Patents
Literature
67 results about "ATP synthase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
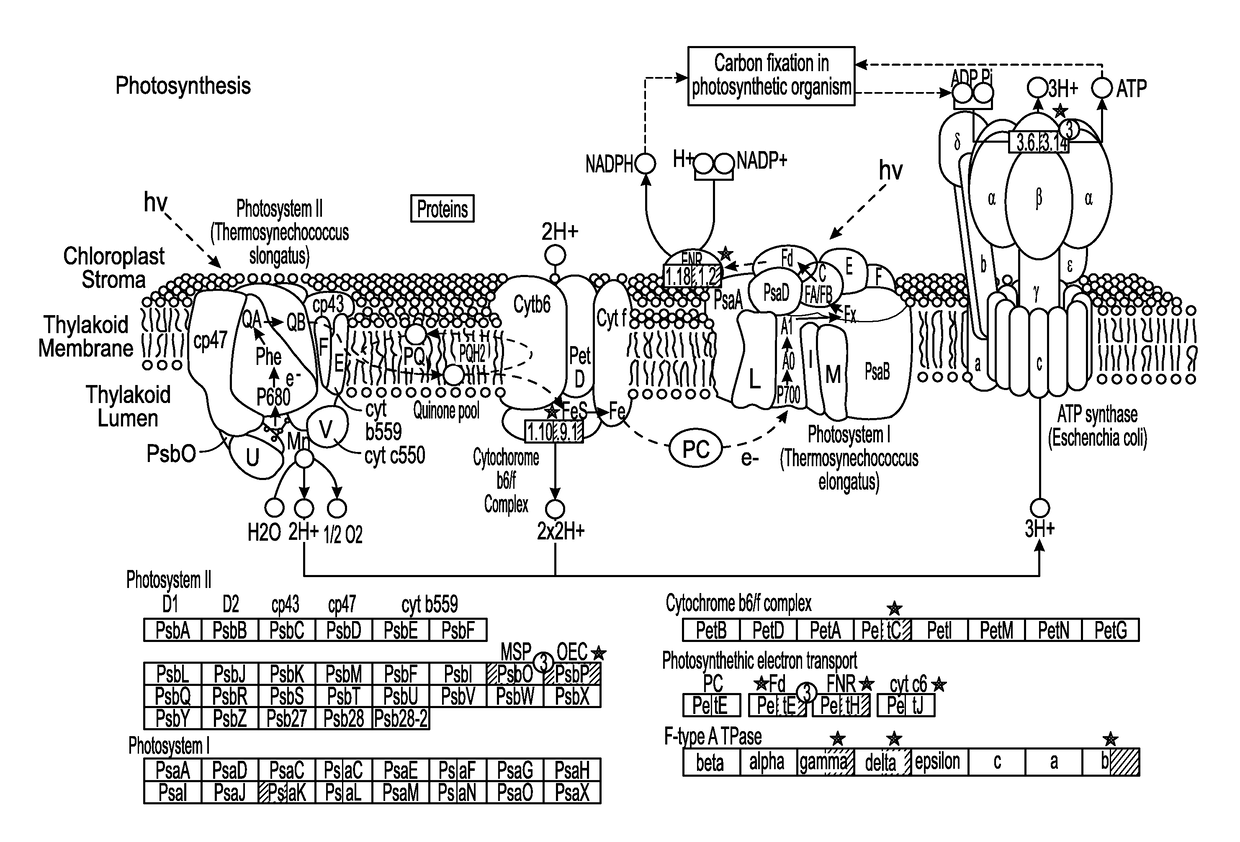
ATP synthase is an enzyme that creates the energy storage molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the most commonly used "energy currency" of cells for all organisms. The formation of ATP from ADP and Pᵢ is energetically unfavorable and would normally proceed in the reverse direction. In order to drive this reaction forward, ATP synthase couples ATP synthesis during cellular respiration to an electrochemical gradient created by the difference in proton (H⁺) concentration across the mitochondrial membrane in eukaryotes or the plasma membrane in bacteria. During photosynthesis in plants, ATP is synthesized by ATP synthase using a proton gradient created in the thylakoid lumen through the thylakoid membrane and into the chloroplast stroma.
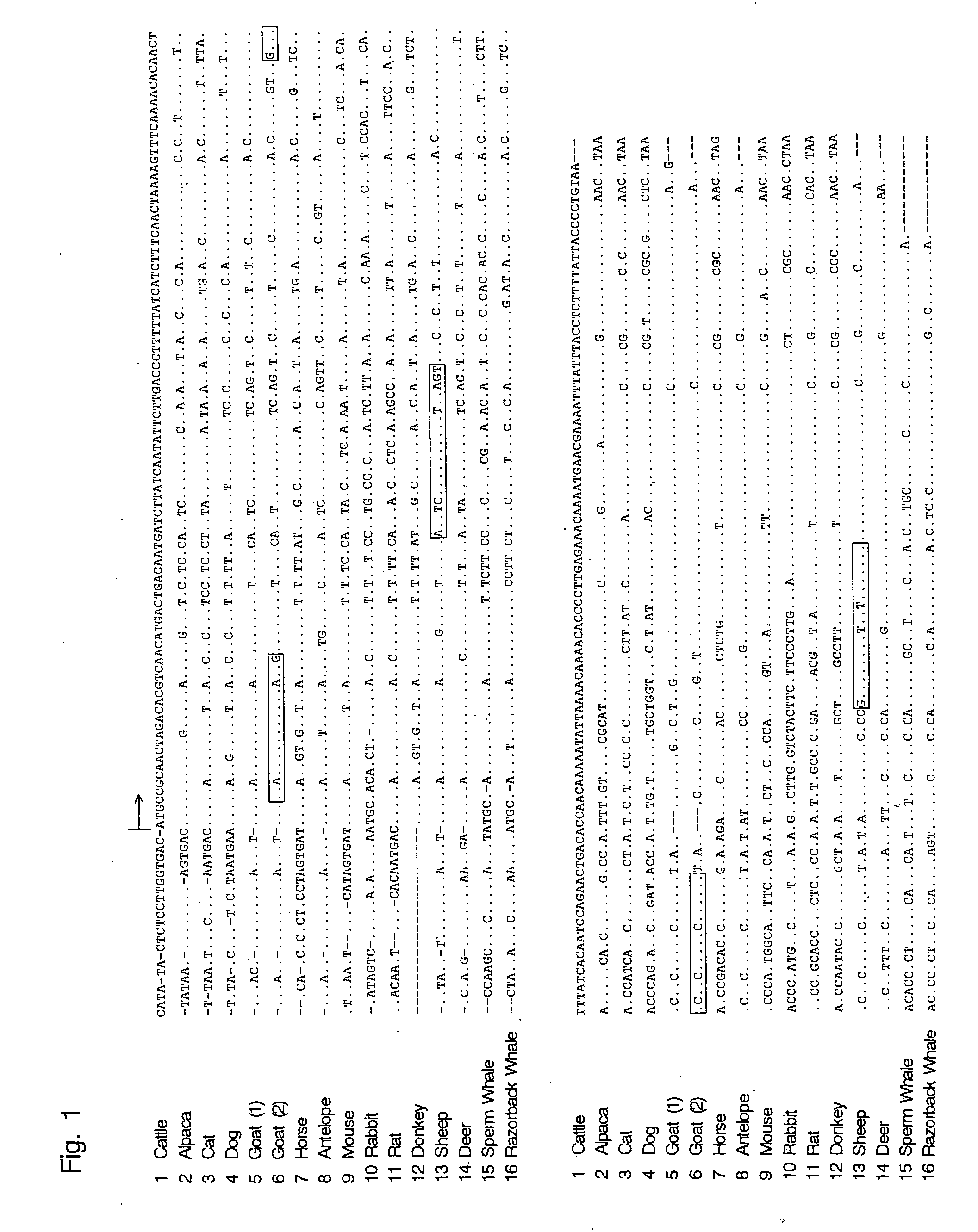
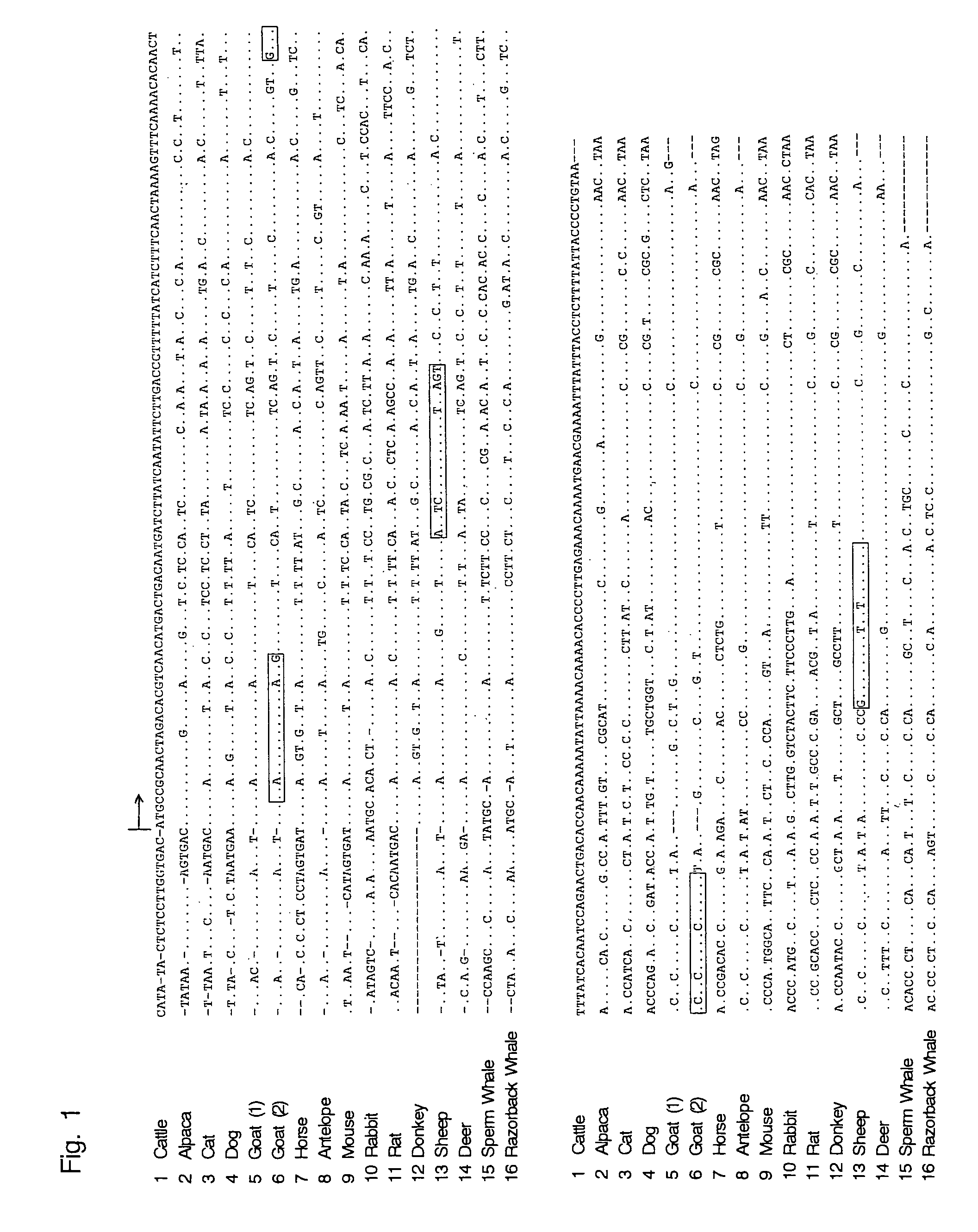
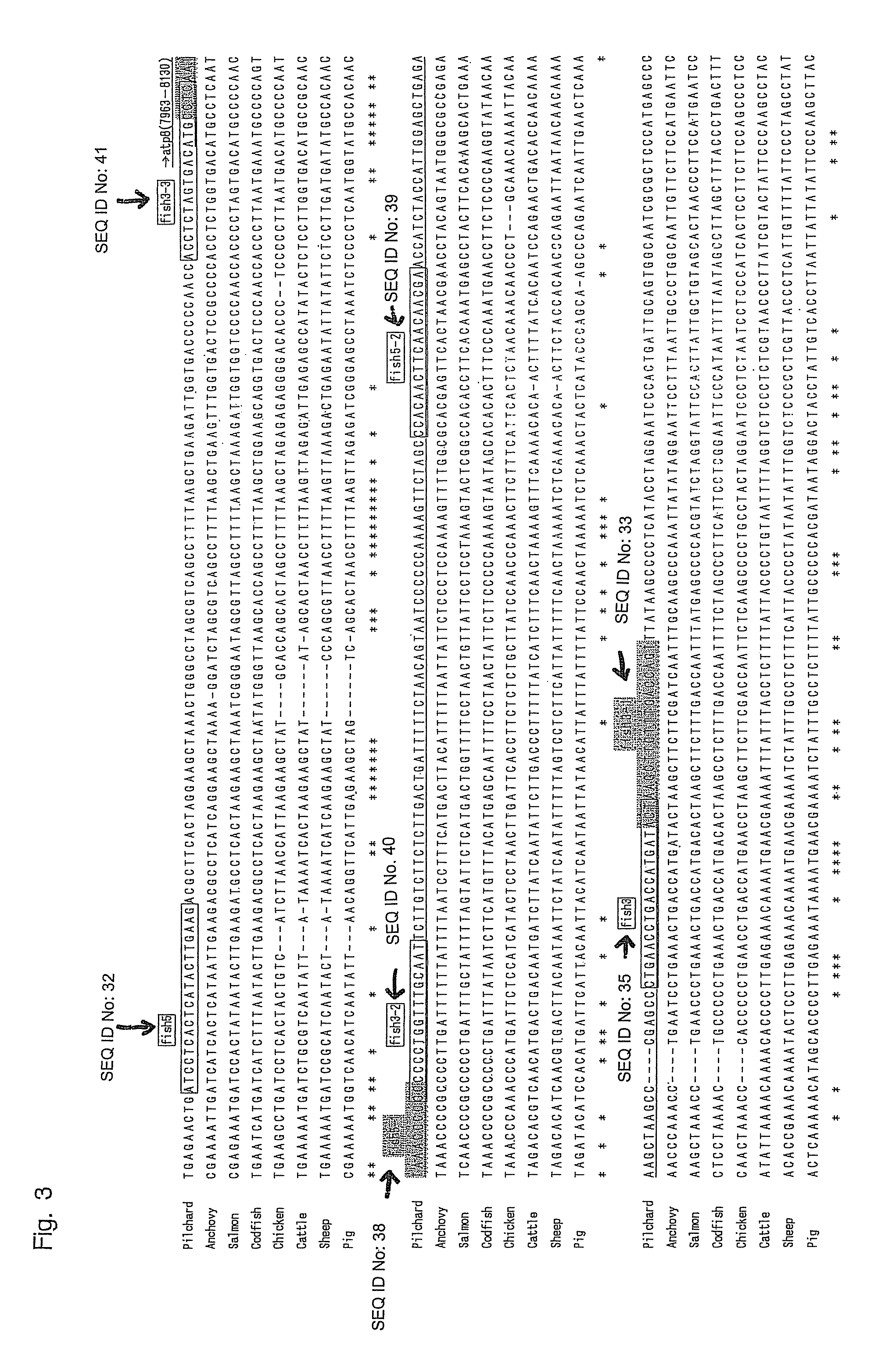
Oligonucleotide sequences that identify species of animal
InactiveUS20050233334A1High sensitivityUseful in detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNAGenome
The present invention provides a method for identifying animal species, said method comprises a step of amplifying a DNA fragment by PCR using a DNA in a sample as a template and animal-specific DNA sequences as a primer pair, wherein the animal-specific DNA sequences are derived from a ATP synthase subunit 8 gene or a region proximal thereto of a mitochondrial genome; and a step of detecting the amplified DNA fragment.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI +1
Method for cultivating transgenic plant with improved insect resistance by using RNA interference technology and special DNA fragment thereof
ActiveCN101851622ANormal growth and reproductionImprove insect resistanceClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumWild type
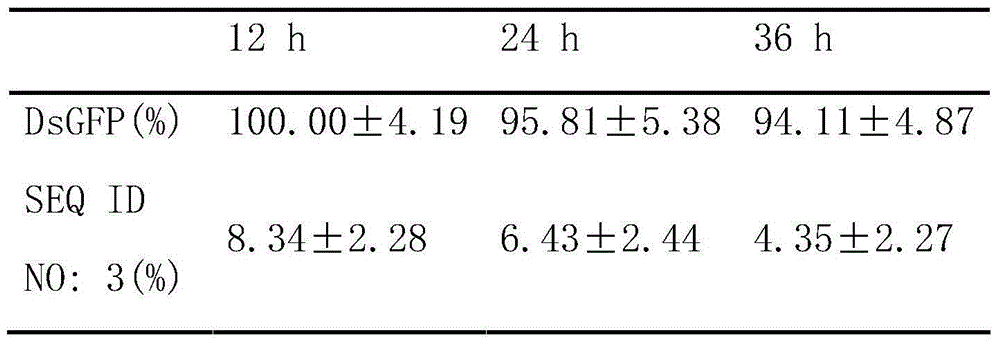
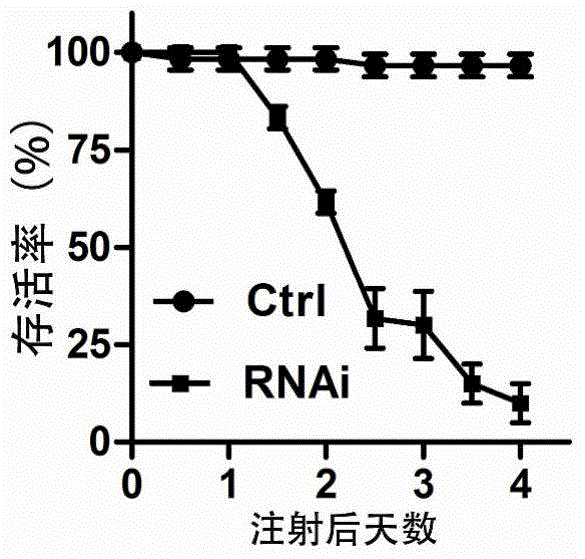
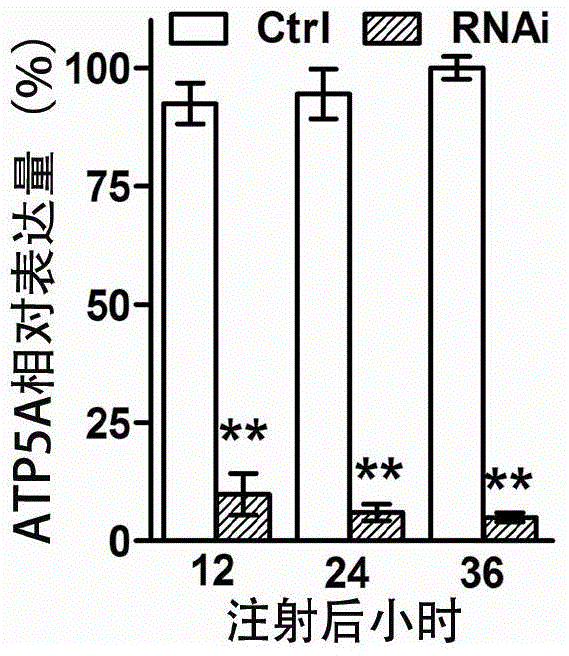
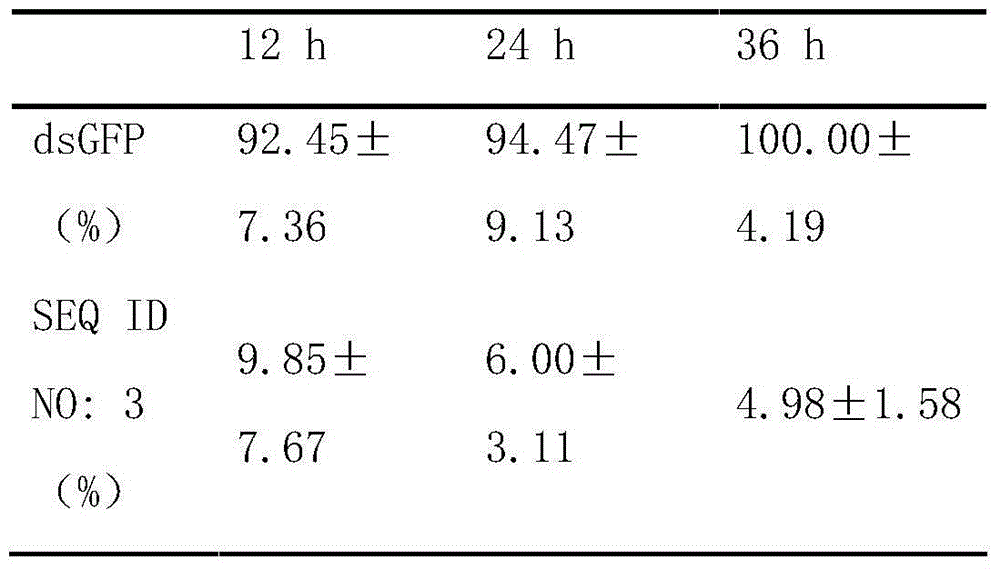
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a transgenic plant with improved insect resistance by using RNA interference technology and a special DNA fragment thereof. The DNA fragment is a gene fragment shown as a formula I, wherein a forward sequence (SEQ) is any one fragment which at least comprises 19bp in full-length cDNA fragments of an ATP synthase E subunit gene; a reverse sequence (SEQ) and the forward sequence (SEQ) are mutually reversely complementary; X is a spacer sequence between the forward sequence (SEQ) and the reverse sequence (SEQ), and the X and the forward sequence (SEQ) or the X and the reverse sequence (SEQ) are both not complementary mutually; and the full-length cDNA of the ATP synthase E subunit gene is shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence table. The invention also aims to provide application of the ATP synthase E subunit gene serving as an RNA interference target gene in cultivating the transgenic plant with improved insect resistance. Experiments prove that aphids inoculated to wild-type tobacco grow and reproduce normally; and aphids inoculated to transgenic tobacco starts to die on the fourth day, dead aphid bodies is blackened after five days and no live aphids can be seen after seven days. The formula (I) is forward sequence (SEQ)-X- reverse sequence (SEQ).
