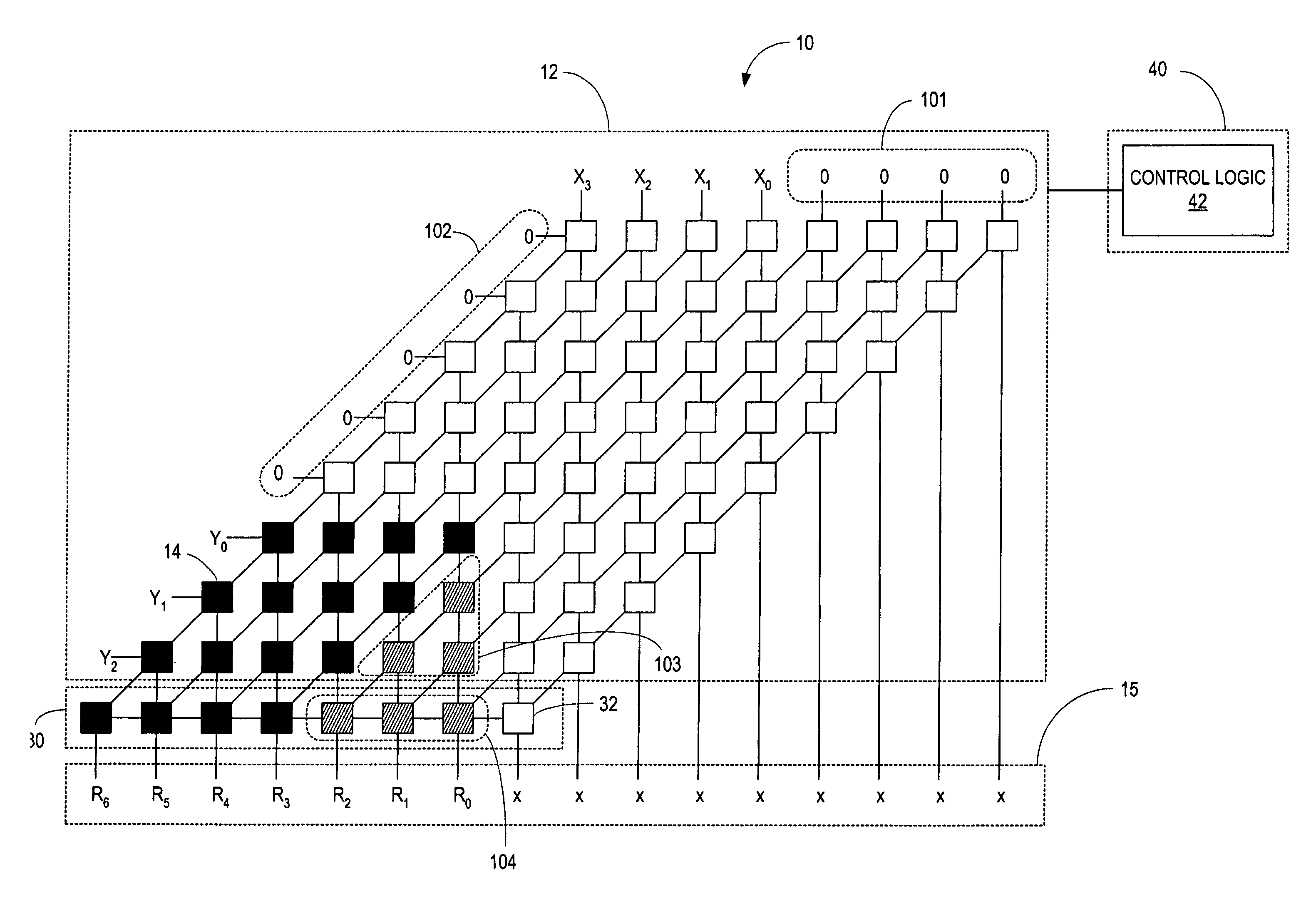
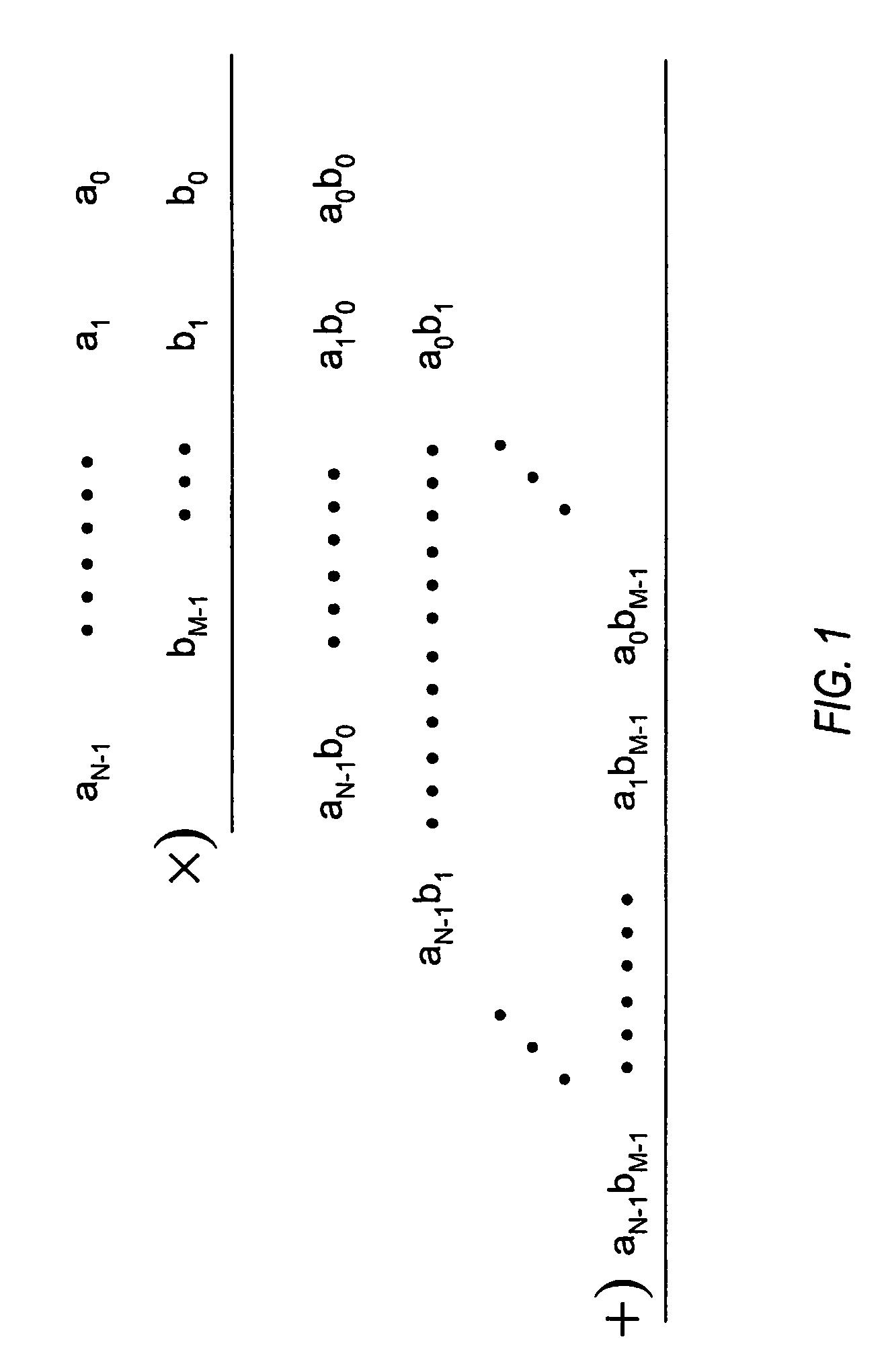
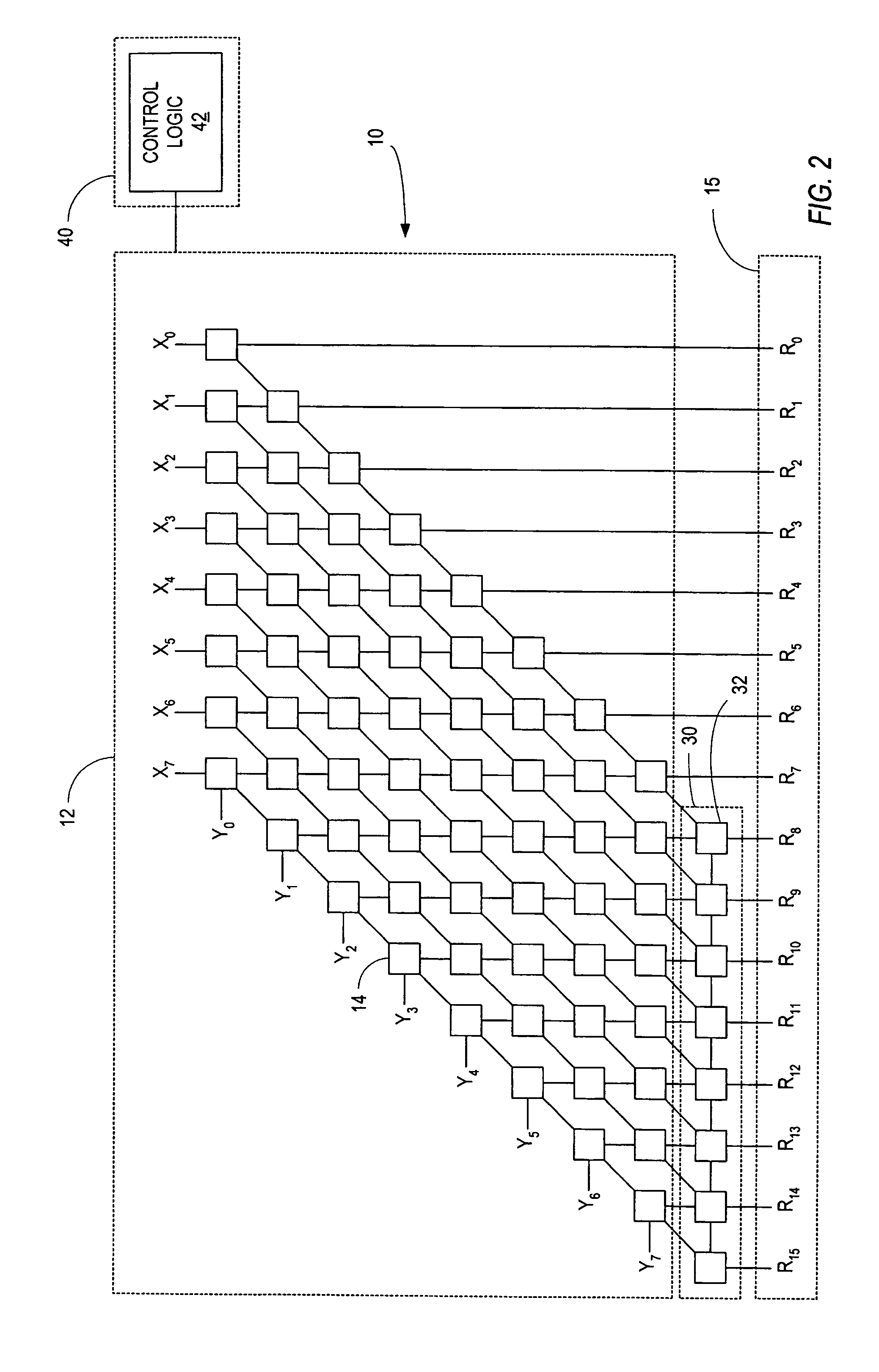
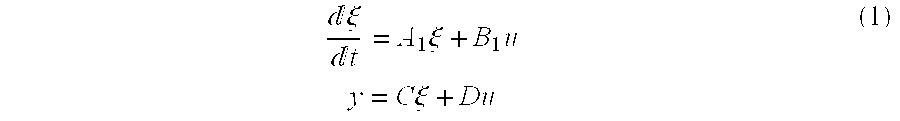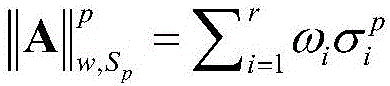Patents
Literature
536 results about "Lagrange multiplier" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematical optimization, the method of Lagrange multipliers is a strategy for finding the local maxima and minima of a function subject to equality constraints (i.e., subject to the condition that one or more equations have to be satisfied exactly by the chosen values of the variables). The basic idea is to convert a constrained problem into a form such that the derivative test of an unconstrained problem can still be applied.
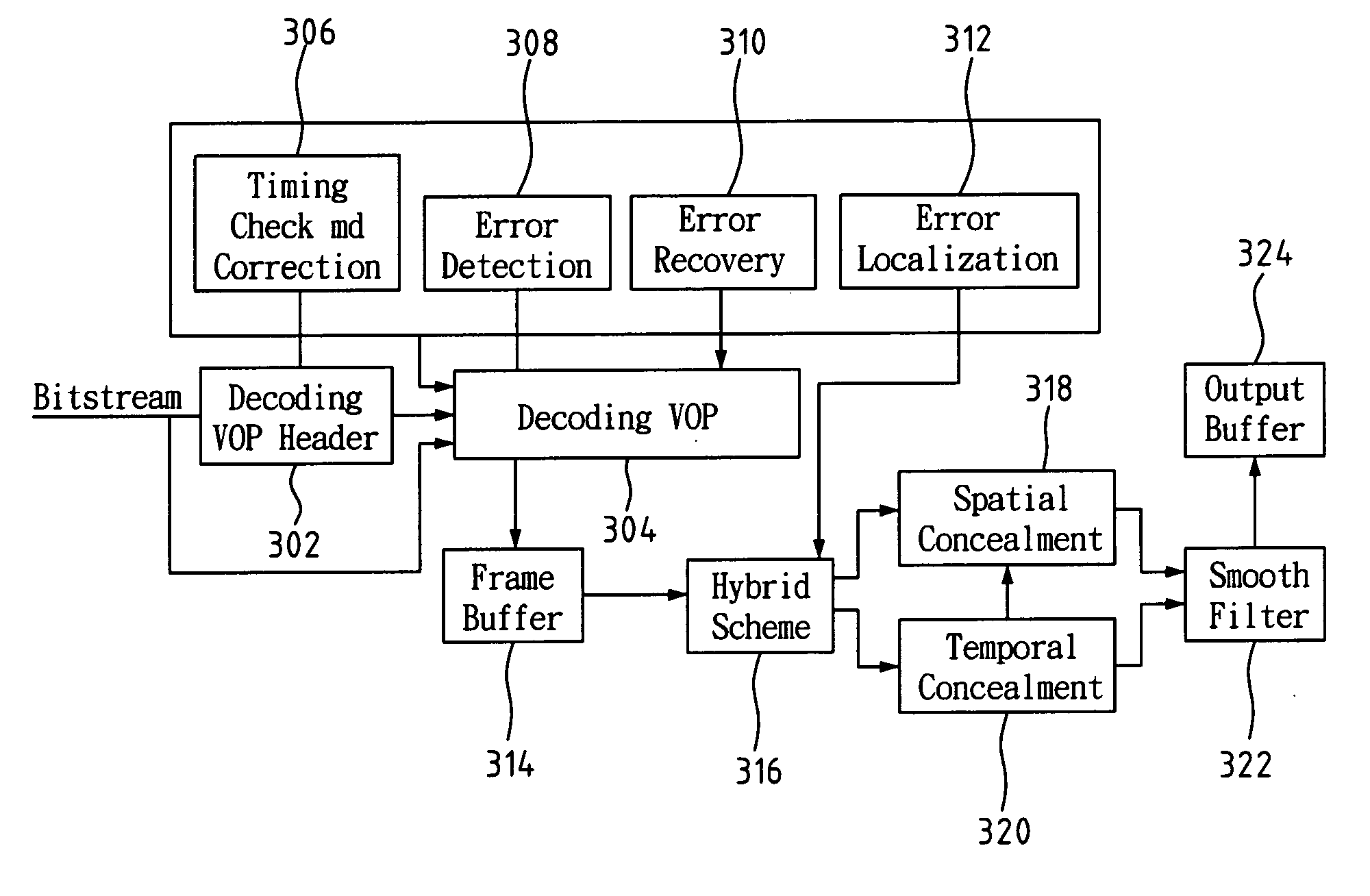
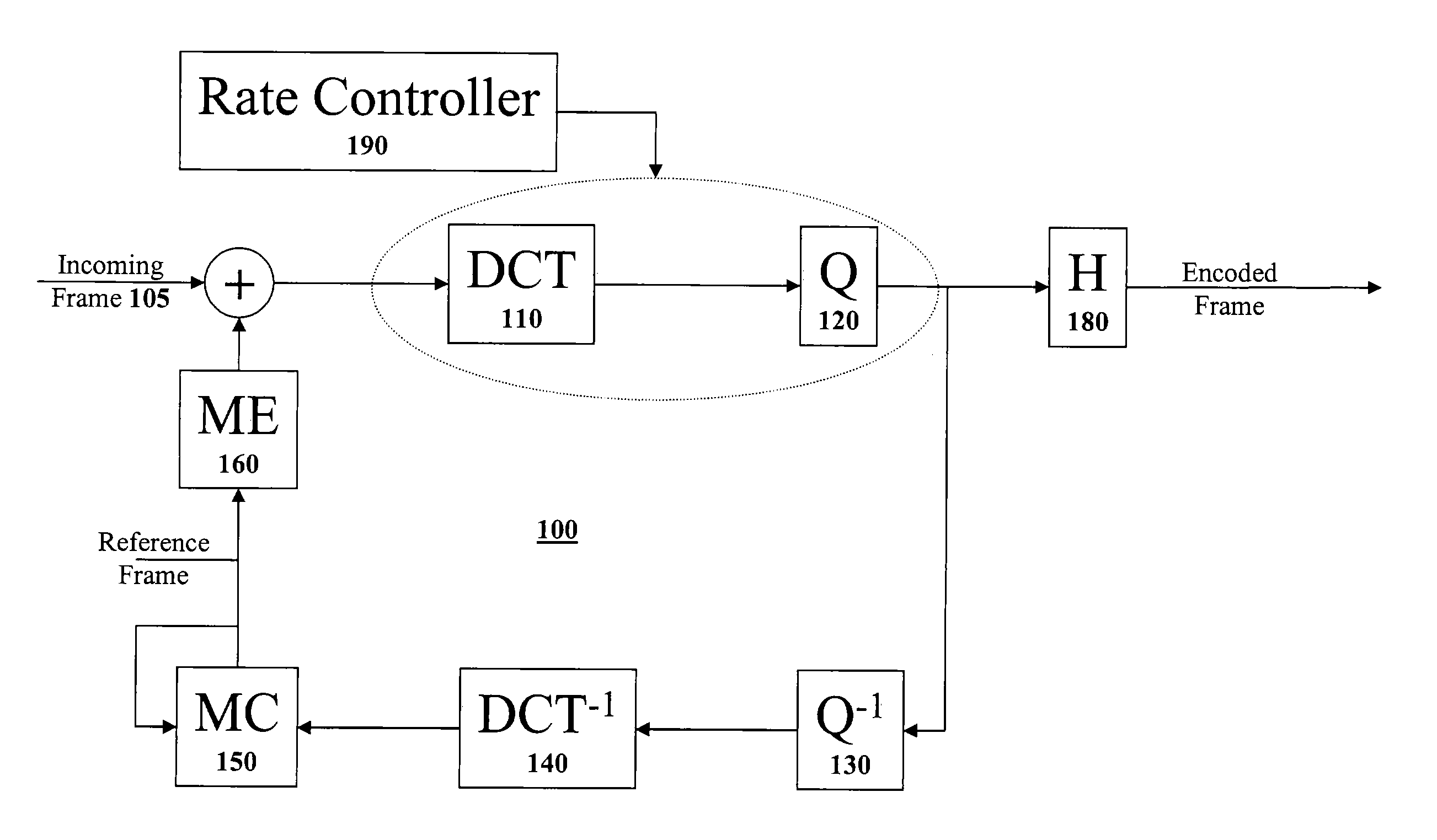
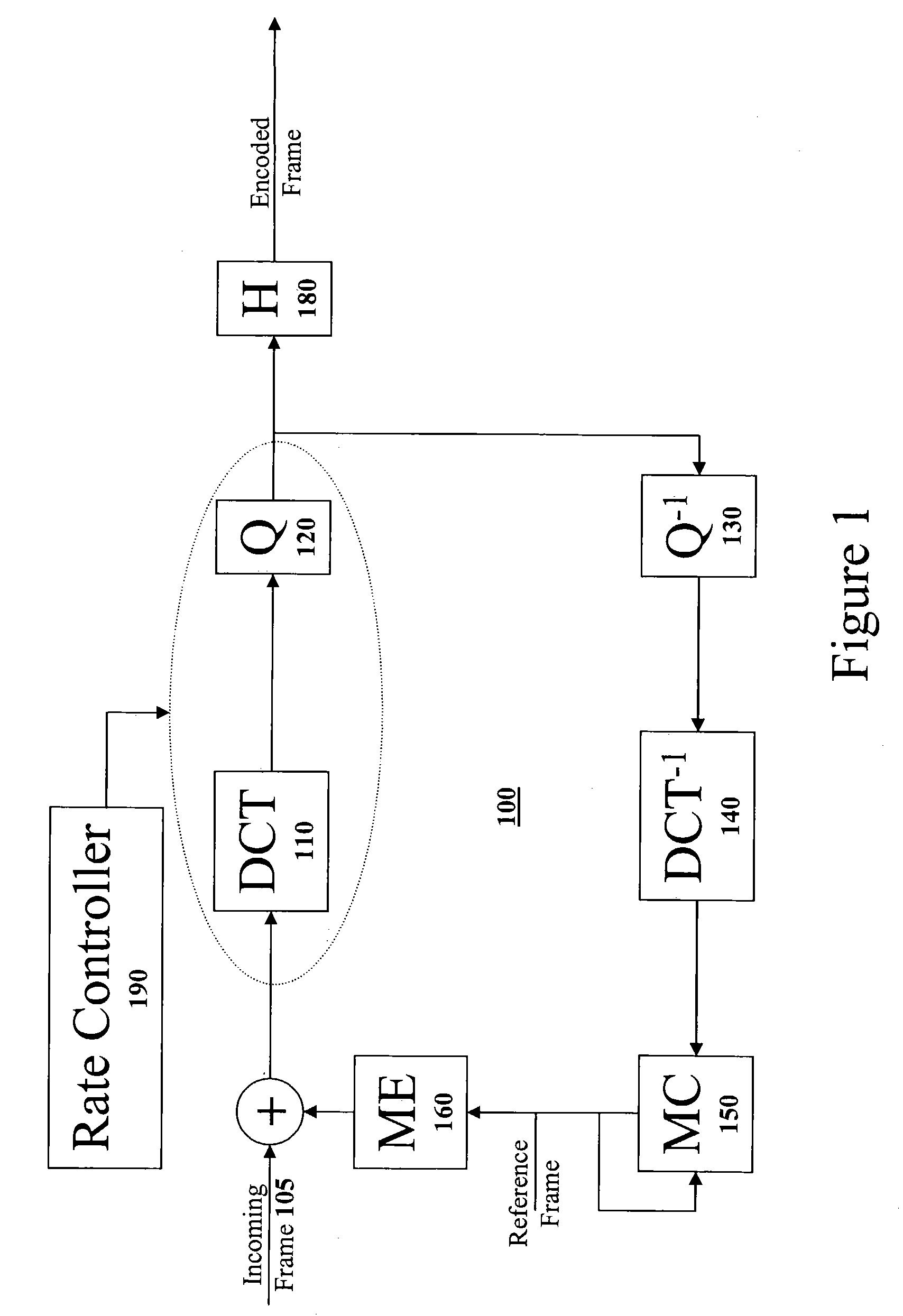
MPEG-4 streaming system with adaptive error concealment
InactiveUS20060104366A1Minimal overheadBest rate-distort balanceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPacket lossError concealment
An MPEG-4 system with error concealment is provided for video service under the network with packet loss. The MPEG-4 system includes an encoder and a decoder. The encoder uses an intra-refreshment technique is used to make coded bitstream more robust against noise in order to stop error propagation. The rate-distortion optimization criterion is also introduced to adaptively update in synchronization with intra-coded blocks adaptively based on the true network condition with minimal overhead. The Lagrange multiplier is modified to achieve the best rate-distortion balance. In addition, a decoder loop is used in the encoder and is synchronized with the true decoder to achieve the best performance and avoid mismatch with the decoder used in the MPEG-4 system. The decoder is able to achieve resilient decoding from any kind of noise and enhance the reconstructed image quality with spatial and temporal hybrid concealment method. The result shows that a 3.65-9.71 dB further improvement on peak-signal-to-noise-ratio (PSNR) can be achieved in comparison with the existing methods that adopt spatial copy and zero motion concealment in decoding.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
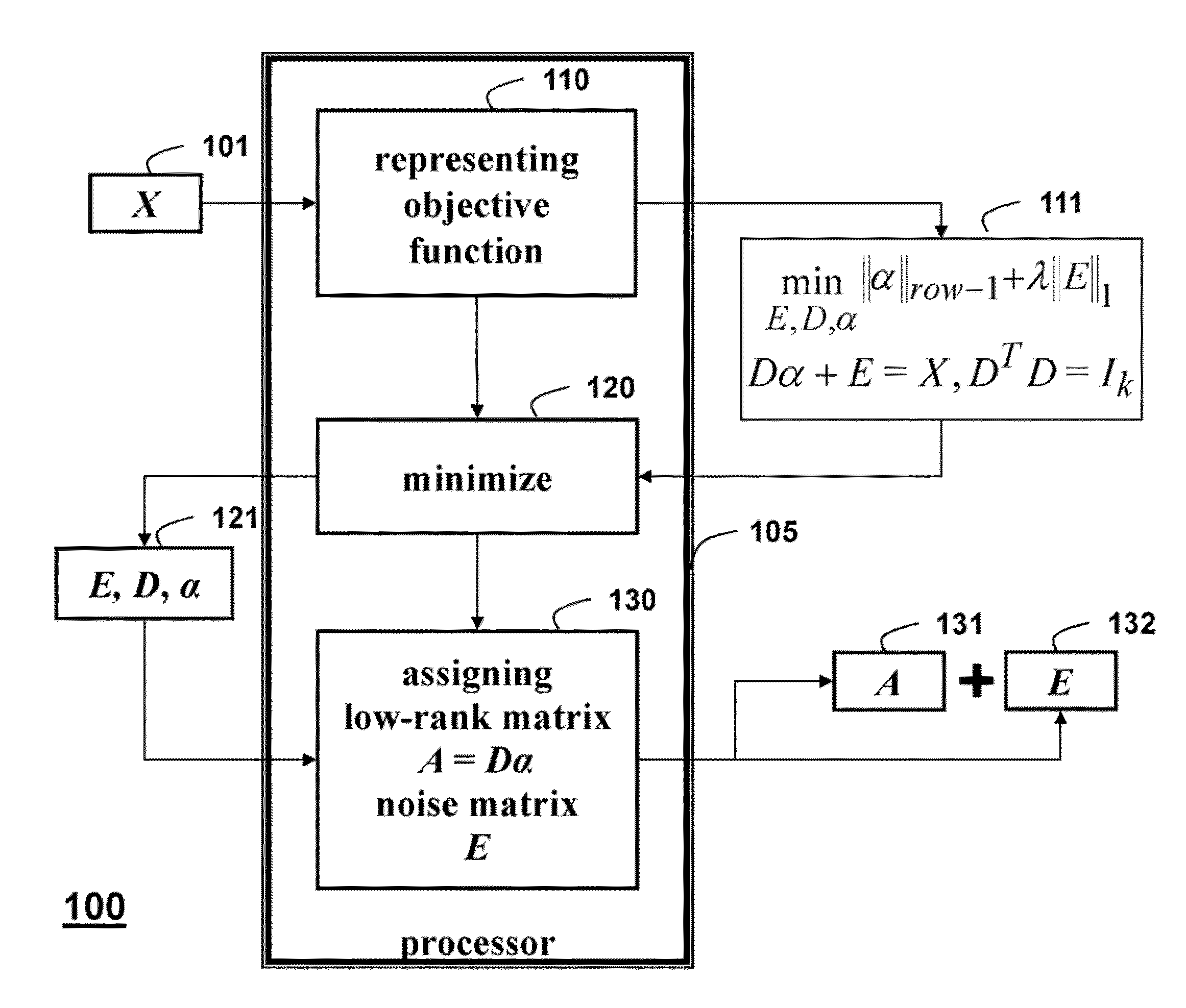
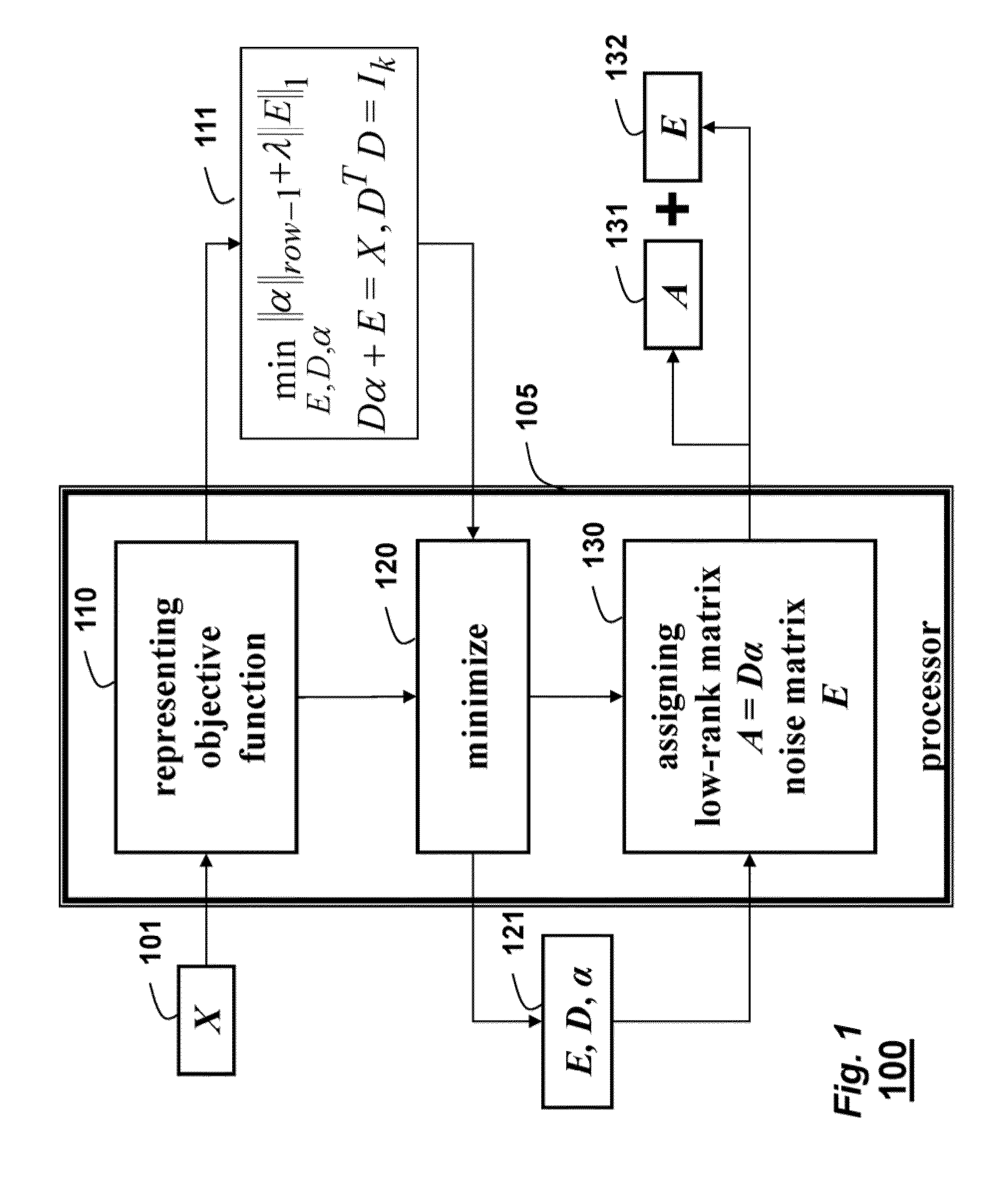
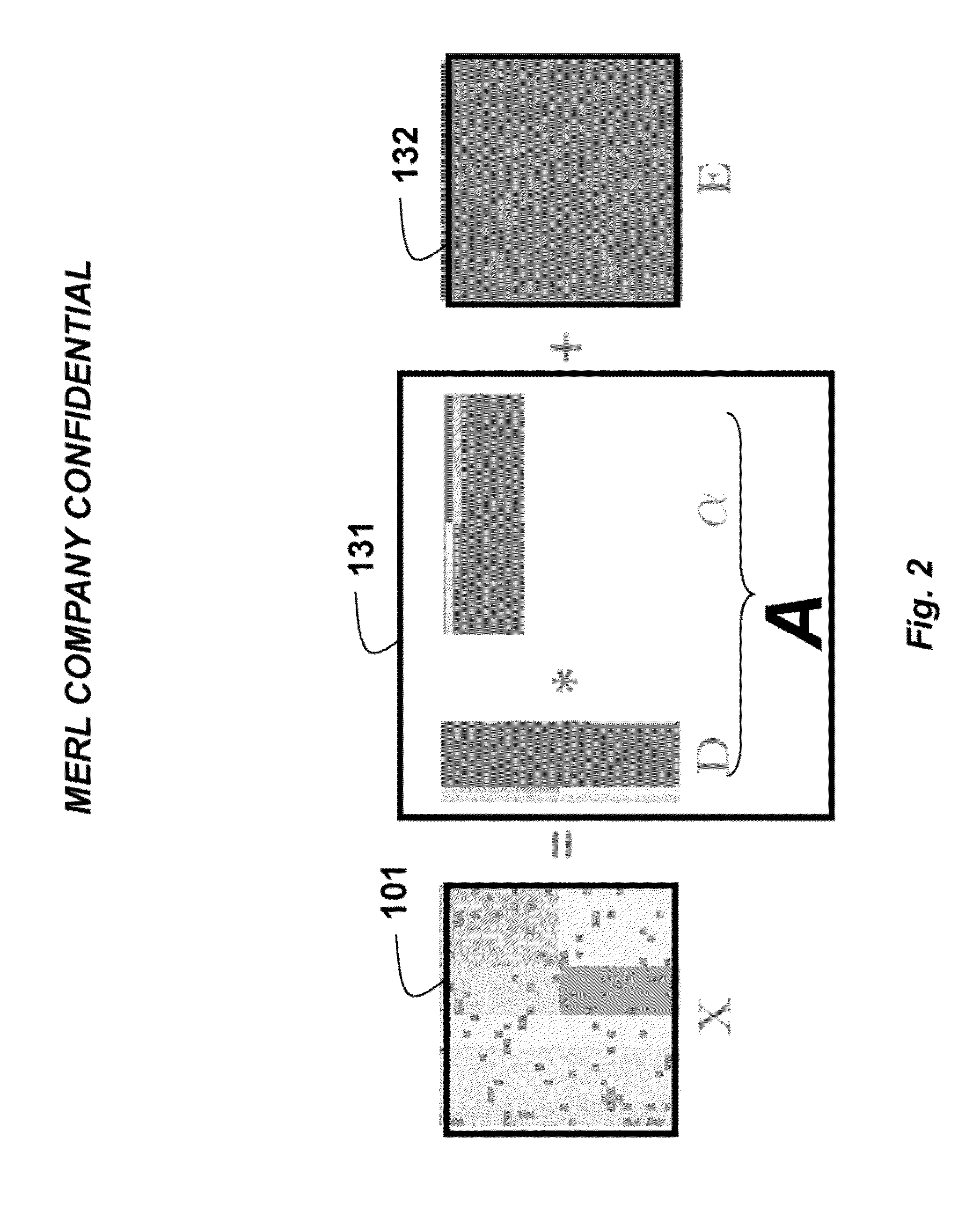
