Patents
Literature
7805 results about "Array data structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computer science, an array data structure, or simply an array, is a data structure consisting of a collection of elements (values or variables), each identified by at least one array index or key. An array is stored such that the position of each element can be computed from its index tuple by a mathematical formula. The simplest type of data structure is a linear array, also called one-dimensional array.
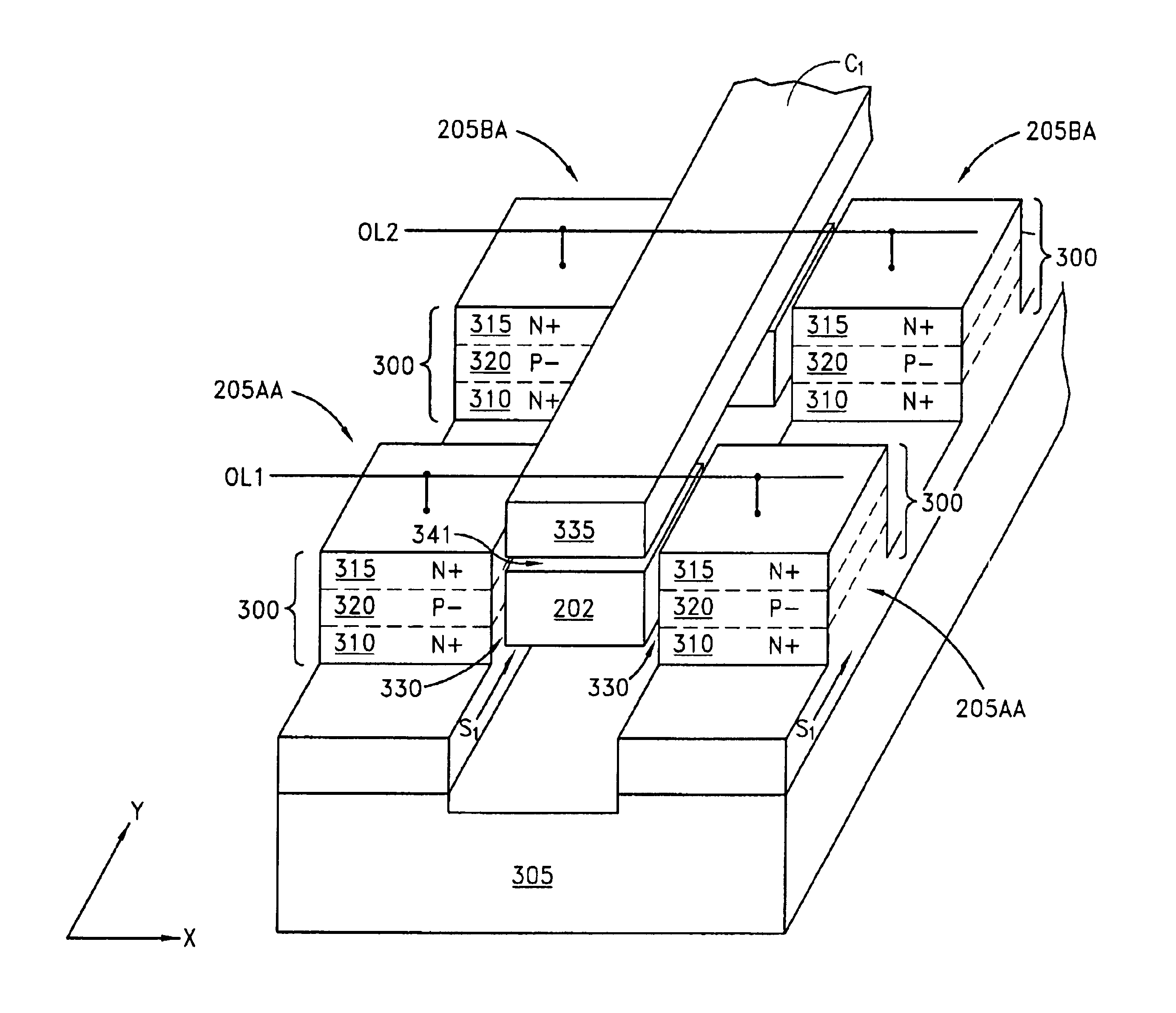
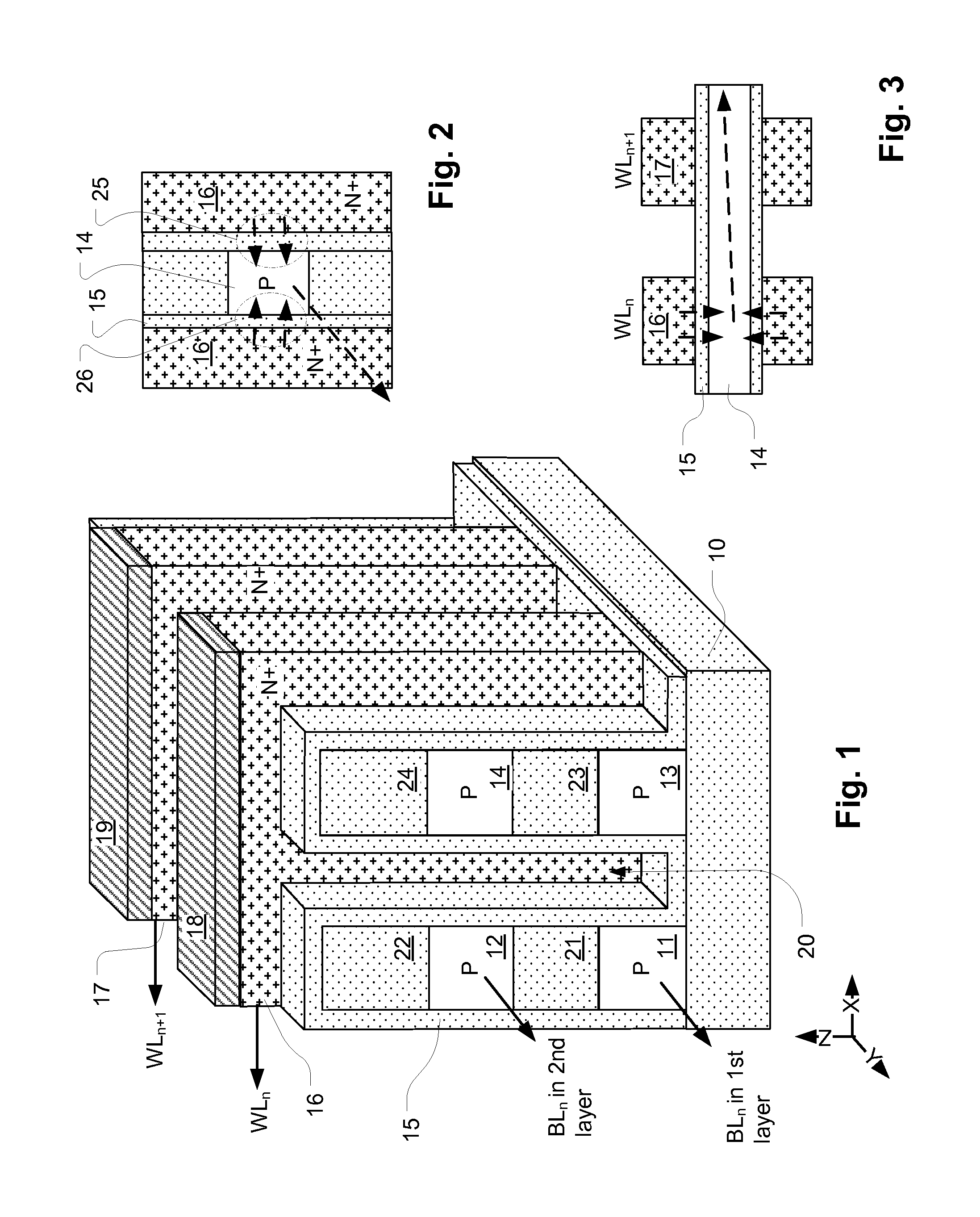
Floating gate transistor with horizontal gate layers stacked next to vertical body
Vertical body transistors with adjacent horizontal gate layers are used to form a memory array in a high density flash electrically erasable and programmable read only memory (EEPROM) or a logic array in a high density field programmable logic array (FPLA). The transistor is a field-effect transistor (FET) having an electrically isolated (floating) gate that controls electrical conduction between source regions and drain regions. If a particular floating gate is charged with stored electrons, then the transistor will not turn on and will provide an indication of the stored data at this location in the memory array within the EEPROM or will act as the absence of a transistor at this location in the logic array within the FPLA. The memory array or the logic array includes densely packed cells, each cell having a semiconductor pillar providing shared source and drain regions for two vertical body transistors that have control gates overlaying floating gates distributed on opposing sides of the semiconductor pillar. Both bulk semiconductor and silicon-on-insulator embodiments are provided. If a floating gate transistor is used to store a single bit of data or to represent a logic function, an area of only 2F<2 >is needed per respective bit of data or bit of logic, where F is the minimum lithographic feature size.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
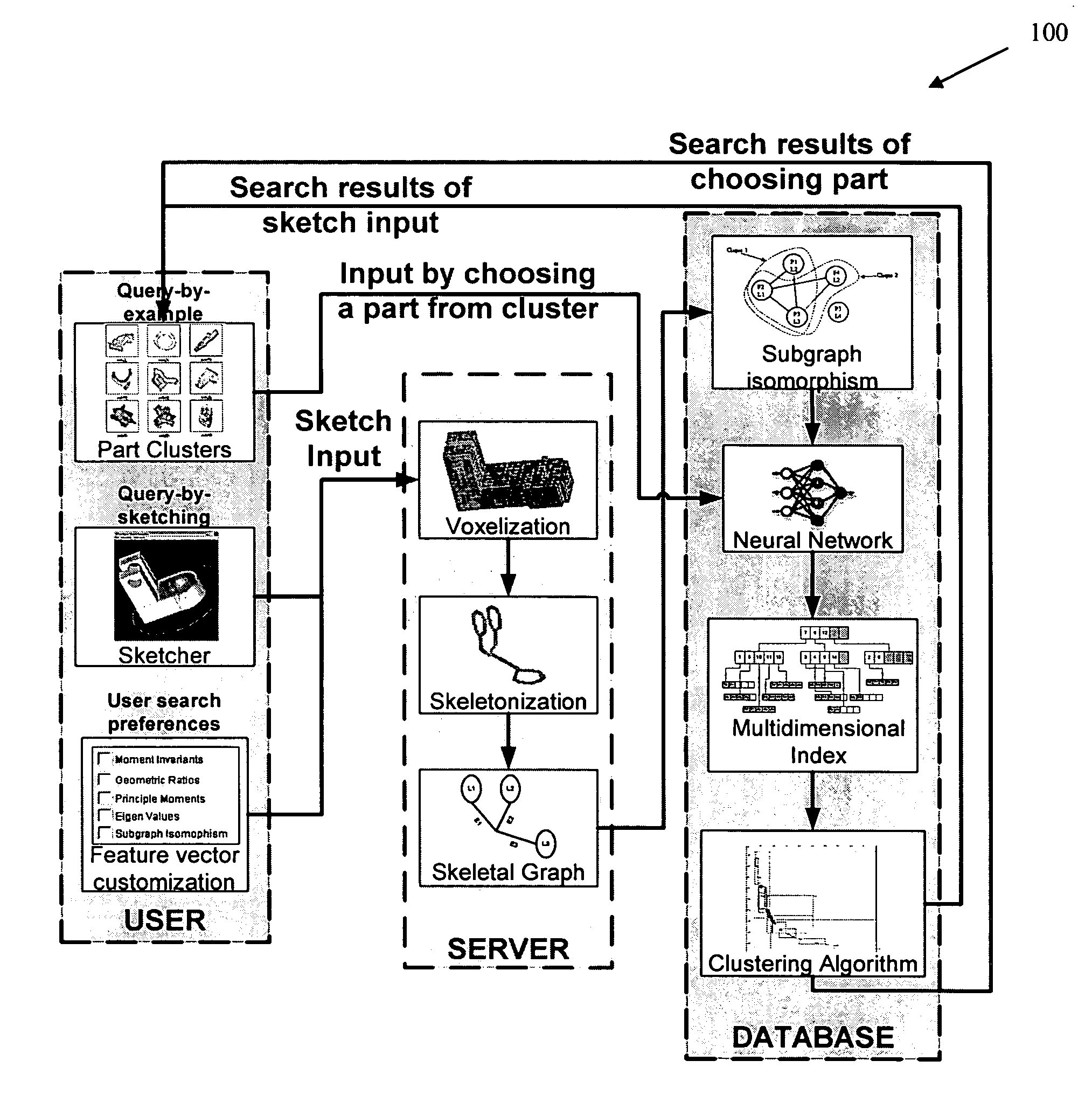
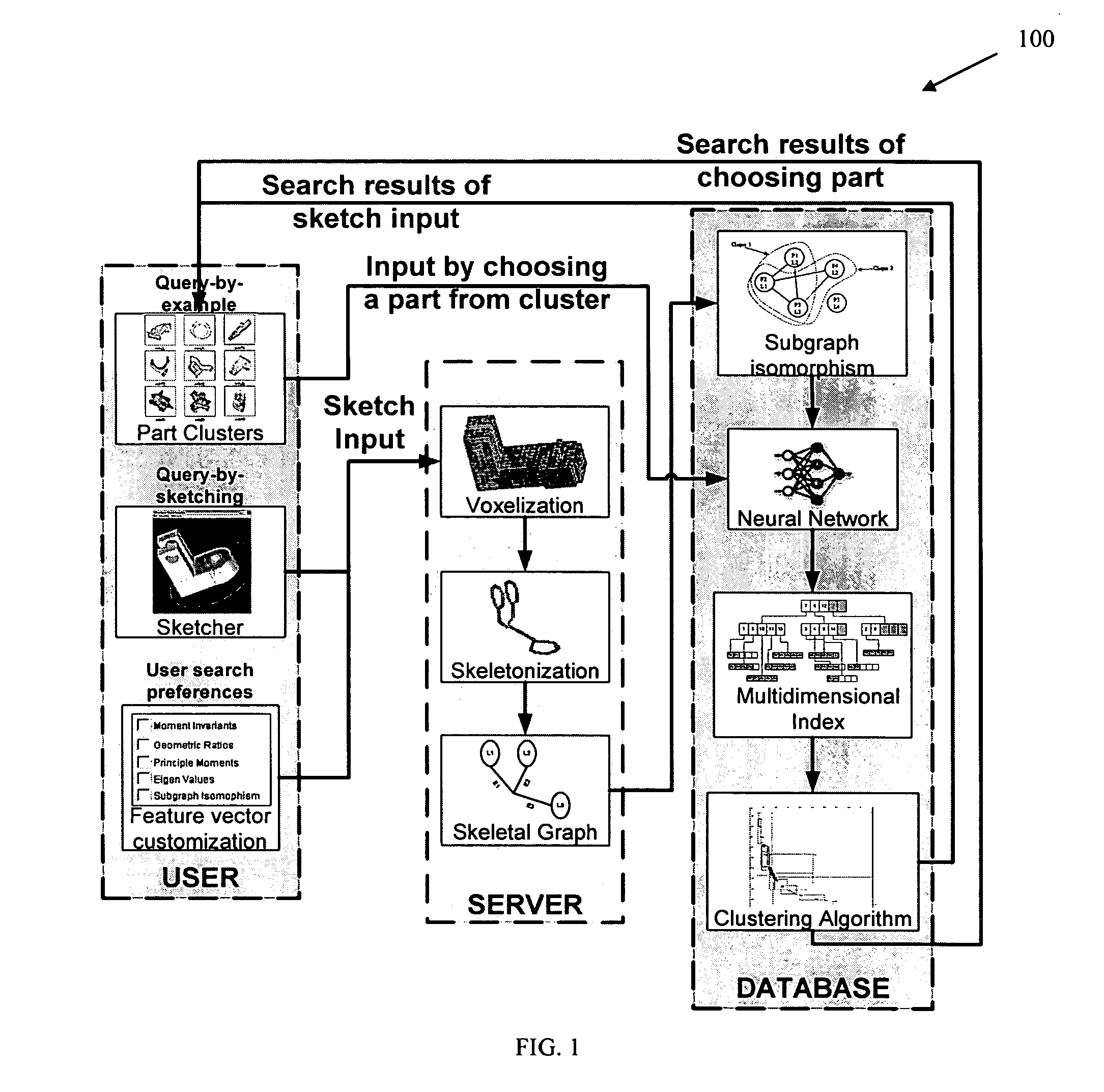
Methods, systems, and data structures for performing searches on three dimensional objects
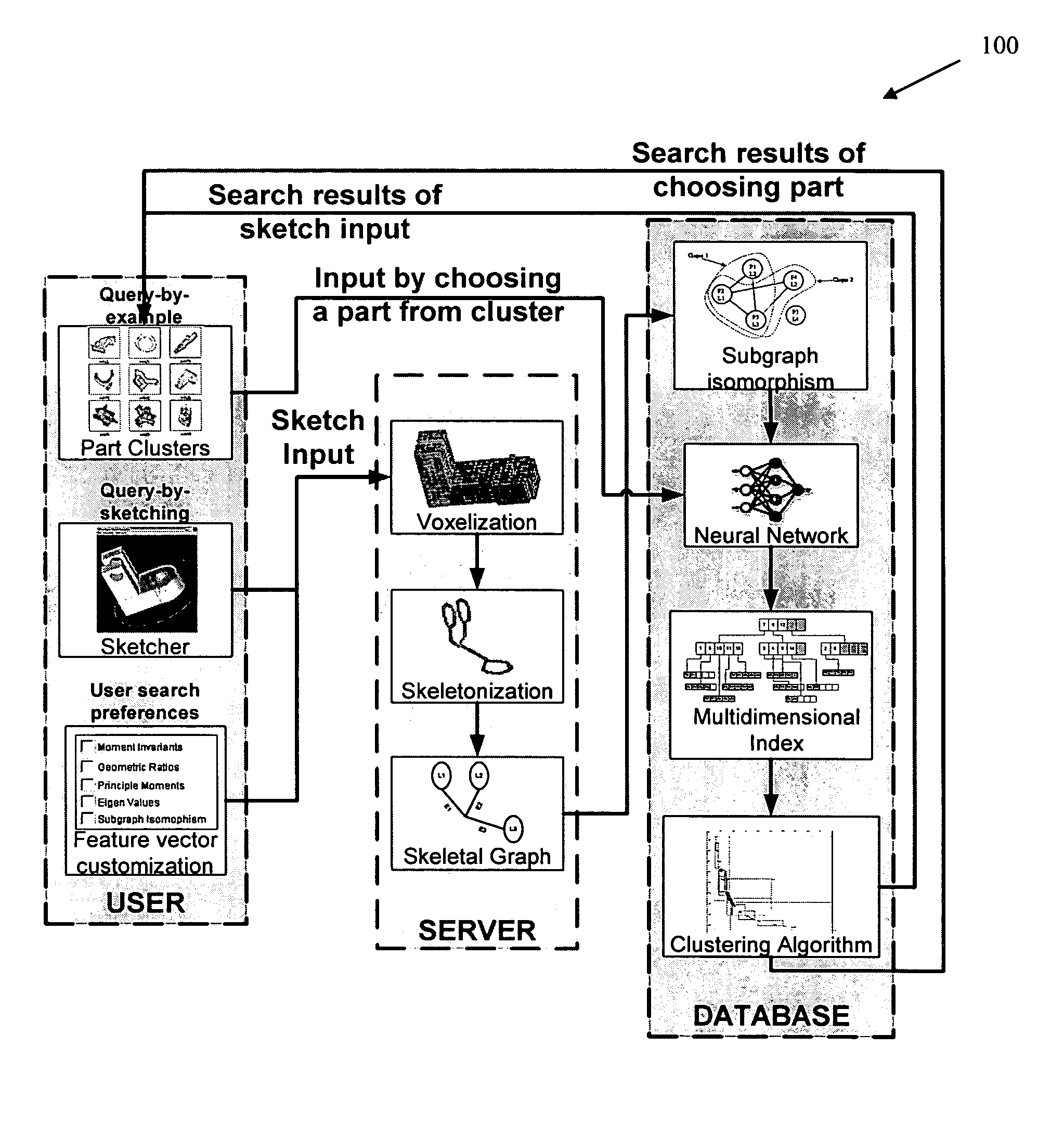
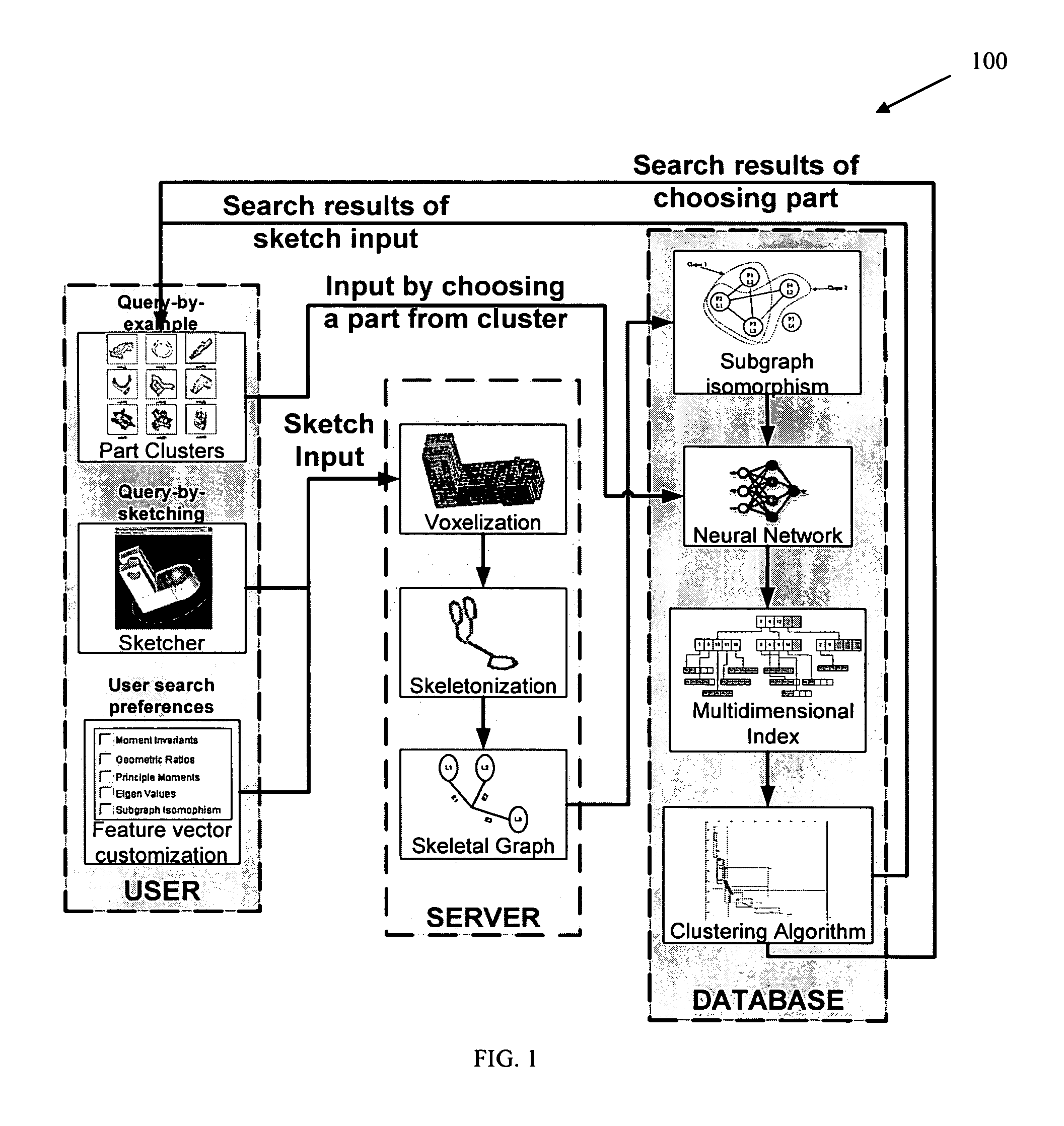
Techniques are provided for searching on three dimensional (3D) objects across large, distributed repositories of 3D models. 3D shapes are created for input to a search system; optionally user-defined similarity criterion is used, and search results are interactively navigated and feedback received for modifying the accuracy of the search results. Search input can also be given by picking 3D models from a cluster map or by providing the orthographic views for the 3D model. Feedback can be given by a searcher as to which models are similar and which are not. Various techniques adjust the search results according to the feedback given by the searcher and present the new search results to the searcher.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Methods apparatus and data structures for enhancing the resolution of images to be rendered on patterned display devices
InactiveUS6393145B2Improve imaging resolutionHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsImage enhancementSub-pixel resolutionArray data structure
Techniques for improving the resolution of images (either analog images, analytic images, or images having a higher resolution than that of a display device) to be rendered on patterned displays. In one aspect of the present invention, an overscaling or oversampling process may accept analytic character information, such as contours for example, and a scale factor or grid and overscale or oversample the analytic character information to produce an overscaled or oversampled image. The overscaled or oversampled image generated has a higher resolution than the display upon which the character is to be rendered. Displaced samples of the overscaled or oversampled image are then combined (or filtered). An analytic image, such as a line drawing for example, may be applied to the oversampling / overscaling process as was the case with the character analytic image. However, since the analytic image may have different units than that of the character analytic image, the scale factor applied may be different. Since an ultra resolution image is already "digitized", that is, not merely mathematically expressed contours or lines between points, it may be applied directly to a process for combining displaced samples of the ultra-resolution image to generate another ultra-resolution image (or an image with sub-pixel information). The functionality of the overscaling / oversampling process and the processes for combining displaced samples may be combined into a single step analytic to digital sub-pixel resolution conversion process.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
Method and apparatus for generating and using enhanced tree bitmap data structures in determining a longest prefix match
ActiveUS20050157712A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsDigital data information retrievalGeneral purposeArray data structure
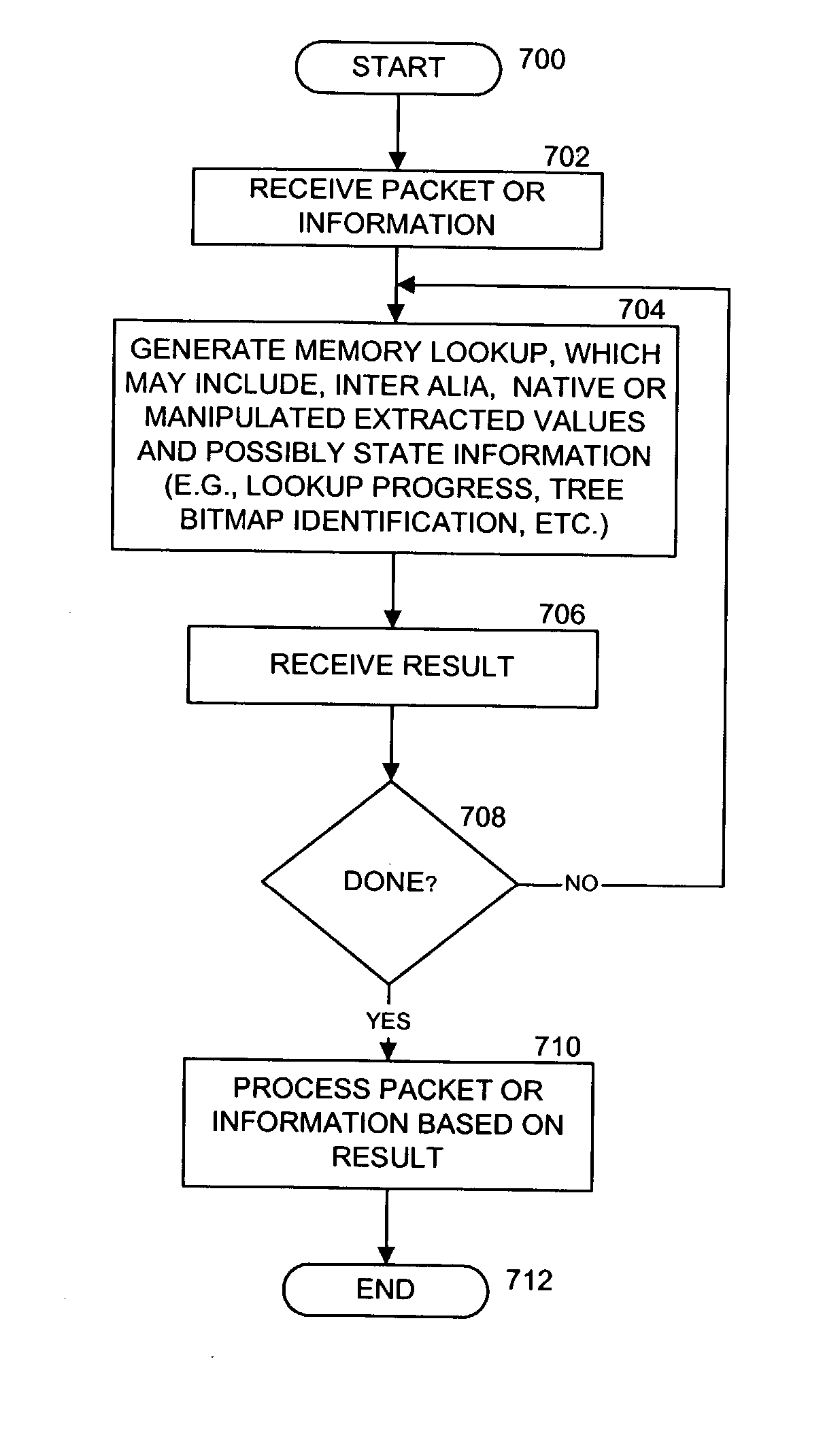
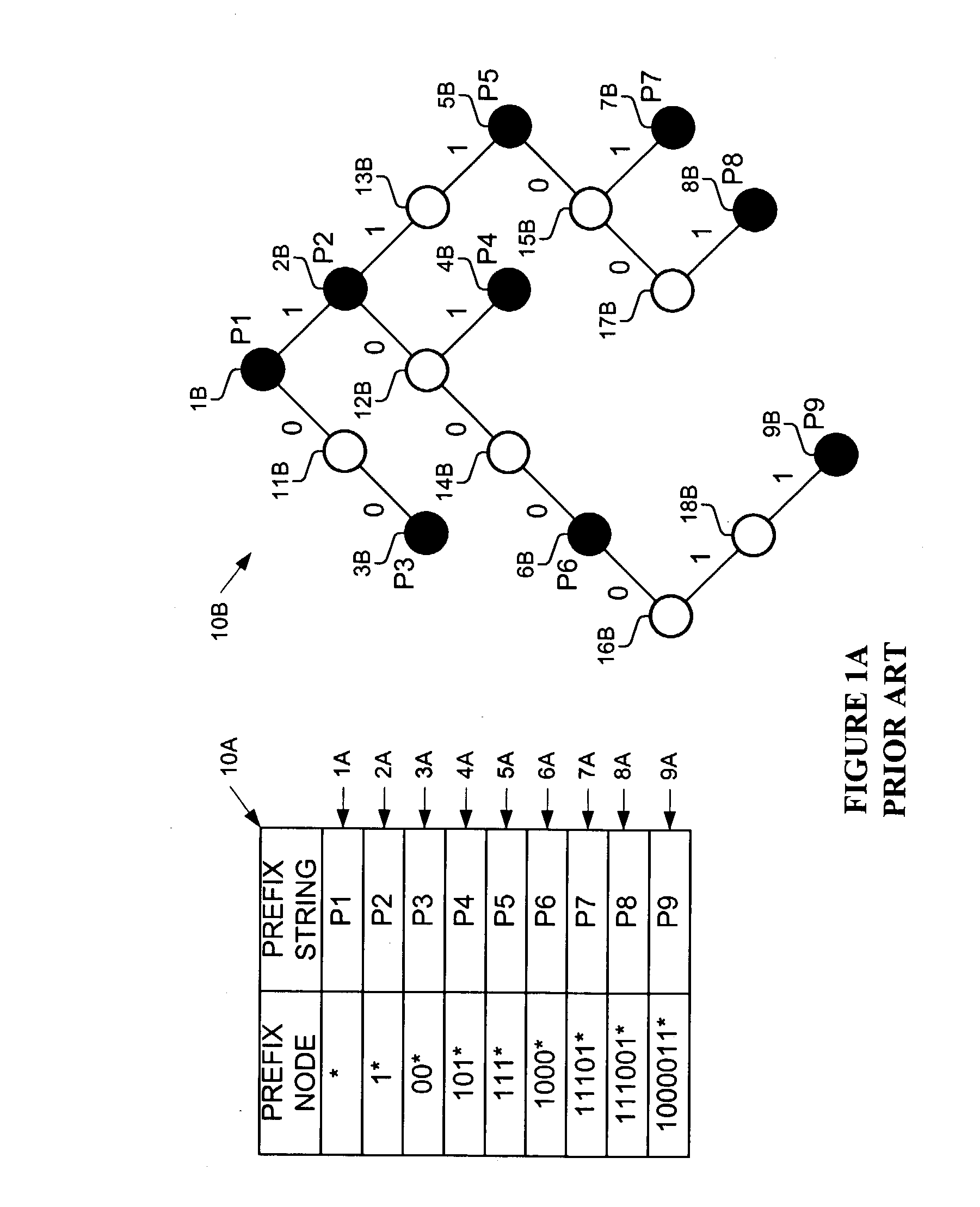
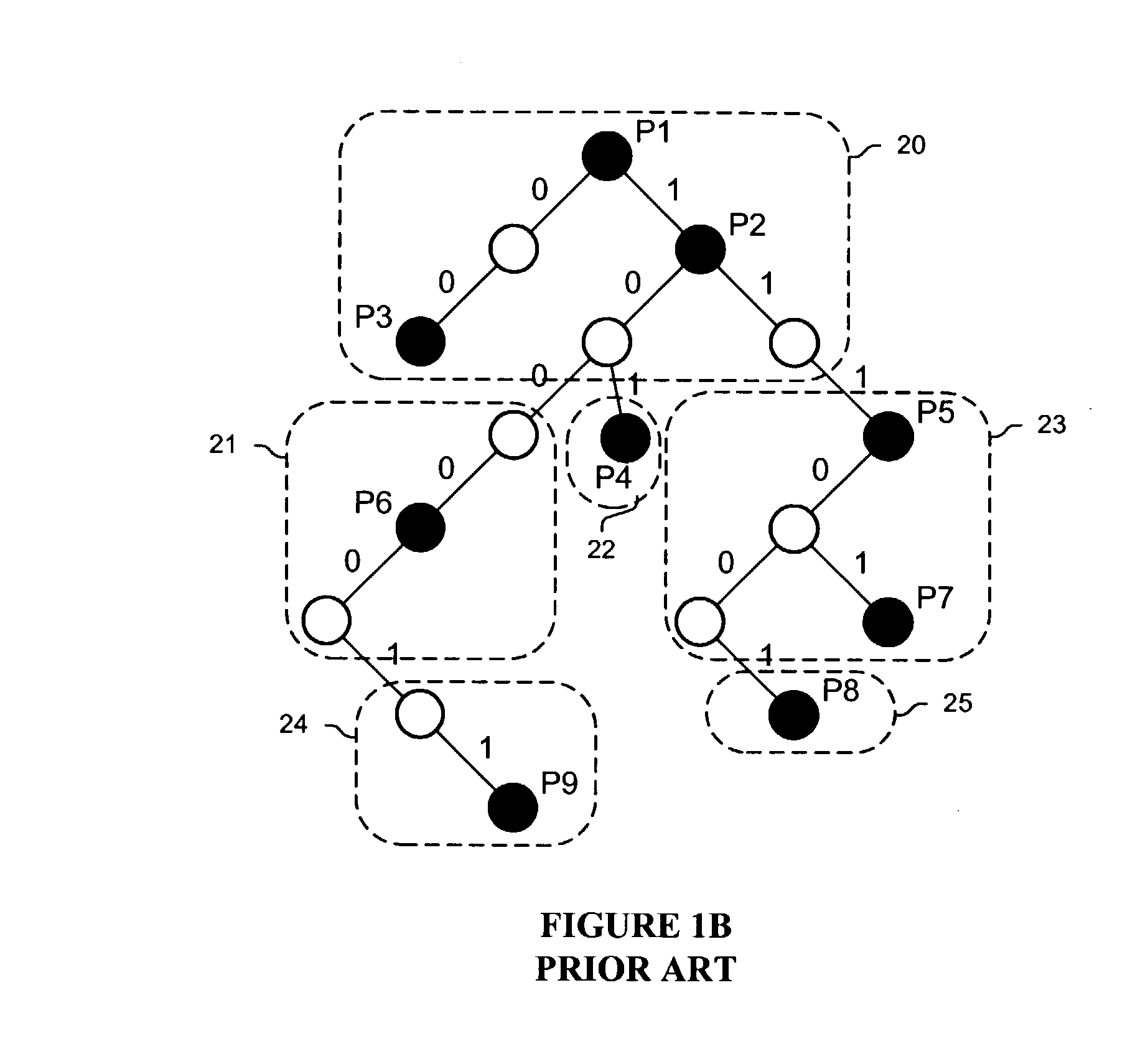
