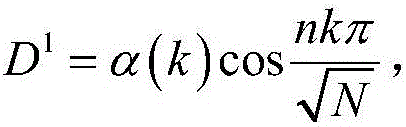Patents
Literature
68 results about "Spatial distortion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Spatial Distortion. Spatial Distortion is the mental ability to distort space; this isn’t used to directly move an object or subject, but rather manipulate the spatial presence of objects.
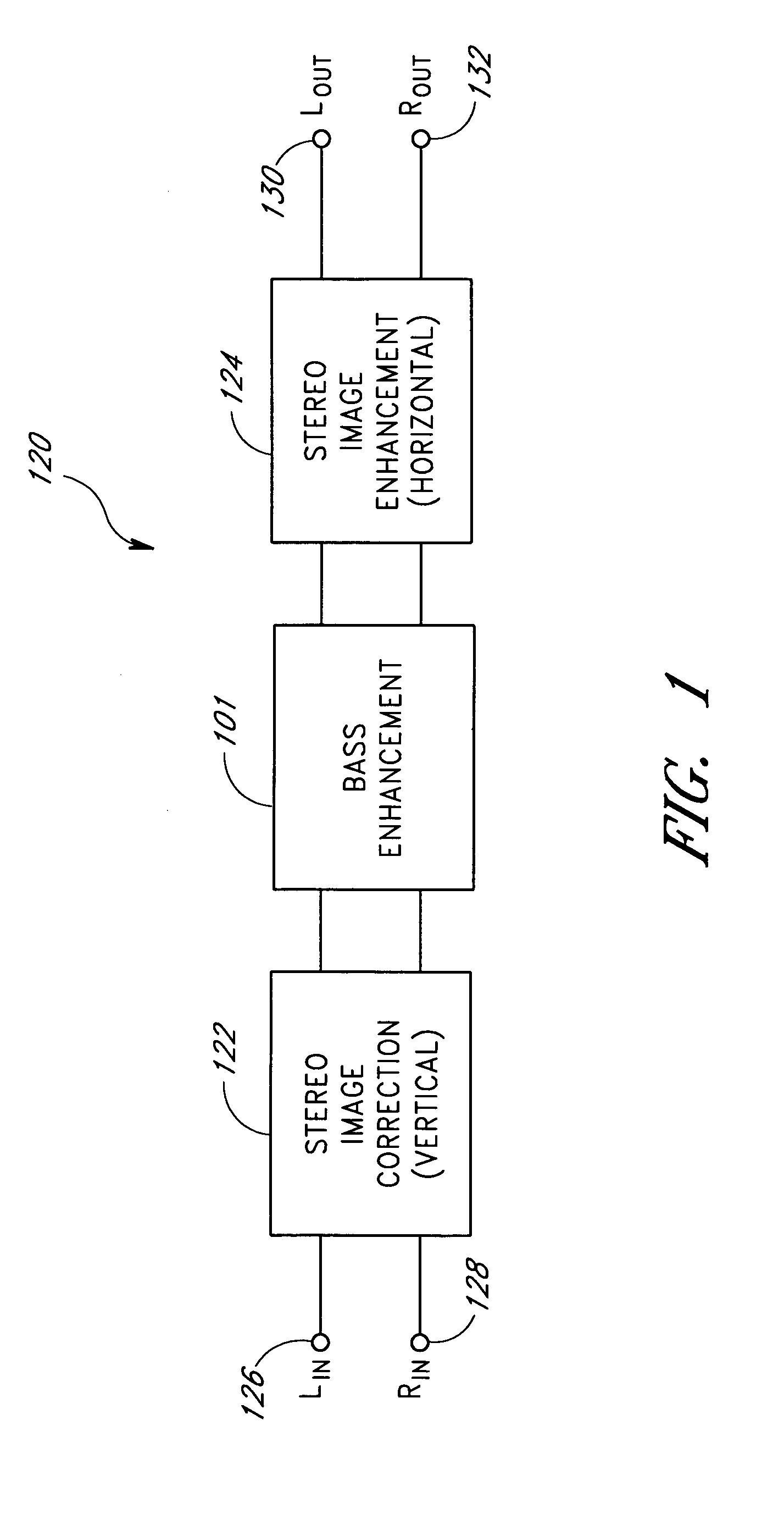
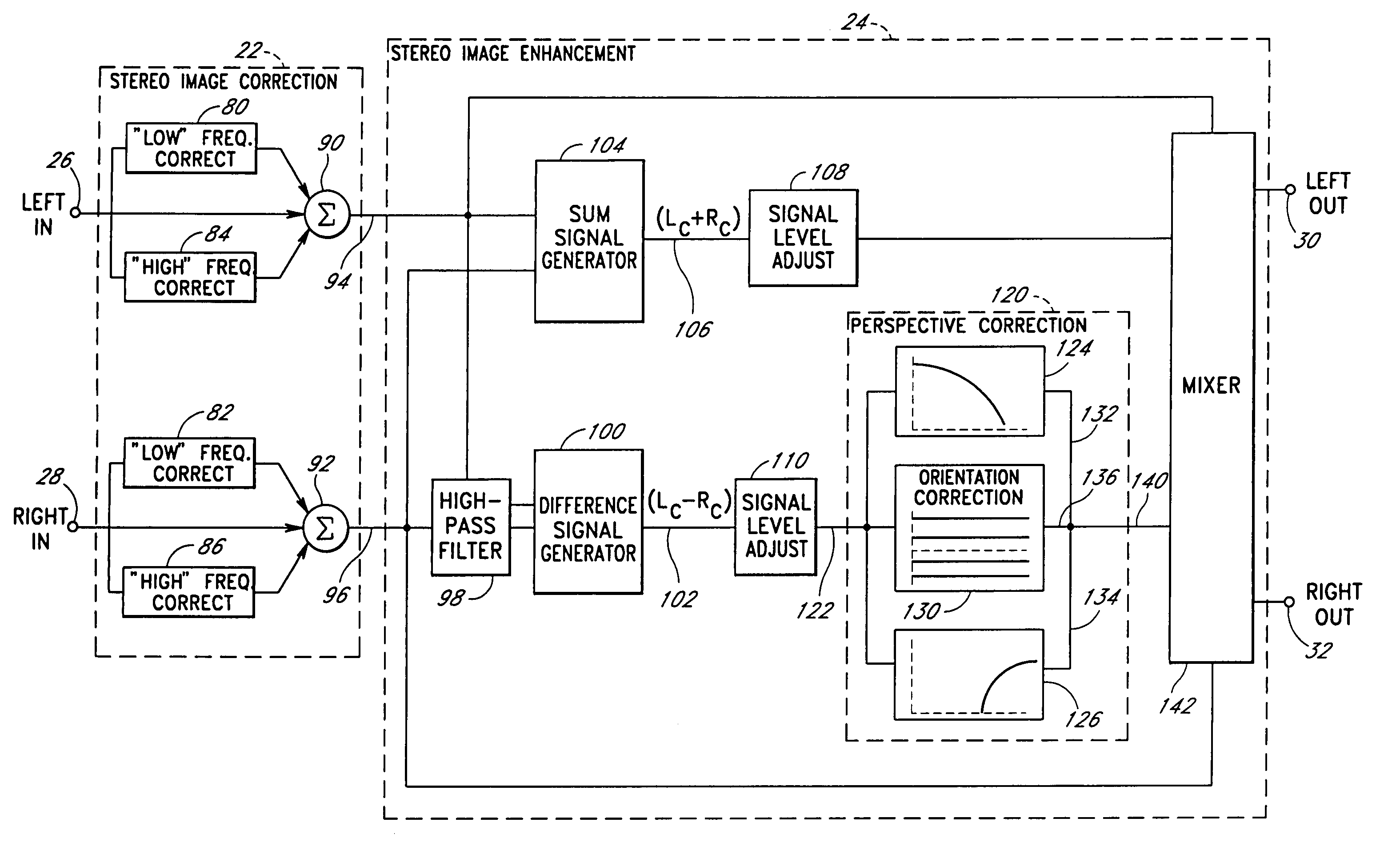
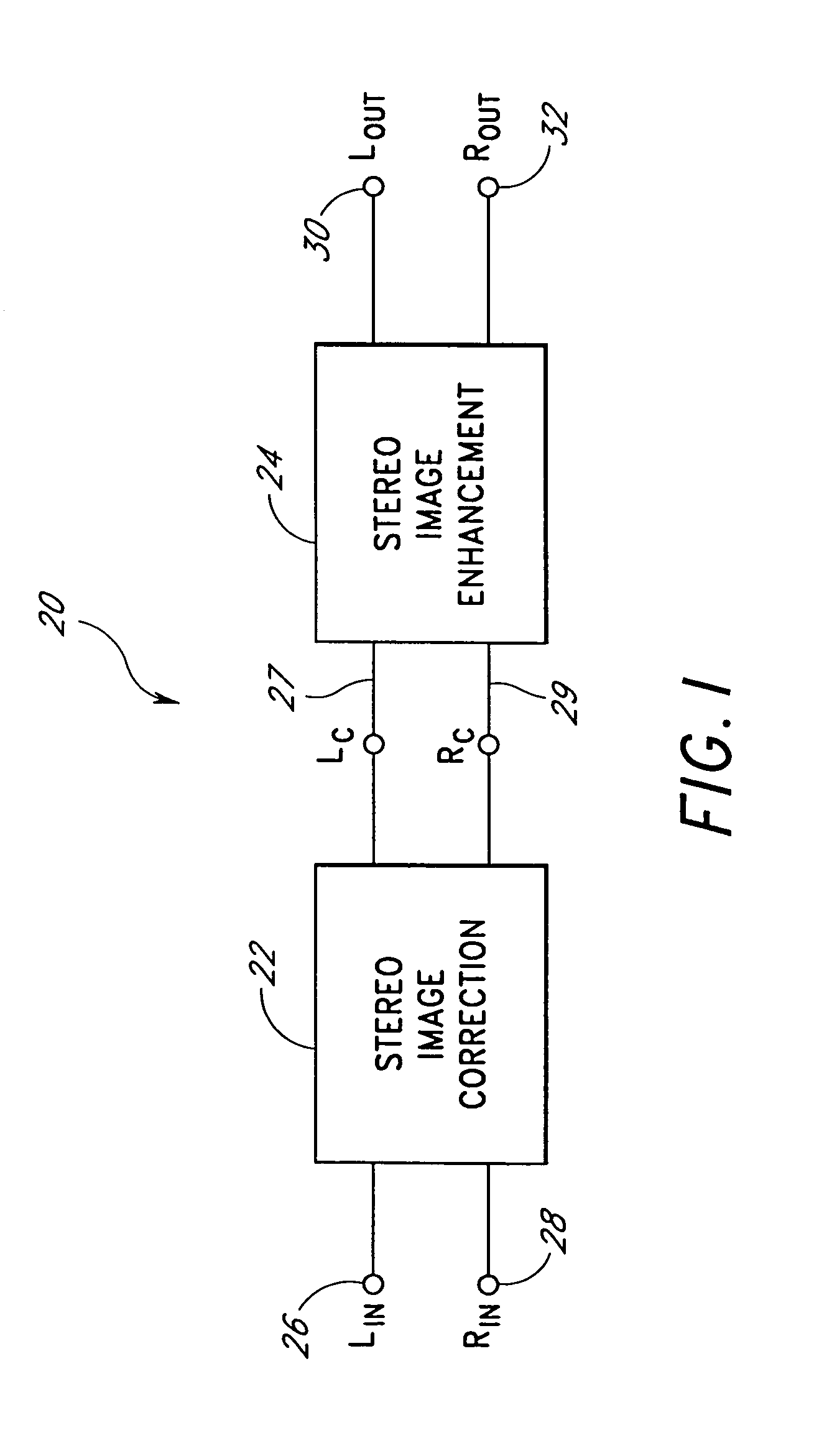
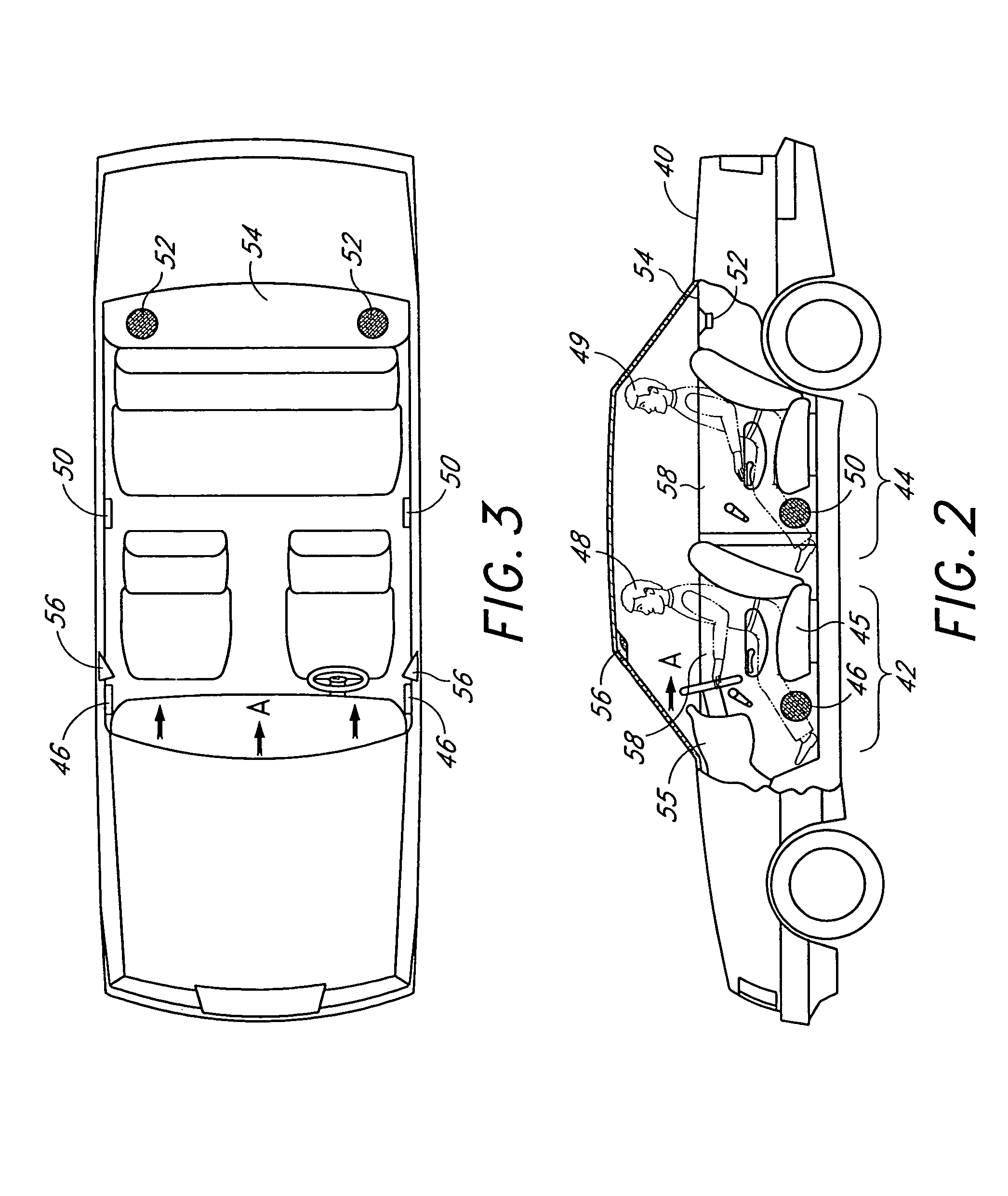
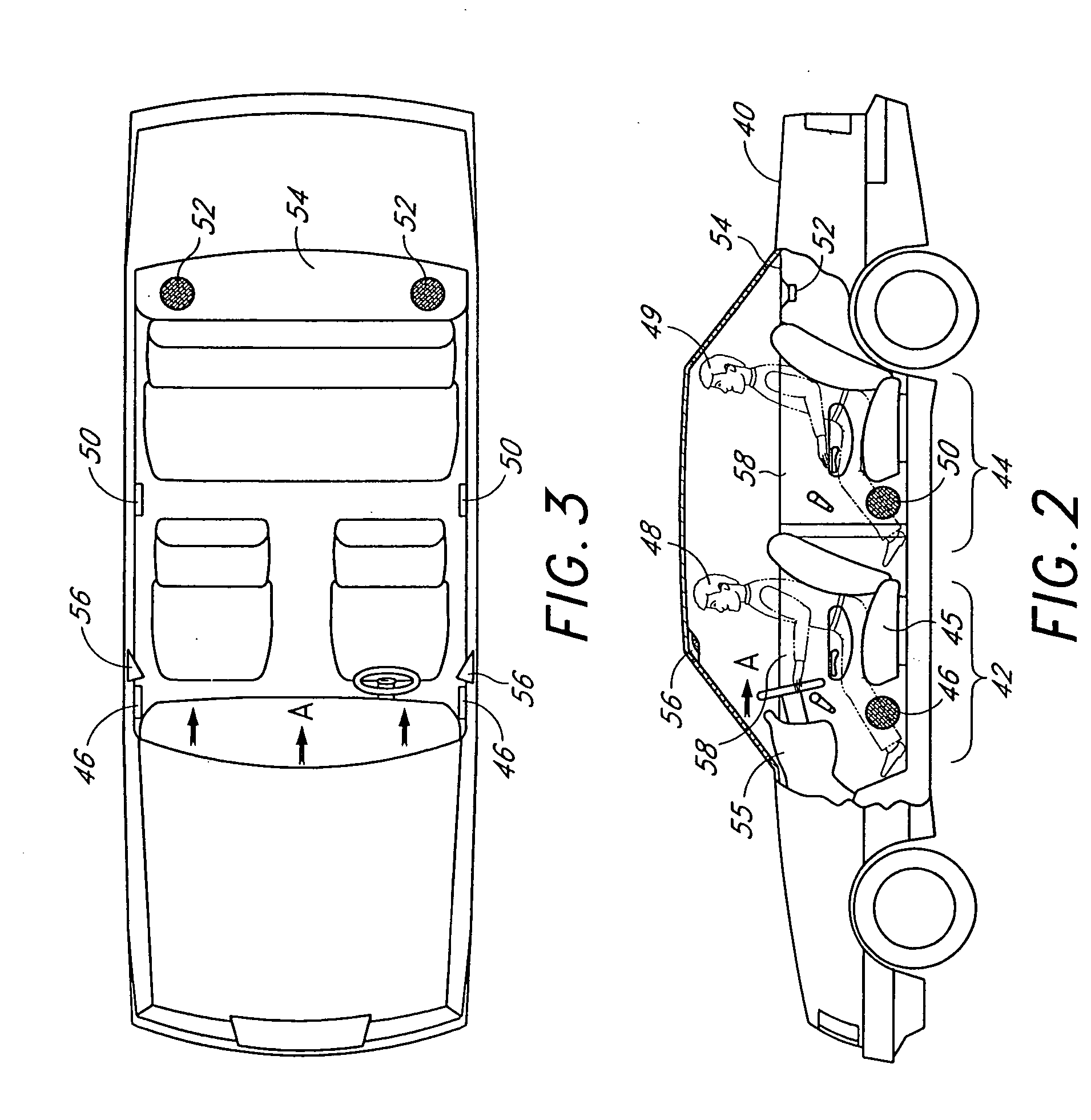
Acoustic correction apparatus
InactiveUS20060126851A1Improve performanceIncrease in sizeHeadphones for stereophonic communicationFrequency response correctionSound imageSound energy
Owner:DTS
Acoustic correction apparatus
InactiveUS7031474B1Improve performanceIncrease in sizeHeadphones for stereophonic communicationFrequency response correctionSound imageSound energy
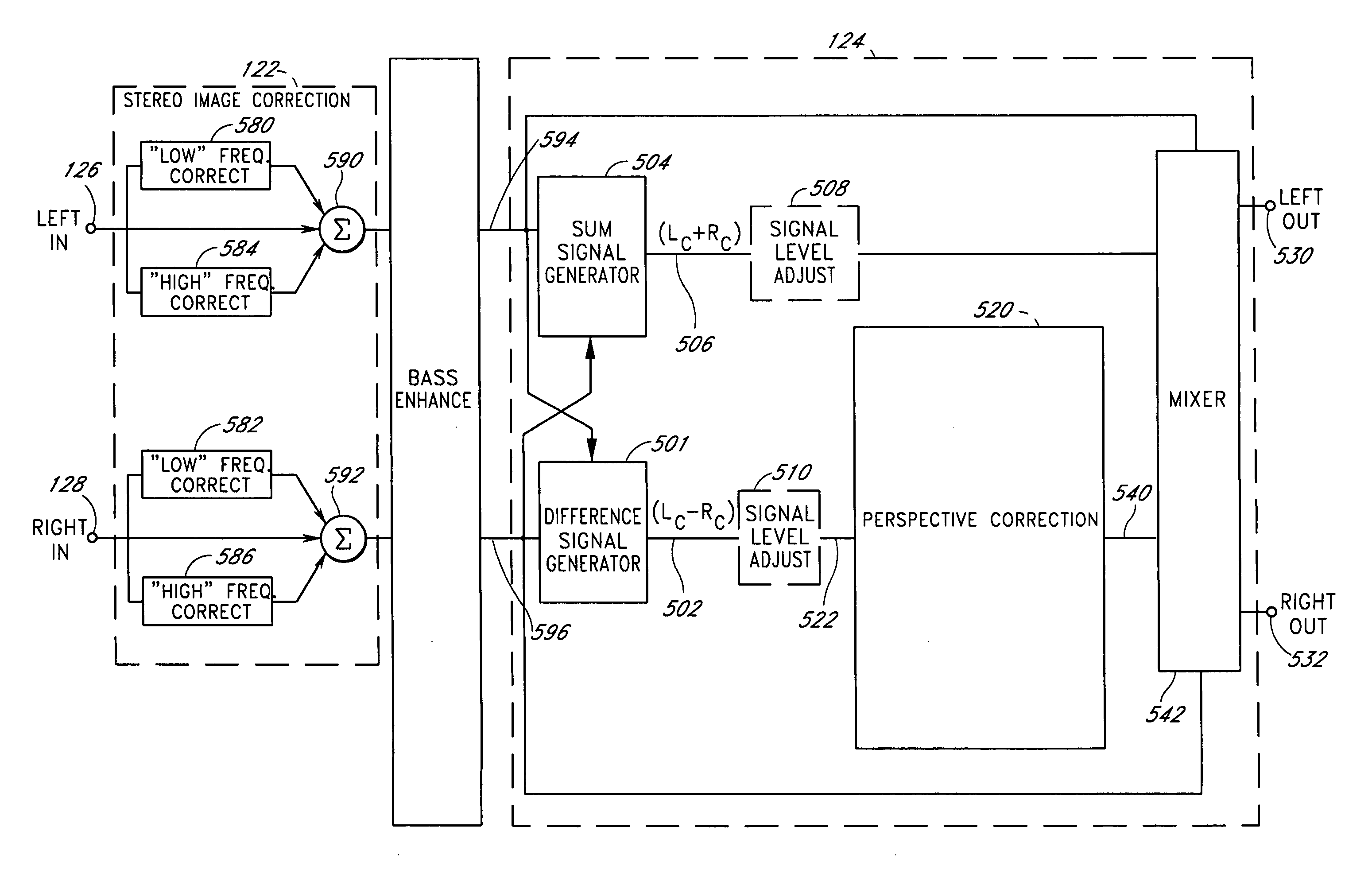
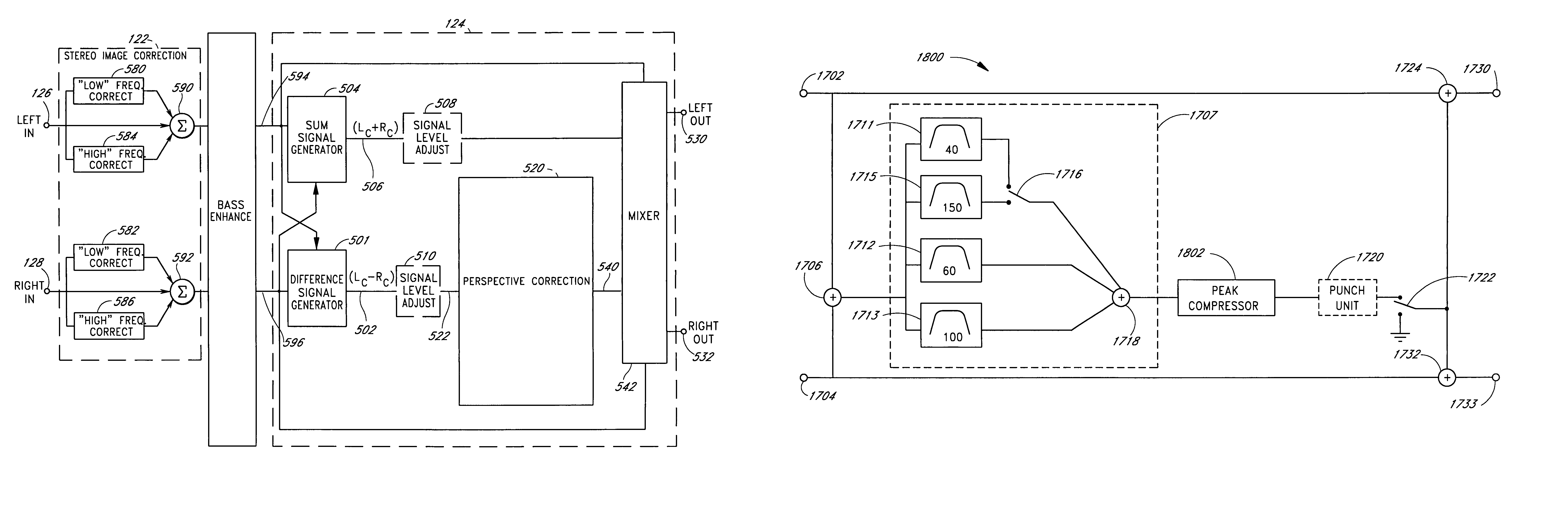
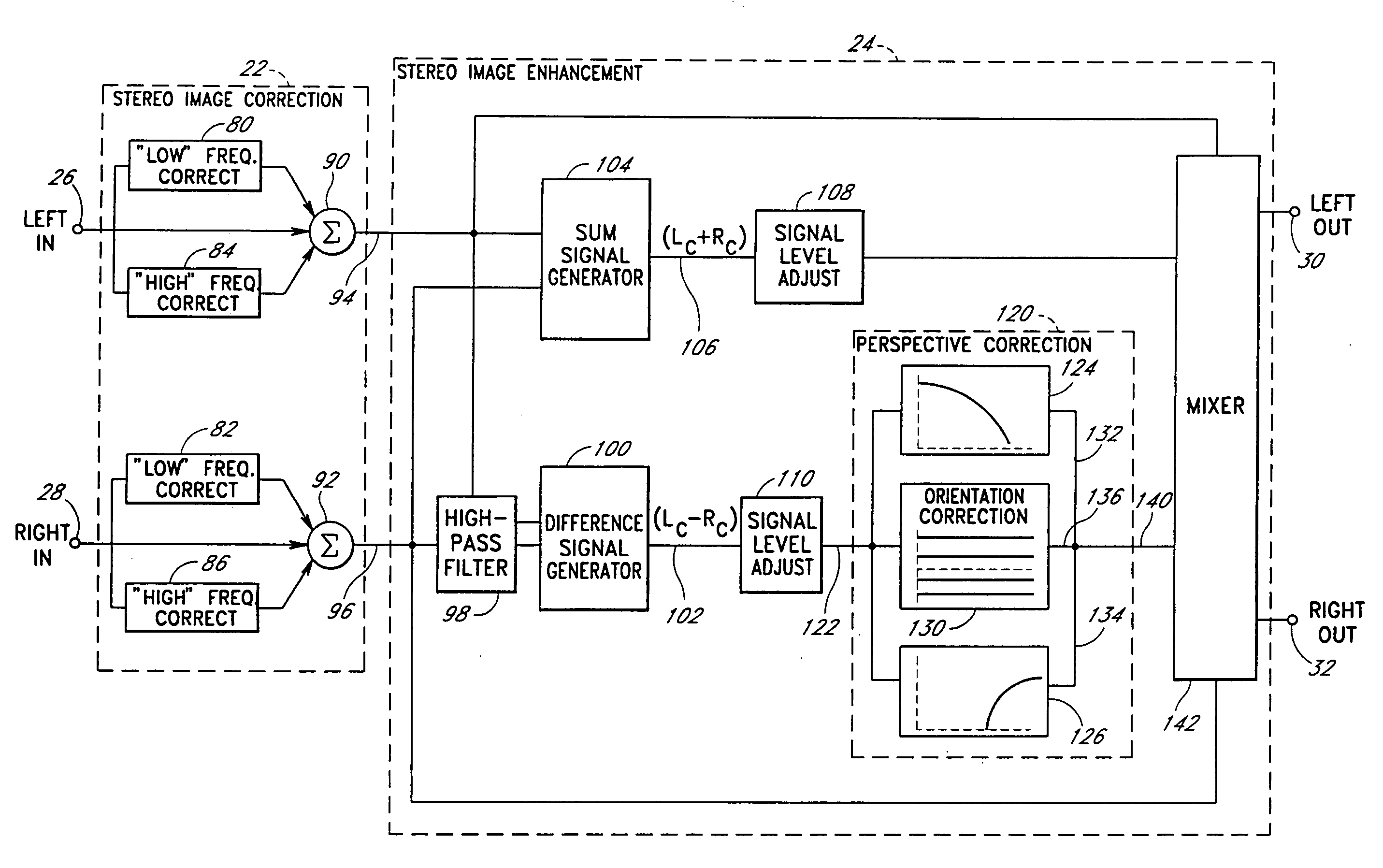
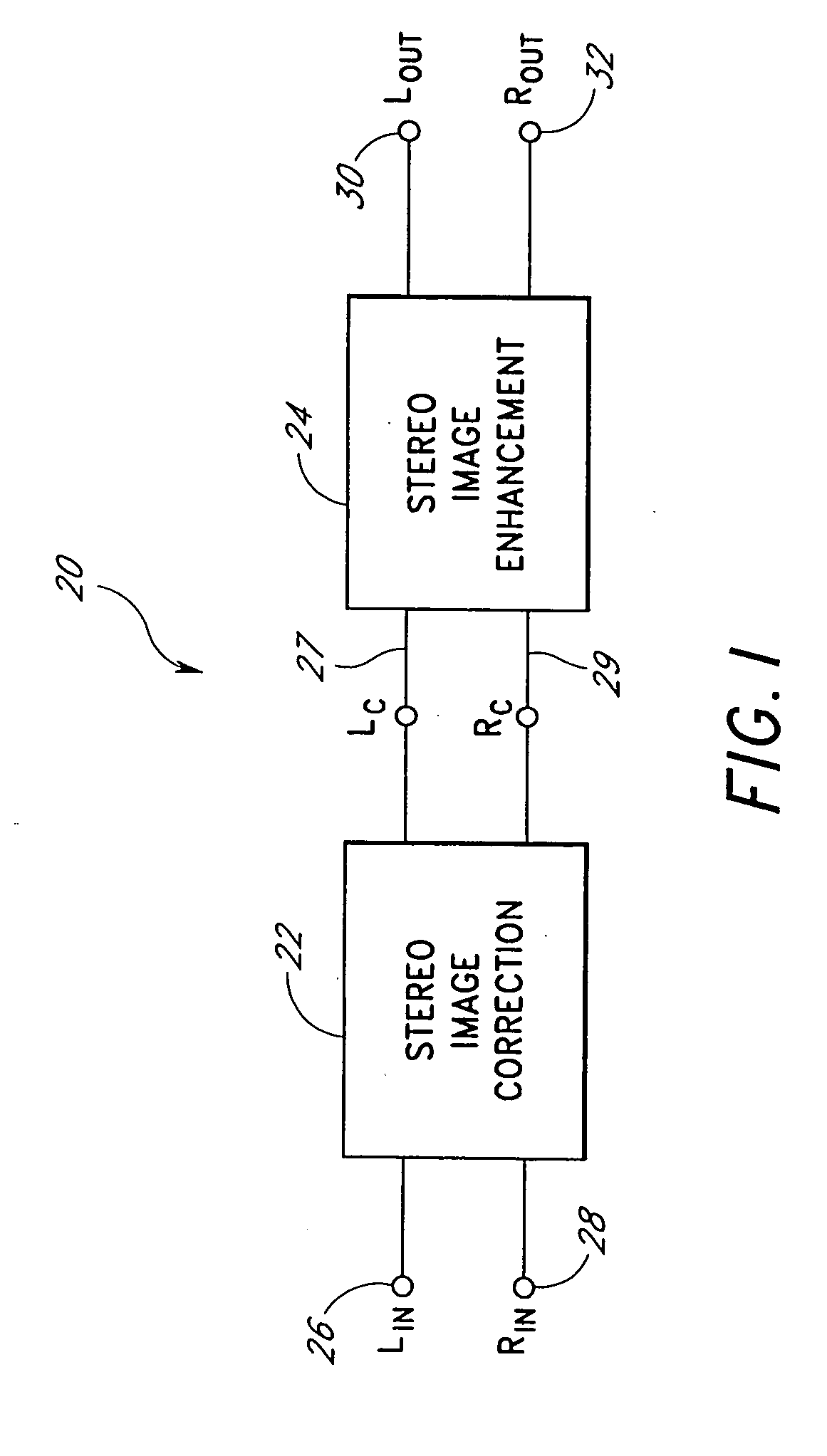
An acoustic correction apparatus processes a pair of left and right input signals to compensate for spatial distortion as a function of frequency when said input signals are reproduced through loudspeakers in a sound system. The sound-energy of the left and right input signals is separated and corrected in a first low-frequency range and a second high-frequency range. The resultant signals are recombined to create image-corrected audio signals having a desired sound-pressure response when reproduced by the loudspeakers in the sound system. The desired sound-pressure response creates an apparent sound image location with respect to a listener. The image-corrected signals can also be spatially-enhanced to broaden the apparent sound image and improve the low frequency characteristics of the sound when played on small loudspeakers.
