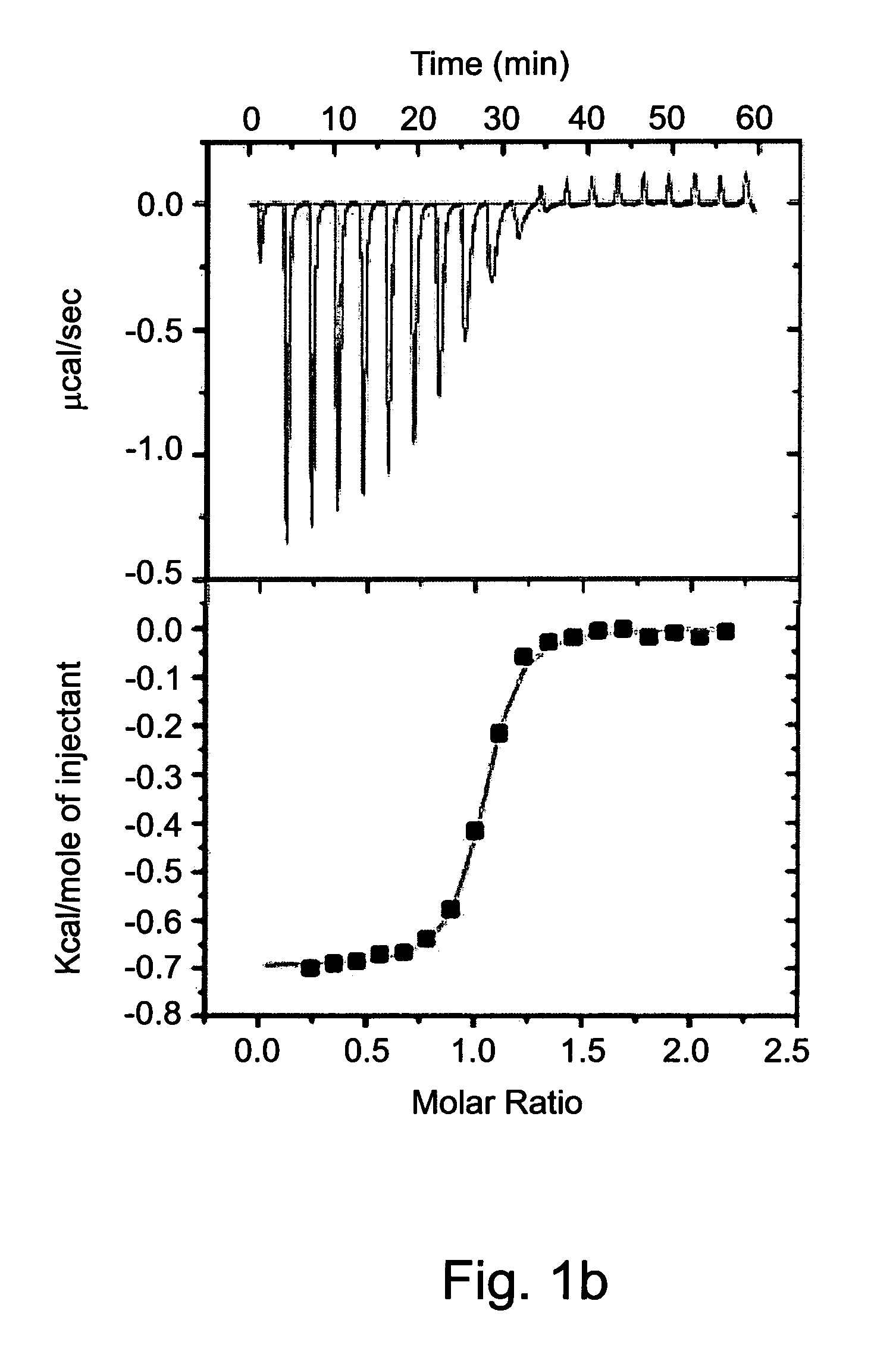
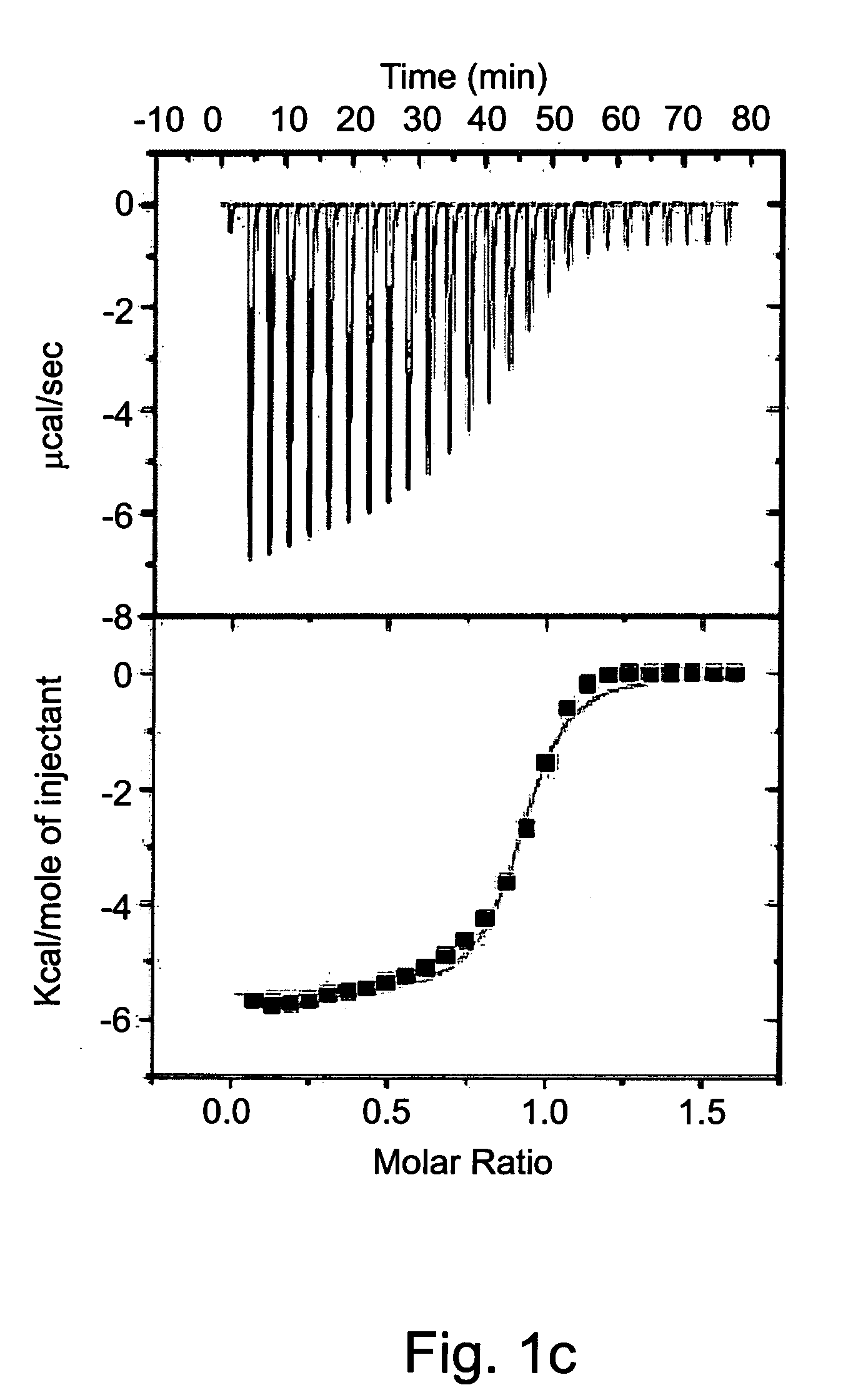
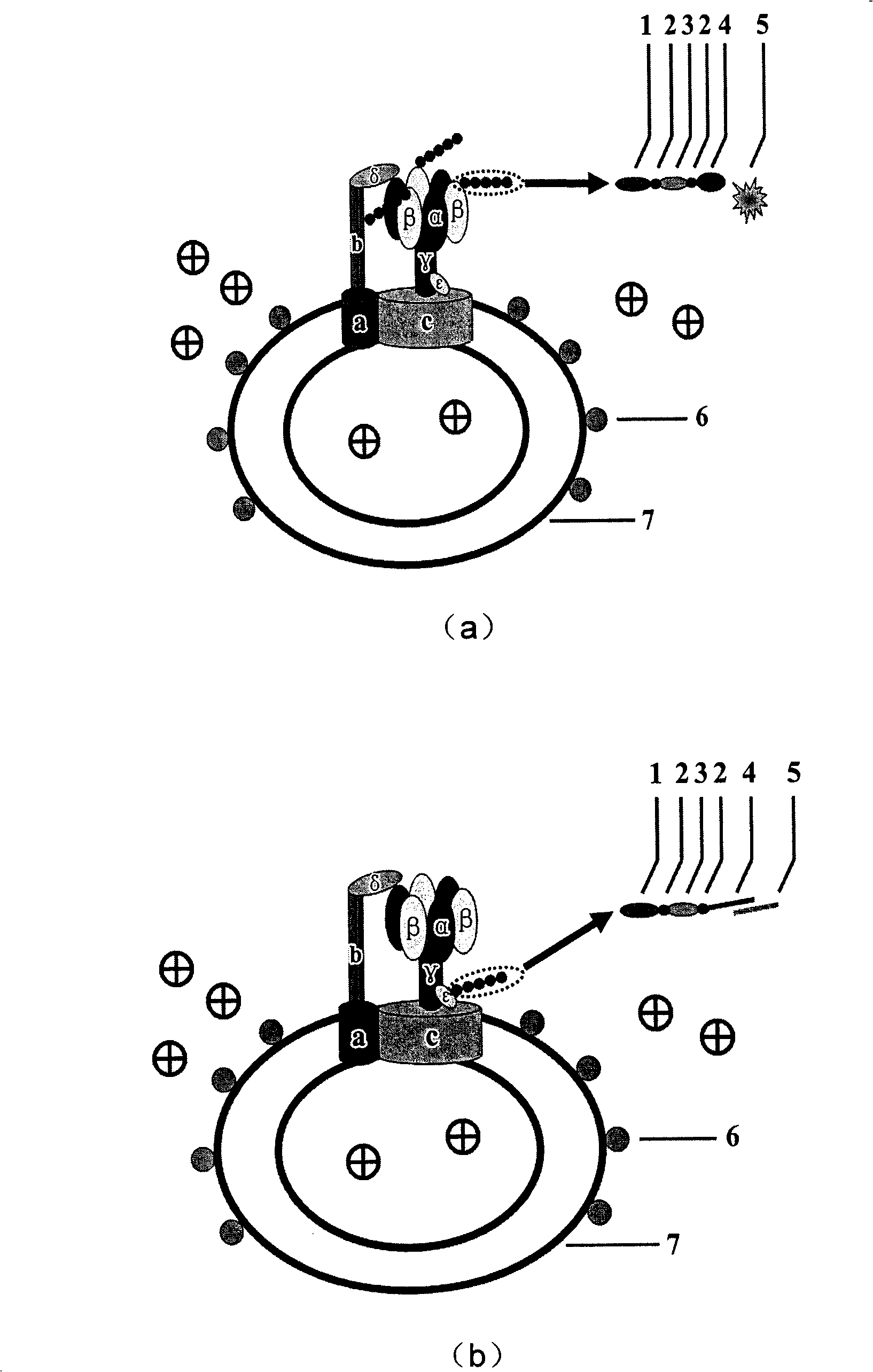
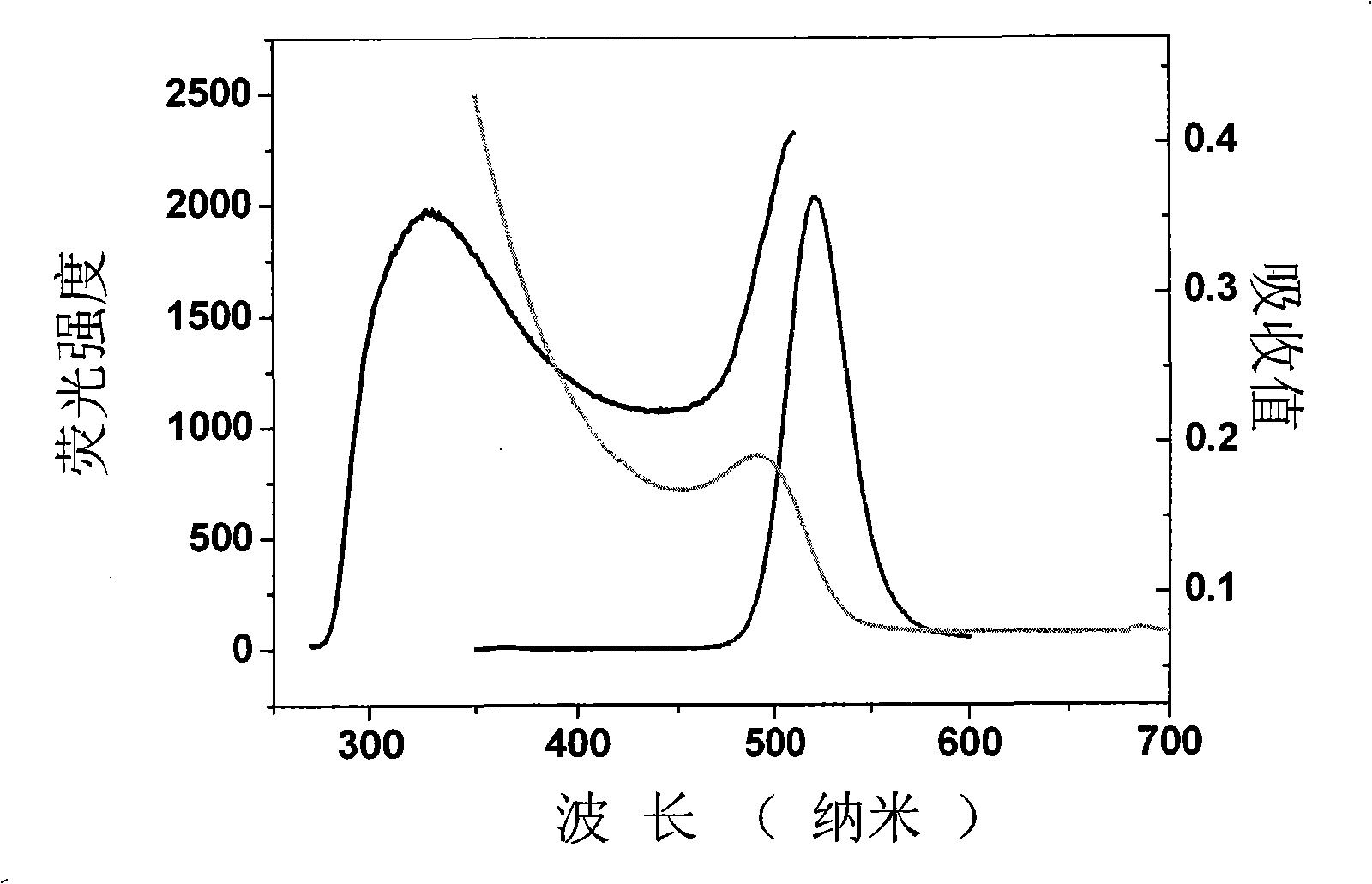
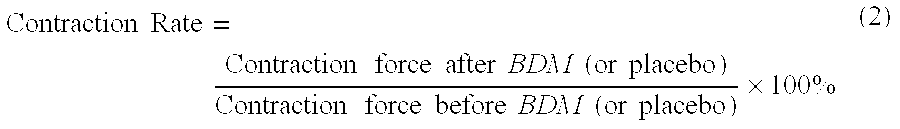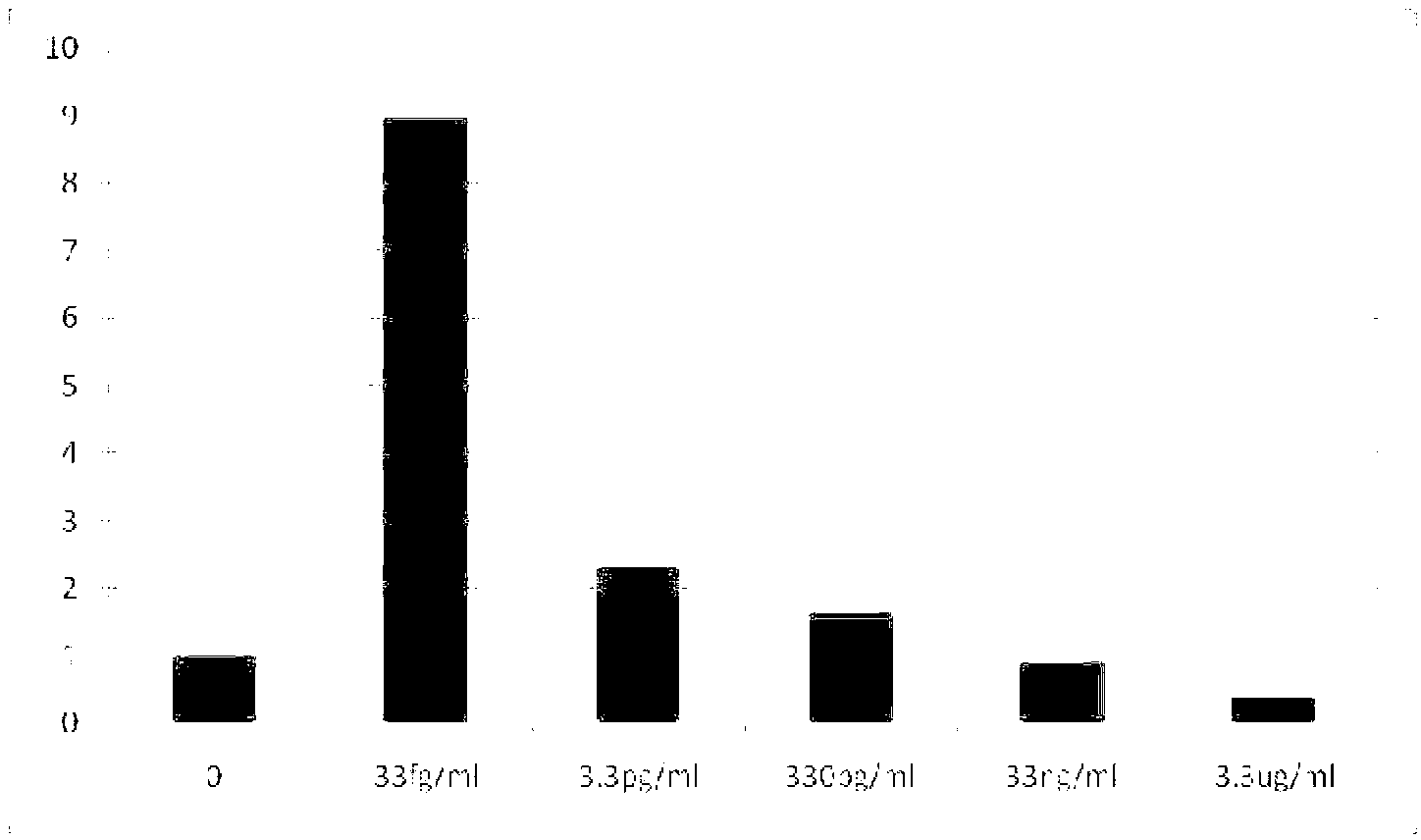Patents
Literature
78 results about "Molecular motor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
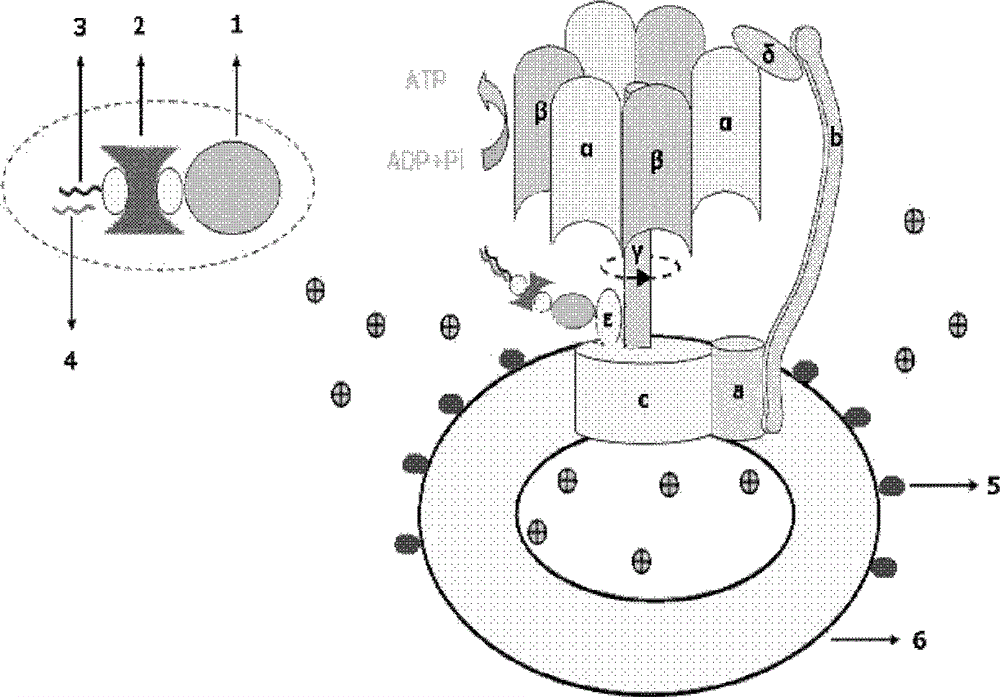
Molecular motors are natural (biological) or artificial molecular machines that are the essential agents of movement in living organisms. In general terms, a motor is a device that consumes energy in one form and converts it into motion or mechanical work; for example, many protein-based molecular motors harness the chemical free energy released by the hydrolysis of ATP in order to perform mechanical work. In terms of energetic efficiency, this type of motor can be superior to currently available man-made motors. One important difference between molecular motors and macroscopic motors is that molecular motors operate in the thermal bath, an environment in which the fluctuations due to thermal noise are significant.
