Patents
Literature
395results about How to "Good planarity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
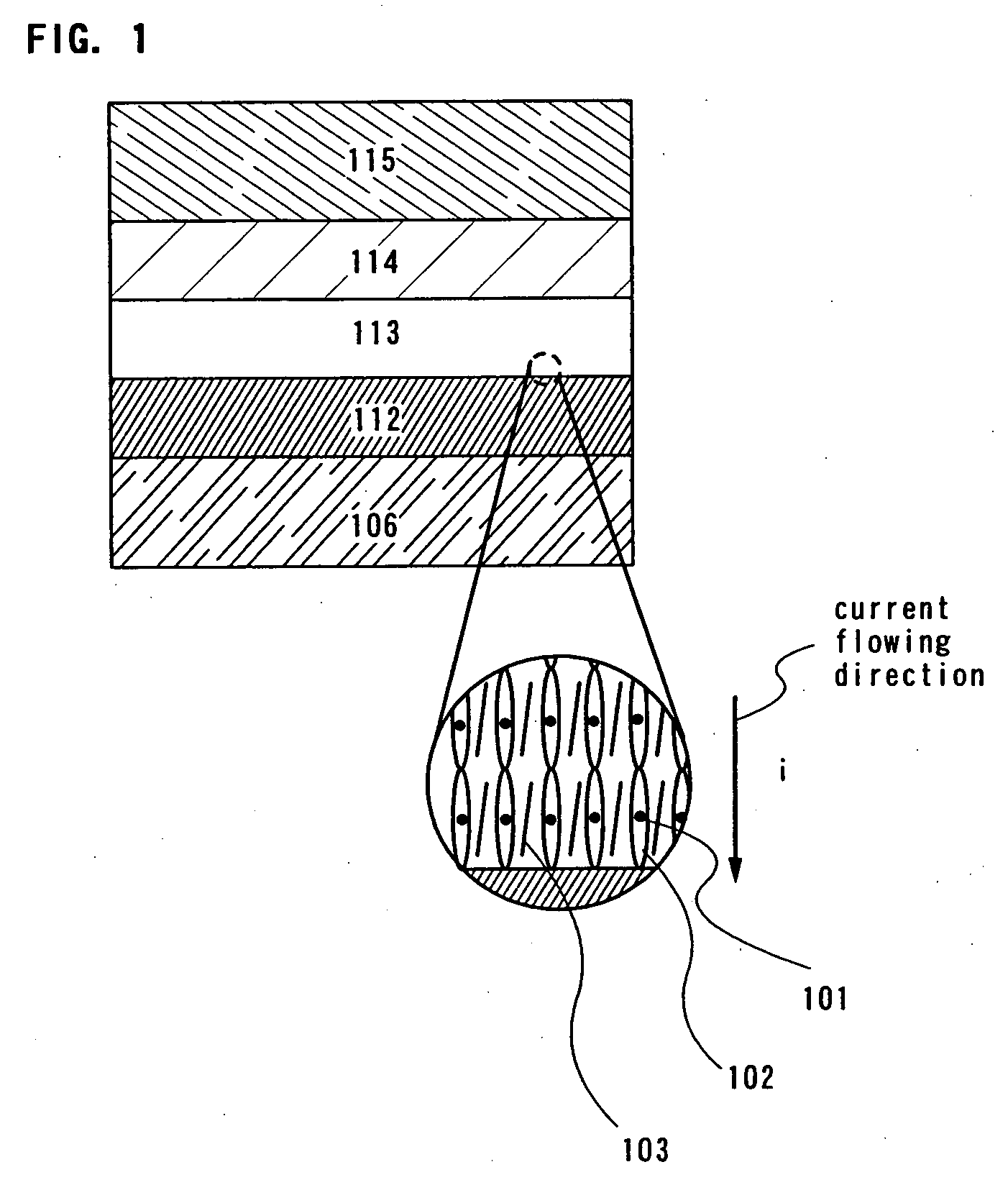
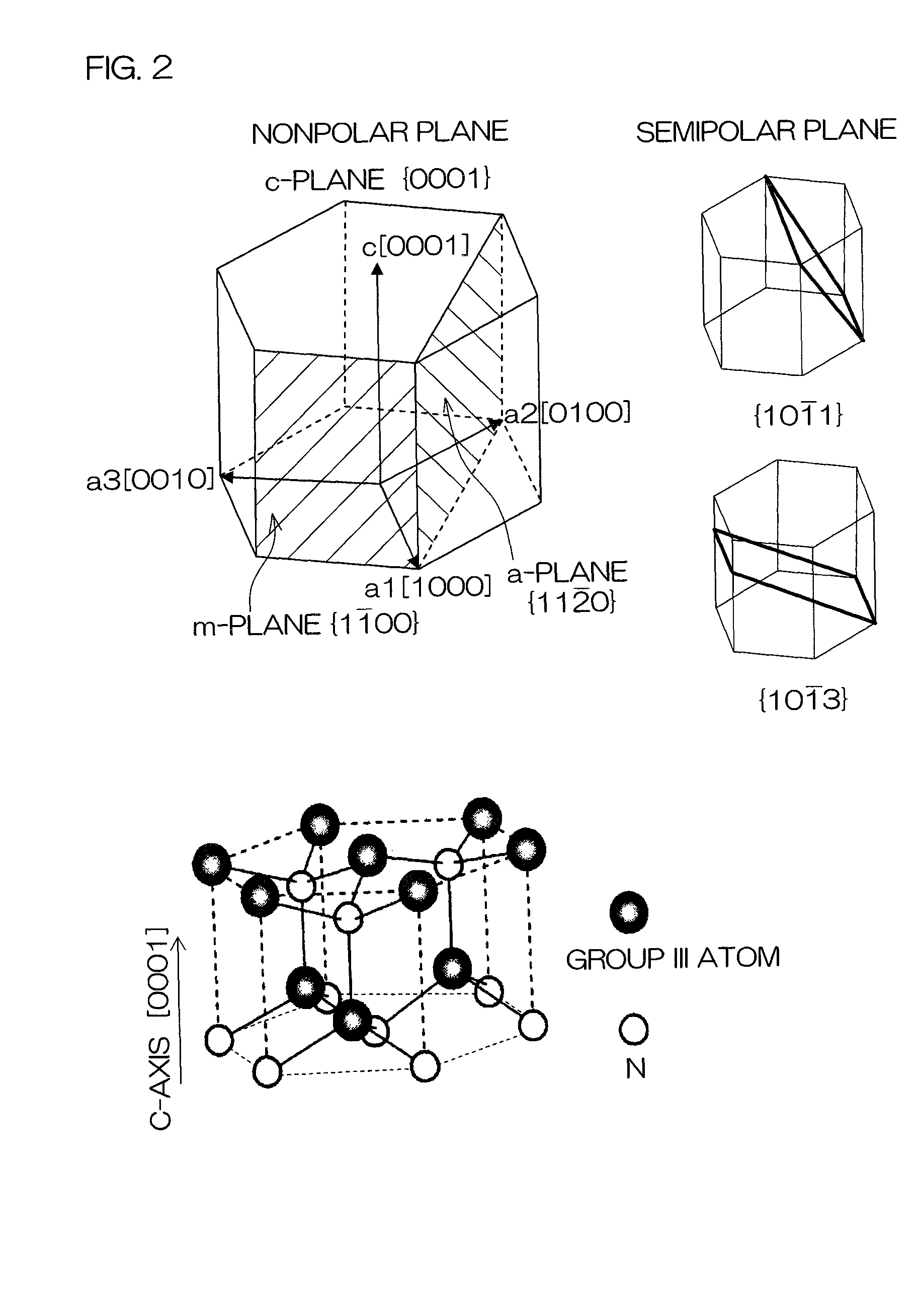
Light-emitting device
ActiveUS8017932B2High incidenceImprove the display effectSolid-state devicesNanoopticsLight emitting deviceNitride semiconductors
A light-emitting device includes a group III nitride semiconductor layer of a multilayer structure consisting of a group III nitride semiconductor having a major surface defined by a nonpolar plane or a semipolar plane and having at least an n-type layer and a p-type layer. A surface of the group III nitride semiconductor layer on a light extraction side is a mirror surface. The light-emitting device may further include a transparent electrode in contact with the surface of the group III nitride semiconductor layer on the light extraction side. In this case, a surface of the transparent electrode on the light extraction side is preferably a mirror surface.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
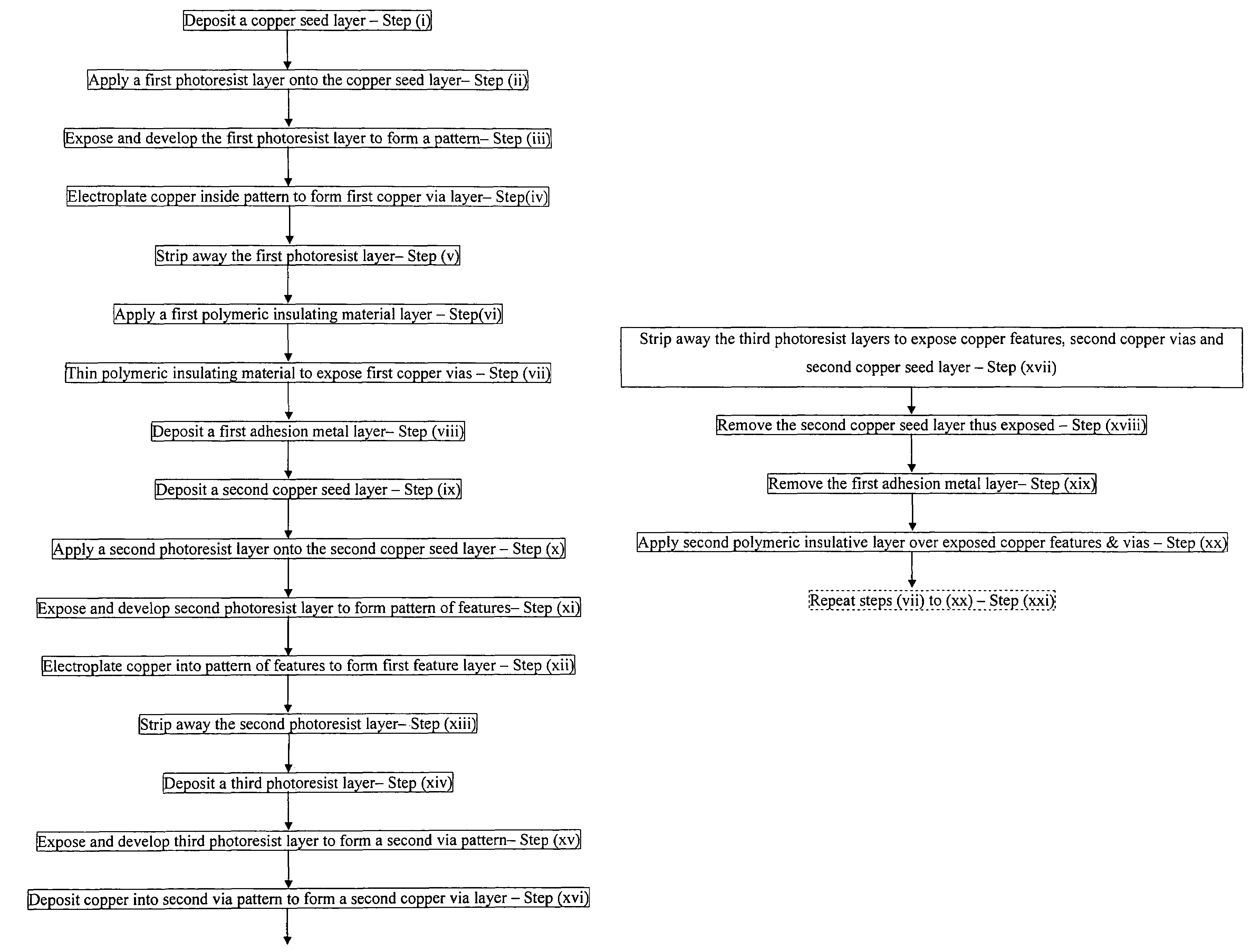
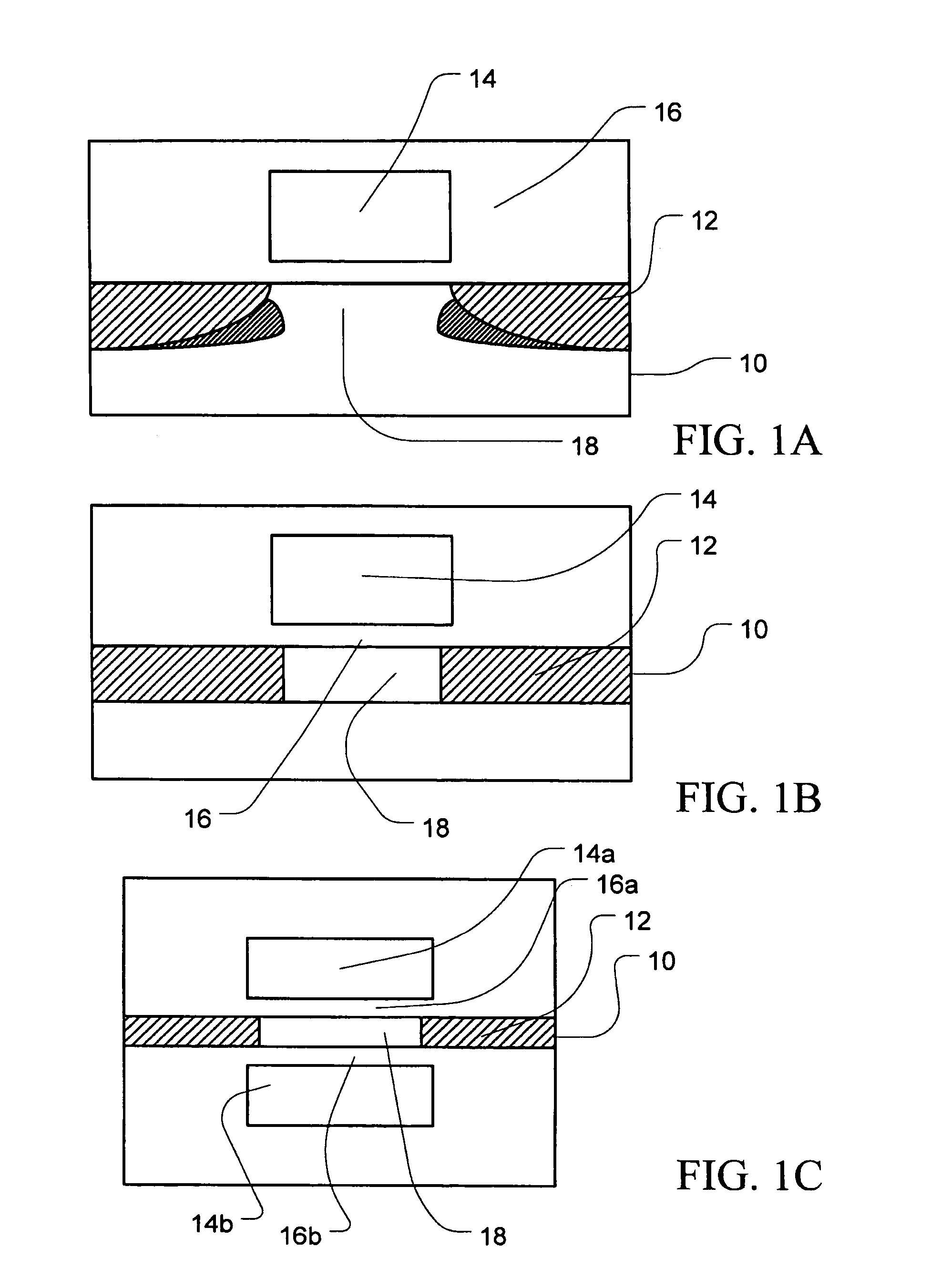
Integrated circuit support structures and their fabrication
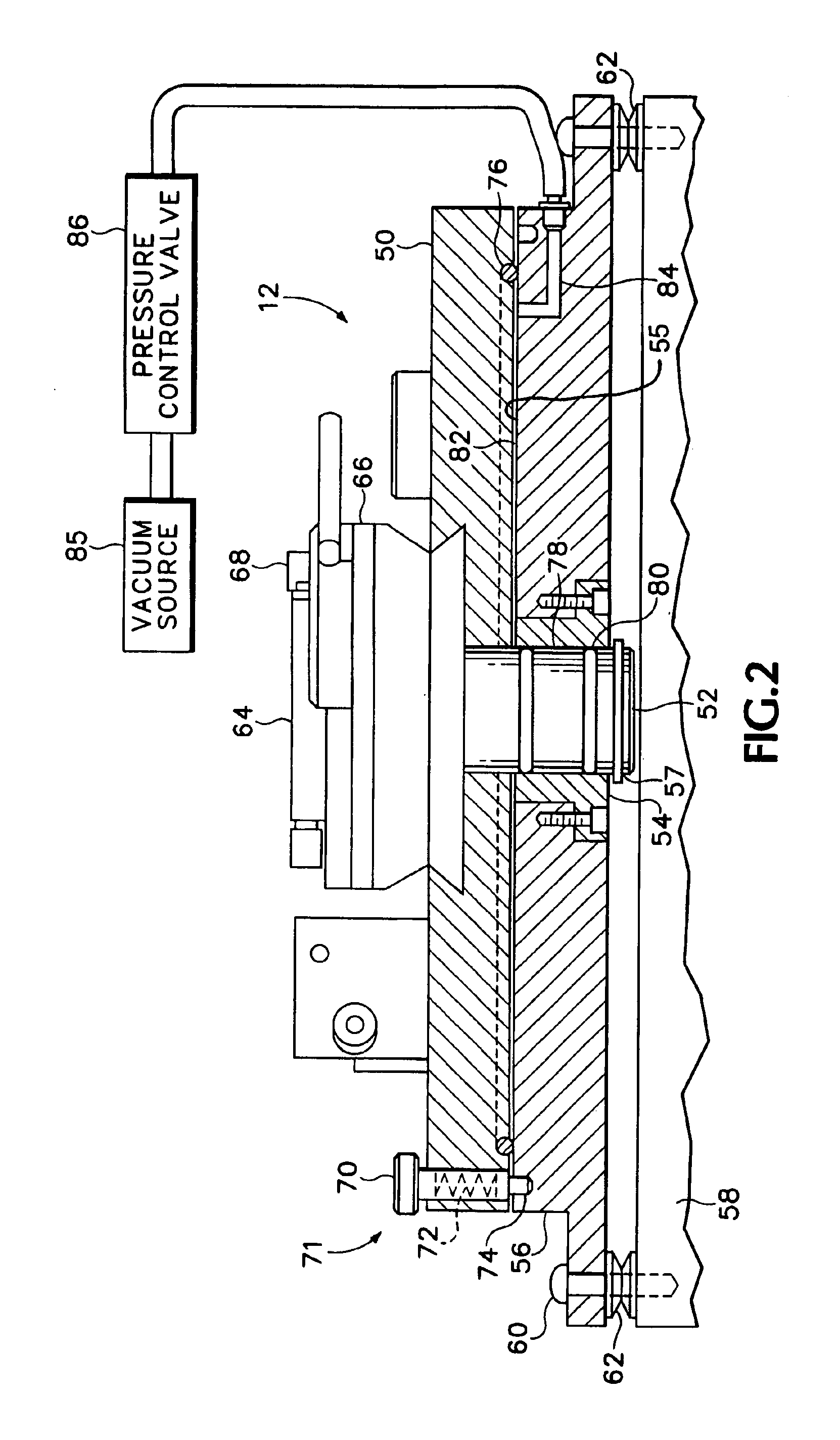
ActiveUS7635641B2Suitable for mass productionHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsEngineering physicsProtection layer
A method of fabricating an electronic substrate comprising the steps of; (A) selecting a first base layer; (B) depositing a first etchant resistant barrier layer onto the first base layer; (C) building up a first half stack of alternating conductive layers and insulating layers, the conductive layers being interconnected by vias through the insulating layers; (D) applying a second base layer onto the first half stack; (F) applying a protective coating of photoresist to the second base layer; (F) etching away the first base layer; (G) removing the protective coating of photoresist; (H) removing the first etchant resistant barrier layer; (I) building up a second half stack of alternating conductive layers and insulating layers, the conductive layers being interconnected by vias through the insulating layers, wherein the second half stack has a substantially symmetrical lay up to the first half stack; (J) applying an insulating layer onto the second hall stack of alternating conductive layers and insulating layers, (K) removing the second base layer, and (L) terminating the substrate by exposing ends of vias on outer surfaces of the stack and applying terminations thereto.