Owner:DTS
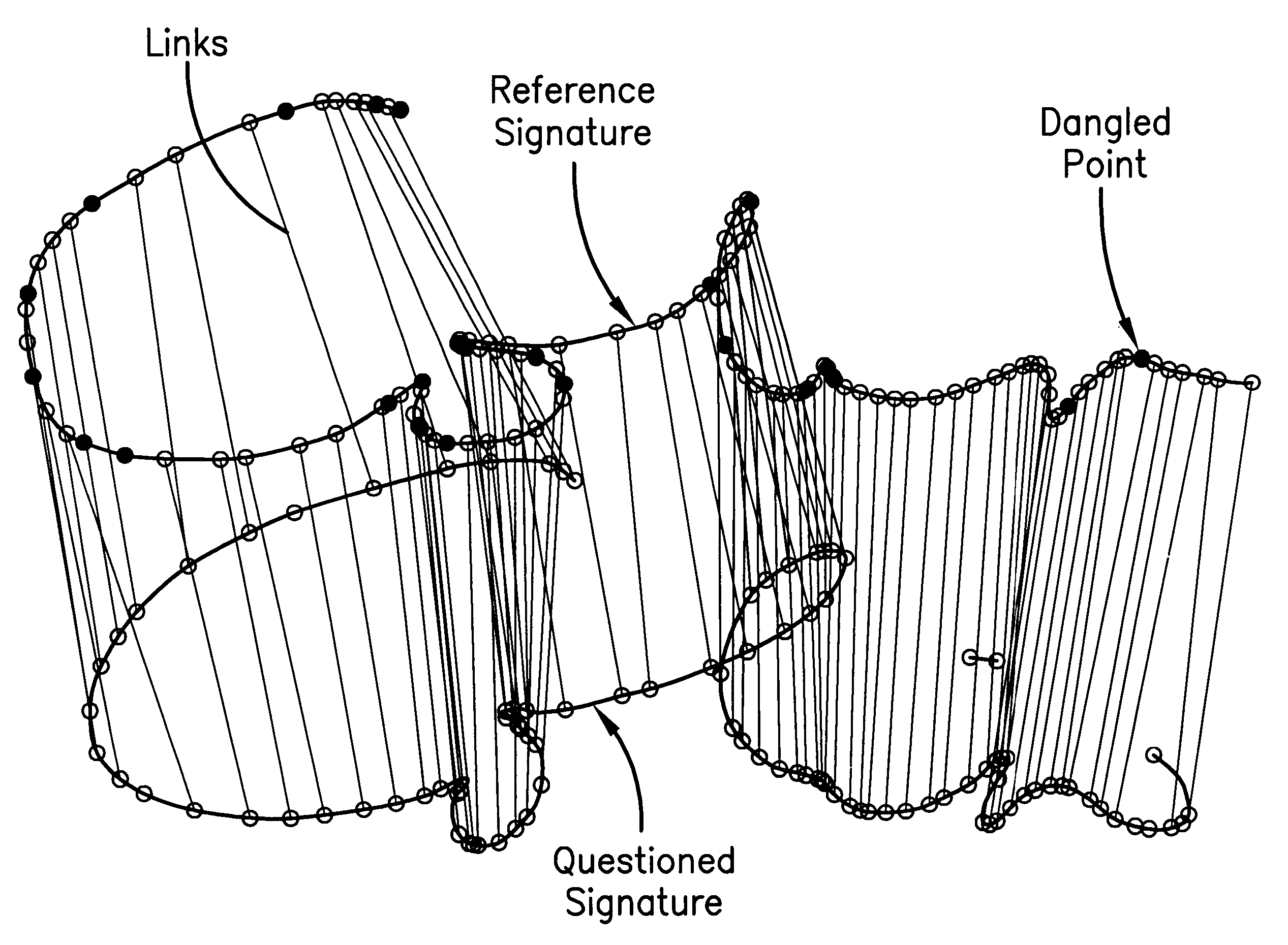
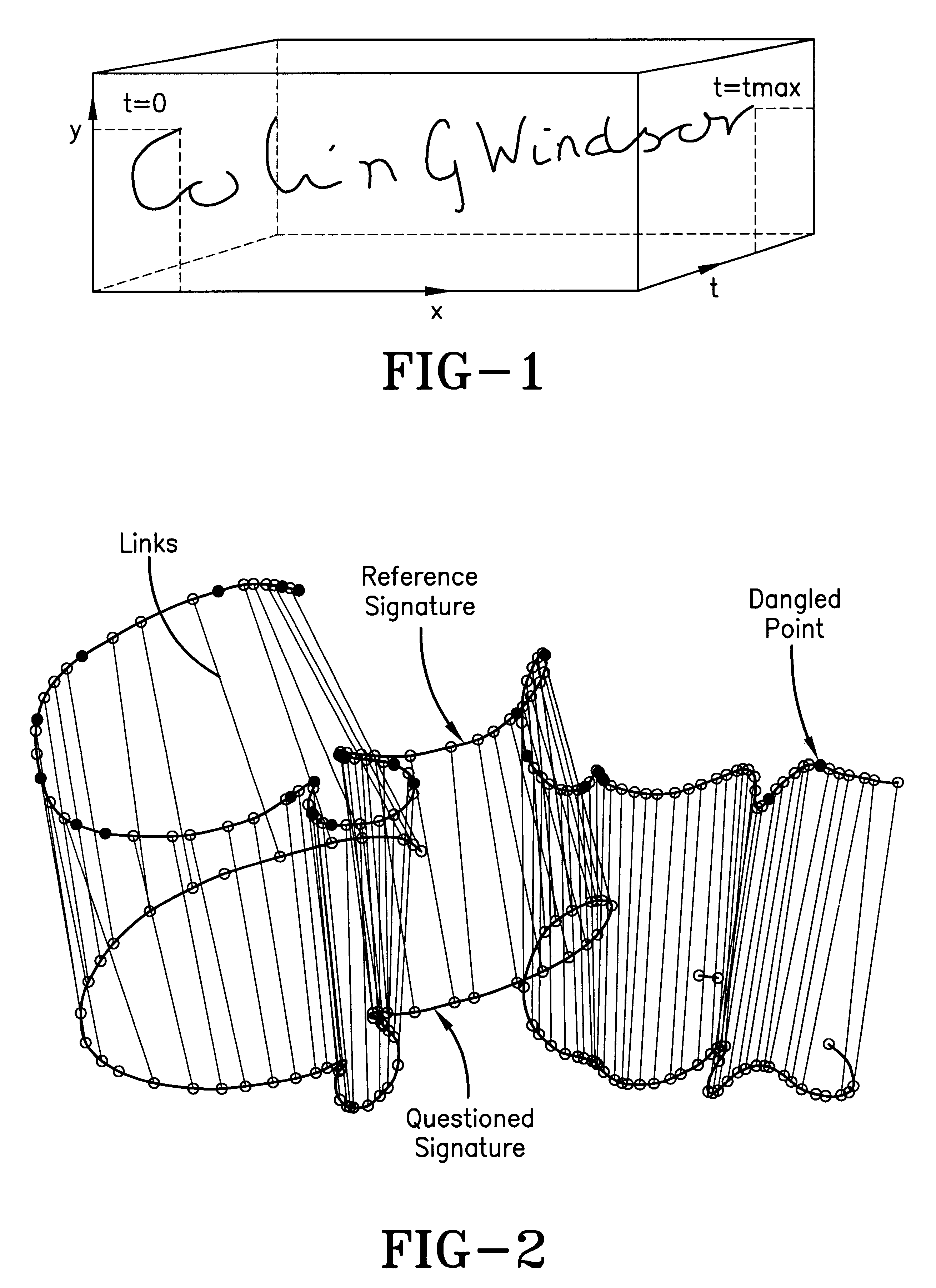
Signature matching
InactiveUS6487310B1Individual entry/exit registersSignature reading/verifyingSpatial correlationAlgorithm
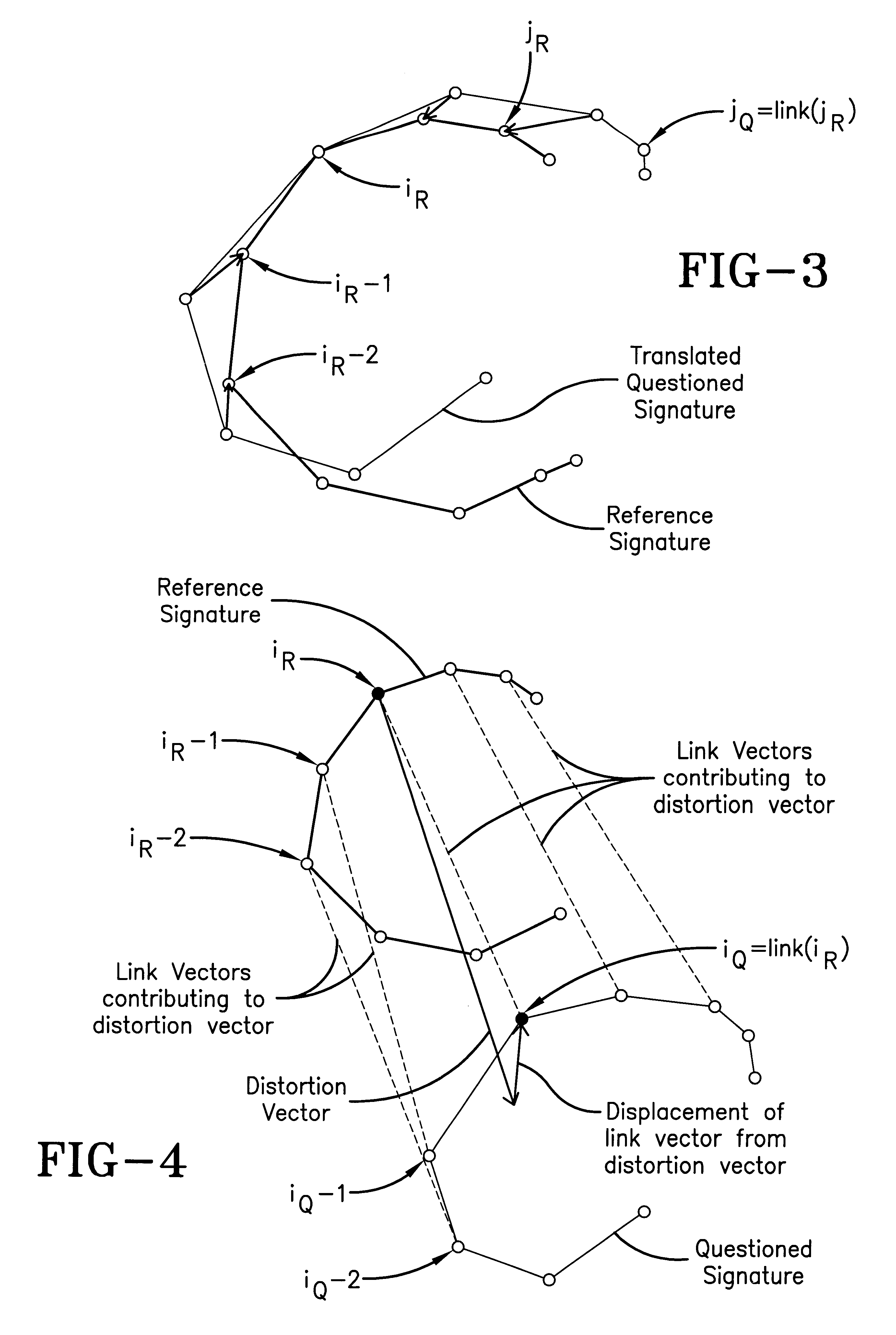
The invention is of an "elastic matching" method for comparing one signature against another, comprising the operations of creating a mapping between corresponding points in two signatures to be compared measured at different times after the commencement of writing the signatures which maximizes the correlation between the local spatial neighborhood of the measured points and simultaneously minimizes the curvature of the elastic spatial distortion from the mapping, providing quantitative measures of both the degree of the spatial correlations and the degree of the non-uniform spatial distortions in the mapping, thereby providing measures of the similarity between the signatures.
Owner:PENOP
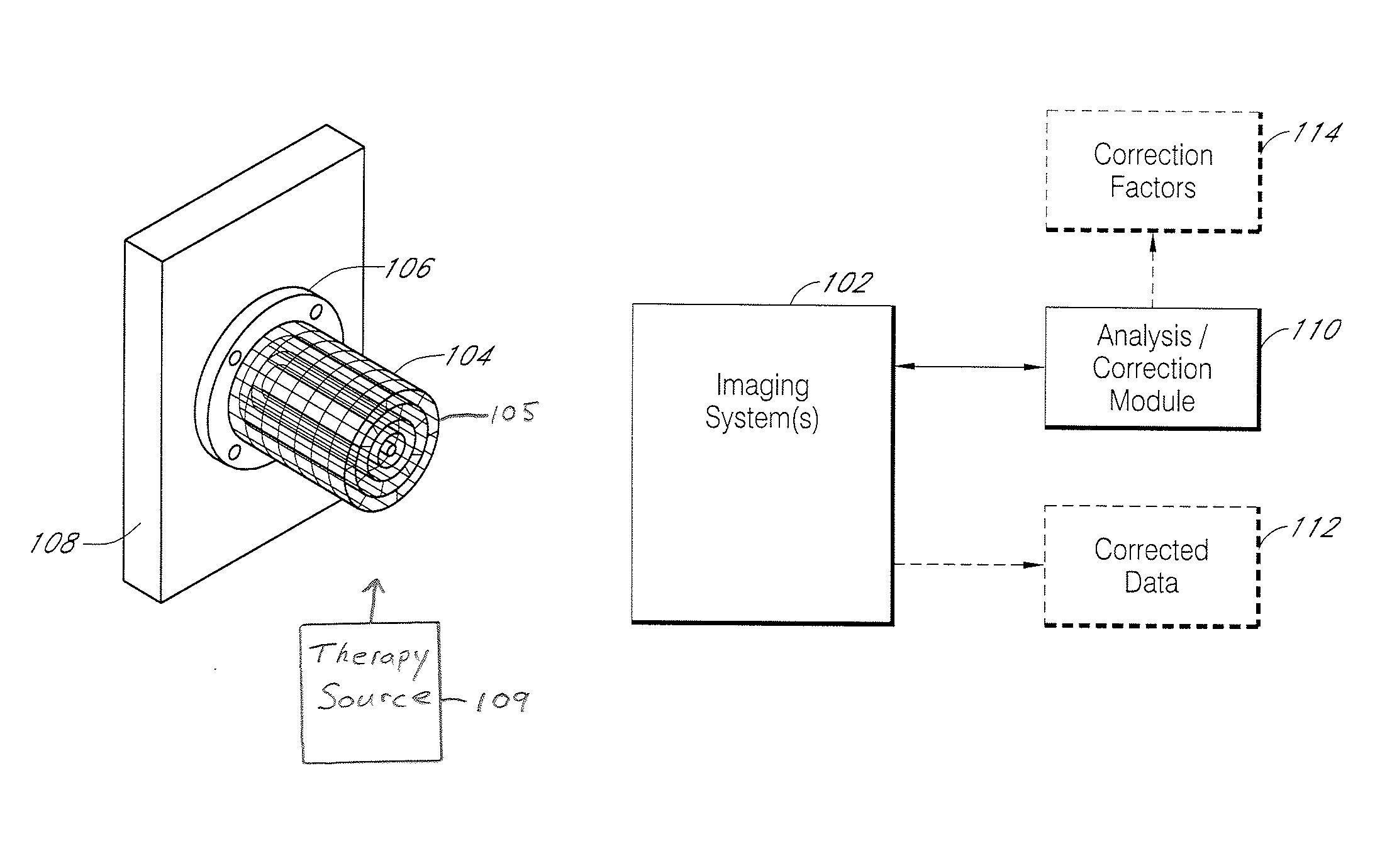
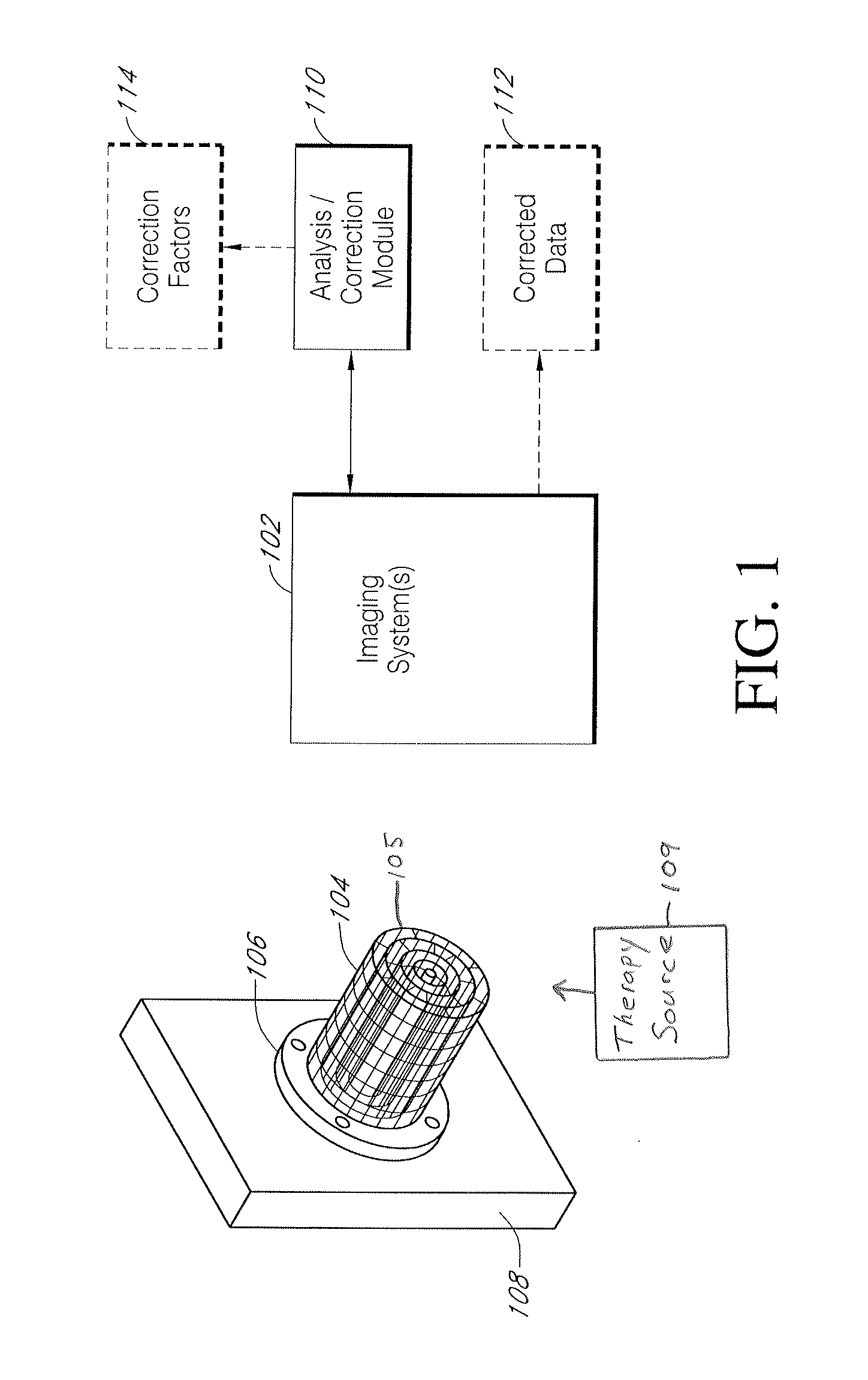
Systems and methods for characterizing spatial distortion in 3D imaging systems
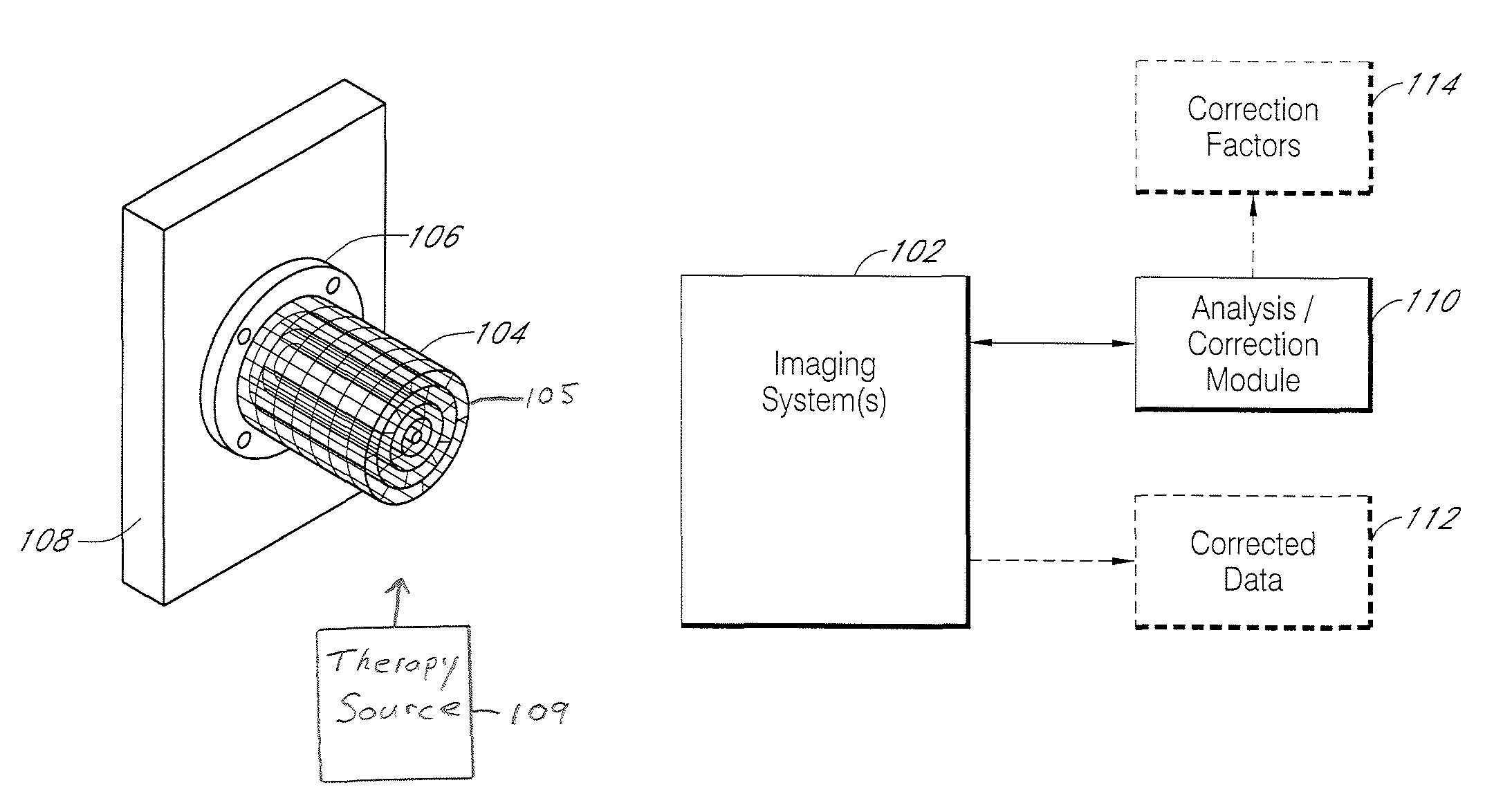
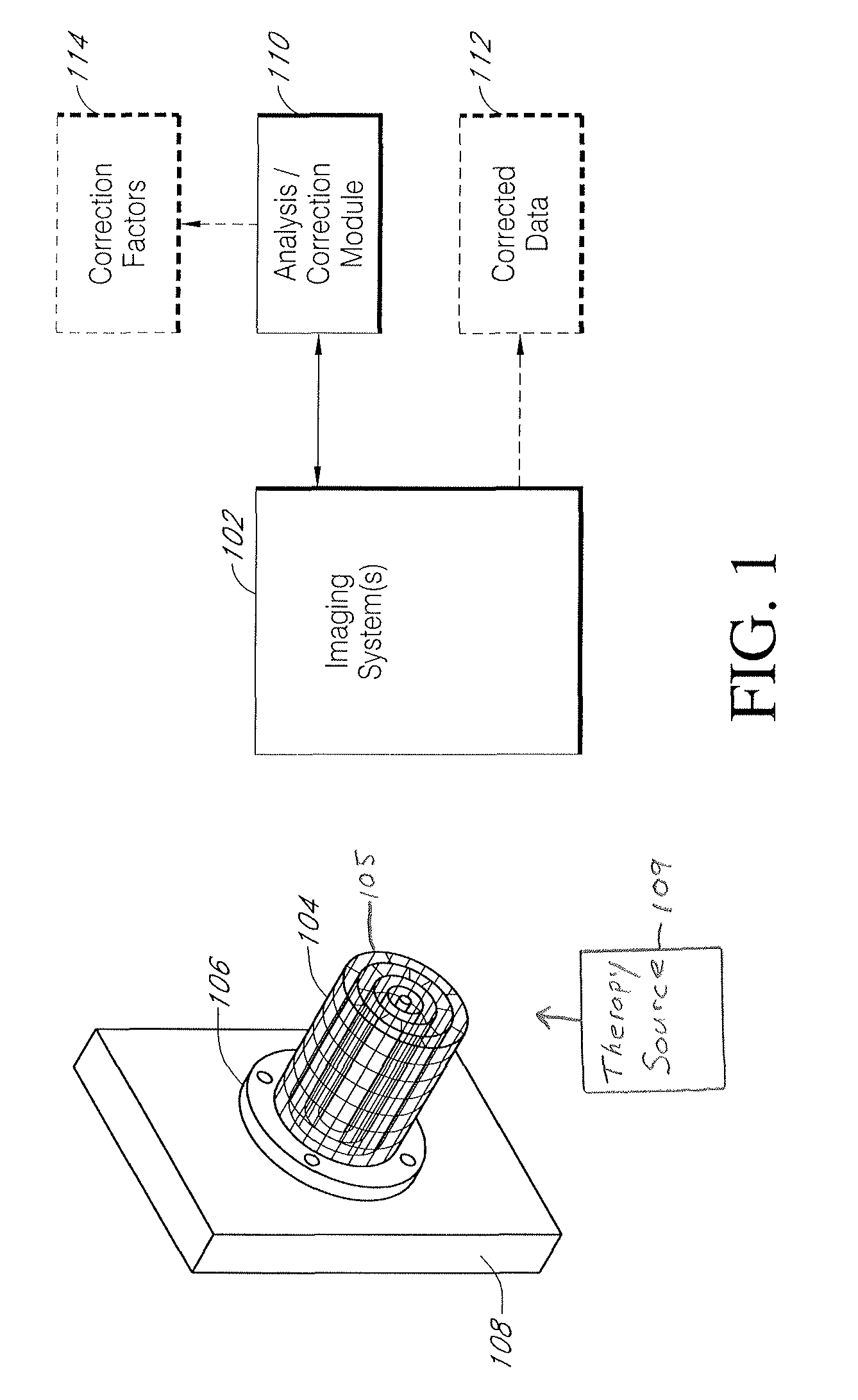
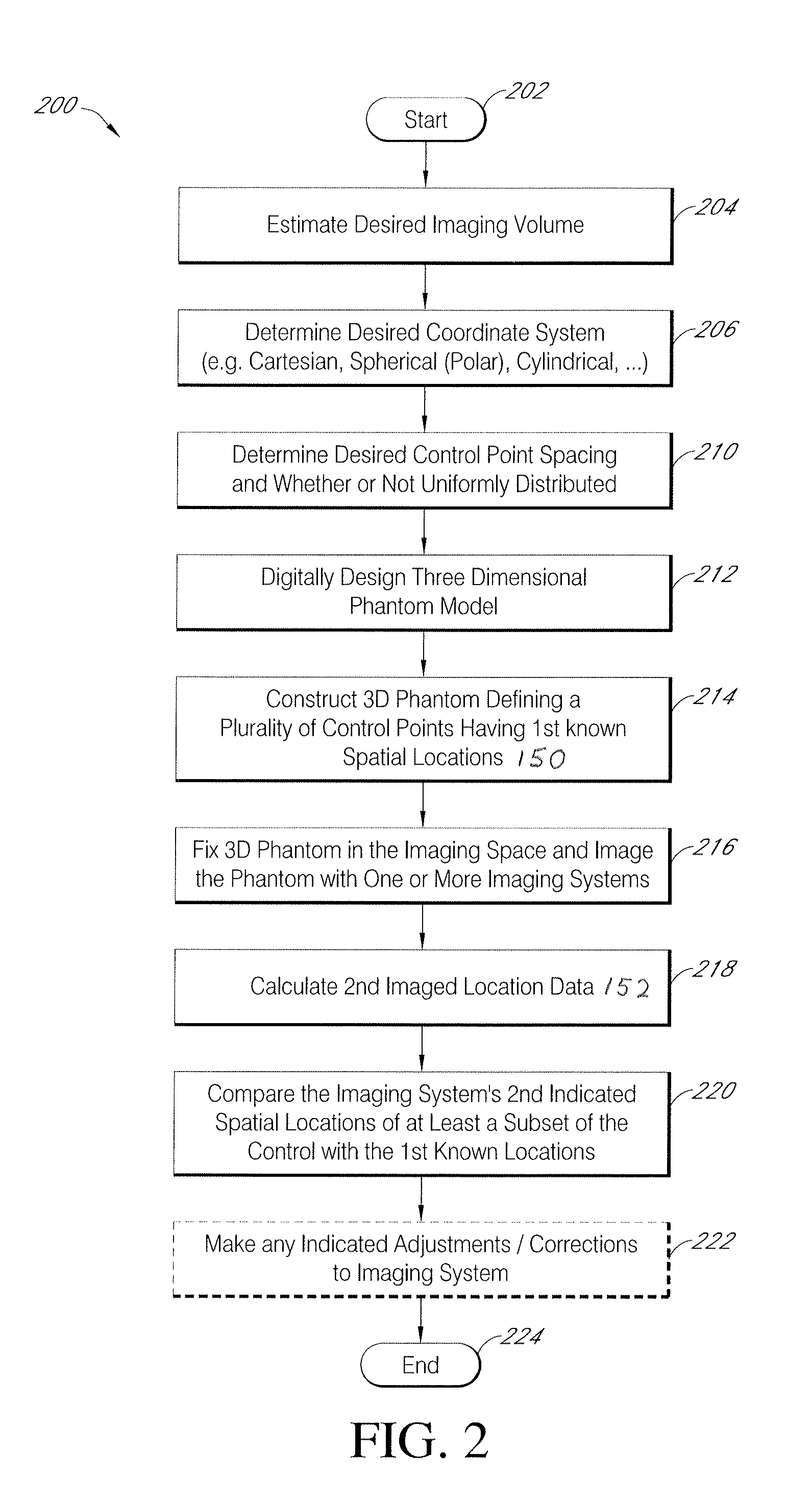
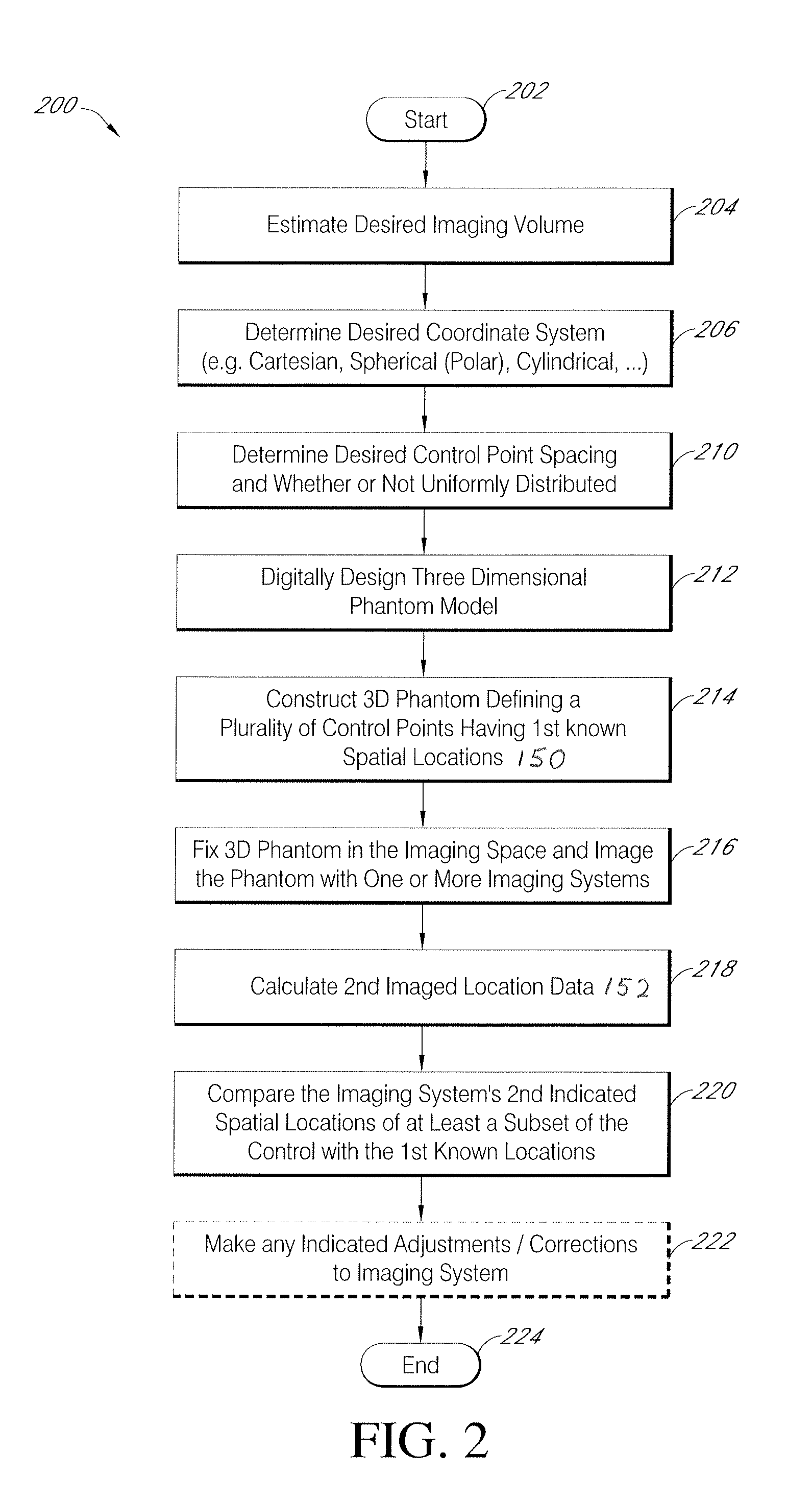
Systems and methods for characterizing spatial distortions in location data determined by an imaging system, for example as employed in imaged guided therapy. A three dimensional phantom is custom formed for a desired imaging space of a given imaging system. The phantom includes a large plurality of control points fixed rigidly in space to a high degree of known accuracy. The phantom is fixed to a stereotactic frame defining a known calibrated reference or zero and imaged. An algorithm customized for the phantom determines the spatial locations of the control points. A comparison is made between the known and the determined spatial locations for at least a subset of the control points. The comparison results in indicia for any determined spatial distortions observed. The raw image data can be manipulated to compensate for any spatial distortion. The control points can have fixed locations known to an accuracy of 100μ or better. The algorithm can determine an initial estimate for the detected location of a control point accurate to ±0.5 pixel or better.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT
Image projection system and method
ActiveUS7384158B2Improve image qualityShorten the optical path lengthTelevision system detailsMirrorsOptical reflectionImaging processing
An image projection system and method is presented for optically projecting an image onto a display surface with visually correct geometry and optimum image quality. The projection system includes an image processing unit for receiving the input image data and generating distortion-compensated image data to compensate for ensuing spatial distortions in the projection system, a projection light engine for receiving the distortion-compensated image data and projecting a distortion-compensated optical image that corresponds to the distortion-compensated image data; and, an optical reflection assembly comprising at least one curved mirror positioned in the optical path of the distortion-compensated optical image emerging from the projection light engine for producing a displayed optical image with reduced distortion on the display surface. The image processing unit distortion-compensates the input image data such that the optical and spatial distortions associated with the projection light engine and optical reflection assembly are substantially reduced in the displayed optical image.
Owner:APPLE INC +1
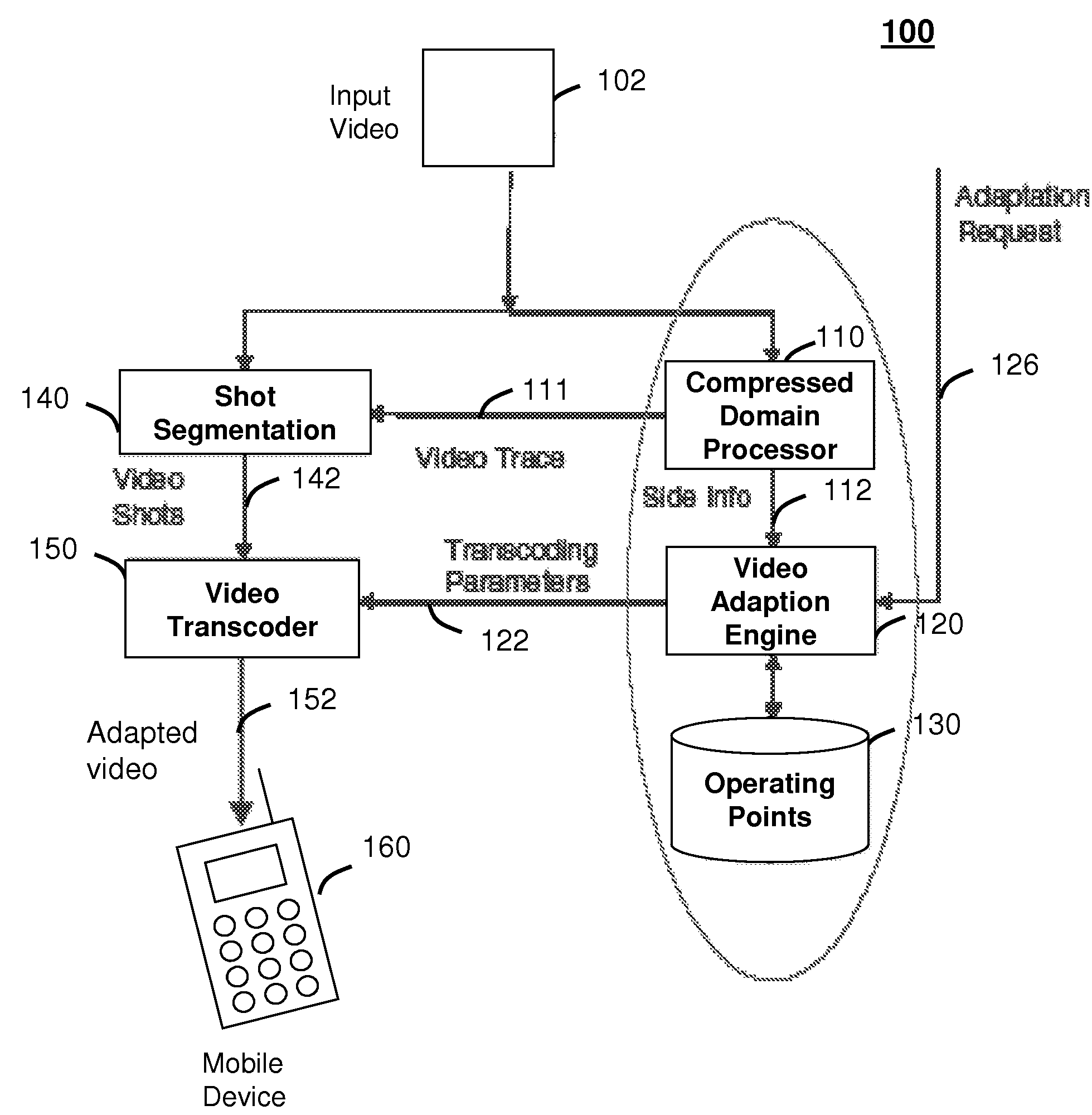
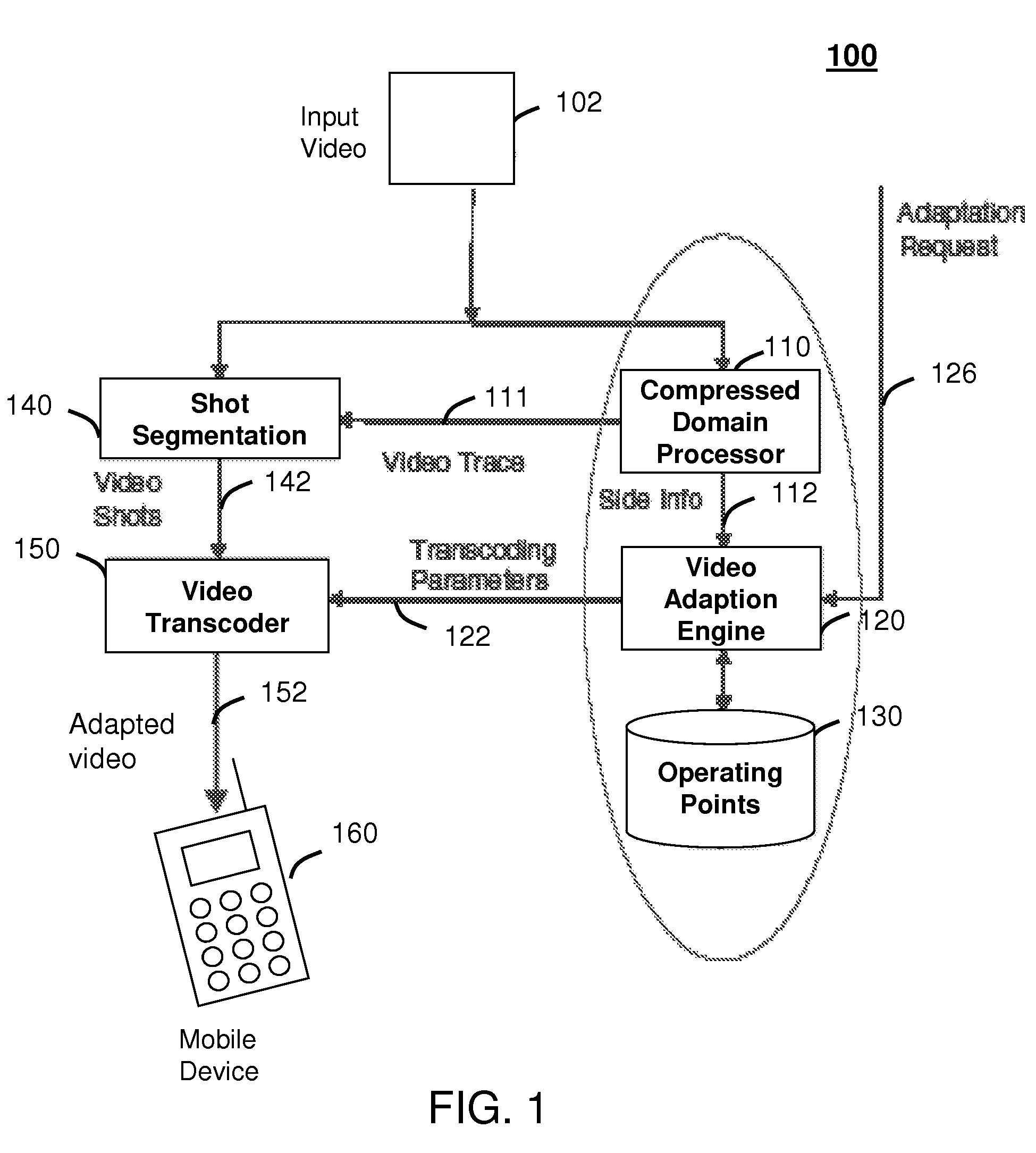
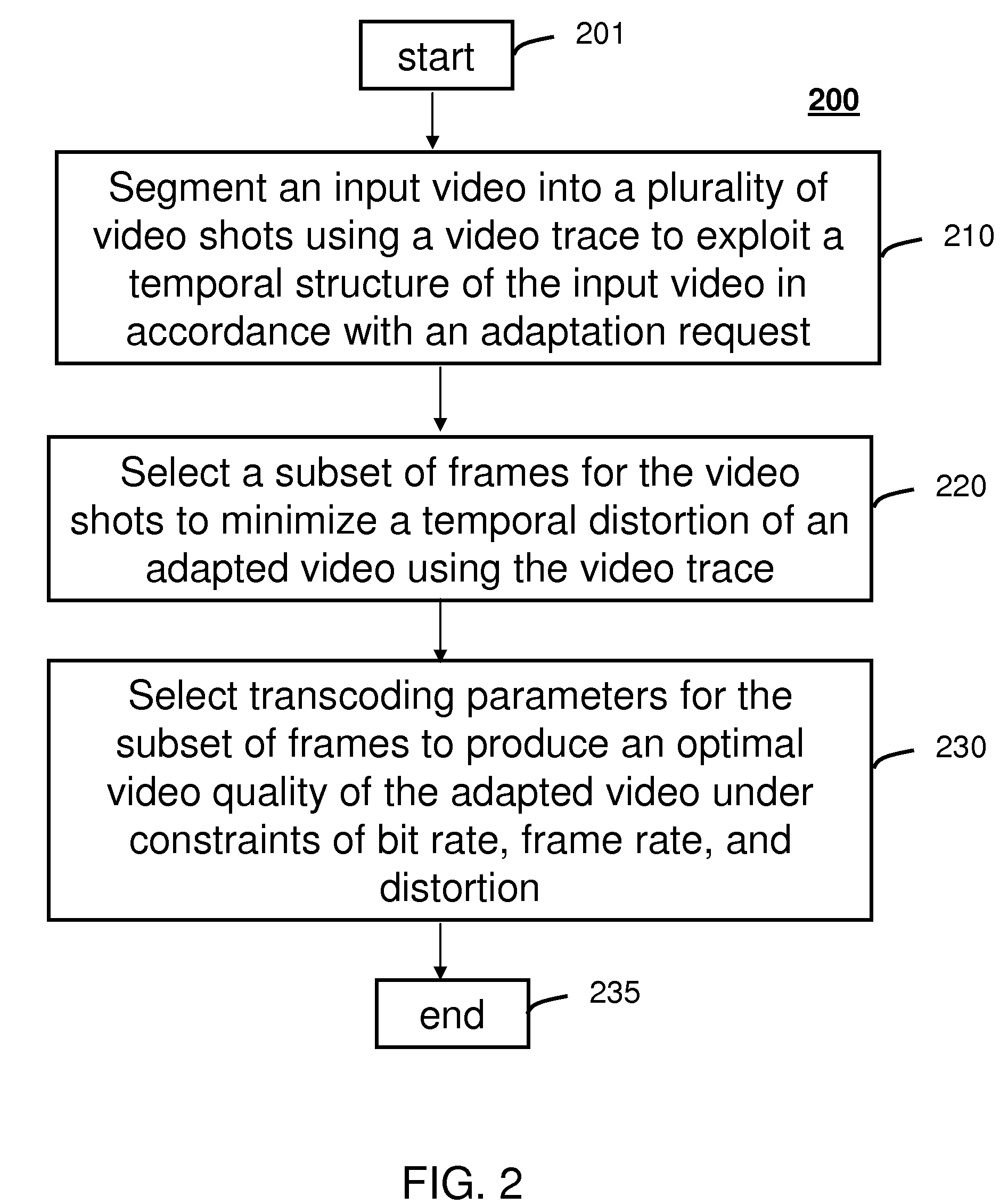
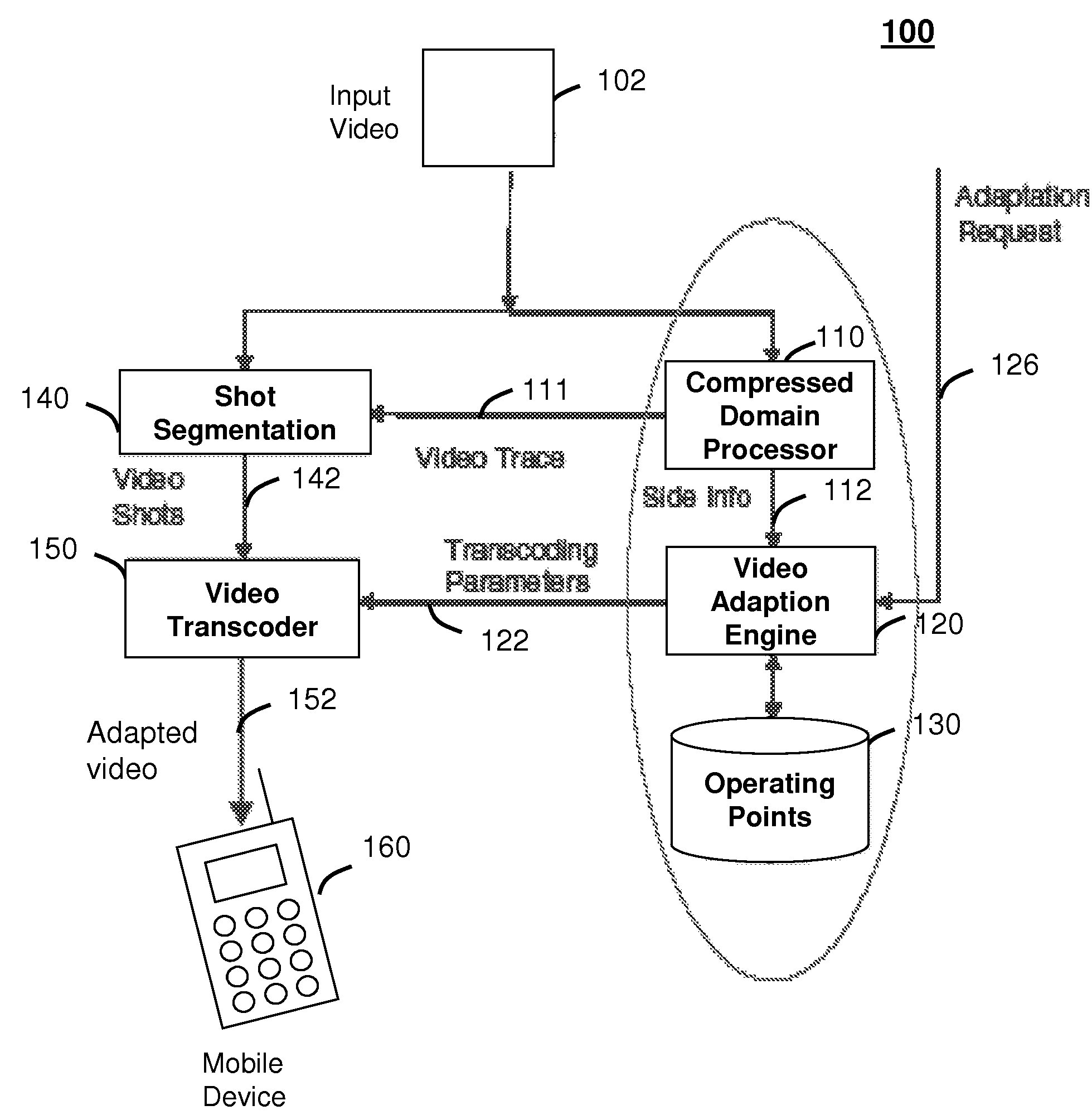
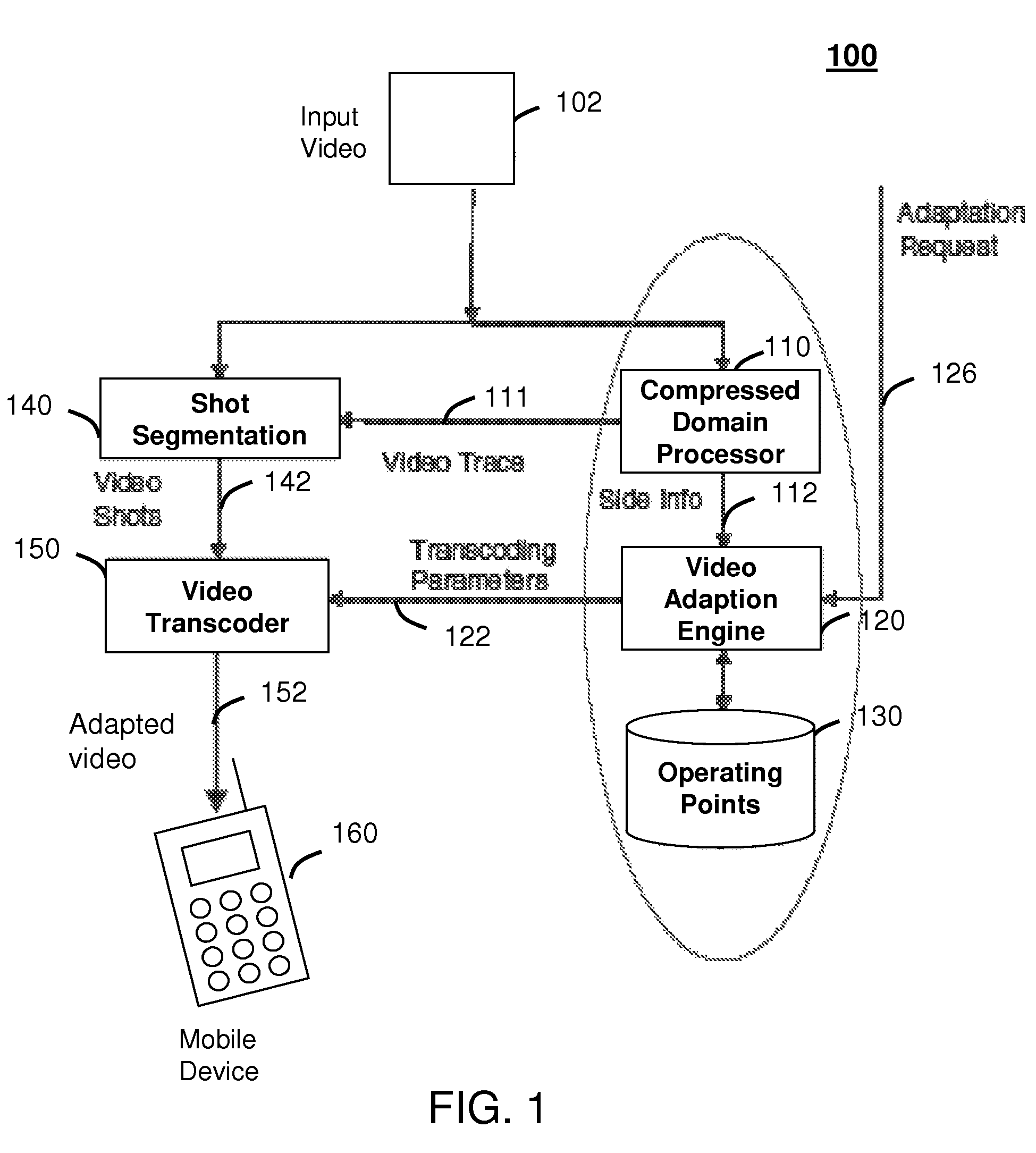
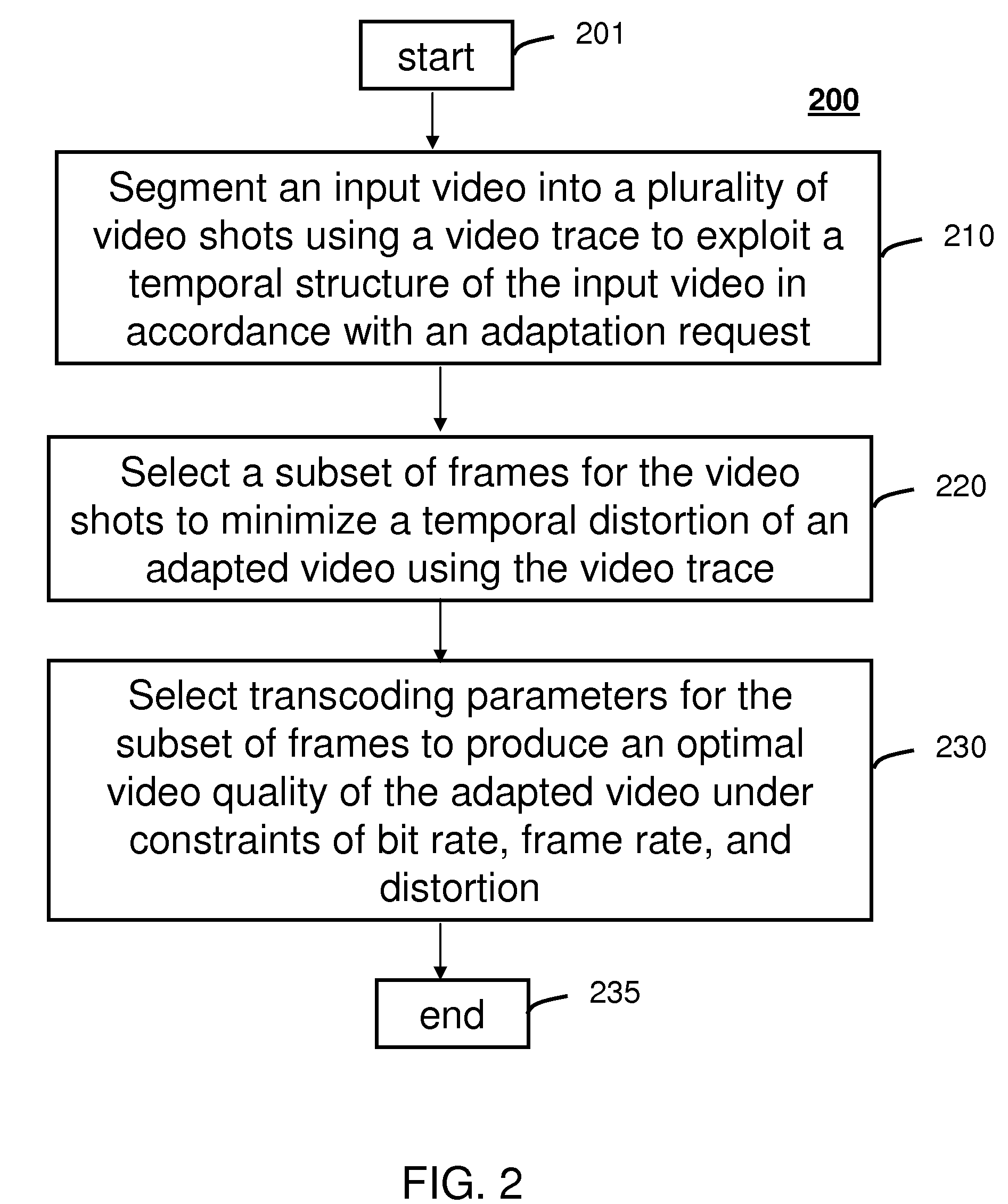
Method and system for intelligent video adaptation
