Patents
Literature
1862 results about "Plant tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Plant Tissue Definition. Plant tissue is a collection of similar cells performing an organized function for the plant. Each plant tissue is specialized for a unique purpose, and can be combined with other tissues to create organs such as leaves, flowers, stems and roots.
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6222100B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemBiocideSeed and root treatmentPlant tissueNovel gene
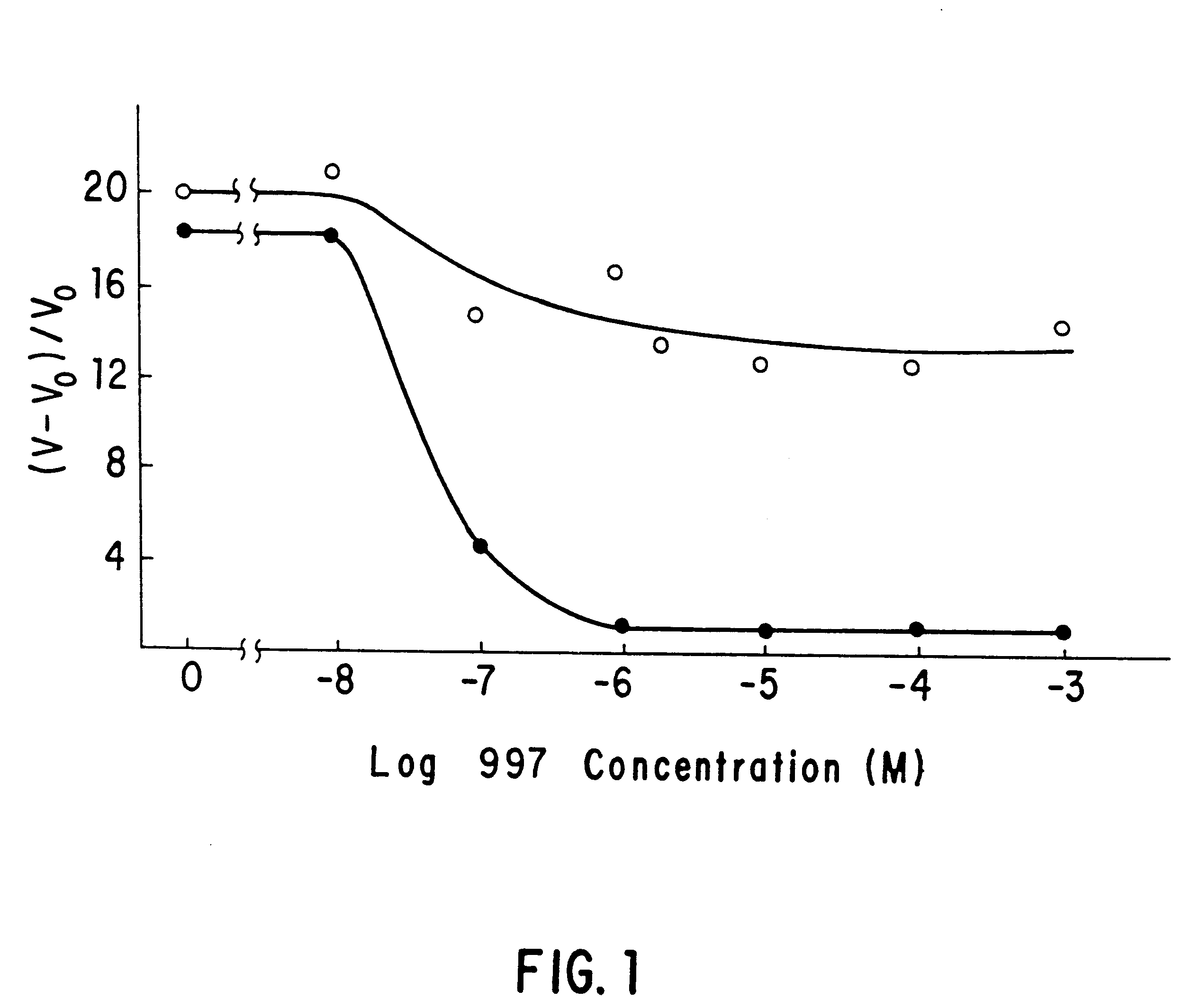
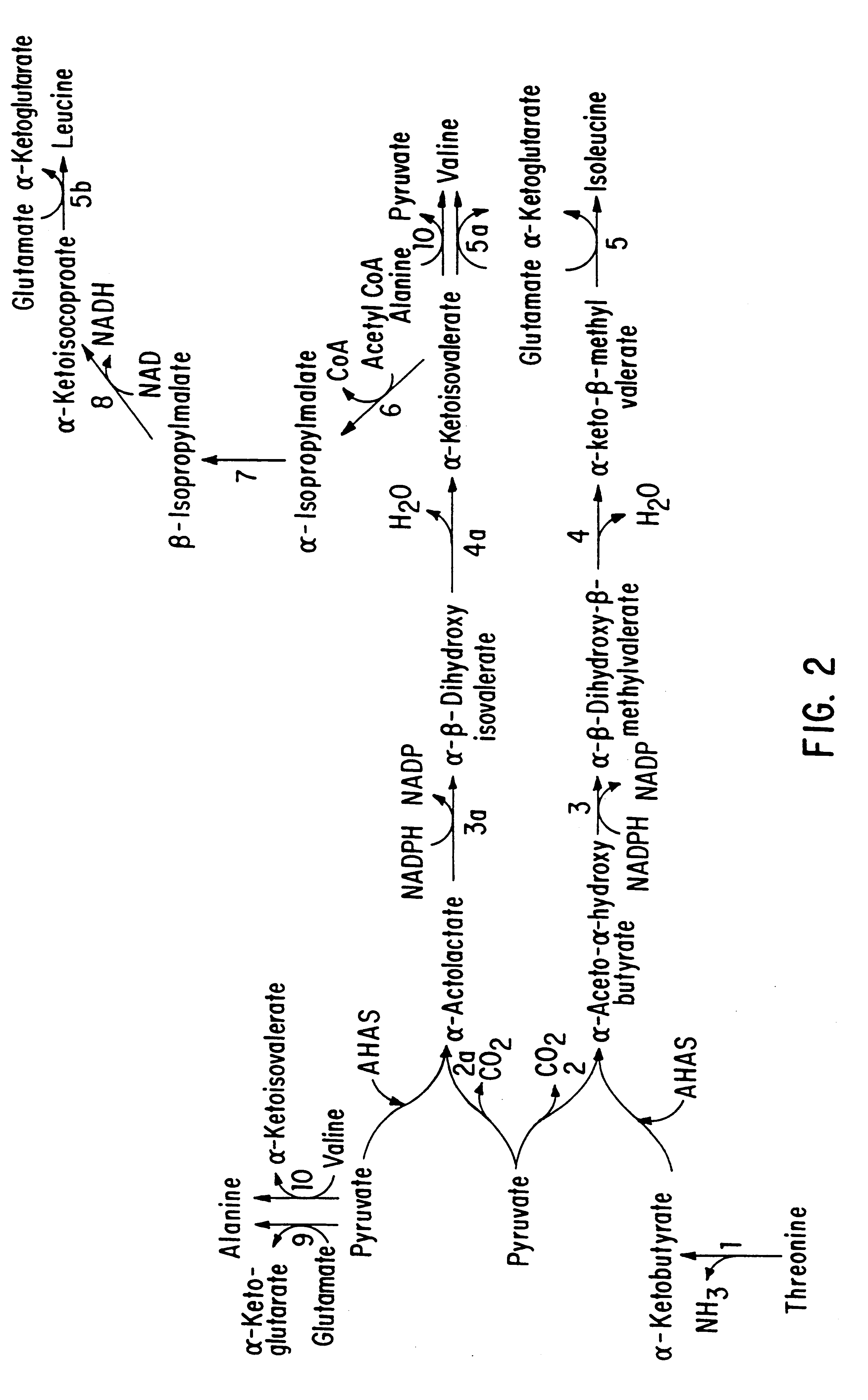
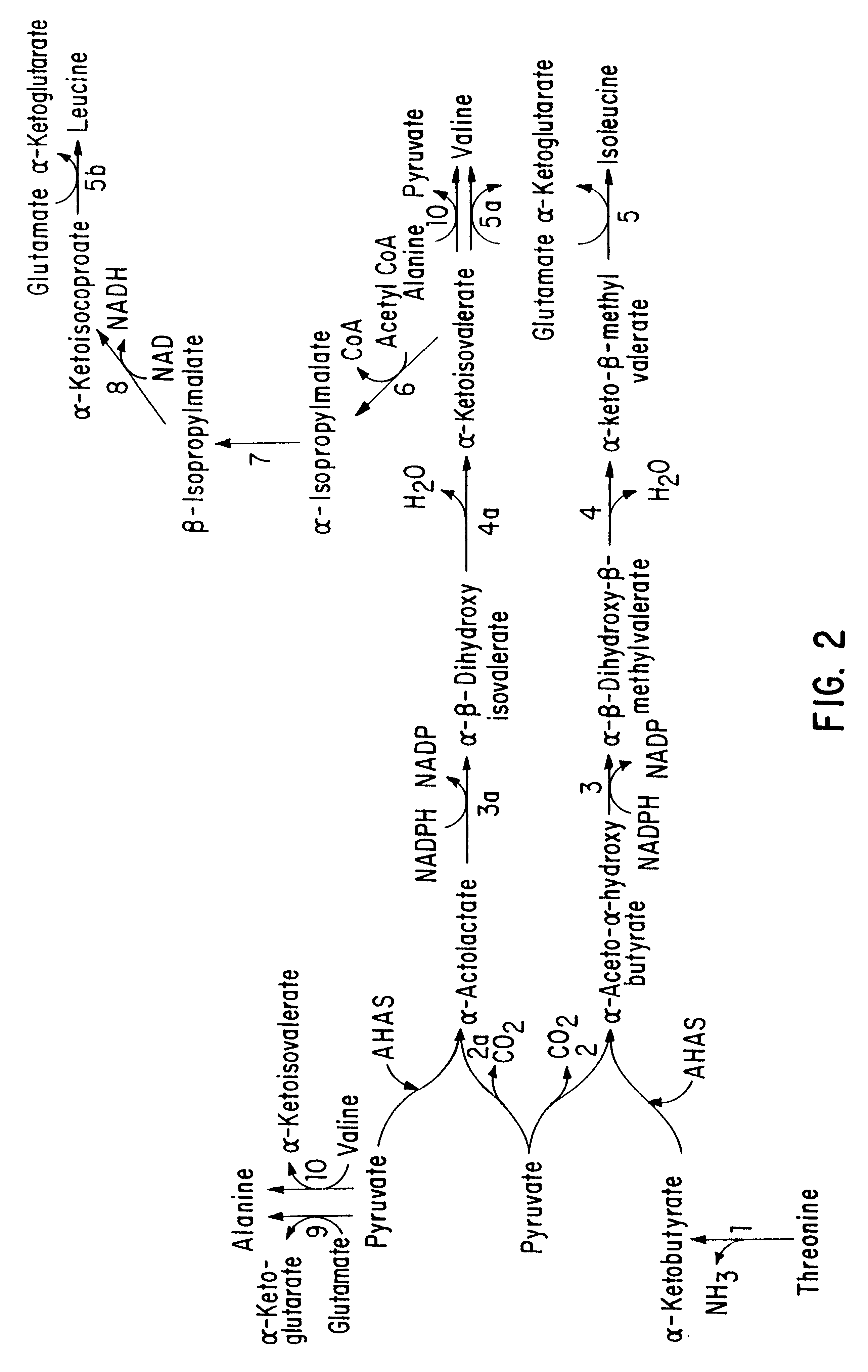
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
Methods to confer herbicide resistance
InactiveUS20070107078A1Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyPlant tissue
Compositions and methods for conferring herbicide resistance to plant cells and bacterial cells are provided. The methods comprise transforming the cells with nucleotide sequences encoding herbicide resistance genes. In particular, herbicide resistance is conferred by expression of proteins with homology to decarboxylase enzymes. Compositions comprise transformed plants, plant tissues, and seeds, as well as transformed bacterial cells.
Owner:ATHENIX
Novel Insecticidal Proteins and Methods for Their Use
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are insecticidal nucleic acids and proteins of bacterial species. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The insecticidal proteins find use in controlling, inhibiting growth or killing lepidopteran, coleopteran, dipteran, fungal, hemipteran, and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6211438B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemMutant preparationVector-based foreign material introductionPlant tissueNovel gene
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
Novel Insecticidal Proteins and Methods for Their Use
ActiveUS20140033361A1Improve pest resistanceImprove toleranceBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyOrder Lepidoptera
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are insecticidal nucleic acids and proteins of bacterial species. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest including plants, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The pesticidal proteins find use in controlling, inhibiting growth or killing Lepidopteran, Coleopteran, Dipteran, fungal, Hemipteran and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:CORTEVA AGRISCIENCE LLC +1
Herbicide resistance in plants
InactiveUS6211439B1Confers resistanceEffectively combat weed problemLyasesPlant genotype modificationPlant tissuePlanting seed