Method for Recovering Low-Rank Matrices and Subspaces from Data in High-Dimensional Matrices
InactiveUS20130191425A1Effective recoveryFaster robust low-rank recoveryDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsAugmented lagrange multiplierAlgorithm
A method recovers an uncorrupted low-rank matrix, noise in corrupted data and a subspace from the data in a form of a high-dimensional matrix. An objective function minimizes the noise to solve for the low-rank matrix and the subspace without estimating the rank of the low-rank matrix. The method uses group sparsity and the subspace is orthogonal. Random subsampling of the data can recover subspace bases and their coefficients from a much smaller matrix to improve performance. Convergence efficiency can also be improved by applying an augmented Lagrange multiplier, and an alternating stepwise coordinate descent. The Lagrange function is solved by an alternating direction method.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
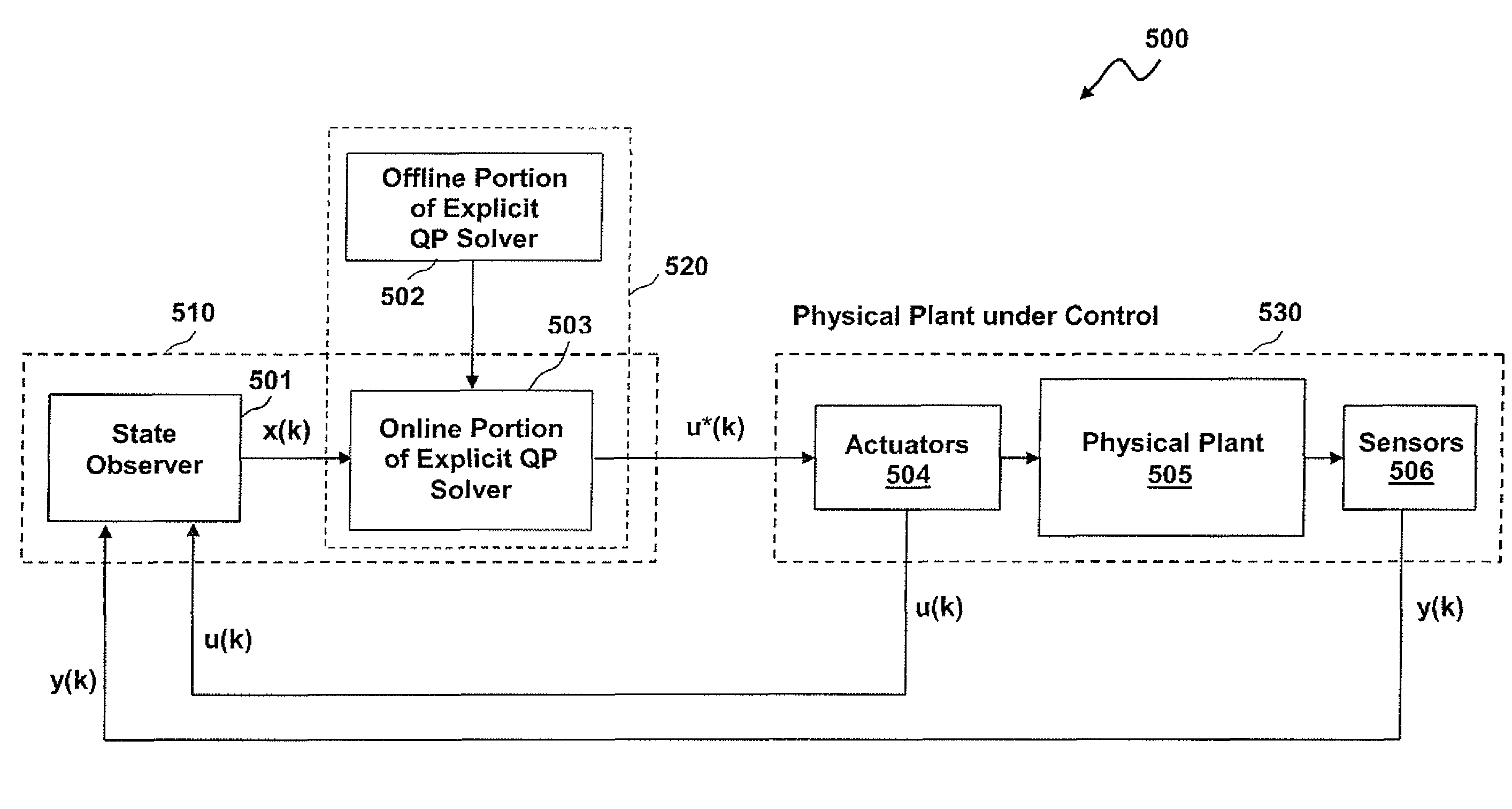
Methods and systems for the design and implementation of optimal multivariable model predictive controllers for fast-sampling constrained dynamic systems
ActiveUS8078291B2Minimize the numberReduce searchComputation using non-denominational number representationAdaptive controlAlgorithmPredictive controller
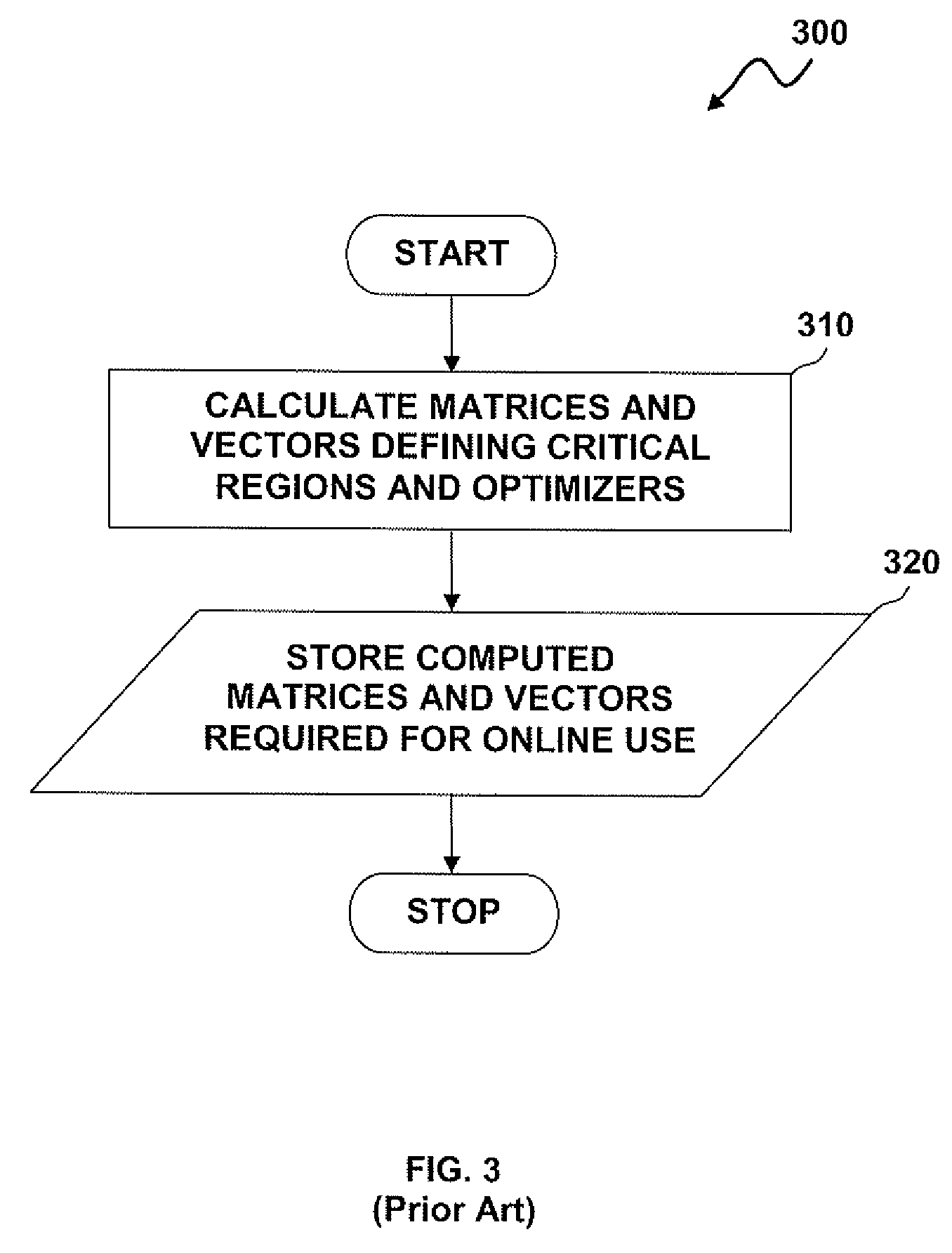
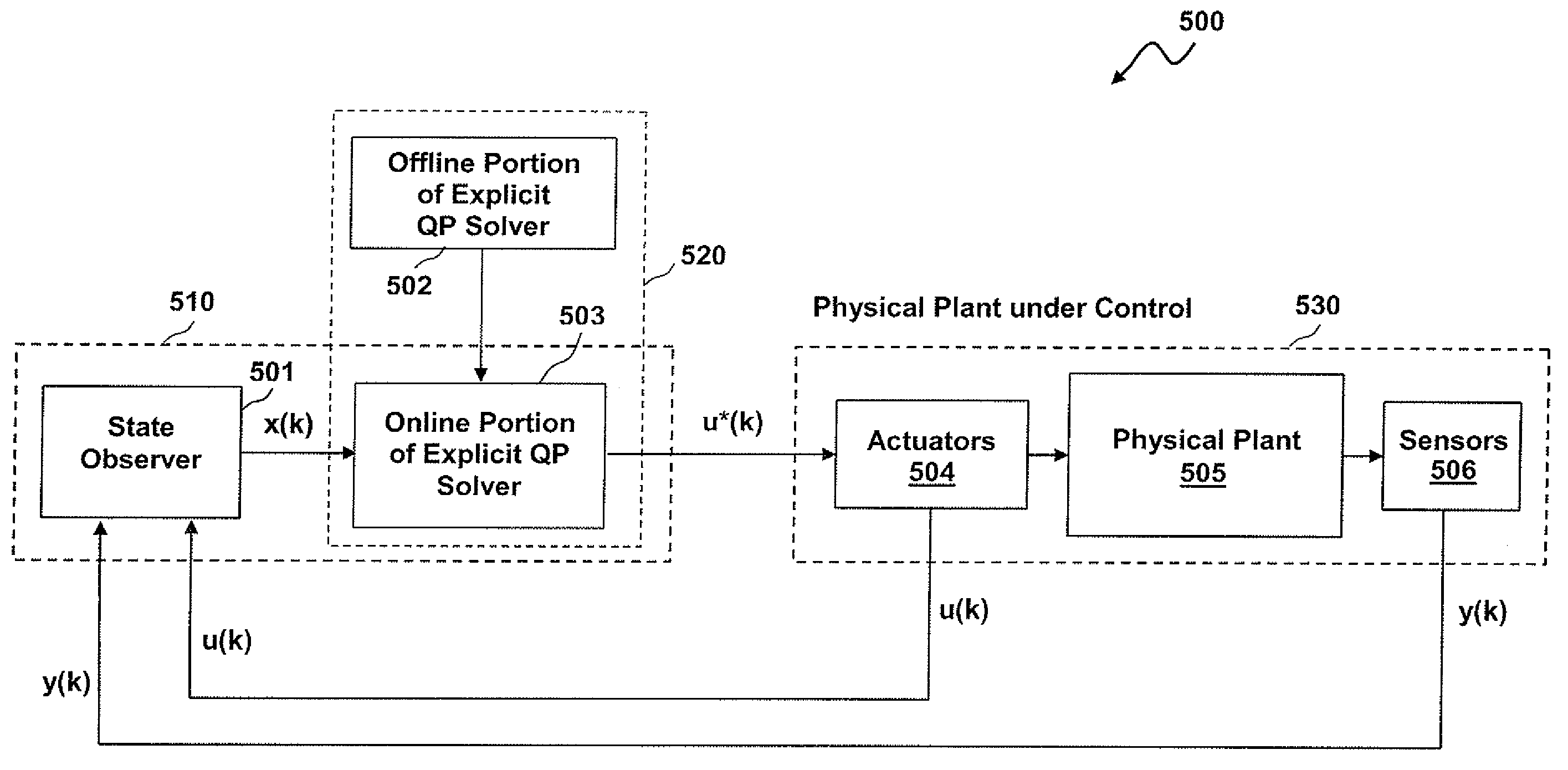
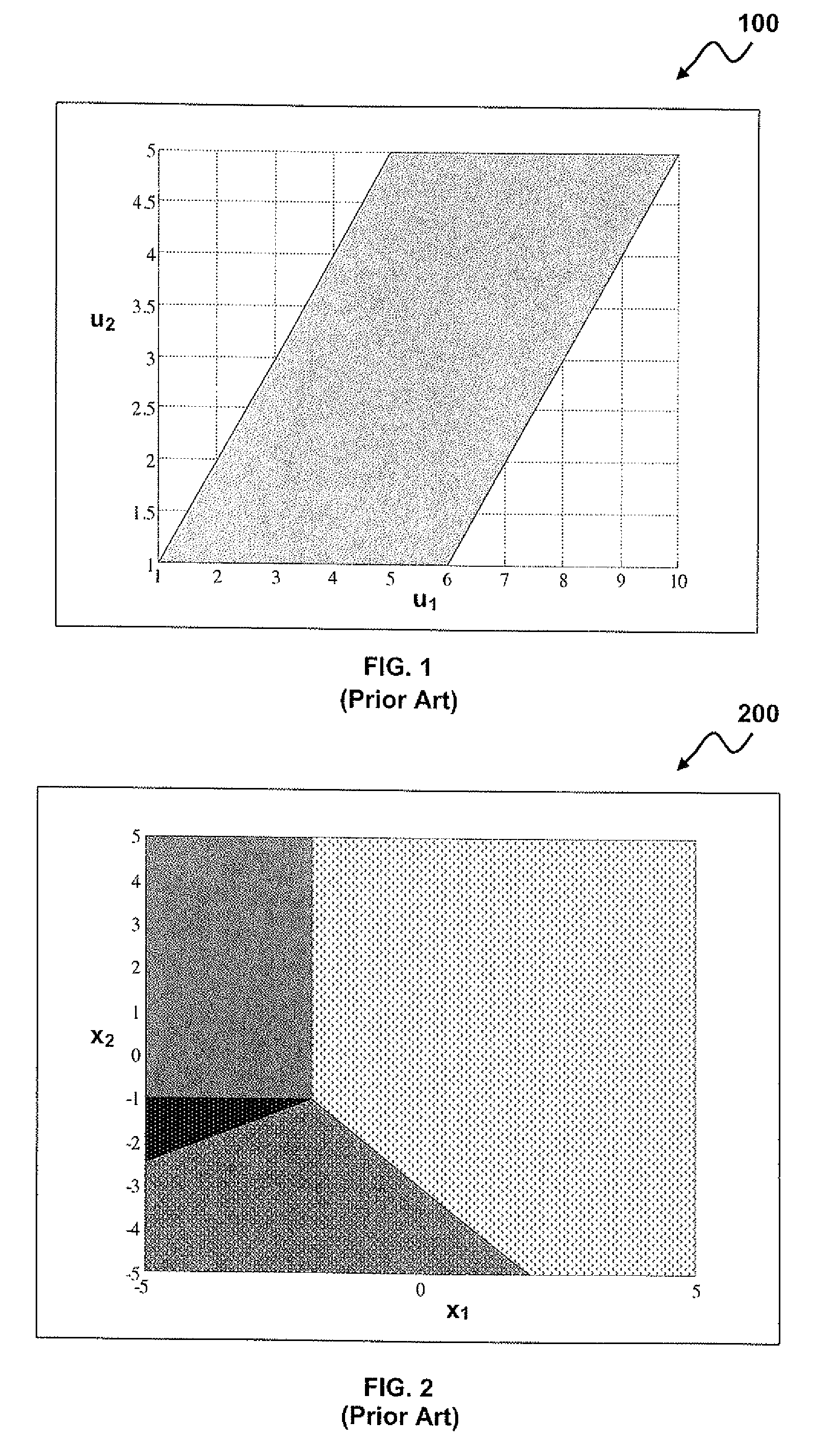
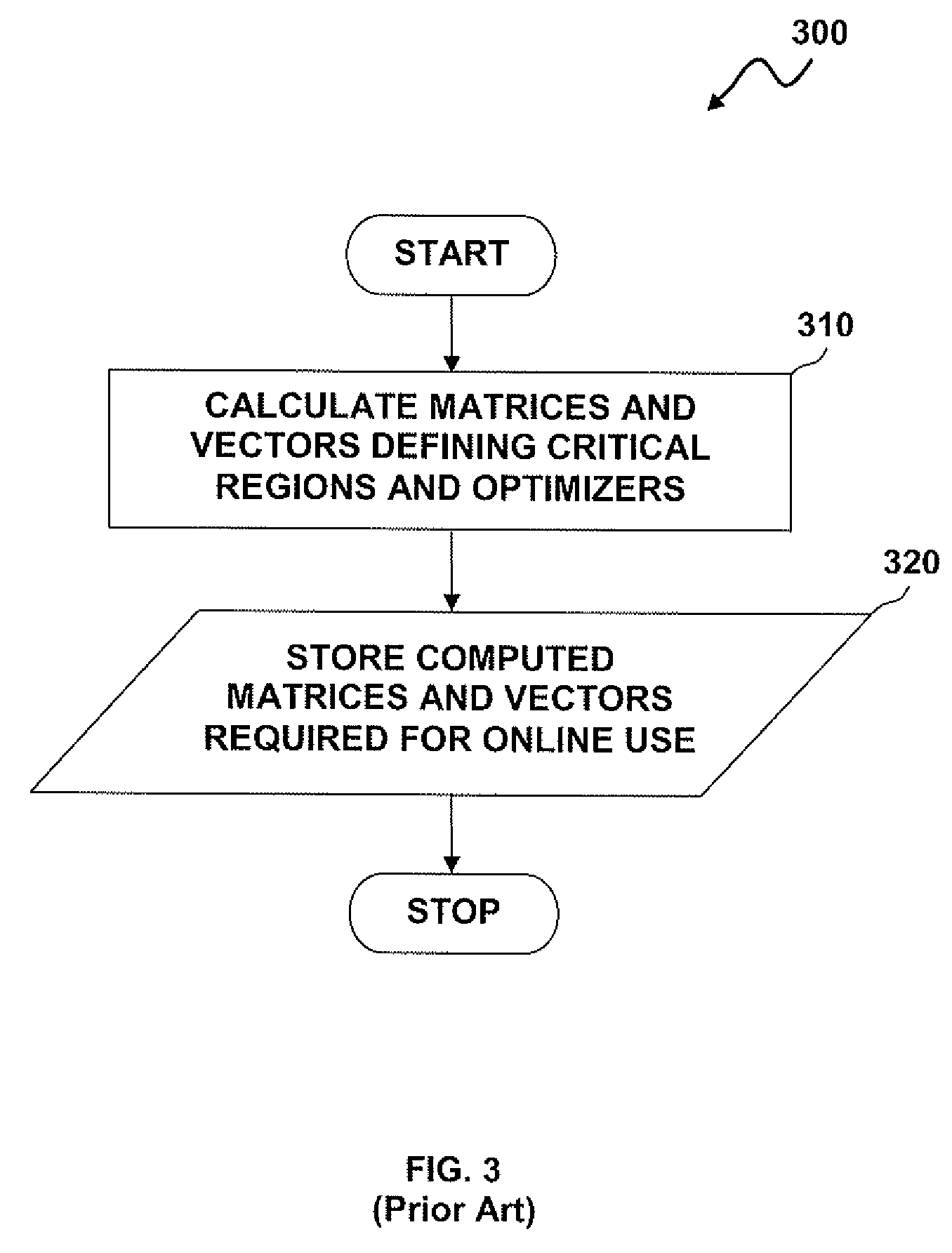
Methods and systems for the design and implementation of optimal multivariable MPC controllers for fast-sampling constrained dynamic systems utilizing a primal-dual feasibility approach and / or a graph approach. The primal-dual feasibility approach can compute and store matrices defining constraints of quadratic programming problems in an off-line part in order to calculate vectors of Lagrange multipliers and an optimizer. Then primal-dual feasibility can be checked in an on-line part using the Lagrange multipliers and the optimizer can provide a unique optimal solution for the constrained dynamic system. The graph approach can compute and store the matrices and the vectors, and also prepare and store a structure of directed graph in off-line part. An optimizer for a given parameter vector can be determined in on-line part using the directed graph, the matrices and the vectors.
