Patents
Literature
1259 results about "Spinal cord" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular structure made up of nervous tissue, which extends from the medulla oblongata in the brainstem to the lumbar region of the vertebral column. It encloses the central canal of the spinal cord, which contains cerebrospinal fluid. The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system (CNS). In humans, the spinal cord begins at the occipital bone, passing through the foramen magnum and entering the spinal canal at the beginning of the cervical vertebrae. The spinal cord extends down to between the first and second lumbar vertebrae, where it ends. The enclosing bony vertebral column protects the relatively shorter spinal cord. It is around 45 cm (18 in) in men and around 43 cm (17 in) long in women. The diameter of the spinal cord ranges from 13 mm (¹⁄₂ in) in the cervical and lumbar regions to 6.4 mm (¹⁄₄ in) in the thoracic area.
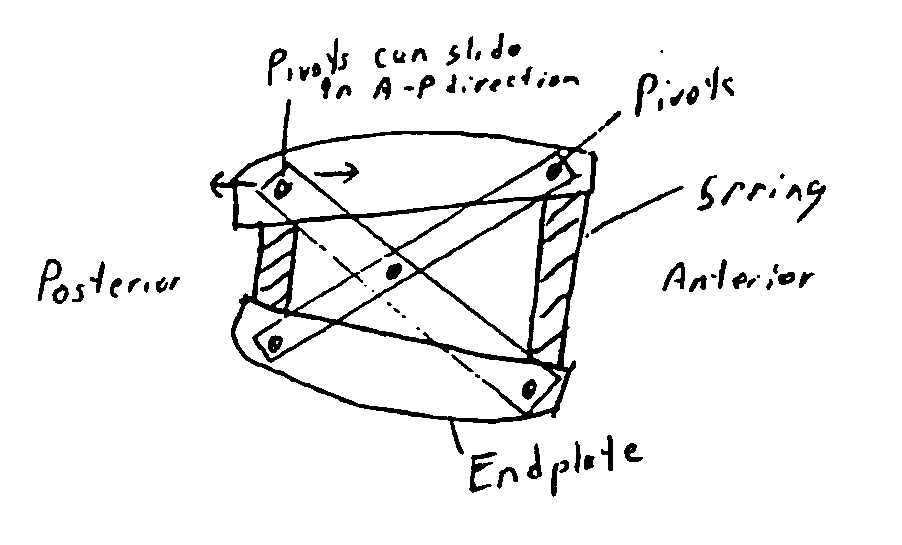
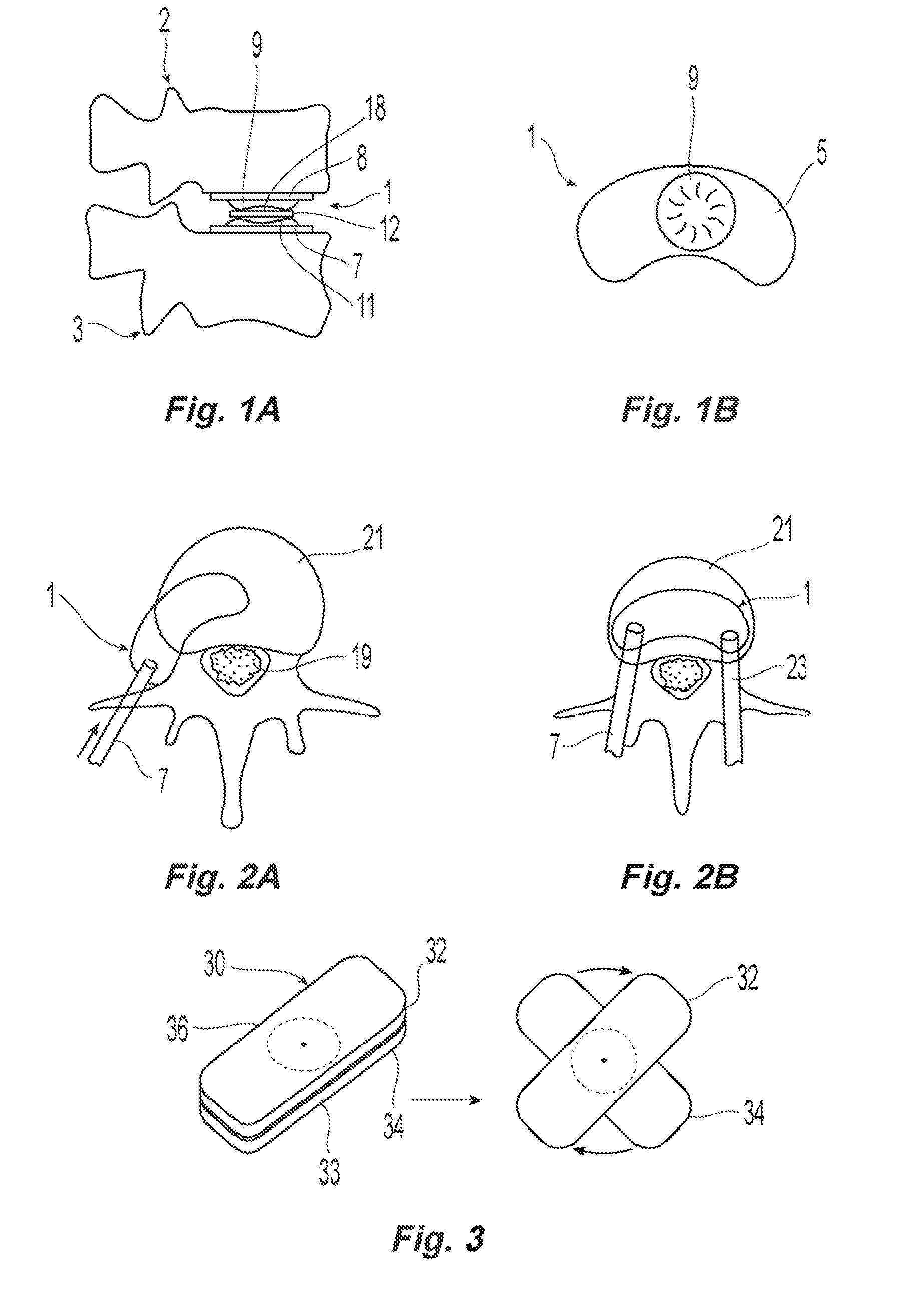
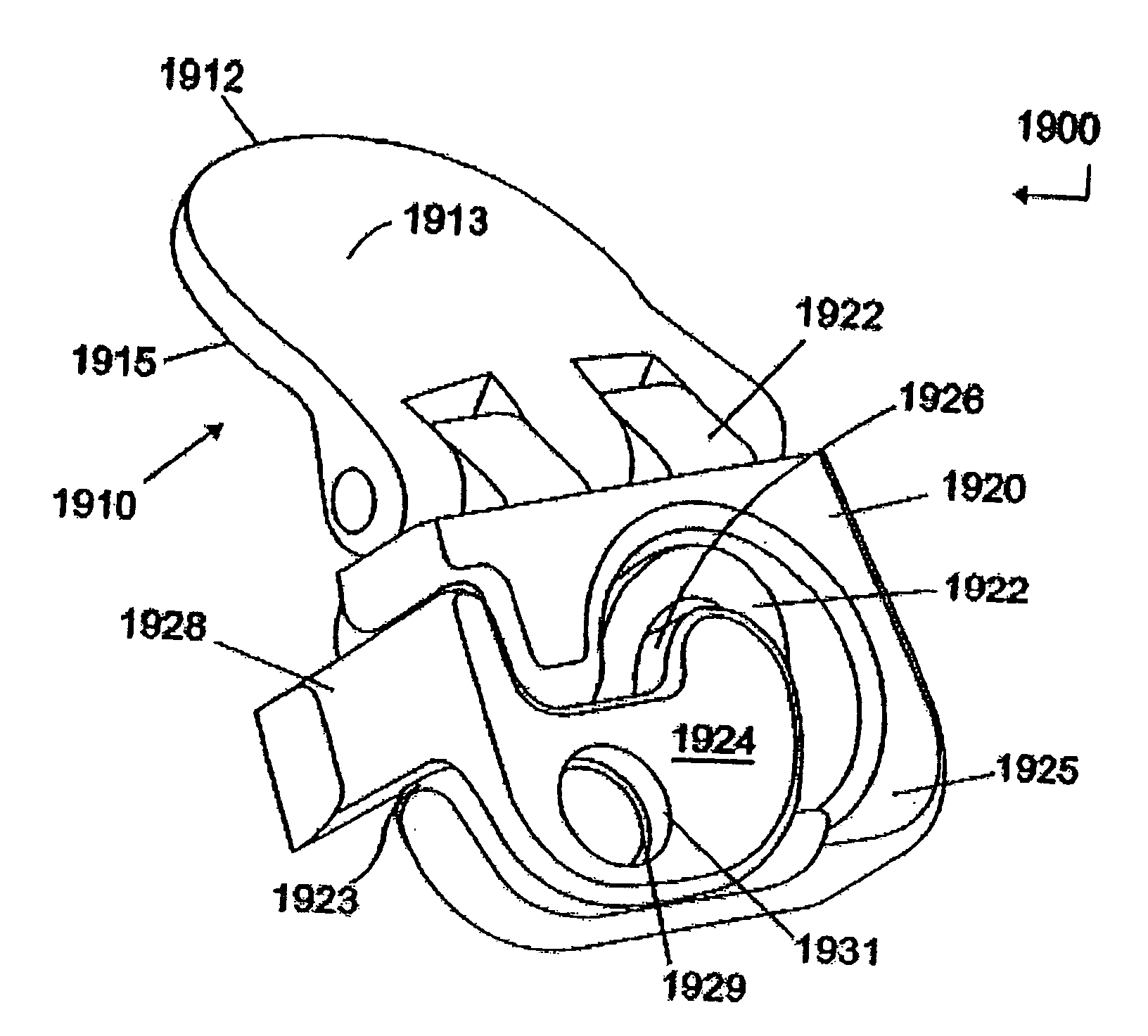
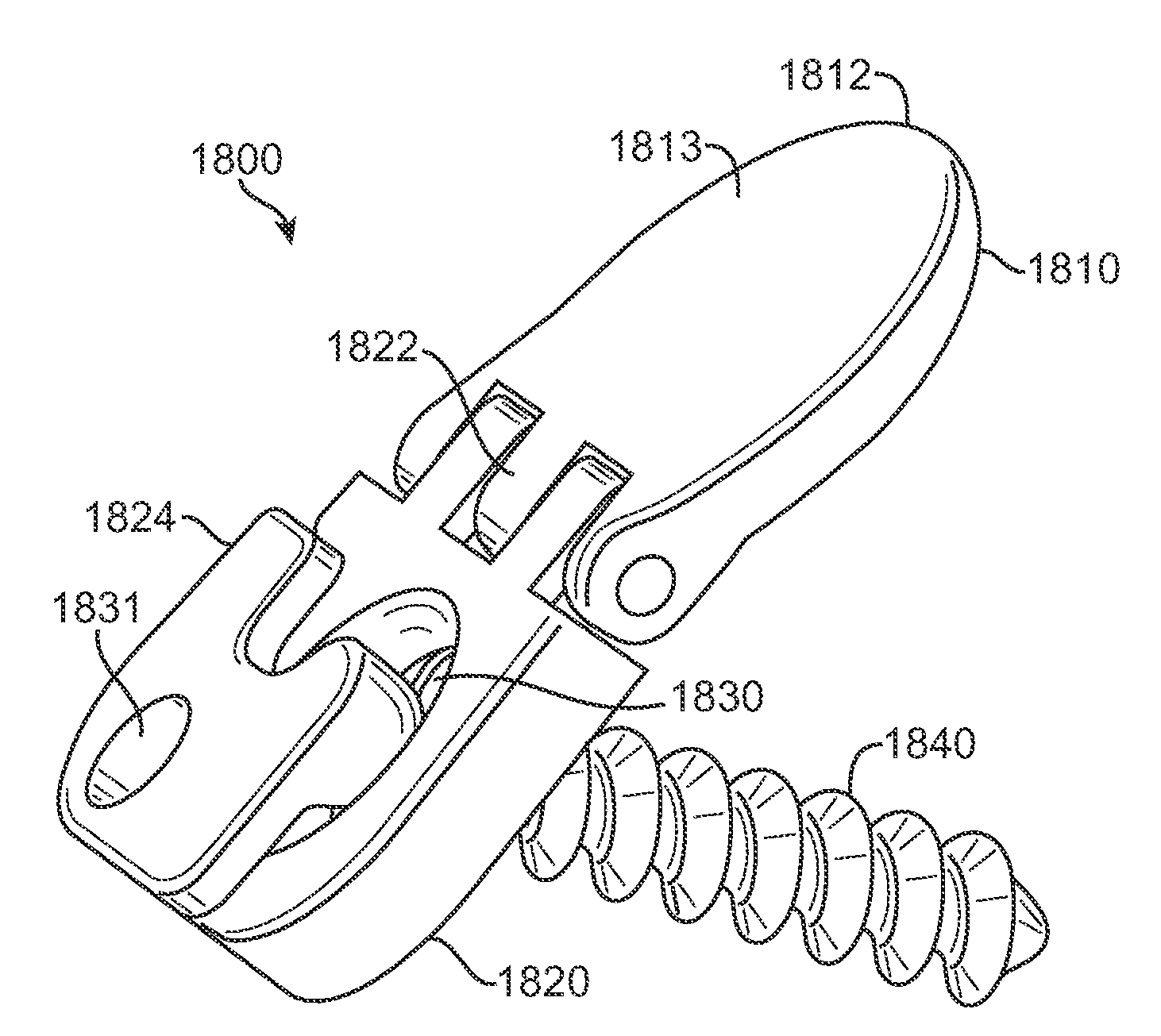
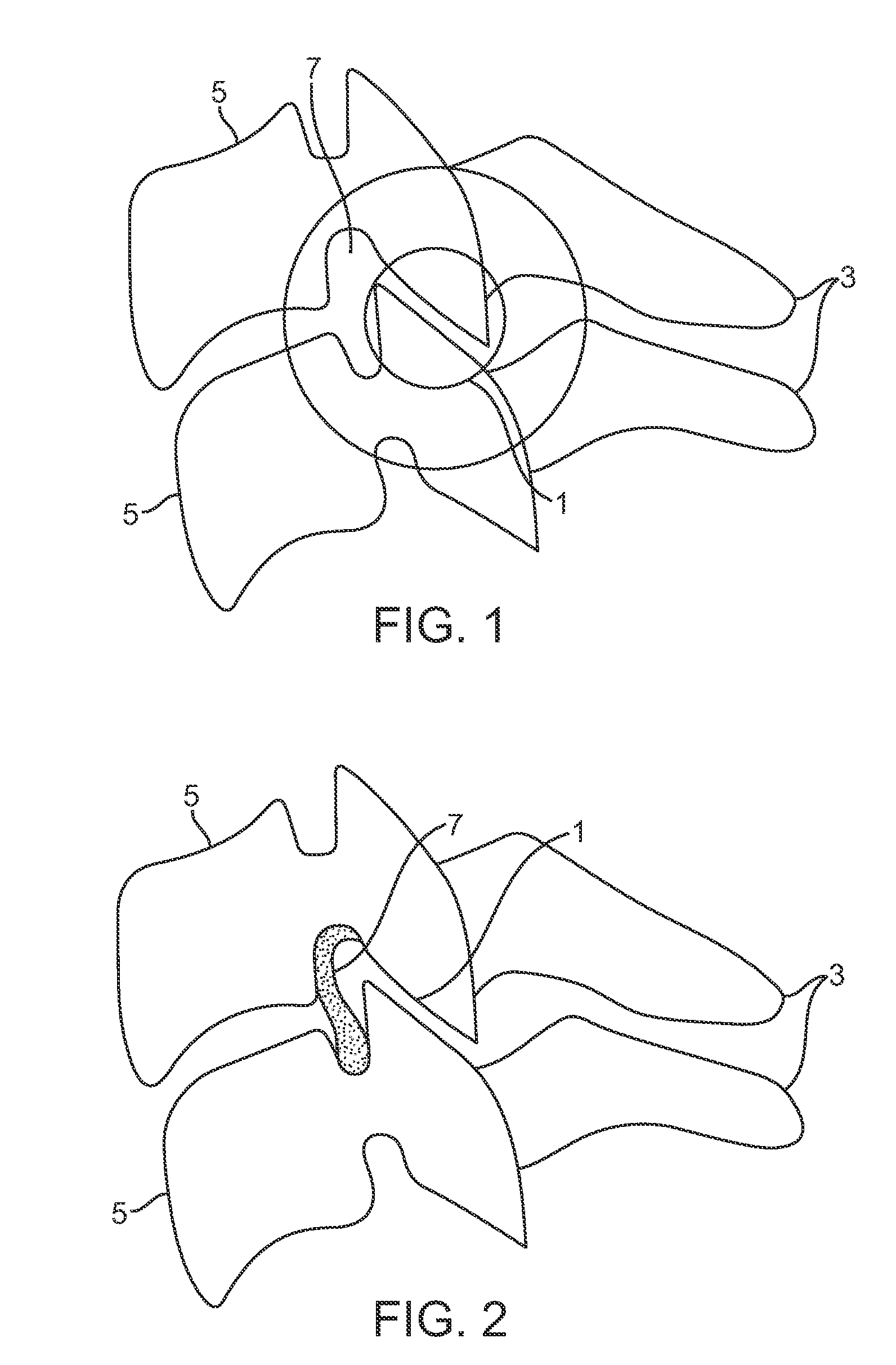
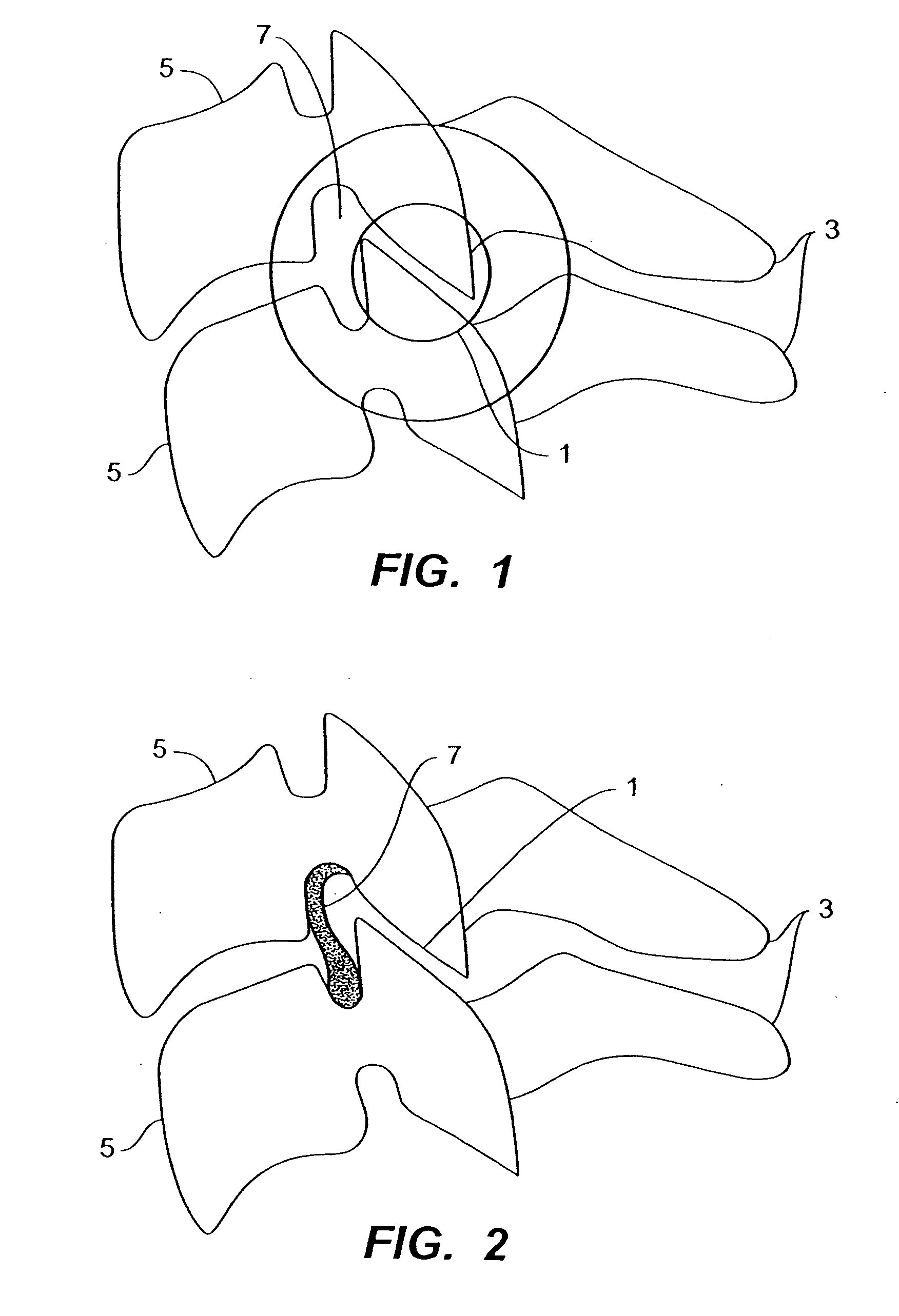
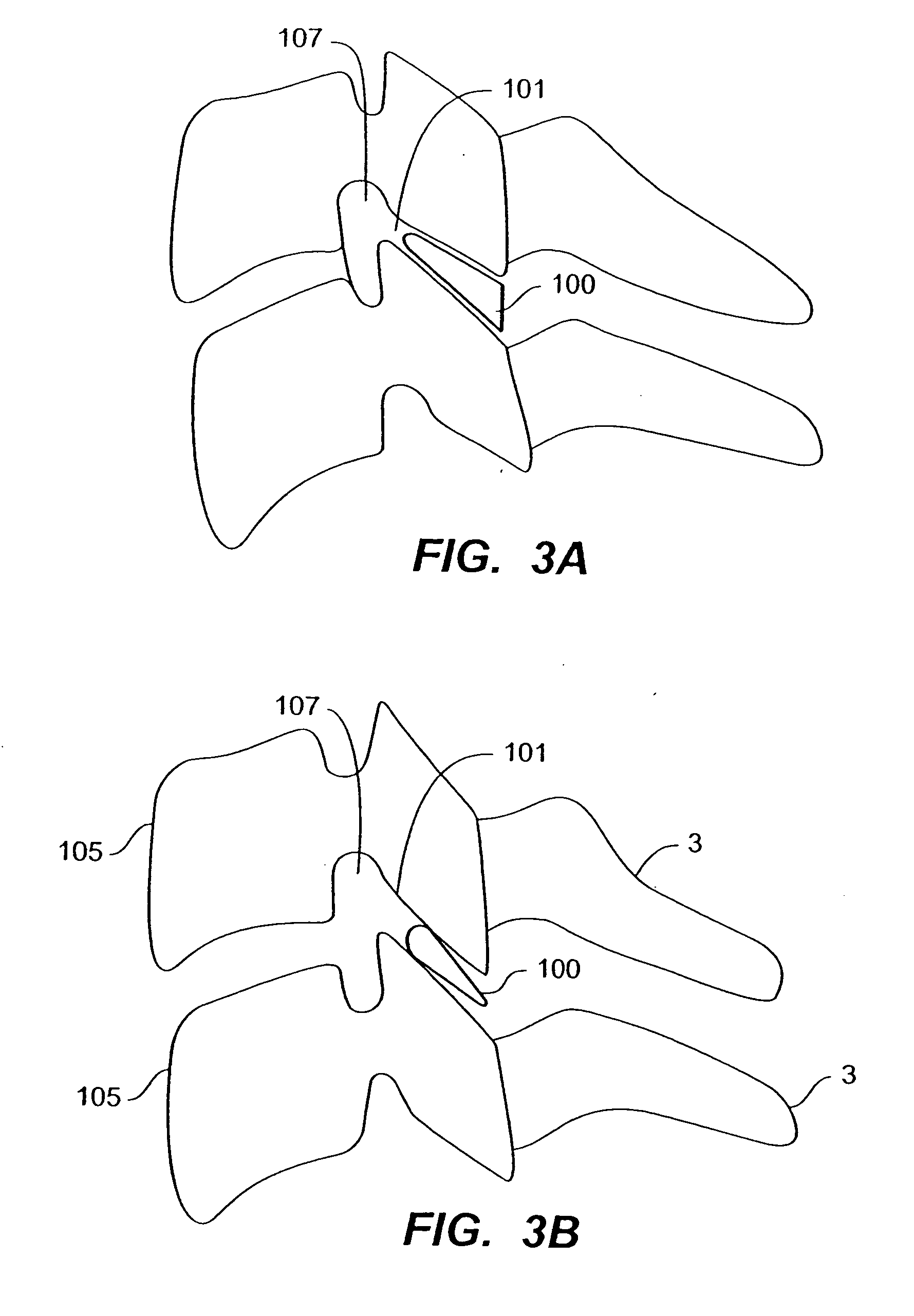
Prosthetic spinal disc replacement
ActiveUS20050043800A1Restrict movementJoint implantsNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSpinal columnSurgical approach
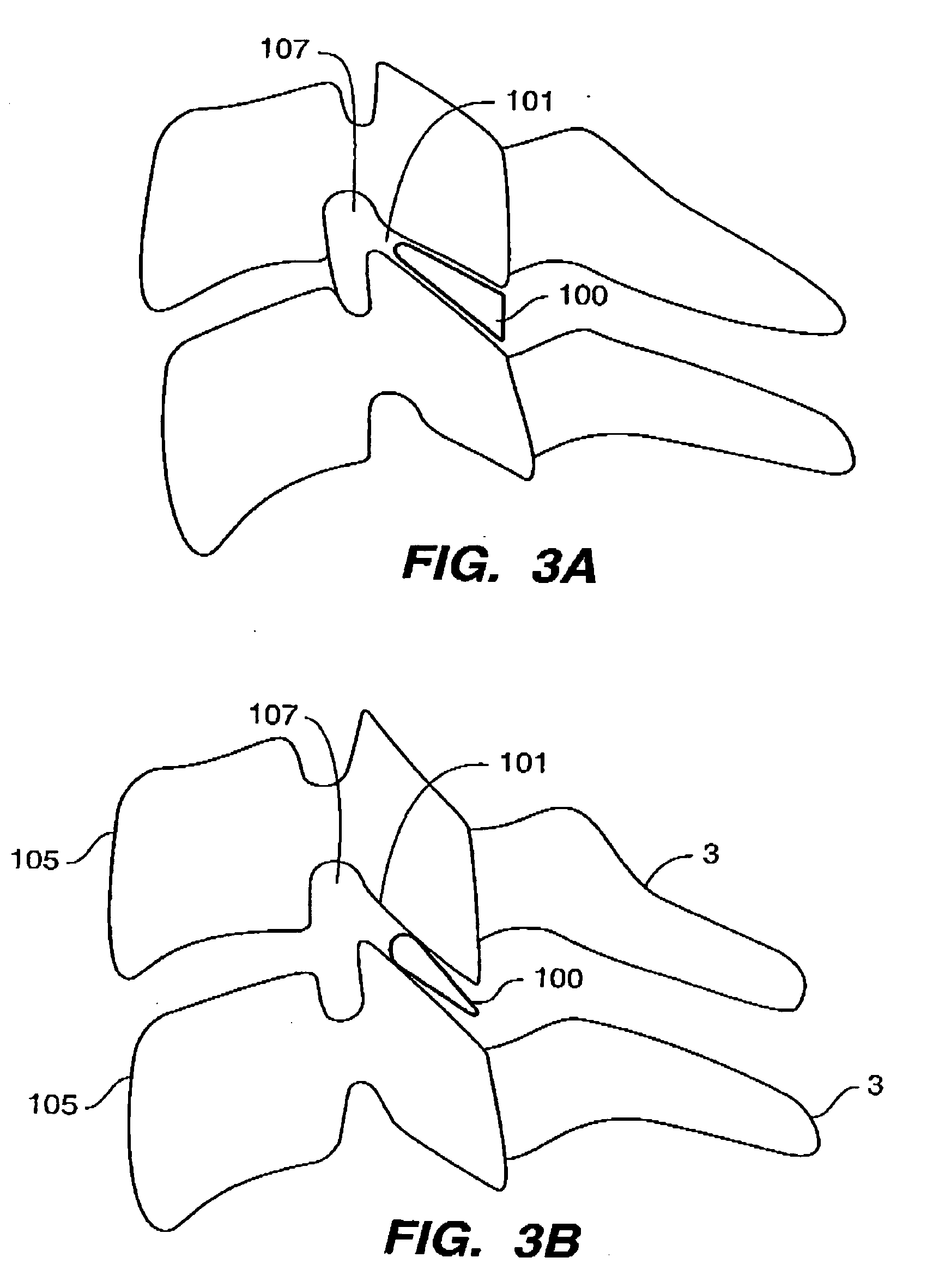
The present invention relates generally to a prosthetic spinal disc for replacing a damaged disc between two vertebrae of a spine. The present invention also relates to a method for implanting a prosthetic spinal disc via posterior or posterior lateral implantation. Other surgical approaches for implanting the prosthetic disc may also be used. The present invention also involves a