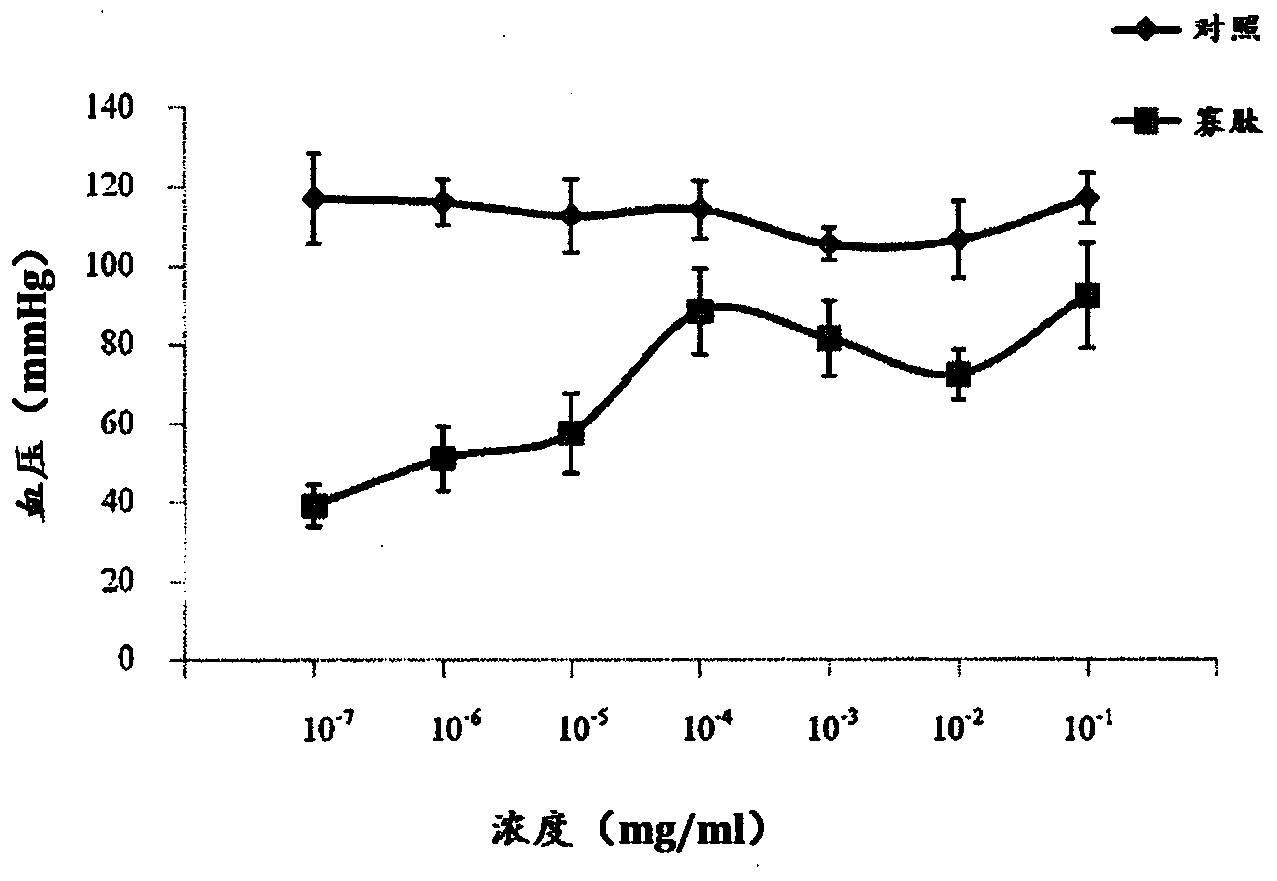
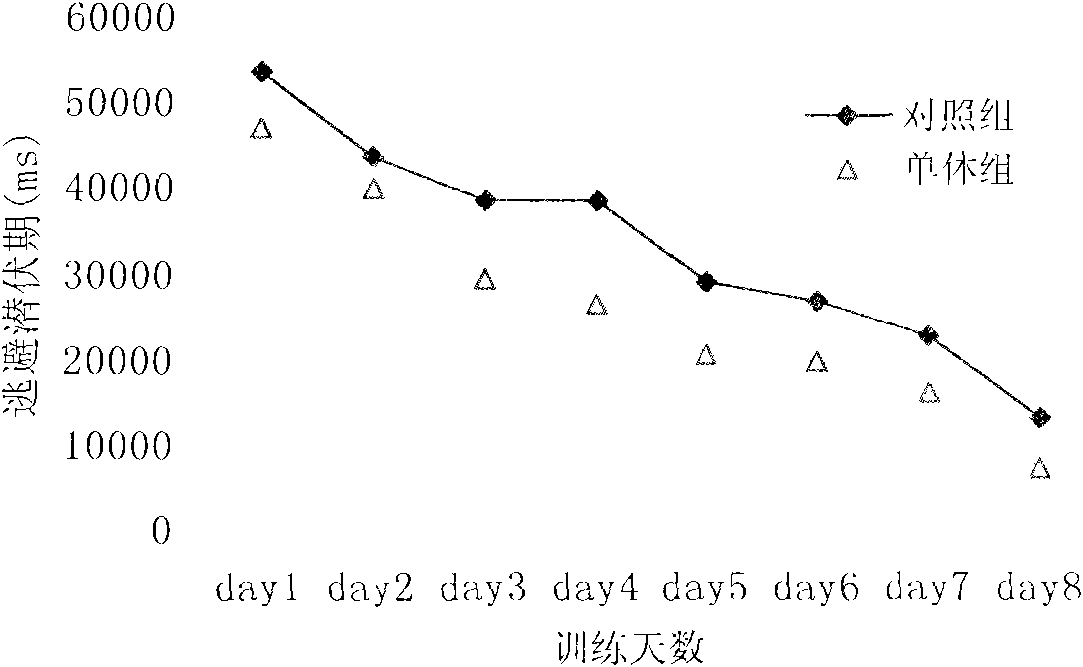Patents
Literature
59 results about "Spatial memory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In cognitive psychology and neuroscience, spatial memory is that part of the memory responsible for the recording of information about one's environment and spatial orientation. For example, a person's spatial memory is required in order to navigate around a familiar city, just as a rat's spatial memory is needed to learn the location of food at the end of a maze. It is often argued that in both humans and animals, spatial memories are summarized as a cognitive map. Spatial memory has representations within working, short-term memory and long-term memory. Research indicates that there are specific areas of the brain associated with spatial memory. Many methods are used for measuring spatial memory in children, adults, and animals.
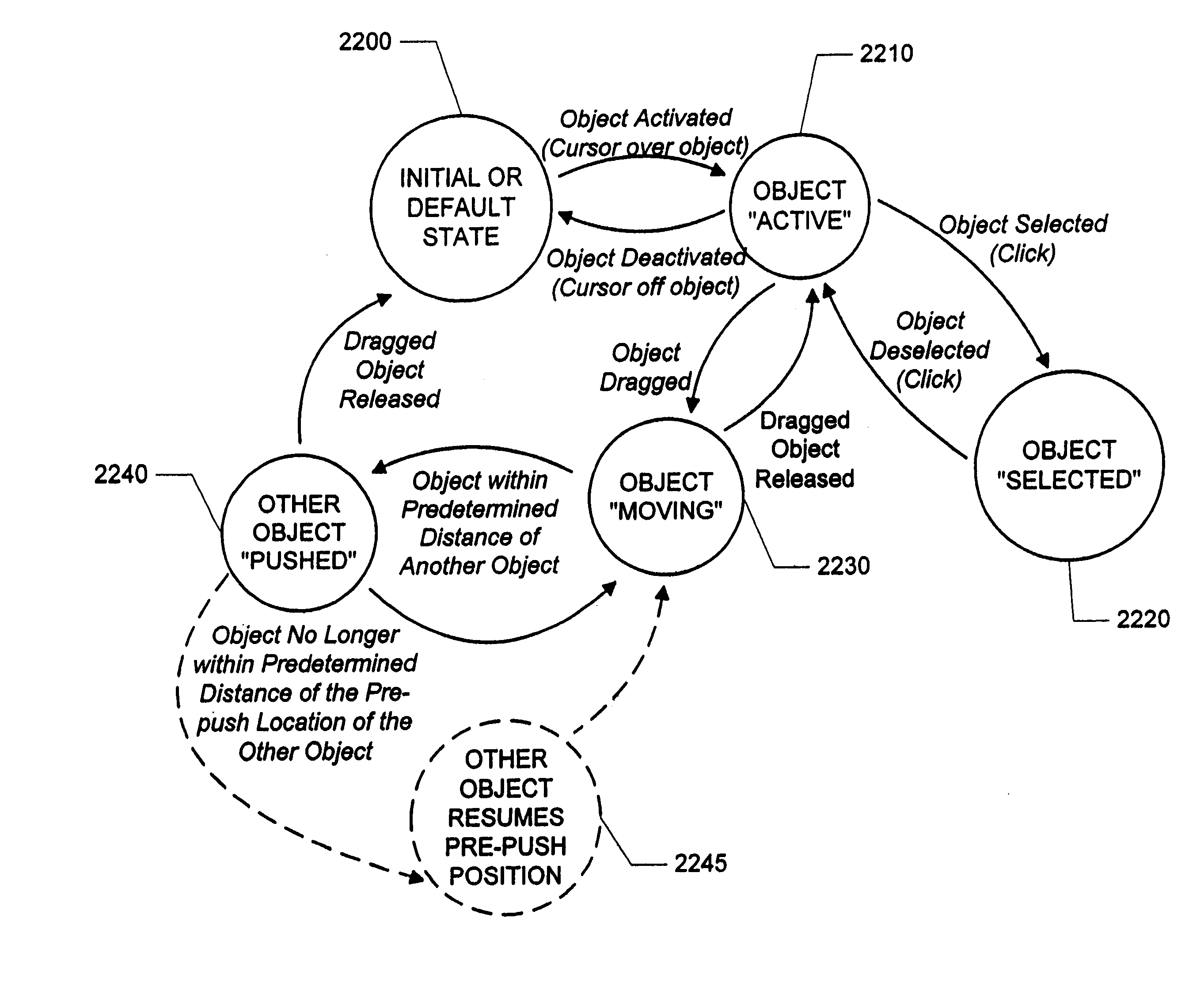
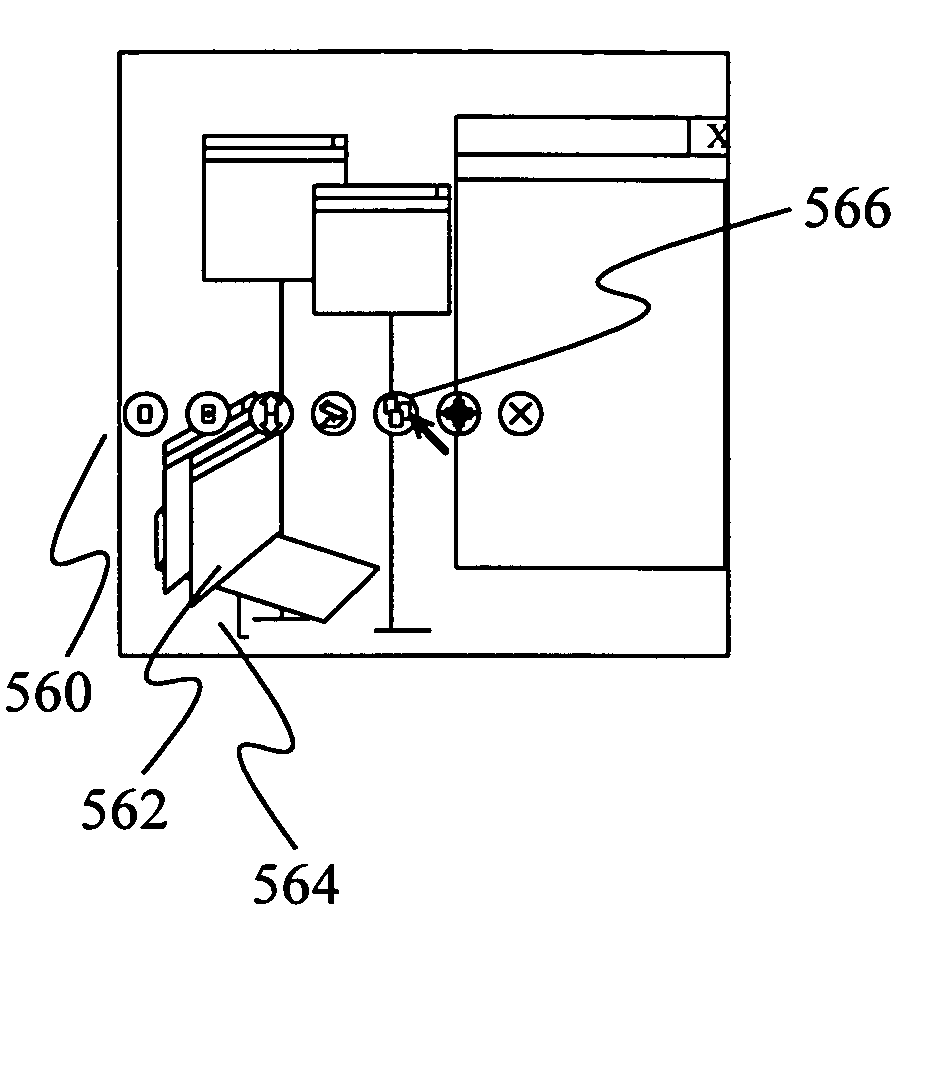
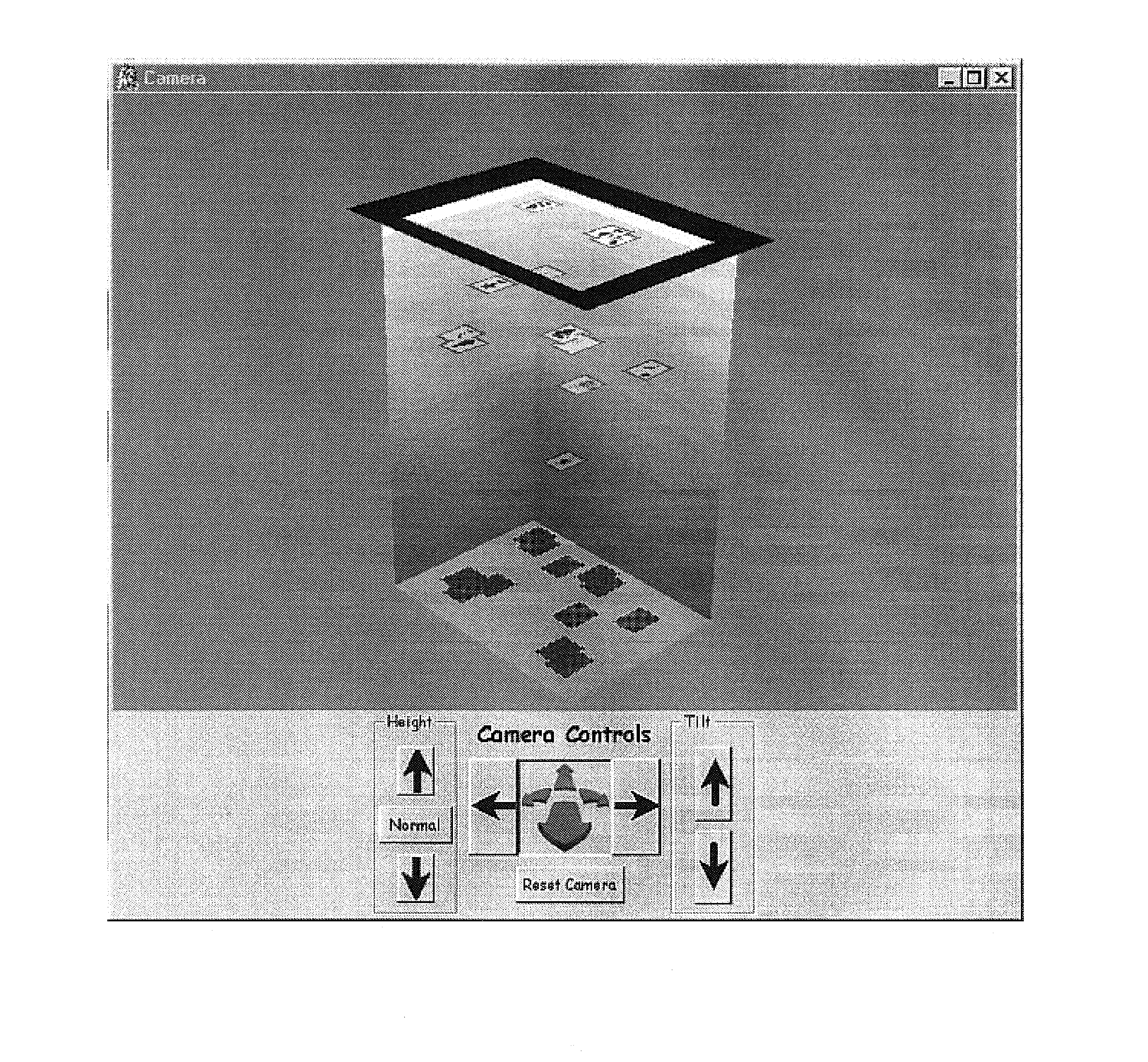
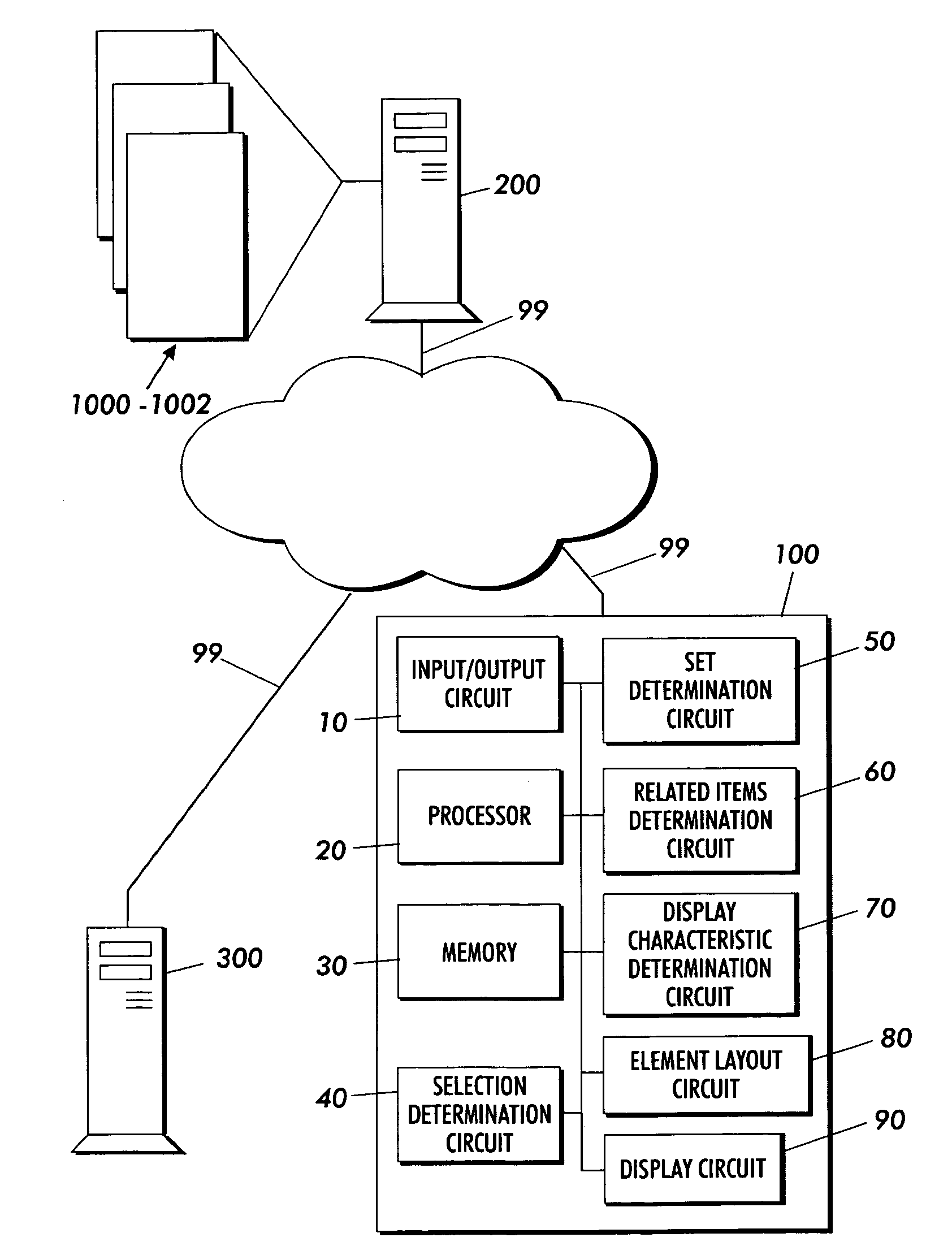
Methods, apparatus and data structures for providing a user interface, which exploits spatial memory in three-dimensions, to objects and which visually groups proximally located objects
InactiveUS6414677B1Increase spacingMore representationInput/output processes for data processing3D-image renderingGraphicsArray data structure
A graphical user interface in which object thumbnails are rendered on a simulated three-dimensional surface which (i) exploits spatial memory and (ii) allows more objects to be rendered on a given screen. The objects may be moved, continuously, on the surface with a two-dimensional input device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for providing a three-dimensional task gallery computer interface
InactiveUS20050010876A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingHuman–computer interactionUser interface
The present invention provides a three-dimensional user interface for a computer system that allows a user to combine and store a group of windows as a task. The image of each task can be positioned within a three-dimensional environment such that the user may utilize spatial memory in order remember where a particular task is located. In further embodiments of the invention, the three-dimensional environment includes a stage, which is used to display the task with the current focus. When a user selects a new task in the gallery, the task is moved to the stage and given focus. If a previous task was on the stage, an image of the previous task is captured. This image is then moved into the task gallery away from the stage. This process allows users to switch between multiple window configurations with a simple action.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods, apparatus and data structures for providing a user interface to objects, the user interface exploiting spatial memory and visually indicating at least one object parameter
InactiveUS7278115B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsImage data processing detailsSearch data structureArray data structure
A graphical user interface in which object thumbnails are rendered in a three-dimensional environment and which exploits spatial memory. The objects may be moved, continuously, with a two-dimensional input device. Pop-up title bars may be rendered over active objects. Intelligent help may be provided to the user, as visual indicators, based on proximity clustering or based on matching algorithms. The simulated location of the object thumbnails in a direction orthogonal to the surface is based on function, such as a linear, polynomial, or exponential function for example, of one or more object properties, such as number of mouse clicks since selected, age, size, etc.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
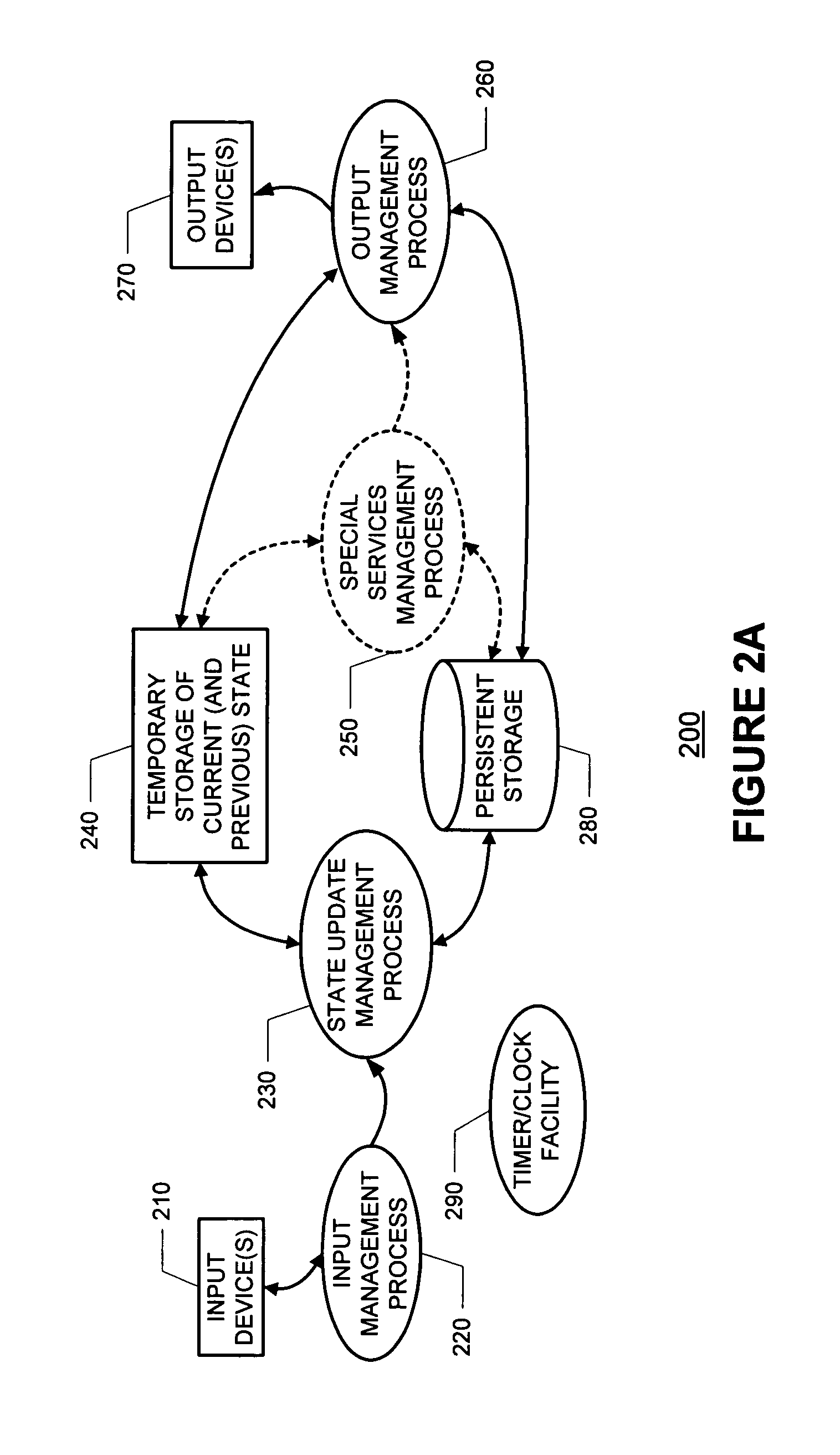
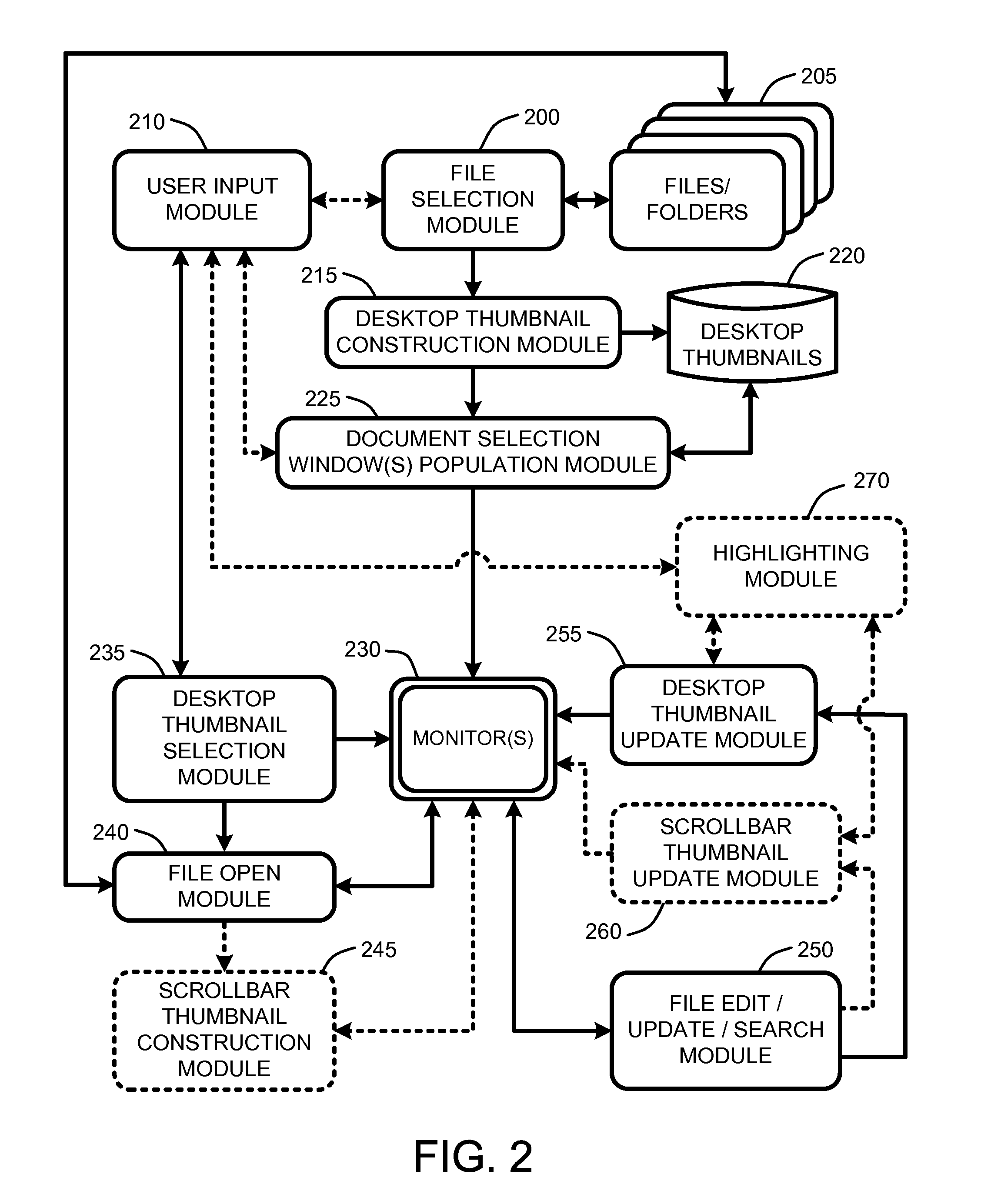
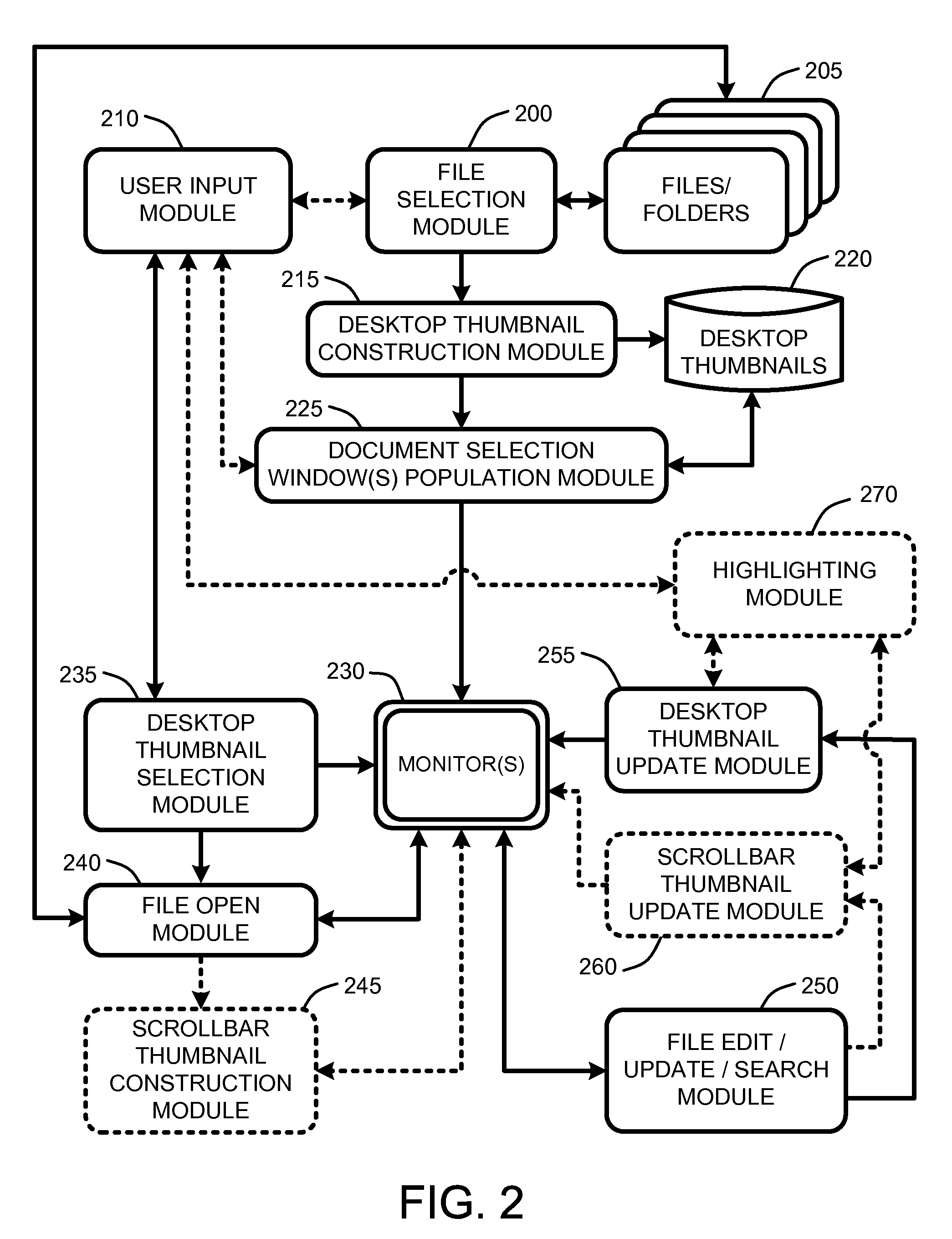
Dynamic thumbnails for document navigation
ActiveUS20080104535A1Easy to navigateProvide utilizationCathode-ray tube indicatorsProgram controlGraphicsThumbnail
A “Spatial Navigator” provides a document navigation environment that leverages user spatial memory. Graphical thumbnail-type representations (“thumbnails”) provide scaled versions of entire documents. Changes to documents are immediately reflected in corresponding thumbnails. Similarly, document search results are highlighted in corresponding thumbnails. One or more dynamic document selection windows present arrangements of a plurality of these thumbnails for user selection and interaction. Each dynamic document selection window provides real-time inter-file navigation by allowing user selection and opening of documents, or any location or portion of a document, through user interaction with the corresponding thumbnail. Once a document is opened, intra-file navigation is enhanced by providing another scaled version of the entire document in a dynamic scrollbar adjacent to a primary document editing / viewing window. Selection of any point within this scrollbar-based thumbnail causes an immediate jump to the corresponding document location in the primary document editing / viewing window.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and apparatus for providing a three-dimensional task gallery computer interface