Owner:GARRETT TRANSPORATION I INC
Broadband sensor location selection using convex optimization in very large scale arrays
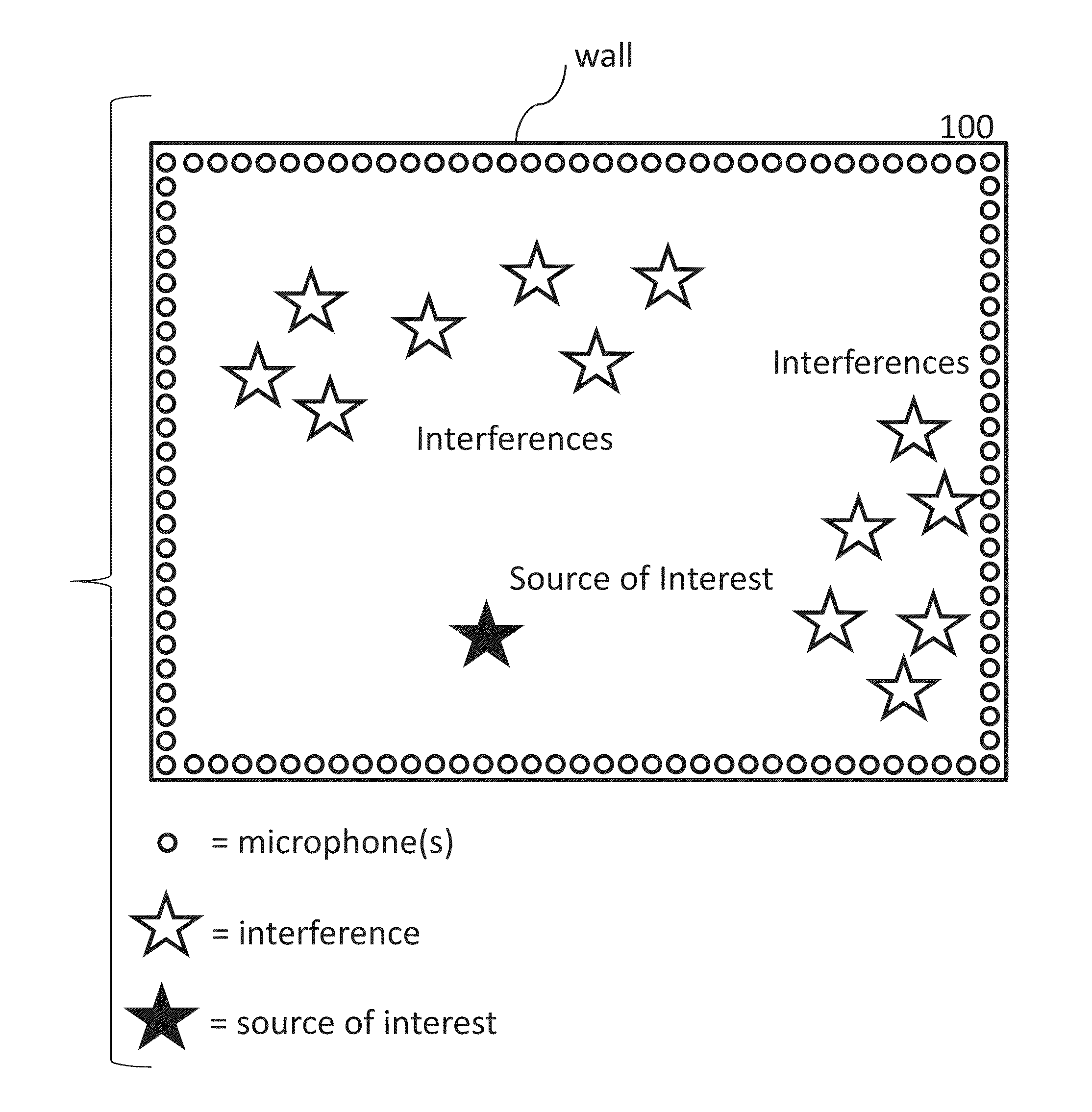
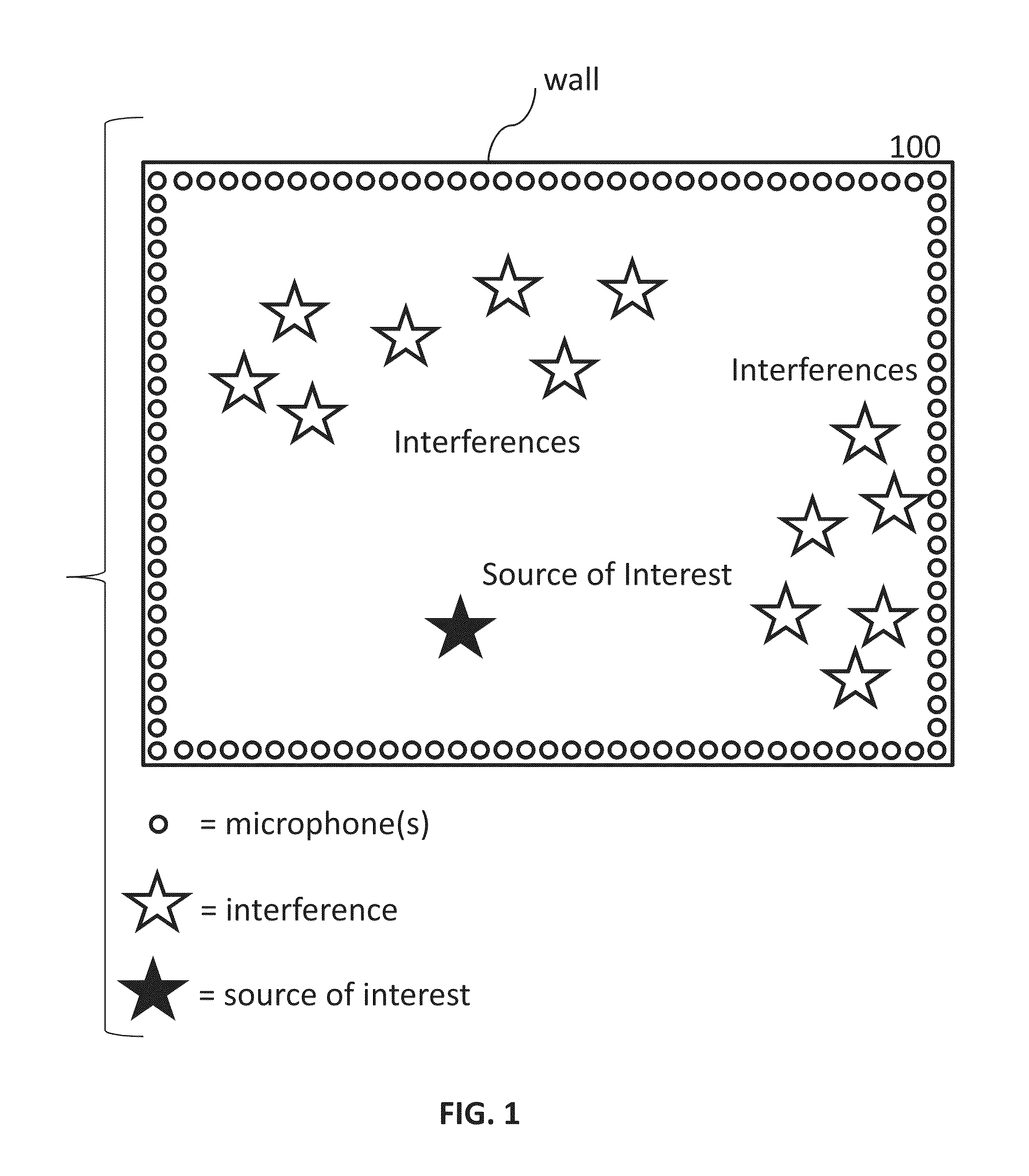
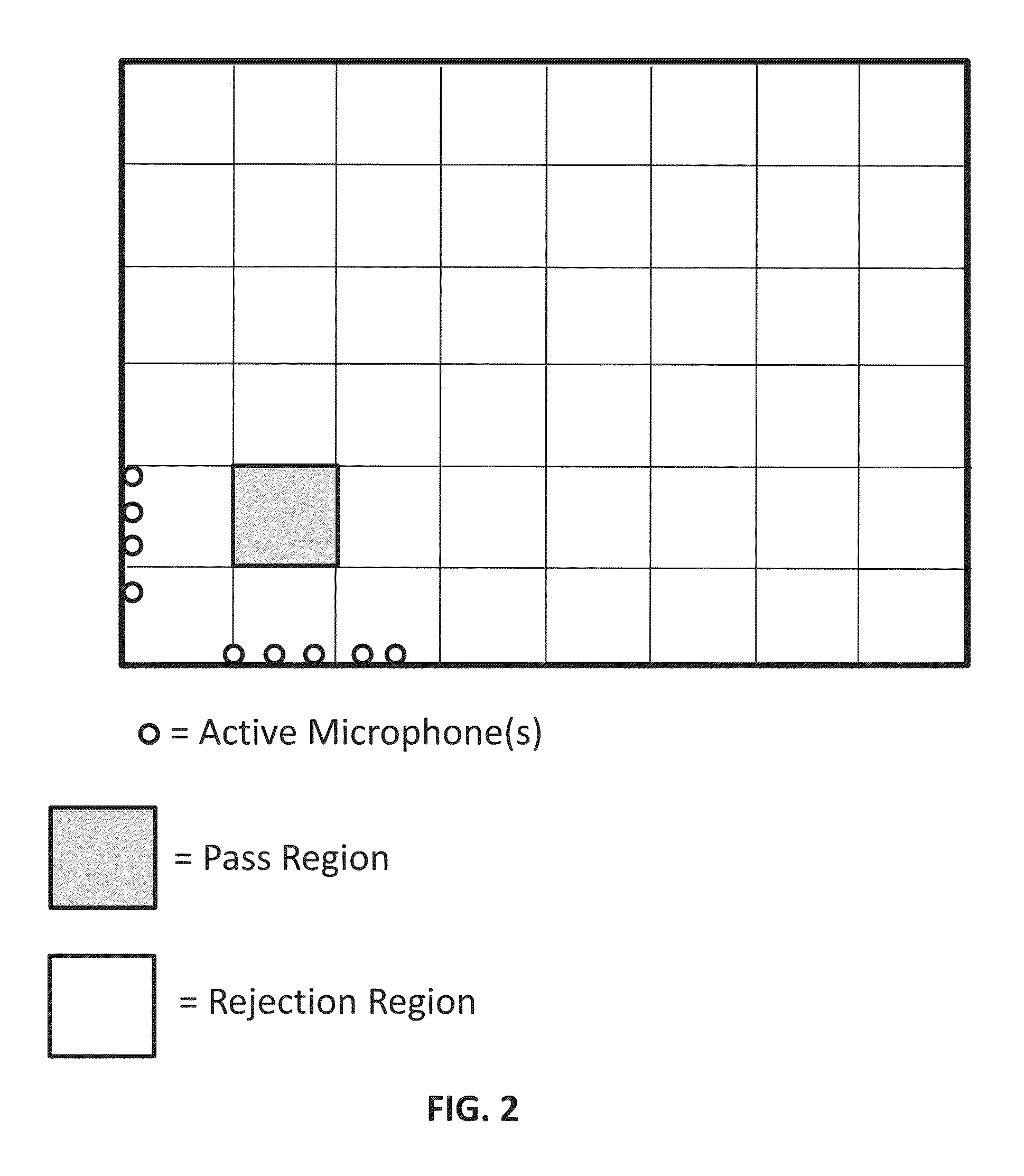
Systems and methods are provided to determine a subset of D microphones in a set of N microphones on a perimeter of a space to monitor a target location. The space is divided into L interference locations. An equation is solved to determine microphone weights for the N microphones by minimizing the maximum gain for signals related to the target location and interference locations, further optimized over an l1 penalty by applying a Lagrange multiplier to an l1 norm of the microphone weights in a manner that determines a set of D non-zero microphones weights and a set of (N−D) microphone weights that are zero or close to zero. Microphone weights are determined for at least 2 different frequencies.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND +1
Method for accurately estimating wind power prediction error interval
InactiveCN105303266AFits the true distributionShorten the lengthForecastingInformation technology support systemElectricityConfidence interval
The invention discloses a method for accurately estimating wind power prediction error intervals. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, obtaining historical wind power data of a wind power plant; secondly, calculating wind power predication errors of all prediction points of the wind power plant, and establishing a wind power predication error distribution model; thirdly, establishing an error probability density function according to the distribution of the predication errors; fourthly, obtaining a confidence interval, meeting a certain confidence level, of the predication errors according to a given wind power predication value; and fifthly, calculating the shortest confidence interval through a Lagrange multiplier algorithm. On the basis of point predication, a probability density function of wind power prediction errors is obtained through interval prediction, and the confidence interval under a certain confidence level is calculated by a probability theory. In this way, the reliability of the interval to contain a wind power point predication value is determined, and the precision of wind power interval prediction is effectively improved.