InactiveUS20080123741A1Quality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTime structureRate distortion
A system (100) and method (200) for efficient video adaptation of an input video (102) is provided. The method can include segmenting (210) the input video into a plurality of video shots (142) using a video trace (111) to exploit a temporal structure of the input video, selecting (220) a subset of frames (144) for the video shots that minimizes a distortion of adapted video (152) using the video trace, and selecting transcoding parameters (122) for the subset of frames to produce an optimal video quality of the adapted video under constraints of frame rate, bit rate, and viewing time constraint. The video trace is a compact representation for temporal and spatial distortions for frames in the input video. A spatio-temporal rate-distortion model (320) provides selection of the transcoding parameters during adaptation.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Acoustic correction apparatus
An acoustic correction apparatus processes a pair of left and right input signals to compensate for spatial distortion as a function of frequency when the input signals are reproduced through speakers in a sound system. The sound-energy of the left and right input signals is separated and corrected in a first low-frequency range and a second high-frequency range. The resultant signals are recombined to create image-corrected audio signals having a desired sound-pressure response when reproduced by the speakers in the sound system. The desired sound-pressure response creates an apparent sound image location with respect to a listener. The image-corrected signals may then be spatially enhanced to broaden the apparent sound image.
Owner:DTS
Acoustic correction apparatus
InactiveUS20060062395A1Enhance the imageBroadening apparent stereo imageTwo-channel systemsLoudspeaker spatial/constructional arrangementsSound imageSound energy
An acoustic correction apparatus processes a pair of left and right input signals to compensate for spatial distortion as a function of frequency when the input signals are reproduced through speakers in a sound system. The sound-energy of the left and right input signals is separated and corrected in a first low-frequency range and a second high-frequency range. The resultant signals are recombined to create image-corrected audio signals having a desired sound-pressure response when reproduced by the speakers in the sound system. The desired sound-pressure response creates an apparent sound image location with respect to a listener. The image-corrected signals may then be spatially enhanced to broaden the apparent sound image.
Owner:DTS
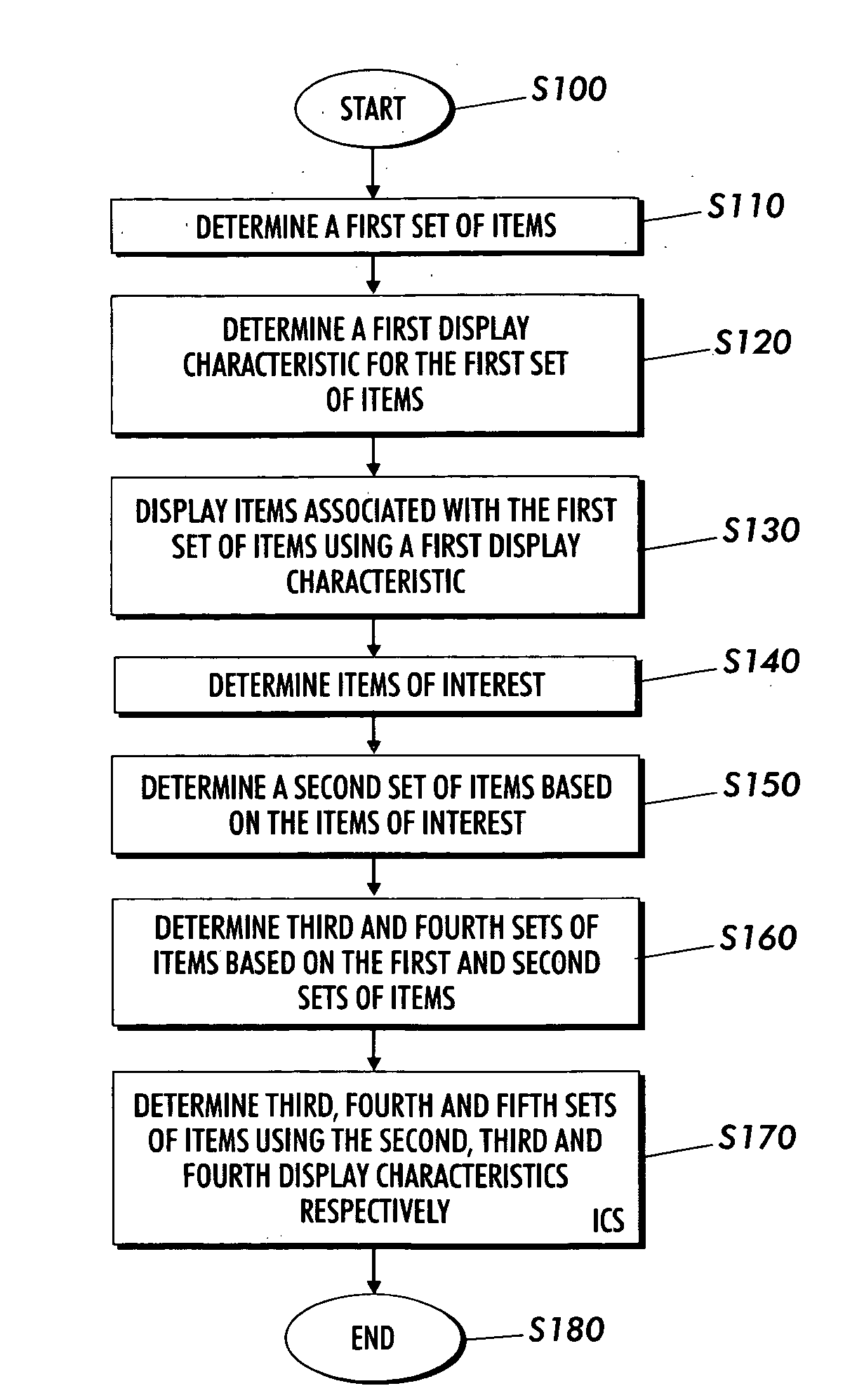
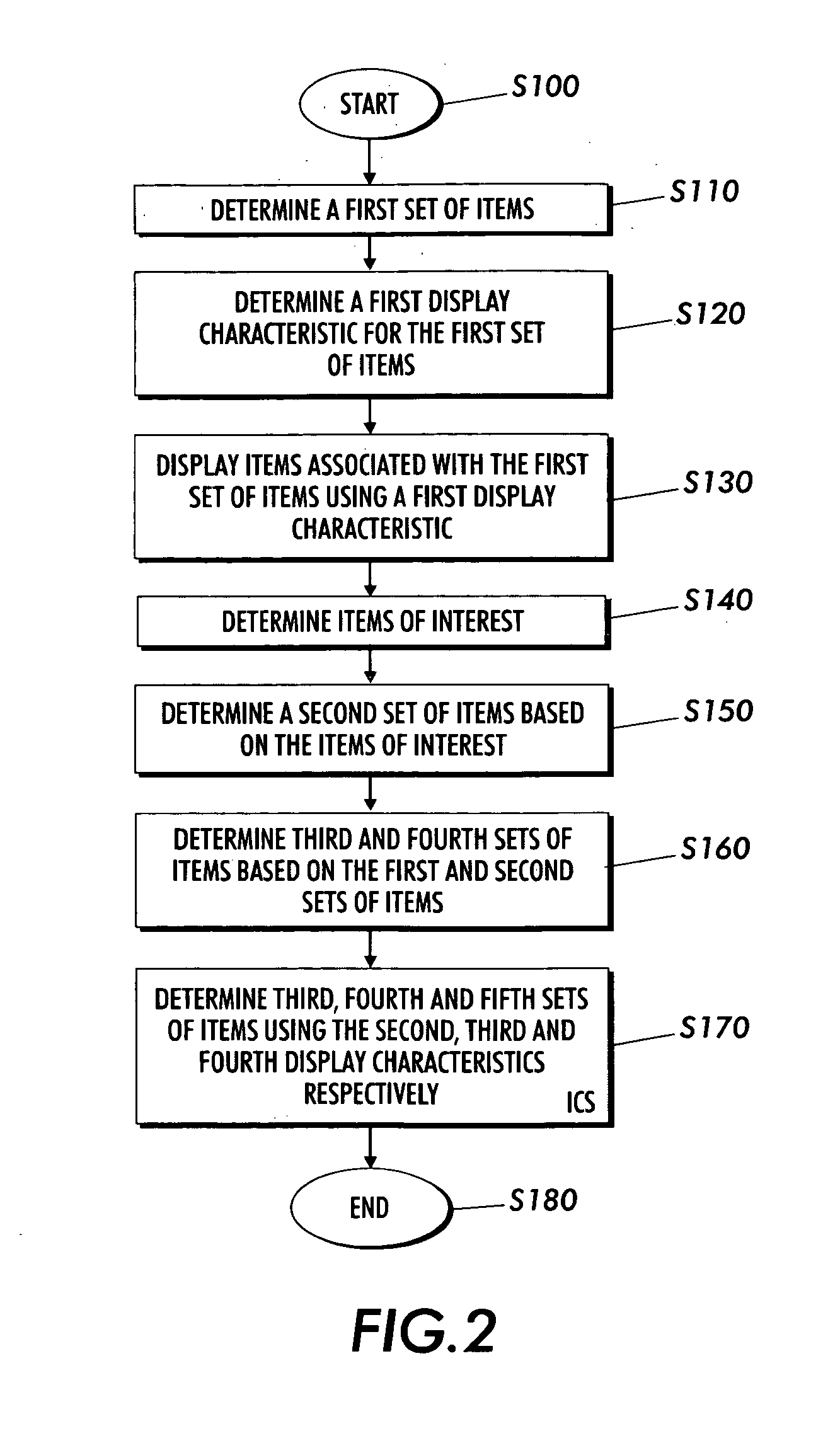
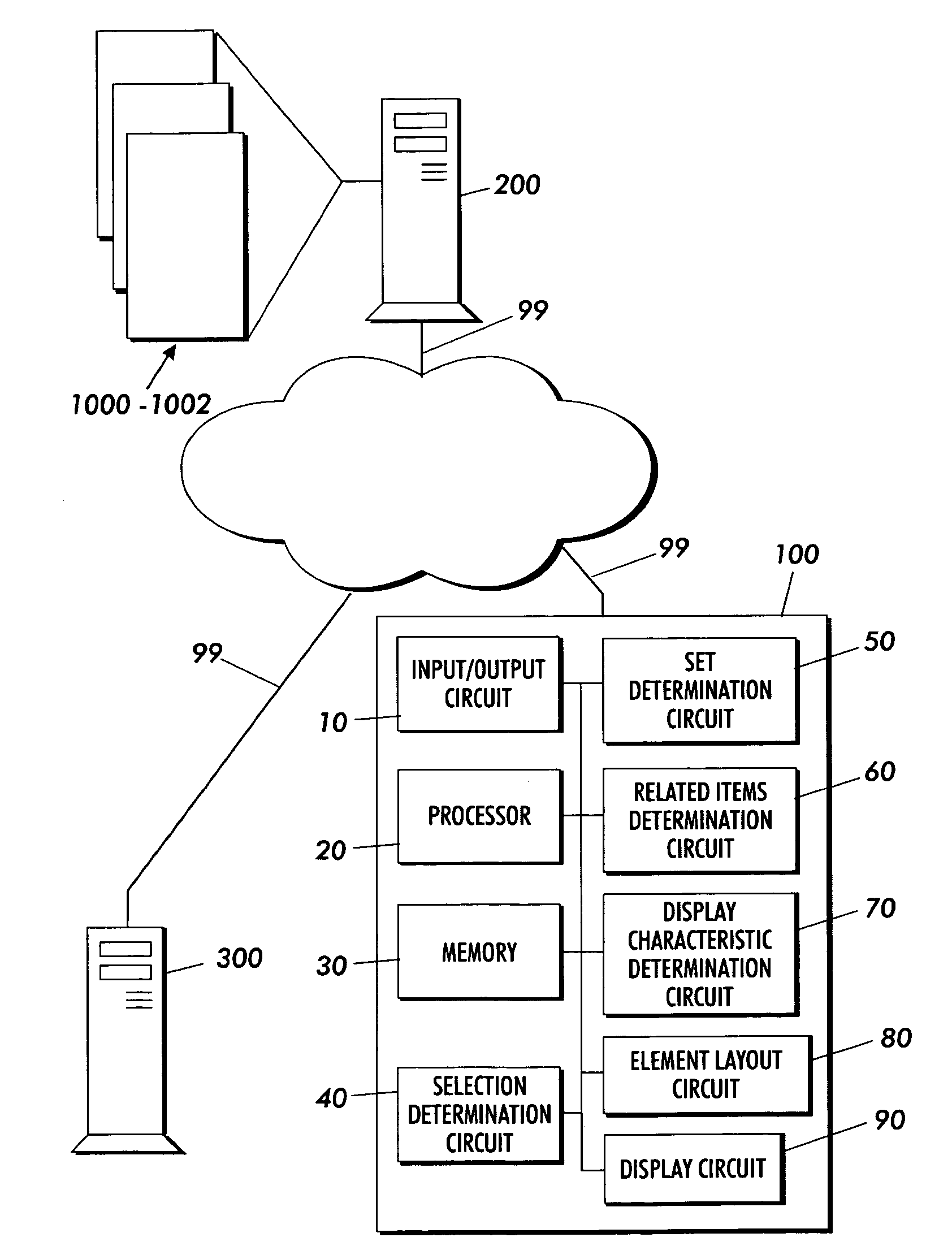
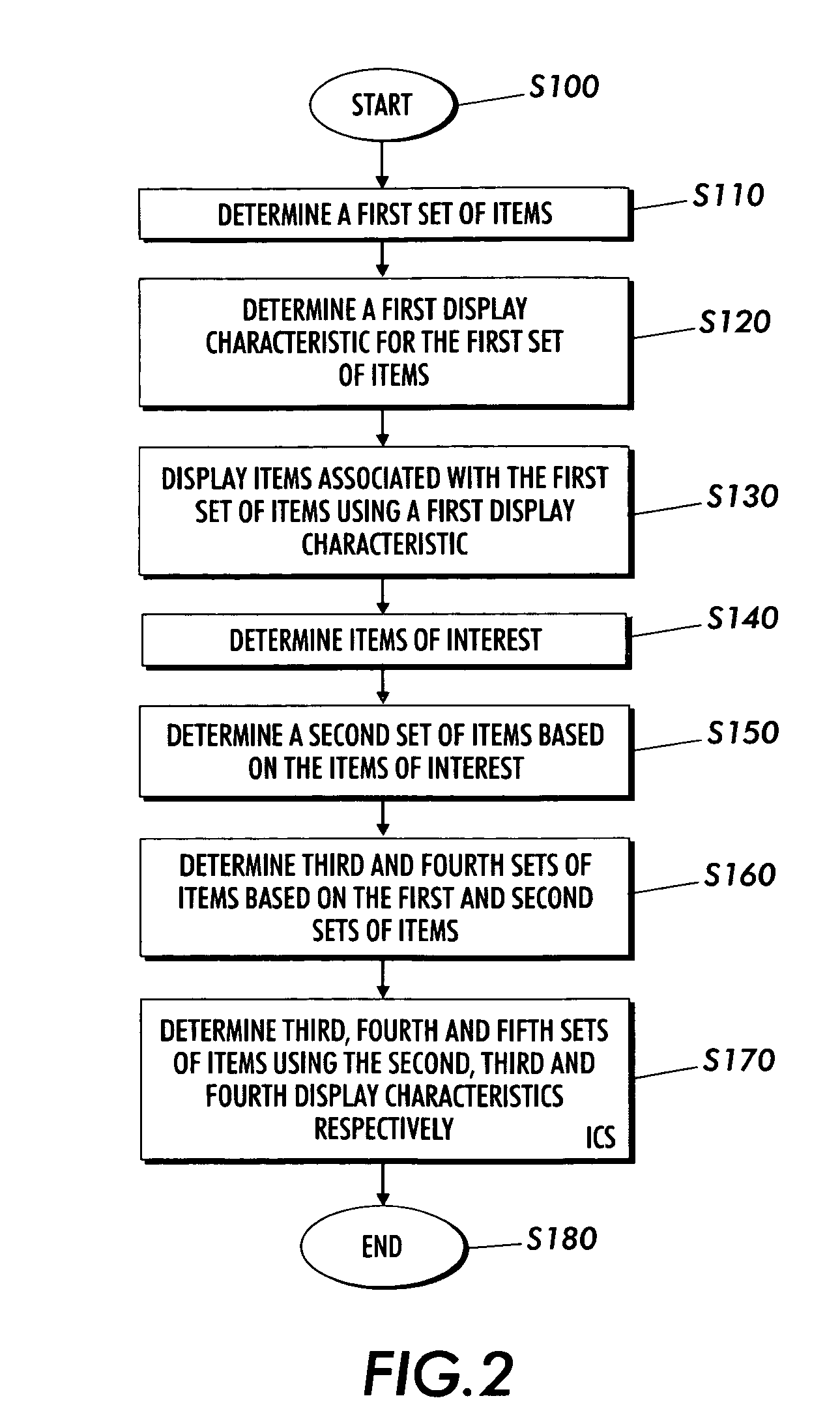
Systems and methods for displaying linked information in a sorted context
InactiveUS20060271883A1Data processing applicationsWeb data navigationInformation repositoryLogical operations
Techniques are presented for determining a first set of display elements, each display element associated with a first display characteristic. An interesting element in the first set of display elements is determined. A second set of elements related to the interesting element is determined. A third set of elements based on the first and second set of elements is determined using intersection, union, subtraction addition and other logical operations. A third set of elements not yet added to the element collection is determined. The elements in the third set are associated with a second or ghosted display characteristic. The elements in the third set are inserted within the sorted context of the visualization based on spatial distortion rules which help to preserve spatial memory cues in the visualization of the element collection. The elements may be documents in an information repository, linked contact information, linked information records in a database or other types of information.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Method for assessing the quality of a distorted version of a frame sequence
