Patents
Literature
858 results about "Tissue surface" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
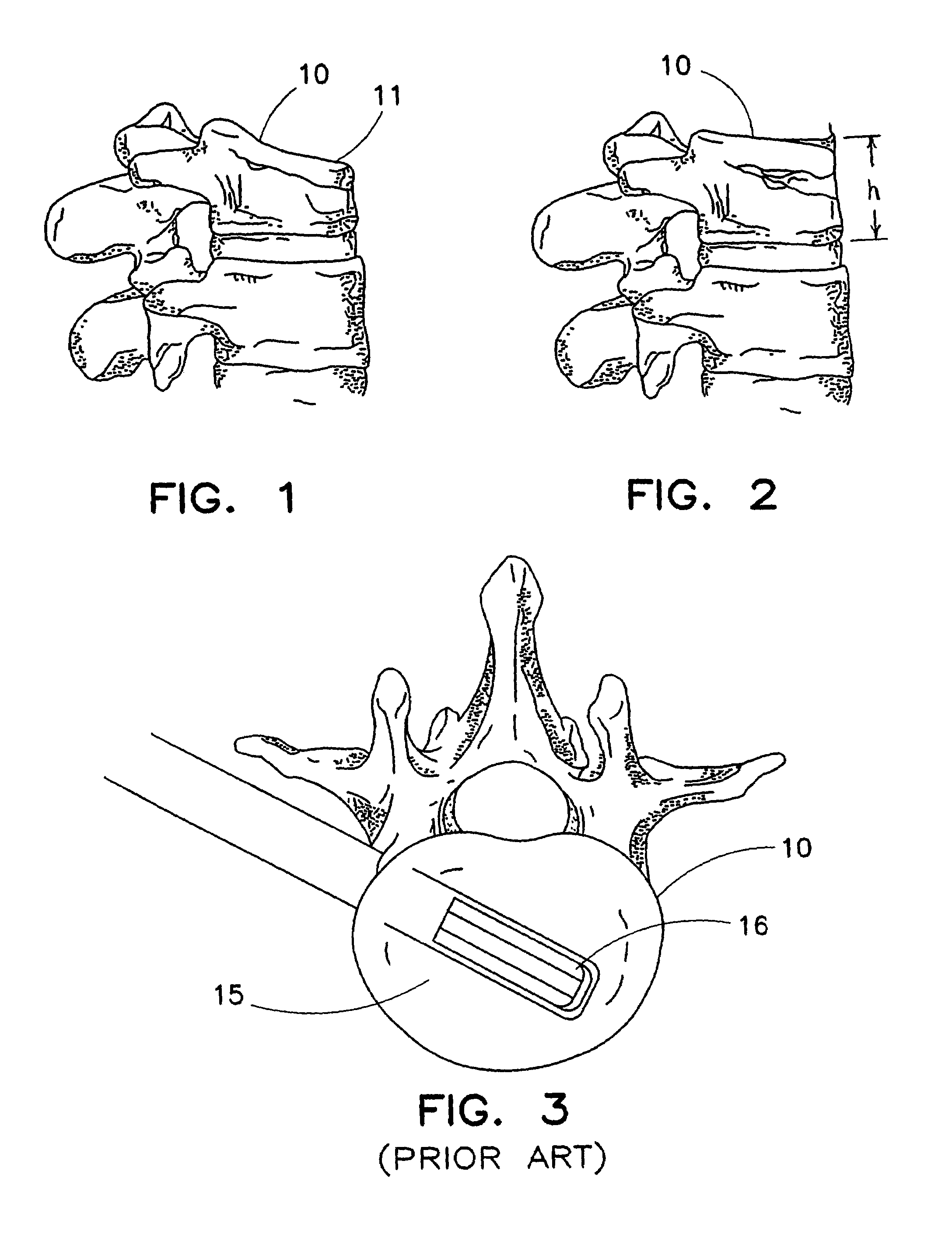
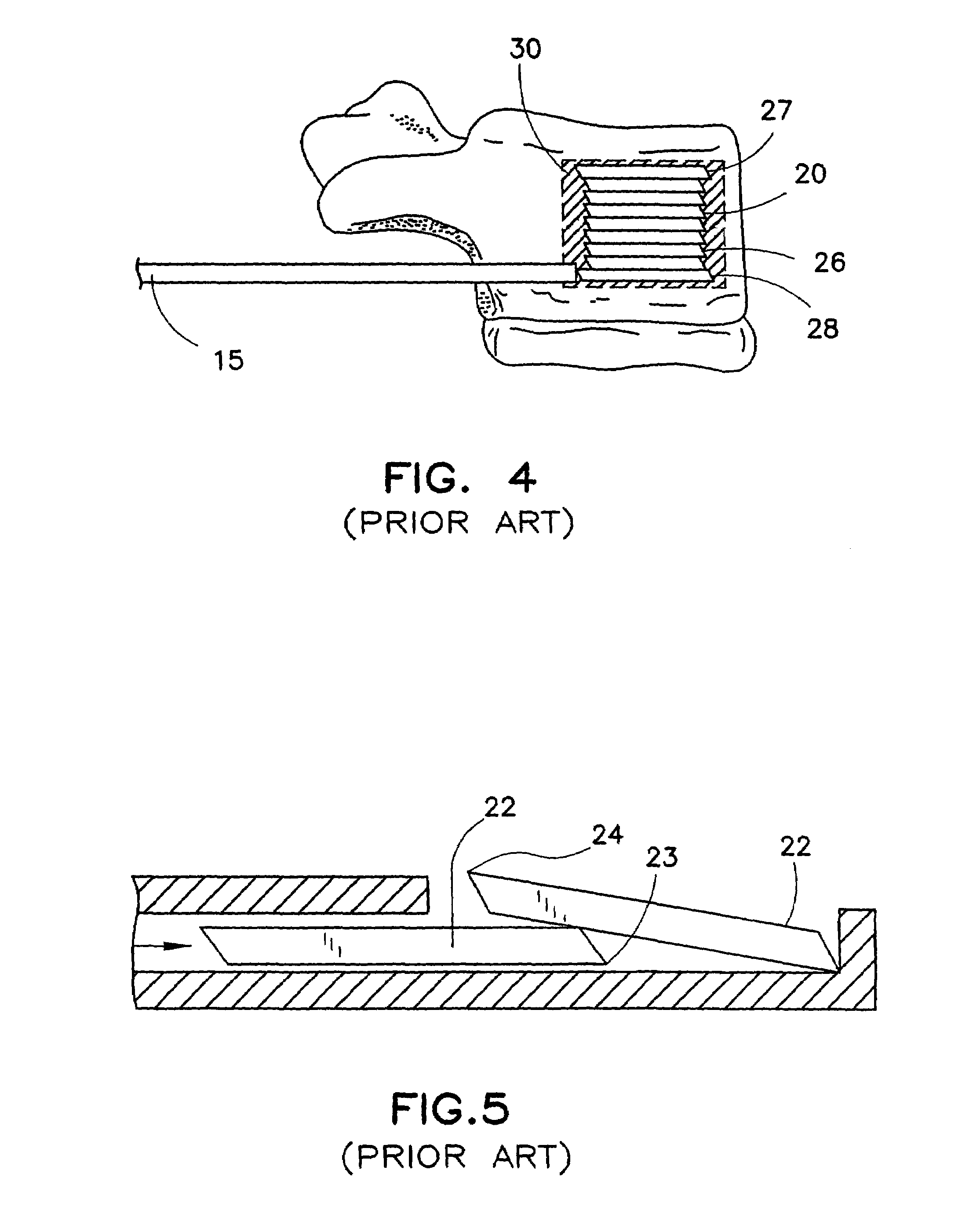
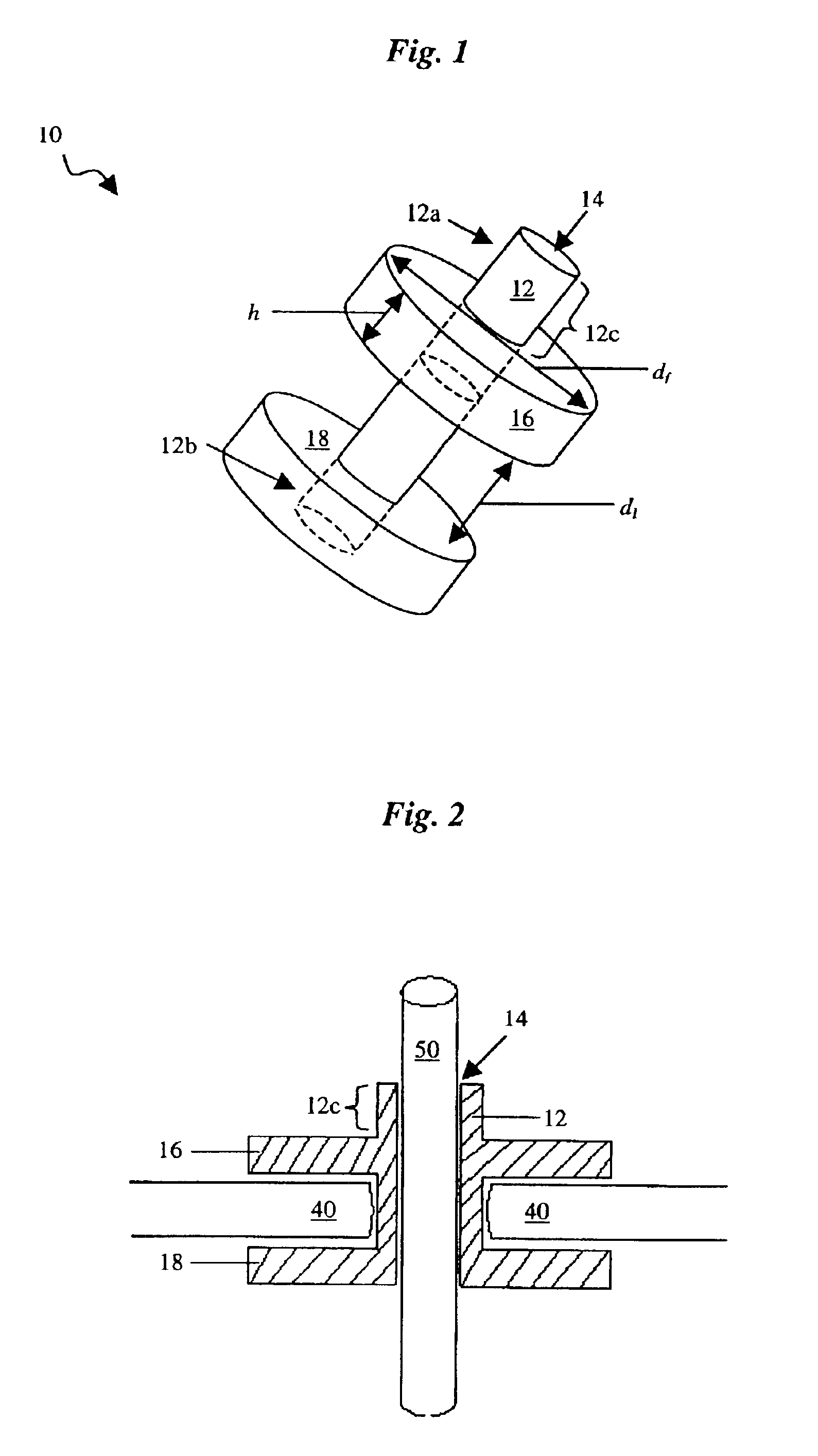
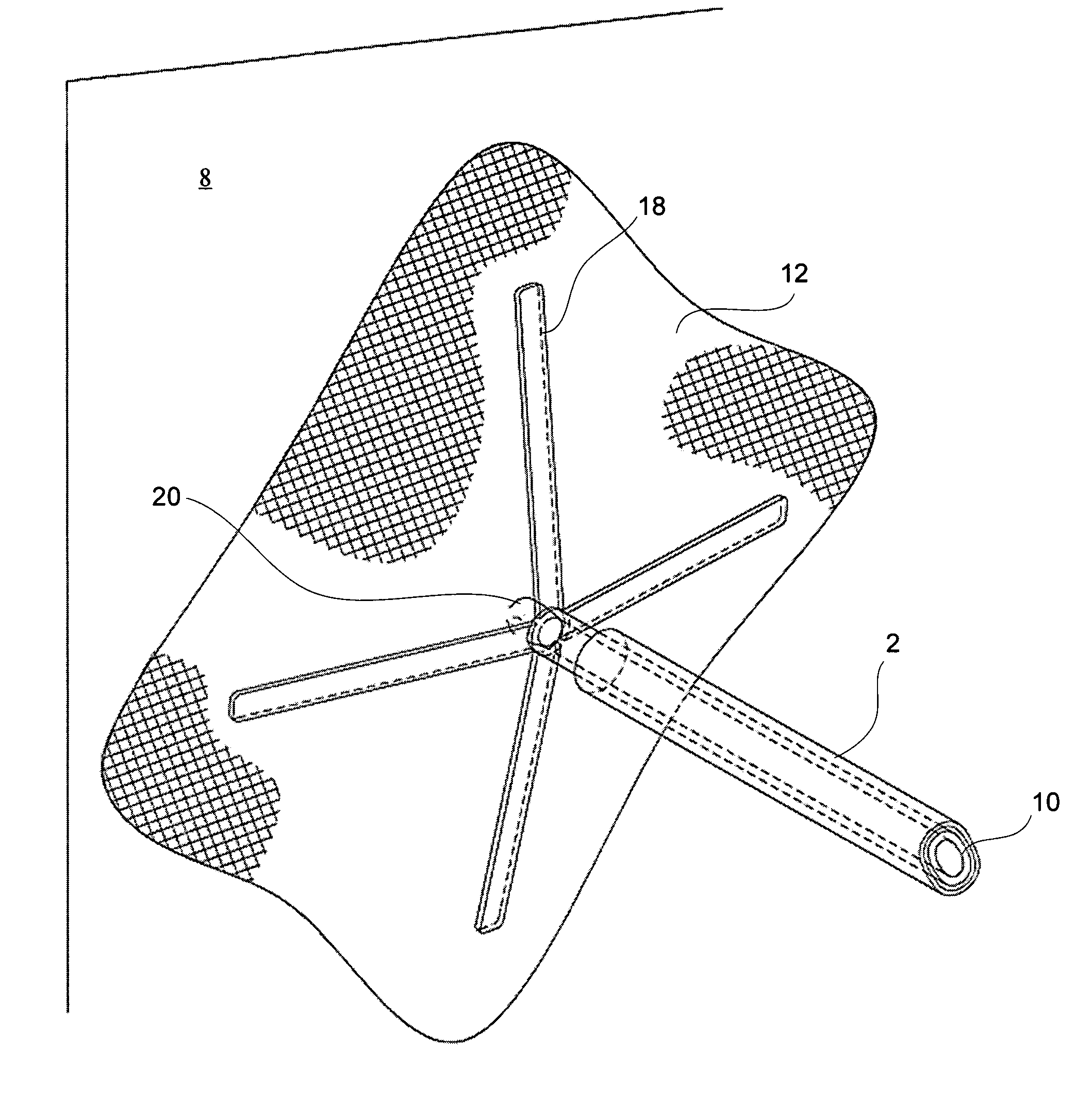
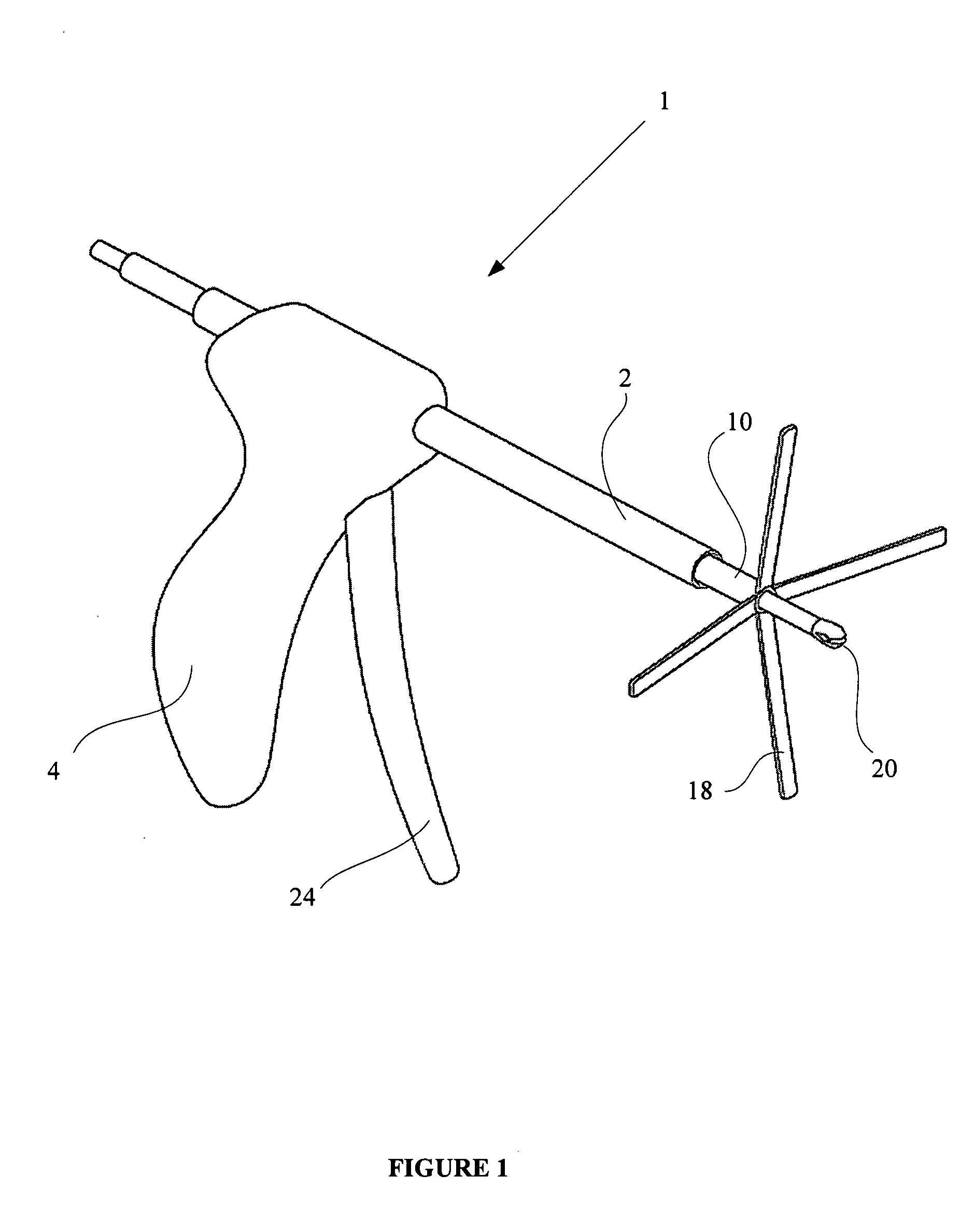
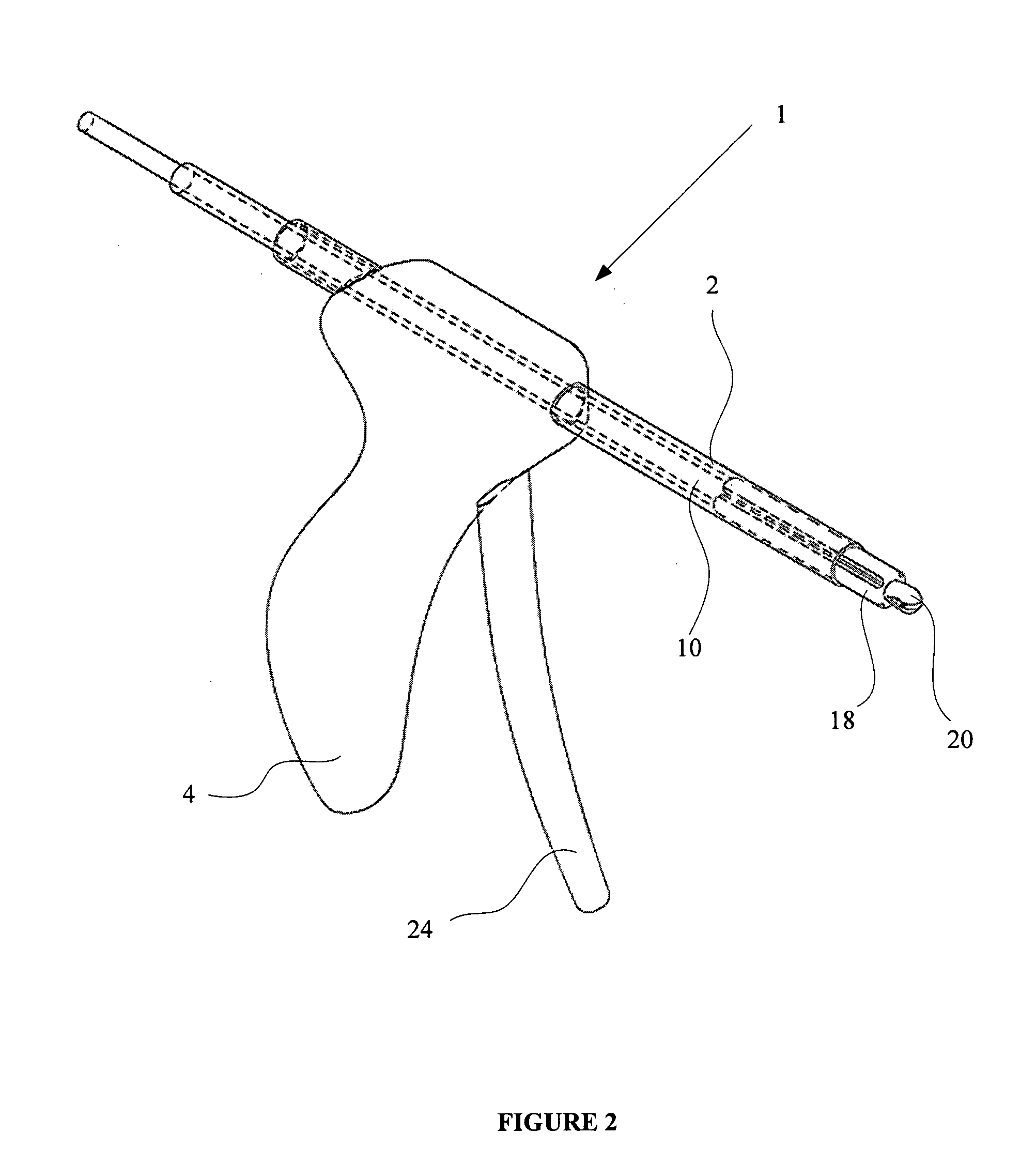
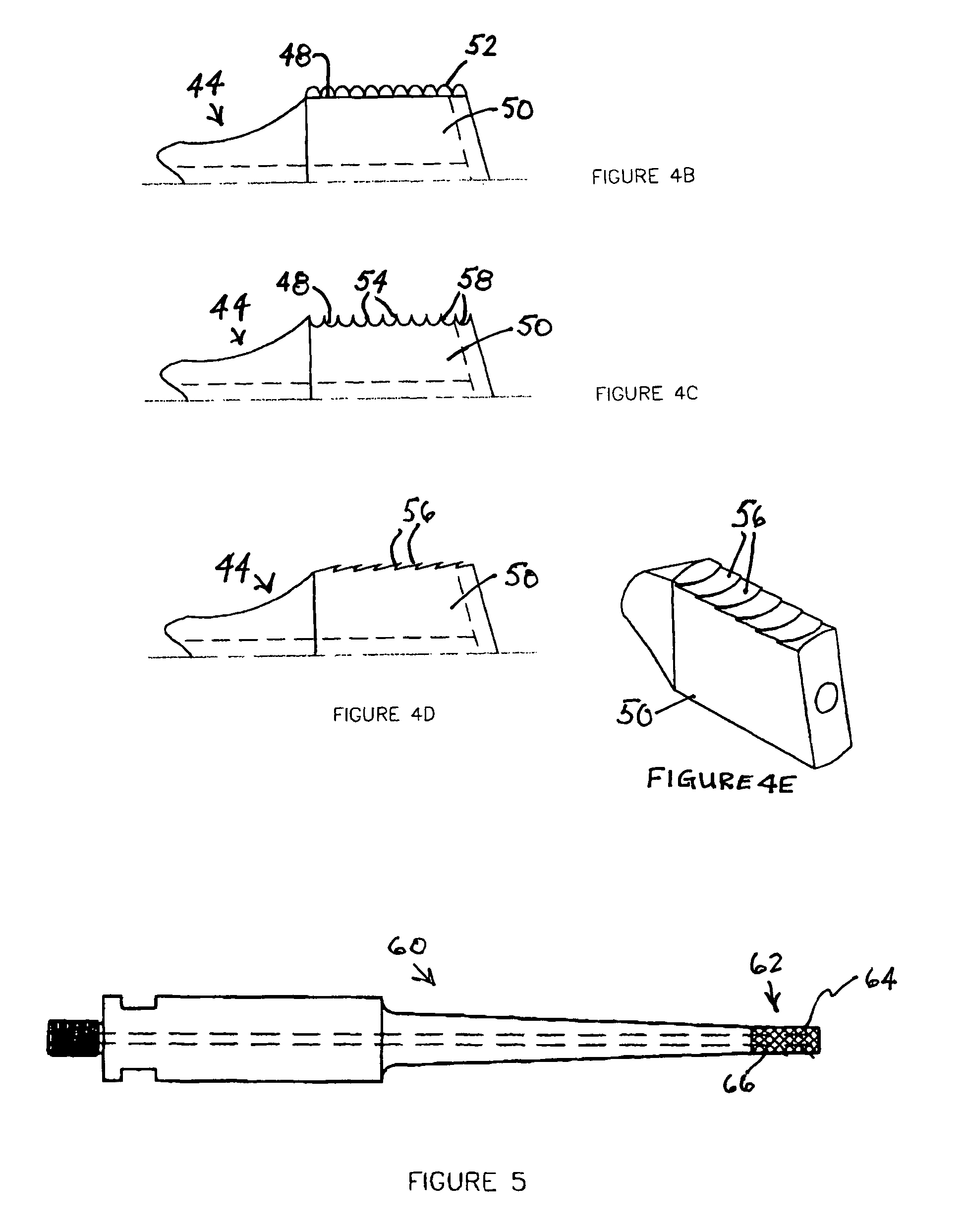
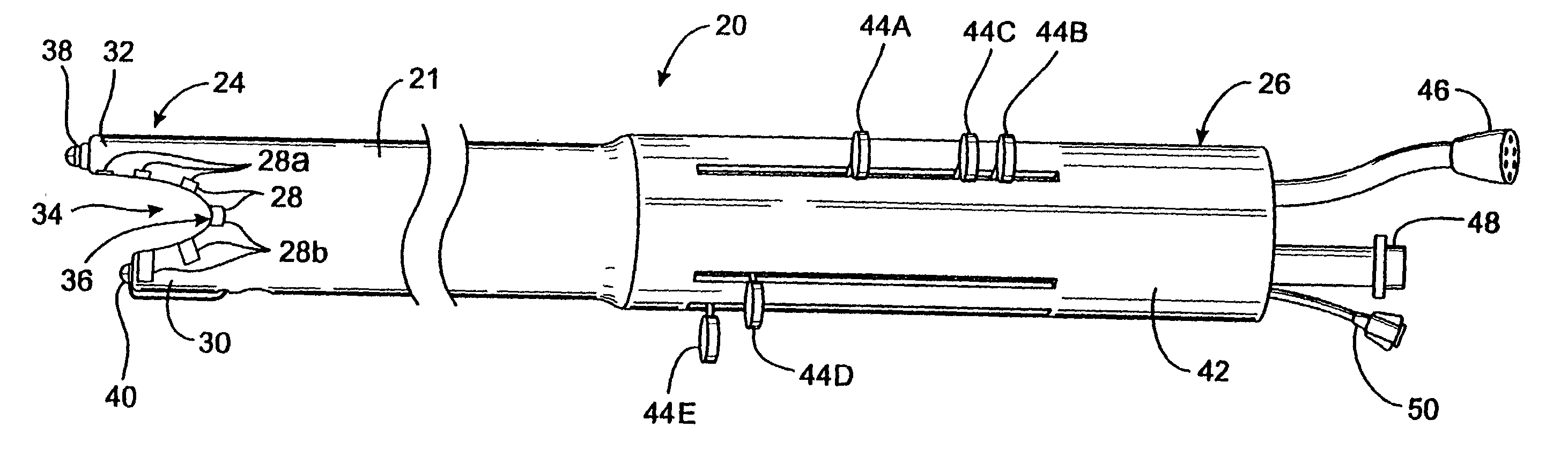
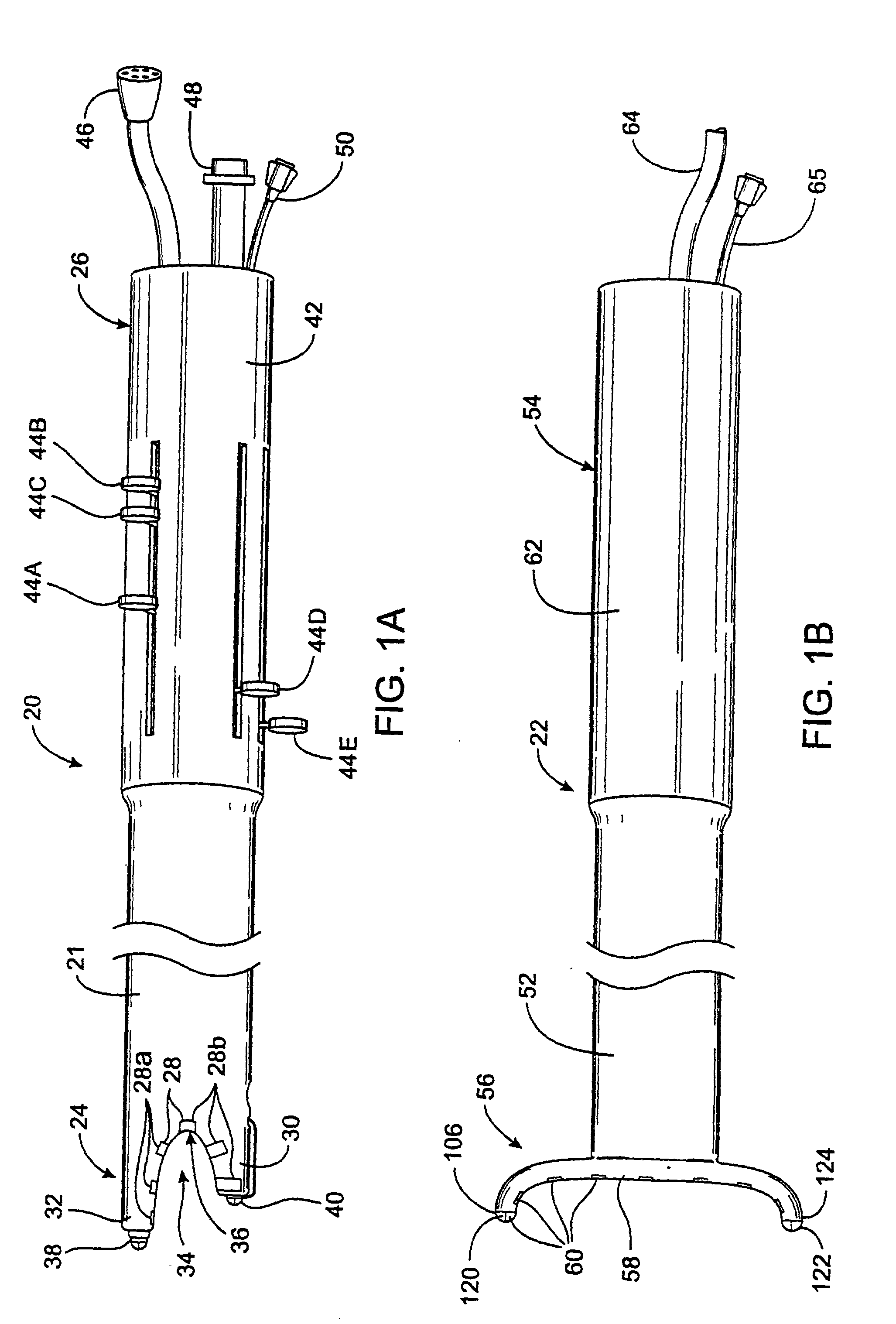
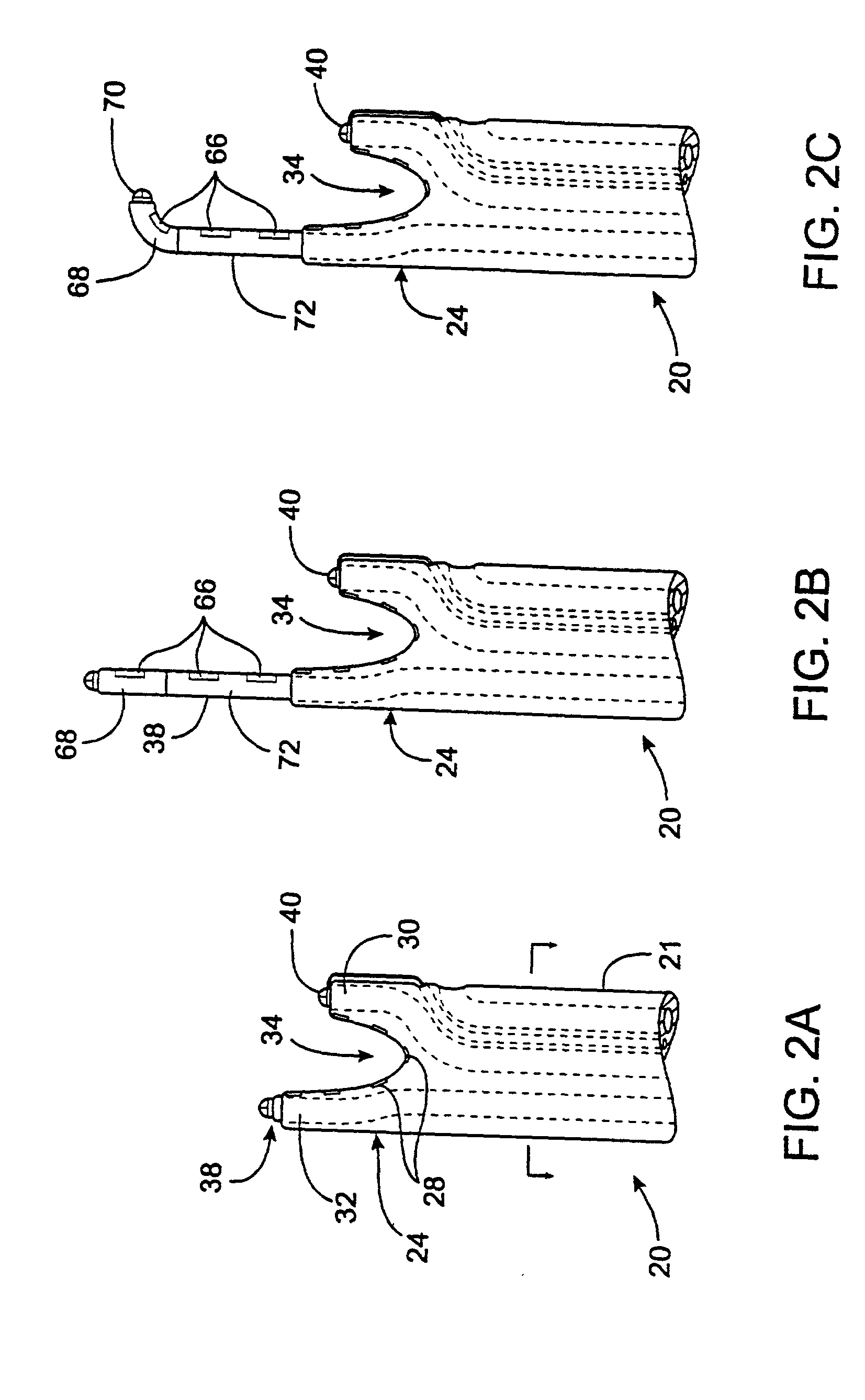
Tissue fastening devices and processes that promote tissue adhesion
ActiveUS8241308B2Improve adhesionOptimize allocationStaplesNailsEndoscopic ProcedureEndoscopic surgery
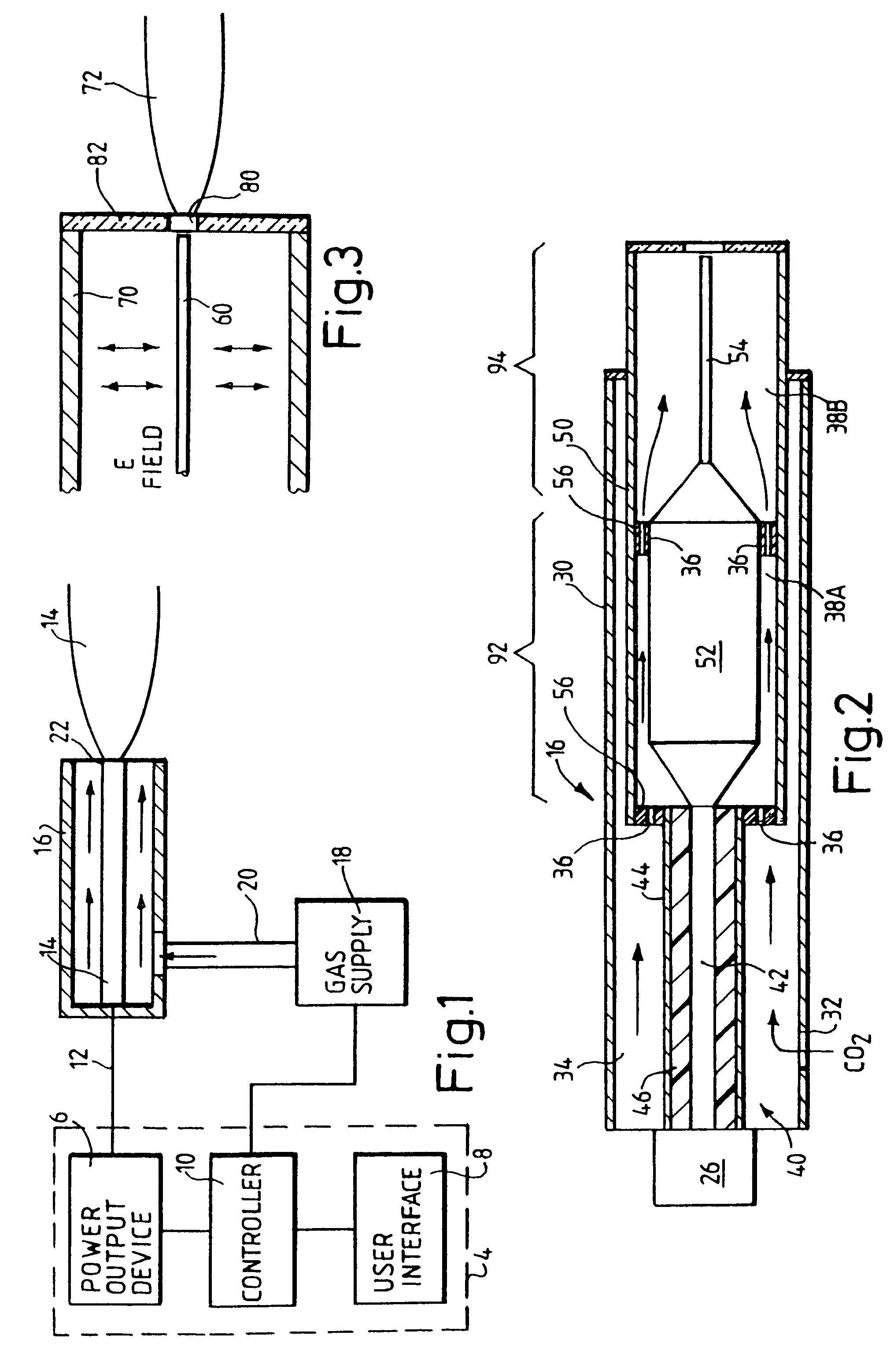
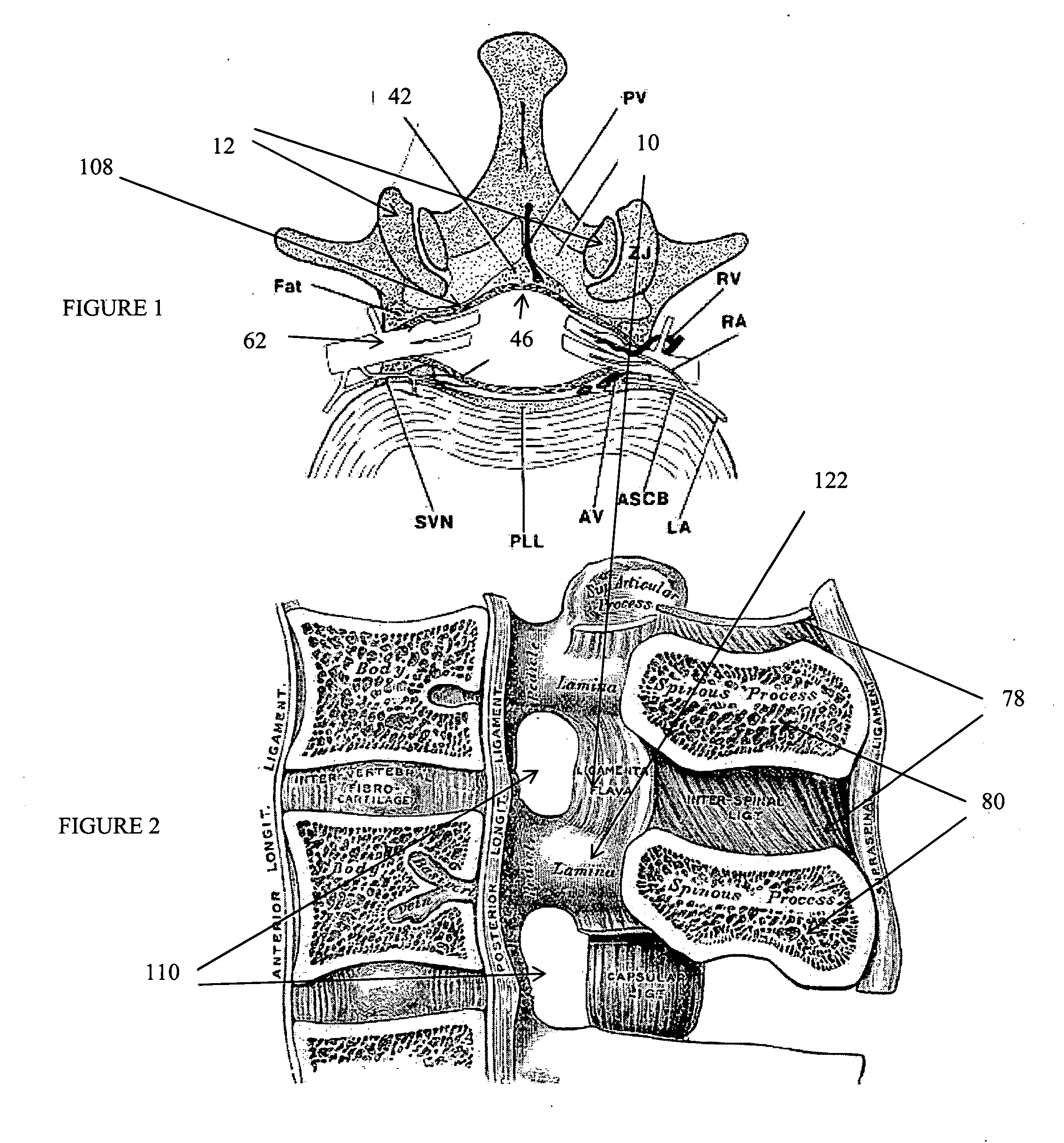
The invention in certain aspects relates to a surgical fastener for fastening tissue segments having tissue surfaces. The fastener includes a first fastener member having a base and a piercing element connected to the base for piercing the tissue segments to be fastened, a second fastener member having an opening for receiving and retaining the piercing element of the first fastener member such that the tissue segments to be fastened are retained between the first and second fastening members, and means for promoting adhesion between the tissue surfaces. The invention also relates to related methods and devices for promoting adhesion of tissue segments and preventing fastener migration, especially in an endoscopic procedure for the treatment of GERD.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Tissue resurfacing
InactiveUS7335199B2Easy to getRapid treatment at the tissue surfaceInstrument handpiecesSurgical instruments for heatingSkin treatmentsSkin surface
