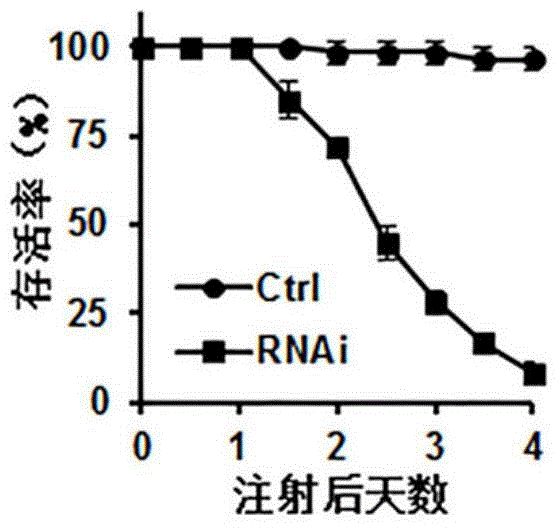
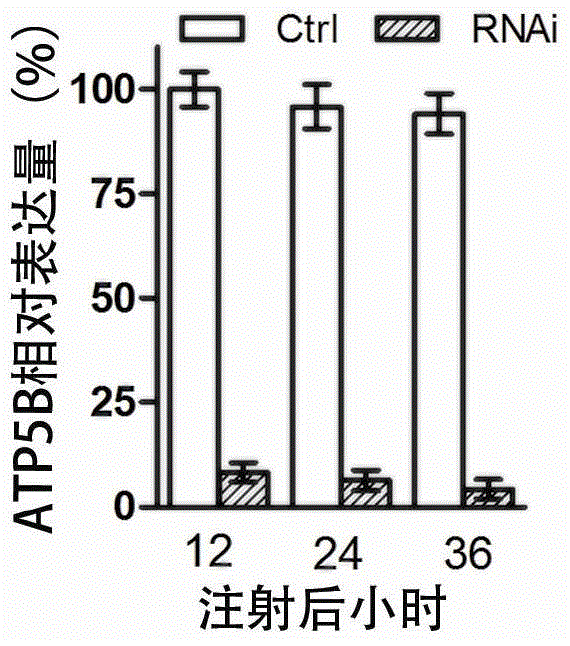
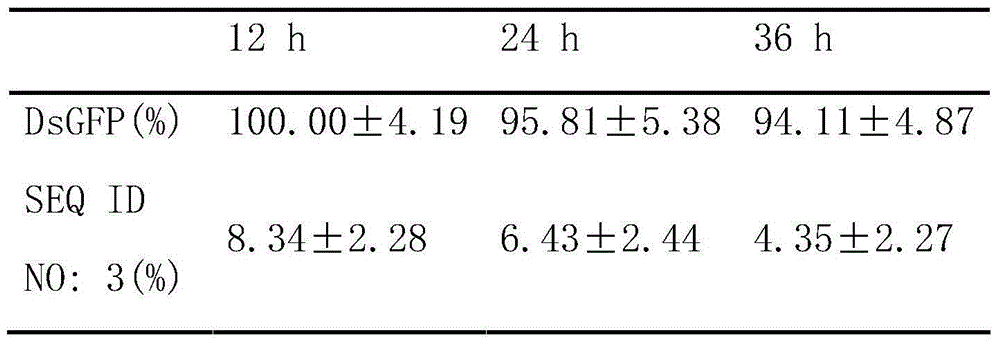
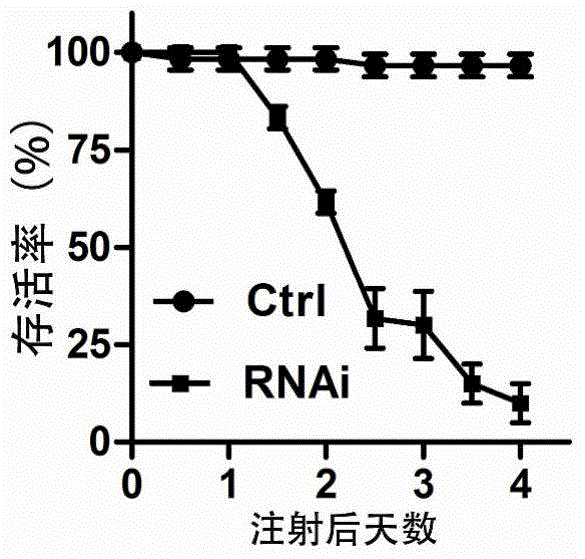
Patents
Literature
183 results about "Subunit gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Infectious bursal disease virus subunit antigen-containing vaccine composition, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103849631AReduce formationIncreased expression of solubleViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesAntigenAdjuvant
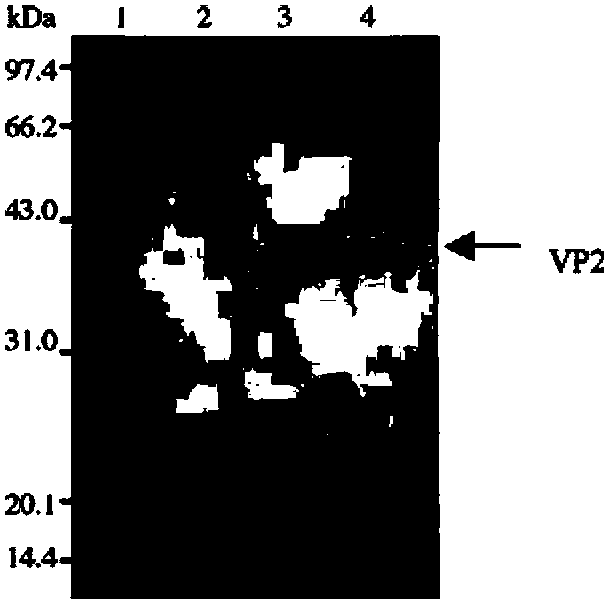
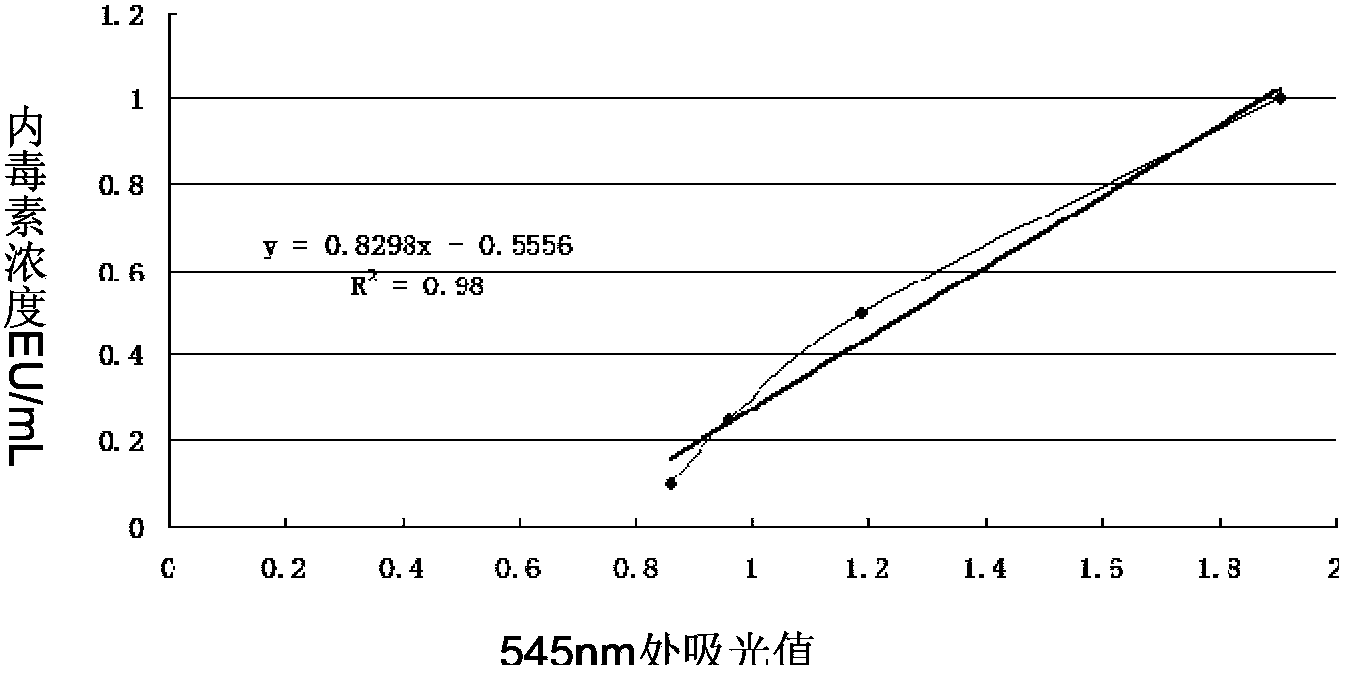
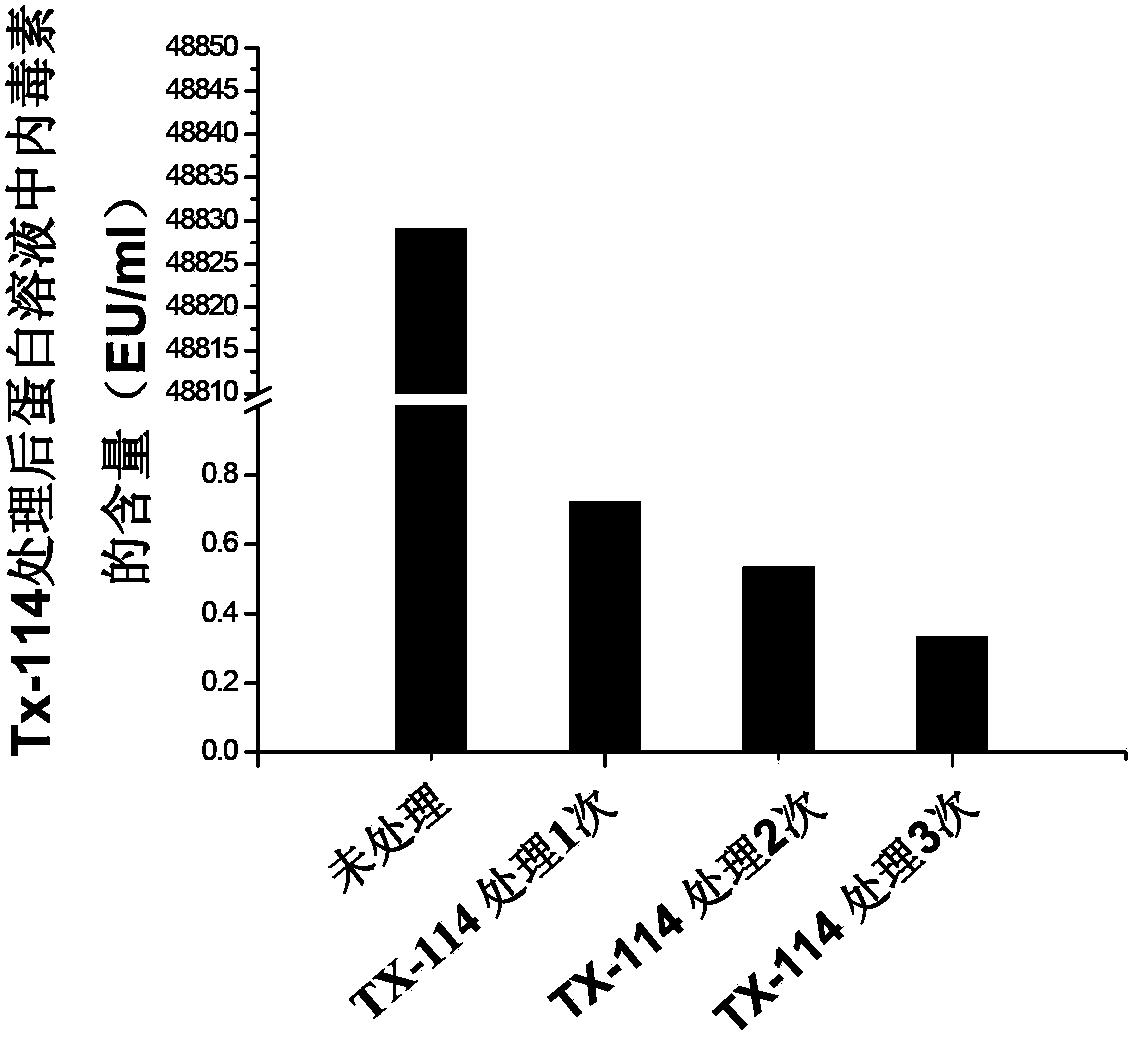
The present invention provides an infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) subunit antigen-containing vaccine composition, which contains an immune amount of recombinant VP2 protein and an adjuvant. According to the present invention, with the subunit gene engineering vaccine composition, the infectious bursal disease can be effectively prevented and controlled; and with the purification technology adopted by the recombinant antigen protein, the endotoxin content in the vaccine composition is significantly reduced, the side reaction of the chicken individuals is significantly reduced, and the safety of the vaccine is substantially increased.