This invention is directed to the production of plants, plant tissues and seeds which are resistant to inhibition by an herbicide which normally inhibits the growth and development of those plants, plant tissues and plant seeds. In particular this invention is directed to altered acetohydroxyacid synthase enzymes which are resistant to inhibition by herbicides which normally inhibit the activity of the synthase before such alteration. This invention further relates to genes encoding such enzymes, and to processes for utilizing these novel genes and enzymes. Further products of the invention include plants, plant tissues and seeds which exhibit resistance to such herbicides resulting from expression of genes encoding herbicide resistant acetohydroxyacid synthase enzyme.
Owner:MGI PHARMA
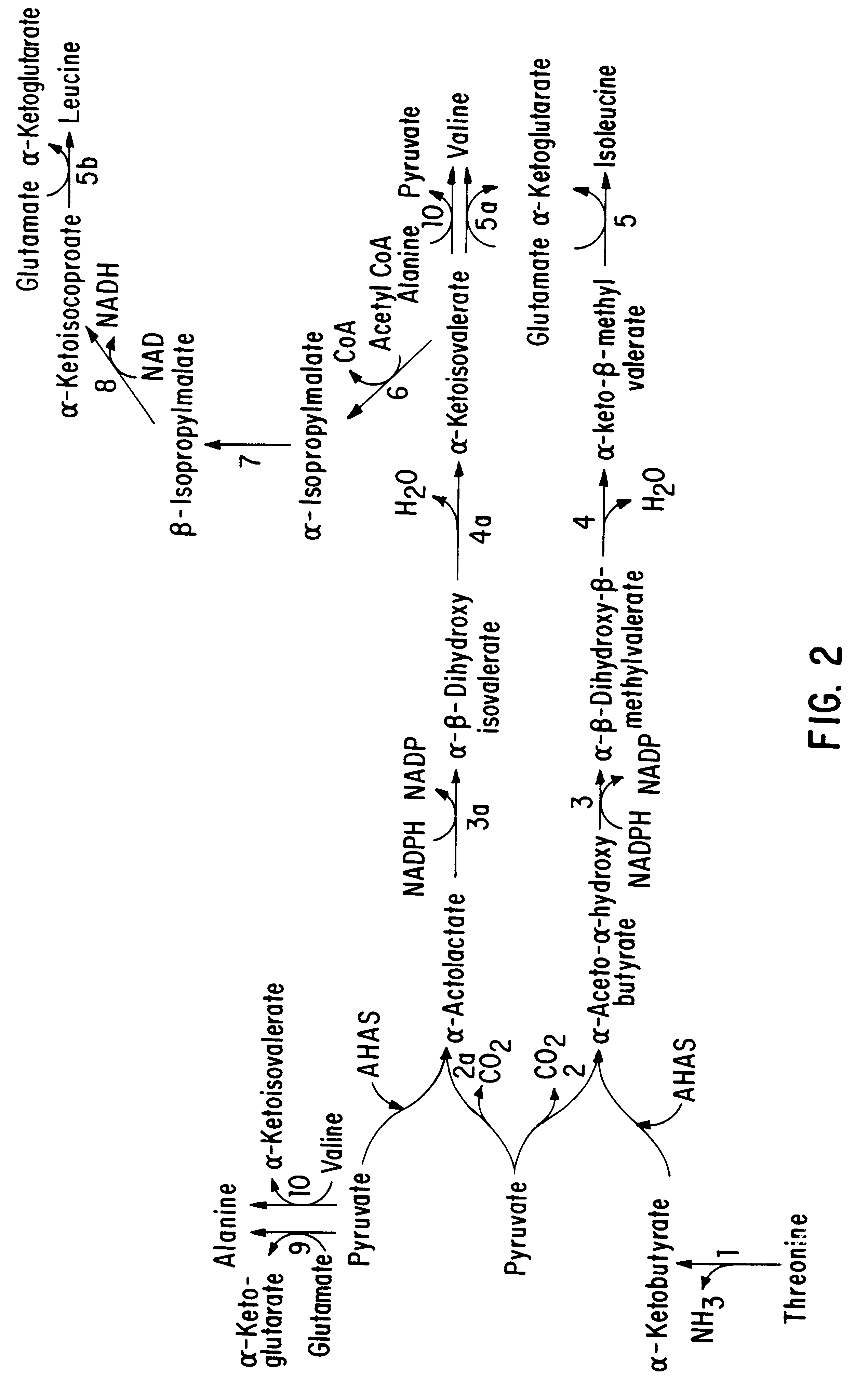
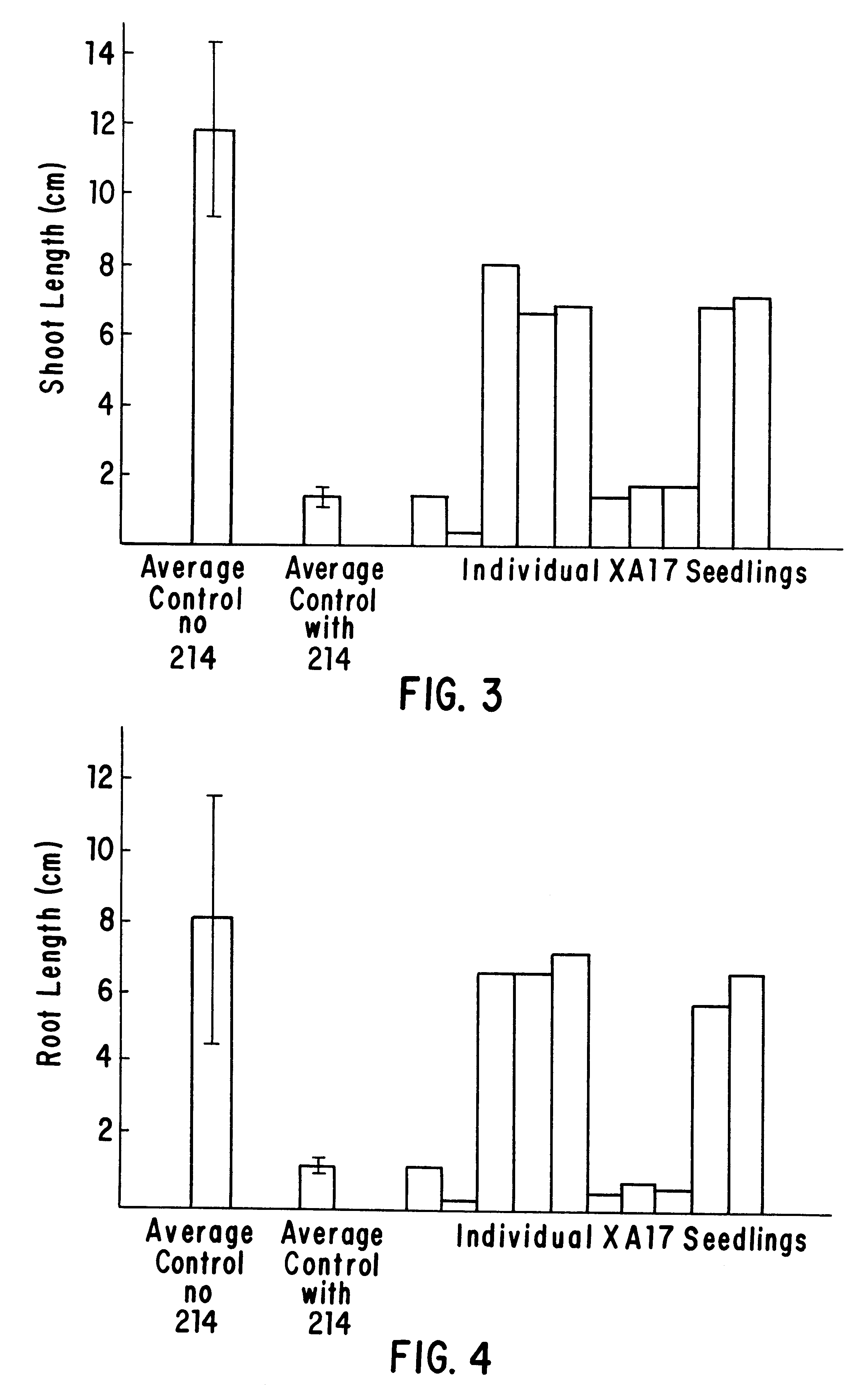
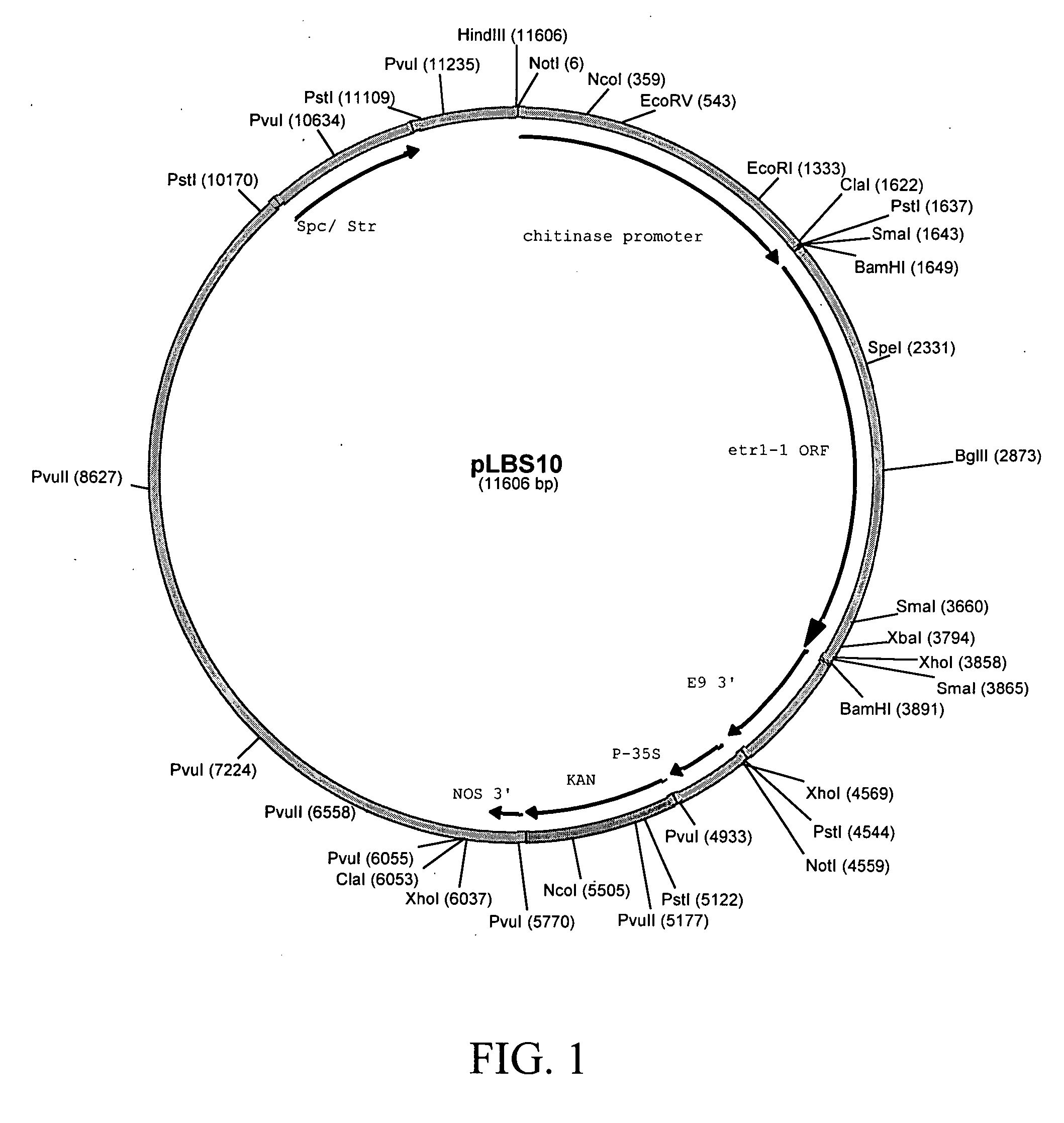
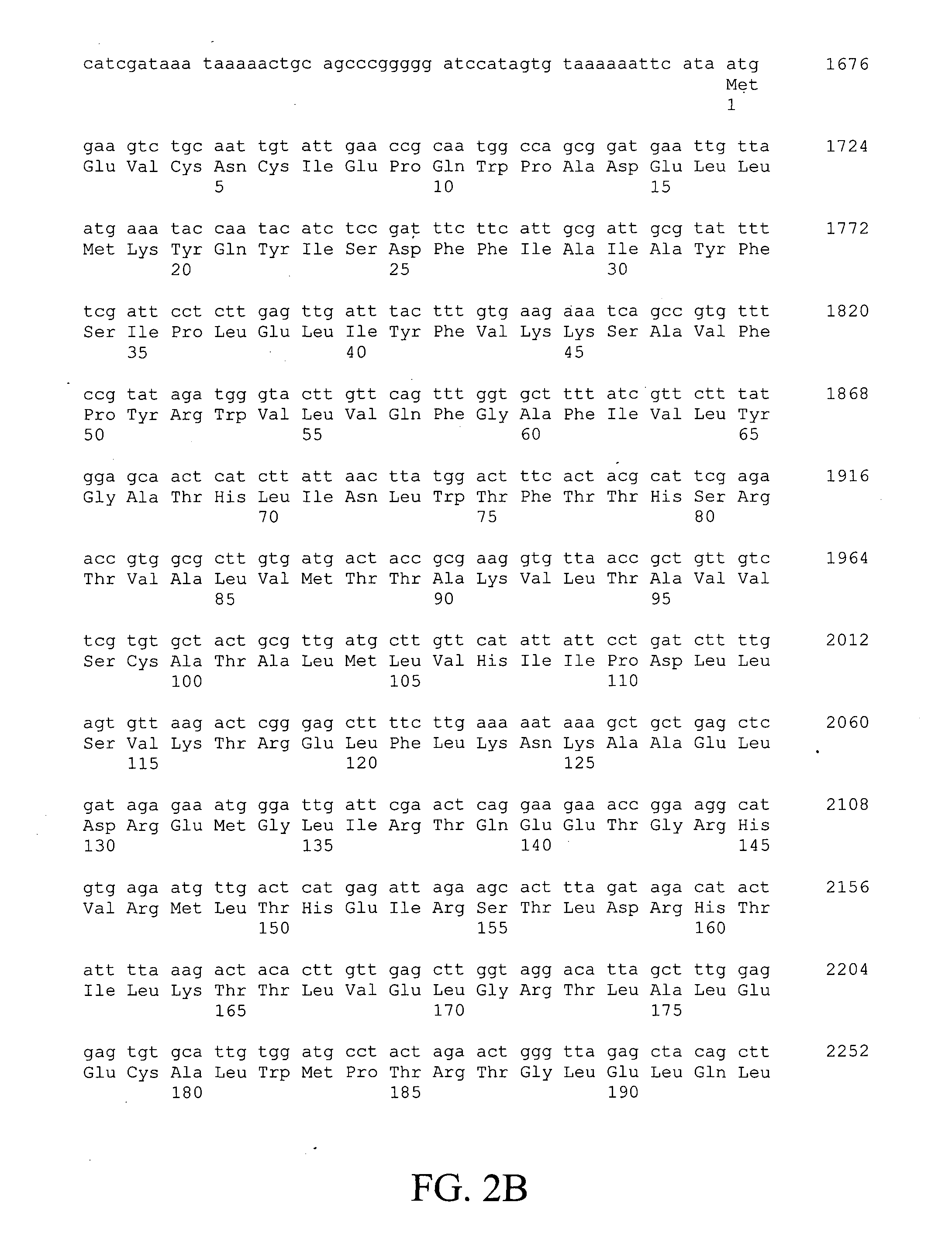
Materials and methods for tissue-specific targeting of ethylene insensitivity in transgenic plants
The subject invention concerns materials and methods for controlling agricultural traits in plants that are mediated by the plant hormone ethylene. One aspect of the invention concerns a polynucleotide that comprises a sequence encoding a mutant ethylene receptor that is operably linked to a regulatory sequence that drives expression of the mutant receptor in a tissue-specific manner. In an exemplified embodiment, the mutant receptor sequence is an etr1-1 sequence, or a functional fragment or variant thereof, and the regulatory sequence is a promoter sequence from a cotton chitinase gene that can promote expression of the mutant ethylene receptor in abscission zone tissue of a plant. The subject invention also concerns plants and plant tissue transformed with the polynucleotide of the subject invention. Plants expressing the polynucleotide of the subject invention do not drop their flowers in response to exposure to ethylene.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA
Cotton variety FM 991B2R
A novel cotton variety, designated as FM 991B2R, is disclosed. The invention relates to seeds, plants, plant cells, plant tissue, harvested products and cotton lint as well as to hybrid cotton plants and seeds obtained by crossing plants of variety FM 991B2R with other plants. The invention also relates to plants and varieties produced by the method of essential derivation from plants of FM 99IB2R and to plants of FM 991B2R reproduced by vegetative methods, including but not limited to tissue culture of regenerable cells or tissue from FM 991B2R.
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC +1
Apparatus for purifying nucleic acids and proteins
InactiveUS20030006193A1Facilitating resuspensionReduce the precipitation rateAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionWater/sewage treatment by substance additionHigh rateBiology
The present invention provides an apparatus for purifying nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA or proteins such as enzymes and antibodies from microorganisms such as viruses and bacteria or animal and plant tissues, the apparatus being capable of fast processing of a plurality of samples. More specifically, the present invention provides an apparatus for purifying nucleic acids or proteins using magnetically attractable particles, the apparatus comprising a plurality of piston pumps; a plurality of nozzles capable of having a