Owner:ENERGIST
Tissue fastening devices and processes that promote tissue adhesion
The invention in certain aspects relates to a surgical fastener for fastening tissue segments having tissue surfaces. The fastener includes a first fastener member having a base and a piercing element connected to the base for piercing the tissue segments to be fastened, a second fastener member having an opening for receiving and retaining the piercing element of the first fastener member such that the tissue segments to be fastened are retained between the first and second fastening members, and means for promoting adhesion between the tissue surfaces. The invention also relates to related methods and devices for promoting adhesion of tissue segments and preventing fastener migration, especially in an endoscopic procedure for the treatment of GERD.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
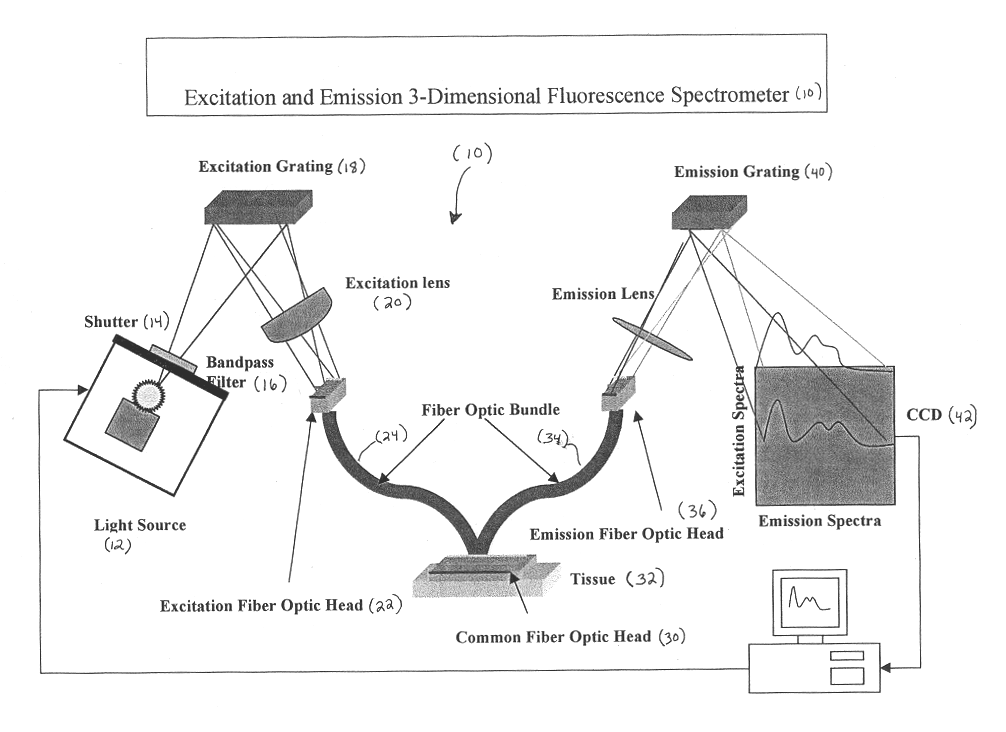
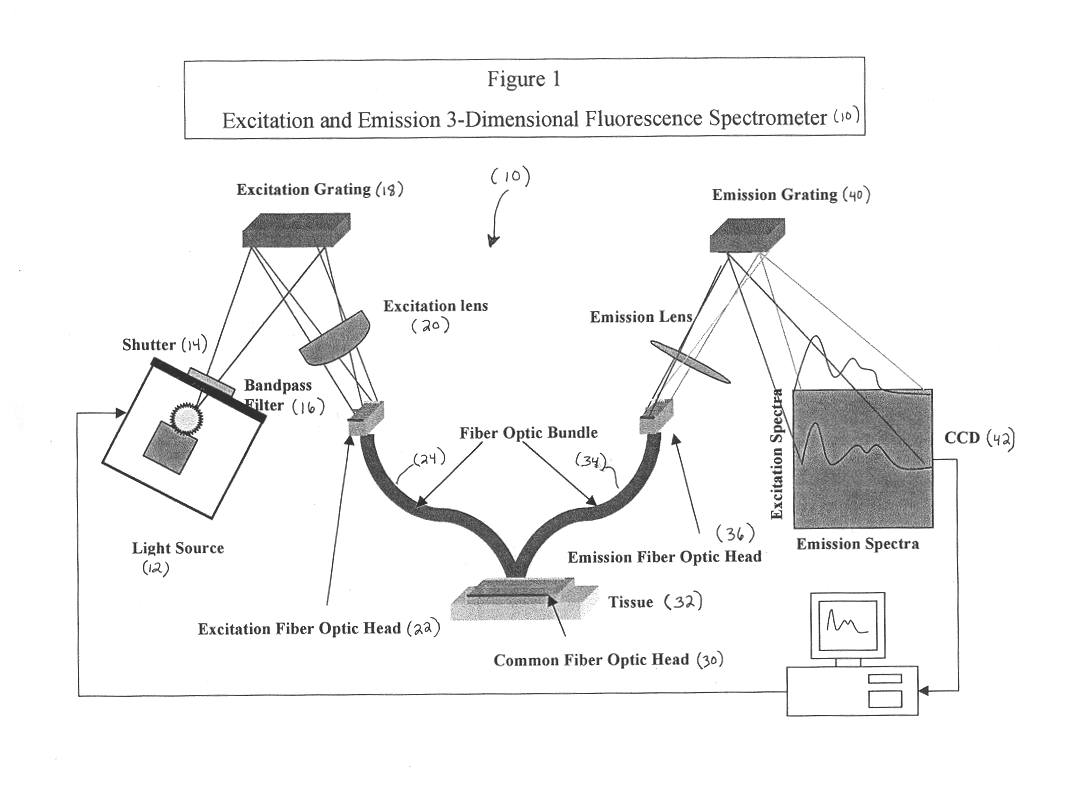
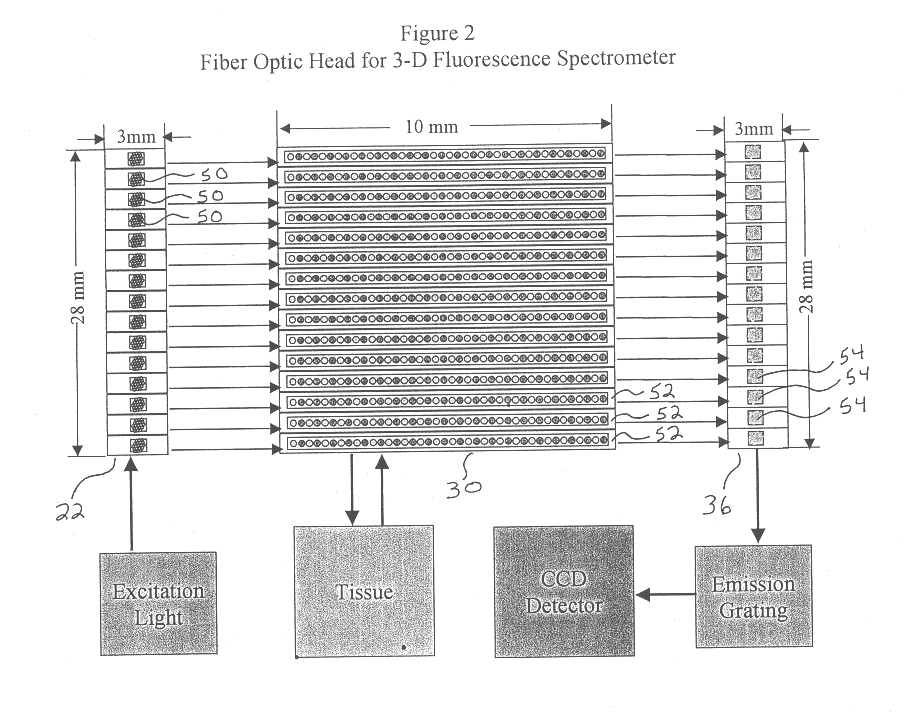
Generation of spatially-averaged excitation-emission map in heterogeneous tissue
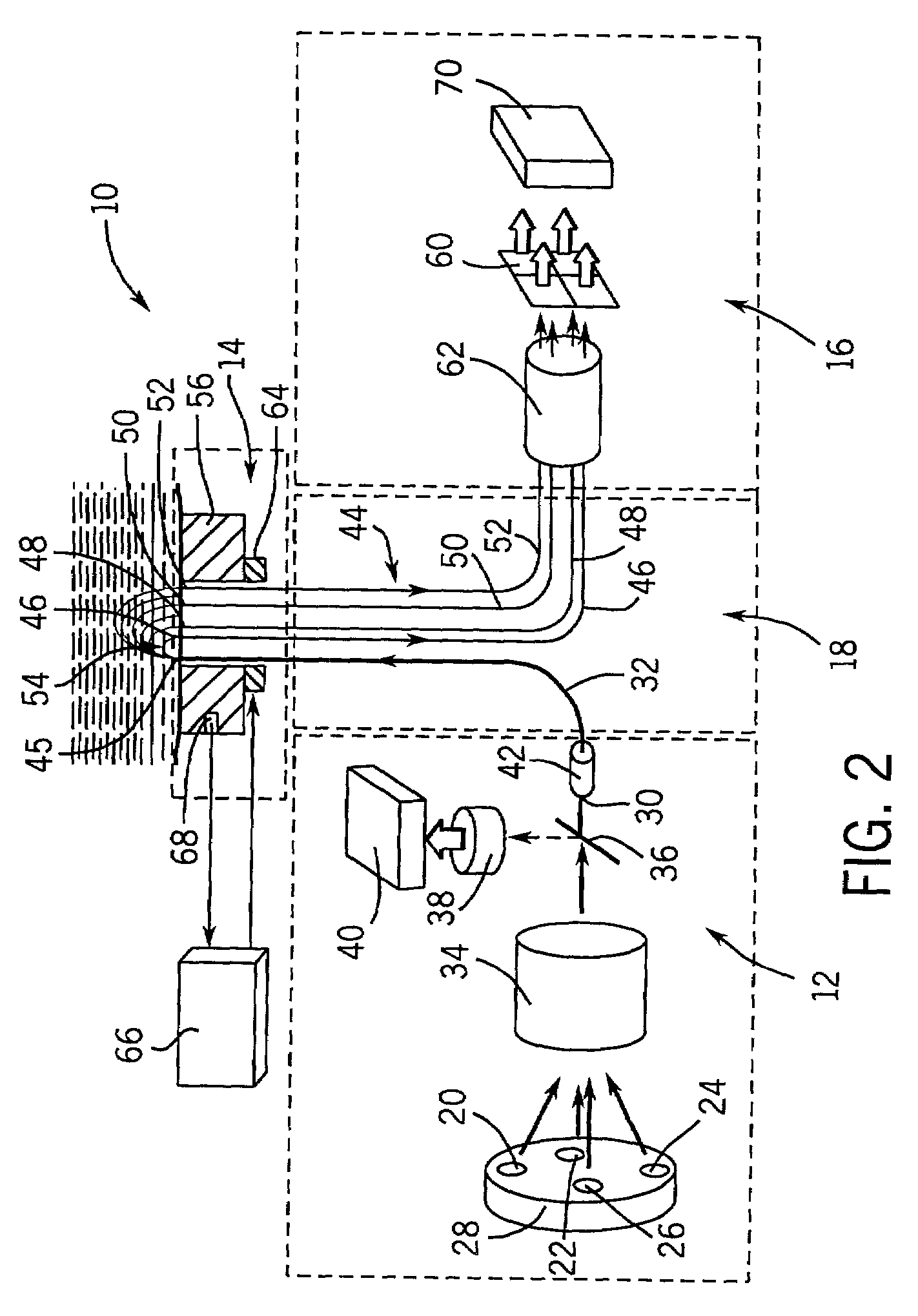
An instrument for evaluating fluorescence of a heterogeneous tissue includes means for exciting a two-dimensional portion of the tissue surface with excitation radiation at a plurality of excitation wavelengths, means for collecting emission radiation from the two-dimensional portion of the tissue surface simultaneously with excitation of the portion, and means for forming a two-dimensional excitation-emission map of the excitation radiation and the simultaneously collected emission radiation and spatially averaging the excitation and emission radiation.
