Patents
Literature
118results about "Sets with desired directivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
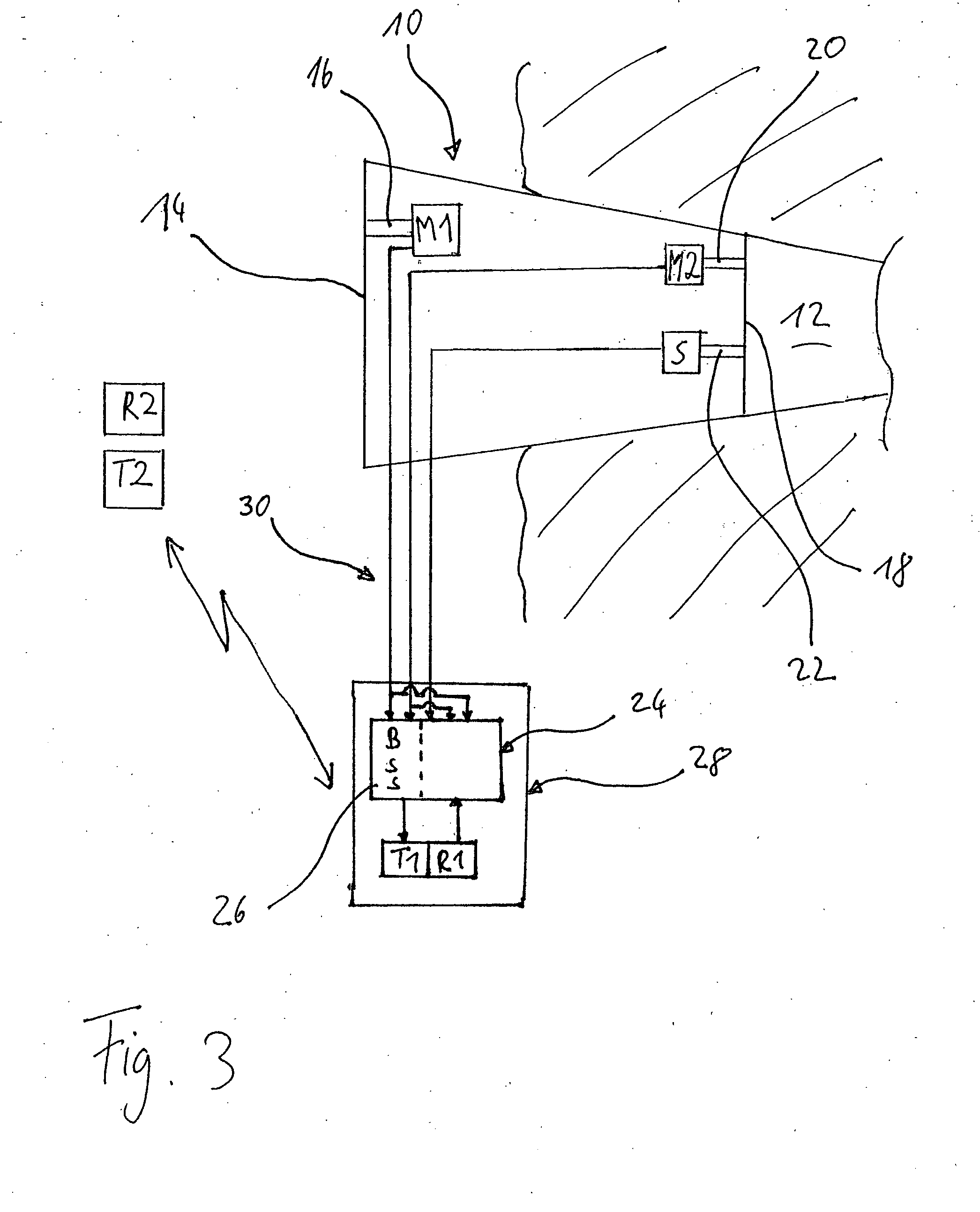
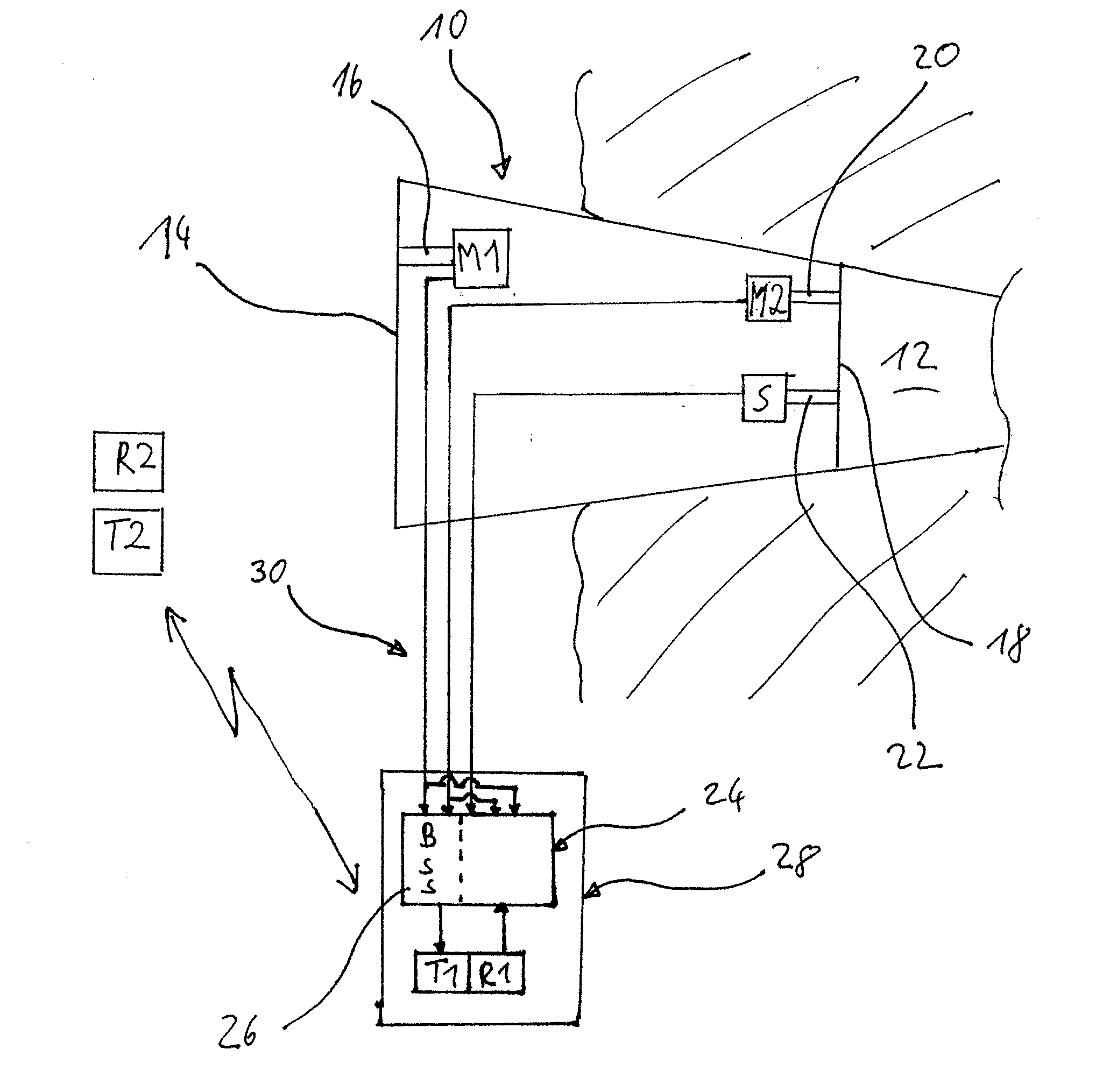
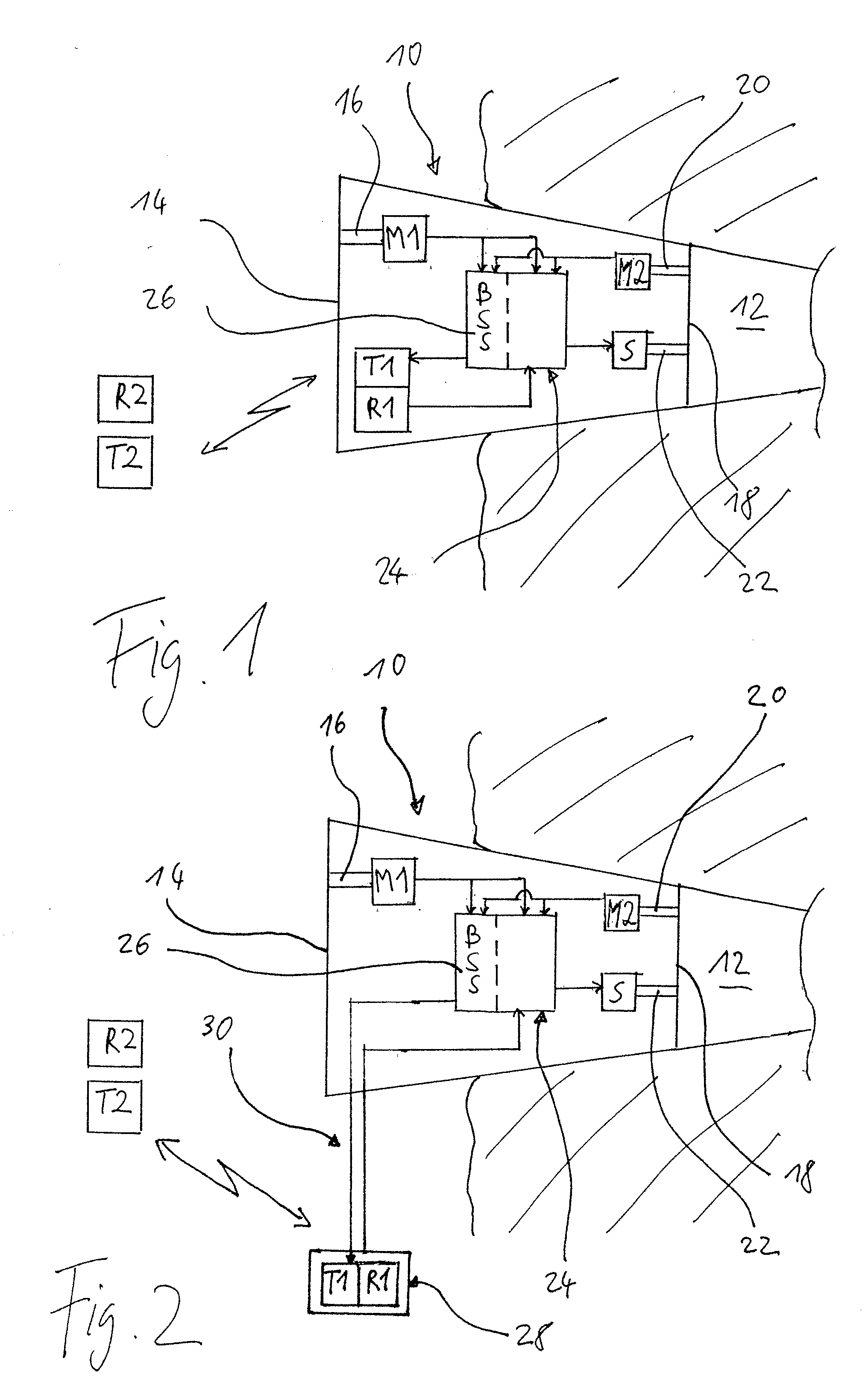
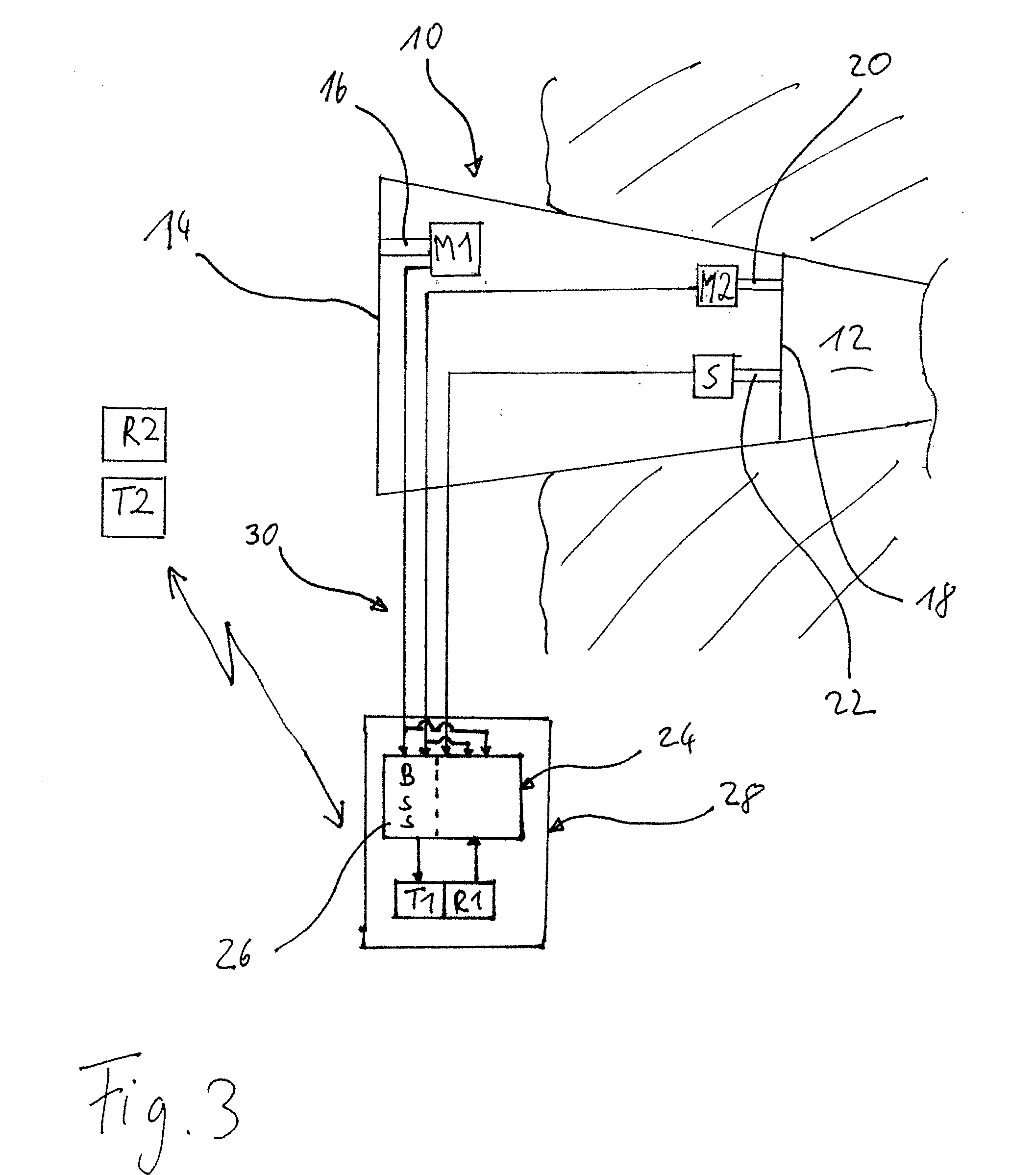
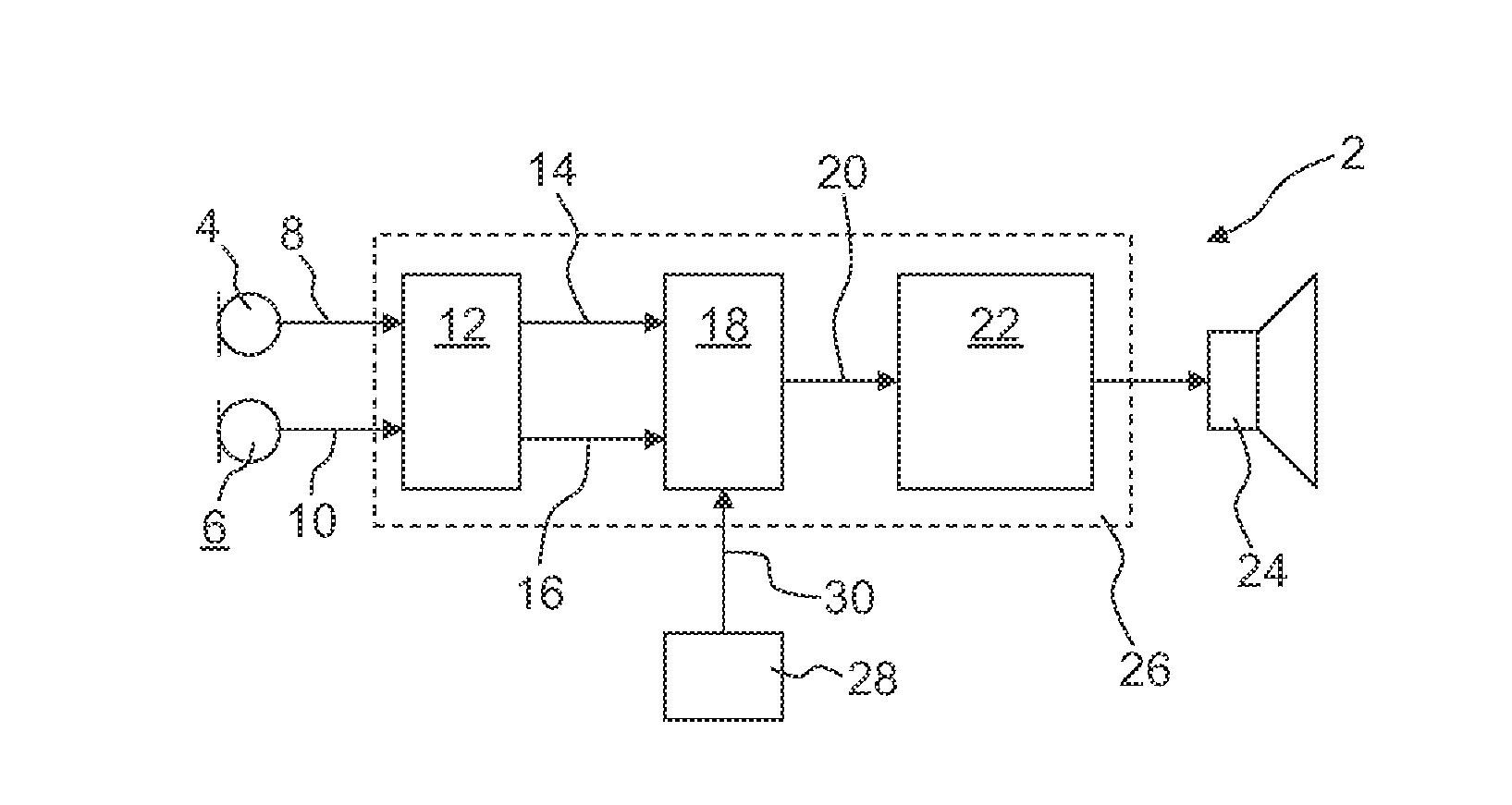
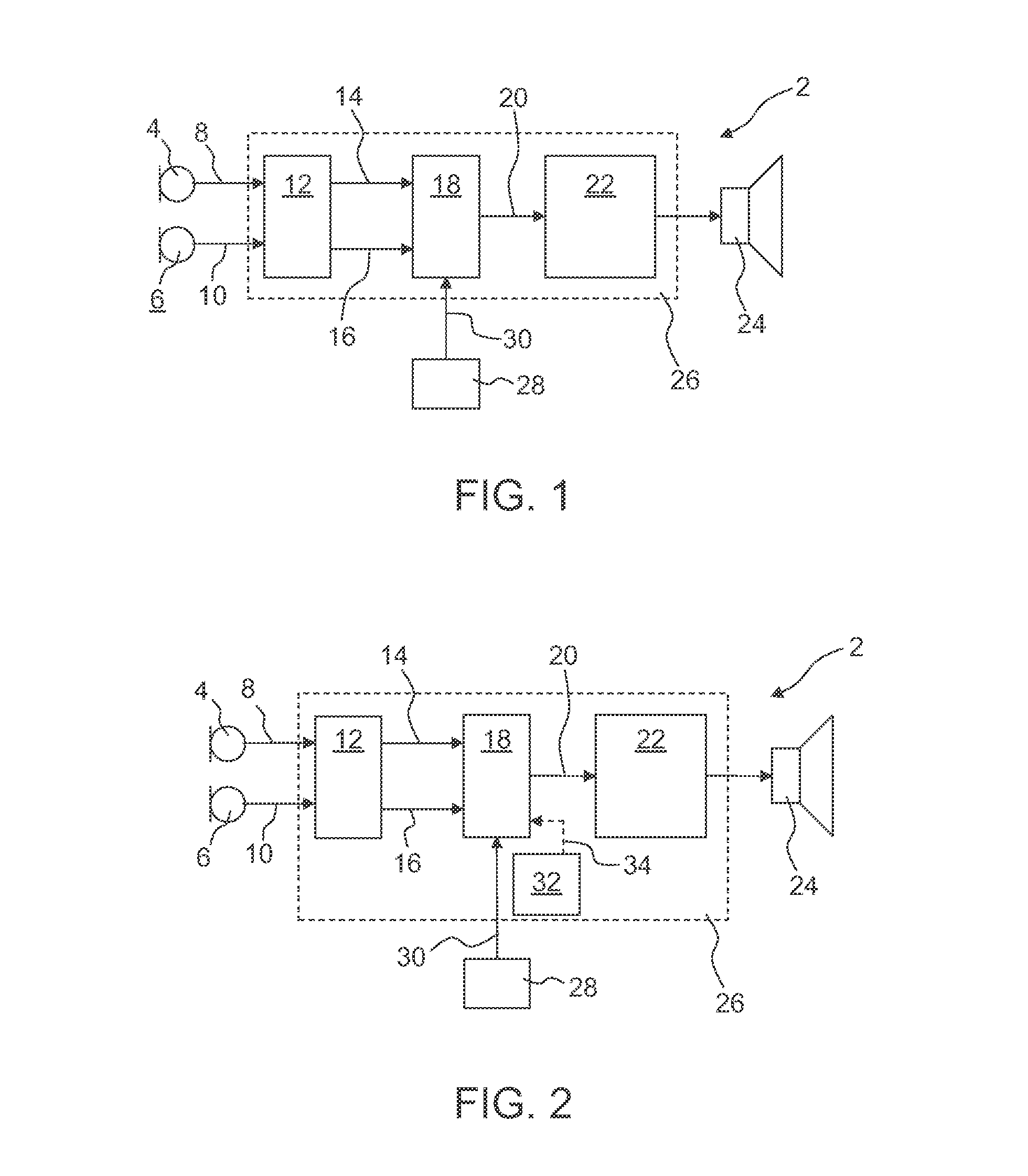
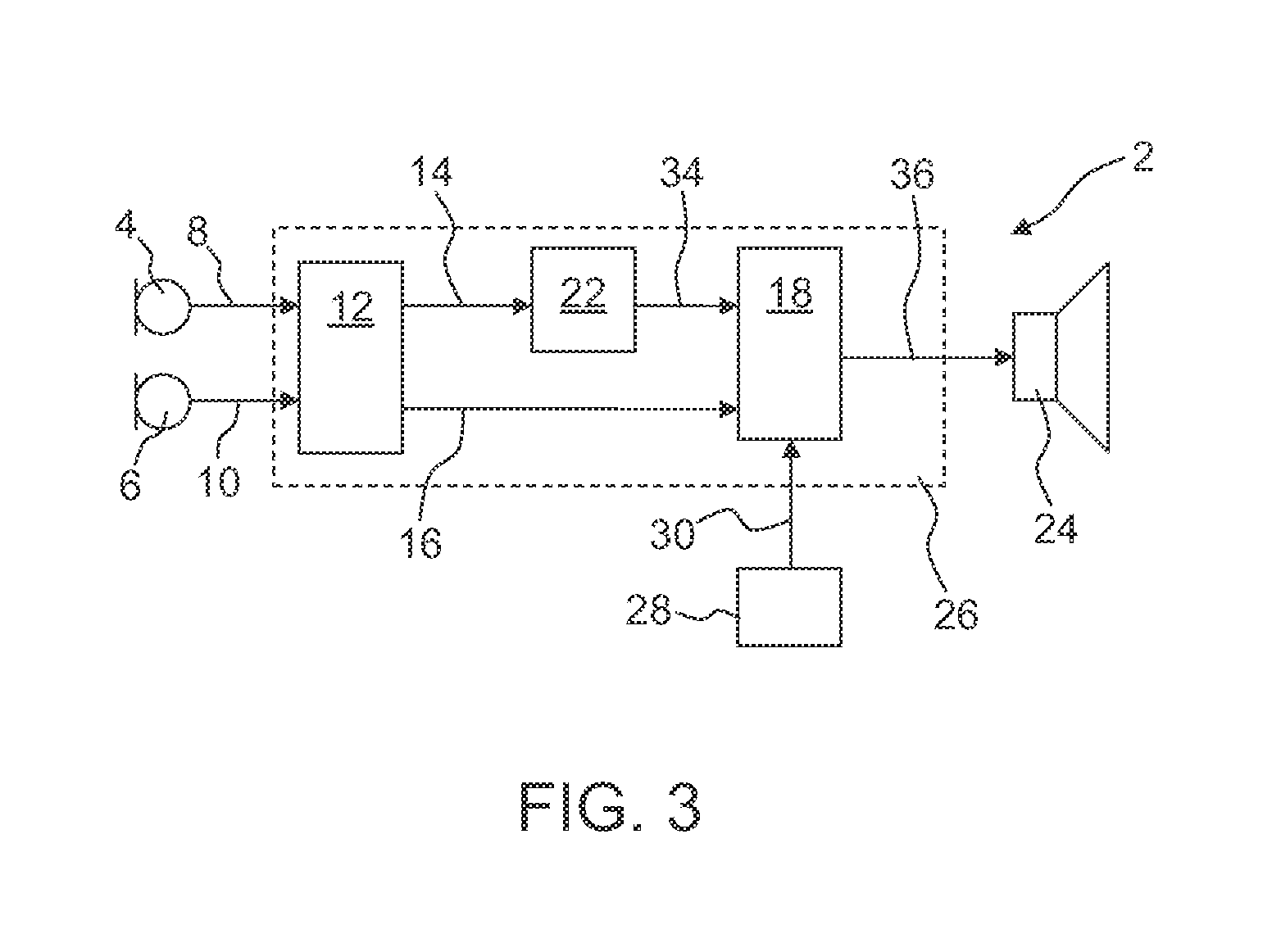
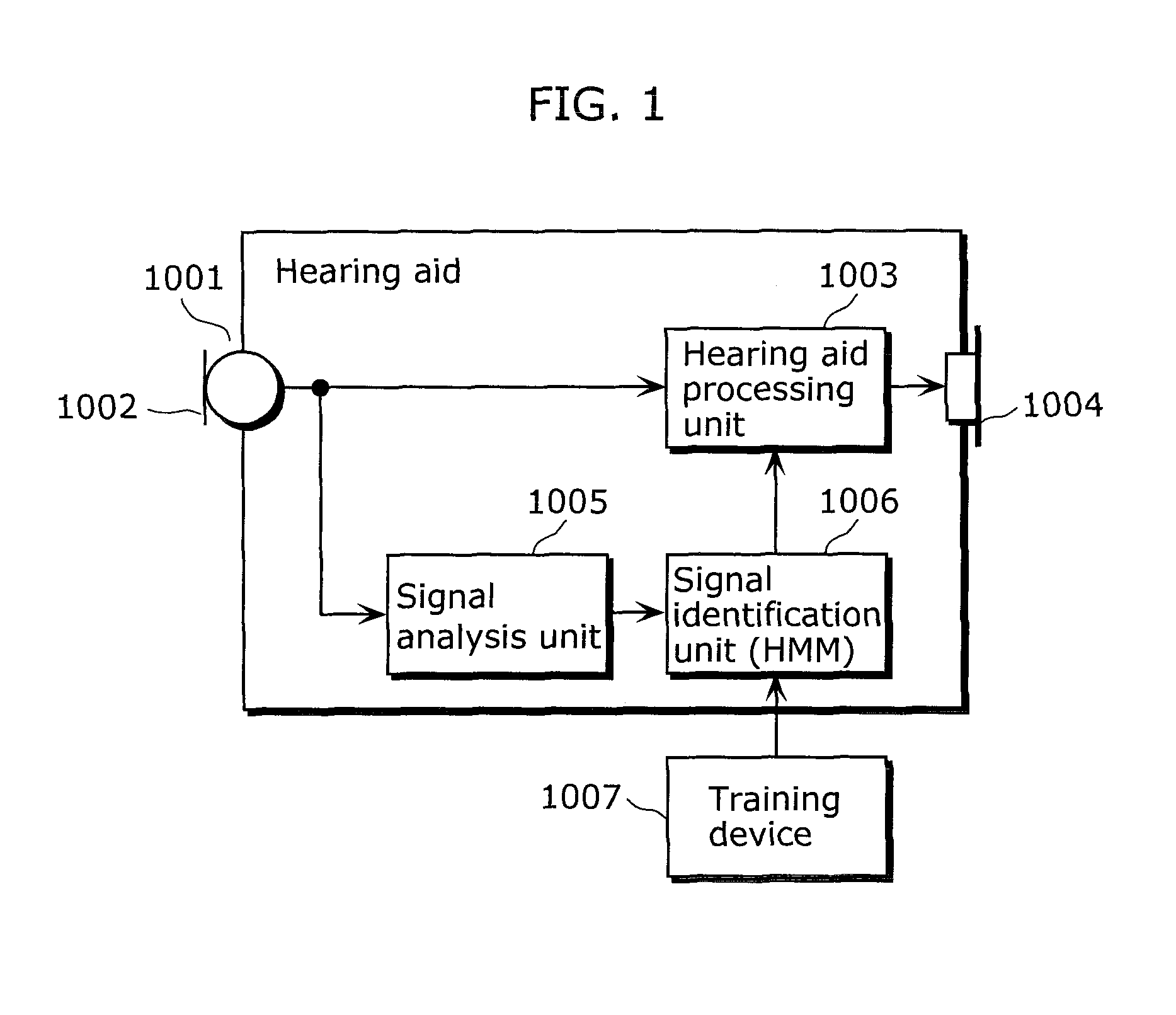
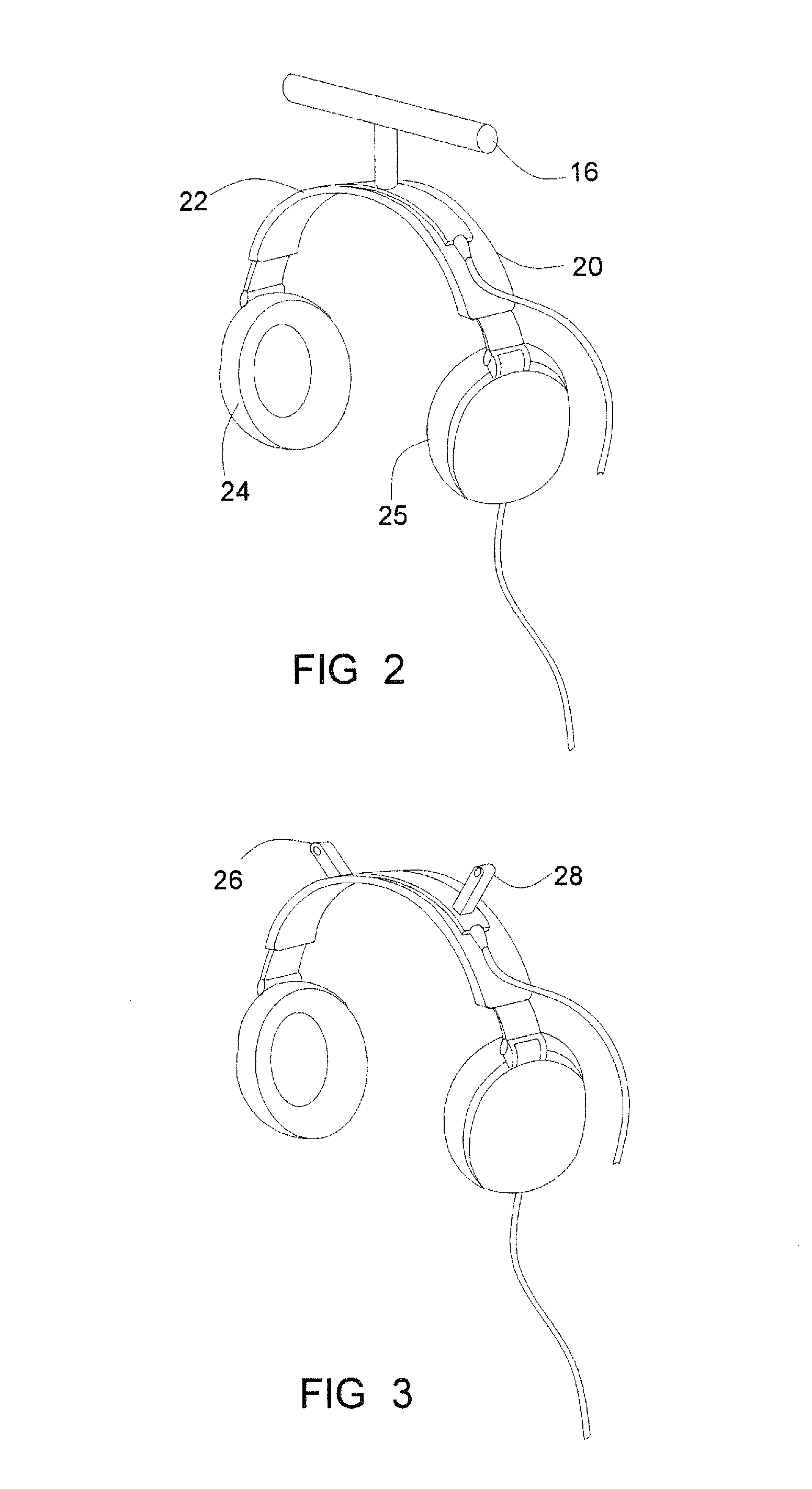
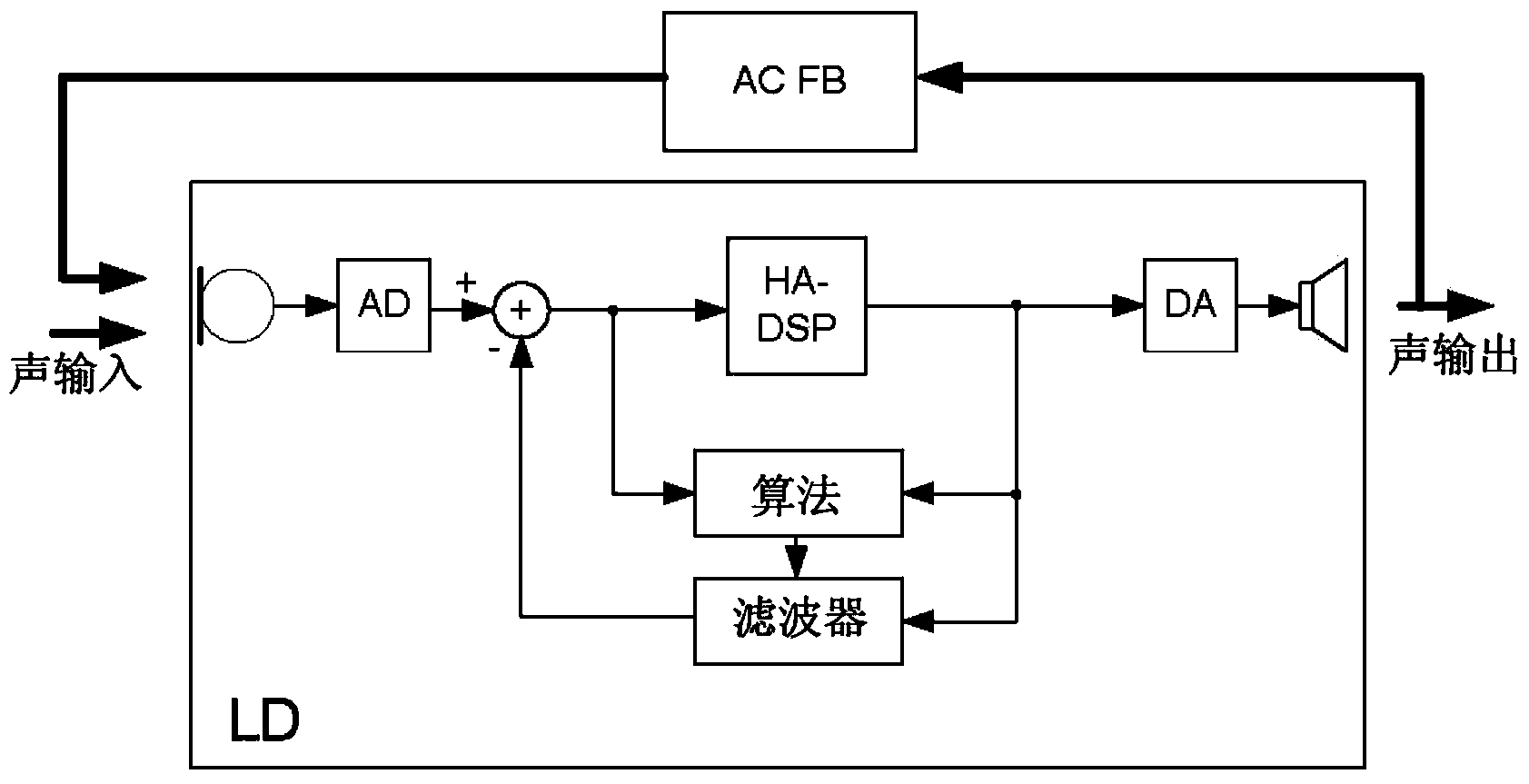
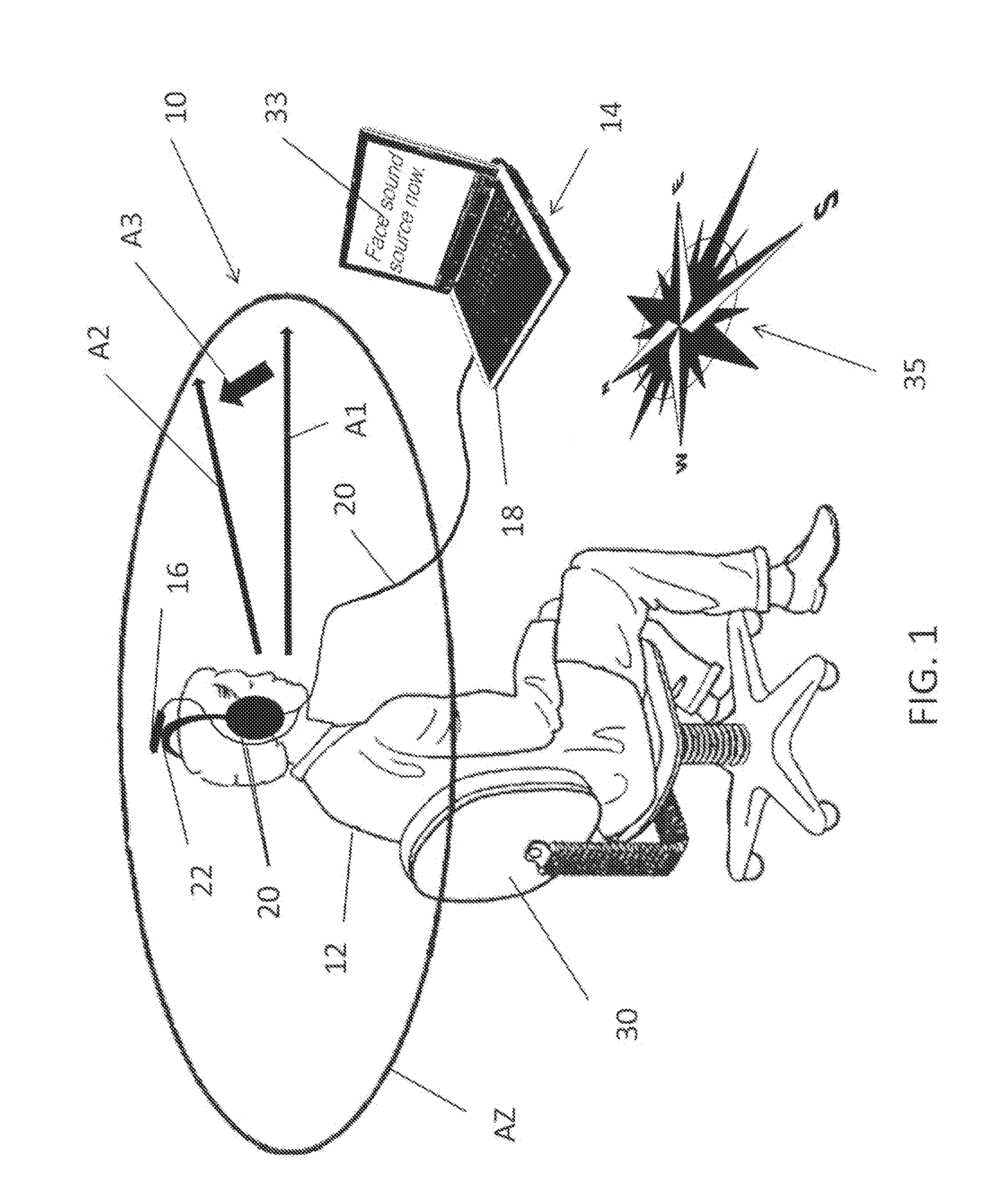
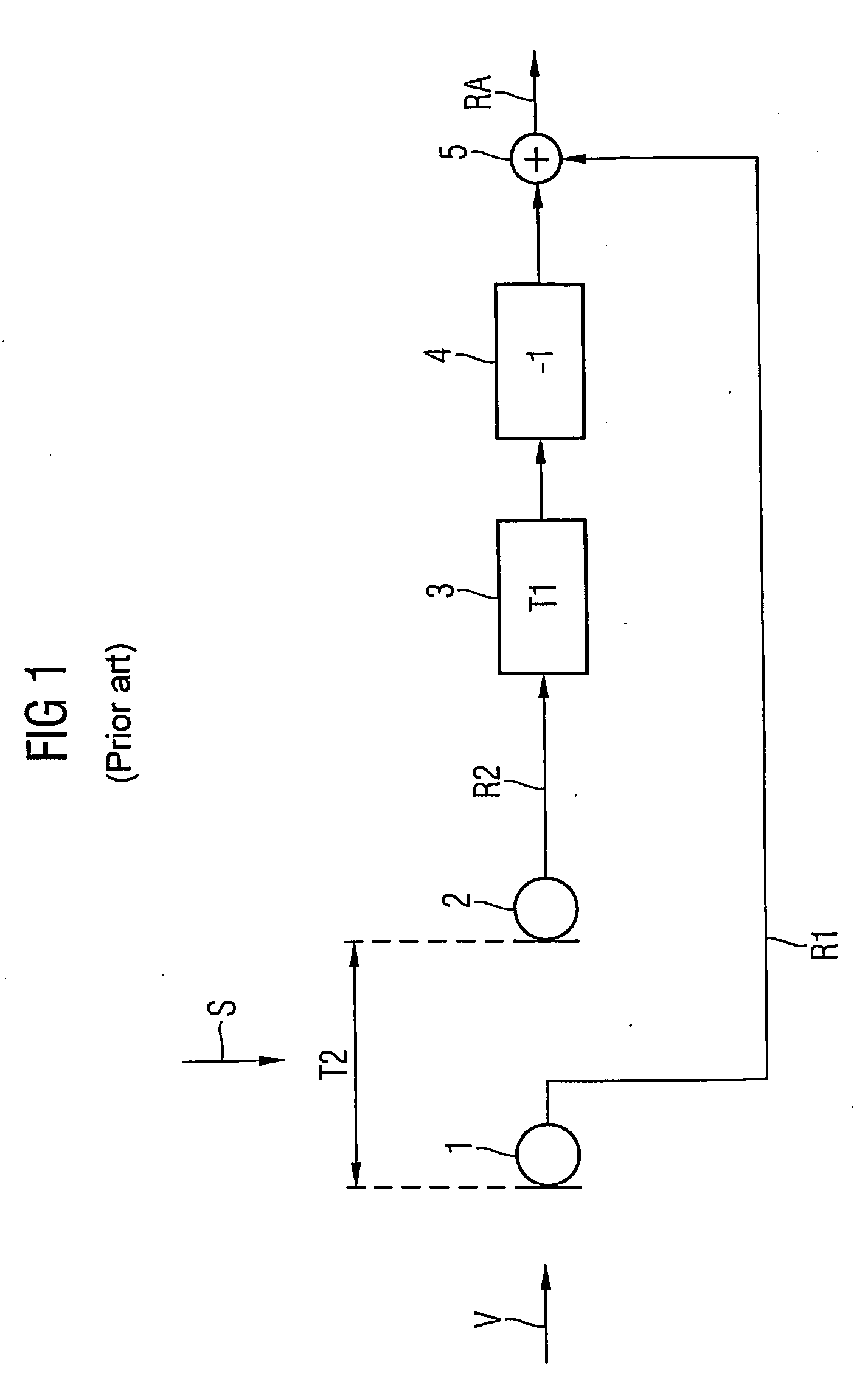
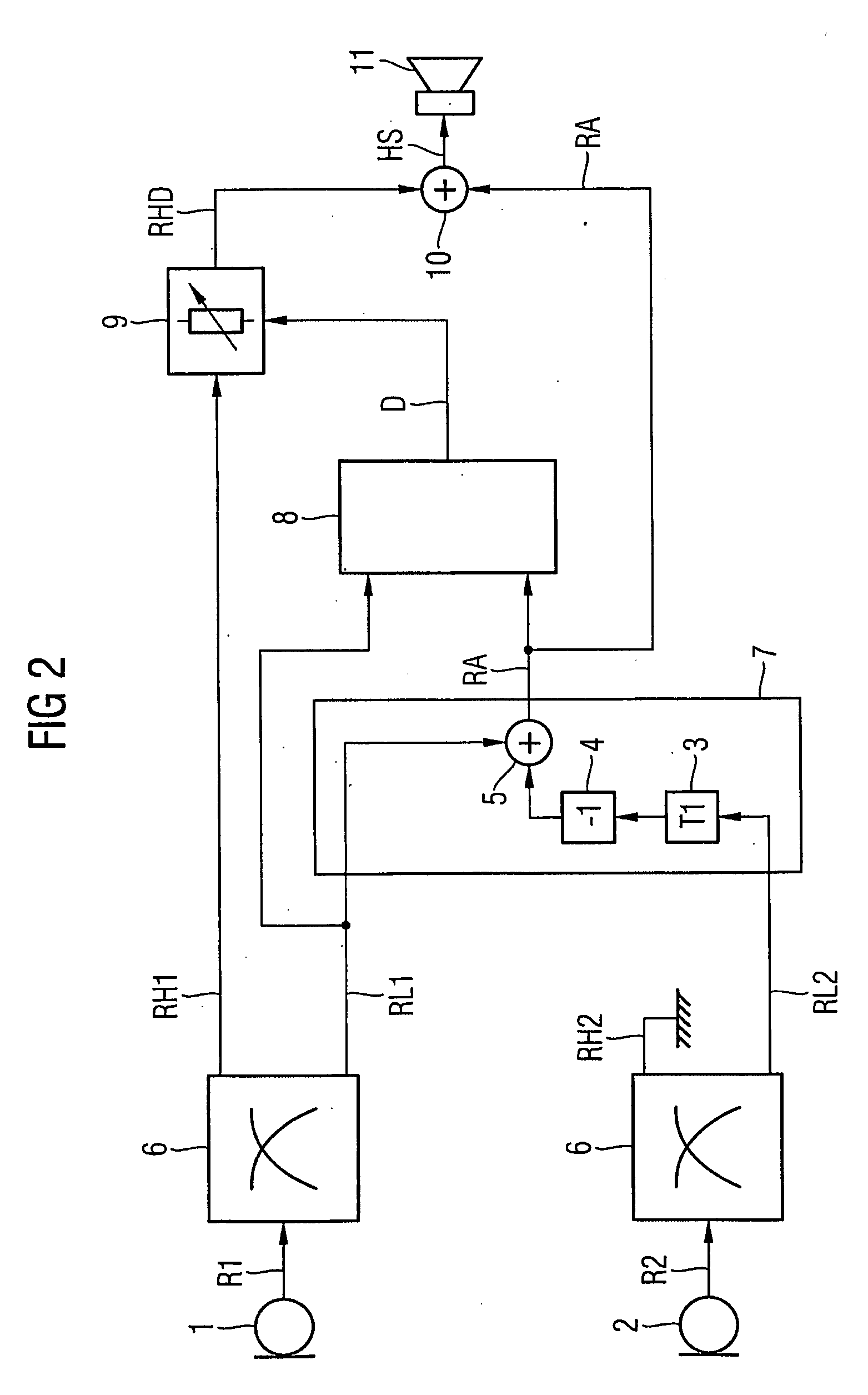
Method for controlling the directionality of the sound receiving characteristic of a hearing aid and a signal processing apparatus
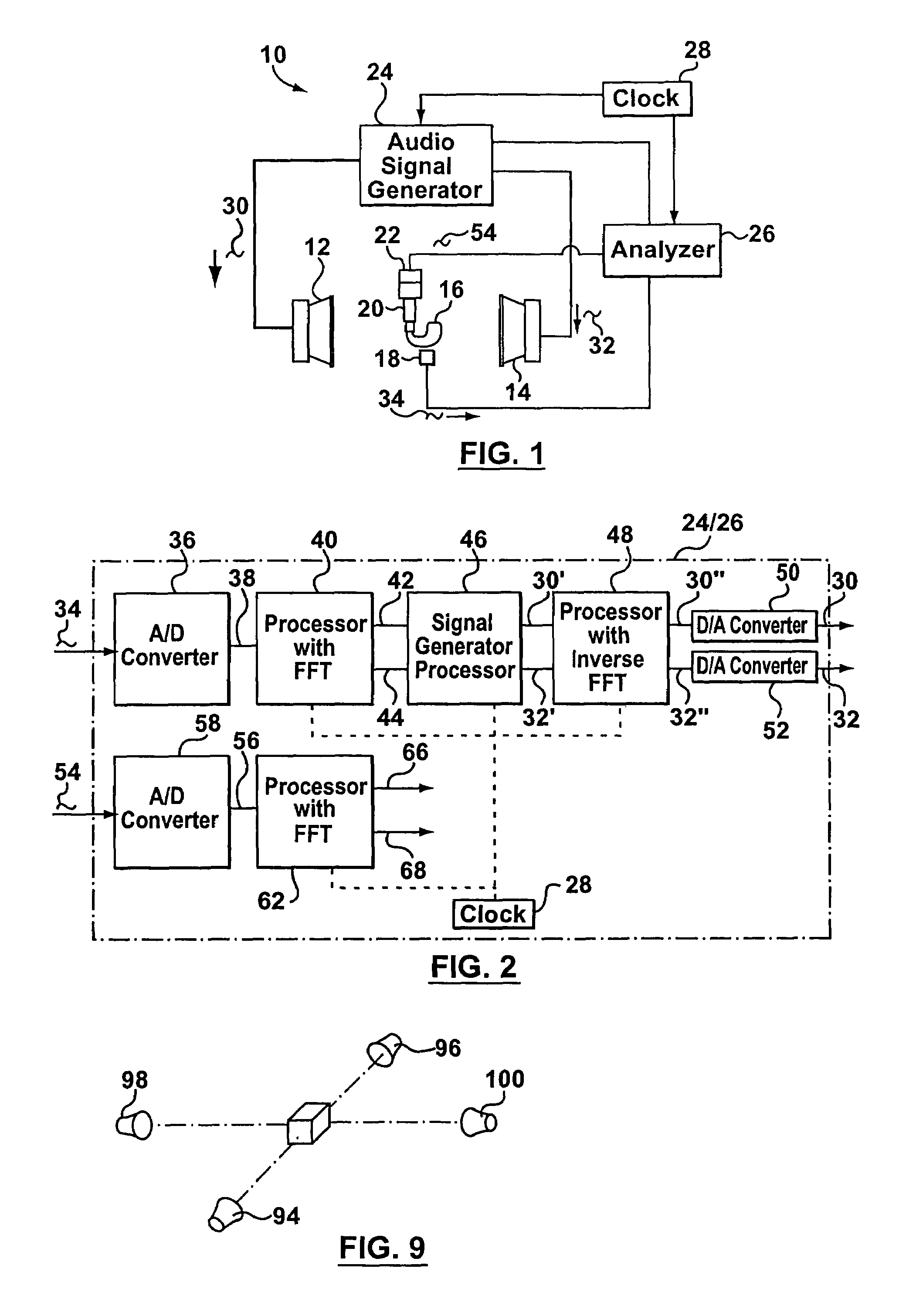
ActiveUS20060177079A1Minimize output signalMinimize microphone noiseDoor/window protective devicesCurtain accessoriesSignal analyzerEngineering
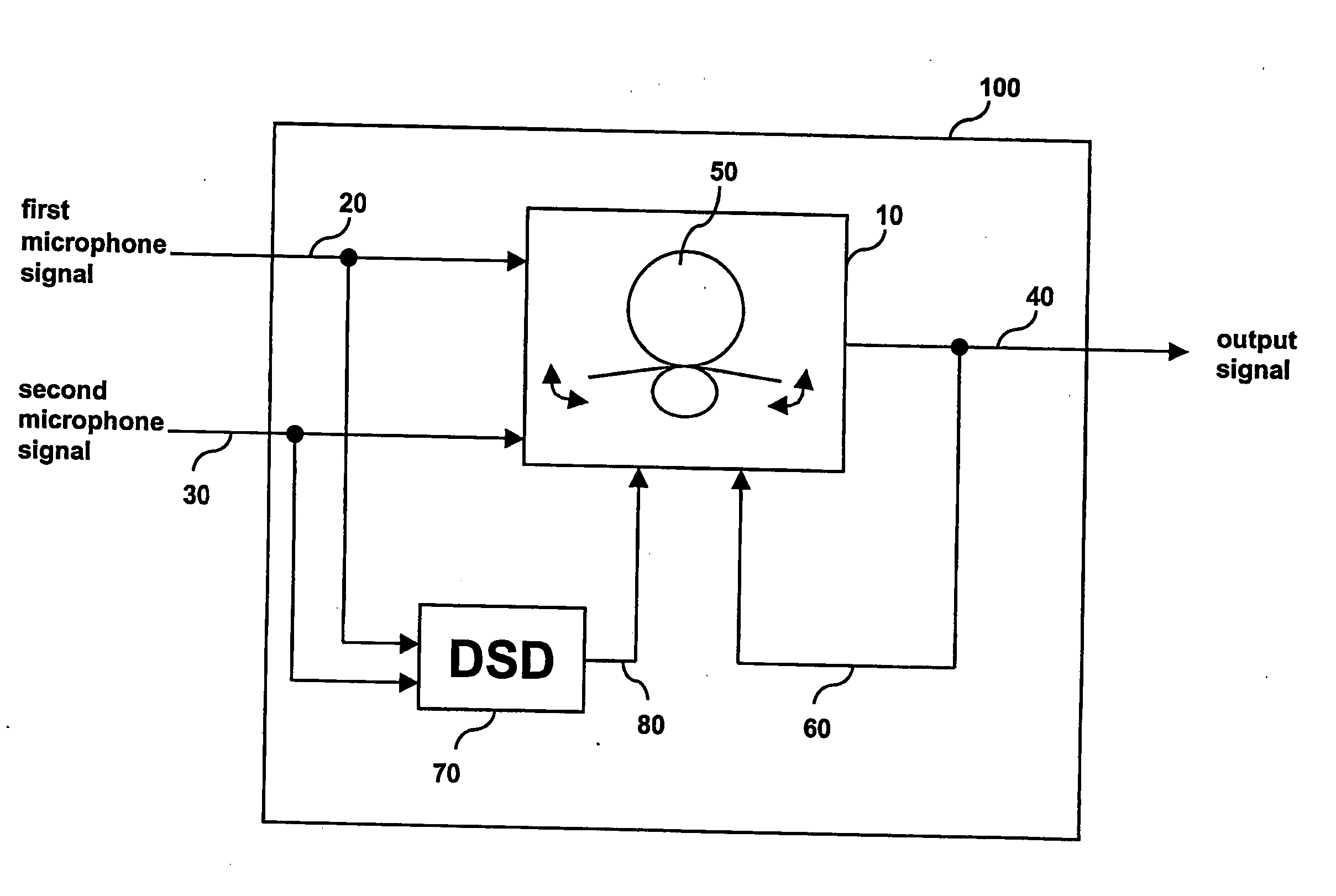
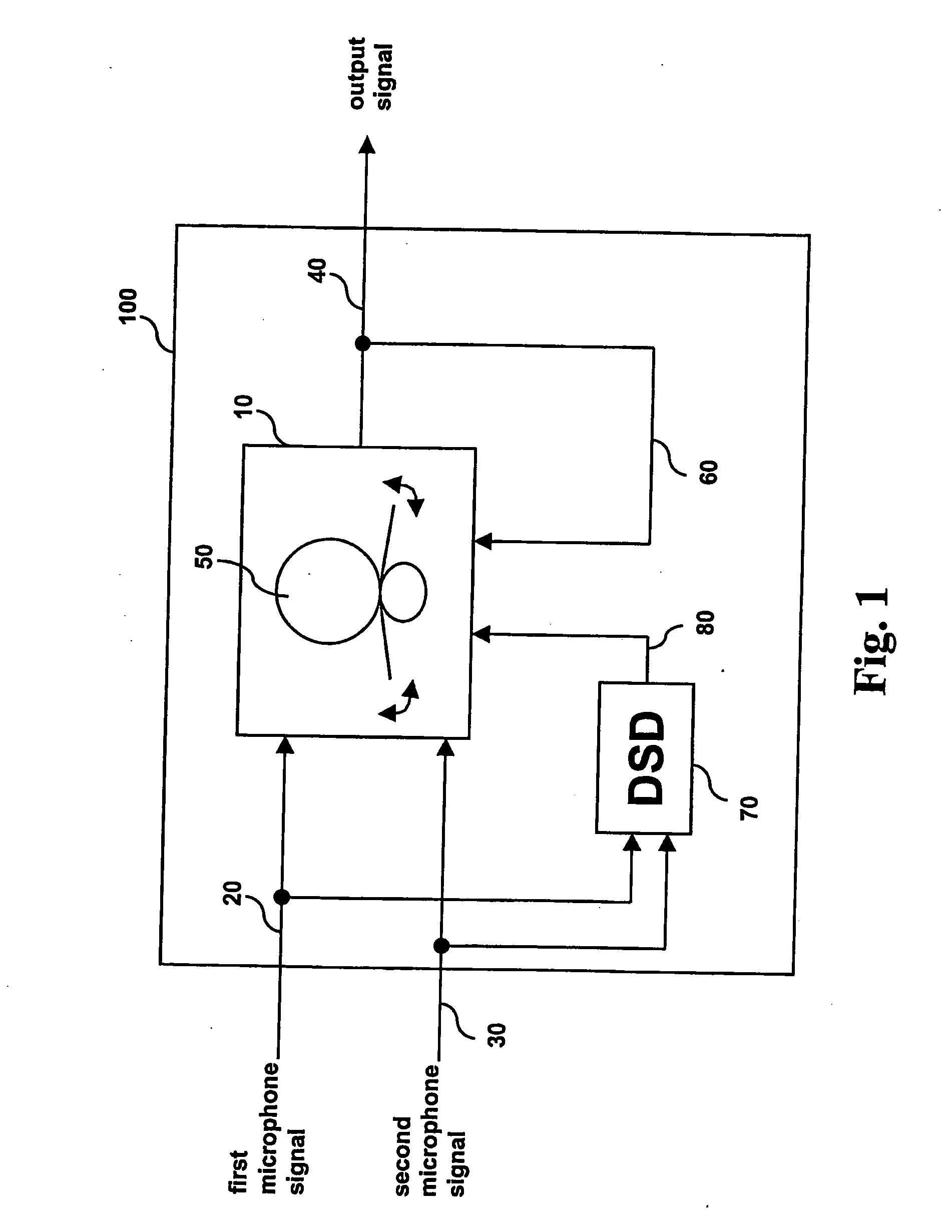
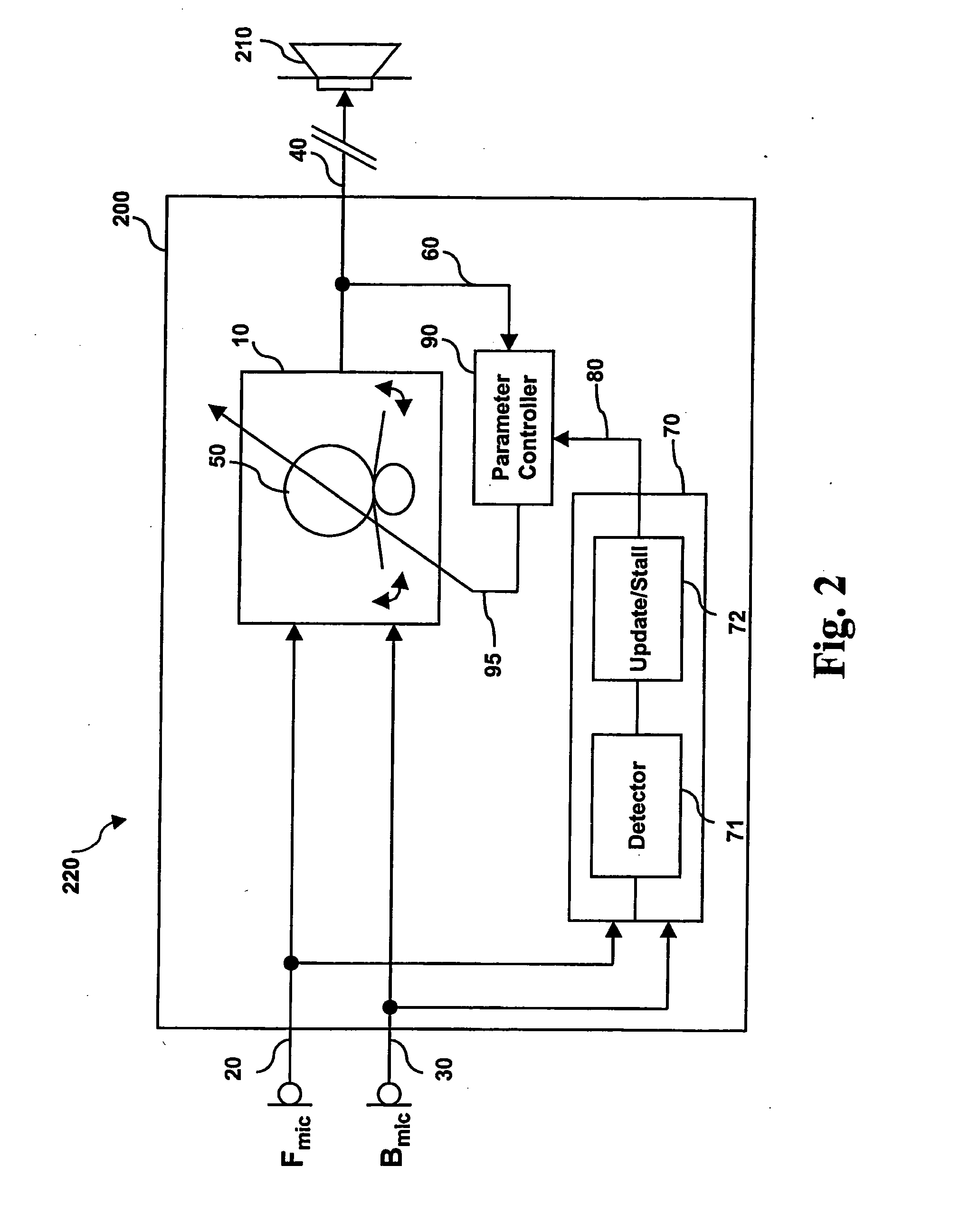
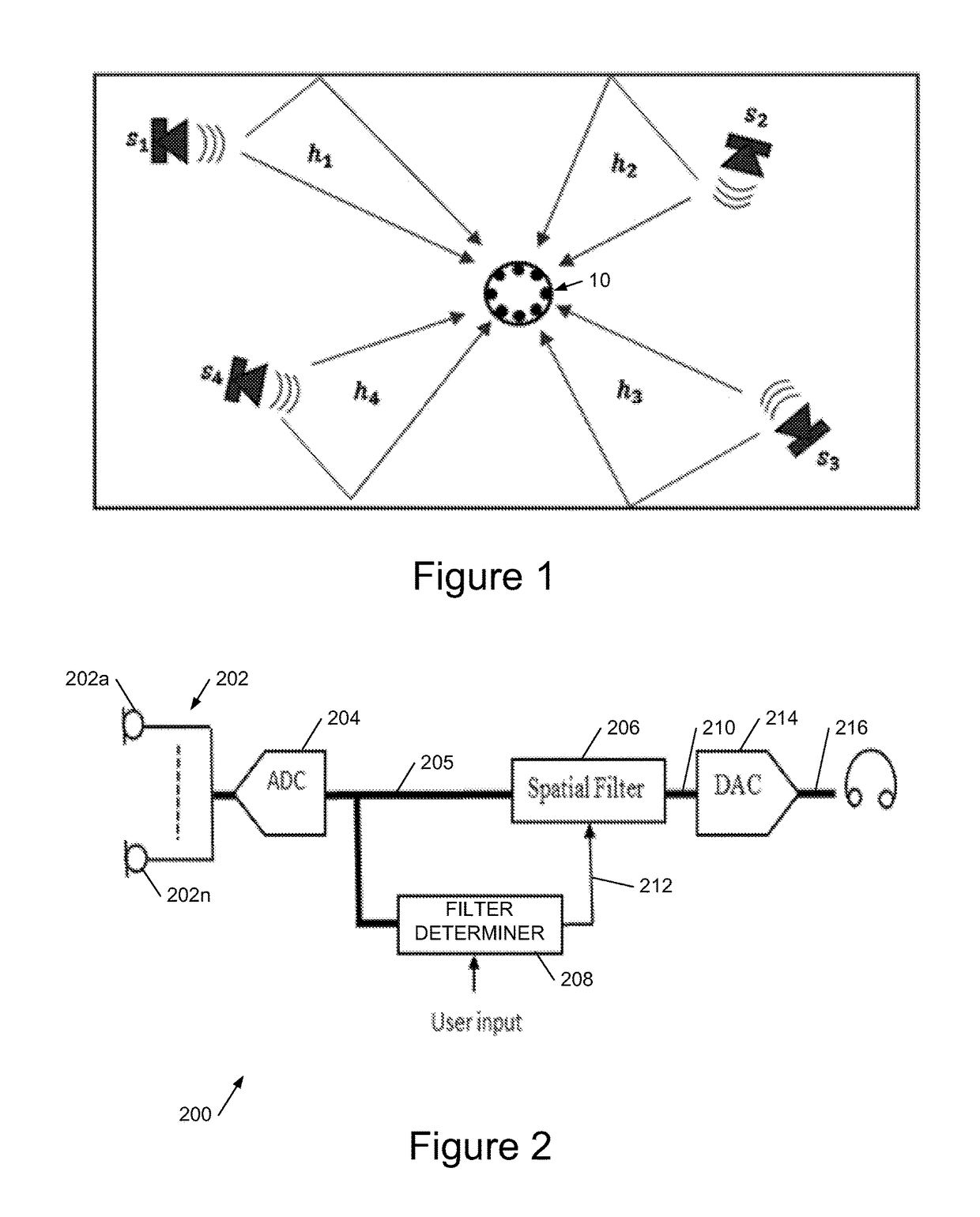
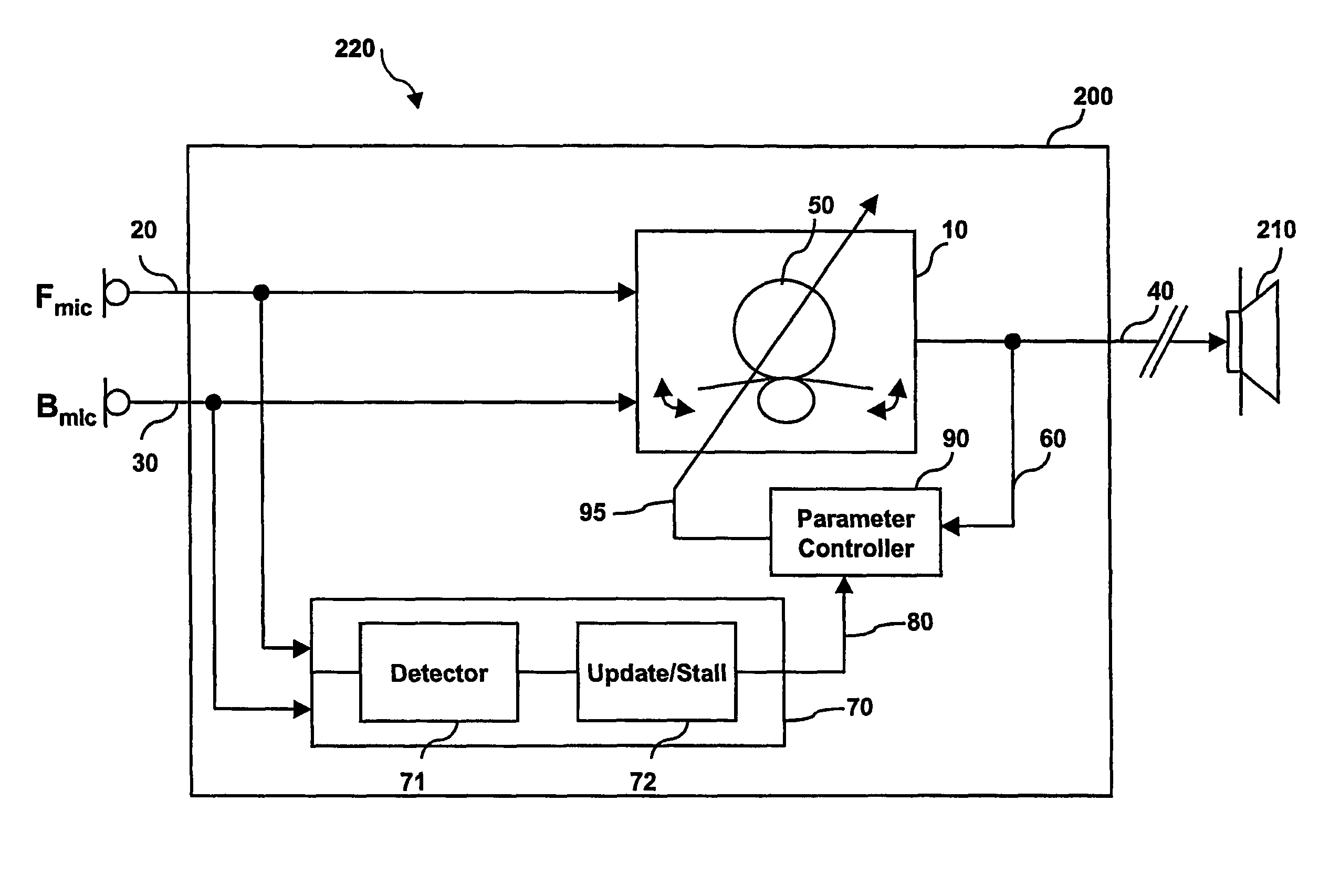