method for implanting the prosthetic spinal disc while either avoiding or minimizing contact with the spinal cord and nerve rootlets, or reducing the time and extent that they need to be repositioned during implantation.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
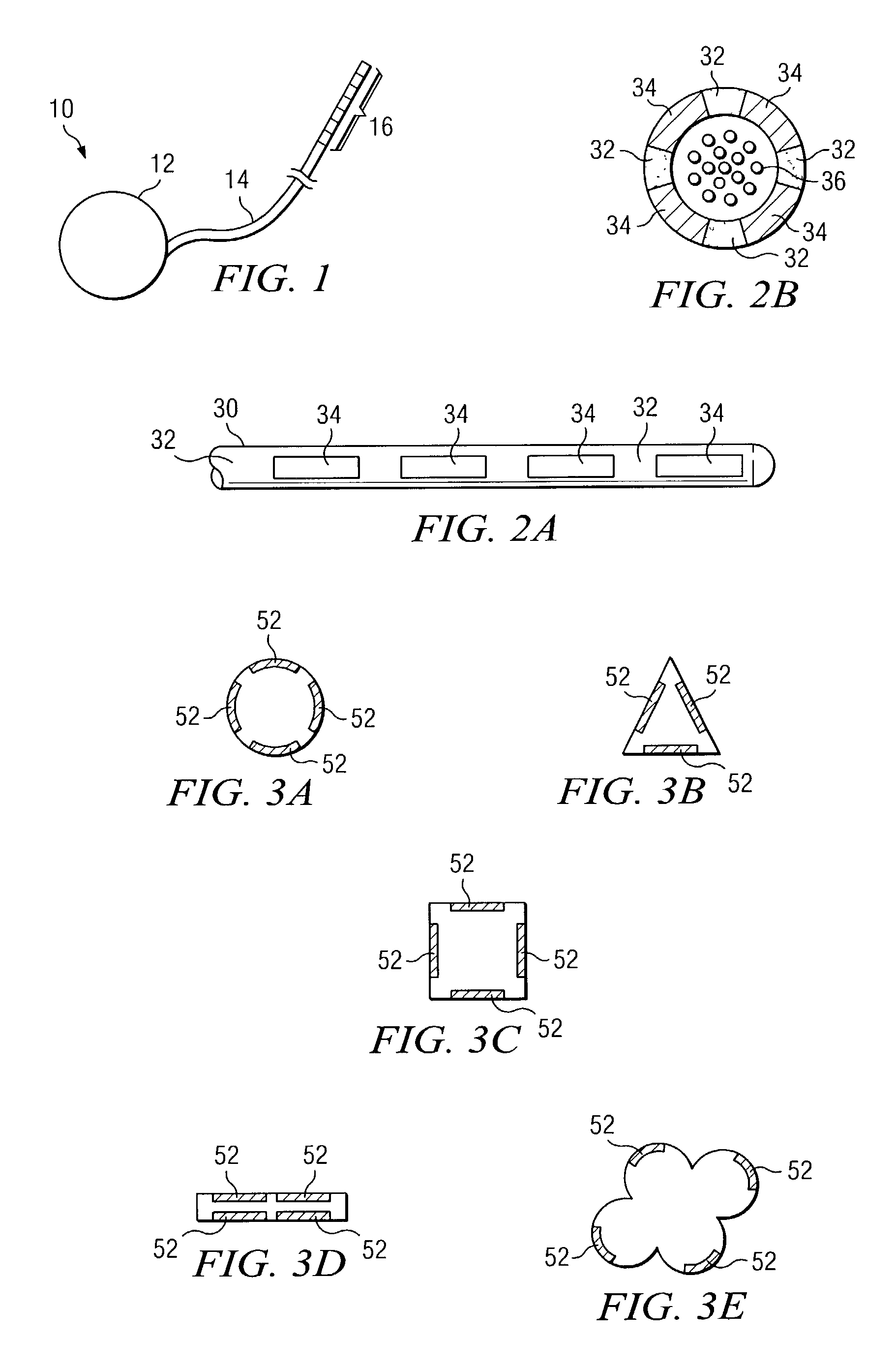
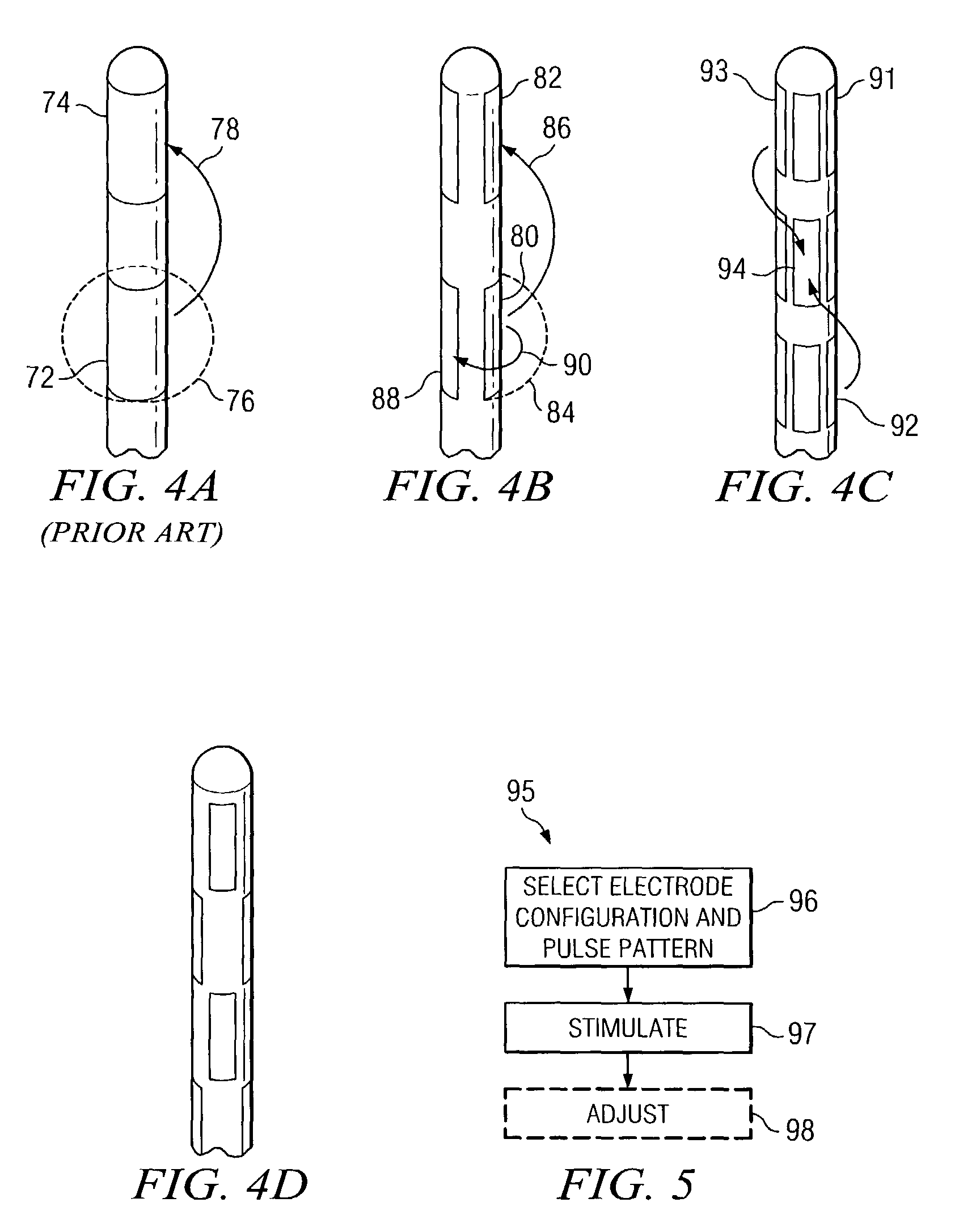
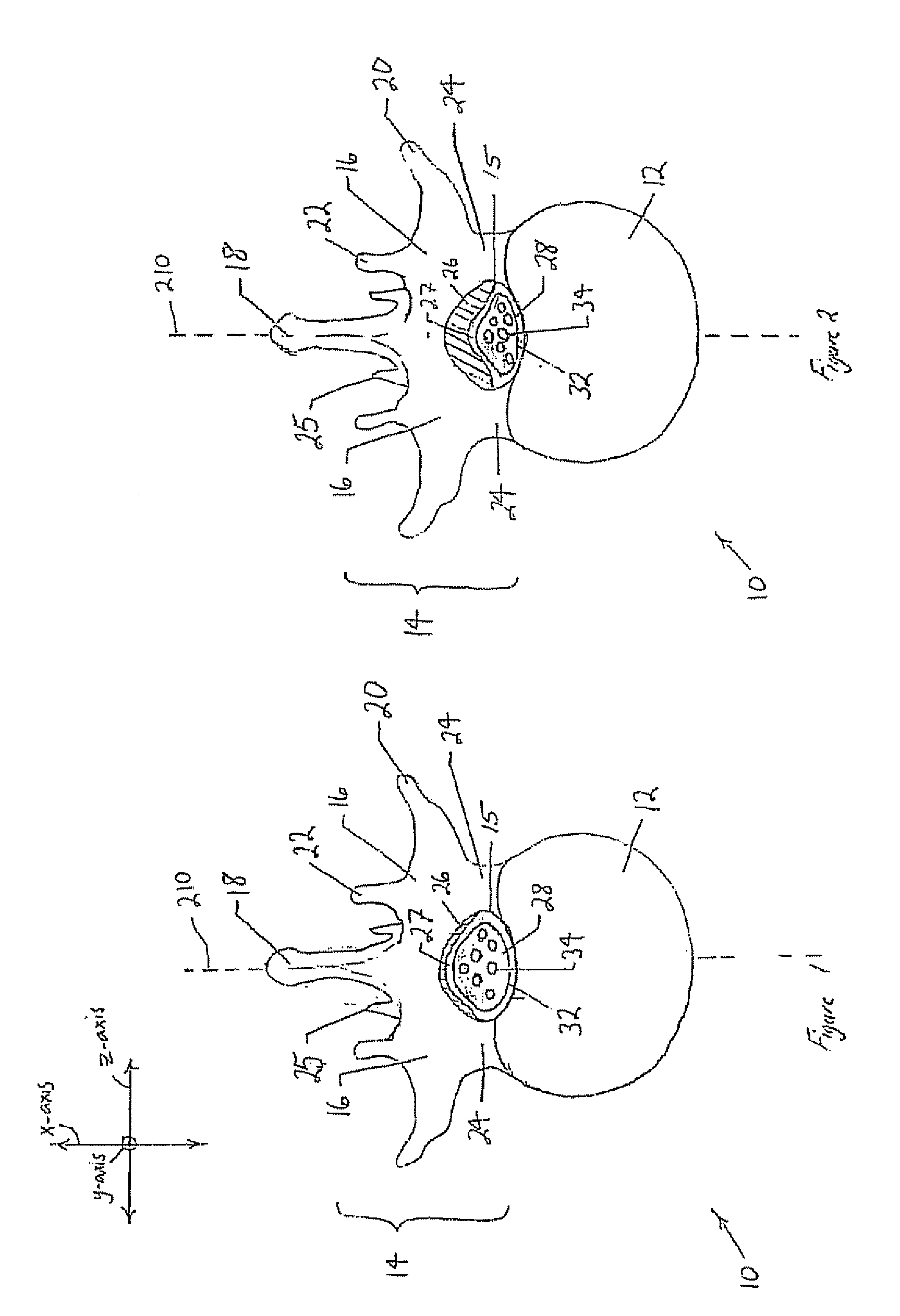
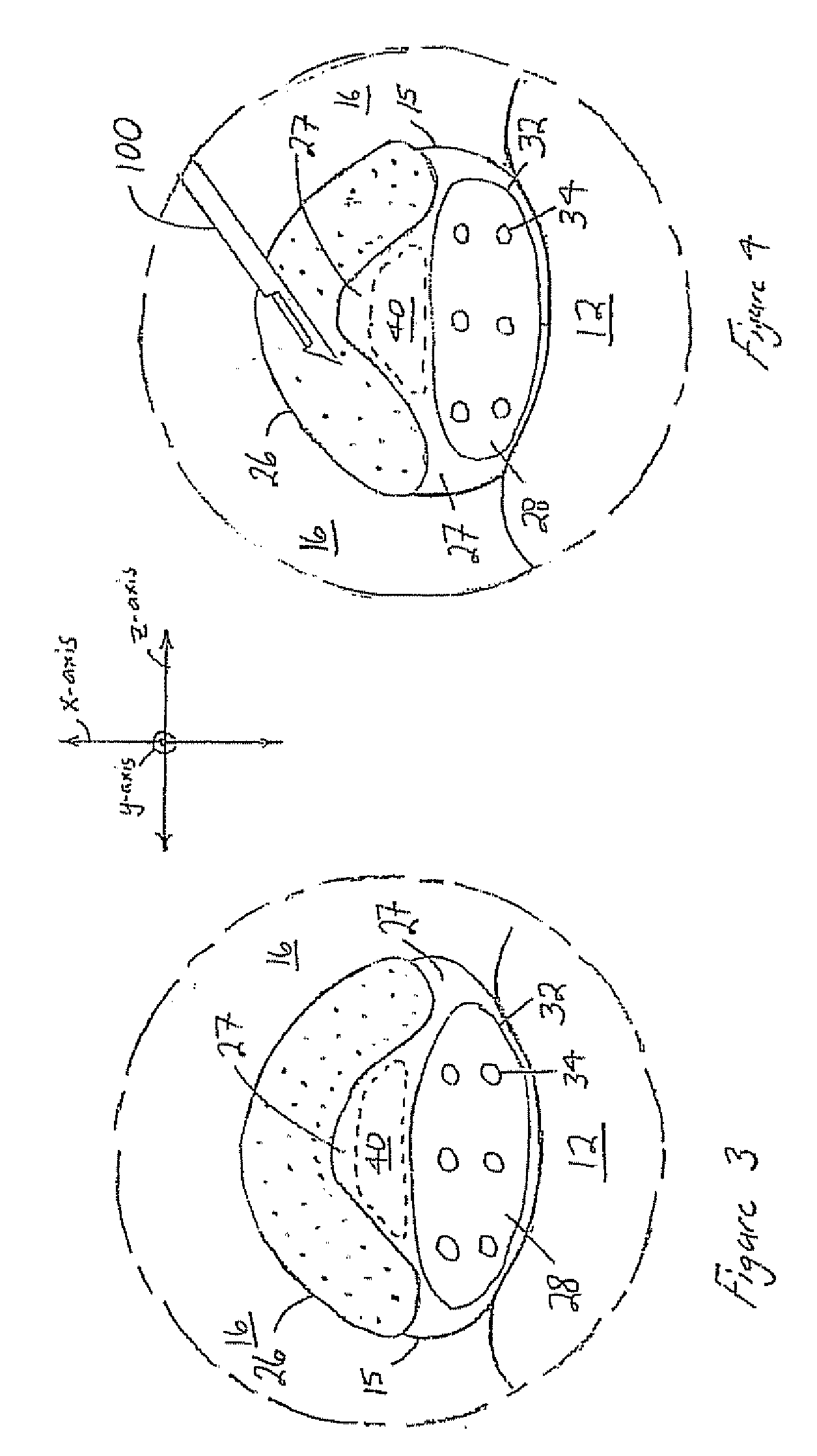
Apparatus for directionally stimulating nerve tissue
This invention relates to an apparatus and method for making such apparatus for providing controlled and directional stimulation patterns for tissue stimulation. The apparatus may be useful in stimulation nervous tissue in the brain, about the spinal cord, on nerve roots, about peripheral nerves, and in muscles, among others. The apparatus includes a implantable pulse generator connected to a lead. The lead has electrodes