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for generating and using an enhanced tree bitmap data structure in determining a longest prefix match, such as in a router, packet switching system. One implementation organizes the tree bitmap to minimize the number of internal nodes that must be accessed during a lookup operation. A pointer is included in each of the trie or search nodes to the best match so far entry in the leaf or results array which allows direct access to this result without having to parse a corresponding internal node. Moreover, one implementation stores the internal node for a particular level as a first element in its child array. Additionally, one implementation uses a general purpose lookup engine that can traverse multiple tree bitmaps or other data structures simultaneously, and perform complete searches, partial searches, and resume partial searches such as after receiving additional data on which to search.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
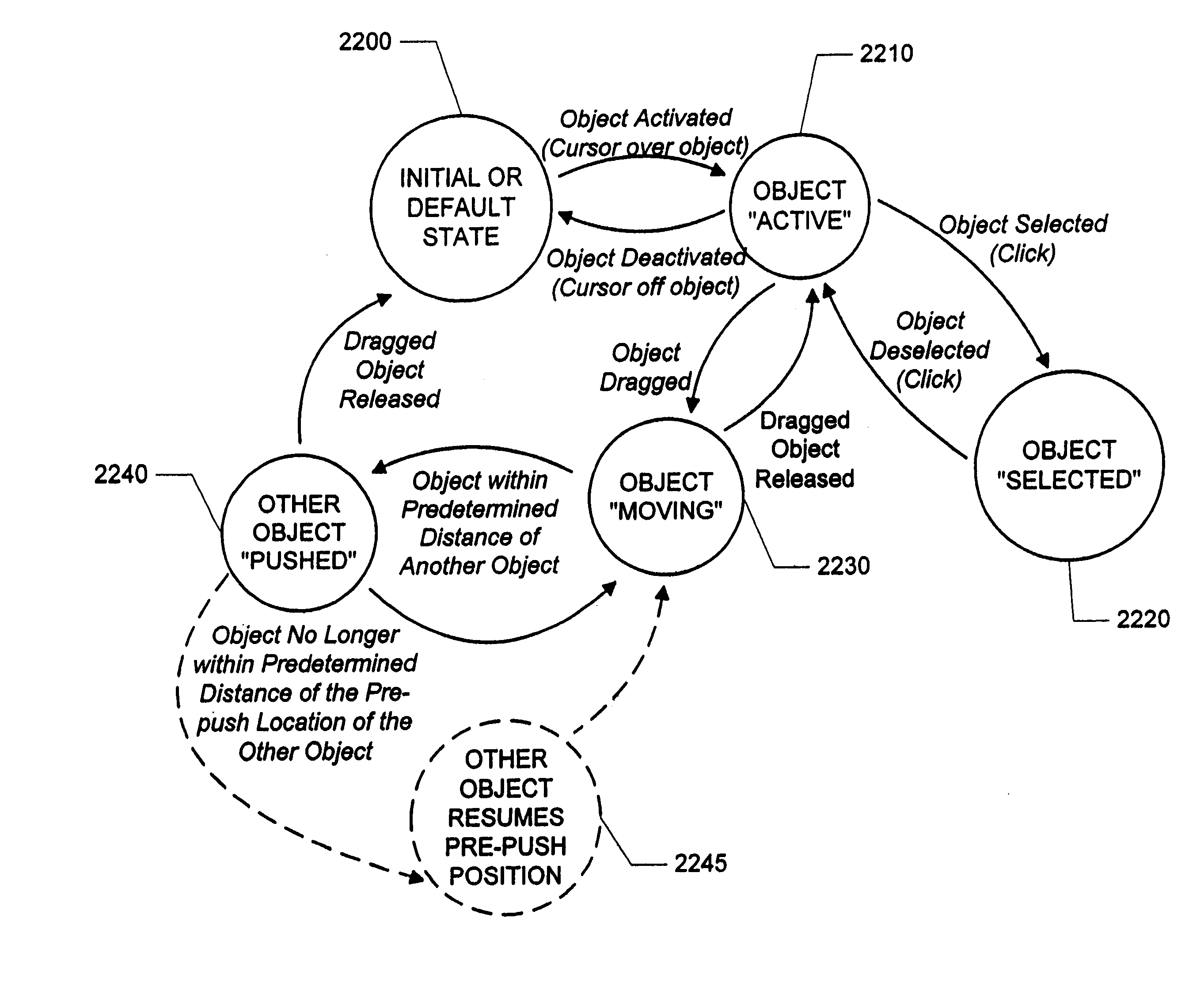
Methods, apparatus and data structures for providing a user interface, which exploits spatial memory in three-dimensions, to objects and which visually groups proximally located objects
InactiveUS6414677B1Increase spacingMore representationInput/output processes for data processing3D-image renderingGraphicsArray data structure
A graphical user interface in which object thumbnails are rendered on a simulated three-dimensional surface which (i) exploits spatial memory and (ii) allows more objects to be rendered on a given screen. The objects may be moved, continuously, on the surface with a two-dimensional input device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
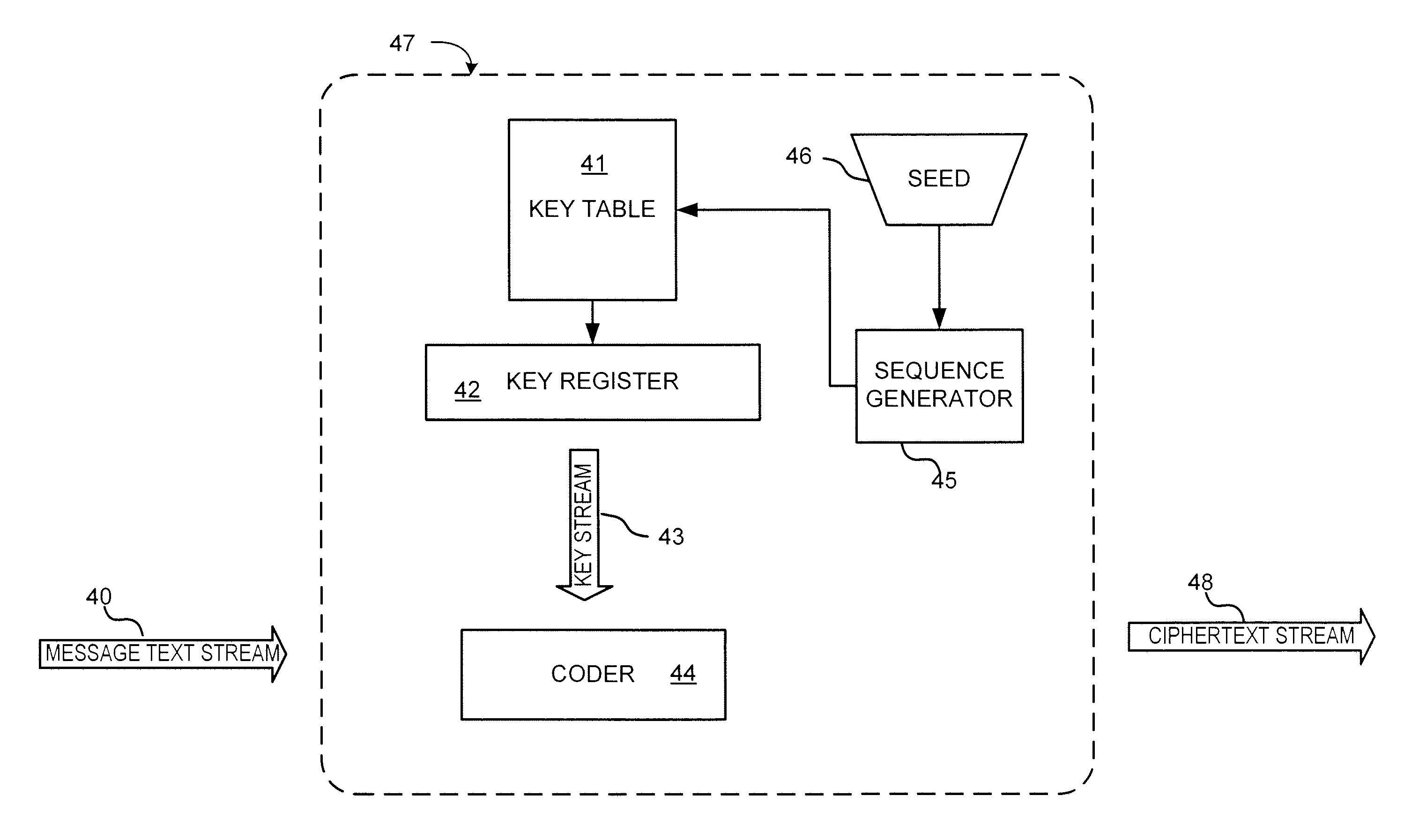
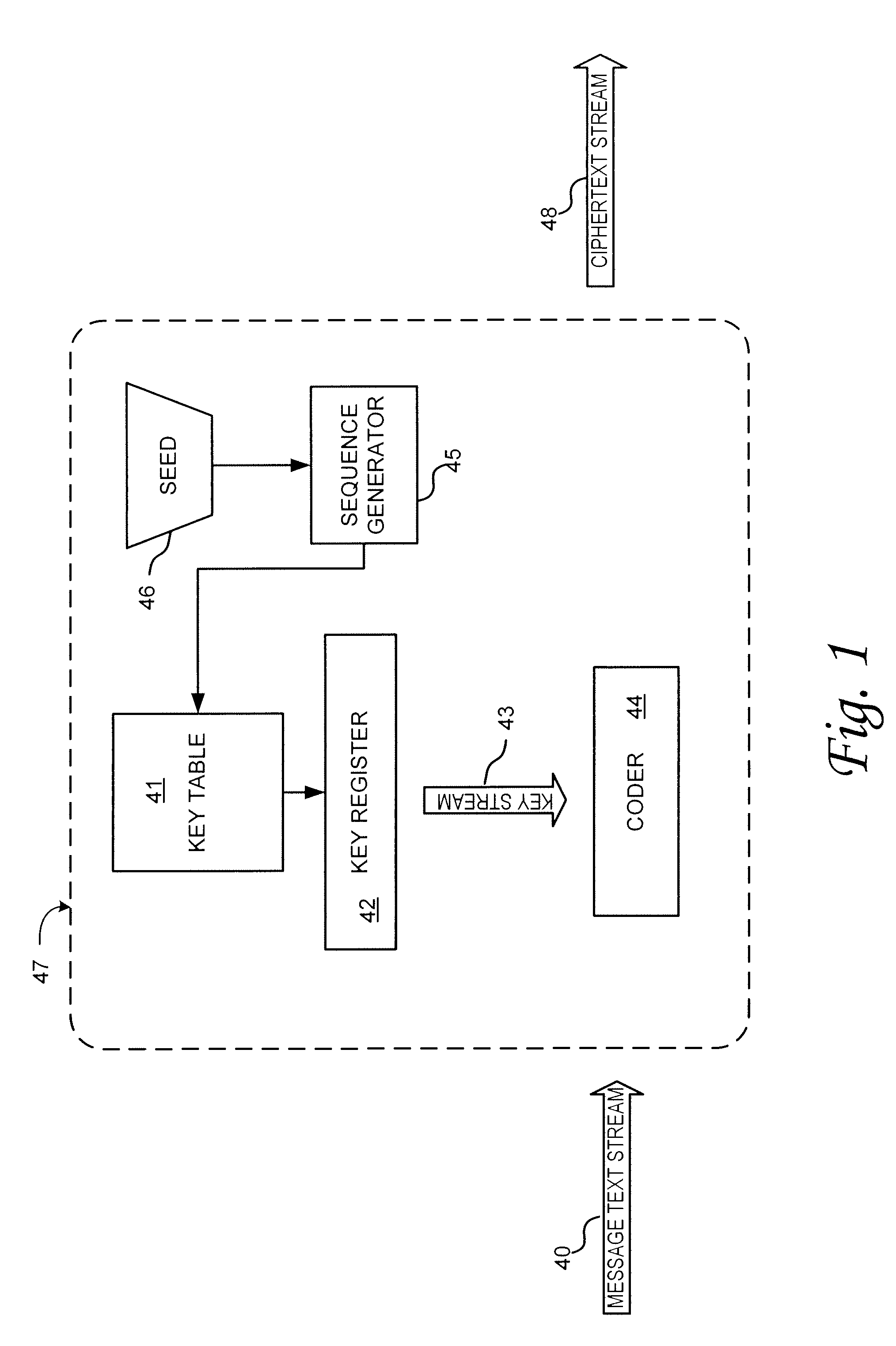
Chaotic cipher system and method for secure communication
ActiveUS20100211787A1Key distribution for secure communicationData stream serial/continuous modificationSecure communicationArray data structure
The present invention provides a method for a data encryption device to perform network communications, the method comprising obtaining an indexed array of encryption keys, wherein the indexed array of encryption keys is shared with a data decryption device; obtaining a message to be encrypted; using a first random or pseudorandom number to determine an index; obtaining a first key from the array of encryption keys, wherein the first key corresponds to the index; selecting a second key from the plurality of encryption keys; encrypting the message using the first key and a second random or pseudorandom number; encrypting the index using the second key and a third random or pseudorandom number; transmitting the encrypted message and the encrypted index to the data decryption device.
Owner:MERCURY MISSION SYST LLC
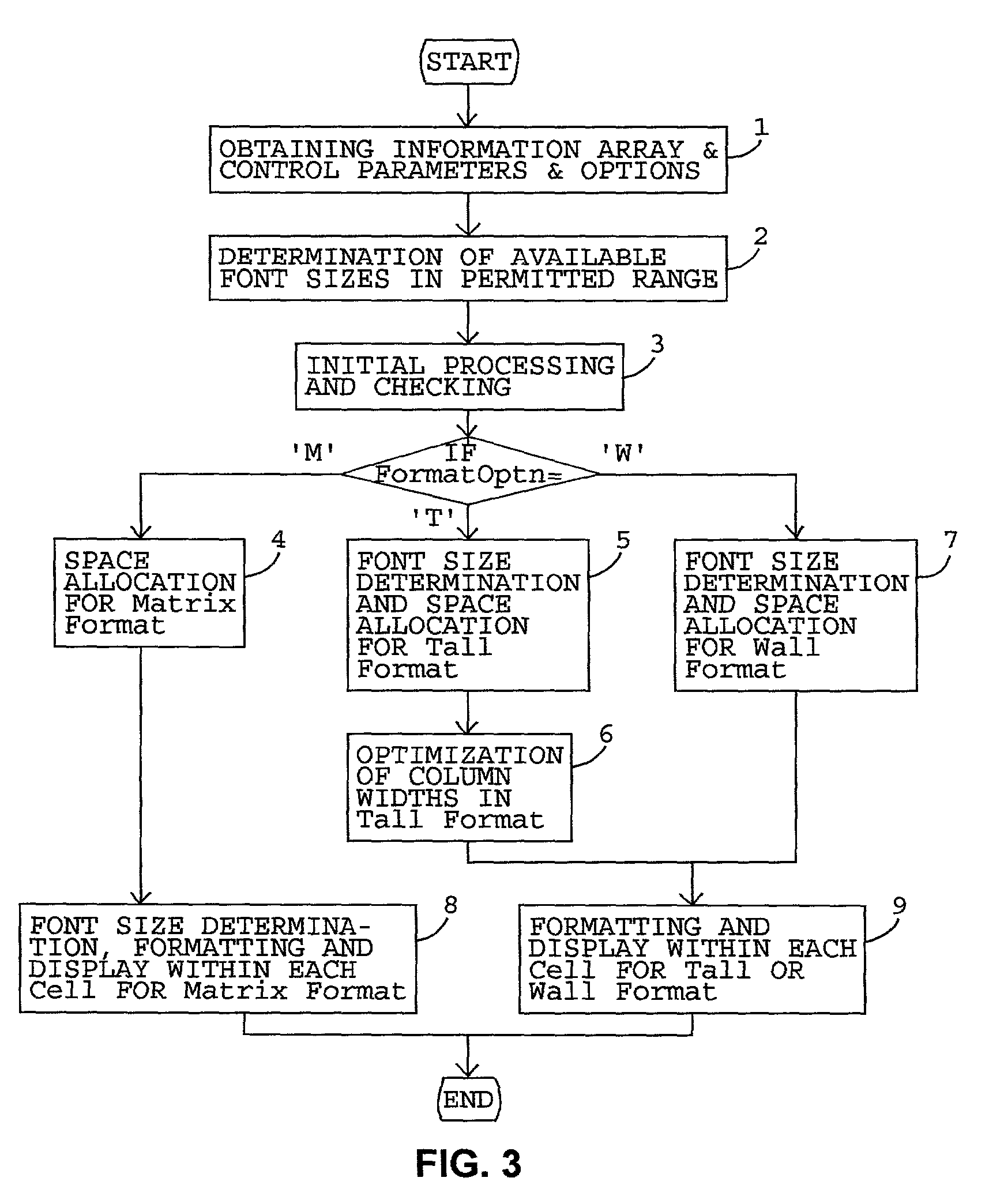
Compacting an information array display to cope with two dimensional display space constraint
ActiveUS8001465B2Maldistribution of minimizedSpace minimizationText processingSpecial data processing applicationsArray data structureCombined use
This invention relates to computer implemented methods for accommodating elements of an information array within the physical constraints of a predetermined two dimensional display space. The maldistribution and wastage of space inherent to matrix format display is sought to be minimized by allocating space based on moderated display space requirement values of larger elements. A measurement of lopsidedness of distribution of larger elements across columns and across rows is used while allocating column widths and row heights. If the display space is inadequate for displaying the array elements in matrix format, then the elements are displayed in Tall / Wall format wherein the row / column alignment of cells, respectively, is not maintained. The information array elements may include text, image or both. Methods such as font size reduction, text abbreviation and image size reduction are used in combination with space allocation methods to fit the array elements into corresponding cells in the display space.
Owner:ARDEN INNOVATIONS LLC
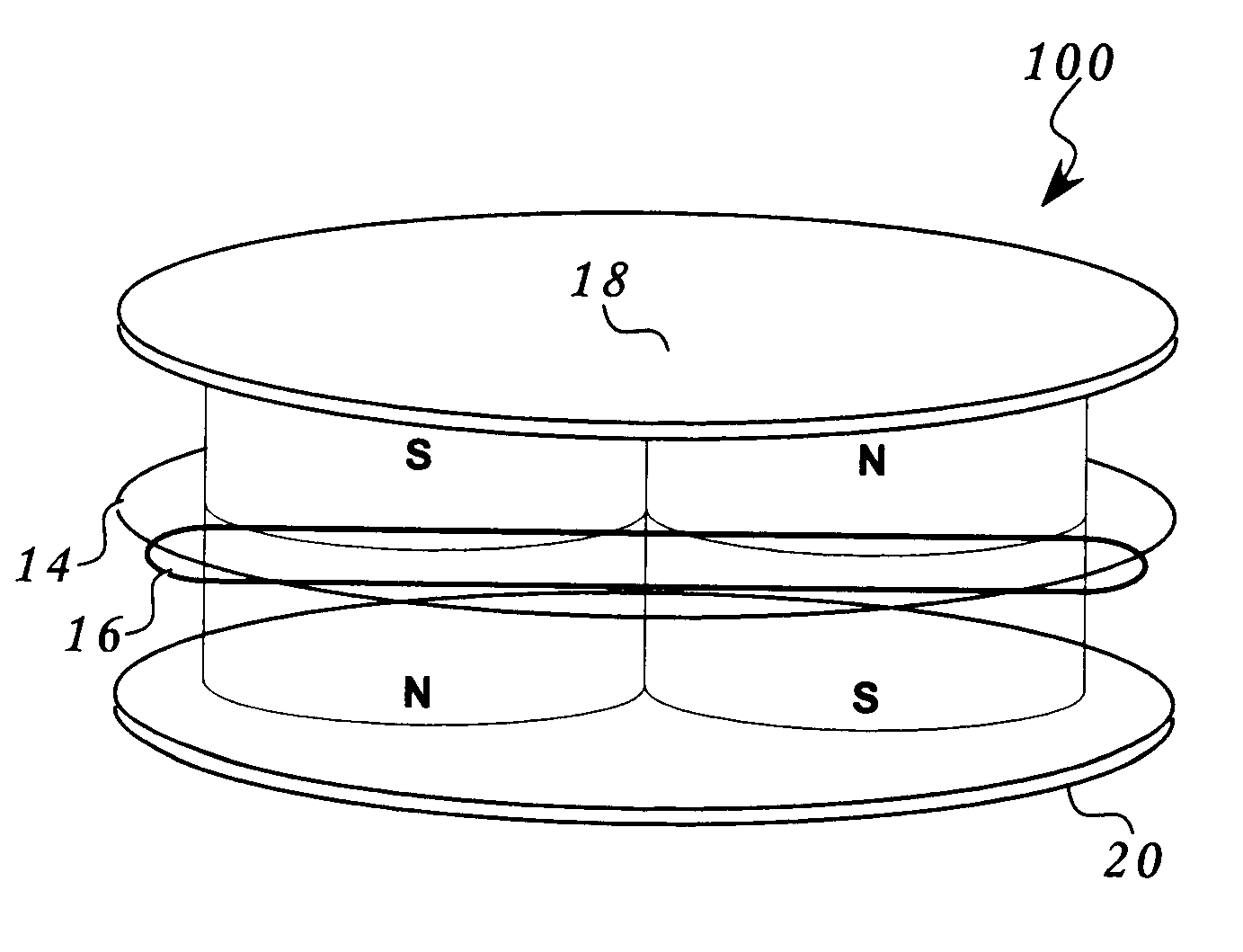
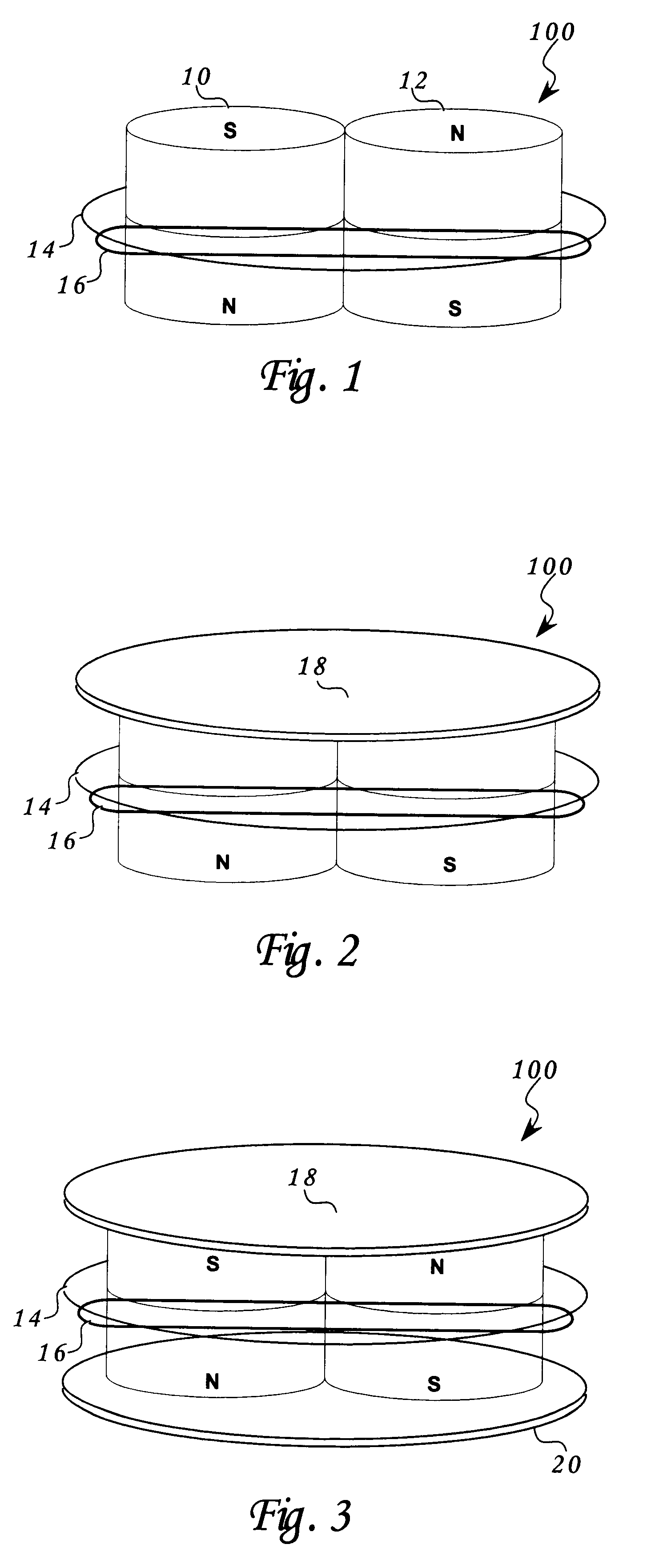
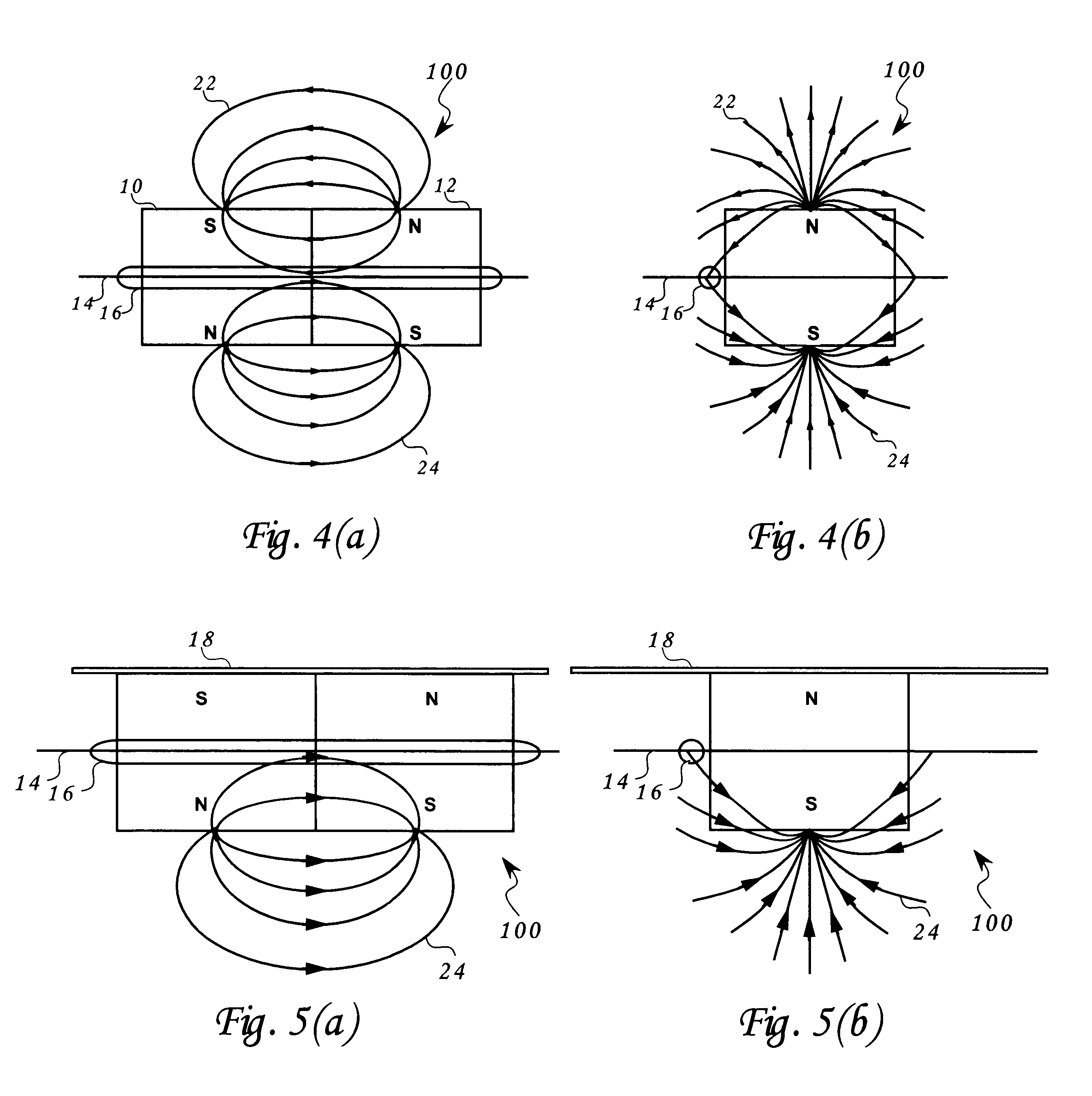
Multifaceted balanced magnetic proximity sensor
An apparatus and method of proximity switch / sensor based generally on a balanceable magnetic pole array. The magnetic pole array contains at least four poles with optional ferromagnetic shunt(s). The proximity of a shunt to a magnetic pole array determines whether the array is balanced or unbalanced. A balanced array is one with a zone where the vector sum of magnetic fields emanating from the array's poles can be made to approach zero. A sensor such as a reed switch is placed in the balanced zone. When the balance of the array is disturbed by the application of one or multiple shunts, the resulting finite magnetic field vector along with the resulting magnetic flux, activates the sensor. This approach can be implemented in a variety of array structures that offer implementation of a variety of logical functions. Multiple shunts and their proximity to the array are used as the logical function's inputs and the sensor's state as the logical function's output.