Owner:RES INST OF ECONOMICS & TECH STATE GRID SHANDONG ELECTRIC POWER +2
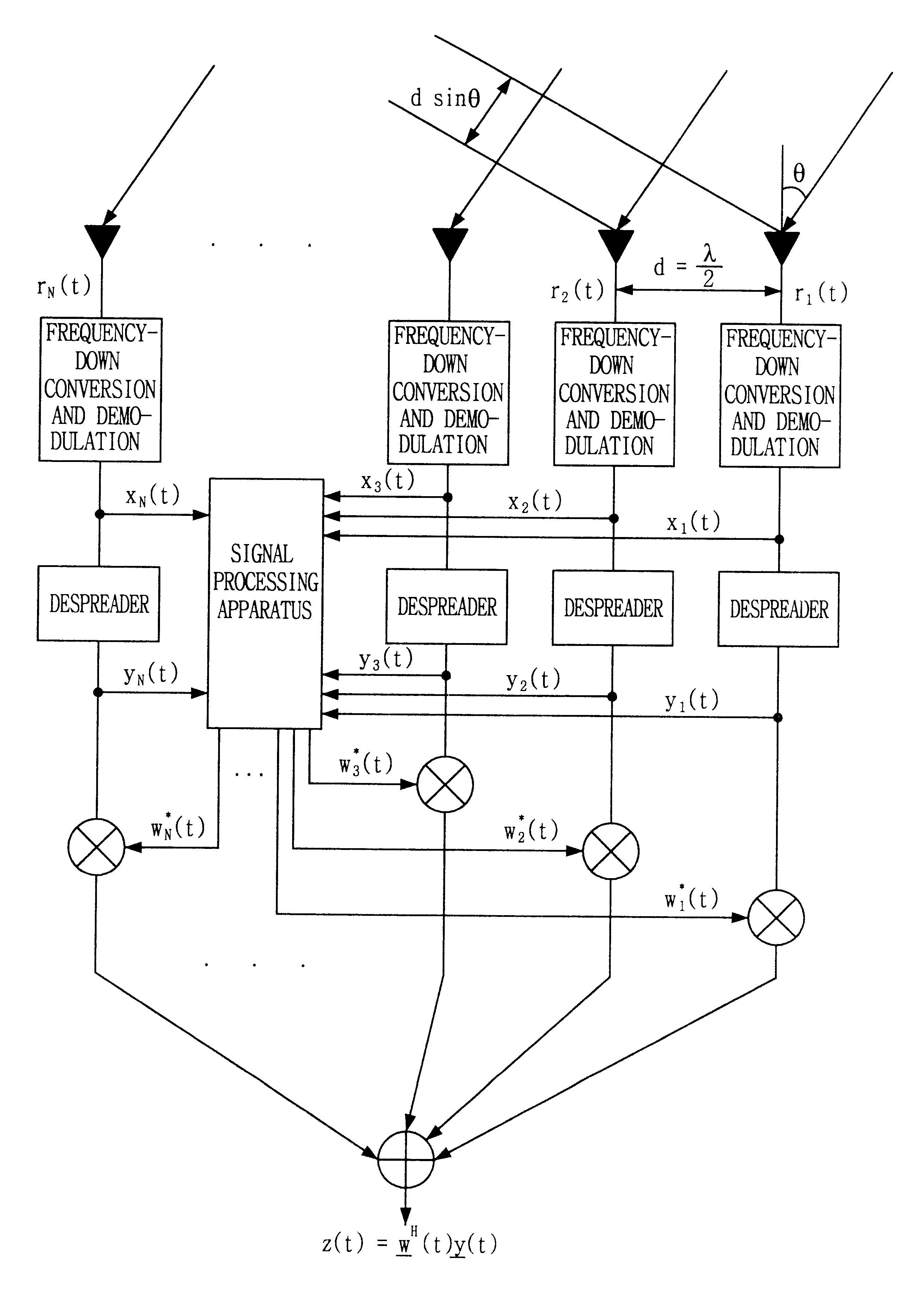
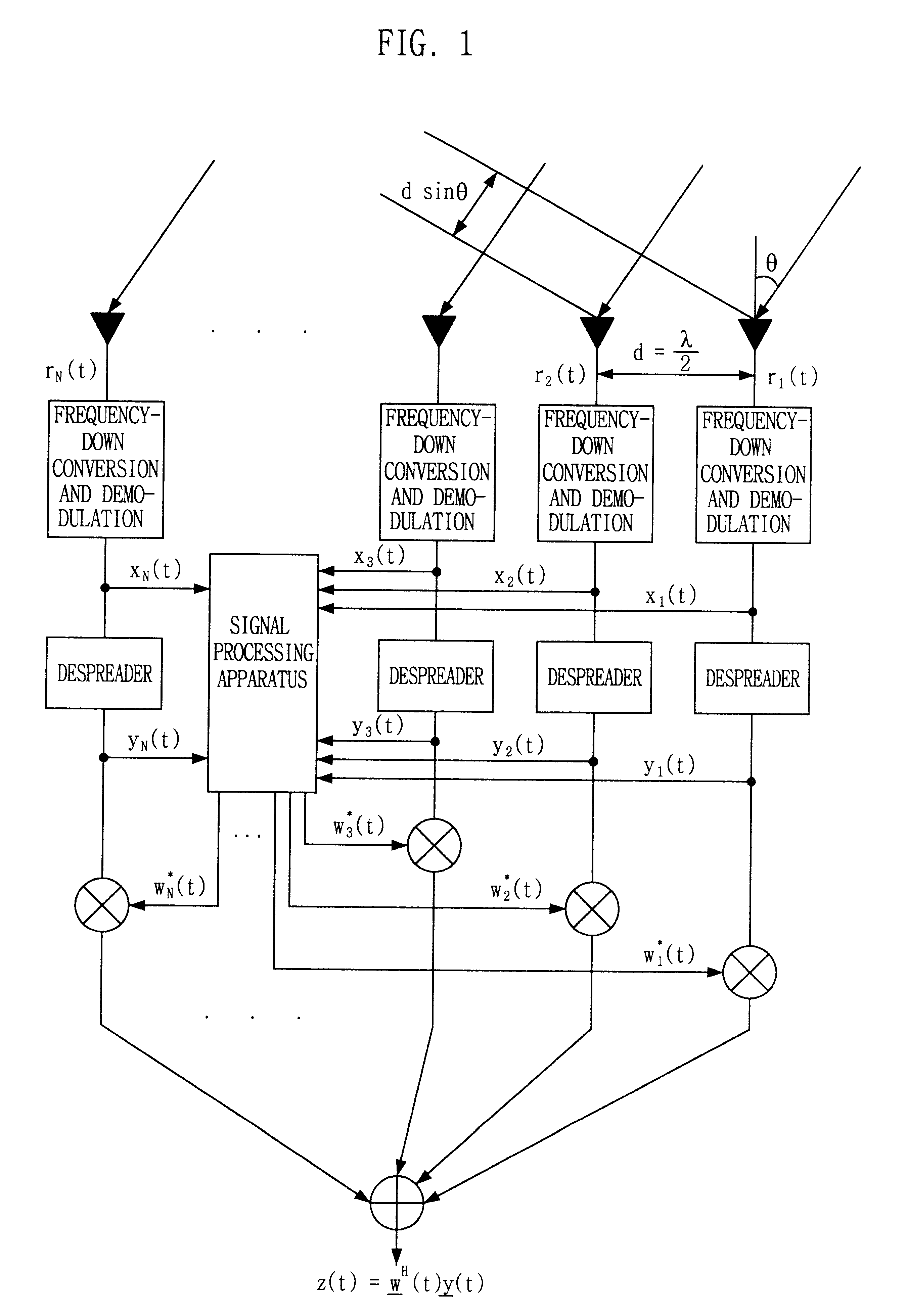
Signal processing method and apparatus for computing an optimal weight vector of an adaptive antenna array system
InactiveUS6462709B1Simple and accurate wayMaximizes the signal to interference plus noise ratioSpatial transmit diversityRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsOff the shelfTarget signal
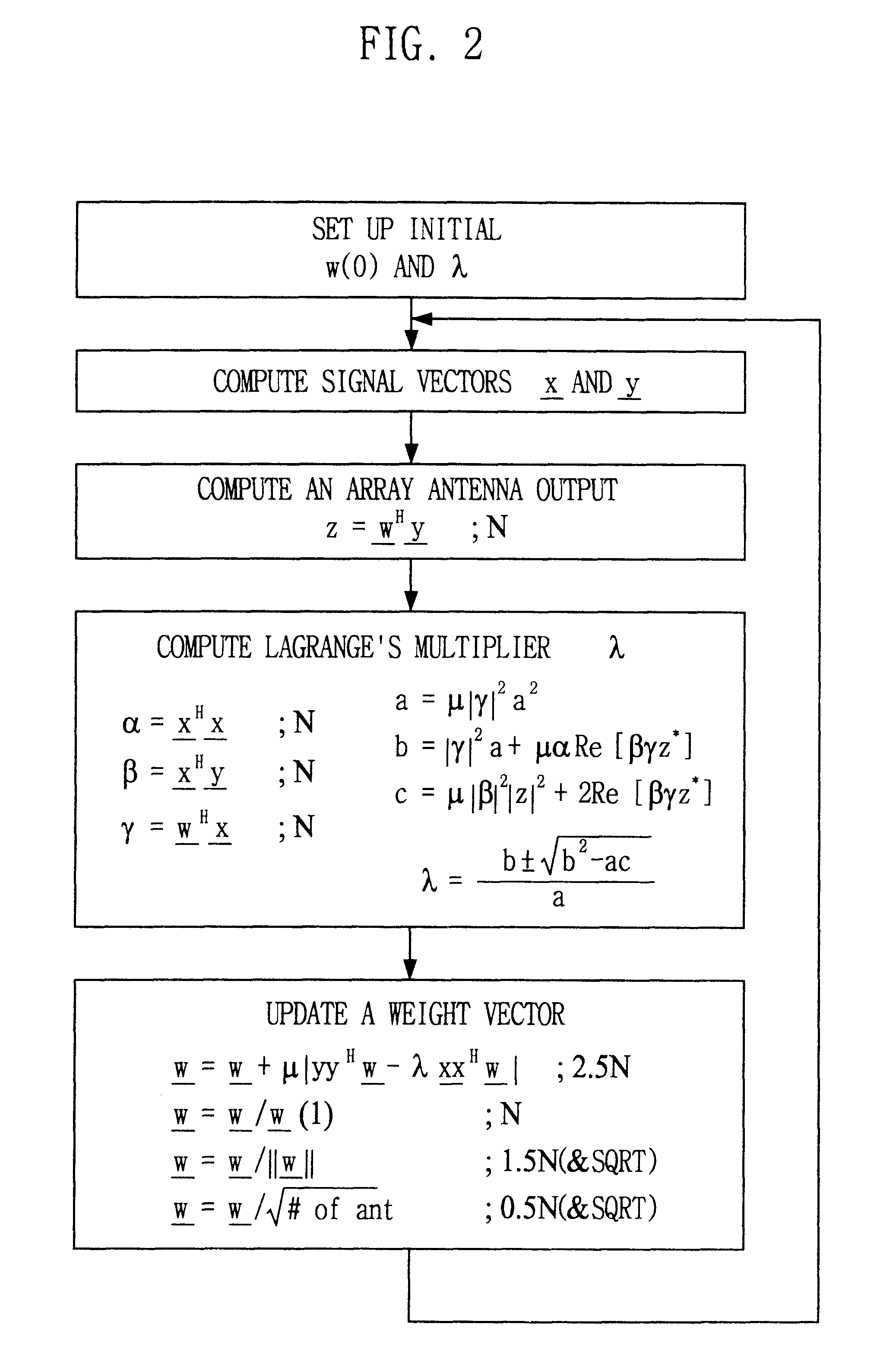
This invention relates to a signal processing method and apparatus for an adaptive array antenna. The objective is to suggest an adaptive procedure of computing the suboptimal weight vector for an array antenna system that provides a beampattern having its maximum gain along the direction of the mobile target signal source in a blind signal environment, where the transmitted data are not known (or not to be estimated) at the receiver. It is the ultimate goal of this invention to suggest a practical way of enhancing both the communication quality and communication capacity through the optimal weight vector of the array system that maximizes SINR(Signal to Interference+Noise Ratio). In order to achieve this goal, the method of Lagrange multiplier is modified in such a way that the suboptimal weight vector is produced with the computational load of about O(8N), which has been found to be small enough for the real-time processing of signals in most land mobile communications with the digital signal processor (DSP) off the shelf, where N denotes the number of antenna elements of the array.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
Proportional fair scheduler for OFDMA wireless systems with QOS constraints
InactiveUS20070248048A1Frequency-division multiplexRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of serviceNon real time
Available bandwidth and power for users demanding real time and non-real time data traffic are scheduled, while maximizing proportional fairness for the users over a plurality of time slots, and meeting quality of service constraints for real time data traffic users. The Lagrangian multipliers are used to define a function which includes the proportional fair capacity over the plurality of time slots, and the total power, the total bandwidth, and rate of the real time users' constraints. A maximum of the function is determined for each time slot by binary searching two parameters while observing the total power and total bandwidth. An optimal allocation of the bandwidth and power for the time slot is calculated using the two parameters.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Low power array multiplier
InactiveUS7546331B2Lower latencyReduce power consumptionComputation using non-contact making devicesArray data structureBinary multiplier
An array multiplier comprises a partial product array including a plurality of array elements and a final carry propagate adder. Operands smaller than a corresponding dimension of the partial product array are shifted toward the most significant row or column of the array to reduce the number of array elements used to compute the product of the operands. Switching activity in the unused array elements may be reduced by turning off power to the array elements or by padding the shifted operands with zeros in the least significant bits. Additional power saving may be achieved by having bypass lines in the partial product array that bypasses non-essential array elements and by feeding partial sum and carry directly to the final carry propagate adder. Elements of the carry propagate adder may also be bypassed to achieve further power reduction.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
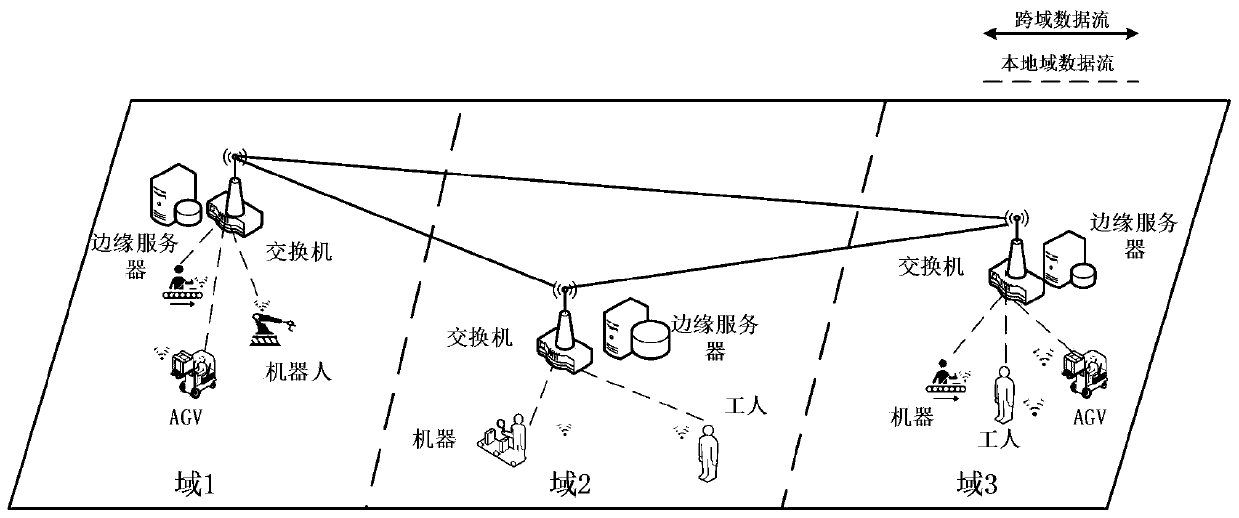
Resource allocation method in distributed heterogeneous environment in mobile edge computing
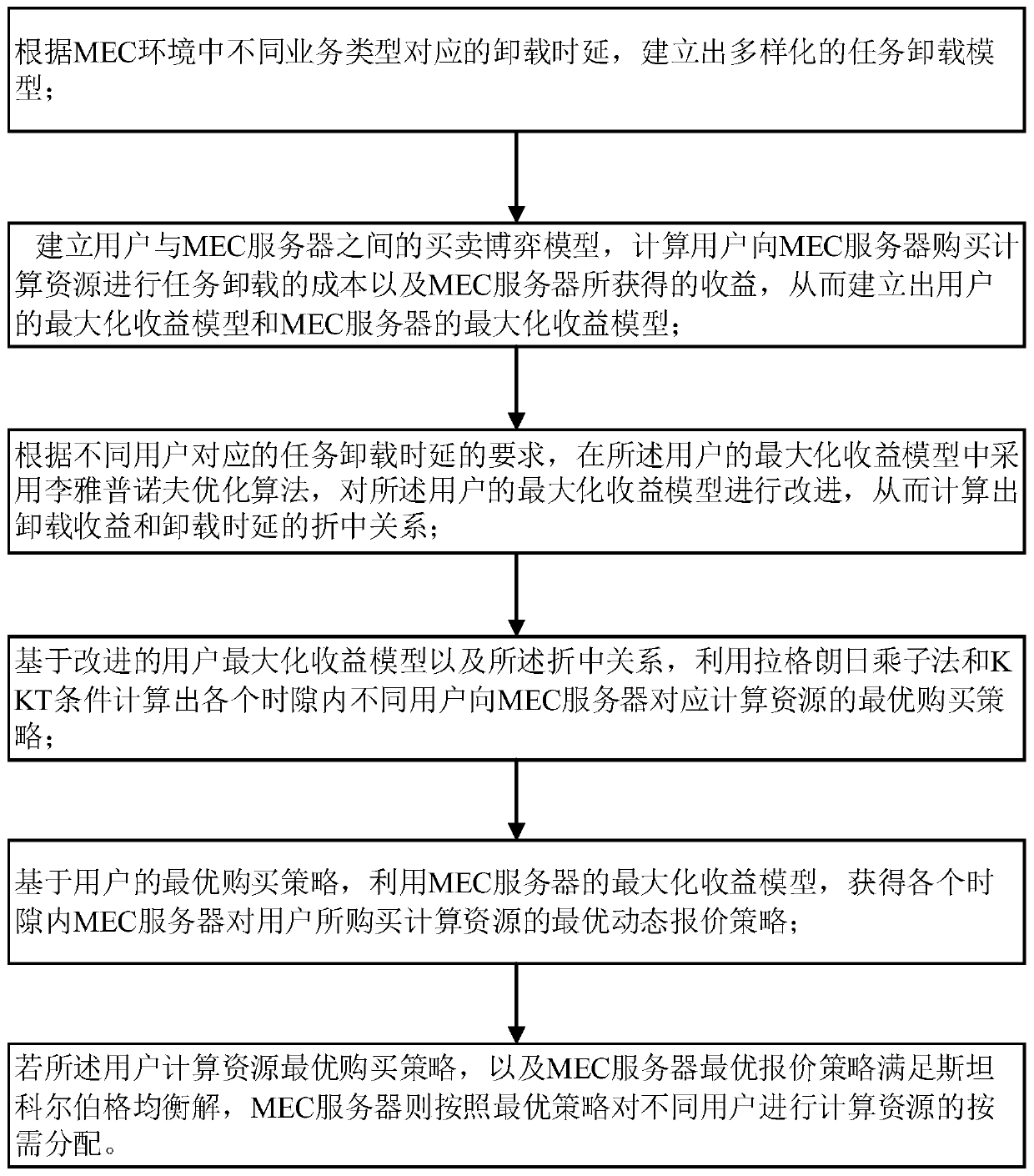
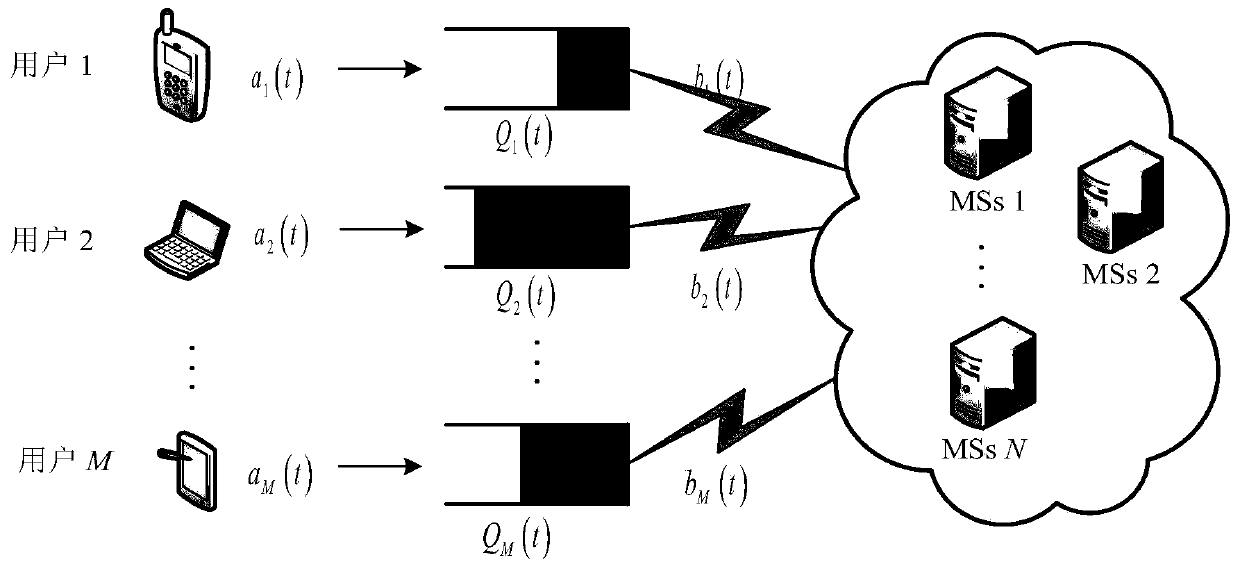
ActiveCN111163521ASignificant heterogeneityAchieve resilienceInference methodsWireless communicationLyapunov optimizationResource assignment
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communication, and relates to a resource allocation method in a distributed heterogeneous environment in mobile edge computing. The method comprises the steps of establishing diversified task unloading models according to unloading delays corresponding to different service types in an MEC environment; establishing a buying and selling game model between the user and the MEC server; respectively establishing maximized income models of the user and the MEC server; adopting a Lyapunov optimization algorithm to improve the user model, and solving an optimal purchase strategy of the user through a Lagrange multiplier method and KKT conditions; solving an optimal quotation strategy of the MEC server based on the strategy; and if the optimal purchase strategy and the optimal quotation strategy satisfy a Stackleberg equilibrium solution, allocating computing resources of different users as required according to the optimal strategy by the MEC server. By means of the method, compromise of user unloading income and time delay can be achieved, and elastic control and on-demand distribution of task unloading and computing resource distribution can be achieved.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for Solving Quadratic Programs for Convex Sets with Linear Equalities by an Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers with Optimized Step Sizes
ActiveUS20150234779A1Minimizes violationMinimizes numberCode conversionComplex mathematical operationsAlgorithmEuclidean vector
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Side-lobe suppression method for three-dimensional array antenna pattern based on improved MOPSO and convex optimization algorithm
ActiveCN106886656AImprove performanceReduce optimization timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsAntenna radiation patternsMathematical model
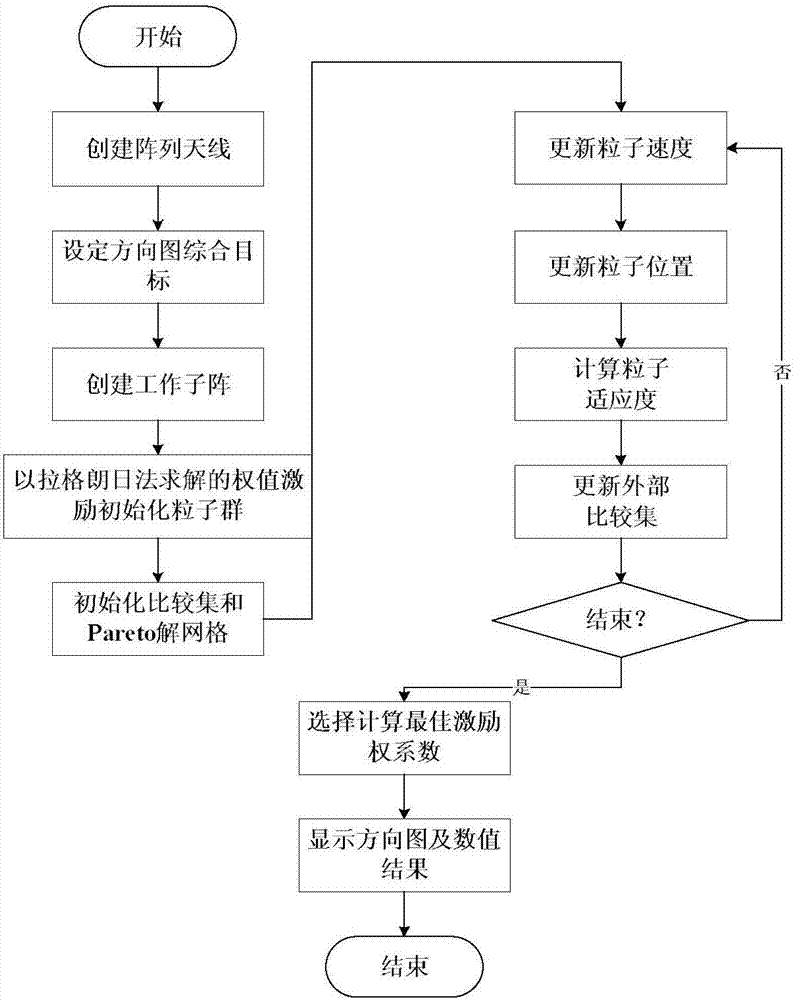
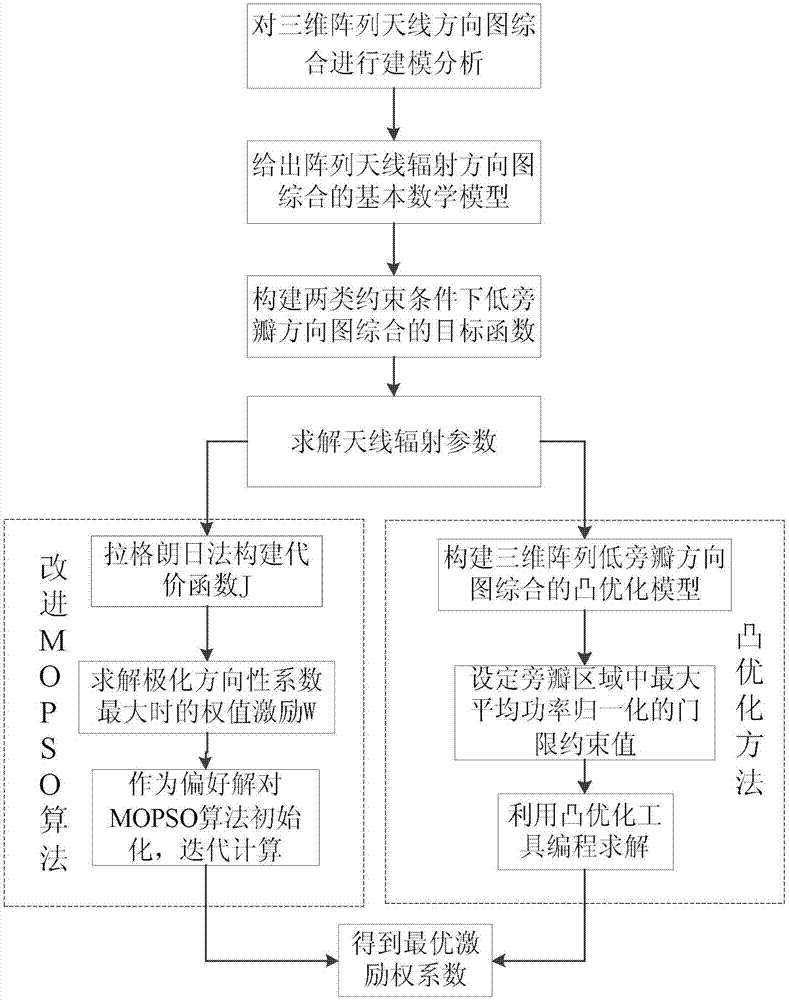
The invention discloses a side-lobe suppression method for a three-dimensional array antenna pattern based on an improved MOPSO and a convex optimization algorithm. Firstly, three-dimensional array antenna pattern synthesis is modeled and analyzed, and a basic mathematic model of the array antenna radiation pattern synthesis is given, and multi-objective functions of low side-lobe pattern synthesis under constraint conditions of an array radiation direction and first side-lobe suppression are constructed respectively; then, the maximal excitation of a polarization directivity coefficient is obtained by a Lagrange multiplier method and is added in the MOPSO algorithm as preference information, an initial population is generated in the vicinity of optimal solutions, and the model is solved by iterative calculation; a convex optimization model of the low side-lobe pattern synthesis is constructed, a convex optimization tool is utilized to solve the corresponding optimal solutions under different threshold constraints, then the three-dimensional array antenna pattern under the low side-lobe constraint is obtained, and therefore the purpose of side-lobe suppression is achieved. According to the side-lobe suppression method for the three-dimensional array antenna pattern based on the improved MOPSO and the convex optimization algorithm, the optimization performance of the algorithms is improved, and the side-lobe suppression problem of the three-dimensional array antenna pattern can be solved efficiently and quickly.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Task unloading method based on power control and resource allocation
