Patents
Literature
50 results about "Interaural time difference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
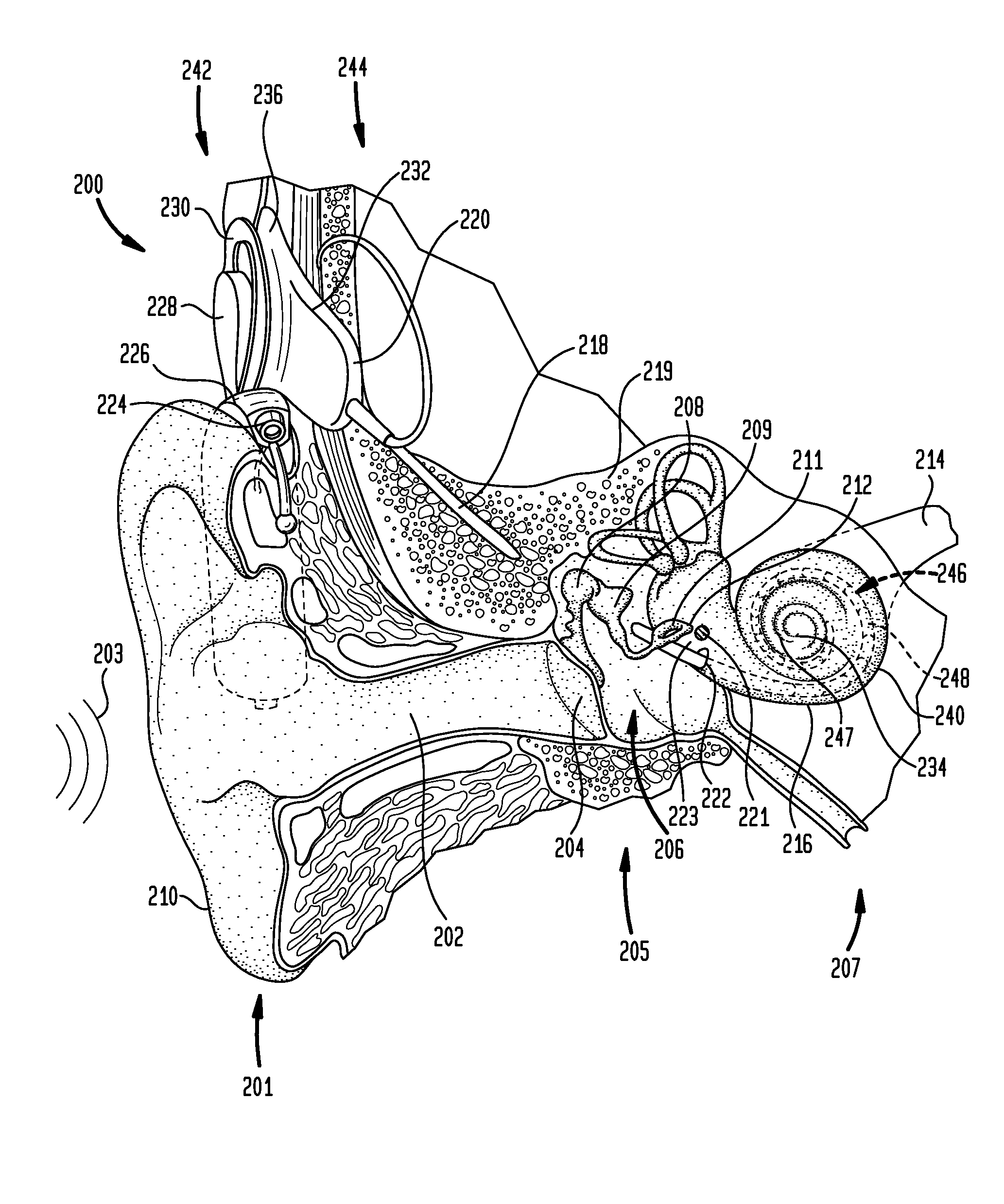
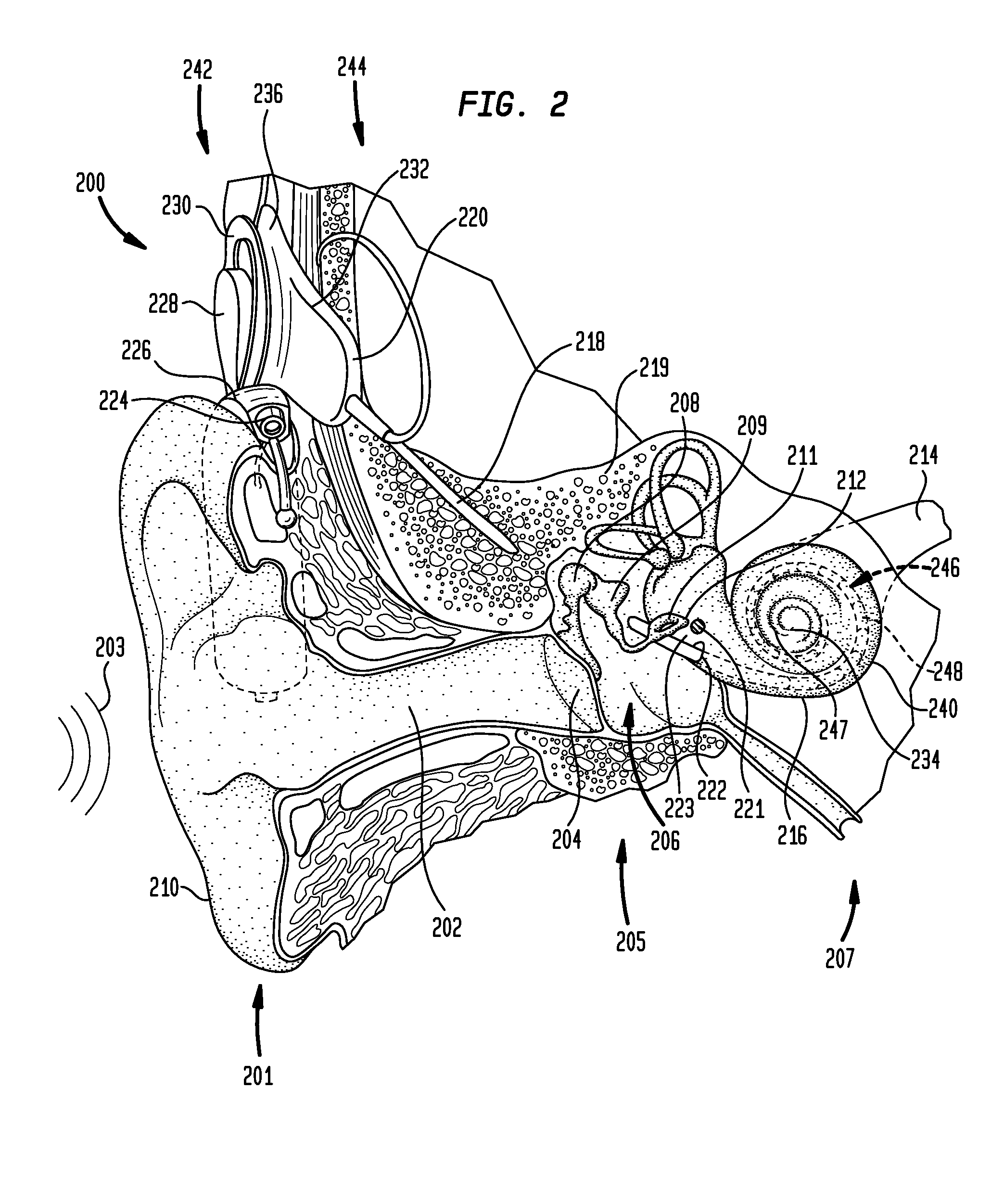
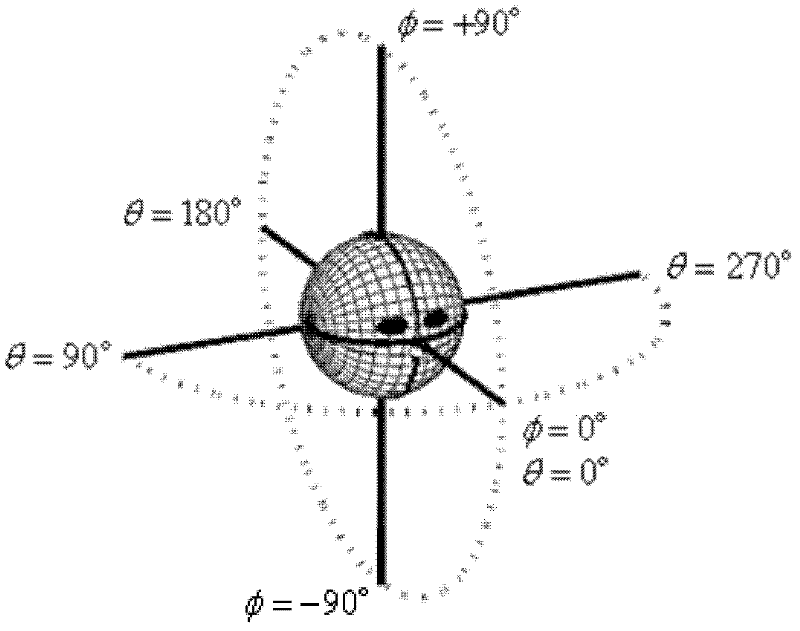
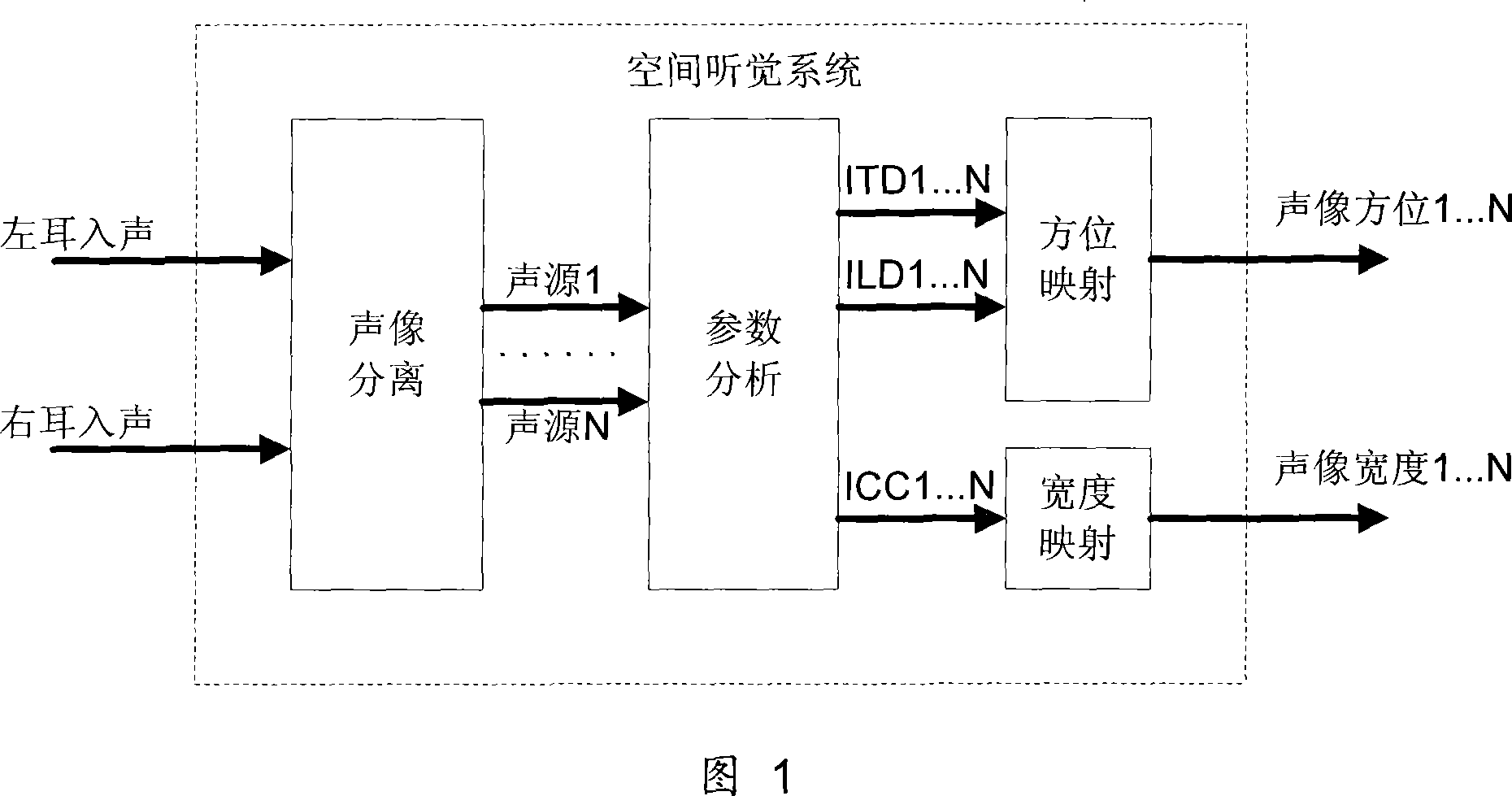
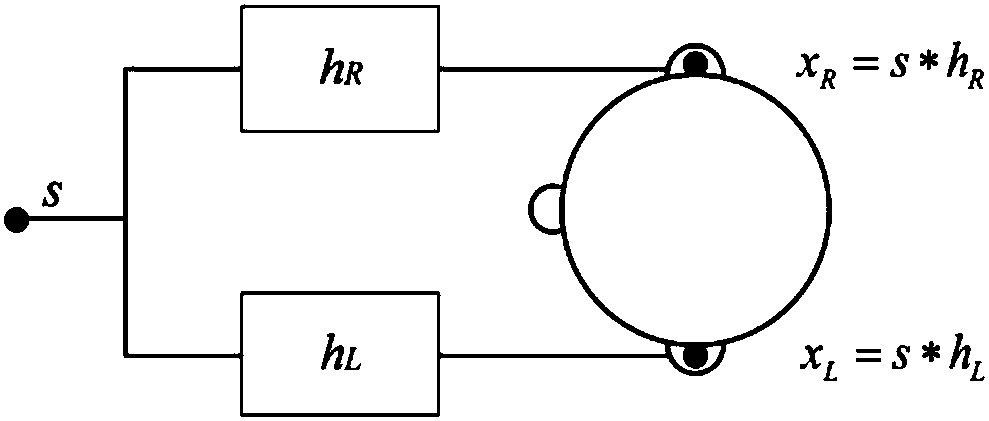
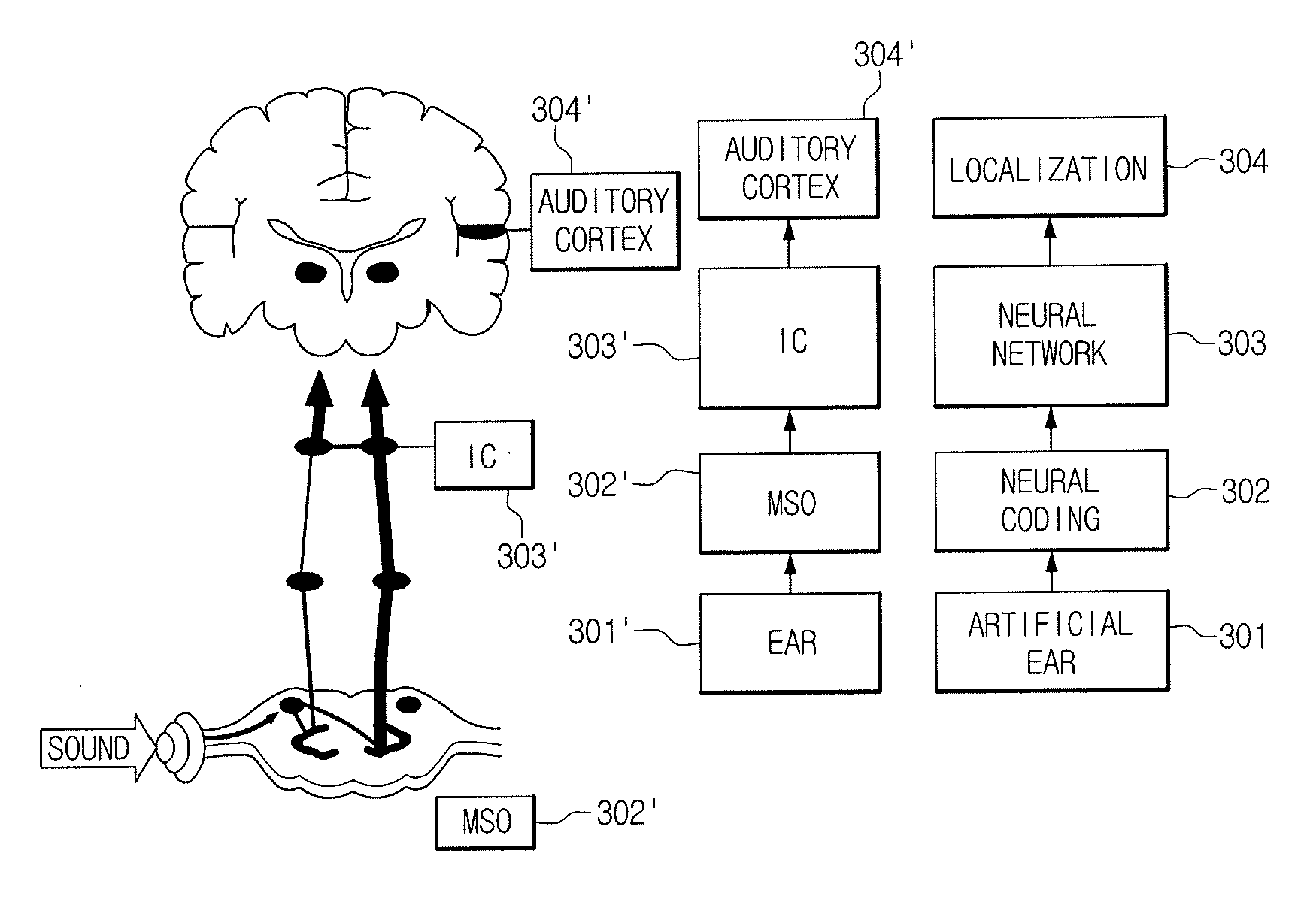
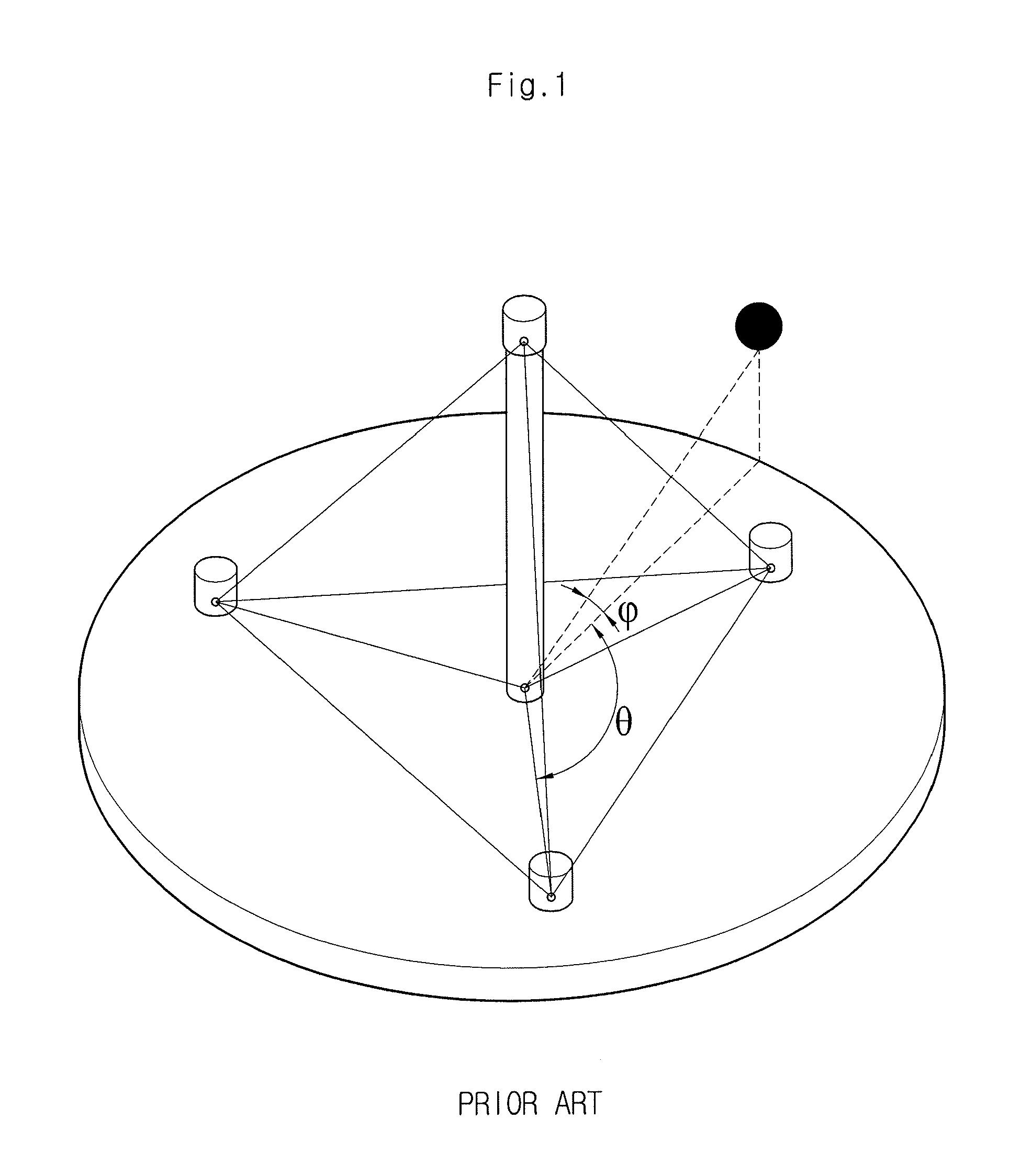
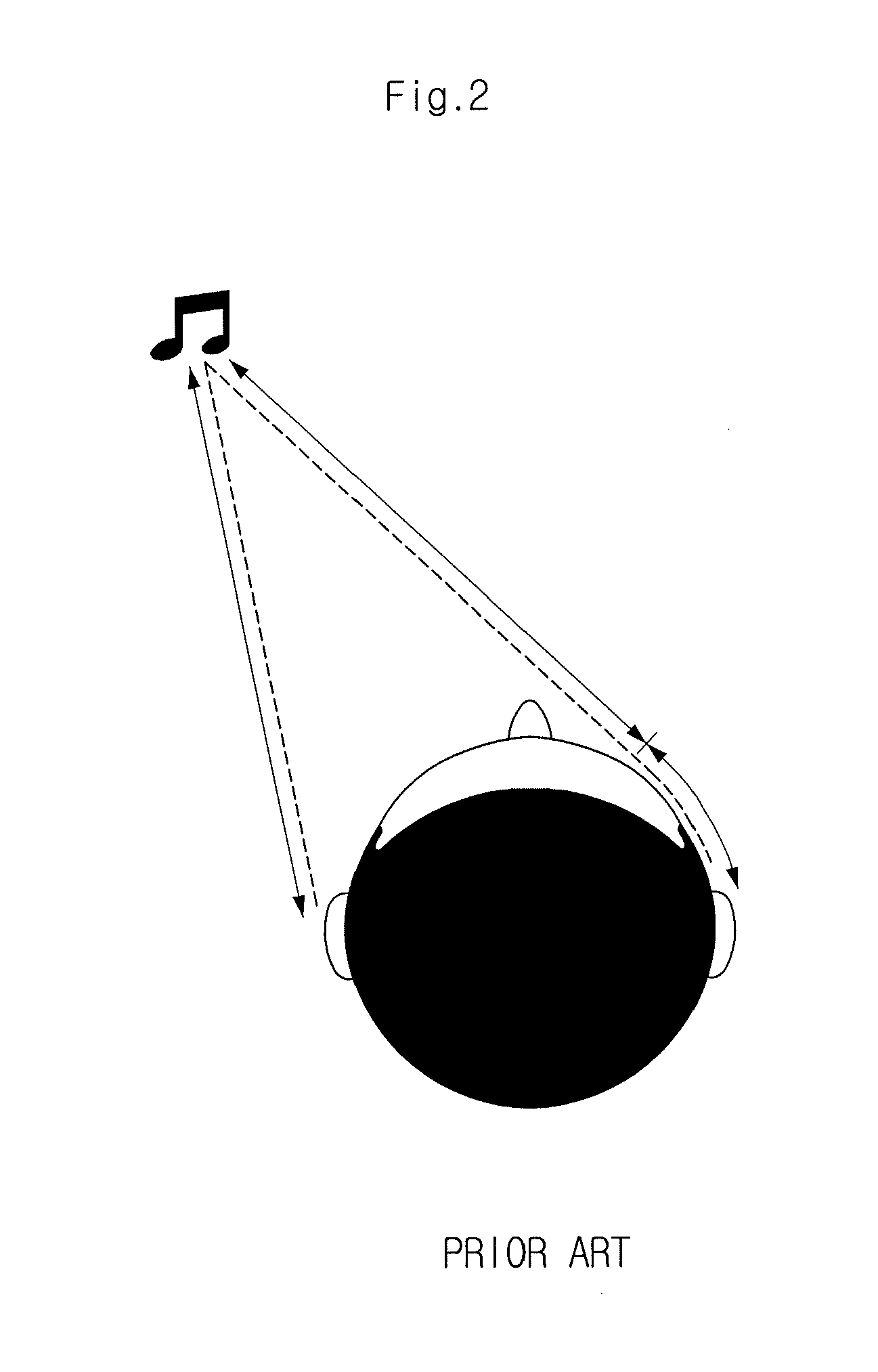
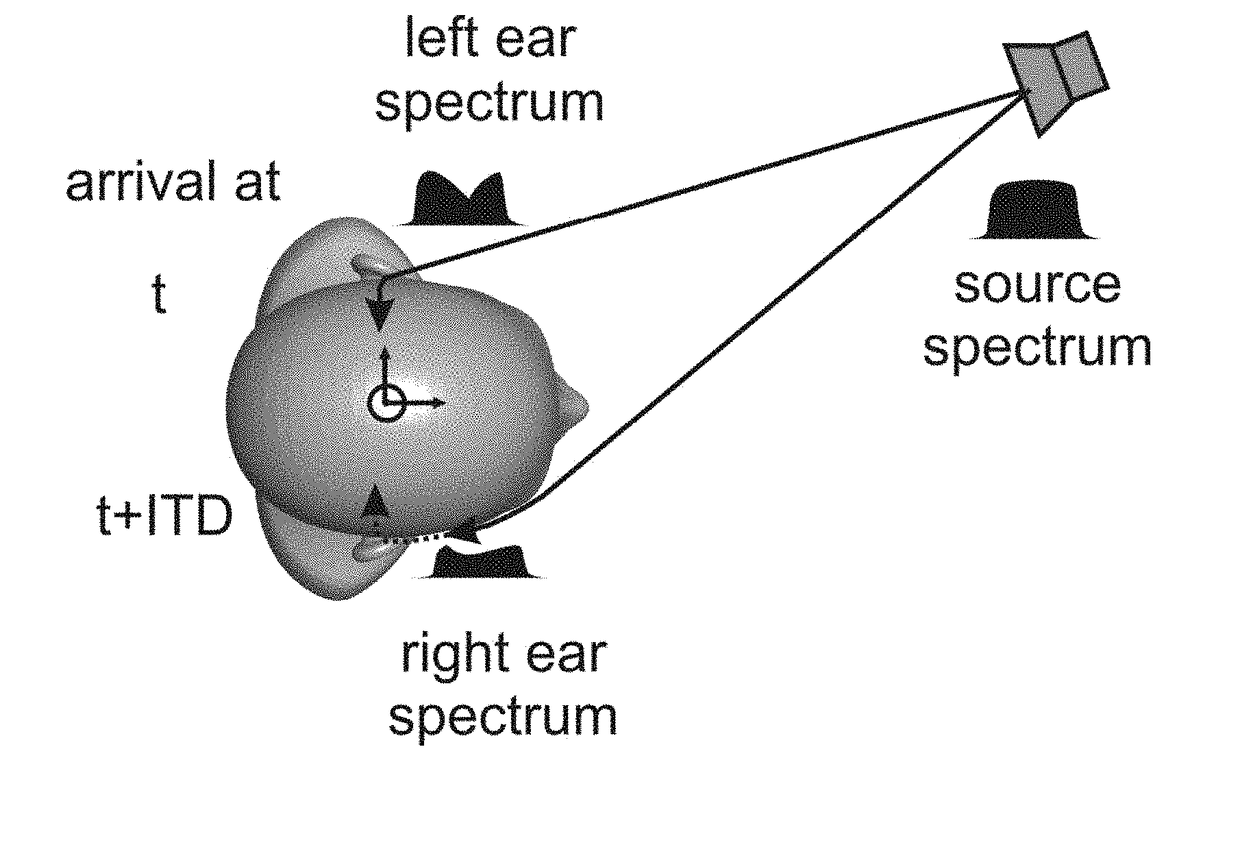
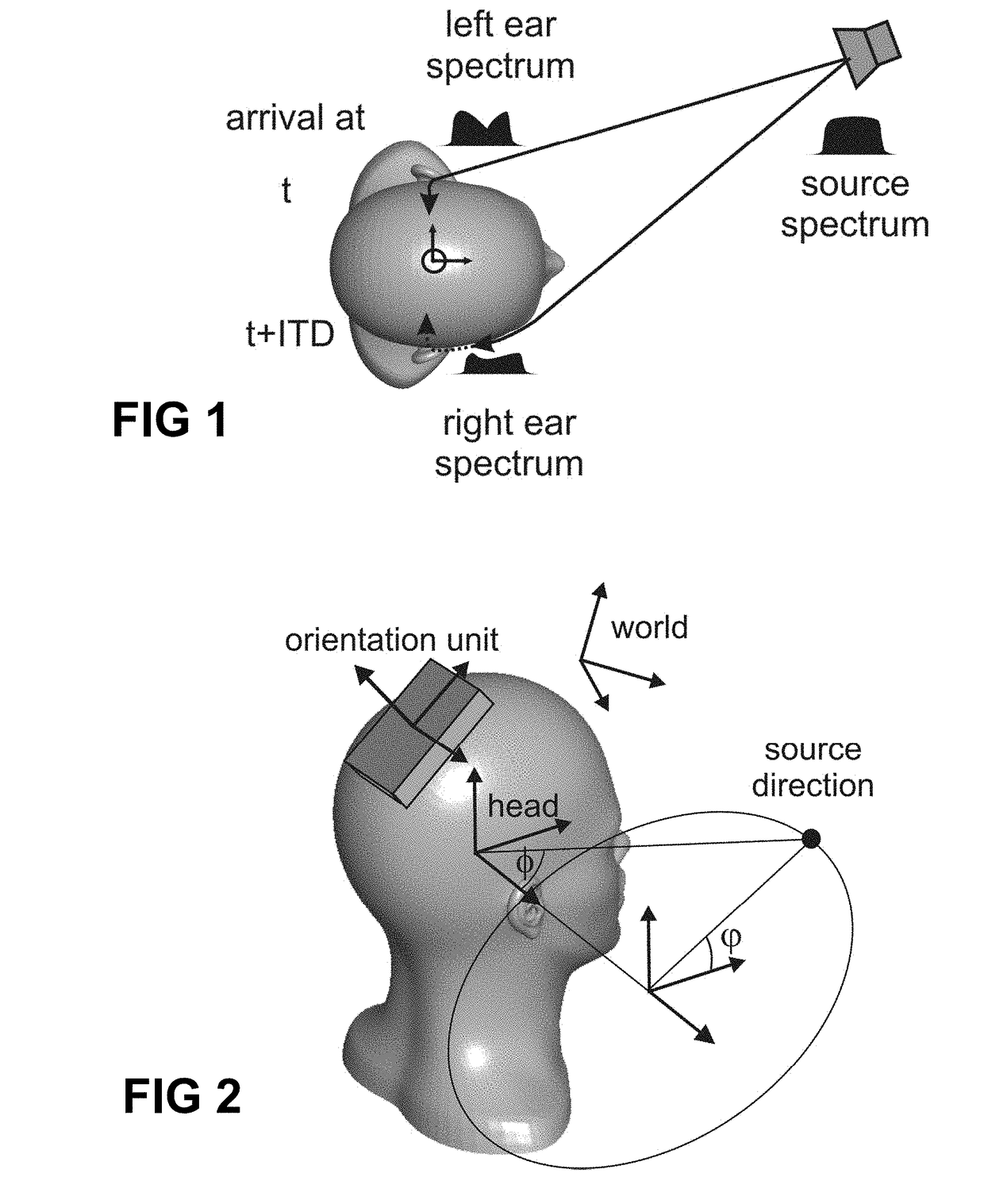
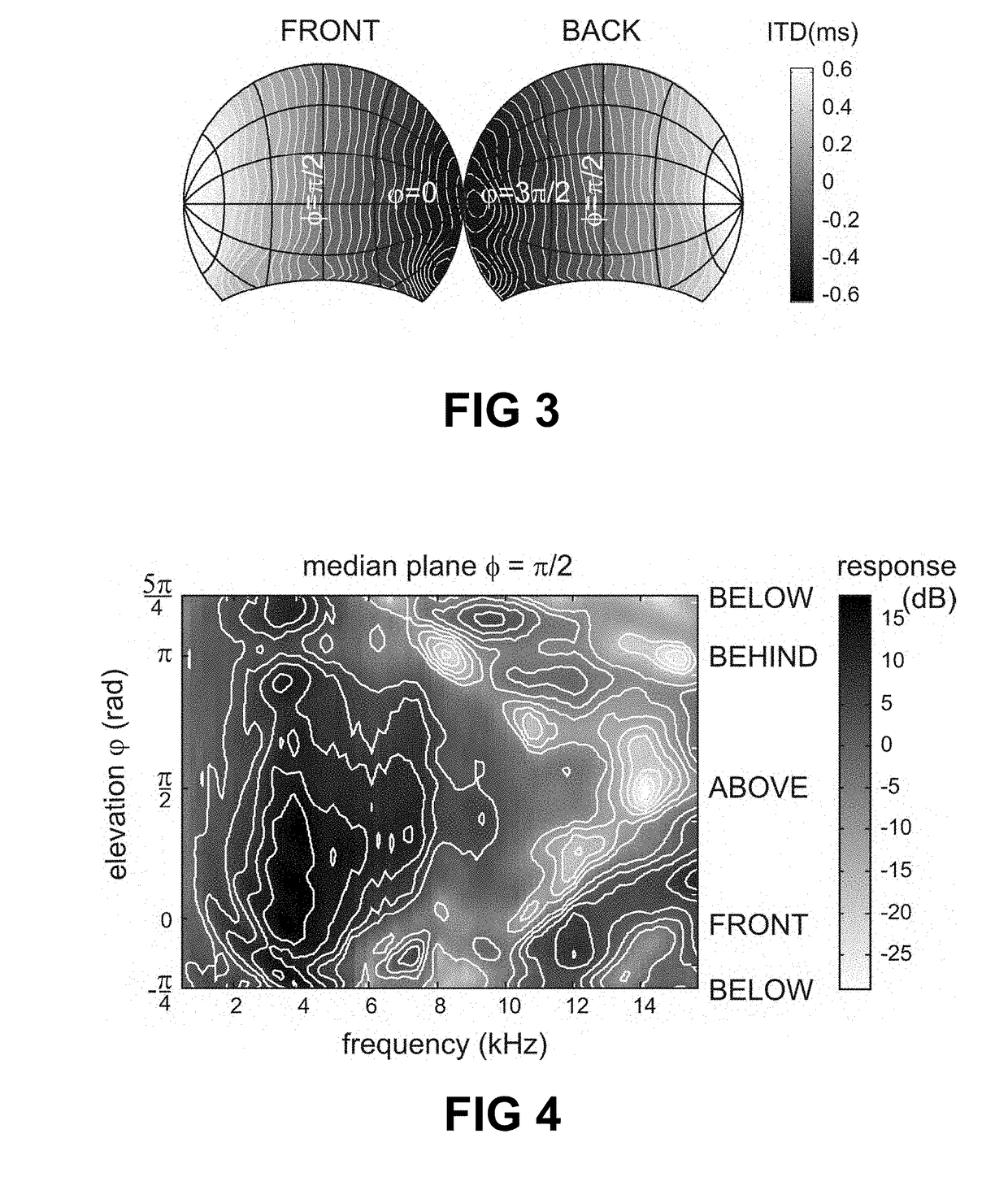
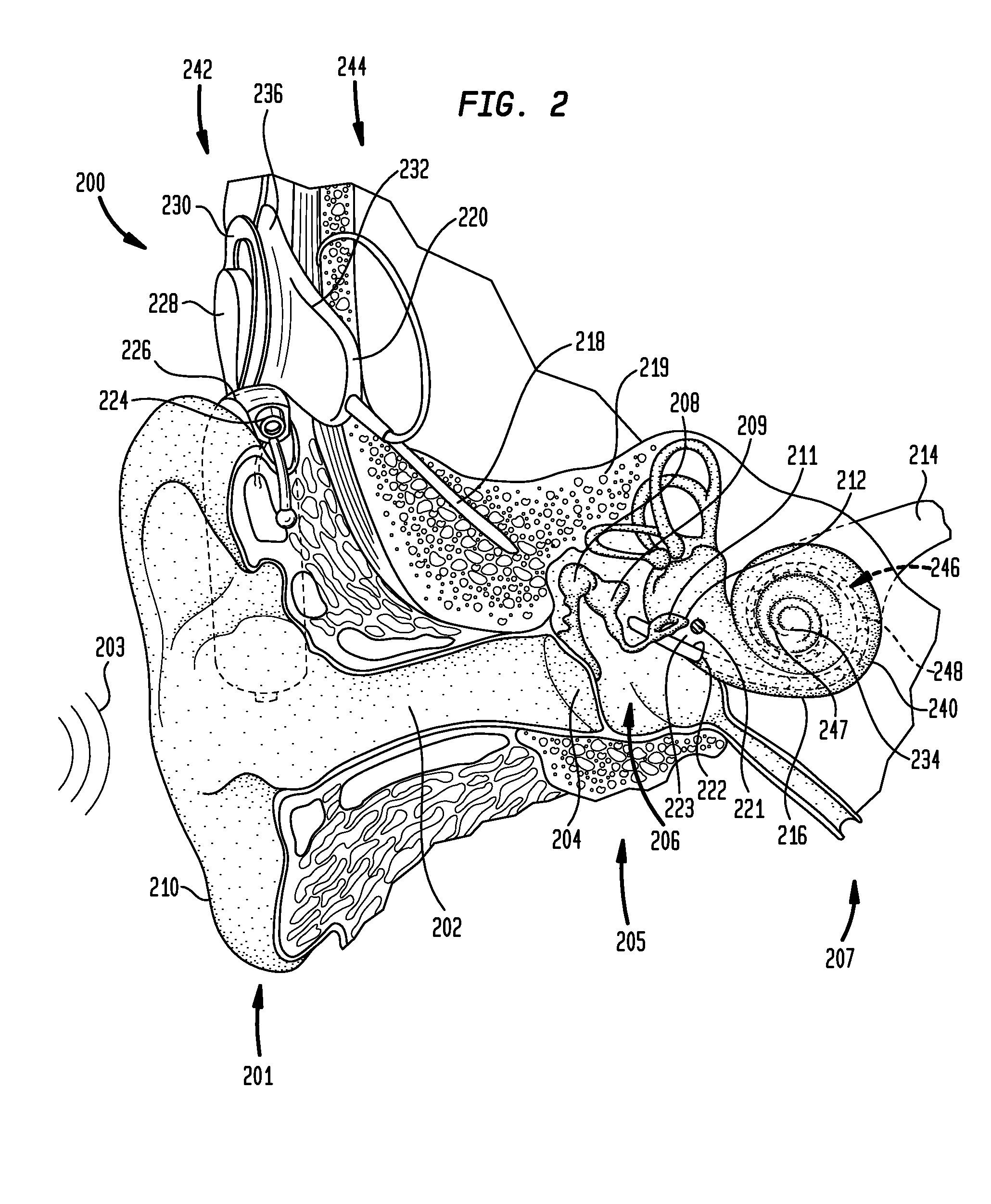
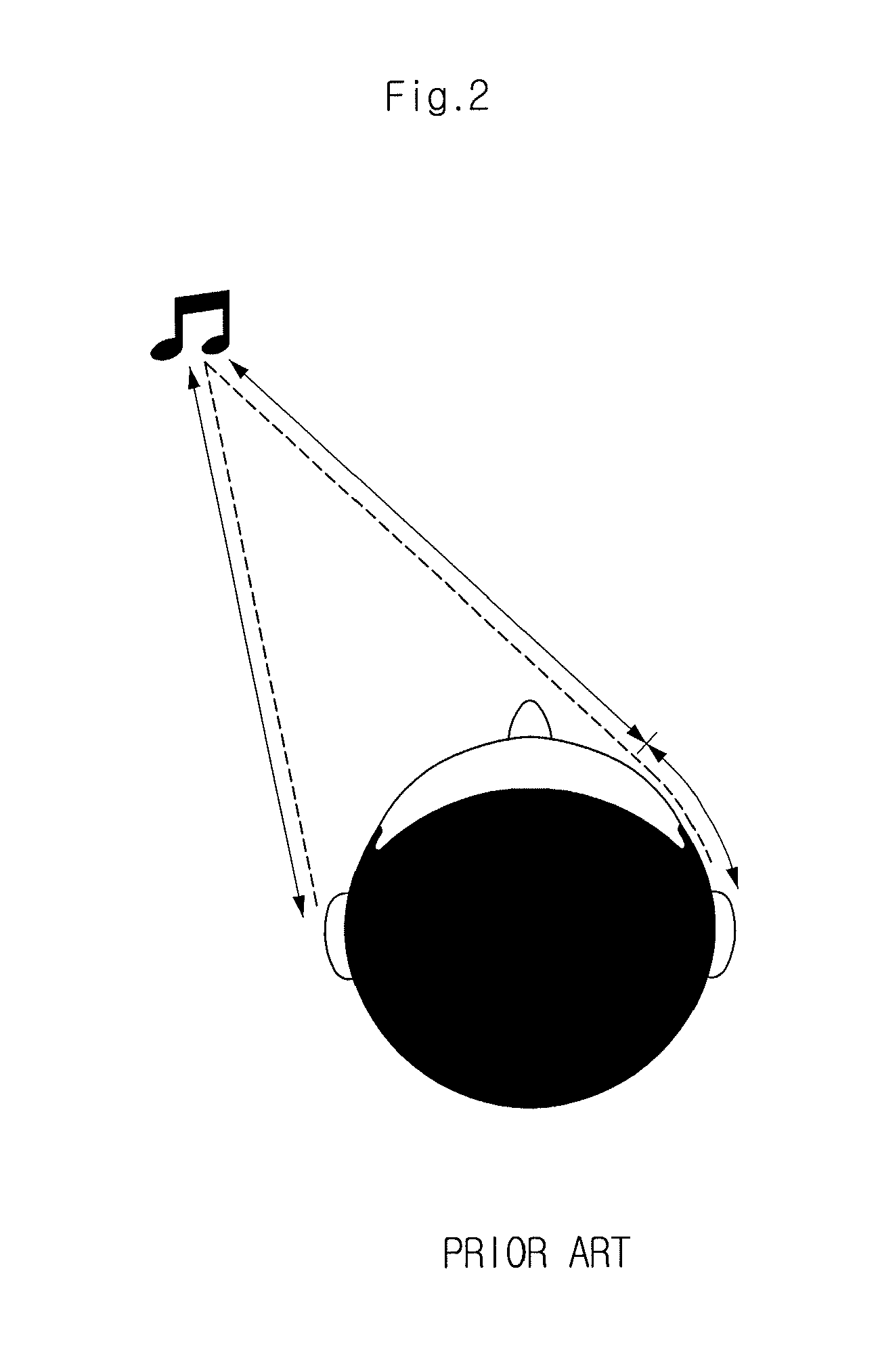
The interaural time difference (or ITD) when concerning humans or animals, is the difference in arrival time of a sound between two ears. It is important in the localization of sounds, as it provides a cue to the direction or angle of the sound source from the head. If a signal arrives at the head from one side, the signal has further to travel to reach the far ear than the near ear. This pathlength difference results in a time difference between the sound's arrivals at the ears, which is detected and aids the process of identifying the direction of sound source.
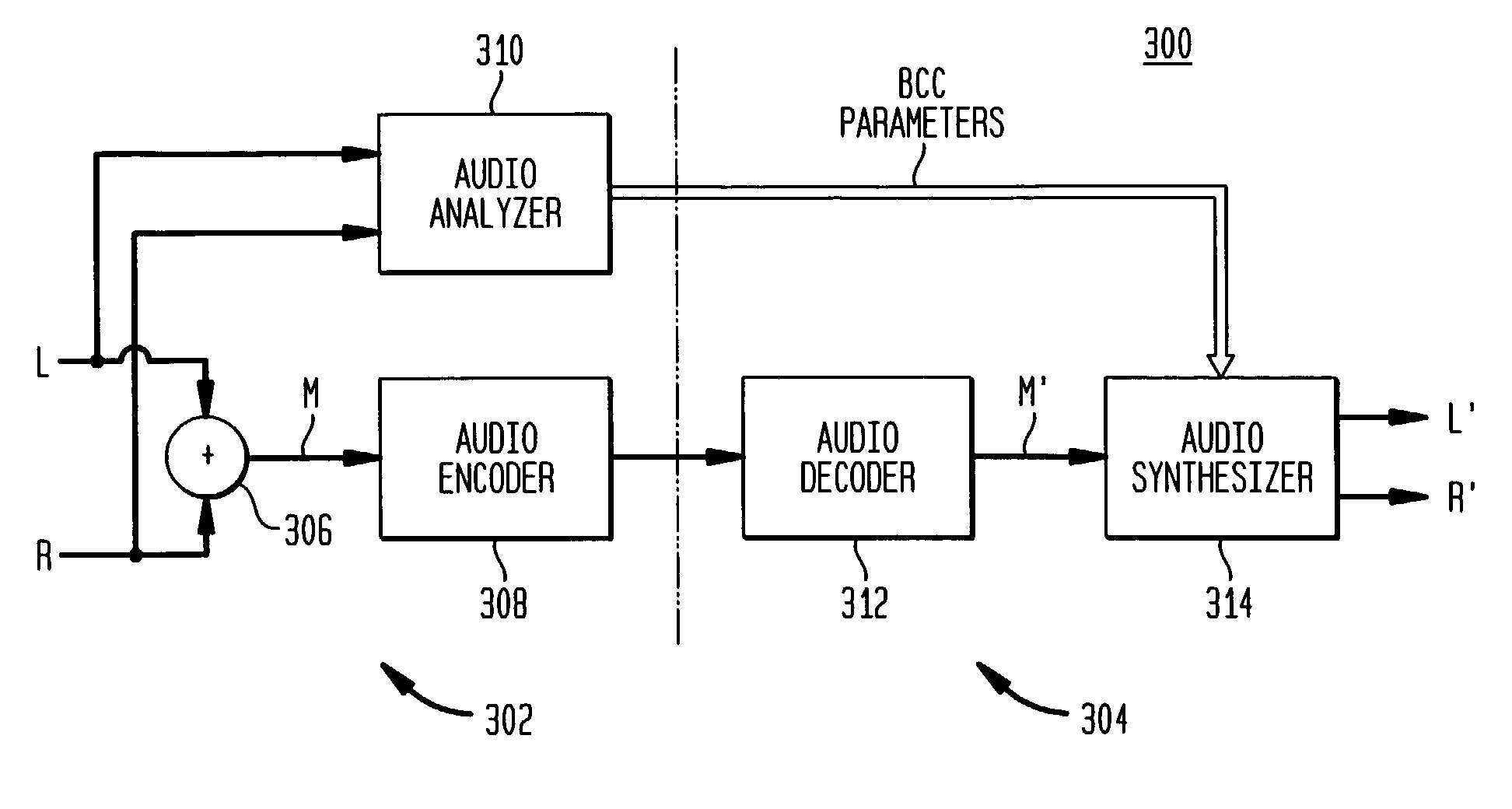
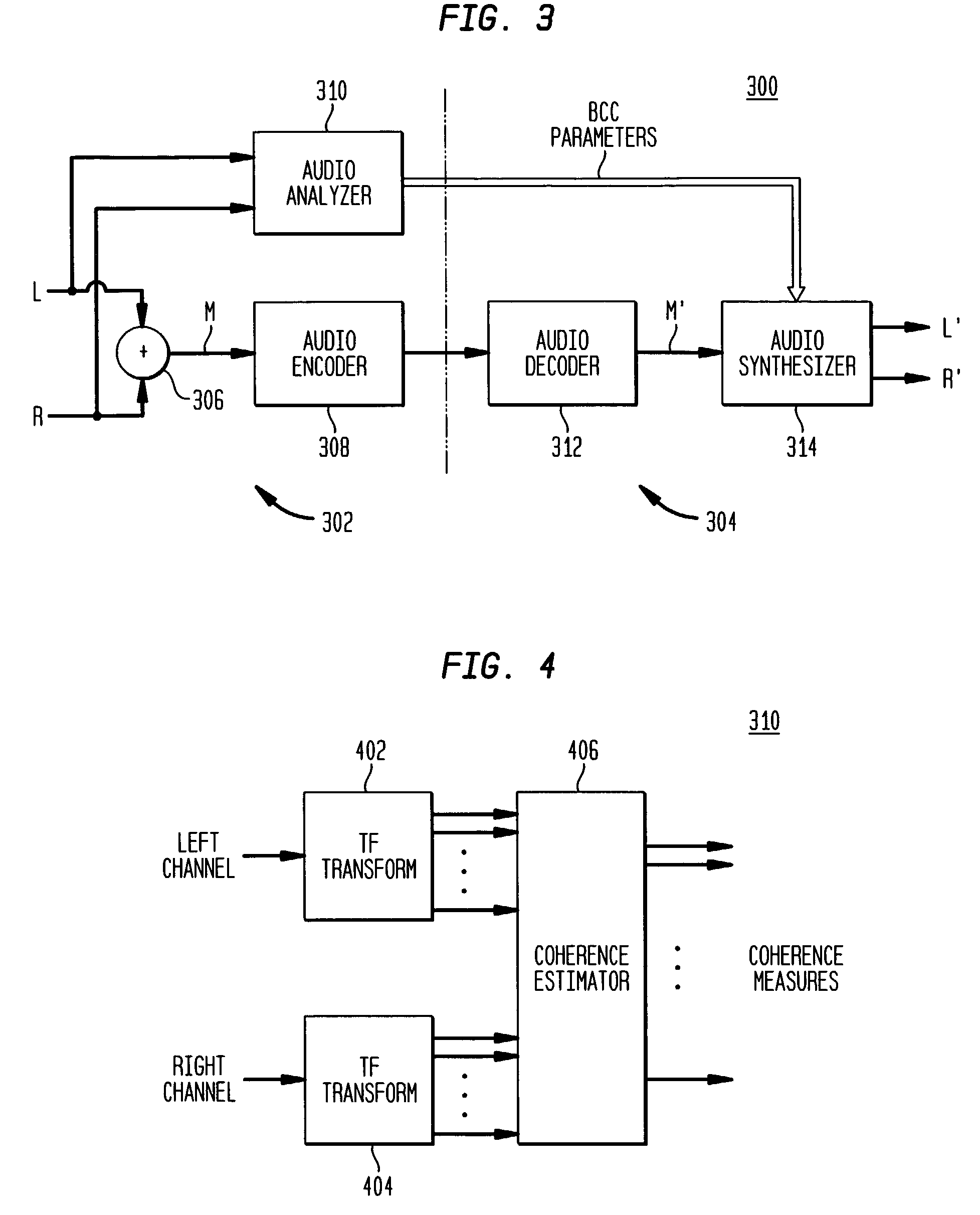
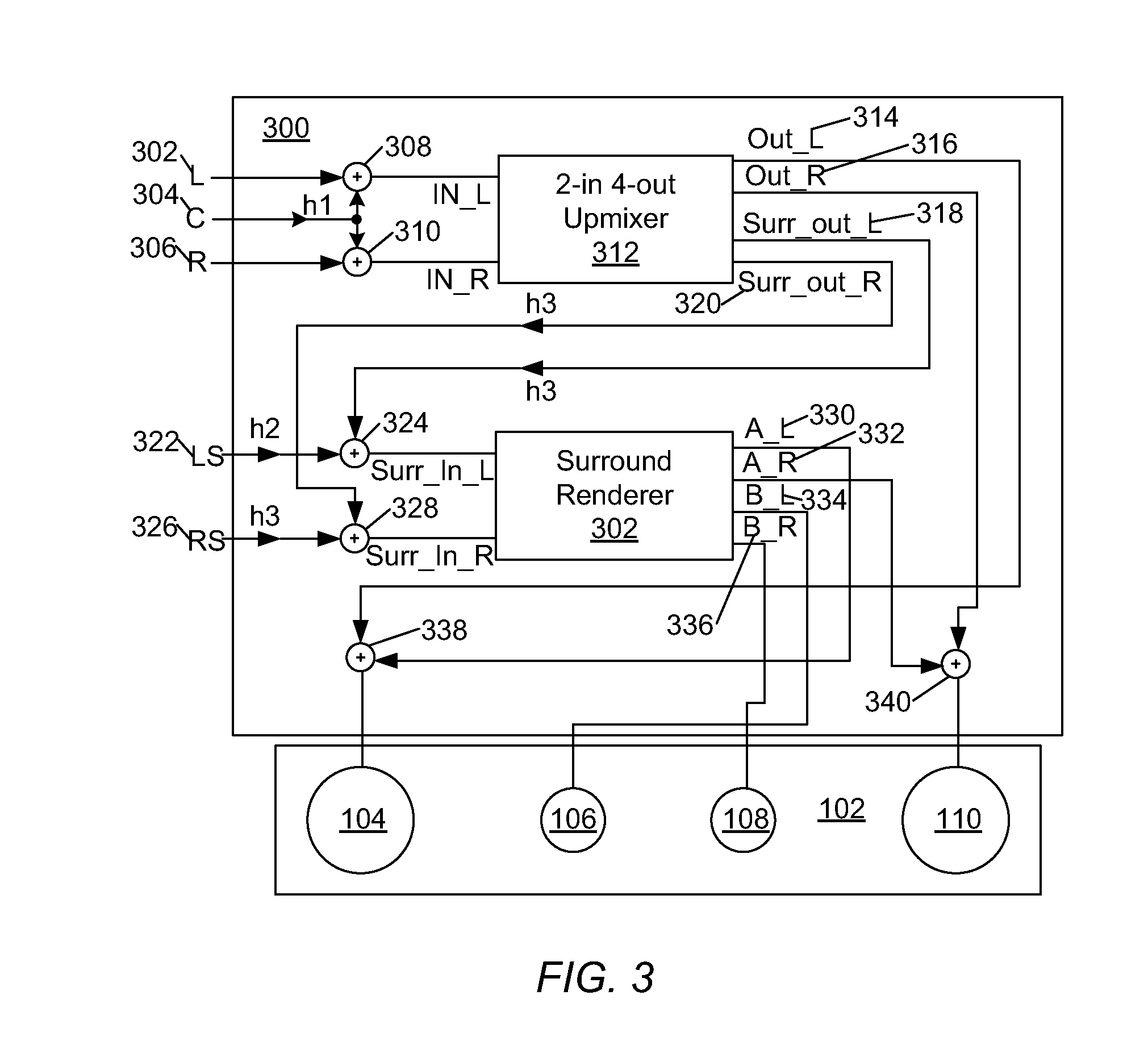
Coherence-based audio coding and synthesis
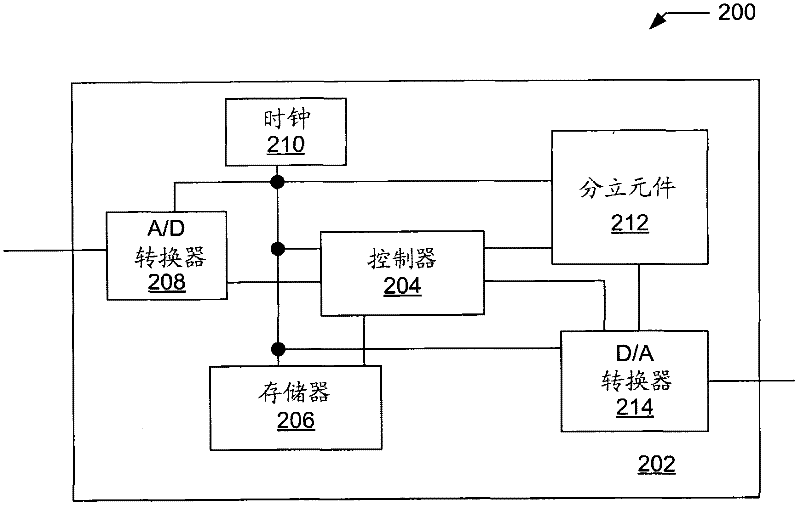
InactiveUS7006636B2Reduce transmission bandwidth requirementsReduce bandwidth requirementsSpeech analysisPseudo-stereo systemsInteraural time differenceVocal tract
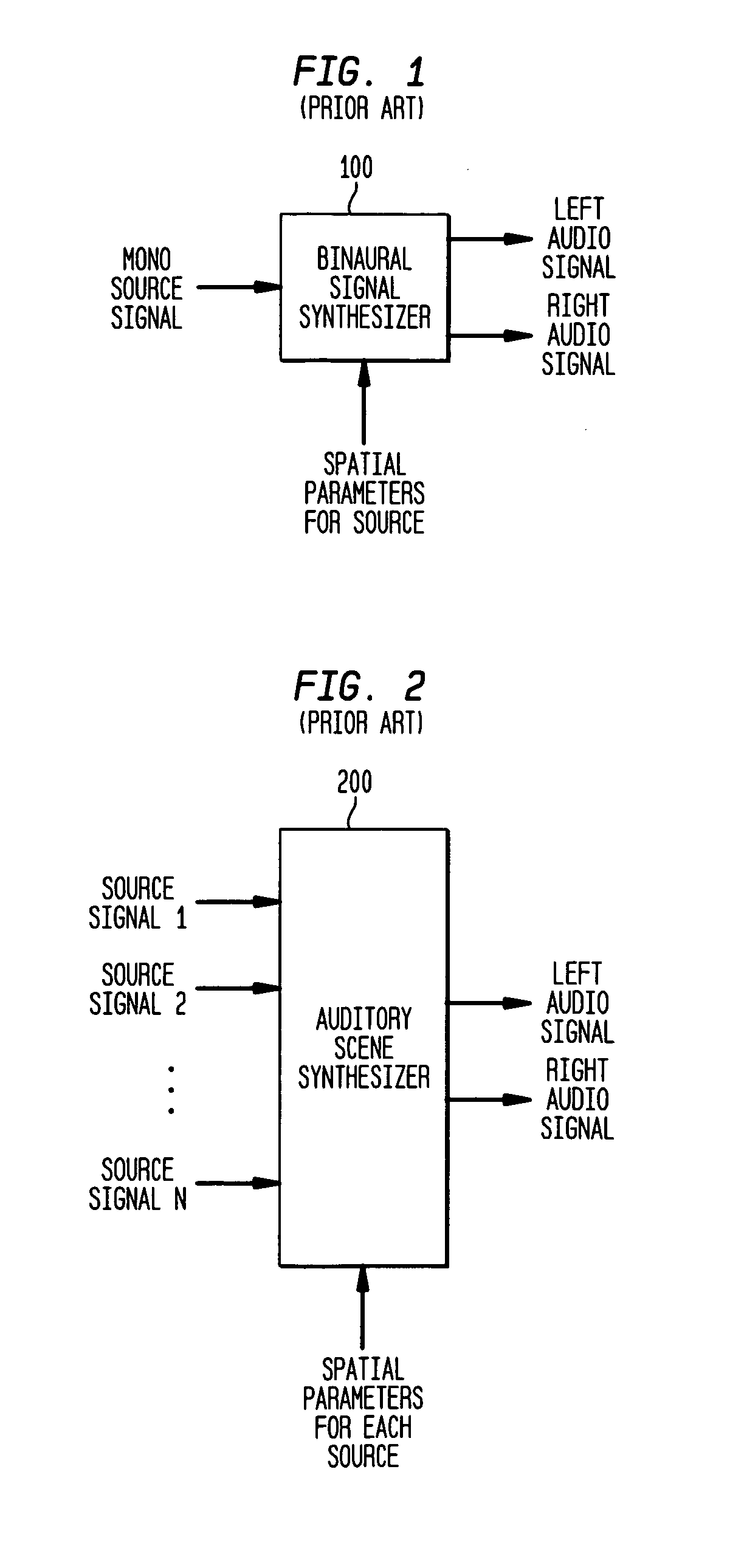
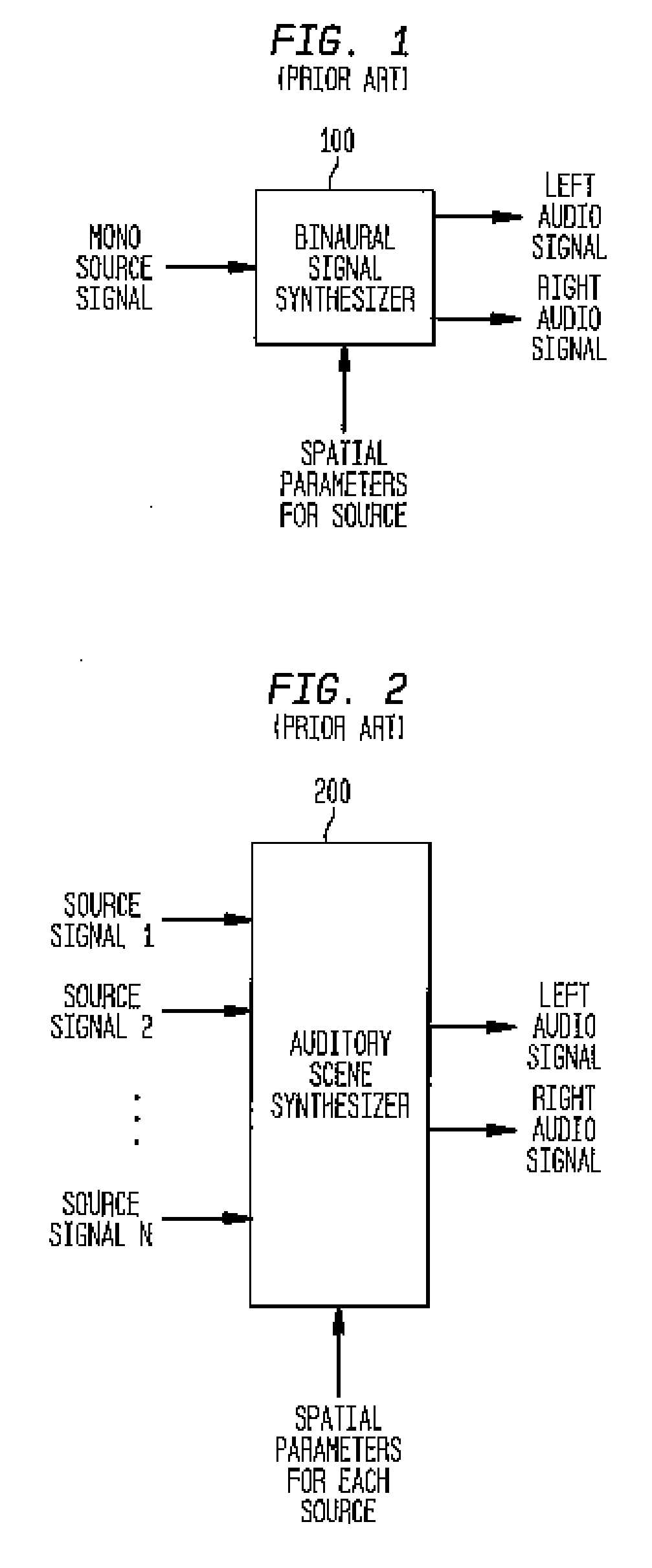
An auditory scene is synthesized from a mono audio signal by modifying, for each critical band, an auditory scene parameter (e.g., an inter-aural level difference (ILD) and / or an inter-aural time difference (ITD)) for each sub-band within the critical band, where the modification is based on an average estimated coherence for the critical band. The coherence-based modification produces auditory scenes having objects whose widths more accurately match the widths of the objects in the original input auditory scene.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Perceptual synthesis of auditory scenes
InactiveUS7116787B2Special service for subscribersStereophonic systemsInteraural time differenceAudio signal flow
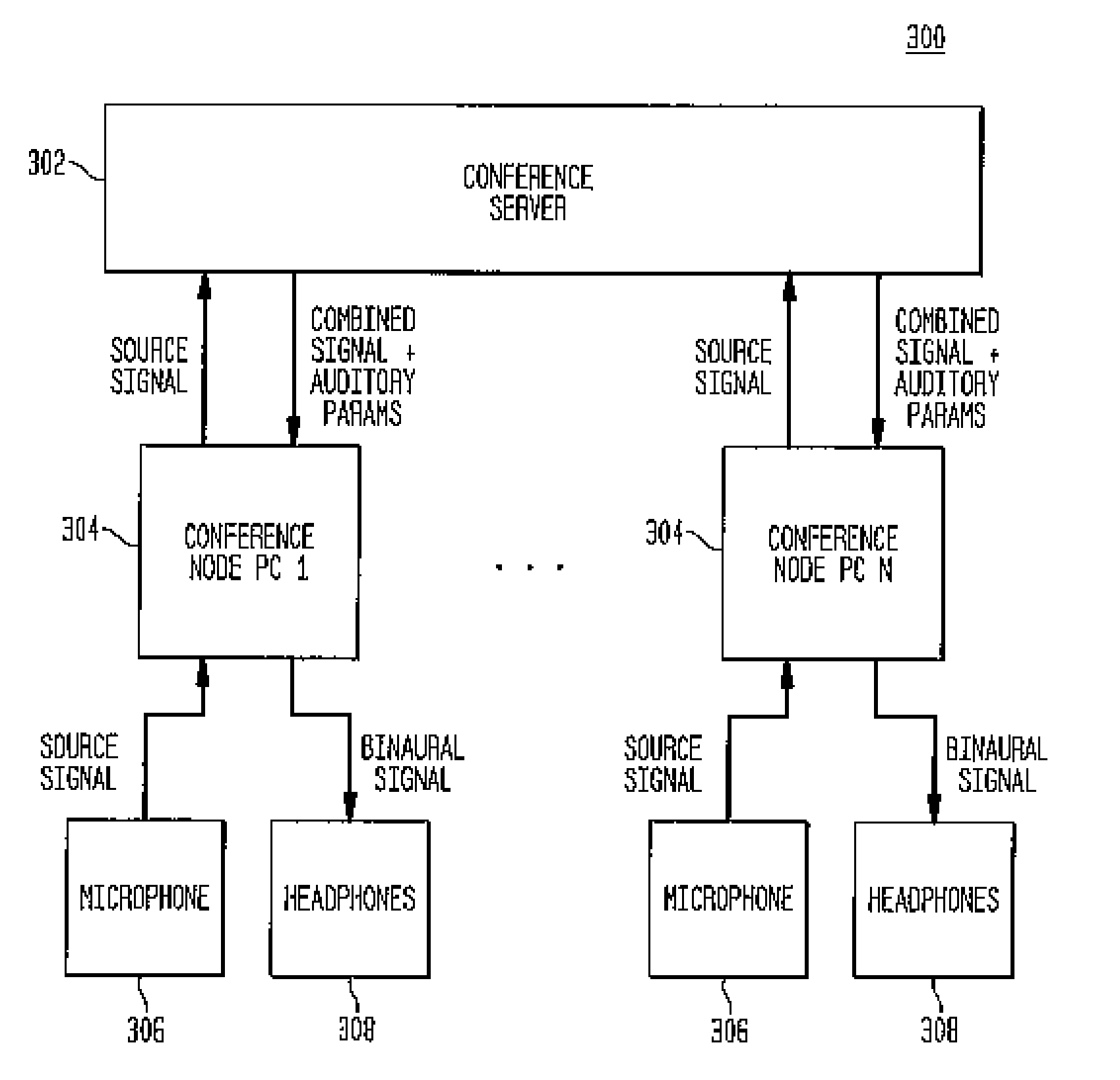
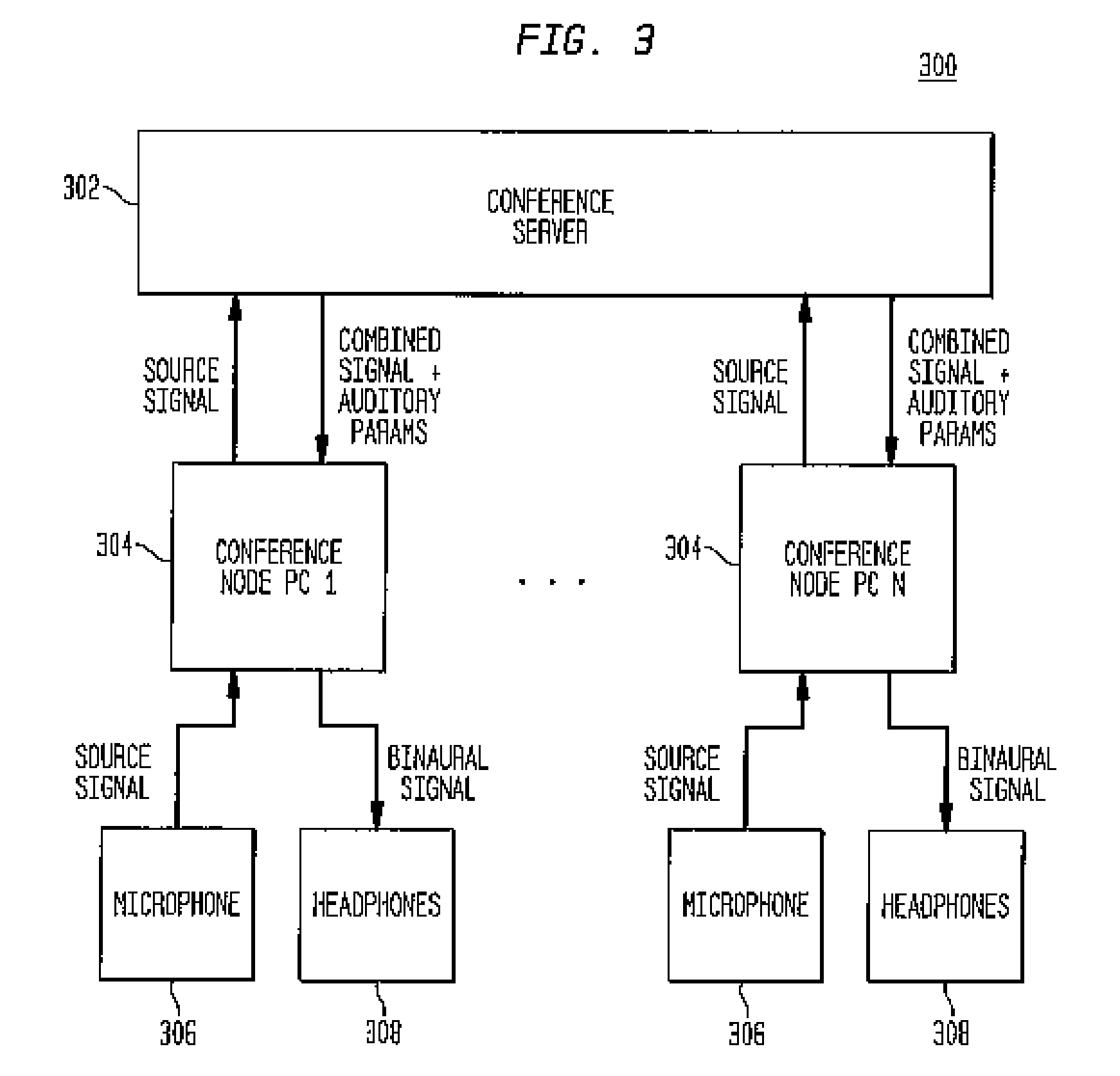
An auditory scene is synthesized by applying two or more different sets of one or more spatial parameters (e.g., an inter-ear level difference (ILD), inter-ear time difference (ITD), and / or head-related transfer function (HRTF)) to two or more different frequency bands of a combined audio signal, where each different frequency band is treated as if it corresponded to a single audio source in the auditory scene. In one embodiment, the combined audio signal corresponds to the combination of two or more different