plurality of disposable tips which are automatically attachable / detachable; and a mechanism which is capable of dispensing a desired amount of a reagent to be used subsequently in the next step into the same number of sections as that of the samples with high accuracy and at a high rate, while a mixture of a sample and a reagent are being mixed (stirred) by the pumps and nozzles, the apparatus being capable of rapidly processing a plurality of samples, wherein a series of steps from mixing (stirring) of the magnetically attractable particles and concentration of the sample to purification is automated with reduced wastes.
Owner:TOYO TOYOBO CO LTD
Apparatus and methods for analyzing and improving agricultural products
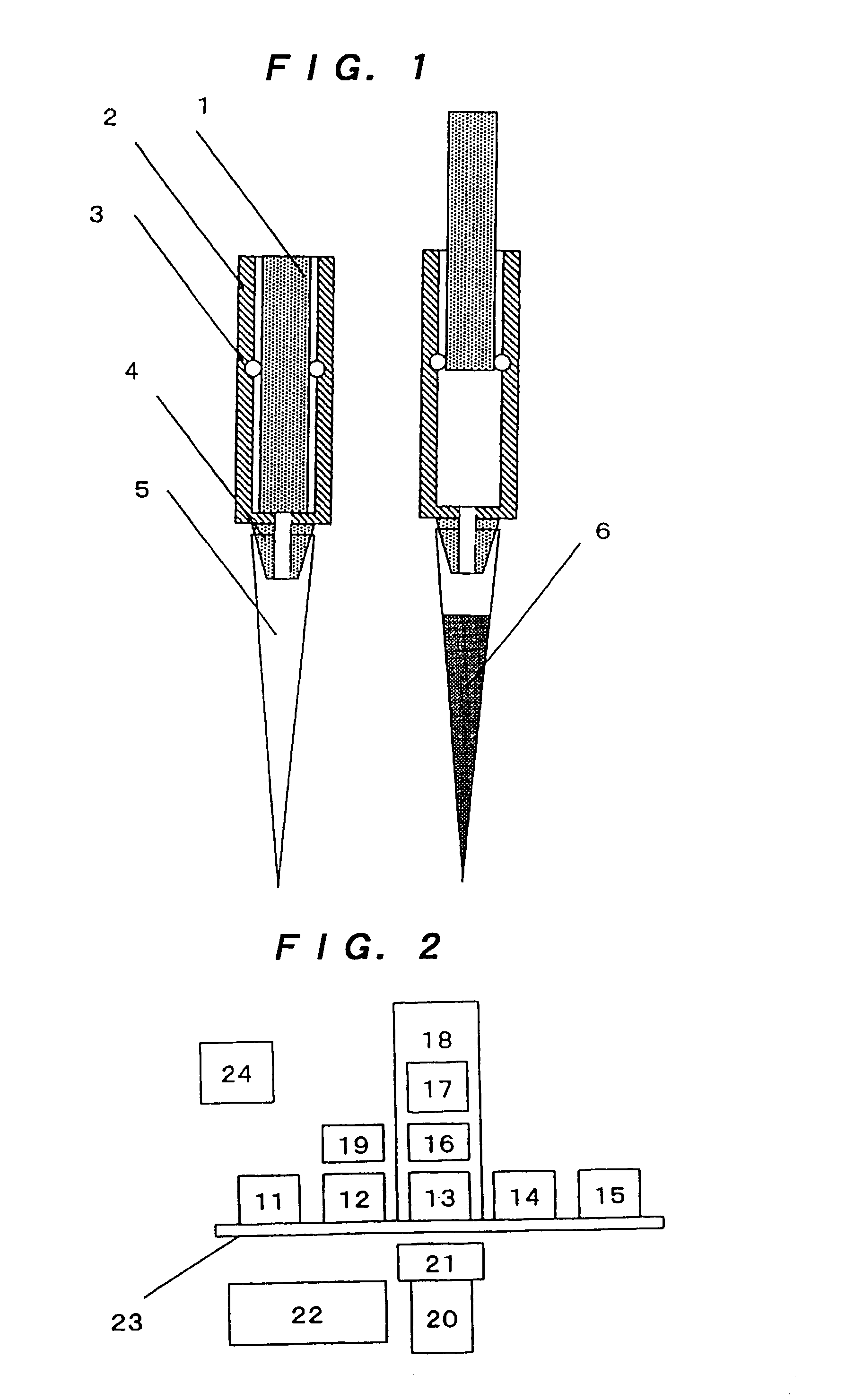
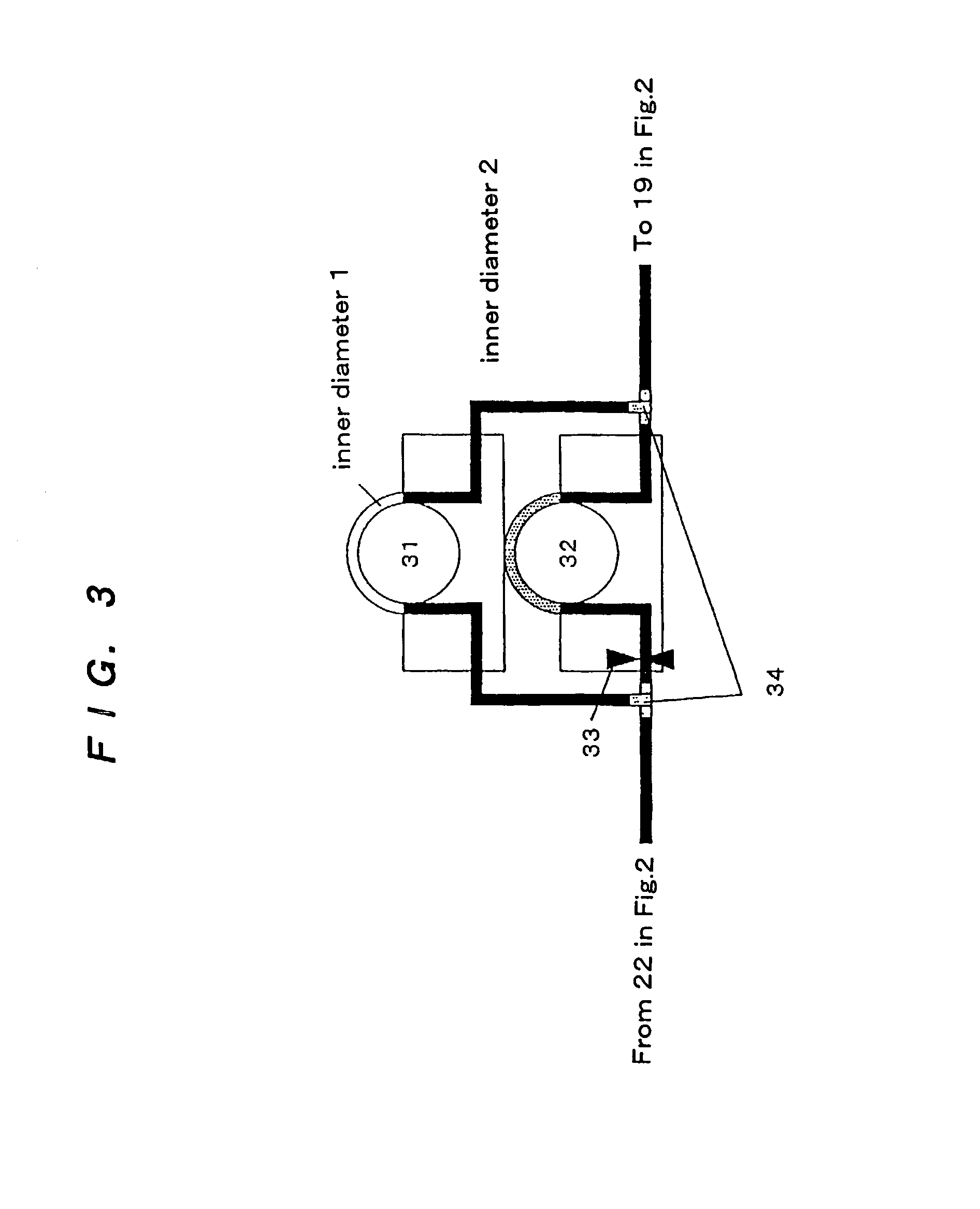
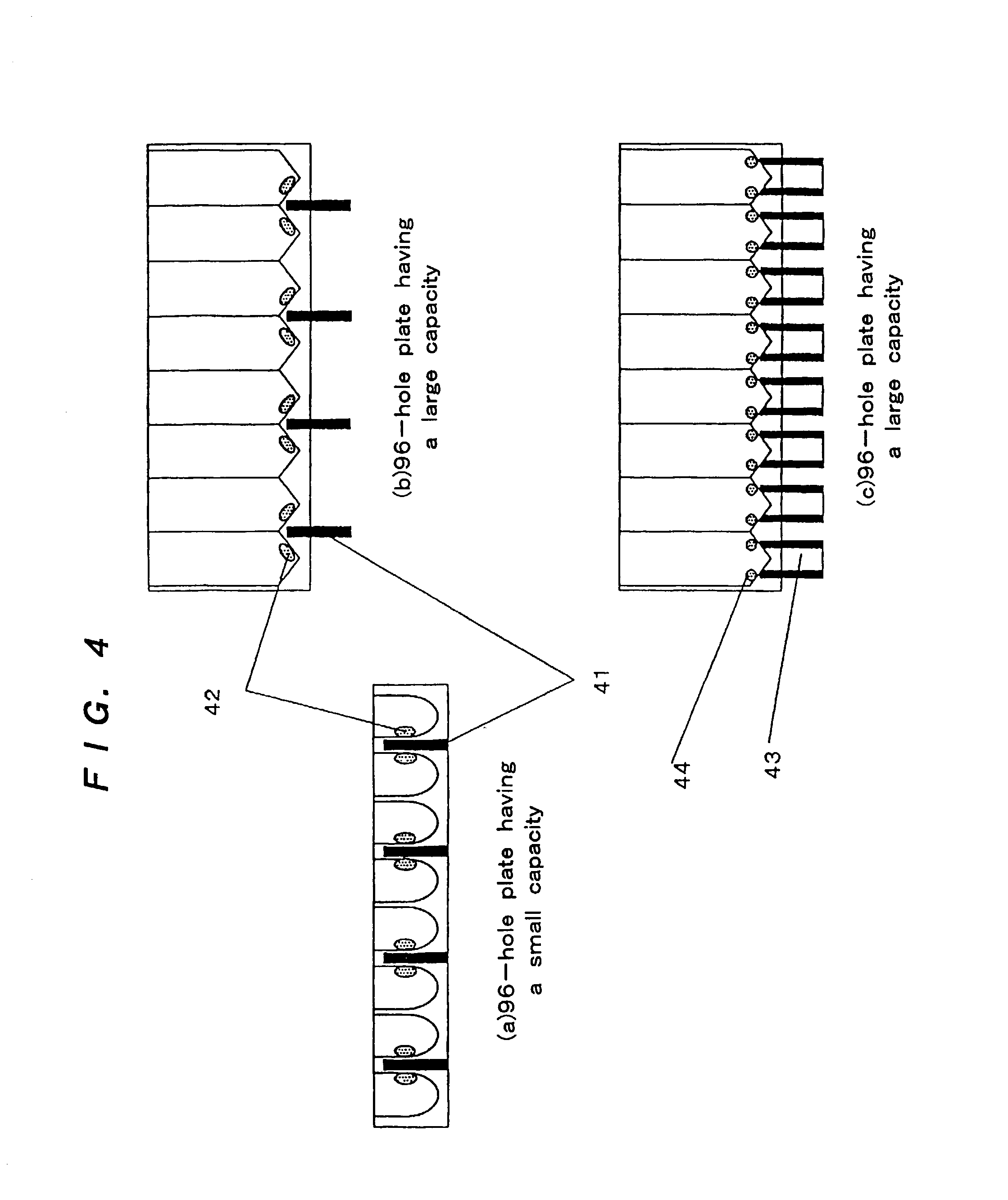
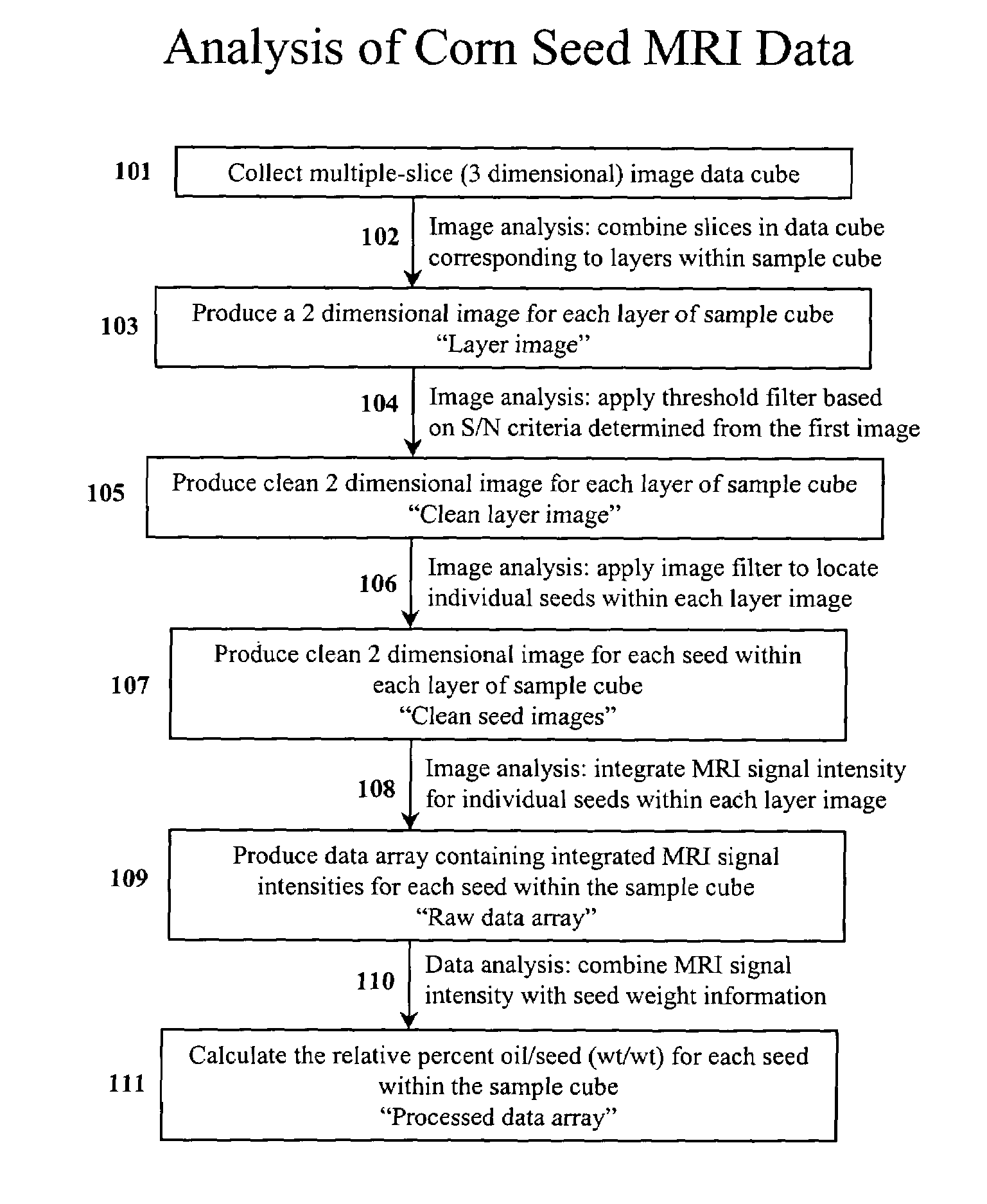
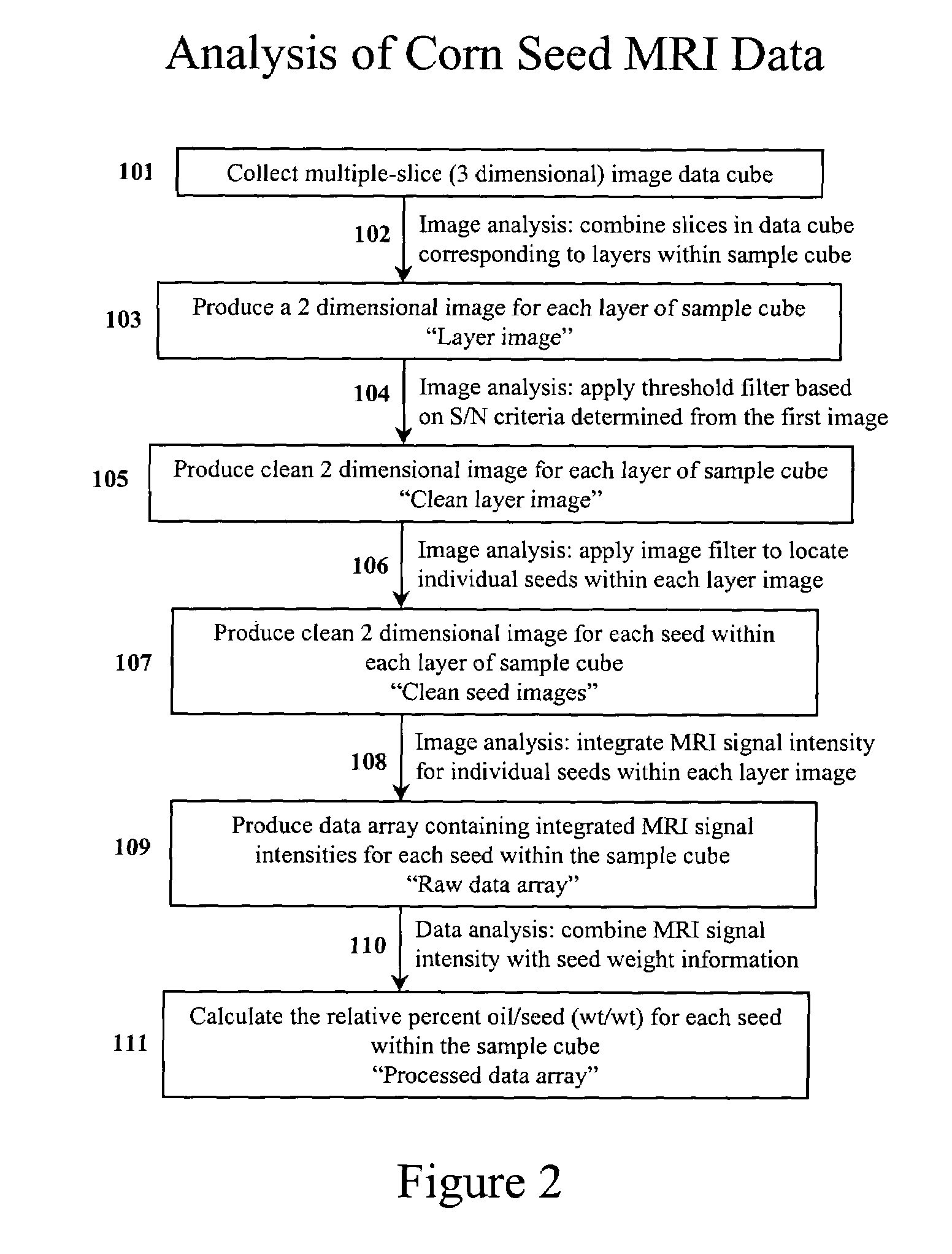
InactiveUS7367155B2Prevent inter-pixel crosstalkSeed and root treatmentLaboratory glasswaresPattern recognitionPlant tissue
A trait of interest is detected as being present within individual ones of a plurality of agricultural samples (such as seeds or plant tissues) by imaging the plurality of samples to form a magnetic resonance image. The image of the plurality of samples is then analyzed to detect image information indicative of the presence of the trait within one or more of the imaged samples. A determination is then made as to whether the trait is exhibited in individual ones of the samples based upon the foregoing analysis. As an example, the samples may be a plurality of seeds, and the detected trait may be oil. A determination is made, based on the image analysis, as to whether each individual seed in the multi-seed image contains oil. A further examination may be made to determine a relative content of oil in each seed as well as a content by weight.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
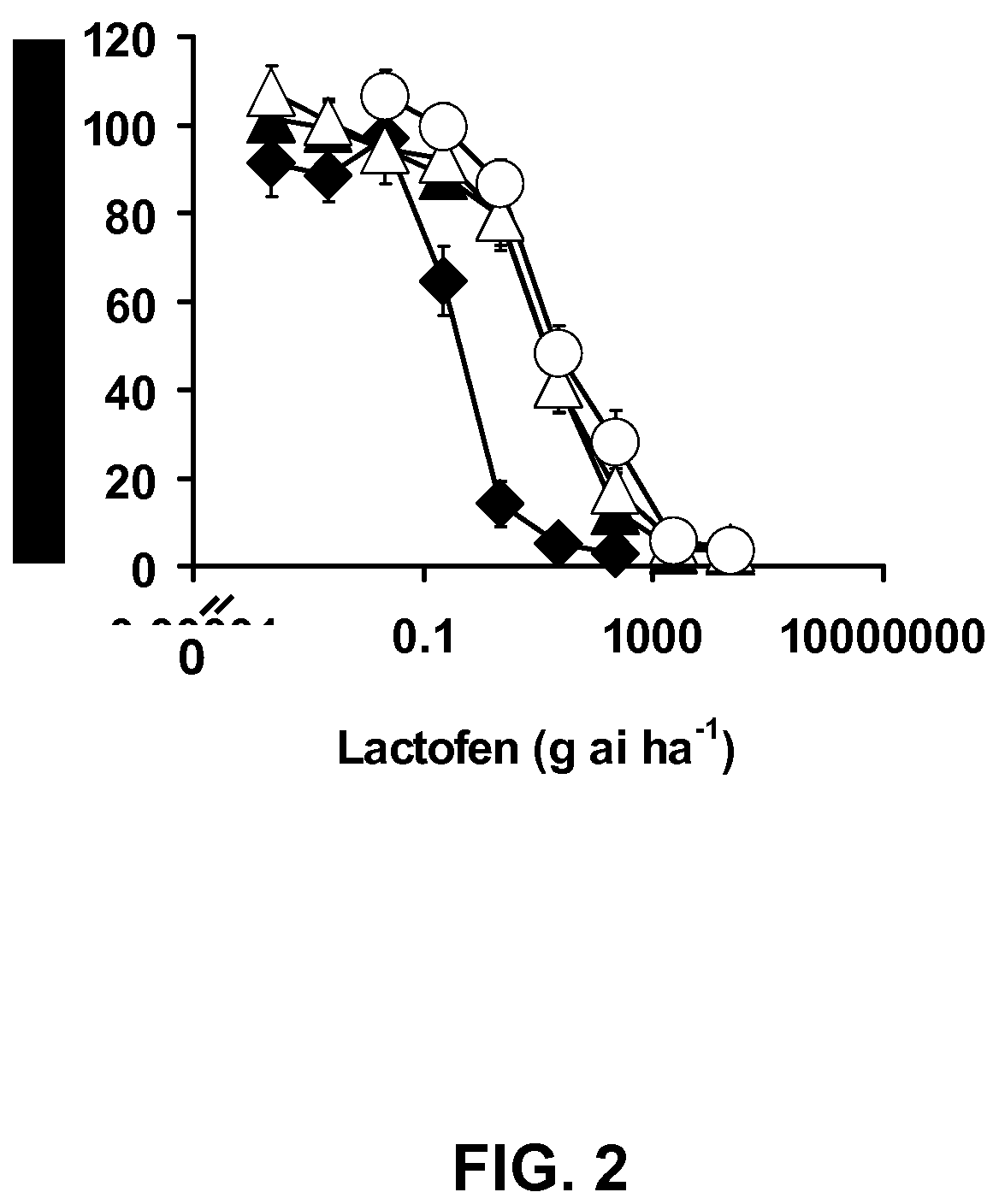
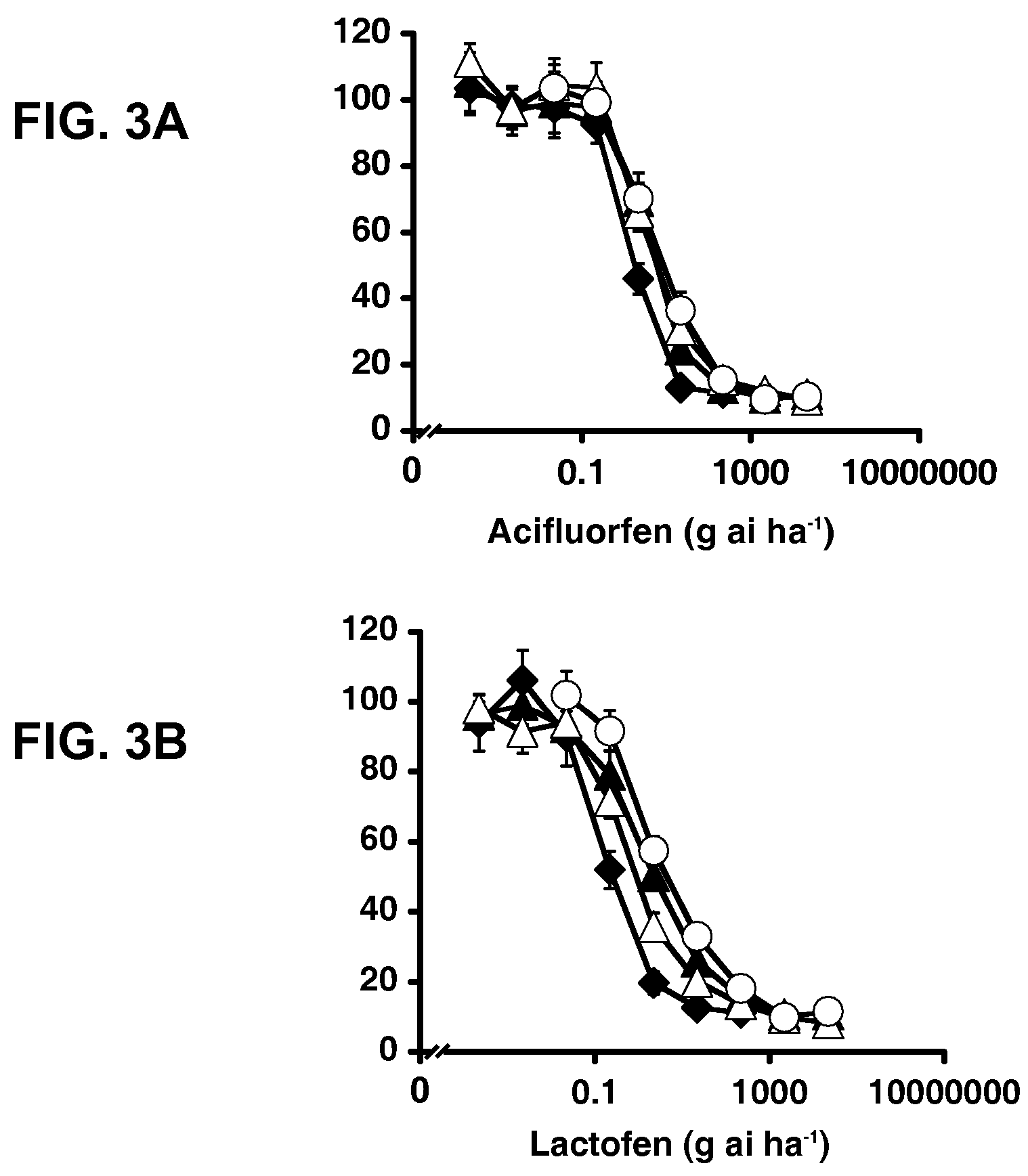
Herbicide Resistance Gene, Compositions and Methods
ActiveUS20100100988A1Improve efficiencyReduce competitionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant tissuePlant cell
The present disclosure provides methods, recombinant DNA molecules, recombinant host cells containing the DNA molecules, and transgenic and genetically engineered plant cells, plant tissue, seeds and plants which contain and express an herbicide resistant protoporphyrinogen oxidase such that they germinate from seed and grow in the presence of an amount of herbicide where the parent plant does not. Such plants are especially appropriate for use in agriculture or horticulture where herbicides are used to kill undesirable plants which might contaminate or compete with the transgenic plant of interest.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Recombinant plant viral vectors
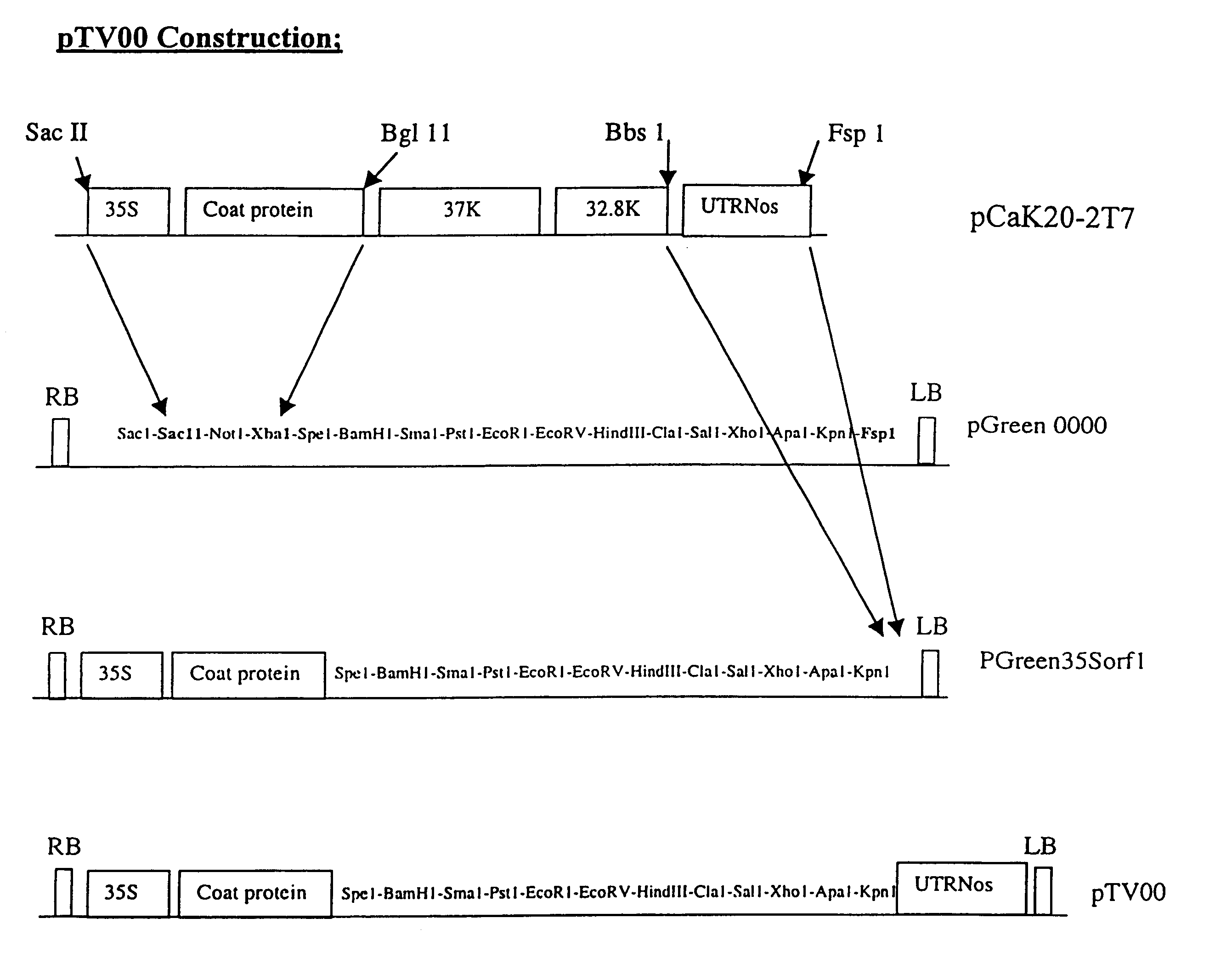
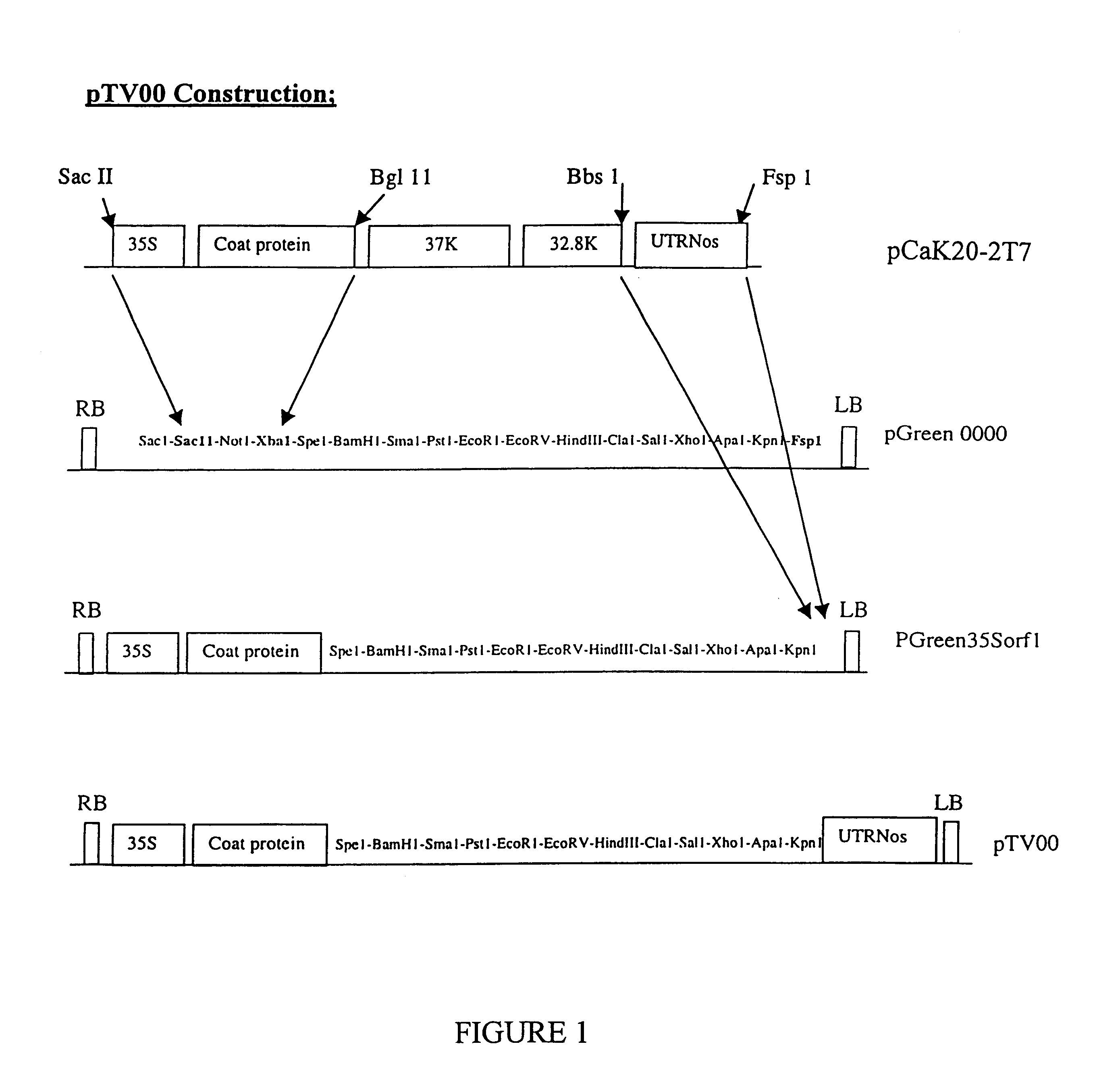
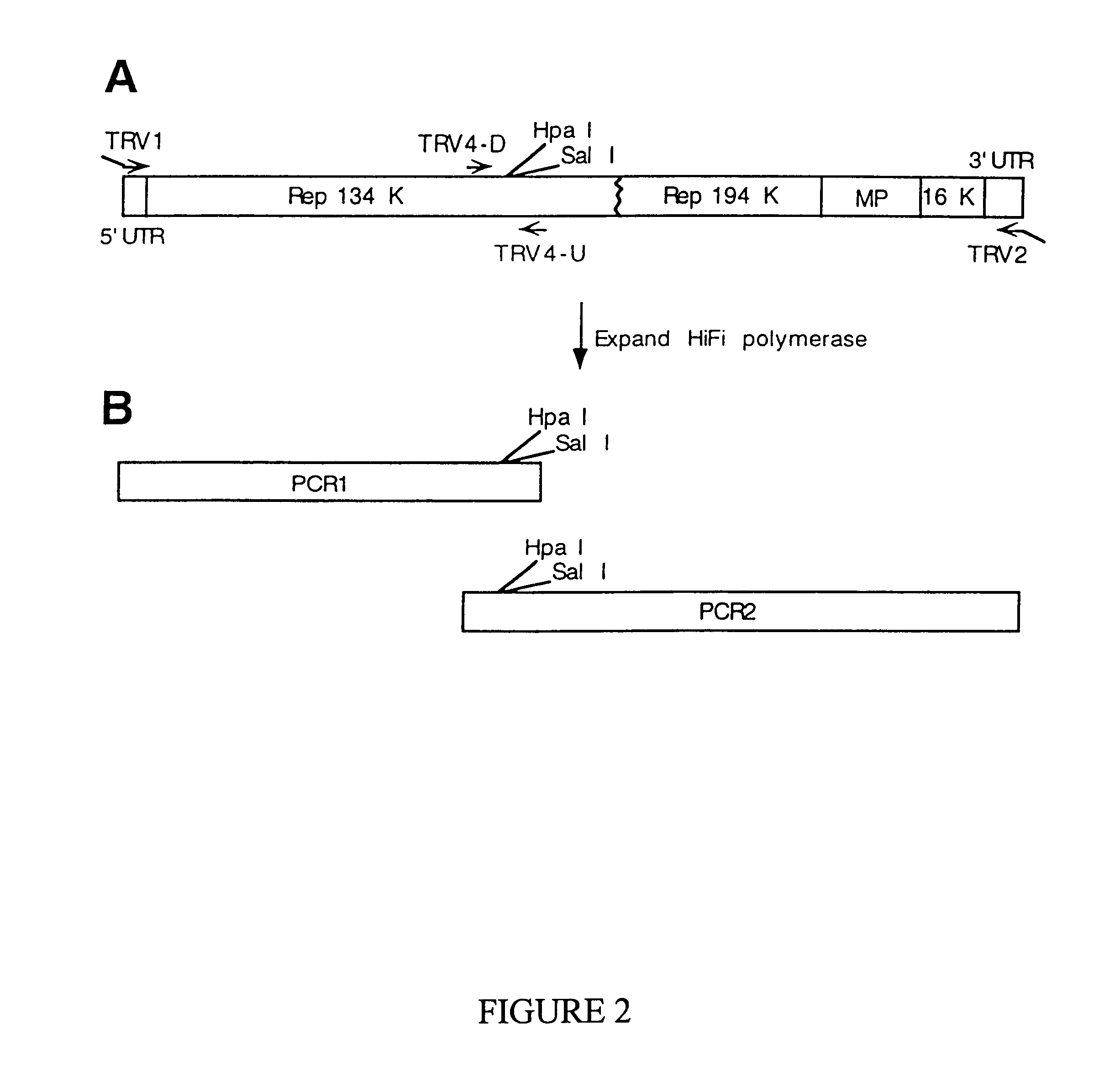