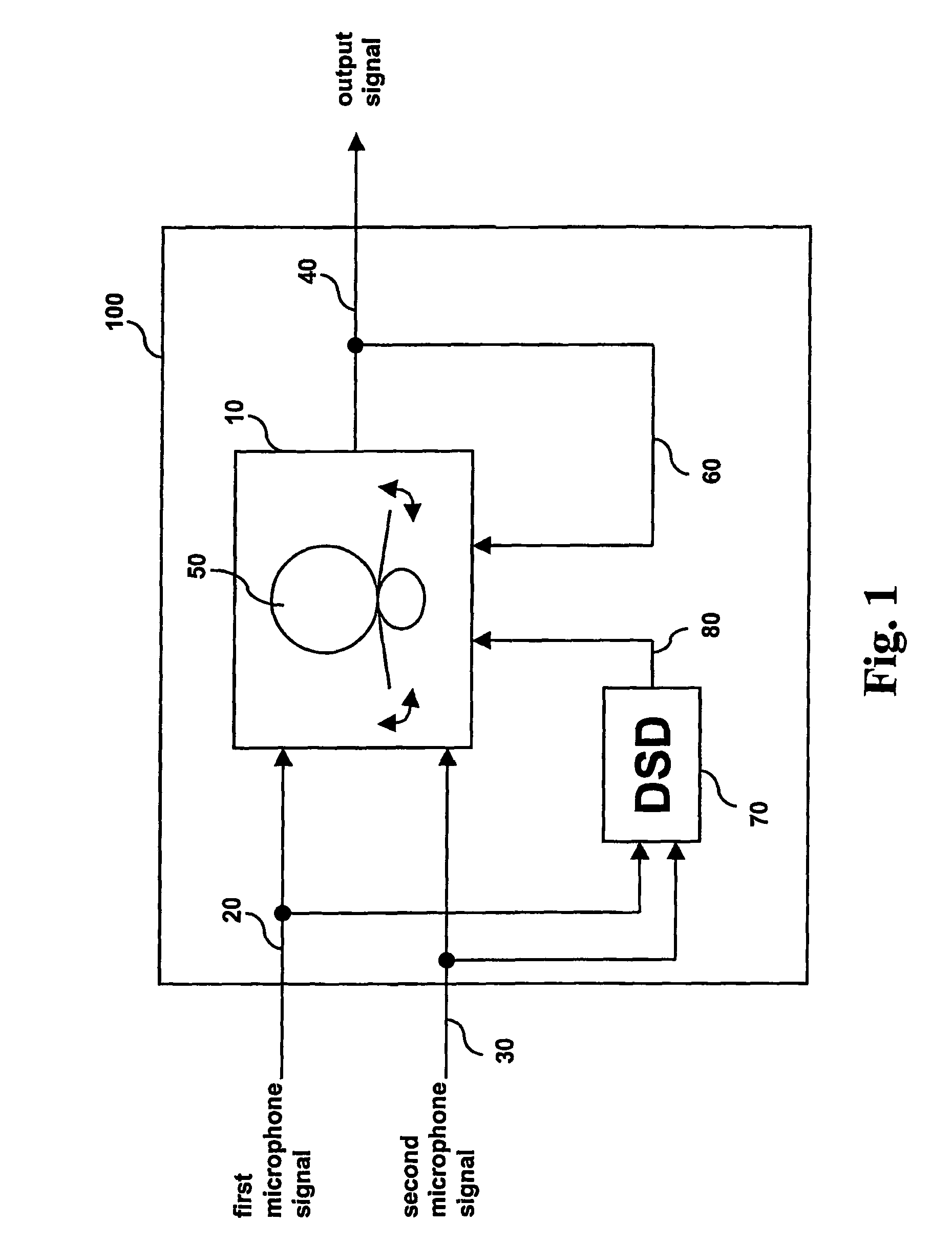
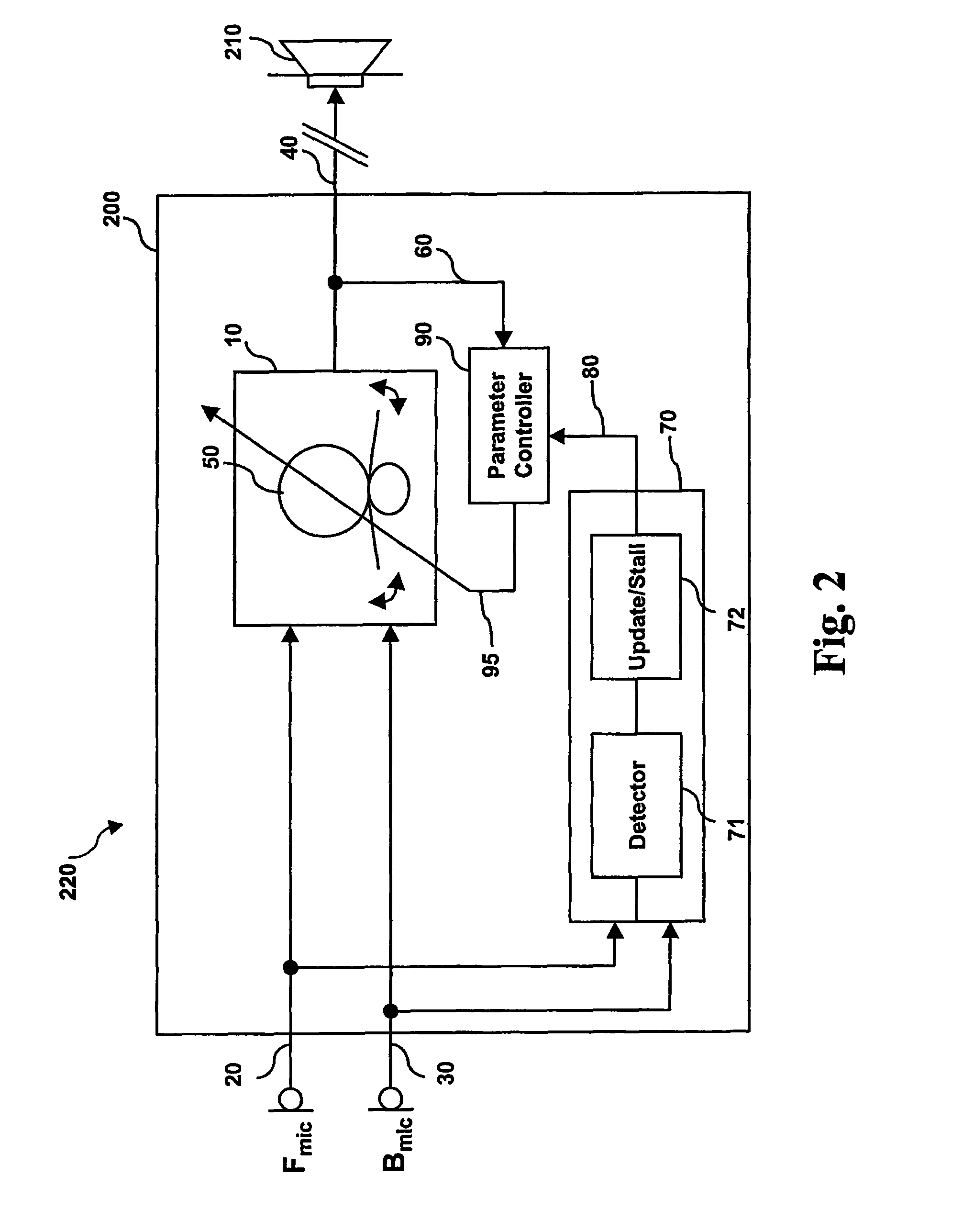
A signal processing apparatus (100) for a hearing aid with a controllable directional characteristic is provided which comprises a directional controller (10) receiving first and second microphone signals (20, 30) and output an output signal (40), a signal analyzer (70) which detects whether at least one of said first and second microphone signals being undesired signals, and wherein said directional controller minimizes the output signal by adjusting the directional characteristic only if the signal analyzer has detected undesired signals.
Owner:WIDEX AS
Blind source separation systems
ActiveUS9668066B1Cost for rotationSave spaceSignal processingSets with desired directivityFrequency spectrumHearing aid
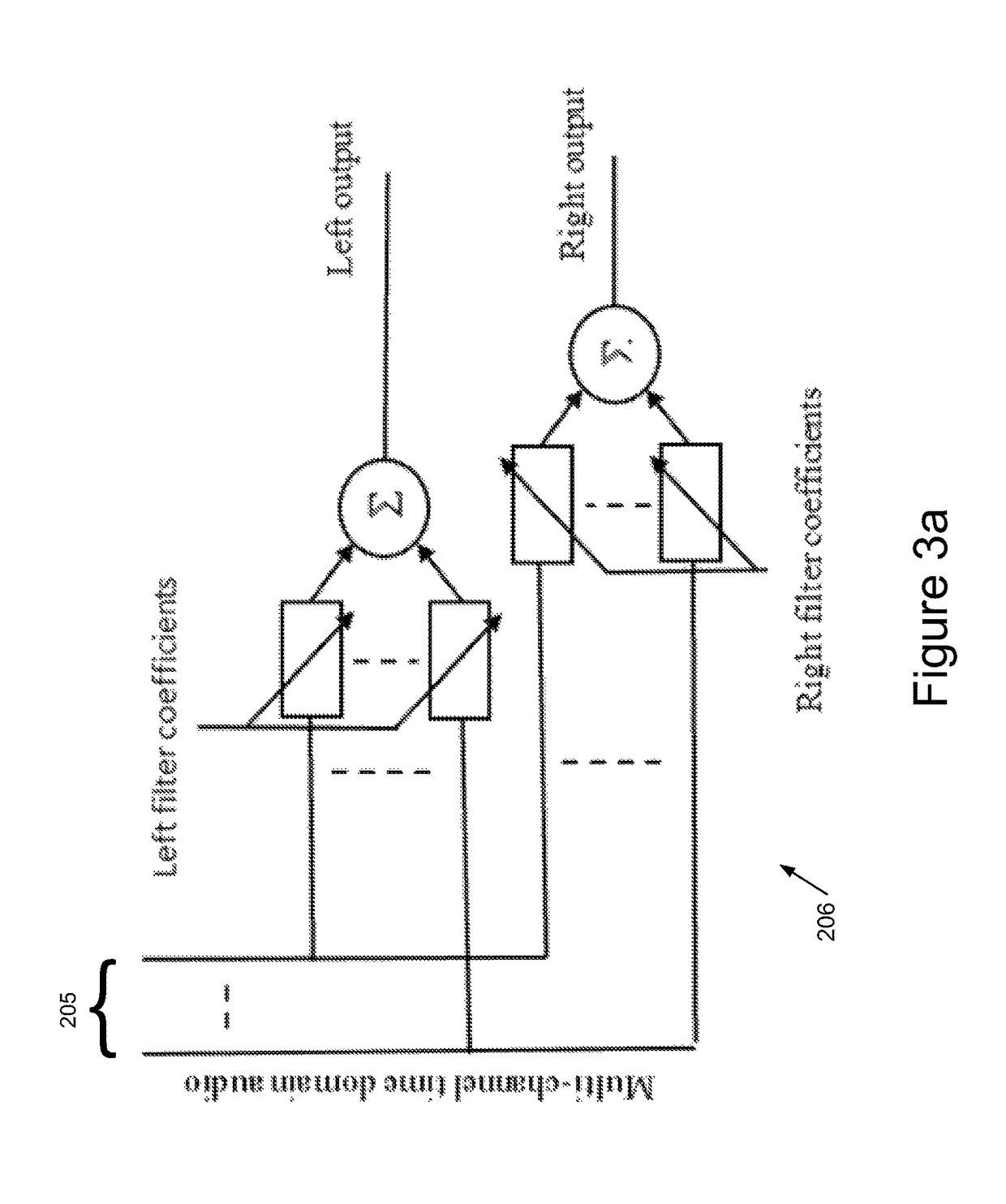
We describe a method of blind source separation for use, for example, in a listening or hearing aid. The method processes input data from multiple microphones each receiving a mixed signal from multiple audio sources, performing independent component analysis (ICA) on the data in the time-frequency domain based on an estimation of a spectrogram of each acoustic source. The spectrograms of the sources are determined from non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) models of each source, the NMF model representing time-frequency variations in the output of an acoustic source in the time-frequency domain. The NMF and ICA models are jointly optimized, thus automatically resolving an inter-frequency permutation ambiguity.
Owner:AUDIOTELLIGENCE LTD
System and method for separation of a user's voice from ambient sound
InactiveUS20070147635A1Easy to separateImprove clarityAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSets with desired directivityComputer scienceSpeech sound
A system for separation of a user's voice from ambient sound, comprising a device to be worn at the user's ear or at least partly in the user's ear canal comprising a first microphone oriented outwardly towards the environment and a second microphone oriented inwardly towards the user's ear canal, and an audio signal processing unit for processing audio signals from the first and second microphone by a blind source separation algorithm adapted to separate the user's voice from ambient sound.
