Patents
Literature
201 results about "Epidural space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
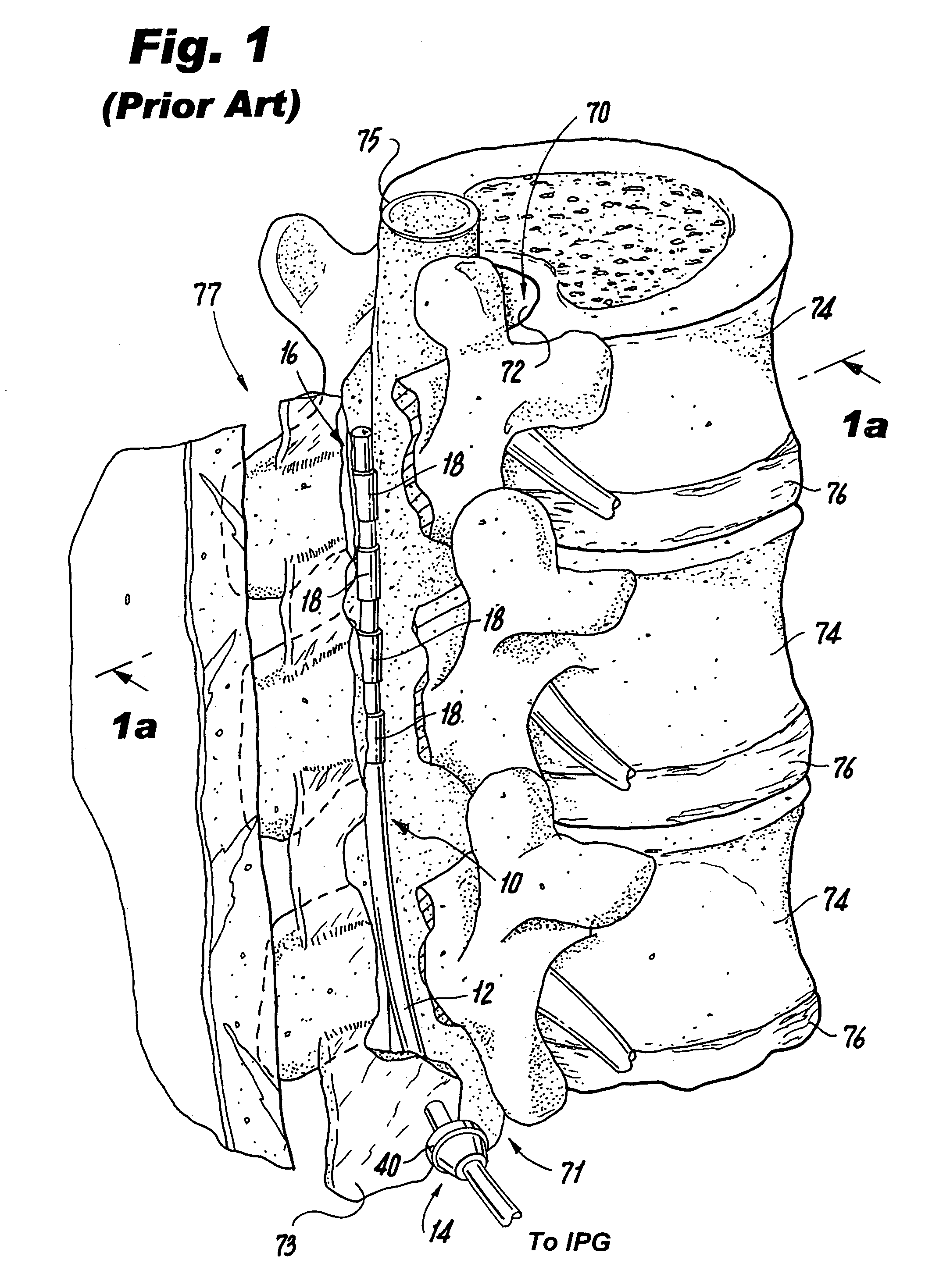
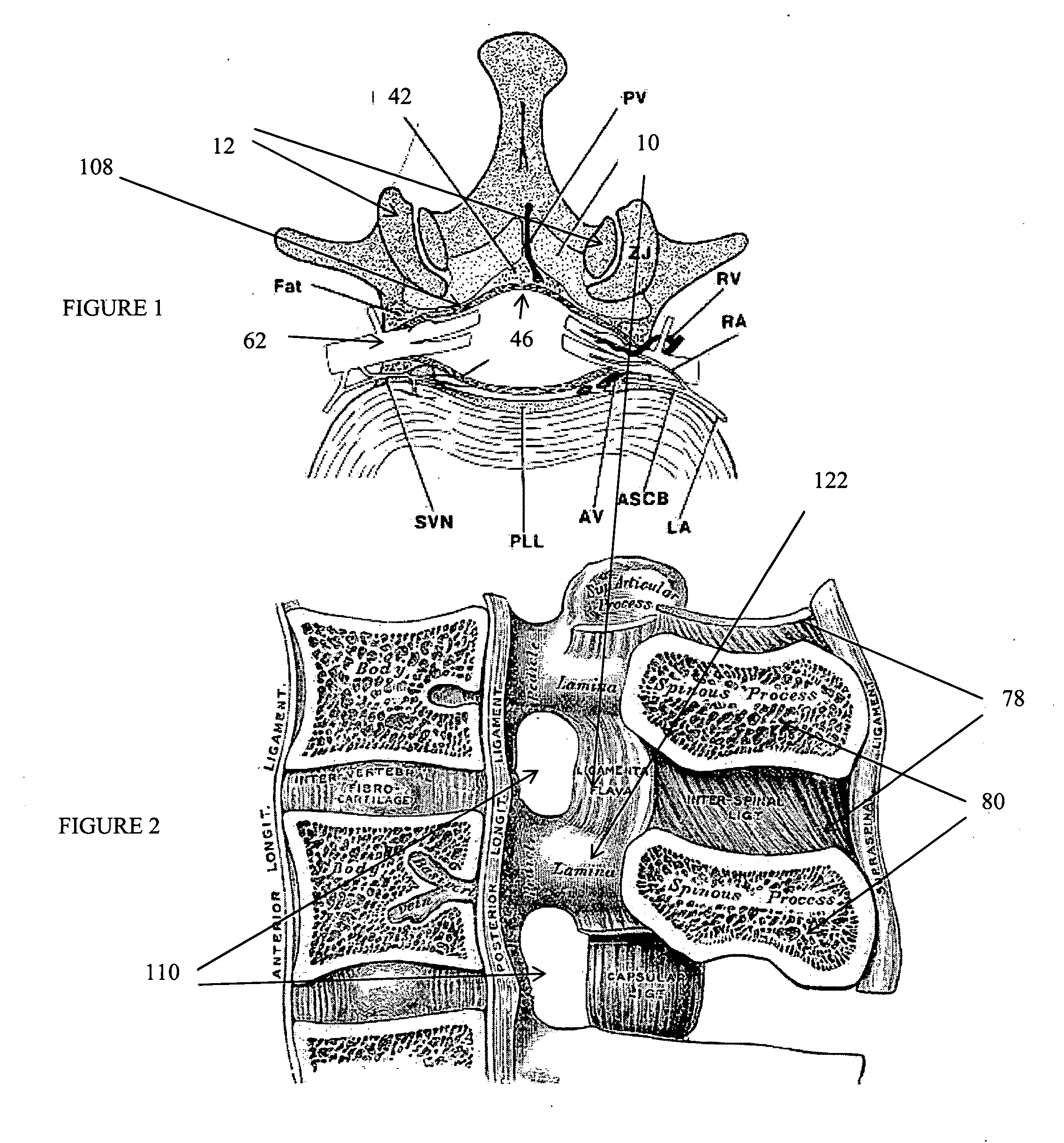
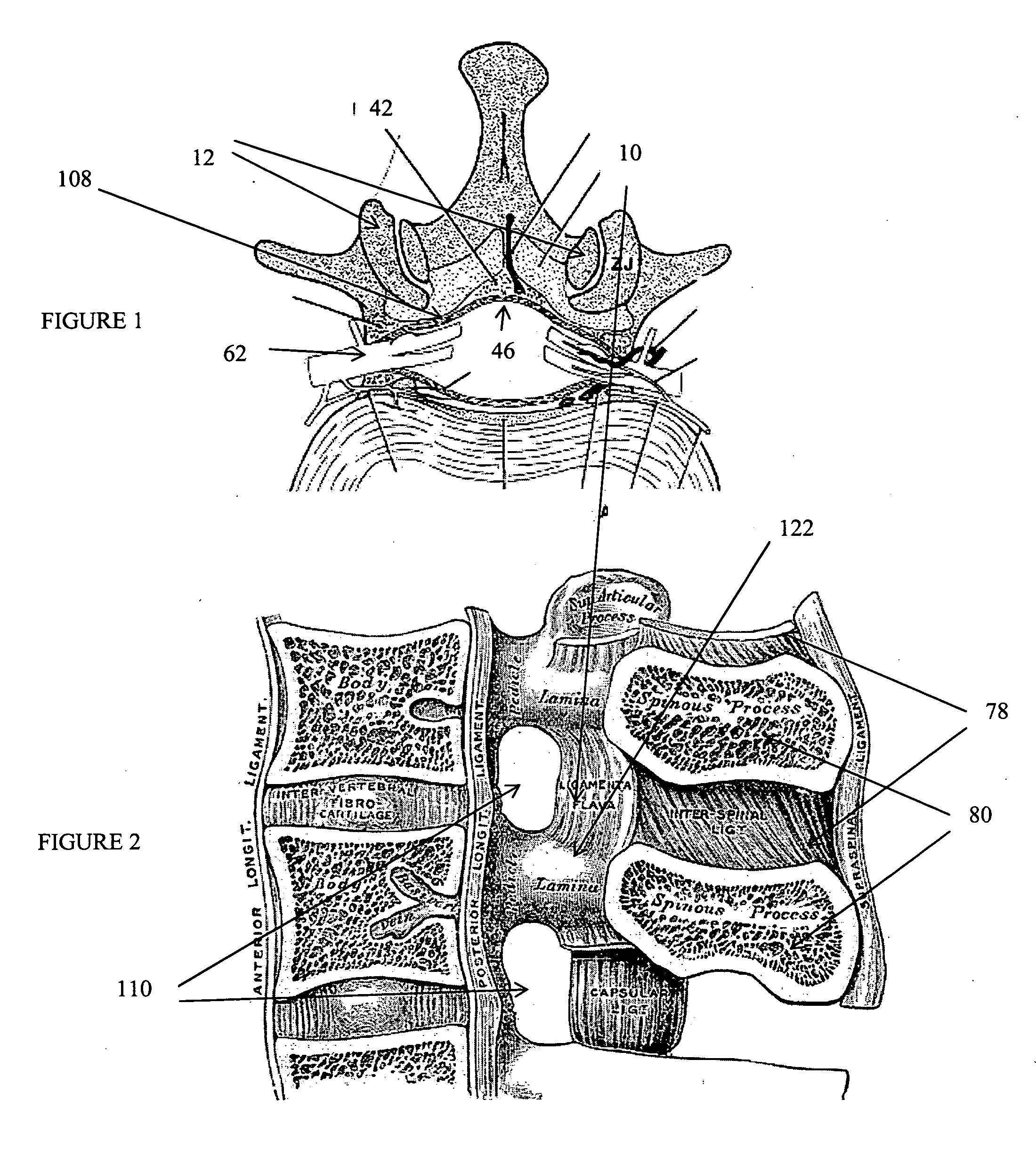
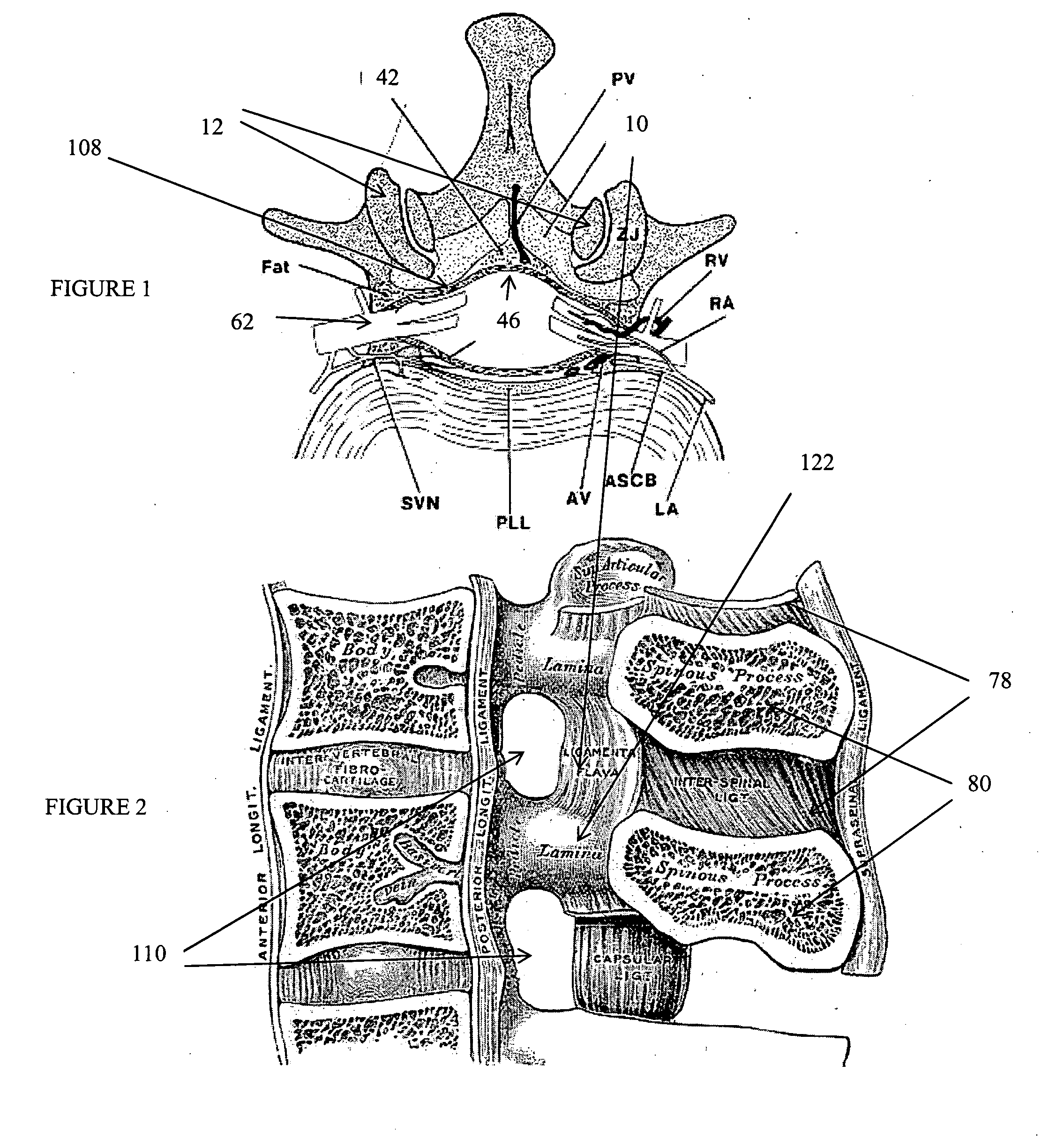
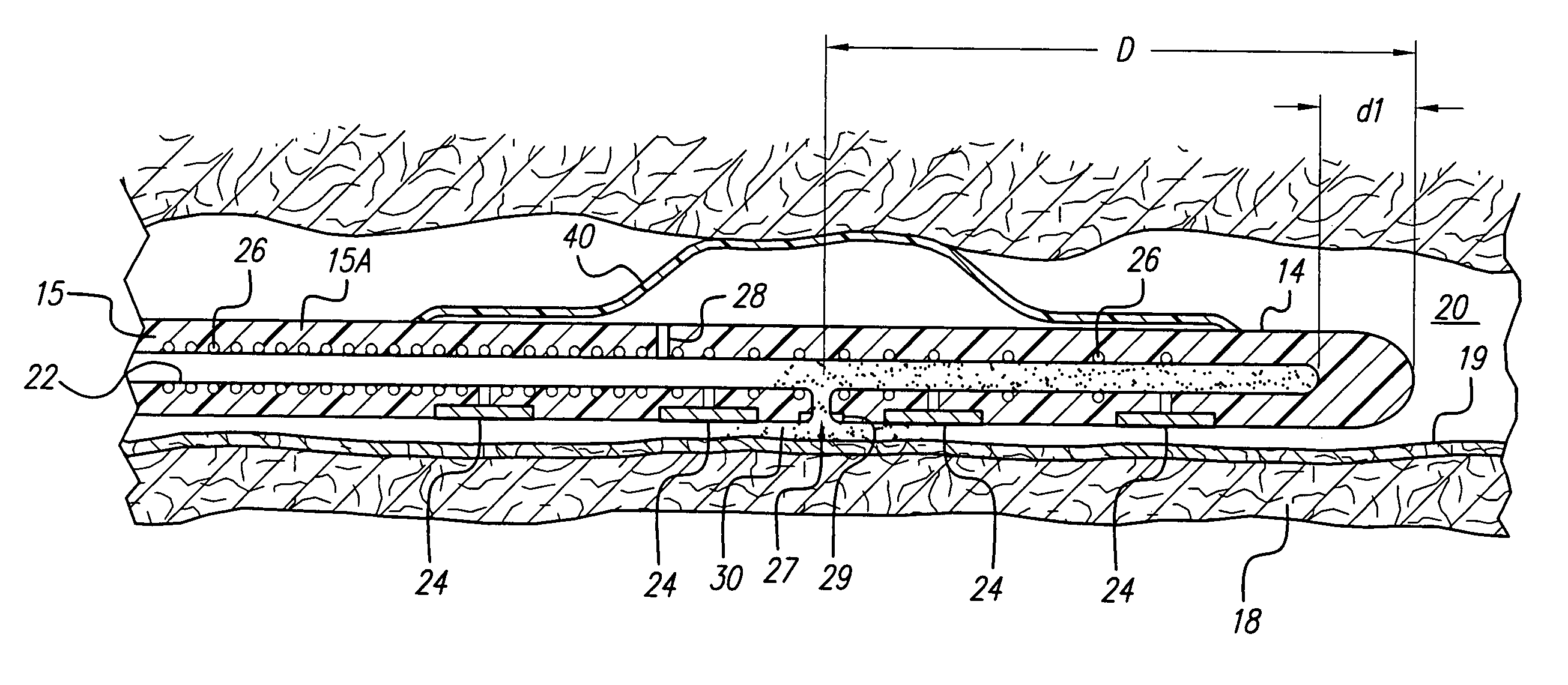
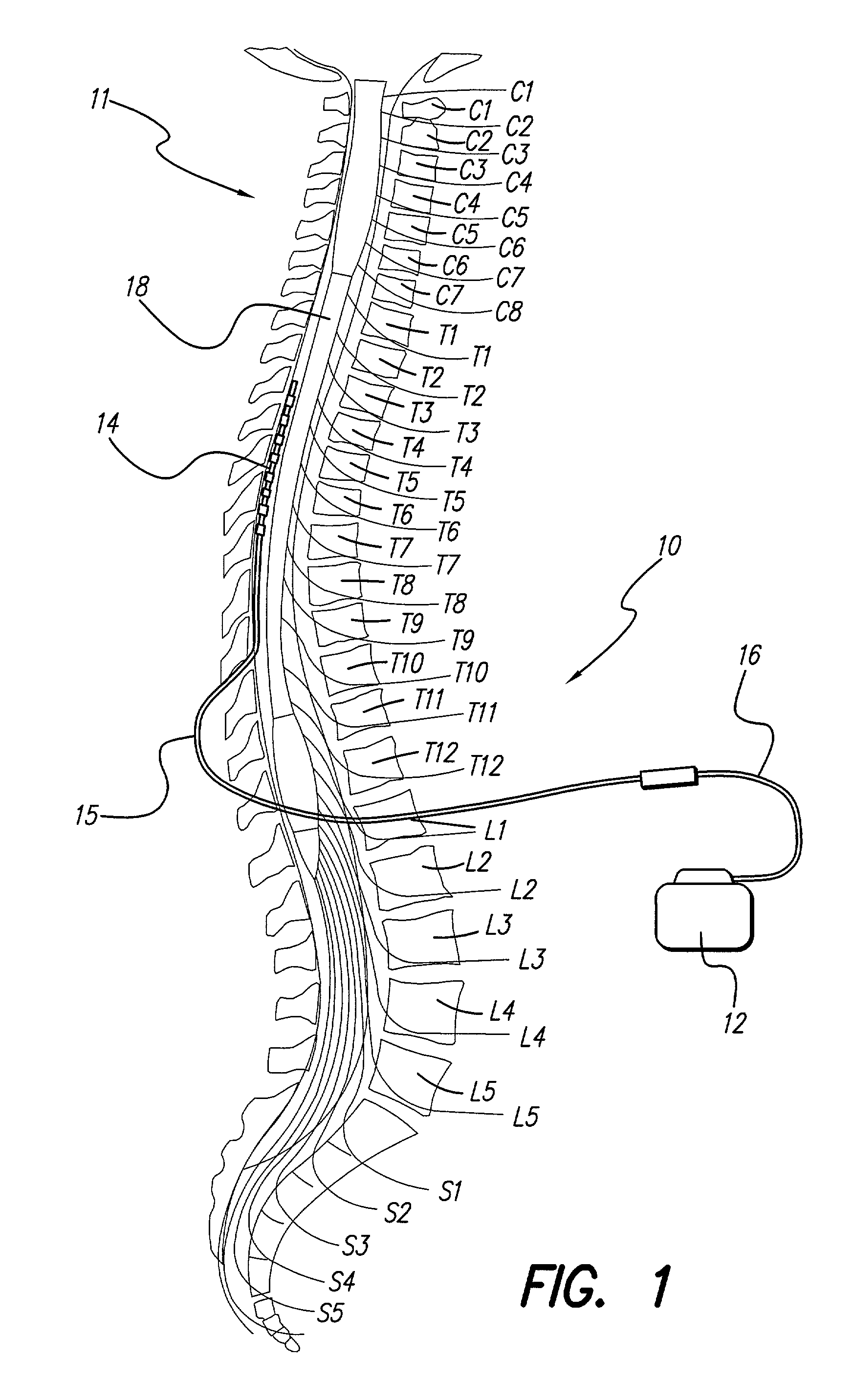
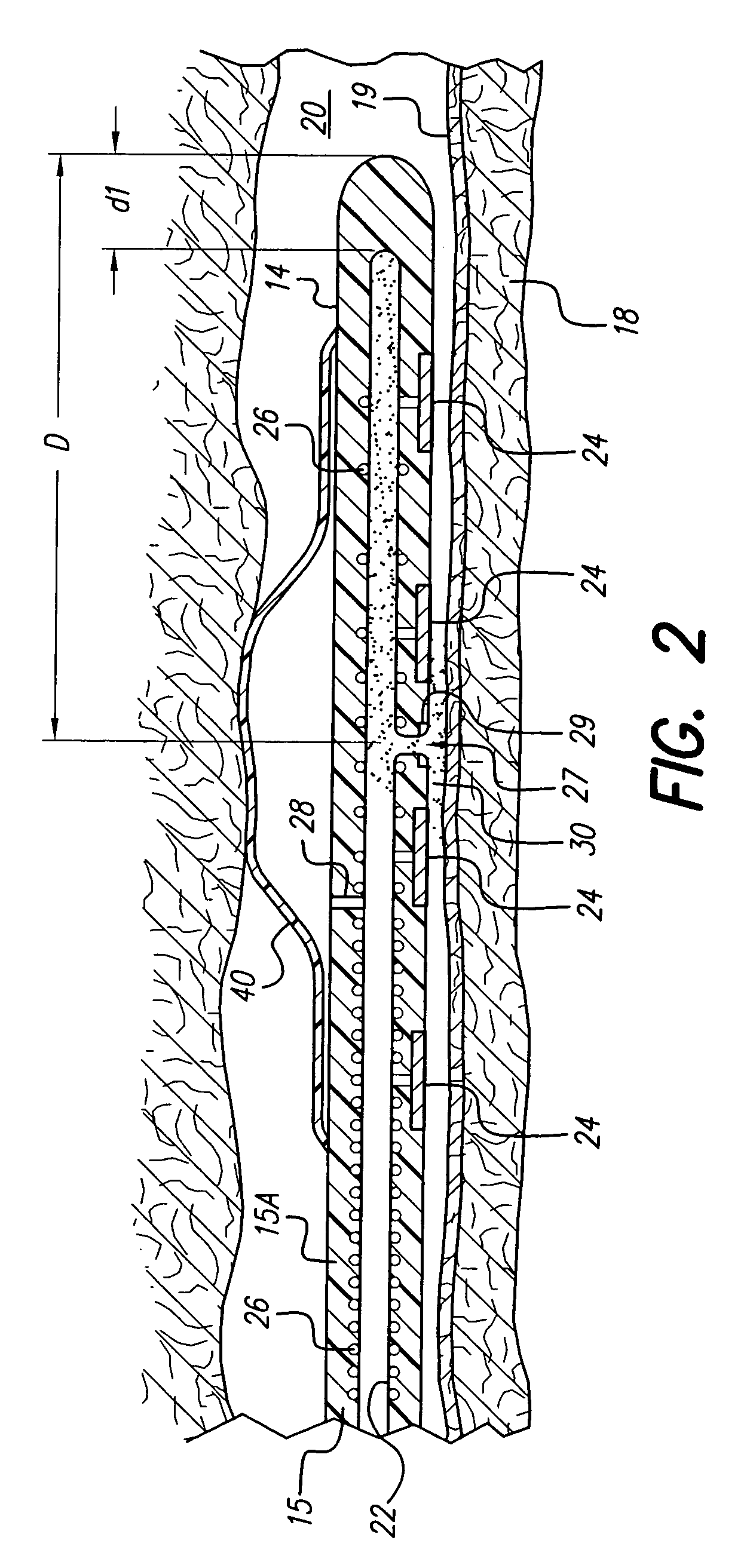
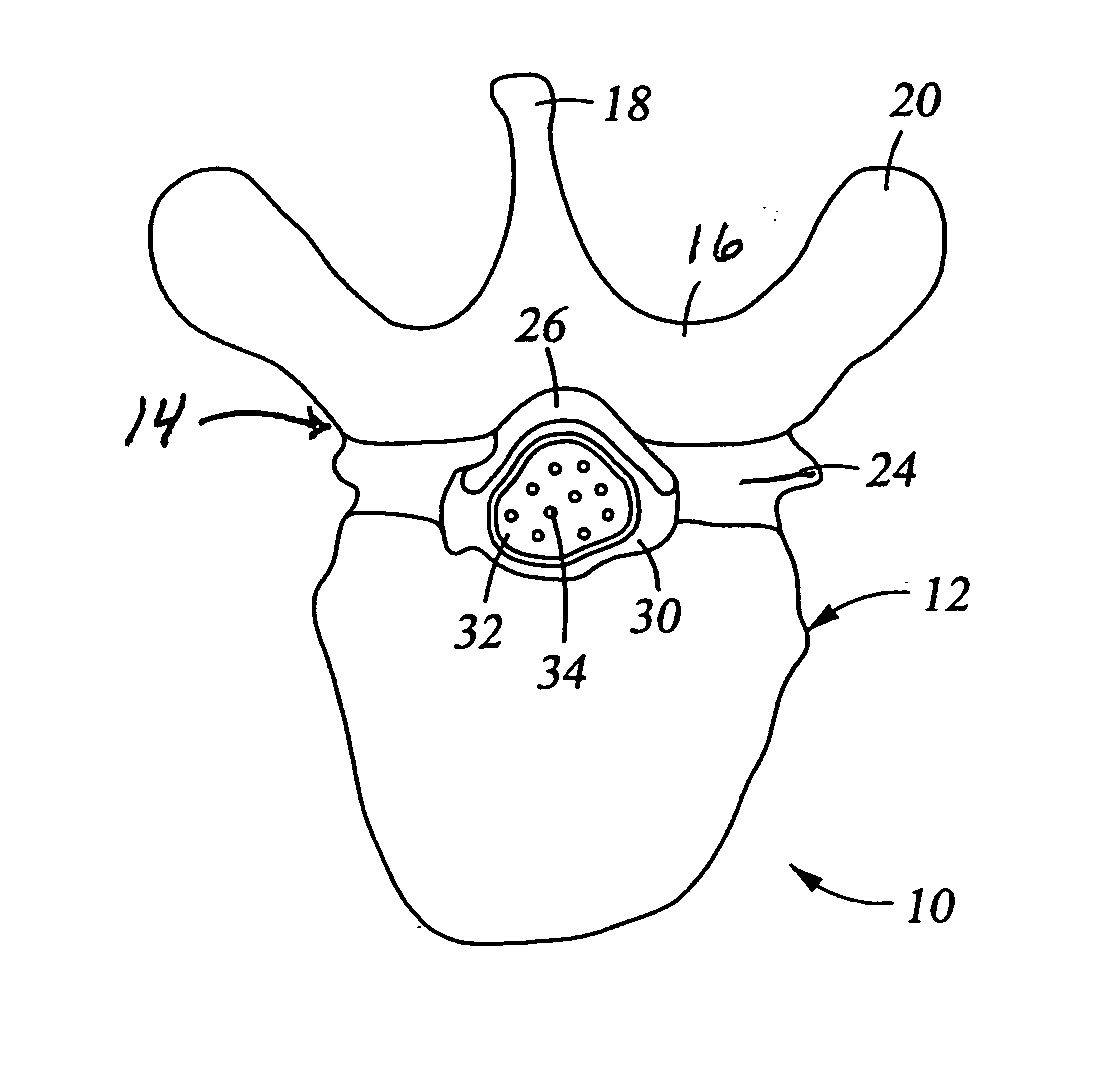
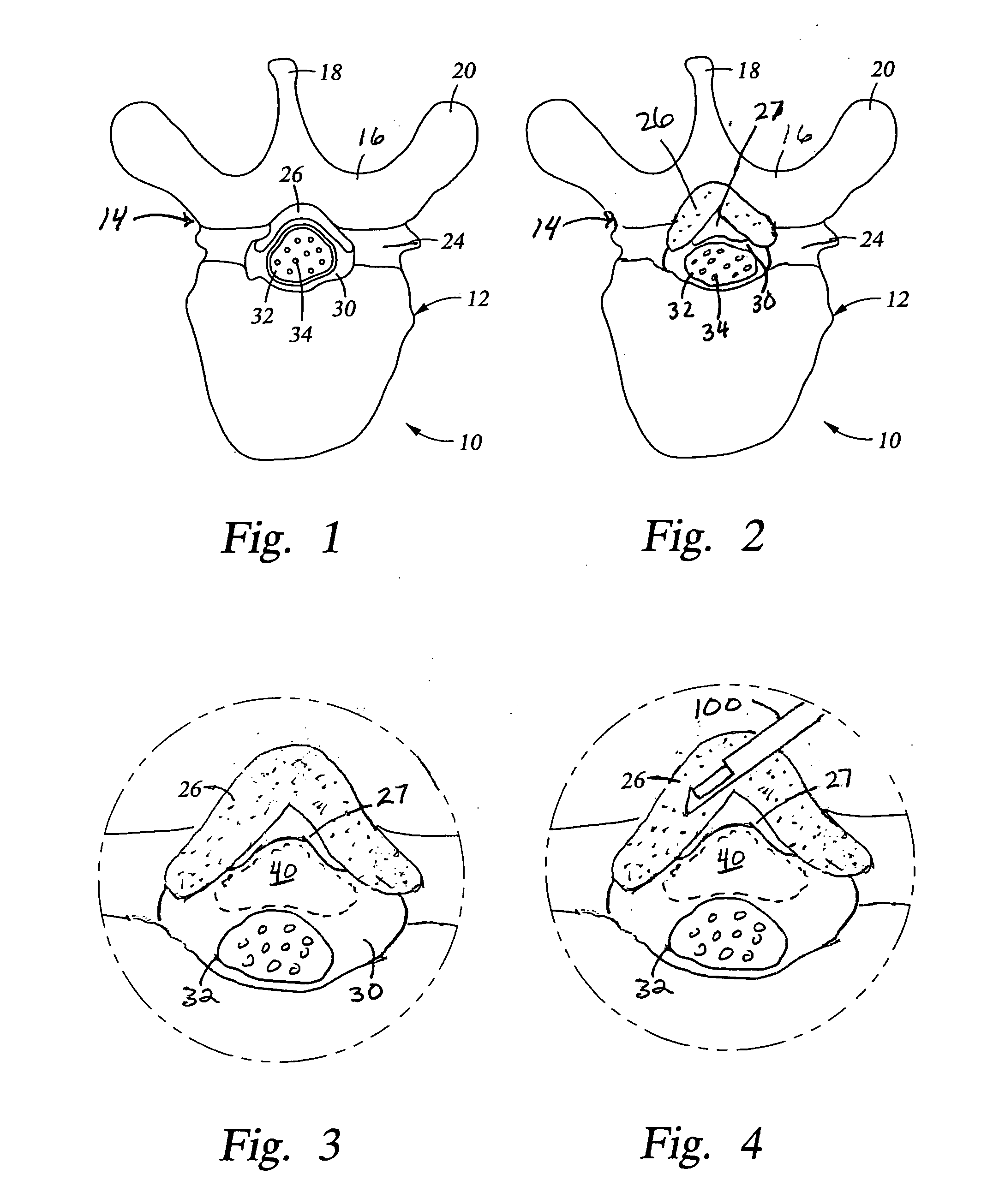
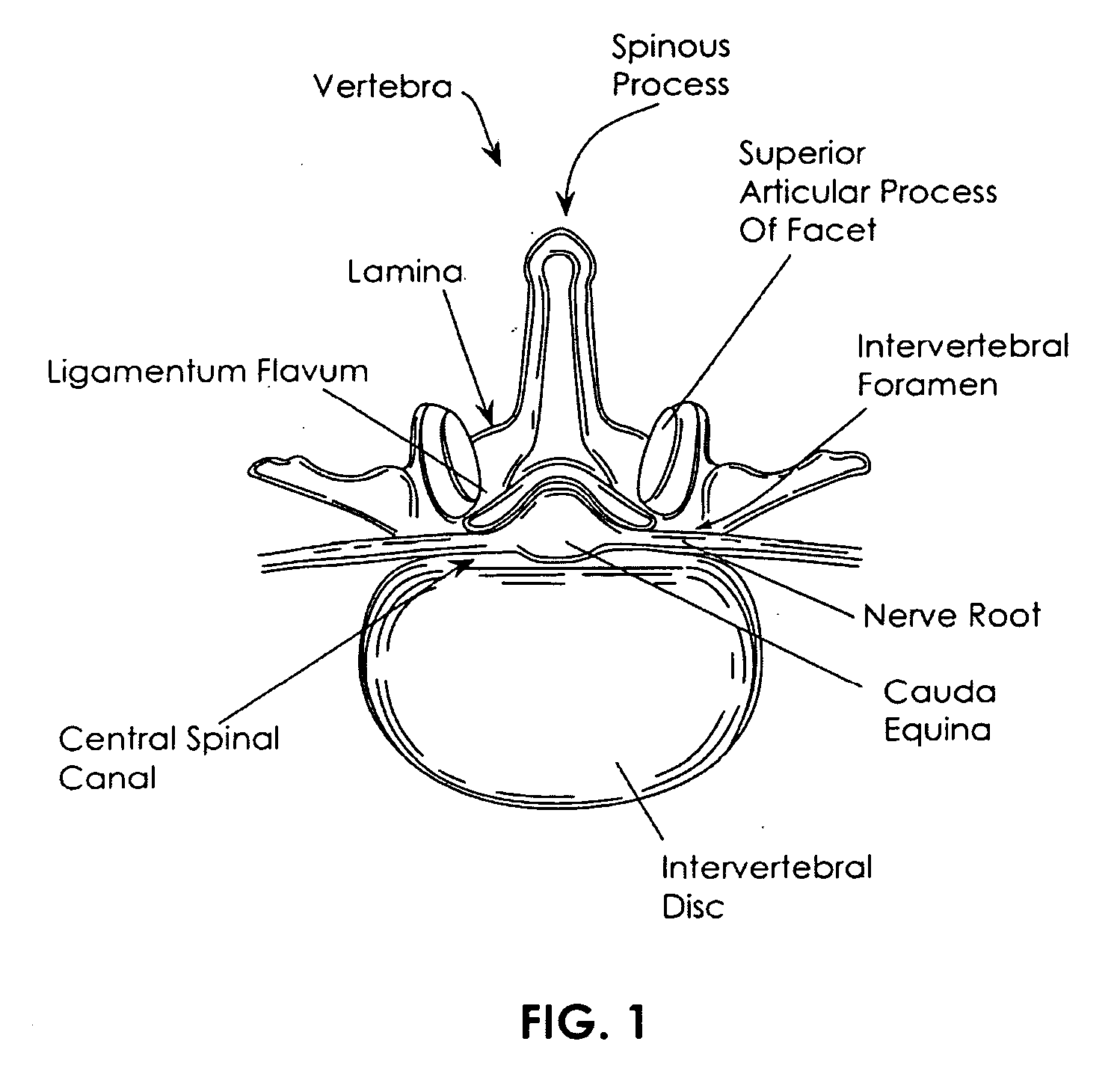
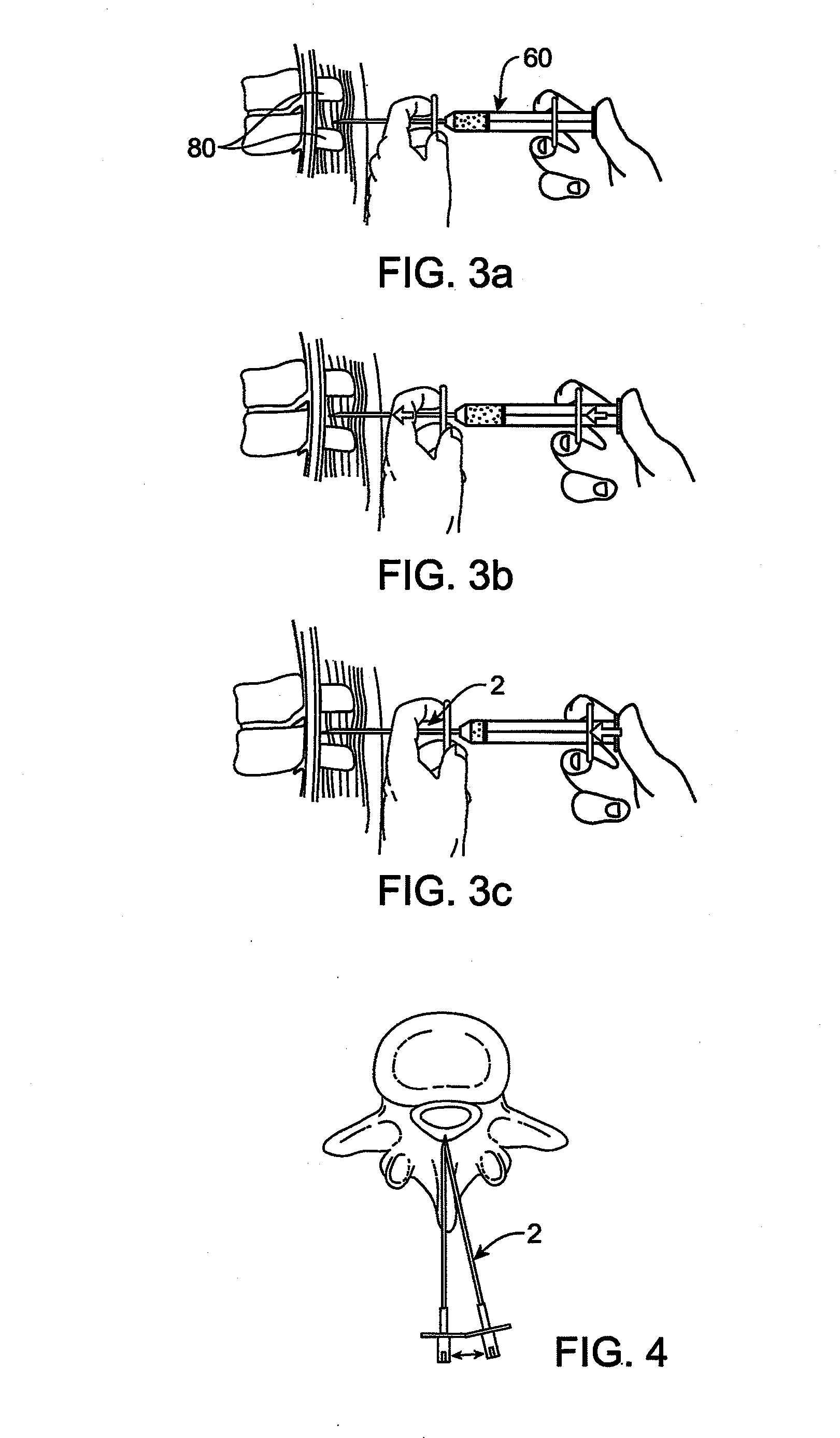
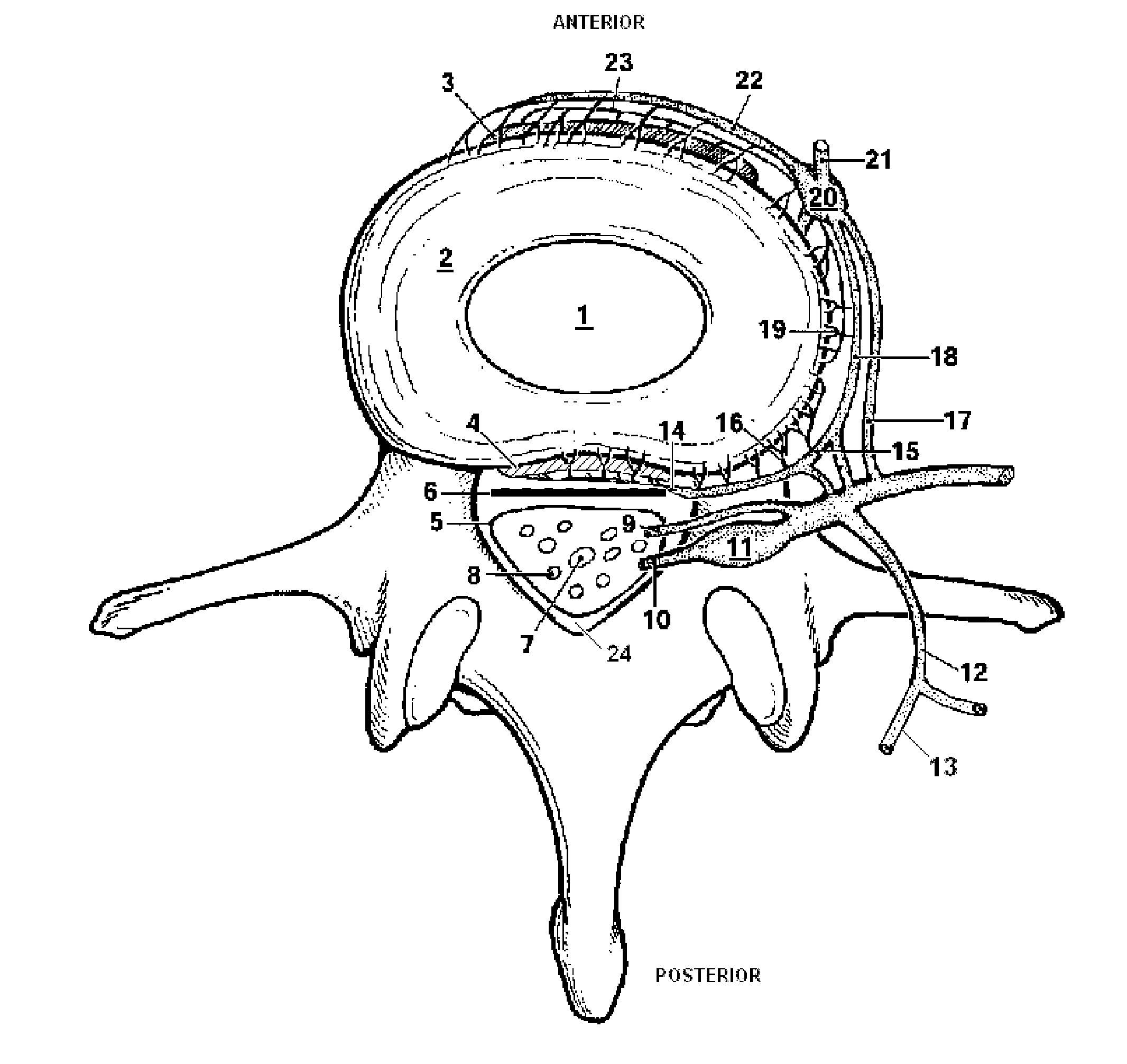