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
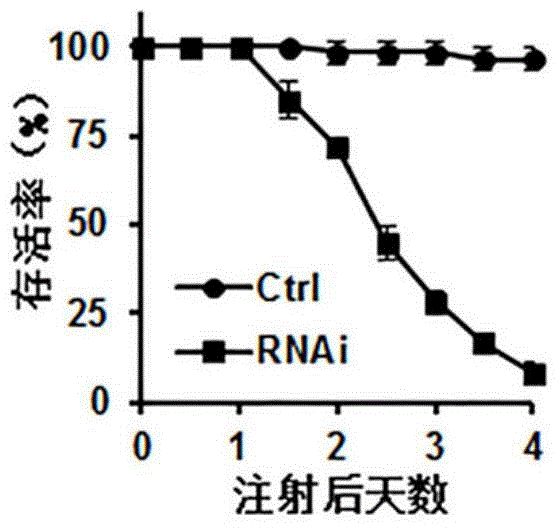
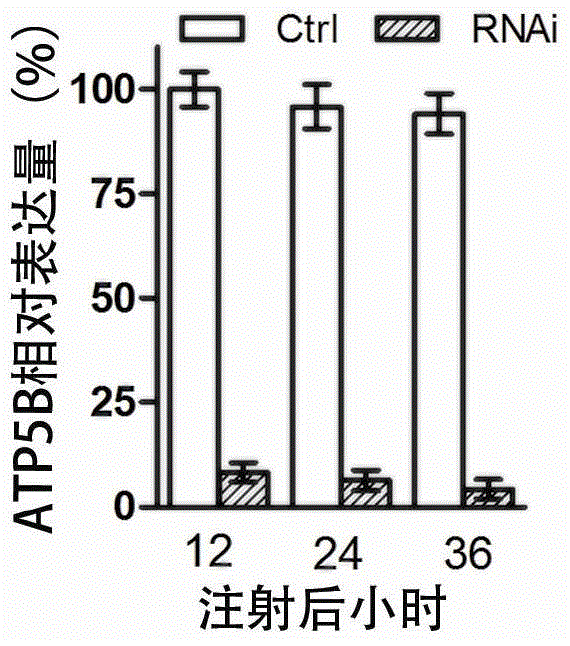
Application of Locusta migratoria ATP synthase beta subunit gene and its dsRNA in pest control
ActiveCN104404042AWill not interfere with the impactCause interferenceBiocideAnimal repellantsConserved sequenceLocust
The invention provides a conserved sequence of locust's ATP synthase beta subunit cDNA, and constructs the RNA, DNA and other constructs thereof. The RNAi technology is utilized to silence the ATP synthase beta subunit in locusts, so that expression of in vivo ATP synthase beta subunit can be significantly inhibited, thus resulting in the lethal effect of locusts. The Locusta migratoria ATP synthase beta subunit gene and its dsRNA can be applied to the RNAi technology for control of Locusta migratoria pests.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene and application of dsRNA of oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene in pest control
ActiveCN104450755AWill not interfere with the impactCause interferenceBiocideAnimal repellantsConserved sequenceMigratory locust
The invention relates to an oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene and application of dsRNA of the oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene in pest control. The oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene disclosed by the invention provides the conserved sequence of ATP synthetase alpha subunit cDNA of a locust, can be used for constructing the constructs, namely RNA, DNA and the like, and obviously inhibits the expression of the ATP synthetase alpha subunit inside a locust body by silencing the ATP synthetase alpha subunit inside the locust body by utilizing an RNAi technology to cause the lethal effect on the locust, thus being applied to the RNAi technology to prevent and control oriental migratory locust pests.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Oligonucleotide sequences that identify species of animal
InactiveUS20100184078A1High sensitivityUseful in detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationDNA fragmentationA-DNA
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI +1
Compositions and Methods for Bioelectricity Production
InactiveUS20080124585A1Reduce consumptionIncrease consumptionBacteriaCell electrodesBiotechnologyATPase
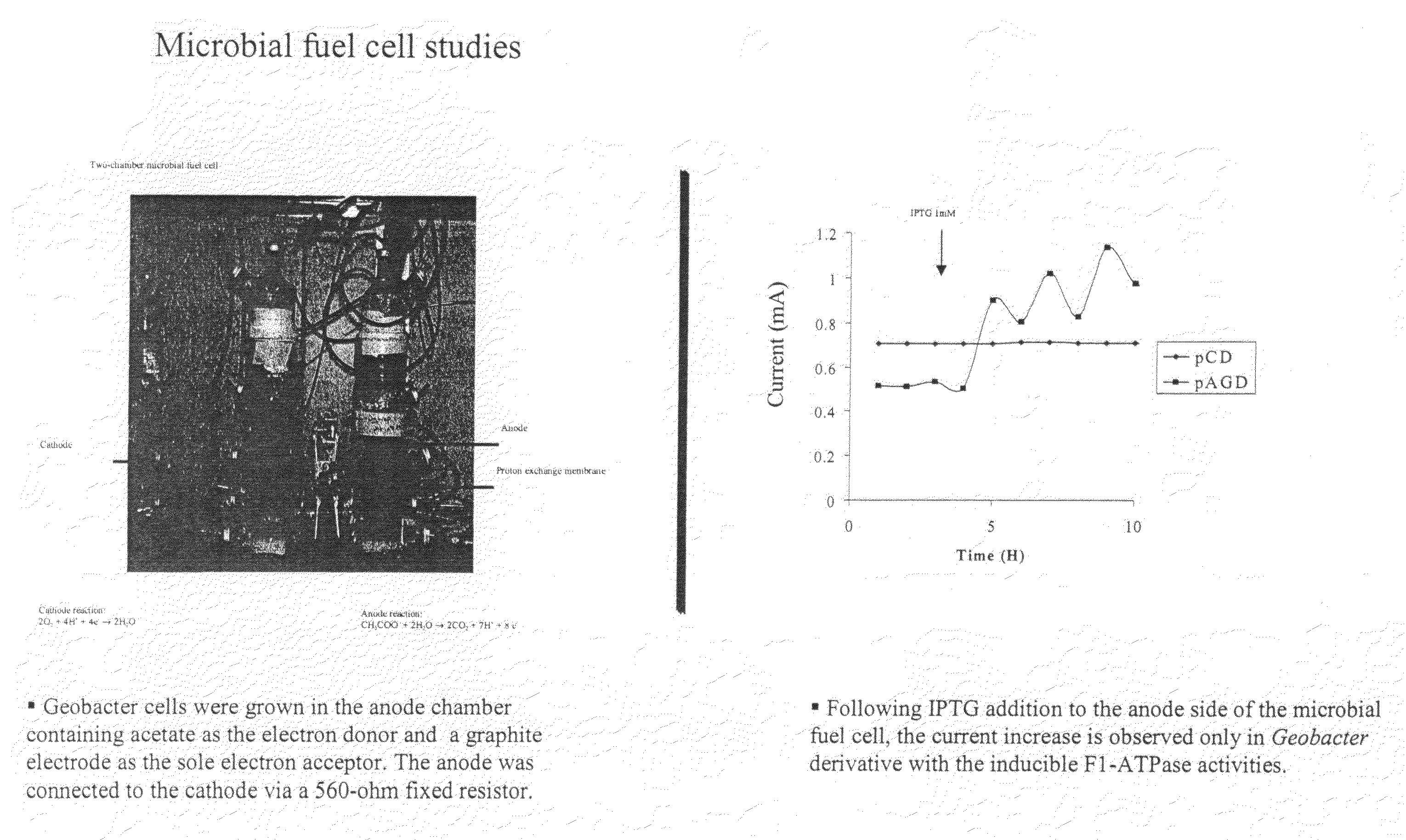
The invention provides a microbial fuel cell having a dissimilatory metal-reducing microbe expressing exogenous or native ATPase subunits, the ATPase subunits assembling into an active ATP synthase and consuming ATP in a futile cycle. The dissimilatory metal-reducing microbe can include an organism selected from the organisms set forth in Table 1. The one or more exogenous ATPase subunits can include a subunit selected from the ATPase subunits set forth in Tables 2 or 3. Also provided is a microbial fuel cell having a dissimilatory metal-reducing microbe expressing one or more exogenous genes encoding a gene product that promotes ATP consumption, the gene products of the one or more exogenous genes having an activity that reduces ATP synthesis, increases ATP consumption or both. The one or more gene products can increase ATP consumption through a futile cycle or through altering a metabolic reaction directly involved in ATP synthesis. Further provided is a microbial fuel cell having a dissimilatory metal-reducing microbe expressing one or more exogenous genes encoding a gene products that increases the electron / mole ratio compared to an unmodified microbe, wherein the increased ratio enhances electron transfer to an electrode. A method of producing electricity from an microbial organism is further provided. The method includes: (a) culturing a microbial fuel cell under anaerobic conditions sufficient for growth, the microbial fuel cell comprising a dissimilatory metal-reducing microbe expressing exogenous ATPase subunits, the ATPase subunits assembling into an active ATP synthase and consuming ATP in a futile cycle when grown under anaerobic conditions, and (b) capturing electrons produced by an increased ATP demand with an electron acceptor.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