Owner:PU LIKE BIO ENG
Method for improving chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production amount of leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene
InactiveCN101775407ALower oxygen levelsIncrease hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeFermentationEnzyme GeneChlamydomonas reinhardtii
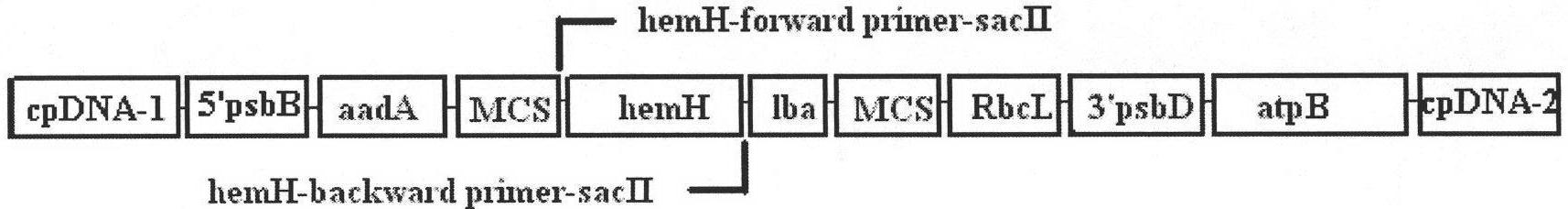
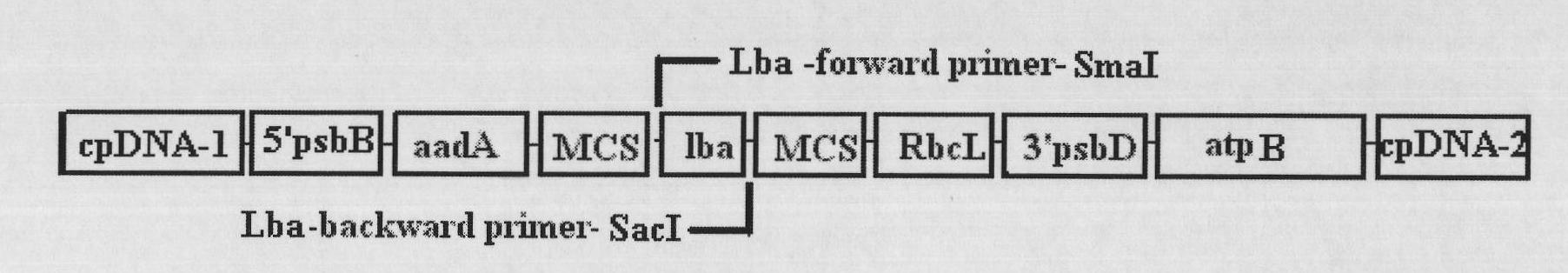
The invention relates to a biological hydrogen production technology, in particular to a method for improving the chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production amount of a leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene. The traditional chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production method has the defects that chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen enzymes are sensitive to oxygen and easily restricted by the oxygen to lose activity, and the chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production effect is limited. The invention discloses an application of a leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene and a globulin subunit gene to hydrogen production by constructing the leghemoglobin ferrous chelate enzyme gene hemH and the globulin subunit gene lba in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast expression vector, transferring the expression vector in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast and expressing the hemH-lba gene in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. The invention has the advantages that the content of oxygen in a closed culture system of the transformed chlamydomonas reinhardtii is reduced obviously faster than that of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii of an un-transformed gene, the oxygen content is kept at a lower level, and the hydrogen production amount is obviously increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Biopesticide and insect preventing and controlling method
ActiveCN101919404AImprove stabilityGood effectBiocideAnimal repellantsNormal growthBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention provides an insect preventing and controlling method, which is to feed lepidopterous insets with a mixture of siRNA for the specific gene of the lepidopterous insets and a cationic polymer, wherein the siRNA is 17 to 50 nt double-chain RNA chemically synthesized in vitro; and the cationic polymer consists of polyethyleneimine (PEI), chitosan, polylysine and gelatin. The invention also relates to a biopesticide, which uses the siRNA for the specific gene of the lepidopterous insets as an active ingredient. In the invention, the gene expression of the lepidopterous insets is inhibited by feeding the lepidopterous insets with the siRNA which contains the specific gene of the lepidopterous insets, such as an interfering insect mitochondrion composite IIIFe-S subunit gene, a cholinesterase gene, a gamma-amino butyric acid receptor gene and the like, to interfere the normal growth and development of the insects, so the effective control of the insects is realized; and pot culture experiment result shows that the biopesticide is very effective.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RIBOBIO
Method for identifying high molecular weight glutenin subunit of wheat through flux
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, which relates to a PCR-based practical flux detection method for molecular markers of the quality characteristics of wheat. In the method, specific molecular markers of NullAx (Glu-A1 locus), Bx7OE(Glu-B1 locus) and Dx5(Glu-D1 locus) subunit genes are selected and multiple PCR systems for simultaneously identifying an important high-quality subunit on Glu-1 locus through one-step reaction are established by optimizing a PCR reaction system and thermal circulation conditions; and in addition, specific amplified products can be effectively separated by common agarose electrophoresis. Compared with single PCR reaction, the method greatly improves the detection efficiency and has reliable identification results and reproducibility through breed and group verification. The invention provides a simple, accurate, rapid and practical method for evaluating breeding materials as well as effectively identifying and selecting high molecular weight glutenin high-quality subunits of filial generation.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
Method for cultivating transgenic plant with improved insect resistance by using RNA interference technology and special DNA fragment thereof
ActiveCN101851622ANormal growth and reproductionImprove insect resistanceClimate change adaptationVector-based foreign material introductionNicotiana tabacumWild type
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a transgenic plant with improved insect resistance by using RNA interference technology and a special DNA fragment thereof. The DNA fragment is a gene fragment shown as a formula I, wherein a forward sequence (SEQ) is any one fragment which at least comprises 19bp in full-length cDNA fragments of an ATP synthase E subunit gene; a reverse sequence (SEQ) and the forward sequence (SEQ) are mutually reversely complementary; X is a spacer sequence between the forward sequence (SEQ) and the reverse sequence (SEQ), and the X and the forward sequence (SEQ) or the X and the reverse sequence (SEQ) are both not complementary mutually; and the full-length cDNA of the ATP synthase E subunit gene is shown as a sequence 1 in a sequence table. The invention also aims to provide application of the ATP synthase E subunit gene serving as an RNA interference target gene in cultivating the transgenic plant with improved insect resistance. Experiments prove that aphids inoculated to wild-type tobacco grow and reproduce normally; and aphids inoculated to transgenic tobacco starts to die on the fourth day, dead aphid bodies is blackened after five days and no live aphids can be seen after seven days. The formula (I) is forward sequence (SEQ)-X- reverse sequence (SEQ).
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Immortalized human liver cell line, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101659941AProlong survival timeEnhance detoxification functionMicrobiological testing/measurementDialysis systemsArtificial liverSupporting system
The invention discloses an immortalized human liver cell line, a preparation method and an application thereof. The immortalized human liver cell line has the main function of primarily cultured humanliver cell. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: transferring SV40T antigen and human telomerase catalyzed subunit gene into primarily cultured separated human normal liver cell by slow virus carrier; and sieving in a cloning way to obtain the immortalized human liver cell line. The immortalized human liver cell line also can be extrinsically amplified in large scales in a microcarrier way. The immortalized human liver cell line can be used for preparing a biological artificial liver support system and preparing the medicament for curing the liver failure.