Owner:OSTERWEIL JOSEF
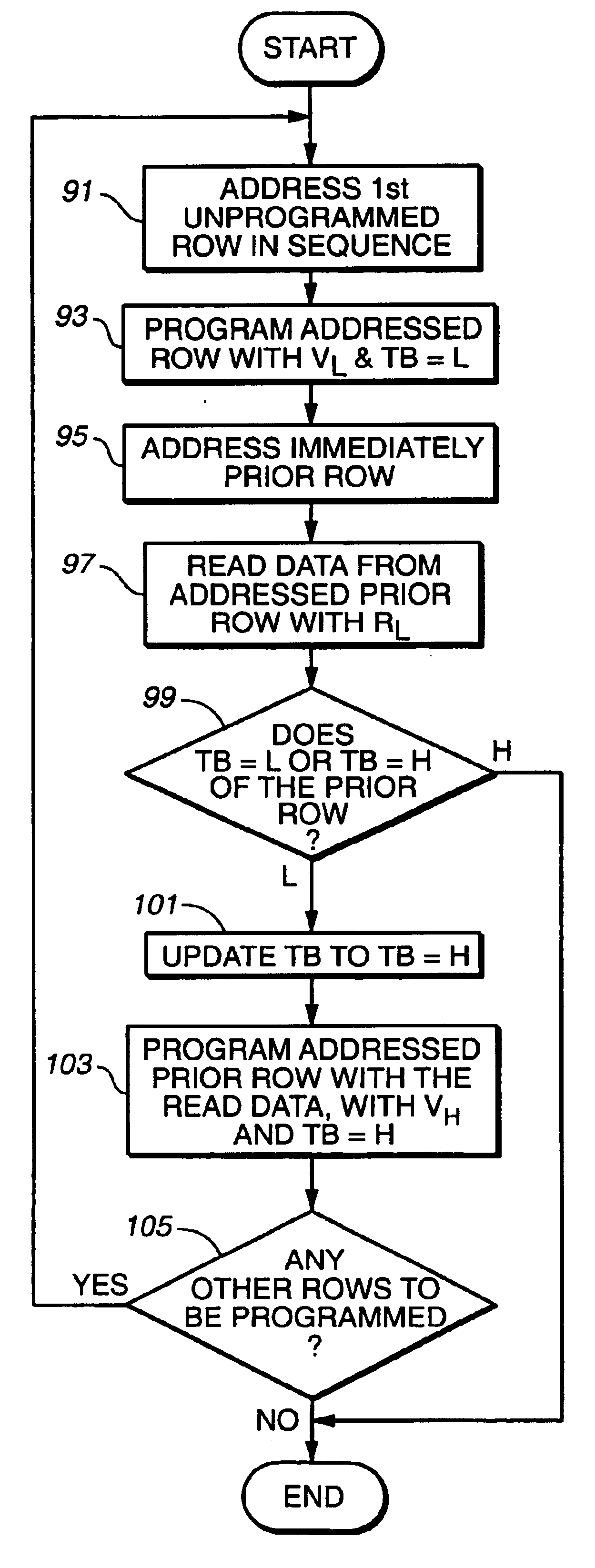
Techniques for reducing effects of coupling between storage elements of adjacent rows of memory cells
Techniques of reducing erroneous readings of the apparent charge levels stored in a number of rows of memory cells on account of capacitive coupling between the cells. All pages of a first row are programmed with a first pass, followed by programming all pages of a second adjacent row with a first pass, after which the first row is programmed with a second pass, and then all pages of a third row are programmed with a first pass, followed by returning to program the second row with a second pass, and so on, in a back-and-forth manner across the rows of an array. This minimizes the effect on the apparent charge stored on rows of memory cells that can occur by later writing data into adjacent rows of memory cells.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Array structure for the application to wireless switch of WLAN and wman
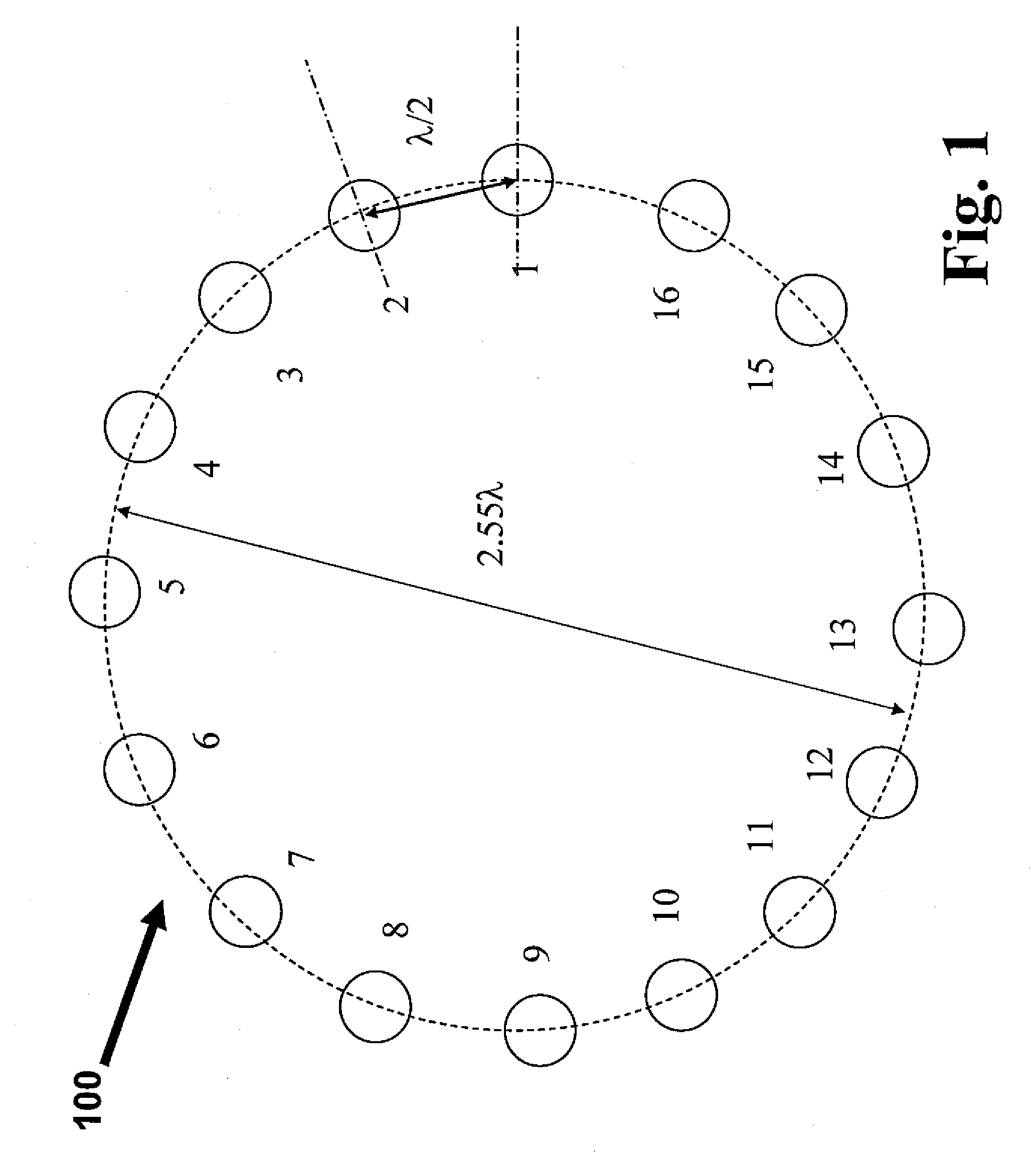
InactiveUS20070257858A1Improve efficiencyLow budgetIndoor communication adaptationIndividually energised antenna arraysArea networkArray data structure
The present invention provides an antenna array structure which includes multiple array elements, and the antenna array structure is using for the application of the WLAN (wireless local area network) or WMAN (wireless metro area network.) Furthermore, the array elements of the present invention are phased arrays or attenuated arrays, and when configuration with different type of the array element is used, the corresponding BFN (beam forming network) can also be implemented in various possibilities. With all the configuration of the present invention, the manufacturers can have a stable array structure for their applications.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
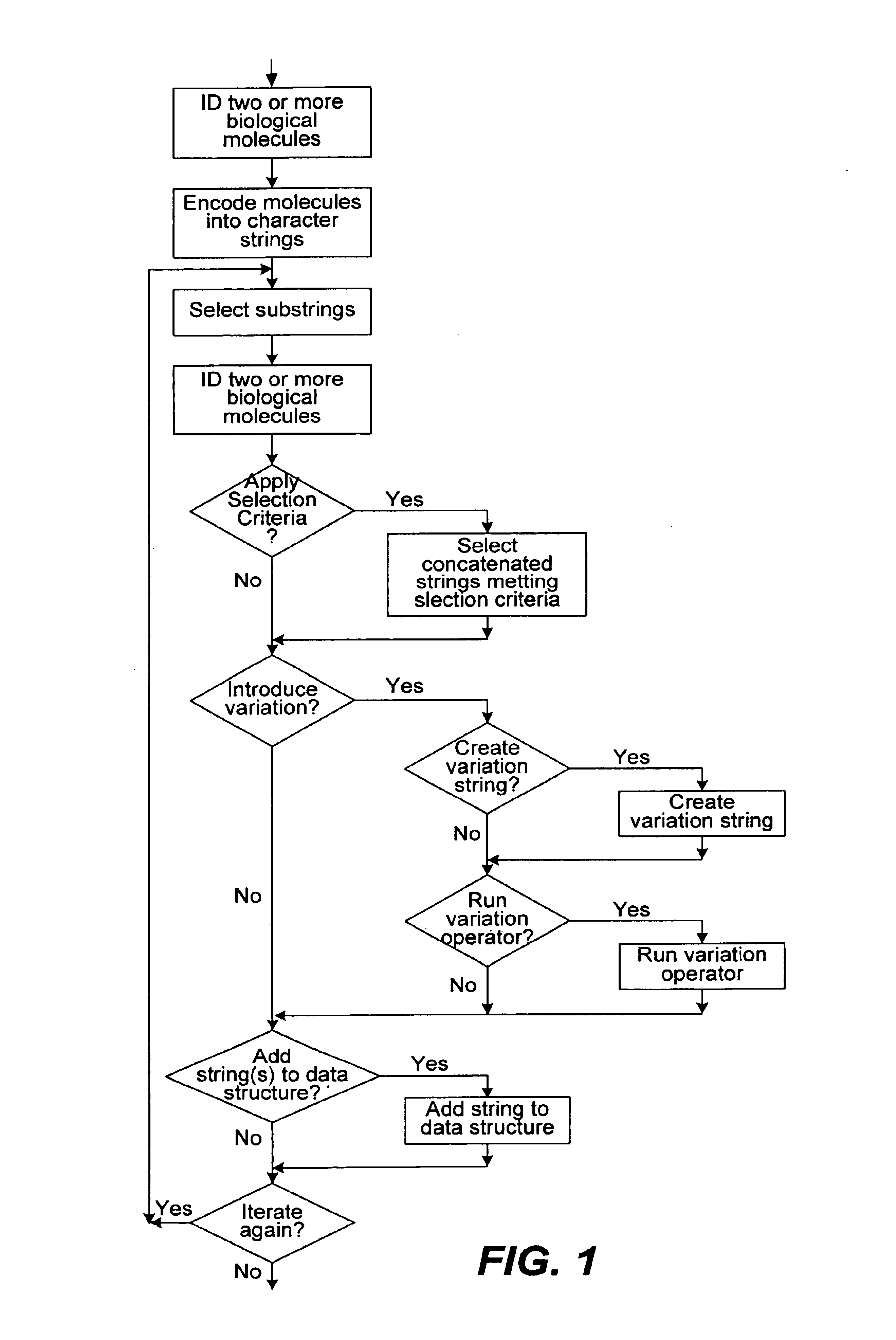
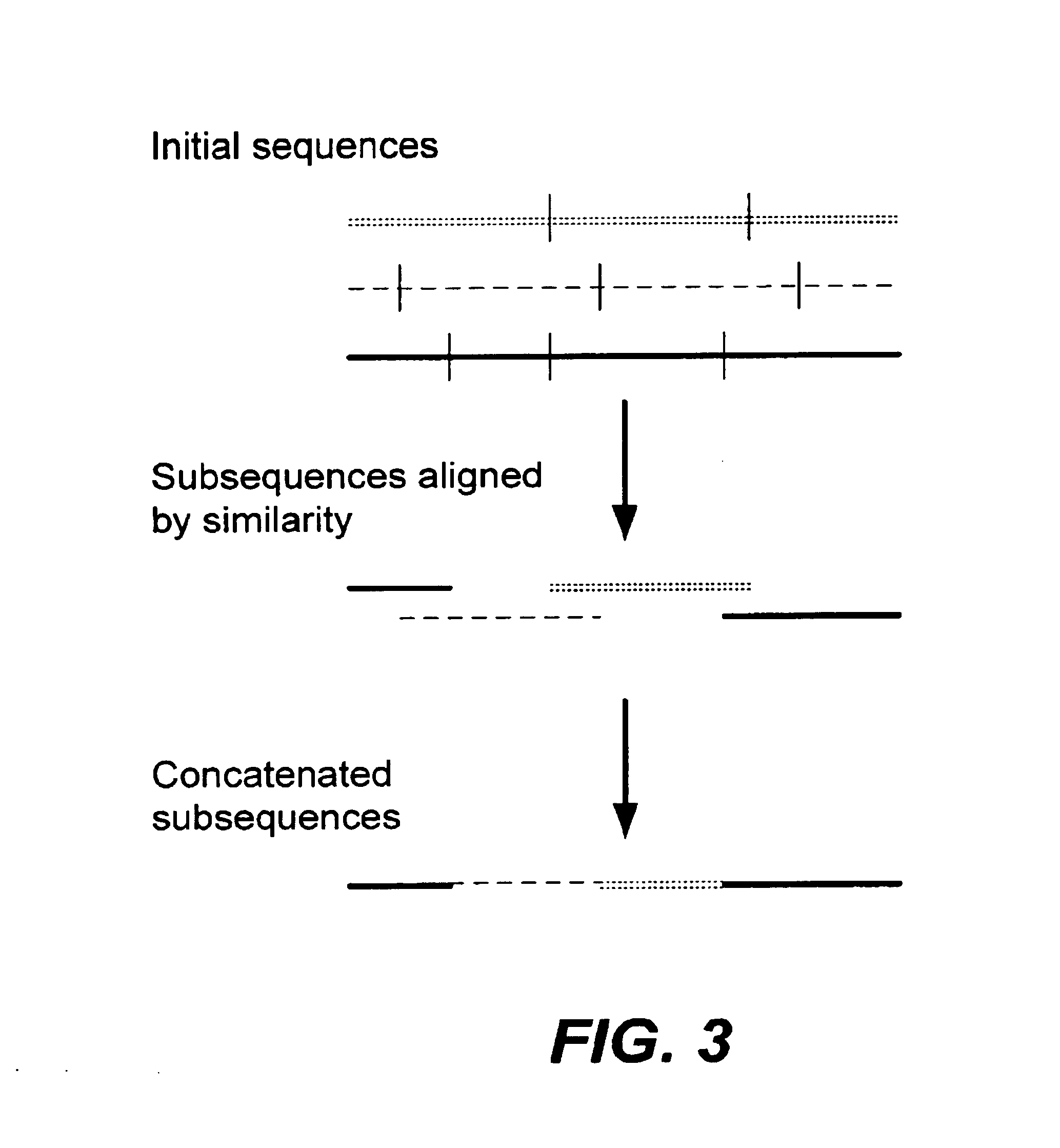
Methods of populating data structures for use in evolutionary simulations
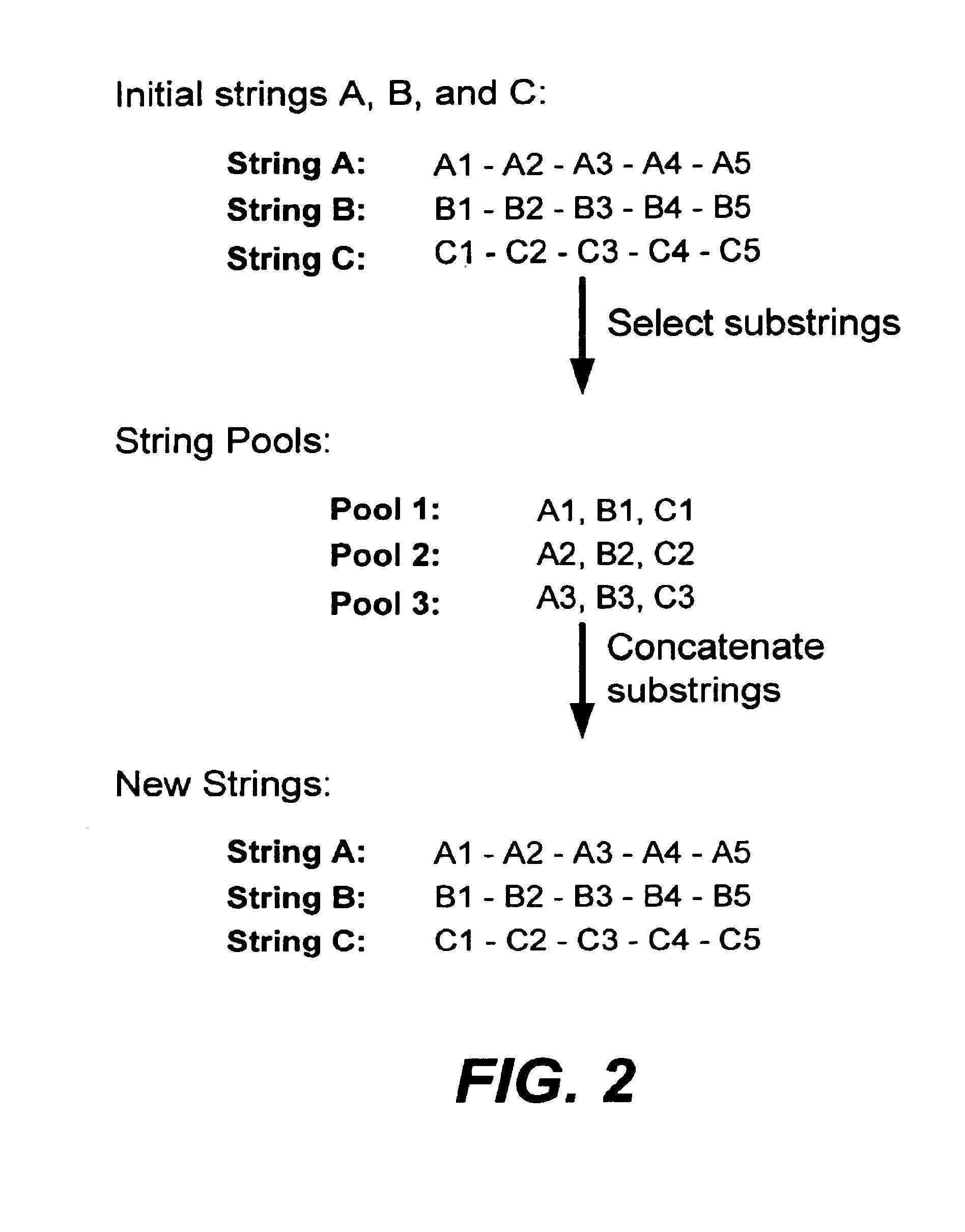
In particular, this invention provides novel methods of populating data structures for use in evolutionary modeling. In particular, this invention provides methods of populating a data structure with a plurality of character strings. The methods involve encoding two or more a biological molecules into character strings to provide a collection of two or more different initial character strings; selecting at least two substrings from the pool of character strings; concatenating the substrings to form one or more product strings about the same length as one or more of the initial character strings; adding the product strings to a collection of strings; and optionally repeating this process using one or more of the product strings as an initial string in the collection of initial character strings.