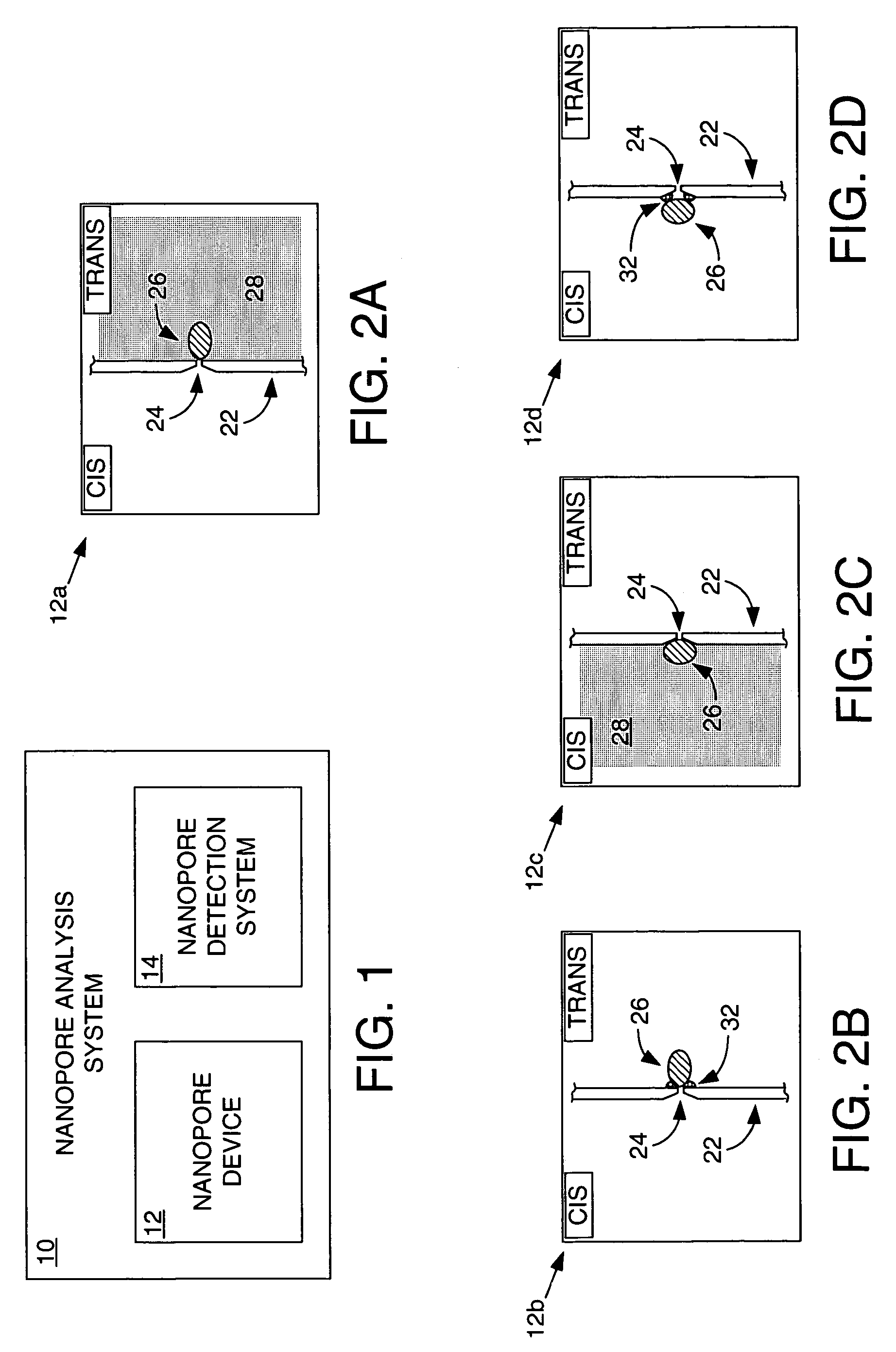
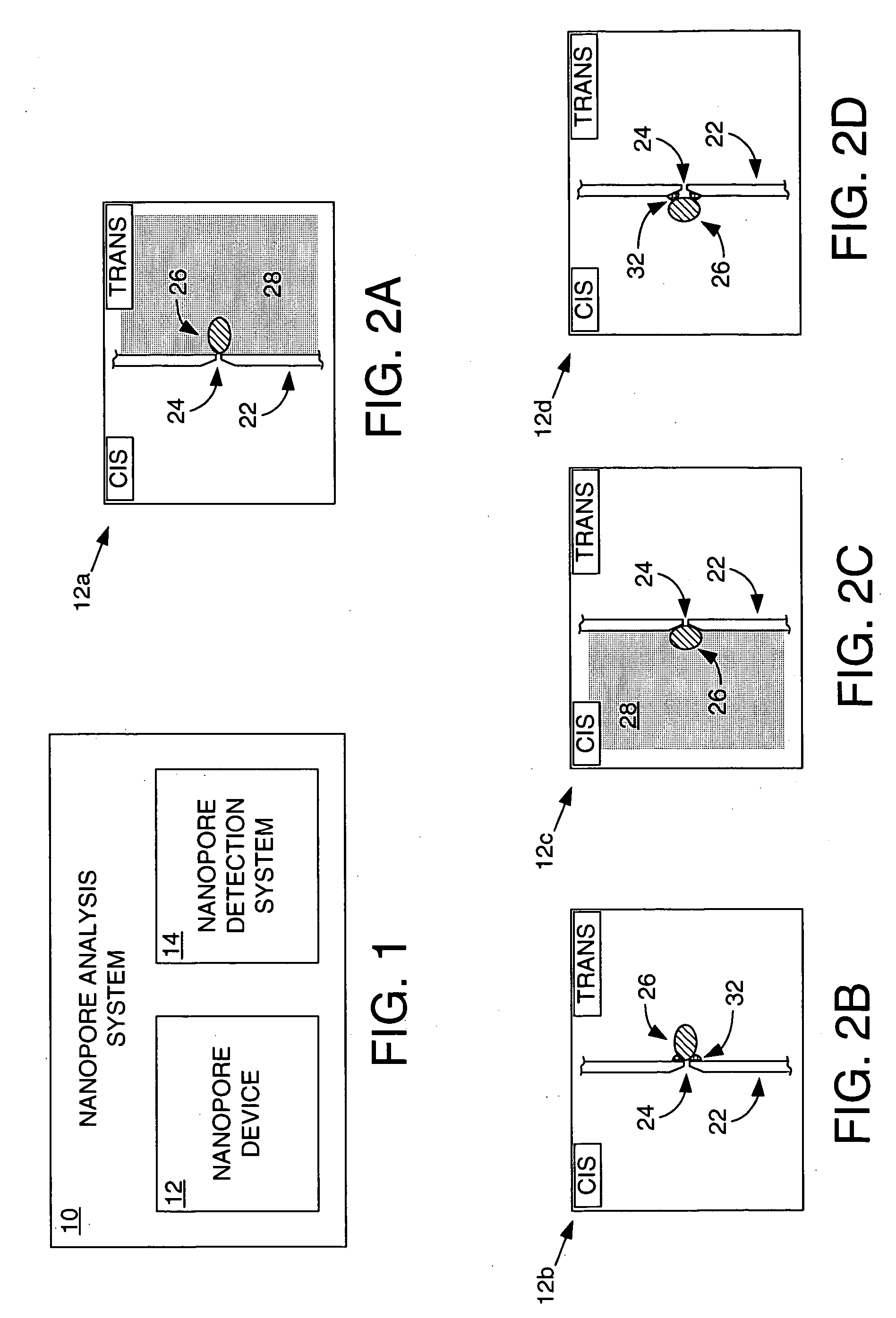
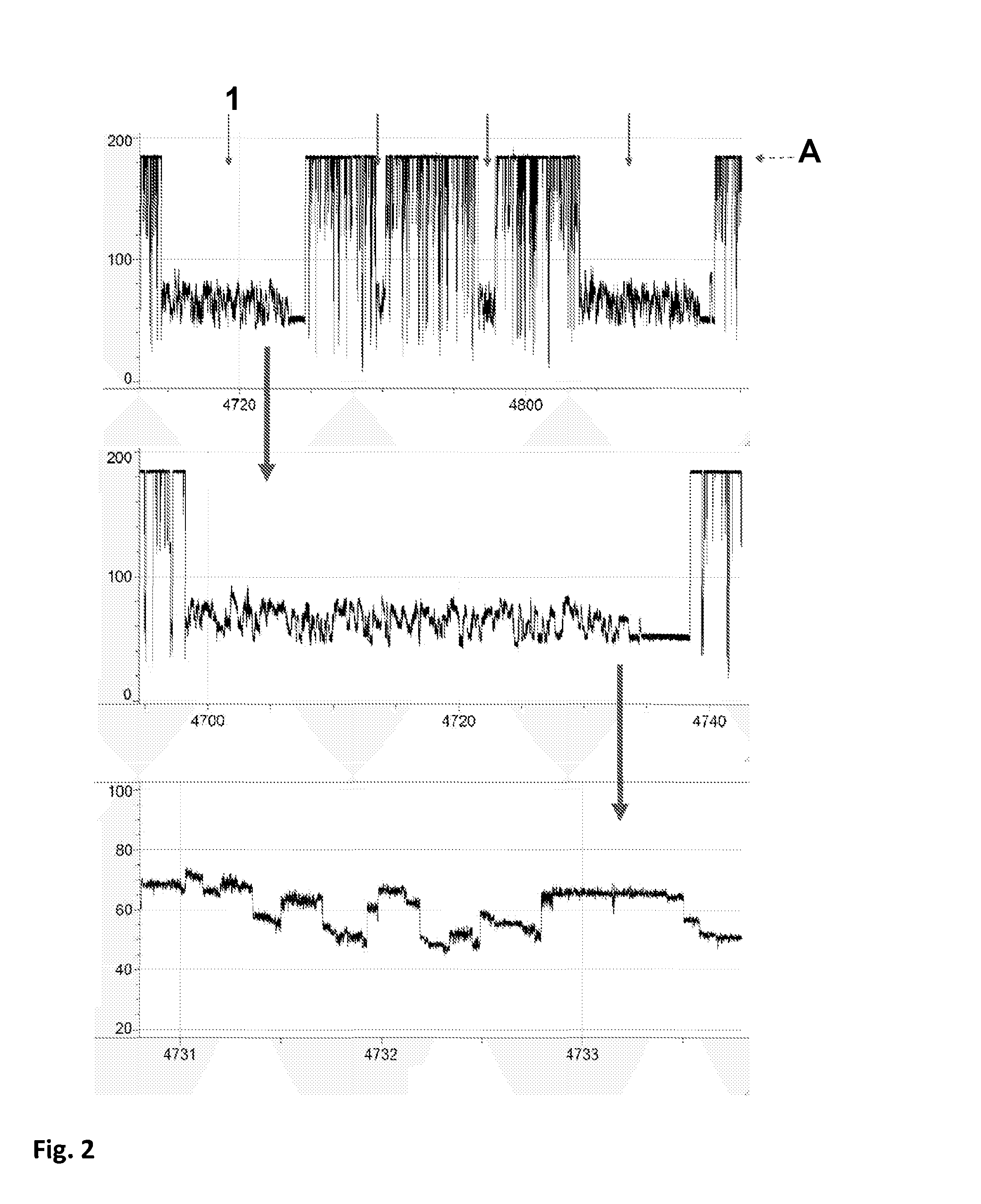
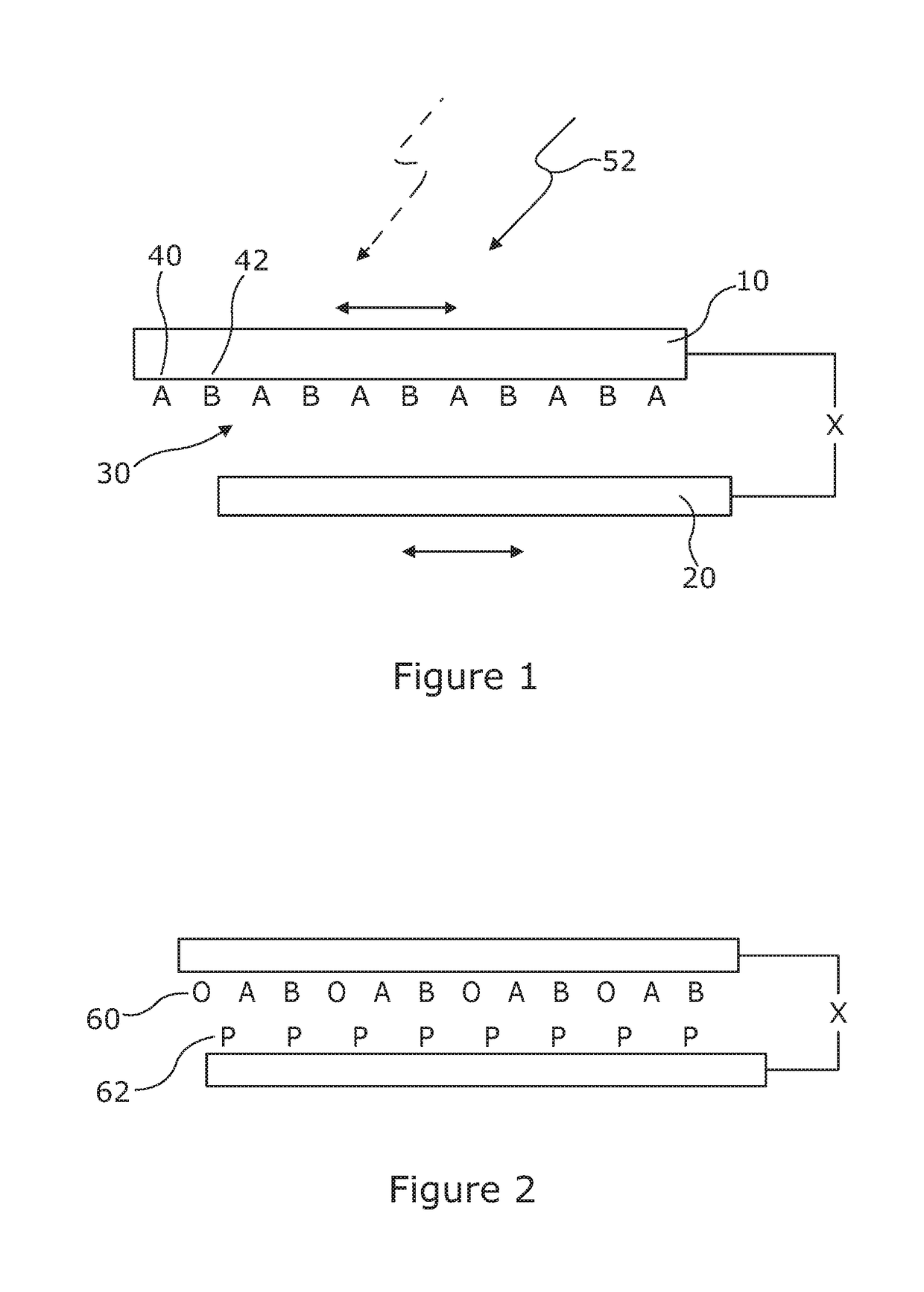
Methods and apparatus for characterizing polynucleotides
ActiveUS7238485B2Reduce probabilityMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCrystallographyMolecular motor
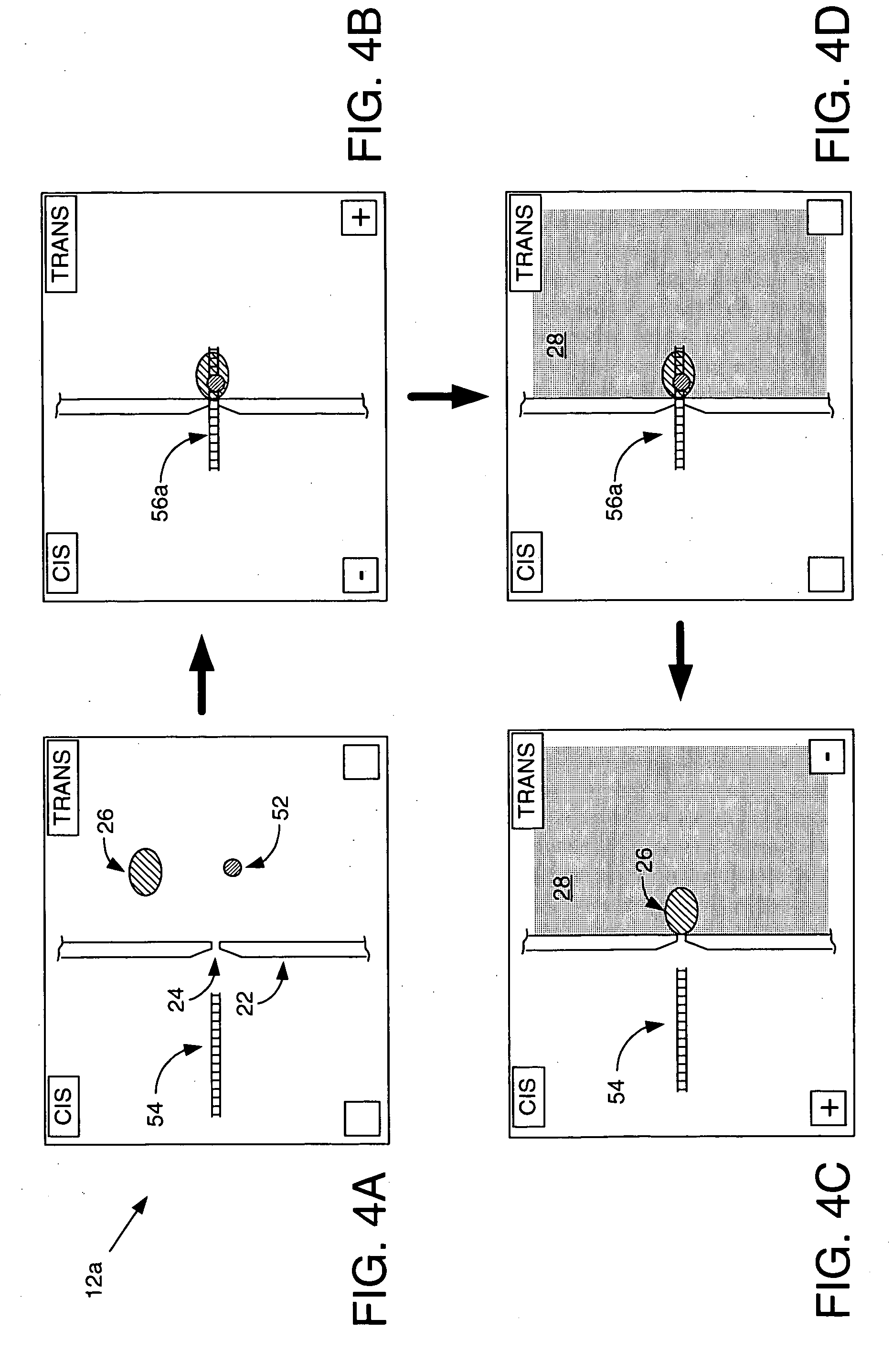
Systems and methods for analysis of polymers, e.g., polynucleotides, are provided. The systems are capable of analyzing a polymer at a specified rate. One such analysis system includes a structure having a nanopore aperture and a molecular motor, e.g., a polymerase, adjacent the nanopore aperture.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
Methods and apparatus for characterizing polynucleotides
ActiveUS20060063171A1Reduce probabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyCrystallographyMolecular motor
Systems and methods for analysis of polymers, e.g., polynucleotides, are provided. The systems are capable of analyzing a polymer at a specified rate. One such analysis system includes a structure having a nanopore aperture and a molecular motor, e.g., a polymerase, adjacent the nanopore aperture.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
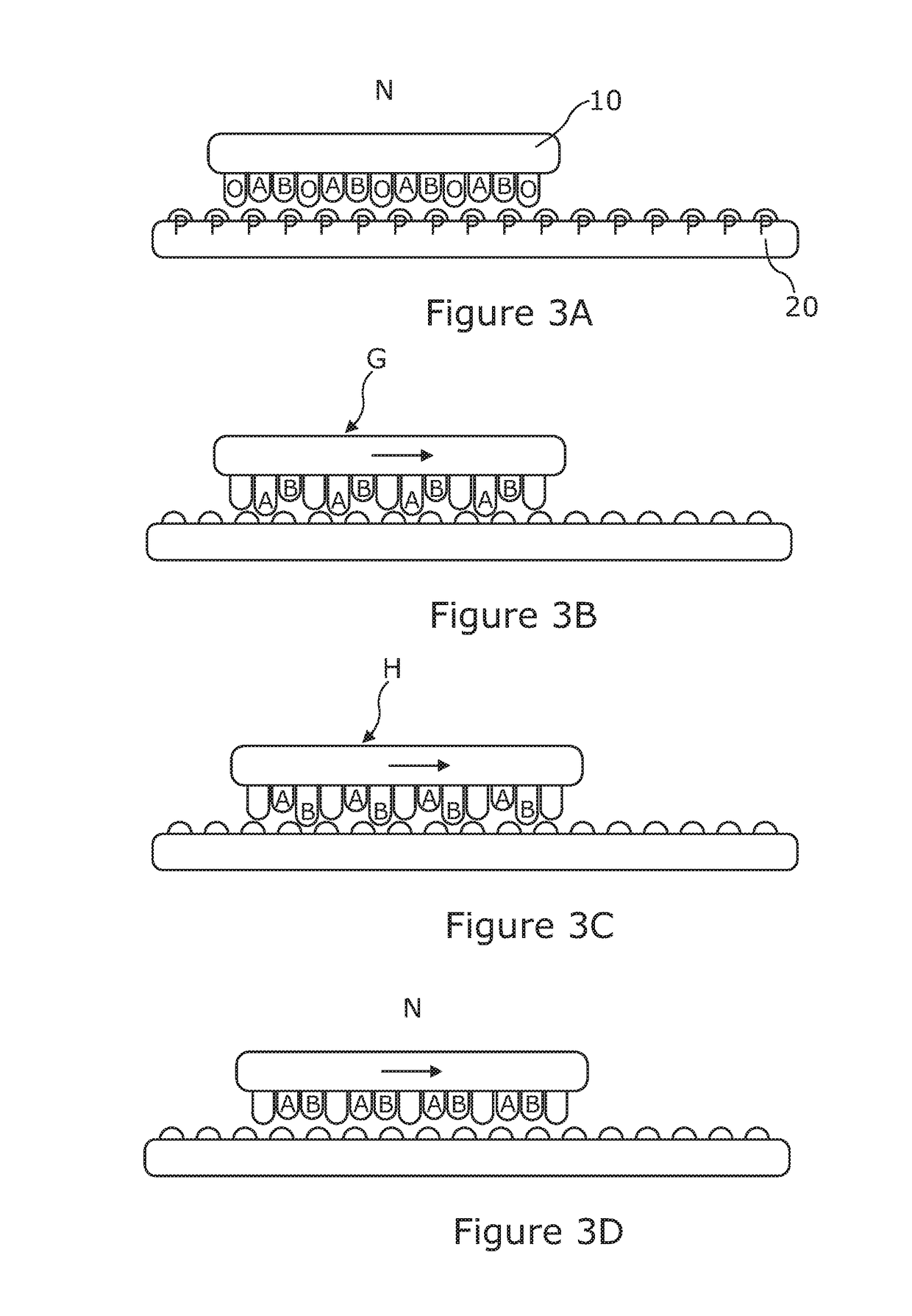
Enzyme method
ActiveUS20140255921A1Improve featuresBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleotideMolecular motor
The invention relates to a new method of characterising a target polynucleotide. The method uses a pore and a Hel308 helicase or amolecular motor which is capable of binding to the target polynucleotide at an internal nucleotide. The helicase or molecular motor controls the movement of the target polynucleotide through the pore.
Owner:OXFORD NANOPORE TECH LTD
Nanometer biological robot and application thereof
InactiveCN101744645AIncrease vitalityCapable of targetingSurgeryPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMolecular motorThrombus
The present invention relates to a nanometer biological robot. The nanometer robot is driven by molecular motors and guided by thrombus antibodies to assist in quickly dissolving thrombi. The rapid rotation of the molecular motors on partial thrombi produces the effect similar to that of a micro power agitator. The molecular motors are driven by light, so the nanometer biological robot is adjustable and controllable. The contact of drugs with fiber proteins is accelerated, the biological and machinery mechanics effect of the nanometer biological robot is synergetic with the medical enzymolysis, and the fibrinolysis is accelerated.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES +1
Method for manufacturing rotary type sensor used for rapidly, sensitively and specifically detecting trace small RNAs
InactiveCN101993820ASimple purification methodUniform sizeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDiseaseFluorescence
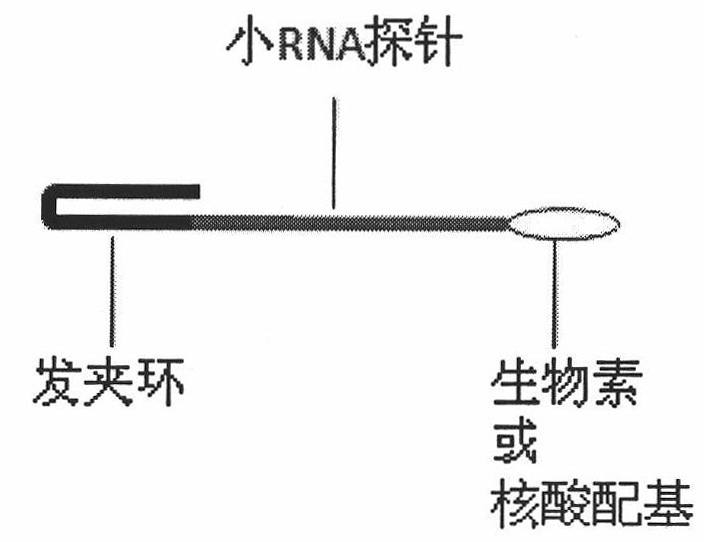
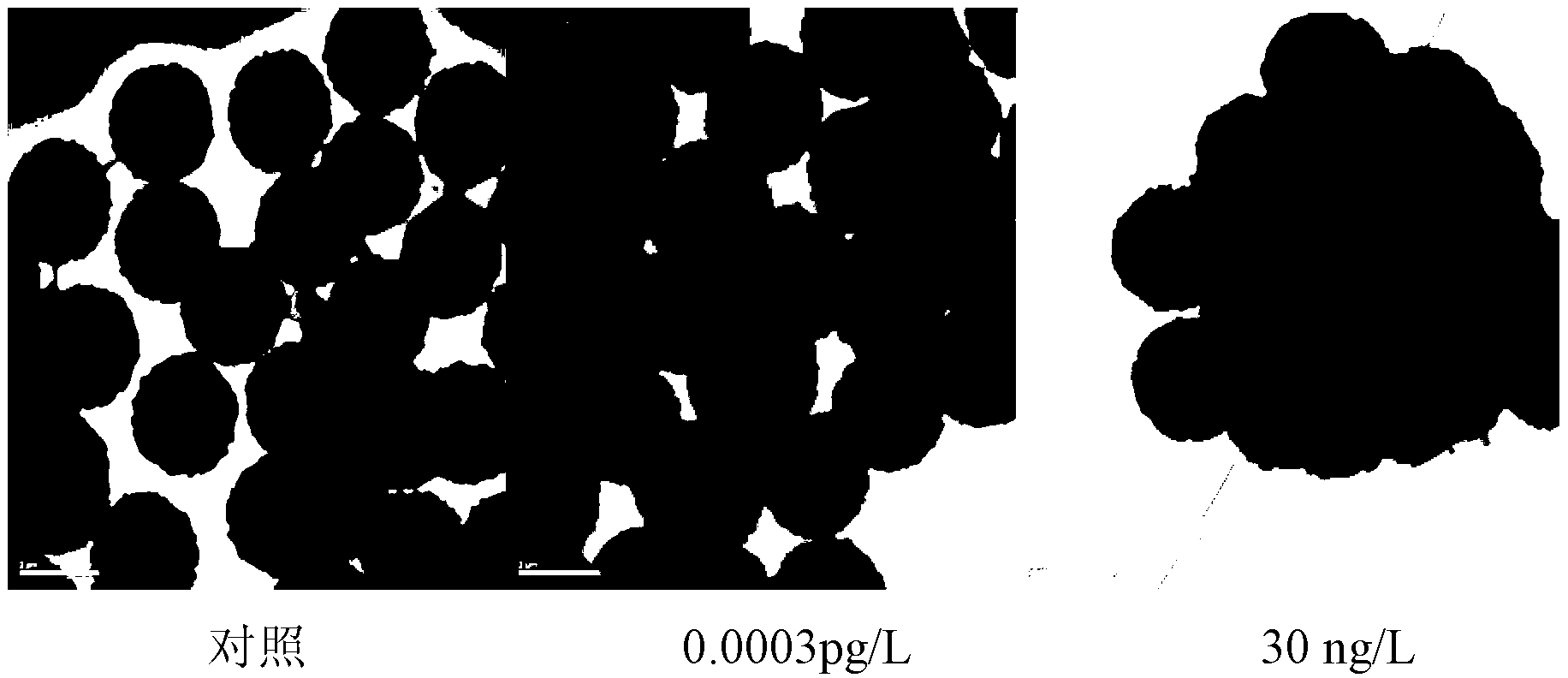
The invention relates to the technical field of method for manufacturing rotary type sensor used for rapidly, sensitively and specifically detecting trace small RNAs, belongs to the technical field of biosensor, in particular relates to establishment and application of a novel rotary type sensor detection method. The invention has the characteristic that sensitivity and specificity when detecting small RNA with low abundance in cell, tissue, body fluid and blood are rapidly, simply and obviously improved. The invention provides a method for manufacturing novel rotary type small RNAs sensor, used for screening, detecting and comparing expression of endogenous small RNA (such as shRNA, miRNA, piRNA, siRNA and the like) and improving the existing chromatophore purification, preparation and fluorescence labelling, design of probe and sensor assembling and preparation technique of related chip. In the invention, FoF1-ATPase has double actions of biosensor and molecular motor. In the detection process, a probe with high specificity on a molecular motor rotates like a propeller, so that centrifugal force and fluidity of peripheral liquid are improved, thus reducing time for target small RNAs to approach the probe and promoting separation of non-target RNA. Thus, the method can rapidly and simply detect small RNA molecules expressed in cell, tissue, body fluid and blood at low abundance with high sensitivity and high specificity and can be used for identifying and comparing variation of small RNA before and after cell differentiation and diagnosis and evaluation of occurrence and development of disease.