InactiveUS20090274390A1Ass qualityQuality improvementImage enhancementImage analysisComputer hardwareFrame sequence
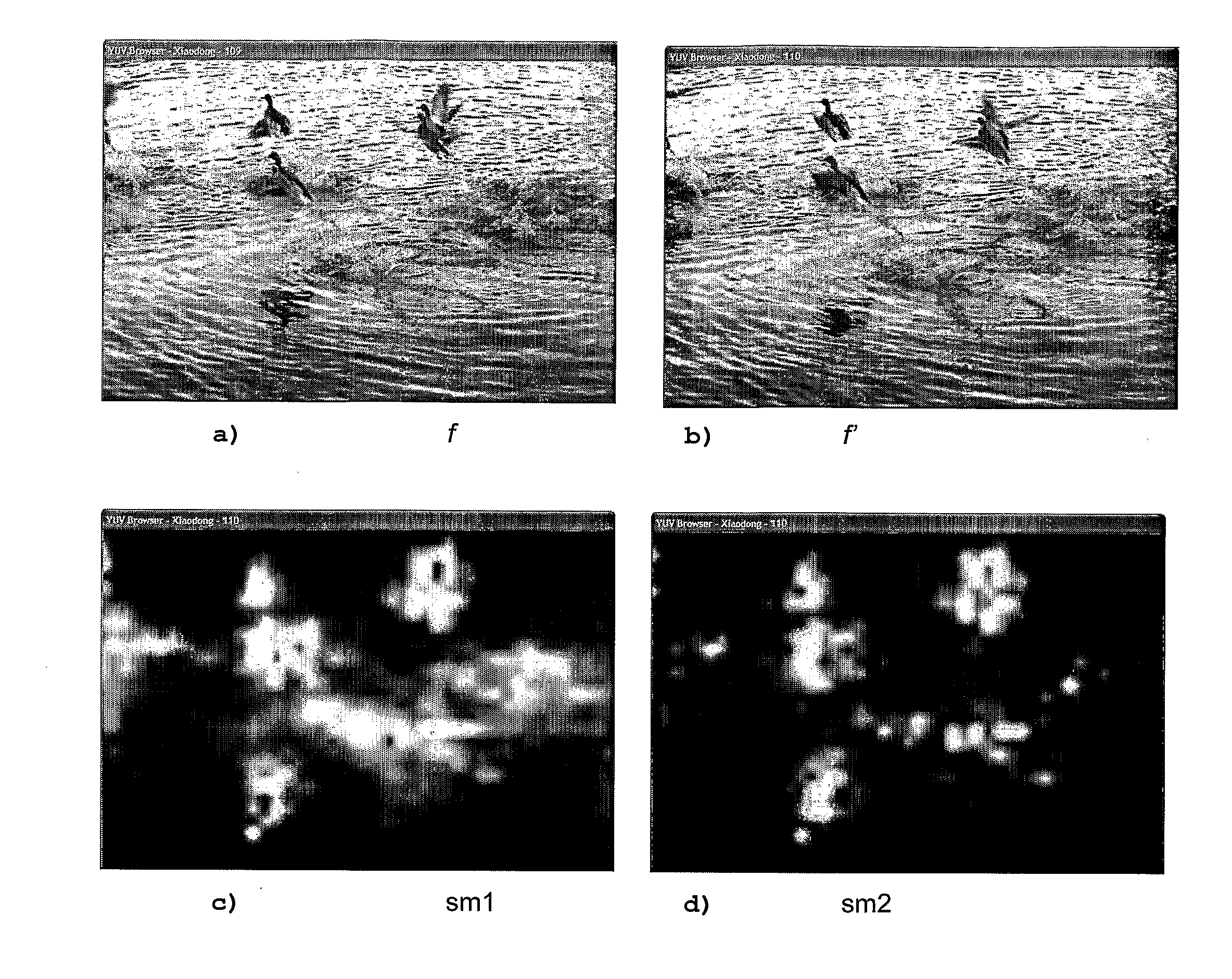
The invention is related to a method for video quality assessment.Said method comprises the steps of determining a last spatial distortion by comparing a block of a last frame (I6) of the sequence with a corresponding block of the distorted version of the last frame, determining, in a last-but-one frame, a best-matching block matching said block of the last frame best, determining a last-but-one spatial distortion by comparing the determined best-matching block of the last-but-one frame with a corresponding block of the distorted version of the last-but-one frame, determining a spatio-temporal perceptual distortion value associated with said block using said determined distortions and using the determined spatio-temporal perceptual distortion value for assessing the quality.The spatial distortion's temporal evolution improves video quality assessment.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
Handheld cellular apparatus for volume estimation
InactiveUS20140368639A1Color television detailsClosed circuit television systemsProgram instructionSpatial distortion
What is disclosed is a wireless cellular device capable of determining a volume of an object in an image captured by a camera of that apparatus. In one embodiment, the present wireless cellular device comprises an illuminator for projecting a pattern of structured light with known spatial characteristics, and a camera for capturing images of an object for which a volume is to be estimated. The camera is sensitive to a wavelength range of the projected pattern of structured light. A spatial distortion is introduced by a reflection of the projected pattern off a surface of the object. And processor executing machine readable program instructions for performing the method of: receiving an image of the object from the camera; processing the image to generate a depth map; and estimating a volume of the object from the depth map. A method for using the present wireless cellular device is also provided.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Multi-scale geometric remote sensing image fusion method based on deep sparse self-coding
ActiveCN106204450AIntegrity guaranteedKeep Spectral InformationImage enhancementImage analysisRemote sensing image fusionImage resolution
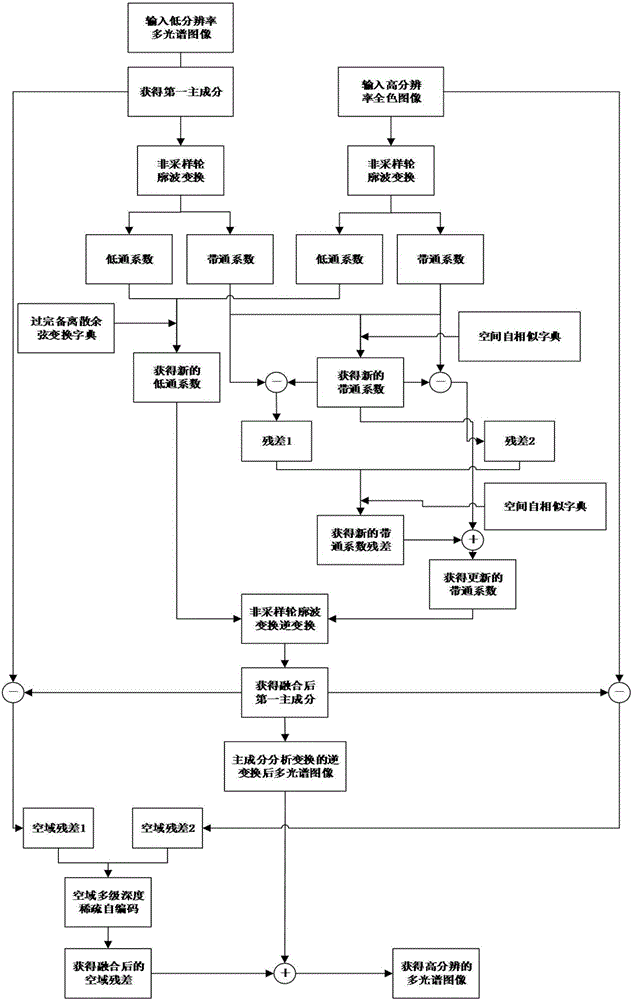
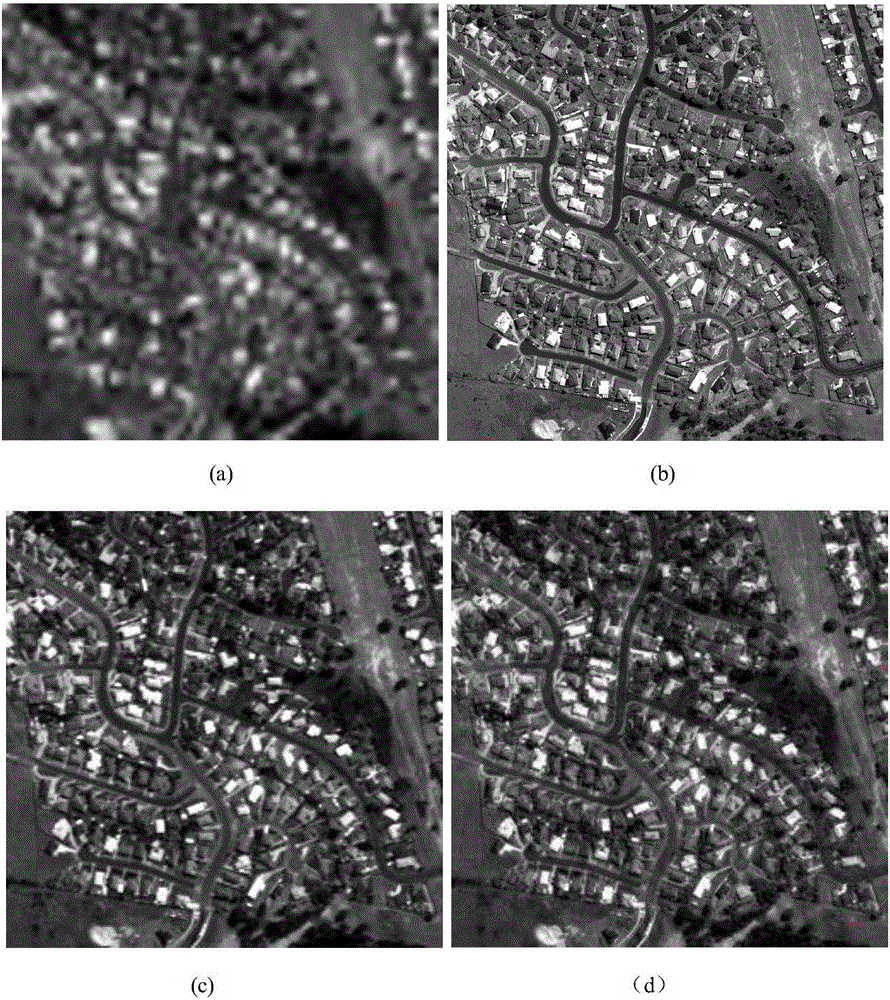
The invention discloses multi-scale geometric remote sensing image fusion based on deep sparse self-coding. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) inputting a low-resolution multispectral image M and high-resolution full-color image P, extracting first principal component C1 of the M; 2) obtaining the low-pass coefficient LM and the band-pass coefficient HM of the C1, and the low-pass coefficient LP and the band-pass coefficient HP of the P; 3) fusing the LM and LP to obtain a low-pass coefficient LN; 4) constructing a space self-similar dictionary DS and fusing the HM and HP to obtain the band-pass coefficient HN under the dictionary DS; 5) updating the HN to obtain the band-pass coefficient HNS; and 6) performing inverse transformation on the LN and the HNS to obtain a fused first principal component C2, updating the C2 to obtain a updated first principal component CS; and 7) performing inverse transformation on the CS to obtain the high-resolution multispectral image. The method reduces the injection of mismatched details, improves the spatial distortions of the fused multispectral images, and can be used for target recognition, terrain classification and remote sensing monitoring.
Owner:XIANYANG NORMAL UNIV
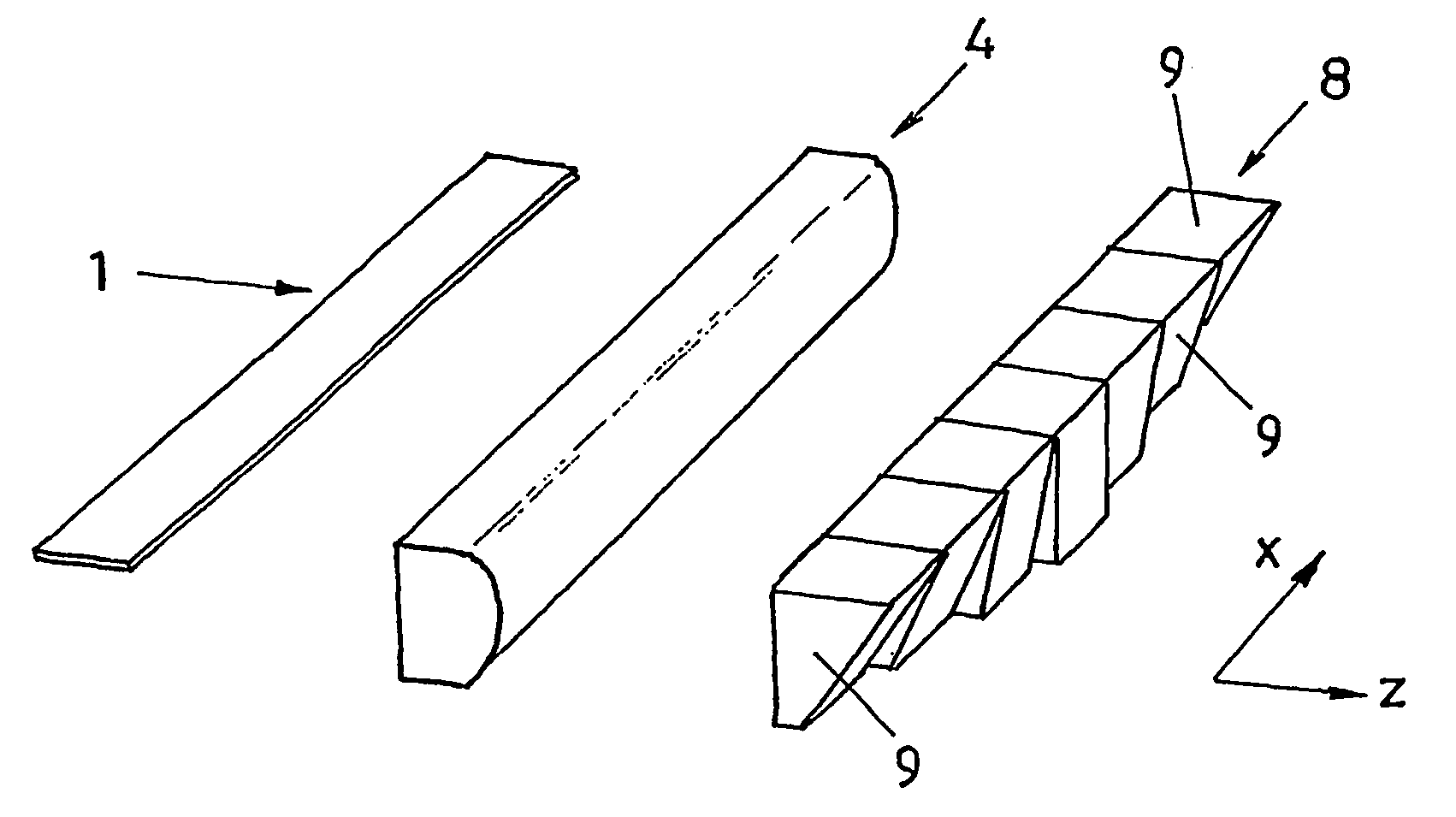