source signals, where each different frequency band corresponds to a region of the combined audio signal in which one of the source signals dominates the others. In this embodiment, the different sets of spatial parameters are applied to synthesize an auditory scene comprising the different source signals. In another embodiment, the combined audio signal corresponds to the combination of the left and right audio signals of a binaural signal corresponding to an input auditory scene. In this embodiment, the different sets of spatial parameters are applied to reconstruct the input auditory scene. In either case, transmission bandwidth requirements are reduced by reducing to one the number of different audio signals that need to be transmitted to a receiver configured to synthesize / reconstruct the auditory scene.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for three-dimensional audio display
InactiveUS7231054B1Stereophonic systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsInteraural time differenceFrequency spectrum
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
System and method for enhancing the binaural representation for hearing-impaired subjects
ActiveUS20140219486A1Improve representationElectrotherapySignal processingInteraural time differenceSound sources
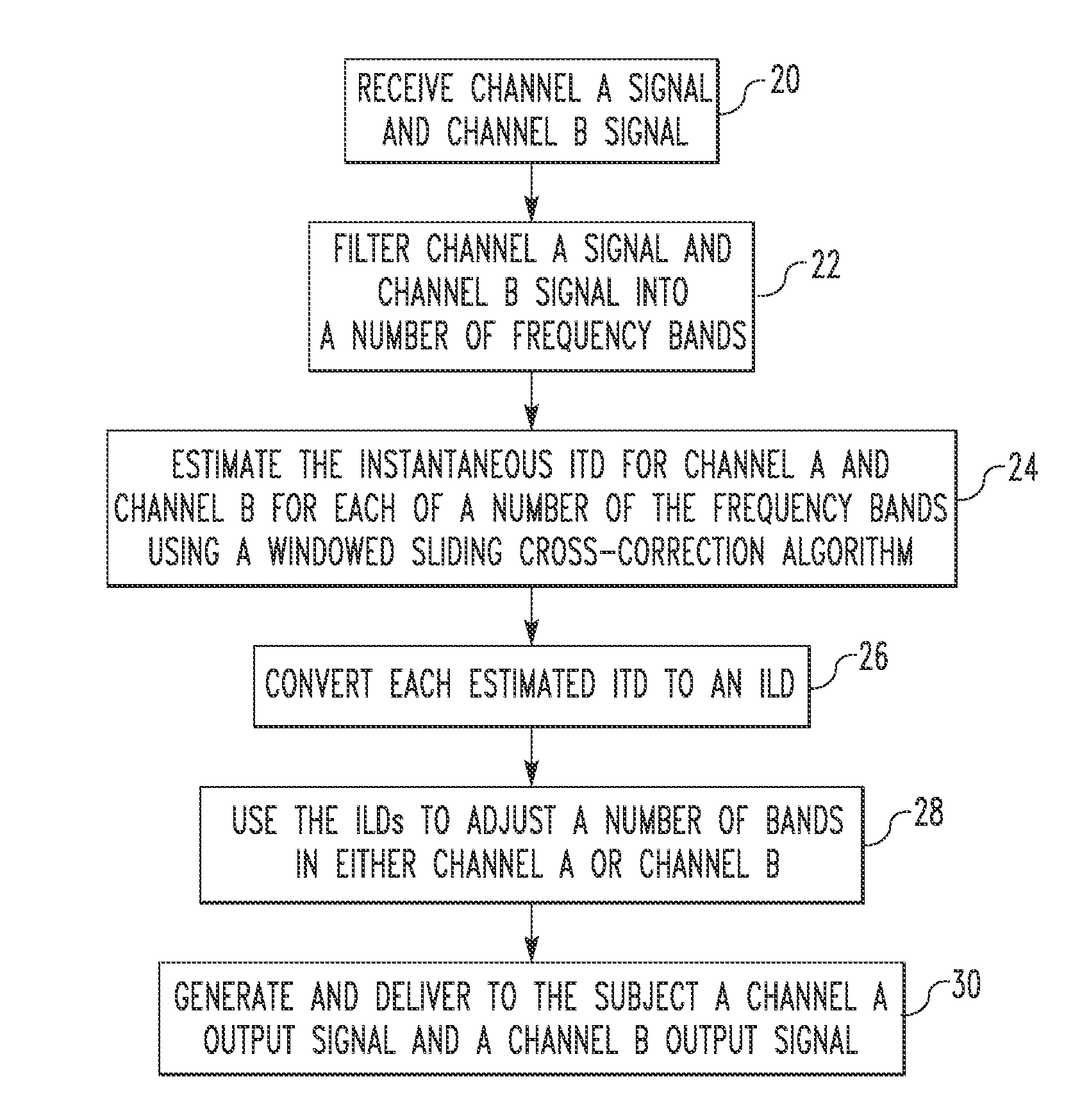
A method of enhancing binaural representation for a subject includes receiving a first signal and a second signal in response to a plurality of sound sources, generating a number of estimated interaural time differences using the first signal and the second signal, converting each of the number of estimated interaural time differences to a corresponding interaural level difference, using one or more of the corresponding interaural level differences to generate an adjusted first signal, and using the adjusted first signal to generate a number of signals delivered to the subject for enhancing the hearing of the subject.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH +1
Binaural Stimulation in Neural Auditory Prostheses or Hearing Aids
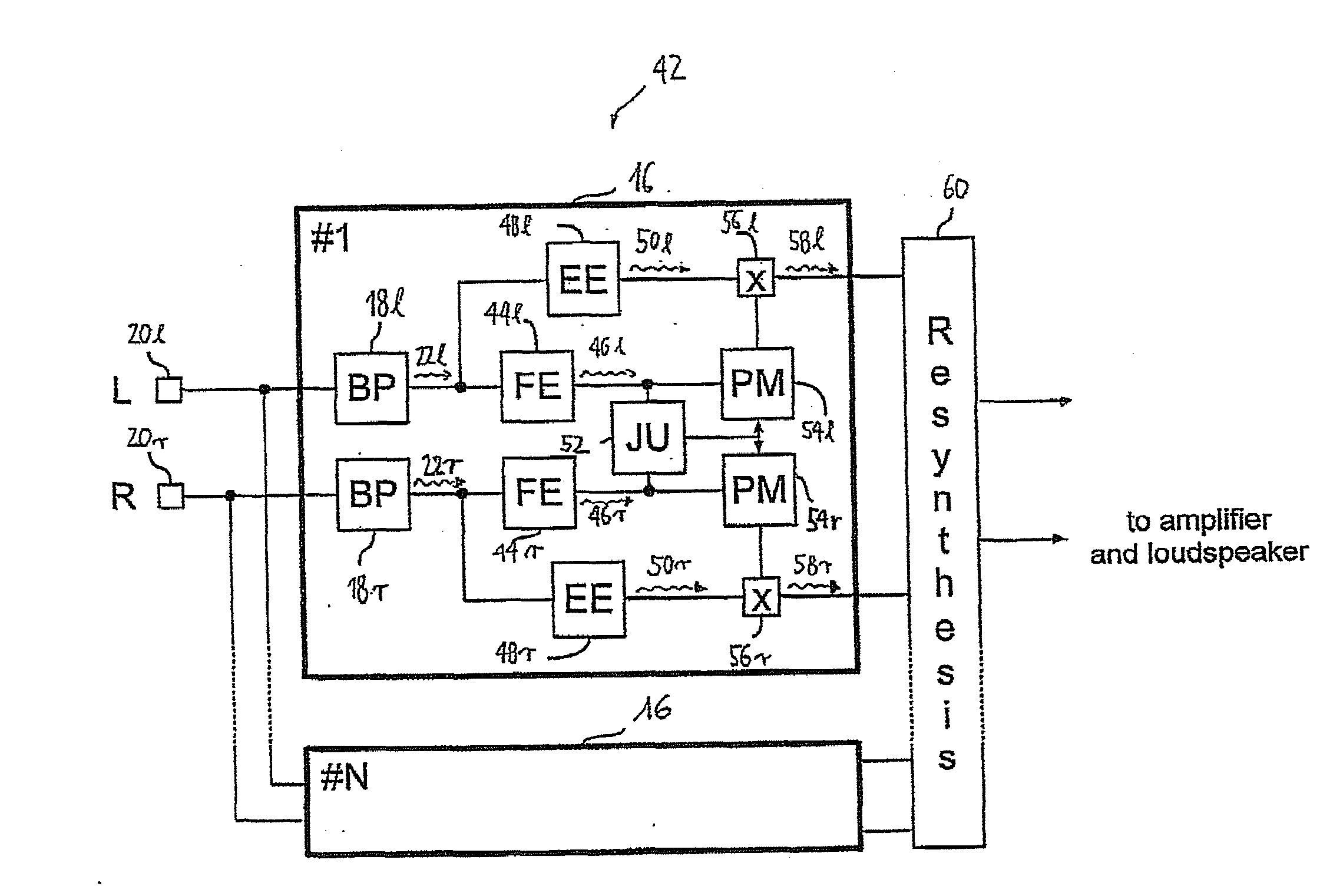
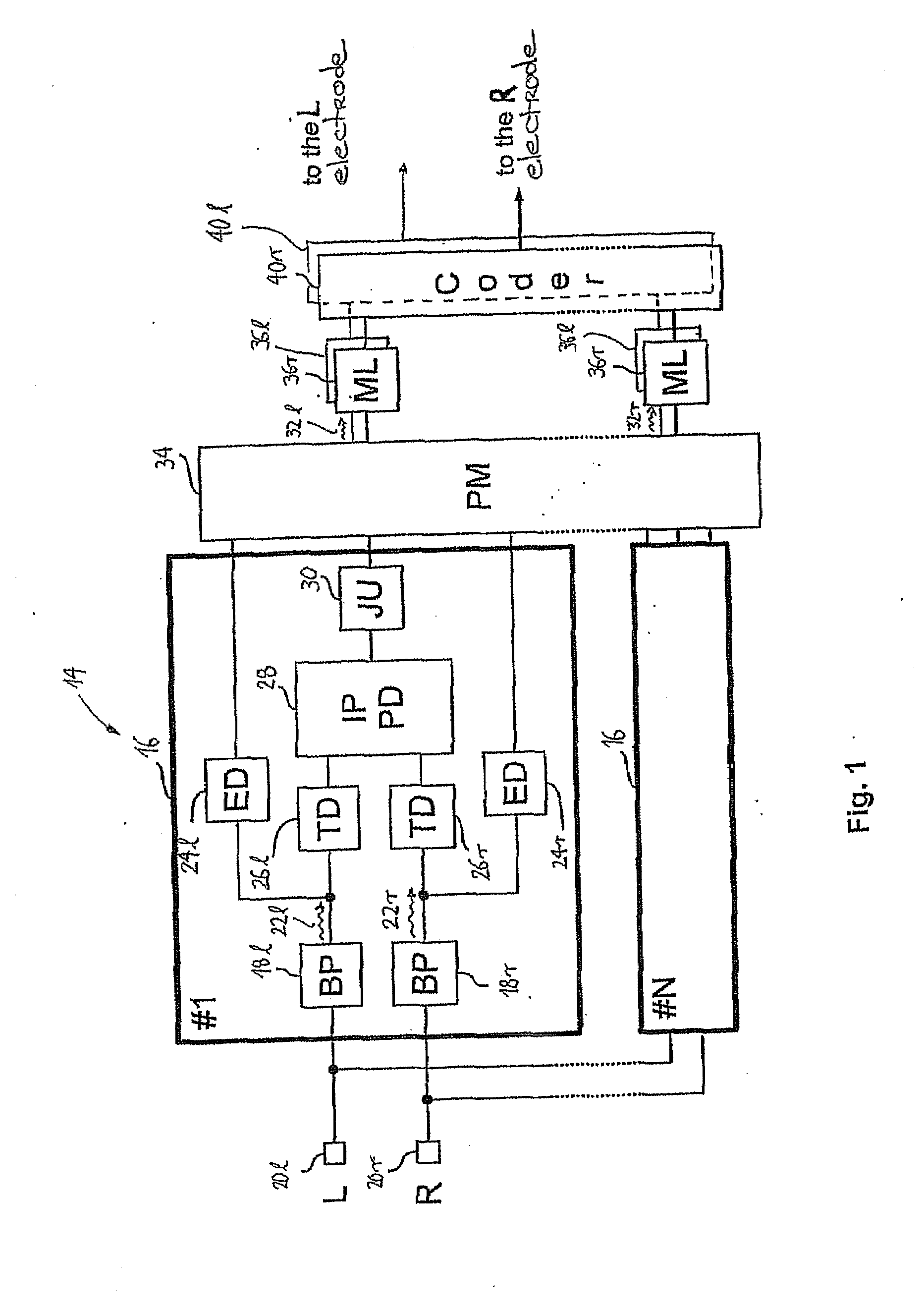
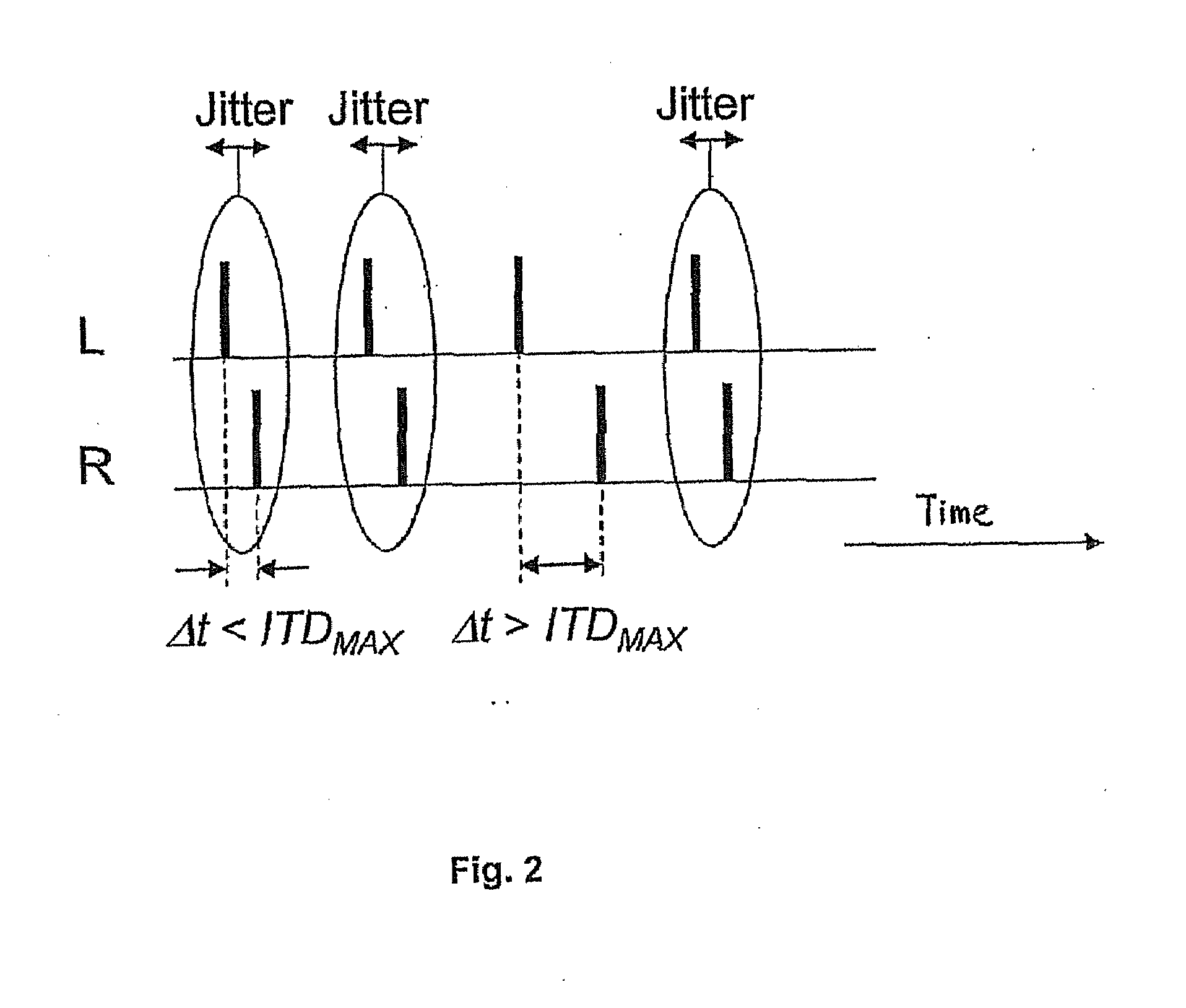
ActiveUS20080319509A1Avoid time-overlapElectrotherapyImplantable hearing aidsInteraural time differenceFine structure
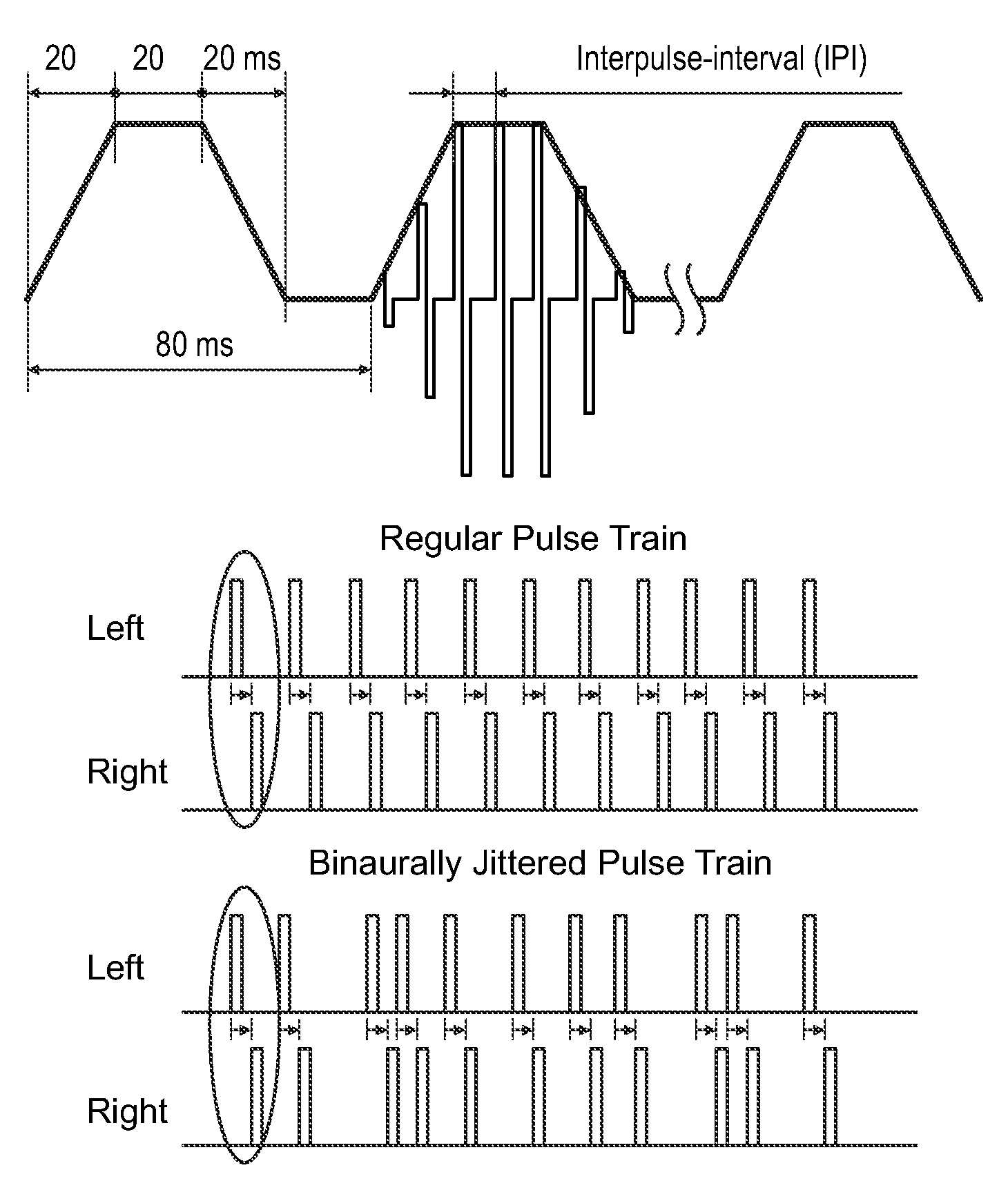
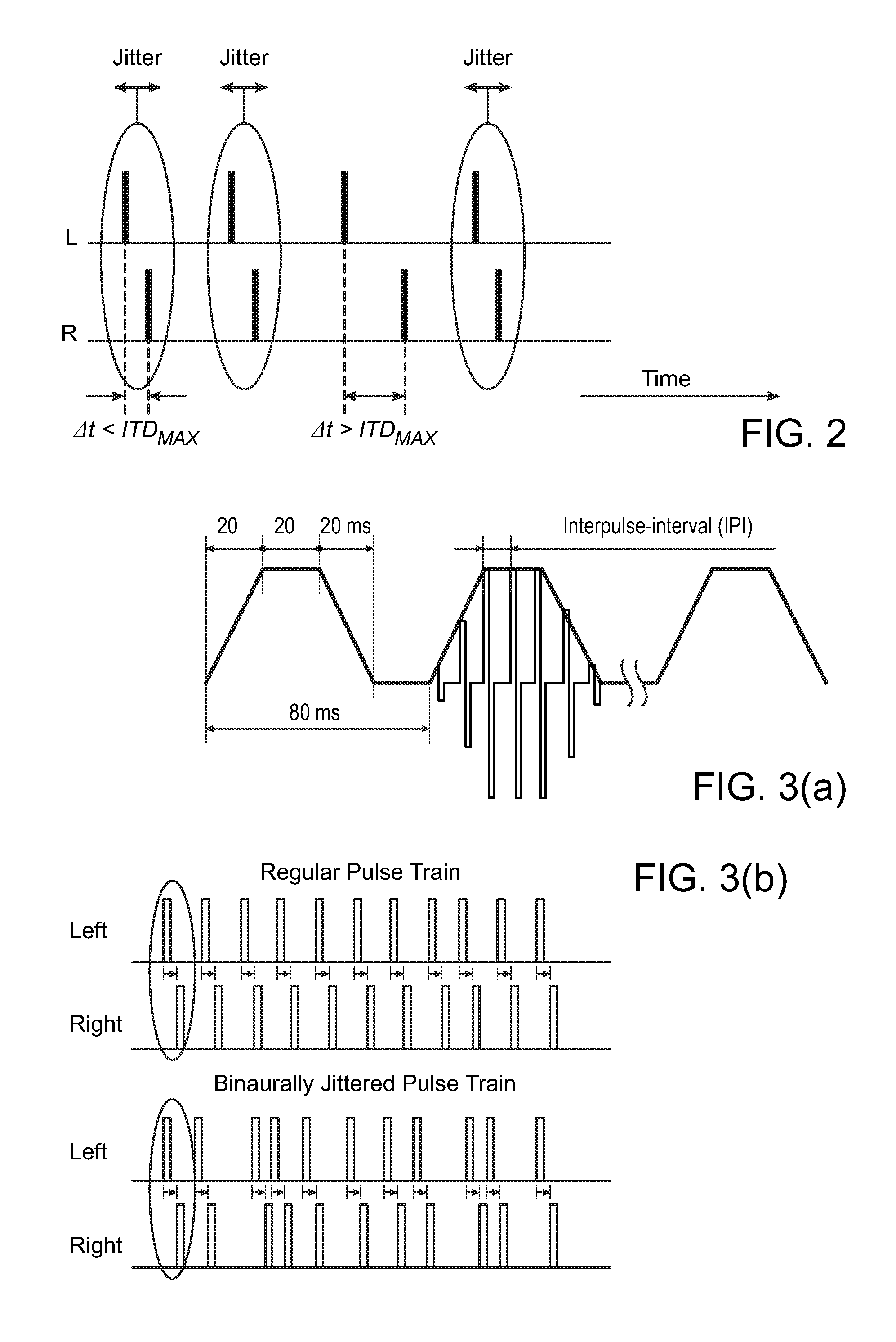
The present invention discloses of binaural stimulation in a neural auditory prosthesis. Binaural acoustic signals are generated that represent sound associated with a user's left and right ears respectively. Based on the binaural acoustic signals, corresponding binaural stimulation signals are generated for electrical stimulation of auditory nerve tissue of the user, wherein the binaural stimulation signals each include a fine structure component with periodic characteristics and interaural time difference (ITD) information. A phase jitter component is added to the binaural stimulation signals to reduce the periodic characteristics of the fine structure component while preserving the interaural time difference (ITD) information.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Dual-channel acoustic signal-based sound source localization method