Owner:殷勤伟 +2
Single molecule detection of bio-agents using the F1-ATPase biomolecular motor
ActiveUS6989235B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsATPaseMolecular motor
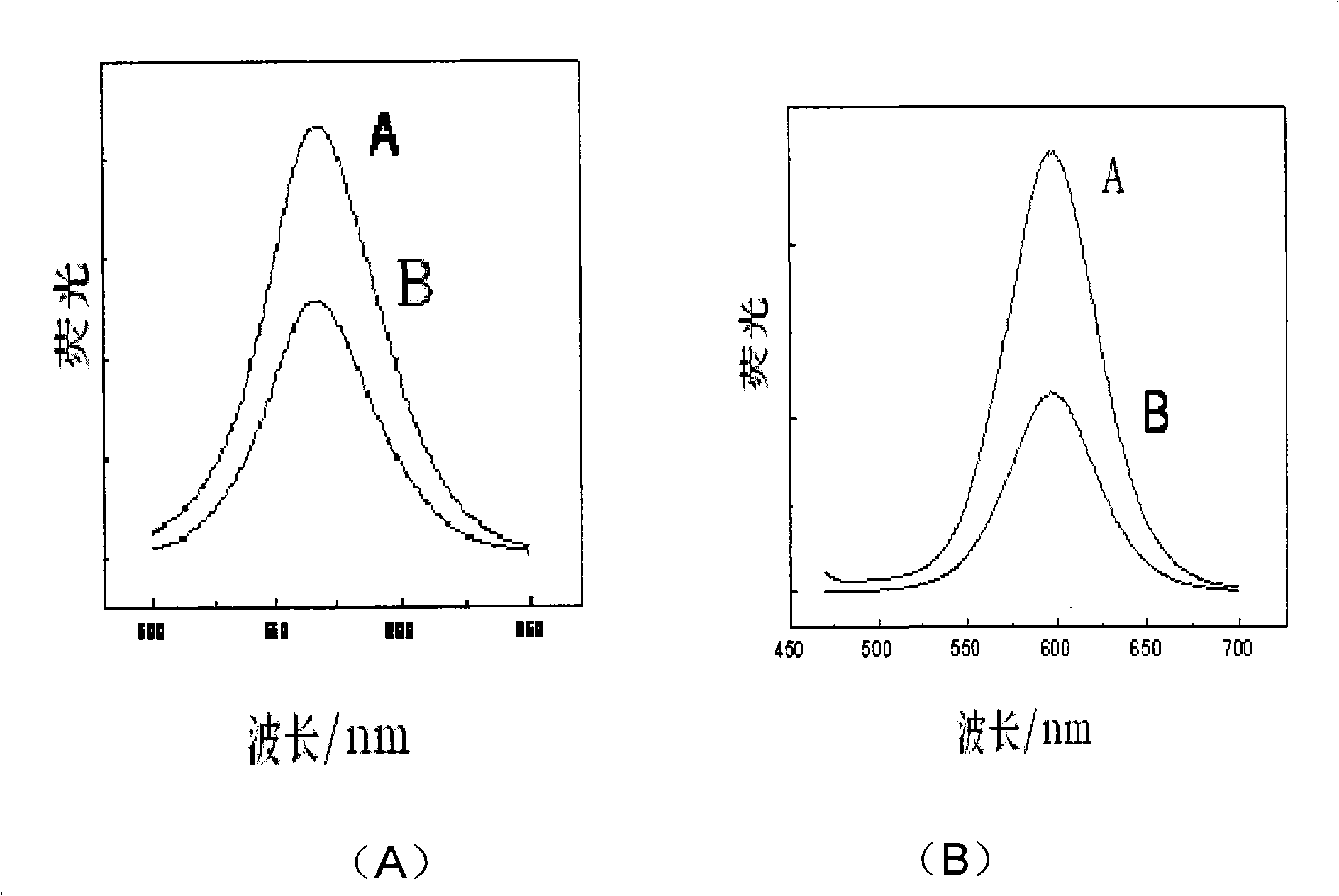
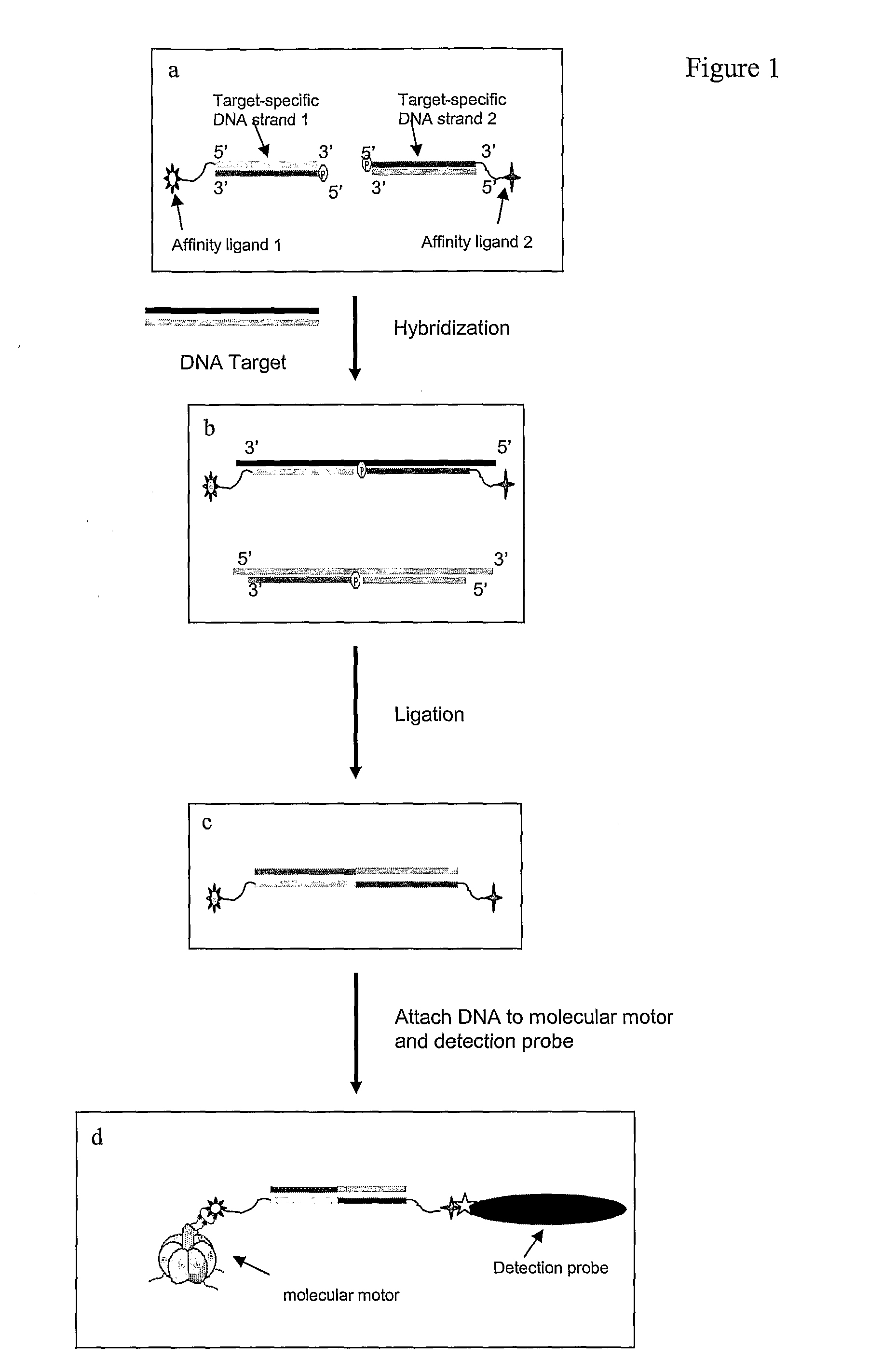
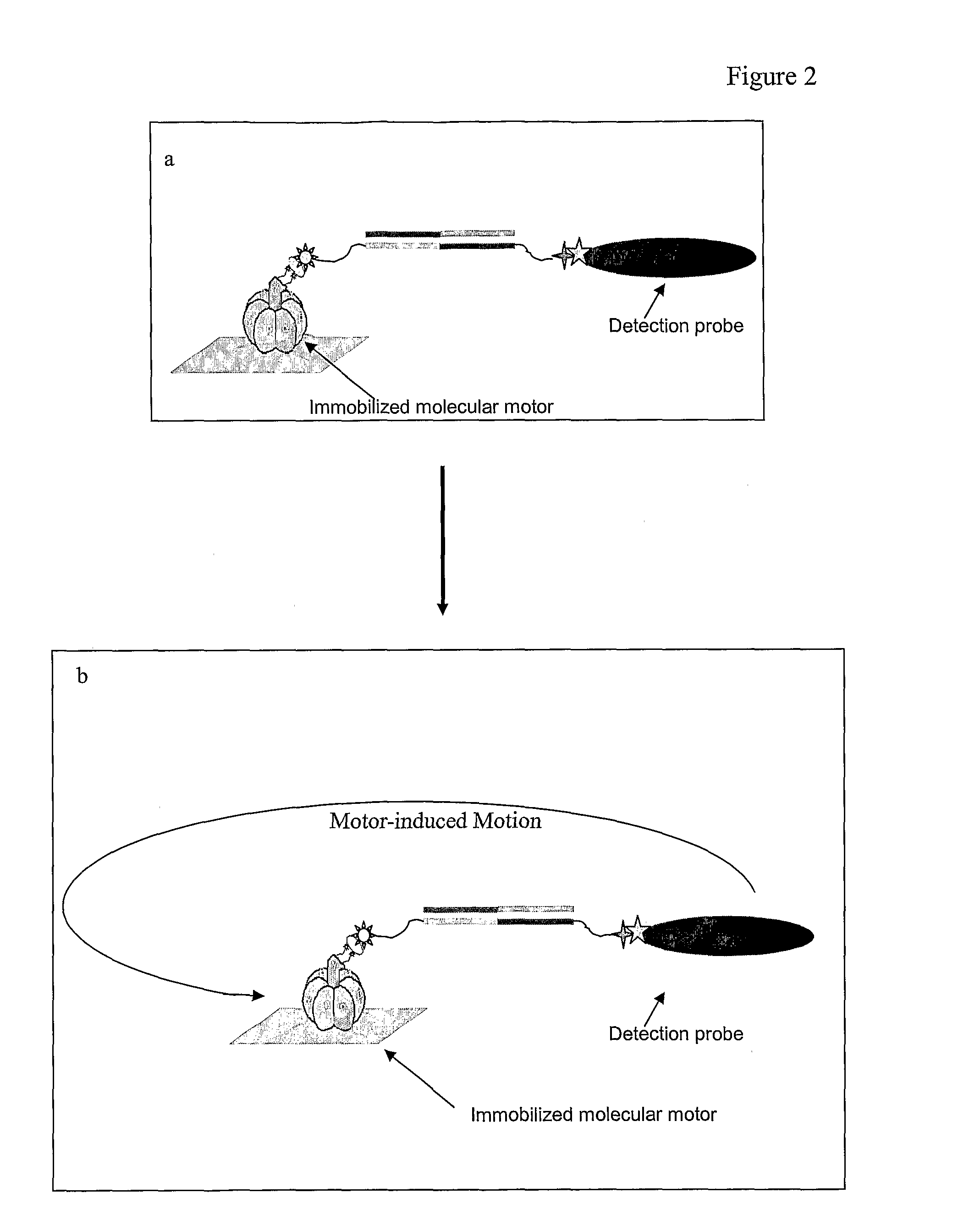
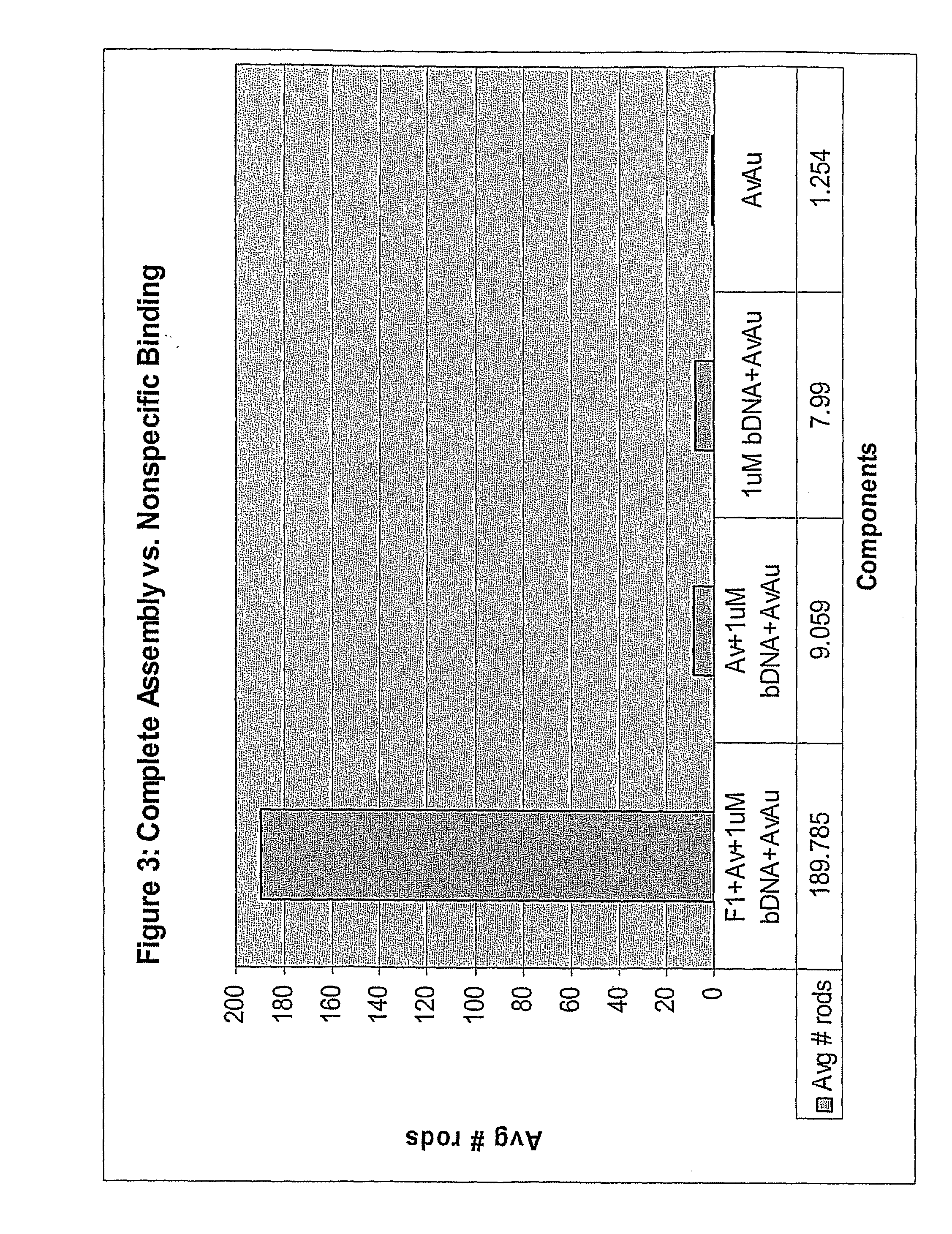
An exemplary system and method of employing DNA hybridization for the detection of bio-agents is disclosed as comprising inter alia a biomolecular rotary motor (150); a capture probe DNA fragment (140) effectively attached to said biomolecular motor (150); a target DNA fragment (130) suitably adapted for hybridization with said capture probe DNA (140); a signal probe DNA fragment (120) suitably adapted for hybridization with said target DNA (130); and a fluorescent bead (100) attached to said signal probe DNA (120). Disclosed features and specifications may be variously controlled, adapted or otherwise optionally modified to improve certain device fabrication parameters and / or performance metrics.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC +1
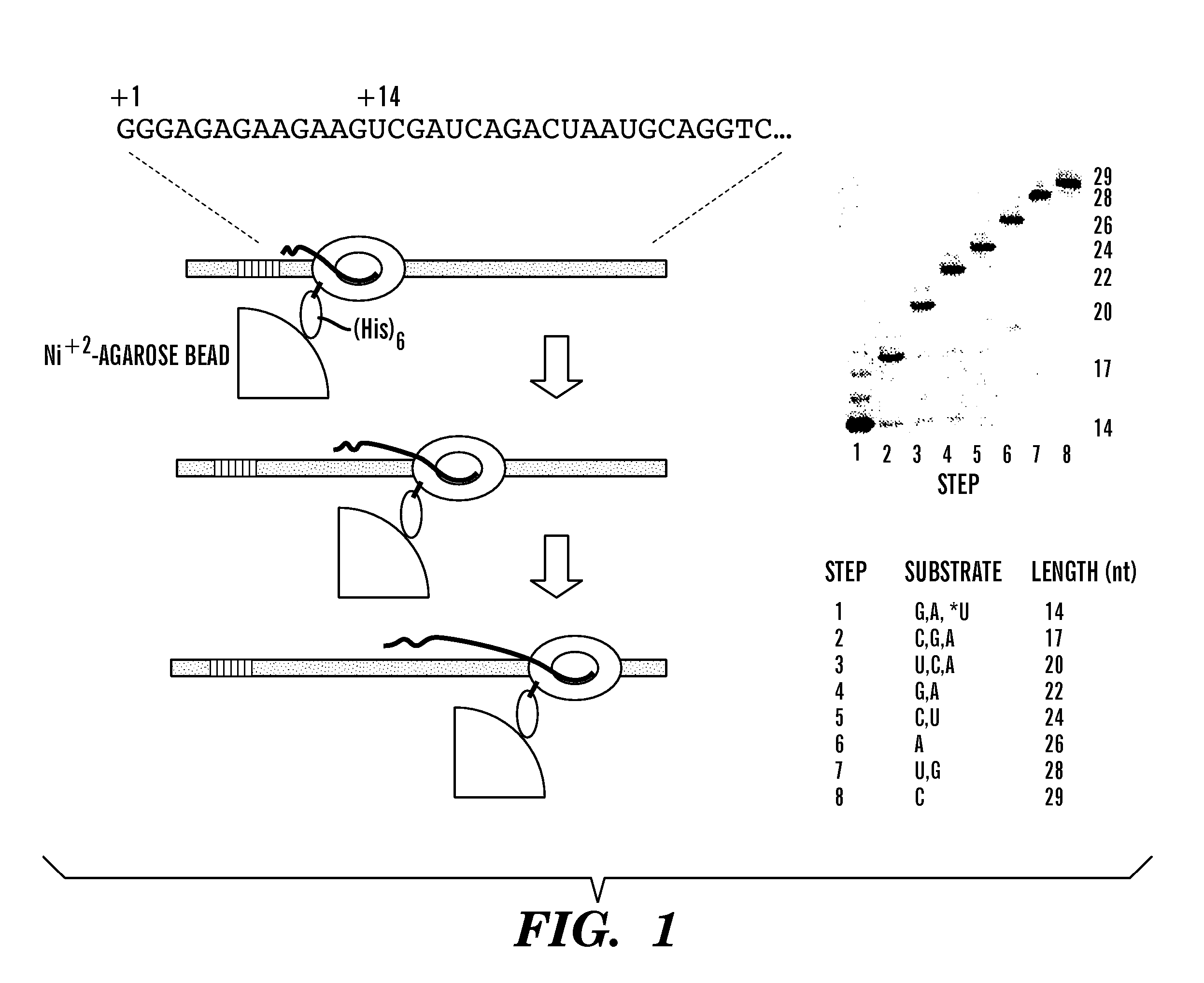
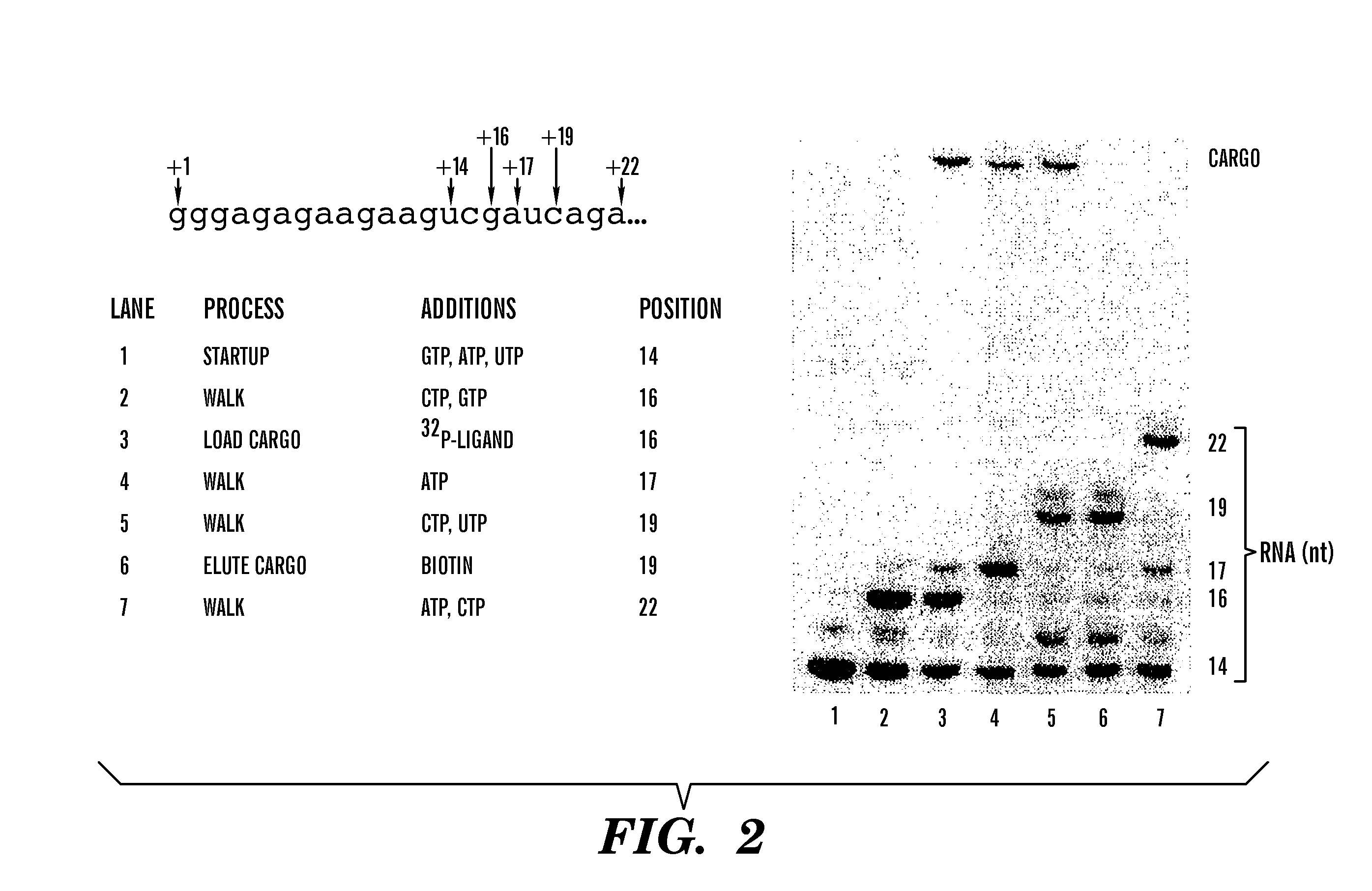
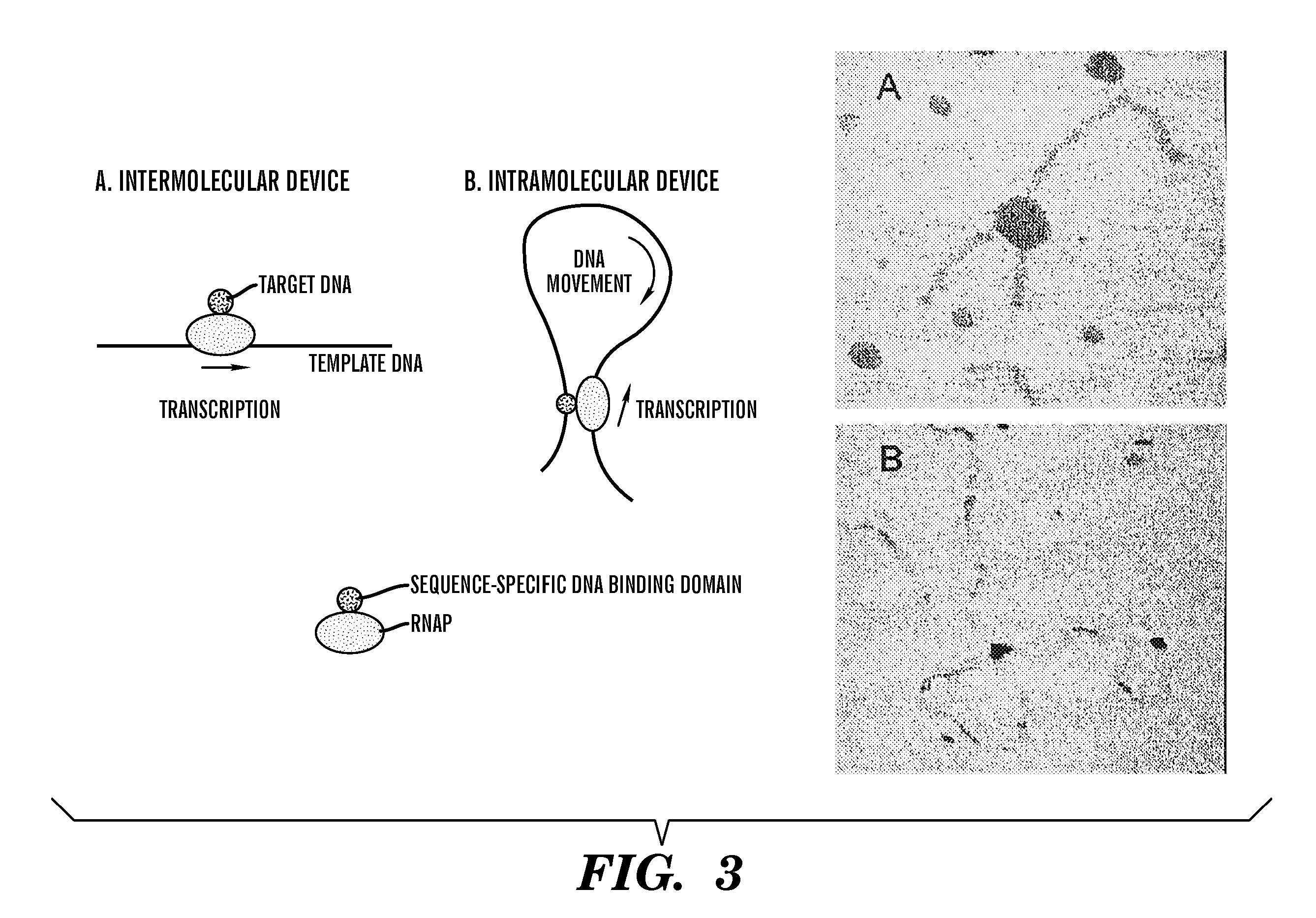
Use of RNA polymerase as an information-dependent molecular motor
InactiveUS20070077575A1Easy to operateOvercome disadvantagesFusion with DNA-binding domainPolypeptide with affinity tagMolecular motorBioinformatics
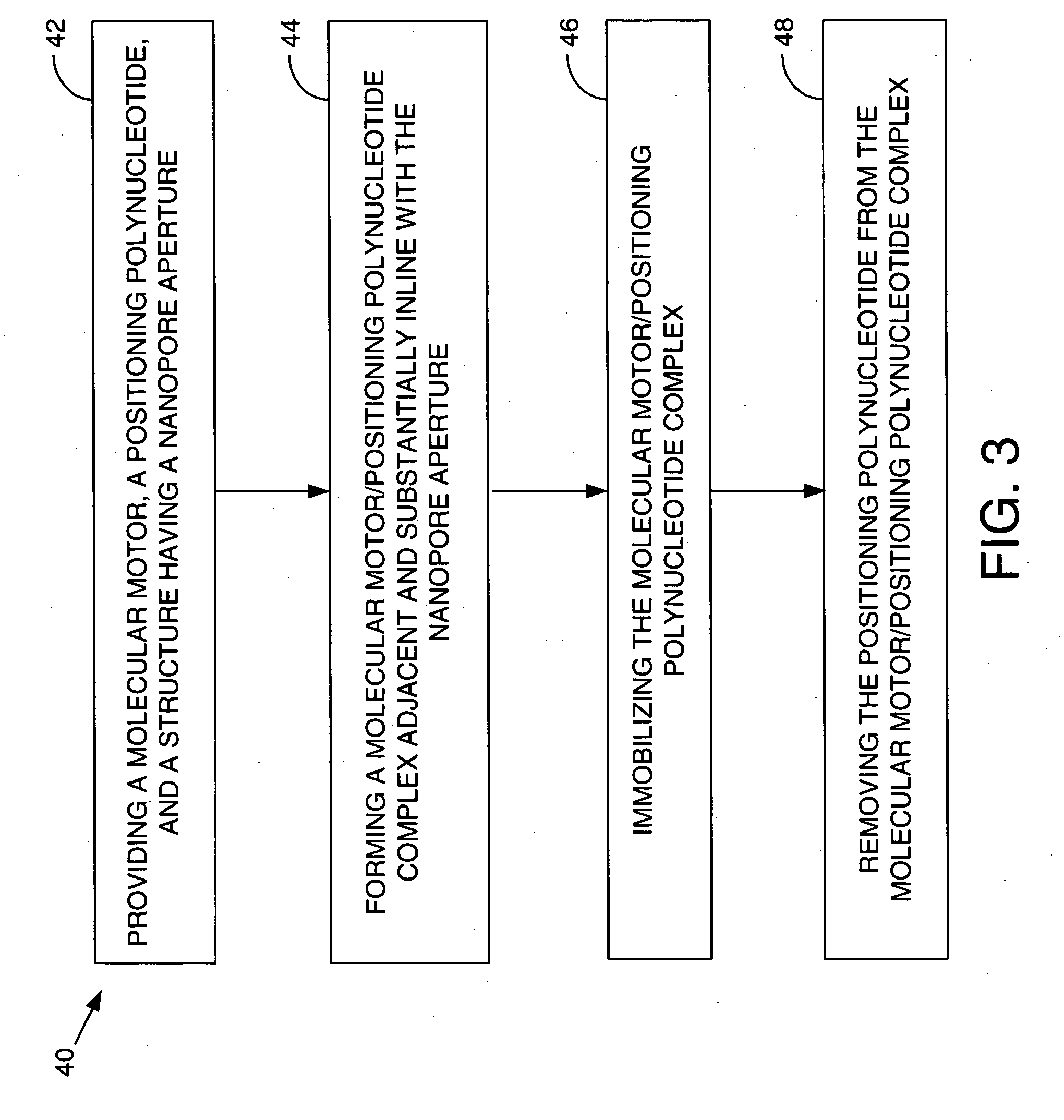
Materials and methods are described in which the information dependence of RNA polymerase is employed to enable its use as a molecular motor adaptable for movement within DNA grid arrays and to actuate, move, position or alter cargo such as physical structures and normally inanimate substances and objects.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
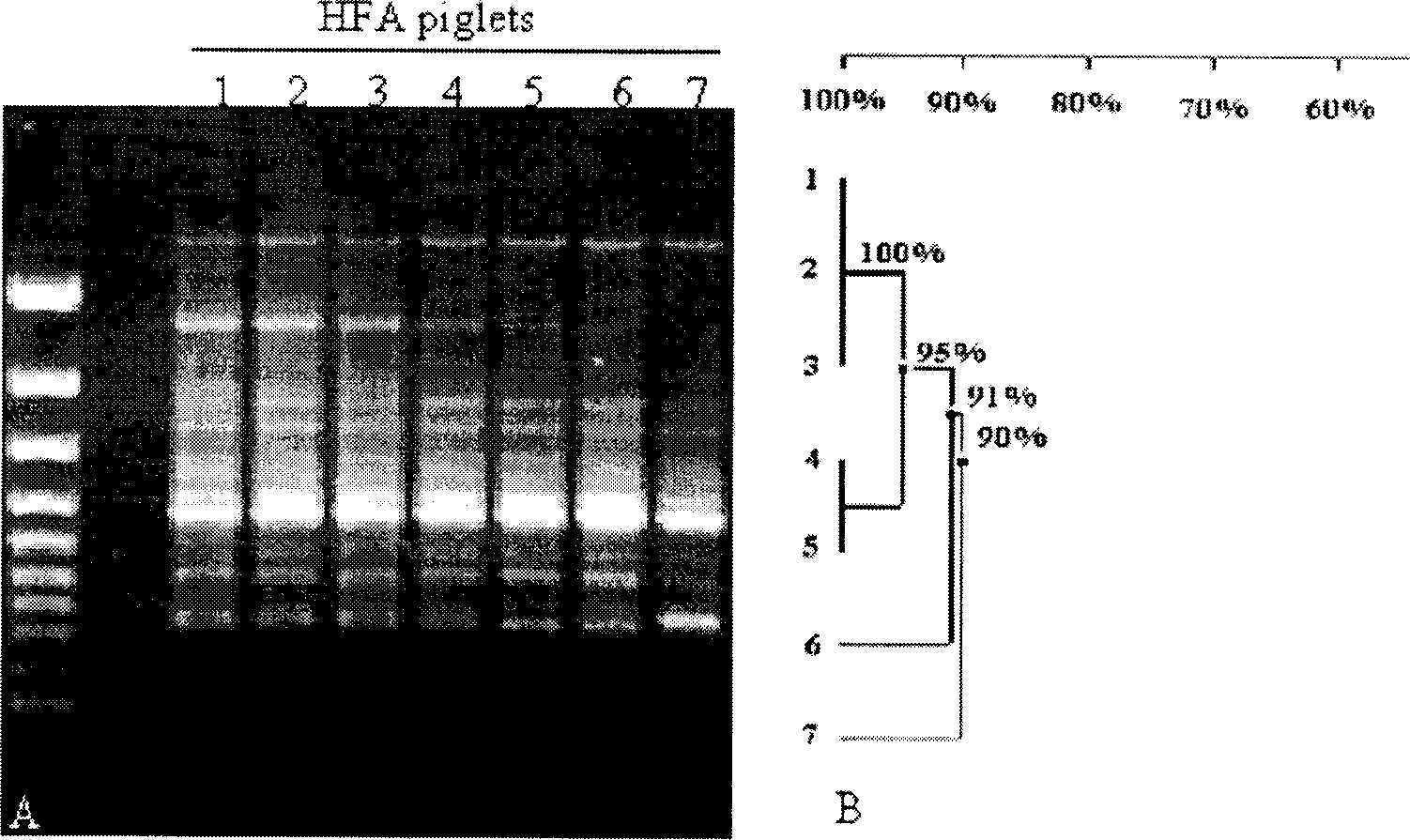
Model construction of human flora-associated piggy and molecular method for detecting flora in intestine tract of baby pig
InactiveCN1840206AFully reflectMicrobiological testing/measurementIn-vivo testing preparationsFecesPositive pressure
Disclosed is a model human-source flora litter model construction and method for detecting flora in litter intestinal tract. The construction steps contain: (1) prepare healthy people fecal bacteria suspension; (2) paunch to farrowing sow to fetch litters; (3) breed the litters in 24-hour aero-ultra filter positive-pressure draft isolation room; (4) inoculate. The detecting steps contain: (1) extract the fecal microbe genome DNA; (2) analyze ERIC-PCR finger spectrum and community DNA crossing; (3) planting analyze bacillus in HFA litter intestinal tract flora; (4) planting analyze HFA bacteroide in HFA litter tract flora. This invention successfully plant human donator's bacillus and bacteroide in litter model intestinal tract. The finger spectrums comparing shows that the flora finger spectrum in litter model intestinal tract has homologous height with that of the human donator. This invention can be used to study the cross-correlation between intestinal tract flora and its host physiology and immune specificity, also it can be used to evaluate regulation and metabolism effect of functional foods or drugs to intestinal tract flora.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
