Patents
Literature
2395 results about "Stereophonic sound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Stereophonic sound or, more commonly, stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that creates an illusion of multi-directional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two or more independent audio channels through a configuration of two or more loudspeakers (or stereo headphones) in such a way as to create the impression of sound heard from various directions, as in natural hearing. Thus the term "stereophonic" applies to so-called "quadraphonic" and "surround-sound" systems as well as the more common two-channel, two-speaker systems. It is often contrasted with monophonic, or "mono" sound, where audio is heard as coming from one position, often ahead in the sound field (analogous to a visual field). Stereo sound has been in common use since the 1970s in entertainment systems such as broadcast radio, TV, recorded music, internet, computer audio, and cinema.
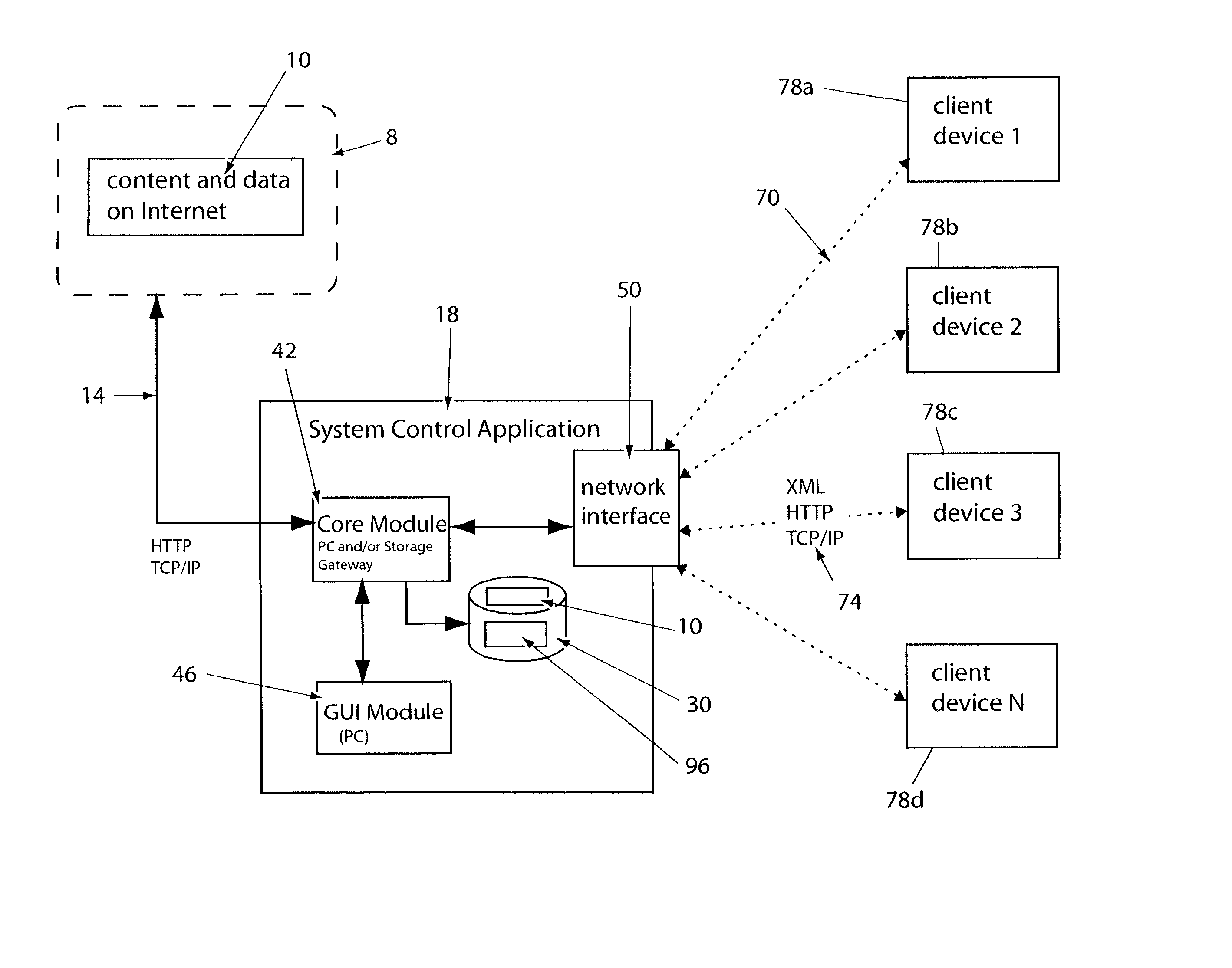
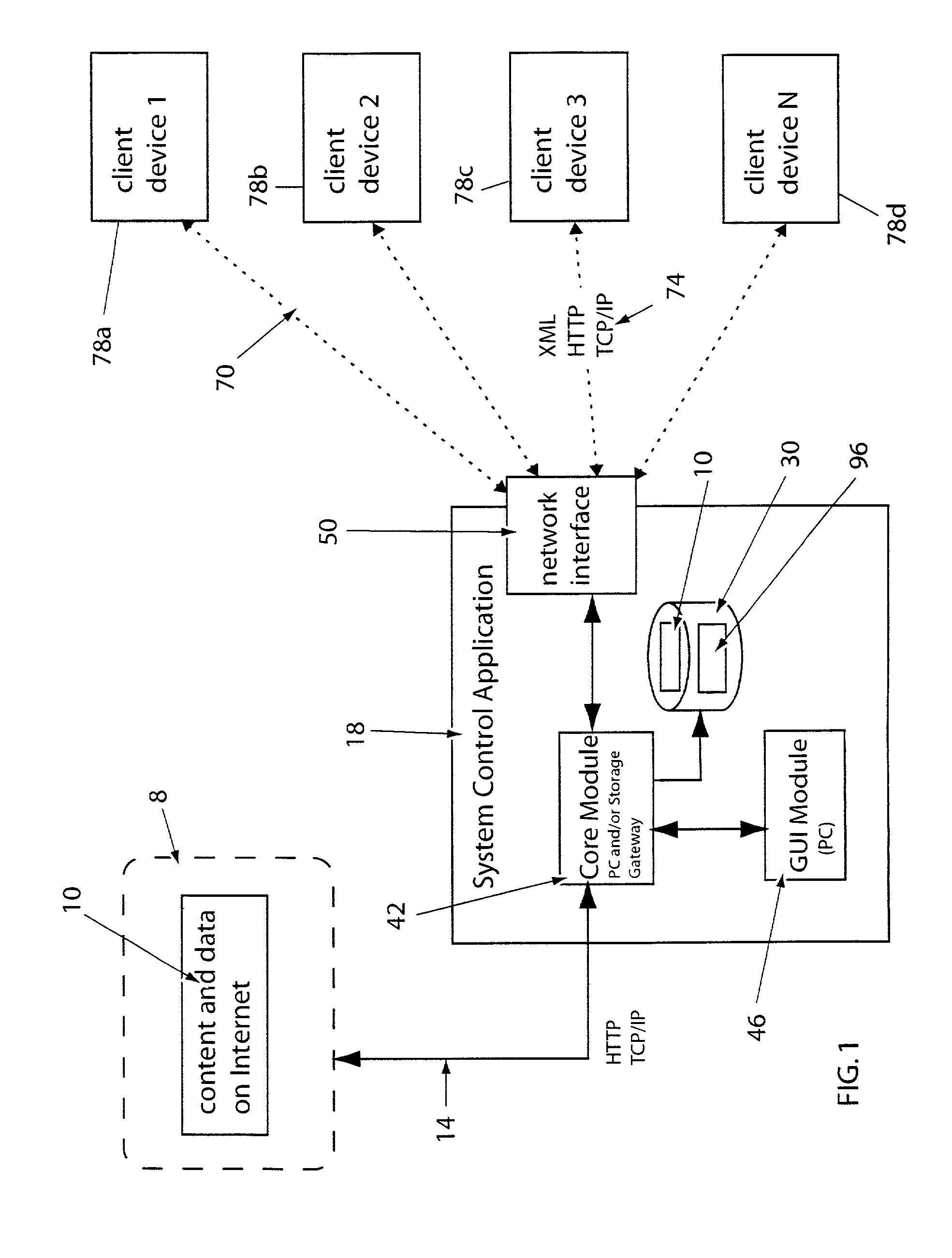
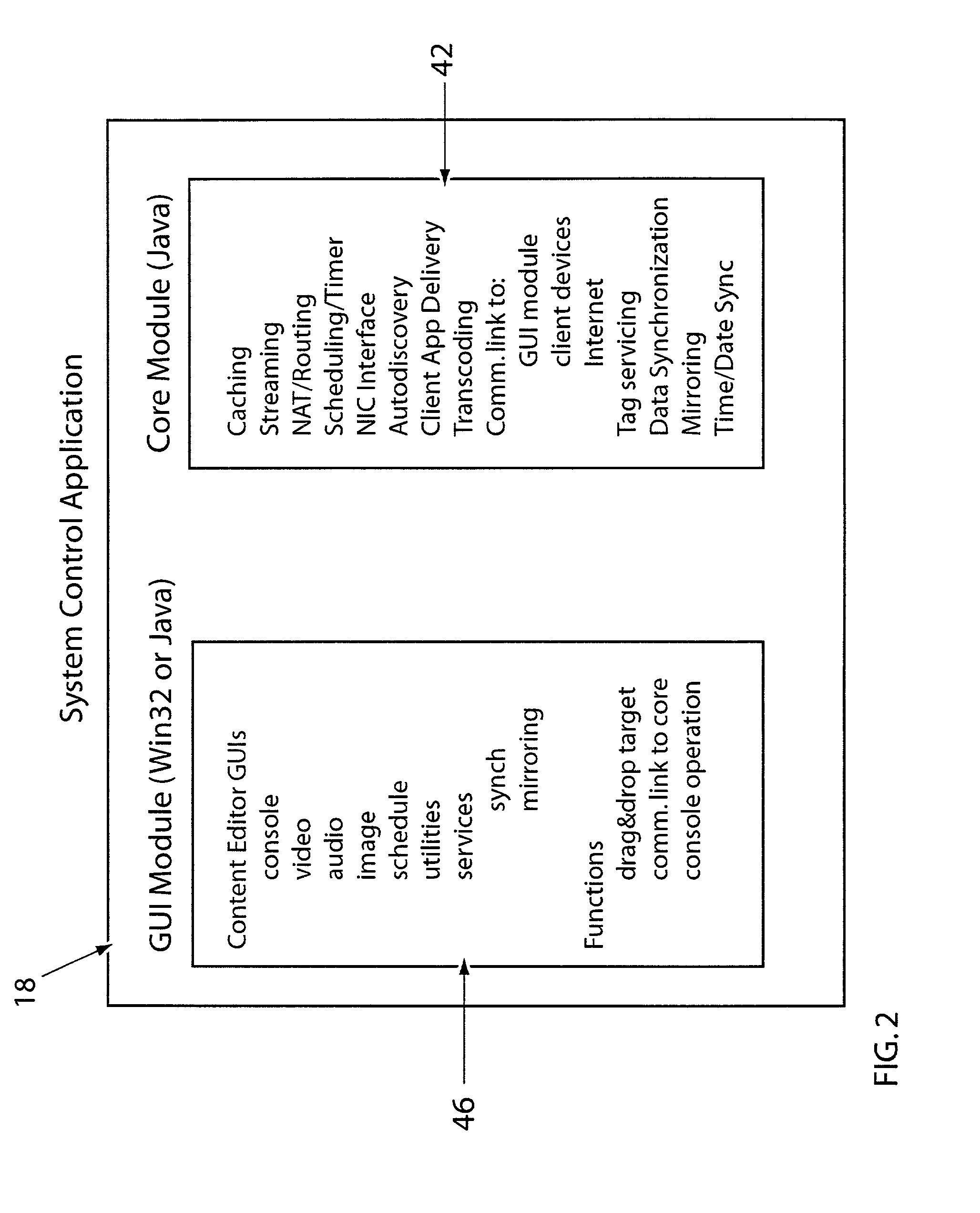
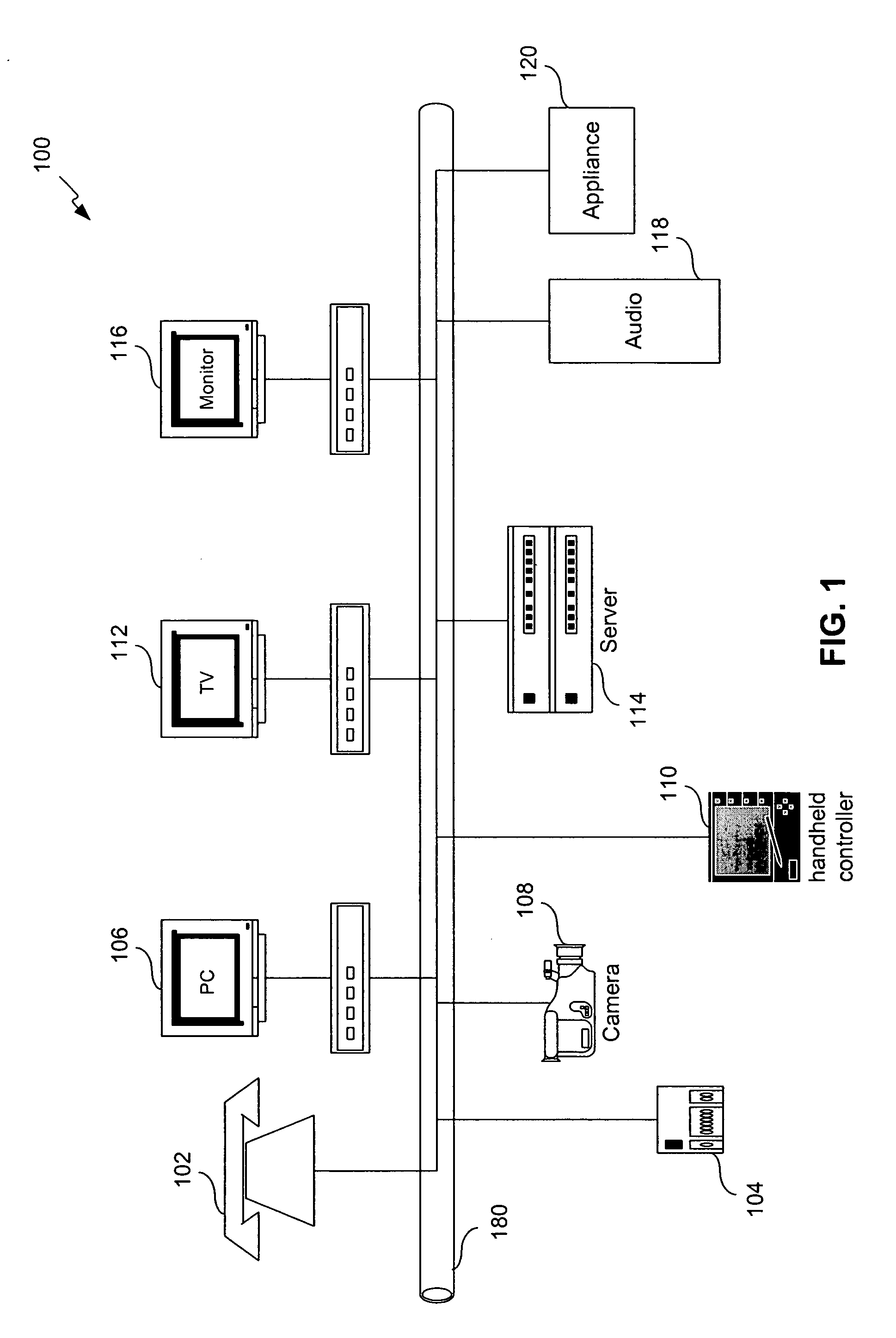
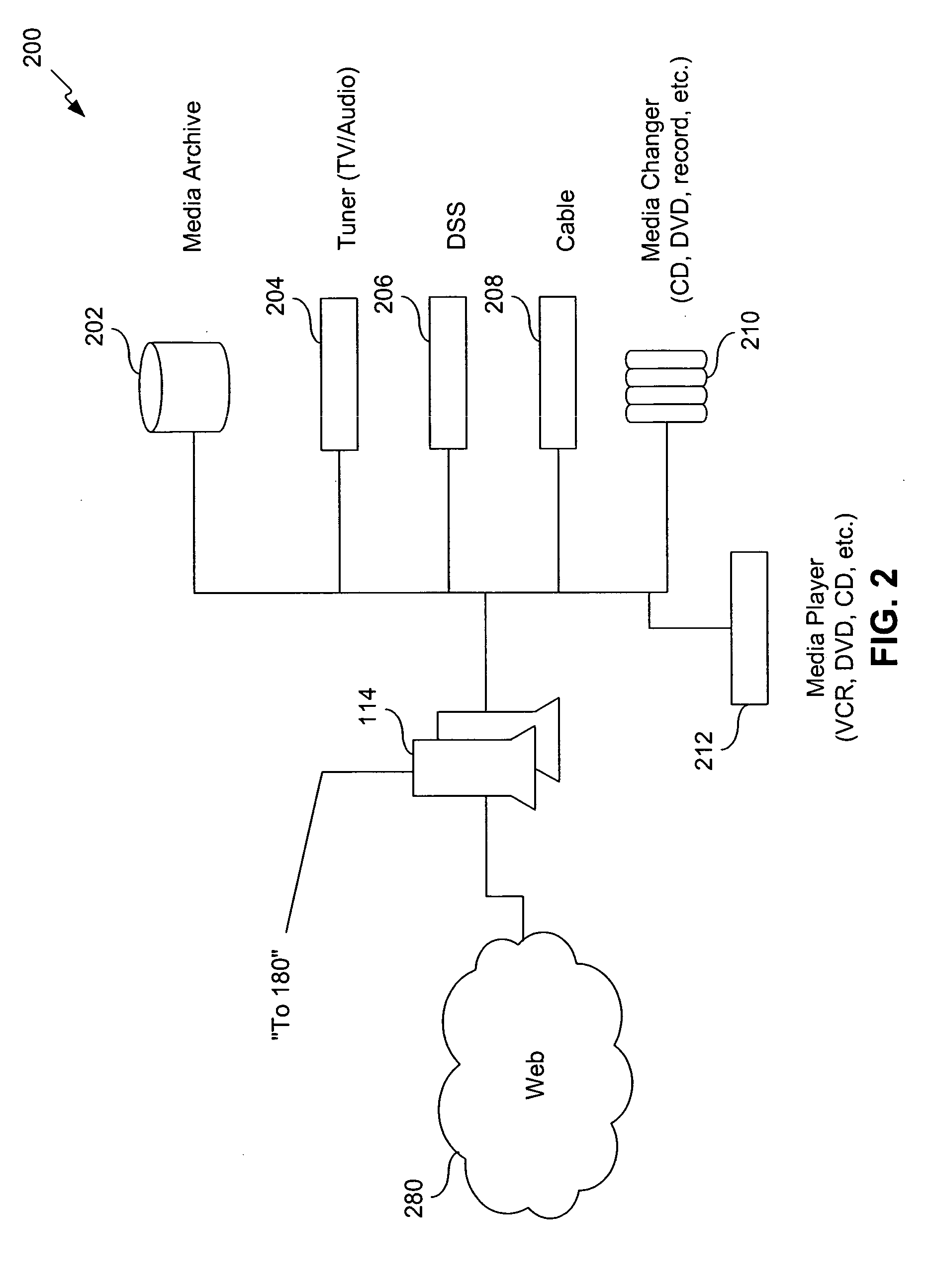
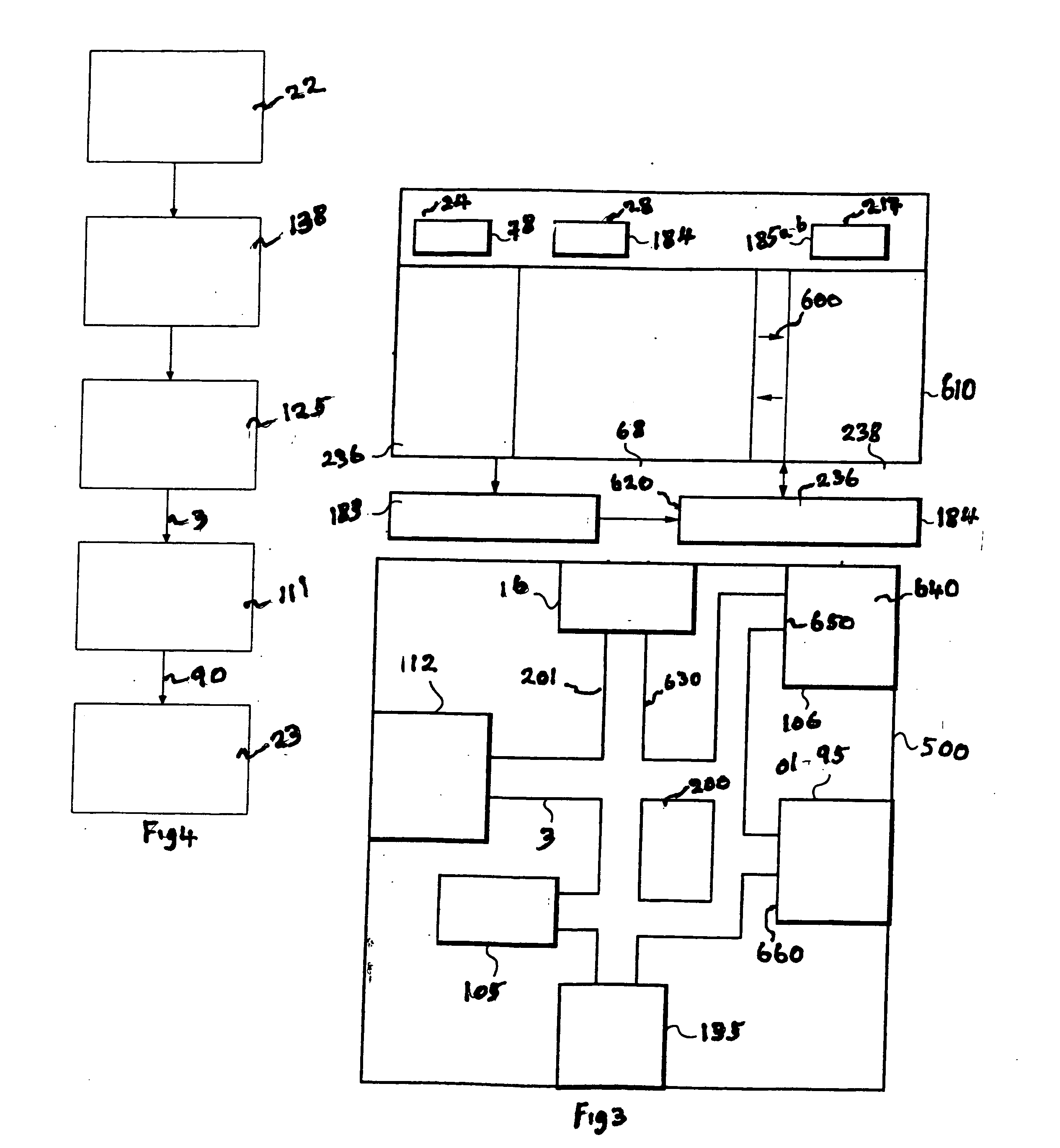
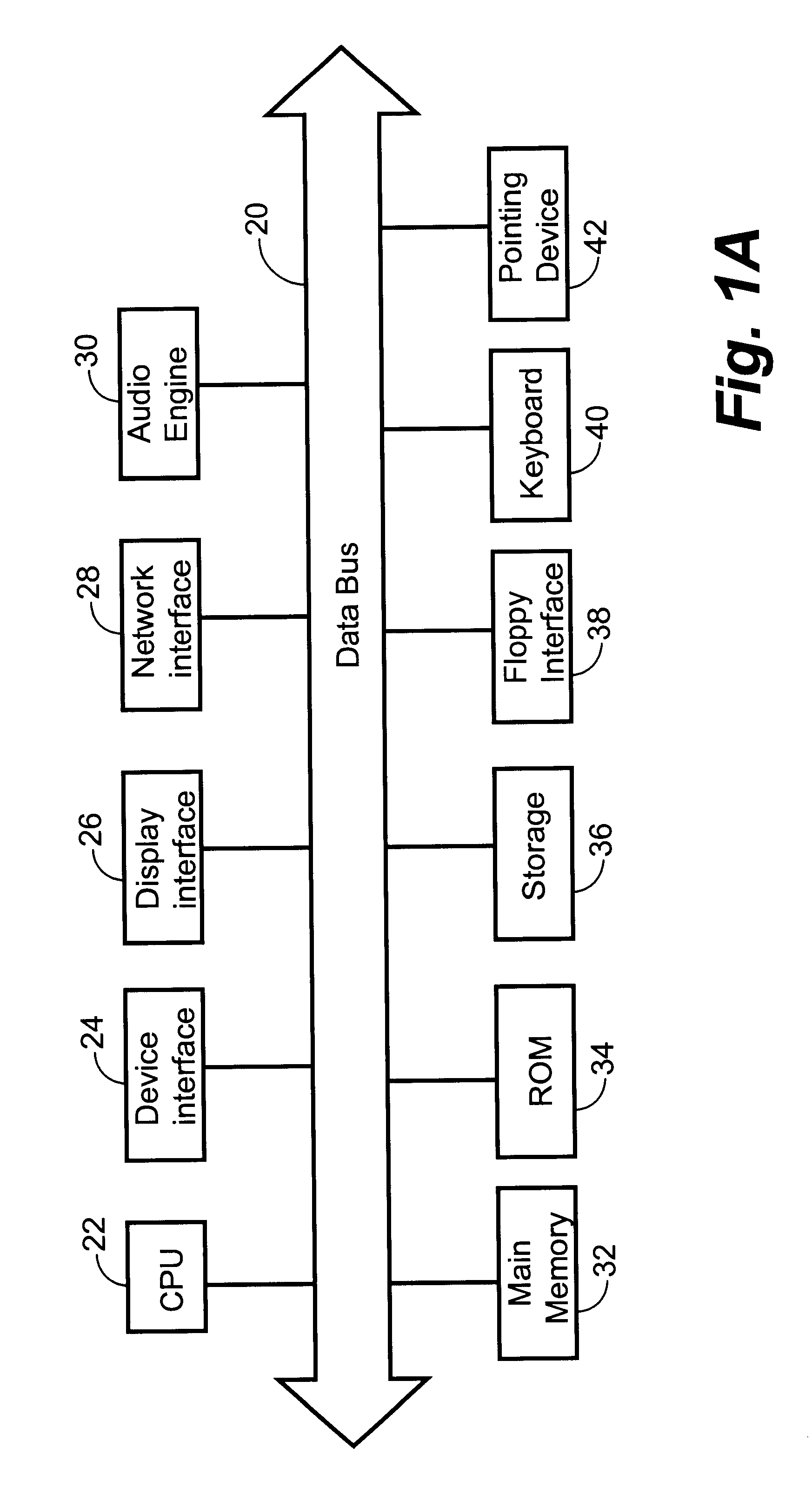
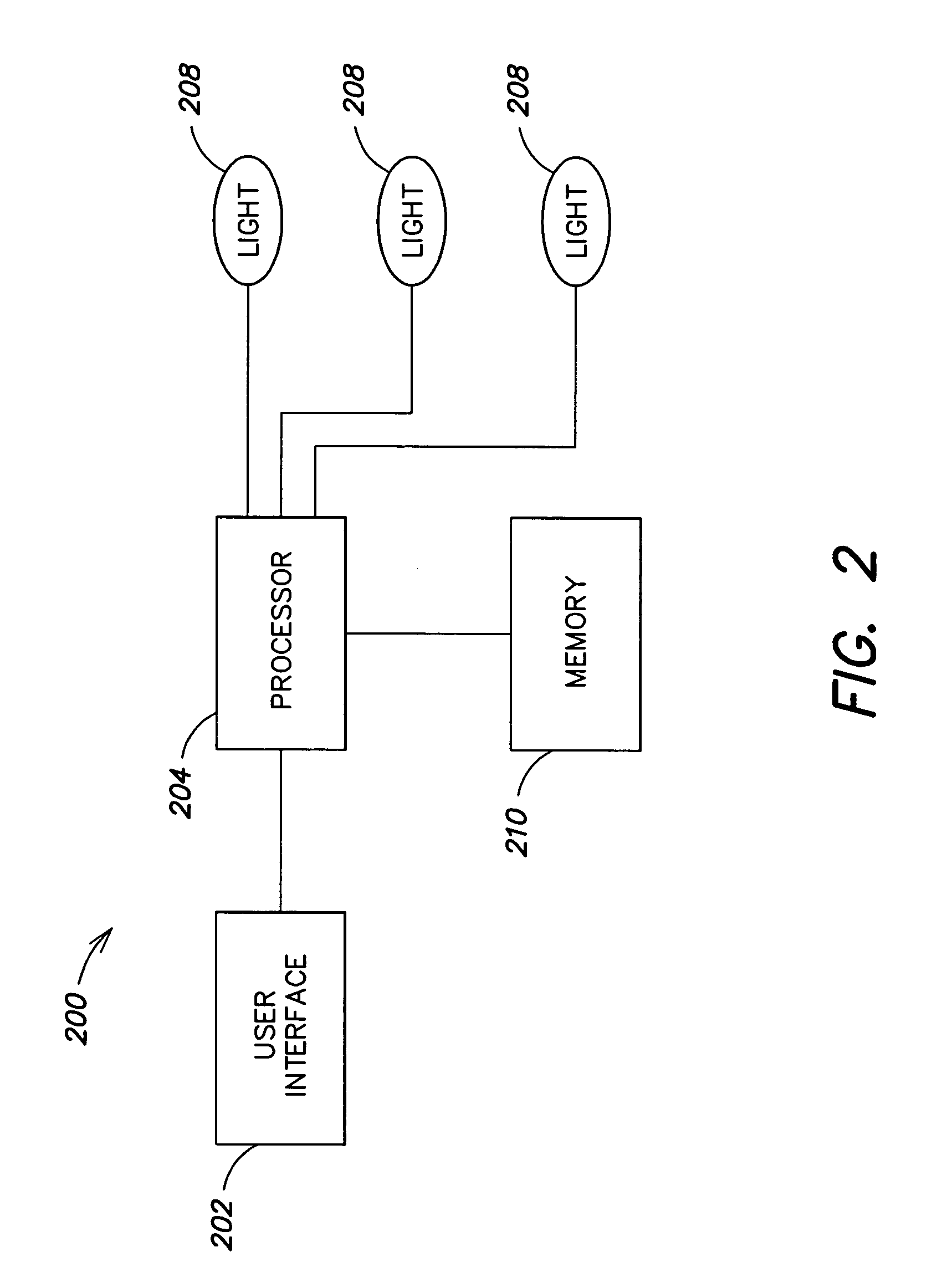
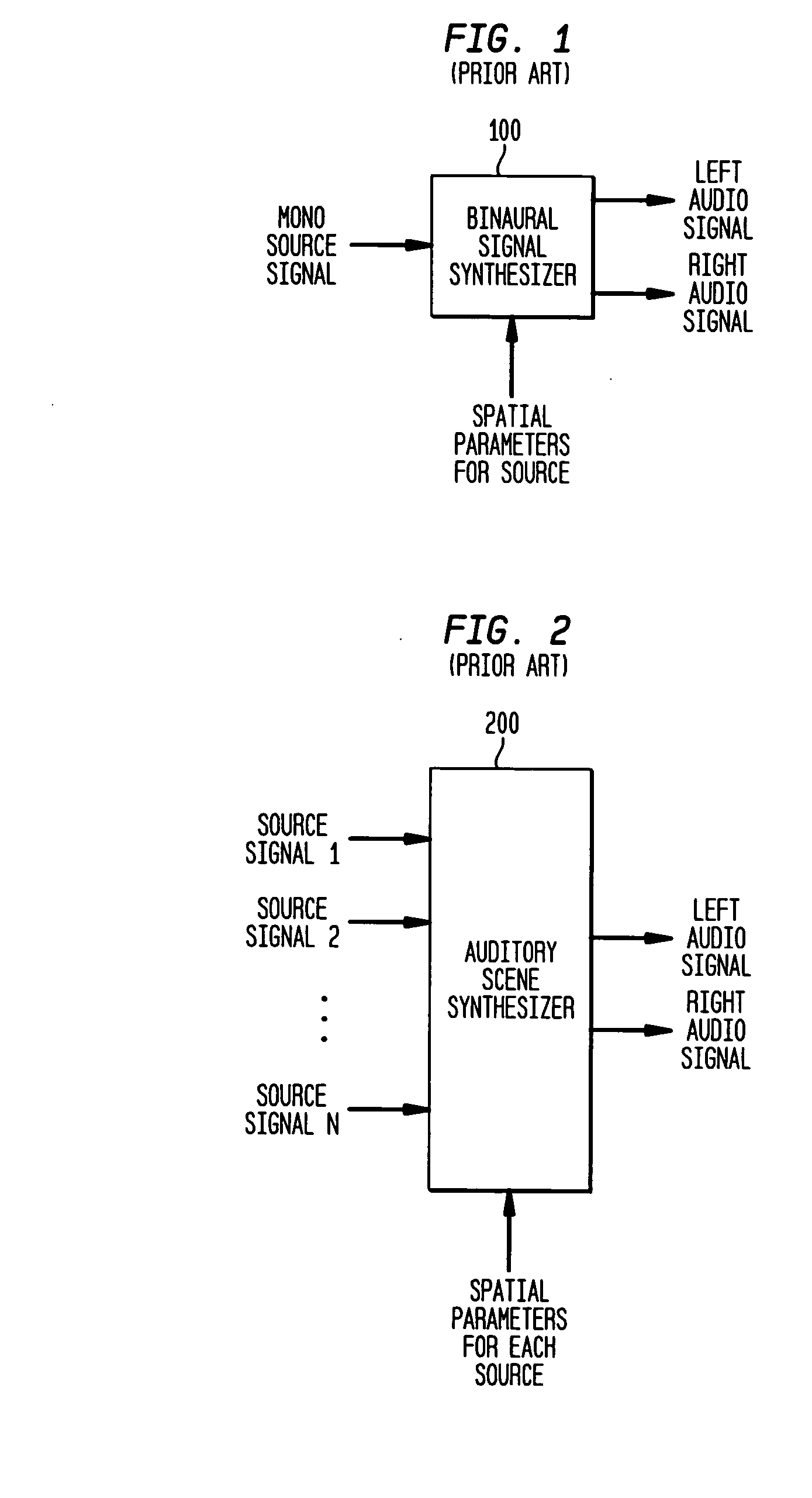
System for providing content, management, and interactivity for thin client devices
InactiveUS20020013852A1Multiple digital computer combinationsSelective content distributionThe InternetProcedural approach
A system is provided for delivering Internet and digital content to a variety of thin client devices. A web portal for accessing and selecting content is used in conjunction with graphical user interfaces on a personal computer for setting up and controlling the content channels. The user interfaces, scheduling, and communication management are controlled by a system control software application running on a local server with an Internet connection. A high speed local area network provides for streaming content from the Internet or local server to thin client devices. A digital audio playback device is connected to the local server via the local area network connection and decodes streamed audio files, and converts them into analog audio signals for input into a conventional stereo. Digital content is streamed automatically from the local server to another Internet playback device, based on end user content preferences and schedule selections.
