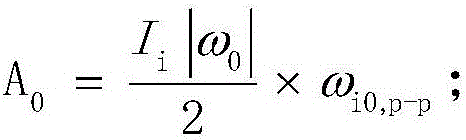Patents
Literature
199 results about "Rapid rotation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
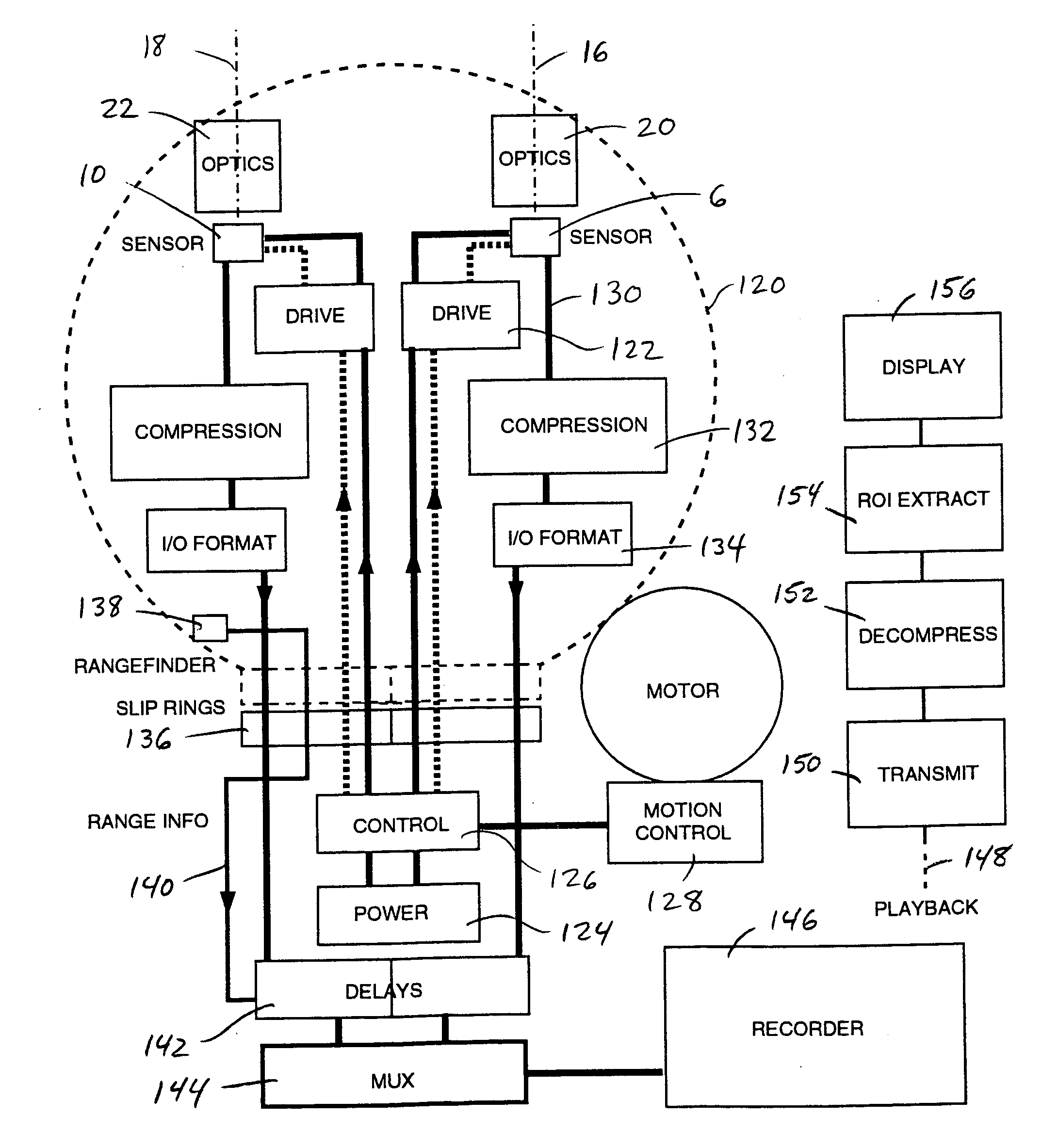
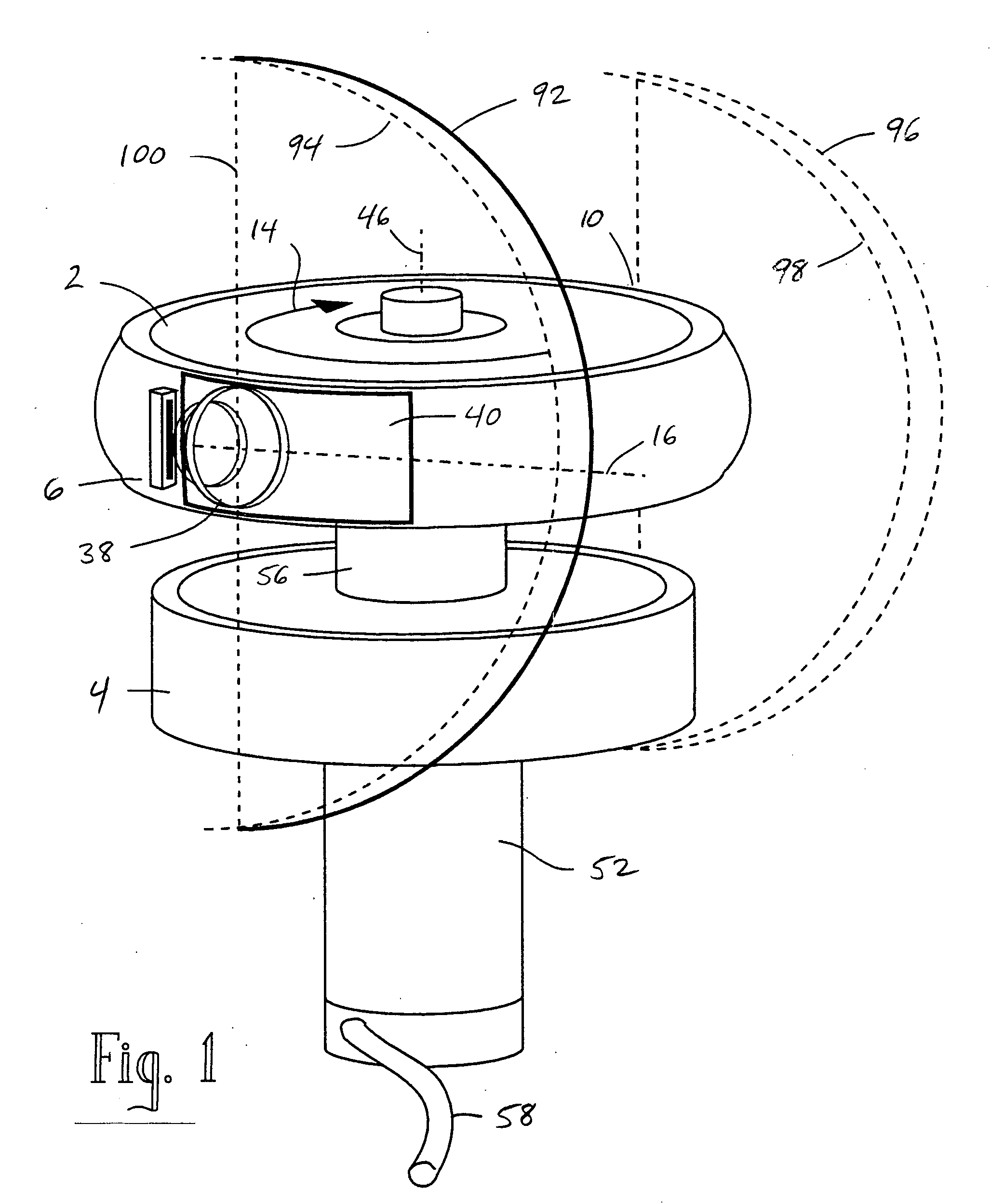
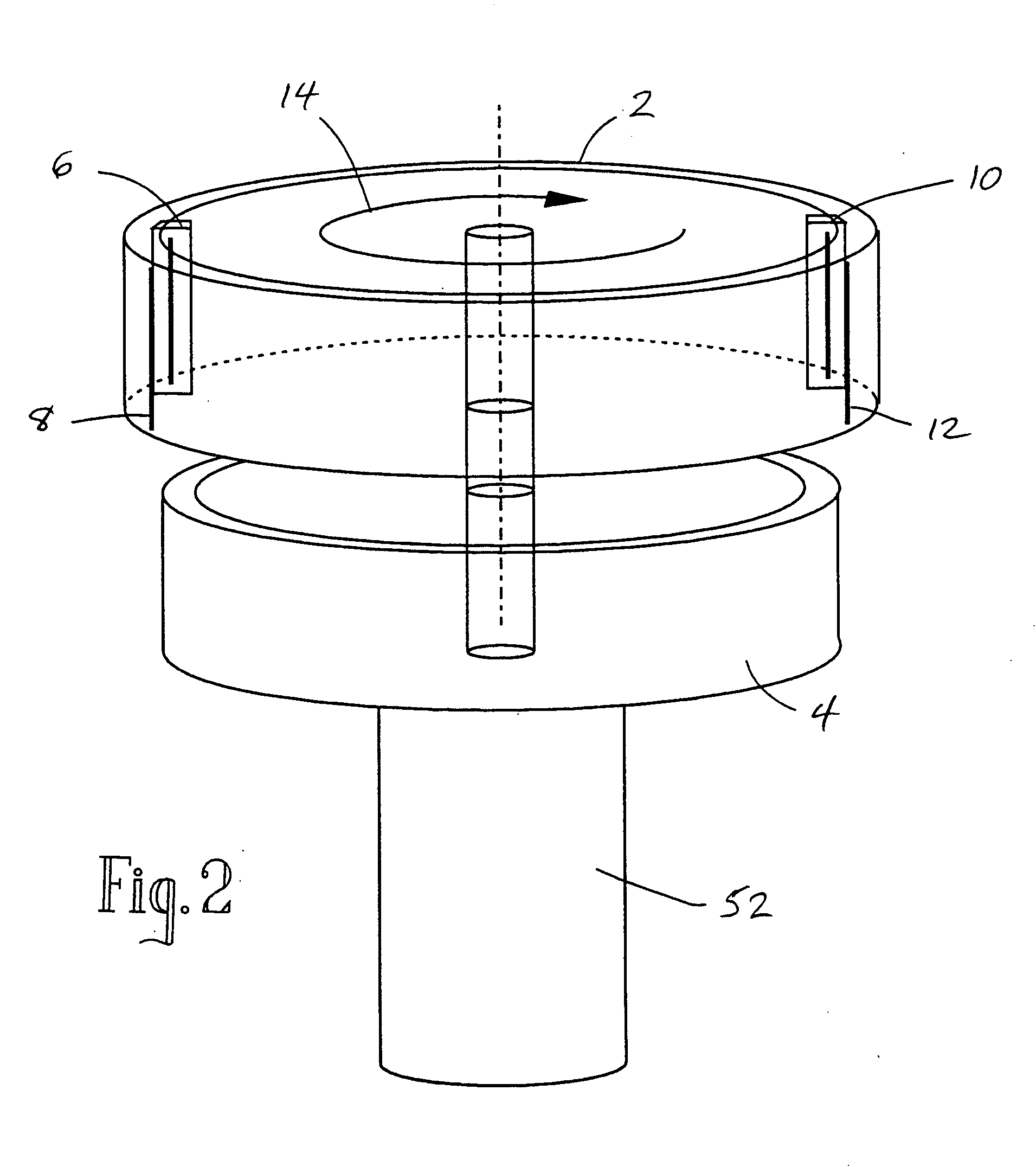
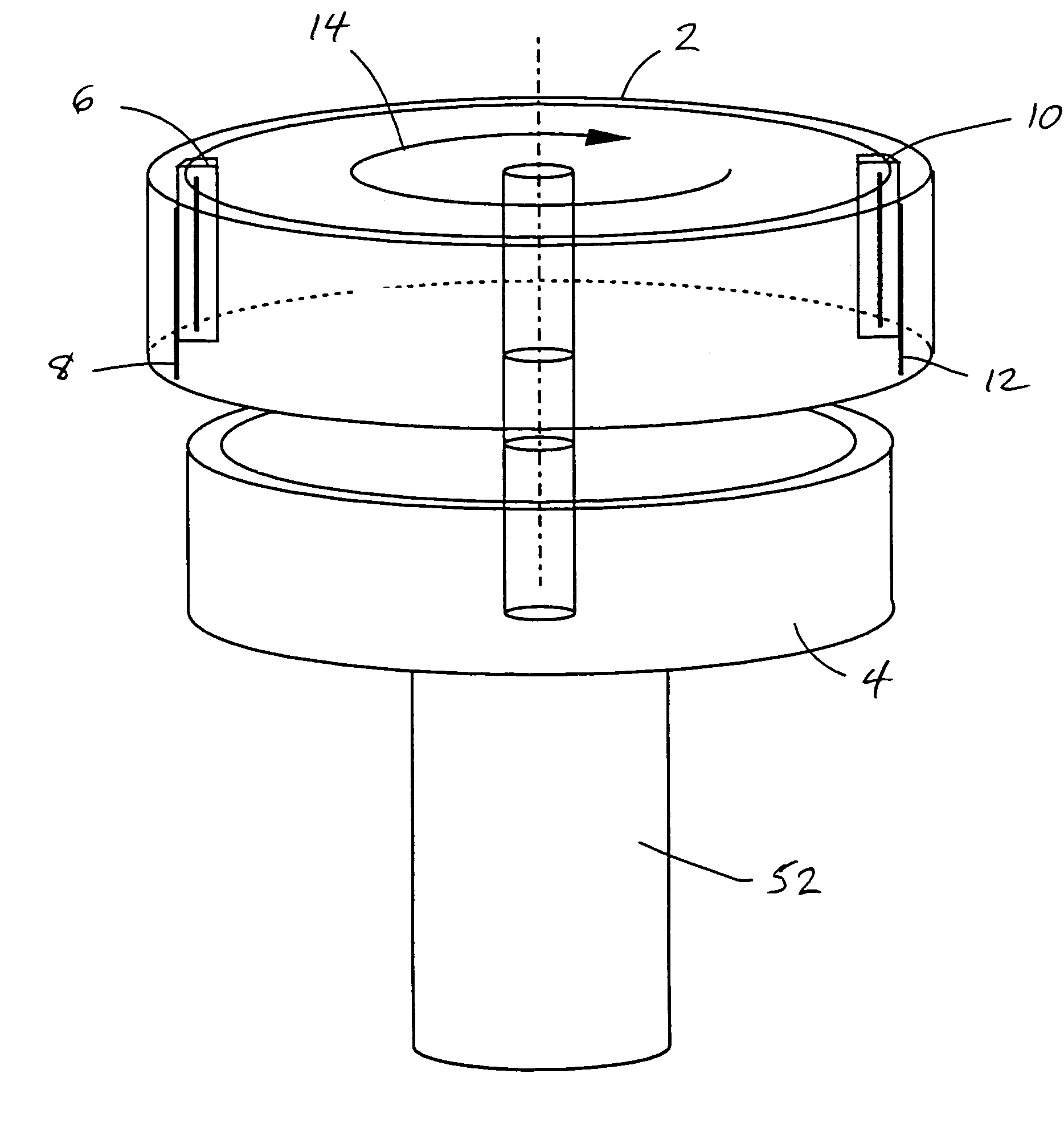
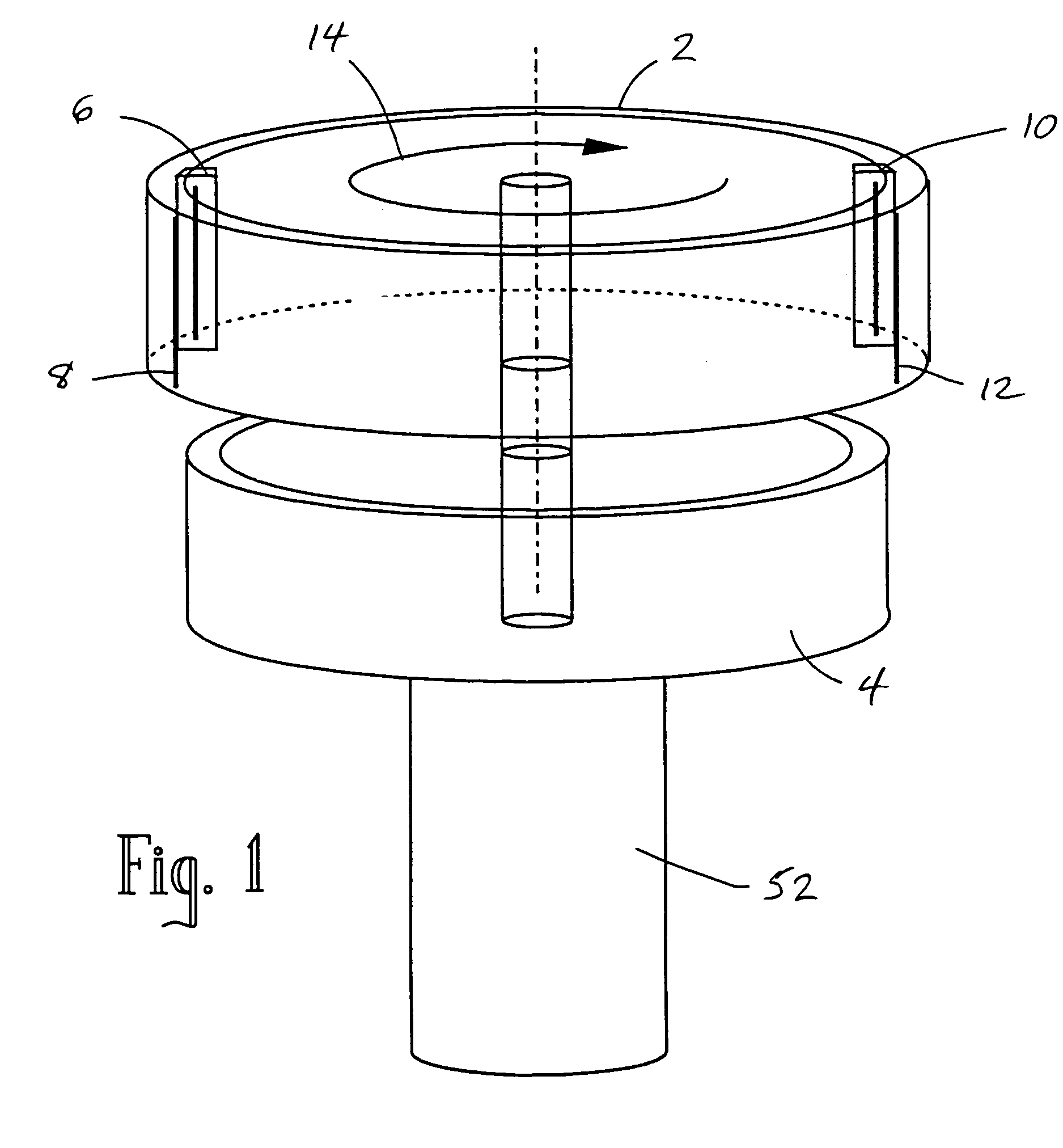
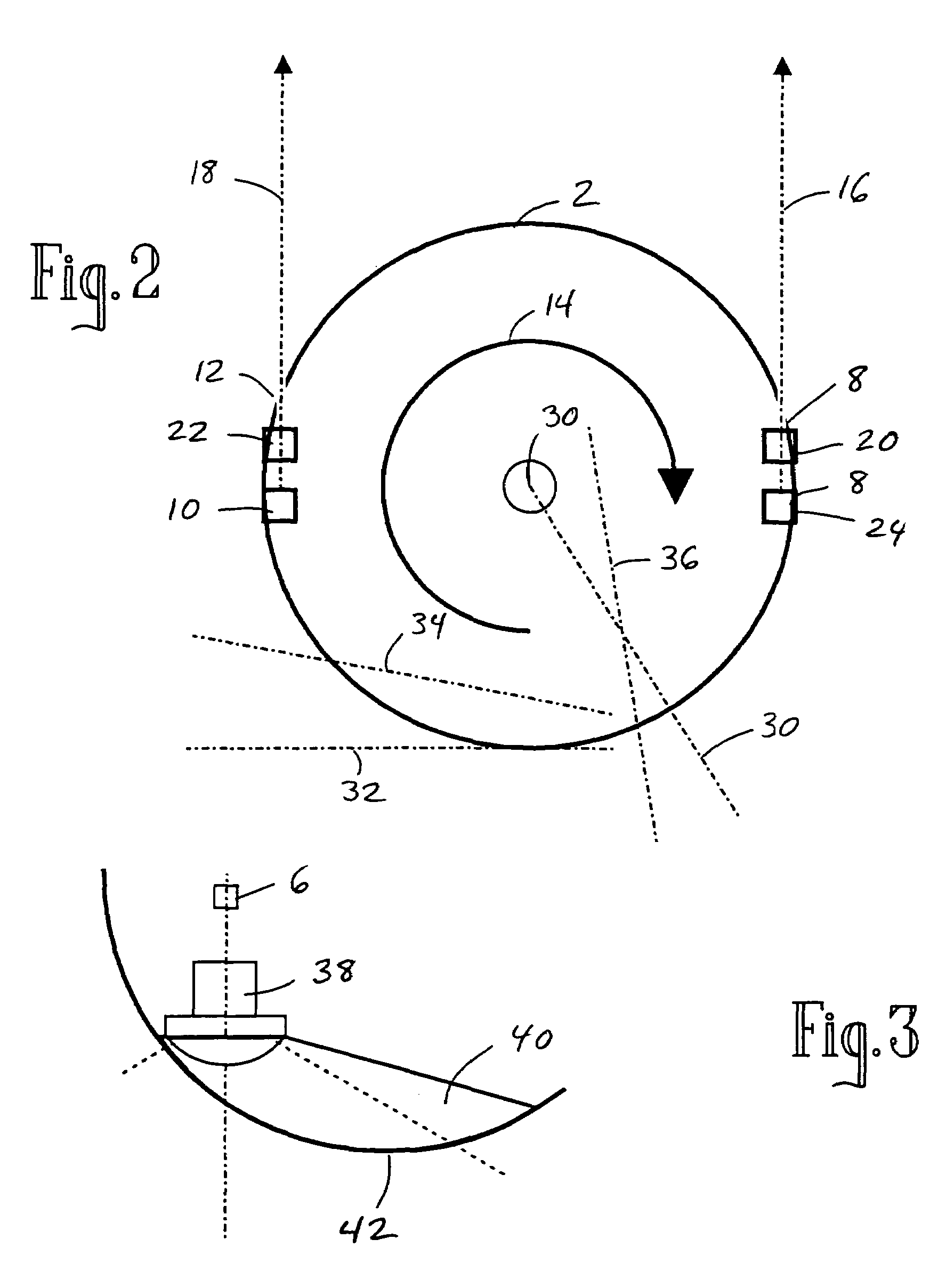
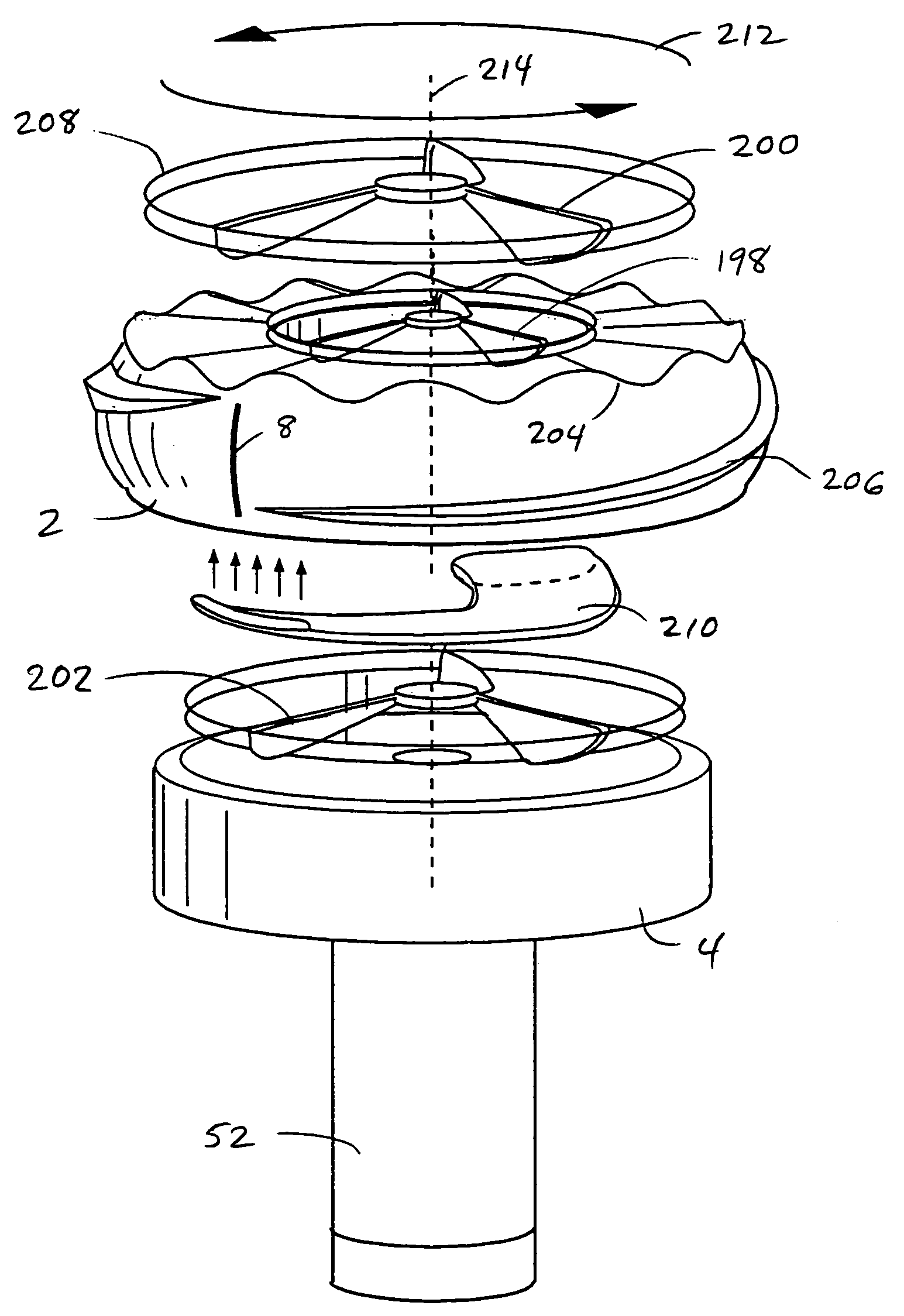
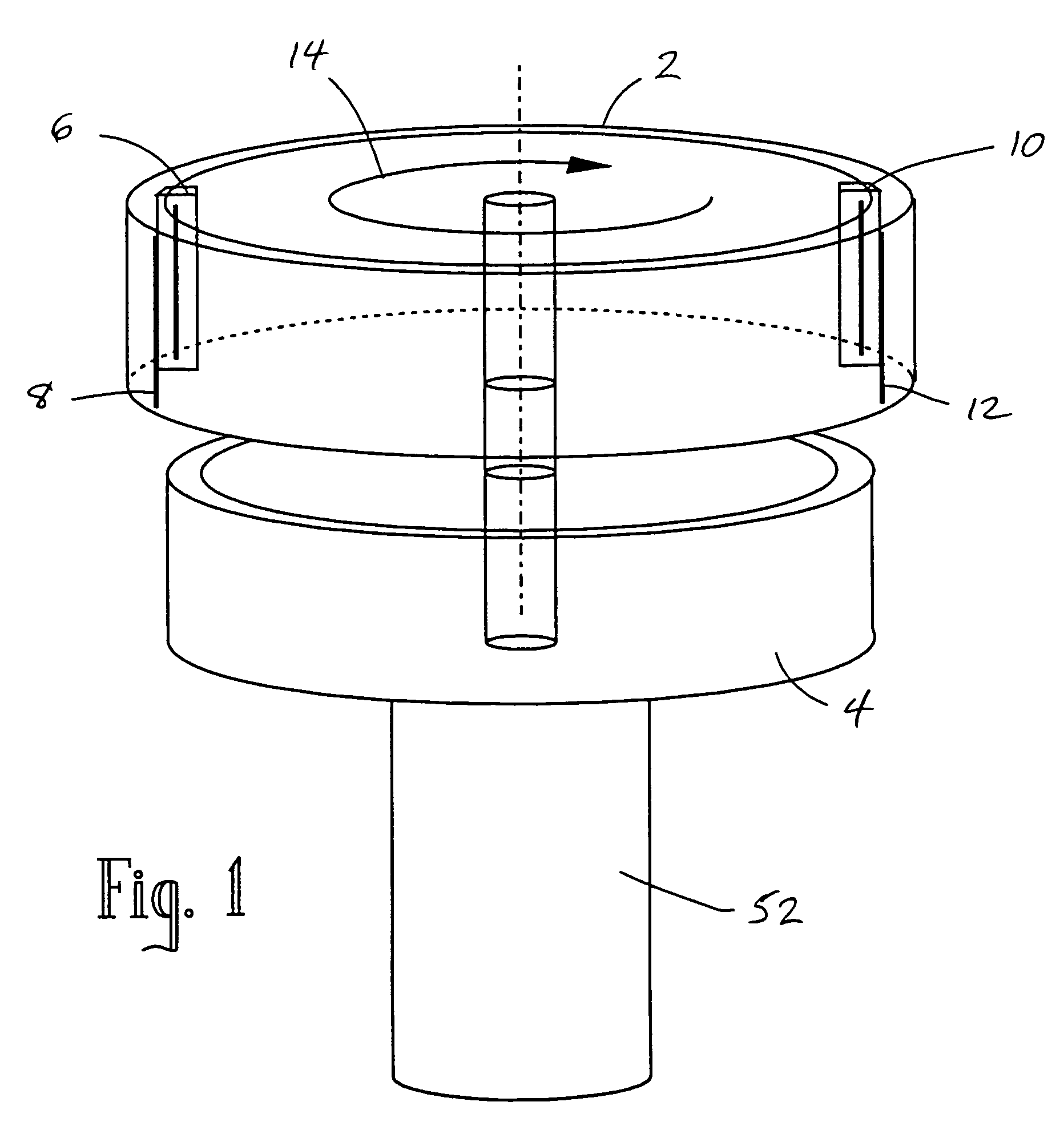
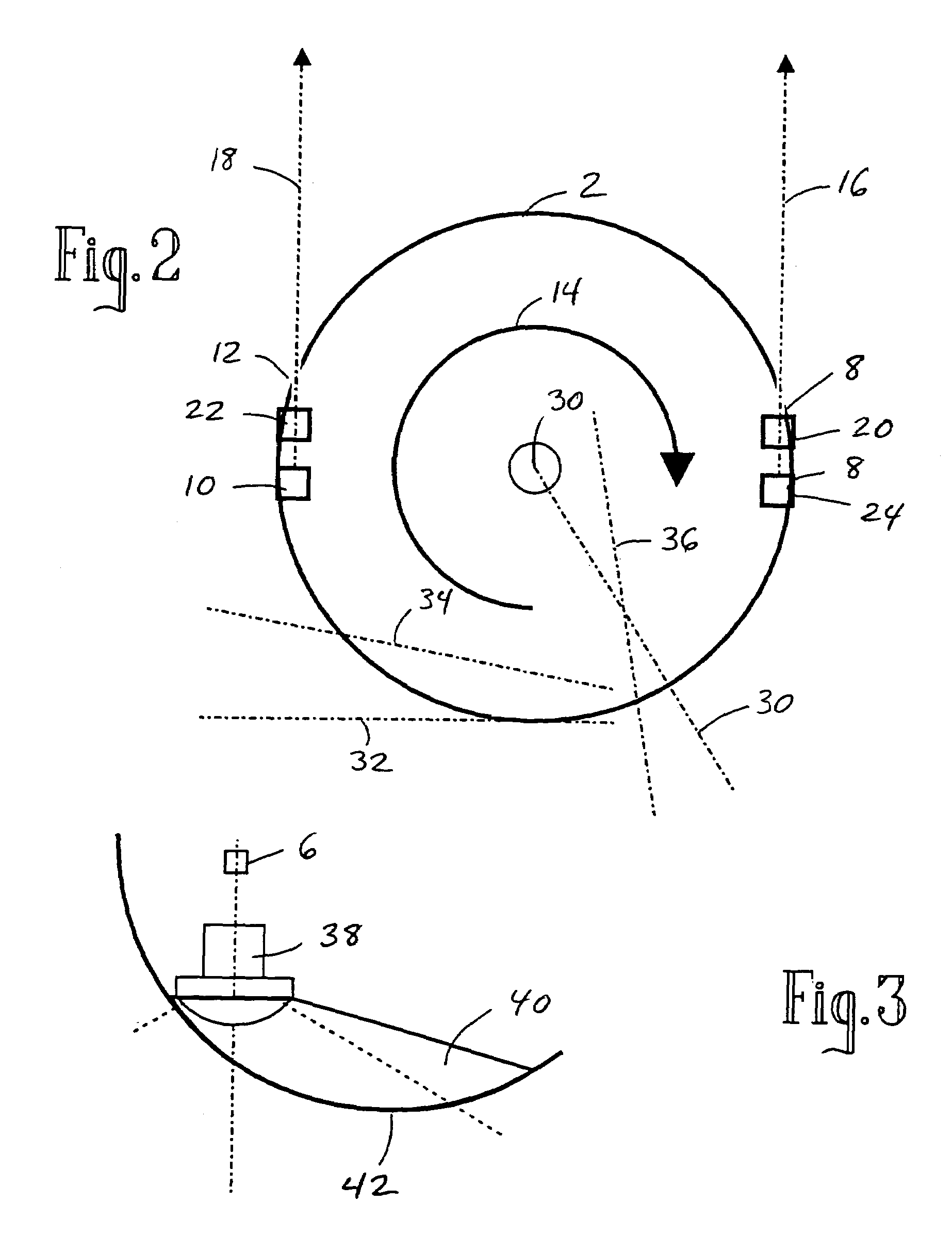
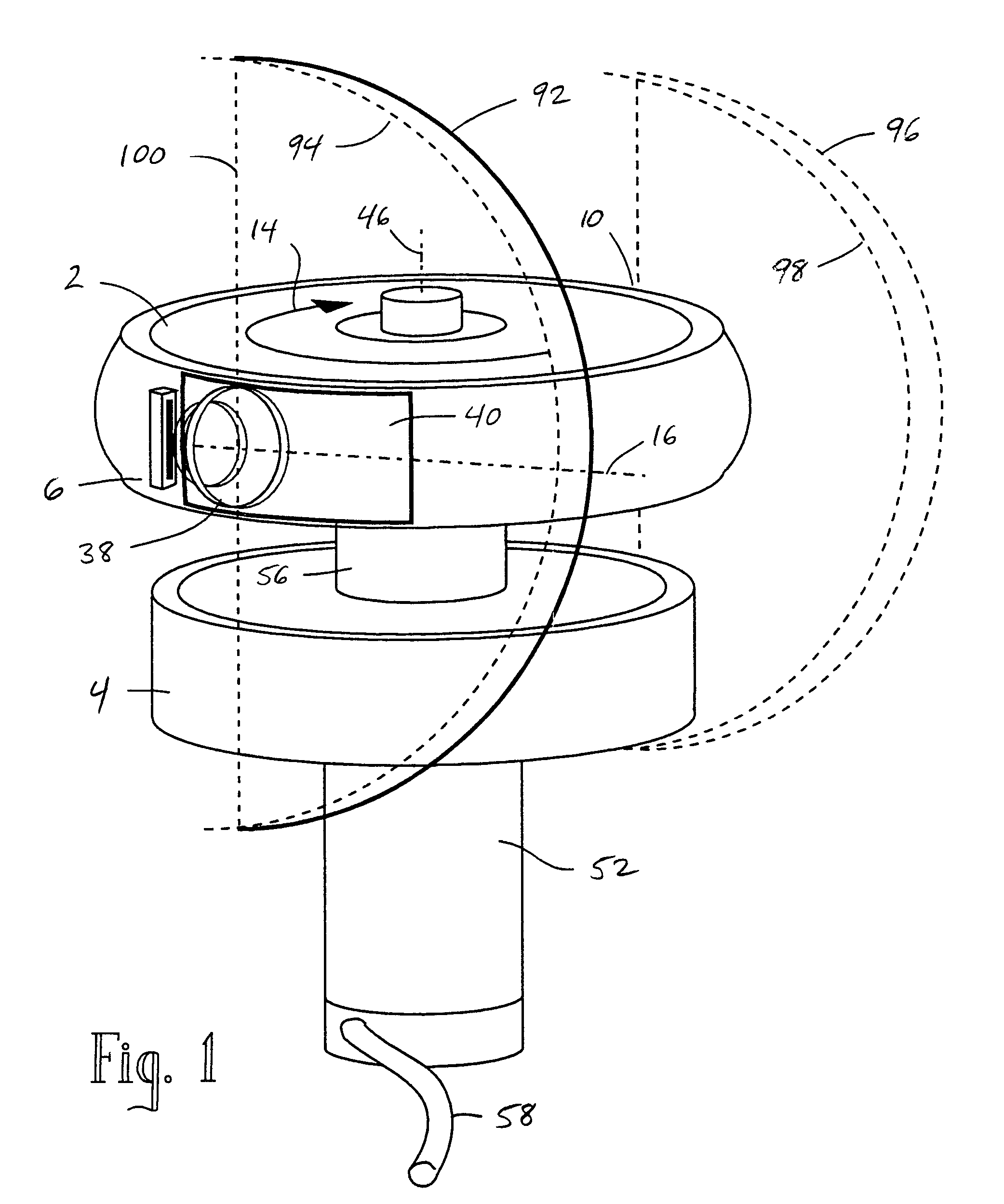
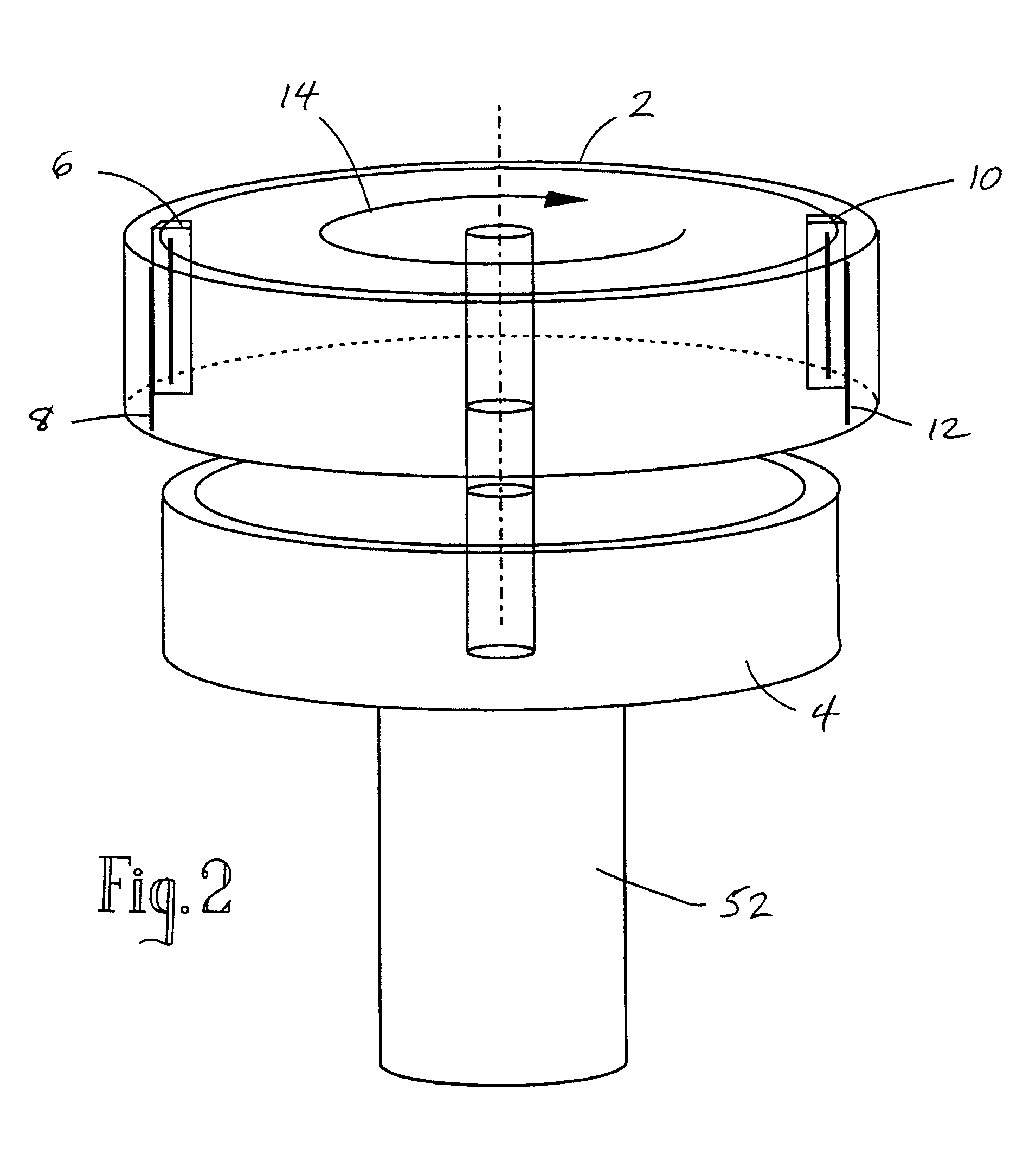
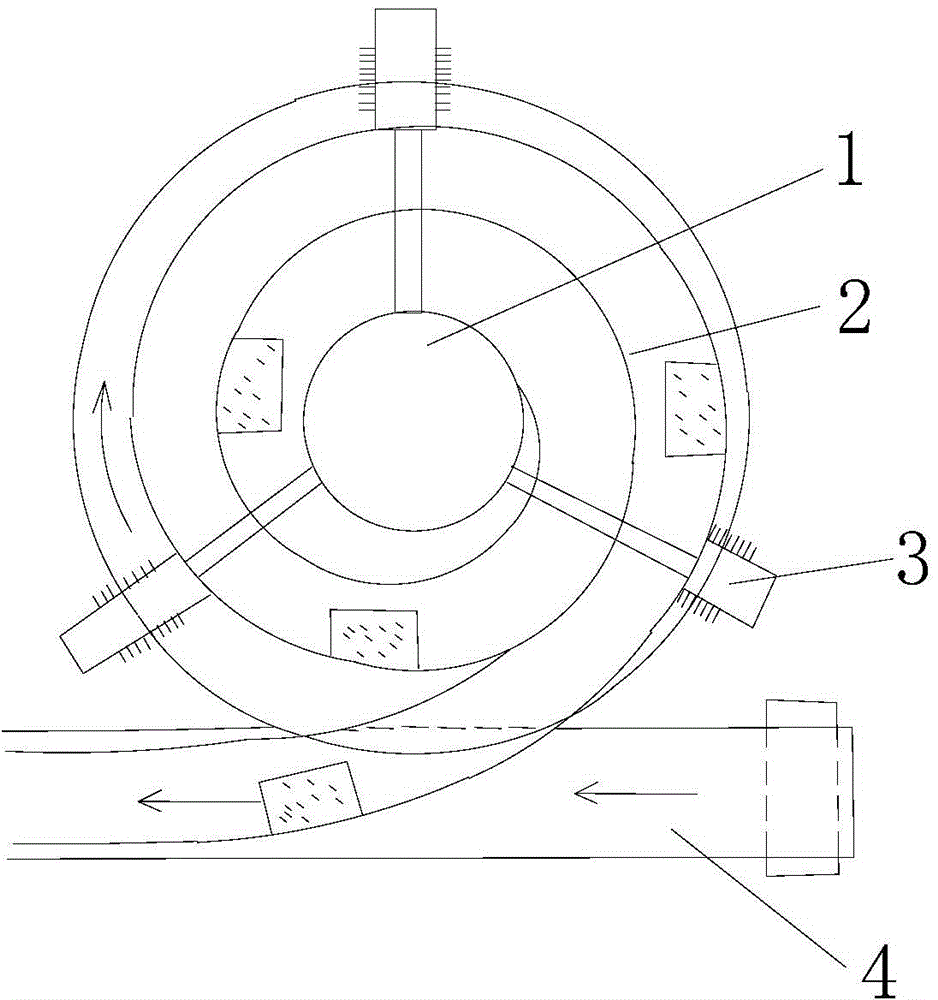
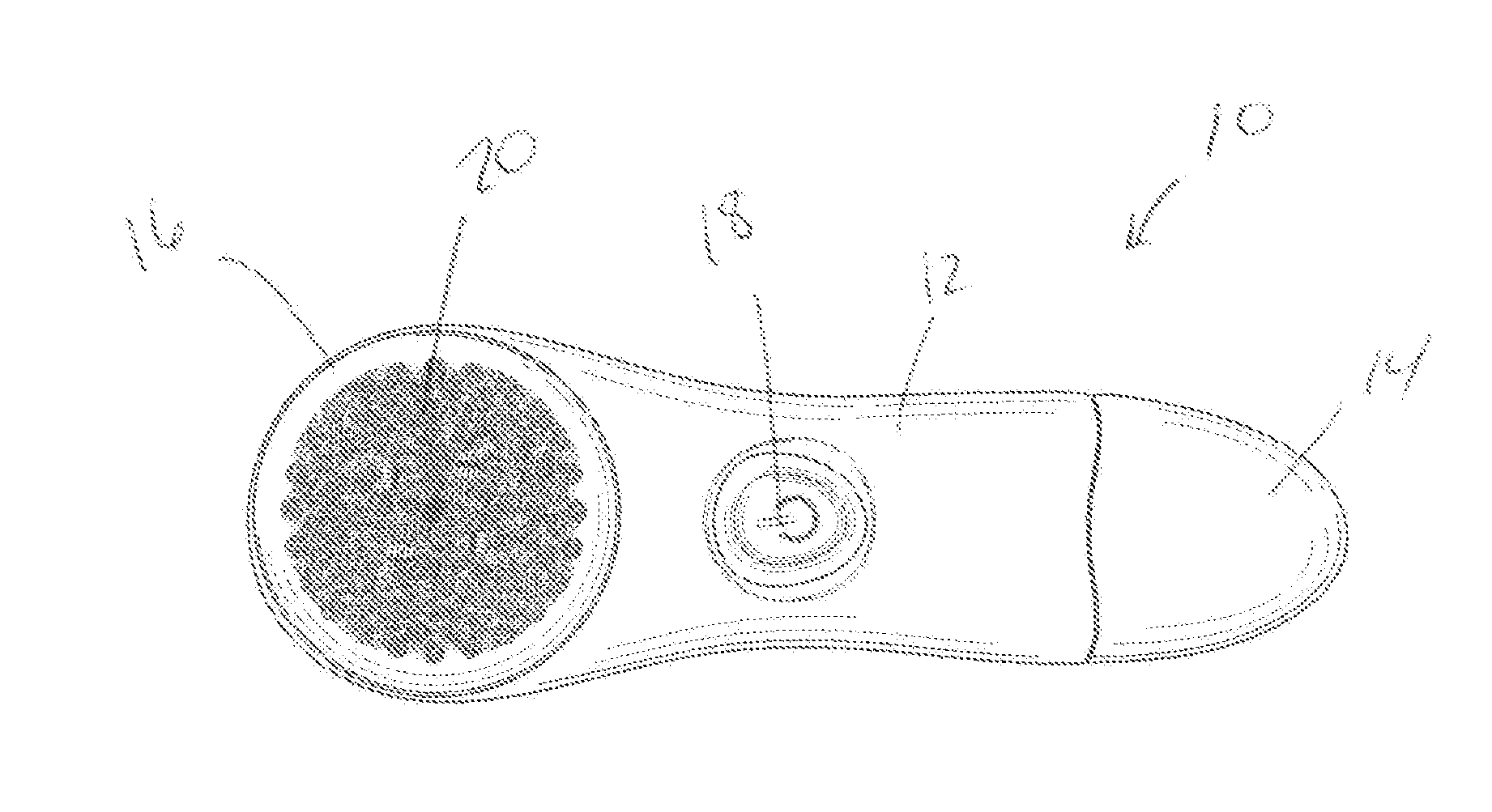
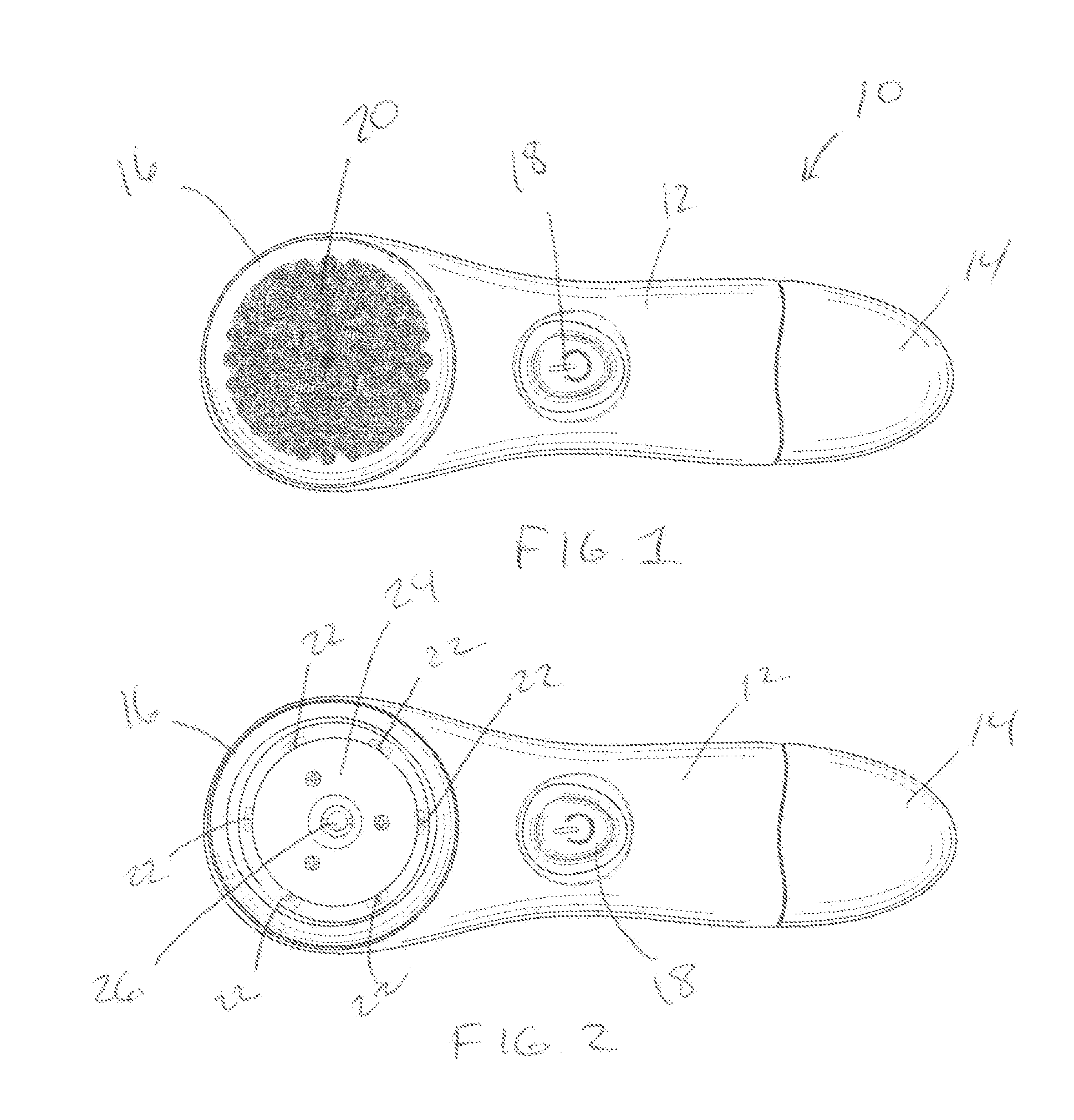