InactiveUS6909443B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingComputerized systemHuman–computer interaction
The present invention provides a three-dimensional user interface for a computer system that allows a user to combine and store a group of windows as a task. The image of each task can be positioned within a three-dimensional environment such that the user may utilize spatial memory in order to remember where a particular task is located. In further embodiments of the invention, the three-dimensional environment includes a stage, which is used to display the task with the current focus. When a user selects a new task in the gallery, the task is moved to the stage and given focus. If a previous task was on the stage, an image of the previous task is captured. This image is then moved into the task gallery away from the stage. This process allows users to switch between multiple window configurations with a simple action.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Dynamic thumbnails for document navigation
ActiveUS7739622B2Easy to navigateProvide utilizationCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingGraphicsThumbnail
A “Spatial Navigator” provides a document navigation environment that leverages user spatial memory. Graphical thumbnail-type representations (“thumbnails”) provide scaled versions of entire documents. Changes to documents are immediately reflected in corresponding thumbnails. Similarly, document search results are highlighted in corresponding thumbnails. One or more dynamic document selection windows present arrangements of a plurality of these thumbnails for user selection and interaction. Each dynamic document selection window provides real-time inter-file navigation by allowing user selection and opening of documents, or any location or portion of a document, through user interaction with the corresponding thumbnail. Once a document is opened, intra-file navigation is enhanced by providing another scaled version of the entire document in a dynamic scrollbar adjacent to a primary document editing / viewing window. Selection of any point within this scrollbar-based thumbnail causes an immediate jump to the corresponding document location in the primary document editing / viewing window.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Systems and methods for displaying linked information in a sorted context
InactiveUS20060271883A1Data processing applicationsWeb data navigationInformation repositoryLogical operations
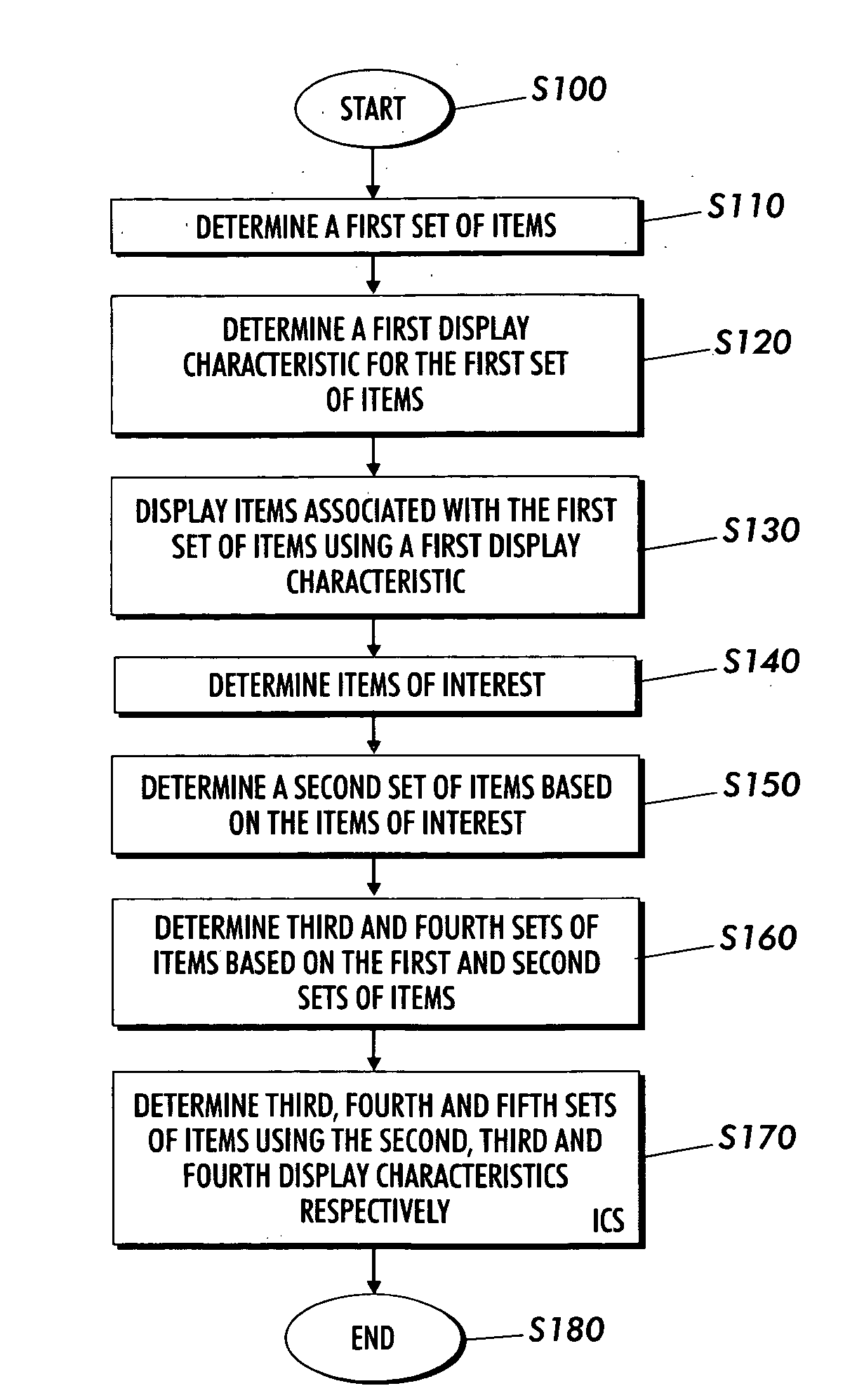
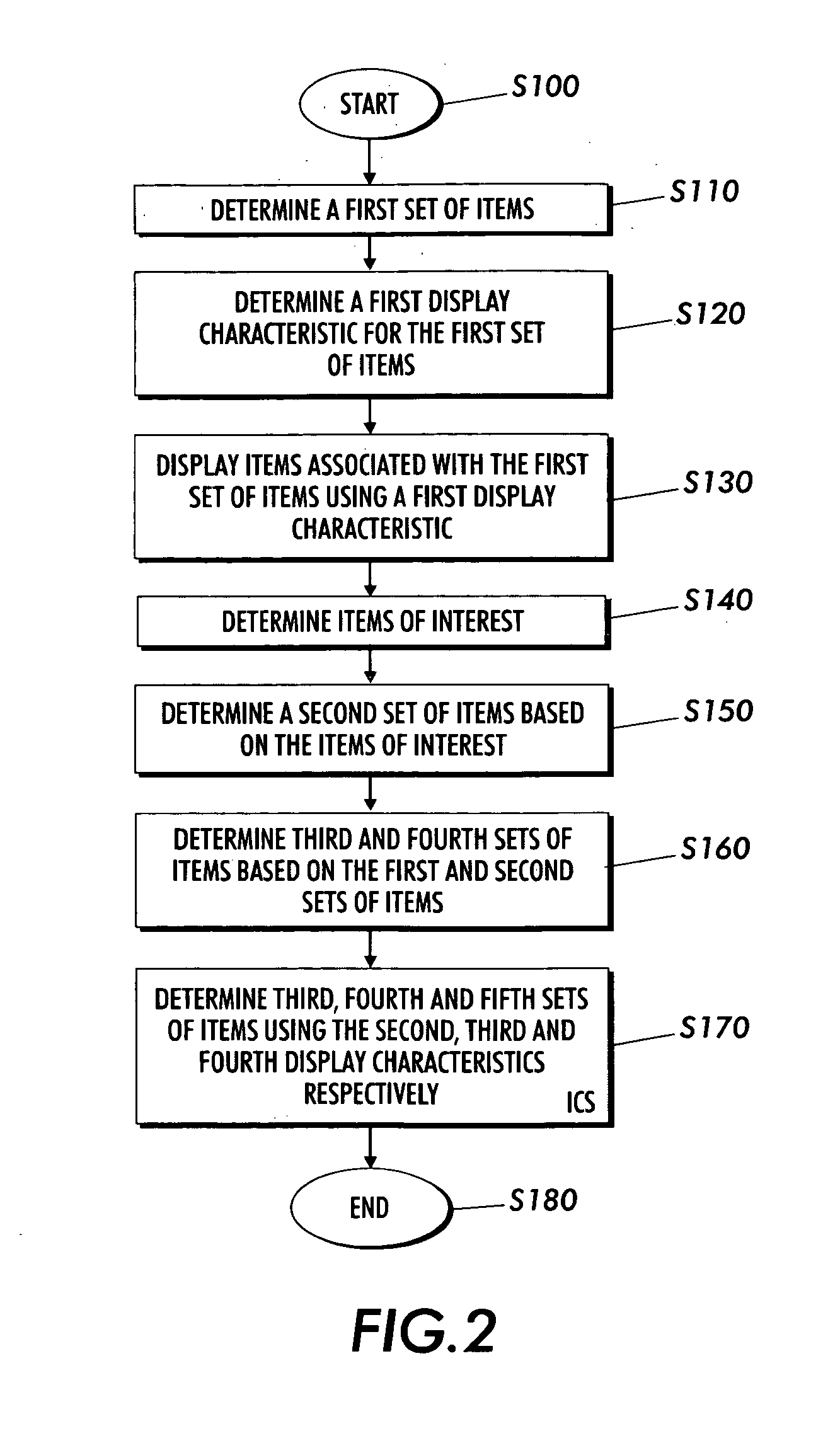
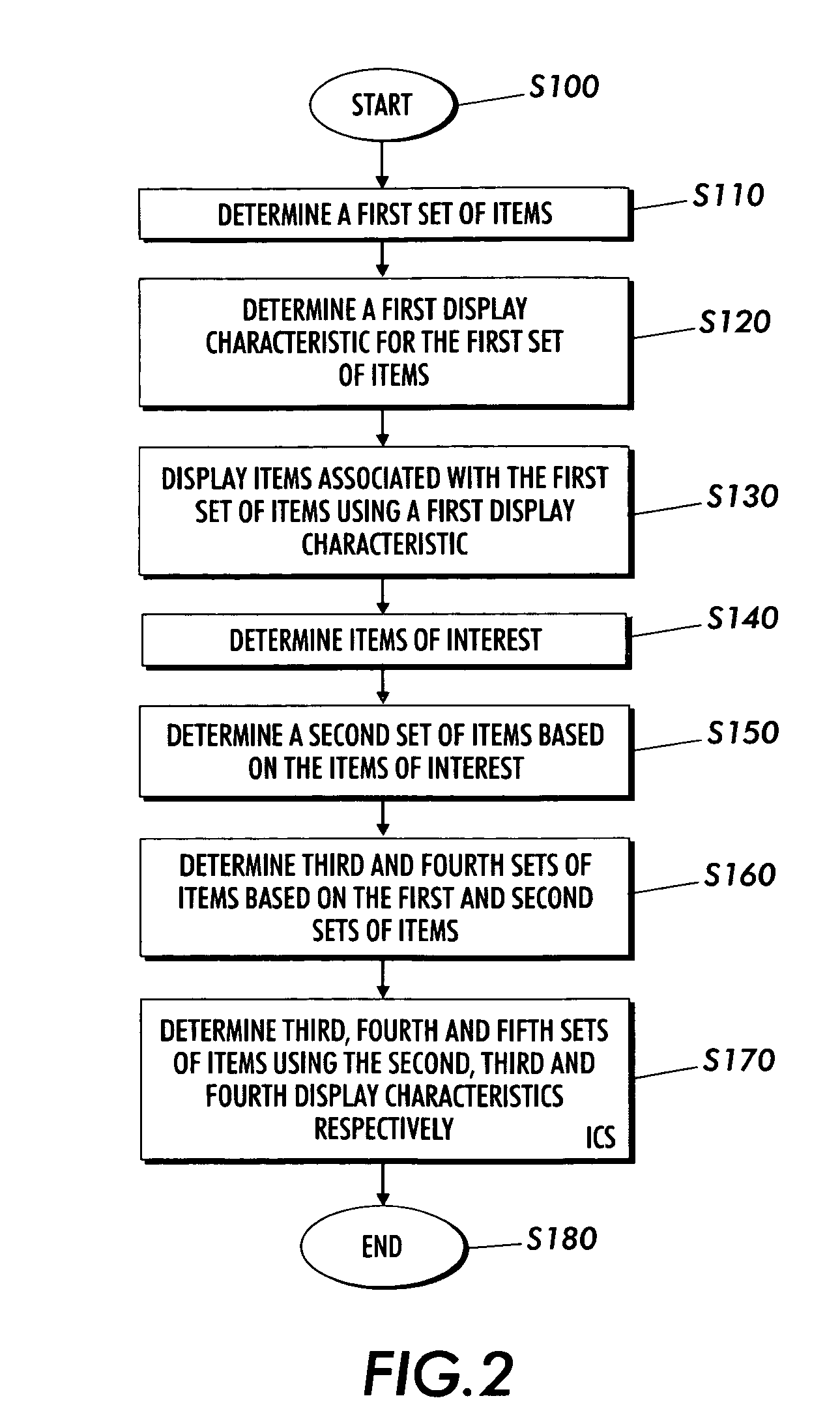
Techniques are presented for determining a first set of display elements, each display element associated with a first display characteristic. An interesting element in the first set of display elements is determined. A second set of elements related to the interesting element is determined. A third set of elements based on the first and second set of elements is determined using intersection, union, subtraction addition and other logical operations. A third set of elements not yet added to the element collection is determined. The elements in the third set are associated with a second or ghosted display characteristic. The elements in the third set are inserted within the sorted context of the visualization based on spatial distortion rules which help to preserve spatial memory cues in the visualization of the element collection. The elements may be documents in an information repository, linked contact information, linked information records in a database or other types of information.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Mouse space memory retention model and intelligent action inspecting system
InactiveCN1817326AInconsistent dwell timeAccurate detectionEducational modelsVeterinary instrumentsMemory retentionData acquisition
A mouse's space memory holding model and its intelligent behavior detection system are disclosed. A circular dark box type labyrinth is used as the behavior data acquiring unit. The mouse to be tested passes through a tubular channel with adjustable one-way gates along a pointed path and closed loop for performing the cyclic training. The signals about the active movement and passive movement caused by electric shock are acquired and processed by the data processing control unit. Said signals are transmitted via PCI bus to the Access database in control system, and then processed by the statistical software package, so controlling and monitoring the behavior of mouse at any time.
