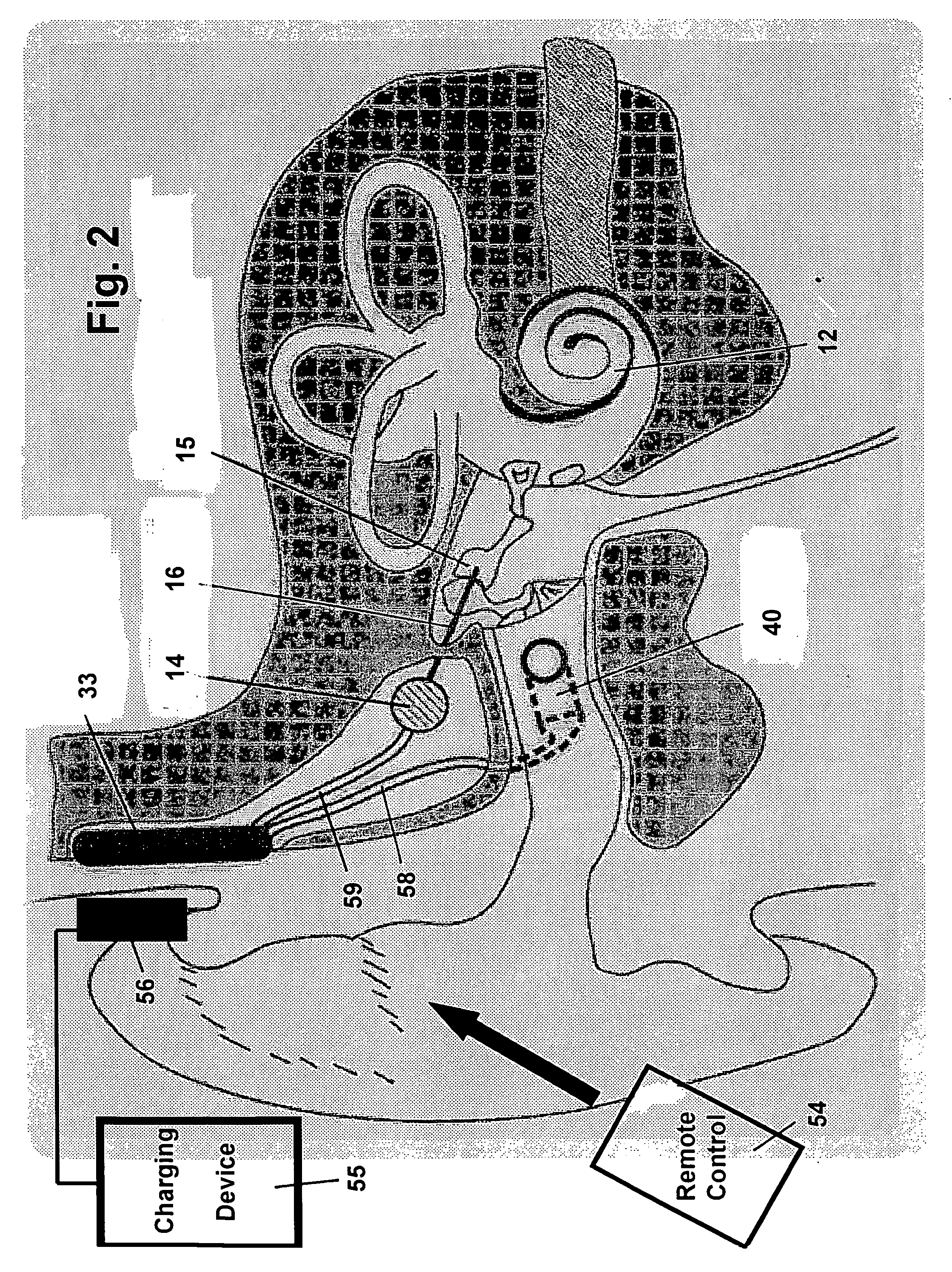Patents
Literature
941results about "Hearing aids signal processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
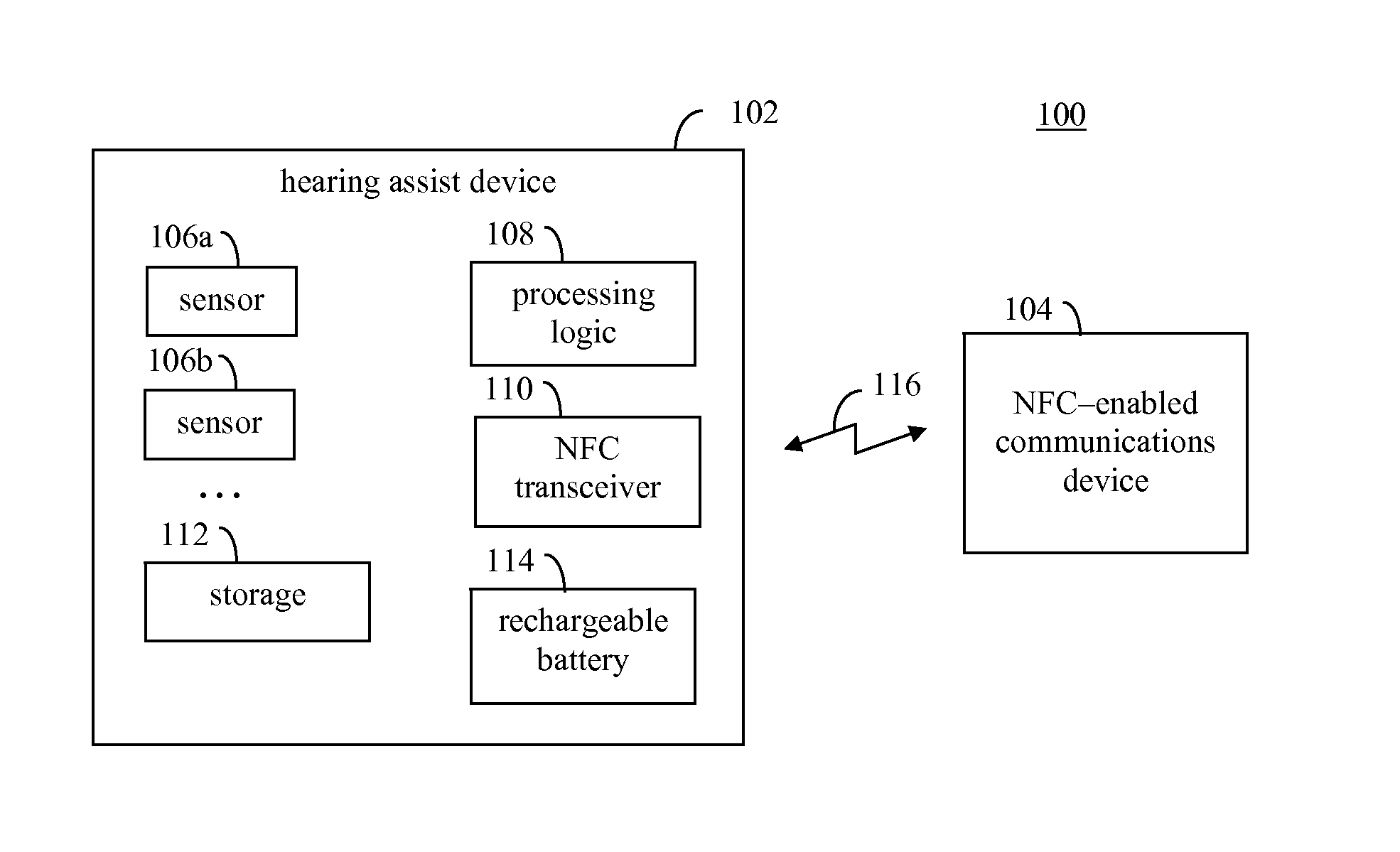
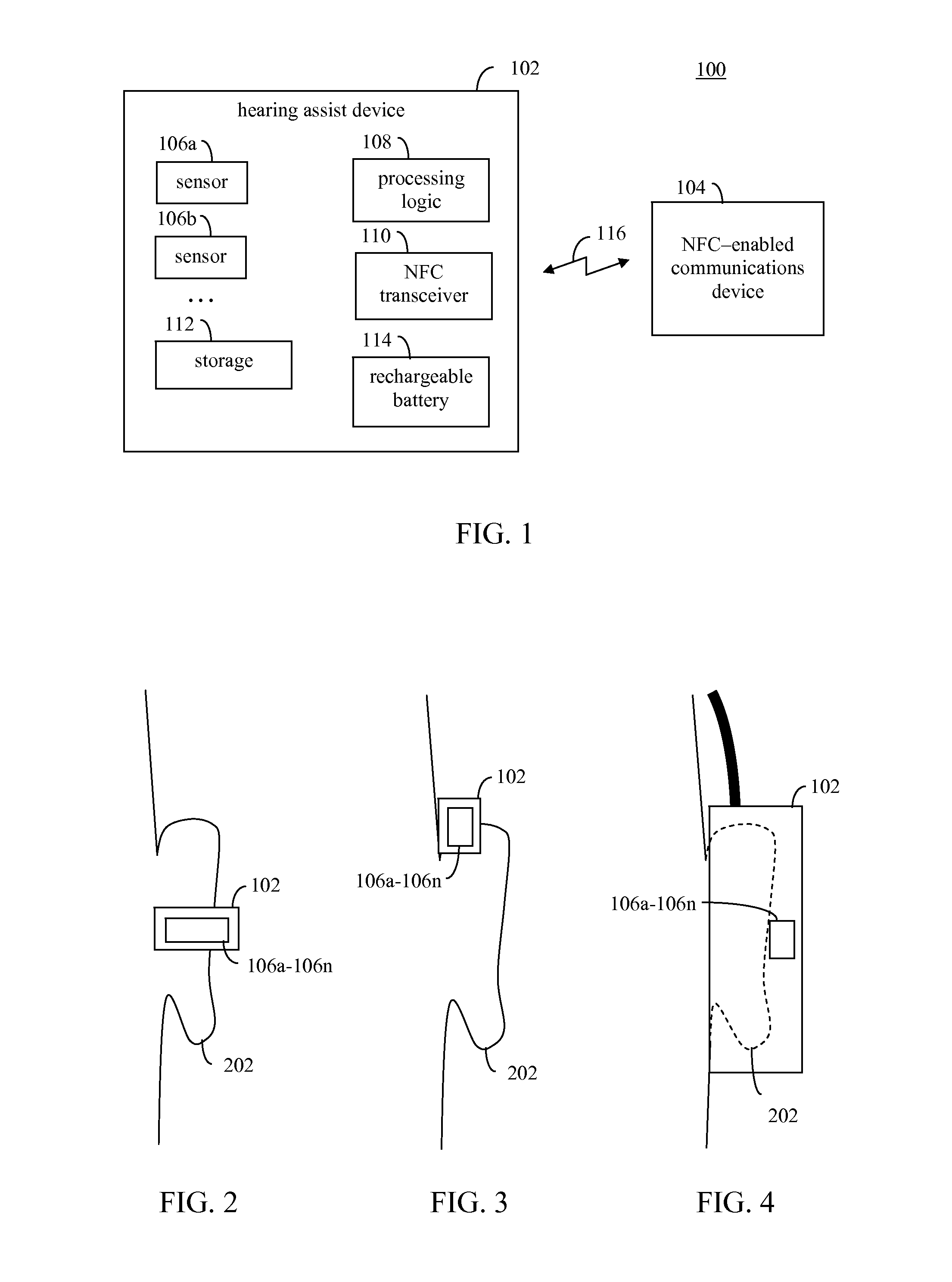
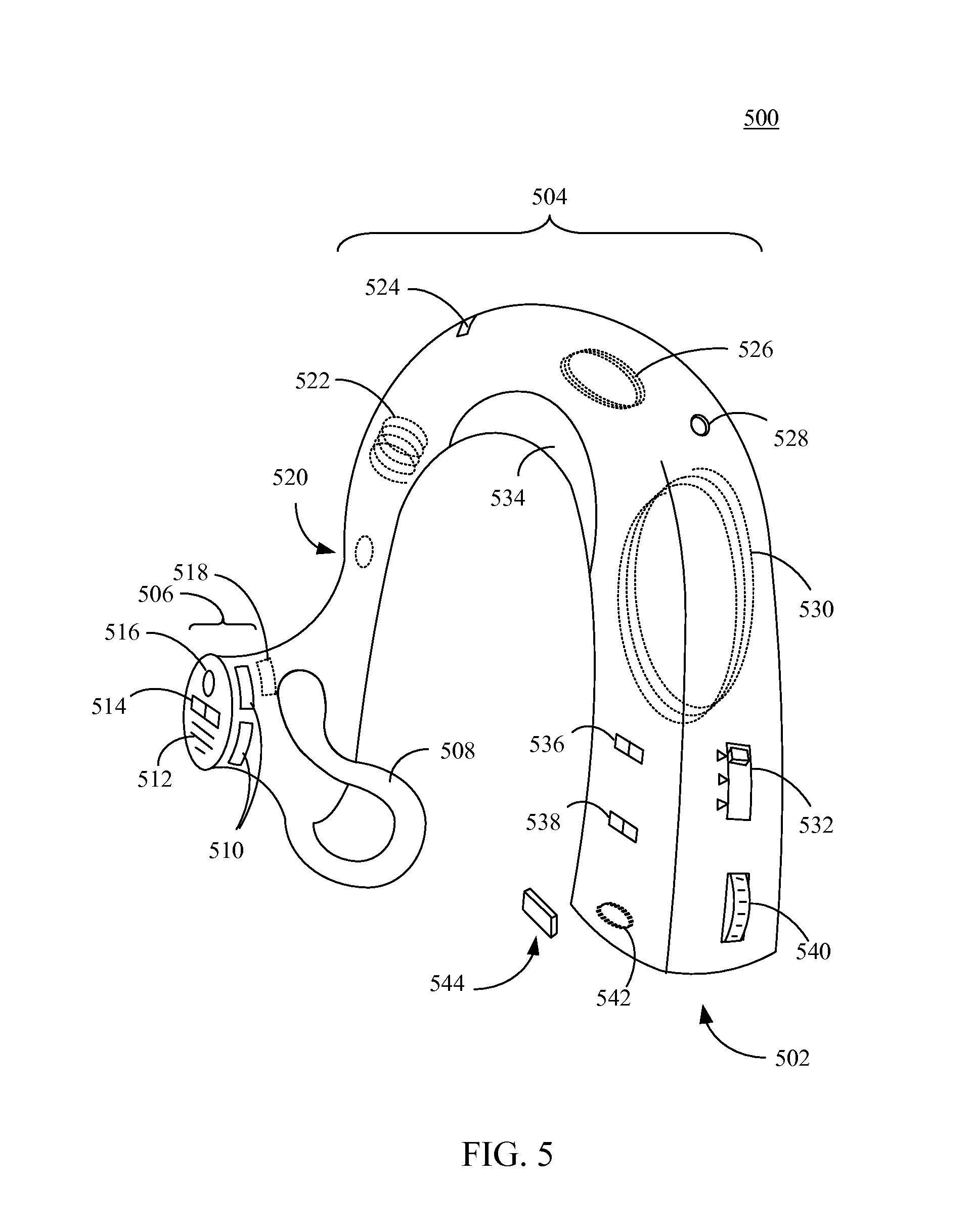
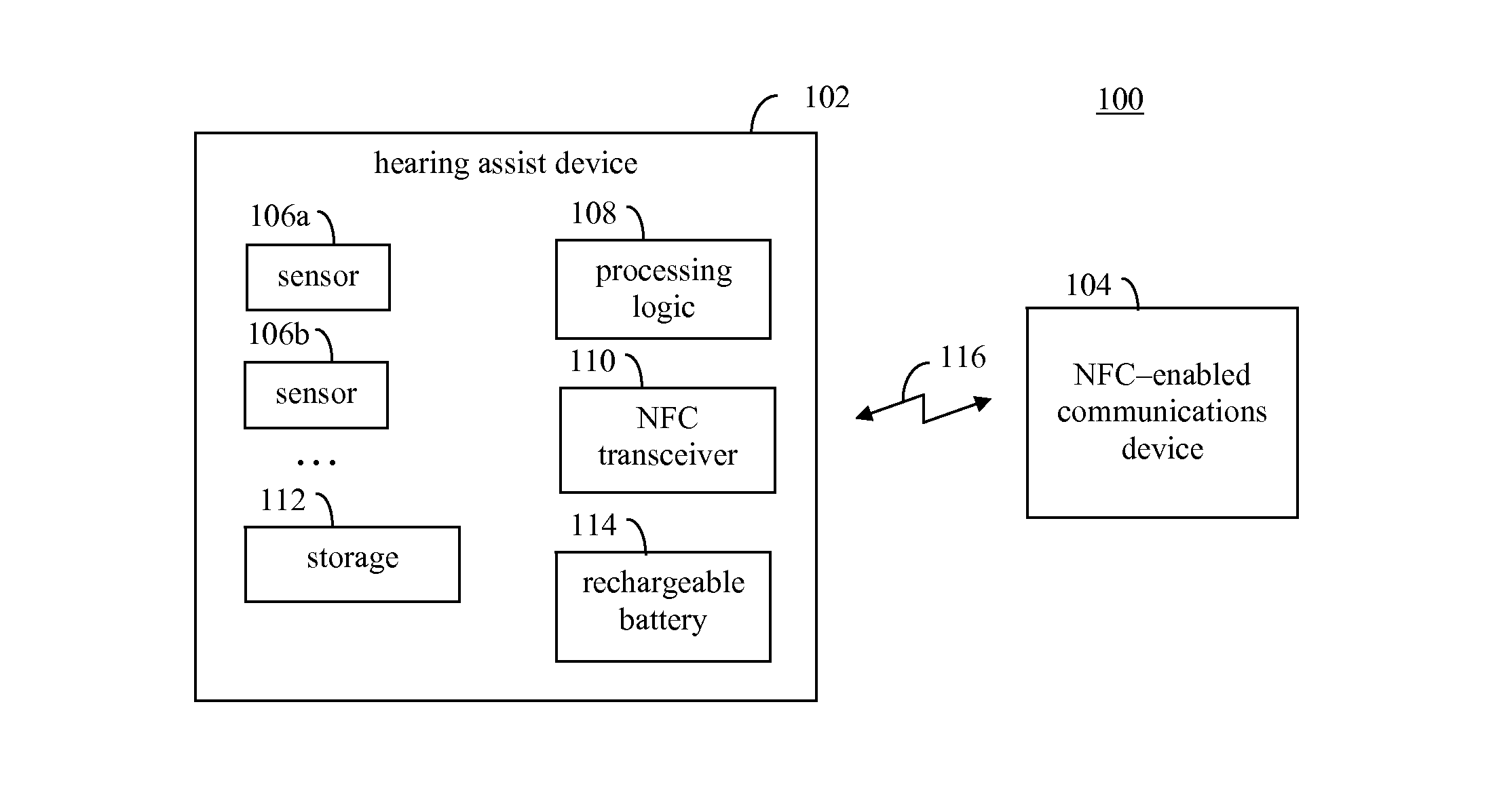
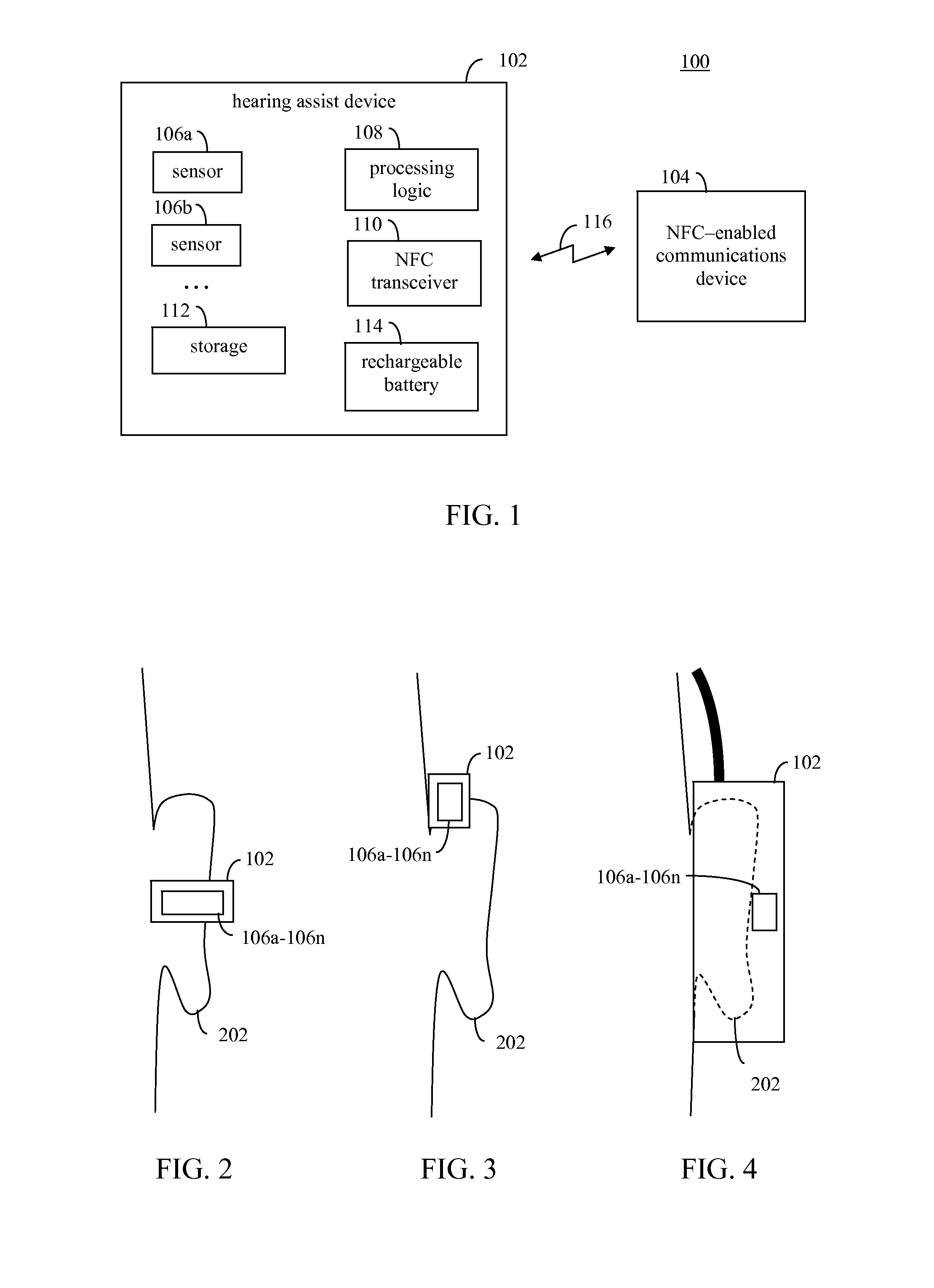
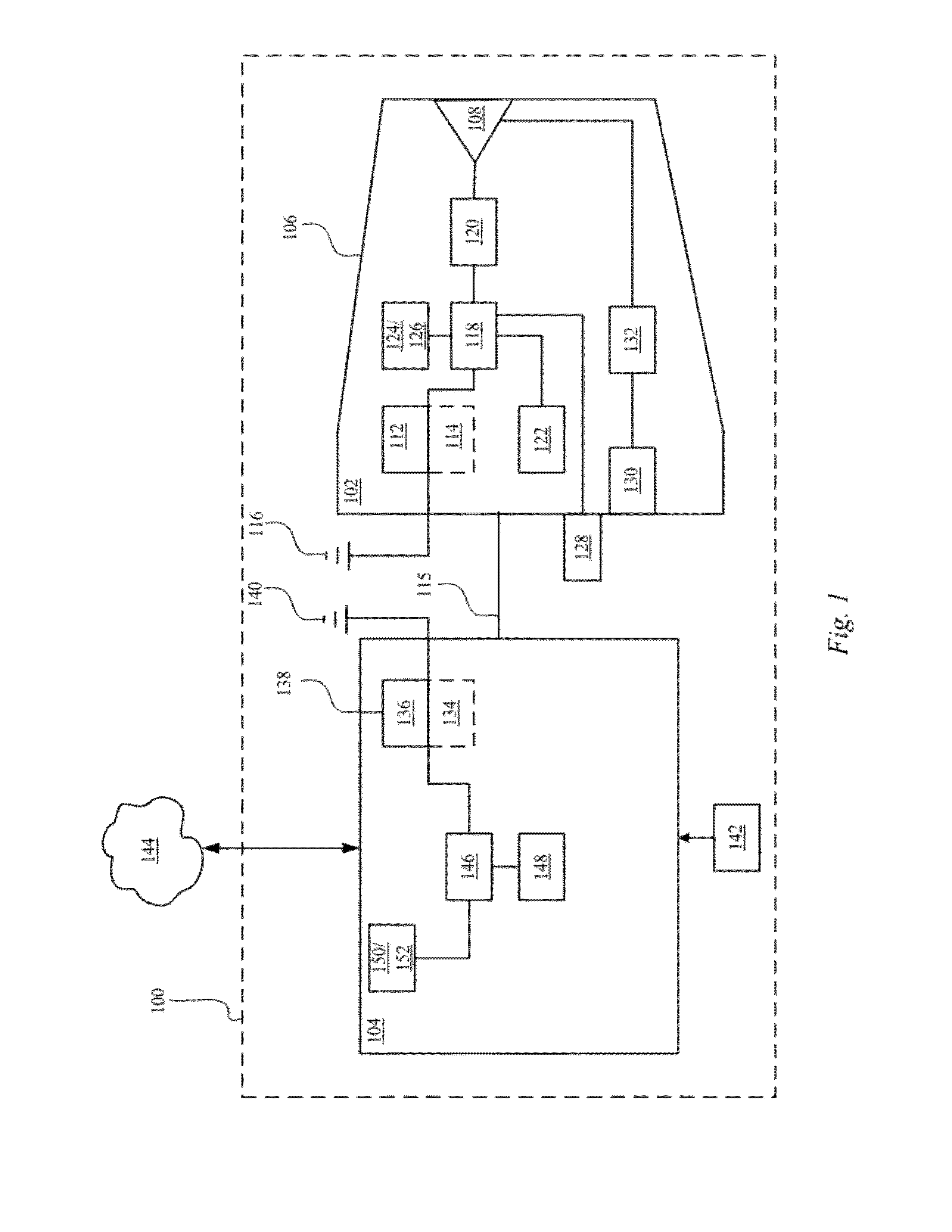
Multisensor hearing assist device for health
InactiveUS20130343585A1Hearing device energy consumption reductionPharmaceutical containersHearing aidRemote analysis
A hearing assist device is associated with an ear of a user. Health characteristics of the user are measured by sensors of the hearing assist device. The measured health characteristics may be analyzed in the hearing assist device, or transmitted from the hearing assist device for remote analysis. Based on the analysis, alerts, instructions, and other information may be displayed to the user in the form of text or graphics, or may be played by the hearing assist device in the form of sound / voice. Medical personnel may be alerted when problems with the user are detected by the hearing assist device. The user may provide verbal commands to the hearing assist device. The hearing assist device may be configured to filter sounds, and may be configured for a personal hearing frequency response of the user. The hearing assist device may be configured for speech recognition to recognize commands.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
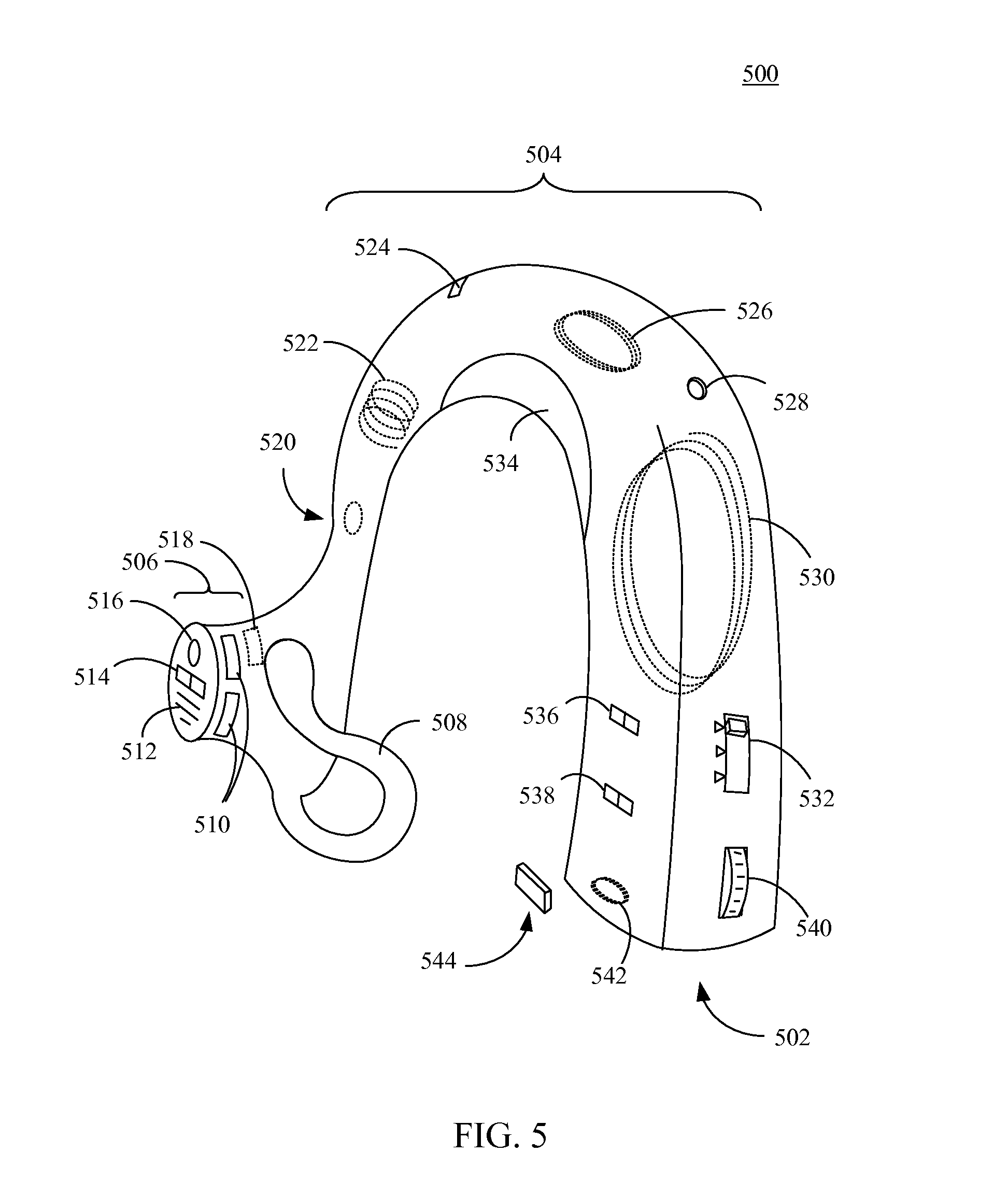
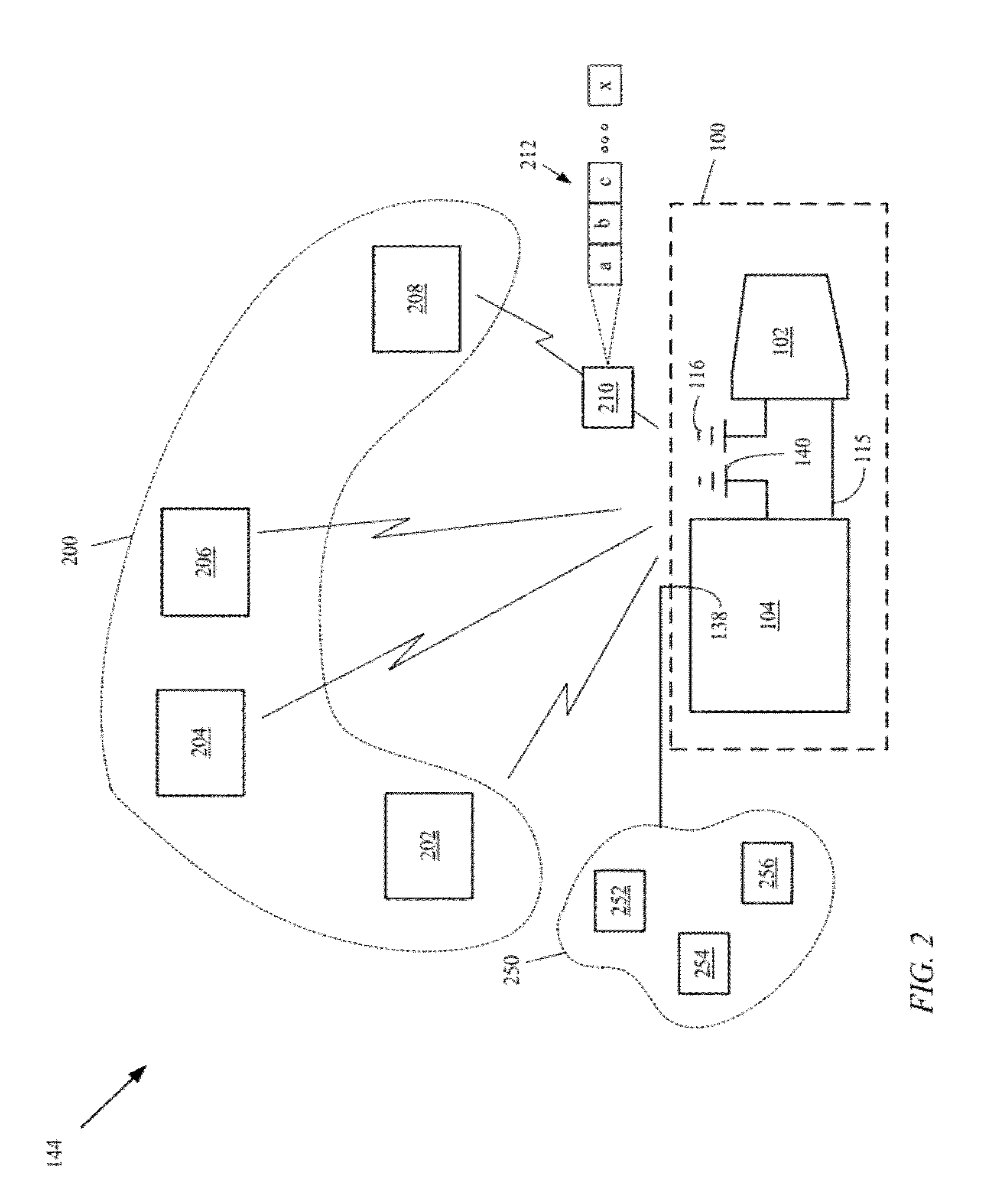
Hearing assist device with external operational support
InactiveUS20130343584A1Hearing device energy consumption reductionPharmaceutical containersHearing aidElectrophonic hearing
Hearing assist devices and devices and services that are capable of providing external operational support thereto are described. In accordance with various embodiments, the performance of one or more functions by a hearing assist device is assisted or improved in some manner by utilizing resources of an external device and / or service to which the hearing assist device may be communicatively connected. Such performance assistance or improvement may be achieved, for example and without limitation, by utilizing power resources, processing resources, storage resources, sensor resources, and / or user interface resources of an external device or service to which the hearing assist device may be communicatively connected.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Ear terminal with microphone for voice pickup
InactiveUS6754359B1Hearing protectionQuality improvementSignal processingHearing aids signal processingEngineeringHeadphones
An ear terminal includes a sealing section arranged for use in the ear meatus of a human, with an inner microphone having a sound inlet for being directed into the meatus and an electronic unit including filtering elements coupled to the inner microphone for filtering the signal from the inner microphone, the filtering elements being programmable to transform the signals based on the sounds received in the ear by the inner microphone into sounds having essentially the characteristics of spoken sounds of the wearer of the ear terminal.