placed about a perimeter. In addition, the lead may include electrodes placed longitudinally along the axis of the lead. By applying charge differences between circumferentially distributed electrodes, a smaller stimulation field may be established. In addition, by stimulating between electrodes distributed longitudinally on the same side, a directional flow field may be established. Such leads are especially useful in deep brain stimulation as the region in which a stimulation field is strong enough to produce tissue stimulation is directional and minimized.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Systems and methods for electrosurgery
InactiveUS7270658B2Use performanceAvoid cloggingSurgical needlesEndoscopesIntervertebral discSpinal cord
Methods and apparatus for selectively applying electrical energy to a target location within a patient's body, particularly including tissue in the spine. In a method of the invention high frequency (RF) electrical energy is applied to one or more active electrodes on an electrosurgical probe in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to remove, contract or otherwise modify the structure of tissue targeted for treatment. In one aspect, a dura mater and spinal cord are insulated from the electrical energy by an insulator positioned on a non-active side of the probe. In another aspect, a plasma is aggressively formed in the electrically conductive fluid by delivering a conductive fluid to a distal end portion of the probe and aspirating the fluid from a location proximal of the return electrode. In another aspect, a distal end of an electrosurgical probe having at least one electrode on a biased, curved, bent, or steerable shaft is guided or steered to a target site within an intervertebral disc having a disc defect for treatment of tissue to be treated at the target site by the selective application of electrical energy thereto.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