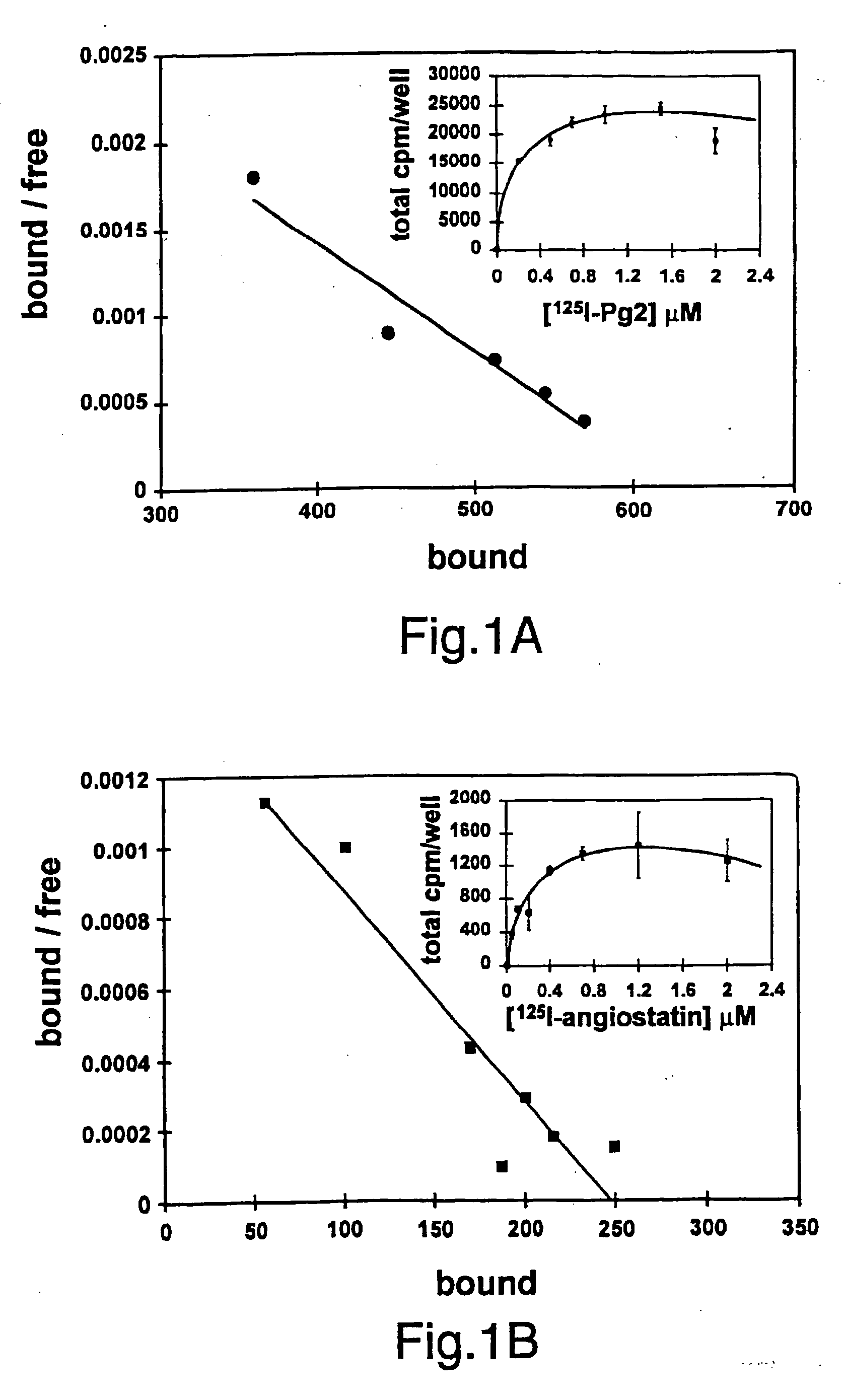
Compositions and methods for promoting or inhibiting angiogenesis
Compounds, compositions and methods for promoting or inhibiting angiogenesis, and screening methods for identifying compounds are disclosed. The compounds bind to F1 ATP synthase particularly to the alpha and / or beta subunits of F1 ATP synthase. When bound to these subunits, they can function as angiostatin agonists, antagonists, partial agonists, inverse agonists, or allosteric modulators. When the compounds mimic or enhance the activity of angiostatin, they inhibit angiogenesis. When the compounds inhibit the ability of angiostatin to bind F1 ATP synthase and are either inactive at inhibiting angiogenesis or directly promote angiogenesis, or if they inhibit the activity of angiostatin, they promote angiogenesis. The compounds can be, for example, antibodies, antibody fragments, enzymes, peptides, nucleic acids such as oligonucleotides, or small molecules. The antibodies can be monoclonal, humanized, or polyclonal antibodies. The compounds can be conjugated to or combined with various cytotoxic agents and / or labeled compounds. Methods for promoting angiogenesis can be used to introduce vasculature to areas in a patient that can benefit from such increased vasculature. Methods for inhibiting angiogenesis can be used to treat disorders mediated by angiogenesis, for example, tumors, autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, and the like.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
Preventing or reducing oxidative stress or oxidative cell injury
InactiveUS20090093441A1Preventing and reducing oxidative stress and oxidative cell injuryPreventing and reducing oxidative stressBiocideOrganic active ingredientsWater insolubleOxidative stress
A water-insoluble cellulose derivative, such as ethyl cellulose is useful for preventing or reducing oxidative stress or oxidative cell injury in tissues of an animal and in particular for influencing the level Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase-1 (SCD1) gene expression or ATP synthase mitochondrial F1 complex assembly factor 1 (ATPAF1) gene expression in non-adipose tissues of the animal.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
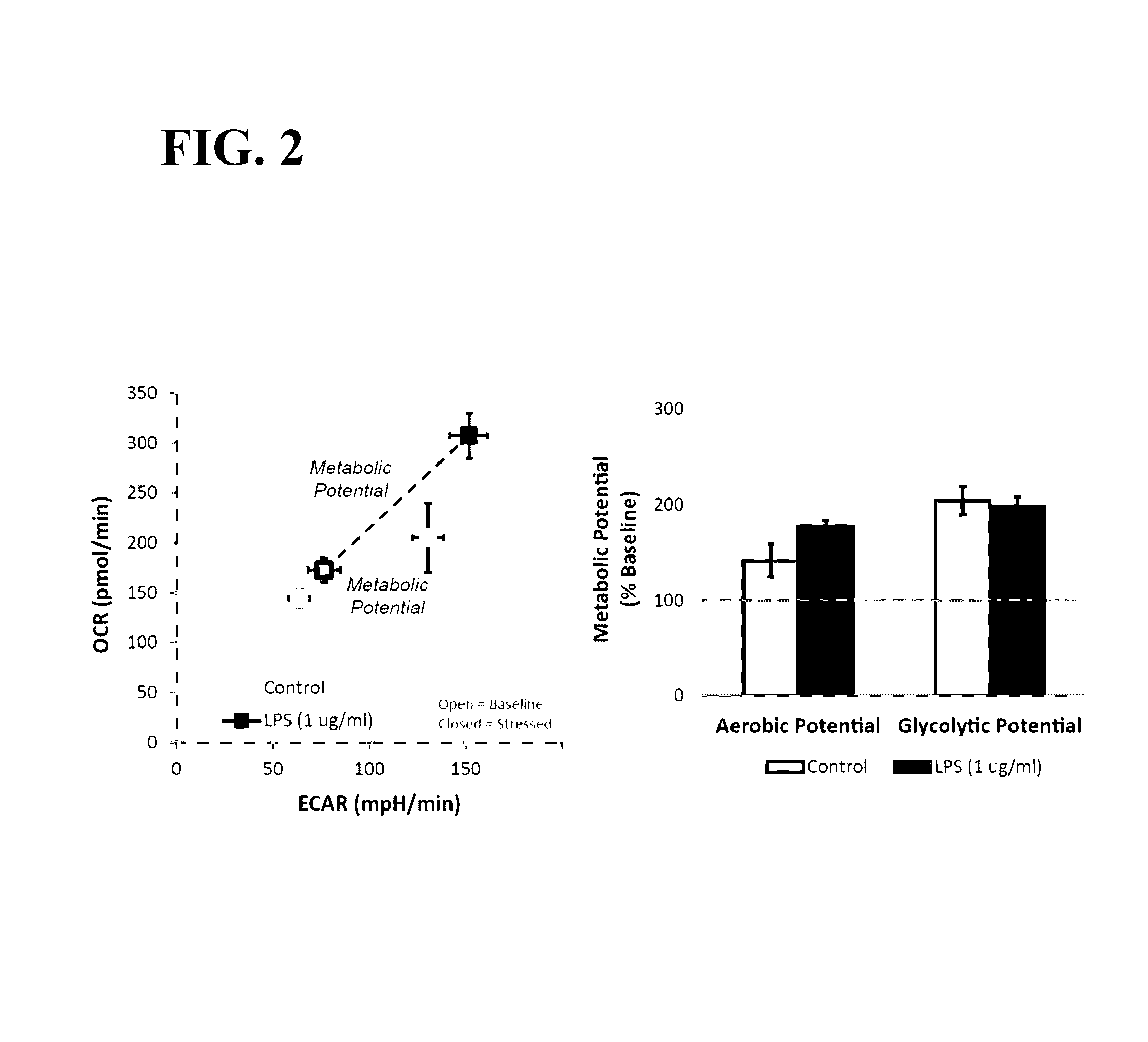
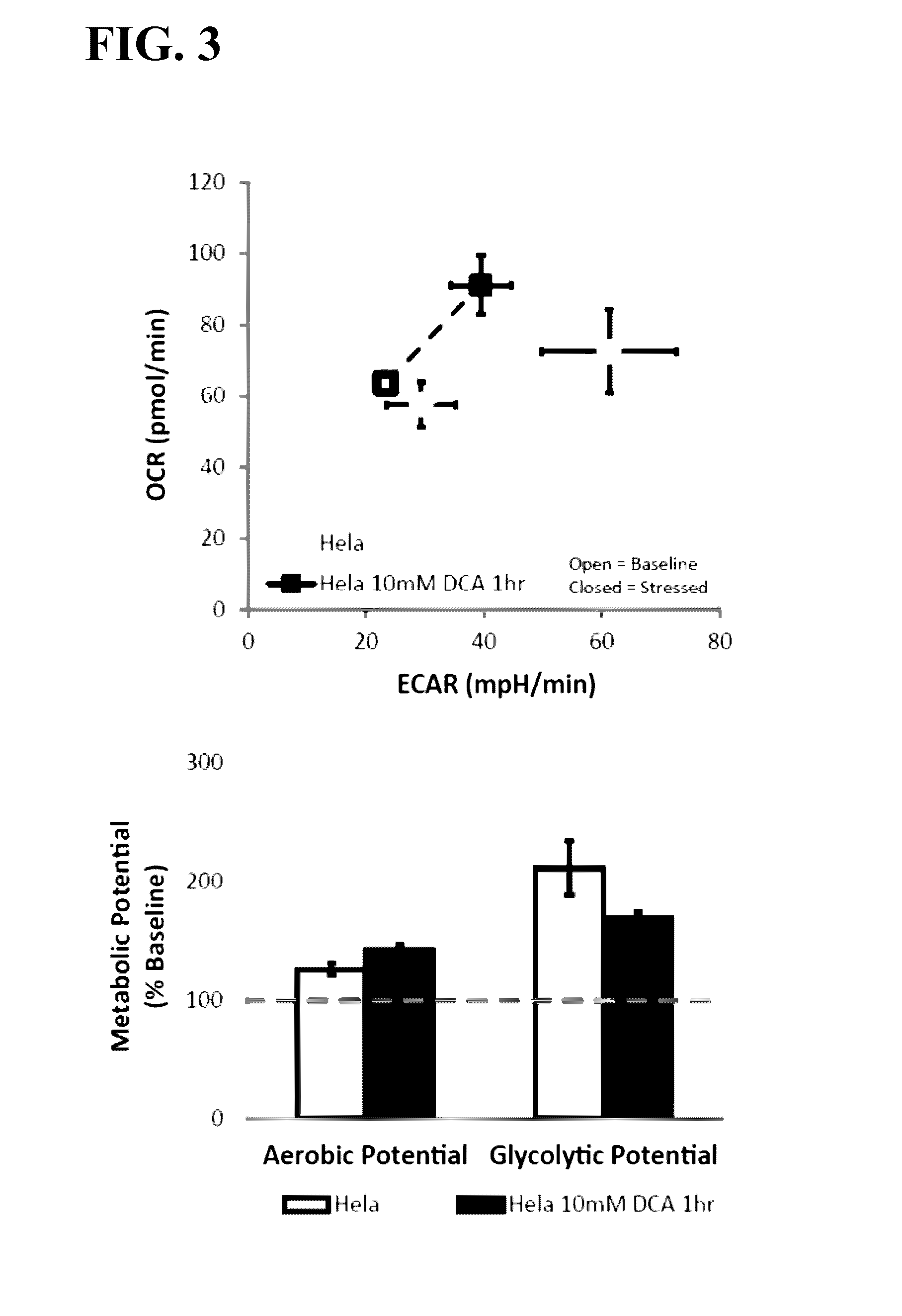
Method and system for determining integrated metabolic baseline and potential of living cells
InactiveUS20160281049A1More dataQuick collectionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCurrent technologyExtracellular acidification
The current technology is related to methods for rapidly determining the metabolic baseline and potential of living cells. Embodiments relate to measuring the activity of each of the two major energy-generating pathways within the cell: mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis, first under baseline conditions, and again after applying a stress to the cells to demand increased energy supply. In some embodiments the stress may be applied by exposing the cells to a combination of two chemical compounds: a mitochondrial uncoupler and an ATP synthase inhibitor. In one embodiment, the metabolic energy generating activity of the mitochondrial respiration pathway is determined by measuring the rate of oxygen consumption by the living cells, and the metabolic energy generating activity of the glycolysis pathway is determined from a measurement of extracellular acidification caused by secretion of protons from the cell. Other embodiments are related to an apparatus for determining a metabolic potential of a cell sample in a well of a multiwell plate.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
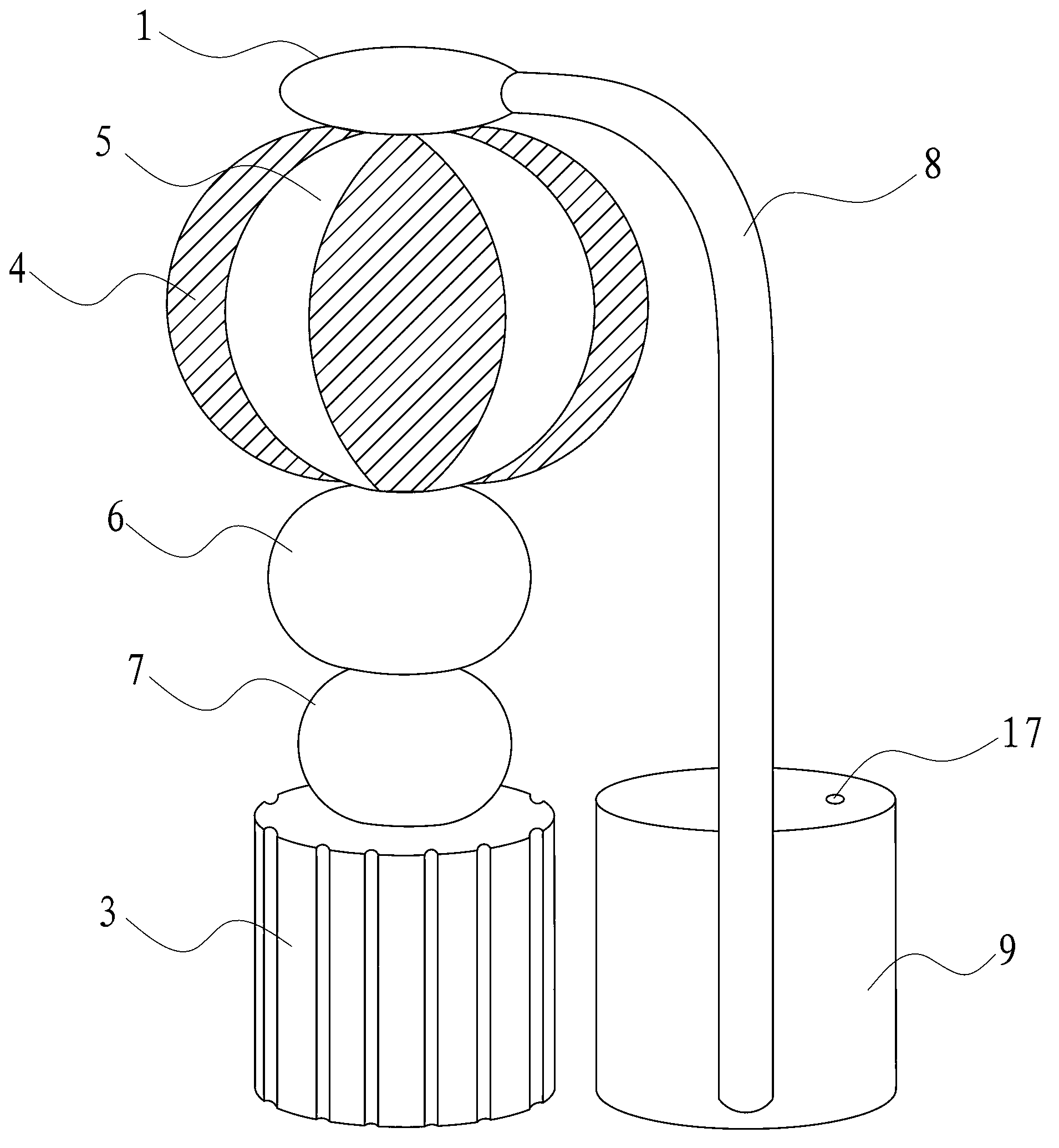
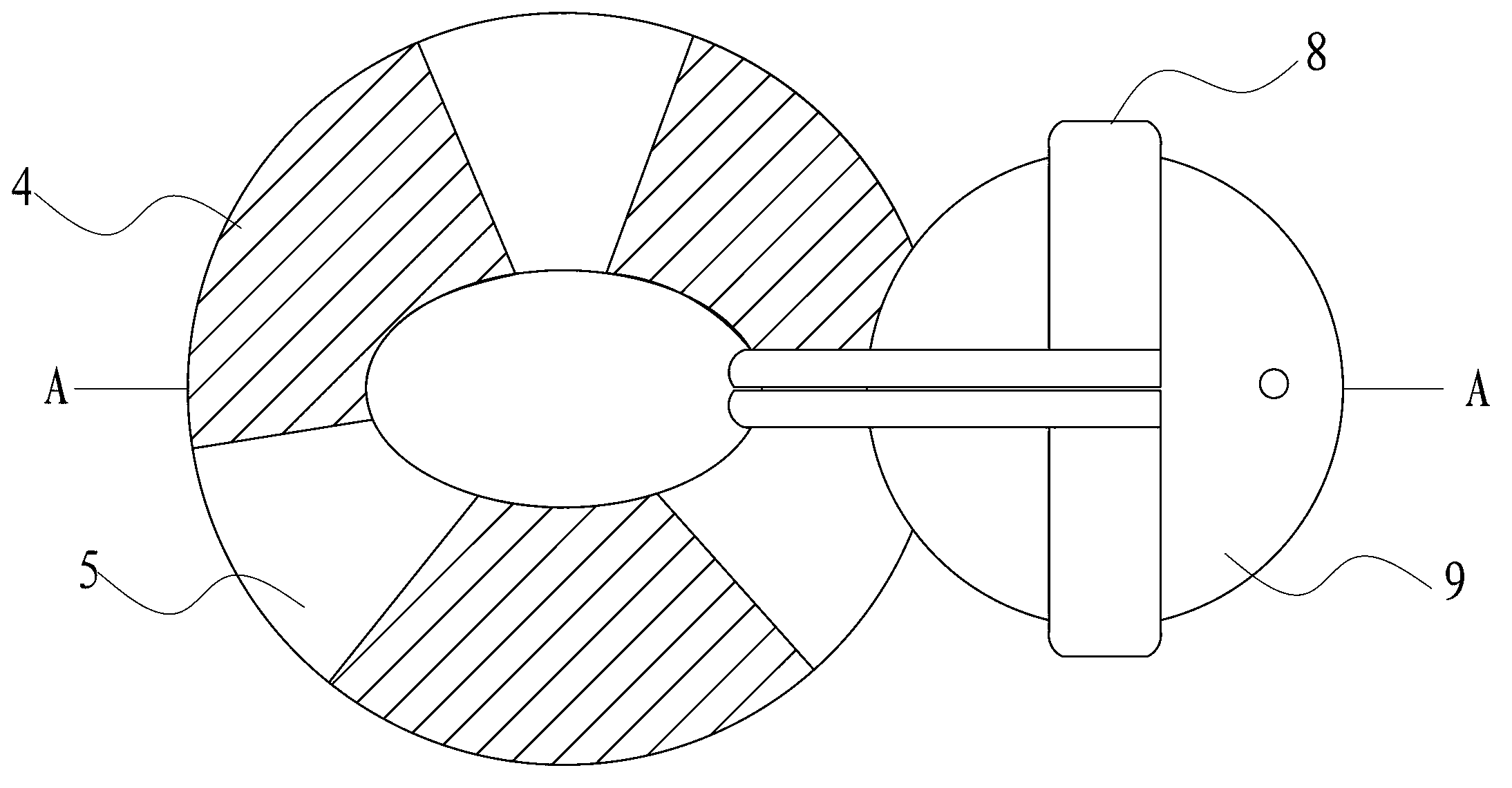
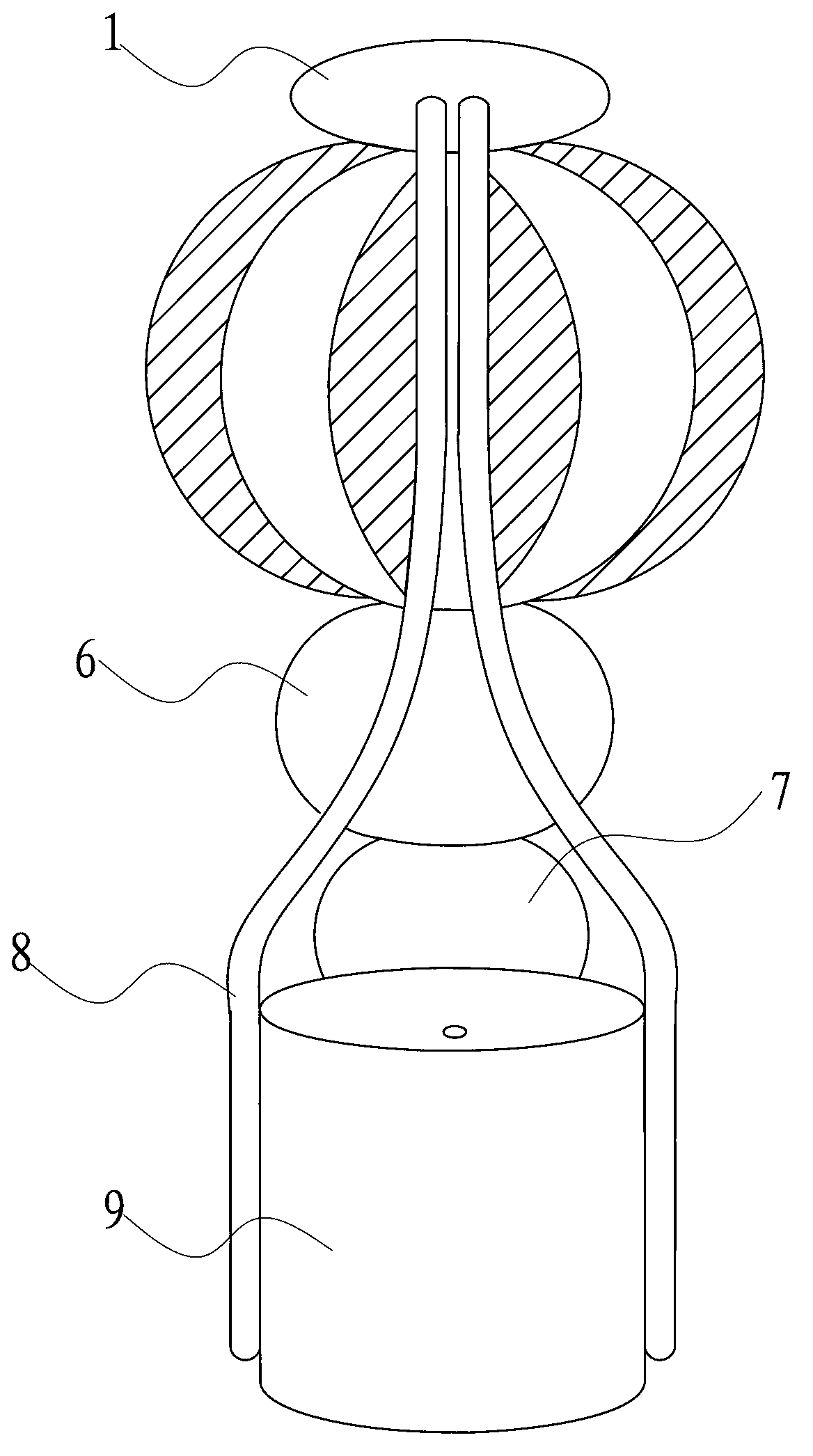
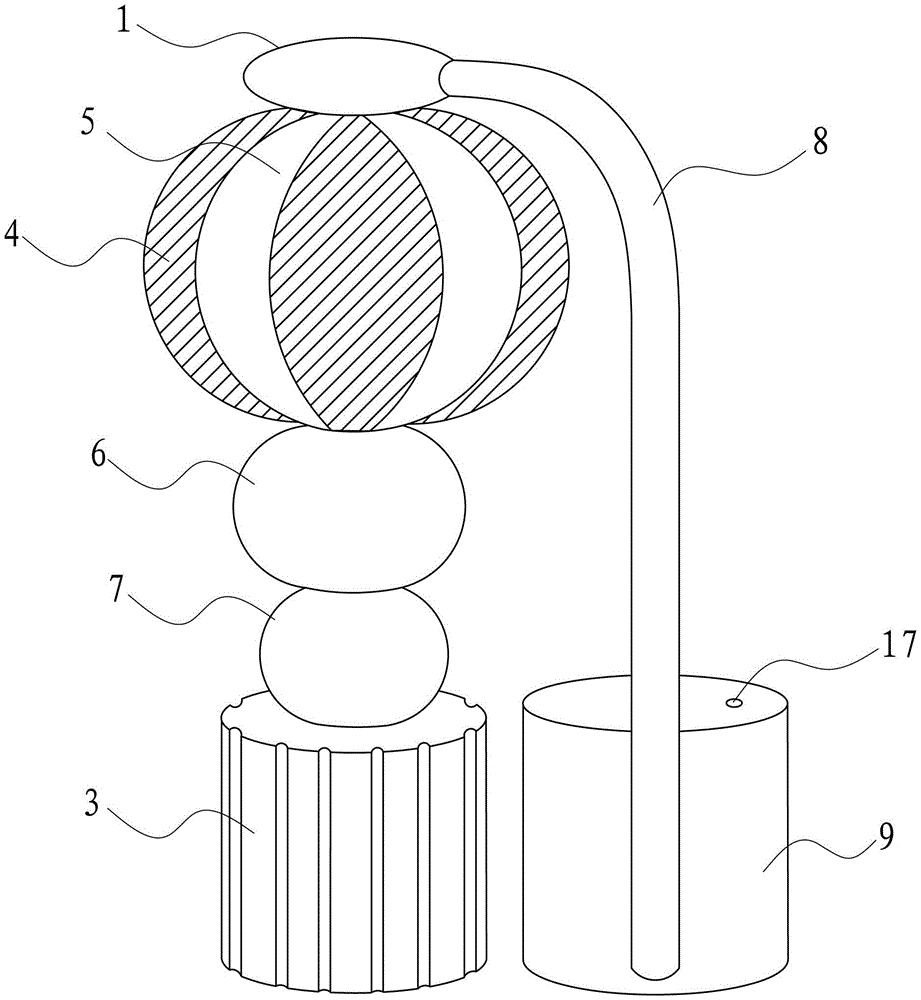