Owner:VIVIANA RES +2
Method, system, and computer program product for managing controlled residential or non-residential environments
InactiveUS20060053447A1Facilitate transmission and receptionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsControl signalDisplay device
A control server, or similar central processor, manages the distribution of data (including audio and video), voice, and control signals among a plurality of devices connected via a wired and / or wireless communications network. The devices include audio / visual devices (such as, televisions, monitors, PDAs, notepads, notebooks, MP3, portable stereo, etc.) as well as household appliances (such as, lighting, ovens, alarm clocks, etc.). The control server supports video / audio serving, telephony, messaging, file sharing, internetworking, and security. A portable controller allows a user to access and control the network devices from any location within a controlled residential and / or non-residential environment, including its surrounding areas. The controllers are enhanced to support location-awareness and user-awareness functionality.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
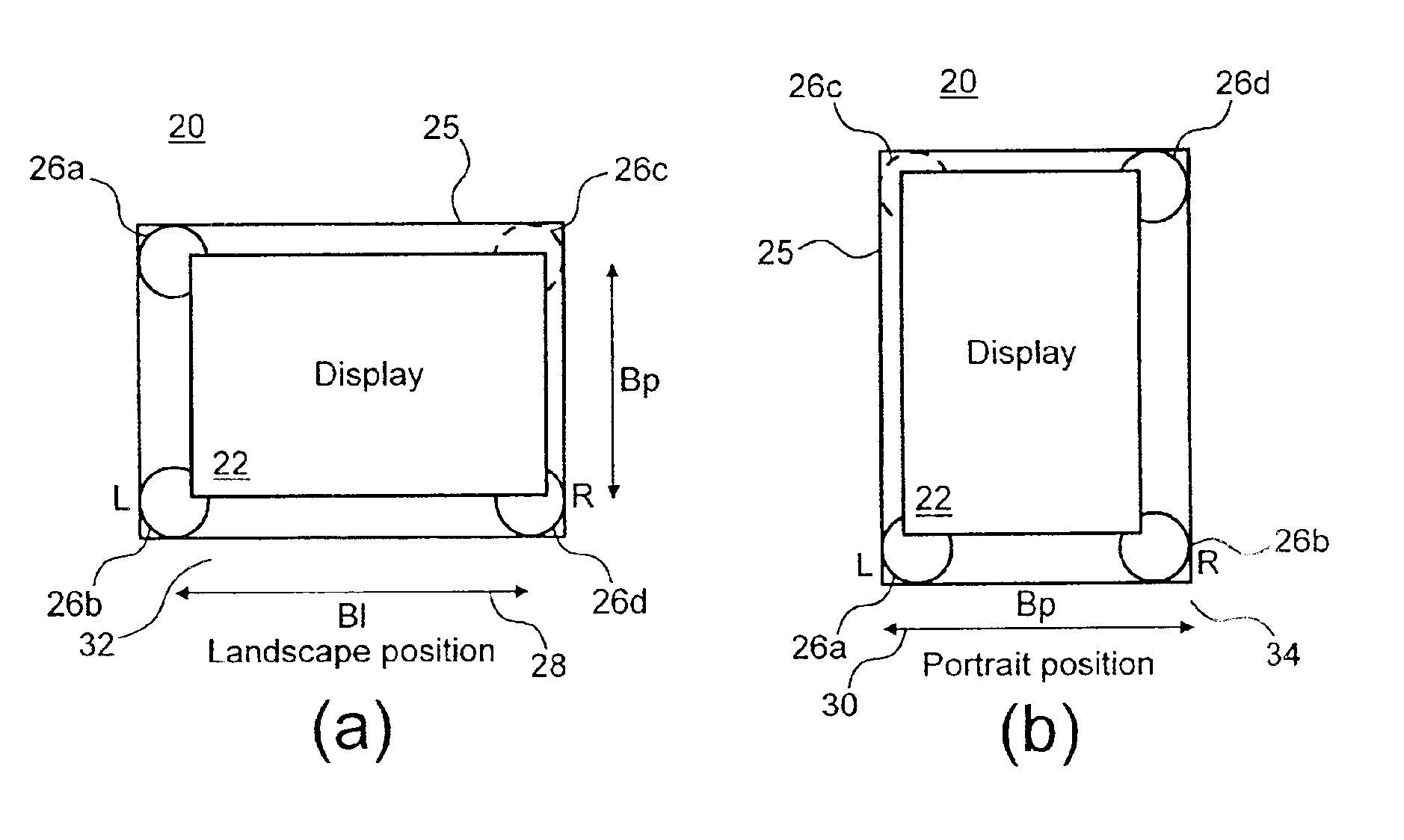
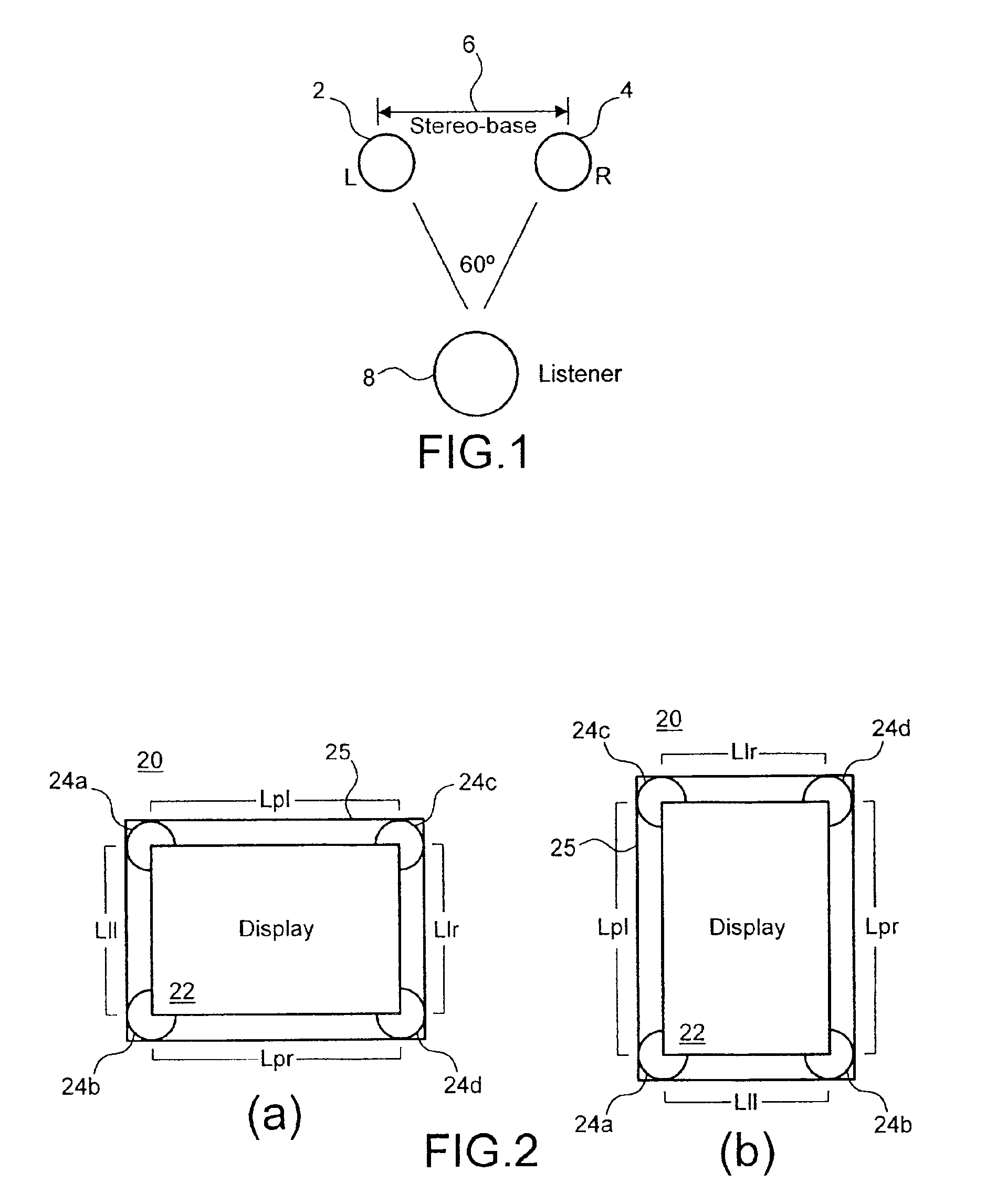
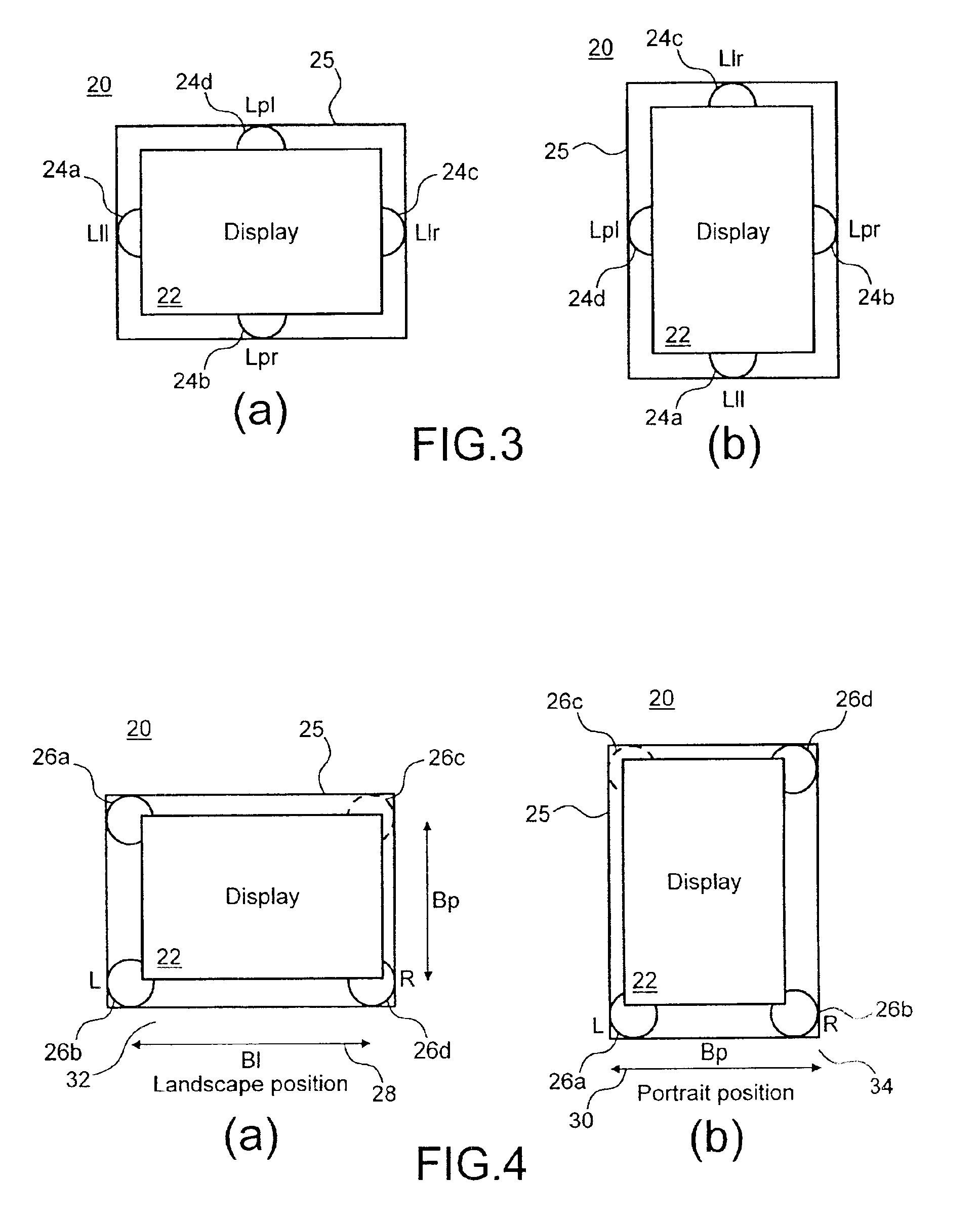
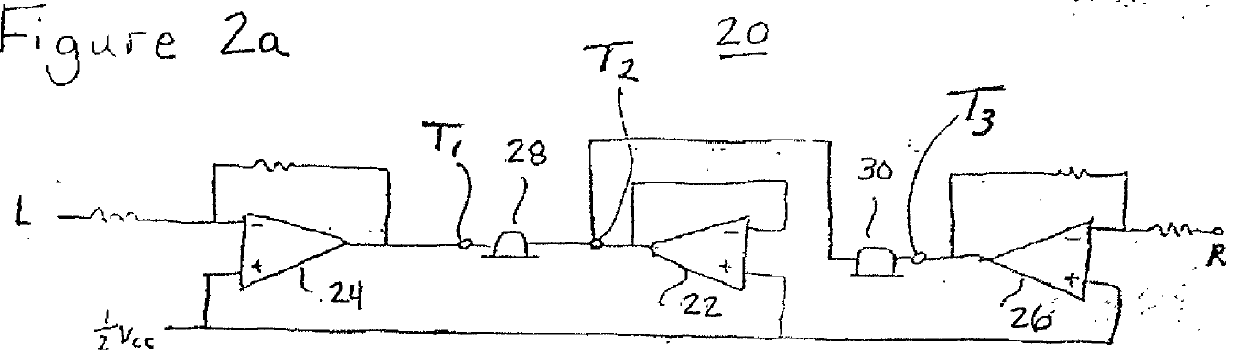
Stereophonic reproduction maintaining means and methods for operation in horizontal and vertical A/V appliance positions
InactiveUS6882335B2Improved audio listeningEnhance the imageTelevision system detailsDevices with sensorDisplay deviceEngineering
Display apparatus including a display and an orientation sensitive interface mechanism is disclosed. In an exemplary embodiment, the orientation sensitive interface includes first and second loudspeaker pairs. The first loudspeaker pair includes first and second loudspeakers and the second loudspeaker pair includes the second and third loudspeaker. The first and second loudspeaker pairs are disposed along transverse directions to each other. The display apparatus comprises a switch which switches between the first loudspeaker pair and the second loudspeaker pair. By providing the respective loudspeaker pairs, and switching between them, it is possible to orient the display apparatus in transverse directions corresponding to respective loudspeaker pairs, yet maintain a substantially stereophonic reproduction for each orientation.
Owner:HTC CORP
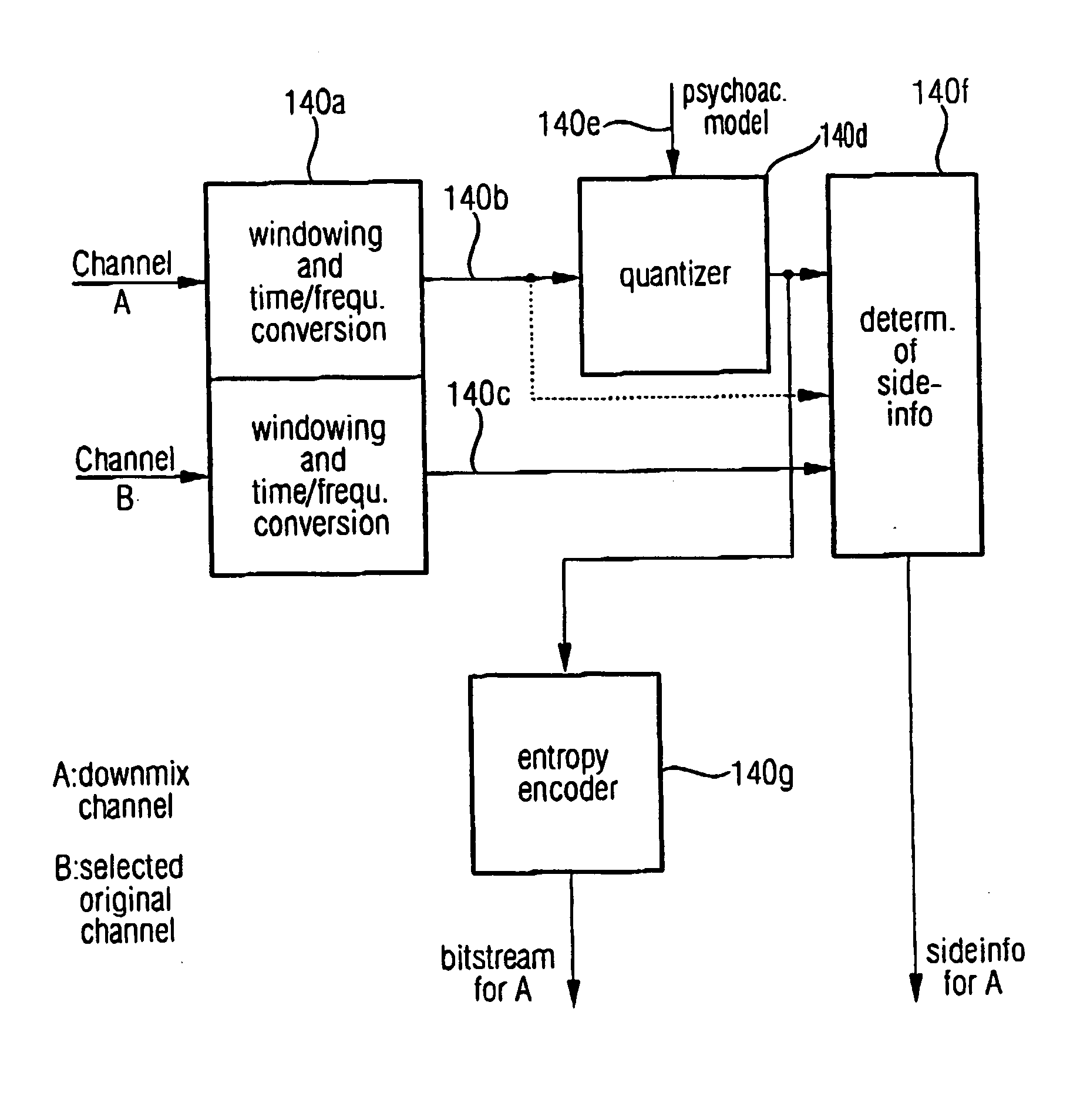
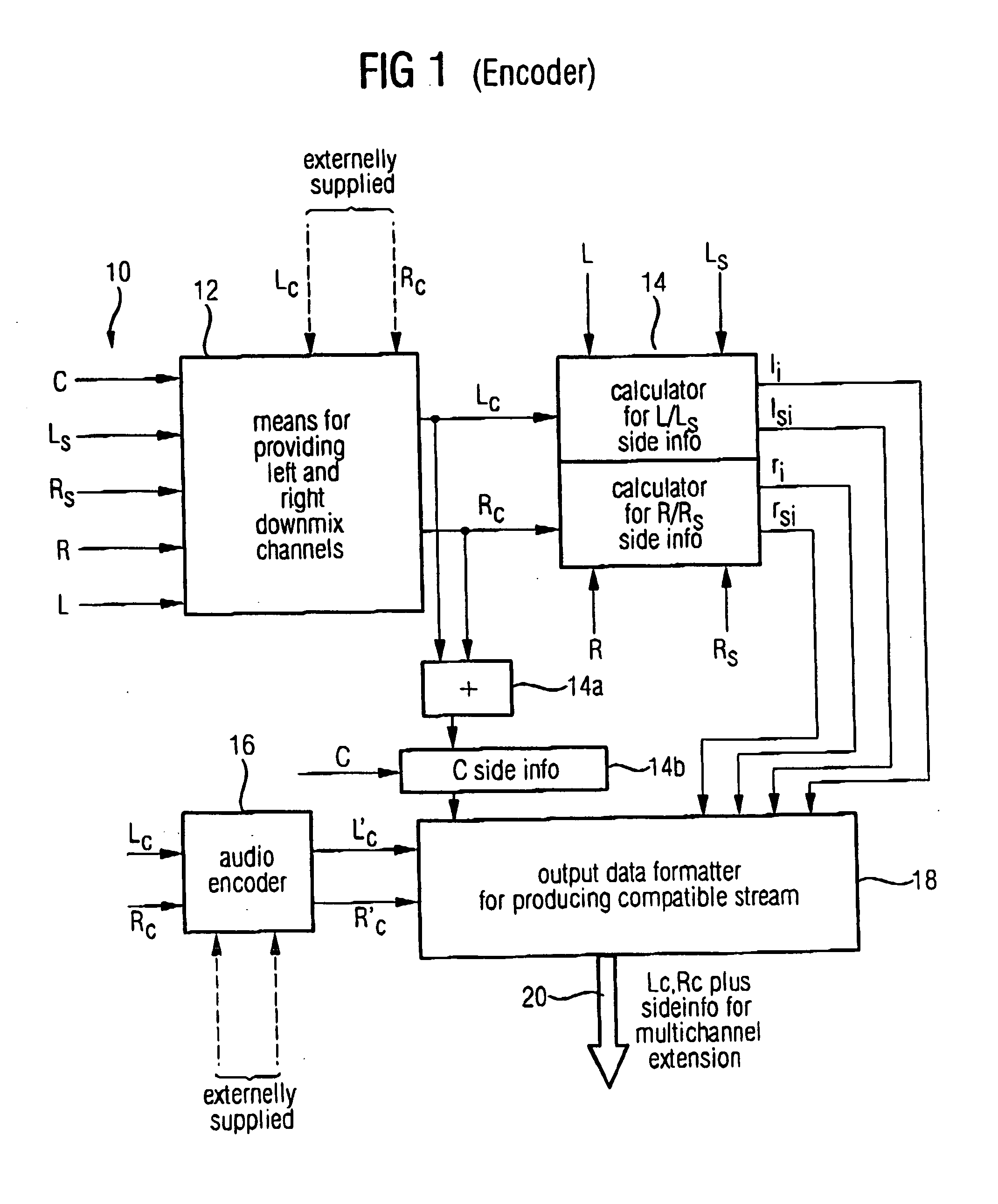
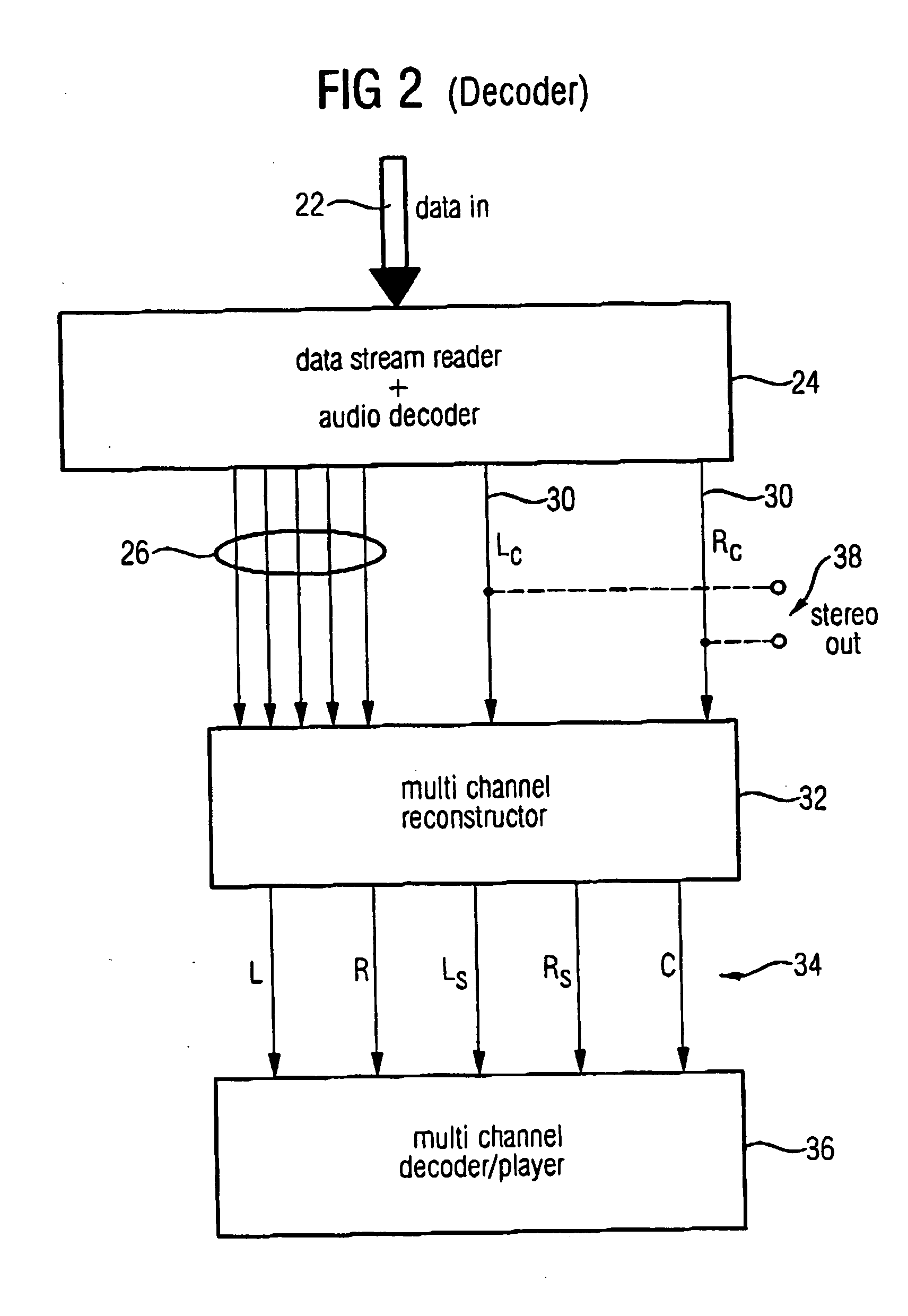
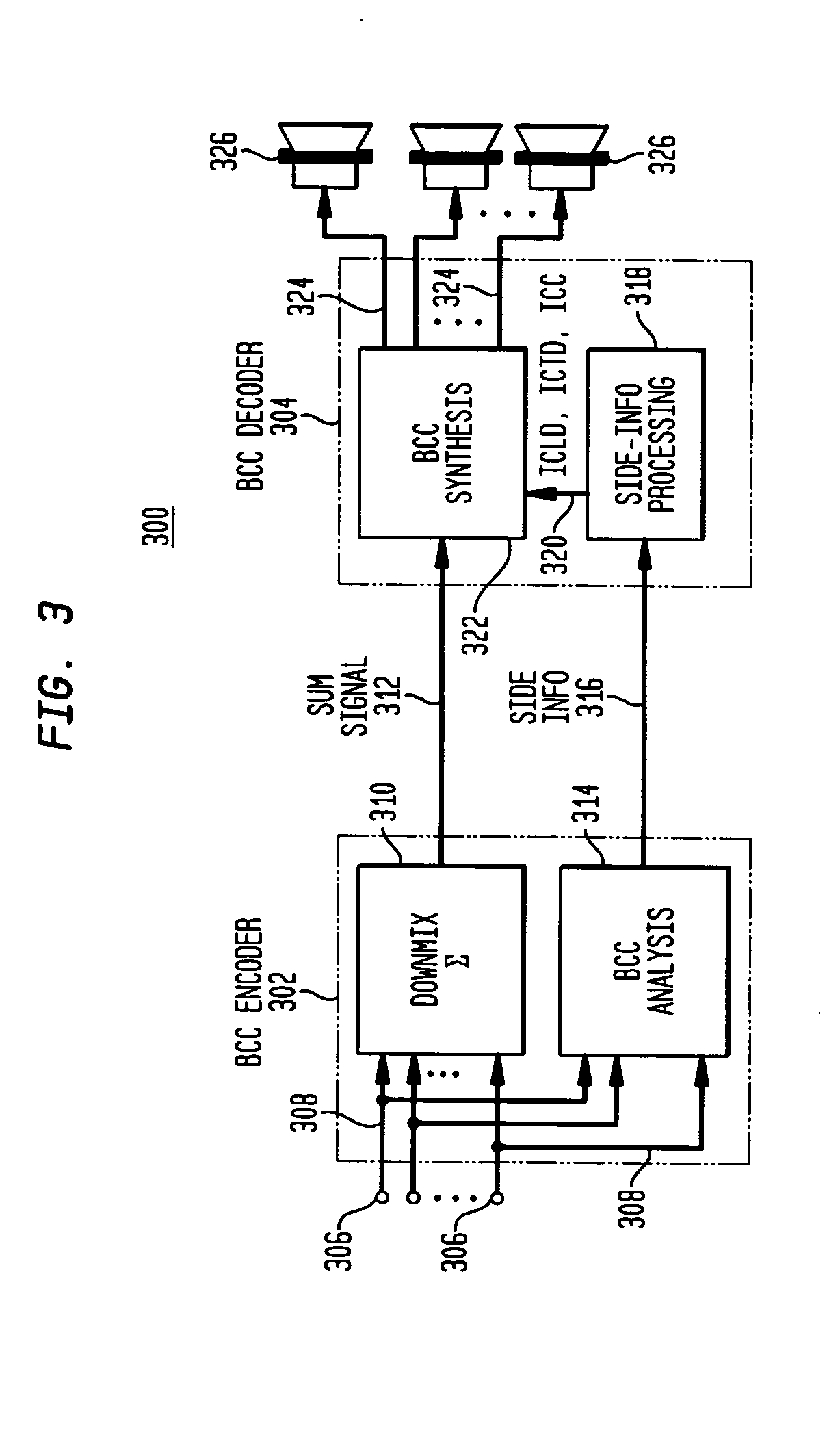
Compatible multi-channel coding/decoding
ActiveUS20050074127A1Suitable for processingEfficient and artifact-reduced encodingSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsSide informationComputer science
In processing a multi-channel audio signal having at least three original channels, a first downmix channel and a second downmix channel are provided, which are derived from the original channels. For a selected original channel of the original channels, channel side information are calculated such that a downmix channel or a combined downmix channel including the first and the second downmix channels, when weighted using the channel side information, results in an approximation of the selected original channel. The channel side information and the first and second downmix channels form output data to be transmitted to a decoder, which, in case of a low level decoder only decodes the first and second downmix channels or, in case of a high level decoder provides a full multi-channel audio signal based on the downmix channels and the channel side information. Since the channel side information only occupy a low number of bits, and since the decoder does not use dematrixing, an efficient and high quality multi-channel extension for stereo players and enhanced multi-channel players is obtained.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