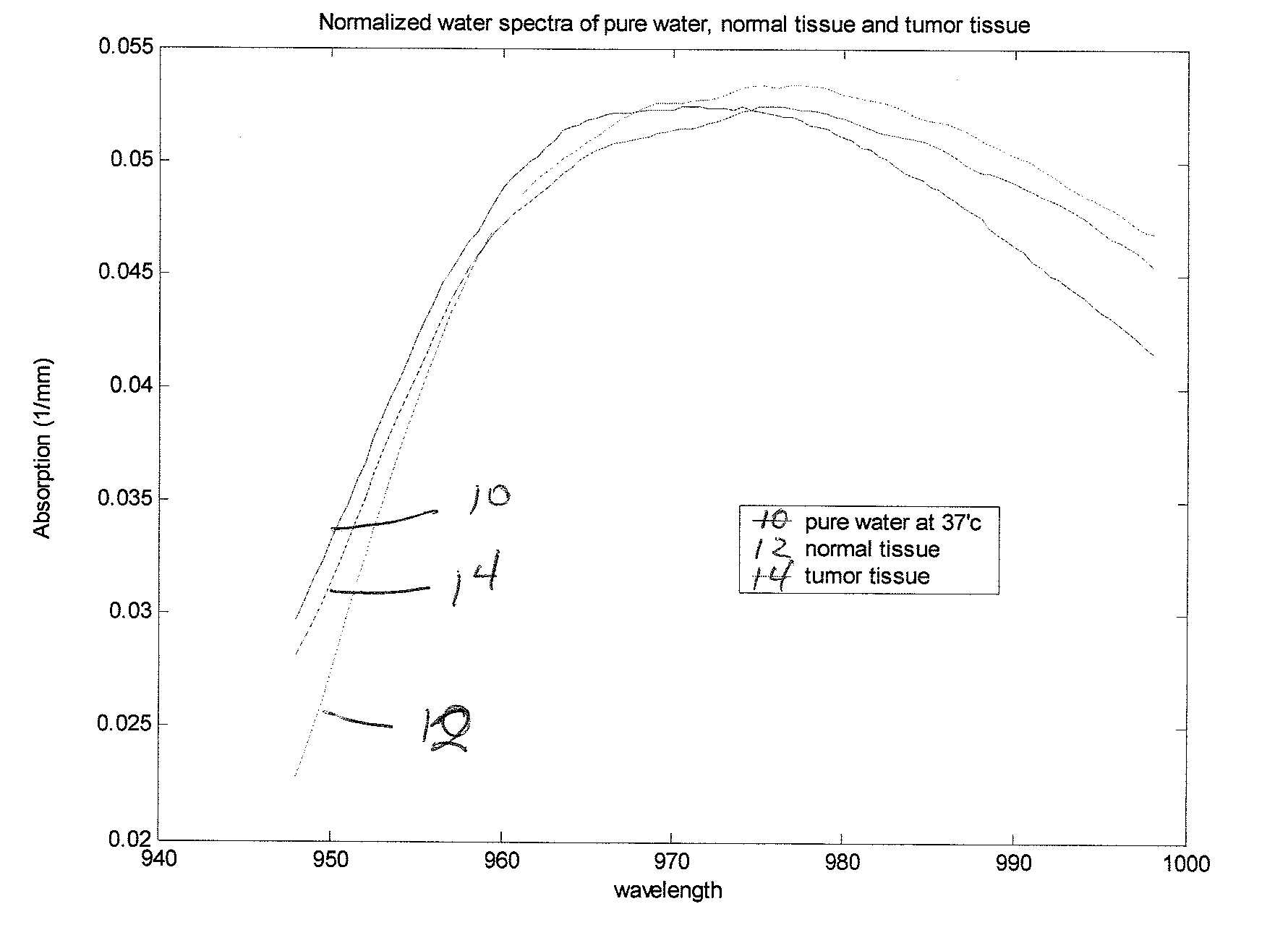
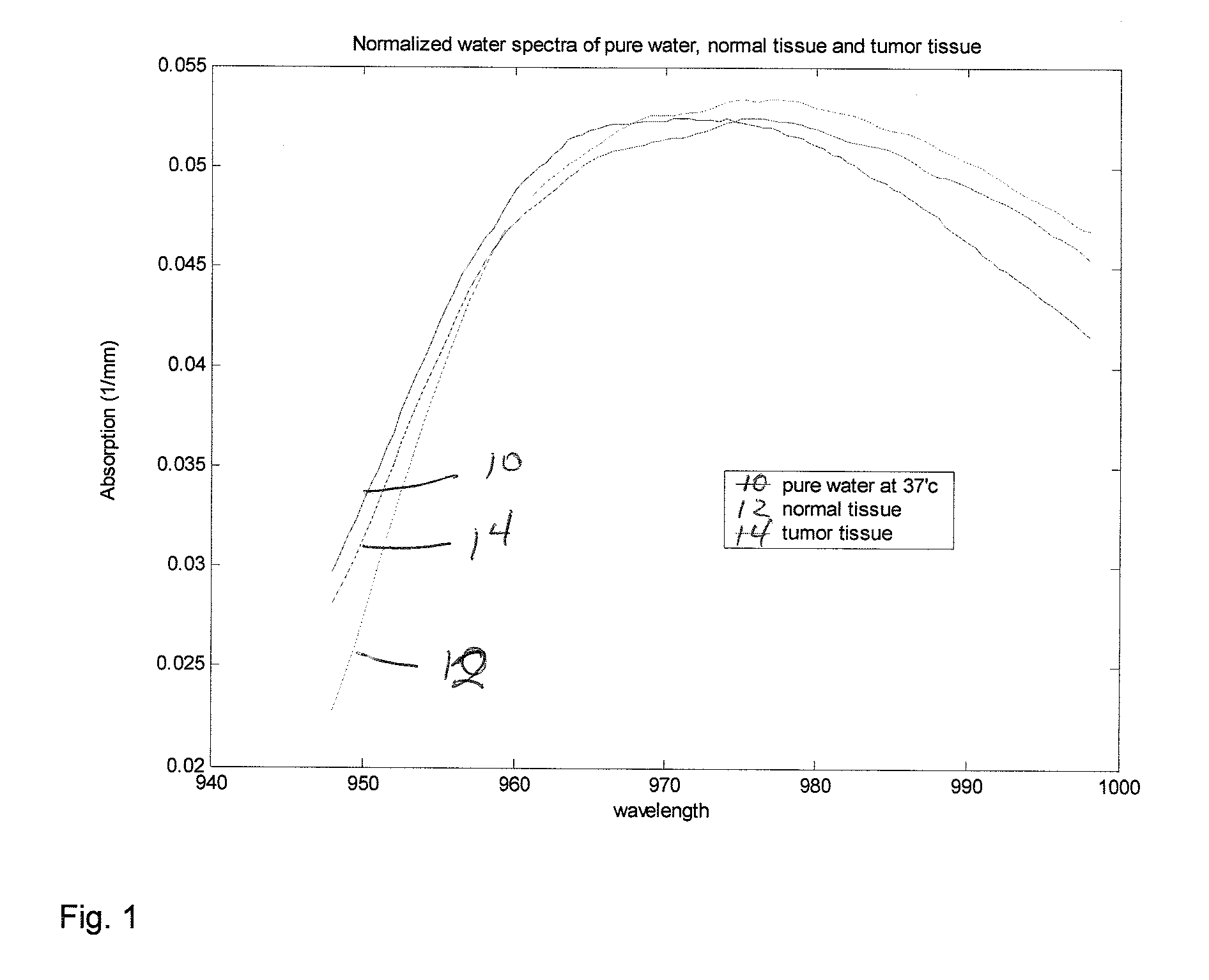
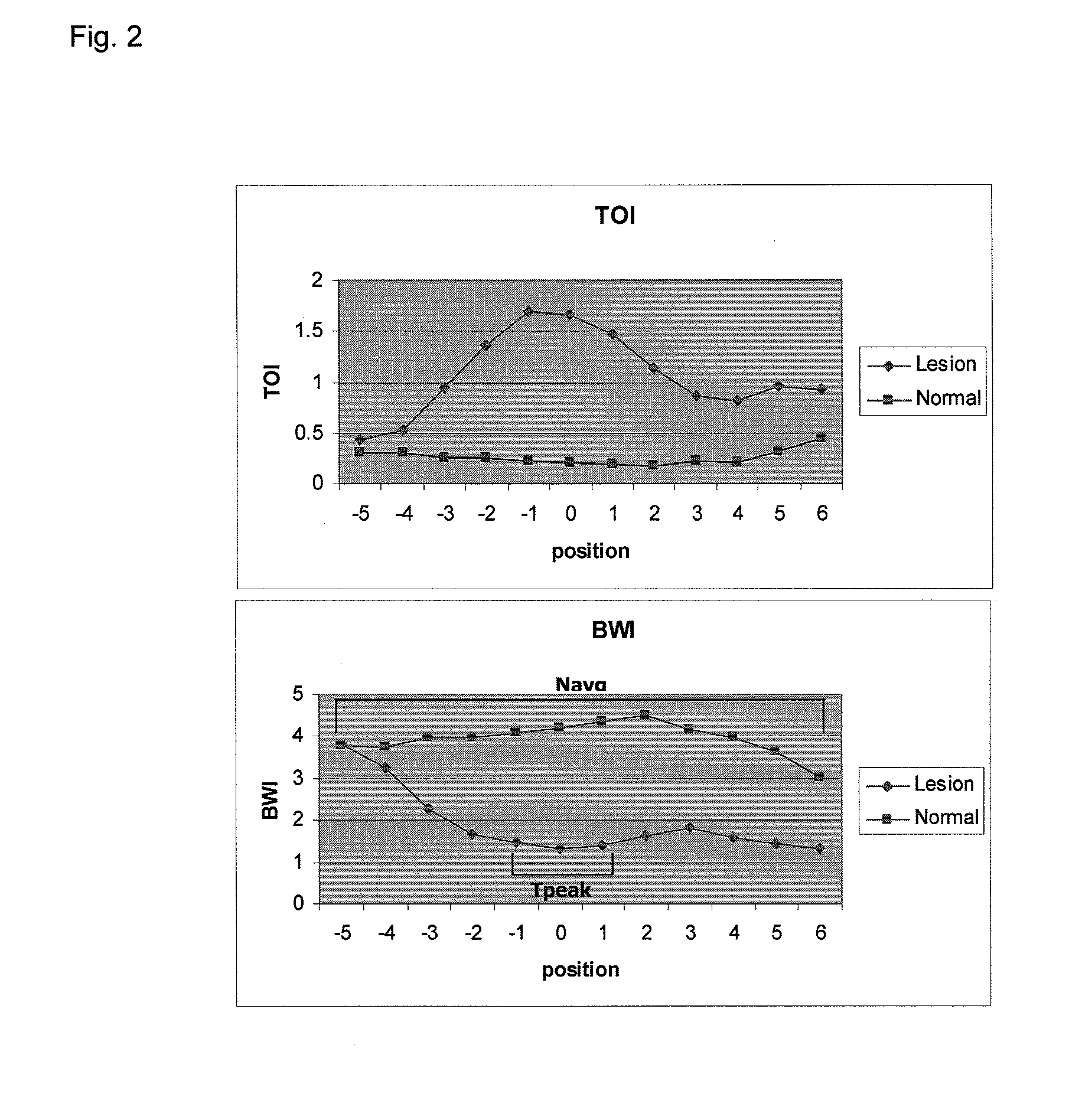
Method and apparatus for assessing the molecular water binding of deep tissue in vivo using nonionizing radiation
InactiveUS20070282179A1Easy to useLow costDiagnostics using lightDiagnostics using spectroscopyNon-ionizing radiationBound water
A method of optically analyzing tissue in vivo in an individual to obtain a unique spectrum for the tissue of the individual includes the steps of optically measuring the tissue of the individual using broadband diffuse optical spectroscopy (DOS) to measure a normalized tissue water spectrum of the individual or noninvasively optically line scanning a tissue site on the individual at a plurality of points, then determining spectral differences between the normalized tissue water spectrum and a pure water spectrum at each point of a line scan, generating a bound water index (BWI) corresponding to the spectral differences, and identifying a tissue state corresponding to the scanned tissue based on the BWI.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Bio-energy muscle relaxants
Human muscle tissues involve striated and smooth muscles. Each muscle tissue possesses its own special function. Differences of physiology functions among the muscle tissues are mainly determined by their various initiation and signal transmission systems, defined as the pre-muscle molecular motor mechanism, or initiating and regulating mechanism. The current medications, drugs, and therapies for diseases and symptoms related abnormal increased muscle tone or excessive muscle contraction are aimed just at the pre-muscle molecular motor mechanisms, whereas without directly intending to effect on the muscle molecular motor mechanism i.e. the contractile apparatus mechanism at all, which, however, is in common for all kinds of muscle tissues. The muscle molecular motor mechanism mainly involves recycling of actin-myosin filament cross-bridge formation and sliding movement. In the process, bio-energy provided by ATP hydrolysis is necessarily required. Therefore, abnormal increased muscle tone or excessive contraction of muscle tissues under diseased conditions may be modified by inhibition of the muscle molecular motor with the actin-myosin ATPase inhibitor, which blocks hydrolysis of ATP, then reduces release of bio-energy for the muscle contraction.Our studies in vitro and in vivo have demonstrated that BDM, an ATPase inhibitor, thereby, its analogues, derivatives, and other chemicals possessing similar effect on ATPase may be used as bio-energy muscle relaxants (general muscle relaxants).