Owner:苏州瑞徕生物科技有限公司
Wheat high-quality high-molecular weight glutenin subunit gene and expressed protein thereof
InactiveCN101798575AImprove processing qualitySignificant contributionMicroorganism based processesPlant peptidesProcess qualityAgricultural science
The invention discloses a wheat high-quality high-molecular weight glutenin subunit gene and an expressed protein thereof. The sequence of the wheat high-quality high-molecular weight glutenin subunit gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The amino acid sequence expressed by the wheat high-quality high-molecular weight glutenin subunit gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. Under the condition of the similar genetic background, major indicators of flour processing quality, such as wet gluten content, Zeleny, farinograph paste formation time, stabilization time and the like of wheat with 5'ylidene (1D*5'gene encode) of the invention are obviously more excellent than wheat with 5 ylidene, therefore, we think that the contribution of the wheat high-quality high-molecular weight glutenin subunit gene 5' to processing quality of the wheat flour is far superior to ylidene 5, and the coded gene 1D*5' has important utility value and development potential on the improvement of the processing quality of wheat variety.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
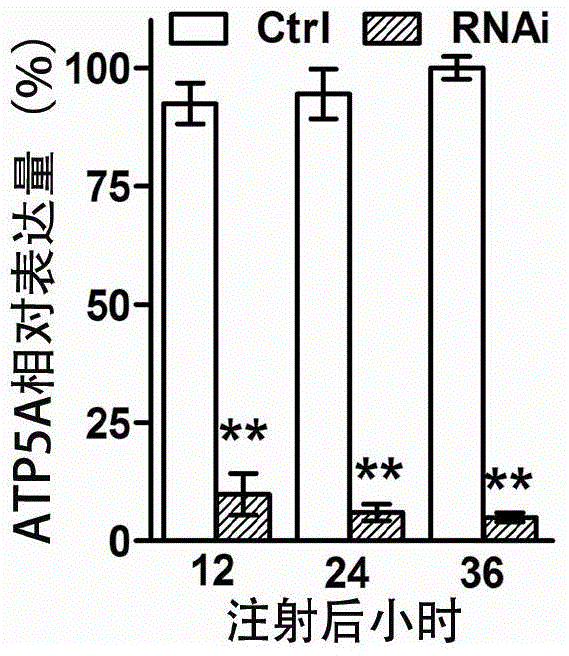
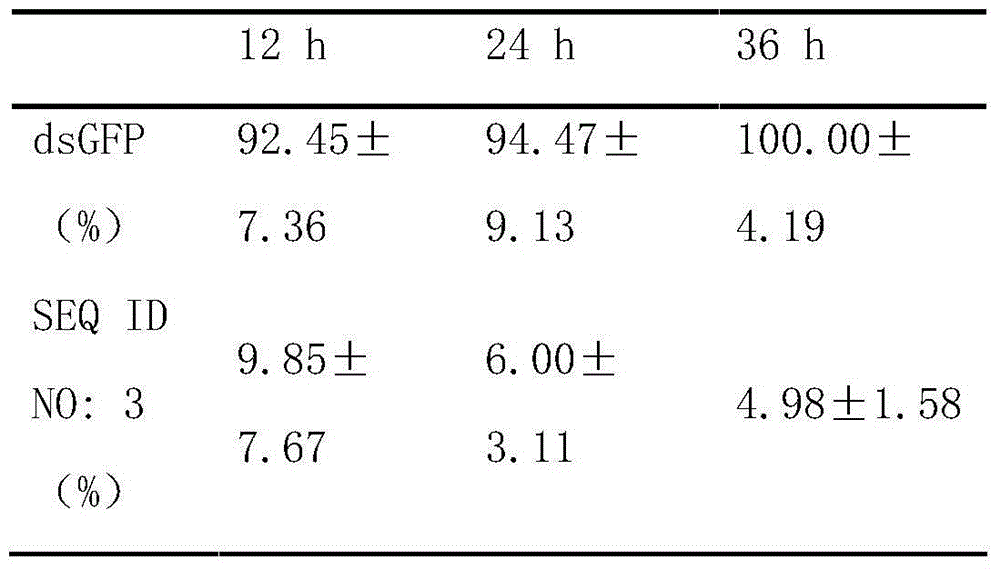
Application of Locusta migratoria ATP synthase beta subunit gene and its dsRNA in pest control
ActiveCN104404042AWill not interfere with the impactCause interferenceBiocideAnimal repellantsConserved sequenceLocust
The invention provides a conserved sequence of locust's ATP synthase beta subunit cDNA, and constructs the RNA, DNA and other constructs thereof. The RNAi technology is utilized to silence the ATP synthase beta subunit in locusts, so that expression of in vivo ATP synthase beta subunit can be significantly inhibited, thus resulting in the lethal effect of locusts. The Locusta migratoria ATP synthase beta subunit gene and its dsRNA can be applied to the RNAi technology for control of Locusta migratoria pests.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene and application of dsRNA of oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene in pest control
ActiveCN104450755AWill not interfere with the impactCause interferenceBiocideAnimal repellantsConserved sequenceMigratory locust
The invention relates to an oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene and application of dsRNA of the oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene in pest control. The oriental migratory locust ATP synthase alpha subunit gene disclosed by the invention provides the conserved sequence of ATP synthetase alpha subunit cDNA of a locust, can be used for constructing the constructs, namely RNA, DNA and the like, and obviously inhibits the expression of the ATP synthetase alpha subunit inside a locust body by silencing the ATP synthetase alpha subunit inside the locust body by utilizing an RNAi technology to cause the lethal effect on the locust, thus being applied to the RNAi technology to prevent and control oriental migratory locust pests.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV +1
Oligonucleotides used for detecting vibrio parahaemolyticus and method of detection therewith
InactiveUS6048697AHigh sensitivityOptimization orderSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNAVibrio parahaemolyticus