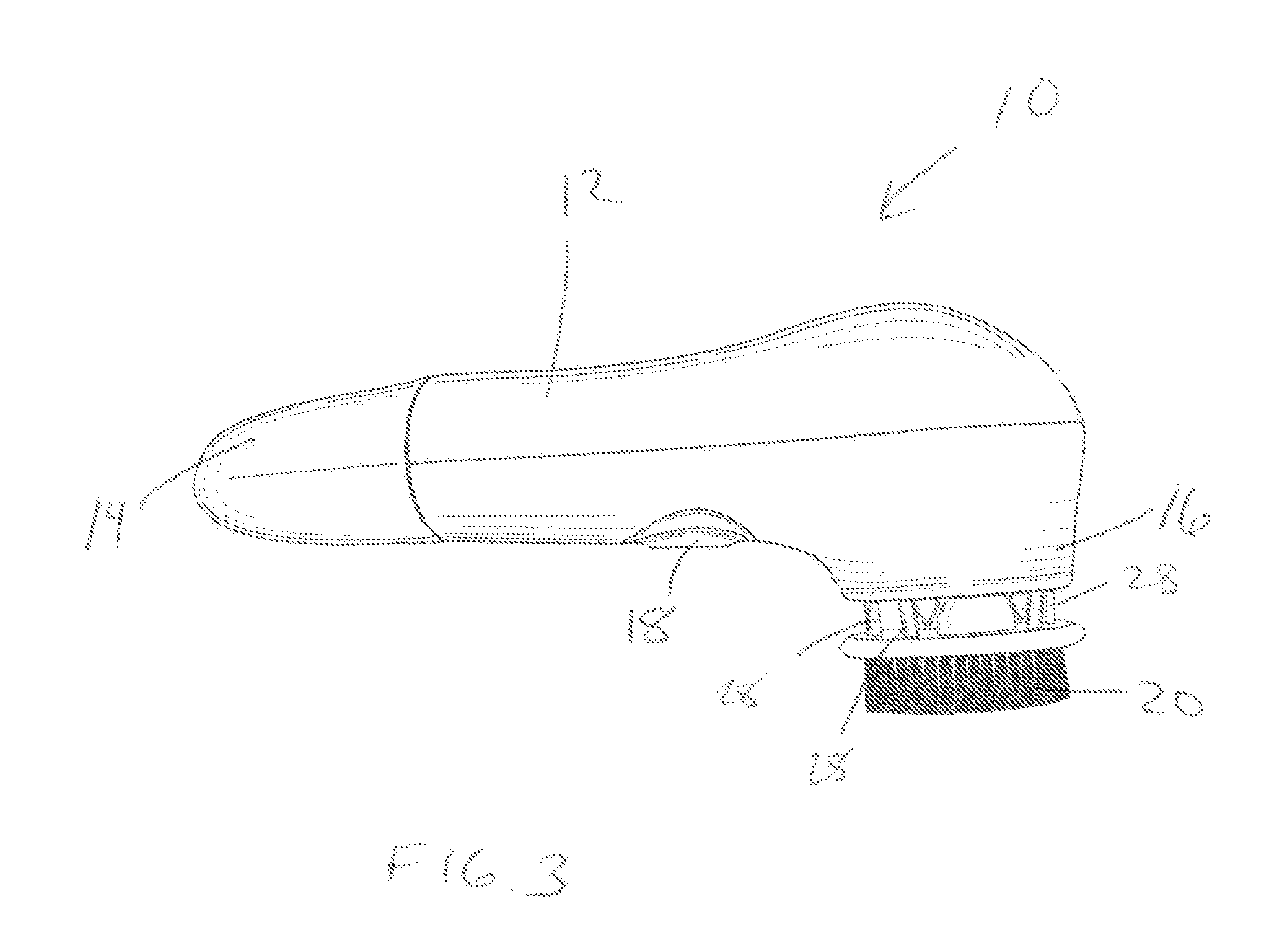
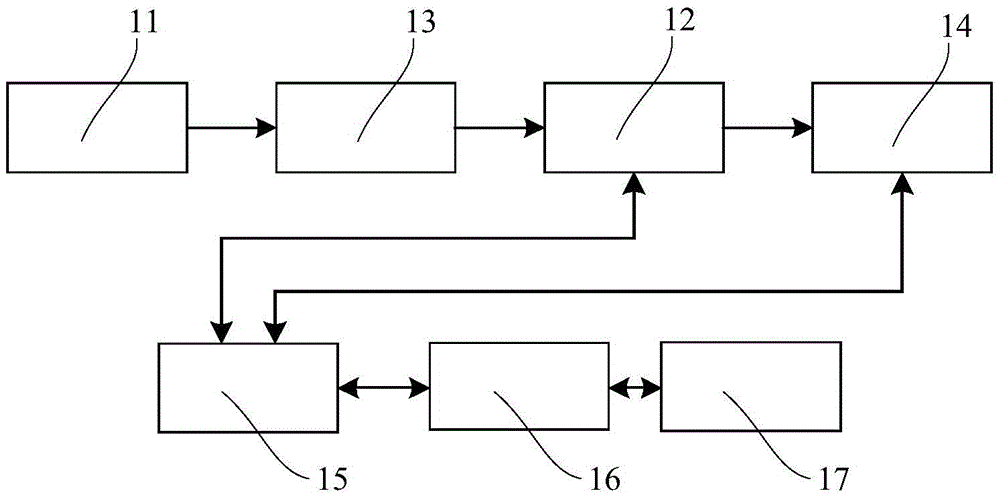
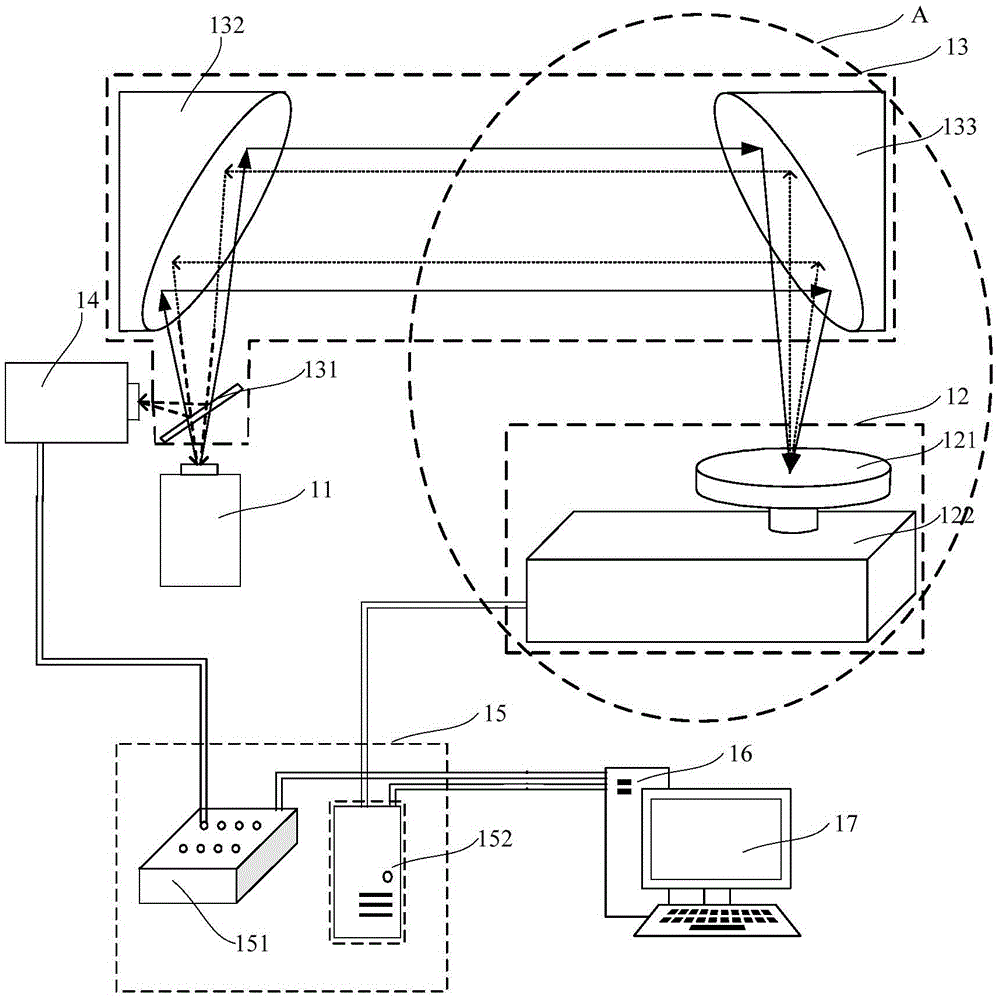
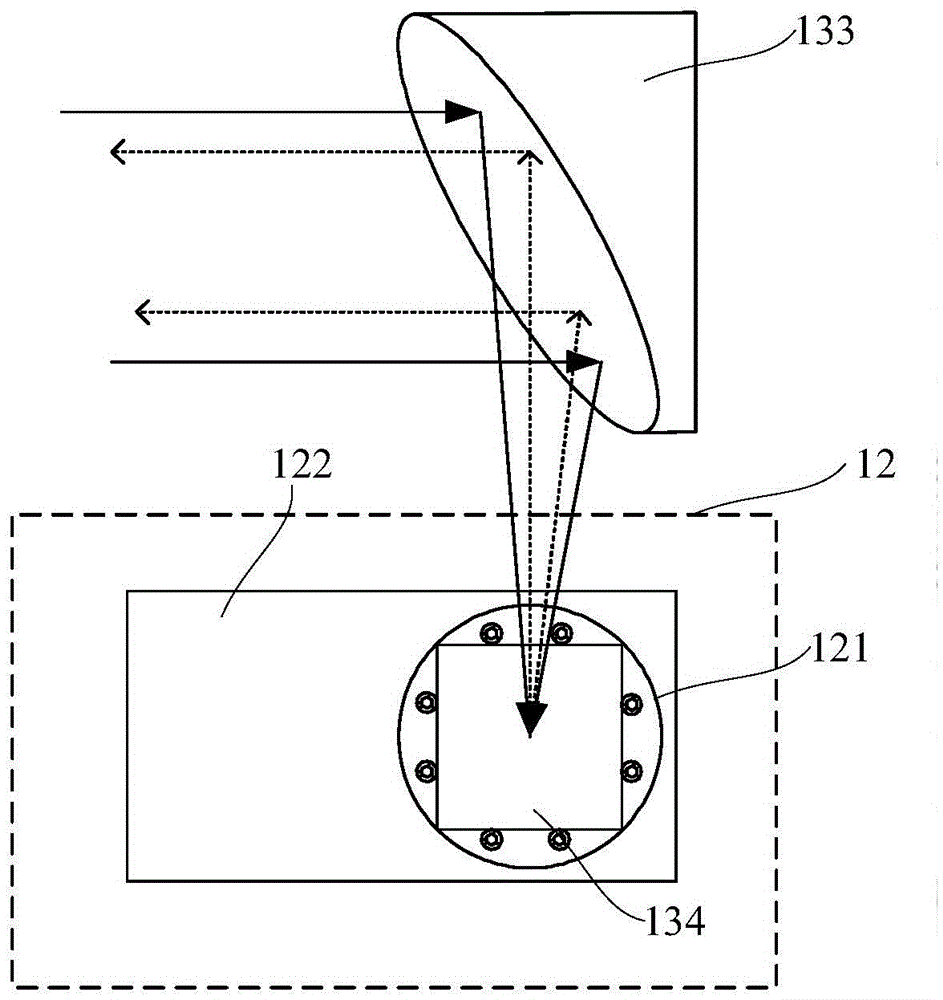
Rotating scan camera
InactiveUS20060072020A1High resolutionHigh light sensitivityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsViewpointsRapid rotation
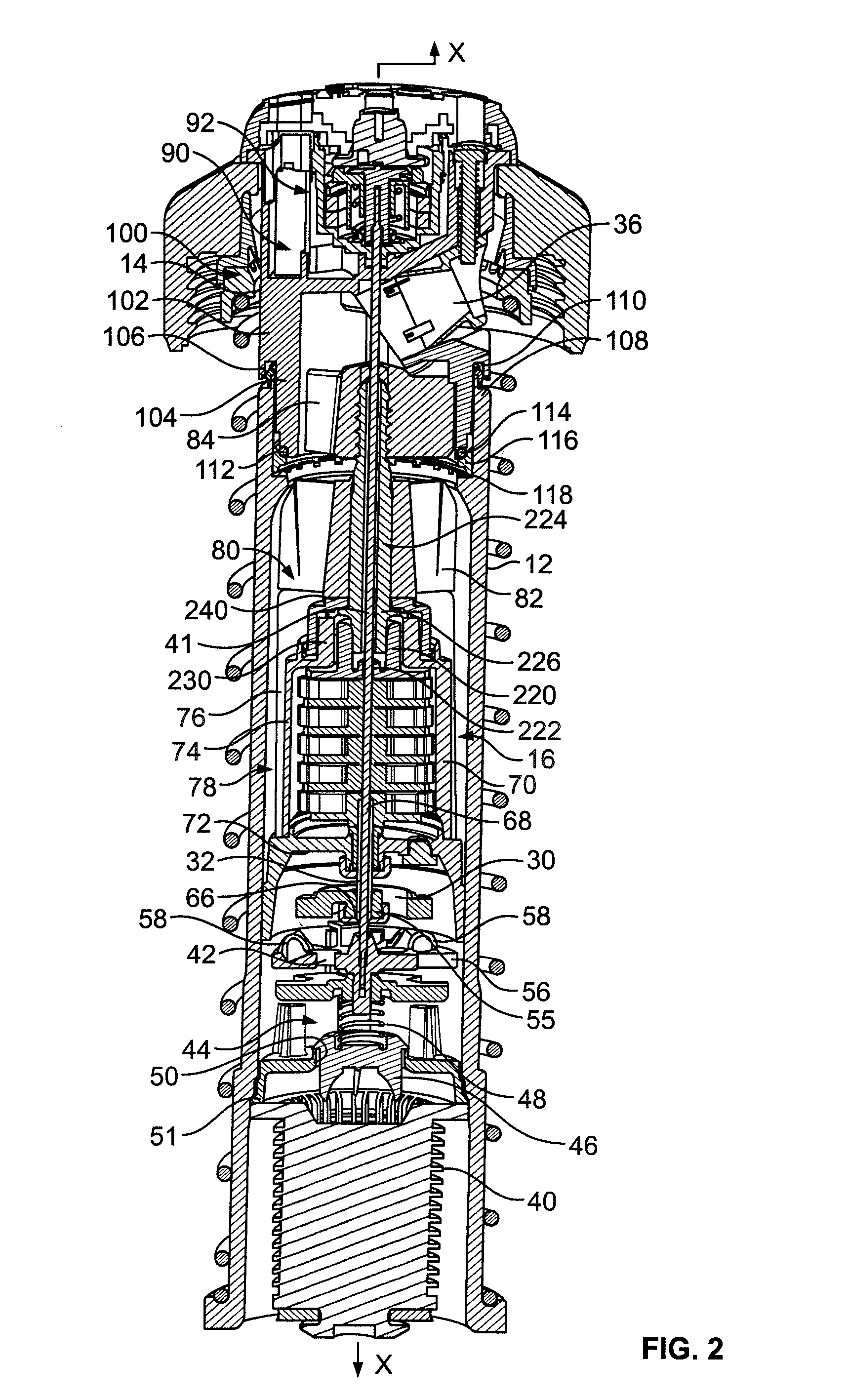
A scanning camera with a rotating drum has one or more sensors characterized by a non-radial optical axis. With two sensors on opposite sides of the drum and facing in substantially the same direction, stereoscopic recording of a panorama is accomplished as the drum rotates. The adjustment of convergence between stereoscopic viewpoints is described that improves the viewing and interpretation of stereoscopic images. Rapid rotation of the scanning camera produces panoramic motion picture recording, with the final frame speed dependent on the sensitivity and speed of the sensor, the resolution desired, and the capabilities of the recording device. The preferred embodiment employs rotating fisheye lenses for a substantially full-sphere field of view. Additional sensors in the same arrangement are used to increase resolution and light sensitivity through multiplexed or additive recording of the image data. Recording image information using film, either internal or external to the camera drum, is also described as a cost-effective alternative to digital media storage.