Owner:SHENYANG MEDICAL COLLEGE
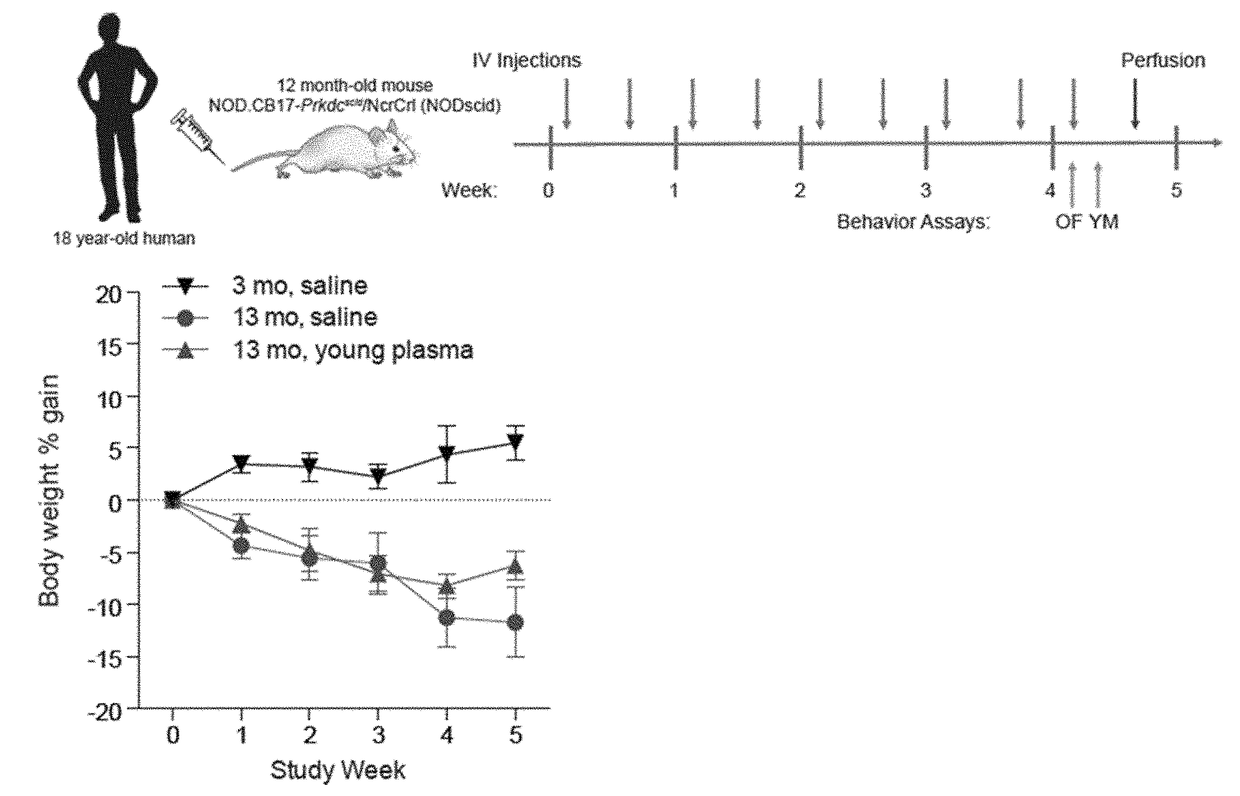
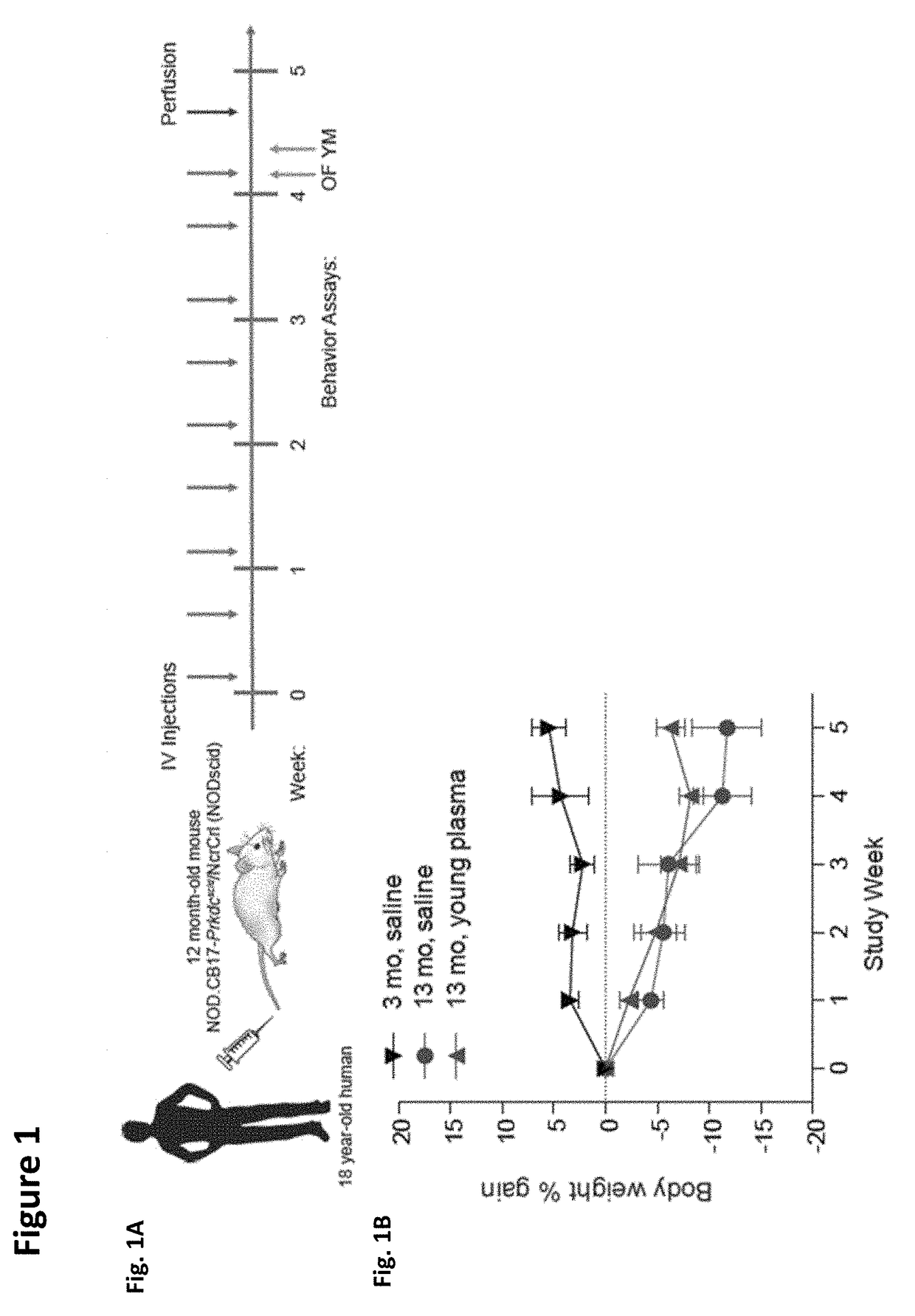
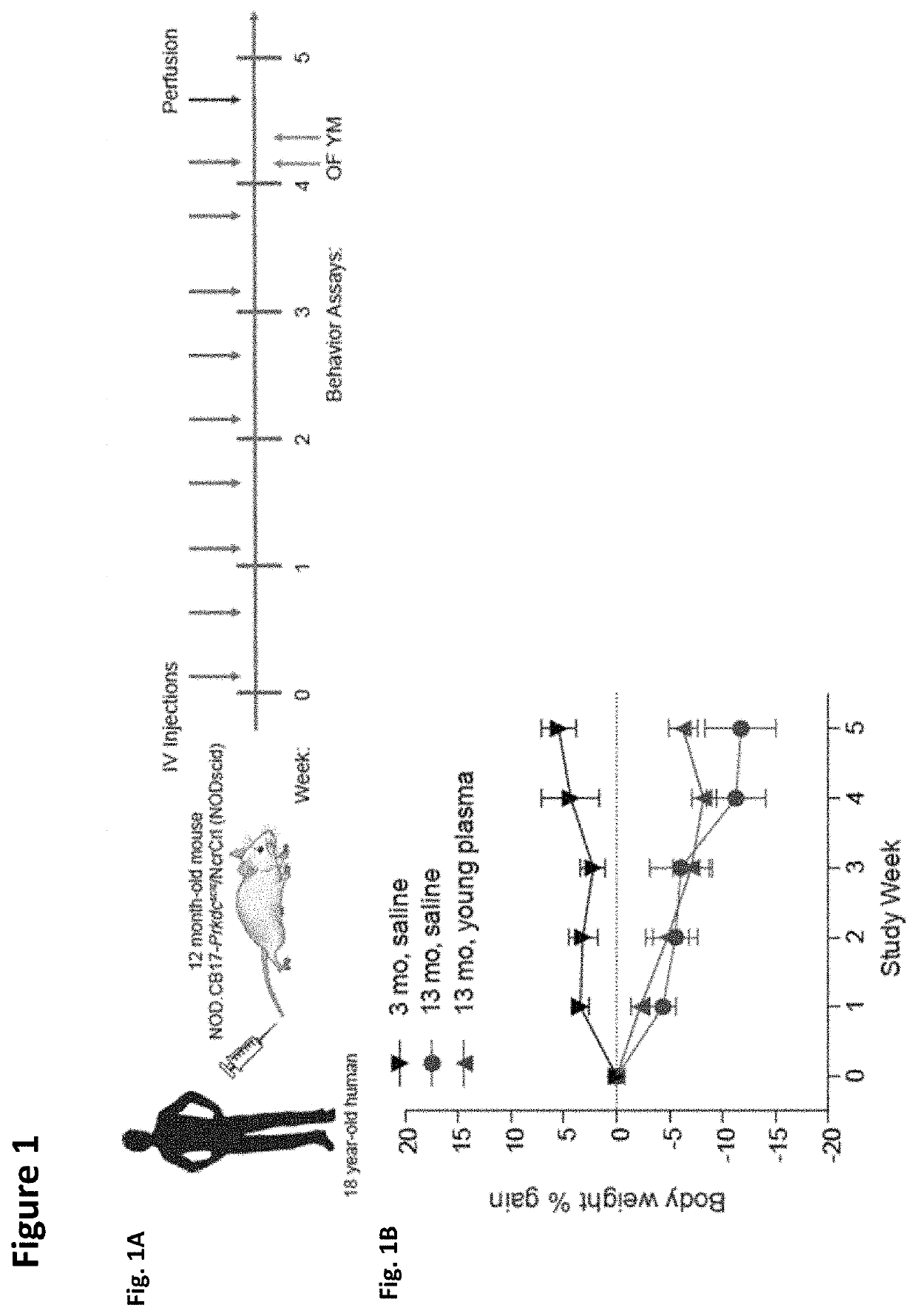
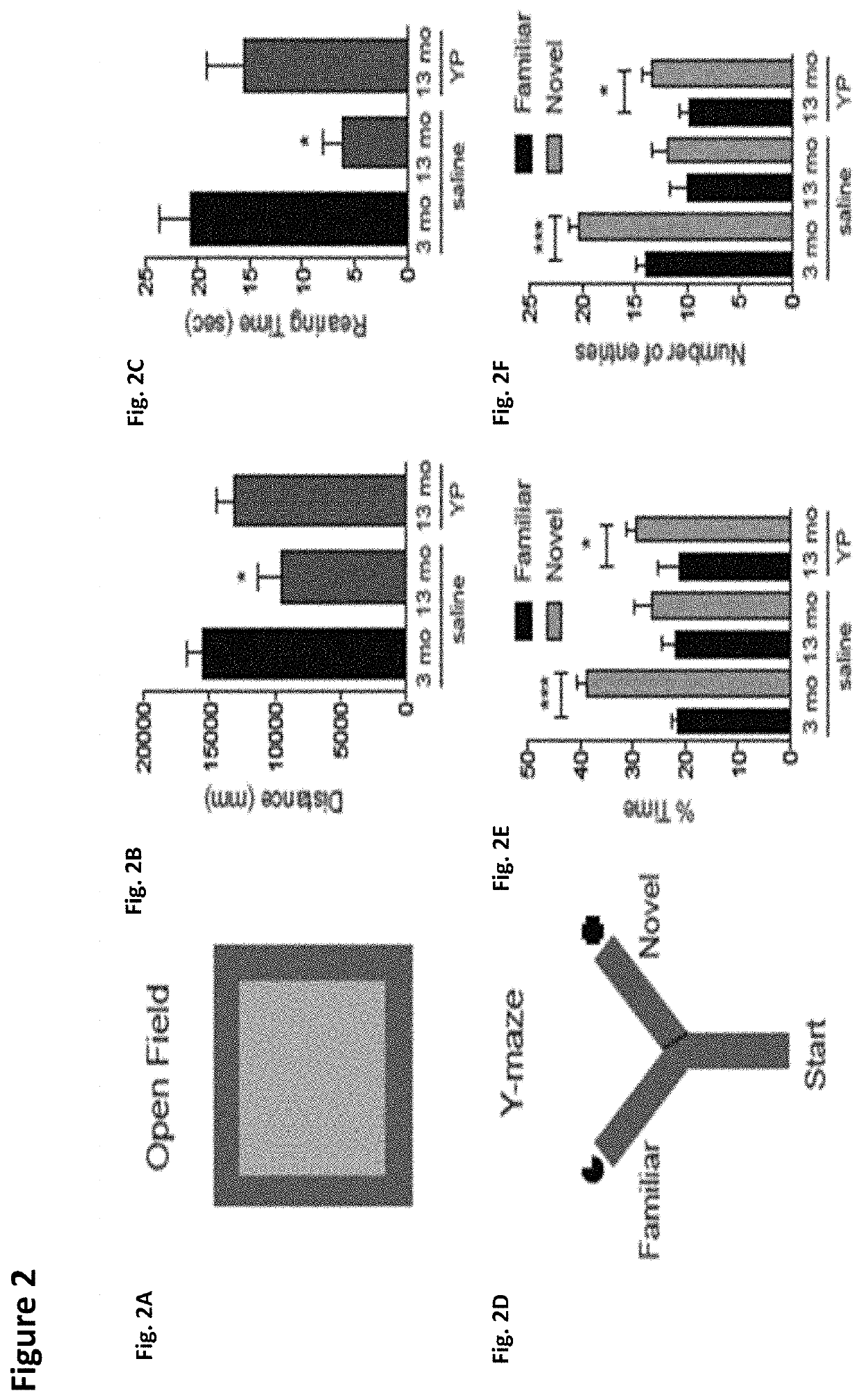
Methods for screening human blood products comprising plasma using immunocompromised rodent models
ActiveUS20170232118A1Compounds screening/testingMammal material medical ingredientsNeurogenesisBlood plasma
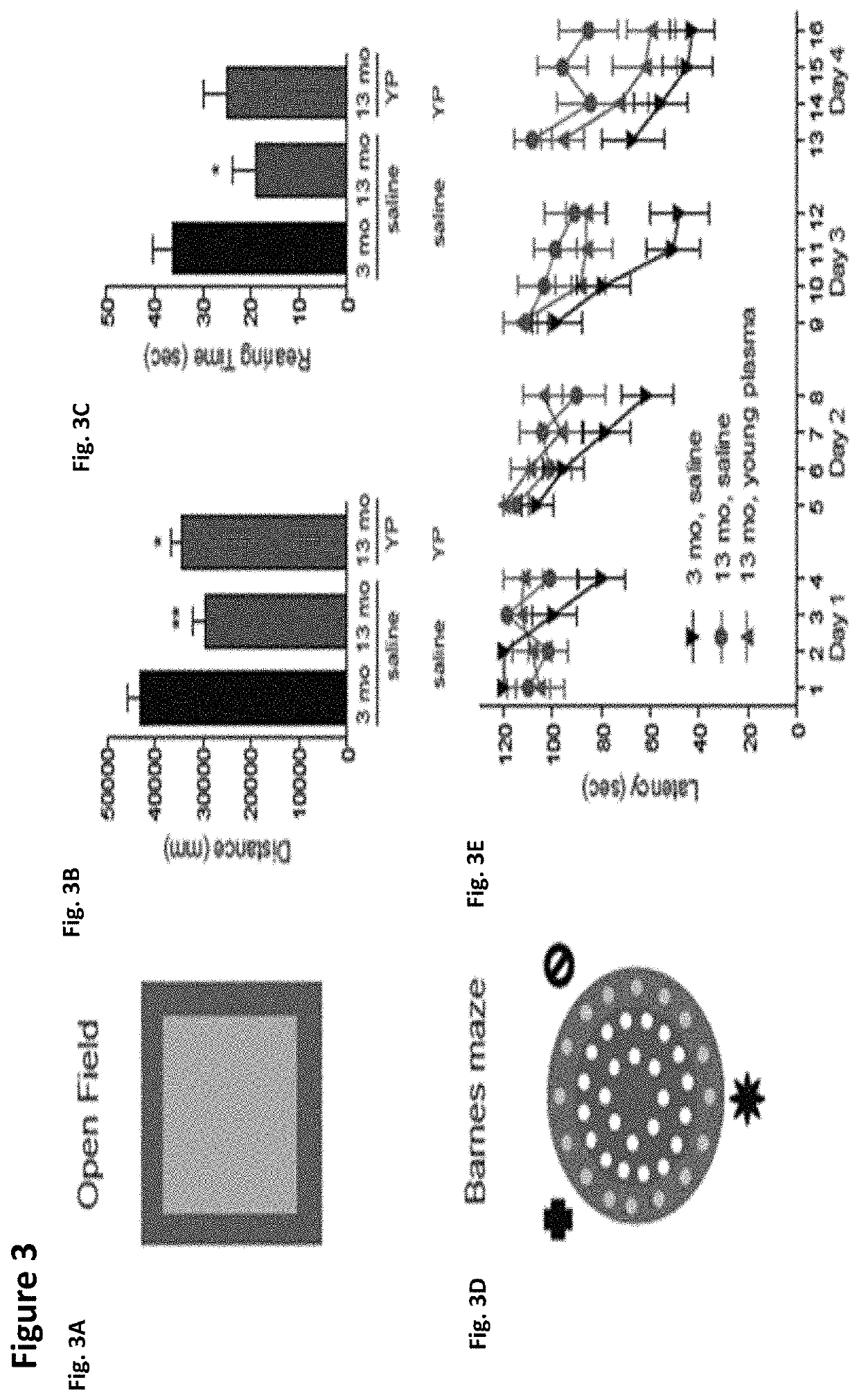
Methods and compositions are provided for screening candidate compositions for activity with respect to treatment of aging-associated conditions, e.g., cognitive impairment conditions or age-related dementia. Aspects of the methods include administering a human blood product comprising plasma, to an immunocompromised animal, e.g., a mouse or a rat, and measuring the effect of the product on an endpoint, e.g., neurogenesis, locomotor activity, anxiety, spatial memory, and hippocampus-dependent memory.
Owner:ALKAHEST INC +2
Systems and methods for backward-compatible constant-time exception-protection memory
Embodiments of the invention provide a table-free technique for detecting all temporal and spatial memory access errors in programs supporting general pointers. Embodiments of the invention provide such error checking using constant-time operations. Embodiments of the invention rely on fat pointers, whose size is contained within standard scalar sizes (up to two words) so that atomic hardware support for operations upon the pointers is obtained along with meaningful casts in-between pointers and other scalars. Optimized compilation of code becomes possible since the scalarized-for-free encoded pointers get register allocated and manipulated. Backward compatibility is enabled by the scalar pointer sizes, with automatic support provided for encoding and decoding of fat pointers in place for interaction with unprotected code.