Owner:PHONAK
System and method for separation of a user's voice from ambient sound
InactiveUS20070160243A1Low costImprove performanceMicrophonesLoudspeakersComputer scienceSpeech sound
A system for separation of a user's voice from ambient sound, comprising a device to be worn at the user's ear or at least partly in the user's ear canal comprising a first microphone oriented acoustically outwardly towards the environment and a second microphone oriented acoustically inwardly towards the user's ear canal, and an audio signal processing unit for processing audio signals from the first and second microphone by a blind source separation algorithm adapted to separate the user's voice from ambient sound.
Owner:PHONAK
Beamforming in hearing aids
A hearing aid system includes a first microphone and a second microphone for provision of electrical input signals, a beamformer for provision of a first audio signal based at least in part on the electrical input signals, the first audio signal having a directional spatial characteristic, wherein the beamformer is configured to provide a second audio signal based at least in part on the electrical input signals, the second audio signal having a spatial characteristic that is different from the directional spatial characteristic of the first audio signal, and a mixer configured for mixing the first audio signal and the second audio signal in order to provide an output signal to be heard by a user.
Owner:GN HEARING AS
Method and apparatus for directional acoustic fitting of hearing aids
ActiveUS20100310101A1Precise sound localizationOvercome deficienciesSignal processingSets with desired directivityUltrasound attenuationMedicine
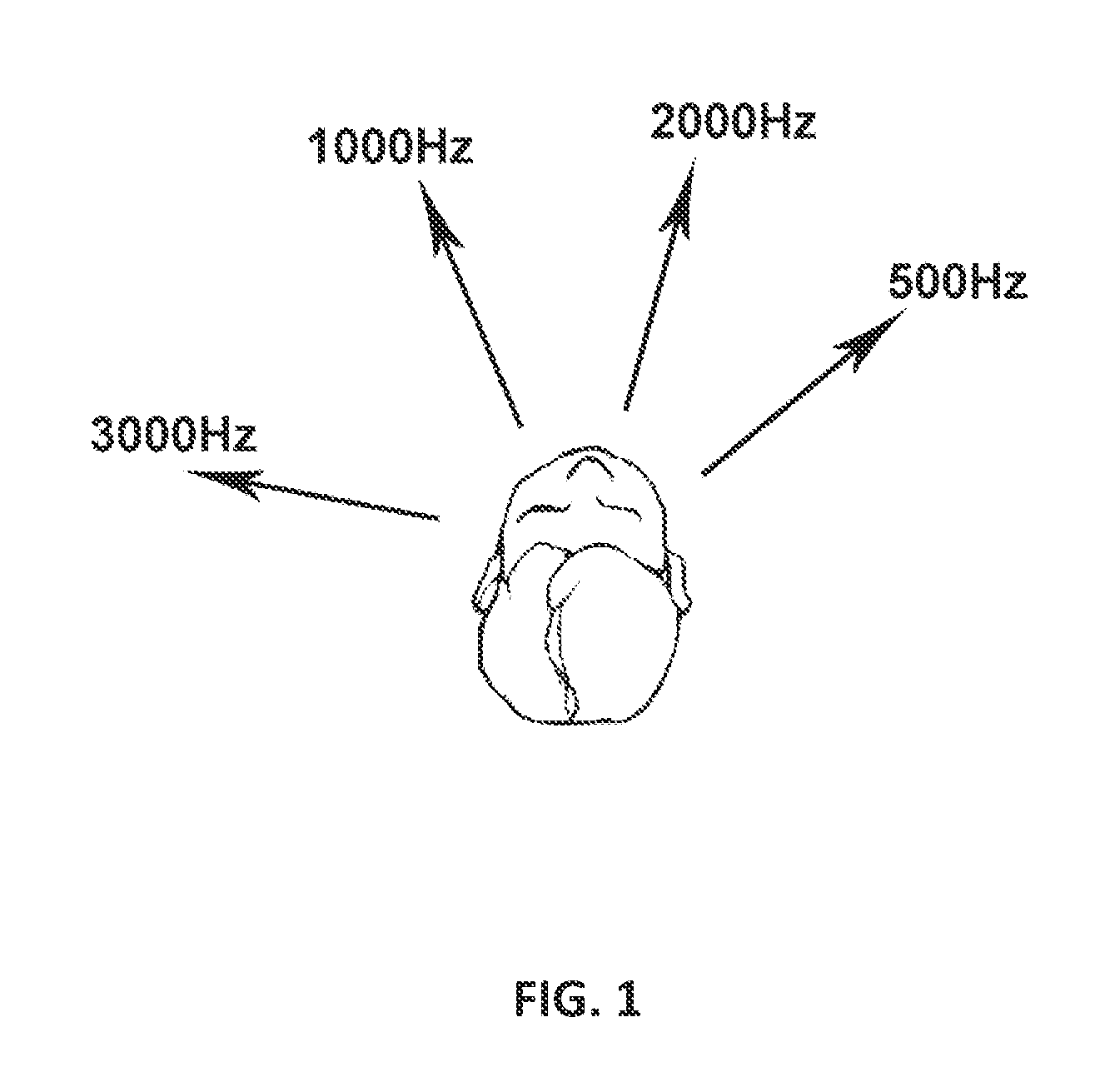
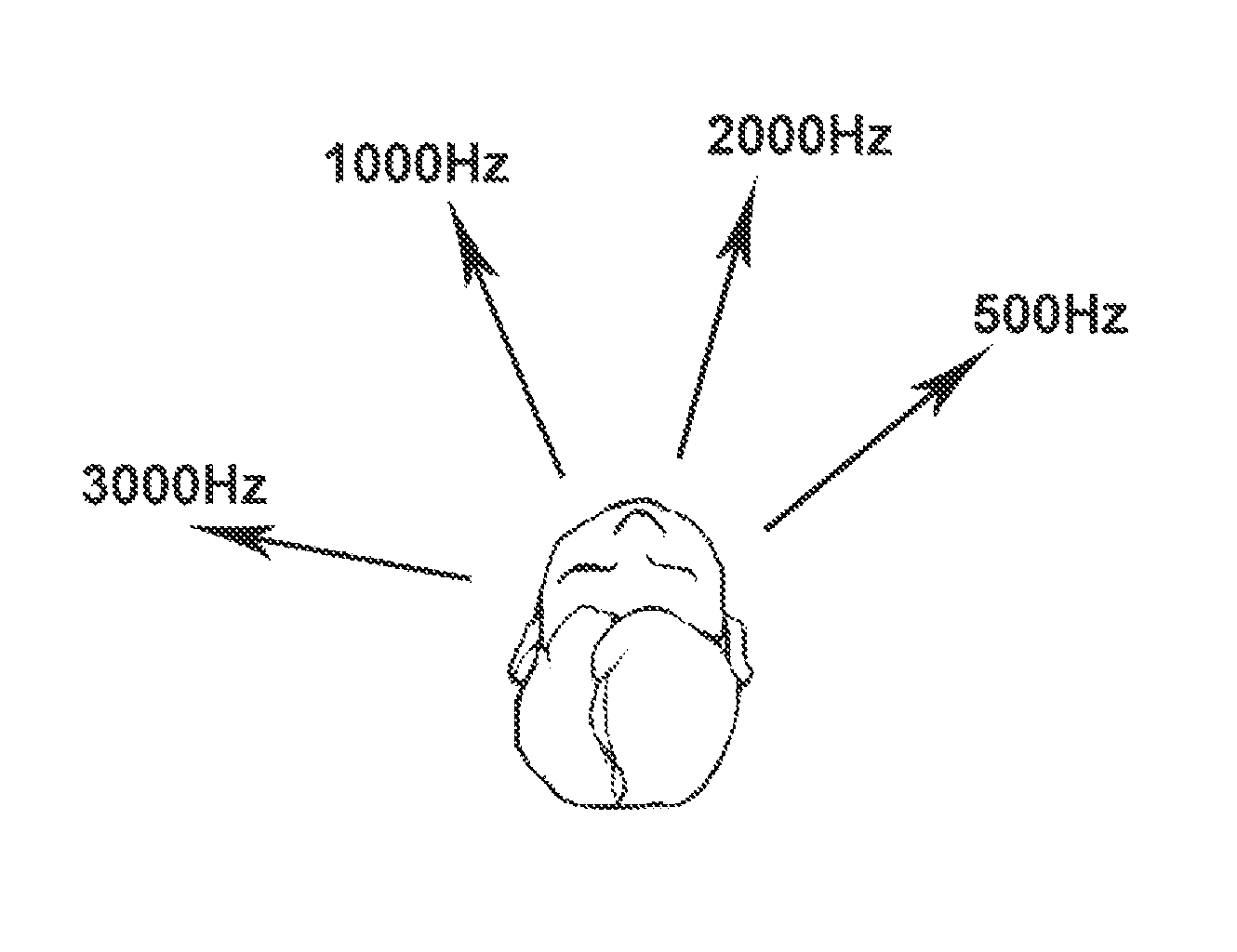
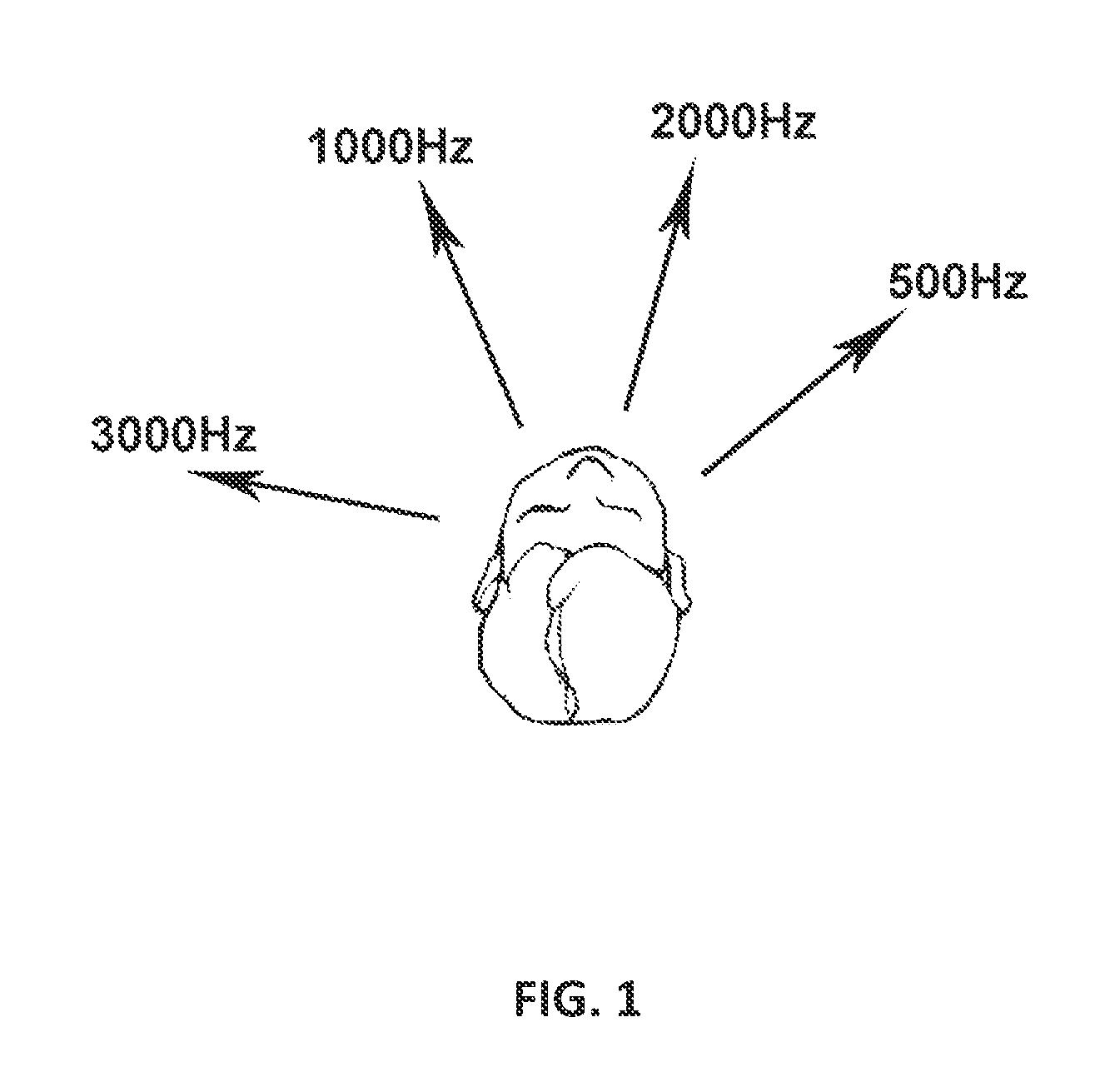
A method of acoustically fitting a hearing aid comprises providing a plurality of audible tones, each having a predetermined frequency through stereo headphones. The tones are provided at specific sound pressure in each ear. The patient changes the relative sound pressure in each ear until a perceived direction of source of the tone is in front of the patient. The amplification or attenuation requirements of a hearing aid are modified based on the difference in the sound pressures required for the left and right ears of the patient for perceived directional sameness for each frequency band-pass channel.
Owner:DEAN ROBERT GARY ANDERSON AS TRUSTEE OF THE D L ANDERSON FAMILY TRUST
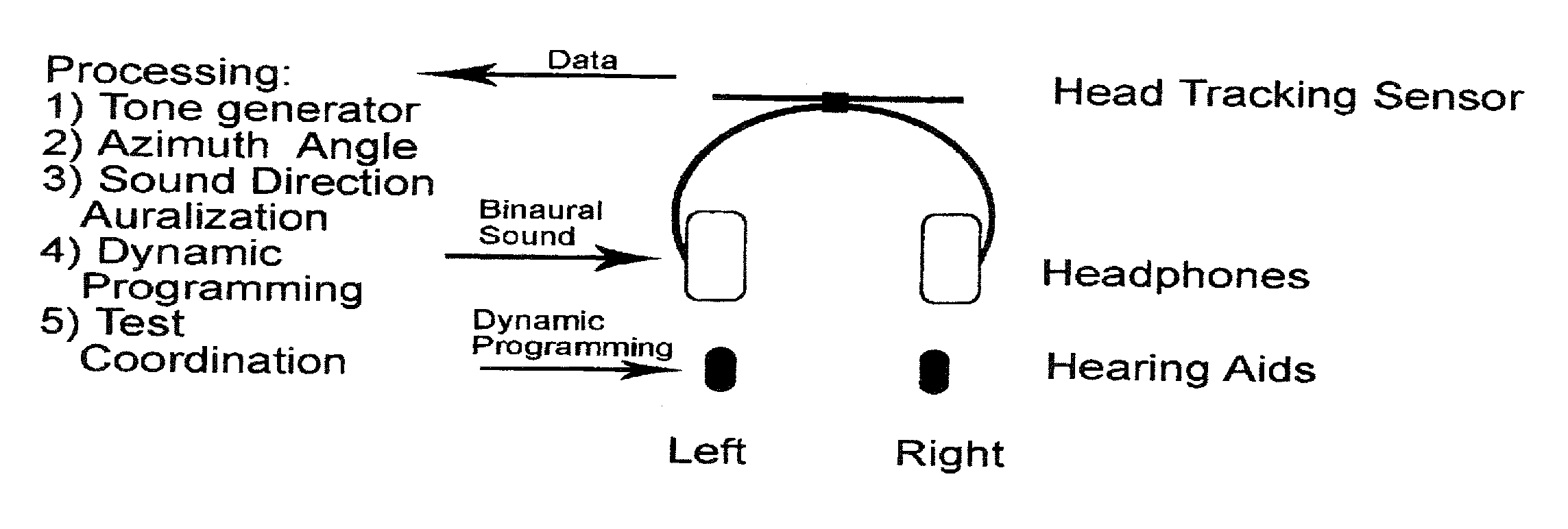
Method of deriving individualized gain compensation curves for hearing aid fitting
ActiveUS20110075853A1Reduce impactReduce fatigueSignal processingSets with desired directivityPersonalizationHearing aid
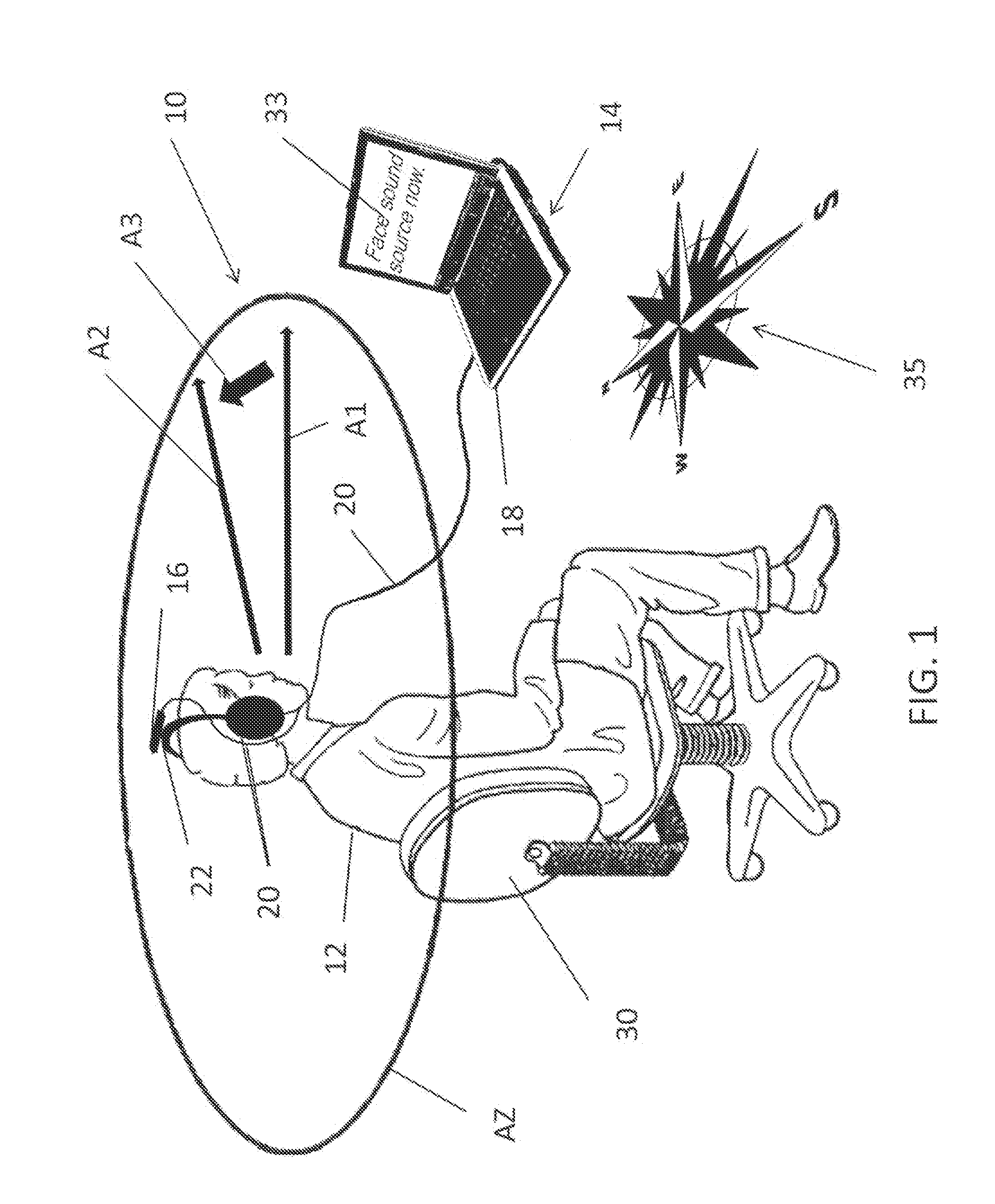
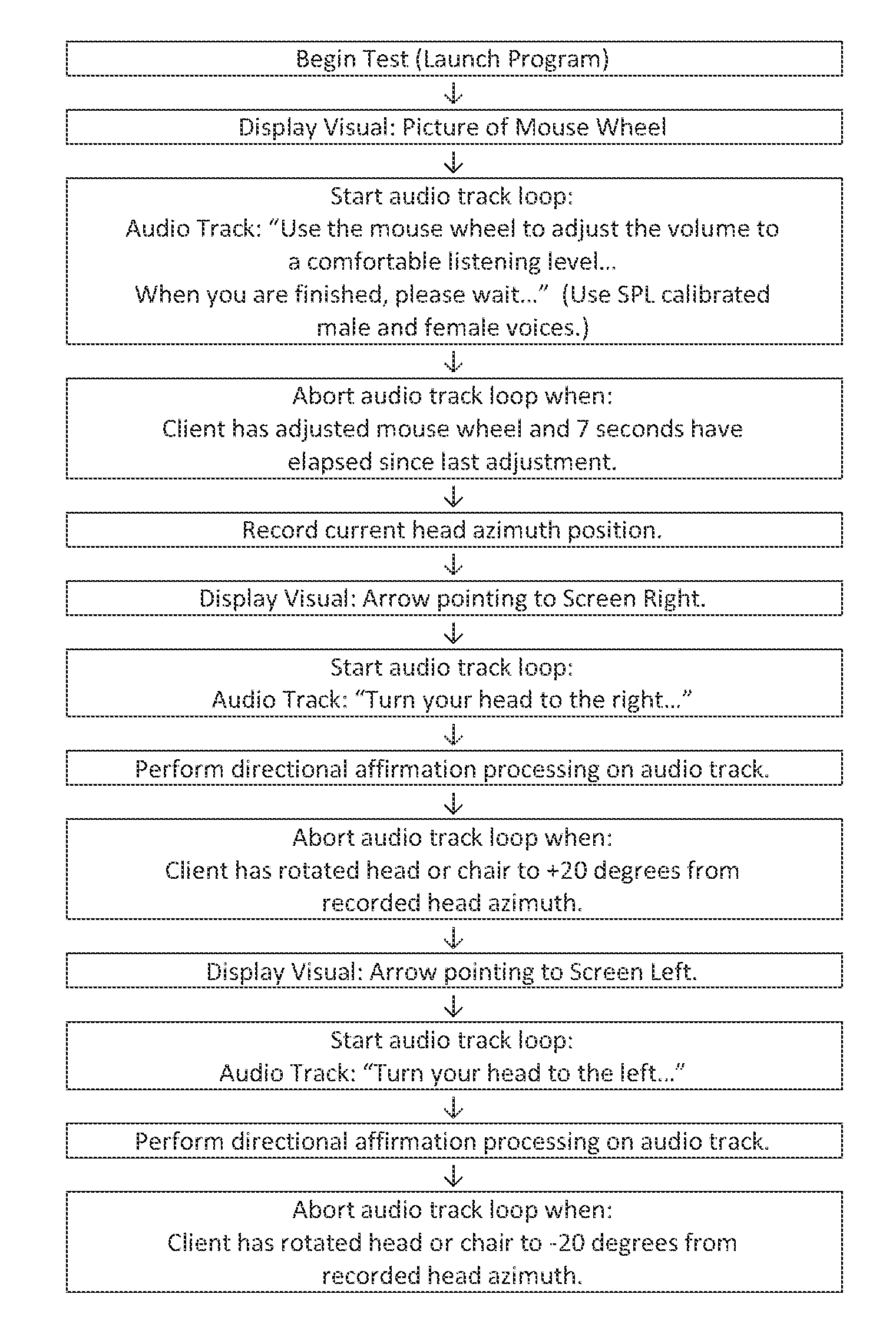
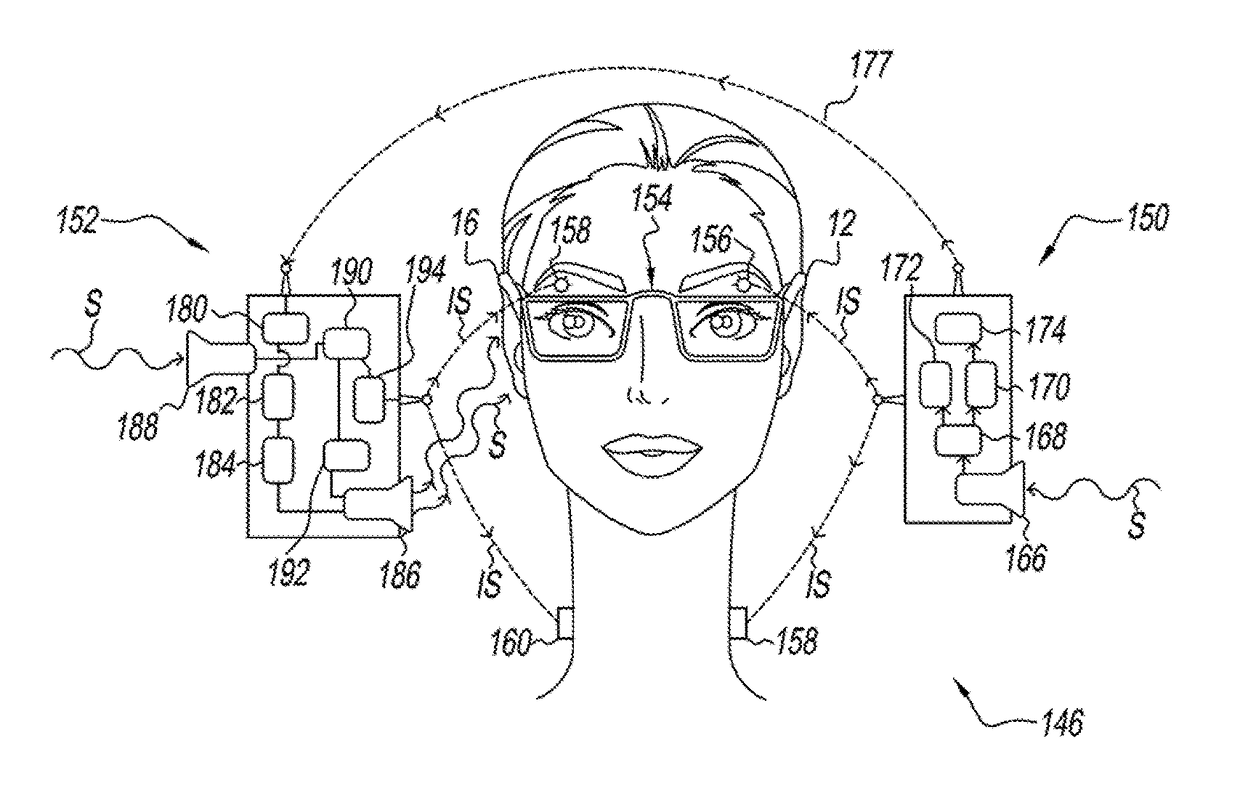
A method of deriving individual gain compensation curves for hearing aid fitting includes providing a system that detects, measures and records head azimuth for sound direction affirmation by a patient and provides a plurality of audio signals through a plurality of test sequences to the ears of the patient, including establishing a comfortable listening level of the patient, establishing binaural balance for right and left ars, establishing loudness discomfort levels of the patient, establishing thresholds-of-hearing levels of the patient and generating a binaurally balanced measurement array of measured equal-loudness levels and measured thresholds-of-hearing levels for both left and right ears.
Owner:DEAN ROBERT GARY ANDERSON AS TRUSTEE OF THE D L ANDERSON FAMILY TRUST
Interactive hearing aid error detection
InactiveUS20190253811A1Improve performanceImprove system performanceEar supported setsSets with desired directivityHearing aidEngineering
The present invention is adapted to assist in optimizing the performance of a hearing aid by detecting conditions which result in sub-optimal performance and assisting a user or health care professional to correct those conditions. The present invention is adapted to optimize the performance of a hearing aid by generating a reference signal which, when broadcast, creates a feedback signal. The feedback signal is then measured, or its characteristics identified, to determine whether the hearing aid system is optimized and, if not, what components or characteristics are not optimized and how to optimize the hearing aid system performance or that of its components.