Owner:ZHUHAI ADVANCED CHIP CARRIERS & ELECTRONICS SUBSTRATE SOLUTIONS TECH
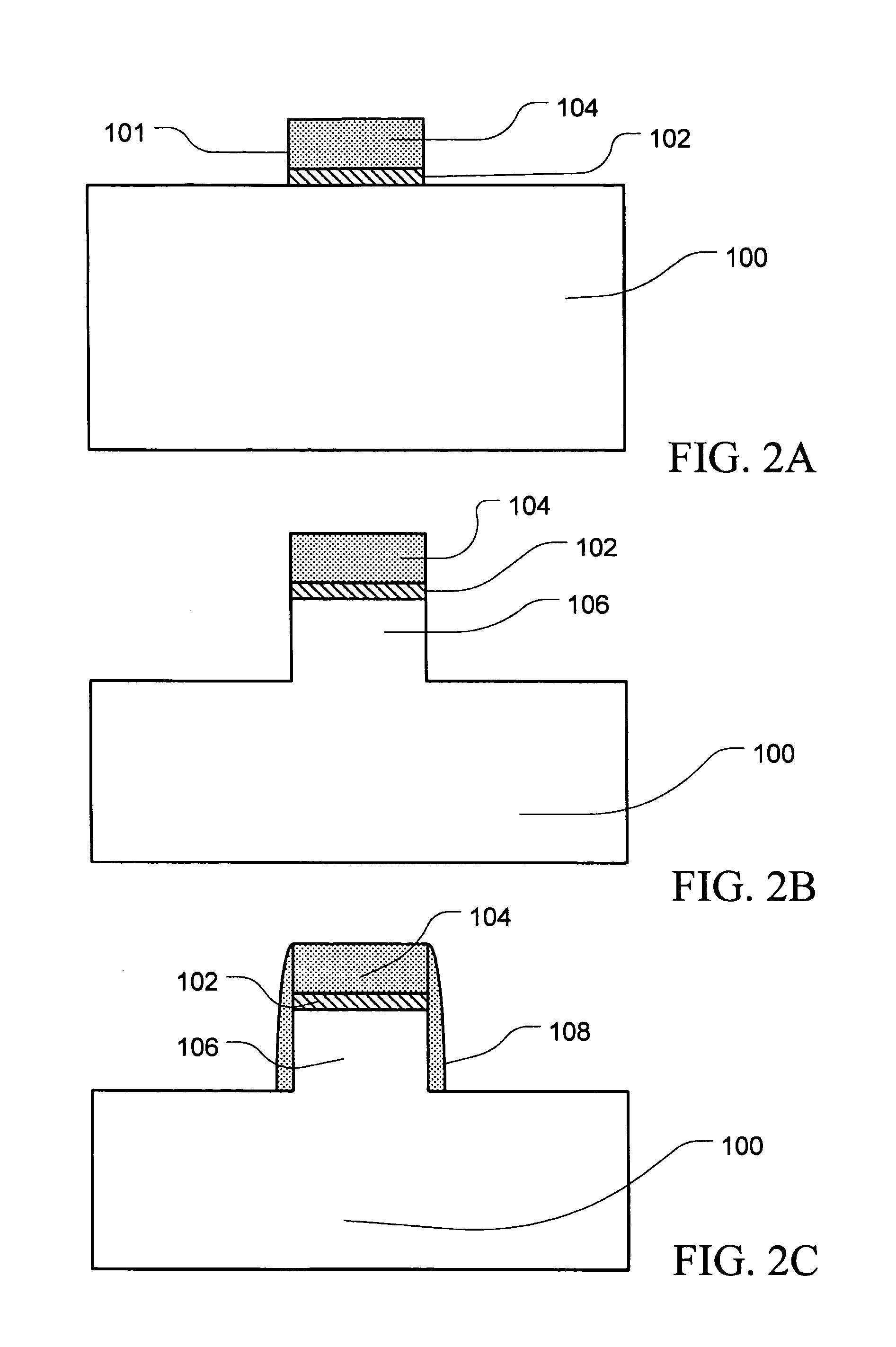
Multi-structured Si-fin and method of manufacture
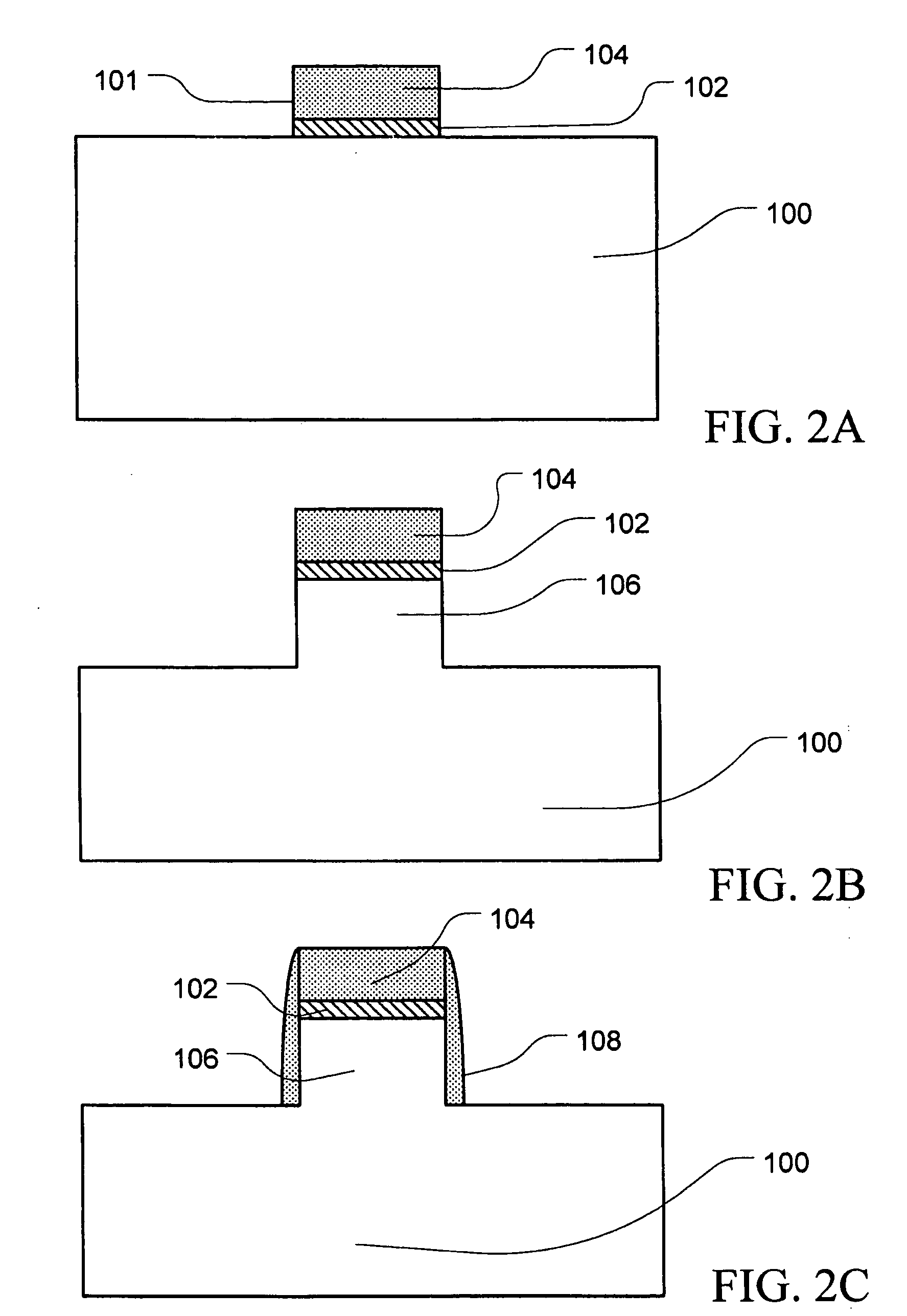
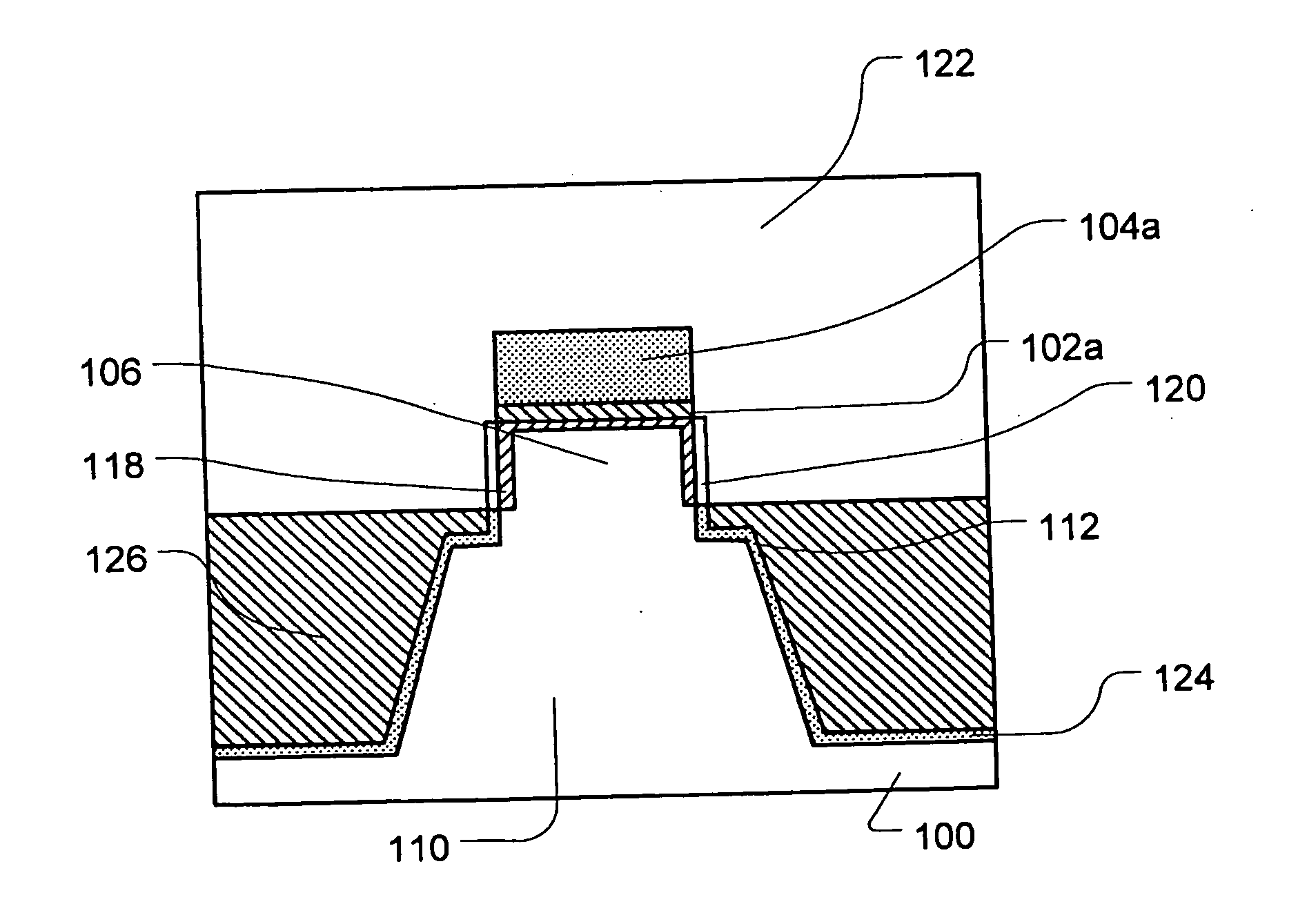
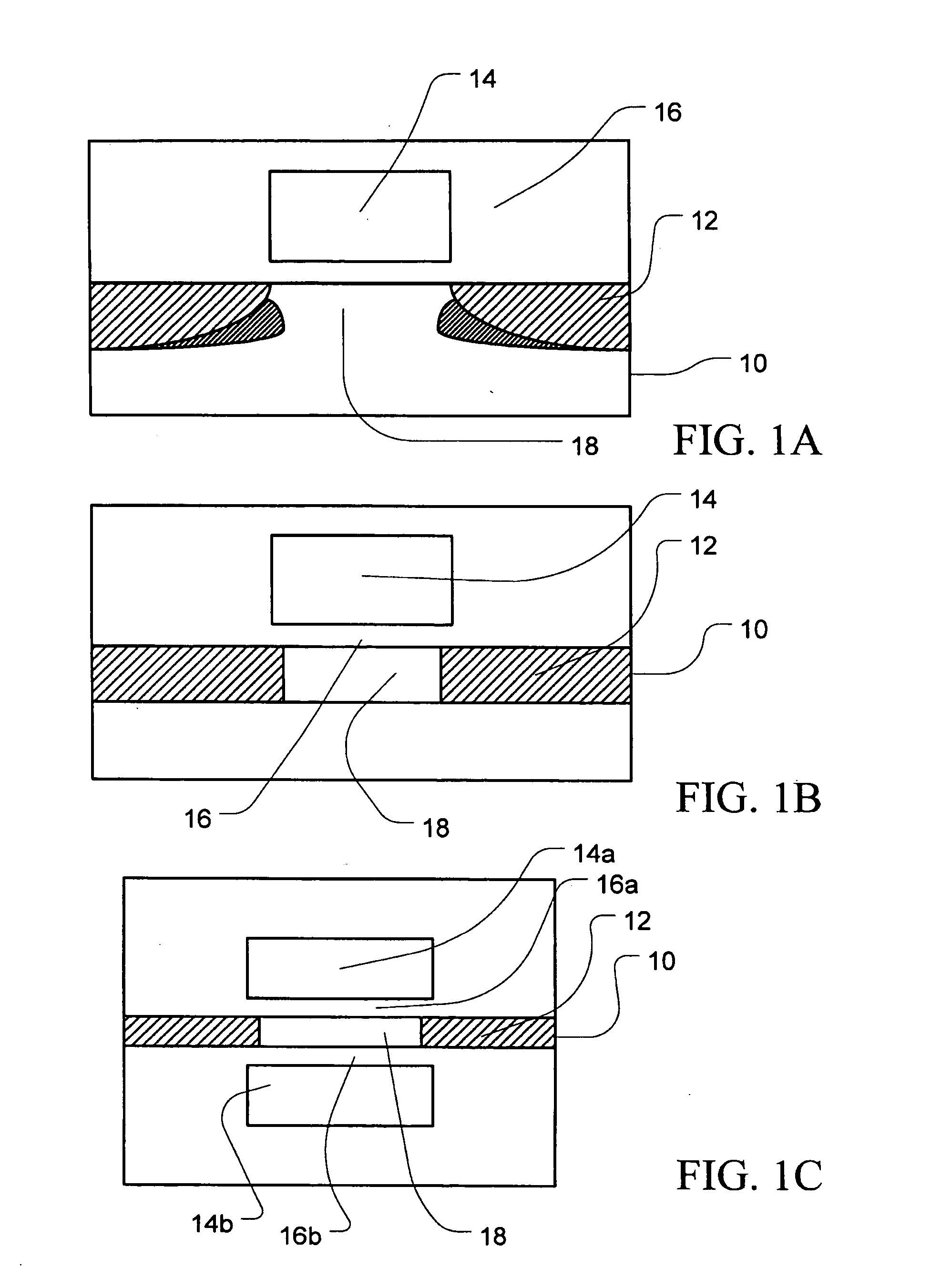
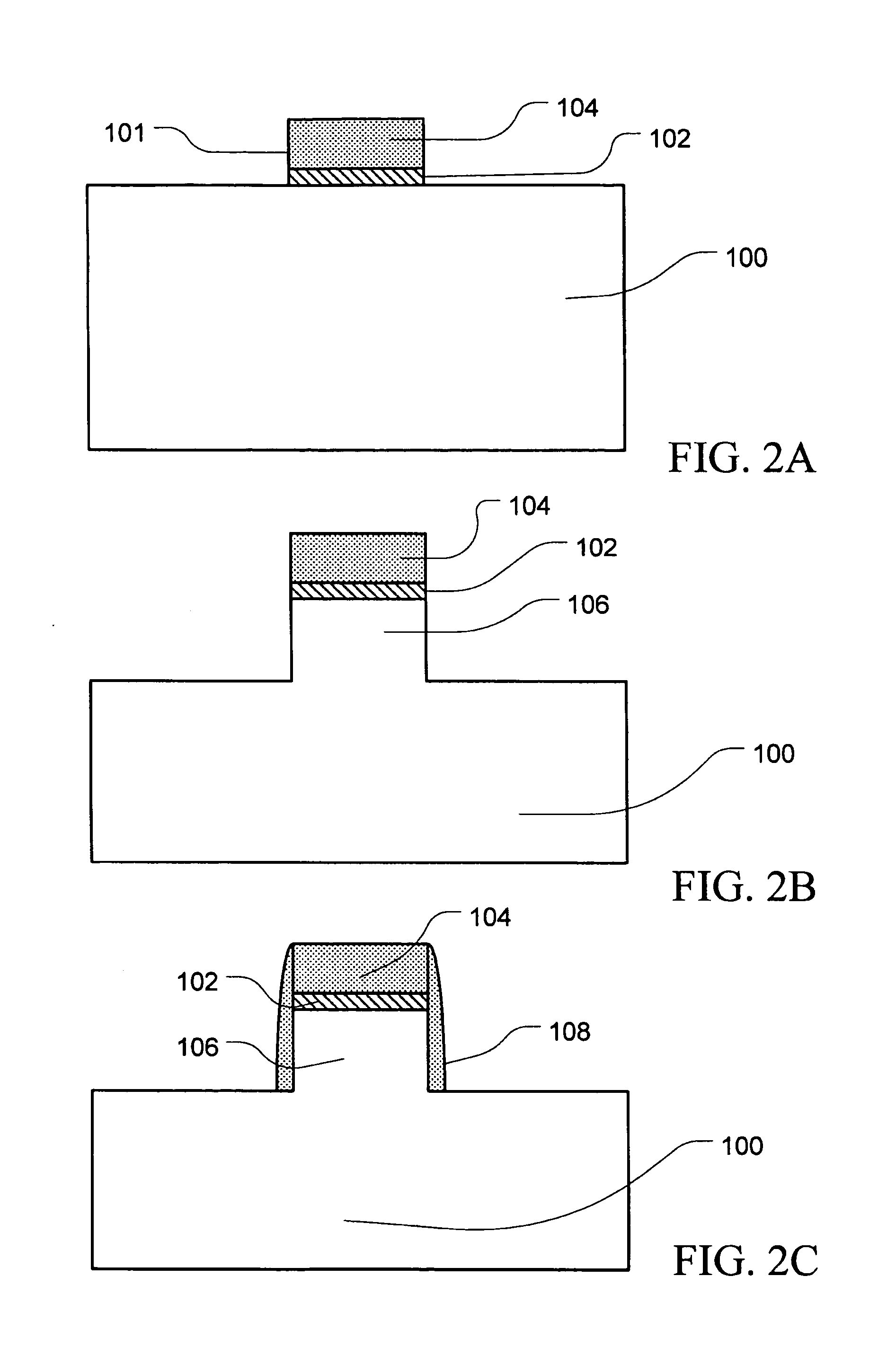
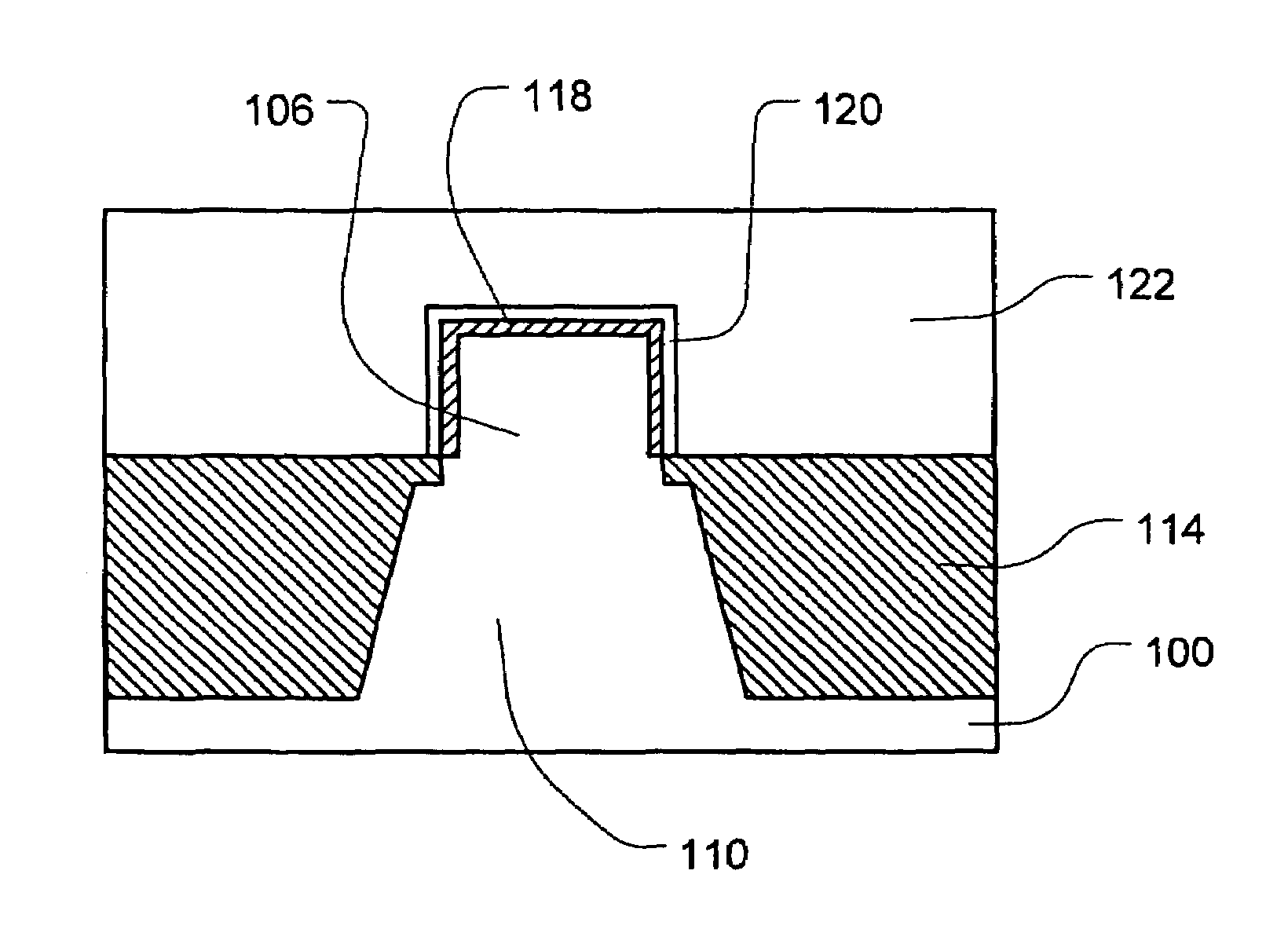
InactiveUS20050035391A1Point becomes highGood planarityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialEngineering
Disclosed is a semiconductor fin construction useful in FinFET devices that incorporates an upper region and a lower region with wherein the upper region is formed with substantially vertical sidewalls and the lower region is formed with inclined sidewalls to produce a wider base portion. The disclosed semiconductor fin construction will also typically include a horizontal step region at the interface between the upper region and the lower region. Also disclosed are a series of methods of manufacturing semiconductor devices incorporating semiconductor fins having this dual construction and incorporating various combinations of insulating materials such as silicon dioxide and / or silicon nitride for forming shallow trench isolation (STI) structures between adjacent semiconductor fins.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-structured Si-fin
InactiveUS7141856B2Point becomes highGood planarityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialEngineering
Disclosed is a semiconductor fin construction useful in FinFET devices that incorporates an upper region and a lower region with wherein the upper region is formed with substantially vertical sidewalls and the lower region is formed with inclined sidewalls to produce a wider base portion. The disclosed semiconductor fin construction will also typically include a horizontal step region at the interface between the upper region and the lower region. Also disclosed are a series of methods of manufacturing semiconductor devices incorporating semiconductor fins having this dual construction and incorporating various combinations of insulating materials such as silicon dioxide and / or silicon nitride for forming shallow trench isolation (STI) structures between adjacent semiconductor fins.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
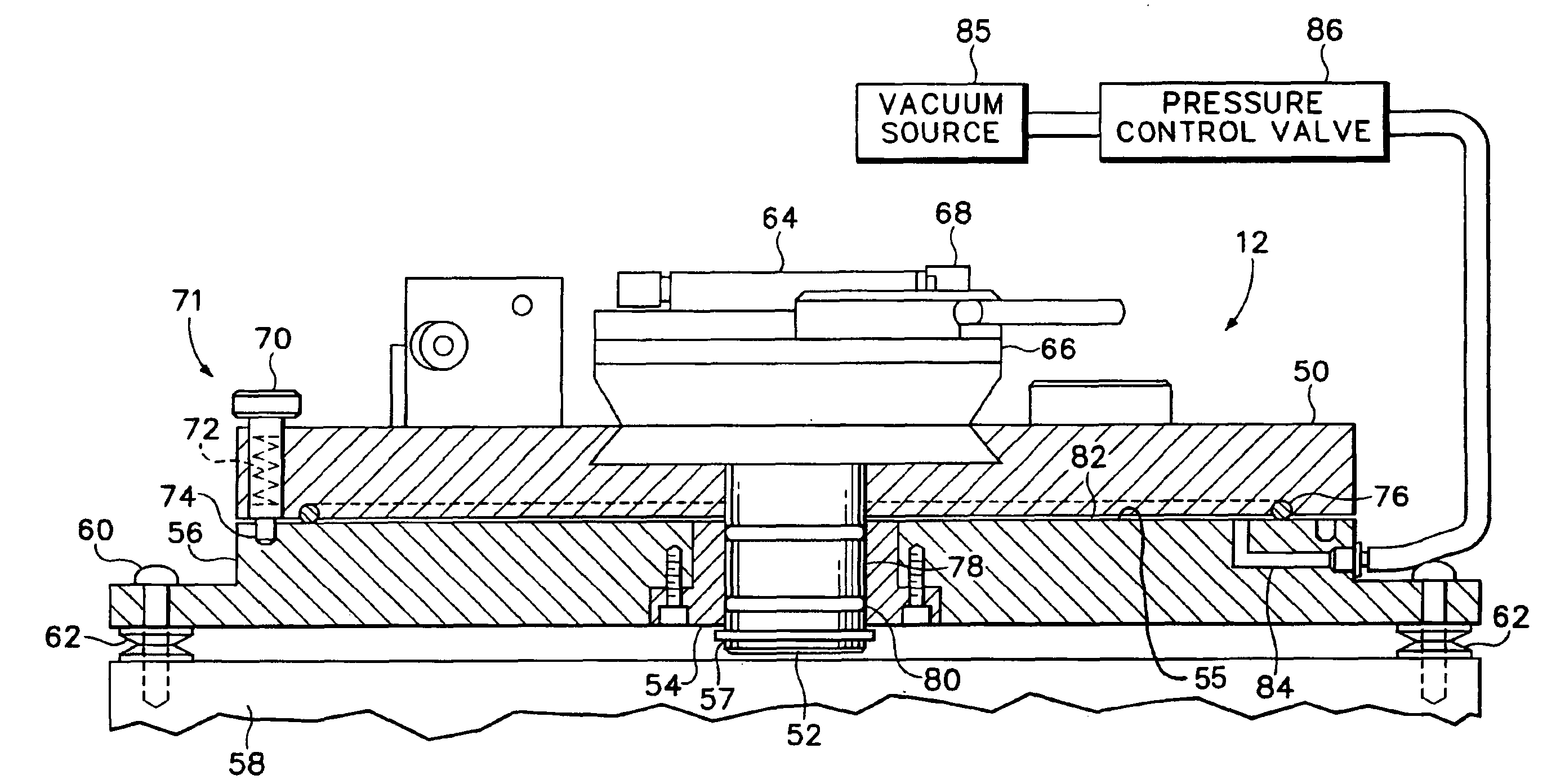
Indexing rotatable chuck for a probe station
InactiveUS6885197B2Improve rigidityPromoting consistent planaritySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingPower stationEngineering
A rotary chuck with indexed rotation promotes rapid rotation of a device under test and increases the productivity of a probe station on which the device is being tested. A device mounting member of a rotatable chuck is supported for rotation on a first surface of a base until a vacuum is applied drawing the device mounting member into contact with a second surface of the base and constraining the device mounting member against rotation.
Owner:CASCADE MICROTECH
Finishing components and elements
InactiveUS6641463B1Easy to organizeReduce manufacturing costPolishing machinesRevolution surface grinding machinesElastomerEngineering
New, versatile finishing surfaces are described. Unitary finishing elements having discrete finishing members attached to unitary resilient body are disclosed for finishing microdevices such as semiconductor wafers. Finishing surfaces such as discrete finishing members can be comprised of a multiphase polymeric composition. The new unitary finishing elements have lower cost to manufacture and high precision. The unitary finishing elements and finishing surfaces can reduce unwanted surface defect creation on the semiconductor wafers during finishing.