Owner:IMMERSIVE LICENSING
Recording a stereoscopic image of a wide field of view
InactiveUS7525567B2Improve stabilityEliminate the problemTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsRapid rotationRotating drum
A scanning camera with a rotating drum has one or more sensors characterized by a non-radial optical axis. With two sensors on opposite sides of the drum and facing in substantially the same direction, stereoscopic recording of a panorama is accomplished as the drum rotates. Rapid rotation of the scanning camera produces panoramic motion picture recording, with the final frame speed dependent on the sensitivity and speed of the sensor, the resolution desired, and the capabilities of the recording device. The preferred embodiment employs rotating fisheye lenses for a substantially fill-sphere field of view. Streamlining of the lens elements on the drum surface is described for quiet operation of the camera, even at high rotation speeds. The rapid rotation of the drum characteristic of motion picture frame rates can improve both the stability and portability of the camera. The gyroscopic effect of the rotating weight of the drum can increase the stability of the camera, and the apparent weight of the camera can be reduced by the lifting effect of aerodynamic elements such as rotors added to the rotating drum. The adjustment of convergence are described that improve the viewing of stereoscopic images. Additional sensors in the same arrangement are used to increase resolution through multiplexed recording of the image data. Recording image information using film, either internal or external to the camera drum, is also described as a cost-effective alternative to digital media storage.
Owner:IMMERSIVE LICENSING
Rotating scan self-cleaning camera
InactiveUS7129971B2Improve stabilityLighter apparent weightTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsRapid rotationFilm frame
A scanning camera with a rotating drum has one or more sensors characterized by a non-radial optical axis. With two sensors on opposite sides of the drum and facing in substantially the same direction, stereoscopic recording of a panorama is accomplished as the drum rotates. Rapid rotation of the scanning camera produces panoramic motion picture recording, with the final frame speed dependent on the sensitivity and speed of the sensor, the resolution desired, and the capabilities of the recording device. The preferred embodiment employs rotating fisheye lenses for a substantially full-sphere field of view. Streamlining of the lens elements on the drum surface is described for quiet operation of the camera, even at high rotation speeds. The rapid rotation of the drum characteristic of motion picture frame rates can improve both the stability and portability of the camera. The gyroscopic effect of the rotating weight of the drum can increase the stability of the camera, and the apparent weight of the camera can be reduced by the lifting effect of aerodynamic elements such as rotors added to the rotating drum. The adjustment of convergence are described that improve the viewing of stereoscopic images. Additional sensors in the same arrangement are used to increase resolution through multiplexed recording of the image data. Recording image information using film, either internal or external to the camera drum, is also described as a cost-effective alternative to digital media storage.
Owner:IMMERSIVE LICENSING
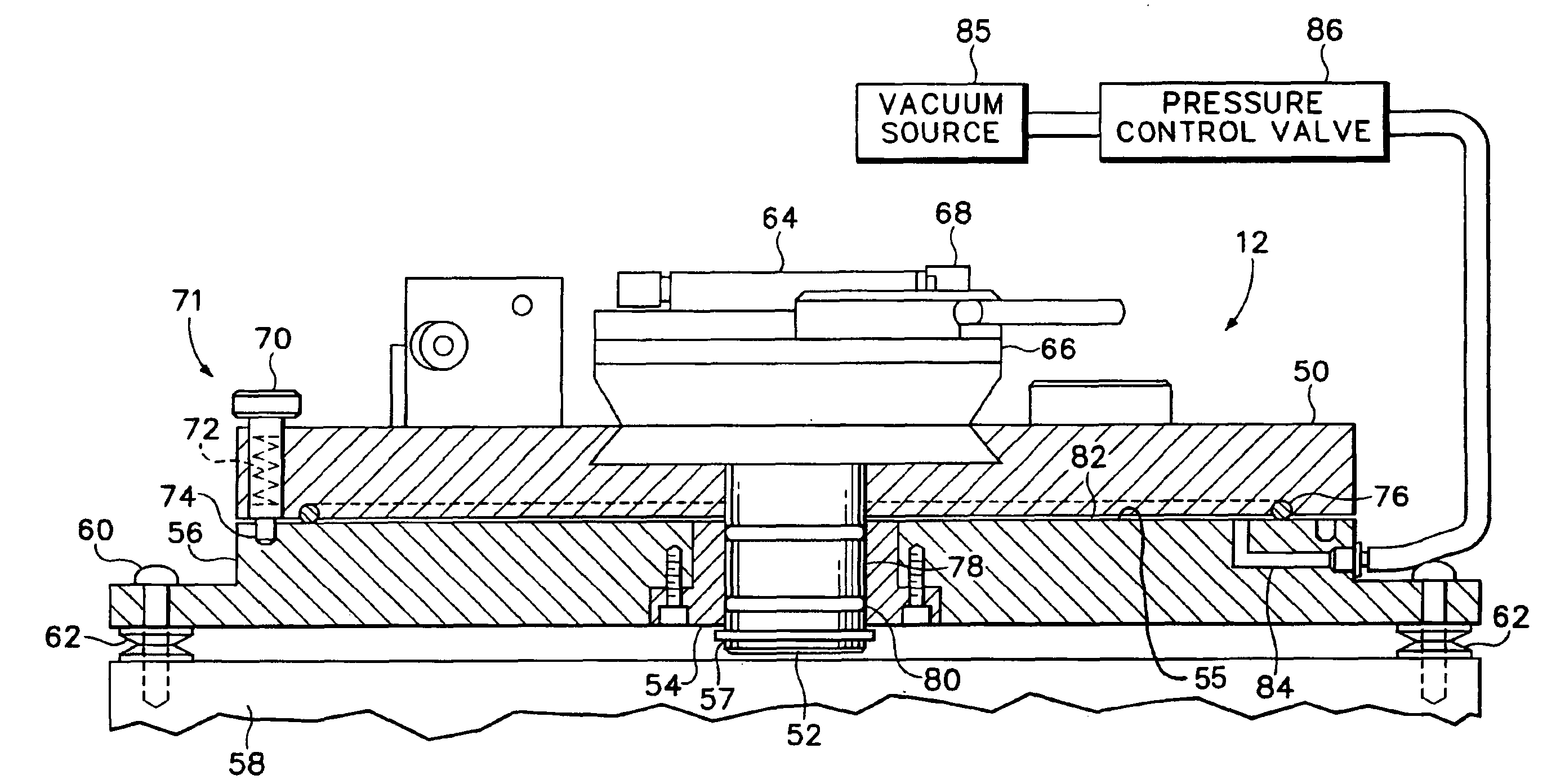
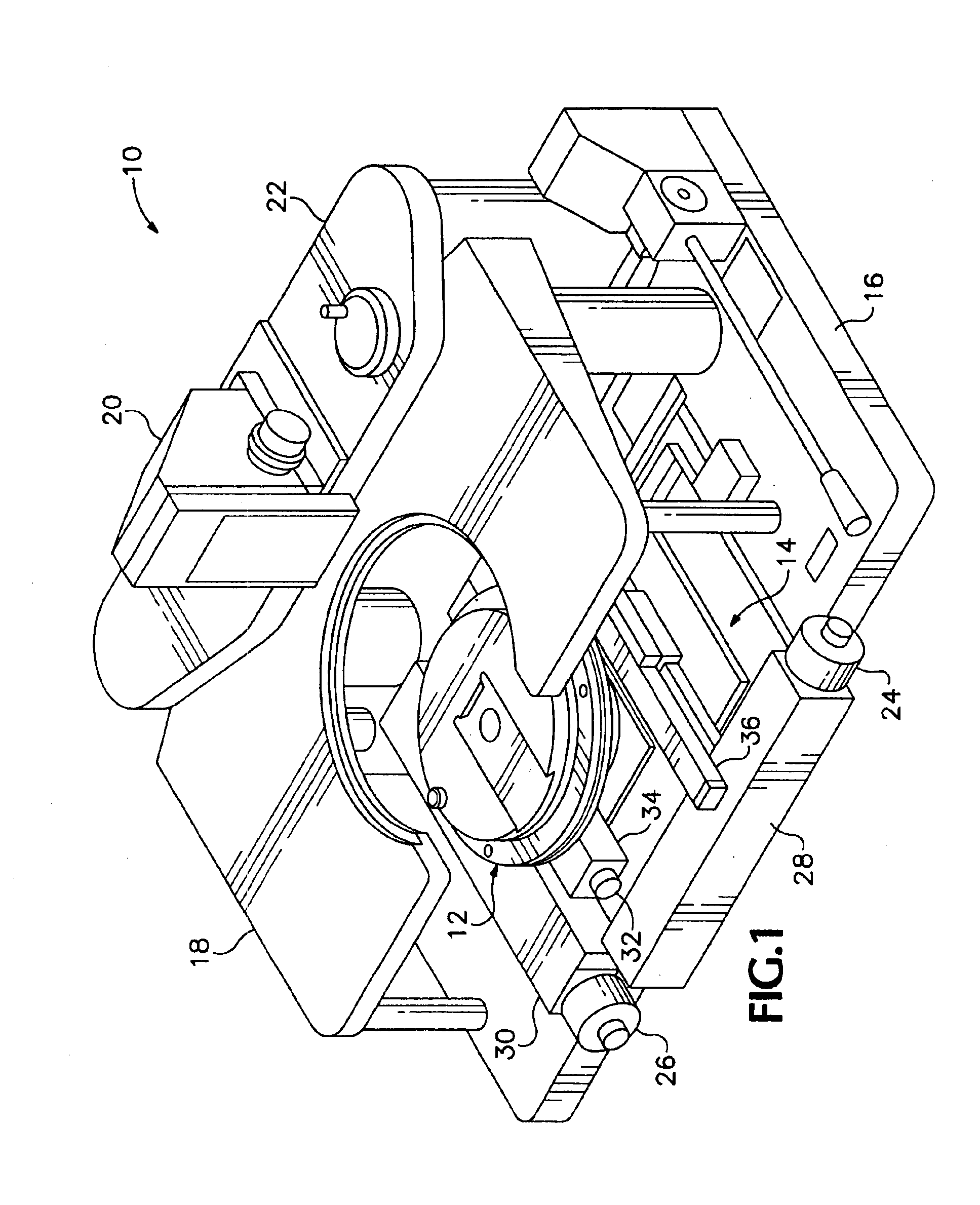
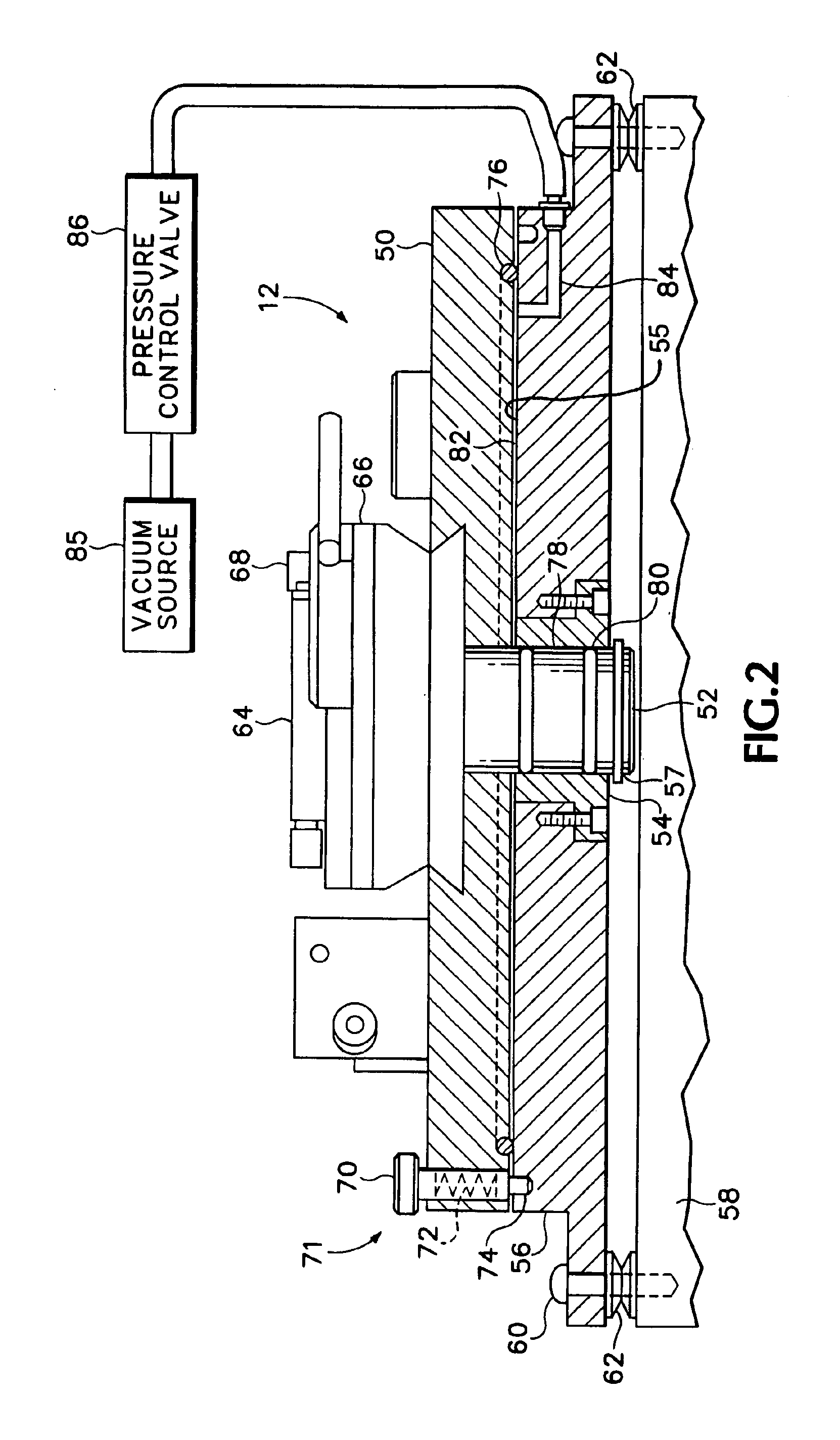
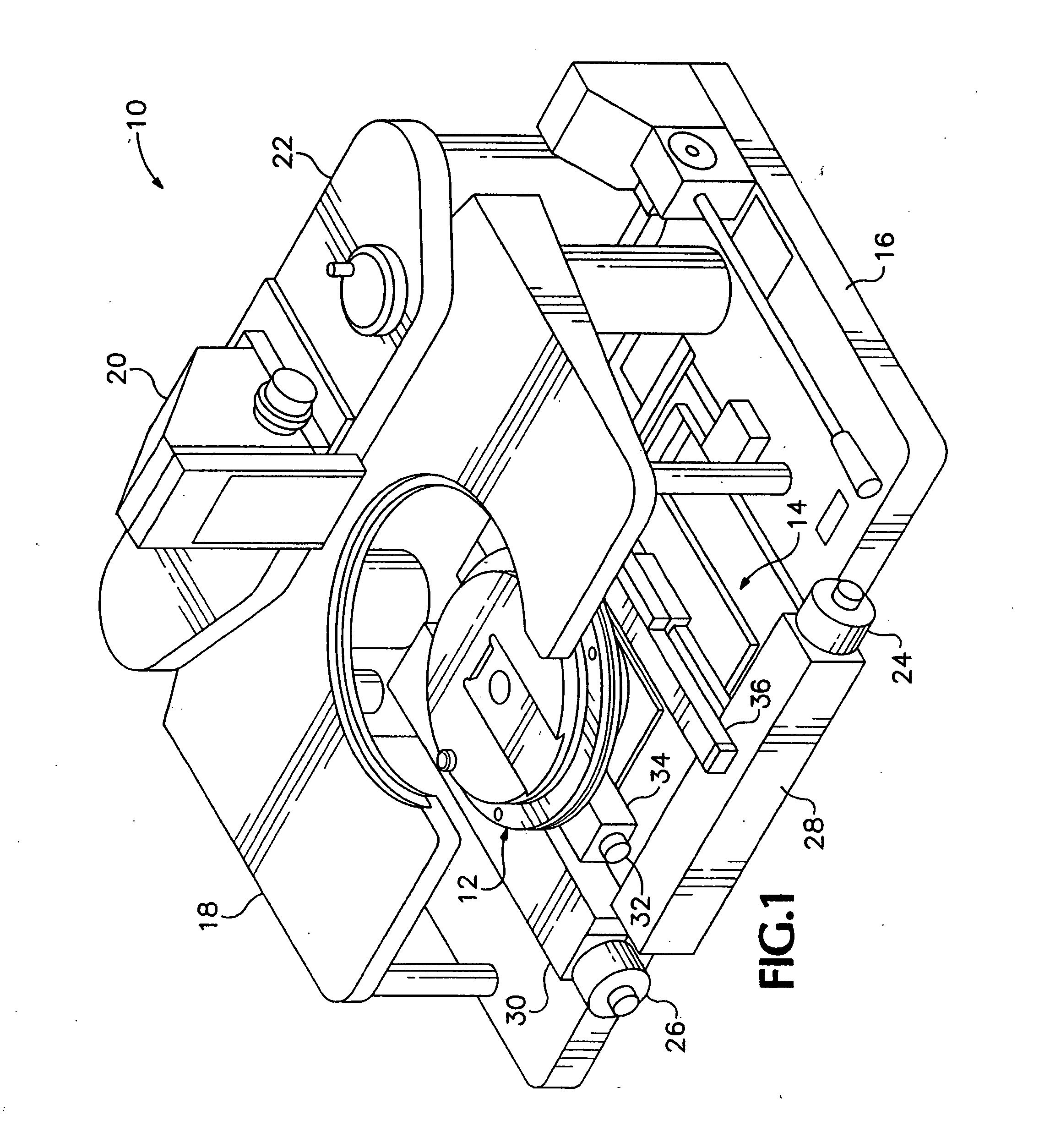
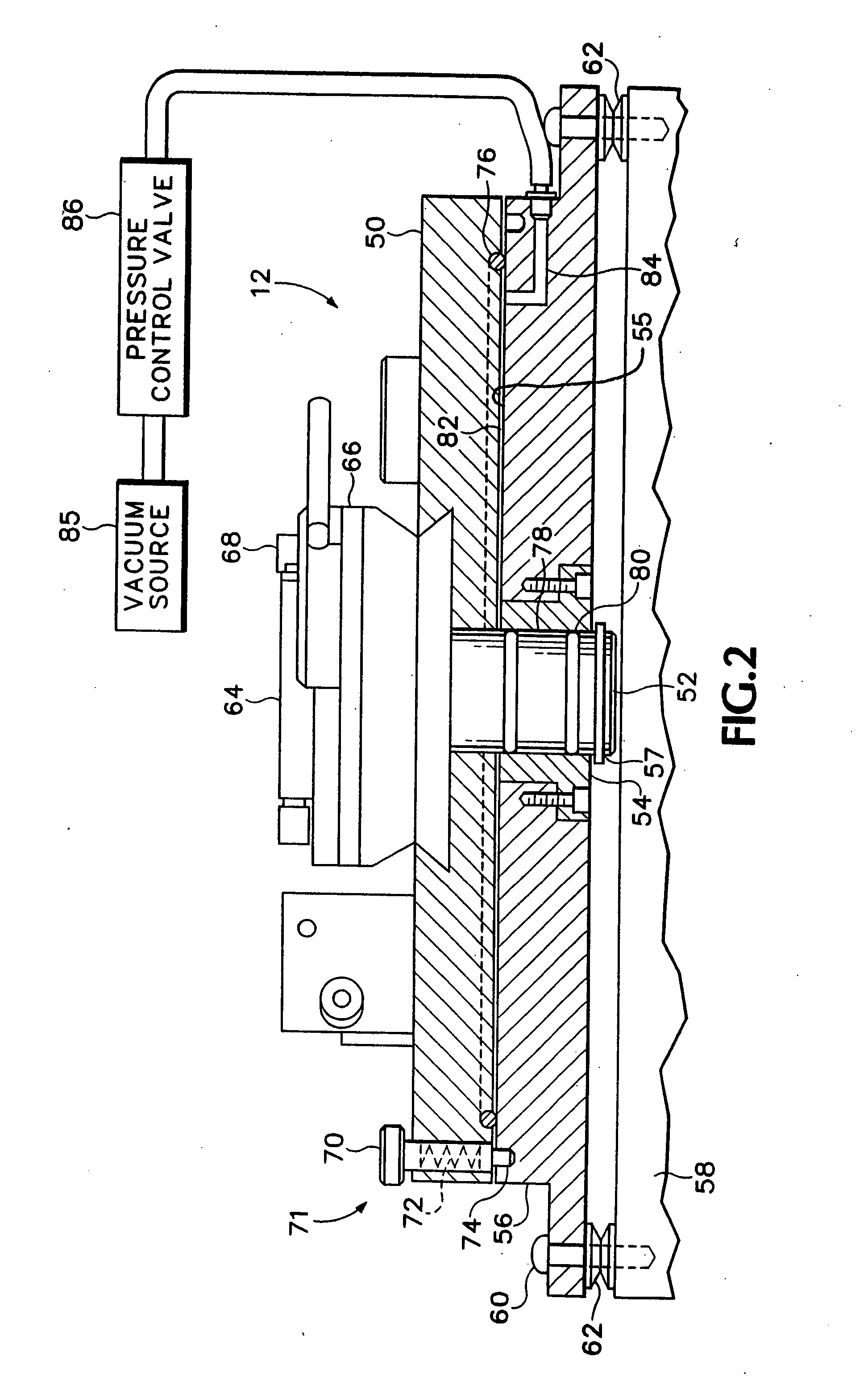
Indexing rotatable chuck for a probe station
InactiveUS6885197B2Improve rigidityPromoting consistent planaritySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingPower stationEngineering
A rotary chuck with indexed rotation promotes rapid rotation of a device under test and increases the productivity of a probe station on which the device is being tested. A device mounting member of a rotatable chuck is supported for rotation on a first surface of a base until a vacuum is applied drawing the device mounting member into contact with a second surface of the base and constraining the device mounting member against rotation.