Owner:YISHENG ZHANG CHONGGANG WANG & PEI WANG
Molecular conformation change-based sequence measuring method
InactiveCN105092647ARapid SequencingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMolecular motorA-DNA
The invention relates to molecular conformation change-based sequence measuring method which can be used for detecting sequences of DNA, RNR, polypeptides or proteins. The method for detecting the sequence of the DNA comprises the following steps: connecting a graphene nanopore device into a circuit; fixing a molecular motor above or in each graphene nanopore; forming a compound body by the molecular motor and DNA template molecules; adding a solution containing single basic groups; when each basic group is compounded into a DNA molecule template by the molecular motor, generating the change of conformation of the molecular motor to influence ionic current passing through each nanopore, wherein the change of the conformation of the molecular motor, caused by each basic group, is different; and analyzing the sequence of the DNA by detecting electrical signals generating when DNA penetrates through the graphene nanopore.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GREEN & INTELLIGENT TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Protein and nucleic acid delivery vehicles, components and mechanisms thereof
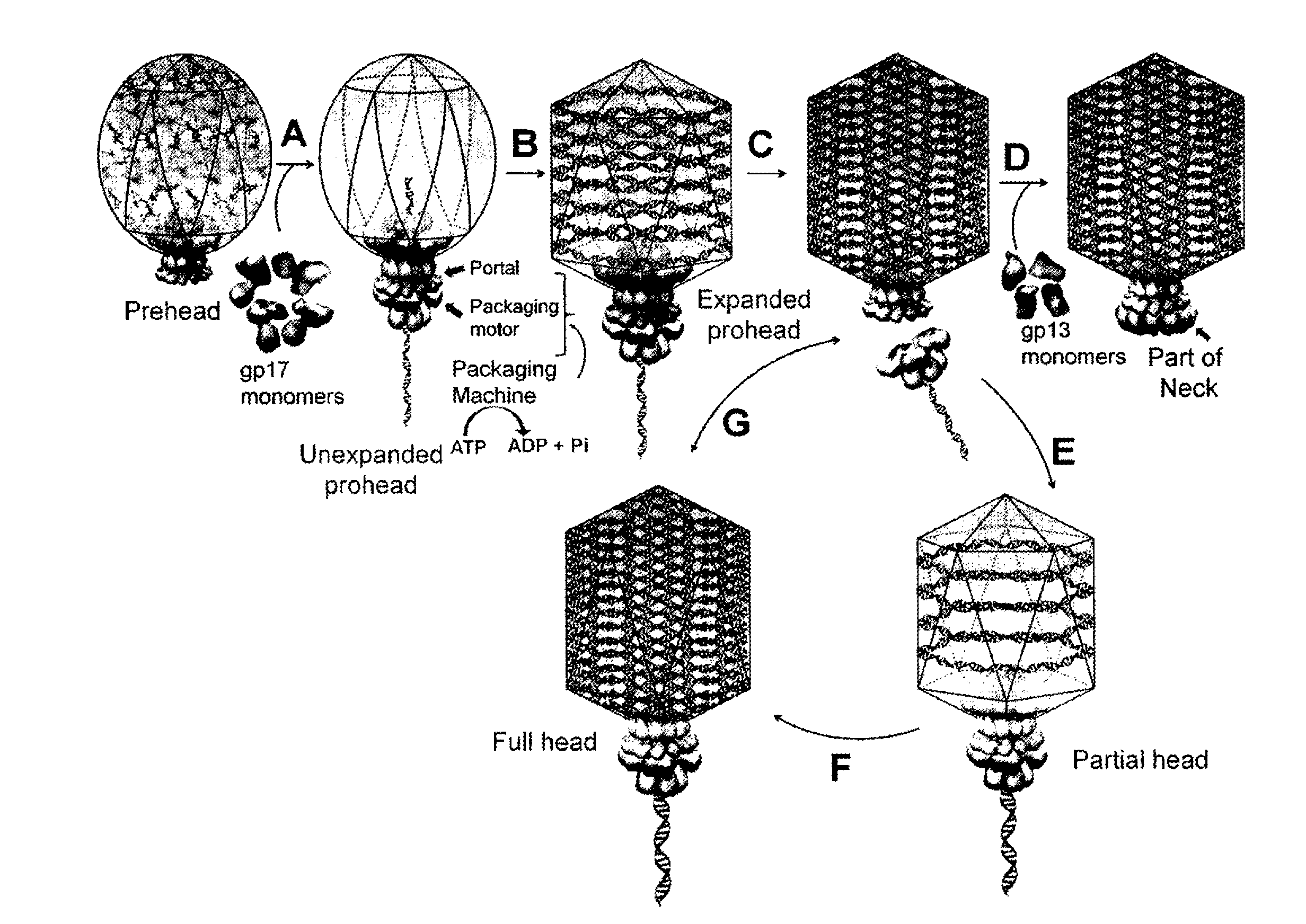
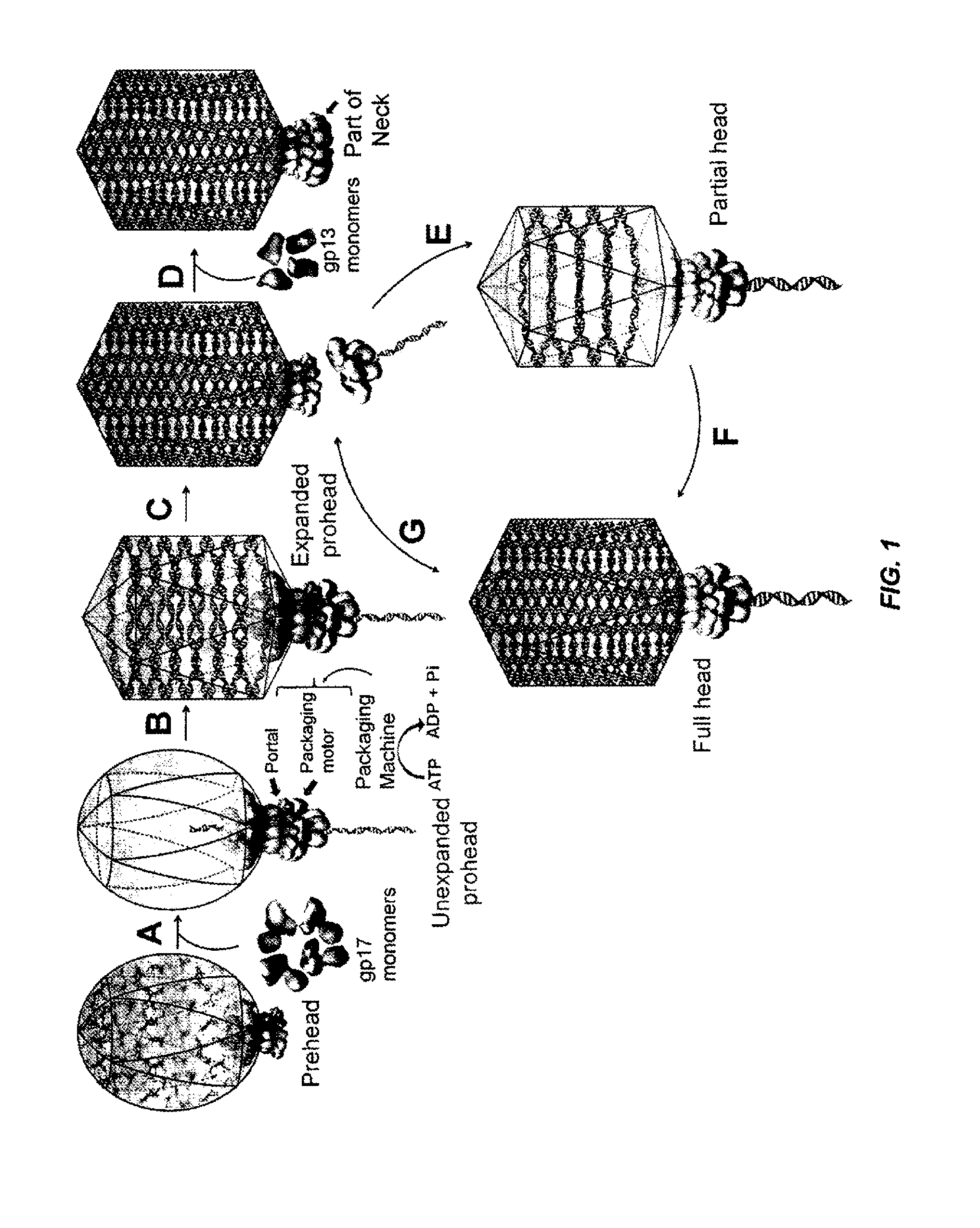
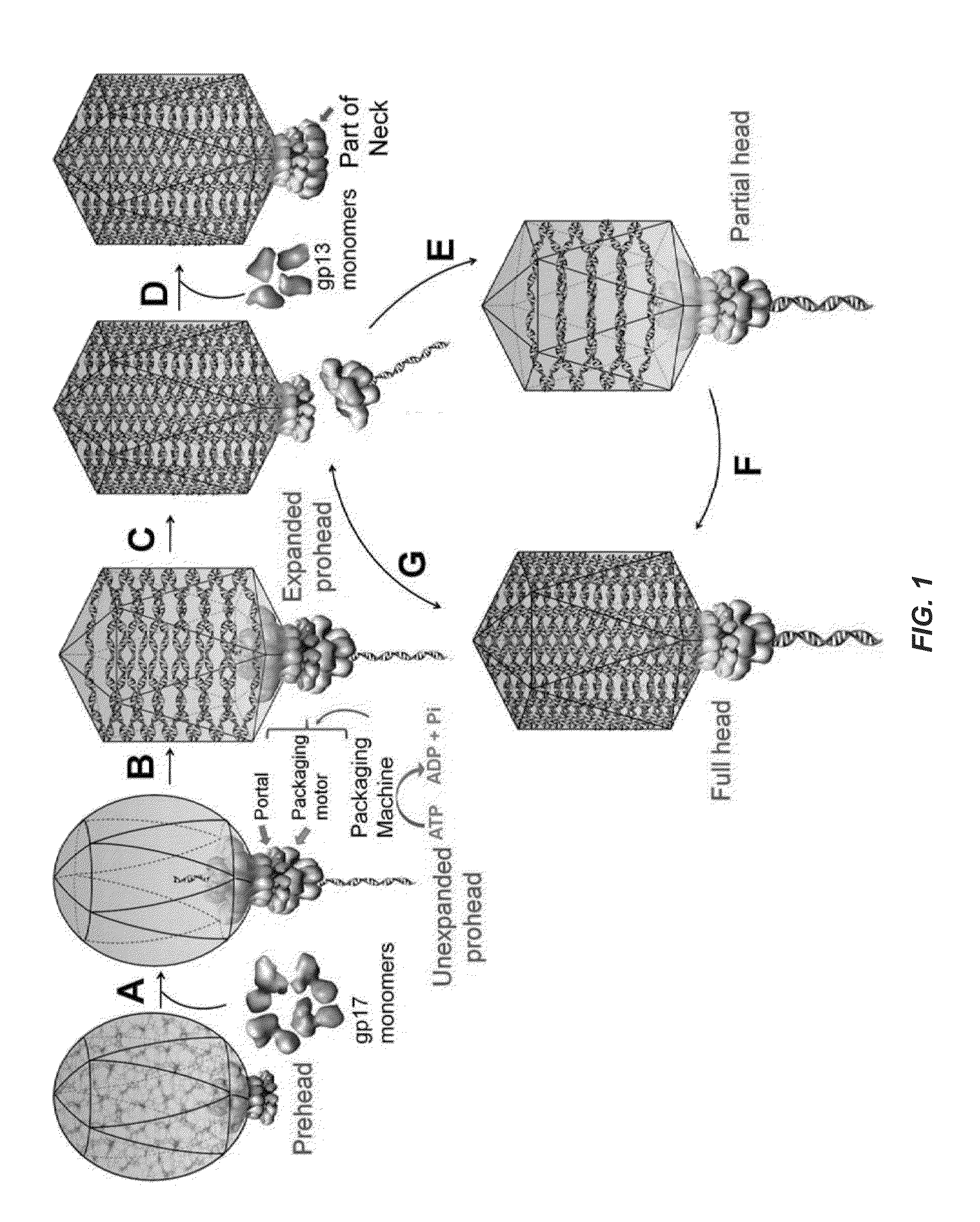
Complex viruses are assembled from simple protein subunits by sequential and irreversible assembly. During genome packaging in bacteriophages, a powerful molecular motor assembles at the special portal vertex of an empty prohead to initiate packaging. An aspect of the invention relates to the phage T4 packaging machine being highly promiscuous, translocating DNA into finished phage heads as well as into proheads. Single motors can force exogenous DNA into phage heads at the same rate as into proheads and phage heads undergo repeated initiations, packaging multiple DNA molecules into the same head. This shows that the phage DNA packaging machine has unusual conformational plasticity, powering DNA into an apparently passive capsid receptacle, including the highly stable virus shell, until it is full. These features allow for the design of a novel class of nanocapsid delivery vehicles.
Owner:CATHOLIC UNIV OF AMERICA
Frictionless molecular rotary motors
A rotaxane consisting of a cucurbituril and an uncharged guest molecule, having low or null affinity therebetween is provided as well as processes for providing the same. Various uses as energy converters (“frictionless” molecular motors), biochips and biosensors using the same are also provided.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
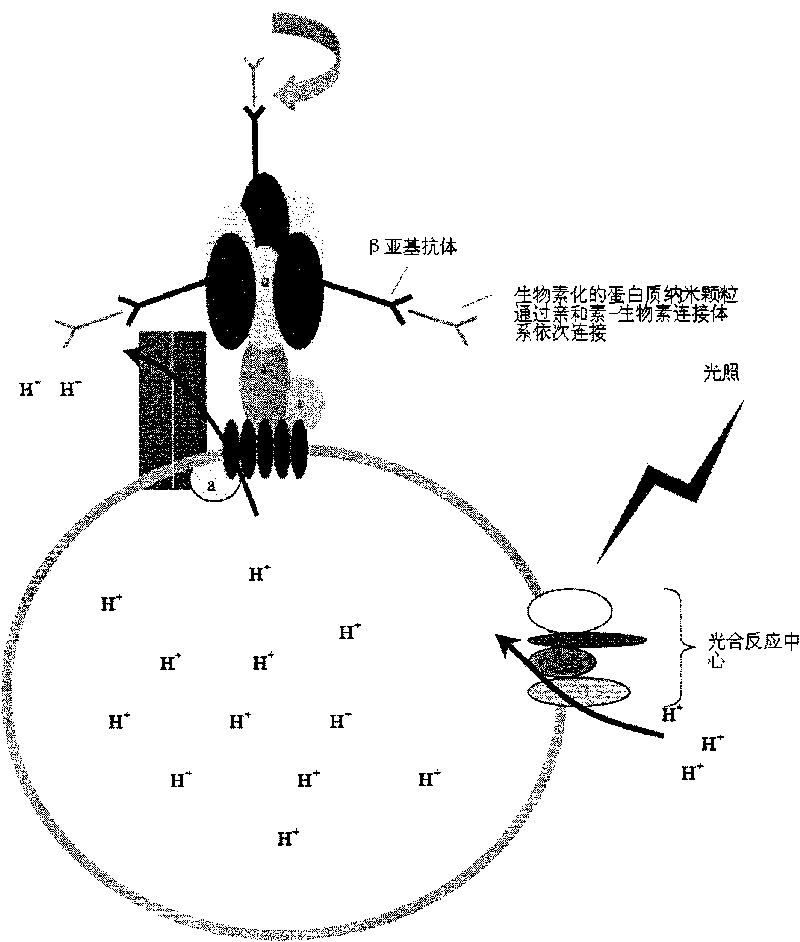
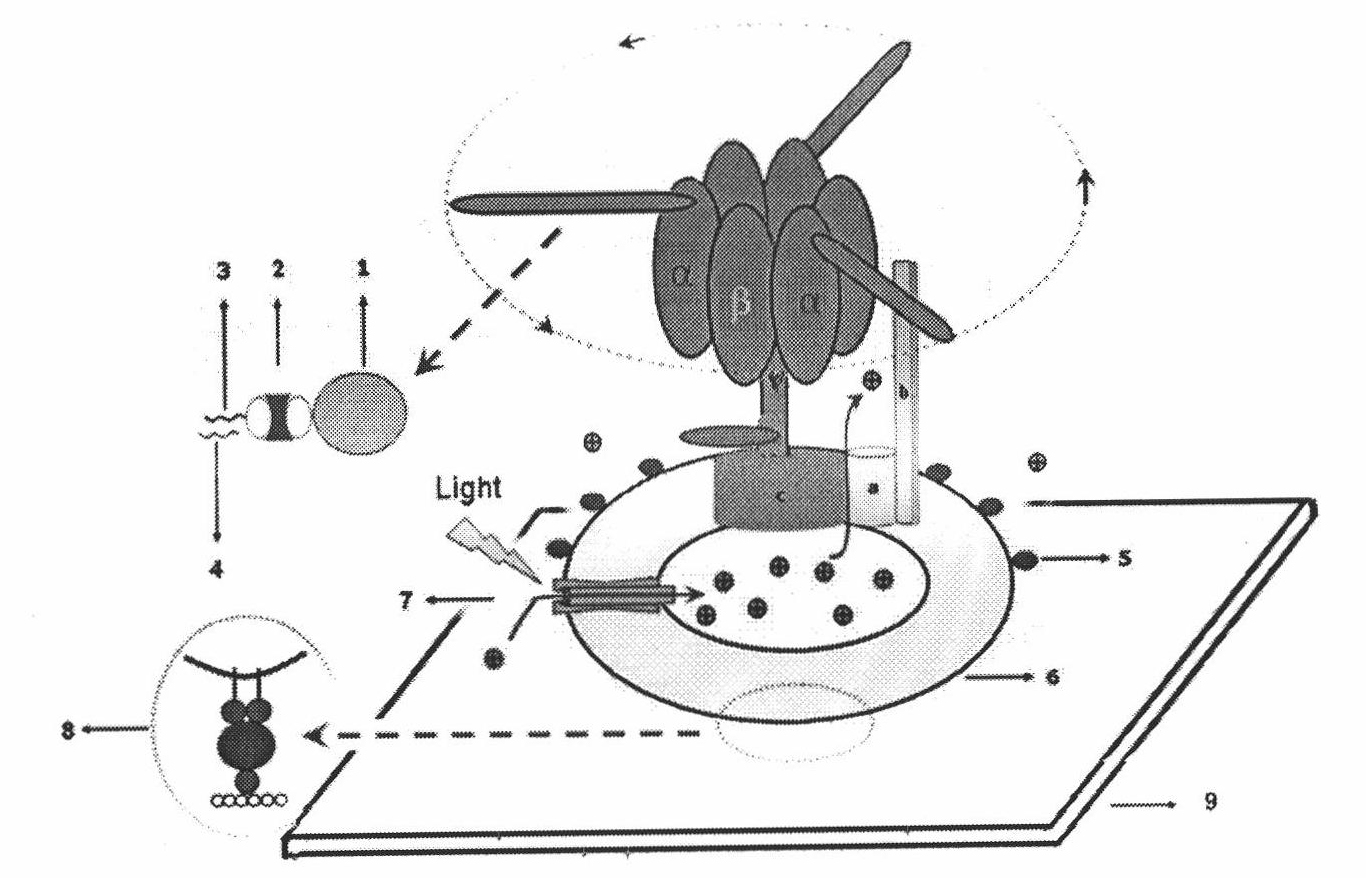
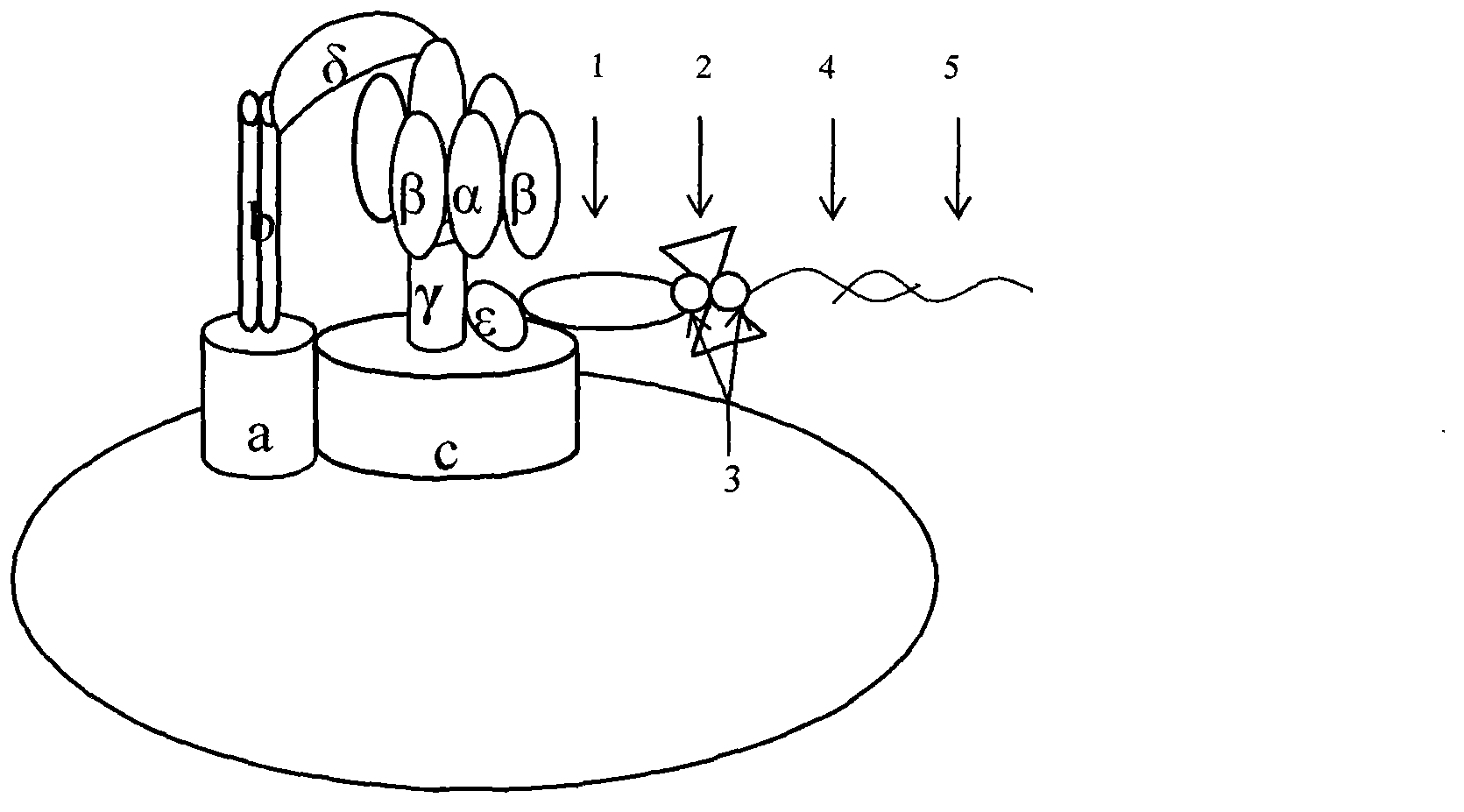
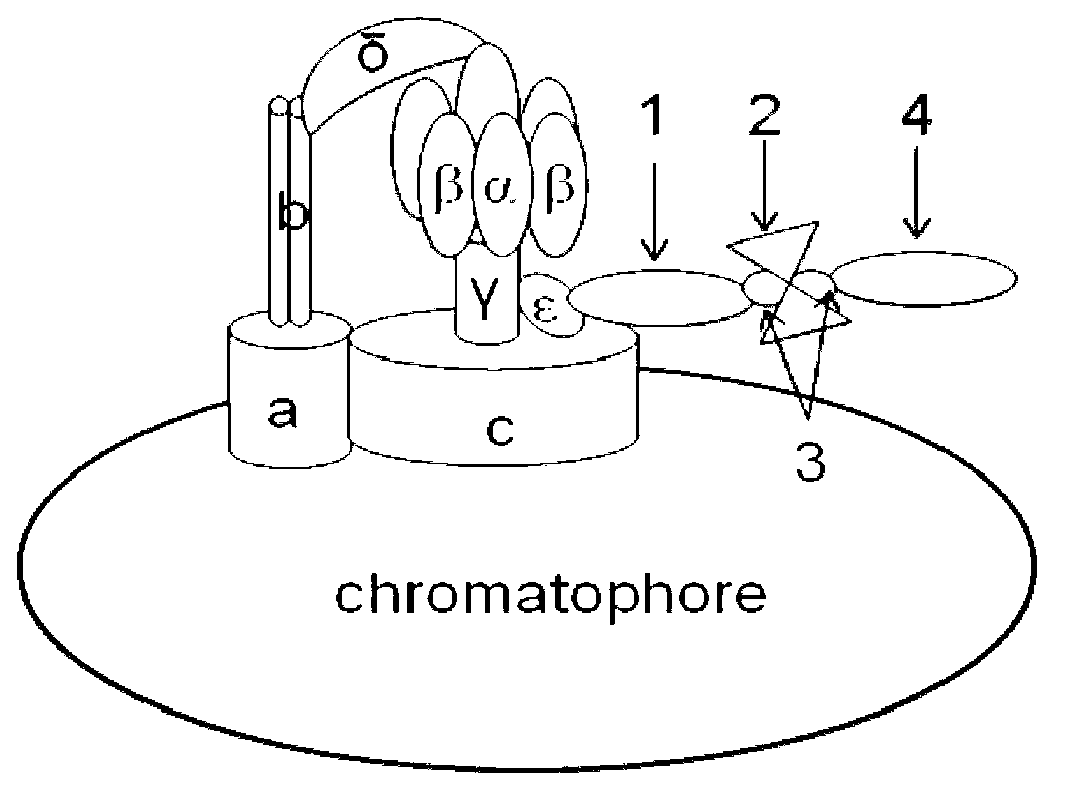
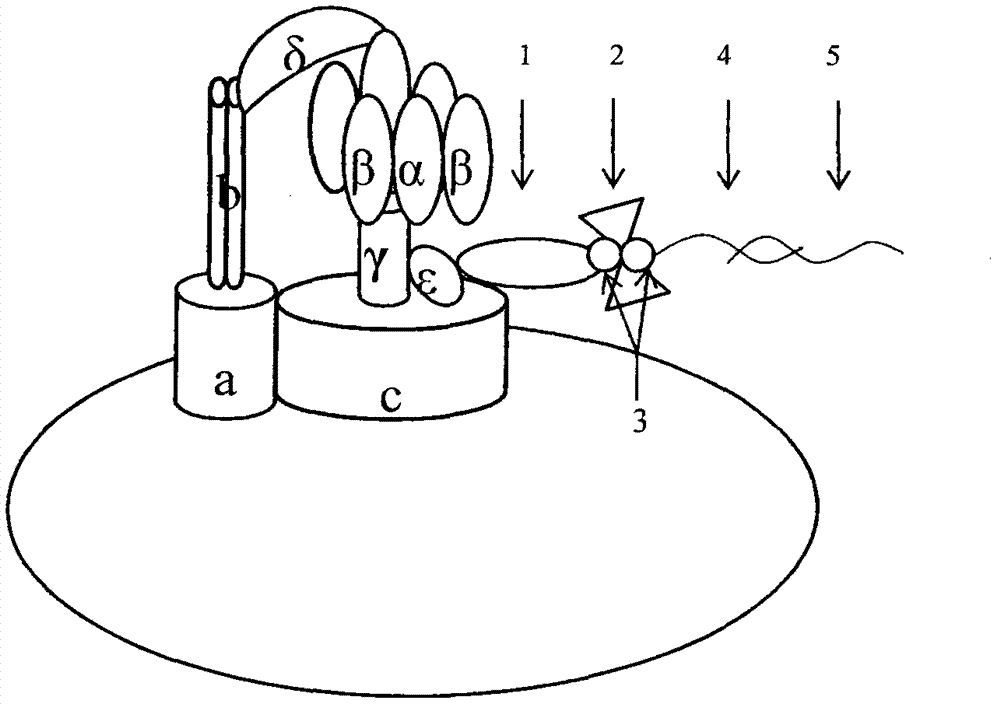
ATP motor rotary type biosensor single molecule analysis and separation technology and method
InactiveCN101334361AImprove resolutionMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceSolubilitySeparation technology
With the aid of basic researches on ATP molecular motor structures and functions, the invention further designs a full-circle biological sensor which is used for analyzing unimolecules that are taken as carrier connecting locus of Epsilon subunits, a preparation method of a plurality of CdTe semiconductor nano crystals that have pH sensitivity, water solubility and high photoluminescence efficiency, and a full-circle ATP motor sensor which is used for marking charge free bodies of ATP motor compounds in a single direction. By adopting the compound that is obtained by combining the full-circle biological sensor with the molecular motor principle and the quantum dot technique, the invention generates a unimolecule device that has novel functions, and combines biological molecule analyzing and separating functions with high resolution capability into a whole; the invention can be developed into a novel analyzing and separating technique with ultra-high resolution in physics, can be widely used in multiple fields of environment, national defense, energy and information, etc., thus having wide application value and enormous economic and social benefits.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Single Molecule Detection Using Molecular Motors
InactiveUS20090035751A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid detectionMolecular motor
The present invention provides methods and compositions for highly sensitive nucleic acid detection, down to the single nucleic acid molecule level. In one aspect, the present invention provides methods for detecting a target nucleic acid comprising: (a) providing first and second target-specific nucleic acids, wherein the first and second target-specific nucleic acids each comprise sequences complementary to the target nucleic acid; wherein the first target specific nucleic acid is bound to a first affinity tag and the second target-specific nucleic acid is bound to a second affinity tag, wherein the first affinity tag is capable of binding to a molecular motor, and wherein the second affinity tag is capable of binding to a detection probe; (b) contacting the first and second target-specific nucleic acids to a sample under conditions whereby the first and second target-specific nucleic acids will hybridize to the target nucleic acid if the target nucleic acid is present in the sample, wherein upon hybridization to the target nucleic acid the first and second target-specific nucleic acids are directly adjacent to each other; (c) ligating the first and second target-specific nucleic acids together; (d) binding the molecular motor t˜ the first affinity tag and the detection probe to the second affinity tag; (e) inducing movement of the molecular motor; and (f) detecting movement of the molecular motor through the detection probe, wherein the movement of the molecular motor serves to detect the target nucleic acid in the sample.