Owner:SEMCON TECH
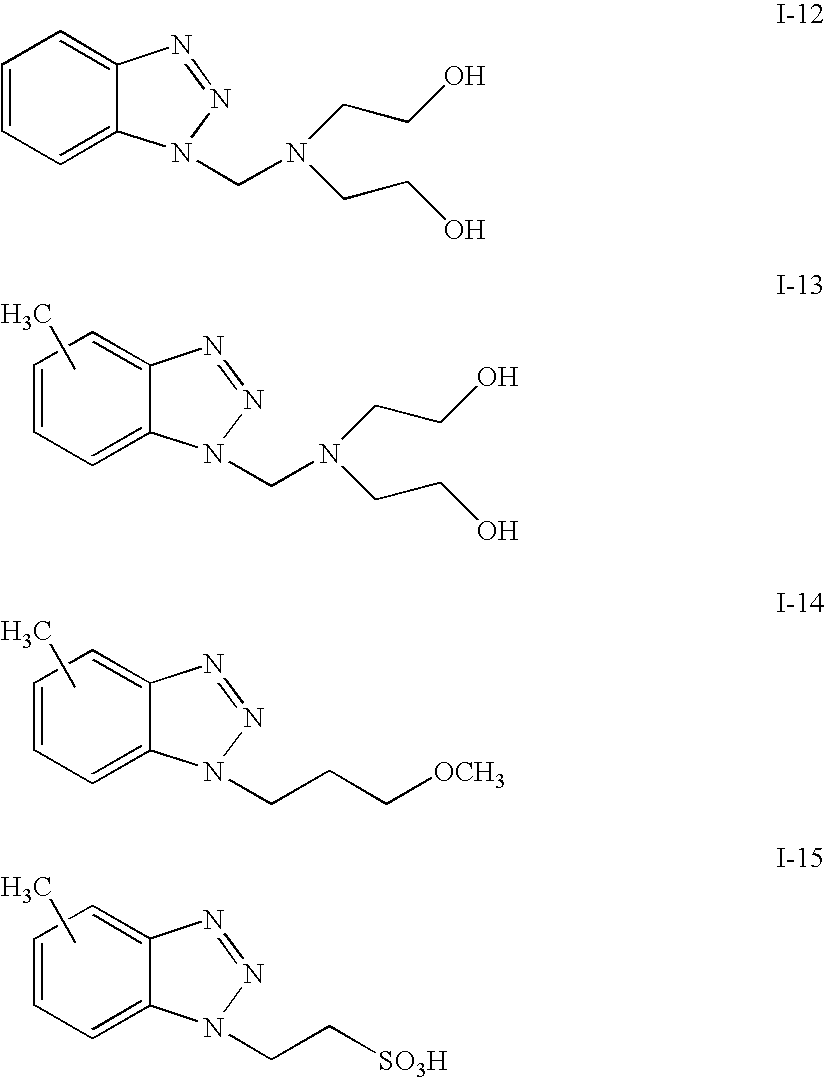
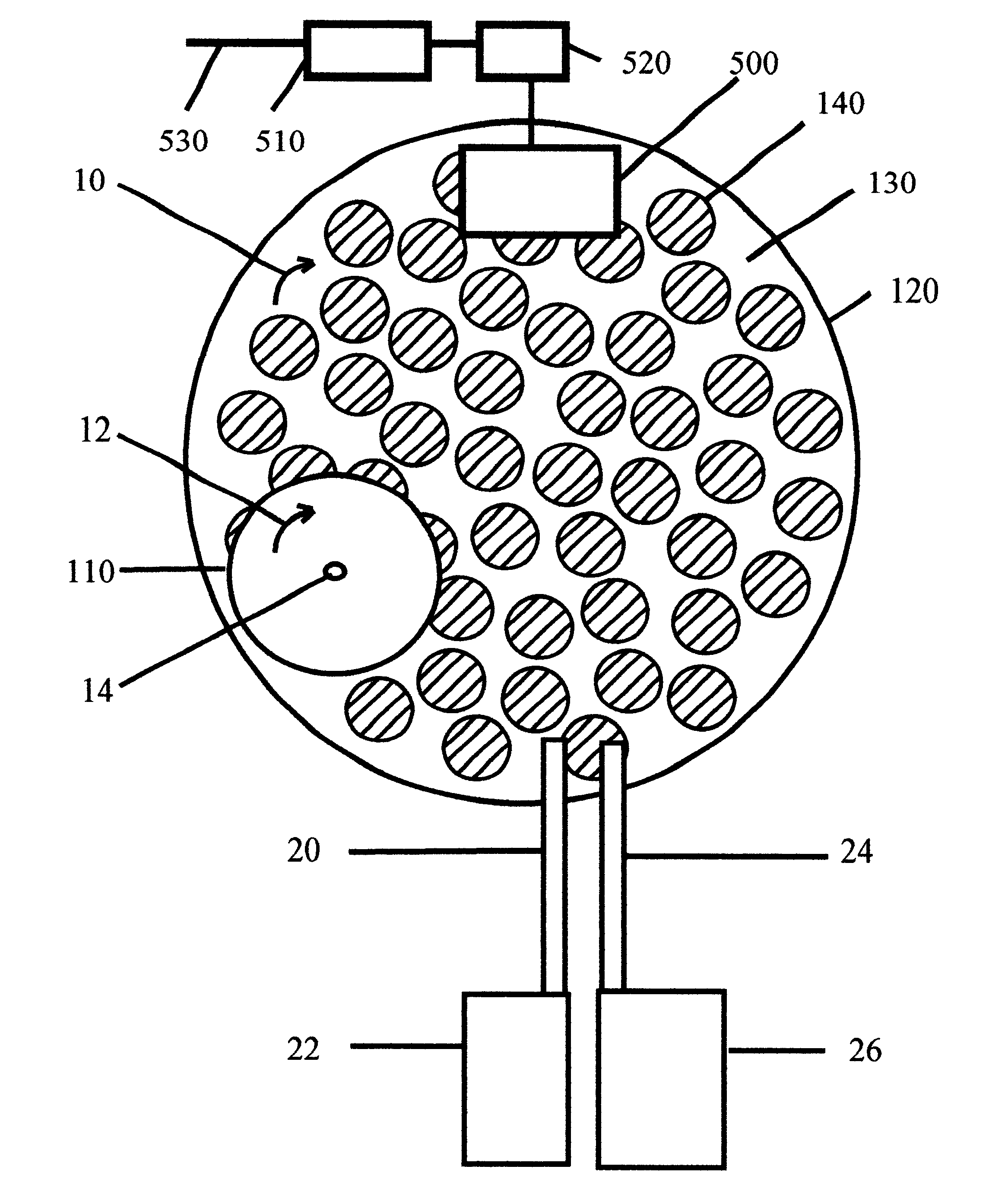
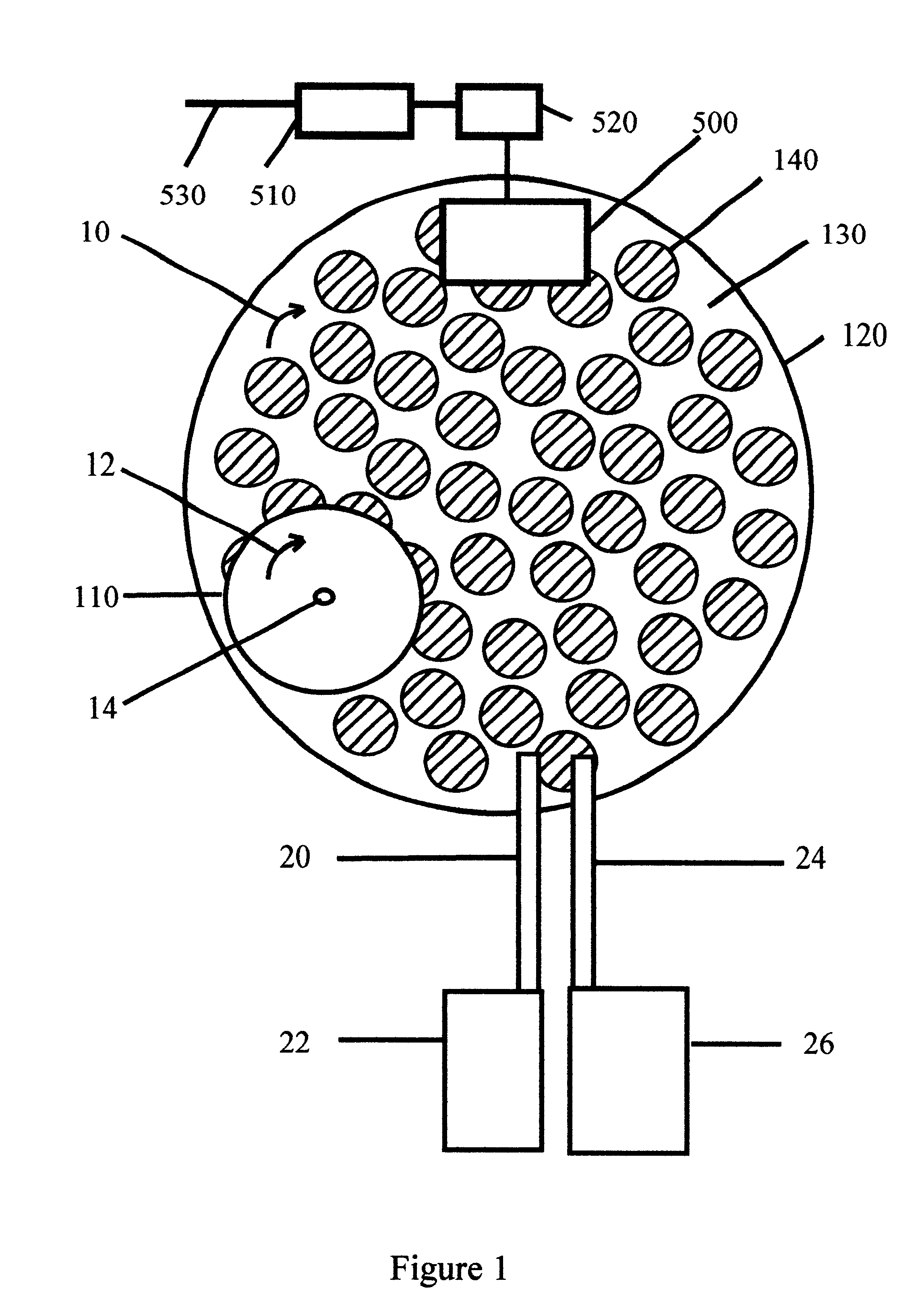
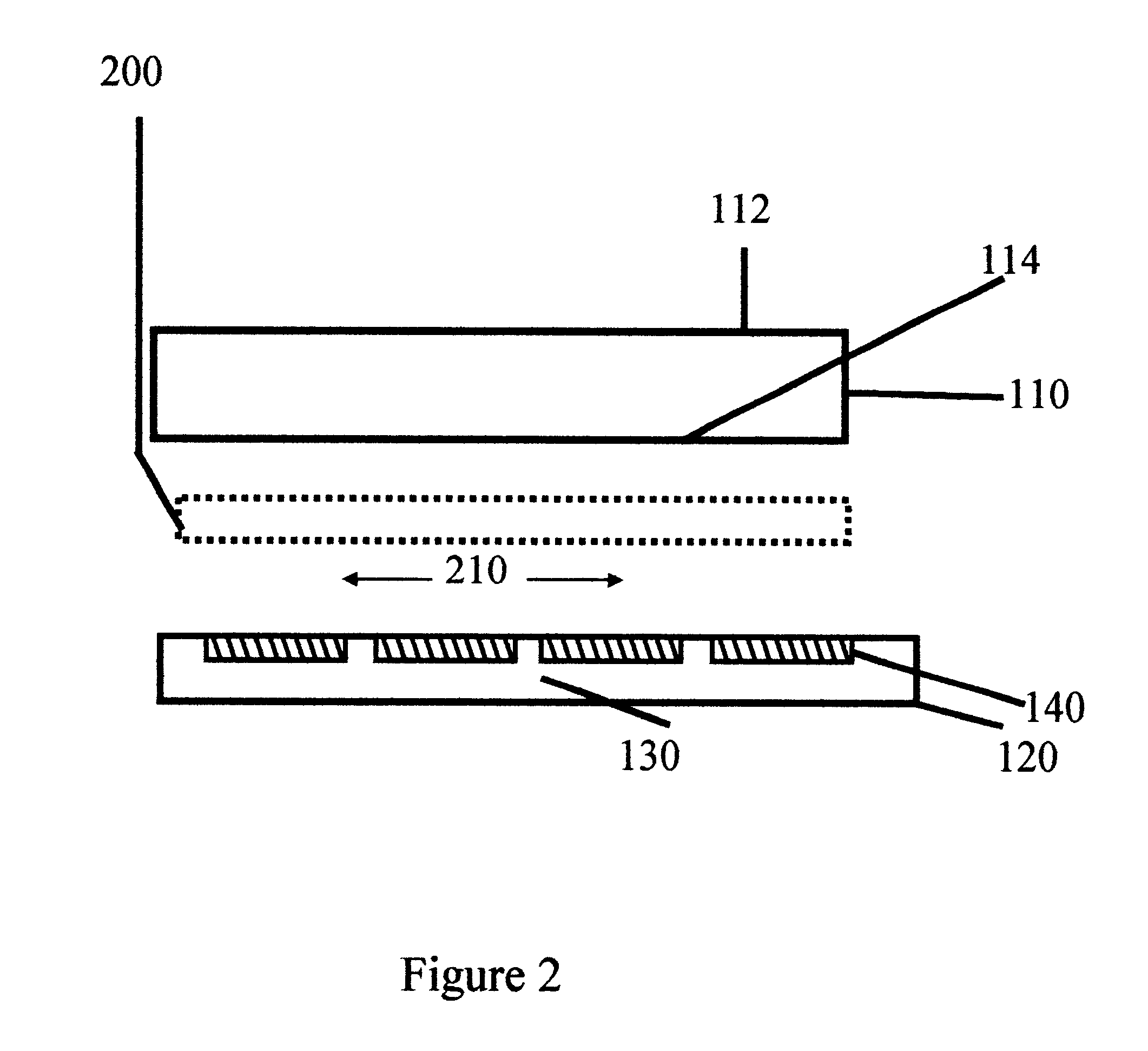
Organic semiconductor material containing naphthalene [1, 2-c: 5, 6-c] di [1, 2, 5] thiadiazole and application thereof
ActiveCN102060982AEasy to manufactureEquilibrium SolubilitySolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal catalystChemical groups
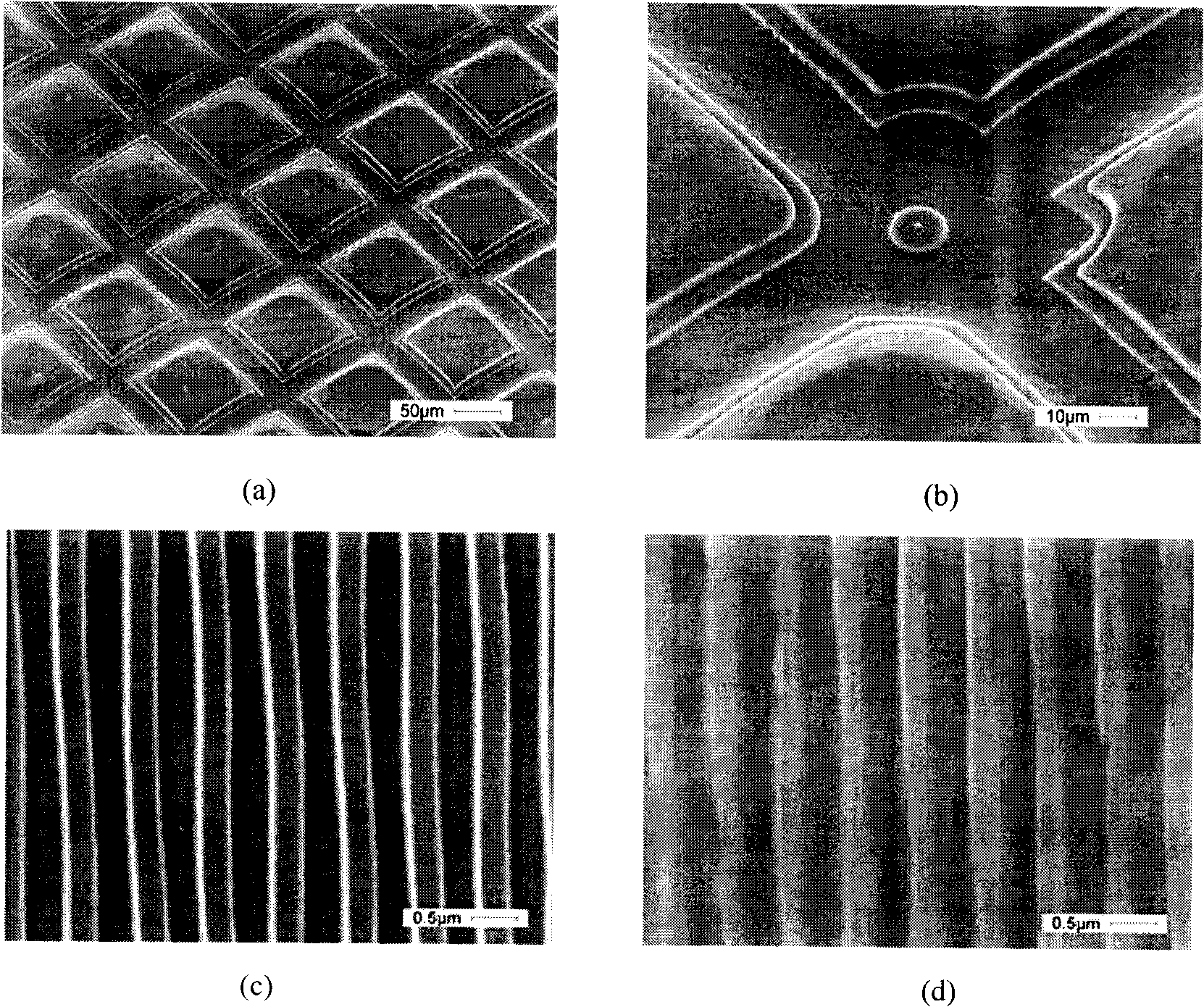
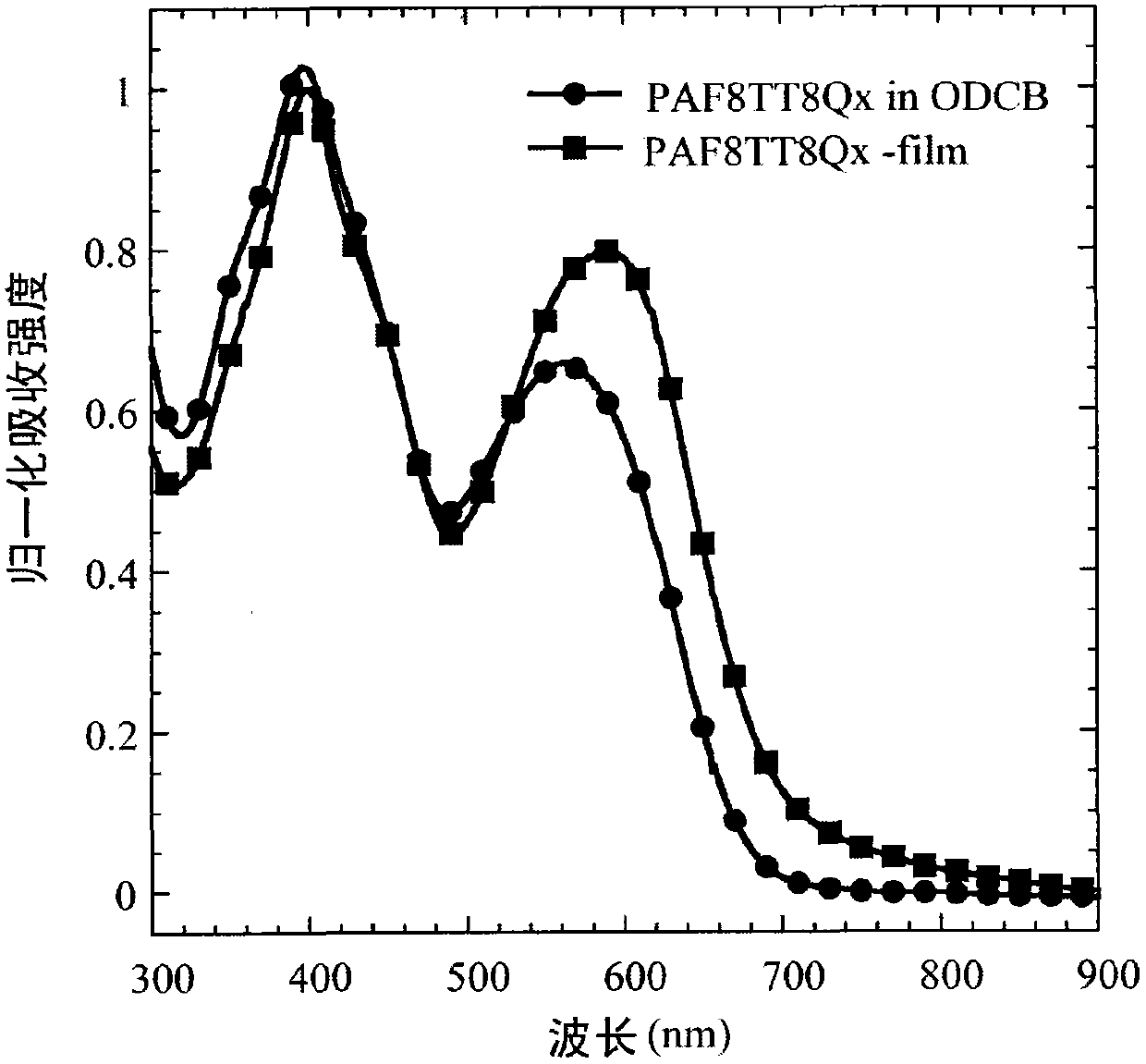
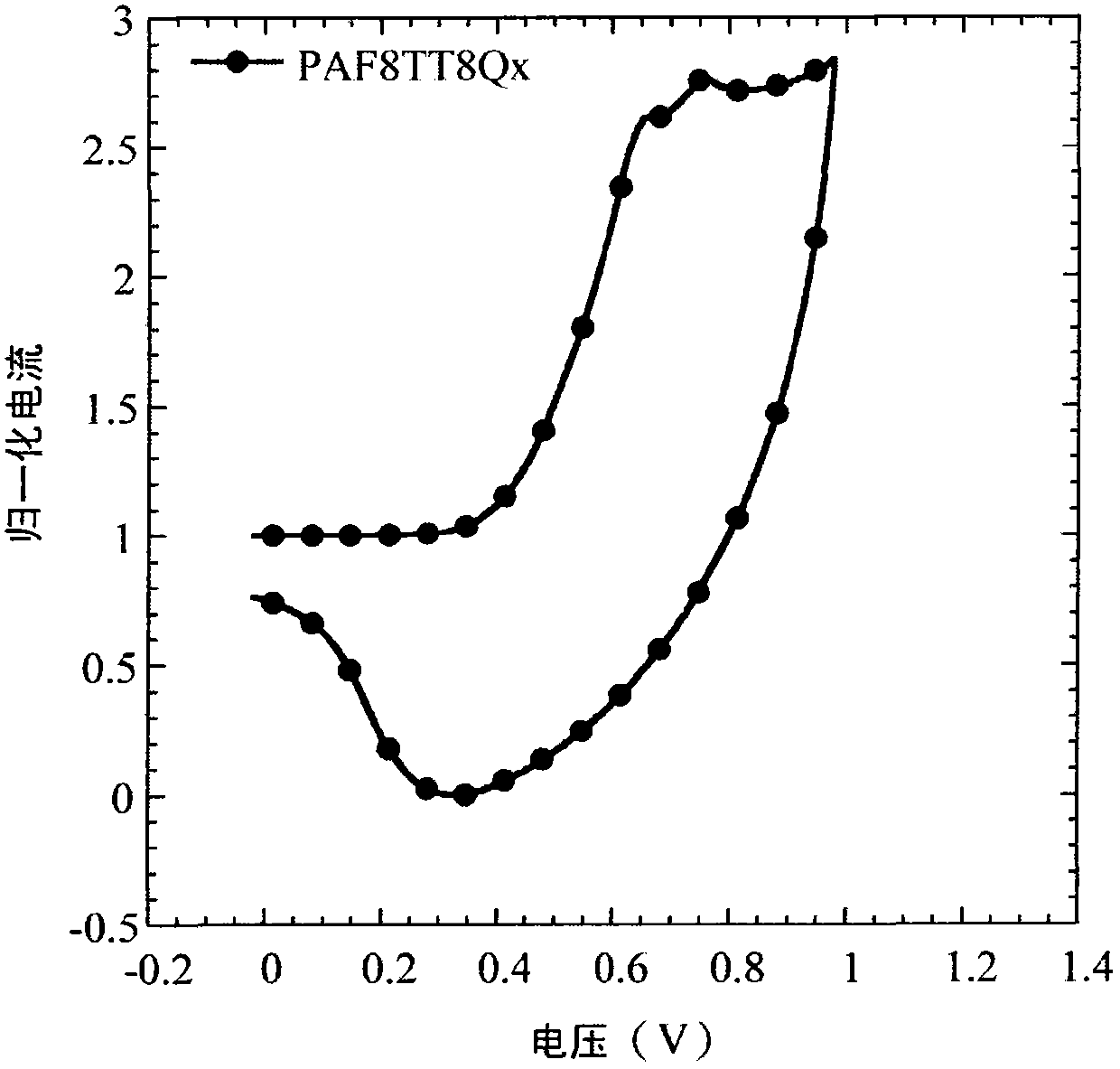
The invention relates to an organic semiconductor material containing naphthalene [1, 2-c: 5, 6-c] di [1, 2, 5] thiadiazole and application thereof, wherein the organic semiconductor material is prepared by reacting the halogenated derivatives with the monomer containing an aromatic group structure under the metal catalyst, wherein the halogenated derivatives are obtained by halogenating the naphthalene [1, 2-c: 5, 6-c] di [1, 2, 5] thiadiazole; the aromatic group is connected with a naphthalene [1, 2-c:5, 6-c] di [1, 2, 5] thiadiazole unit in a conjugate manner. The organic semiconductor material is characterized by containing 3, 7 substituted decorative[1, 2-c: 5, 6-c] di [1, 2, 5] thiadiazole chemical groups; as the naphthalene [1, 2-c:5, 6-c] di [1, 2, 5] thiadiazole has excellent electron-withdrawing ability and planarity, the organic semiconductor material can excellently adjust the photoelectric property, has excellent photoelectric performance, and is applied to the field of organic photoelectric components.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Multi-structured Si-fin and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20070048947A1Improve planarity and uniformityHigh materialTransistorSolid-state devicesSilicon nitrideEngineering
Disclosed is a semiconductor fin construction useful in FinFET devices that incorporates an upper region and a lower region with wherein the upper region is formed with substantially vertical sidewalls and the lower region is formed with inclined sidewalls to produce a wider base portion. The disclosed semiconductor fin construction will also typically include a horizontal step region at the interface between the upper region and the lower region. Also disclosed are a series of methods of manufacturing semiconductor devices incorporating semiconductor fins having this dual construction and incorporating various combinations of insulating materials such as silicon dioxide and / or silicon nitride for forming shallow trench isolation (STI) structures between adjacent semiconductor fins.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
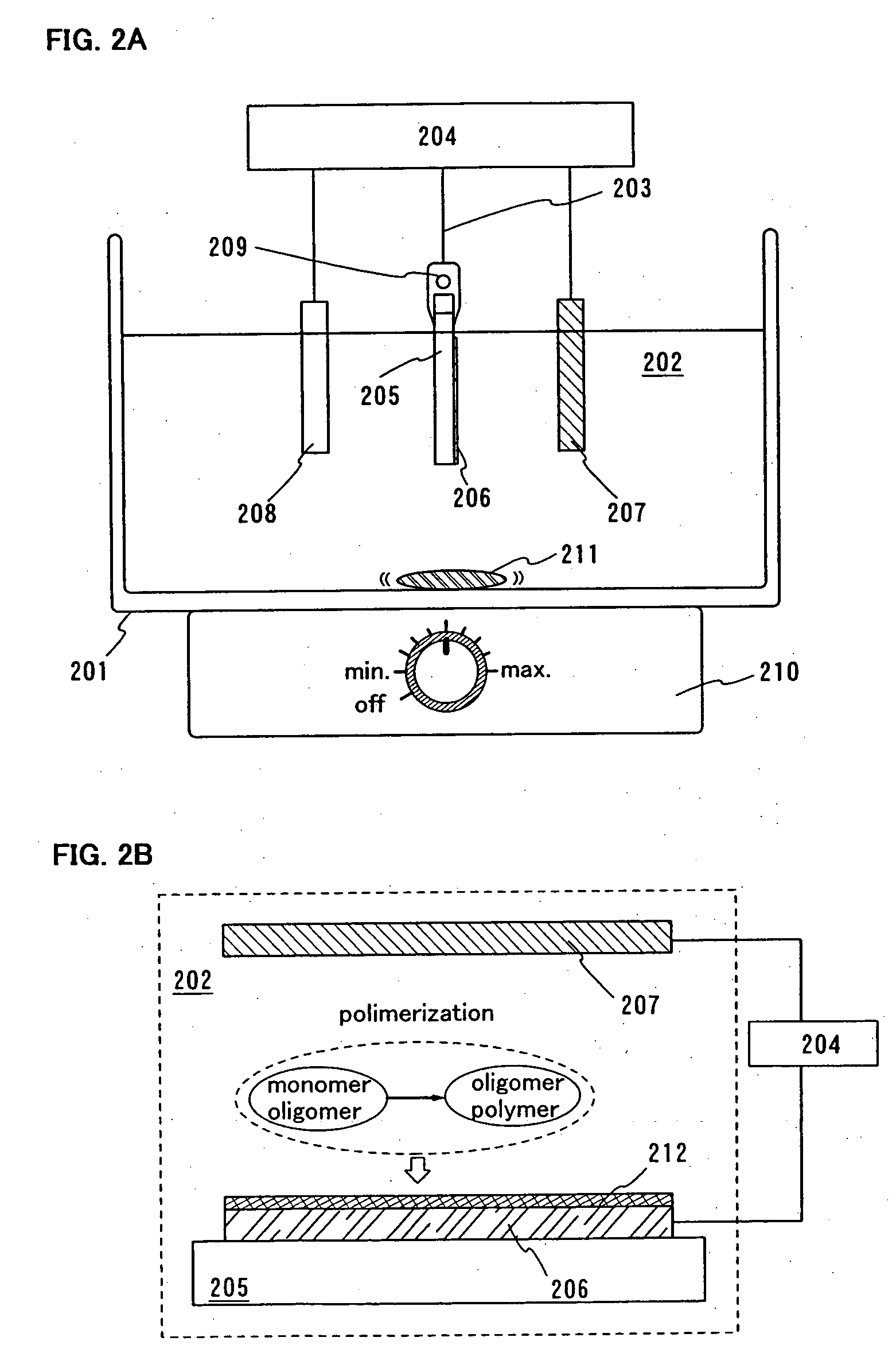
Light emitting device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20050001543A1Reduce and eliminate generationEasily deterioratedDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesSimple Organic CompoundsCompound (substance)
A light emitting element containing an organic compound has a defect that the light emitting element is easily deteriorated by various factors; therefore, it is the biggest issue of the light emitting element that the light emitting element is formed with high reliability (longer lifetime). An objective of the present invention is to reduce or eliminate generation of the above described various defective modes of the light emitting element containing an organic compound. According to the present invention, current efficiency-luminance characteristics can be improved by orienting organic compound molecules in an applying direction of current. In addition, deterioration can be prevented by using a crystallization inhibitor.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Novel integrated circuit support structures and their fabrication
ActiveUS20070082501A1Suitable for mass productionHigh yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuit aspectsEngineering physicsProtection layer
A method of fabricating an electronic substrate comprising the steps of; (A) selecting a first base layer; (B) depositing a first etchant resistant barrier layer onto the first base layer; (C) building up a first half stack of alternating conductive layers and insulating layers, the conductive layers being interconnected by vias through the insulating layers; (D) applying a second base layer onto the first half stack; (F) applying a protective coating of photoresist to the second base layer; (F) etching away the first base layer; (G) removing the protective coating of photoresist; (H) removing the first etchant resistant barrier layer; (I) building up a second half stack of alternating conductive layers and insulating layers, the conductive layers being interconnected by vias through the insulating layers, wherein the second half stack has a substantially symmetrical lay up to the first half stack; (J) applying an insulating layer onto the second hall stack of alternating conductive layers and insulating layers, (K) removing the second base layer, and (L) terminating the substrate by exposing ends of vias on outer surfaces of the stack and applying terminations thereto.
