Method for inducing in vitro directed differentiation of stem cells through non-contact coculture
A technology for inducing cells and stem cells, applied in the field of non-contact co-culture induced stem cells in vitro directed differentiation, which can solve the problems of difficult separation and purification of stem cells, limited area of semi-permeable membrane, and increased risk of clinical application, etc. Directed differentiation, easy suspension effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1: Non-contact co-culture induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into osteoblasts in vitro
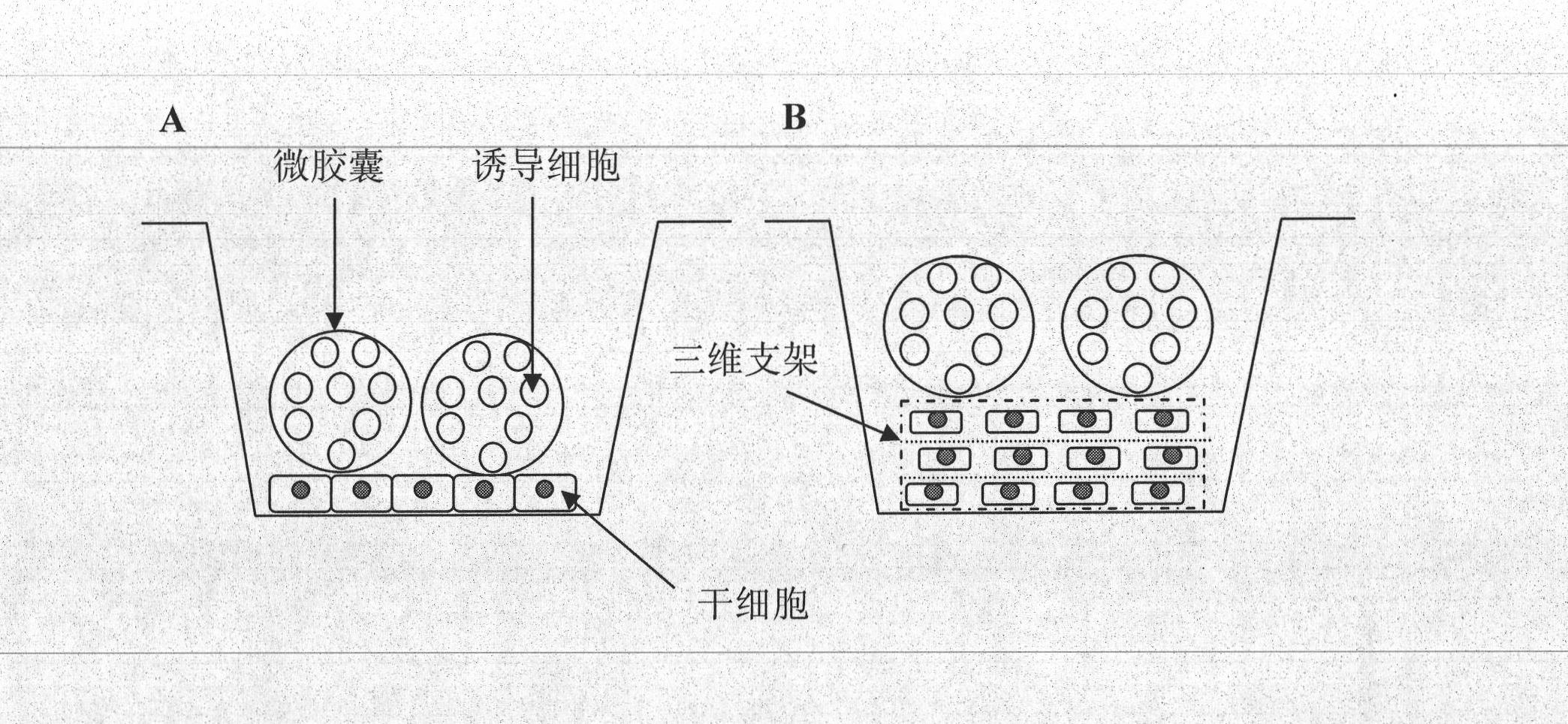
[0032] Sodium alginate-polylysine microcapsules embedded with BMP-2 gene transfected CHO cells were prepared by electrostatic droplet method. The prepared microcapsules were added to the cell culture medium and cultivated in an incubator (see literature: Optimization of the Seeding Density in Microencapsulated Recombinant CHO Cell Culture. Ying Zhang, Jing Zhou, Xulang Zhang, Weiting Yu, Xin Guo, Wei Wang , Xiaojun Ma.Chemical and Biochemical Engineering Quarterly, 2008, 22(1): 105-111), the culture medium was regularly replaced every 3 days.