Audio playback device and method of its operation
InactiveUS20070087686A1Surround sound field/effectImproved audio playbackLoudspeaker enclosure positioningStereophonic systemsMobile deviceLoudspeaker
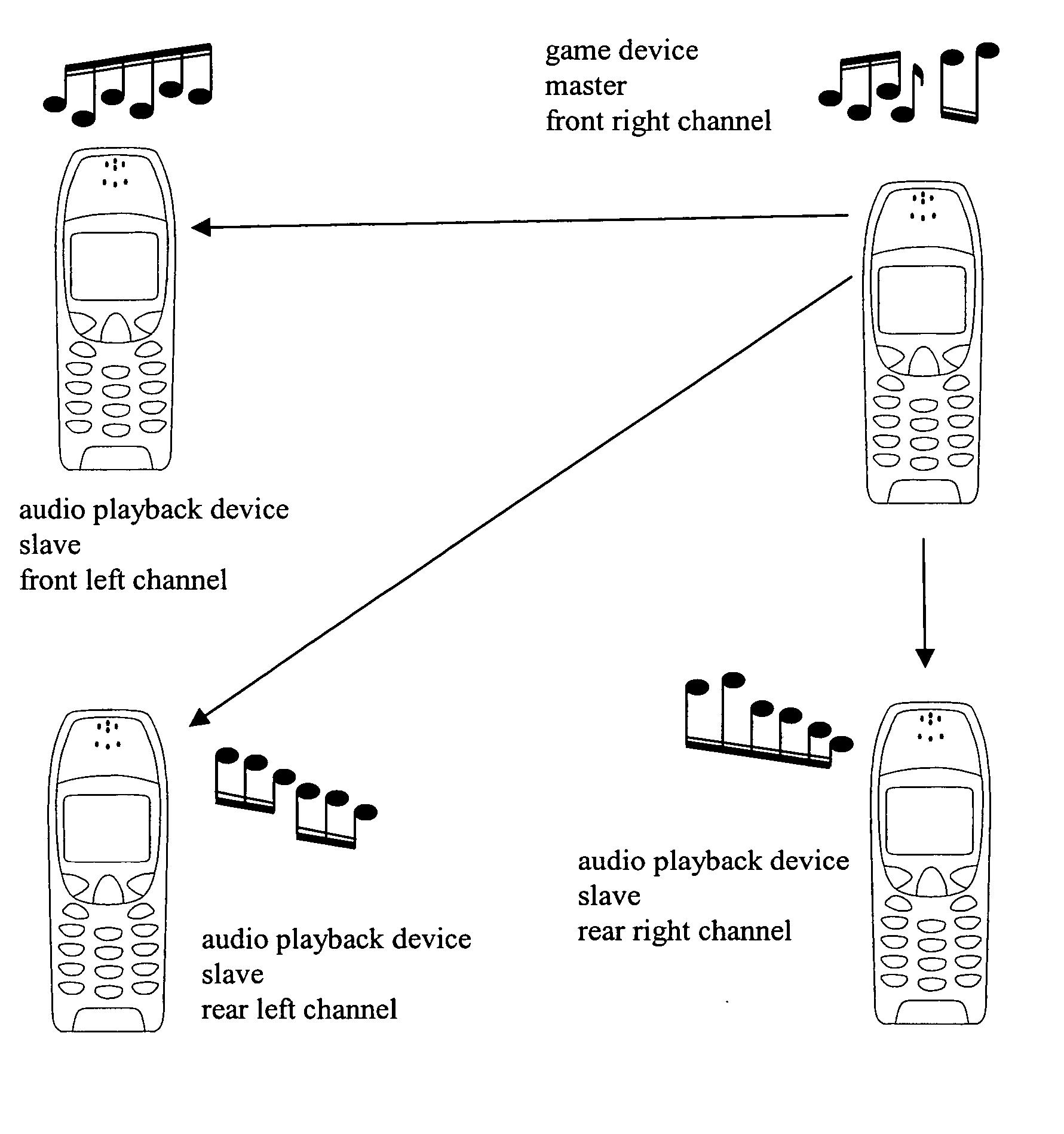
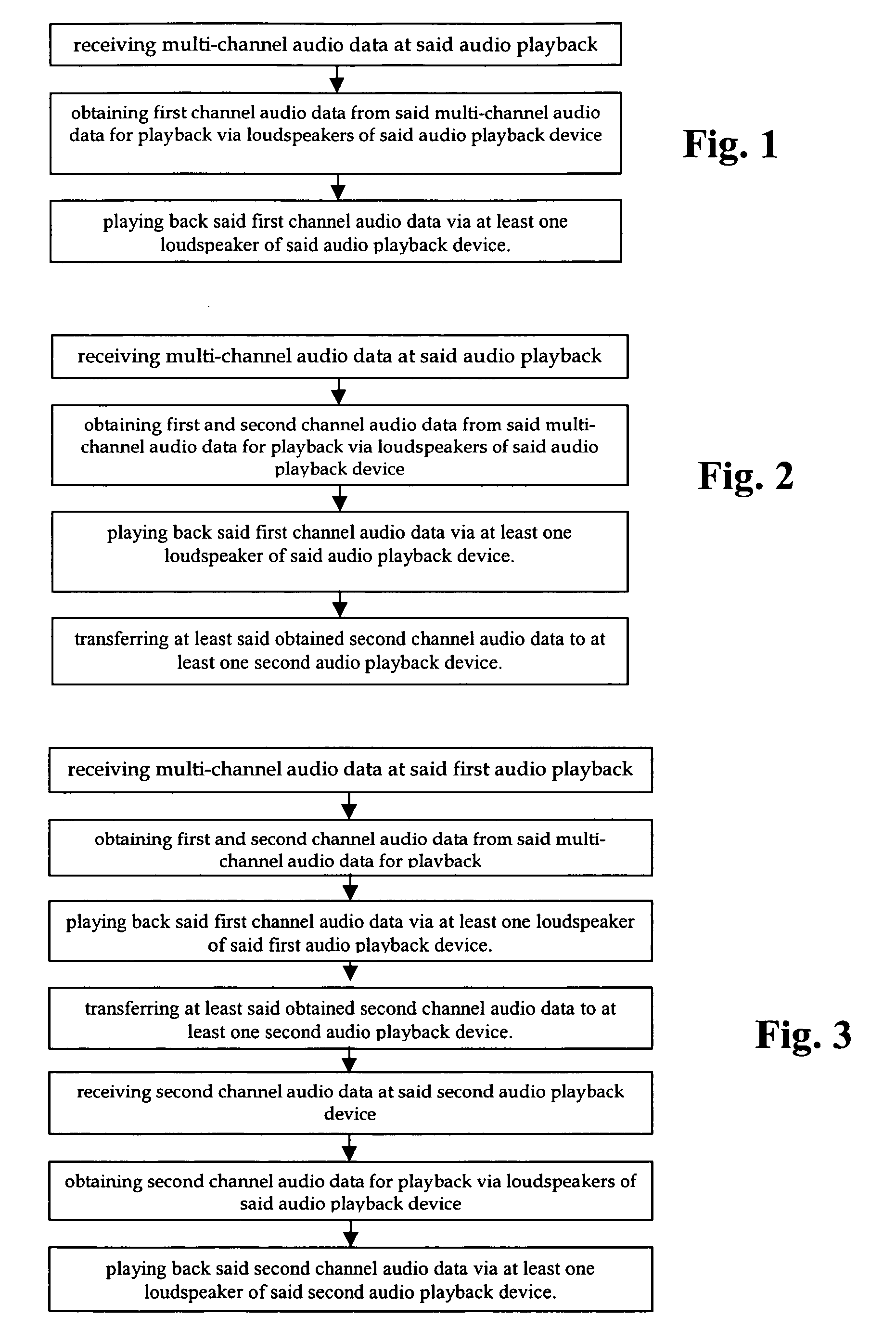
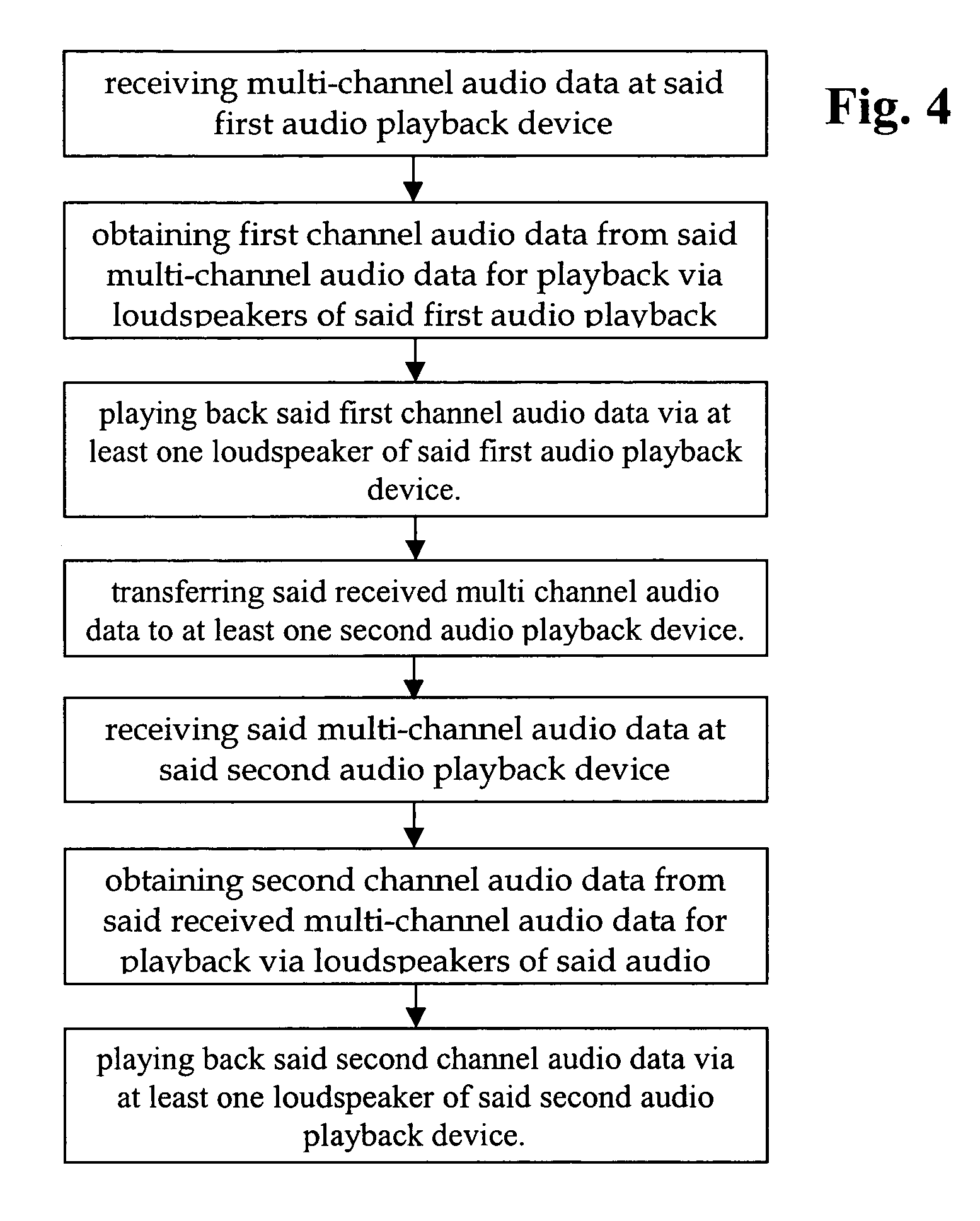
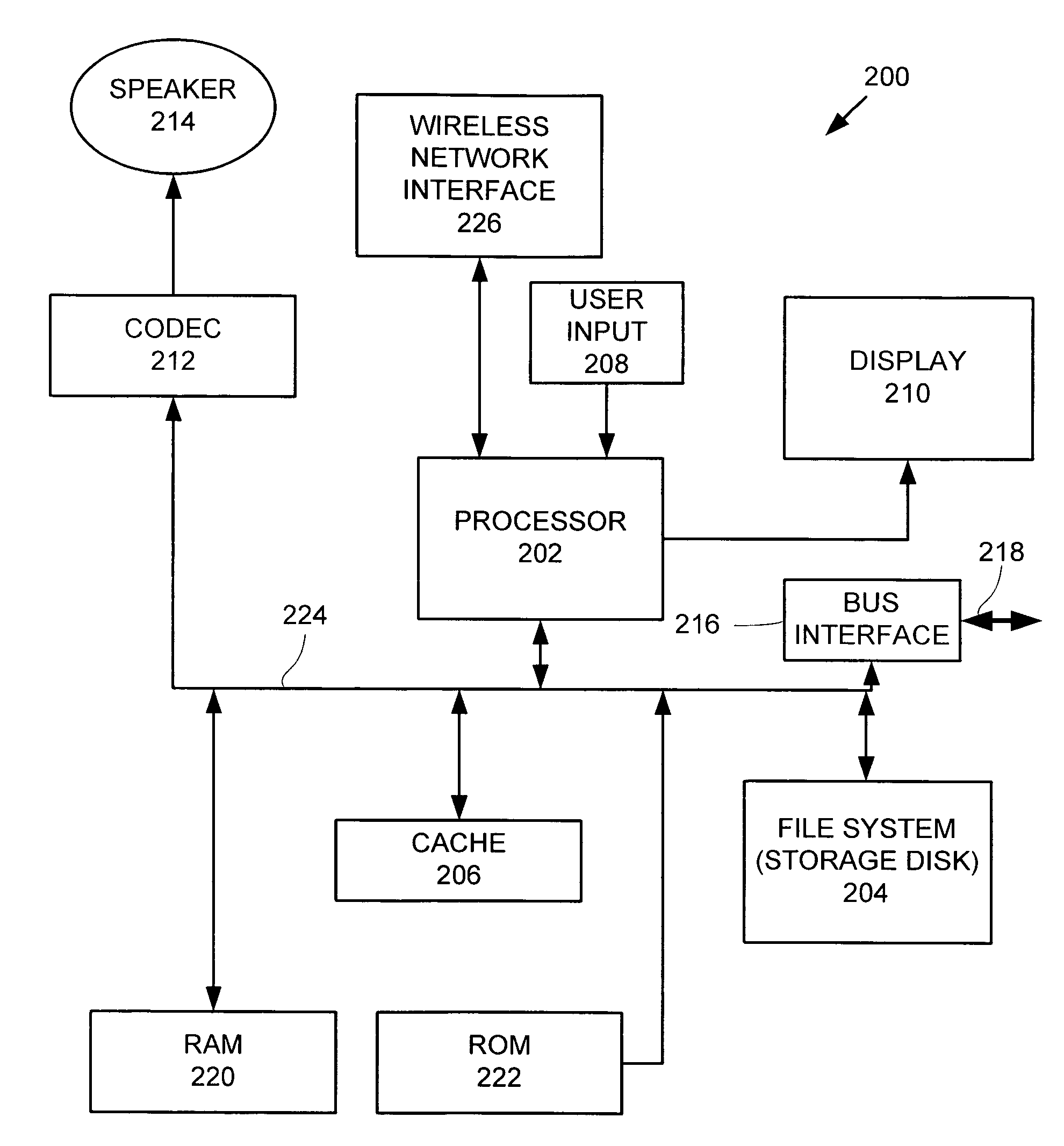
The invention relates to mobile audio playback devices and methods of its operation for enhanced music and sound experience for mobile devices. To provide stereo and surround sound, the present invention provides an audio playback device with a receiving means for receiving multi-channel audio data, obtaining means connected to the receiving means, for obtaining first channel audio data from the multi-channel audio data for playback on the audio playback device, and playback means having at least one loudspeaker, and being connected to the obtaining means for outputting the first channel audio data. The other not selected audio channels or all received audio data may be transferred to other terminals for playback or may be discarded.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
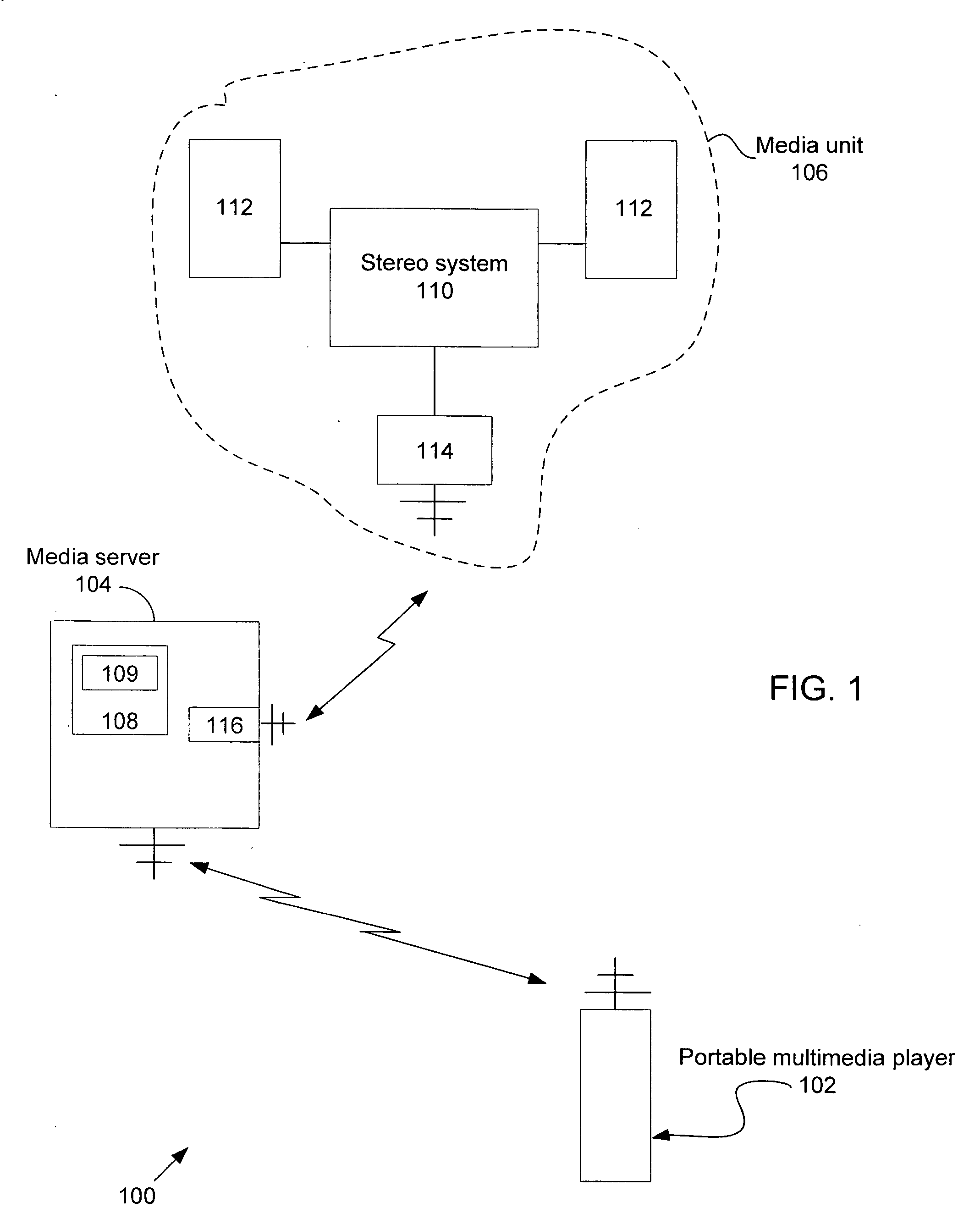
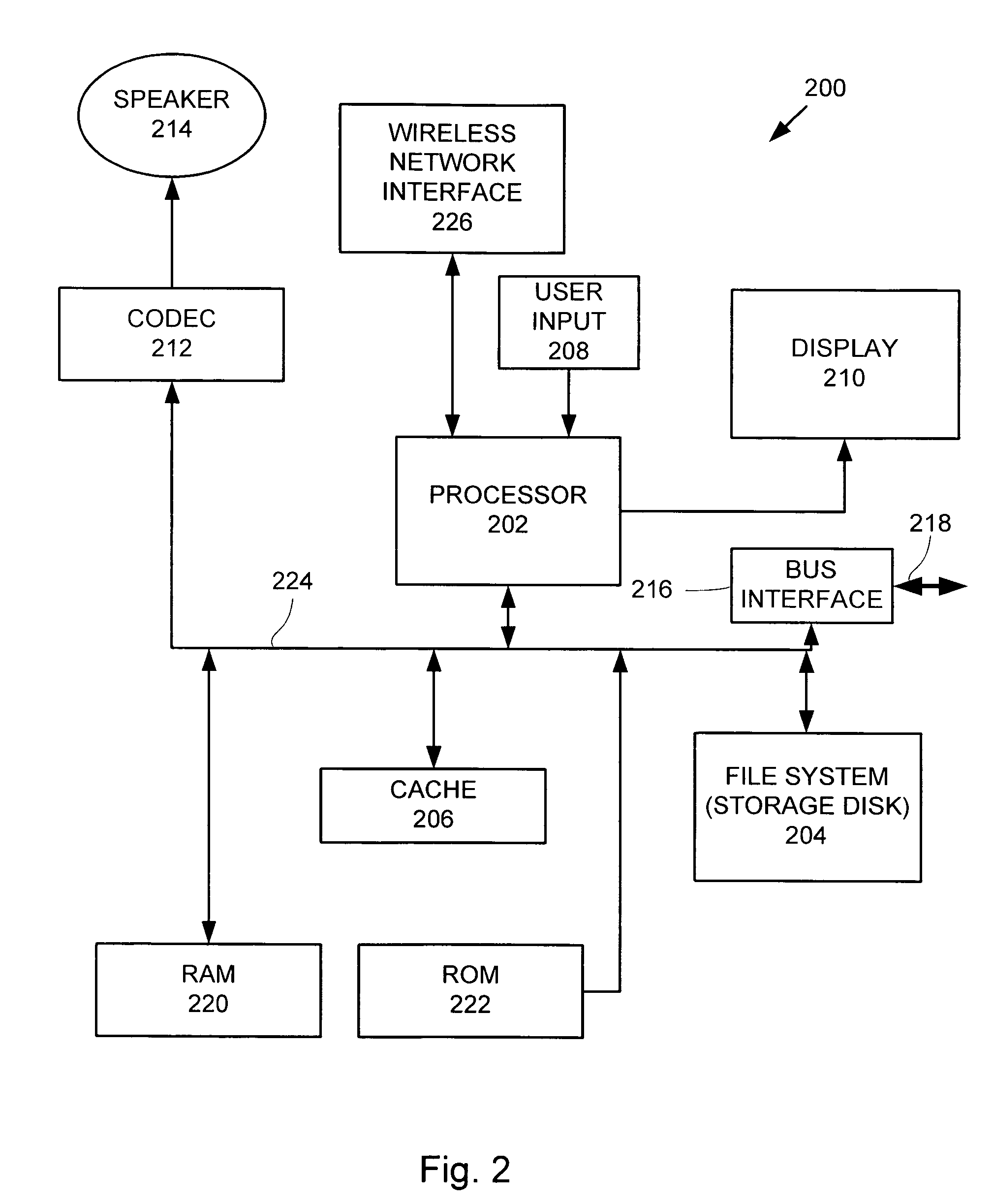
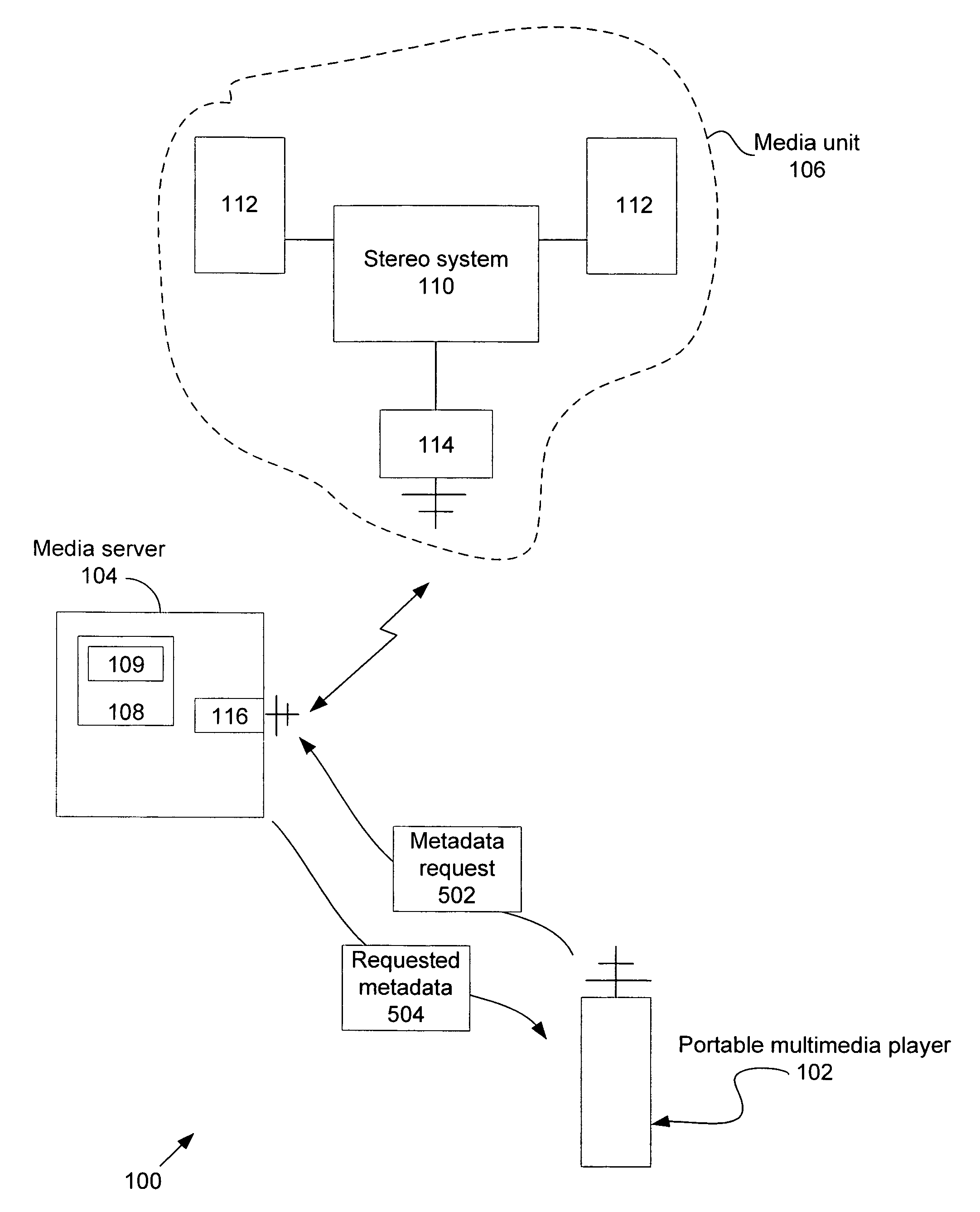
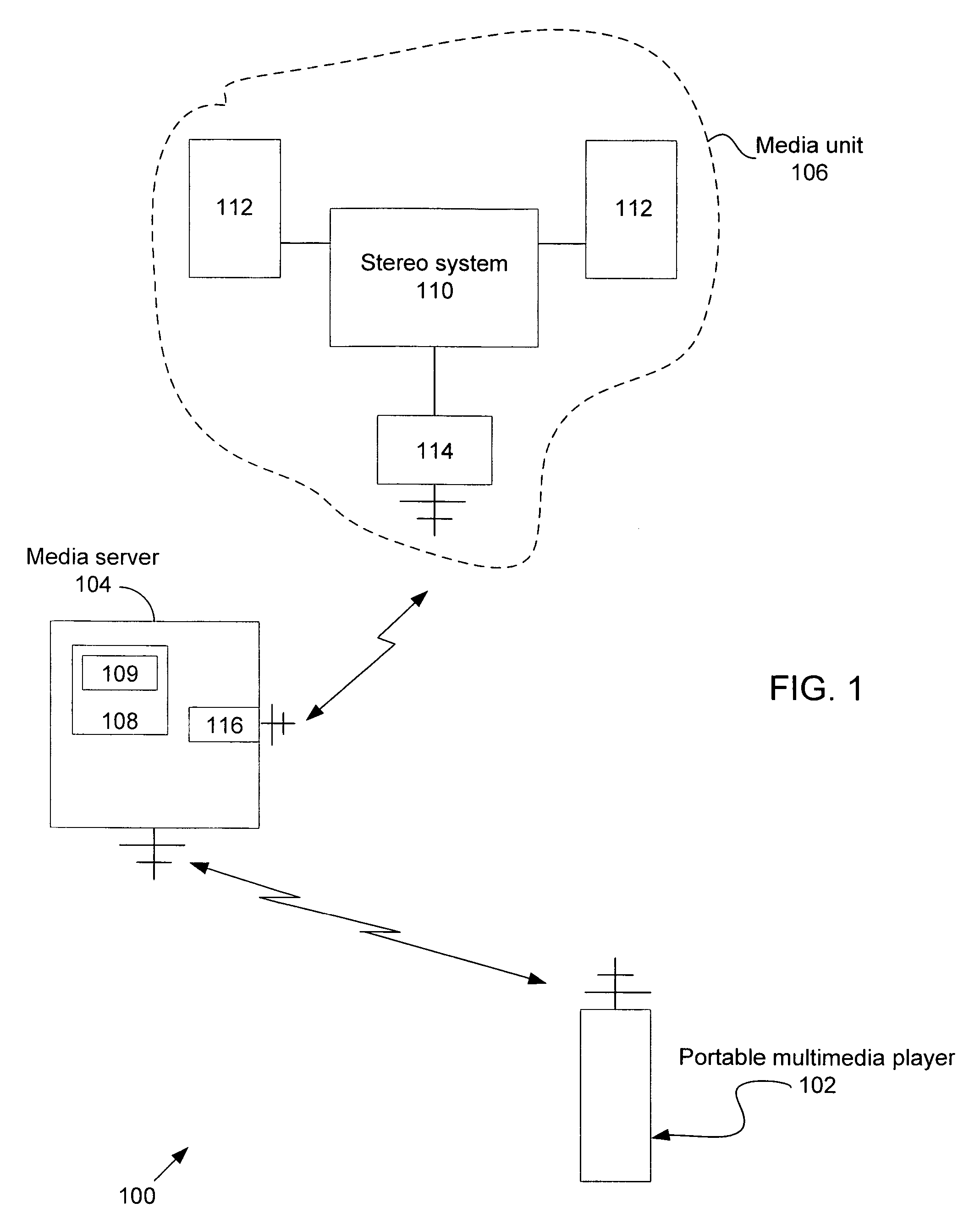
Portable media player as a low power remote control and method thereof
ActiveUS20070169115A1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram loading/initiatingRemote controlMedia server
A portable multimedia player is used to wirelessly access and control a media server that is streaming digital media by way of a wireless interface to a media unit such as a stereo / speakers in the case of streaming digital audio. In one embodiment, the portable multimedia player is wirelessly synchronized to a selected one(s) of a number of digital media files stored on the media server in such a way that digital media file metadata (song title, author, etc.) associated with the selected digital media file(s) only is transferred from the media server to be stored in the portable media player.
Owner:APPLE INC
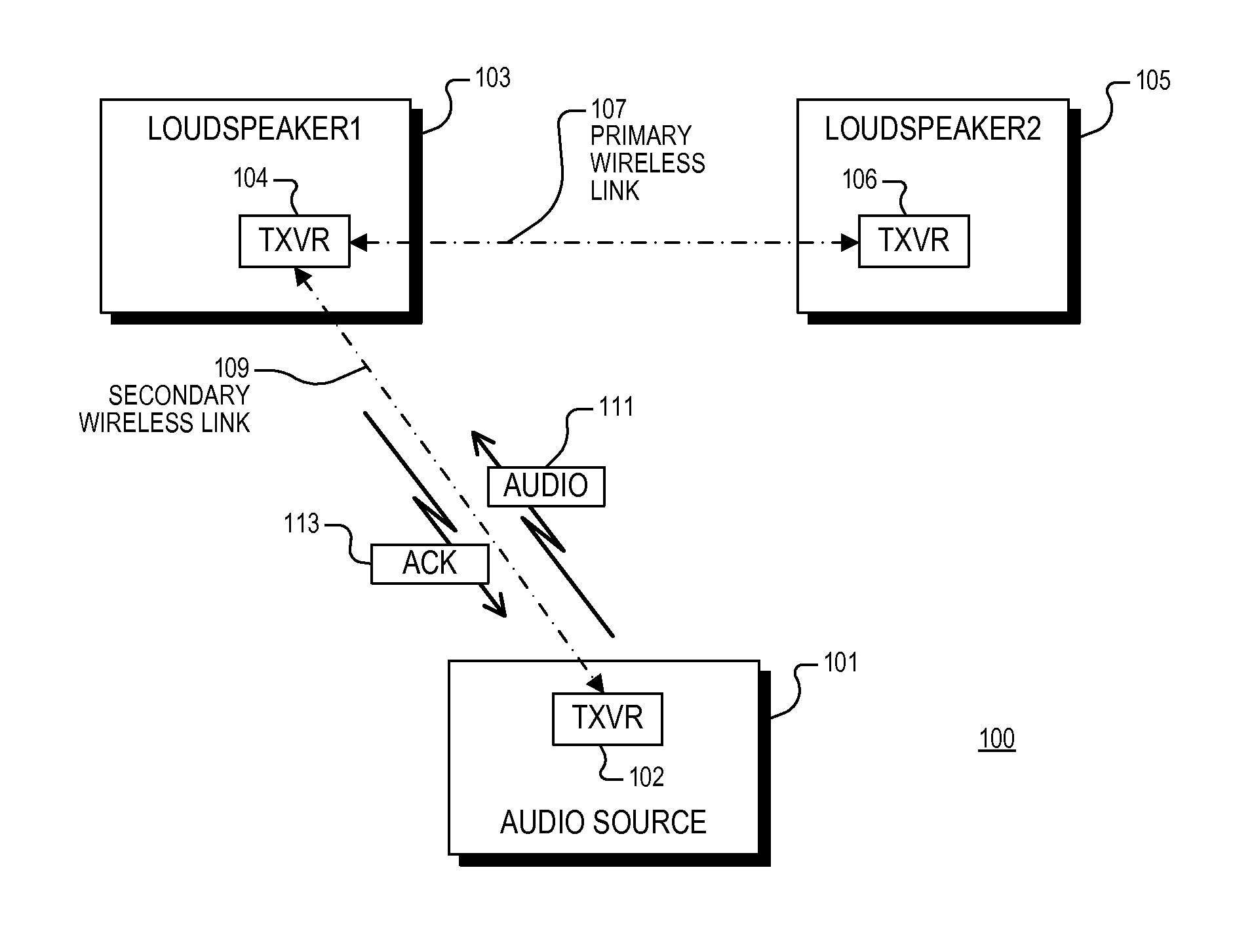
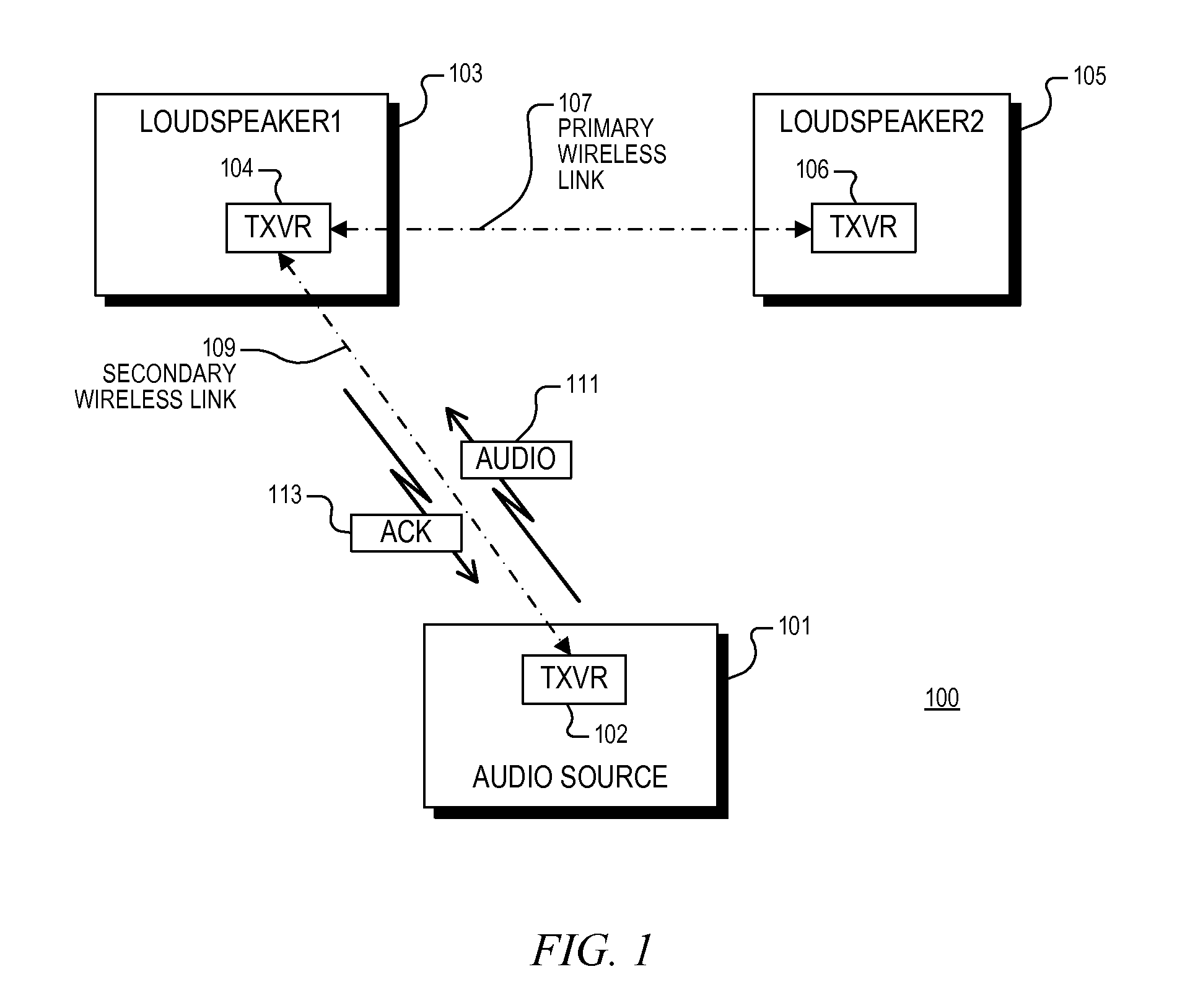
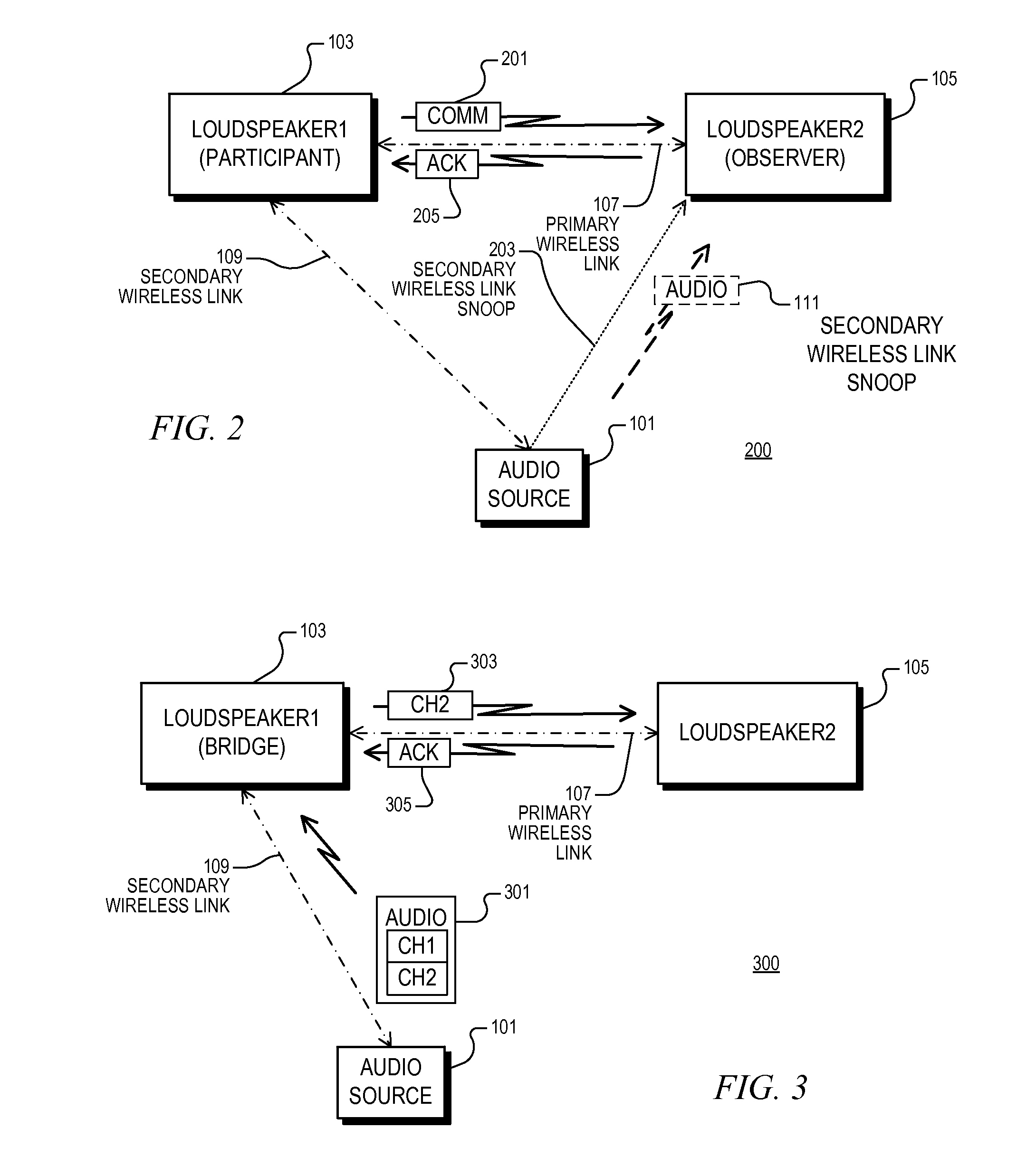
Un-tethered wireless stereo speaker system
ActiveUS20120058727A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelService provisioningTransceiverWireless transceiver
A wireless speaker system configured to receive stereo audio information wirelessly transmitted by an audio source including first and second loudspeakers. The first loudspeaker establishes a bidirectional secondary wireless link with the audio source for receiving and acknowledging receipt of the stereo audio information. The first and second loudspeakers communicate with each other via a primary wireless link, and the first and second loudspeakers are configured to extract first and second audio channels, respectively, from the stereo audio information. A wireless audio system including an audio source and first and second loudspeakers, each having a wireless transceiver. The first and second loudspeakers communicate via a primary wireless link. The audio source communicates audio information to the first loudspeaker via a secondary wireless link which is configured according to a standard wireless protocol. The first loudspeaker is configured to acknowledge successful reception of audio information via the secondary wireless link.