Owner:CODEXIS MAYFLOWER HLDG LLC
Software transactional memory for dynamically sizable shared data structures
ActiveUS20040015642A1Data processing applicationsError preventionArray data structureComputer science
We propose a new form of software transactional memory (STM) designed to support dynamic-sized data structures, and we describe a novel non-blocking implementation. The non-blocking property we consider is obstruction-freedom. Obstruction-freedom is weaker than lock-freedom; as a result, it admits substantially simpler and more efficient implementations. An interesting feature of our obstruction-free STM implementation is its ability to use of modular contention managers to ensure progress in practice.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
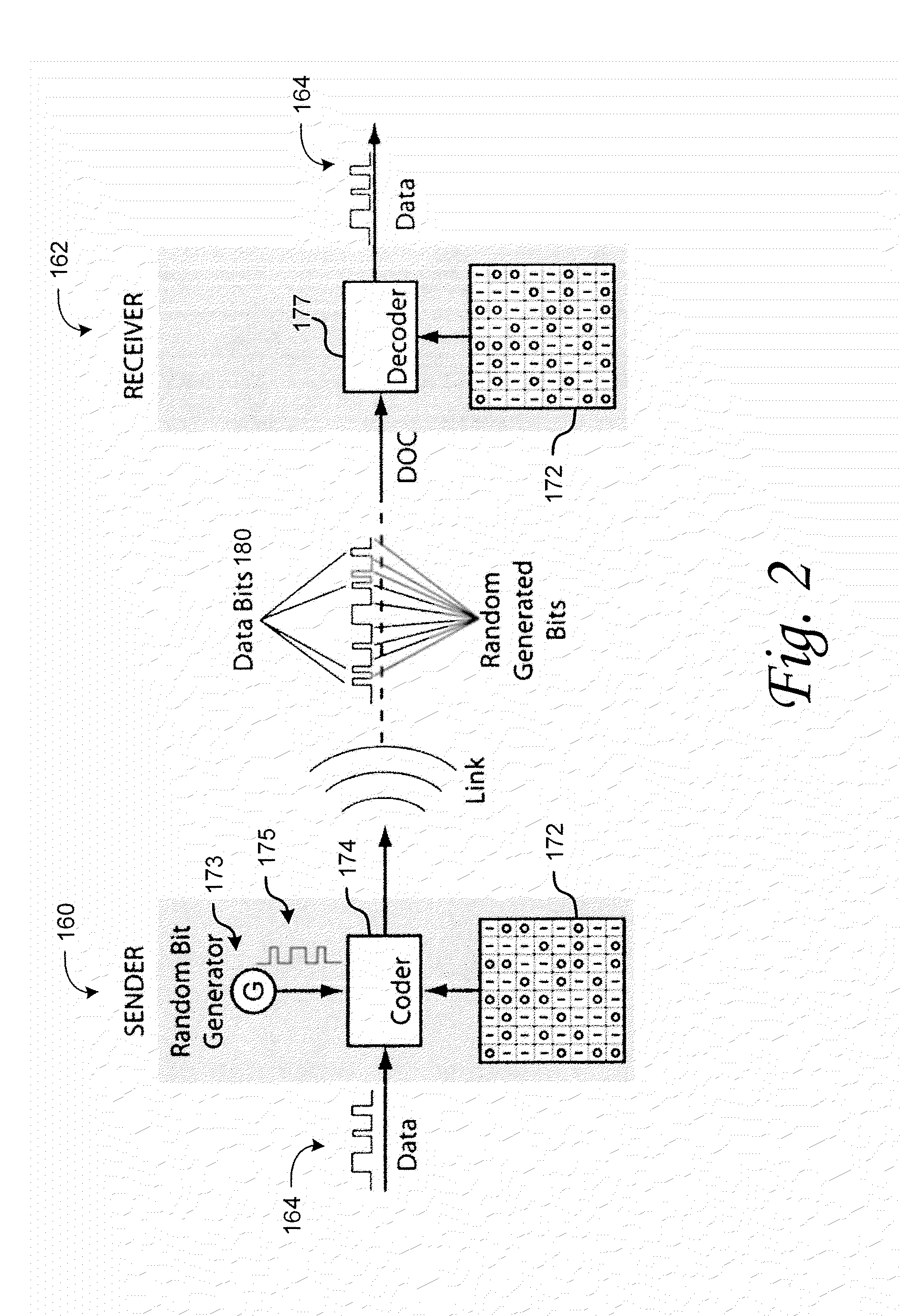
Validation service for payment cards with preloaded dynamic card verification values
InactiveUS20090150295A1Improve securityUser identity/authority verificationElectronic credentialsPaymentPersonalization
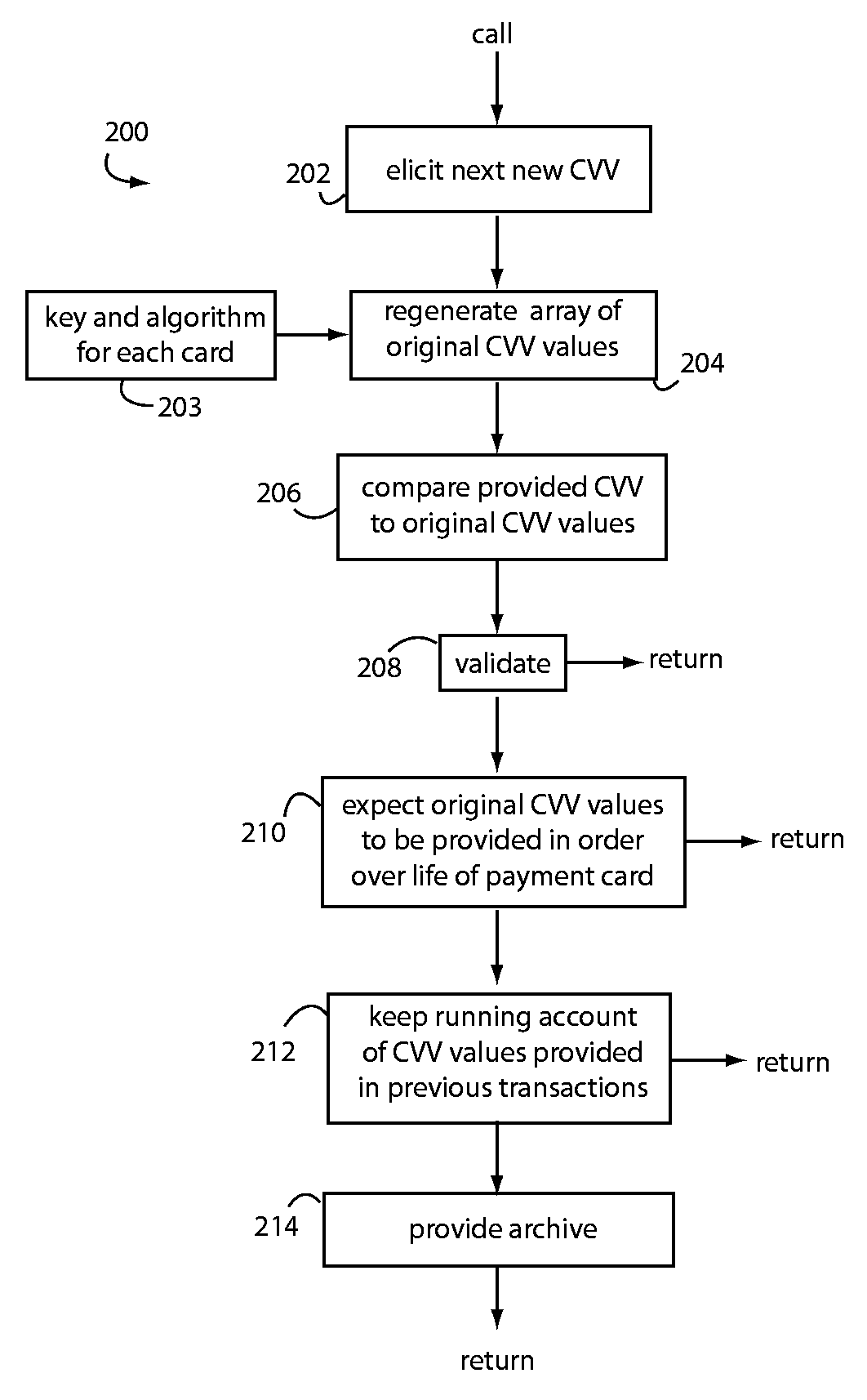
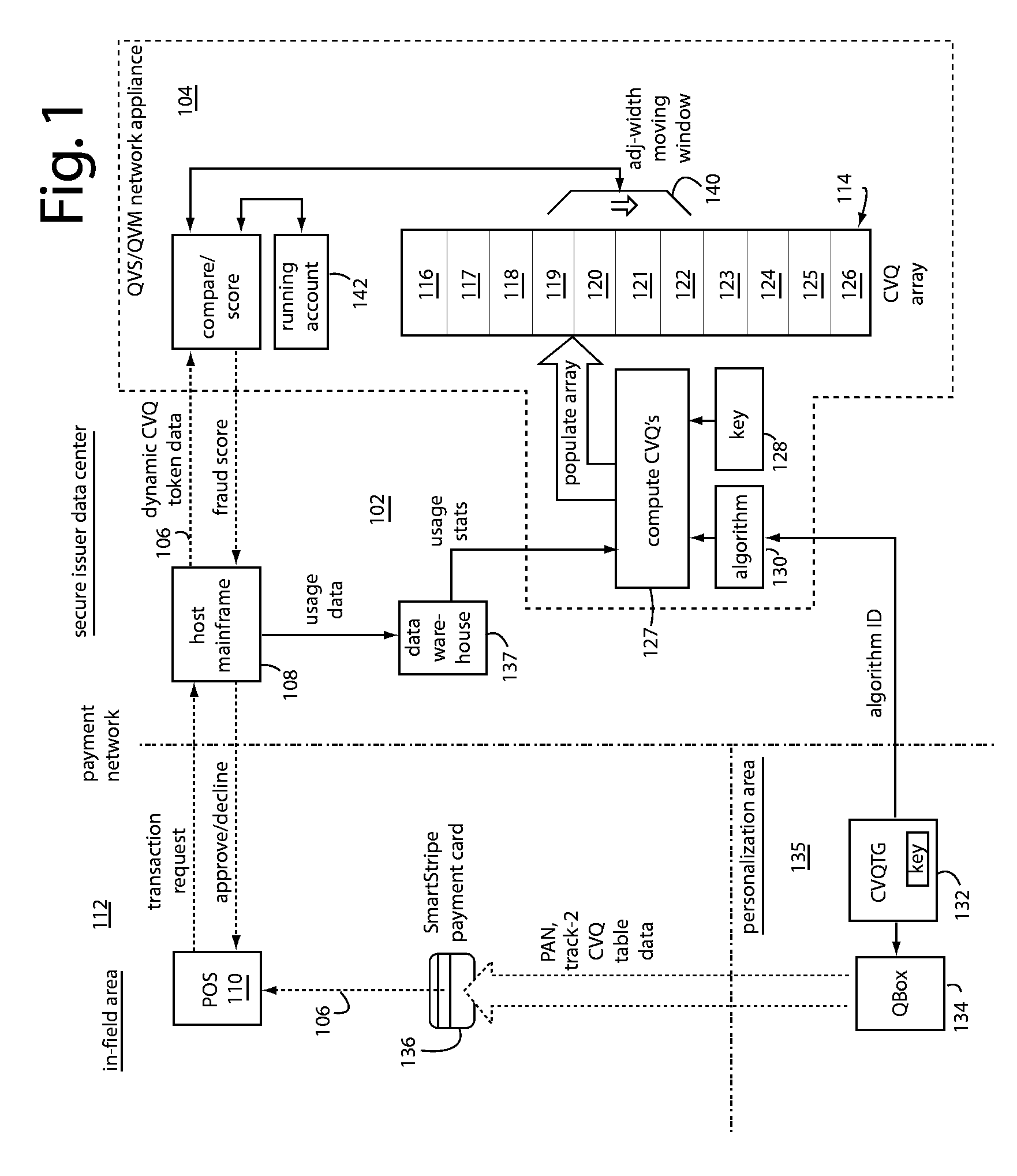
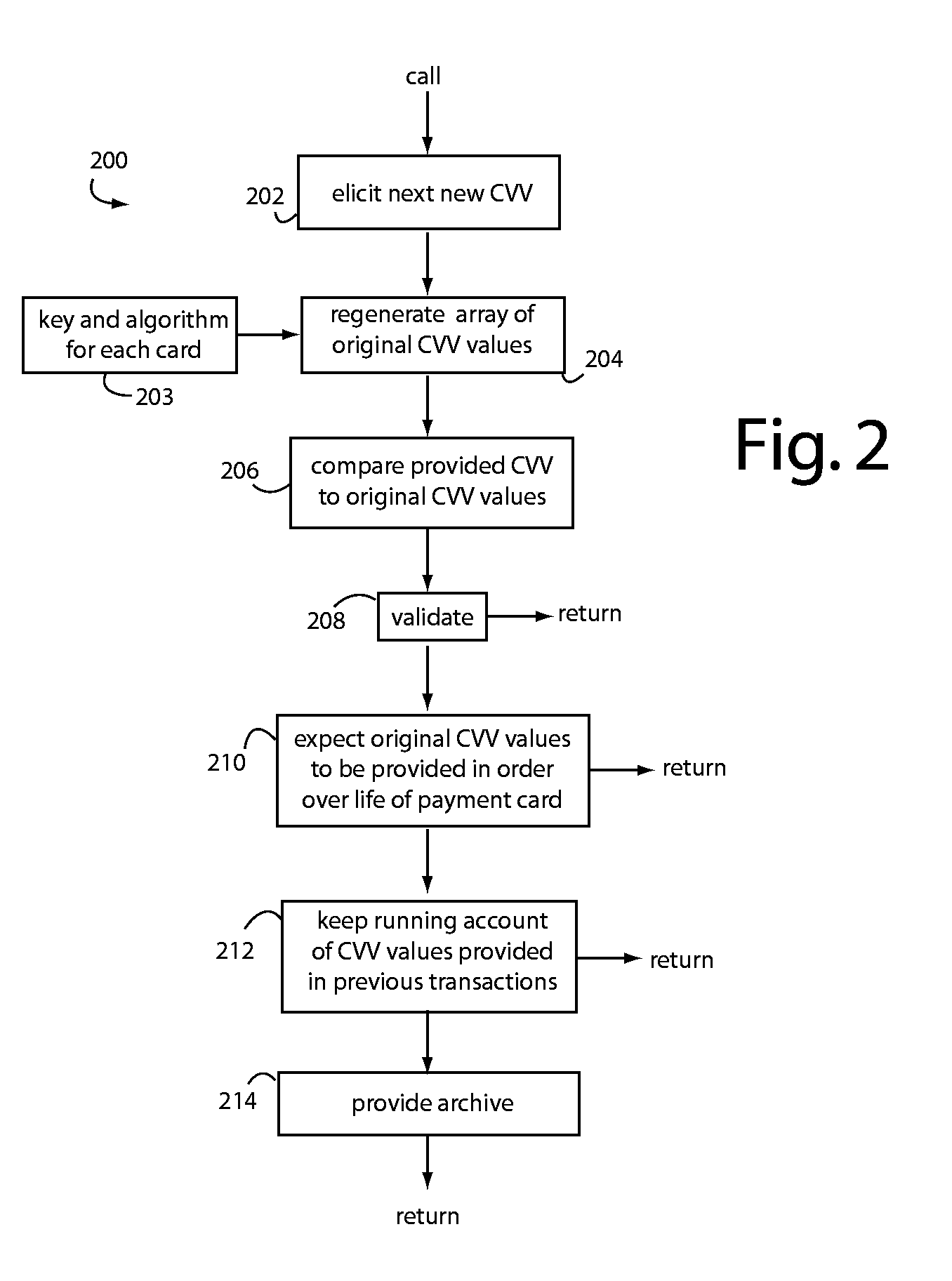
QSecure Validation Service (QVS™) is part of the QSecure Suite and includes a CVQ Table Generator (QTG) for use with a QBox™ card personalizer. In general, the QVS / QVM compares dynamic CVQ token data fetched by an issuer authorization host from a transaction then occurring in the field. An array of acceptable CVQ values computed in real-time from the original keys and algorithms used by the QTG and QBox to personalize the particular card are applied in the comparison. There is an order to the CVQ values in such array, and the dynamic CVQ token data will step through these over time. Small deviations in the order actually received can normally occur for reasons other than fraud, so a moving window of acceptance is needed to cope with normal deviations. A running account of which CVQ values have already been used is maintained for, or by, the QVS, and these help predict where the acceptance window should next be positioned in the array of acceptable CVQ values.
Owner:COIN
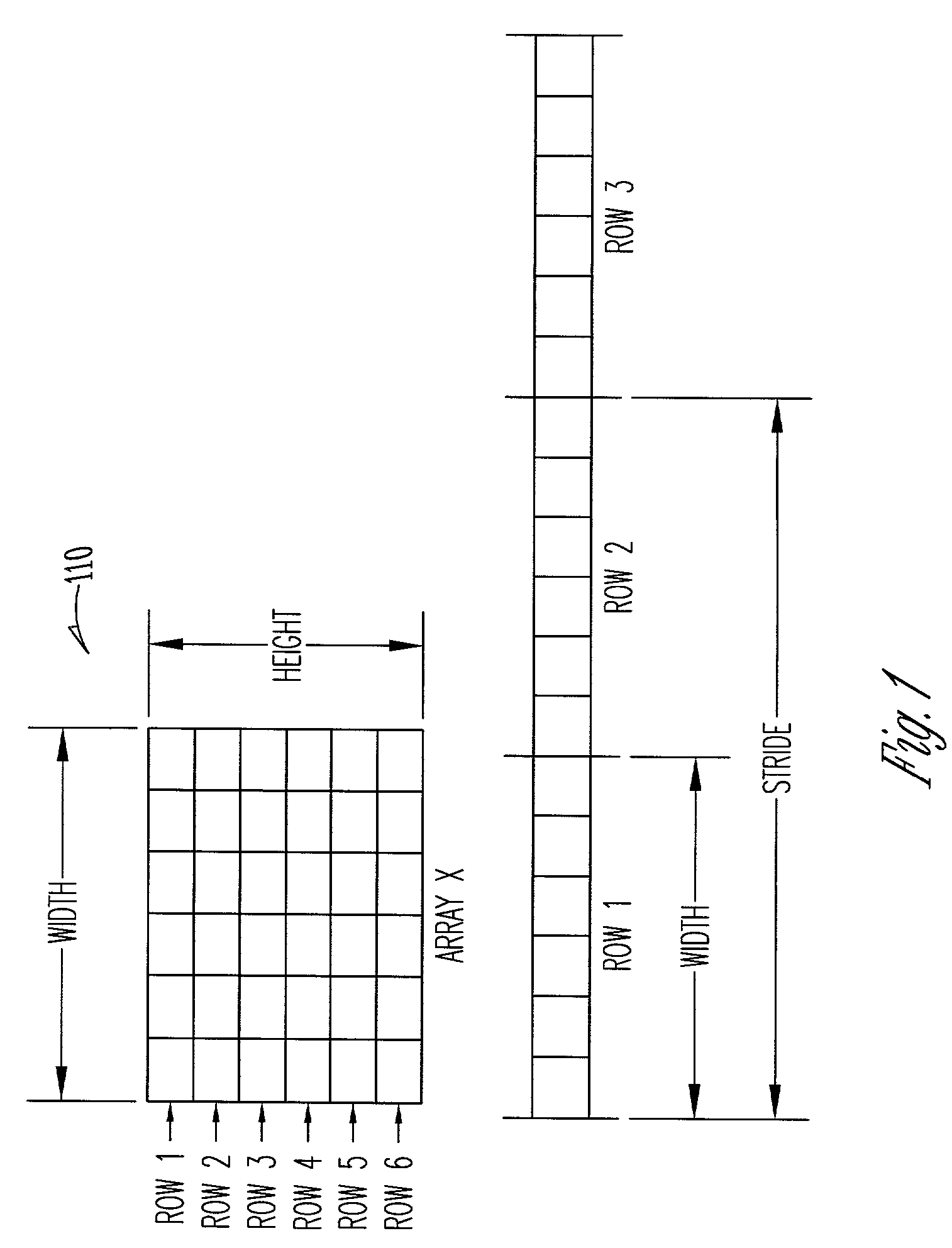
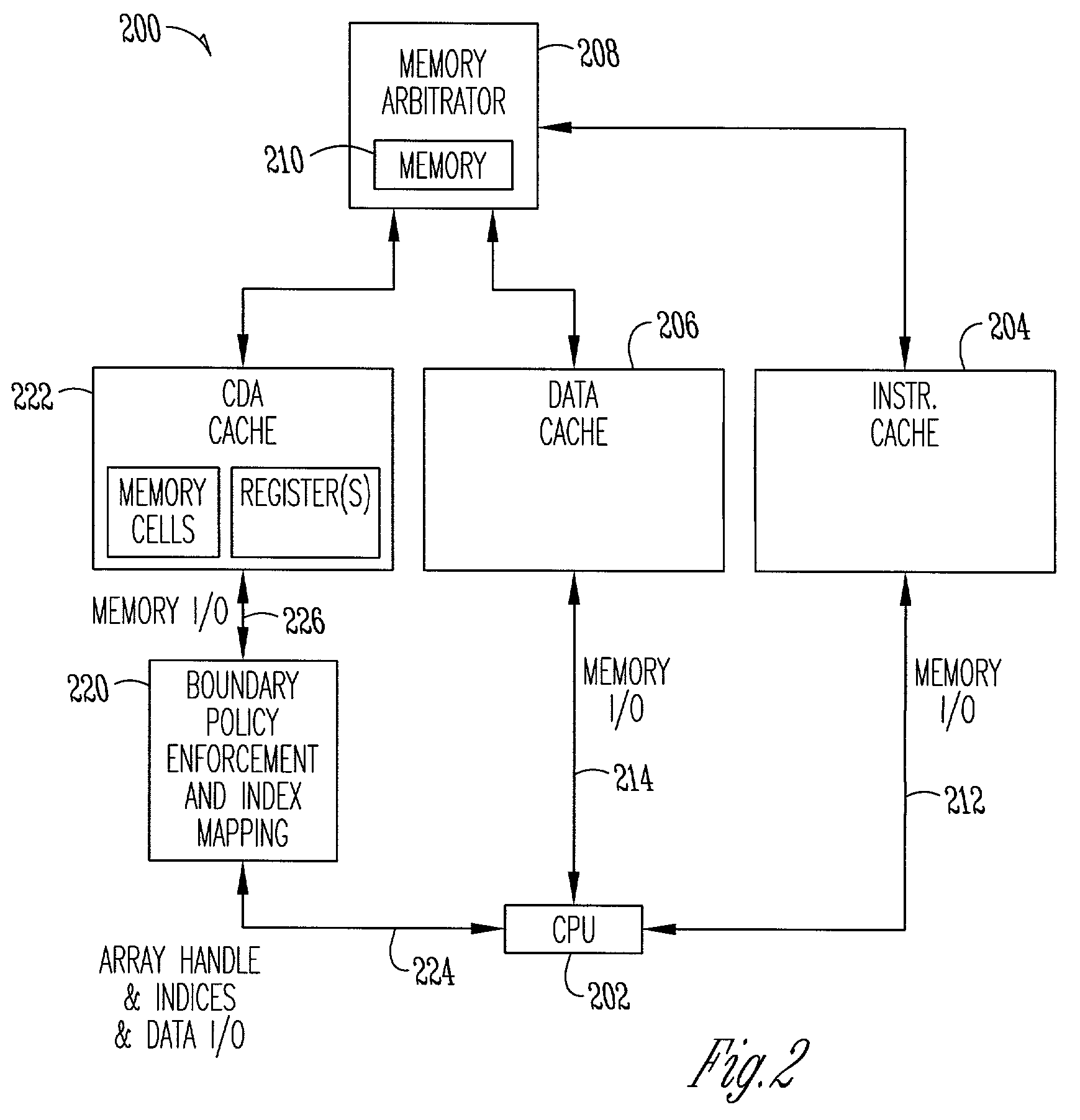
Dynamic arrays and overlays with bounds policies
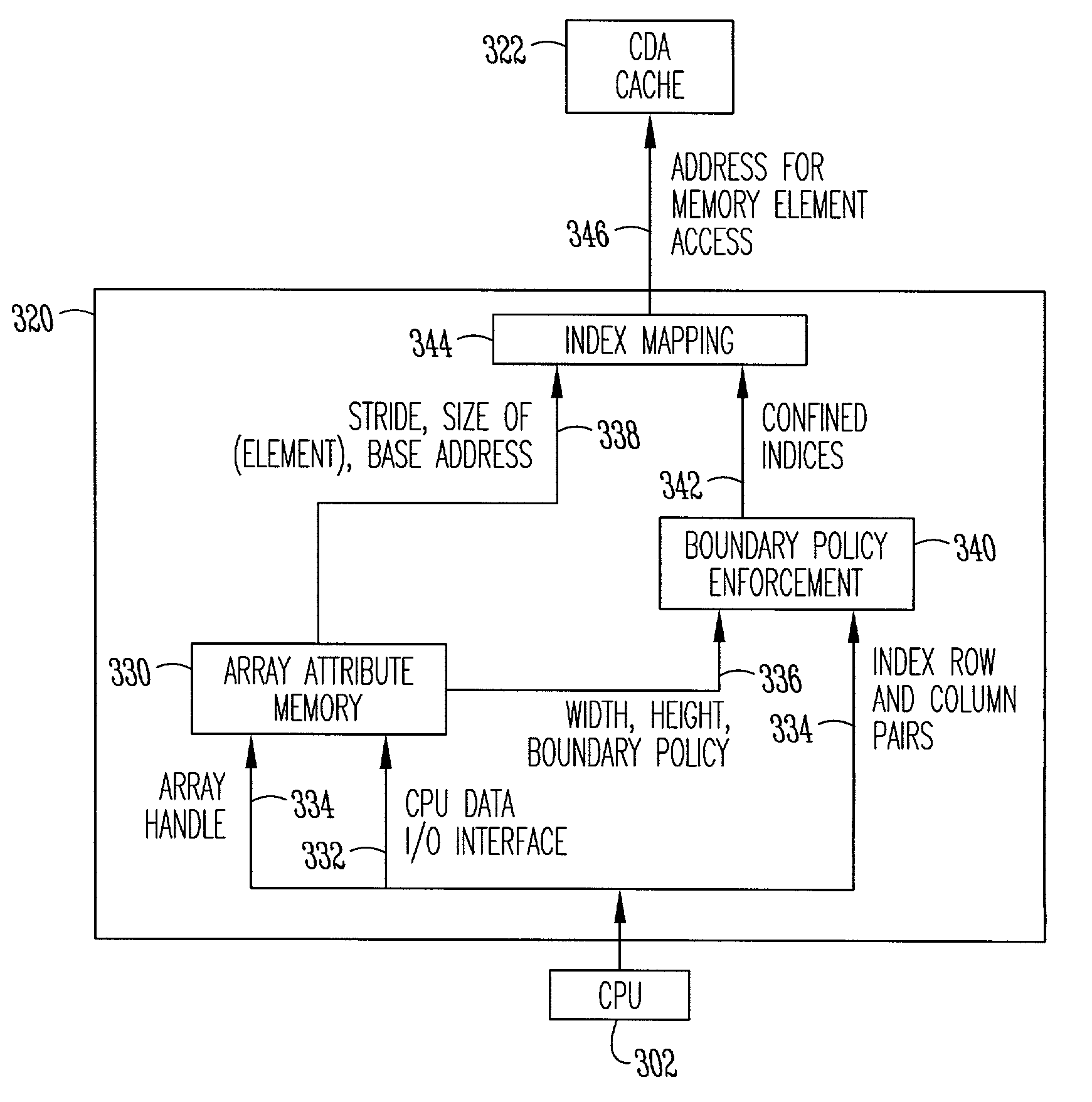
InactiveUS7062761B2Simplify the codeEfficient accessResource allocationProgramming languages/paradigmsArray data structureOperating system
Systems and methods are provided for writing code to access data arrays. One aspect provides a method of accessing a memory array. Data is provided within a one-dimensional array of allocated memory. A dimensional dynamic overlay is declared from within a block of statements, and the declaration initializes various attributes within an array attribute storage object. The data is accessed from within the block of statements as a dimensional indexed array using the array attribute storage object. Another aspect provides a method of creating and accessing a dimensional dynamic array. A dimensional dynamic array is declared from within a block of statements, and memory storage for the array is dynamically allocated. A dynamic overlay storage object is also provided and its attributes are initialized from the dynamic array declaration. The data is accessed as a dimensional indexed array from within the block of statements using the array attribute storage object.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
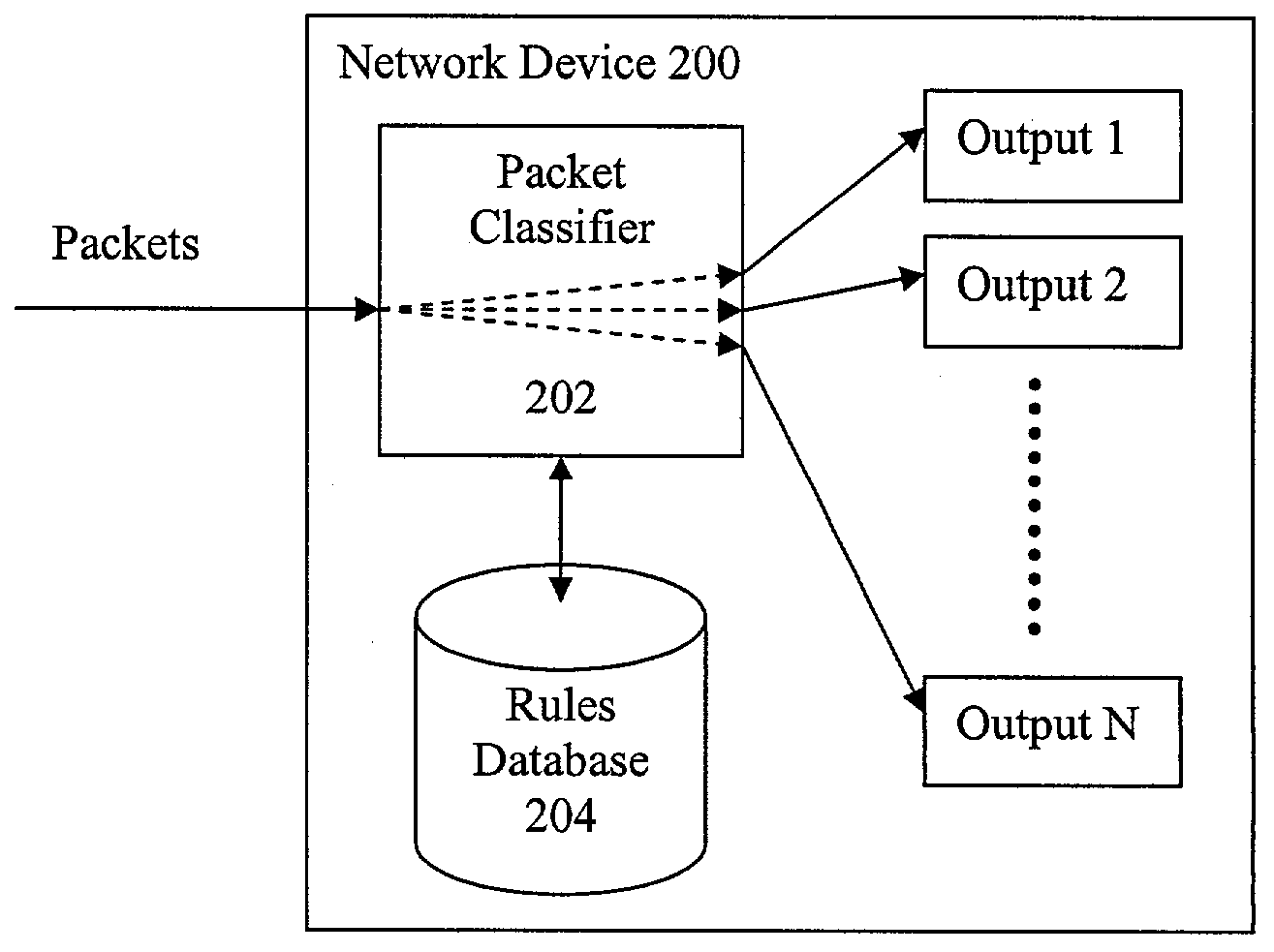
Fast IP packet classification with configurable processor
InactiveUS7227842B1Accelerate packet classificationQuick classificationError preventionTransmission systemsArray data structureAlgorithm
A novel solution for fast packet classification includes a novel data structure to store classifier rules which enables fast packet classification, which structure employs bitmaps for each field of the incoming packet for which classification is desired. A fast packet classification algorithm using the novel data structure allows the matching rule with the highest priority to be quickly obtained. A novel rule update algorithm allows new classifier rules to be added into the data structure incrementally. In one practical implementation of a classification engine employing the structures and algorithms of the present invention, a configurable processor with customized instructions is used to accelerate packet classification.