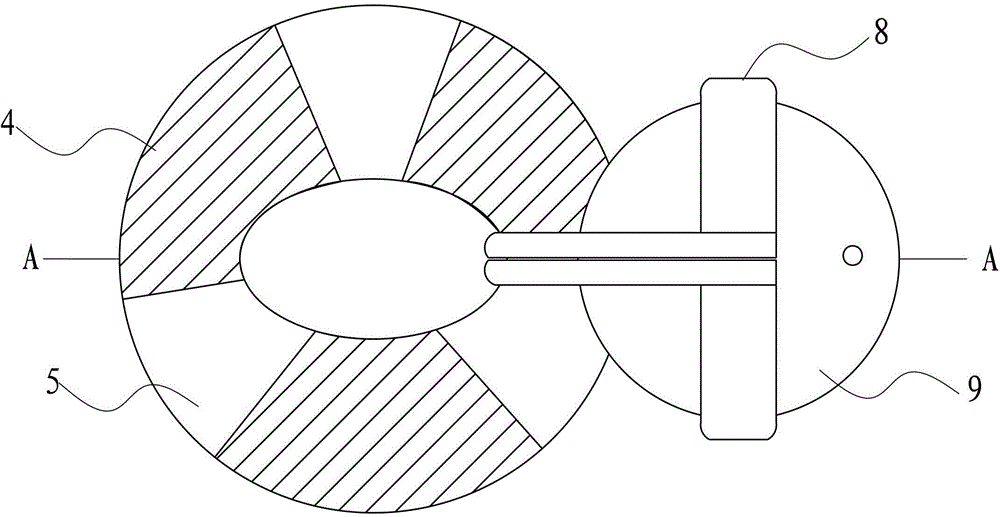
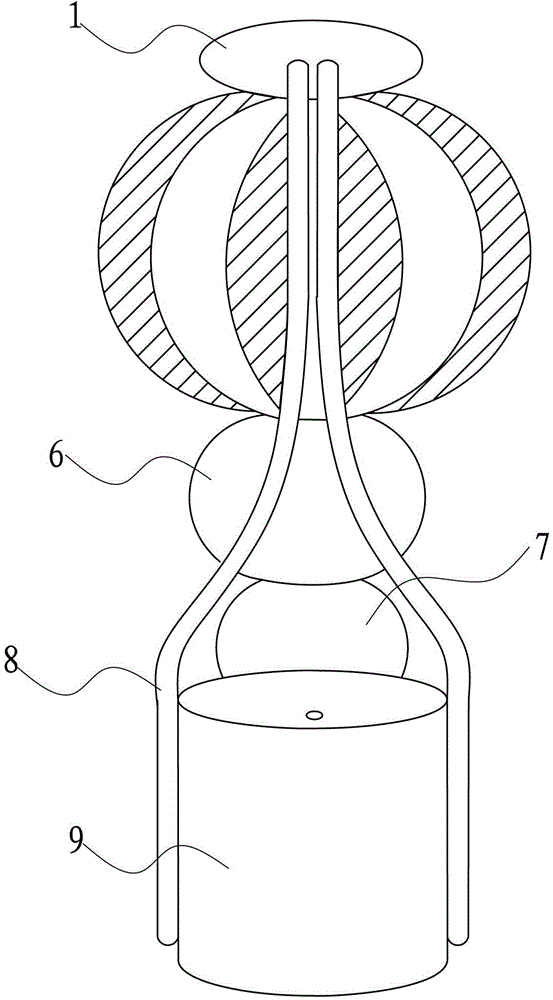
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase model training aid
InactiveCN102938225ASmooth rotationReduce frictionEducational modelsEngineeringAdenosine triphosphate
The invention discloses an adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase model training aid which comprises a rotating part and a support part and is characterized in that the rotating part comprises a shaft lever, an inserting pedal ball, a first ball body and a second ball body, wherein the inserting pedal ball, the first ball body and the second ball body are sequentially sleeved on the shaft lever from top to bottom; and the support part comprises a shaft lever base, a connection rod base, bent connection rods and top balls arranged at the front ends of the connection rods, wherein the connection rods are symmetrically arranged on the outer surface of the connection rod base, the top end of the shaft lever is in rotating connection with the top balls, and the lower end of the shaft lever is in rotating connection with the shaft lever base. The ATP synthase model training aid is simple in structure, convenient to carry and capable of displaying the appearance structure and working principle of the ATP synthase.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
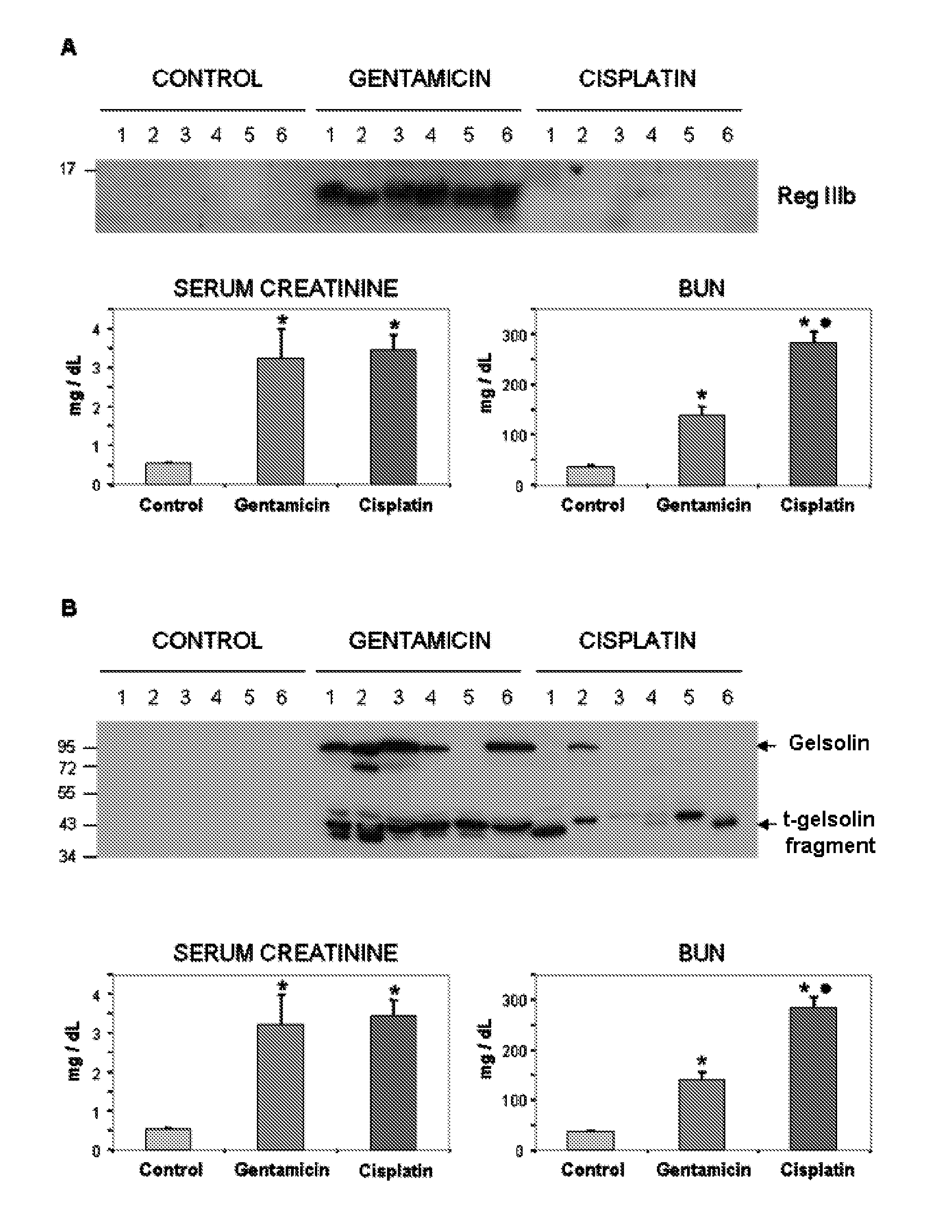
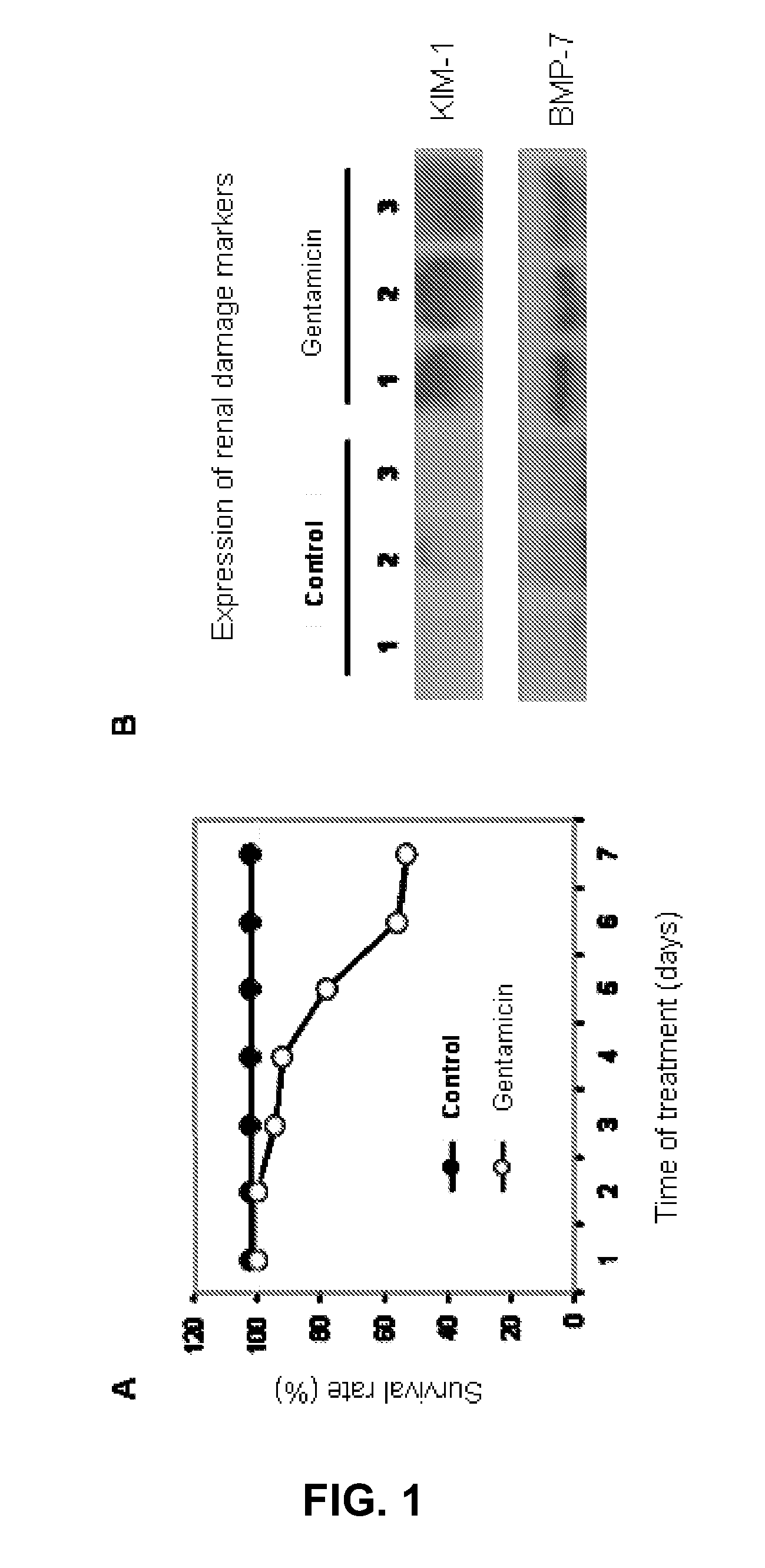
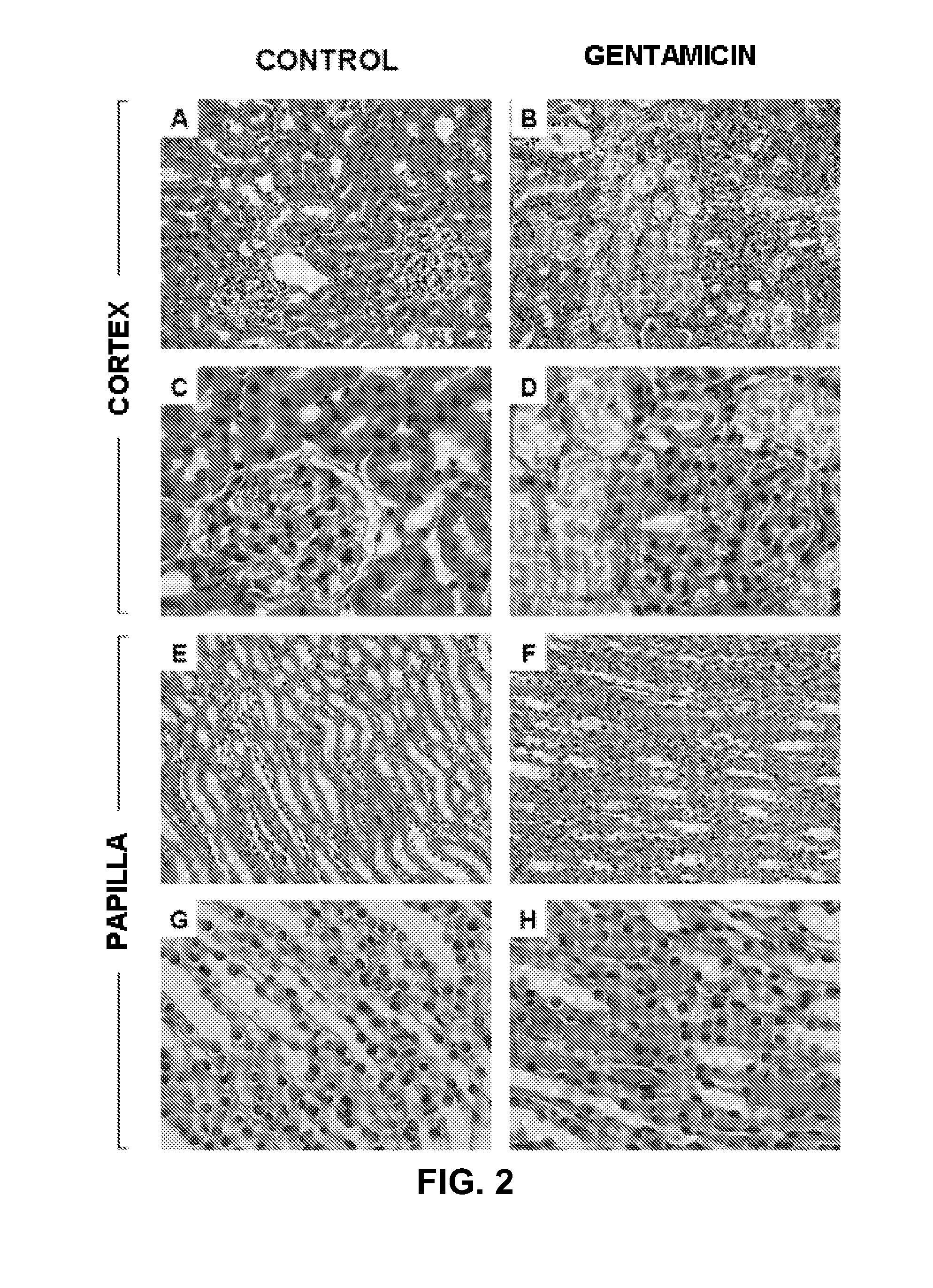
Method for the detection of renal damage
InactiveUS20120220480A1Damage causedFailure causedLibrary screeningDisease diagnosisAlpha-enolaseFetuin b
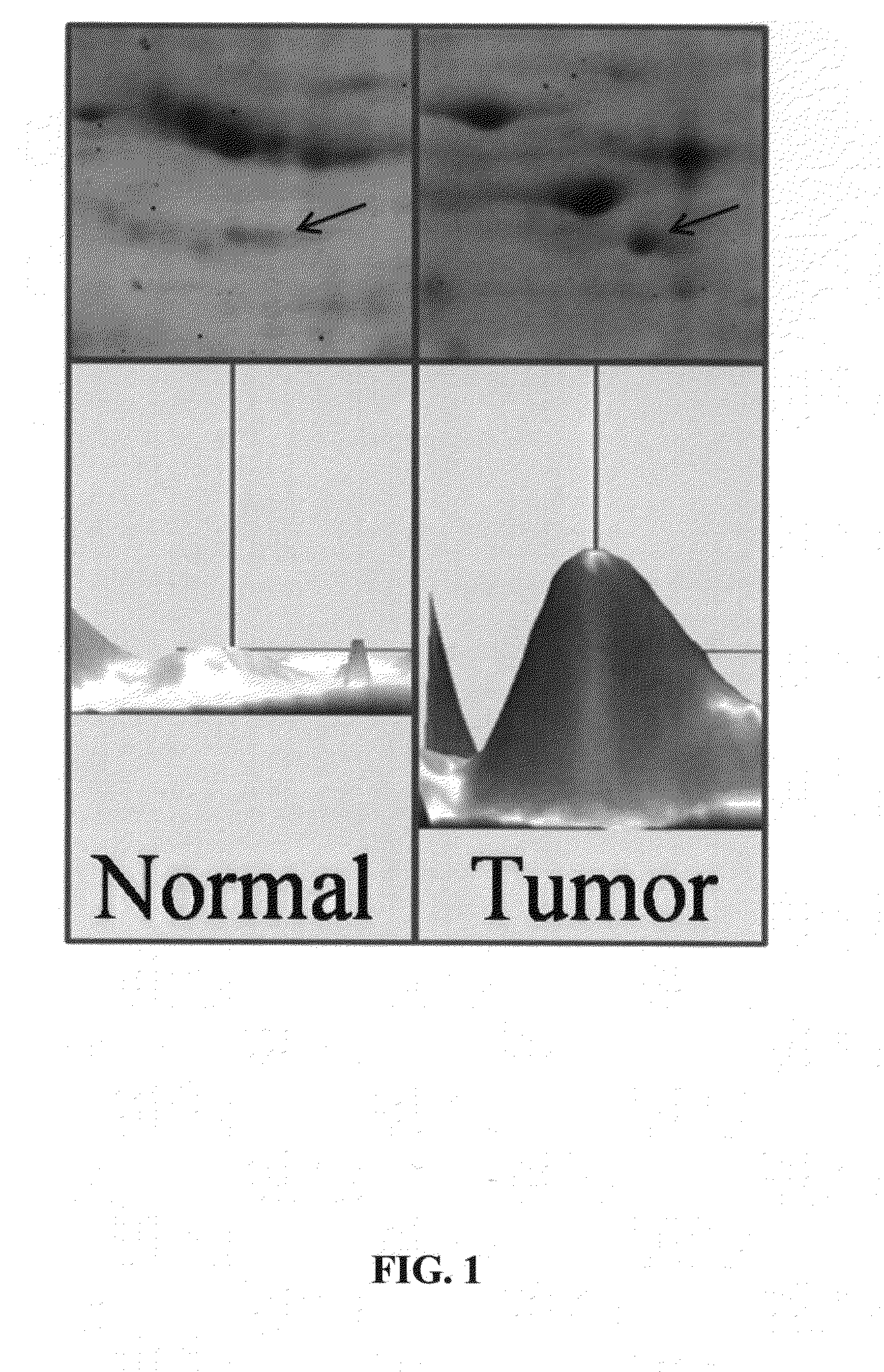
The invention relates to a method for determining the presence of renal damage in an individual and also to a method for detecting one or several proteins selected from the list comprising Reg3B, fetuin B, Ras-related GTP-binding protein A serine protease inhibitor A3L, subunit 1 of COP9, gamma subunit of ATP synthase, gelsolin, ribonuclease UK114, aminoacylase 1A, alpha-enolase, keratin 5, parvalbumin alpha, ribonuclease 4 or serine protease inhibitor A3K. The renal damage may be acute renal failure. Said renal pathologies may be caused by the administration of a nephrotoxic agent, wherein the nephrotoxic agent may be an aminoglycoside antibiotic such as gentamicin, or cisplatin. The invention also provides means to differentiate the renal damage or renal failure induced by gentamicin from that induced by cisplatin, through the biochemical analysis of the urinary level of Reg3B and / or gelsolin, or fragments thereof.
Owner:UNIV DE SALAMANCA
Lipoprotein receptor
Owner:MEDICAL RESEARCH COUNCIL
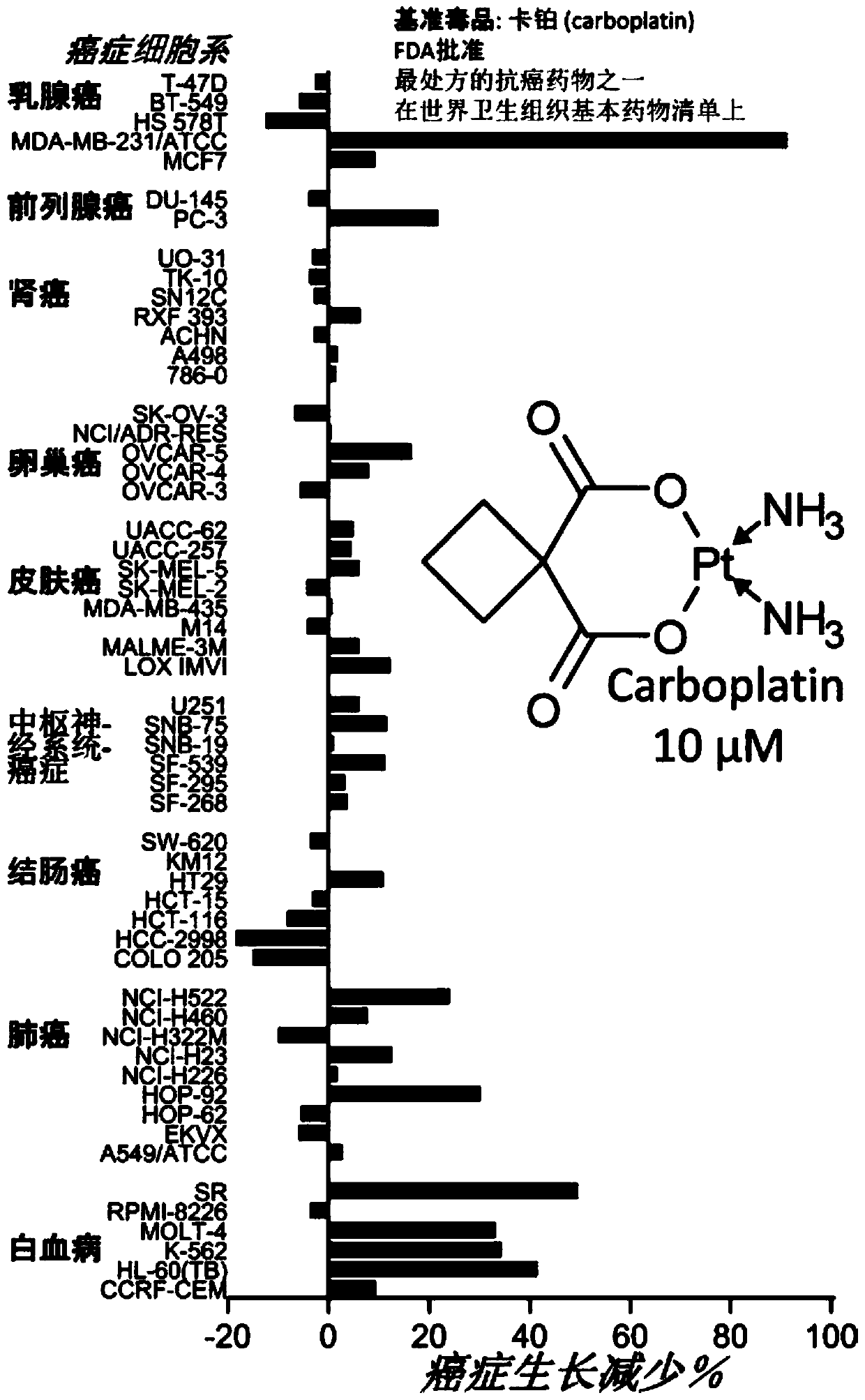
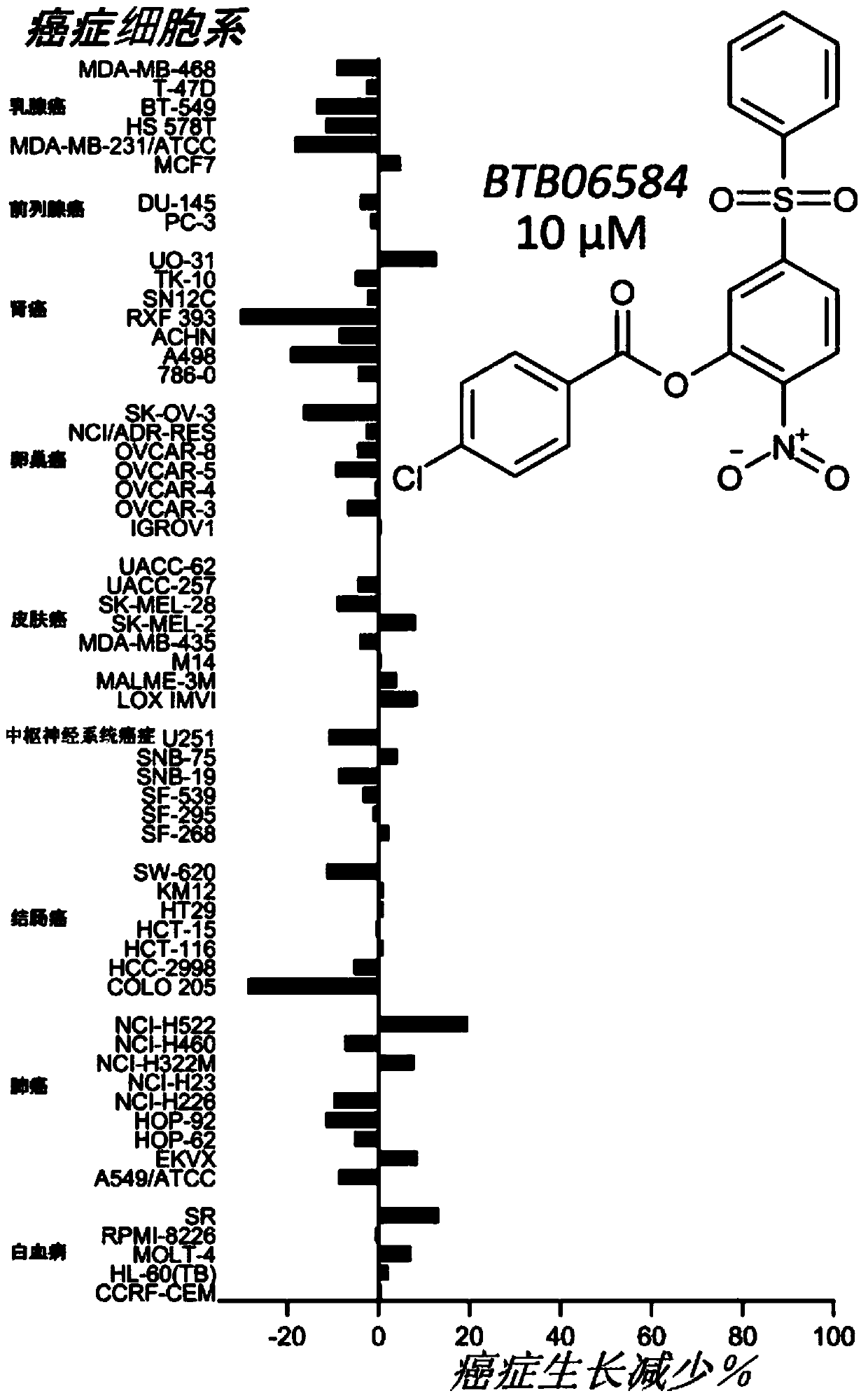
Method of treating cancer using atp synthase inhibitors
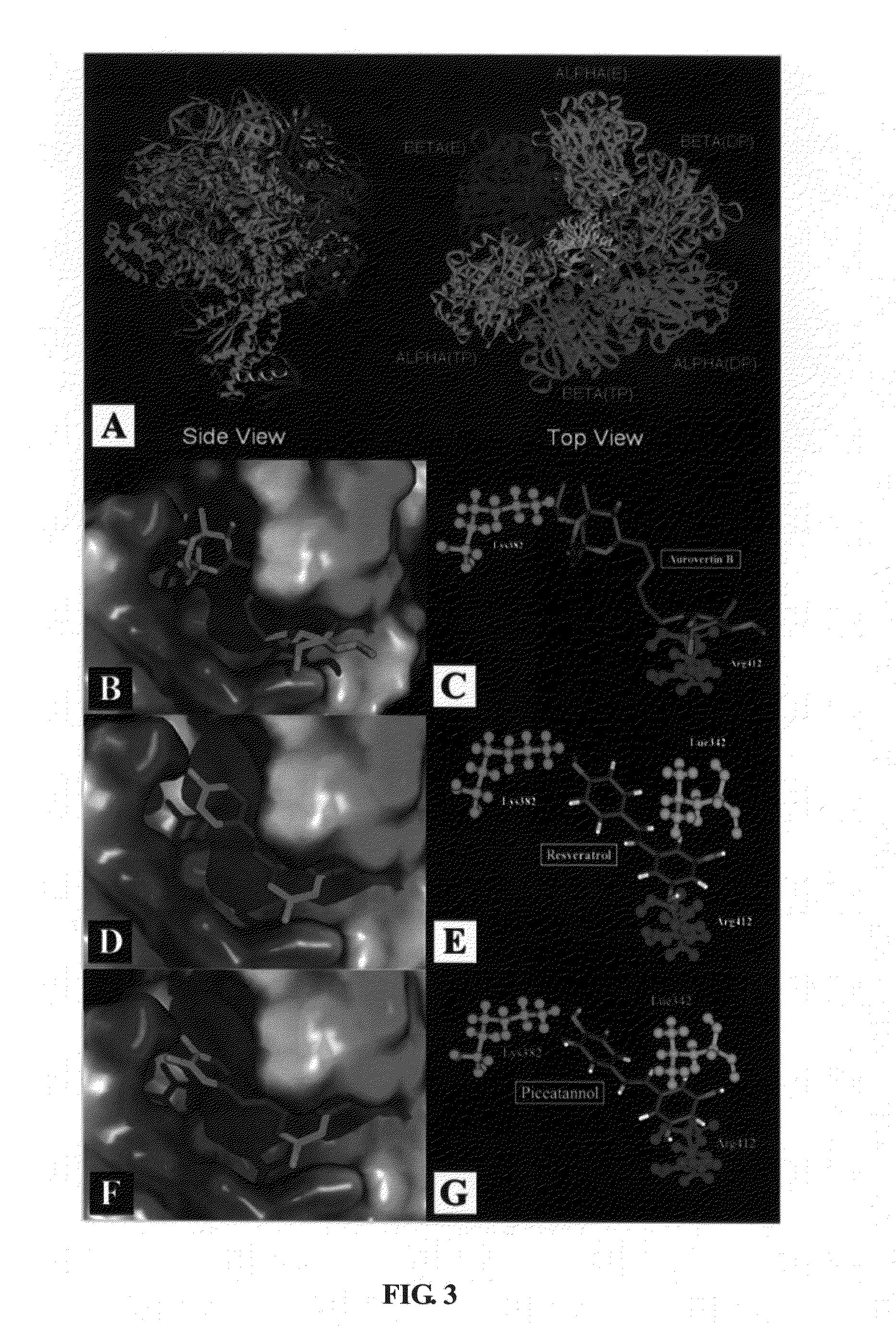
The present invention is directed to a method of treating cancer in a subject in need of such a treatment by administering an inhibitor of ATP synthase in a pharmaceutically effective amount, preferably, the inhibitor contains one pyrone ring. The present invention also provides for a pharmaceutical composition comprising an inhibitor of ATP synthase, preferably, the inhibitor is aurovertin B.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Glycolipid Mixture with Anti-Inflammatory Activity Obtained from Oscillatoria Planktothrix
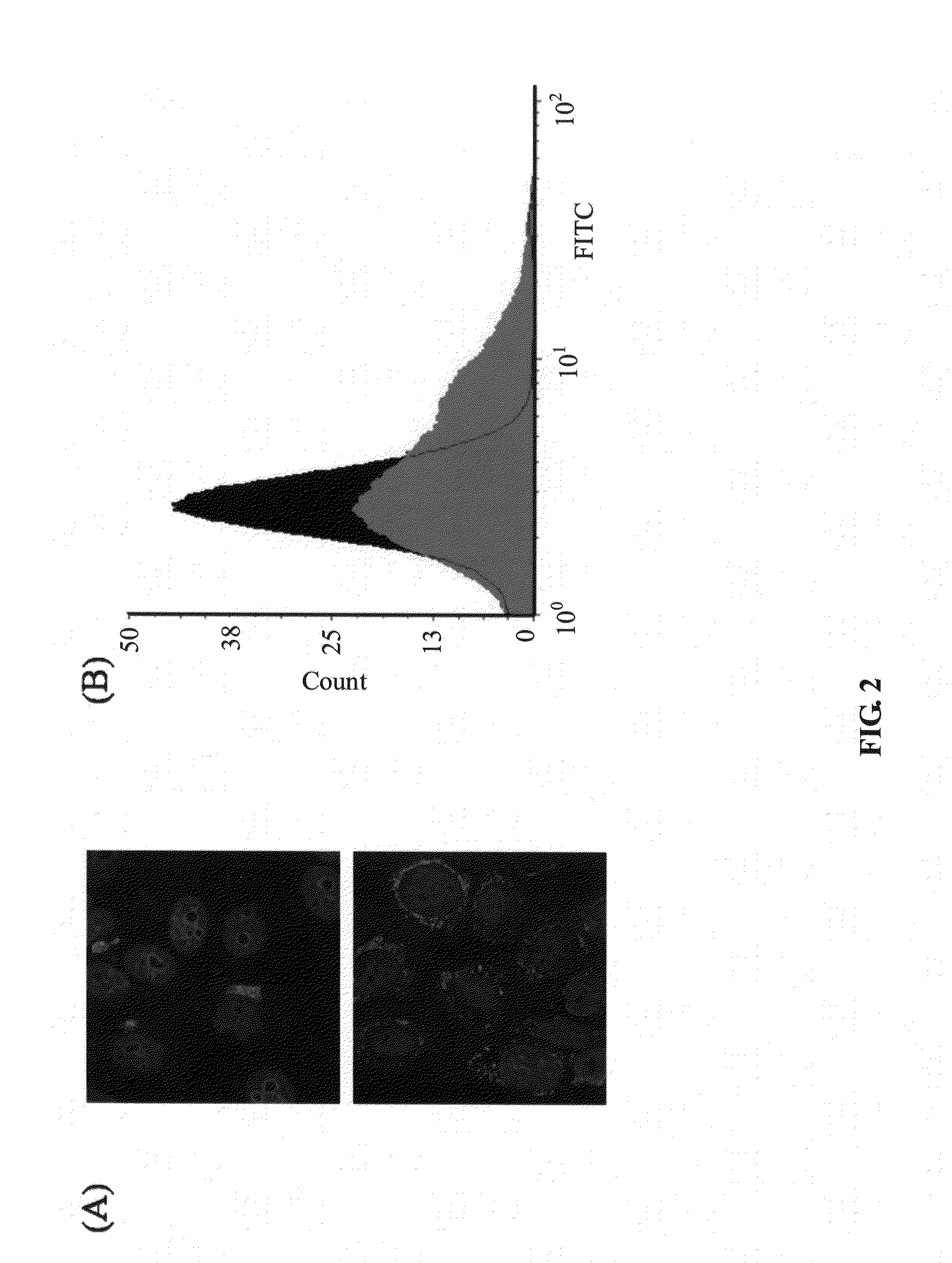
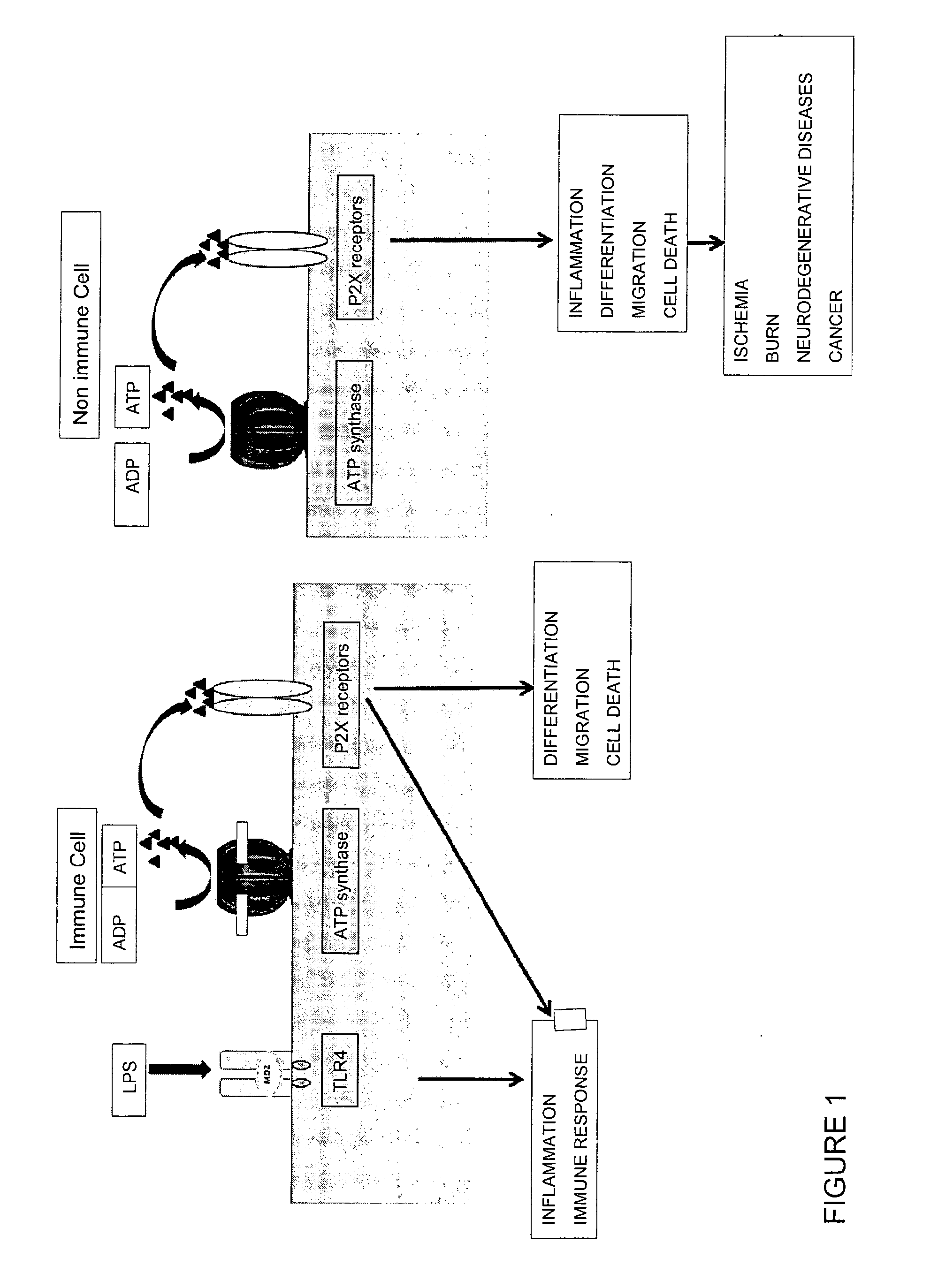
It was observed that a highly purified preparation of polar glycolipids extracted from cells of the cyanobacterium Oscillatoria Planktothrix is characterized by the presence of at least one species of high molecular weight glycolipid comprising one or more units of rhamnose. In such mixture, having a level of nucleic acid contamination lower than (or equal to) 3%, an inhibitory activity toward ATP synthase (ATP-SX) was identified which is capable of decreasing the level of extracellular ATP and thereby the extent of the inflammatory response. The glycolipid mixture is especially useful in inflammation induced by ischemic stimuli, cancer or autoimmune diseases (such as multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis), psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, autoimmune thyroiditis, systemic lupus erythematosus), in addition to systemic inflammatory states such as systemic inflammatory syndrome (SIRS), sepsis, vasculitis, or in localized inflammatory states, such as neurodegenerative diseases or asthma.