Owner:CASCADE MICROTECH
Powered lower bobbin feed system for deflector type rotary braiding machines
A Powered Lower Bobbin Feed (“PLBF”) system is disclosed for improving the operation of deflector type rotary braiding machines, such as the Wardwell Rapid Braider. The PLBF eliminates or reduces the impulsive tension spikes set up by the deflection and feed process in current rotary braiding machines by uniquely controlling the lower bobbin filament feed. These tension spikes result from: the rapid rotational acceleration and deceleration required of the lower bobbin as a result of the feed process; the lever arm tension control and bobbin ratchet mechanism; and the shape of the filament deflector surface. Such failure limits the operating speed of rotary braiding machines, the minimum size of filament that can be braided effectively, or the ability to maintain the quality of the braid produced. By eliminating or reducing these spikes, the PLBF therefore can increase the working speed of circular braiding machines and improve the uniformity of braided filaments generated by such machines at a given speed. In the preferred embodiment, the PLBF comprises: a slip ring designed to provide power to the lower bobbins; a variable speed powered lower bobbin concept; a feedback control system for the bobbins to assure bobbin feed matches braid consumption; and an improved, more contoured, deflector surface to minimize feed tension spikes. The new contour can be created: by retrofitting existing deflectors with a spline; or, by making new deflectors that incorporate the overall contour of a retrofitted deflector.
Owner:STOLBERGER
Rotating scan camera
InactiveUS7791638B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMultiplexingViewpoints
A scanning camera with a rotating drum has one or more sensors characterized by a non-radial optical axis. With two sensors on opposite sides of the drum and facing in substantially the same direction, stereoscopic recording of a panorama is accomplished as the drum rotates. The adjustment of convergence between stereoscopic viewpoints is described that improves the viewing and interpretation of stereoscopic images. Rapid rotation of the scanning camera produces panoramic motion picture recording, with the final frame speed dependent on the sensitivity and speed of the sensor, the resolution desired, and the capabilities of the recording device. The preferred embodiment employs rotating fisheye lenses for a substantially full-sphere field of view. Additional sensors in the same arrangement are used to increase resolution and light sensitivity through multiplexed or additive recording of the image data. Recording image information using film, either internal or external to the camera drum, is also described as a cost-effective alternative to digital media storage.
Owner:IMMERSIVE LICENSING
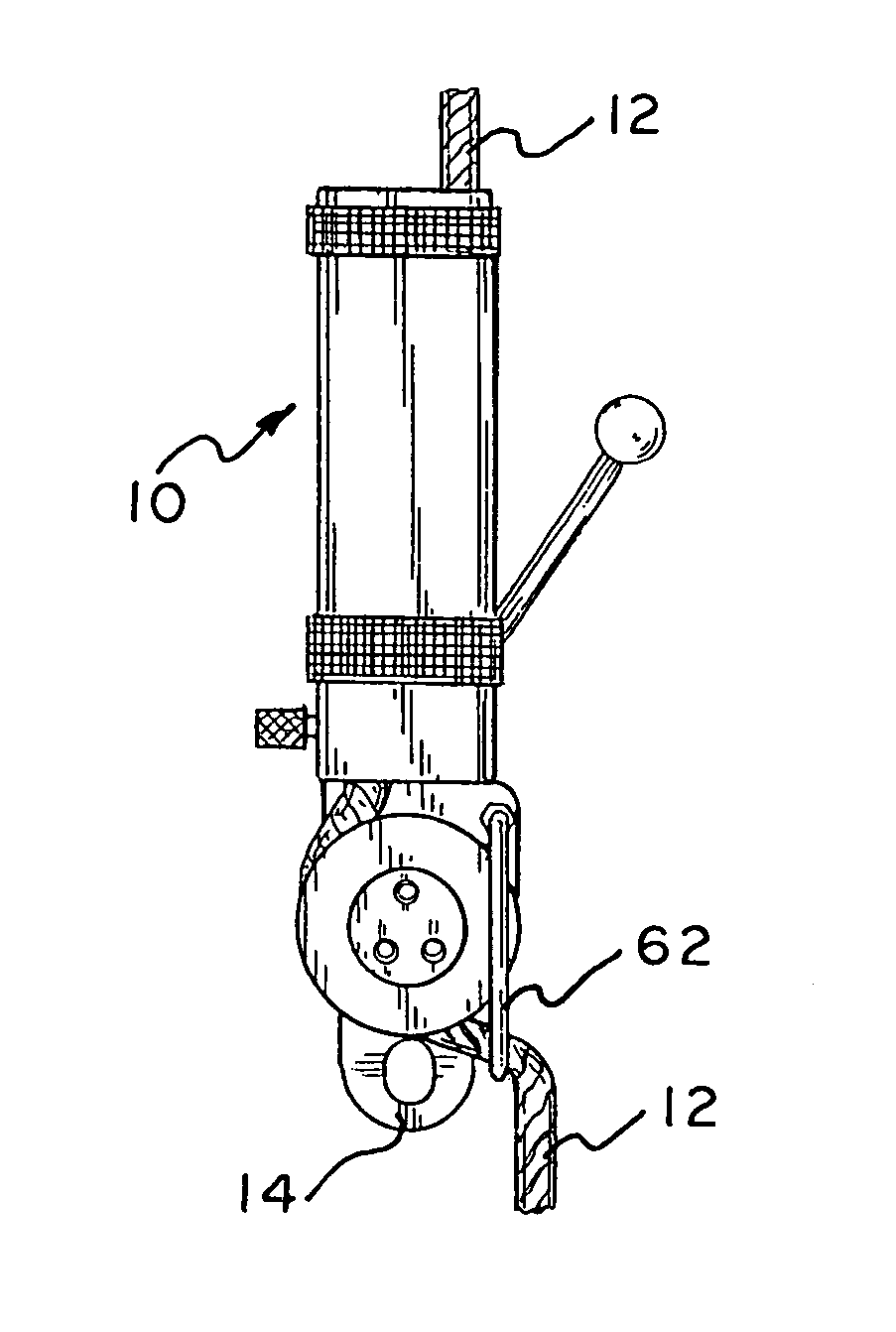
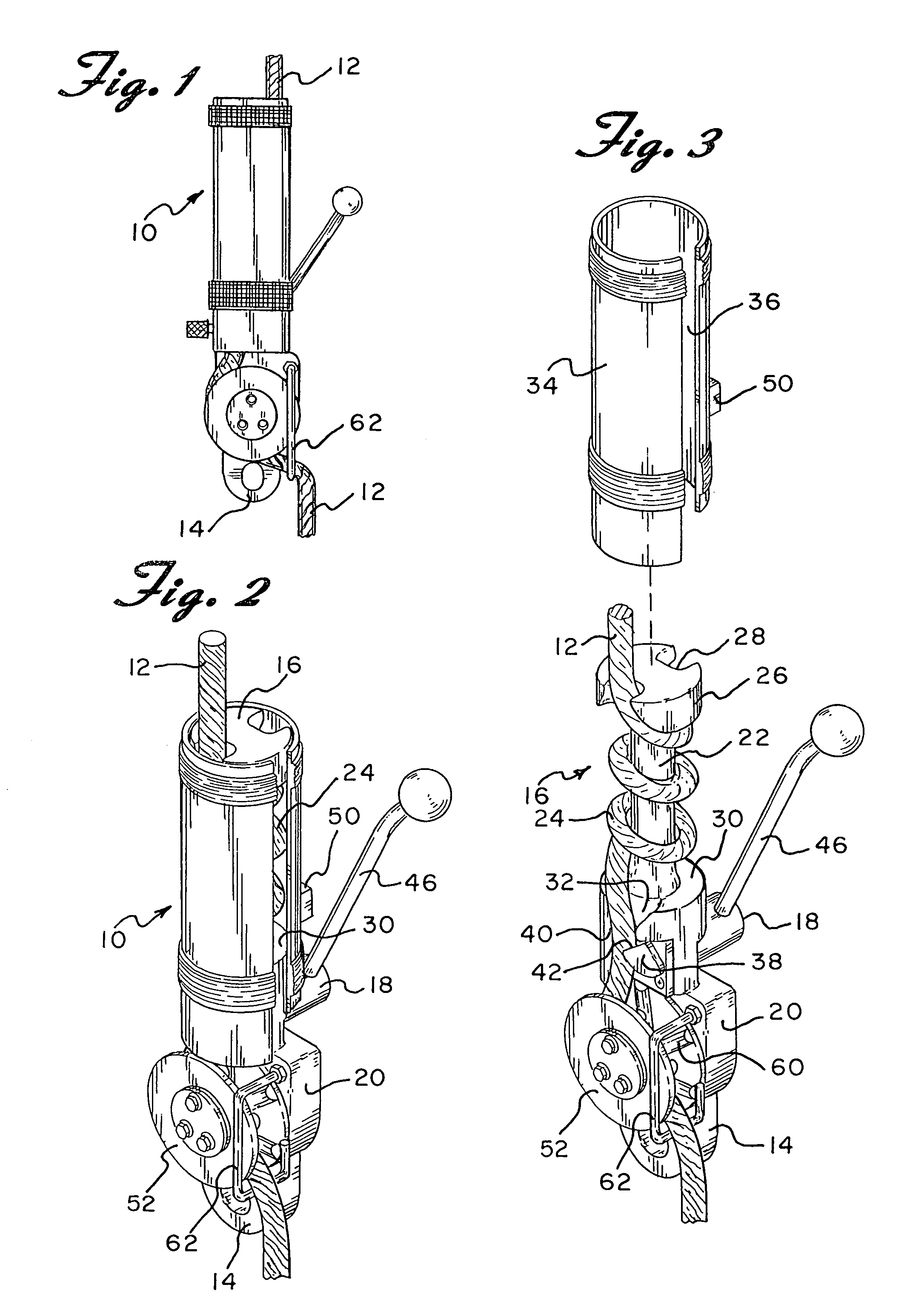
Descent controller with safety brake
InactiveUS6962238B1Preventing accidental freefallEasy to moveBuilding rescueEngineeringCentrifugal force
A descent controller for lowering a workman or other person along a vertically extending rope from an elevated position to a relatively lower position includes a friction device that may be in the form of a cylinder having a plurality of turns of rope wrapped therearound or a plurality of spaced apart horizontal bars with the rope woven between the bars. The friction device interacts with said rope to retard the movement of the controller along the rope. A lever operated pawl is mounted beneath the friction device and is used by the workman to applying an adjustable force on said rope in order to control his descent down the rope. A centrifugal brake is mounted below the lever centrifugal brake. The centrifugal brake includes a wheel mounted for rotation and has the rope passing around at least a portion of said wheel. Included within the brake is a pawl brake mounted for rotation with the wheel and a fixed stop member. Upon sensing rapid rotation of the wheel, the pawl brake moves outwardly by centrifugal force to engage the fixed stop member and applies a positive stopping force on the wheel to prevent movement of the descent controller relative to said rope thereby preventing accidental freefall.
Owner:OSTROBROD MEYER
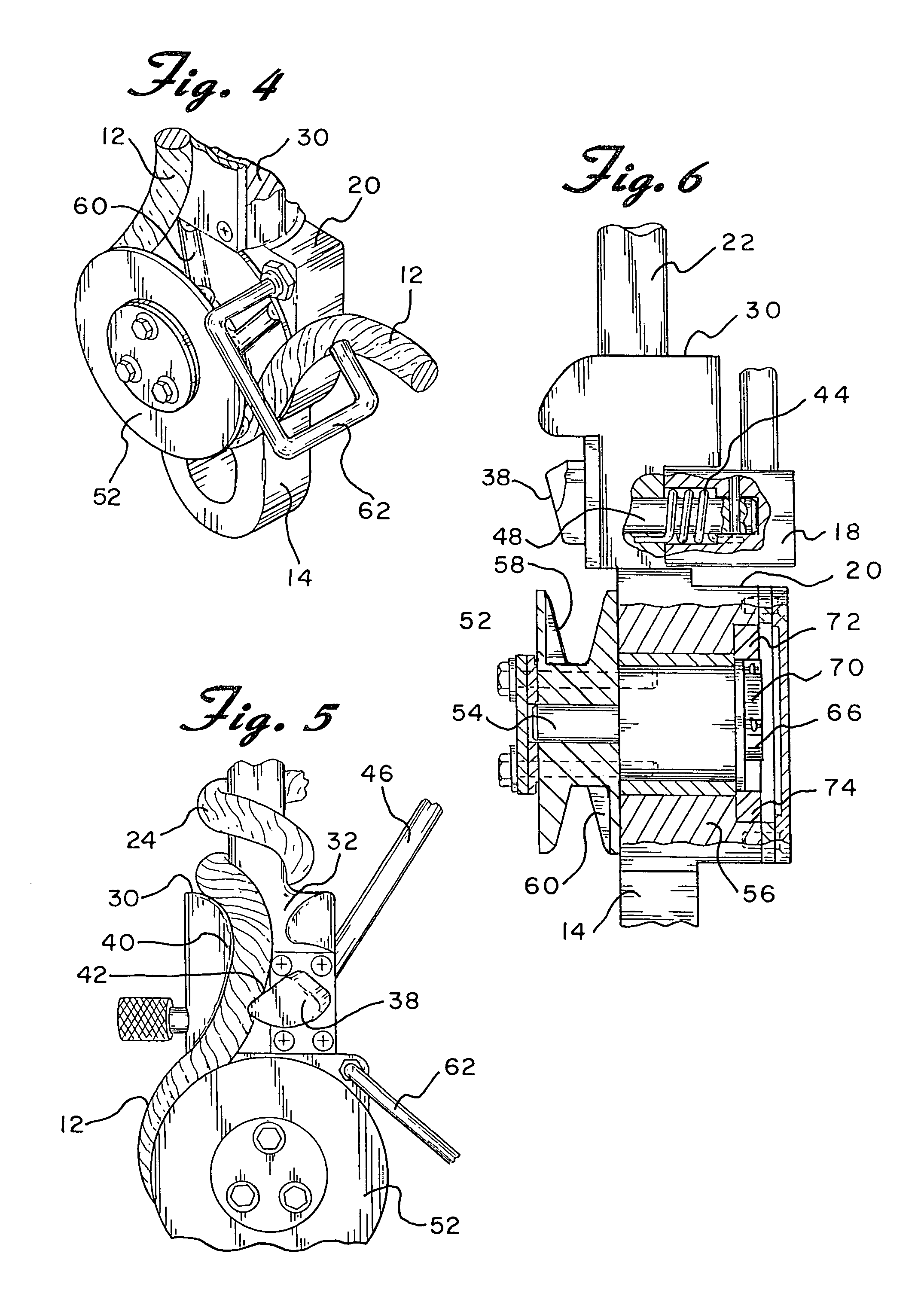
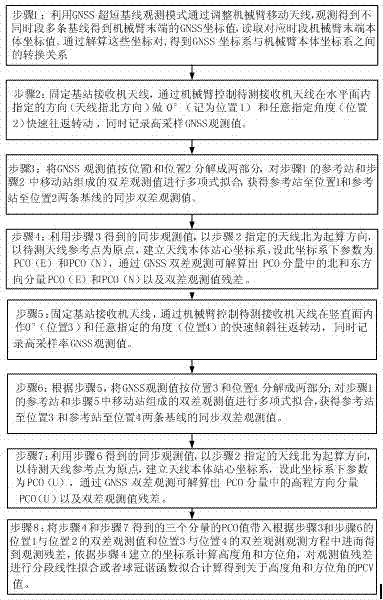
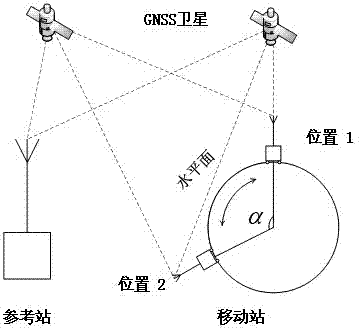
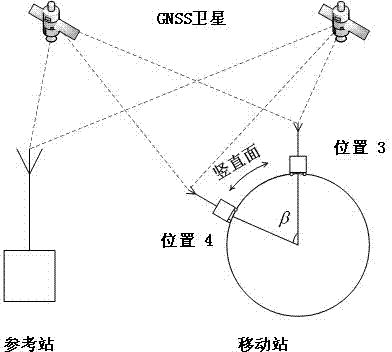
Correction method for absolute antenna phase center of outdoor GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver based on precision mechanical arm
ActiveCN104502926AImprove calibration accuracyRealize CalibrationSatellite radio beaconingObservational errorNavigation system
The invention belongs to the fields of antenna measuring technique and satellite navigation and positioning, and relates to a correction method for the absolute antenna phase center of an outdoor GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) receiver based on a precision mechanical arm. In view of the problem that conventional outdoor GNSS observation cannot obtain a high-precision correction model for the absolute antenna phase center of a receiver, a majority of common errors are eliminated through ultra-short baseline observation, the absolute phase center offset (PCO) of a receiver antenna and the separation of phase center variation (PCV) are realized through rapid rotation and inclination of the high-precision mechanical arm, finally the PCO is resolved through a least squares algorithm, and fitting calculation of the PCV is carried out for observation residual. According to the correction method, outdoor operation can be carried out, the correction precision of 1mm for the PCO and PCV can be reached, the correction method is suitable for accurate calibration of the PCO and PCV of the receiver capable of tracking the signals of satellite navigation systems such as a GPS (Global Positioning System), a BDS (Beidou Navigation System), a GLONASS (Global Navigation Satellite System) and Galileo, and thus the systematic measuring error caused by imprecision of the PCO and PCV of the receiver can be eliminated, and the user positioning precision is further improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Rotating disc type candy feeding device
The invention discloses a rotating disc type candy feeding device. The rotating disc type candy feeding device comprises a conical disc, a spiral groove, a fur brush and a conveying belt, wherein the spiral groove is formed in the outer edge of the disc surface of the conical disc, the spiral groove is linked with the disc surface of the conical disc and gradually spreads outwards, a drive motor is arranged on a cone portion of the conical disc, a rotation mechanism where the fur brush can be installed is arranged on the disc surface of the conical disc, the rotation mechanism is driven by the drive mechanism, the rotation direction of the rotation mechanism is opposite to the rotation direction of the conical disc driven by the drive motor, the conveying belt is arranged at the bottom of the spiral groove, and the conveying belt is communicated with the outermost layer of the spiral groove. The rotating disc type candy feeding device is simple in structure. Due to rapid rotation of the conical disc, messy candies are scattered along the conical disc under functions of centrifugal force, and slide into the spiral groove, and then are driven by the rotating conical disc to move in spiral mode. Furthermore, the stacked candies can be separated by the fur brush which reversely rotates, and the candies after being tidies fall onto the conveying belt, and then are conveyed by the conveying belt.
Owner:CHANGZHOU GAUSS PRECISION TOOLS
Indexing rotatable chuck for a probe station
InactiveUS20050127927A1Shorten shaft lengthGood planaritySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProduction rateRapid rotation
A rotary chuck with indexed rotation promotes rapid rotation of a device under test and increases the productivity of a probe station on which the device is being tested. A device mounting member of a rotatable chuck is supported for rotation on a first surface of a base until a vacuum is applied drawing the device mounting member into contact with a second surface of the base and constraining the device mounting member against rotation.