Owner:CERCACOR LAB INC
Method for treating obstructive sleep disorder includes removing tissue from the base of tongue
InactiveUS7090672B2Stiffening the surrounding tissue structureUseful in treatmentSuture equipmentsHeart valvesThermal energyTongue root
A method for treating obstructive sleep disorders includes accessing the interior of the tongue through an incision made in the skin in the vicinity of the jaw of a patient; advancing an instrument through the incision into the interior of the tongue; and removing an amount of tissue from the interior of the base of the tongue with the instrument. The present invention includes forming a cavity or plurality of channels in the tongue. The cavity may be collapsed using a suture, fastener or bioadhesive. An emplaced suture may be provided to hold the cavity in a collapsed position thereby reducing the degree of obstruction. Additionally, thermal energy may be applied to the tissue surface immediately surrounding the channels to cause thermal damage to the tissue surface, thereby creating hemostasis and stiffening the surrounding tissue structure.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Surgical Cutting Guide
ActiveUS20080275452A1Prevent deviationComputer-aided planning/modellingNon-surgical orthopedic devicesEngineeringSurgical department
The present invention is directed to a surgical cutting guide for guiding a surgical instrument along a cutting path located on a biological tissue. The surgical guide includes a contact surface that conforms to a surface associated with the tissue and at least one guide for restricting movement of a surgical instrument in a first direction and for allowing the movement of the surgical instrument in a second direction along a cutting path across the surface of the tissue. The guide further contains a stop for restricting movement of the surgical instrument in the second direction along the cutting path. The stop is based at least, in part, on patient specific information.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Multi-modality ablation device
ActiveUS7074218B2Minimum activation timeEffects damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyRadio frequencyUltrasound energy
An instrument for ablation of tissue. The instrument including: a body having at least one surface for contacting a tissue surface, the at least one surface being substantially planar; an ultrasonic transducer disposed in the body for generating ultrasonic energy and directing at least a portion of the ultrasonic energy to the tissue surface, the ultrasonic transducer being operatively connected to an ultrasonic generator; at least one radio-frequency electrode disposed on the at least one surface for directing radio frequency energy to the tissue surface, the at least one radio-frequency electrode being operatively connected to a power source; and one or more switches for selectively coupling at least one of the ultrasonic transducer to the ultrasonic generator and the at least one radio-frequency electrode to the power source.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Intralumenal contact sensor
InactiveUS6942657B2Eliminate aberrant wave conductionReduce lossDiagnosticsCatheterLight treatmentLaser light
An apparatus and method for phototherapy are described in which laser light or other radiation is projected from within a catheter, through a balloon member, and toward the surface of tissue. The light reflected from body fluids or the tissue surface is captured by a collecting device located within the catheter, e.g., within the balloon member, and the intensity of the reflected light is ascertained. The apparatus and method provides for accurately positioning the apparatus against the tissue treatment site.
Owner:CARDIOFOCUS INC
Tissue distraction device
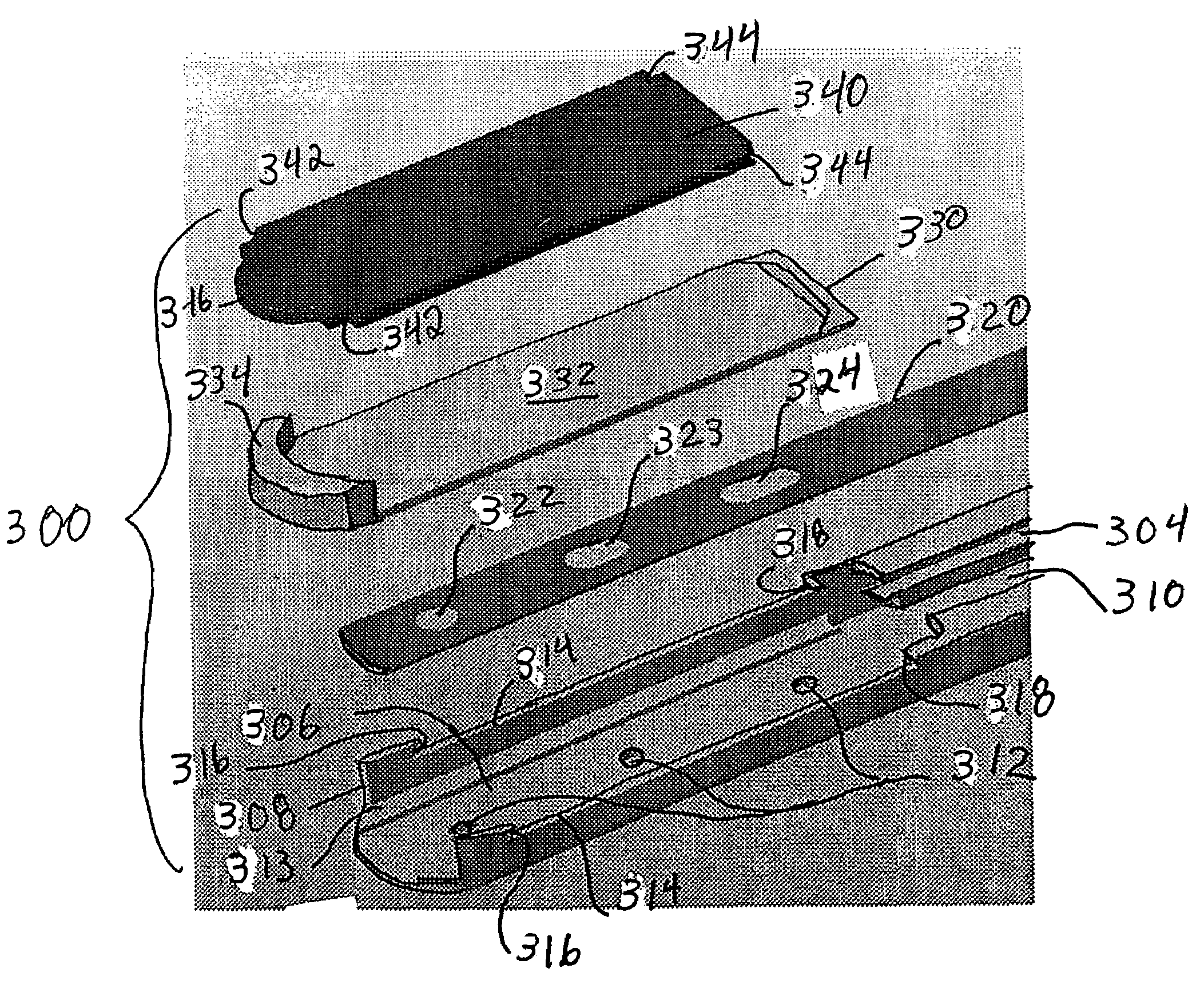
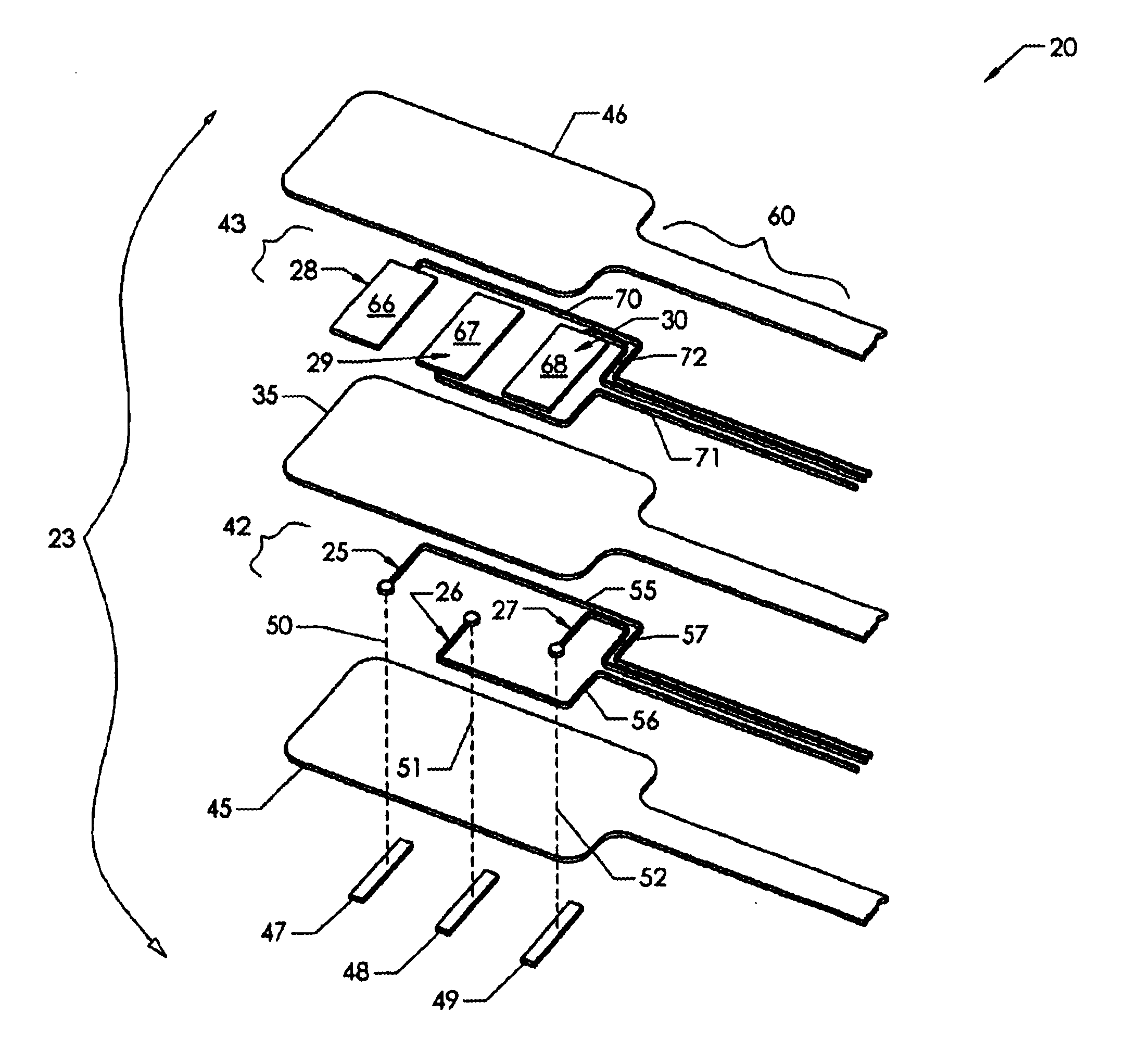
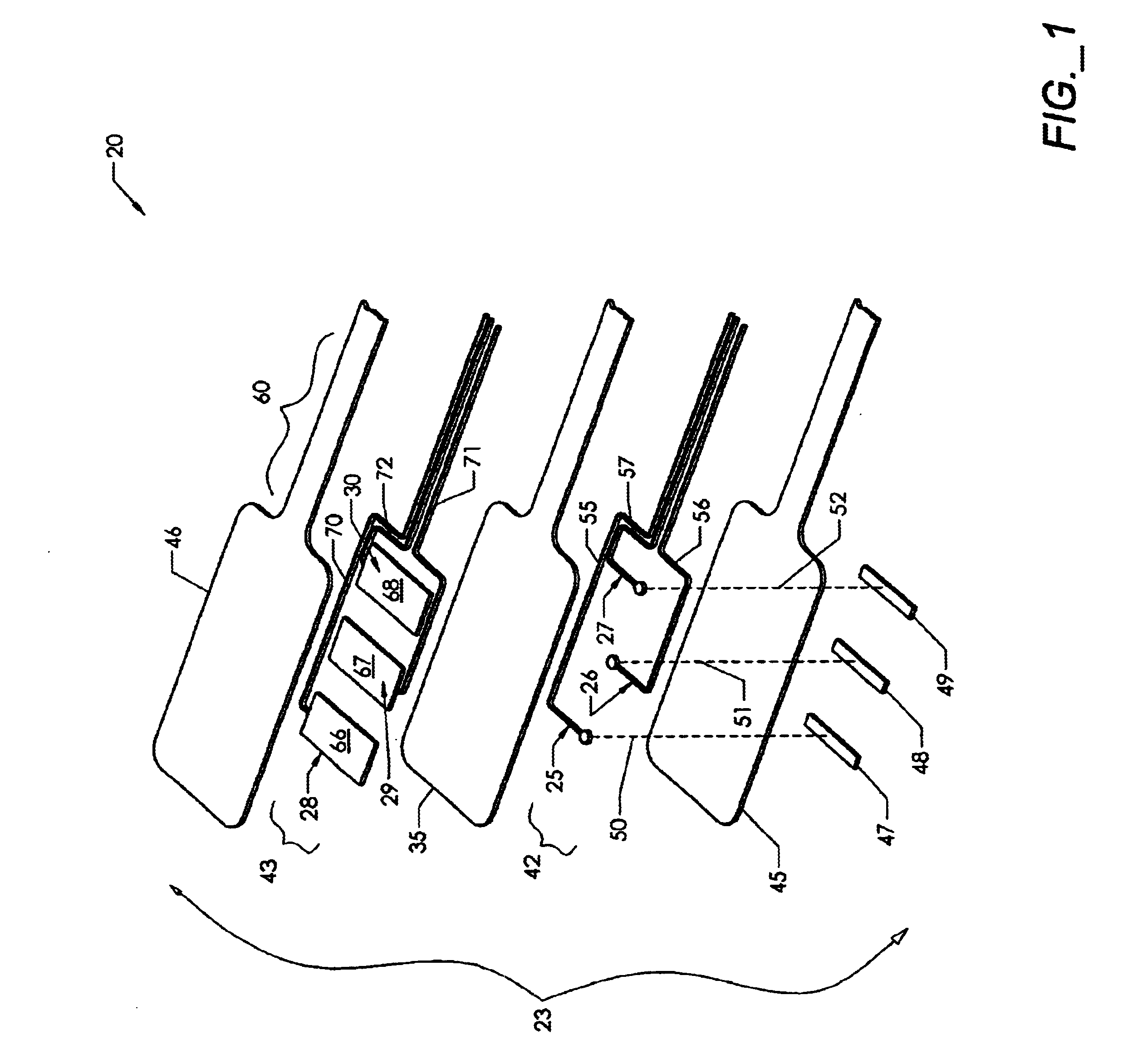
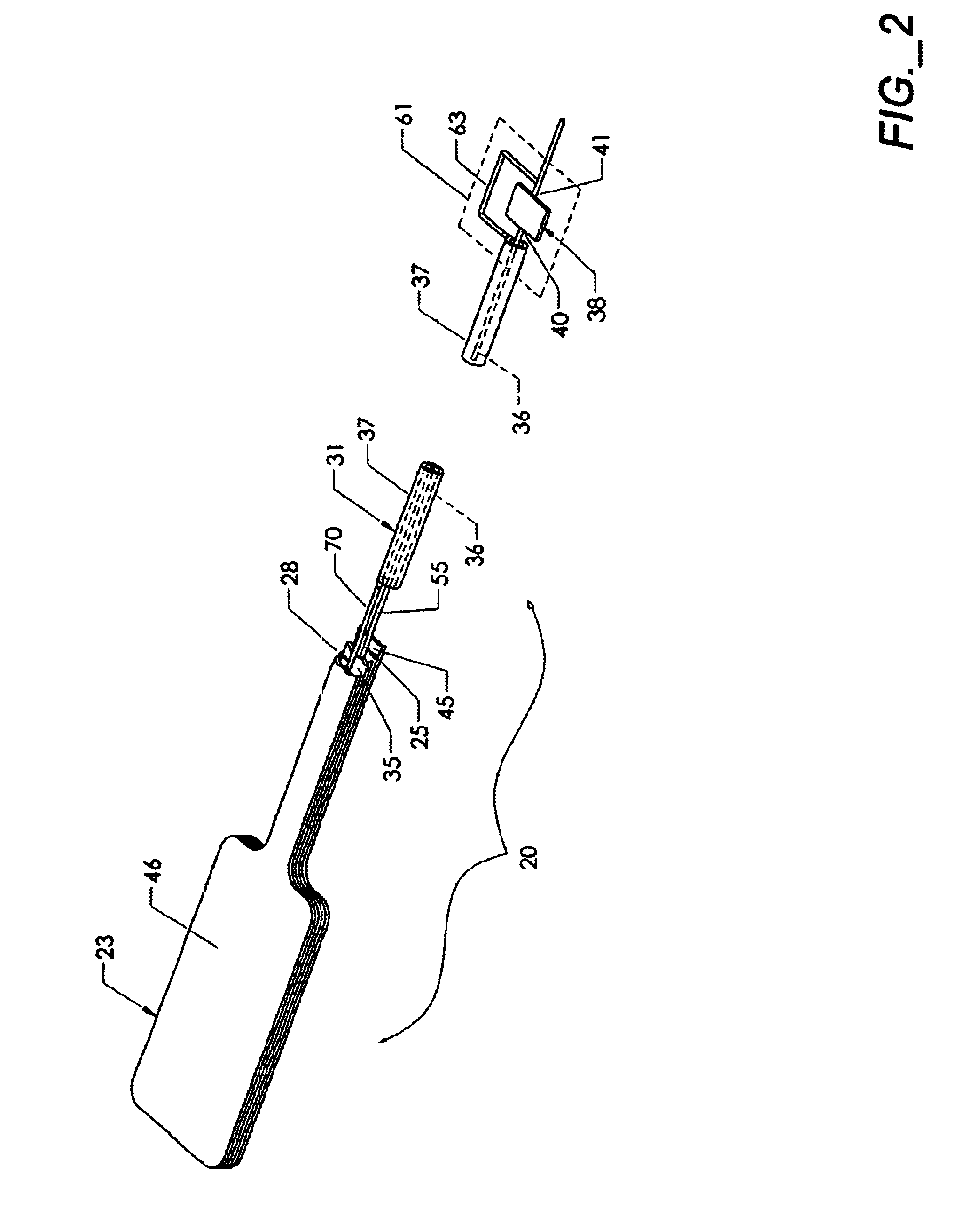
ActiveUS6997929B2Avoid relative motionInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsDistractionWafer stacking
An apparatus and method for distracting, in a given direction, and supporting two tissue surfaces is provided. A plurality of wafers are consecutively inserted using a wafer insertion apparatus between the two tissue surfaces to create a column of wafers. A detachable wafer assembly is provided that includes a base wafer initially associated with a track assembly of a wafer insertion apparatus. The base wafer is dislodged from the track assembly so that the base wafer is left within the distraction site as the track assembly is removed. A top cap wafer is provided that is situated at the top of the wafer stack, in which the top cap wafer is larger than the remaining wafers to form a gap surrounding the stack to receive biologic material.