[0033] Microencapsulated BMP-2 transgenic cells were mixed with 1×10 4 cells / cm 2 Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells seeded at a density of two-dimensional adherent culture were co-cultured according to the above culture conditions, and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells cultured alone were used as a control...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Example 2: Non-contact co-culture induces embryonic stem cells to differentiate into cardiomyocytes in vitro
[0035] Sodium alginate-chitosan microcapsules embedded with human cardiac muscle cell line HCM were prepared by air jet method. The prepared microcapsules were added to the cell culture fluid, and cultivated in an incubator, and the culture fluid was regularly replaced every 3 days, and the culture conditions were the same as in Example 1.
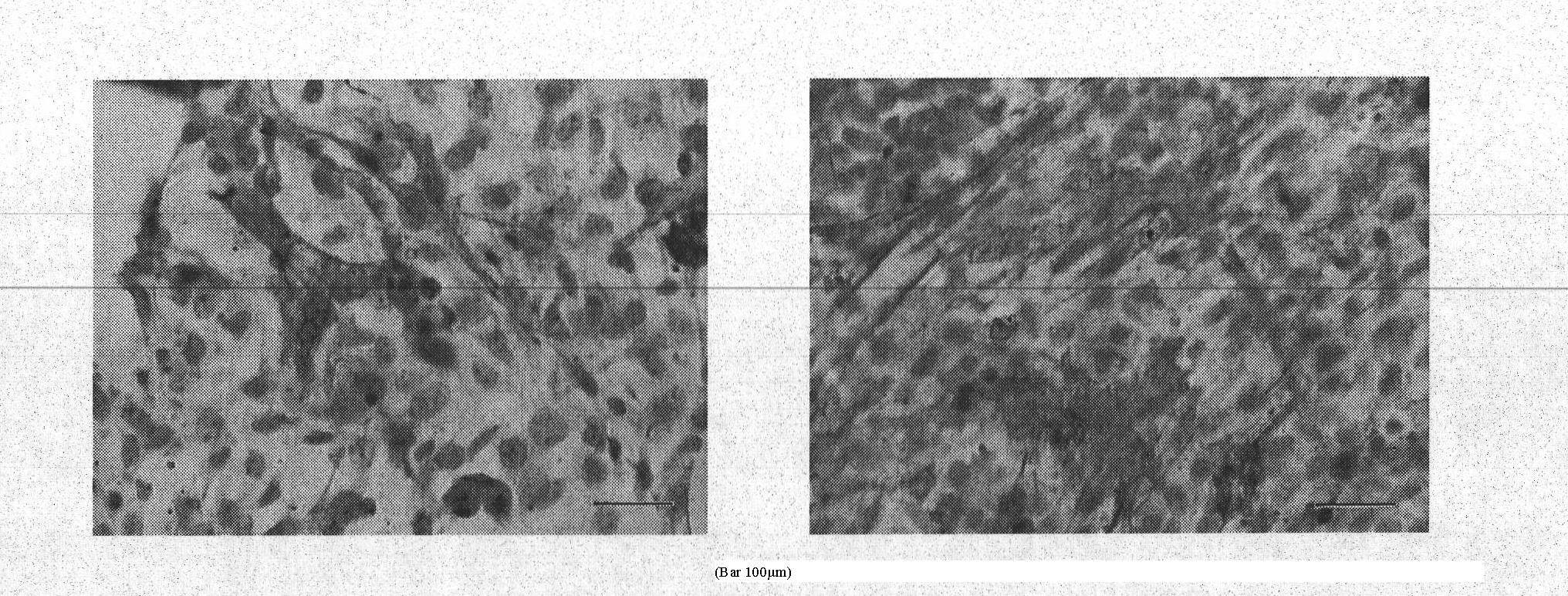
[0036] Microencapsulated HCM cells were mixed with 1 × 10 4 cells / cm 2 Two-dimensional adherent cultured mouse embryonic stem cells inoculated at a density of 100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000ss to h See the experimental results Figure 5 . The results showed that the mouse embryonic stem cells in the co-culture group had differentiated into cardiomyocytes, which was significantly different from that in the control group.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Example 3: Non-contact co-culture in a bioreactor induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into three-dimensional neural tissues in vitro
[0038] Sodium alginate-chitosan microcapsules embedded with SD rat olfactory ensheathing cells were prepared by electrostatic droplet method. The prepared microcapsules were added to the olfactory ensheathing cell culture medium, cultured in an incubator, and the culture medium was regularly replaced every 3 days. The culture conditions are the same as in Example 1.