Owner:TENSILICA
Method, system, program, and data structure for a dense array storing character strings
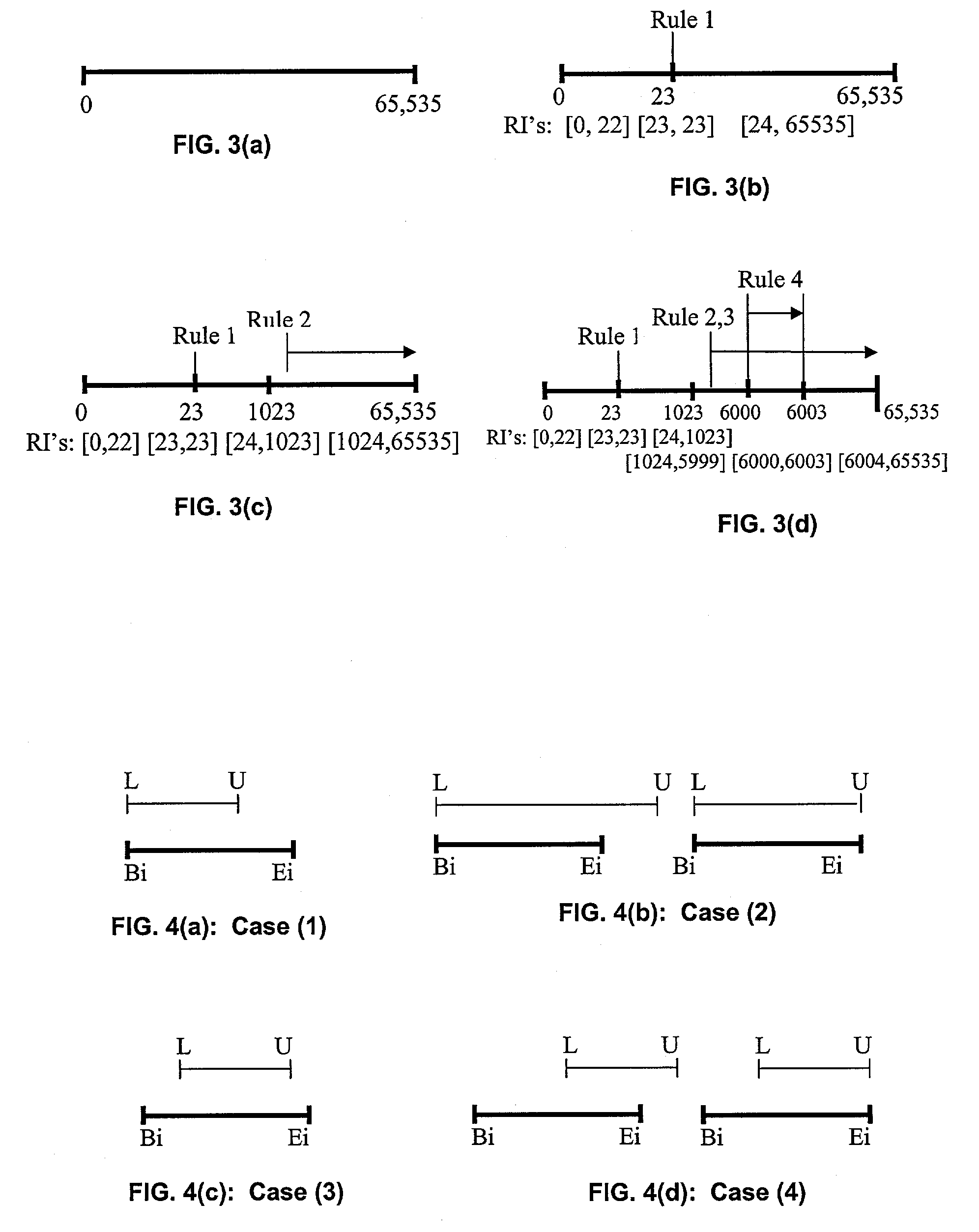
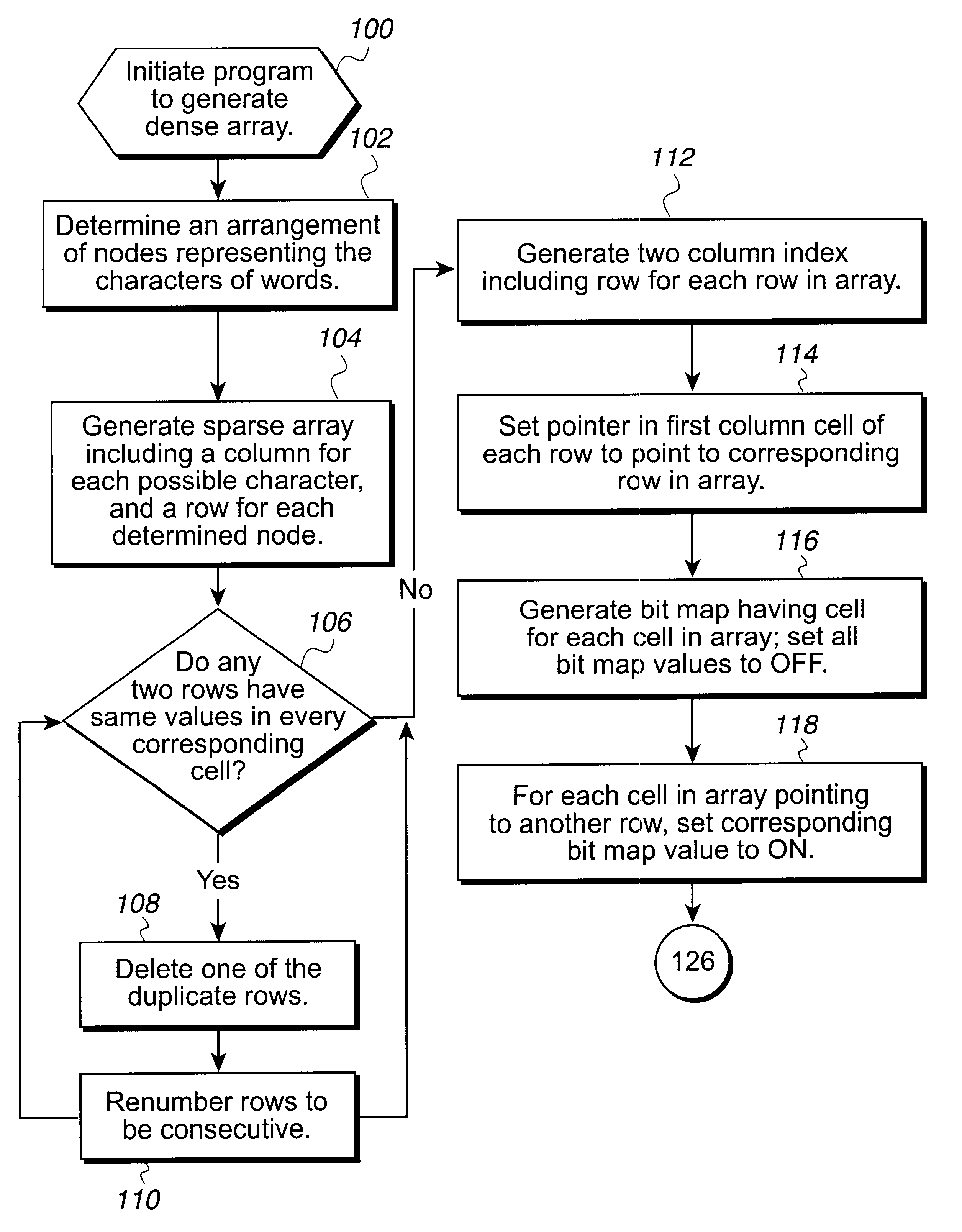
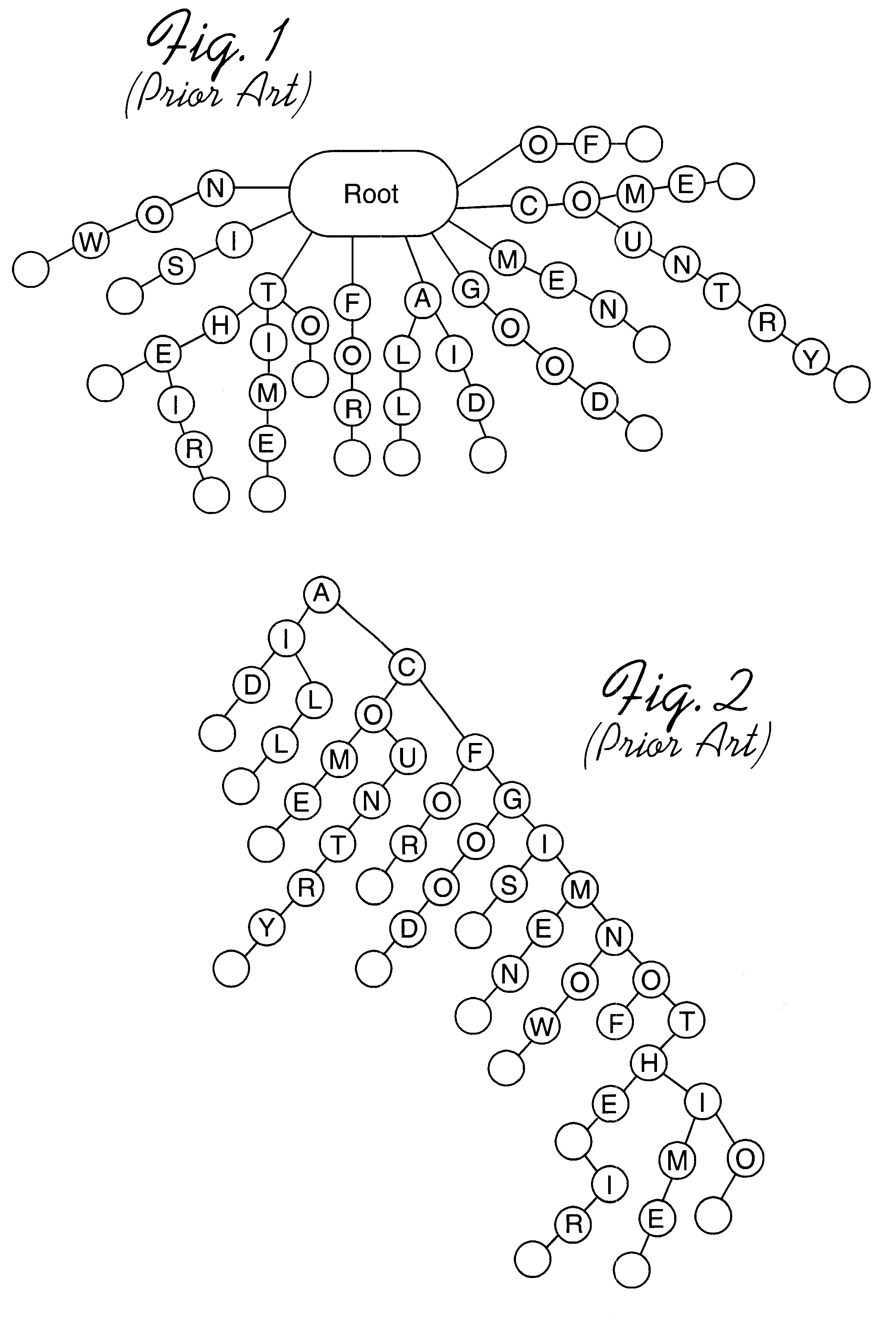
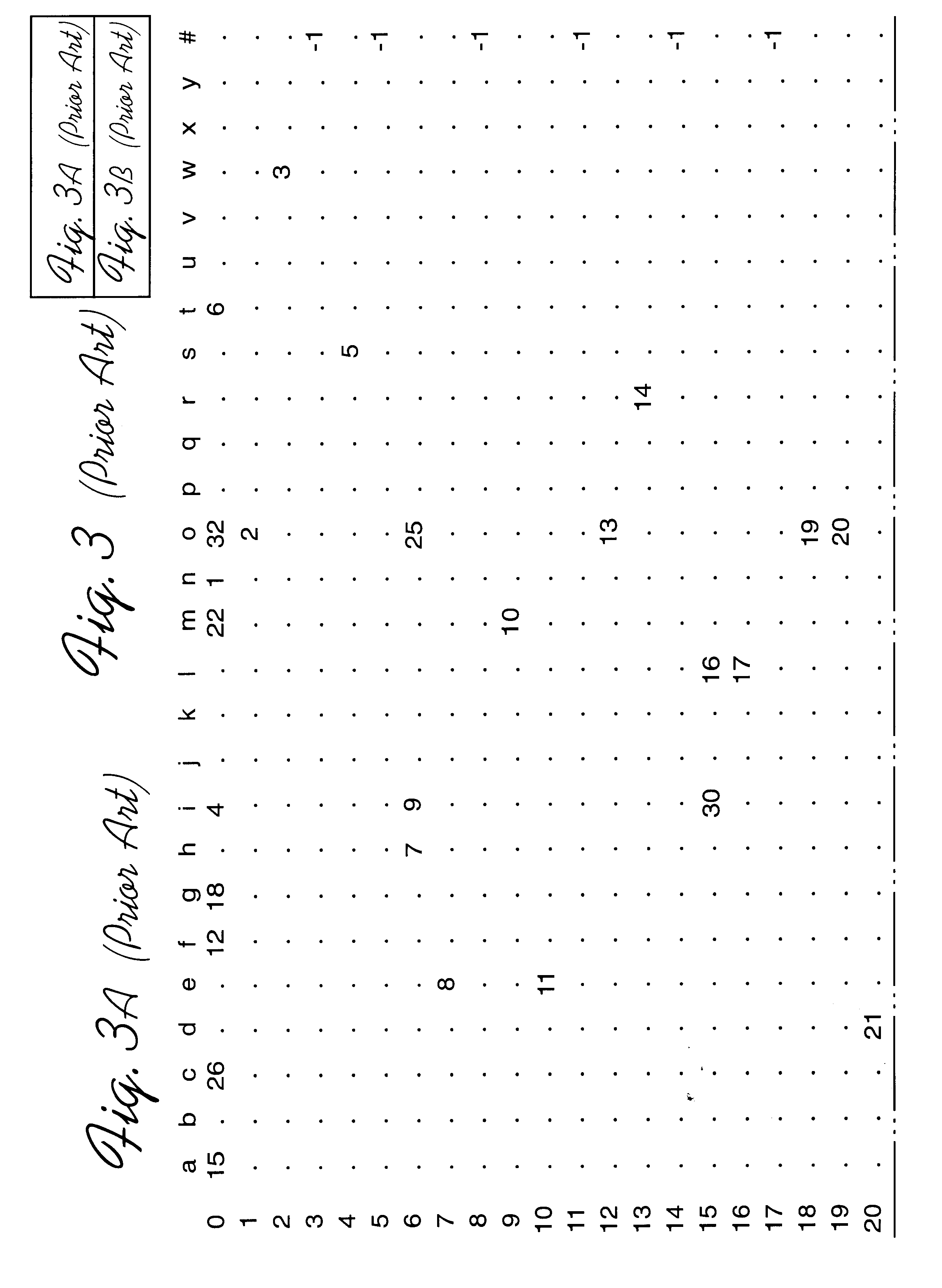
InactiveUS6470347B1Reduce in quantityLess storage spaceData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalArray data structureTheoretical computer science
Disclosed is a system, method, and program for generating a data structure in computer memory for storing strings, such as words in a dictionary. Each string includes at least one character from a set of characters. An arrangement of nodes is determined to store the characters such that the arrangement of the nodes is capable of defining a tree structure. An array data structure is generated to store the nodes. The array includes a row for each node and a column for each character in the set of characters. A non-empty cell identifies a node for the character indicated in the column of the cell that has descendant nodes in the row indicated in the cell content for the node. The array data structure is processed to eliminate at least one row in the array data structure to reduce a number of bytes needed to represent the array data structure. In this way, the array data structure following the processing requires less bytes of storage space then before the processing.
Owner:IBM CORP
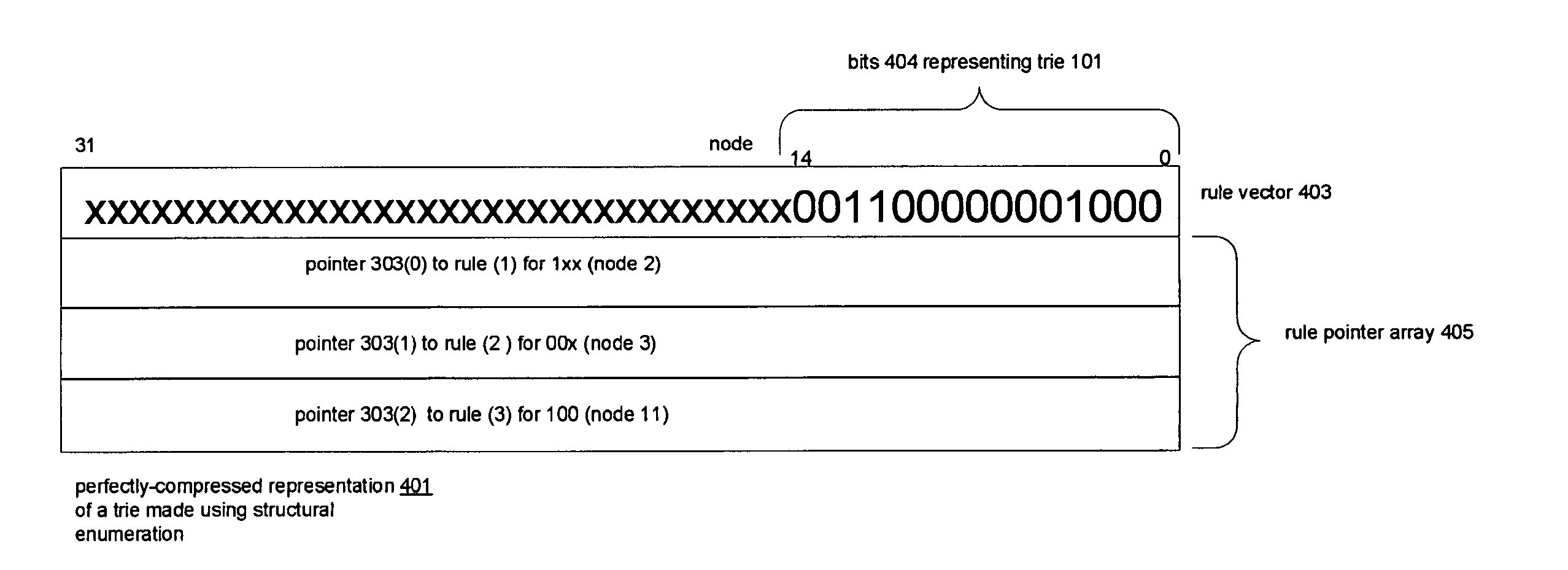
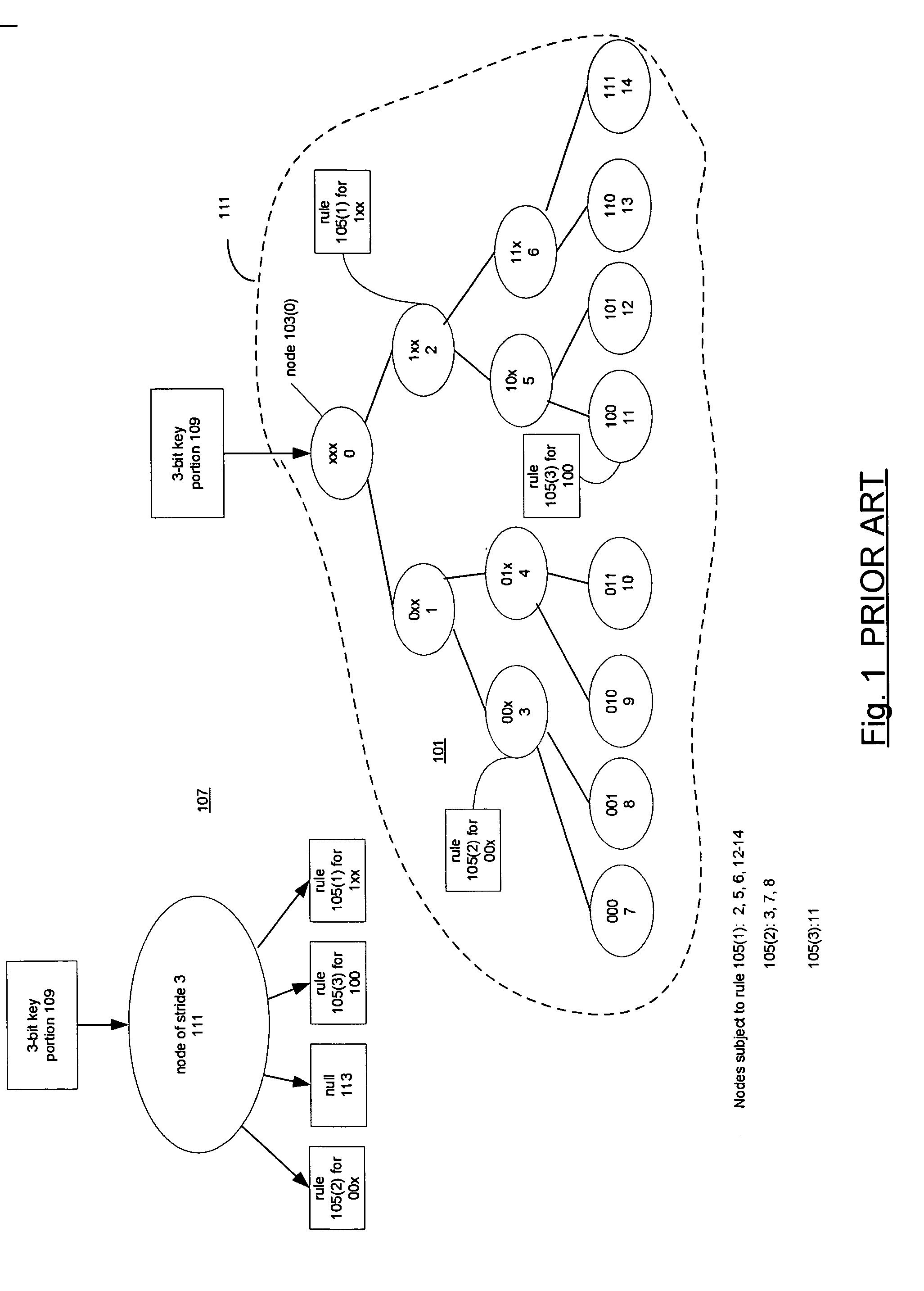
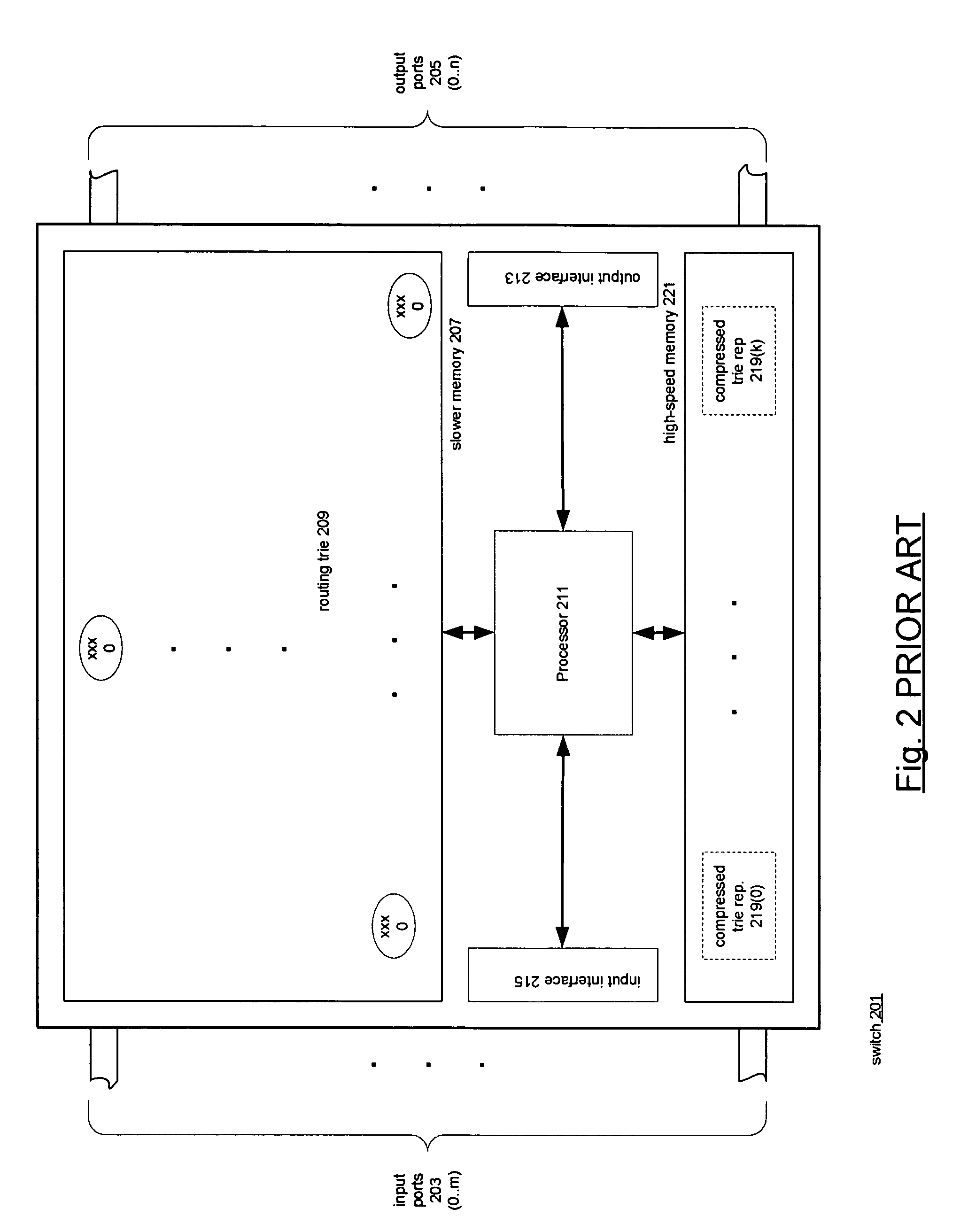
Compressed representations of tries
InactiveUS20060288024A1Digital data processing detailsTransmissionArray data structureTheoretical computer science
Techniques for representing nodes of tries. Associated with the nodes are keys and rules. A node of a trie having a stride n>1 is represented by a trie having a stride of 1 and the stride 1 trie is represented by a bit string termed a structural enumeration. The structural enumeration has a bit for each node of the trie of stride 1. If the node has a key and rule associated with it, the bit is set; otherwise it is not. The representation of a node of stride n>1 includes the node's structural enumeration and an array of rule pointers. The array has an entry for each rule associated with the node and the entries have the same order in the array as the set bits for their keys in the structural enumeration. Nodes having large strides may be represented by subdividing them into subtries.
Owner:FREESCALE SEMICON INC
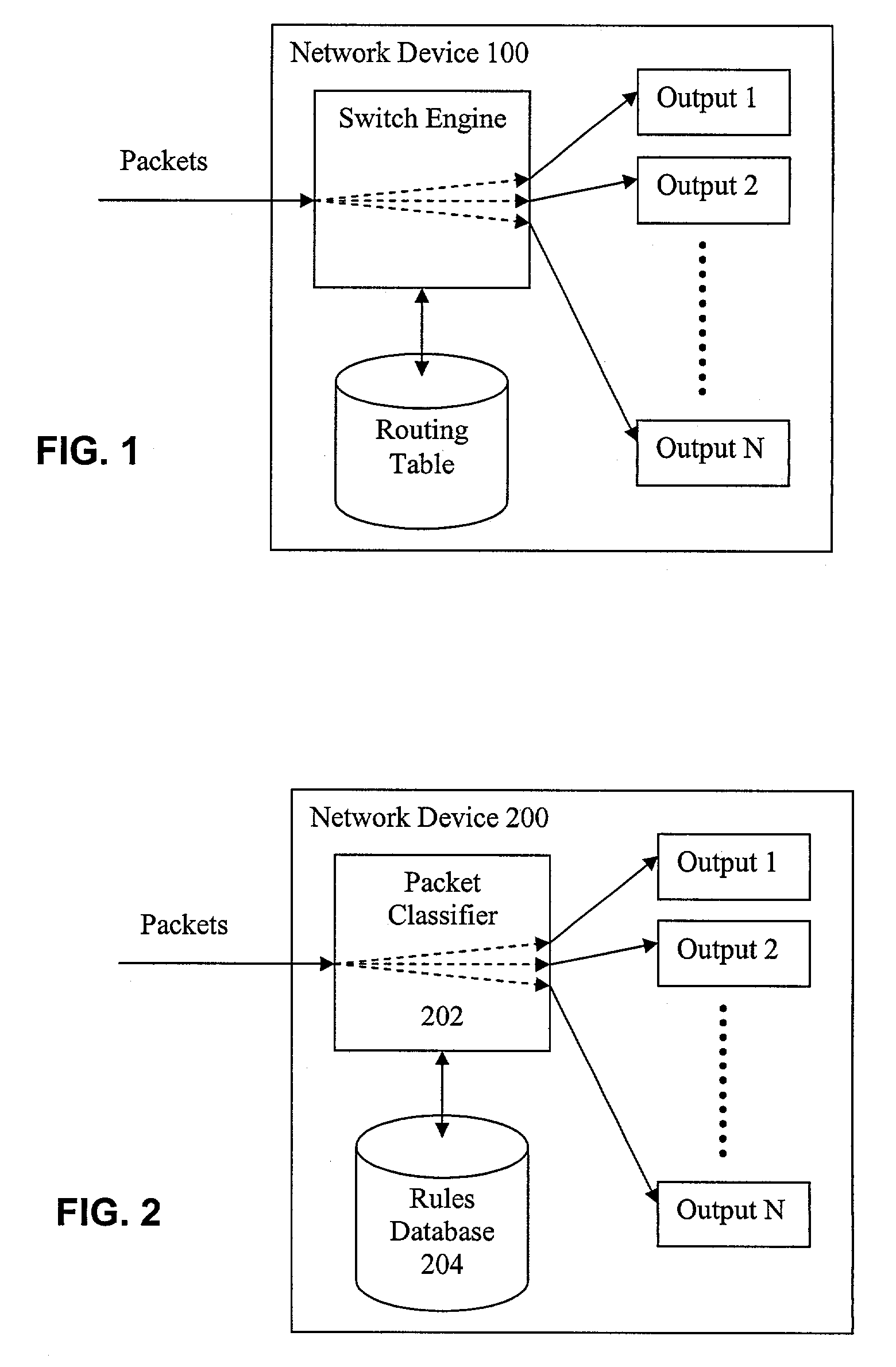
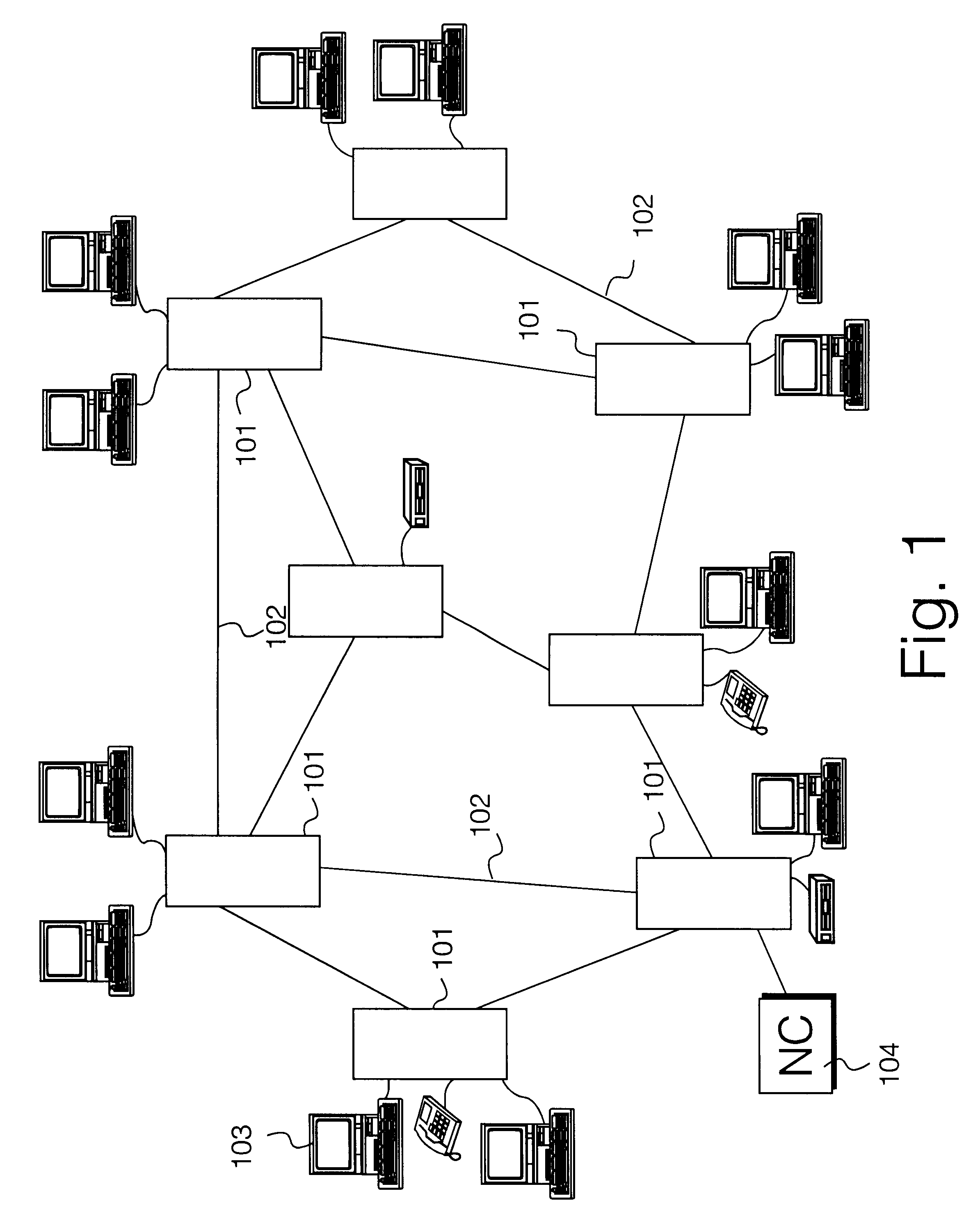
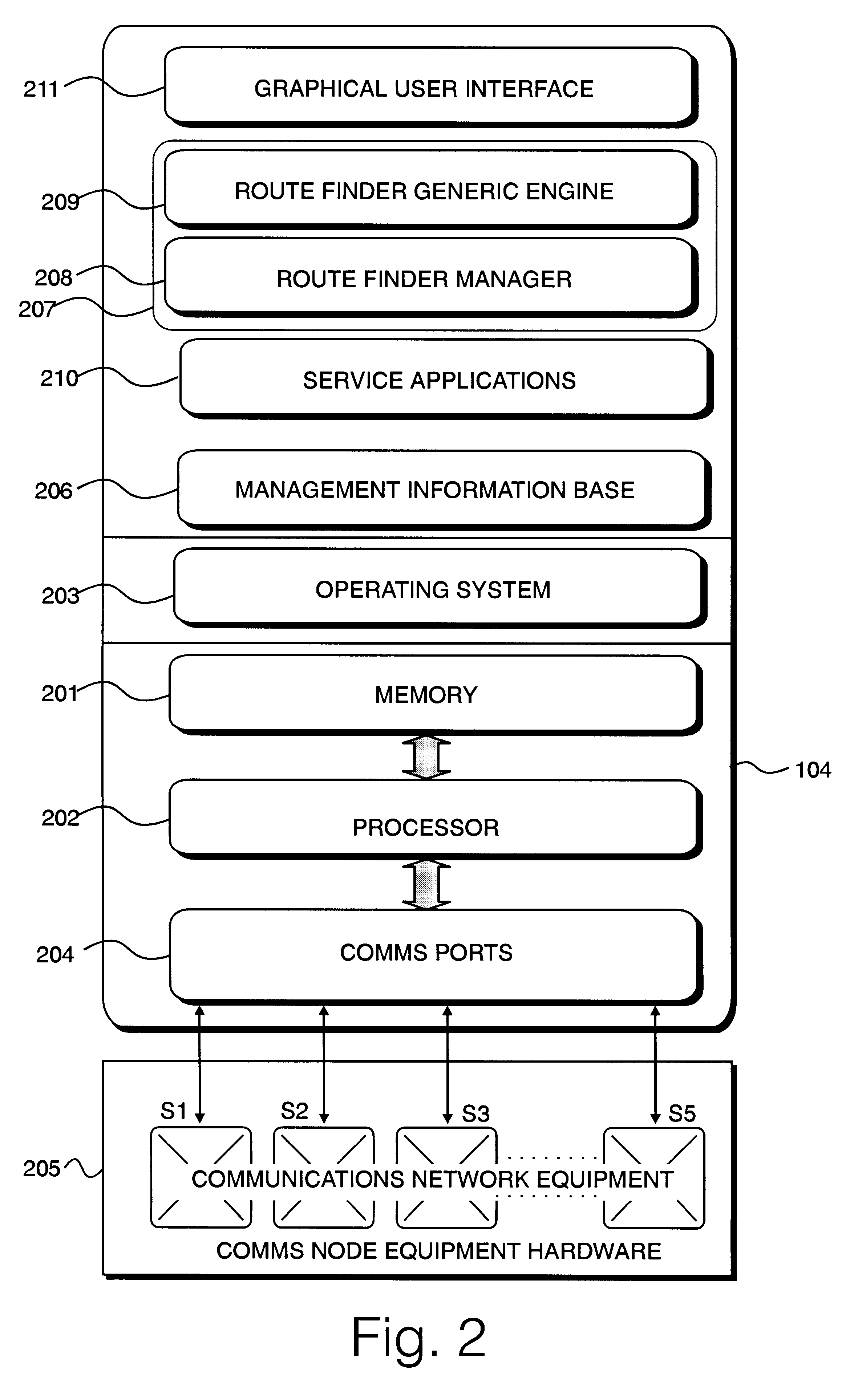
Traffic route finder in communications network
InactiveUS6314093B1Equally distributedCostMultiplex communicationData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityArray data structure
A route finder means and method for finding routes to satisfy a plurality of connection requests in a communications network comprising a plurality of nodes connected by a plurality of links. A cost is assigned to each network link. Arrays of eight shortest paths of links between each pair of nodes in the network are created. Bit strings comprising for example a 3 bit binary number for each point-to-point connection request are generated. Each 3 bit number is an index to one element of the shortest path array for each connection request's source and destination nodes. The bit strings are assembled into population members which are manipulated by genetic algorithms. The fitness of the population members is evaluated by calculating the cost of traversing the routes represented by the bit strings. The route finder means and method has an ability to split traffic over multiple routes, and to handle different traffic types, eg different bit rate traffic types. The route finder means and method is generic to a plurality of different communications network types.