Owner:HONEYWELL HEARING TECH
Hearing system and method for operating a hearing system
ActiveUS20130142345A1Satisfactory performanceSatisfactory hearing performanceHearing aids signal processingSets with customised acoustic characteristicsTransducerAuditory system
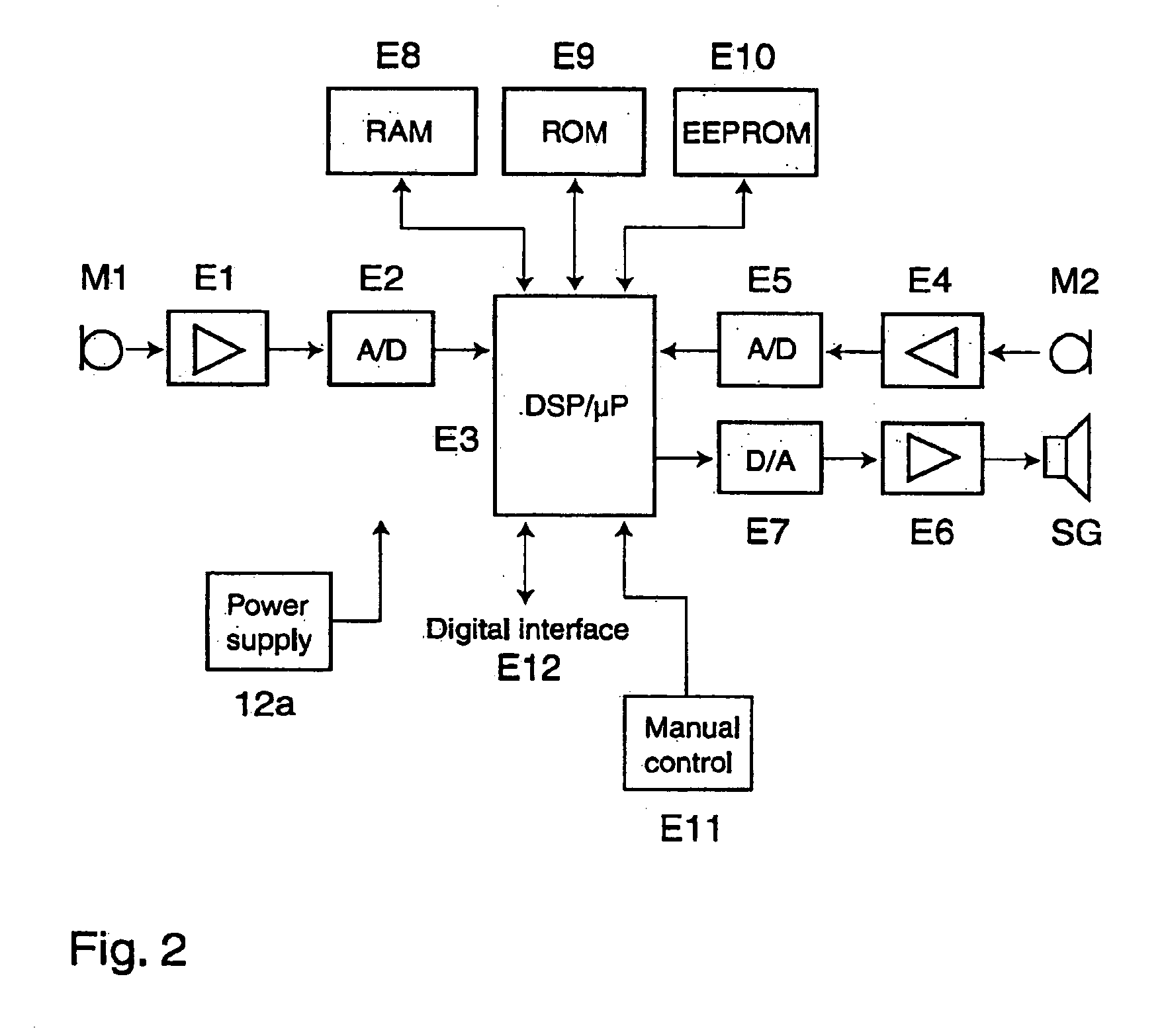
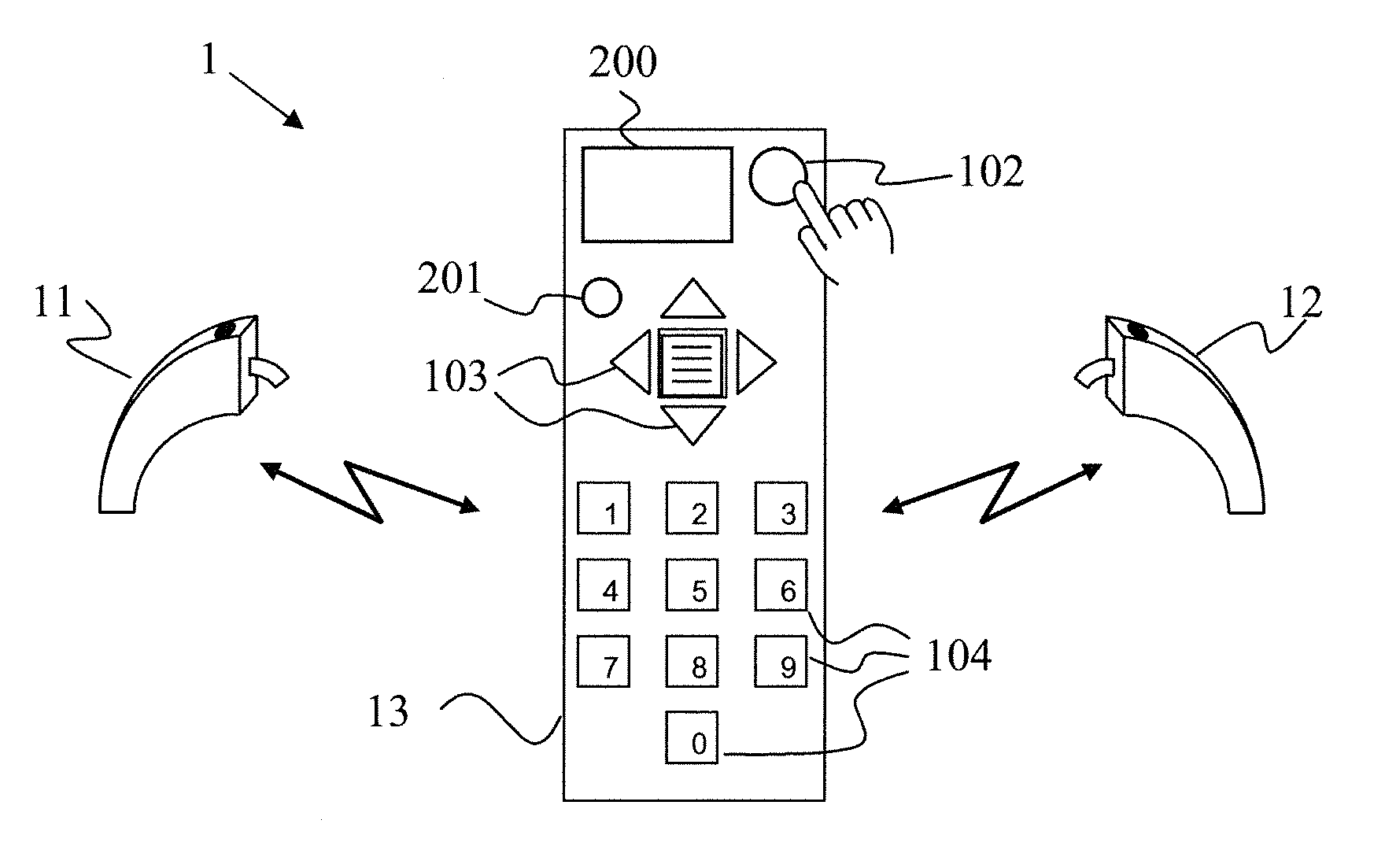
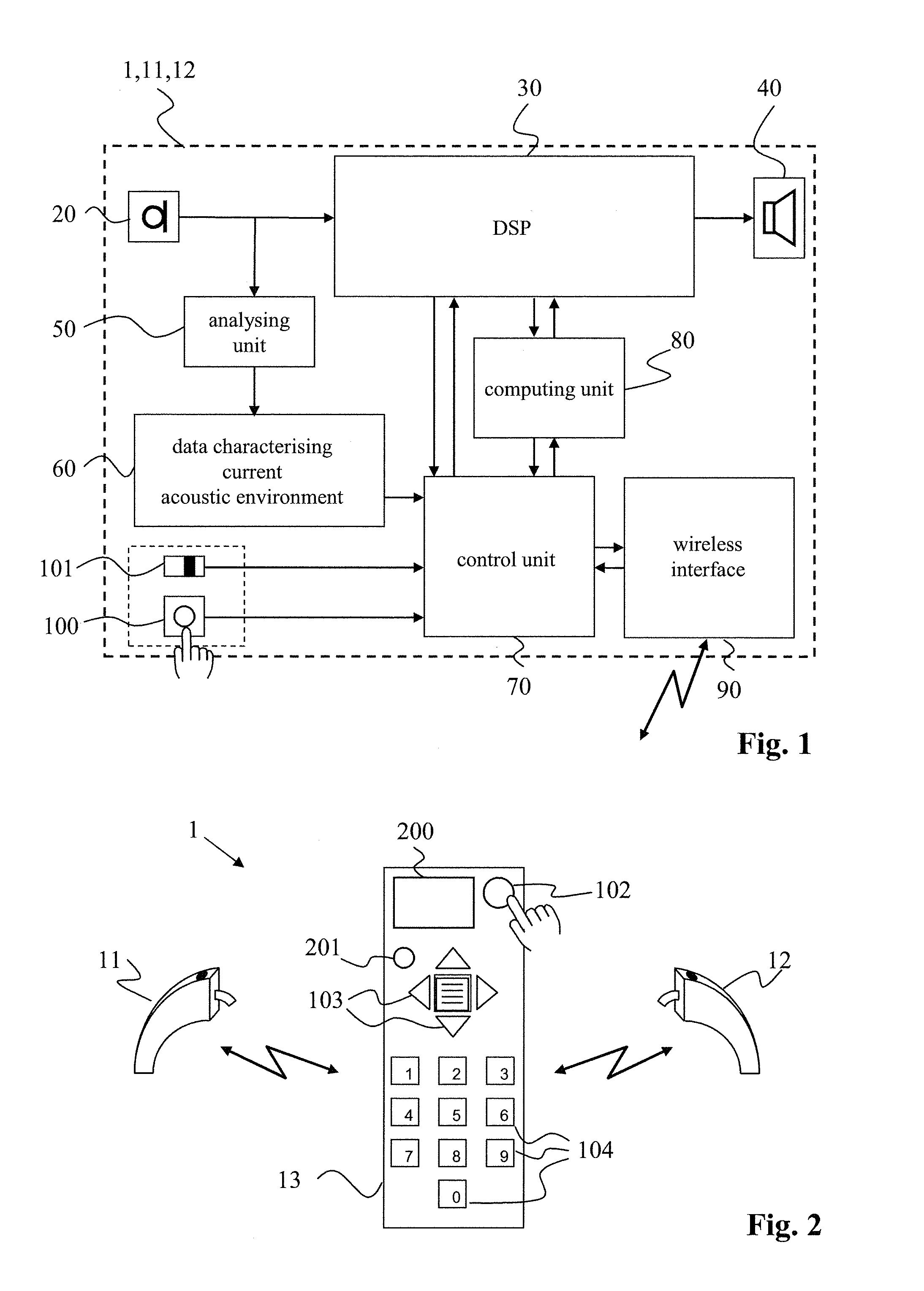
A hearing system (1) capable of assisting a user of the hearing system (1) to find a location where satisfactory hearing performance is achievable is described. The hearing system (1) comprises at least one hearing device (11, 12) with an input transducer (20), an output transducer (40), and a processing unit (30) operatively connected to the input transducer (20) as well as to the output transducer (40). The hearing system (1) further comprises a first means (50) for determining from a signal of the input transducer (20) at least one parameter (60) representative of a current acoustic environment at a current location, and a second means (40, 200, 201) for indicating to a user of the hearing system (1) a degree of suitability of the current location to achieve satisfactory hearing performance based on the at least one parameter (60).
Owner:SONOVA AG
Hearing aid and processes for adaptively processing signals therein
ActiveUS6912289B2Improve performancePromote activationMicrophonesHearing aids signal processingFrequency spectrumHearing aid
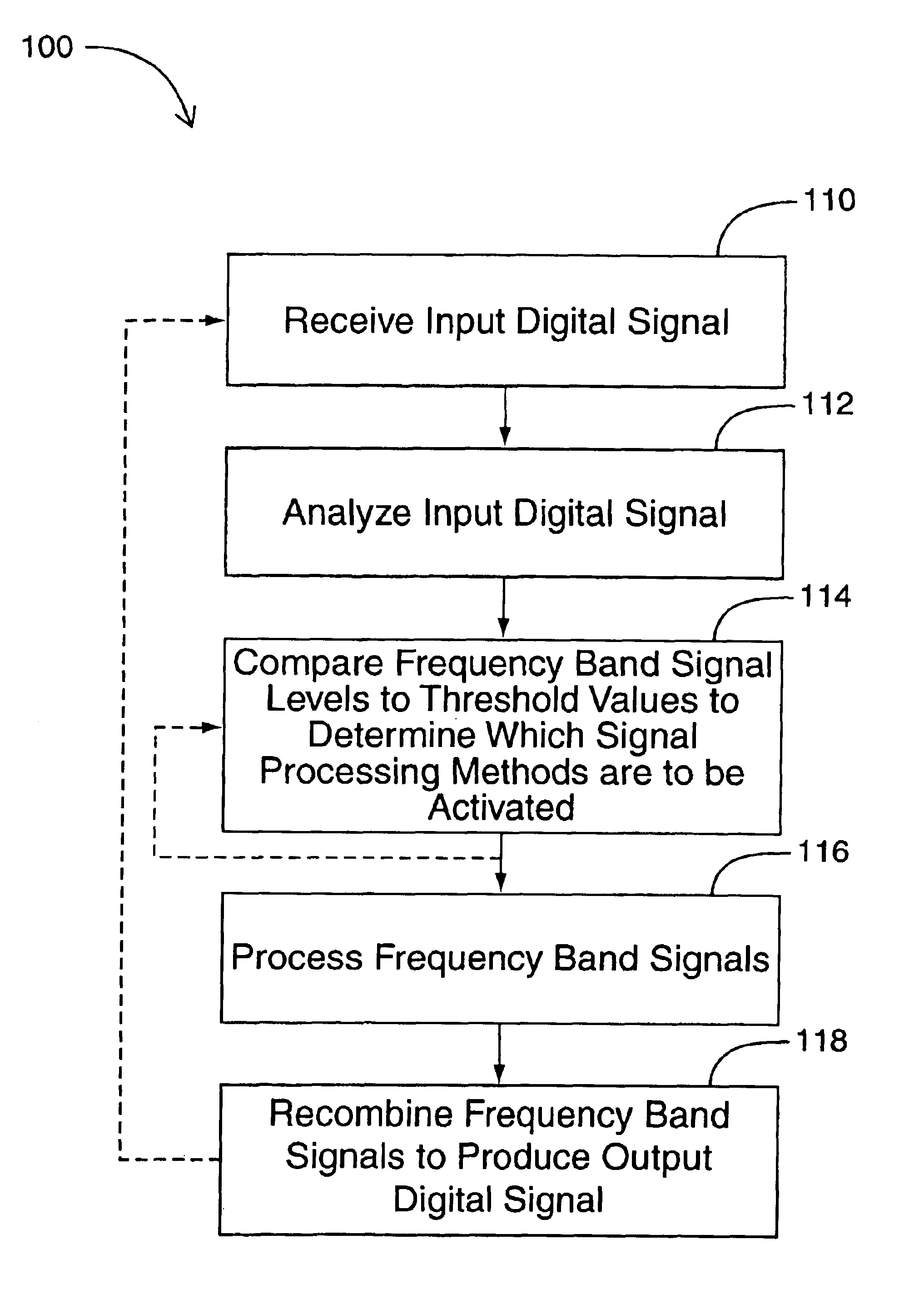
An improved hearing aid, and processes for adaptively processing signals therein to improve the perception of desired sounds by a user thereof. In one broad aspect, the present invention relates to a process in which one or more signal processing methods are applied to frequency band signals derived from an input digital signal. The level of each frequency band signal is computed and compared to at least one plurality of threshold values to determine which signal processing schemes are to be applied. In one embodiment of the invention, each plurality of threshold values to which levels of the frequency band signals are compared, is derived from a speech-shaped spectrum. Additional measures such as amplitude modulation or a signal index may also be employed and compared to corresponding threshold values in the determination.
Owner:UNITRON HEARING
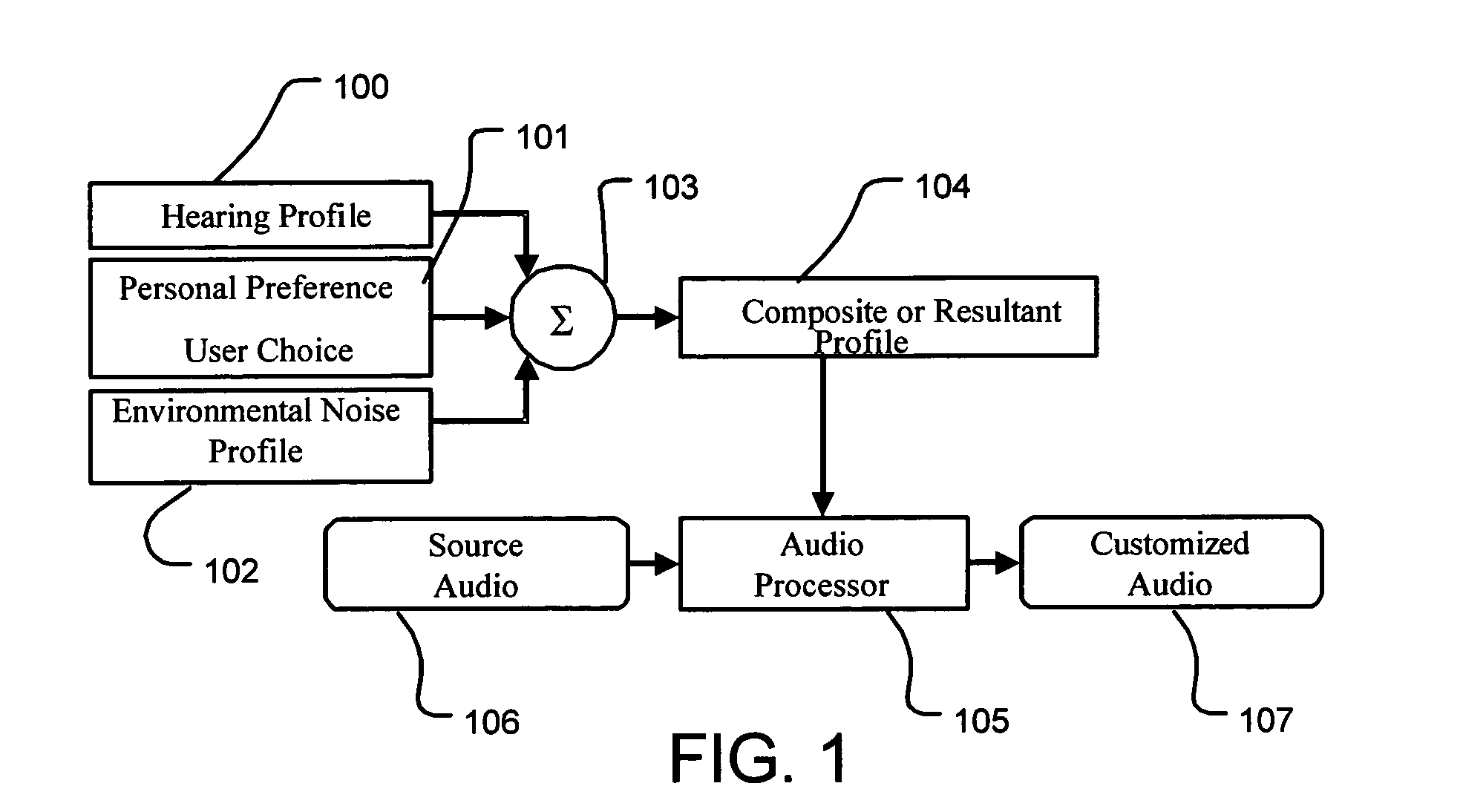
Sound enhancement for mobile phones and other products producing personalized audio for users
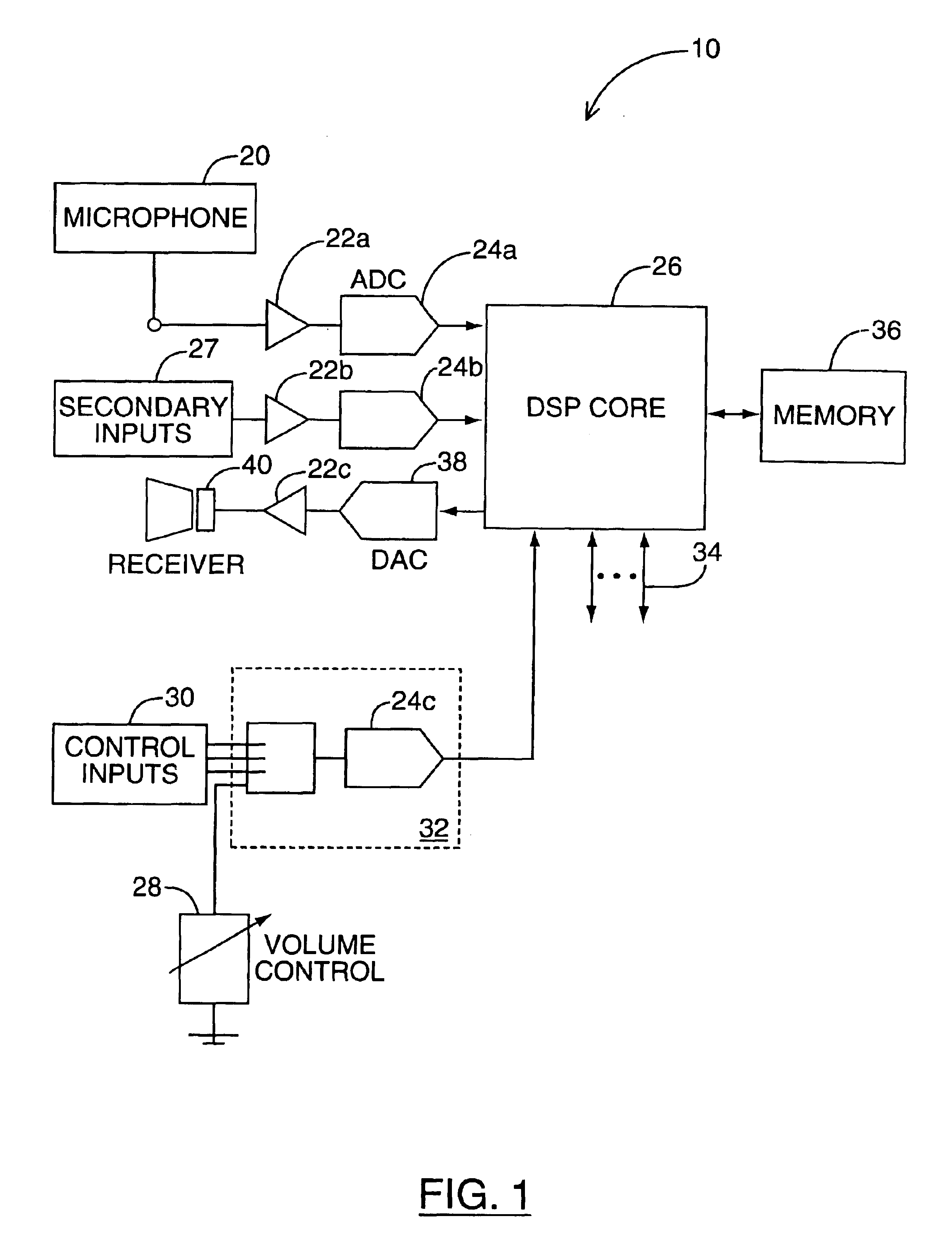
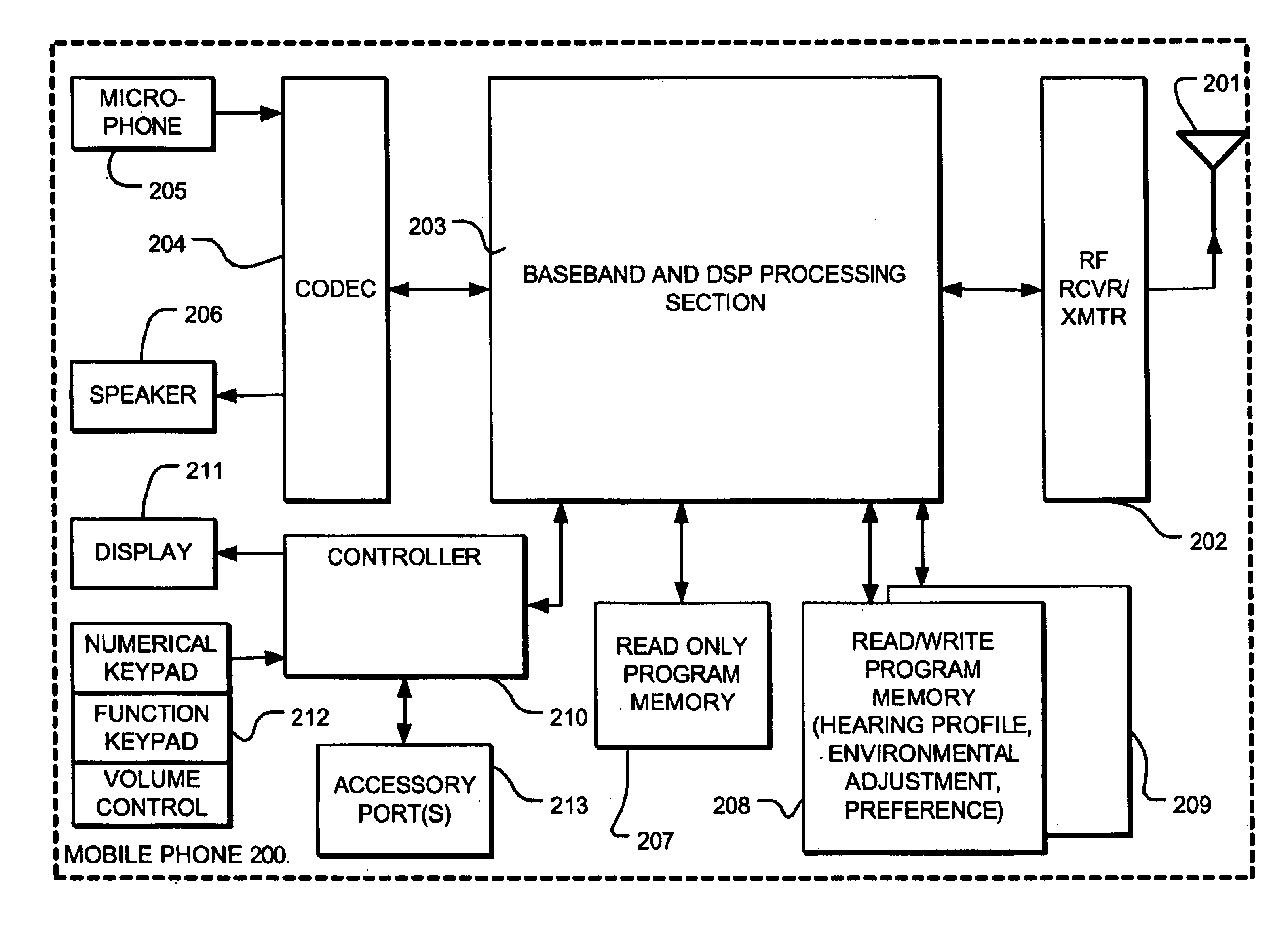
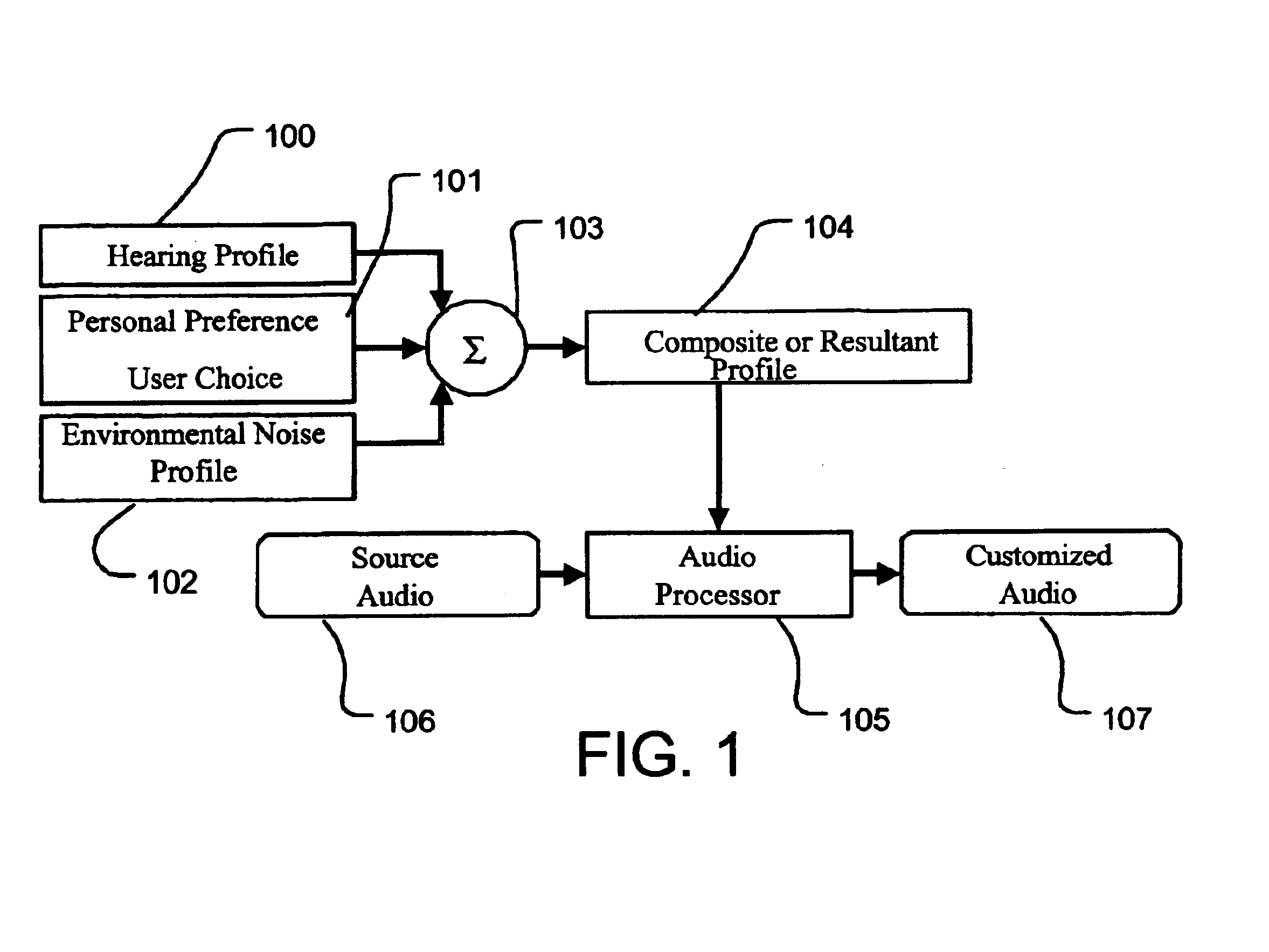
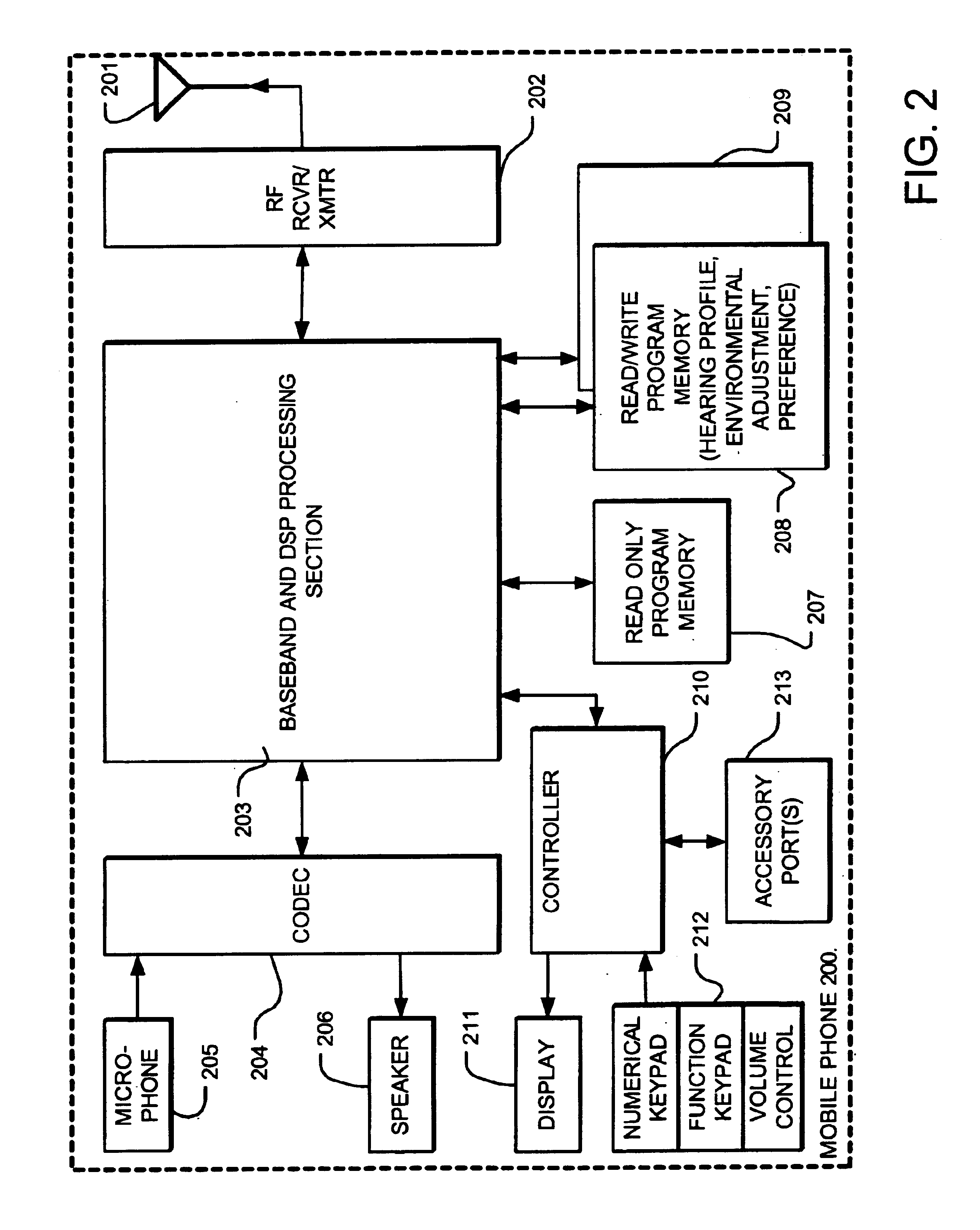
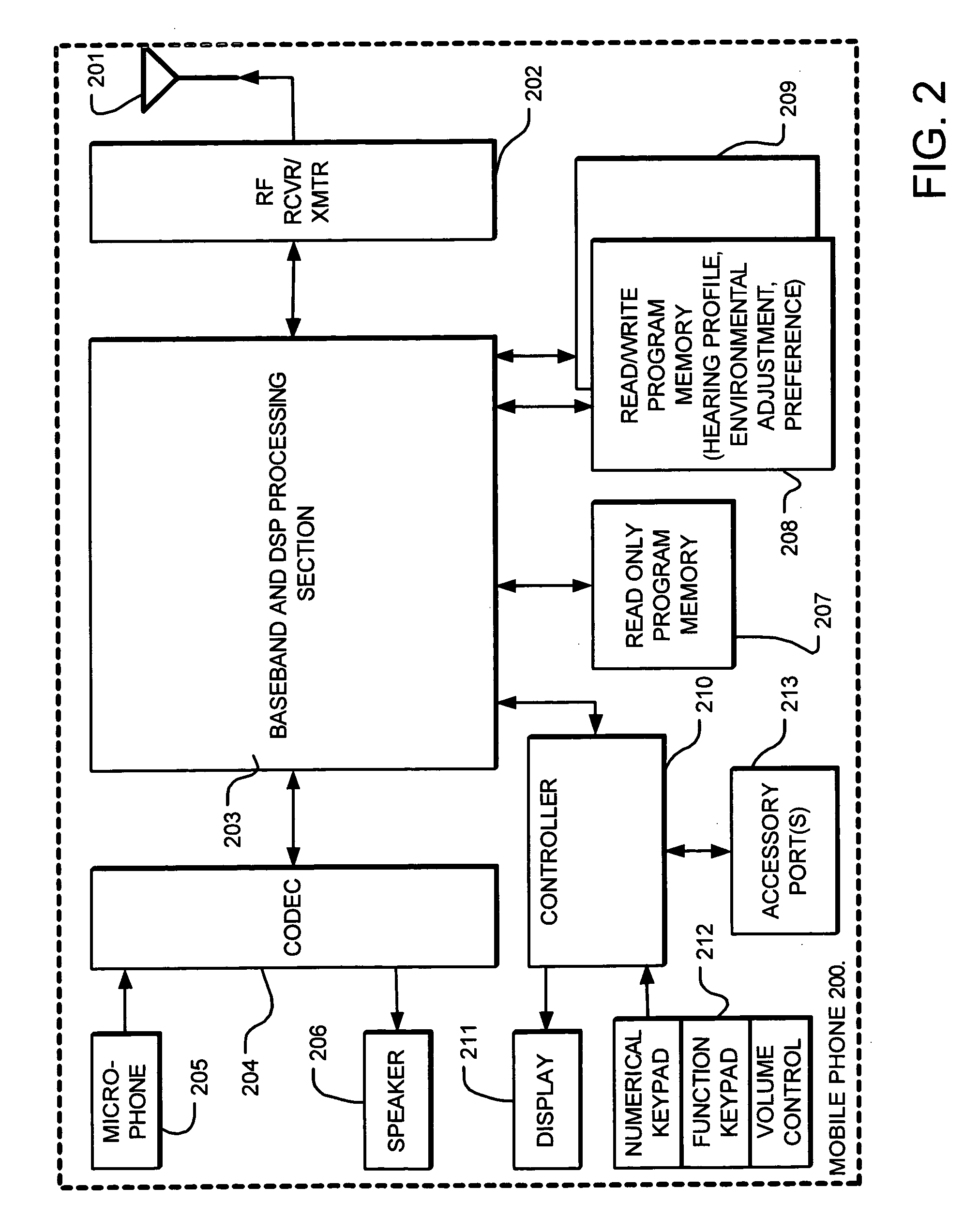
InactiveUS6944474B2Easy to receiveImprove soundStereophonic circuit arrangementsHearing impaired stereophonic signal reproductionInstruction memoryEnvironmental noise
A mobile phone or other personal communication device includes resources applying measures of an individual's hearing profile, personal choice profile, and induced hearing loss profile, separately or in combination, to build the basis of sound enhancement. A personal communication device thus comprises a transmitter / receiver coupled to a communication medium for transmitted receiving audio signals, control circuitry that controls transmission, reception and processing of call and audio signals, a speaker, and a microphone. The control circuitry includes logic applying one or more of a hearing profile of the user, a user preference related hearing, and environmental noise factors in processing the audio signals. The control circuitry may includes instruction memory and an instruction execution processor such as a digital signal processor.