InactiveCN102438189AFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsInteraural time differenceSound sources
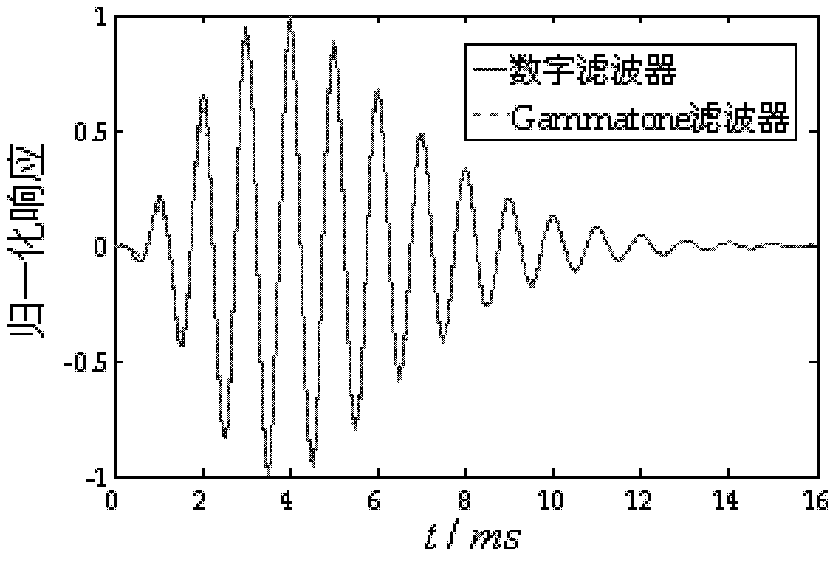
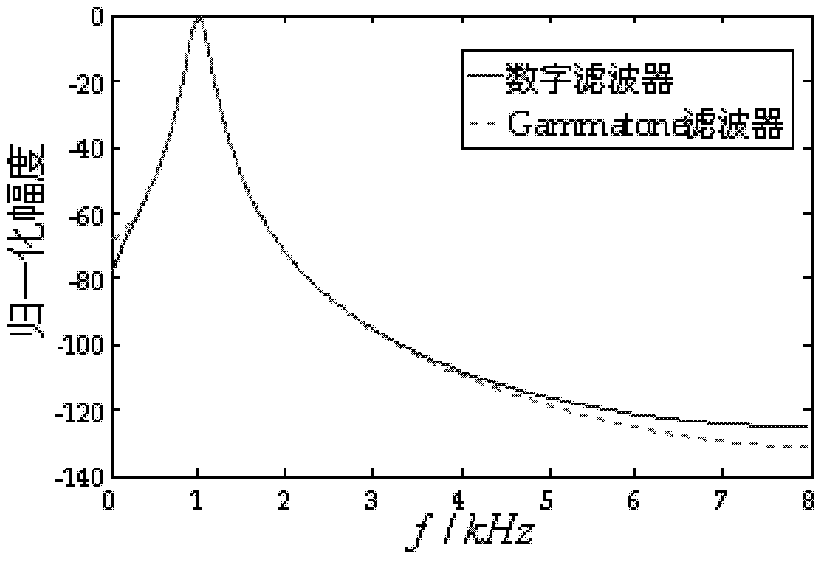
The invention relates to a dual-channel acoustic signal-based sound source localization method which is an improved sound source localization method. In the method, the mean value and the variance of the interaural time difference (ITD) and the interaural intensity difference (IID) of each frequency band are taken as characteristic clues for the localization of the azimuth of a sound source to set up an azimuth mapping model. In the actual localization of the sound source, dual-channel acoustic signals are inputted, the inputted acoustic signals are subjected to frequency band allocation and filtering processing by a Gammatone filter group which is similar to a human aural filter, then, are inputted to a characteristic extraction module, the localization information on the ITD and the IID of each subband is extracted, the localization clues on the ITD and the IID of each subband are integrated based on a Gaussian mixture model (GMM), and the likelihood values of the ITD and the IID on the corresponding frequency band of each azimuth angle are obtained and are served as the decision values for azimuth estimation. The system has higher sound source localization performance.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Binaural sound source positioning method based on binaural matching filter
ActiveCN103901401AImprove estimation accuracyEnsure real-time requirementsPosition fixationInteraural time differenceSound sources
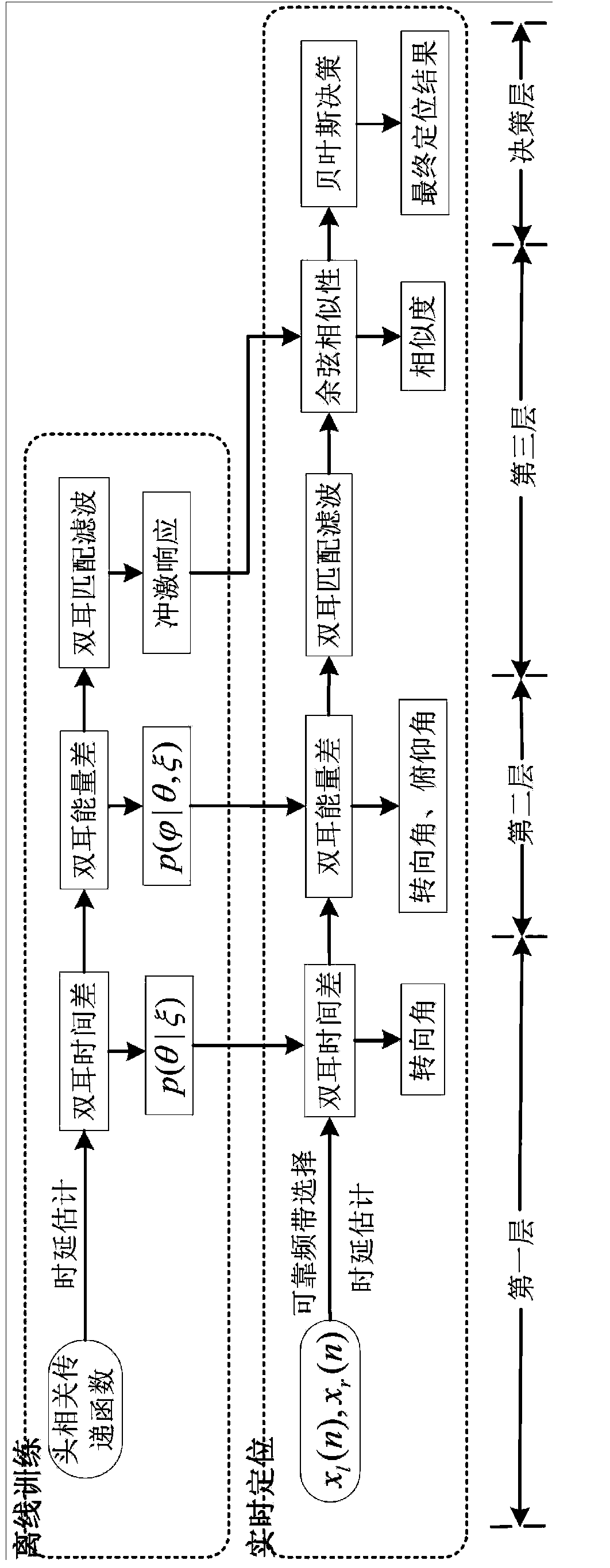
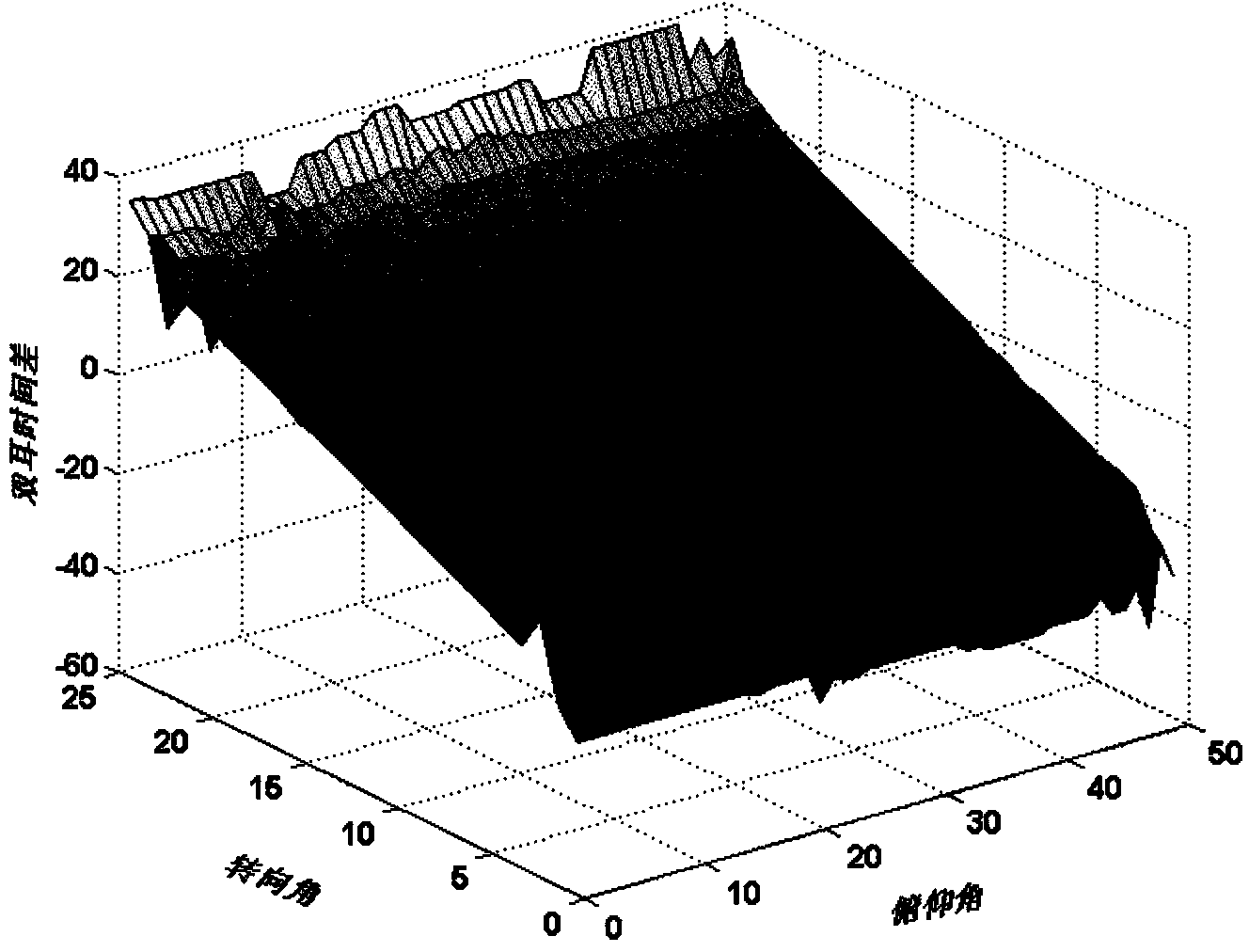
The invention discloses a novel binaural sound source positioning method based on a Bayesian hierarchical mode. Firstly, a reliable frequency band selection mechanism guarantees that a frequency band selected for estimating an interaural time difference is reliable, and estimation accuracy of the time difference is improved; secondly, an interaural intensity difference is used for shrinking a candidate direction set obtained in the first layer; thirdly, the fact that a binaural matching filter is used as novel binaural positioning characteristics is proposed in the third layer, the binaural matching filter describes differences between binaural signals, and the relation between the interaural time difference and the interaural intensity difference can be shown sufficiently; finally, searching space is gradually reduced in a three-layer positioning process, so that the direction with the maximum probability is obtained by adopting Bayesian decision criterions. By means of a hierarchical positioning system, the number of times of characteristic machining can be reduced effectively, time complexity of algorithms is reduced, and the real-time requirement of the sound source positioning system is guaranteed.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