Owner:EARLENS CORP
Method of Audio Signal Processing and Hearing Aid System for Implementing the Same
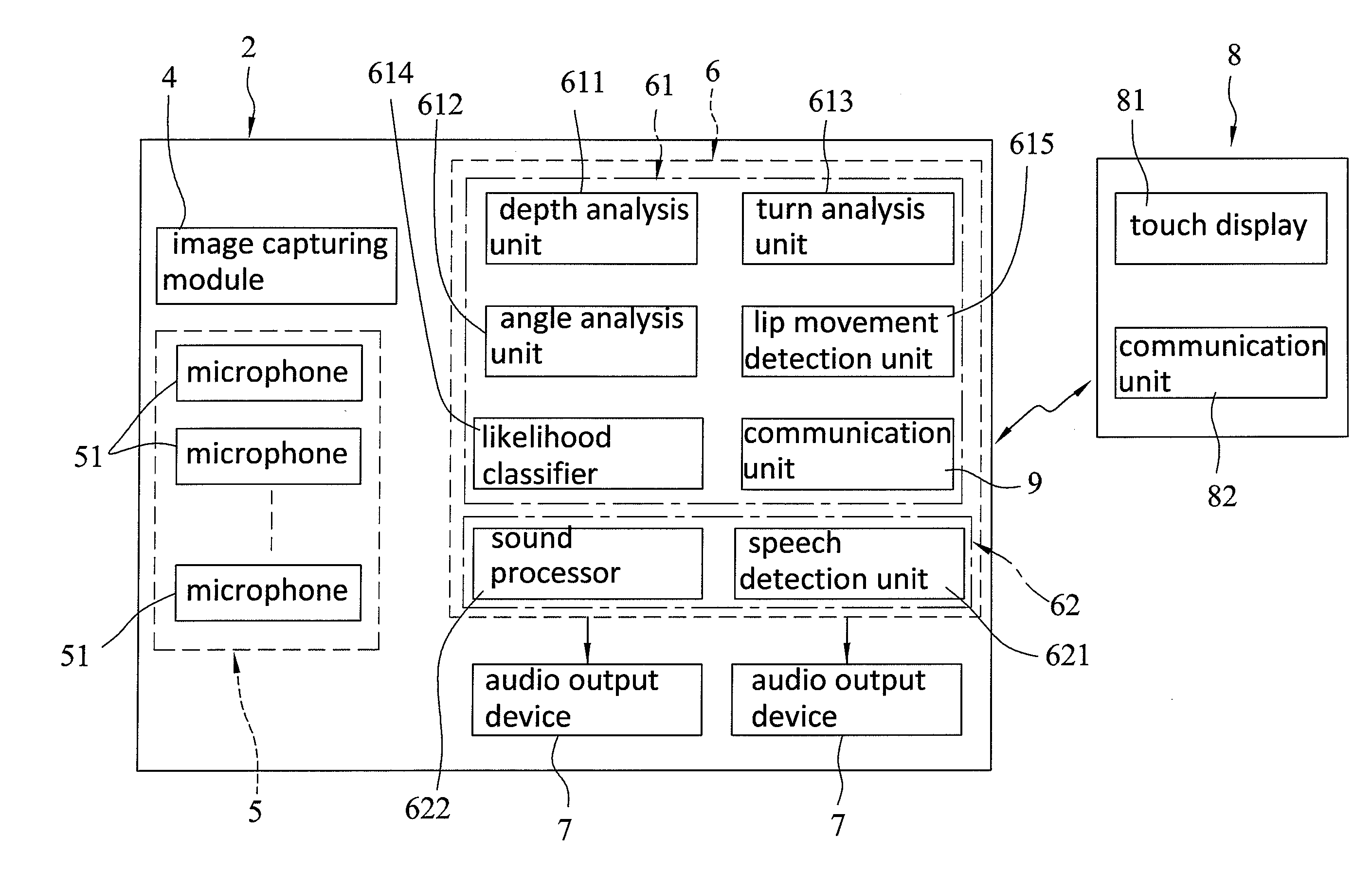
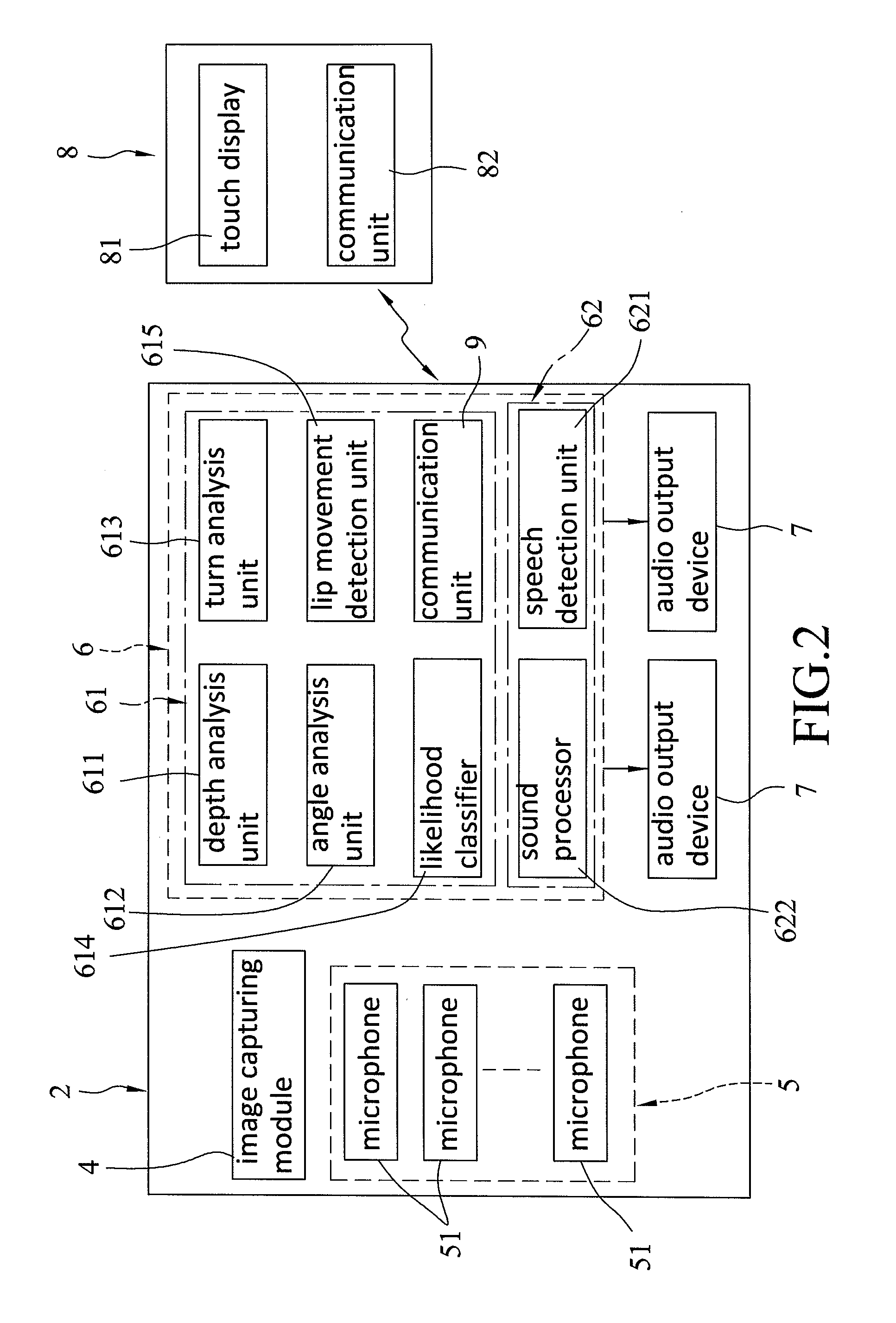
In a method of audio signal processing, a hearing aid system is configured to: collect sound information of a surrounding environment of the hearing aid system; capture an image of the surrounding environment of the hearing aid system; perform a directional signal processing operation on the sound information so as to generate an output audio signal; the output audio signal containing an extracted voice signal that comes from an area corresponding to a location of a target object in the image; and output the output audio signal.
Owner:LIU CHING FENG +1
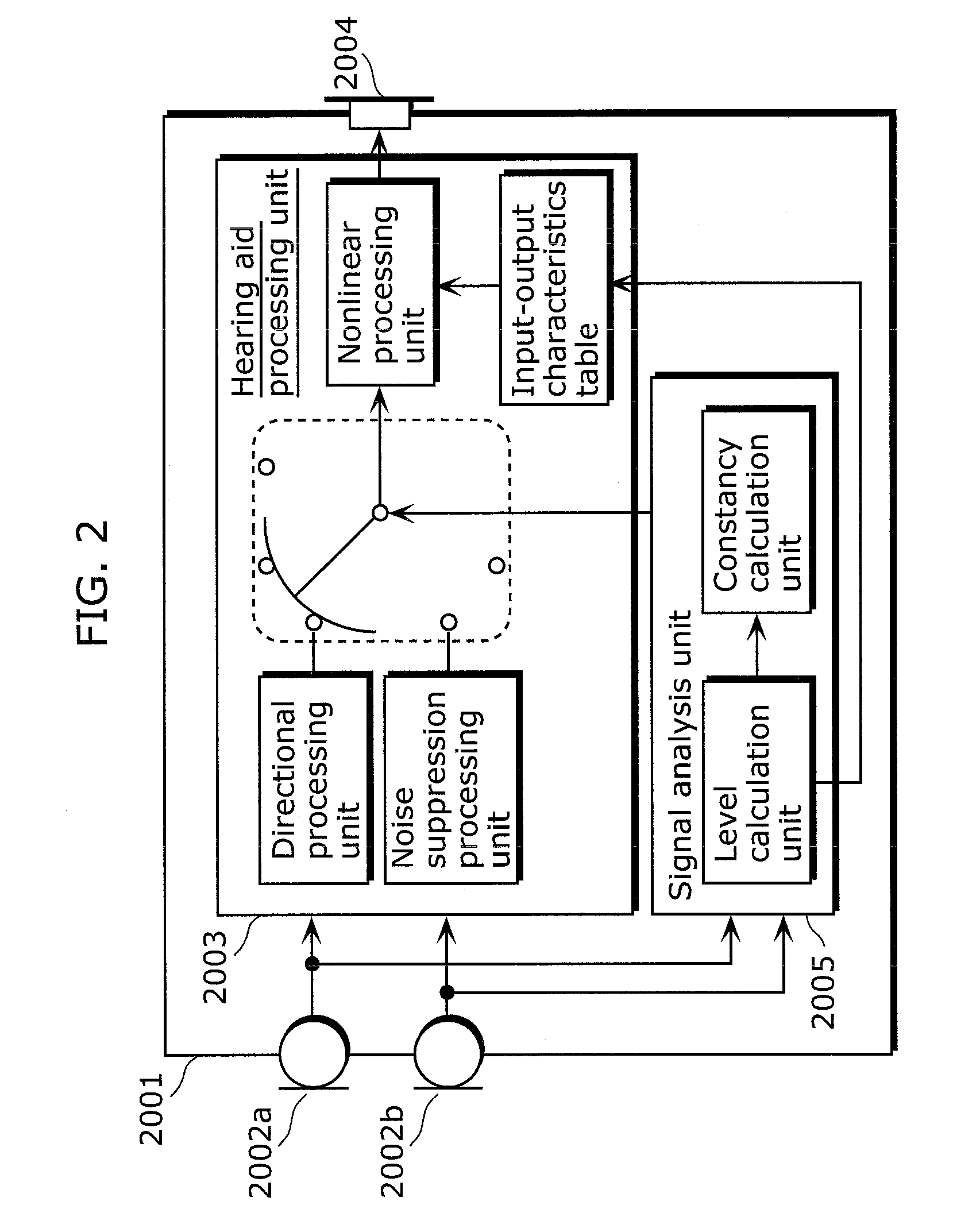
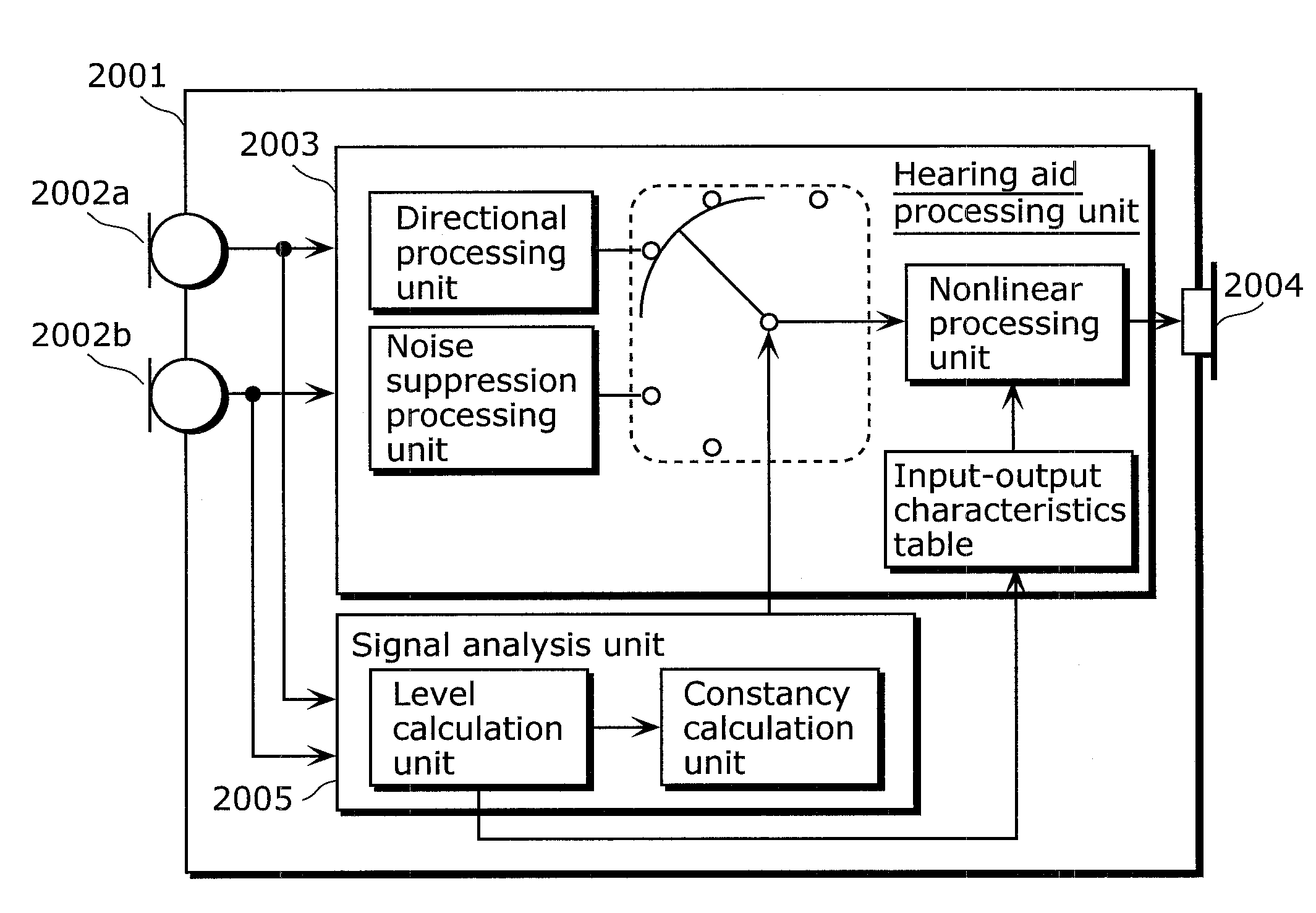
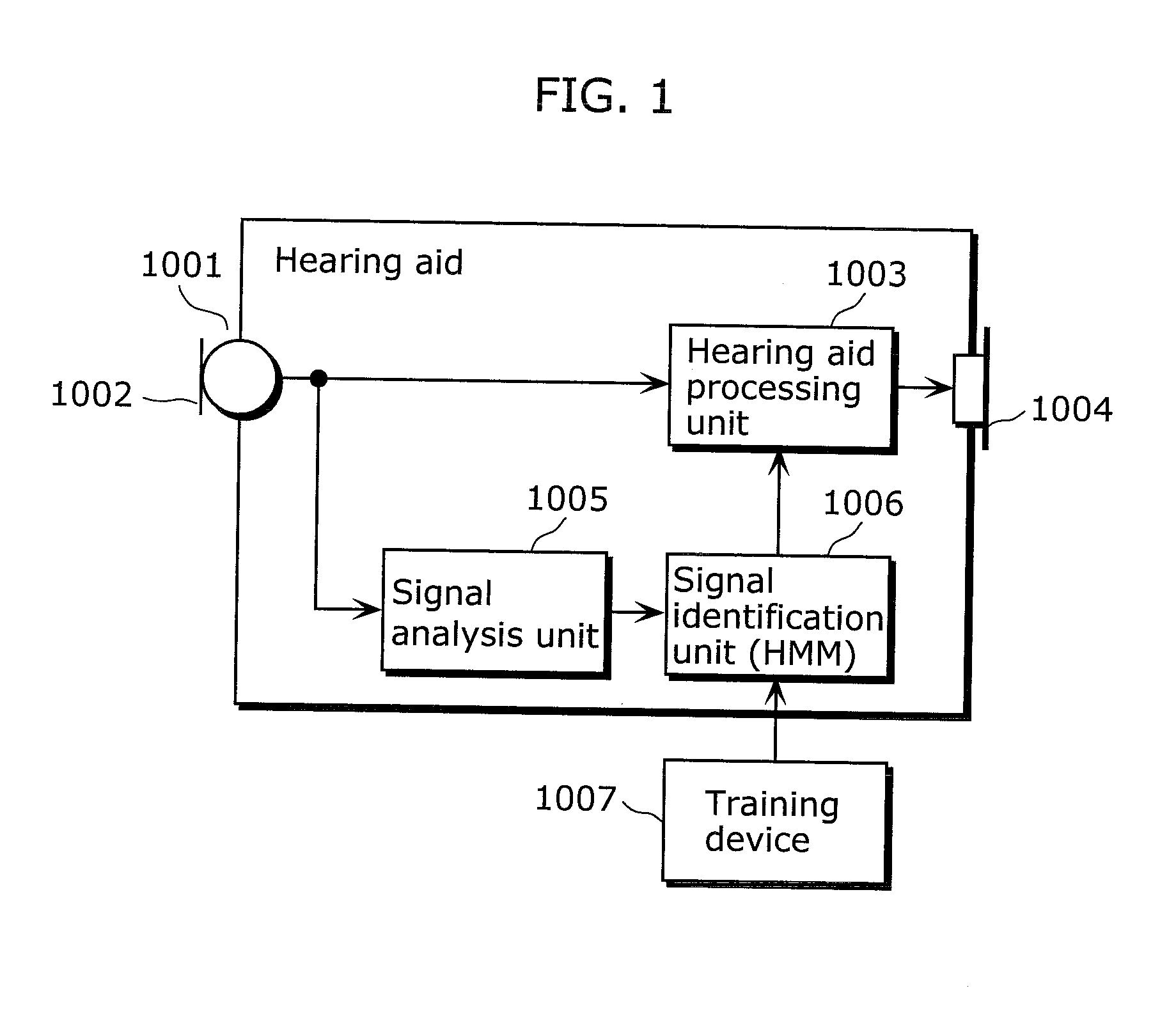
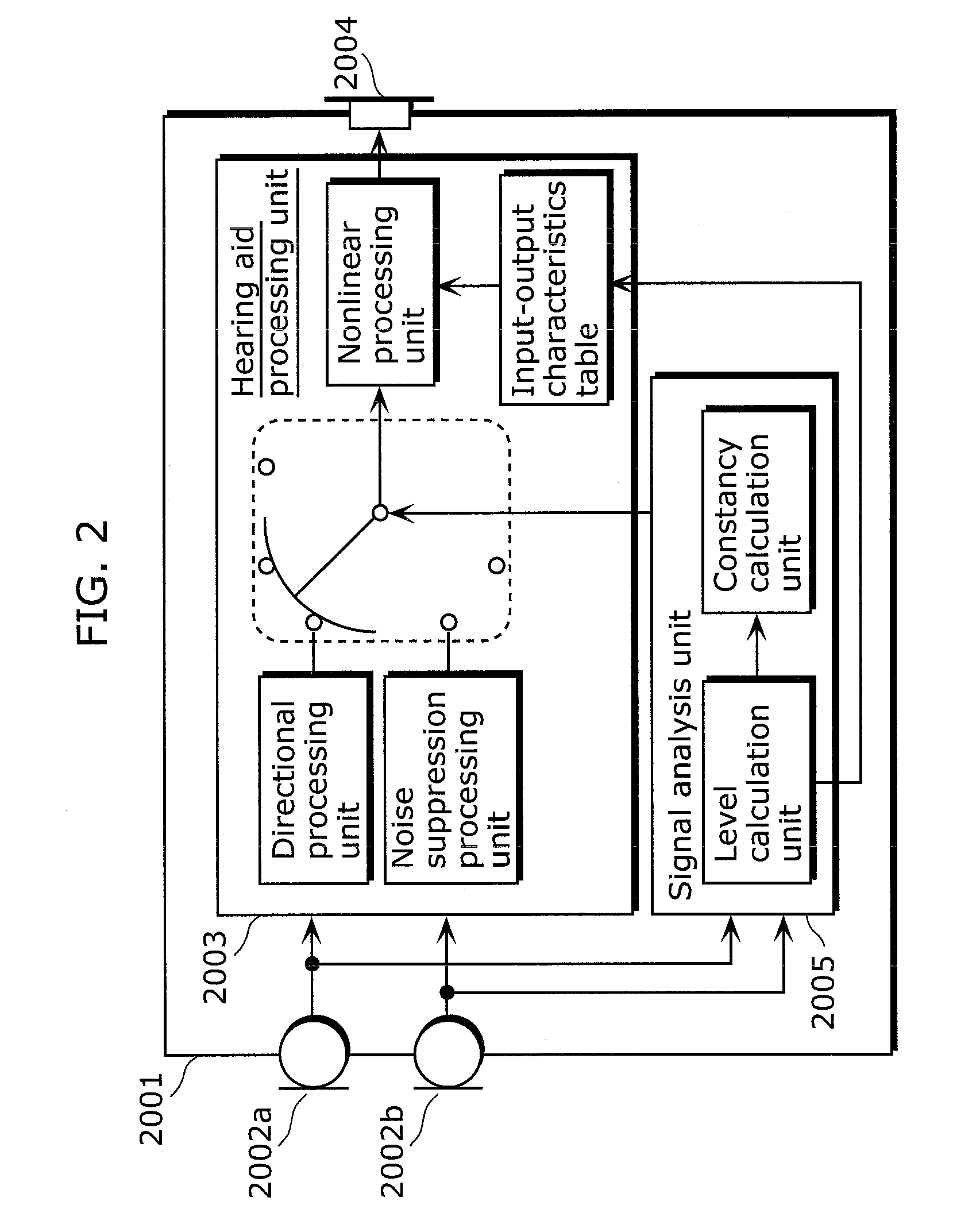
Hearing aid, hearing aid system, walking detection method, and hearing aid method
ActiveUS8391524B2Easily detect walking stateMicrophonesSets with desired directivityPedometerEngineering
A hearing aid that analyzes a surrounding acoustic environment and automatically switches between a plurality of hearing aid processing reduces noise by limiting directionality, when the user is in a noisy outdoor location. However, in the case where directionality is limited to the front when the user is walking or the like, the user is put in extreme danger because he / she cannot notice sound of danger approaching from behind. Behavior analysis of identifying a walking state of the user is necessary in addition to environmental analysis, but typical walking detection using a sensor as in the case of a pedometer and the like is not applicable to a device worn at an ear such as a hearing aid. On the basis of an occurrence pattern of wind noise when walking, the walking state of the user is identified in the case where pulse-like wind noise occurs repeatedly. This enables walking detection to be performed using an existing structure, with there being no need to provide a sensor or the like. Hence, it is possible to provide a hearing aid that can be safely used even outdoors.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method and apparatus for directional acoustic fitting of hearing aids
ActiveUS20140029775A1Precise sound localizationOvercome deficienciesSignal processingSets with desired directivityUltrasound attenuationMedicine
A method of acoustically fitting a hearing aid comprises providing a plurality of audible tones, each having a predetermined frequency through stereo headphones. The tones are provided at specific sound pressure in each ear. The patient changes the relative sound pressure in each ear until a perceived direction of source of the tone is in front of the patient. The amplification or attenuation requirements of a hearing aid are modified based on the difference in the sound pressures required for the left and right ears of the patient for perceived directional sameness for each frequency band-pass channel.
Owner:DEAN ROBERT GARY ANDERSON AS TRUSTEE OF THE D L ANDERSON FAMILY TRUST
Hearing aid, hearing aid system, walking detection method, and hearing aid method
ActiveUS20110135126A1Easily detect walking stateMicrophonesSets with desired directivityPedometerEngineering
A hearing aid that analyzes a surrounding acoustic environment and automatically switches between a plurality of hearing aid processing reduces noise by limiting directionality, when the user is in a noisy outdoor location. However, in the case where directionality is limited to the front when the user is walking or the like, the user is put in extreme danger because he / she cannot notice sound of danger approaching from behind. Behavior analysis of identifying a walking state of the user is necessary in addition to environmental analysis, but typical walking detection using a sensor as in the case of a pedometer and the like is not applicable to a device worn at an ear such as a hearing aid. On the basis of an occurrence pattern of wind noise when walking, the walking state of the user is identified in the case where pulse-like wind noise occurs repeatedly. This enables walking detection to be performed using an existing structure, with there being no need to provide a sensor or the like. Hence, it is possible to provide a hearing aid that can be safely used even outdoors.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of focusing a hearing instrument beamformer
ActiveCN103475974ASets with desired directivityFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsSpatial OrientationsHead movements
The invention relates to a method of focusing a hearing instrument beamformer, aiming to comfortably and visually realize the automatic adaption of the beam width and / or beam direction. A spatial orientation and / or position of the head of the hearing instrument user are / is first captured. When no head movements are captured, the acoustic signals are picked up with directional dependency. Then the amplification of acoustic signals is boosted that originate from a focus solid angle in front of the head of the hearing instrument user, compared with acoustic signals from other solid angles. This activates or increases directivity. Then the focus solid angle is decreased to gradually focus and to increase directivity, until the level of acoustic signals from the focus solid angle, actually the presence of the desired signals in the focus solid angle (purely theoretically the probability that the desired signal is present in the focus solid angle), reduces on account of reducing the focus solid angle.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Speaker
ActiveCN102845077AImmersive Sound EffectsTransducers for sound channels pluralityFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsEngineeringLoudspeaker
Provided are a speaker and a speaker system. The speaker includes a main unit and a sub unit. The main unit emits a sound in a first direction. The sub unit is formed integrally with the main unit and emits a sound in a second direction different from the first direction.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
A hearing assistance device with brain-computer interface
InactiveCN104244157ASets with desired directivityAcquiring/recognising eyesBrain computer interfacingComputer science
The present disclosure relates to a communication device. The device comprises input for receiving sound signal to be processed and presented to a user, and output for outputting the processed signal to a user perceivable as sound. The processing is performed by use of a processor for processing the sound signal in dependence of a setting or a set of setting to compensate a hearing loss profile. Further, the communication device comprises a bio-signal acquisition and amplifier component in communication with a user interface for providing the biosignals as input to the user interface, the user interface controlling the setting or set of setting for operation of the communication device.