Disclosed are nucleic acid vectors which comprise: (a) a transfer nucleotide sequence comprising (i) a plant active promoter, operably linked to (ii) a recombinant tobacco rattle virus (TRV) cDNA (preferably derived from TRV RNA2) which includes at least cis acting elements permitting replication of the cDNA; a subgenomic promoter operably linked to a sequence encoding a TRV coat protein; and a heterologous nucleotide sequence which is foreign to the virus;(b) border sequences which permit the transfer of the transfer nucleotide sequence into a plant genome. Such vectors may be used as expression vectors or for achieving viral induced gene silencing (VIGS) of a target gene, wherein the heterologous nucleotide sequence is a targeting sequence which corresponding to that gene. Example vectors include pTV00 and vectors which are derived from PTV00 and have the characteristics thereof. Also disclosed are associated processes, methods, viruses or viral particle, kits, host cells and plant tissues.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD
Reagents and methods for storage and processing of biological samples for DNA analysis
ActiveUS20060147944A1Long-term stabilityStable in long-termSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSample purificationPlasmid
The present invention describes reagents and methods for storing and / or processing of biological samples for direct use in PCR and other DNA applications. After storage, the preserved DNA in the samples may then be processed and analyzed by known methods, e.g., PCR. the present invention provides in one aspect, a method for simple and rapid storage and / or processing of nucleic acids, such as DNA, from various sources, including but not limited to body fluids, various solutions, cells, plants, tissues, bacterial cell lysates containing plasmids, etc. The present invention further comprises reagents and methods employing glycols at alkaline pH to process biological samples and make DNA usable in PCR without further sample purification. Accordingly, the present invention provides in one aspect, a method for simple and rapid processing of nucleic acids, such as DNA, from various sources, including but not limited to body fluids, various solutions, cells, plants, tissues, bacterial cell lysates containing plasmids, etc.
Owner:MOLECULAR RES CENT
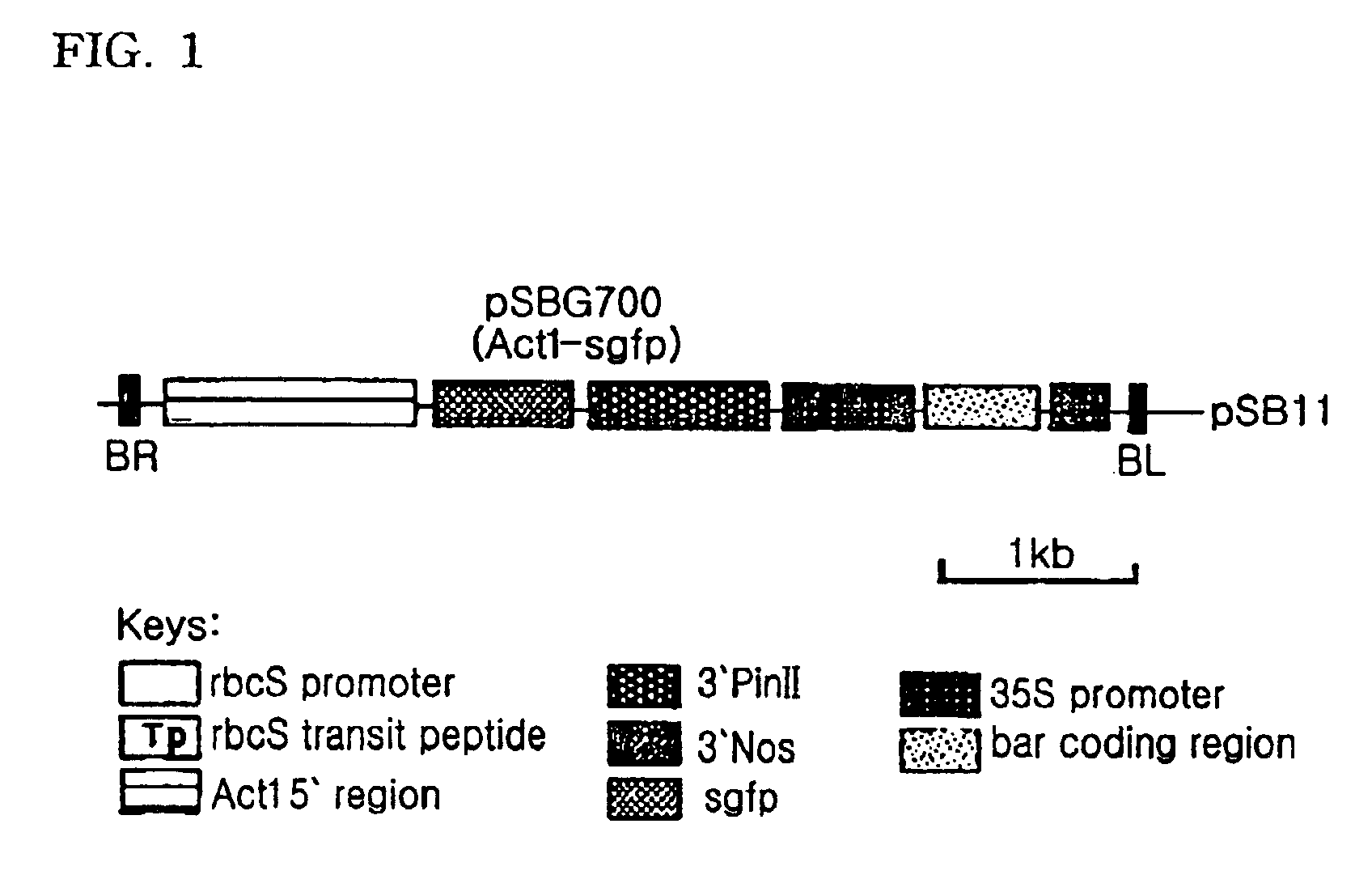
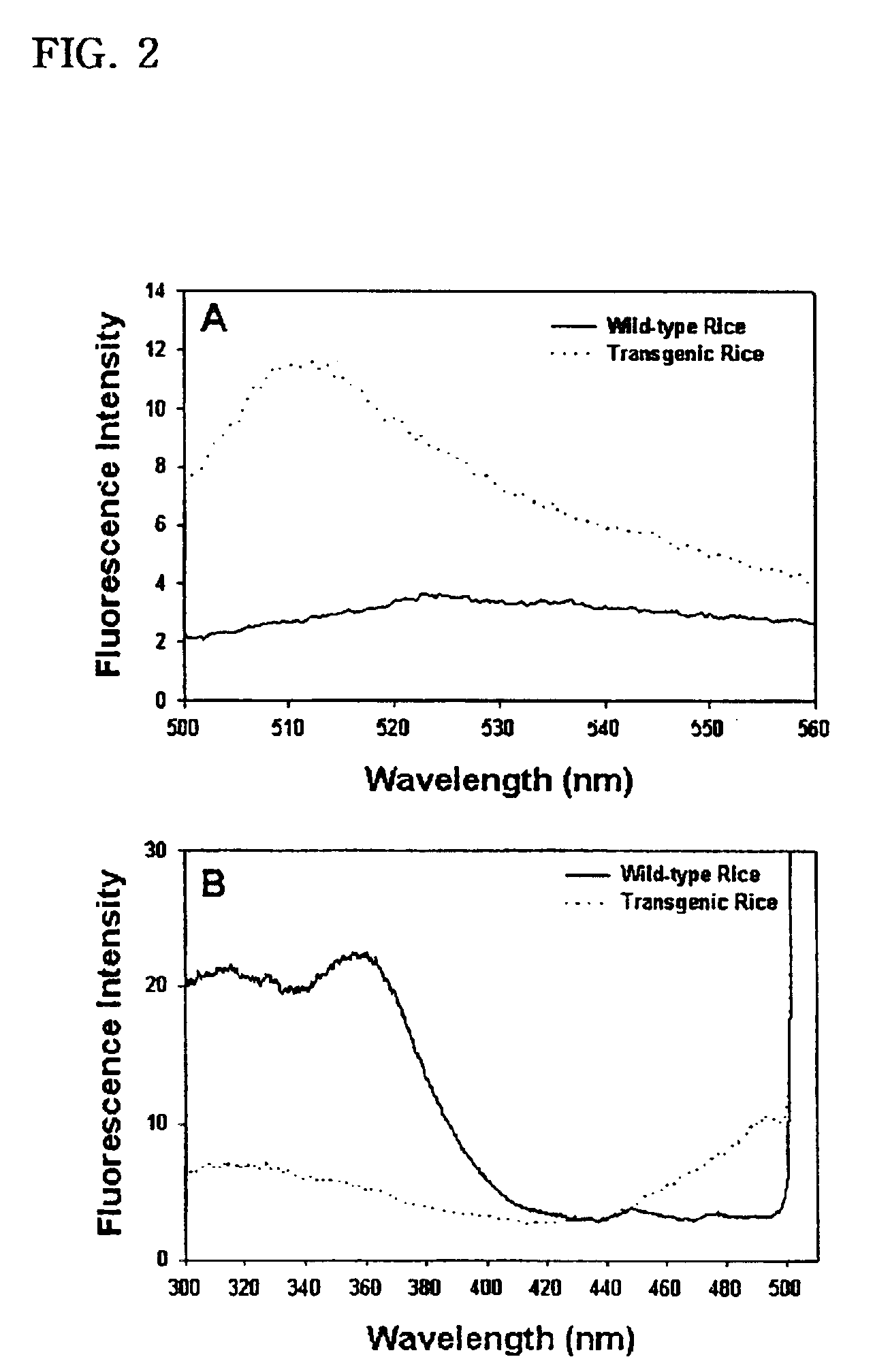
Vivo monitoring method of transgenic plants and system using the same
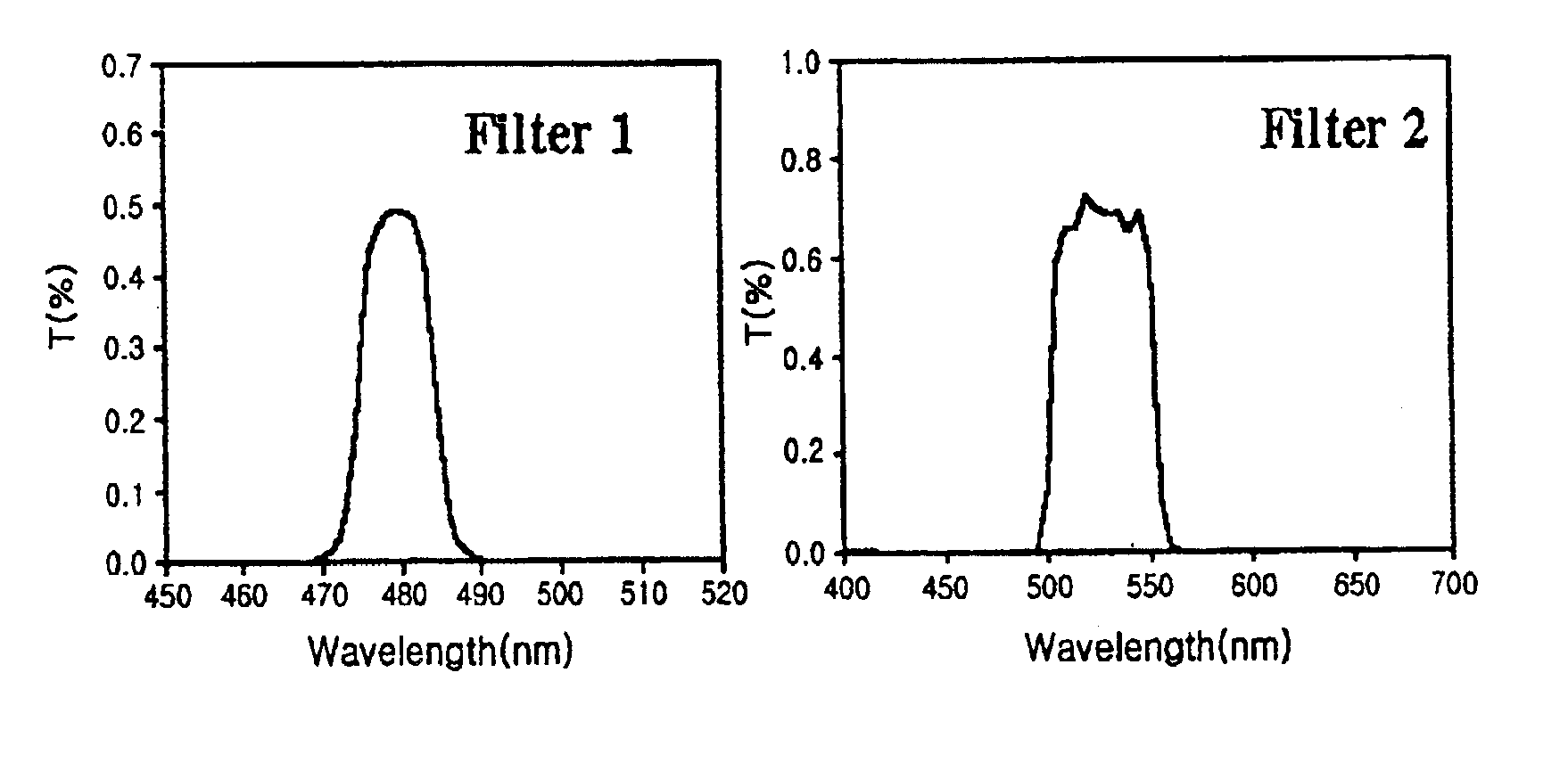
The present invention relates to a method for visualizing GFP expression in callus, various tissue and organ of the transgenic plants as image and system using the same. The said method needs no other additional genetic product, substrate or cofactor and can detect very simply and quickly GFP expression by using the said system of the present invention consisting of a CCD camera, a light source, band-pass filter and data processing computer, so it provides many advantages for selection of transgenic seeds, for studying of gene expression in the tissue or organ of plants, or for studying of specificity of each development step.