Owner:ZHUHAI ADVANCED CHIP CARRIERS & ELECTRONICS SUBSTRATE SOLUTIONS TECH
Low-temperature diffusion welding method for magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy
InactiveCN101920393AAvoid generatingHigh bonding strengthNon-electric welding apparatusSolder maskAxial pressure
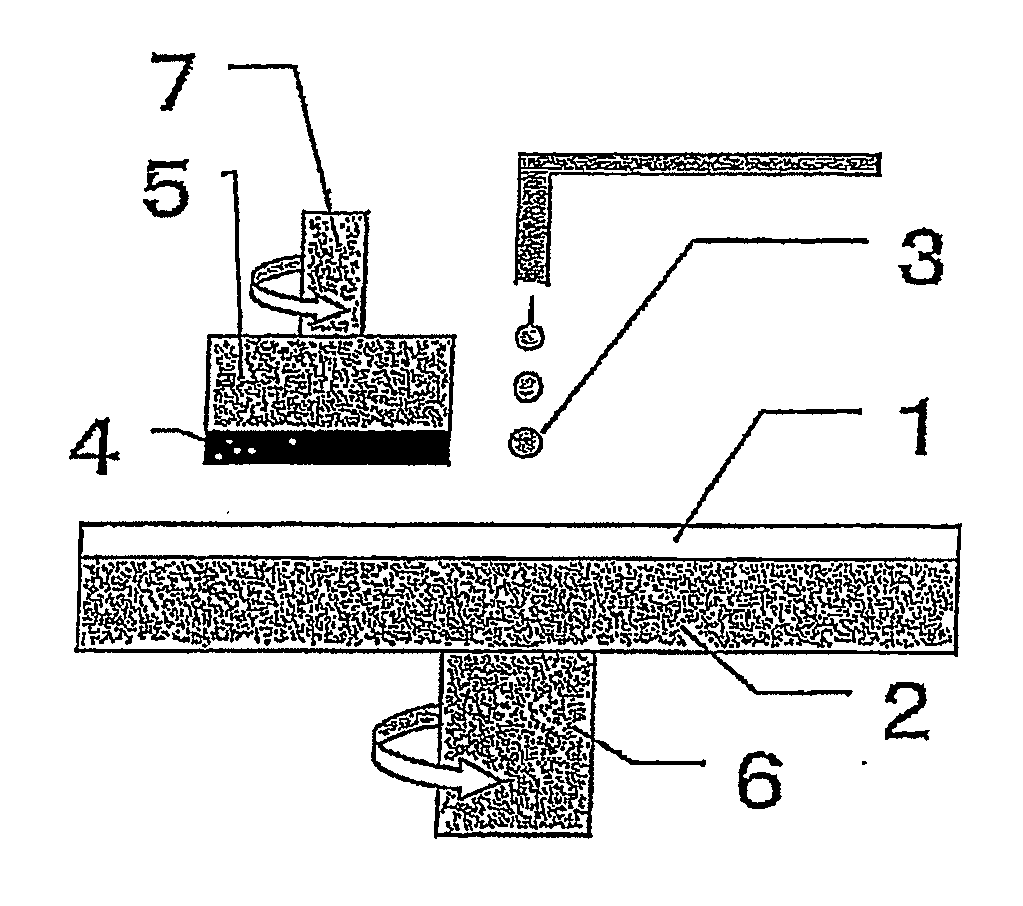
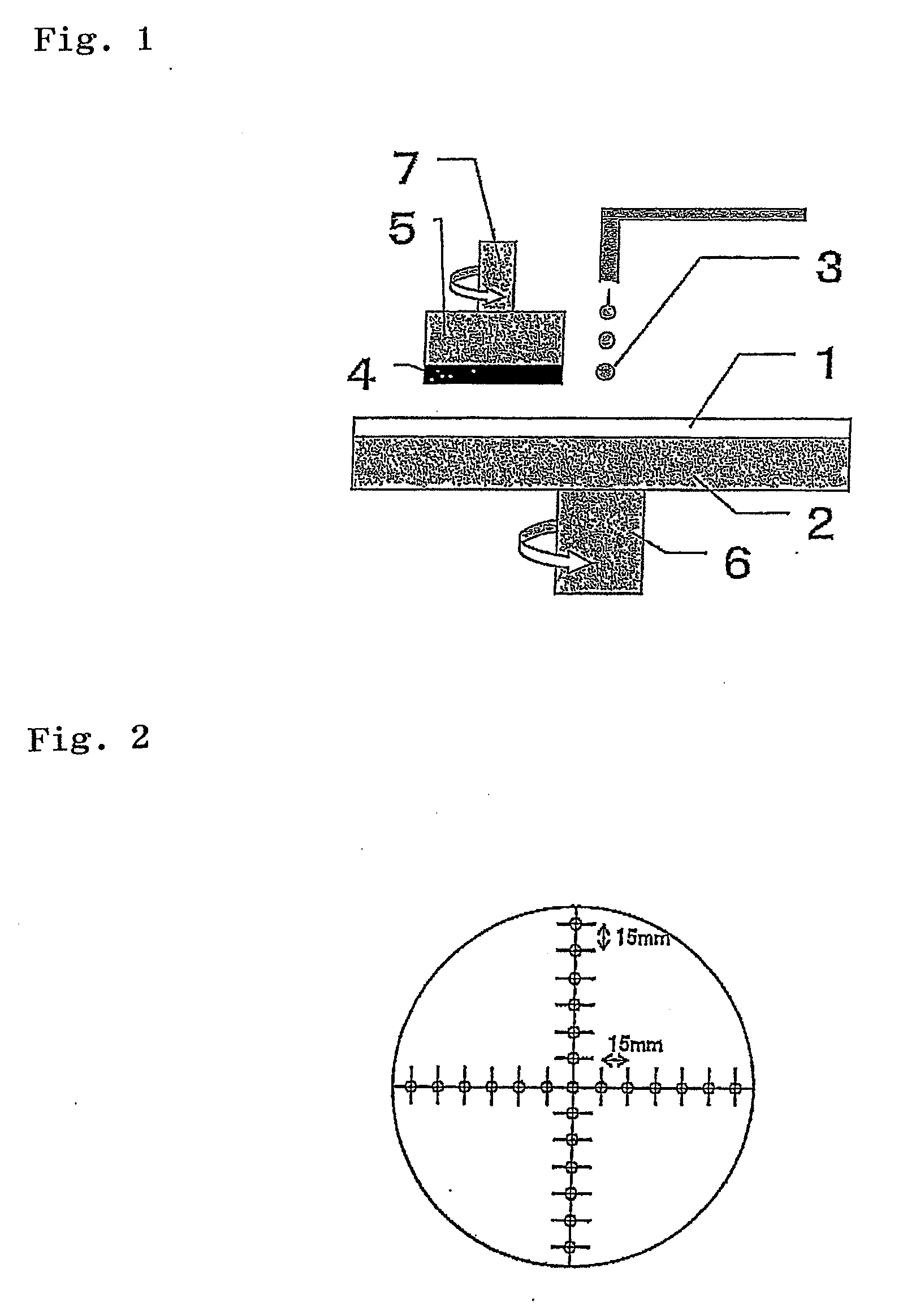
The invention discloses a low-temperature diffusion welding method for magnesium alloy and aluminum alloy. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) workpiece surface cleaning: processing a magnesium alloy plate and an aluminum alloy plate to a specified size, and removing oxide layers from to-be-welded surfaces thereof; (2) workpiece assembly: placing a tin-zinc alloy foil serving as a middle layer between the aluminum alloy plate and the magnesium alloy plate, and placing a solder mask on and below the plates respectively to form a welded workpiece; and (3) charging the workpiece into a furnace and welding: putting the welded workpiece into a vacuum diffusion welding furnace, performing heating and heat preservation, applying an axial pressure to the welded workpiece when the heat preservation begins, and releasing the pressure when the heat preservation is finished. The method can effectively overcome the defect that the prior art cannot realize high-quality welding between the Mg alloy and the Al alloy, is suitable for reliable welding between the Mg alloy and the Al alloy of different categories, is particularly suitable for welding the thin magnesium alloy plate and the thin aluminum alloy plate, and has good welding planarity, high parallel precision and integral compactness.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
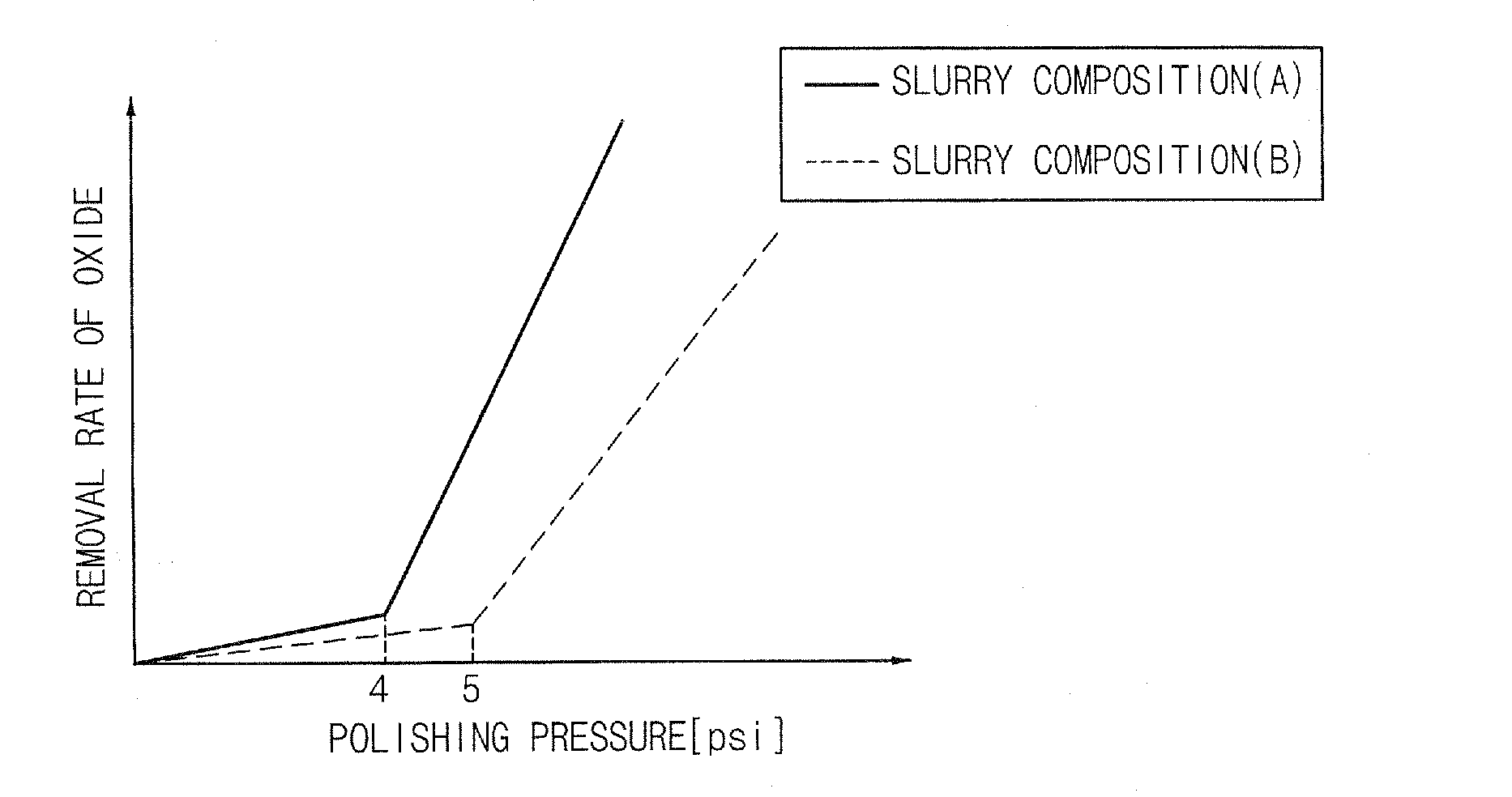
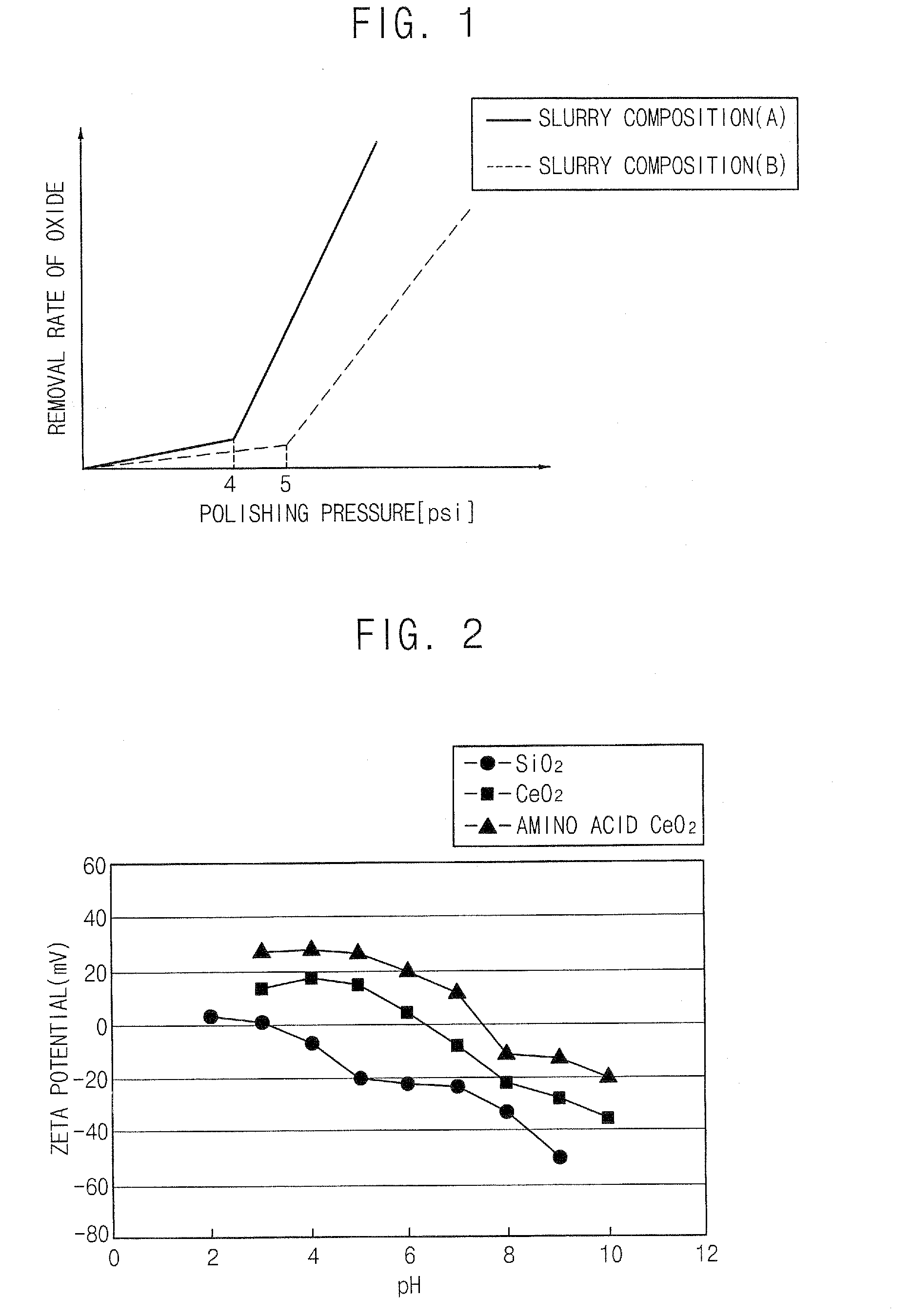
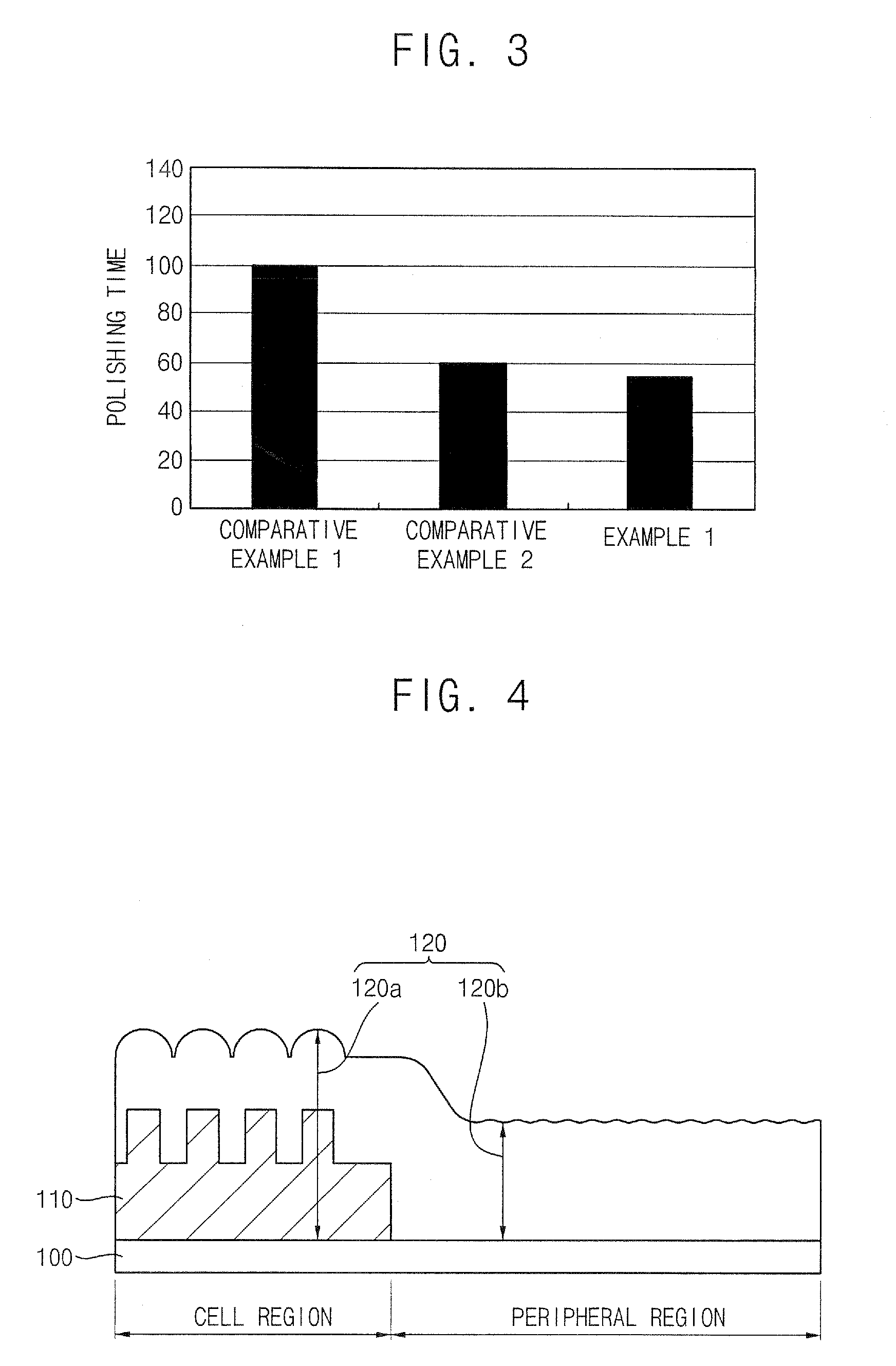
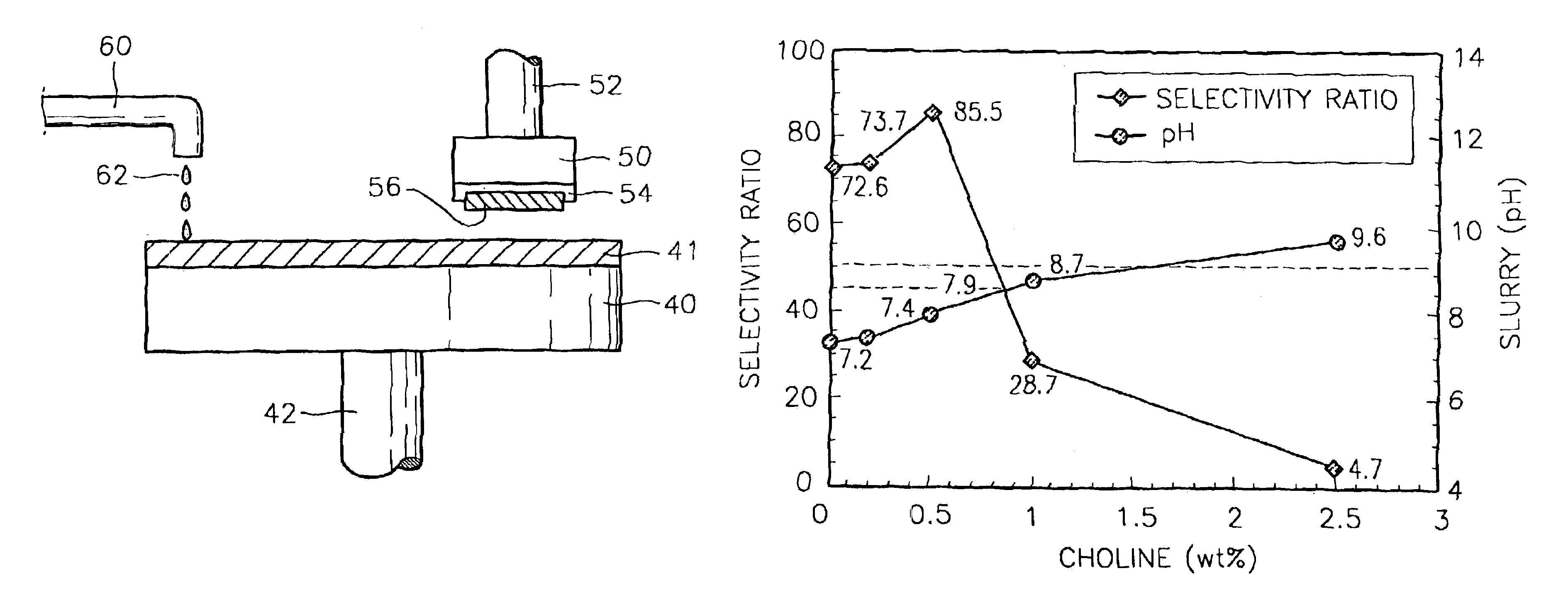
Slurry compositions and methods of polishing a layer using the slurry compositions
ActiveUS20080081542A1Shorten polishing timeLow polishing pressurePigmenting treatmentPolishing machinesPh controlSlurry
In a slurry composition and a method of polishing a layer using the slurry composition, the slurry composition includes from about 3 to 20 percent by weight of an abrasive, from about 0.1 to 3 percent by weight of an ionic surfactant, from about 0.01 to 0.1 percent by weight of a nonionic surfactant, from about 0.01 to 1 percent by weight of a polish accelerating agent including an amino acid compound, and a remainder of an aqueous solution including a basic pH-controlling agent and water. The slurry composition including the nonionic surfactant and the polish accelerating agent may be used for speedily polishing a stepped upper portion of a silicon oxide layer, and may also enable a lower portion of the silicon oxide layer to function as a polish stop layer.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for manufacturing semiconductor substrate
InactiveUS20080248629A1Avoid pollutionVariation of depth is reducedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSingle crystalSilicon oxide
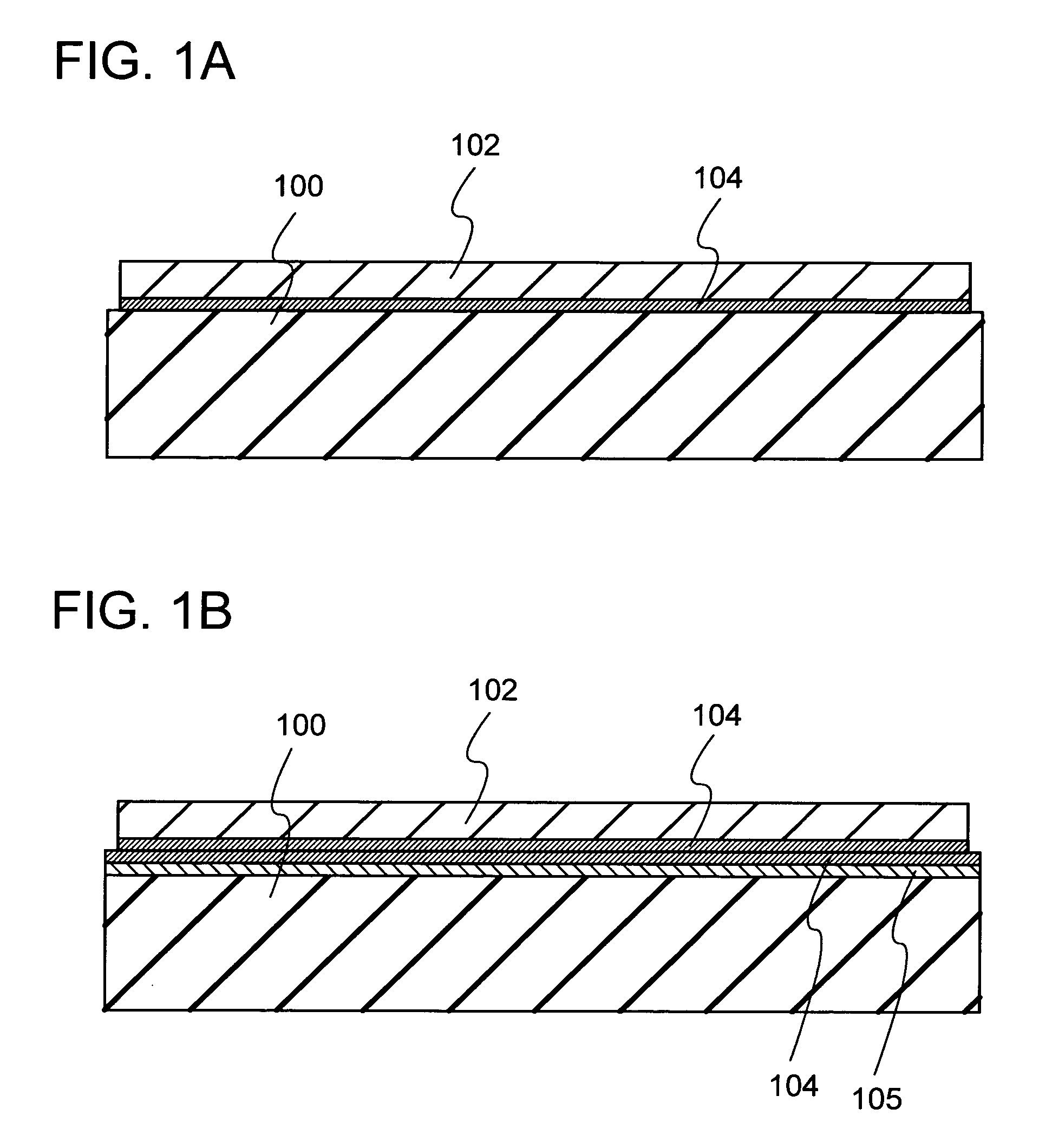
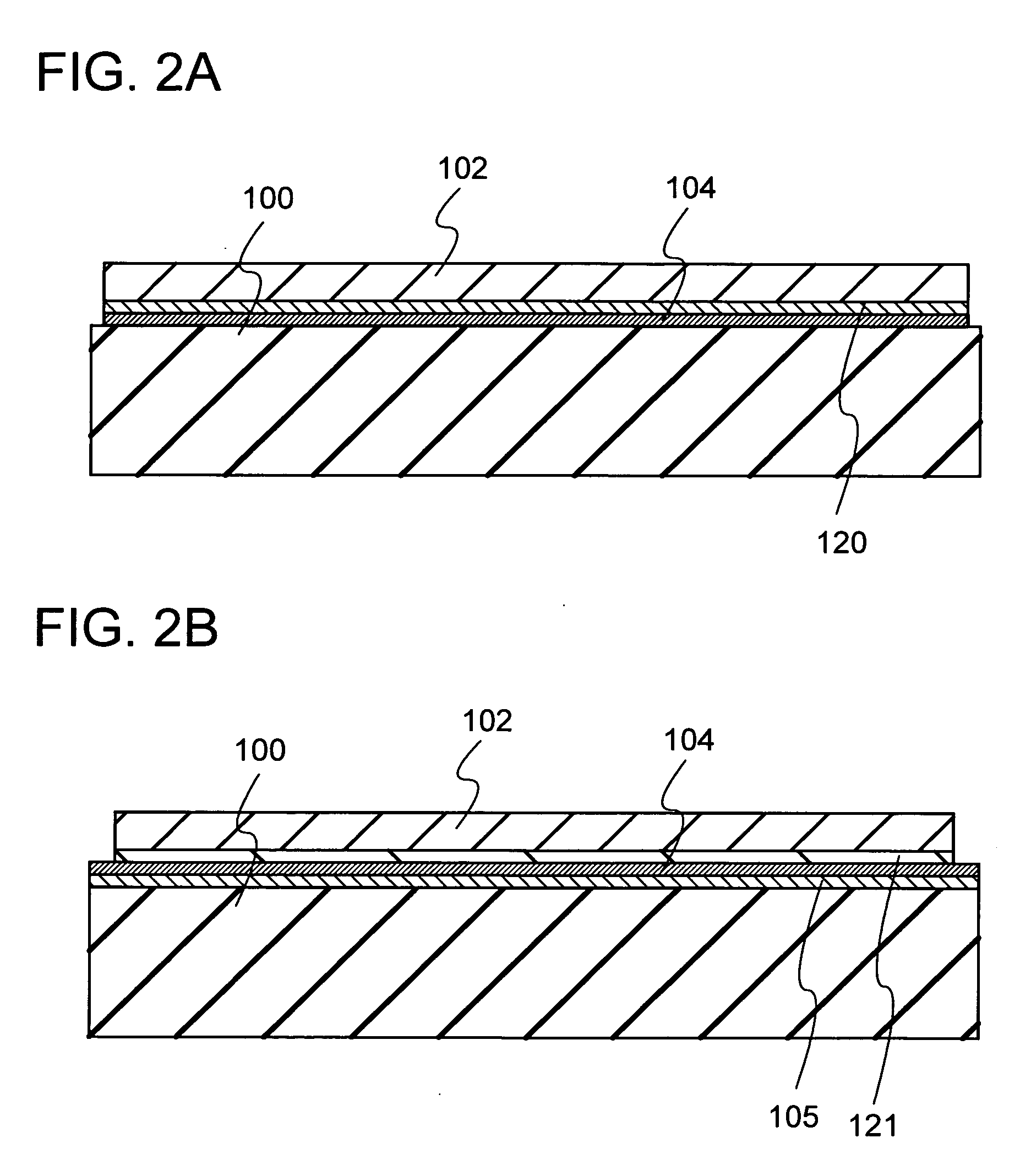
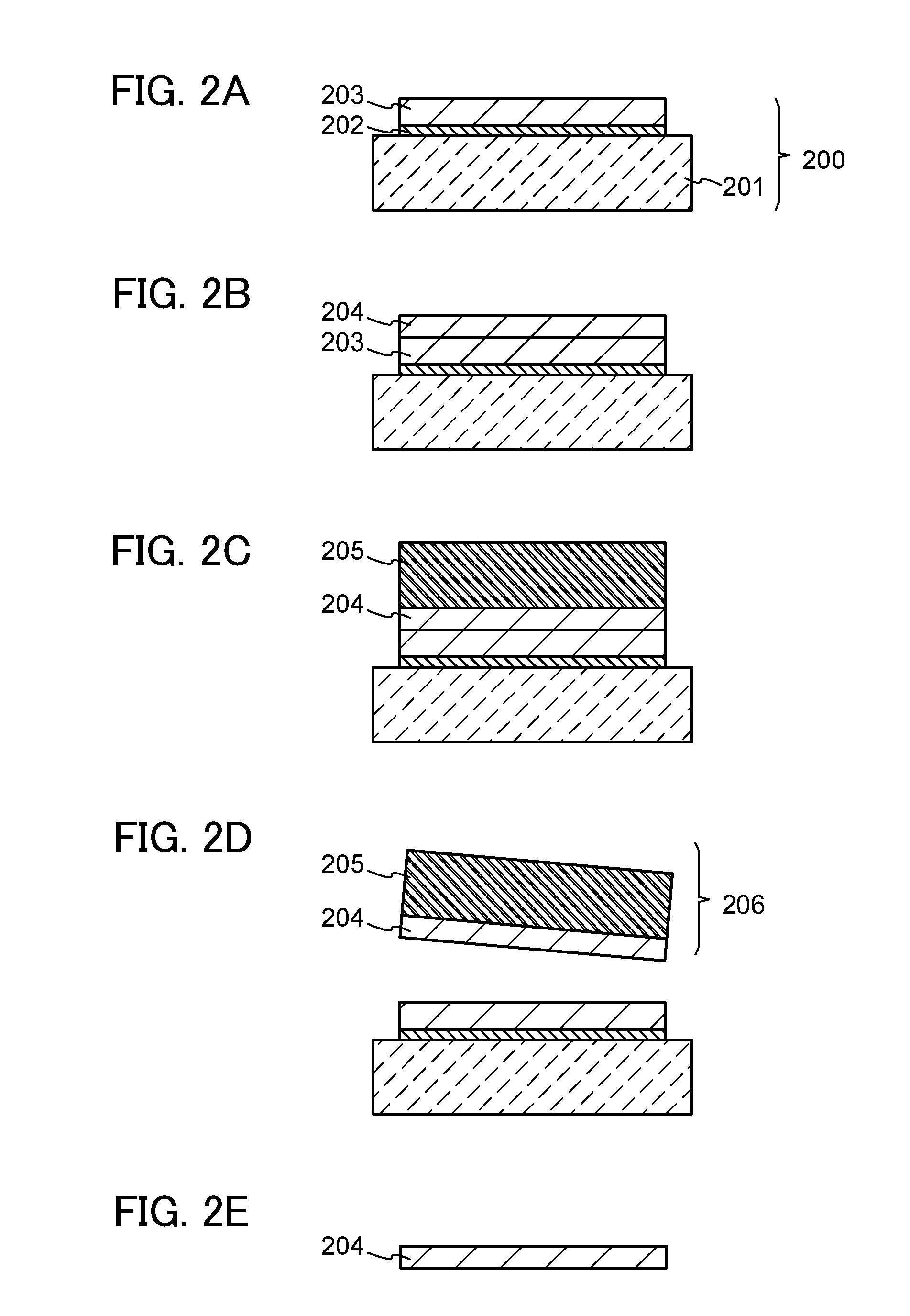
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor substrate is provided, which comprises a step of irradiating a single crystal semiconductor substrate with ions to form an embrittlement layer in the single crystal semiconductor substrate, a step of forming a silicon oxide film over the single crystal semiconductor substrate, a step of bonding the single crystal semiconductor substrate and a substrate having an insulating surface with the silicon oxide film interposed therebetween, a step of performing a thermal treatment, and a step of separating the single crystal semiconductor substrate with a single crystal semiconductor layer left over the substrate having the insulating surface.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Polishing pad