Owner:CASCADE MICROTECH
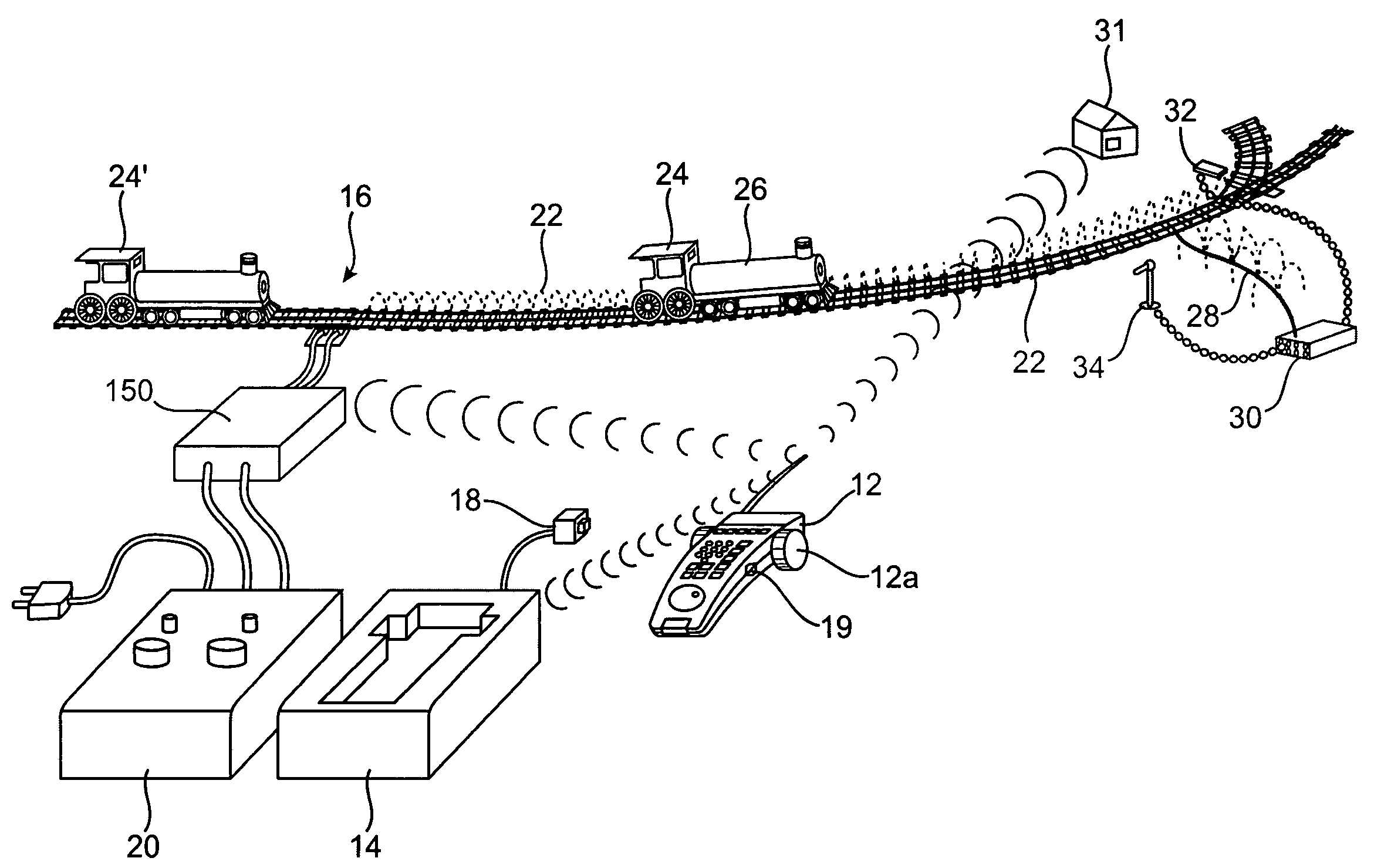
Model railroad velocity controller
ActiveUS7312590B1Fast spinShort elapsed timeDC motor speed/torque controlEmergency protective circuit arrangementsAngular distanceEngineering
Control over velocity of a model train may be determined based upon the speed of rotation of a control knob. A processor receives electronic pulses indicating rotation of the knob beyond a predetermined increment of angular distance. The processor calculates the amount of power ultimately conveyed to the model train based not only upon the number of pulses received, but also upon the elapsed time between these pulses. The shorter the elapsed time between pulses, the greater the change in power communicated to the train. Initially, a user can rapidly rotate the knob to attain coarse control over a wide range of velocities, and then rotate the knob more slowly to achieve fine-grained control over the coarse velocity. Utilizing the control scheme in accordance with embodiments of the present invention, in a compact and uninterrupted physical motion, a user can rapidly exercise both coarse and fine control over velocity of a model train.
Owner:WACHOVIA BANK N A ADMINISTRATIVE AGENT
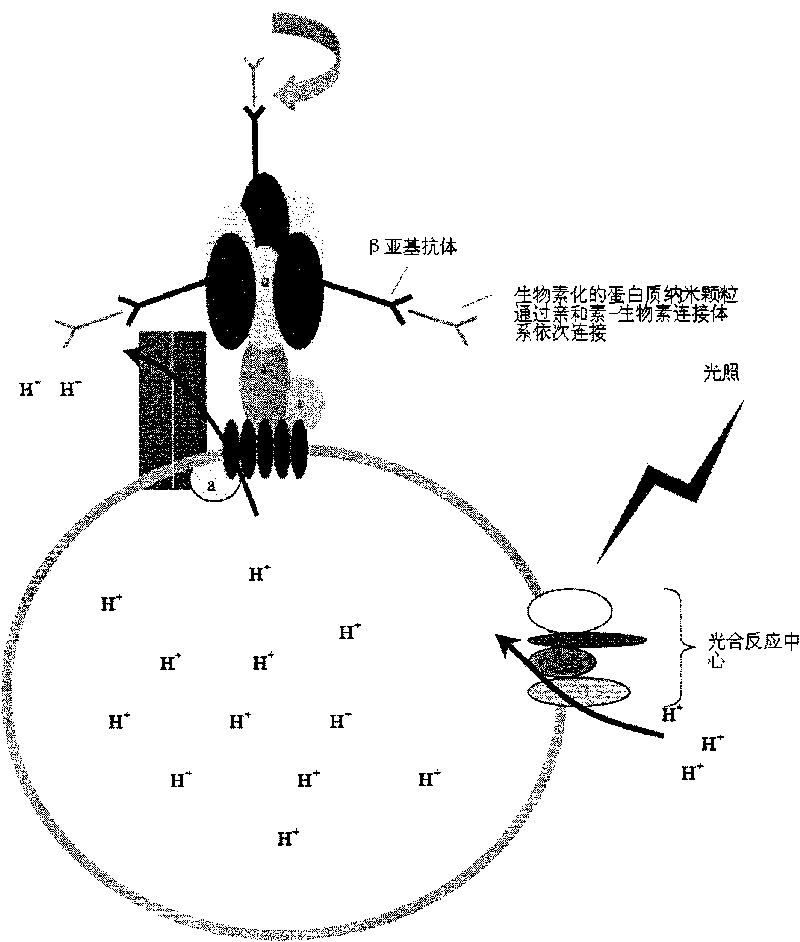
Nanometer biological robot and application thereof
InactiveCN101744645AIncrease vitalityCapable of targetingSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMolecular motorThrombus
The present invention relates to a nanometer biological robot. The nanometer robot is driven by molecular motors and guided by thrombus antibodies to assist in quickly dissolving thrombi. The rapid rotation of the molecular motors on partial thrombi produces the effect similar to that of a micro power agitator. The molecular motors are driven by light, so the nanometer biological robot is adjustable and controllable. The contact of drugs with fiber proteins is accelerated, the biological and machinery mechanics effect of the nanometer biological robot is synergetic with the medical enzymolysis, and the fibrinolysis is accelerated.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES +1
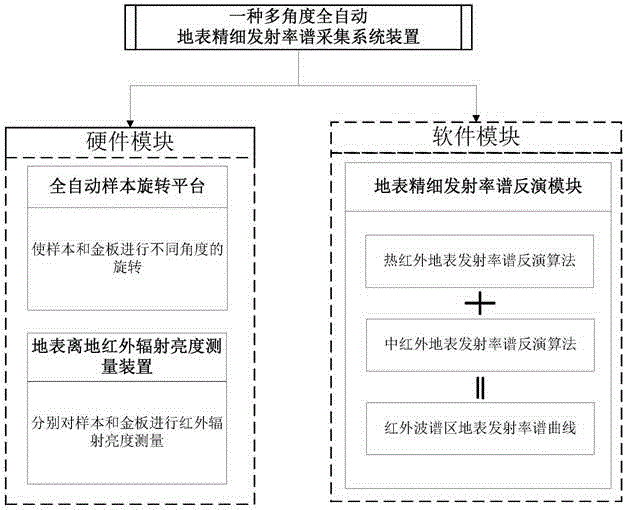
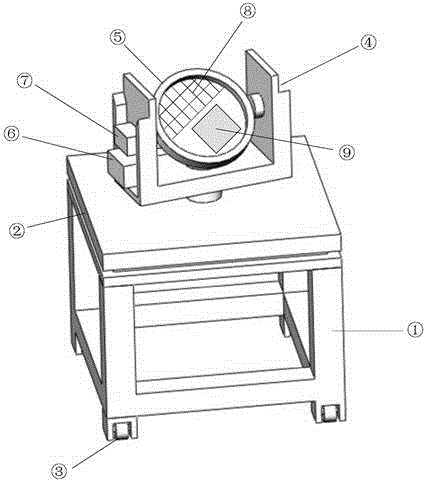
Multi-angle full-automatic earth surface fine emissivity spectrum collecting system device
InactiveCN104155007AResolve inconsistenciesQuick spin toggleEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryMeasurement deviceEarth surface
A multi-angle full-automatic earth surface fine emissivity spectrum collecting system device is composed of a full-automatic sample rotary platform, an earth surface off-ground infrared radiance measurement device and an earth surface fine emissivity spectrum inversion module. The full-automatic sample rotary platform realizes rapid rotation through an electric rotary platform carried on a movable tabletop, and can remotely control the rotary platform to be switched between a sample and a metal plate in a rotary mode according to a set rotation angle and pace; the earth surface off-ground infrared radiance measurement device mainly adopts a Fourier transform infrared wavelength dispersive spectrometer for observation and measurement and collects and stores off-ground radiance data of the sample and the metal plate within the wave length range of 3-16 micrometers with the cooperation of the full-automatic sample rotary platform; the obtained off-ground infrared radiance data are input to the built earth surface fine emissivity spectrum inversion module, and an emissivity spectral line of the sample within the wave length range of 3-16 micrometers is obtained.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
Dual-Function Skin Cleansing Apparatus
InactiveUS20160120375A1Effectively aid in removalSkin stimulationCarpet cleanersBrush bodiesEngineeringDual function
Embodiments of the present invention relate a dual function cleansing apparatus. Specifically, the present invention relates to embodiments of a facial cleansing apparatus having one or more brushes that may have a rapid rotation or an oscillation. More specifically, embodiments of the present invention include a facial cleansing device having a rotating brush and an oscillating brush. In a preferred embodiment, the rotating brush has a rotating motion, and the oscillating brush has an oscillating motion that is driven by a single motor.
Owner:EPICARE
Novel optical fiber coiling device of laser device
InactiveCN107814261APrevent winding breakagePlay a role of buffer protectionFilament handlingActive medium shape and constructionAdhesive discCoupling
The invention discloses a novel optical fiber coiling device of a laser device. The optical fiber coiling device includes a coiling motor, a supporting frame, a fixing plate, a base, an adjustable conveying plate structure, a rapid rotation seat structure, a rapid disassembly optical fiber coiling wheel structure, a connecting shaft, a coupling, a buffering rubber roller, a fixing shaft, a connecting sleeving, a baffle ring and a main switch. According to the novel optical fiber coiling device of the laser device, through the arrangement of the buffering rubber roller, the fixing shaft, the connecting sleeving and the baffle ring, the problem that the optical fiber is too hard resulting in the fact that coiling is broken in the coiling process can be prevented, and the effect of cushion protection can be achieved. Through the arrangement of a conveying connection bolt and nut and a fixing adhesive disc, safe fixation is convenient to conduct in the conveying process, and stability andreliability in the conveying process are ensured; and through the arrangement of a conveying fixing steel plate and a damping spring, the effect of cushion protection can be achieved and the problem that violent waggle appeared in the conveying or coiling process affects the work of conveying or coiling is prevented.
Owner:张家港初恒激光科技有限公司
Variable velocity sprinkler transmission
A sprinkler having a water-driven drive mechanism or motor for rotating a sprinkler head is disclosed where the drive mechanism converts a constant input rate into a variable rate to reduce tailing from overly-rapid rotation and to promote full develop of water stream discharge profile. The drive mechanism includes continuously engaged members including one or more planet gears each having an offset or eccentrically positioned engagement portion for driving a second gear member. As the planet gear rotates, the movement of the engagement portion has a radial component relative to the second gear, and the rotational velocity of the second gear is related to the radial position of the engagement portion.
Owner:RAIN BIRD CORP
False twister main shaft grinding device convenient to use
InactiveCN107877275AEasy to useEasy to operateRevolution surface grinding machinesDrive wheelElectric machine
The invention relates to the technical field of textile processing, and discloses an easy-to-use false twister spindle grinding device, which includes a machine body, a receiving box is placed on the inner bottom wall of the machine body, and an electric pusher is fixedly connected to one side of the middle part of the inner wall of the machine body. The outer surface of the push rod on the electric push rod is fixedly sleeved with a fourth bearing, and the other side of the middle part of the inner wall of the body is fixedly connected with the first motor, and one side of the fourth bearing is connected to the first motor. The output shafts are all fixedly connected with clamping pipes. In the present invention, the driving wheel is rotated through the working rotation of the third motor, and the driving wheel drives the driven wheel to rotate through the belt. One side of the driven wheel is fixedly connected with a rotating shaft, and the outer surface of the rotating shaft is fixedly sleeved with a grinding roller, so that the The grinding roller rotates quickly to grind the outer surface of the main shaft of the false twister. The grinding device is easy to operate, saves time and effort, and improves the working efficiency of grinding.
Owner:绍兴瑞豪机械有限公司
SLAM system based on multi-view panoramic inertia navigation
PendingCN108846867ALarge field of viewSolve the problem of limited field of viewImage analysisGeometric image transformationRobot environmentSimulation
The invention discloses a SLAM system based on multi-view panoramic inertia navigation. A 360 panoramic vision model is constructed, the high-precision vision SLAM and space movement tracking are realized through lightweight-level embedded parallel computation by combining the inertia navigation to closely couple and fuse with the vision feature, the problem that the environment sending method isinsufficient in information acquisition and uncertain in fast rotation in the prior art is solved, and an effective automatic measure is provided for robot environment modeling and positioning navigation in strong light / weak texture / movement fuzzy and like complex environments. The system precision and robustness are improved, the sufficiency of the autonomous navigation of the robot is guaranteed, and the lightweight and the device can be realized through the design way of the embedded system.
Owner:安徽云能天智能科技有限责任公司
Emulsification stirring apparatus
InactiveCN104001442AQuick responseStir the reaction to mix wellRotary stirring mixersMixing methodsDrive shaftWater flow
A disclosed emulsification stirring apparatus comprises a reaction container, a high-shear emulsification motor and a stirring shaft, the stirring shaft is arranged in the reaction container, the lower end of the stirring shaft is fixedly provided with a rotation stator, the stirring shaft is connected with a driving shaft of the high-shear emulsification motor, the reaction container also is provided with a stirring frame, the upper end part of the stirring frame is in the shape of a cylinder, the periphery of the cylinder is provided with a gear ring, the gear ring is connected with rotation gears in an engage manner, the rotation gears are fixedly installed on a transverse motor, the upper end part of the stirring frame consists of three stirring ribs spirally distributed in the shape of a triangle, and a fixed cover is arranged outside of the rotation stator. The emulsification stirring apparatus solves the problem of insufficiently uniform stirring of conventional stirrers, and is compact and reasonable in designed structure. A double stirring shaft structure is employed, a small stirrer with relatively rapid rotation speed is arranged at the bottom of the reaction container, the stirring frame is arranged above the small stirrer, and the upper end part of the stirring frame is formed by the three stirring ribs, so that water flow is formed and makes vertical motion, sufficient mixing and rapidly reaction speed are realized during a stirring reaction.
Owner:浙江永隆科技有限公司
Rapid-switching high-frequency waveguide switch
ActiveCN103066757AEliminate positioning vibrationSufficient static locking torqueSynchronous machinesStructural associationMicrowaveMetallic materials
A rapid-switching high-frequency waveguide switch comprises an electric coupler (1), a motor assembly (2), a shell body (3) and a guided assembly (4). The electric coupler (1) and the motor assembly (2) are fixed above the shell body (3), and the shell body (3) is buckled and connected on the guided assembly (4). The guided assembly (4) achieves switching of two radio frequency passages through two arch-shaped passage holes. The motor assembly (2) is used as a drive system, achieves rapid rotation of a guided rotor, produces location locking torque, and achieves movement precise control and movement location of ninety-degree-angle movement. The rapid-switching high-frequency waveguide switch has the advantages of being simple and reliable in structure, low in difficulty of processing and assembling, free from introducing extra non-metallic material, capable of achieving rapid switch of a switch on the premise of guaranteeing the microwave performance of the switch.
Owner:CHINA AEROSPACE TIMES ELECTRONICS +1
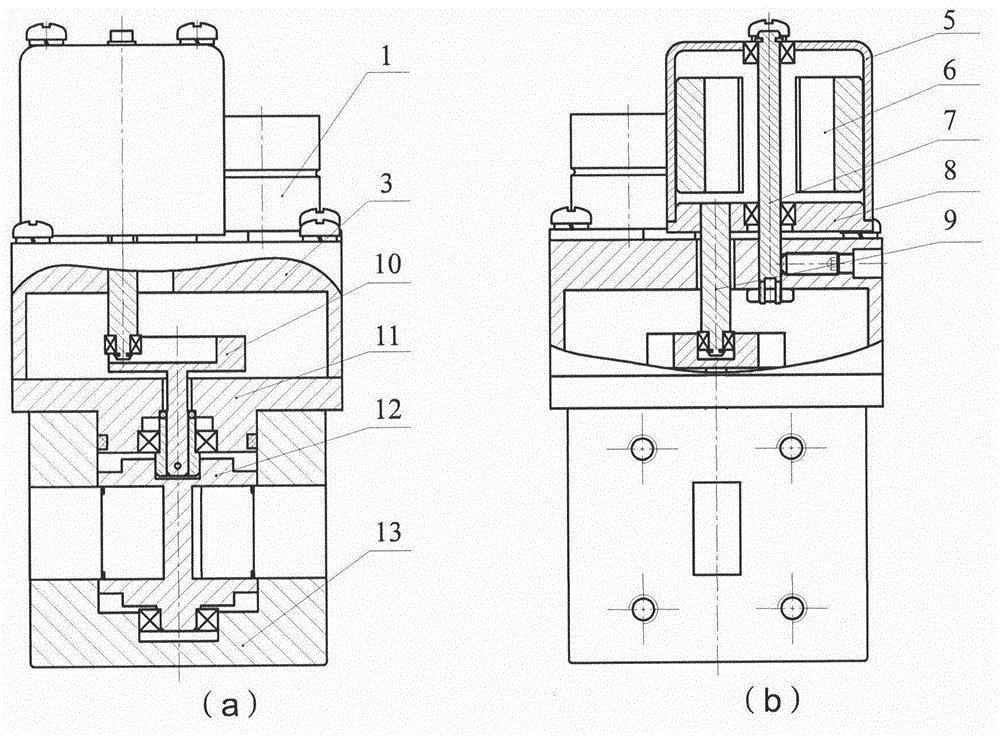
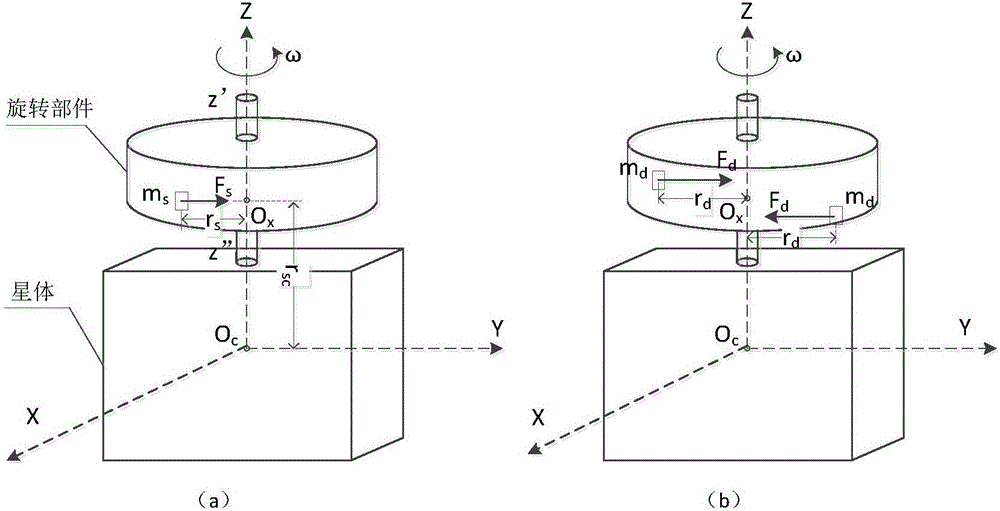
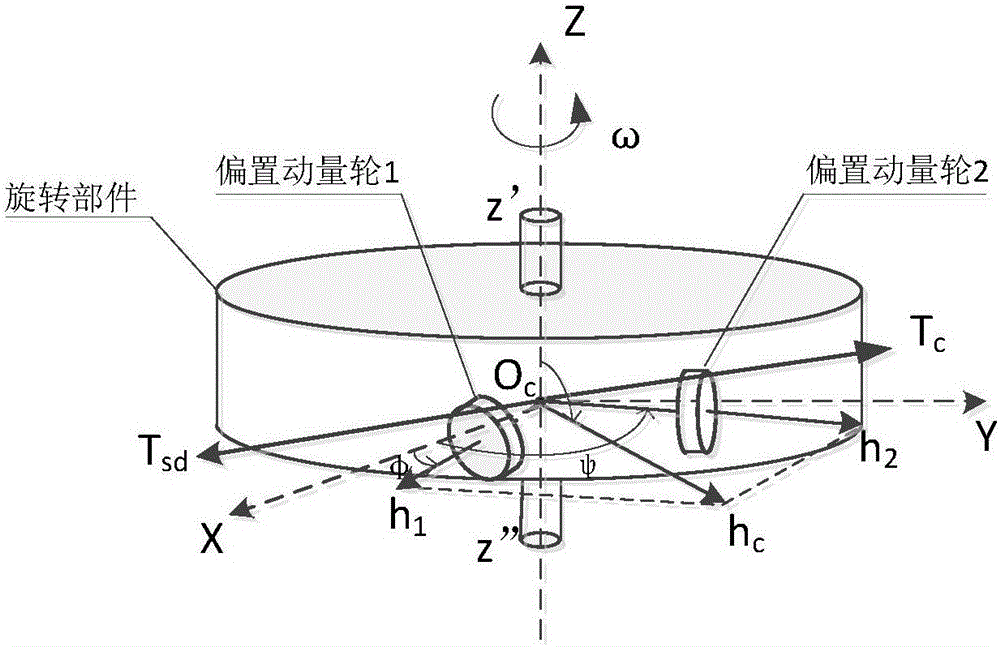
Self-compensating method for dynamic and still unbalancing disturbance moment of satellite rotating part
InactiveCN106586034ASimplify the development processEasy to implementCosmonautic vehiclesSpacecraft guiding apparatusMomentumCalibration result
The invention discloses a self-compensating method for a dynamic and still unbalancing disturbance moment of a satellite rotating part. The dynamic and still unbalancing disturbance moment produced by quick rotating of the rotating part on a satellite can influence the stability of the satellite and reduce the control precision of the satellite. A traditional method for eliminating a dynamic and still unbalancing disturbance moment of a rotating part comprises the steps that the rotating part is subjected to dynamic balancing, and then, active control over dynamic and still unbalancing disturbance is conducted through a satellite attitude control system. The traditional method has limitation to application of rotating parts which are large in inertia, high in rotating speed and irregular in shape. According to the self-compensating method for the dynamic and still unbalancing disturbance moment of the satellite rotating part, two small bias momentum wheels are arranged on the rotating part of the satellite, and the rotating speed of the two bias momentum wheels is set according to the on-orbit calibration result of dynamic and still unbalancing disturbance so that the dynamic and still unbalancing disturbance moment produced during rotating of the rotating part can be eliminated. The self-compensating method is simple, obvious in effect and low in cost, and engineer achieving can be facilitated.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENG CENT FOR MICROSATELLITES
Terahertz wave rapid rotation scanning imaging system and method
InactiveCN105607140AImproving imaging timeImprove imaging effectGeological detection using milimetre wavesOptical detectionRotary stageSynchronous control
The invention provides a terahertz wave rapid rotation scanning imaging system and method, and the system comprises a terahertz quantum cascading laser, an objective table, a transmission gathering optical path system, a terahertz quantum well detector, a signal collection processing module, a synchronous control module, and an image display module. The system employ the terahertz quantum cascading laser as the radiation source, employs the photoconduction-type terahertz quantum well detector as the detector, employs the self-designed rotating table and translation platform, a signal transmission gathering optical path and a signal collection processing module, completes the terahertz wave rapid rotation scanning imaging, and remarkably improve the imaging duration and effect. The system and method achieves the actual application of the technology of terahertz wave rapid rotation scanning imaging, successfully improves the imaging speed and effect, and is of great significance to the development and popularization of the technology of terahertz wave rapid rotation scanning imaging.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Moss cleaner
The invention belongs to the field of cleaning equipment and discloses a moss cleaner comprising a body and a cleaning unit. The body comprises a drive unit and a control panel; the drive unit in connection with the cleaning unit drives the cleaning unit; the control panel is used for controlling operating states of the drive unit; the cleaning unit rotates to clean moss. The cleaning unit is rotatably connected to a motor. The motor drives the cleaning unit to rotate fast for cleaning, and cleaning speed is high. The motor is mounted on the body to allow convenient holding or convenient position changing for the cleaner. An air jet unit is disposed inside the cleaning unit and capable of blowing away the cleaned moss in time, continual cleaning is facilitated, and cleaning effect is guaranteed. Air inlets are arranged in a ventilation field chamber which is sealed, and air can smoothly enter a connecting shaft while the connecting shaft rotates fast. A screw nut at the tail of the body allows connection of an extension bar, moss at far places such as a pool bottom is convenient to clean, and cleaning effect is guaranteed.