Owner:DONGBU HANNONG CHEMICAL CO +1
Nonlinear System Identification Techniques and Devices for Discovering Dynamic and Static Tissue Properties
ActiveUS20110054354A1Quickly mechanical propertyLow costDiagnostics using suctionDiagnostics using pressureAccelerometerEngineering
A device for measuring a mechanical property of a tissue includes a probe configured to perturb the tissue with movement relative to a surface of the tissue, an actuator coupled to the probe to move the probe, a detector configured to measure a response of the tissue to the perturbation, and a controller coupled to the actuator and the detector. The controller drives the actuator using a stochastic sequence and determines the mechanical property of the tissue using the measured response received from the detector. The probe can be coupled to the tissue surface. The device can include a reference surface configured to contact the tissue surface. The probe may include a set of interchangeable heads, the set including a head for lateral movement of the probe and a head for perpendicular movement of the probe. The perturbation can include extension of the tissue with the probe or sliding the probe across the tissue surface and may also include indentation of the tissue with the probe. In some embodiments, the actuator includes a Lorentz force linear actuator. The mechanical property may be determined using non-linear stochastic system identification. The mechanical property may be indicative of, for example, tissue compliance and tissue elasticity. The device can further include a handle for manual application of the probe to the surface of the tissue and may include an accelerometer detecting an orientation of the probe. The device can be used to test skin tissue of an animal, plant tissue, such as fruit and vegetables, or any other biological tissue.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Herbicide resistance gene, compositions and methods
ActiveUS7842856B2Improve efficiencyReduce competitionBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant tissuePlant cell
The present disclosure provides methods, recombinant DNA molecules, recombinant host cells containing the DNA molecules, and transgenic and genetically engineered plant cells, plant tissue, seeds and plants which contain and express an herbicide resistant protoporphyrinogen oxidase such that they germinate from seed and grow in the presence of an amount of herbicide where the parent plant does not. Such plants are especially appropriate for use in agriculture or horticulture where herbicides are used to kill undesirable plants which might contaminate or compete with the transgenic plant of interest.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Herbicide Resistance Gene, Compositions and Methods
ActiveUS20070050863A1Improve efficiencyReduce competitionImmunoglobulinsOxidoreductasesPlant cellAdemetionine