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 00991 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 6, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 6, 1999 PCT Filed Mar. 25, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 35970 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 2, 1997An oligonucleotide is provided which has a nucleotide sequence derived from SEQ ID NO:1, characterized in that it contains at least one site capable of amplifying a nucleotide sequence characteristic of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. The oligonucleotide may have a nucleotide sequence not derived from SEQ ID NO:3, or incapable of amplifying nucleotide sequences originating in Vibrio alginolyticus and Vibrio harveyi, and may be represented by SEQ ID NO:5 or SEQ ID NO:6. A method of detecting Vibrio parahaemolyticus in a specimen is also provided which comprises preparing a primer set comprising two of the above oligonucleotides, selectively amplifying therewith a DNA gyrase subunit B gene sequence contained in the specimen as a target, and determining whether or not there is a gyrB unit specific for Vibrio parahaemolyticus in the specimen. Also provided is a primer which reacts specifically with a gyrB gene of Vibrio parahaemolyticus to thereby differentiate and identify the same among other Vibrios and strains other than the genus Vibrio. The Vibrio parahaemolyticus-specific primer serves to detect 285-bp gyrB gene fragments specific for this Vibrio by the PCR method without the necessity for DNA extraction or like operations from bacterial cells.
Owner:NIPPON SUISAN KAISHA LTD
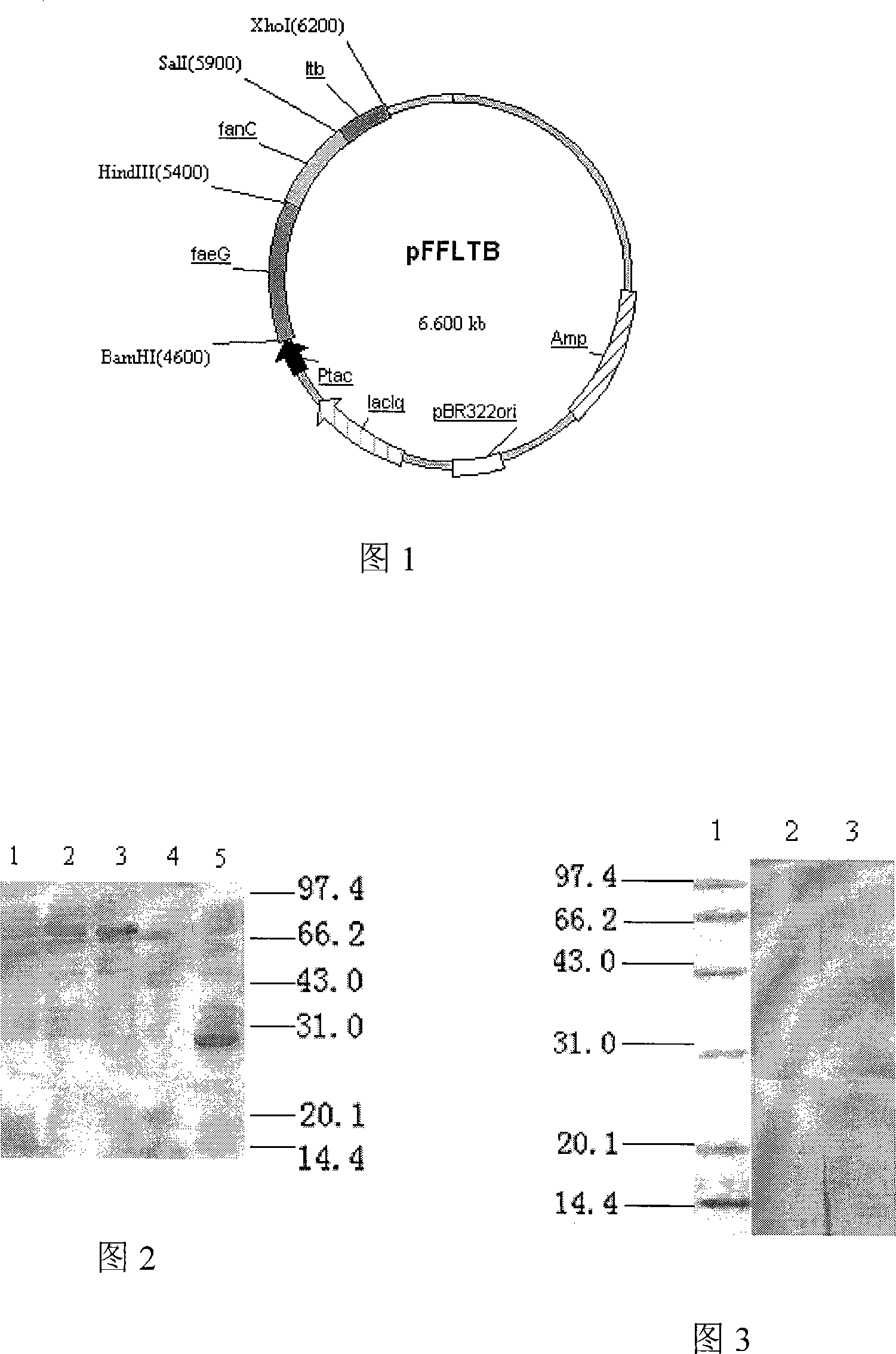
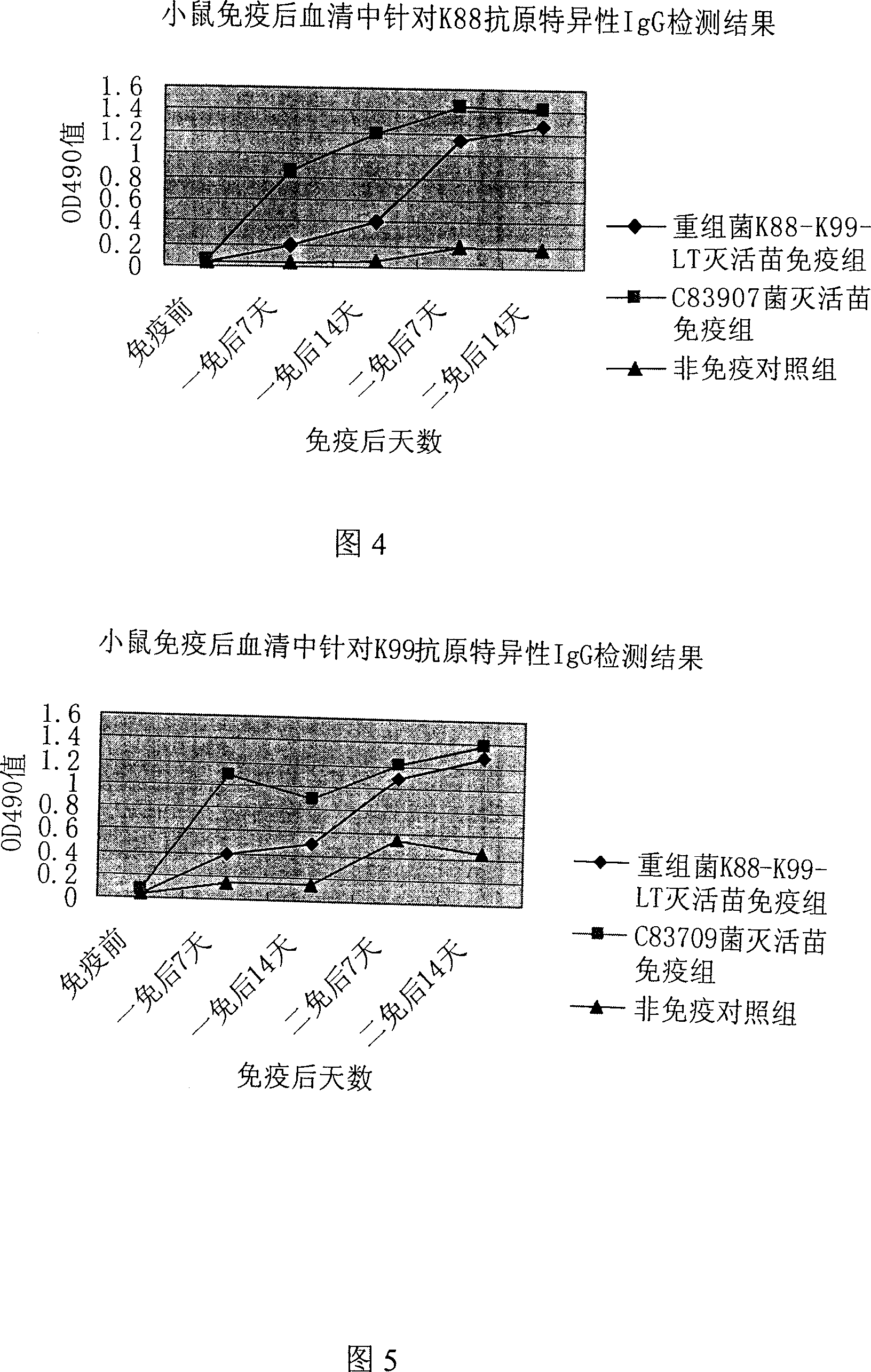
Colibacillus gene engineering bacterin K88-K99-LT for firstborn piglet diarrhea and construction method thereof
InactiveCN101121937AImprove protectionAntibacterial agentsAntibody medical ingredientsEscherichia coliWestern blot
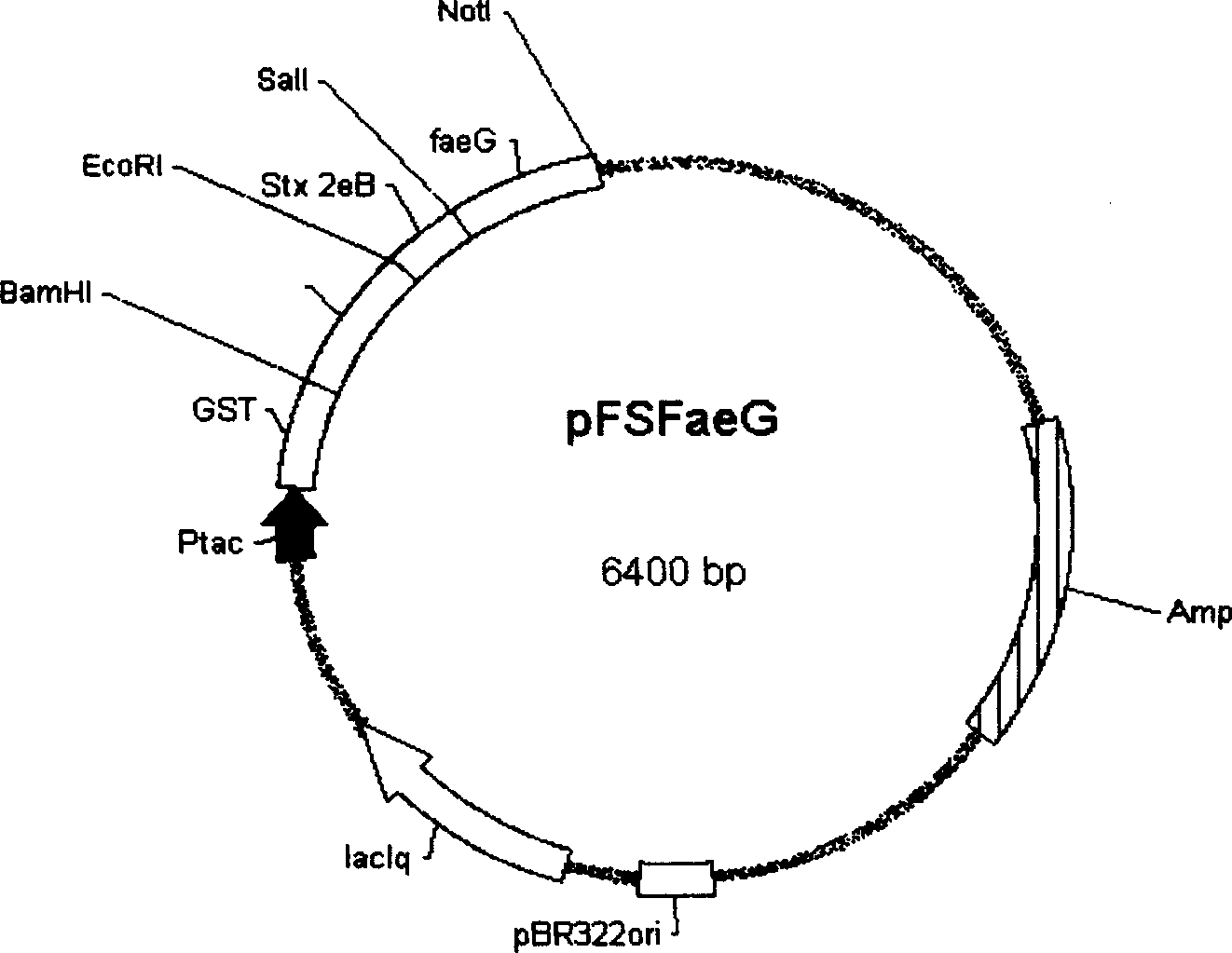
The invention relates to Escherichia coli genetic engineering vaccine 987P-ST-F41 for curing diarrhea of baby pigs and the constitution method, pertaining to the field of veterinary technology. The major subunit gene faeG segment of the expanded K88, the major subunit gene fanC segment of K99 and the major subunit gene ltb segment of LT linked to the pronucleus expression vector pGEX-6P-1 in series in a faeG-fanC-ltb manner; after transformation of host bacteria BL21, IPTG induction expression is conducted, and proved by SDS-PAGE and Western-blot that the objective gene is expressed. The vaccine is capable to prevent diarrhea of baby pigs, and the safety and immunogenicity are reliable.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Wheat 1B†ù14 gene, its coded protein and its promotor
The present invention provides a gene for coding wheat 1BX14 subunit, protein coded by said gene and promotor for inducing said gene to make expression. Said invented IBX14 subunit gene had best possess SEQ ID NO:1 indicated nucleotide sequence, and the coded protein had best possess SEQ ID No.2 indicated amino acid sequence. Said invention also provides the method for identification of wheat strain containing 1BX14 gene and DNA primer used for said method.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing recombinant human nerve growth factor by using Escherichia coli expression system
ActiveCN102839182AHigh bioactivityEasy to prepareFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliInclusion bodies
The invention discloses a method preparing a recombinant human nerve growth factor by using an Escherichia coli expression system. Beta-subunit genes of the recombinant human nerve growth factor comprise 6 histidine purification sites, an enterokinase cleavage site and a beta-subunit gene encoding mature peptide of modified human nerve growth factor and a molecular chaperone gene. The beta-subunit genes of the recombinant human nerve growth factor have high expression quantity in the Escherichia coli; generated inclusion body protein has high-efficiency renaturation under the assist of the molecular chaperone; and the recombinant human nerve growth factor obtained by nickel column affinity chromatography after the molecular chaperone is cleavaged accurately by the enterokinase, has a purity greater than 99% and biological activity greater than 500,000 AU / mg.