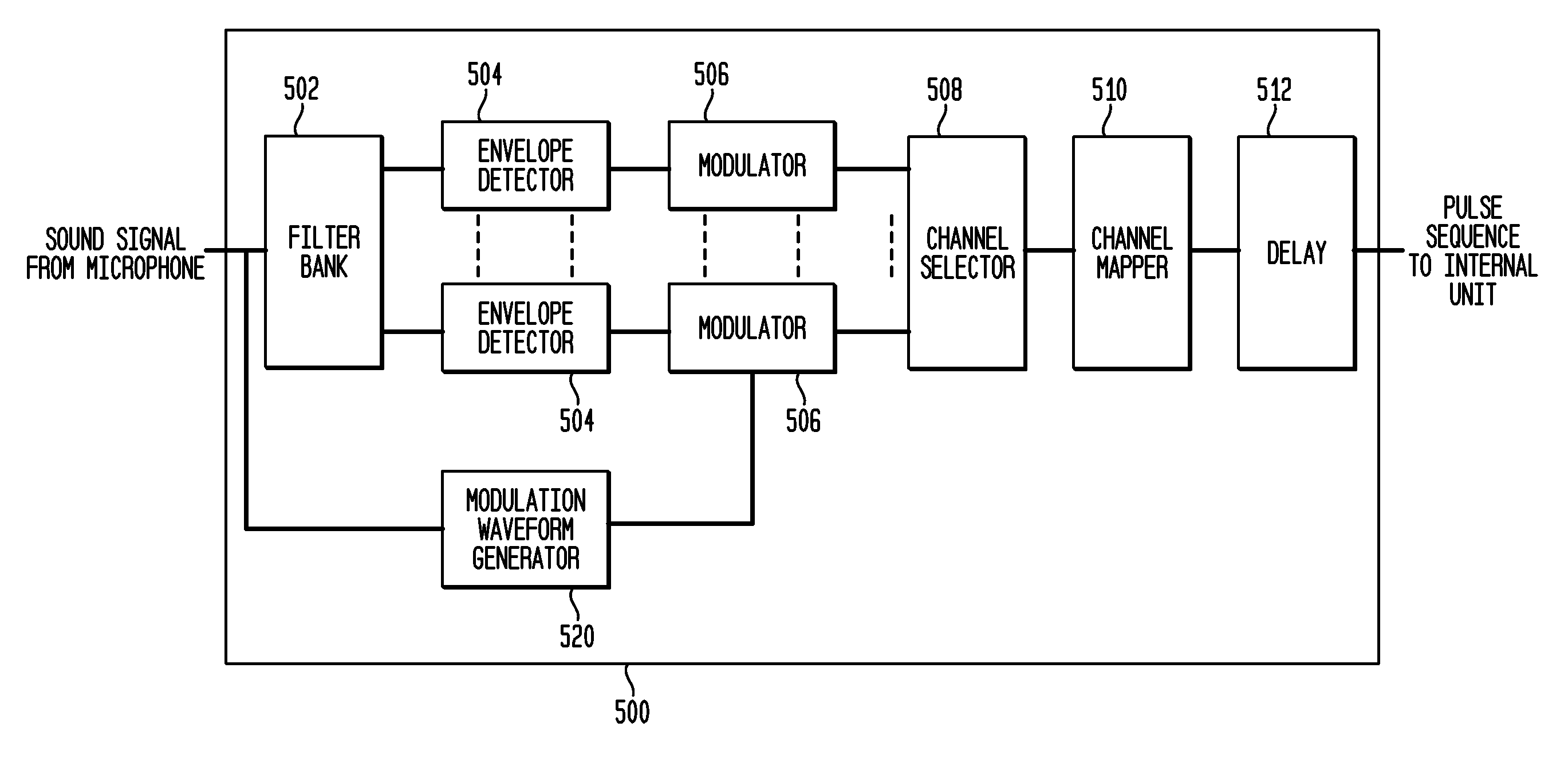
Interaural time difference enhancement strategy
Aspects of the present invention are generally directed to a modulation enhancement strategy that helps improve ITD perception by explicitly modulating the electrical stimulation signal. In an embodiment, the timing of the applied modulations is based on amplitude inflections (i.e., peaks or troughs) in the received sound signal. In an embodiment, the identified inflections (i.e., peaks or troughs) represent the most energetic portions of the signal over a particular time period (e.g., the time period prior to the inflection having a length equal to the expected fundamental period of the signal. Further, in an embodiment, the cochlear implant applies a delay to the stimulation signal to help maintain interaural timing cues. The application of this delay helps account for the traveling wave delay in the acoustic path of the opposite ear in embodiments in which the opposite ear is fitted with a hearing aid or is not fitted with a hearing device.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Binaural sound source localization method based on sub-band signal to noise ratio estimation
InactiveCN102565759APrecise positioningPosition fixationInteraural time differenceSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
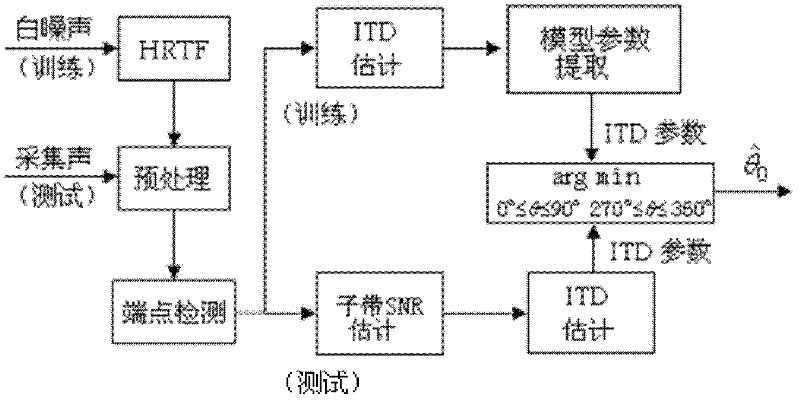
A binaural sound source localization method based on sub-band signal to noise ratio estimation is an improved sound source localization method, wherein the mean value of the ITD (Interaural Time Difference) of various orientations is used as the localization characteristic clue for the sound source orientation to build an orientation mapping model; during the actual sound source localization, a dual-channel acoustic signal is input, the input acoustic signal is firstly subjected to frequency domain transformation, a frequency domain is divided into a plurality of sub-bands, signal to noise ratio estimation is carried out in each sub-band, according to the sub-band signal to noise ratio, the power spectrum of the corresponding sub-band is selected to calculate the ITD parameters of each frame, one-by-one match is performed according to the orientation characteristic model built by the ITD characteristic parameters and a training module, and based on the Euclidean distance measurement, the orientation is output. With the binaural sound source localization method, the performance of sound source localization in noisy environments can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
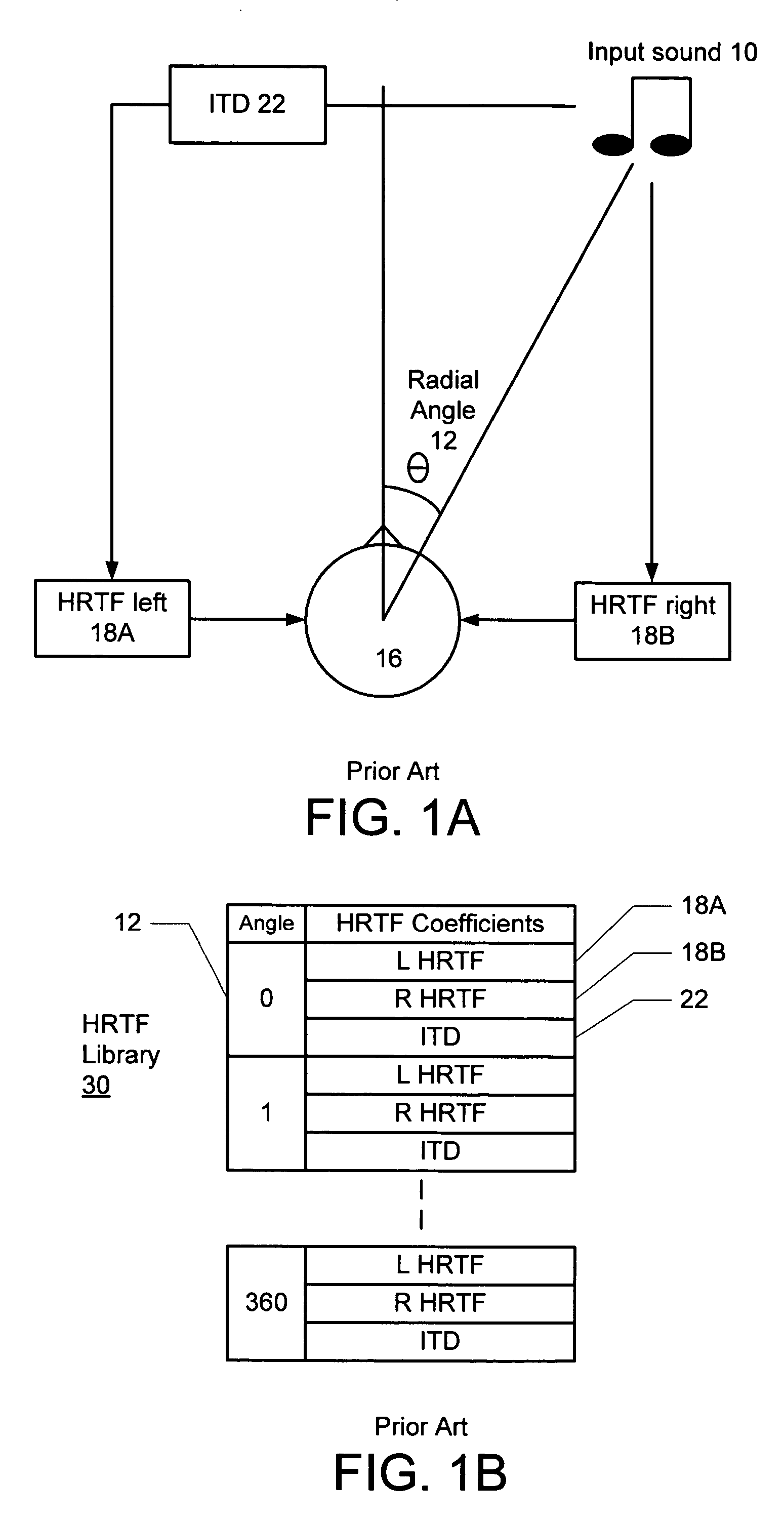
Asymmetric HRTF/ITD storage for 3D sound positioning