ActiveUS20100048102A1Improve the level ofHigh polishing rateAbrasion apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEndcappingPolyol
A polishing pad capable of maintaining a high level of dimensional stability upon moisture absorption or water absorption and providing high polishing rate includes a polishing layer of a polyurethane foam having fine cells, wherein the polyurethane foam includes a cured product of a reaction of (1) an isocyanate-terminated prepolymer (A) that includes an isocyanate monomer, a high molecular weight polyol (a), and a low molecular weight polyol, (2) an isocyanate-terminated prepolymer (B) that includes a polymerized diisocyanate and a polyethylene glycol with a number average molecular weight of 200 to 1,000, and (3) a chain extender.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS ELECTRONICS MATERIALS CMP HLDG INC
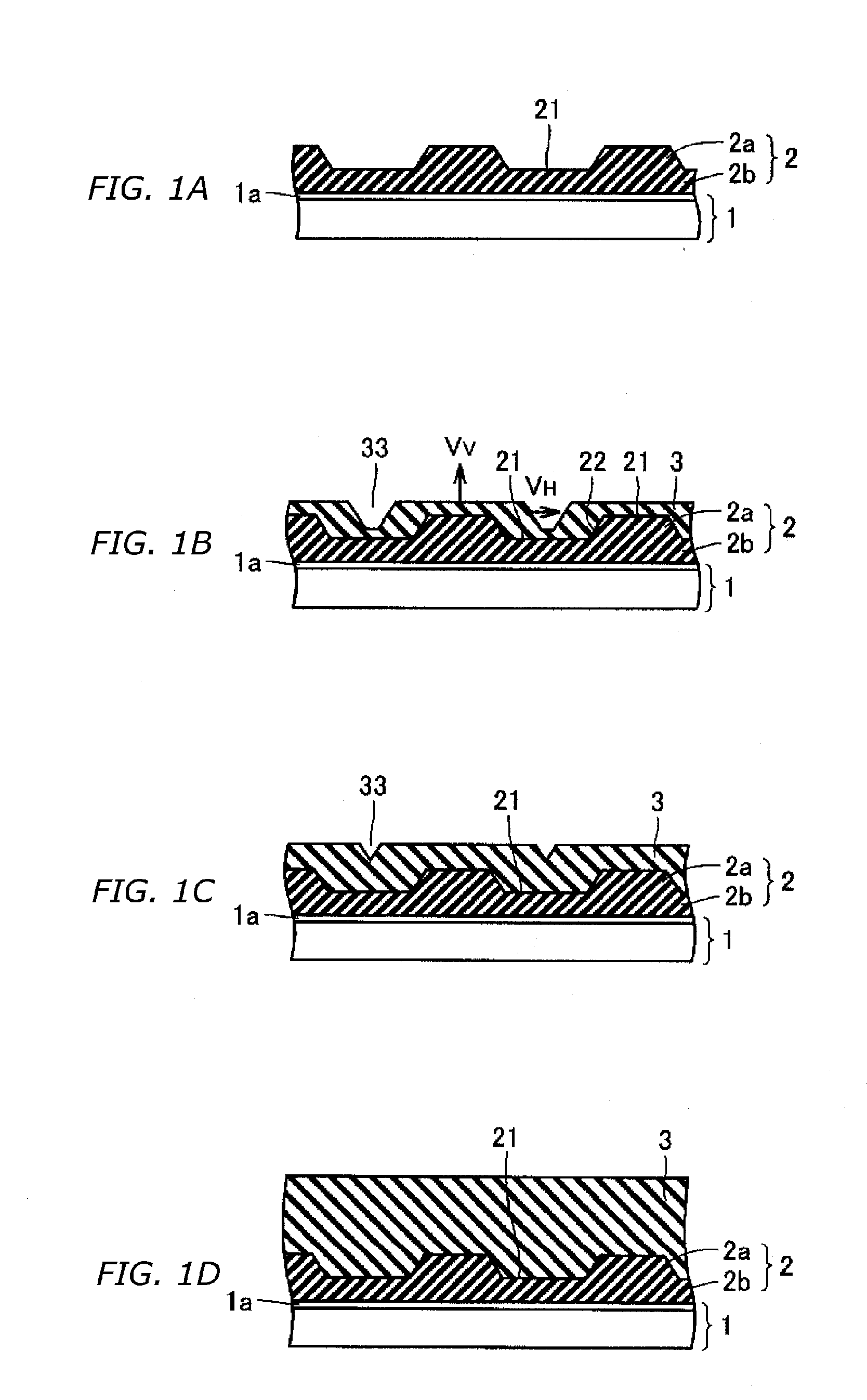
Semiconductor device and method of manufacturing the same
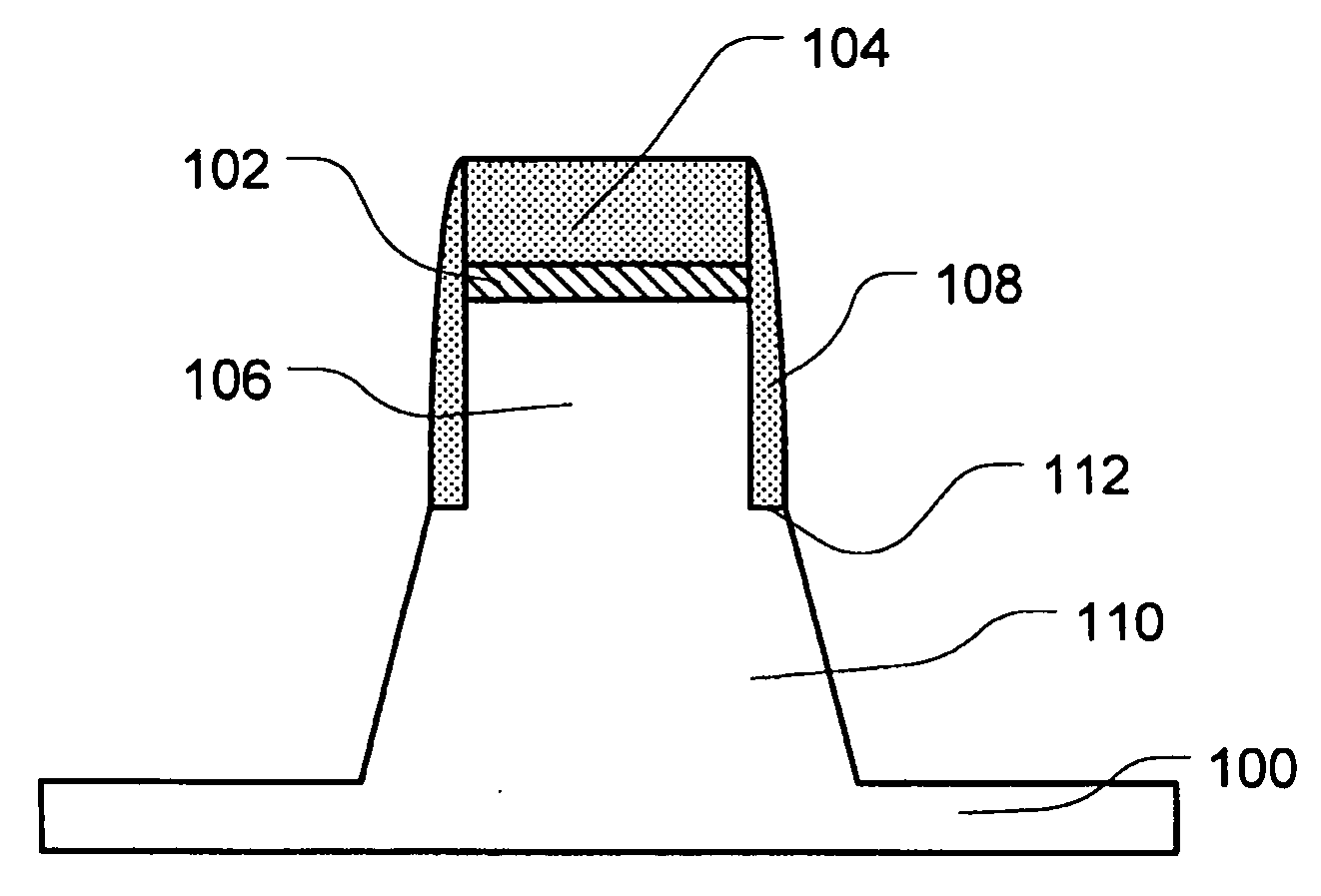
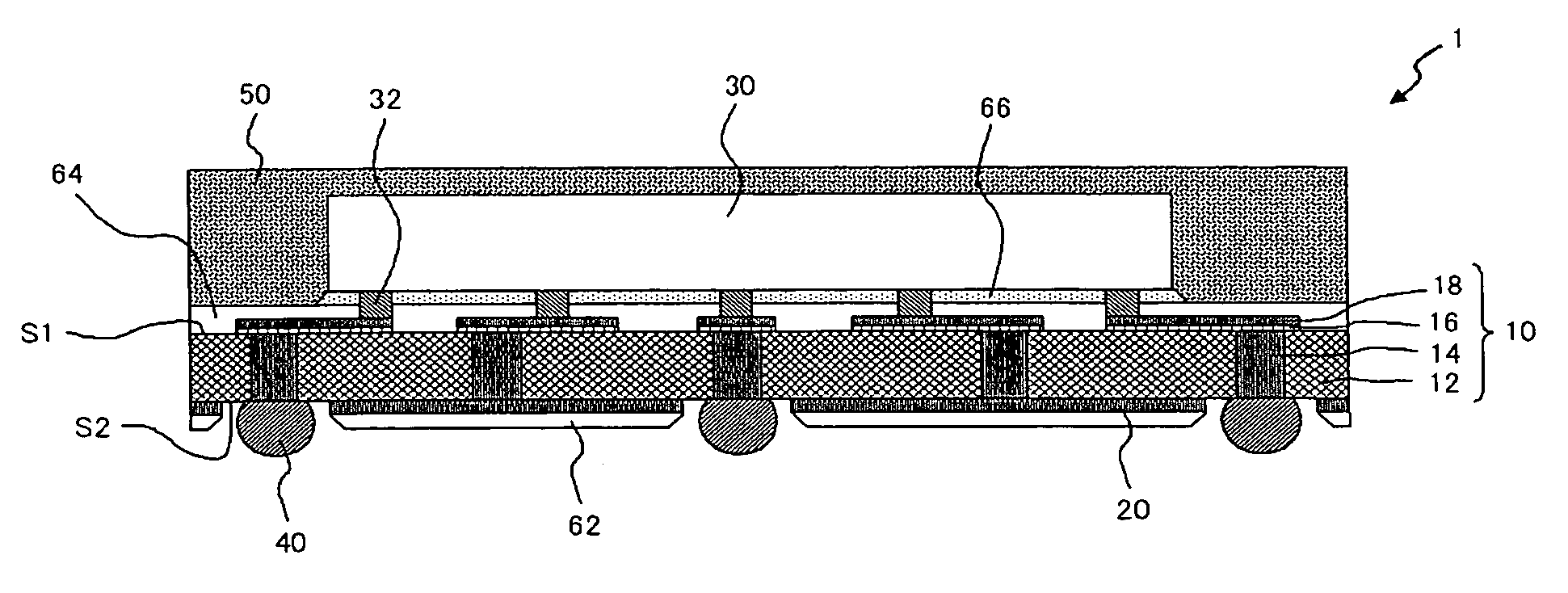
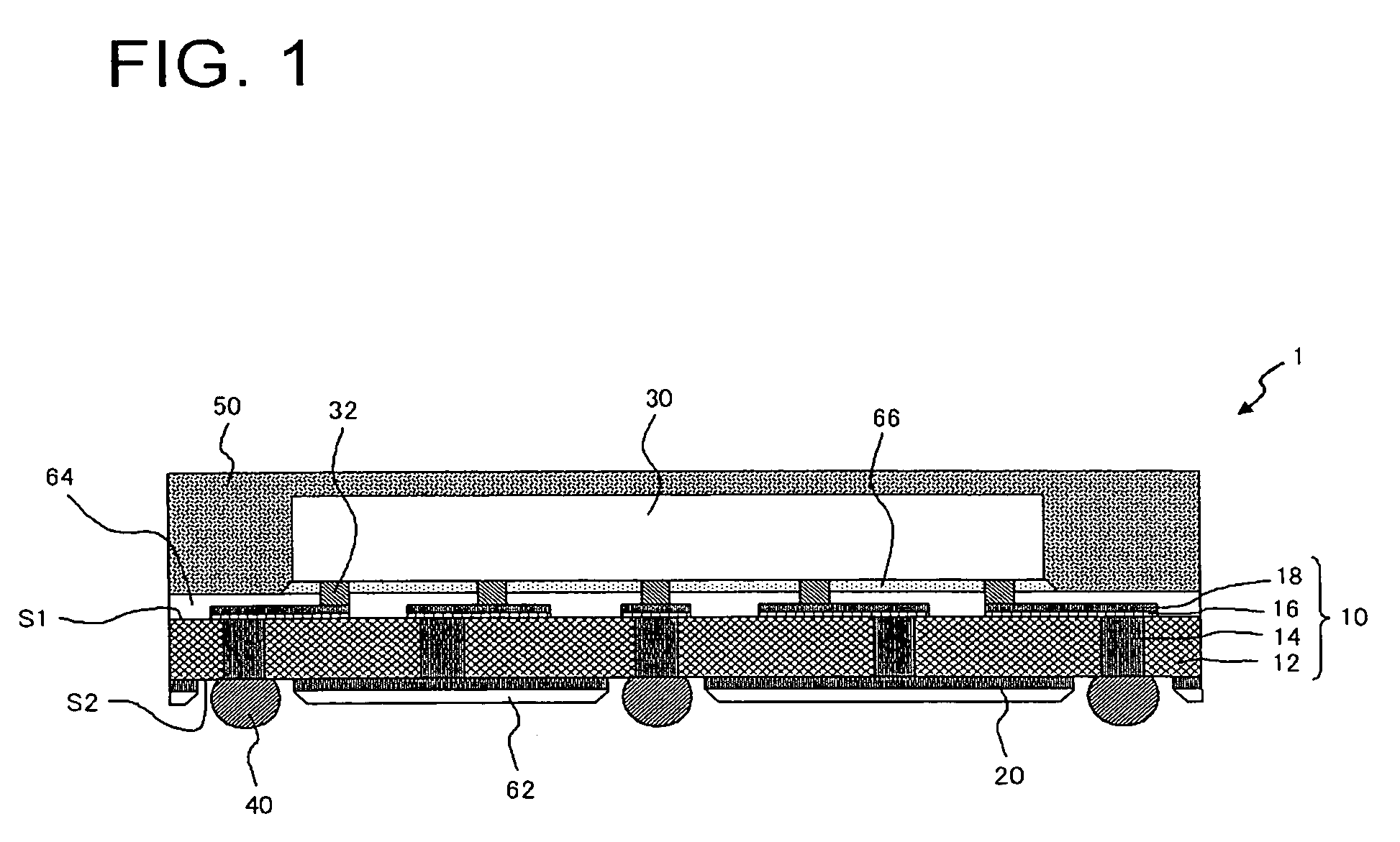
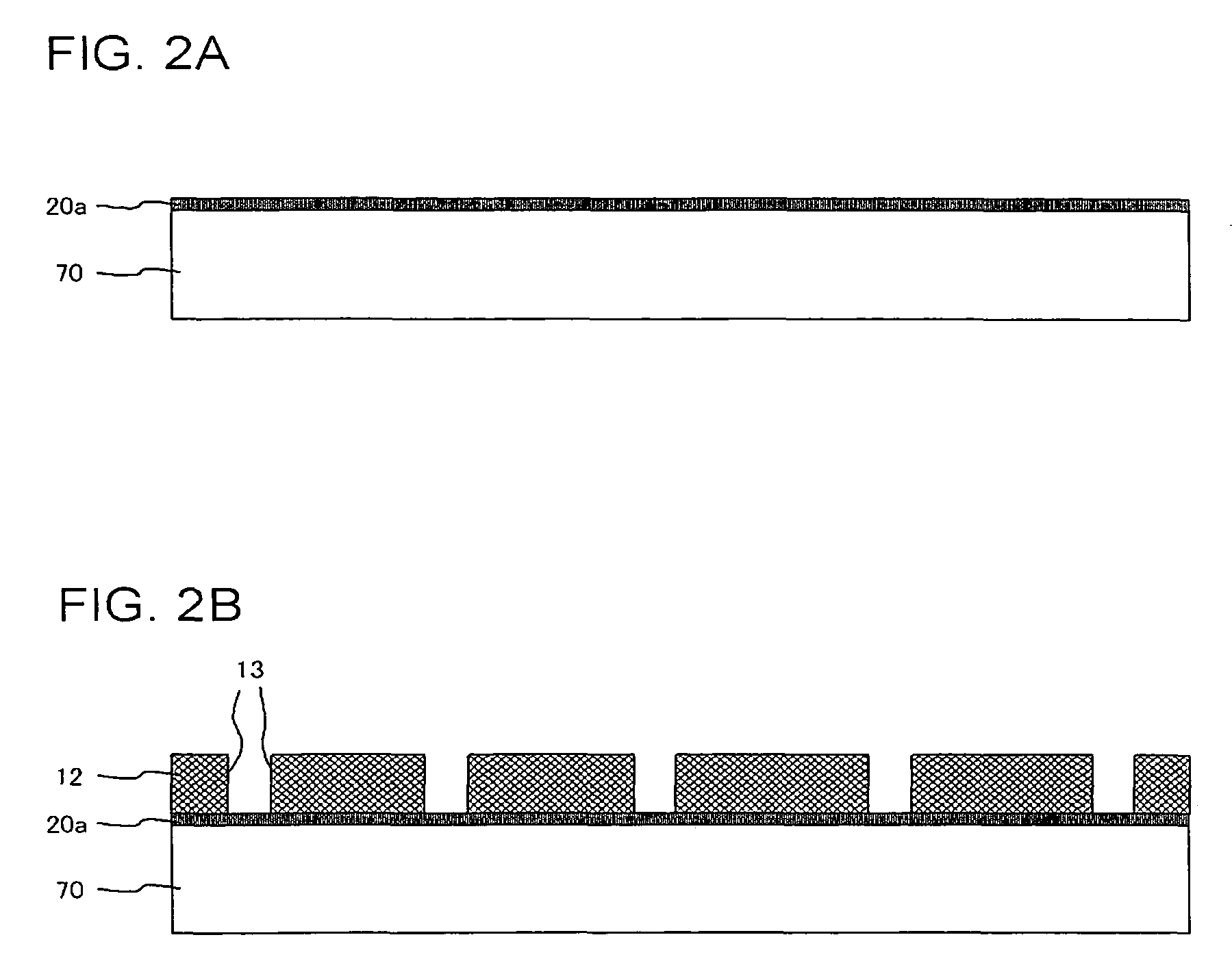
InactiveUS7800233B2Good planaritySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductorMetal
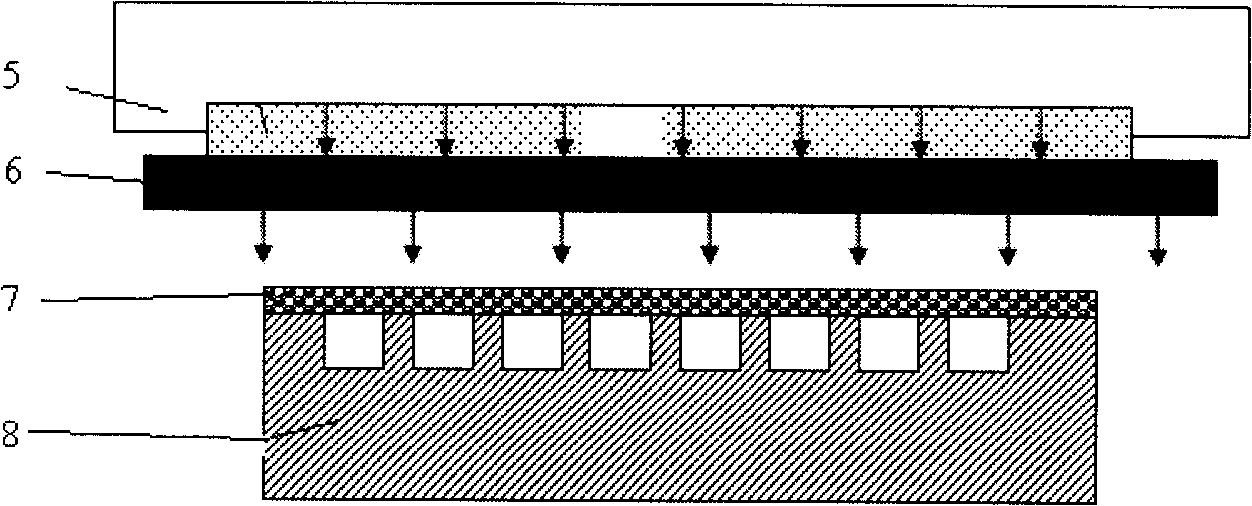
A method of manufacturing according to an embodiment of the present invention includes forming a seed metal layer 20a on a supporting substrate 70, forming an interconnect layer 10 including an interconnect 18 on the seed metal layer 20a, removing the supporting substrate 70 after forming the interconnect layer 10, and patterning the seed metal layer 20a thus to form an interconnect 20 after removing the supporting substrate.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method for impacting micro-plasticity forming with strong laser and device thereof
InactiveCN101254574AHigh surface hardnessHigh sensitivitySemi-permeable membranesPiezoelectric/electrostrictive/magnetostrictive devicesShock waveElectrolysis
A plastic micro-forming method by using strong laser shock and a device thereof belong to the field of micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) processing and laser micro-processing technology. The method is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: polishing both sides of a target for experiment by electrolysis; pressing a transparent optical medium with a thickness of micrometer level on a press plate as a constrained layer; tightly pressing a metal flying plate on the optical medium; fastening the optical medium, the metal flying plate, the target and a template on a special target clamping machine through the press plate; turning on a nano-second pulsed laser; adjusting the optical path to focus the laser outputted from the nano-second pulse laser on the target surface; subjecting the nano-second pulsed laser to single emission to achieve single pulse laser shock on the target. The method can generate ultrahigh pressure and strain rate during production of a sample, and the application of pressure of the generated shock wave has higher planarity, completeness and repeatability, thus improving surface rigidity of micro-metal parts and improving micro-sensing sensitivity. Accordingly, a micro-driving device can provide higher drive force, torsional moment and energy.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Ink jet recording medium
InactiveUS20050069655A1Good planaritySuppressing loss of imageDuplicating/marking methodsCoatingsGlass transitionPigment