Owner:HIMPP
Noise estimation for use with noise reduction and echo cancellation in personal communication
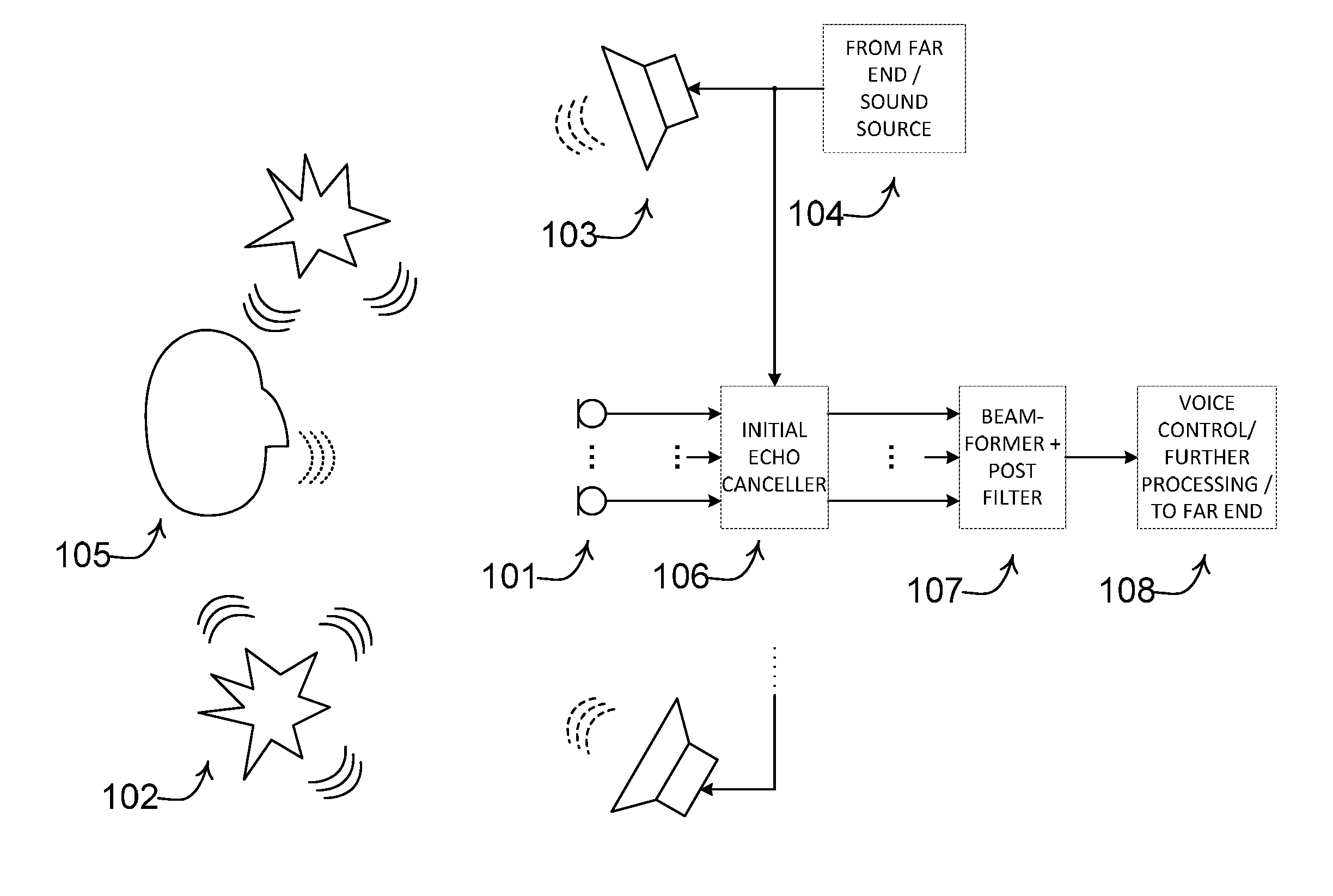
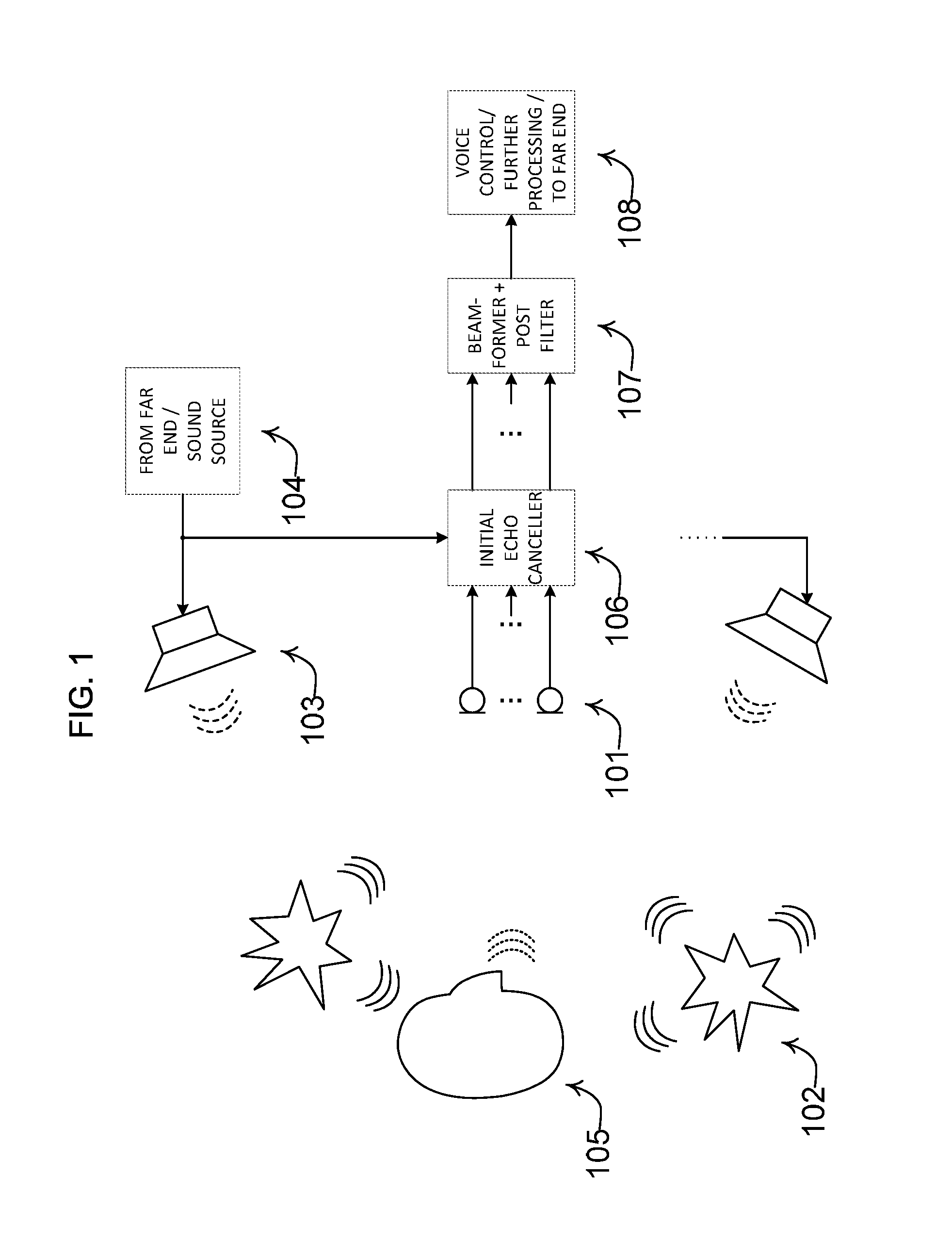
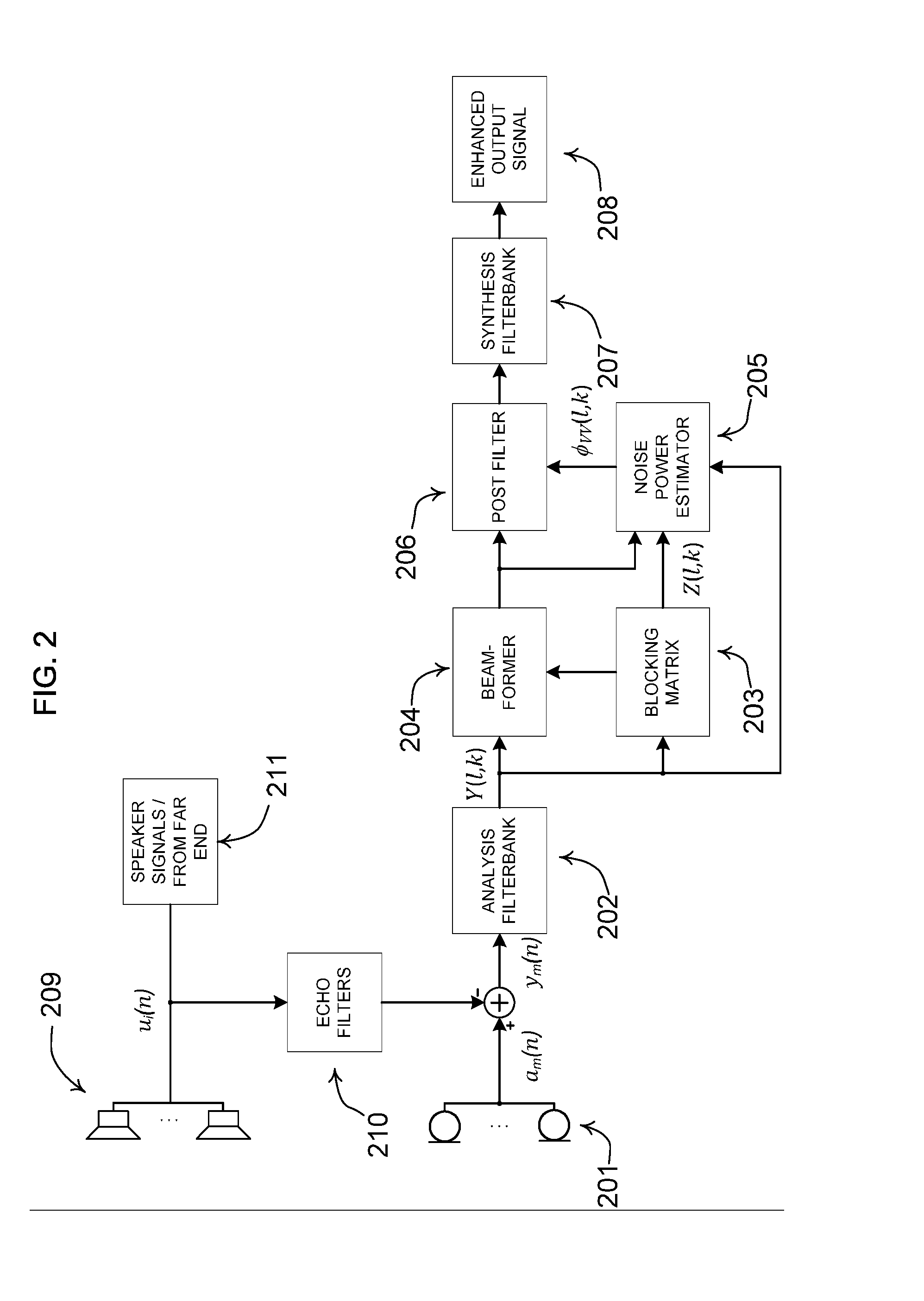
ActiveUS20140056435A1Improve recognition rateImprove sound qualityInterconnection arrangementsEar treatmentNoise correctionEngineering
A method comprises processing M subband communication signals and N target-cancelled signals in each subband with a set of beamformer coefficients to obtain an inverse target-cancelled covariance matrix of order N in each band; using a target absence signal to obtain an initial estimate of the noise power in a beamformer output signal averaged over recent frames with target absence in each subband; multiplying the initial noise estimate with a noise correction factor to obtain a refined estimate of the power of the beamformer output noise signal component in each subband; processing the refined estimate with the magnitude of the beamformer output to obtain a postfilter gain value in each subband; processing the beamformer output signal with the postfilter gain value to obtain a postfilter output signal in each subband; and processing the postfilter output subband signals to obtain an enhanced beamformed output signal.
Owner:OTICON
Method for dynamic suppression of surrounding acoustic noise when listening to electrical inputs
ActiveUS20110137649A1Improved listening comfortAccurate monitoringHearing device active noise cancellationHearing aids signal processingElectricityEngineering
A listening instrument includes a) a microphone unit for picking up an input sound from the current acoustic environment of the user and converting it to an electric microphone signal; b) a microphone gain unit for applying a specific microphone gain to the microphone signal and providing a modified microphone signal; c) a direct electric input signal representing an audio signal; d) a direct gain unit for applying a specific direct gain to the direct electric input signal and providing a modified direct electric input signal; e) a detector unit for classifying the current acoustic environment and providing one or more classification parameters; f) a control unit for controlling the specific microphone gain applied to the electric microphone signal and / or the specific direct gain applied to the direct electric input signal based on the one or more classification parameters.
Owner:OTICON
Sound enhancement for hearing-impaired listeners
InactiveUS20070127748A1Enhance spectral cuesSpeech analysisHearing aids signal processingFrequency spectrumSpeech sound
A method of enhancing sound heard by a hearing-impaired listener comprises monitoring the sound in an environment in which the listener is located; and manipulating the frequency of high frequency components of the sound in a high frequency band, with little, if any, distortion to components of the sound in a speech frequency band, to enhance spectral cues to aid the listener in sound externalisation and spatialisation.