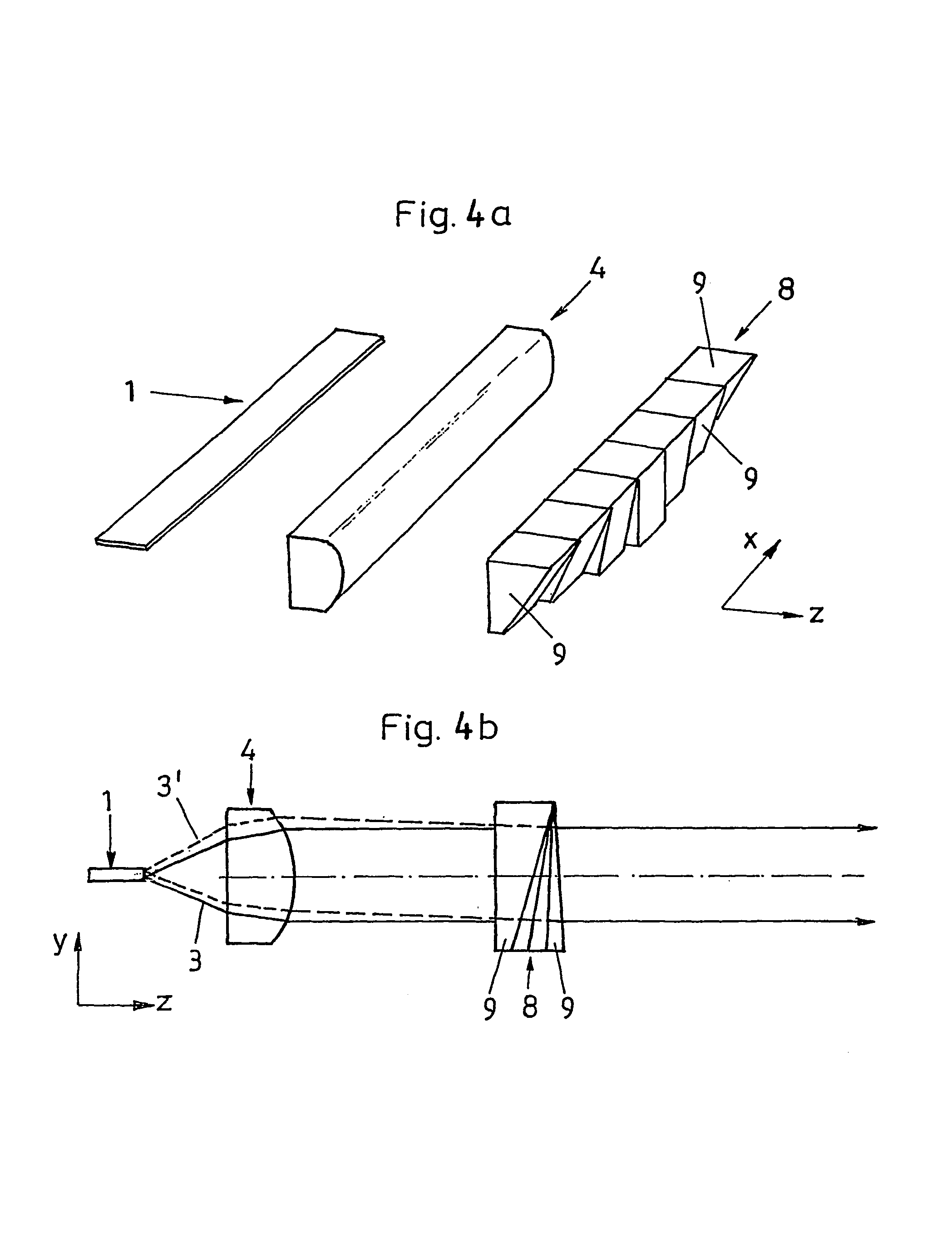
Assembly for correcting laser illumination emitted from a laser light source and method for producing said assembly
The invention relates to an assembly for correcting laser illumination emitted from a laser light source, comprising a laser light source, which has linear emission sources that are arranged in a row in a first direction (X), whereby in addition, the emission sources that are arranged essentially in a row are at least partially offset relative to the row in a perpendicular direction (Y) in relation to the first direction (X). The assembly also comprises corrective elements, which can correct the laser illumination emitted from the laser light source in such a way that the spatial distortion of the laser illumination, caused by the offset position of the emission sources relative to the row, is compensated. According to the invention, the corrective elements are configured as a plate array that comprises a number of plate elements consisting of substantially plane-parallel plates that are transparent to the laser illumination used. At least two of the plate elements have a different thickness and the corrective mans is located in the laser illumination emitted from the laser light source, in such a way that the light beams emitted from at least two emission sources that are offset in relation to one another are subjected to a respective beam offset of a different magnitude by two different plate elements, thus compensating the distortion caused by the offset position of the emission sources. The invention also relates to a method for producing the aforementioned assembly.
Owner:LIMO GMBH
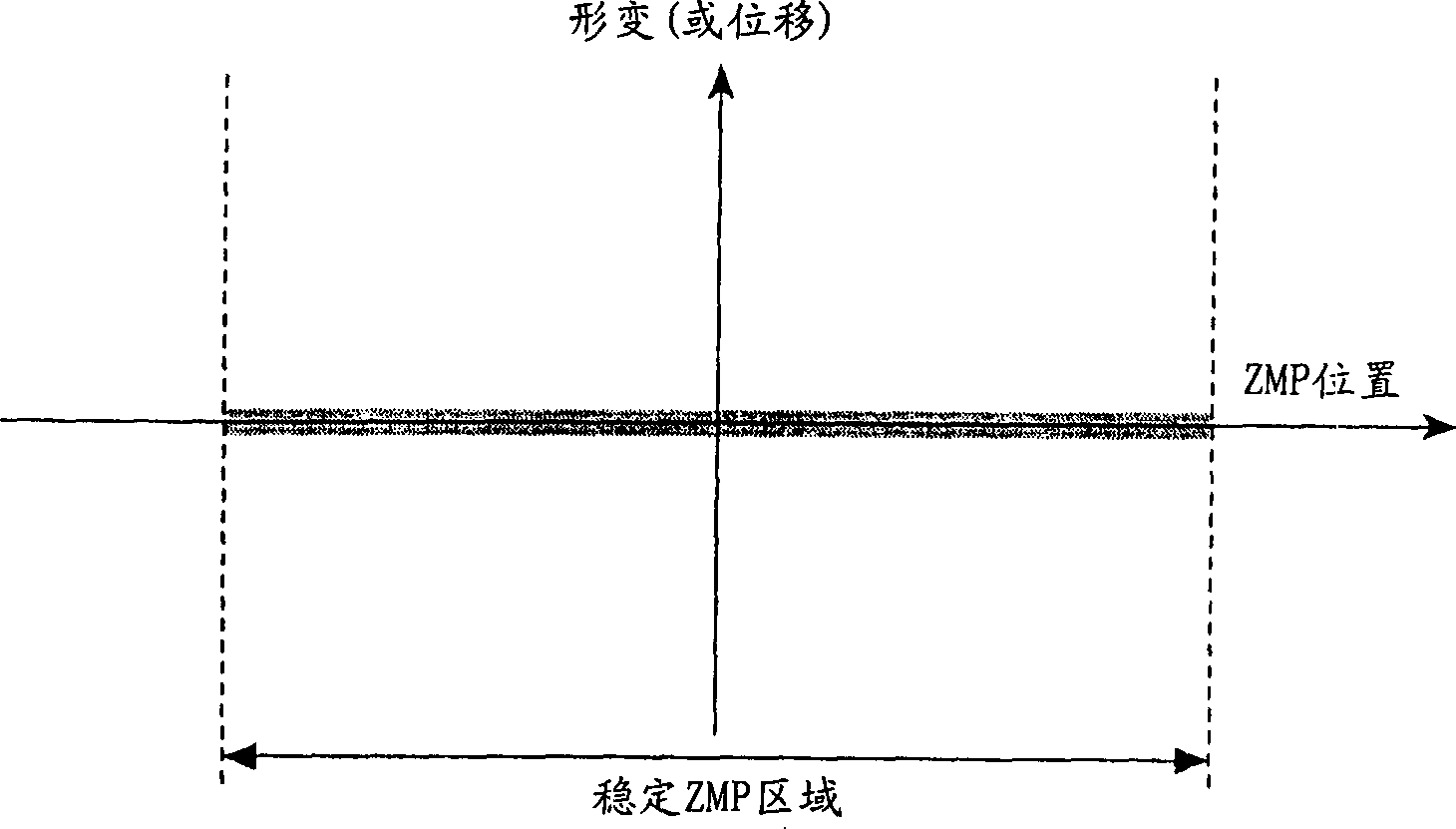
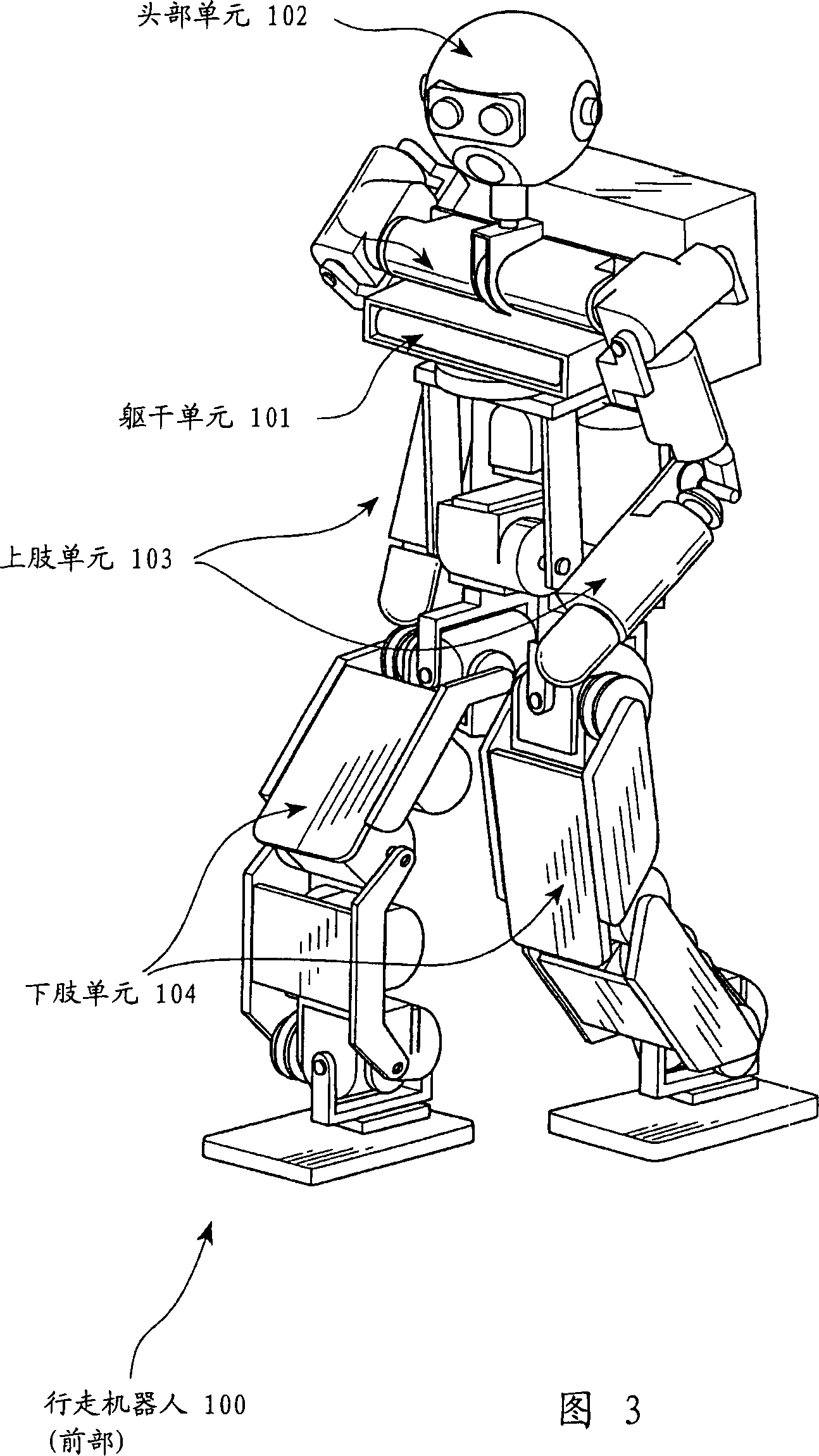
Legged mobile robot and control method thereof, leg structure and mobile leg unit for legged mobile robot
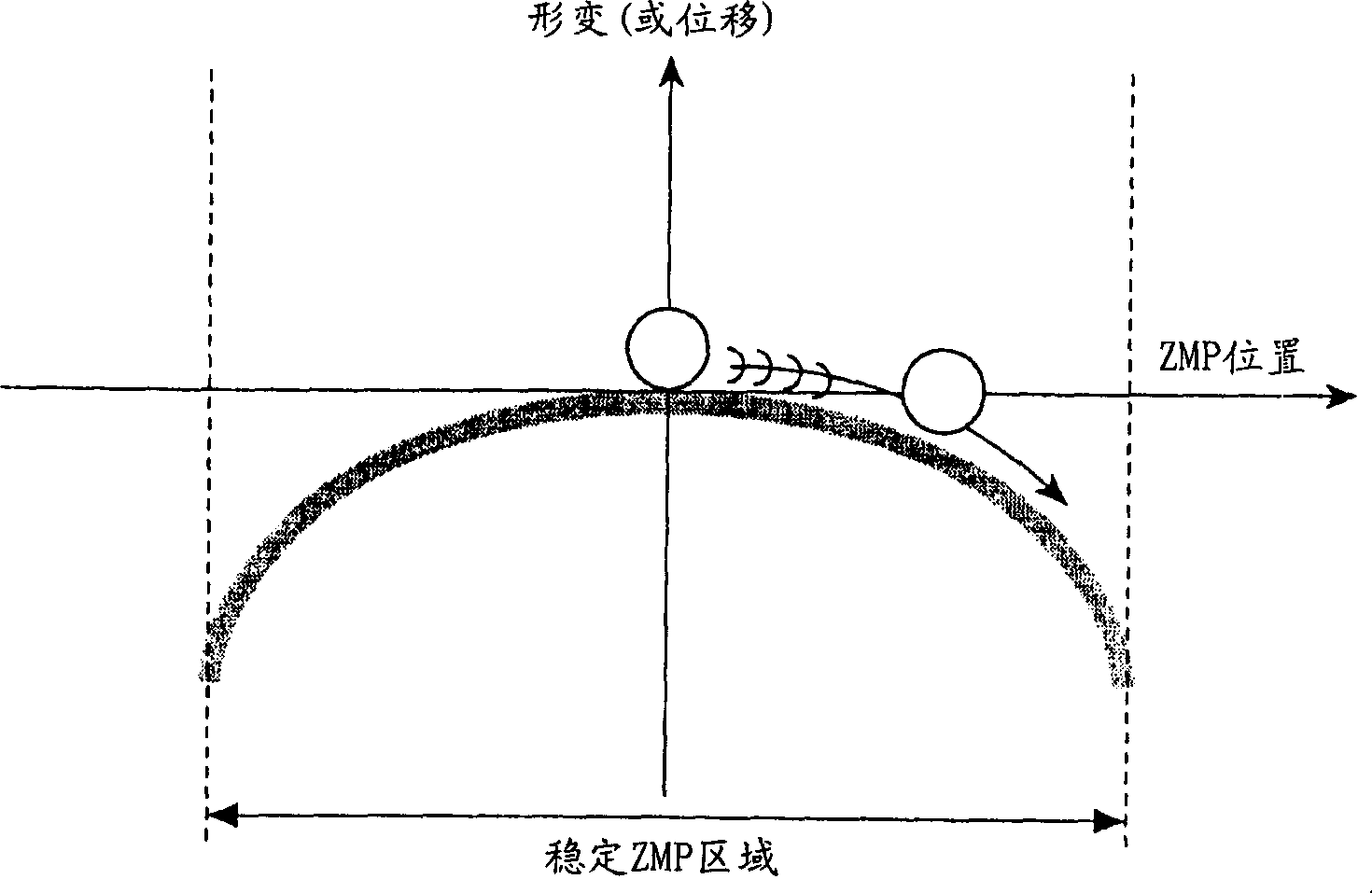
A legged mobile robot the body of which can be controlled in attitude stabilization by using ZMP stability determining norms with a relatively slow sampling period. The legged mobile robot has a ZMP stable region comprising a supporting polygon formed by a sole contact point of a mobile leg with the road surface, and a ZMP behavior space in which deformation or momentum of the robot body is generated so that the ZMP is directed toward generally the center of the ZMP stable region. Regarding the sign of the deformation (or momentum) of the robot in the ZMP behavior space, the negative sign is defined to be the direction in which a spatial distortion causing the ZMP toward the edge of the stable region is produced while the positive sign is defined to be the direction in which a spatial distortion causing the ZMP toward the center of the stable region is produced.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
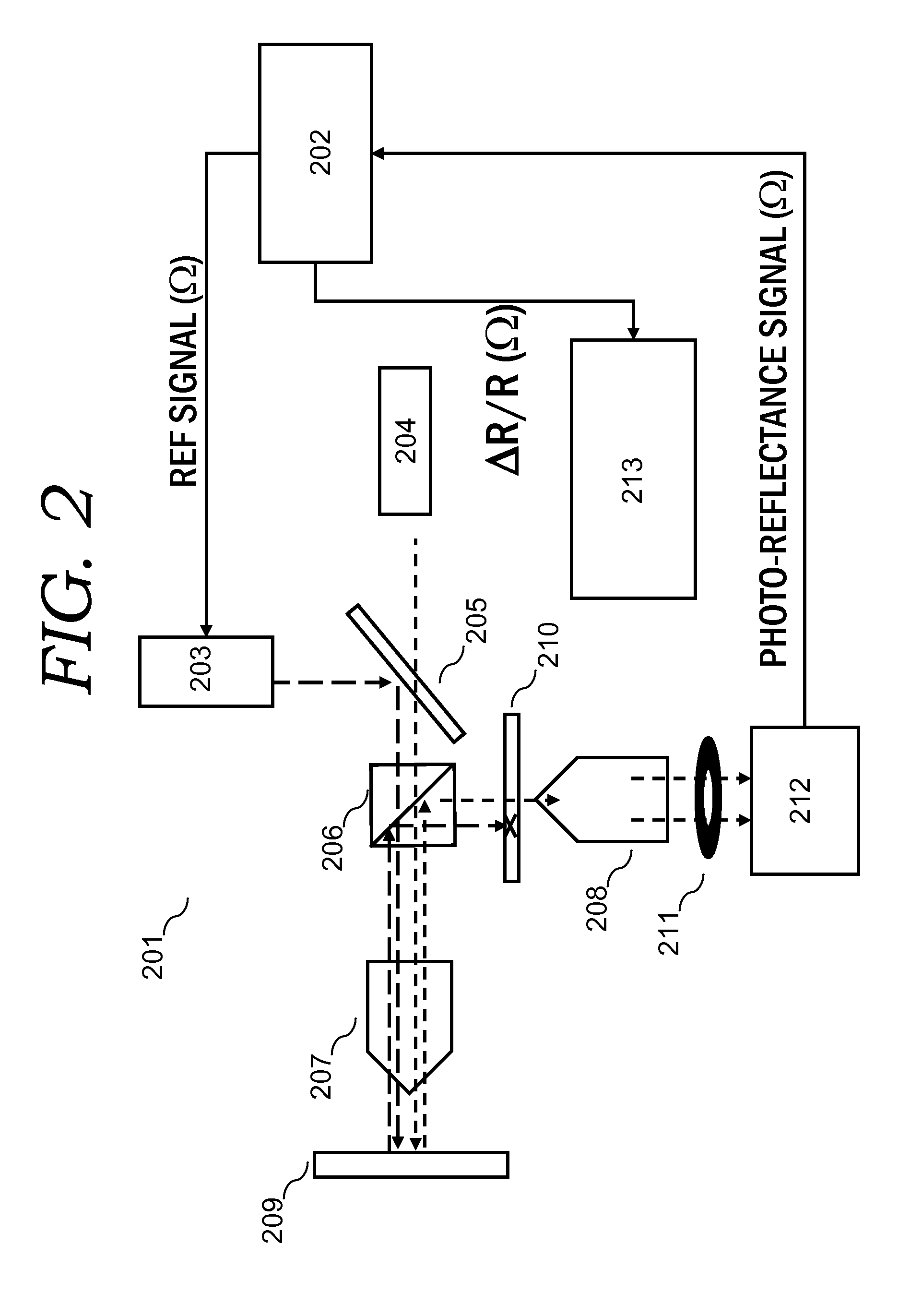
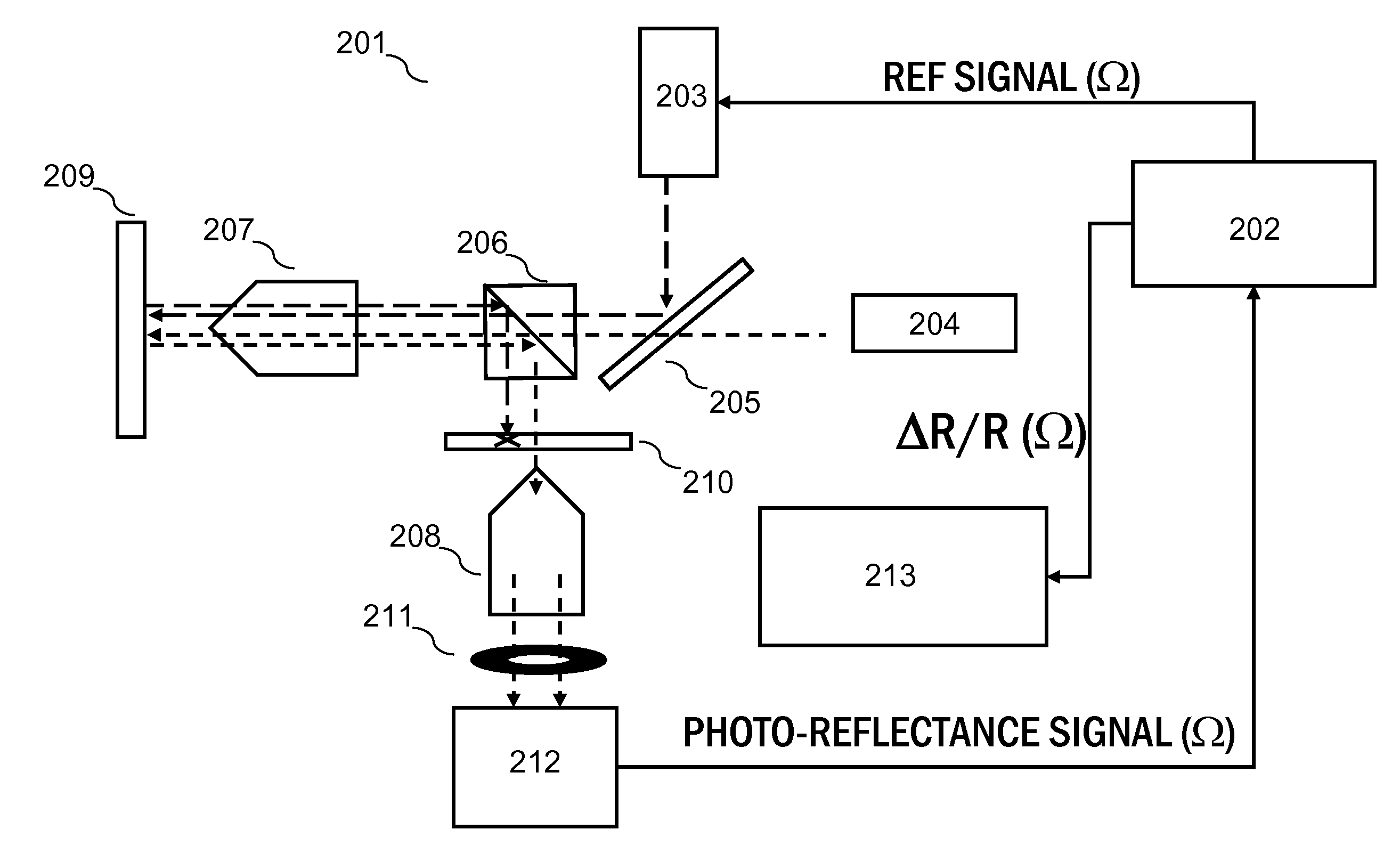
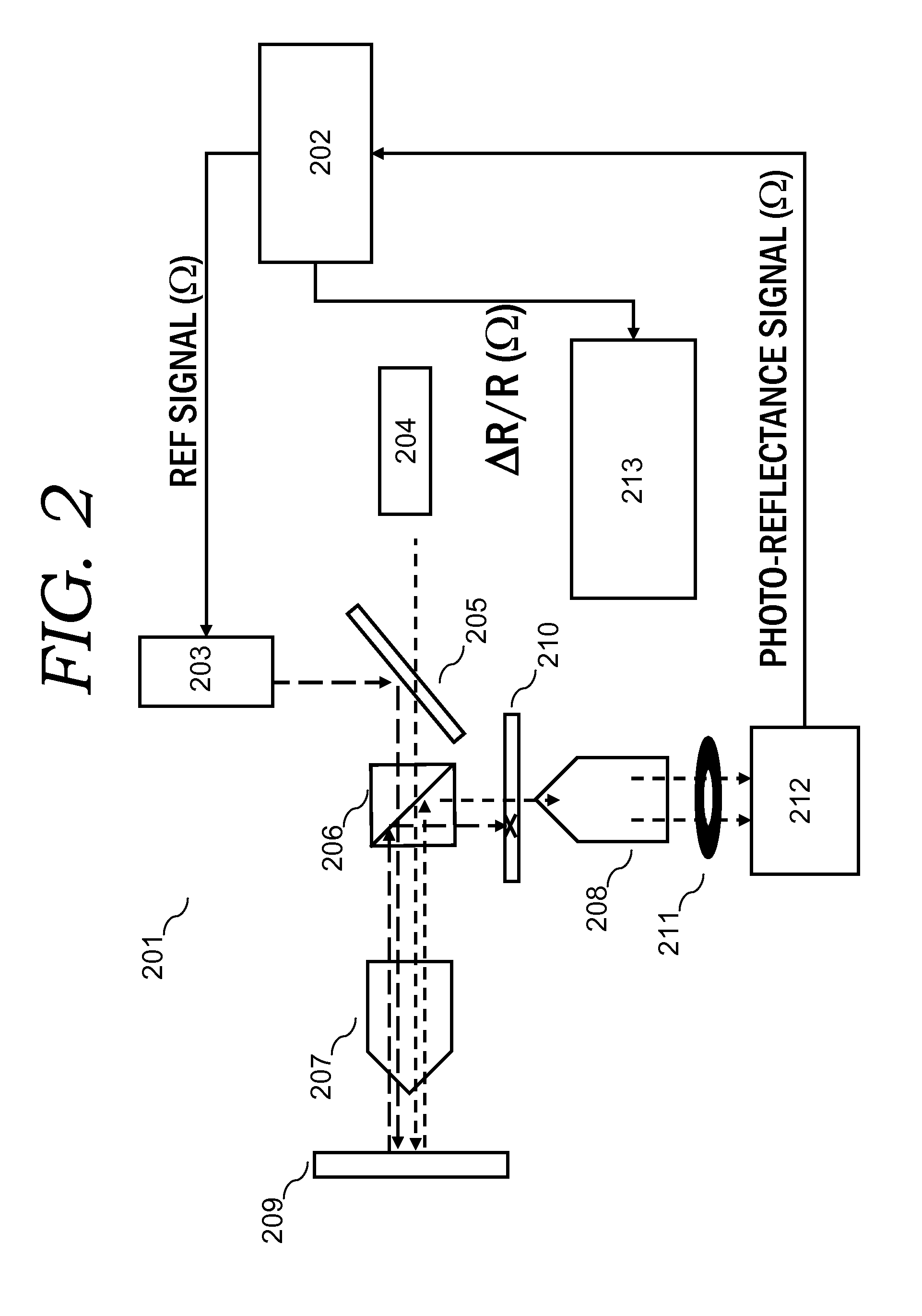
Method and Apparatus of Z-Scan Photoreflectance Characterization
ActiveUS20100315646A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsSemiconductor structureLight beam
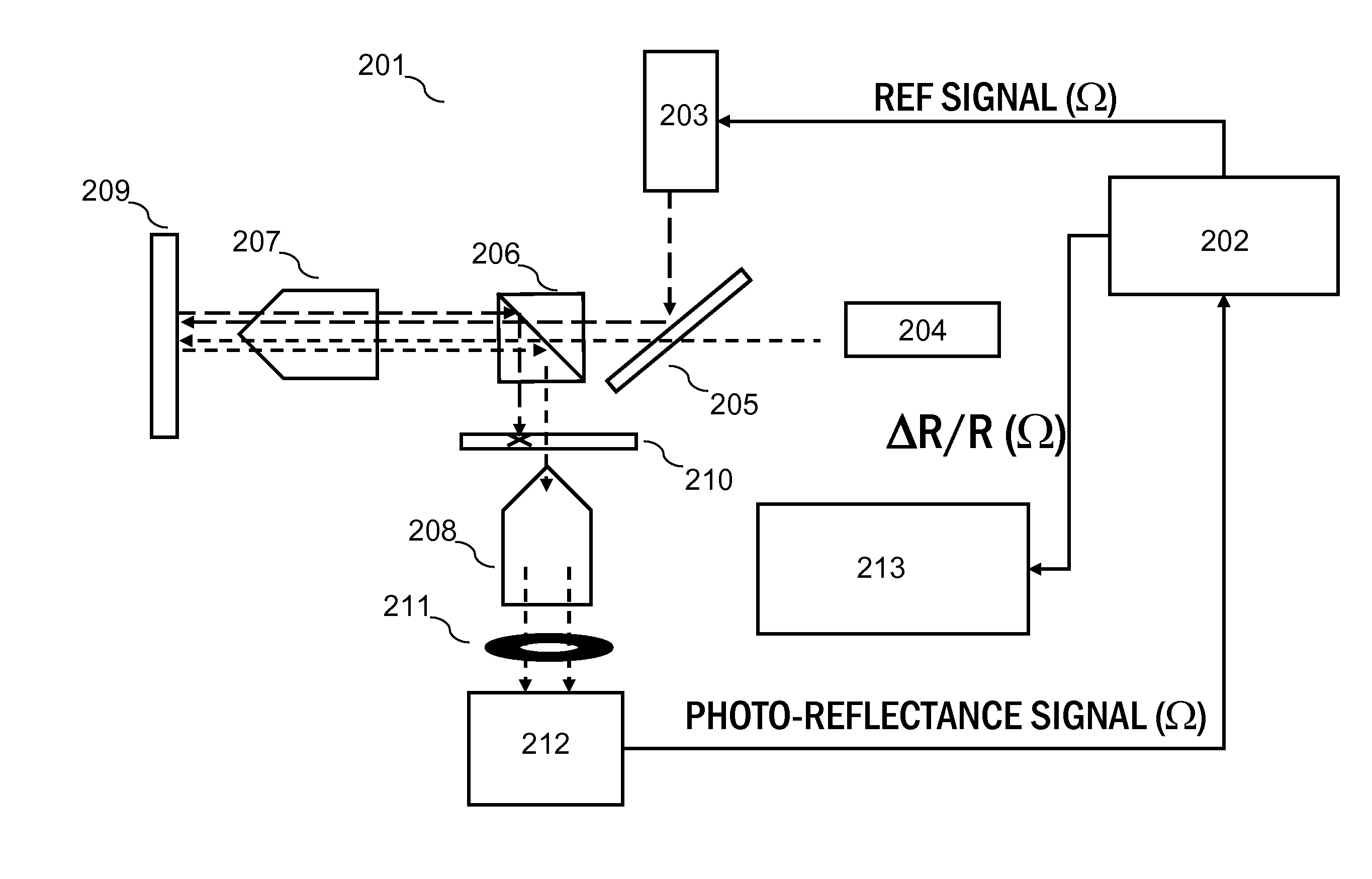
A method of z-scan photo-reflectance characterization of semiconductor structures and apparatus for same has been developed. The method and apparatus provides the ability to independently measure electro-refractive and electro-absorptive nonlinearities that occur in conventional photo-reflectance signals. By performing a series of photo-reflectance measurements, each containing photo-modulated nonlinear optical signals, with the sample at a multiplicity of positions along the focal length of the probe light column, and with an aperture fixtured in the reflected probe path, precision characterization of both electro-refractive and electro-absorptive nonlinearities is attained. The Z-scan photo-reflectance method and apparatus characterizes spatial distortions of a coherent photo-reflectance probe light beam due to electro-refractive and electro-absorptive effects.