Owner:OTICON
Beamforming in hearing aids
Owner:GN HEARING AS
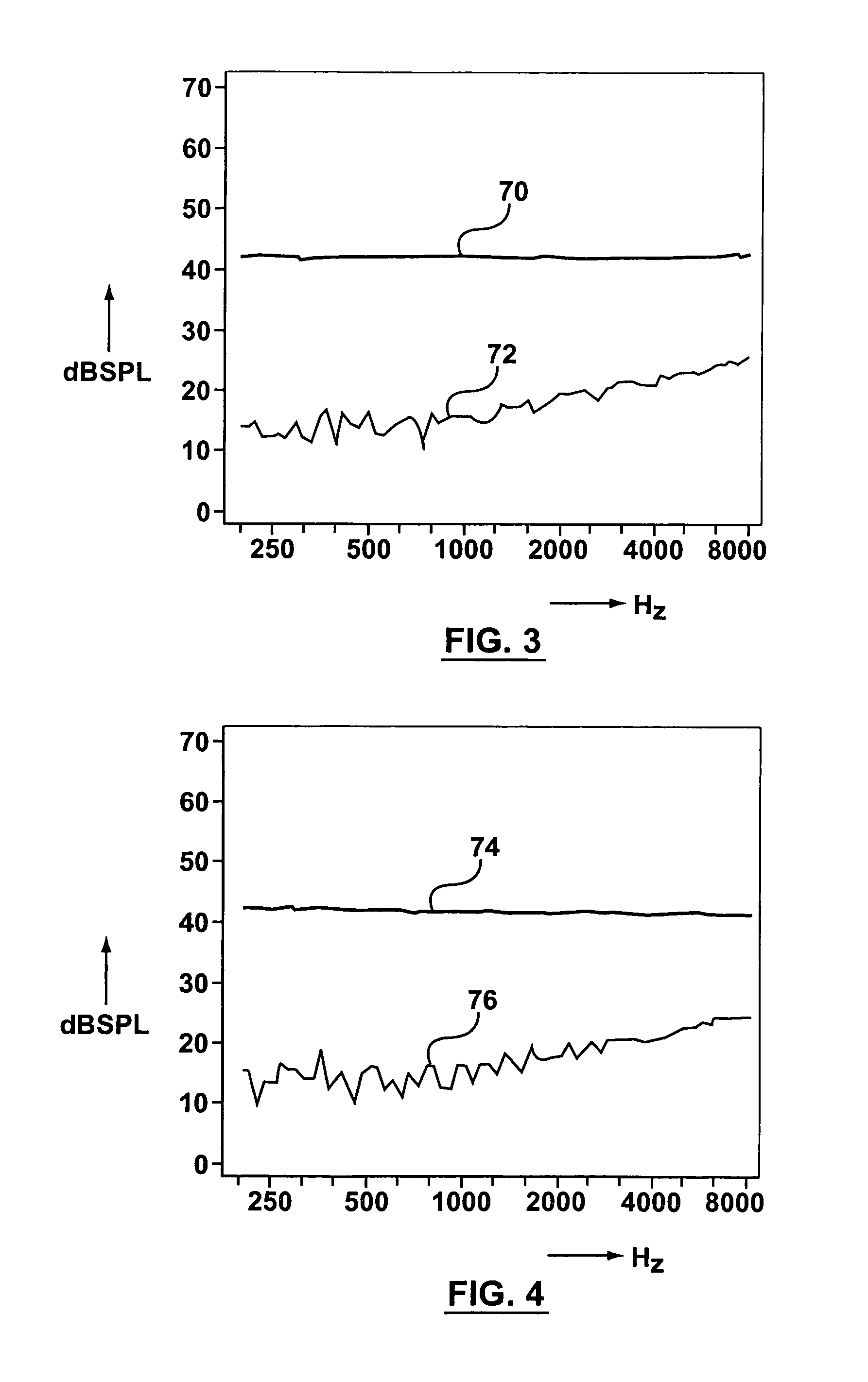
Directional hearing aid tester
ActiveUS20050053250A1Test accurateAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSets with desired directivityHearing aidLoudspeaker
Method and apparatus for testing a directional acoustic device such as a directional hearing aid having level-dependent non-linear circuitry, in which two or more speakers are placed at desired positions relative to the hearing aid, e.g. in front and behind the hearing aid. The speakers are excited simultaneously with broadband excitation signals formed from components which are orthogonal to each other, e.g. sinusoids, where the bin frequencies of the Direct Fourier Transform (“DFT”) of one excitation signal are different from the bin frequencies of the other excitation signal. Thus, the response to each excitation signal can easily be extracted without filtering, allowing the directional characteristics of the hearing aid to be evaluated.
Owner:RHINOMETRICS
Directional hearing aid tester
ActiveUS7062056B2Test accurateAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSets with desired directivityFourier transform on finite groupsHearing aid
Method and apparatus for testing a directional acoustic device such as a directional hearing aid having level-dependent non-linear circuitry, in which two or more speakers are placed at desired positions relative to the hearing aid, e.g. in front and behind the hearing aid. The speakers are excited simultaneously with broadband excitation signals formed from components which are orthogonal to each other, e.g. sinusoids, where the bin frequencies of the Direct Fourier Transform (“DFT”) of one excitation signal are different from the bin frequencies of the other excitation signal. Thus, the response to each excitation signal can easily be extracted without filtering, allowing the directional characteristics of the hearing aid to be evaluated.
Owner:RHINOMETRICS
Automatic switching between omnidirectional and directional microphone modes in a hearing aid
ActiveCN101433098ASets with desired directivityHearing aids signal processingFrequency spectrumEngineering
Owner:GN HEARING AS
Deep learning-based binaural sound source positioning method in digital hearing aid
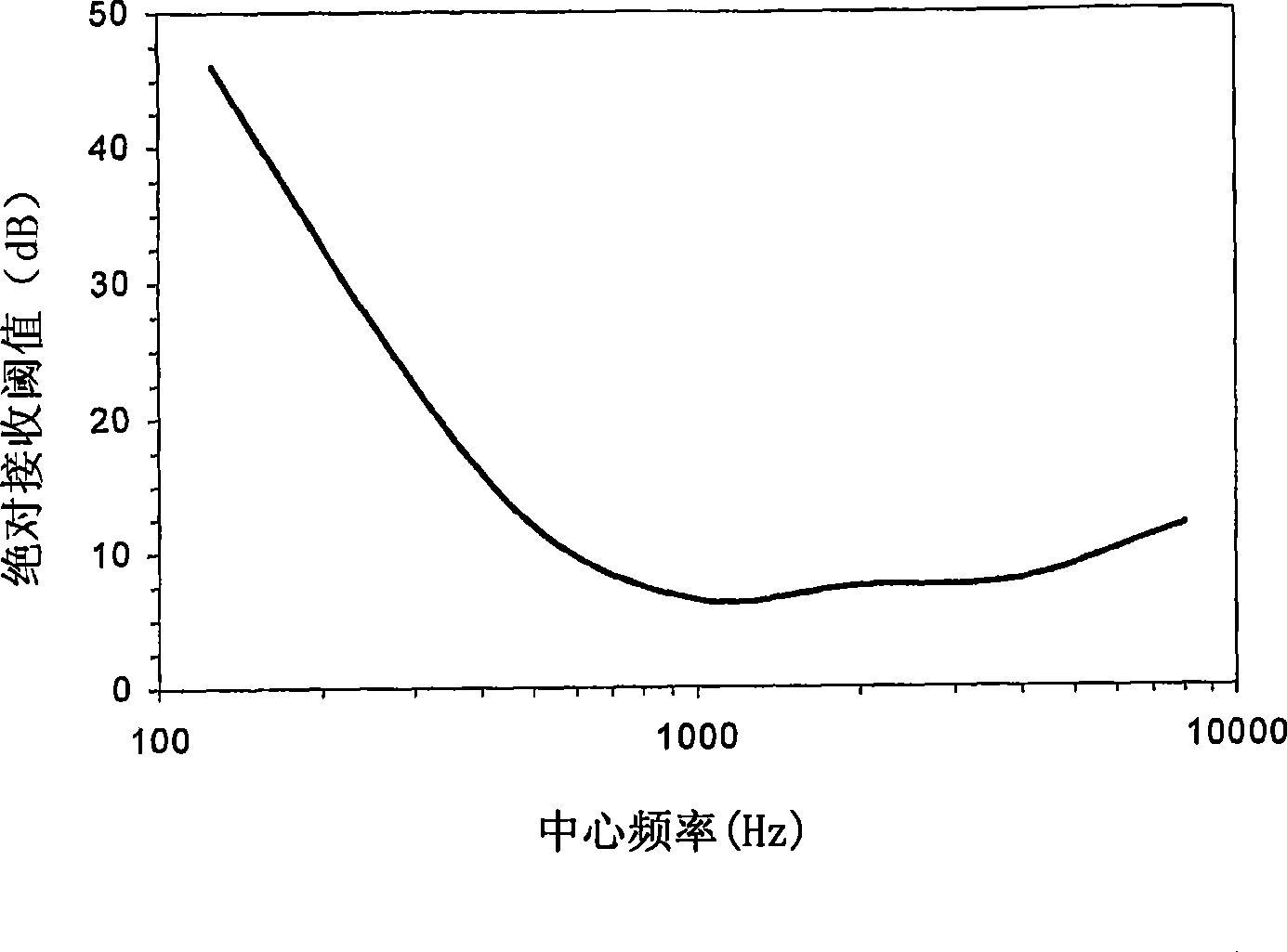
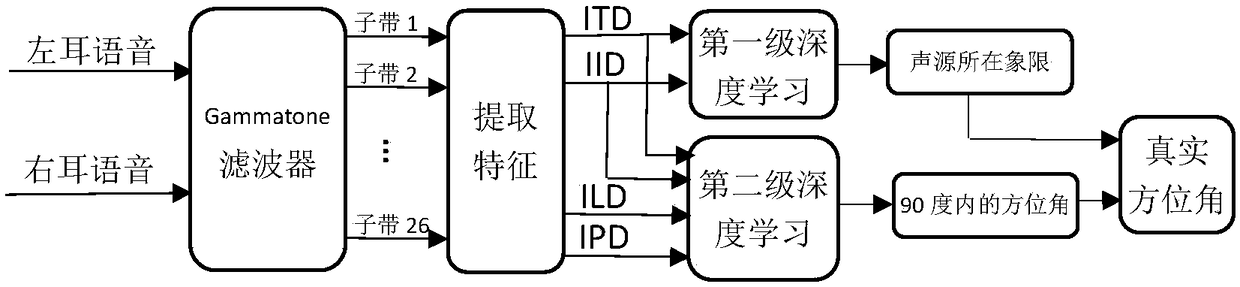
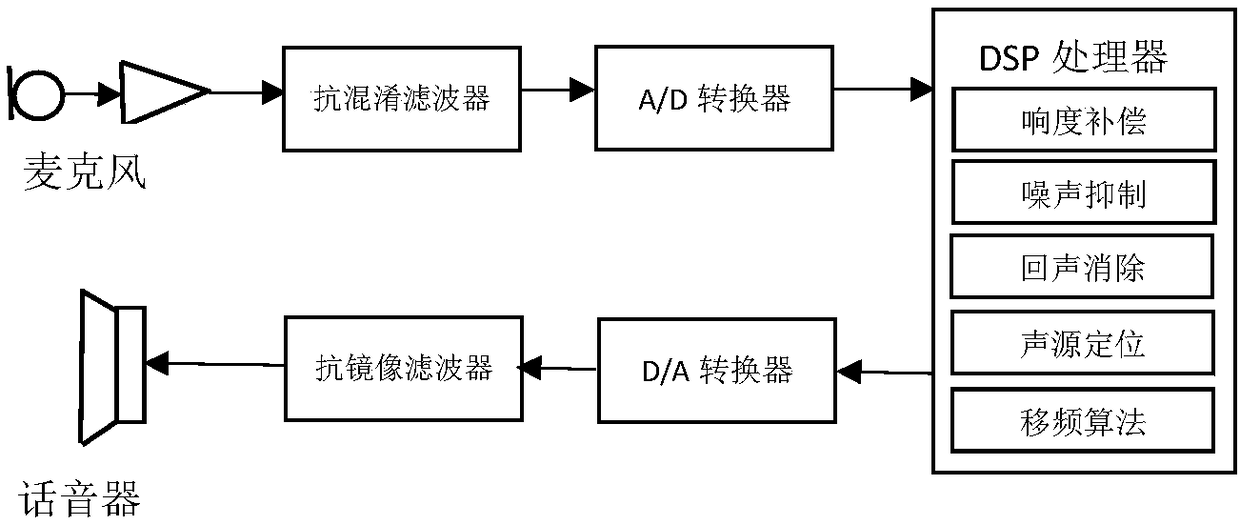
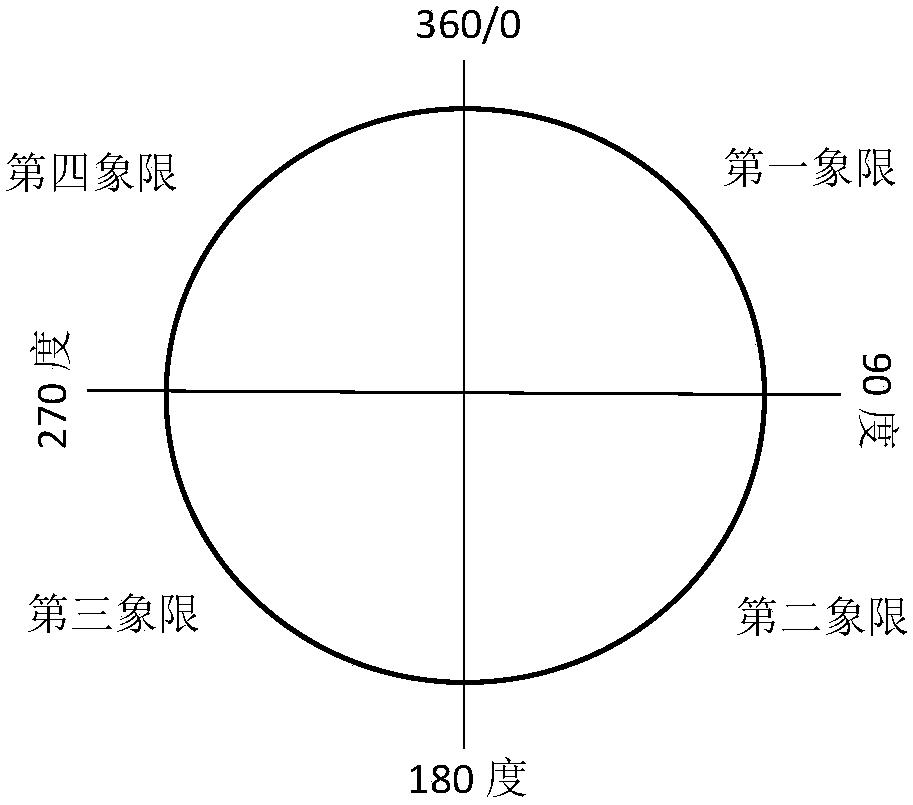
ActiveCN108122559AImprove learning abilityStrong offline trainingSpeech analysisSets with desired directivityInteraural time differencePattern recognition
The invention discloses a deep learning-based binaural sound source positioning method in a digital hearing aid. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, decomposing a binaural sound sourcesignal into a plurality of channels through a gammatone filter, extracting a high-energy channel through a weighting coefficient, then extracting a first type of features by using a head-related-transform function (HRTF), namely an Interaural Time Difference (ITD) and an Interaural Intensity Difference (IID) which are used as inputs of deep learning, and dividing a horizontal plane into four quadrants to narrow a positioning range; secondly, extracting a second type of features of head-related transform, namely an Interaural Level Difference (ILD) and an Interaural Phase Difference (IPD); andfinally, in order to realize more precise positioning, taking the first and second types of four features as inputs of next deep learning, thereby obtaining an azimuth angle of sound source positioning. Precise positioning of 72 azimuth angles is realized on the horizontal plane from 0 degree to 360 degrees at a step length of 5 degrees.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Hearing aid for people having asymmetric hearing loss
ActiveUS20170085998A1Different tonal qualityImprove fidelitySignal processingBone conduction transducer hearing devicesTransducerSignal transition