Owner:SPINEWAVE
Precision ablating method
Methods of ablating tissue in an alimentary tract are provided. The methods include advancing an ablation structure into an alimentary tract while supporting the ablation structure with an endoscope. The methods further include a step of moving at least part of the ablation structure with respect to the endoscope and toward a tissue surface, before activating the ablation structure to ablate a tissue surface.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
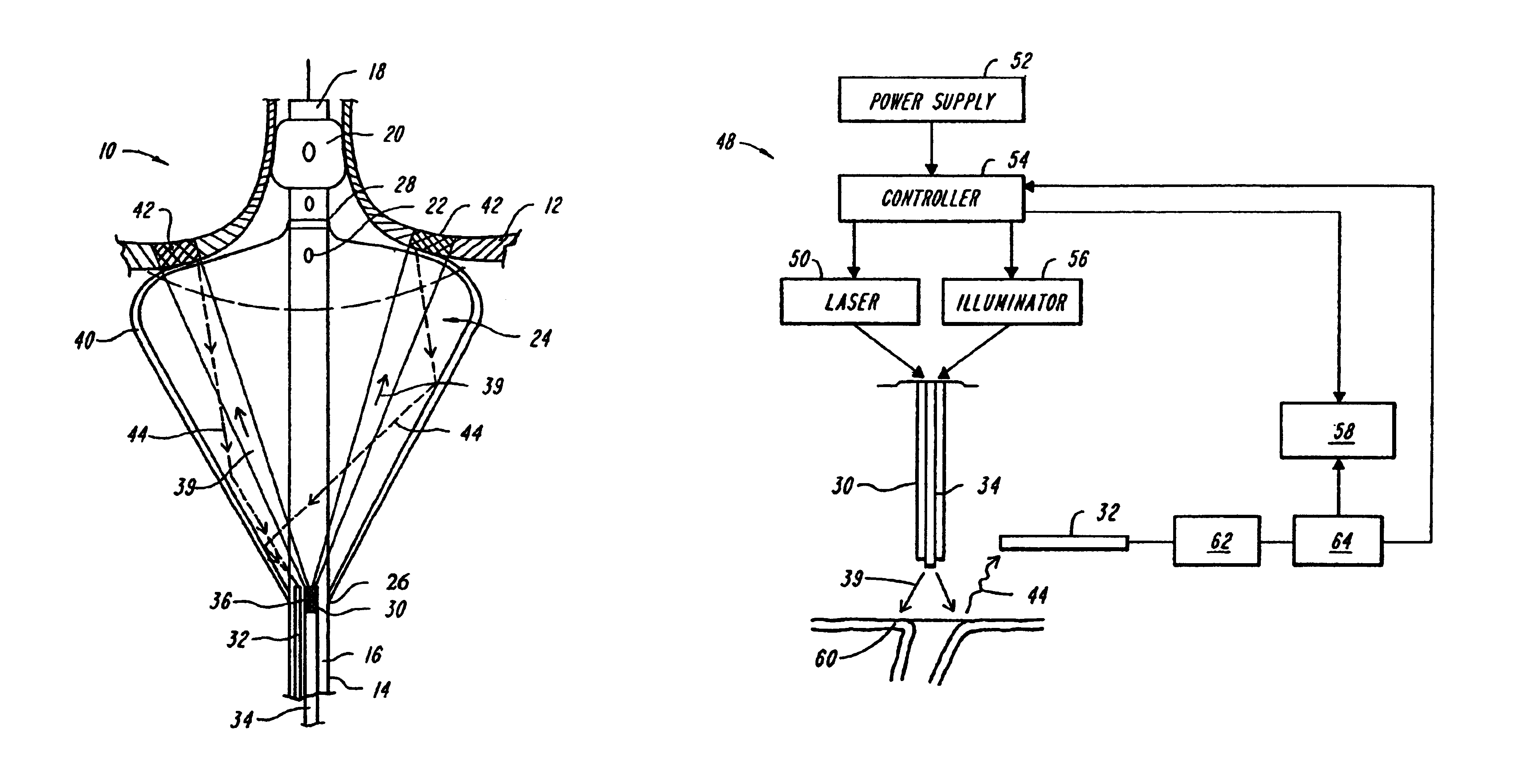
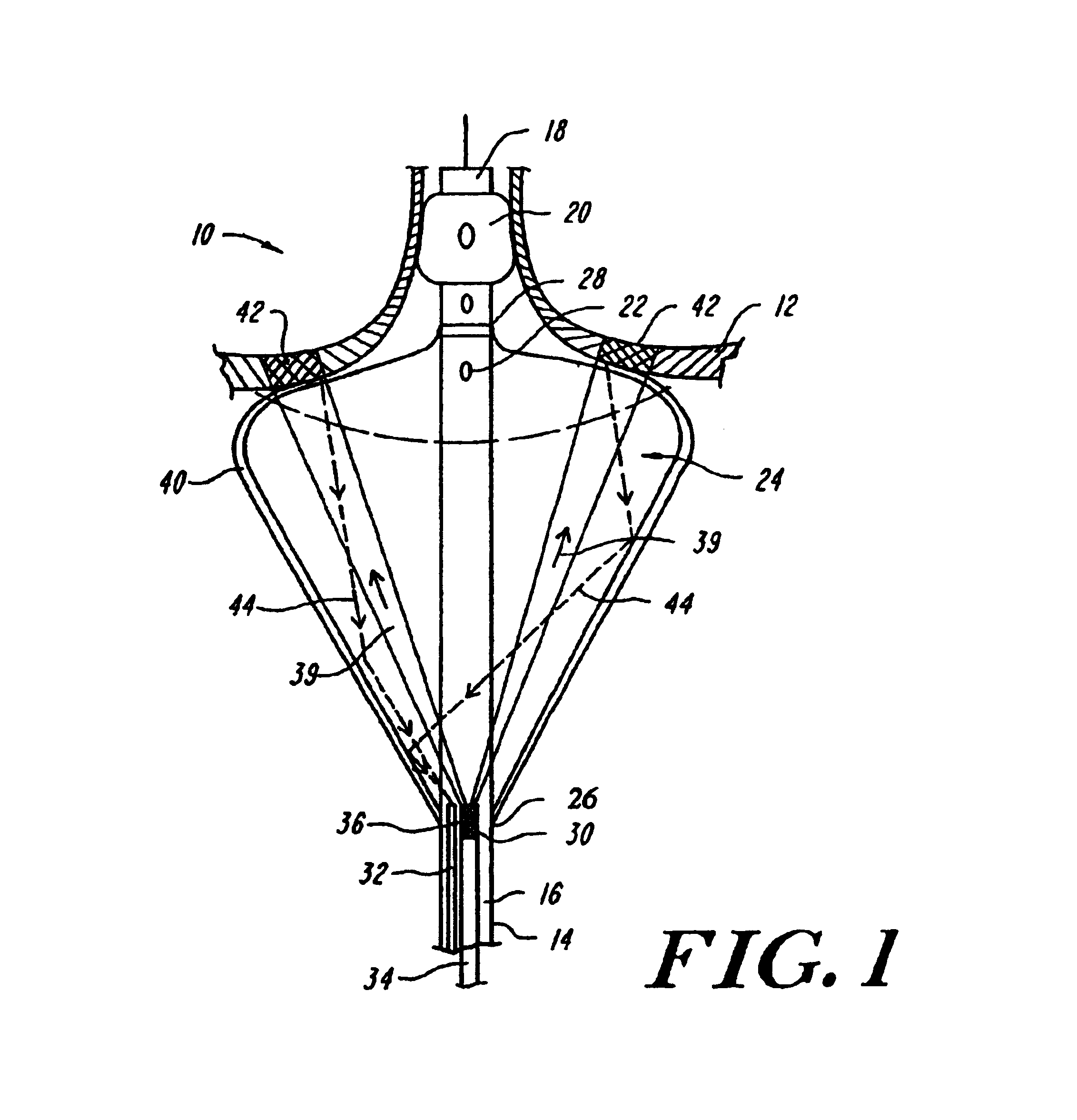
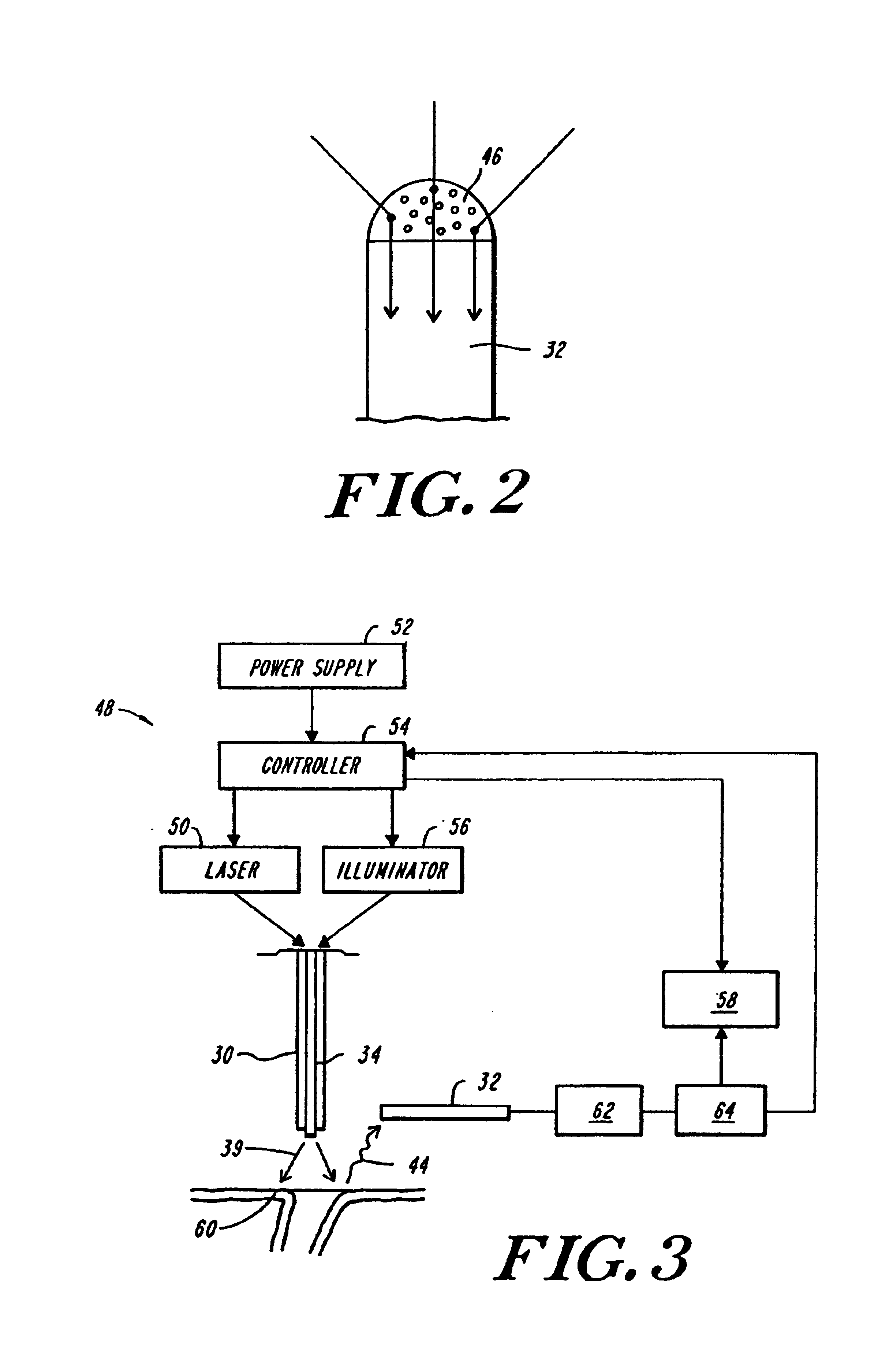
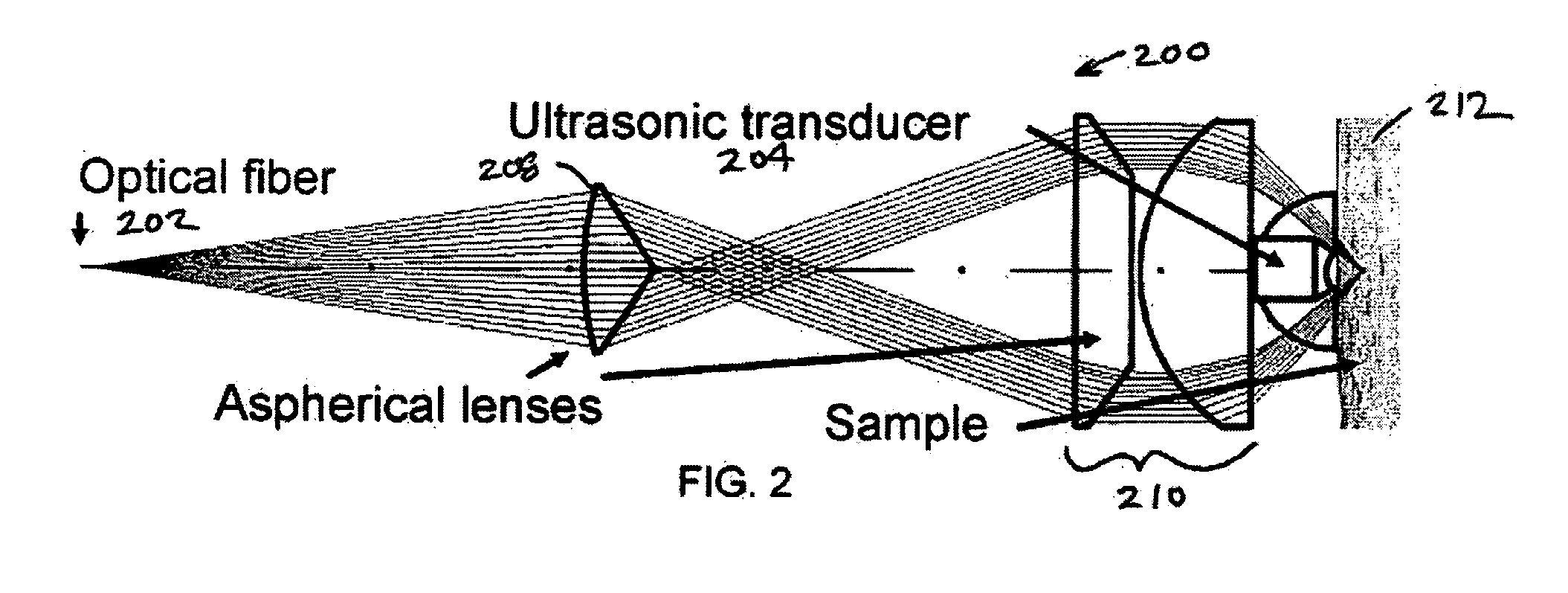
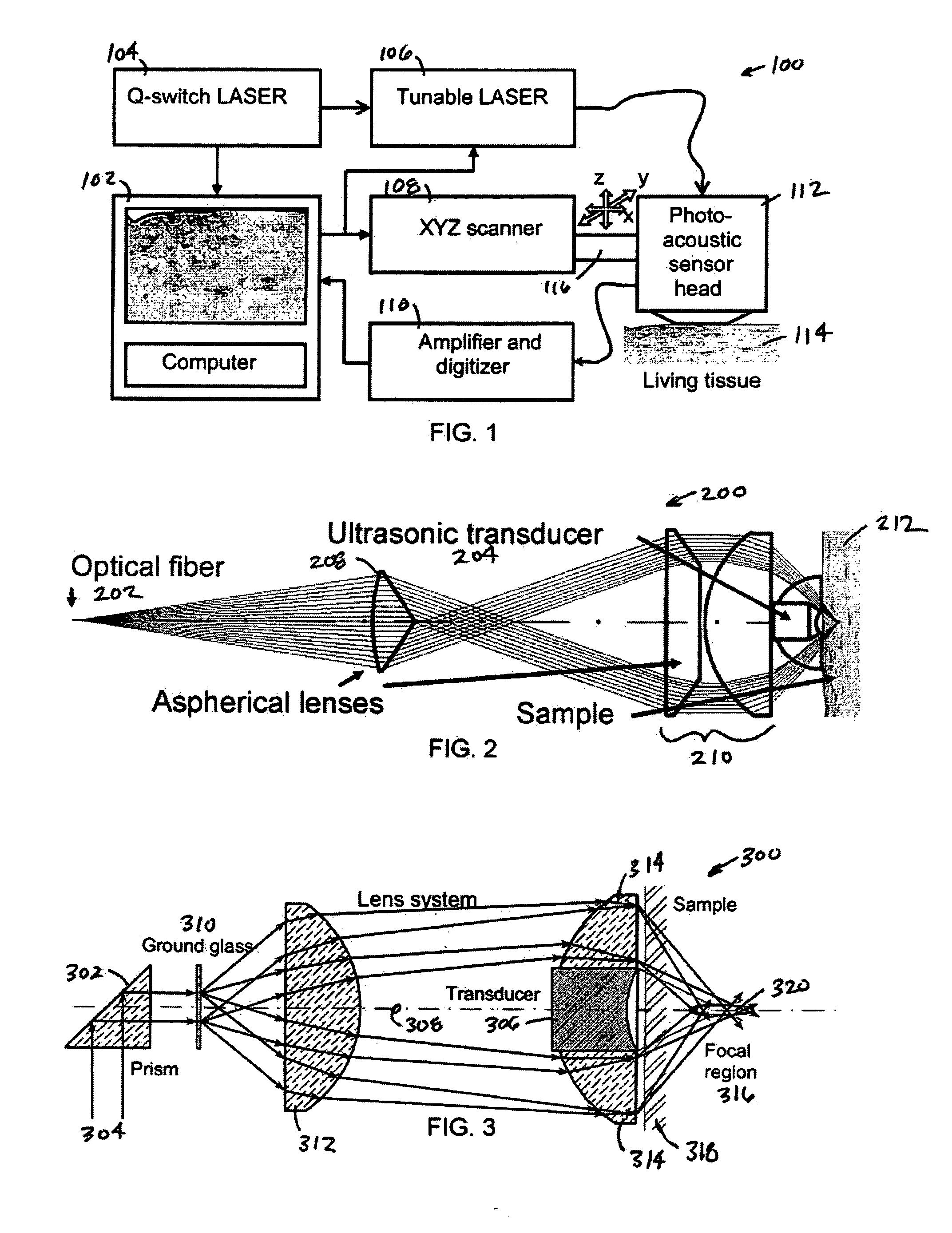
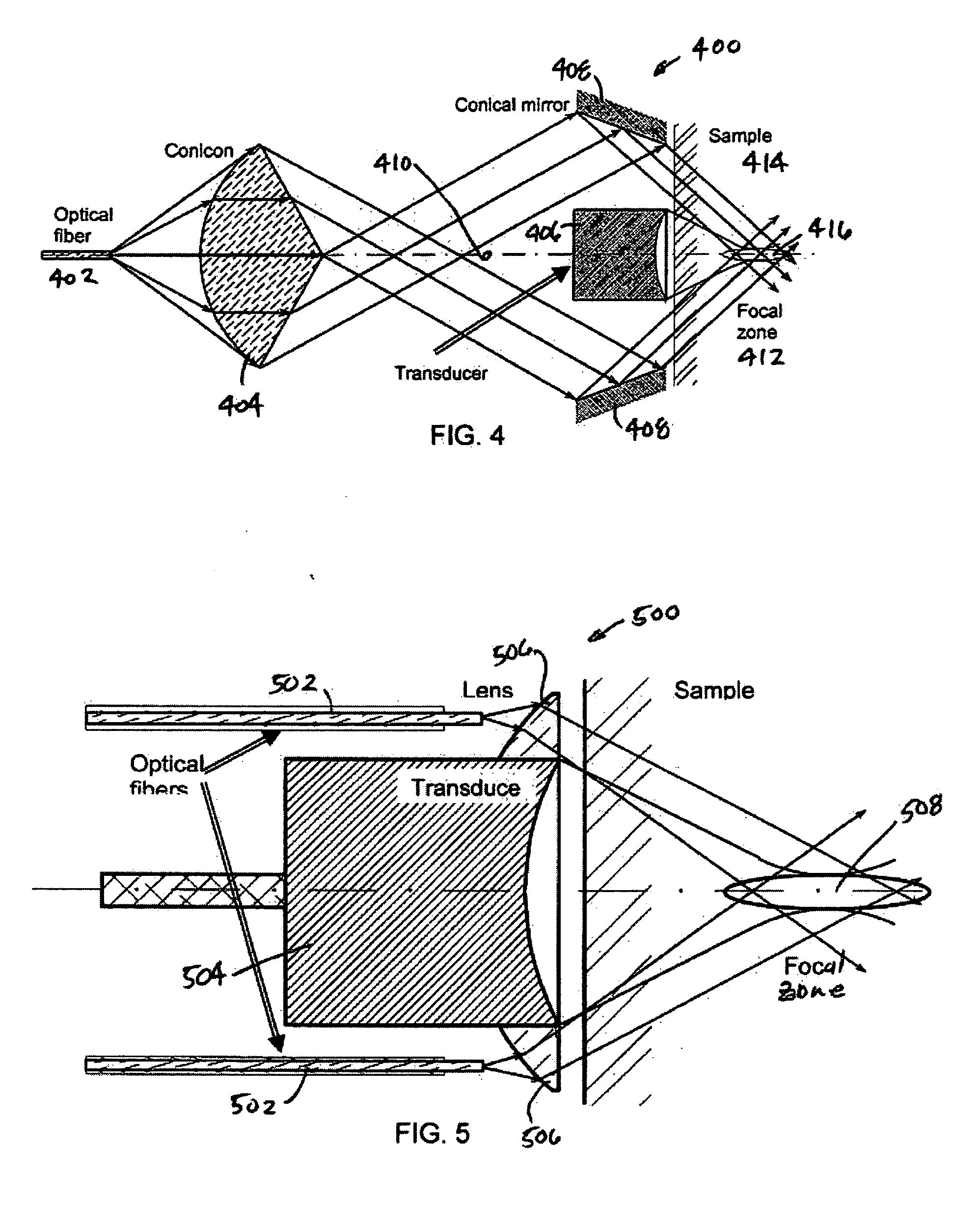
Method, system and apparatus for dark-field reflection-mode photoacoustic tomography
InactiveUS20060184042A1Enhance the imageMinimize interferenceCatheterDiagnostics using tomographyUltrasonic sensorAcoustic wave
The present invention provides a method, system and apparatus for reflection-mode microscopic photoacoustic imaging using dark-field illumination that can be used to characterize a target within a tissue by focusing one or more laser pulses onto a surface of the tissue so as to penetrate the tissue and illuminate the target, receiving acoustic or pressure waves induced in the target by the one or more laser pulses using one or more ultrasonic transducers that are focused on the target and recording the received acoustic or pressure waves so that a characterization of the target can be obtained. The target characterization may include an image, a composition or a structure of the target. The one or more laser pulses are focused with an optical assembly of lenses and / or mirrors that expands and then converges the one or more laser pulses towards the focal point of the ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY
Tissue surface treatment apparatus and method
InactiveUS7278991B2Minimize injuryAvoid structureSurgical needlesCatheterCritical structureTarget tissue
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Apparatus and method for treating tumors near the surface of an organ