Owner:SUZHOU IND PARK QINGYUAN HUAYAN WATER
Textile yarn drying device
InactiveCN107816862ADry evenlyGuaranteed uniformityDrying gas arrangementsDrying chambers/containersThermal energyCoupling
The invention relates to the technical field of textiles, and discloses a yarn drying device for textiles, which includes a body, the top of the body is fixedly connected with a first fixing frame, and one side of the first fixing frame is fixedly connected with a motor. The output shaft of the motor is fixedly connected with a rotating shaft through a coupling, the middle part of the top of the body is inlaid with a bearing, the bottom of the rotating shaft passes through the bearing and extends to the inside of the body, and the bottom of the rotating shaft is fixedly connected with a mounting block . In this textile yarn drying device, the motor works through the rotating shaft to quickly rotate the placement basket, thereby throwing out the moisture inside the yarn on the yarn hanging rod, and at the same time, the blower can blow out the heat inside the heating chamber, and evenly align the yarn The yarn is heated and dried, thereby ensuring the uniformity of yarn drying, improving the utilization rate of heat energy, reducing the waste of heat, thereby saving production costs, and the drying of spinning yarn is relatively uniform, which improves the quality of the product , thereby improving production efficiency.
Owner:宿迁至诚纺织品股份有限公司
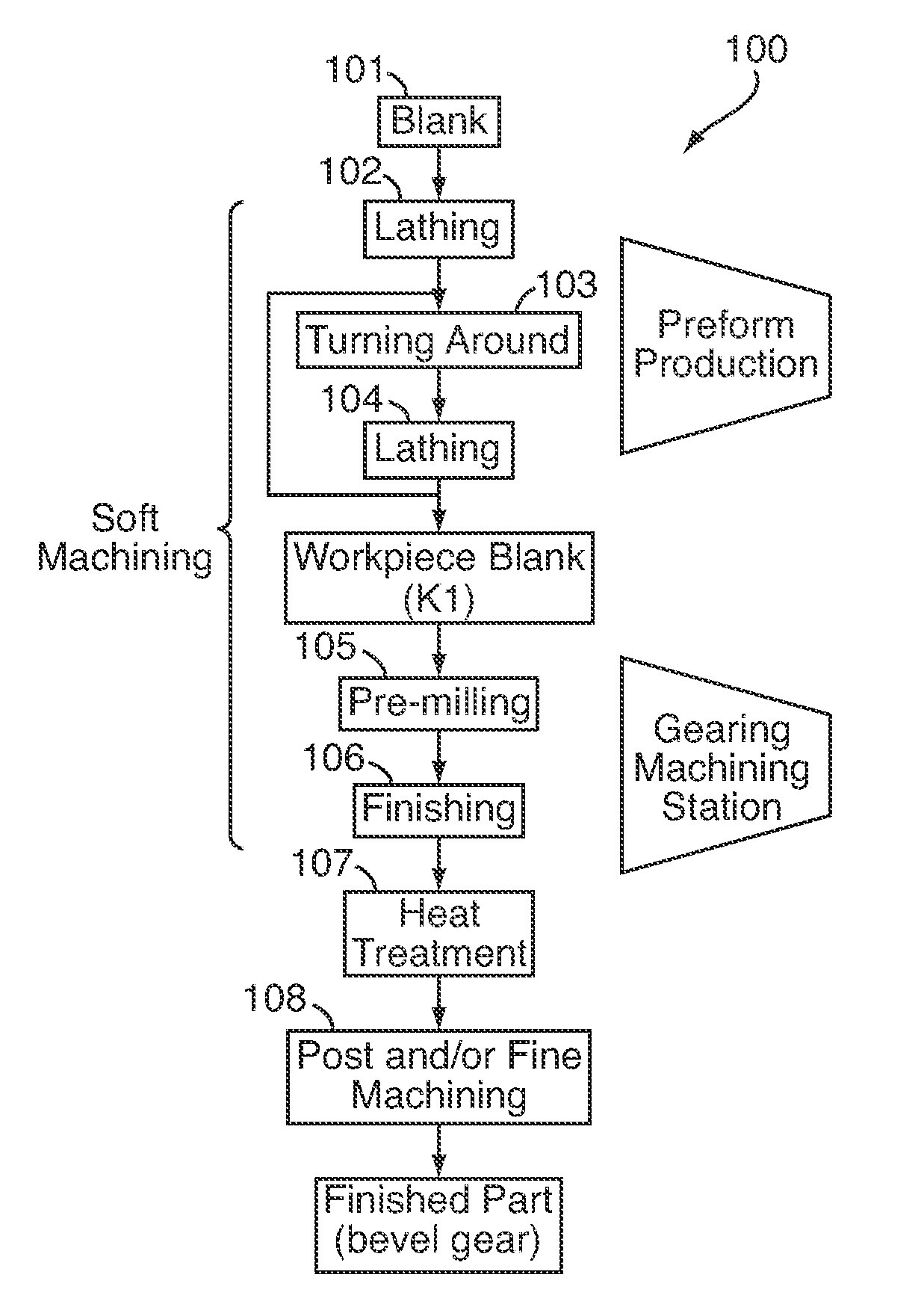
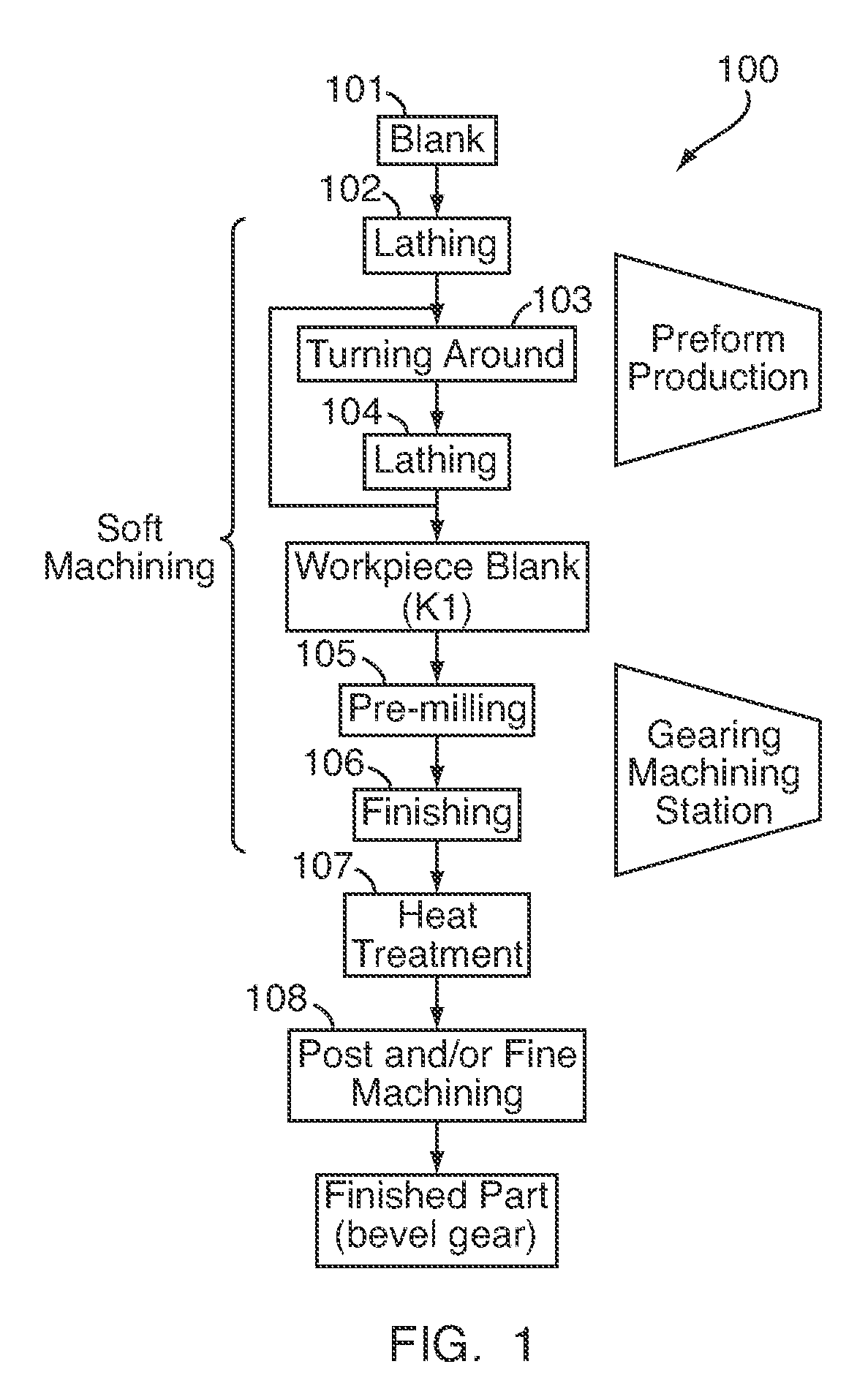
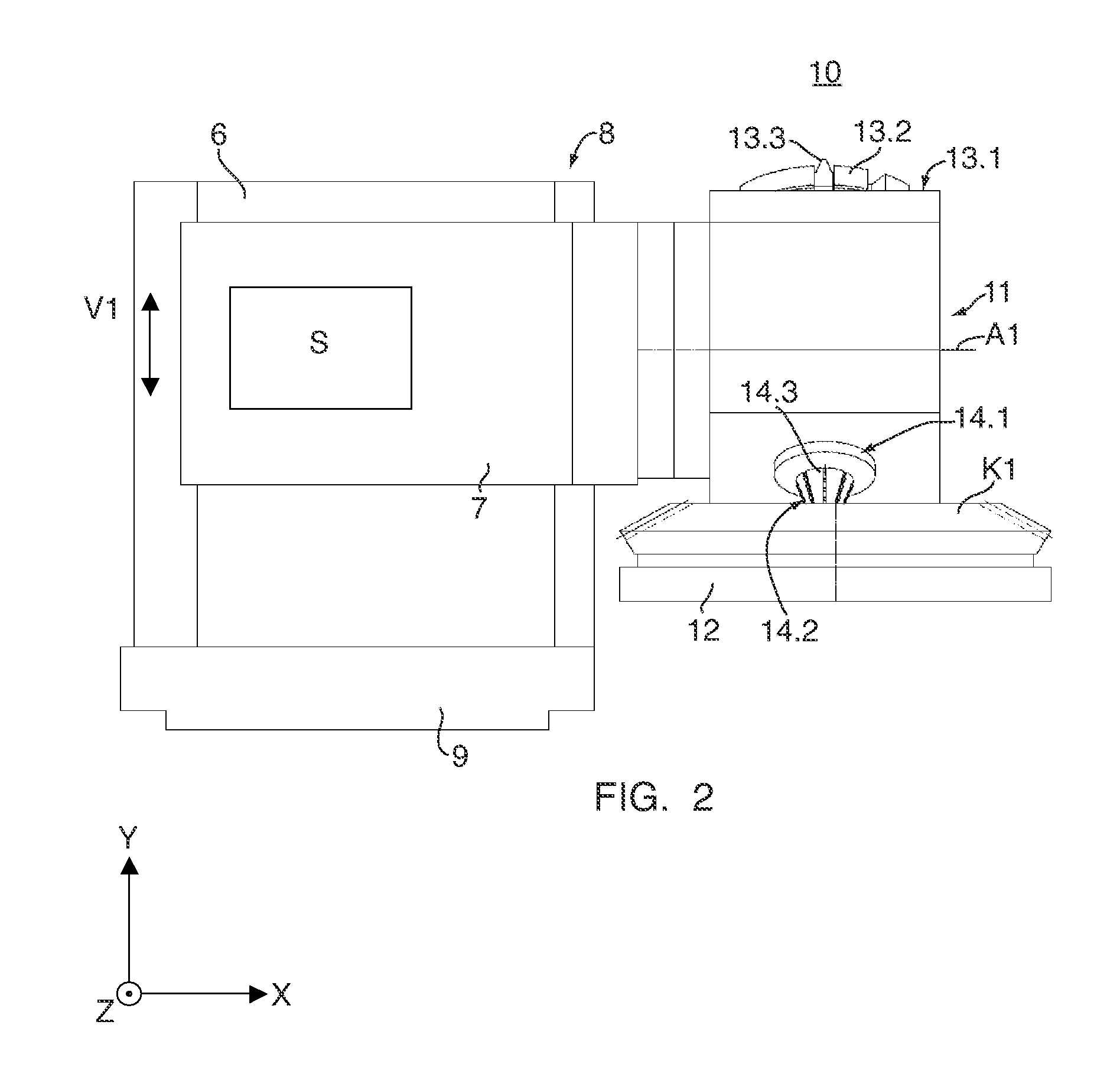
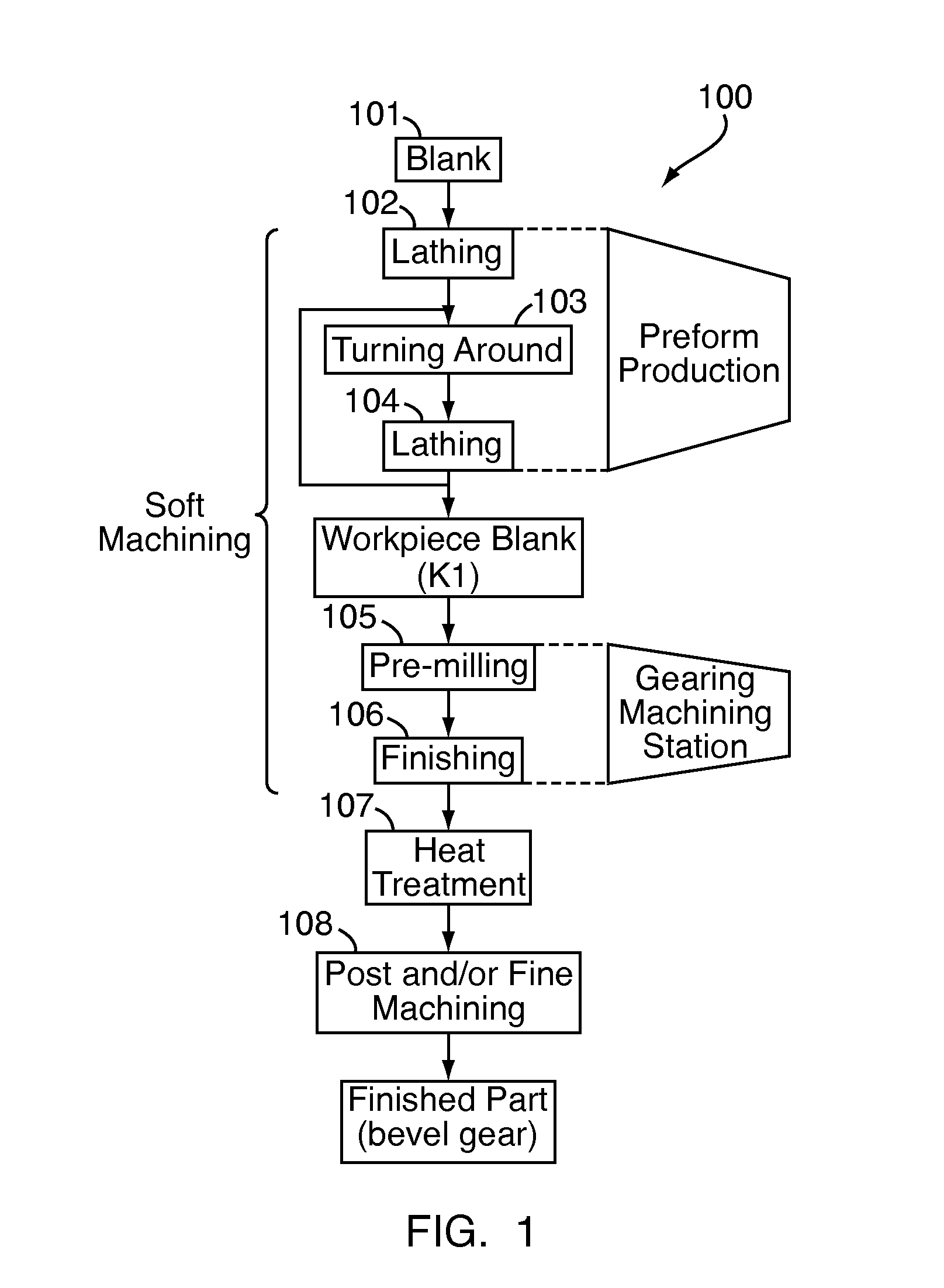
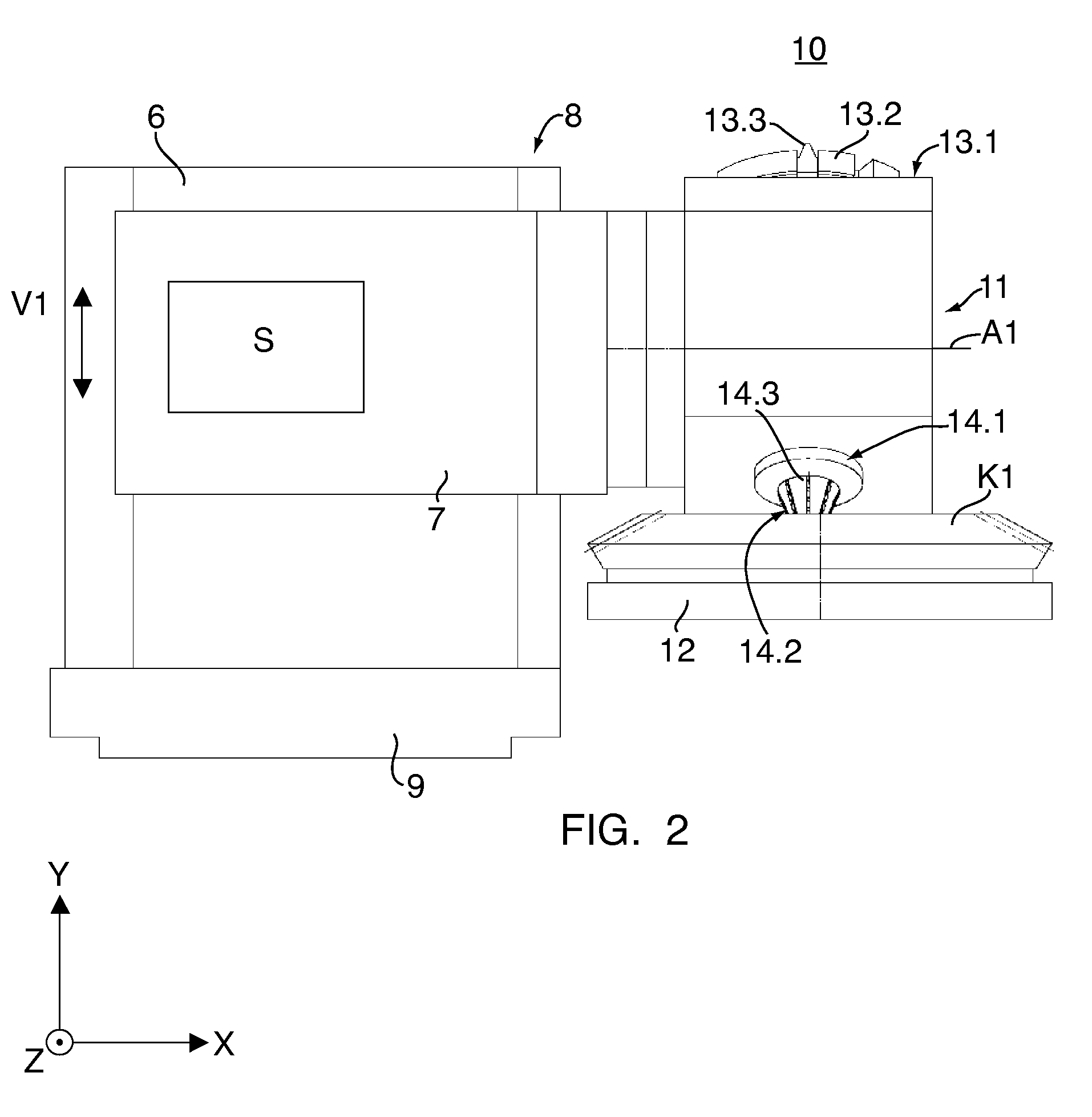
Device and method for soft machining of bevel gears and use of the device
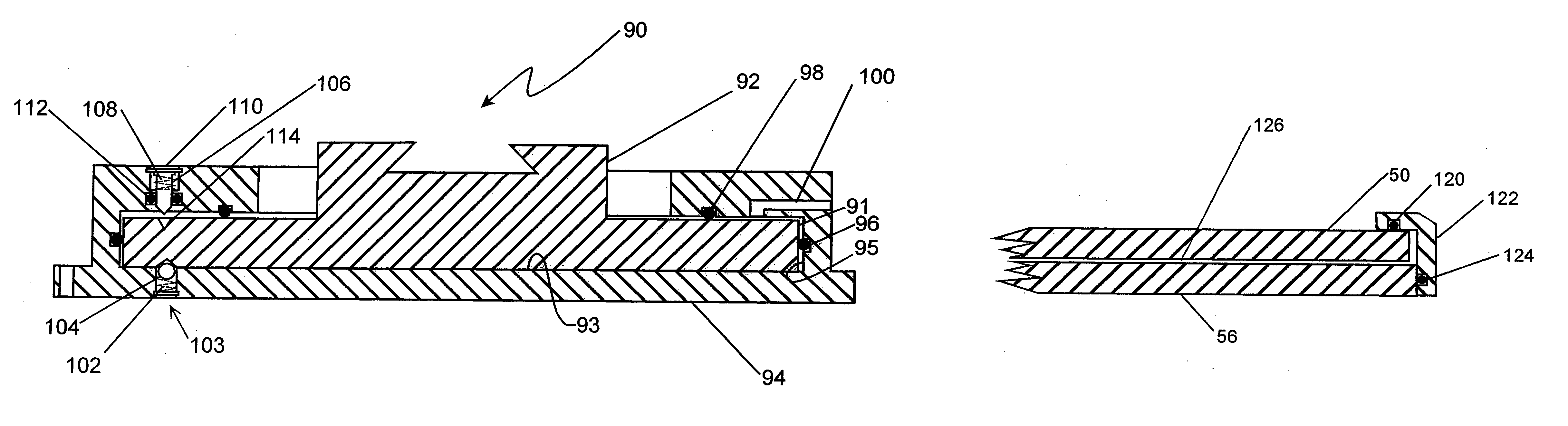
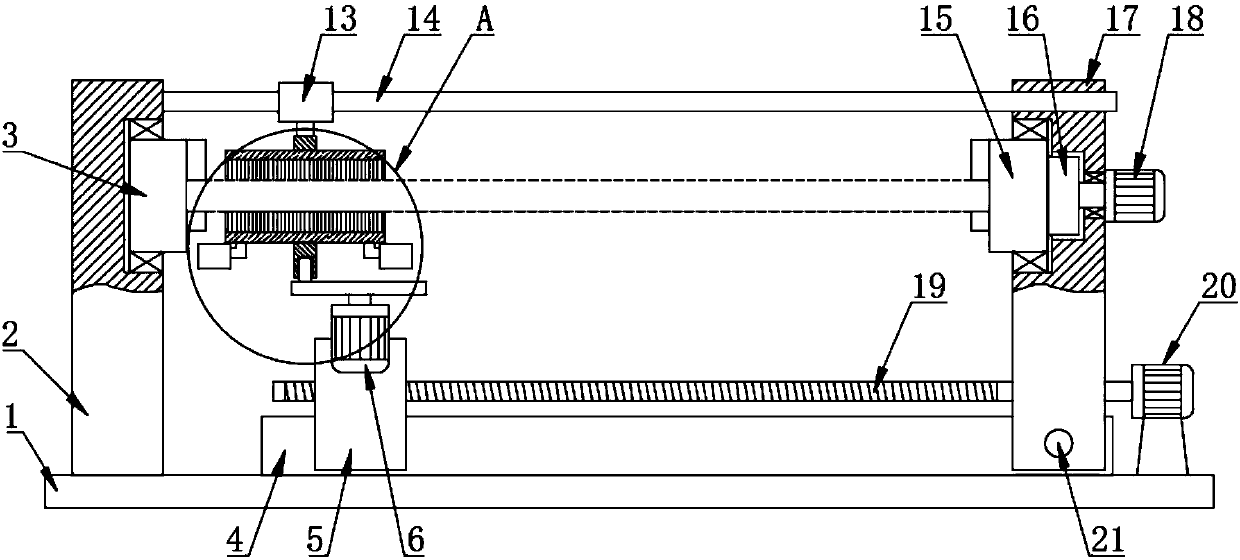
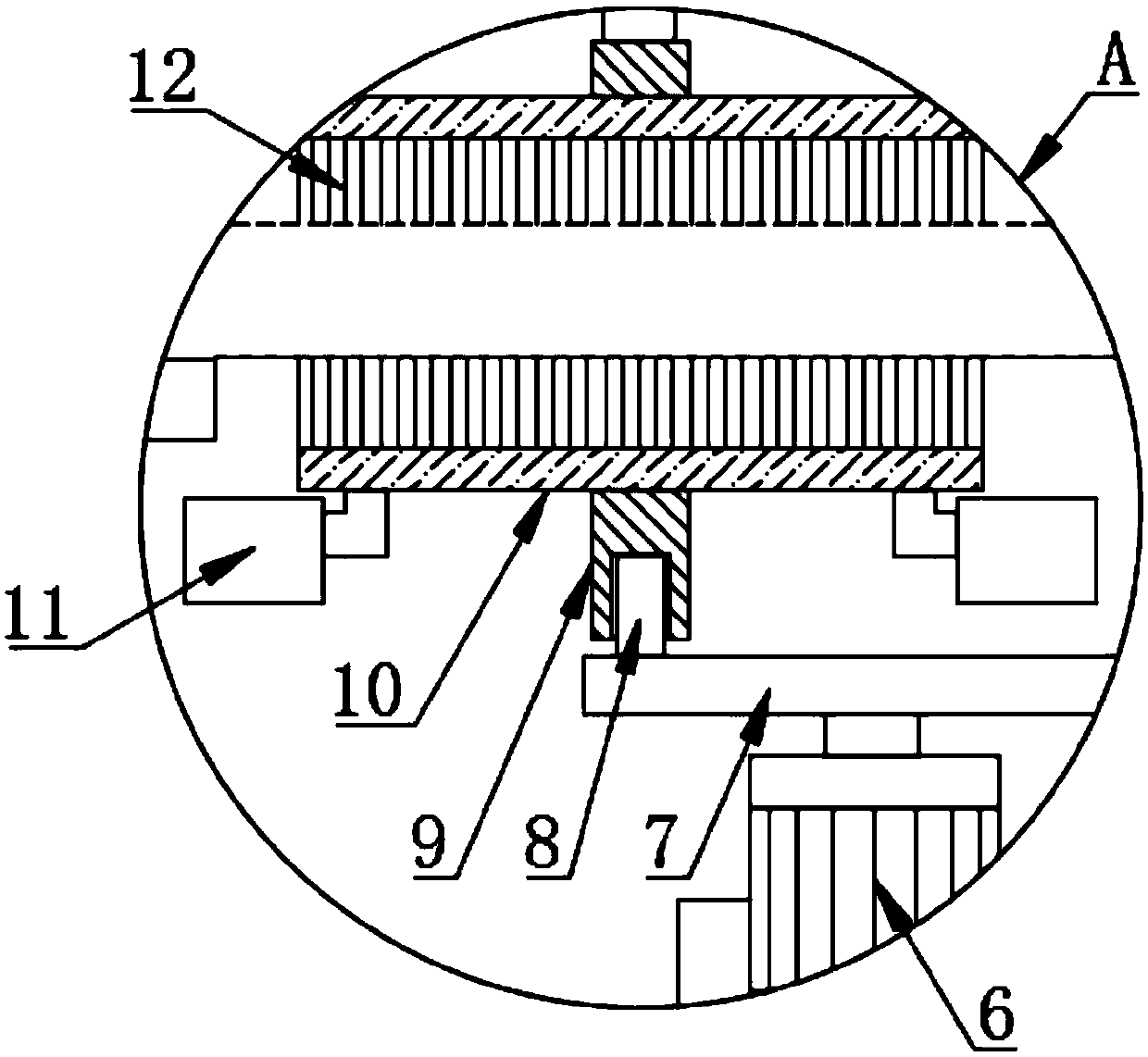
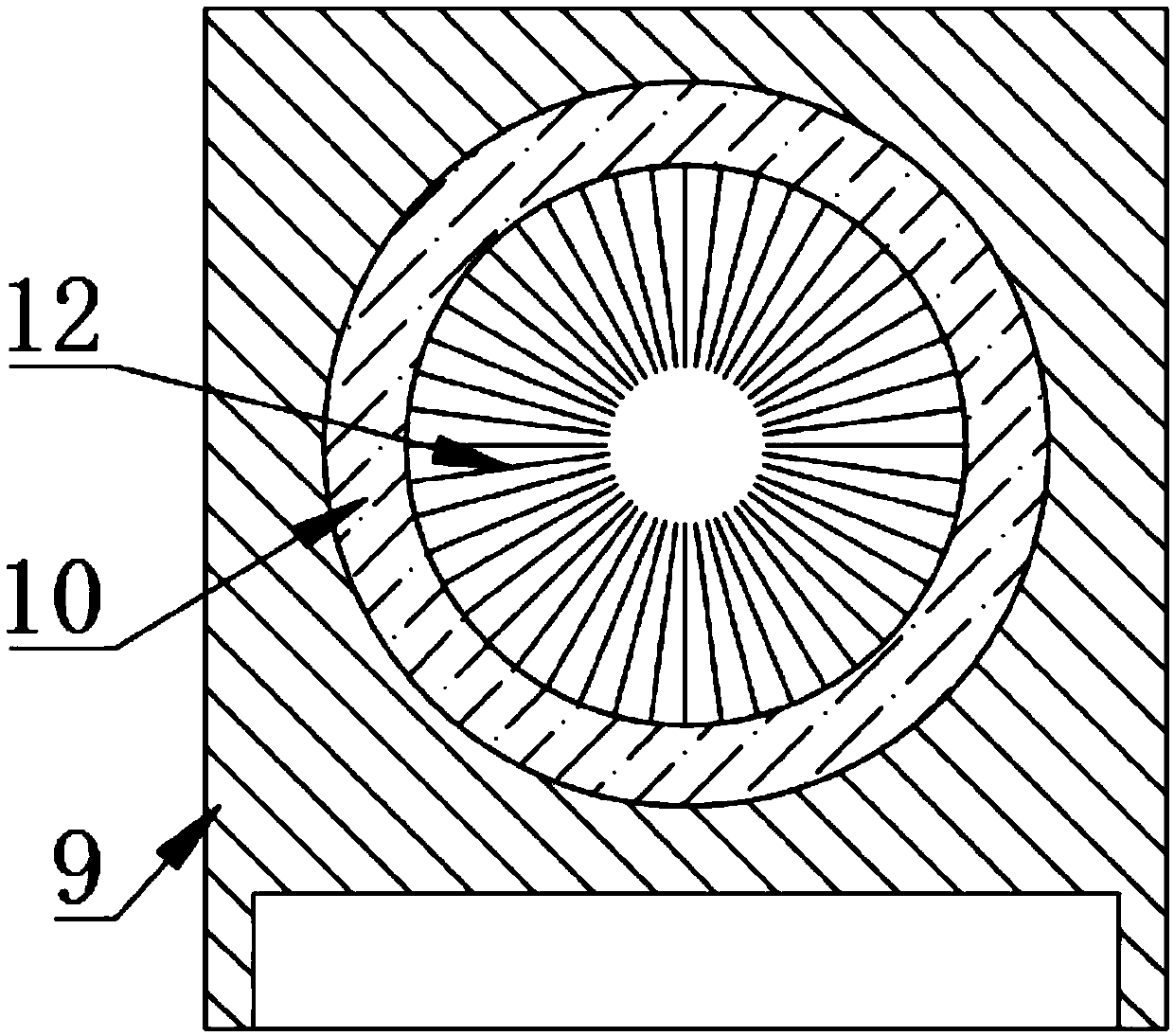
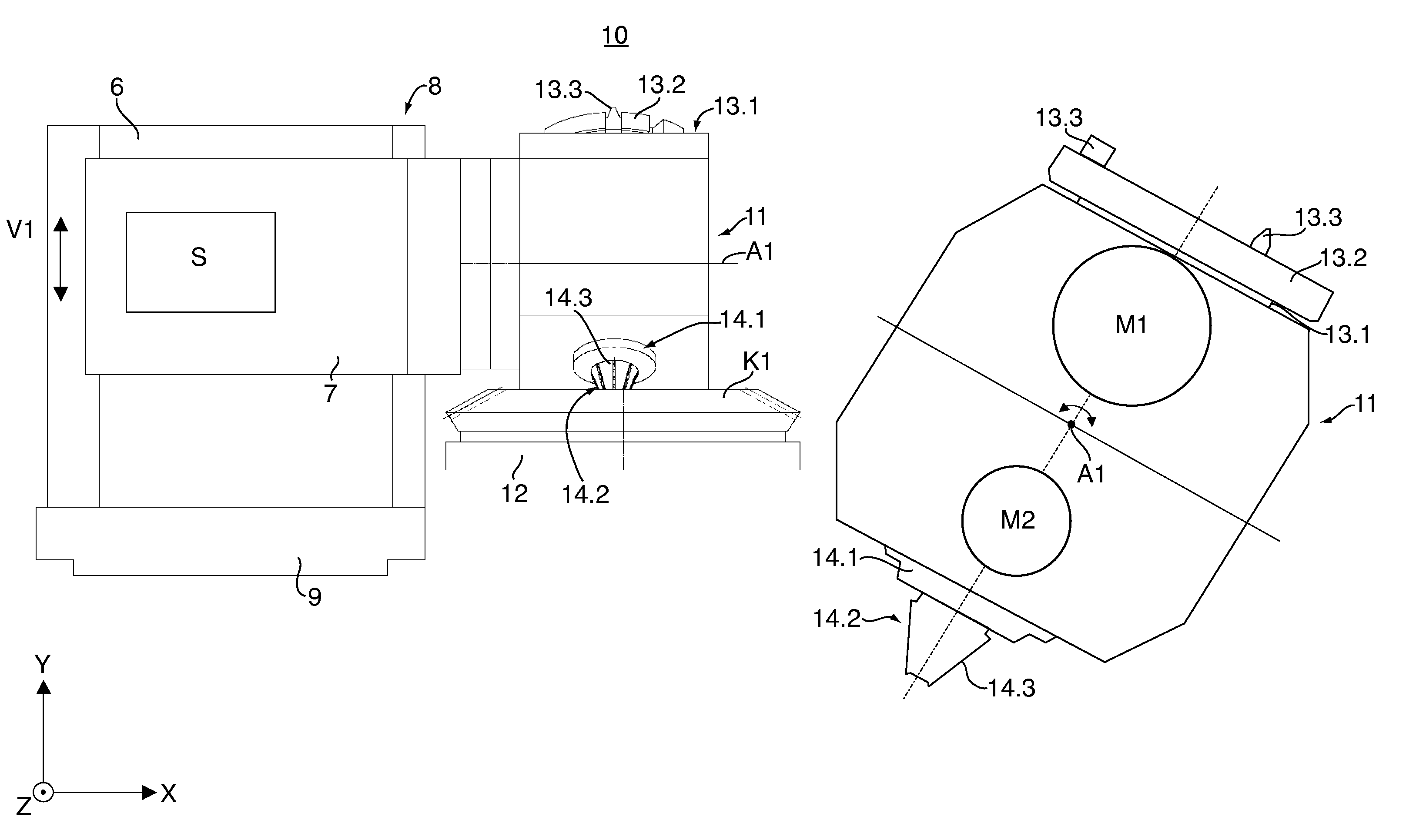
InactiveUS20070283545A1Cost-effectiveAutomatic/semiautomatic turning machinesMilling machinesSlow rotationMachining process
A device (10) for soft machining of bevel gears, having a receptacle (12) for receiving a bevel gear blank (KI) and having a tool spindle (13.1) for receiving a cutter head (13.2). The device comprises a machining arm (11) having a pivot axis (Al) which has the tool spindle (13.1) for receiving the cutter head (13.2) on a first side and has a tool spindle (14.1) for receiving an end-milling cutter (14.2) on a second side. A CNC controller (S) puts the end-milling cutter (14.2) into rapid rotation to cut a predefined number of tooth gaps on the bevel gear blank (K1). After the machining arm (11) is pivoted, the cutter head used as the bevel gear finishing tool (13.2) is used. It is put into slower rotation to machining the bevel gear blank (K1) using the bevel gear finishing tool (13.2) in a post-machining process
Owner:KLINGELNBERG AG
Tire pressure monitoring system without requirement of assembly
The invention relates to a tire pressure monitoring system without requirement of assembly. According to the system, a tire pressure monitoring sensor capable of movement inside the tire comprises a housing, wherein a pressure sensing / sending unit, one or a plurality of batteries, and an antenna for sending a signal of an internal tire pressure instruction are accommodated in the housing. In one embodiment, components are assembled inside the housing, such that the centre of gravity and the geometric center of the housing are the same. During the tire rotation process, a monitor independently rotates inside the tire, and is particularly applicable for the tire with the characteristic of slow rotation, such as a tire used in a gantry system. Optionally the pressure monitoring components are assembled inside the housing, such that the centre of gravity deviates the geometric center of the housing. With the centripetal force generated during the tire rotation process, the monitor and the tire rotate together, and the monitor is applicable for the tire with the characteristic of rapid rotation, such as an automobile tire. The tire pressure monitoring system comprises the monitor and a receiver, wherein the receiver is positioned outside the tire, and is provided for receiving the monitoring signal.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Quenching machine tool capable of preventing bending deformation of slender rod piece during quenching