Owner:BLUEGREEN BIOTECH
Productivity and Bioproduct Formation in Phototropin Knock/Out Mutants in Microalgae
ActiveUS20180187170A1Reduced PHOT expressionHigh genetic stabilityHydrolasesUnicellular algaeElectron micrographsChlamydomonas reinhardtii
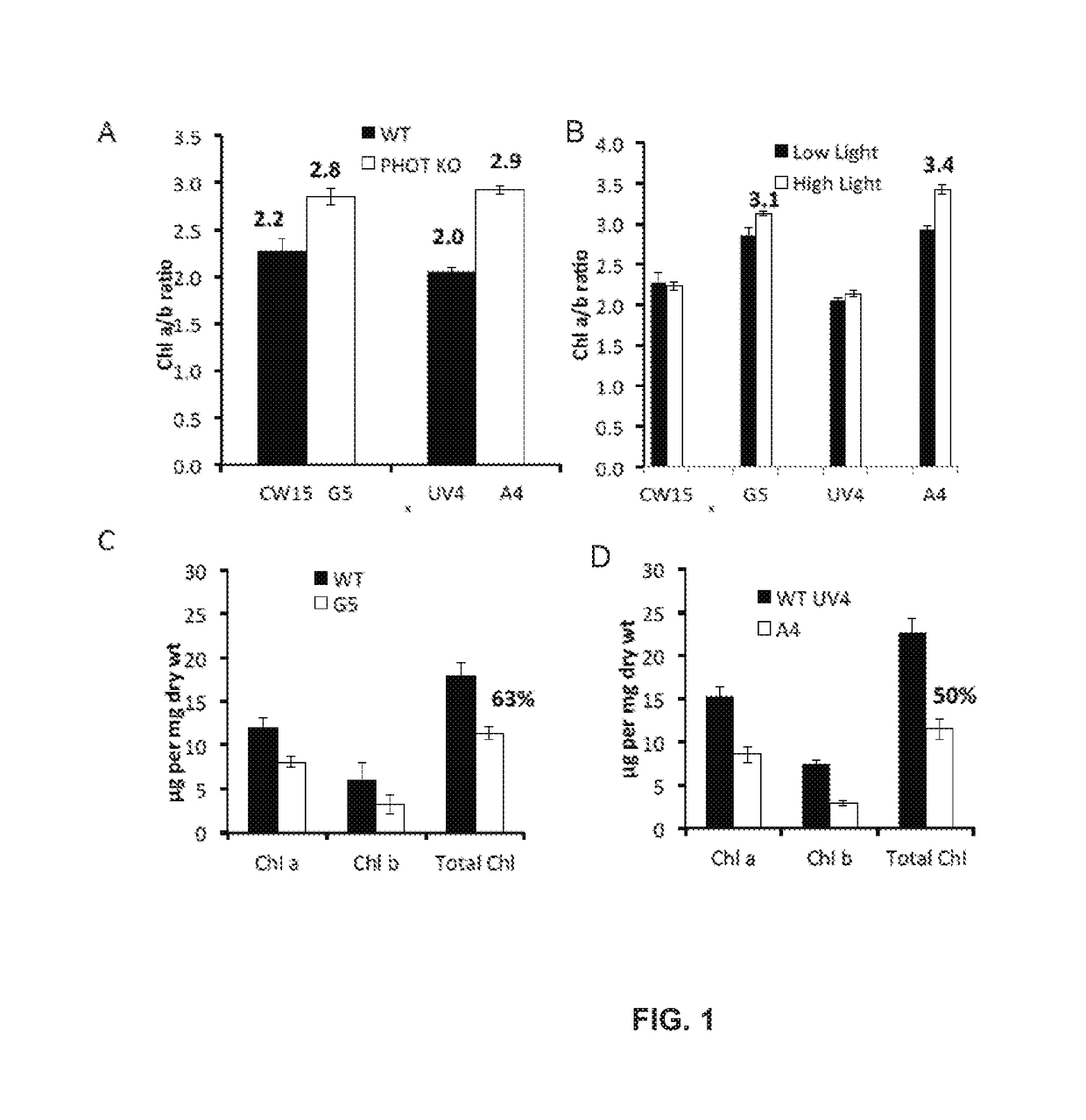
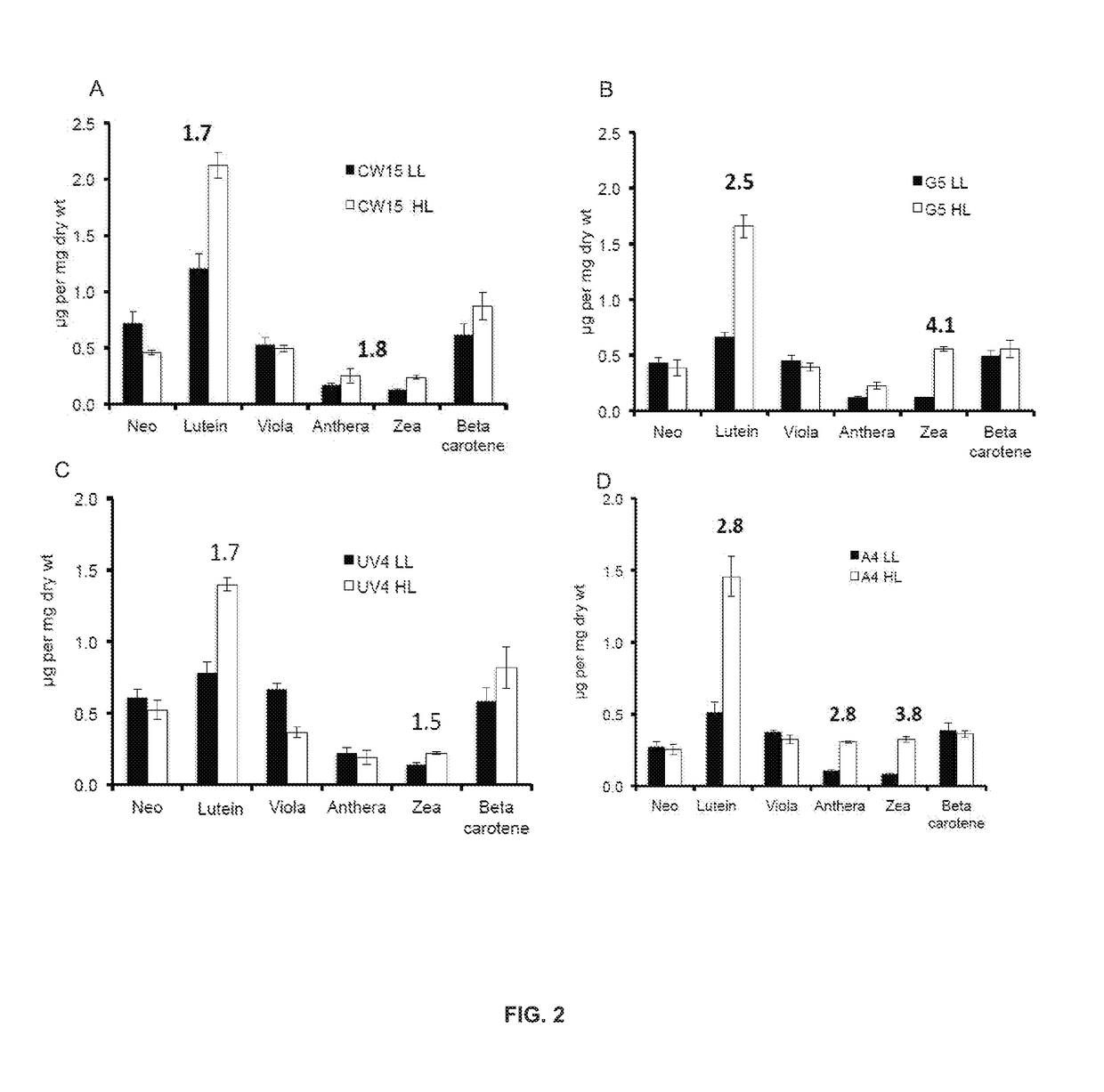
Phototropin is a blue light receptor, which mediates a variety of blue-light elicited physiological processes in plants and algae. In higher plants these processes include phototropism, chloroplast movement and stomatal opening. In the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, phototropin plays a vital role in progression of the sexual life cycle and in the control of the eye spot size and light sensitivity Phototropin is also involved in blue-light mediated changes in the synthesis of chlorophylls, carotenoids, chlorophyll binding proteins. We compared the transcriptome of phototropin knock out (PHOT KO) mutant and wild-type parent to analyze differences in gene expression in high light grown cultures (500 μmol photons m−2 s−1). Our results indicate the up-regulation of genes involved in photosynthetic electron transport chain, carbon fixation pathway, starch, lipid, and cell cycle control genes. With respect to photosynthetic electron transport genes, genes encoding proteins of the cytochrome b6f and ATP synthase complex were up regulated potentially facilitating proton-coupled electron transfer. In addition genes involved in limiting steps in the Calvin cycle Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (RuBisCO), Sidoheptulose 1,7 bisphosphatase (SBPase), Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (3PGDH) and that mediate cell-cycle control (CDK) were also up regulated along with starch synthase and fatty acid biosynthesis genes involved in starch and lipid synthesis. In addition, transmission electron micrographs show increased accumulation of starch granules in PHOT mutant compared to wild type, which is consistent with the higher expression of starch synthase genes. Collectively, the altered patterns of gene expression in the PHOT mutants were associated with a two-fold increase in growth and biomass accumulation compared to wild type when grown in environmental photobioreactors (Phenometrics) that simulate a pond environment. In conclusion, our studies suggest that phototropin may be a master gene regulator that suppresses rapid cell growth and promotes gametogenesis and sexual recombination in wild type strains.
Owner:NMC INC +1
Insecticidal and acaricidal composition
ActiveCN111657281AImprove the effect of prevention and controlSynergistic effect is obviousBiocideAnimal repellantsChemical compoundBiochemistry
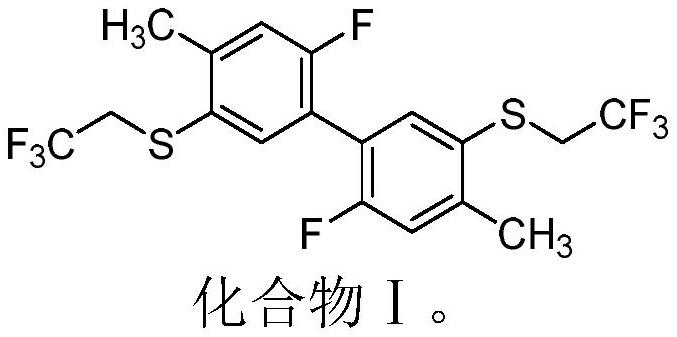
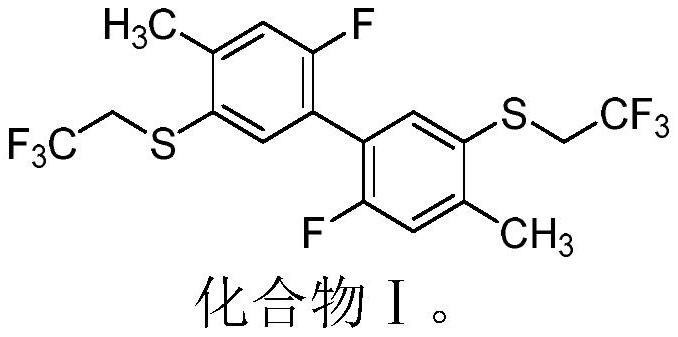
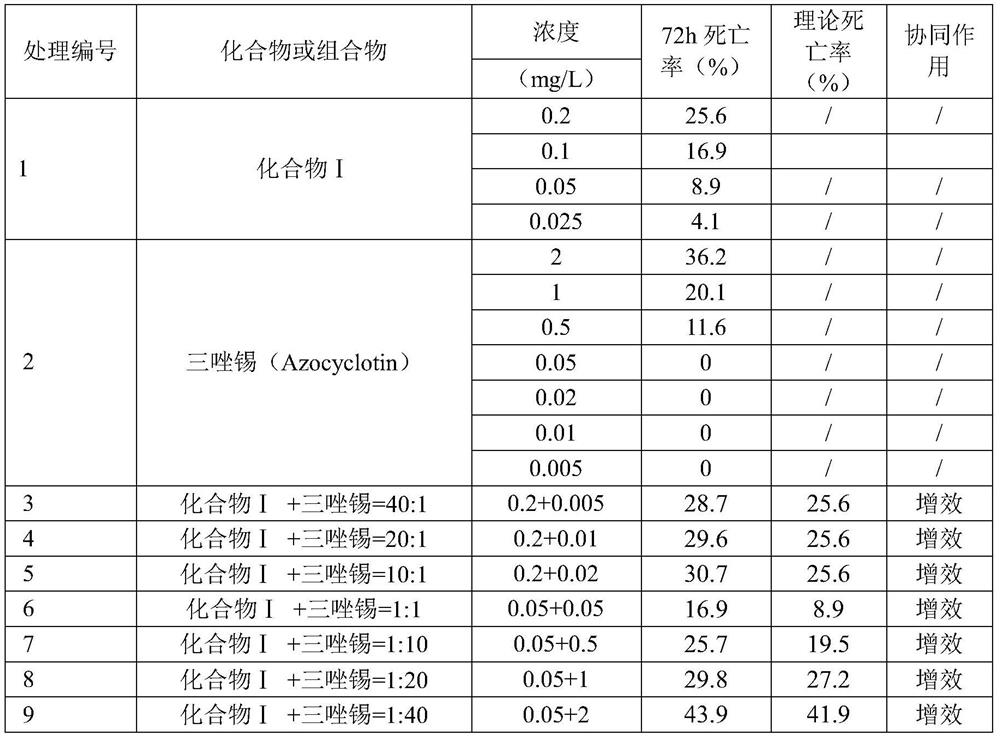
The invention belongs to the field of insecticidal and acaricidal agents, and relates to an insecticidal and acaricidal composition containing an ATP synthetase inhibitor insecticidal / acaricidal agent. The composition contains an active component A and an active component B, wherein the weight part ratio of the active component A to the active component B is 1:99-99:1, the active component A is selected from a compound I, the active component B is selected from an ATP synthase inhibitor insecticide / acaricide, and the structure of the active component A is defined in the specification. The composition of the invention has the advantages of obvious synergism, resistance delaying and the like, and can be used for preventing and treating various pests.