Owner:XITRONIX CORP
Systems and methods for displaying linked information in a sorted context
InactiveUS7562085B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsInformation repositoryLogical operations
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
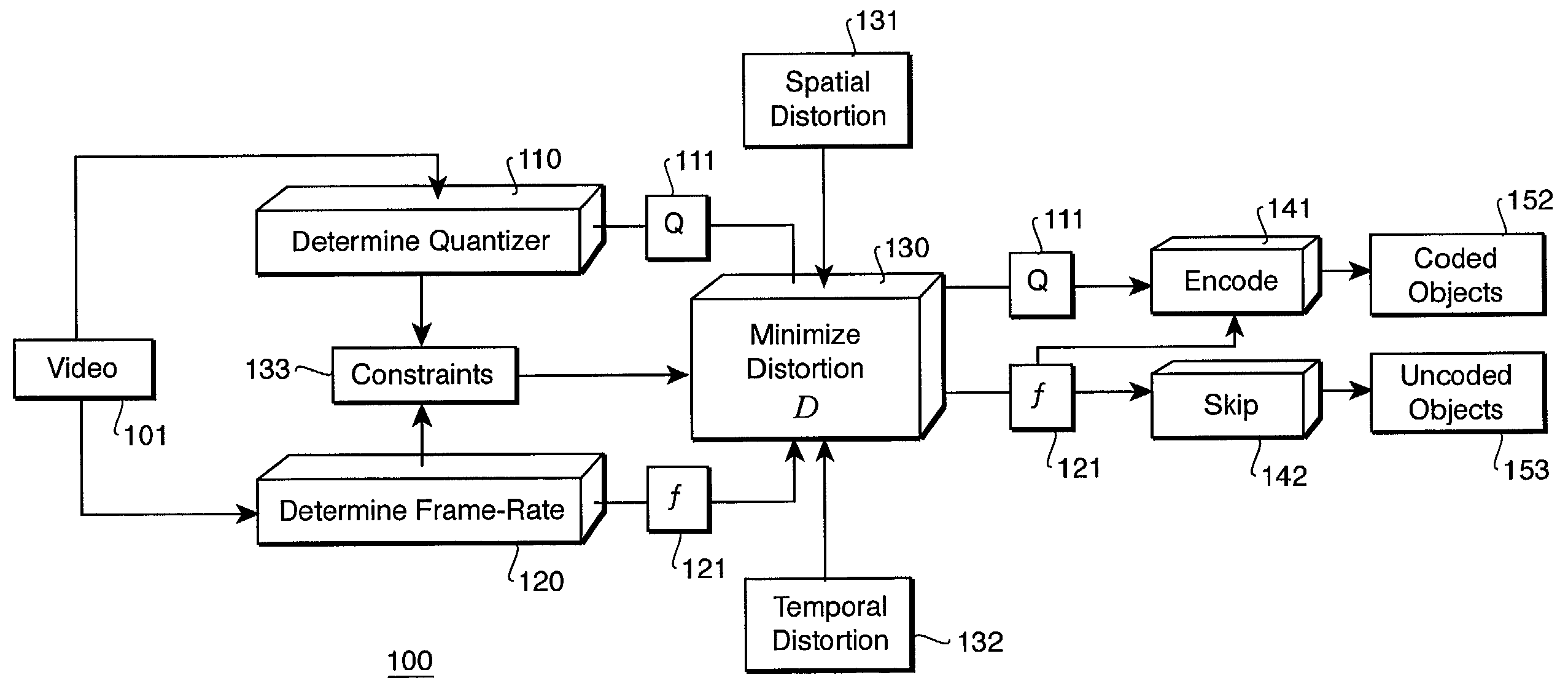
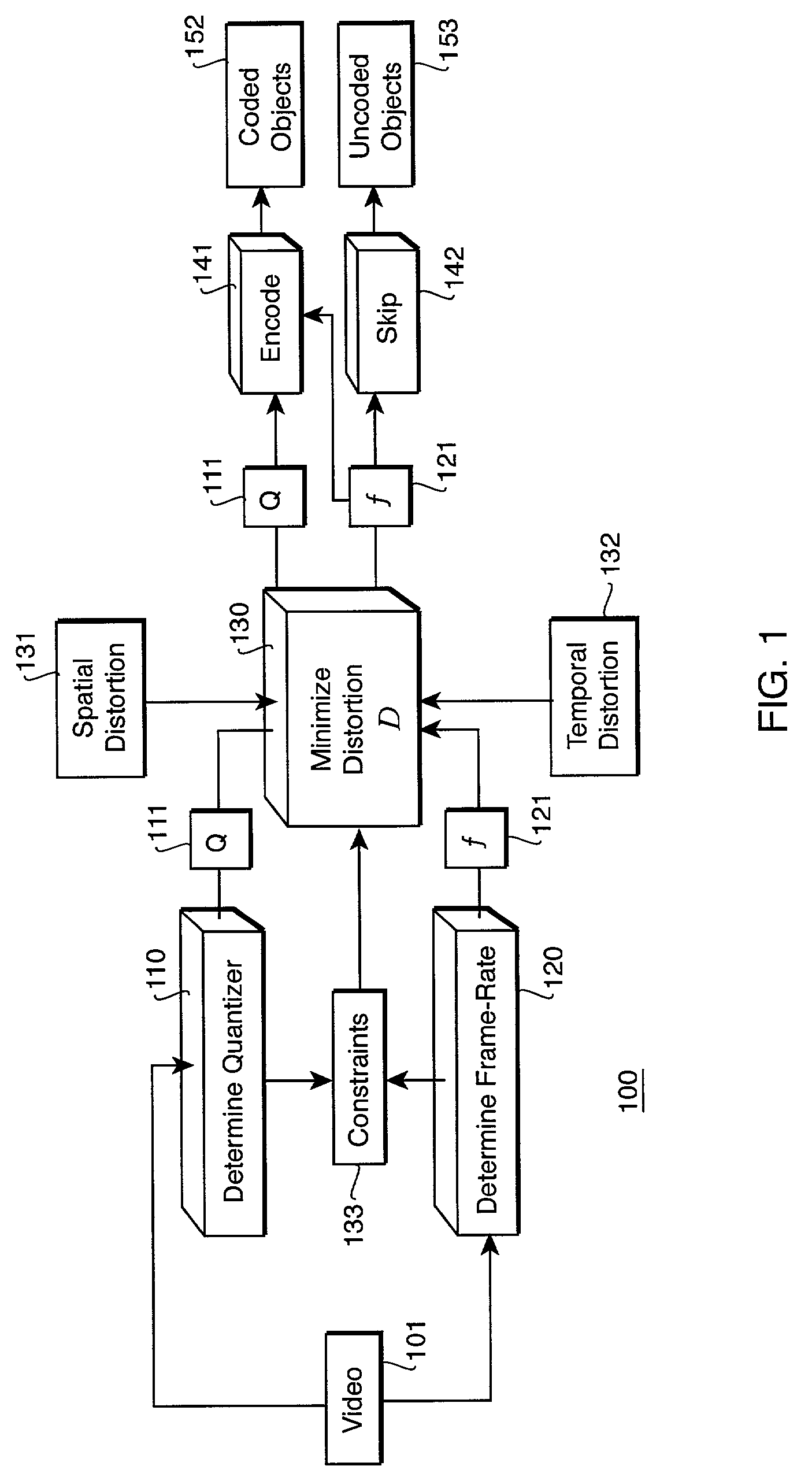
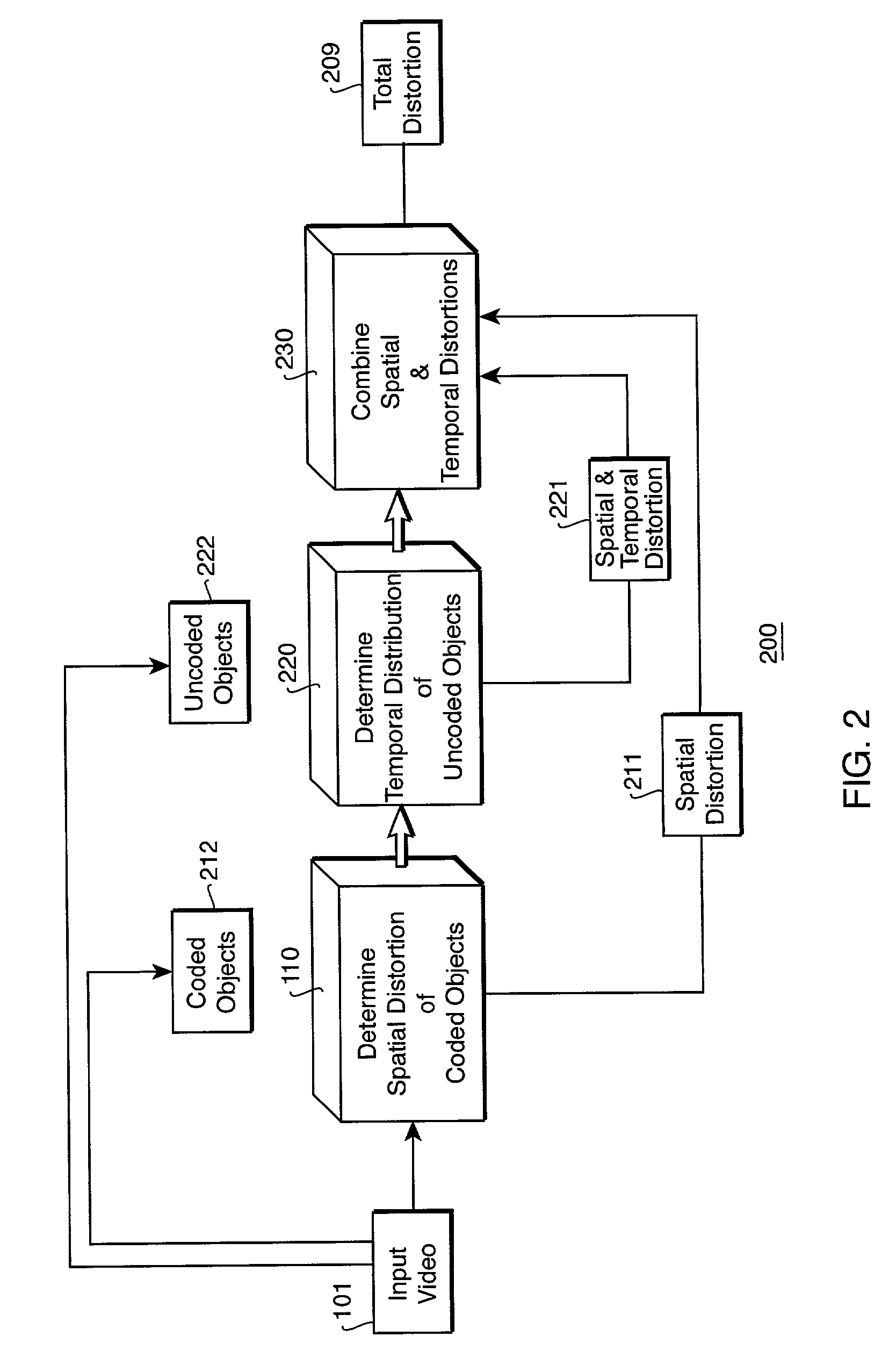
Encoding a video with a variable frame-rate while minimizing total average distortion
InactiveUS7209519B2Optimally minimize average total distortionMinimize distortionPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCode conversionTime distortionPattern recognition
A method encodes a video as video objects. For each candidate object, a quantizer parameter and a skip parameter that jointly minimizes an average total distortion in the video are determined while satisfying predetermined constraints. The average total distortion includes spatial distortion of coded objects and spatial and temporal distortion of uncoded objects. Then, the candidate objects is encoded as the coded objects with the quantizer parameter and the skip parameter, and the candidate objects is skipped as the uncoded objects with the skip parameter.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
1,2,3-Triazole unit-based micro-molecular luminescent material and application thereof
ActiveCN105176521ASingle structureMolecular weight determinationOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesEvaporationLight-emitting diode
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic photoelectric materials, and discloses a 1,2,3-triazole unit-based micro-molecular luminescent material and an application thereof. The molecular weight, the pi electron conjugate degree, the intramolecular charge transfer and other properties of the material can be adjusted through adopting 1,2,3-triazole as a skeleton unit and changing the kind, the position and the quantity of units connected with the skeleton unit. The organic donor-receptor connection luminescent material can realize intramolecular charge transfer, and reduces the carrier imbalance problem of unipolar luminescent materials in order to simplify the structure of a device and improve the performances of the device. Two adjacent units connected with the triazole unit have spatial distortion due to steric hindrance, so the structural non-planarity is reduced, and the accumulation degree of the material is reduced, thereby the aggregation quenching of the material and luminescence of an exciplex are inhibited. The material can be used in evaporation organic micro-molecular electroluminescent diodes.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Systems and methods for characterizing spatial distortion in 3D imaging systems
InactiveUS20100021029A1Reduce spacingImage enhancementImage analysisSpatial distortionImage-Guided Therapy
Systems and methods for characterizing spatial distortions in location data determined by an imaging system, for example as employed in imaged guided therapy. A three dimensional phantom is custom formed for a desired imaging space of a given imaging system. The phantom includes a large plurality of control points fixed rigidly in space to a high degree of known accuracy. The phantom is fixed to a stereotactic frame defining a known calibrated reference or zero and imaged. An algorithm customized for the phantom determines the spatial locations of the control points. A comparison is made between the known and the determined spatial locations for at least a subset of the control points. The comparison results in indicia for any determined spatial distortions observed. The raw image data can be manipulated to compensate for any spatial distortion. The control points can have fixed locations known to an accuracy of 100μ or better. The algorithm can determine an initial estimate for the detected location of a control point accurate to ±0.5 pixel or better.