An ink jet recording medium having an ink receiving layer on a support, wherein the support comprises a composition containing thermoplastic resin fine particles and a white pigment at least on the receiving layer forming surface side which at least the ink receiving layer is formed, and the support is subjected to heating and pressing treatment in a temperature range of not less than the glass transition temperature of the thermoplastic resin fine particles.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Polishing liquid for metal and polishing method using the same
ActiveUS20090239380A1Improve polishing rateGood planarityOther chemical processesNanoinformaticsColloidal silicaElectrical conductor
A liquid for polishing a metal is provided that is used for chemically and mechanically polishing a conductor film including copper or a copper alloy in production of a semiconductor device, and a polishing method using the metal-polishing liquid is also provided. The liquid includes: (a) colloidal silica particles having an average primary particle size of from 10 nm to 25 nm and an average secondary particle size of from 50 nm to 70 nm; (b) a metal anticorrosive agent; (c) at least one compound selected from the group consisting of a surfactant and a water-soluble polymer compound; (d) an oxidizing agent; and (e) an organic acid.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
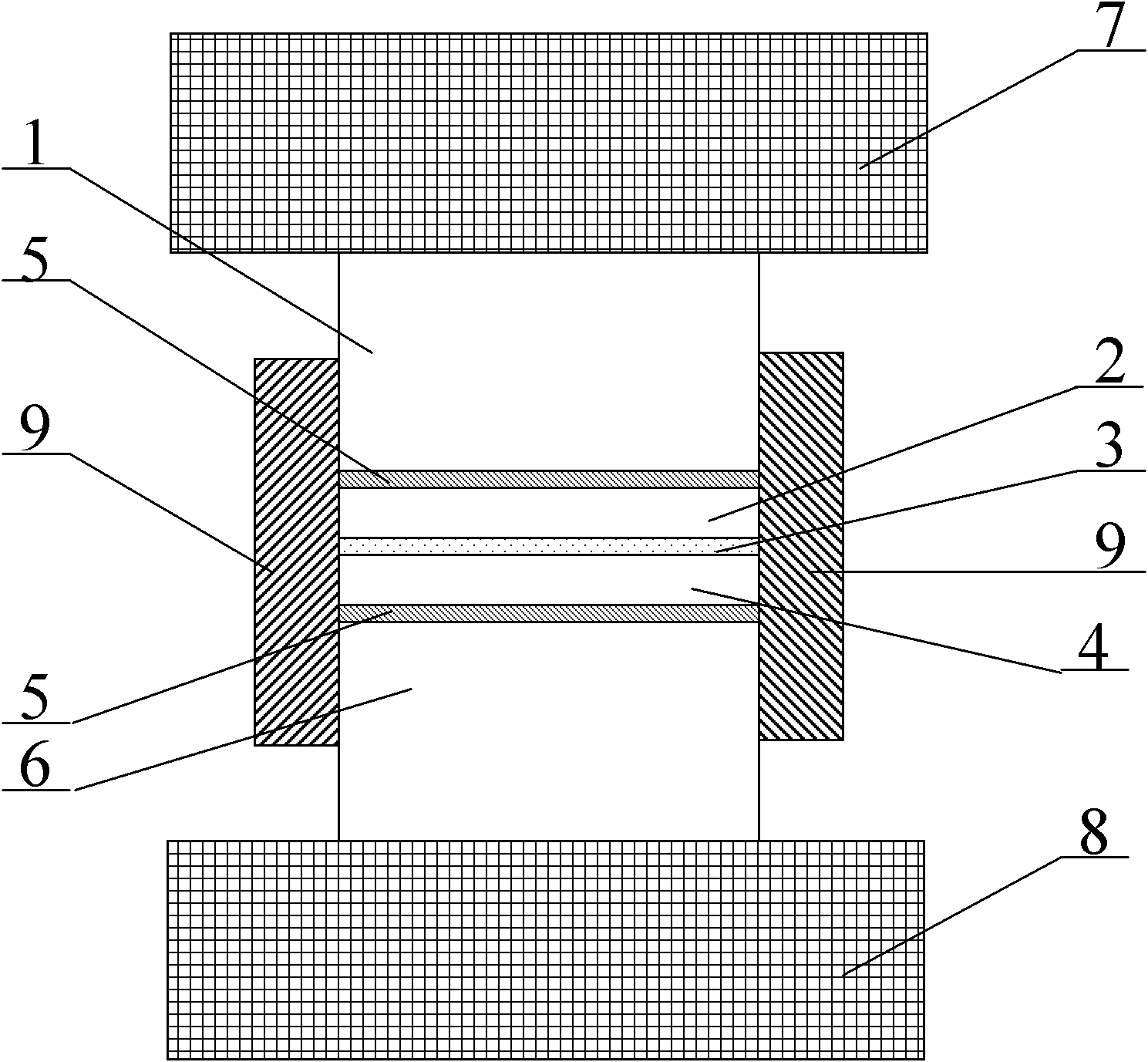
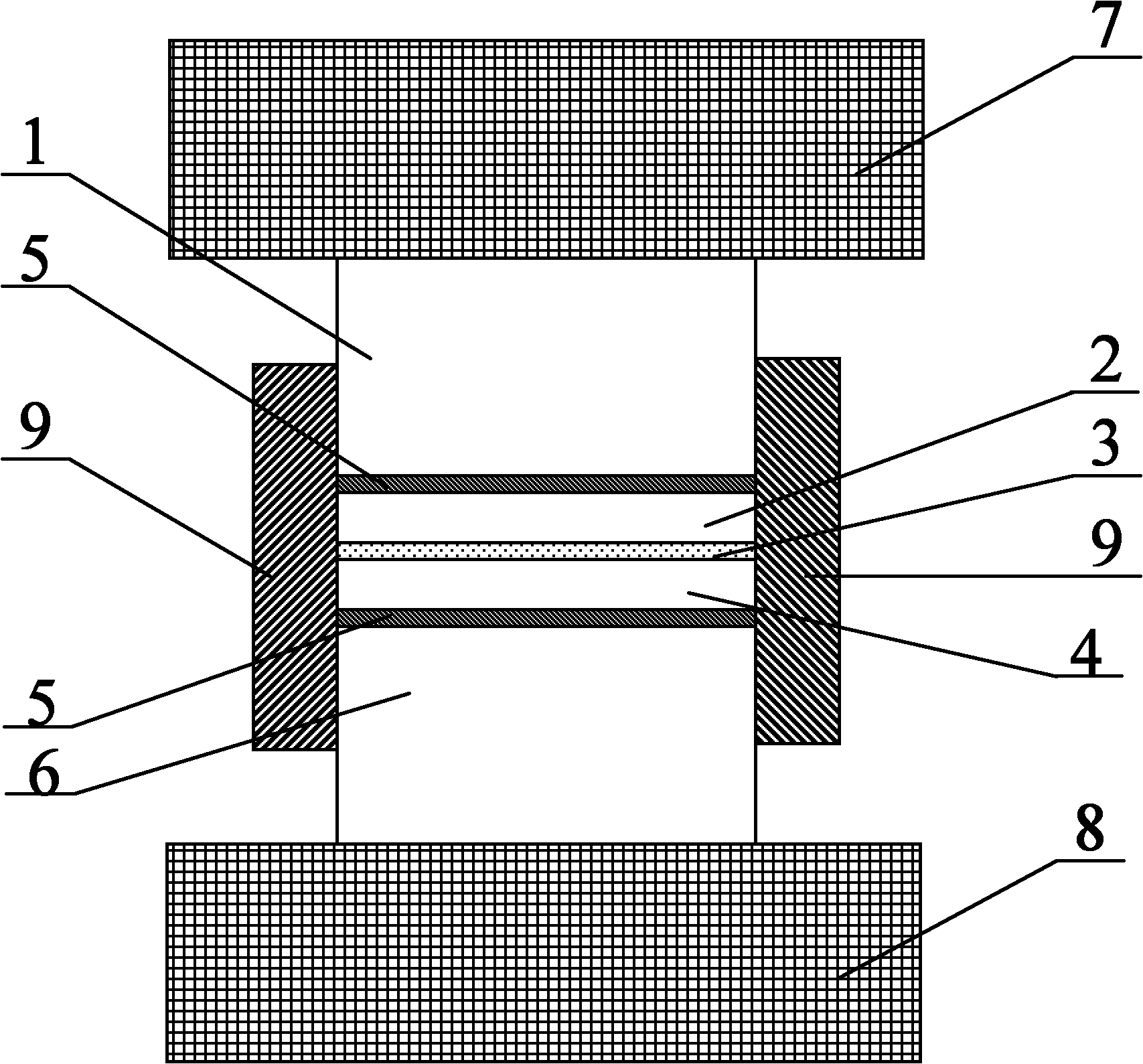
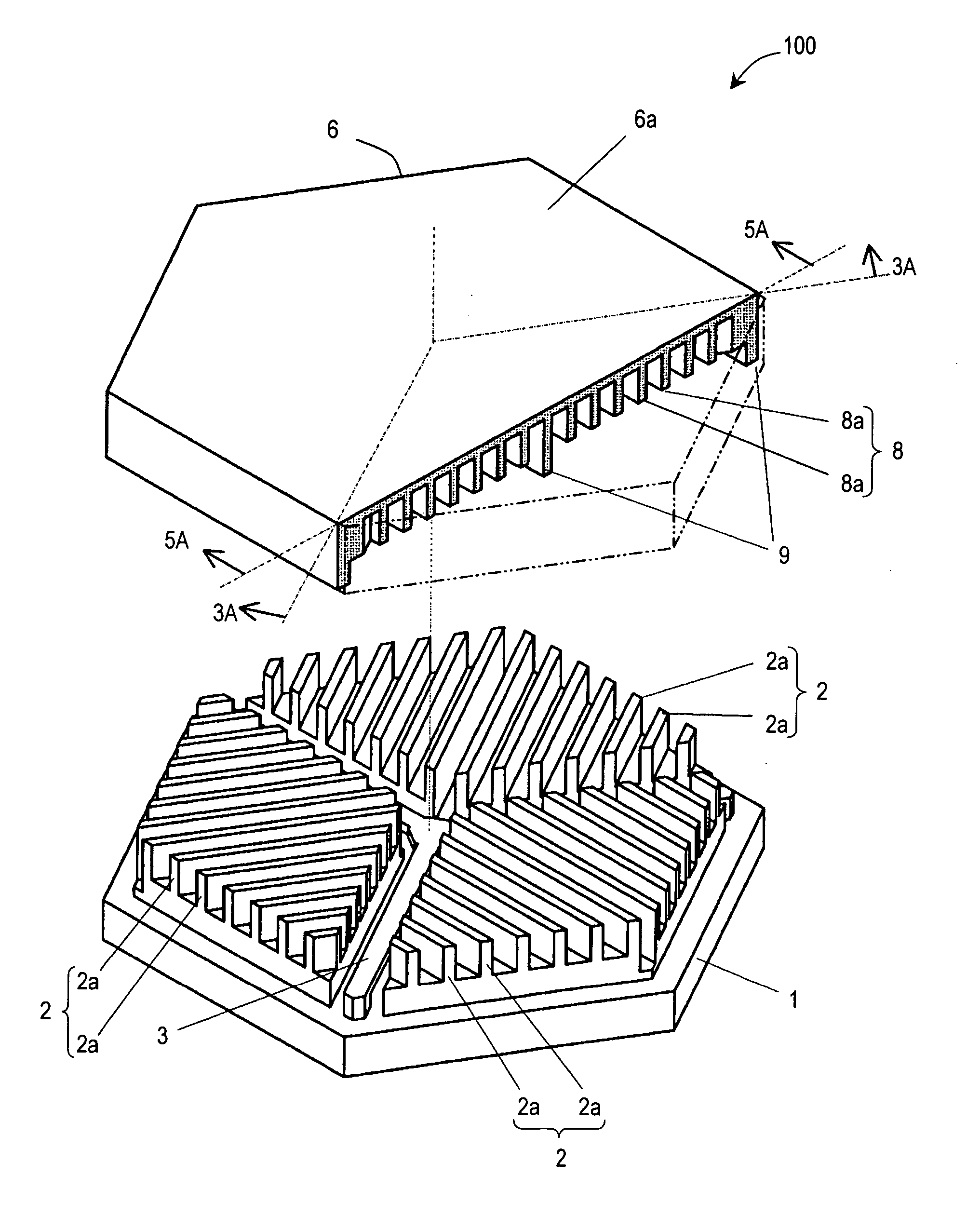
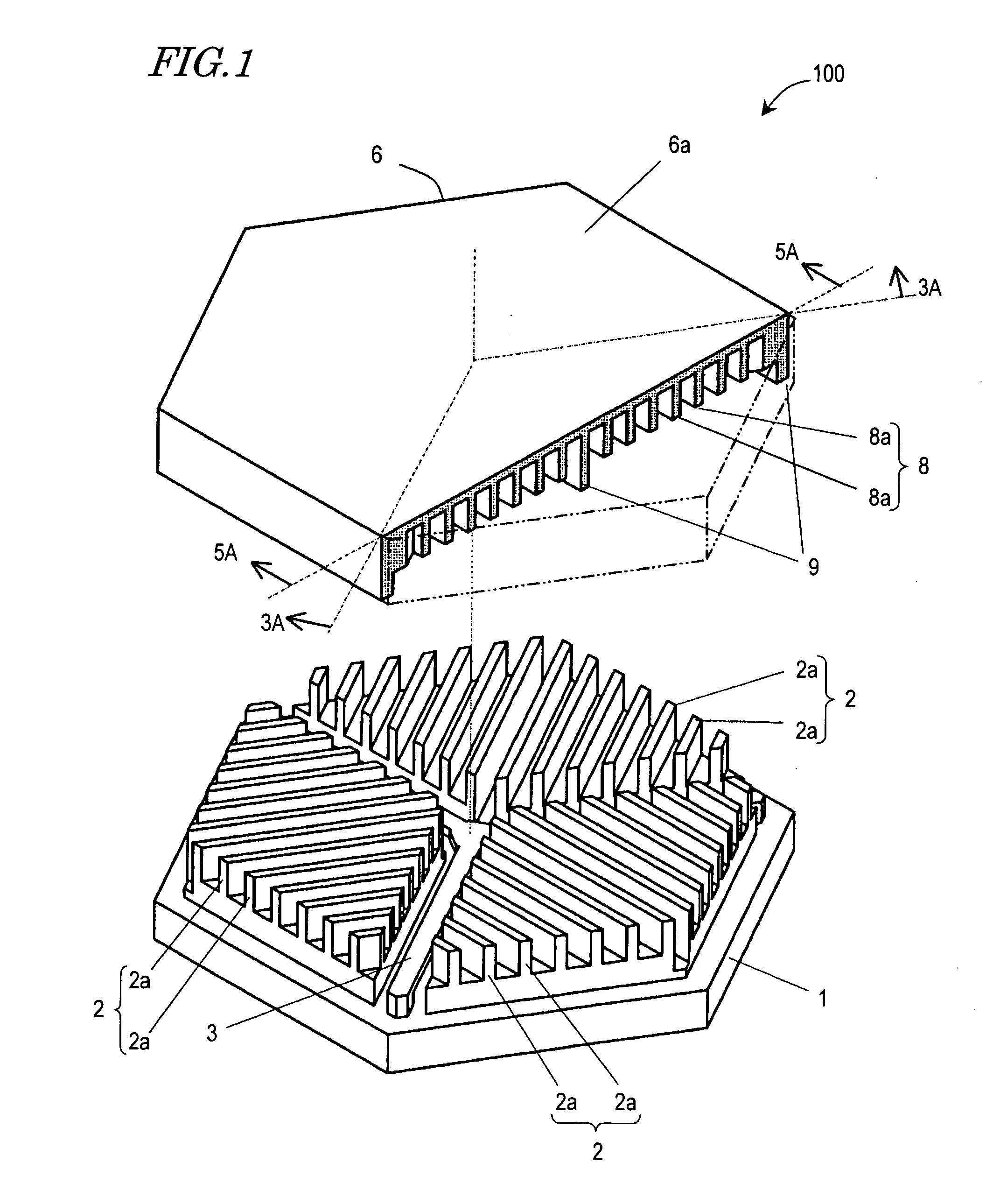
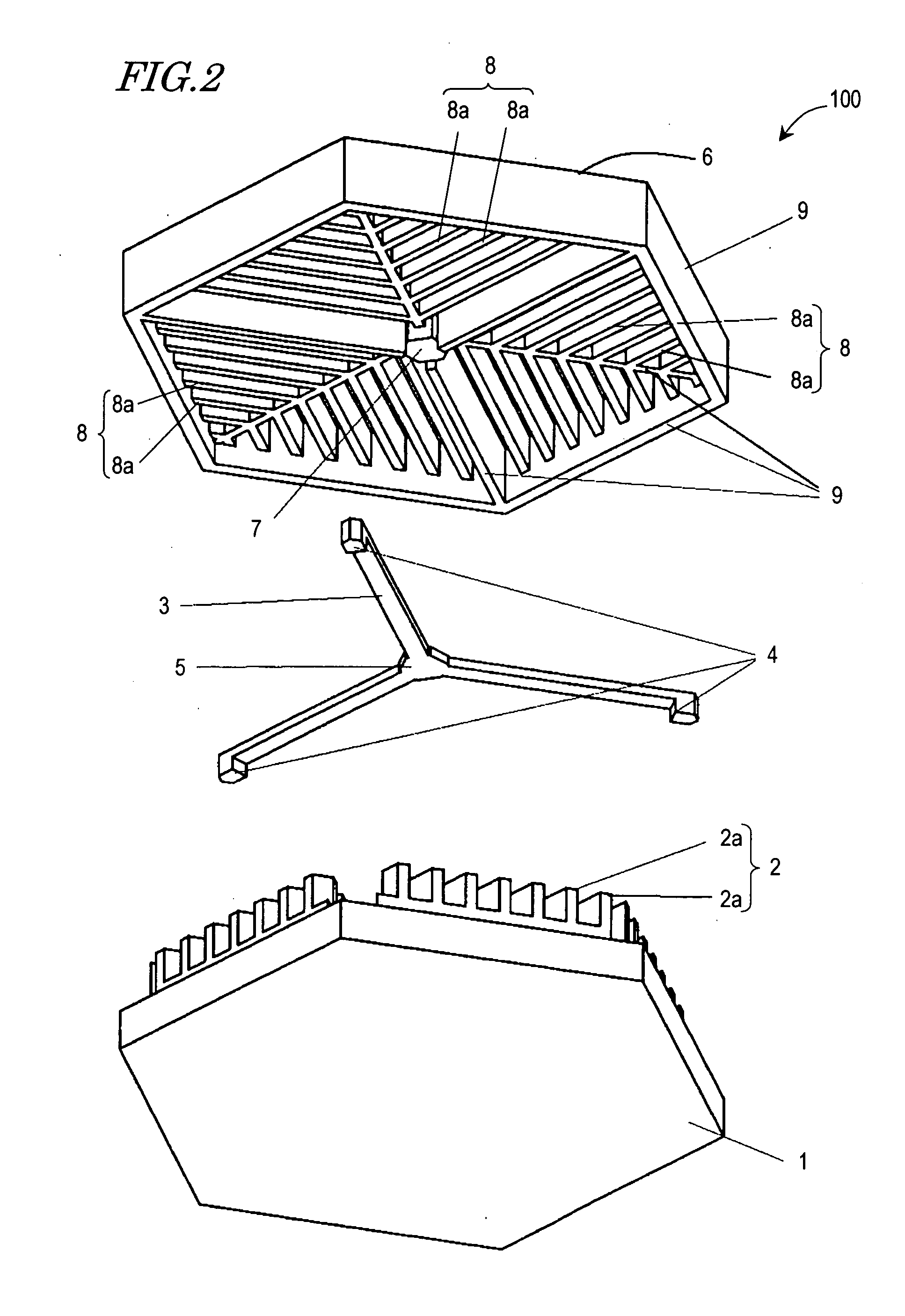
Microactuator
InactiveUS20050236928A1Reduce quality problemsImprove rigidityPiezoelectric/electrostrictive devicesElectrostatic motorsEngineeringMicroactuator
There has been a trade-off between the rigidity and the mass of a movable section of a microactuator, and also between the rigidity of the movable section and the electrostatic force. A microactuator 100 includes: a base 1; a first comb electrode 2 supported by the base 1; a movable section 6 having a second comb electrode 8 opposing the first comb electrode 2, and at least one reinforcement rib 9 protruding toward the base 1; and an elastic supporting member 3 for supporting the movable section 6 so as to allow the movable section 6 to be displaced with respect to the base 1. The height of the second comb electrode 8 is different from the height of the at least one reinforcement rib 9.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Benzodithiophene polymer, its preparation method, semiconductor composition containing it, and solar cell using it
InactiveCN104086752AImprove solubilityGood film formingOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesHalogenSide chain
The invention discloses a benzodithiophene polymer, its preparation method, a semiconductor composition containing it, and a solar cell using it. The benzodithiophene polymer has a structure represented by a formula shown in the specification; and in the formula, A1, A2, A3, B1, B2 and B3 are respectively independently selected from hydrogen, C1-C30 alkyl groups, C1-C30 alkyloxy groups, cyan groups, nitro groups, ester groups, aryl groups with four following substituent groups RX, heteroaryl groups with four following substituent groups RX, aralkyl groups with four following substituent groups RX, halogen atoms, halogenated alkyl groups, heteroalkyl groups, alkenyl groups and alkynyl groups; the substituent groups RX comprise hydrogen, C1-C30 alkyl groups, C1-C30 alkyloxy groups, ester groups, sulfonyl groups or fluorinated alkyl groups. The introduction of a thiophene side chain to benzodithiophene makes the obtained polymer molecule have a high conjugate degree, so it is in favor of improving the carrier mobility of the above polymer material.