Owner:SHENYANG SINOCHEM AGROCHEMICALS R&D CO LTD
Molecular motor lipid vesicle composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112656696AImprove delicate vitalityImprove solubilityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsMolecular motorPhospholipid
The invention relates to a molecular motor lipid vesicles composition, a preparation method and an application of the composition. The composition has the effects of improving the solubility and long-term effect of molecular motors and promoting absorption, and the assembly structure of the molecular motor lipid vesicles is a closed structure or a cell compartment containing molecular motor ATP synthase and lipid bilayers thereof and having biological membrane properties, the molecular motor lipid vesicles called vesicles, niosolnes are also called liposomes in the past, the biological membrane containing the molecular motor has a lipid bilayer structure, so that the biological membrane has moisturizing, whitening and anti-aging effects when being applied to the field of cosmetics, achieves the effects of improving the stability, improving the solubility and the long-term effect of the molecular motor and promoting absorption, and is simple and convenient in production process, and low in cost, and the defects that the lipidosome adopting phospholipid needs to be purified, is easy to oxidize and degrade and the like are avoided.
Owner:HANGZHOU UMOTOR BIOTECH CO LTD
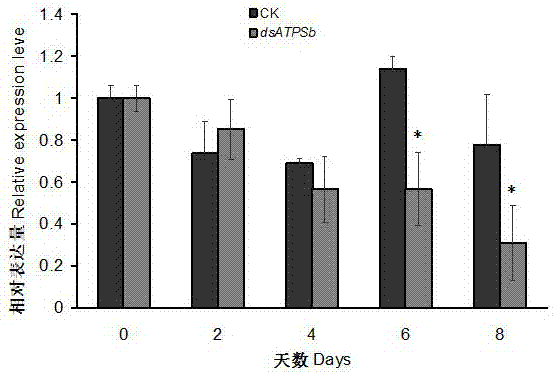
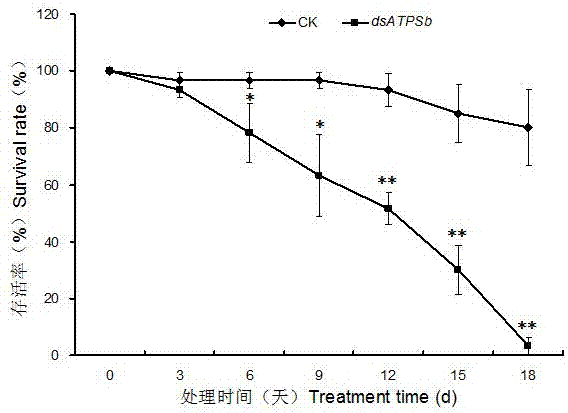
ATPSb gene related to survival of brown planthopper and encoded protein as well as application thereof
The invention discloses a ATPSb gene related to survival of a brown planthopper and encoded protein as well as application thereof. The ATPSb gene is characterized in that the ATPSb gene has nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 1, a gene code ATP synthase b subunit, plays an important role in keeping normal survival of the brown planthopper, which cause the decreasing of the survival rate if the role is inhibited. The protein encoded by the ATPSb gene has the amino sequence shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. The application of the ATPSb gene and encoded protein is used for researching pesticide and biologically controlling the brown planthopper. According to the invention, the RNA interference on the ATPSb gene is successfully conducted, the results show that the survival rate of pests is reduced,the survival of the pests is obviously inhabited, so that the functions that the pests are inhabited and the biologically controlling is fully realized are hopefully realized at the same time.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method for recombinant production of procambarus clarkii ATP synthase F0 subunit 6 protein
The invention relates to a method for recombinant production of procambarus clarkii ATP synthase F0 subunit 6 protein, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. According to the method, an atp6 gene is obtained through whole-gene synthesis, a recombinant expression vector pColdII-atp6 is constructed and transforms an escherichia coli expression strain BL21(DE3) to achieve efficient expression, and then an important foundation is laid for the following intensive study for the molecular mechanism of the procambarus clarkii ovary 'eyestalk excision effect'.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Preparation method and use of chimeric human anti-murine monoclonal antibody for inhibiting angiostatin acceptor
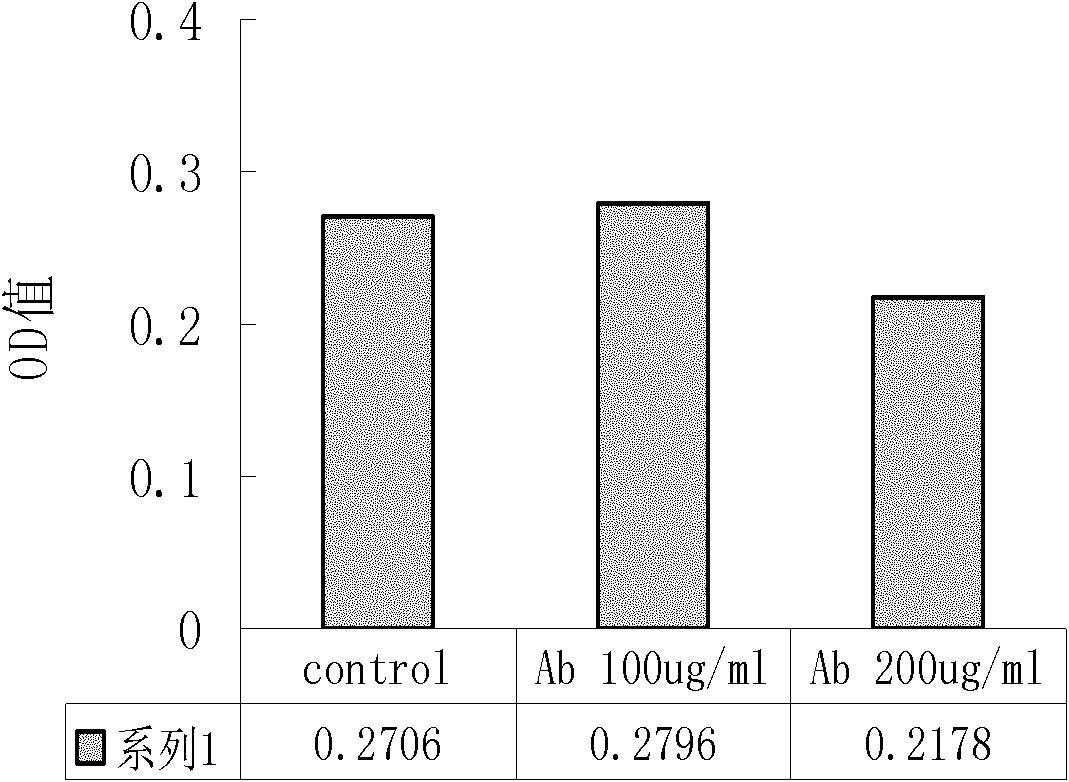
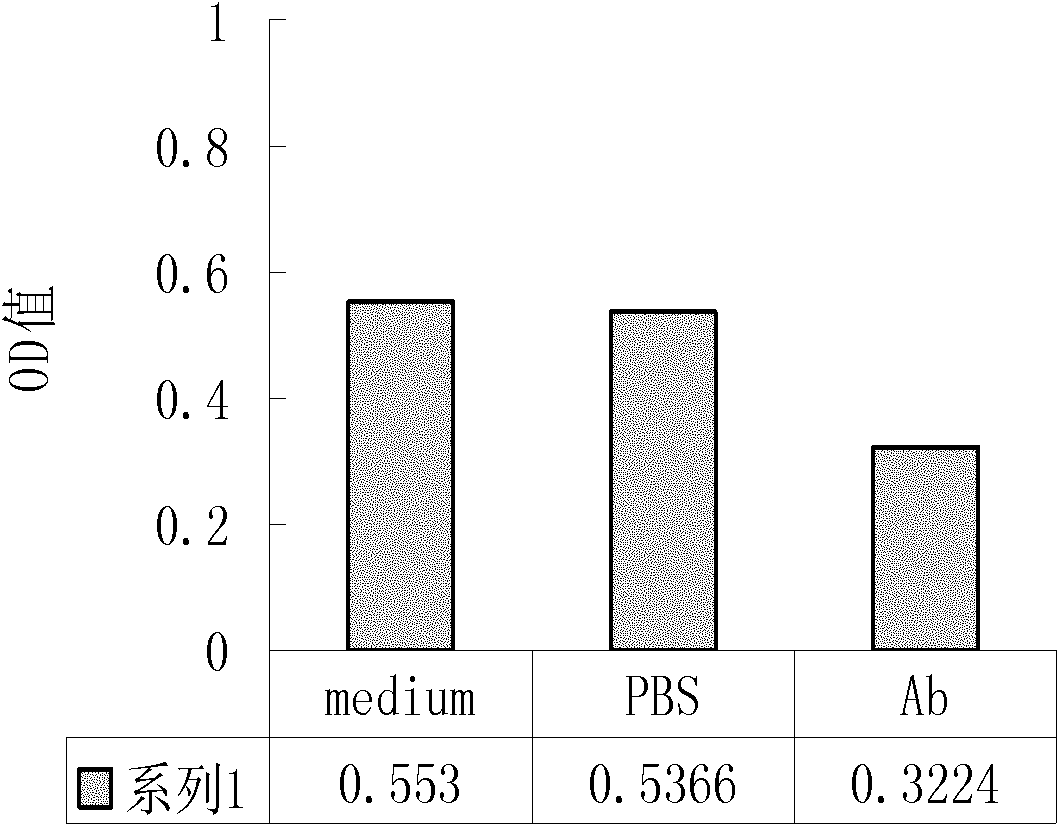
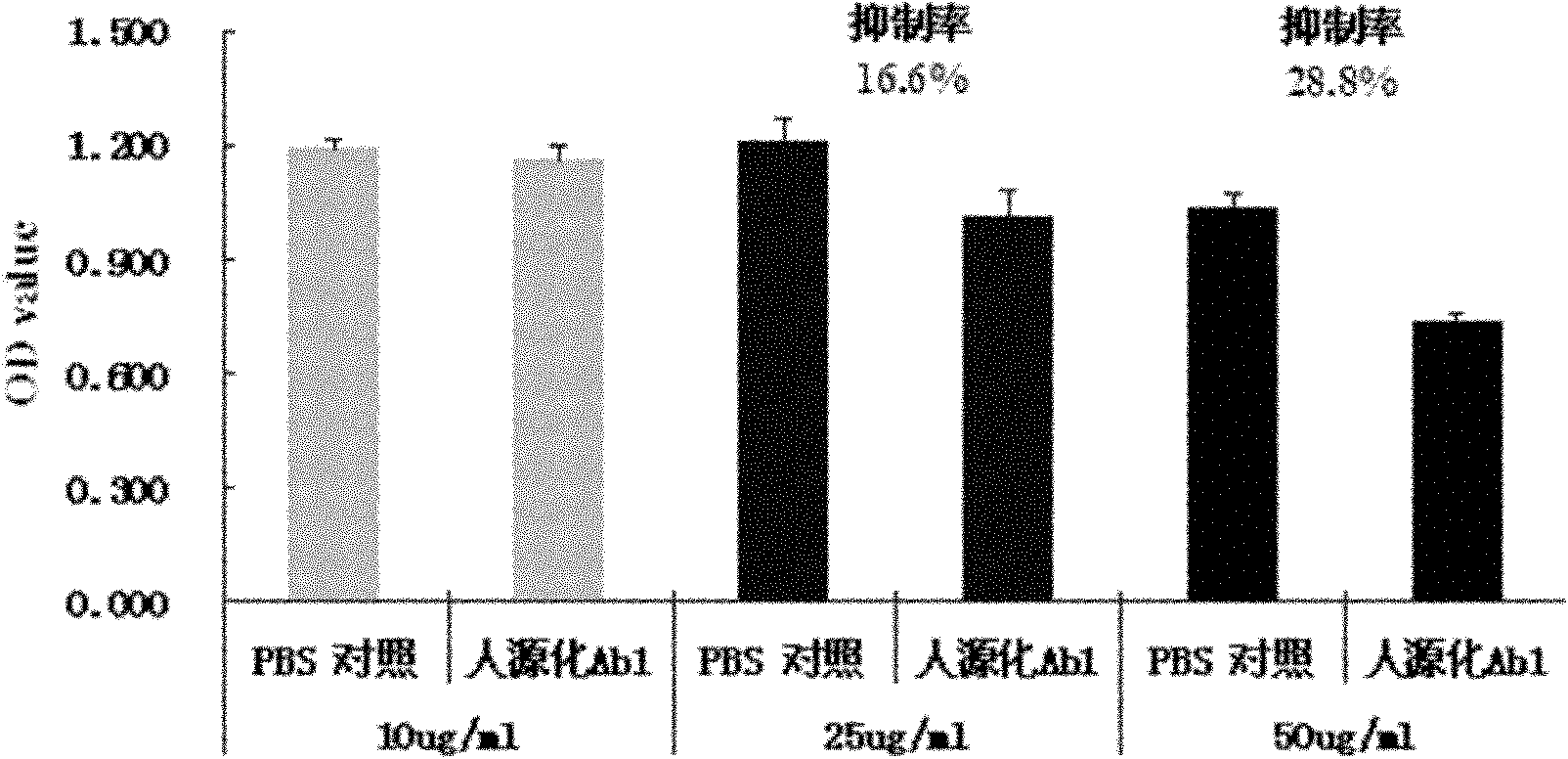
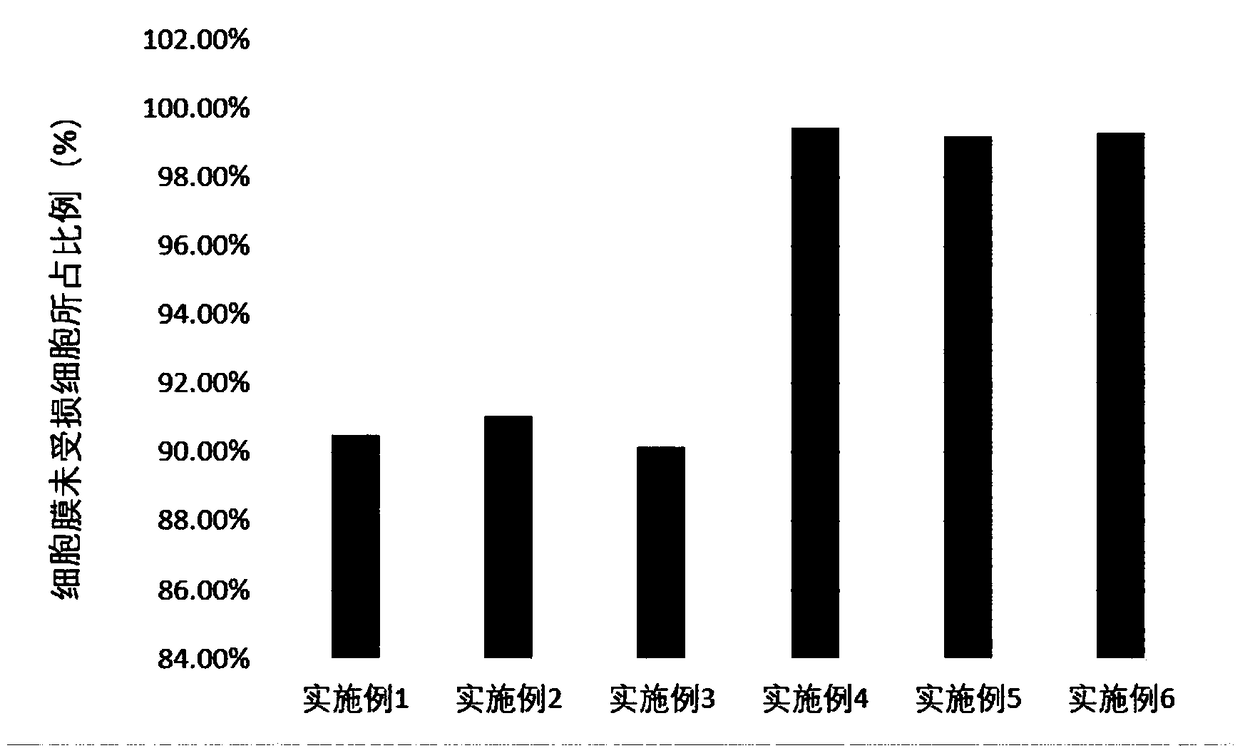
InactiveCN102464720AInhibit synthesisSuitable for in vivo applicationFungiHybrid immunoglobulinsApoptosisCell membrane
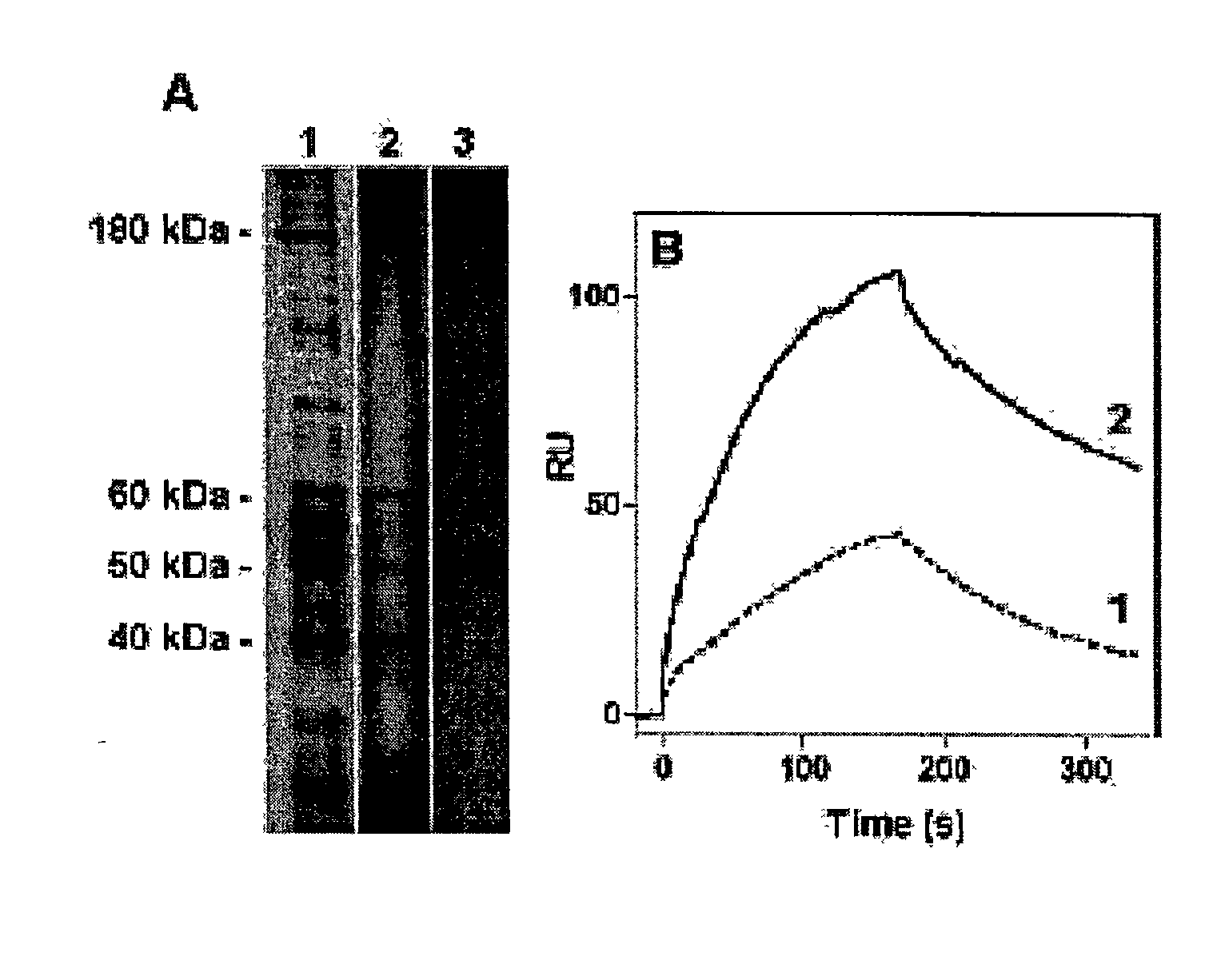
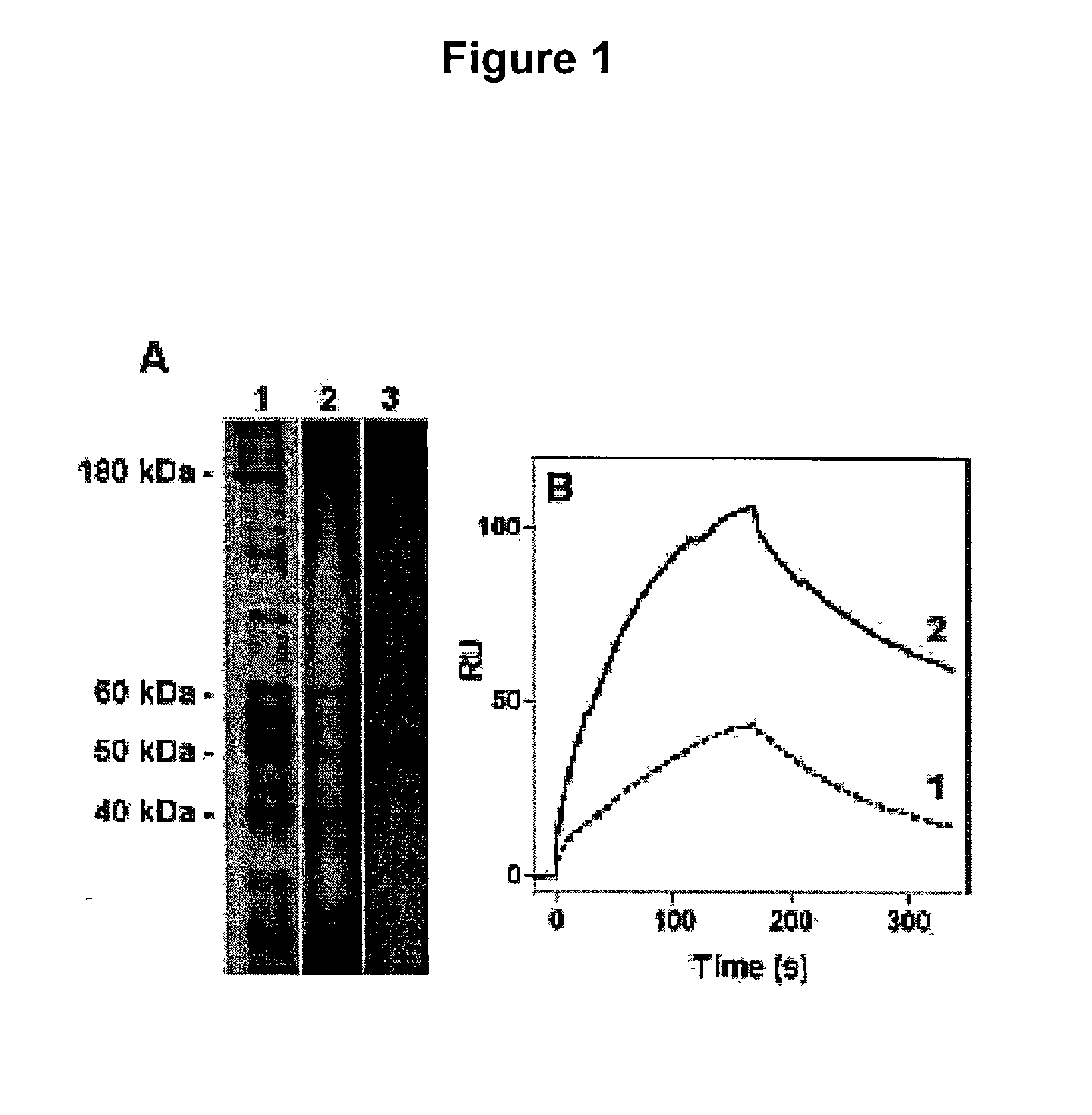
The invention discloses a chimeric human anti-murine monoclonal antibody for inhibiting an angiostatin acceptor, and its preparation method and use. The chimeric human anti-murine monoclonal antibody for inhibiting the angiostatin acceptor comprises an antibody light-chain unit and an antibody heavy-chain unit, wherein a heavy chain is connected to a light chain through a disulfide bond. The chimeric human anti-murine monoclonal antibody for inhibiting the angiostatin acceptor is a chimeric antibody, can maintain human adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase-resistant activity and is suitable for be used in vivo. The chimeric human anti-murine monoclonal antibody for inhibiting the angiostatin acceptor has obvious effects of inhibiting proliferation of a breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231, has certain effects of inhibiting proliferation of a lung cancer cell A549, a liver cancer cell HepG2, and a cell PC-3 and a cell HUVEC of the prostate, causes apoptosis of associated cells, specifically binds with tumor tissue, and specifically identifies a tumor cell membrane and an endothelial cell membrane. In addition, the chimeric human anti-murine monoclonal antibody for inhibiting the angiostatin acceptor can inhibit activity of ATP synthase on surfaces of tumor cell membranes and endothelial cell membranes, formation of vessels in vitro, and moving of the cell HUVEC and the breast cancer cell MDA-MB-231 in vitro, and is meaningful to antitumor therapy.