Owner:LOMA LINDA UNIV MEDICAL CENT
Gait/balance analyzer
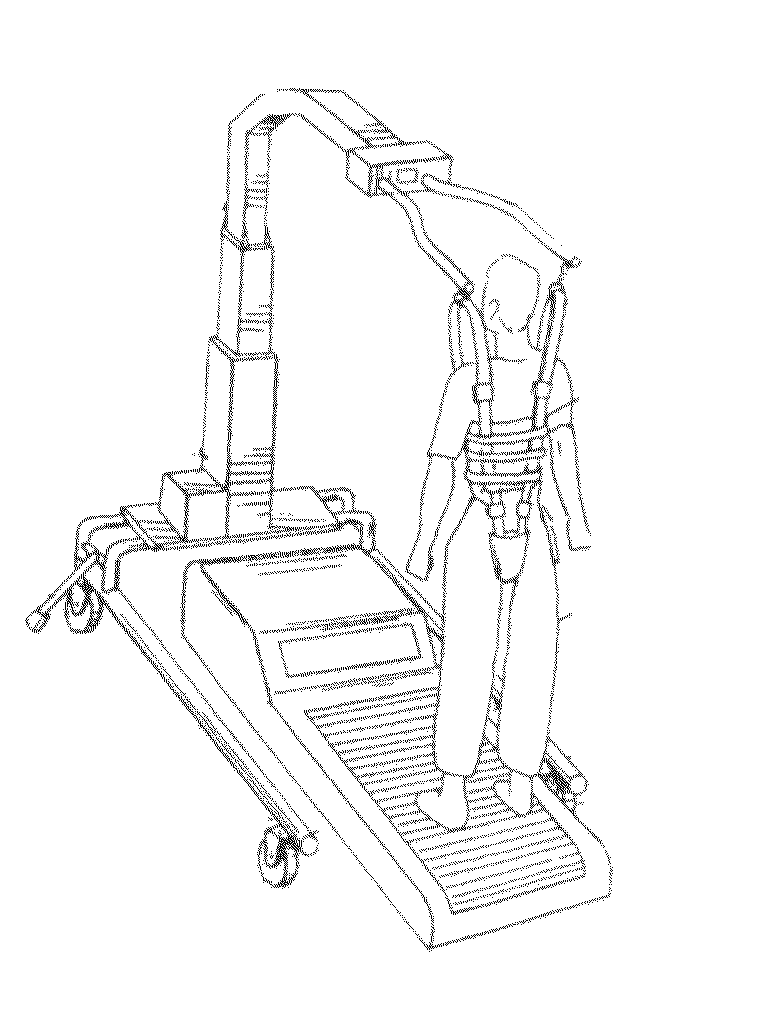
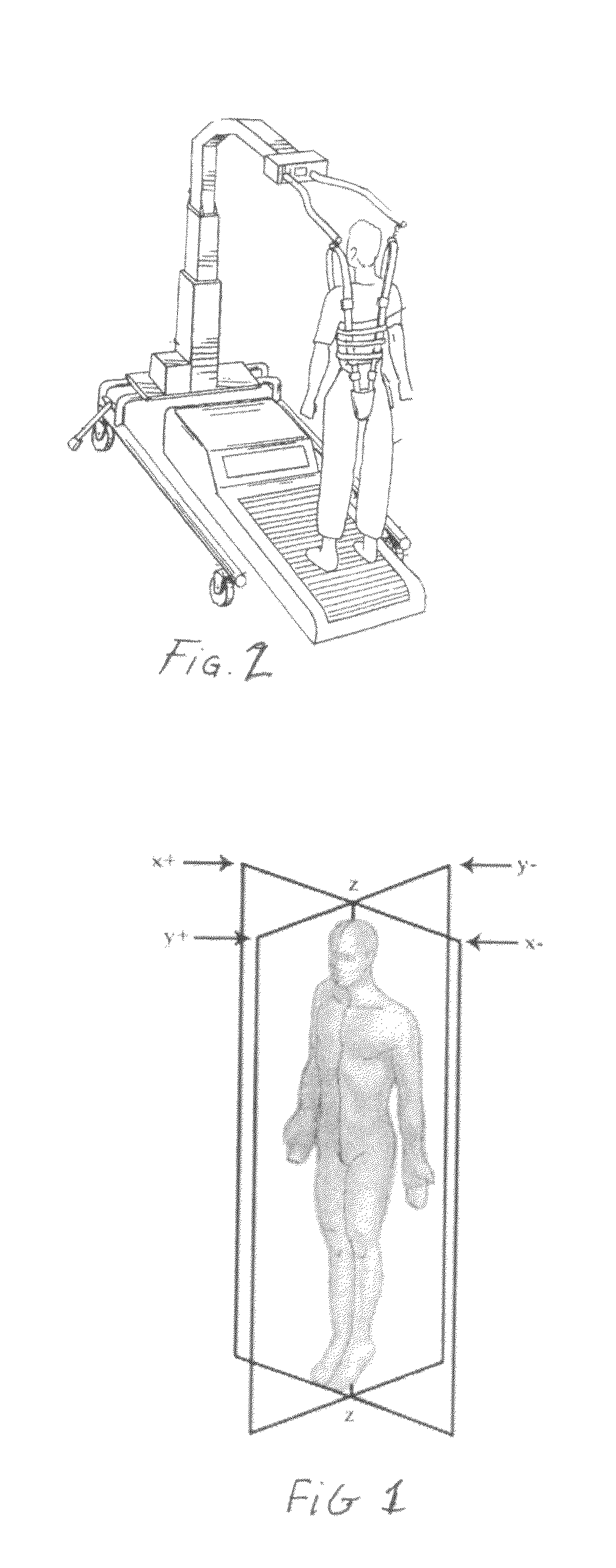
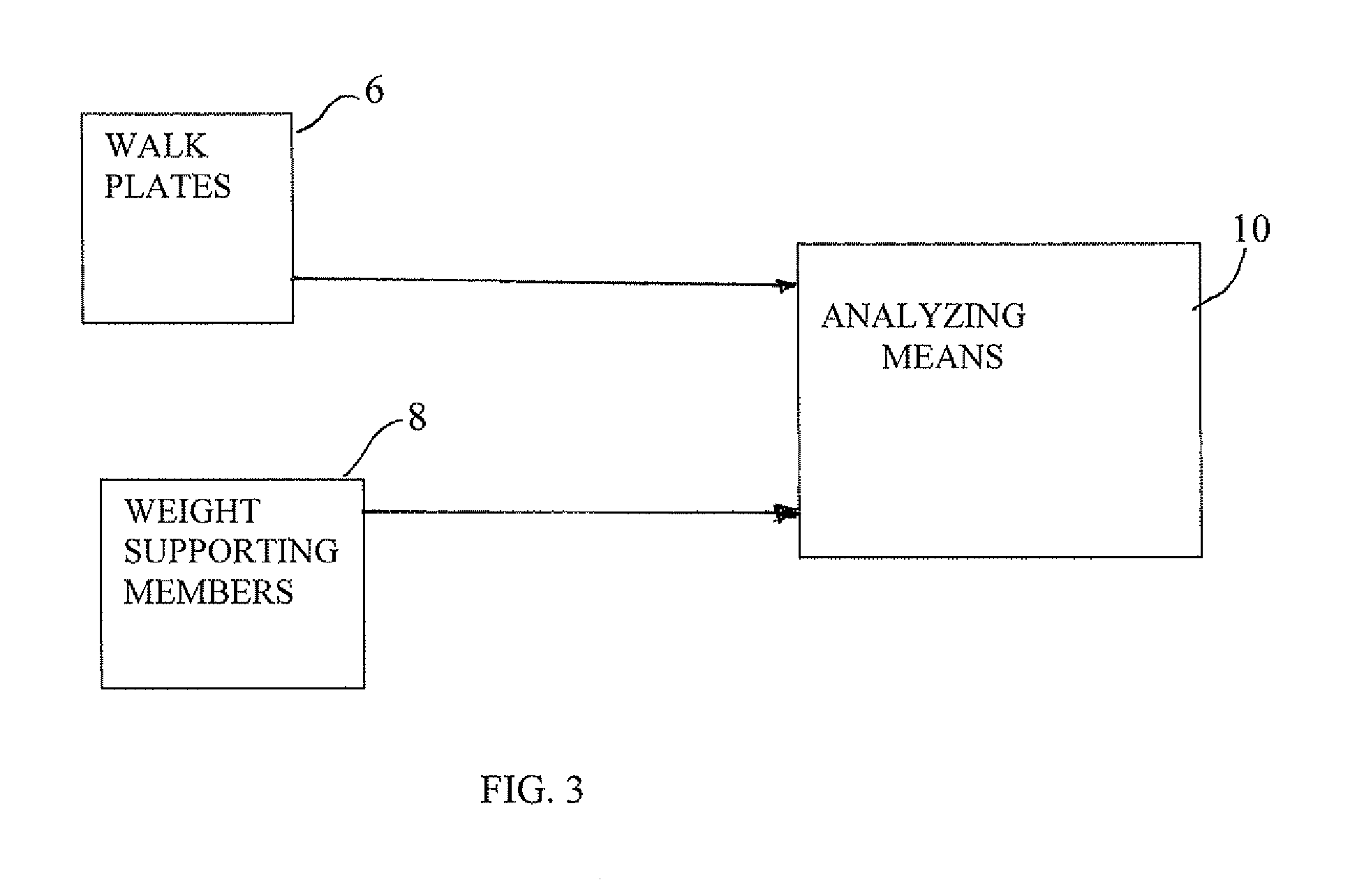
An apparatus for analyzing gait and balance to determine visual spatial distortion including a treadmill having a movable tread, at least a weight bearing sensor for measuring weight bearing pressure in right, left, front and rear directions provided under said tread and an analyzer for analyzing lean coupled to output of said weight bearing sensor.
Owner:PADULA WILLIAM V
Method for measuring video quality using a reference, and apparatus for measuring video quality using a reference
InactiveUS20130100350A1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsPattern recognitionVideo quality
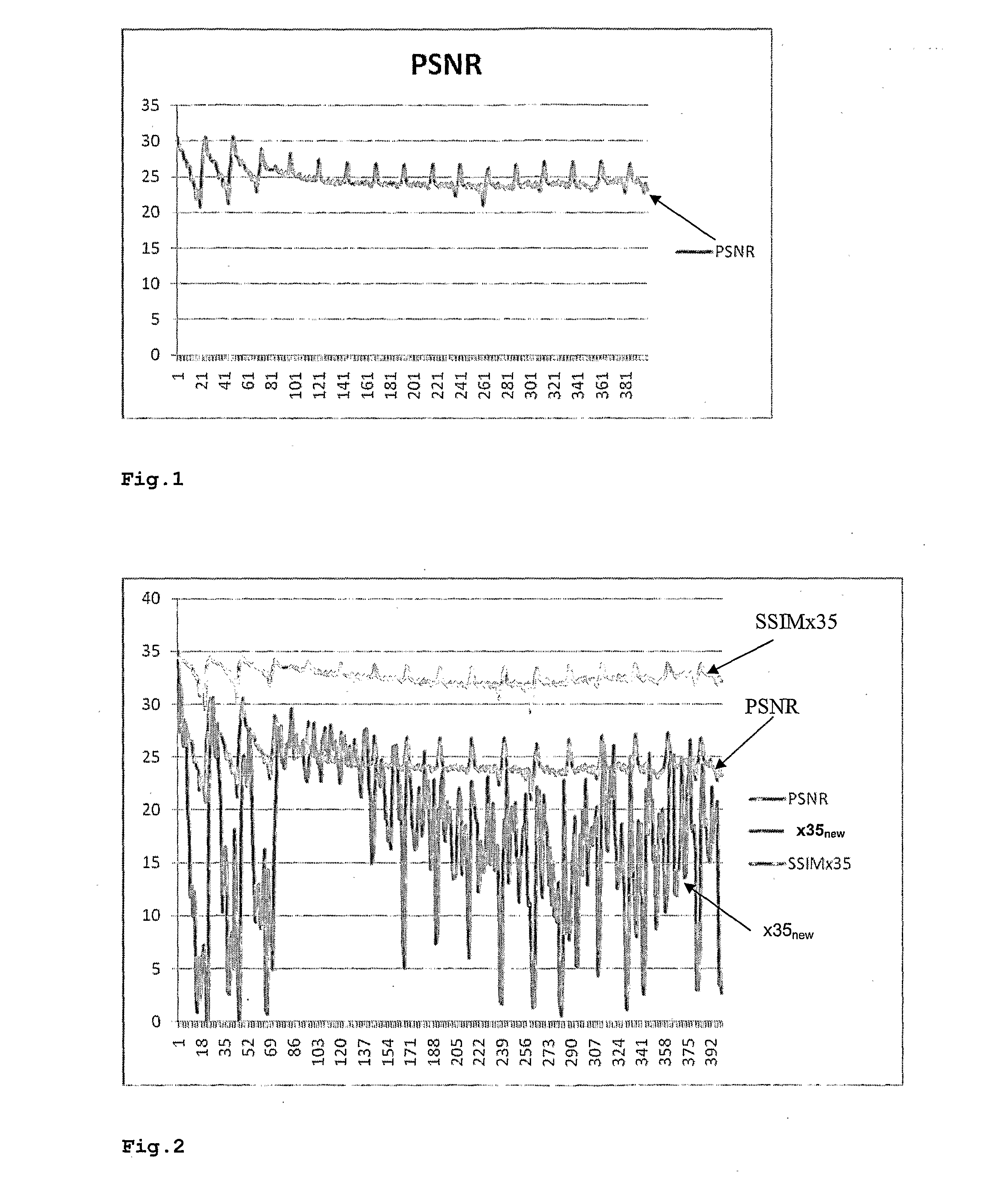
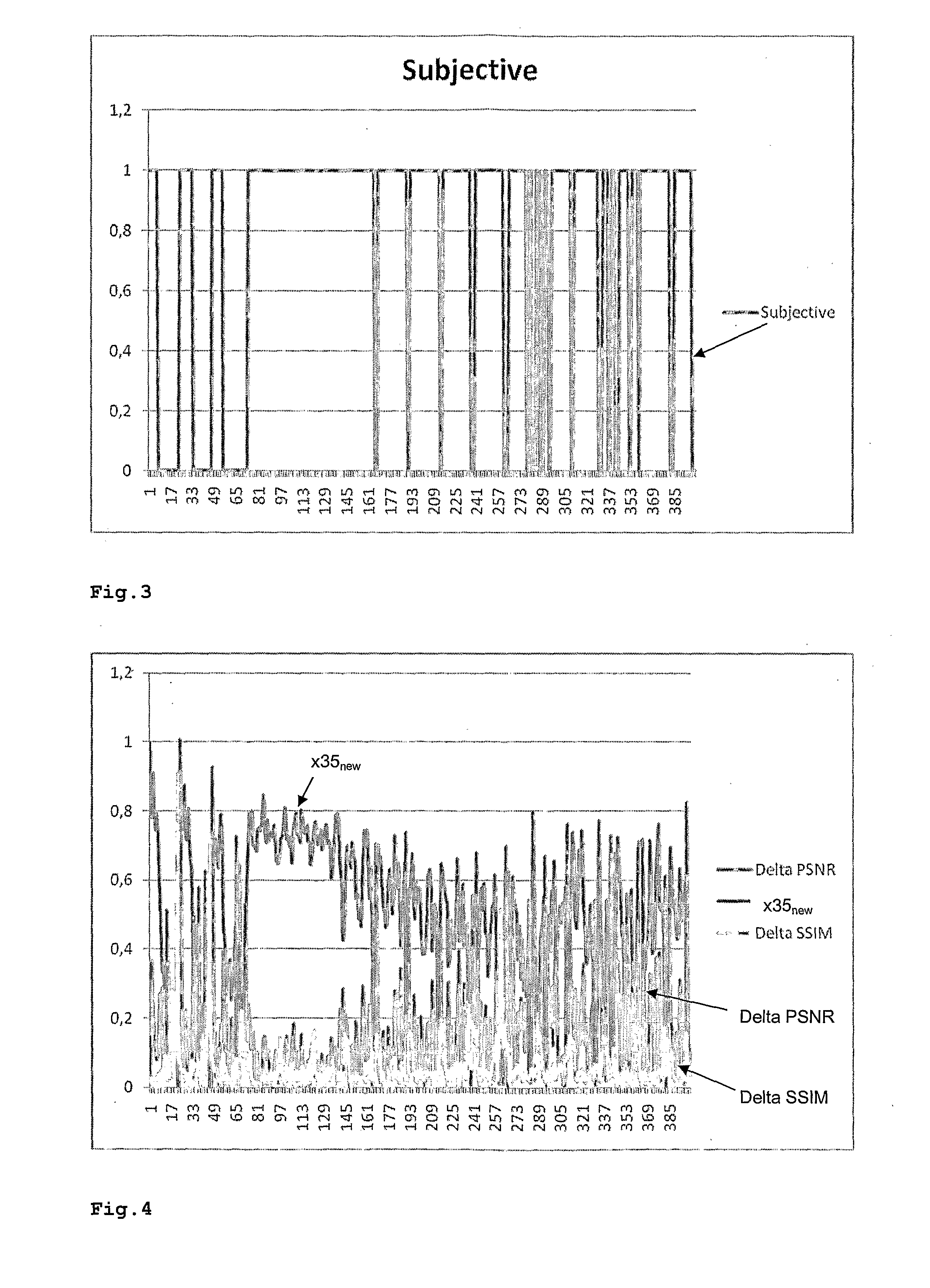
The purpose of an objective video quality evaluation is to automatically assess the quality of video sequences in agreement with human quality perception. The invention addresses the effects of the introduction of a temporal dimension by focusing on the temporal evolutions of spatial distortions, since it has been found that a spatial quality variation cannot be evaluated by simple subtraction of the spatial quality of neighbouring frames. An improved method for estimating perceived video quality comprises steps of calculating a first similarity map between adjacent frames of a current sequence, calculating a second similarity map between the corresponding reference frames, and calculating (smg3) a third similarity map, which provides a numerical quality value.