Owner:APPLE INC
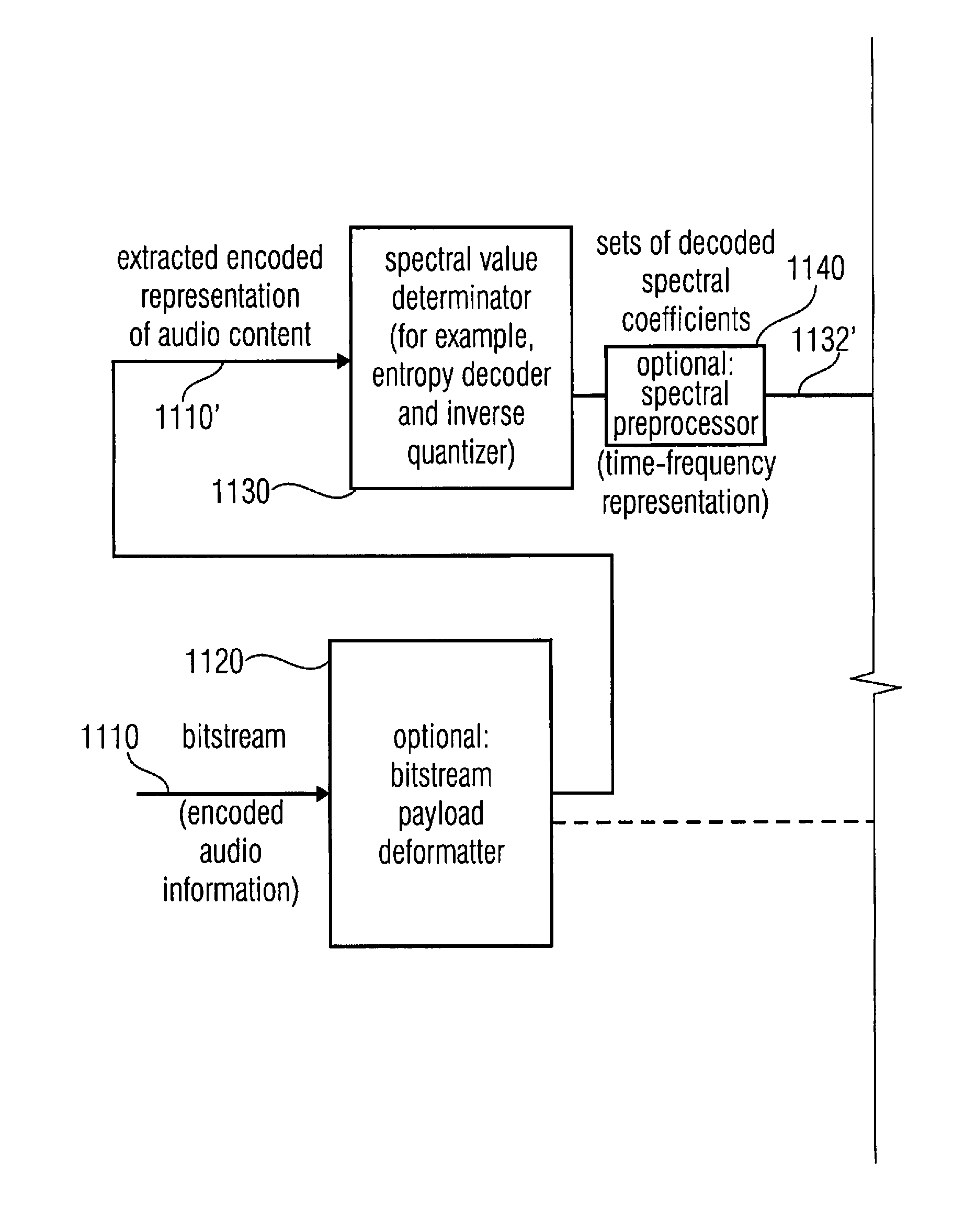
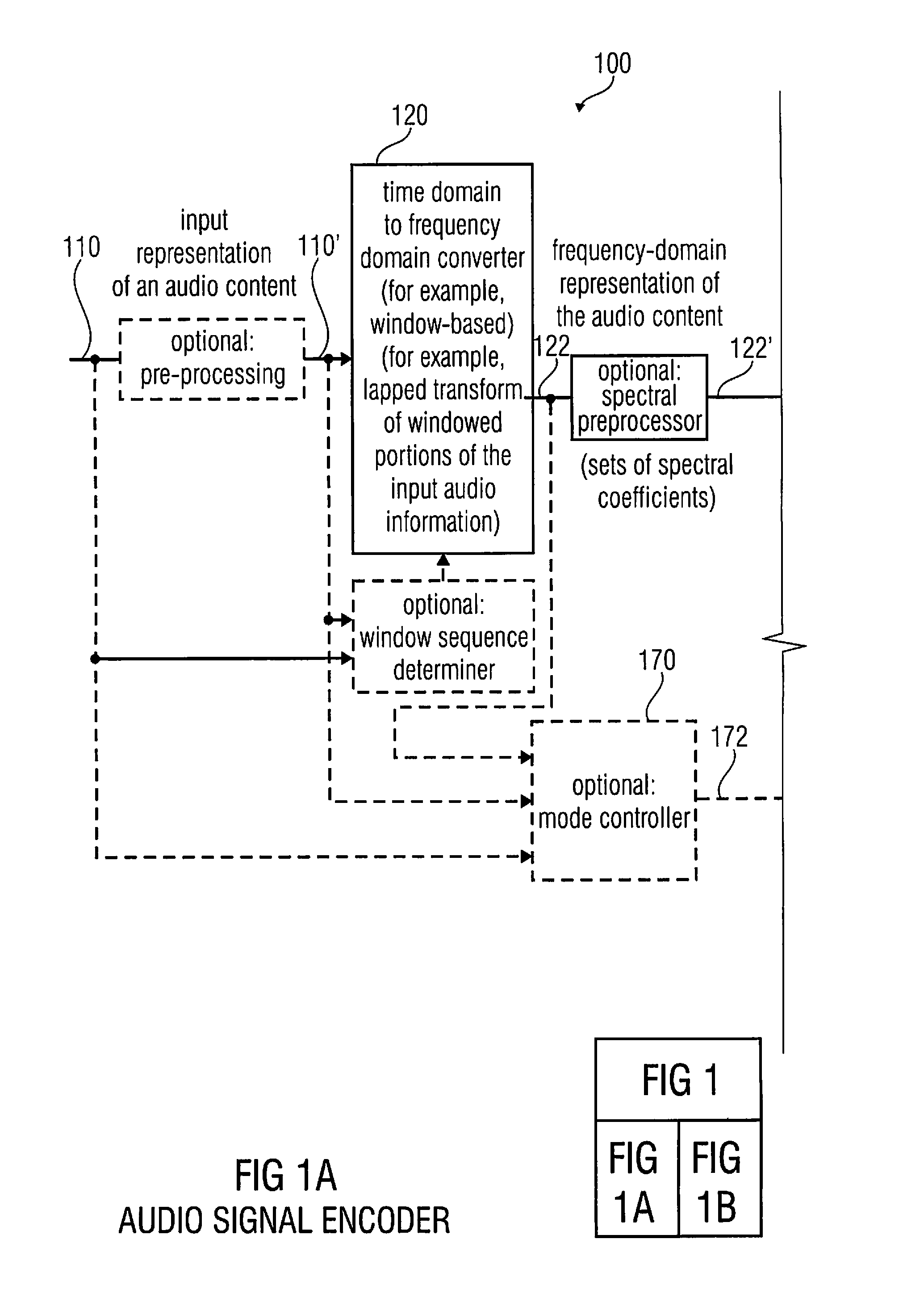
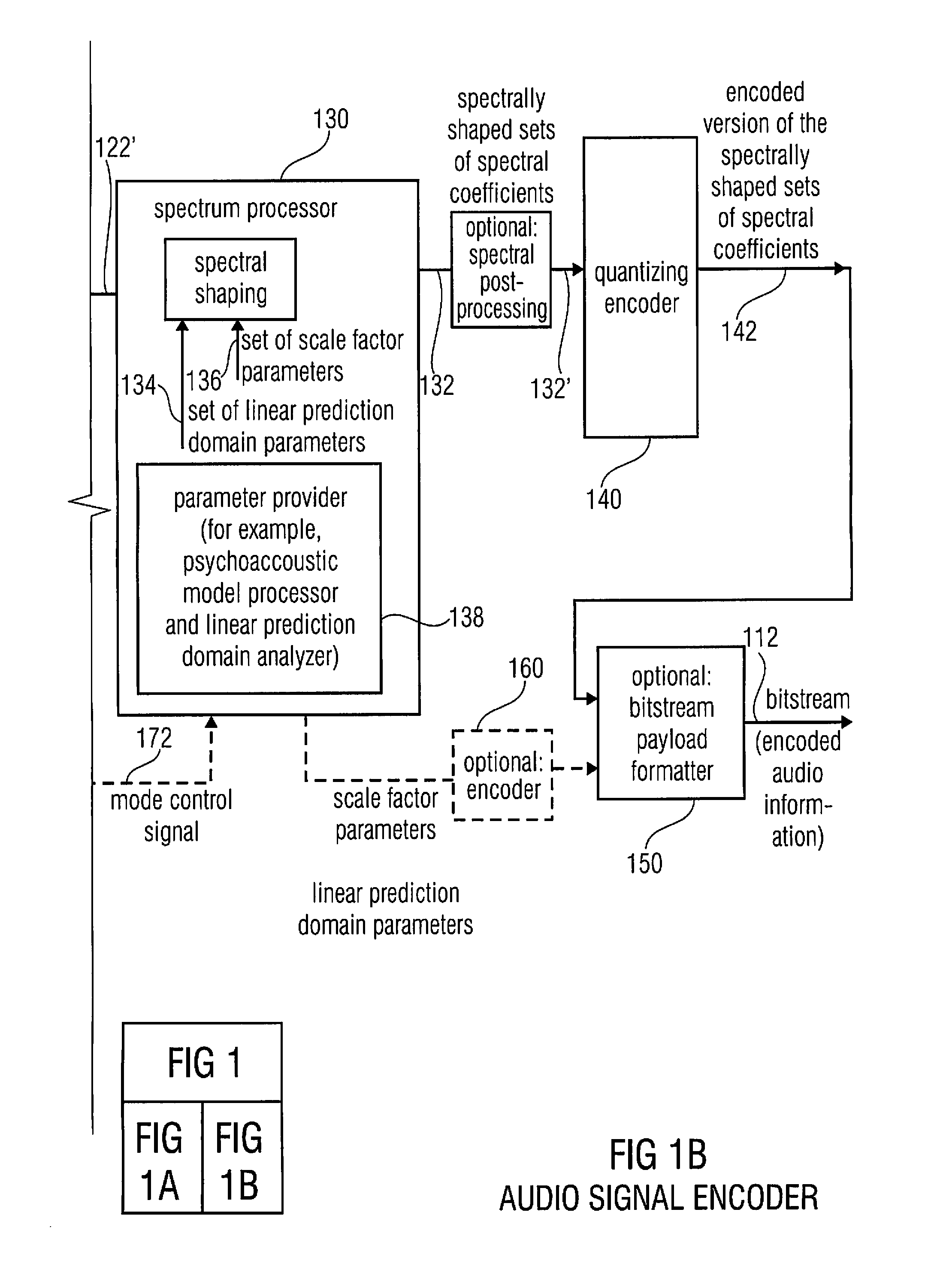
Multi-mode audio signal decoder, multi-mode audio signal encoder, methods and computer program using a linear-prediction-coding based noise shaping
ActiveUS20120245947A1Without inacceptable artifactEasy transitionSpeech analysisLinear prediction codingFrequency spectrum
A multi-mode audio signal decoder has a spectral value determinator to obtain sets of decoded spectral coefficients for a plurality of portions of an audio content and a spectrum processor configured to apply a spectral shaping to a set of spectral coefficients in dependence on a set of linear-prediction-domain parameters for a portion of the audio content encoded in a linear-prediction mode, and in dependence on a set of scale factor parameters for a portion of the audio content encoded in a frequency-domain mode. The audio signal decoder has a frequency-domain-to-time-domain converter configured to obtain a time-domain audio representation on the basis of a spectrally-shaped set of decoded spectral coefficients for a portion of the audio content encoded in the linear-prediction mode and for a portion of the audio content encoded in the frequency domain mode. An audio signal encoder is also described.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Methods, apparatus and data structures for providing a uniform representation of various types of information
InactiveUS20030014421A1Complete efficientlyDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsTask analysisComputer users
Methods and apparatus for analyzing tasks performed by computer users by (i) gathering usage data, (ii) converting logged usage data into a uniform format, (iii) determining or defining task boundaries, and (iv) determining a task analysis model by "clustering" similar tasks together. The task analysis model may be used to (i) help users complete a task (such help, for example, may be in the form of a gratuitous help function), and / or (ii) to target marketing information to users based on user inputs and the task analysis model. The present invention also provides a uniform semantic network for representing different types of objects in a uniform way.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for mapping strings for comparison
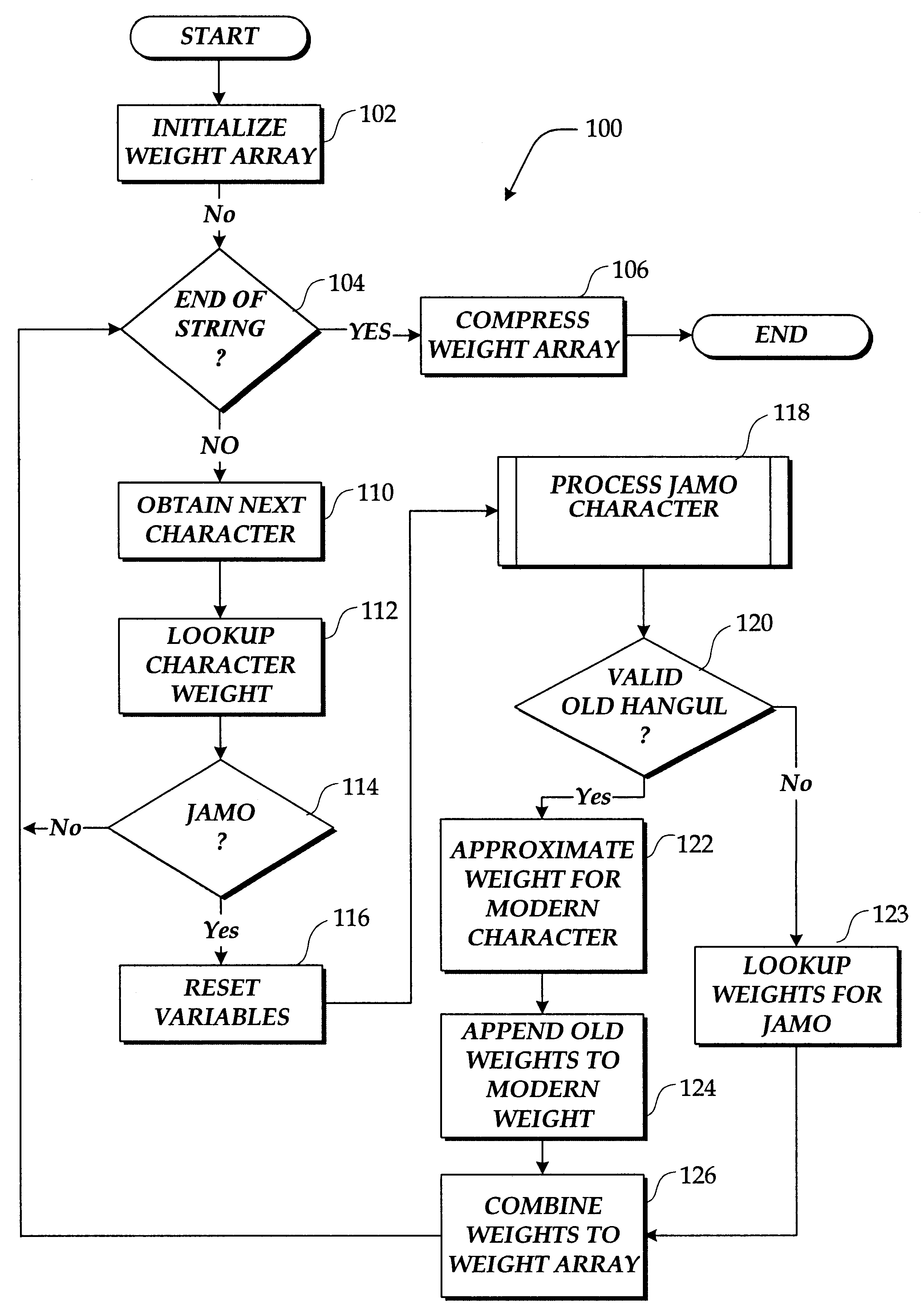
InactiveUS6873986B2Natural language translationData processing applicationsArray data structureAlgorithm
A method and system for mapping a number of characters in a string, wherein the string comprises a combination of characters representing indexed expressions and a combination of characters representing non-indexed expressions. One embodiment produces a weight array that can be utilized to compare a first and second string having indexed and non-indexed expressions. In one embodiment, a method generates a set of special weights for characters that represent indexed and non-indexed expressions. The method then associates a weight value of an indexed expression with the specific group of characters representing a specific non-indexed expression, and generates a weight array by retrieving a plurality of special weights associated with the specific group of characters representing the specific non-indexed expression and the associated weight value of the indexed expression.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
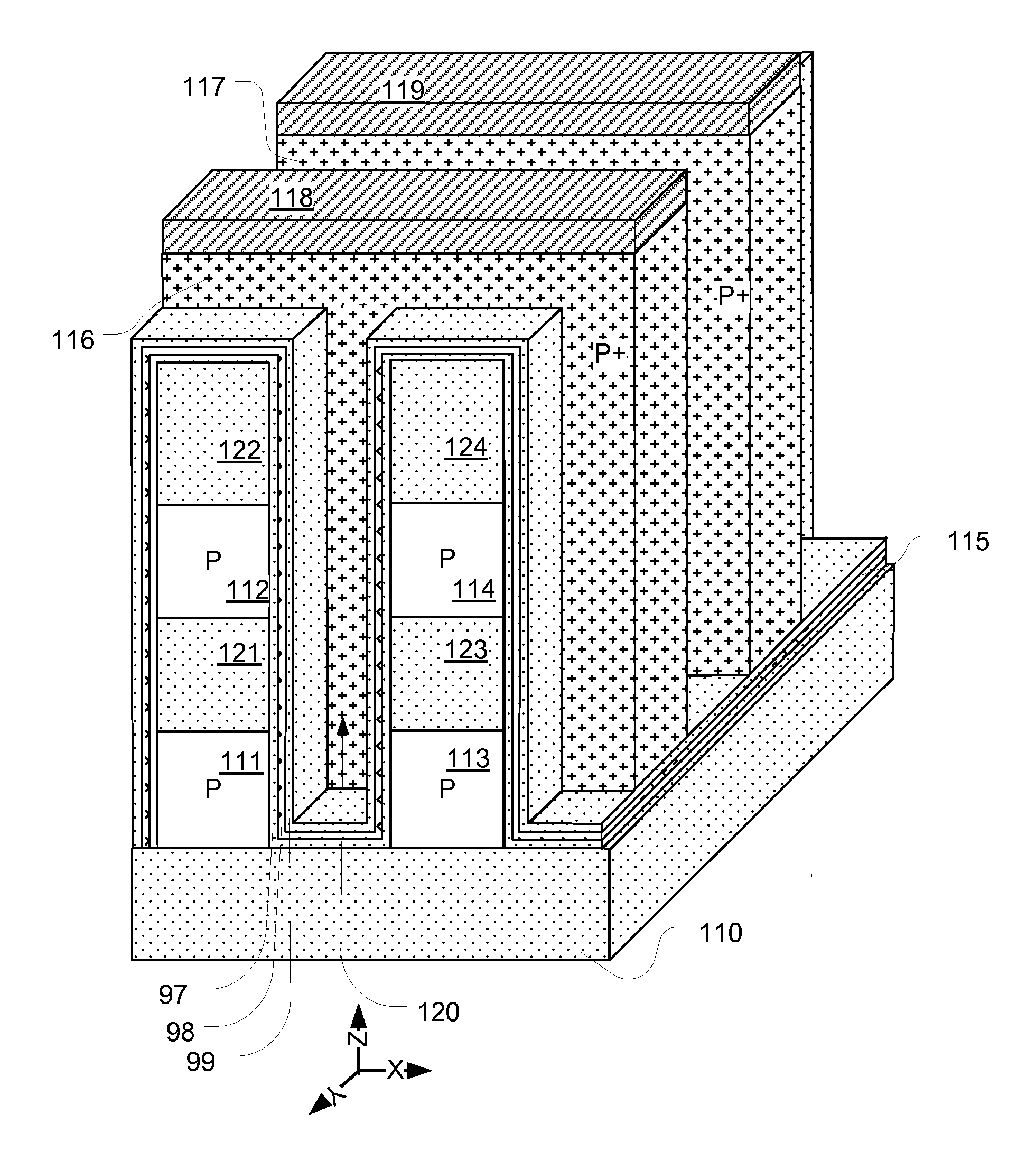
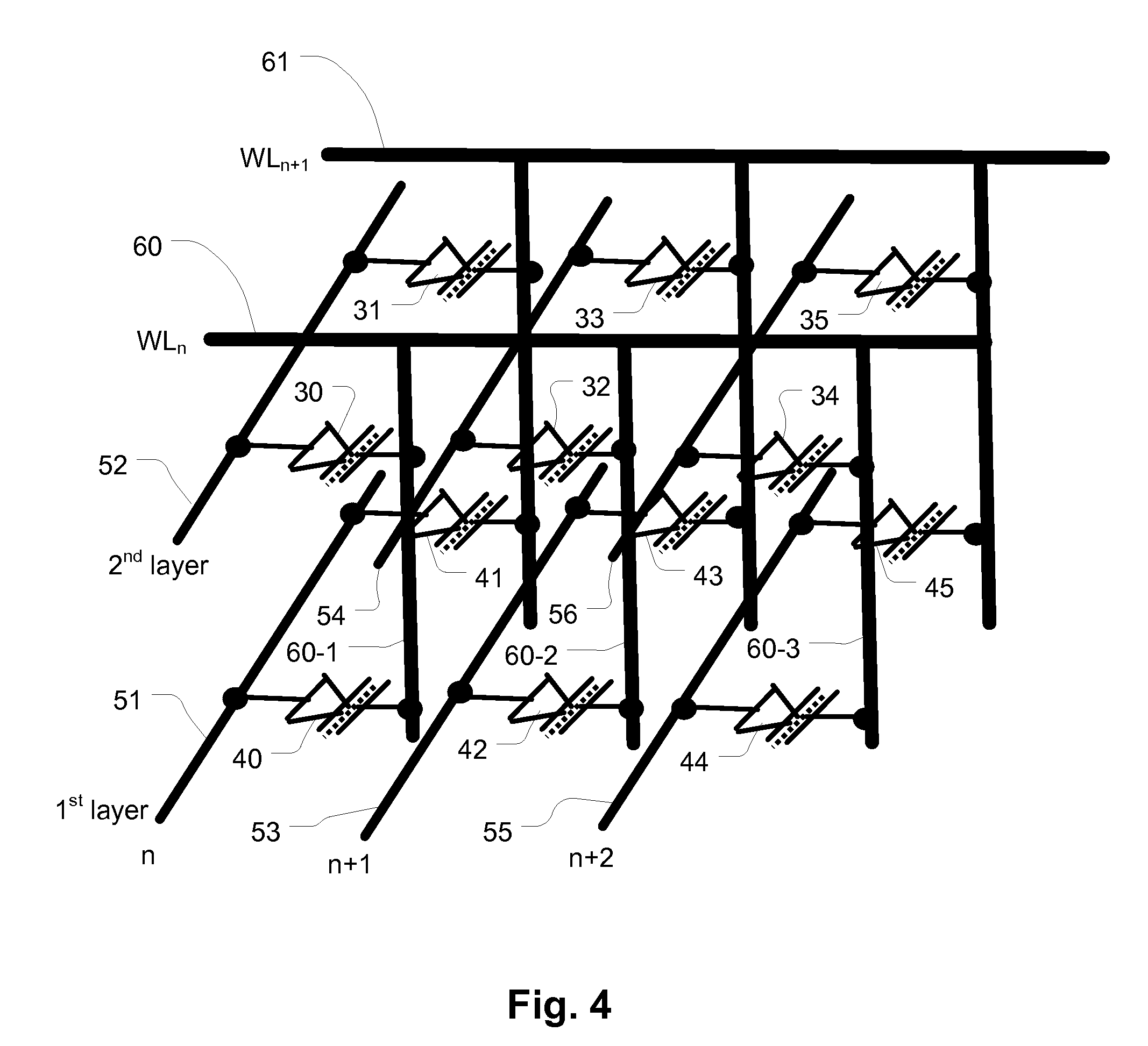
Memory Architecture of 3D Array With Alternating Memory String Orientation and String Select Structures
ActiveUS20120182806A1Increase pitchImproved gate structureSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesArray data structureConductive materials
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
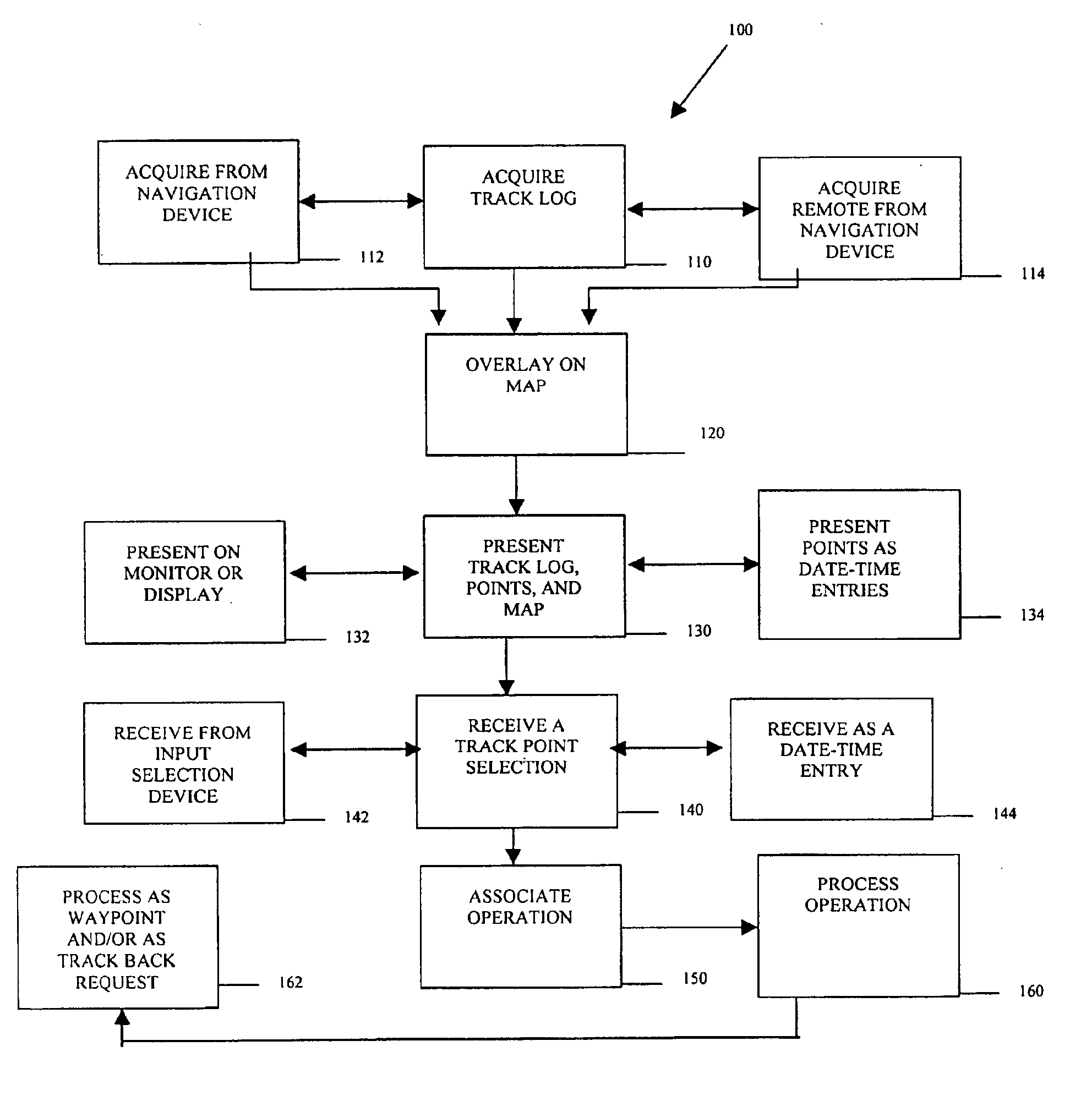
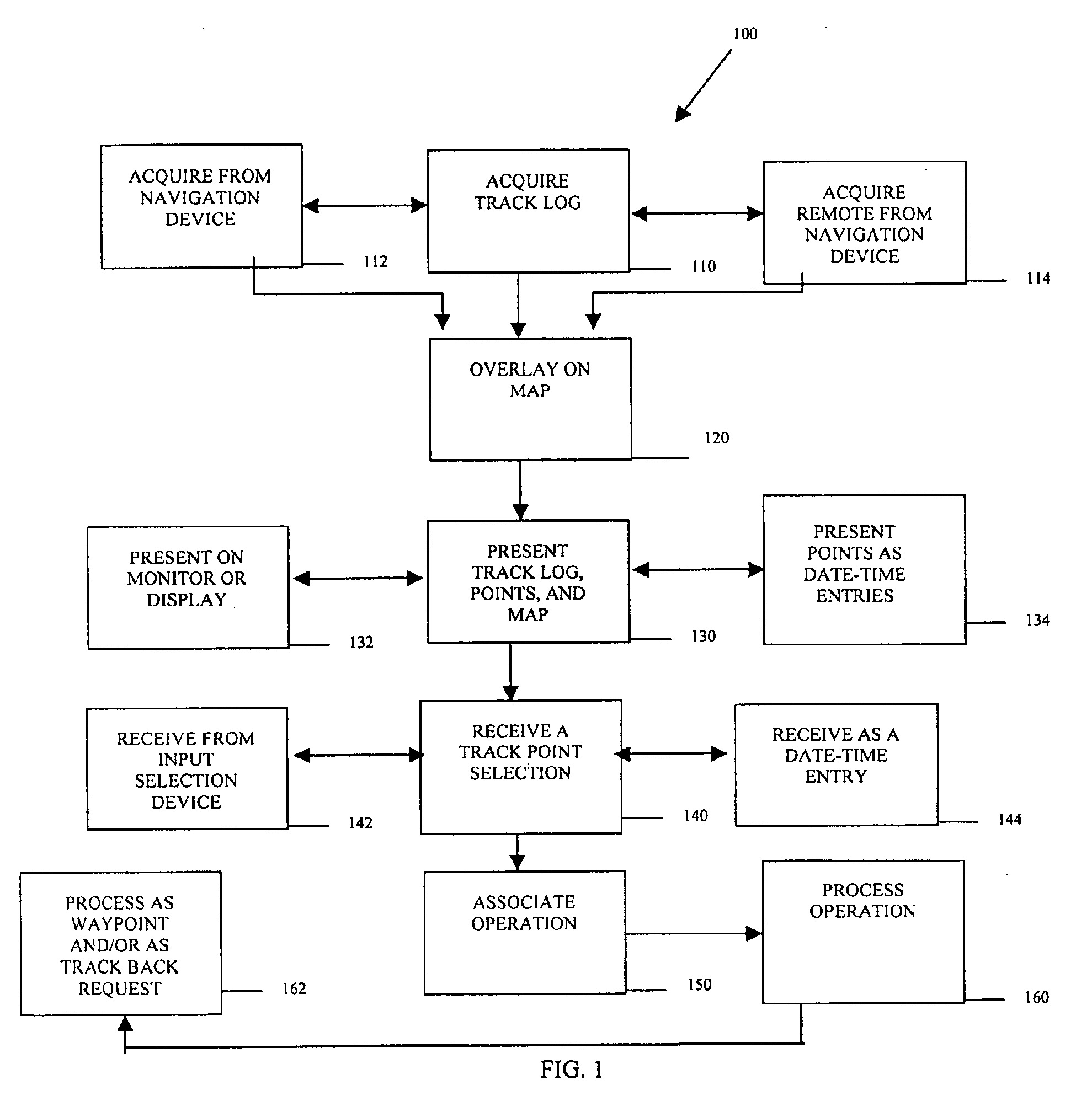
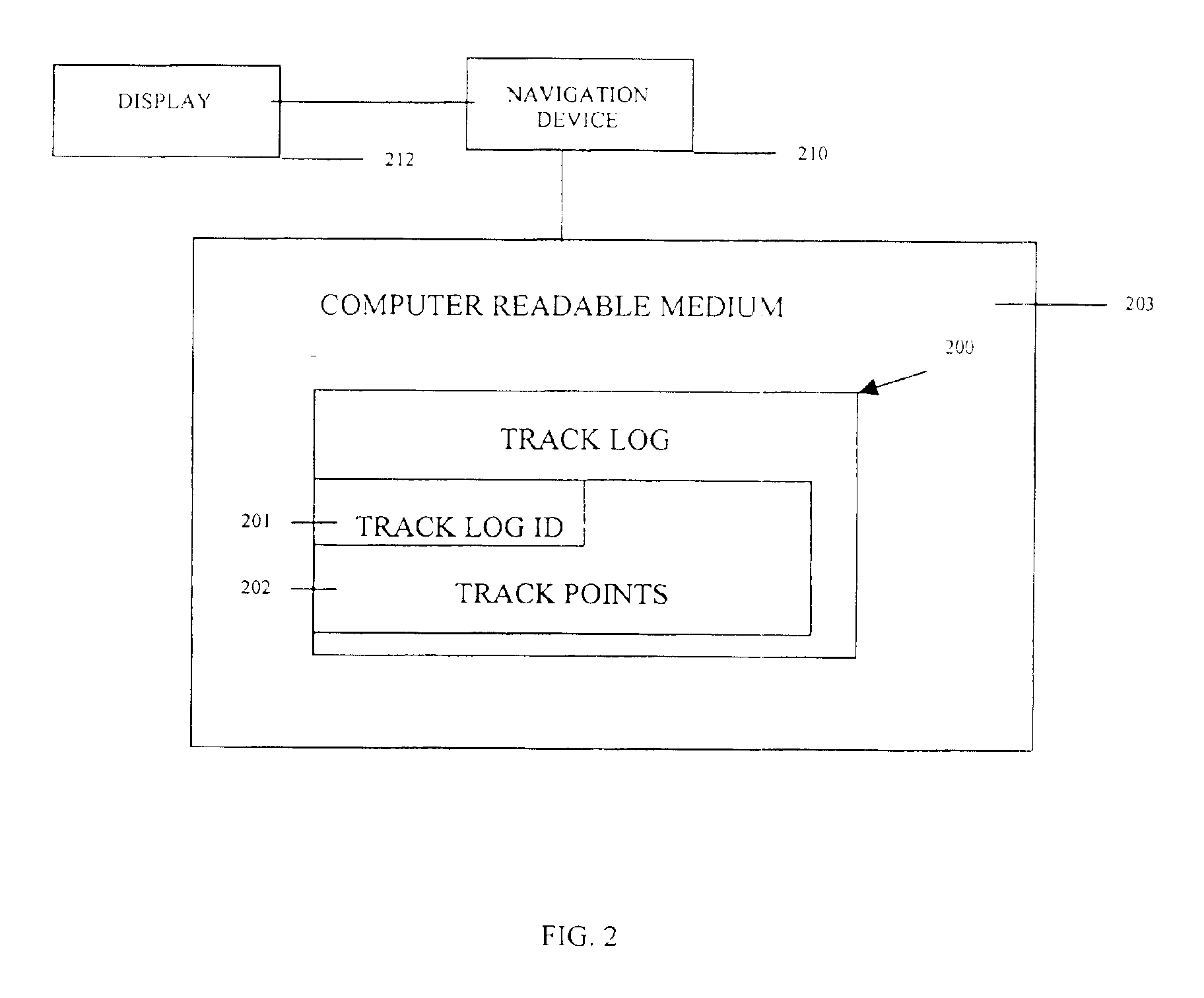
Methods, data structures, and systems for processing track logs
InactiveUS6845318B1Speed up the processSpeed controllerInstruments for road network navigationComputer visionArray data structure
Methods, data structures, and systems provide techniques for processing track logs. A track log is represented as a plurality of track points. The track points represent geographic positions previously traversed. The track log and the track points are overlaid on a map and presented on a display in communication with a portable navigation device. Track points are graphically selected and identified via the display. Any graphically selected track point is also associated with a selectable operation for immediate, automatic, and / or subsequent execution on the portable navigation device.