Owner:VAST AUDIO PTY LTD
System for rehabilitation of a hearing disorder
InactiveUS7376563B2Improve understandingAdverse effectElectrotherapyElectric tinnitus maskersEngineeringHearing perception
A system for rehabilitation of a hearing disorder which comprises at least one acoustic sensor for picking up an acoustic signal and converting it into an electrical audio signal, an electronic signal processing unit for audio signal processing and amplification, an electrical power supply unit which supplies individual components of the system with current, and an actuator arrangement which is provided with one or more electroacoustic, electromechanical or purely electrical output-side actuators or any combination of these actuators for stimulation of damaged hearing, wherein the signal processing unit has a speech analysis and recognition module and a speech synthesis module.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
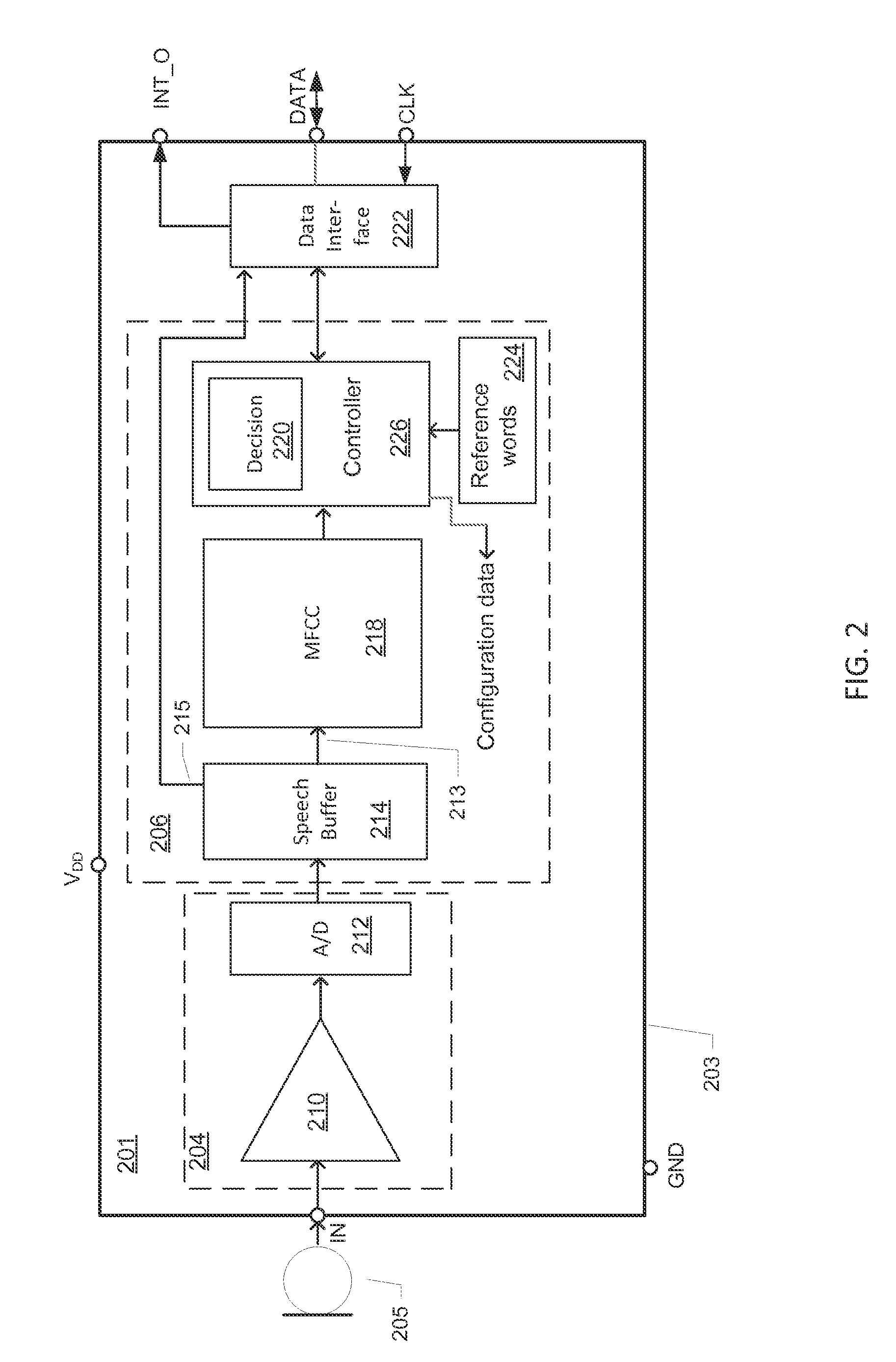
Microphone circuit assembly and system with speech recognition
ActiveUS20140257813A1Reduce consumptionReduce loadHearing aids signal processingSpeech recognitionAnalog-to-digital converterApplication processor
A microphone circuit assembly for an external application processor, such as a programmable Digital Signal Processor, may include a microphone preamplifier and analog-to-digital converter to generate microphone signal samples at a first predetermined sample rate. A speech feature extractor is configured for receipt and processing of predetermined blocks of the microphone signal samples to extract speech feature vectors representing speech features of the microphone signal samples. The microphone circuit assembly may include a speech vocabulary comprising a target word or target phrase of human speech encoded as a set of target feature vectors and a decision circuit is configured to compare the speech feature vectors generated by the speech feature extractor with the target feature vectors to detect the target speech word or phrase.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INT UNLTD
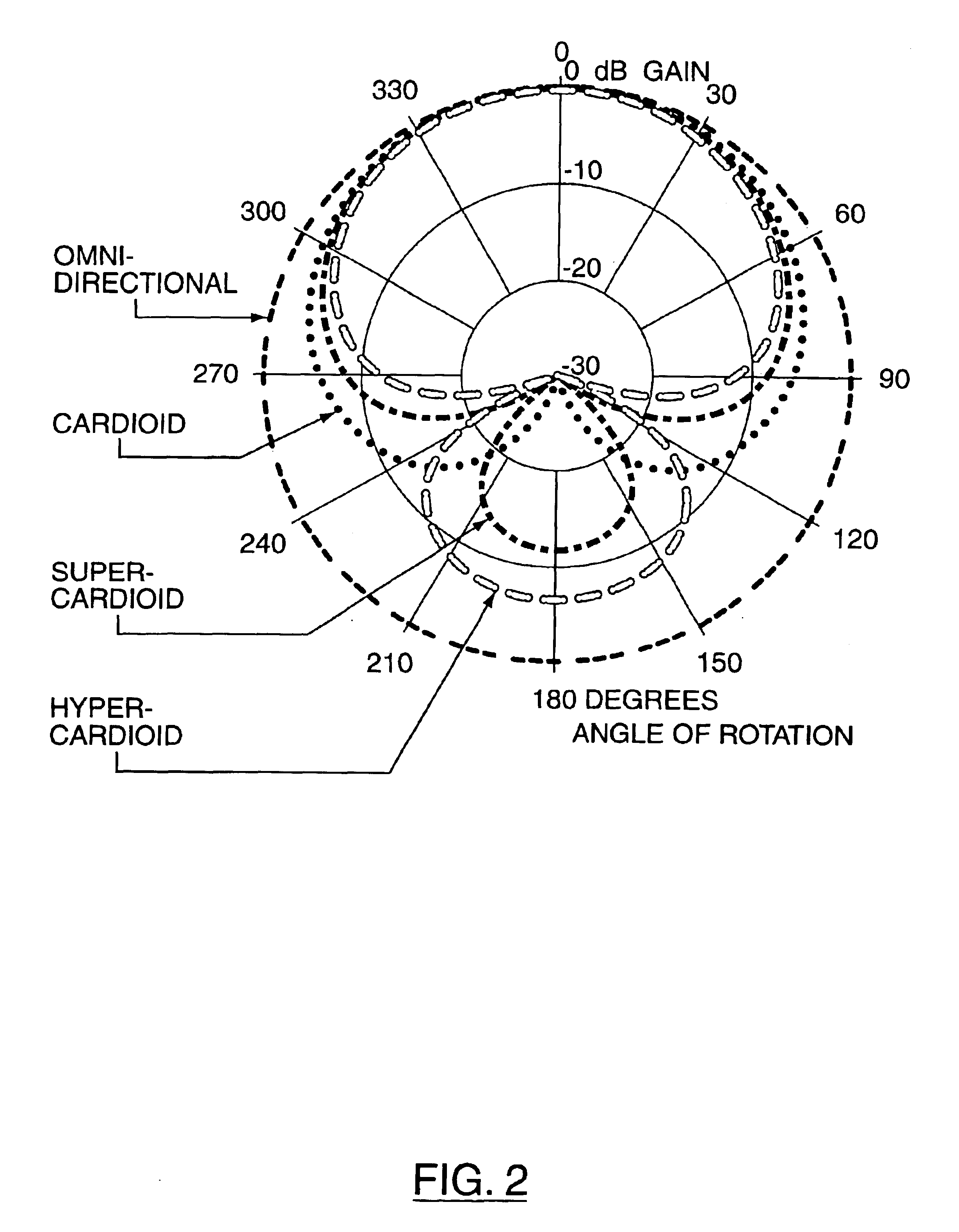
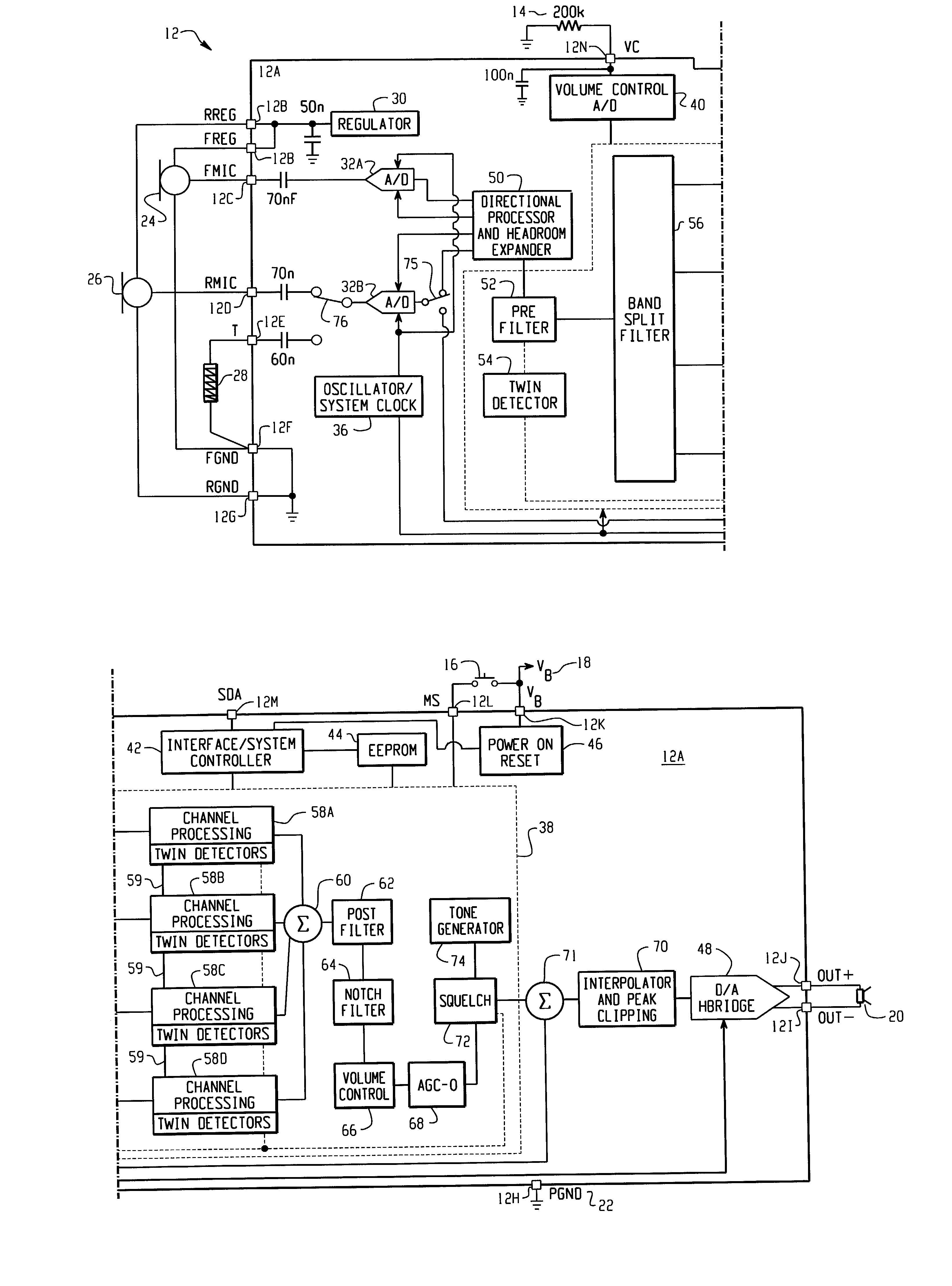
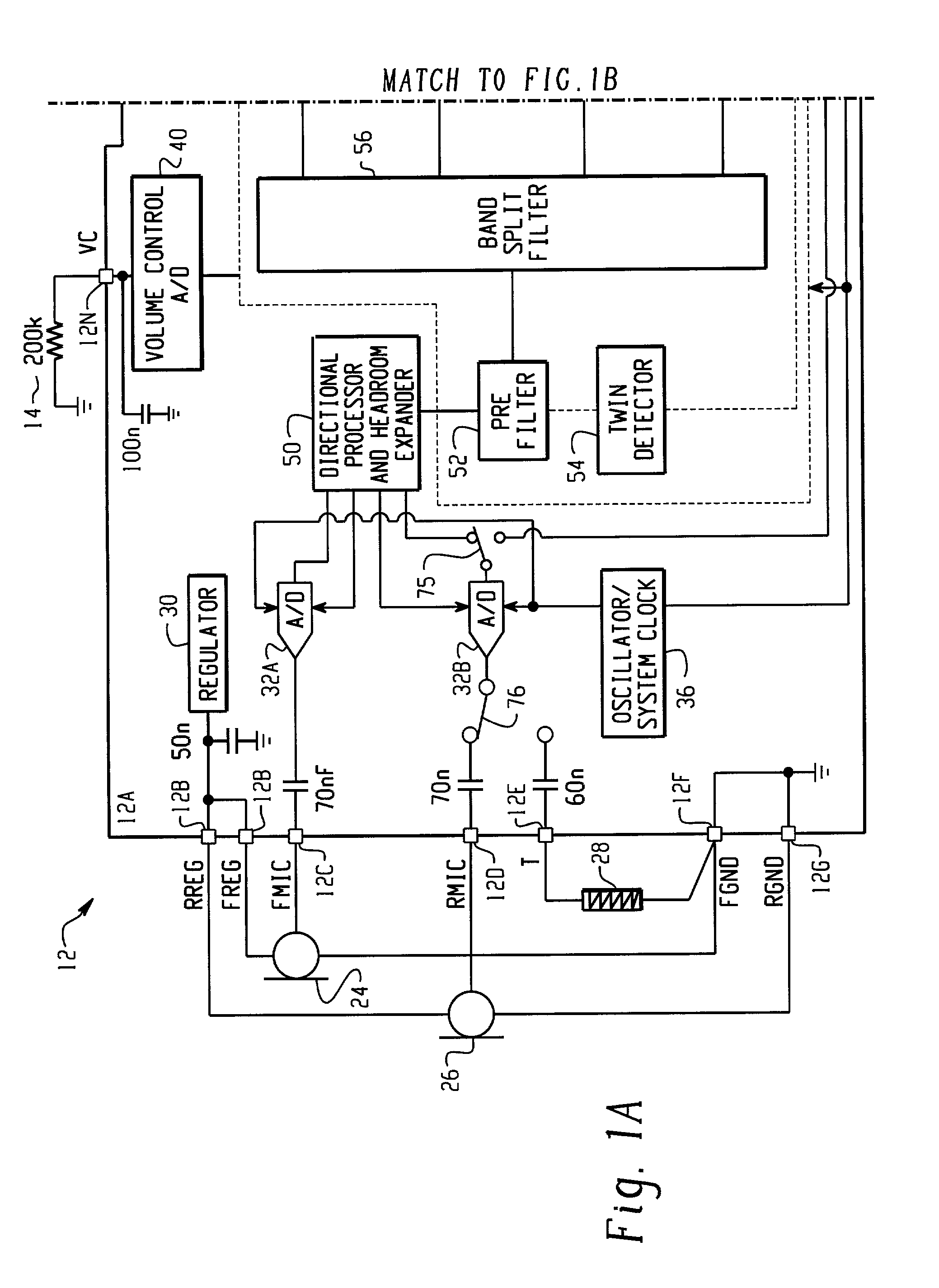
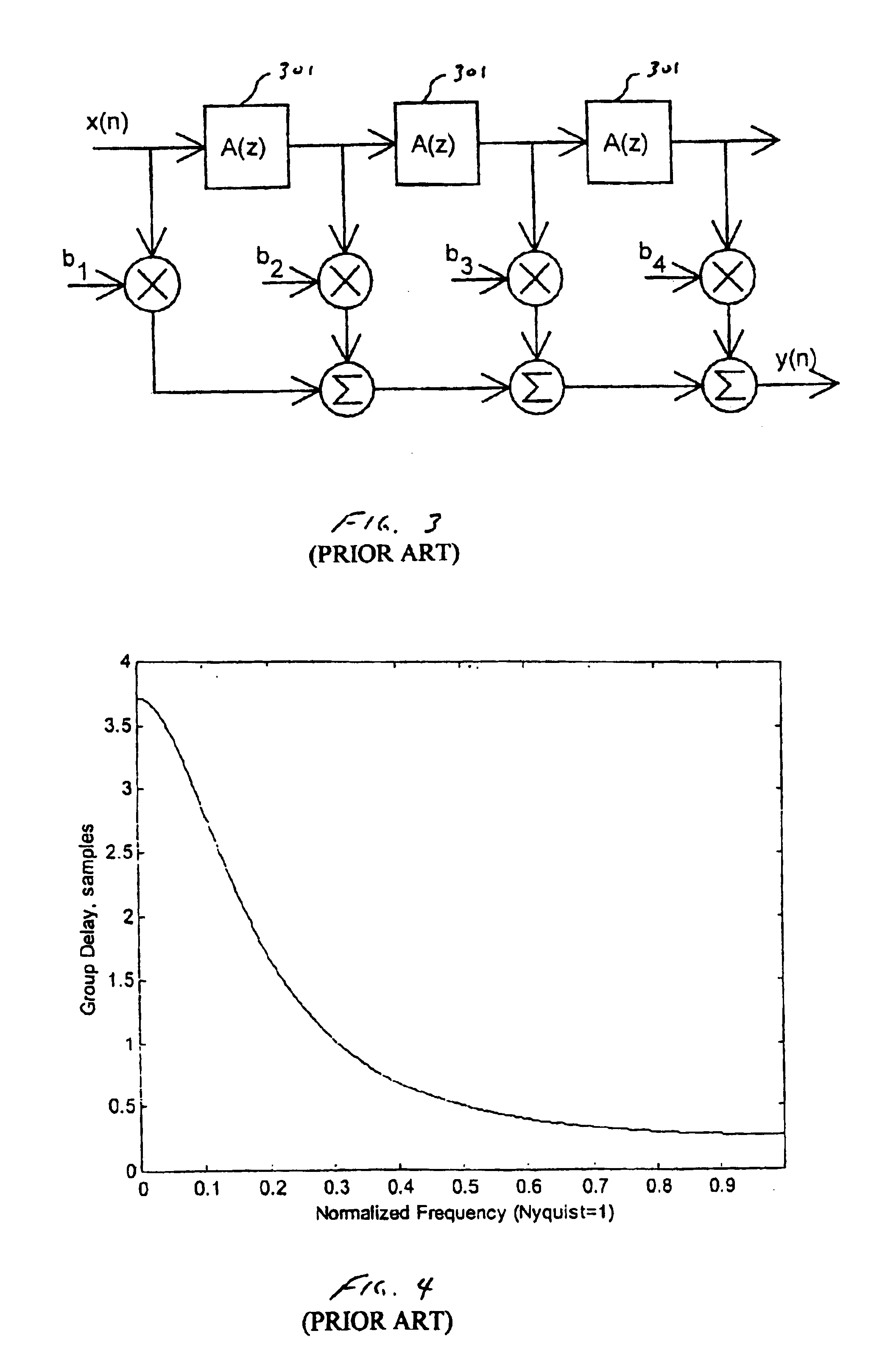
Method for controlling the directionality of the sound receiving characteristic of a hearing aid and a signal processing apparatus
ActiveUS20060177079A1Minimize output signalMinimize microphone noiseDoor/window protective devicesCurtain accessoriesSignal analyzerEngineering
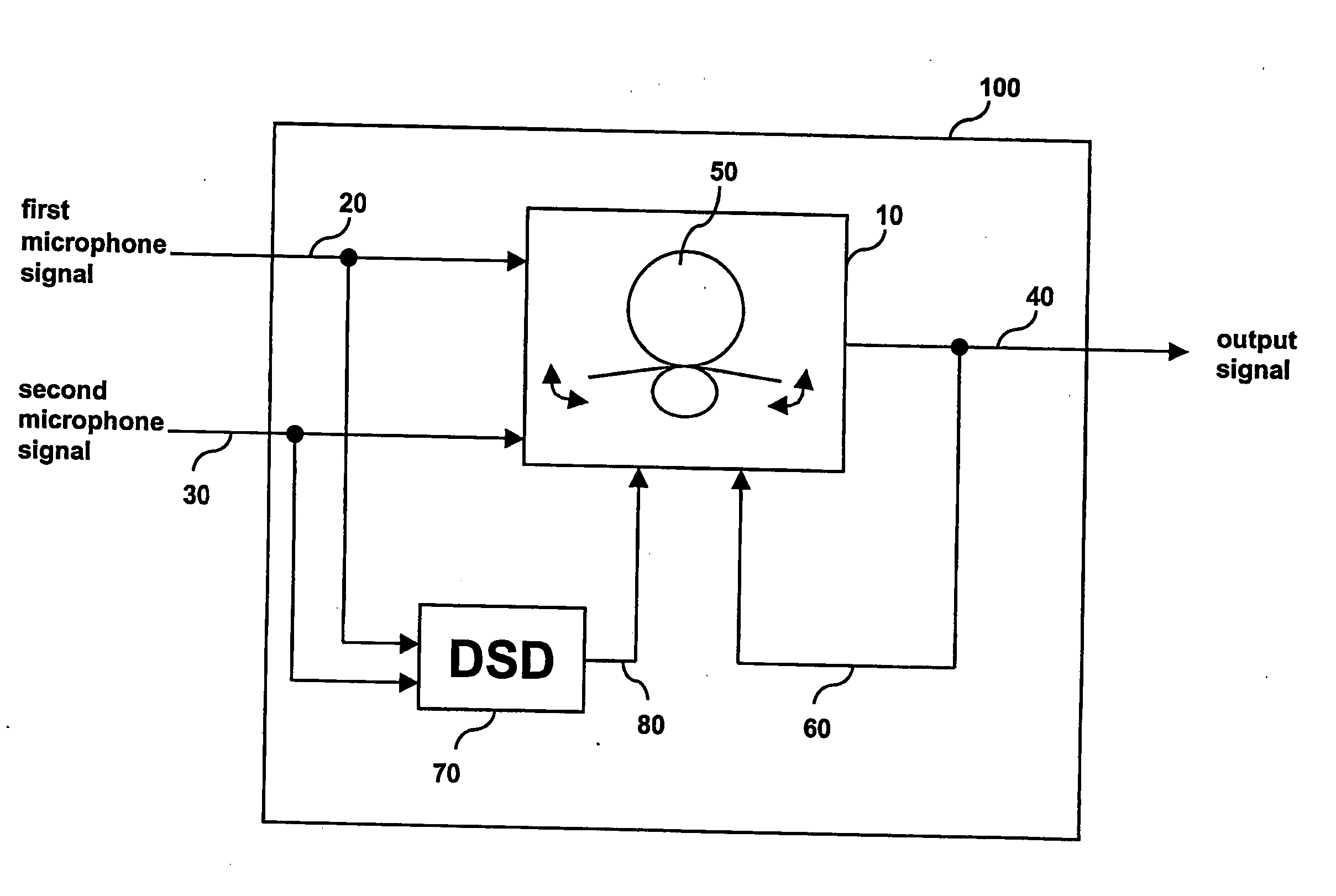
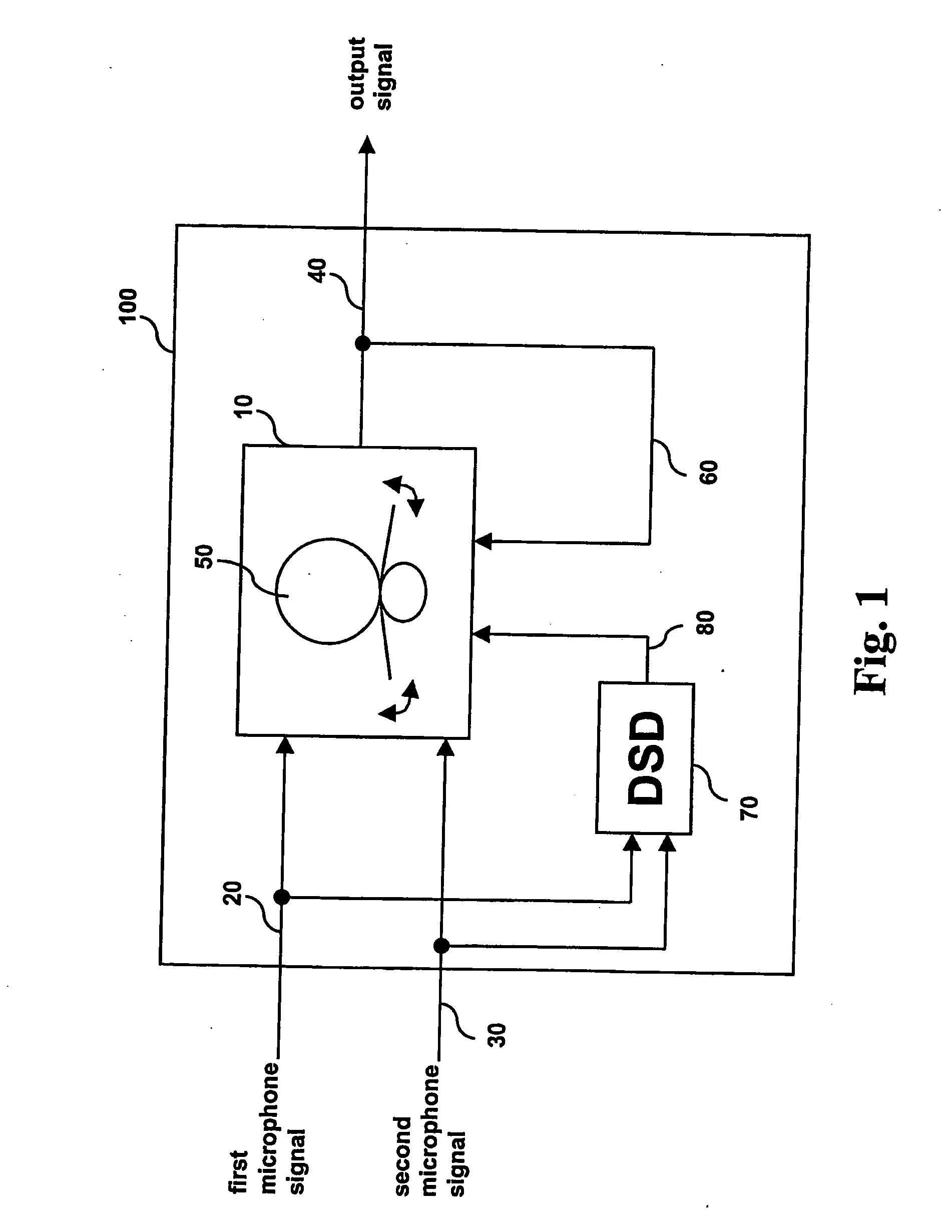
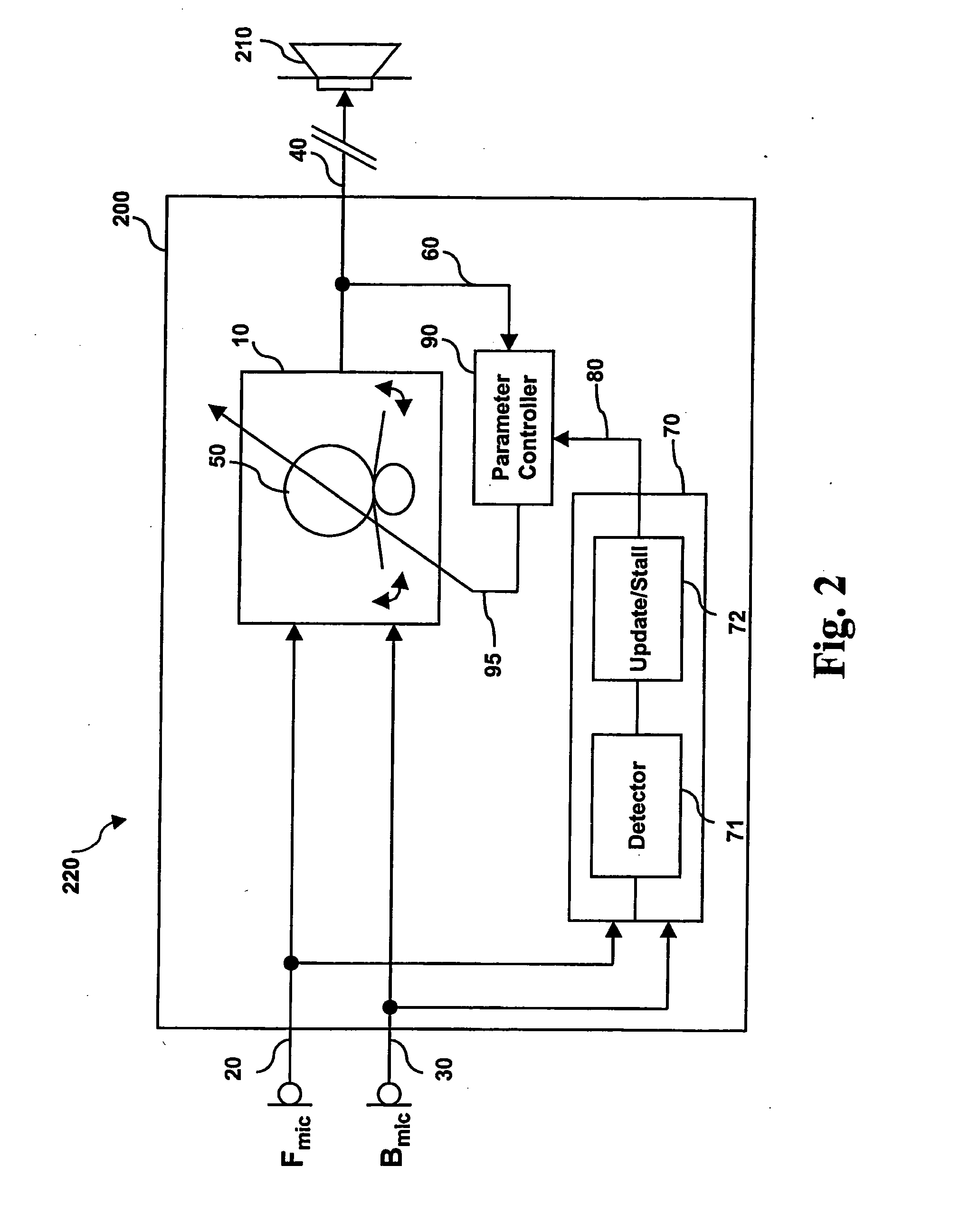
A signal processing apparatus (100) for a hearing aid with a controllable directional characteristic is provided which comprises a directional controller (10) receiving first and second microphone signals (20, 30) and output an output signal (40), a signal analyzer (70) which detects whether at least one of said first and second microphone signals being undesired signals, and wherein said directional controller minimizes the output signal by adjusting the directional characteristic only if the signal analyzer has detected undesired signals.
Owner:WIDEX AS
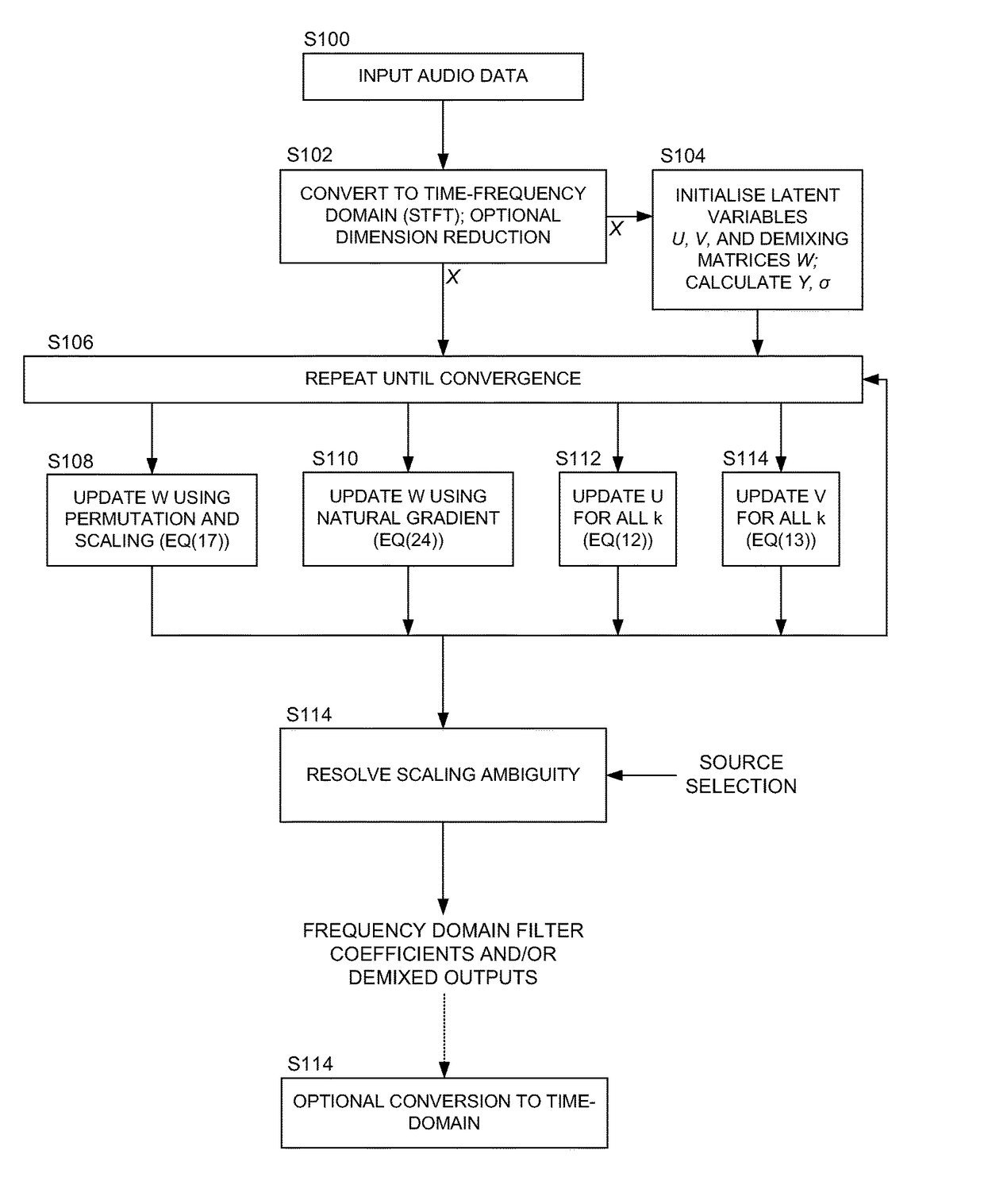
Method and apparatus for demixing of degenerate mixtures
InactiveUS6430528B1Reduce environmental noiseAccurately determineDigital computer detailsHearing aids signal processingChannel parameterTime windows
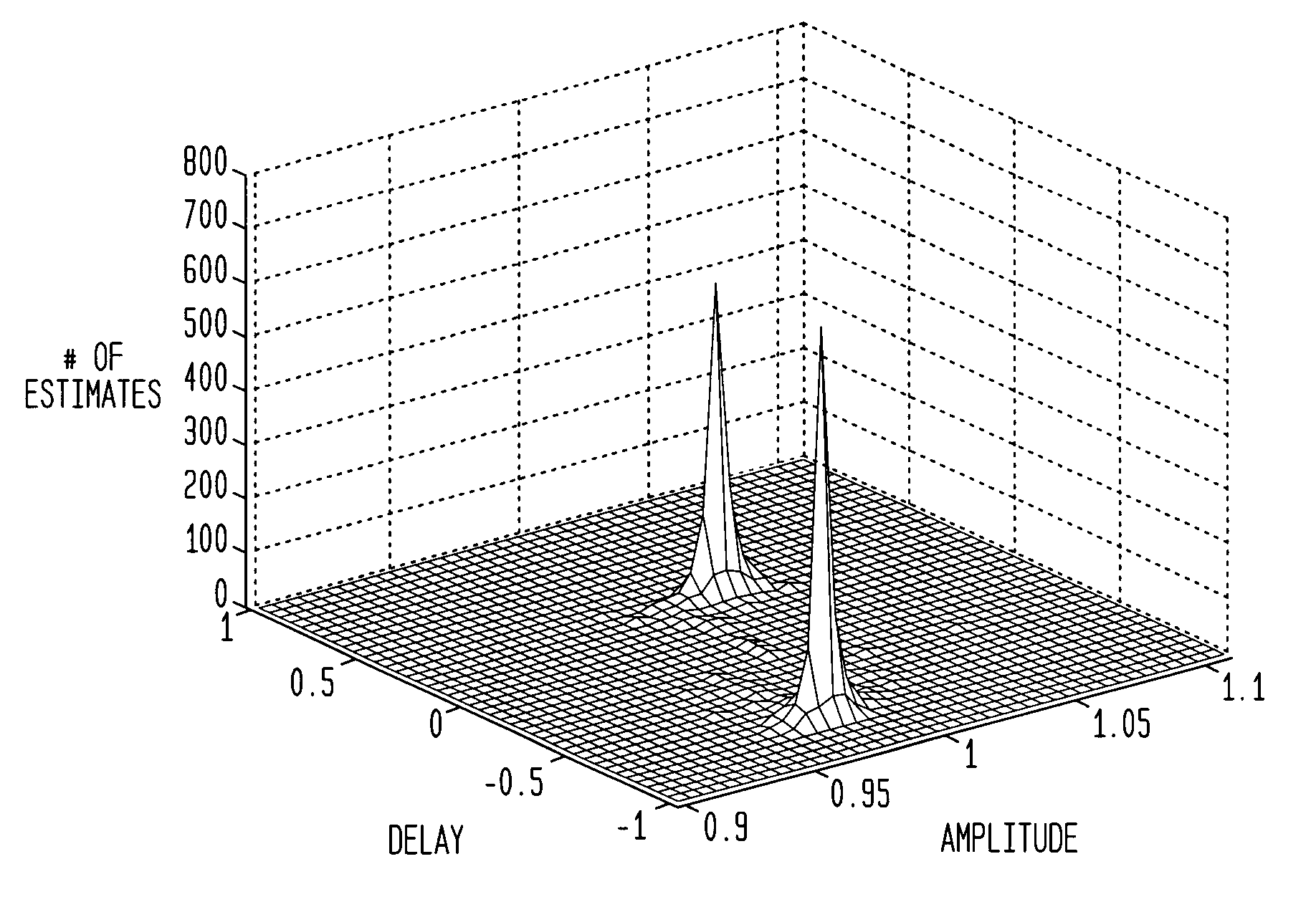
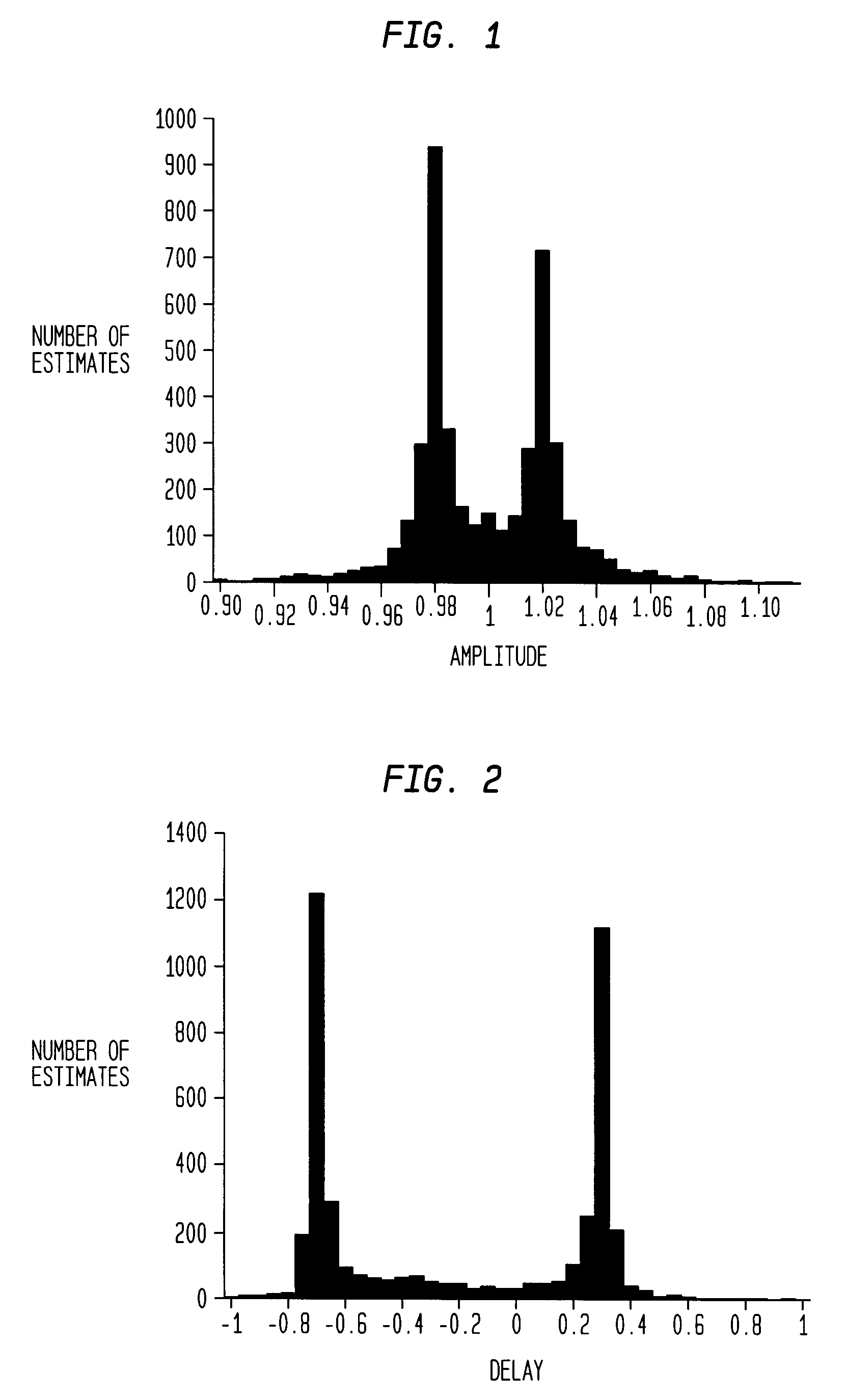
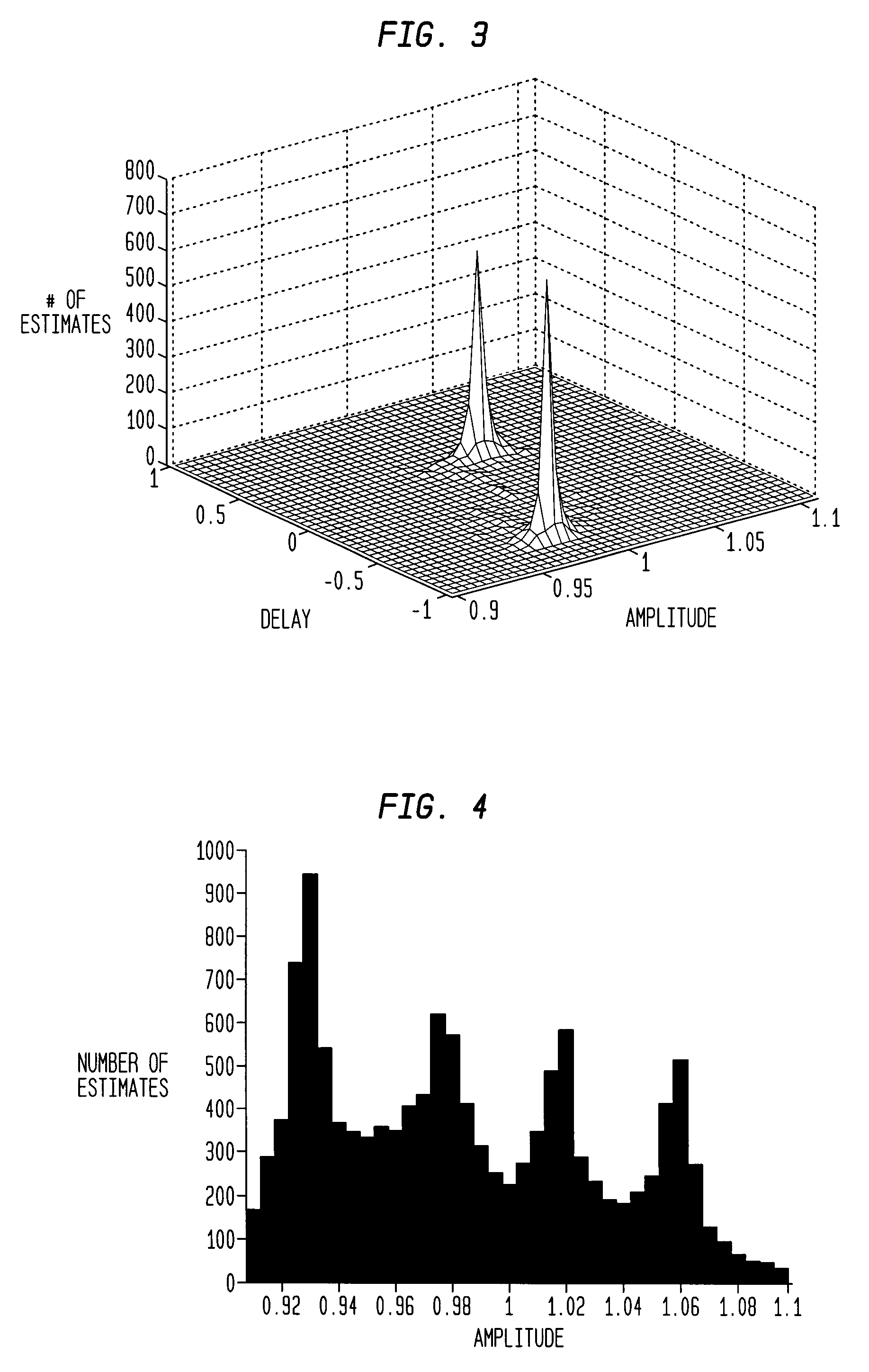
A method and system for blind channel estimation comprises acquiring two mixtures of at least one at least weakly W-disjoint orthogonal source signal, calculating point-by-point ratios of a transform of a time-window of each of said mixture signals, determining channel parameter estimates from said ratios, constructing a histogram of said channel parameter estimates, repeating the calculating, determining and constructing steps for successive time windows of the mixture signals, and selecting as estimates of said channel parameters those estimates associated with identified peaks on said histogram.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP