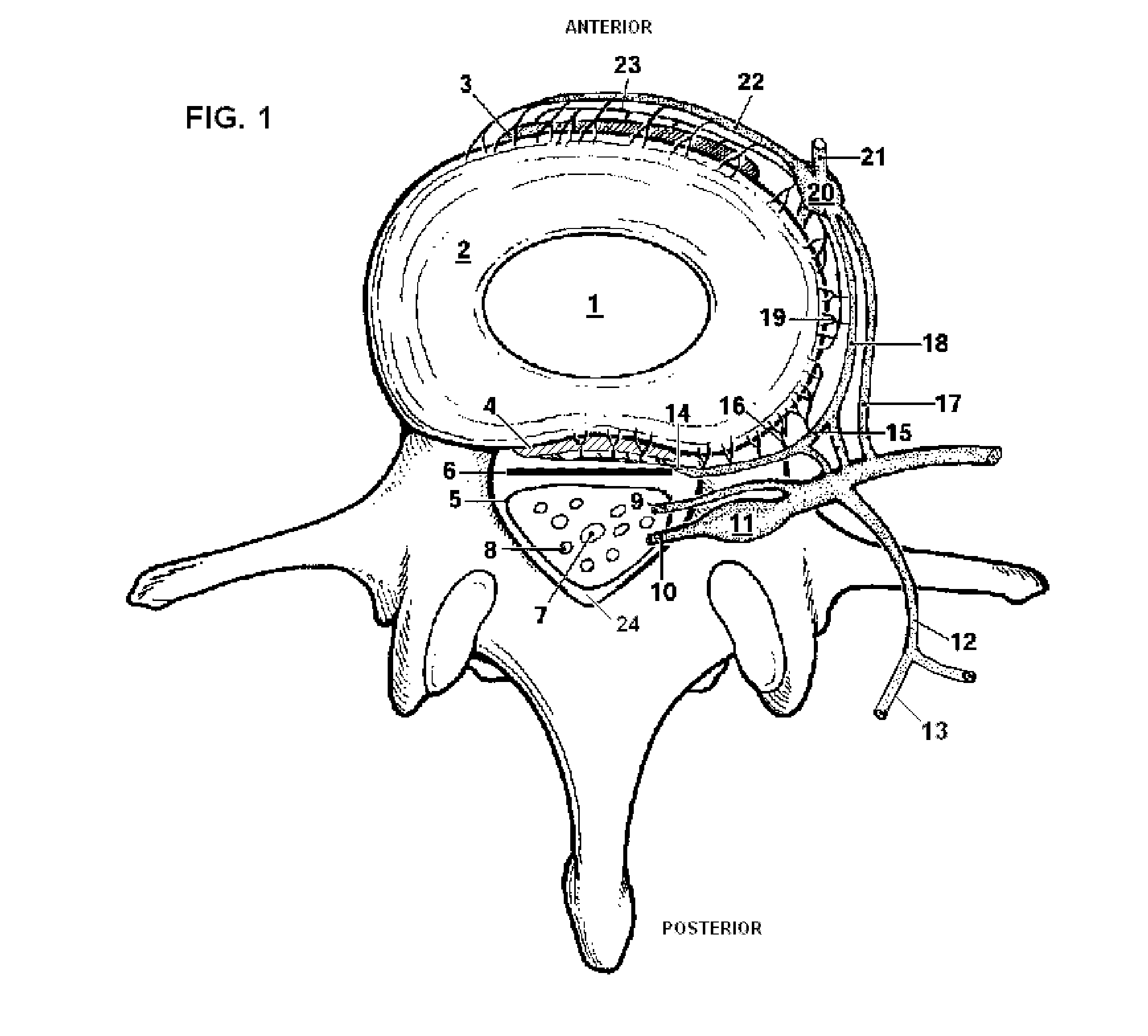
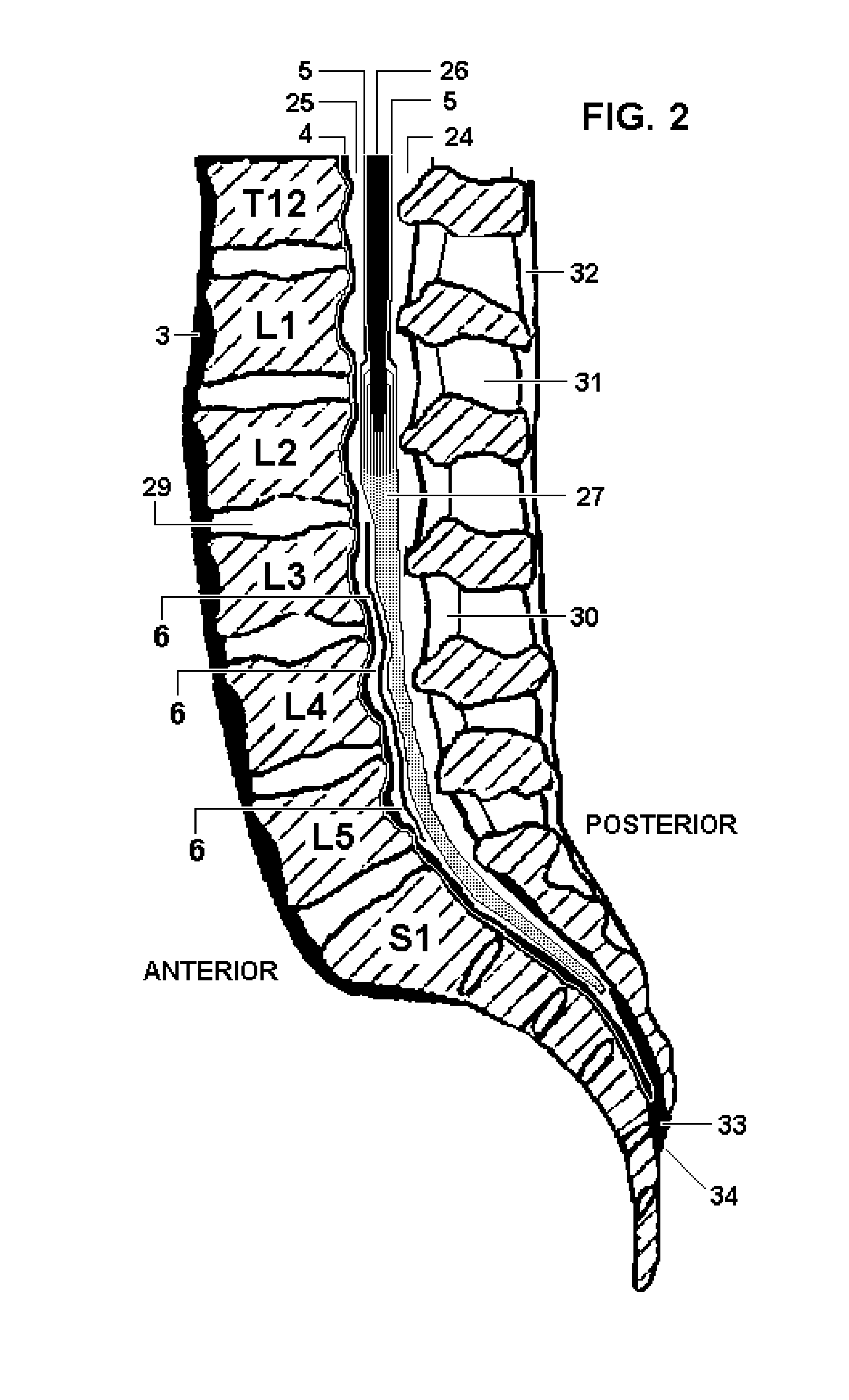
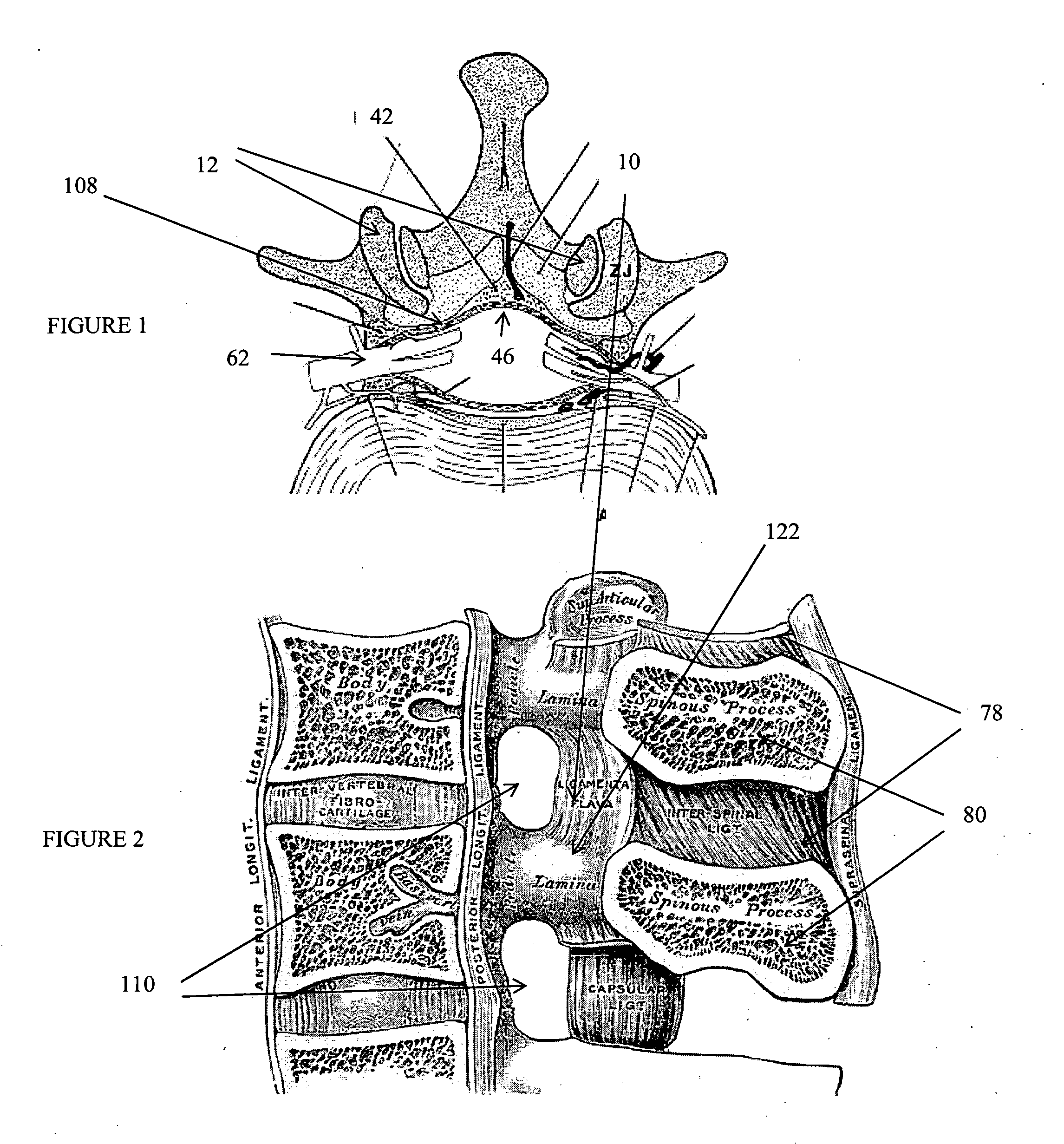
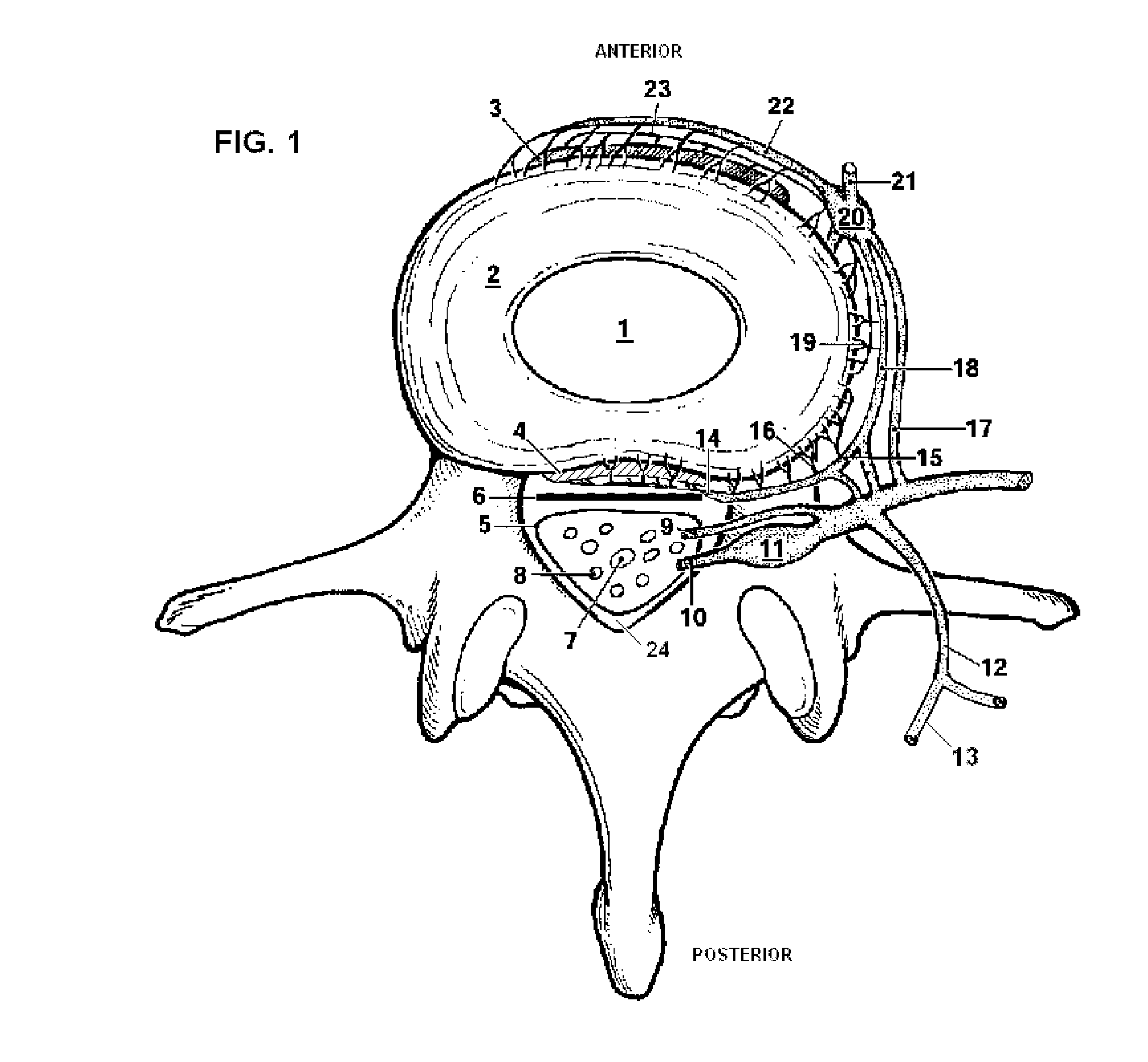
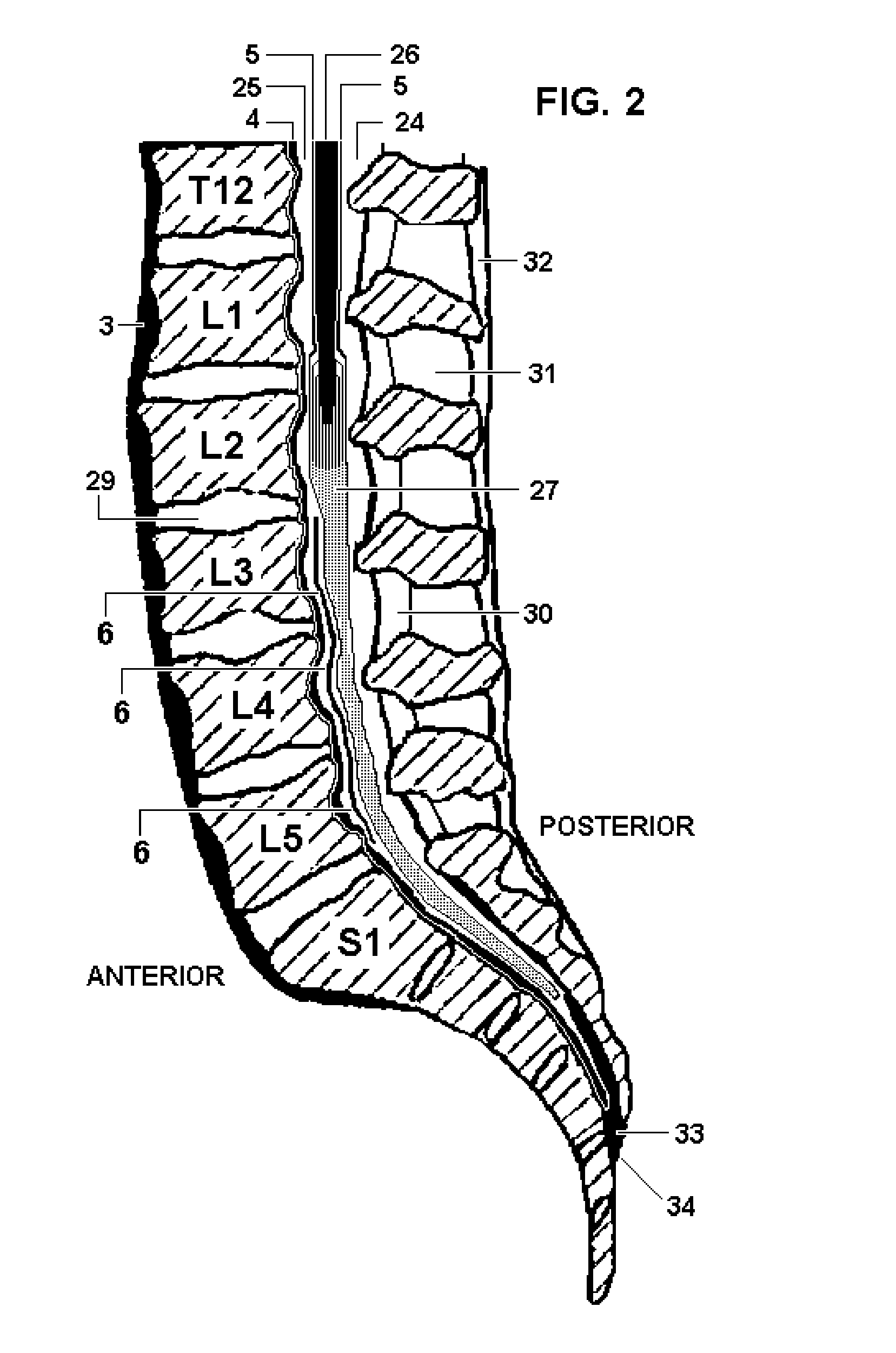
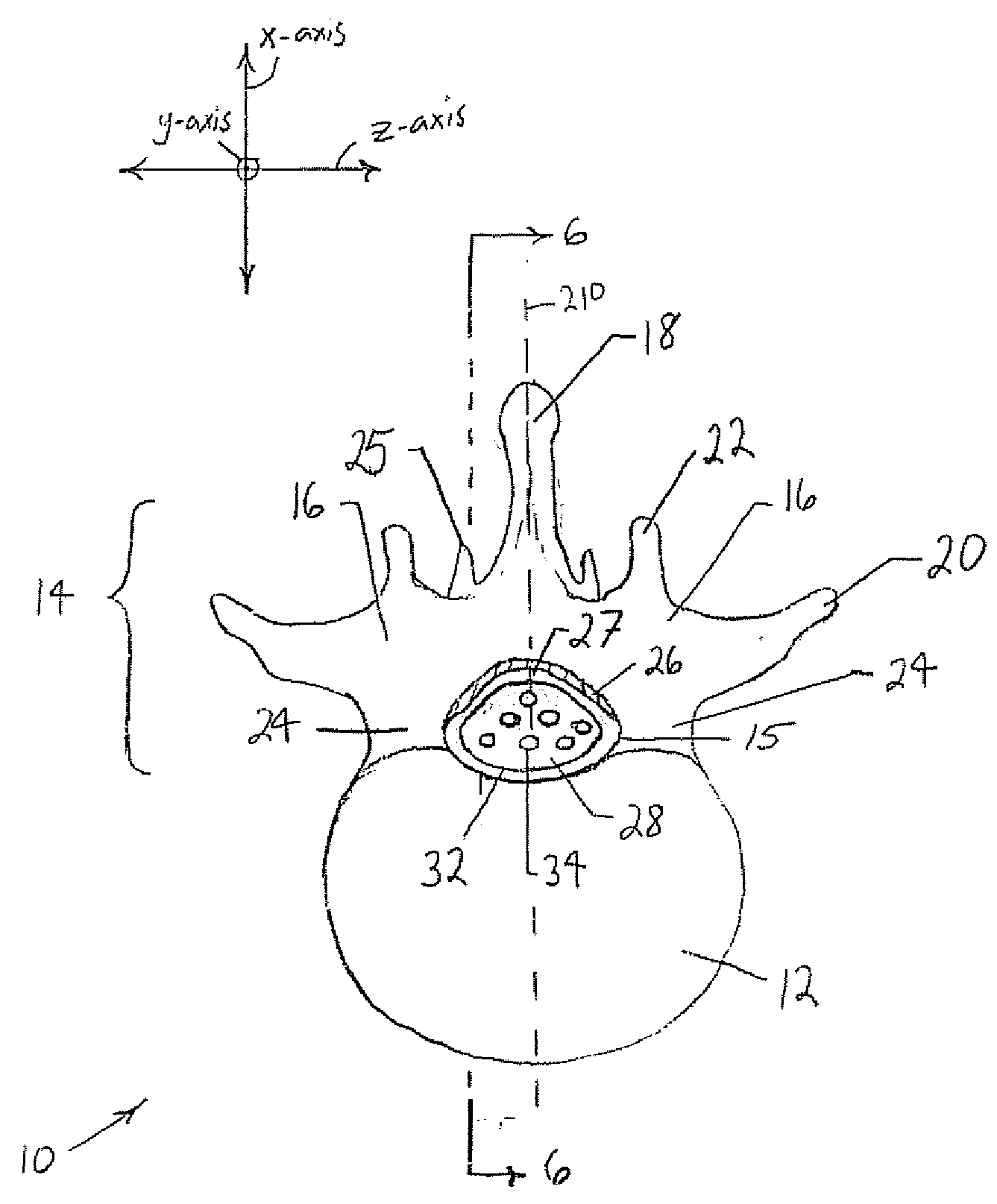
Dura mater is the outermost meningeal layer that covers the brain and spinal cord. It consists of two layers; the inner meningeal layer and the outer periosteal layer. The potential space between the layers of the dura mater is called the epidural space. The epidural space exists around both the brain and the spinal cord.