Owner:GARMIN
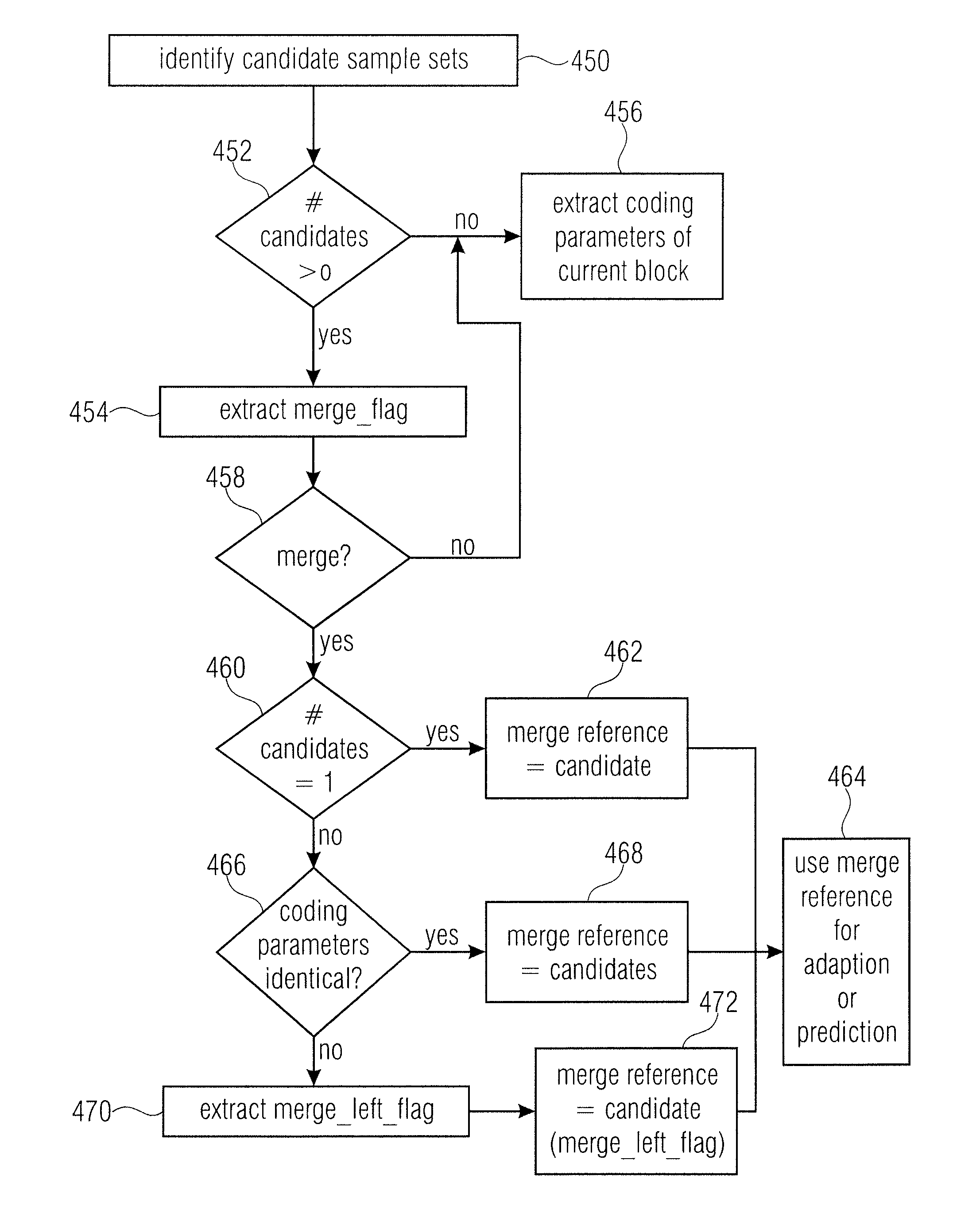
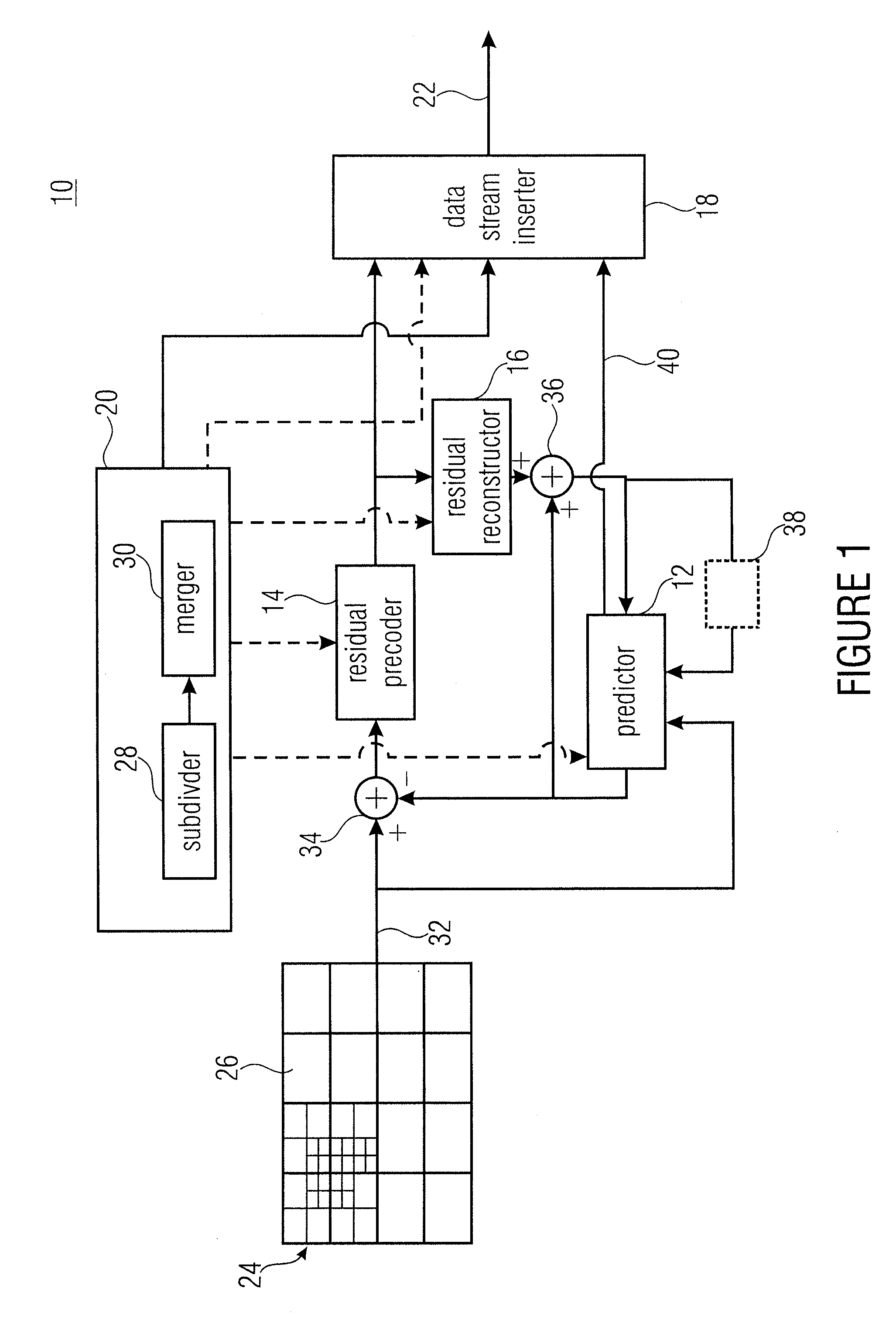
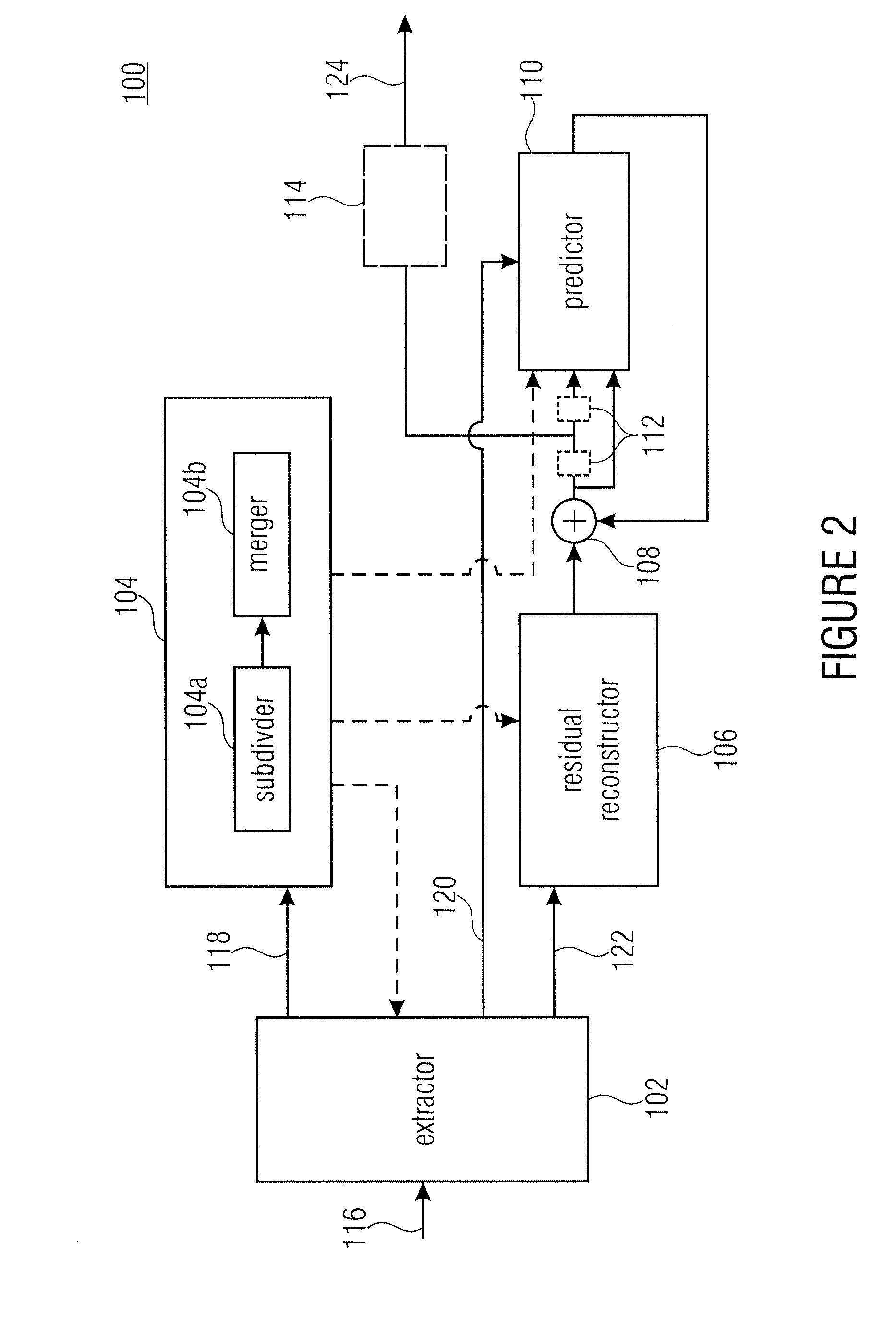
Inheritance in sample array multitree subdivision
ActiveUS20130034157A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer architectureRound complexity
A better compromise between encoding complexity and achievable rate distortion ratio, and / or to achieve a better rate distortion ratio is achieved by using multitree sub-divisioning not only in order to subdivide a continuous area, namely the sample array, into leaf regions, but using the intermediate regions also to share coding parameters among the corresponding collocated leaf blocks. By this measure, coding procedures performed in tiles—leaf regions—locally, may be associated with coding parameters individually without having to, however, explicitly transmit the whole coding parameters for each leaf region separately. Rather, similarities may effectively exploited by using the multitree subdivision.
Owner:GE VIDEO COMPRESSION LLC
Columnar storage of a database index
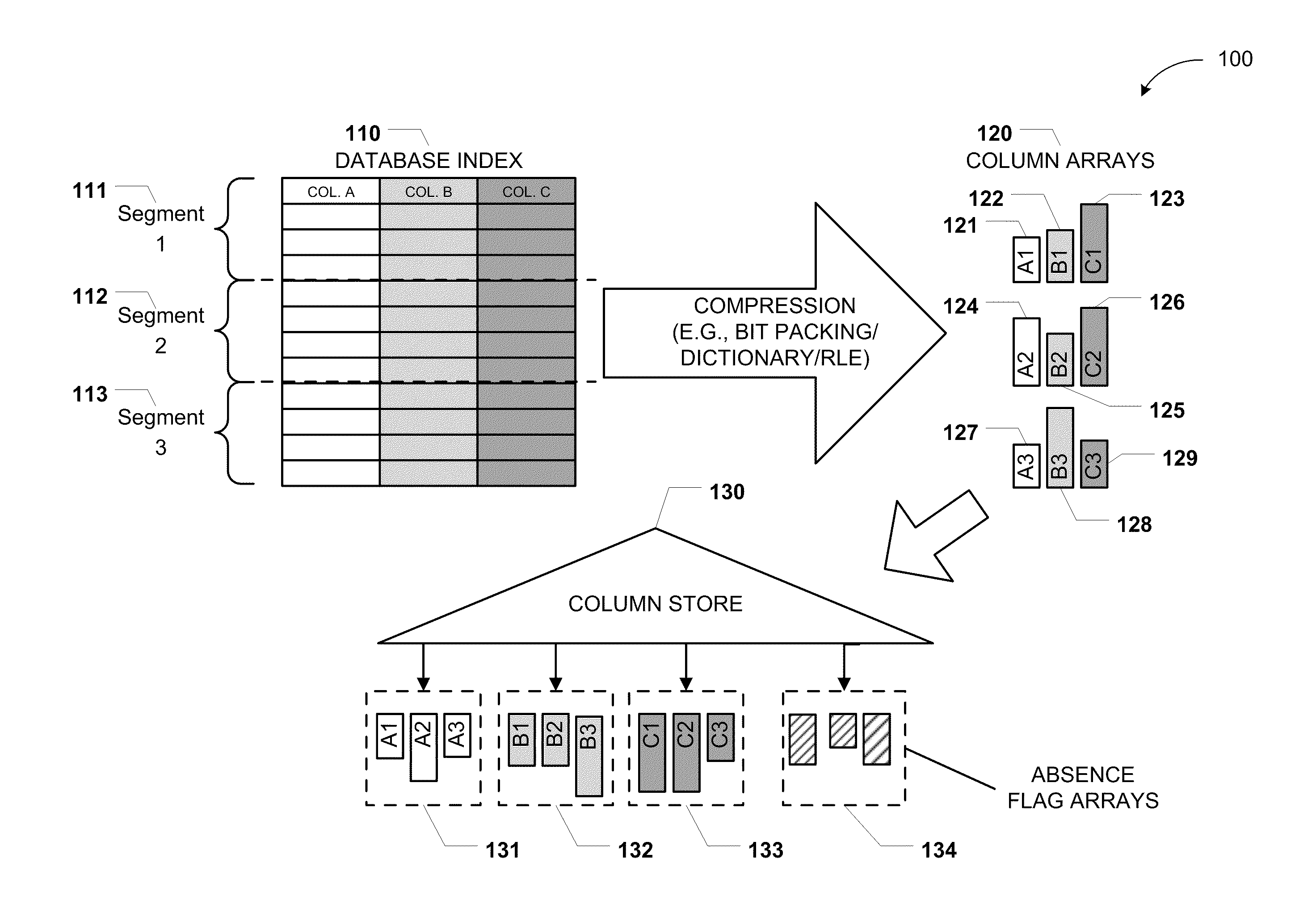
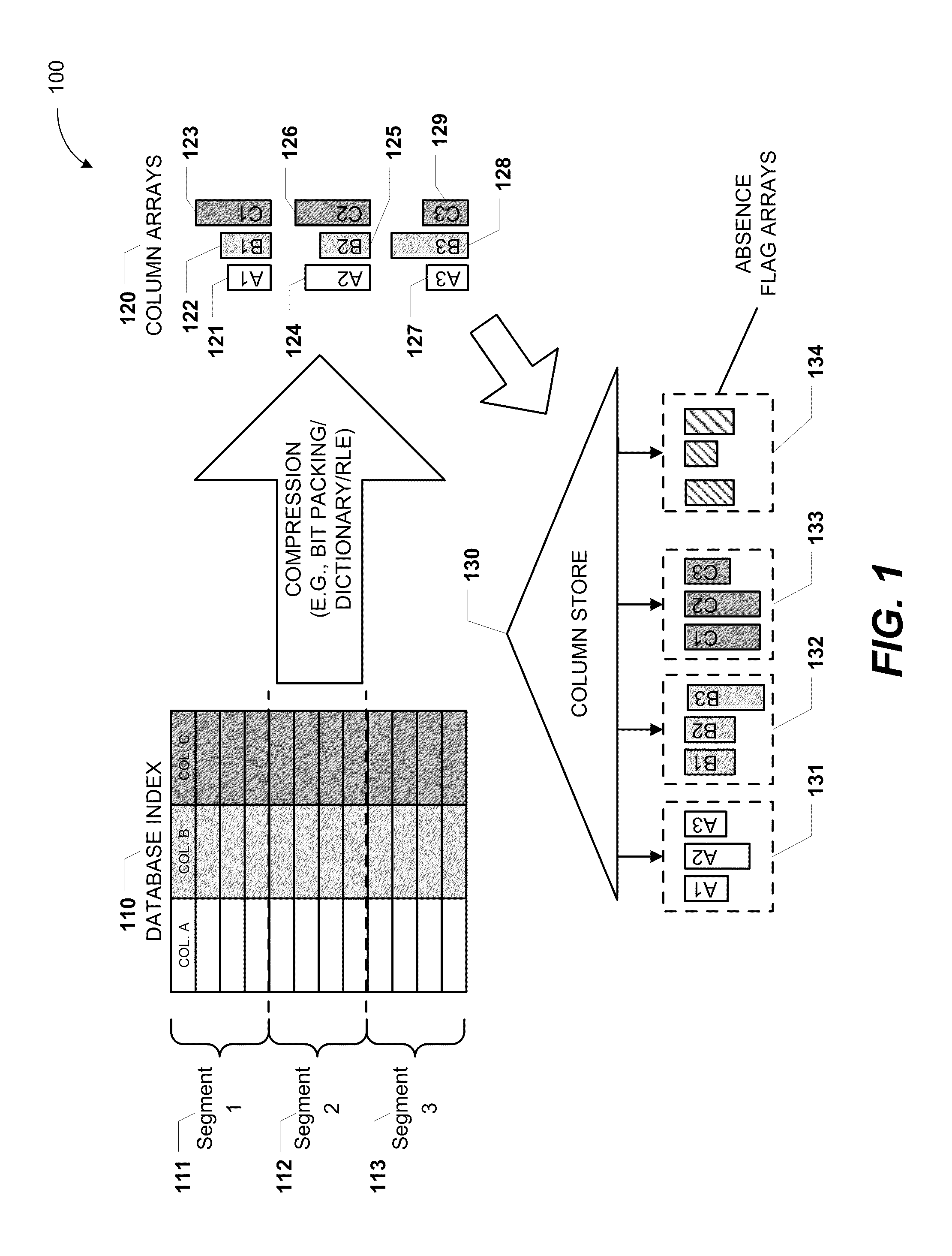
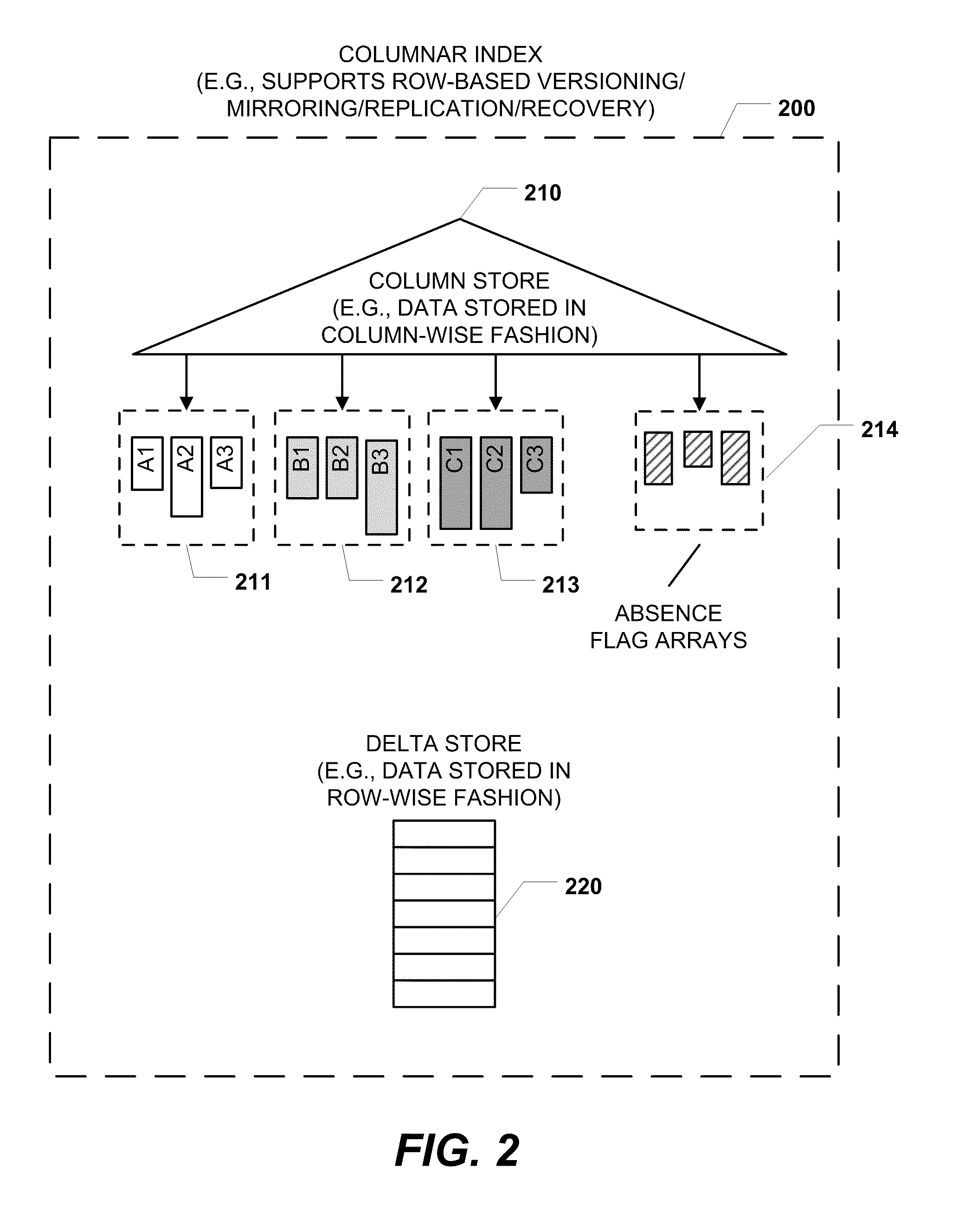
ActiveUS20110219020A1Fast column-wise processing of queryMaintain compatibilityDigital data processing detailsHierarchical databasesArray data structureDatabase index
Methods, systems, and computer-readable media of columnar storage of a database index are disclosed. A particular columnar index includes a column store that stores rows of the columnar index in a column-wise fashion and a delta store that stores rows of the columnar index in a row-wise fashion. The column store also includes an absence flag array. The absence flag array includes entries that indicate whether certain rows have been logically deleted from the column store.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
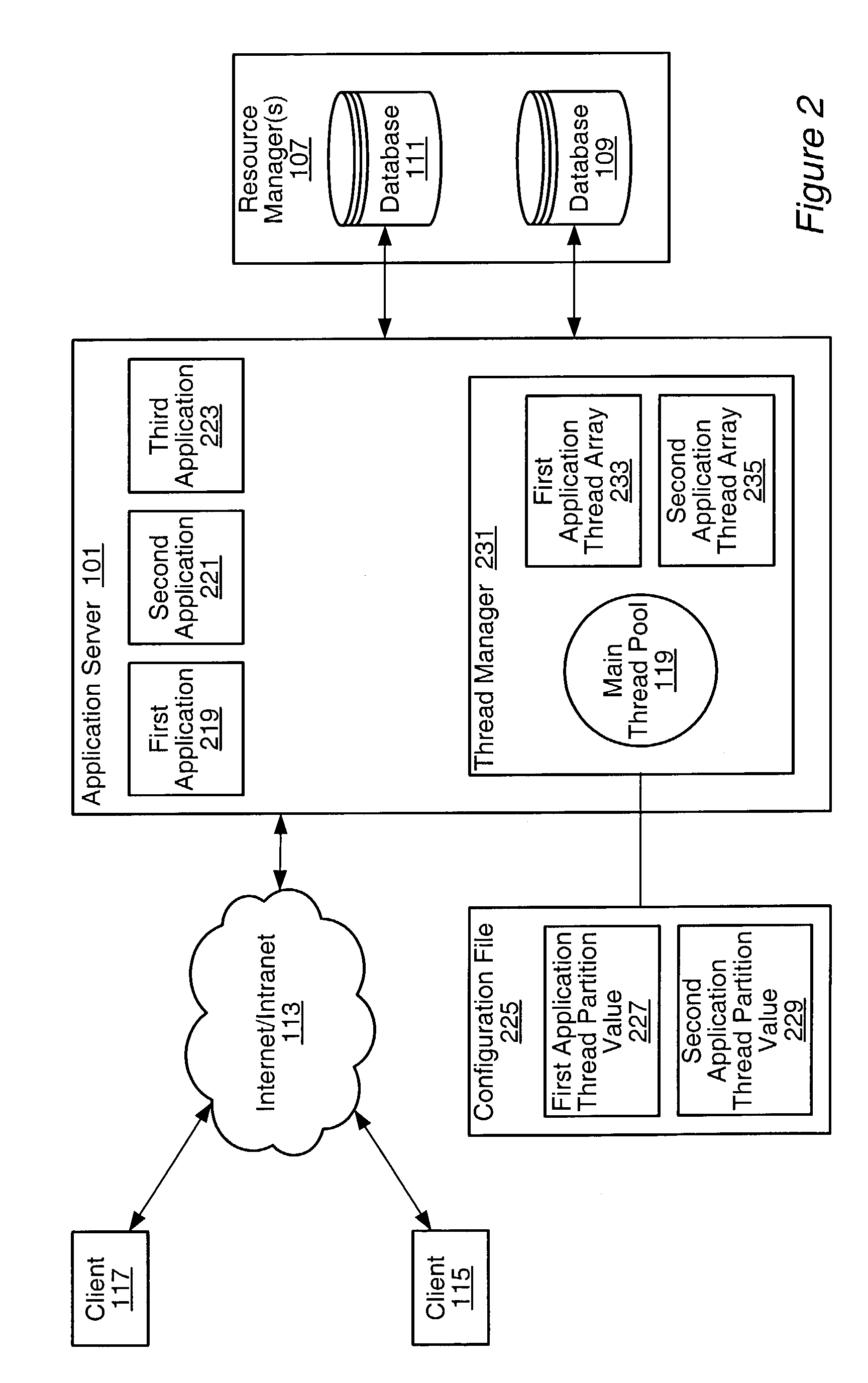
Thread level application partitioning
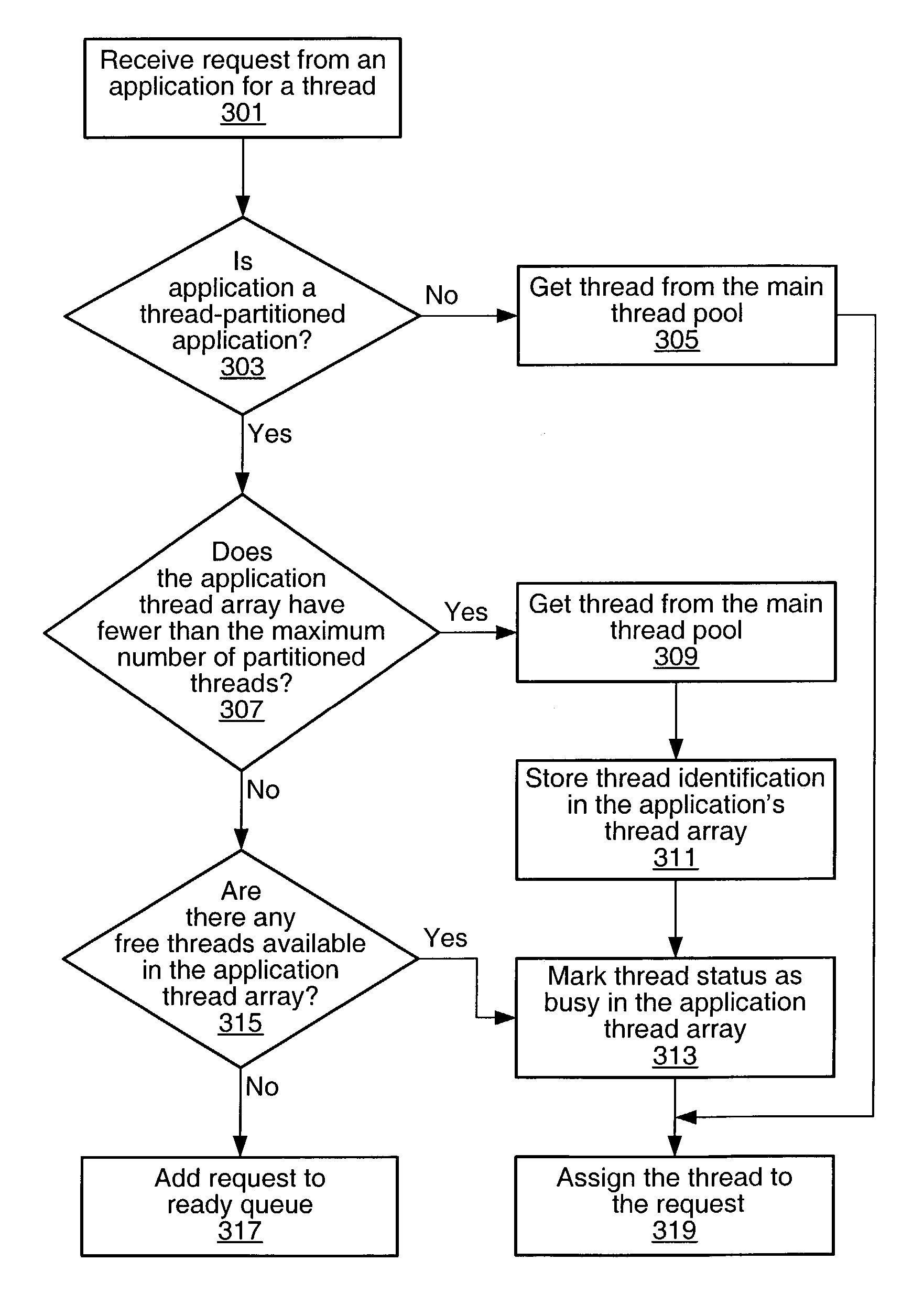
A system and method for managing threads and thread requests in an application server. If the application is a thread-partitioned application with a request, the thread manager may determine if an application thread array for the application has less than the maximum number of threads partitioned for the application. If it does, the thread manager may retrieve a thread from the main thread pool, and assign it to the request. If it does not, the thread manager may determine if there are any free threads in an application thread array, and if there are, one of the free threads in the application thread array may be assigned to the request. If there are no free threads available in the application thread array, the request may be added to a ready queue.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Methods, systems, and data structures for performing searches on three dimensional objects
Techniques are provided for searching on three dimensional (3D) objects across large, distributed repositories of 3D models. 3D shapes are created for input to a search system; optionally user-defined similarity criterion is used, and search results are interactively navigated and feedback received for modifying the accuracy of the search results. Search input can also be given by picking 3D models from a cluster map or by providing the orthographic views for the 3D model. Feedback can be given by a searcher as to which models are similar and which are not. Various techniques adjust the search results according to the feedback given by the searcher and present the new search results to the searcher.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
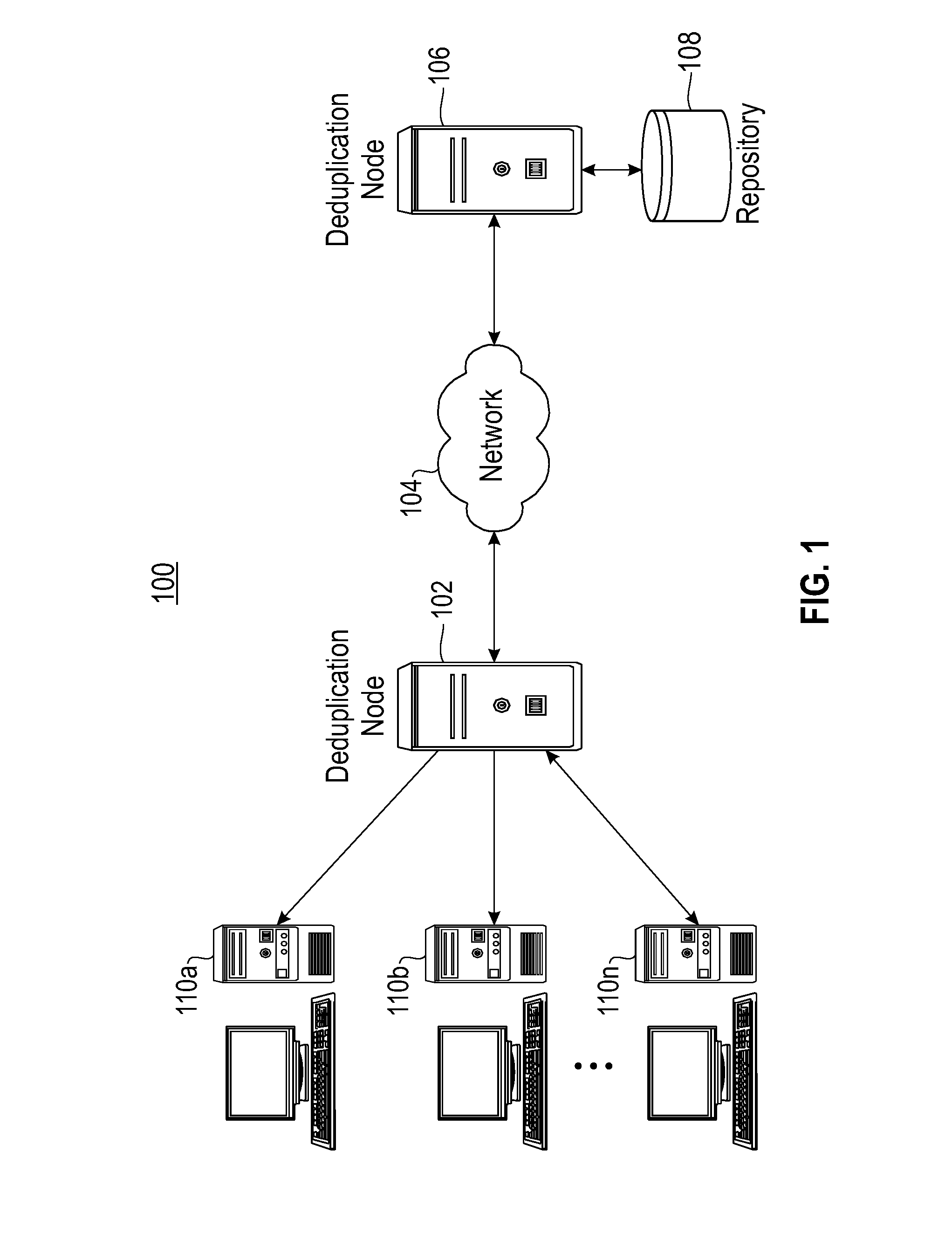
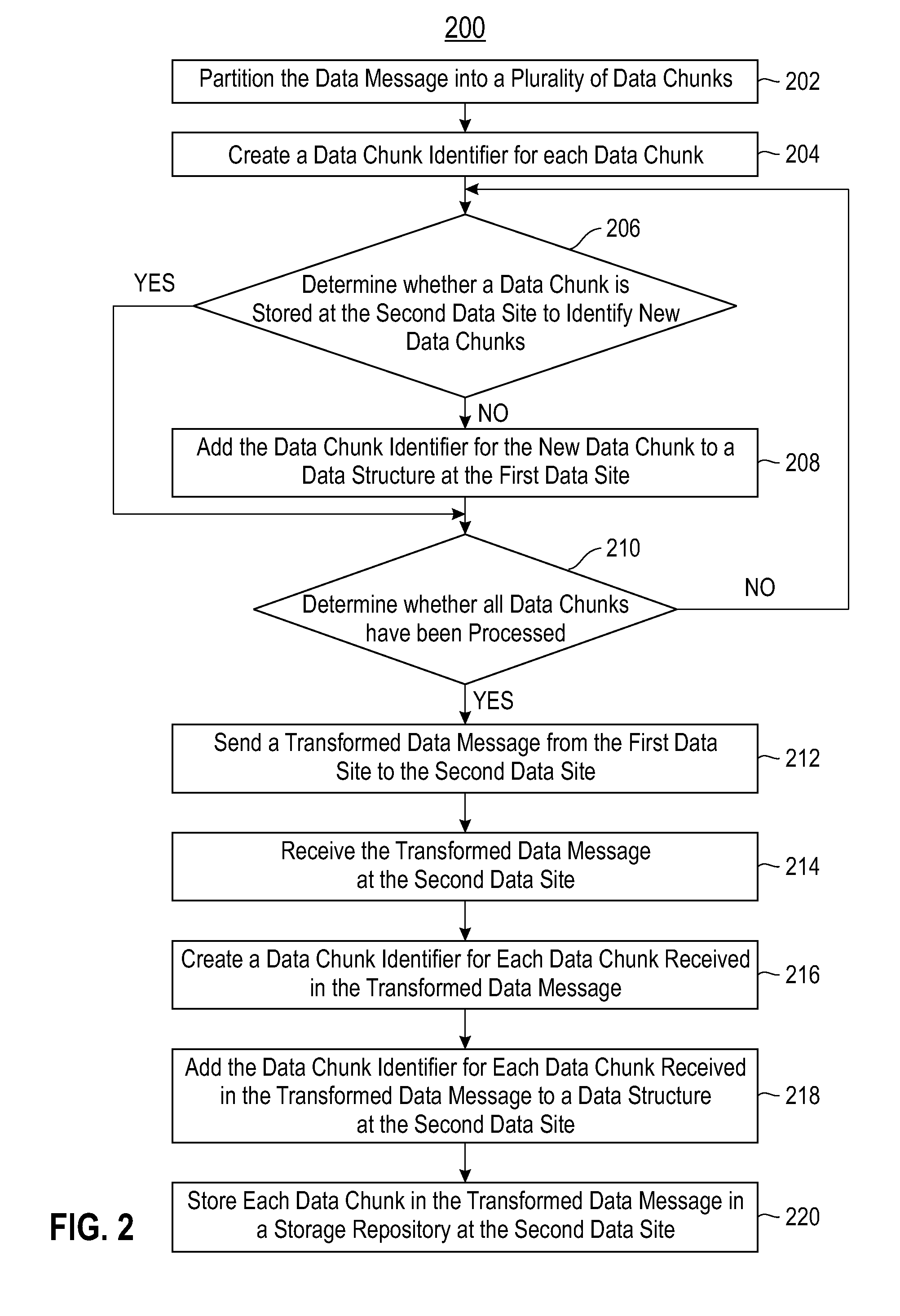
Optimizing Data Transmission Bandwidth Consumption Over a Wide Area Network
ActiveUS20110258161A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsArray data structureData transmission