Owner:IBM CORP
Methods, apparatus and data structures for providing a user interface to objects, the user interface exploiting spatial memory and visually indicating at least one object parameter
A graphical user interface in which object thumbnails are rendered in a three-dimensional environment and which exploits spatial memory. The objects may be moved, continuously, with a two-dimensional input device. Pop-up title bars may be rendered over active objects. Intelligent help may be provided to the user, as visual indicators, based on proximity clustering or based on matching algorithms. The simulated location of the object thumbnails in a direction orthogonal to the surface is based on function, such as a linear, polynomial, or exponential function for example, of one or more object properties, such as number of mouse clicks since selected, age, size, etc.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
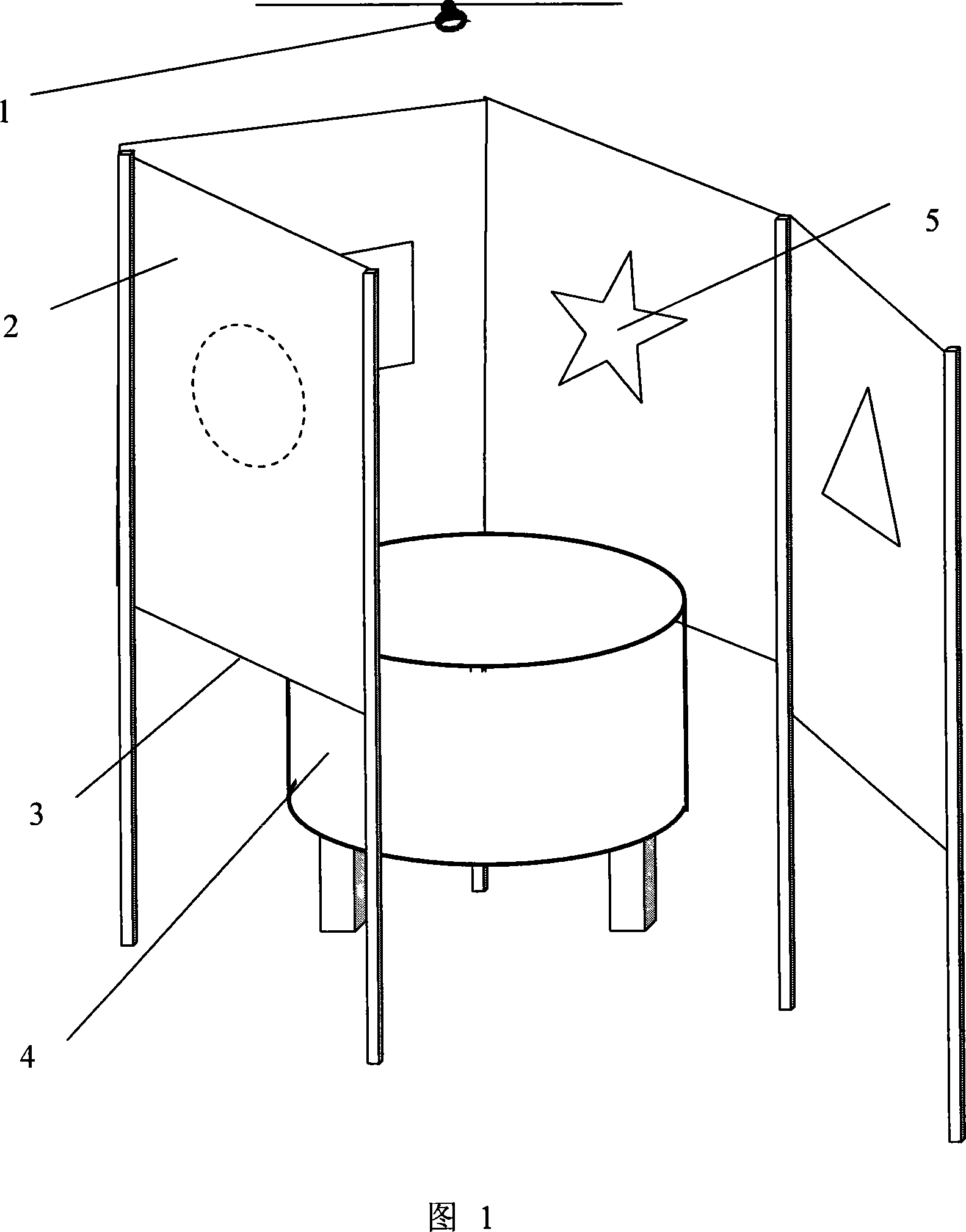
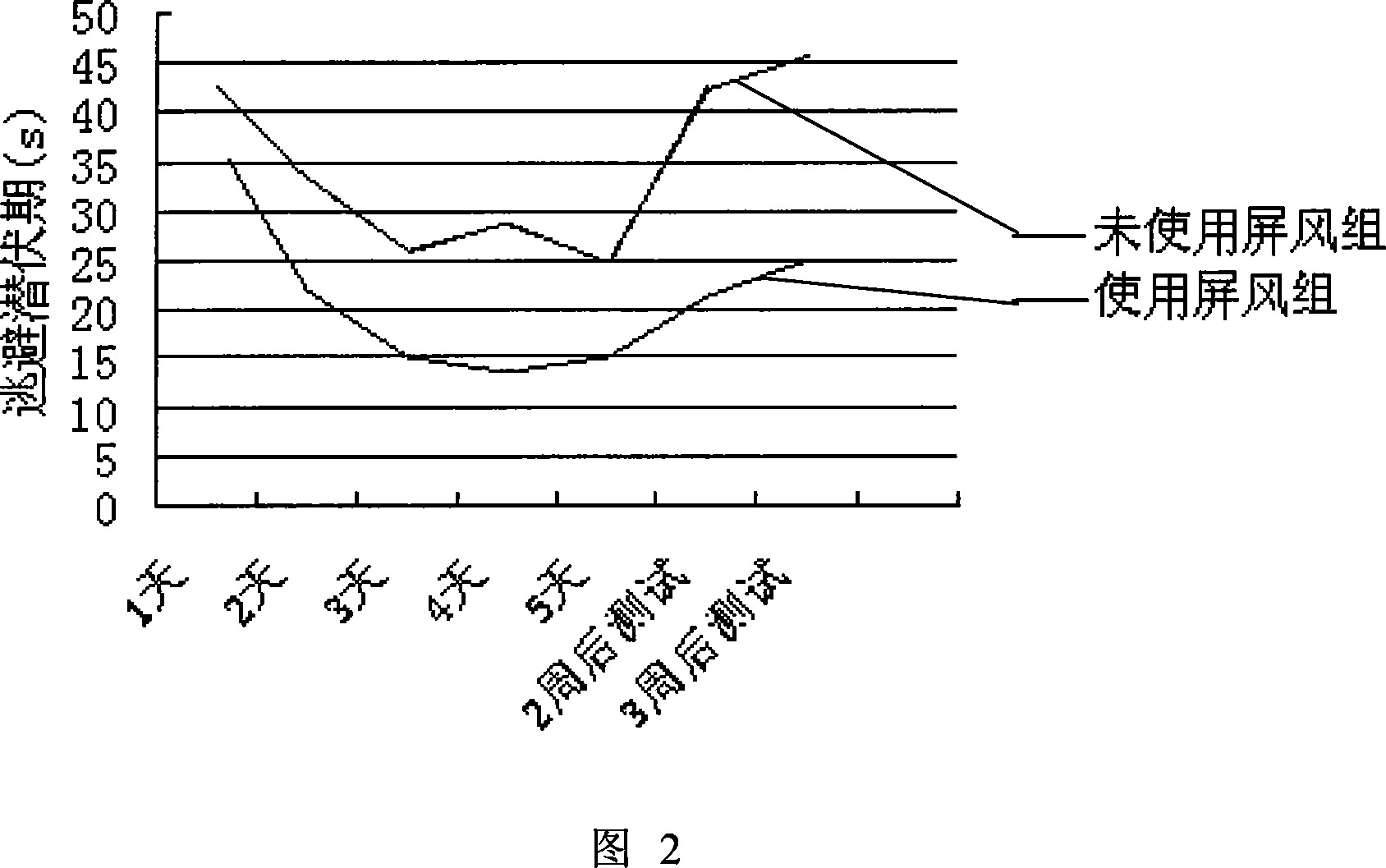
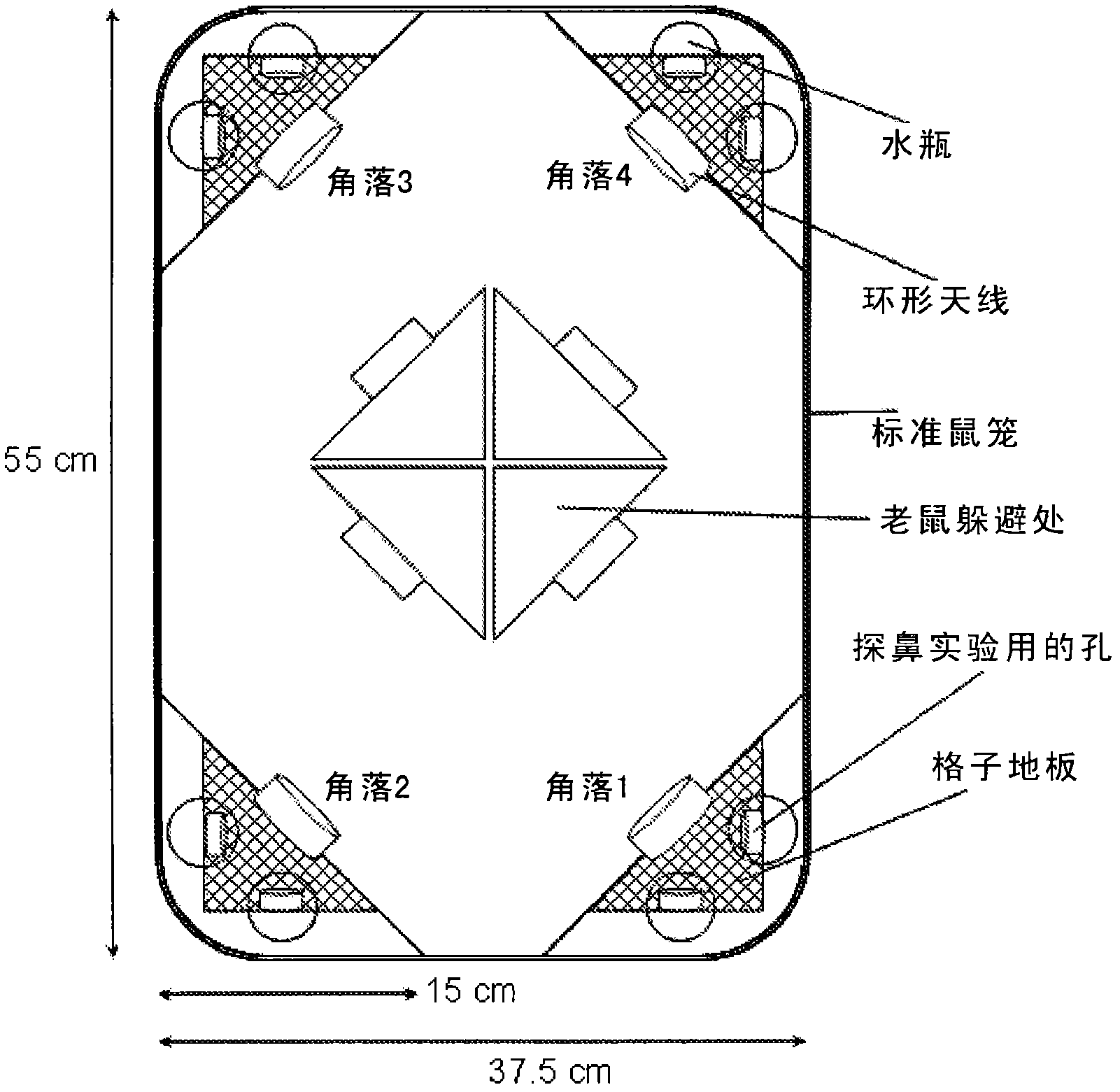
Method and device for reinforcing spatial memory of water maze laboratory animal
InactiveCN101142900AImprove spatial memorySpatial memory enhancementTaming and training devicesWater mazeComputerized system
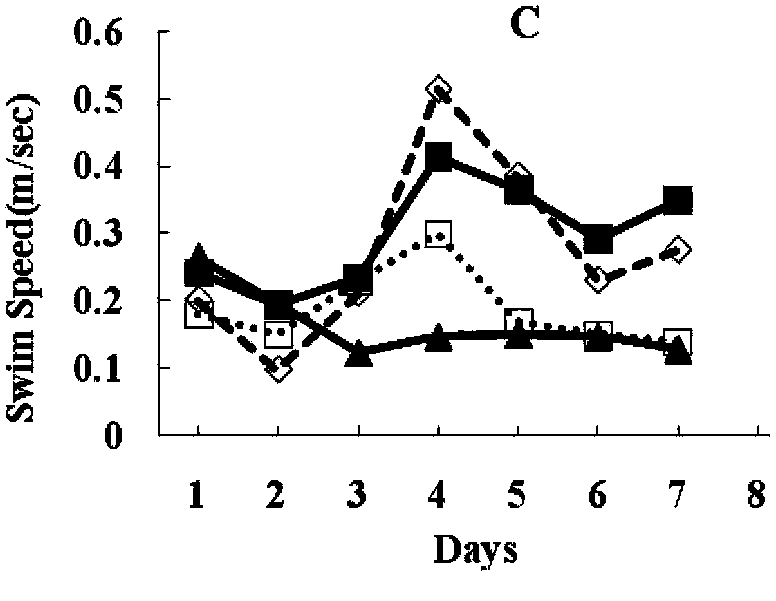
The invention provides a method and a device for enhancing spatial memory of water maze test animal. The method comprises a water tank for animal swimming and a platform arranged in the water, a camera and a computer system. The invention is characterized in that the method also comprises a visual reference system; the visual reference system arranges a septum above the surrounding of the water tank to isolate interference from outside; the visual reference system also arranges a plurality of fixed pictures on the internal side of the septum as memory reference of the animal and the fixed picture is contrast with the color of the septum. By building the water maze standard visual reference system, the invention ensures that the test animal can avoid interference from outside in the process of swimming, meanwhile, when the test animal swims in the water tank, the fixed picture in the system as the visual reference of the animal is good for enhancing spatial memory ability of the animal and reducing system error of a plurality of repeated tests. The test result shows that the invention can significantly enhance spatial memory of a rat in the water maze test and ensures that the spatial memory can maintain a longer time.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Application of gastrodin to preparing medicaments for preventing and treating Alzheimer's disease
InactiveCN103385884AReduce inflammationImprove toleranceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseAmyloid
The invention discloses an application of gastrodin to preparing medicaments for preventing and treating Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease, and pathological characteristics comprise neuro fibrillary tangles formed in cells, hyperplasia of reactive microglia and glial cell, and the like, wherein the extracellular deposition of amyloid A beta is the main pathogenetic reason of AD. An AD small mouse taking a gastrodin-containing fodder is substantially improved in spatial-memory learning ability, substantially reduced in A beta level in brain and serum, and substantially reduced in amyloid plaques and microglia in brain tissue, and thus it is indicated that gastrodin is capable of preventing A beta deposition and decreasing active components causing AD mouse brain gastrodin.
Owner:KUNMING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Systems and methods for displaying linked information in a sorted context
InactiveUS7562085B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsInformation repositoryLogical operations
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Malicious application processing method and apparatus, and terminal
ActiveCN105718788ASave space memoryEfficiencyPlatform integrity maintainanceSoftware engineeringComputer terminal
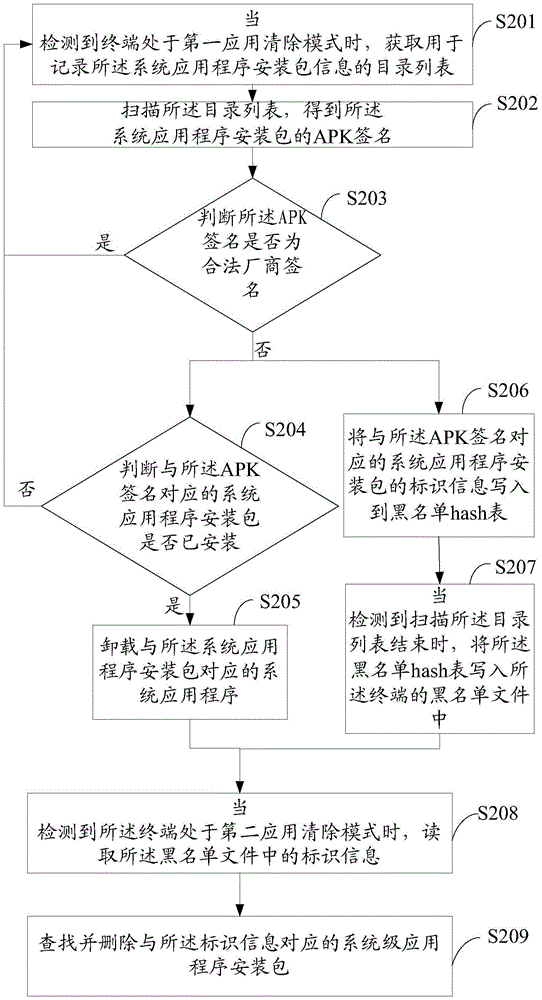
Embodiments of the present invention provide a malicious application processing method and apparatus, and a terminal. The method comprises: when it is detected that a terminal is in a first application erasure mode, acquiring an APK signature of a system application installation package; if it is determined that the APK signature is an illegal manufacturer signature, loading identification information of the system application installation package corresponding to the APK signature into a blacklist file of the terminal; and when it is detected that the terminal is in a second application erasure mode, searching for and erasing the system application installation package corresponding to the identification information in the blacklist file. With adoption of the technical scheme provided by the present invention, spatial memory of the terminal can be saved, and efficiency of erasing malicious applications is improved.
Owner:YULONG COMPUTER TELECOMM SCI (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Real-time virtual machine memory scheduling method and device
InactiveCN106776048AAvoid wastingRelieve memory pressureResource allocationSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationStressed stateHost memory
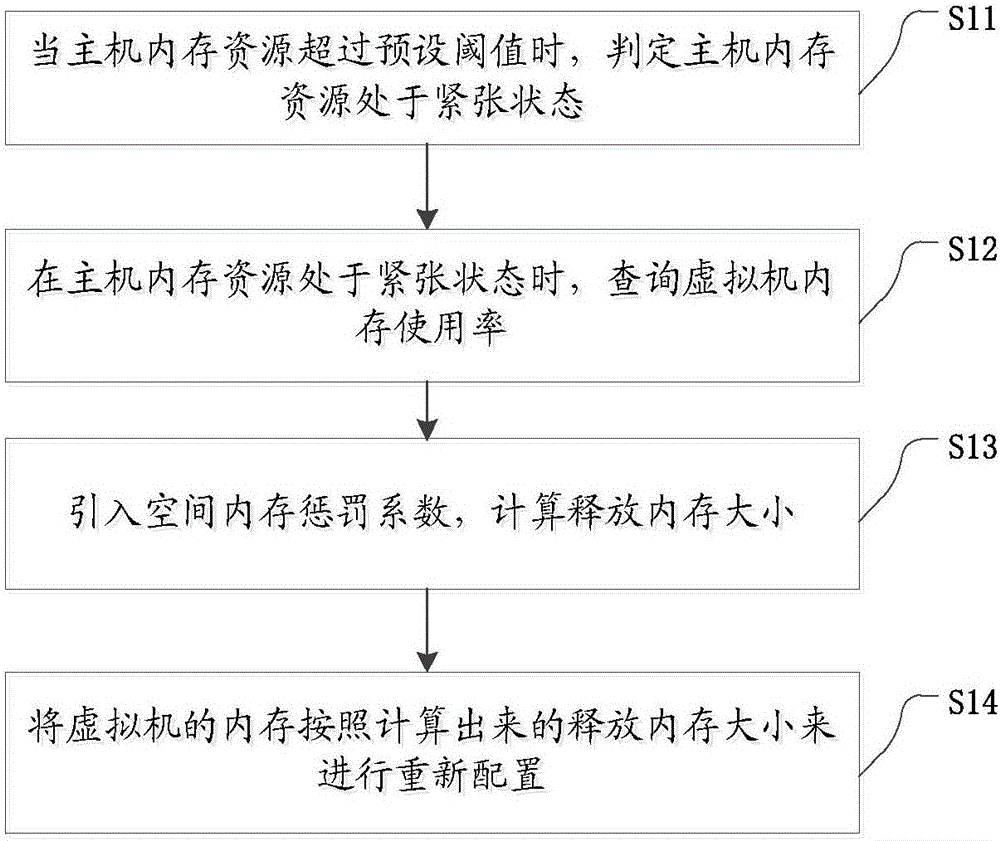
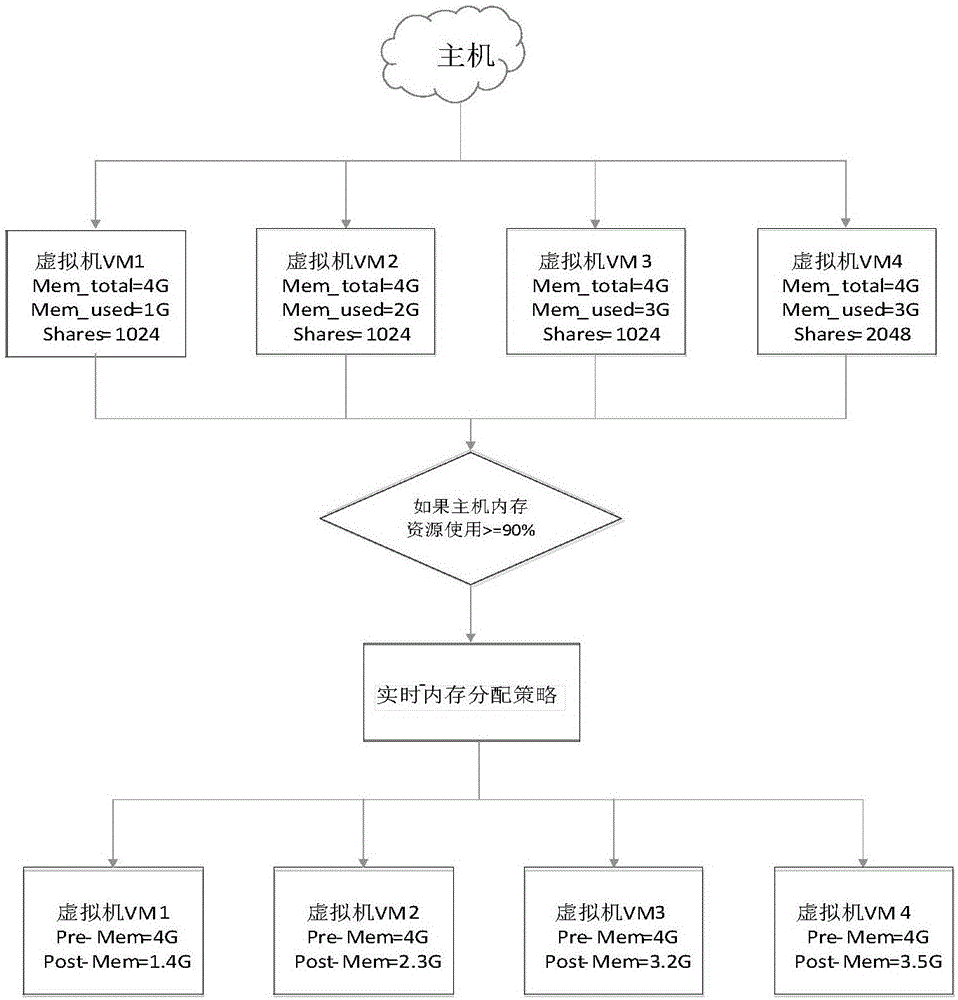
The invention discloses a real-time virtual machine memory scheduling method and device. The memory scheduling method comprises the steps that when the memory resource of a mainframe exceeds the preset threshold value, the memory resource of the mainframe is determined to be in a stressed state; when the memory resource of the mainframe is in a stressed state, the memory usage rate of a virtual machine is queried; the spatial memory punishment coefficient is introduced, the size of the released memory is calculated; the memory of the virtual machine is reallocated according to the calculated size of the released memory. According to the memory scheduling method, the optimization of memory allocation is achieved, and wastes of memory resources are avoided.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
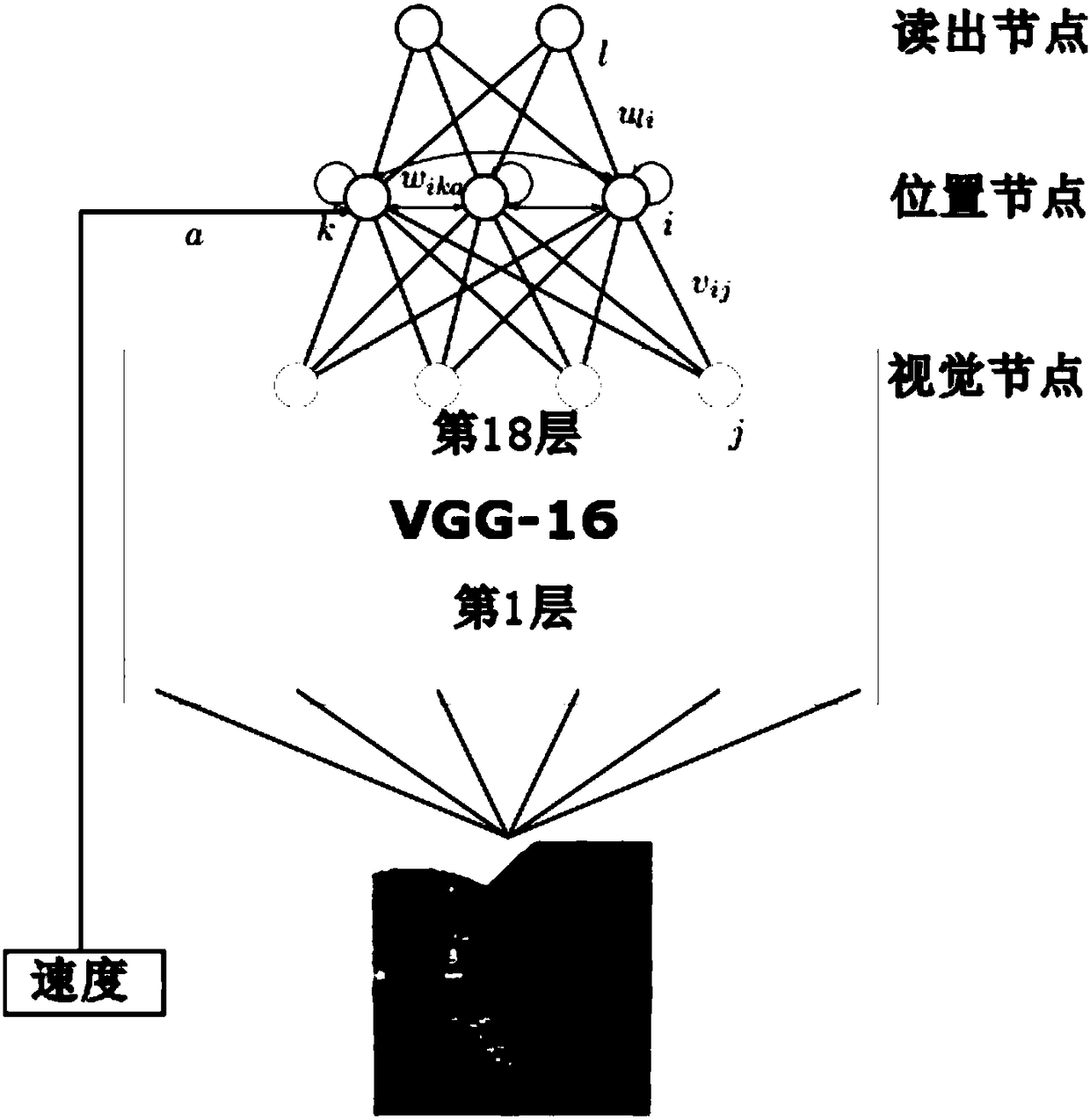
Robot navigation method based on visual perception and spatial cognitive neural mechanism
ActiveCN109240279AImprove biomimicryStrong bionicPosition/course control in two dimensionsSimultaneous localization and mappingNODAL