ActiveUS20060062409A1Reduce decreaseReduce functionStereophonic systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsInteraural time differenceComputer science
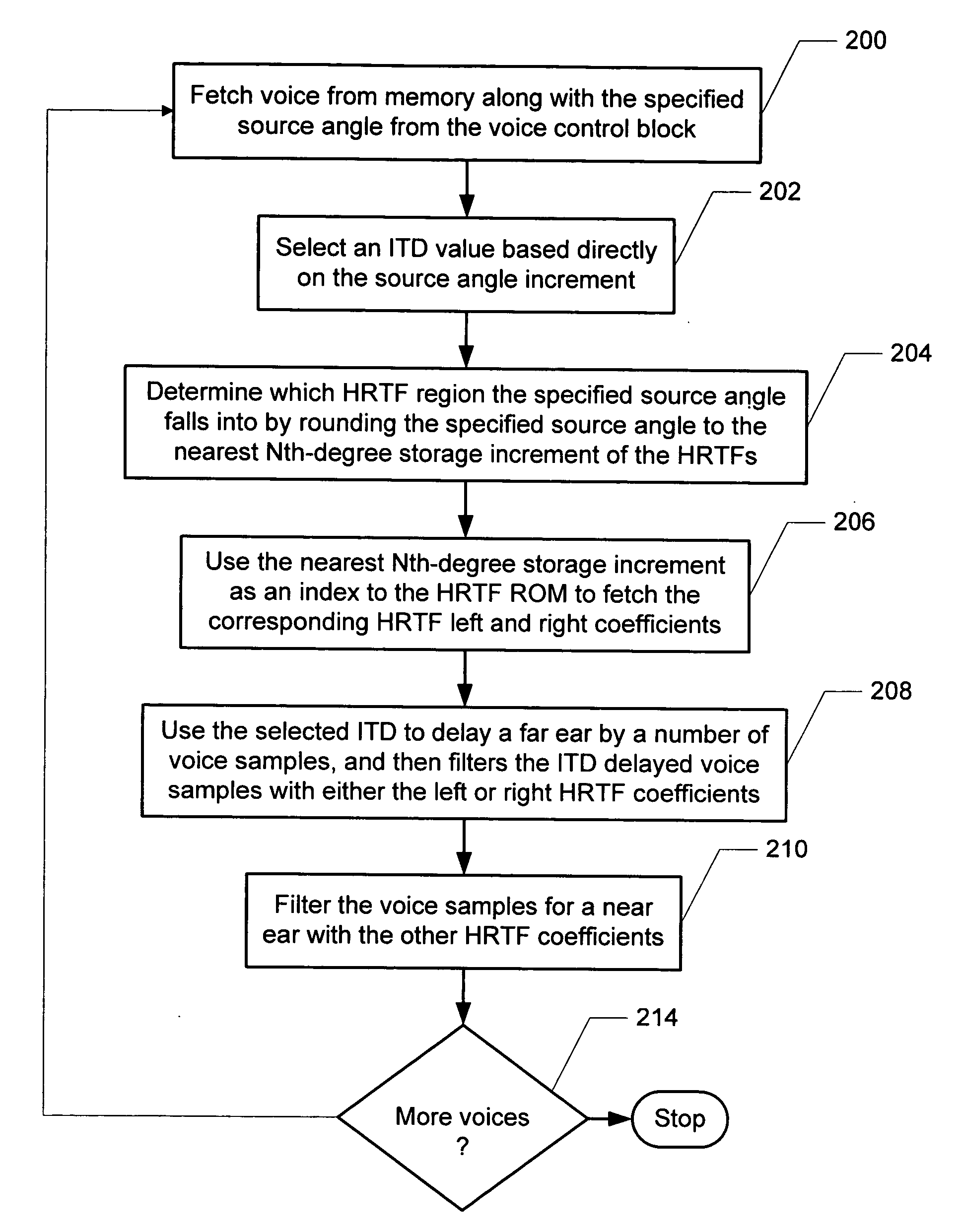
A method and system for reducing head related transfer function (HRTF) storage requirements for 3-D sound processing of an input sound having a specified source angle increment is provided. Interaural time difference (ITD) values are selected based directly on the source angle increment; and HRTFs for processing the input sound are stored in angle increments larger than the source angle increment.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
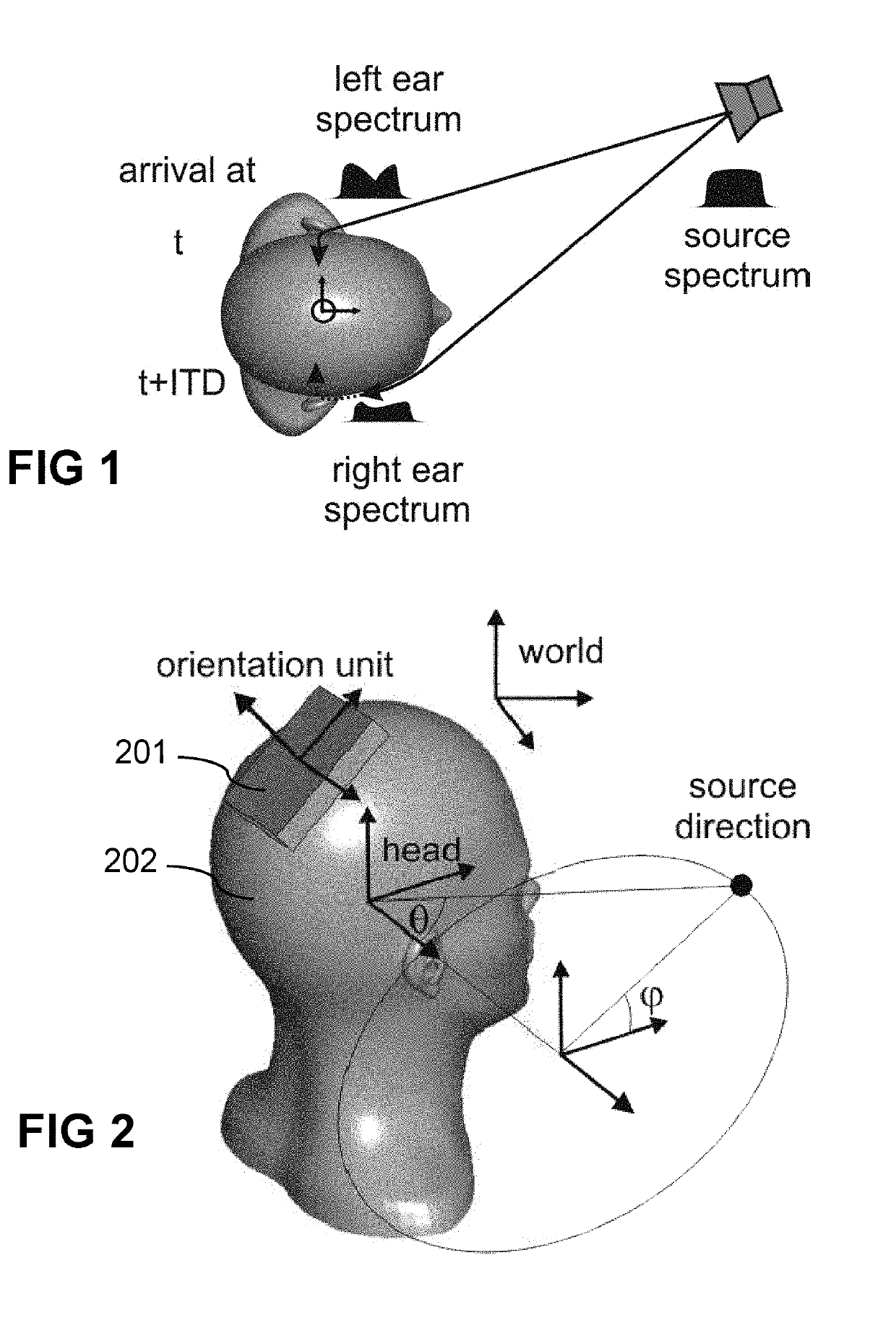
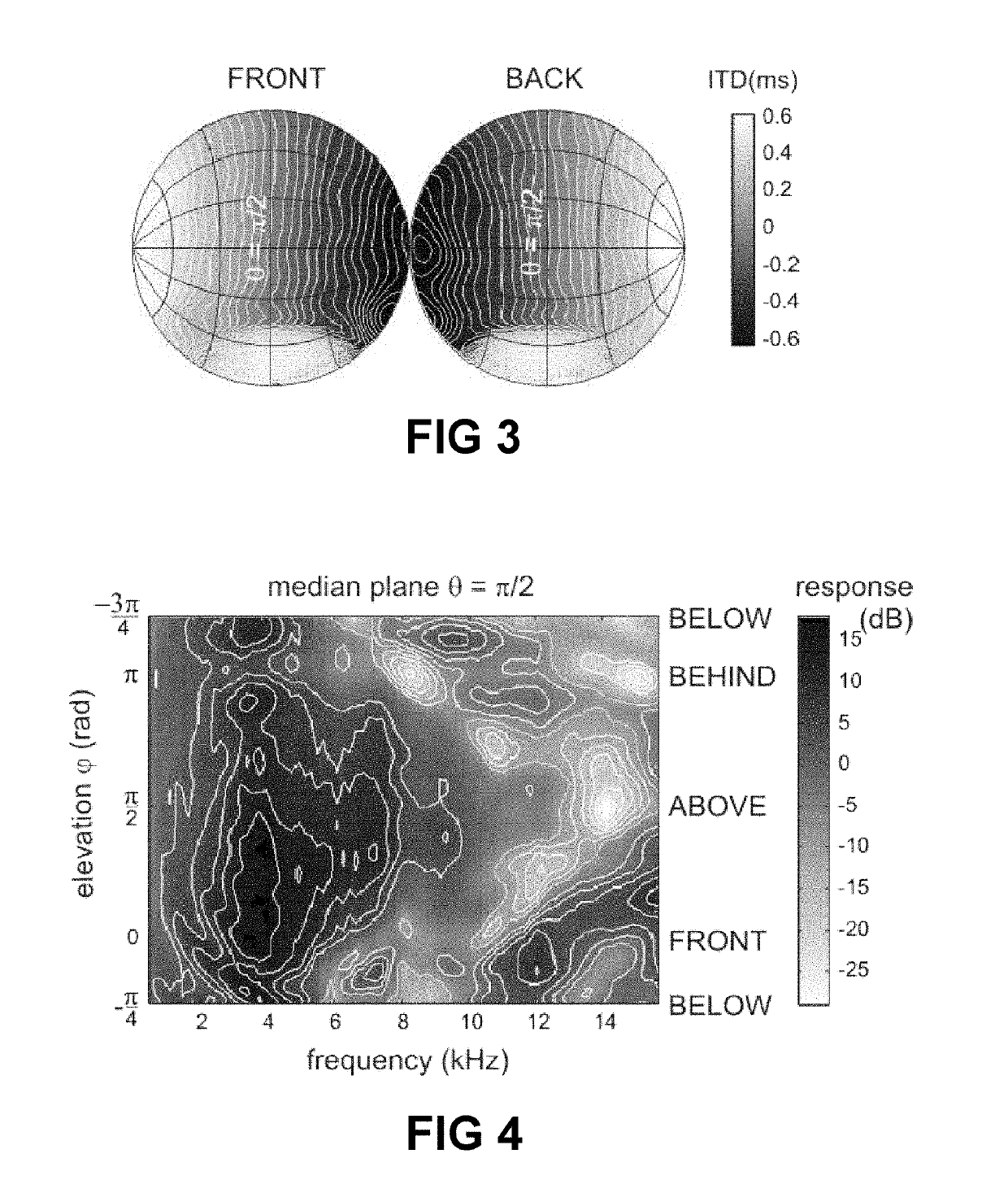
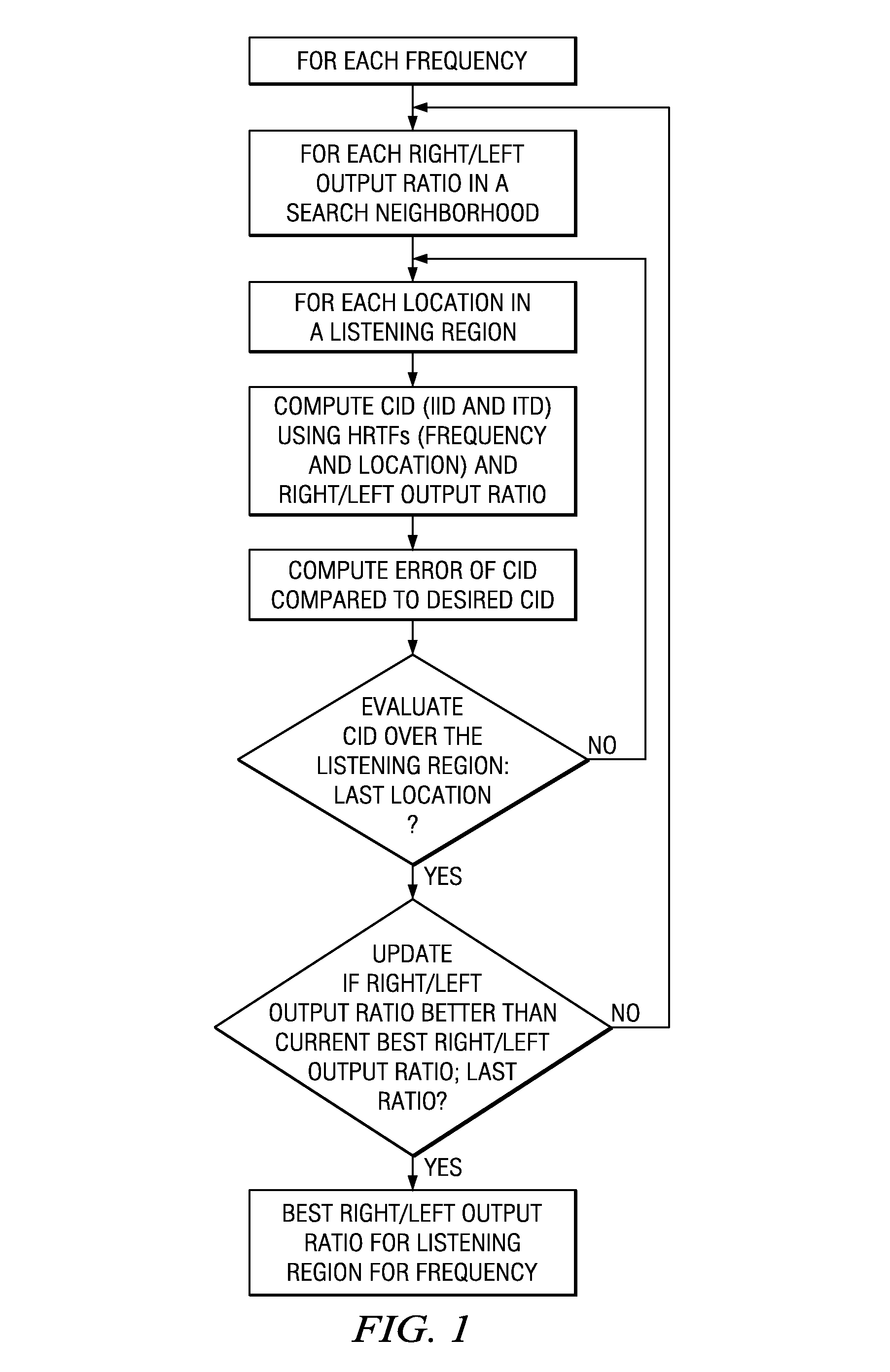
Method of determining a personalized head-related transfer function and interaural time difference function, and computer program product for performing same
ActiveUS20190208348A1Potential inaccuracy of the orientation sensor unitMore freeSignal processingHeadphones for stereophonic communicationInteraural time differenceData set
A method of estimating an individualized head-related transfer function and an individualized interaural time difference function of a particular person, comprises the steps of: a) obtaining a plurality of data sets comprising a left and a right audio sample from in-ear microphones, and orientation information from an orientation unit, measured in a test-arrangement where an acoustic test signal is rendered via a loudspeaker and the person is moving the head; b) extracting interaural time difference values and / or spectral values, and corresponding orientation values; c) estimating a direction of the loudspeaker relative to the head using a predefined quality criterion; d) estimating an orientation of the orientation unit relative to the head; e) estimating the individualized ITDF and the individualized HRTF. A computer program product may be provided for performing the method, and a data carrier may contain the computer program.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ANTWERP
Binaural stimulation in neural auditory prostheses or hearing aids
ActiveUS7920923B2Avoid time-overlapElectrotherapyImplantable hearing aidsInteraural time differenceFine structure
The present invention discloses of binaural stimulation in a neural auditory prosthesis. Binaural acoustic signals are generated that represent sound associated with a user's left and right ears respectively. Based on the binaural acoustic signals, corresponding binaural stimulation signals are generated for electrical stimulation of auditory nerve tissue of the user, wherein the binaural stimulation signals each include a fine structure component with periodic characteristics and interaural time difference (ITD) information. A phase jitter component is added to the binaural stimulation signals to reduce the periodic characteristics of the fine structure component while preserving the interaural time difference (ITD) information.