Owner:ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS A BODY OF THE STATE OF ARIZONA ACTING FOR & ON BEHALF OF ARIZONA STATE UNVERSITY
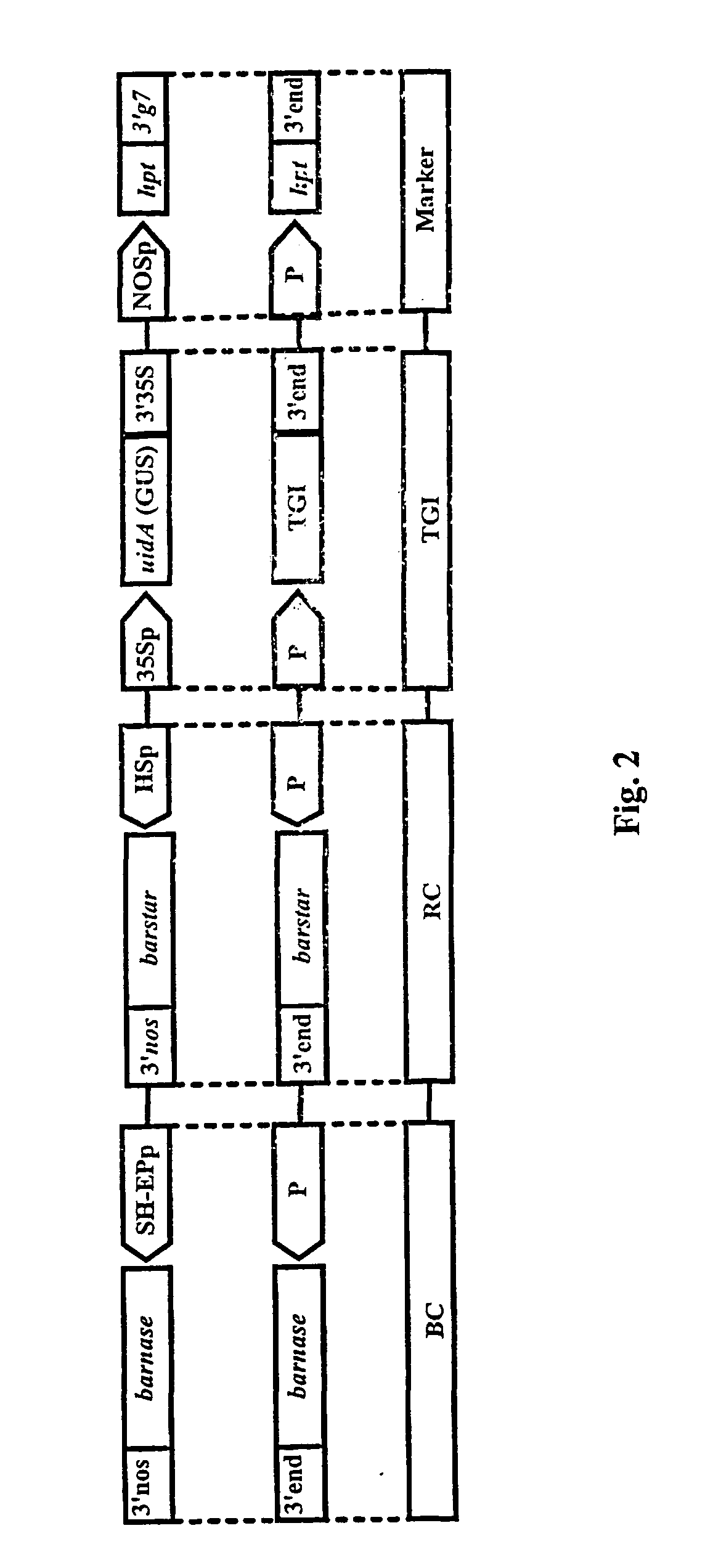
Molecular control of transgene escape by a repressible excision system
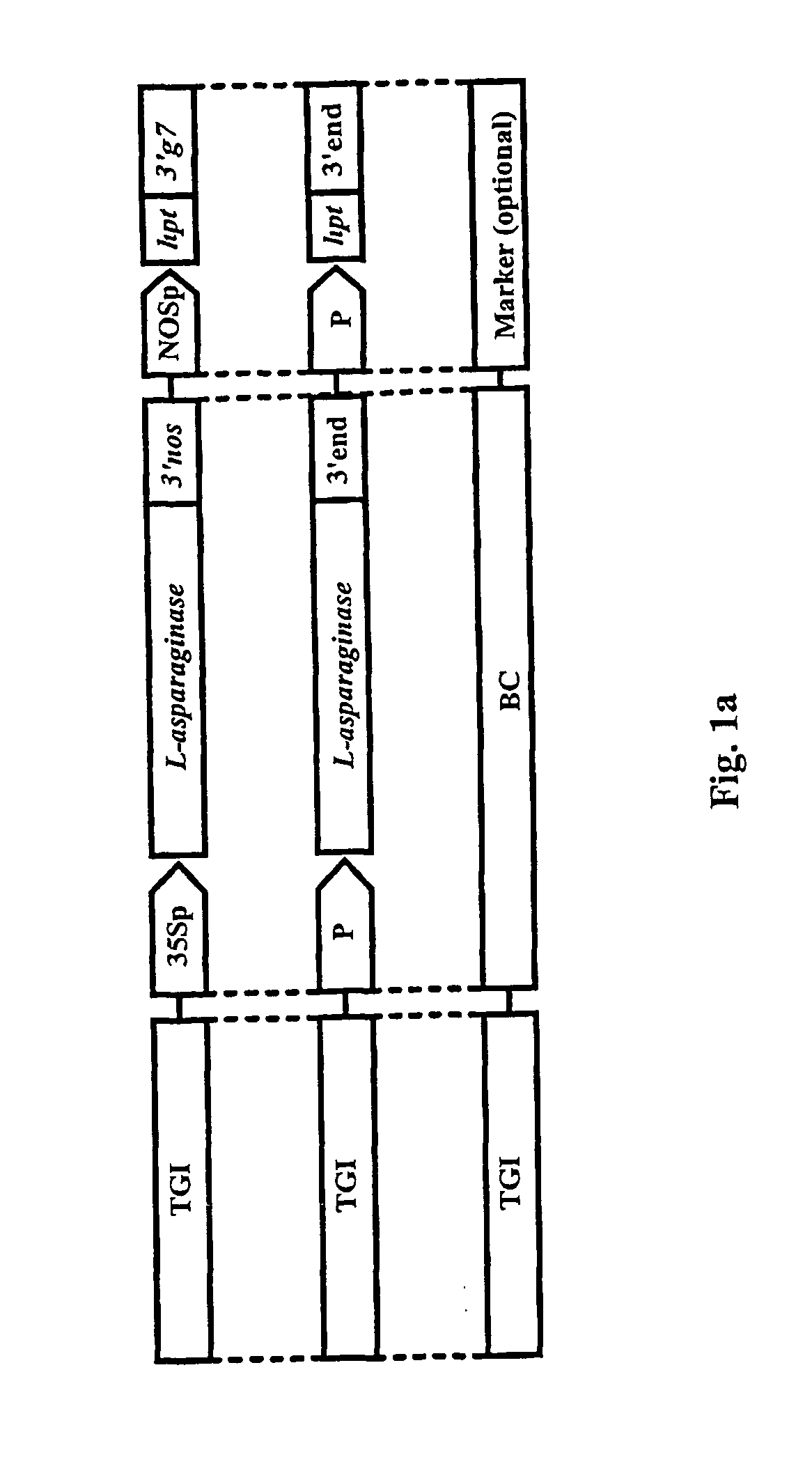
InactiveUS20020007500A1Prevent escapeClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesMolecular motorOrganism
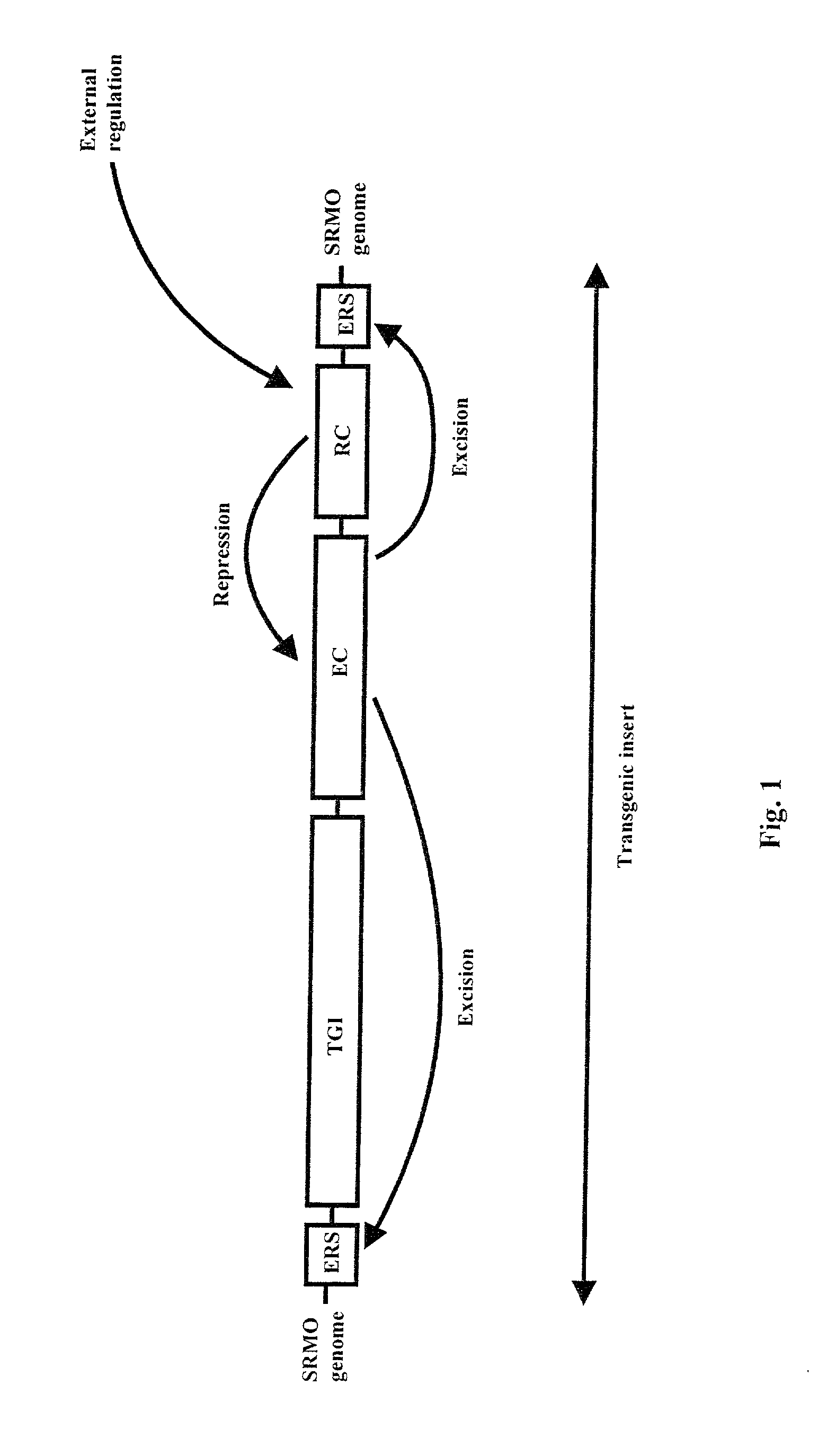
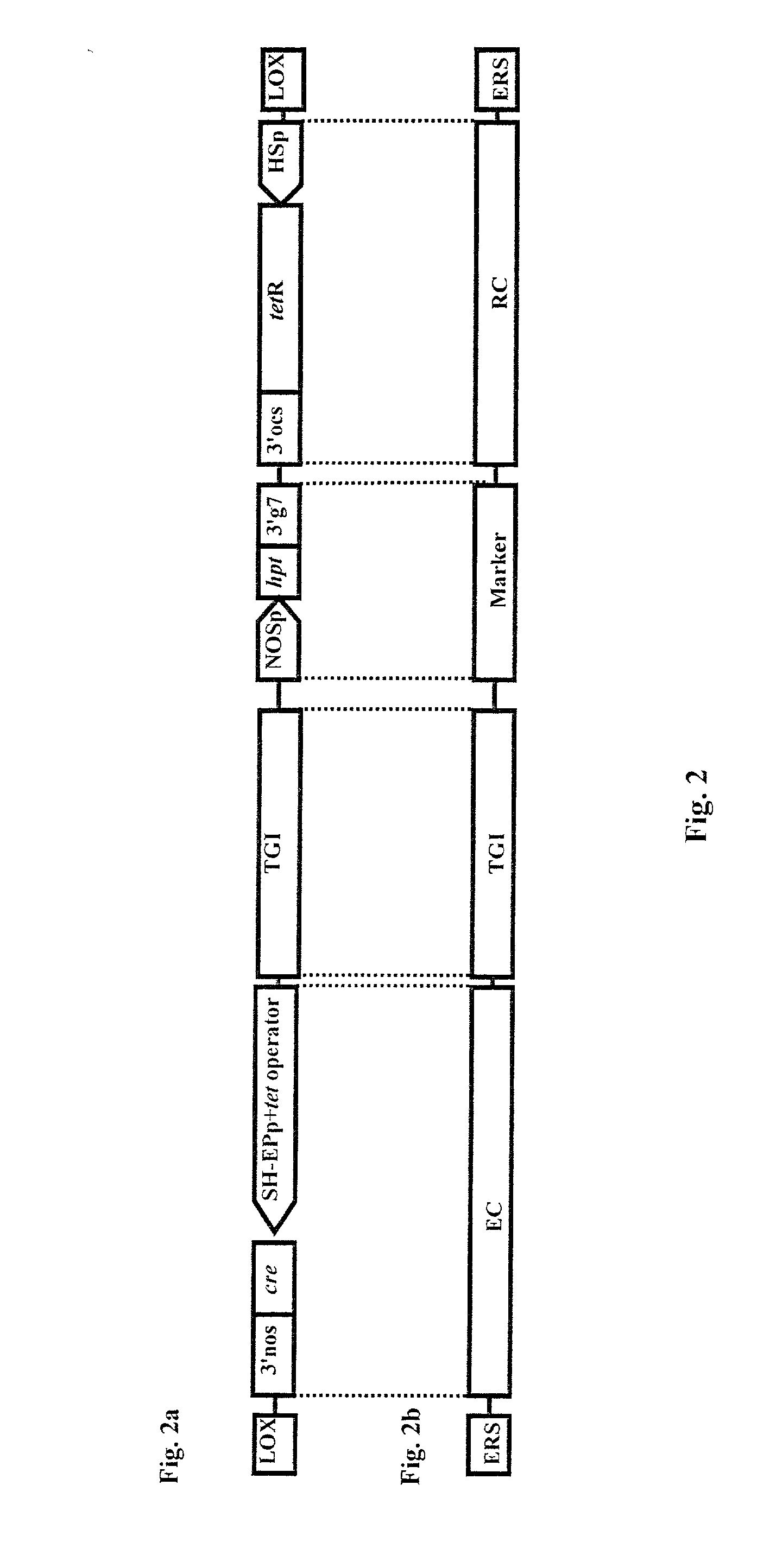
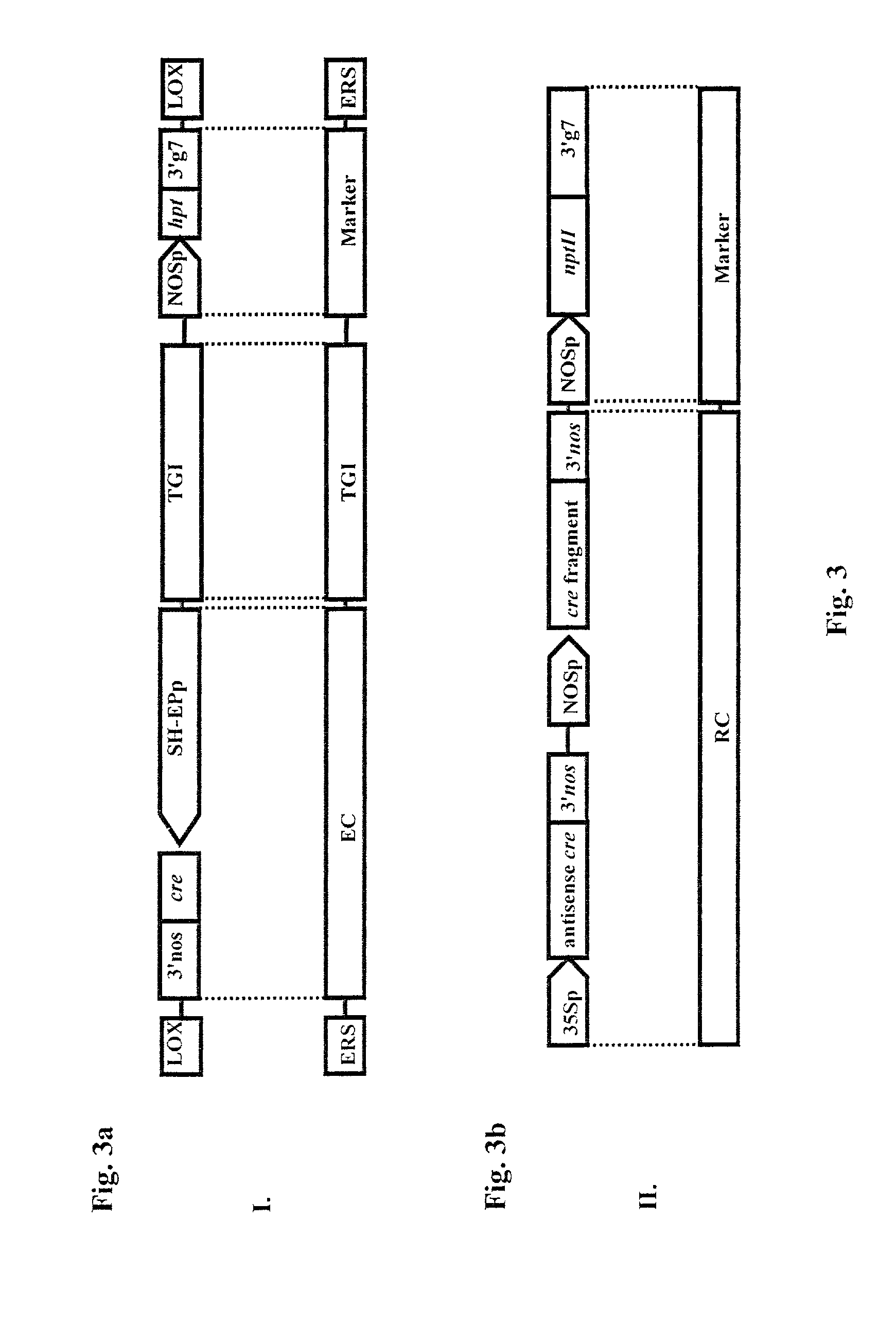
The present invention is related to a method and a system for controlling the transgene segregation and spread. Escape of the gene of interest (TGI) into the environment is prevented by a repressible excision system (RES), which can be controlled by externally applicable means and comprises an excision construct (EC) having a gene encoding recombinase closely linked to the (TGI) and flanked by excision recognition sites (ERSs). The externally applicable means for controlling the repression of the expression of the gene encoding the recombinase enzyme is achieved with or without a repressor construct (RC). The action of the repressible excision system (RES) leads to excision of the transgenic insert, whenever a transgenic organism and the externally applicable means are withdrawn, which occurs if a transgenic organism escapes from the human control.