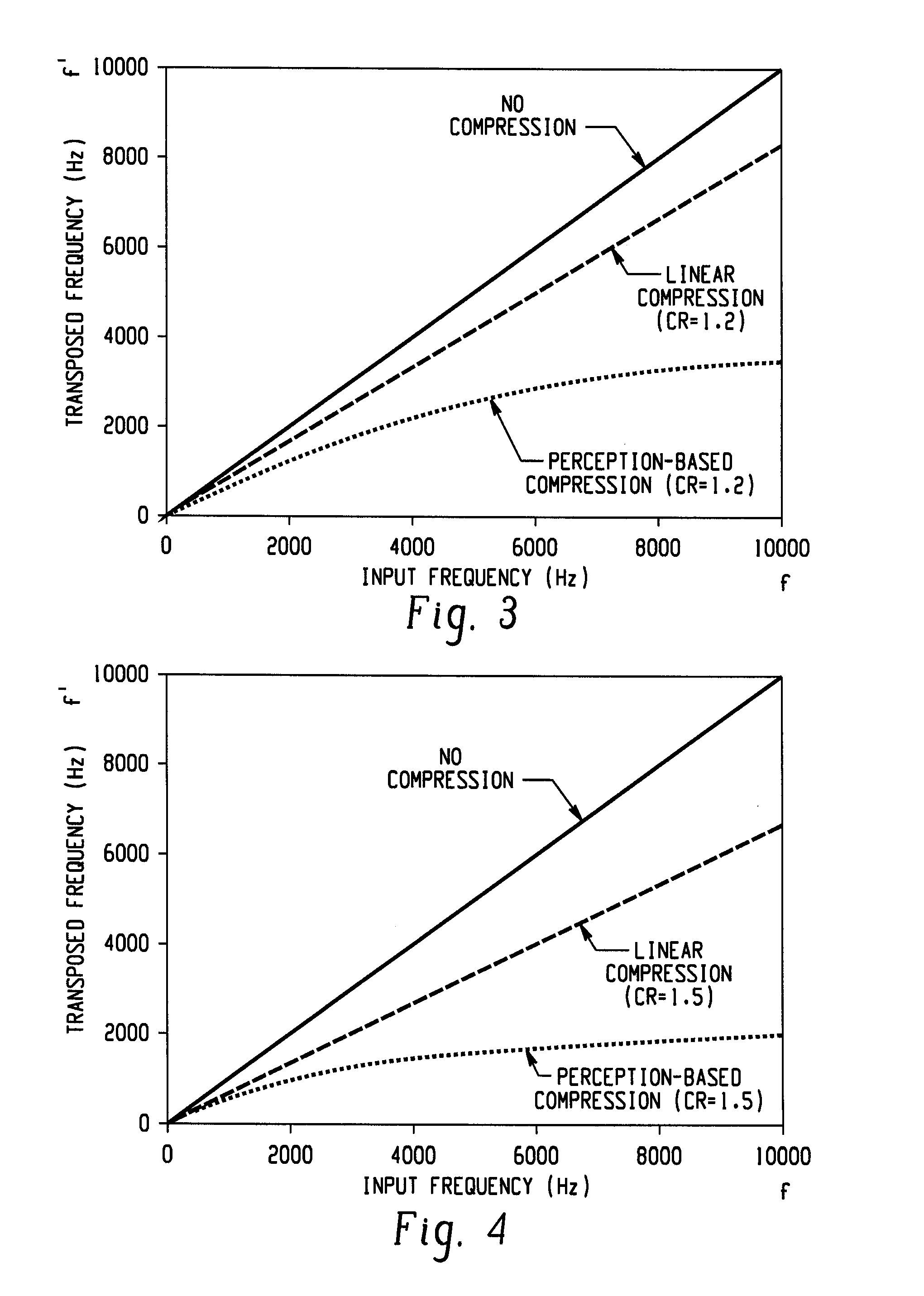
Method for frequency transposition and use of the method in a hearing device and a communication device
InactiveUS7248711B2Frequency efficiencyImprove transmission qualityHearing aids signal processingFrequency spectrumHearing apparatus
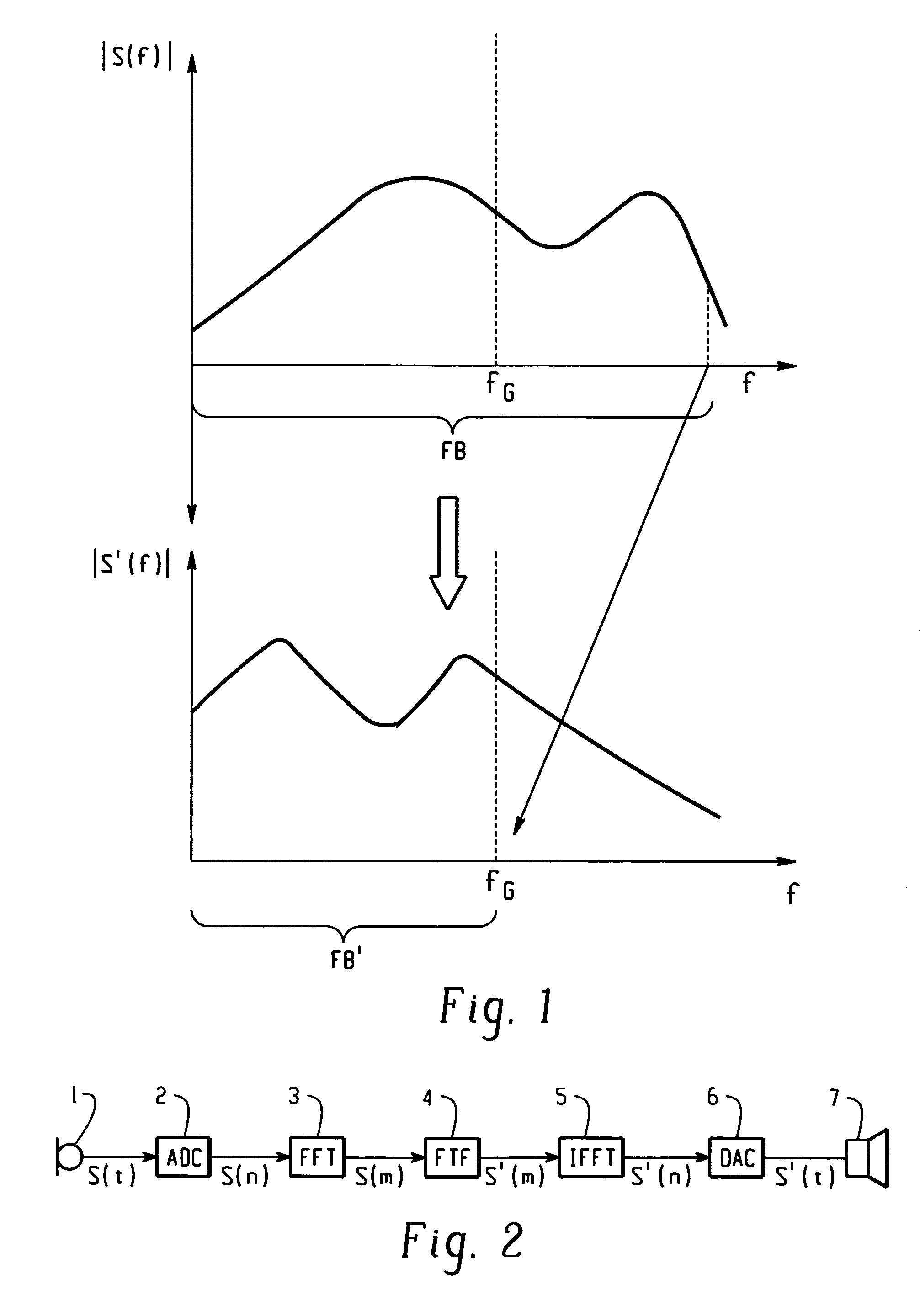
A method for frequency transposition in a communication device Or a hearing device, respectively, is disclosed by transforming an acoustical signal into an electrical signal (s) and by transforming the electrical signal from time domain into frequency domain to obtain a spectrum (S). A frequency transposition is being applied to the spectrum (S) in order to obtain a transposed spectrum (S′), whereby the frequency transposition is being defined by a nonlinear frequency transposition function. Thereby, it is possible to transpose lower frequencies almost linearly, while higher frequencies are transposed more strongly. As a result thereof, harmonic relationships are not distorted in the lower frequency range, and at the same time, higher frequencies can be moved to a lower frequency range, namely to an audible frequency range of the hearing impaired person. The transposition scheme can be applied to the complete signal spectrum without the need for switching between non-transposition and transposition processing for different parts of the signal. Therefore, no artifacts due to switching are encountered. A higher transmission quality is obtained because more information is taken into account for the transmission.
Owner:SONOVA AG
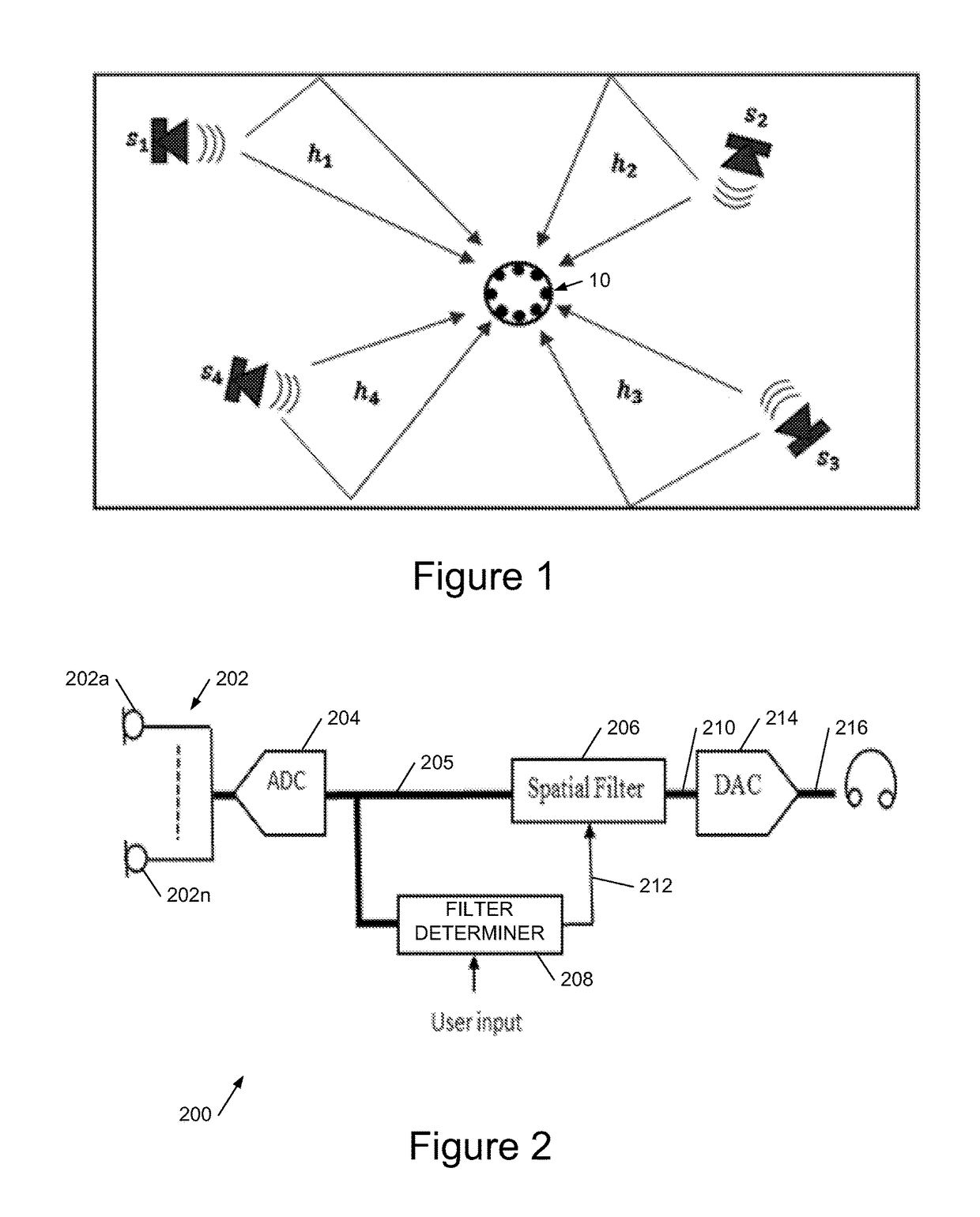
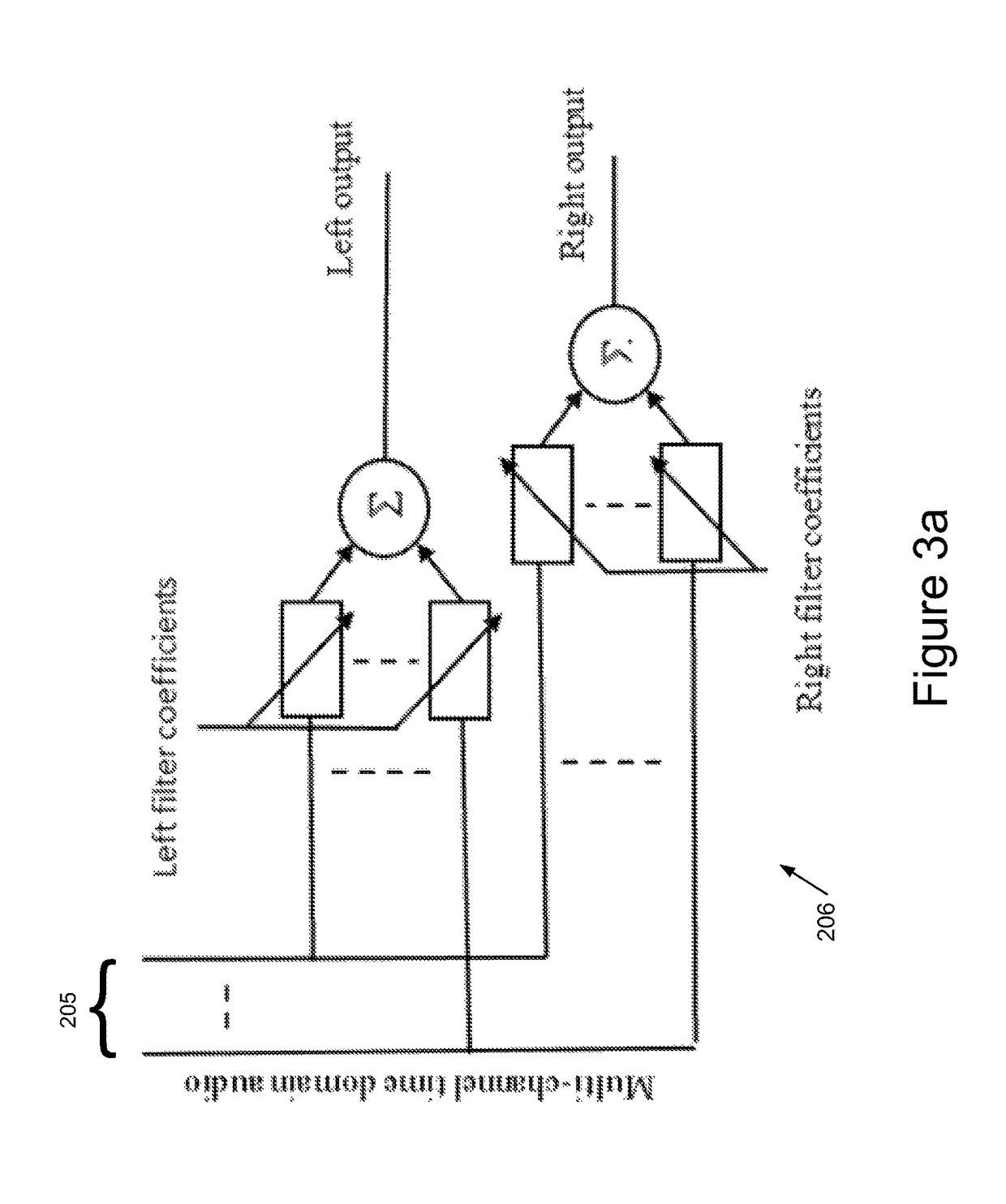
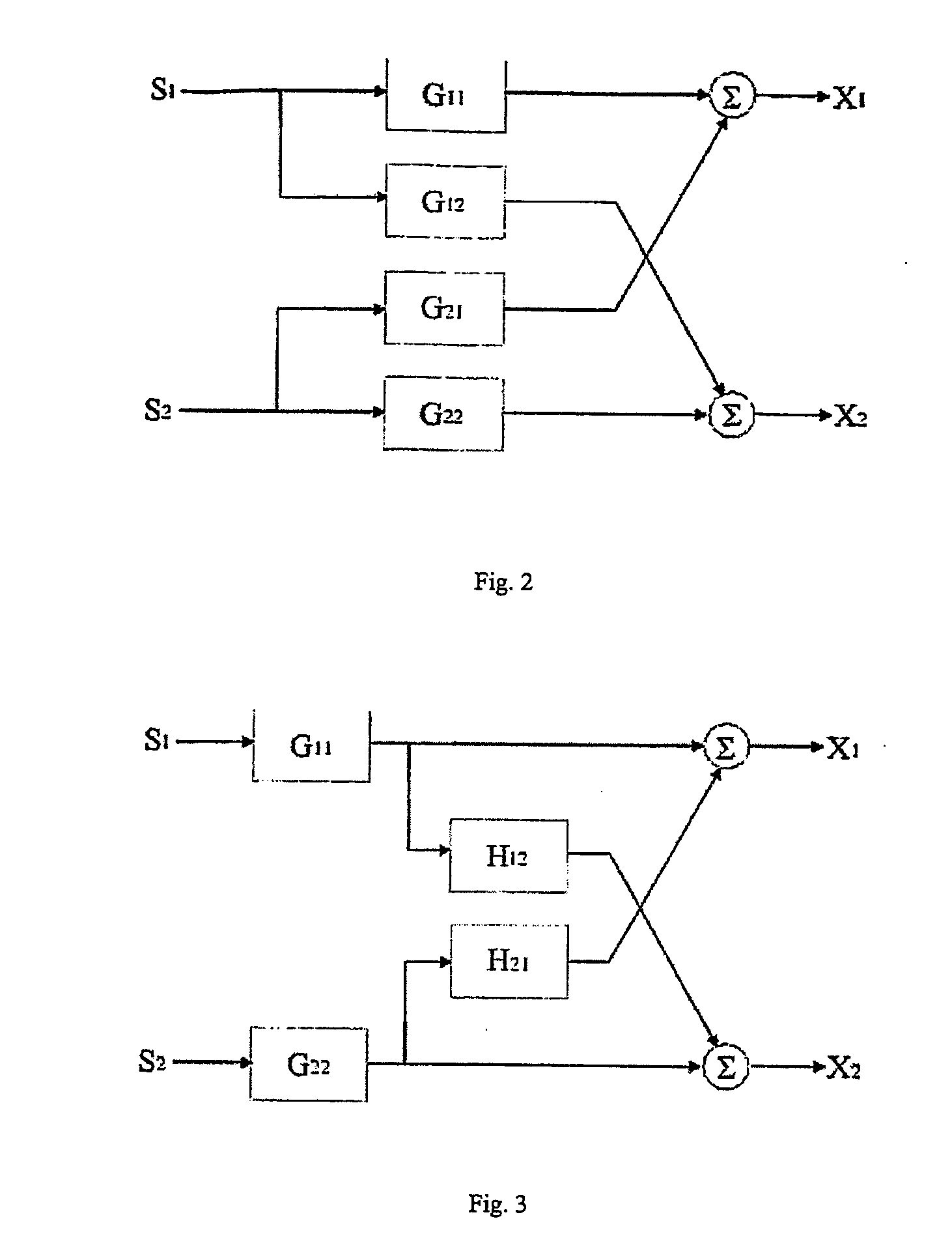
Blind source separation systems
ActiveUS9668066B1Cost for rotationSave spaceSignal processingSets with desired directivityFrequency spectrumHearing aid
We describe a method of blind source separation for use, for example, in a listening or hearing aid. The method processes input data from multiple microphones each receiving a mixed signal from multiple audio sources, performing independent component analysis (ICA) on the data in the time-frequency domain based on an estimation of a spectrogram of each acoustic source. The spectrograms of the sources are determined from non-negative matrix factorization (NMF) models of each source, the NMF model representing time-frequency variations in the output of an acoustic source in the time-frequency domain. The NMF and ICA models are jointly optimized, thus automatically resolving an inter-frequency permutation ambiguity.
Owner:AUDIOTELLIGENCE LTD
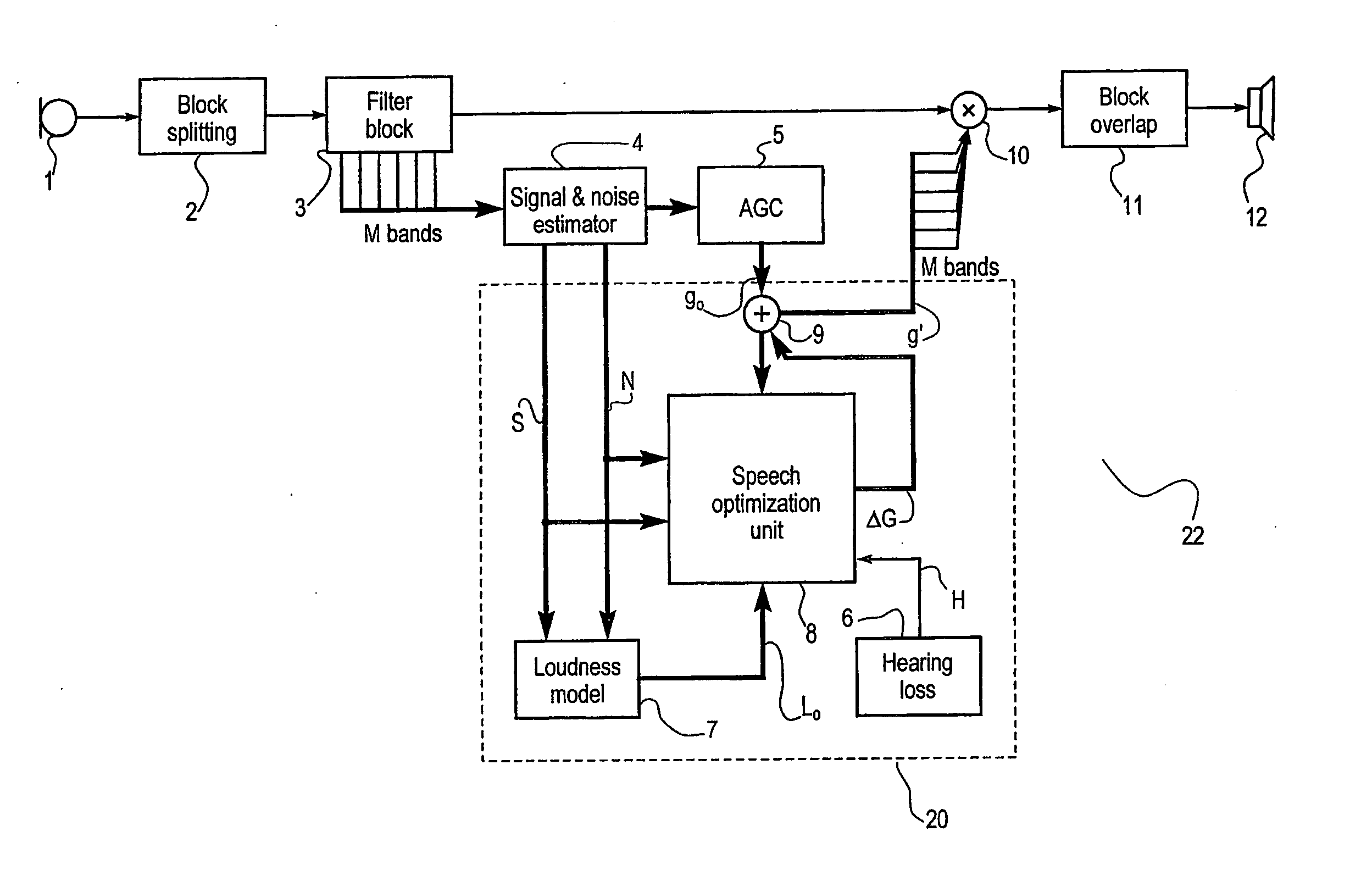
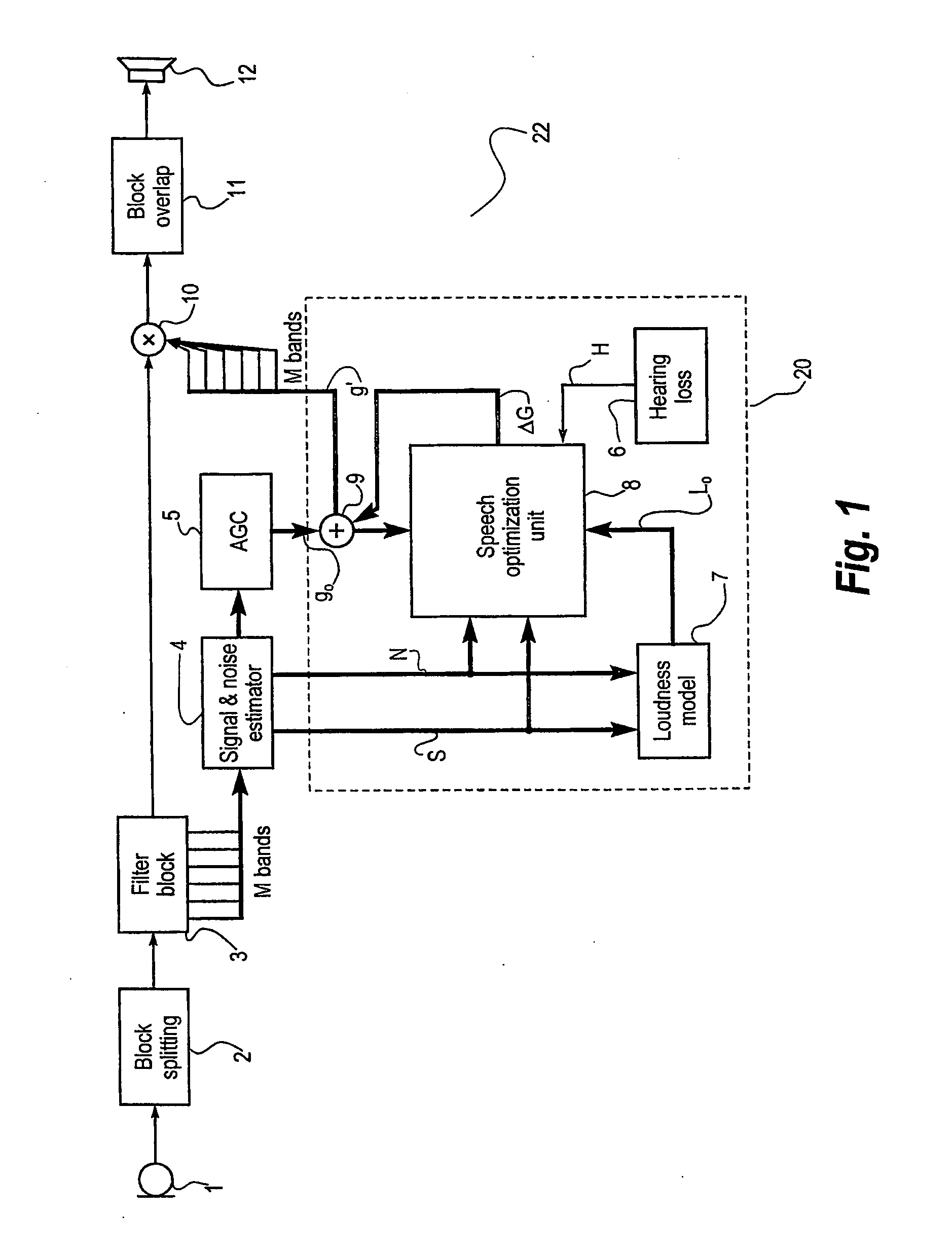
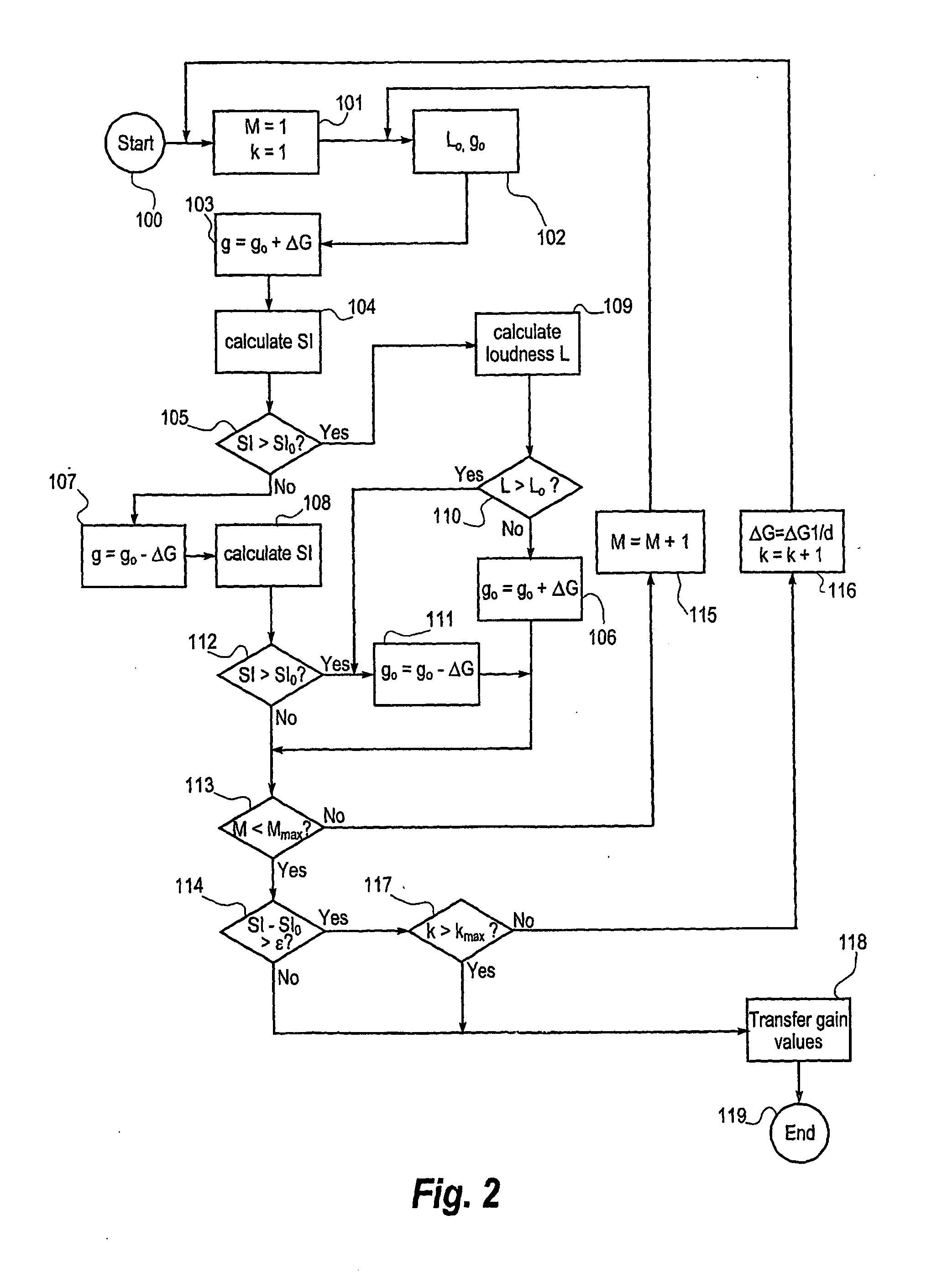
Hearing aid and a method for enhancing speech intelligibility
ActiveUS20050141737A1Improve speech claritySpeech analysisHearing aids signal processingTransducerHearing aid
A hearing aid (22) having a microphone (1), a processor (53) and an output transducer (12), is adapted for obtaining an estimate of a sound environment, determining an estimate of the speech intelligibility according to the sound environment estimate, and for adapting the transfer function of the hearing aid processor in order to enhance the speech intelligibility estimate. The method according to the invention achieves an adaptation of the processor transfer function suitable for optimizing the speech intelligibility in a particular sound environment. Means for obtaining the sound environment estimate and for determining the speech intelligibility estimate may be incorporated in the hearing aid processor, or they may be wholly or partially implemented in an external processing means (56), adapted for communicating data to the hearing aid processor via an appropriate link.