Owner:MED EL ELEKTROMEDIZINISCHE GERAETE GMBH
Perceptual synthesis of auditory scenes
InactiveUS20070003069A1Special service for subscribersStereophonic systemsInteraural time differenceComputer science
An auditory scene is synthesized by applying two or more different sets of one or more spatial parameters (e.g., an inter-ear level difference (ILD), inter-ear time difference (ITD), and / or head-related transfer function (HRTF)) to two or more different frequency bands of a combined audio signal, where each different frequency band is treated as if it corresponded to a single audio source in the auditory scene. In one embodiment, the combined audio signal corresponds to the combination of two or more different source signals, where each different frequency band corresponds to a region of the combined audio signal in which one of the source signals dominates the others. In this embodiment, the different sets of spatial parameters are applied to synthesize an auditory scene comprising the different source signals.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
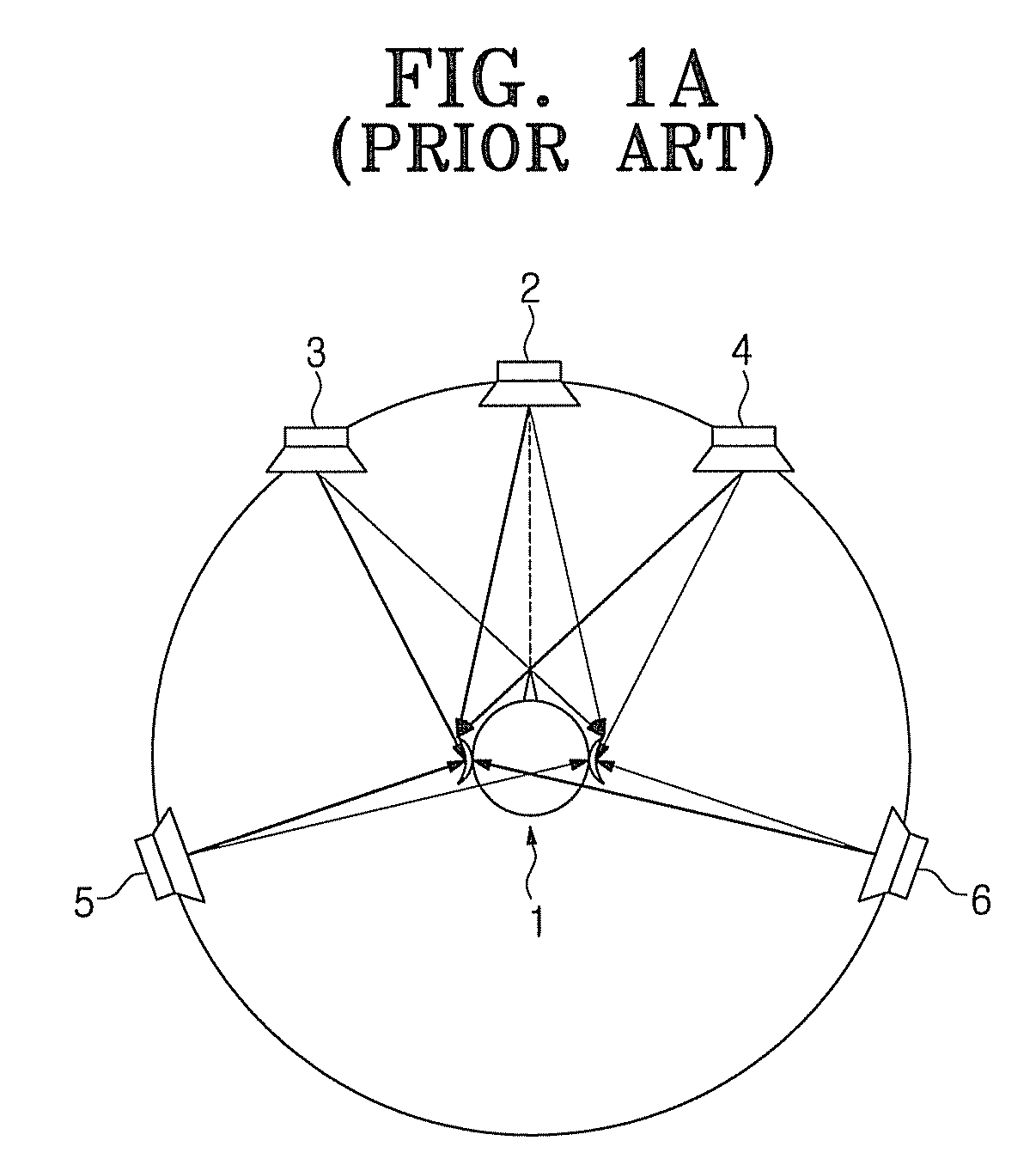
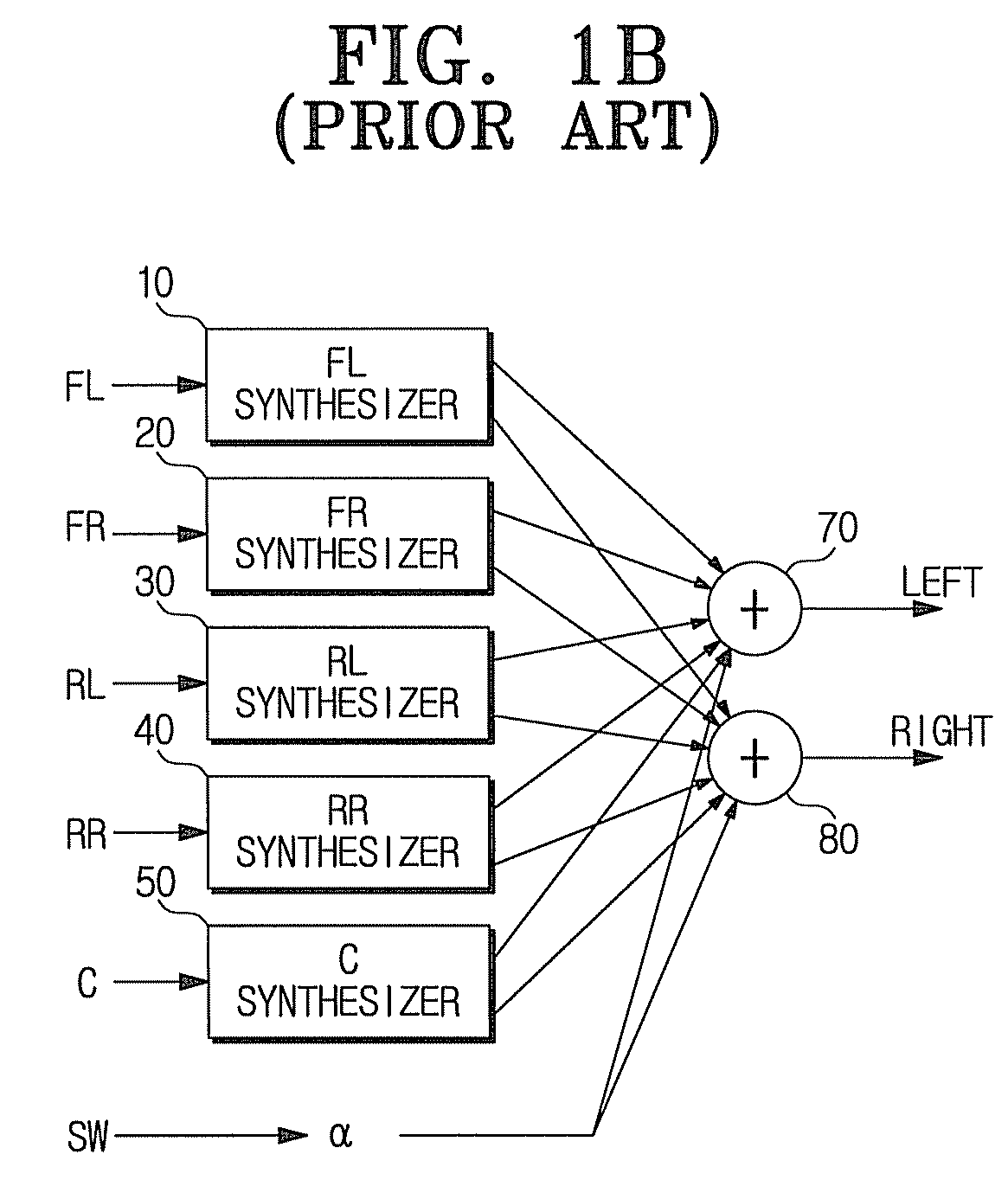
Stereophonic sound output apparatus and early reflection generation method thereof
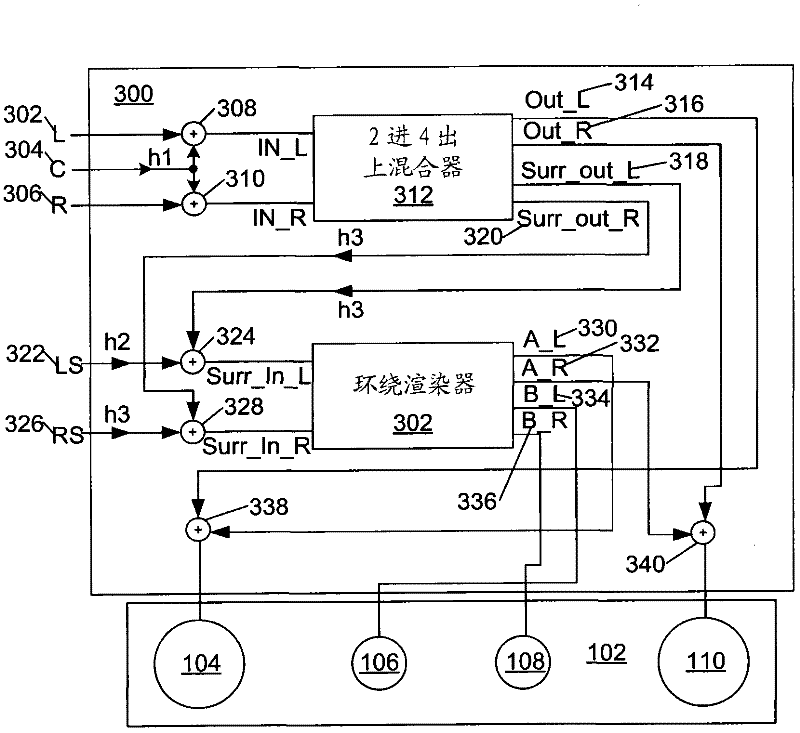
ActiveUS20080205675A1Reduce computing timeEfficient implementationPseudo-stereo systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsInteraural time differenceVocal tract
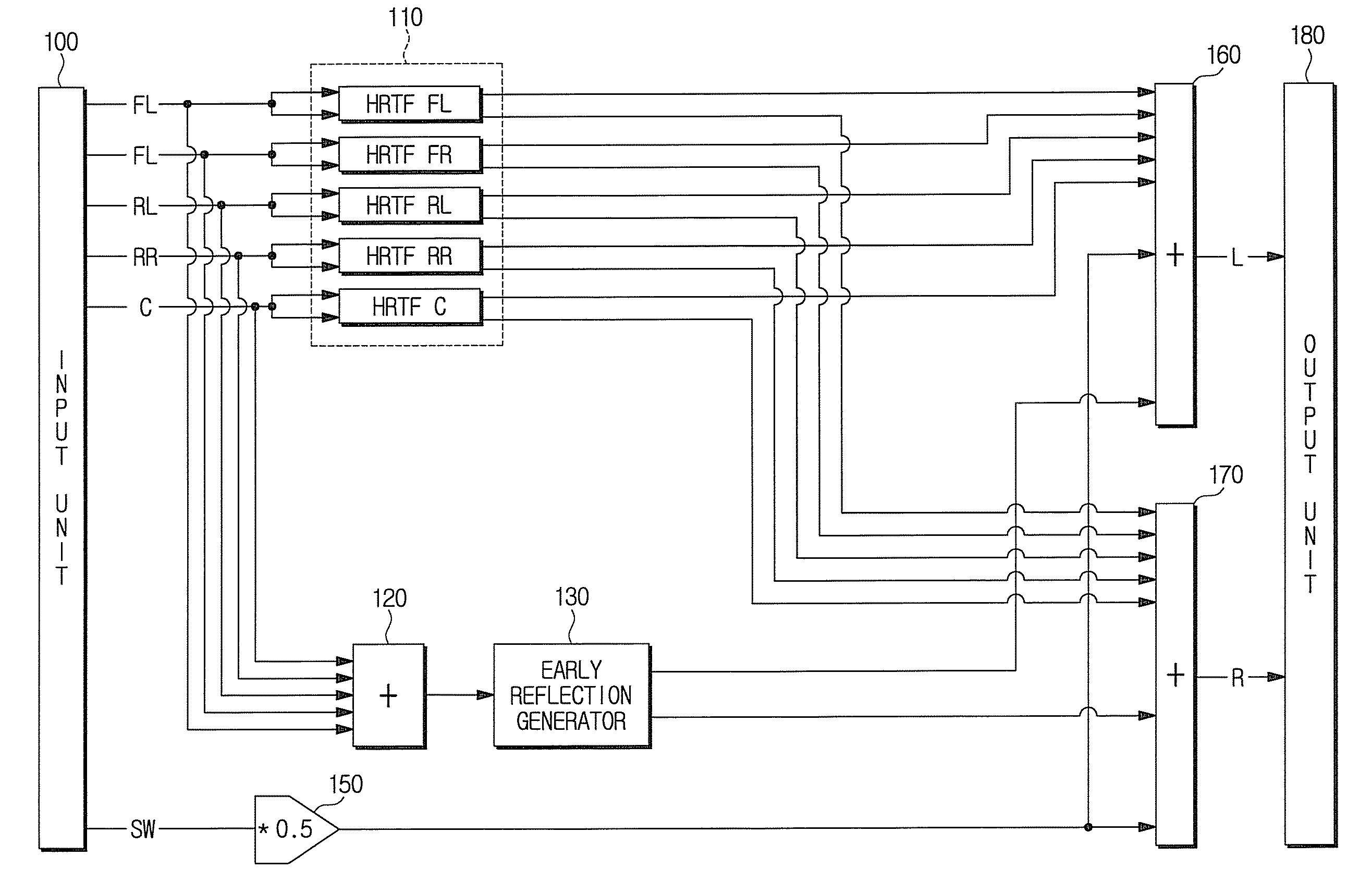
A stereophonic sound output apparatus and an early reflection generation method thereof. The stereophonic sound output apparatus includes an early reflection generator to implement an early reflection when a 5.1 channel audio signal is down-mixed to a 2-channel audio signal to play back a 5.1 channel audio signal through a 2-channel headphone. The early reflection generator generates early reflections in pairs in which there is an appropriate time difference between the left side reflections and the right side reflections by generating an interaural time difference between two input audio signals and filtering. It is possible to copy the characteristics of early reflections in a real listening room. It is also possible to implement an early reflection similar to a real reflection measured in an apparatus for playing back the 5.1 channel audio signal through 2-channel headphone. A natural 5.1 channel effect may also be obtained using little computation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
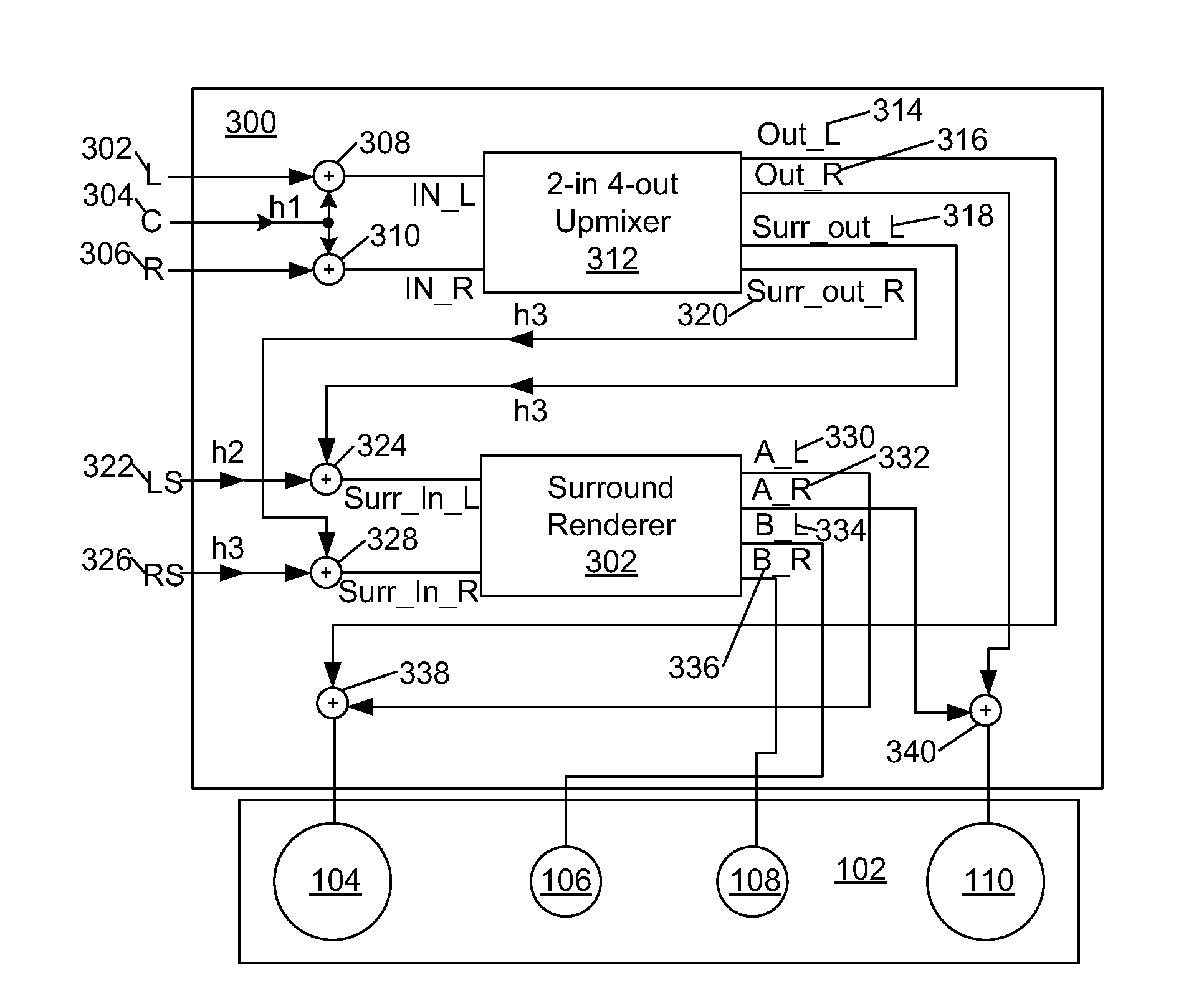
Speaker array for virtual surround rendering
InactiveUS20120155650A1Low off-axis colorationLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsStereophonic systemsInteraural time differenceLoudspeaker
A device and method for generation of virtual surround sound with a two-way approach is provided. The device and method employs a first order head-related model designed to resemble interaural time difference localization and inter-aural level difference localization cues in the respective frequency bands while avoiding phantom imaging and excessive coloration.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
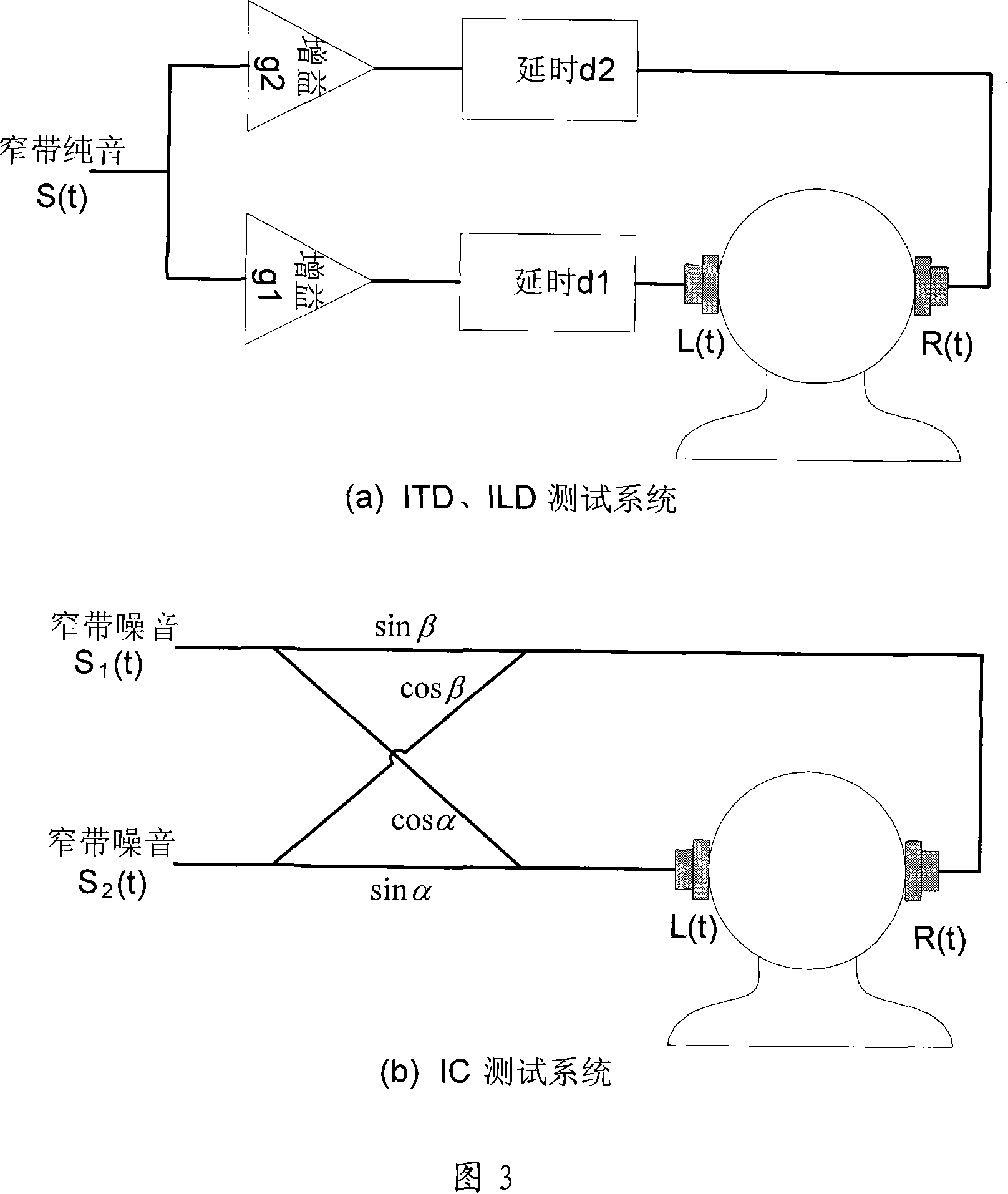
Method and device for measuring binaural sound time difference ILD critical apperceive characteristic
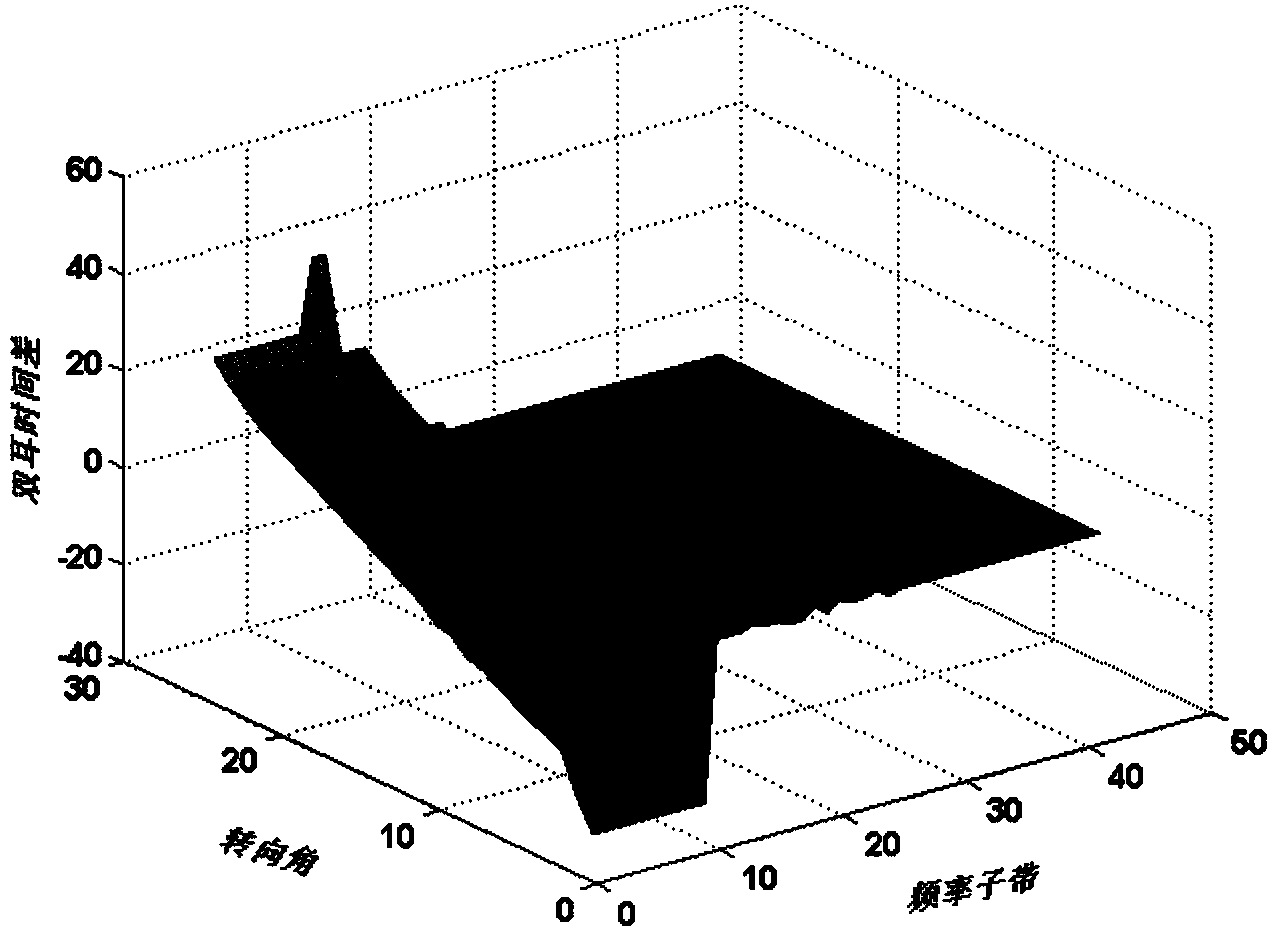
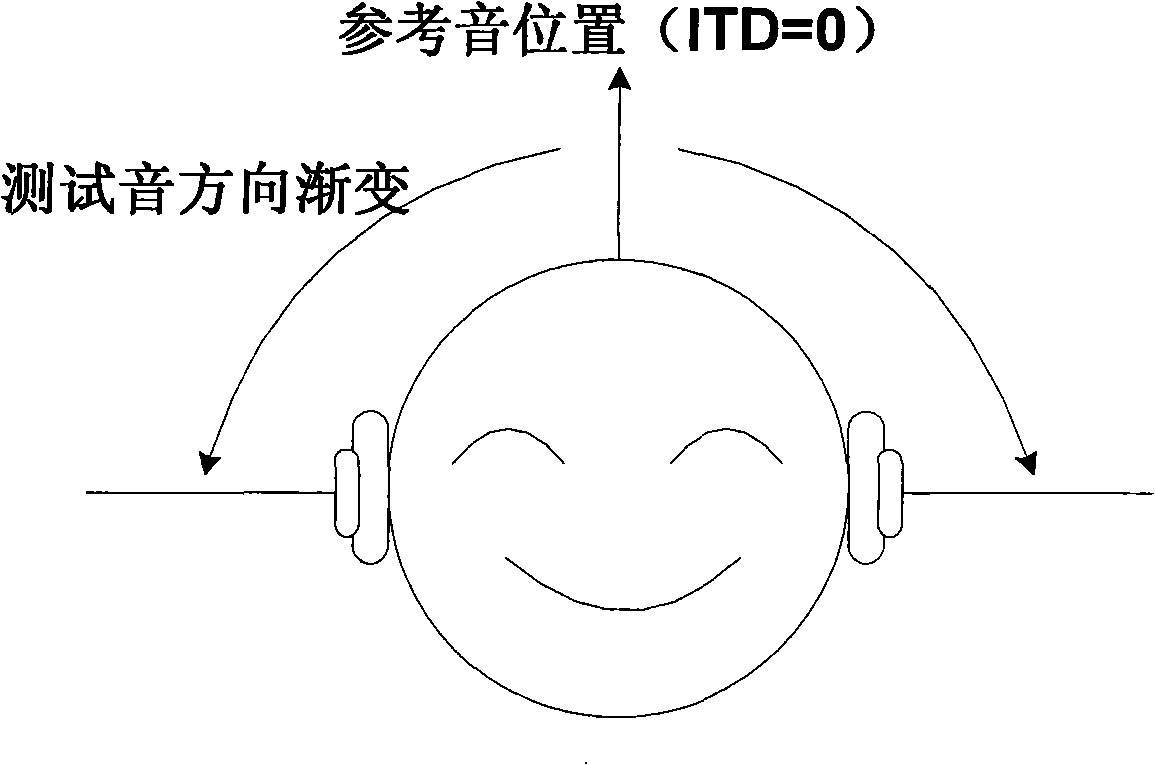
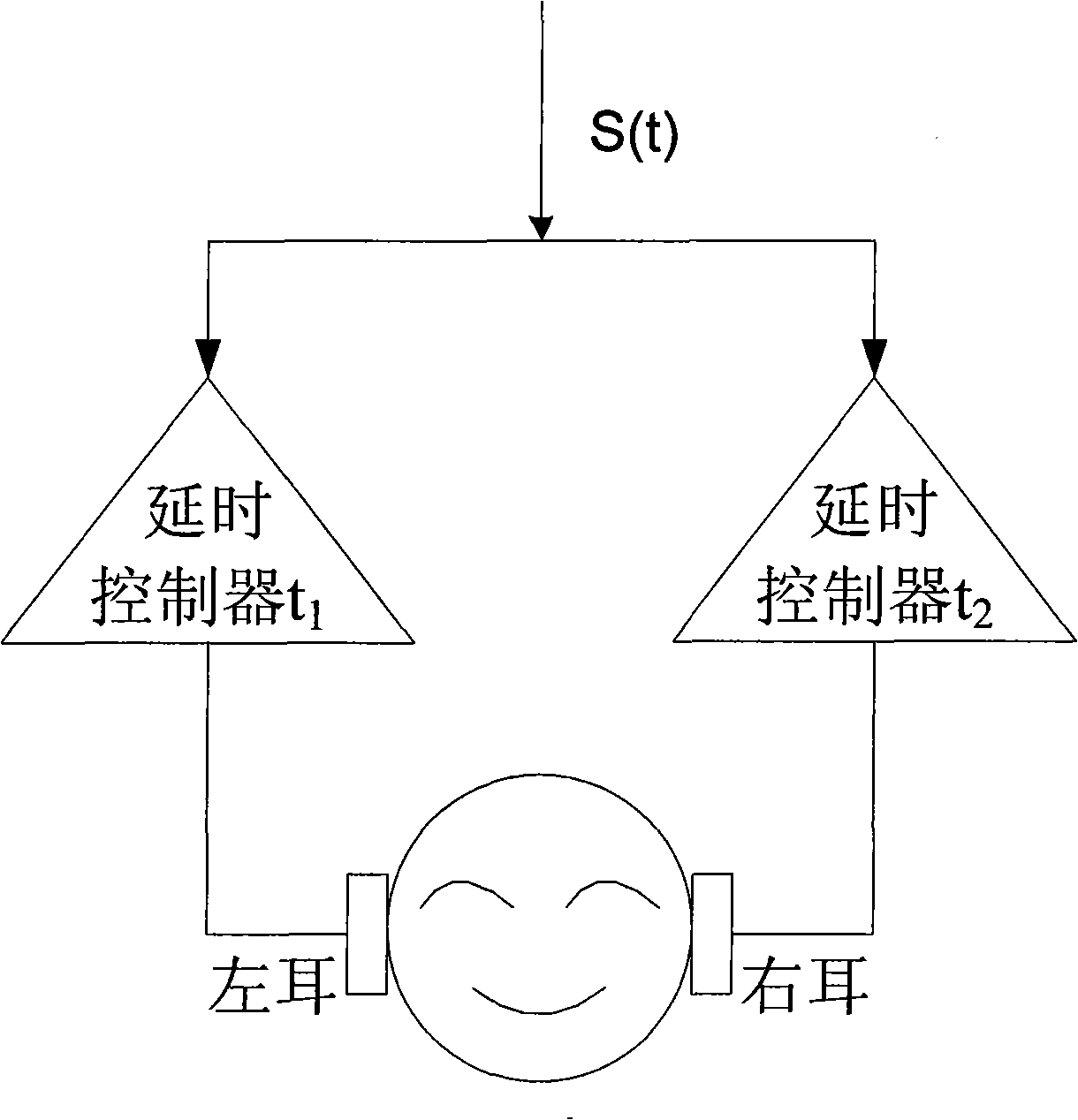
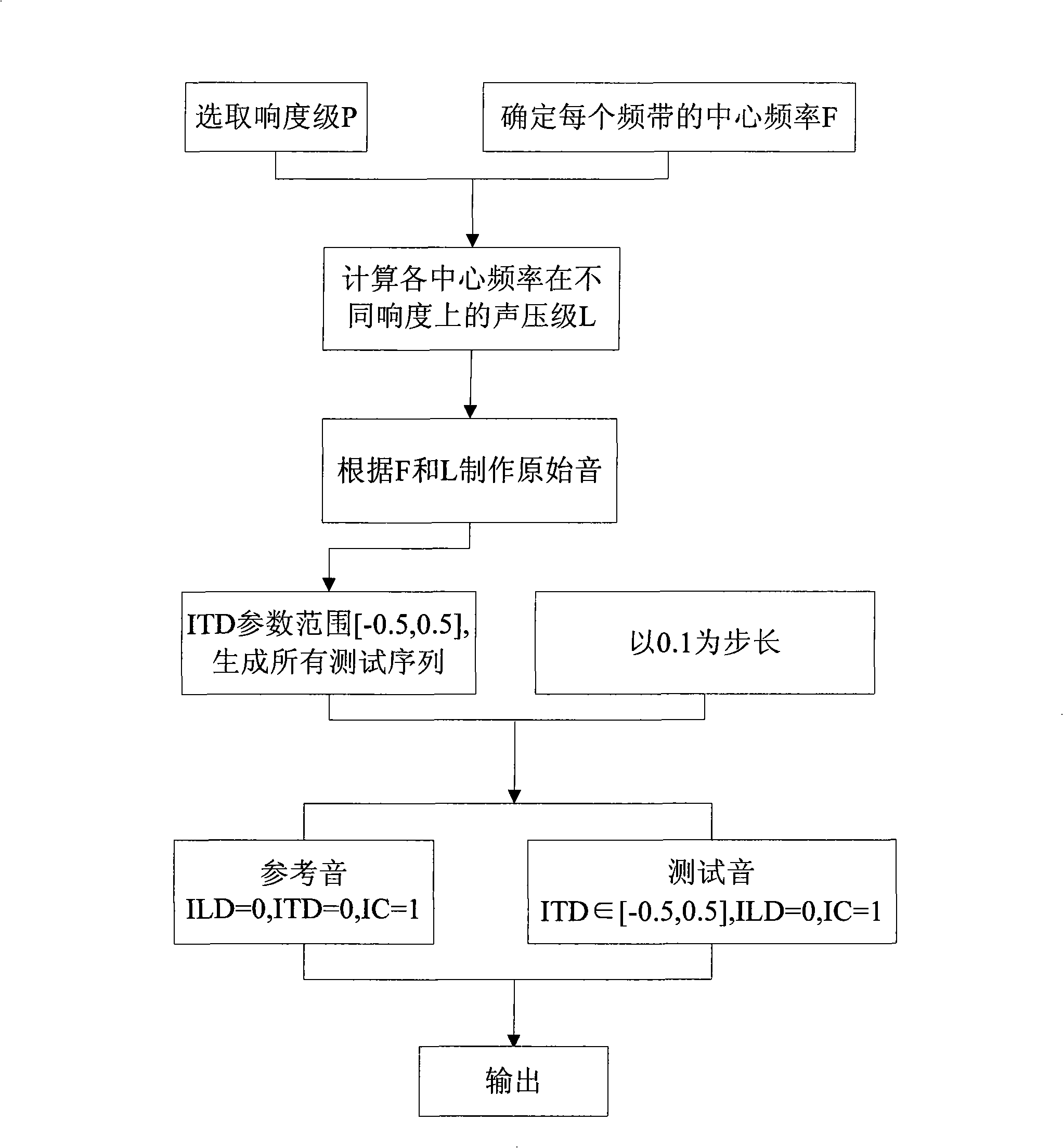
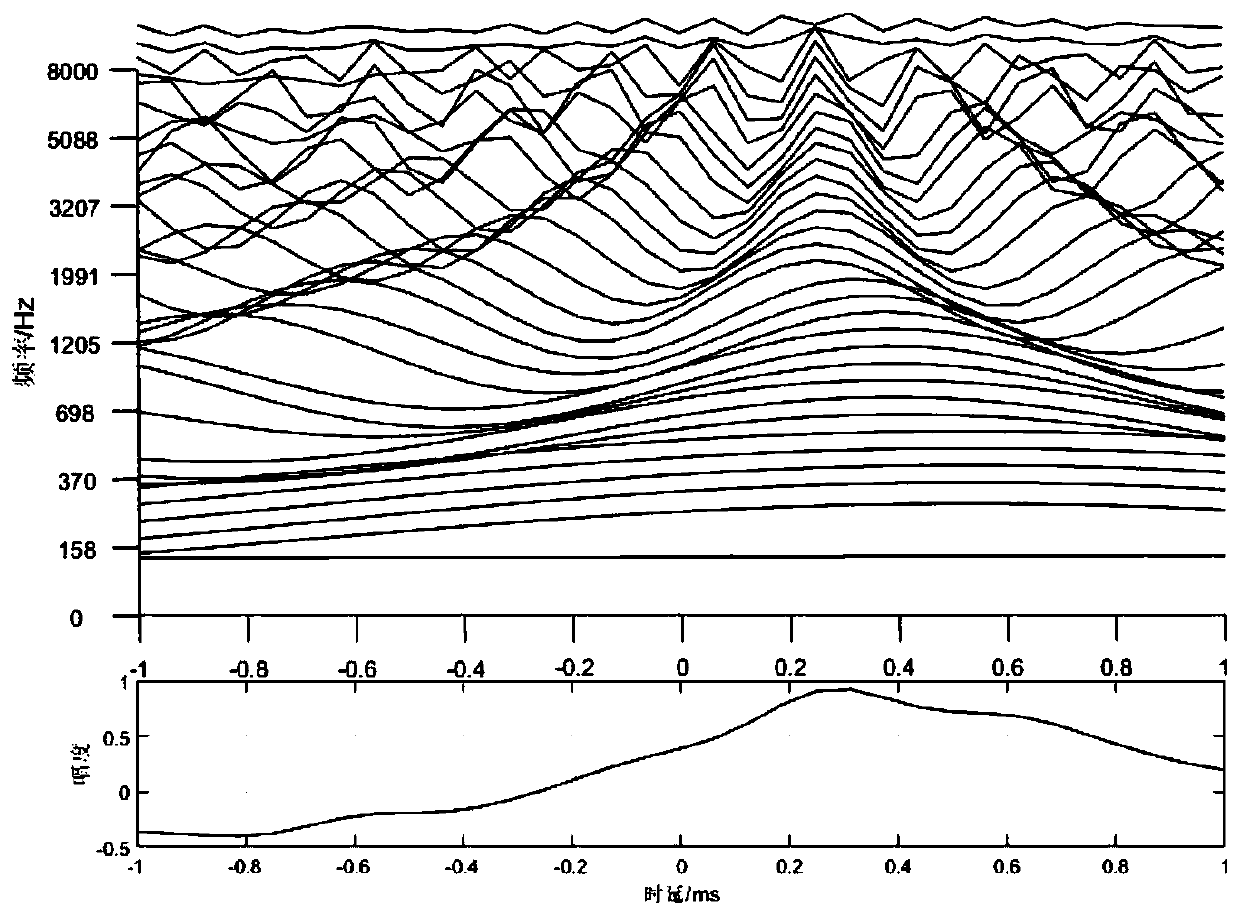
In spatial audio coding, interaural time difference is one of the important parameters for an auditory system to identify sound emanate direction. The invention discloses a method for measuring the critical perception characteristic of the interaural time difference (hereinafter referred to as ITD) parameters; the method comprises the following steps: a partitioning rule of Bark frequency bands is adopted for the test source, the center frequency of the Bark frequency bands is chosen as an original audio frequency, meanwhile, the original audio maintains a constant sound pressure level; then the gradient test sound at the listening position is produced by a method for equidistantly or nonlinearly changing an ITD value according to the perception principle of the ITD; finally, a critical perception value JND of the ITD parameters is obtained by a subjective test method. The method realizes quantitative analysis of the ITD critical perception characteristic of signals with the frequencies ranging from 20Hz to 20KHz, solves the defect that only qualitative description exists in the traditional ITD characteristic analysis, and solves the problem of removing the subjective redundancy of the ITD parameters from the spatial audio coding, which are beneficial for optimization analysis.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Recording data training method, multi-track audio surrounding method and recording data training device
ActiveCN104581602ASolve the problem that good listening effect cannot be obtainedDeaf amplification systemsInteraural time differenceChannel data
The invention discloses a recording data training method, a multi-track audio surrounding method and a recording data training device, and belongs to the field of audio processing. The recording data training method comprises the following steps: according to an hearing environment of a user, modeling to obtain a virtual hearing model; according to physiological data of the head of the user, modeling to obtain a virtual dummy head model; calculating to obtain interaural time difference (ITD) corresponding to direct waves of each sound track; calculating to obtain interaural latency difference (ILD) corresponding to direct waves of each sound track. The multi-track audio surrounding method comprises the following steps: obtaining original multi-track audio content; according to the ITD and the ILD obtained by the recording data training method, performing conversion on sound data of each sound track in the multi-track audio content to obtain left channel data and right channel data which correspond to each sound track; mixing the left sound channel data corresponding to each sound track into target left channel data and mixing right sound channel data corresponding to each sound track into target right sound channel data to generate stereo audio content.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KUGOU TECH
Space parameter selection method for parameter stereo coding
InactiveCN101149925AGuaranteed stereo sound qualityGuaranteed sound qualitySpeech analysisStereophonic systemsInteraural time differenceComputer science
The space parameter selection method for parameter stereo coding is disclosed. Three space parameters of interaural time difference, interaural intensity difference and interaural correlation degree are used for describing the space information in stereo signals. Signals are classified into three frequency ranges of low, middle and high frequency. According to the coding rate of the space parameters, different space parameter combinations are selected in each frequency range to describe space information. Advantage: raised effect of space information expression and coding efficiency of parameter stereo.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Virtualizer sweet spot expansion