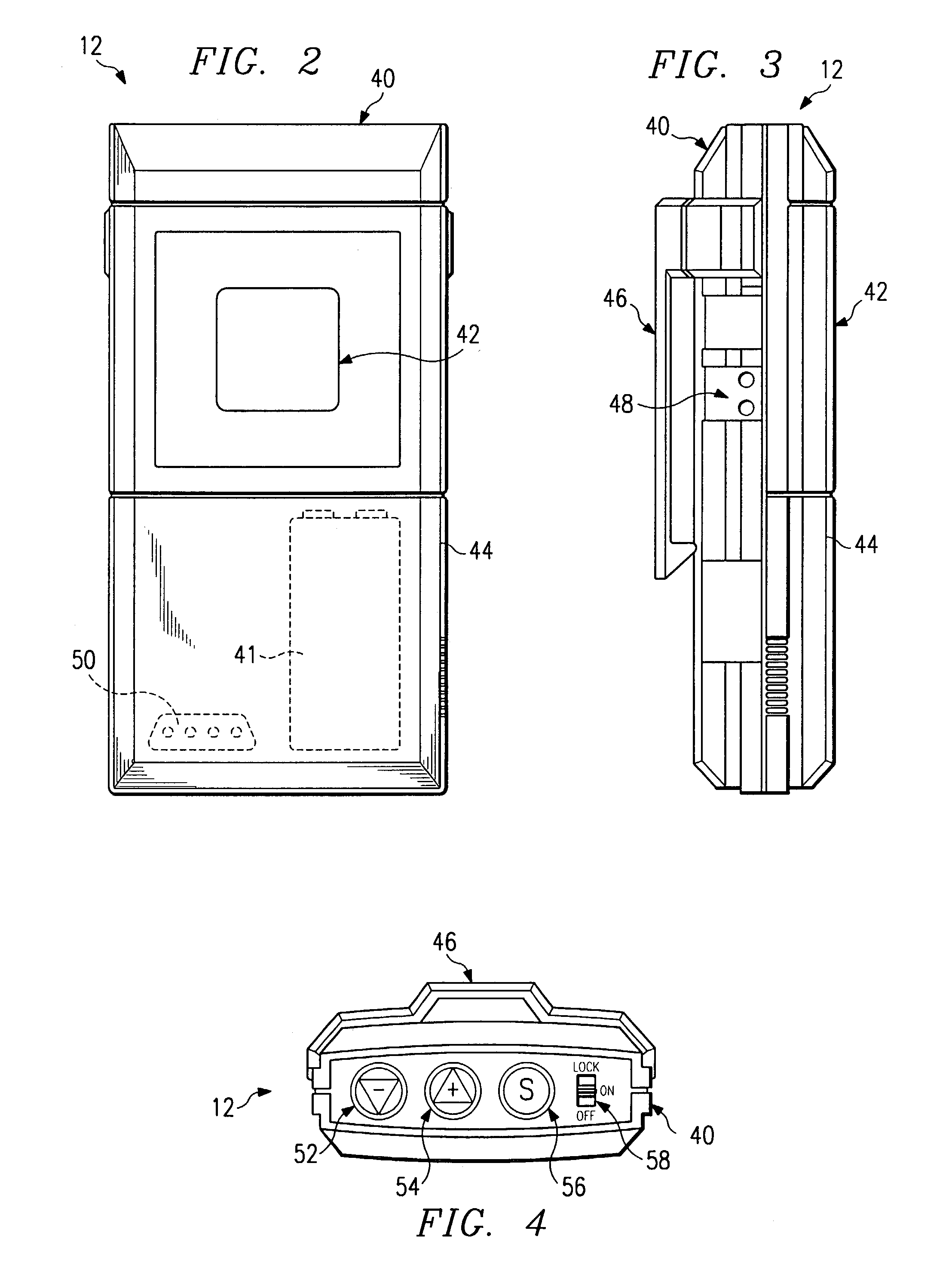
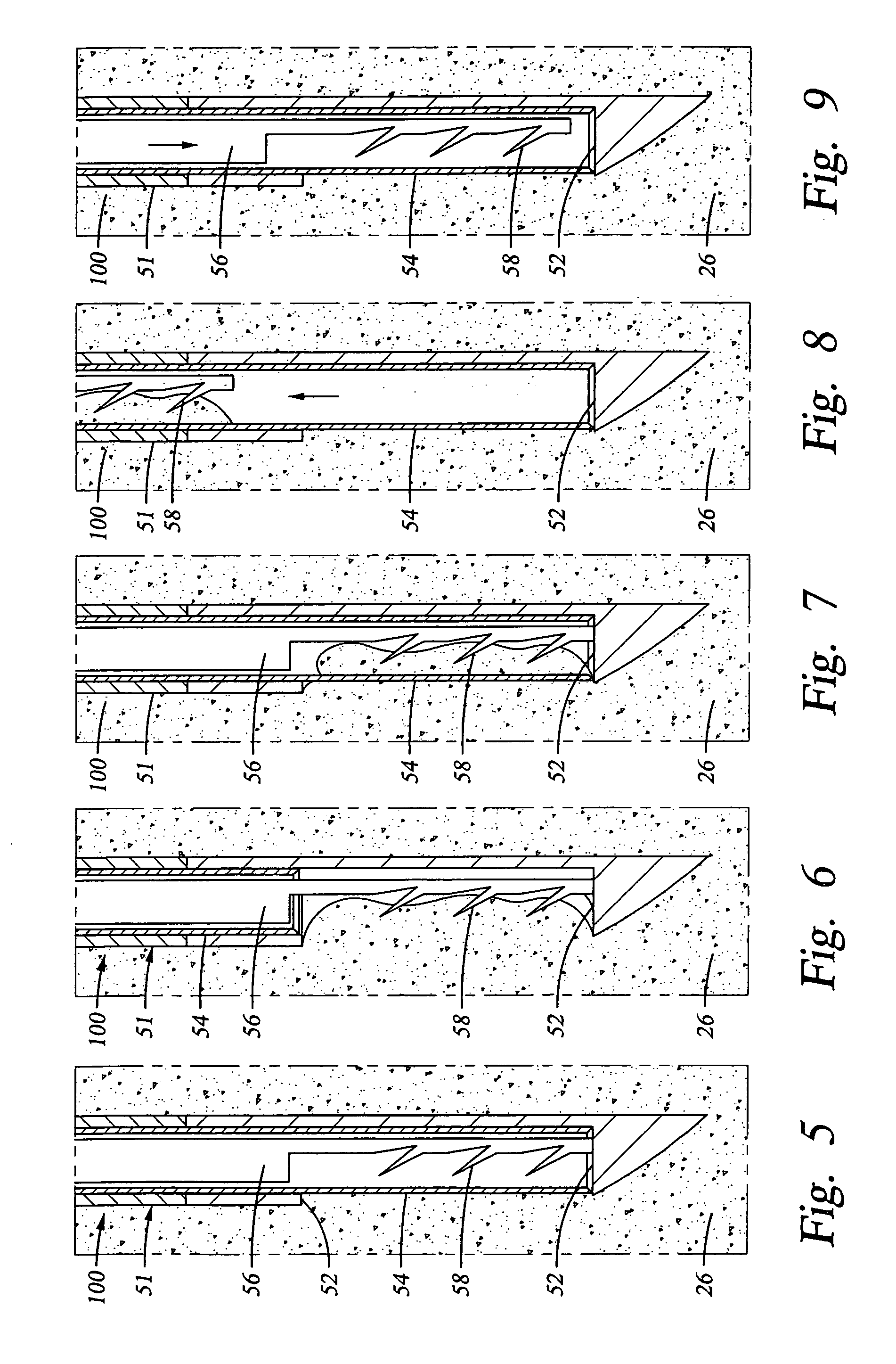
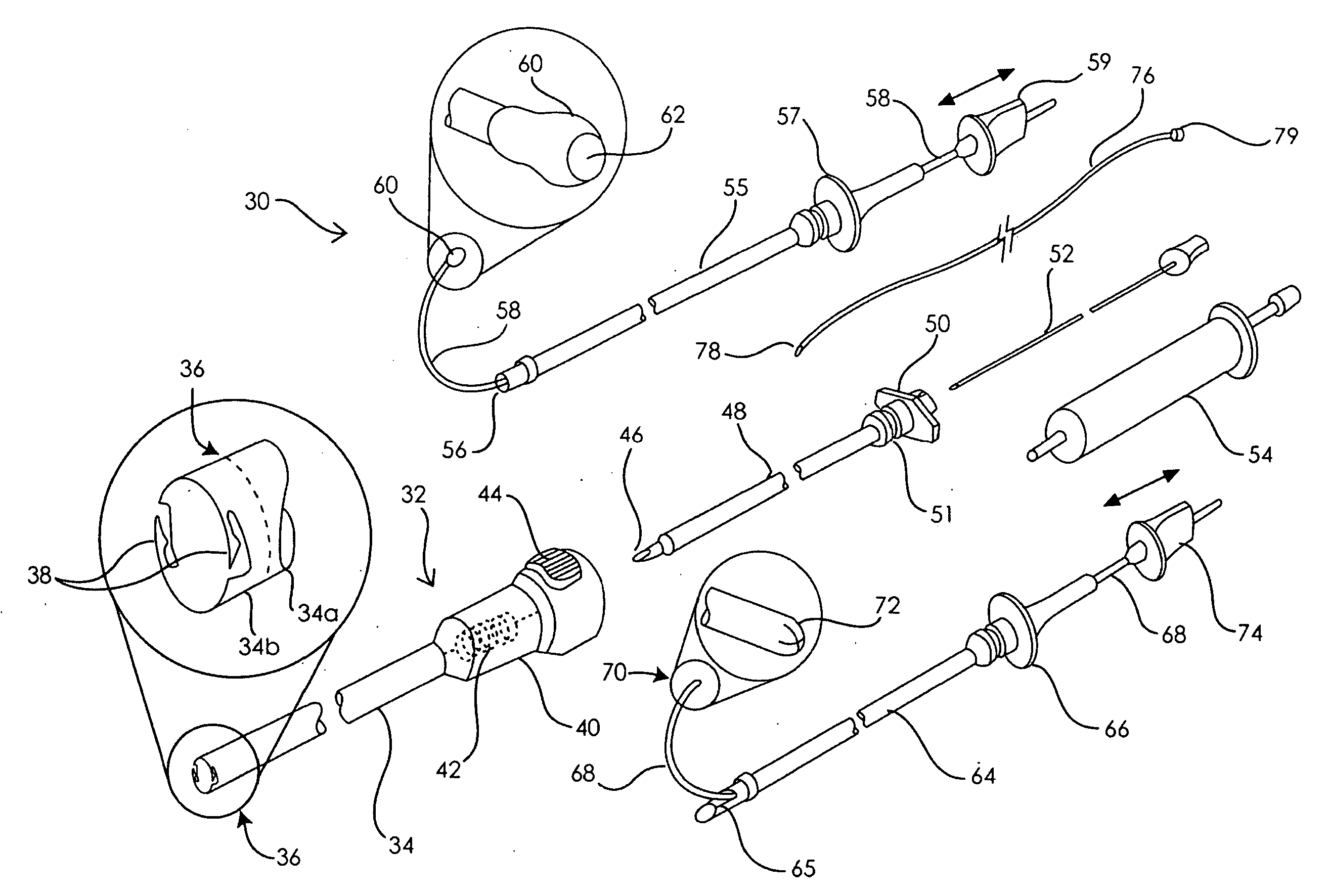
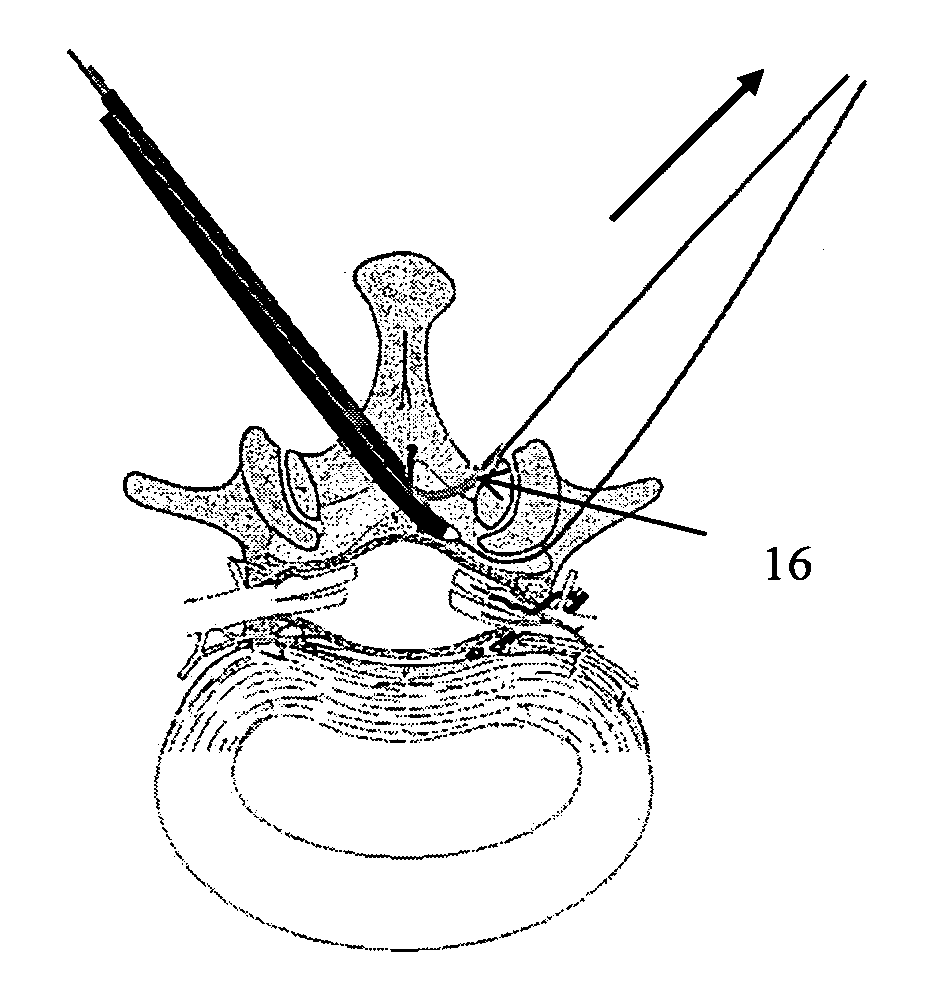
Devices and methods for selective surgical removal of tissue
ActiveUS7738969B2Improve securityAvoid injuryCannulasAnti-incontinence devicesSurgical removalVascular structure
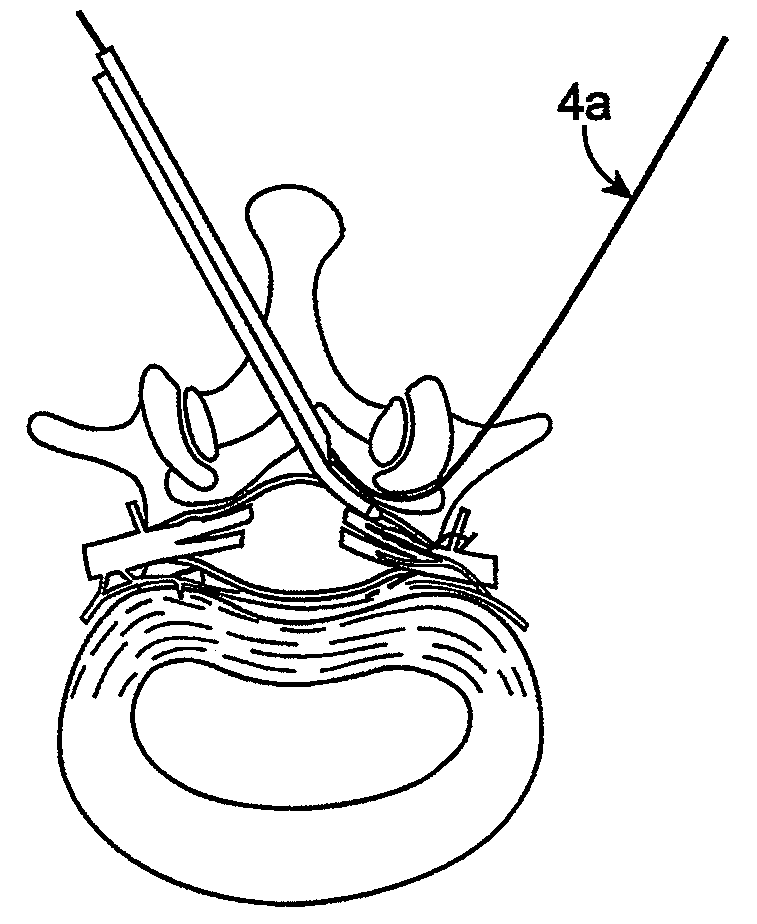
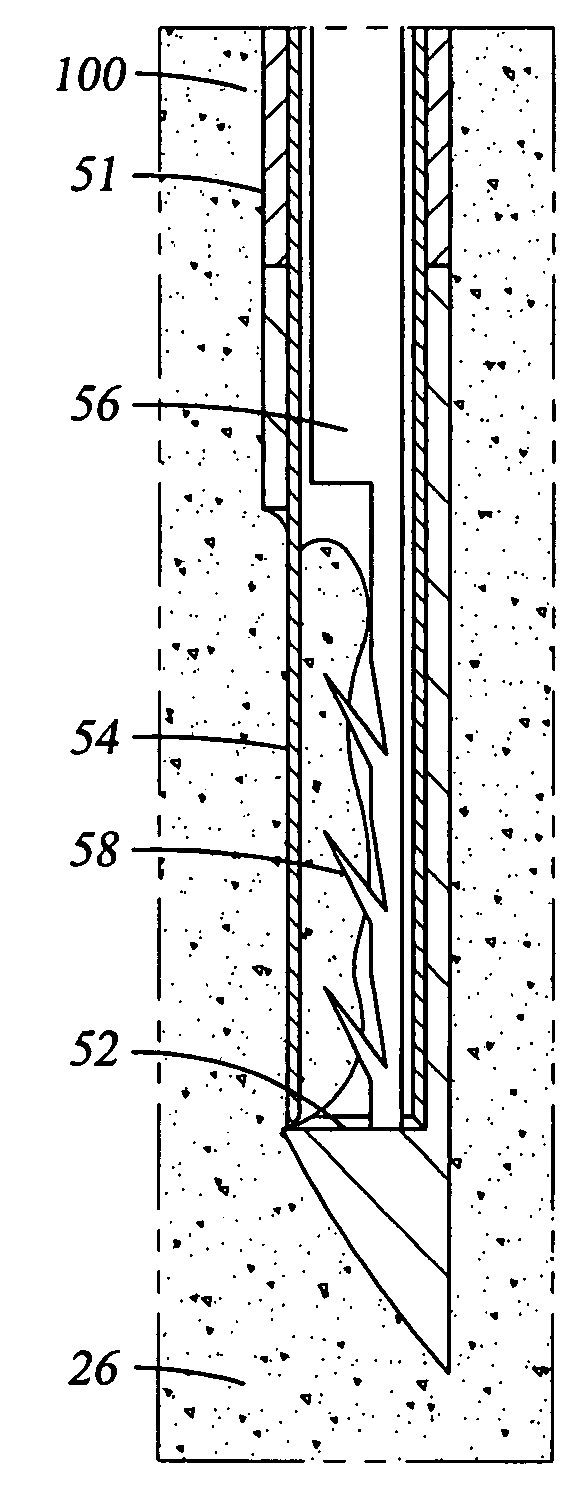
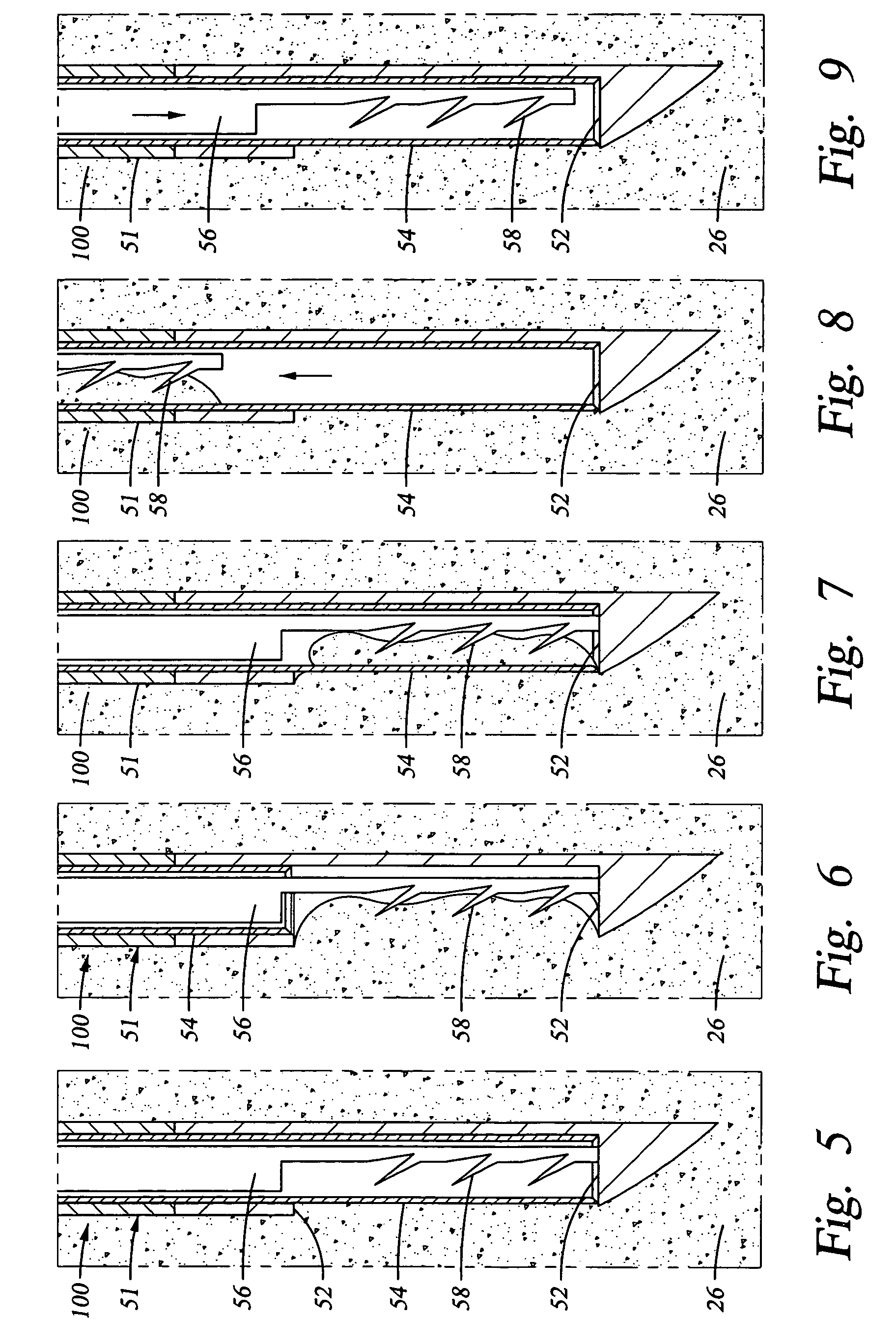
Methods and apparatus are provided for selective surgical removal of tissue. In one variation, tissue may be ablated, resected, removed, or otherwise remodeled by standard small endoscopic tools delivered into the epidural space through an epidural needle. The sharp tip of the needle in the epidural space, can be converted to a blunt tipped instrument for further safe advancement. The current invention includes specific tools that enable safe tissue modification in the epidural space, including a barrier that separates the area where tissue modification will take place from adjacent vulnerable neural and vascular structures. A nerve stimulator may be provided to reduce a risk of inadvertent neural abrasion.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC +1
Positive fixation percutaneous epidural neurostimulation lead
InactiveUS20060041295A1Direction easyInhibit migrationSpinal electrodesTransvascular endocardial electrodesLinear configurationSignal generator
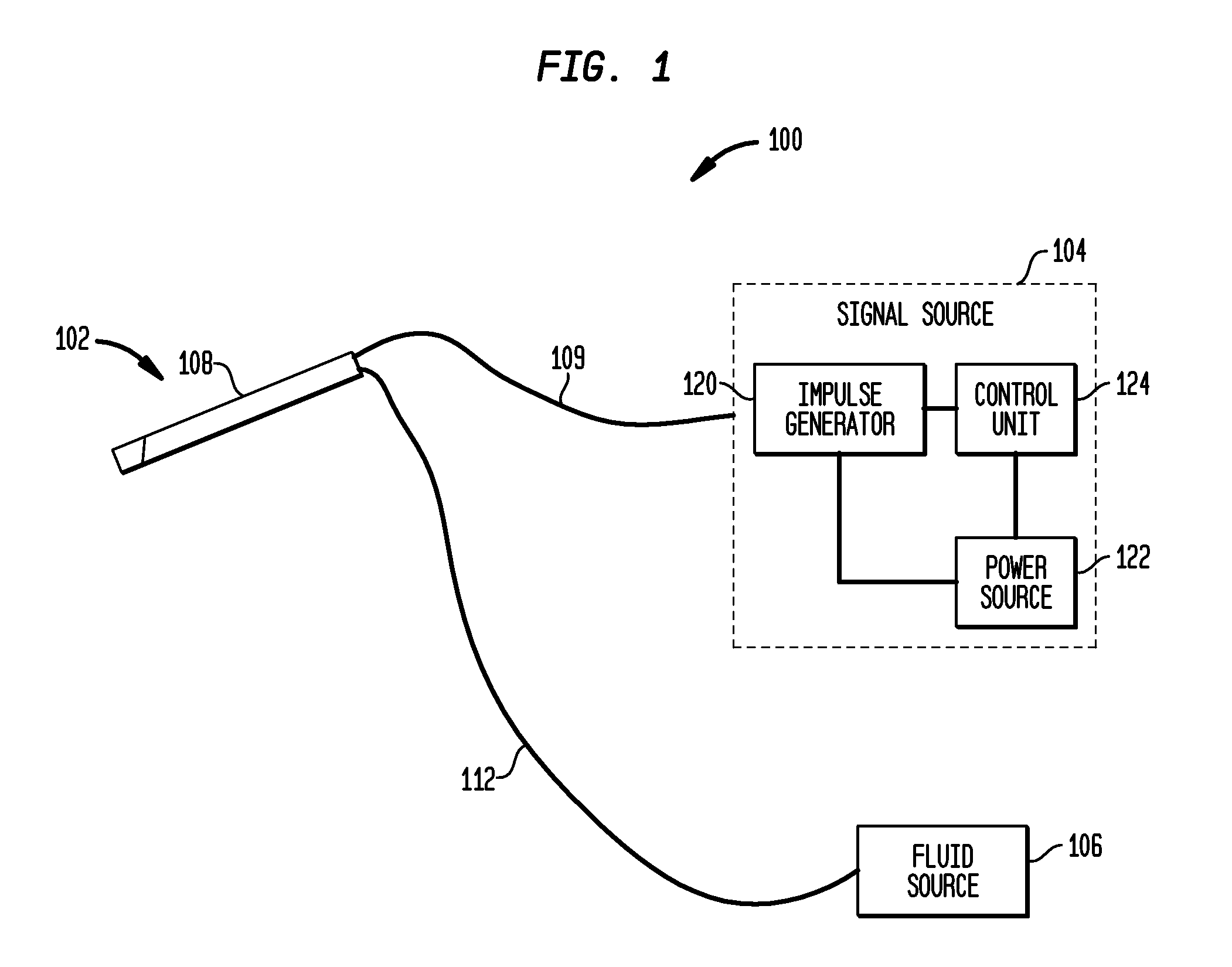
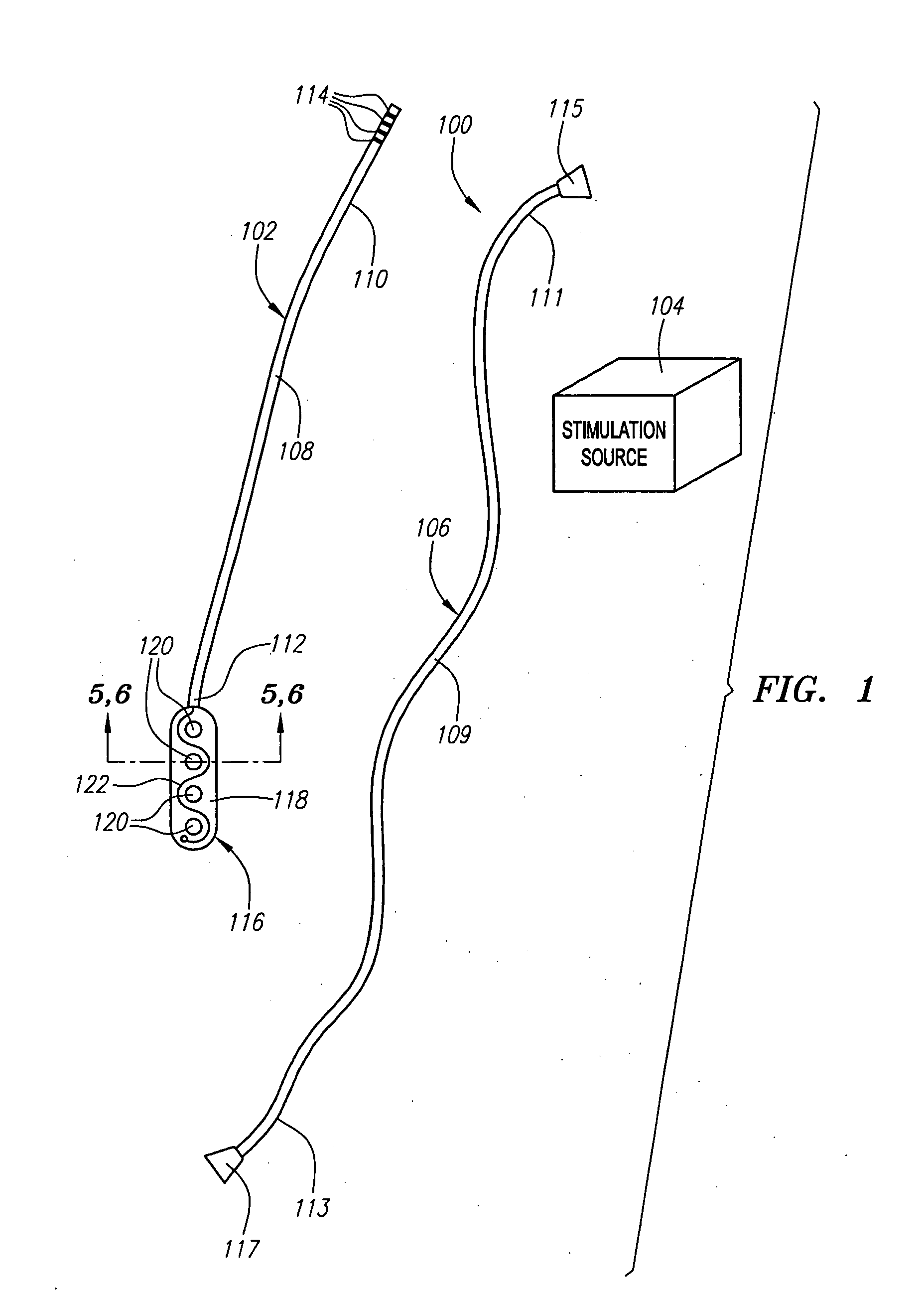
Disclosed is a lead for percutaneous insertion into an epidural space of a spinal canal, which includes an elongated lead body having opposed proximal and distal end portions. At least one electrode for stimulating a patient is operatively associated with the distal end portion of the lead body. Structure for conducting signals extends through the lead body to connect the electrode to a connecting structure operatively associated with the proximal end portion of the lead body. The connecting structure is capable of engaging a signal generator such that signals can be conducted from a signal generator to the electrode. The distal end portion of the lead body is adapted for movement between a first state, in which the distal end portion has a generally linear configuration, and a second state, in which the distal end portion has an undulating configuration.