Owner:UNICORP
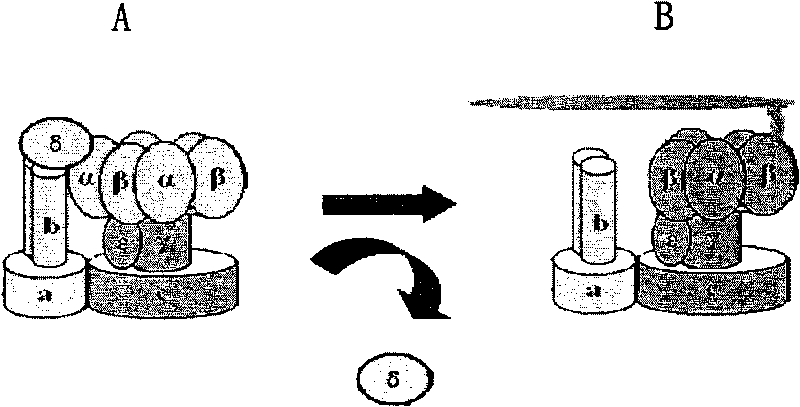
Biomolecule motor magnetic regulating and controlling device
A nano-class magnetic regulating controller of biomotor features that a controllable magnetic rotor is installed on the platform of microscope, and under the action of external motor, it can rotate fast and drive the molecular motor in specimen platform to rotate.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Light-driven rotary molecular motors
InactiveUS20110077394A1Silicon organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationLight energyMolecular motor
Compounds of Formula (1) are disclosed.Cb is a carbocyclic or heterocyclic group having an atom within the cyclic structure selected from C, N, Si, and Cr and singly bound to A. A is CR, COR, CSR, CNR2, CCN, CCONR2, CNO2, CNNAr, CX′, or N. Cr is a chromophore having a substantially planar cyclic structure. The compounds function as nanometer-scale rotary molecular motors powered and controlled by light energy. The design of the molecular motor devices is flexible so that the rotary direction, drive light wavelength, and other physical characteristics can be varied. The compounds can be chemically functionalized to allow it to be integrated into or attached to a variety of structures. The device can be used in applications where mechanical power, positional control, and information encoding are to be generated at the size scale of individual molecules.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT NEVADA SYST OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF NEVADA RENO
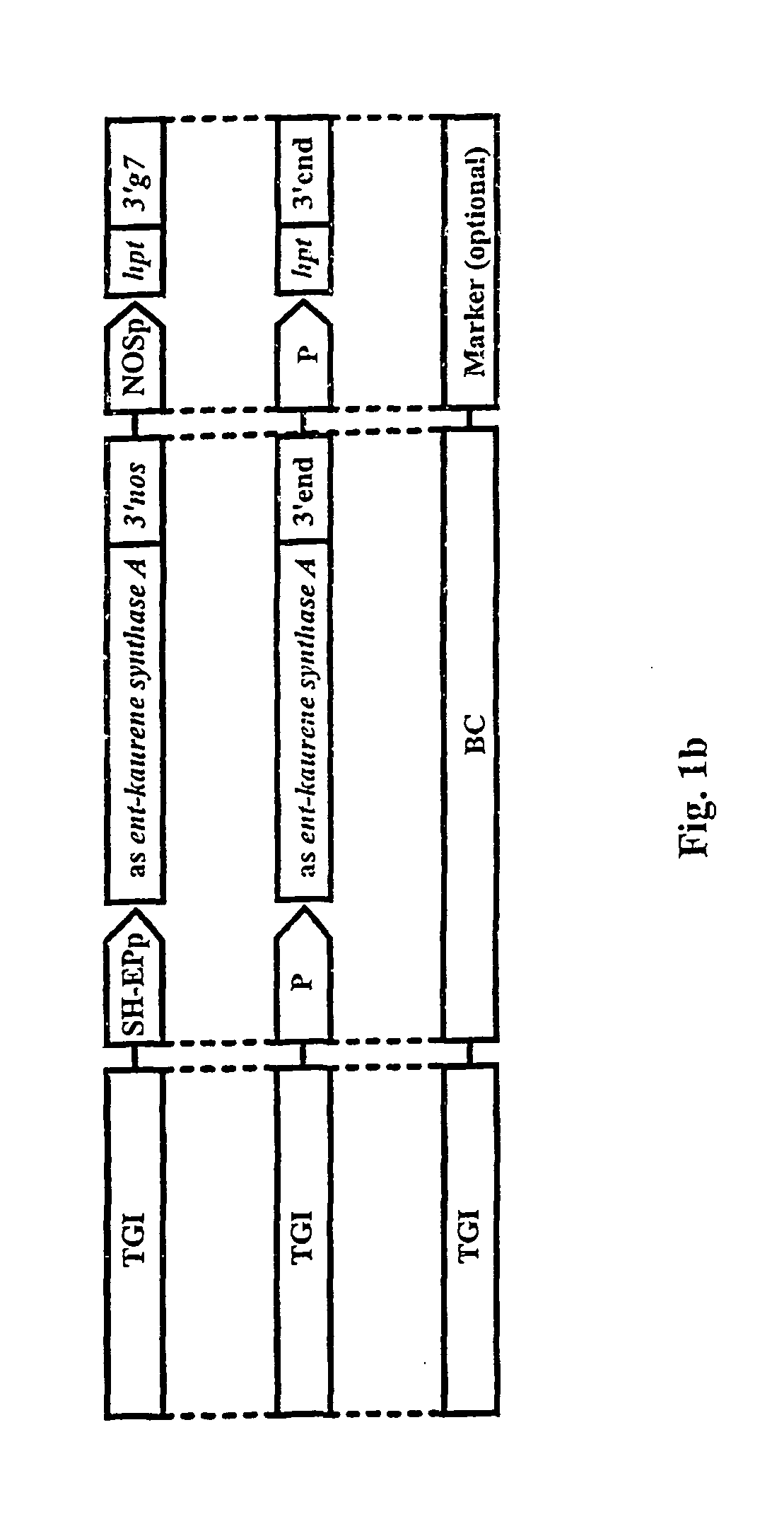
Molecular control of transgene segregation and its escape by a recoverable block of function (RBF) system
InactiveUS6849776B1Avoid environmentAvoid separationSugar derivativesHydrolasesDNA constructMolecular motor
The invention is related to a method and a DNA construct for controlling transgene segregation in a sexually reproducing multicellular organism (SRMO), especially in such SRMOs which are susceptible of interbreeding with their cultured or wild-type relatives. The method and construct allows the farmer to reuse the transgenic crop without risk for escape of the transgene into the environment. The DNA construct is a recoverable block of function (RBF) system comprising at least one blocking construct (BC), and at least one means for recovering the blocked functions. The BC has a capacity of blocking at least one molecular or physiological function essential for the development and / or reproductive cycle of the SRMO. The BC is closely linked to the transgene of intereset (TGI). The blocked function is recoverable by an external treatment or intervention, which is optionally combined with one or more recovering constructs (RC). Different types of RBFs, including single, full, delayed, double, multiple and reversed delayed RBF are disclosed.
Owner:UNICROP LTD
Construction and detection method of biomolecular motor resonance sensor
InactiveCN102798715AIncrease the probability of collisionReduce reaction detection timeMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNonlinear phenomenaEngineering
The invention provides a construction and detection method of a biomolecular motor resonance sensor. According to the invention, in the process of constructing rotary biological sensors, the phenomenon that activation / suppression exists between load and rotation speed is found and nonlinear relationship exists between signal change and load. The nonlinear phenomenon between rotation and load cannot be explained by common theories of mechanics, but can be described by the resonance theory. According to the invention, motor rotary type sensors are developed into resonance type sensors. The regulation and control factors of the sensors of such type are more complicated and the regulation and control requirements are higher; but once resonance conditions are found to develop the application of the sensors to a higher level, larger principle and technology breakthroughs of the biological sensors are obtained; and after the products are put into use, direct economic benefit and huge social benefit can be generated.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Molecular control of transgene segregation and its escape by a recoverable block of funtion (rbf) system
InactiveUS20040025200A1Leak to environmentInhibition of segregationClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesDNA constructWild type
The invention is related to a method and a complex of DNA constructs for providing an increased level of control of transgene segregation in Sexually Reproducing Multicellular Organisms (SRMOs), which are prone to out-crossing with their wild-type or cultivated relatives. The method and constructs allow the farmer to reuse the transgenic crop. without risk. The RBF system comprises one or more Transgenes of Interest (TGIs) encoding desired gene products, one or more Blocking Constructs (BC), and one or more user-controlled means for recovering the blocked functions. The BC has the capacity of blocking at least one function essential for the survival and / or reproduction of the SRMO. Preferably more than one BC flanking the TGIs are used. The BC may be located in close proximity to the TGI, preferably in an intron or flanking the TGIs. The blocked function is recoverable by user-controlled interventions preferably applicable under confined conditions. The intervention is combined with one or more Recovering Constructs (RC). Different types of RBF systems are disclosed. The Double and Triple and Segregating RBF systems and intron-inserted BC are the preferred embodiments of the present invention. The Transgenic Inserts (TI) of the Triple RBF system and their interactions are shown in FIG. 10.
Owner:UNICROP LTD
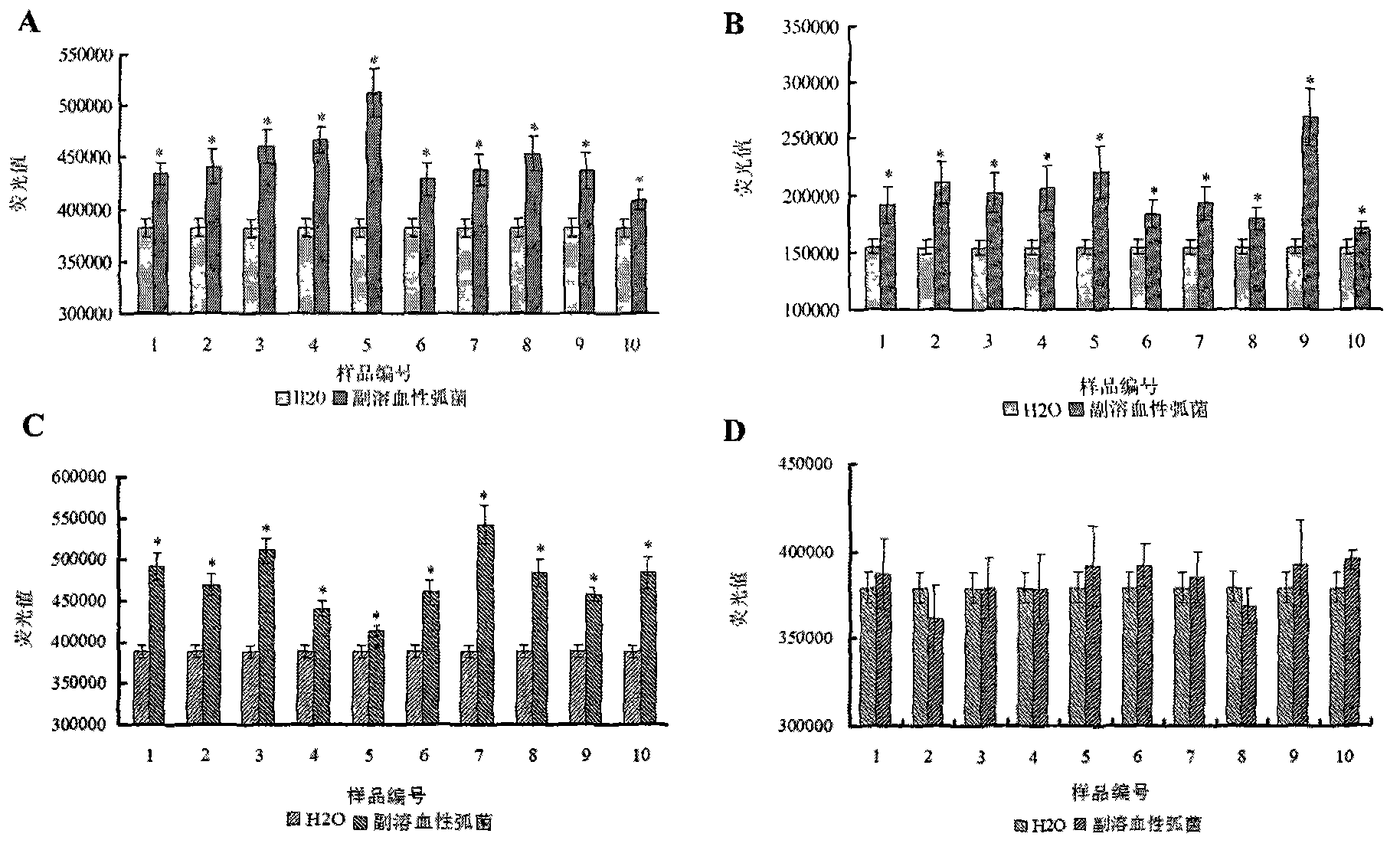
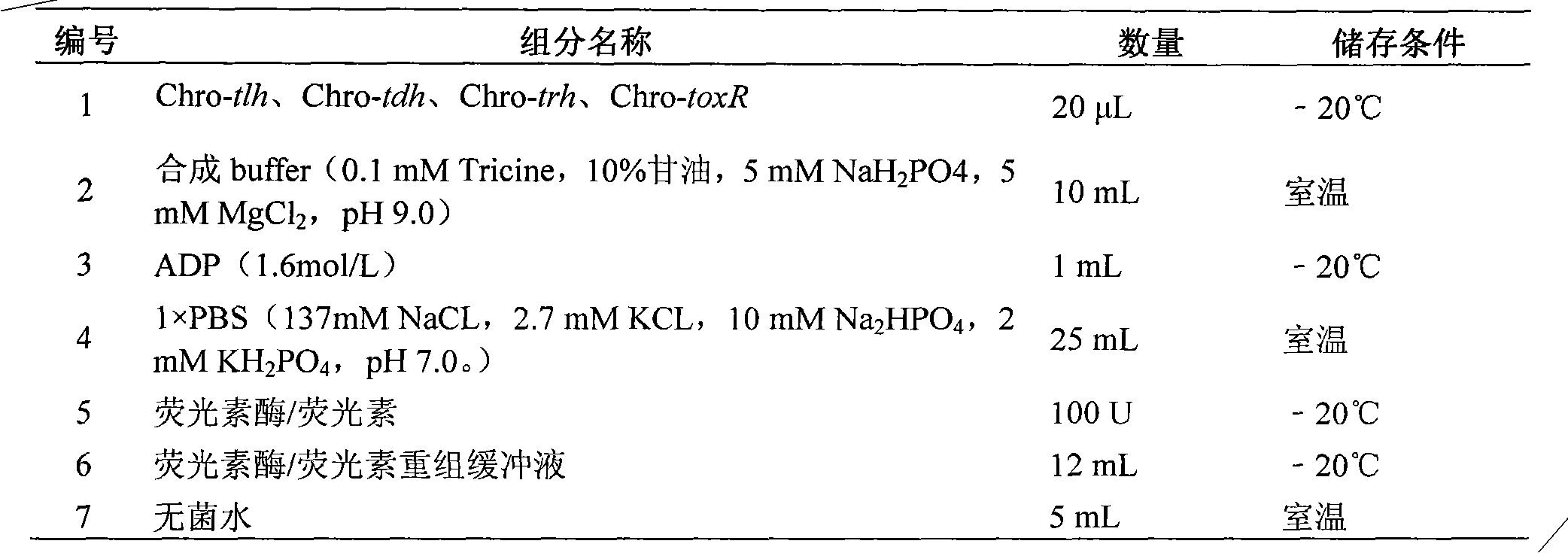
Molecular motor biosensor kit used in vibrio parahaemolyticus molecular typing
ActiveCN102936625AQuick checkStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesVirulent characteristicsMolecular motor
The invention belongs to a kit used for carrying out rapid molecular typing determination upon vibrio parahaemolyticus pathogenicity. Specifically, vibrio parahaemolyticus species-specific genes tlh and toxR and virulence genes tdh and trh are detected by using F0F1-ATPase molecular motor biosensors Chro-tlh, Chro-tdh, Chro-trh, and Chro-toxR in the kit. On the one hand, with the detections upon species-specific genes tlh and toxR, a target strain can be identified. On the other hand, with the detections upon tdh and trh, the target strain pathogenicity can be determined. A method comprises that: F0F1-ATPase molecular motor biosensors in the kit are constructed; molecular typing is carried out by using the F0F1-ATPase molecular motor biosensors; and vibrio parahaemolyticus pathogenicity is determined according to a typing result. The kit has the advantages of high sensitivity, high speed, simple operation, and low cost.
Owner:PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA BEIJING ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU +1
Biosensor and method of detecting vibrio parahemolyticus thereby
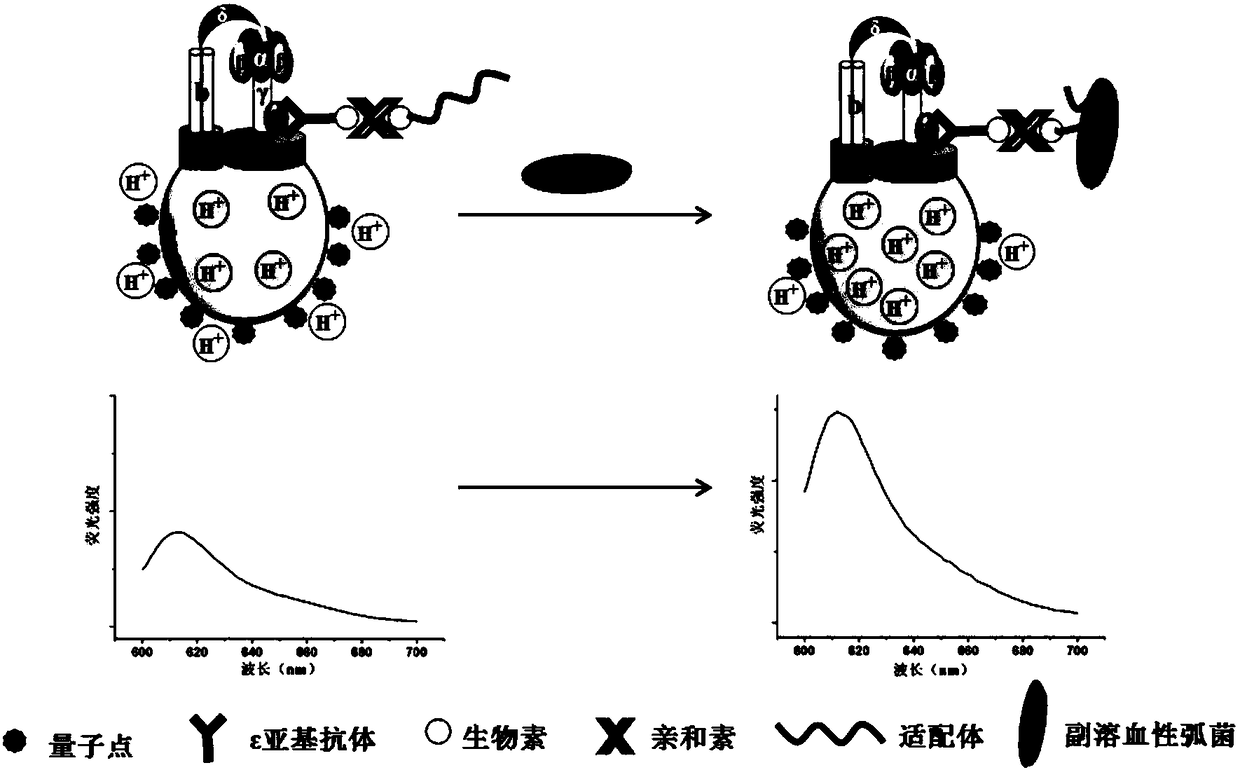
InactiveCN108120703AImprove stabilityReduce manufacturing costFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceBiology
The invention provides a method of detecting vibrio parahemolyticus based on an aptamer recognizing quantum dot labelled molecular motor biosensor. The aptamer of vibrio parahemolyticus is specifically recognized as a recognizing probe by labeling a pH sensitive quantum dot fluorescent nanomaterial to the surface of a color carrier. An F0F1 ATPas molecular motor aptamer sensing system is constructed by connecting the recognizing probe to a F0F1-ATPase molecular motor by means of an epsilon subunit antibody-biotin-avidin-5' end biotinylated vibrio parahemolyticus aptamer system. The lowest detection limit to the vibrio parahemolyticus by the method can reach 7cfu / mL, and the method can be applied to detecting vibrio parahemolyticus in shrimp meat samples, and is accurate and reliable in result.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Molecular Motor
There is disclosed a microscale or nanoscale stepper motor in which one or more arrays of corresponding types of optically switchable molecular actuators are used to drive progressive motion between bodies of the motor.
Owner:DEXLER KIM ERIC
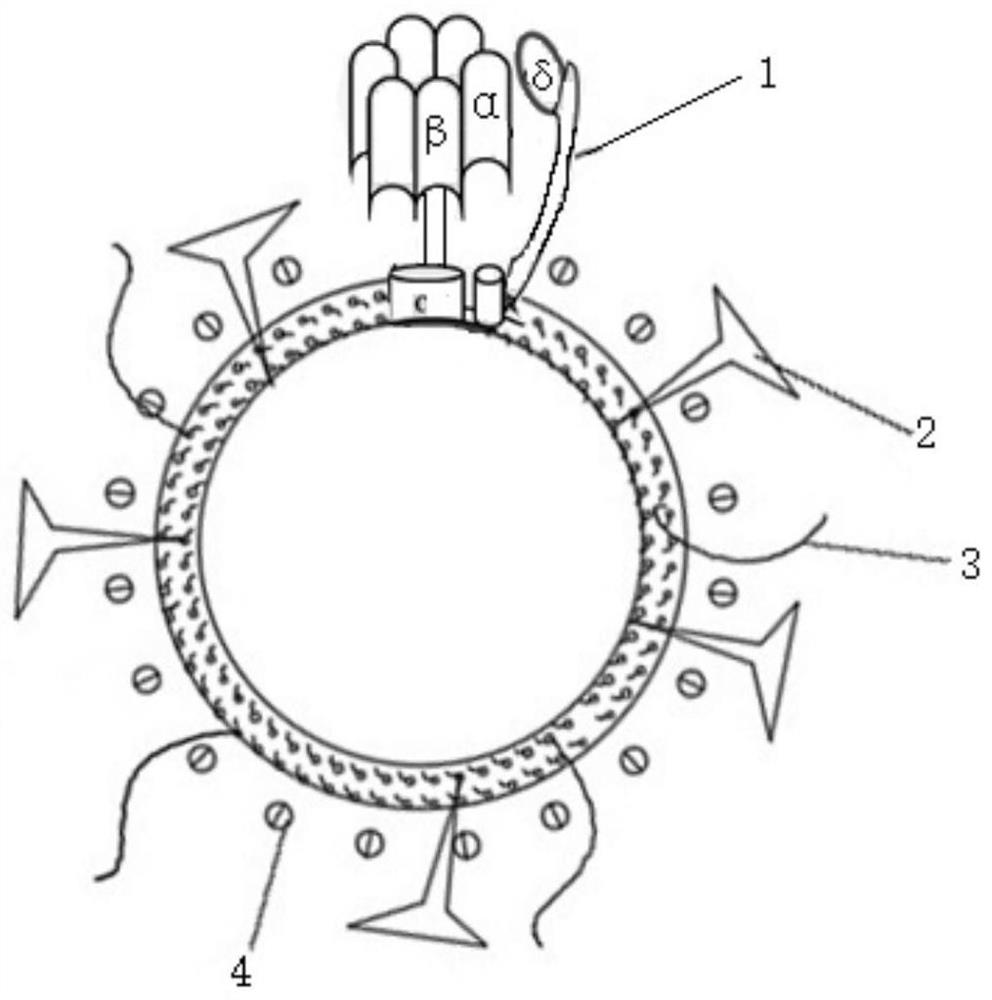
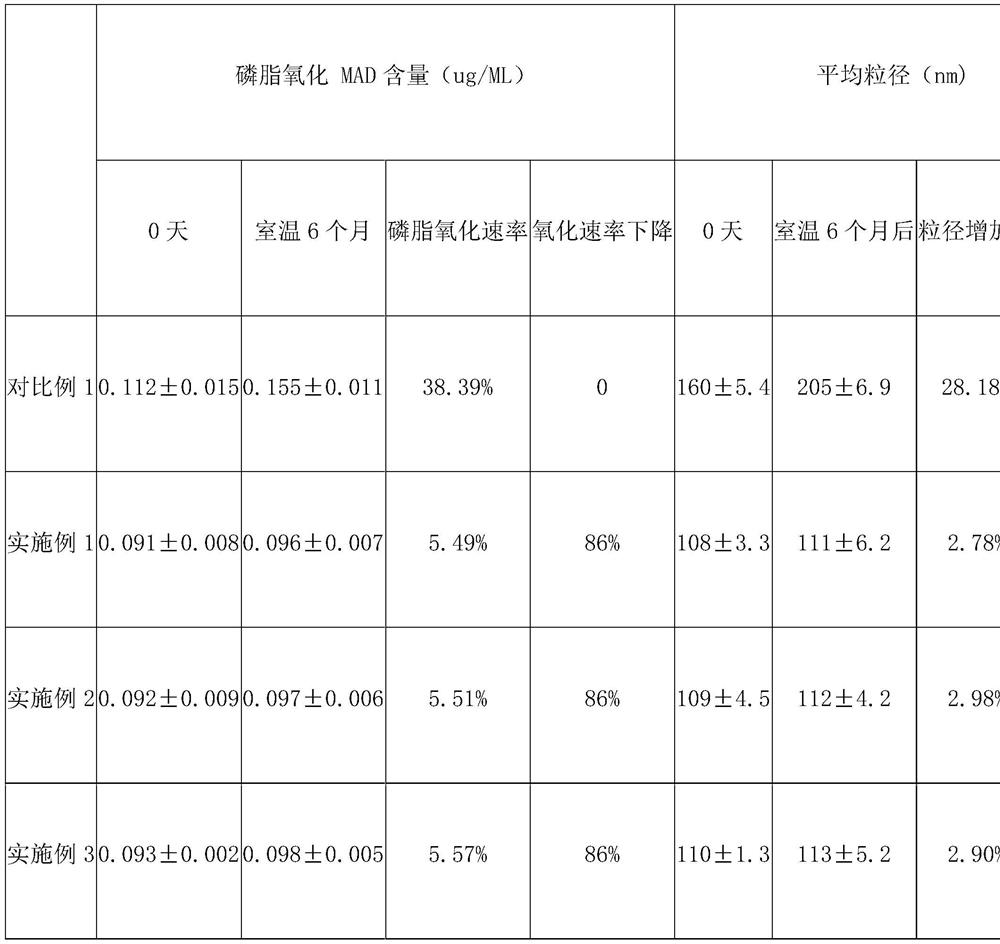
Molecular motor lipid vesicle composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112656696AImprove delicate vitalityImprove solubilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMolecular motorPhospholipid
The invention relates to a molecular motor lipid vesicles composition, a preparation method and an application of the composition. The composition has the effects of improving the solubility and long-term effect of molecular motors and promoting absorption, and the assembly structure of the molecular motor lipid vesicles is a closed structure or a cell compartment containing molecular motor ATP synthase and lipid bilayers thereof and having biological membrane properties, the molecular motor lipid vesicles called vesicles, niosolnes are also called liposomes in the past, the biological membrane containing the molecular motor has a lipid bilayer structure, so that the biological membrane has moisturizing, whitening and anti-aging effects when being applied to the field of cosmetics, achieves the effects of improving the stability, improving the solubility and the long-term effect of the molecular motor and promoting absorption, and is simple and convenient in production process, and low in cost, and the defects that the lipidosome adopting phospholipid needs to be purified, is easy to oxidize and degrade and the like are avoided.