ActiveCN111245651AReduce offload overheadReduce time complexityData switching networksQuality of serviceOptimal decision
The invention discloses a task unloading method based on power control and resource allocation, and relates to the field of industrial Internet of Things. The method comprises the steps: establishinga cross-domain network model of an industrial field; constructing a calculation model of an equipment task; according to the model, constructing a mixed integer nonlinear programming model for communication power control, resource allocation and calculation unloading problems; decomposing a problem into three sub-problems; solving an optimal communication power and a resource allocation strategy by utilizing convex optimization knowledge, a Lagrange multiplier method and a KKT (Karush-Kuhn-Tucker) condition; after substituting an original target function, solving an optimal decision of a taskcalculation position by utilizing a deep reinforcement learning algorithm, and obtaining an optimal strategy of communication power, resource allocation and the calculation position of task unloading.The method can obtain the optimal strategy in industrial network task unloading, and has the technical effects of reducing the task delay, reducing the equipment energy consumption and ensuring the service quality.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Aircraft multi-objective optimization method based on self-adaptive agent model
ActiveCN104866692ASave optimization design costImprove approximation accuracySpecial data processing applicationsPhysical planningEngineering
The invention discloses an aircraft multi-objective optimization method based on a self-adaptive agent model, relates to a multi-objective optimization method for treating complex aircraft design, and belongs to the field of aircraft design optimization. According to the aircraft multi-objective optimization method, an integrated preference function is constructed by use of a physical planning method to realize the conversion of the multi-objective optimization problem into a single-objective optimization problem reflecting design preference; next, the self-adaptive agent model is constructed from the integrated preference function and constraint conditions to take the place of a high-accuracy analysis model, and therefore, the problem of great time taken in calculation of optimization design is solved; finally, the constraint problem is converted into a non-constraint problem by use of an augmentation Lagrange multiplier method, and the non-constraint problem is solved by use of a genetic algorithm. The aircraft multi-objective optimization method has the advantages that the solving process of the aircraft multi-objective optimization method taking much time in calculation is simple and efficient, and therefore, a Pareto noninferior solution meeting the requirements of a user can be obtained quickly to shorten the design period of the aircraft, and the design cost is reduced. Besides, the aircraft multi-objective optimization method is high in universality and convenient for program development.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
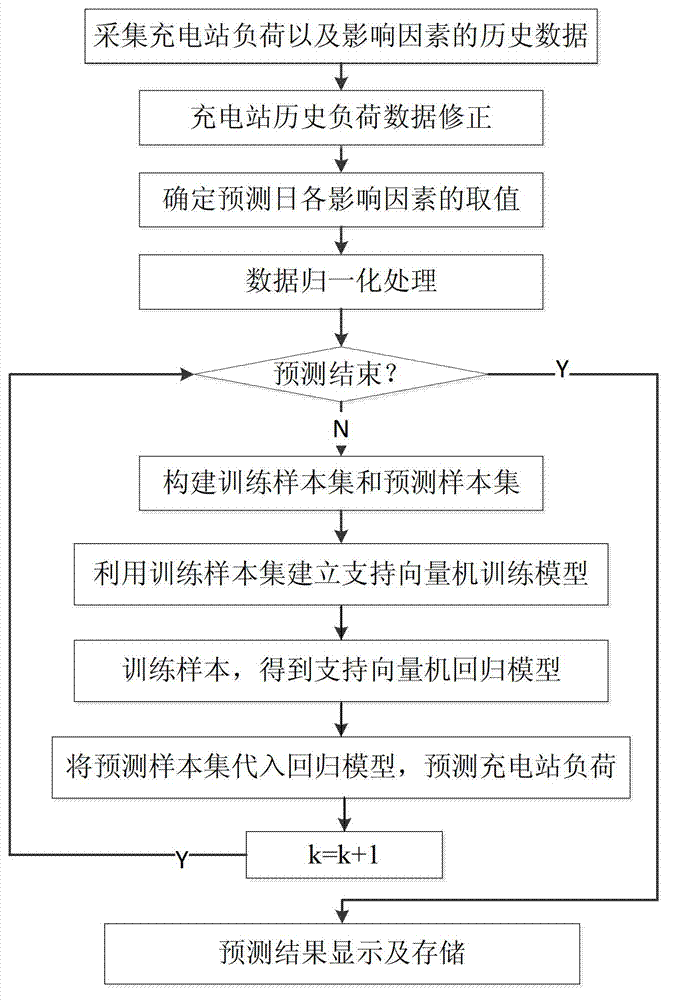
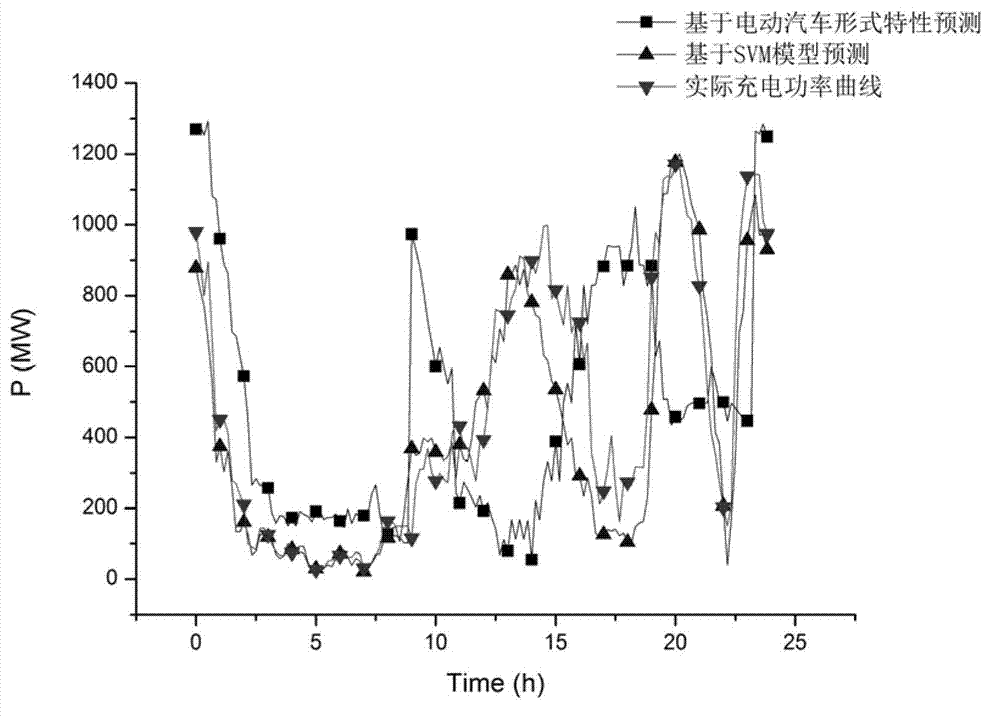
Electric vehicle charging station load prediction method based on support vector machine
ActiveCN103400203AHigh outputHigh precisionForecastingSystems intergating technologiesSupport vector machineEngineering
The invention provides an electric vehicle charging station load prediction method based on a support vector machine. The electric vehicle charging station load prediction method based on the support vector machine comprises the following steps of: collecting charging station load before a prediction day and historical data of factors which affect the charging station load; constructing a training sample set according to the historical data; training by the training sample set to obtain the Lagrange multiplier of a support vector machine regression function; according to the Lagrange multiplier, establishing a support vector machine prediction model; and substituting the prediction sample set into the support vector machine prediction model to obtain a charging station load prediction value. According to the electric vehicle charging station load prediction method based on the support vector machine, which is disclosed by the invention, the electric vehicle charging station load prediction precision can be effectively improved, and a more reliable basis is provided for an electric power dispatching department to regulate a dispatching plan, regulate system reserve capacity and optimize the generator set capacity.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Pattern detection in sensor networks
InactiveUS20160156652A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionAugmented lagrange multiplierData set
A method of detecting an anomaly in a sensor network for diagnosing a network attack may include receiving a data set comprising a plurality of vector-valued measurements from a plurality of sensors, and decomposing the data set into a low-rank component L and a sparse component S using an Augmented Lagrange Multiplier (ALM) method. In one embodiment, at least one of L or S can be determined using an exact minimizer of a Lagrangian in the ALM method, L can represent patterns that occur in a relatively large number of the plurality of sensors, and S can represent patterns that occur in a relatively small number of the plurality of sensors. The method may also include ascertaining, using the computer system, the anomaly in the data set based on the patterns in the sparse component S.
Owner:NUMERICA CORP
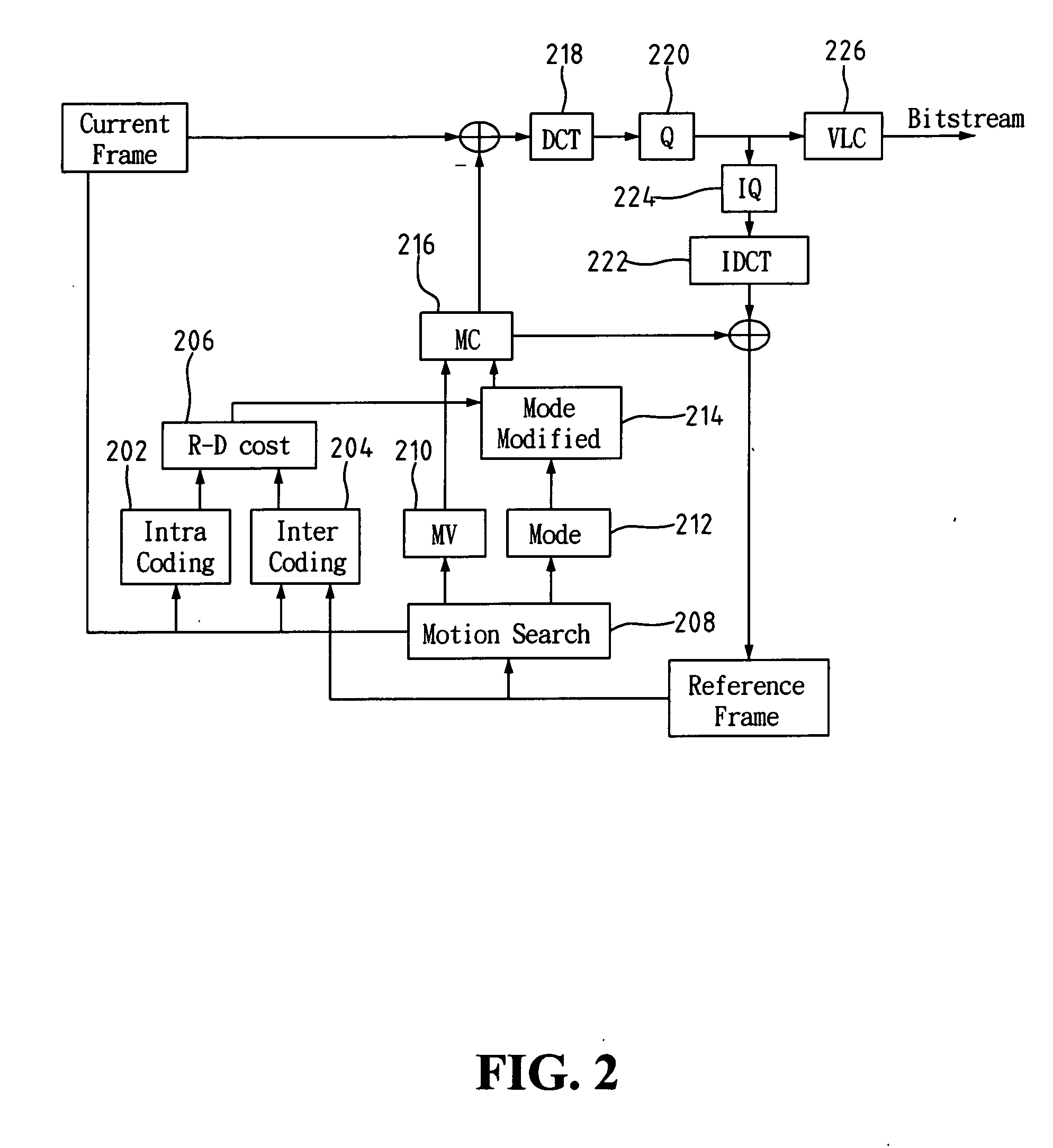
Method and apparatus for control of rate-distortion tradeoff by mode selection in video encoders
InactiveUS7042943B2Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningRate distortionBuffer overflow
A Method And Apparatus For Control of Rate-Distortion Tradeoff by Mode Selection in Video Encoders is Disclosed. The system of the present invention first selects a distortion value D near a desired distortion value. Next, the system determines a quantizer value Q using the selected distortion value D. The system then calculates a Lagrange multiplier lambda using the quantizer value Q. Using the selected Lagrange multiplier lambda and quantizer value Q, the system begins encoding pixelblocks. If the system detects a potential buffer overflow, then the system will increase the Lagrange multiplier lambda. If the Lagrange multiplier lambda exceeds a maximum lambda threshold then the system will increase the quantizer value Q. If the system detects a potential buffer underflow, then the system will decrease the Lagrange multiplier lambda. If the Lagrange multiplier lambda falls below a minimum lambda threshold then the system will decrease the quantizer value Q.
Owner:APPLE INC
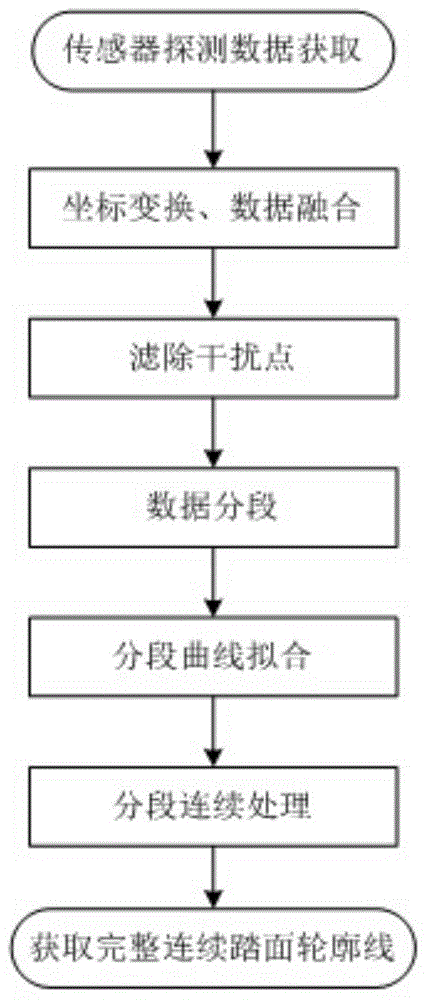
Method and device for obtaining wheel set tread contour line of urban rail train