Owner:APPLE INC
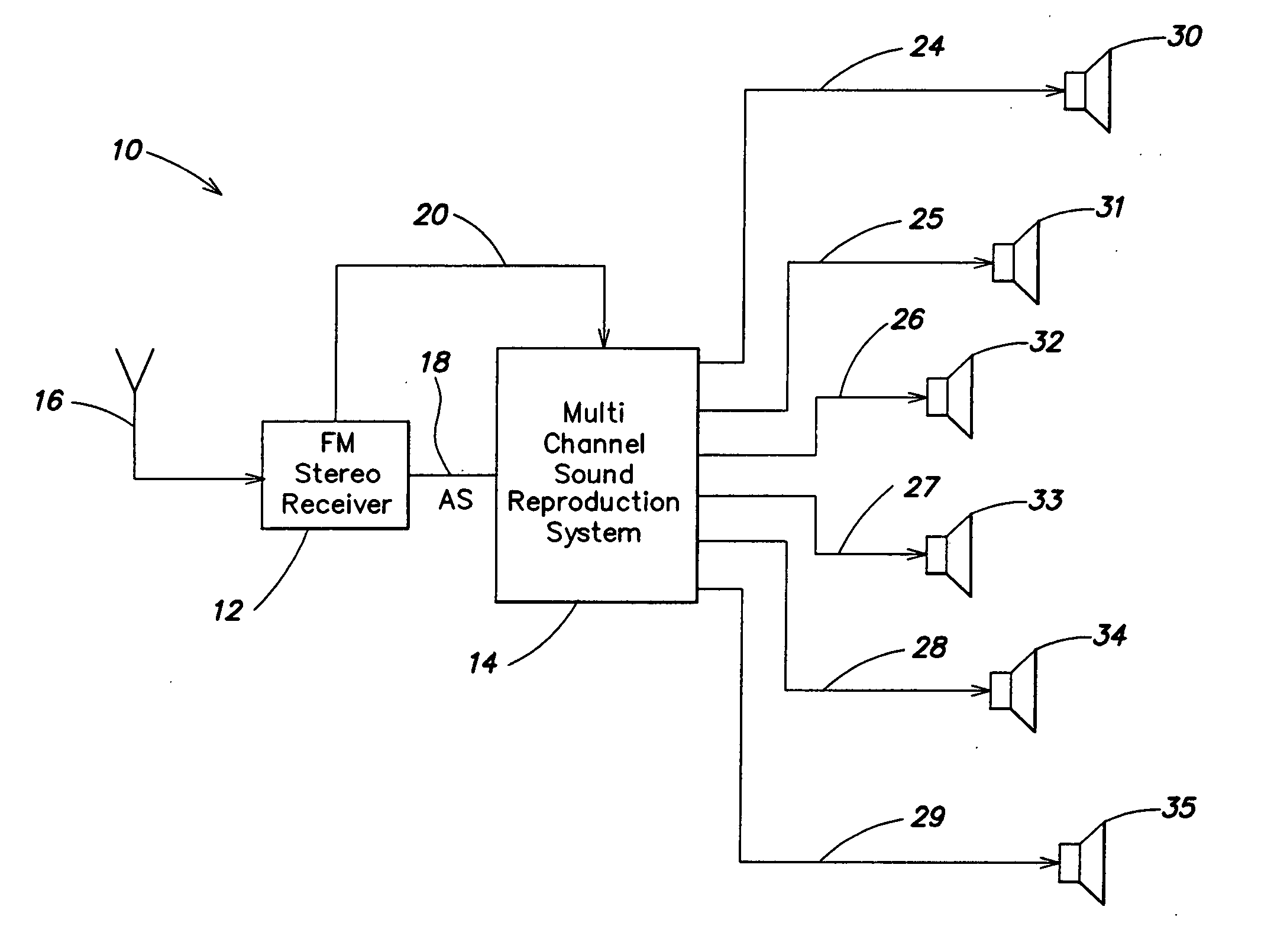
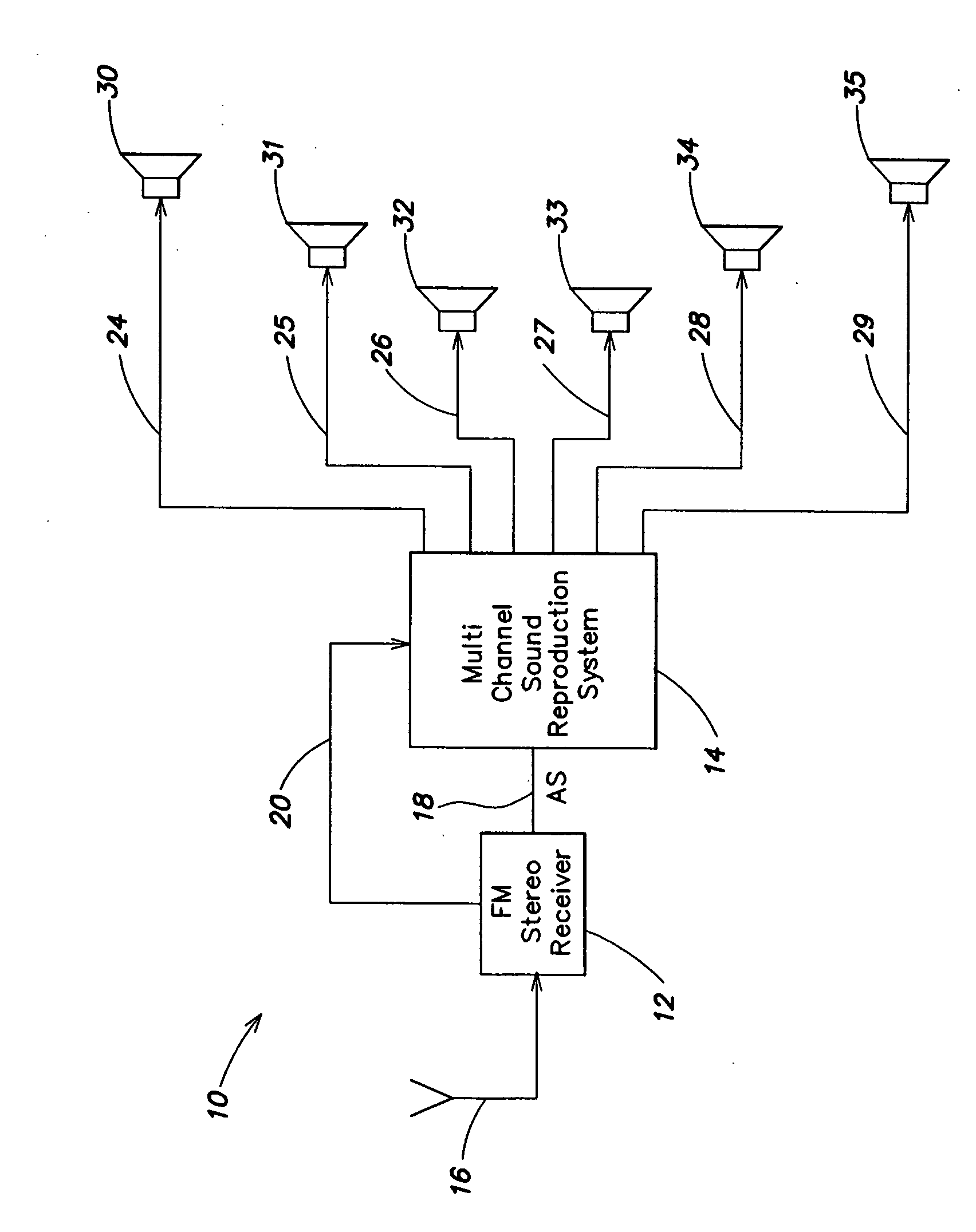
Apparatus for multichannel sound reproduction system
InactiveUS20070003067A1Improve acoustic patternAvoid driftingBroadcast information characterisationBroadcast circuit arrangementsControl signalVocal tract
The sound reproduction of a multichannel sound reproduction system with a plurality of speakers which is connected to the output of an FM stereo receiver is controlled by a control signal derived from the reception quality. Preferably, the control signal from the FM stereo receiver for controlling the stereo and mono components is also employed to control the multichannel sound reproduction system. For example, stereo, pseudo-stereo or mono reproduction are provided in the multichannel sound reproduction system in response to the stereo component within the output signal.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
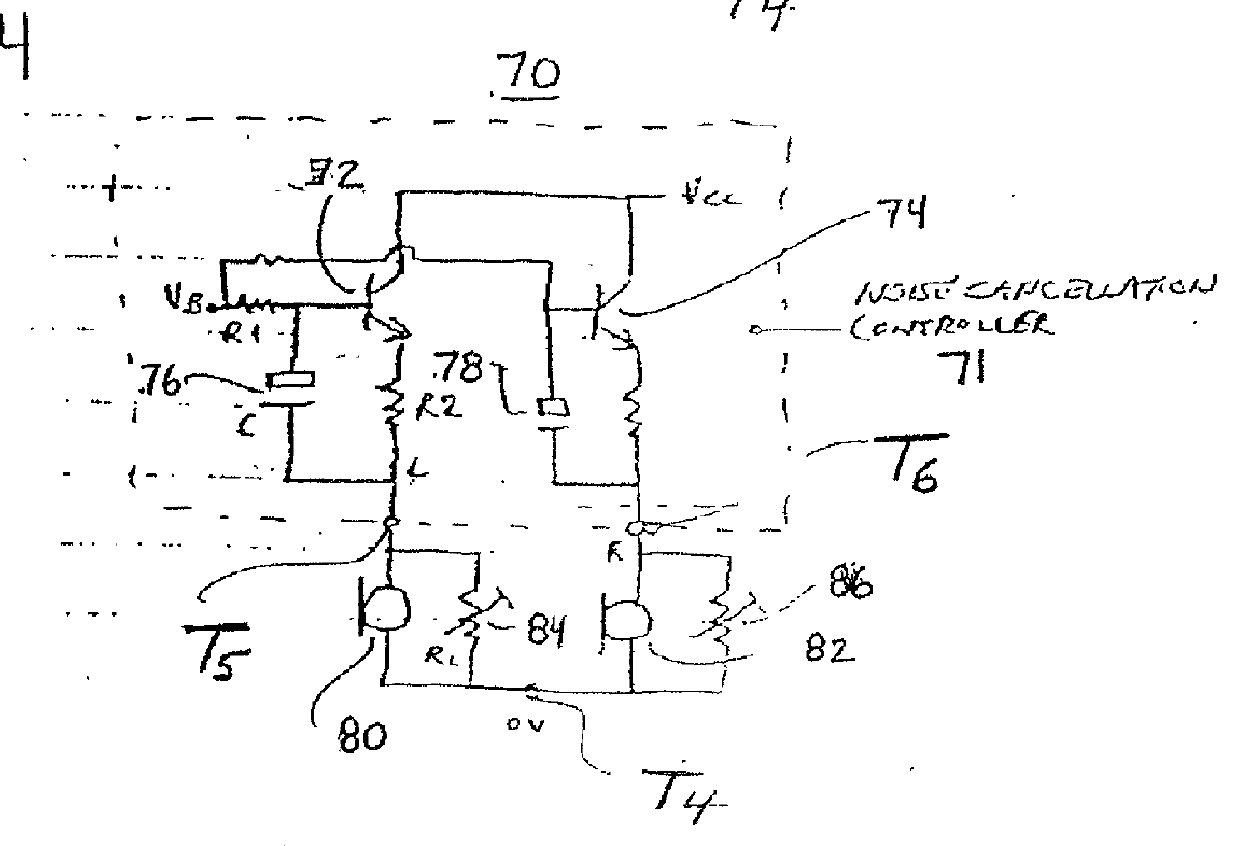
Noise cancellation system for active headsets
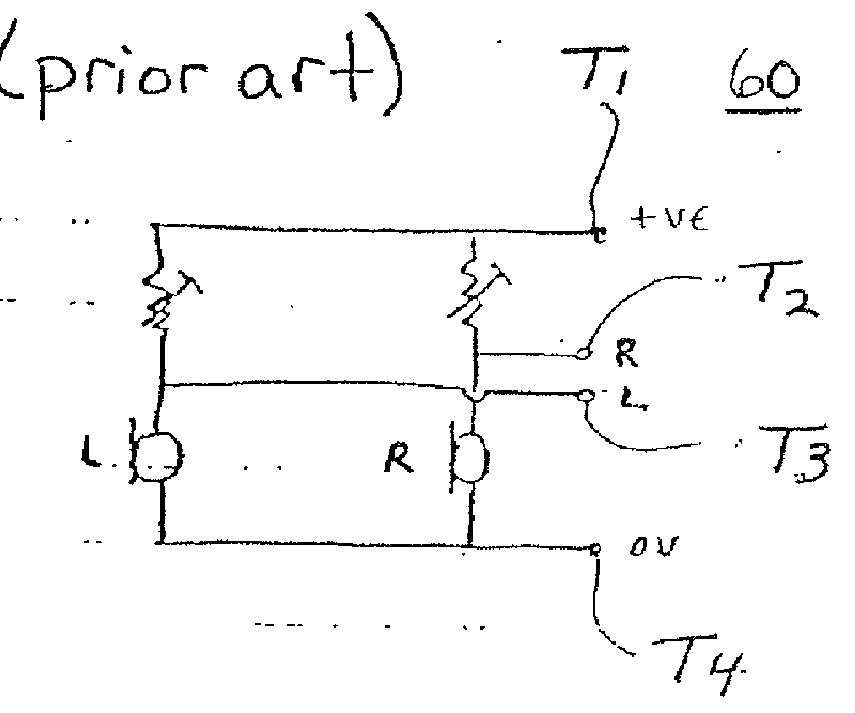
InactiveUS20010053228A1Headphones for stereophonic communicationStereophonic circuit arrangementsElectricityElectrical connection
An active headset system is provided with compatibility with existing socket configurations in a way that minimizes the number of electrical connections. The number of connections between the active headset and the remote noise cancellation circuitry is reduced through the use of a common contact, having a controlled impedance, that serves as an input connection to corresponding terminals of the two earphones of the active headset. According to another aspect of the present invention, the transients associated with plugging in or unplugging stereo jack plugs or up to a seven pin connector into an active headset may be overcome by a transient detector in the noise cancellation circuitry. Yet another aspect of the present invention concerns the powering of the noise cancellation circuitry whether the noise cancellation circuitry is placed inside the active headset or at least partially internal to a remote external device.
Owner:NCT GROUP
Entertainment device configured for interactive detection and security vigilant monitoring in communication with a control server
InactiveUS20070256105A1Facilitate transmission and receptionClosed circuit television systemsBurglar alarmSensor arrayEngineering
Home security detectors configured with the control components of the home comprising interactive detectors enhanced to support location-awareness and home occupant-awareness and functionality. The system includes at least one motion sensor configured with communication devices operatively arranged to transmit information about any motion of occupants in the various sections of the home as part of the information about the occupancy of the home during an emergency. At least one sensor is provided in various rooms of a home each sensing a state of the home. A central communication device is coupled, wired or wirelessly, directly or indirectly, to each home sensor configured to transmit the state of the home. The number of occupants in the home are determined by at least one body heat sensor and at least one heartbeat sensor each configured with the interactive detectors to detect the presence of emergency and home occupants and to know the present situations such as their heartbeats, such that the number of occupants and their locations are determinable from the number of detected body heat and their security and safety conditions are determinable by their heartbeats. The detection method includes the steps of sensing a state of the home and transmitting the state of the home to at least a server. Images of the home are captured by at least a camera means configured with at least a MOS and / or CMOS based active sensor array for producing real-time images and stored in the server for wireless retrieval. The images ideally include at least an intruder of the home. The server is configured with a central processor for enabling controlling security vigilance monitoring and for enabling rapid distribution of detection data, voice, and other detection signals within the monitoring environment. The system establishes a network which includes configuring home audio / visual devices, media destination means such as televisions, monitors, PDAs, notepads, notebooks, MP3, wireless stereo, cell phones etc for the detection means. The control server supports video / audio servings, telephony, messaging, file sharing, internetworking, and security monitoring and allows home occupants to access and control the home network environment from any location within a controlled residential, commercial / industrial and / or non-residential, commercial / industrial environment with at least a computer means such as a cell phone.
Owner:COSTA VERDI SERIES 63 OF ALLIED SECURITY TRUST I
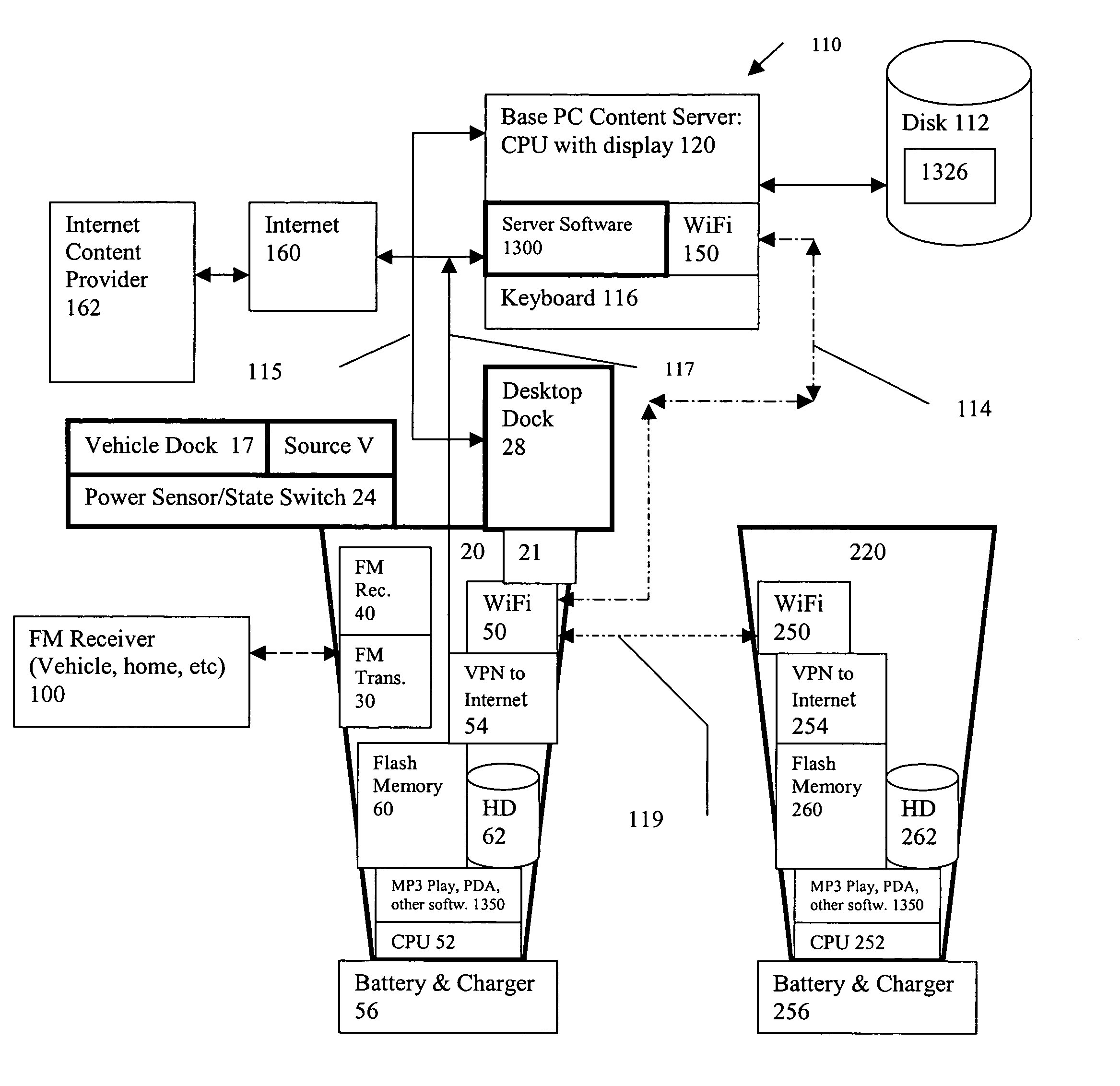
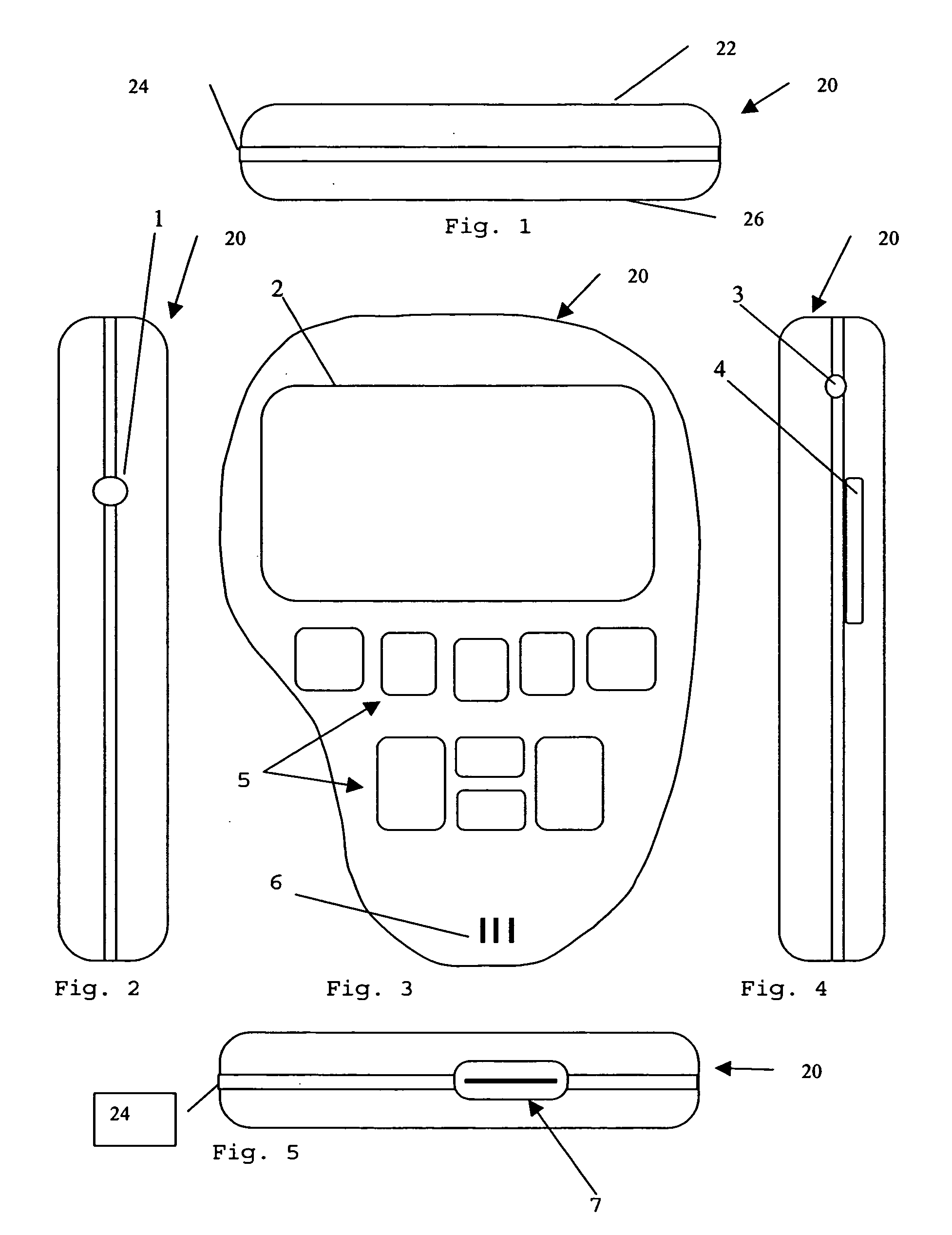
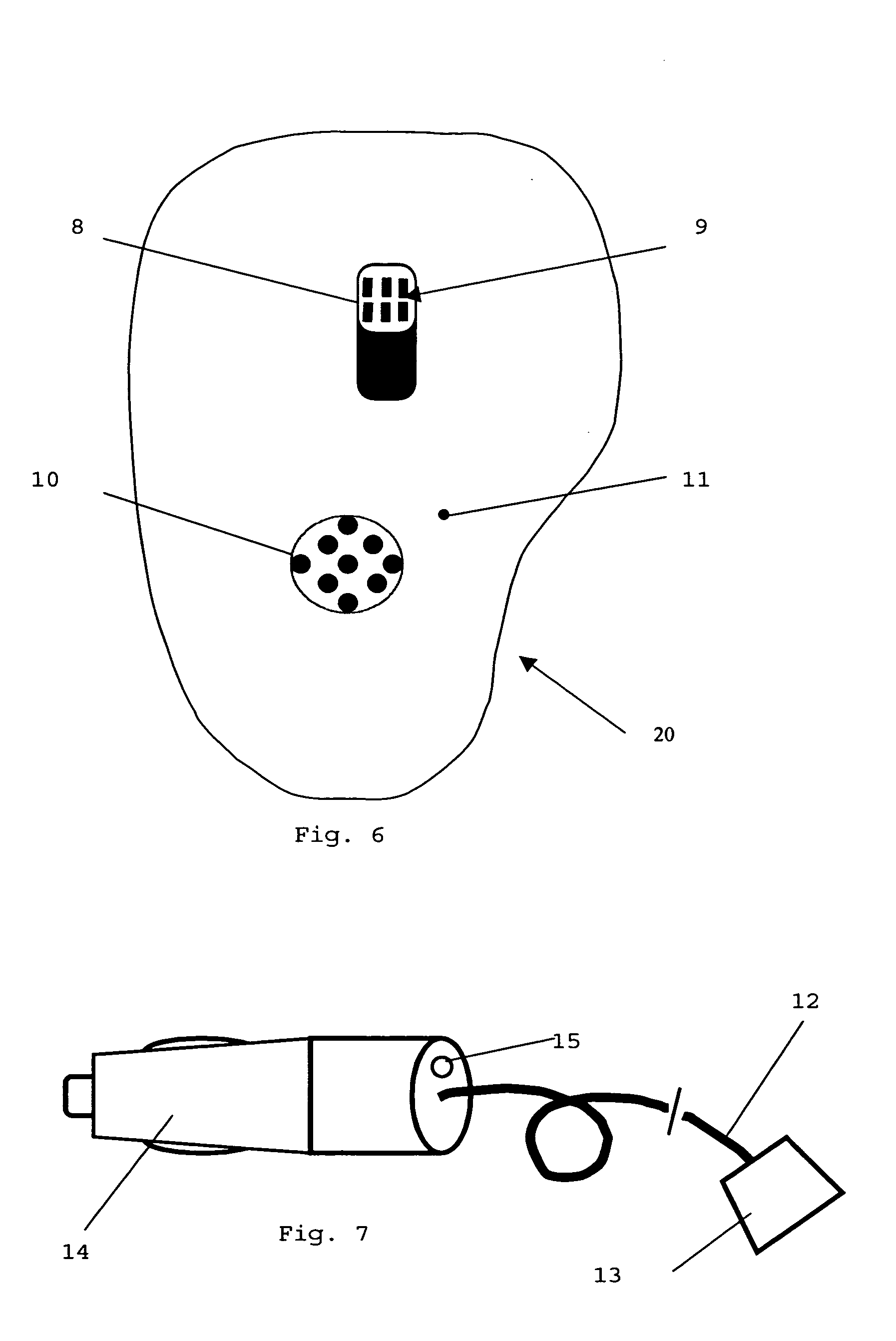
Handheld portable wireless digital content player
InactiveUS20040117442A1Drawback can be obviatedReduced strengthElectrophonic musical instrumentsRecord information storageComputer hardwareIn vehicle
A portable handheld digital content player has an integrated wireless interface, an integrated FM transmitter and an integrated auto on and auto off feature for ease of use in vehicles. The player and associated software on a base content server provide automated broadband wireless content downloads to the player while in a vehicle and transfer of audio to the vehicle stereo via FM band transmission without the use of an accessory. The player integrates an FM scan function to search for a suitable frequency for transmitting within the FM band. The player integrates some PDA-like functionality including personal contact information, appointment calendar, user schedule, email in addition to others.