Owner:SUZHOU INDAL PARK HUMAN ANTIBODOMICS DEV
Method for collecting nitrosobacteria
ActiveCN108486019AImprove liquidityImprove the immunityBacteriaMicroorganism preservationATPaseFreeze-drying
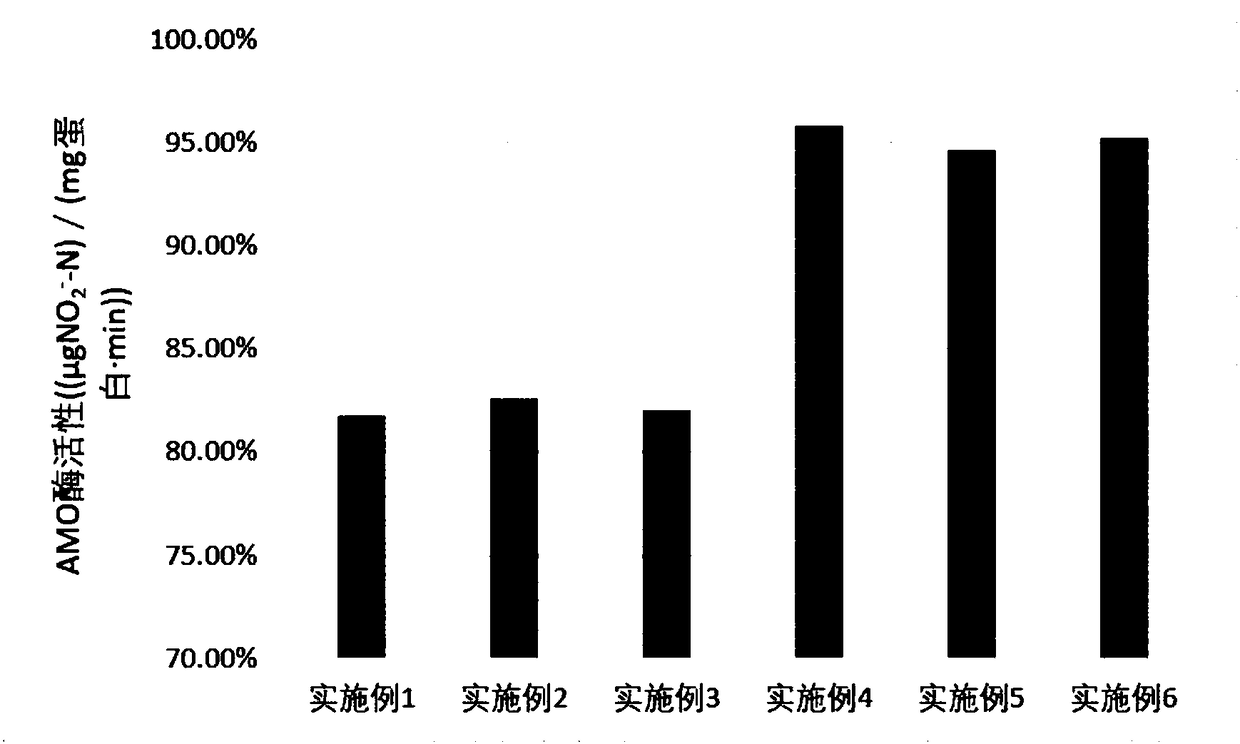
The invention discloses a method for collecting nitrosobacteria. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a protective agent, namely adding 2-4 parts of sodium glutamate, 18-25 parts oftripotassium phosphate and 1-3 parts of cysteine into 90-120 parts of sterile water, and uniformly mixing to obtain the protective agent; 2) adding thalli, namely 0.8-1.2 times that of the volume of nitrosobacteria thalli into the protective agent obtained in the step 1), and performing shock re-suspending so as to obtain a mixed solution; and 3) freezing and preserving, namely performing freeze drying on the mixed solution obtained in the step 2), freezing and preserving at a temperature of 70-90 DEG C, and performing activation transfer every 2-3 months. The method disclosed by the inventionhas the beneficial effects that damage of freeze drying on the nitrosobacteria thalli can be greatly reduced, and the nitrosobacteria survival rate and activities of ATP synthase and ammonia monooxygenase (AMO) in the preservation process are improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
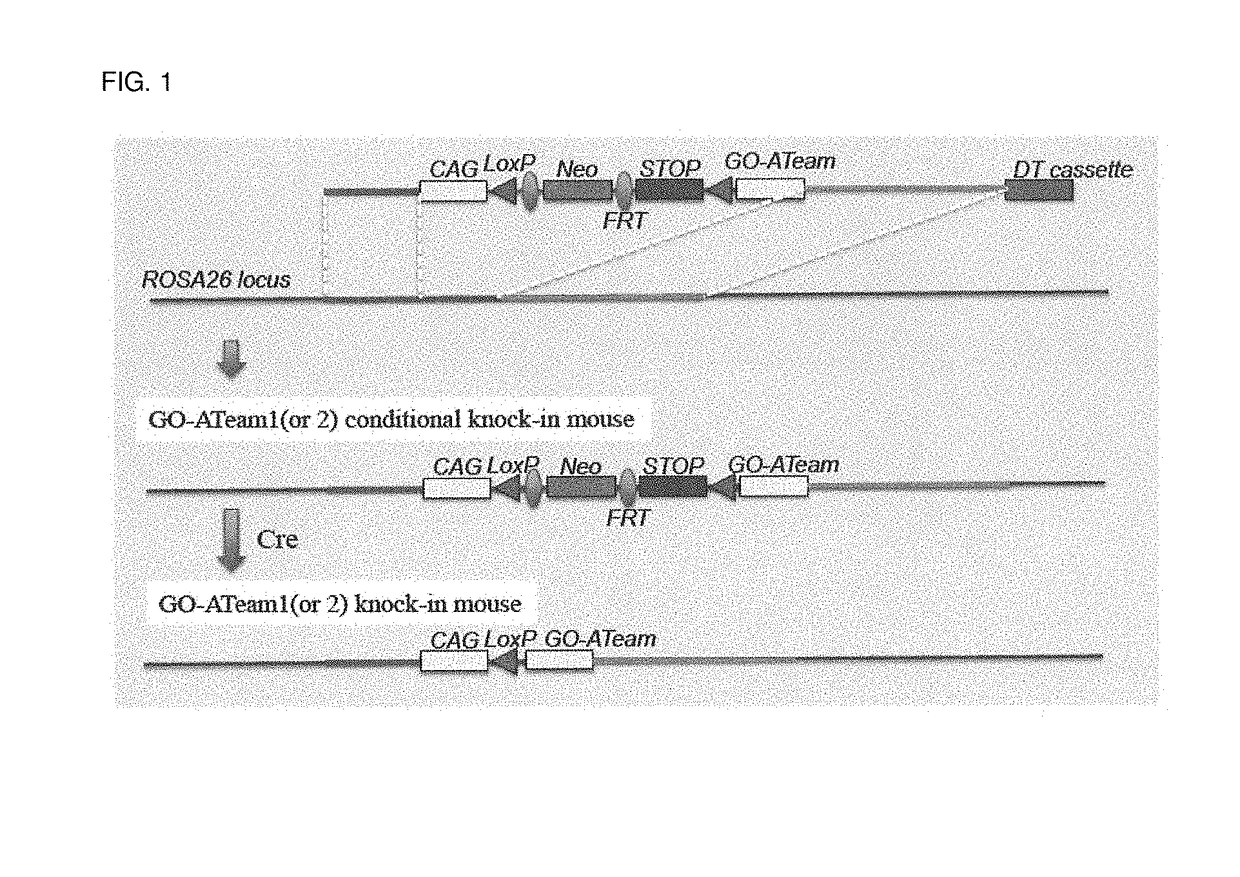
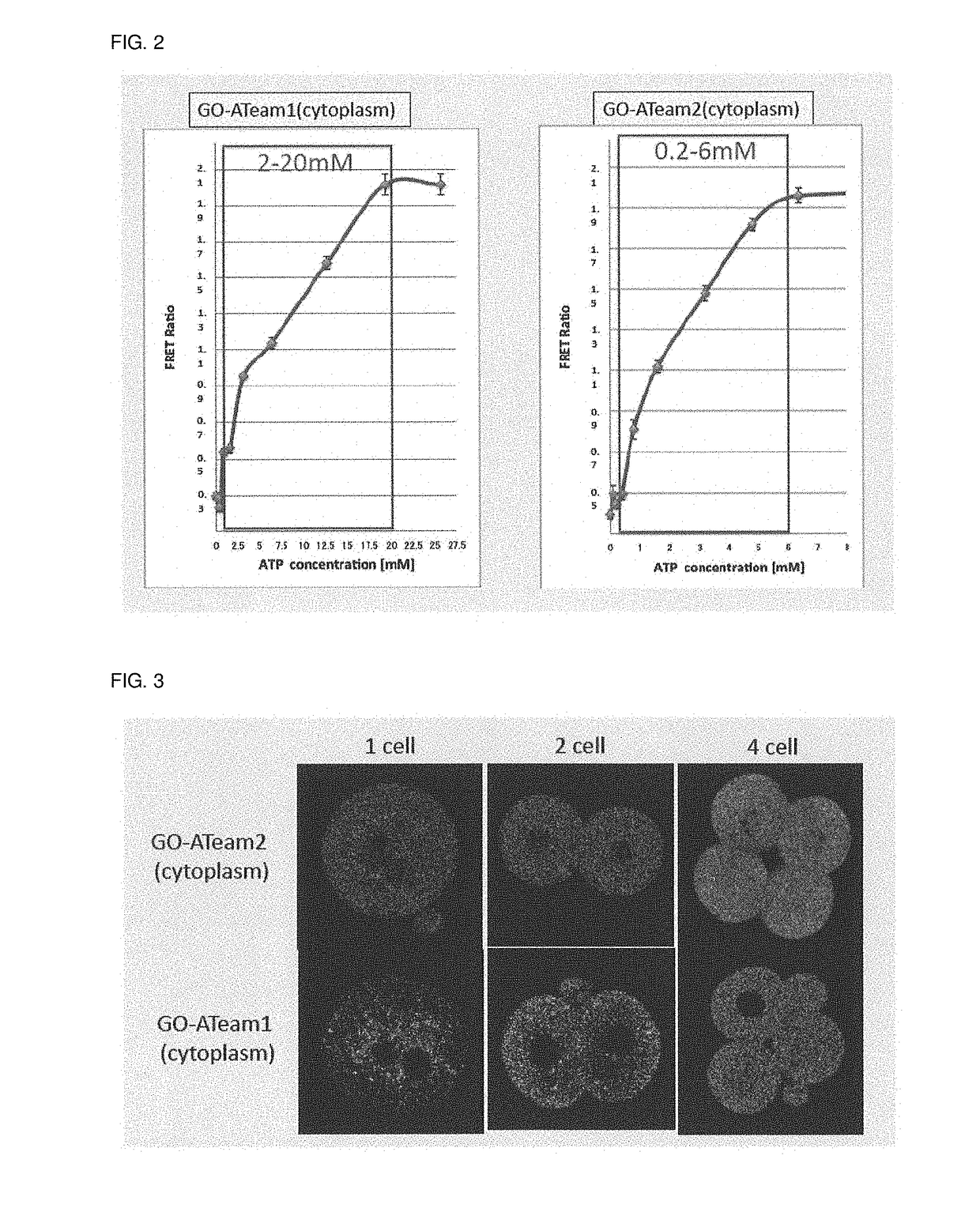
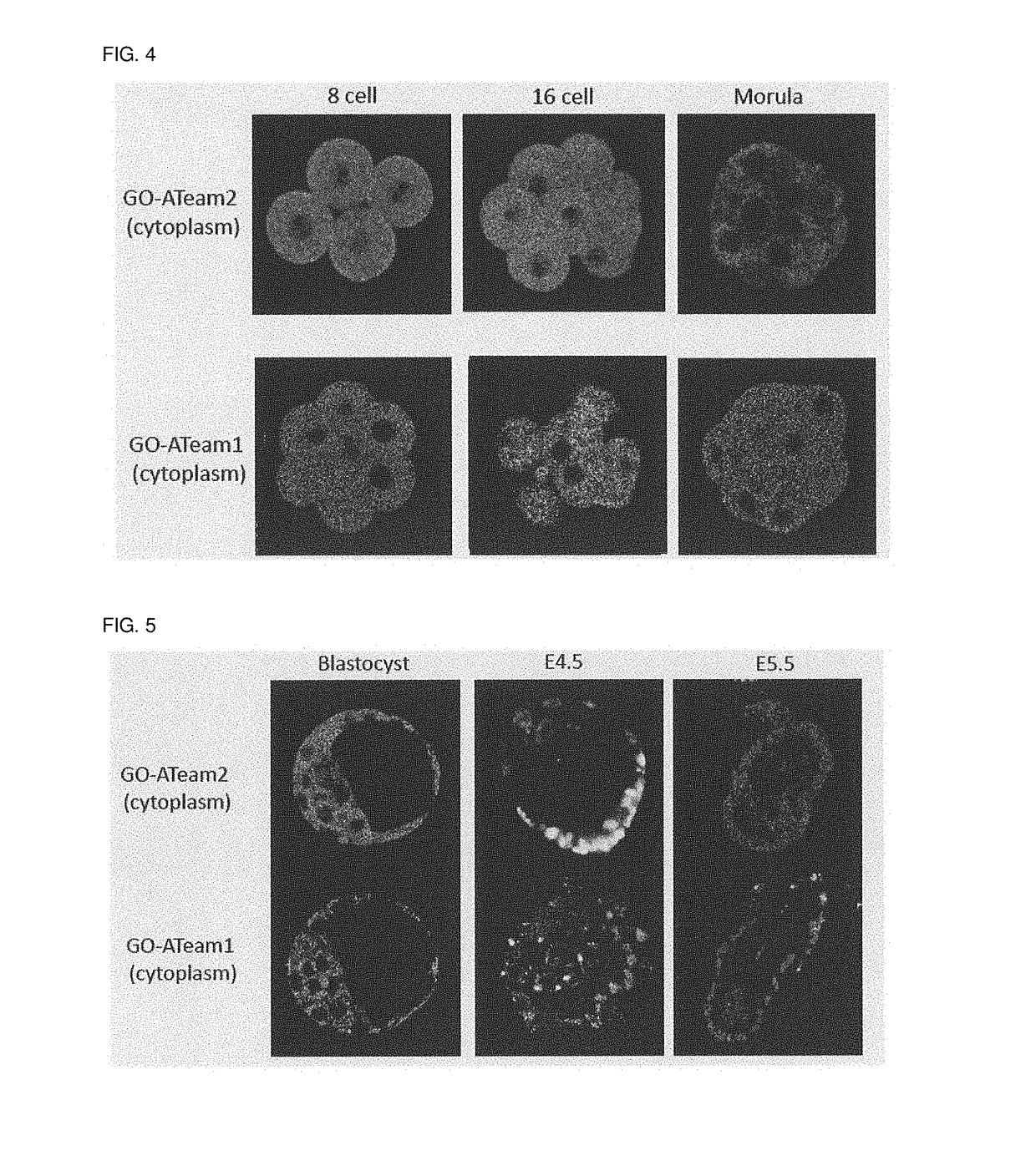
Atp-visualizing animal and use thereof
Provided are a transgenic non-human mammal expressing a fusion protein, wherein the fusion protein comprises an ε subunit of an ATP synthase and two distinct fluorescent proteins as a donor and an acceptor for FRET, one of the fluorescent proteins being placed at an amino terminal moiety of the ε subunit and the other being placed at a carboxyl terminal moiety of the ε subunit, and a method of screening for an agent for preventing or treating diseases in a mammal in need thereof, comprising using an above transgenic non-human mammal.