Owner:WIDEX AS
Providing notification sounds in a customizable manner
ActiveUS20120213393A1Hearing aids signal processingHearing aids testing/monitoringReal-time computing
Broadly speaking, the embodiments disclosed herein describe an apparatus, system, and method that allow a user to perceive notifications (audible or otherwise) corresponding to an external event in any manner deemed appropriate.
Owner:APPLE INC
Mobile phones and other products producing personalized hearing profiles for users
InactiveUS20050260985A1Easy to receiveImprove soundStereophonic circuit arrangementsHearing impaired stereophonic signal reproductionEnvironmental noiseInstruction memory
A mobile phone or other personal communication device includes resources applying measures of an individual's hearing profile, personal choice profile, and induced hearing loss profile, separately or in combination, to build the basis of sound enhancement. A personal communication device thus comprises a transmitter / receiver coupled to a communication medium for transmitted receiving audio signals, control circuitry that controls transmission, reception and processing of call and audio signals, a speaker, and a microphone. The control circuitry includes logic applying one or more of a hearing profile of the user, a user preference related hearing, and environmental noise factors in processing the audio signals. The control circuitry may includes instruction memory and an instruction execution processor such as a digital signal processor.
Owner:SOUND ID INC
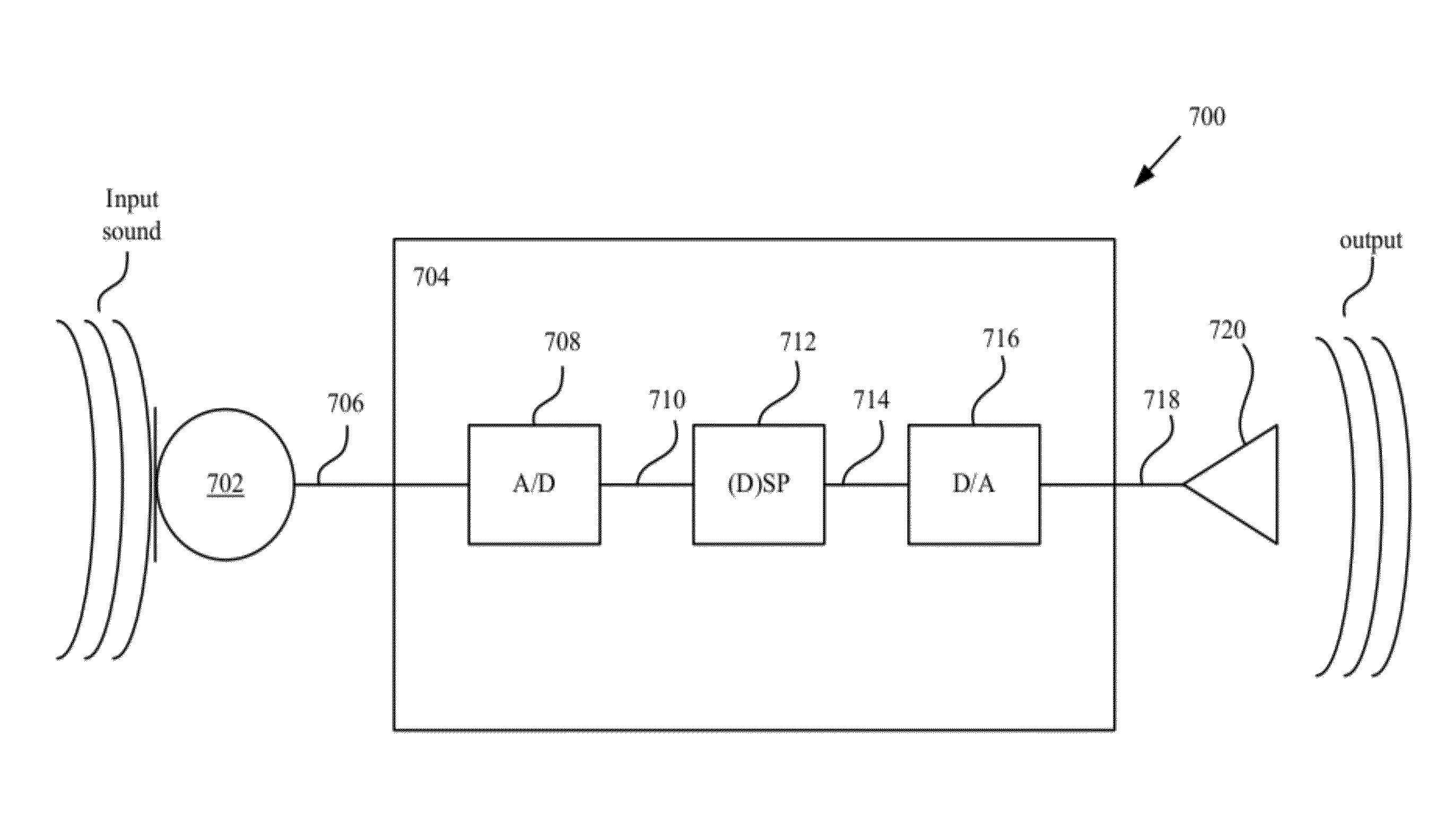
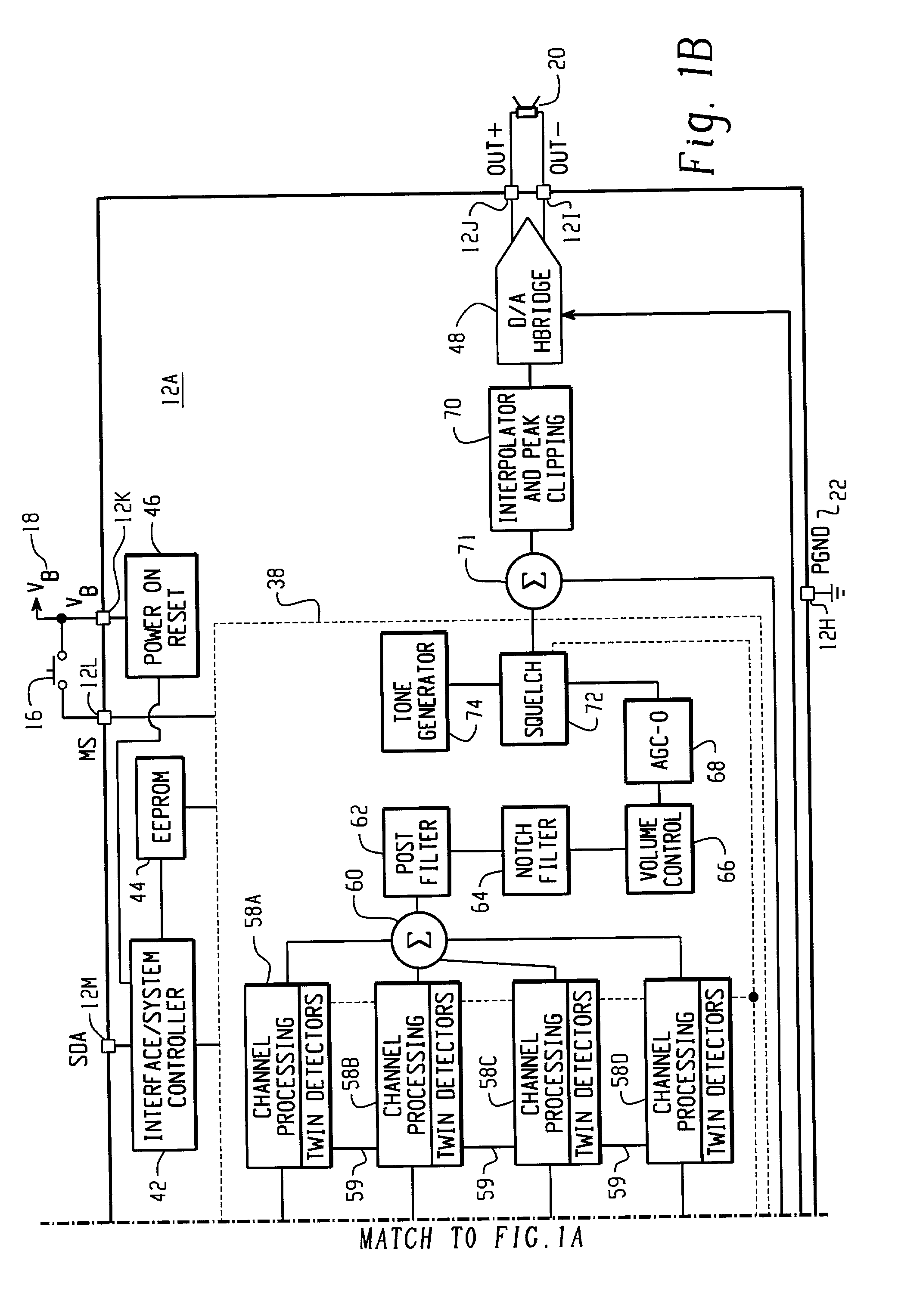
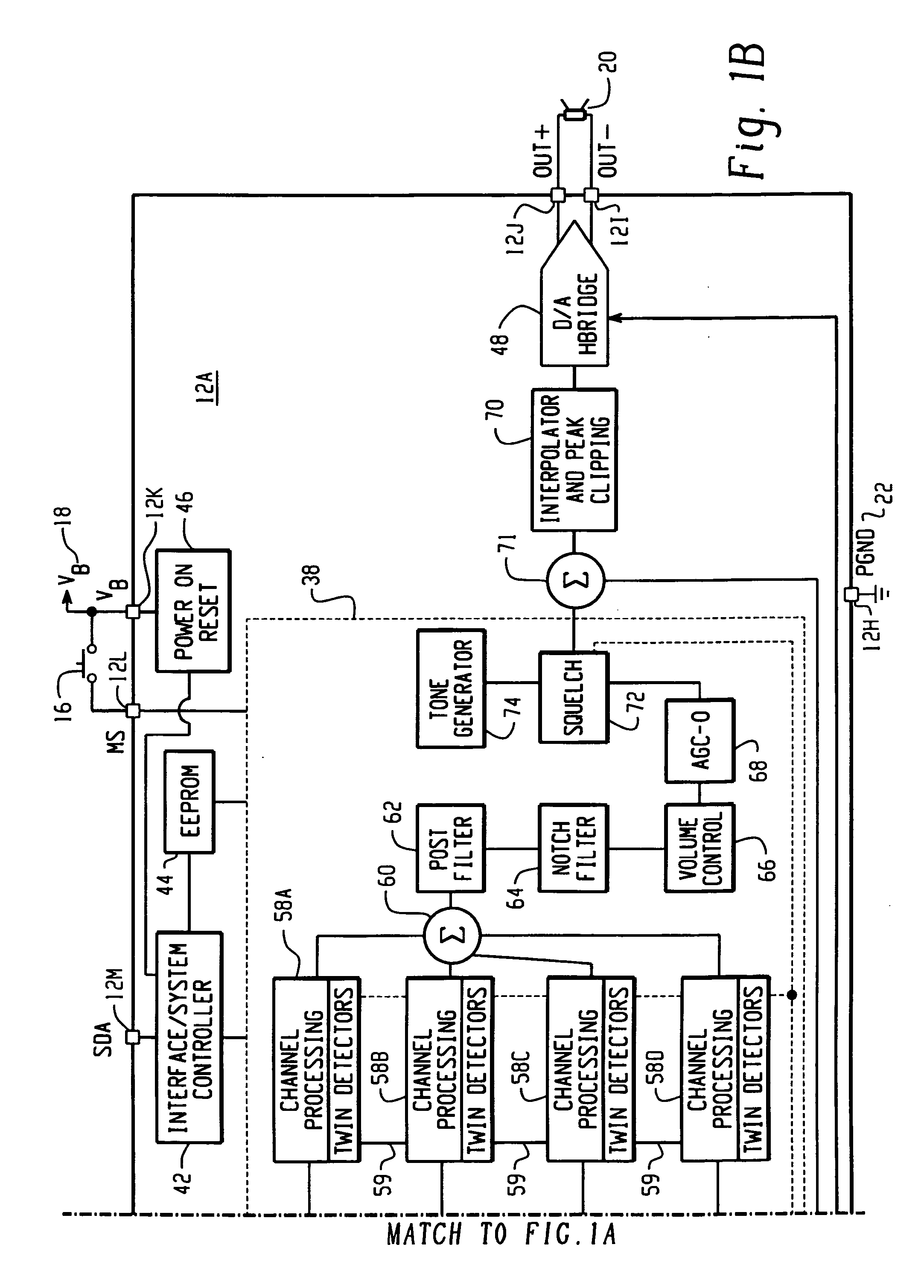
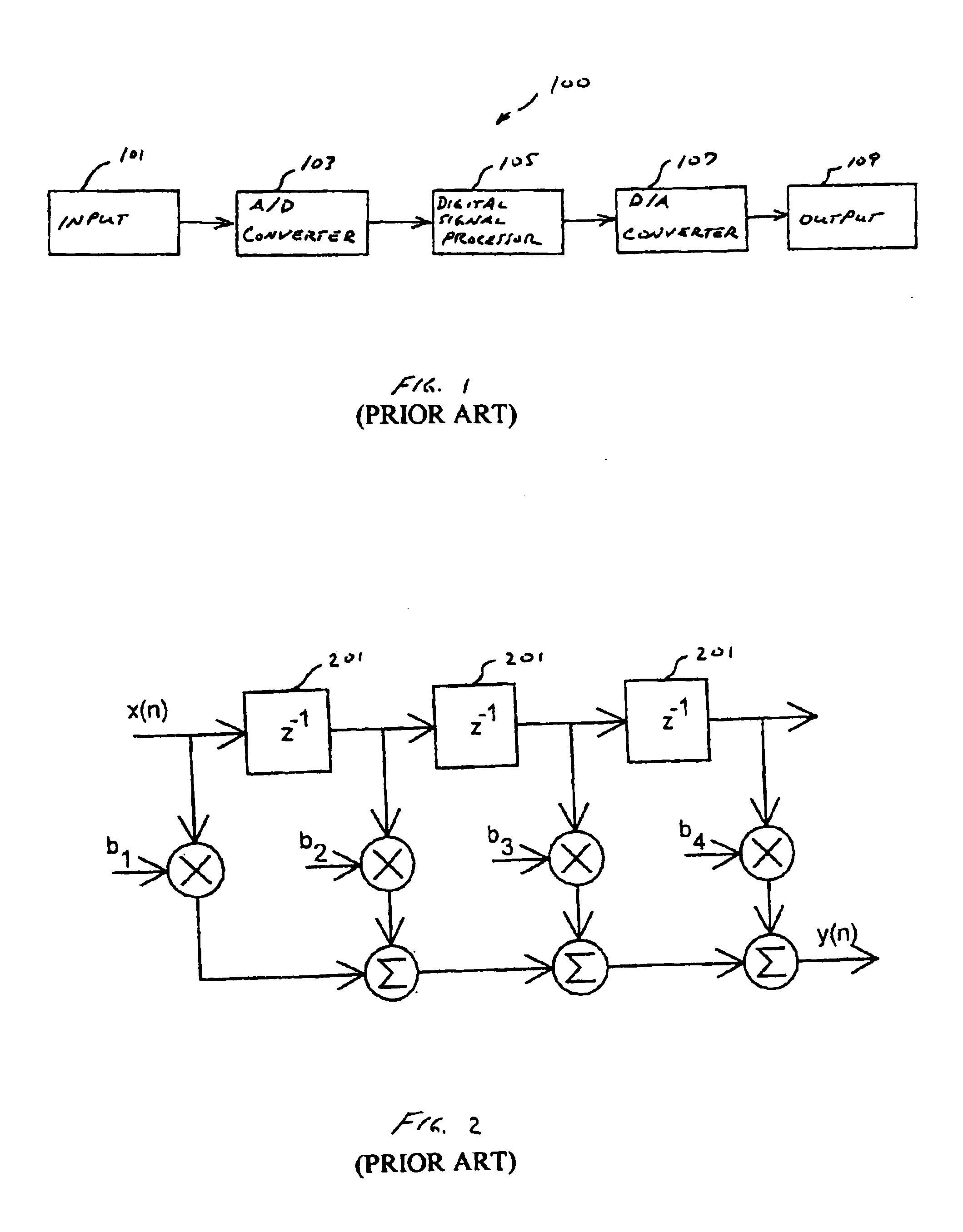
Inter-channel communication in a multi-channel digital hearing instrument
A multi-channel digital hearing instrument is provided that includes a microphone, an analog-to-digital (A / D) converter, a sound processor, a digital-to-analog (D / A) converter and a speaker. The microphone receives an acoustical signal and generates an analog audio signal. The A / D converter converts the analog audio signal into a digital audio signal. The sound processor includes channel processing circuitry that filters the digital audio signal into a plurality of frequency band-limited audio signals and that provides an automatic gain control function that permits quieter sounds to be amplified at a higher gain than louder sounds and may be configured to the dynamic hearing range of a particular hearing instrument user. The D / A converter converts the output from the sound processor into an analog audio output signal. The speaker converts the analog audio output signal into an acoustical output signal that is directed into the ear canal of the hearing instrument user.
Owner:HIMPP
External microphone array and hearing aid using it
ActiveUS20150049892A1Reduces and even eliminatesEnhance listening experienceMicrophonesElectrical transducersSound sourcesRemote control
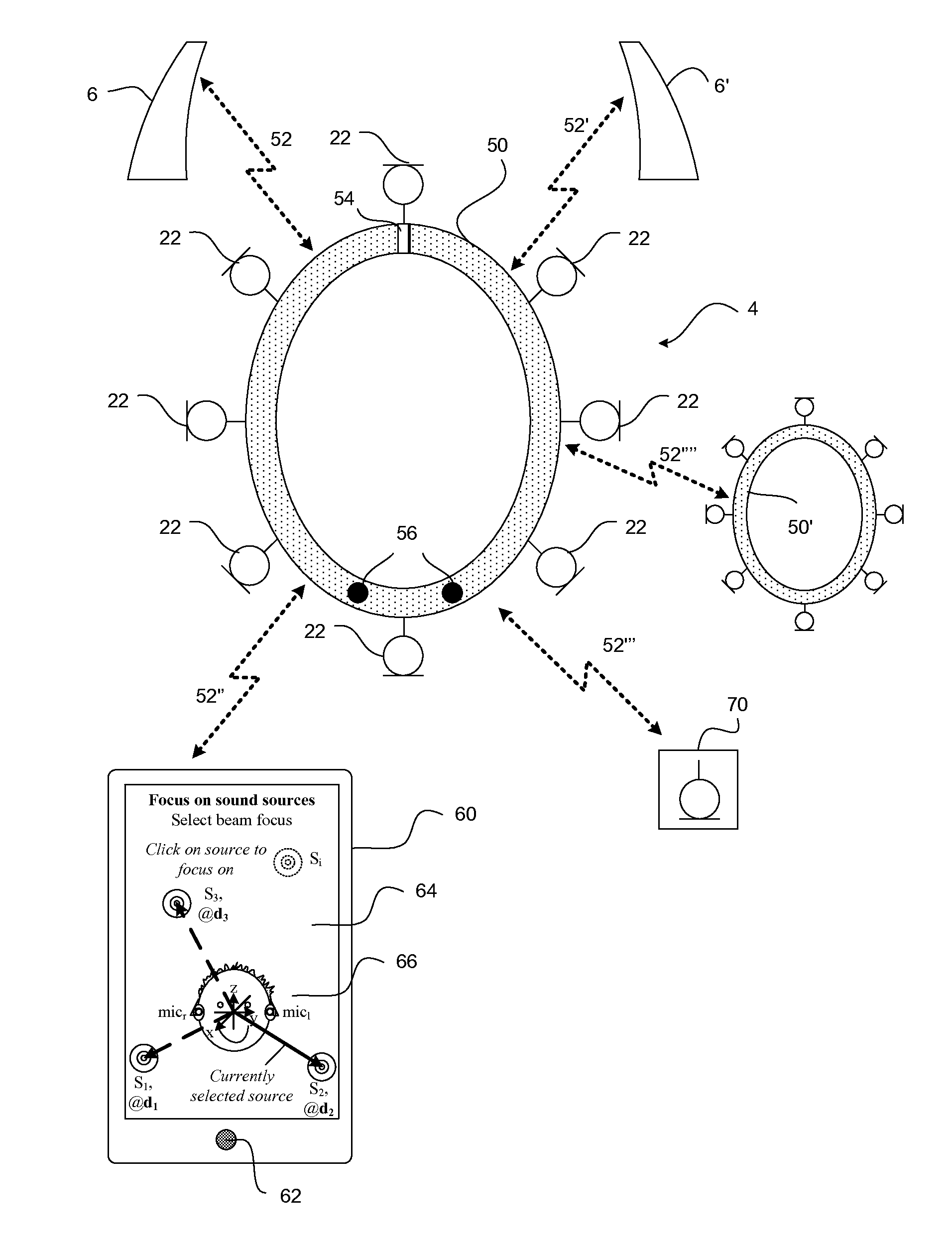
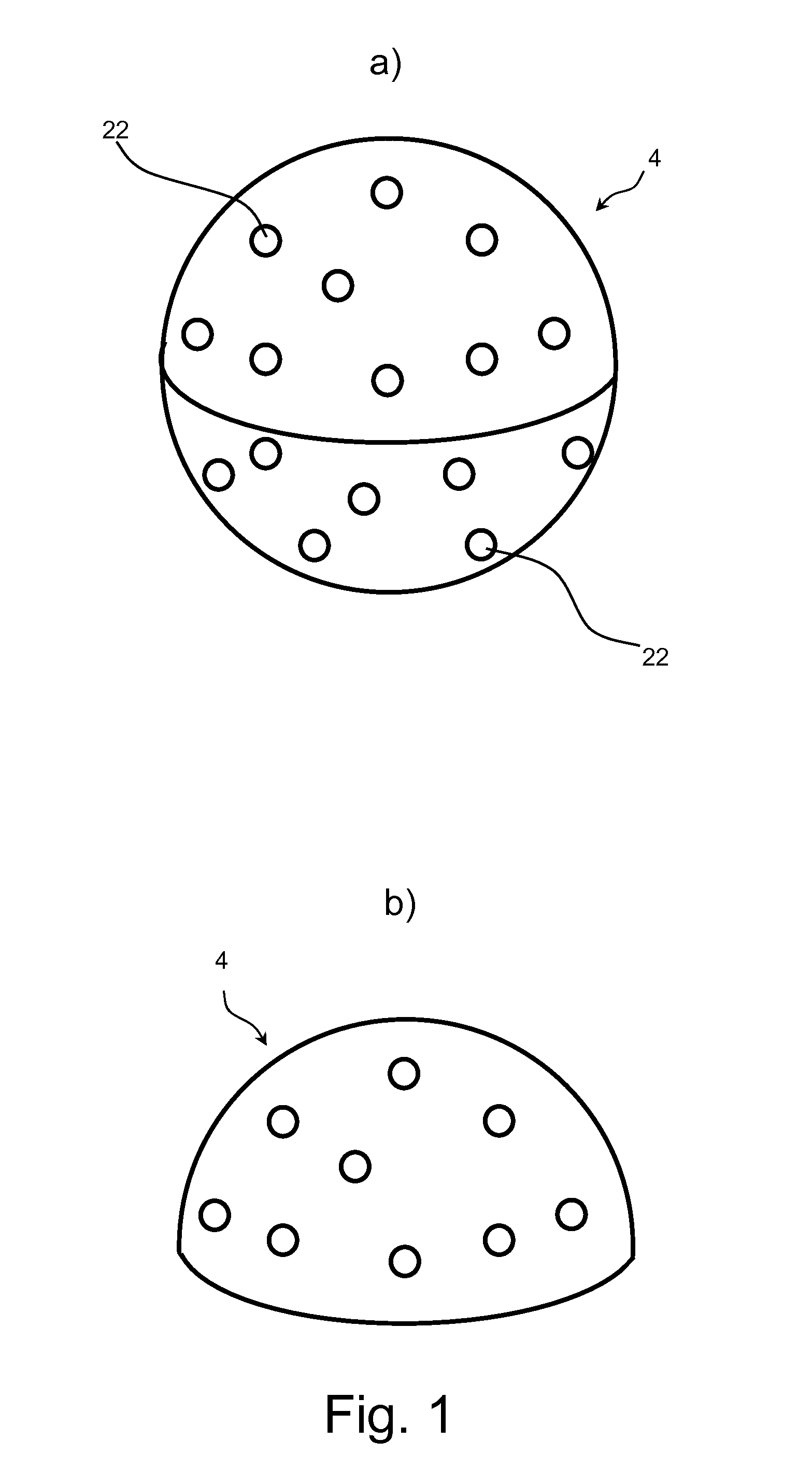
An external microphone array is configured to be used with a hearing aid and comprises a number of microphones configured to detect one or more sound signals from a sound source and means for wirelessly sending the detected sound signal to at least one hearing aid. The external microphone array comprises means for automatically determining the direction of the sound source either by: a) receiving a wireless signal transmitted from a remote control; b) by receiving acoustic signals picked up by the hearing aid(s) and by further comparing the signals with signals received by the external microphone array. The external microphone array may e.g. take the form of a sphere, a hemi-sphere or a neckband.