ActiveCN103589832AFast spinReduce the amount of bending deformationIncreasing energy efficiencyFurnace typesNumerical controlMotor drive
The invention relates to a quenching machine tool capable of preventing bending deformation of a slender rod piece during quenching. The quenching machine tool comprises a tool body, a track, a bracket mechanism and quenching equipment installed on a numerical control sliding table. The bracket mechanism consists of a headstock and a tailstock disposed on the track, and two sets of middle supporting frames. The headstock is provided with a spring clamp head and a drive motor, and the tailstock is provided with a live center and a drive air cylinder. Each middle supporting frame comprises a base, a center frame and three center frame rollers installed on the center frame. The three center frame rollers are arranged in the shape of an isosceles triangle. After loading, the wheel surfaces press against a rod body. Both ends of the rod piece are fixed through the spring clamp head and the live center. The to-be-quenched part of the rod piece is positioned between the two sets of middle supporting frames. The rod body passes through the voids between the three rollers on the center frame. During quenching, the motor drives rapid rotation of the rod piece through the spring clamping head, so that the rod piece can be evenly heated and cooled. And through the action of the three center frame rollers, bending deformation of the rod piece is further restricted, and the quality of the quenching piece is improved.
Owner:ZHENJIANG TIANXIANG PRECISION ELECTRIC MACHINERY
Rotary Fluidized Bed Device and Method for Using Said Device
ActiveUS20090022632A1Increase centrifugal forceEasy to separateFlow mixersChemical/physical/physico-chemical stationary reactorsFluidized bedEngineering
The present invention relates to a device with a rotating fluidized bed in one or a succession of cylindrical chambers, in which injectors (12), distributed around the fixed circular wall (2) of said cylindrical chamber(s), inject along this wall, in successive layers, one or more fluids (13), which entrain the solid particles (17), passing through this / these chamber(s), in a movement of rapid rotation whereof the centrifugal force concentrates these particles along this wall, thereby forming a fluidized bed rotating around a central duct or a plurality of central ducts (3), through which the fluids are removed. The present invention further relates to a method of catalytic polymerization, drying or other treatments of solid particles in suspension in a rotating fluidized bed or of catalytic conversion of fluids passing through said rotating fluidized bed using a device according to the present invention.
Owner:DE BROQUEVILLE
Adjustable round steel rust removing device
InactiveCN107932285AImprove rust removal efficiencyImprove rust removal effectGrinding drivesGrinding machinesEngineeringRapid rotation
The invention discloses an adjustable round steel rust removing device. The adjustable round steel rust removing device comprises a base. A fixing base is fixedly arranged on the left side of the topof the base. A groove is formed in the right end face of the fixing base and internally and rotationally provided with a first three-jaw chuck. A sliding rail is fixedly arranged on the top of the base, and the upper portion of the sliding rail is in sliding connection with a movable base. A step groove in the left end face of the movable base is internally rotationally connected with a second three-jaw chuck. The right end face of the second three-jaw chuck is fixedly connected with a rotation disc. A motor is fixedly arranged on the right end face of the movable base, and the motor is fixedly connected with the rotation disc. A guiding square rod is fixedly connected to the top of the right end face of the fixing base and is in sliding connection with a guiding sleeve. The bottom of theguiding sleeve is fixedly connected with an installing block through a support, and a rust removing barrel is fixedly arranged in the installing block. The adjustable round steel rust removing devicecan conduct rust removal on round steel different in length and diameter, and the application range is wide; and through rapid rotation of the round steel and friction of a rust removal brush in the rust removing barrel, rust can be removed, and the rust removing efficiency is high.
Owner:宁波市江北义盈工贸有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com