Owner:NEUROPOINT MEDICAL
Devices and methods for tissue access
ActiveUS20060089633A1Easy to disassembleEliminate needCannulasAnti-incontinence devicesSurgical departmentNerve stimulation
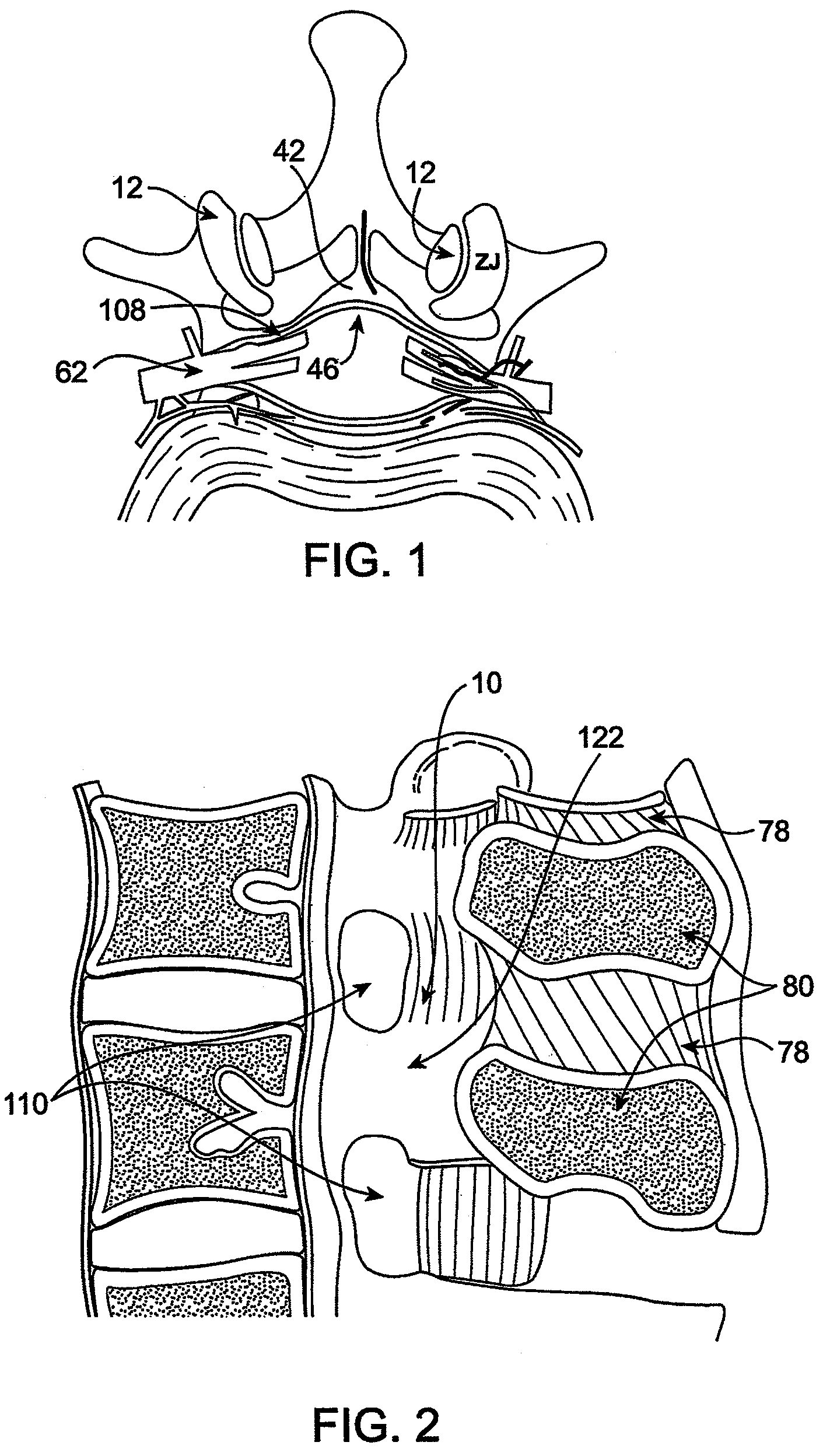
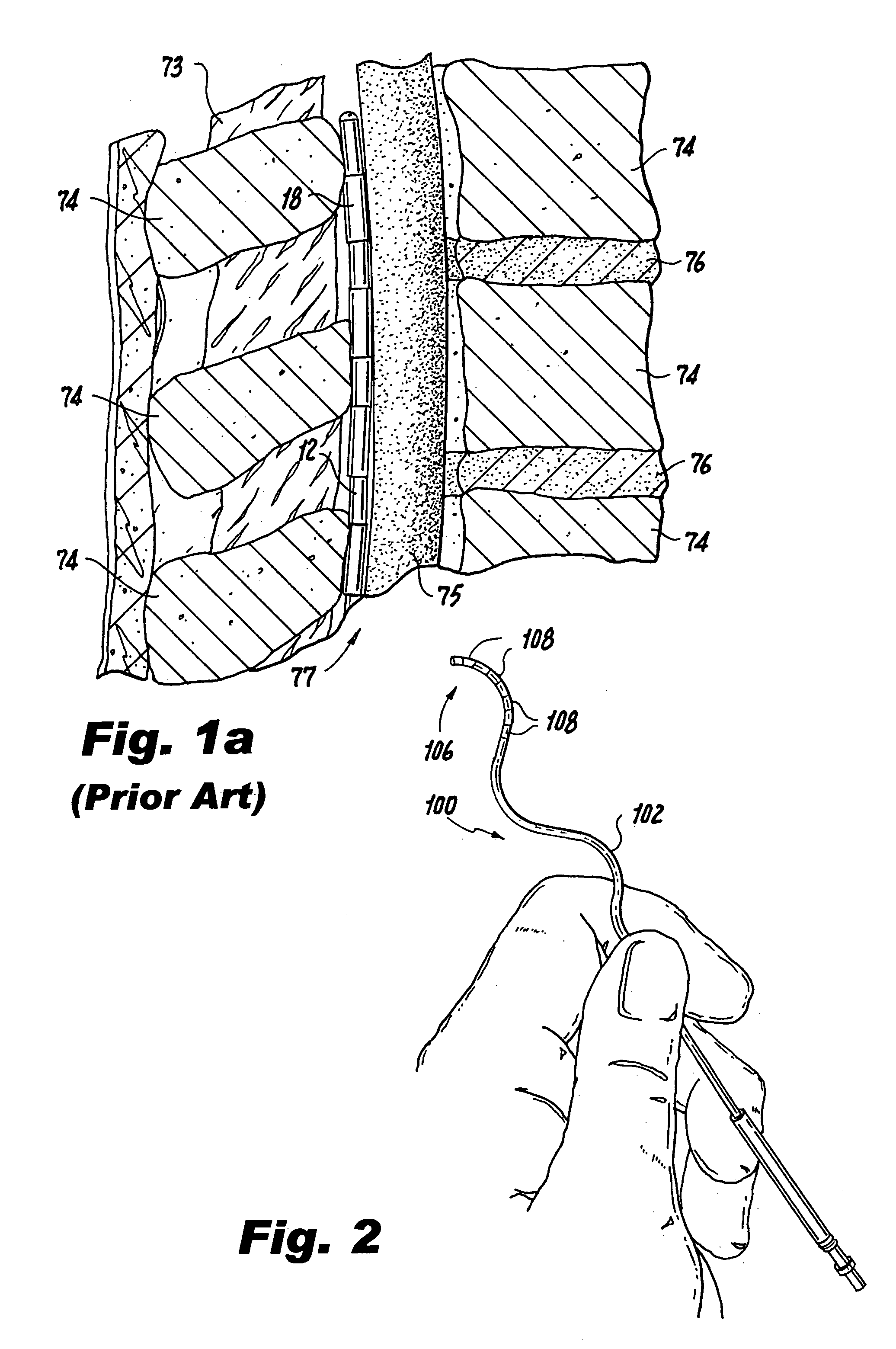
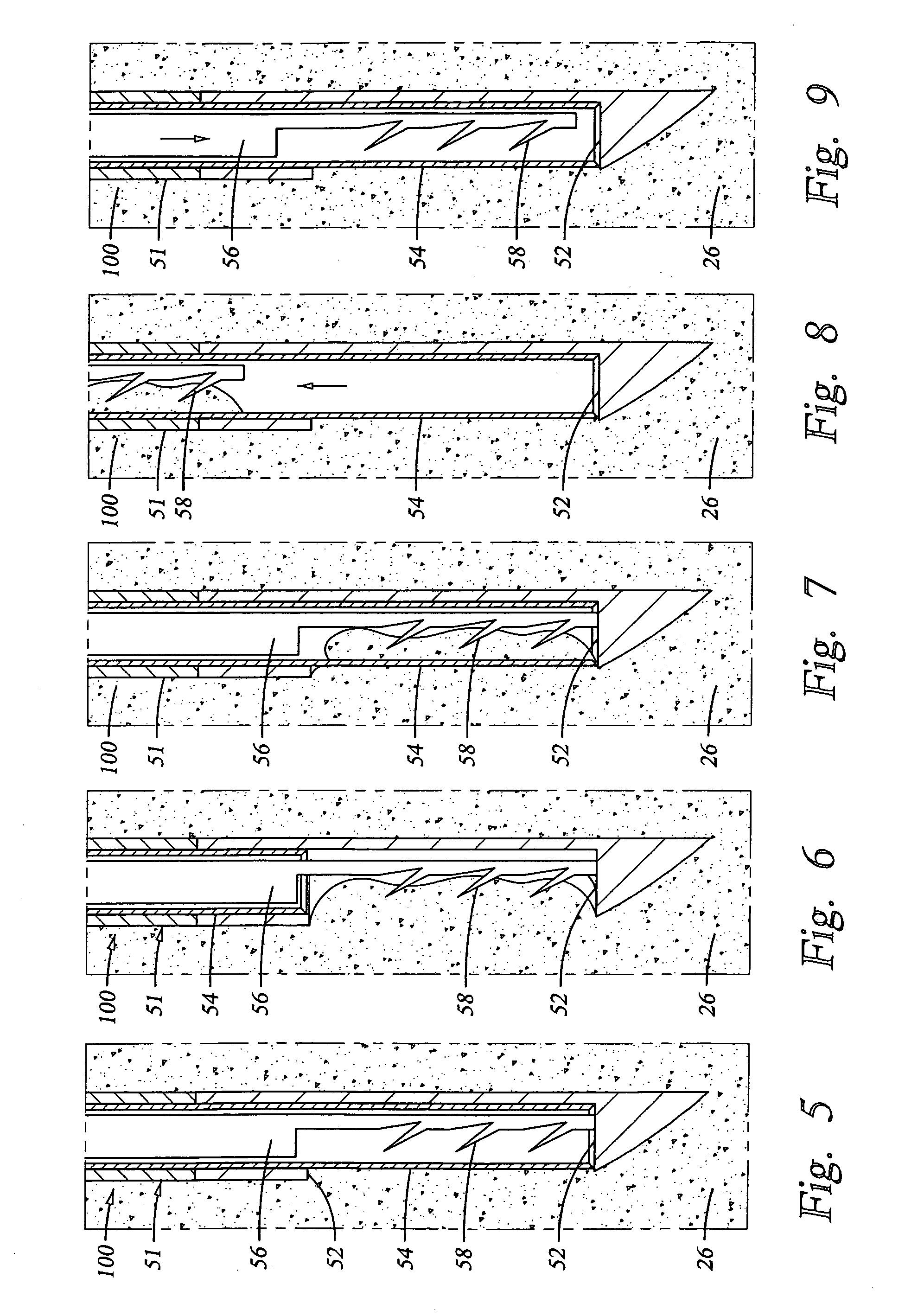
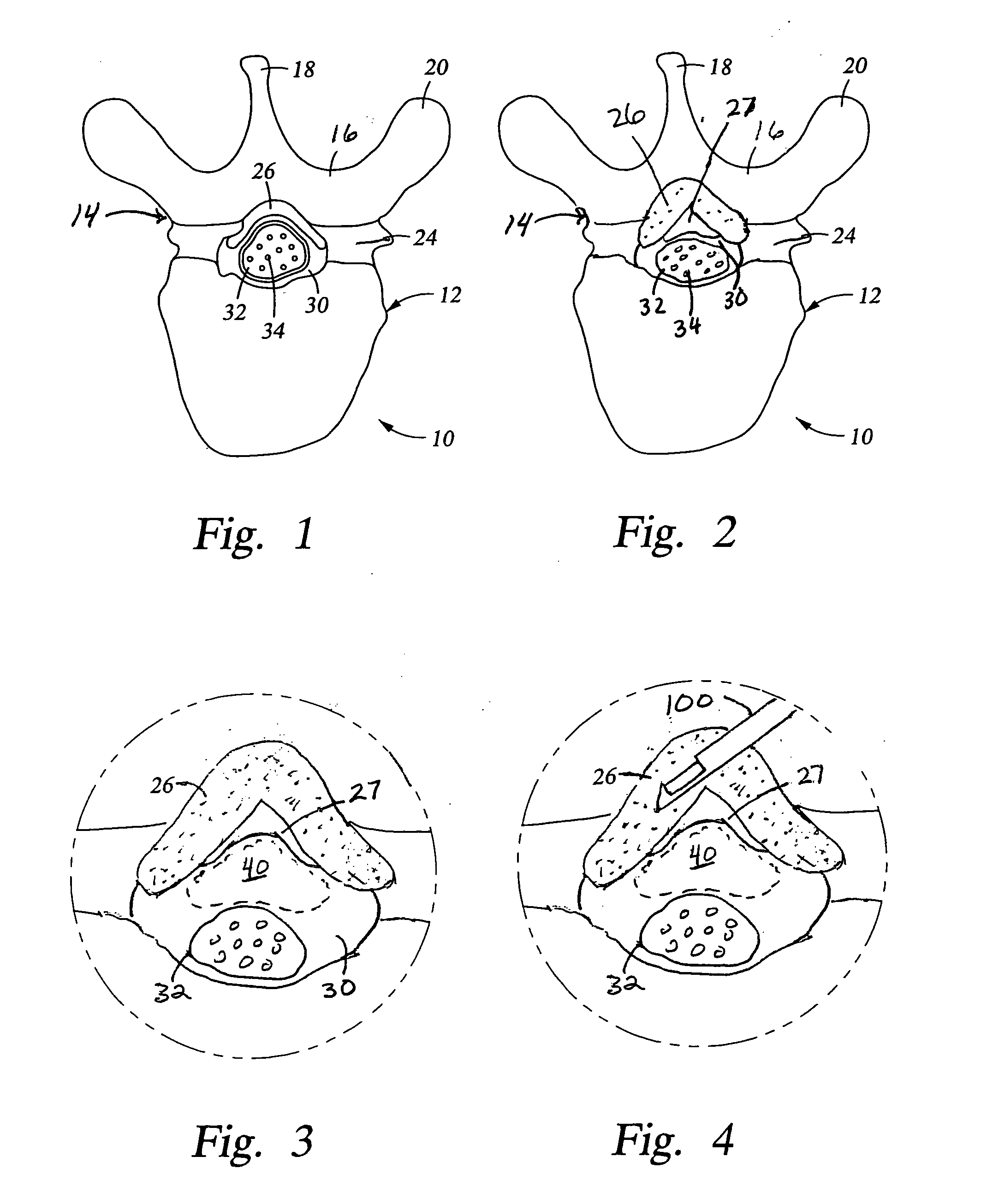
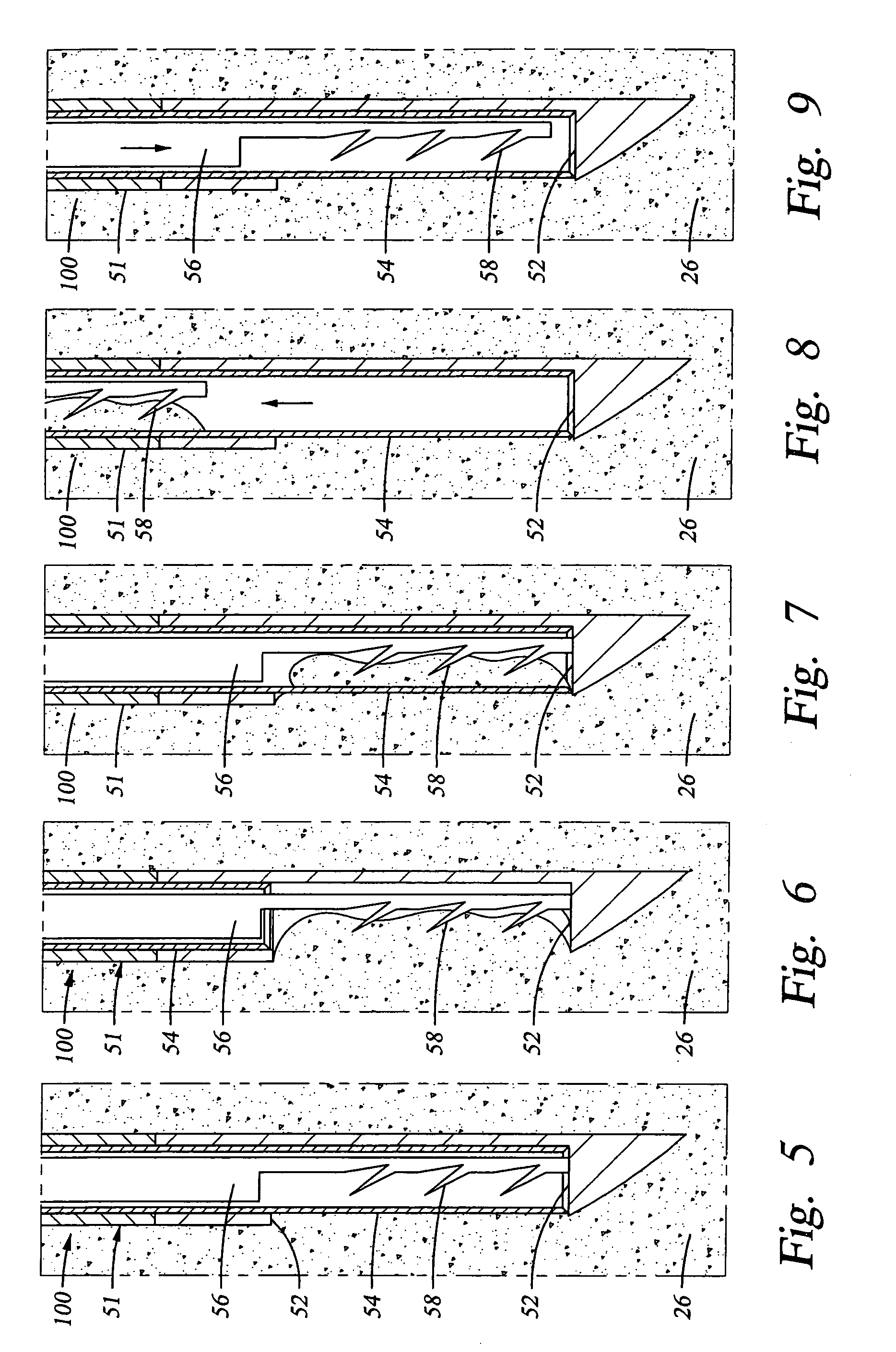
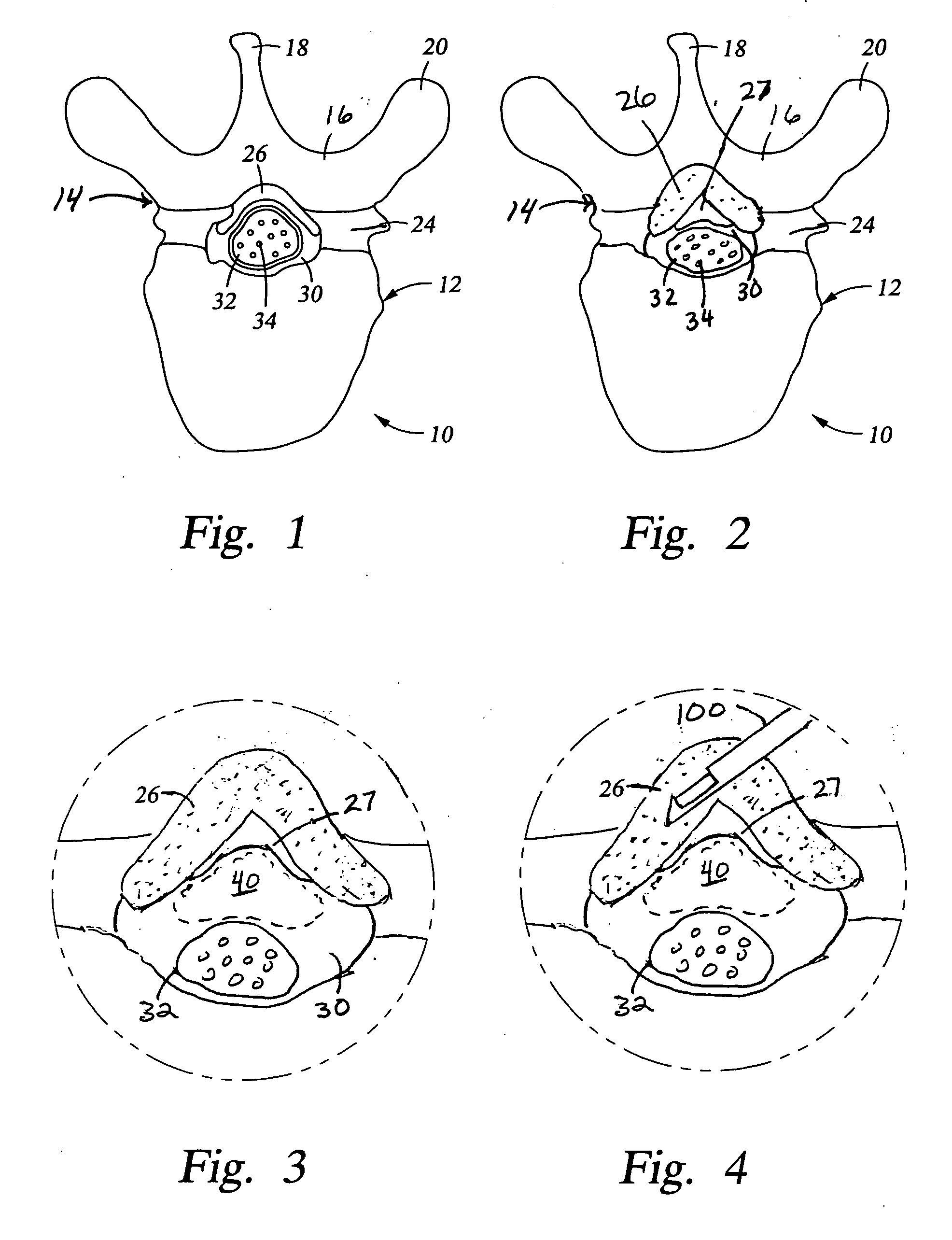
Methods and apparatus are provided for selective surgical removal of tissue, e.g., for enlargement of diseased spinal structures, such as impinged lateral recesses and pathologically narrowed neural foramen. In one variation, tissue may be ablated, resected, removed, or otherwise remodeled by standard small endoscopic tools delivered into the epidural space through an epidural needle. Once the sharp tip of the needle is in the epidural space, it is converted to a blunt tipped instrument for further safe advancement. A specially designed epidural catheter that is used to cover the previously sharp needle tip may also contain a fiberoptic cable. Further embodiments of the current invention include a double barreled epidural needle or other means for placement of a working channel for the placement of tools within the epidural space, beside the epidural instrument. The current invention includes specific tools that enable safe tissue modification in the epidural space, including a barrier that separates the area where tissue modification will take place from adjacent vulnerable neural and vascular structures. In one variation, a tissue abrasion device is provided including a thin belt or ribbon with an abrasive cutting surface. The device may be placed through the neural foramina of the spine and around the anterior border of a facet joint. Once properly positioned, a medical practitioner may enlarge the lateral recess and neural foramina via frictional abrasion, i.e., by sliding the abrasive surface of the ribbon across impinging tissues. A nerve stimulator optionally may be provided to reduce a risk of inadvertent neural abrasion. Additionally, safe epidural placement of the working barrier and epidural tissue modification tools may be further improved with the use of electrical nerve stimulation capabilities within the invention that, when combined with neural stimulation monitors, provide neural localization capabilities to the surgeon. The device optionally may be placed within a protective sheath that exposes the abrasive surface of the ribbon only in the area where tissue removal is desired. Furthermore, an endoscope may be incorporated into the device in order to monitor safe tissue removal. Finally, tissue remodeling within the epidural space may be ensured through the placement of compression dressings against remodeled tissue surfaces, or through the placement of tissue retention straps, belts or cables that are wrapped around and pull under tension aspects of the impinging soft tissue and bone in the posterior spinal canal.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC +1
Devices and methods for tissue access
InactiveUS20060095028A1Improve securityAvoid injuryEar treatmentCannulasAccess methodSurgical removal
Methods and apparatus are provided for selective surgical removal of tissue. In one variation, tissue may be ablated, resected, removed, or otherwise remodeled by standard small endoscopic tools delivered into the epidural space through an epidural needle. The sharp tip of the needle in the epidural space, can be converted to a blunt tipped instrument for further safe advancement. The current invention includes specific tools that enable safe tissue modification in the epidural space, including a barrier that separates the area where tissue modification will take place from adjacent vulnerable neural and vascular structures. A nerve stimulator may be provided to reduce a risk of inadvertent neural abrasion.
Owner:BAXANO
Devices and methods for tissue access
InactiveUS20060122458A1Enabling symptomatic reliefApproach can be quite invasiveCannulasDiagnosticsSurgical departmentNerve stimulation
Methods and apparatus are provided for selective surgical removal of tissue, e.g., for enlargement of diseased spinal structures, such as impinged lateral recesses and pathologically narrowed neural foramen. In one variation, tissue may be ablated, resected, removed, or otherwise remodeled by standard small endoscopic tools delivered into the epidural space through an epidural needle. Once the sharp tip of the needle is in the epidural space, it is converted to a blunt tipped instrument for further safe advancement. A specially designed epidural catheter that is used to cover the previously sharp needle tip may also contain a fiberoptic cable. Further embodiments of the current invention include a double barreled epidural needle or other means for placement of a working channel for the placement of tools within the epidural space, beside the epidural instrument. The current invention includes specific tools that enable safe tissue modification in the epidural space, including a barrier that separates the area where tissue modification will take place from adjacent vulnerable neural and vascular structures. In one variation, a tissue removal device is provided including a thin belt or ribbon with an abrasive cutting surface. The device may be placed through the neural foramina of the spine and around the anterior border of a facet joint. Once properly positioned, a medical practitioner may enlarge the lateral recess and neural foramina via frictional abrasion, i.e., by sliding the tissue removal surface of the ribbon across impinging tissues. A nerve stimulator optionally may be provided to reduce a risk of inadvertent neural abrasion. Additionally, safe epidural placement of the working barrier and epidural tissue modification tools may be further improved with the use of electrical nerve stimulation capabilities within the invention that, when combined with neural stimulation monitors, provide neural localization capabilities to the surgeon. The device optionally may be placed within a protective sheath that exposes the abrasive surface of the ribbon only in the area where tissue removal is desired. Furthermore, an endoscope may be incorporated into the device in order to monitor safe tissue removal. Finally, tissue remodeling within the epidural space may be ensured through the placement of compression dressings against remodeled tissue surfaces, or through the placement of tissue retention straps, belts or cables that are wrapped around and pull under tension aspects of the impinging soft tissue and bone in the posterior spinal canal.