ActiveCN104163188ARelatively small errorWith online non-contact measurementWheel-rims surveying/measuringContact typeEngineering
The invention discloses a method and device for obtaining a wheel set tread contour line of an urban rail train. The device comprises two sets of 2D laser displacement sensors installed on the two sides of a rail in a mirror symmetry mode. The laser detection faces of the two sets of sensors are located on the same plane, and the integral device is lower than the rail surface. The method comprises the steps that after the sensors detect wheels at the same time to obtain detection point coordinates, the output points of the two sets of sensors are combined to a same coordinate system through coordinate transformation and coordinate translation; the x-coordinate value of the right end face of a tread is obtained, and a filtering window is established based on the x-coordinate value to remove interference points of measuring data; the x-coordinate value of the right end face of the tread is obtained, and measured data points are divided into K number sets according to the actual situations; least squares curve fitting is carried out on the data points of each number set; coordinate values of segment points are obtained, and each segment curve is smoothened into an integral tread contour line according to the lagrange multiplier method. The method and device have the advantages of being high in speed and precision, easy to operate, capable of carrying out online non-contact type measurement, and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
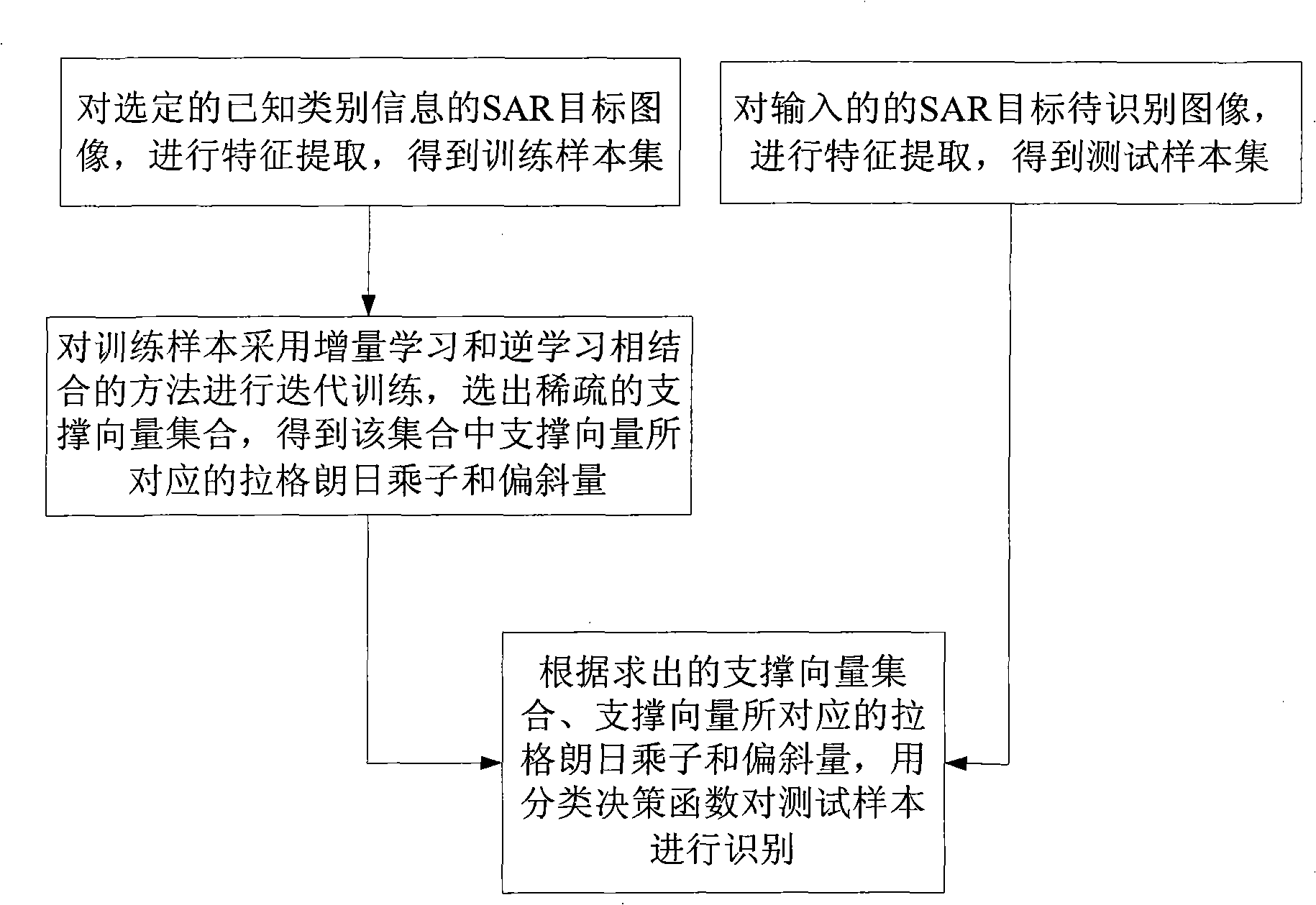
SAR target recognition method based on sparse least squares support vector machine
InactiveCN101551856ASmall amount of calculationShorten recognition timeCharacter and pattern recognitionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFeature extractionImaging processing
The invention discloses a SAR target recognition method based on a sparse least squares support vector machine, which belongs to the technical field of image processing and mainly solves the problem that the existing method need a long time for SAR target recognition. The realization process comprises the following steps of: firstly respectively implementing feature extraction to the selected target images with known classification information and images to be recognized to obtain training samples and test samples; and then applying iterative training to the training samples by using the combination of incremental learning method and reversal learning method to select a sparse support vector set and obtain a Lagrange multiplier and deflection corresponding to the support vectors in the set; and finally using a classification decision function to recognize the test samples according to the obtained support vector set, the Lagrange multiplier and deflection corresponding to the support vectors. The invention has the advantage of shortening recognition time under the condition of equivalent recognition precision and can be used for detection and recognition of SAR target.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
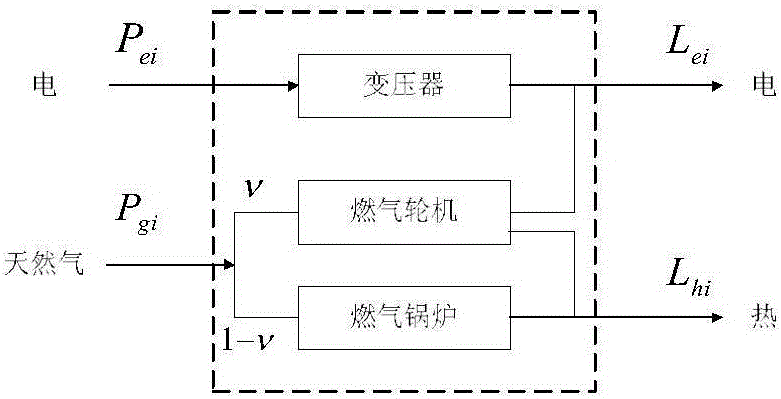
Modeling and optimized dispatching method of electrical series-parallel system on the basis of energy center
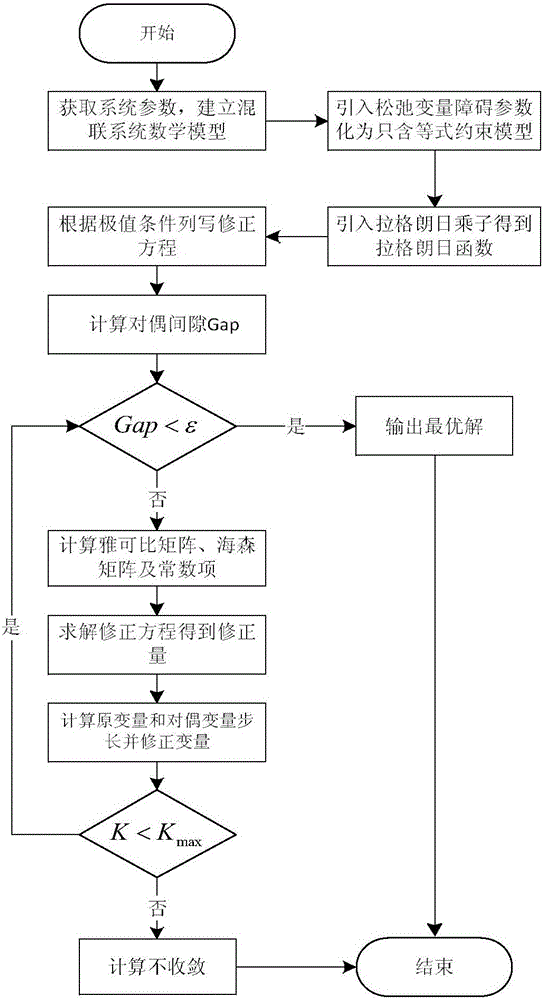
ActiveCN105046369AImprove convenienceForecastingSystems intergating technologiesSlack variableSimulation
The invention discloses a modeling and optimized dispatching method of an electrical series-parallel system on the basis of an energy center. The modeling and optimized dispatching method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing an electrical network, a natural gas network and an energy hub model, and coupling the electrical network with the natural gas network through an energy hub to form the electrical series-parallel system; then, taking total energy cost as a target function, and considering various constraint conditions to establish an optimized dispatching mathematic model of the electrical series-parallel system; and carrying out solving by a primal-dual interior-point method, importing a slack variable and a barrier parameter in sequence in a solving process so as to change the model into a model which only contains an equality constraint, then, importing a Lagrange multiplier to obtain a Lagrange function, and solving a non-linear equation set formed by a KKT (Karush-Kuhn-Tucker) condition of the Lagrange function by a Newton method. A constructed example simulation result indicates that an optimization effect on the electrical series-parallel system by the modeling and optimized dispatching method is superior to an independent optimization effect.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Perceptual-based video coding method
InactiveUS20110142124A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionVideo encodingAlgorithm
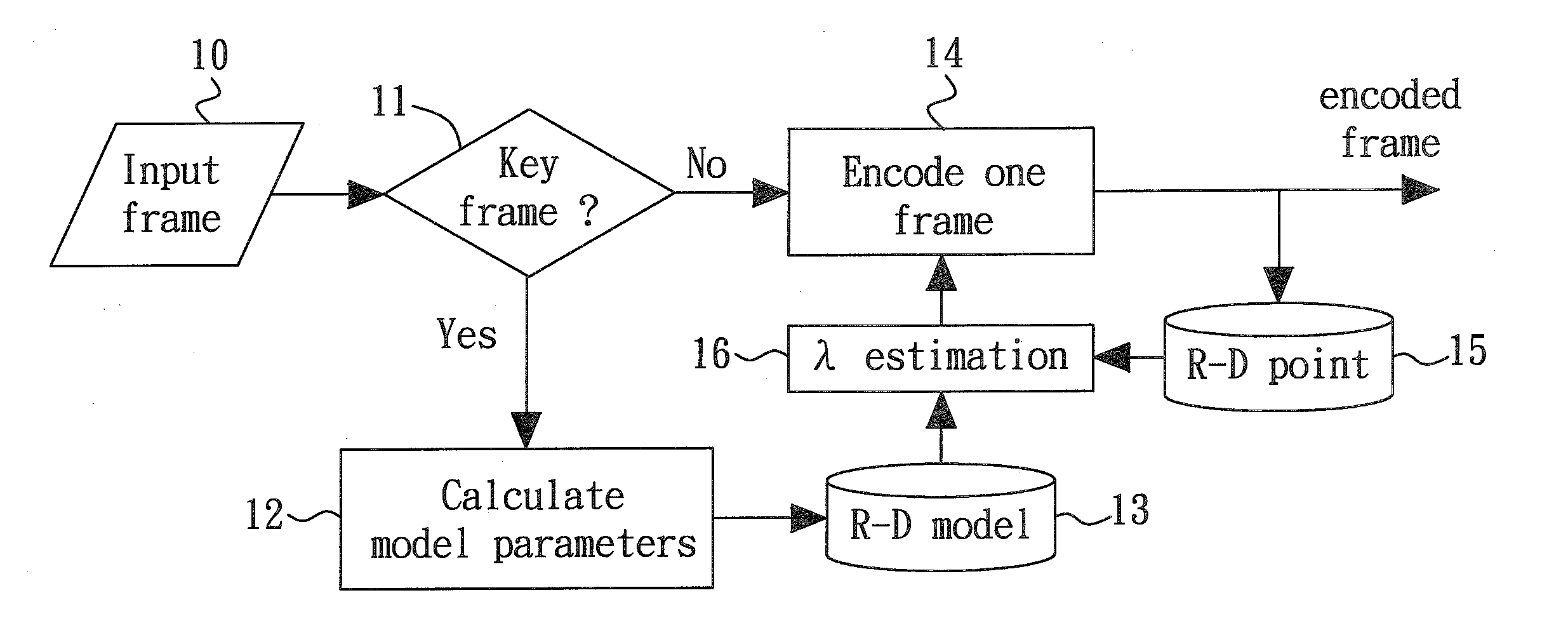
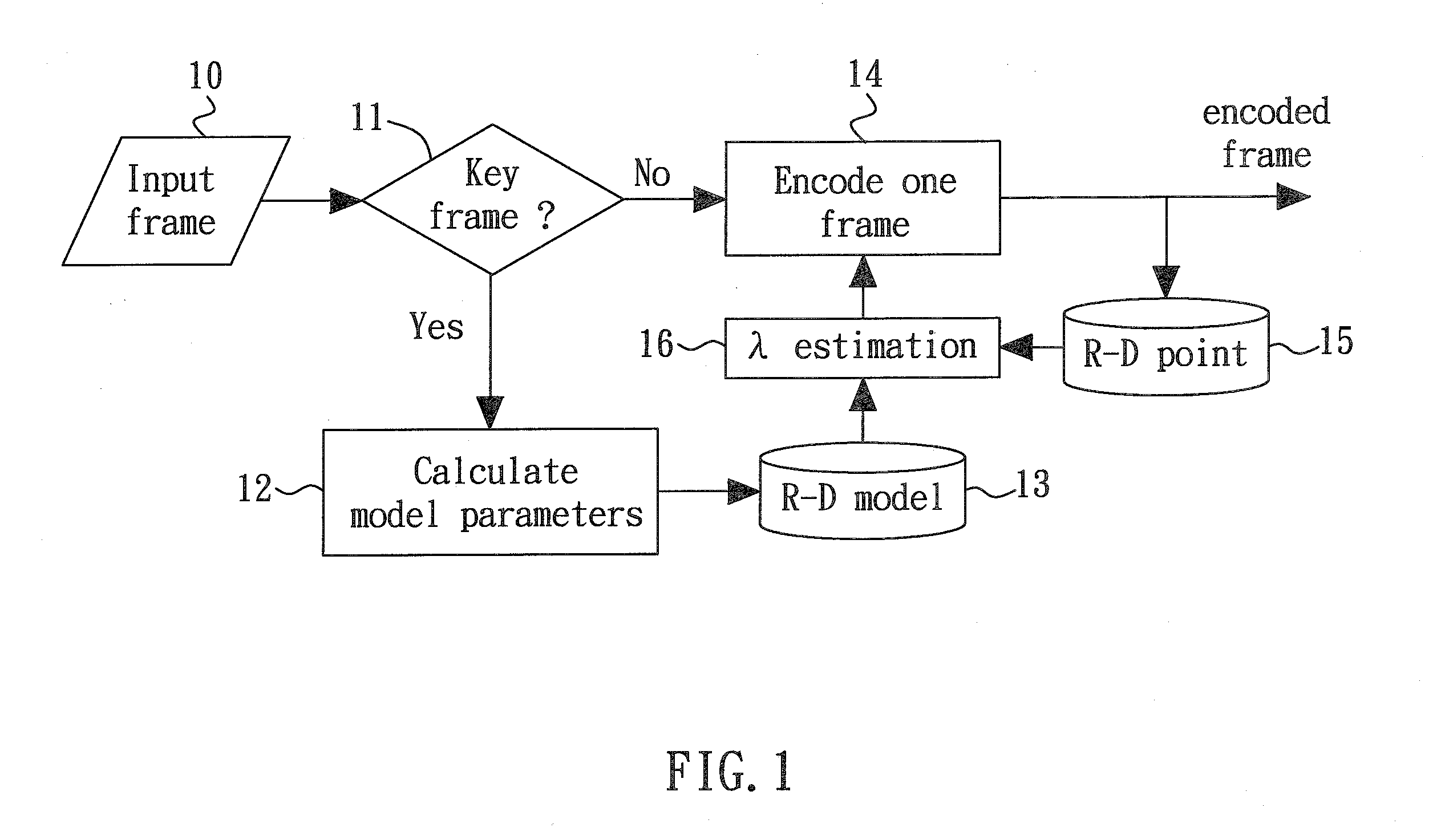
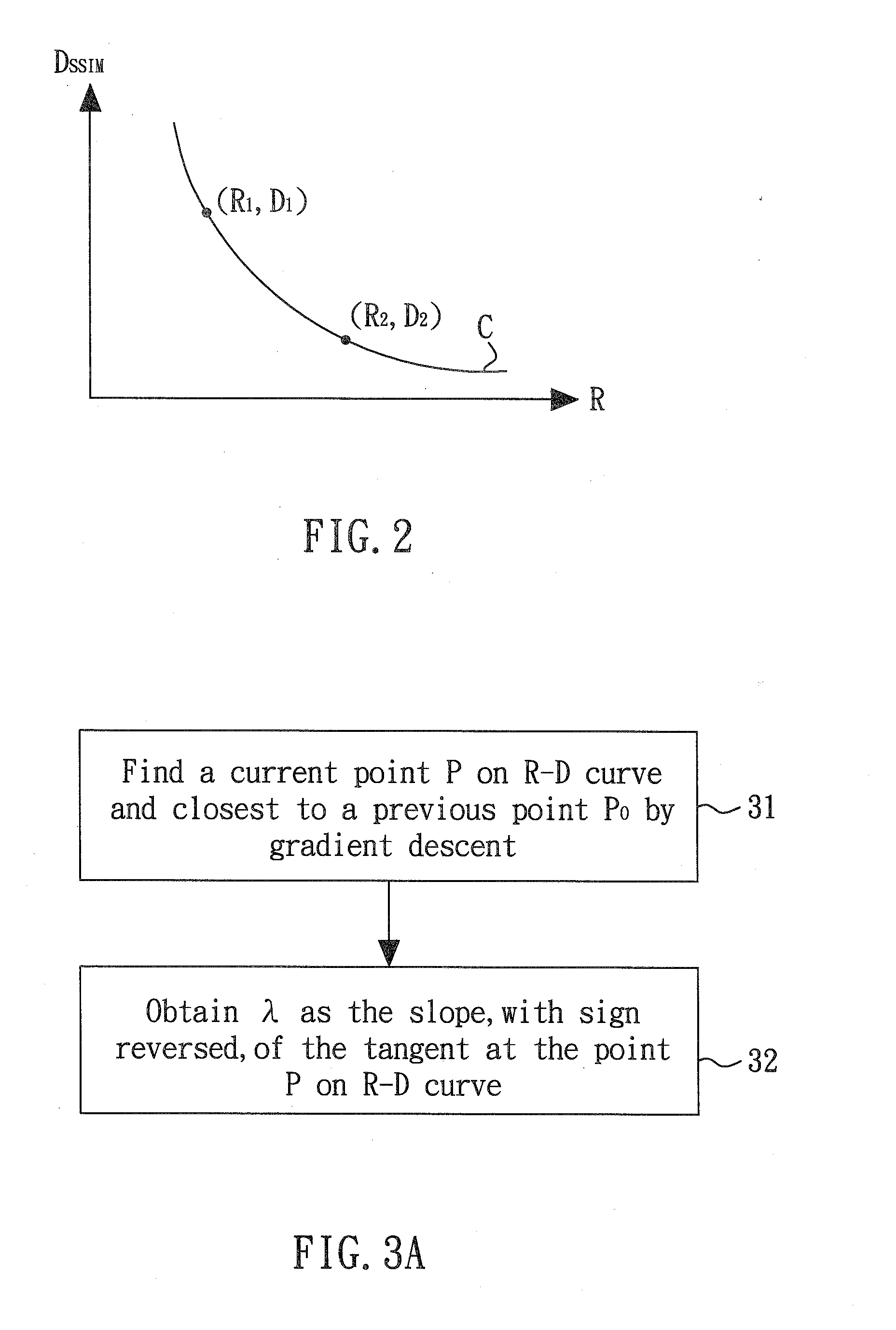
A perceptual-based video coding method provides a perceptual-based rate-distortion (R-D) curve as a predictive R-D curve. The Lagrange multiplier for a current frame is then determined by deciding a slope, with sign reversed, of a tangent to the predictive R-D curve at a current point that is on the predictive R-D curve and closest to a previous R-D point of a previous encoded frame. The current frame is then encoded according to the determined Lagrange multiplier.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Variable load, variable output charge-based voltage multipliers
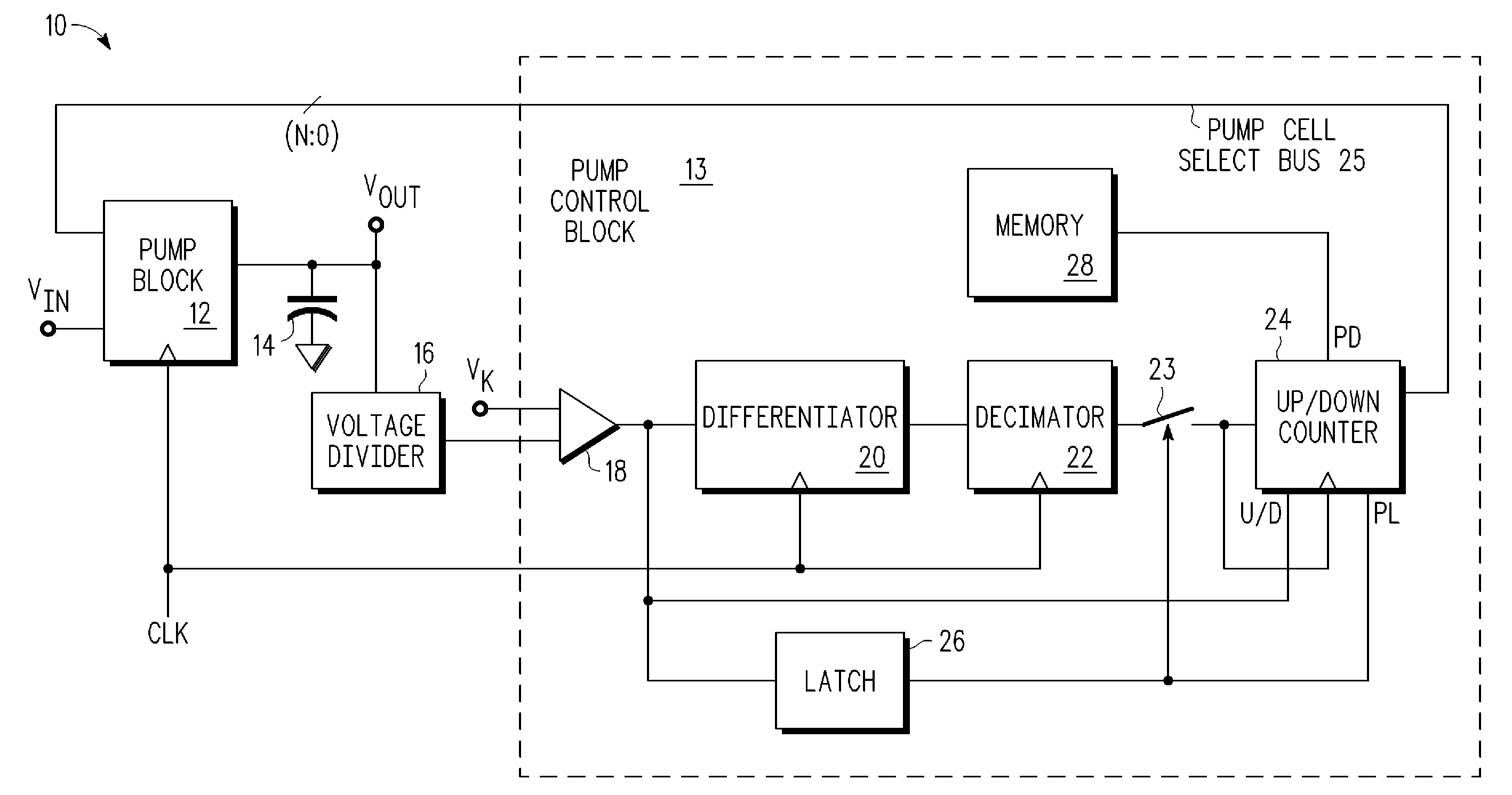
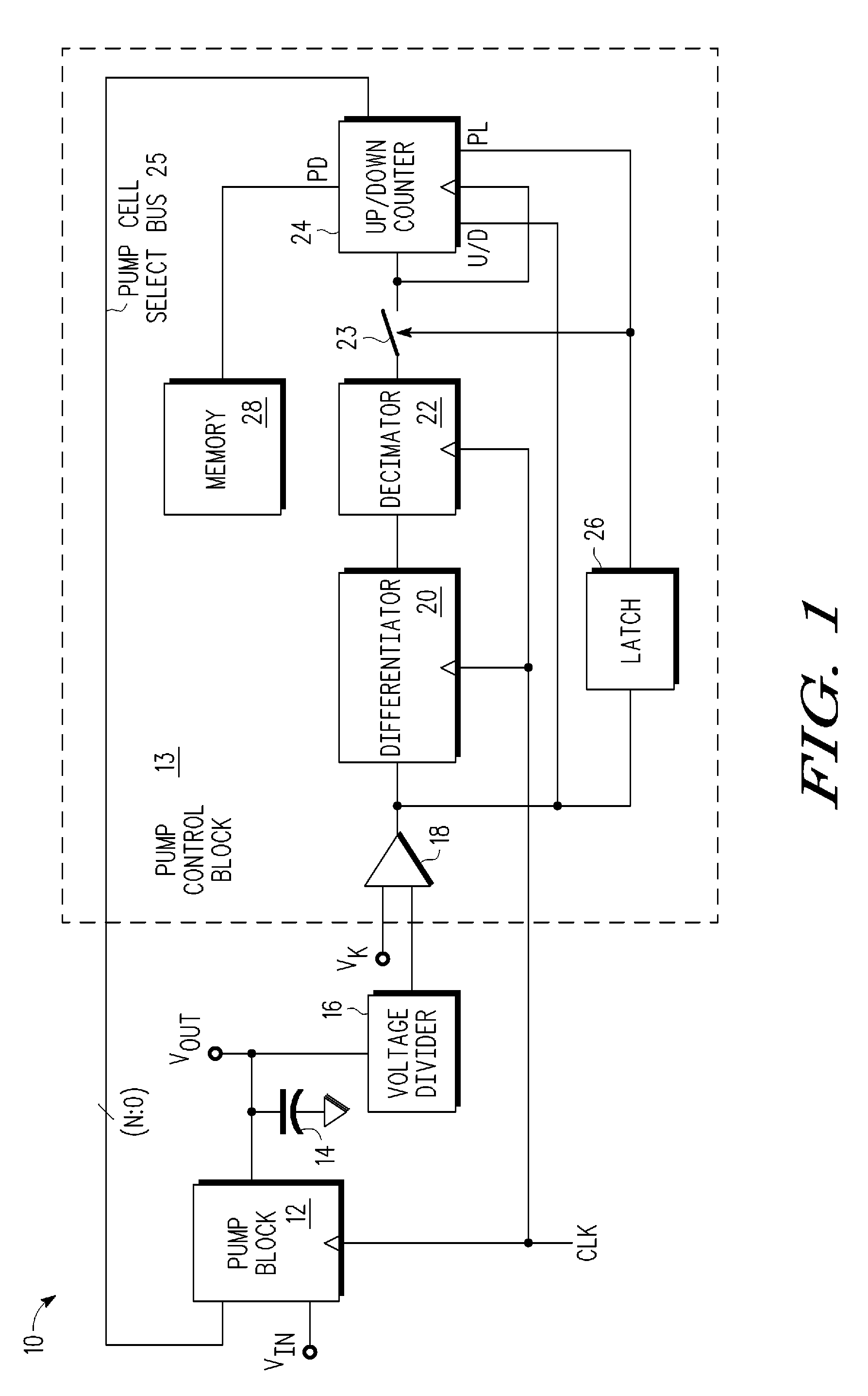
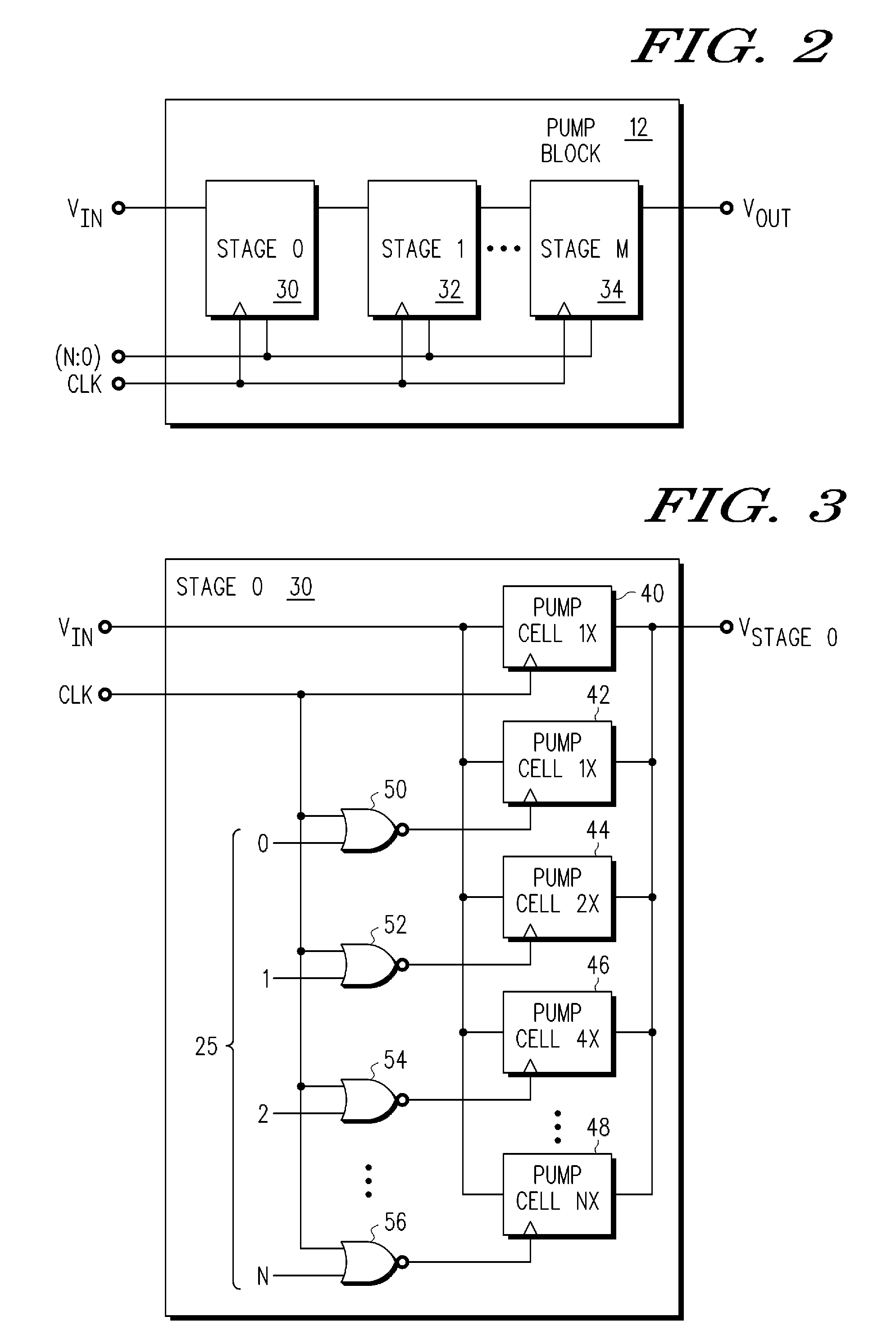
ActiveUS20090097285A1Ac-dc conversionApparatus without intermediate ac conversionVoltage multiplierEngineering
A charge-based voltage multiplier device comprising a charge-pump circuit and a charge-pump controller is provided. The charge-pump circuit is configured to multiply an input voltage signal (Vin) into an output voltage signal (Vout), the charge-pump circuit includes a plurality of charge-pump stages, wherein at least one of the charge-pump stages includes a weighted capacitor array of pump cells. The charge-pump controller is configured to provide a pump cell select to selectively control the weighted capacitor array of pump cells of the at least one of the charge-pump stages of the charge-pump circuit.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Recursive feature elimination method using support vector machines
ActiveUS20110106735A1Reduce in quantityMinimize the numberKernel methodsDigital computer detailsSupport vector machineAlgorithm
Identification of a determinative subset of features from within a group of features is performed by training a support vector machine using training samples with class labels to determine a value of each feature, where features are removed based on their the value. One or more features having the smallest values are removed and an updated kernel matrix is generated using the remaining features. The process is repeated until a predetermined number of features remain which are capable of accurately separating the data into different classes. In some embodiments, features are eliminated by a ranking criterion based on a Lagrange multiplier corresponding to each training sample.