Owner:WUHAN HITECK BIOLOGICAL PHARMA
Human interleukin-12 recombinant insect virus strain and its prepn
InactiveCN1357622AEfficient formationViruses/bacteriophagesFermentationWhite blood cellInfective disorder
The present invention discloses a human interleukin-12 recombinant insect virus strain, the recombinant Autographa california multiple nuclear polyhedrosis virus AcNPV-hIL12 virus strain, CCTCC No.2 V200108 and its preparation. The recombinant virus strain is inserted into human interleukin-12 expressing box, and the expressing box includes double promoter sequence, P35 subunit DNA encoding sequence of human interleukin-12 and P40 subunit DNA encoding sequence. P35 subunit gene locates in the downstream of Polyhederin and P40 subunit gene locates in the downstream of P10 promoter. The present invention can express human interleukin-12, and the cell factor is safe and reliable to human body and suitable for treating tumor bacteria, virus and various infections diseases.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
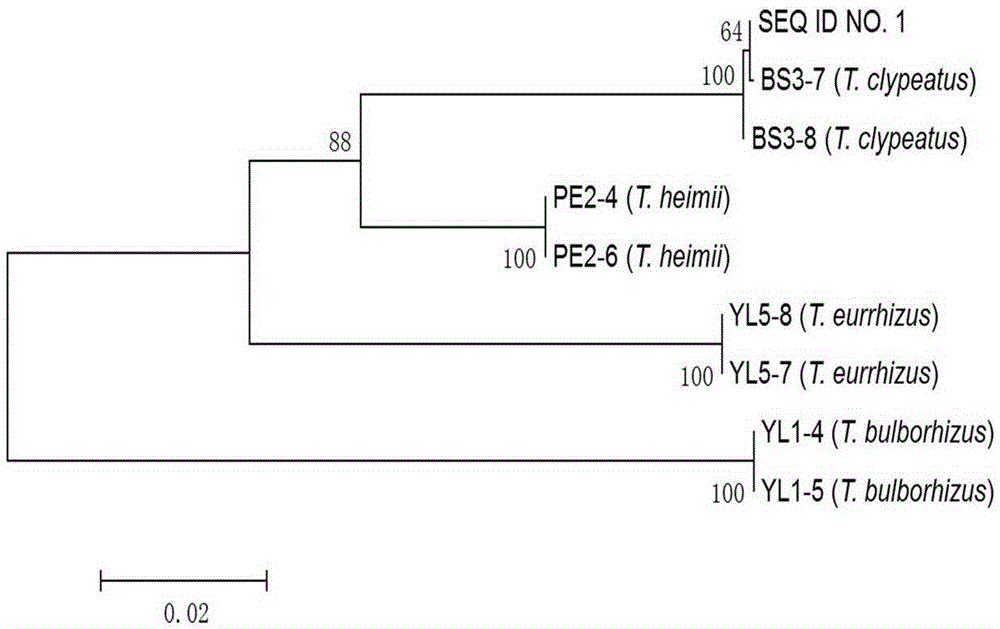
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) barcode reference gene of termitomyces clypeatus and application of DNA barcode reference gene of termitomyces clypeatus
InactiveCN105238794AEasy to expandEasy to compareMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringMolecular identificationReference genes
The invention belongs to the field of fungus species identification and relates to a reference gene for molecular identification of Termitomyces clypeatus and a molecular identification method. Sequences of adopted primers are RPB2B-f: 5'-CCGCAAAGGCTGGTGTATC-3' and RPB2B-r: 5'-TTCGAATGAGTTCAAGTGT-3', and the primers can be used for amplification of large-subunit gene (RPB2) of RNA (ribonucleic acid) polymerase II of the termitomyces clypeatus to obtain a reference detection gene. The termitomyces clypeatus can be quickly and accurately identified according to RPB2 gene DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence differences. The RPB2 gene overcomes the defect of difficulty in identification of traditional termitomyces clypeatus forms and has the advantages of universality and easiness in amplification and comparison, reliability and accuracy in identification are greatly improved, and a powerful research implement is provided for excavation, protection and utilization of genetic resources of the termitomyces clypeatus.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
Process for the isolation of a nontoxinogenic vibrio cholerae strain and a process for preparing cholera vaccine from said vibrio cholerae strain
A process for the isolation of nontoxinogenic V. cholerae strain and a process for preparing a cholera vaccine from said V. cholerae strain, said process comprising (a) isolating V. cholerae from the stool of a patient suffering from cholera by spreading the stool on a selector medium specific for V. cholerae, (b) separating the non-toxinogenic V. cholerae strain from the population of the V. cholerae strains isolated in step (a), and (c) incorporating immunogenic cholera toxin (ctx) B subunit gene into the chromosome of the strain by conventional methods to produce the vaccine.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES +2
Method for improving yield of chlamydomonas reinhardtii biological hydrogen production through soybean hemoglobin genes
InactiveCN101845461AIncrease hydrogen productionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesChlamydomonas reinhardtiiChloroplast
The invention belongs to a biological hydrogen production technology, particularly to a method for improving the yield of chlamydomonas reinhardtii biological hydrogen production through soybean hemoglobin genes. Traditional chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production has the disadvantages that chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogenase is sensitive to oxygen and is easily inhabited by the oxygen to inactivate; and the hydrogen production effect of chlamydomonas is limited. The invention discloses application of soybean hemoglobin globulin subunit genes in chlamydomonas reinhardtii hydrogen production, the soybean hemoglobin globulin subunit genes lba are constructed in a chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast expression vector, and the expression vector is transformed into chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast, so that the lba genes are expressed in the chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. The decrease of the oxygen content in a closed culture system of the transformed chlamydomonas reinhardtii is markedly quicker than that of the chlamydomonas reinhardtii of the untransformed genes, the oxygen content can be kept at a lower level, and the hydrogen yield is markedly increased; the method is applicable for all microalgae for hydrogen production.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Calcineurin catalytic subunit gene and application thereof