Owner:HANGZHOU UMOTOR BIOTECH CO LTD
Molecular motor biosensor kit for molecular subtyping of salmonella
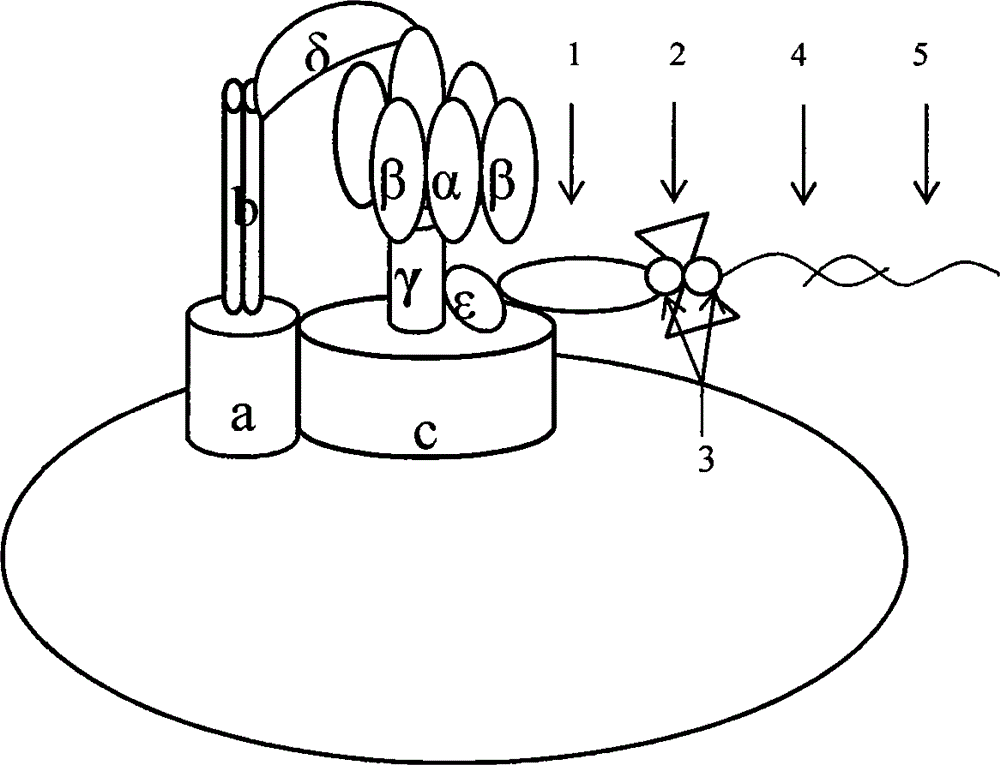
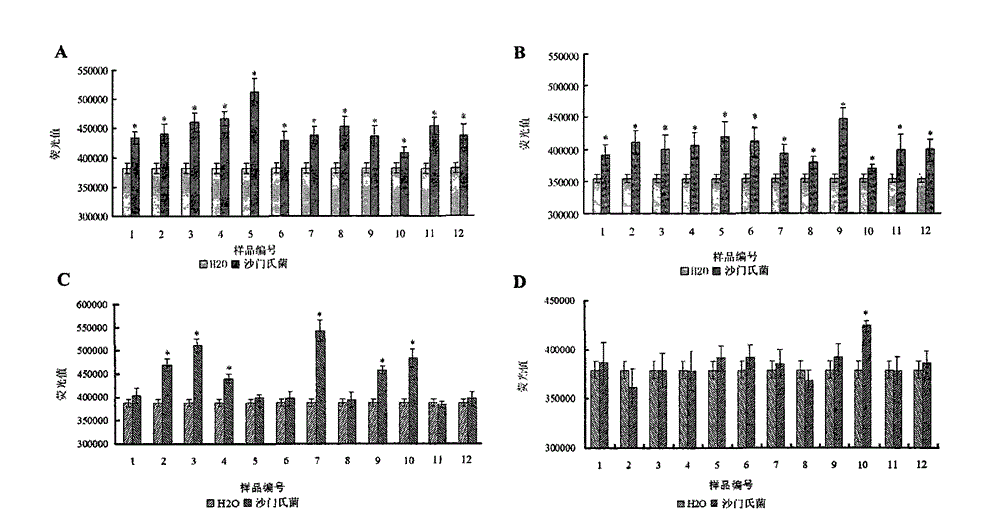
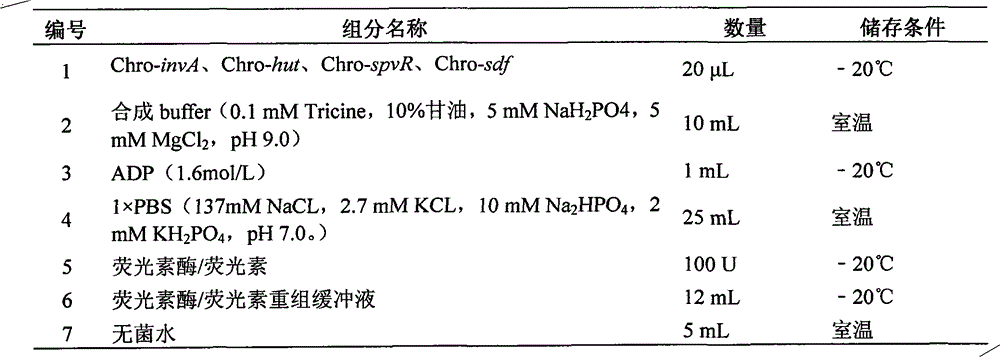
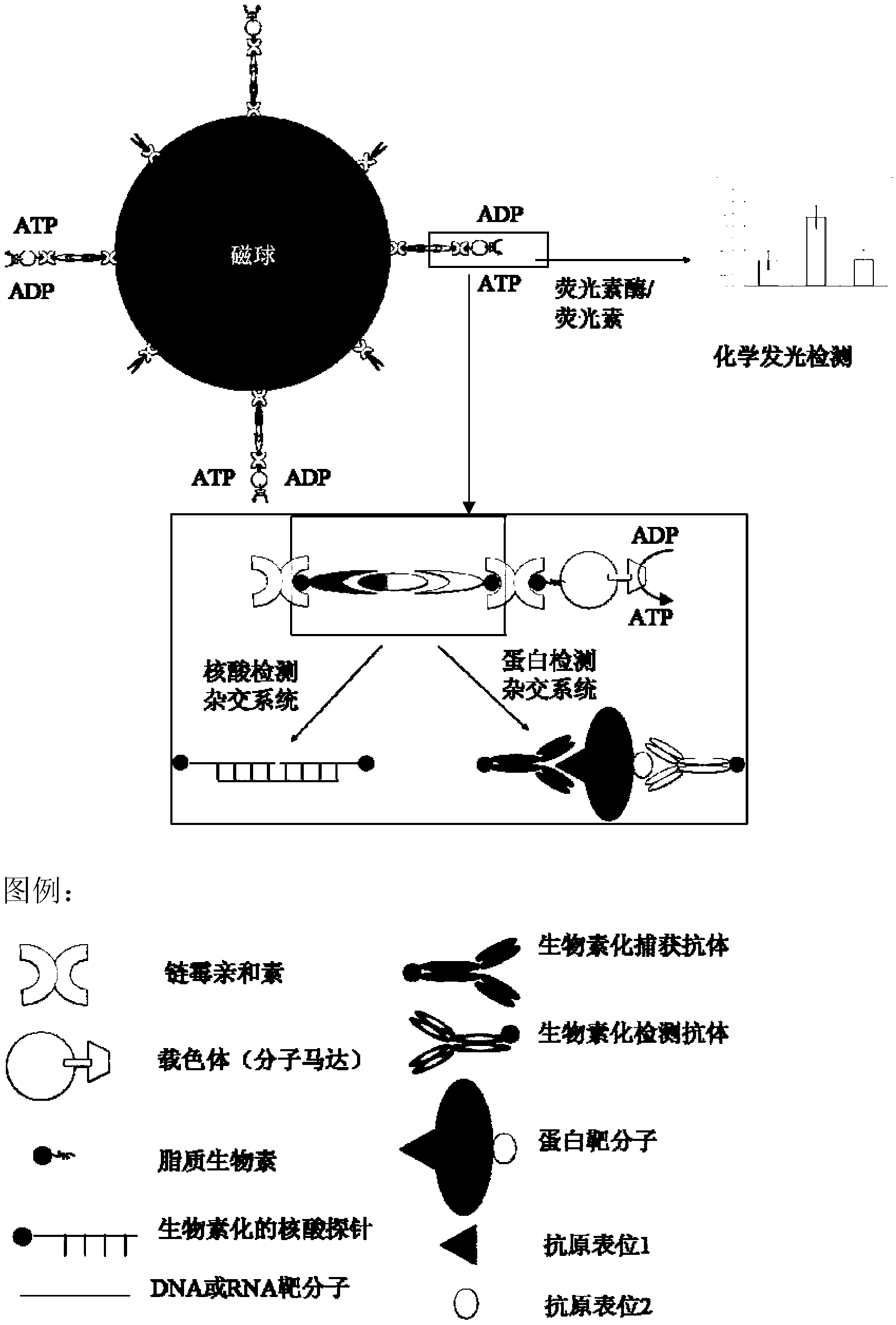
InactiveCN102912021AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMolecular motorSalmonella Be
The invention belongs to a kit for quickly performing molecular subtyping determining to salmonella, and particularly relates to the technology of utilizing an F0F1-ATPase molecular motor biosensor Chro-invA, Chro-hut, Chro-spvR and Chro-sdf in the kit to detect specific gene invA and hut of the salmonella, toxic plasmid gene spvR and salmonella enteritidis strain specific gene sdf, so as to determine whether the salmonella contains toxic plasmid and whether the salmonella is the salmonella enteritidis in a subtyping way. The kit has functions that 1, the invA and the hut of the salmonella is detected, so as to identify target bacterium; 2, the spvR can be detected to determine whether the target bacterium carries the toxic plasmid; and 3, the sdf is detected to determine whether the target bacterium is the salmonella enteritidis. The method can be used for establishing the F0F1-ATPase molecular motor biosensor in the kit, carrying out molecular subtyping of the F0F1-ATPase molecular motor biosensor, and determining whether the salmonella contains the toxic plasmid and whether the salmonella is the salmonella enteritidis in a subtyping way according to a subtyping result. The method has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, fast, simple to operate, and low in cost.
Owner:BEIJING ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT +1
Biosensor construction and detection method based on molecular motor, magnetic enrichment and double-probe hybridization
InactiveCN103308690AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingSignalling moleculesSingle strand
The invention relates to a detection method of biomacromolecule, and in particular relates to a method for detecting the biomacromolecule by utilizing the signal amplification characteristic of the ATP molecular motor in terms of time and space and high temperature resistance thereof, high specificity of double-antibody hybridization and double-probe hybridization, high flexibility and fastness of magnetic enrichment and magnetic separation, and the high flexibility of the chemiluminiscence detection technology, and reduction of the non-specific hybridization by the single-stranded nuclease degradation and mismatched double-strand. A novel biosensor construction and detection method is capable of separating the signal molecule from the reaction system, storing the signal molecule to measure for multiple times and facilitating the comparison of the samples in different batches, and according to the method, the super-flexibility, fastness, high specificity and avoidance of amplification can be realized.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Method of assisting to identify irradiated lipid-containing foods
InactiveCN103175816AMeet the detection rangeShorten detection timeFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiotin-streptavidin complexPhosphate
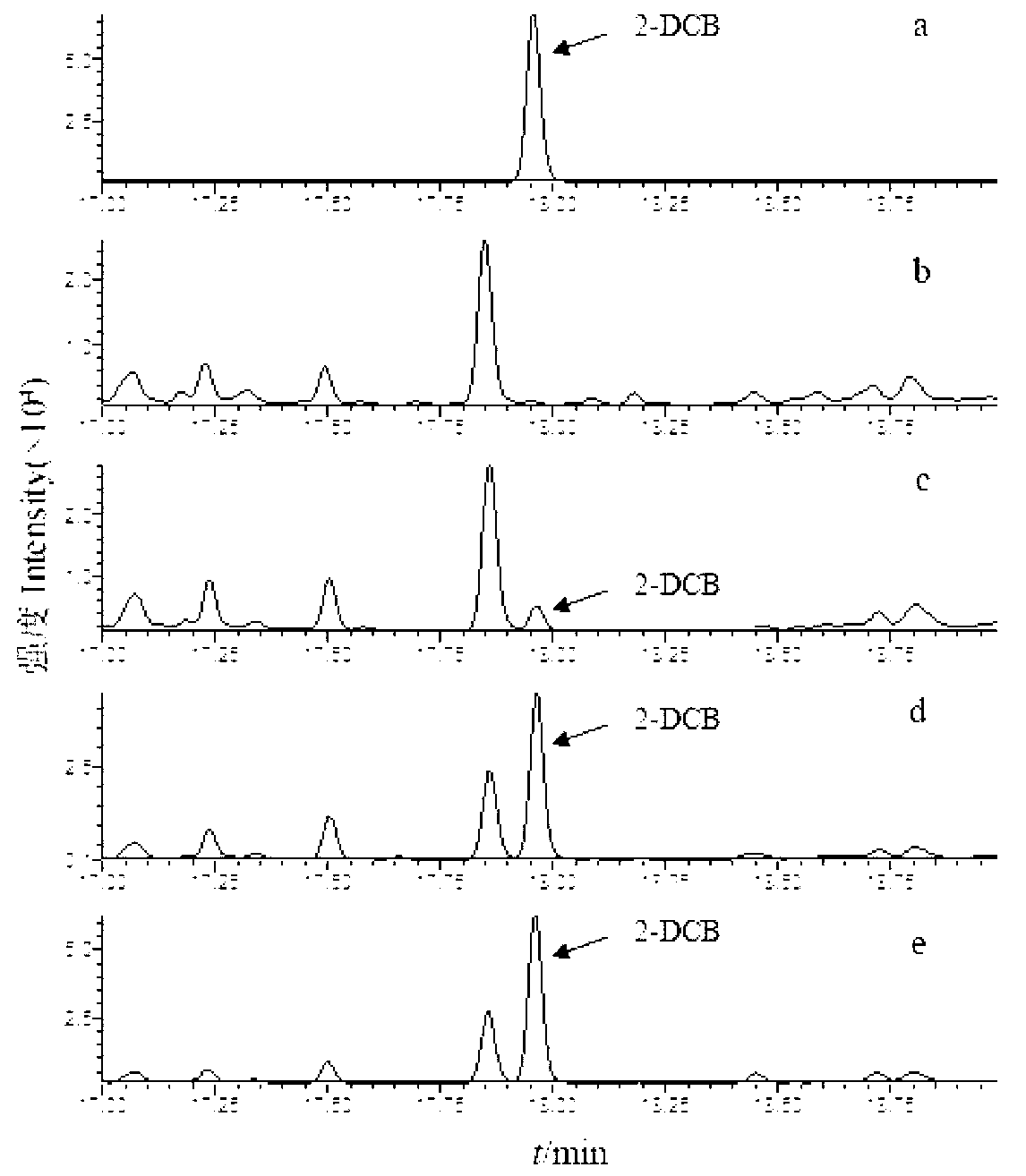
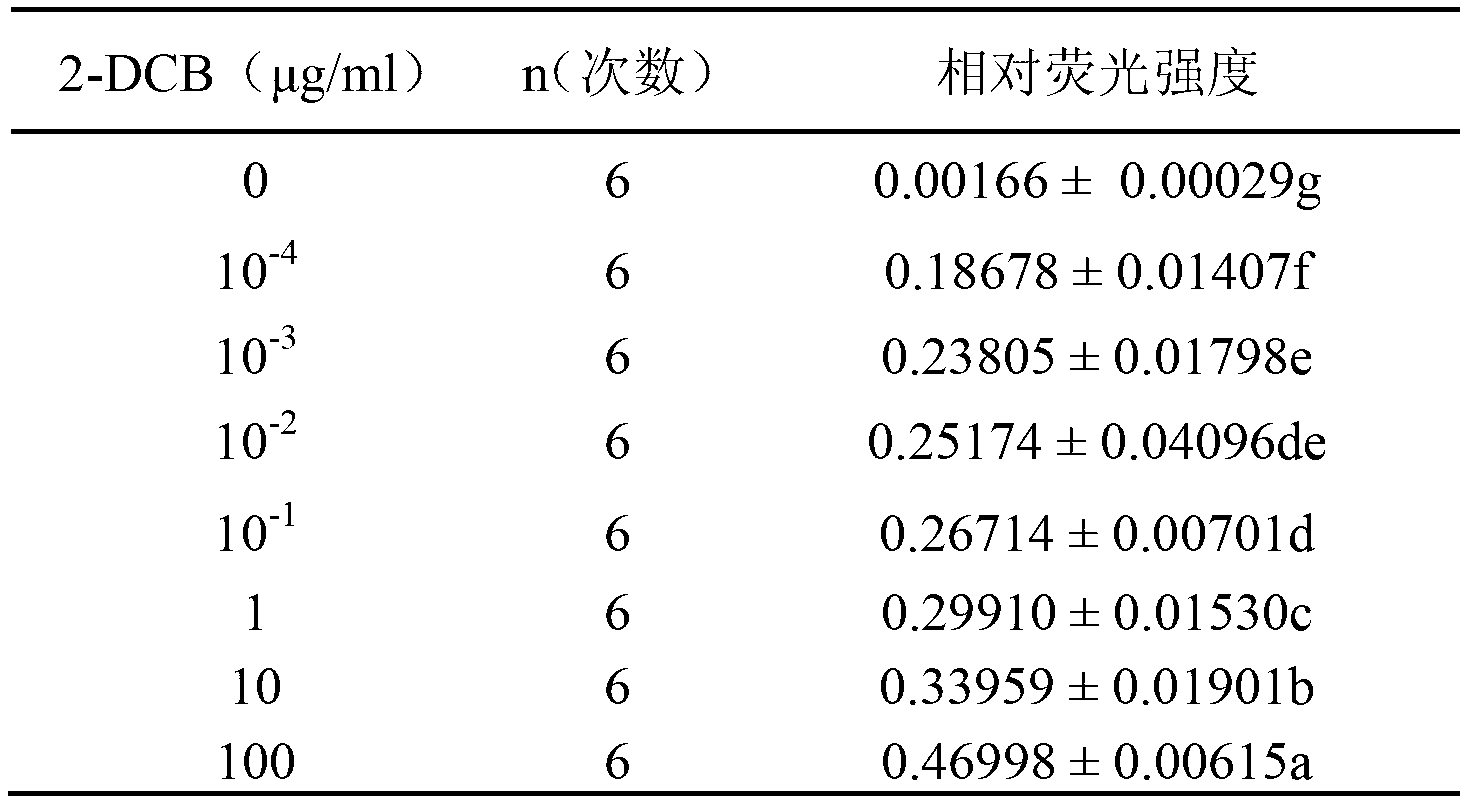
The invention discloses a method of assisting to identify irradiated lipid-containing foods. The method comprises the steps of: (1) sequentially connecting a biotinylated epsilon subunit clonal antibody, streptavidin and a biotinylated 2-dodecyl cyclobutanone polyclonal antibody on epsilon subunit of F0F1-ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) synthase to obtain a molecular motor biosensor; (2) extracting lipid-containing foods which are not irradiated by using a solvent to obtain a solvent extracting solution a, carrying out reaction on the solvent extracting solution a and the molecular motor biosensor under the condition with the existence of a start buffer solution, adding a PBS (Phosphate Buffer Solution) into a reaction system to stop the reaction, uniformly mixing a reaction solution of the reaction system and a fluorescein / luciferase solution, and detecting a mixture by using an ultra-weak luminescence instrument to obtain the fluorescence intensity of the lipid-containing foods which are not irradiated; and (3) extracting the lipid-containing foods to be identified by using a solvent to obtain a solvent extracting solution b, and carrying out the same operations in the step (2) on the solvent extracting solution b to obtain the fluorescence intensity of the lipid-containing foods to be identified, thus realizing identification of the lipid-containing foods. With the adoption of the method of identifying the irradiated lipid-containing foods, the detection time can be shortened to be about 10mins, and in addition, the detection sensitivity of 2-DCB (Dodecyl Cyclobutanone) can reach 10-4 micrograms / mL, thus satisfying the existing detection range of the irradiated lipid-containing foods.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Protein and nucleic acid delivery vehicles, components and mechanisms thereof
ActiveUS20130196416A1Organic active ingredientsMicroencapsulation basedDelivery vehicleMolecular motor
Complex viruses are assembled from simple protein subunits by sequential and irreversible assembly. During genome packaging in bacteriophages, a powerful molecular motor assembles at the special portal vertex of an empty prohead to initiate packaging. An aspect of the invention relates to the phage T4 packaging machine being highly promiscuous, translocating DNA into finished phage heads as well as into proheads. Single motors can force exogenous DNA into phage heads at the same rate as into proheads and phage heads undergo repeated initiations, packaging multiple DNA molecules into the same head. This shows that the phage DNA packaging machine has unusual conformational plasticity, powering DNA into an apparently passive capsid receptacle, including the highly stable virus shell, until it is full. These features allow for the design of a novel class of nanocapsid delivery vehicles.
Owner:CATHOLIC UNIV OF AMERICA
F0F1-ATPase rotary molecular motor sensor kit for detecting Vibrio cholera
InactiveCN103088111AQuick checkHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiologyF0F1-ATPase
An F0F1-ATPase rotary molecular motor sensor kit for detecting Vibrio cholera belongs to the field of the rapid detection of food microbes, and mainly solves an overlong time (about 5 days) problem of traditional detection methods. The kit is mainly characterized in that an F0F1-ATPase rotary molecular motor sensor on a chromatophore is utilized, an F0F1-ATP synthase can rapidly rotate, and the coupling between a catalytic site and proton transfer is established through rotating the F0F1-ATP synthase. An ompW probe is connected to the epsilon subunit of the ATP synthase, a sample to be measured and a negative contrast substance are respectively combined with a biosensor, the ATP outputs 20min after the ATP catalytic synthesis are compared, the ATP synthetic outputs can be measured through the amount of H<+> in the environment, and the H<+> amount can be obtained through the fluorescence intensity of H-DHPE. The kit can realize the rapid, sensitive and high-flux detection of the Vibrio cholera in the sample to be measured.
Owner:PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA BEIJING ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com