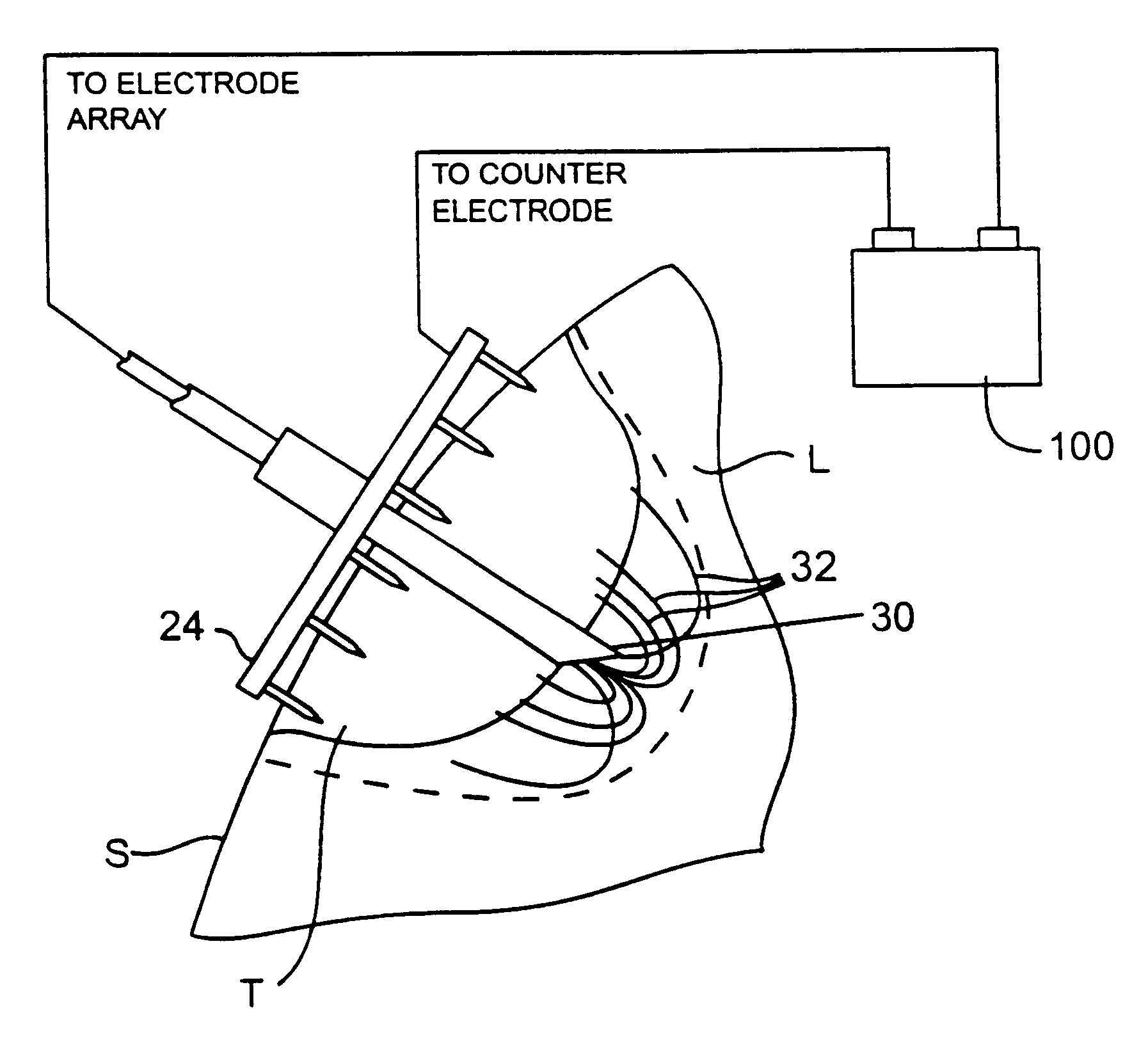
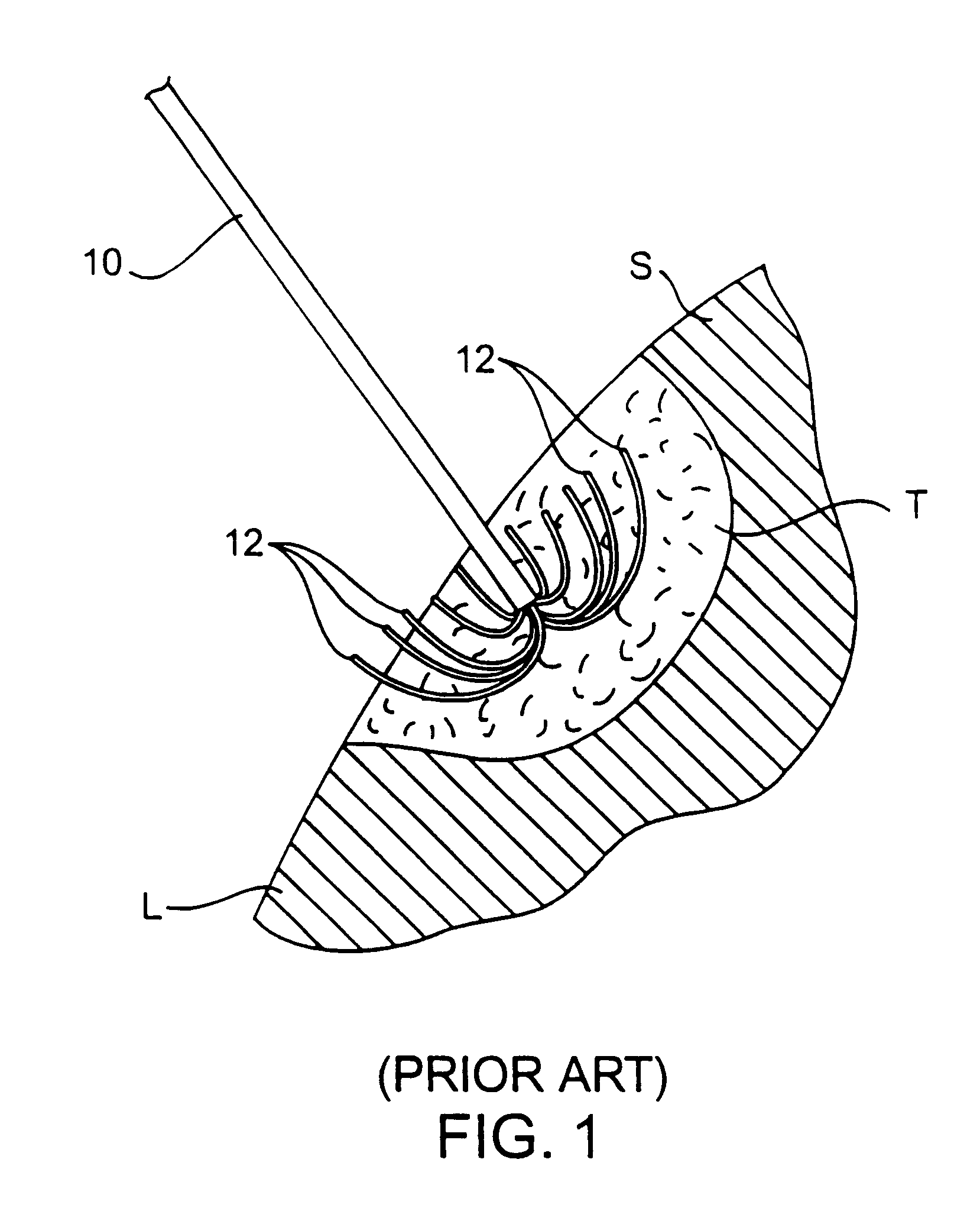
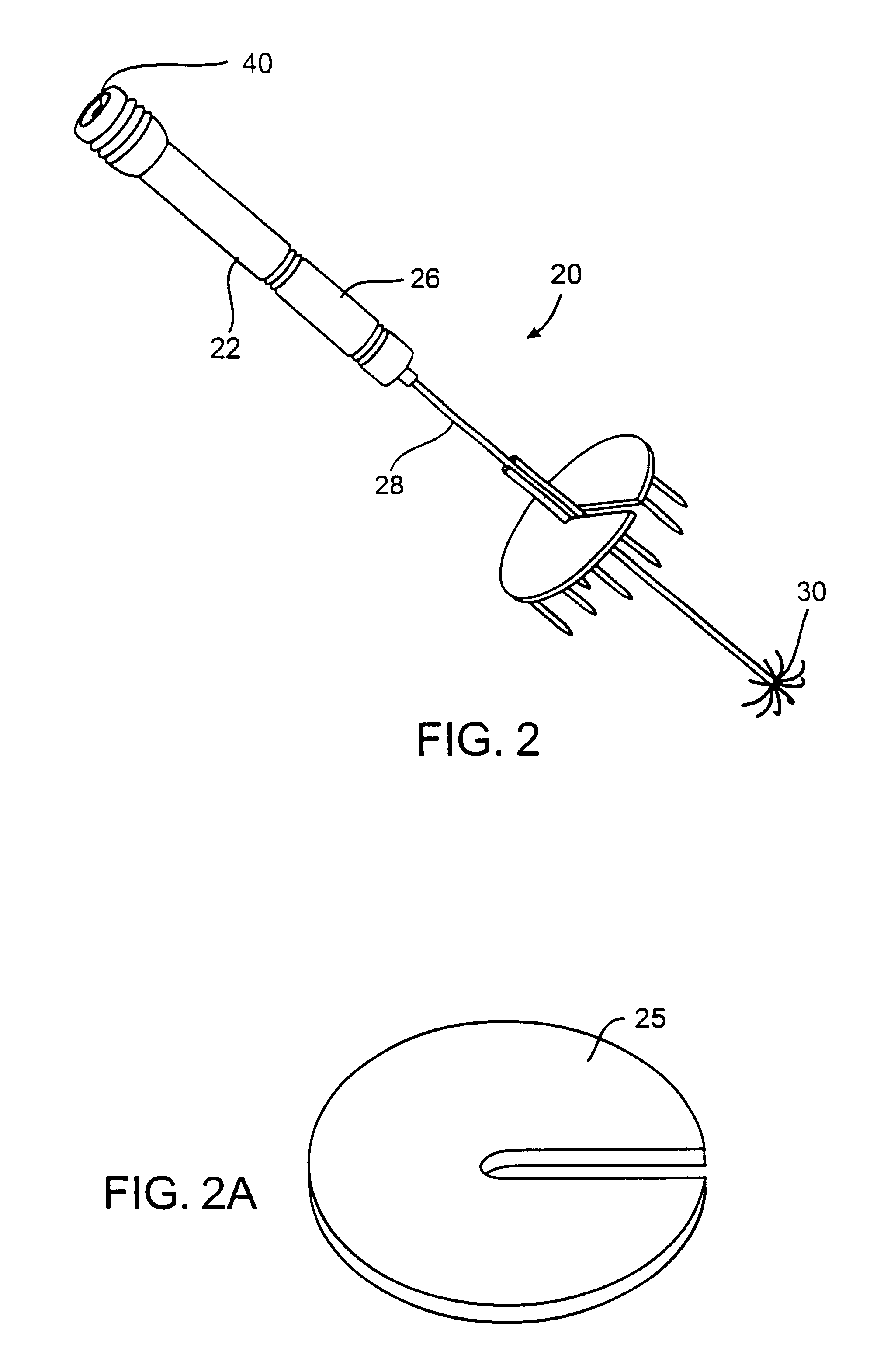
InactiveUS6337998B1Avoid flowPrevent heat lossElectrotherapySurgical needlesAbnormal tissue growthTherapeutic Area
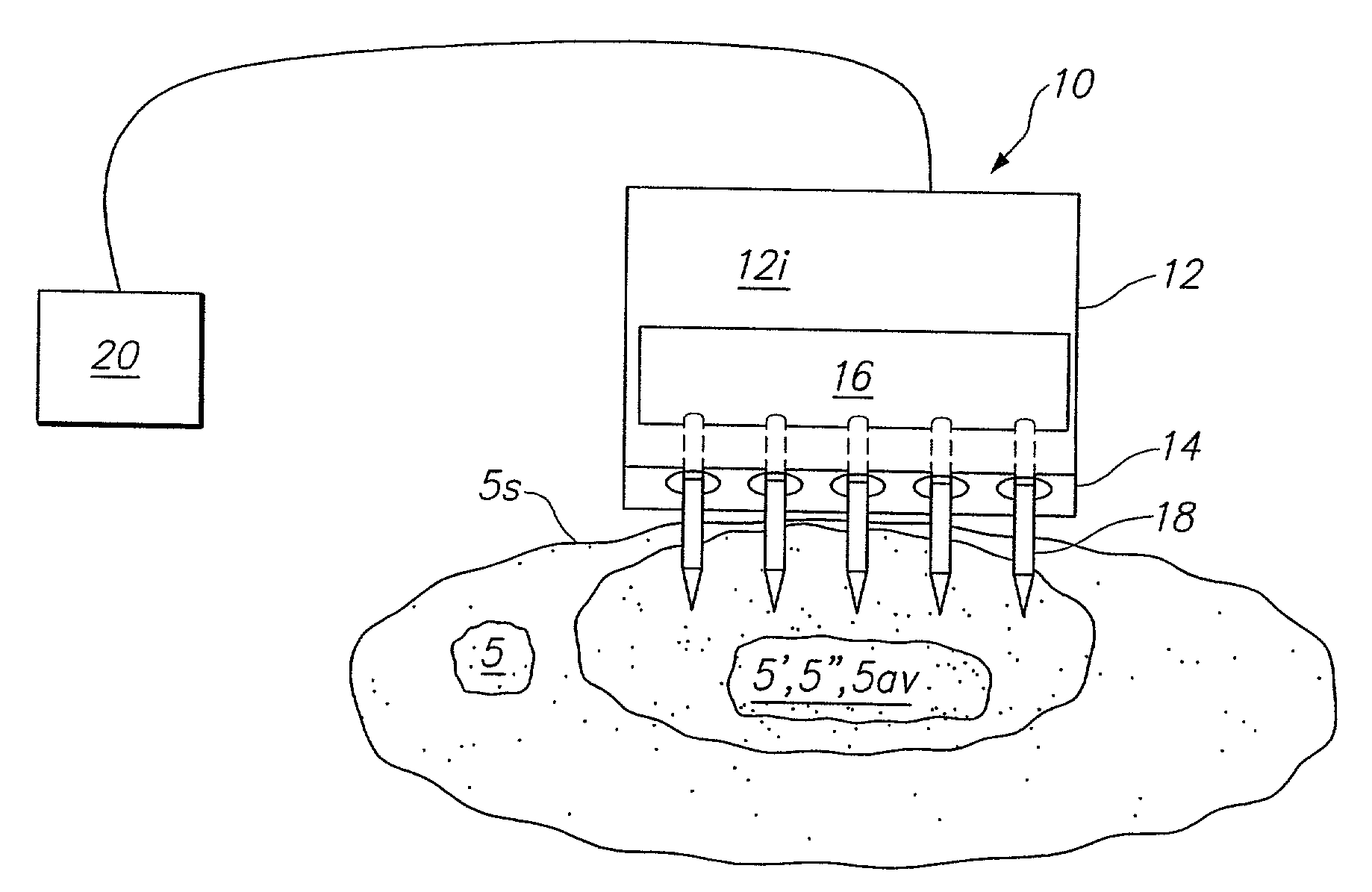
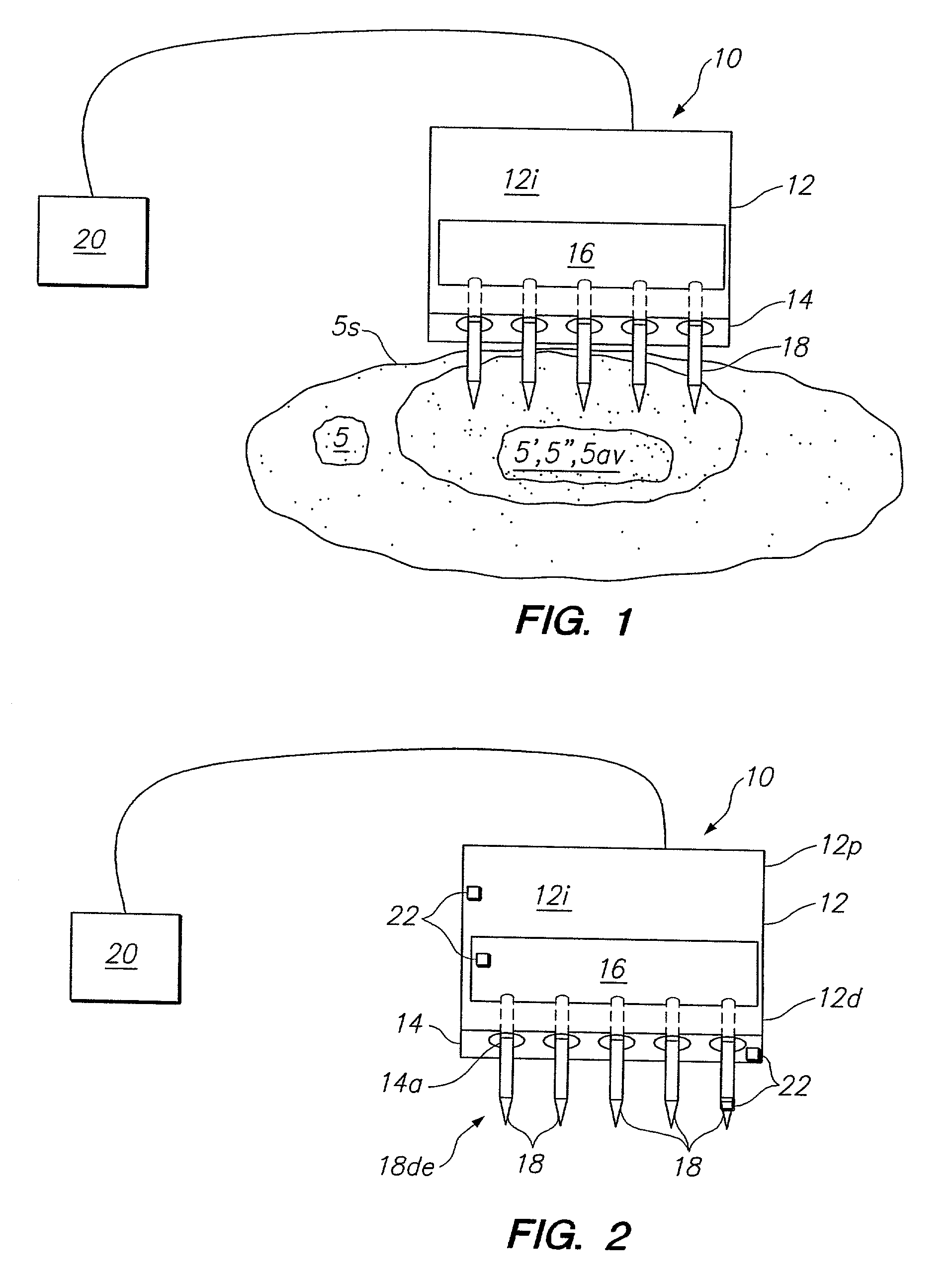
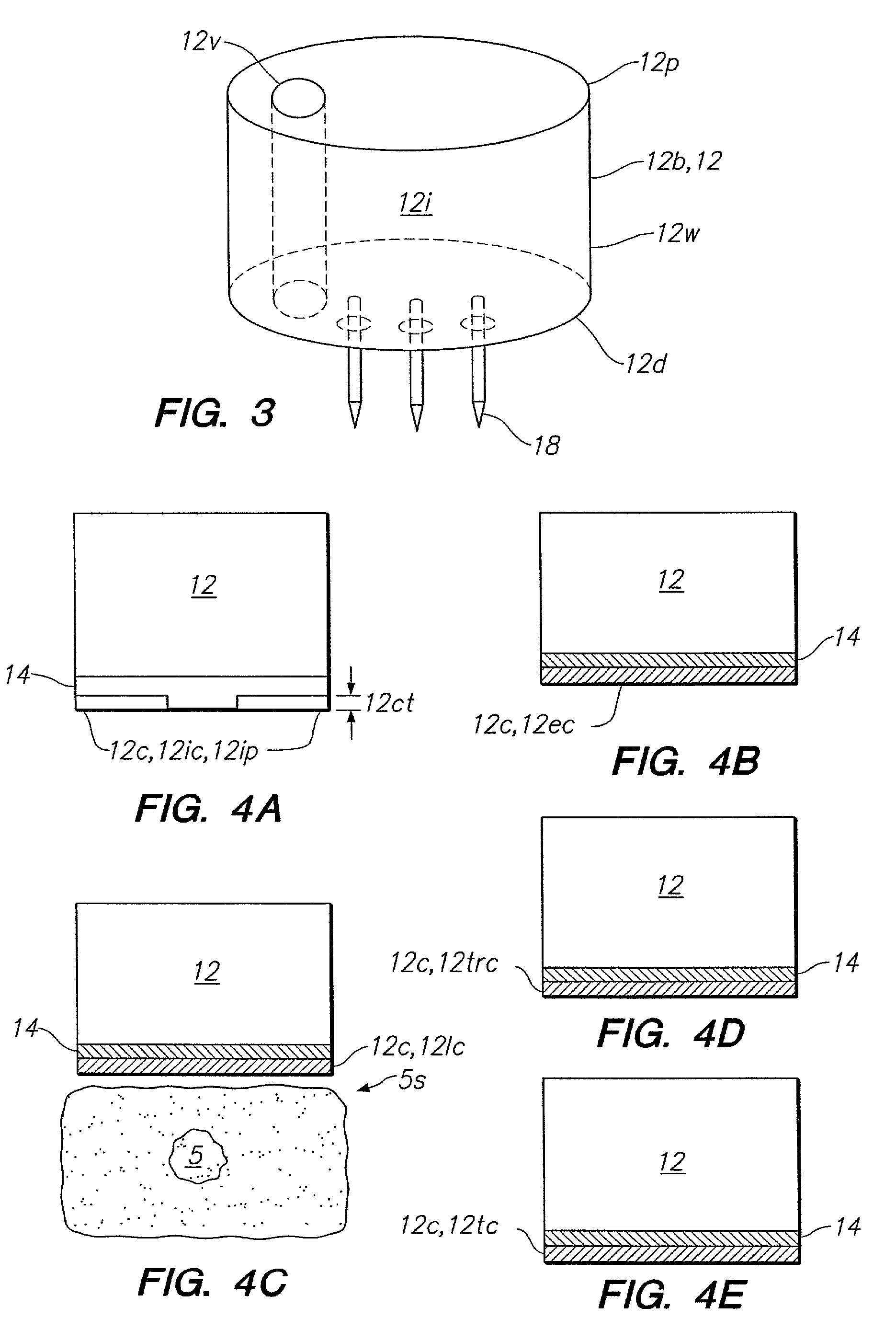
A system for treating a target region in tissue beneath a tissue surface comprises a probe for deploying an electrode array within the tissue and a surface electrode for engaging the tissue surface above the treatment site. Preferably, surface electrode includes a plurality of tissue-penetrating elements which advance into the tissue, and the surface electrode is removably attachable to the probe. The tissue may be treated in a monopolar fashion where the electrode array and surface electrode are attached to a common pole on an electrode surgical power supply and powered simultaneously or successively, or in a bipolar fashion where the electrode array and surface electrode are attached to opposite poles of the power supply. The systems are particularly useful for treating tumors and other tissue treatment regions which lie near the surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
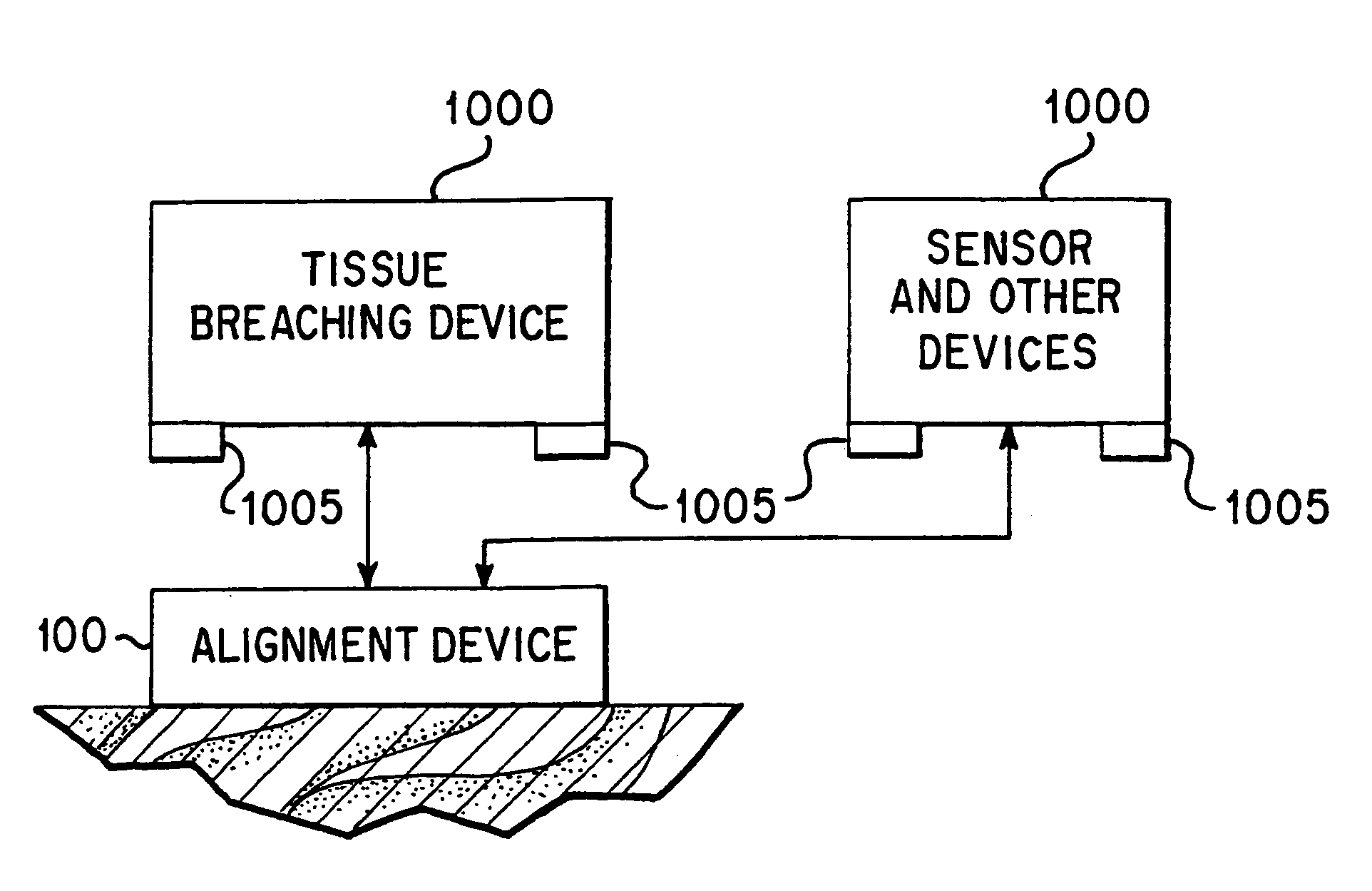
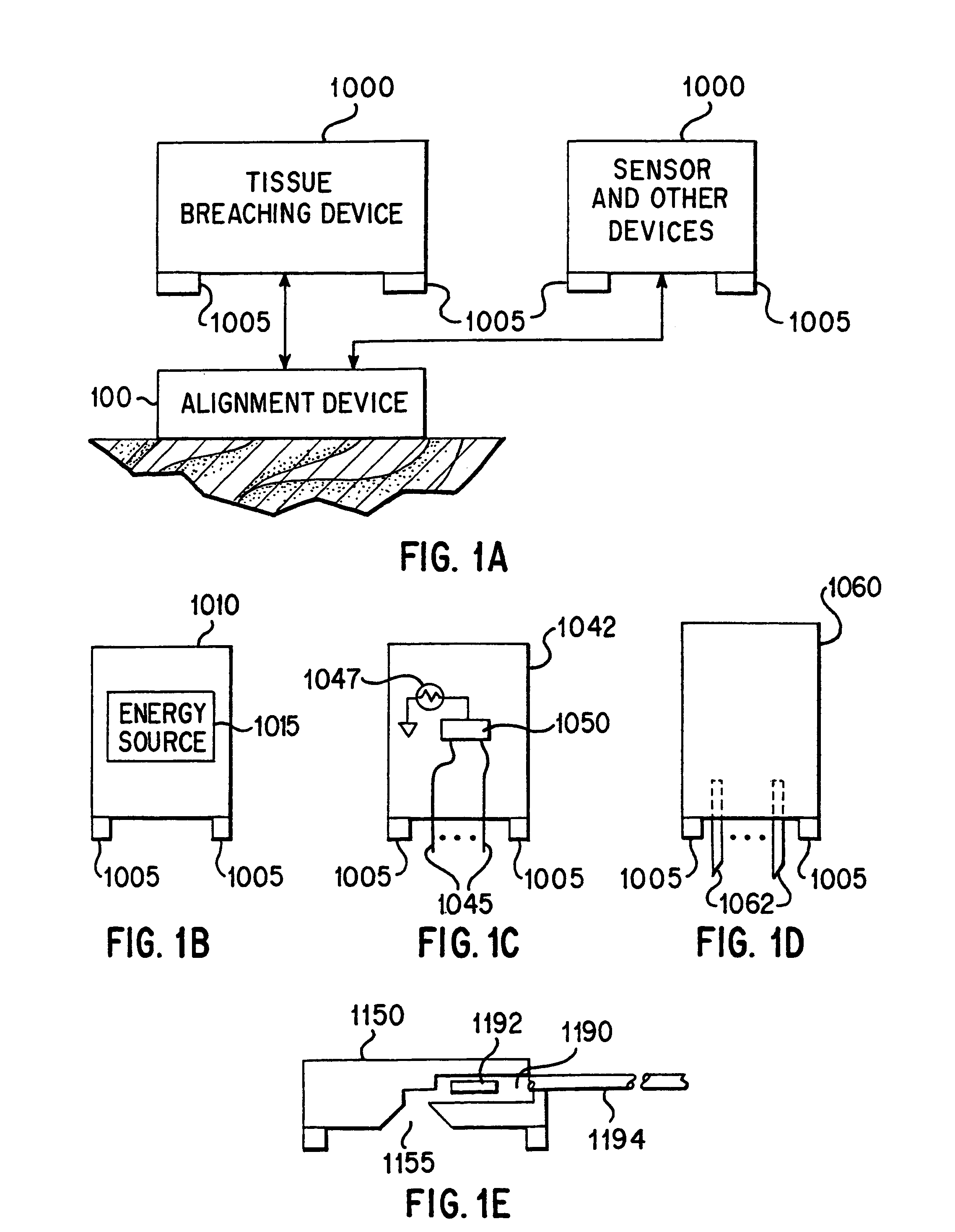
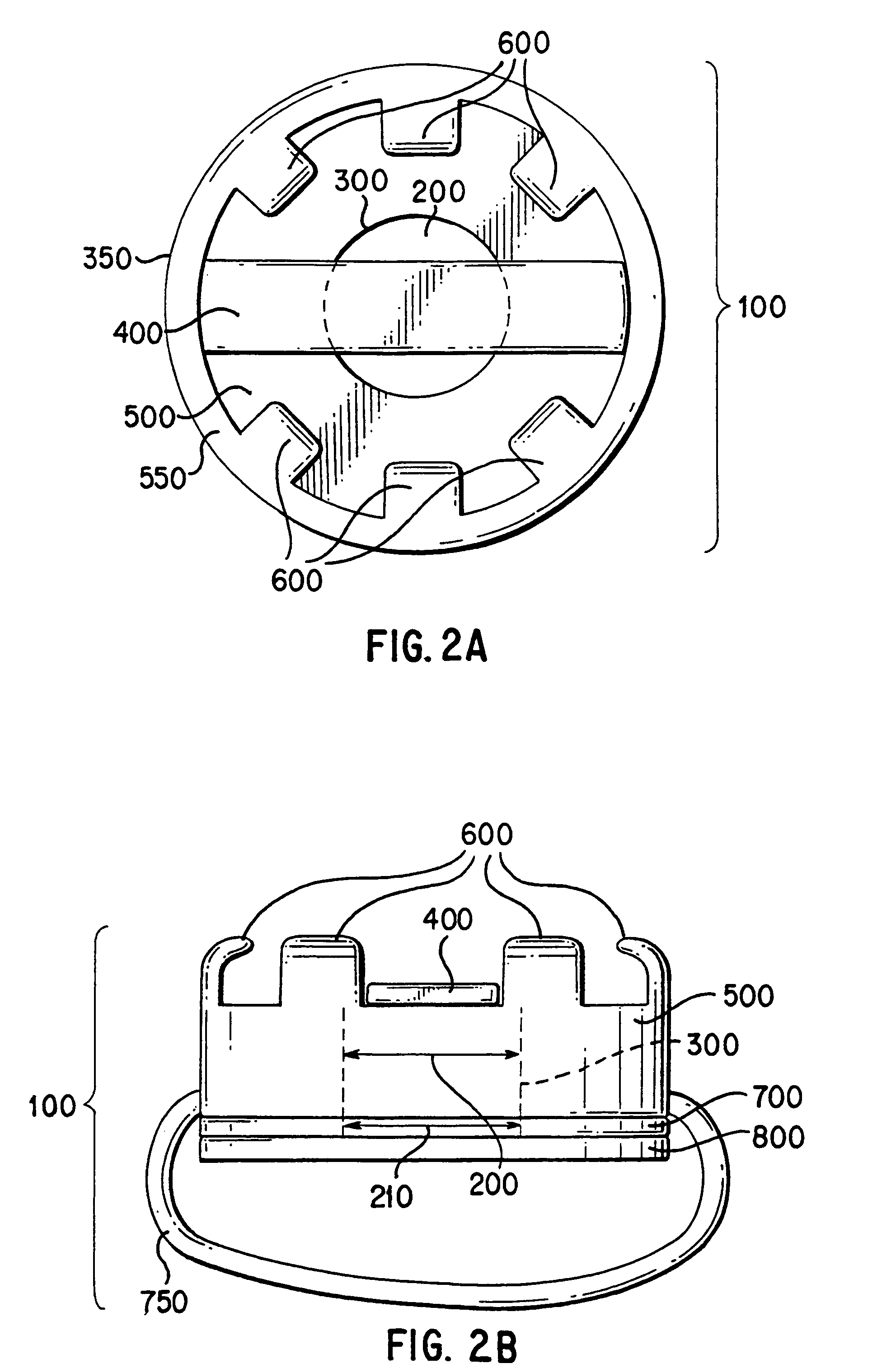
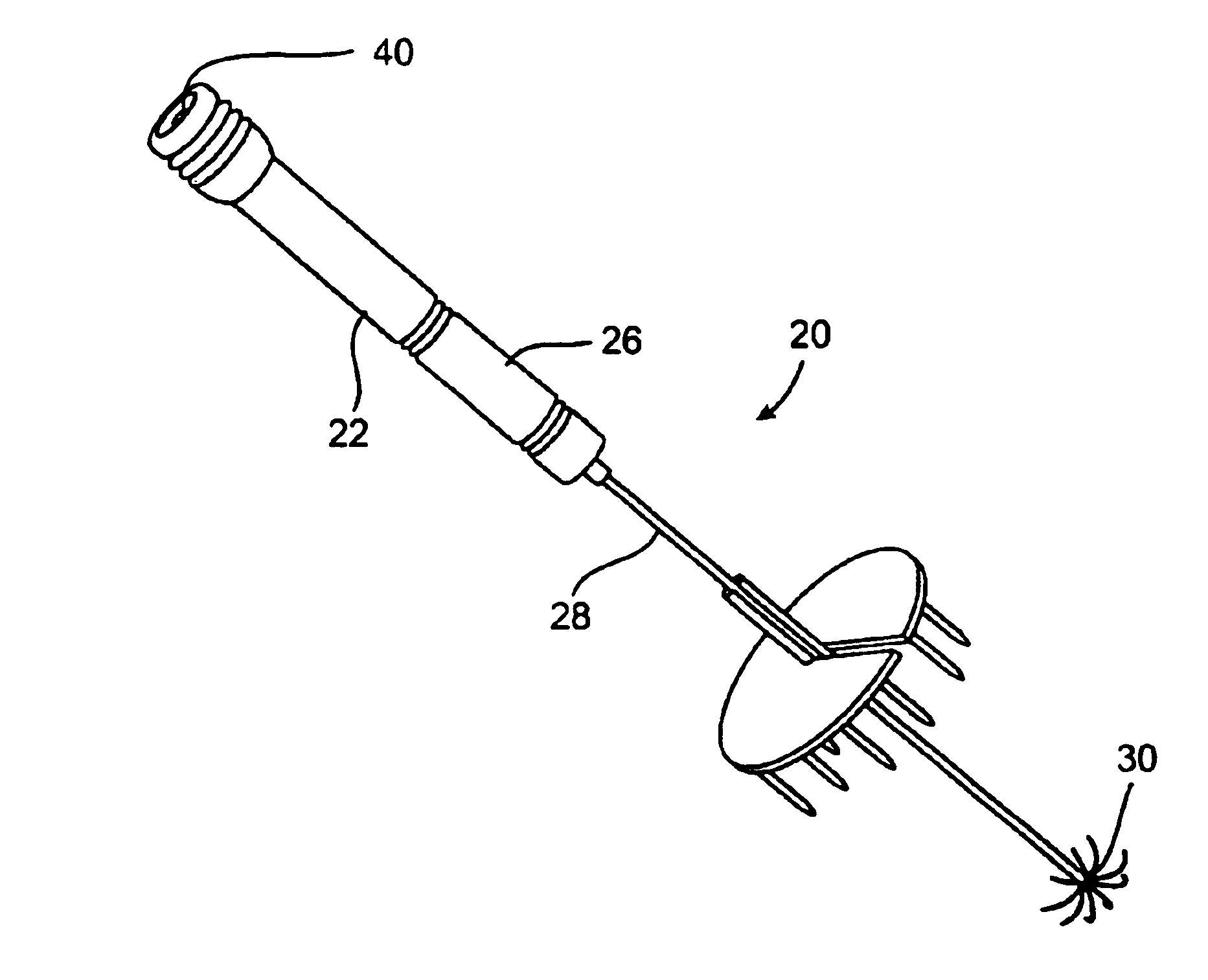
Integrated alignment devices, system, and methods for efficient fluid extraction, substance delivery and other applications
InactiveUS6925317B1Guaranteed alignmentEasy accessSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAnalyteMonitoring system
An alignment device and related systems and methods for aligning at least one apparatus with respect to a surface of a tissue. The alignment device comprises a tissue interface member suitable for positioning on the surface of the tissue and mating with the apparatus to maintain alignment of the apparatus during an operation of the apparatus. The alignment device is useful to align various apparatus that are part of a continuous analyte monitoring system.