Owner:OTICON
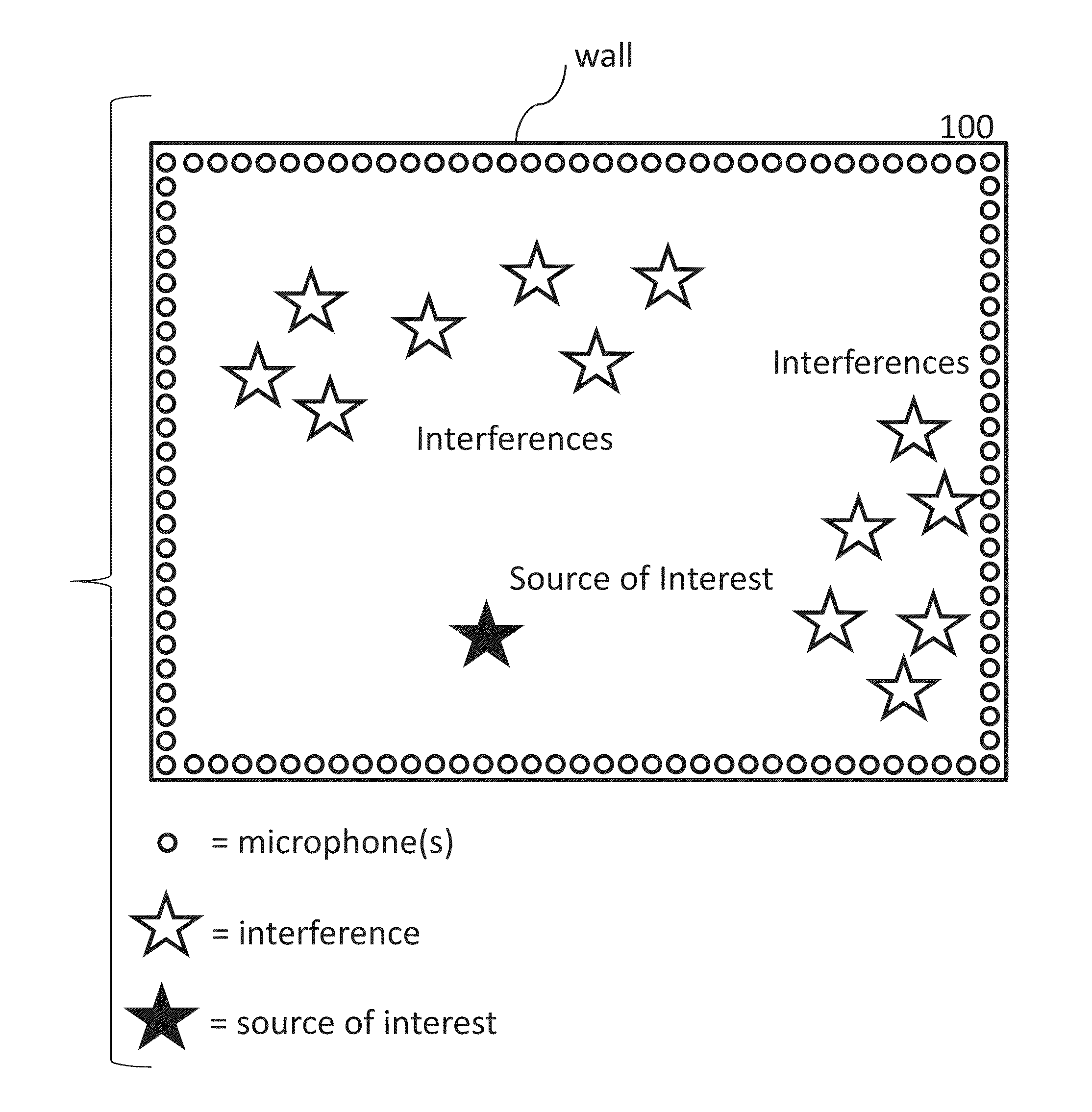
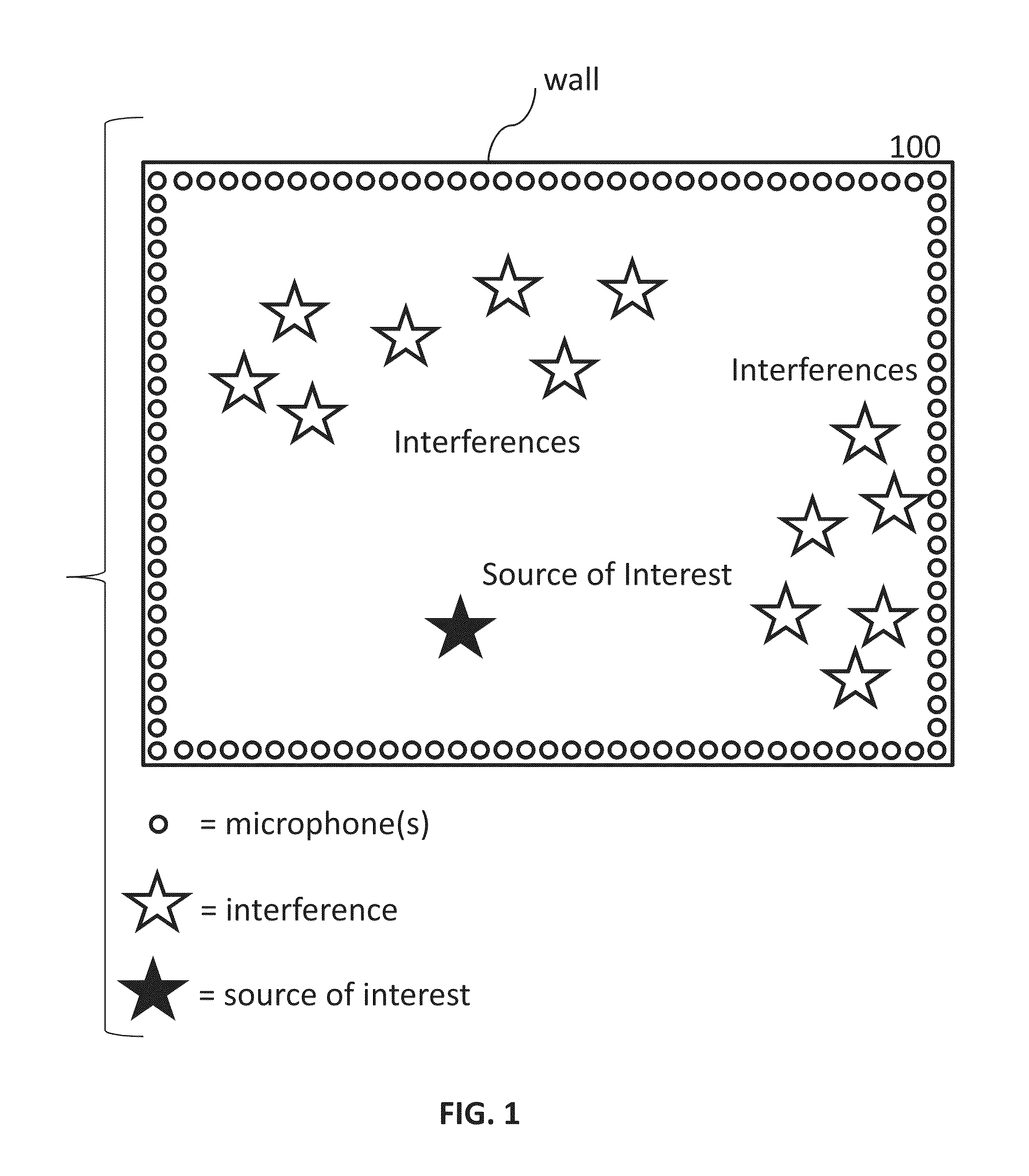
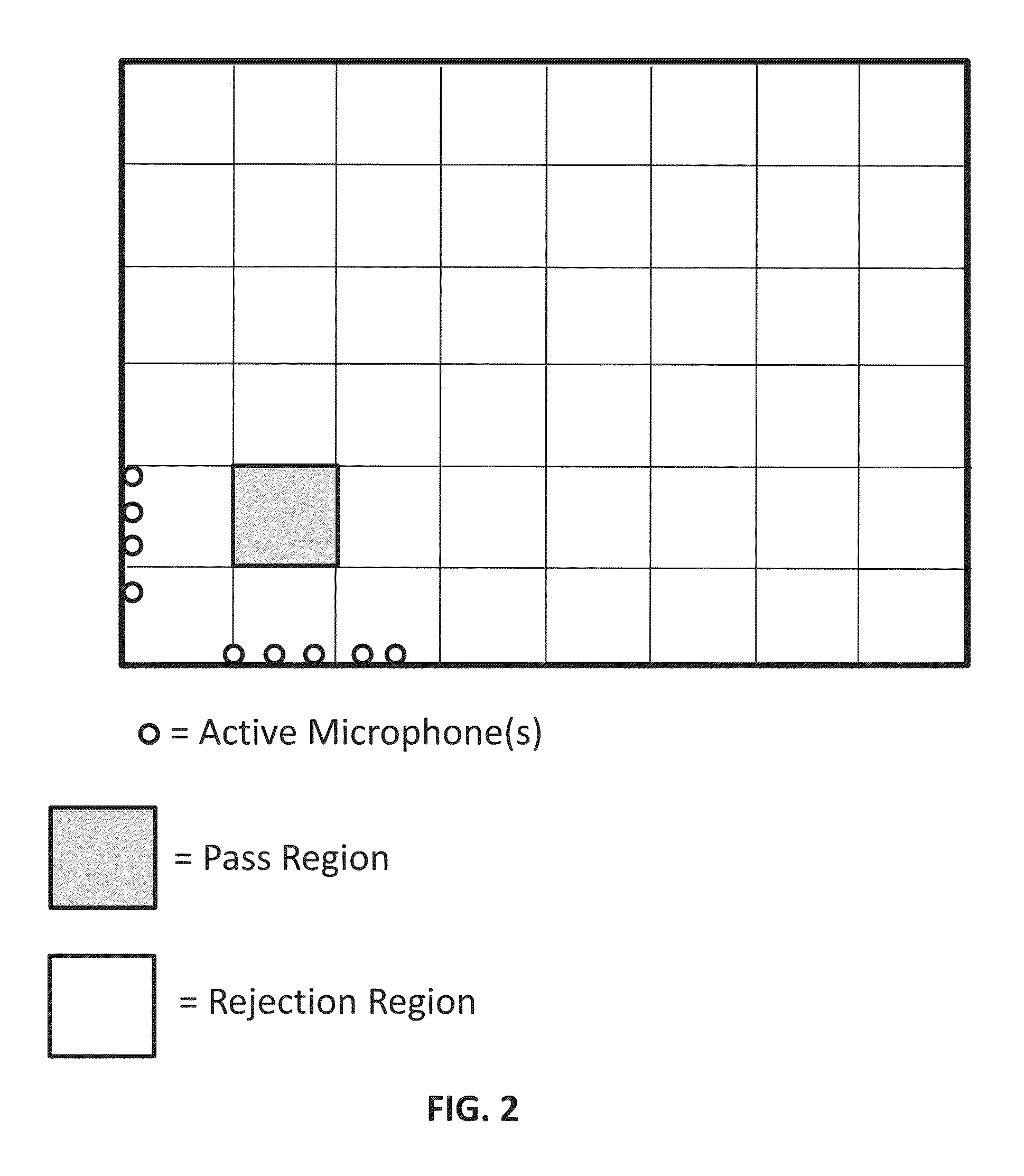
Broadband sensor location selection using convex optimization in very large scale arrays
Systems and methods are provided to determine a subset of D microphones in a set of N microphones on a perimeter of a space to monitor a target location. The space is divided into L interference locations. An equation is solved to determine microphone weights for the N microphones by minimizing the maximum gain for signals related to the target location and interference locations, further optimized over an l1 penalty by applying a Lagrange multiplier to an l1 norm of the microphone weights in a manner that determines a set of D non-zero microphones weights and a set of (N−D) microphone weights that are zero or close to zero. Microphone weights are determined for at least 2 different frequencies.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
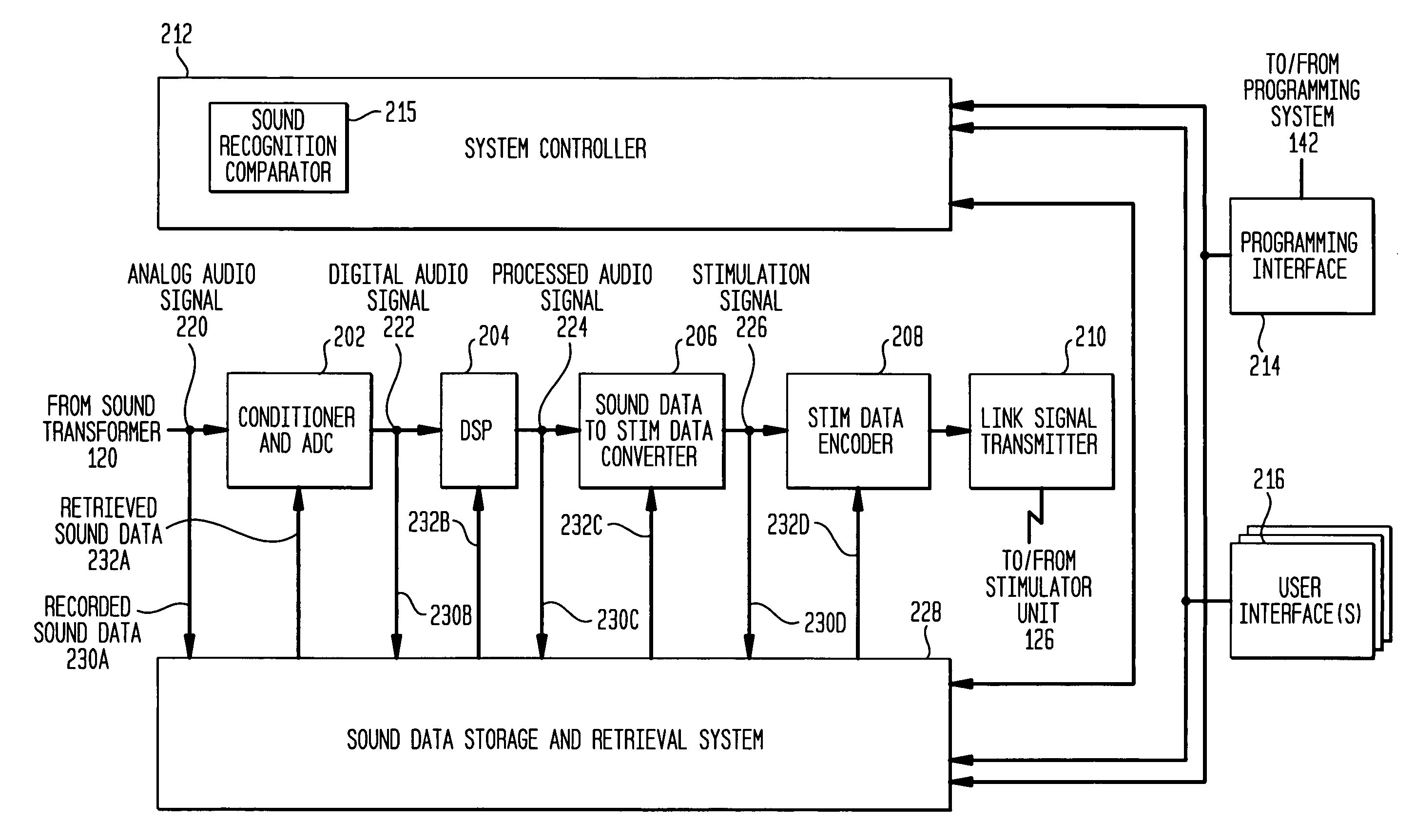
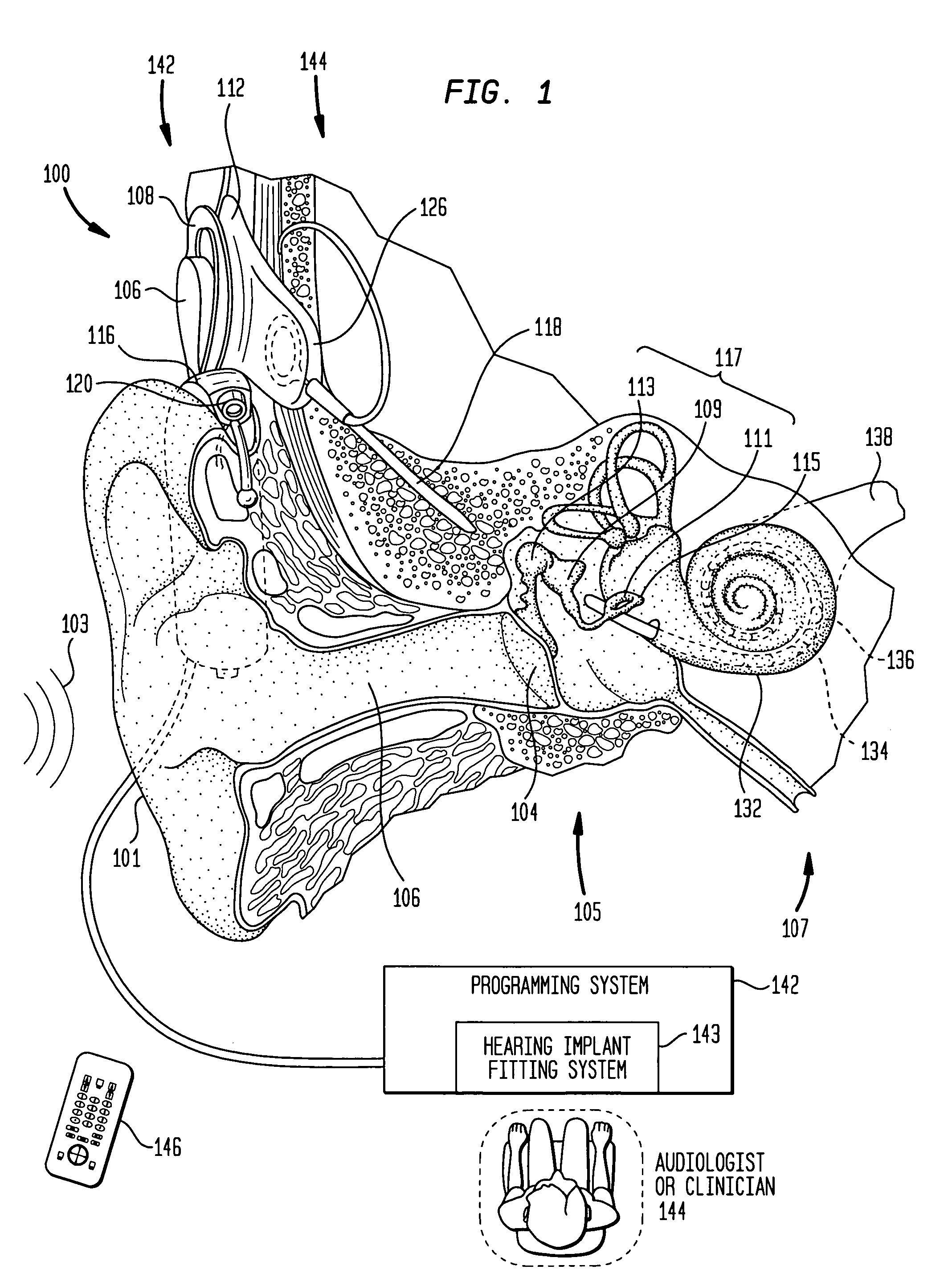
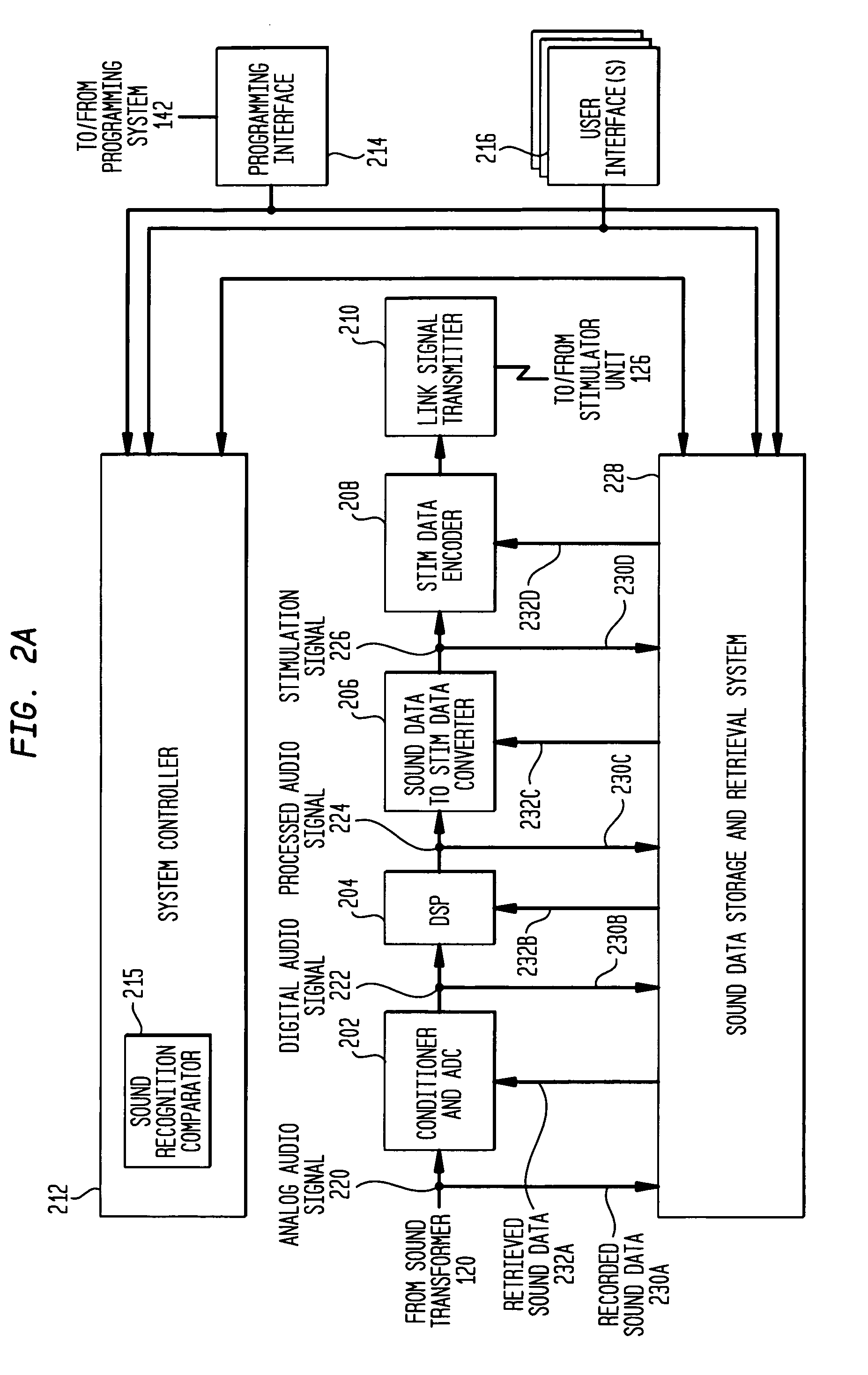
Recording and retrieval of sound data in a hearing prosthesis
A hearing prosthesis for delivering stimuli to a hearing-impaired recipient is disclosed, the hearing prosthesis comprising: a sound transducer for converting received sound signals into electric audio signals; a sound processor for converting said electric audio signals into stimuli signals; a stimulator for delivering said stimuli to the recipient; a memory for storing data representative of sound signals; and a controller configured to cause selected sound data to be retrieved from said memory and processed by said sound processor.
Owner:COCHLEAR LIMITED
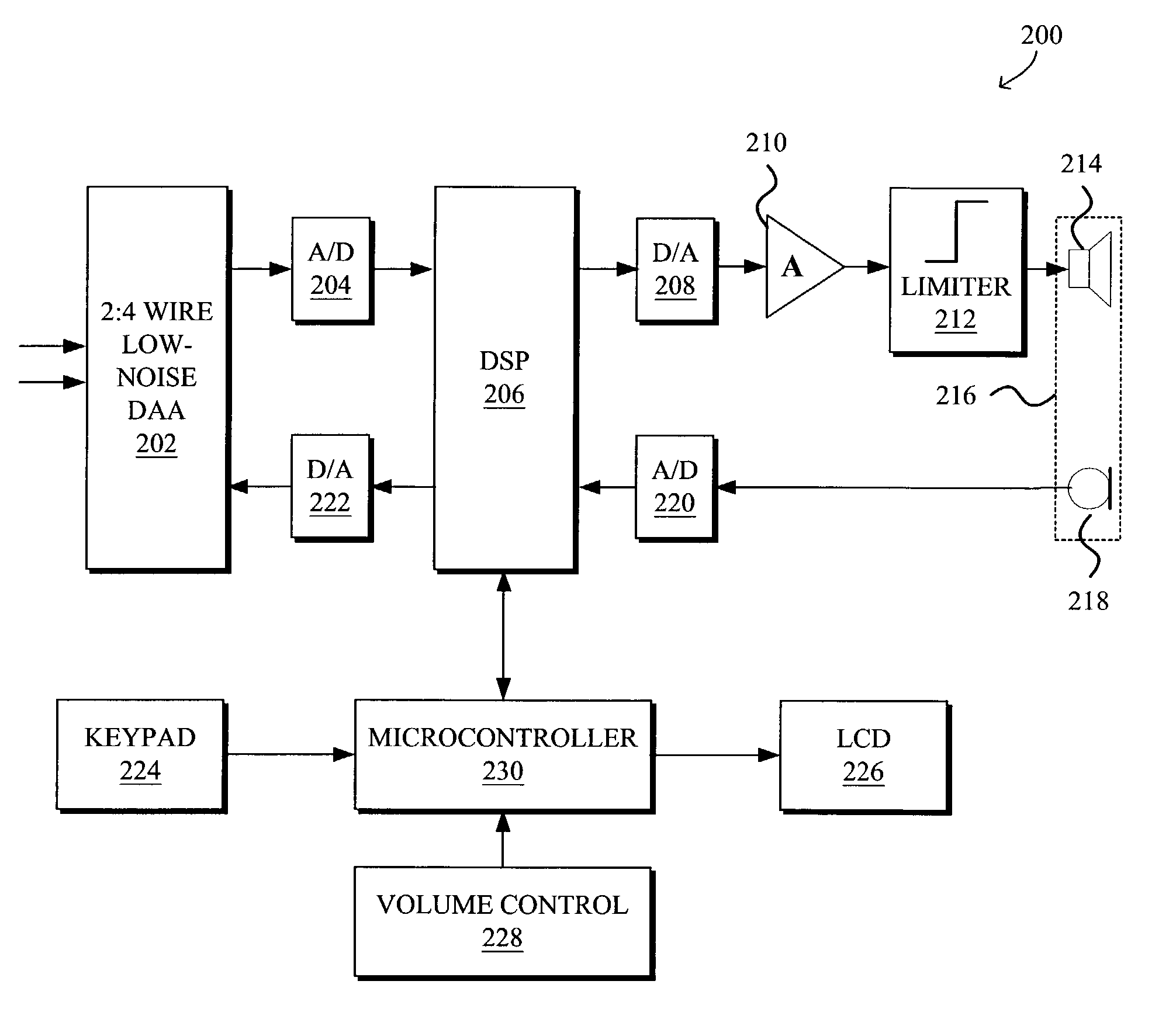
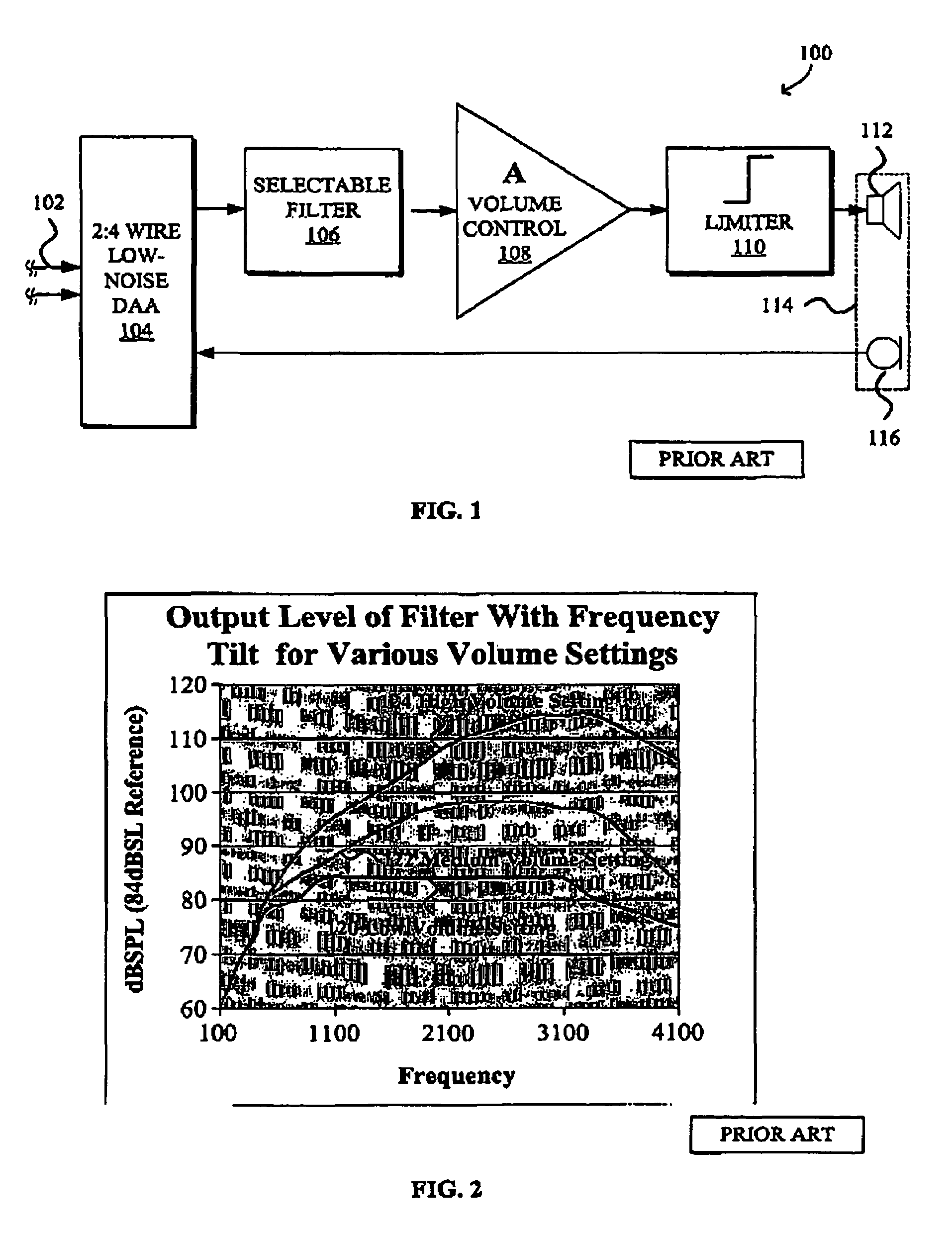
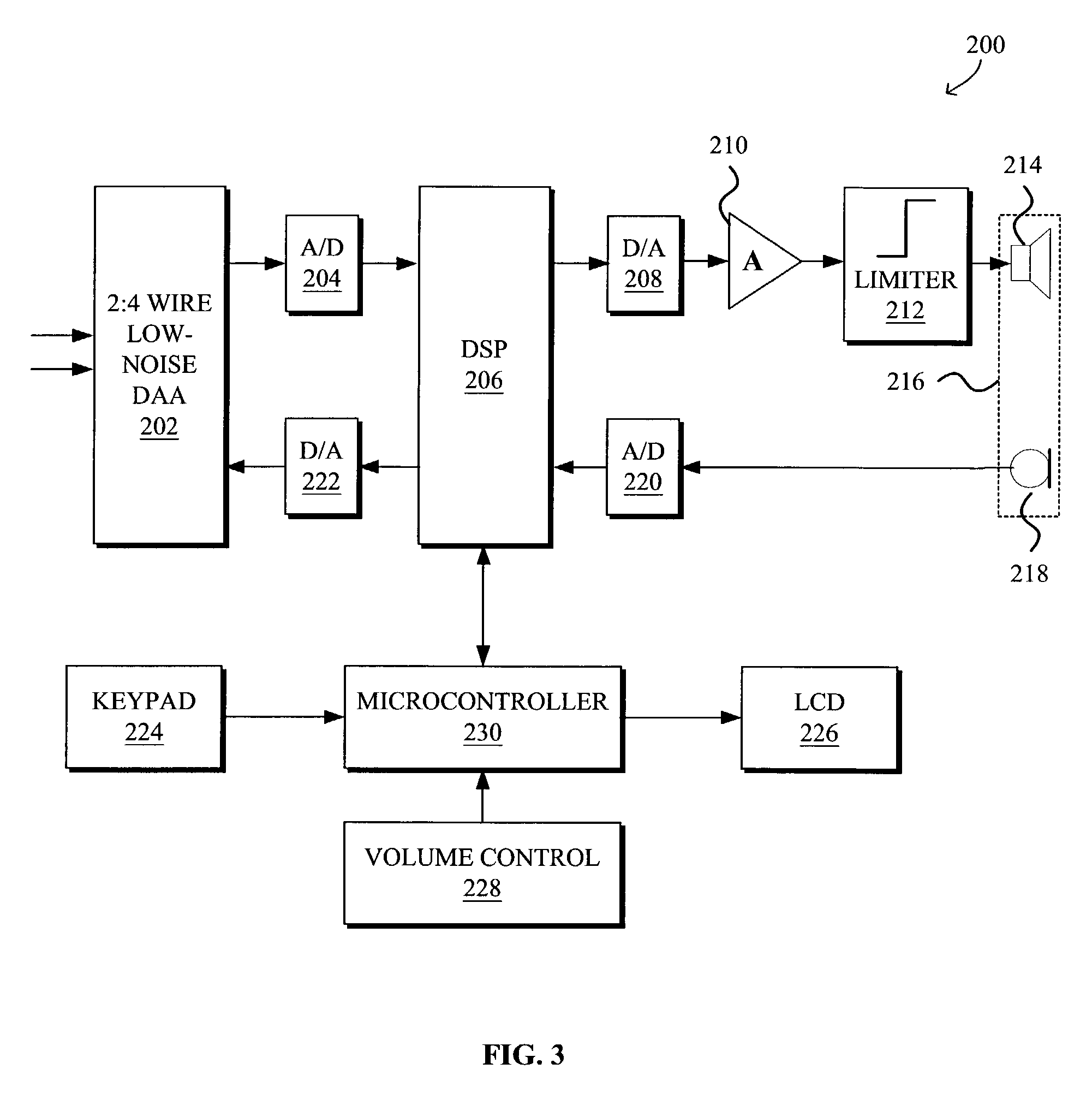
DSP-enabled amplified telephone with digital audio processing
InactiveUS7042986B1Improve intelligibilityInterconnection arrangementsStereophonic circuit arrangementsFinite impulse responseDigital signal processing
A DSP-enabled system and method for increasing intelligibility of audio on amplified telephones by providing digital audio processing customizable based on characteristics of hearing loss specific to individual end users are disclosed. The DSP-enabled amplified telephone generally comprises a DSP capable of implementing at least one digital processing mode for processing audio input, a volume control for allowing the user to select a volume control level, and a controller for interfacing between the DSP and the volume control. The DSP is optionally programmable to implement a processing mode selected from multiple processing modes that the DSP is capable of implementing. The mode is selected based upon the user's hearing loss characteristics. The DSP may be further customized by being programmed with frequency response, compression ratio, and / or knee point according to hearing loss characteristics of the user. The DSP may implement digital TILL, BILL, and / or PILL (treble, bass, and programmable increase at low levels, respectively), all of which apply more amplification to softer inputs than to louder inputs, as well as input compression, output compression, and / or finite impulse response (FIR) filter tone control.