An exemplary embodiment includes partitioning a data message to be communicated from a first data site to a second data site into data chunks; generating a data chunk identifier for each data chunk; determining whether the data chunks are stored at the second data site; when at least one data chunk is not stored at the second data site, adding the data chunk identifier for each data chunk not stored at the second data site to a data structure at the first data site; sending a transformed data message from the first date site to the second data site; wherein, when at least one data chunk is already stored at the second data site, rather than including that data chunk, the transformed data message instead includes at least one tuple to enable the data message to be reconstructed at the second data site without sending the previously stored data chunk, the transformed data message also includes each data chunk not stored at the second data site.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method, system, program, and data structures for mapping logical blocks to physical blocks
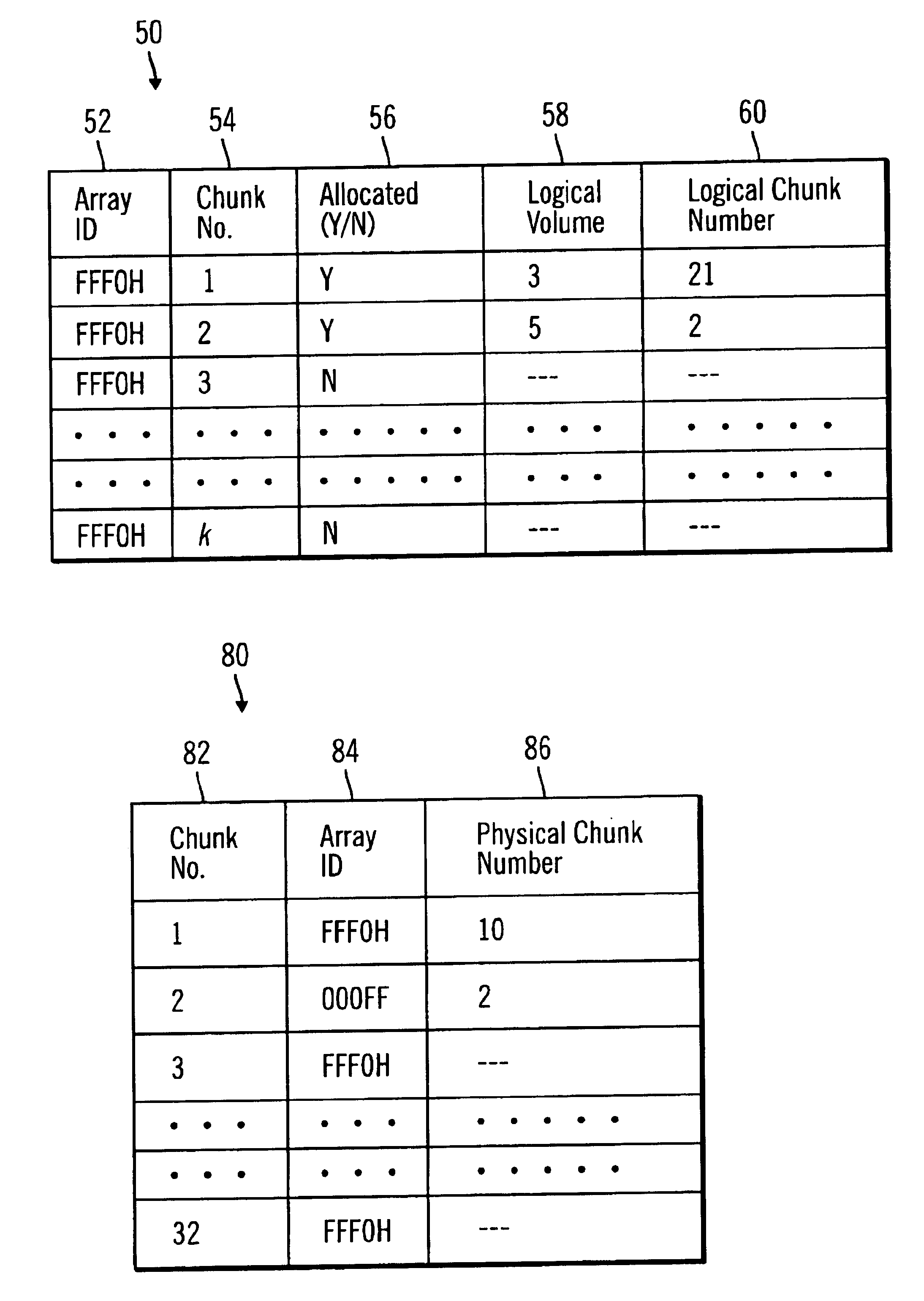
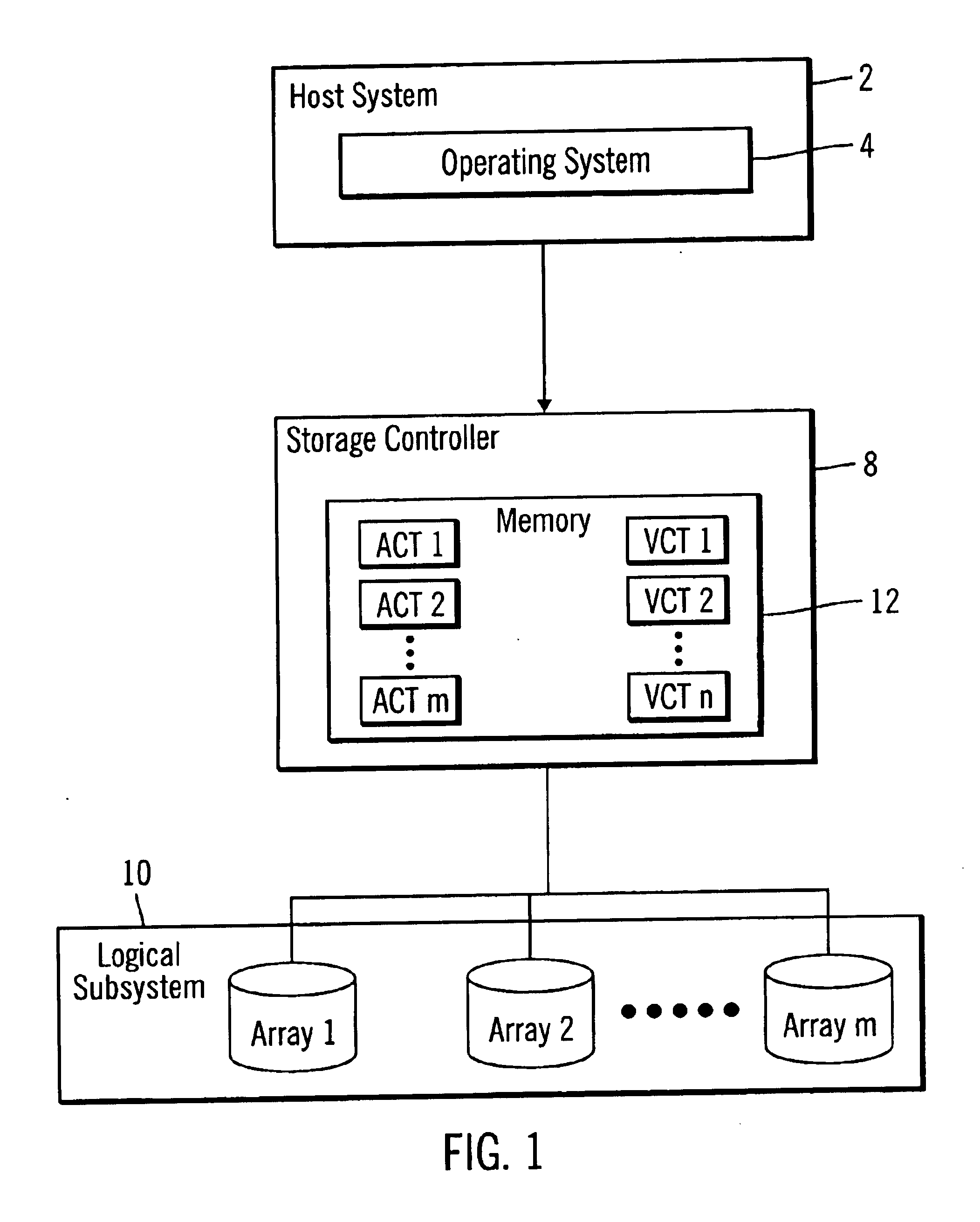
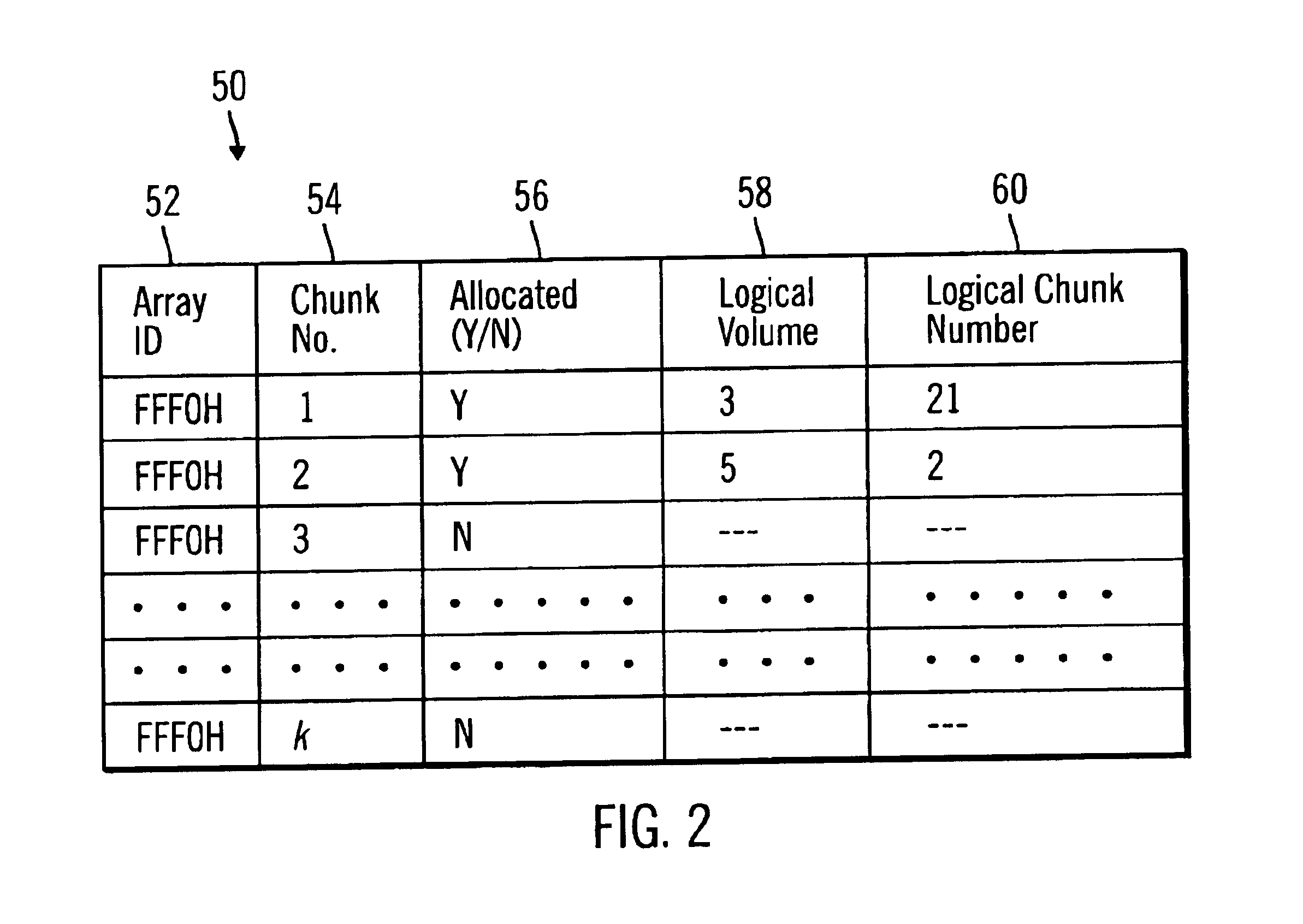
InactiveUS6839827B1Increase in sizeAvoid performanceInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationArray data structureControl store
Disclosed is a method, system, program, and data structure for a storage controller to map logical blocks to physical storage blocks. The storage controller is in communication with at least one host system that views a logical storage space. The storage controller defines the logical storage space as a sequence of logical chunks, wherein each logical chunk comprises a plurality of logical blocks in the logical storage space. The storage controller further defines a physical storage space as a sequence of physical chunks, wherein each physical chunk comprises a plurality of physical blocks in the physical storage system. The storage controller associates each logical chunk in the sequence of logical chunks defining the logical storage space with one physical chunk in the physical storage system. Further, the contiguous logical chunks are capable of being associated with non-contiguous physical chunks.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods apparatus and data structures for enhancing the resolution of images to be rendered on patterned display devices
InactiveUS20010048764A1Improve imaging resolutionHigh resolutionImage enhancementTelevision system detailsSub-pixel resolutionArray data structure
Techniques for improving the resolution of images (either analog images, analytic images, or images having a higher resolution than that of a display device) to be rendered on patterned displays. In one aspect of the present invention, an overscaling or oversampling process may accept analytic character information, such as contours for example, and a scale factor or grid and overscale or oversample the analytic character information to produce an overscaled or oversampled image. The overscaled or oversampled image generated has a higher resolution than the display upon which the character is to be rendered. Displaced samples of the overscaled or oversampled image are then combined (or filtered). An analytic image, such as a line drawing for example, may be applied to the oversampling / overscaling process as was the case with the character analytic image. However, since the analytic image may have different units than that of the character analytic image, the scale factor applied may be different. Since an ultra resolution image is already "digitized", that is, not merely mathematically expressed contours or lines between points, it may be applied directly to a process for combining displaced samples of the ultra-resolution image to generate another ultra-resolution image (or an image with sub-pixel information). The functionality of the overscaling / oversampling process and the processes for combining displaced samples may be combined into a single step analytic to digital sub-pixel resolution conversion process.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com