Owner:ALTEA THERAPEUTIC CORP +1
Topically applied clotting material
A composition, system, articles and method for the enhancement of clotting in wounds with extravascular blood flow, especially where the surface of the tissue has been broken is described. The system consists of biotolerable, porous particulates applied to the surface of a wound with liquid blood thereon. The porous nature of the particulate material, either free-flowing or packaged or restrained on or in a surface, enhances clotting. Chemical or biochemical agents, such as additional clotting agents, therapeutic agents, antibiotics, clot strengthening agents (such as fibrous structural materials), and the like may optionally be included on, with or within the porous particles. The particles may comprise such diverse materials as organics, metallics, inorganics, ceramics, and the like, both natural and artificial. It is generally preferred that the pore size distribution lies within a general range, and this range may vary from animal to animal and condition to condition, but generally falls within about 0.5 to 1000 nanometers or 3,000 to 200,000 Daltons.
Owner:MEDAFOR
Apparatus and method for treating tumors near the surface of an organ
InactiveUS6889089B2Enhances uniform electrosurgical treatment of tissueEliminate needSurgical needlesSurgical instruments for heatingAbnormal tissue growthElectrode array
A system for treating a target region in tissue beneath a tissue surface comprises a probe for deploying an electrode array within the tissue and a surface electrode for engaging the tissue surface above the treatment site. Preferably, surface electrode includes a plurality of tissue-penetrating elements which advance into the tissue, and the surface electrode is removably attachable to the probe. The tissue may be treated in a monopolar fashion where the electrode array and surface electrode are attached to a common pole on an electrode surgical power supply and powered simultaneously or successively, or in a bipolar fashion where the electrode array and surface electrode are attached to opposite poles of the power supply. The systems are particularly useful for treating tumors and other tissue treatment regions which lie near the surface.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Devices and methods for tissue access
ActiveUS20060089633A1Easy to disassembleEliminate needCannulasAnti-incontinence devicesSurgical departmentNerve stimulation
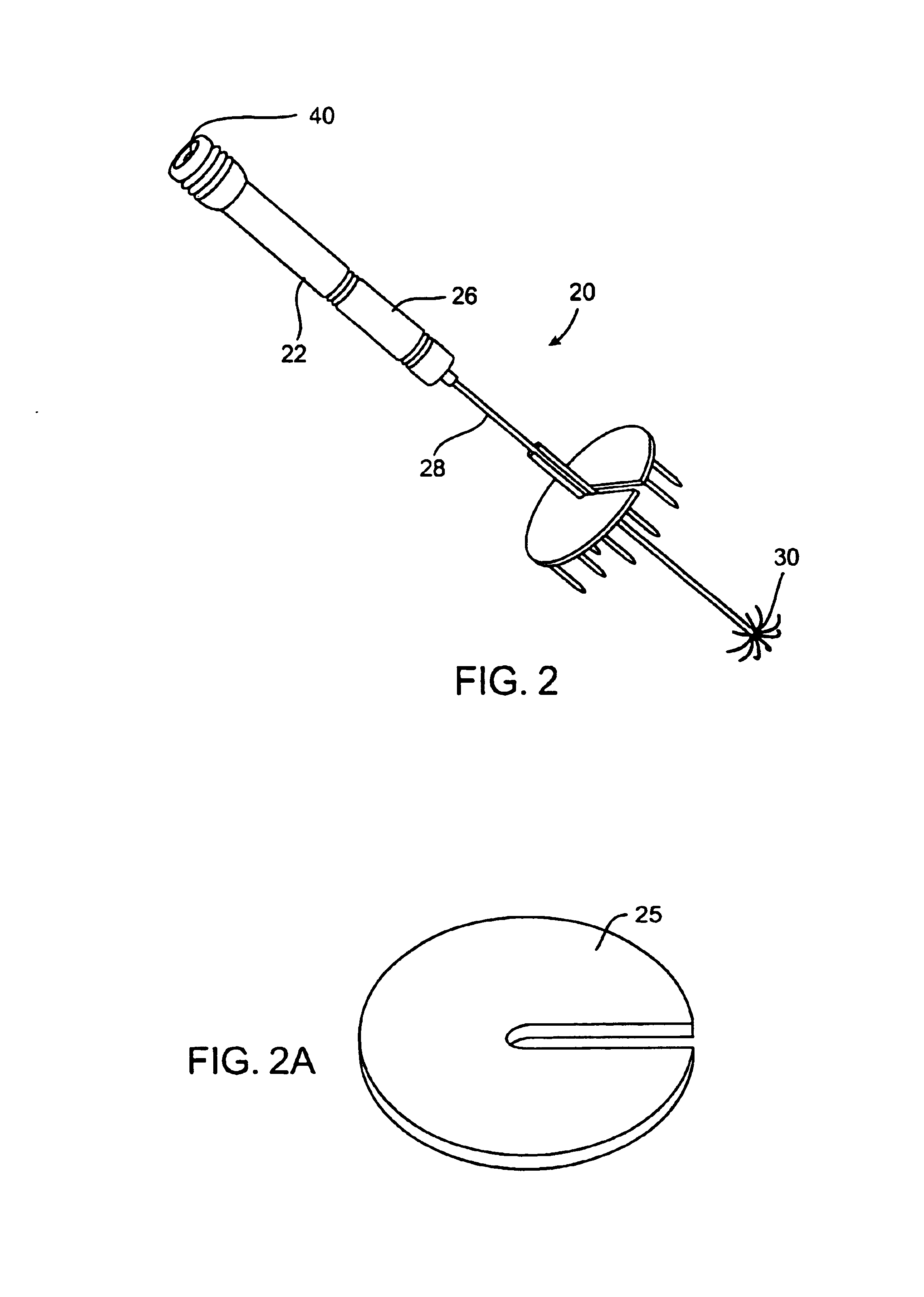
Methods and apparatus are provided for selective surgical removal of tissue, e.g., for enlargement of diseased spinal structures, such as impinged lateral recesses and pathologically narrowed neural foramen. In one variation, tissue may be ablated, resected, removed, or otherwise remodeled by standard small endoscopic tools delivered into the epidural space through an epidural needle. Once the sharp tip of the needle is in the epidural space, it is converted to a blunt tipped instrument for further safe advancement. A specially designed epidural catheter that is used to cover the previously sharp needle tip may also contain a fiberoptic cable. Further embodiments of the current invention include a double barreled epidural needle or other means for placement of a working channel for the placement of tools within the epidural space, beside the epidural instrument. The current invention includes specific tools that enable safe tissue modification in the epidural space, including a barrier that separates the area where tissue modification will take place from adjacent vulnerable neural and vascular structures. In one variation, a tissue abrasion device is provided including a thin belt or ribbon with an abrasive cutting surface. The device may be placed through the neural foramina of the spine and around the anterior border of a facet joint. Once properly positioned, a medical practitioner may enlarge the lateral recess and neural foramina via frictional abrasion, i.e., by sliding the abrasive surface of the ribbon across impinging tissues. A nerve stimulator optionally may be provided to reduce a risk of inadvertent neural abrasion. Additionally, safe epidural placement of the working barrier and epidural tissue modification tools may be further improved with the use of electrical nerve stimulation capabilities within the invention that, when combined with neural stimulation monitors, provide neural localization capabilities to the surgeon. The device optionally may be placed within a protective sheath that exposes the abrasive surface of the ribbon only in the area where tissue removal is desired. Furthermore, an endoscope may be incorporated into the device in order to monitor safe tissue removal. Finally, tissue remodeling within the epidural space may be ensured through the placement of compression dressings against remodeled tissue surfaces, or through the placement of tissue retention straps, belts or cables that are wrapped around and pull under tension aspects of the impinging soft tissue and bone in the posterior spinal canal.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC +1
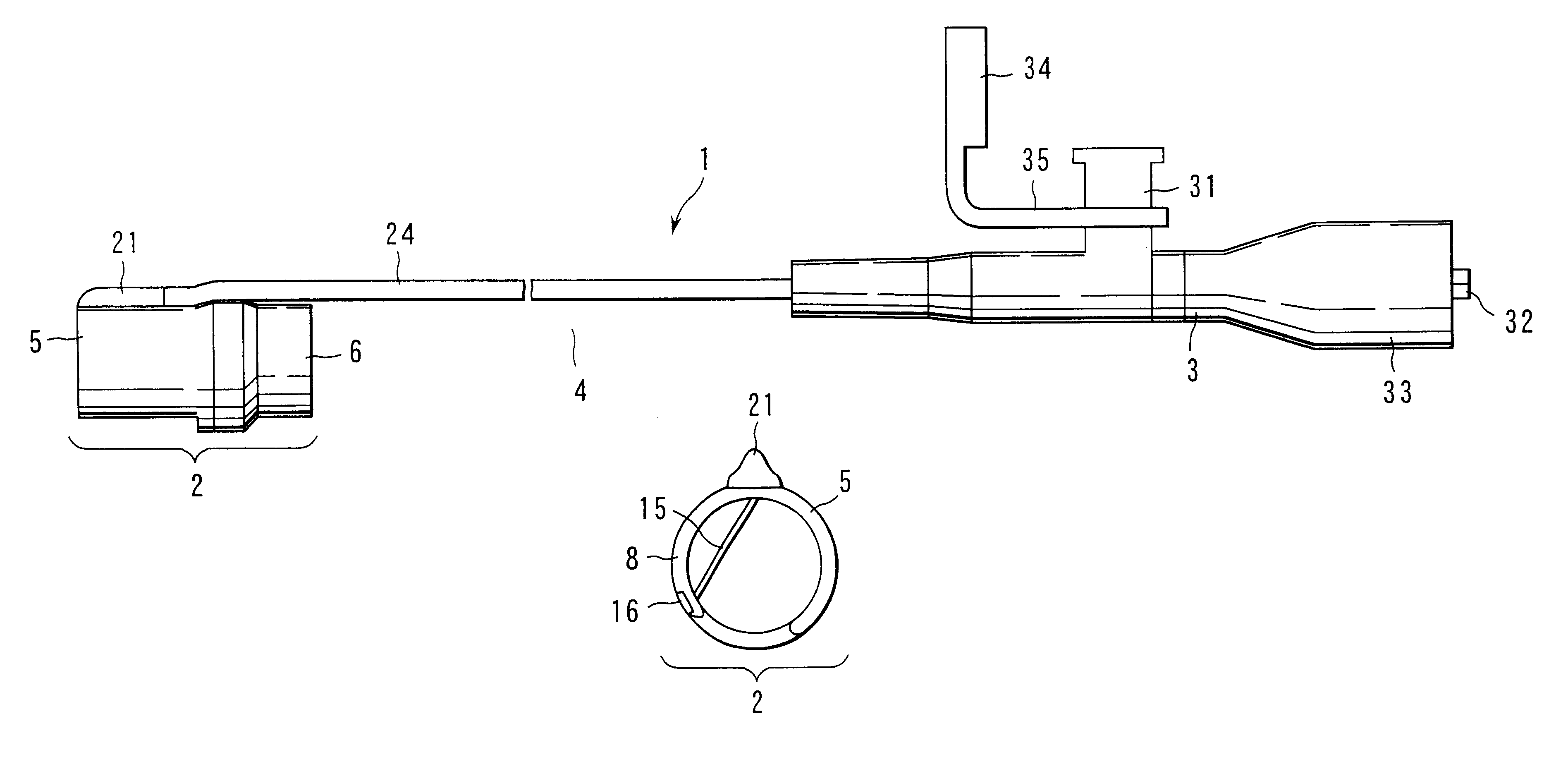
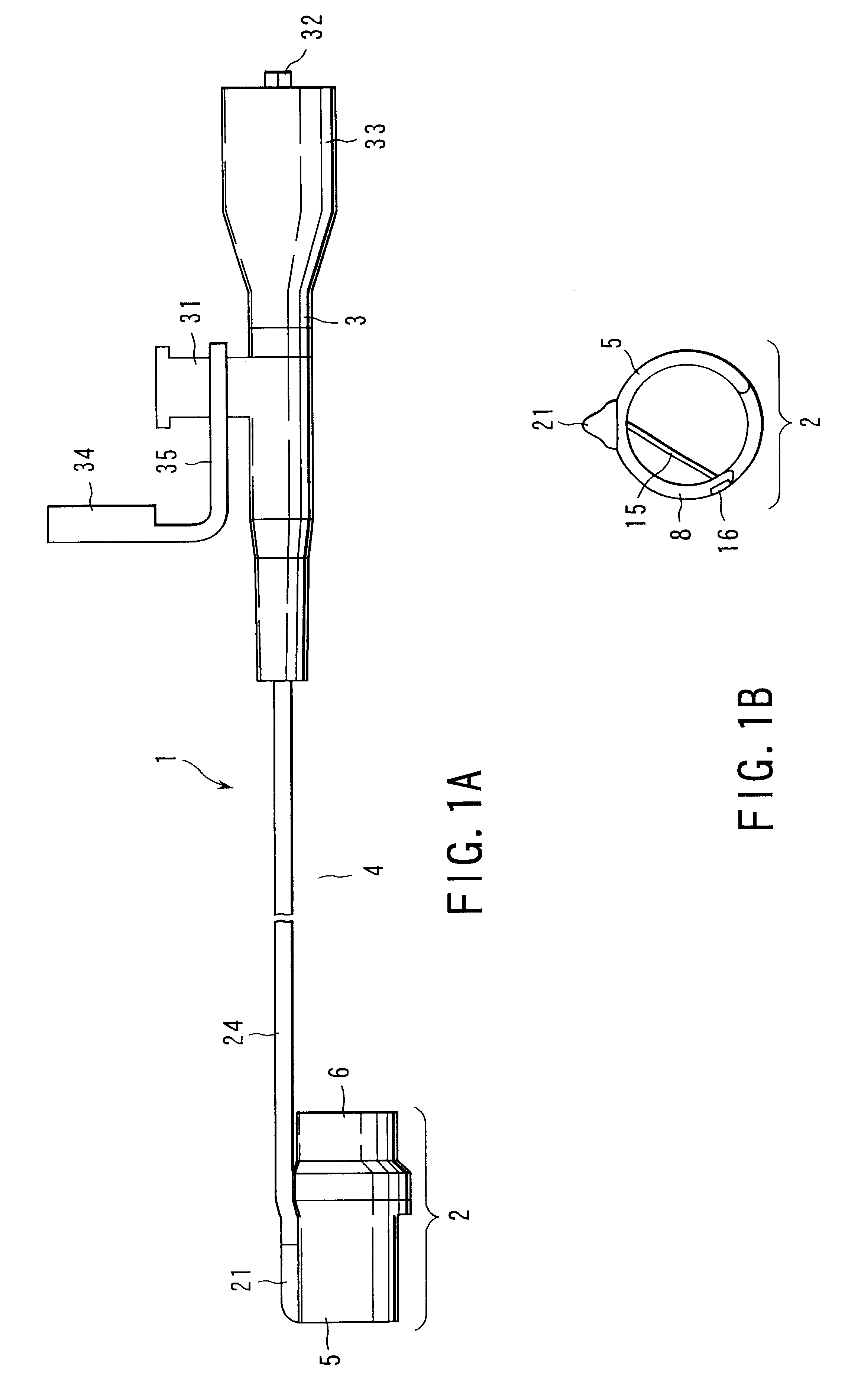
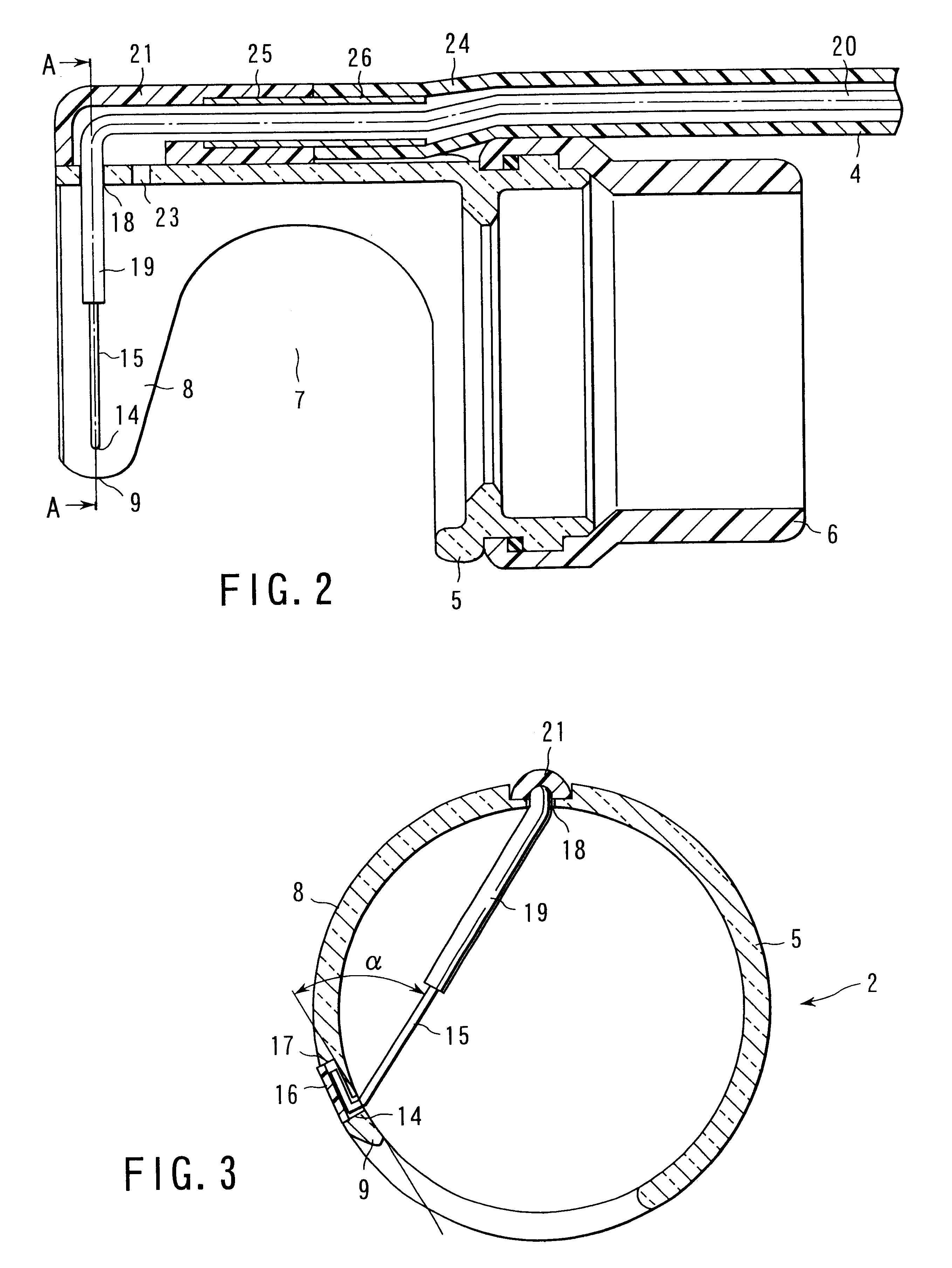
Treatment apparatus for endoscope