Owner:SONIQCAST
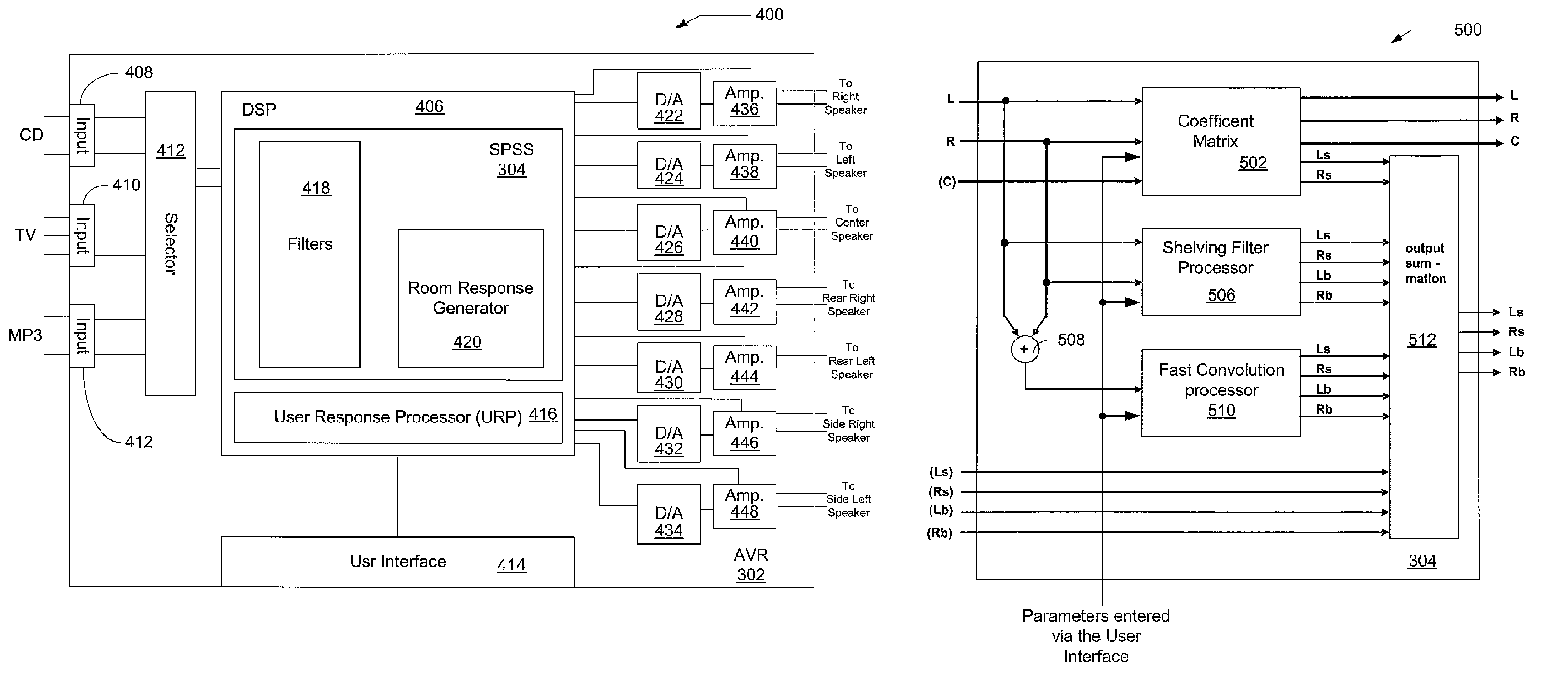
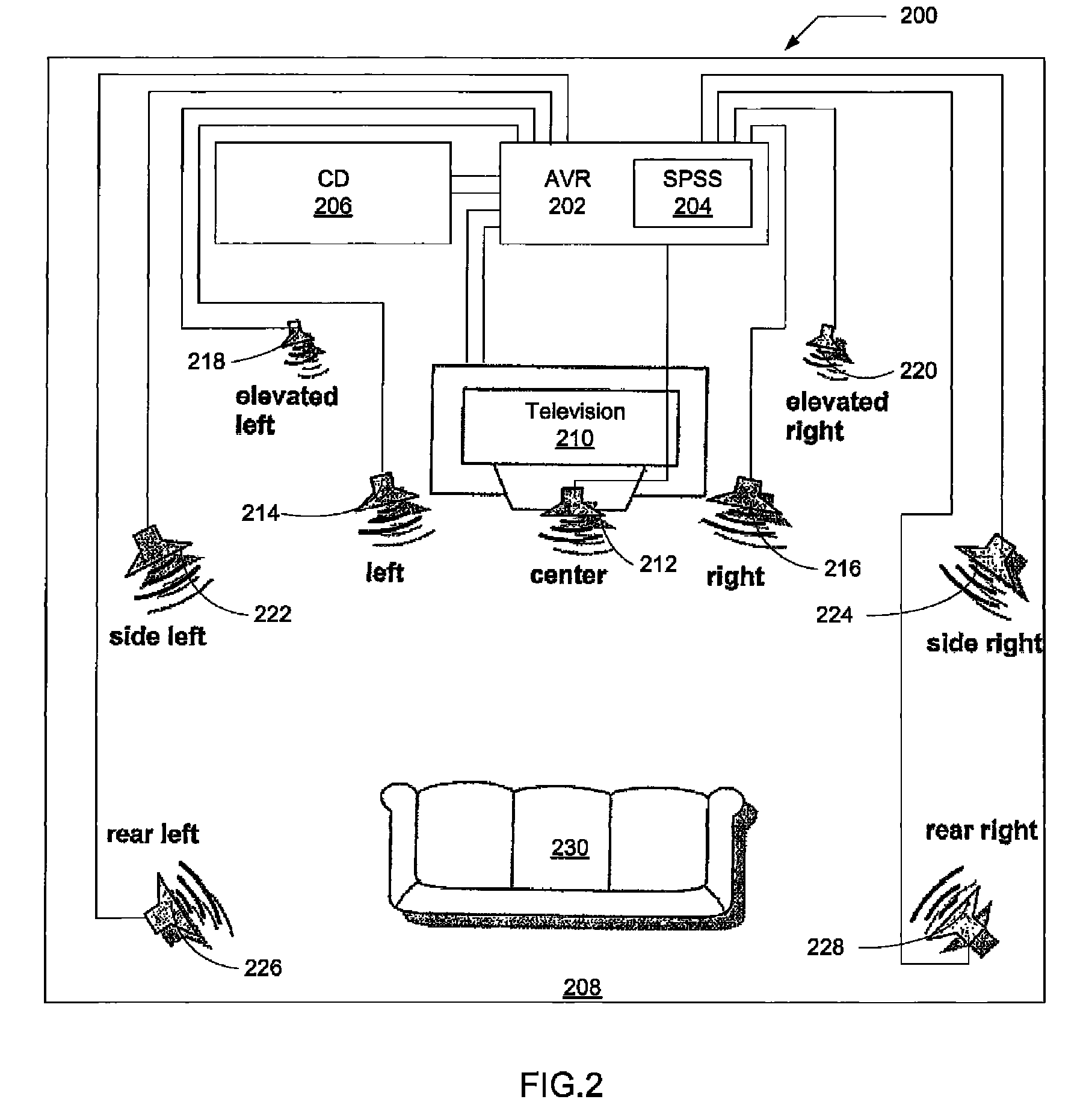
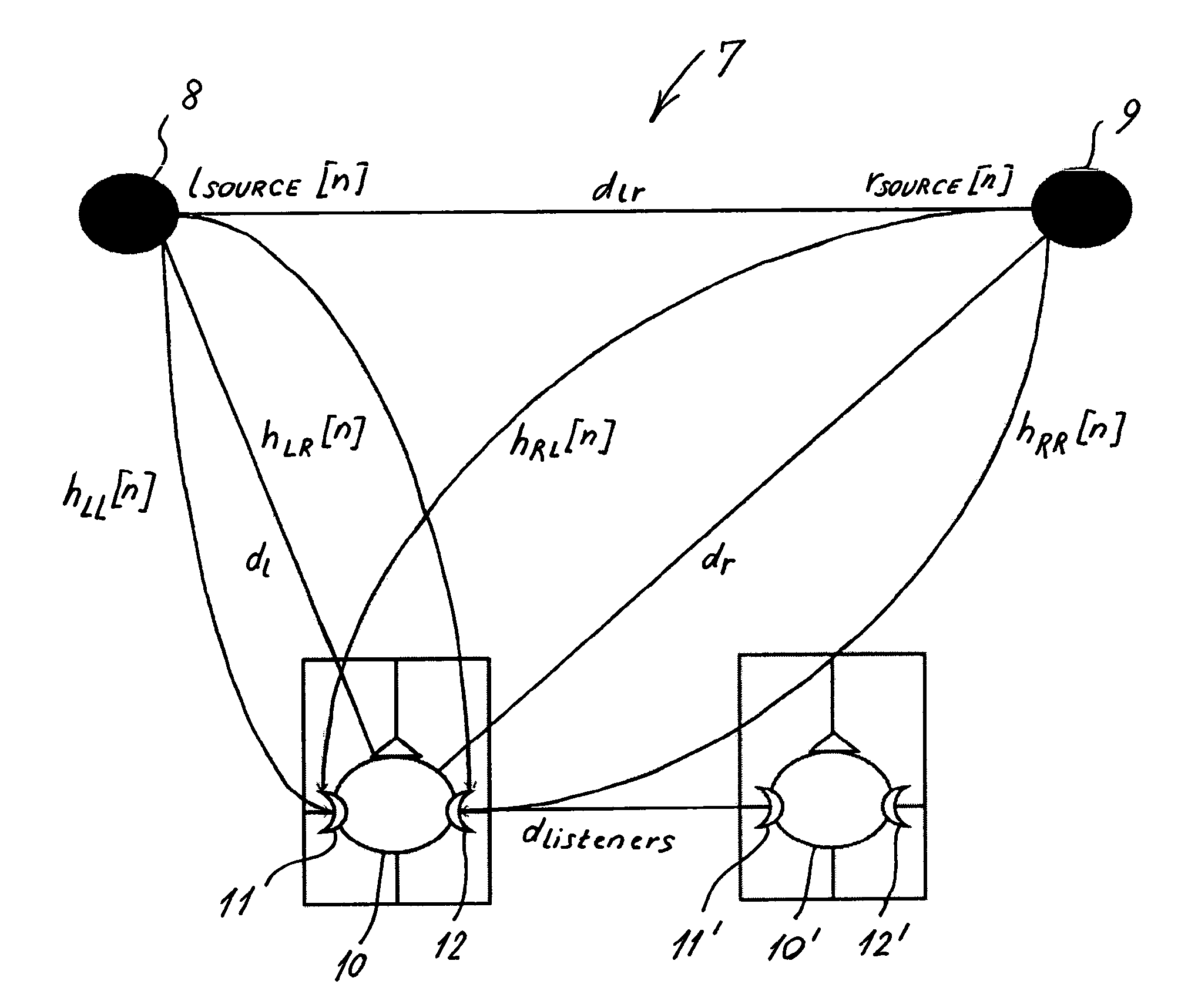
Spatial processing stereo system
A spatial processing stereo system (“SPSS”) that receives audio signals and a limited number of user input parameters associated with the spatial attributes of a room, such as “room size”, “stage distance”, and “stage width”. The input parameters are used to define a listening room and generate coefficients, room impulse responses, and scaling factors that are used generate additional surround signals.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
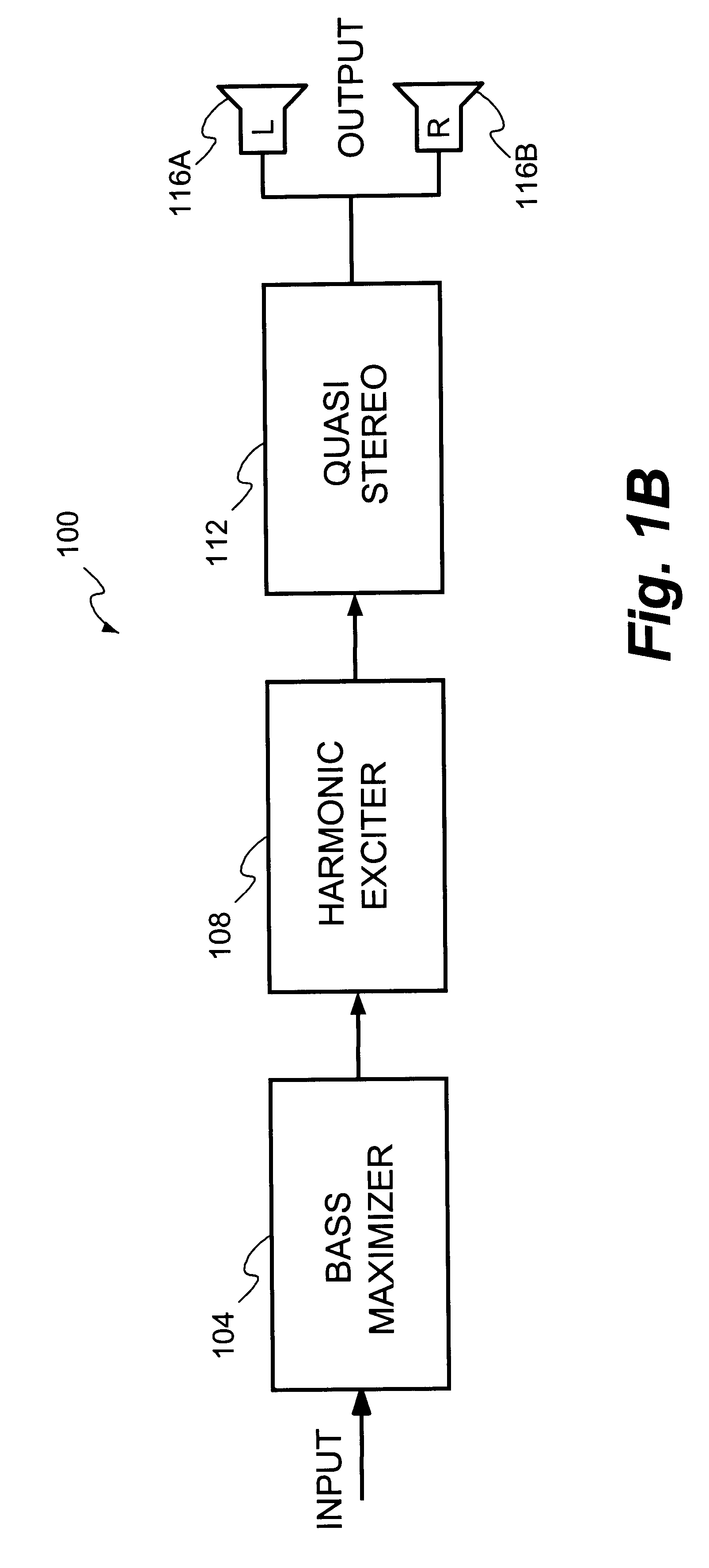
Method and system for enhancing audio signals
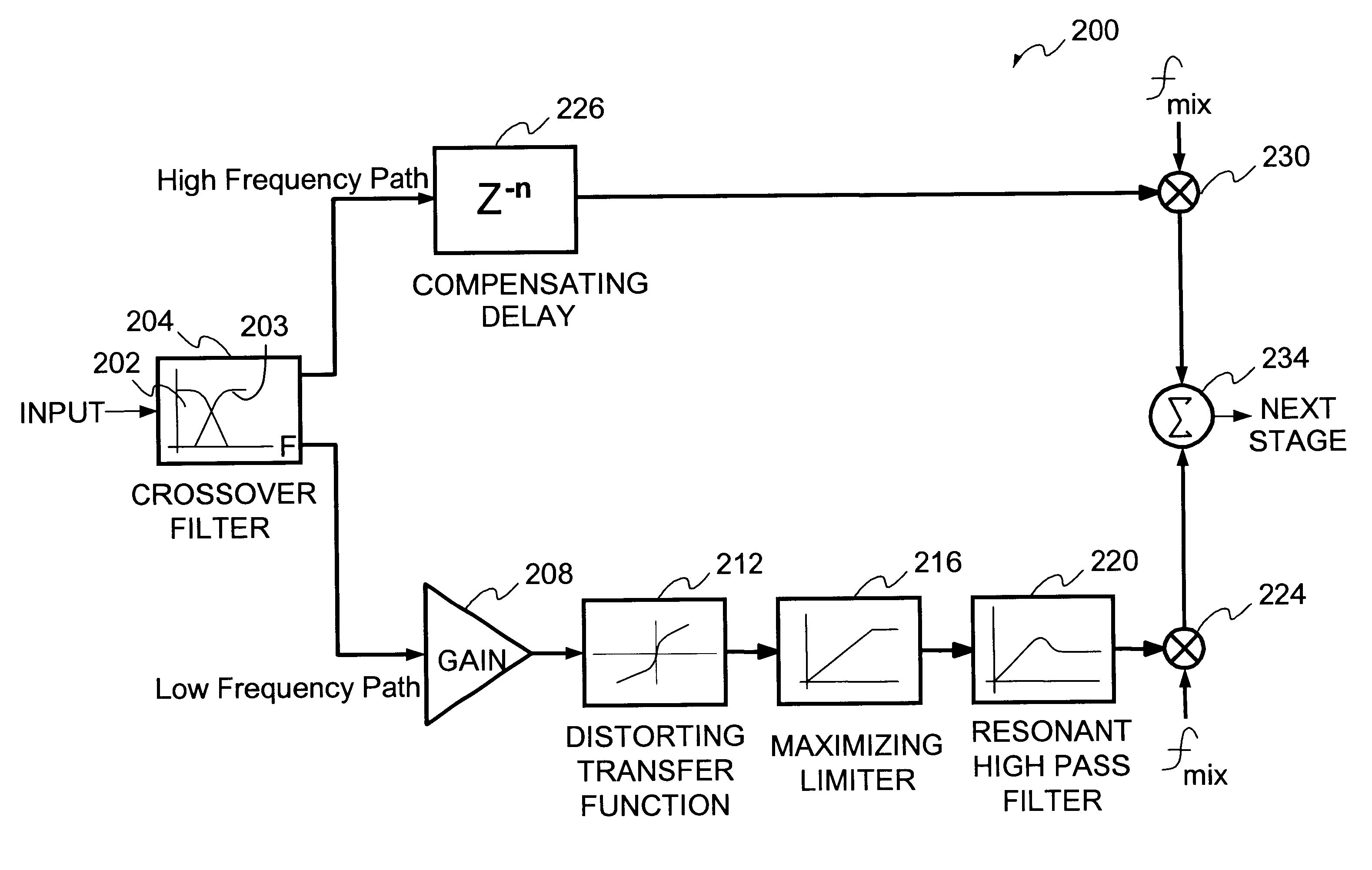
InactiveUS6606388B1Facilitates separate modificationFacilitates enhancementElectrophonic musical instrumentsGain controlHarmonicComputer module
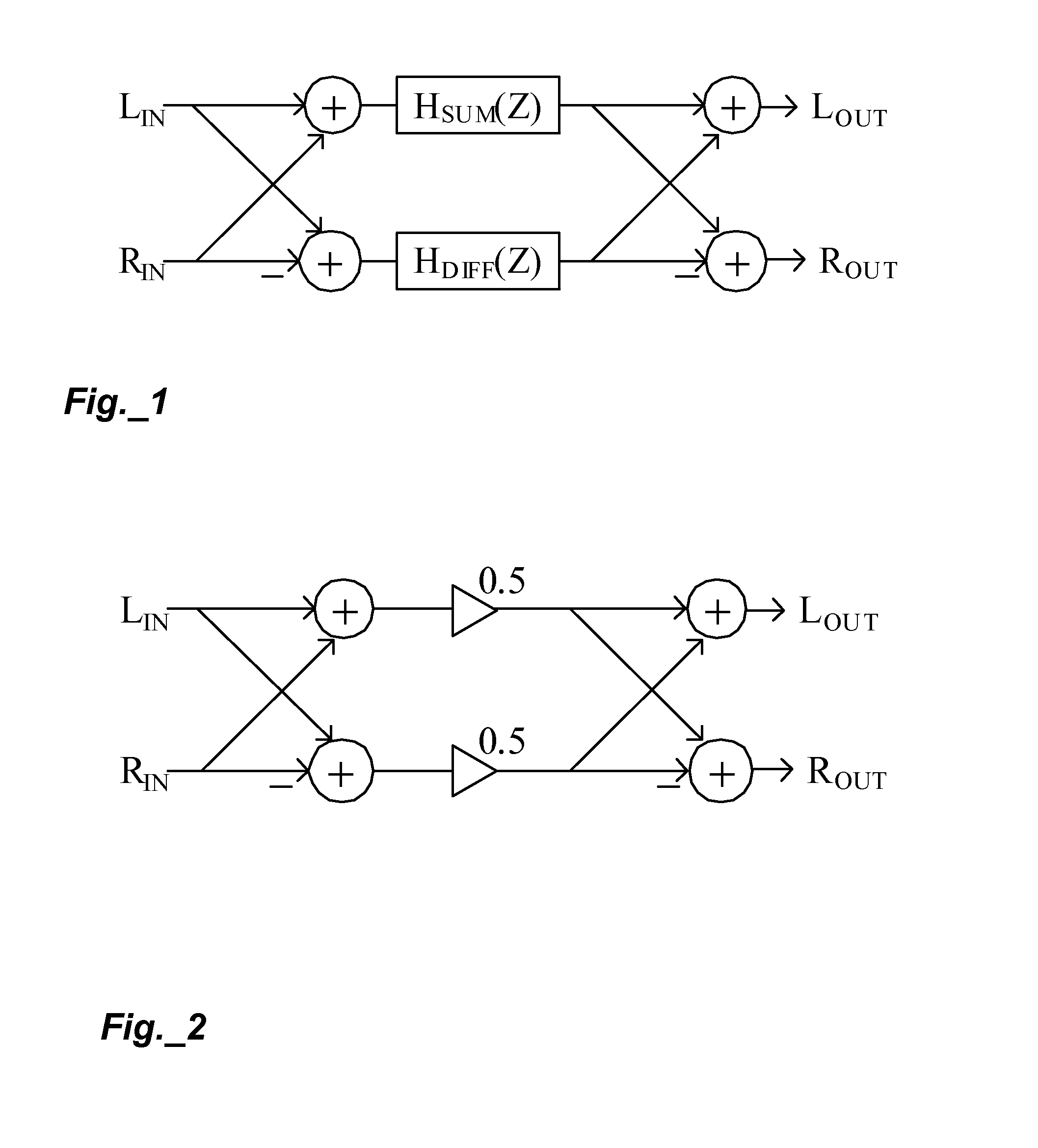
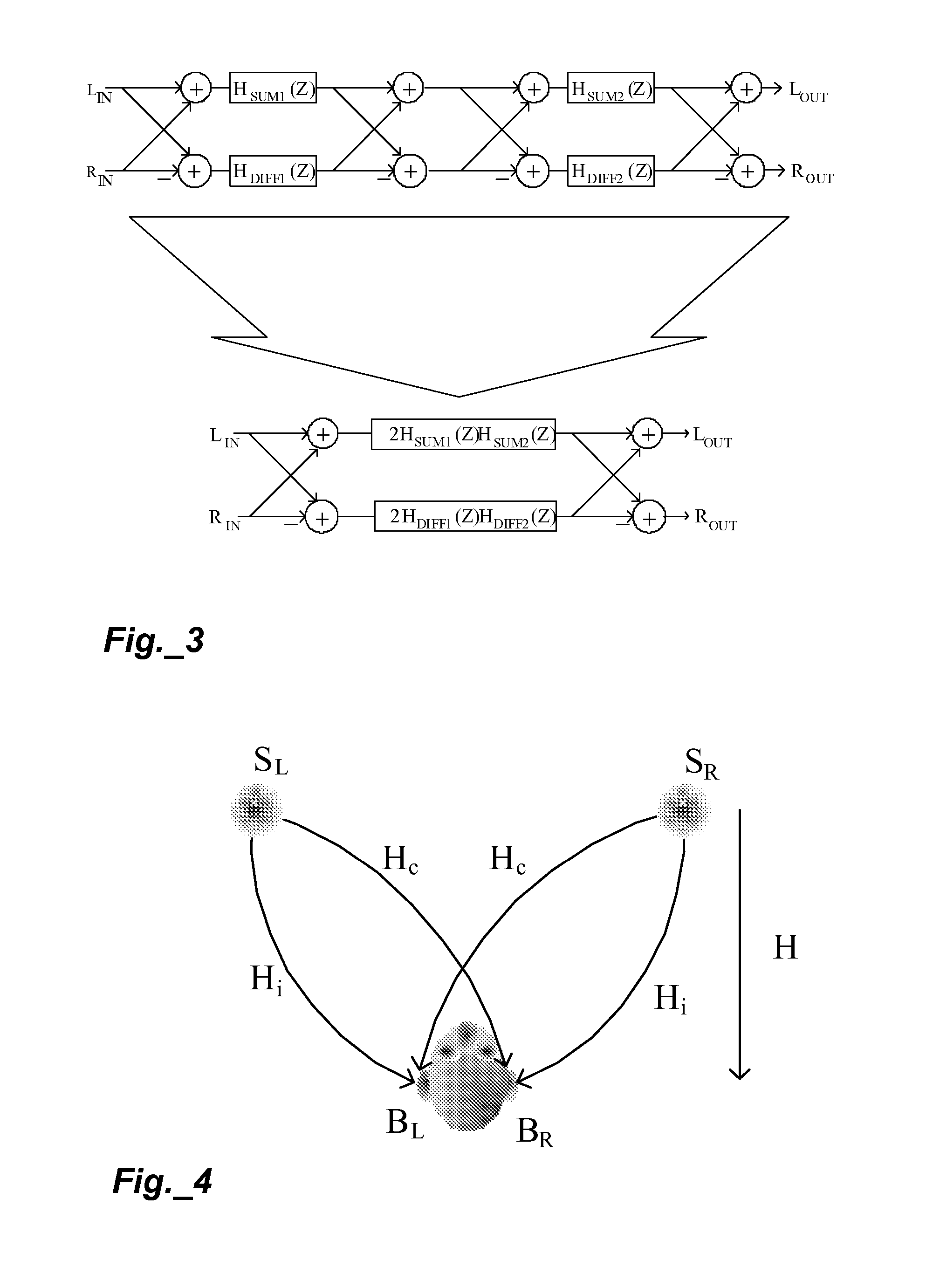
A technique for enhancing audio signals generated from compressed digital audio files is described. The technique uses a Bass Maximizer module, a Harmonic Exciter module and a Quasi Stereo module. The Bass Exciter module enhances the intensity, depth and punch of the bass audio content by creating harmonic sequences from low frequency components contained in the original input signal. The Harmonic Exciter module adds to the treble audio content of the original input signal by generating harmonic series from the high frequency components contained in the input signal. The Quasi Stereo Module creates a stereo image of the enhanced input signal by adding and subtracting delayed and filtered versions of the enhanced input signal with itself to create left and right channeled stereo-like outputs. The technique provides a useful tool to regenerate from an audio signal more pleasant and joyful sounds.
Owner:ARBORETUM SYST
Systems and methods of generating control signals
Separating a source in a stereo signal having a left channel and a right channel includes transforming the signal into a short-time transform domain; computing a short-time similarity measure between the left channel and the right channel; classifying portions of the signals having similar panning coefficients according to the short-time similarity measure; segregating a selected one of the classified portions of the signals corresponding to the source; and reconstructing the source from the selected portions of the signals.
Owner:SIGNIFY NORTH AMERICA CORP
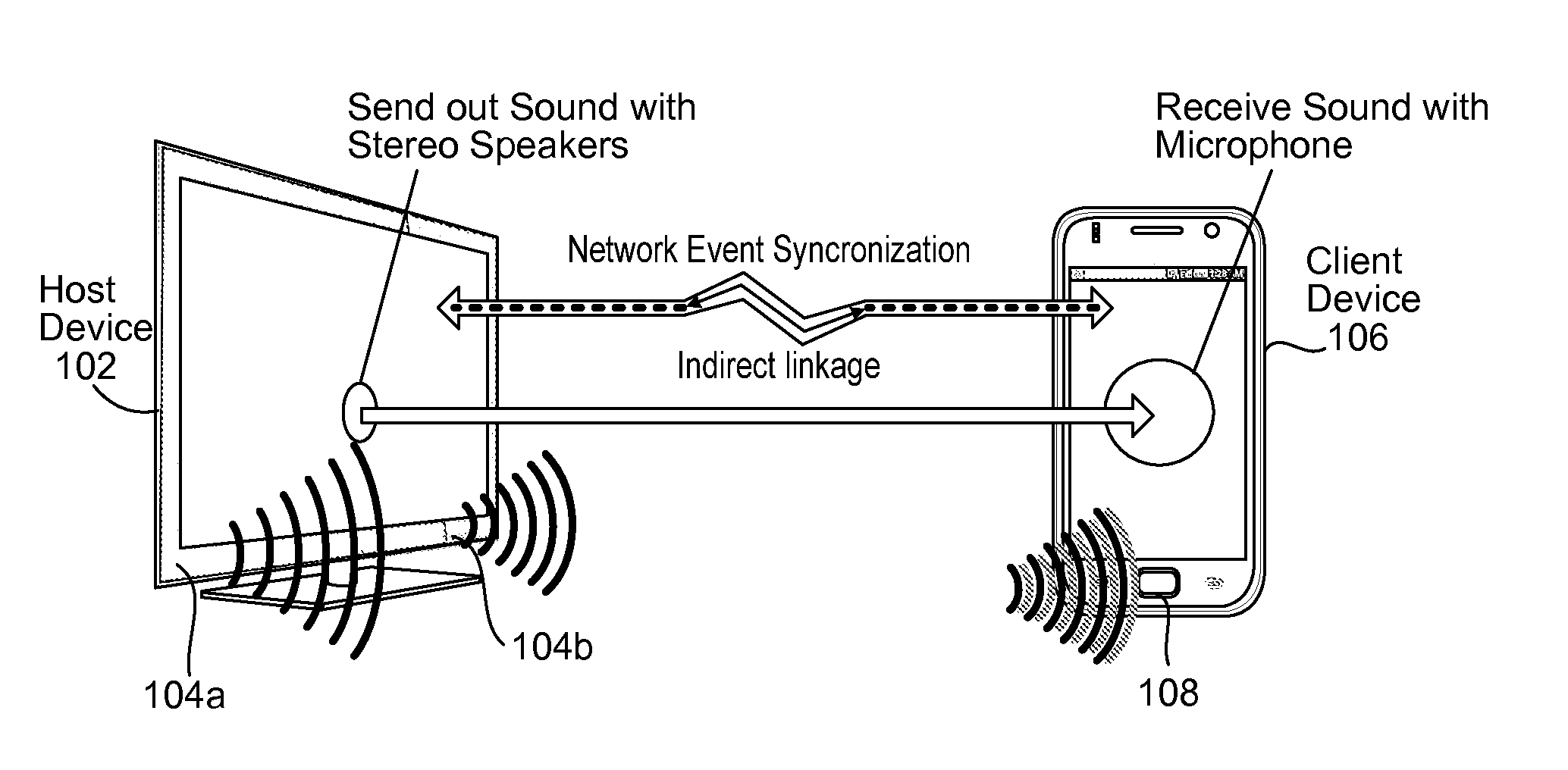
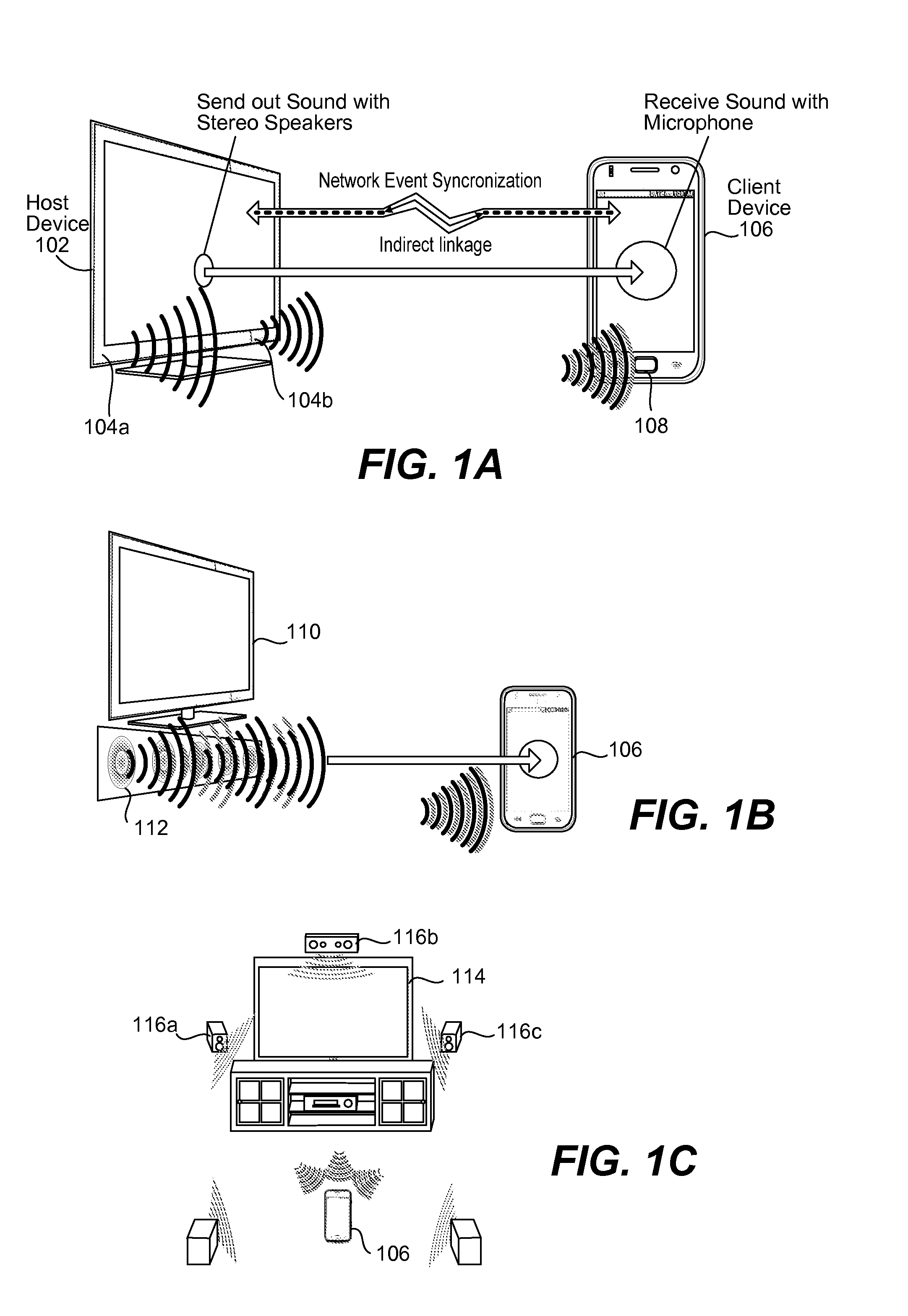
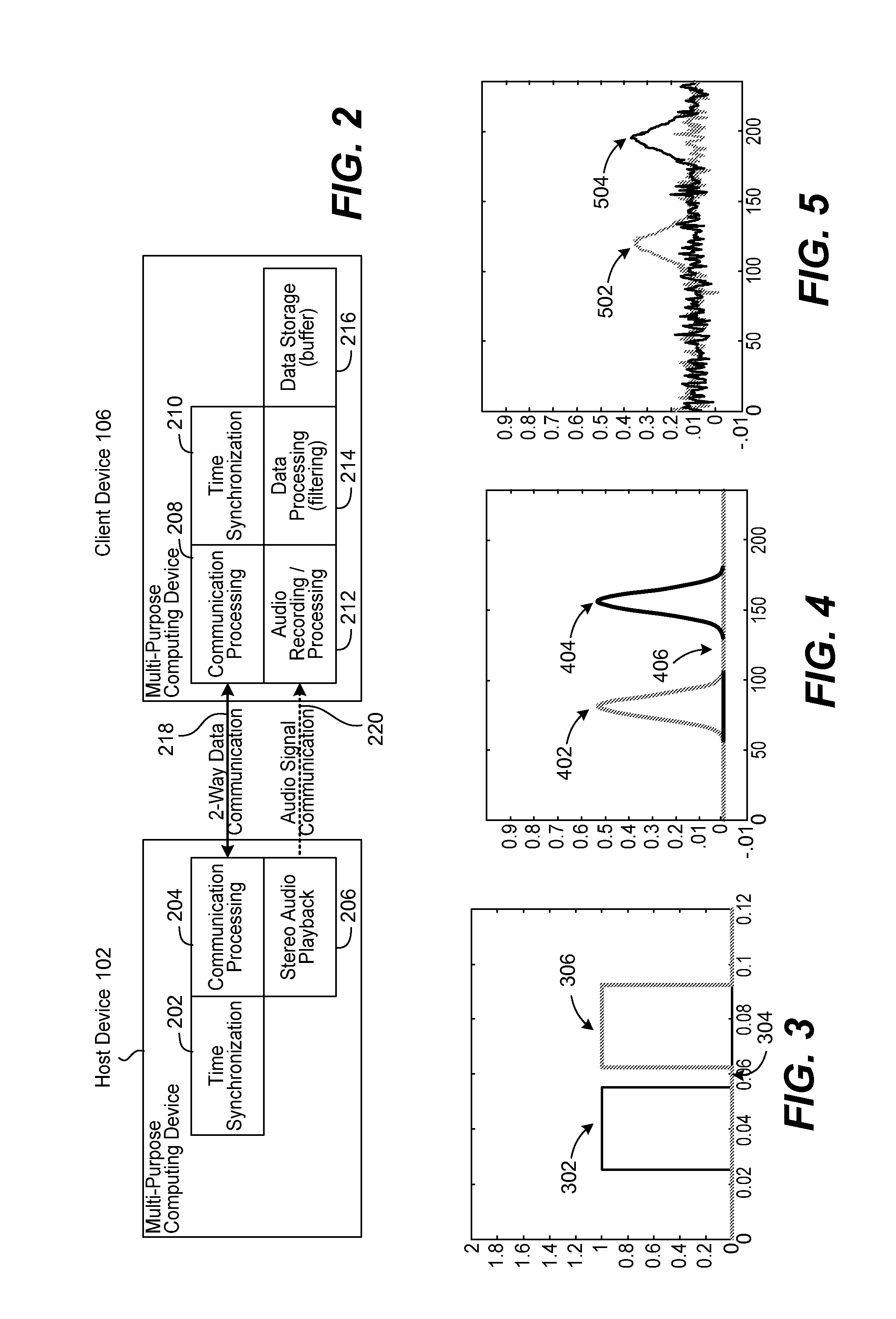
Position determination of devices using stereo audio
InactiveUS20120127831A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationHand held devicesLoudspeaker
Methods and systems for determining and utilizing spatial correlative information relating to two or more devices to determine device positioning are described. Using audio signals emitted from stereo speakers, for example, associated with a first device and a microphone associated with the second device, the distance and angle between the two devices and as their relative positions can be determined. No other sensors or specialized accessories are needed on either device to calculate the distance and angles. The devices need only be loaded with the appropriate software which, when executed, is able to carry out steps of the present invention. The usefulness of one or both of the devices may be enhanced by knowing the distance and angle data between the devices. For example, one device may be a TV having stereo speakers and the other device may be a handheld device, such as a smartphone, having a microphone.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
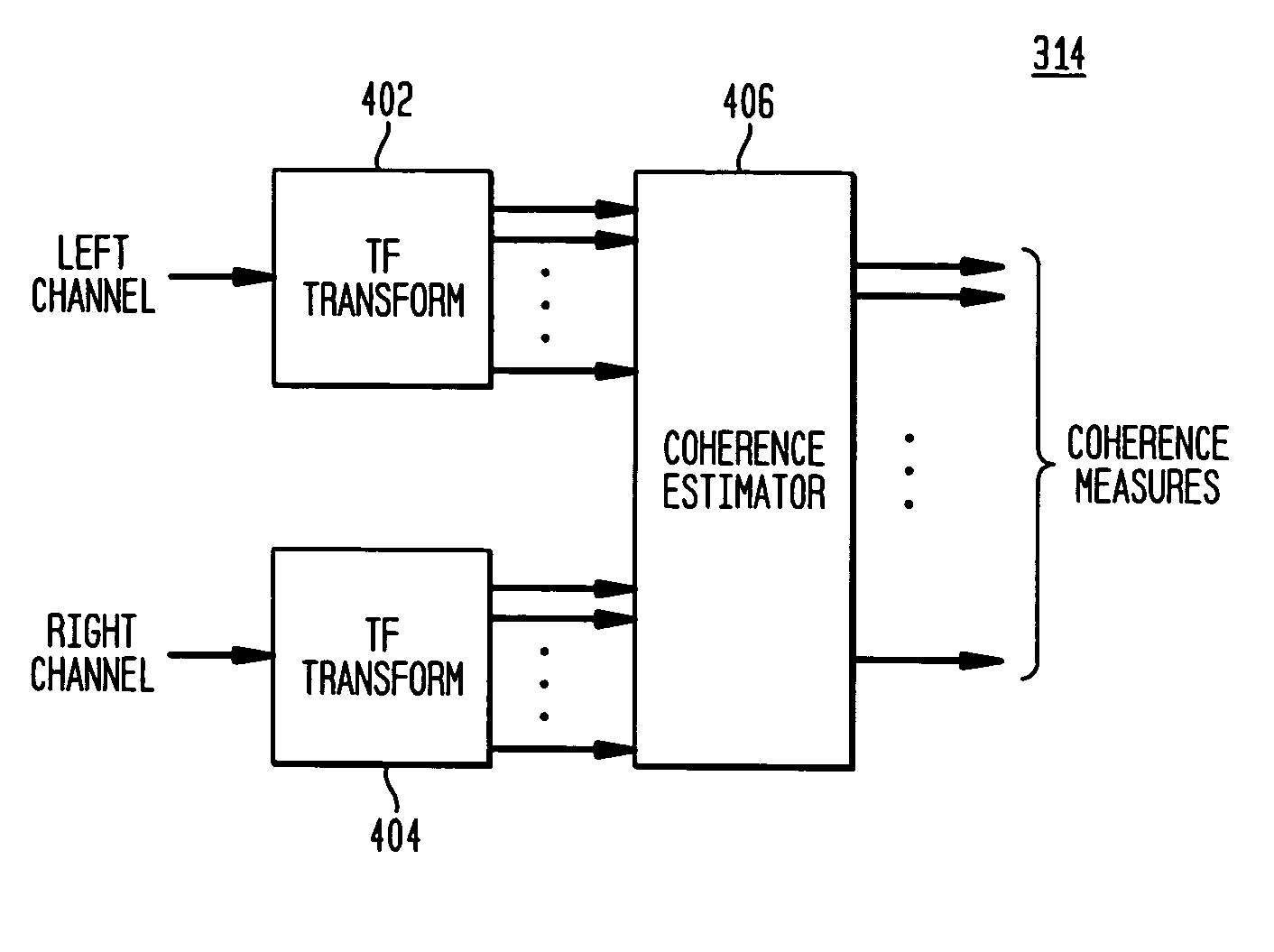
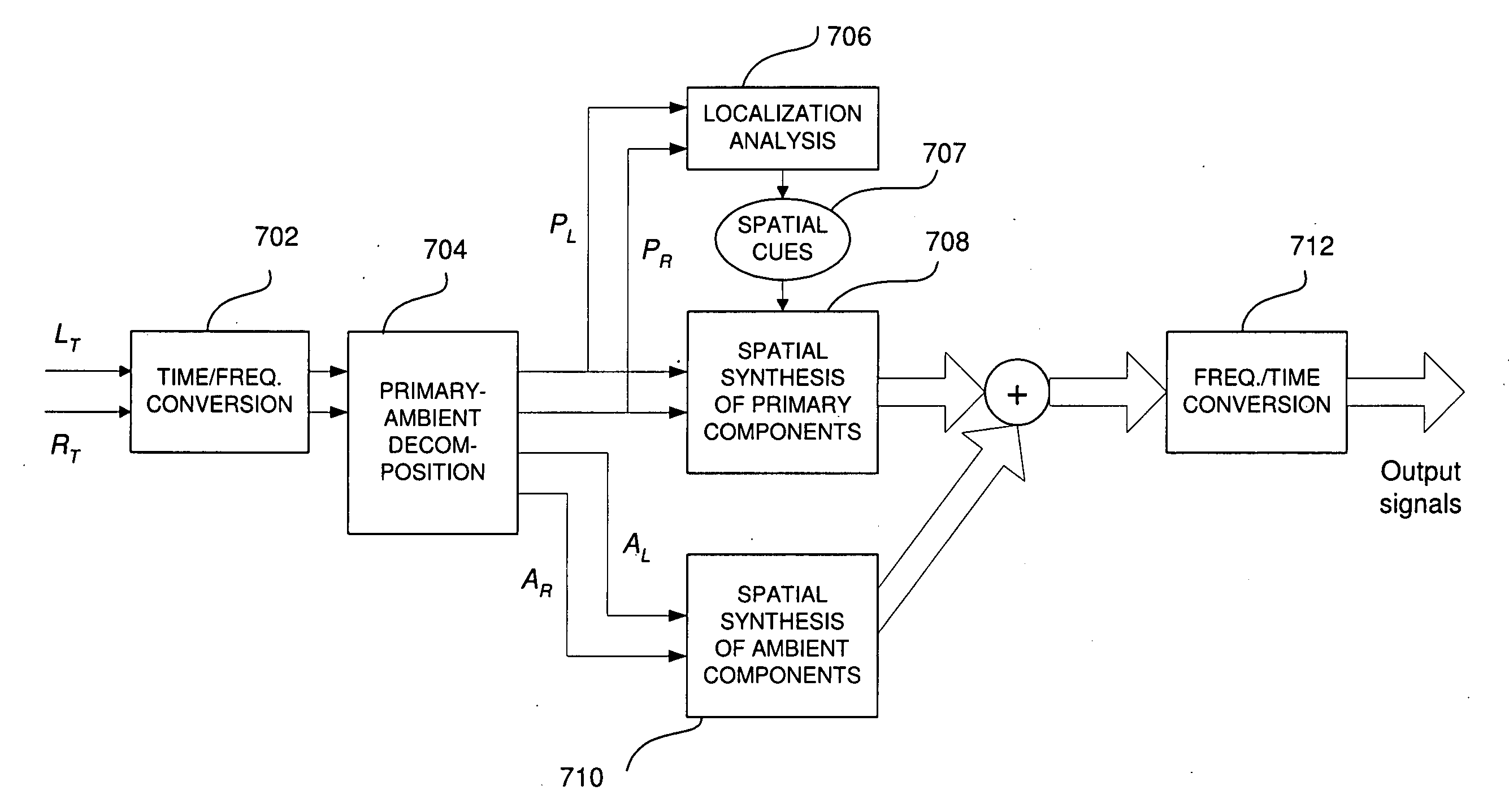
Late reverberation-based synthesis of auditory scenes
ActiveUS20050180579A1Reduce transmission bandwidth requirementsReduce bandwidth requirementsGain controlSpeech analysisComputation complexityChannel correlation
A scheme for stereo and multi-channel synthesis of inter-channel correlation (ICC) (normalized cross-correlation) cues for parametric stereo and multi-channel coding. The scheme synthesizes ICC cues such that they approximate those of the original. For that purpose, diffuse audio channels are generated and mixed with the transmitted combined (e.g., sum) signal(s). The diffuse audio channels are preferably generated using relatively long filters with exponentially decaying Gaussian impulse responses. Such impulse responses generate diffuse sound similar to late reverberation. An alternative implementation for reduced computational complexity is proposed, where inter-channel level difference (ICLD), inter-channel time difference (ICTD), and ICC synthesis are all carried out in the domain of a single short-time Fourier transform (STFT), including the filtering for diffuse sound generation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Portable media player as a low power remote control and method thereof
A portable multimedia player is used to wirelessly access and control a media server that is streaming digital media by way of a wireless interface to a media unit such as a stereo / speakers in the case of streaming digital audio. In one embodiment, the portable multimedia player is wirelessly synchronized to a selected one(s) of a number of digital media files stored on the media server in such a way that digital media file metadata (song title, author, etc.) associated with the selected digital media file(s) only is transferred from the media server to be stored in the portable media player.