Owner:MAGNOLIA LICENSING LLC
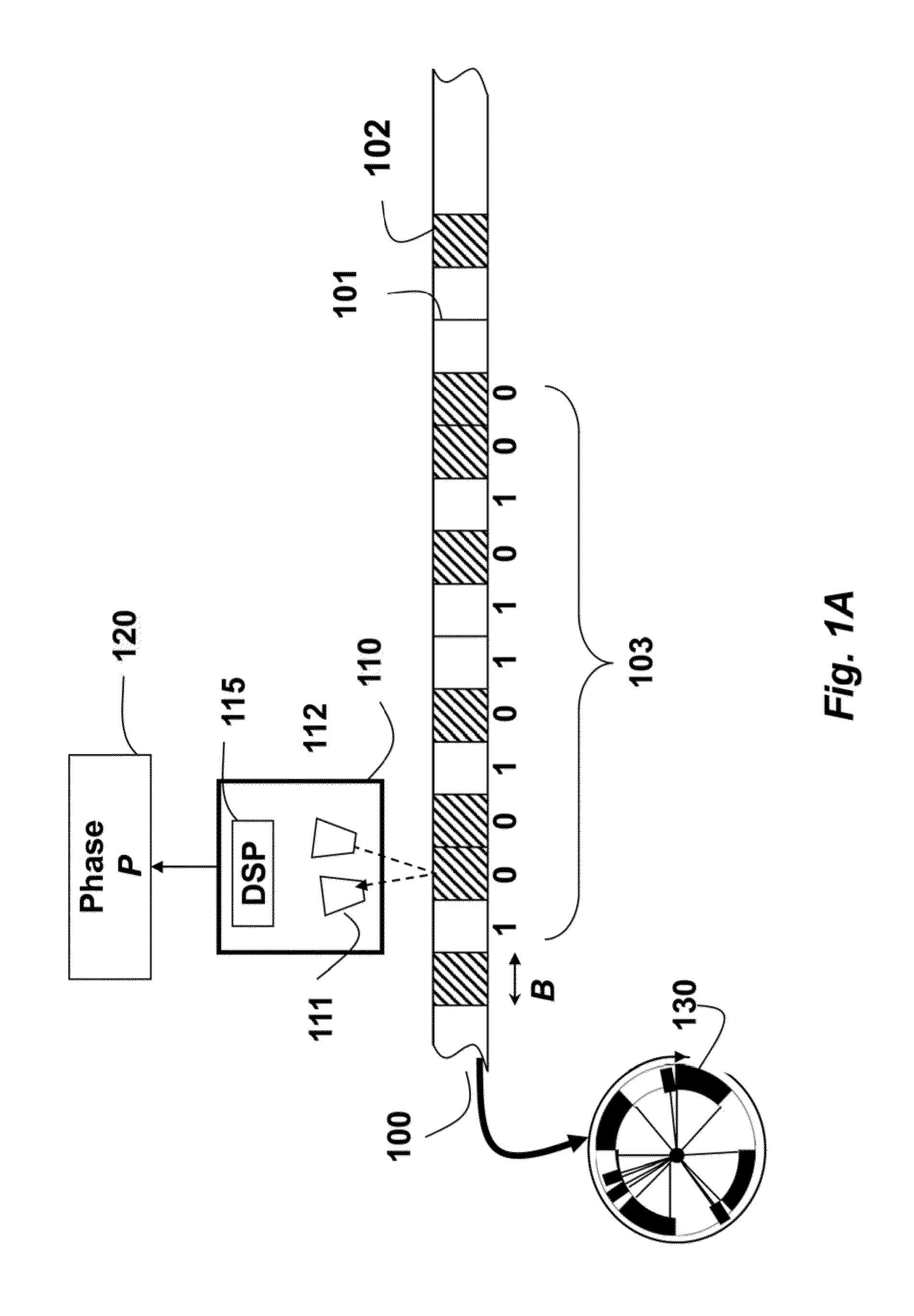
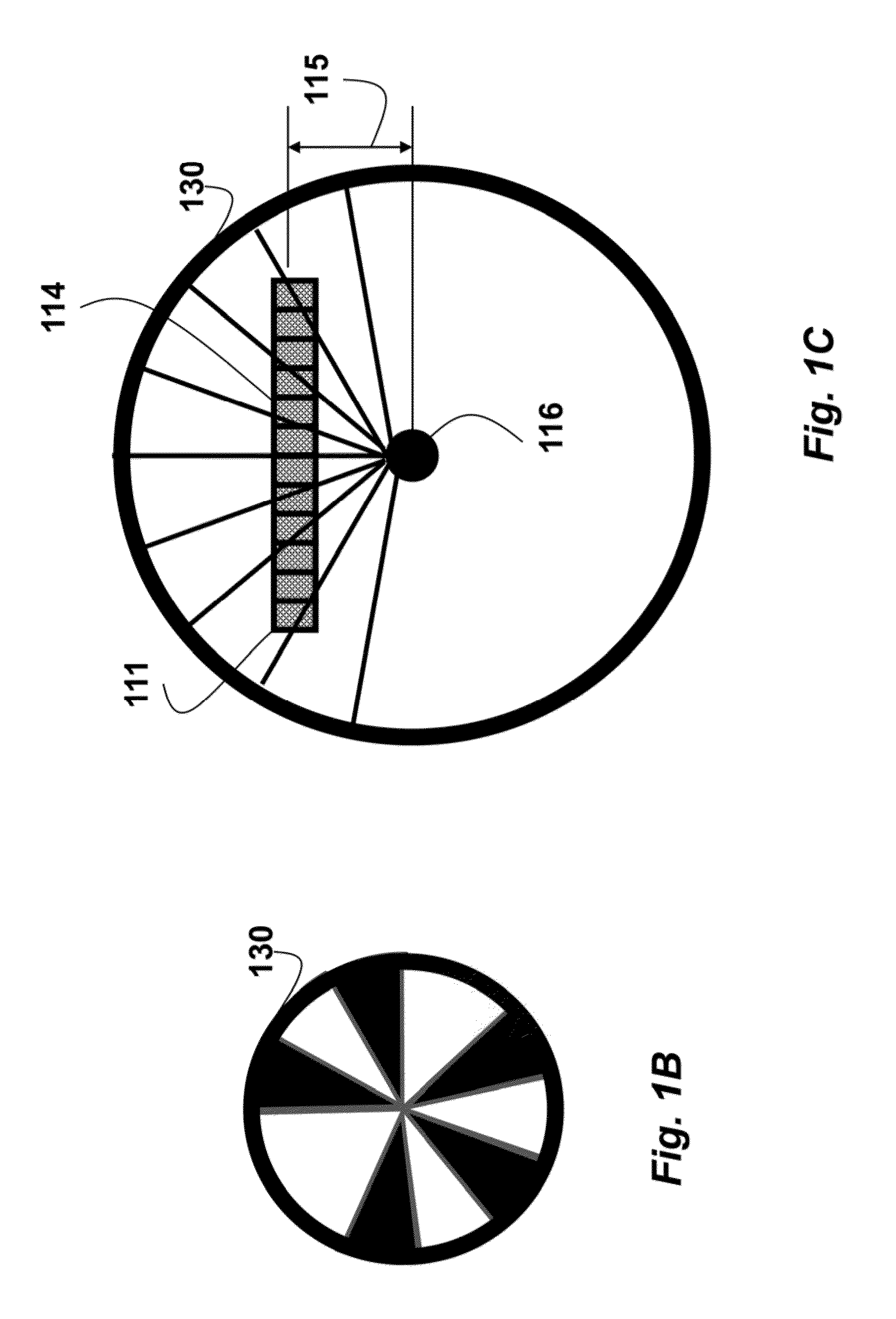
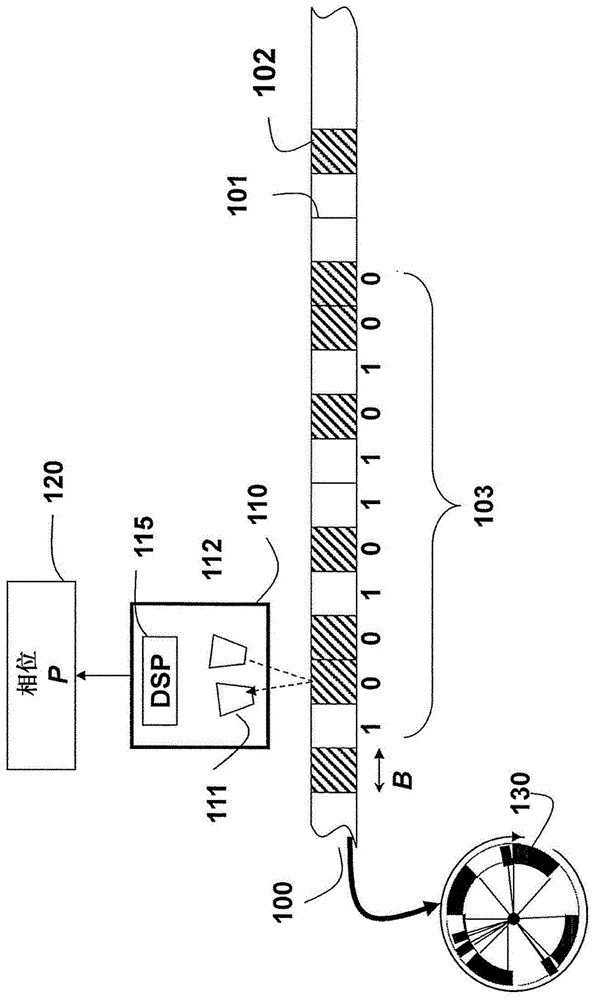
Self-calibrating single track absolute rotary encoder
ActiveUS9423281B2Reduces cost and complexityWave based measurement systemsCalibration apparatusSpatial distortionRotary encoder
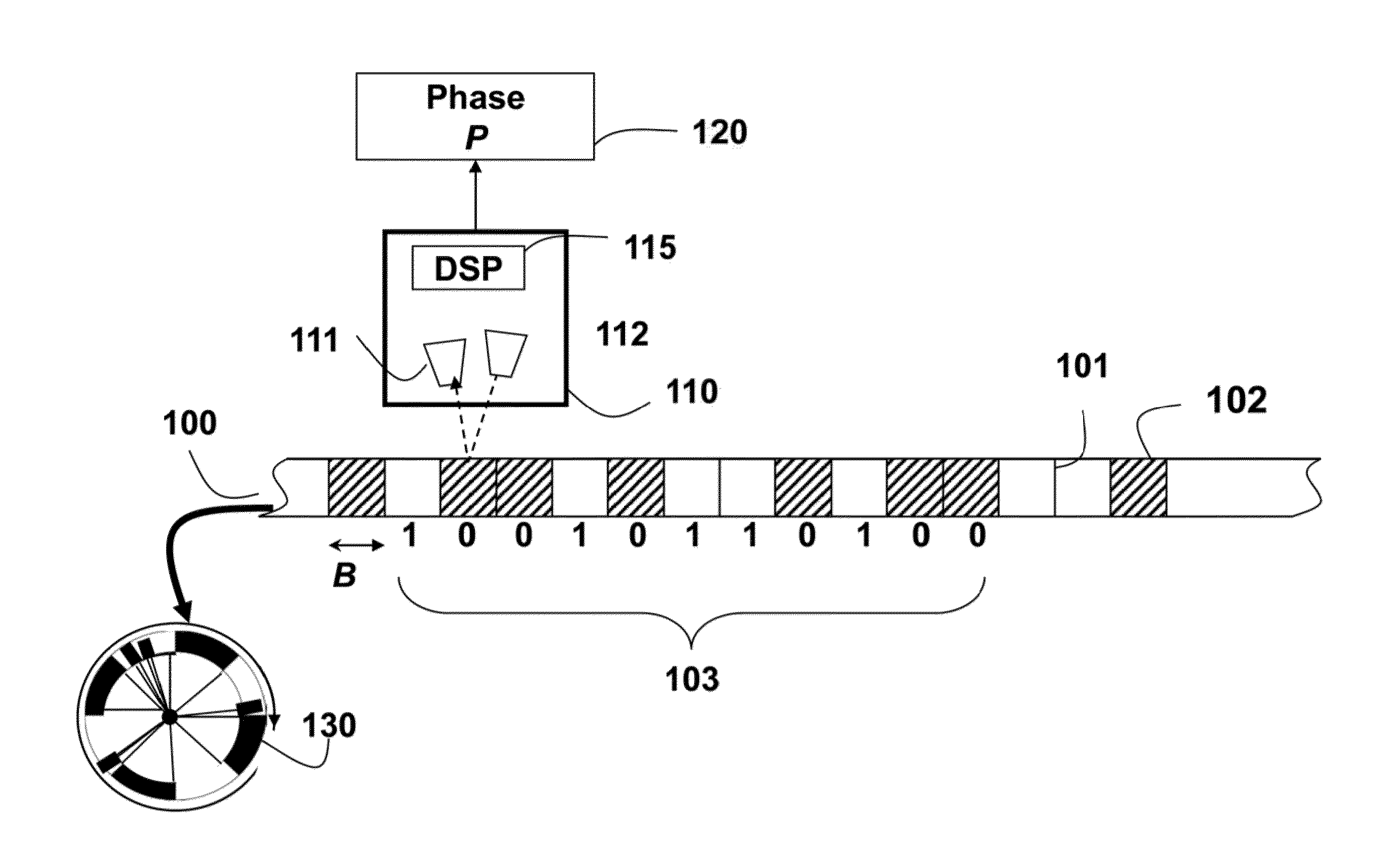
A rotary encoder includes a single read-head and a circular scale. The encoder is self-calibrated by acquiring calibration samples with the read-head for rotational angles of the circular scale, and estimating spatial frequency and spatial distortion parameters of the encoder from the calibration samples.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Device for performing synchronous focusing shaping on distorted femtosecond laser pulse and control method
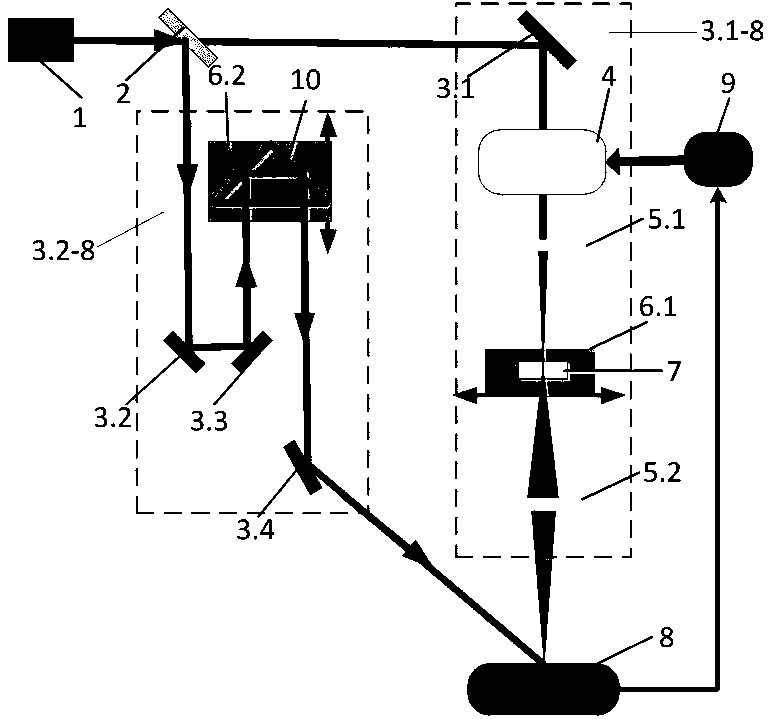
InactiveCN110048293ASolve dispersionAchieve spatial resolutionLaser detailsOptical elementsTime distortionBeam splitter
The invention relates to a method for performing focusing shaping control on a distorted femtosecond laser pulse. The method is characterized in that an optical inverse diffusion algorithm is writtenaccording to a time inversion principle; a phase shift holographic algorithm is written according to a holographic interference principle; light beams output from a laser 1 are incident on a beam splitter 2 and are divided into two parts, one part entering a sample light path 3.1-8 and the other part entering a reference light path 3.2-8. The light beams in the reference light path 3.2-8 are reflected onto an isosceles prism 10 by a second mirror 3.2 and a third mirror 3.3, the light beams are reflected to a fourth mirror 3.4 by the isosceles prism 10, and the light beams are reflected by thefourth mirror 3.4 and then input to a two-dimensional spectrometer 8. According to the method in the invention, the spatial freedom of the wave-front in a spatial light modulator is controlled by running the optical inverse diffusion algorithm through a computer, thereby realizing simultaneous focusing shaping control on the spatial distortion and time distortion of the femtosecond laser pulse.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH AT WEIHAI
Table top image calibration phantom
ActiveUS20180035970A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsRadiation measurementGrid patternImage calibration
A device for measuring image quality properties of an image acquisition device while the subject or object is being scanned contains an embedded grid pattern to measure spatial distortion along the length of the image acquisition table. The device also contains reference materials, which may run along the length of the device, for measuring fundamental imaging properties such as signal strength, noise, and resolution. Automated software can detect the device within an acquisition, measure its properties, and provide data and reports on the quality of the image acquisition.
Owner:ACCUMETRA LLC
Method and apparatus of z-scan photoreflectance characterization
ActiveUS8300227B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementScattering properties measurementsSemiconductor structureLight reflection
A method of z-scan photo-reflectance characterization of semiconductor structures and apparatus for same has been developed. The method and apparatus provides the ability to independently measure electro-refractive and electro-absorptive nonlinearities that occur in conventional photo-reflectance signals. By performing a series of photo-reflectance measurements, each containing photo-modulated nonlinear optical signals, with the sample at a multiplicity of positions along the focal length of the probe light column, and with an aperture fixtured in the reflected probe path, precision characterization of both electro-refractive and electro-absorptive nonlinearities is attained. The Z-scan photo-reflectance method and apparatus characterizes spatial distortions of a coherent photo-reflectance probe light beam due to electro-refractive and electro-absorptive effects.
Owner:XITRONIX CORP
Method for self-calibrating a rotary encoder
ActiveCN105229424ALow costReduce complexityConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyGreek letter betaClassical mechanics
A method for self-calibrating a rotary encoder including a single read-head (111) and a circular scale (101), comprises the steps of: acquiring calibration samples (150) by the read-head for rotational angles (Theta) of the circular scale; and estimating spatial frequency (F) and spatial distortion parameters (Alpha, Beta) of the encoder from the calibration samples for self-calibrating the rotary encoder.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
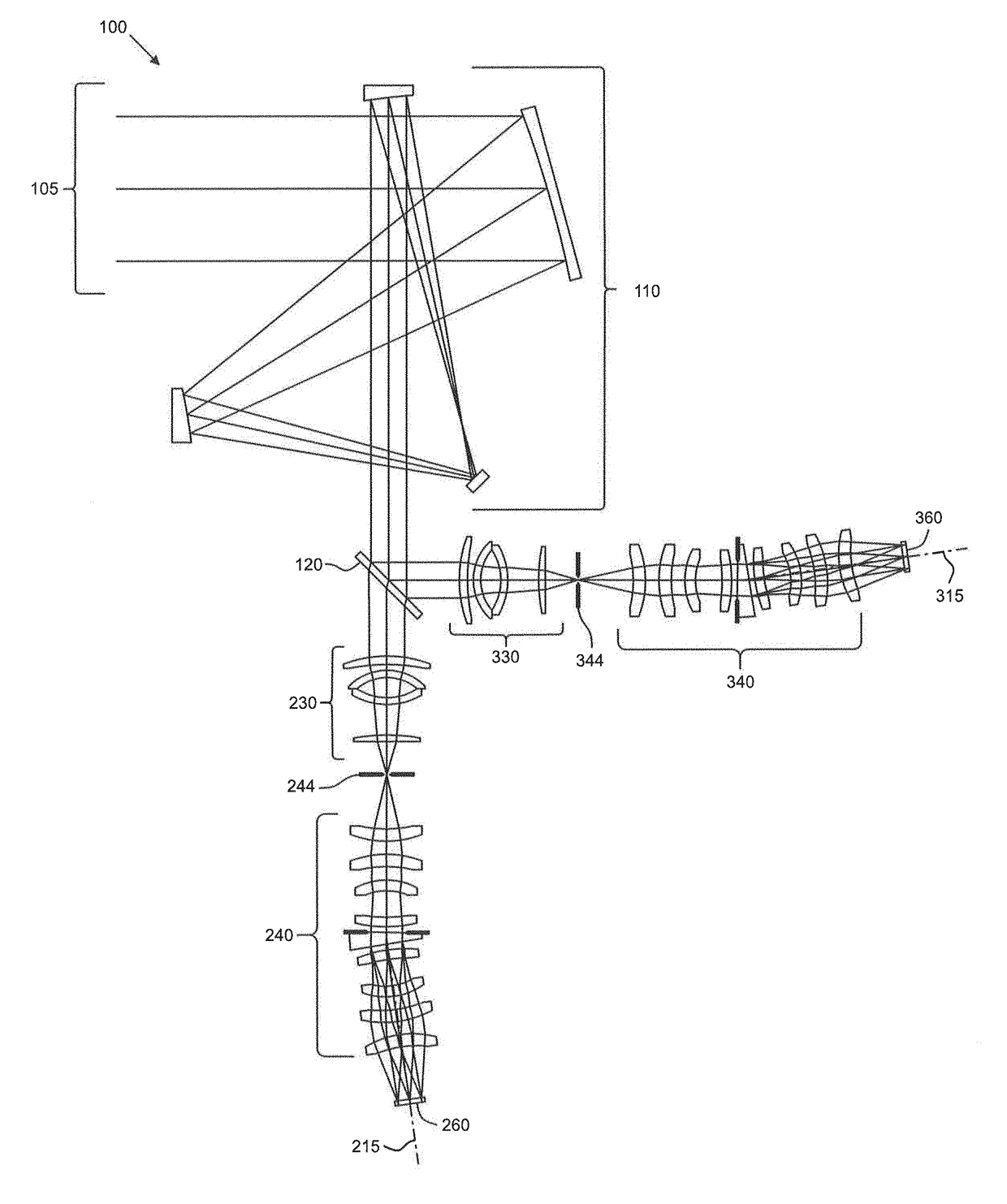
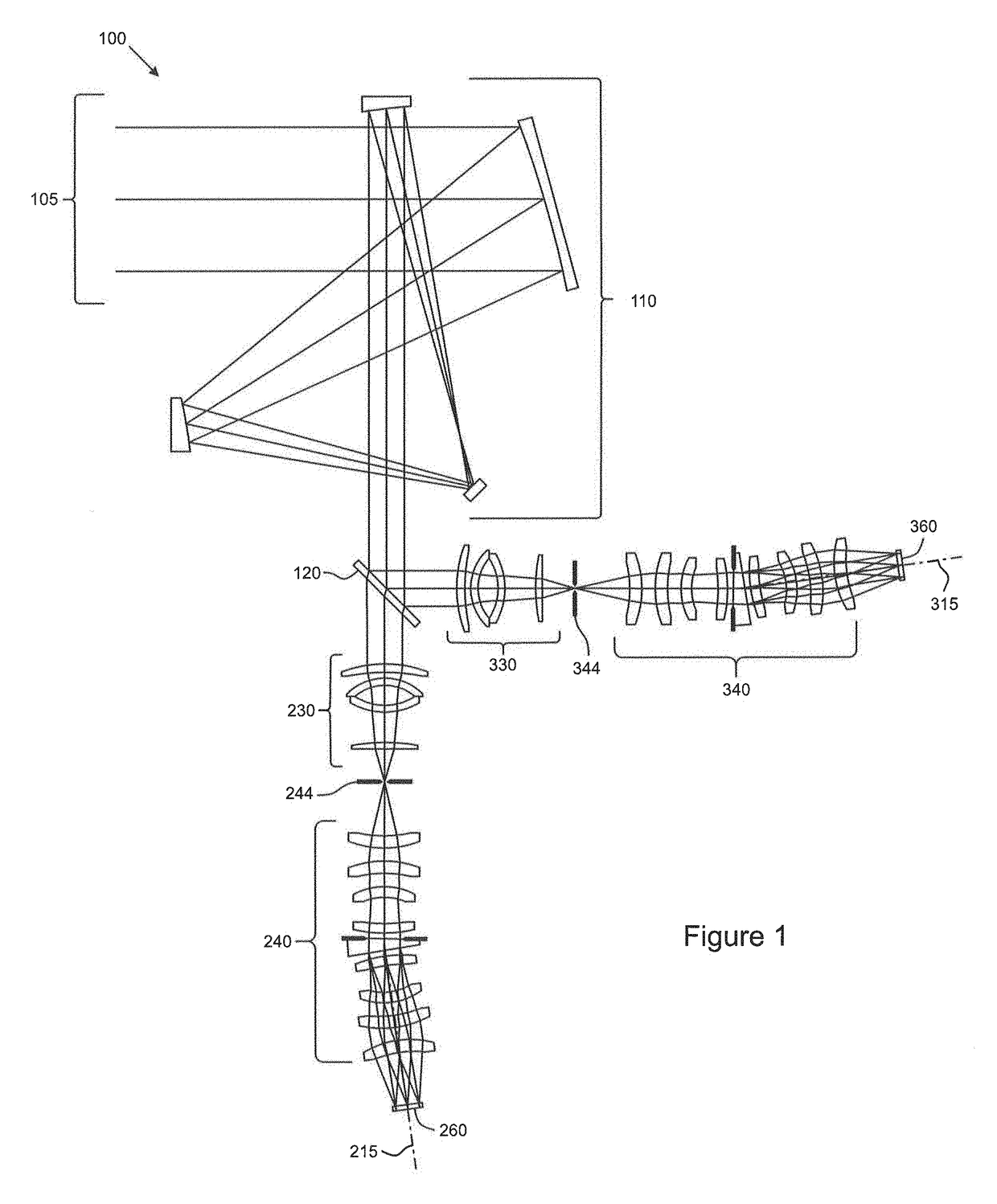
Enhanced co-registered optical systems
ActiveUS10012543B1Improve fidelityImprove discriminationRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSystem combinationSpatial distortion
An imaging optical system including a plurality of imaging optical sub-systems, each having at least one optical element and receiving light from a source, and a plurality of spectrometer optical sub-systems, each spectrometer optical sub-system receiving light from at least one of the imaging optical sub-systems, each imaging optical sub-system and spectrometer optical sub-system combination having a spatial distortion characteristic, each spatial distortion characteristic having a predetermined relationship to the other spatial distortion characteristics.
Owner:WAVEFRONT RES
Preparation method and application of micro-porous polymer
InactiveCN109293886AGood gas adsorption performanceGood planarityOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesHydrogenOrganic solvent
The invention provides a preparation method and an application of a micro-porous polymer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: sequentially adding a monomer, an anhydrous organic solvent and an anhydrous catalyst into a dried pressure-resistant tube, performing magnetic stirring under a dark condition, and extracting ad drying the obtained crude product to obtain the micro-porouspolymer. The preparation method adopts the monomer obtained by polymerizing indanone groups or indolyl groups in order to synthesize the polymer and increases the spatial distortion of the monomer toincrease the specific surface area of the polymer in order to achieve a good gas adsorption performance, so the prepared micro-porous polymer is suitable for storing and transporting hydrogen and other gases.
Owner:HEBEI UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method and system for intelligent video adaptation
InactiveUS8761248B2Quality improvementColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionTime structureRate distortion
A system (100) and method (200) for efficient video adaptation of an input video (102) is provided. The method can include segmenting (210) the input video into a plurality of video shots (142) using a video trace (111) to exploit a temporal structure of the input video, selecting (220) a subset of frames (144) for the video shots that minimizes a distortion of adapted video (152) using the video trace, and selecting transcoding parameters (122) for the subset of frames to produce an optimal video quality of the adapted video under constraints of frame rate, bit rate, and viewing time constraint. The video trace is a compact representation for temporal and spatial distortions for frames in the input video. A spatio-temporal rate-distortion model (320) provides selection of the transcoding parameters during adaptation.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
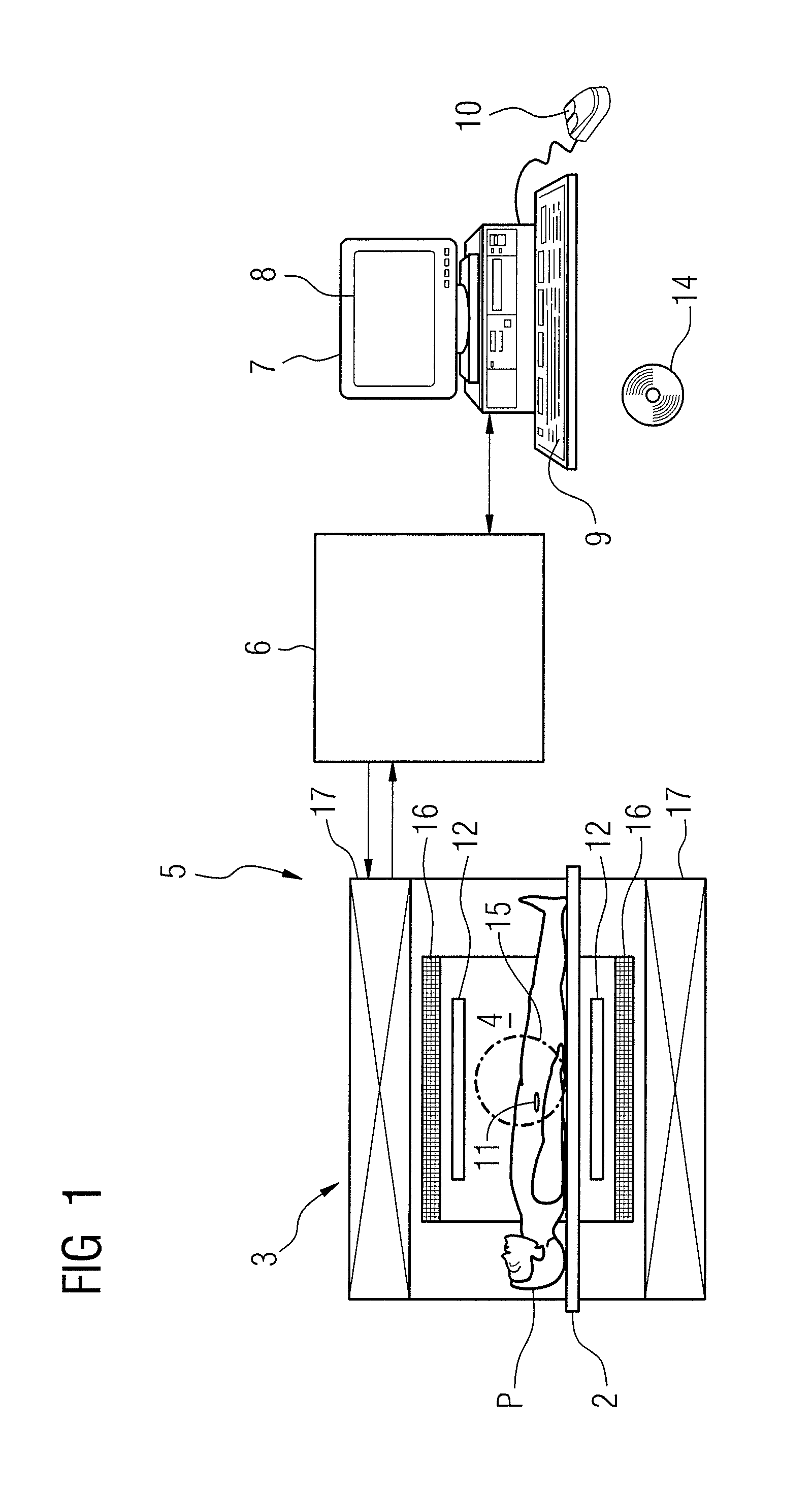
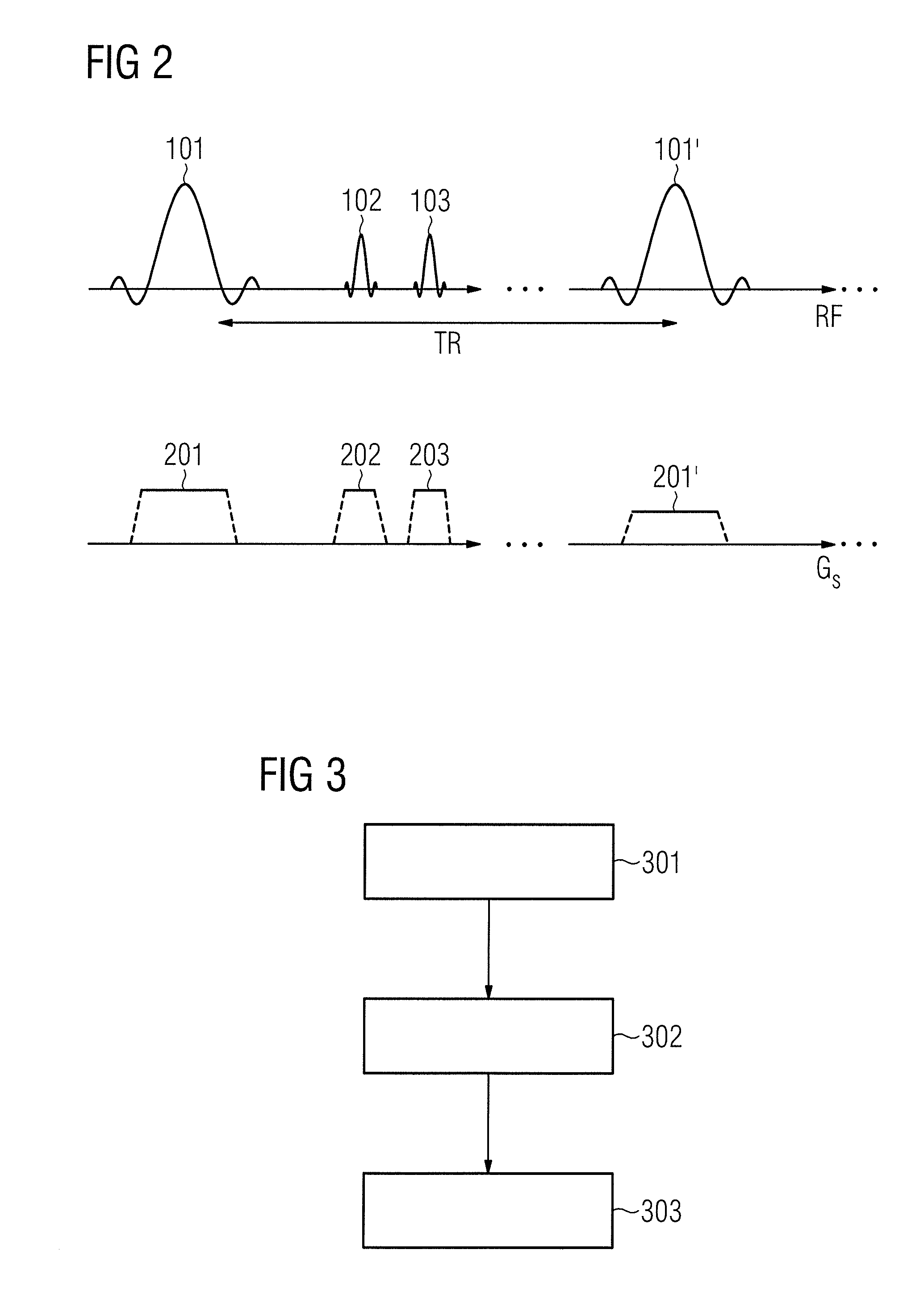
Method for generating a pulse sequence to acquire magnetic resonance data, and operating method and magnetic resonance system employing the generated pulse sequence
ActiveUS20120139539A1Avoid signal lossMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceSpatial distortion
In a method for generating a pulse sequence for operating a magnetic resonance (MR) system for acquiring data from an examination subject having an interfering object in the patient's body, the bandwidths of at least two of the RF (radio-frequency) pulses in the pulse sequence are matched such that the matched RF pulses respectively excite a congruent slice when they are radiated into an examination subject under the effect of a slice selection gradient of identical amplitude. The matching of the RF pulses in the manner ensures so that the respective slices excited by the at least two RF pulses are subject to the same nonlinearities and inhomogeneities, and therefore the same spatial distortions, and so that signal losses due to inconsistent excitations of the two pulses are avoided. The image data that can be acquired with the pulse sequence are therefore optimized.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com