InactiveCN104195152AIncrease aluminum resistanceReduce contentFungiHydrolasesEscherichia coliNucleotide
The invention discloses a calcineurin catalytic subunit gene which is cloned in a cryptococcus humicolus BSLL1-1 strain. The nucleotide sequence of the calcineurin catalytic subunit gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1 and is used for coding the protein with an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2; the protein is expressed in escherichia coli, and the calcineurin catalytic subunit gene is further successfully expressed in saccharomyces cerevisiae. According to the calcineurin catalytic subunit gene, the saccharomyces cerevisiae is enhanced in aluminum resistant capacity, genetically engineered bacteria are capable of adsorbing (or absorbing) activated aluminum contained in a culture medium, and the genetically engineered bacteria of the saccharomyces cerevisiae have application prospect of reducing the content of activated aluminum contained in acid soil.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
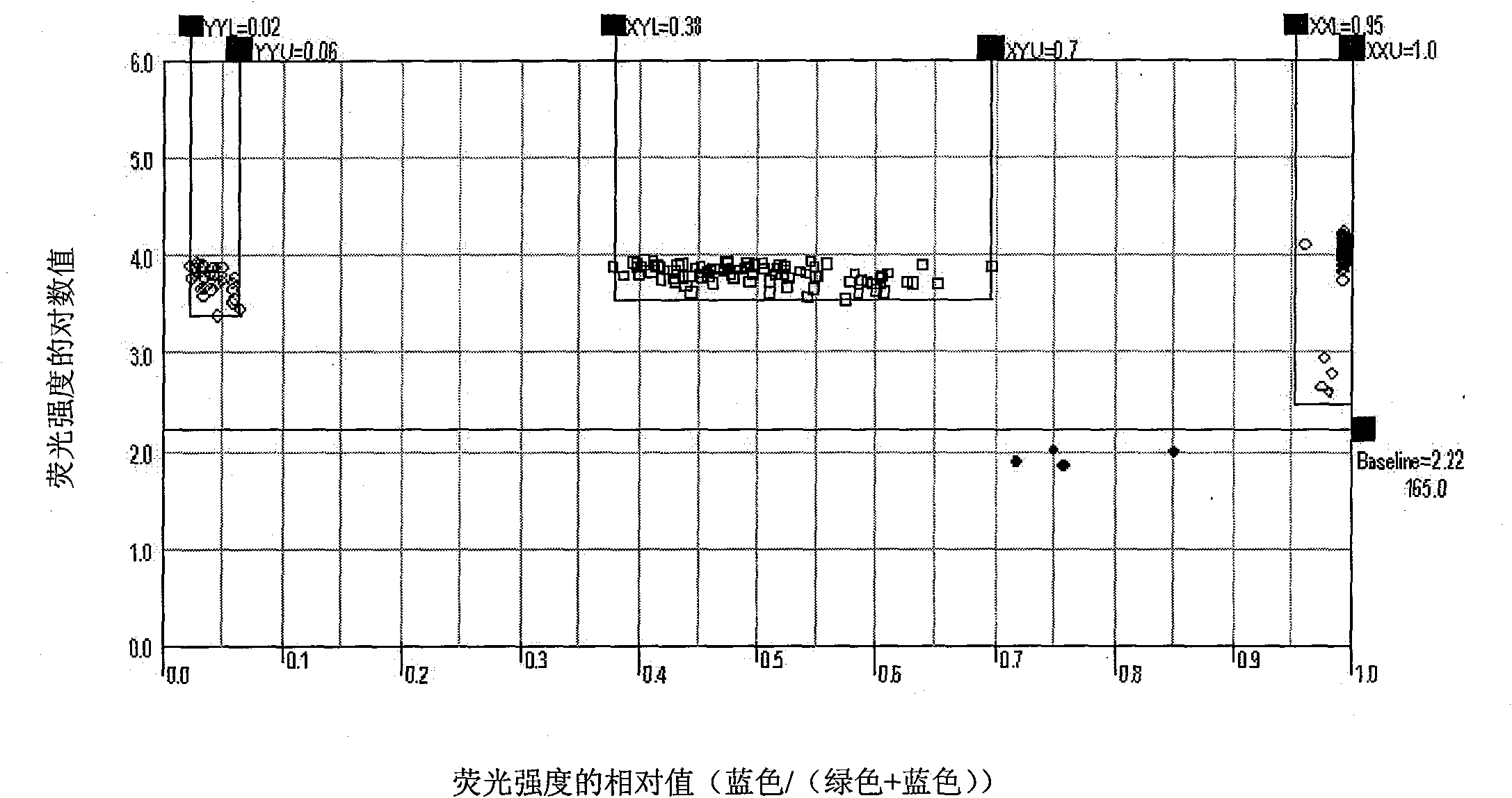
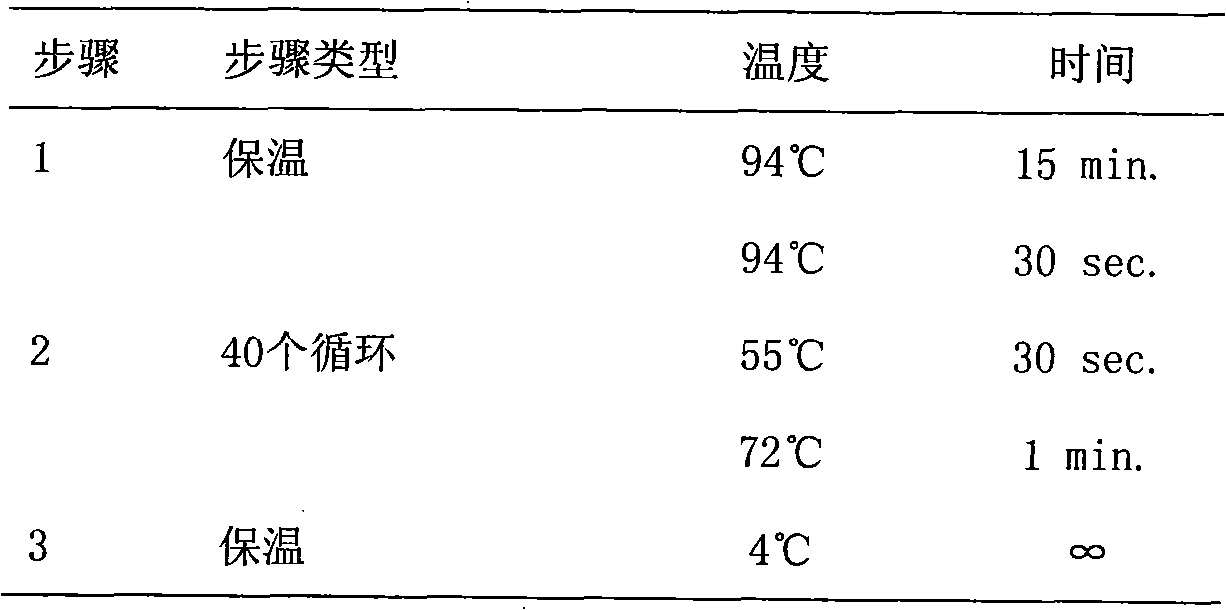
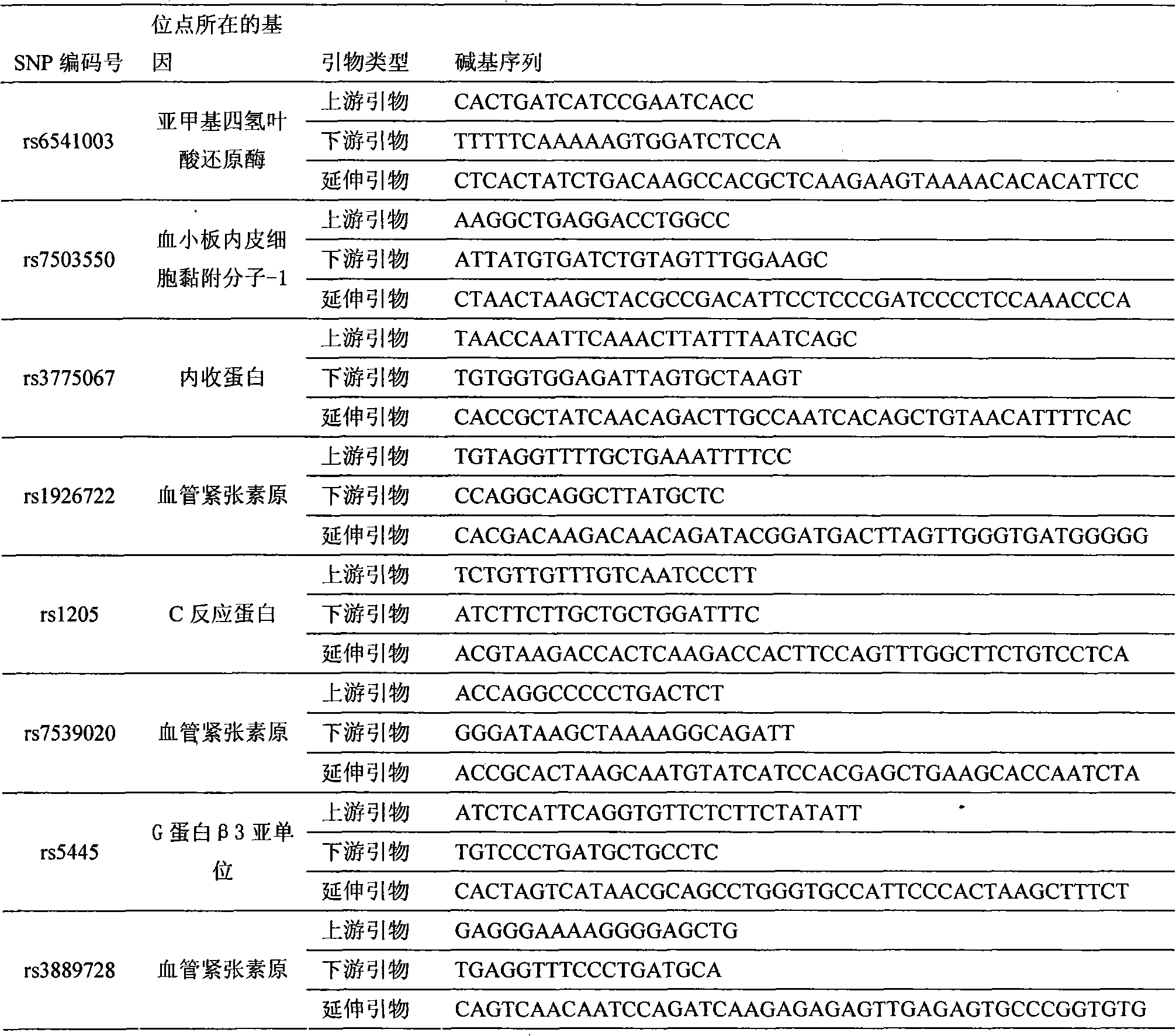
Method for simultaneously detecting 32 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) locus genotypes
InactiveCN101851672AImprove throughputEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementHepatic lipaseAngiotensinogen mrna
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously detecting 32 labeled single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) loci. In the method, adducin-1, platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1), C-reactive protein (CRP), endothelial constitutive nitric oxide synthase (ecNOS), plasma cell membrane glycoprotein-1 (PC-1), L-selectin, G-protein beta3 subunit gene, angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE), angiotensin II type 1 receptor gene, proangiotensin, methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) and hepatic lipase gene which are published on an international haplotype diagram engineering database are selected for detecting 32 labeled single nucleotide polymorphisms of the Han nationality in China; three primers are designed for each single nucleotide polymorphism (two PCR amplification primers and one extension primer); and the single nucleotide polymorphism loci are subjected to genotyping through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification, extension and hybridization and by applying an SNP stream genotyping system. The detection method has the advantages of quickness, accuracy, high throughput, simple operation, microscale and the like.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA
Primers and probes for detecting fox component in food and feed
ActiveCN103060435AFast evolutionGuaranteed check outMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceRedox enzymesMicrobiology
The invention belongs to technology of qualitative detection of animal-derived components in food and feed, and particularly relates to a primer / probe group for detecting fox component in food and feed. The invention selects mitochondrion cytochrome C redox enzyme I subunit gene sequence of fox, and designs a group of specific primers and probes. After using the primers and probes, the real-time fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) technology can be adopted to quickly, sensitively and specifically detect the fox component in food and feed. The primers and probes can also be provided together with other reagents in the form of a kit, and is used for nucleic acid amplification reaction. The method is simple to operate and has favorable repetitiveness.
Owner:山东众合天成检验有限公司
dsRNA (double-stranded ribonucleic acid) for inhibiting expression of wheat aphid cytochrome c oxidase viic subunit gene and application thereof
The invention discloses a dsRNA (double-stranded ribonucleic acid) for inhibiting expression of wheat aphid cytochrome C oxidase VIIc subunit gene and application thereof. The invention provides a dsRNA molecule disclosed as Sequence 2 in the sequence table. The invention also provides a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) molecule for coding the RNA molecule. The invention also provides application of the RNA molecule or the DNA molecule, which is at least one of the following (1) to (4): (1) preventing and treating aphids; (2) promoting death of aphids; (3) inhibiting growth of aphids; and (4) inhibiting expression of the aphid in-vivo cytochrome C oxidase VIIc subunit gene. The dsRNA has important application value in preventing and treating aphids in agricultural production.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Primer for amplifying specific regions of common pathogenic type Legionella gyrB genes and application thereof
ActiveCN102168131AEasy to operateThe preparation method is simple and easyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesEpidemiologic surveyLegionella bozemanii