The hearing aid apparatus includes a first hearing aid member and a second hearing aid member. The first hearing aid member is placeable on a patient's body, and includes a first transducer for receiving sounds that would be received by the patient's first ear and converting these received sounds into first transmittable signals. The second hearing aid is placeable on a patient's body adjacent to the patient's second ear, and includes a receiver for receiving the first transmittable electrical signals and a second transducer for converting the first transmittable electrical signals into sound signals configured for delivery to the patient's second ear.
Owner:EAR TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for directional acoustic fitting of hearing aids
ActiveUS8553897B2Precise sound localizationOvercome deficienciesSignal processingSets with desired directivityUltrasound attenuationMedicine
A method of acoustically fitting a hearing aid comprises providing a plurality of audible tones, each having a predetermined frequency through stereo headphones. The tones are provided at specific sound pressure in each ear. The patient changes the relative sound pressure in each ear until a perceived direction of source of the tone is in front of the patient. The amplification or attenuation requirements of a hearing aid are modified based on the difference in the sound pressures required for the left and right ears of the patient for perceived directional sameness for each frequency band-pass channel.
Owner:DEAN ROBERT GARY ANDERSON AS TRUSTEE OF THE D L ANDERSON FAMILY TRUST
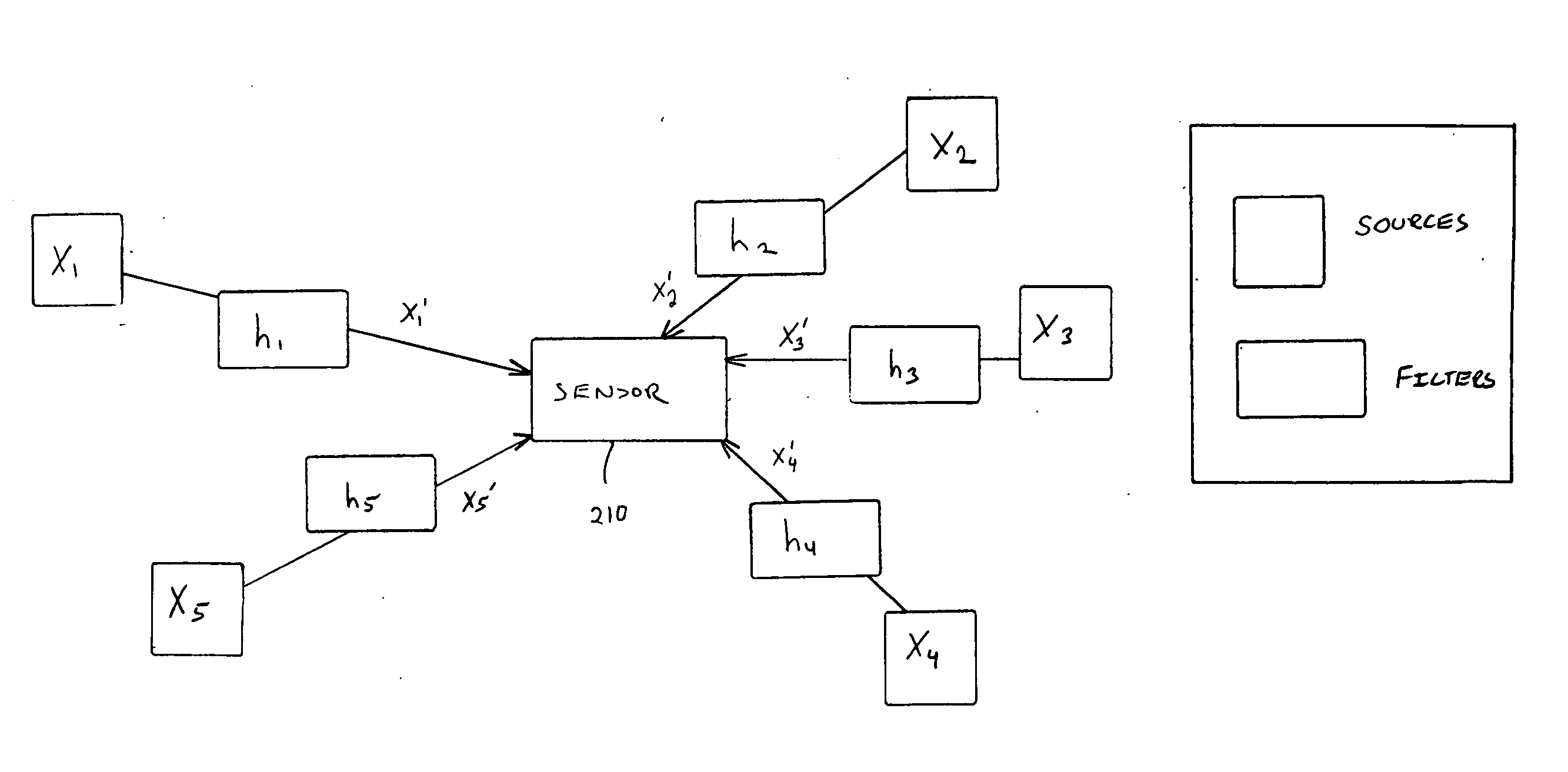
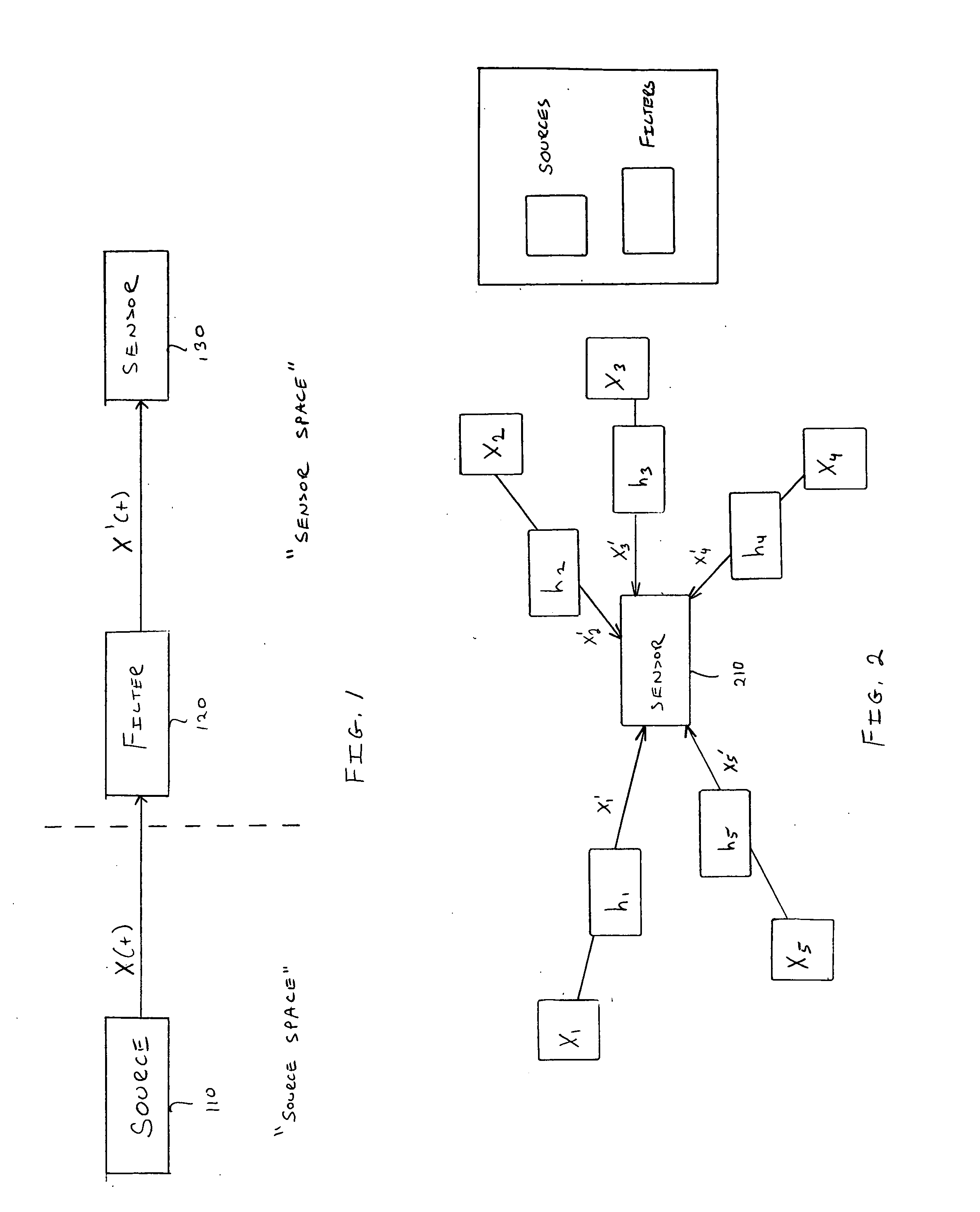
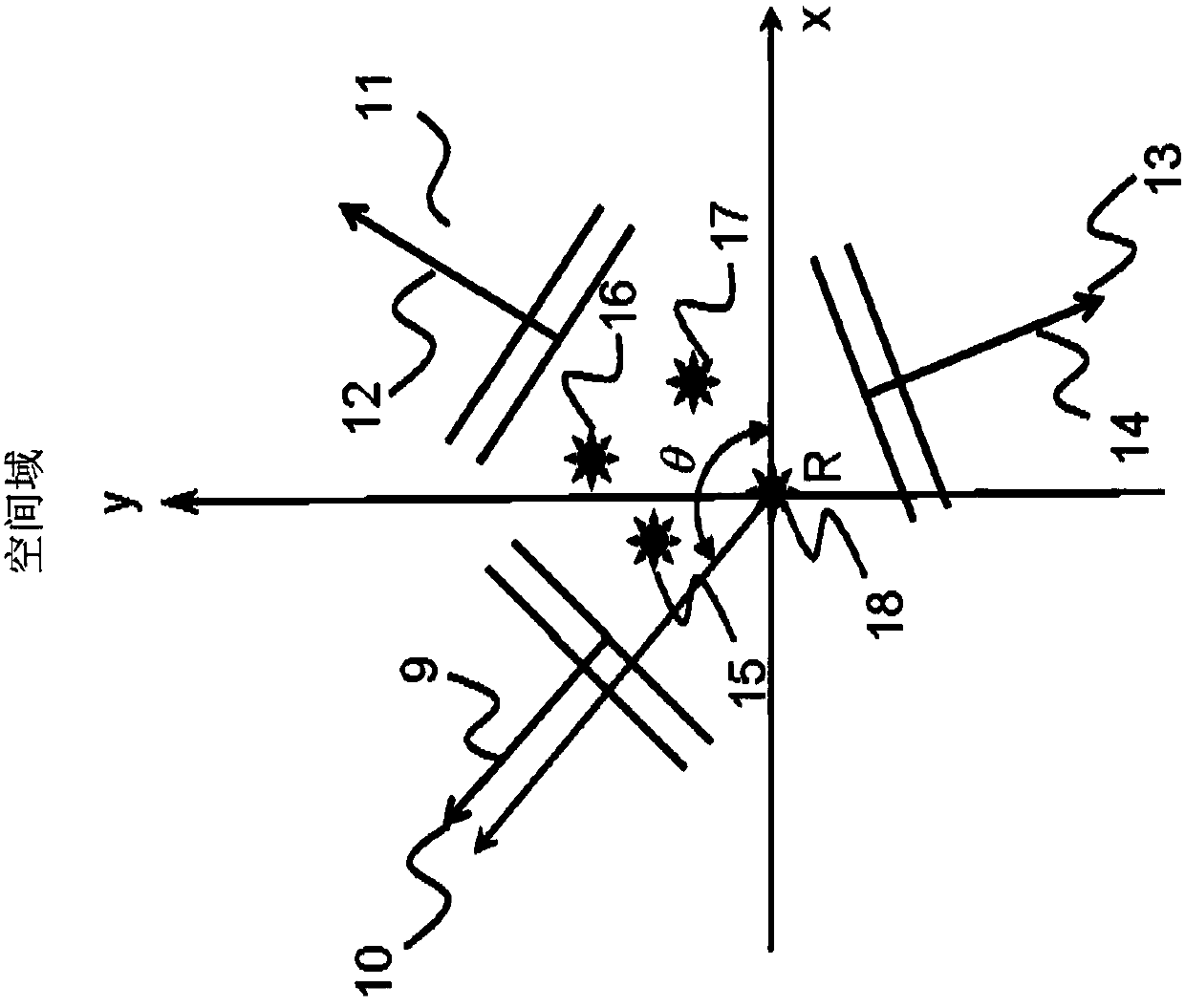
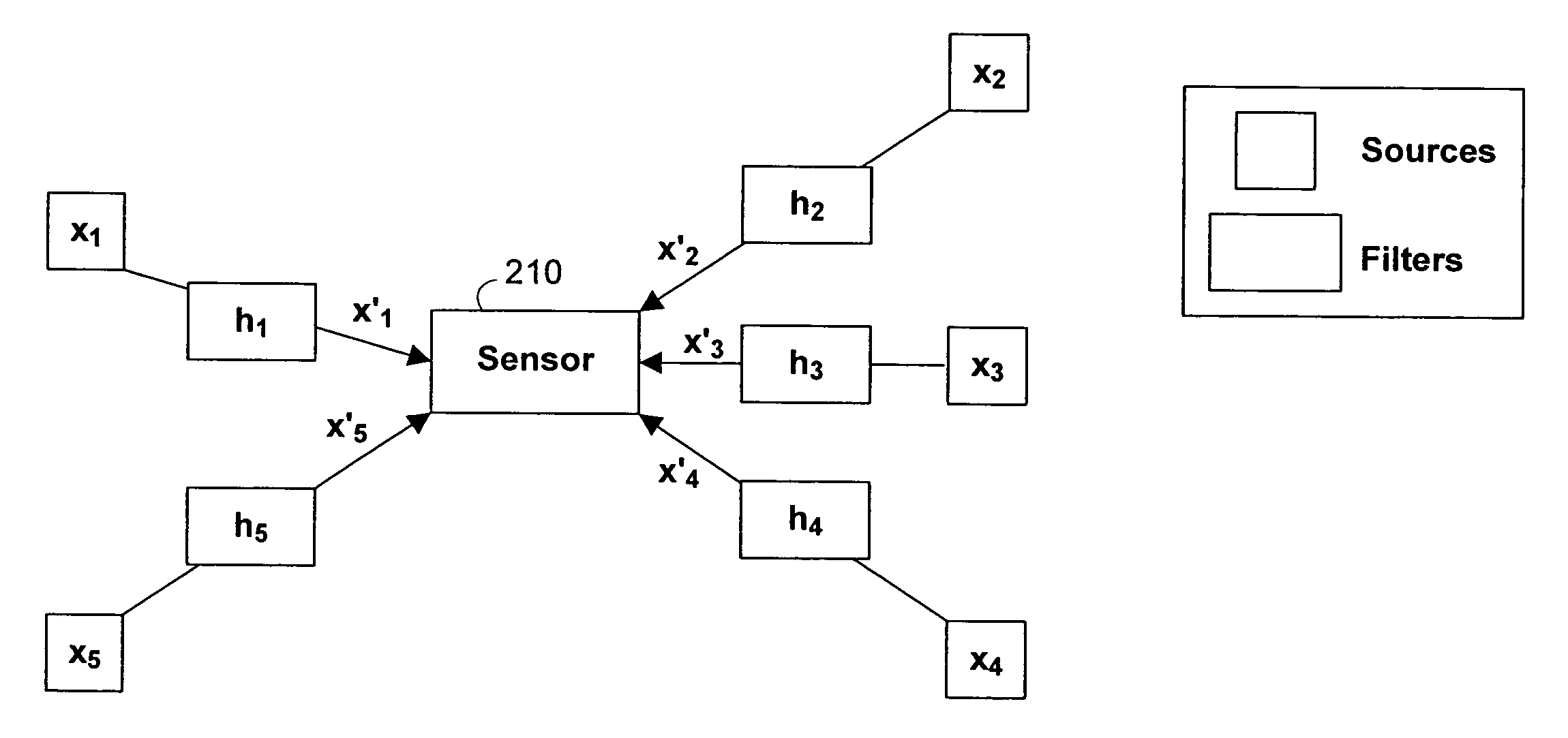
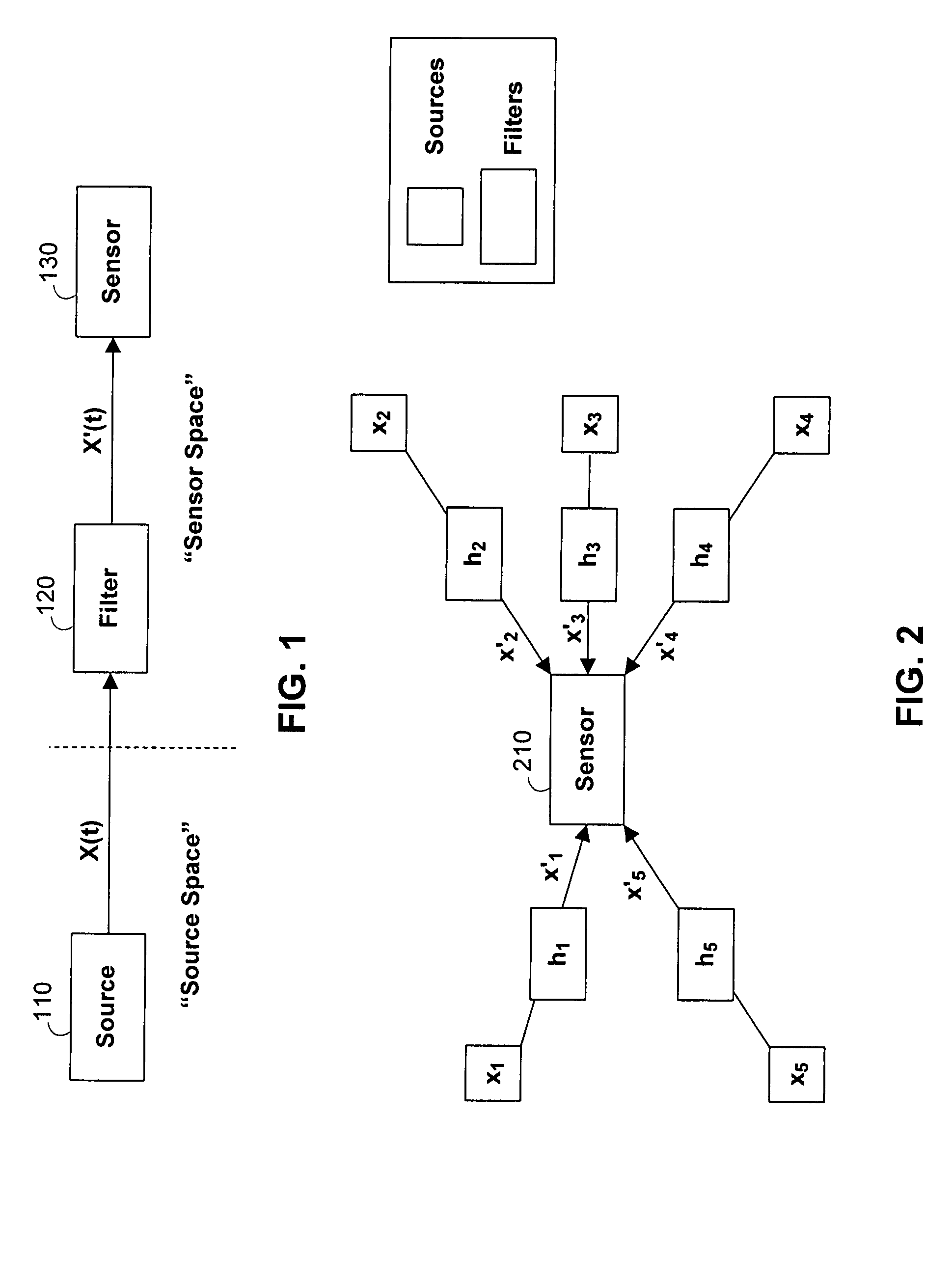
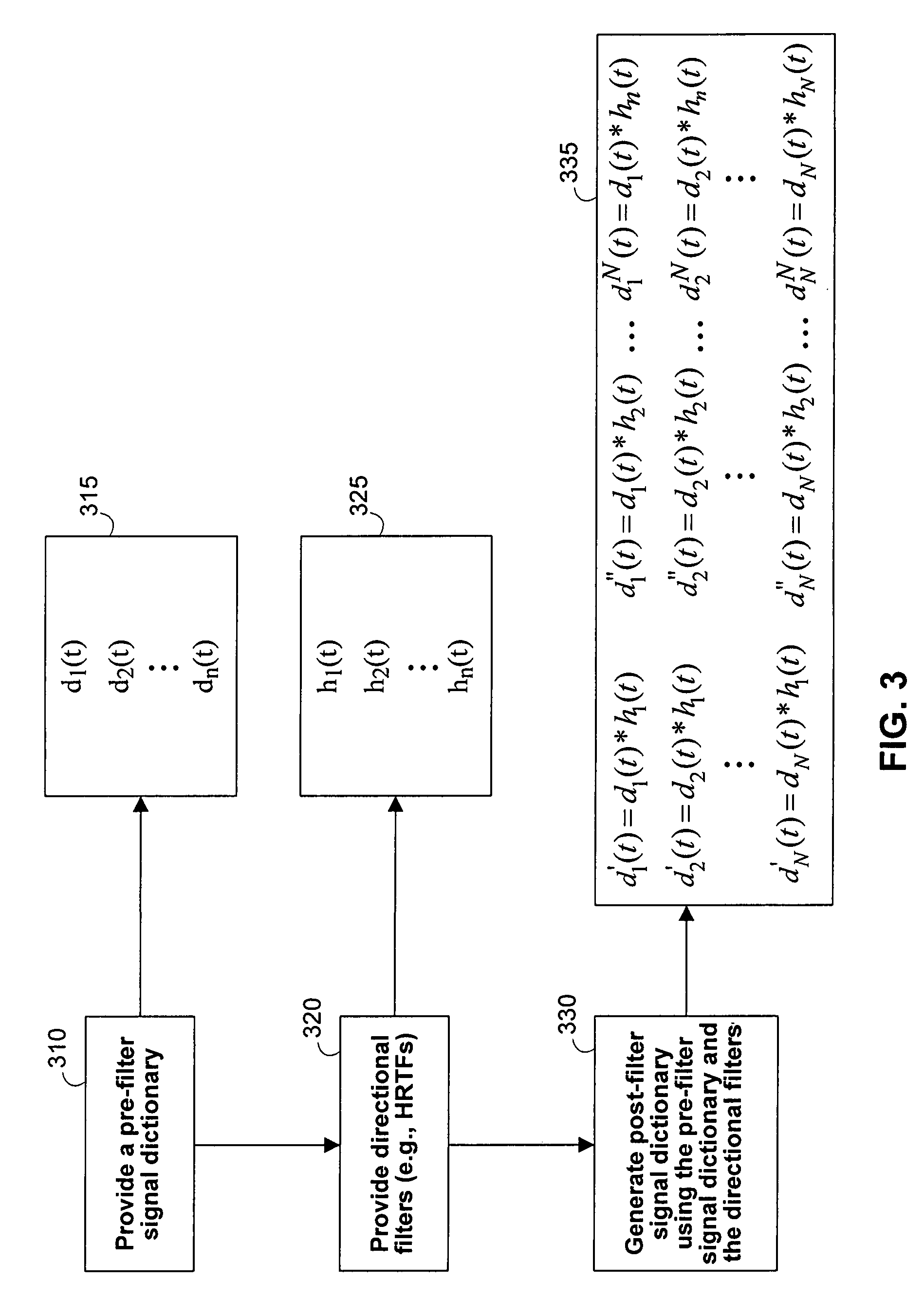
Systems and methods for separating multiple sources using directional filtering
InactiveUS20050213777A1Eliminate needMiniaturization trendAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSets with desired directivityComputer scienceBasis function
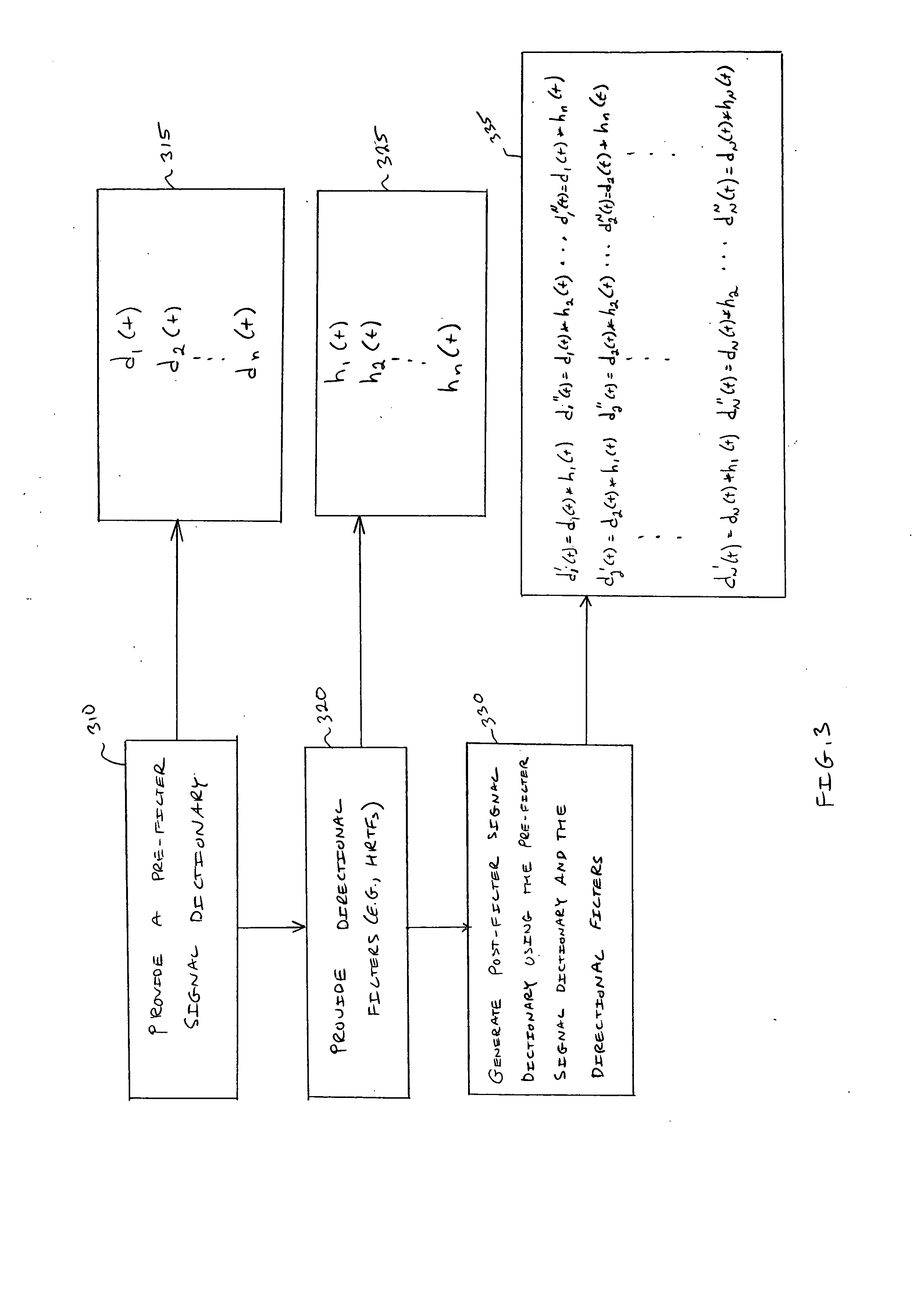
Systems and methods for performing source separation are provided. Source separation is performed using a composite signal and a signal dictionary. The composite signal is a mixture of sources received by a sensor. The signal dictionary is a database of filtered basis functions that are formed by the application of directional filters. The directional filters approximate how a particular source will be received by the sensor when the source originates from a particular location. Each source can be characterized by a coefficient and a filtered basis function. The coefficients are unknown when the sources are received by the sensor, but can be estimated using the composite signal and the signal dictionary. Various ones of the sources may be selectively reconstructed or separated using the estimated value of the coefficients.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC +1
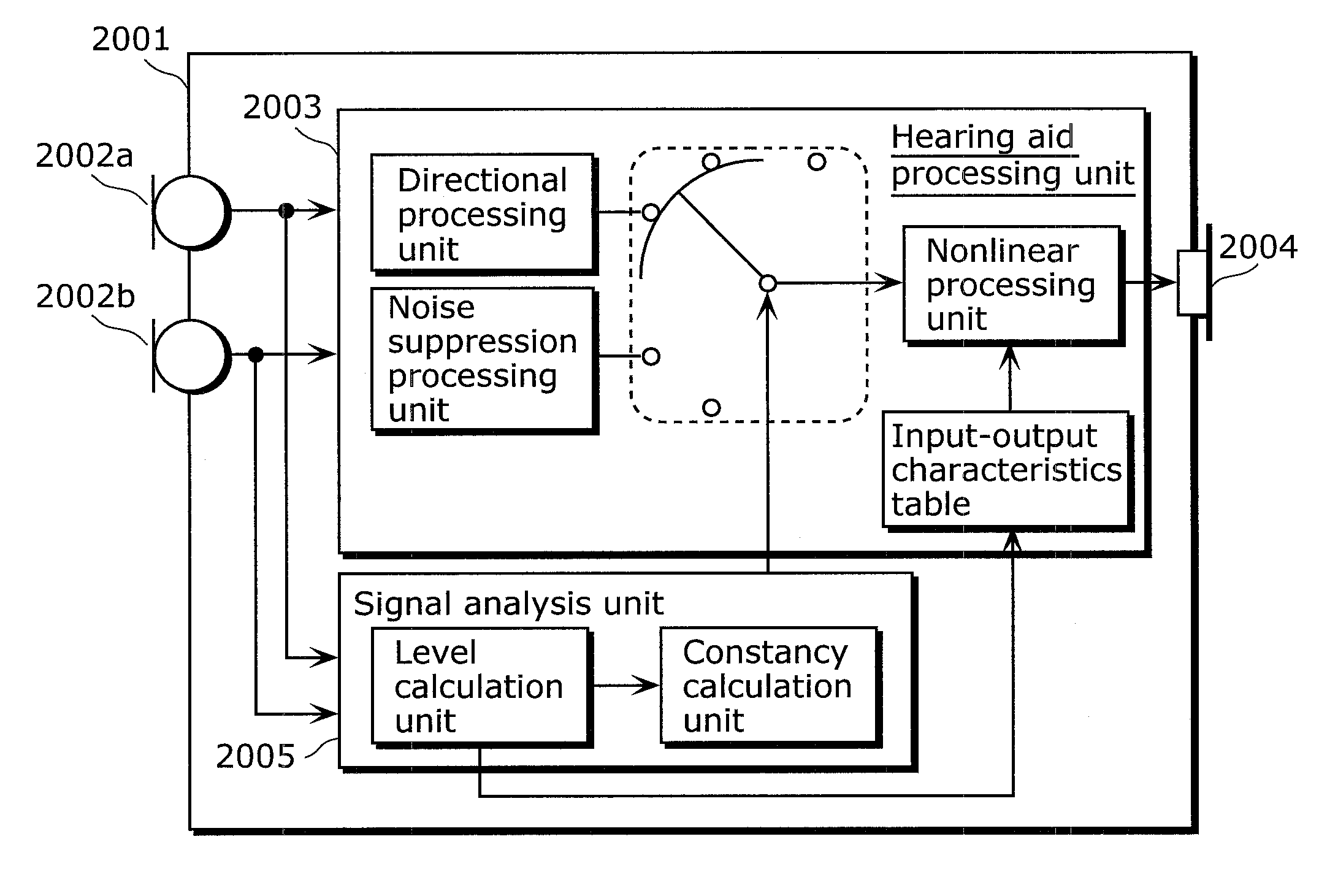
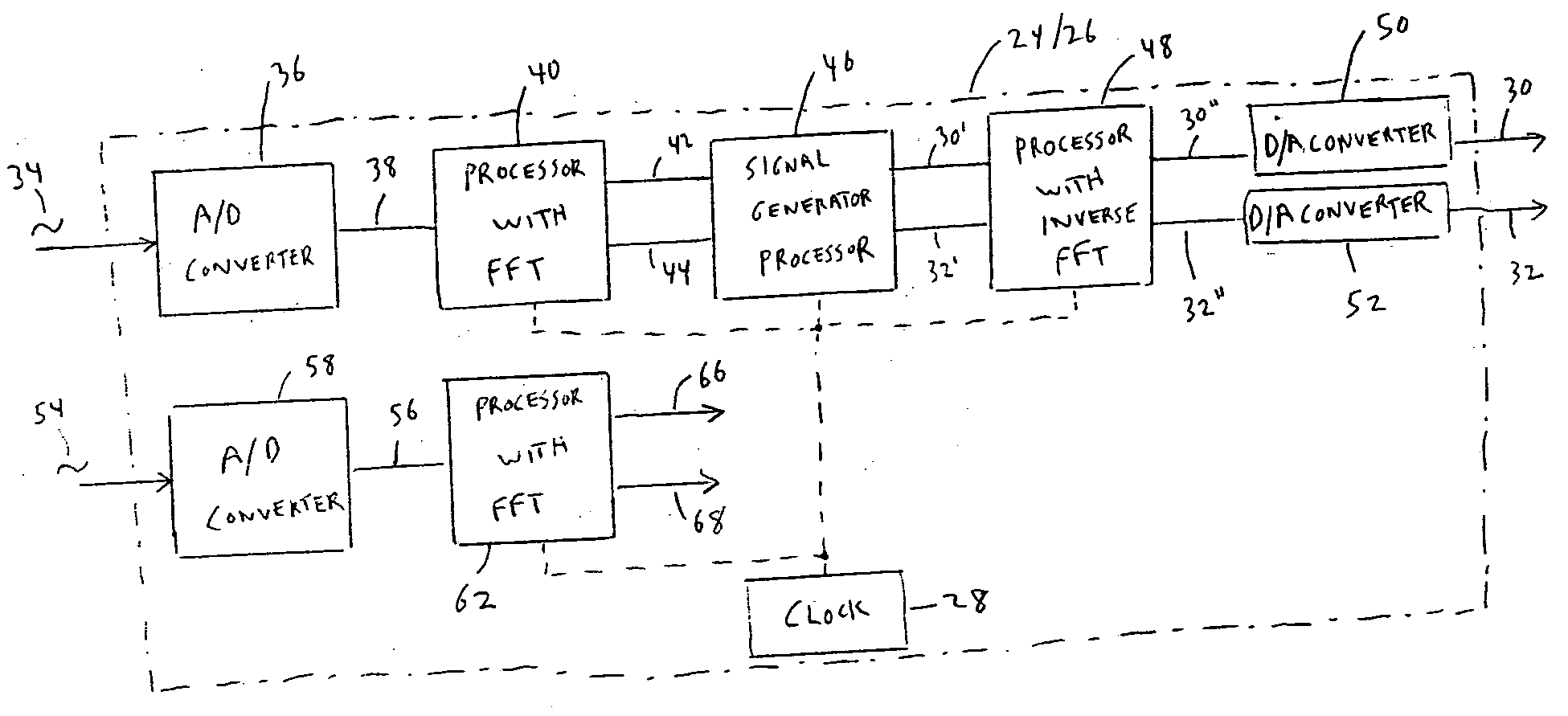
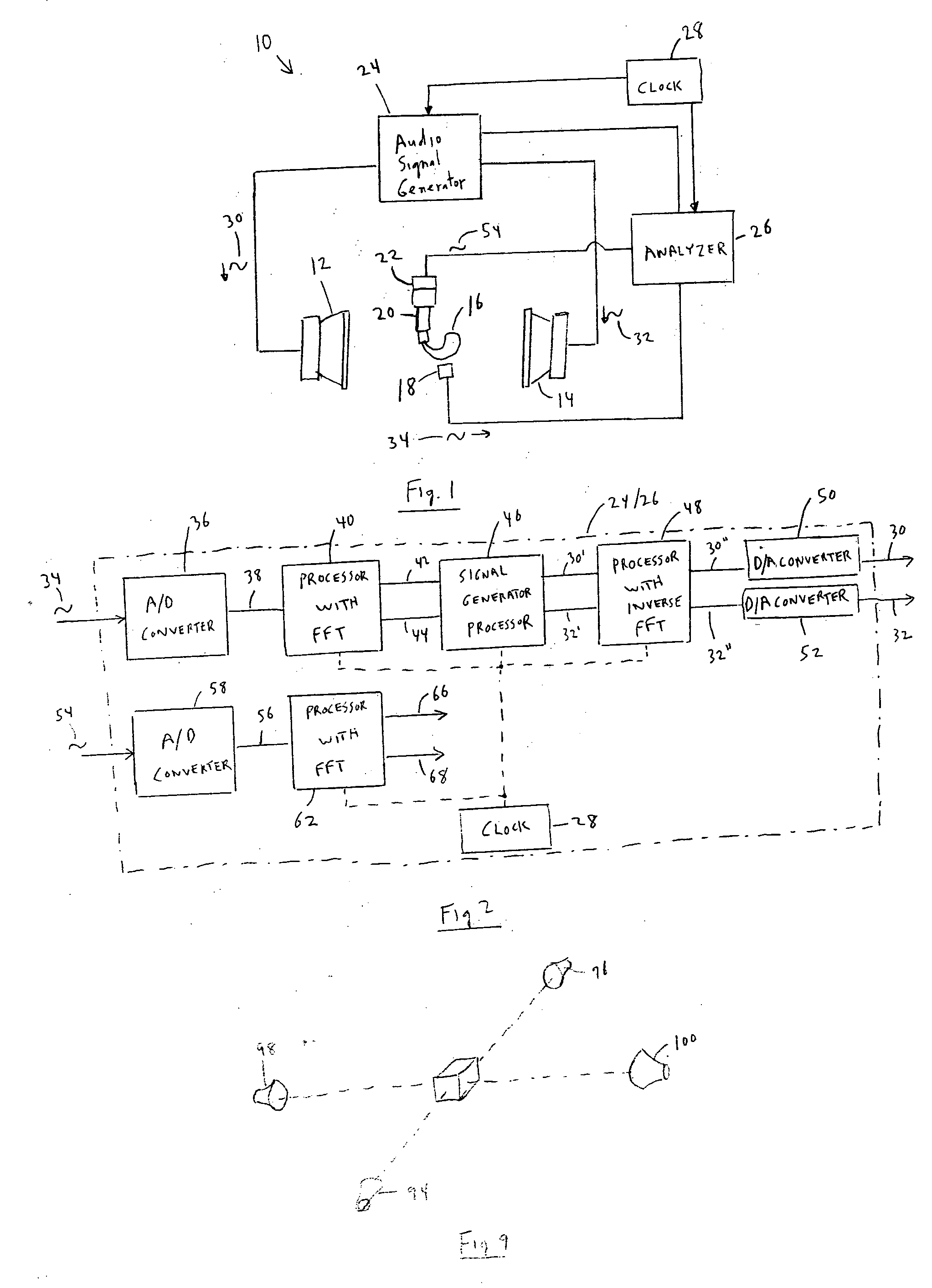
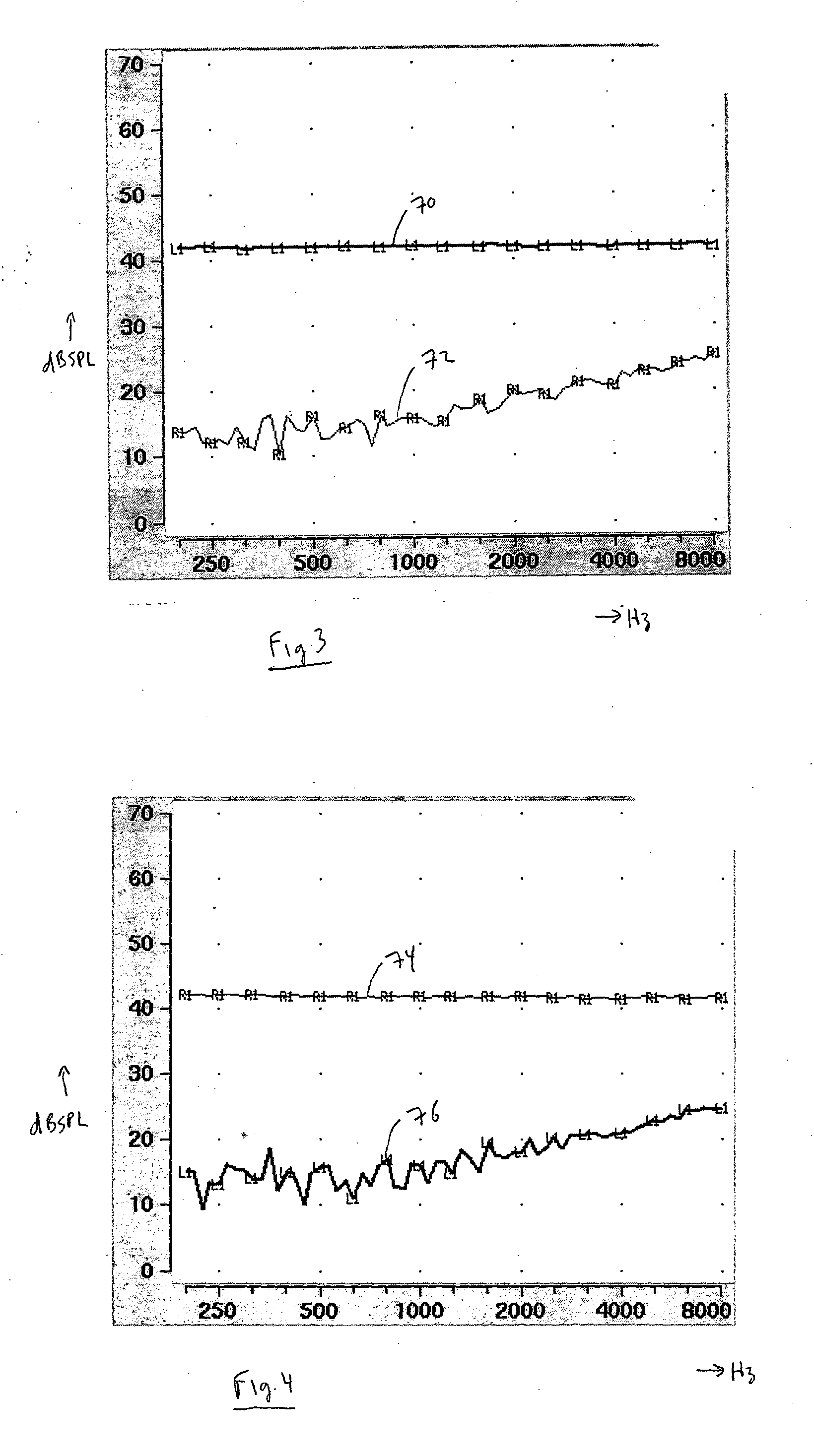
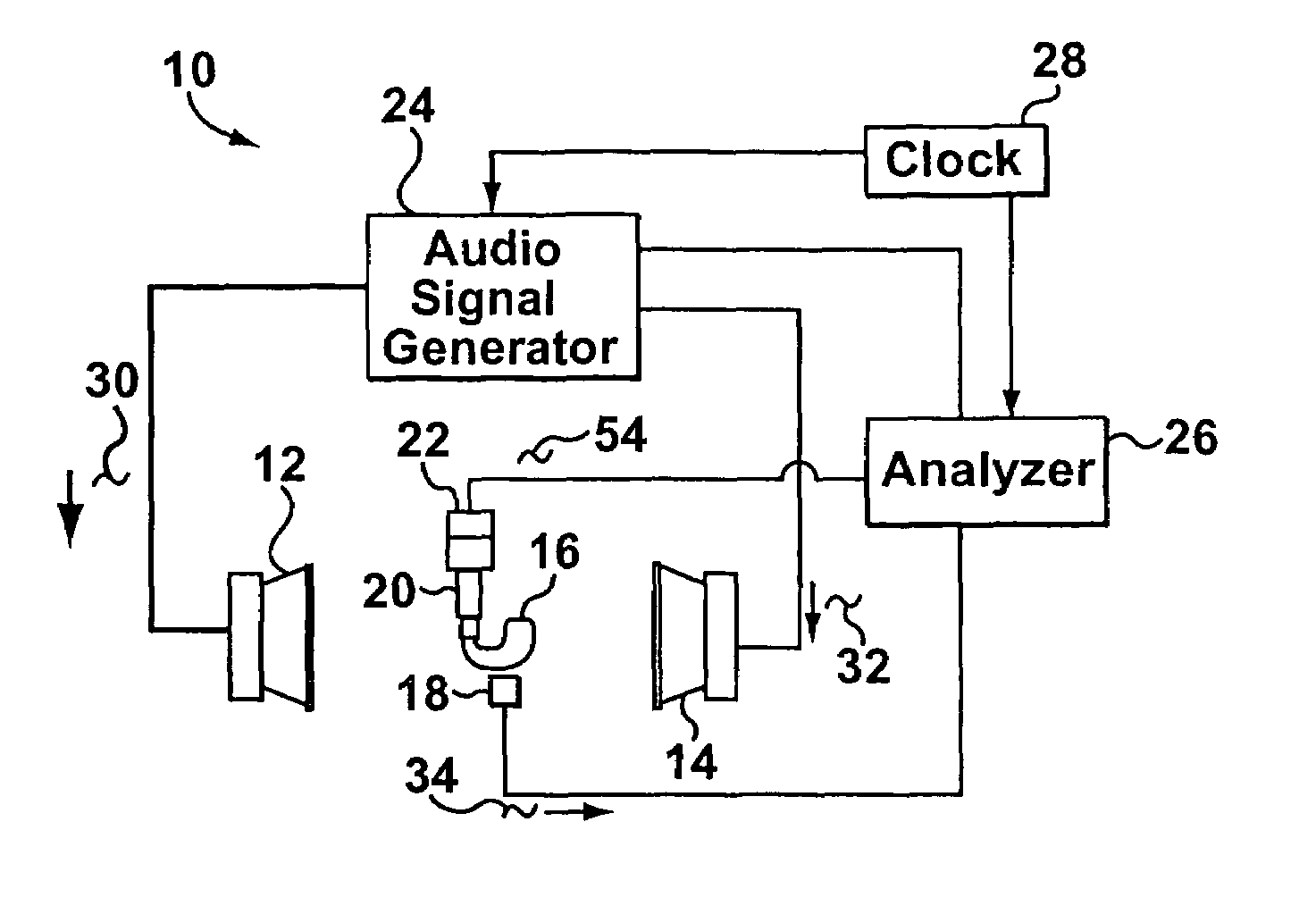
Method for controlling the directionality of the sound receiving characteristic of a hearing aid and a signal processing apparatus
ActiveUS7933423B2Minimize output signalImprove abilitiesDoor/window protective devicesCurtain accessoriesSignal analyzerEngineering
A signal processing apparatus (100) for a hearing aid with a controllable directional characteristic is provided which comprises a directional controller (10) receiving first and second microphone signals (20, 30) and output an output signal (40), a signal analyzer (70) which detects whether at least one of said first and second microphone signals being undesired signals, and wherein said directional controller minimizes the output signal by adjusting the directional characteristic only if the signal analyzer has detected undesired signals.