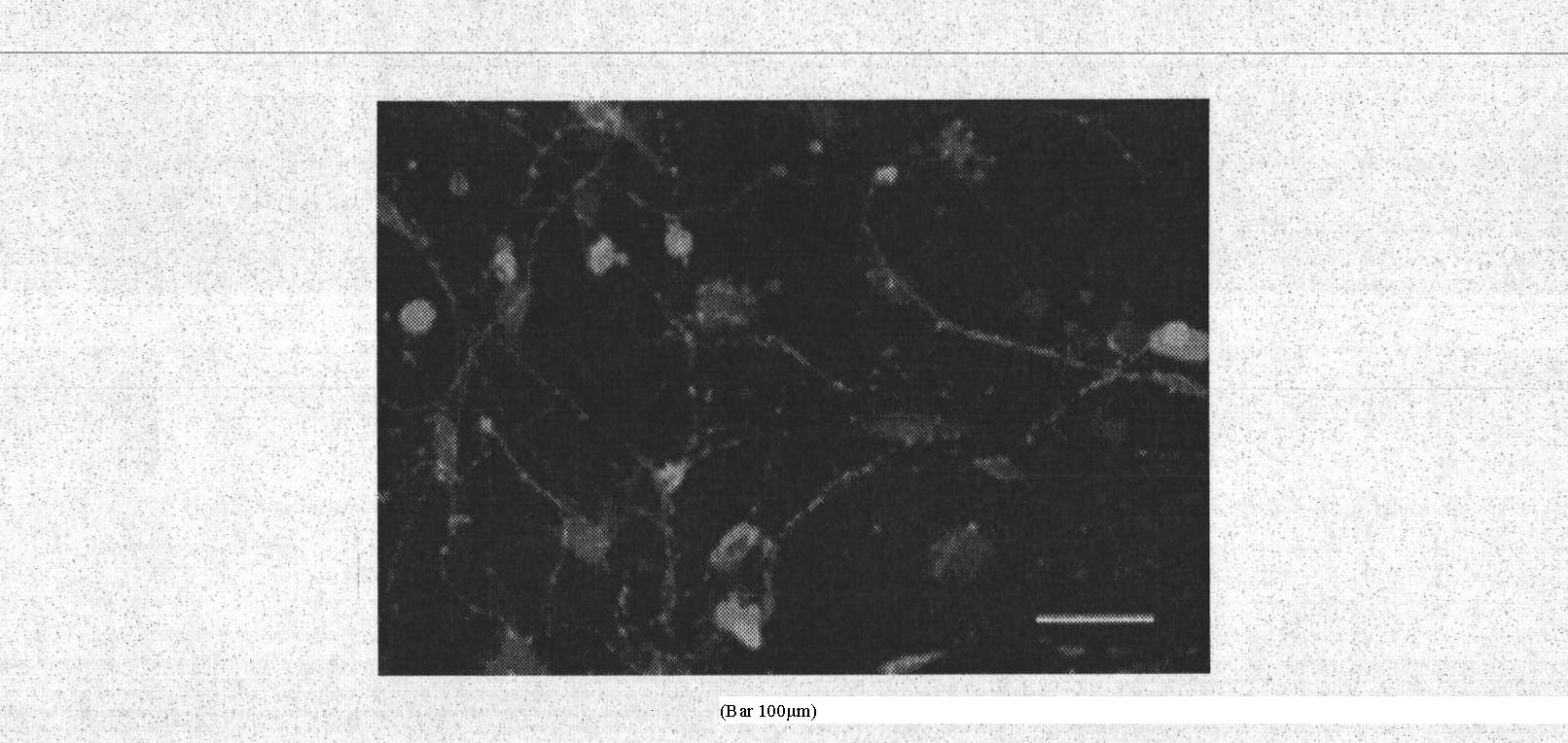
[0039] Microencapsulated olfactory ensheathing cells were mixed with 2×10 6 cells / cm 3 SD rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells seeded at a density of 3D chitosan scaffolds were co-seeded into a rotary bioreactor for dynamic co-culture. On the 20th day of dynamic co-culture, the cells in the scaffold material Perform βIII-tubulin / Hoechst33342 immunofluorescence detection. See the experimental results Figure 6 . The results showed that the bon...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com