The invention relates to a primer for respectively amplifying specific regions of gyrB genes (DNAgyrase B subunit gene, hereinafter referred to as gyrB) in Legionella micdadei, Legionella bozemanii and Legionella longbeachae, but also provides a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) reagent kit comprising the primer for amplifying the specific regions of gyrB genes in Legionella micdadei, Legionella bozemanii and Legionella longbeachae. The PCR reagent kit for detecting Legionella micdadei, Legionella bozemanii and Legionella longbeachae is simple, convenient and quick and has good specificity and high sensitivity, can be applied to the fields of supervision and detection of water bodies and clinic samples, detection of pathogenic bacteria in drinking water, bacteriology classification, epidemiology survey and the like and has profound and lasting social benefit and great economic benefit.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Heat-resistant nitrile hydratase, engineering bacteria and application thereof in production of amide by catalyzing hydration reaction of nitrile compounds
InactiveCN107881163AHigh expressionHigh activityFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousEscherichia coli
The invention discloses heat-resistant nitrile hydratase, engineering bacteria and application thereof in production of amide by catalyzing hydration reaction of nitrile compounds. The heat-resistantnitrile hydratase contains alpha-subunit coding genes with a base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.4, beta-subunit coding genes with a base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.5, and active element coding genes with a base sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.6. The nitrile hydratase genes are cloned from aurantimonas manganoxydans SI859A and successfully subjected to heterologous expression in E. coli BL21 (DE3), so as to obtain nitrile hydratase with high expression quantity and high activity and proteins with specific activities reaching 404.5U / mg. The nitrile hydratase has high catalytic activity on aromatic nitrile compounds and aliphatic nitrile compounds, and is a kind of nitrile hydratase with wide substrate spectrum, high thermal stability and excellent industrial application potential.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
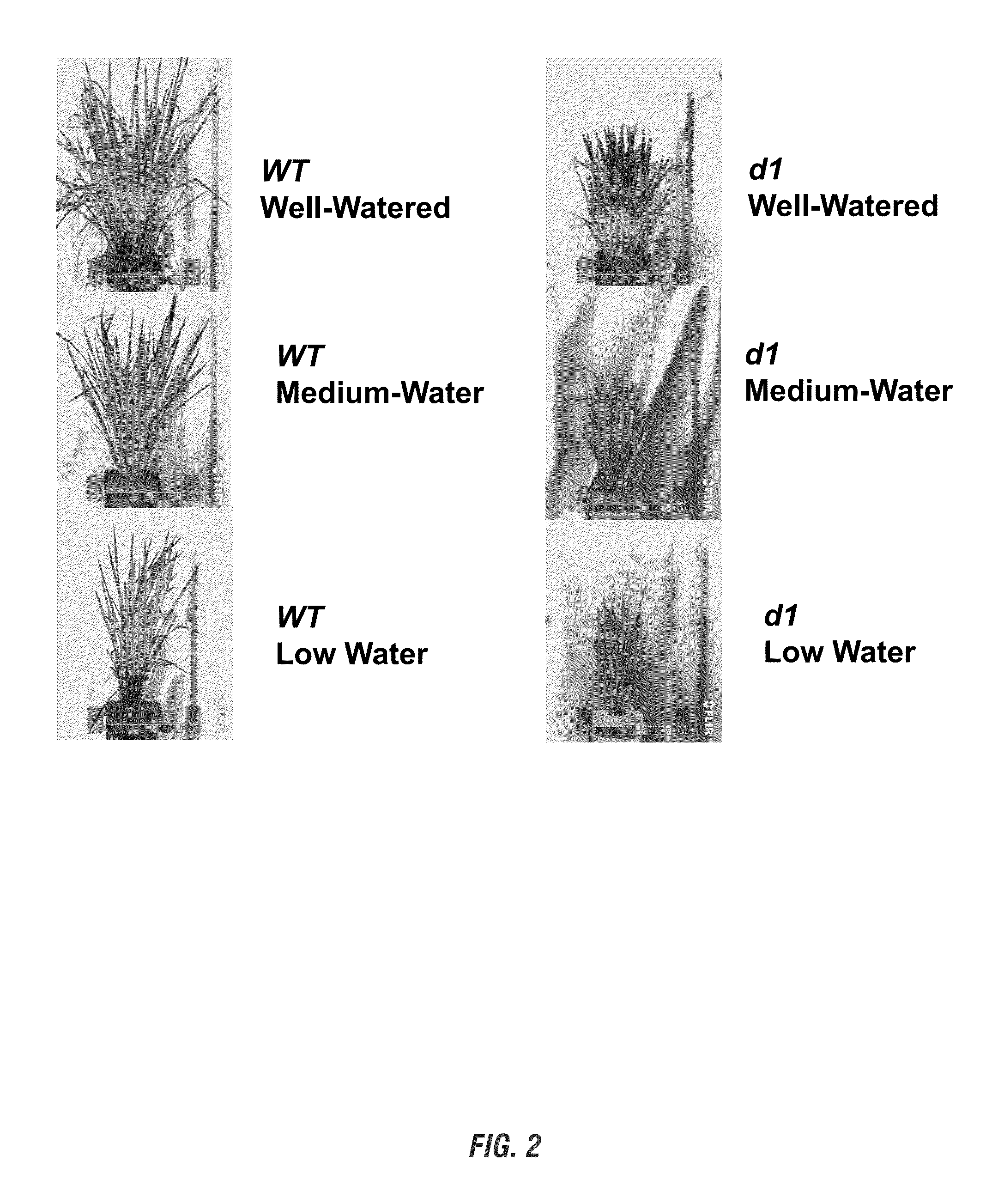
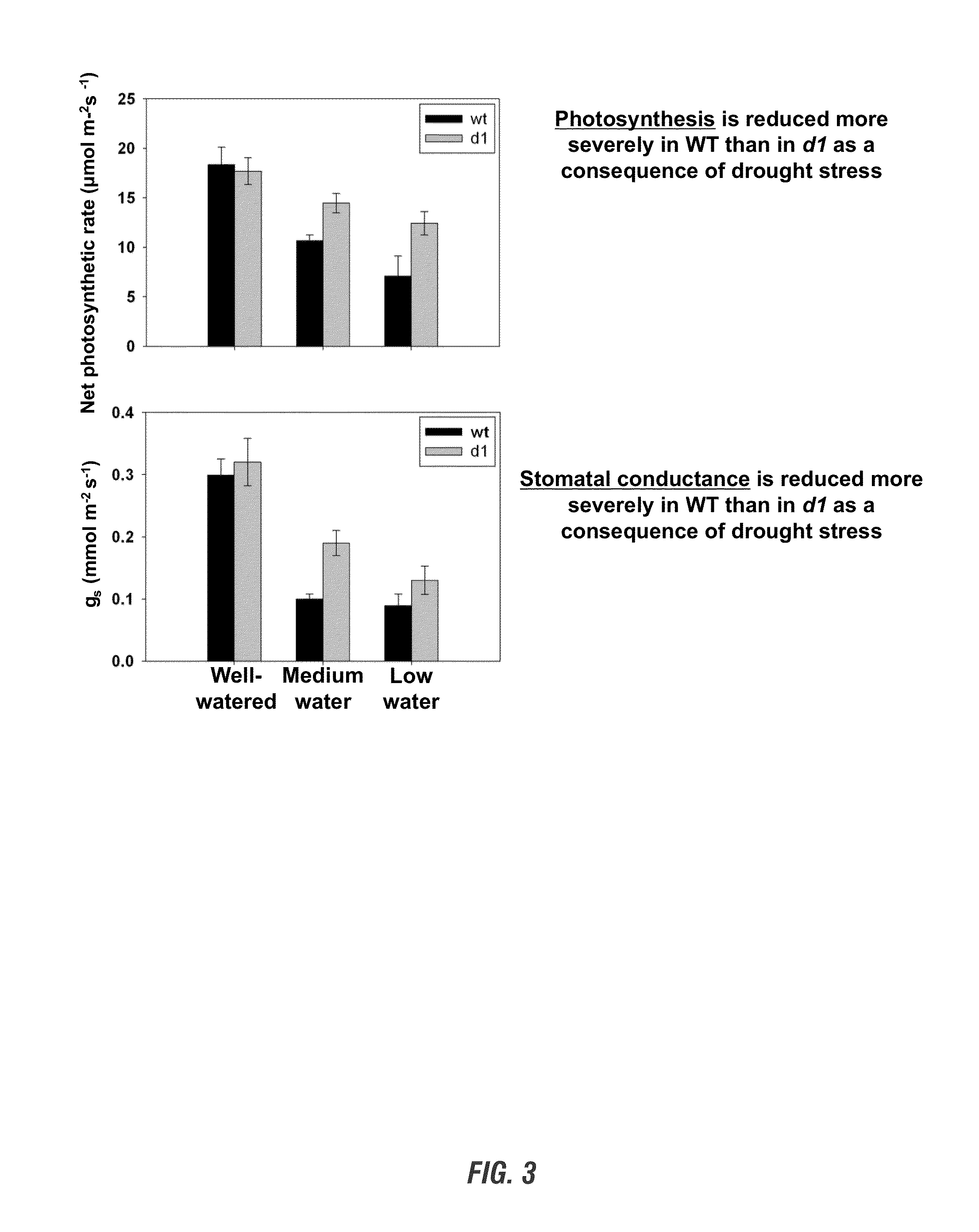
Methods of improving drought tolerance and seed production in rice
ActiveUS20140007266A1Reduce the overall heightHigh seed productionSugar derivativesHydrolasesBiotechnologyPlant tissue
The invention provides for compositions and methods for producing plants that have higher yield in drought conditions by manipulating the G-proteins such as the rice alpha subunit gene, RGA1. In particular, the present invention provides for plants, varieties, lines, and hybrids, as well as plant tissues and plant seeds that contain modified G-protein activity, particularly RGA1 activity to engineer drought tolerance and improved seed production in plants, as well as improved tolerance to high density planting
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Preparation method of high fluorescence intensity recombinant phycobiliprotein concatermer
ActiveCN106916839AAvoid mutual interferenceHigh fluorescence intensityNucleic acid vectorHybrid peptidesEscherichia coliLyase
The present invention belongs to the field of fluorescent proteins in biotechnology, and particularly relates to a preparation method of a high fluorescence intensity recombinant phycobiliprotein concatermer. According to the preparation method, a streptavidin gene is linked to an allophycocyanin alpha subunit gene through a linker sequence; on the basis, one or a plurality of allophycocyanin alpha subunit genes are connected in series through linker sequences to form a fusion gene; and the fusion gene, a phycobiliprotein lyase gent and a phycoerythrobilin biosynthetic enzyme gene co-express in Escherichia coli to obtain the recombinant allophycocyanin concatermer with characteristics of biotin binding ability and high fluorescence intensity. According to the present invention, tn the immunofluorescence assay, the recombinant phycobiliprotein concatermer can achieve the strong fluorescent signal compared to the recombinant phycobiliprotein monomer; and the prepared recombinant phycobiliprotein concatermer can be adopted as the fluorescent marker for immunofluorescence detection in the field of biology and biomedicine.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cattle enteropeptidase catalyzing subunit gene and its gene engineering production process