ActiveUS8085958B1Stereophonic systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsInteraural time differencePsychoacoustics
Audio loudspeaker virtualizers and cross-talk cancellers and methods use a combination of interaural intensity difference and interaural time difference to define virtualizing filters. This allows enlargement of a listener's sweet spot based on psychoacoustic effects.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
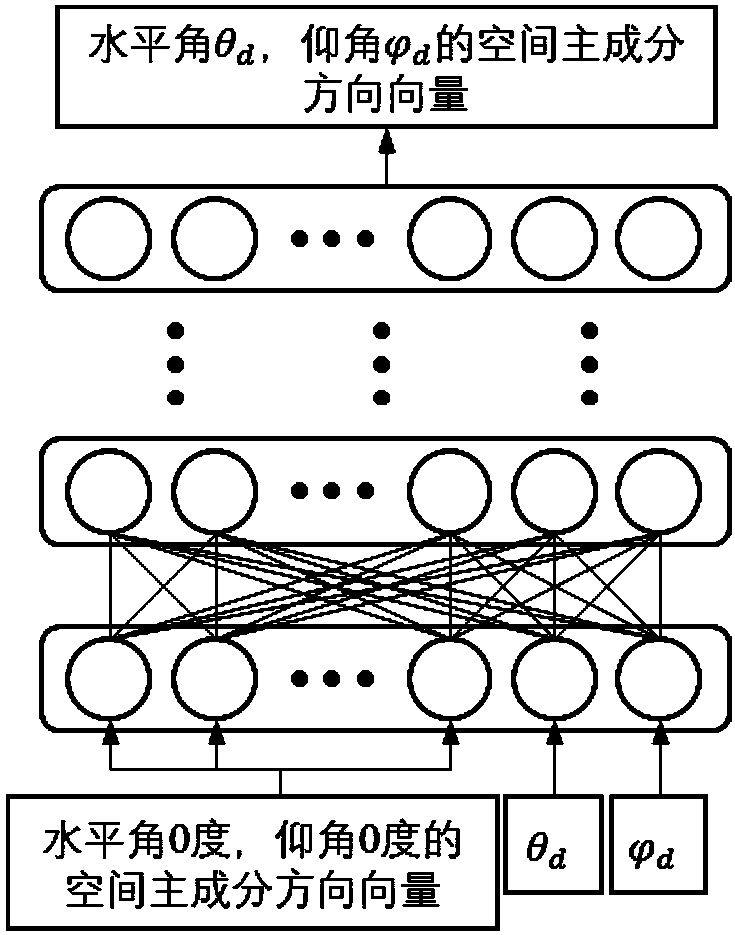
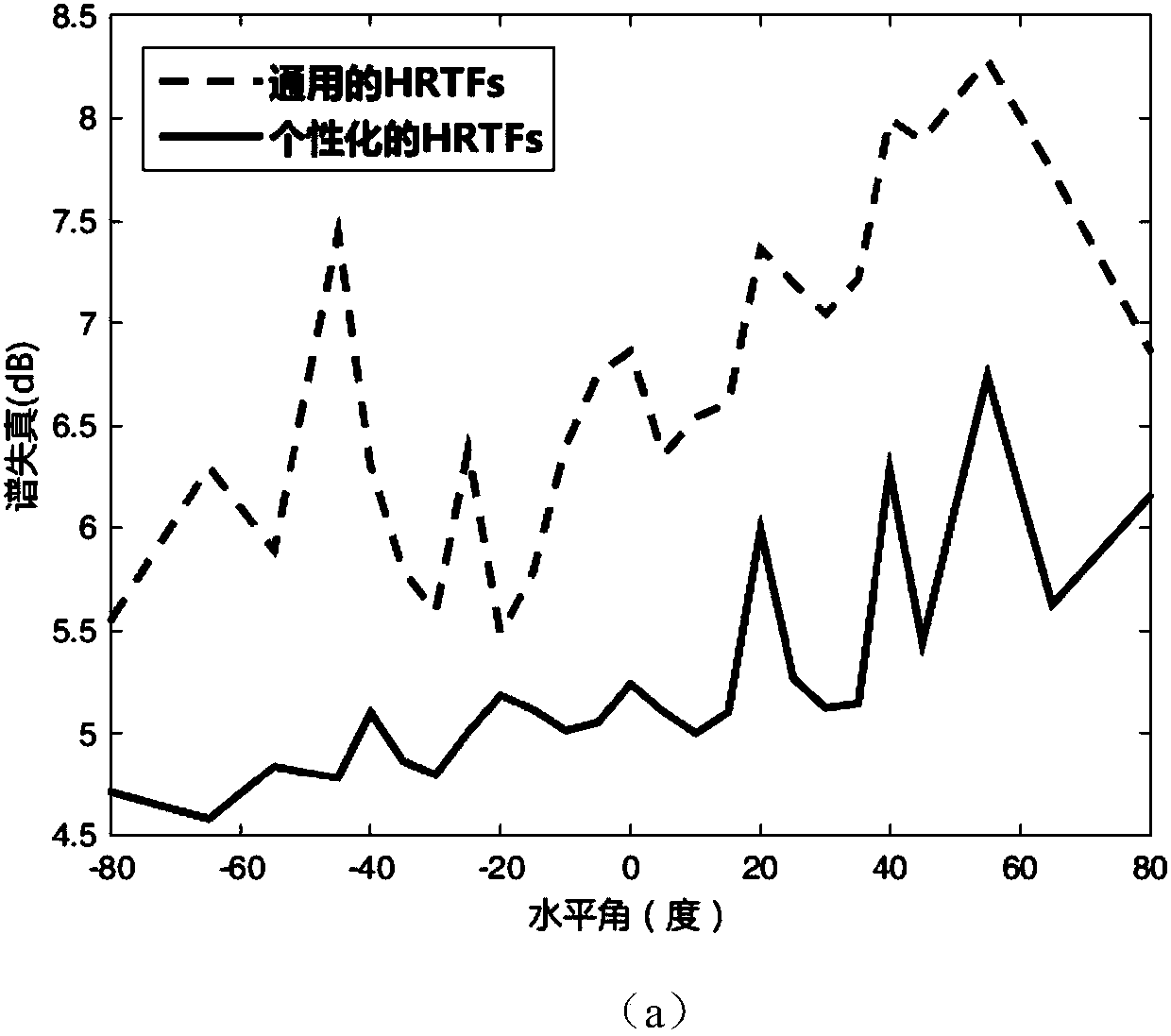
Personalized head-related transfer function modeling method based on deep neural network
ActiveCN108596016AImplement HRTF predictionCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesInteraural time differencePersonalization
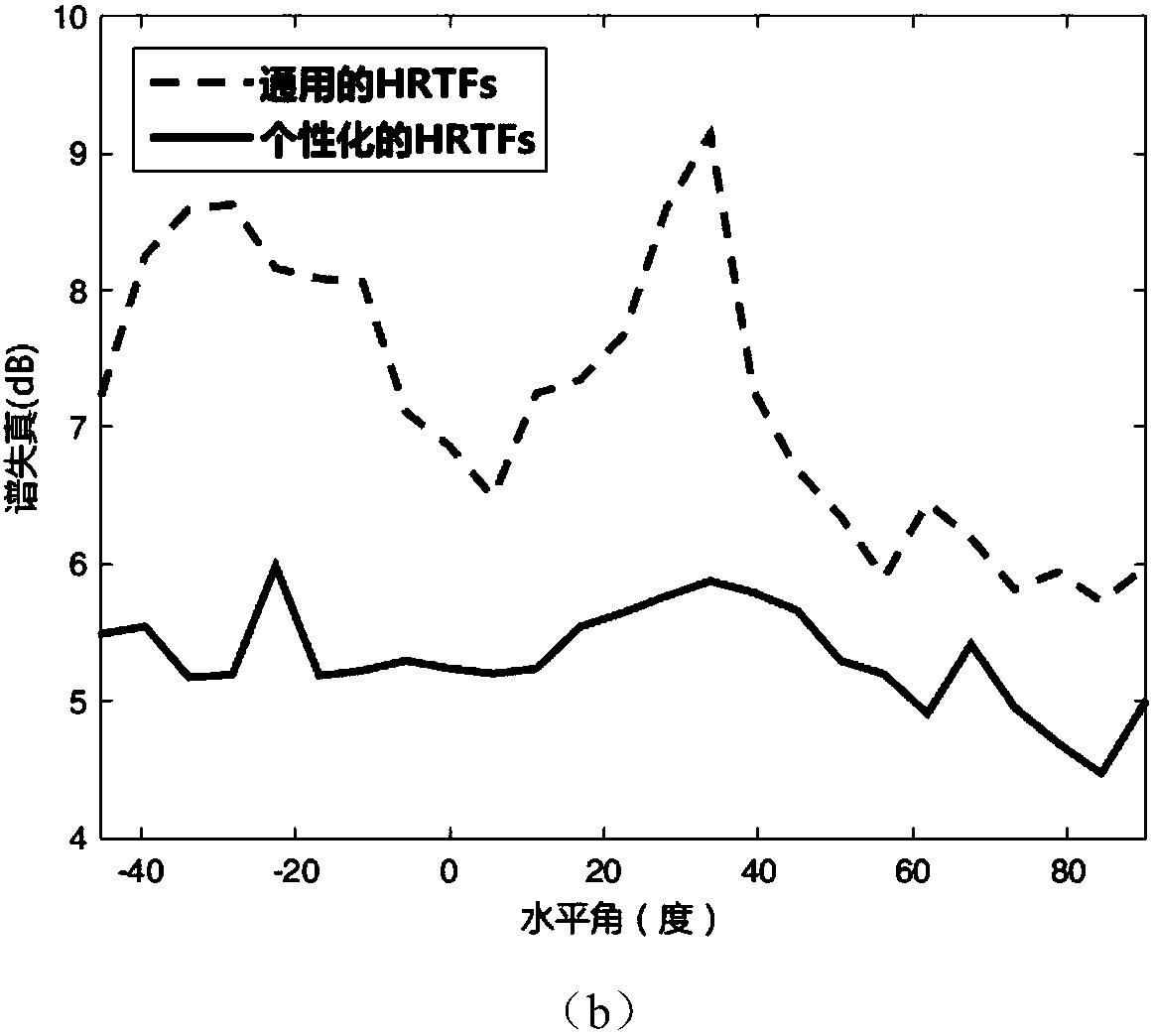
The invention discloses a personalized head-related transfer function modeling method based on a deep neural network. According to the method, HRTF data is decomposed on the basis of spatial principalcomponent analysis, and spatial principal components, spatial principal component coefficients and an average spatial function are all modeled by a neural network, wherein the spatial principal components and the average spatial function are only related to a spatial direction, and the spatial principal component coefficients are functions of a frequency and personalized characteristic parameters. The deep neural network is utilized to model the spatial principal components, the average spatial function and an interaural time difference, spatial direction information such as a horizontal angle and an elevation angle is introduced into a network input layer, and the neural network is utilized to model spatial principal component coefficients on the basis of human body measurement parameters. On the basis of the above model, a personalized HRTF in any direction in space can be obtained according to a small number of human body measurement parameters of a subject.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Deep learning-based binaural sound source positioning method in digital hearing aid
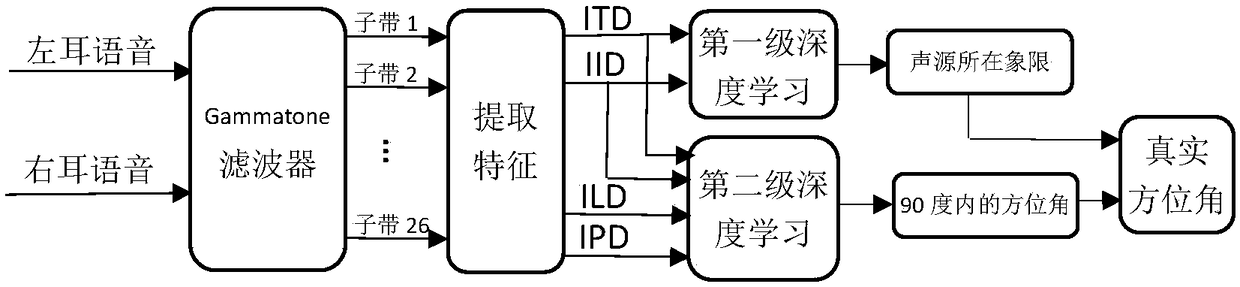
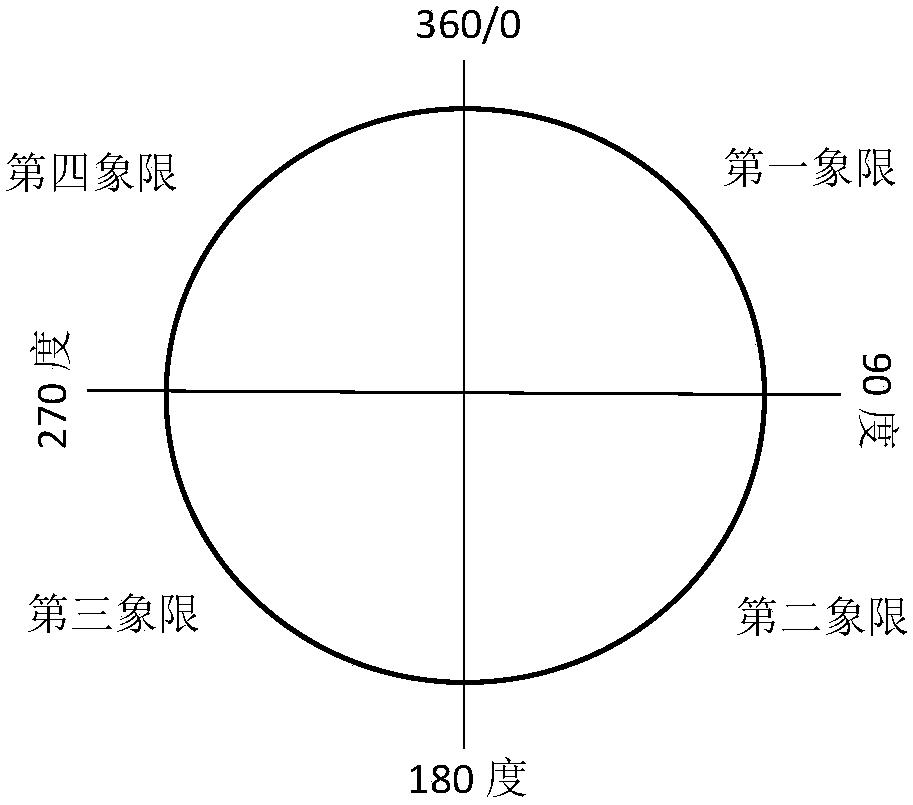
ActiveCN108122559AImprove learning abilityStrong offline trainingSpeech analysisSets with desired directivityInteraural time differencePattern recognition
The invention discloses a deep learning-based binaural sound source positioning method in a digital hearing aid. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, decomposing a binaural sound sourcesignal into a plurality of channels through a gammatone filter, extracting a high-energy channel through a weighting coefficient, then extracting a first type of features by using a head-related-transform function (HRTF), namely an Interaural Time Difference (ITD) and an Interaural Intensity Difference (IID) which are used as inputs of deep learning, and dividing a horizontal plane into four quadrants to narrow a positioning range; secondly, extracting a second type of features of head-related transform, namely an Interaural Level Difference (ILD) and an Interaural Phase Difference (IPD); andfinally, in order to realize more precise positioning, taking the first and second types of four features as inputs of next deep learning, thereby obtaining an azimuth angle of sound source positioning. Precise positioning of 72 azimuth angles is realized on the horizontal plane from 0 degree to 360 degrees at a step length of 5 degrees.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
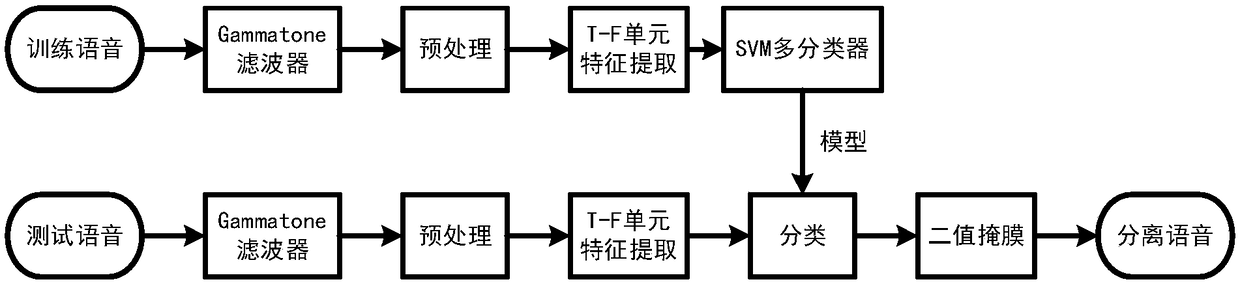
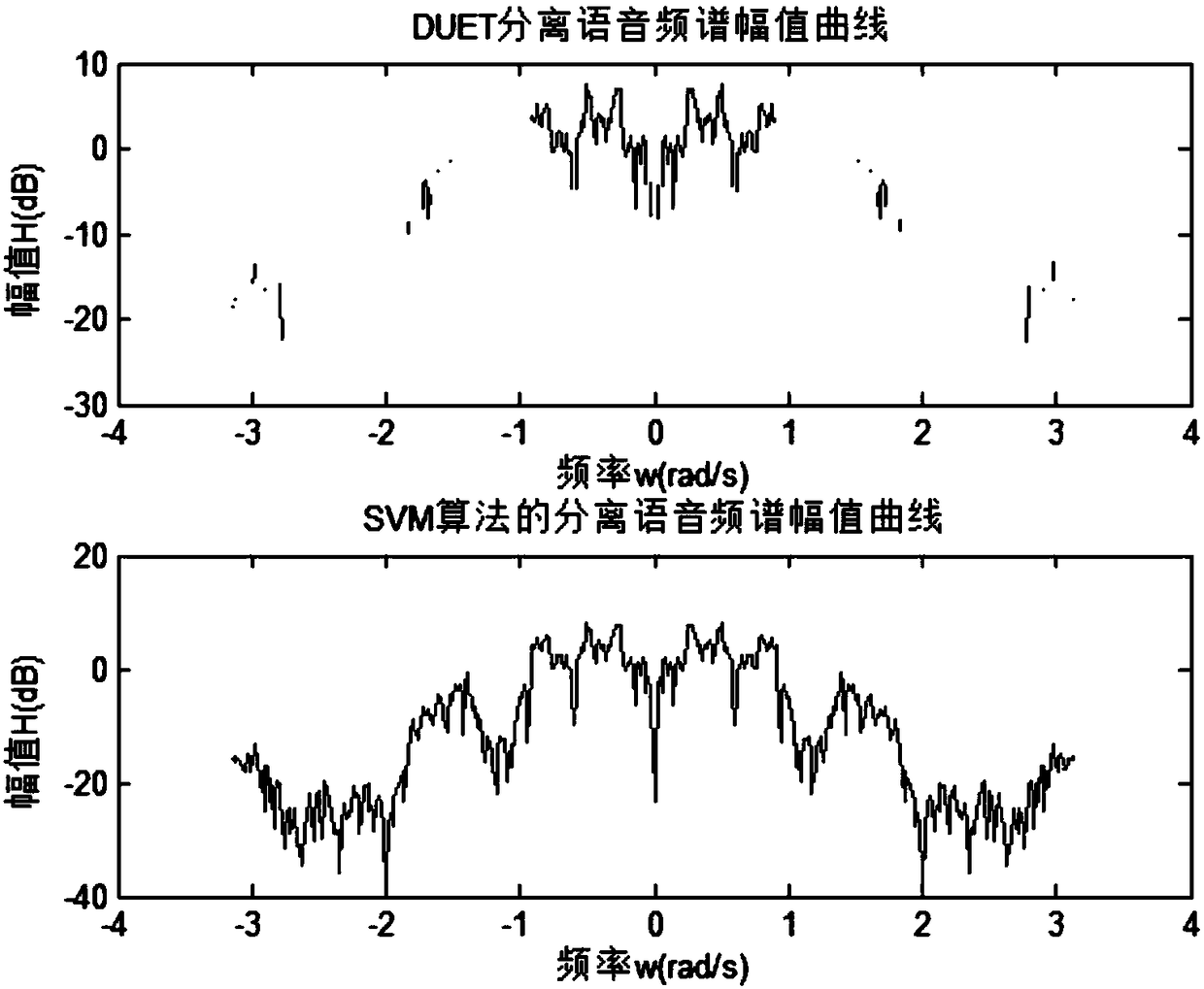
Binaural speech separation method based on support vector machine
ActiveCN108091345AAchieve robustnessImprove robustnessSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionInteraural time differenceSound sources
The invention discloses a binaural speech separation method based on a support vector machine. The method comprises the steps that after a binaural signal passes through a Gammatone filter, the interaural time difference ITD and the parameter interaural intensity difference IID of each sub-band acoustic signal are extracted; in a training phase, the sub-band ITD and IID parameters extracted from apure mixed binaural signal containing two sound sources are used as the input features of the support vector machine SVM, and the SVM classifier of each sub-band is trained; and in a test phase, in an environment with reverberation and noise, the sub-band features of a test mixed binaural signal containing two sound sources are extracted, and the SVM classifier of each sub-band is used to classify the feature parameters of each sub-band to separate each sound source in mixed speech. According to the invention, the method is based on the classification capability of the support vector machinemodel; robust binaural speech separation in a complex acoustic environment is realized; and the problem of frequency point data loss is effectively solved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
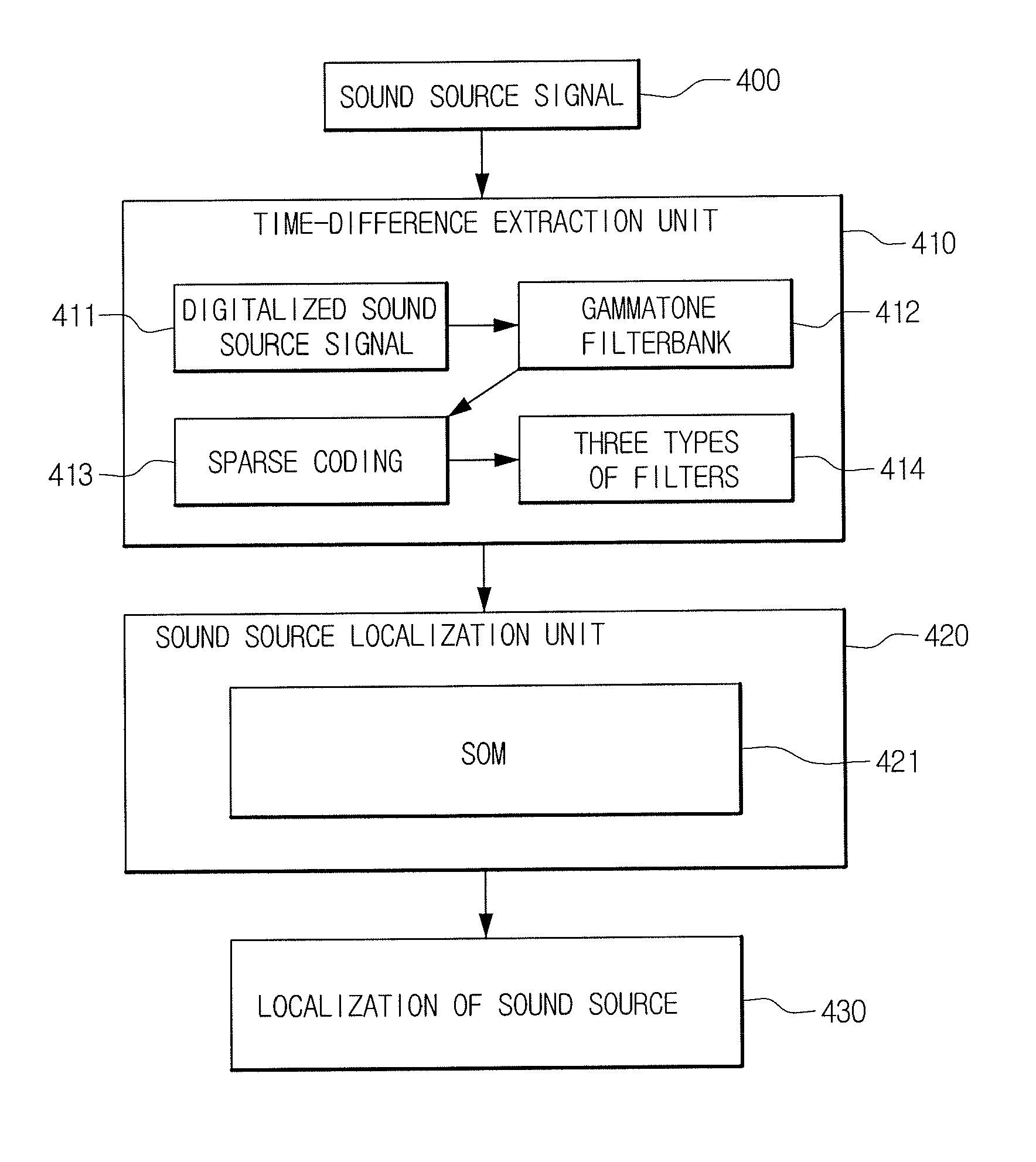
Sound source localization system and method
ActiveUS20110222707A1Microphones signal combinationTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsInteraural time differenceLocalization system
A sound source localization system includes a plurality of microphones for receiving a signal as an input from a sound source; a time-difference extraction unit for decomposing the signal inputted through the plurality of microphones into time, frequency and amplitude using a sparse coding and then extracting a sparse interaural time difference (SITD) inputted through the plurality of microphones for each frequency; and a sound source localization unit for localizing the sound source using the SITDs. A sound source localization method includes receiving a signal as an input from a sound source; decomposing the signal into time, frequency and amplitude using a sparse coding; extracting an SITD for each frequency; and localizing the sound source using the SITDs.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
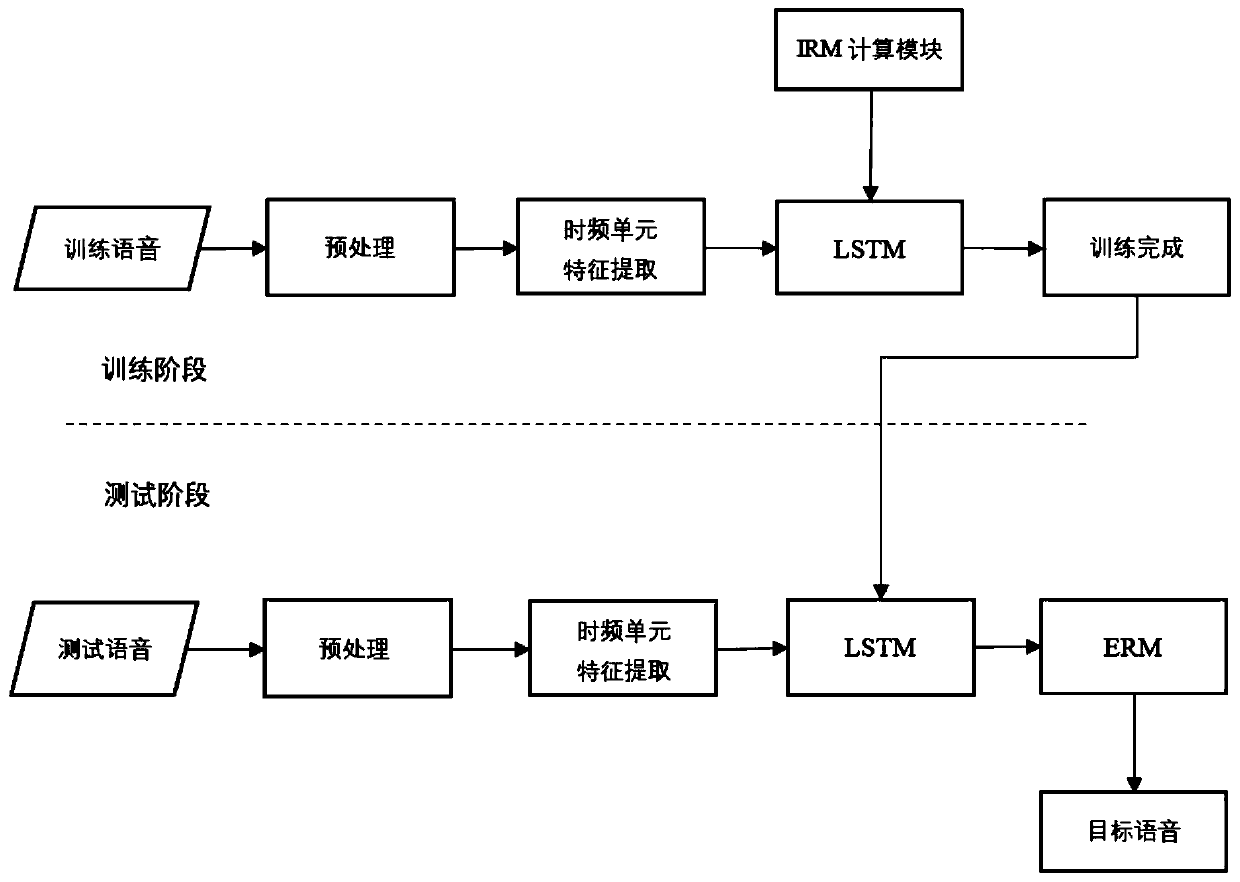
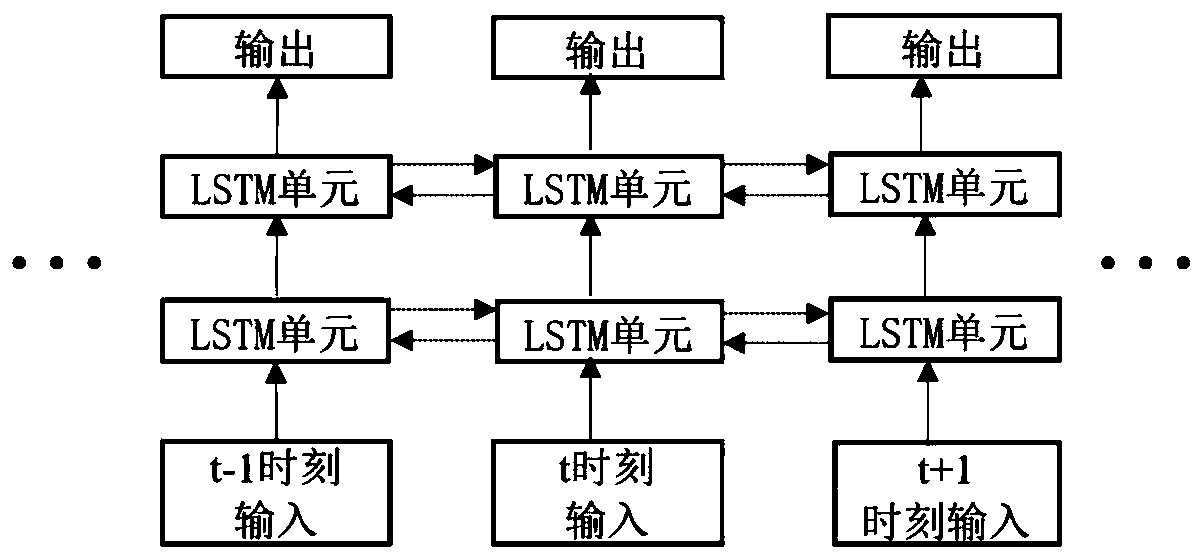
Binaural speech separation method based on LSTM (Long Short Term Memory) network
ActiveCN110728989AEasy to separateImprove robustnessSpeech analysisInteraural time differenceFrequency Unit