Owner:BAXANO
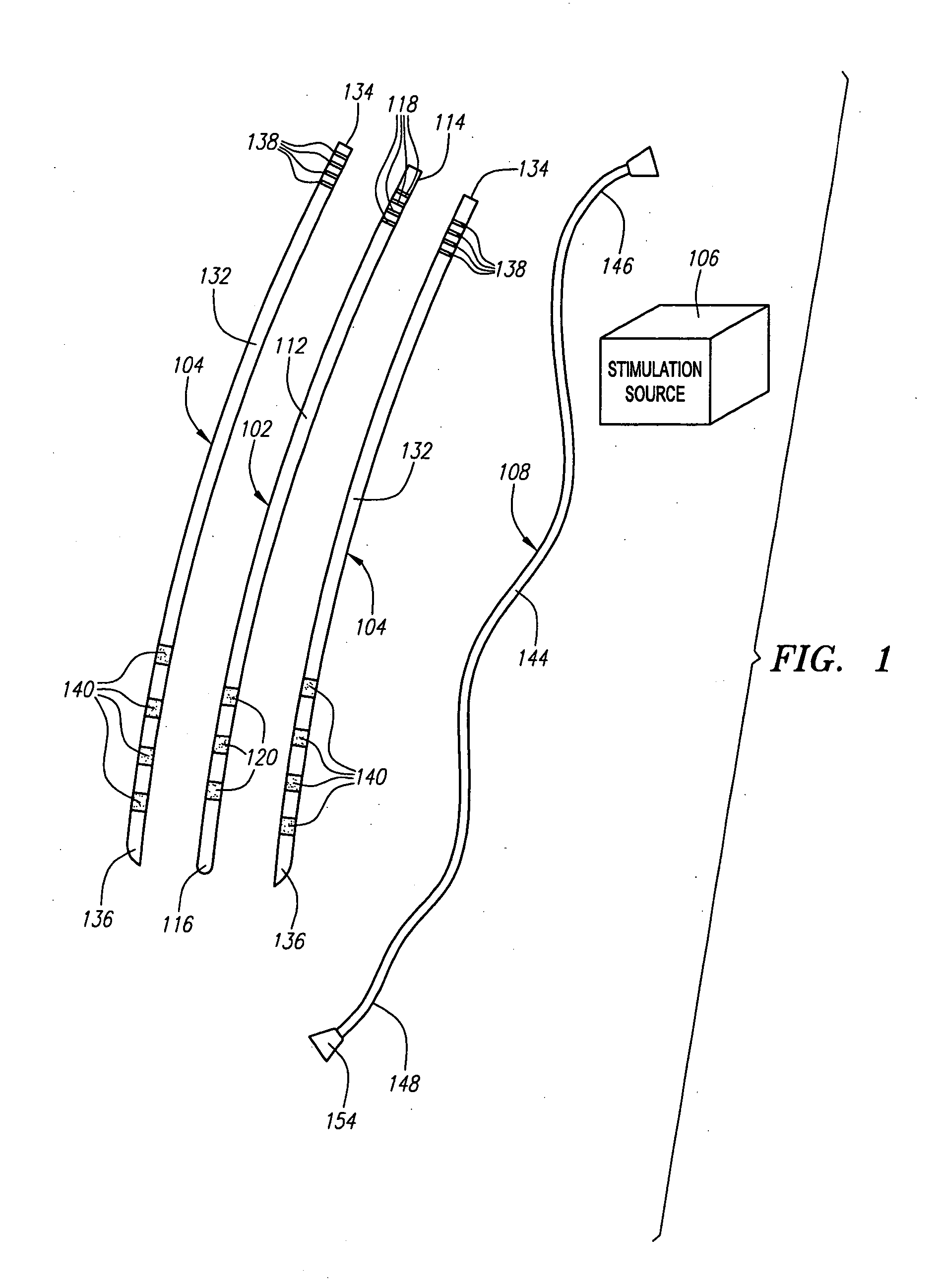
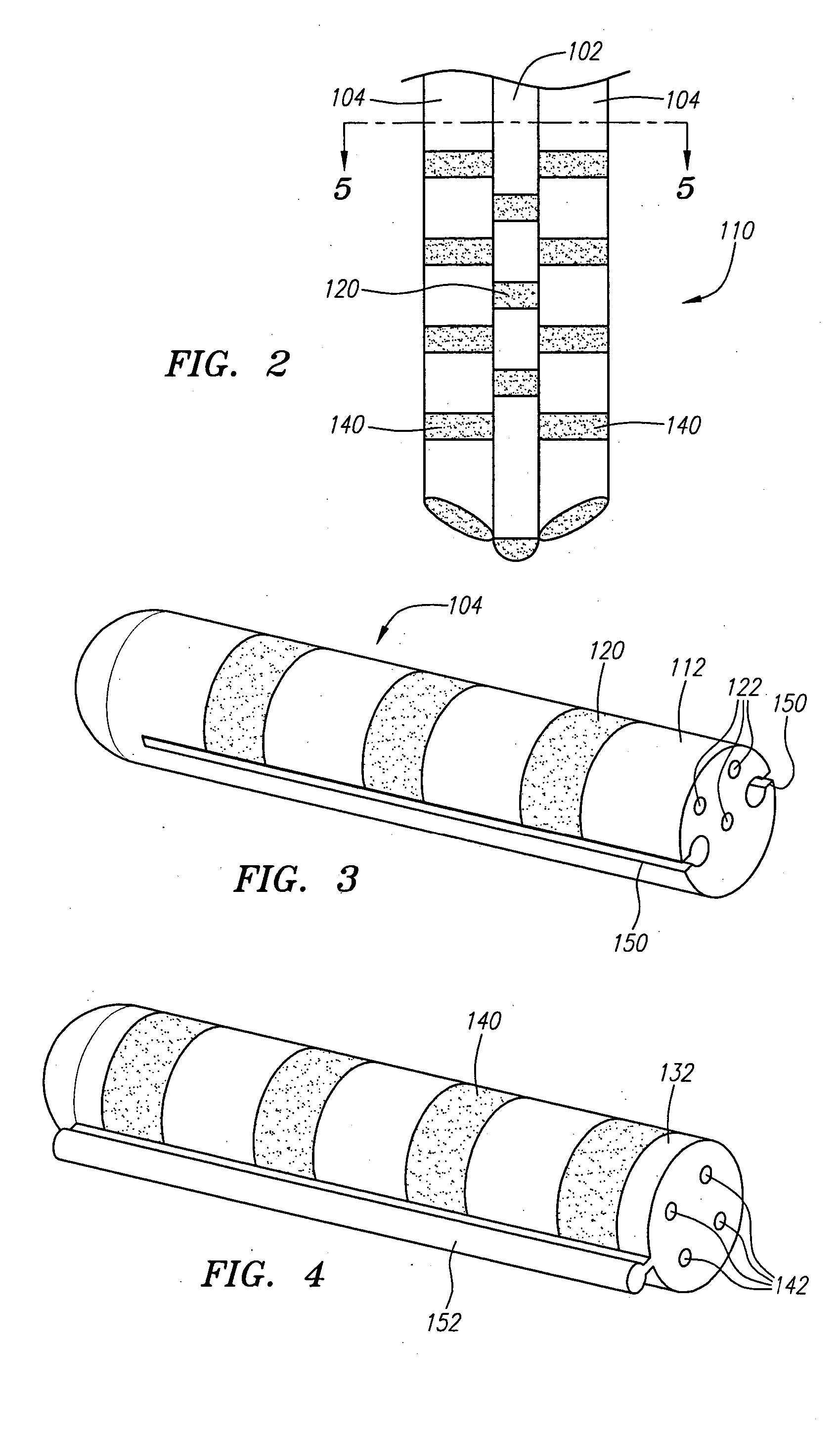
Modular stimulation lead network
InactiveUS20050203599A1More stabilityMinimize damageSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesCouplingChronic pain
A medical kit and method for treating an ailment, such as chronic pain is provided. The kit comprises first and second medical leads, e.g., stimulation leads. Each lead comprises an elongated body and at least one operative element. The first medical lead comprises a coupling mechanism, such as a slot, and the second medical lead comprises a complementary mechanism, such as a rail, that slidably engages the coupling mechanism of the first medical lead. The method may comprise delivering the first medical lead into a patient's body, e.g., into the epidural space of the patient, and delivering the second medical lead into the patient's body by sliding the complementary coupling mechanism of the second medical lead along the coupling mechanism of the first medical lead.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Leadless neurostimulation device and method including the same
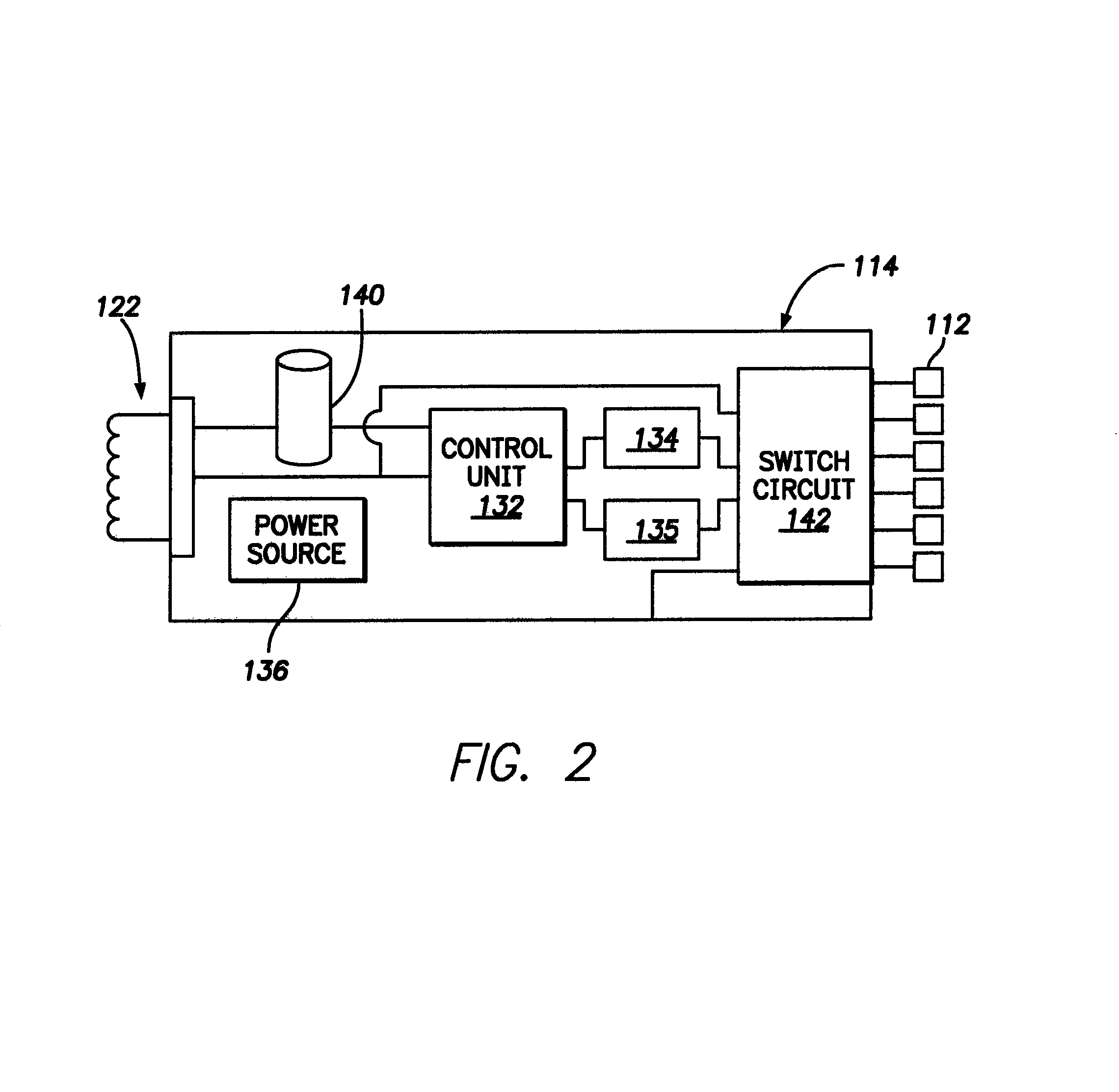
Leadless neurostimulation (NS) device including a device body and electrodes positioned along an active side of the device body. The electrodes form a multi-electrode array that is configured to interface with nervous tissue of a patient and supply electrical pulses to the nervous tissue. The NS device also includes an electronic sub-system that is coupled to the device body. The electronic sub-system includes switching circuitry, a power source, and an inductive coil that is operably coupled to the power source. The inductive coil is configured to receive electrical power through inductive coupling with an external coil. The device body, including the inductive coil coupled thereto, is sized and shaped to be disposed within an epidural space of a patient.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Devices and methods for tissue modification
ActiveUS20060095059A1Easy to disassembleEliminate needCannulasAnti-incontinence devicesSurgical departmentNerve stimulation
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC +1
Neural stimulation lead fixation
An implantable lead having at least one electrode contact at or near its distal end prevents undesirable movement of the electrode contact from its initial implant location. One embodiment relates to a spinal cord stimulation (SCS) lead. A balloon may be positioned on the electrode lead array. The balloon is filled with air, liquid or a compliant material. When inflated, the balloon stabilizes the lead with respect to the spinal cord and holds the lead in place. The pressure of the balloon is monitored or otherwise controlled during the filling process in order to determine at what point the filling process should be discontinued. An elastic aspect of the balloon serves as a contained relief valve to limit the pressure the balloon may place on the surrounding tissues when the epidural space is constrained.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Spinal ligament modification kit
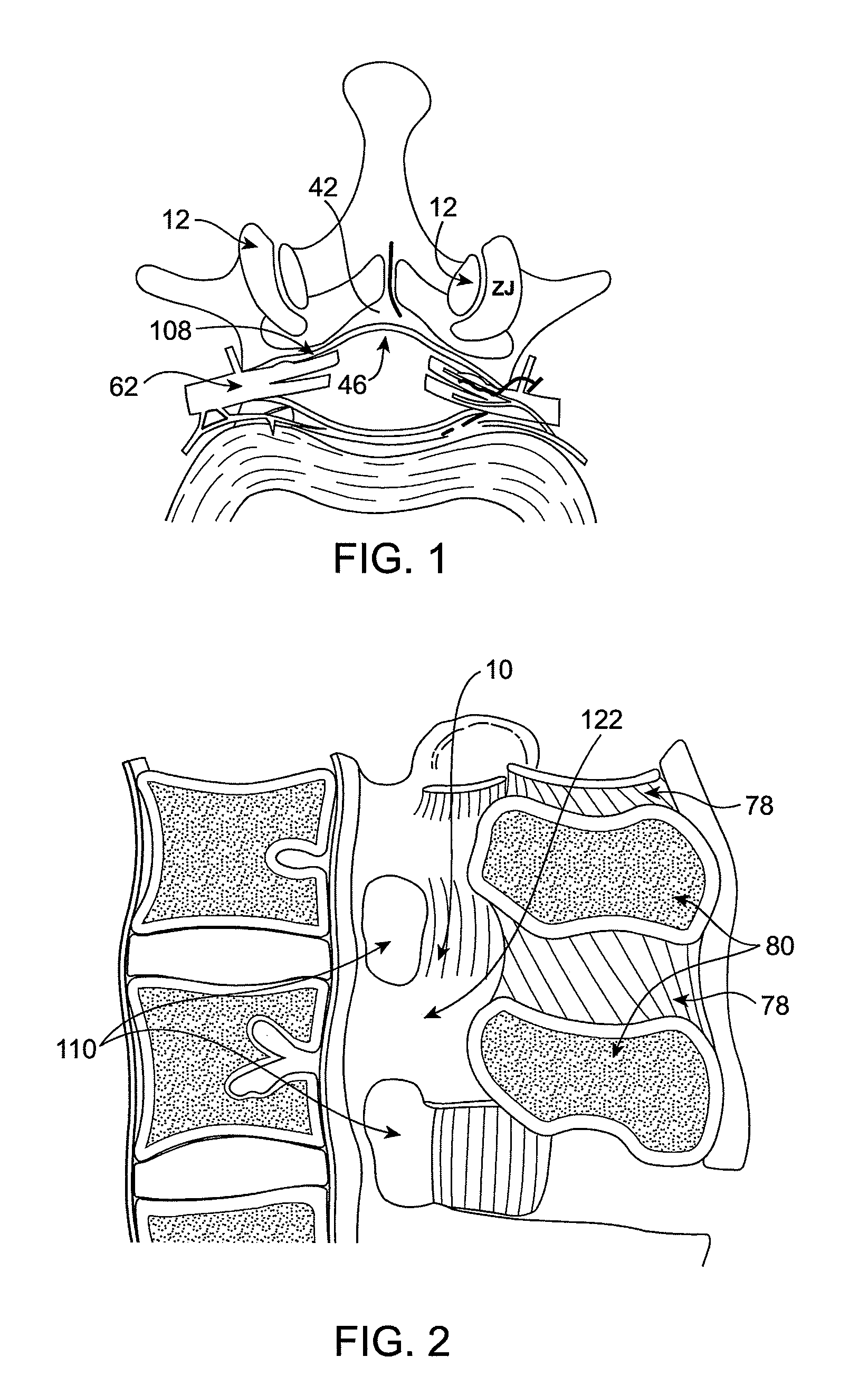
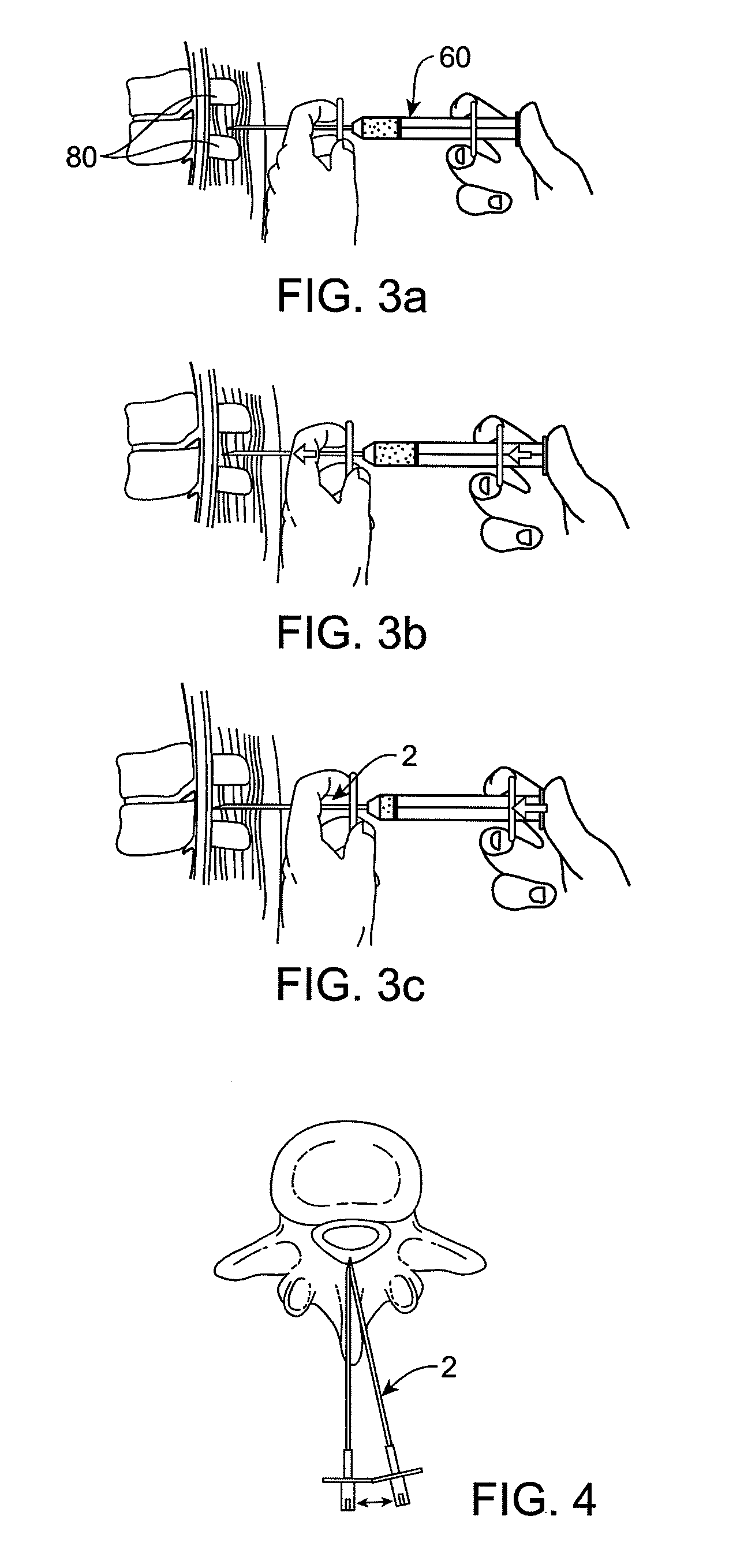
InactiveUS20060036211A1Prevent leakageUse minimizedSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSpinal ligamentsSpinal column
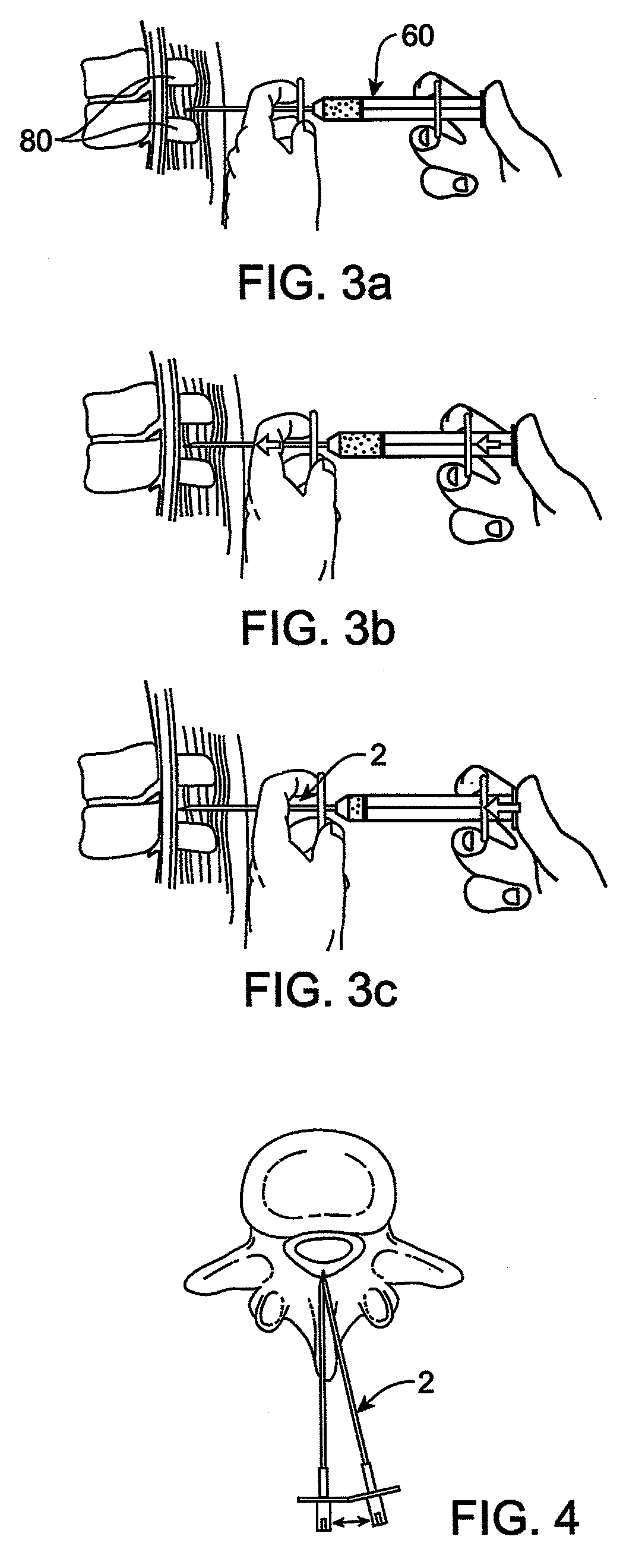
A method for treating stenosis in a spine comprises percutaneously accessing the epidural space in a stenotic region of interest, compressing the thecal sac in the region of interest to form a safety zonem, inserting a tissue removal tool into tissue in the working zone, using the tool to percutaneously reduce the stenosis; and utilizing imaging to visualize the position of the tool during at least a part of the reduction step. A tissue excision system for performing percutaneous surgery, comprises a cannula comprising a tissue-penetrating member having a distal end defining an aperture on one side thereof, an occluding member slidably received on or in the cannula and closing the aperture when the occluding member is adjacent the cannula distal end, means for engaging adjacent tissue via the aperture, and cutting means for resecting a section of the engaged tissue.
Owner:VERTOS MEDICAL
Multiprogrammable tissue stimulator and method
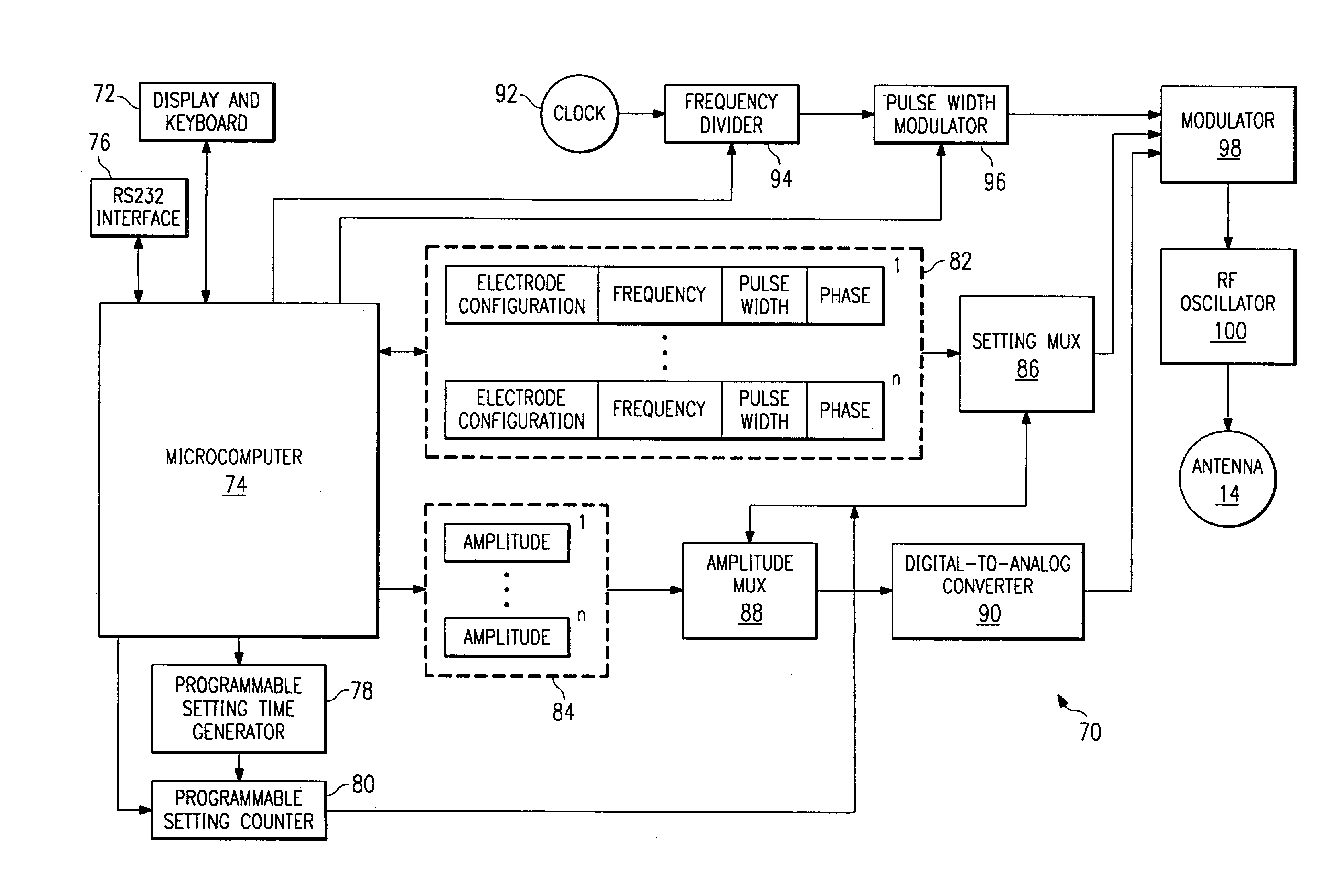
An electronic stimulation system is used to control pain over multiple regions of a patient's body. The system has one or more percutaneous leads, each having multiple electrodes, implanted within the patient's epidural space parallel to the axis of the spinal cord. The leads are connected to either a totally implanted system or a radio frequency system. The system is able to treat pain over different regions of a patient's body by “simultaneously” stimulating the patient with at least three different stimulation settings. “Simultaneous” stimulation involves sequentially stimulating the patient with the multiple stimulation settings such that the patient receives the cumulative effect of each stimulation setting, while not perceiving the transition from one stimulation setting to another.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Method and device for enhanced delivery of a biologically active agent through the spinal spaces into the central nervous system of a mammal
InactiveUS6913763B2Promotes high patient compliancePromotes acceptanceElectrotherapyMedical devicesDiseaseNervous system
A delivery method and implantable apparatus that allows for controlled, enhanced and (pre)-programmable administration of a biologically active agent into the spinal structures and / or the brain via the epidural space of a mammal, particularly of a human being and including a feedback regulated delivery method and apparatus specifically in the treatment of neurological diseases and chronic pain.
Owner:INTRABRAIN INT
Devices and methods for tissue modification
ActiveUS20060089609A1Enabling symptomatic reliefApproach can be quite invasiveCannulasAnti-incontinence devicesSurgical removalEpidural needles
Methods and apparatus are provided for selective surgical removal of tissue. In one variation, tissue may be ablated, resected, removed, or otherwise remodeled by standard small endoscopic tools delivered into the epidural space through an epidural needle. The sharp tip of the needle in the epidural space, can be converted to a blunt tipped instrument for further safe advancement. The current invention includes specific tools that enable safe tissue modification in the epidural space, including a barrier that separates the area where tissue modification will take place from adjacent vulnerable neural and vascular structures. A nerve stimulator may be provided to reduce a risk of inadvertent neural abrasion.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC +1
Spinal ligament modification
ActiveUS20060036272A1Prevent leakageUse minimizedSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSpinal ligamentsSpinal column
A method for treating stenosis in a spine comprises percutaneously accessing the epidural space in a stenotic region of interest, compressing the thecal sac in the region of interest to form a safety zonem, inserting a tissue removal tool into tissue in the working zone, using the tool to percutaneously reduce the stenosis; and utilizing imaging to visualize the position of the tool during at least a part of the reduction step. A tissue excision system for performing percutaneous surgery, comprises a cannula comprising a tissue-penetrating member having a distal end defining an aperture on one side thereof, an occluding member slidably received on or in the cannula and closing the aperture when the occluding member is adjacent the cannula distal end, means for engaging adjacent tissue via the aperture, and cutting means for resecting a section of the engaged tissue.