Owner:APPLE INC
Phase-Amplitude 3-D Stereo Encoder and Decoder
ActiveUS20090092259A1Preserving source separationSpeech analysisStereophonic systemsSound sourcesSpatial analysis
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
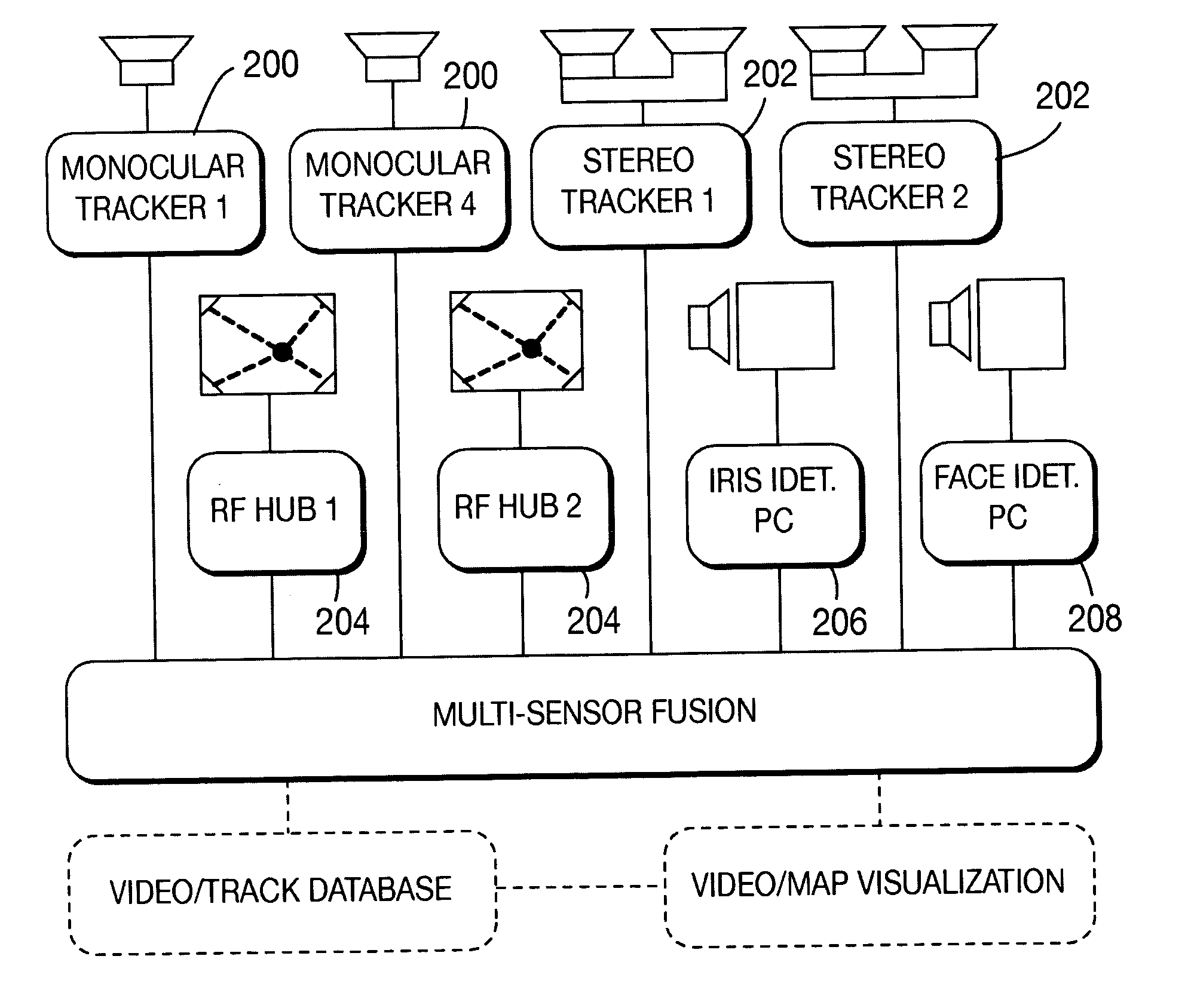
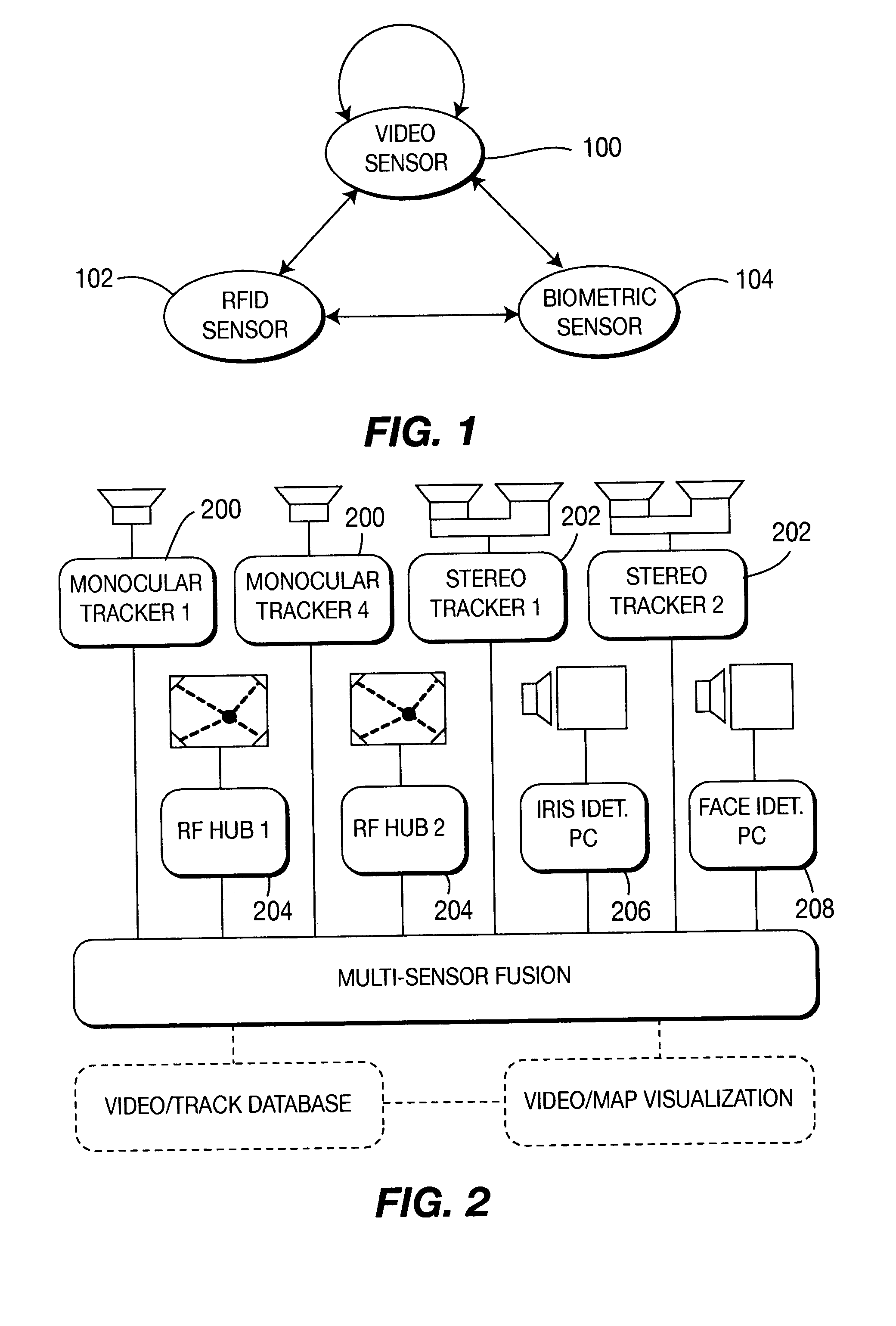
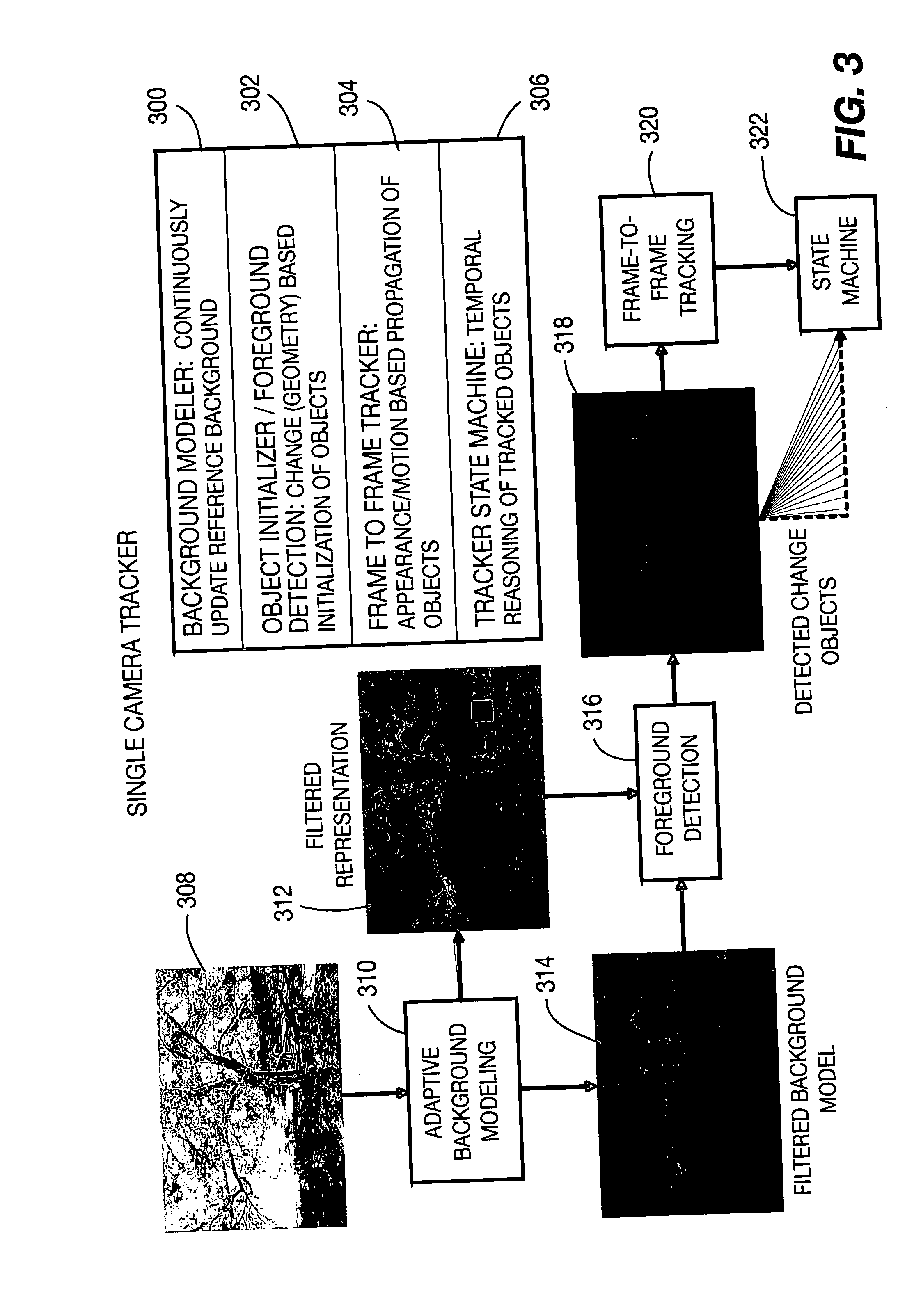
Method and apparatus for stereo, multi-camera tracking and RF and video track fusion
A unified approach, a fusion technique, a space-time constraint, a methodology, and system architecture are provided. The unified approach is to fuse the outputs of monocular and stereo video trackers, RFID and localization systems and biometric identification systems. The fusion technique is provided that is based on the transformation of the sensory information from heterogeneous sources into a common coordinate system with rigorous uncertainties analysis to account for various sensor noises and ambiguities. The space-time constraint is used to fuse different sensor using the location and velocity information. Advantages include the ability to continuously track multiple humans with their identities in a large area. The methodology is general so that other sensors can be incorporated into the system. The system architecture is provided for the underlying real-time processing of the sensors.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Multichannel sound reproduction method and device
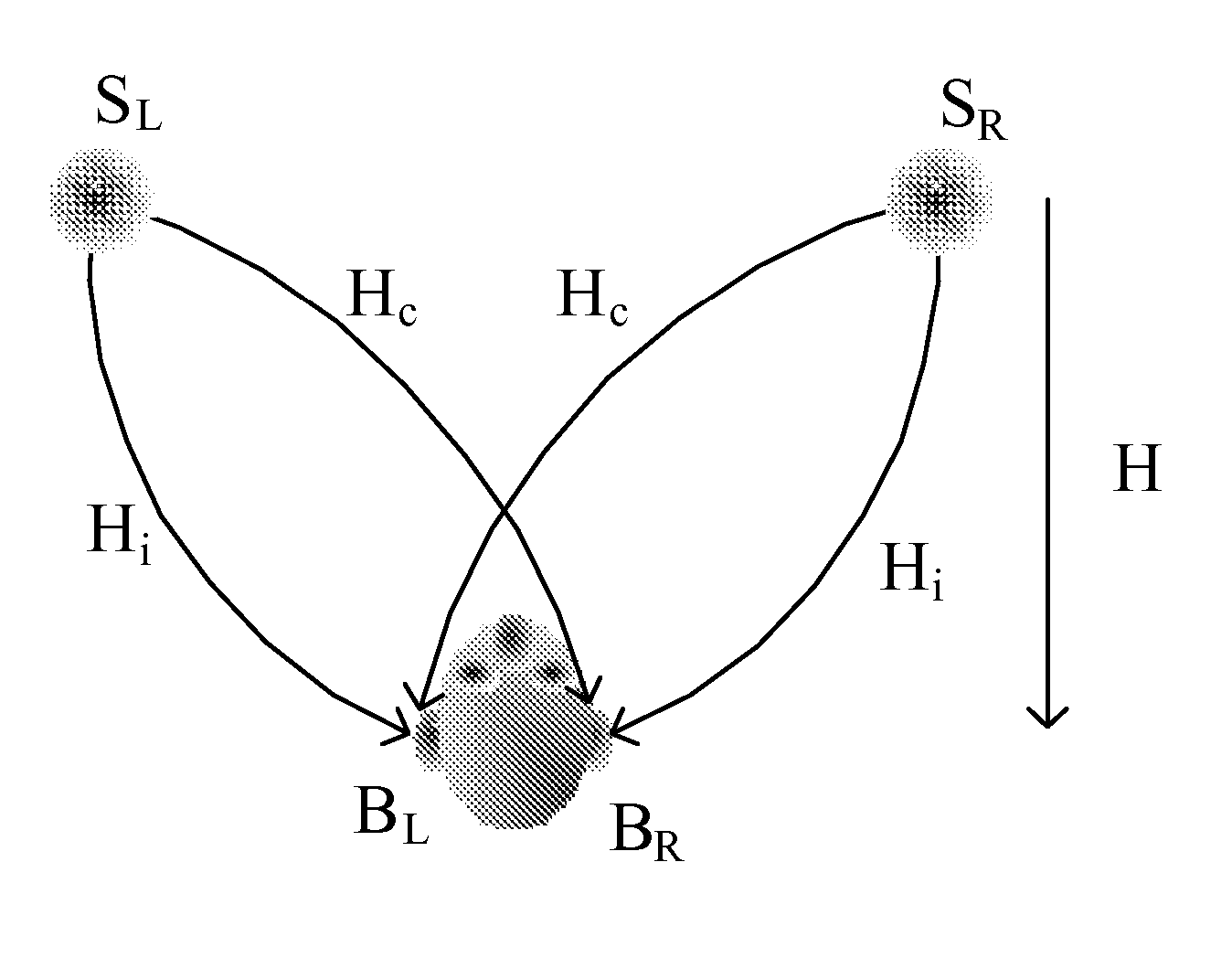
ActiveUS20130010970A1Reduce impactEasy to predictPseudo-stereo systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsSurround soundStereophonic sound
The present invention relates to a method for selecting auditory signal components for reproduction by means of one or more supplementary sound reproducing transducers, such as loudspeakers, placed between a pair of primary sound reproducing transducers, such as left and right loudspeakers in a stereophonic loudspeaker setup or adjacent loudspeakers in a surround sound loudspeaker setup, the method comprising the steps of (i) specifying azimuth angle range within which one of said supplementary sound reproducing transducers is located or is to be located and a listening direction; (Ii) based on said azimuth angle range and said listening direction, determining left and right interaural level difference limits and left and right interaural time difference limits, respectively; (iii) providing a pair of input signals for said pair of primary sound reproducing transducers; (iv) pre-processing each of said input signals, thereby providing a pair of pre-processed input signals; (v) determining interaural level difference and interaural time difference as a function of frequency between said pre-processed signals; and (vi) providing those signal components of said input signals that have interauial level differences and interaural time differences in the interval between said left and right interaural level difference limits, and left and right interaural time difference limits, respectively, to the corresponding supplementary sound reproducing transducer. The invention also relates to a device for carrying out the above method and systems of such devices.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST MFG KFT
Depth information measurement apparatus and mixed reality presentation system
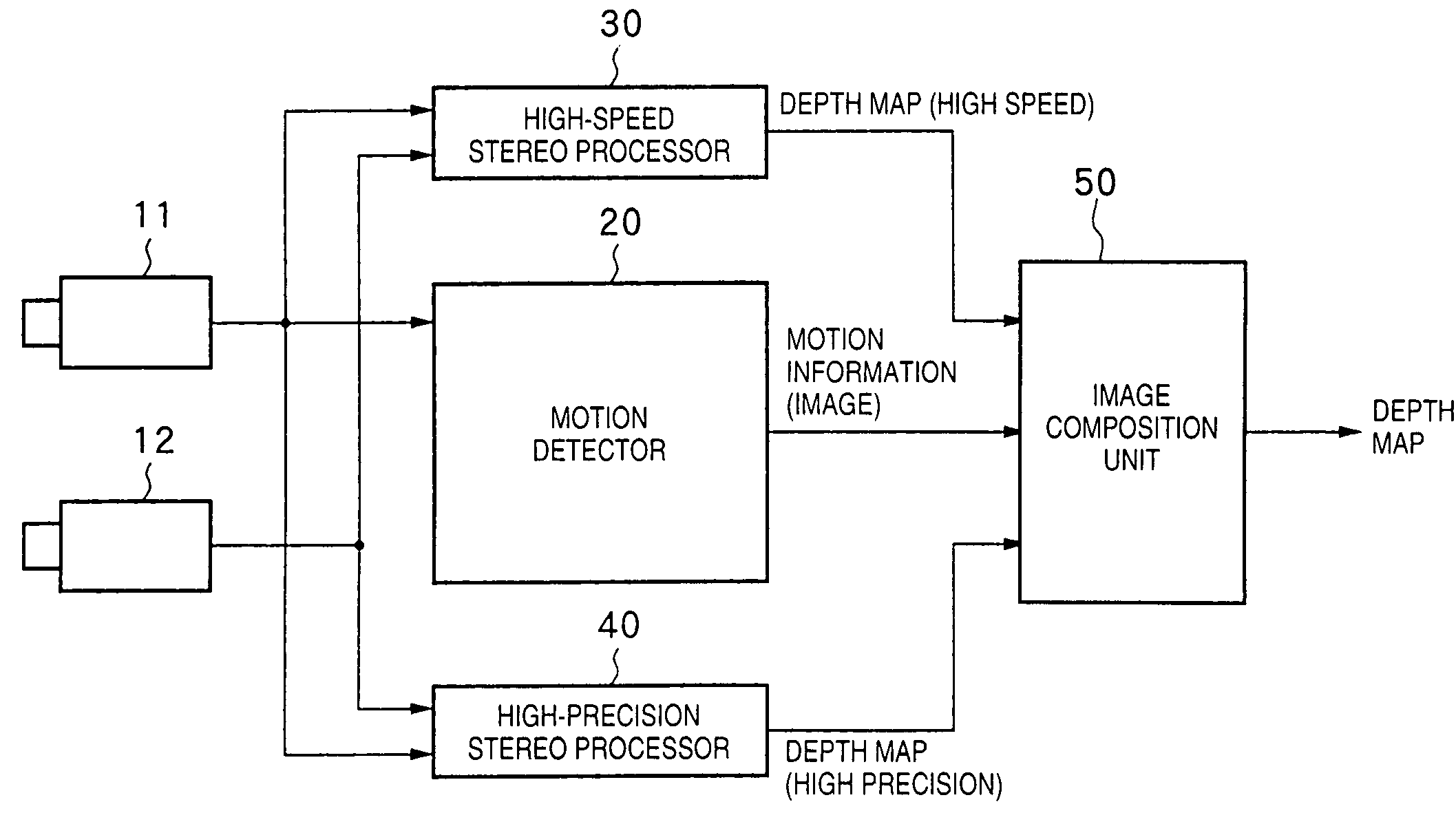
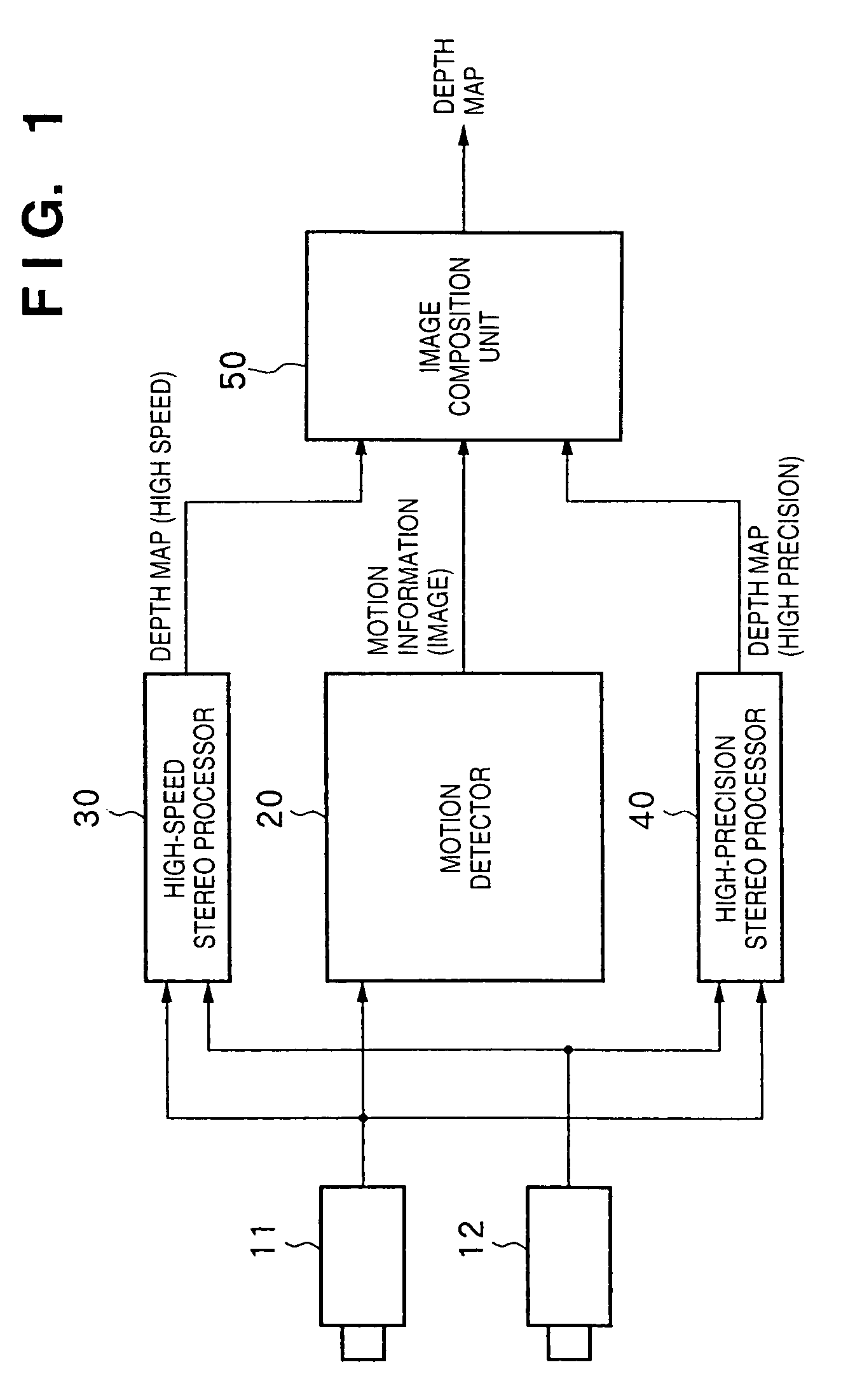
InactiveUS7295697B1Improve accuracyImage enhancementDetails involving processing stepsStereophonic soundStereo image
There is disclosed a depth information generation apparatus capable of acquiring high-precision depth information within a short computation time. A depth information generation apparatus of this invention generates depth information at the capture position of a reference image from the reference image, and at least one peripheral image that forms a stereo image pair with the reference image, and has a high-speed stereo processor (30) for generating depth information at high speed from the reference image and peripheral image, and a high-precision stereo processor (40) for generating high-precision depth information. A motion detector (20) detects a motion in an image, and instructs an image composition unit (50) to select the output from the high-speed stereo processor (30) for a portion with a large motion, and the output from the high-precision stereo processor (40) for other portions. The image composition unit (50) composites the outputs from the high-speed stereo processor (30) and high-precision stereo processor (40) in accordance with an instruction from the motion detector (20), and outputs a depth map as final depth information.