The invention discloses a binaural speech separation method based on an LSTM (Long Short Term Memory) network. The ITD (Inter-aural Time Difference), the IID (Interaural Intensity Difference) and theCCF (Cross Correlation Function) of each time frequency unit of a training binaural speech signal are extracted to be used as separation space features; space features of a current frame and front andback 5 frames of the time frequency units in the same subband are used as input parameters of a two-way LSTM network to be trained; and a separation model based on the LSTM is obtained. At the test stage, the space features of the current frame and the front and back 5 frames of the time frequency units of a test binaural speech signal are used as input parameters, obtained through training, of the two-way LSTM network, and are used for estimating shielding values of the target speech of the current time frequency unit so as to perform speech separation according to a shielding value. The separation result shows that compared with a method based on a deep neural network, the binaural speech separation method based on the LSTM network provided by the invention has the advantages that the subjective evaluation index is obviously improved, and the algorithm generalization performance is good.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Computer program and method of determining a personalized head-related transfer function and interaural time difference function
ActiveUS20180035226A1Good computer program productLarge user groupInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingInteraural time differencePersonalization
A method of estimating an individualized head-related transfer function (HRTF) and an individualized interaural time difference function (ITDF) of a particular person, comprising the steps of: a) obtaining a plurality of data sets (Li, Ri, Oi), each comprising a left and a right audio sample (Li, Ri) from a pair of in-ear microphones, and orientation information (Oi) from an orientation unit, measured in a test-arrangement whereby an acoustic test signal is rendered via a loudspeaker; b) storing the data sets in a memory; c) estimating the directions of the loudspeaker relative to the person based on the orientation data and the audio data; d) estimating the ITDF based on the data sets and on the estimated relative position / orientation; e) estimating the HRTF, based on the data sets and based on the estimated relative position / orientation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ANTWERP
Method for locating a sound source, and humanoid robot using such a method
ActiveCN106030331ASimple calculationDirection/deviation determination systemsInteraural time differenceSound sources
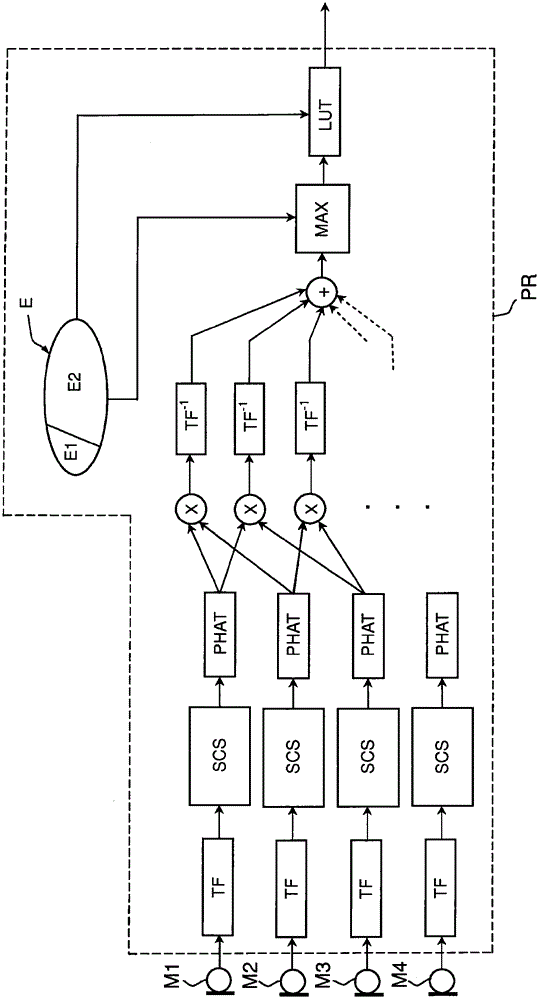
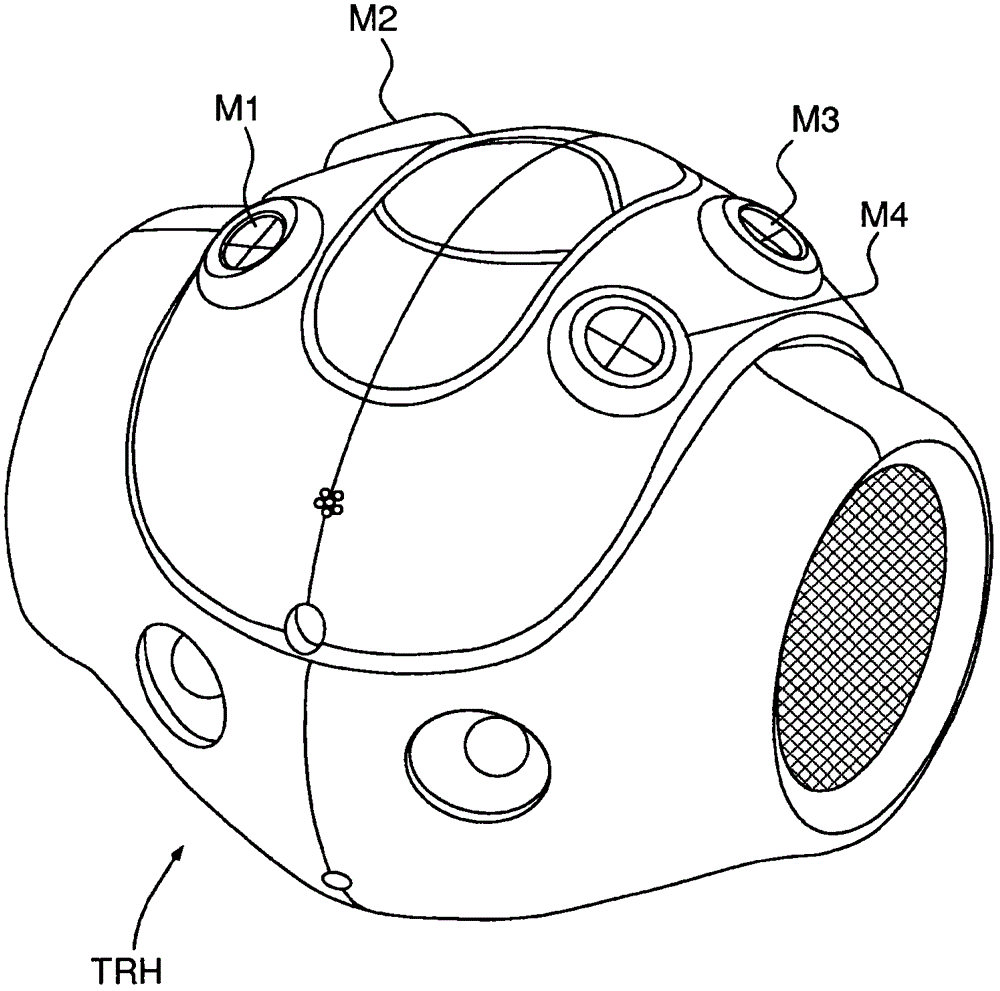
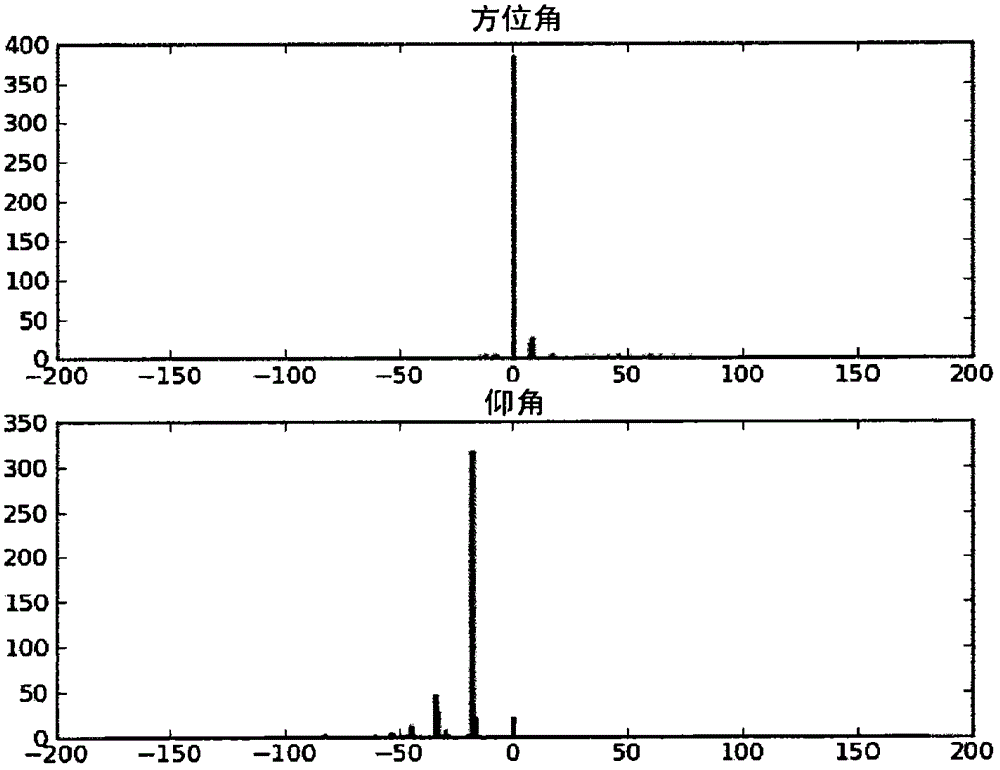
The invention relates to a method for locating a sound source by maximizing a directed response strength calculated for a plurality of vectors of the interauricular time differences forming a set (E) that includes: a first subset (E1) of vectors compatible with sound signals from a single sound source at an unlimited distance from said microphones; and a second subset (E2) of vectors that are not compatible with sound signals from a single sound source at an unlimited distance from said microphones. Each vector of said first subset is associated with a direction for locating the corresponding single sound source, and each vector of said second subset is associated with the locating direction associated with a vector of said first subset closest thereto according to a predefined metric. The invention also relates to a humanoid robot including: a set of at least three microphones (M1, M2, M3, M4), preferably arranged on a surface higher than the head thereof; and a processor (PR) for implementing one such method.
Owner:ALDEBARAN ROBOTICS SA
Speaker array for virtual surround rendering
ActiveCN102611966AStereophonic circuit arrangementsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsInteraural time differenceLoudspeaker
An approach and device for generation of virtual surround sound with a two-way approach that employs a first order head-related models have been used that resemble interaural time difference localization and inter-aural level difference localization cues in the respective frequency bands while avoiding phantom imaging and excessive coloration.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Interaural time difference enhancement strategy
Aspects of the present invention are generally directed to a modulation enhancement strategy that helps improve ITD perception by explicitly modulating the electrical stimulation signal. In an embodiment, the timing of the applied modulations is based on amplitude inflections (i.e., peaks or troughs) in the received sound signal. In an embodiment, the identified inflections (i.e., peaks or troughs) represent the most energetic portions of the signal over a particular time period (e.g., the time period prior to the inflection having a length equal to the expected fundamental period of the signal. Further, in an embodiment, the cochlear implant applies a delay to the stimulation signal to help maintain interaural timing cues. The application of this delay helps account for the traveling wave delay in the acoustic path of the opposite ear in embodiments in which the opposite ear is fitted with a hearing aid or is not fitted with a hearing device.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
Sound source localization system and method
ActiveUS8270632B2Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesStereophonic circuit arrangementsInteraural time differenceLocalization system
A sound source localization system includes a plurality of microphones for receiving a signal as an input from a sound source; a time-difference extraction unit for decomposing the signal inputted through the plurality of microphones into time, frequency and amplitude using a sparse coding and then extracting a sparse interaural time difference (SITD) inputted through the plurality of microphones for each frequency; and a sound source localization unit for localizing the sound source using the SITDs. A sound source localization method includes receiving a signal as an input from a sound source; decomposing the signal into time, frequency and amplitude using a sparse coding; extracting an SITD for each frequency; and localizing the sound source using the SITDs.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Method and apparatus for recognizing sound source
ActiveCN113366549AImprove recognition rateRoad vehicles traffic controlStereophonic circuit arrangementsInteraural time differenceSound sources
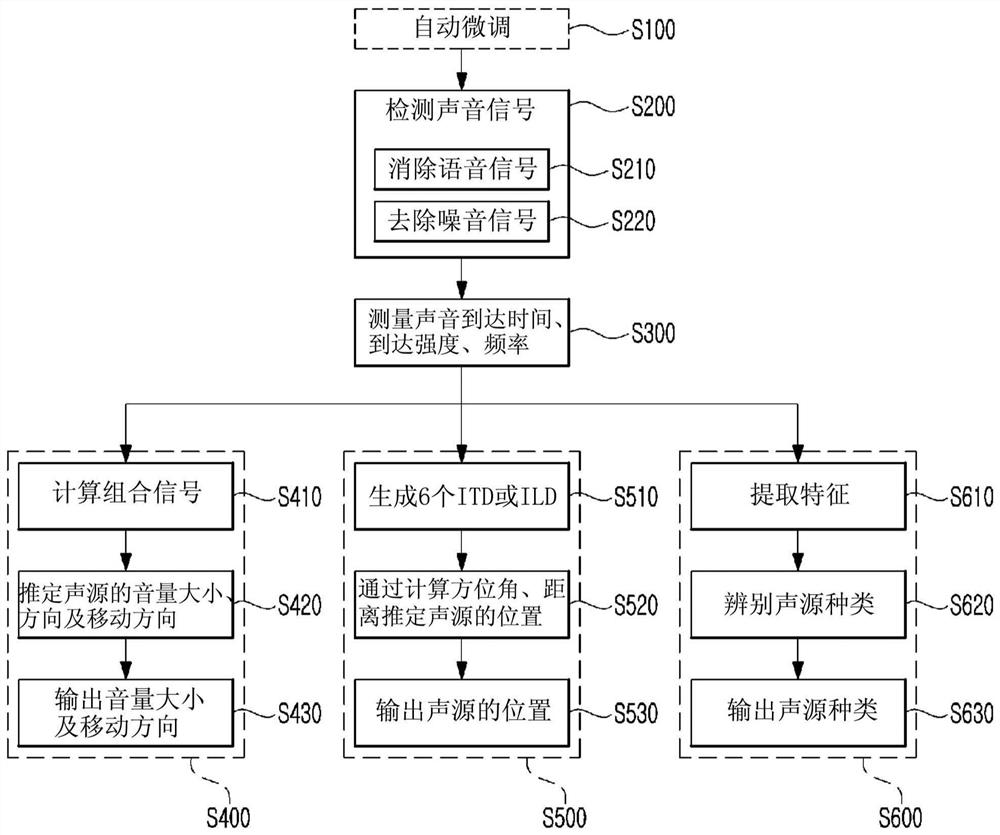
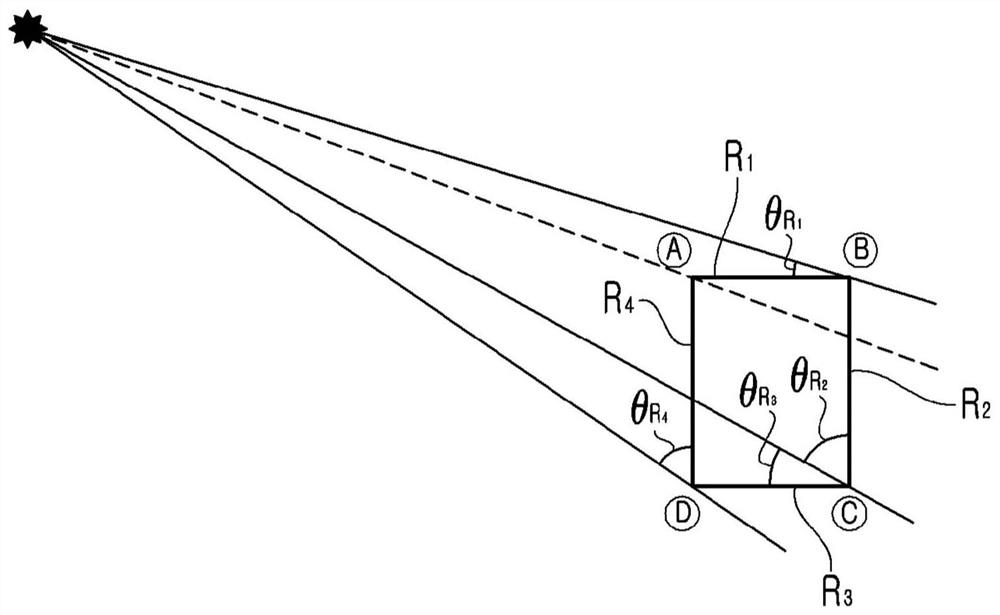
The present invention relates to a method and an apparatus for recognizing a sound source. According to the sound source recognition method of the present invention, an acoustic signal is detected by four acoustic sensors arranged in a rectangular shape when viewed in a horizontal direction, an acoustic arrival time is measured, six Interactive Time Differences (ITDs) are generated on the basis of the difference between the acoustic arrival times of the respective sound sensors, and the position of the sound source is estimated on the basis of the six ITDs. In addition, features of the sound source are extracted and classified by using a sum signal from the four acoustic sensors to determine the type of the sound source.
Owner:金永彦
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com