Owner:VERTOS MEDICAL
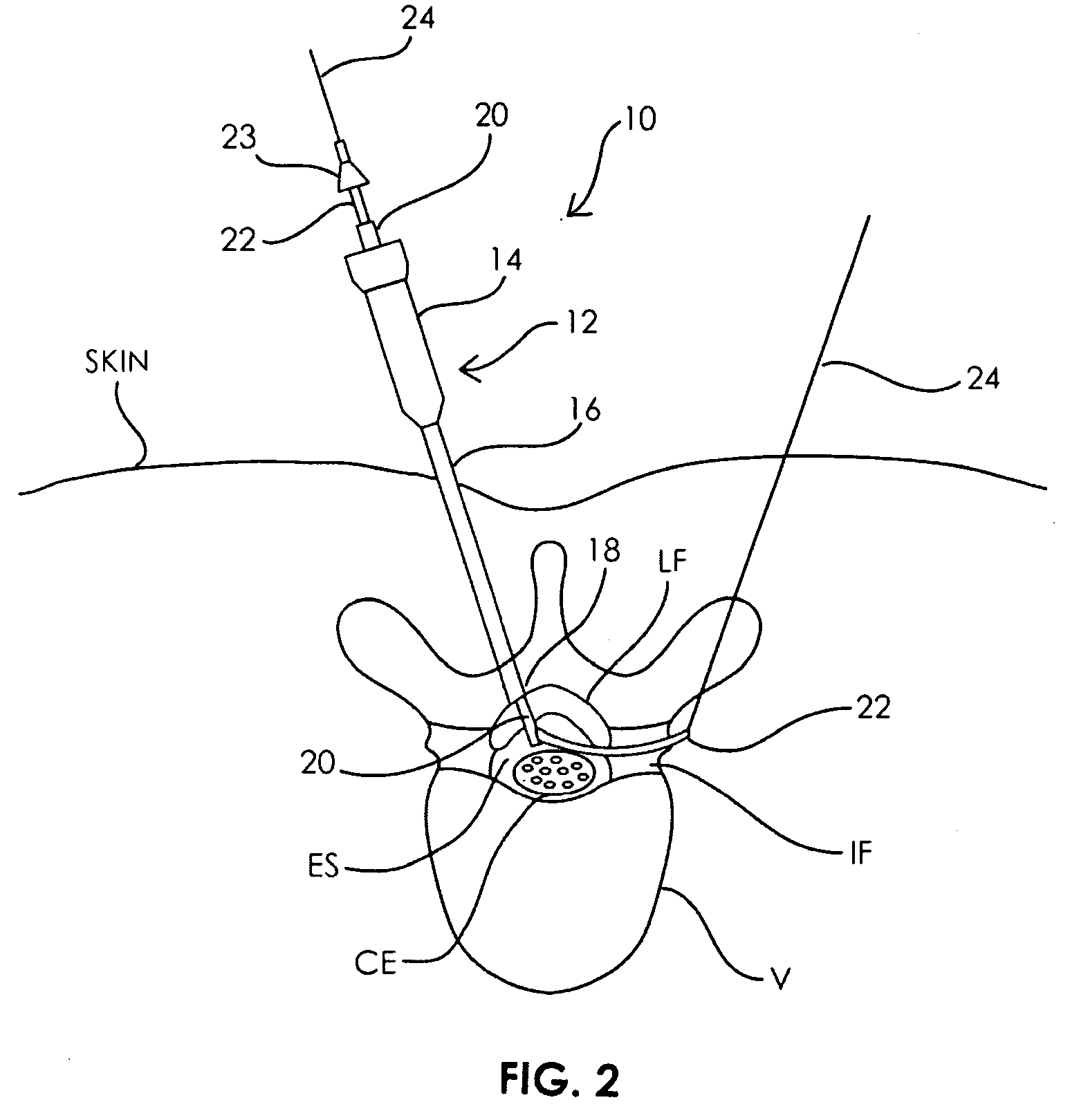
Spinal access system and method
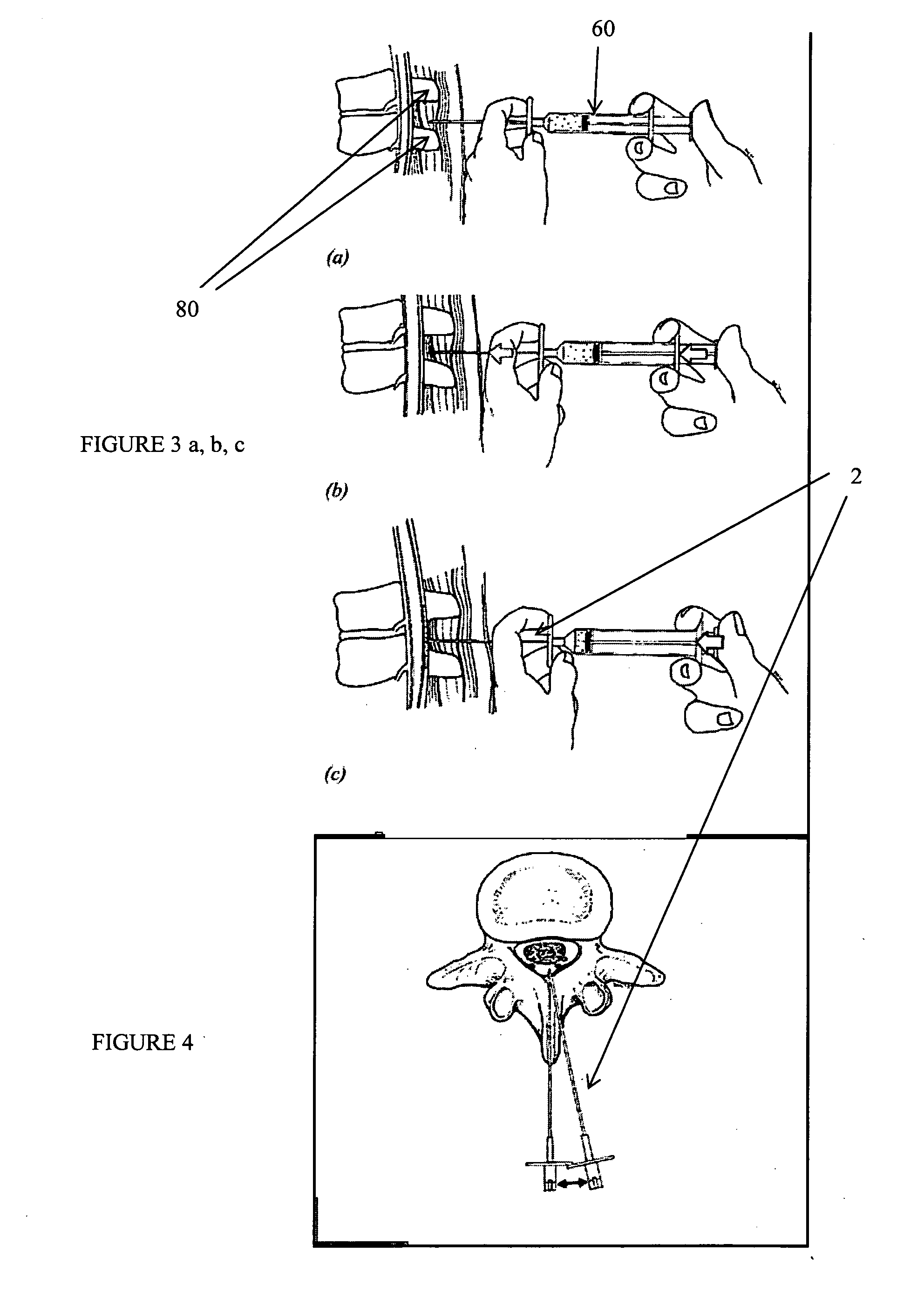
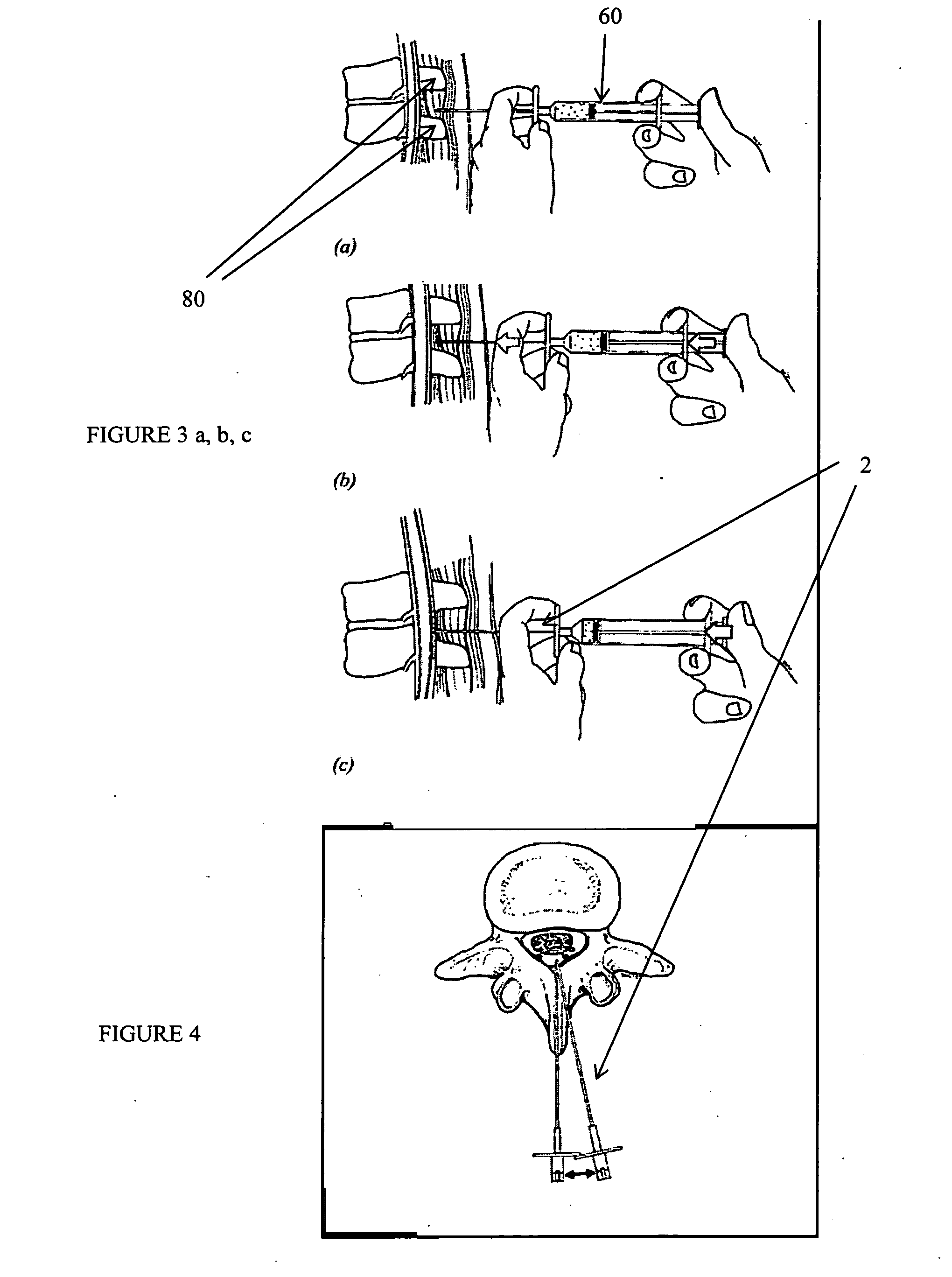
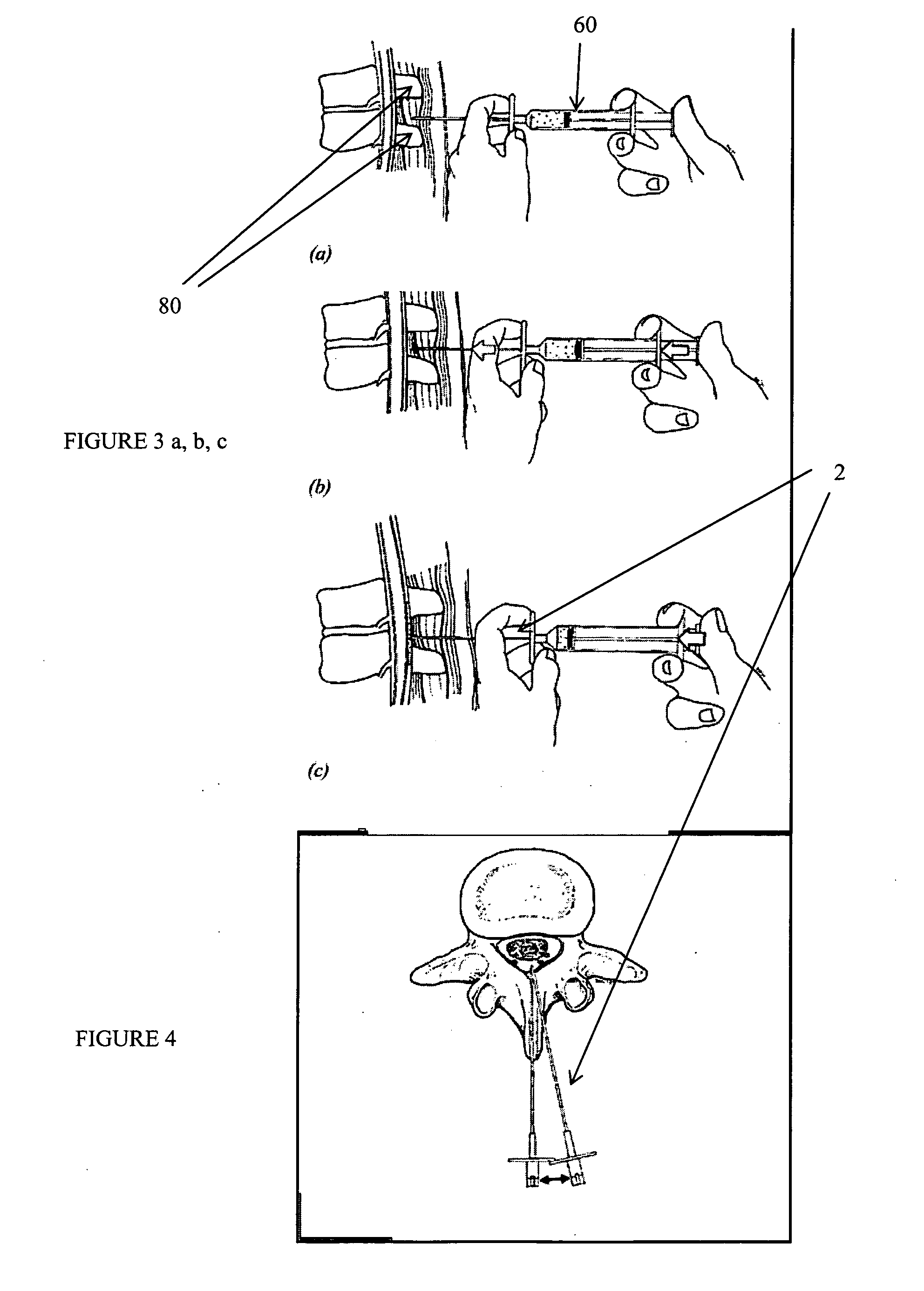
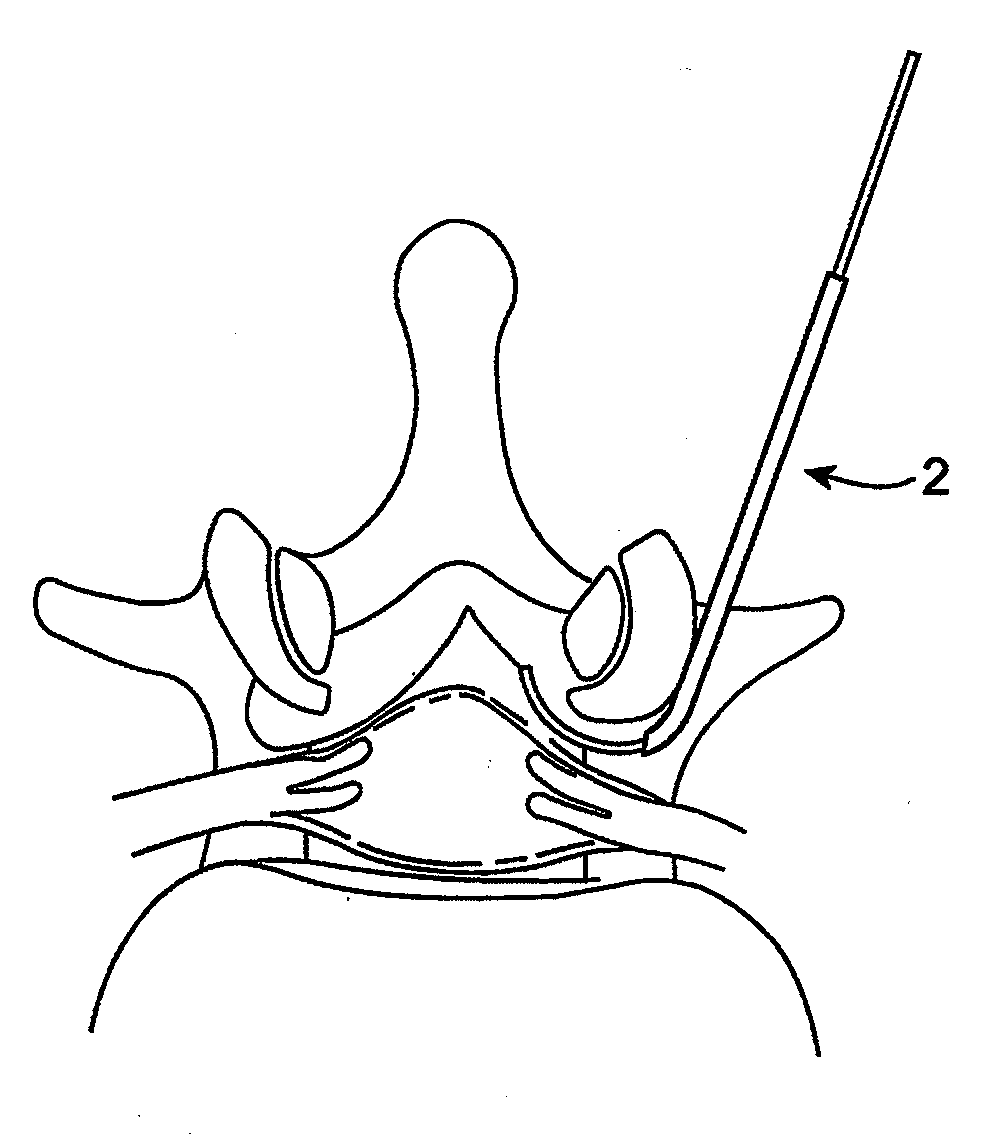
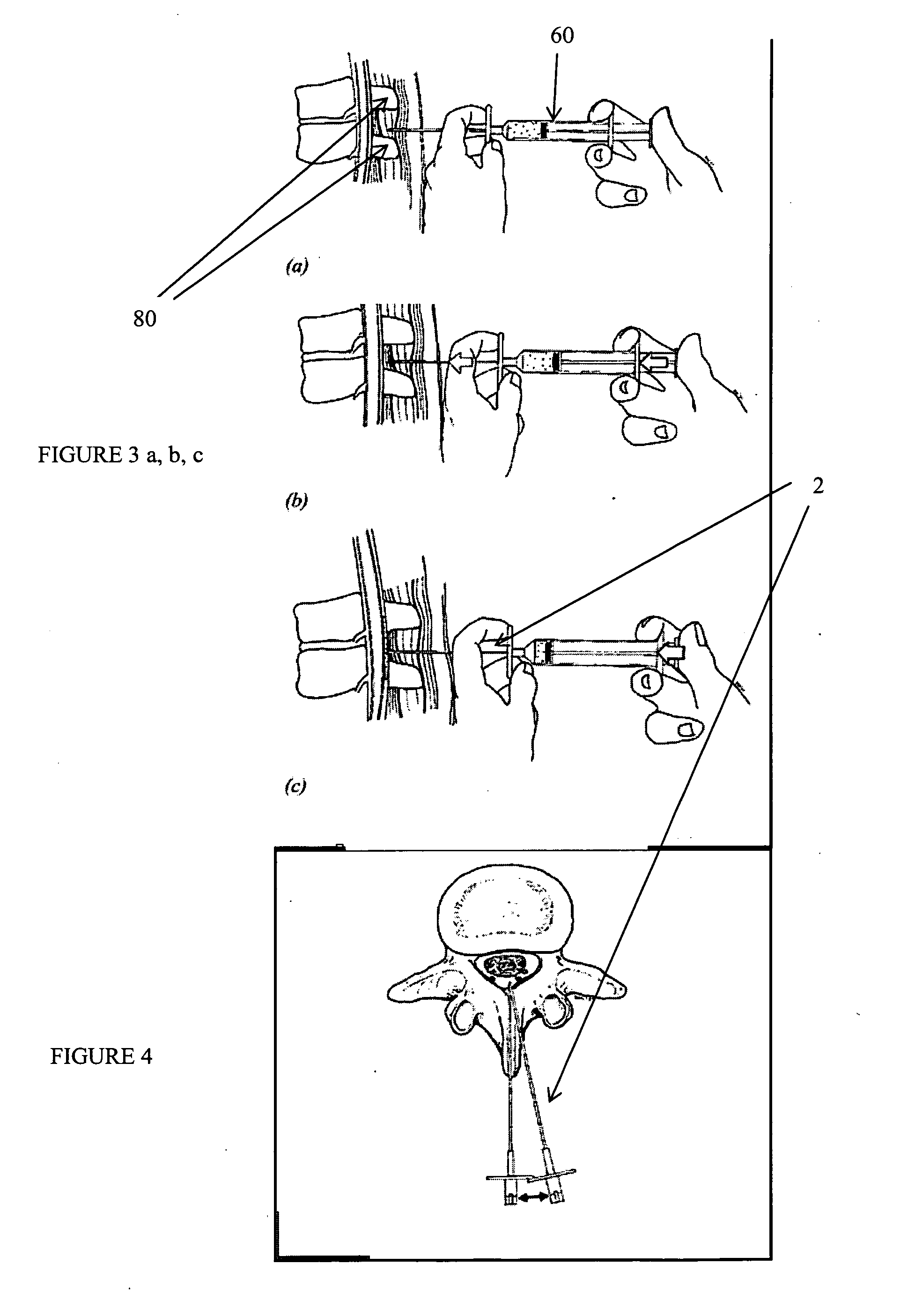
Described herein are devices and systems for accessing a spine and particularly the epidural region of the spine and methods of using these systems and devices to access the spine or regions of the spine. In particular, cannulas that may be anchored to the ligamentum flavum or the periosteum are described. Ligamentum flavum access tools are also described. These tools may be used with (or without) an anchoring cannula to penetrate the ligamentum flavum and provide access to the epidural space without risk of injury to other structures within the epidural space. The devices, methods and systems described herein are particularly useful in minimally invasive surgical (MIS) uses. The devices, methods and systems described herein may be used for performing spinal decompressions and other spinal procedures.
Owner:BAXANO
Devices and methods for tissue modification
InactiveUS20100094231A1Improve securityAvoid injuryCannulasDiagnosticsSurgical removalEpidural needles
Owner:BAXANO
Spinal ligament modification devices
InactiveUS20060036271A1Prevent leakageUse minimizedSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSpinal ligamentsSpinal column
A method for treating stenosis in a spine comprises percutaneously accessing the epidural space in a stenotic region of interest, compressing the thecal sac in the region of interest to form a safety zonem, inserting a tissue removal tool into tissue in the working zone, using the tool to percutaneously reduce the stenosis; and utilizing imaging to visualize the position of the tool during at least a part of the reduction step. A tissue excision system for performing percutaneous surgery, comprises a cannula comprising a tissue-penetrating member having a distal end defining an aperture on one side thereof, an occluding member slidably received on or in the cannula and closing the aperture when the occluding member is adjacent the cannula distal end, means for engaging adjacent tissue via the aperture, and cutting means for resecting a section of the engaged tissue.
Owner:VERTOS MEDICAL
Devices and methods for tissue modification
ActiveUS20090204119A1Enabling symptomatic reliefApproach can be quite invasiveSpinal electrodesCannulasSurgical removalVascular structure
Methods and apparatus are provided for selective surgical removal of tissue. In one variation, tissue may be ablated, resected, removed, or otherwise remodeled by standard small endoscopic tools delivered into the epidural space through an epidural needle. The sharp tip of the needle in the epidural space, can be converted to a blunt tipped instrument for further safe advancement. The current invention includes specific tools that enable safe tissue modification in the epidural space, including a barrier that separates the area where tissue modification will take place from adjacent vulnerable neural and vascular structures. A nerve stimulator may be provided to reduce a risk of inadvertent neural abrasion.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC +1
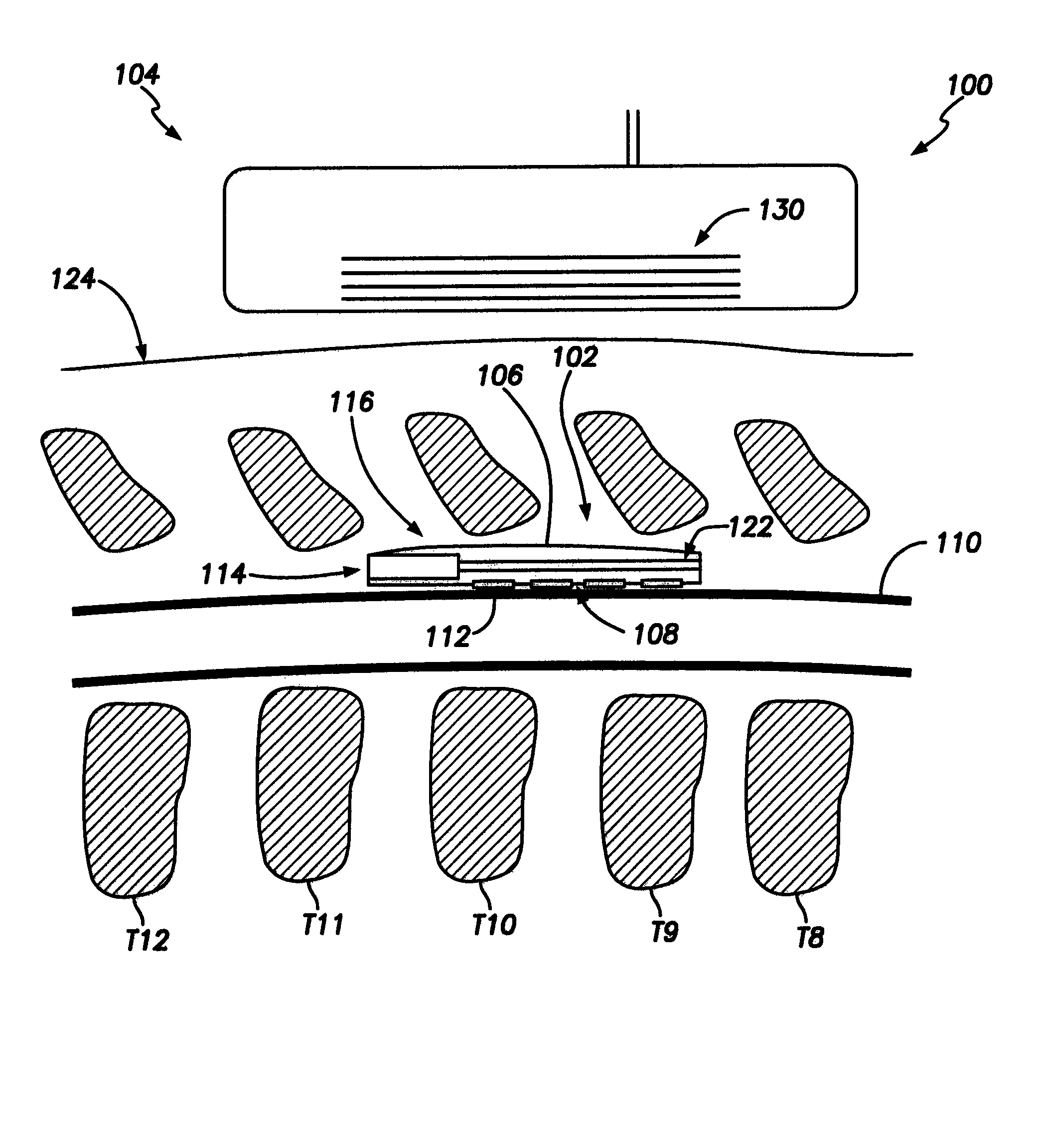
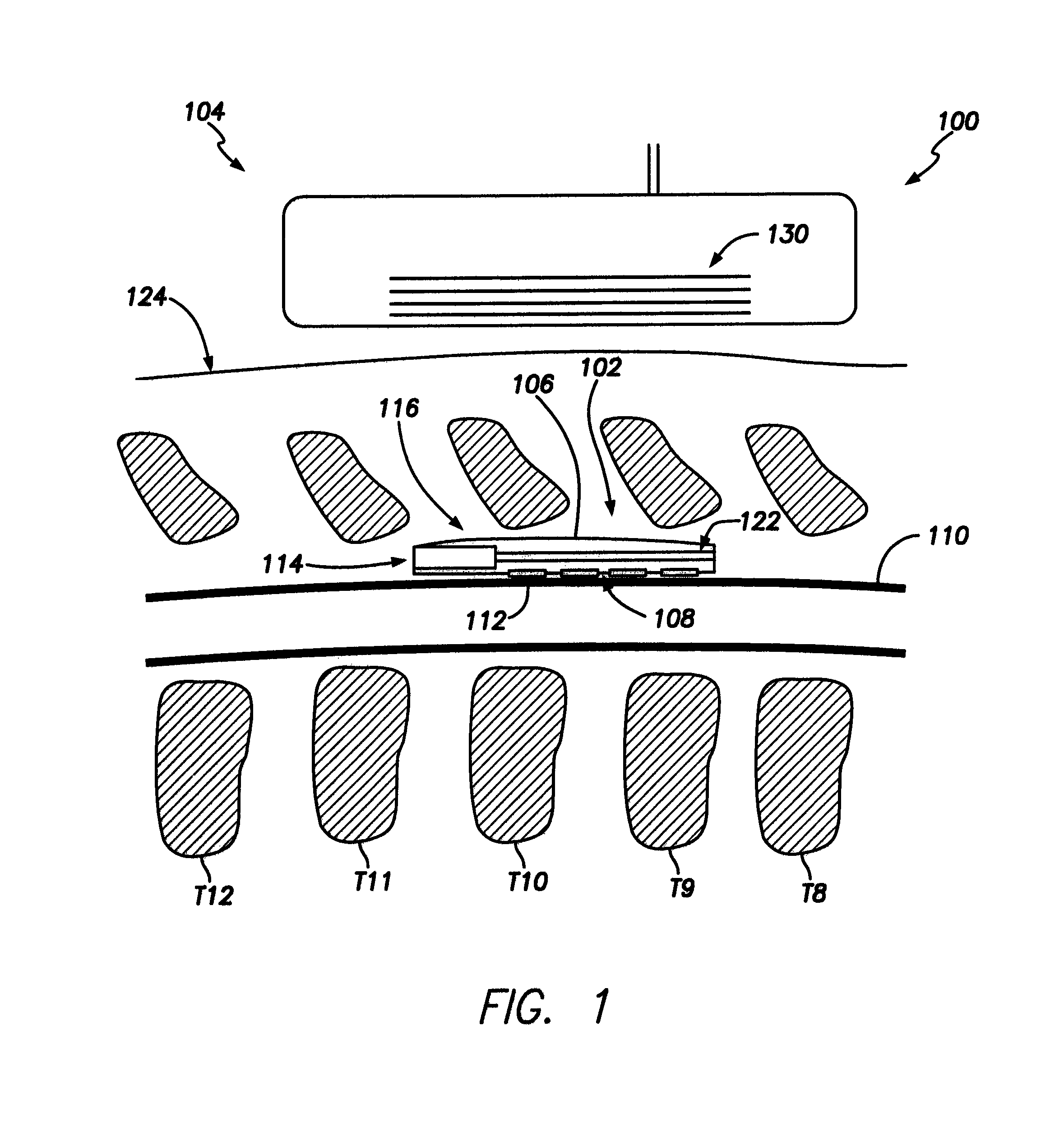
System and Method for Electrical Stimulation of the Lumbar Vertebral Column
ActiveUS20120215218A1Inhibit migrationPrevent rotationSpinal electrodesSurgical instruments for heatingElectrical impulseElectrical stimulations
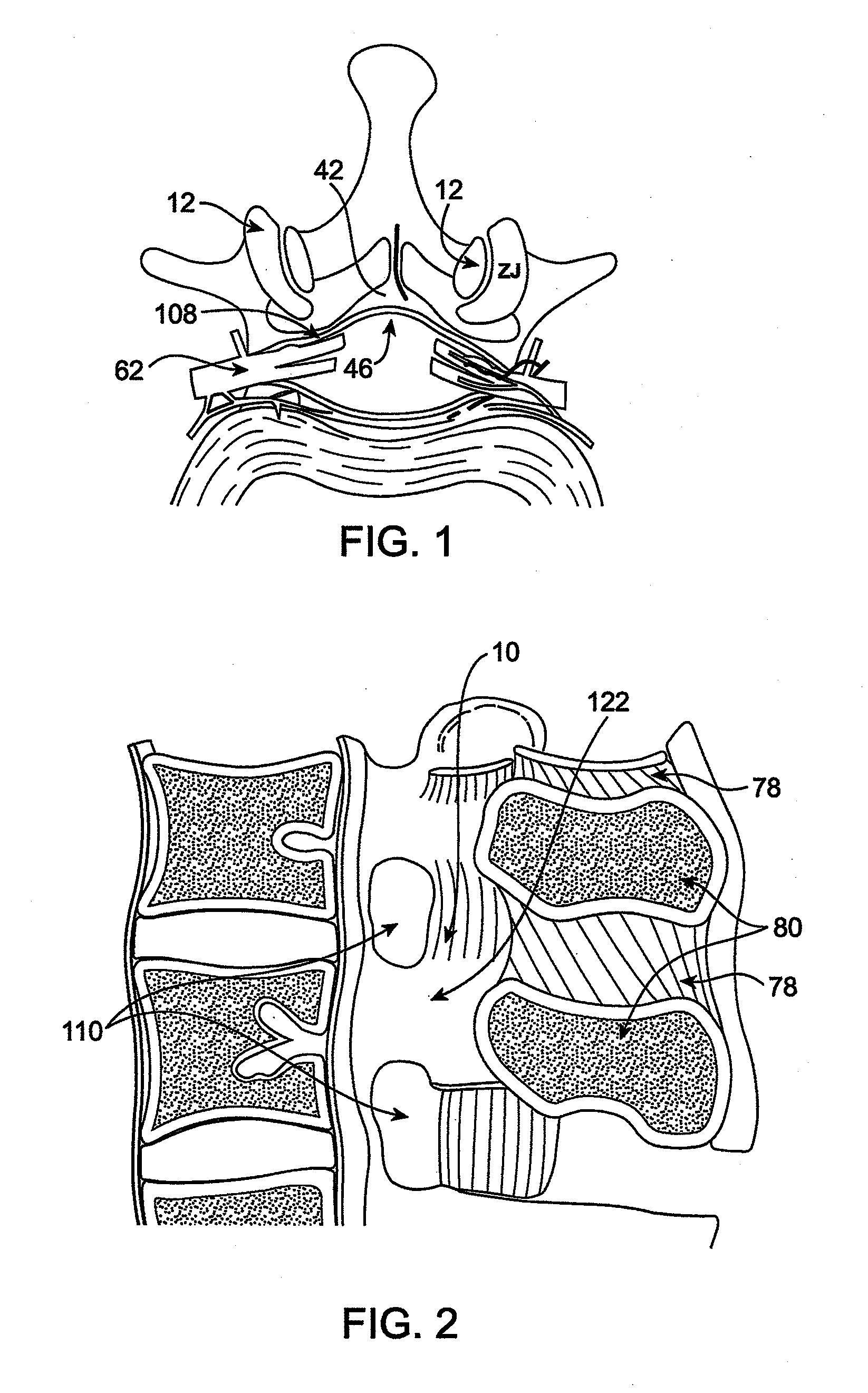
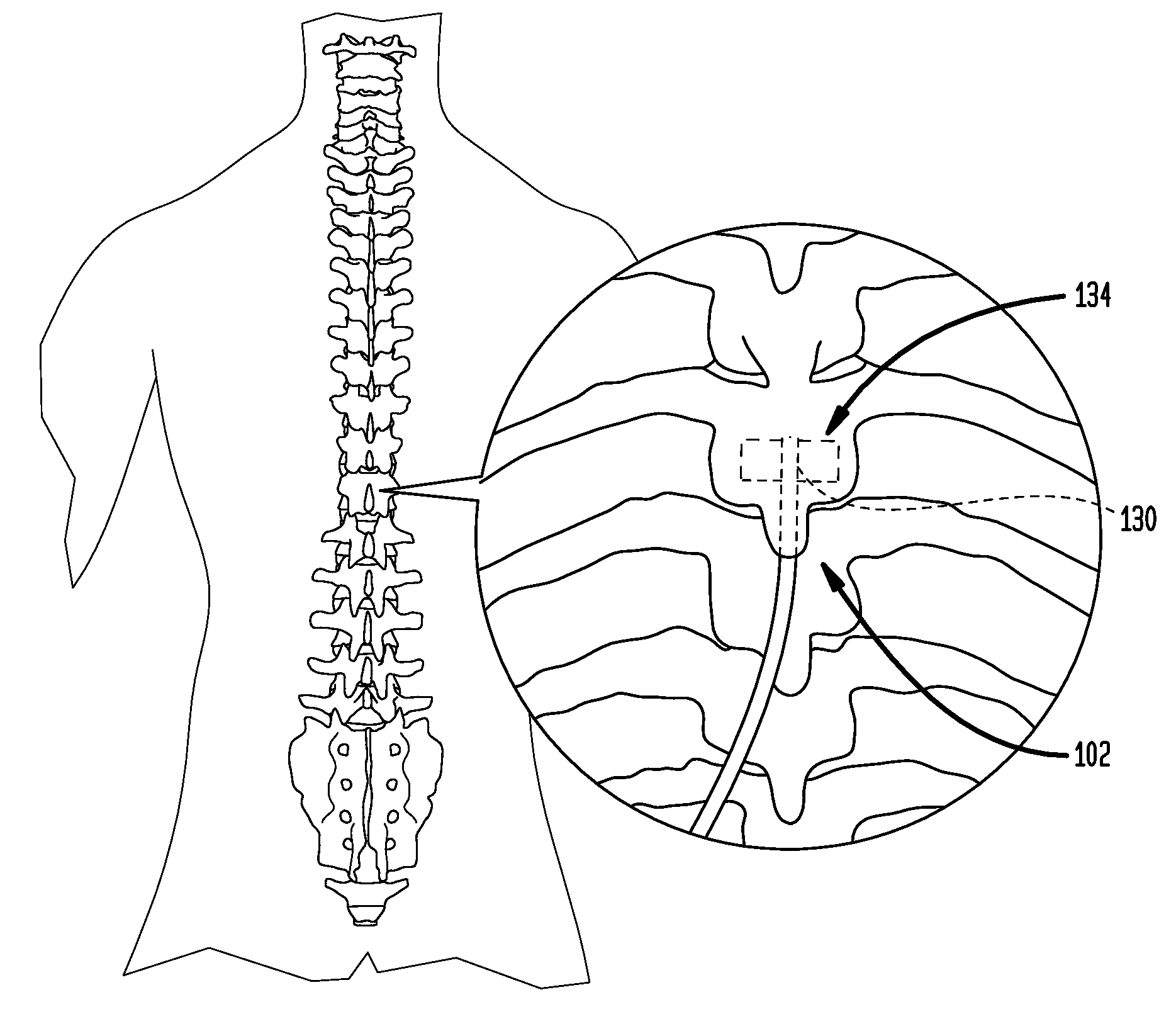
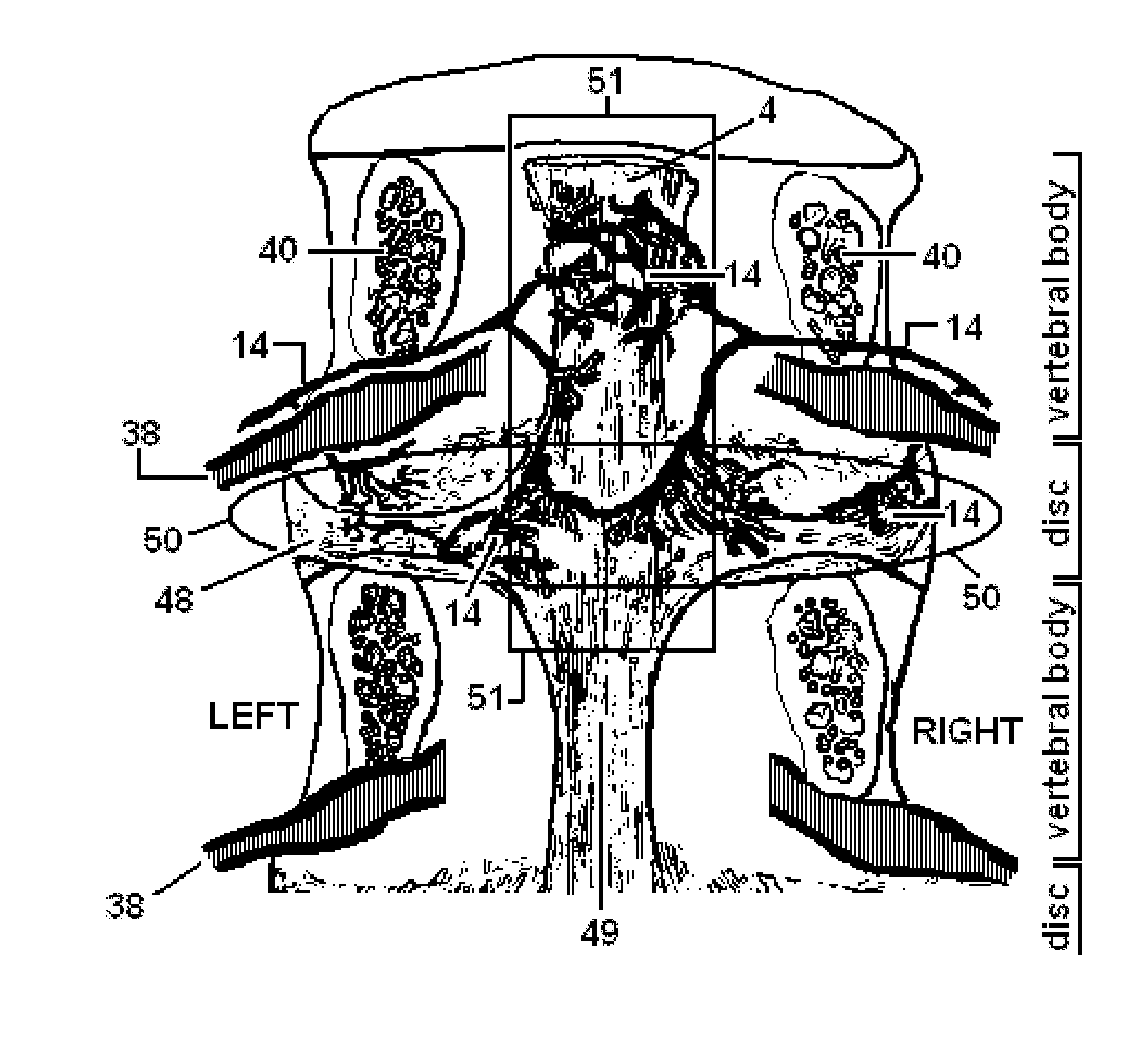
Disclosed methods and devices treat chronic lower back pain from degenerated or injured intervertebral discs. Electrodes connected to a pulse generator deliver electrical impulses to nerves located within the posterior longitudinal ligament and annulus fibrosus of lumbar intervertebral discs. The stimulation reduces back pain reversibly, adjustably, and with almost complete coverage of the pain-generating region. A temporary percutaneous lead and a permanent paddle lead are used. The percutaneous lead, designed to prevent inappropriate stimulation of the thecal sac, is inserted using a specially-designed introducer cannula and lead blank. The paddle lead is configured individually for implantation in the anterior epidural space of each patient. Electrical stimulation parameters may also be selected so as to ablate the nerves, using non-thermal irreversible electroporation, or using joule heating wherein a thermal insulator covers substantially all of the thecal sac, thereby shielding the thecal sac from potential heat damage.