The invention relates to a robot navigation method based on visual perception and a spatial cognitive neural mechanism. The collected visual images are transformed into visual nodes representing position and orientation angle information of the robot through a neural network to form a visual cell; a visual code of the visual cell is transformed into a spatial description of the environment, and acognitive map, similar to what is formed in the brain when the mammal freely moves, is constructed; and positioning and navigation of the robot are realized based on the cognitive map. According to aneural computation system of environment perception and spatial memory, the robot completes a series of tasks such as visual processing, spatial representation, self-positioning, and map update, thereby realizing robotic navigation with high bionics and strong autonomy in an unknown environment. Compared with the traditional simultaneous localization and mapping SLAM technology, the robot navigation method based on visual perception and the spatial cognitive neural mechanism in the invention avoid a series of complex calculations such as manual design visual features and feature point matchingand greatly improve the robustness of the system to factors such as illumination changes, viewing angle changes, object motion and the like in the natural environment.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of compound in treatment of senile dementia by inhibiting amyloid protein accumulation
InactiveCN108309962AImprove learning and memory abilityEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderAmyloidPediatrics
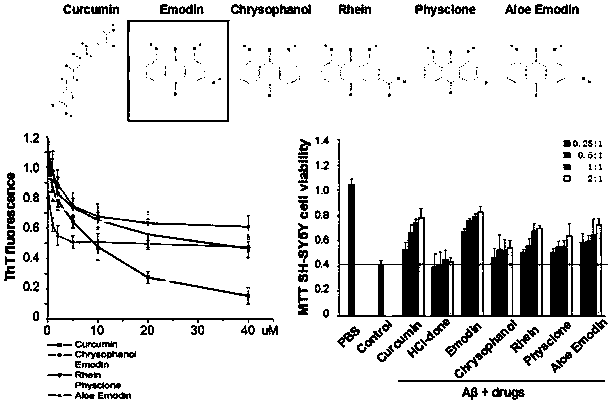
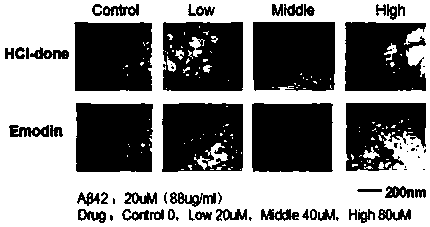
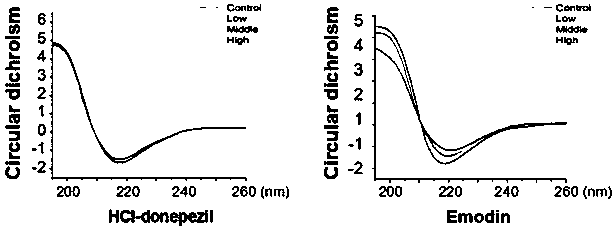
The invention discloses application of emodin in antagonizing accumulation of amyloid beta protein, improving cognitive memory ability and reducing senile plaques. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is neurodegenerative disease characterized by neurofibrillary tangles, amyloid beta (A beta) protein plaque deposition and cognitive decline, wherein A beta protein extracellular toxicity accumulation is considered to be one of the main links in the pathogenesis of AD. The emodin is found to be capable of significantly inhibiting the accumulation of A beta protein 1-42 monomers so as to prevent the monomersfrom forming fibers, and is also found to be capable of inhibiting the formation of a beta secondary structure, improving the spatial memory learning ability of AD mice and obviously clearing amyloidplaques in brain tissues of APP / PS1 double-transgenic AD model mice; therefore, the emodin can be applied to the treatment of AD and the research and development of related drugs.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
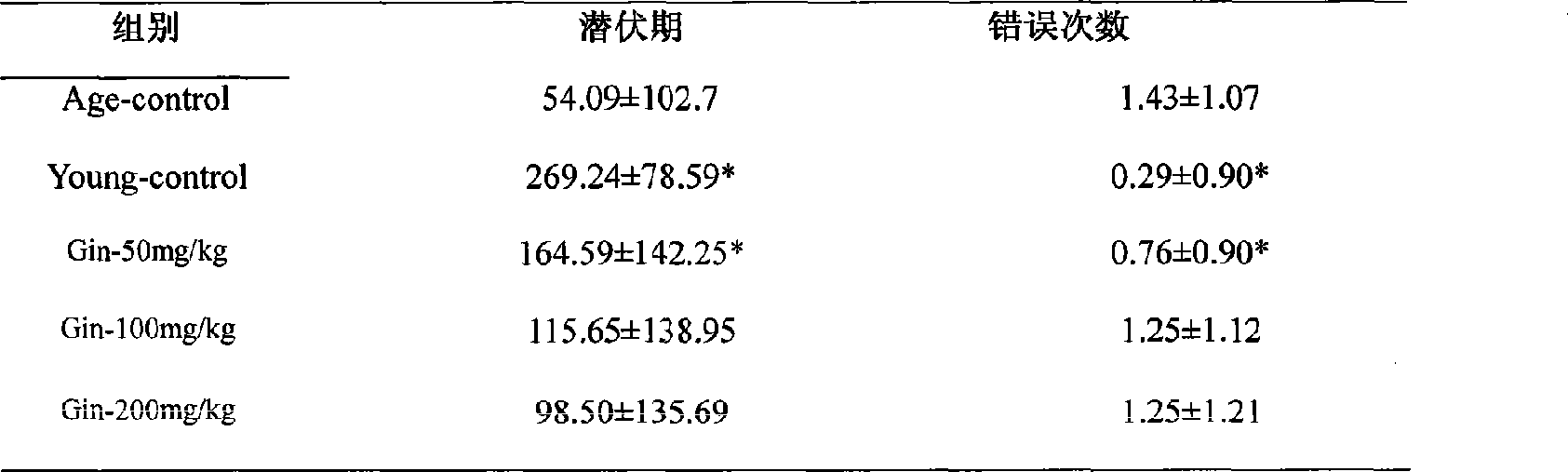
Use of ginsenoside in preparing food and medicine for preventing age associated memory impairment and Alzheimer's disease associated dysmnesia
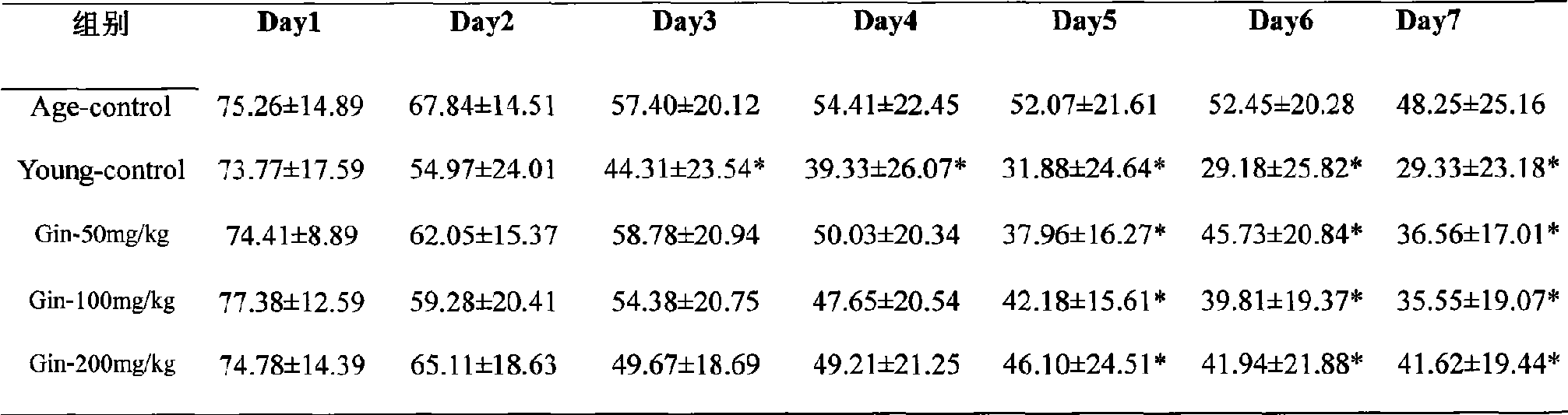
The invention relates to the use of ginsenosides in the preparation of foods and drugs for preventing age-associated memory decline and Alzheimer's disease-related memory impairment. The experiments confirm that the ginsenosides can significantly improve the passive avoidance ability, the active avoidance ability and the space memory exploration ability of mice and have the obvious function of preventing the age-associated memory decline and the Alzheimer's disease-related memory impairment by giving the ginsenosides to C57BL / 6J mice and SAMP8 mice from the animal middle-aged period to the old-aged period of the C57BL / 6J mice or the time which should occur the Alzheimer's disease-related memory impairment of the SAMP8 mice.
Owner:珍奥集团股份有限公司 +1
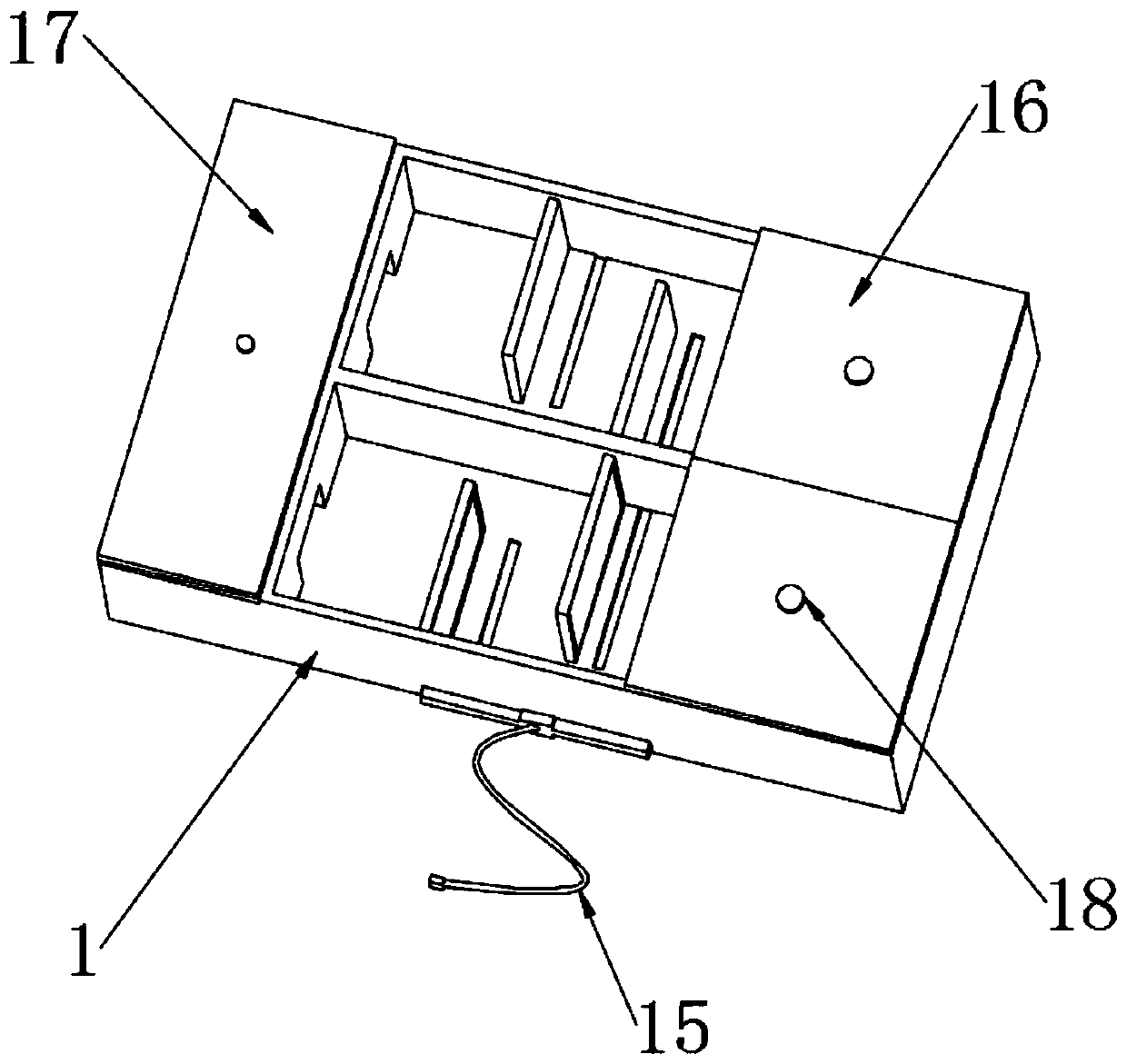
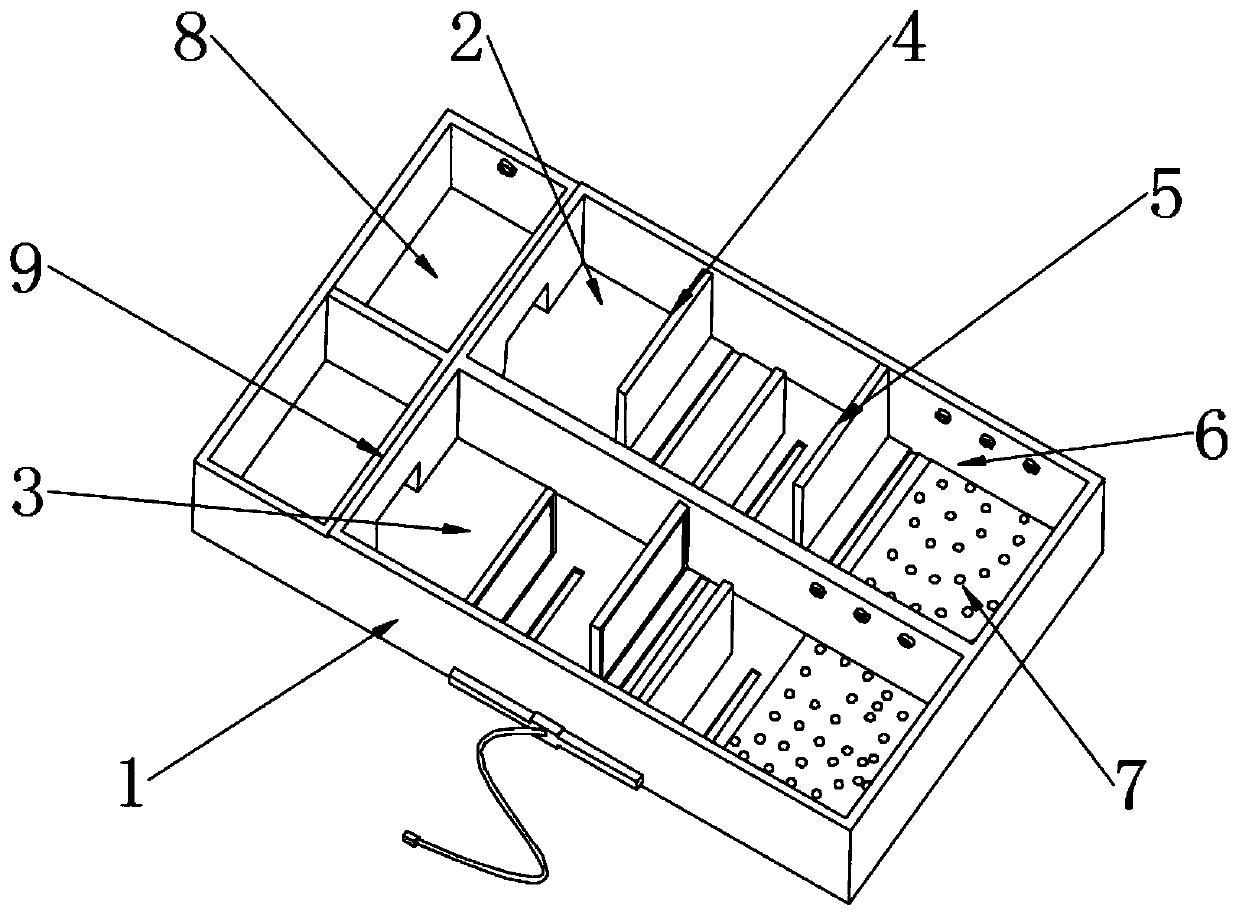
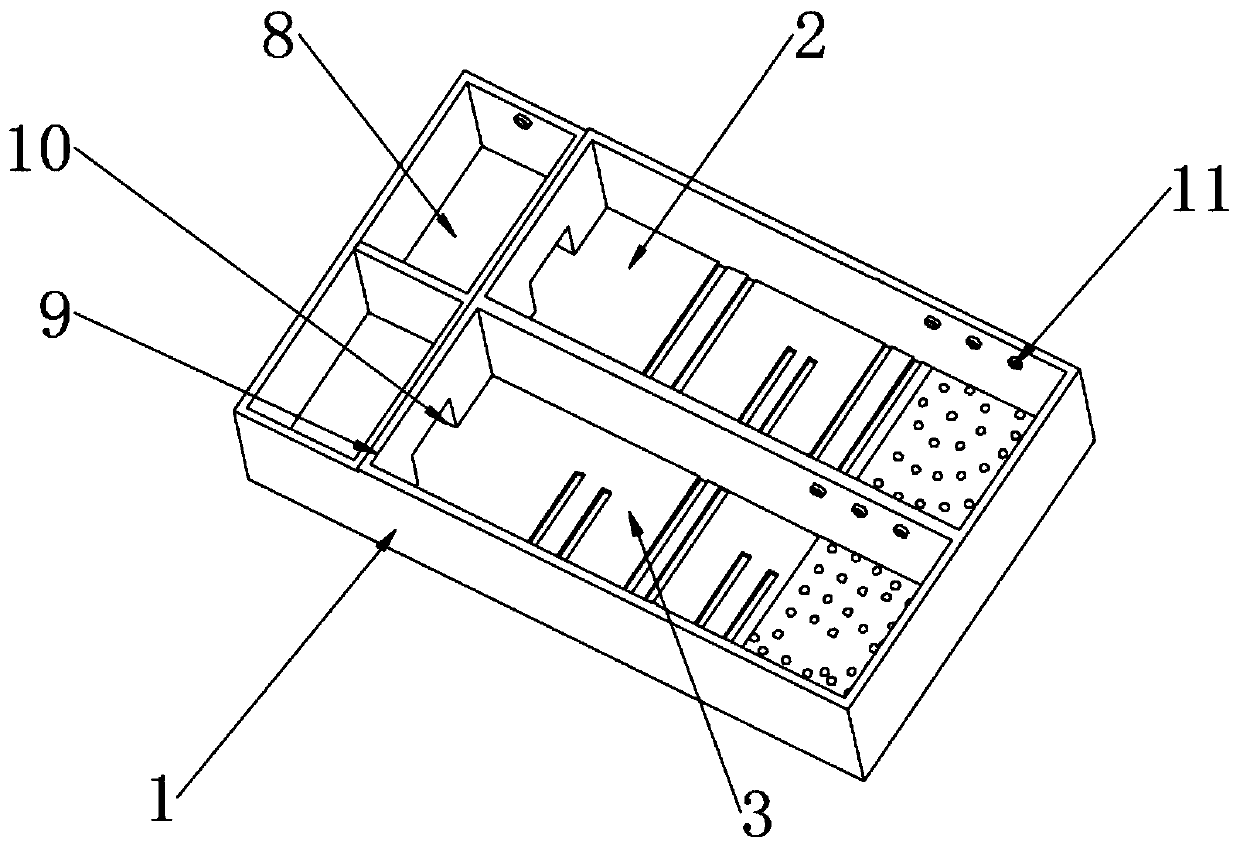
Mouse learning and memory behavior training and testing device
InactiveCN110122366AShort timeScientific and reasonable structureTaming and training devicesFood storageComputer science
The invention discloses a mouse learning and memory behavior training and testing device. The device comprises a training box, wherein the inside of the training box is divided into a first training channel and a second training channel; blocking plates are mounted at the centers inside the first training channel and the second training channel. The mouse learning and memory behavior training andtesting device is scientific and reasonable in structure and safe and convenient to use; by functions of the first training channel, the second training channel, the blocking plates, partition platesand food storage rooms, experiment mice are induced by mouse grains to move; meanwhile, the blocking plates are used for blocking to enable routes to be bent and complicated, and accordingly, the experiment mice are trained to memorize the routes, certain spatial memory is produced; heating plates are added to the blocking plate in the second training channel to stimulate the experiment mice, so that time for the experiment mice to generate memory is shorter under stimulation, LED strong lights are regularly started inside the food storage rooms, the experiment mice can generate memory on time, and operation is simple and reliable.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
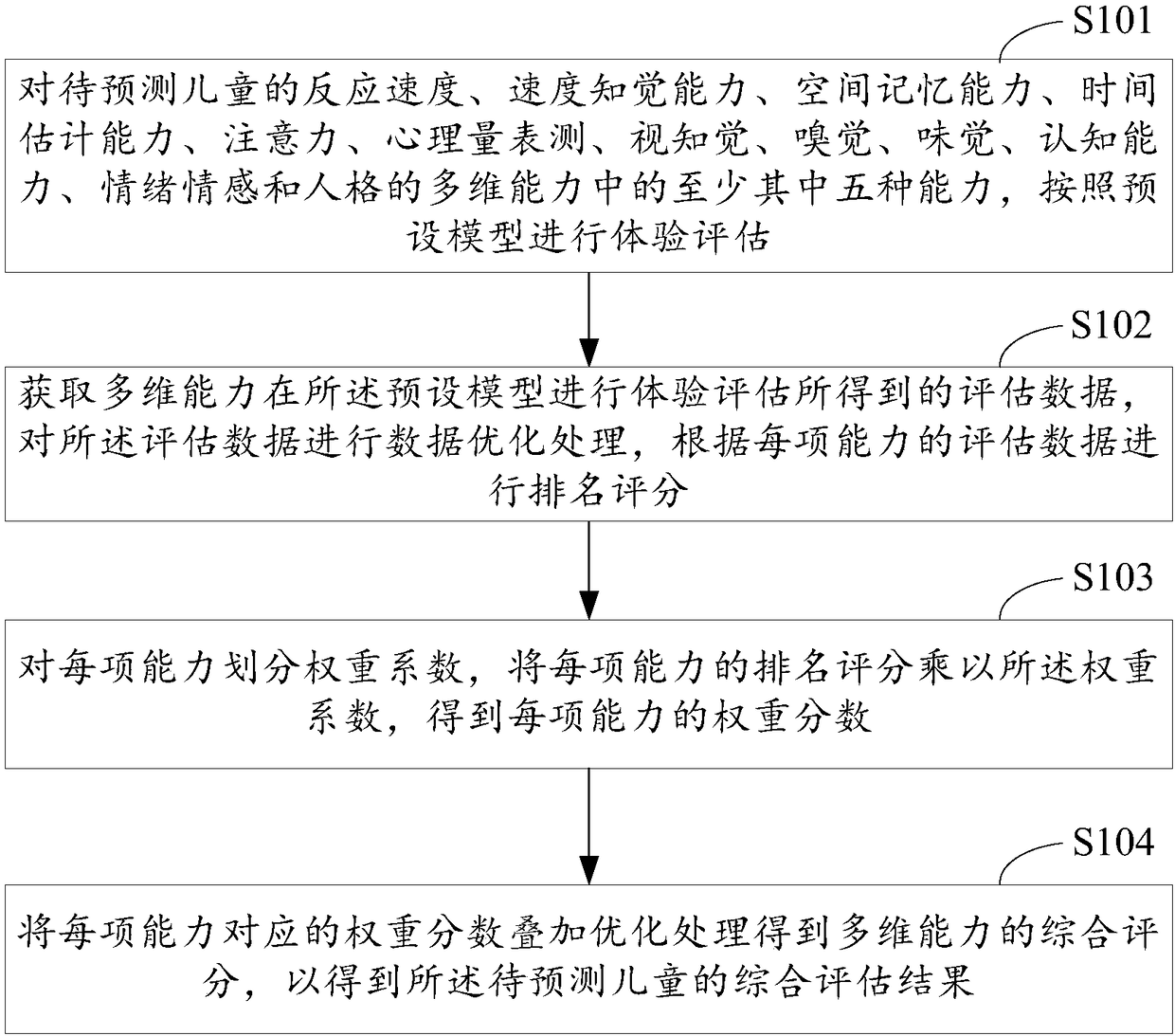
Comprehensive evaluating method and system for predicting children multi-dimensional ability
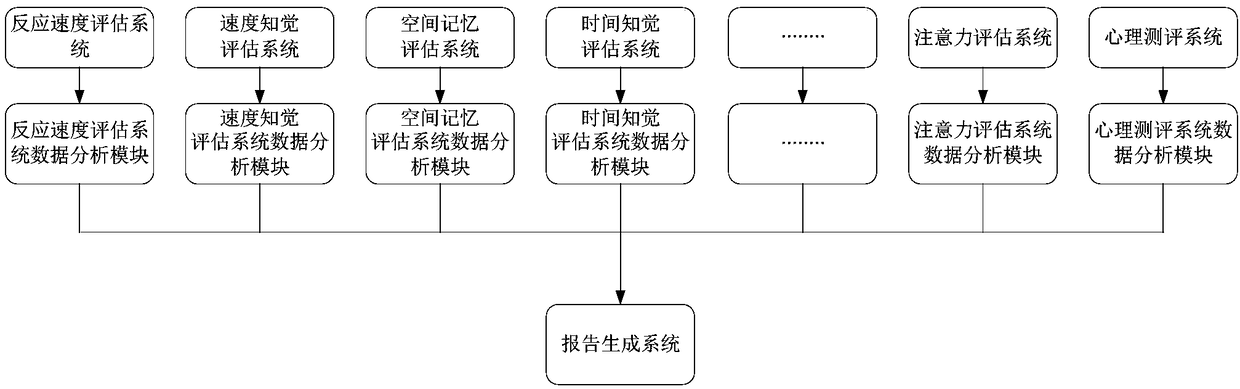
InactiveCN108256698AEasy to understandAvoiding adverse developmental conditions for childrenPhysical therapies and activitiesForecastingEvaluation resultWeight coefficient
The application relates to the technical field of intelligent evaluation, and provides a comprehensive evaluating method and a comprehensive evaluating system for predicting children multi-dimensionalability. The method includes steps of carrying out experience evaluation on a multi-dimensional ability of a child to be predicted according to a preset model, and acquiring the evaluation data of the multi-dimensional ability acquired by performing experience evaluation on the preset model, performing data optimal treatment on the evaluation data and carrying out rank scoring; multiplying the rank score of every ability by the weight coefficient to obtain the weight percent of every ability; performing superposition optimizing treatment on the weight percent corresponding to every ability toobtain the comprehensive score of the multi-dimensional ability and obtain the comprehensive evaluation result of the child to be predicted. The application can evaluate multiple cognitive competences of the child, such as reaction speed, speed awareness ability and space memory ability; a user can conveniently and uniformly learn about advantages and shortcomings of the child, so as to carry outdirective training and cultivation on the child and avoid some adverse situations to children's growth.