Owner:PLANTRONICS
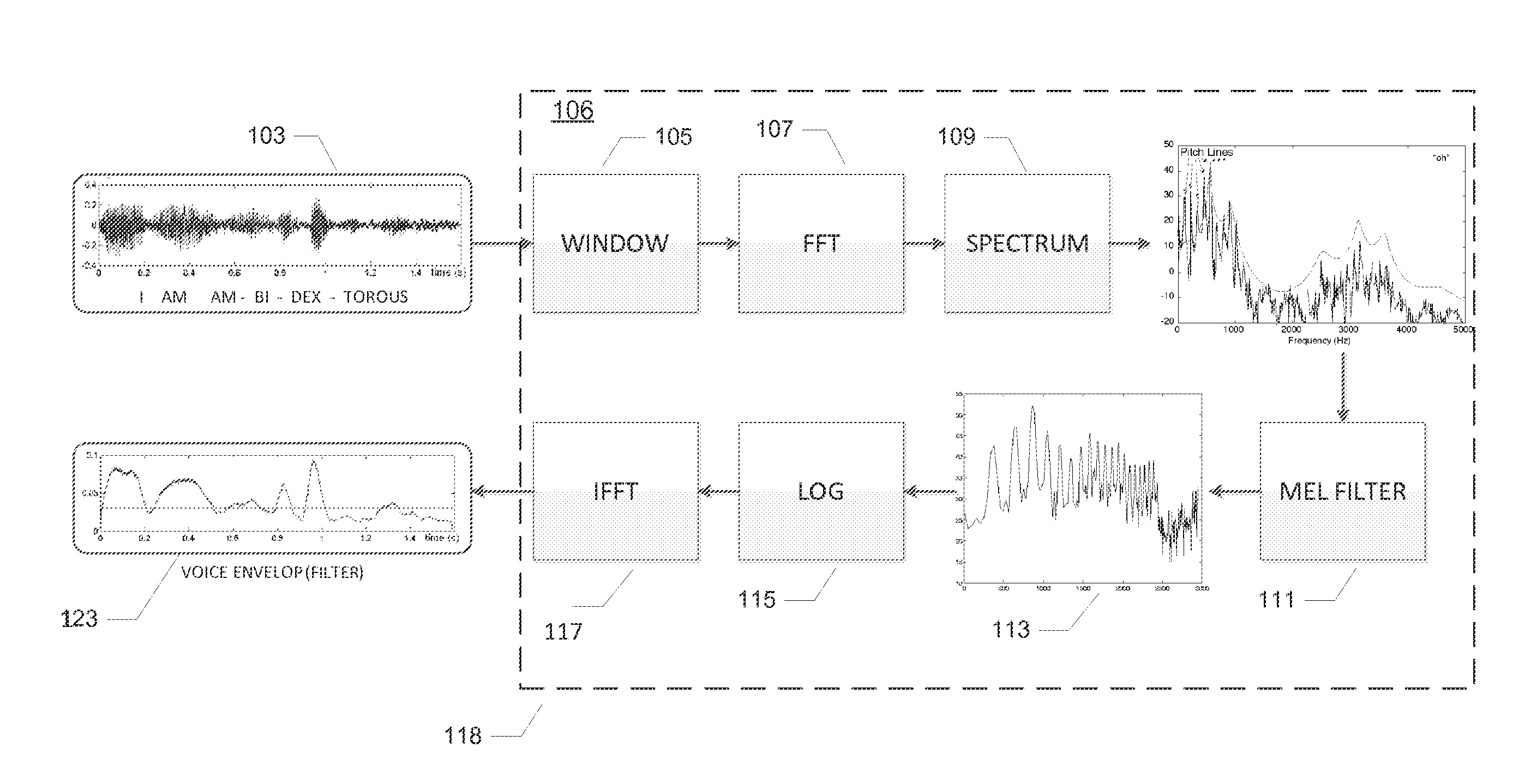
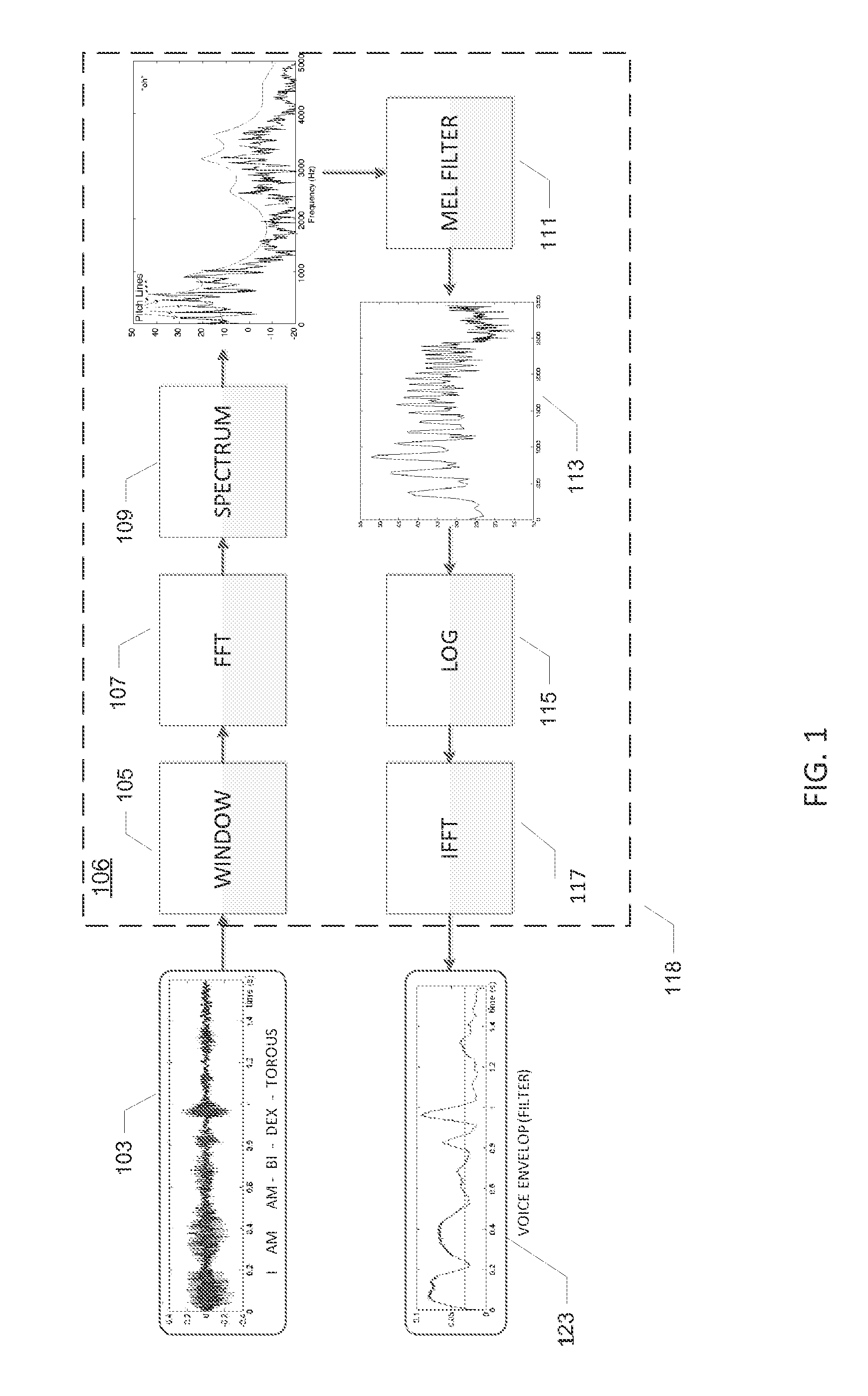
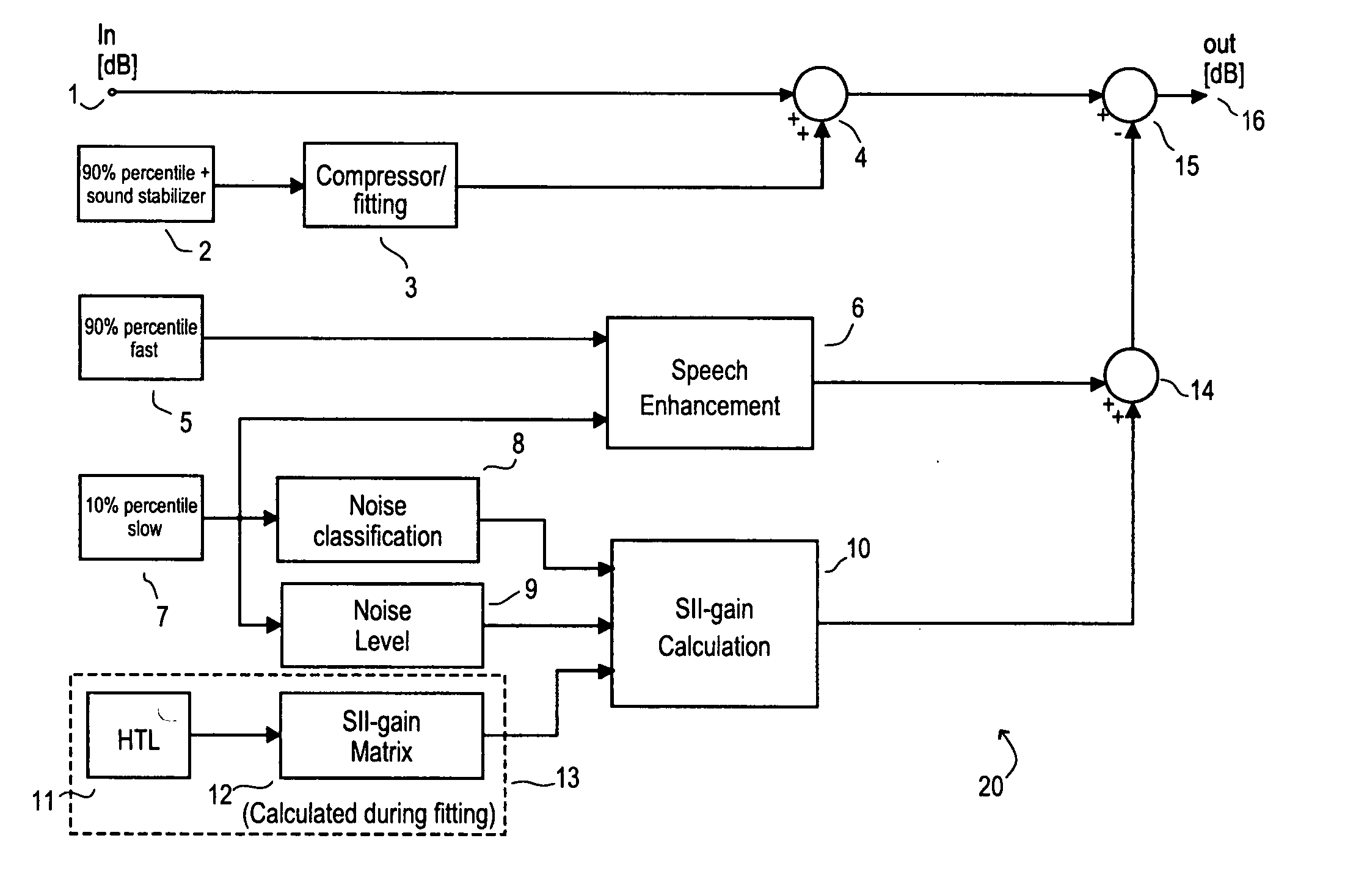
Method for processing audio-signals
ActiveUS20070100605A1Enhance speech signalSpeech analysisHearing aids signal processingMicrophone signalComputer science
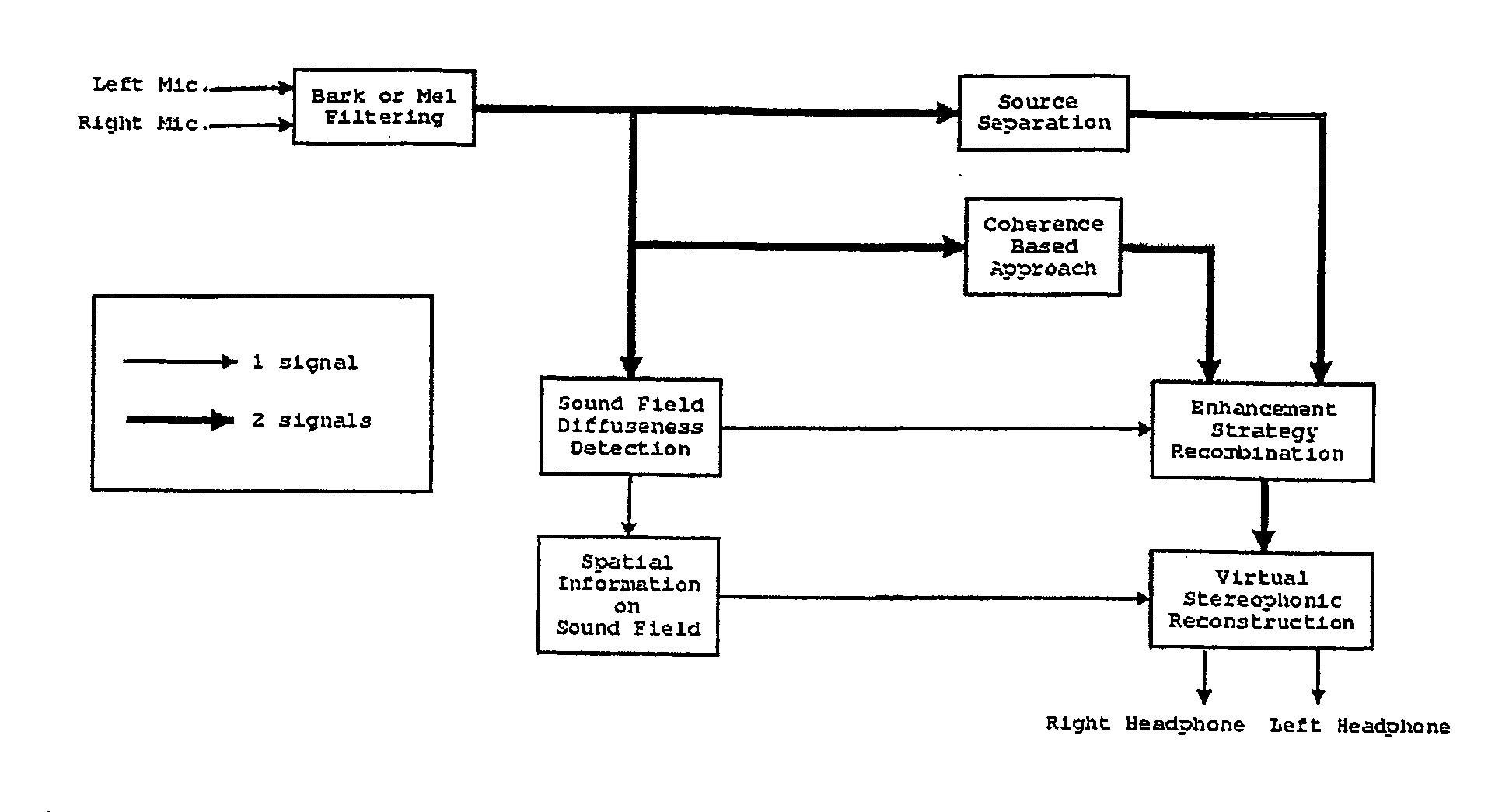
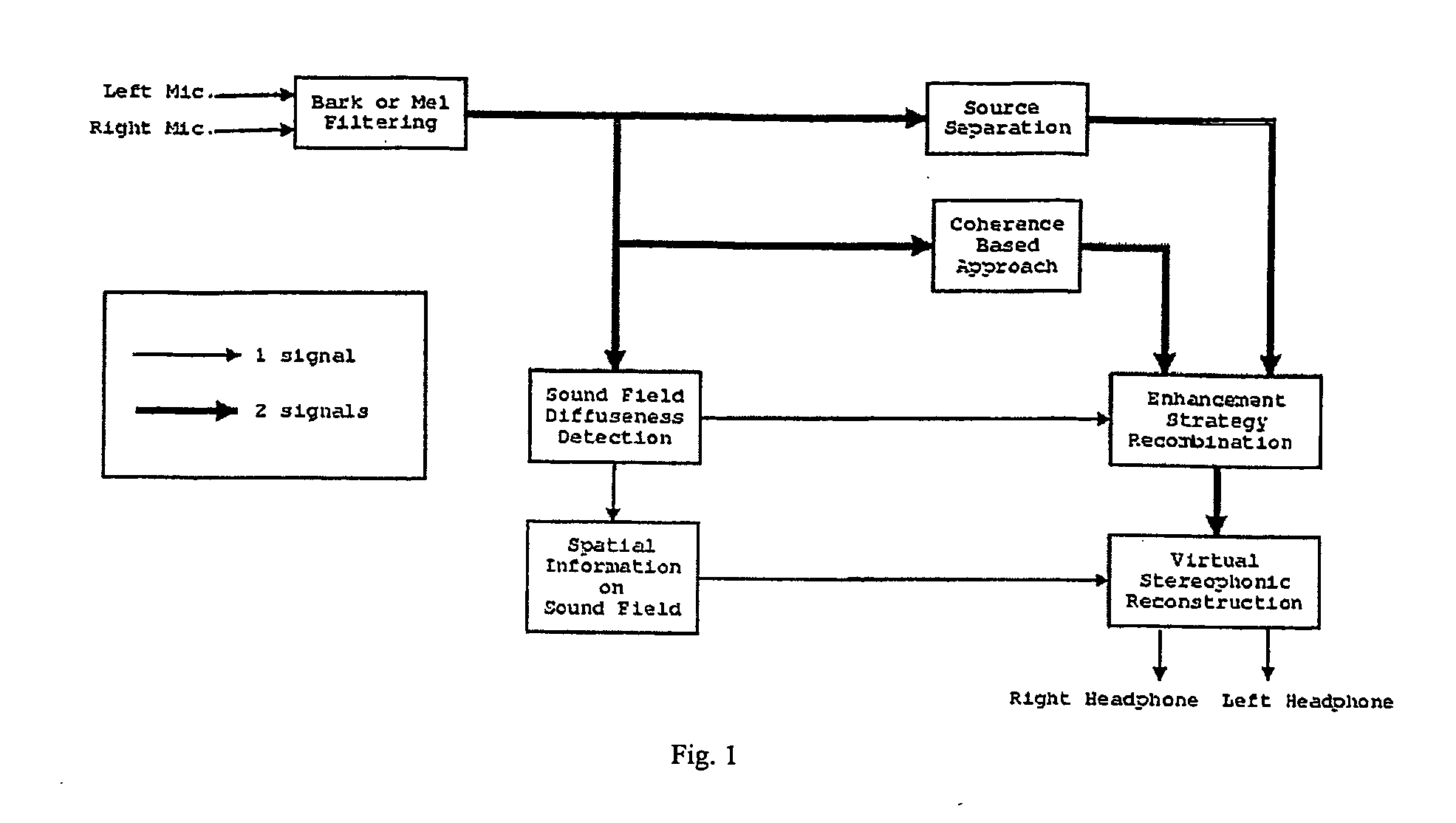
The invention regards a method for processing audio-signals whereby audio signals are captured at two spaced apart locations and subject to a transformation in the perceptual domain (Bar or Mel), whereupon: a) a (blind or supervised) source separation process is performed to give a first estimate of the wanted signal parts and the noise parts of the microphone signals and b) a coherence based separation process is performed to give a second estimate of the wanted signal parts and the noise parts of the microphone signals, and where further a sound field diffuseness detection is performed on the at least two signals, whereby further the sound field diffuseness detections is used to mix the output from the blind source separation and the coherence based separation process in order to achieve the best possible signal. The transfer functions calculated from the source separation are used to reconstruct a virtual stereophonic sound field in restore the spatial information about the source position in the enhanced signals.
Owner:OTICON
Hearing aid and a method of processing signals
ActiveUS20060204025A1Reduce the amount of noiseMinimize effect of noiseMicrophonesGain controlTransducerHearing aid
A hearing aid (30) comprises a microphone (71), a signal processing means (20) and an output transducer (22), and the signal processing means (20) comprises a set of audio processing parameters mapped to a set of stored noise classes (12) and means (8) for classifying the background noise for the purpose of optimizing the frequency response in order to minimize the effects of the background noise. The hearing aid may further comprise a neural net for controlling the frequency response. A method for reducing a noise component in a signal is also devised, which method comprises classification of the noise component, comparing the noise component to a set of known noise components, and adapting the processed audio signals according to a corresponding set of frequency response parameters.
Owner:WIDEX AS
Sound perception using frequency transposition by moving the envelope
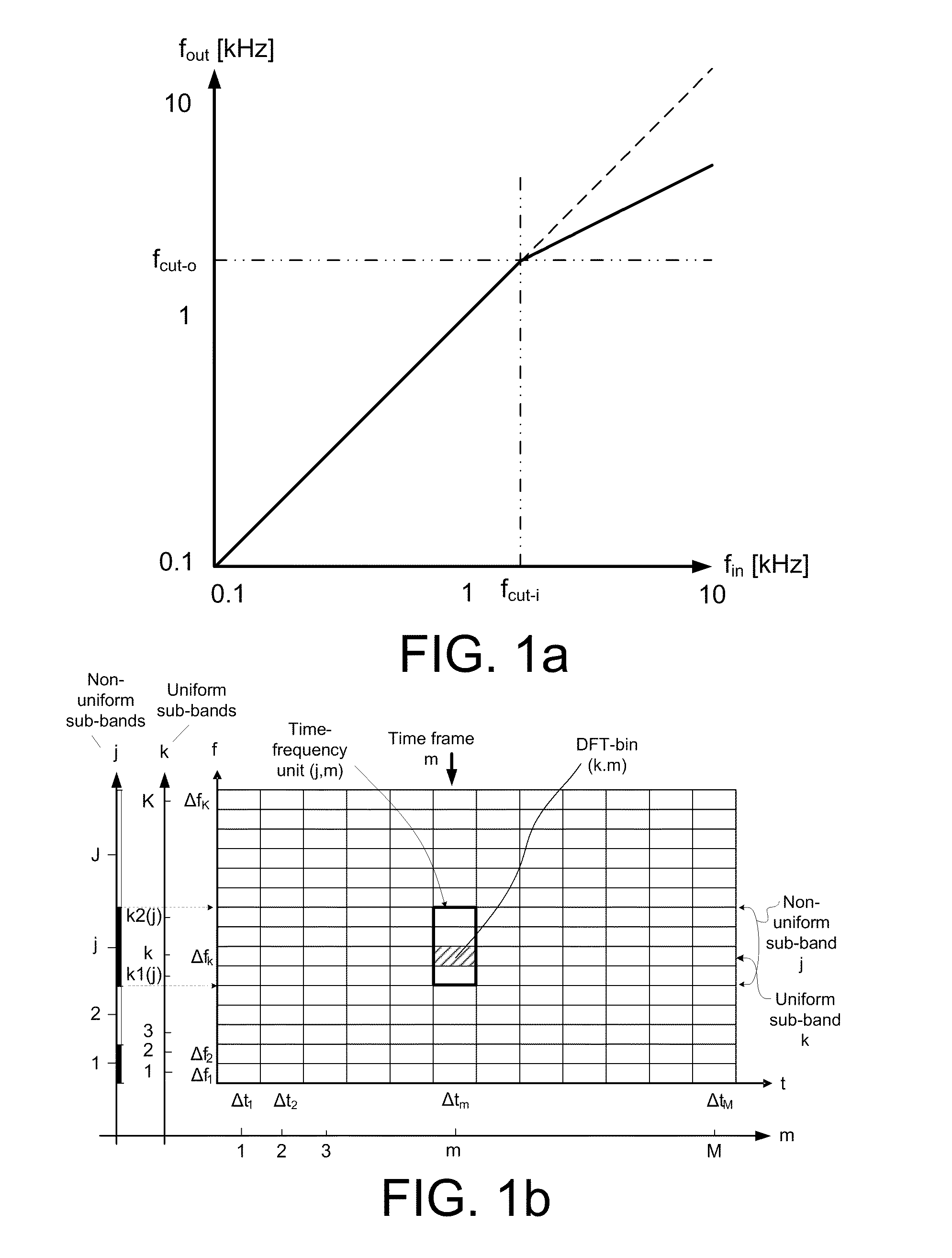
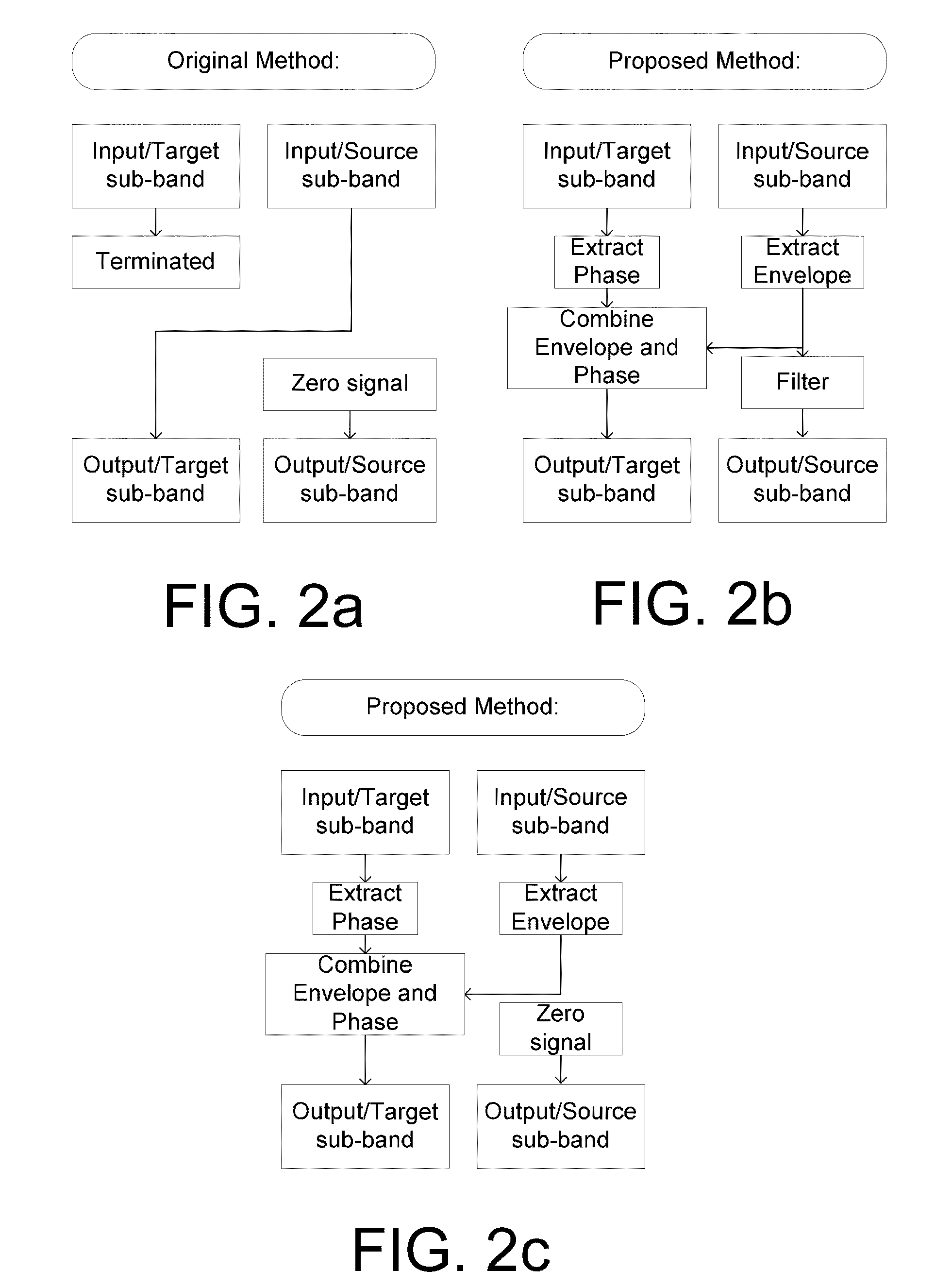
ActiveUS20110249843A1Facilitate cognitionImprove sound qualityHearing aids signal processingTransducer casings/cabinets/supportsSound perceptionSound quality
The application relates to a method of improving a user's perception of an input sound. The application further relates to an audio processing device and to its use. The object of the present application is to increase the sound quality of a sound signal as perceived by a user, e.g. a hearing impaired user. The method comprises a) Defining a critical frequency fcrit between a low frequency range and a high frequency range; b) Analyzing an input sound in a number of frequency bands below and above said critical frequency; c) Defining a cut-off frequency fcut below said critical frequency fcrit; d) Identifying a source frequency band above said cut-off frequency fcut; e) Extracting the envelope of said source band; f) Identifying a corresponding target band below said critical frequency fcrit; g) Extracting the phase of said target band; h) Combining the envelope of said source band with the phase of said target band. This has the advantage of increasing the sound quality, and the potential to further improve speech intelligibility in frequency transposition, e.g. frequency lowering systems. The invention may e.g. be used in communication devices, such as telephones, or listening devices, e.g. hearing instruments, headsets, head phones, active ear protection devices or combinations thereof.
Owner:OTICON
Hearing aid and processes for adaptively processing signals therein
ActiveUS20050078842A1Improve performancePromote activationMicrophonesHearing aids signal processingFrequency spectrumHearing aid
An improved hearing aid, and processes for adaptively processing signals therein to improve the perception of desired sounds by a user thereof. In one broad aspect, the present invention relates to a process in which one or more signal processing methods are applied to frequency band signals derived from an input digital signal. The level of each frequency band signal is computed and compared to at least one plurality of threshold values to determine which signal processing schemes are to be applied. In one embodiment of the invention, each plurality of threshold values to which levels of the frequency band signals are compared, is derived from a speech-shaped spectrum. Additional measures such as amplitude modulation or a signal index may also be employed and compared to corresponding threshold values in the determination.
Owner:UNITRON HEARING
Spectral enhancement using digital frequency warping
InactiveUS6980665B2Improve speech intelligibilityImproving speech perceived speech qualityElectrophonic musical instrumentsHearing aids signal processingFrequency spectrumHandling system
A frequency-warped processing system using either sample-by-sample or block processing is provided. Such a system can be used, for example, in a hearing aid to increase the dynamic-range contrast in the speech spectrum, thus improving ease of listening and possibly speech intelligibility. The processing system is comprised of a cascade of all-pass filters that provide the frequency warping. The power spectrum is computed from the warped sequence and then compression gains are computed from the warped power spectrum for the auditory analysis bands. Spectral enhancement gains are also computed in the warped sequence allowing a net compression-plus-enhancement gain function to be produced. The speech segment is convolved with the enhancement filter in the warped time-domain to give the processed output signal. Processing artifacts are reduced since the frequency-warped system has no temporal aliasing.
Owner:GN HEARING AS
Balanced armature based valve
ActiveUS20160255433A1Mitigate one or more amplified or echo-like soundsIn the ear hearing aidsHearing device energy consumption reductionElectric machineryEngineering
A balanced armature (“BA”) based valve is described. The valve includes a motor having a coil assembly and a magnetic system, an armature extending through or being located adjacent to the motor, a drive pin coupled to the armature, and a valve flap of a membrane having a hole therein. The valve flap is actuated by the drive pin into open and closed positions, in response to respective motions of the armature. A housing contains the motor, the armature, the drive pin, and the membrane. In one embodiment, the membrane is attached to the housing and divides the housing into an upper space and a lower space, and there is airflow through the hole, between the upper space and the lower space, only when the valve flap is open. A first spout of the housing may deliver sound generated by an acoustic driver in the housing into a wearer's ear canal, and is also open to the upper space. A second spout of the housing is open to the bottom space and to an ambient environment. Other embodiments are also described.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com