A treatment apparatus to treat a tissue in a body cavity is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a base disposed in the vicinity of a tip-end portion of an endoscope, and an in-tissue inserting portion including a base end supported by the base and a tip end insertable in the tissue in the body cavity in a direction substantially parallel to the surface of the tissue, and extending to the tip end from the base end in a tapered shape. The in-tissue inserting portion has an inner side disposed in the vicinity of the surface of the tissue when inserted into the tissue. The apparatus further comprises a high-frequency electrode, for treating the tissue, supported by the base and disposed in the vicinity of the inner side of the in-tissue inserting portion, and a cable which supplies power to the high-frequency electrode from a high-frequency power source outside the body.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
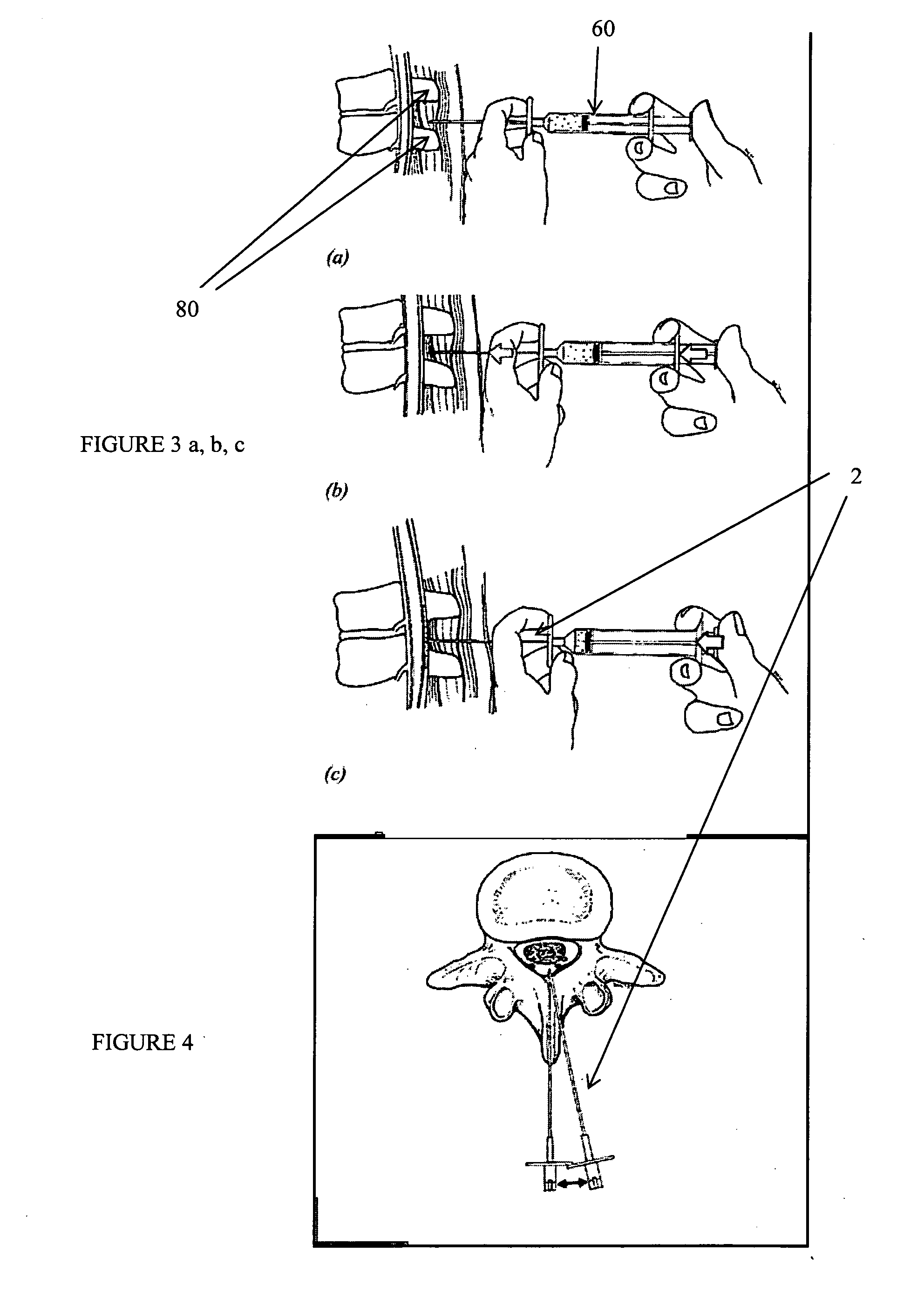
Percutaneous access device
A percutaneous access device is provided including a sleeve having an inner lumen extending therethrough that is adapted to slidably receive a catheter, and at least one flange disposed around the sleeve and adapted to be positioned adjacent a tissue surface. In a preferred embodiment, the device includes a first flange disposed around the sleeve and adapted to be positioned adjacent a first tissue surface, and a second flange disposed around the sleeve and spaced apart from the first flange such that the second flange is adapted to be disposed adjacent a second tissue surface opposed to the first tissue surface. In use, the flanges 16, 18 are positioned on opposed sides of tissue so that the device 10 is effective to prevent tissue surrounding the percutaneous access device from coming into contact with the catheter as it is introduced through the sleeve 12. The device also includes an antimicrobial agent that is effective to protect against bacterial colonization on and around the access device, the catheter, and the tissue surface surrounding the access device.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI SWITZERLAND SARL
Method for optical measurements of tissue to determine disease state or concentration of an analyte
A method for collecting optical data at two morphologically similar, substantially non-overlapping, and preferably adjacent, areas on the surface of a tissue, while the temperature in each area is being maintained or modulated according to a temperature program. The optical data obtained are inserted into a mathematical relationship, e.g., an algorithm, that can be used to predict a disease state (such as the diabetes mellitus disease state) or the concentration of an analyte for indicating a physical condition (such as blood glucose level). This invention can be used to differentiate between disease status, such as, for example, diabetic and non-diabetic. The method involves the generation of a calibration (or training) set that utilizes the relationship between optical signals emanating from the skin under different thermal stimuli and disease status, e.g., diabetic status, established clinically. This calibration set can be used to predict the disease state of other subjects. Structural changes, as well as circulatory changes, due to a disease state are determined at two morphologically similar, but substantially non-overlapping areas on the surface of human tissue, e.g., the skin of a forearm, with each area being subjected to different temperature modulation programs. In addition to determination of a disease state, this invention can also be used to determine the concentration of an analyte in the tissues. This invention also provides an apparatus for the determination of a disease state, such as diabetes, or concentration of an analyte, such as blood glucose level, by the method of this invention.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
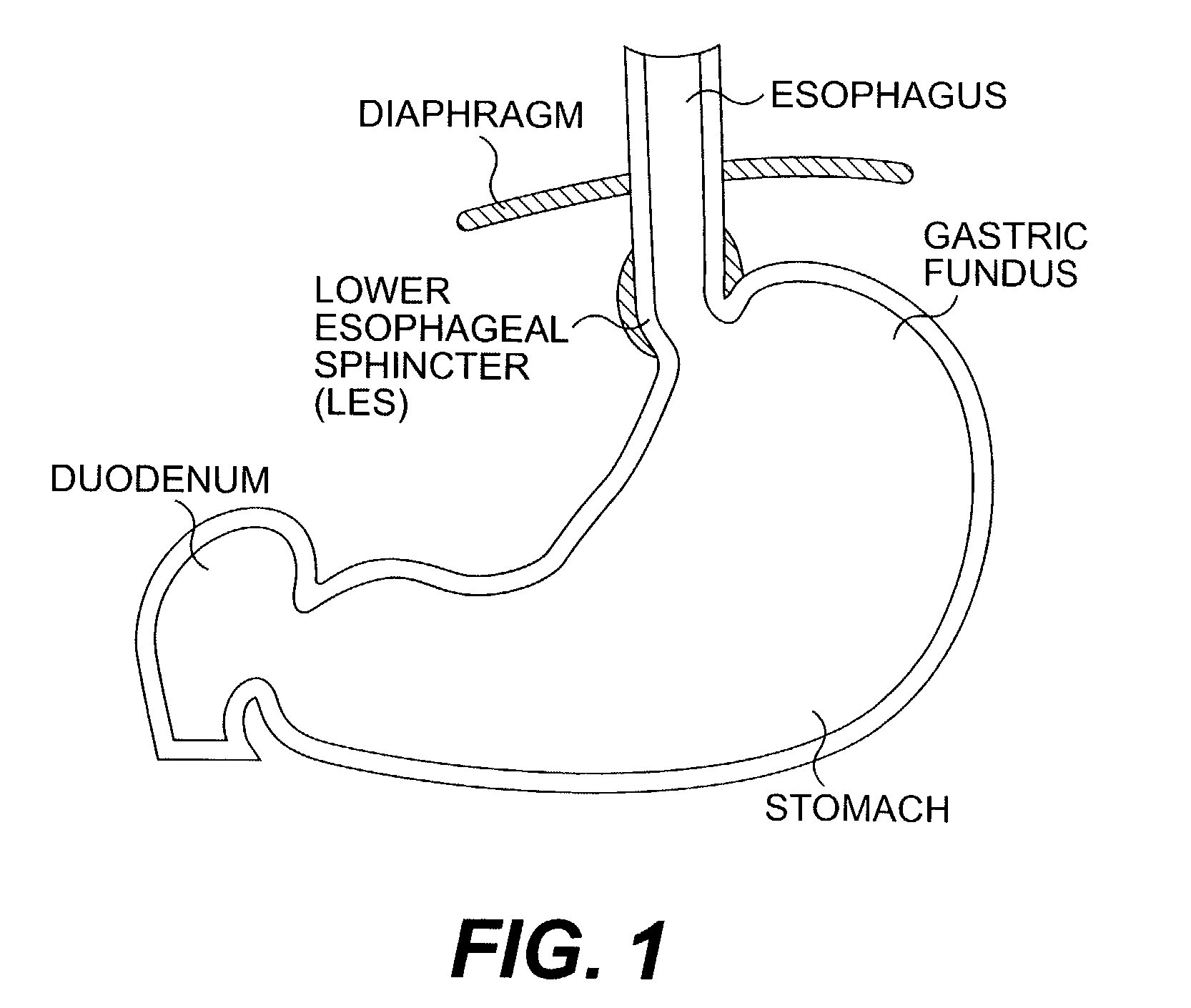
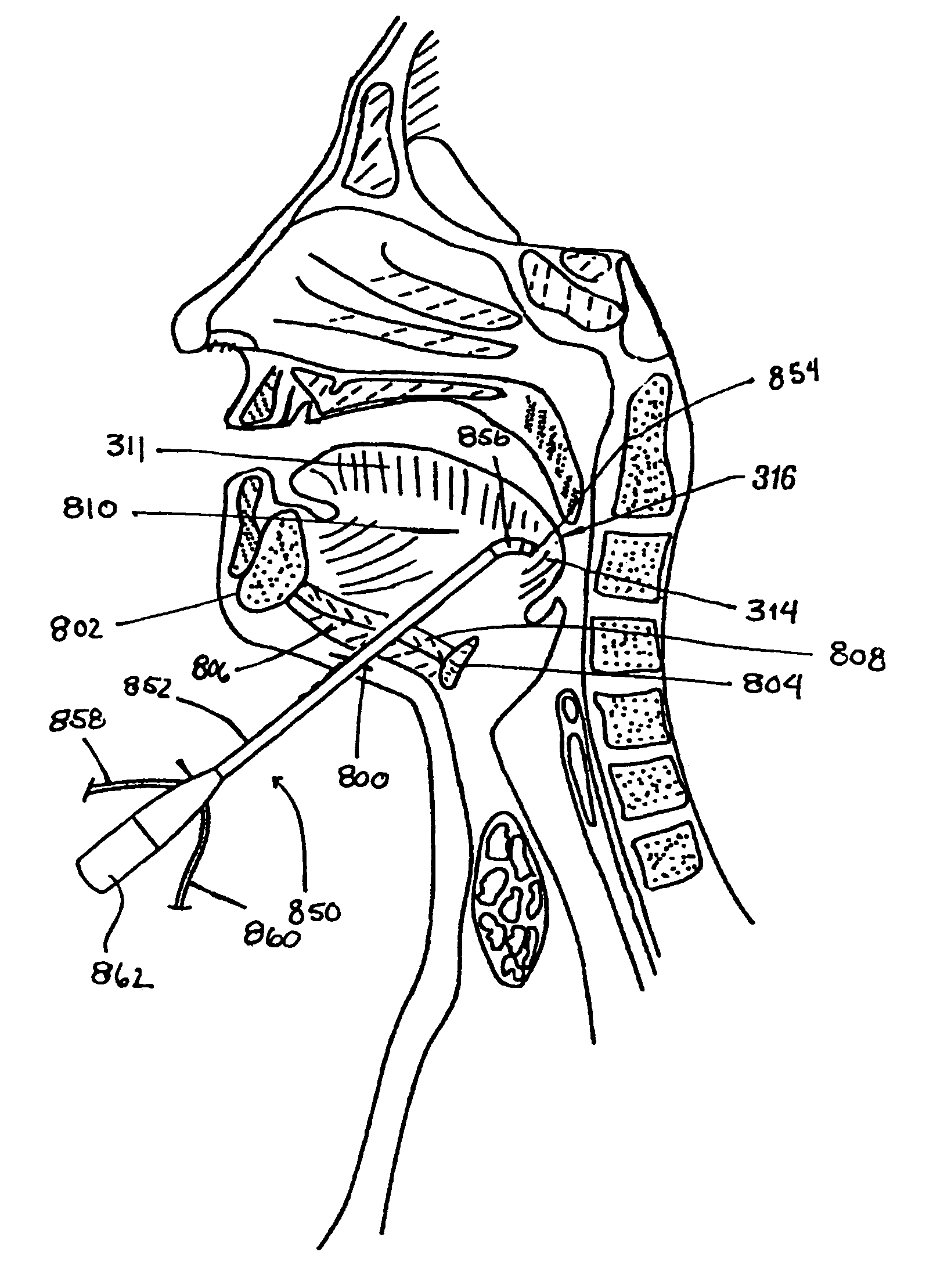
Method and apparatus for endoscopic repair of the lower esophageal sphincter
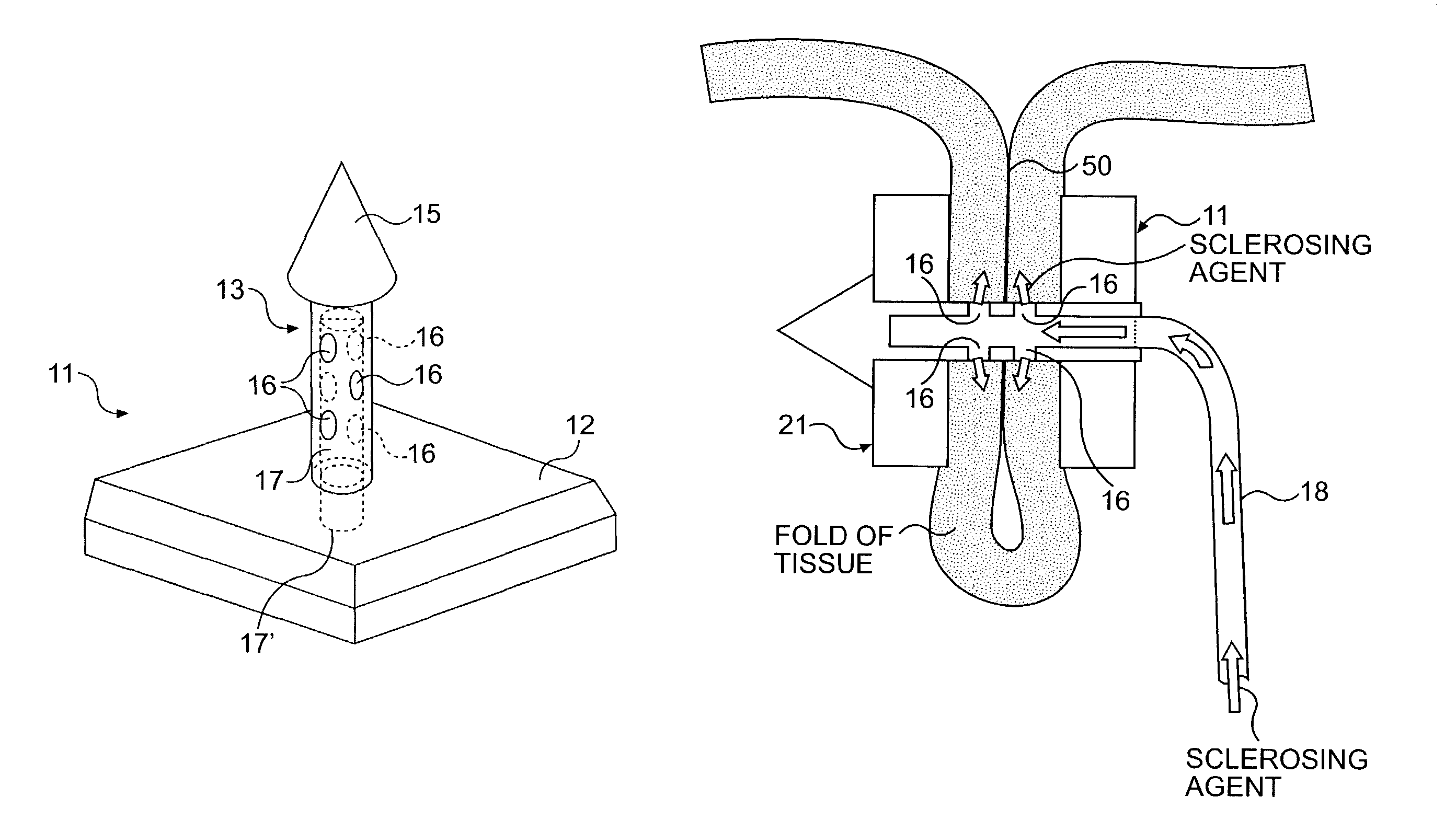
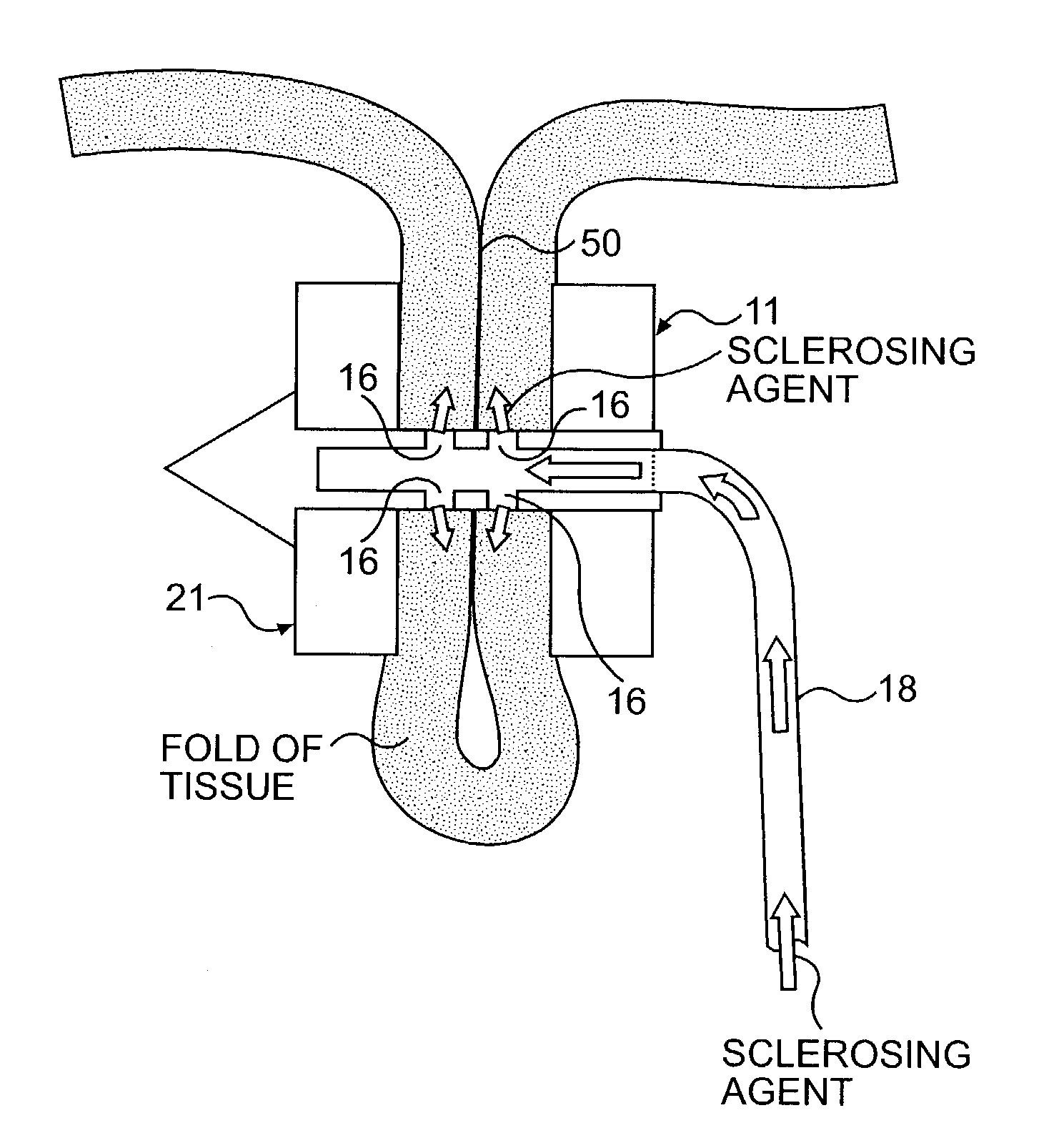
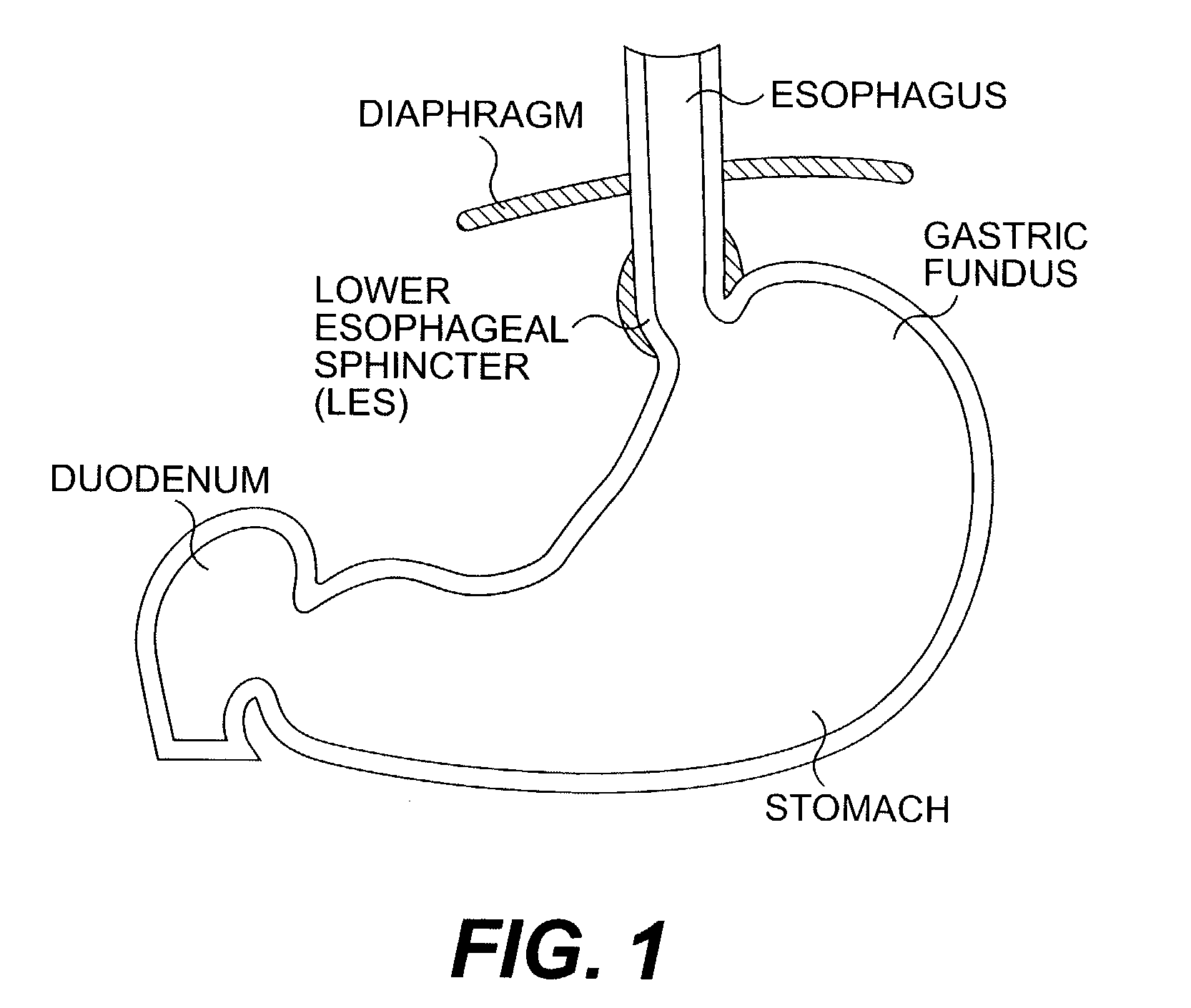
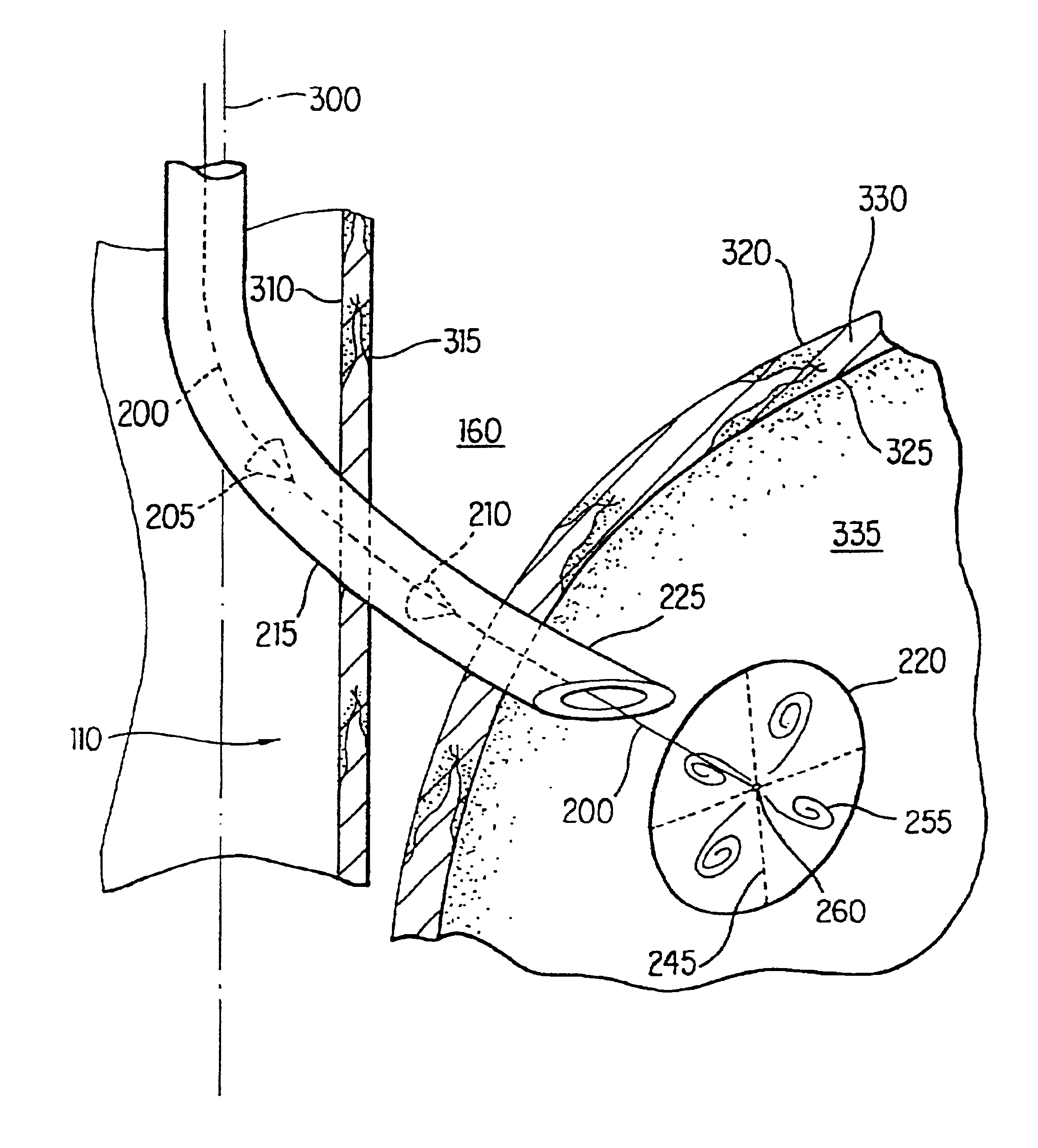
The present invention includes a method and apparatus for adhering tissue to one another. In an embodiment of the present invention the two tissues to be joined, for example the lower esophagus and the fundus of the stomach, are first placed adjacent to one another. Next a first restraint is placed near the outside surface of one of the tissues and a second restraint is placed near the outside surface of the other tissue. An irritant is then placed between the two adjacent tissues. The restraints, and consequently the tissue surfaces, are then drawn together. As the touching irritated tissue surfaces heal they will become bonded to one another and their need for the mechanical fastening of the restraints, to secure them together, will be diminished.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Medical instruments and methods for using the same
InactiveUS20070185506A1Quickly and easily releasingAttachment of the sheet to the surface quicker and easierDisinfectionProsthesisHuman bodyHernia surgical mesh
A medical instrument used to position a surgical mesh sheet to a surface of the human body. The instrument contains a mechanism for holding the mesh sheet against the tissue surface in more than two locations during the attaching process, making attachment of the sheet to the surface quicker and easier. The instrument also contains a mechanism for grasping and then quickly and easily releasing the mesh sheet from the instrument once it is in place. The invention can also be used to hold the mesh in position without the use of the mechanism that grips the mesh.