Owner:LIPANI JOHN D
Devices and methods for selective surgical removal of tissue
ActiveUS20060094976A1Improve securityAvoid injuryCannulasAnti-incontinence devicesTissue remodelingLateral recess
Methods and apparatus are provided for selective surgical removal of tissue, e.g., for enlargement of diseased spinal structures, such as impinged lateral recesses and pathologically narrowed neural foramen. In one variation, tissue may be ablated, resected, removed, or otherwise remodeled by standard small endoscopic tools delivered into the epidural space through an epidural needle. Once the sharp tip of the needle is in the epidural space, it is converted to a blunt tipped instrument for further safe advancement. A specially designed epidural catheter that is used to cover the previously sharp needle tip may also contain a fiberoptic cable. Further embodiments of the current invention include a double barreled epidural needle or other means for placement of a working channel for the placement of tools within the epidural space, beside the epidural instrument. The current invention includes specific tools that enable safe tissue modification in the epidural space, including a barrier that separates the area where tissue modification will take place from adjacent vulnerable neural and vascular structures. In one variation, a tissue removal device is provided including a thin belt or ribbon with an abrasive cutting surface. The device may be placed through the neural foramina of the spine and around the anterior border of a facet joint. Once properly positioned, a medical practitioner may enlarge the lateral recess and neural foramina via frictional abrasion, i.e., by sliding the tissue removal surface of the ribbon across impinging tissues. A nerve stimulator optionally may be provided to reduce a risk of inadvertent neural abrasion. Additionally, safe epidural placement of the working barrier and epidural tissue modification tools may be further improved with the use of electrical nerve stimulation capabilities within the invention that, when combined with neural stimulation monitors, provide neural localization capabilities to the surgeon. The device optionally may be placed within a protective sheath that exposes the abrasive surface of the ribbon only in the area where tissue removal is desired. Furthermore, an endoscope may be incorporated into the device in order to monitor safe tissue removal. Finally, tissue remodeling within the epidural space may be ensured through the placement of compression dressings against remodeled tissue surfaces, or through the placement of tissue retention straps, belts or cables that are wrapped around and pull under tension aspects of the impinging soft tissue and bone in the posterior spinal canal.
Owner:SPINAL ELEMENTS INC +1
Methods and apparatus for spinal cord stimulation using expandable electrode
InactiveUS20100057178A1Increase the areaLarge treatment areaSpinal electrodesBalloon catheterEffective treatmentBody tissue
The present invention provides systems, apparatus and methods for selectively applying electrical energy to body tissue. More specifically, systems and methods are provided for introducing a spinal cord stimulation electrode device into a patient's epidural space through a small portal, such as a percutaneous penetration, and then expanding the electrode device once inside the epidural space to achieve a larger footprint of contact on the dura. This substantially prevents migration of the electrode within the epidural space and provides for more efficient and effective treatment.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
Collapsible/expandable tubular electrode leads
InactiveUS20050203600A1Inhibit tissue growthEasy retrievalSpinal electrodesExternal electrodesSpinal cordSurgical department
A medical lead and method of treating a patient are provided. The medical lead comprises an electrically insulative tubular membrane, a resilient spring element associated with the insulative membrane, and at least one electrode associated with the insulative membrane. In the preferred embodiment, the tubular membrane has a non-circular cross-sectional shape. The spring layer is configured to urge that insulative membrane into an expanded geometry. The medical lead is configured to be collapsed into a compact form for percutaneous delivery into the patient, thereby obviating the need to perform an invasive surgical procedure on the patient. The body formed by these elements, when expanded, can be sized to fit within the epidural space of a patient. The patient can be treated by placing the medical lead into a collapsed state by applying a compressive force to the medical lead, percutaneously delivering the collapsed medical lead into the patient adjacent tissue to be treated, and placing the medical lead into an expanded state by releasing the compressive force. In one preferred method, the stimulation lead is used to stimulate tissue, such as spinal cord tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
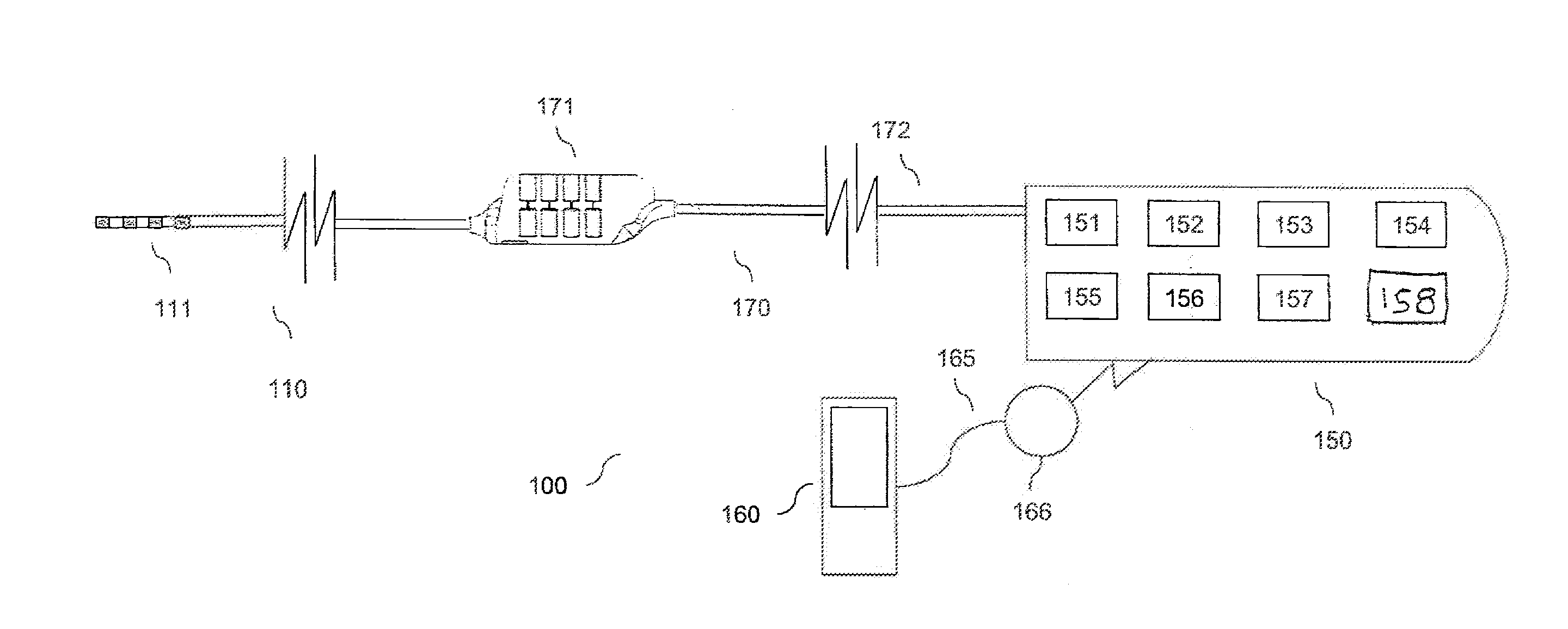
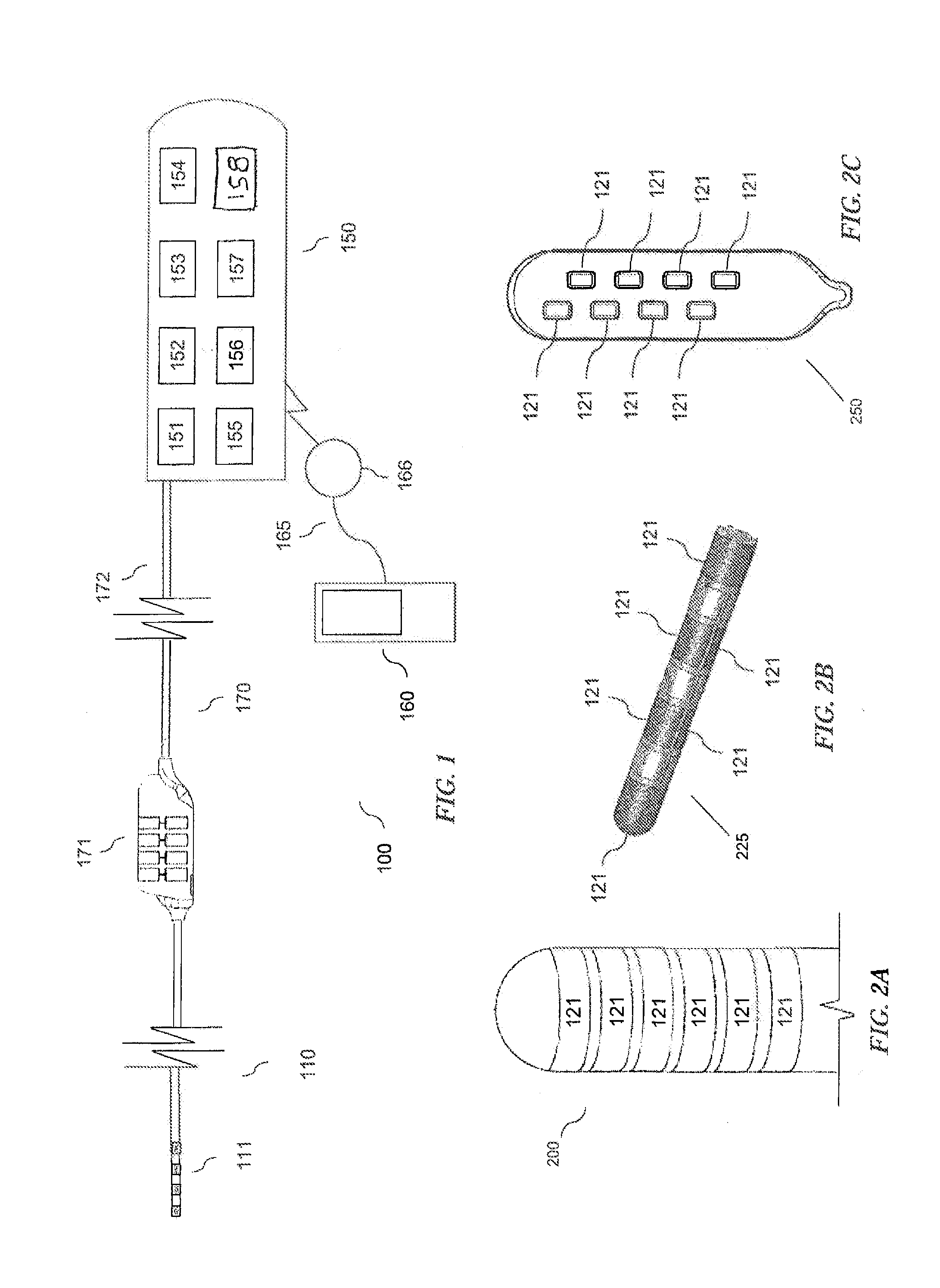
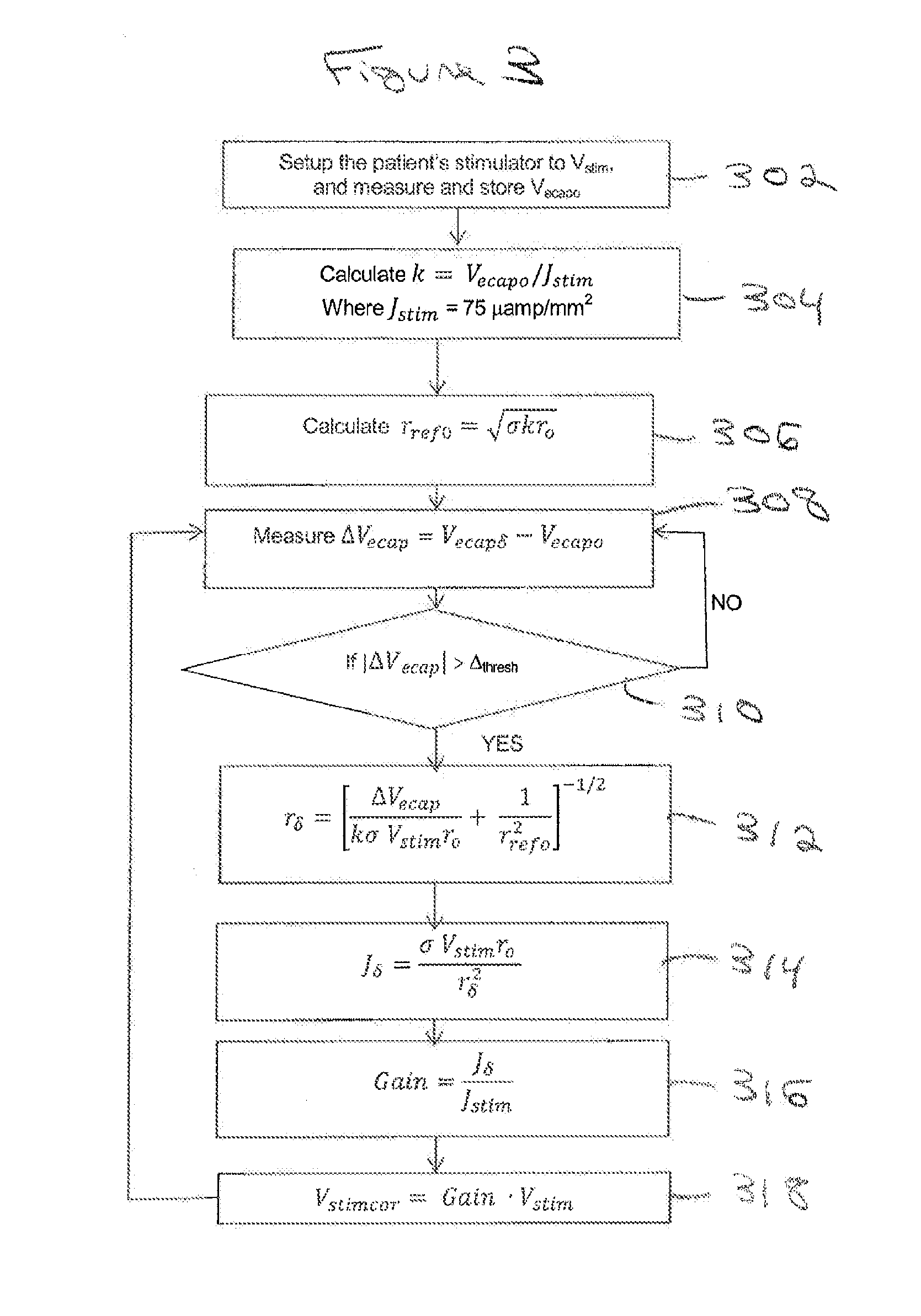
Method and system for non-linear feedback control of spinal cord stimulation
ActiveUS20150360031A1ElectrotherapyArtificial respirationEvoked compound action potentialSpinal column
A system of non-linear feedback control for spinal cord stimulation is provided. The system comprises a lead adapted to be implanted within an epidural space of a dorsal column of a patients spine, and a pulse generator (PG) electrically coupled to the lead. The PG is configured to deliver spinal cord stimulation (SCS) therapy. The system also comprises a sensing circuitry configured to sense an evoked compound action potential (ECAP) response that propagates along the neural pathway. The system also comprises a processor programmed to operation, in response to instructions stored on a non-transient computer-readable medium, to obtain a baseline ECAP response when the lead and spinal cord tissue properties are in baseline states; analyze ECAP responses relative to the baseline ECAP response to obtain an ECAP feedback difference indicative of a change in at least one of the baseline state of the lead and the baseline state of the spinal cord tissue properties. The processor is also programmed to adjust an SCS therapy based on the ECAP feedback.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
Spinal ligament modification devices
InactiveUS20060184175A1Secure bootReduce stenosisSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesSpinal ligamentsSpinal column
A method for treating stenosis in a spine comprises percutaneously accessing the epidural space in a stenotic region of interest, compressing the thecal sac in the region of interest to form a safety zonem, inserting a tissue removal tool into tissue in the working zone, using the tool to percutaneously reduce the stenosis; and utilizing imaging to visualize the position of the tool during at least a part of the reduction step. A tissue excision system for performing percutaneous surgery, comprises a cannula comprising a tissue-penetrating member having a distal end defining an aperture on one side thereof, an occluding member slidably received on or in the cannula and closing the aperture when the occluding member is adjacent the cannula distal end, means for engaging adjacent tissue via the aperture, and cutting means for resecting a section of the engaged tissue.
Owner:VERTOS MEDICAL
Steerable fiberoptic epidural balloon catheter and scope
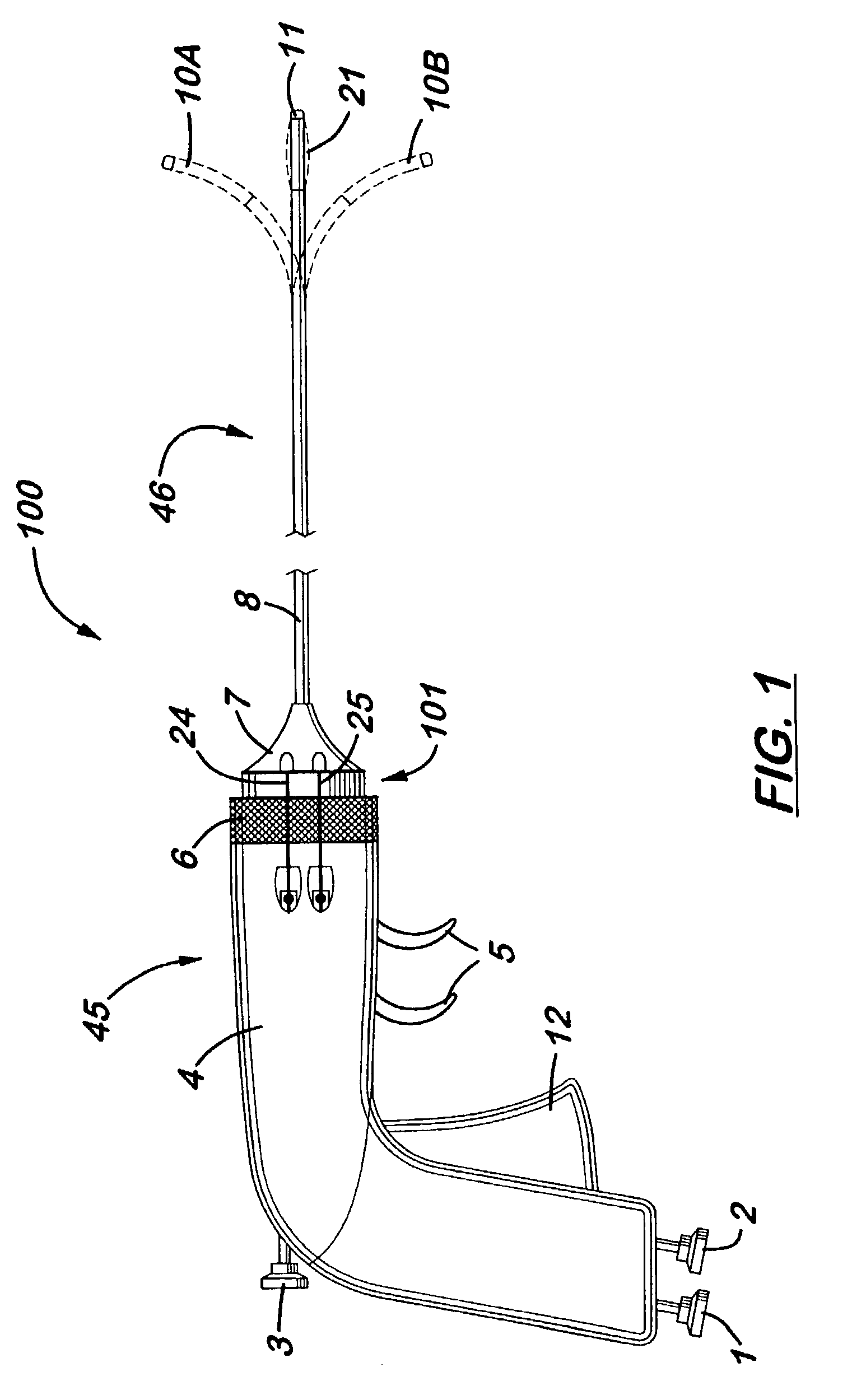
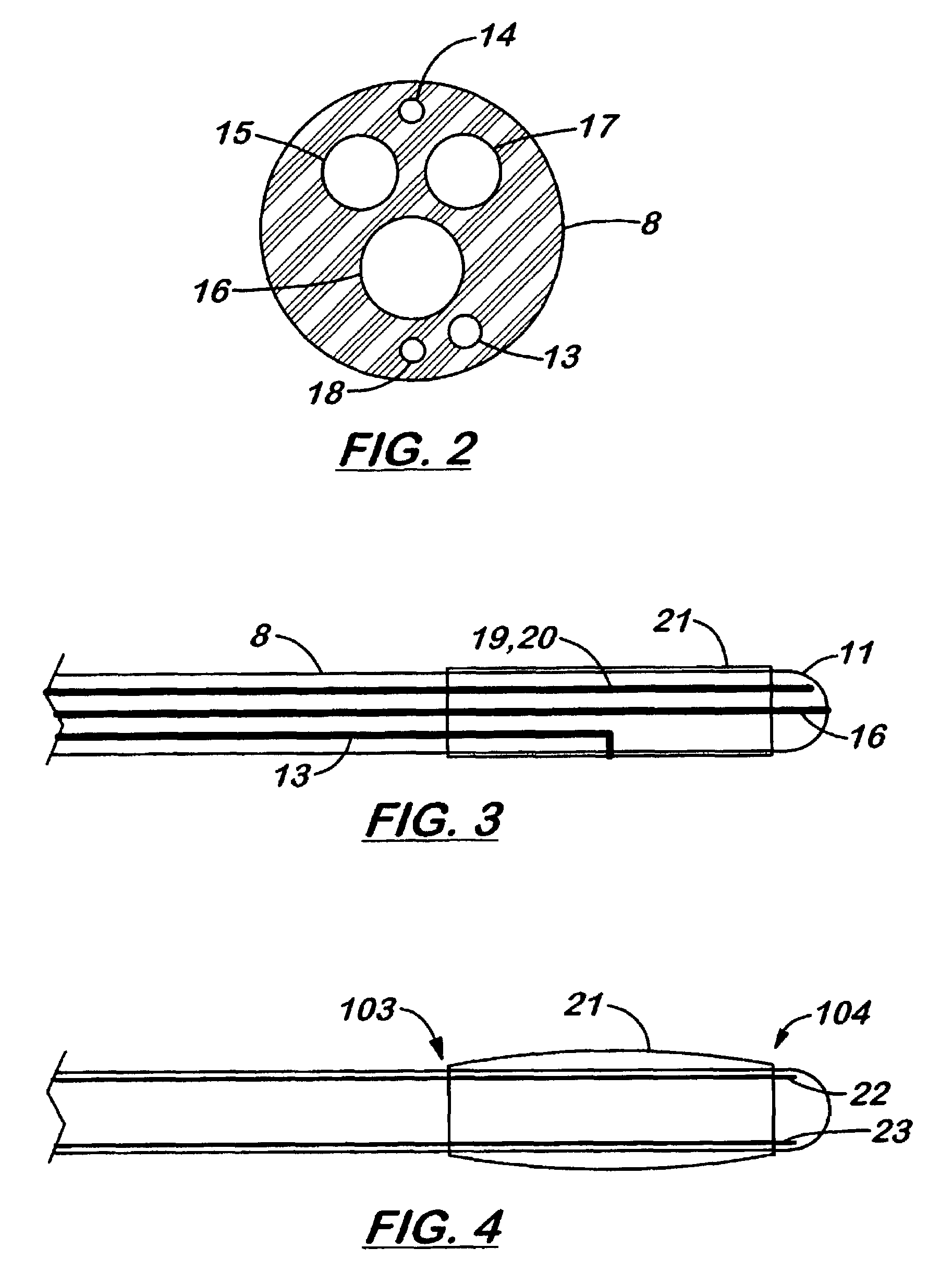
Devices for and methods of treating afflictions occurring in a body cavity, such as the epidural space. The methods and devices provide for fluoroscopic assisted placement of a fiber optic catheter / scope with a balloon tip. These devices and methods would perform decompression surgery, neuroplasty, and mechanical lysis of adhesions (and other afflictions), as well as allowing small operating and therapeutic instruments under direct visualization.