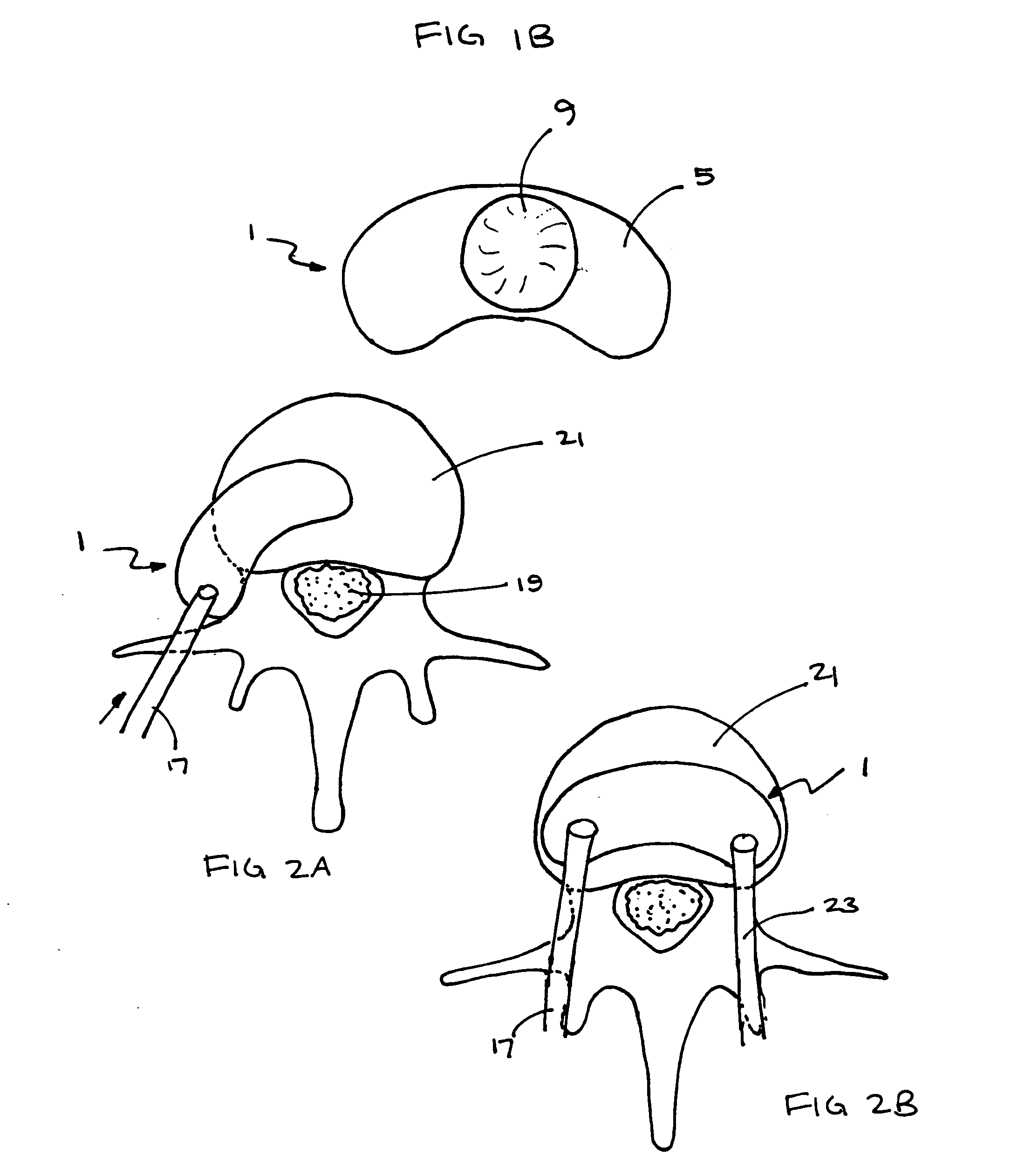
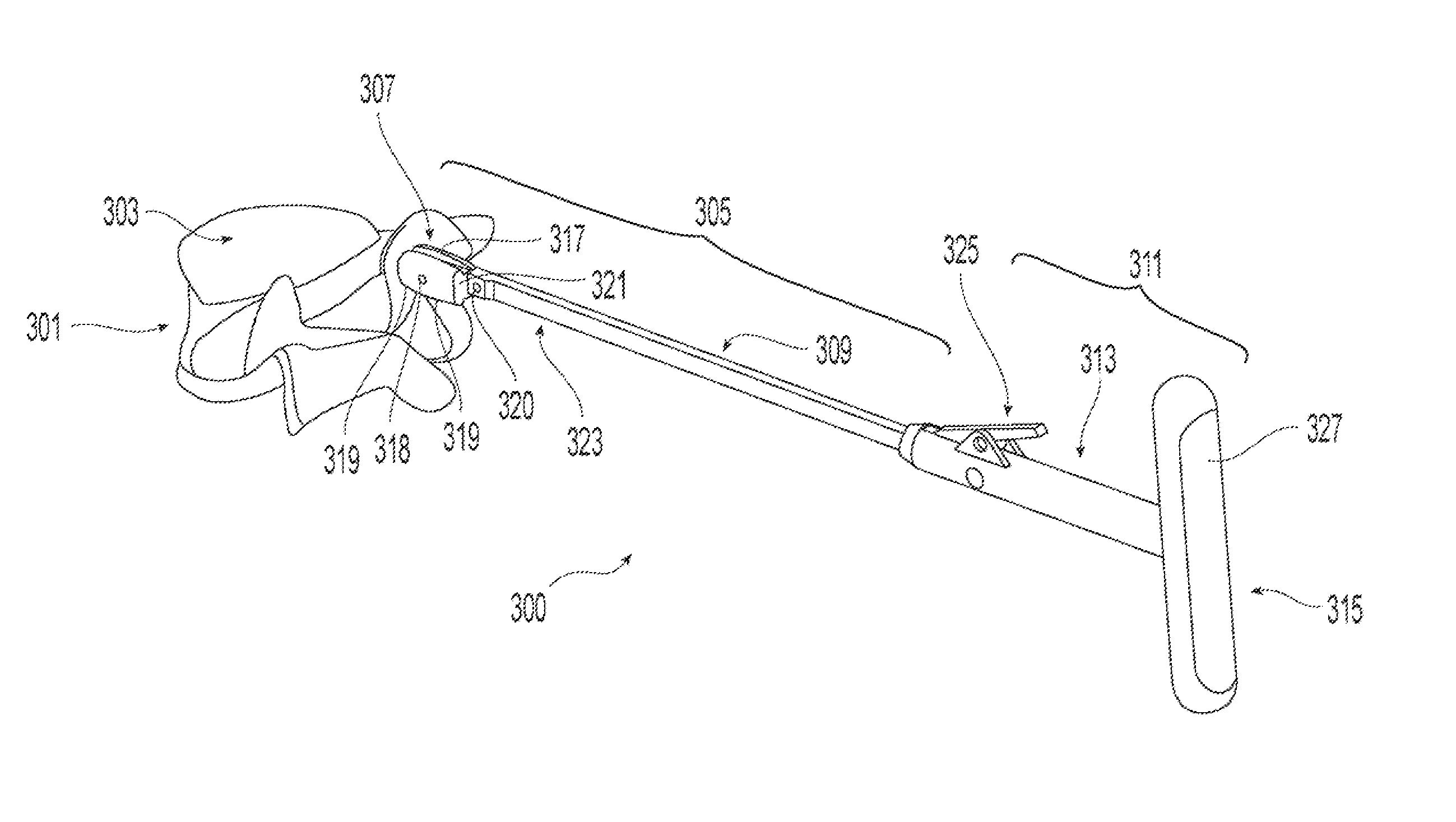
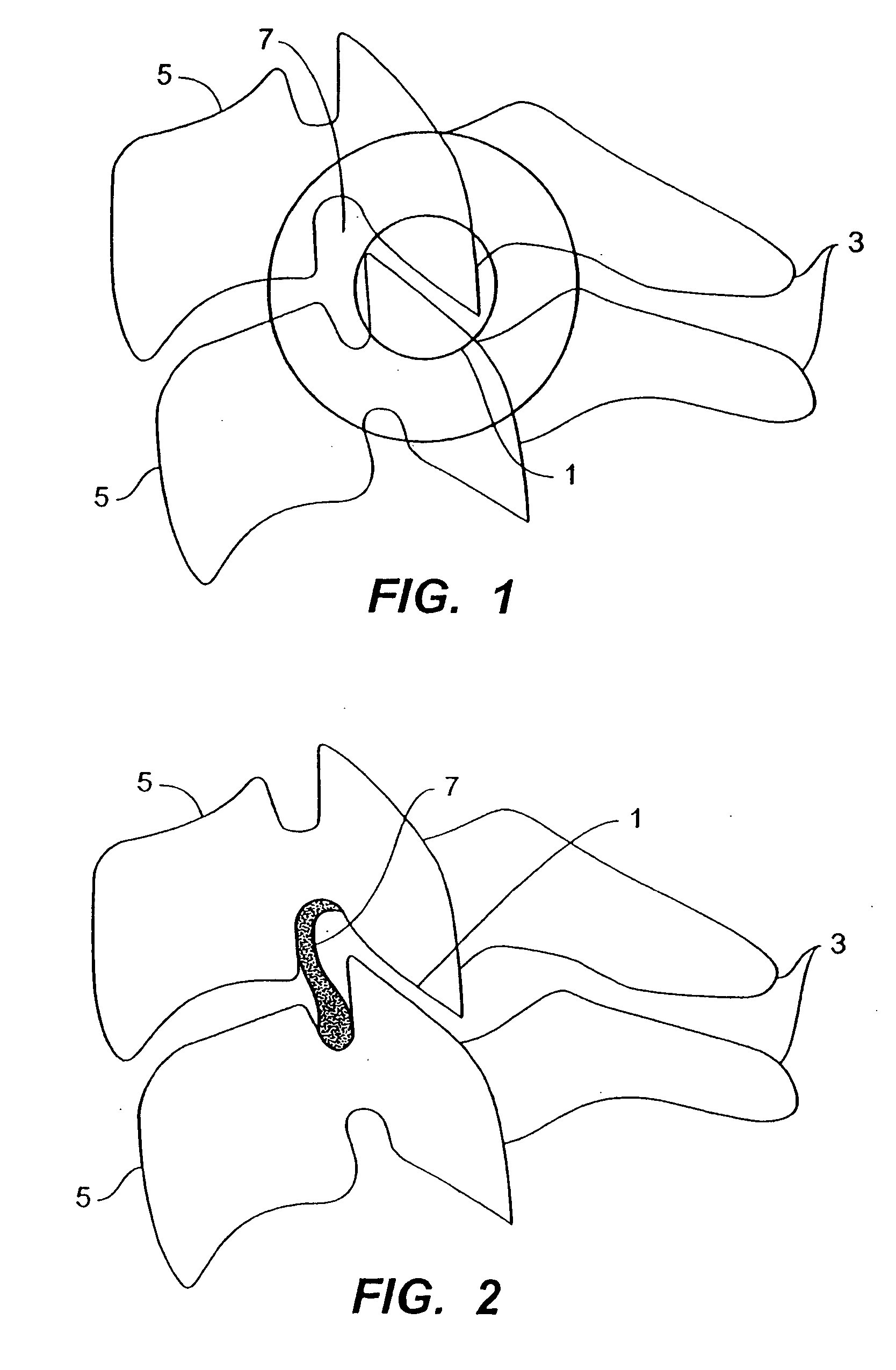
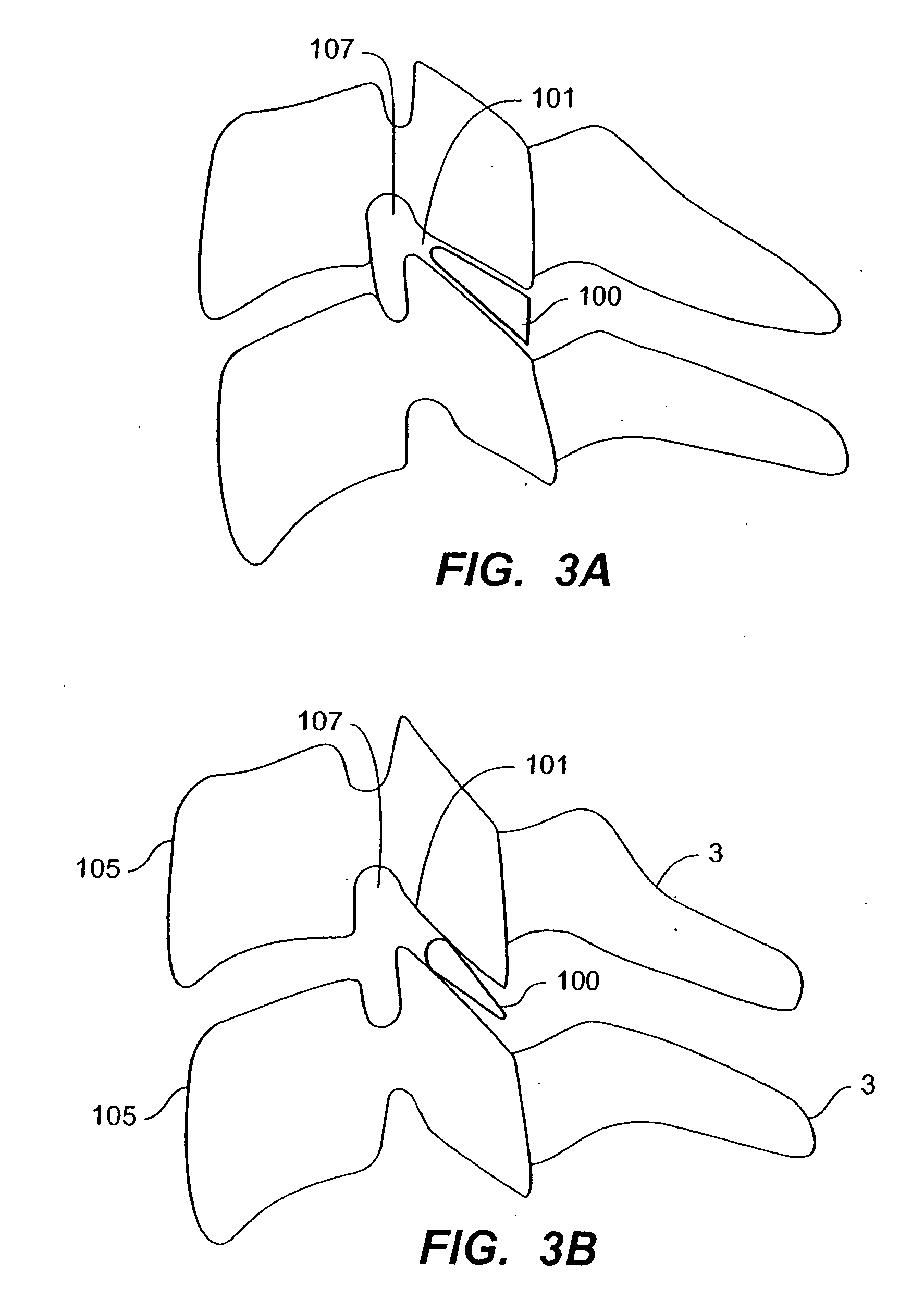
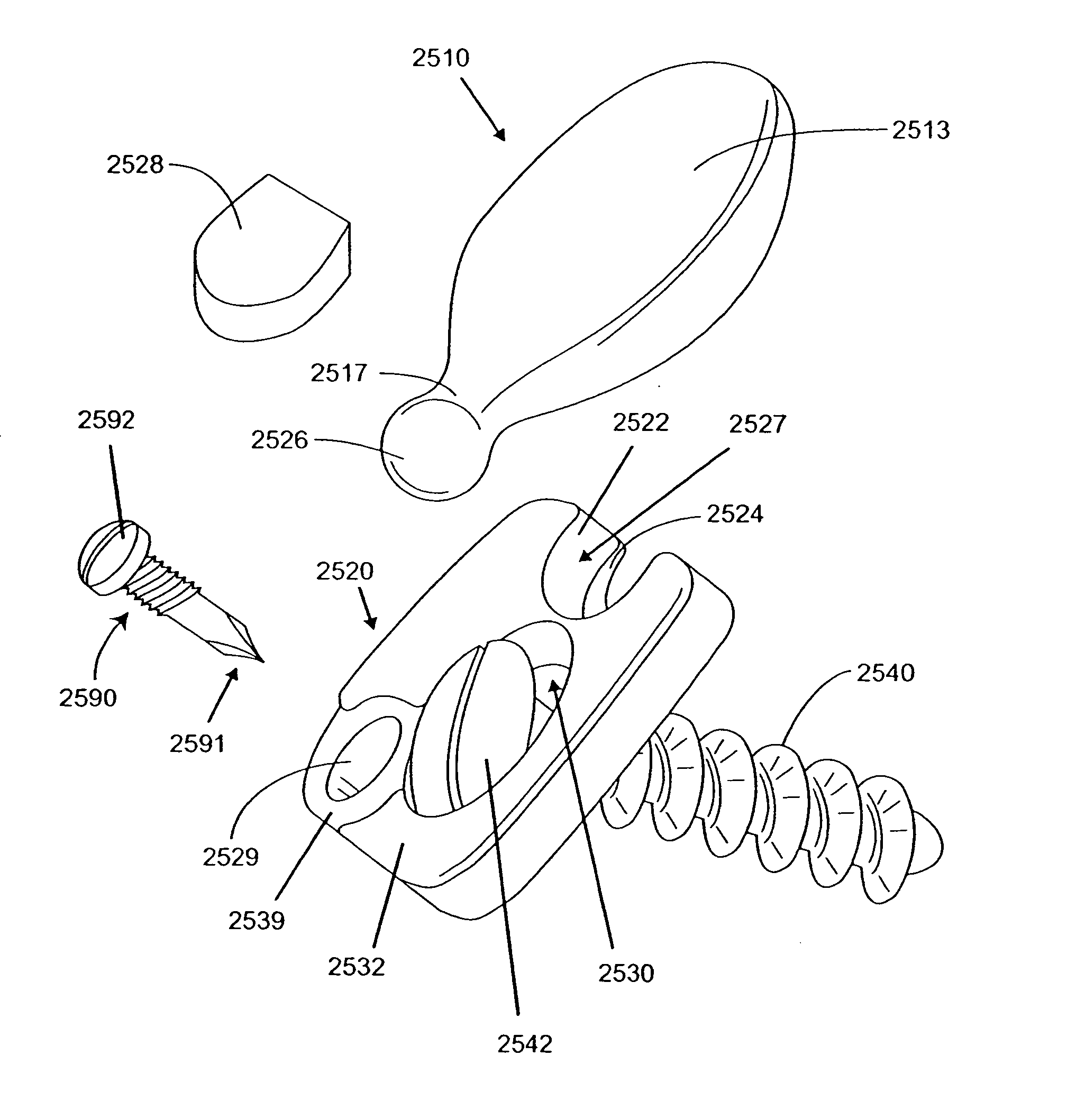
Inter-cervical facet implant with surface enhancements
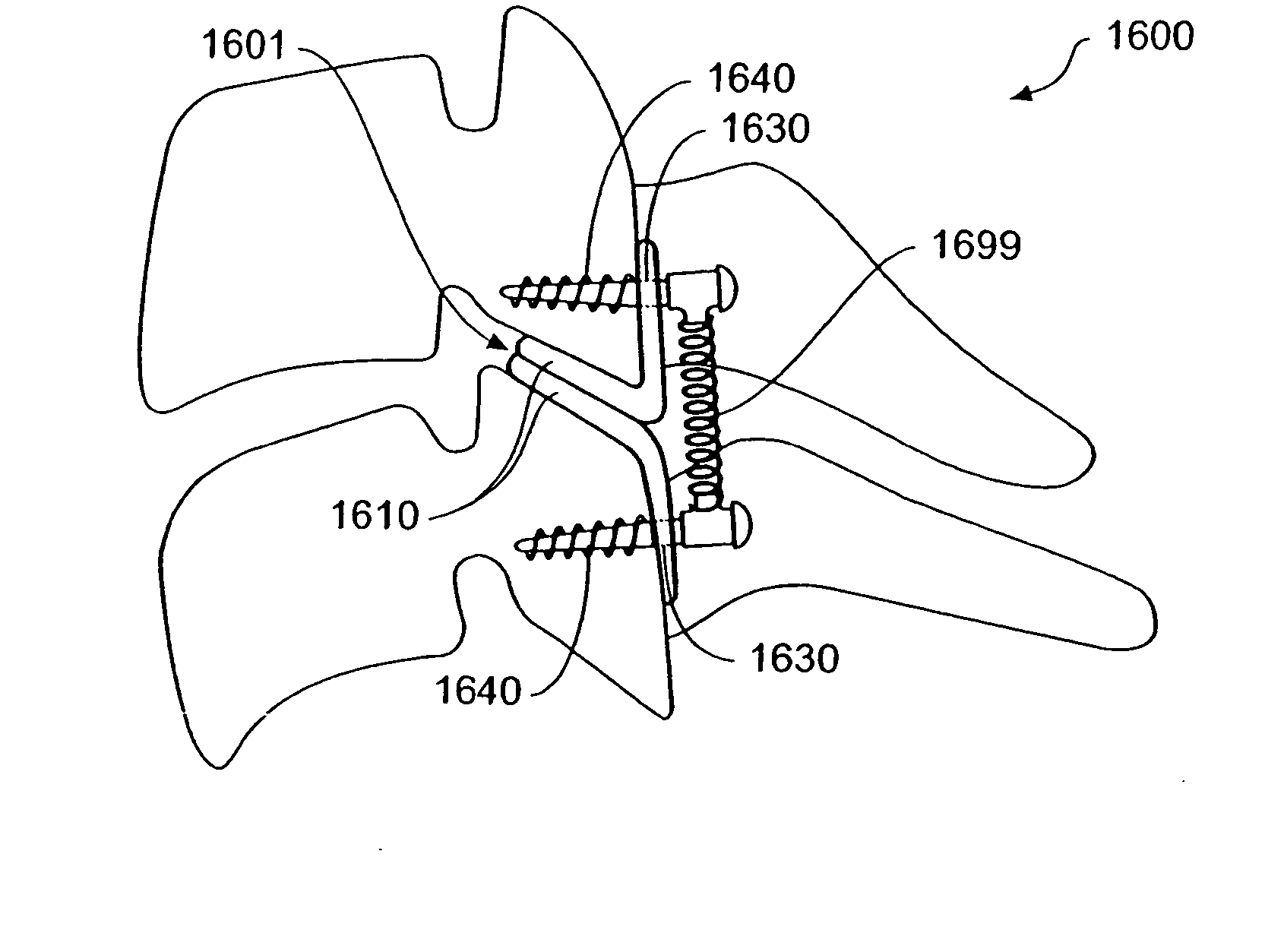
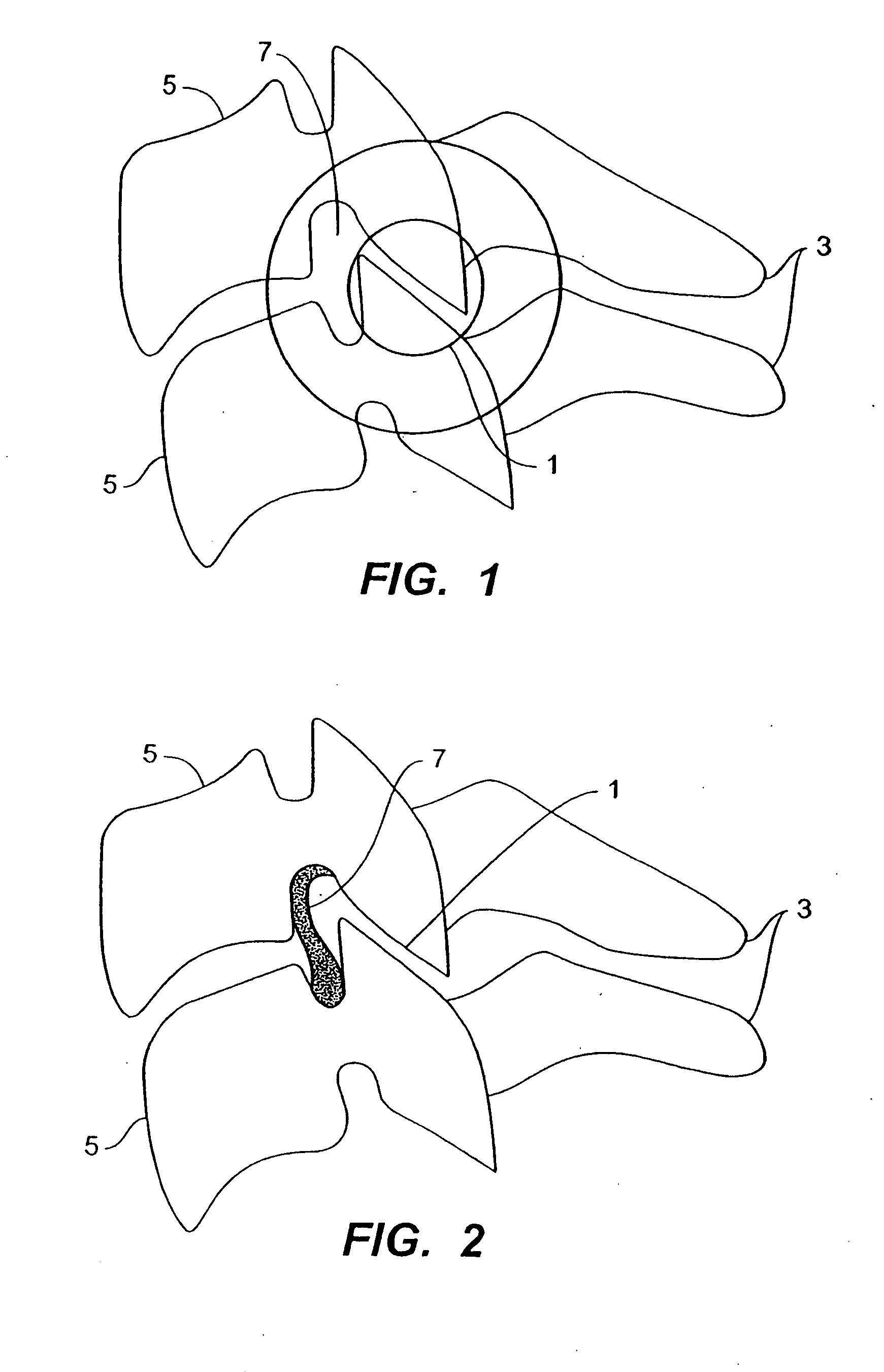
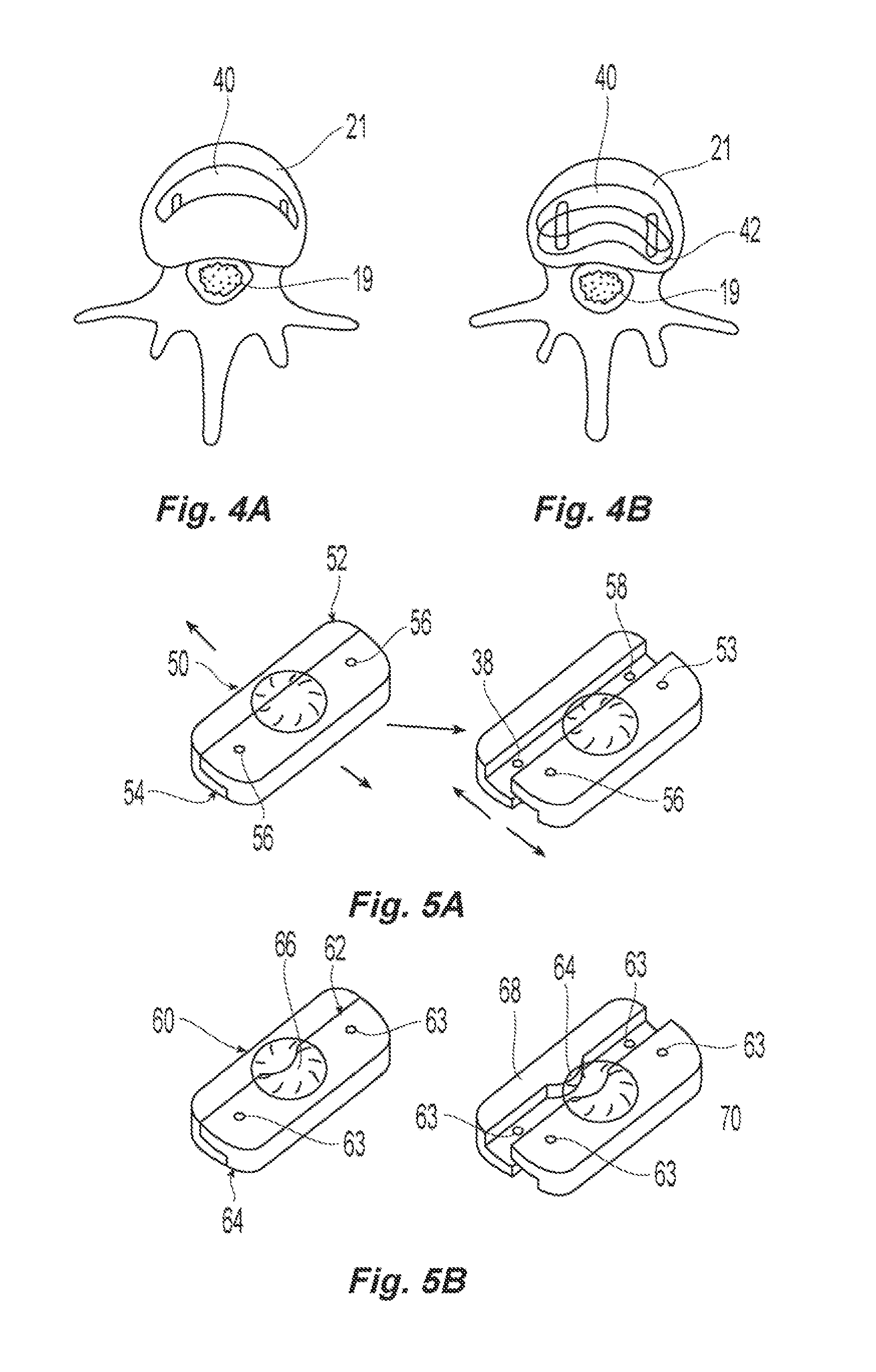
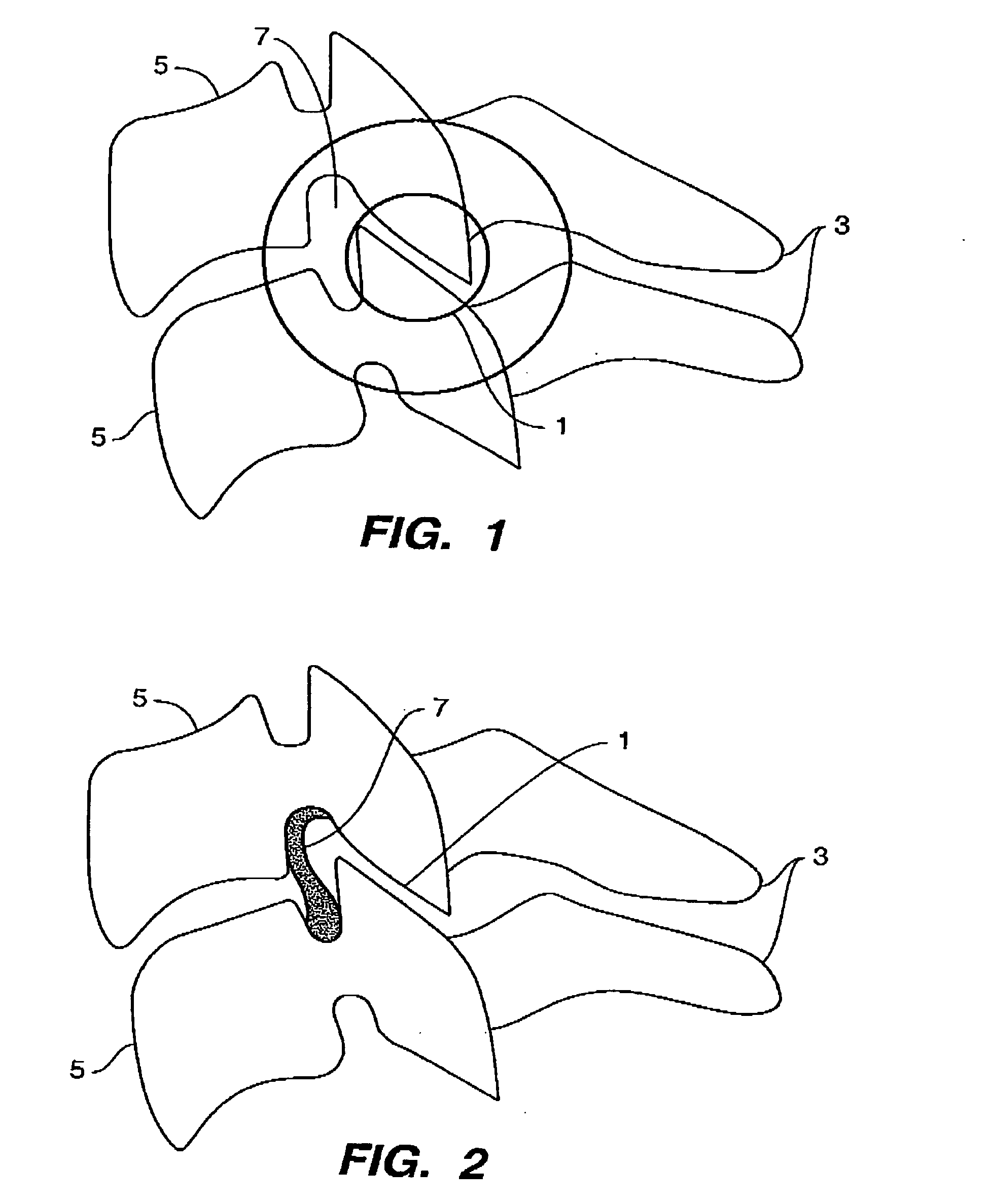
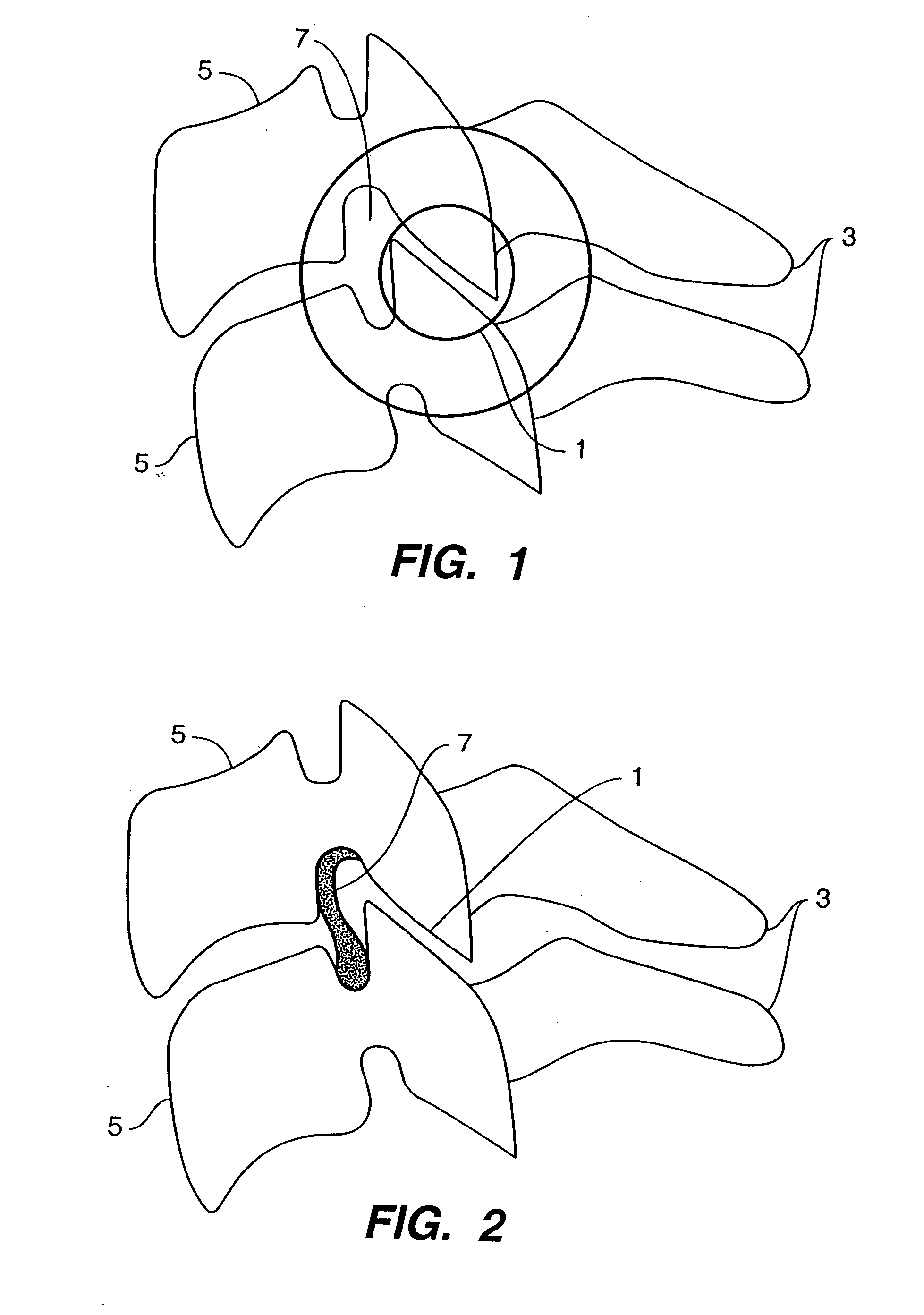
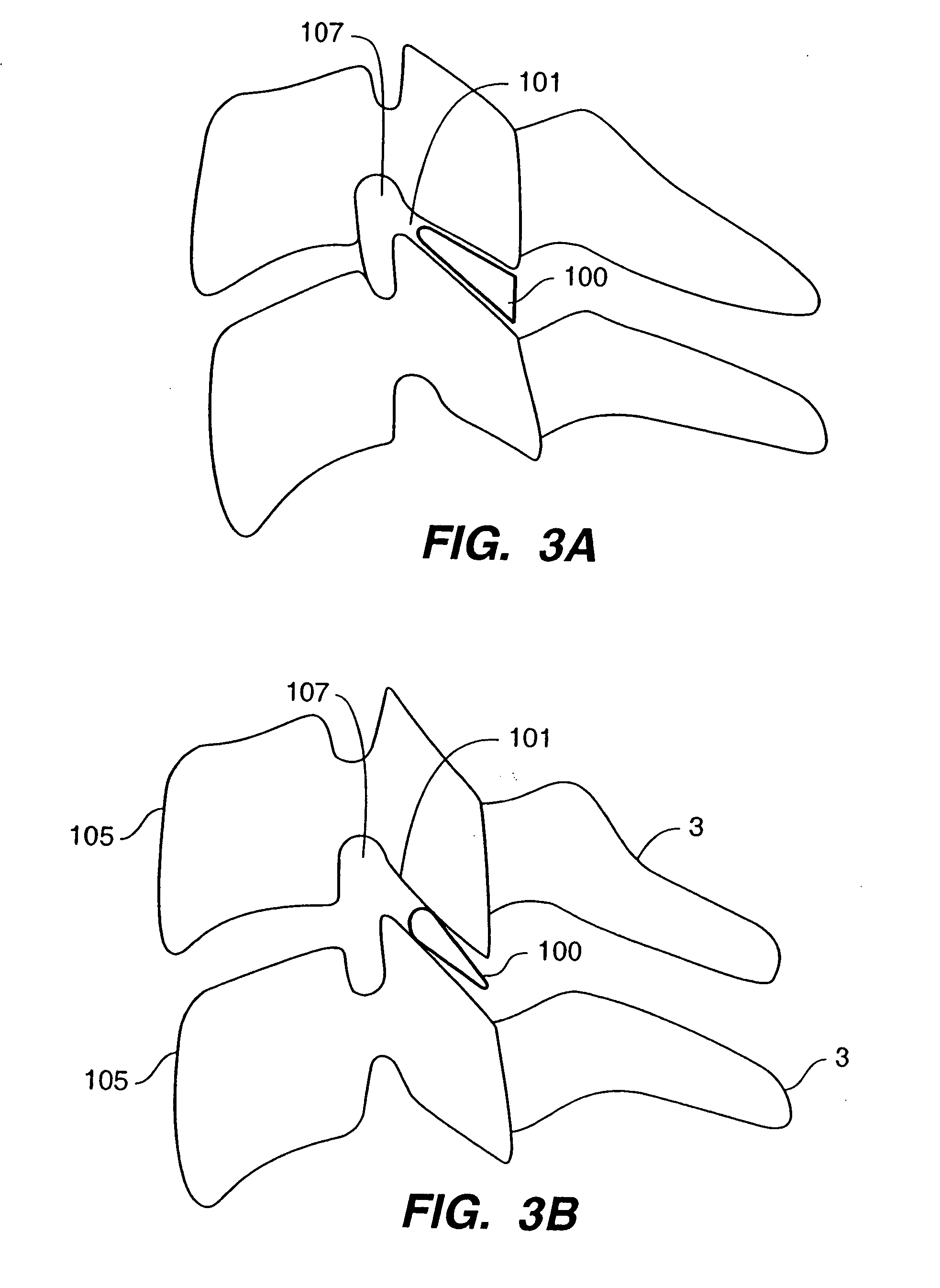
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
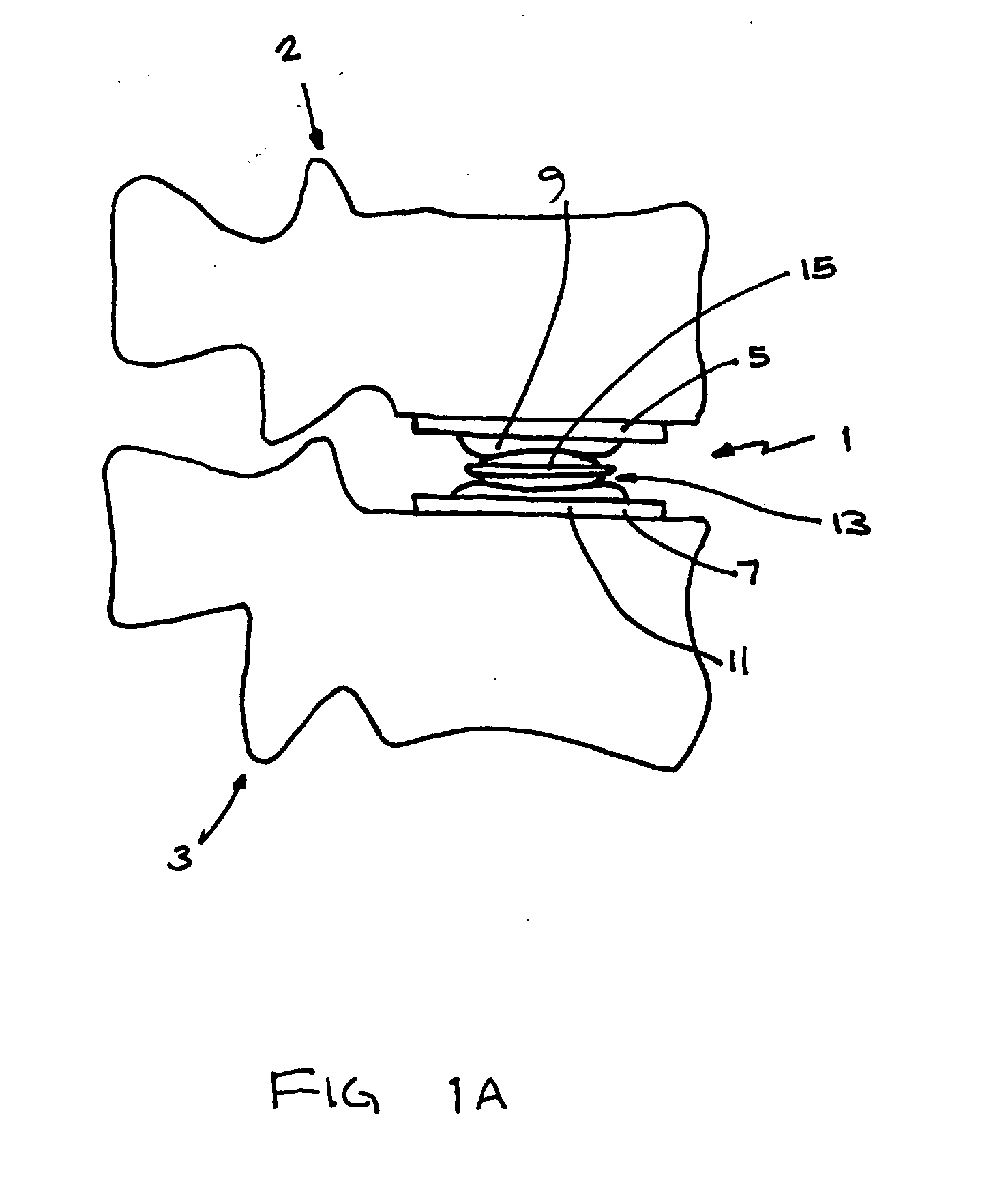
Spinal disc nucleus implant
InactiveUS20050043796A1Accurate removalMinimally invasiveJoint implantsSpinal implantsIntervertebral discSpinal cord