Owner:HUANENG CLEAN ENERGY RES INST +1
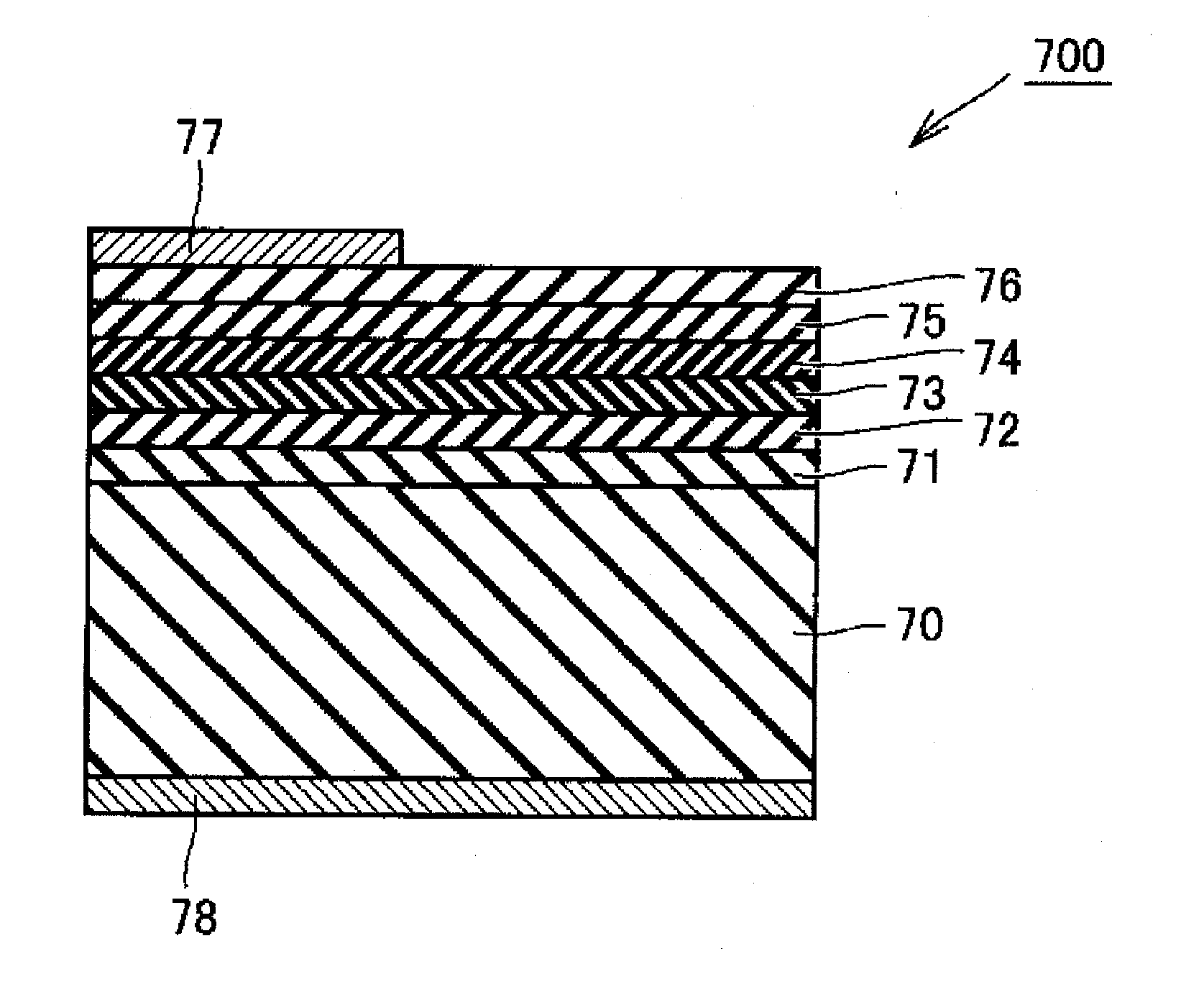
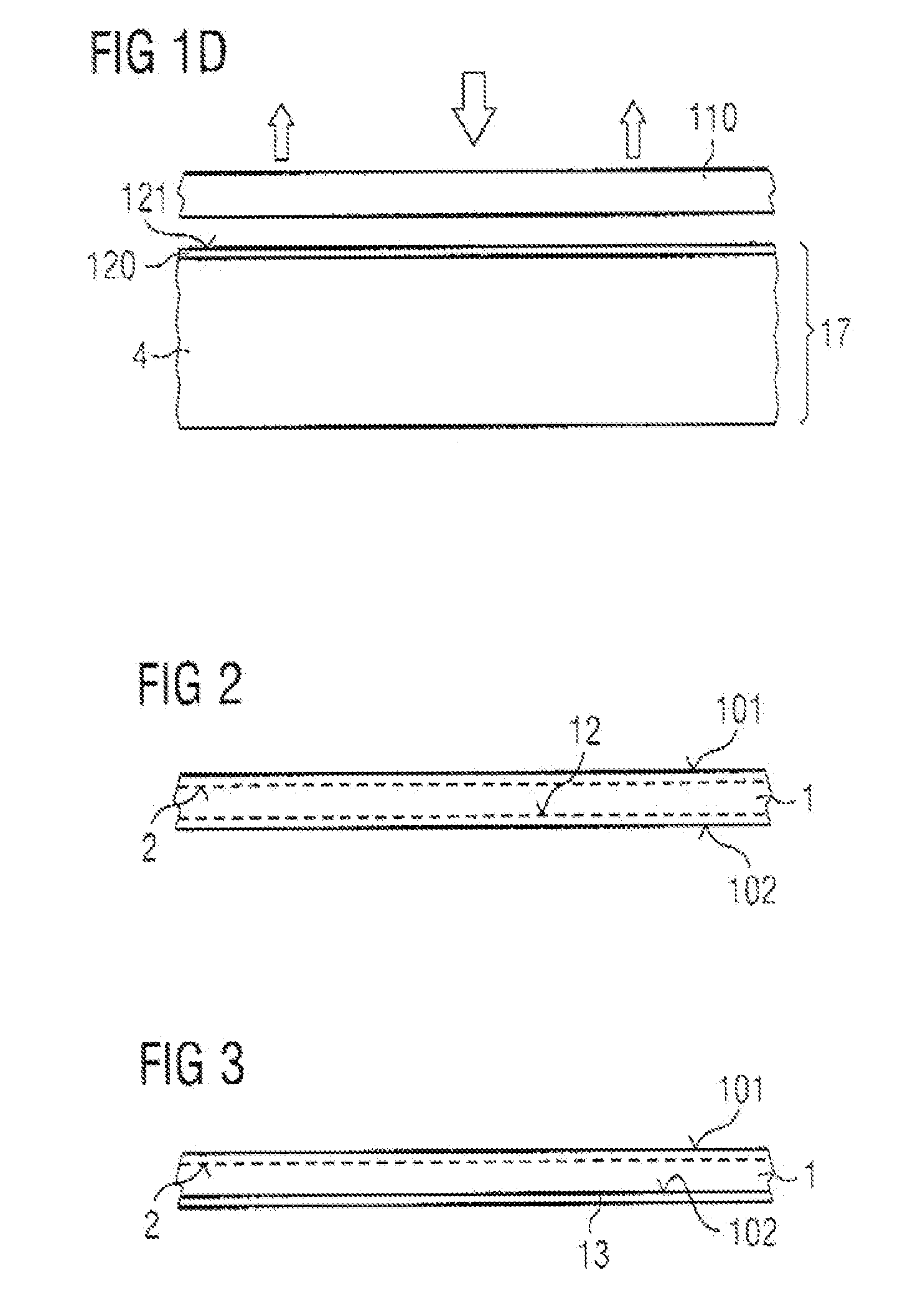
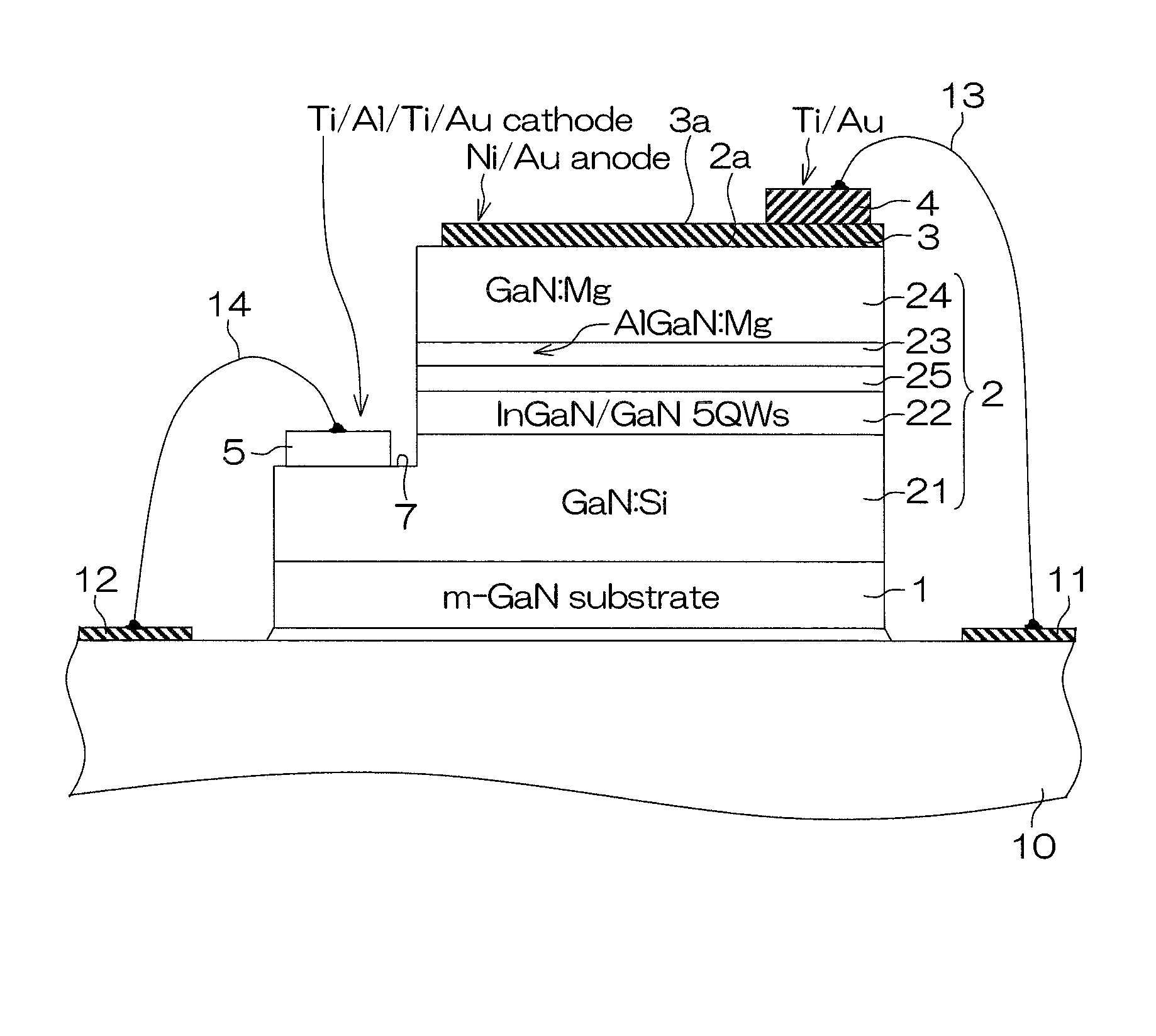
Group III Nitride Crystal Substrate, Method of Its Manufacture, and Group-III Nitride Semiconductor Device
ActiveUS20050164419A1Reduce dislocation densityReduce manufacturing costPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsVolumetric Mass DensityVapor phase
Affords a Group-III nitride crystal substrate that is of low dislocation density and is inexpensive to manufacture, a method of manufacturing such a substrate, and Group-III nitride semiconductor devices that incorporate the Group-III nitride crystal substrate. The Group-III nitride crystal substrate manufacturing method includes: a step of growing, by liquid-phase epitaxy, a first Group-III nitride crystal (2) onto a base substrate (1); and a step of growing, by vapor-phase epitaxy, a second Group-III nitride crystal (3) onto the first Group-III nitride crystal (2). The Group-III nitride crystal substrate, produced by such a manufacturing method, has a dislocation density of 1×107 dislocations / cm2.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
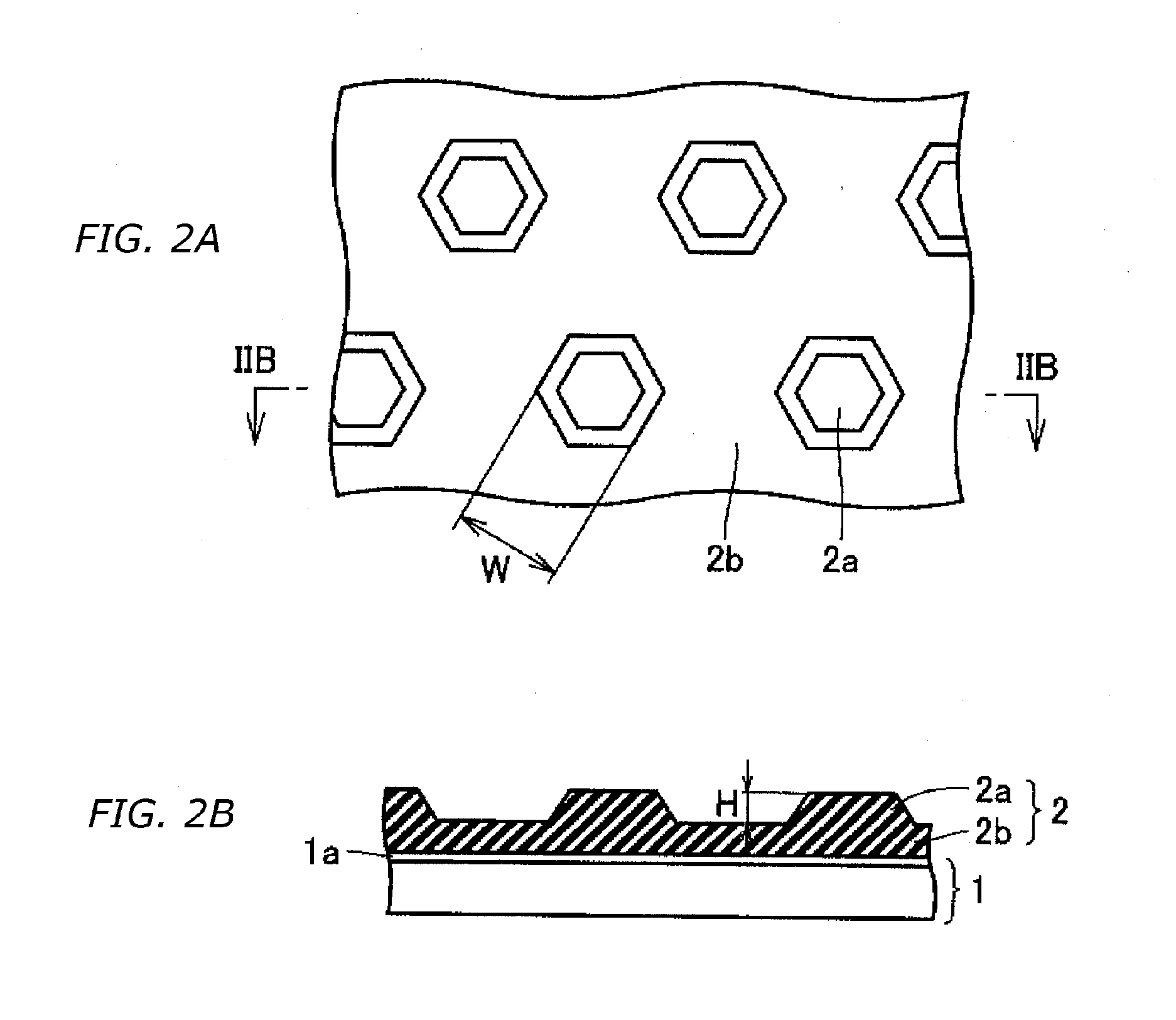
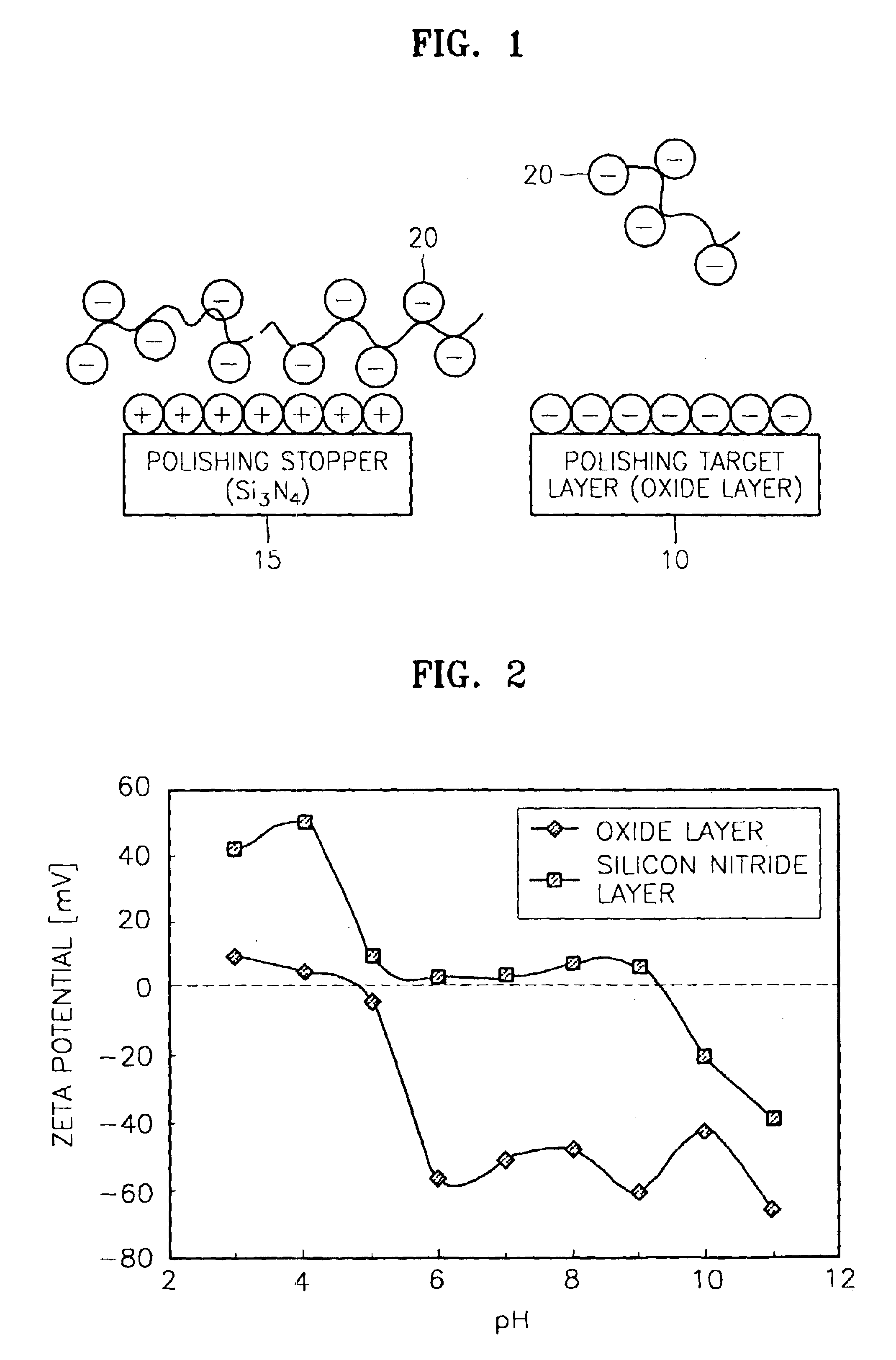
Chemical mechanical polishing slurry and chemical mechanical polishing method using the same
ActiveUS6887137B2High planarityHigh selectivity ratio characteristicPigmenting treatmentPolishing machinesCompound (substance)Oxide
Slurries for chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) are provided including a high planarity slurry and high selectivity ratio slurry. A high planarity slurry includes at least one kind of metal oxide abrasive particle and an anionic polymer passivation agent having a first concentration. A high selectivity ratio slurry includes at least one kind of the metal oxide abrasive particle, the passivation agent in a second concentration that is less than the first concentration of the passivation agent for the high planarity slurry, one of a quaternary amine and the salt thereof, and a pH control agent. The high selectivity ratio slurry has a pH in a range of about over an isoelectric point of a polishing target layer and less than an isoelectric point of a polishing stopper. In addition, a CMP method using the CMP slurries having high planarity and high selectivity ratio is provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Indexing rotatable chuck for a probe station
InactiveUS20050127927A1Shorten shaft lengthGood planaritySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduction rateRapid rotation
A rotary chuck with indexed rotation promotes rapid rotation of a device under test and increases the productivity of a probe station on which the device is being tested. A device mounting member of a rotatable chuck is supported for rotation on a first surface of a base until a vacuum is applied drawing the device mounting member into contact with a second surface of the base and constraining the device mounting member against rotation.
Owner:CASCADE MICROTECH
Multi-structured Si-fin and method of manufacture
InactiveUS7534686B2Point becomes highGood planarityTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringSilicon dioxide
Disclosed is a semiconductor fin construction useful in FinFET devices that incorporates an upper region and a lower region with wherein the upper region is formed with substantially vertical sidewalls and the lower region is formed with inclined sidewalls to produce a wider base portion. The disclosed semiconductor fin construction will also typically include a horizontal step region at the interface between the upper region and the lower region. Also disclosed are a series of methods of manufacturing semiconductor devices incorporating semiconductor fins having this dual construction and incorporating various combinations of insulating materials such as silicon dioxide and / or silicon nitride for forming shallow trench isolation (STI) structures between adjacent semiconductor fins.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Triazine compound and light-emitting device
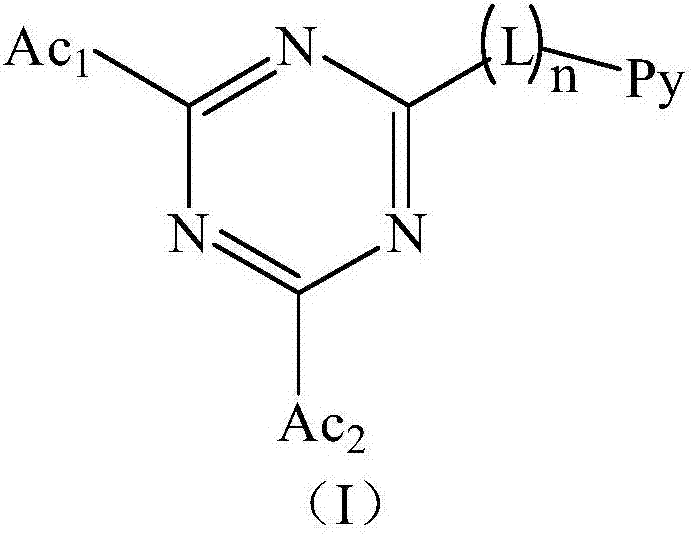
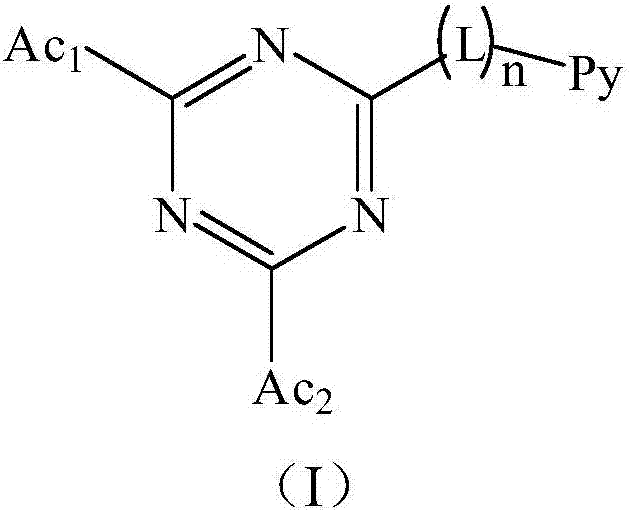
InactiveCN106892901AGood planarityRealize the designOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesTriazeneNitrogen
The invention relates to a triazine compound. The structural formula of the triazine compound is as shown in formula I, wherein L is substituted or non-substituted C6-C24 arylidene; n is 0 or 1; Py is substituted or non-substituted C3-C24 nitrogen-containing heterocyclic groups or nitrogen-containing heterocyclic condensation groups; Ac1 and Ac2 are substituted or non-substituted C12-C48 nitrogen-containing heterocyclic condensation groups; Ac1 and Ac2 can be identical ort different. The invention further relates to a light-emitting device containing the triazine compound. When two nitrogen-containing heterocyclic condensation groups are connected with a triazine group, certain angles are formed between the nitrogen-containing heterocyclic condensation groups and the triazine group due to steric hindrance, and TADF design is achieved.