The present disclosure provides methods, recombinant DNA molecules, recombinant host cells containing the DNA molecules, and transgenic plant cells, plant tissue, seeds and plants which contain and express an herbicide resistant protoporphyrinogen oxidase such that they germinate from seed and grow in the presence of an amount of herbicide where the parent plant does not. Such plants are especially appropriate for use in agriculture or horticulture where herbicides are used to kill undesirable plants which might contaminate or compete with the transgenic plant of interest.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Herbicide resistance gene, compositions and methods
ActiveUS7671254B2Improve efficiencyReduce competitionImmunoglobulinsOxidoreductasesPlant tissuePlant cell
The present disclosure provides methods, recombinant DNA molecules, recombinant host cells containing the DNA molecules, and transgenic plant cells, plant tissue, seeds and plants which contain and express an herbicide resistant protoporphyrinogen oxidase such that they germinate from seed and grow in the presence of an amount of herbicide where the parent plant does not. Such plants are especially appropriate for use in agriculture or horticulture where herbicides are used to kill undesirable plants which might contaminate or compete with the transgenic plant of interest.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
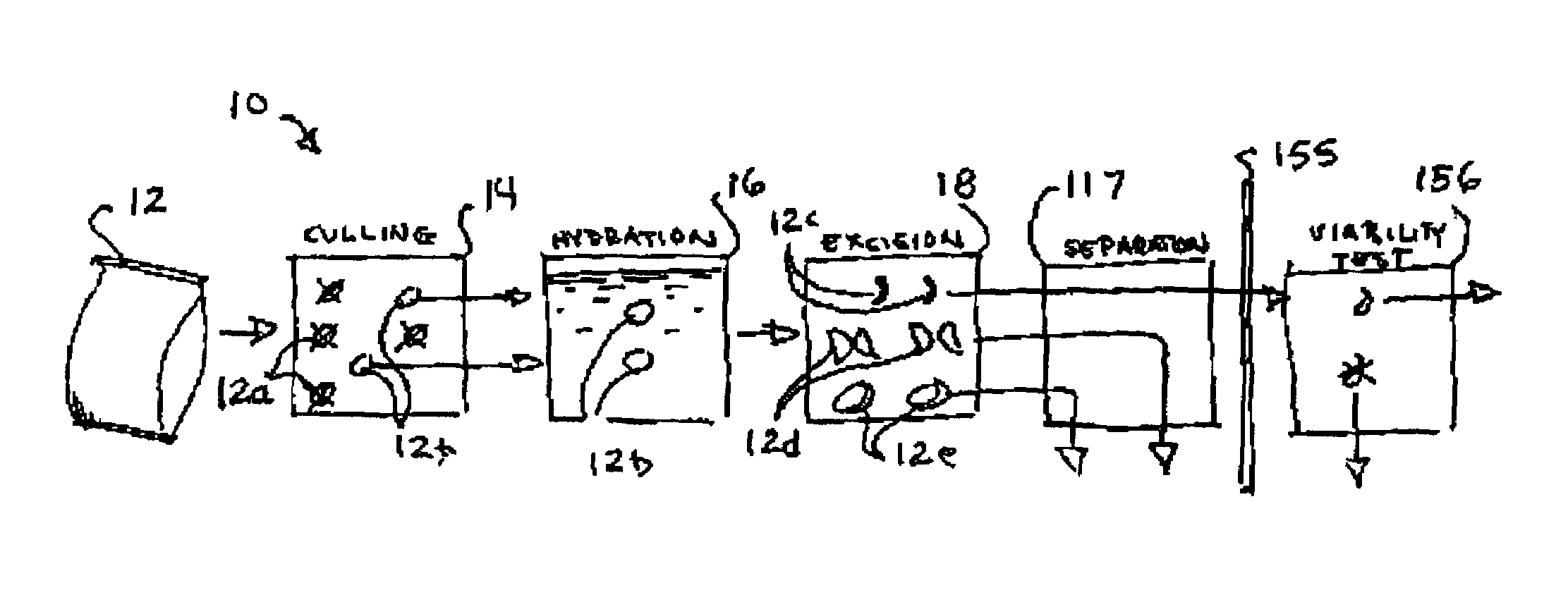
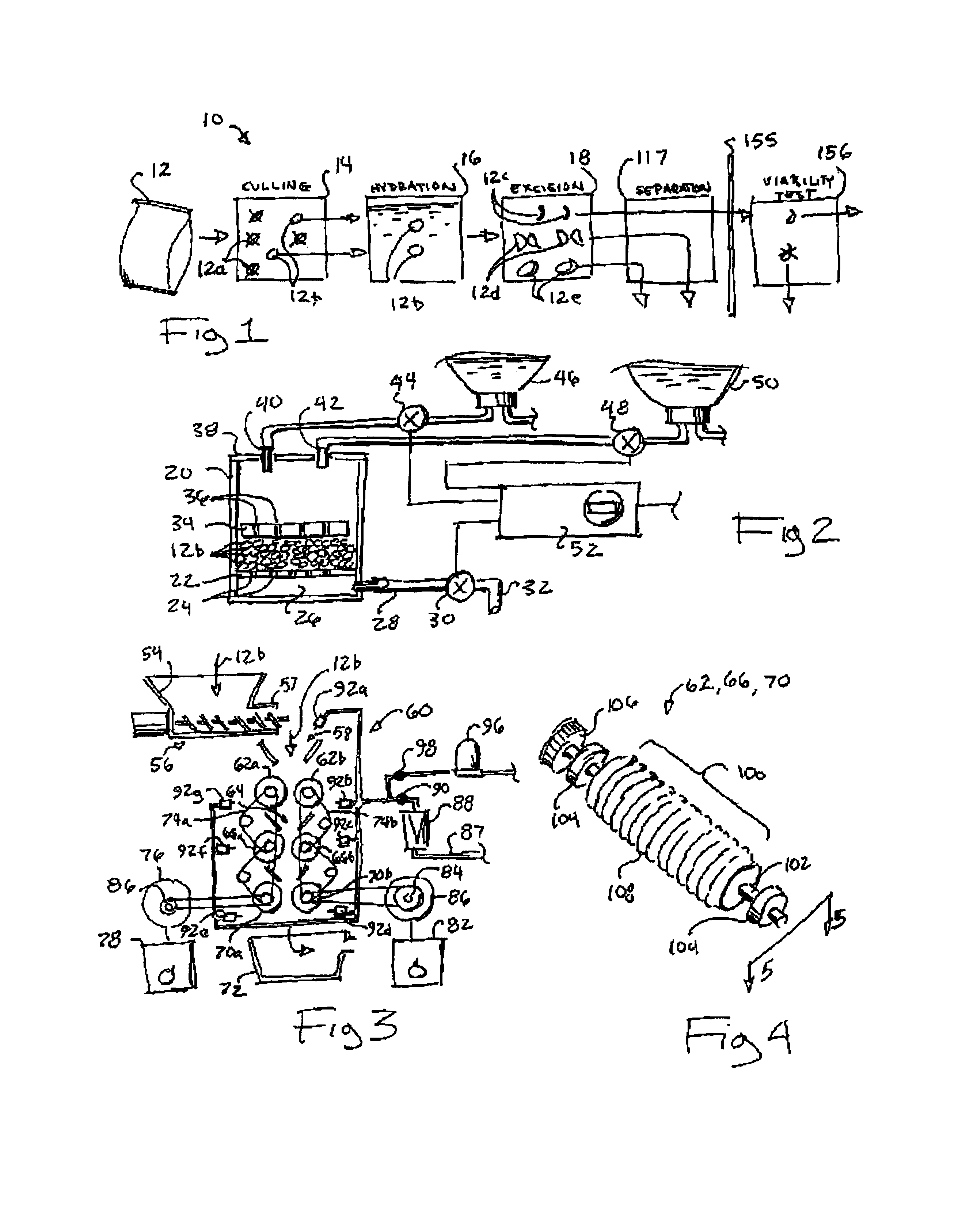
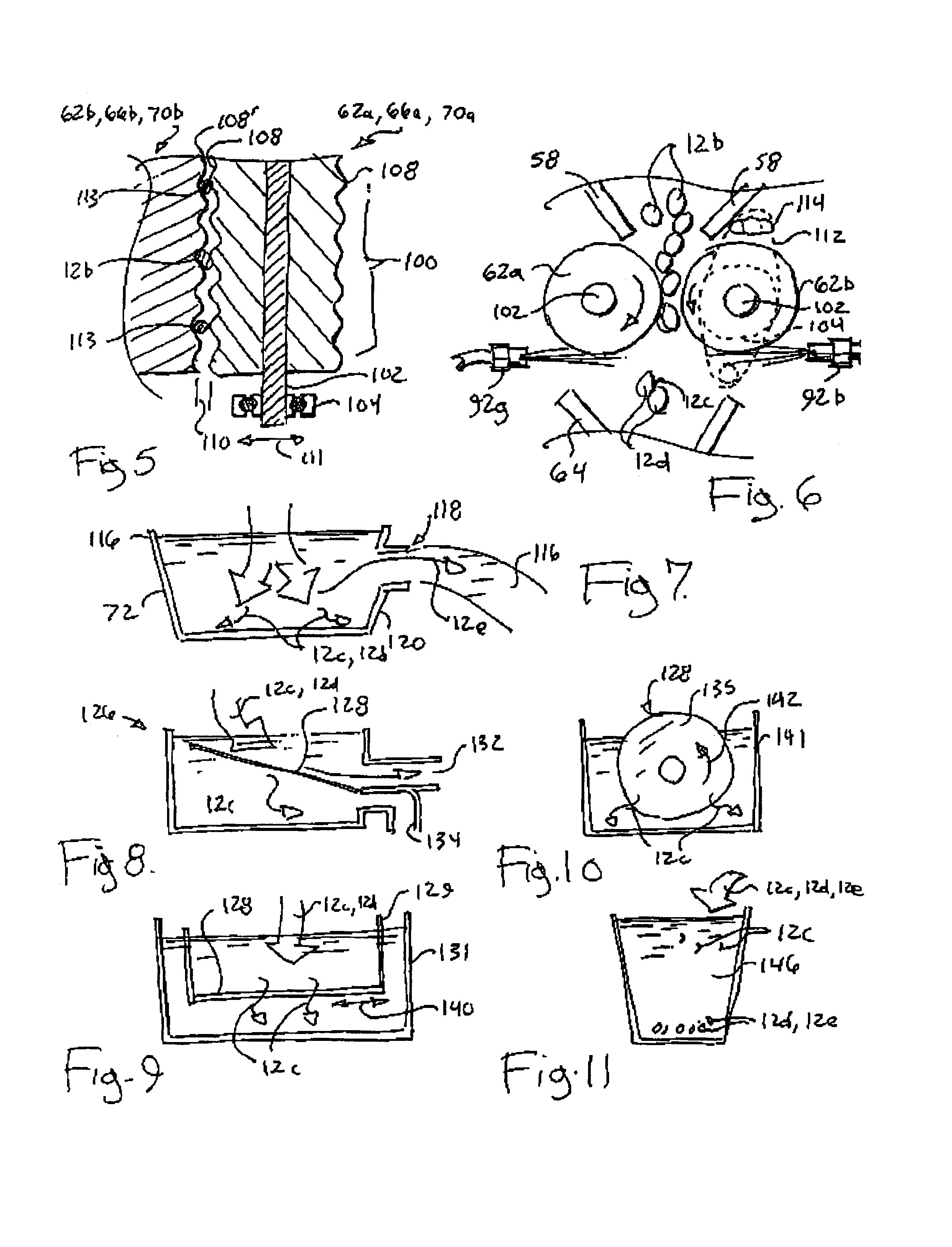
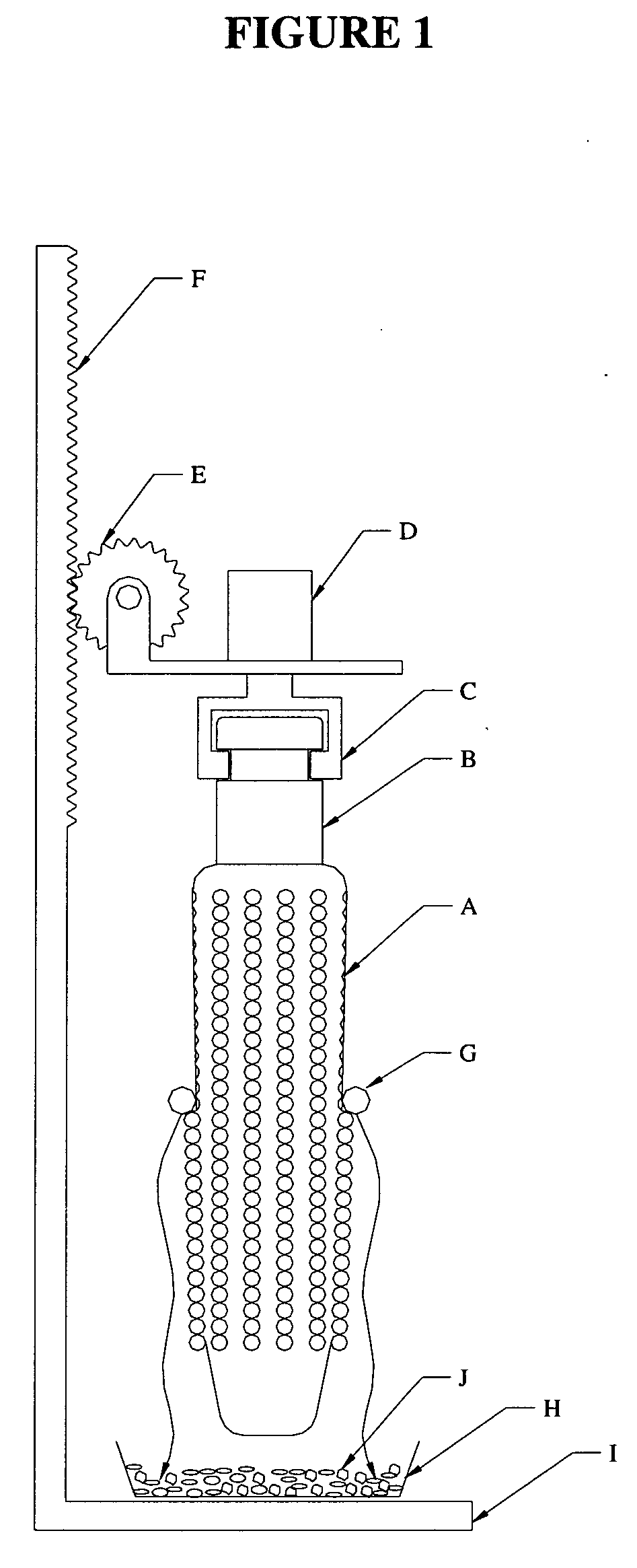
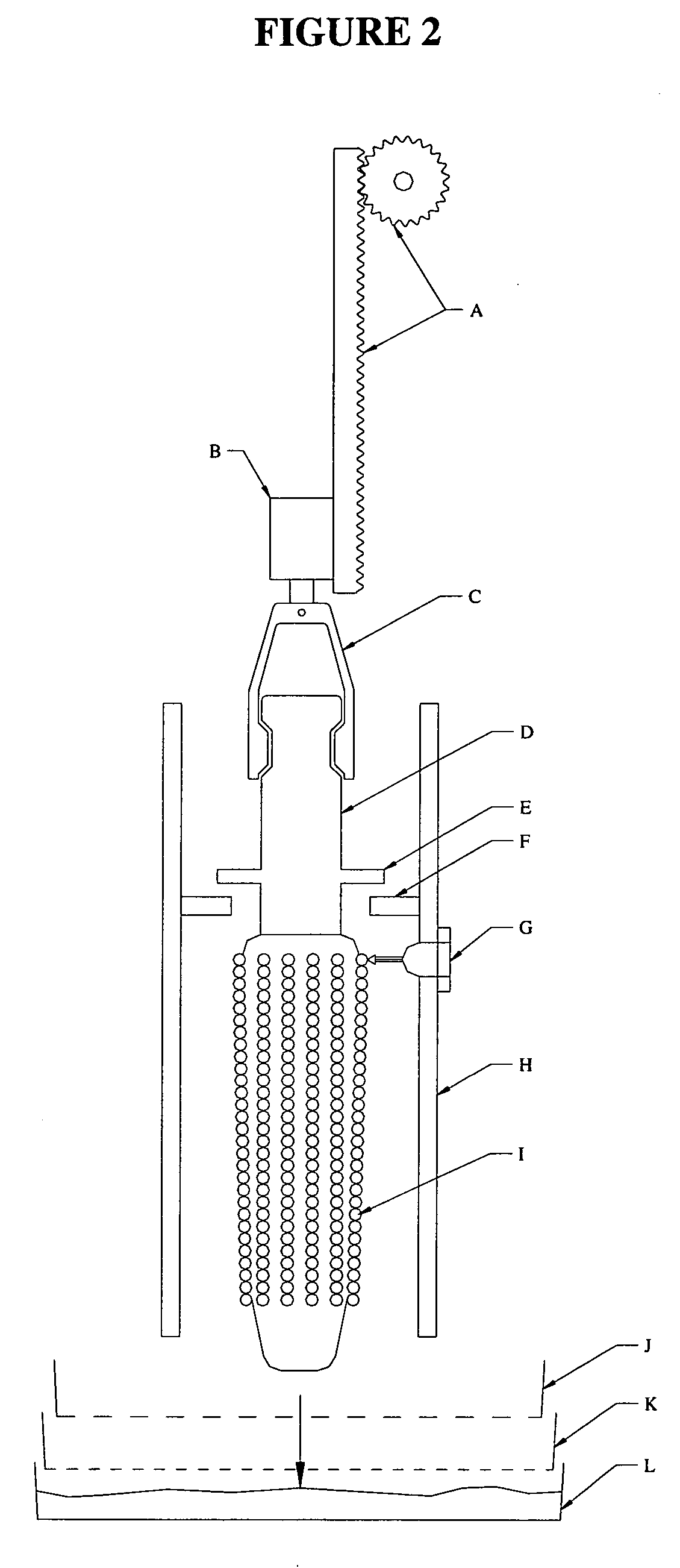
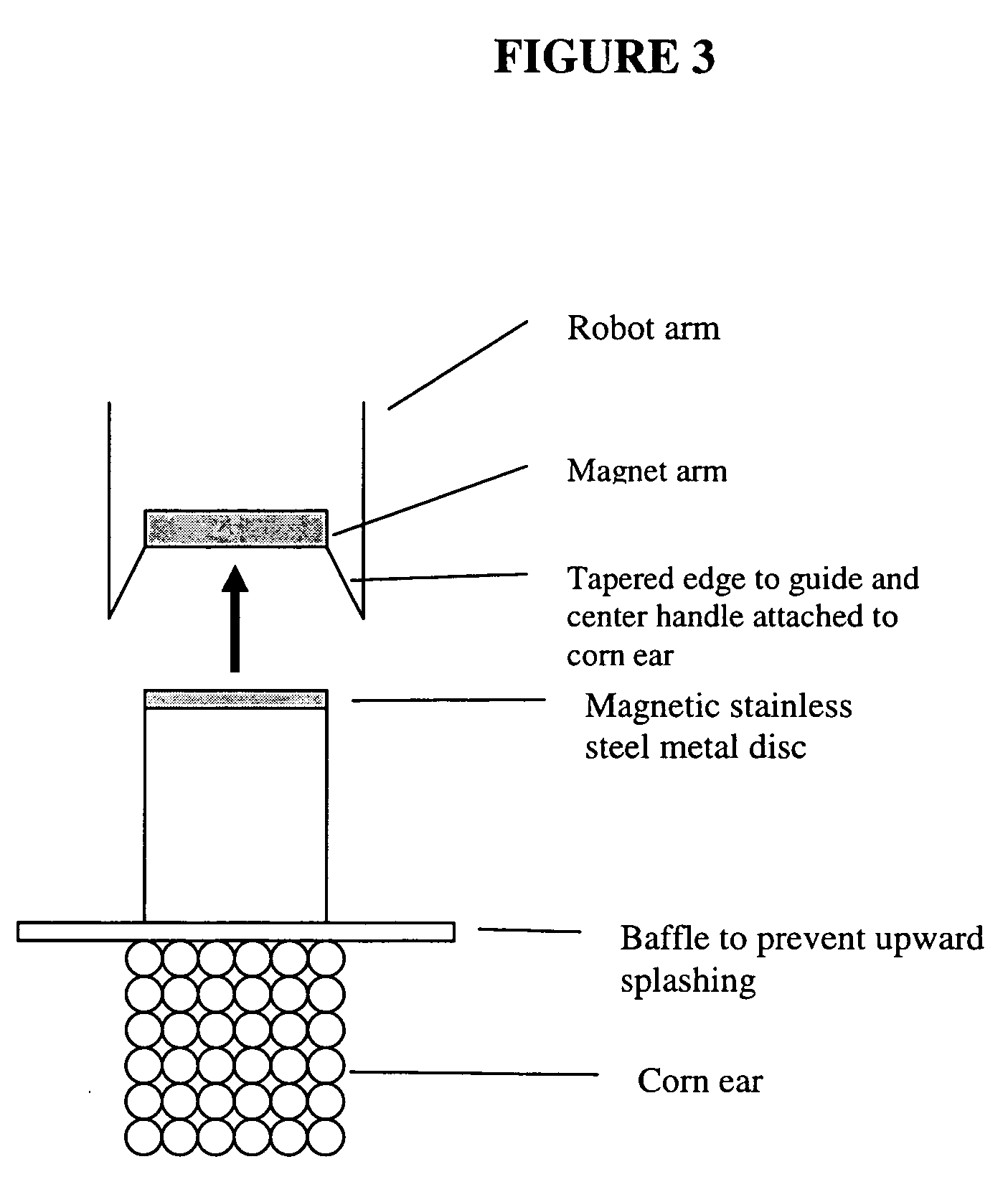
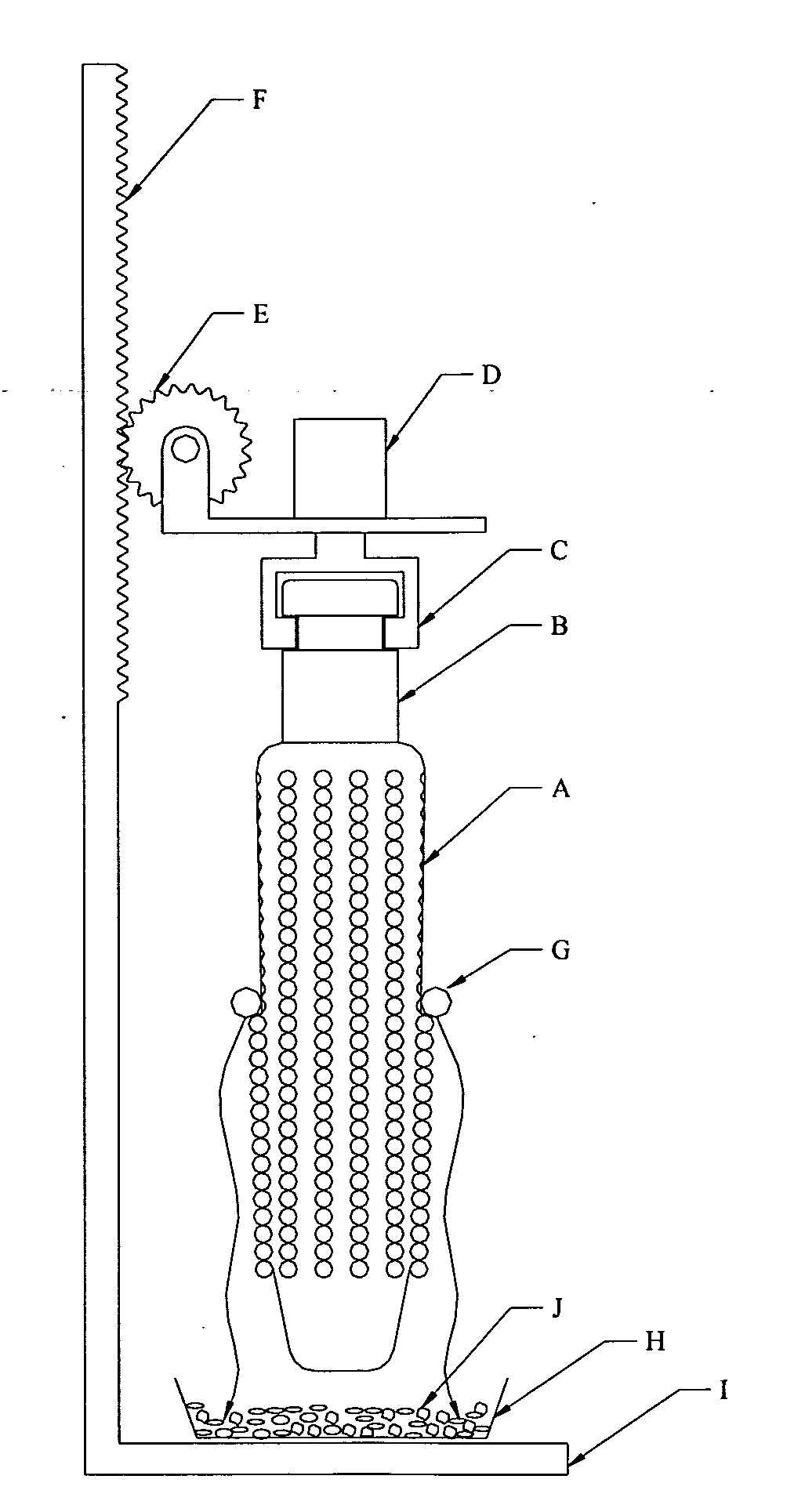
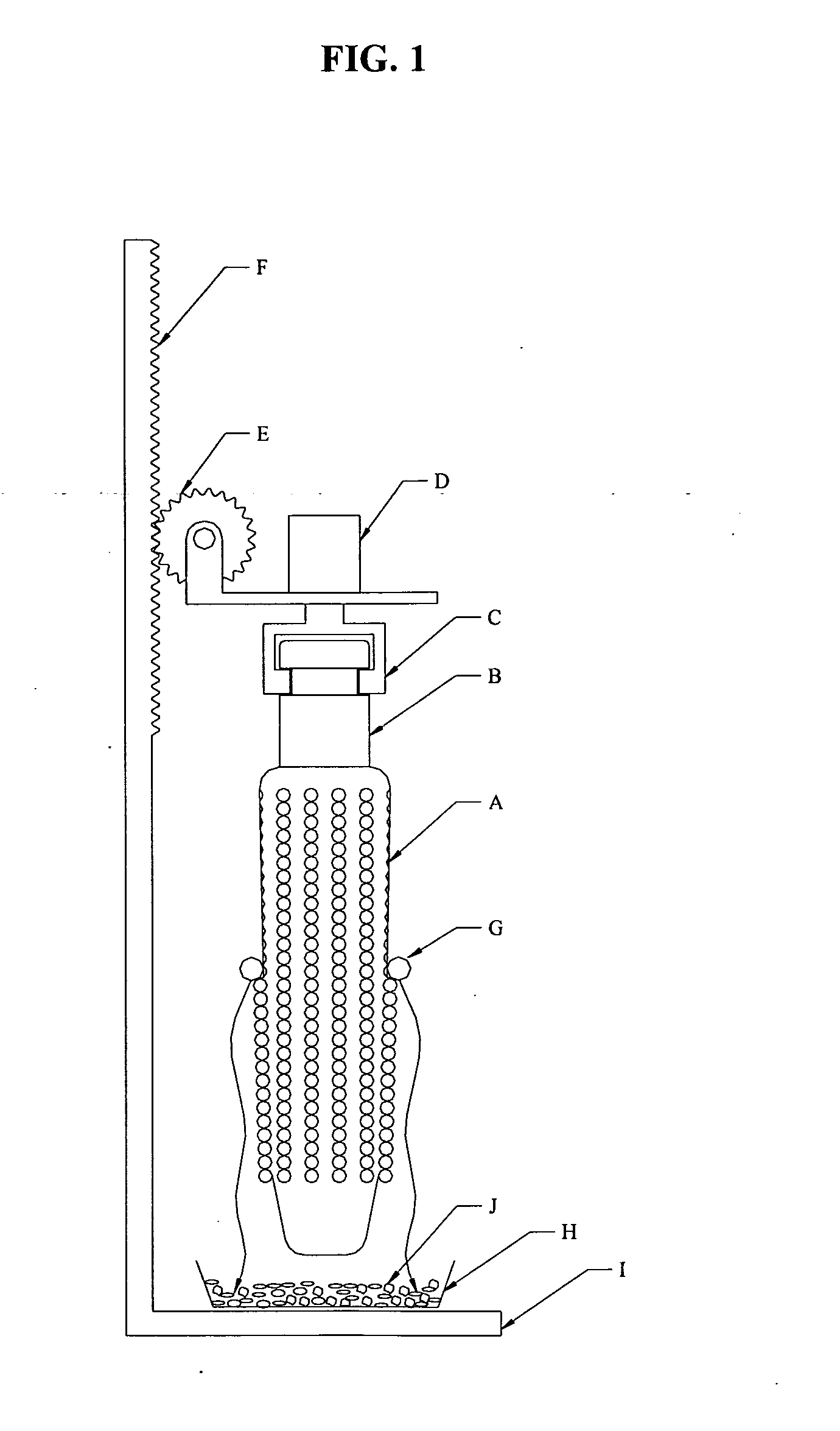
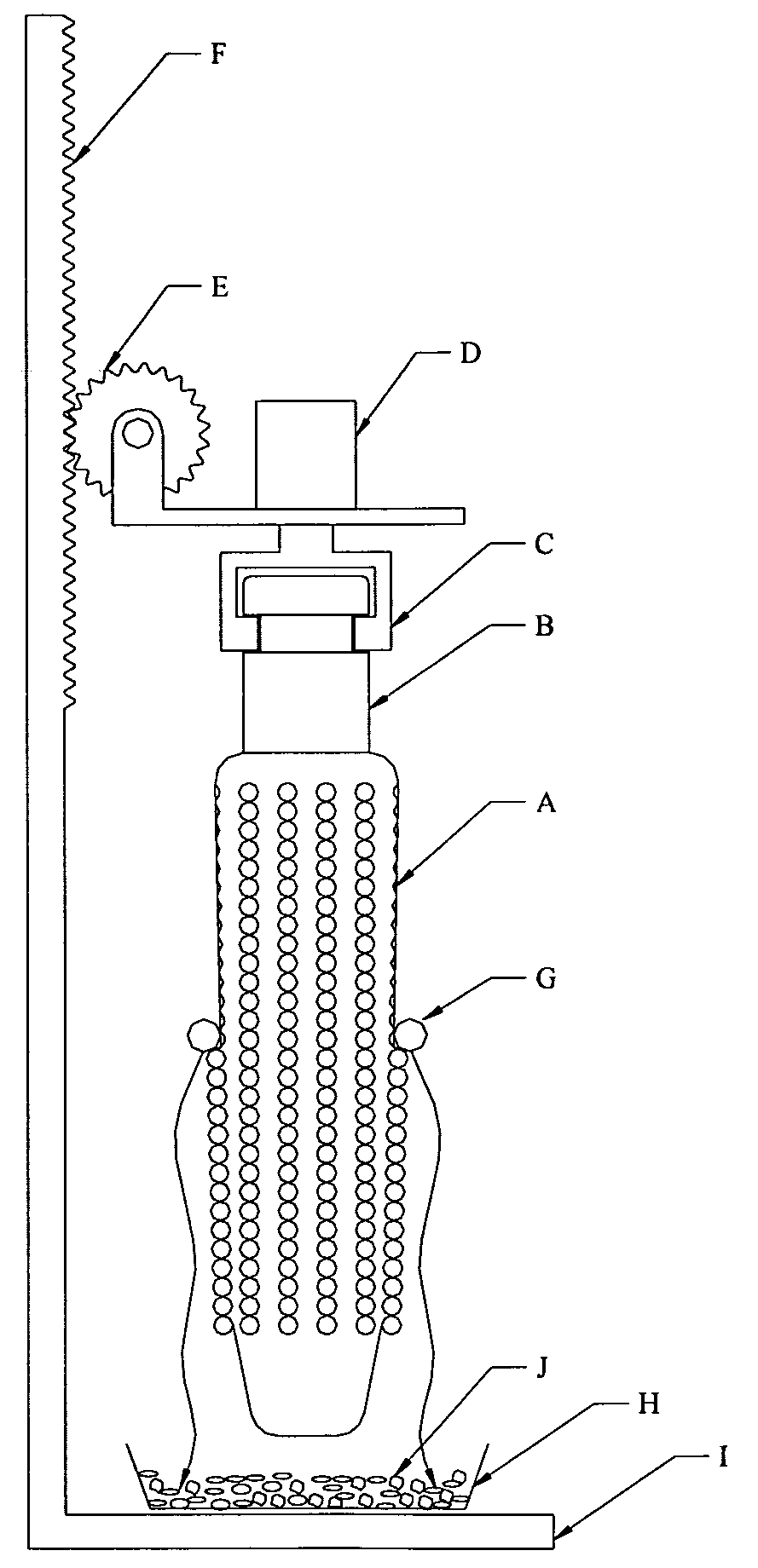
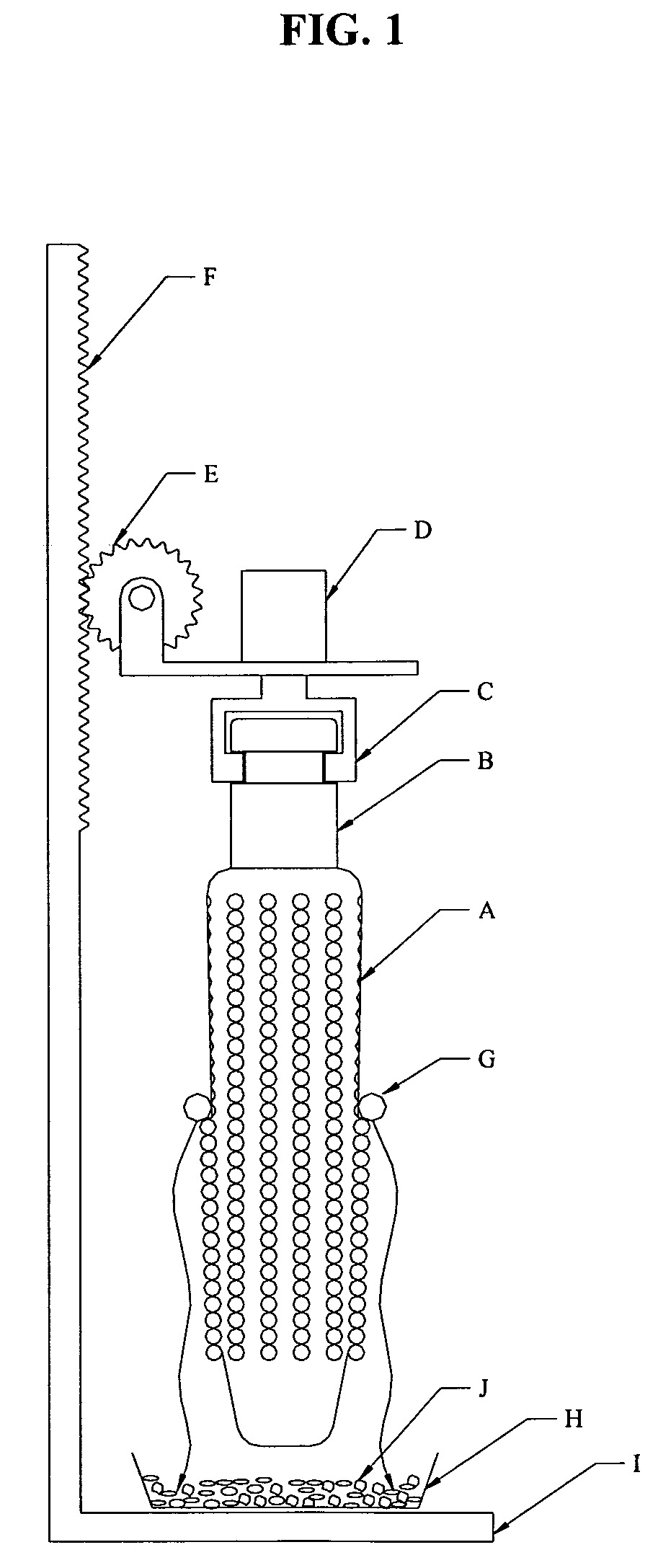
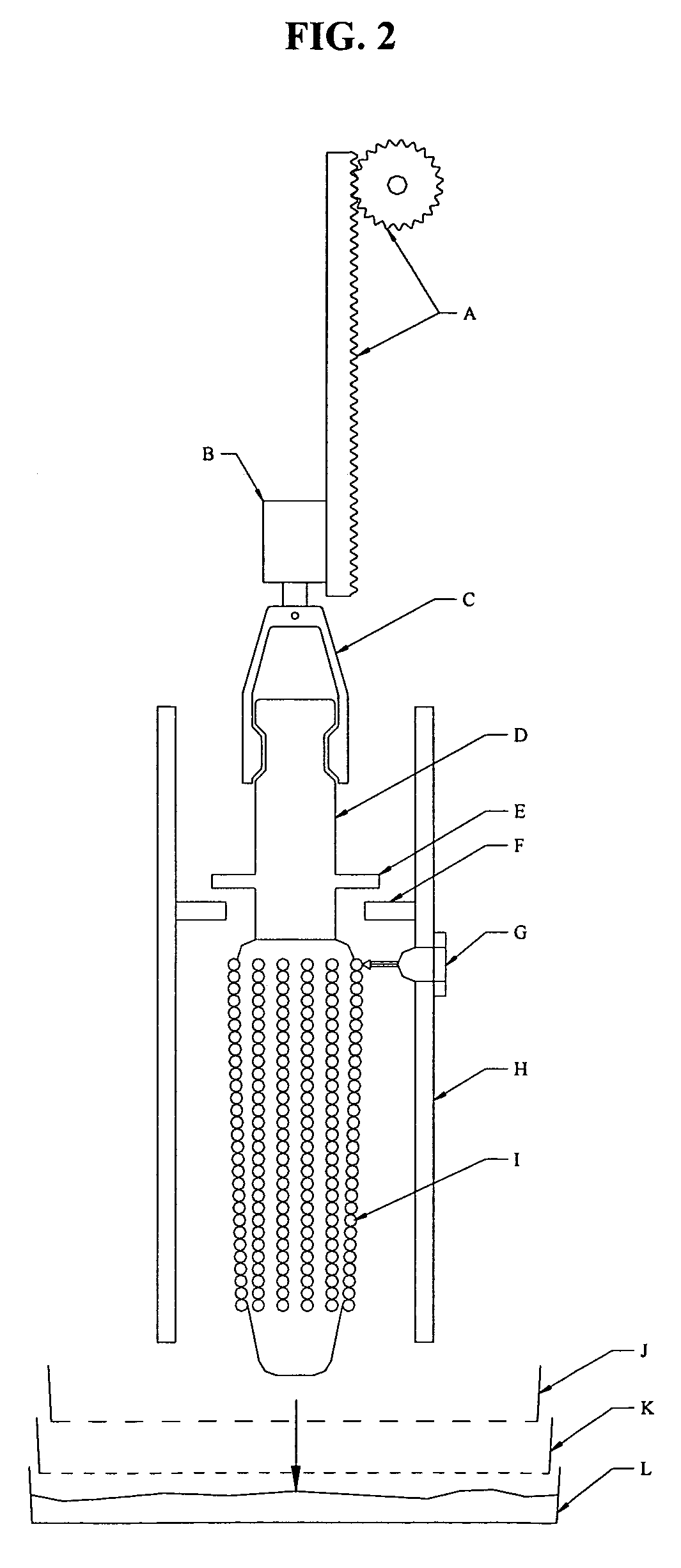
Method and apparatus for preparation of genetically transformable plant tissue
A process of mechanical separation of embryos from seeds for genetic transplantation employs counter-rotating cylinders together with one or more culling, hydration, separation, and viability testing steps to provide high-throughput of viable, transplantable tissue.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
LED array for illuminating cell well plates and automated rack system for handling the same
InactiveUS7160717B2Improve storage efficiencyReduce amountBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCells/wellPlant tissue
An assembly for promoting the growth of plant tissues that includes a plurality of plates each defining an array of wells wherein each of the wells contains a tissue sample. Support for the plates is provided by a rack having a plurality of vertically stacked shelves that may include one or more register depressions that urge the plates into predetermined positions. Light for the tissue samples is provided by a plurality of light-emitting diode arrays each mounted on a circuit board. Each circuit board is supported by a respective card edge connector of the rack so that the light-emitting diodes are in proximity to the plates supported on one of the shelves therebelow. Preferably, the light-emitting diode array corresponds to the well array supported in the registered position on the shelf therebelow so that each light-emitting diode is centered above a respective one of the wells.