Owner:JACKSON KELLY
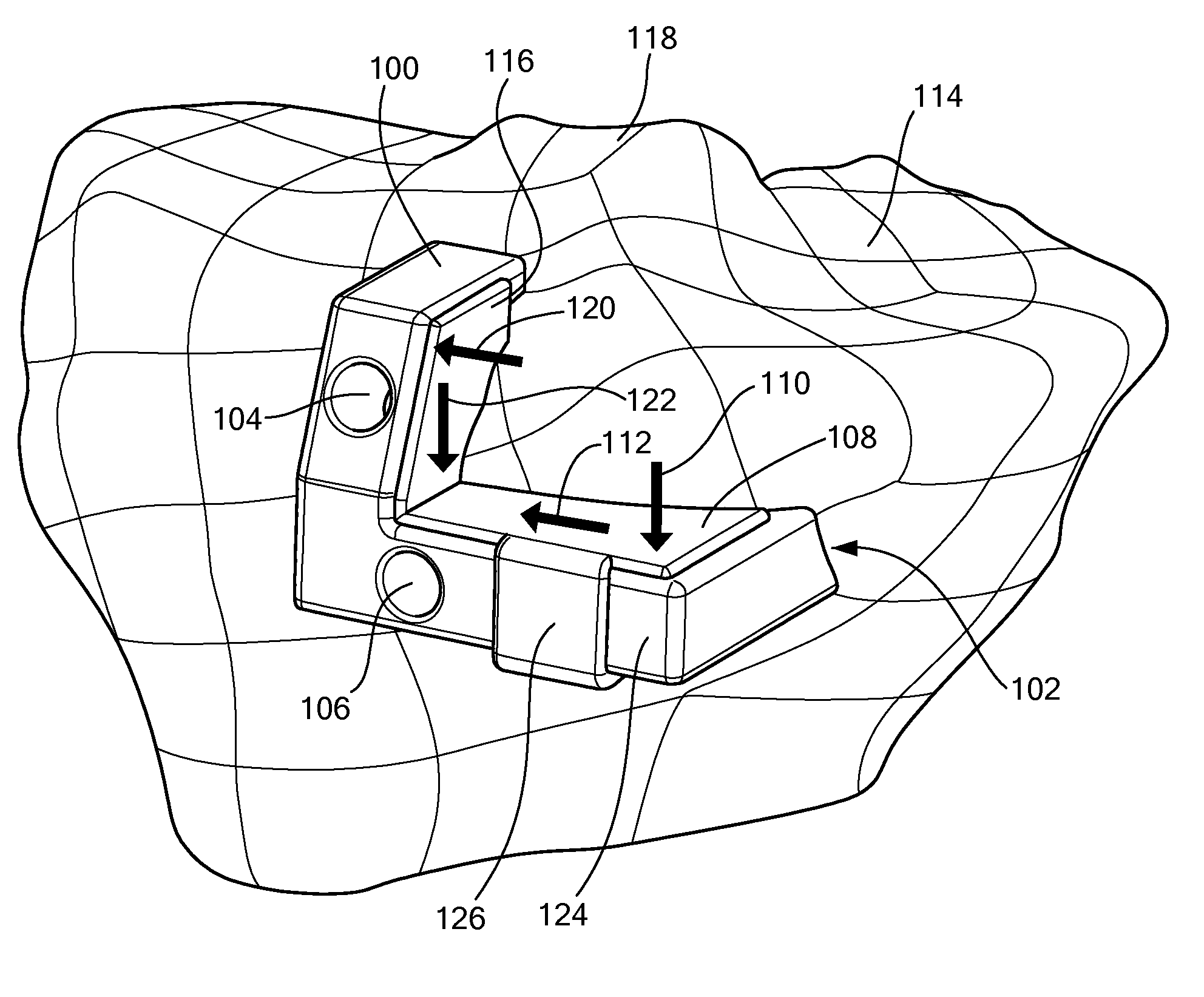
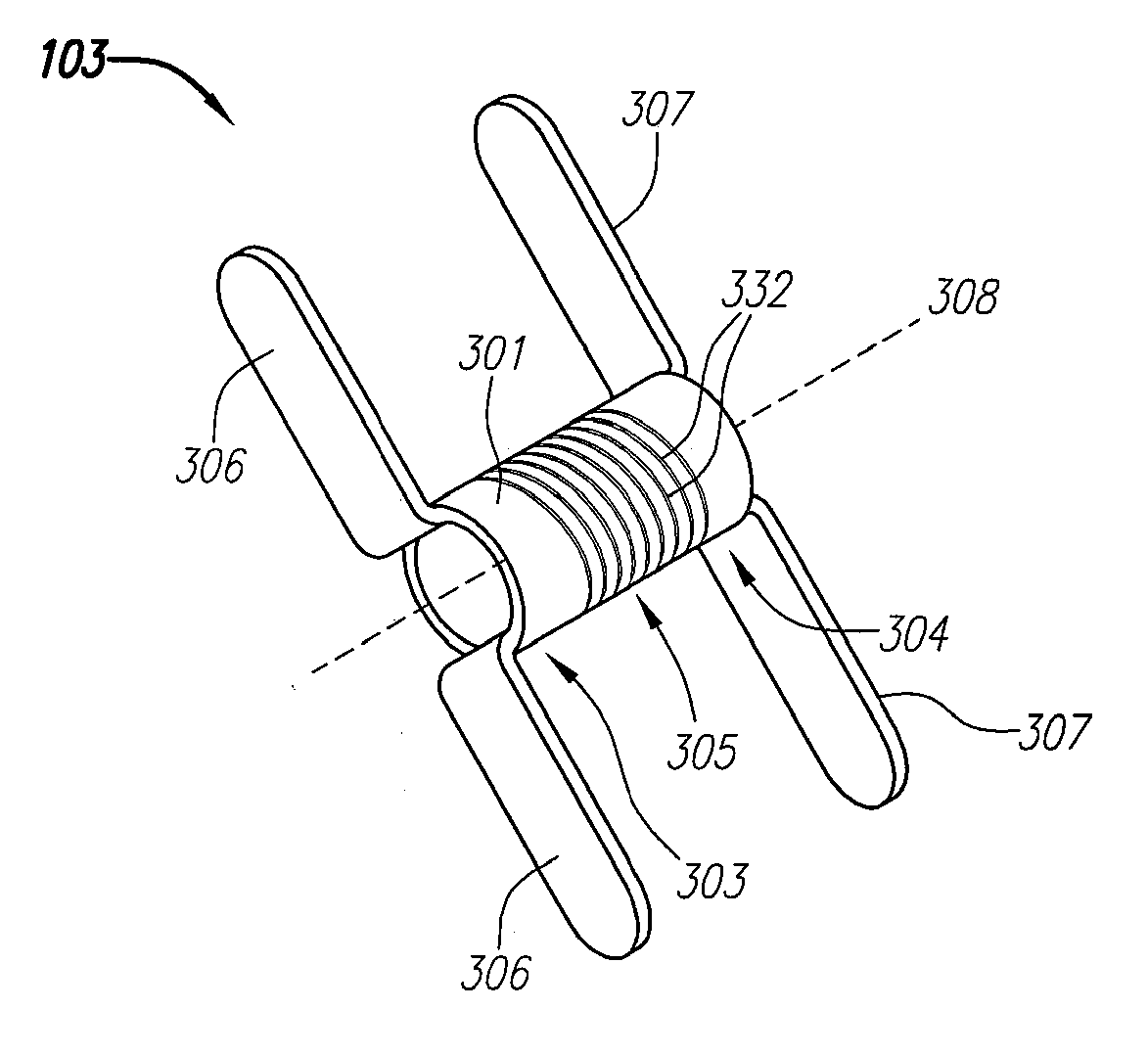
Clip-Based Systems And Methods For Treating Septal Defects
Systems and methods for treating internal tissue defects, such as septal defects, with clip-based devices are provided. An exemplary clip-based device includes a tubular body having at least a first and a second deflectable member coupled thereto. The first and second members are coupled on opposite ends of the tubular body and configured to deflect between an undeployed configuration and a deployed configuration. In the deployed configuration, each member extends outwardly away from the tubular body in a position configured to abut a tissue surface. The first and second members are preferably configured to maintain a tissue wall therebetween and at least partially close any opening in the tissue wall.
Owner:ABBOTT RYAN +6
Surgical tool positioning based on sensed parameters
ActiveUS10398517B2Slow its advancementSurface be reducedProgramme controlProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringActuator
Devices, systems, and methods are provided in which movement of a tool is controlled based on sensed parameters. In one embodiment, an electromechanical tool is provided having an instrument shaft and an end effector formed thereon. The electromechanical tool is configured to be mounted on an electromechanical arm, and the electromechanical tool is configured to move with or relative to the electromechanical arm and perform surgical functions. A controller is operatively coupled to the electromechanical arm and the electromechanical tool and is configured to retard advancement of the electromechanical tool toward a tissue surface based on a sensed amount of displacement of a tissue surface, a strain on the tissue of the patient, the temperature of the electromechanical tool, or the like.
Owner:CILAG GMBH INT
Devices and methods for tissue access
InactiveUS20060122458A1Enabling symptomatic reliefApproach can be quite invasiveCannulasDiagnosticsSurgical departmentNerve stimulation
Methods and apparatus are provided for selective surgical removal of tissue, e.g., for enlargement of diseased spinal structures, such as impinged lateral recesses and pathologically narrowed neural foramen. In one variation, tissue may be ablated, resected, removed, or otherwise remodeled by standard small endoscopic tools delivered into the epidural space through an epidural needle. Once the sharp tip of the needle is in the epidural space, it is converted to a blunt tipped instrument for further safe advancement. A specially designed epidural catheter that is used to cover the previously sharp needle tip may also contain a fiberoptic cable. Further embodiments of the current invention include a double barreled epidural needle or other means for placement of a working channel for the placement of tools within the epidural space, beside the epidural instrument. The current invention includes specific tools that enable safe tissue modification in the epidural space, including a barrier that separates the area where tissue modification will take place from adjacent vulnerable neural and vascular structures. In one variation, a tissue removal device is provided including a thin belt or ribbon with an abrasive cutting surface. The device may be placed through the neural foramina of the spine and around the anterior border of a facet joint. Once properly positioned, a medical practitioner may enlarge the lateral recess and neural foramina via frictional abrasion, i.e., by sliding the tissue removal surface of the ribbon across impinging tissues. A nerve stimulator optionally may be provided to reduce a risk of inadvertent neural abrasion. Additionally, safe epidural placement of the working barrier and epidural tissue modification tools may be further improved with the use of electrical nerve stimulation capabilities within the invention that, when combined with neural stimulation monitors, provide neural localization capabilities to the surgeon. The device optionally may be placed within a protective sheath that exposes the abrasive surface of the ribbon only in the area where tissue removal is desired. Furthermore, an endoscope may be incorporated into the device in order to monitor safe tissue removal. Finally, tissue remodeling within the epidural space may be ensured through the placement of compression dressings against remodeled tissue surfaces, or through the placement of tissue retention straps, belts or cables that are wrapped around and pull under tension aspects of the impinging soft tissue and bone in the posterior spinal canal.
Owner:BAXANO
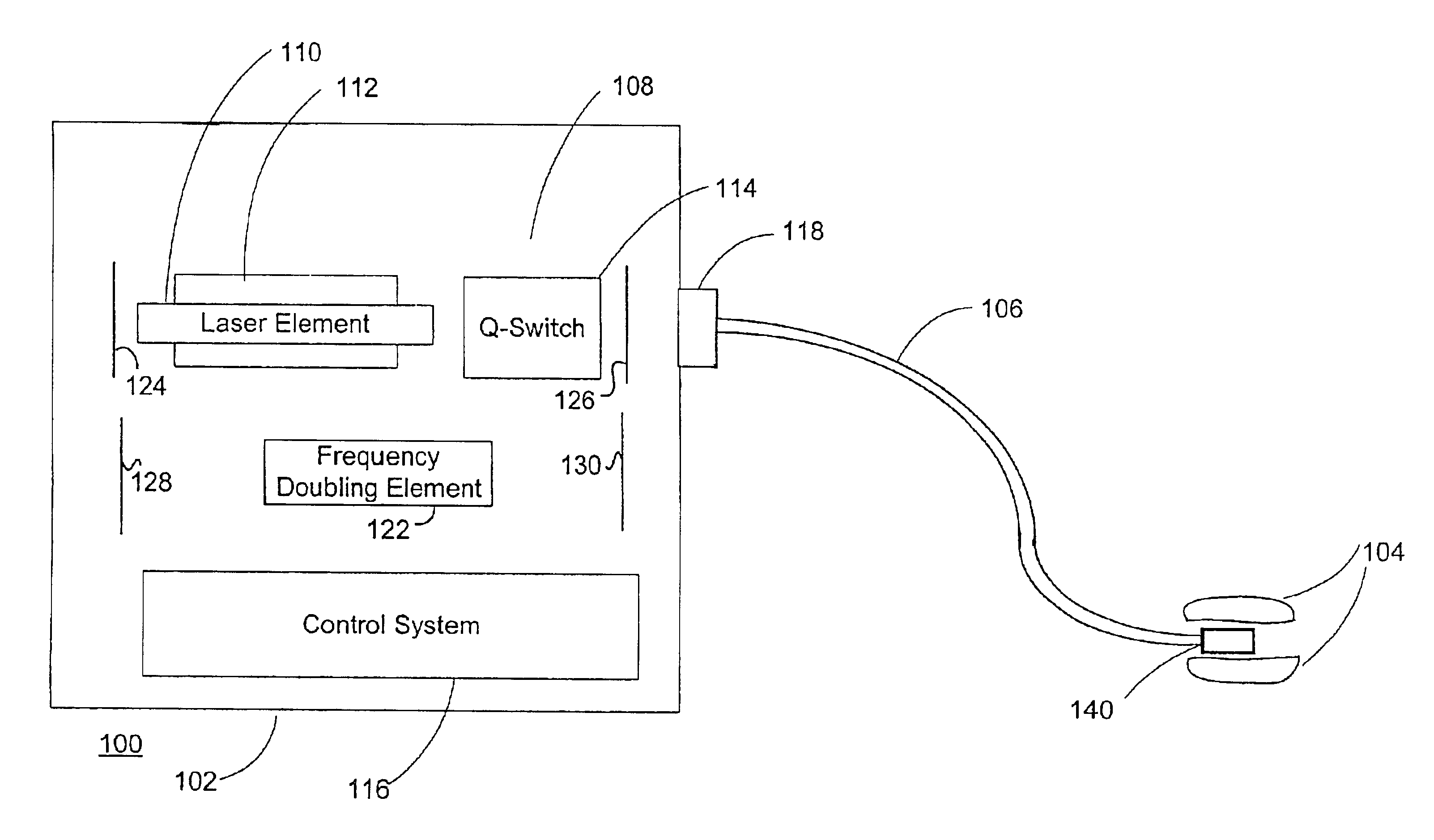
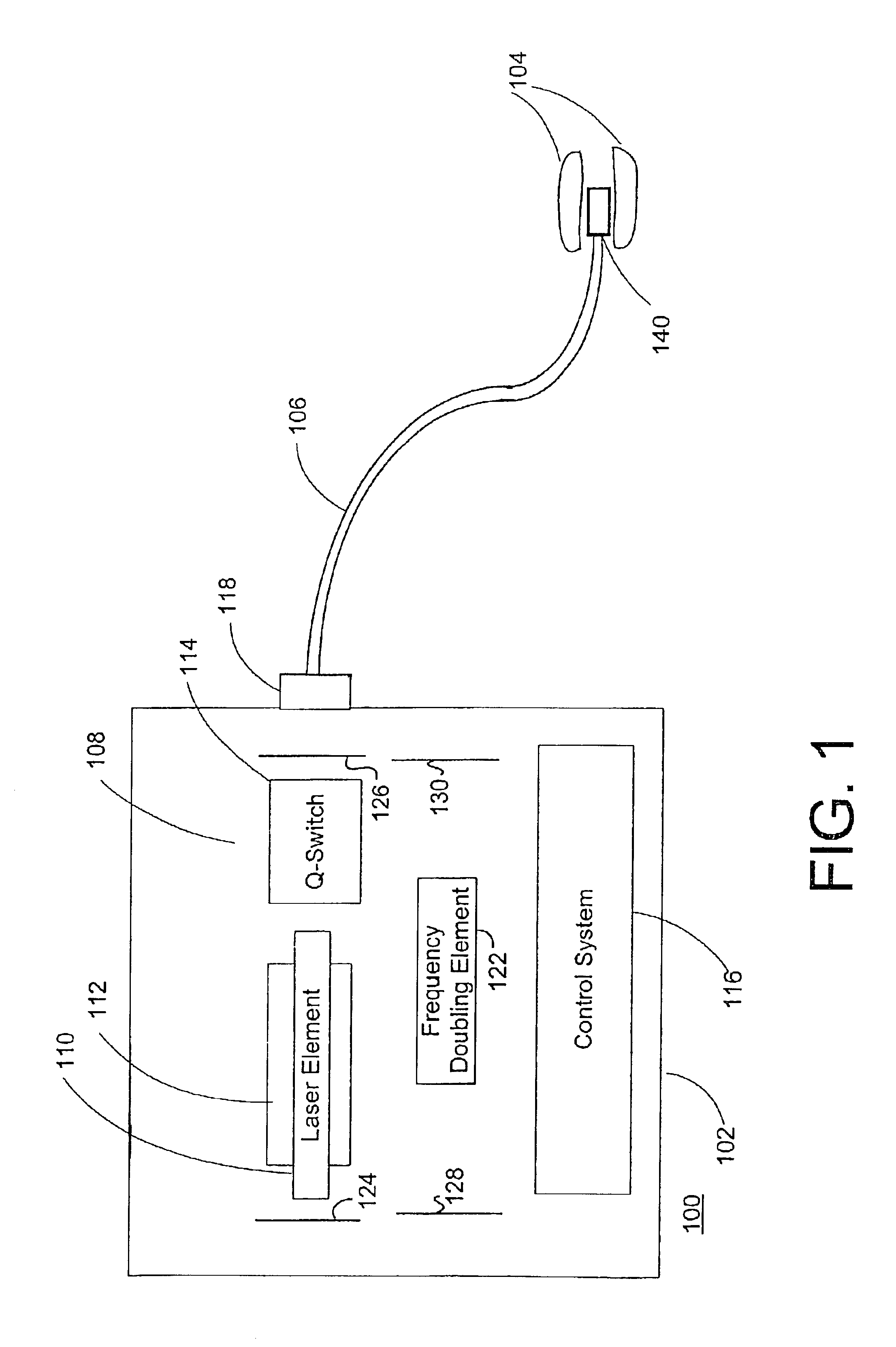
Method and system for photoselective vaporization of the prostate, and other tissue
InactiveUS6986764B2Reduce incidenceLess side effectsEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsOptical radiationMedicine
A method for photoselective vaporization of prostate tissue includes delivering laser radiation to the treatment area on the tissue, via an optical fiber for example, wherein the laser radiation has a wavelength and irradiance in the treatment area on the surface of the tissue sufficient because vaporization of a substantially greater volume of tissue than a volume of residual coagulated tissue caused by the laser radiation. The laser radiation is generated using a neodymium doped solid-state laser, including optics producing a second or higher harmonic output with greater than 60 watts average output power. The delivered laser radiation has a wavelength for example in a range of about 200 nm to about 650 nm, and has an average irradiance in the treatment area greater than about 10 kilowatts / cm2, in a spot size of at least 0.05 mm2.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
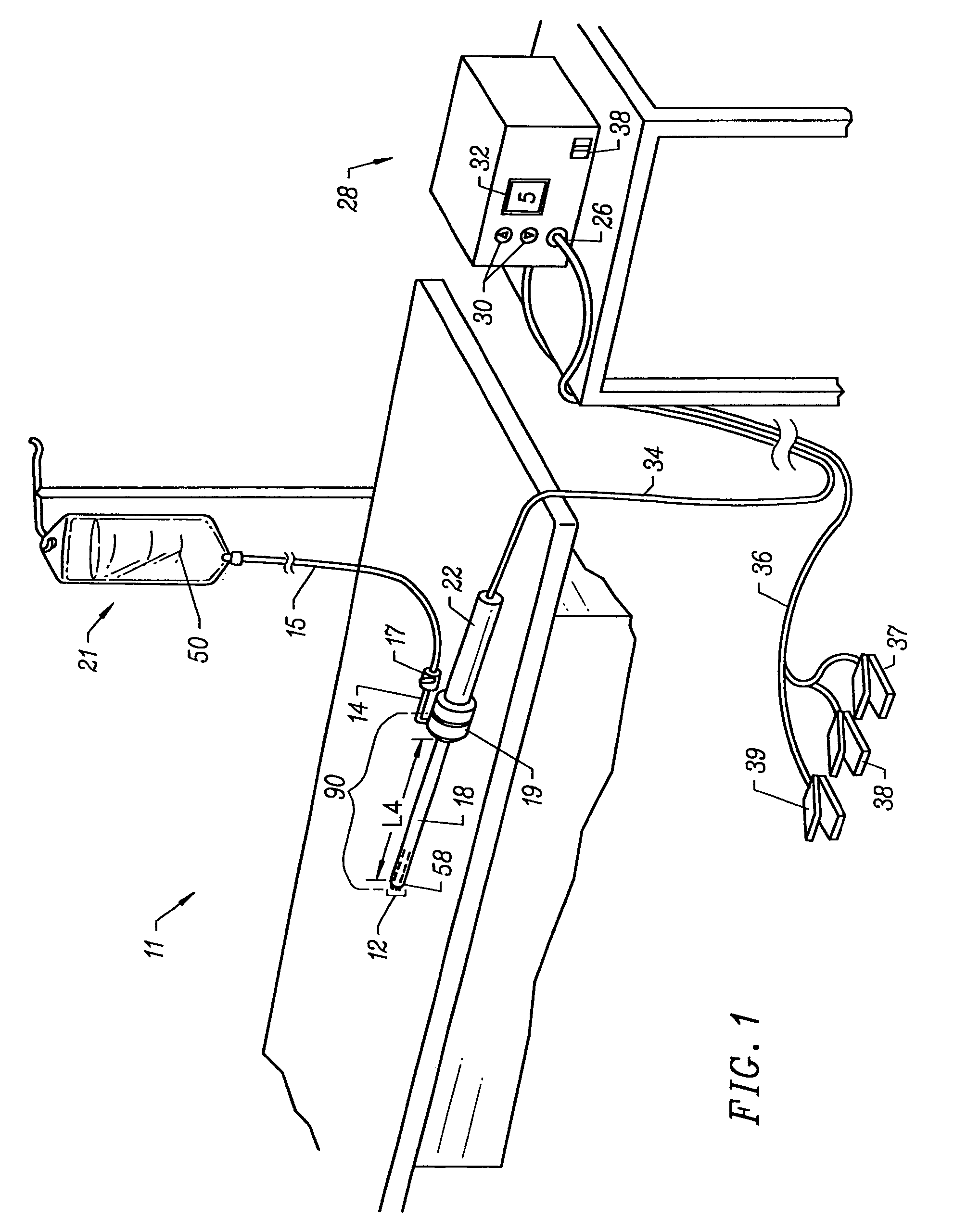
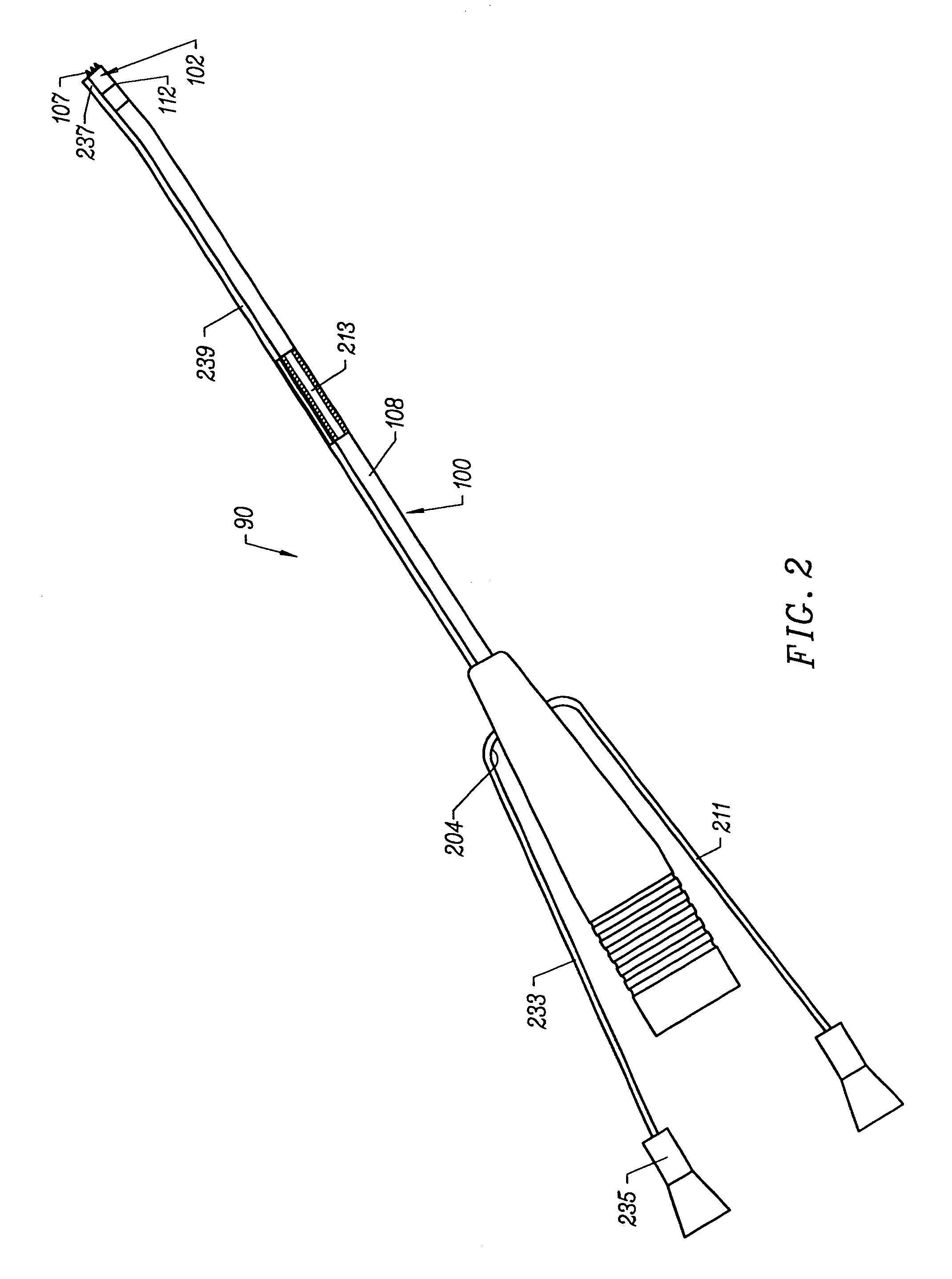
Electrical means to normalize ablational energy transmission to a luminal tissue surface of varying size
Methods and devices for measuring the size of a body lumen and a method for ablating tissue that uses the measurement to normalize delivery of ablational energy from an expandable operative element to a luminal target of varying circumference are provided. The method includes inserting into the lumen an expandable operative element having circuitry with resistivity or inductance that varies according to the circumference of the operative element, varying the expansion of the operative element with an expansion medium, measuring the resistivity of the circuitry, and relating the resistivity or inductance to a value for the circumference of the operative element. In some embodiments the sizing circuit includes a conductive elastomer wrapped around the operative element. Other embodiments of the method apply to operative elements that include an overlapping energy delivery element support in which the overlap varies inversely with respect to the state of expansion, and which is configured with sizing electrodes that sense the amount of the overlap.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Ultrasonic wound debrider probe and method of use
ActiveUS7931611B2Shorten the timeImprove surgical efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryUltrasonic cavitationMedical treatment
An ultrasonic medical probe comprises an elongate shaft formed integrally with a head portion having a distal end face oriented at least partially transversely to a longitudinal axis of the shaft. The shaft is provided with an internal longitudinal channel or bore extending to the end face. The end face is formed with an indentation communicating with the channel or bore at a distal end thereof, whereby liquid is guided over an extended surface of the end face relative to the channel or bore. The head portion also has a lateral surface extending substantially parallel to the longitudinal axis of the probe. The lateral surface is provided with at least one outwardly or radially extending projection. The projection enables the application of ultrasonic cavitation energy to a tissue surface that is in contact with the lateral or side surface of the probe head.
Owner:MISONIX INC
Device and method for forming a lesion
InactiveUS20020128639A1Minimize complexityLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCannulasControl systemEngineering
A control system alters one or more characteristics of an ablating element to ablate tissue. In one aspect, the control system delivers energy nearer to the surface of the tissue by changing the frequency or power. In another aspect, the ablating element delivers focused ultrasound which is focused in at least one dimension. The ablating device may also have a number of ablating elements with different characteristics such as focal length.
Owner:EPICOR
Surface electromyographic electrode assembly
InactiveUS6865409B2Easily conform to body contourAvoid pollutionSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical conductorEngineering
An electrode assembly for use on a surface of biological tissue to measure bio-electric signals including an electrode apparatus having an electrode device adapted to directly contact the surface of the biological tissue. The electrode apparatus receives and transmits bio-electric signals measured across the biological tissue having a first voltage and a minute first current. A signal transmission line is included having a signal transmission conductor electrically coupled at one portion to the electrode device for transmission of the bio-electric signals. The transmission includes a second conductor electrically coupled to the amplifier apparatus and arranged to substantially shield the transmission conductor from ambient electric fields generated from sources external to the transmission line. A high impedance amplifier device is included having a signal input and a signal output. The signal input is electrically coupled to another portion of the signal transmission conductor for receipt of the transmitted bio-electric signals. The signal output is electrically coupled to the shield conductor, in a feedback loop, for receipt of at least a portion of the transmitted bio-electric signals, such that the voltage of the signals at the signal input of the high impedance amplifier device is maintained substantially equal to the voltage of the signals output from the signal output thereof.
Owner:KINESENSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com