Owner:CANON KK
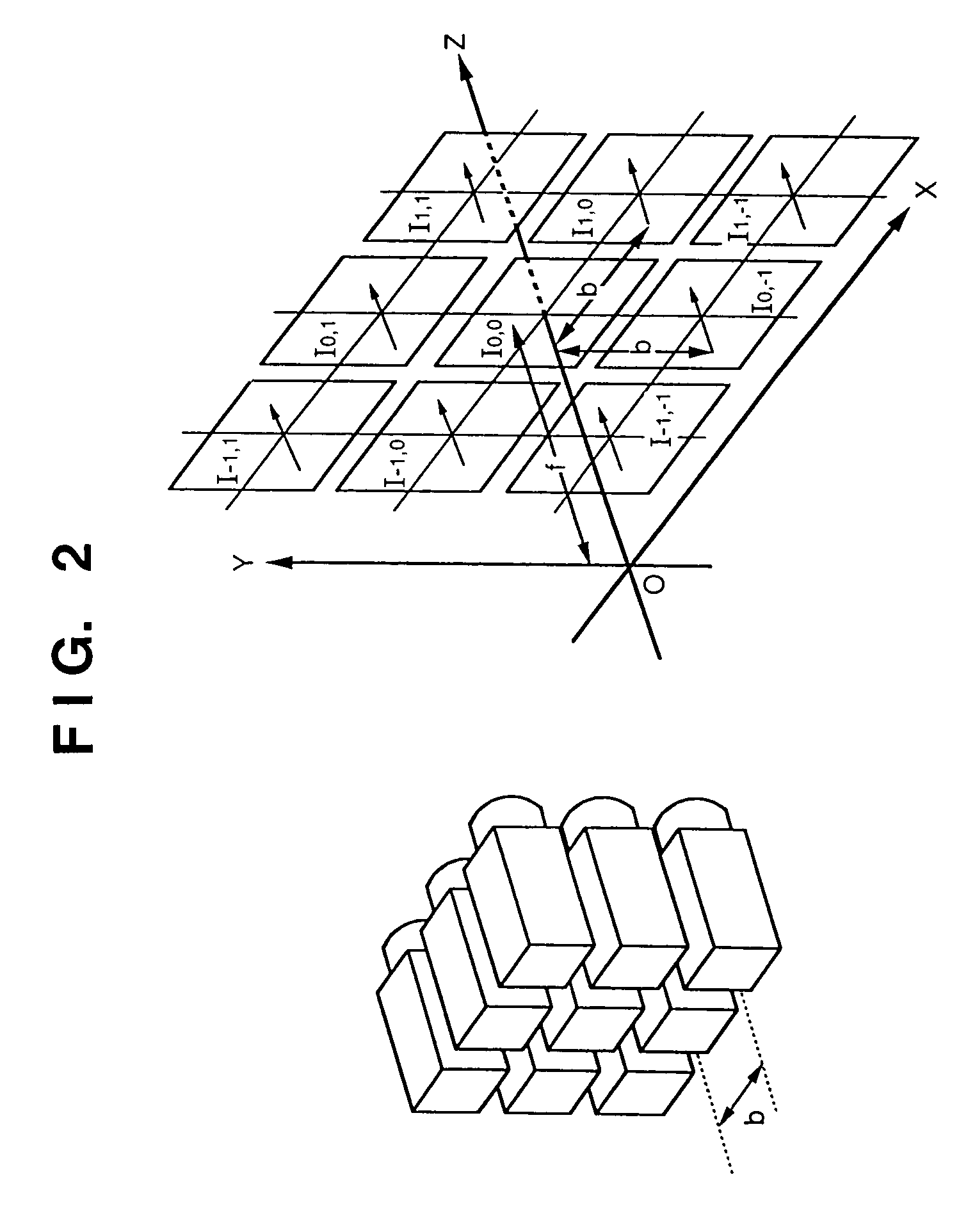
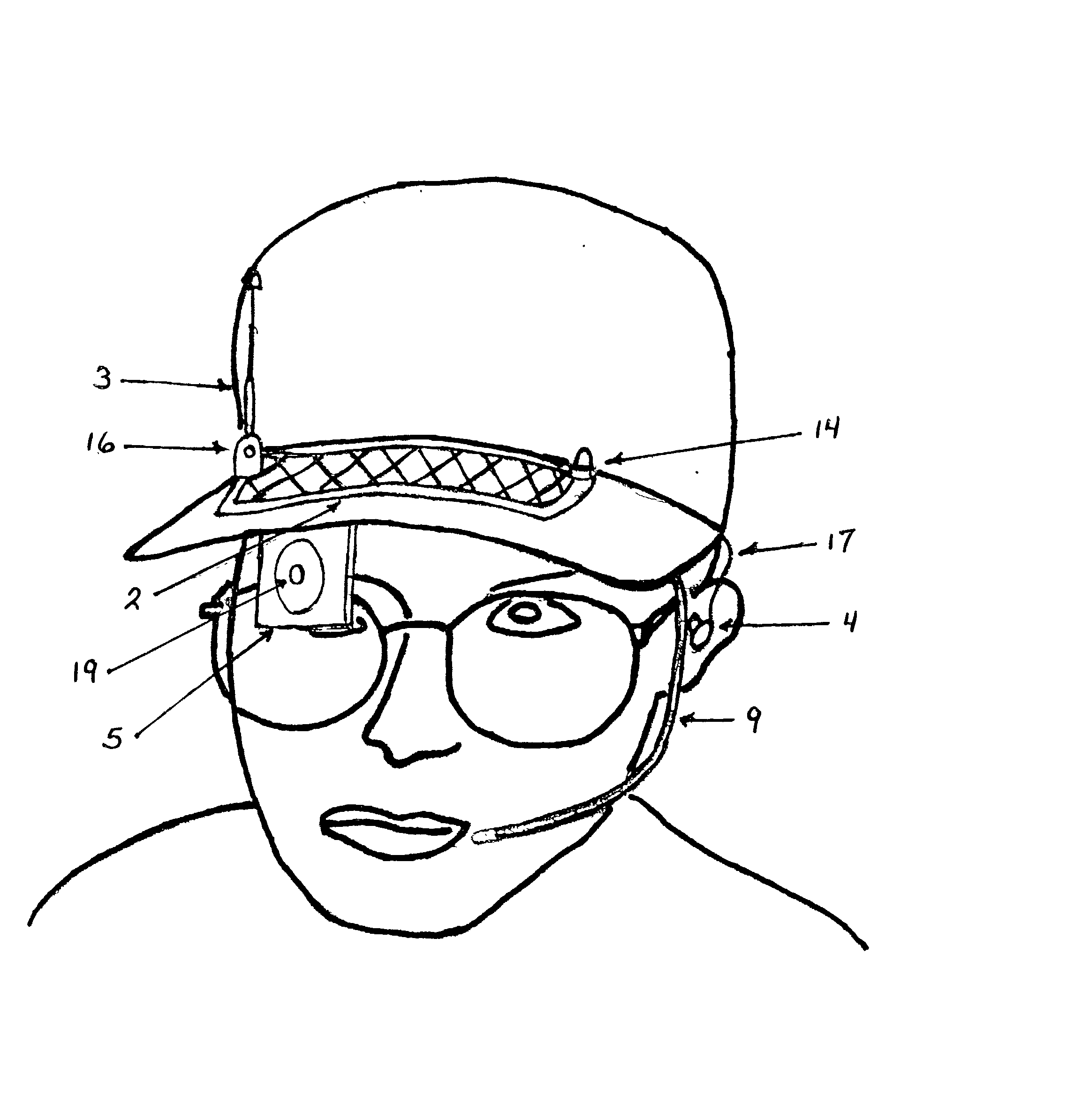
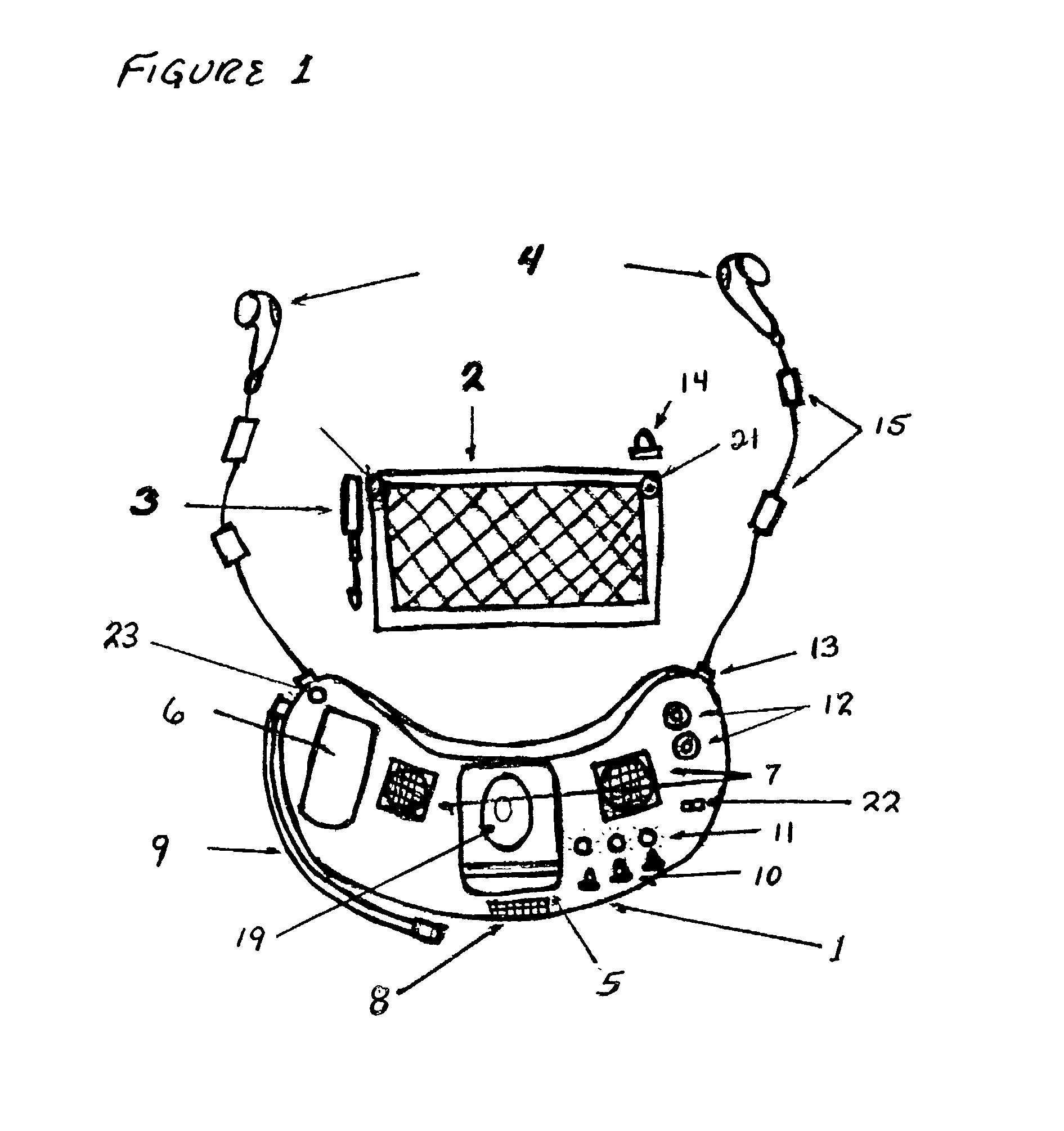
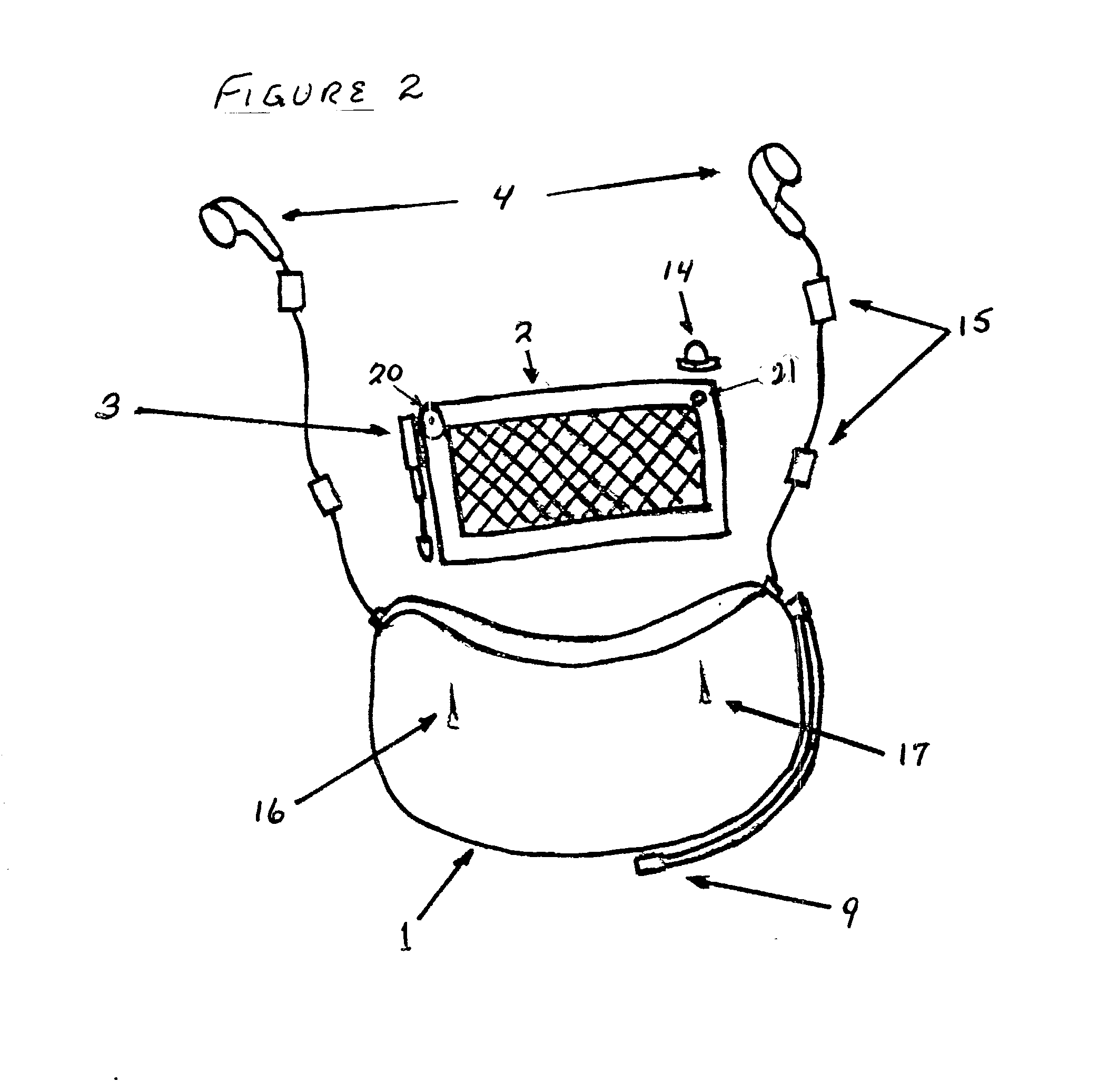
Hands free solar powered cap/visor integrated wireless multi-media apparatus
InactiveUS20020186180A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails for portable computersCamera lensElectrical battery
A apparatus whereby the functional electronics components of popular consumer communications and entertainment products can be repackaged in a molded plastic module that would be mounted underneath and follow the contour of the visor of a head wearable cap / visor providing the user with a hands free, continuous power, virtually invisible multi-media capability. The module would feature, a drop down visual display, drop down camera lens for low resolution digital photography, rechargeable battery, stereo speakers and earphones, a microphone and microphone boom, manual push button controls and LED indicator lights, input / output jacks, and an interactive voice capability. A flexible solar cell and antenna would be mounted on the upper surface of the head wearable cap / visor providing the wireless link and continuous power to the electronics module. All components would be secured to the head wearable cap visor via two active pins that protrude from the upper surface of the electronic module, pierce the visor, and mate up with the solar cell and antenna on the upper surface of the visor.
Owner:DUDA WILLIAM
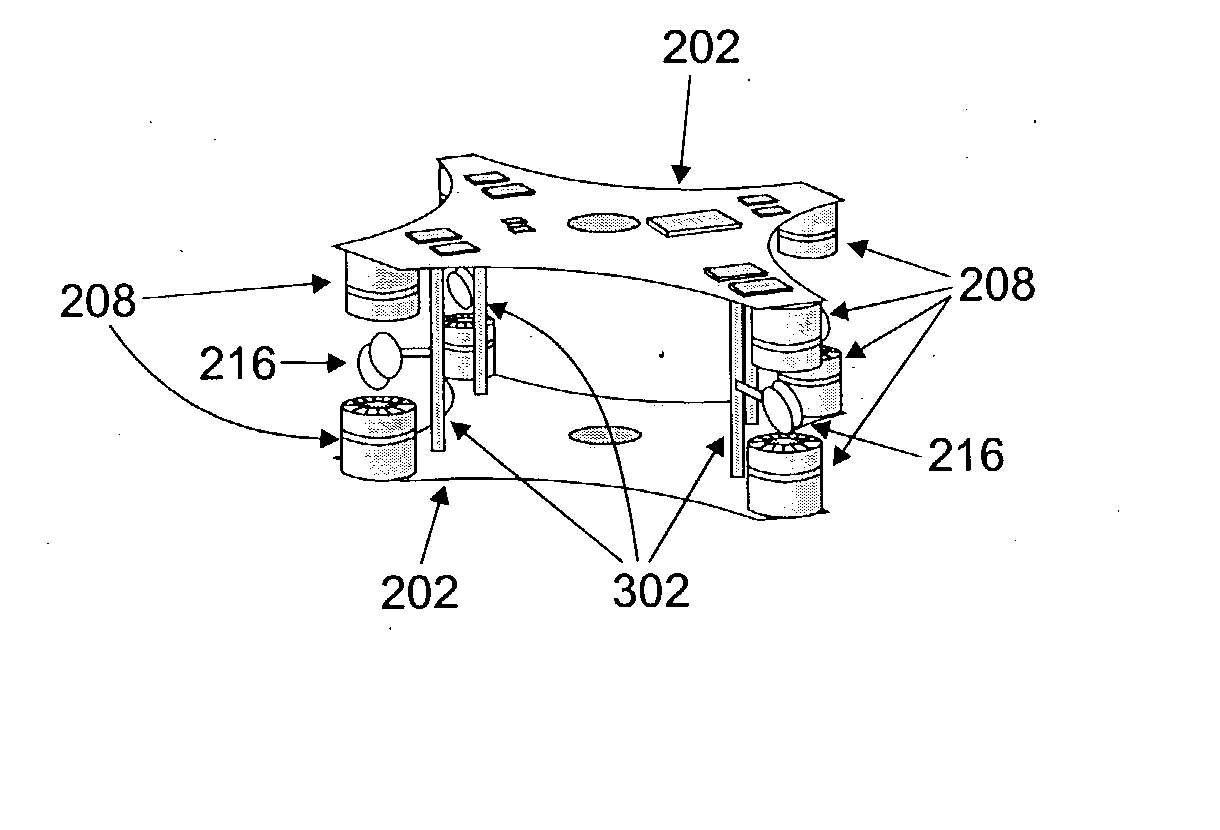
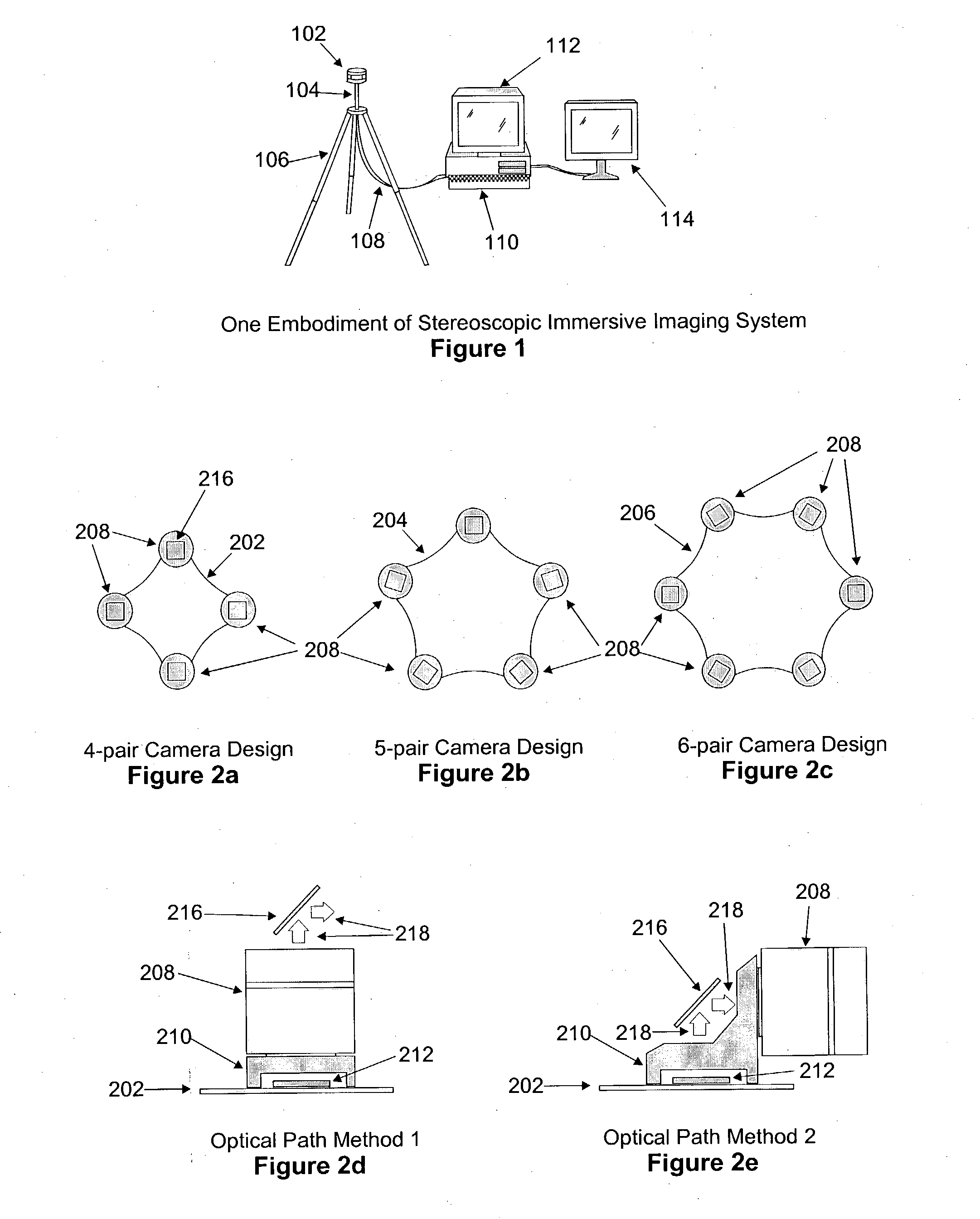
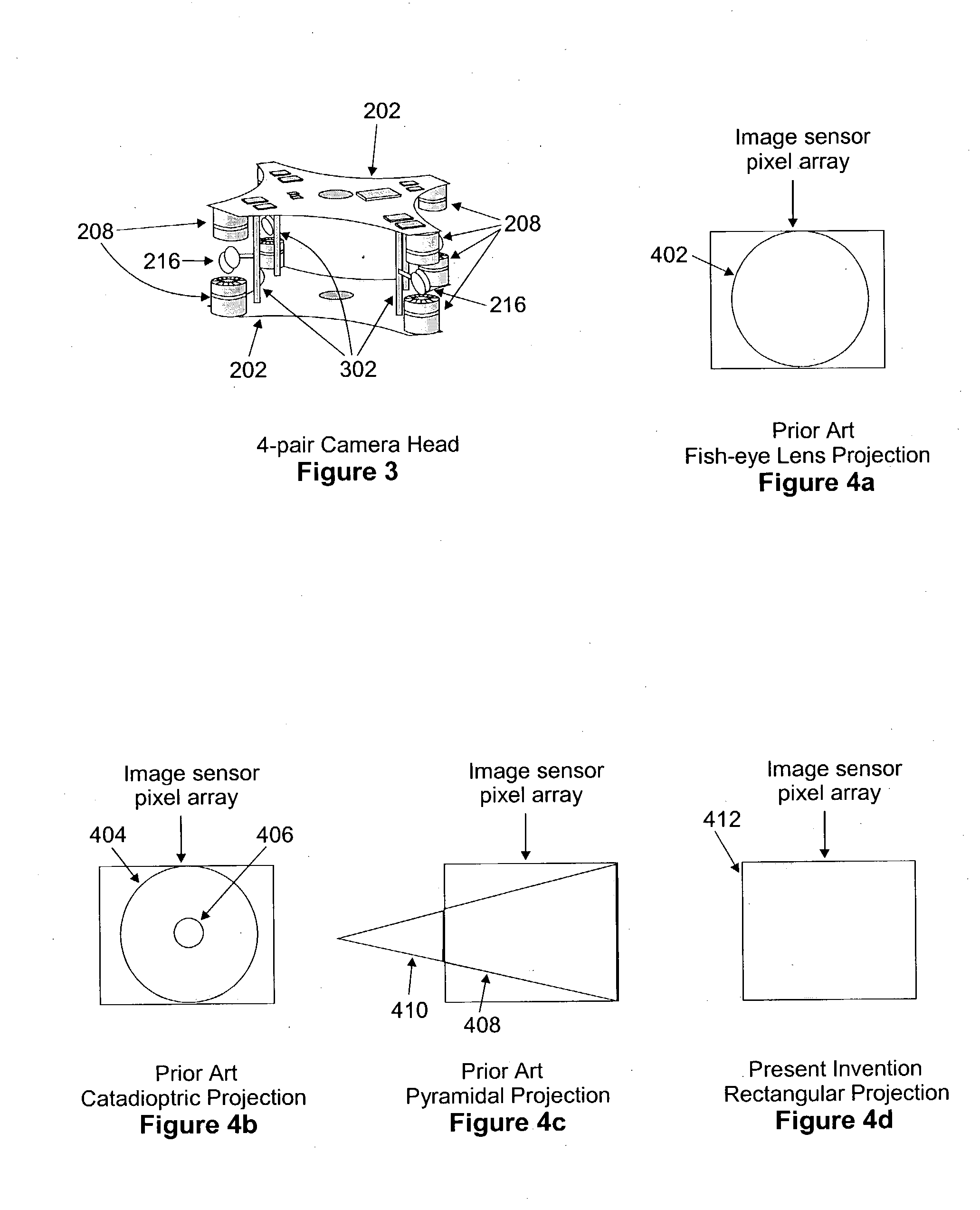
Immersive imaging system
InactiveUS20040027451A1Simple inputHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsStereoscopic videoImaging data
A system, method and device for the capture and display of high-resolution stereoscopic or monoscopic wide fields-of-view (FOV) at still or video rates, presenting techniques and designs for distance measuring, for changing the working stereo capture range of a stereoscopic image capture device, and for playing pre-recorded or transmitted stereoscopic video image data through a player unit. The system supports multiple independent viewers and image analysis sub-systems of various types utilizing hardware, software and firmware. Further included is a stereoscopic videoconferencing embodiment that captures and transmits an entire room's view and automatically directs focus of images.
Owner:IMAGE MASTERS
Computer-based universal remote control system
InactiveUS6111569ATelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsVideocassette recorderRemote control
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Video and audio conferencing system with spatial audio
ActiveUS20060104458A1Good directional beamEasy to separateMicrophonesSignal processingSide informationDisplay device
In some embodiments, spatially realistic audio may be provided for a conference call. Voices from participants on the left side of a display, in a conference call, may be directed through audio on the left side of the display at the other conferencing system in the conference call (similarly for voices from the center and right side of the display). In some embodiments, two speakers may be used in the system to create synthesized stereo sound at a location specified by directional information received as side information along with the existing audio channel. The location may be determined by using beamforming with integrated microphones on a camera or speakerphone. In some embodiments, the audio signal and directional information may be sent in the form of a left audio channel and a right audio channel.
Owner:LIFESIZE INC
Spatial audio enhancement processing method and apparatus
The present invention describes techniques that can be used to provide novel methods of spatial audio rendering using adapted M-S matrix shuffler topologies. Such techniques include headphone and loudspeaker-based binaural signal simulation and rendering, stereo expansion, multichannel upmix and pseudo multichannel surround rendering.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
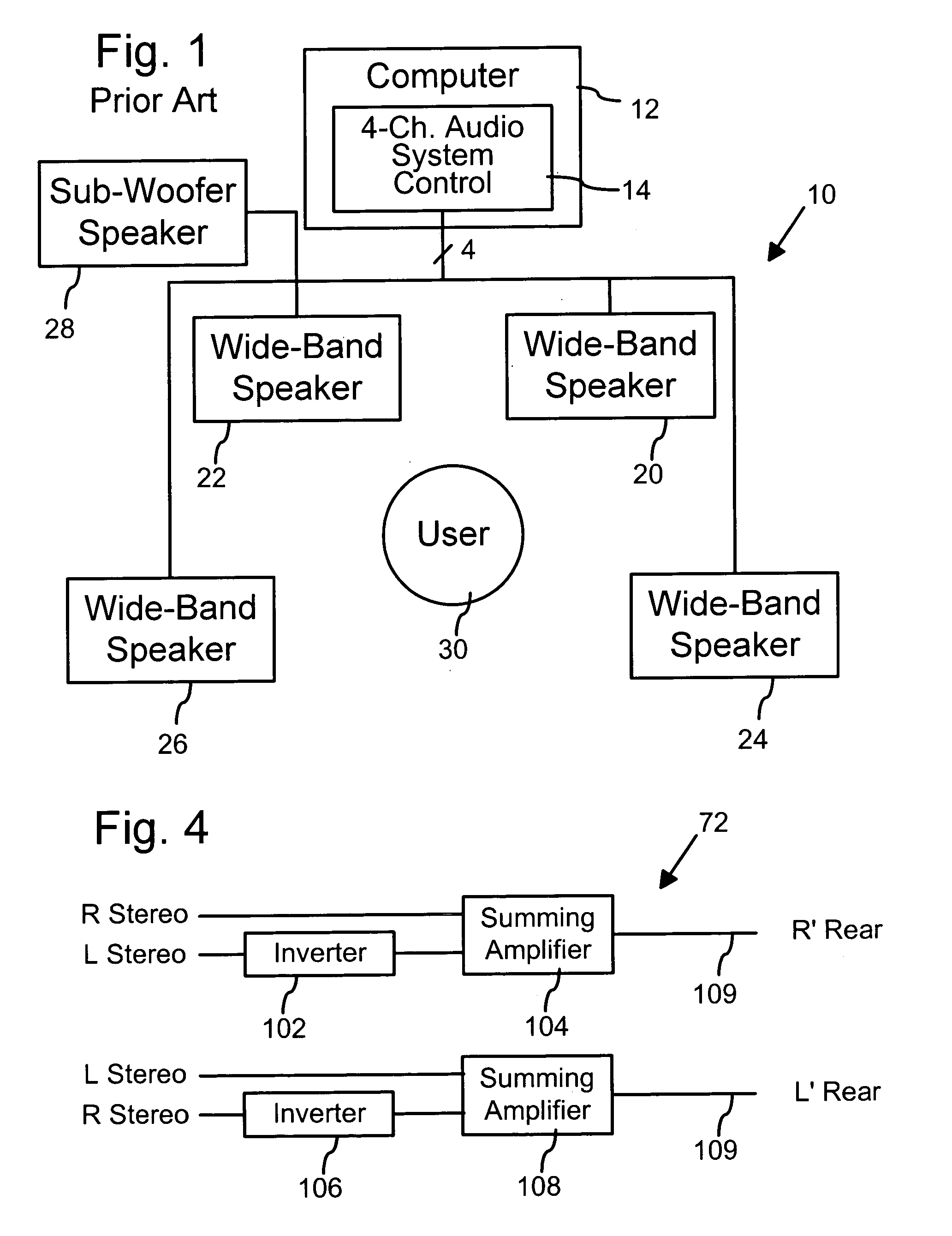
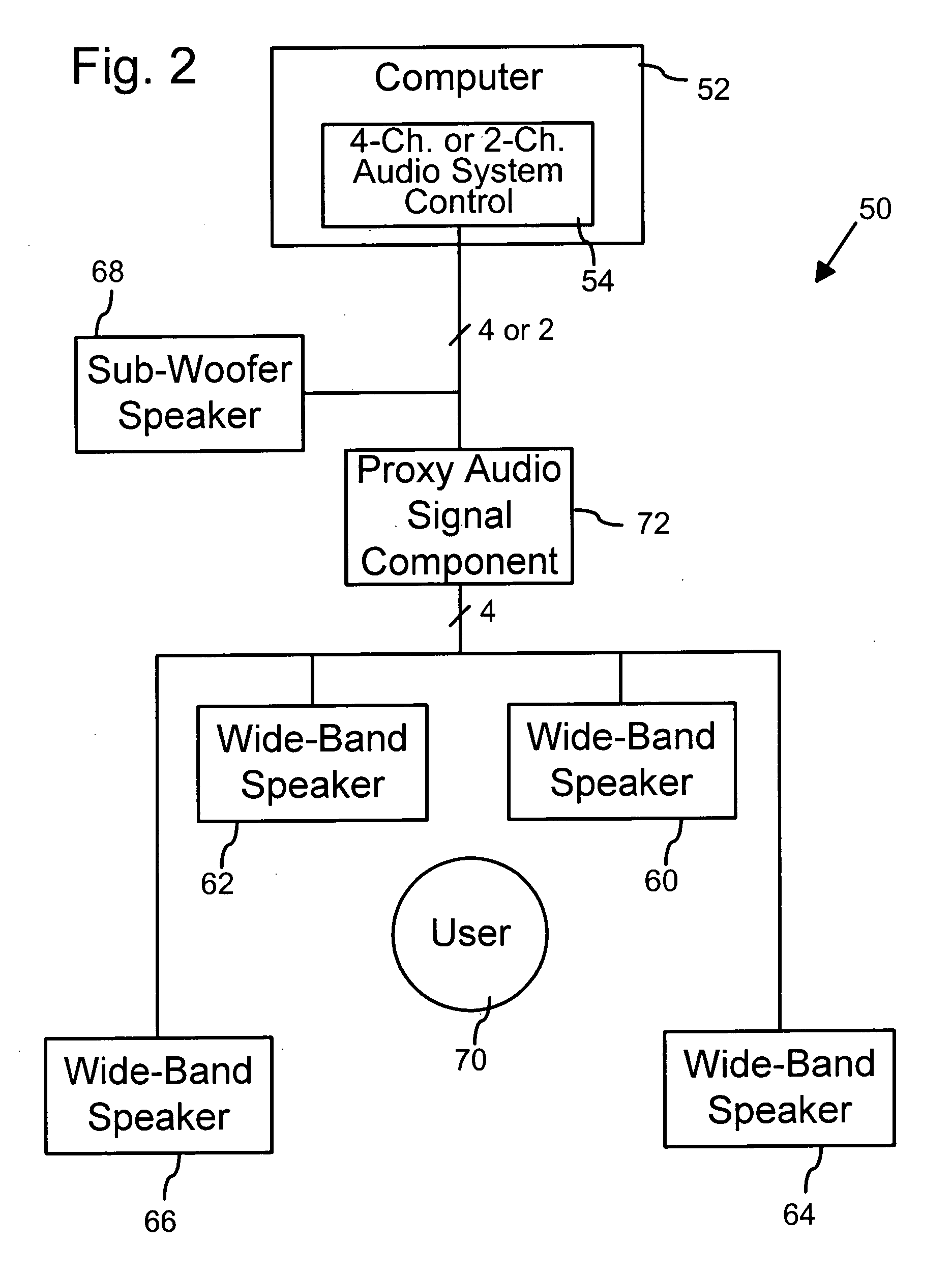
Universal four-channel surround sound speaker system for multimedia computer audio sub-systems
InactiveUS6934394B1Simple and compactStereophonic circuit arrangementsSound input/outputComputer speakersVocal tract
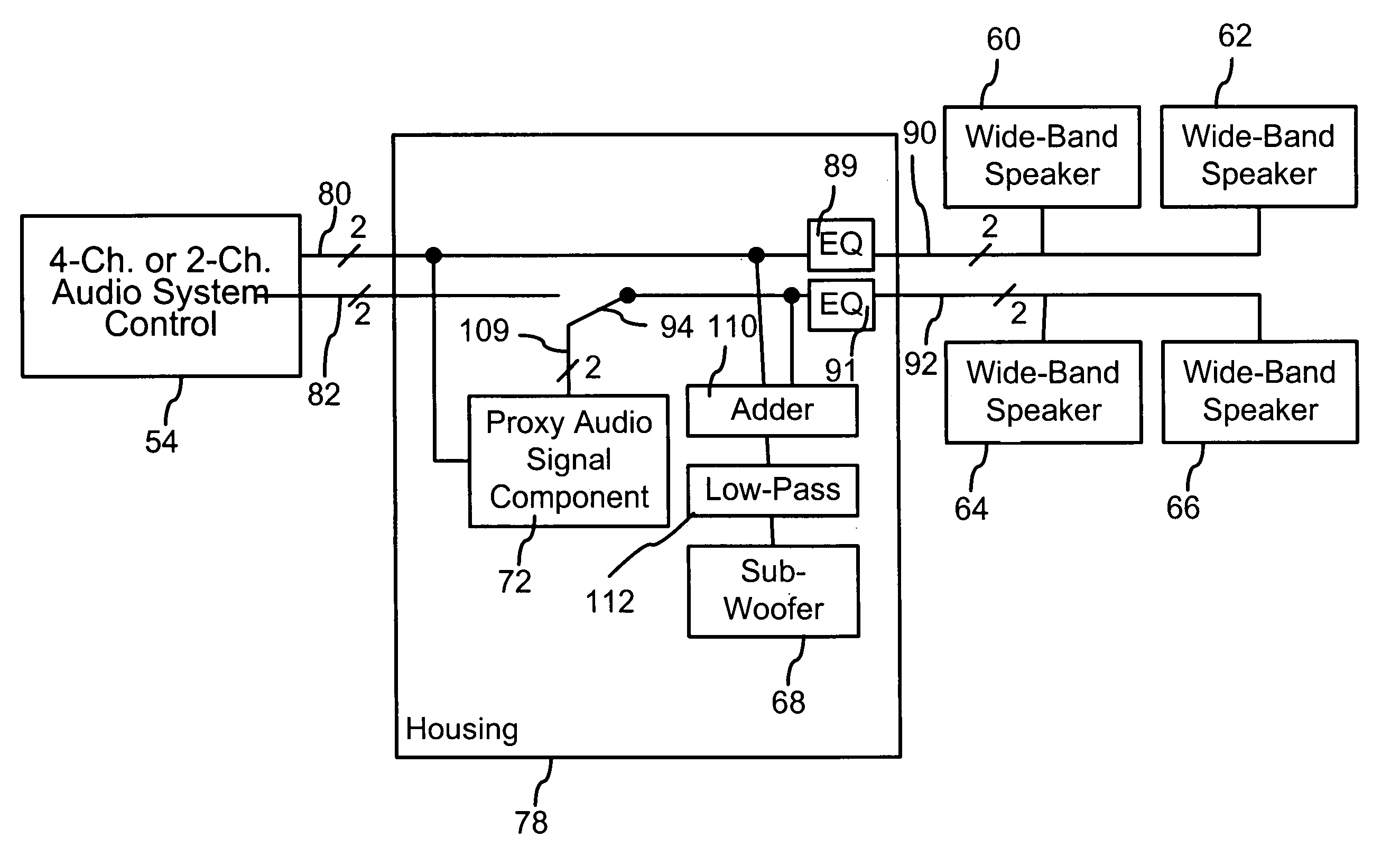
A universal four-channel multimedia computer speaker system is connectable to audio sub-system control circuits (e.g., “sound cards”) of both the four-channel type and the conventional two-channel (stereo) type. With the audio sub-system control circuit being of a four-channel type, the universal four-channel audio system functions as a conventional multimedia computer four-channel surround sound audio system. With a four audio channel multimedia computer work and the audio sub-system control circuit being of a conventional two-channel (stereo) type, the universal four-channel audio system is configured to provide one pair of wide-band speakers (e.g., the front) with distinct audio playback according to respective right-front and left-front audio channels in a four or two audio channel multimedia computer work such as a game, music, etc. The universal four-channel audio system is configured to provide at the rear speakers distinct audio playback that are generated from the right-front and left-front audio channels in the four or two audio channel multimedia computer work. With respect to the rear speakers, the universal four-channel audio system includes a proxy audio signal component that provides respective right and left rear proxy audio signals to proximate the typical sound of actual right and left rear audio signals carried on a four audio channel multimedia computer work or simulated surround signals generated from conventional two channel multimedia work.