Owner:ADVANCED PAIN CENT
System and Methods for Diagnosis and Treatment of Discogenic Lower Back Pain
ActiveUS20150005680A1Inhibit migrationPrevent rotationSpinal electrodesDiagnosticsClosed loopElectrical impulse
Methods and devices to treat discogenic lumbar back pain are disclosed. Electrodes are implanted within the anterior epidural space of the patient. A pulse generator that is connected to the electrodes delivers electrical impulses to sympathetic nerves located within the posterior longitudinal ligament (PLL) of the lumbar spine and outer posterior annulus fibrosus of the intervertebral disc. In alternate embodiments, energy directed to nerves in the PLL may be from light or mechanical vibrations, or the nerves may be cooled. The electrodes may also be used diagnostically to correlate spontaneous nerve activity with spinal movement, fluctuations in autonomic tone and the patient's experience of pain. The electrodes may also be used to generate diagnostic evoked potentials. The diagnostic data are used to devise parameters for the therapeutic nerve stimulation. Automatic analysis of the data may be incorporated into a closed-loop system that performs the nerve stimulation automatically.
Owner:LIPANI JOHN D
Ipsilateral Approach to Minimally Invasive Ligament Decompression Procedure
A method for treating stenosis in a spine of a patient having a median plane, wherein the spine includes a spinal canal having a posterior surface, a dural sac and an epidural space between the posterior surface and dural sac, the location of the stenosis determining a region of interest in the spine. In an embodiment the method comprises the steps of a) generating at least one view of a portion of the spinal canal in the region of interest; b) compressing the dural sac in the region of interest by injecting a fluid to form a safety zone and establish a working zone in the region of interest, the safety zone lying between the working zone and the dural sac; c) percutaneously accessing the epidural space in the region of interest on a first side of the median plane; d) inserting a tissue removal tool into tissue in the working zone on the first side of the median plane; e) using the tissue removal tool to percutaneously reduce the stenosis on the first side of the median plane; and f utilizing the at least one view to position the tissue removal too during at least a part of step d) and at least part of step e)
Owner:VERTOS MEDICAL
Collapsible/expandable electrode leads
ActiveUS20050203602A1Providing mechanical stabilityFacilitate collapsing of the medical leadSpinal electrodesHead electrodesSpinal cordSurgical department
A medical lead and method of treating a patient are provided. The medical lead comprises an electrically insulative membrane, a resilient spring element associated with the insulative membrane, and at least one electrode associated with the insulative membrane. The spring layer is configured to urge that insulative membrane into an expanded geometry. The medical lead is configured to be collapsed into a compact form for percutaneous delivery into the patient, thereby obviating the need to perform an invasive surgical procedure on the patient. The body formed by these elements, when expanded, can be sized to fit within the epidural space of a patient. The patient can be treated by placing the medical lead into a collapsed state by applying a compressive force to the medical lead, percutaneously delivering the collapsed medical lead into the patient adjacent tissue to be treated, and placing the medical lead into an expanded state by releasing the compressive force. In one preferred method, the stimulation lead is used to stimulate tissue, such as spinal cord tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
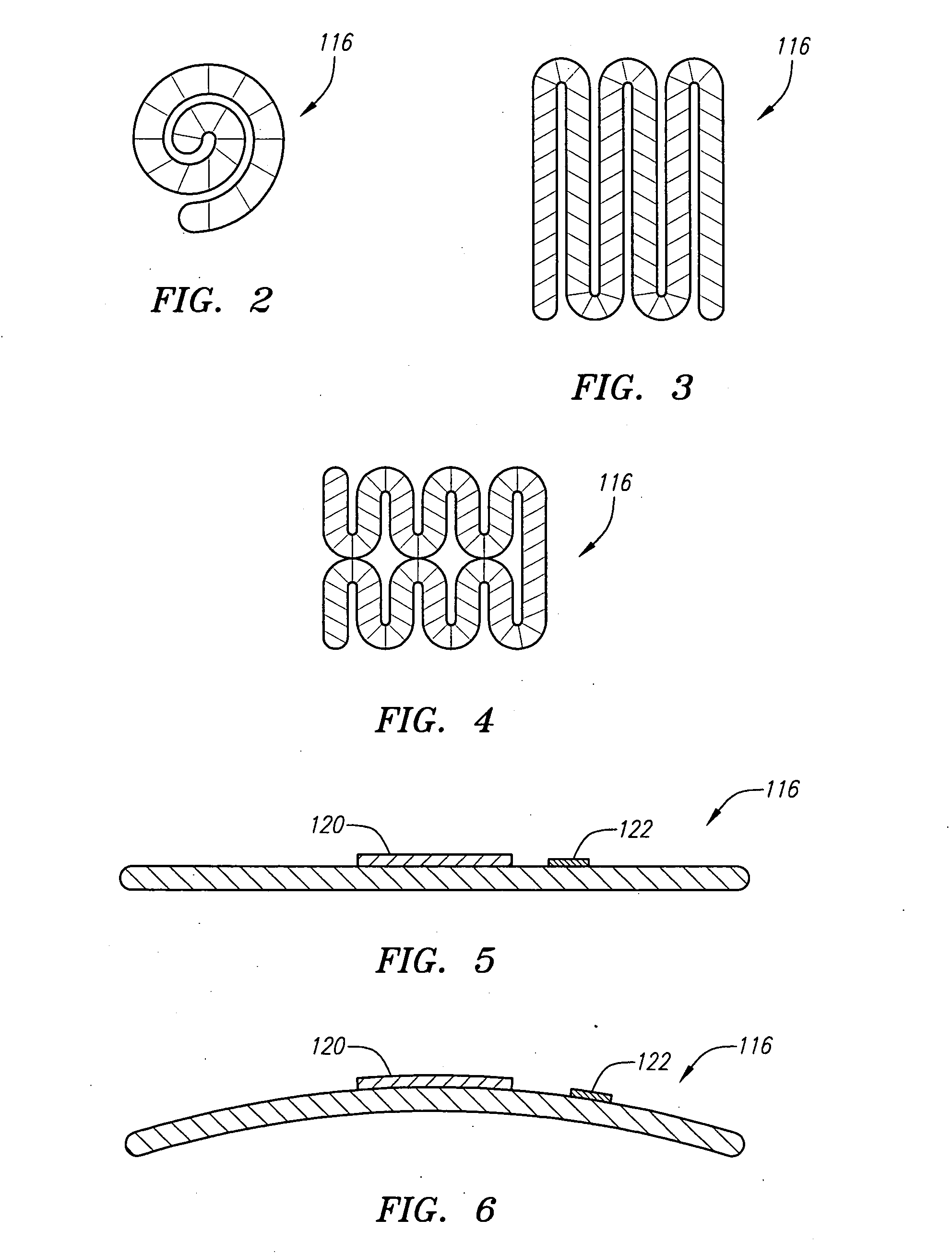
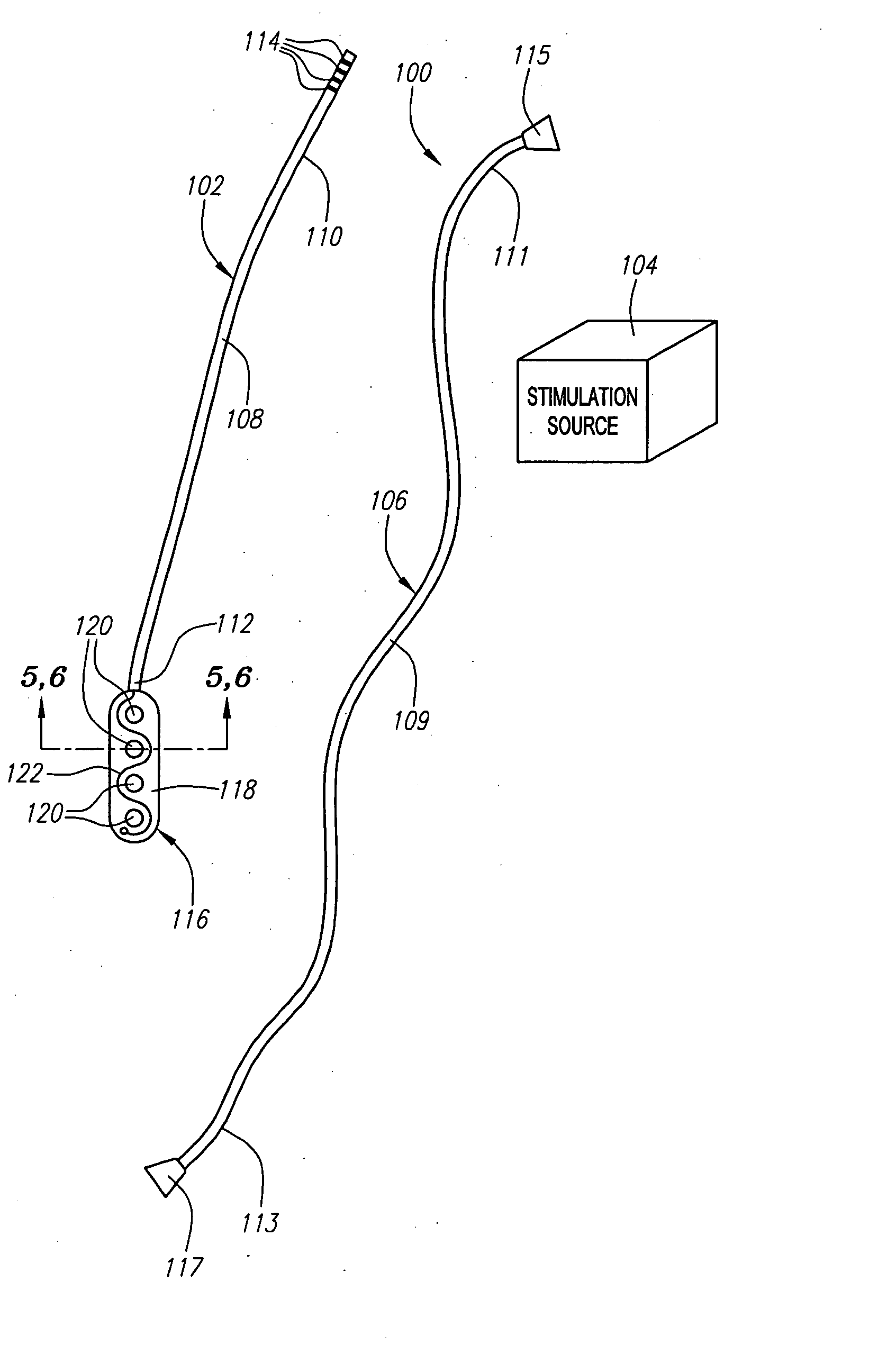
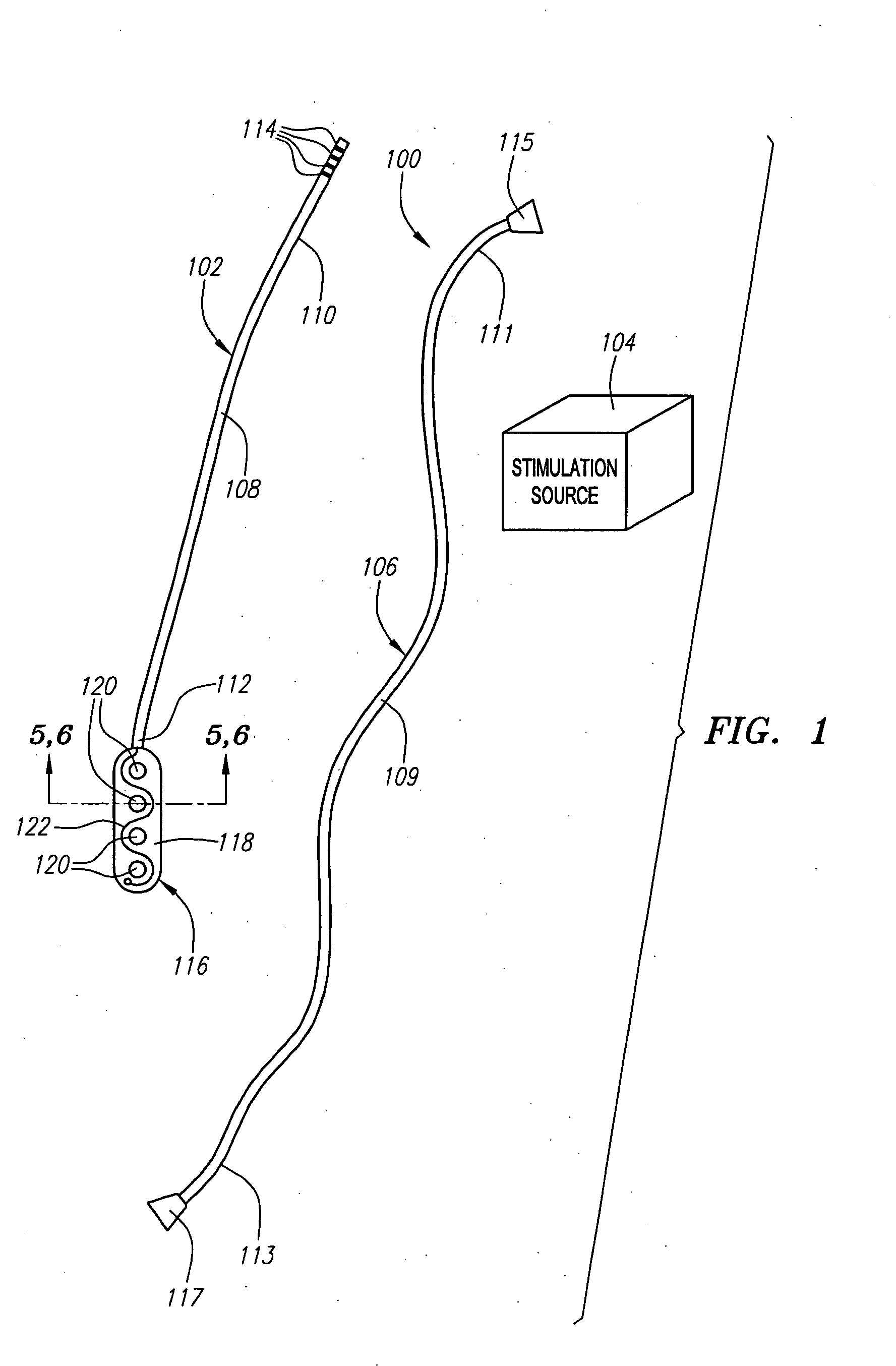
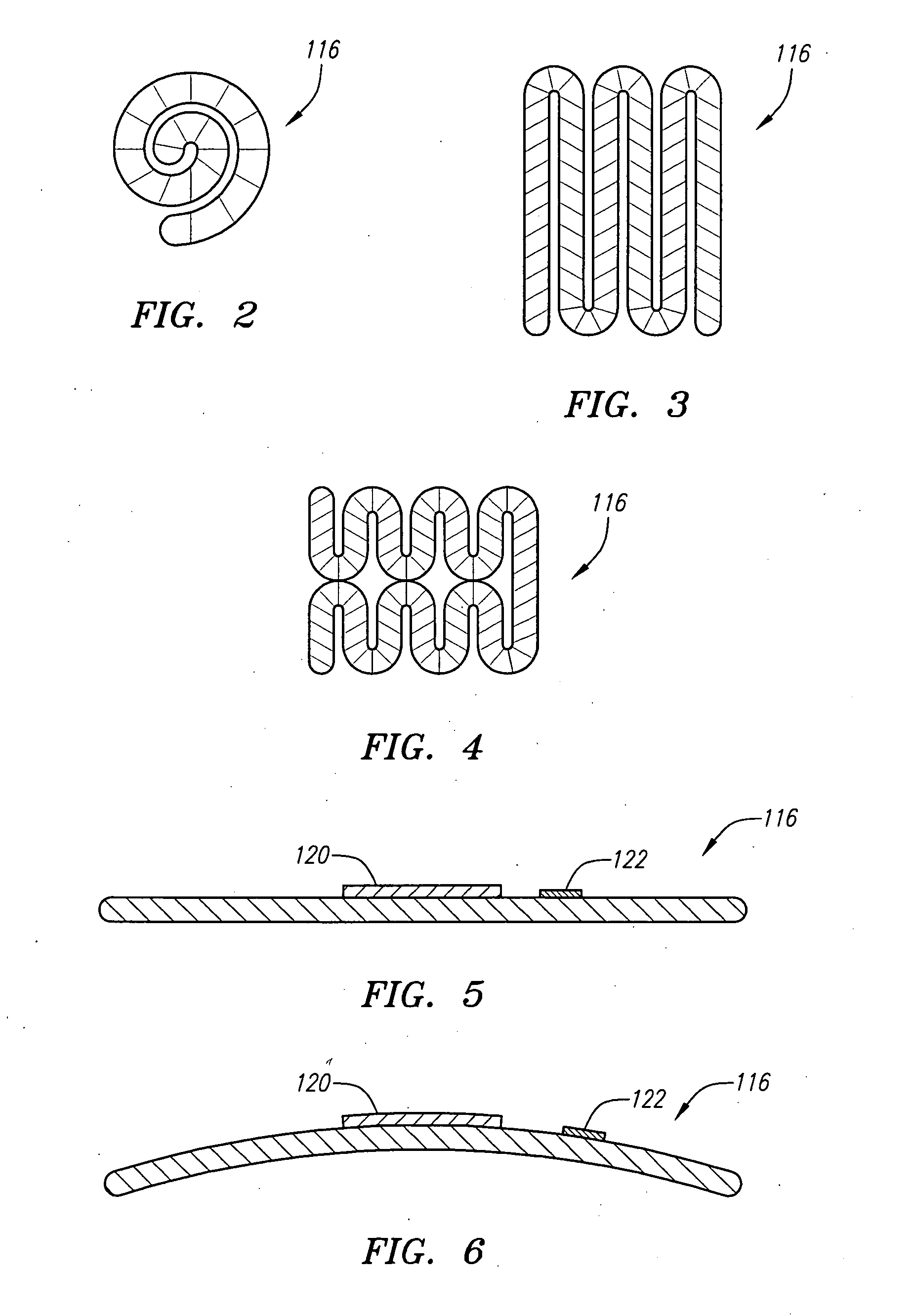
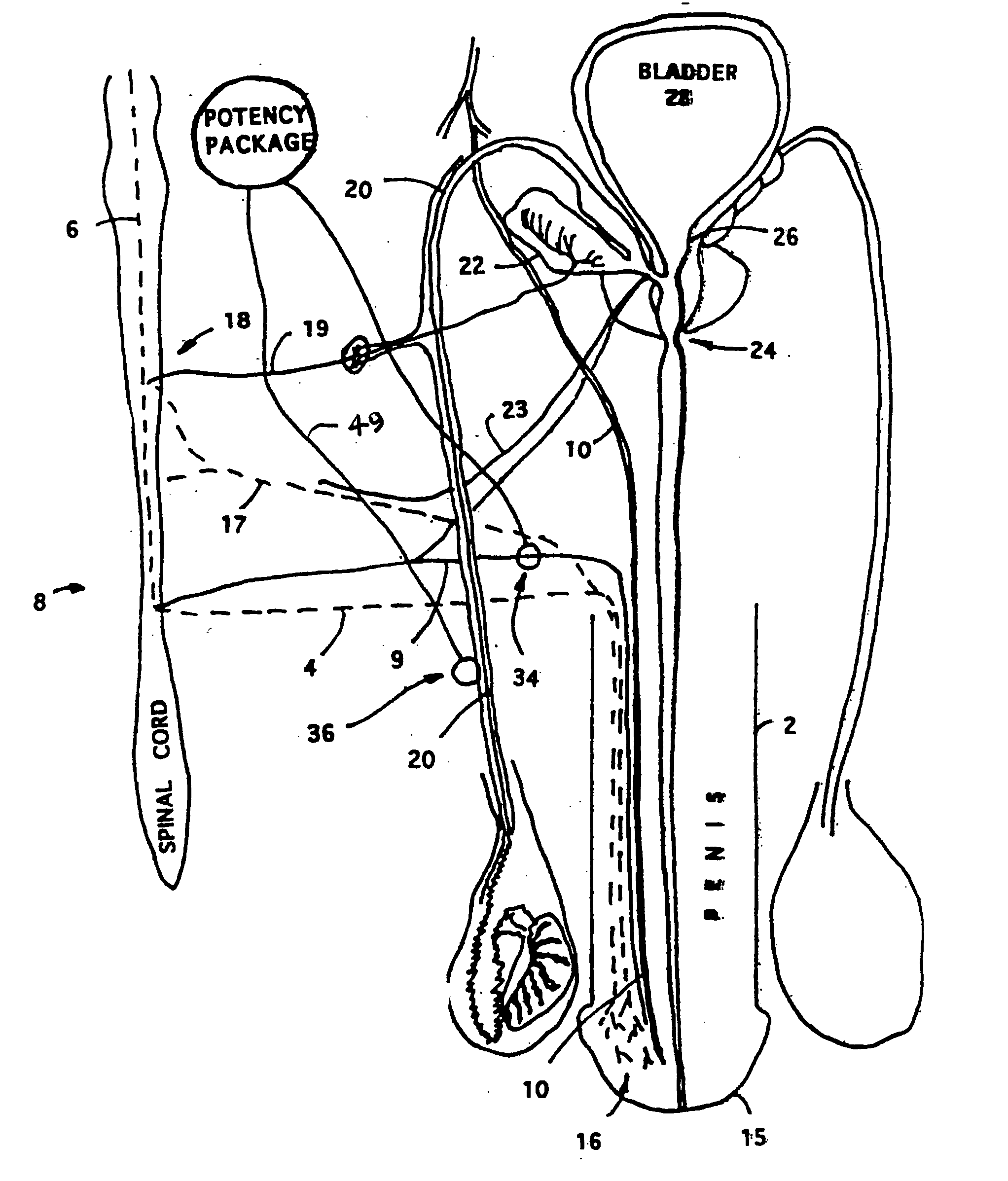
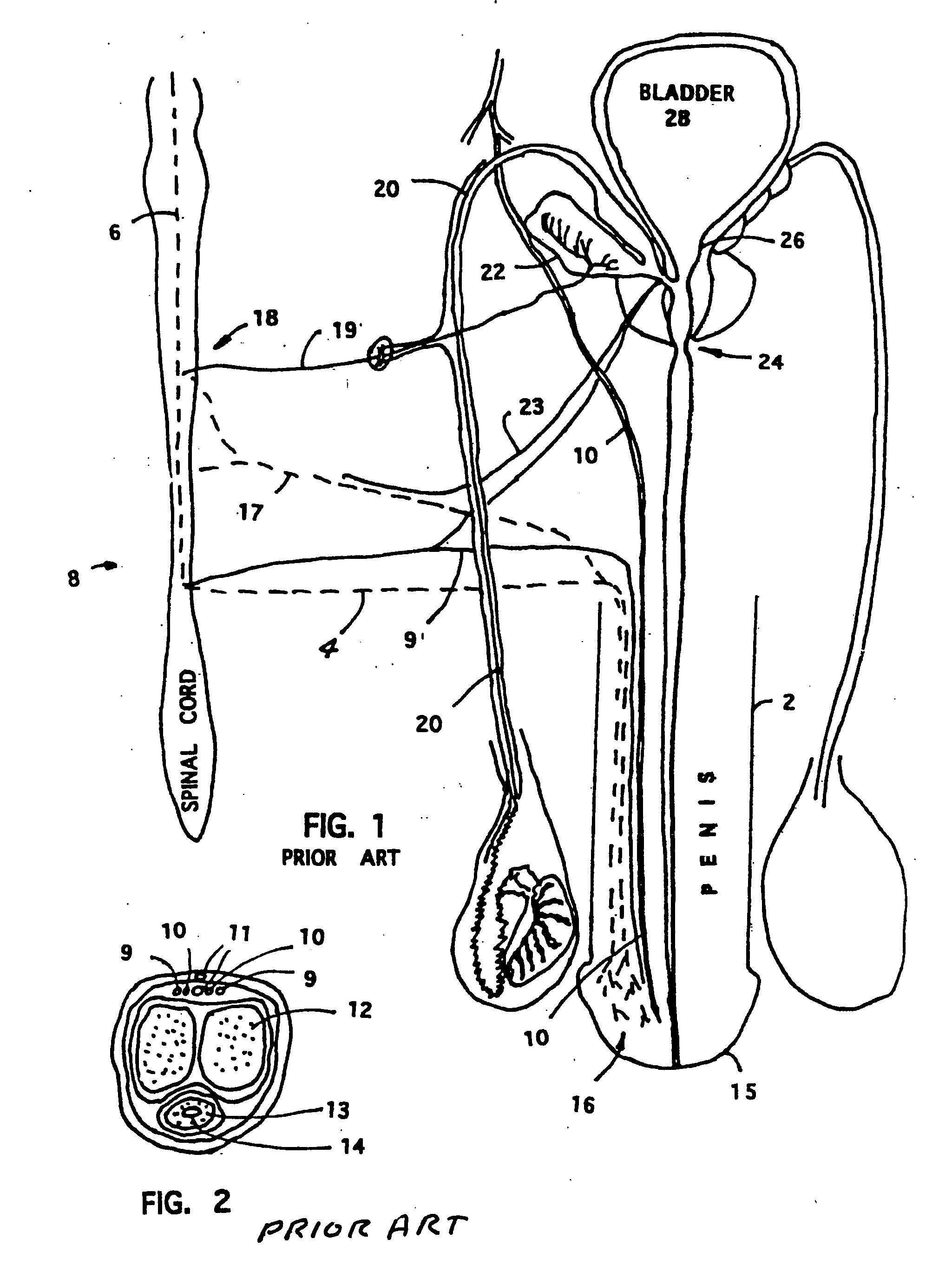
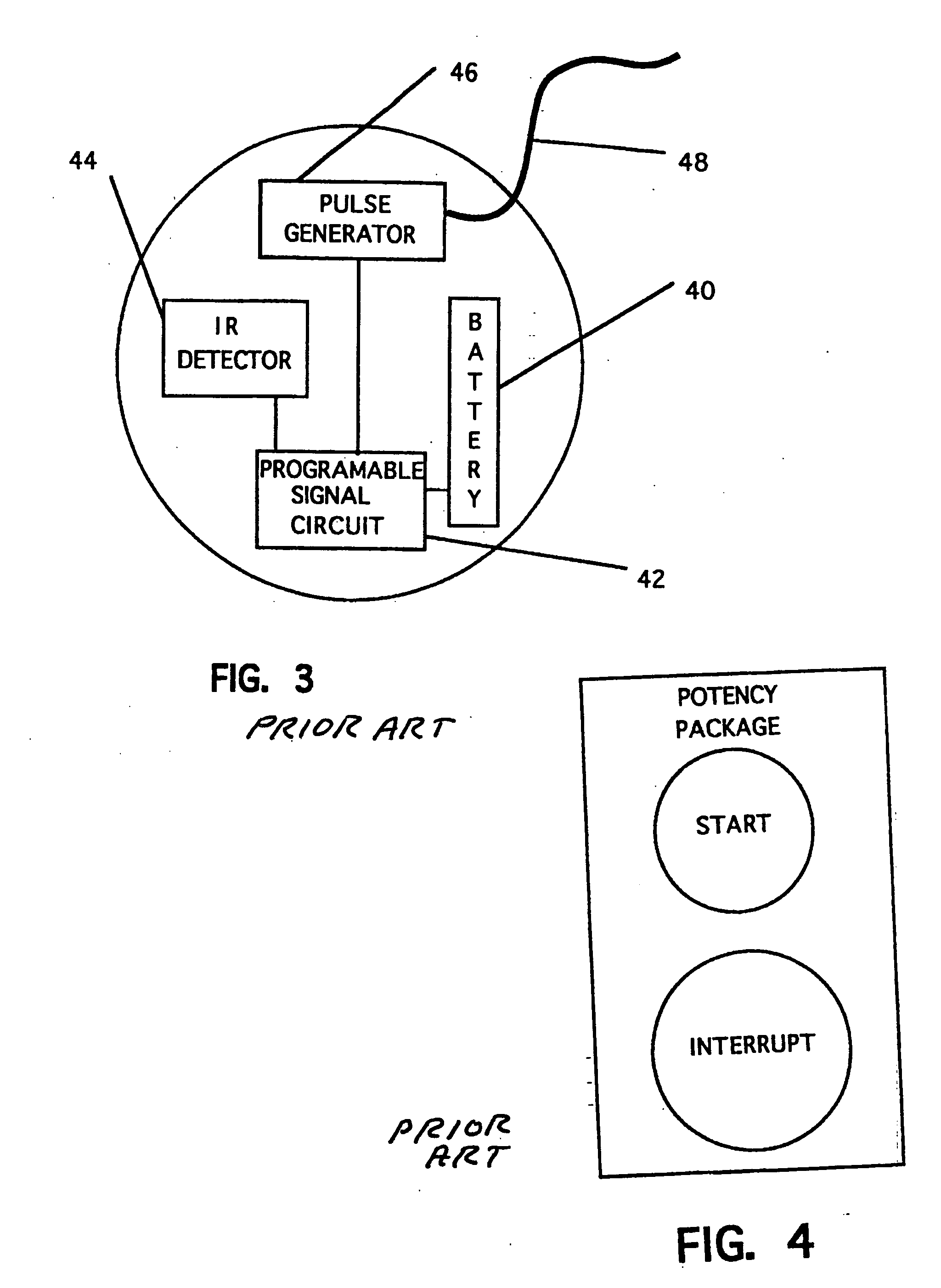
Potency package
InactiveUS20060129028A1Stimulates arousalEscalationElectrotherapyNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSpinal columnElectrical conductor
A device and method for male impotence correction and female anorgasmy. An electronic stimulator with at least one pulse generator is implanted inside the body. At least one electrode is installed in the epidural space in the sacrum section of the spinal column and a conductor running under the user's skin electrically connects the electrode to the pulse generator. The stimulator is programmable and may be controlled from outside the body. Upon command initiated by the user or the user's lover the stimulator produces very short low-voltage electrical pulses in the sacrum section that are picked up by the nerves leading to the sex organs of the user, which stimulates arousal in the user's reproductive systems. The pulses are similar to the pulses generated by heart pacemakers. In other preferred embodiments the stimulator includes one or two drug chambers and a tube extending from each chamber to a nerve for producing stimulation of a sex organ. The present invention works on both males and females. In a preferred embodiment, the programmable electronic stimulator is implanted under the skin in the patient's back. Stimulation of the nerves coming out from the parasympathetic part of the spinal cord causes dilatation of the penile arteries in the male and in the clitoris arteries of the female, which results in an erection in the male and pre-orgasmic sensation in the female. In female, the stimulation of the sacral part of the spinal cord increases sexual desire and escalation to the level of orgasm. A preferred embodiment provides for emission stimulation. Emission is stimulated by electrical excitation of the sacral part of the spinal cord by increasing the voltage of the previous impulses. The device may be preprogrammed to set in motion the emission and ejaculation process at a predetermined time interval after the start of the erection process.
Owner:KRAKOUSKY ALEXANDER A
Implantable medical lead and system, and method of use thereof
InactiveUS20050021119A1Precise positioningEliminate needSpinal electrodesHead electrodesSpinal columnManaged pain
Implantable medical leads, lead assemblies, and methods for implanting the leads into the human body, for example, for use within the epidural spaces of the spinal column to manage pain. A stylet lumen extends within the lead between a side-wall stylet entrance port and a lead distal region. In use, exemplary stylets may be inserted through the lead stylet port to stiffen only the distal portion of the lead, and the distal portion of the lead inserted through an introducer needle into the human body. The stiffened distal portion of the lead may be short and easily controllable.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com