Owner:BIOLEX THERAPEUTICS INC
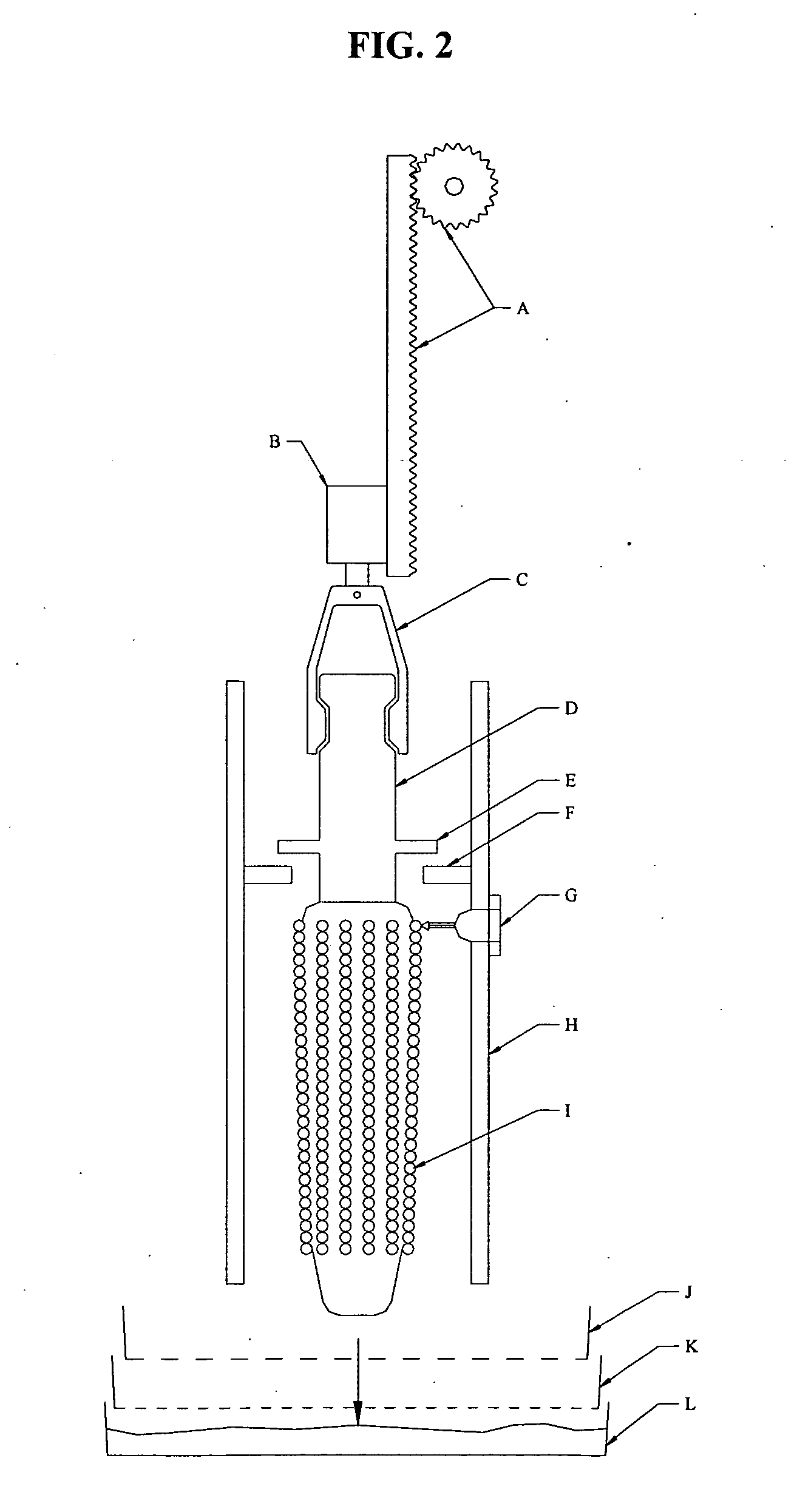
Method and apparatus for substantially isolating plant tissues
ActiveUS20050246786A1Improve reliabilityReduce harmOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationPlant tissueGMO Plants
The present invention discloses and claims methods and devices for the rapid mechanical isolation of monocot plant tissues suitable for transformation or tissue culture. The invention includes mechanical devices for substantially isolating target plant tissues for use as transformable explants, and propagation of transgenic plants and plant tissues.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for substantially isolating plant tissues
ActiveUS20090142837A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPlant tissueEmbryo
The present invention provides methods and devices for the rapid isolation of monocot plant embryos suitable for transformation or tissue culture. The invention includes mechanical devices for substantially isolating plant embryos for use as transformable explants. Media suitable for isolating plant embryos and methods for their preparation are also provided.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Methods for stable transformation of plants
InactiveUS6858777B2Improve conversion efficiencyImprove transformation efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationAxillary budNicotiana tabacum
Multiple shoot structures are induced from plant tissues (e.g., shoot apices or axillary buds on an artificial medium) to produce multiple shoot cultures. These multi-shoot cultures are then transformed by known transformation methods. Plants are subsequently regenerated from the transformed cells. Crops that may be efficiently transformed by this method include plants normally recalcitrant to transformation such as sugar beet, sunflower, soybean, cotton, tobacco, tomato, peanuts, melons, watermelon, squash, Brassica, and pepper.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
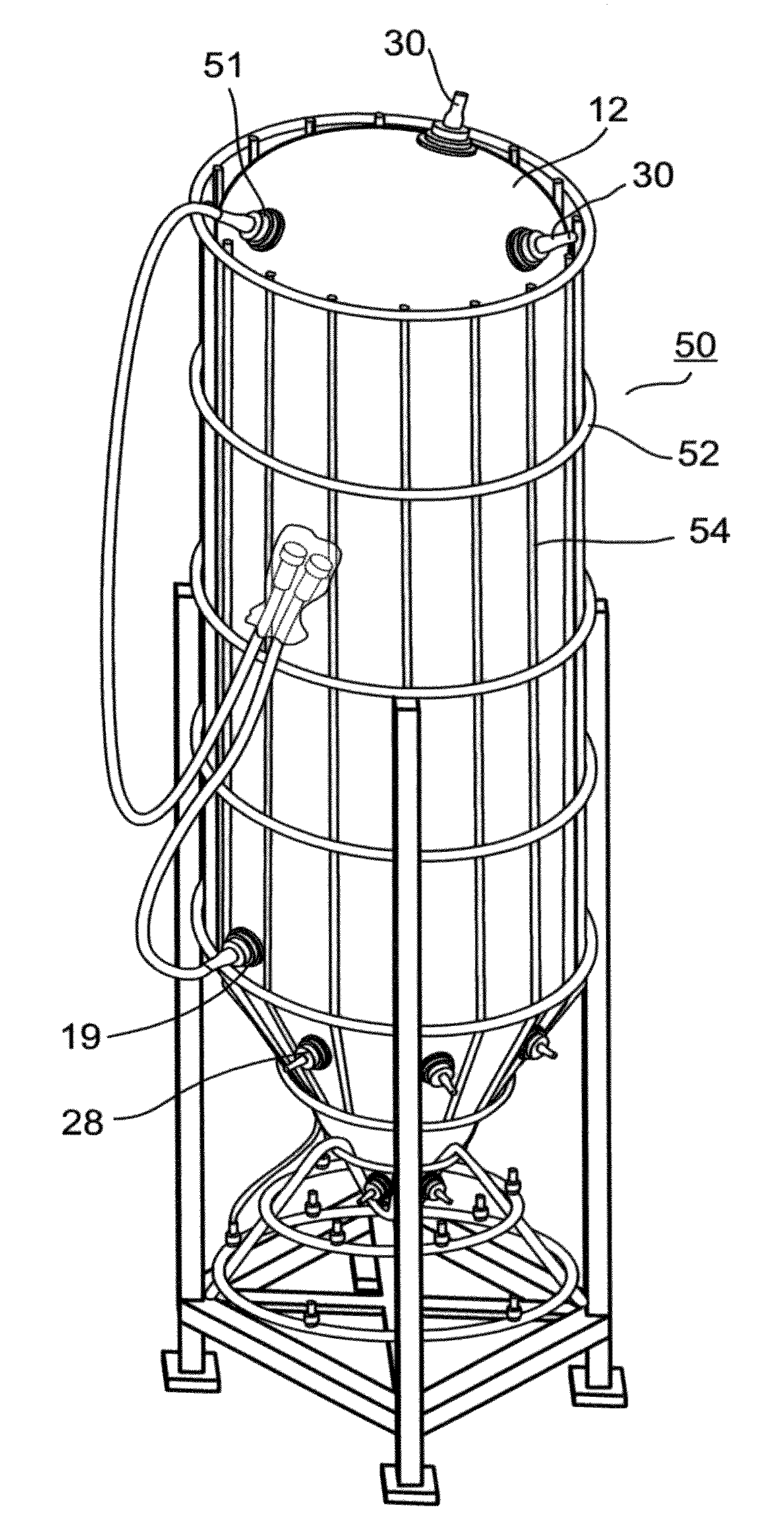
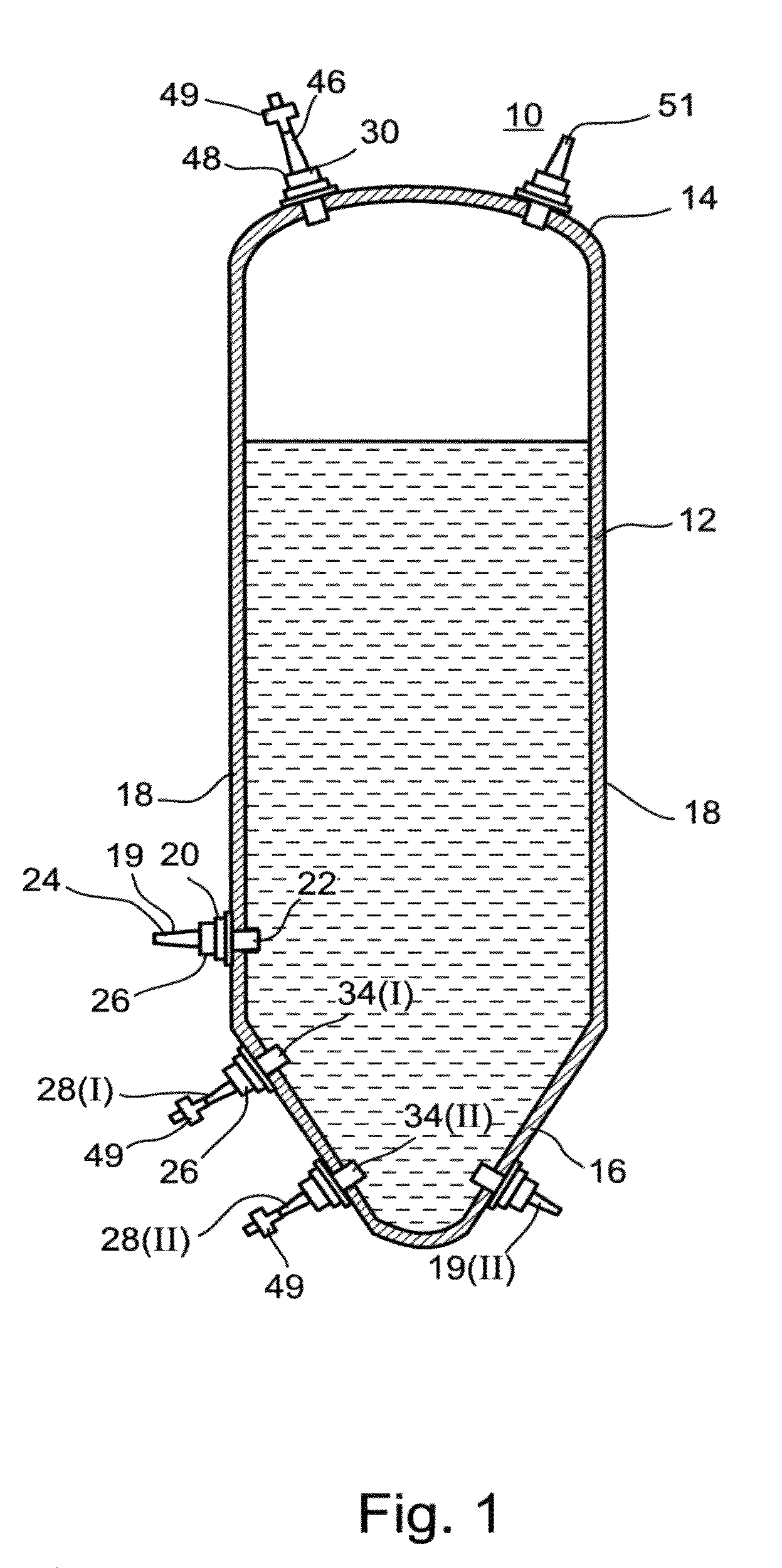
Large scale disposable bioreactor
ActiveUS20100112700A1Easy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPlant tissuePlant cell
A reusable, disposable device for culturing plant tissues or cells including a non-rigid container having dimensions and gas exchange ports designed for maintaining oxygen saturation and shear forces suitable for culturing plant tissue or cells in 400 liters or more of culture medium is provided. Also provided are methods for producing a catalytically active human recombinant protein in a plant cell, using the disposable device of one of the embodiments of the instant specification.