Owner:BIOWULF TECH +1
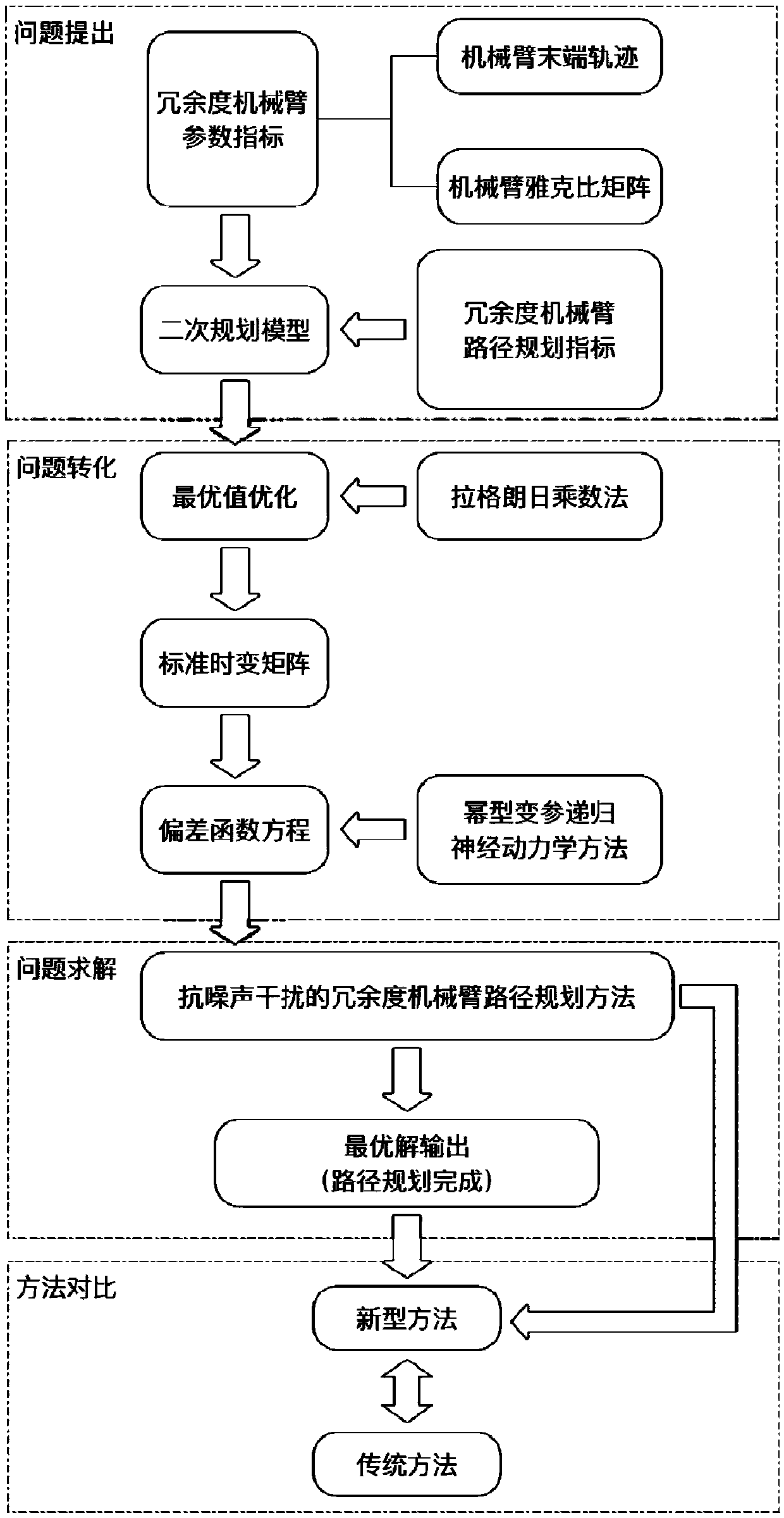
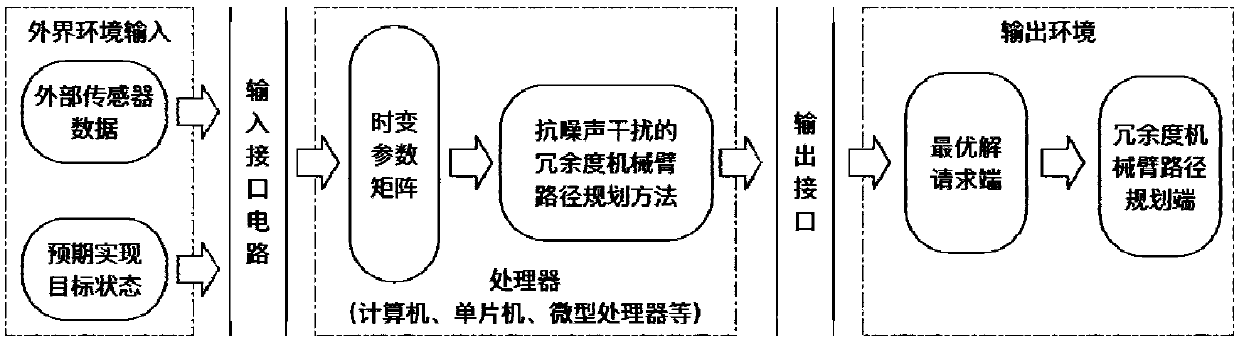
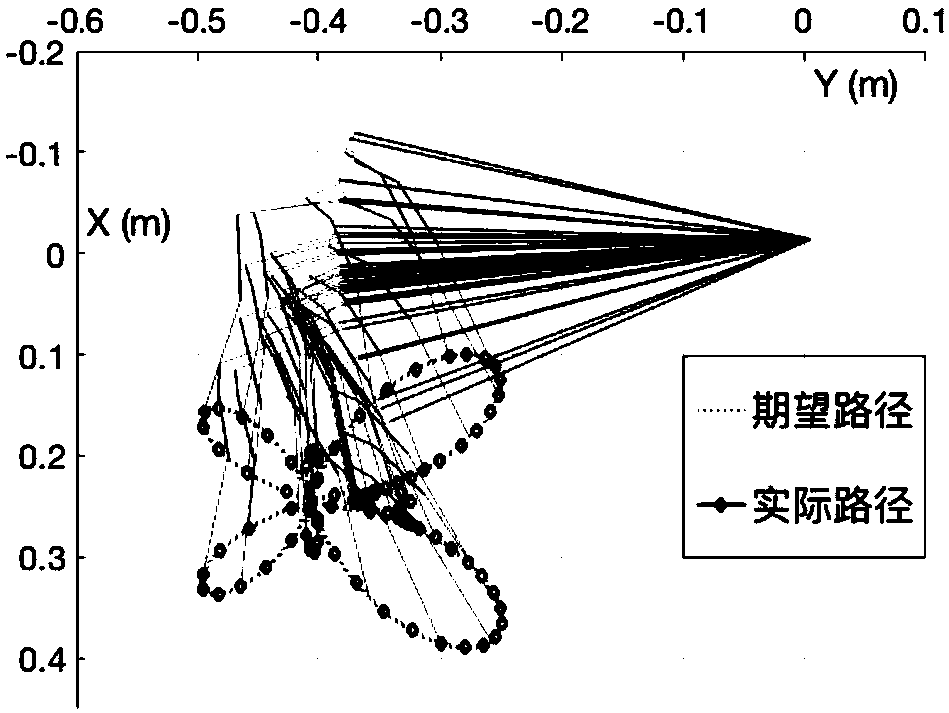
Anti-noise-interference redundant manipulator path planning method
ActiveCN108015763AHas global convergence propertiesCalculation speedProgramme-controlled manipulatorRobustificationDynamic method
The invention discloses an anti-noise-interference redundant manipulator path planning method and a system. The method comprises the steps of (1) building a time-varying quadratic planning model according to an actual redundant manipulator parameter index, and introducing a performance index of a redundant manipulator; (2) using a lagrange multiplier method for carrying out optimal value optimization on the time-varying quadratic planning model; (3) designing a standard matrix equality according to an optimization formula; (4) designing a deviation function equation of the system according toan actual physical model system and the standard matrix equality; and (5) designing the anti-noise-interference redundant manipulator path planning method according to the deviation function equationand a power type varying parameter recursion neurodynamics method, wherein a network state solution solved by the method is an optimal solution. According to the anti-noise-interference redundant manipulator path planning method and the system provided by the invention, with the interference of an outside noise environment, an actual motion path of a redundant manipulator can further coincide withan expected path, so that the calculating speed is greatly improved, and the method has the characteristics of high precision, fast convergence, high instantaneity, good robustness and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
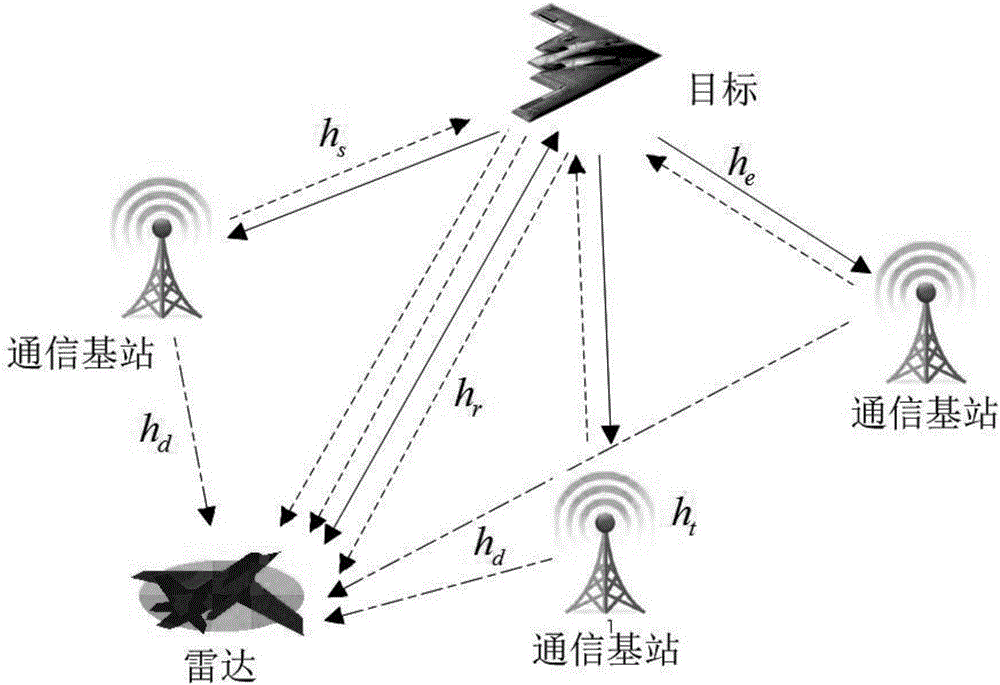
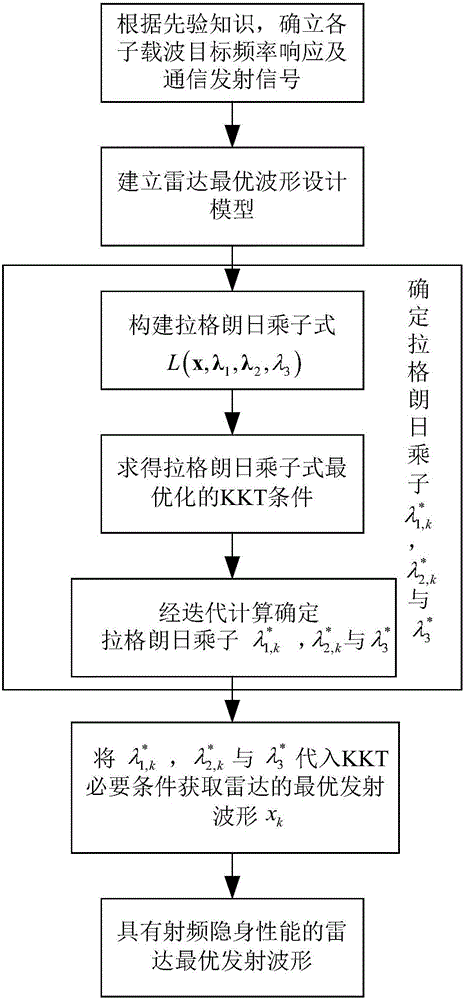
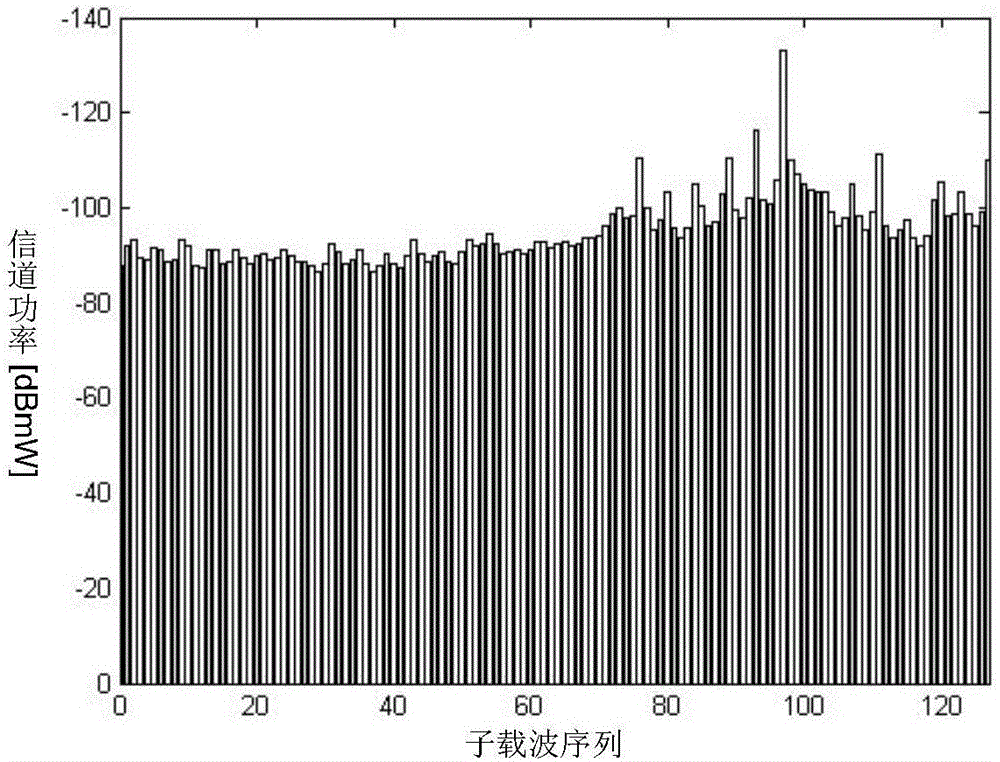
Radar optimal waveform design method based on radio frequency stealth in frequency spectrum shared environment
ActiveCN106680780AGuaranteed channel capacityGuaranteed communication qualityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionRadar systemsFrequency spectrum
The present invention discloses a radar optimal waveform design method based on radio frequency stealth in a frequency spectrum shared environment, belonging to the radar design and manufacturing field. The method comprises: obtaining priori knowledge of detection area target frequency response of a radar and communication system and signals of a communication system, and assuming that the echo of the communication signals reflected through the target to the radar can be received and processed by the radar; and establishing an optimal waveform design mathematic model; and employing the Lagrange multiplier method to solve the optimal waveform design mathematic model and performing iterative computation to determine the optimal emission waveform of the radar system. The minimization of the total emission power of the radar is taken as a target, the emission waveform of the radar system is subjected to adaptive optimization design in the conditions of satisfying a certain target parameter estimation performance and the communication system channel capacity so as to ensure the channel capacity and the communication quality of the communication system and allow the radar system to ensure the optimal radio frequency stealth performance in the condition of satisfying a certain target parameter estimation performance.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
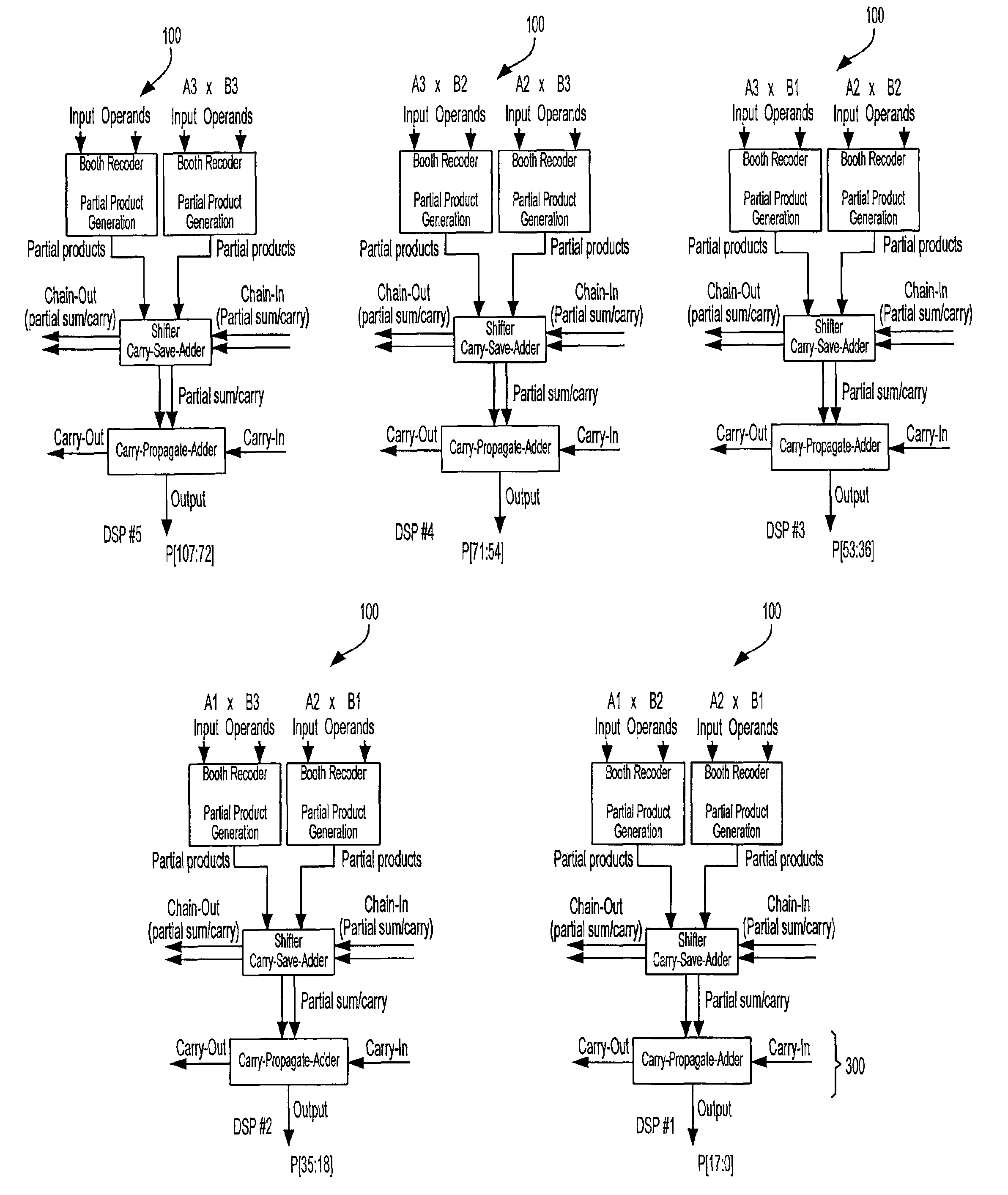
DSP block for implementing large multiplier on a programmable integrated circuit device
ActiveUS8307023B1Reducing and eliminating relianceExtensive operationComputation using non-contact making devicesBinary multiplierComputer architecture
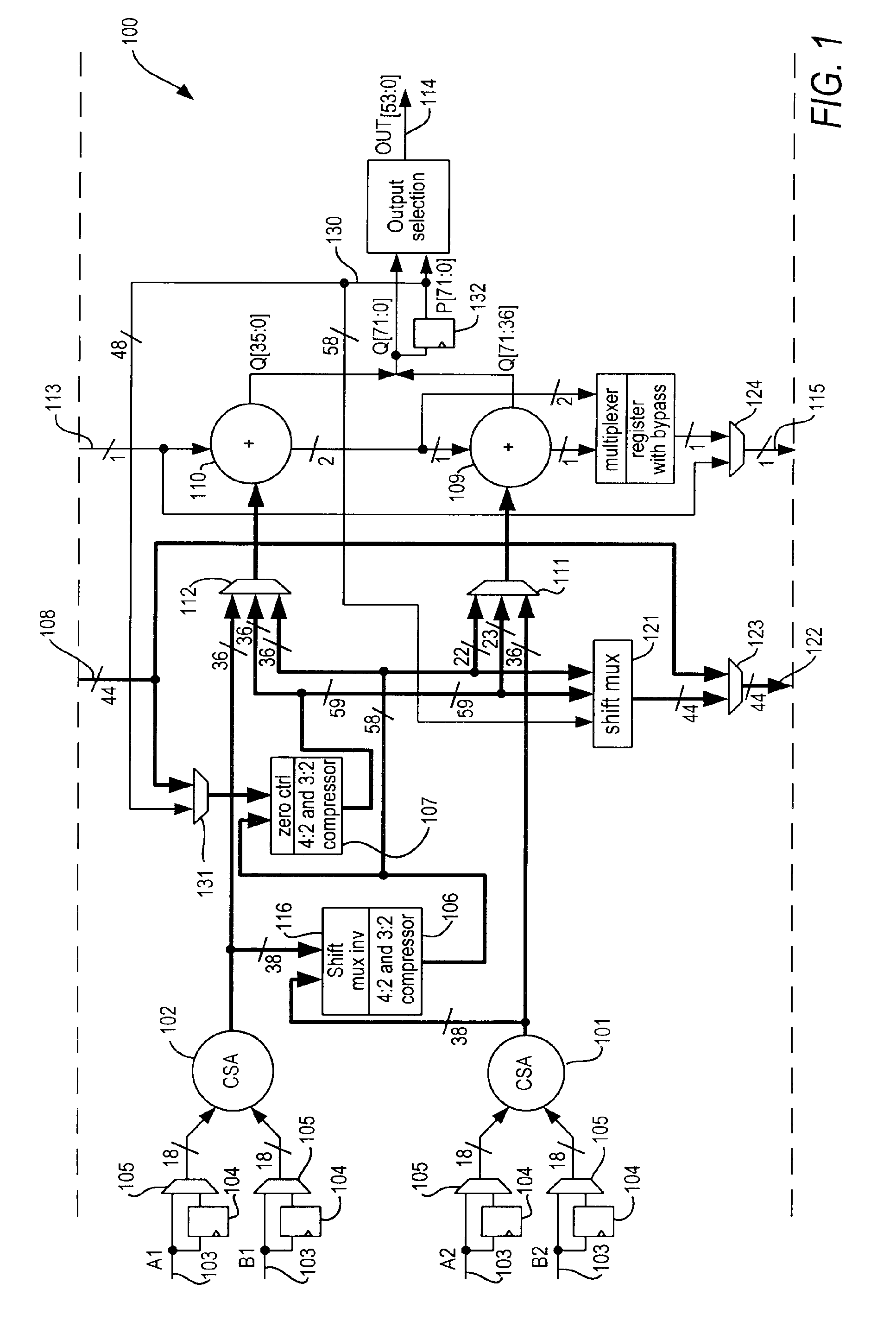
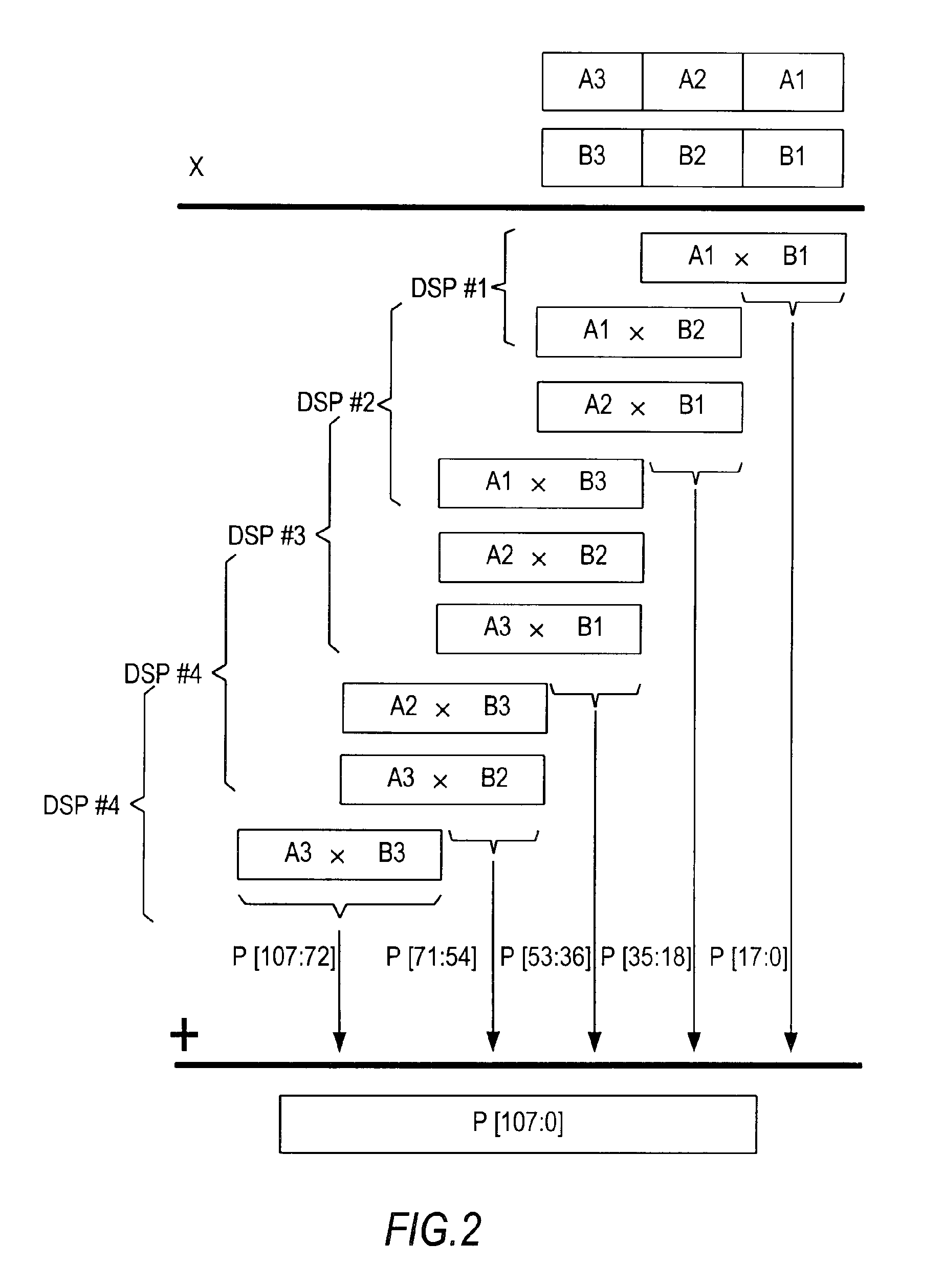
A programmable integrated circuit device includes a plurality of specialized processing blocks. Each specialized processing block may be small enough to occupy a single row of logic blocks. The specialized processing blocks may be located adjacent one another in different logic block rows, forming a column of adjacent specialized processing blocks. Each specialized processing block includes one or more multipliers based on carry-save adders whose outputs are combined using compressors. Chain-in and chain-out connections to the compressors allow adjacent specialized processing blocks to be cascaded to form arbitrarily large multipliers. Each specialized processing block also includes a carry-propagate adder, and the carry-propagate added in the final specialized processing block of the chain provides the final result. The size of the multiplication that may be performed is limited only by the number of specialized processing blocks in the programmable integrated circuit device.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
System and method for solving equality-constrained quadratic program while honoring degenerate constraints
InactiveUS20060282178A1Improve accuracyIncreased complexityAdaptive controlMatrix decompositionAlgorithm
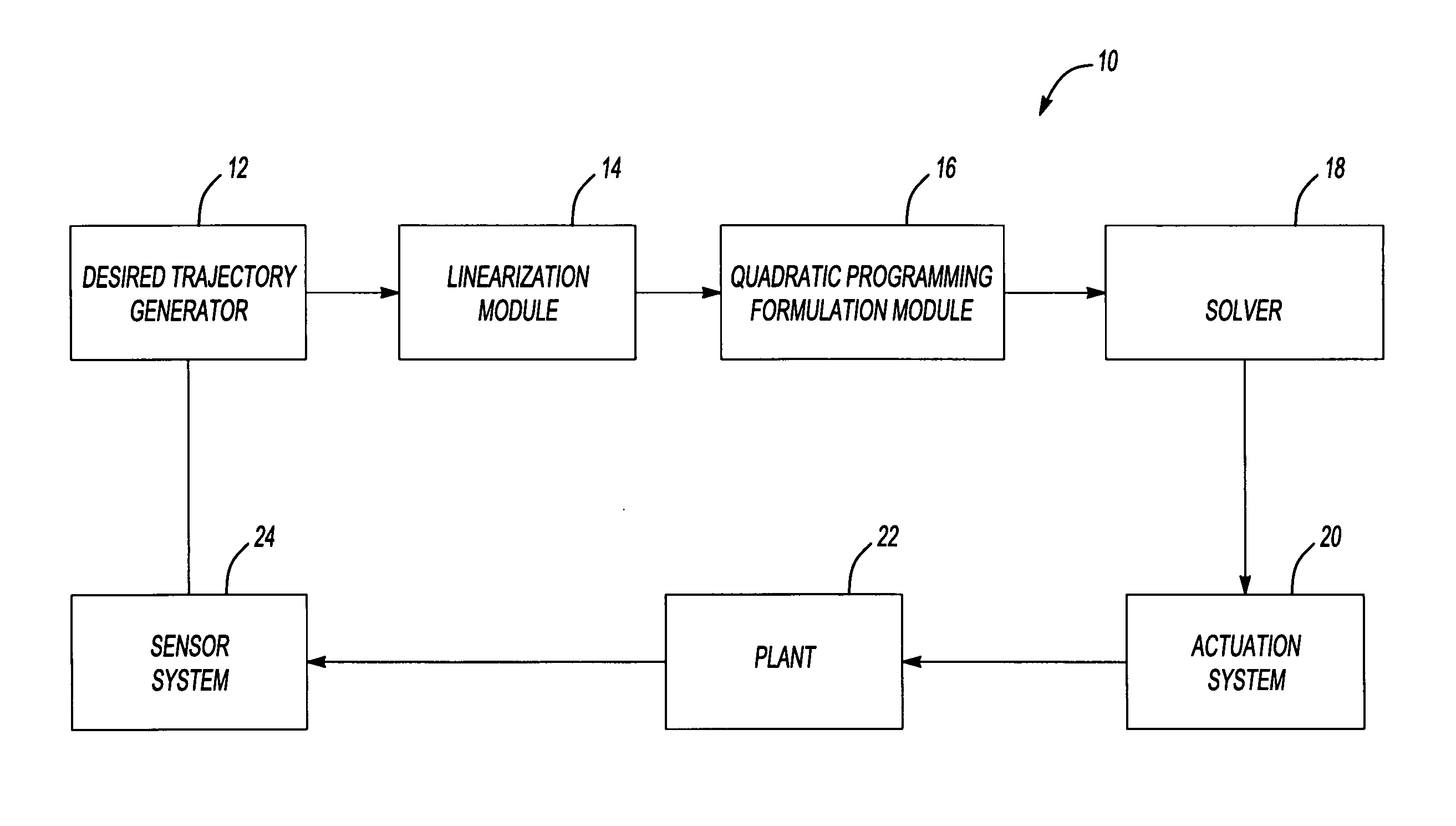
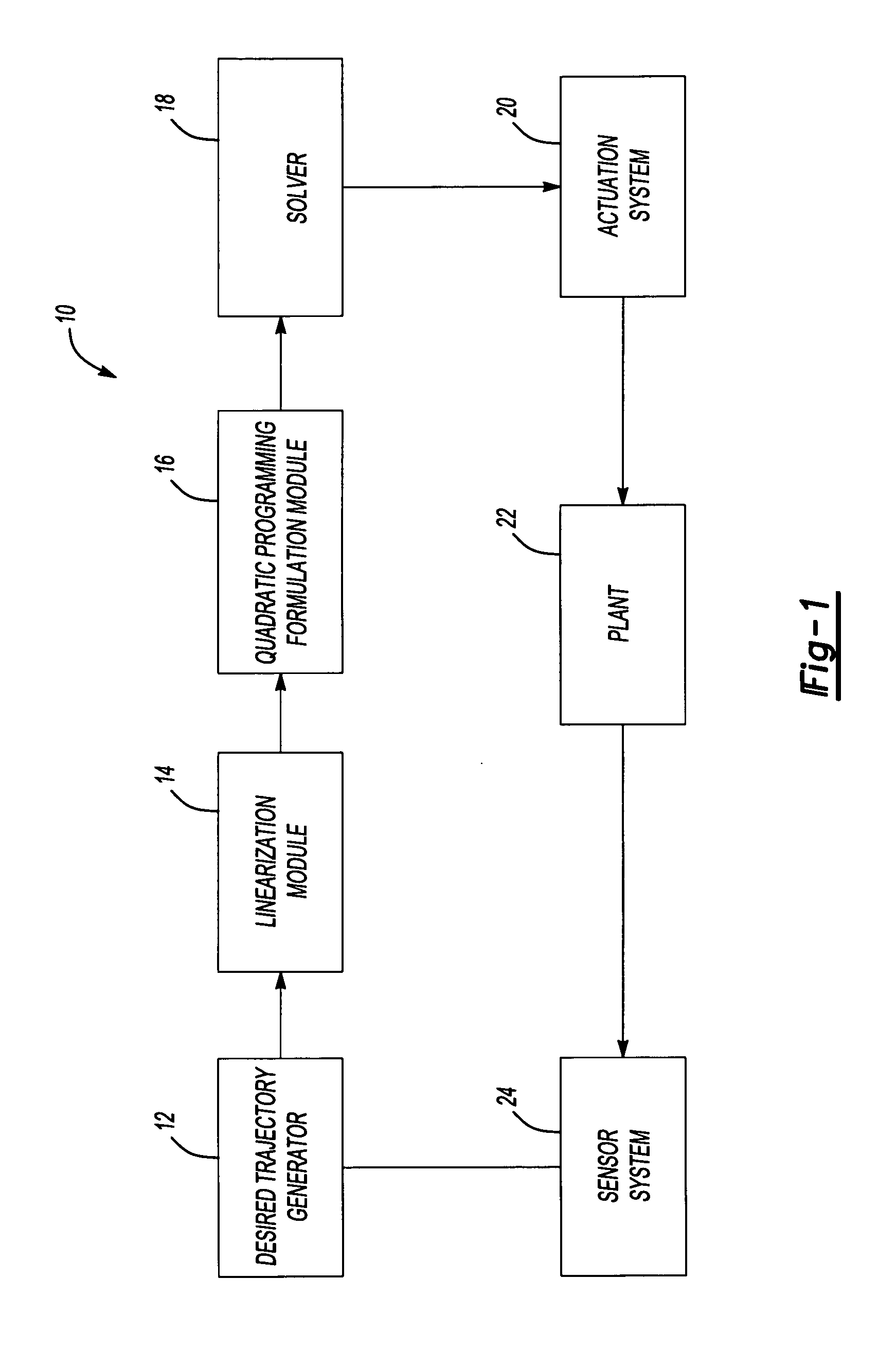
A system and method more accurately solves equality-constrained a quadratic program without significantly increasing computational load. The solver can be used to iteratively determine the solution to a general quadratic program via an active set method. The algorithm determines which of the equality constraints are binding and which constraints are not. The non-binding constraints are dropped from the active set and the objective function improved. The non-binding constraints are identified based upon the signs of the Lagrange multipliers of the equality constraints. The algorithm determines the optimization variables and the Lagrange multipliers independently of one another based upon a single matrix factorization.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