Owner:AAC MICROTECH CHANGZHOU
Organic semiconducting polymer and solar battery comprising same
InactiveCN102718946AGood planarityIncrease the open circuit voltageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOrganic semiconductorSolar battery
The invention provides an organic semiconducting polymer and a solar battery comprising the same. The organic semiconducting polymer has a structure as shown in a chemical formula (1).
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +2
Method for manufacturing semiconductor substrate and method for manufacturing semiconductor device
InactiveUS20100129948A1Increase the number of timesImprove productivityFinal product manufactureSolid-state devicesProduction rateLaser light
An object is to manufacture a semiconductor substrate having a single crystal semiconductor layer with favorable characteristics, without requiring CMP treatment and / or heat treatment at high temperature. In addition, another object is to improve productivity of semiconductor substrates. Vapor-phase epitaxial growth is performed by using a first single crystal semiconductor layer provided over a first substrate as a seed layer, whereby a second single crystal semiconductor layer is formed over the first single crystal semiconductor layer, and separation is performed at an interface of the both layers. Thus, the second single crystal semiconductor layer is transferred to the second substrate to provide a semiconductor substrate, and the semiconductor substrate is reused by performing laser light treatment on the seed layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
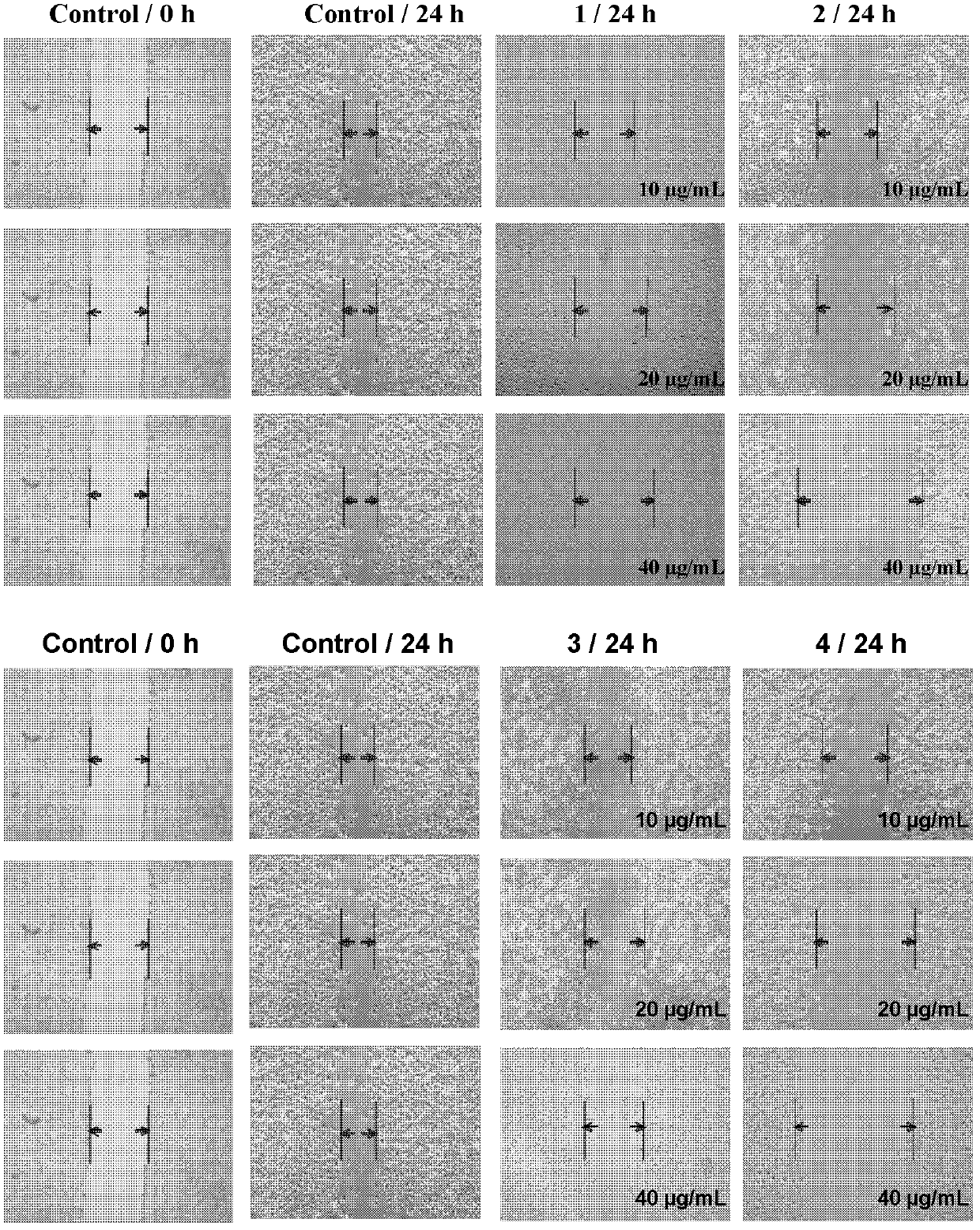
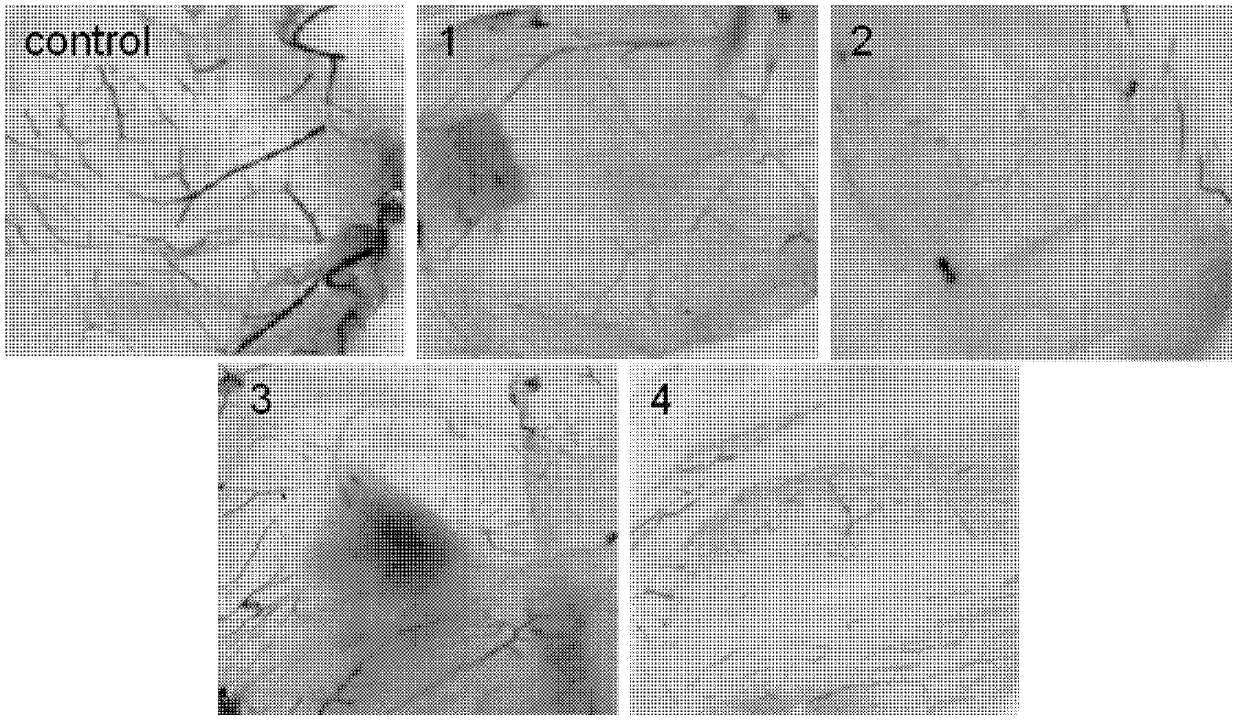
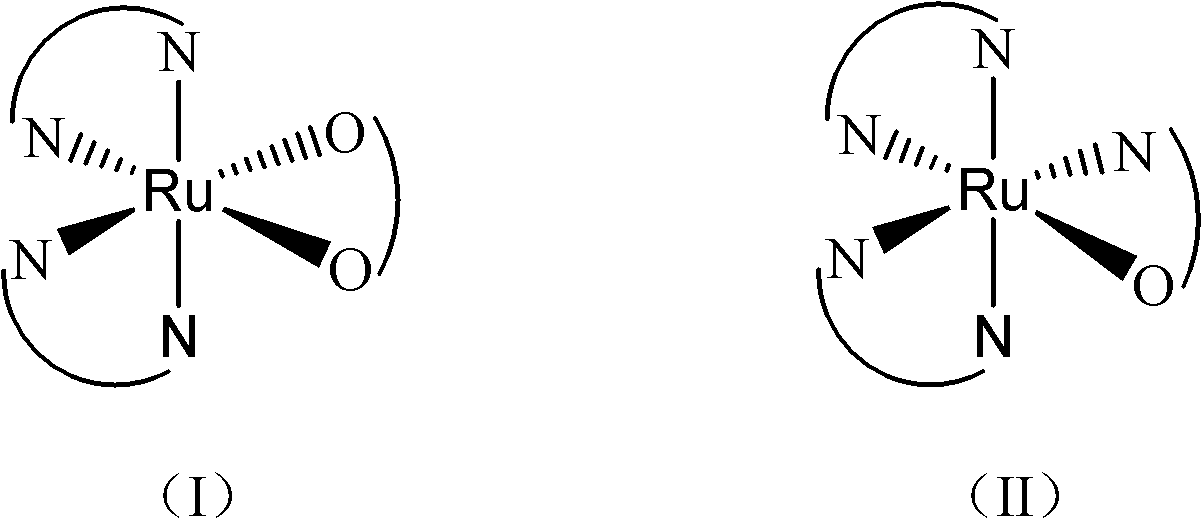
Ruthenium complex capable of inhibiting tumor angiogenesis and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102516309AImprove stabilityImprove solubilityOrganic active ingredientsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsSolubilityLithium chloride
The invention belongs to the field of chemical drugs, and discloses a ruthenium complex capable of inhibiting tumor angiogenesis and a preparation method and application thereof. The ruthenium complex provided by the invention has a structure shown in a formula I or II. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dropwise adding a silver nitrate solution to a sodium salt solution, stirring and reacting, then filtering, washing and vacuum drying a precipitate, and thereby obtaining a ligand O-O; taking ruthenium chloride, L, and lithium chloride to be dissolved in N-, N-dimethyl formamide, heating and refluxing under the protection of argon atmosphere to obtain an intermeidate Ru (L2) Cl22 +; allowing the ligand O-O and the Ru (L2) Cl22 + to be dissolved in an ethanol / water mixed solvent, heating and refluxing to obtain the ruthenium complex shown in the formula I; and allowing the Ru (L2) Cl22 +, 8- hydroxyquinoline, and ammonium acetate to be dissolved in ethanol, and heating and refluxing under the protection of argon atmosphere to obtain the ruthenium complex shown in the formula II. The ruthenium complex has the advantages of good stability, uneasiness in hydrolysis, good solubility, low toxicity, and the ability to inhibit tumor angiogenesis, and is easily absorbed by the human body.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
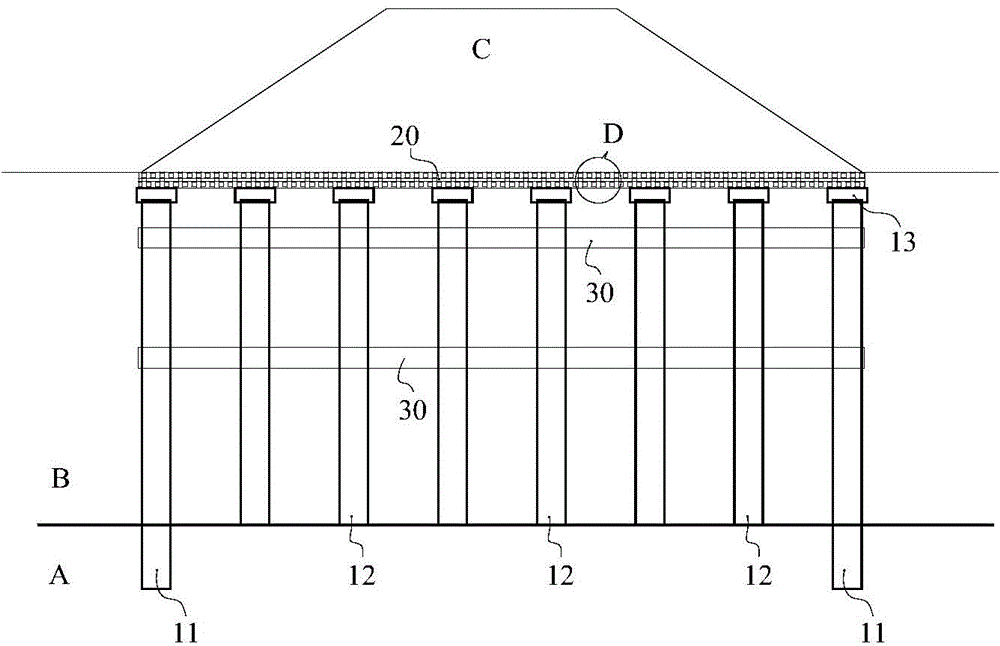
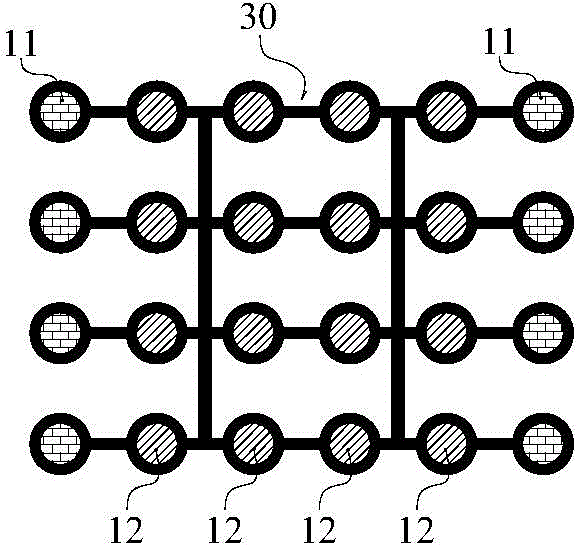
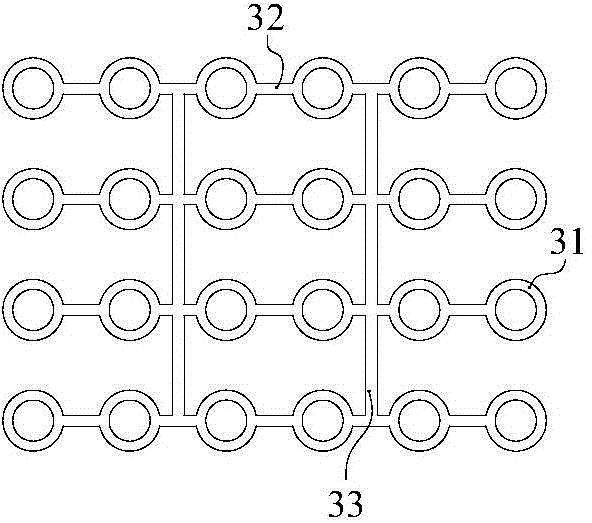
Soft soil foundation combined pile net structure
The invention discloses a soft soil foundation combined pile net structure, aims at effectively improving reinforcing effect and saving project investment and comprises cast-in-place piles, pressed piles, pile caps, guide fixing frame lattices and a cushion body. The cast-in-place piles are arranged around the boundary of a filling body at intervals, bottoms of the cast-in-place piles enter a bedrock layer below a soft soil layer by certain depth, the pressed piles are arranged in the soft soil layer within a range of the cast-in-place piles at intervals, bottoms of the pressed piles are pressed in the top surface of the bedrock layer, the pile caps are arranged at the tops of the cast-in-placed piles and the pressed piles and fixedly connected with the cast-in-placed piles and the pressed piles, the guide fixing frame lattices are positioned in the soft soil layer and transversely restrain the cast-in-place piles and the pressed piles, and the cushion body is laid between the tops of the piles caps and the undersurface of the filling body.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY ERYUAN ENG GRP CO LTD +1
Method of fabricating a quasi-substarte wafer and semiconductor body fabricated using such a quasi-substarte wafer
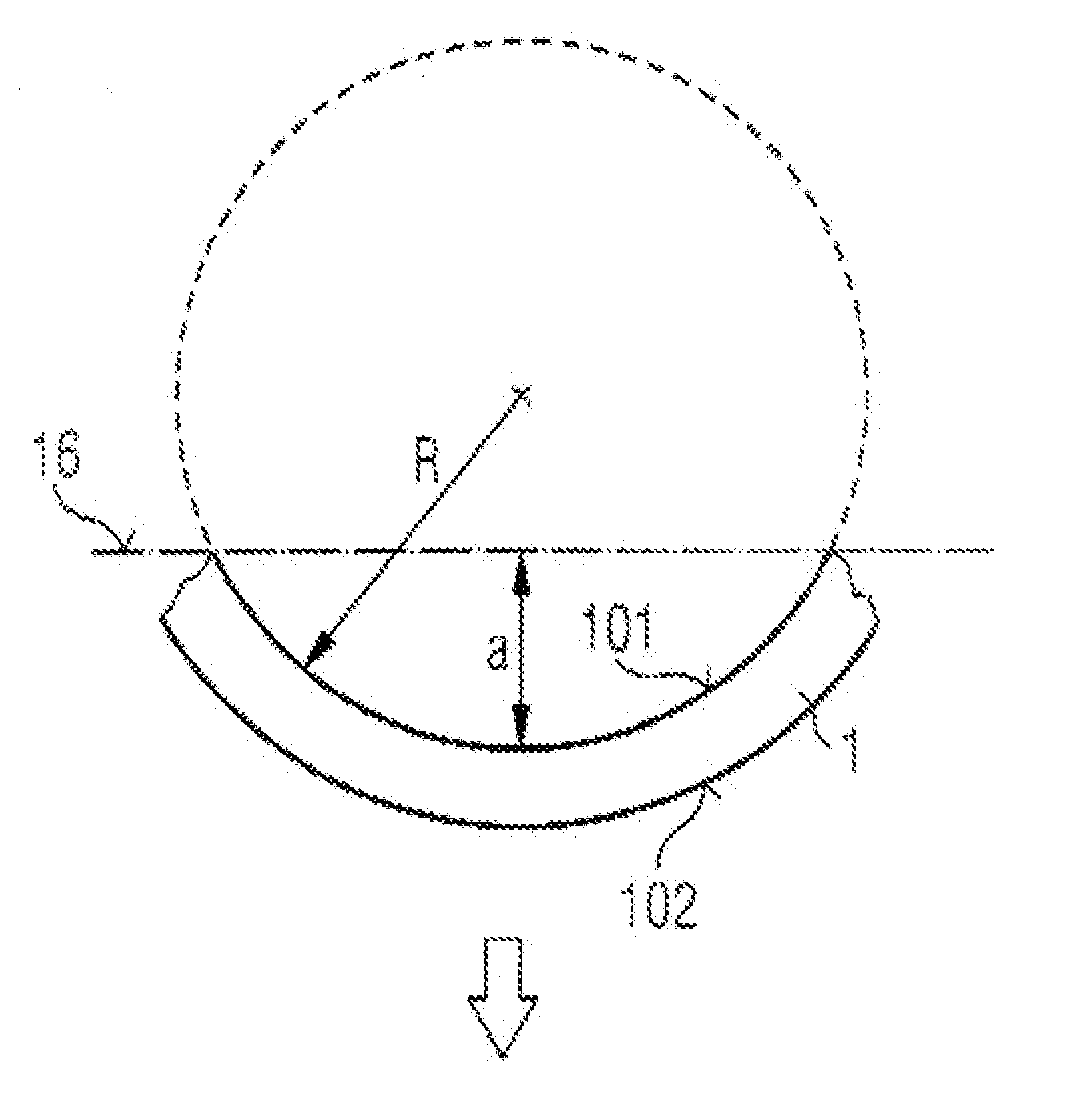
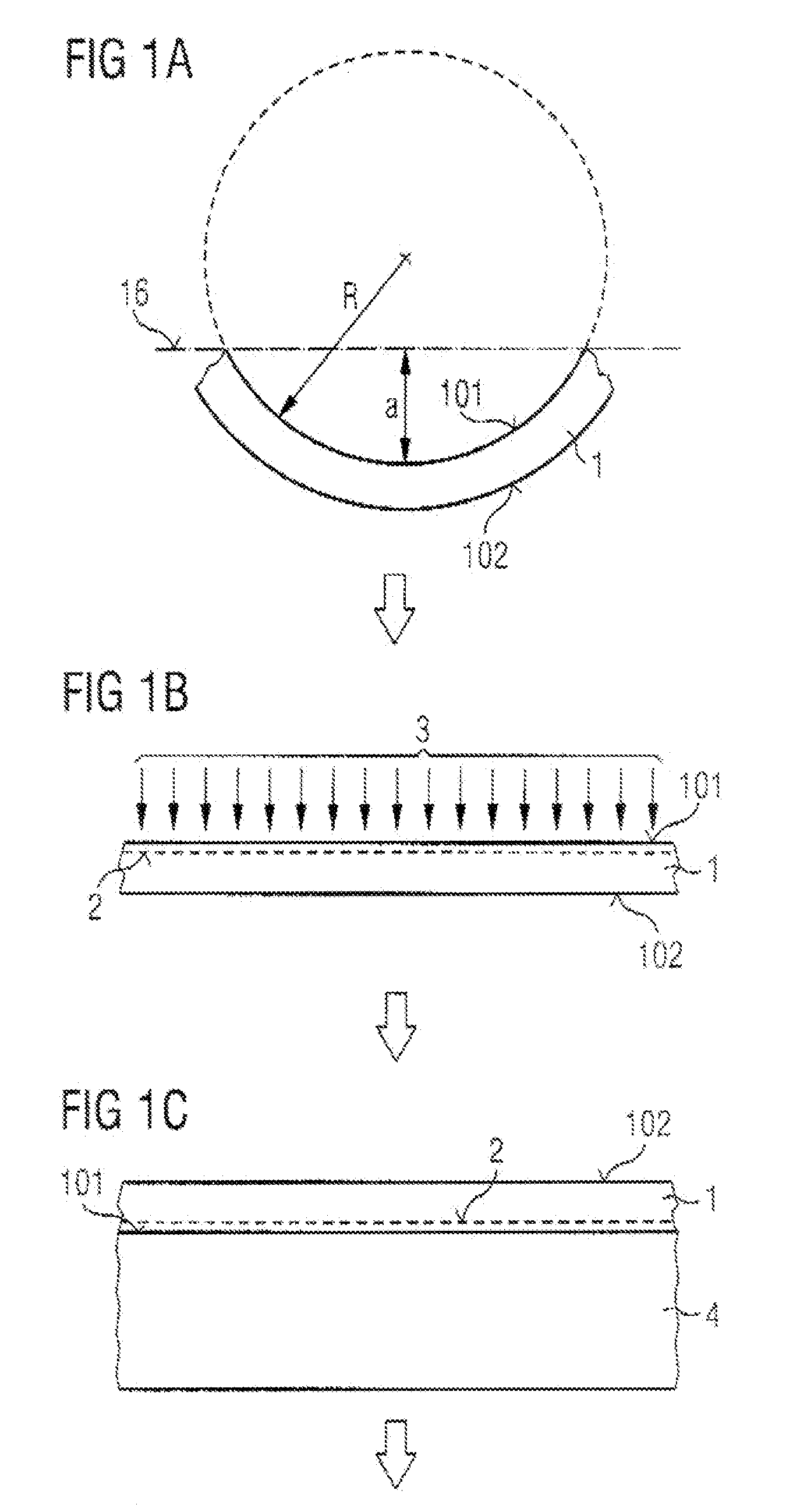
ActiveUS20070175384A1Good planarityImprove mechanical stabilityPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthEngineeringSemiconductor
Disclosed are a method of fabricating a quasi-substrate wafer (17) with a subcarrier wafer (4) and a growth layer (120), and a semiconductor body fabricated using such a quasi-substrate wafer (17). In the method of fabricating a quasi-substrate wafer (17), a growth substrate wafer (1) is fabricated that is provided with a separation zone (2) and comprises the desired material of the growth layer (120). The growth substrate wafer (1) is provided with a stress that counteracts a stress generated by the formation of the separation zone, and / or the stress generated by the formation of the separation zone is distributed, by structuring a first main face (101) of the growth substrate wafer (1) and / or the separation zone (2), to a plurality of subregions along the first main face (101). The growth substrate wafer (1) with separation zone (2) exhibits no or only slight bowing.
Owner:OSRAM OLED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![Organic semiconductor material containing naphthalene [1, 2-c: 5, 6-c] di [1, 2, 5] thiadiazole and application thereof Organic semiconductor material containing naphthalene [1, 2-c: 5, 6-c] di [1, 2, 5] thiadiazole and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/60086426-a8d6-48fe-83a2-b88c7b9342e9/HSA00000374537600011.PNG)
![Organic semiconductor material containing naphthalene [1, 2-c: 5, 6-c] di [1, 2, 5] thiadiazole and application thereof Organic semiconductor material containing naphthalene [1, 2-c: 5, 6-c] di [1, 2, 5] thiadiazole and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/60086426-a8d6-48fe-83a2-b88c7b9342e9/HSA00000374537600012.PNG)
![Organic semiconductor material containing naphthalene [1, 2-c: 5, 6-c] di [1, 2, 5] thiadiazole and application thereof Organic semiconductor material containing naphthalene [1, 2-c: 5, 6-c] di [1, 2, 5] thiadiazole and application thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/60086426-a8d6-48fe-83a2-b88c7b9342e9/HSA00000374537600021.PNG)