Owner:SUZHOU ZHONGKE ADVANCED TECH RES INST CO LTD +1
Cognitive map construction method based on space and motion joint coding
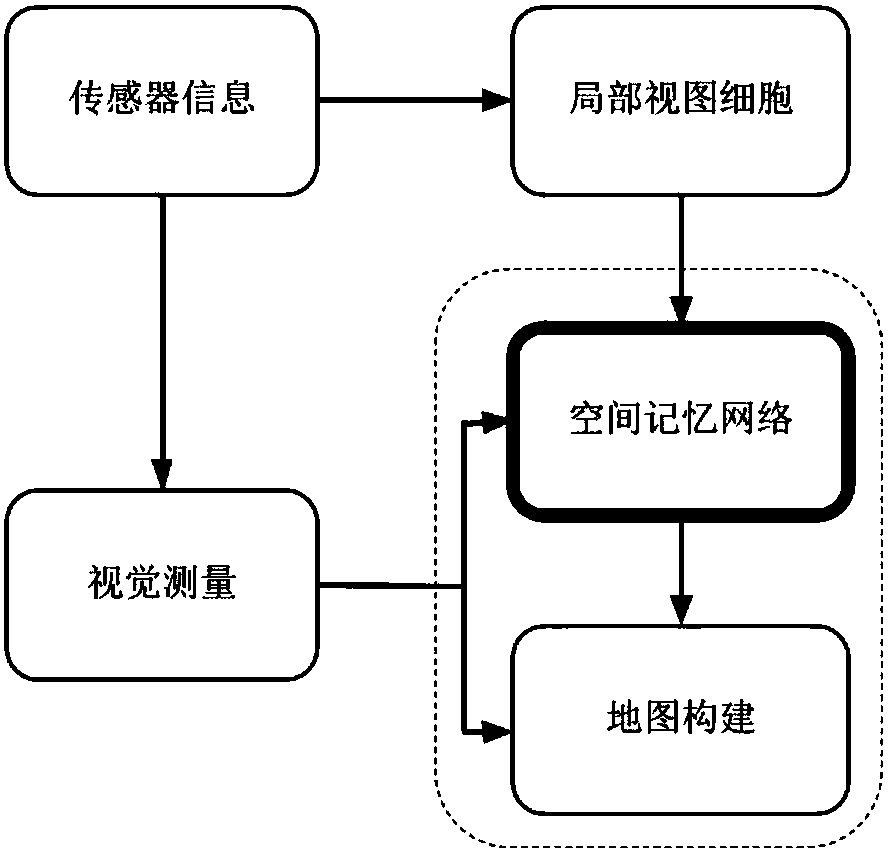
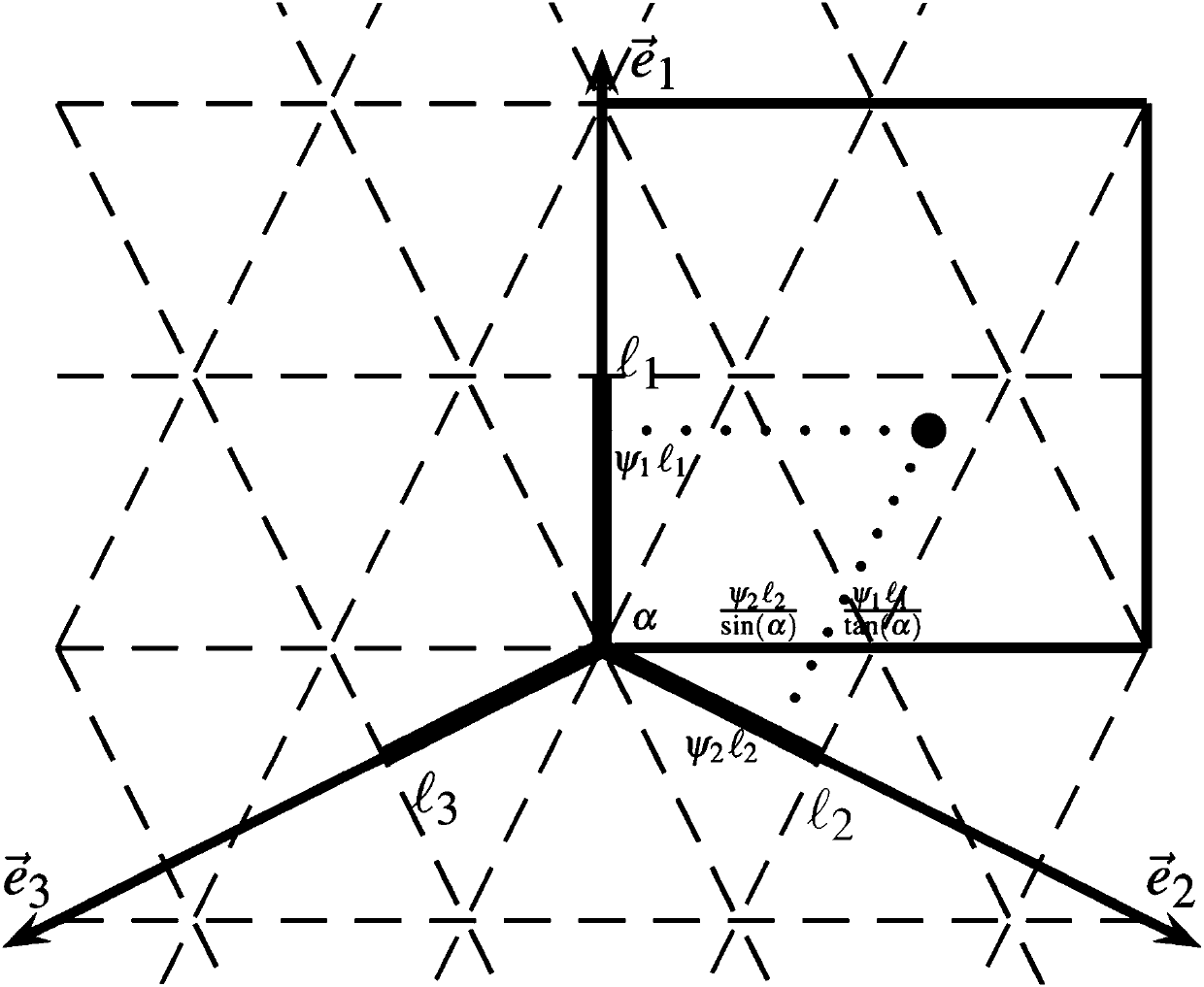
ActiveCN110019582AStable codingHigh biological fidelityBiological neural network modelsGeographical information databasesVisual perceptionPositioning system
The invention relates to a cognitive map construction method based on space and motion joint coding, and belongs to the technical field of robot navigation. A sniffing layer-hippocampus neural circuitin an internal positioning system of the brain of a mammal is considered; a continuous attractor neural network model-spatial memory network is formed by utilizing spatial navigation coding characteristics of position cells, head orientation cells, grid cells and velocity cells, space and motion characteristics of animals are coded at the same time, and path integration is carried out on angularvelocity and linear velocity. In the network, the asymmetric connection weights among the neurons generate system inherent activity peaks capable of spontaneously moving, once speed input exists, theattractor network can steadily integrate the linear speed and the angular speed, and stable robot head direction and position coding is formed. And local view cells are formed through single-camera visual input, so that the accumulative error of path integration can be corrected. According to the invention, a consistent half-meter topological map can be stably constructed by using a single camera.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF AUTOMATION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of cornflower-3-O-galactoside in preparing foods or medicaments for improving cognitive functions of old people
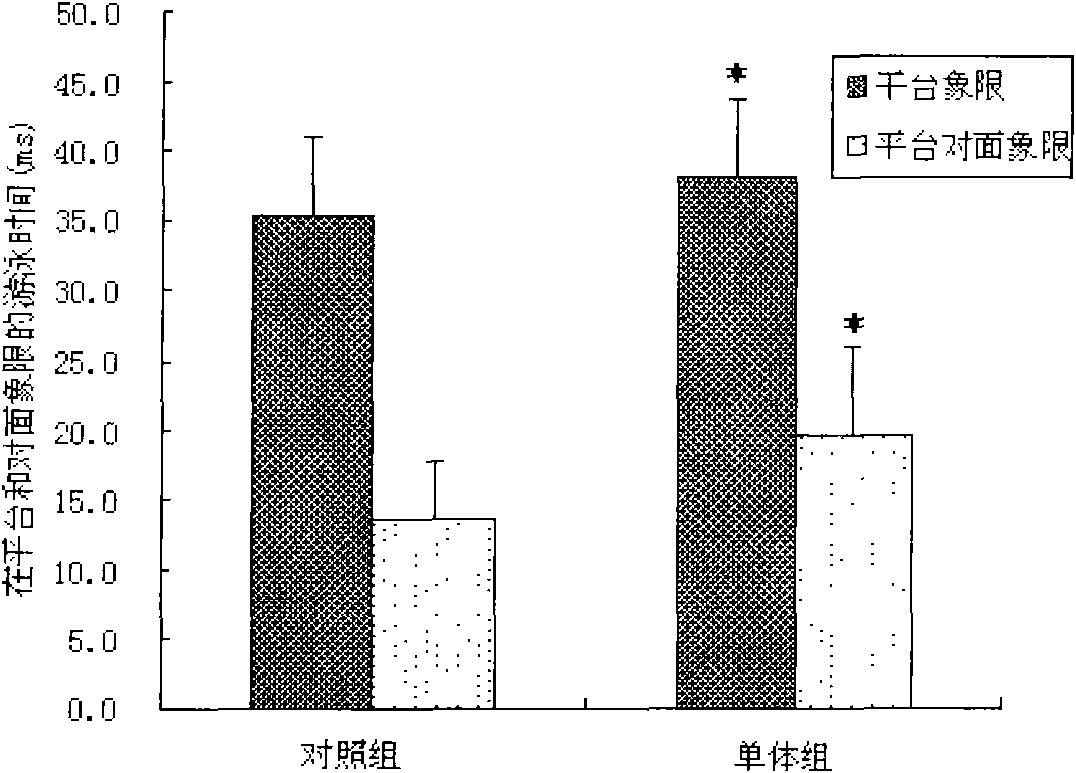
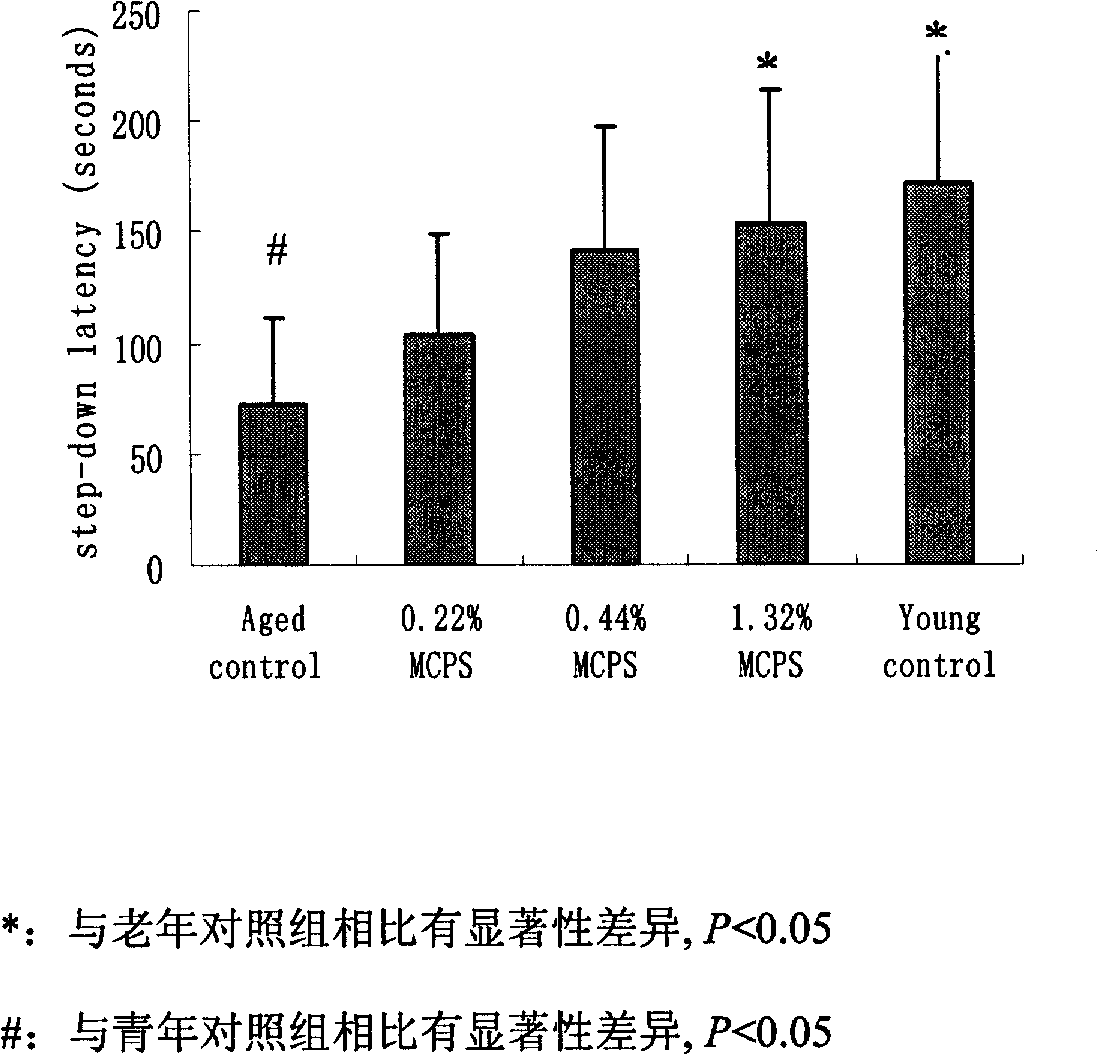
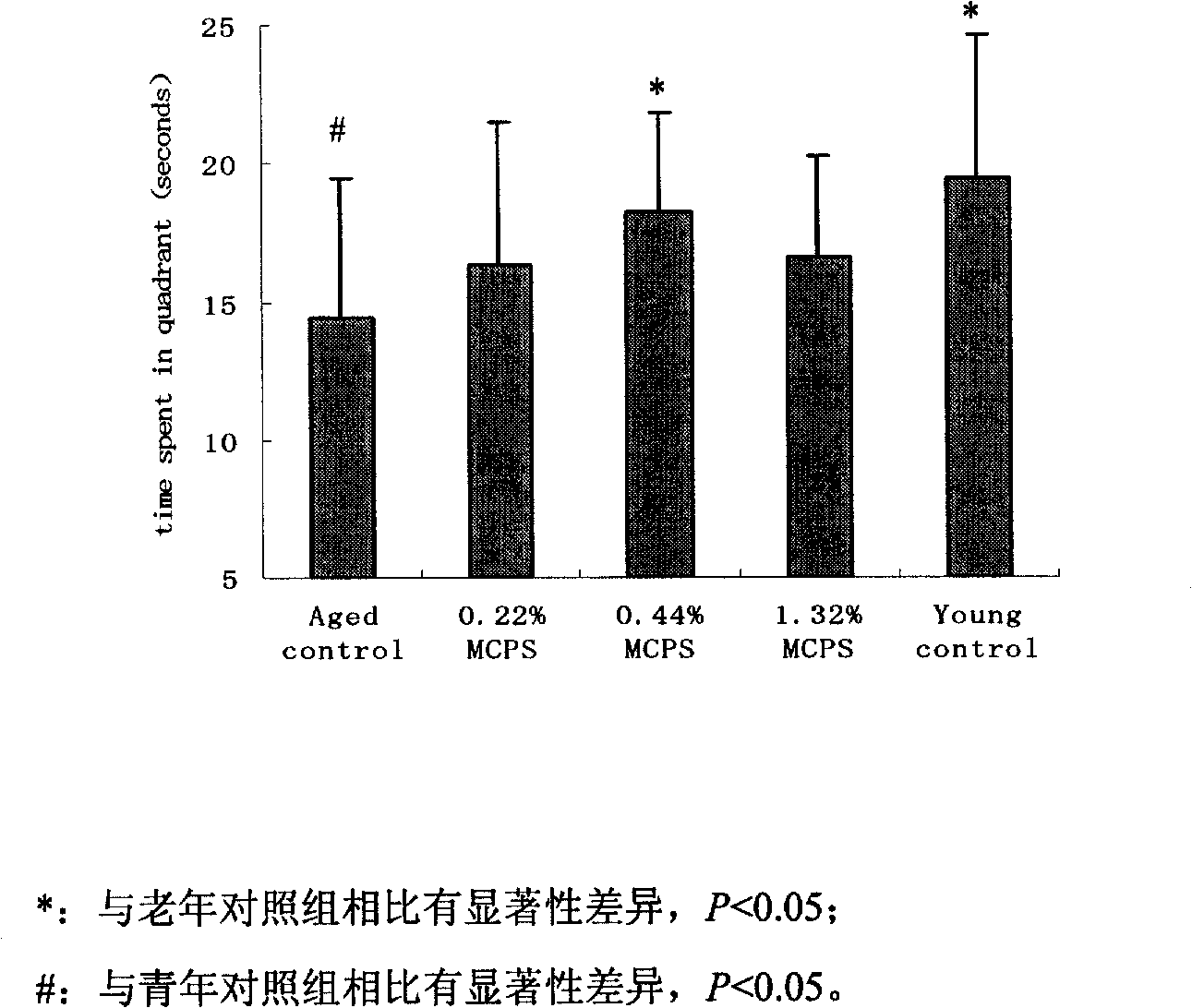
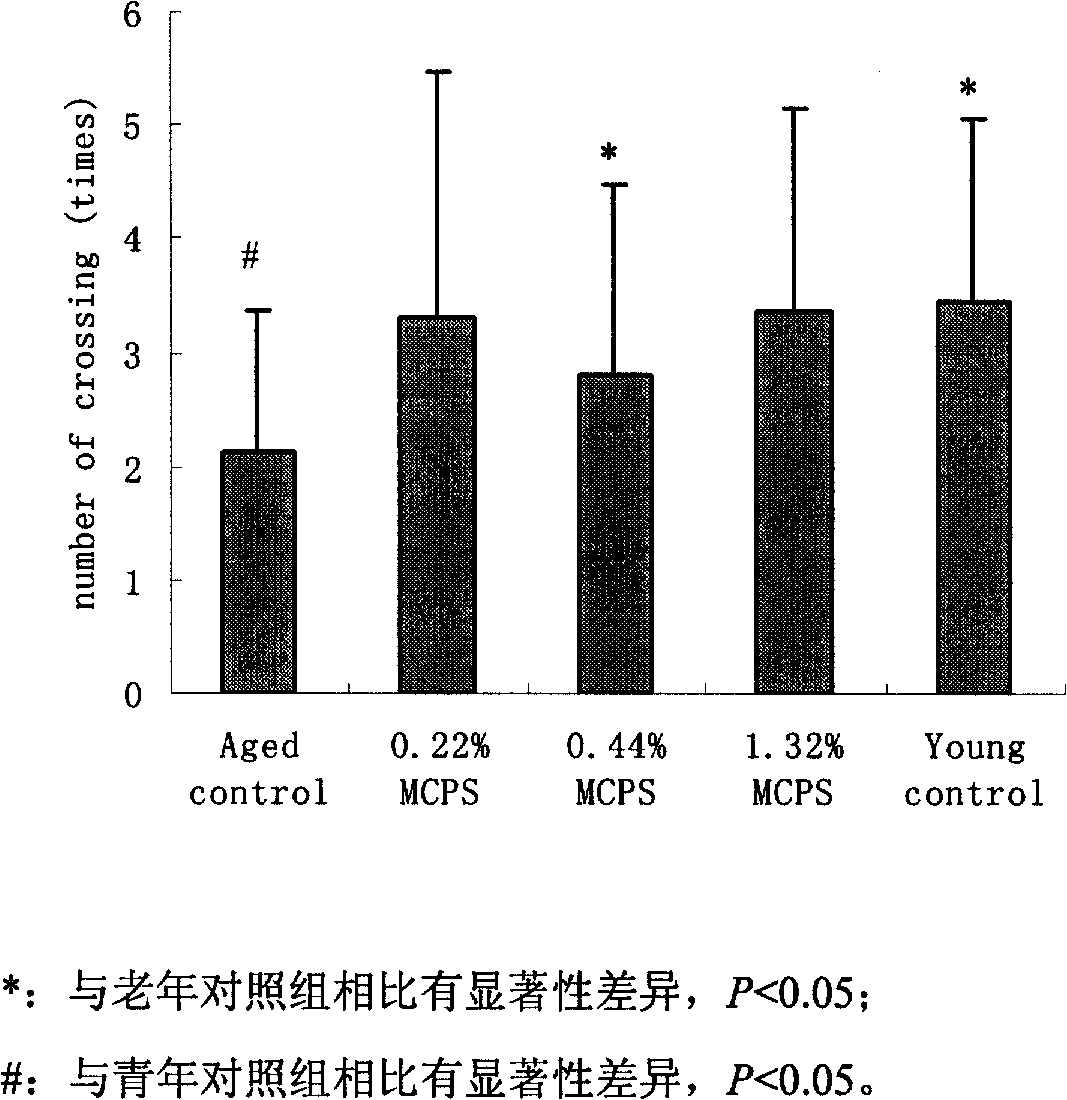
InactiveCN101669637ADark avoidance latency extendedExtended Quadrant DurationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderApoptosisNerve cells
The invention discloses an application of cornflower-3-O-galactoside in preparing foods or medicines for improving cognitive functions of old people. Results from animal experiments show that: compared with a control group (mice are fed with distilled water), the step-through latencies of animals fed with the cornflower-3-O-galactoside are all evidently prolonged; the escape latencies of mice in Morris water maze are evidently shortened; the duration time on a platform quadrant is evidently prolonged, and times of crossing the platform are evidently increased. The hint shows that the spatial memory ability of the old-aged mice compensated with the cornflower-3-O-galactoside can be evidently improved. Compared with an H2O2 model group, the LDH activity of hippocampal nerve cell supernate inthe group fed with the cornflower-3-O-galactoside evidently decreases and the nerve cells apoptosis rate evidently decreases. The hint shows that the cornflower-3-O-galactoside can evidently suppressthe hippocampal nerve cell apoptosis induced by H2O2 and play a protection role in the hippocampal nerve cells damaged by H2O2.