Owner:PROTALIX
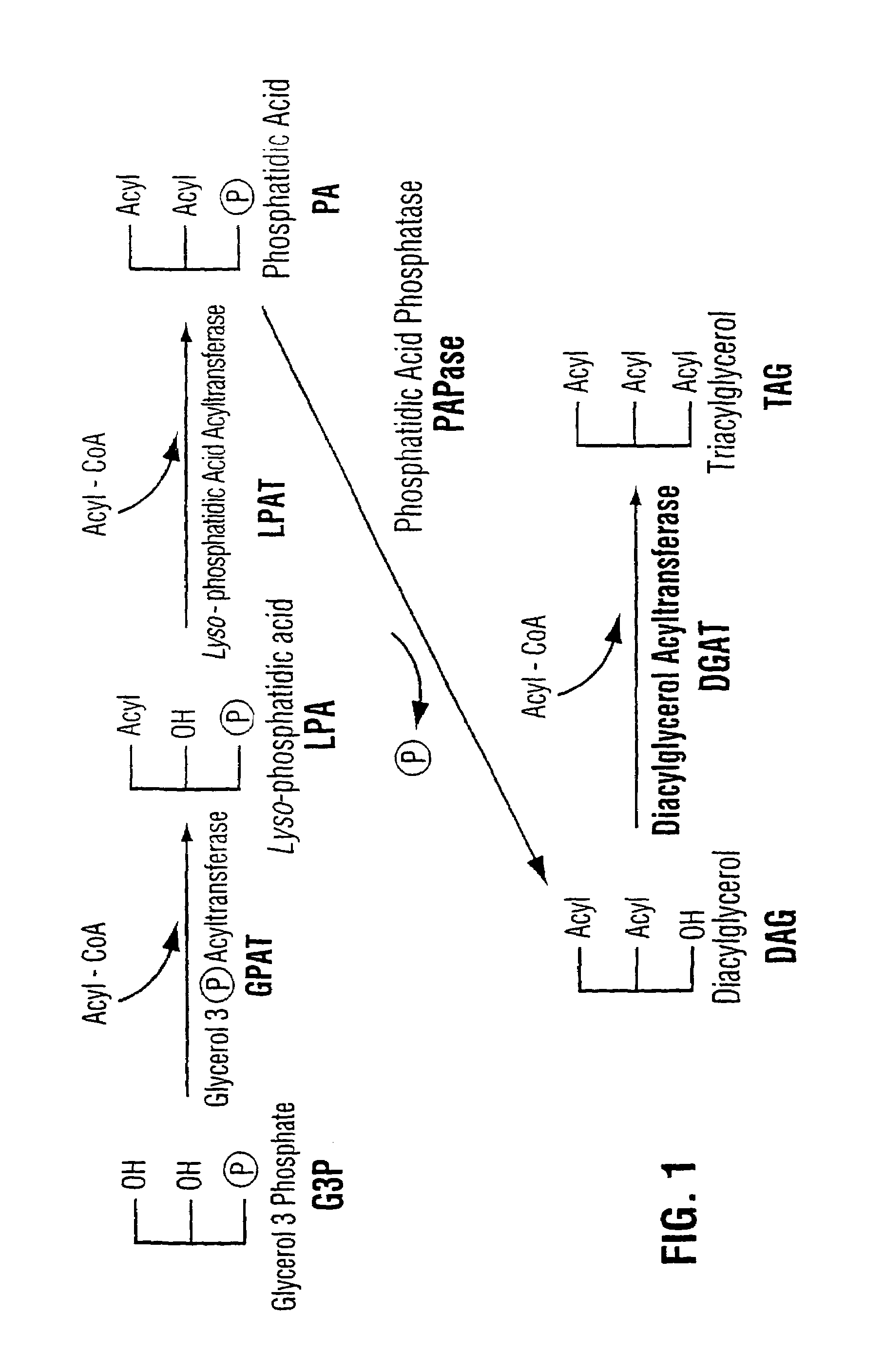
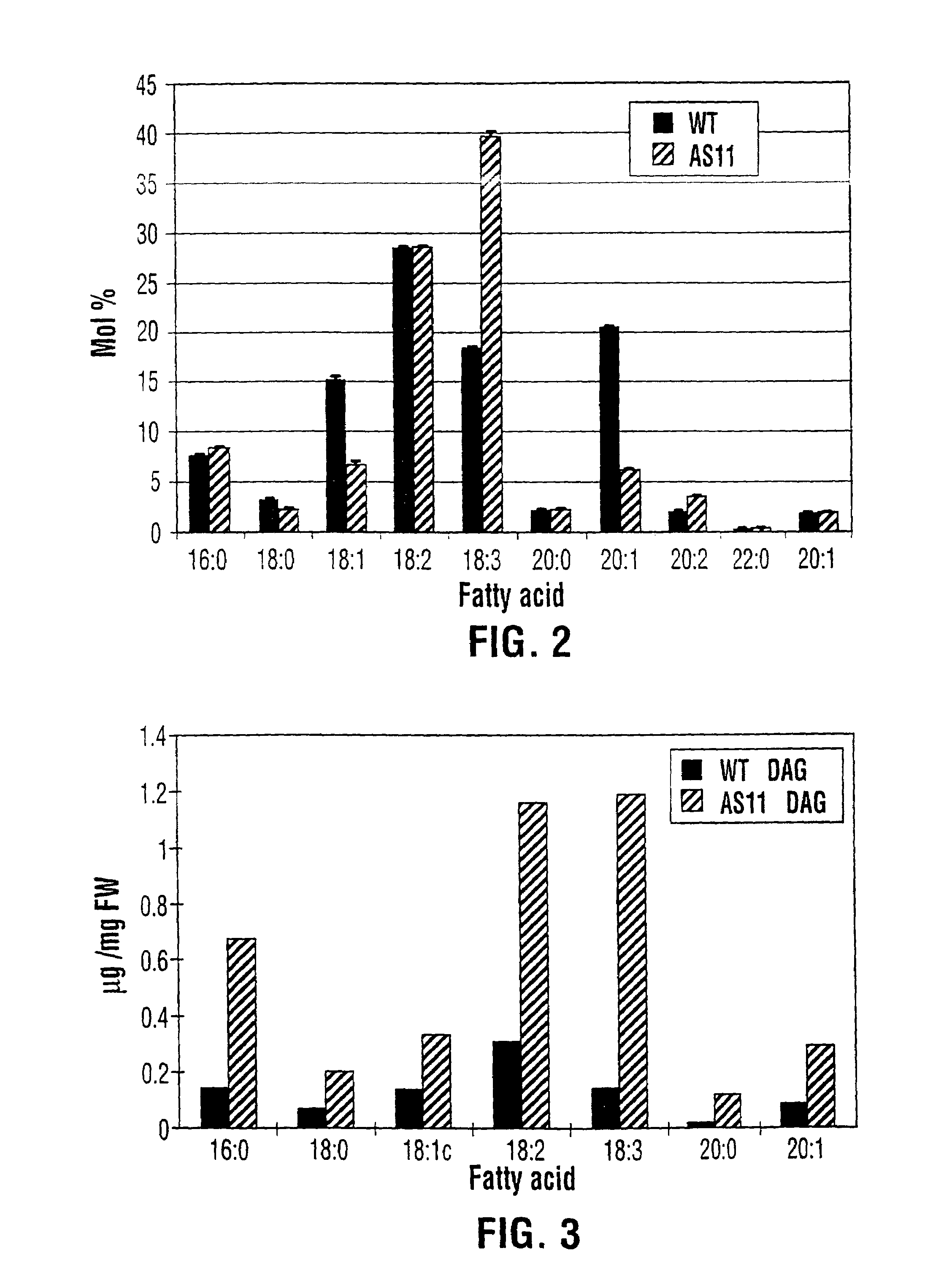
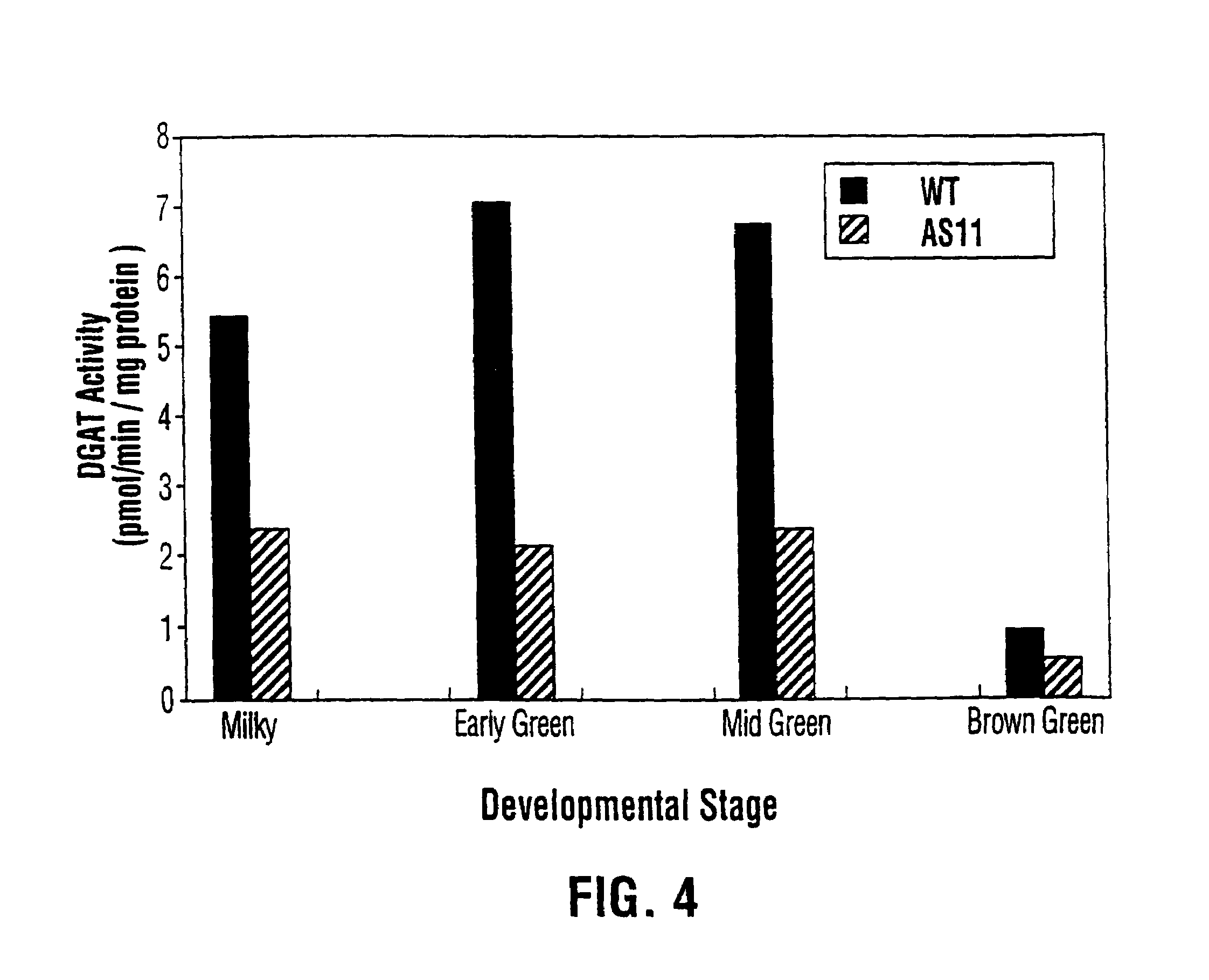
Diacylglycerol acyltransferase gene from plants
InactiveUS7015373B1Reduced DGAT activityReduce rateSugar derivativesTransferasesBrassicaceaePlanting seed
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Methods and compositions for introduction of exogenous dsrna into plant cells
This invention provides a method to silence an endogenous target gene expression in plants by applying a specific dsRNA onto the exterior surface of a plant. Application, such as by spraying or brushing a plant with dsRNA is done without wounding the plant tissue and cells such as by mechanical-type wounding, particle bombardment or mechanical infection with viral vectors. The present invention enables the regulation of gene expression in plants. In some embodiments of the invention, the dsRNA is directed to an essential gene of a plant pathogen or pest, whereby the pathogen and / or pest damage is controlled, resulting in desired agronomic performance.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Insecticidal proteins and methods for their use
ActiveUS20160186204A1Improve pest resistanceImprove toleranceBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBiotechnologyOrder Lepidoptera
Compositions and methods for controlling pests are provided. The methods involve transforming organisms with a nucleic acid sequence encoding an insecticidal protein. In particular, the nucleic acid sequences are useful for preparing plants and microorganisms that possess insecticidal activity. Thus, transformed bacteria, plants, plant cells, plant tissues and seeds are provided. Compositions are insecticidal nucleic acids and proteins of bacterial species. The sequences find use in the construction of expression vectors for subsequent transformation into organisms of interest including plants, as probes for the isolation of other homologous (or partially homologous) genes. The pesticidal proteins find use in controlling, inhibiting growth or killing Lepidopteran, Coleopteran, Dipteran, fungal, Hemipteran and nematode pest populations and for producing compositions with insecticidal activity.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC +1
Method and apparatus for substantially isolating plant tissues
The present invention provides methods and devices for the rapid isolation of monocot plant embryos suitable for transformation or tissue culture. The invention includes mechanical devices for substantially isolating plant embryos for use as transformable explants. Media suitable for isolating plant embryos and methods for their preparation are also provided.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Compositions and methods for producing fermentable carbohydrates
InactiveUS20110201059A1Increasing total locked carbohydrate contentGenetic engineeringFermentationMicroorganismYeast
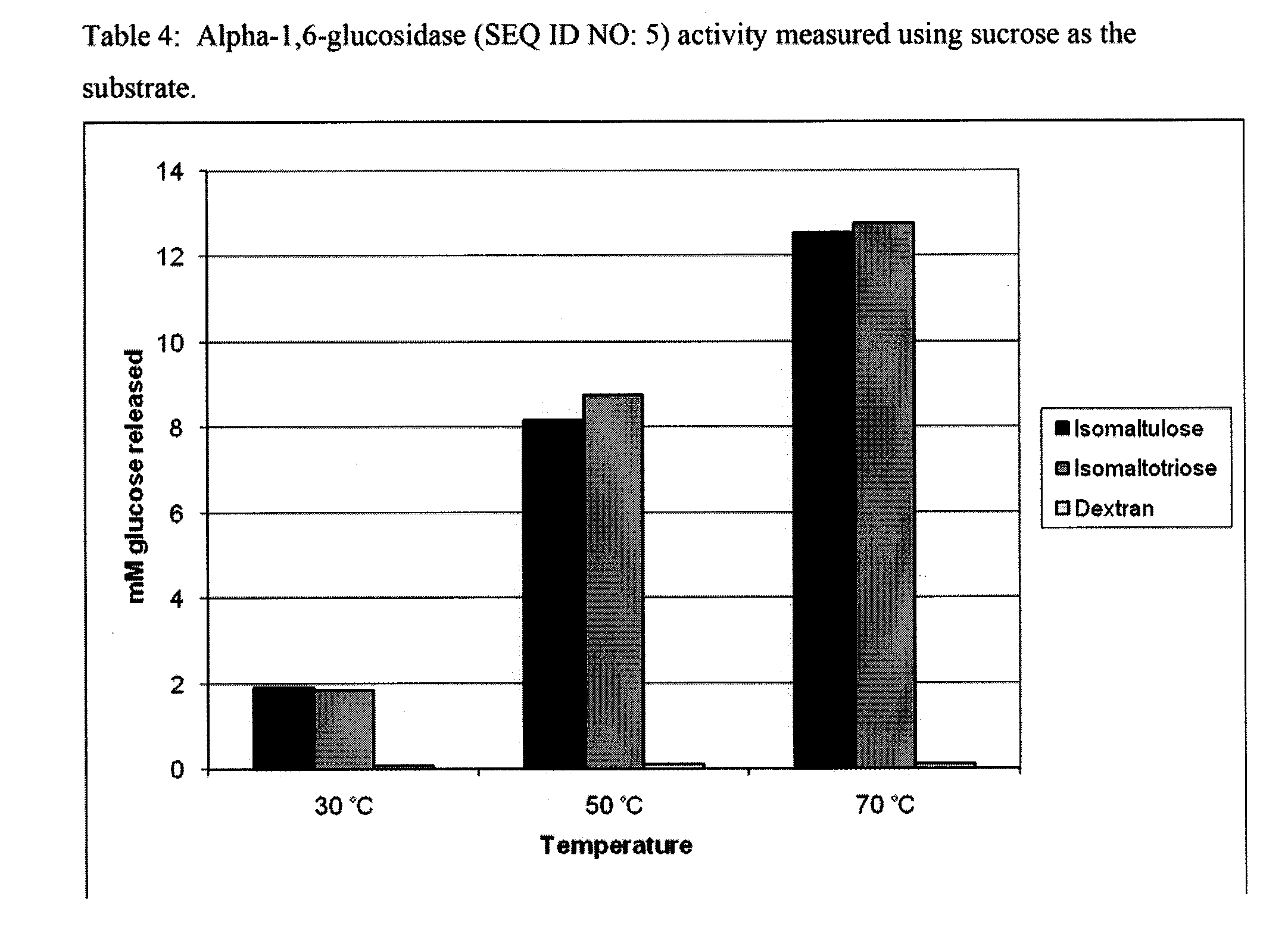
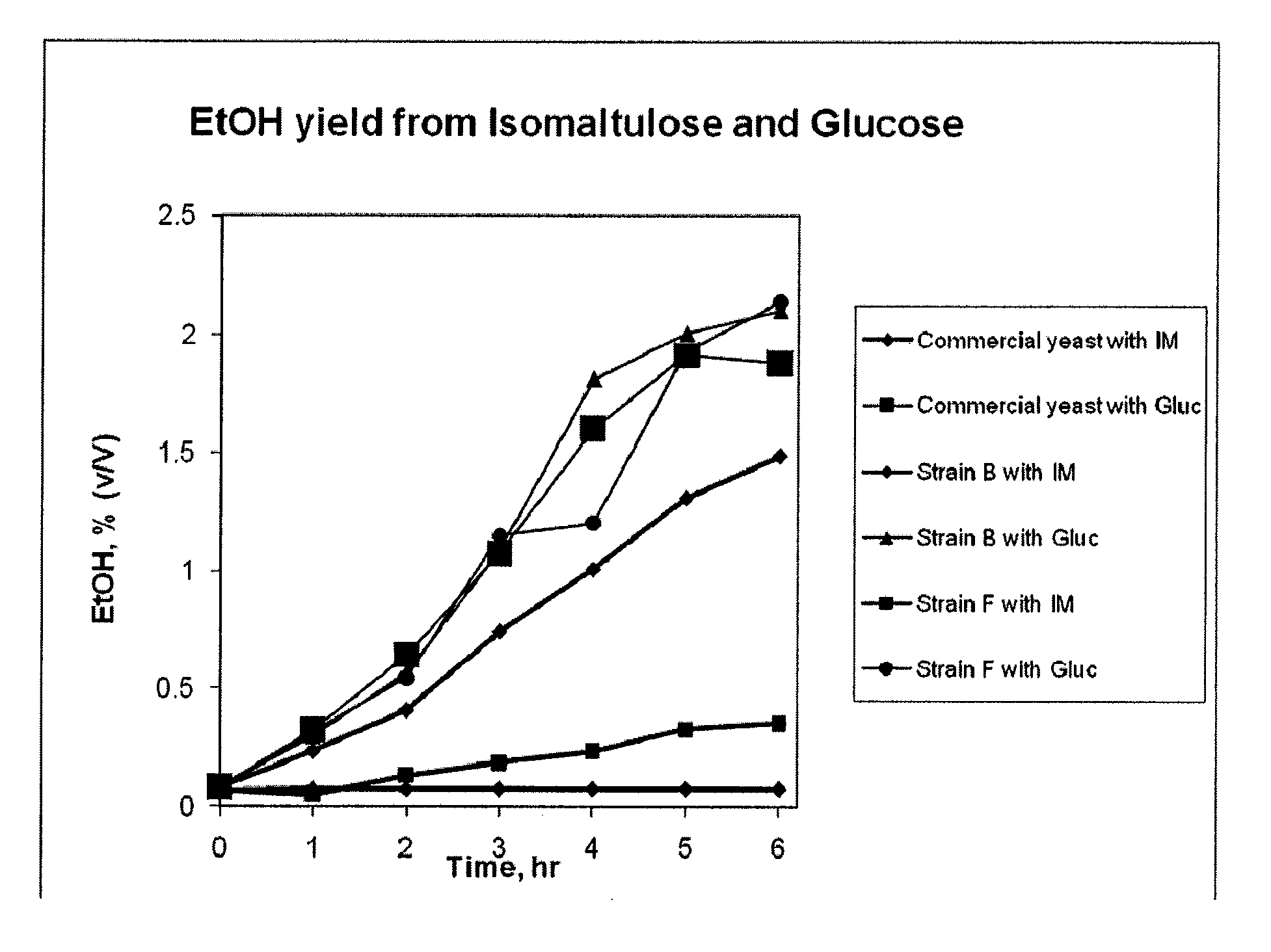
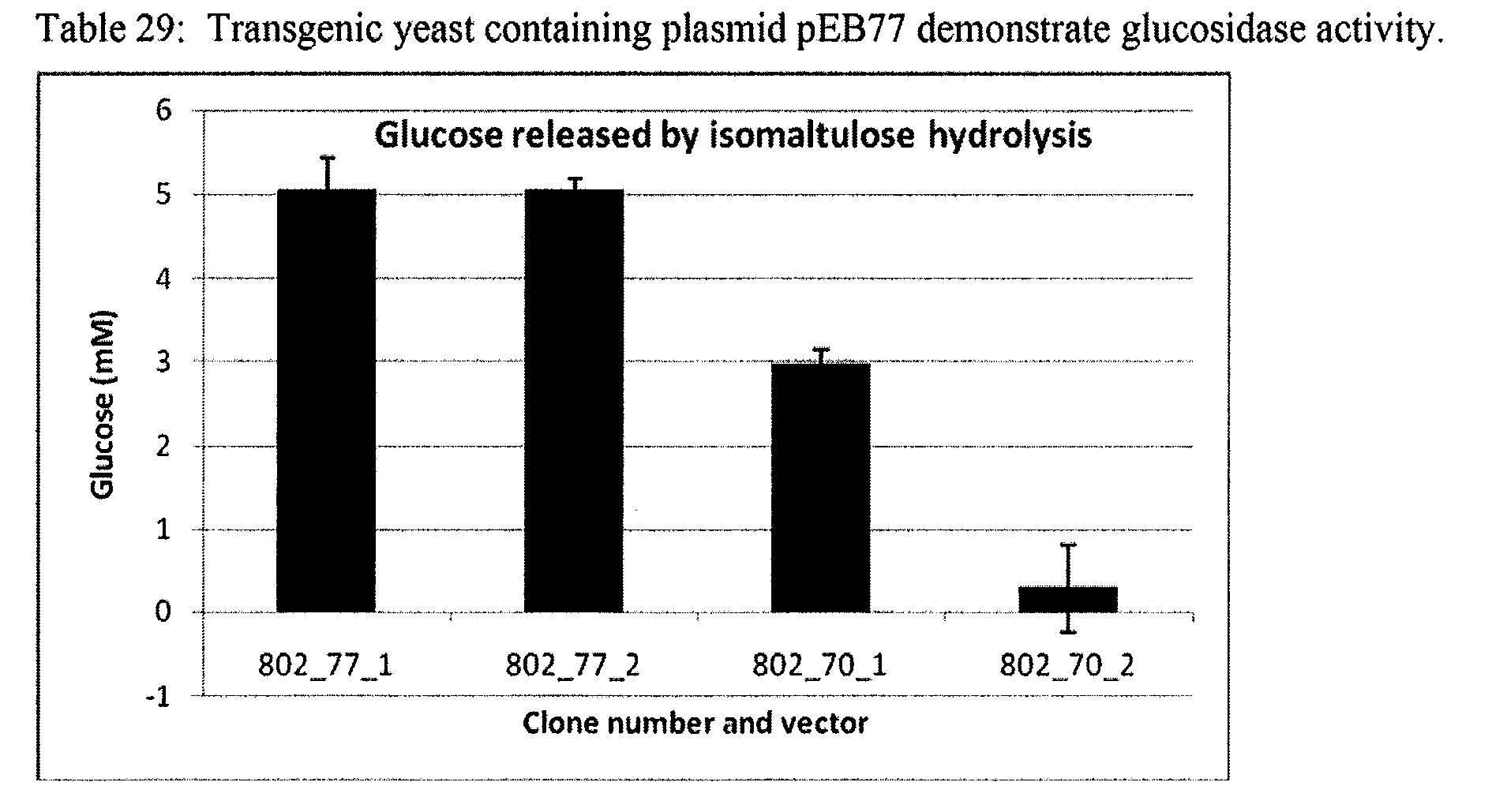
Provided herein are methods for producing fermentable sugar obtained from a plant tissue. The methods include providing transgenic plant material comprising one or more locked carbohydrates and contacting plant material with an enzyme capable of converting the locked carbohydrate into a fermentable sugar. The methods are useful for providing sugar or sugar pre-cursors for several industrial purposes including ethanol production. The invention also encompasses plants and plant parts that produce a lock enzyme to yield a locked carbohydrate, with the consequence of accumulating the locked carbohydrate in the plant. The invention also encompasses providing a key enzyme able to convert locked carbohydrates to fermentable sugars. Key enzymes can be provided by transgenic plants or plant parts, transgenic microbes, transgenic yeast, microbes or yeast.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com