Method for cultivating transgenic plant with improved insect resistance by using RNA interference technology and special DNA fragment thereof
A fragment and gene technology, applied in the field of using RNA interference technology to cultivate transgenic plants with improved insect resistance and its special DNA fragments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Embodiment 1, the cultivation of insect-resistant transgenic plants
[0032] 1. Construction of recombinant expression vector
[0033] 1. Synthesis of the target gene
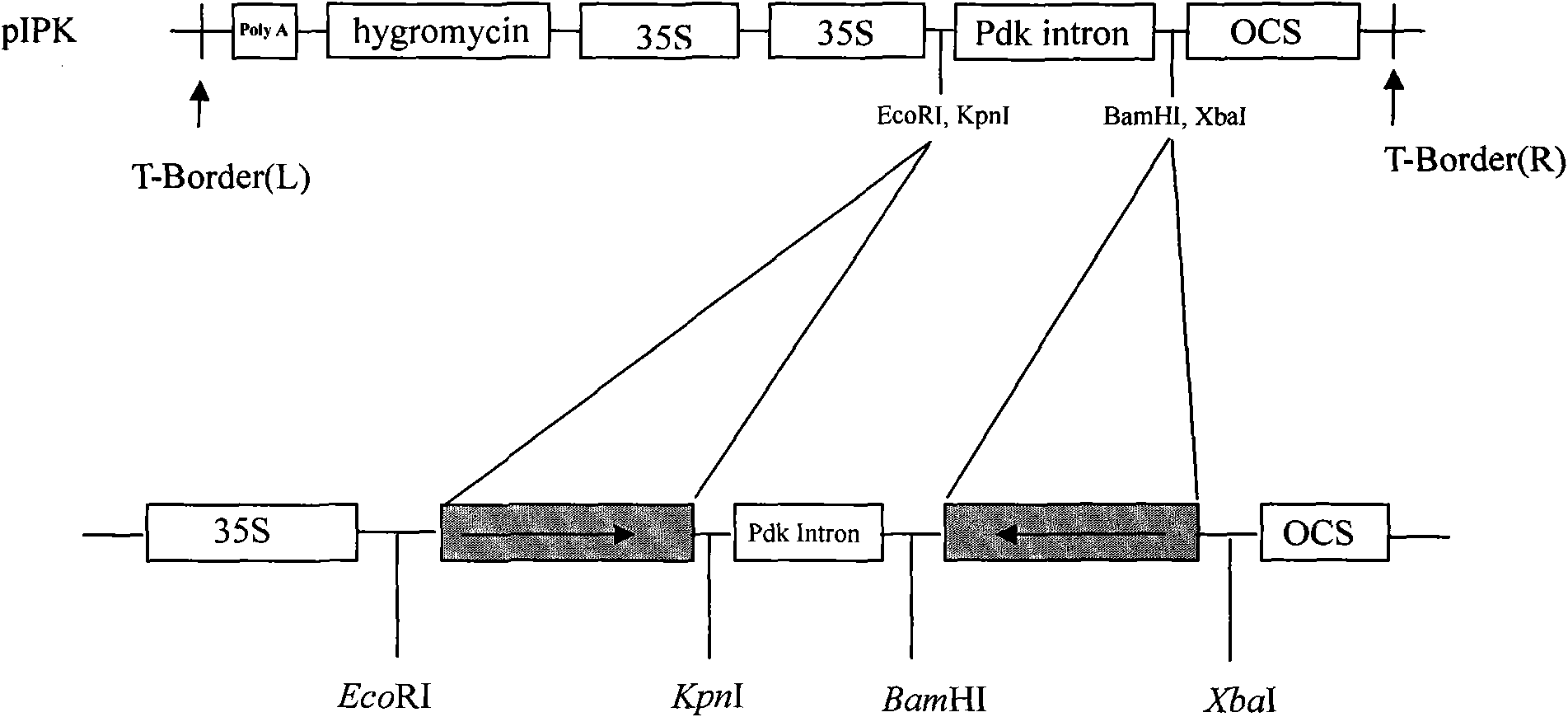
[0034] Obtain the sequence (NM_001162178) of aphid ATPase E subunit gene mRNA according to http: / / www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov online information, its specific cDNA sequence is as shown in sequence 1 in the sequence list, synthesizes two according to this sequence Primers were paired and endonuclease sites were introduced (primer 1: 5'TTTGAATTCAGCGACTCAAGATCATGGAG3'; primer 2: 5'TTTGGTACCCTGCCACTTCTTCAACTAAT 3'; primer 3: 5'TTTTCTAGAAGCGACTCAA GATCATGGAG 3'; primer 4: 5'TTTGGATCCCCTGCCACTTCTTCAACTAAT 3').
[0035] Extract the total RNA of the peach aphid (Myzus persicae) of Aphididae (Aphididae), reverse transcribe into cDNA, use the cDNA as a template, carry out PCR amplification with the above-mentioned primer 1 and primer 2, and obtain fragment 1; use the above-mentioned primer 3 and primer 4 were amplified...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com