Owner:INST OF HYGIENE & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE PLA ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL
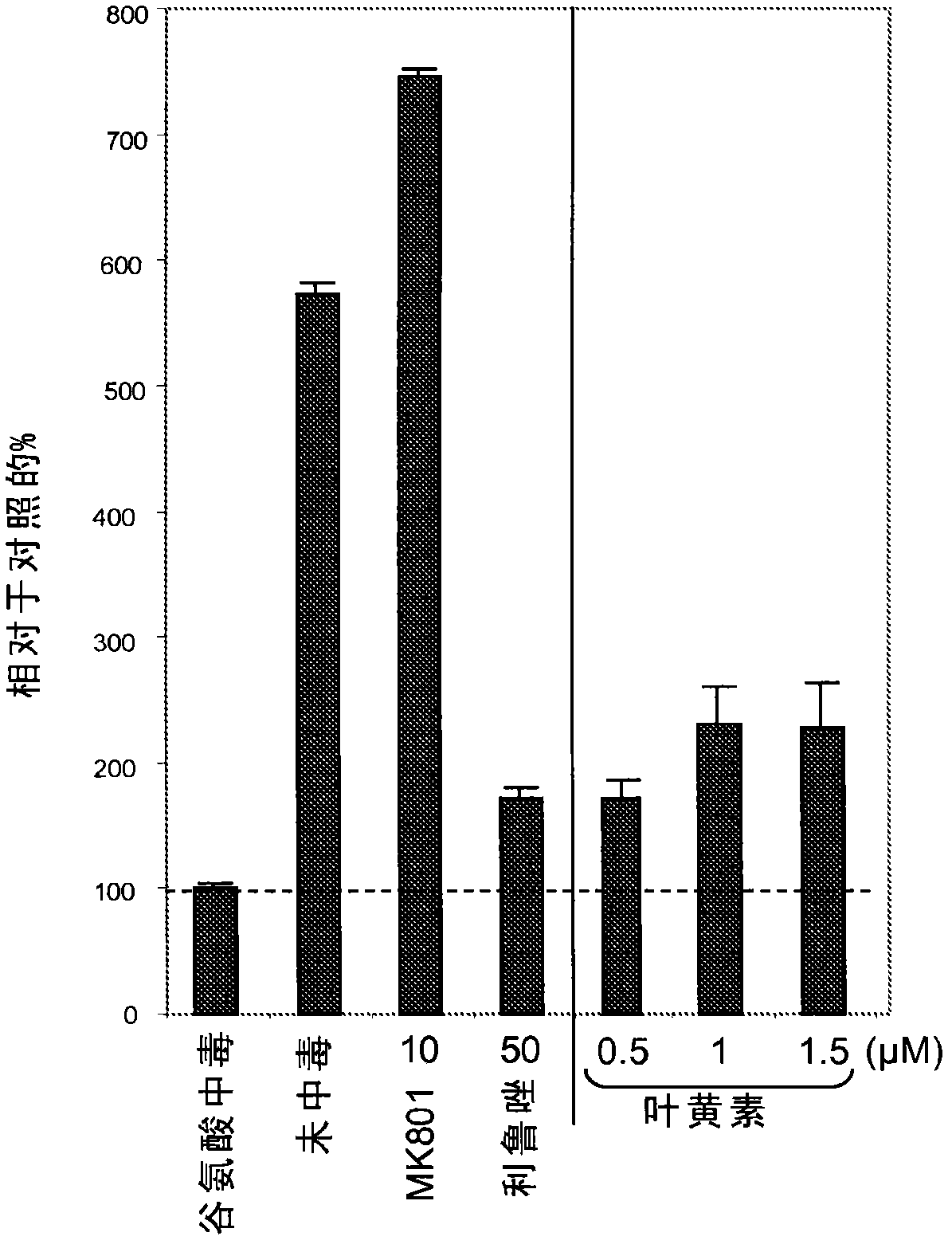
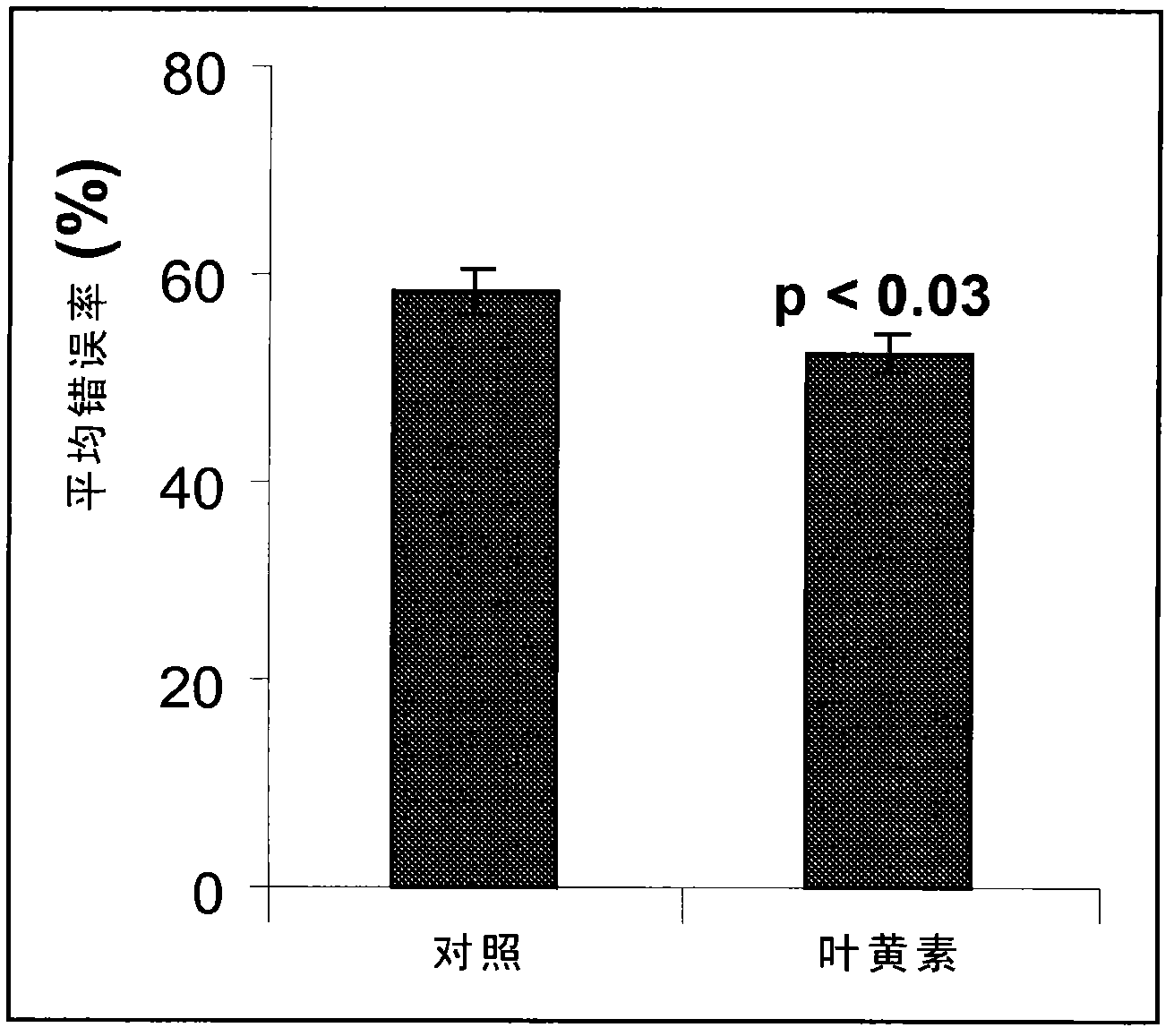
Use of lutein containing compositions to improve certain aspects of memory
InactiveCN102612364AEnhance memoryNervous disorderHydroxy compound active ingredientsZeaxanthinComputer science
This invention relates to a method of enhancing an aspect of memory in a healthy individual, wherein the aspect of memory is selected from the group consisting of: associative memory, spatial memory and memory under stress comprising: administering a composition consisting of: a) an effective amount of either lutein or the combination of lutein and zeaxanthin; and b) an appropriate carrier; and observing the enhanced associative memory, spatial memory or memory under stress.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Methods for screening human blood products comprising plasma using immunocompromised rodent models
ActiveUS10905779B2Compounds screening/testingMammal material medical ingredientsImmune compromisedNeurogenesis
Owner:ALKAHEST INC +2
Use of sea collagen peptide in preparing medicine or food capable of improving senility memory function
InactiveCN101491543AImprove old memory functionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityOligopeptide
The invention relates to a marine collagen peptide product and application of the marine collagen peptide product in preparing a medicine or food for improving senile memory. Marine collagen peptide is a group of oligopeptide mixtures with low molecular weight produced by hydrolyzing fishskins of marine fishes (salmon, tilapia, and the like). 70 to 80 percent of molecular weight of oligopeptide is distributed between 200 and 1000Da. The marine collagen peptide product has the characteristics of easy absorption, quick absorption, low viscosity, good water solubility, and the like. An experiment proves that a senile mouse is provided with the marine collagen peptide so as to can remarkably improve the abilities of passive avoidance, active avoidance and spatial memory exploration of the senile mouse, and the marine collagen peptide product has the efficacy of improving the senile memory.
Owner:珍奥集团股份有限公司 +1
Walnut peptide colon positioning mini-pills and preparation method thereof
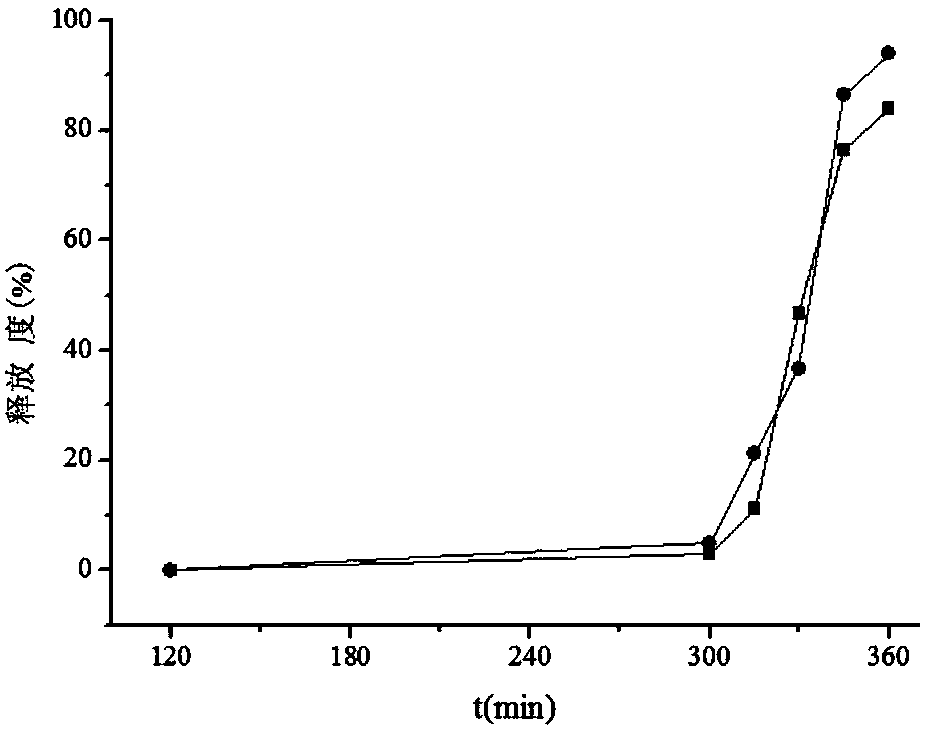
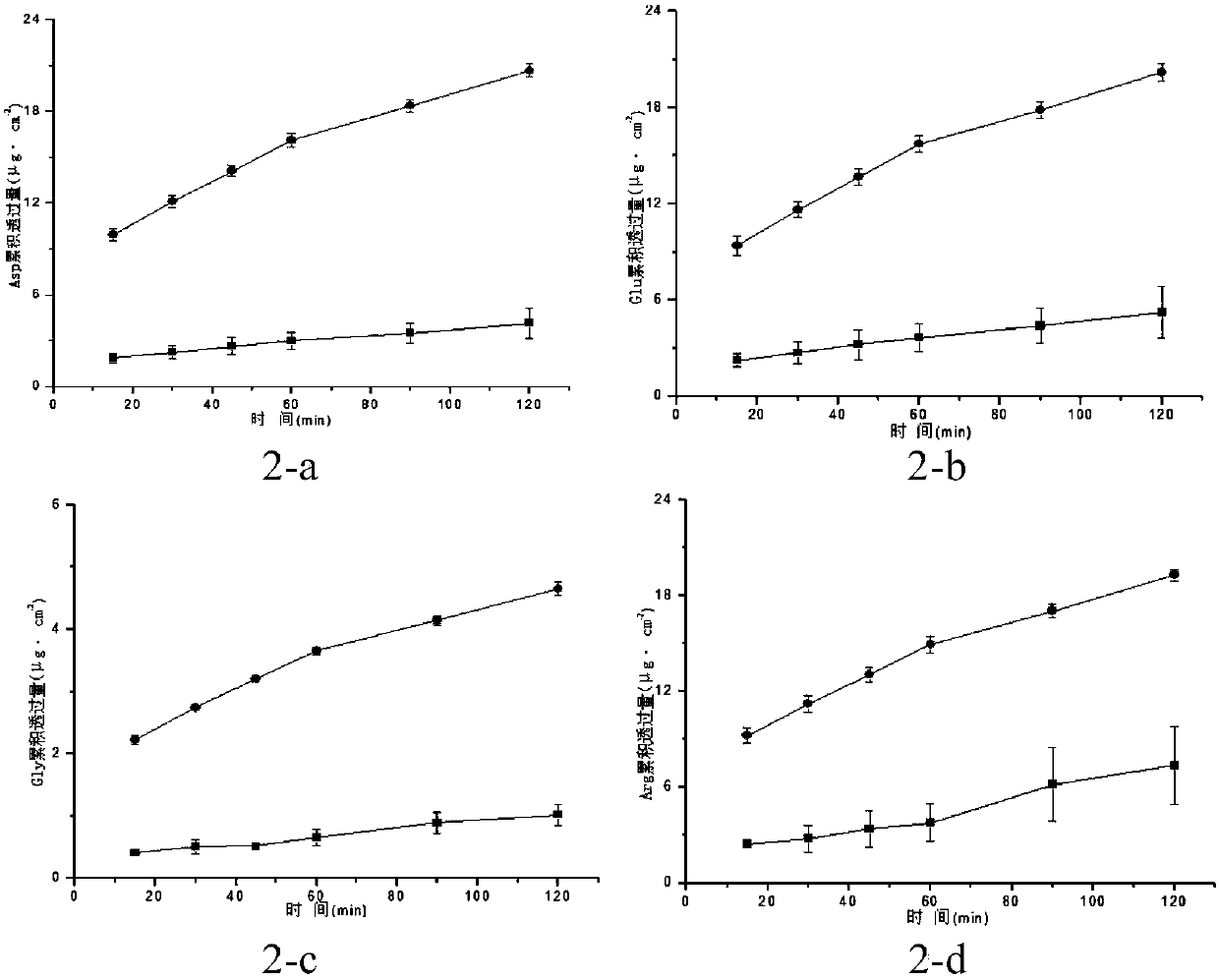
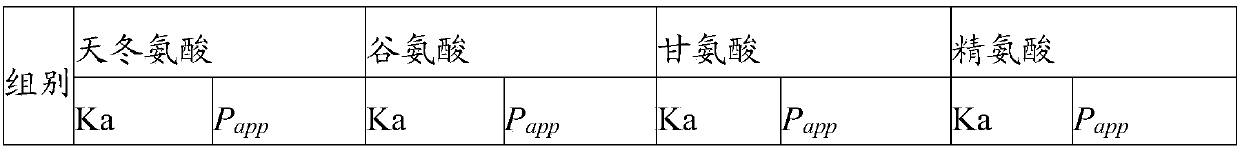
InactiveCN108201140AImprove spatial memoryIncreased speed through the water mazeFood shapingFood ingredient functionsAdhesiveGastric fluid
The invention relates to the technical field of a health-care food new preparation, in particular to walnut peptide colon positioning mini-pills and a preparation method thereof. Each of the walnut peptide colon positioning mini-pills provided by the invention consists of a pill core and a coating layer, wherein the pill cores are prepared from walnut peptide, an excipient, an adhesive and a wetting agent. For the prepared walnut peptide colon positioning mini-pills, the particle diameters are 10-2000[mu]m, the release degree in stimulated gastric juice within 120min is smaller than 2%, the release degree in stimulated intestinal fluid within 5h is smaller than 10%, and the release degree in stimulated colon fluid within 1h is greater than 95%. Compared with walnut peptide raw materials, the absorption efficiency in colons is obviously improved, and the health-care food new preparation has high oral administration biological availability. The walnut peptide colon positioning mini-pillsprovided by the invention can improve the spatial memory capacity of rats for the position of a platform, and increase the speed of the rats passing through a water maze.