Owner:WIDEX AS
Speech intelligibility enhancing system
ActiveUS20190356991A1Improve protectionLimited amountIn the ear hearing aidsHearing aids signal processingUltrasound attenuationCoupling
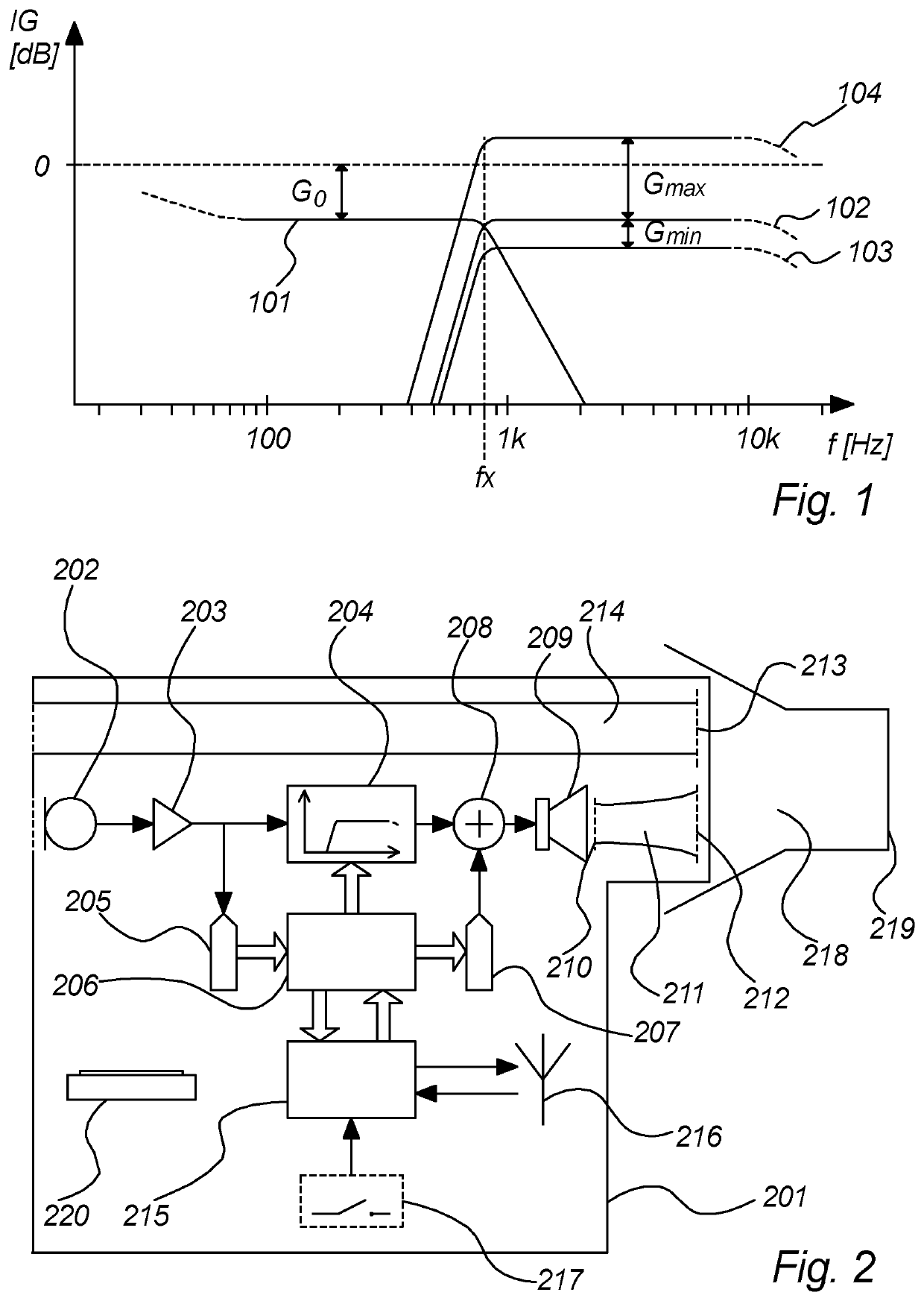
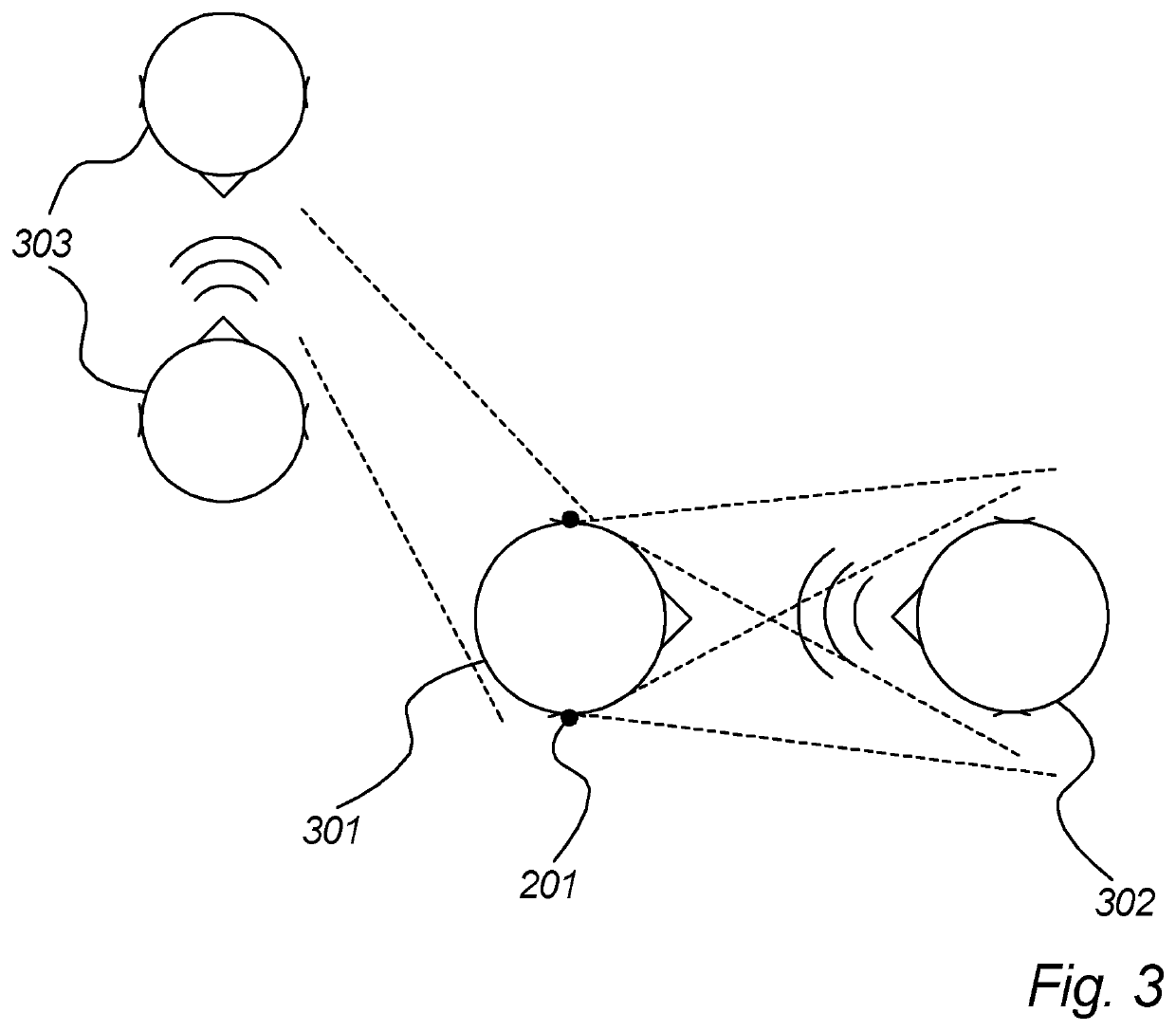
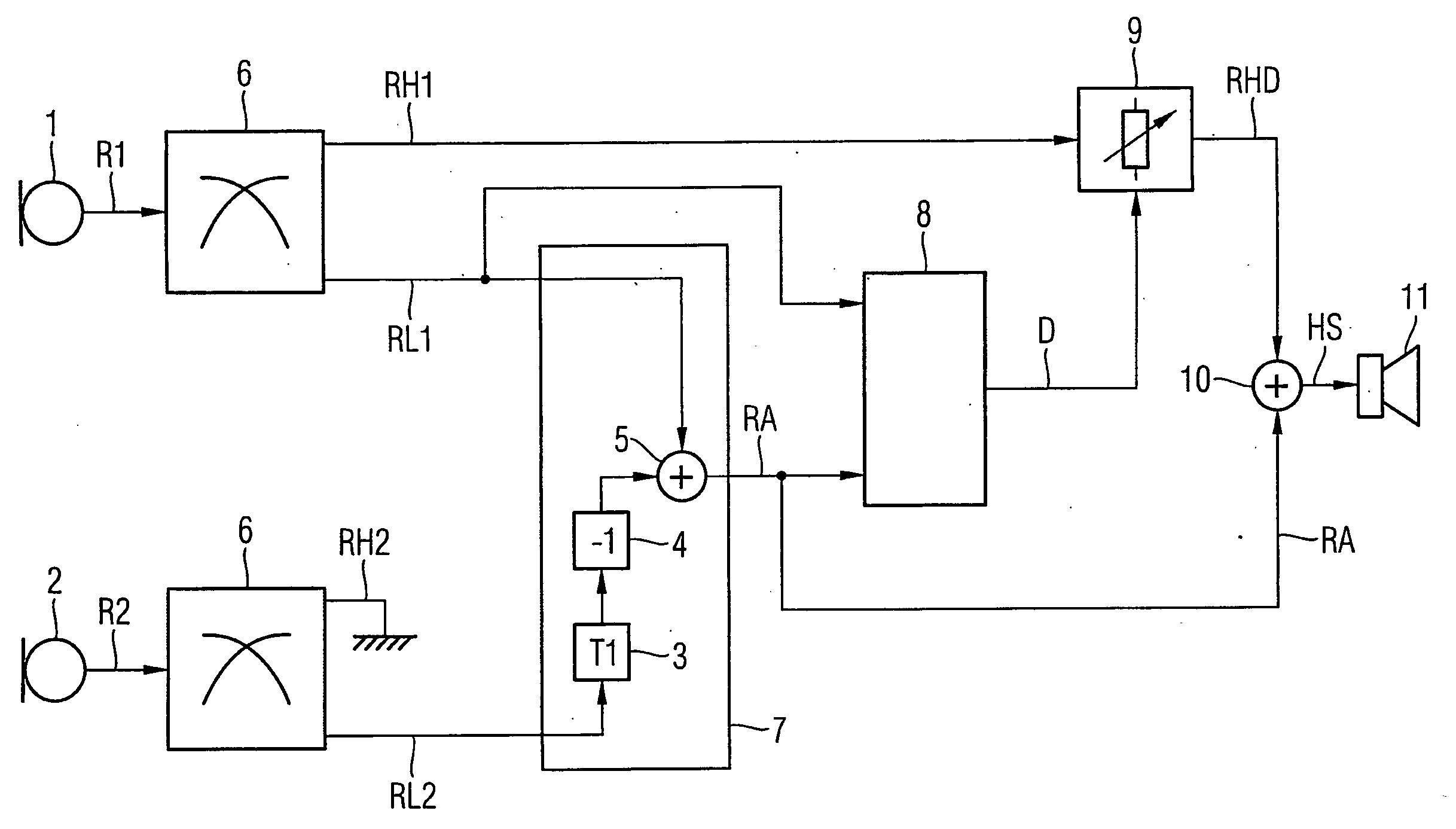
A speech intelligibility enhancing system for difficult acoustical conditions is disclosed, the speech intelligibility enhancing system comprising at least one ear plug (201) for insertion in an ear canal (218) of a person, the at least one ear plug being arranged with an ear canal facing portion (401) and an environment facing portion (402), and the at least one ear plug comprising an acoustically attenuating path (214; 214, 213) comprising a vent (214) coupling said environment facing portion (402) with said ear canal facing portion (401); and an electroacoustic path (202, 204, 209; 202, 203, 204, 208, 209, 210, 211, 212) comprising a microphone (202) at said environment facing portion (402), a variable gain (204) and a loudspeaker (209) at said ear canal facing portion (401); wherein said acoustically attenuating path (214; 214, 213) is arranged with a transfer function from said environment facing portion (402) to said ear canal facing portion (401) having a low pass characteristic having a low pass cut¬off frequency and said low pass characteristic attenuating sound by a nominal attenuation (Go) for frequencies below said cut-off frequency.
Owner:LIZN APS
Method for operating a hearing device and microphone system for hearing device
ActiveUS20090279724A1Increased frequency rangeCompromises perceptionPiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesSignal processingEngineeringHearing apparatus
A method for operating a hearing device, an associated microphone system comprising at least two omnidirectional microphones, and a hearing device are provided. The microphones emit microphone signals and are electrically interconnected with one another in order to form directional characteristics. A damping of the upper frequency range of the microphone signals is determined from the lower frequency range of the microphone signals. The impression of a wide-band directional microphone is produced as a result.
Owner:SIVANTOS PTE LTD
Direction of arrival estimation in miniature device using a sound sensor array
InactiveCN107592601AMinimize energy consumptionMicrophonesElectrical transducersSensor arraySound sources
The application discloses direction of arrival estimation in a miniature device using a sound sensor array. The miniature device is a hearing device which includes a sound system for estimating the direction of arrival of acoustical signals emitted by one or more sound sources, wherein the system includes a sound sensor unit including an array of M sound receiving transducers, each providing an electric input signal; a sampling unit used for providing at least one sample of a surrounding sound field; and a processing unit comprising a model unit comprising a parametric model configured to be able to describe the sound field at the array as a function of the direction of arrival in a region surrounding and adjacent to the array, a model optimizing unit configured to optimize said model based on said sound samples, a cost optimizing unit configured to minimize a cost function of the model with respect to said direction of arrivals, and an estimating unit configured to estimate the direction of arrival based on said parametric model with the optimized parameters and the optimized cost function.
Owner:OTICON
Systems and methods for separating multiple sources using directional filtering
InactiveUS7280943B2Source separationEliminate needAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSets with desired directivityComputer scienceBasis function
Systems and methods for performing source separation are provided. Source separation is performed using a composite signal and a signal dictionary. The composite signal is a mixture of sources received by a sensor. The signal dictionary is a database of filtered basis functions that are formed by the application of directional filters. The directional filters approximate how a particular source will be received by the sensor when the source originates from a particular location. Each source can be characterized by a coefficient and a filtered basis function. The coefficients are unknown when the sources are received by the sensor, but can be estimated using the composite signal and the signal dictionary. Various ones of the sources may be selectively reconstructed or separated using the estimated value of the coefficients.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC +1
Method of deriving individualized gain compensation curves for hearing aid fitting
ActiveUS8879745B2Reduce impactReduce fatigueSignal processingSets with desired directivityPersonalizationHearing aid
A method of deriving individual gain compensation curves for hearing aid fitting includes providing a system that detects, measures and records head azimuth for sound direction affirmation by a patient and provides a plurality of audio signals through a plurality of test sequences to the ears of the patient, including establishing a comfortable listening level of the patient, establishing binaural balance for right and left ears, establishing loudness discomfort levels of the patient, establishing thresholds-of-hearing levels of the patient and generating a binaurally balanced measurement array of measured equal-loudness levels and measured thresholds-of-hearing levels for both left and right ears.
Owner:DEAN ROBERT GARY ANDERSON AS TRUSTEE OF THE D L ANDERSON FAMILY TRUST
Enhanced blind source separation algorithm for highly correlated mixtures
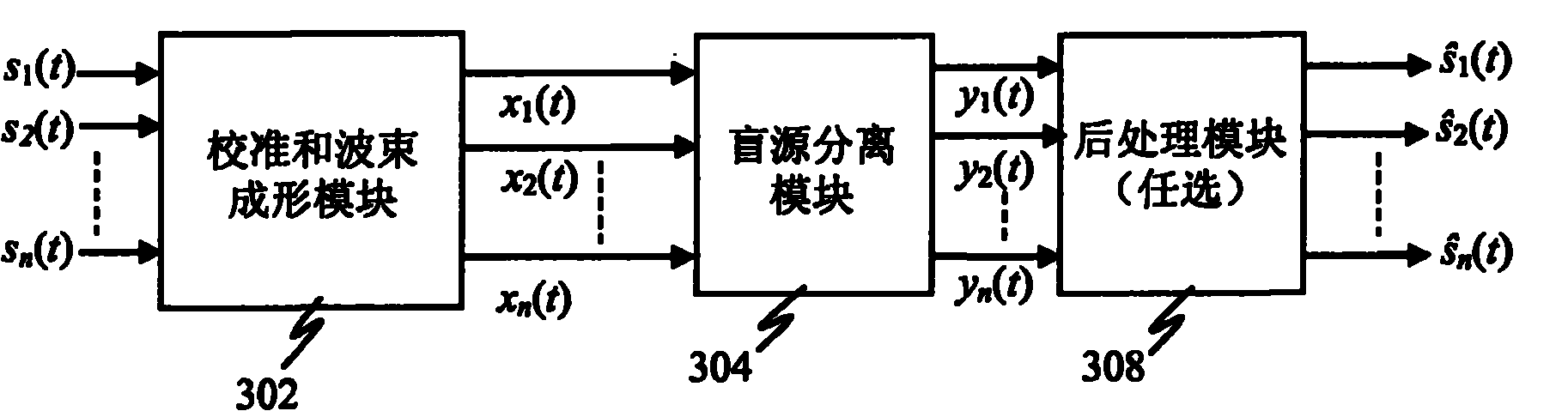
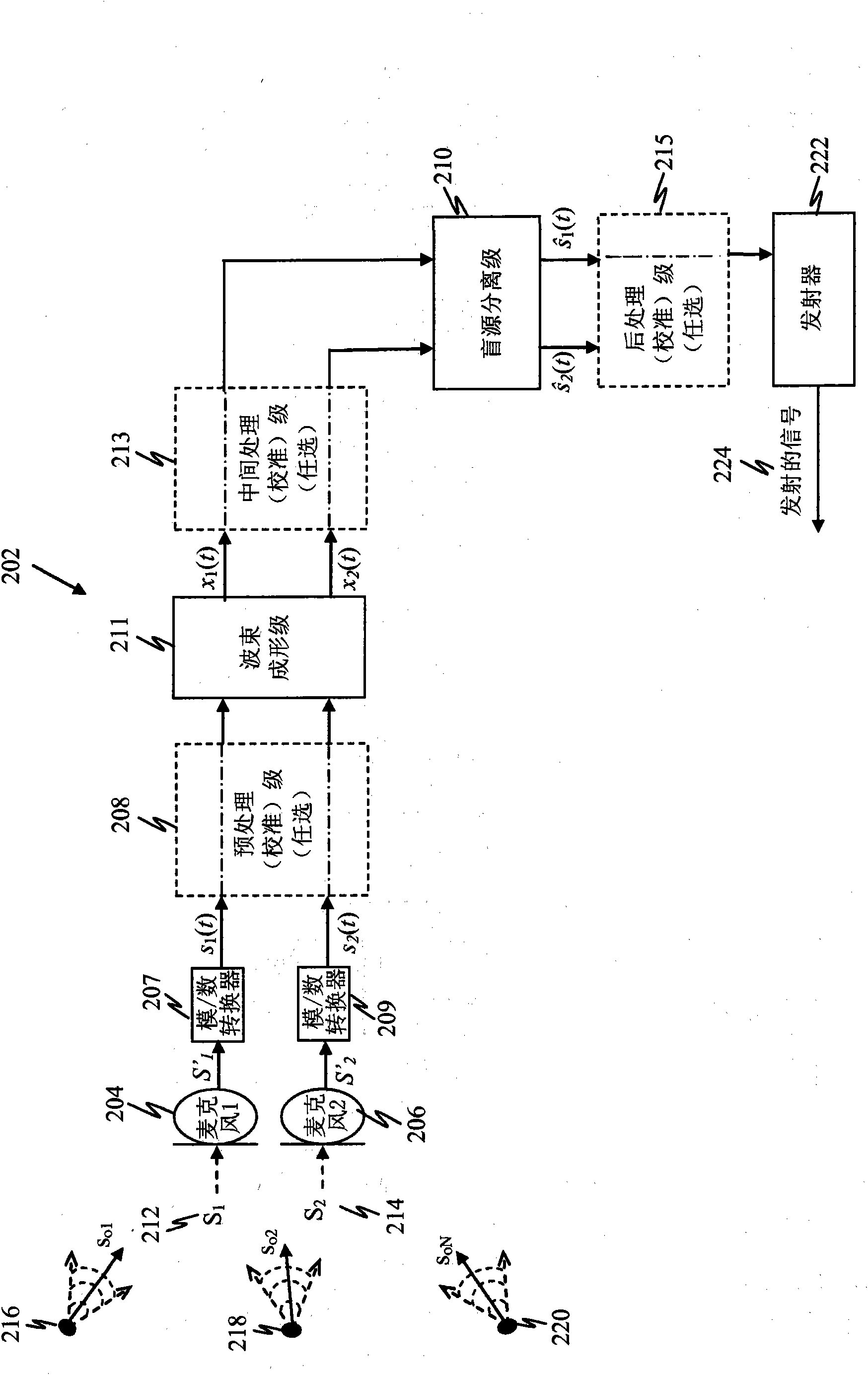
InactiveCN101904182ASpeech analysisSets with desired directivityComputer scienceBlind source separation algorithm
An enhanced blind source separation technique is provided to improve separation of highly correlated signal mixtures. A beamforming algorithm is used to precondition correlated first and second input signals in order to avoid indeterminacy problems typically associated with blind source separation. The beamforming algorithm may apply spatial filters to the first signal and second signal in order to amplify signals from a first direction while attenuating signals from other directions. Such directionality may serve to amplify a desired speech signal in the first signal and attenuate the desired speech signal from the second signal. Blind source separation is then performed on the beamformer output signals to separate the desired speech signal and the ambient noise and reconstruct an estimate of the desired speech signal. To enhance the operation of the beamformer and / or blind source separation, calibration may be performed at one or more stages.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com