The present invention belongs to the field of biological engineering technology. The cattle enteropeptidase catalyzing subunit gene encodes the cattle enteropeptidase catalyzing subunit and has the activity of discriminating serine protease of enteropeptidase and cutting specific amino acid sequence. The gene may be obtained from cattle's intestinal tissue by gene cloning technology. The cattle enteropeptidase catalyzing subunit may be prepared through gene engineering process and may be discriminated specifically as proteinase and used to cut the substrate containing enteropeptidase cutting site. One of the application is as tool proteinase for the specific breakage of recombinant fusion protein and the present invention is especially suitable for the research in gene engineering, biochemistry, molecular biology, etc.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
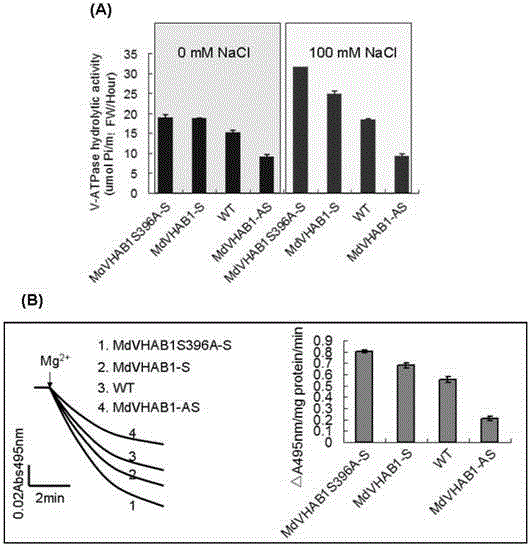
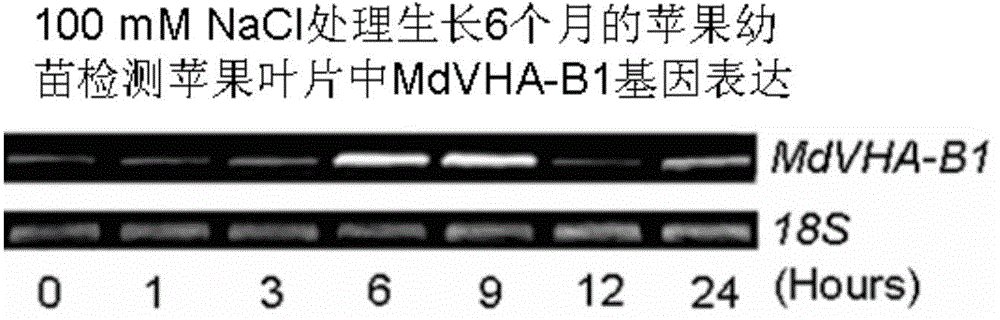
Apple V-ATPase subunit gene MdVHA-B1S396A and stress-resistance application thereof
ActiveCN104531718AImprove resilience to adversityImprove the ability to resist salt stressFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionSalinityV-ATPase
The invention relates to apple V-ATPase subunit gene MdVHA-B1S396A and stress-resistance application thereof. An MdVHA-B1 gene is separated from an apple; then, a serine residue at the 396 position is mutated into alanine through carrying out a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) bridging method for two times so as to obtain the MdVHA-B1S396A gene; the expression level of transgenic apple healing can be further increased through over-expression of the gene in apple tree healing; and simultaneously, the adversity ability of transgenic apple healing, such as salinity resistance and the like, can be further increased.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for cultivating starch-content-increased transgenic plant through multi-gene transformation
InactiveCN103173485AImprove conversion rateHigh total starch contentTransferasesFermentationGranule-Bound Starch SynthaseSucrose synthetase
The invention discloses a method for cultivating a starch-content-increased transgenic plant through multi-gene transformation. According to the transgenic plant cultivation method provided by the invention, a selection marker gene, an adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase small subunit gene, an adenosine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase large subunit gene, a sucrose synthase gene, and a granule-bound starch synthase gene are introduced into a target plant, such that a transgenic plant is obtained. The total starch content of the transgenic plant is higher than that of the target plant. As a result of experiment of the invention, a plurality of genes can be simultaneously transferred in one-time through one time of gene gun bombardment, such that transgenic material cultivation period and work load can be greatly shortened. Specifically, the 4 genes related to starch metabolism are simultaneously transferred in, such that the total starch content of a transgenic regenerated plant is higher than that of wild-type plant.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
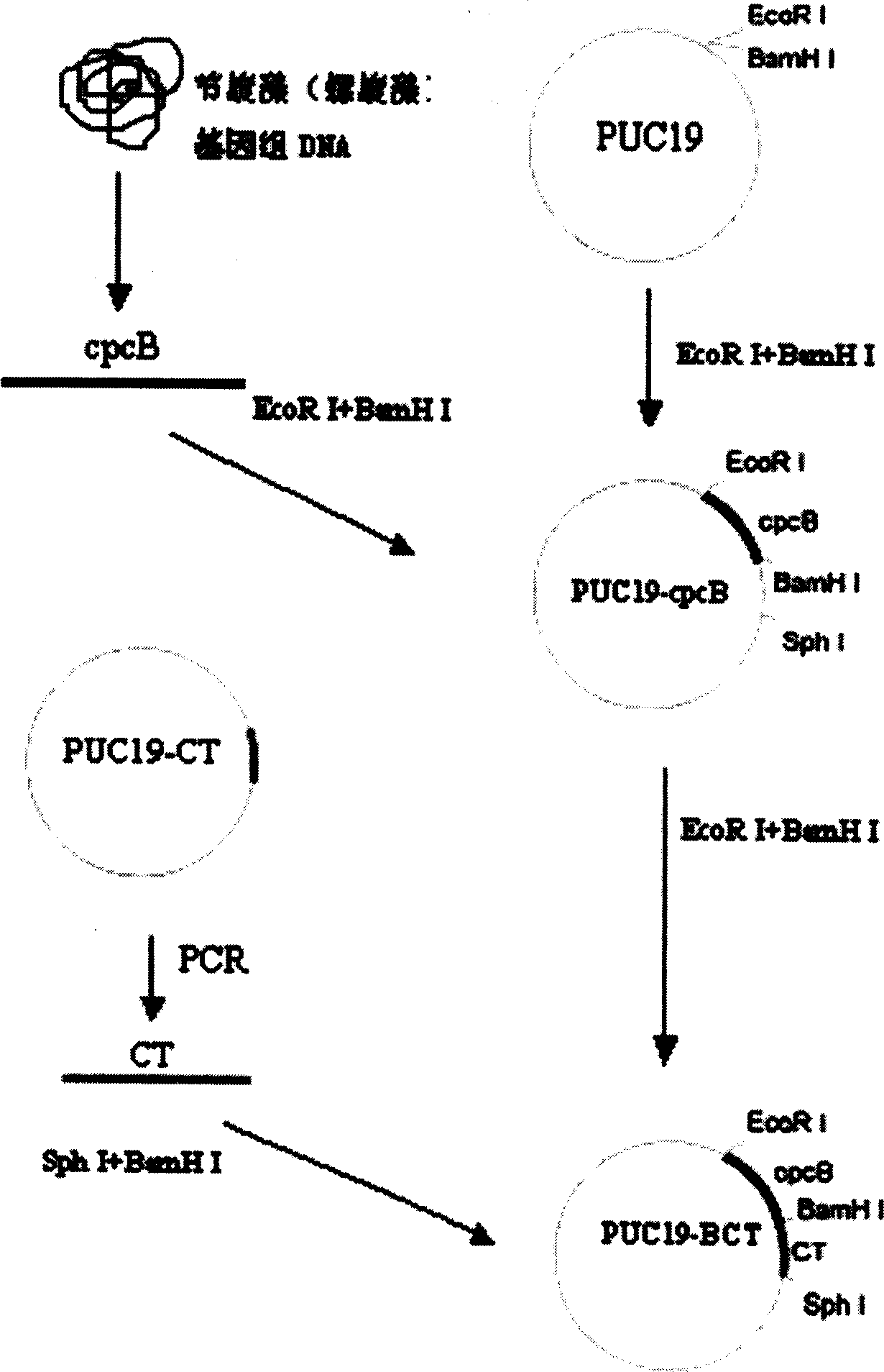
Fusion protein and method for preparing same
InactiveCN1721446AGood antigenicityLow antigenicityHybrid peptidesDNA/RNA fragmentationRecombinant salmon calcitoninCancer research
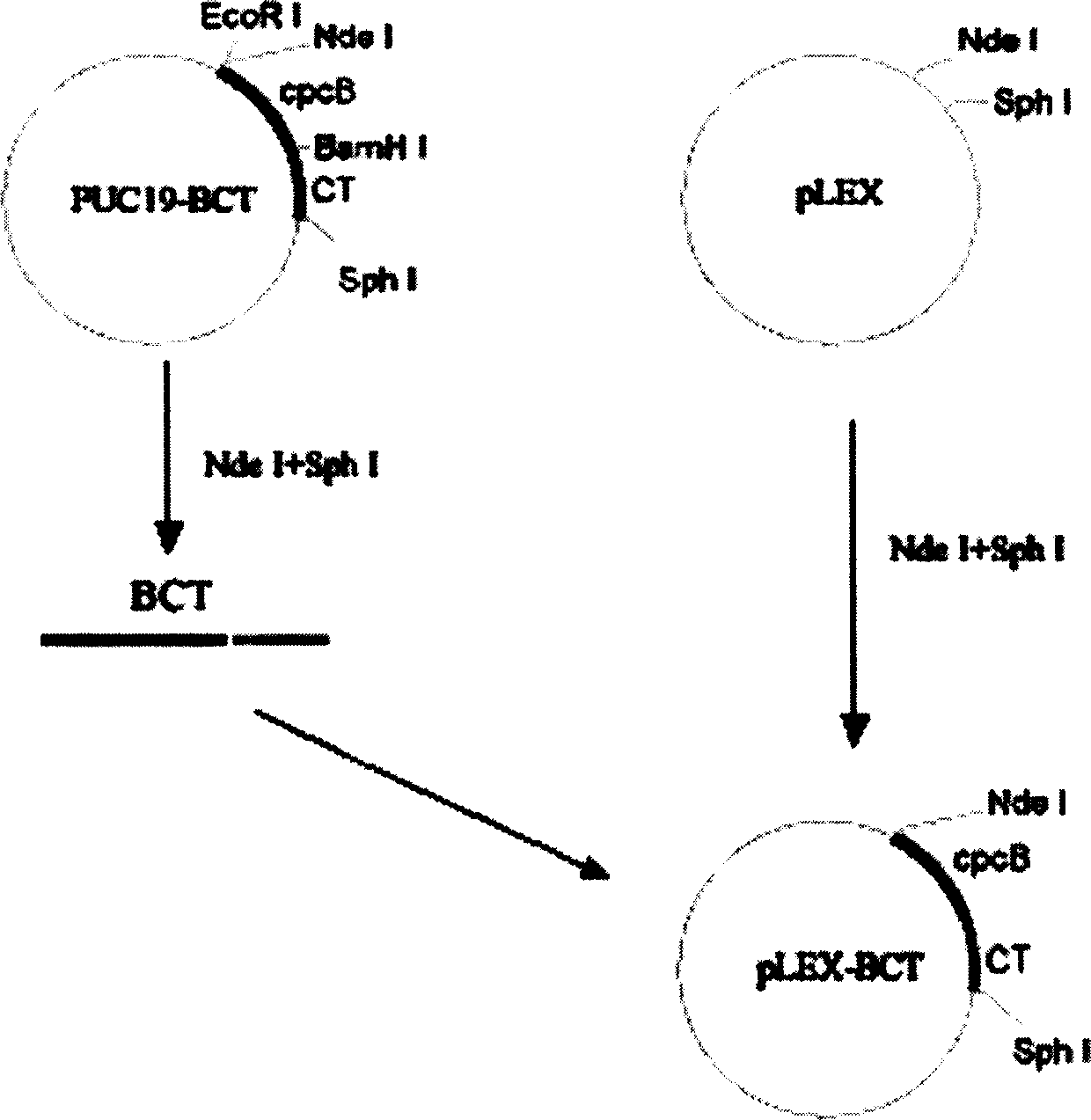
The present invention is fusion protein constituted through fusing phycocyanin beta-subunit gene in the upstream of human and salmon calcitonin chimera gene. The fusion protein has length 648 bp, molecular weight 23 KDa, amino acid sequence with 100 % homology with the sequence shown in SEQ No. 2 and polypeptide with 213 residues; and has prokaryotic expression vector with preservation number of CCTCC1261. The calcitonin chimera gene has length 102 bp; and the phycocyanin beta-subunit gene is cpcB gene of length 519 bp and polypeptide coding 171 amino acid residues. The constitution of the fusion protein needs no processing and purification, and this ensures the high expression amount of the calcitonin, increases the stability in clinical application, lowers the antigenicity of calcitonin and raises its bioactivity.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Gene engineering vaccine for weaning pigling diarrhea and pig hydrops disease
The gene engineering vaccine for pigling weaning diarrhea (PWD) and pig edema disease (ED) belongs to the field of stockbreeding and veterinary technology. Primer containing specific cleavage site is first designed based on the faeG(F4), fedA(F18) and Stx 2e B subunit gene sequences; protective antigen gene is amplified through PCR process with PWD and ED colibucillus plasmid operate or genome DNA as template; said gene is directionally connected serially to the expressive plasmid pGEX-6P-1, used to transform host bacillus BL21 and IPTG inducing expressed; and the expression of the target gene is SDS-PAGE and Western-blot proved. The recombinant bacilli expressing the above-said three protective antigen genes are immunized to mouse and pig via different ways so as to evaluate the immunogenicity and safety. Test shows that the vaccine may be used to prevent PWD and ED effectively.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com