Owner:INFINITUS (CHINA) CO LTD
Application of compound in improvement of cognition and memory ability and reduction of senile plaques
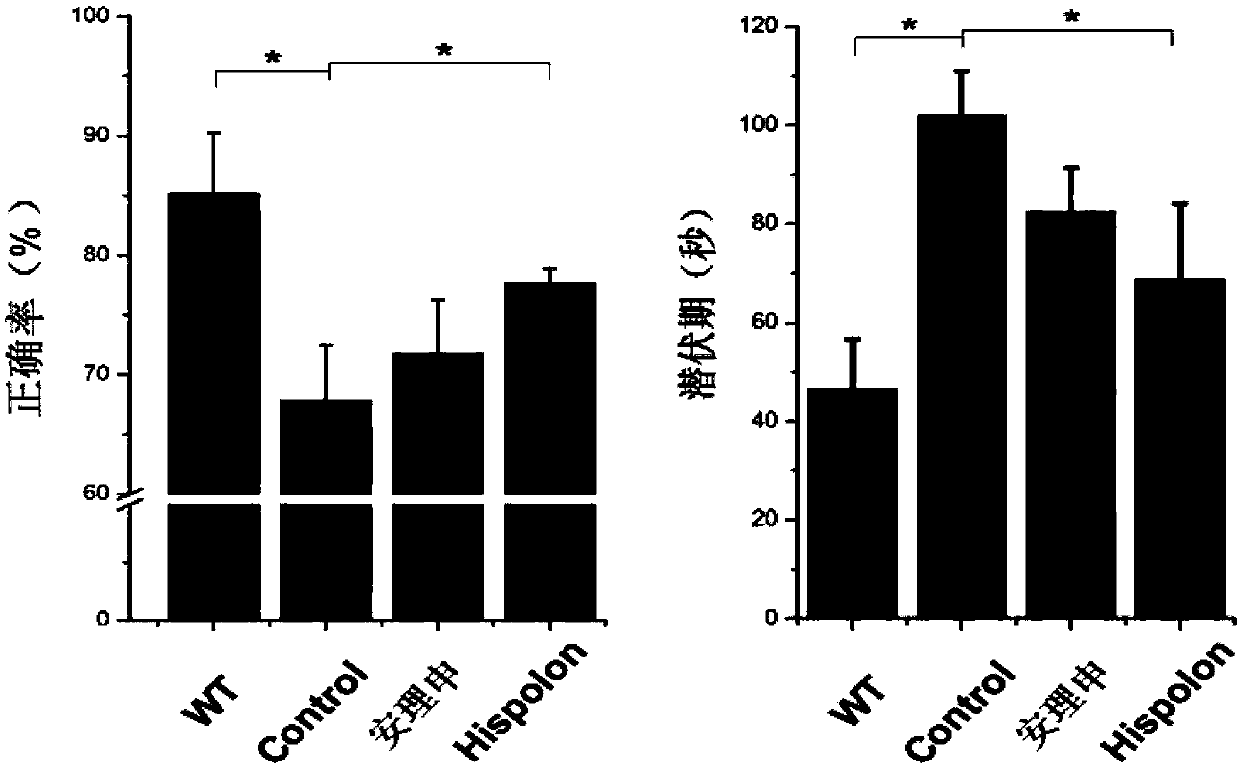
InactiveCN107648209AClearing Effect Improvement EffectNervous disorderKetone active ingredientsDiseaseFiber
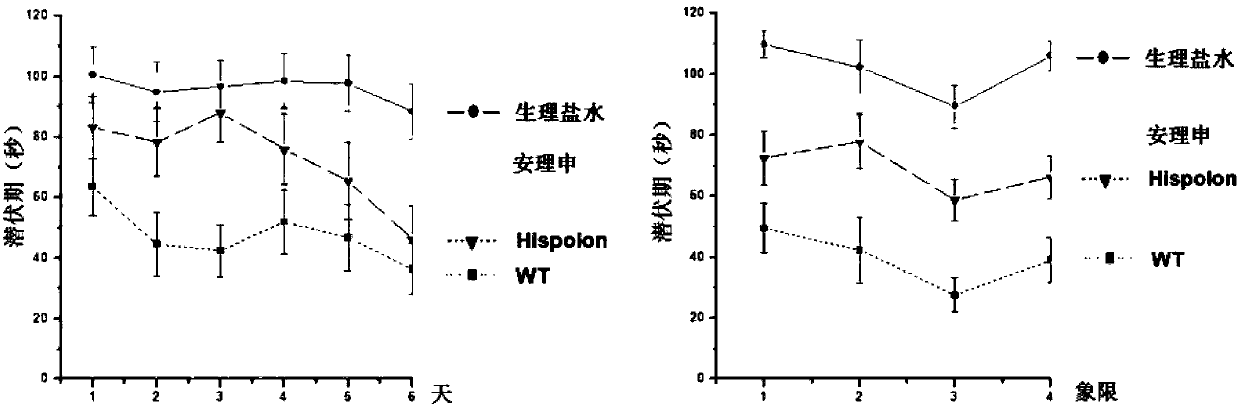
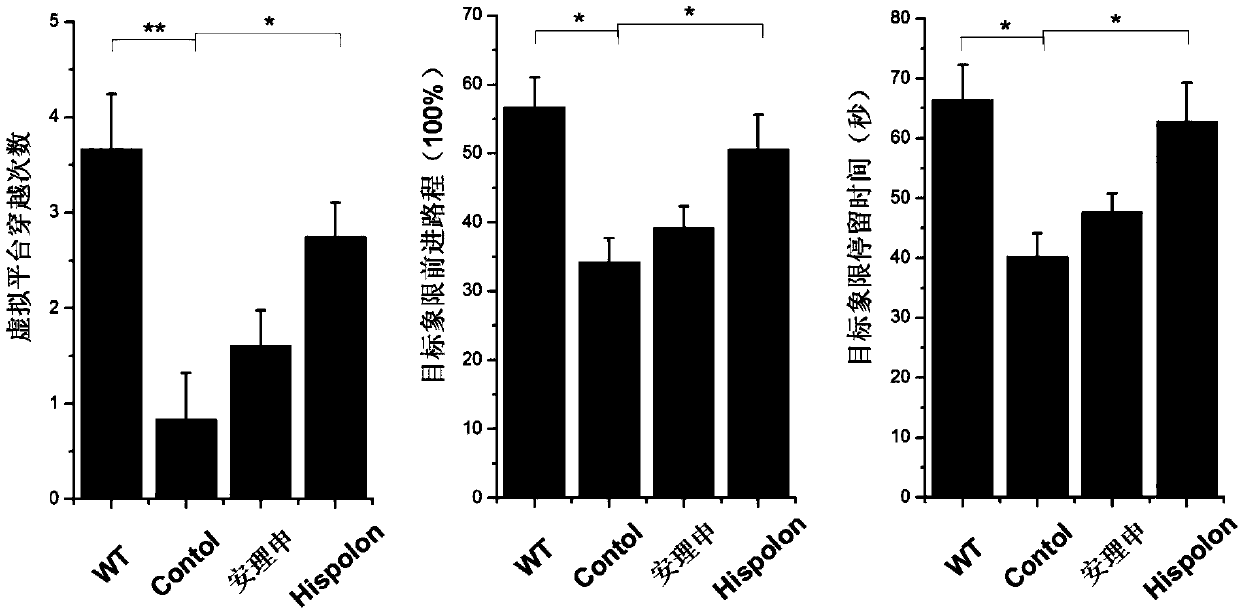
The invention discloses an application of Hispolon in the improvement of the cognition and memory ability and the reduction of senile plaques. Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease with nerve cell fiber entanglement, amyloid beta-protein (Abeta) plaque deposition and cognition function decline as pathologic characteristics, wherein Abeta extracellular toxic accumulation is considered as one of main attack links of the AD. It is found that the Hispolon can improve the spatial memory learning ability of AD mice and obviously clear amyloid plaques in APP / PS1 double transgenic ADmodel mice brain tissues, which shows that the Hispolon can be applied to the treatment of the AD and the development of related drugs.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
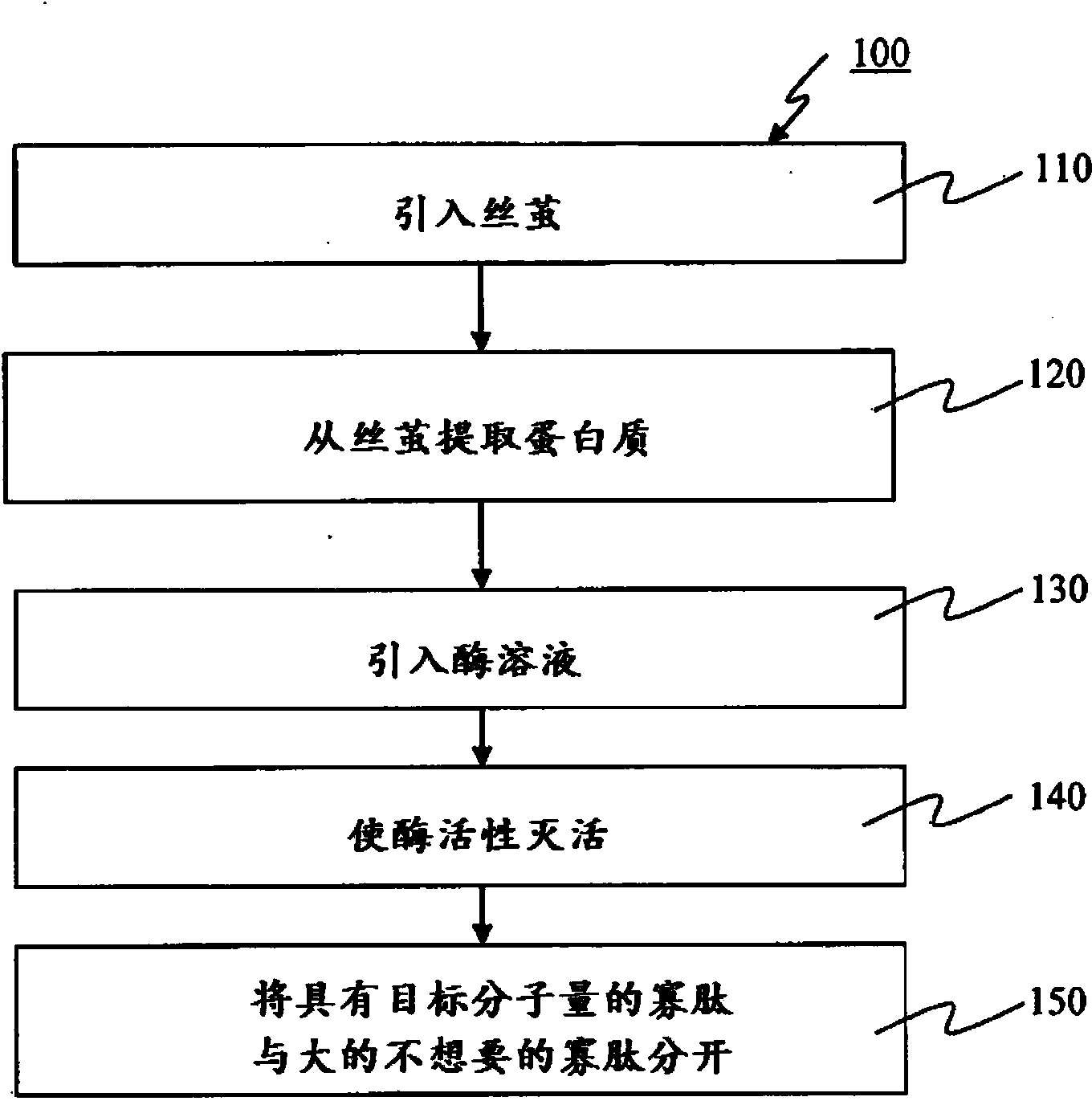
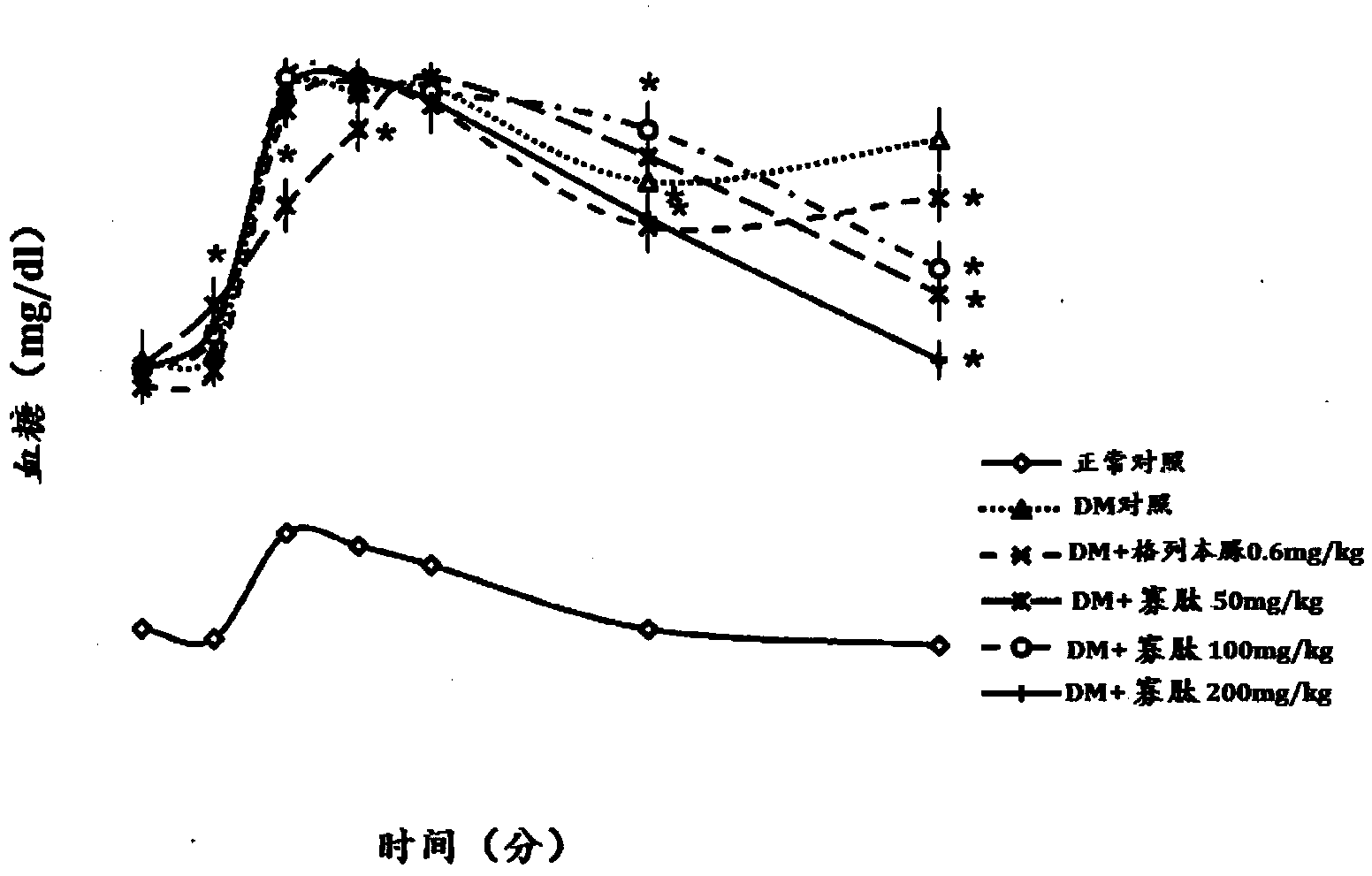
Silk-based bioactive oligopeptide compositions and manufacturing process therefor
A process for preparing or manufacturing target molecular weight silk-derived oligopeptides with bioactive properties includes providing silk cocoon, extracting proteins or peptides from the silk cocoon, introducing an enzyme solution to obtain oligopeptides, and separating target oligopeptides from other peptides. Silk-derived oligopeptides in accordance with the present disclosure possess one or more of antioxidant properties, cholesterol lowering activity, lipid oxidation prevention properties, blood sugar lowering properties, blood pressure lowering properties, natural killer cell enhancement activity, insulin production enhancement activity, body weight regulatory activity, central nervous system stimulant properties, and neuroprotective, cognitive function protective, memory protective, and / or neural function improvement properties (e.g., memory deficit alleviation, spatial memory improvement, recognition memory improvement, learning improvement, synaptic transmission facilitation, and anti -neurodegenerative properties).
Owner:AGRI RES DEV AGENCY PUBLIC ORG
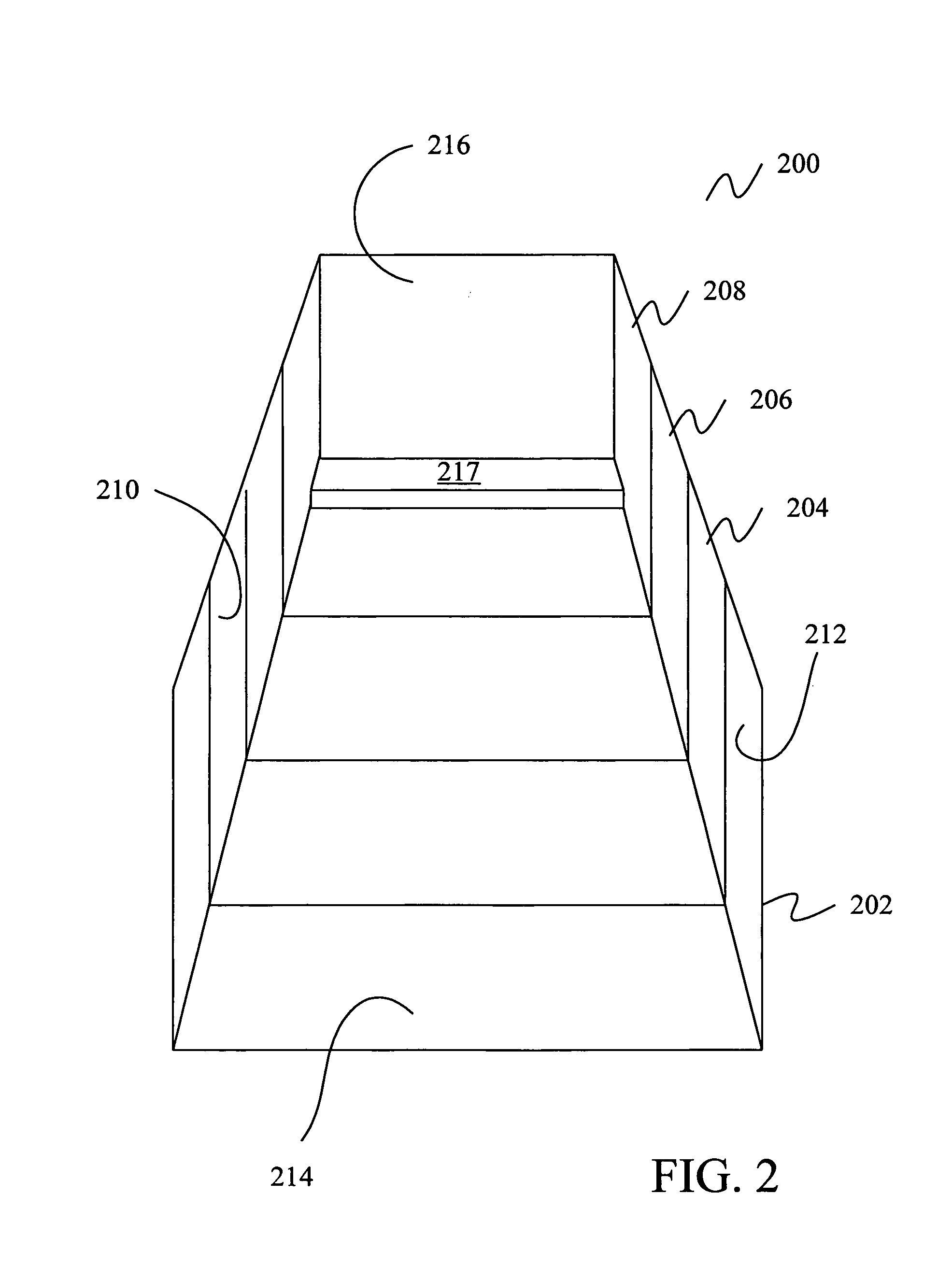
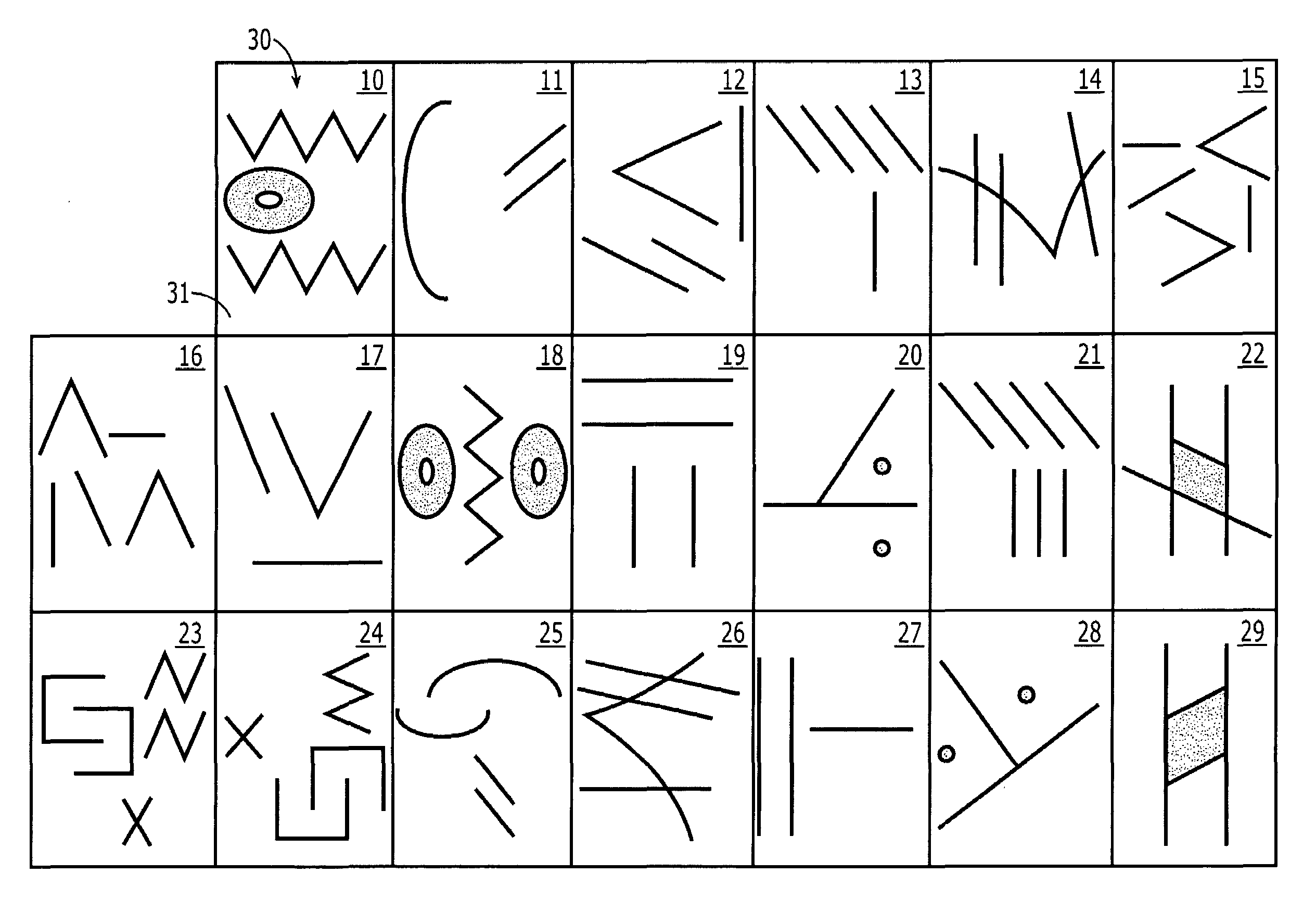
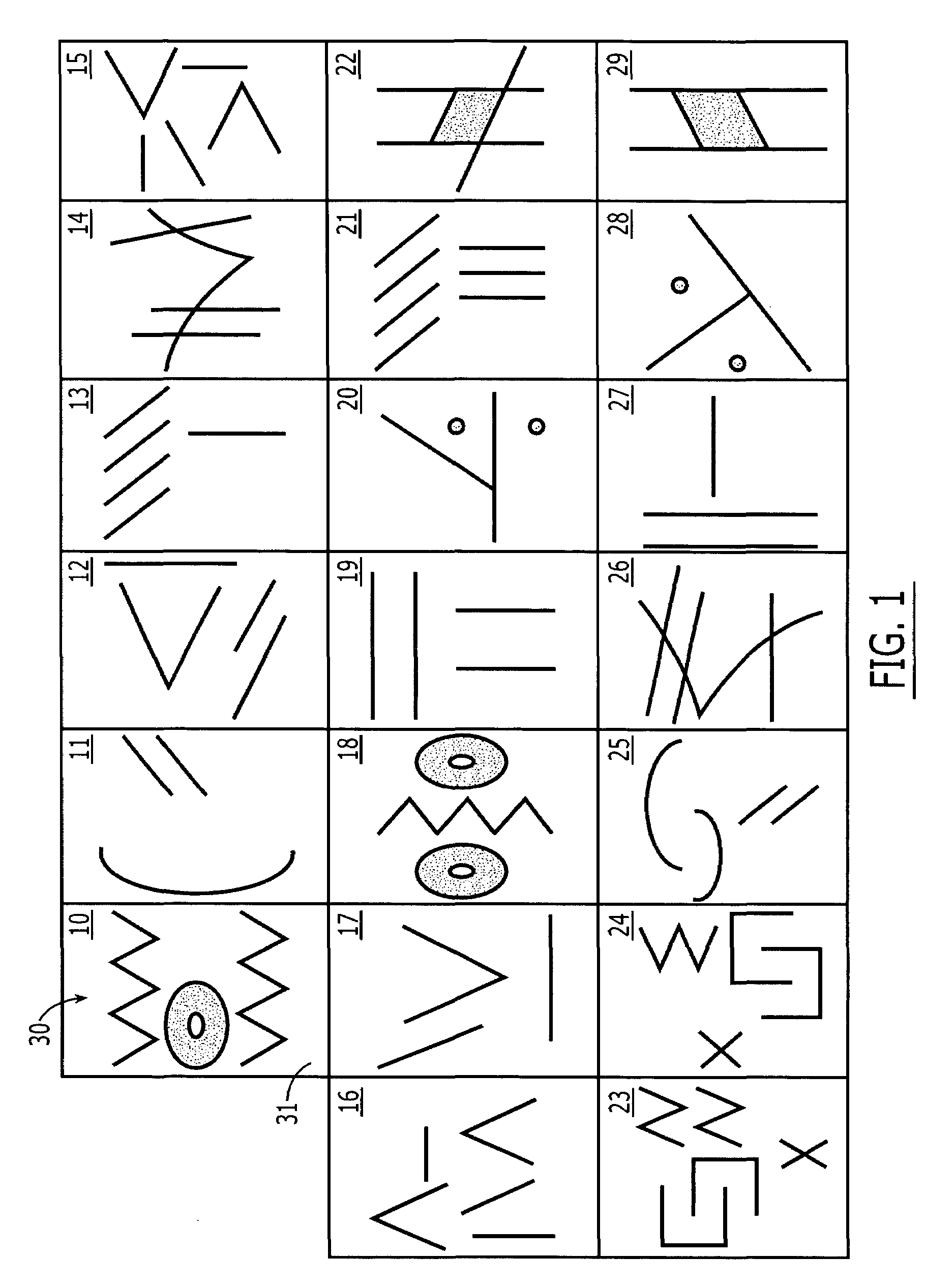
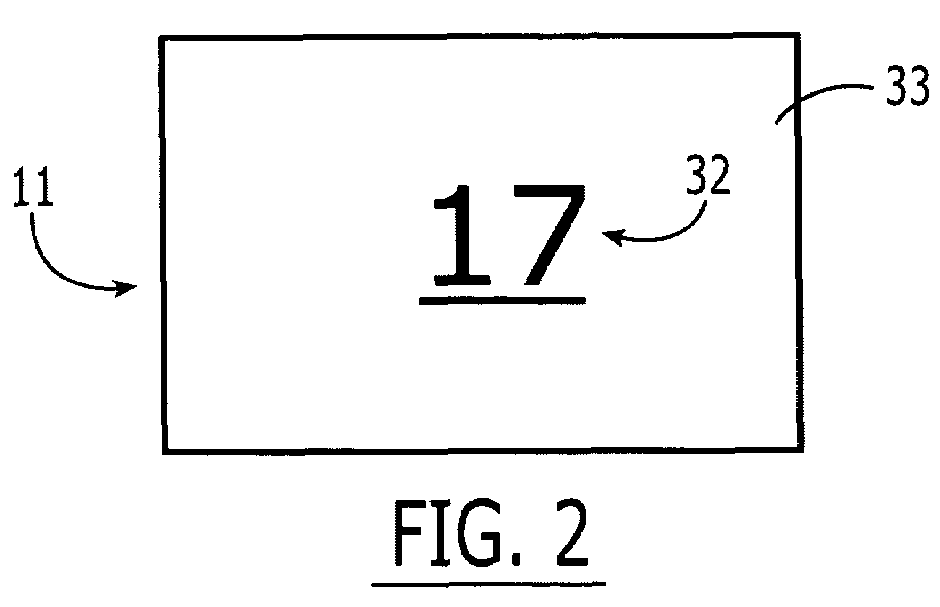
Spatial memory assessment and associated methods
A neuropsychological assessment includes cards having a first indicium on a top face and an index indicium on a bottom face. A display includes an arrangement of images, each image corresponding to one of the first indicia, the image number fewer than or equal to the card number. A receptacle has depressions for holding a card, each having an aperture therethrough positioned commensurate with the index indicium's location. At least some of the depressions are positioned analogously to the display arrangement. A trial is administered by revealing the display to an examinee. The display is removed from examinee view, and the examinee is instructed to reproduce the arrangement of the images by selecting a card having a first indicium corresponding to an image and placing the selected card within a selected depression on the receptacle in a position that corresponds to a position of the corresponding image on the display.
Owner:PSYCHOLOGICAL CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com