Owner:LOGITECH EURO SA
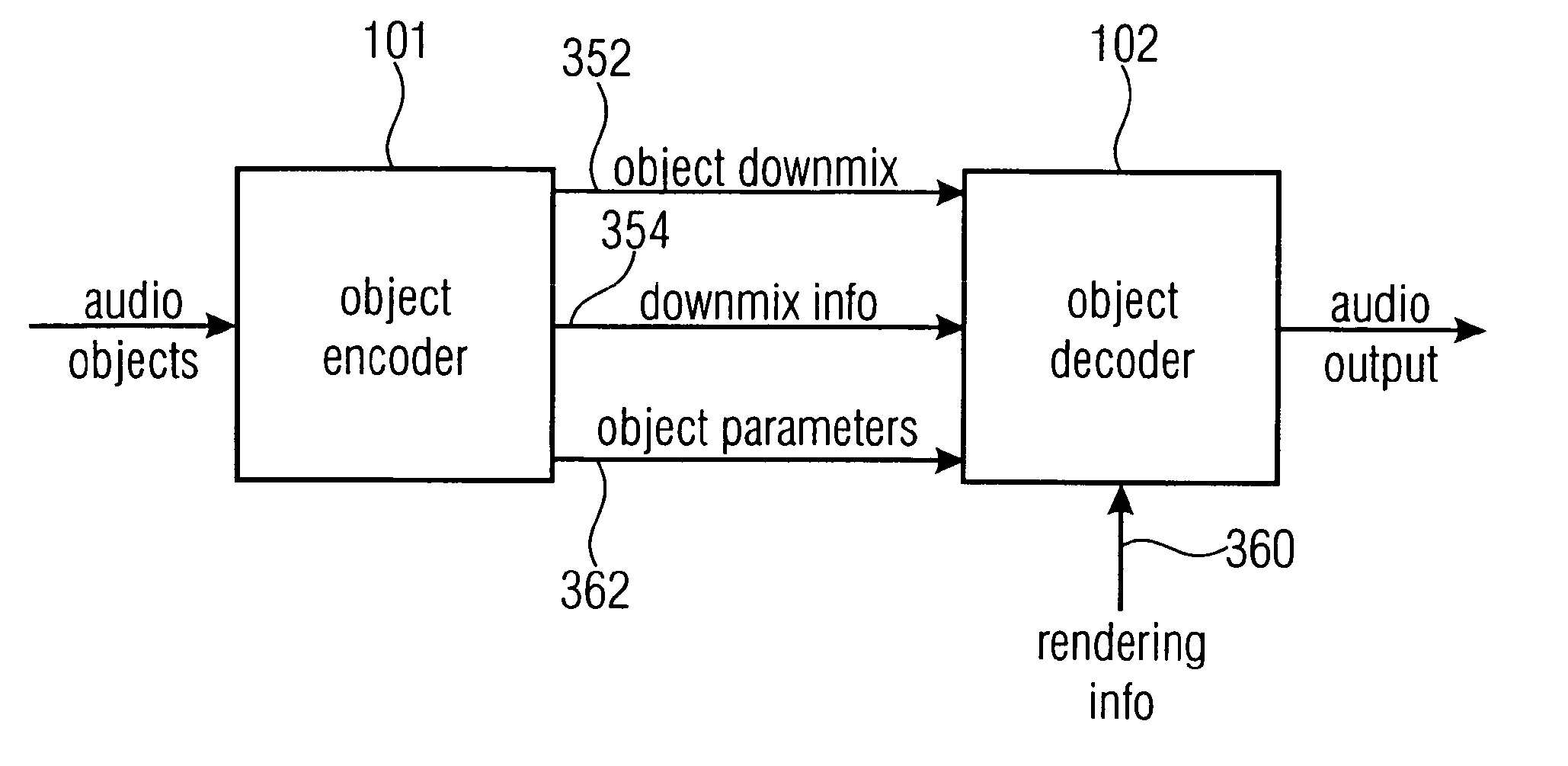
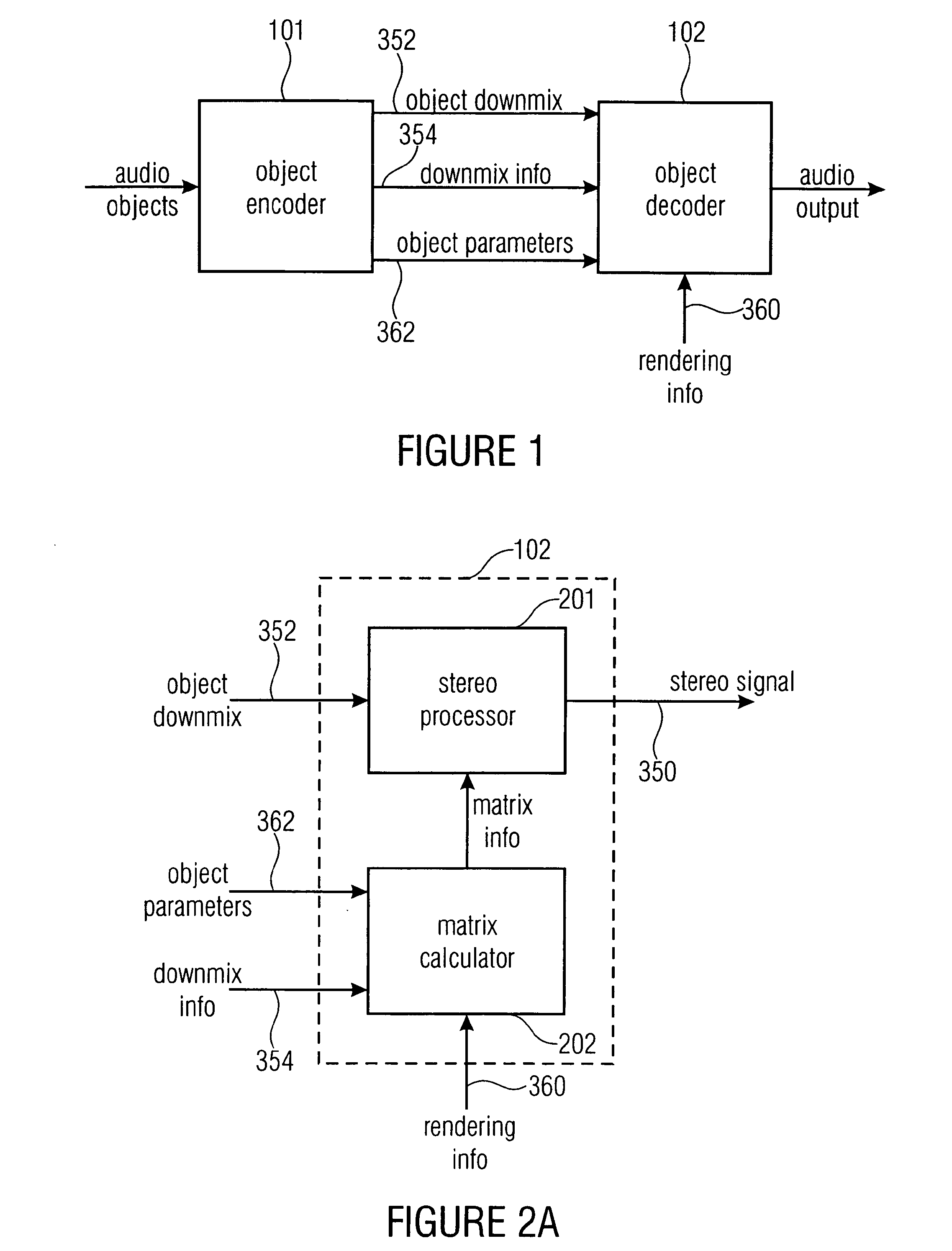
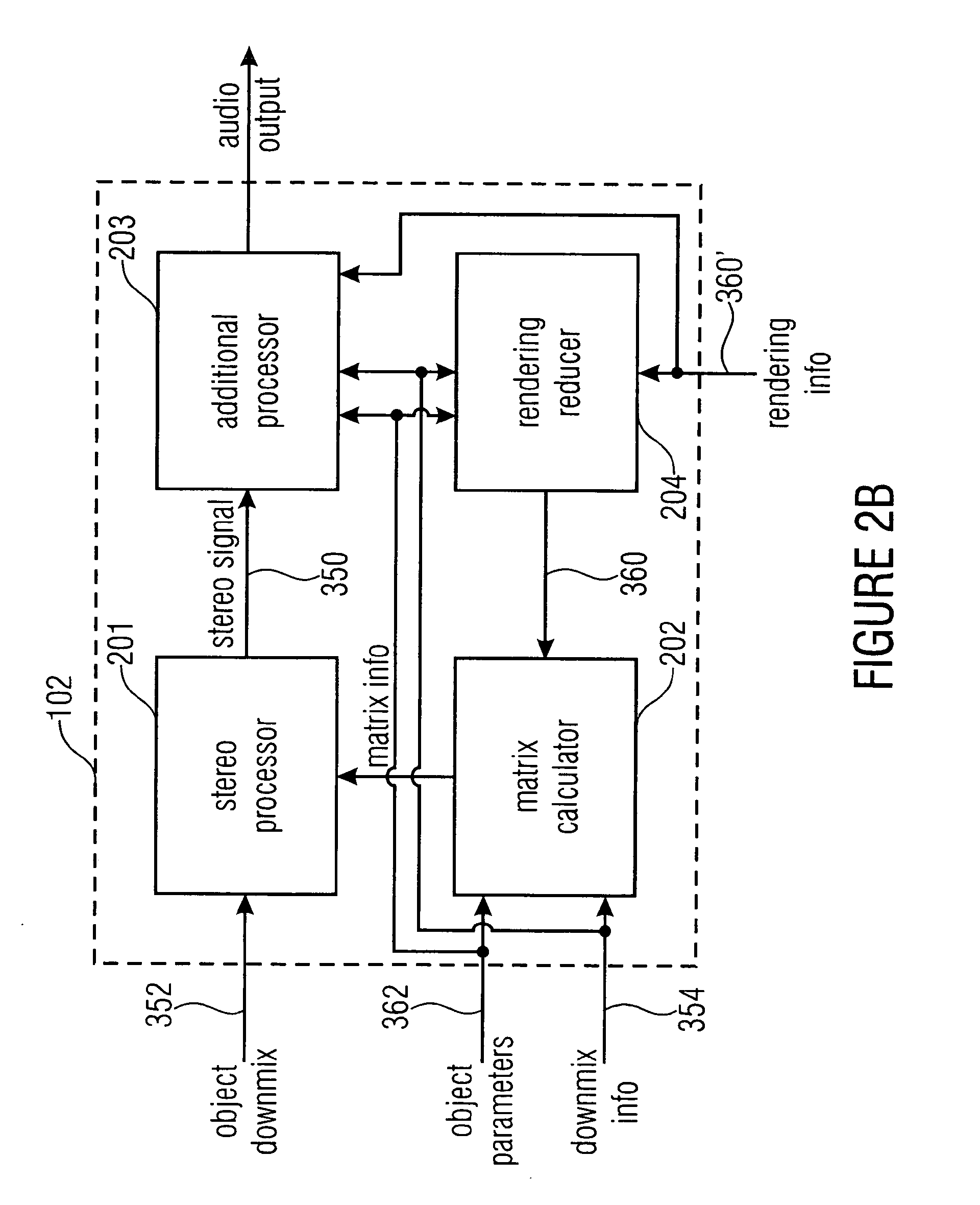
Apparatus and method for synthesizing an output signal
An apparatus for synthesizing a rendered output signal having a first audio channel and a second audio channel includes a decorrelator stage for generating a decorrelator signal based on a downmix signal, and a combiner for performing a weighted combination of the downmix signal and a decorrelated signal based on parametric audio object information, downmix information and target rendering information. The combiner solves the problem of optimally combining matrixing with decorrelation for a high quality stereo scene reproduction of a number of individual audio objects using a multichannel downmix.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
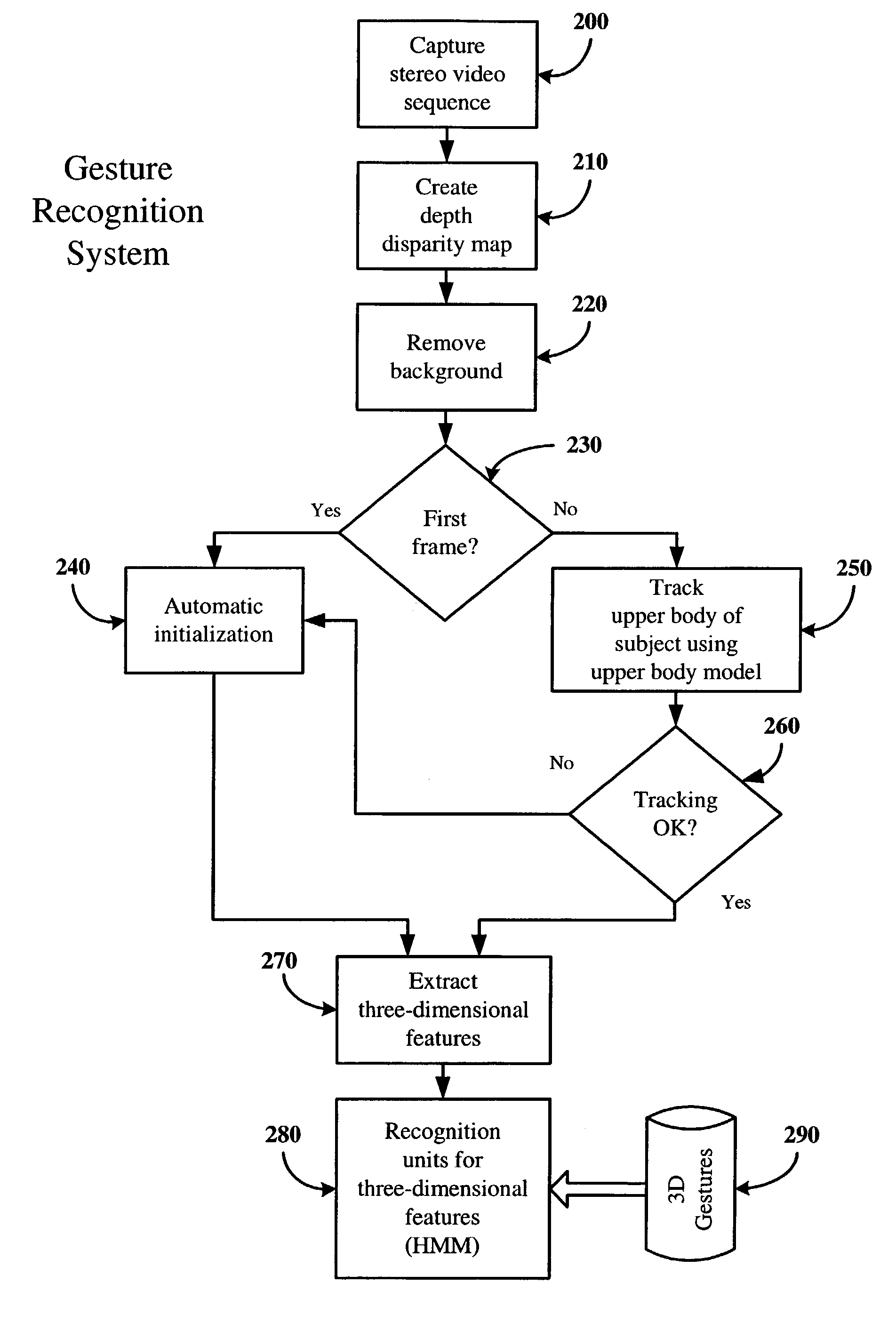
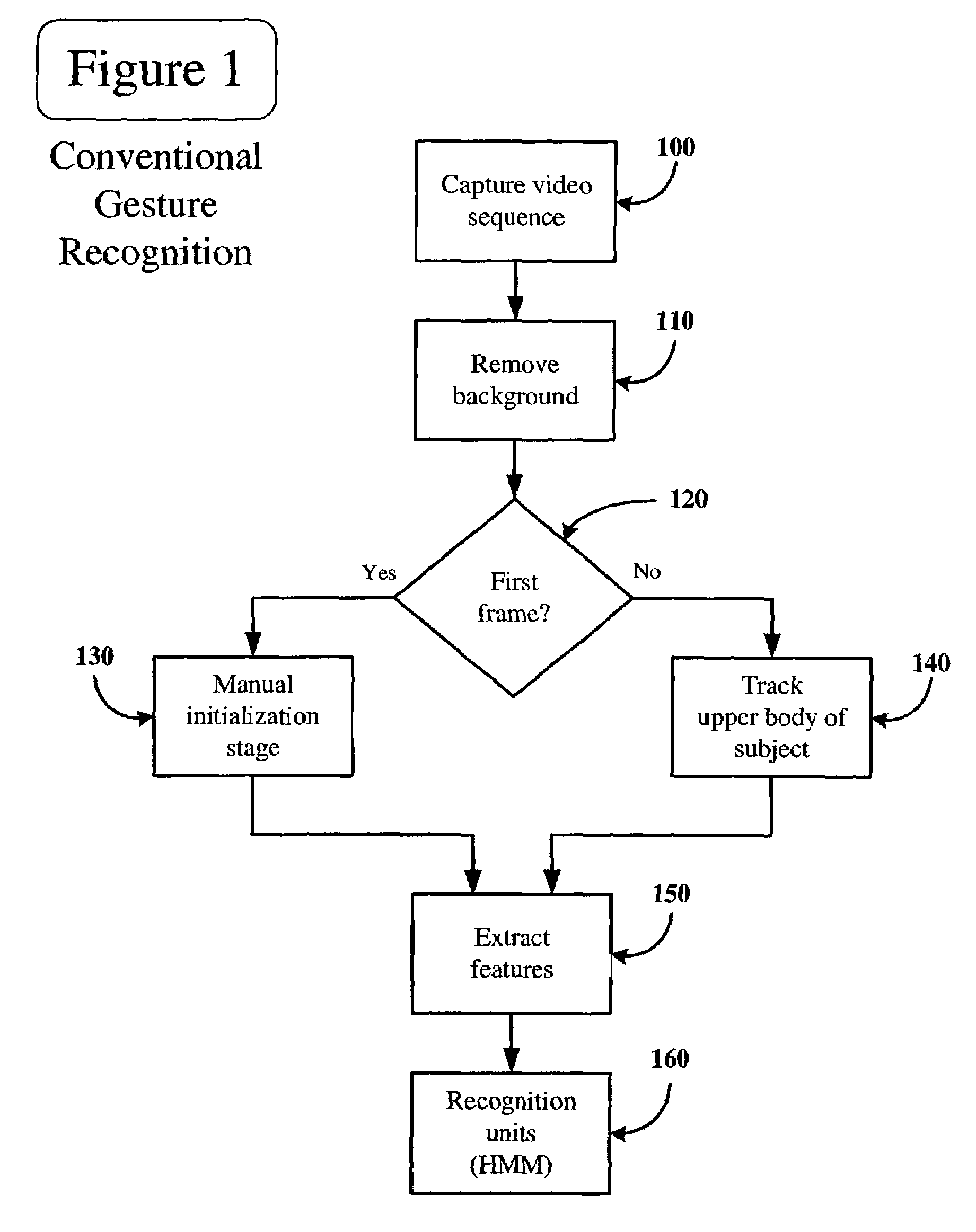
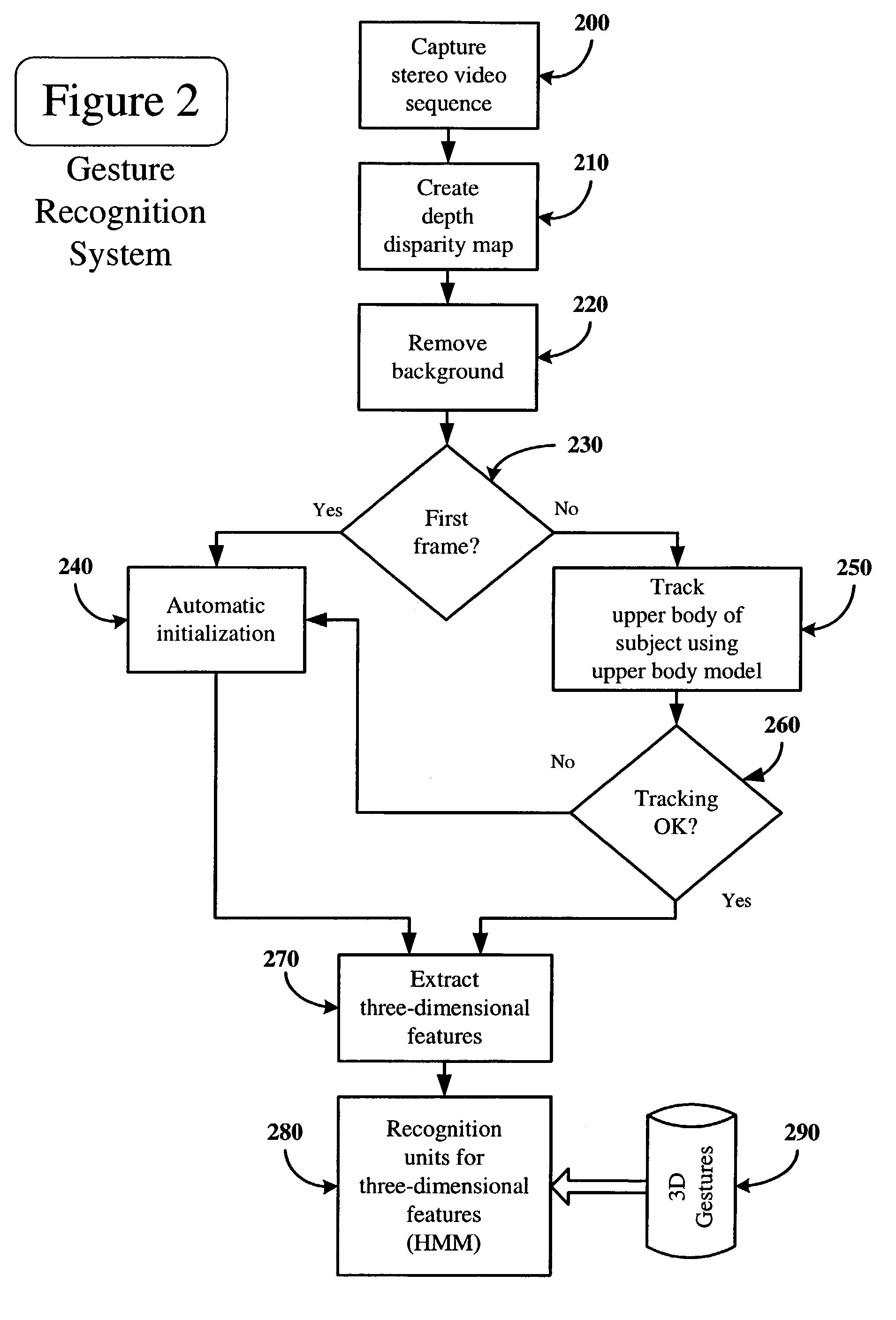
Dynamic gesture recognition from stereo sequences
InactiveUS7274800B2Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionHide markov modelComputer vision
According to an embodiment, an apparatus and method are disclosed for dynamic gesture recognition from stereo sequences. In an embodiment, a stereo sequence of images of a subject is obtained and a depth disparity map is generated from the stereo sequence. The system is initiated automatically based upon a statistical model of the upper body of the subject. The upper body of the subject is modeled as three planes, representing the torso and arms of the subject, and three Gaussian components, representing the head and hands of the subject. The system tracks the upper body of the subject using the statistical upper body model and extracts three-dimensional features of the gestures performed. The system recognizes the gestures using recognition units, which, under a particular embodiment, utilizes hidden Markov models for the three-dimensional gestures.
Owner:INTEL CORP
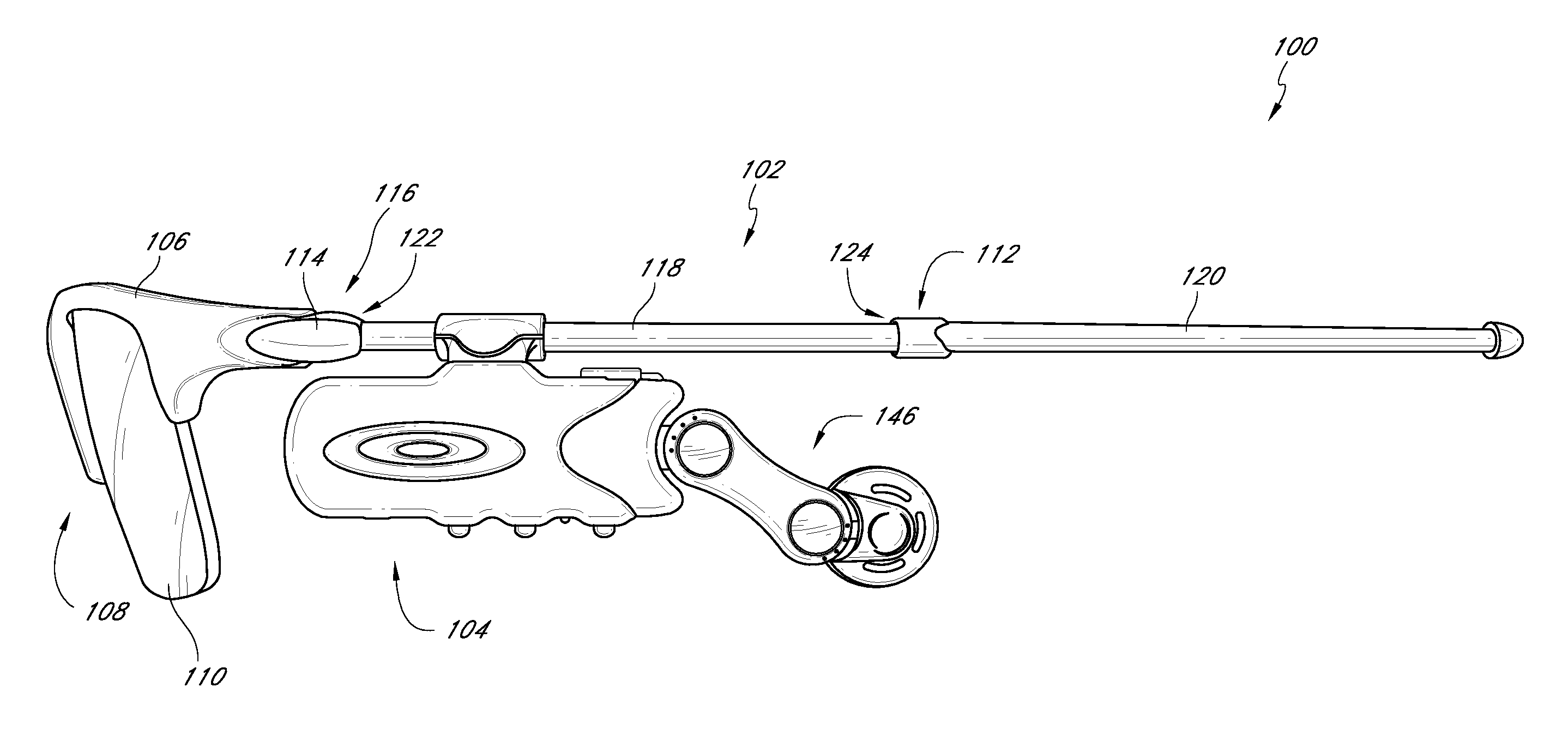
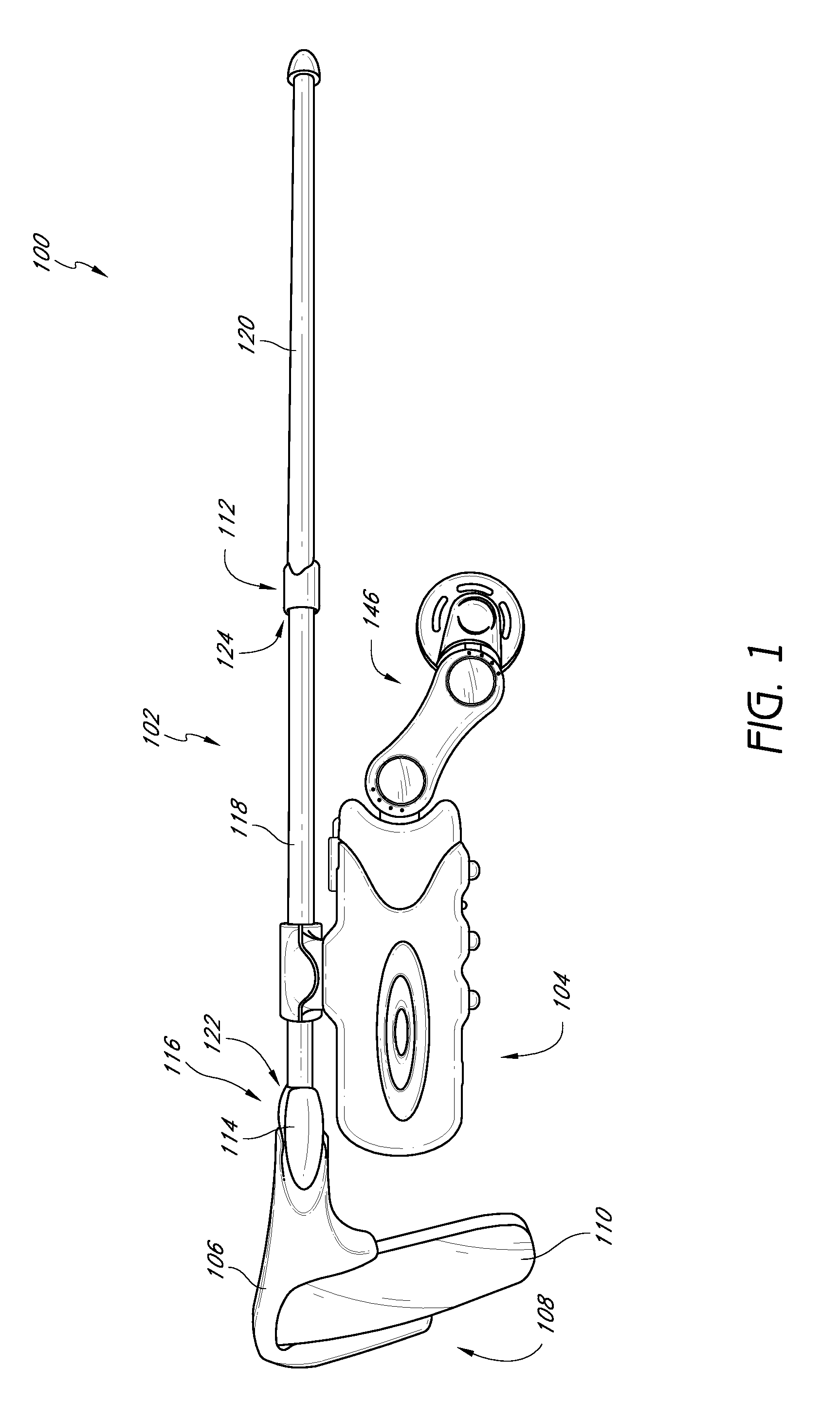
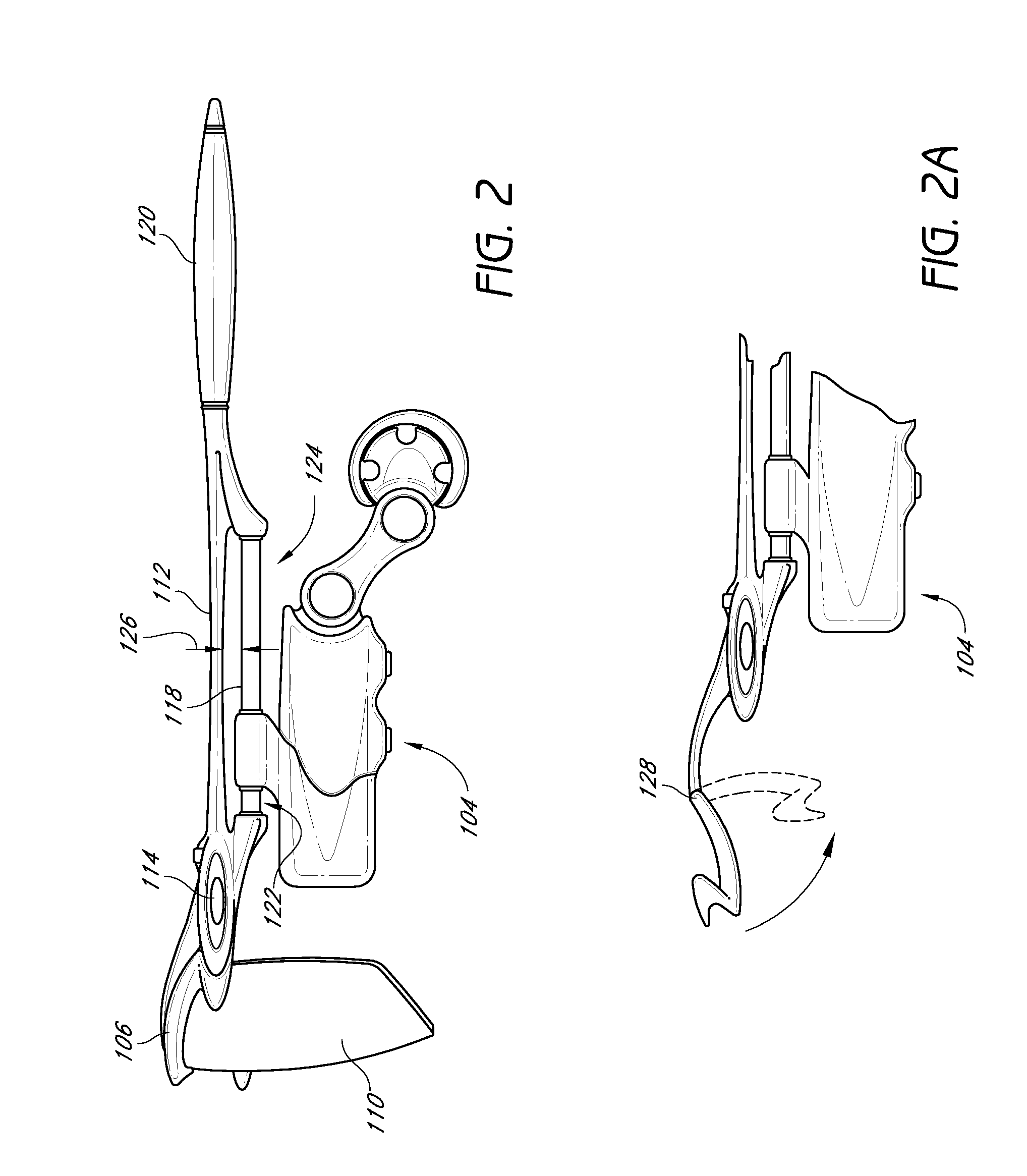
Eyewear with detachable adjustable electronics module
A detachable adjustable electronics module may be removably or permanently connected to eyewear. The module may include electronics for processing audio and / or video input and / or output signals. The module may be provided with an adjustable arm, for adjustably carrying a speaker. The module and / or the speaker may be adjusted relative to the wearer in any of the anterior-posterior direction, the inferior-superior direction and laterally. Rotation adjustments may also be accomplished. Eyewear may be provided with only a single module, on a single side, or with two modules, one on each side, such as to provide stereo audio or dual mono sound.
Owner:OAKLEY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com