Methods and systems for the design and implementation of optimal multivariable model predictive controllers for fast-sampling constrained dynamic systems
ActiveUS20090254202A1Minimize the numberSaveMathematical modelsComputation using non-denominational number representationGraphicsDirected graph
Methods and systems for the design and implementation of optimal multivariable MPC controllers for fast-sampling constrained dynamic systems utilizing a primal-dual feasibility approach and / or a graph approach. The primal-dual feasibility approach can compute and store matrices defining constraints of quadratic programming problems in an off-line part in order to calculate vectors of Lagrange multipliers and an optimizer. Then primal-dual feasibility can be checked in an on-line part using the Lagrange multipliers and the optimizer can provide a unique optimal solution for the constrained dynamic system. The graph approach can compute and store the matrices and the vectors, and also prepare and store a structure of directed graph in off-line part. An optimizer for a given parameter vector can be determined in on-line part using the directed graph, the matrices and the vectors.
Owner:GARRETT TRANSPORATION I INC
Method for solving unit commitment of wind-fire energy storing-saving and emission-reducing unit
InactiveCN103632309AIncrease profitSuppression of Oscillating PhenomenaData processing applicationsGenetic modelsElectric power systemDecomposition
The invention discloses a method for solving unit commitment of wind-fire energy storing-saving and emission-reducing unit. A decomposition-coordination thought is adopted, the unit commitment of a wind-fire power storage system is decomposed into an upper and lower layer optimization problem, the wind-fire power storage system is decomposed into fire power subsystems, wind power subsystems and water pumping energy-storing subsystems by using Lagrangian relaxation, and each subsystem is coordinated by using a self-adaptive Lagrange multiplier on an upper layer; each subsystem on a lower layer is solved by using a self-adaptive genetic algorithm. An entire optimization process comprises the following steps: determining the outputs of the wind power subsystems and the outputs of the water pumping energy-storing subsystems as well as spinning reserve which can be provided by the water pumping energy-storing subsystems according to a load curve; transmitting obtained results to the fire power subsystems respectively; coordinating and allocating in parallel on the basis by using each fire power subsystem to determine corresponding start-stop sequences and optimal outputs. According to the method, the wind power fan stop, the peak-shaving energy consumption of fire power units and the running cost can be reduced effectively, and the safety, robustness and energy saving and emission reducing capabilities of the system are further improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Sparse and low-rank matrix approximation-based hyperspectral image restoration method
InactiveCN106408530AEasy to implementAchieve denoising effectImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionMulti band
The invention relates to a sparse and low-rank matrix approximation-based hyperspectral image restoration method and belongs to the image processing field. The method includes the following steps that: a hyperspectral data sequence affected by mixed noises is acquired, or simulated mixed noises are artificially added into a clear hyperspectral image sequence, so that hyperspectral data to be processed can be obtained; the multi-band hyperspectral image data are segmented into a plurality of small data blocks, and each three-dimensional data block is pieced into one two-dimensional data matrix; a weighted Schatten p-normal type low-rank matrix approximation model is constructed for each two-dimensional data matrix; an extended Lagrange multiplier method is adopted to solve the model to obtain mixed noise-removed two-dimensional data matrixes; each two-dimensional data matrix is restored into three-dimensional hyperspectral data, so that a mixed noise-removed multi-band hyperspectral image can be obtained; and the above steps are repeated by using an iteration method to obtain a better restoration effect. The method can be effectively applied to fields such as remote sensing, geography, agriculture and military fields.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
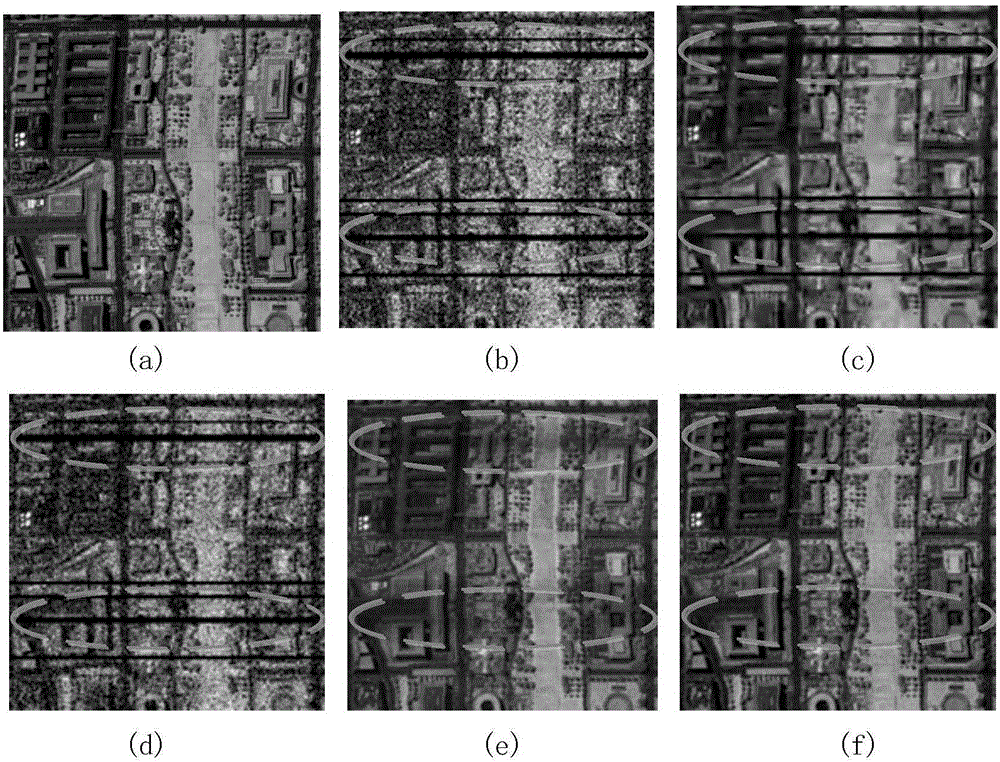
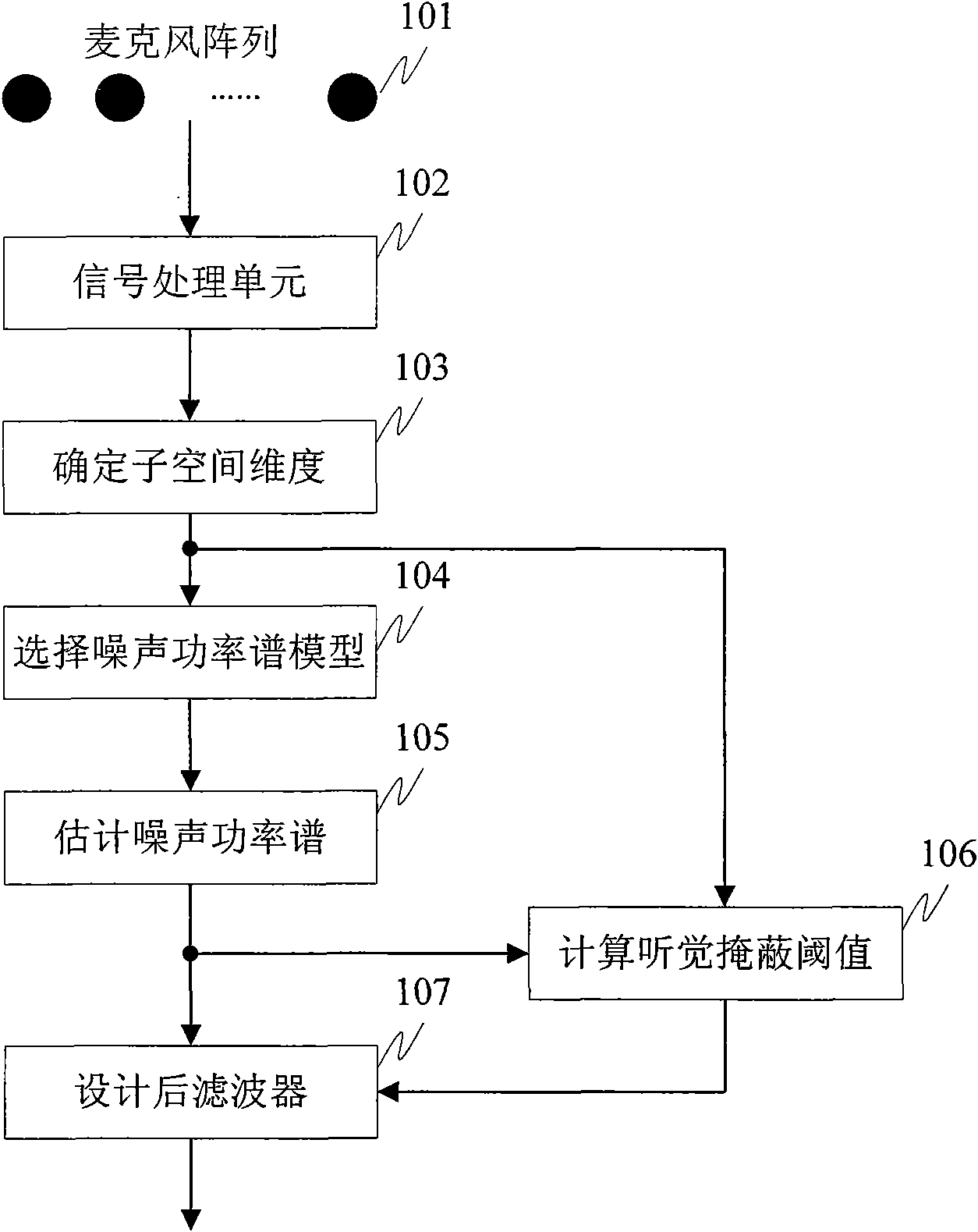
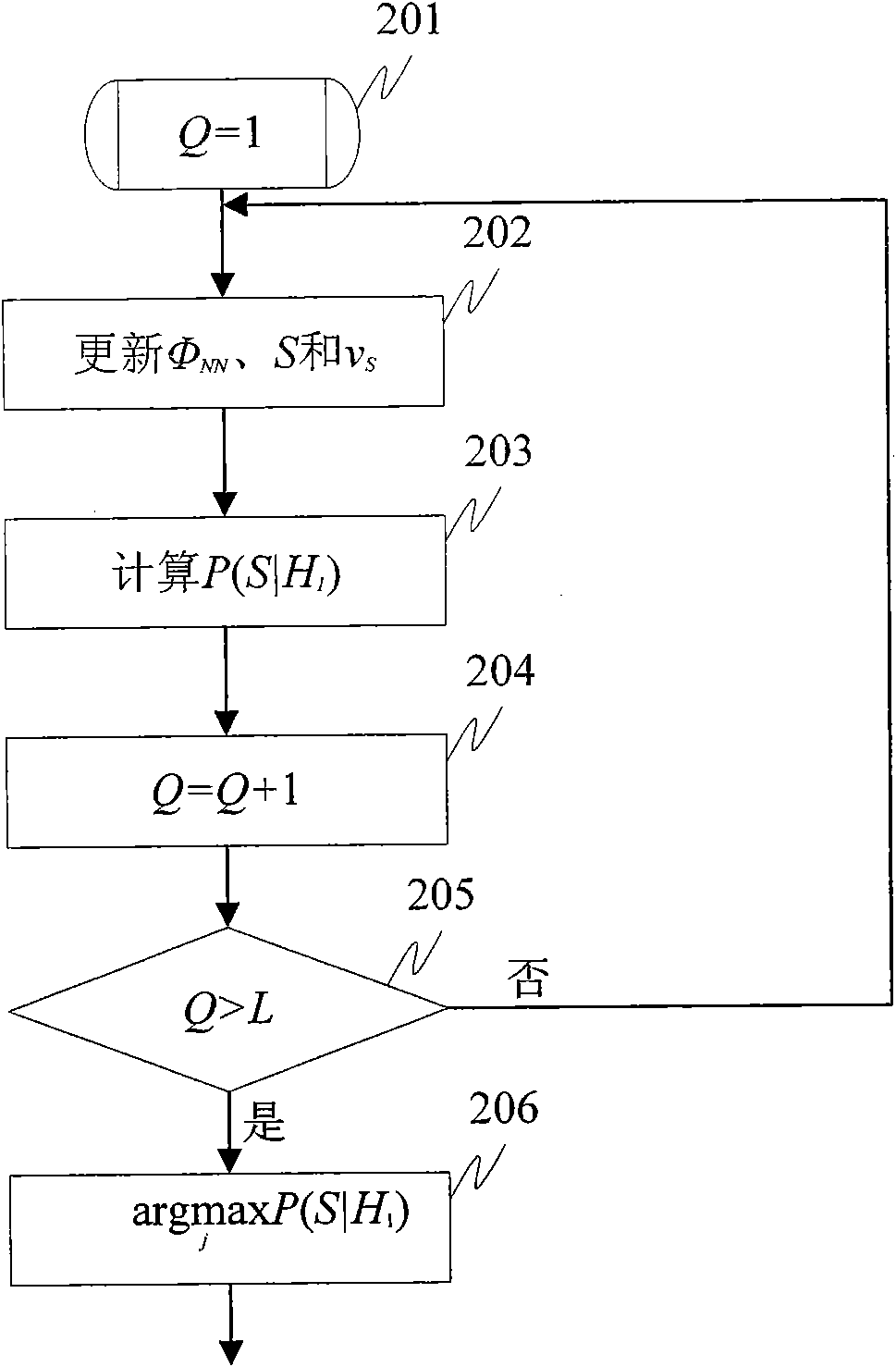
Microphone array postfiltering sound enhancement method based on multi-models and hearing characteristic
ActiveCN101778322ASmall distortionReduce estimation errorSpeech analysisFrequency/directions obtaining arrangementsNoise power spectrumSignal subspace
The invention discloses a microphone array postfiltering sound enhancement method based on multi-models and hearing characteristic, aiming at two important factors influencing the postfiltering sound enhancement performance of a microphone array, i.e. accurate estimation for signal parameters and suitable compromise between increasing noise reduction performance and reducing voice distortion. Thescheme of the invention comprises the following steps of carrying out time domain alignment on signals collected by the microphone array, and carrying out short-time Fourier transform and characteristic value analysis based of power spectrum; determining the dimensionality of a signal subspace through the existence probability of target voice signal in maximation noise-carried voice signals; self-adaptively selecting a distribution model of a noise power spectrum in the noise-carried voice signals; estimating noise power spectrum by utilizing a conditional probability; estimating an auditory masking threshold value based on the signal subspace; and estimating a postfilter by combining Lagrange multipliers according to the auditory sensing characteristics.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com