Owner:YAMAMOTO MASAMICHI
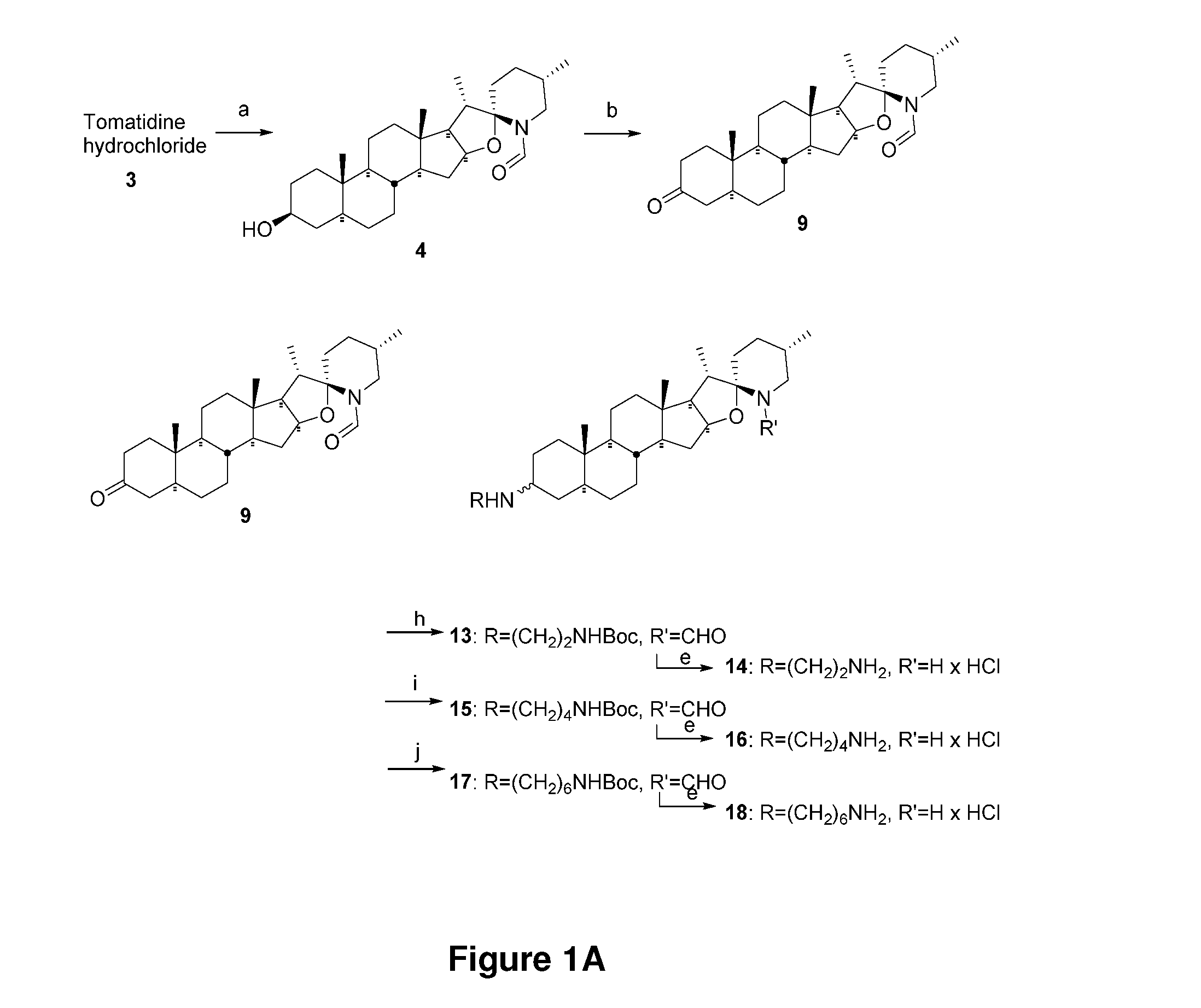
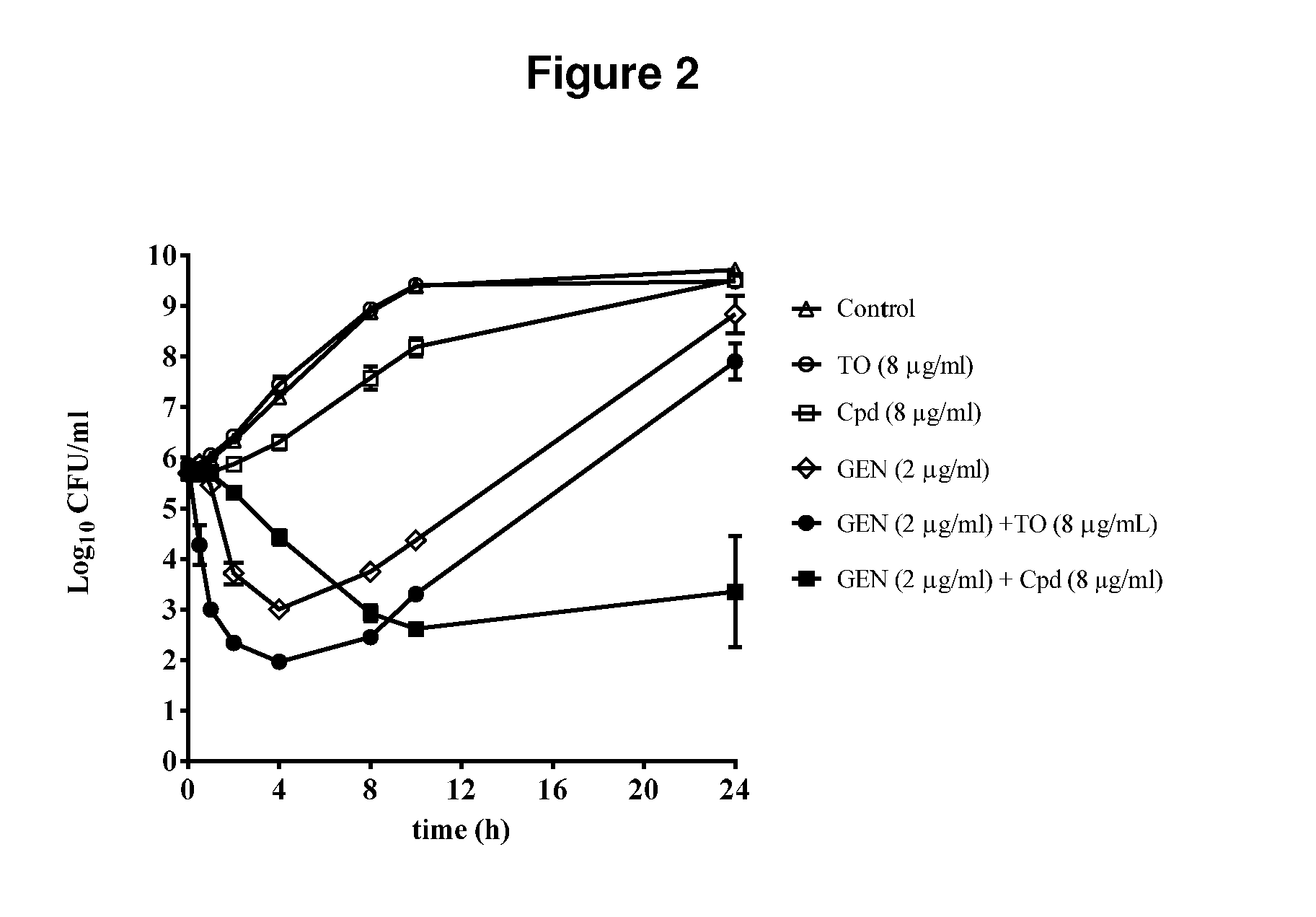
Atp synthase inhibitors and steroid alkaloids and uses thereof as antimicrobial agents and as potentiators for aminoglycosides against pathogenic bacteria
ActiveUS20160317556A1Promote growthReduced survivalAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsCompound (substance)Pathogenic bacteria
The present invention provides bacterial ATP synthase inhibitors such as a compound of formula (I): (Formula (I)) (A) in combination with an aminoglycoside antibiotic for preventing or treating a bacterial infection in a subject; or (B) (a) for preventing or treating an infection caused by an electron transport-deficient bacteria in a subject; or (b) for the disinfection, sterilization and / or antisepsis of an object contaminated with an electron transport-deficient bacteria. There are provided compositions and kits using such compounds and inhibitors.
Owner:SCOPRA SCI & GENIE SEC
Compositions and methods for promoting or inhibiting angiogenesis
InactiveUS20060216296A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsAbnormal tissue growthDisease
Compounds, compositions and methods for promoting or inhibiting angiogenesis, and screening methods for identifying compounds are disclosed. The compounds bind to F1 ATP synthase particularly to the alpha and / or beta subunits of F1 ATP synthase. When bound to these subunits, they can function as angiostatin agonists, antagonists, partial agonists, inverse agonists, or allosteric modulators. When the compounds mimic or enhance the activity of angiostatin, they inhibit angiogenesis. When the compounds inhibit the ability of angiostatin to bind F1 ATP synthase and are either inactive at inhibiting angiogenesis or directly promote angiogenesis, or if they inhibit the activity of angiostatin, they promote angiogenesis. The compounds can be, for example, antibodies, antibody fragments, enzymes, peptides, nucleic acids such as oligonucleotides, or small molecules. The antibodies can be monoclonal, humanized, or polyclonal antibodies. The compounds can be conjugated to or combined with various cytotoxic agents and / or labeled compounds. Methods for promoting angiogenesis can be used to introduce vasculature to areas in a patient that can benefit from such increased vasculature. Methods for inhibiting angiogenesis can be used to treat disorders mediated by angiogenesis, for example, tumors, autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis, and the like.
Owner:DUKE UNIV +1
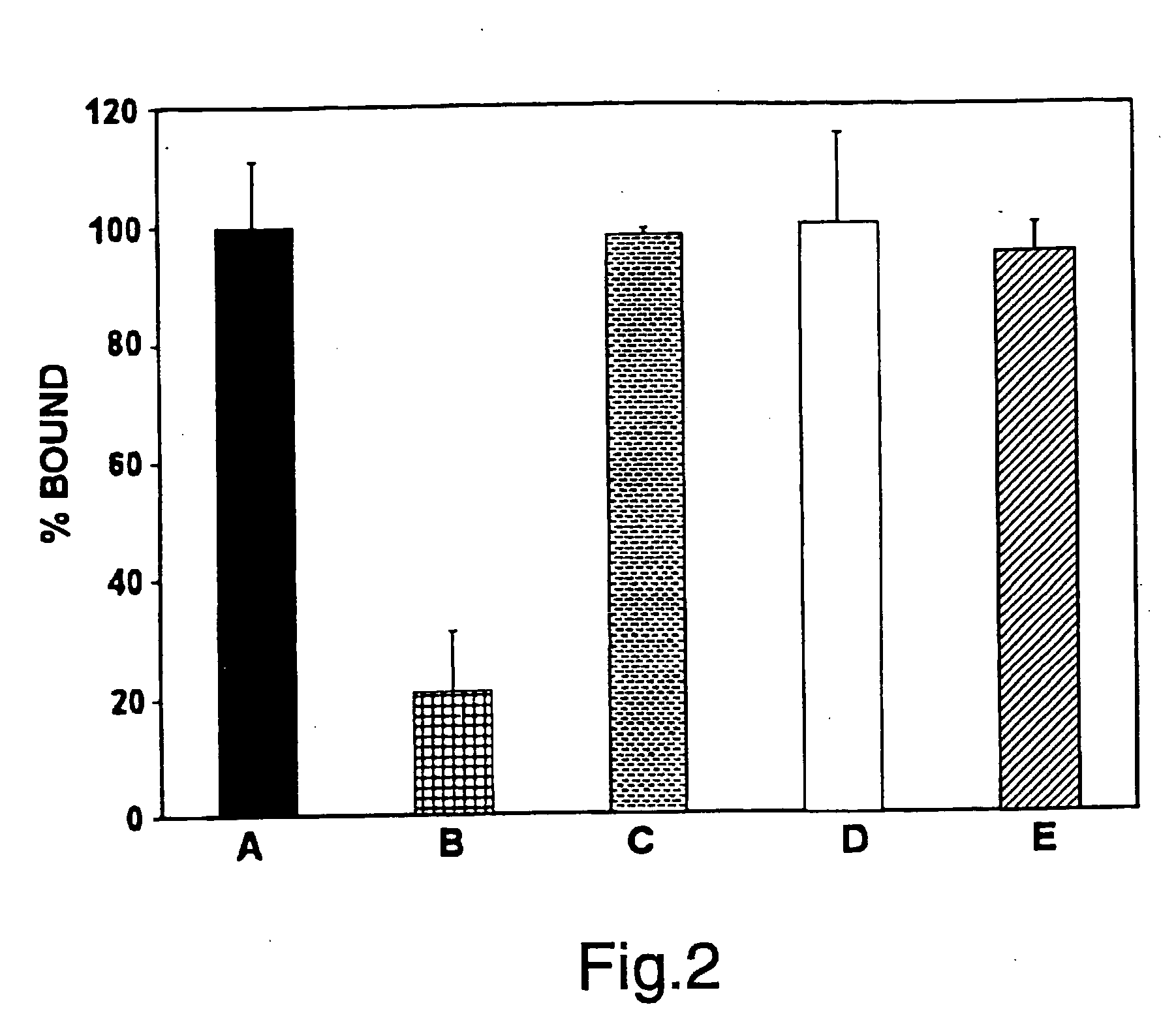
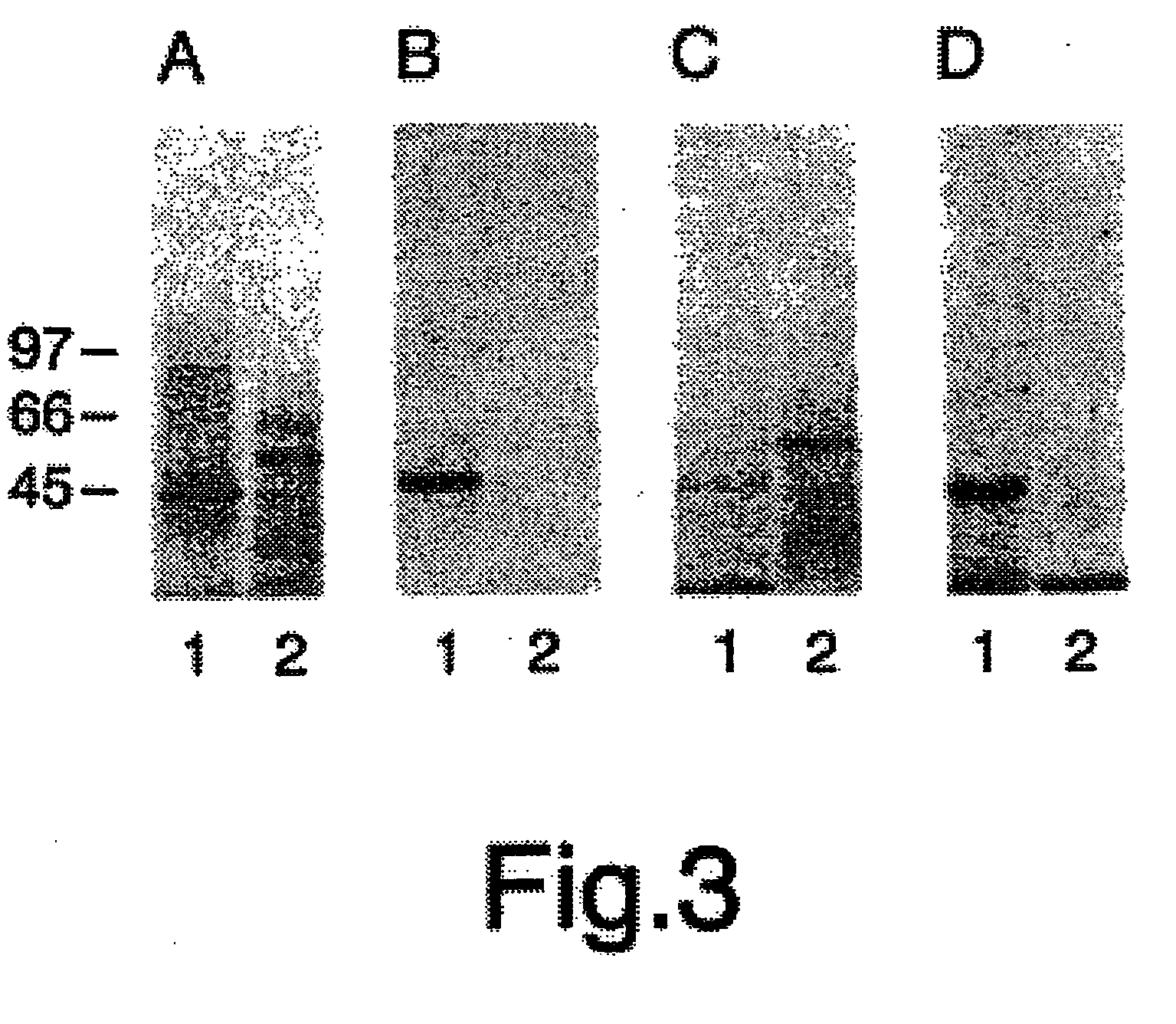
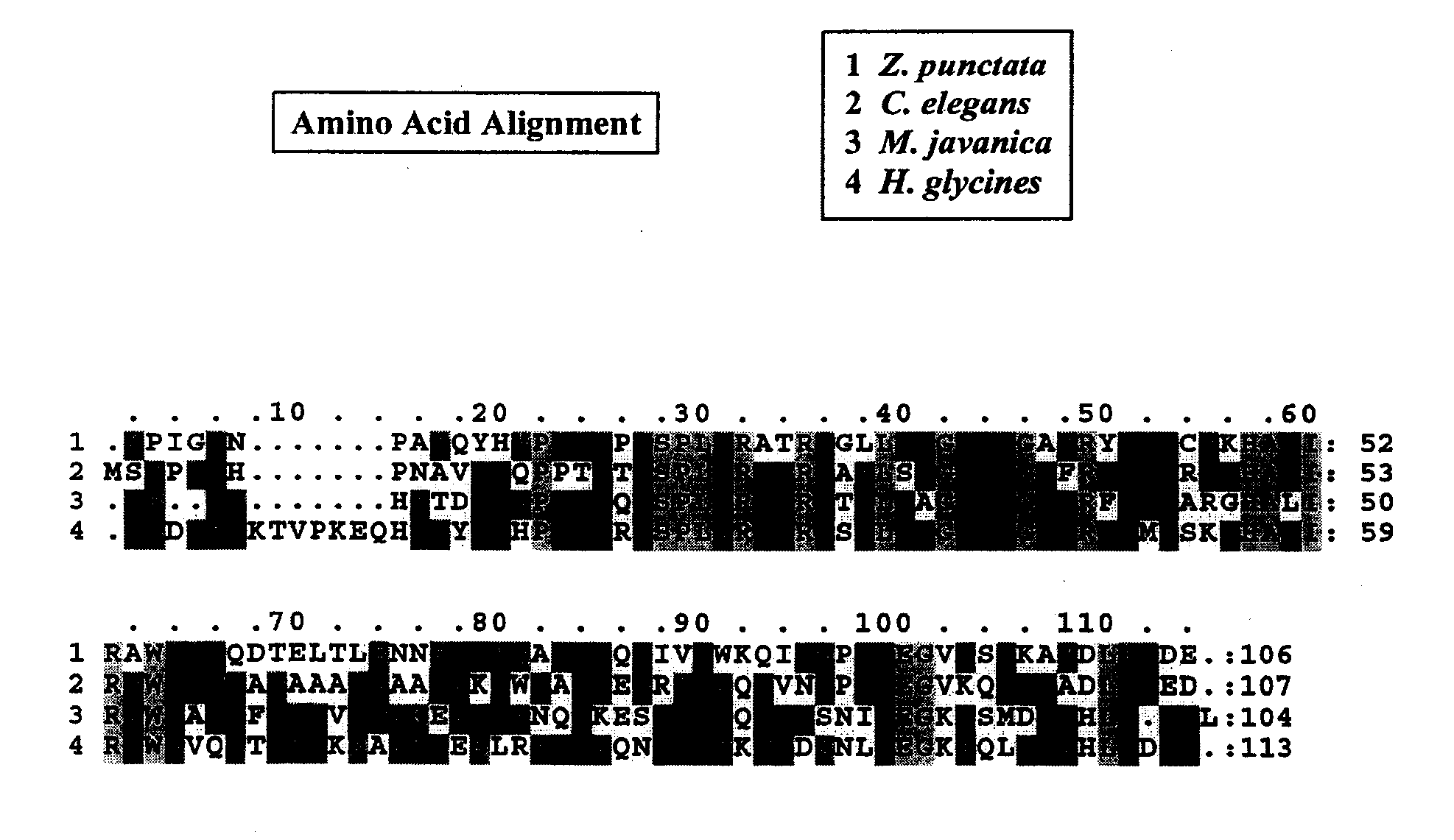
Nematode ATP Synthase Subunit E-Like Sequences
Nucleic acid molecules from nematodes encoding ATP synthase subunit E polypeptides are described. ATP synthase subunit E-like polypeptide sequences are also provided, as are vectors, host cells, and recombinant methods for production of ATP synthase subunit E-like nucleotides and polypeptides. Also described are screening methods for identifying inhibitors and / or activators, as well as methods for antibody production.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Genetically engineered bacterium for high expression of Procambarus clarkia ATP synthase F0 subunit 8
The invention relates to a method for high expression of a Procambarus clarkia ATP synthase F0 subunit 8 protein by the aid of an Escherichia coli expression system and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. An atp8 gene is obtained through total gene synthesis, a recombinant expression vector pColdII-atp8 is constructed and an Escherichia coli expression strain BL21(DE3) is converted for high expression, and an important foundation is laid for subsequent deep research on a molecular mechanism of the Procambarus clarkia ovary eyestalk-ablation effect.
Owner:FRESHWATER FISHERIES RES CENT OF CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) synthase model training aid
InactiveCN102938225BSmooth rotationReduce frictionEducational modelsEngineeringAdenosine triphosphate
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Oligonucleotide sequences that identify species of animal
InactiveUS8158772B2High sensitivityUseful in detectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA fragmentationA-DNA
Methods for identifying animal species involving amplifying a DNA fragment by PCR using a DNA in a sample as a template and animal-specific DNA sequences as a primer pair, the animal-specific DNA sequences derived from a ATP synthase subunit 8 gene or a region proximal thereto of a mitochondrial genome; and detecting the amplified DNA fragment.
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI +1
Therapeutic modulators of the reverse mode of atp synthase
Compounds of the following formula (I) slow the ATP-hydrolysing mode of ATP synthase and are useful for treating various diseases and disorders including cancer, particularly cancers that utilize theWarburg effect.
Owner:迈克尔大卫福雷斯特
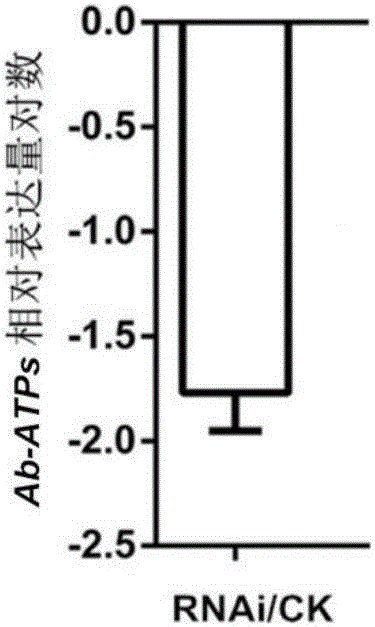
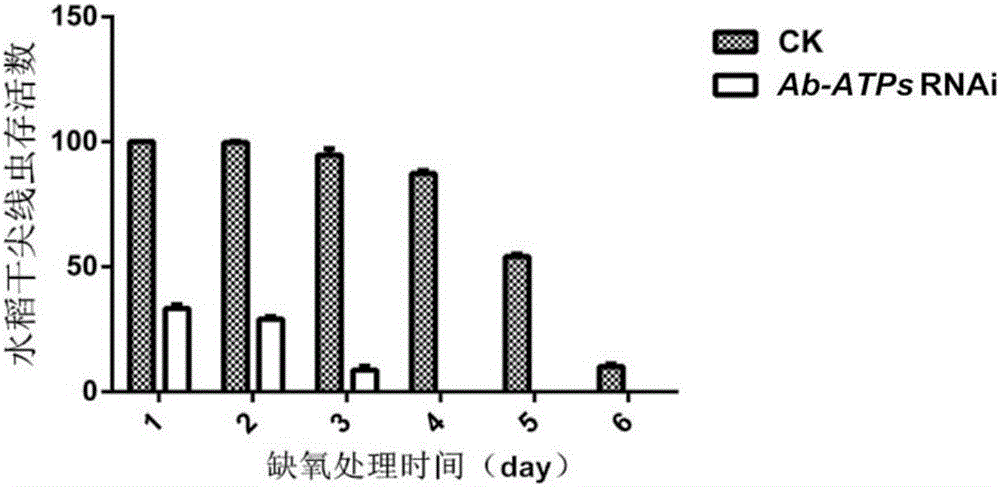
ATP synthetase gene for prevention and control of aphelenchoides besseyi christie, and primers and application thereof
The invention relates to an ATP synthetase gene for prevention and control of aphelenchoides besseyi christie, and primers and an application thereof. The gene has the sequence shown in a sequence table SEQ No.1. A primer group for construction of the aphelenchoides besseyi christie ATP synthase gene comprises an upstream primer Ab-ATPs-F shown in the sequence table SEQ No.2 and a downstream primer Ab-ATPs-R shown in the sequence table SEQ No.3. The application of the gene in prevention and control of the aphelenchoides besseyi christie is provided. The ATP synthetase gene has the expression up-regulated after the aphelenchoides besseyi christie is subjected to hypoxia stress, so the gene is indicated to play a role in the hypoxia stress resisting process of the aphelenchoides besseyi christie. Through the study of the gene, the gene has important biological significance and potential application value in the prevention and control of the aphelenchoides besseyi christie.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com