A device and method for repairing spinal discs in which the nucleus has been damaged. A central section of the nucleus is cored out using a device which ablates the tissue using RF energy. A nucleus implant comprising a shape memory material is placed in the central section of the disc through a cannula, which implant is activated by body heat to expand and fill the central section, such that the implant emulates the functions and strength of the disc's natural nucleus.
Owner:SENTRON MEDICAL
Inter-cervical facet joint fusion implant
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
Closed-loop neuromodulation for prevention and treatment of cardiac conditions
InactiveUS7218964B2Reduced activityImprove heart functionCatheterRespiratory organ evaluationClosed loop feedbackSpinal cord
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Neural blocking therapy
A method and apparatus are disclosed for treating a variety of conditions include treating a disorder associated with neural activity near a region of a brain. In such condition, the method includes placing an electrode to create a field near said region, creating said field with parameters selected to at least partially block neural activity within said field. For treating a tissue sensation, the method includes identifying a target area of tissue to be treated and placing an electrode to create a field near the target area, and creating the field with parameters selected to at least partially block neural activity within the target area. For treating a condition associated with neural activity of a spinal cord, the method includes placing an electrode to create a field near a nerve associated with the spinal cord, and creating the field with parameters selected to at least partially block neural activity within the nerve.
Owner:FLATHEAD PARTNERS LLC +1
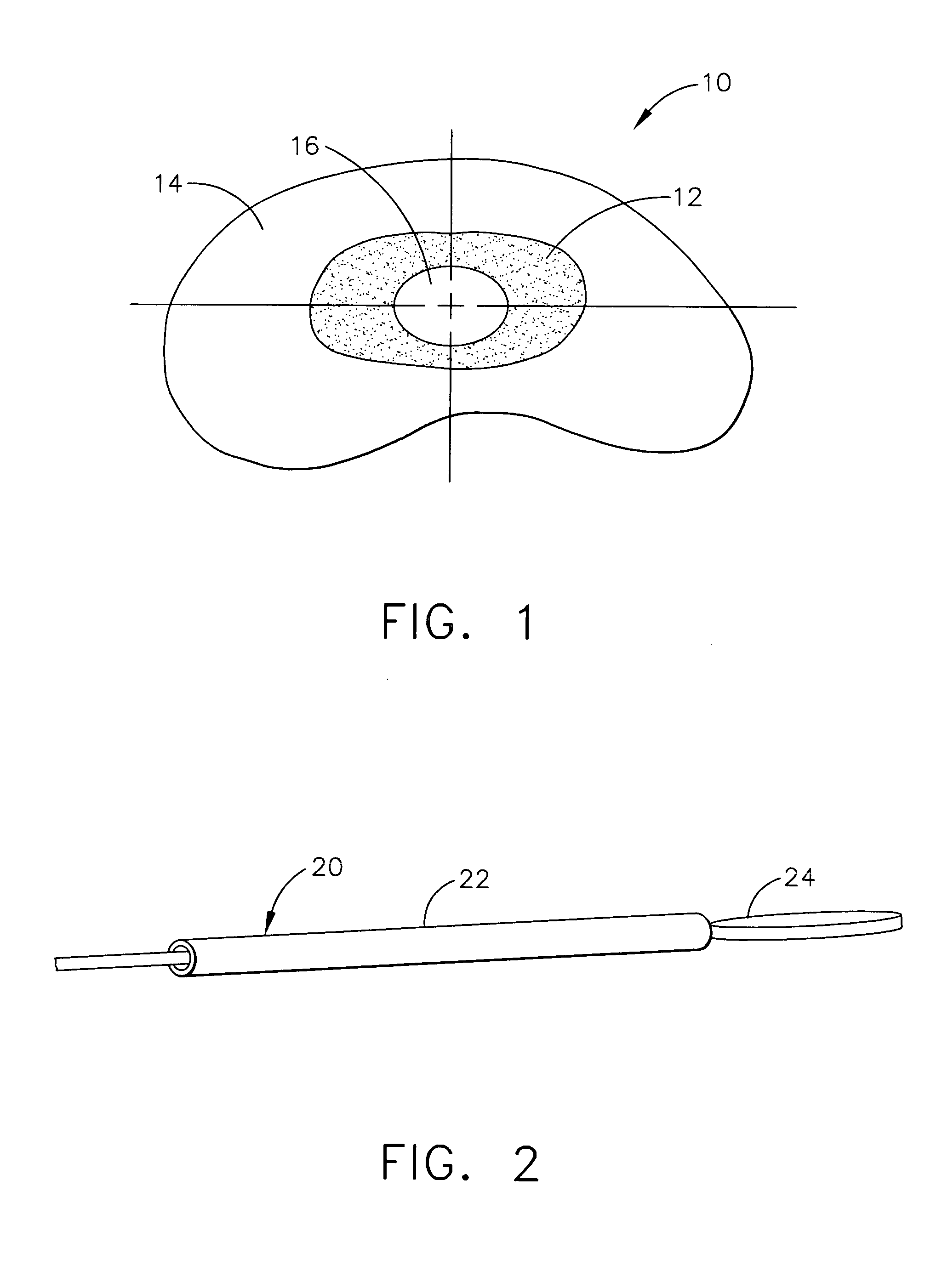
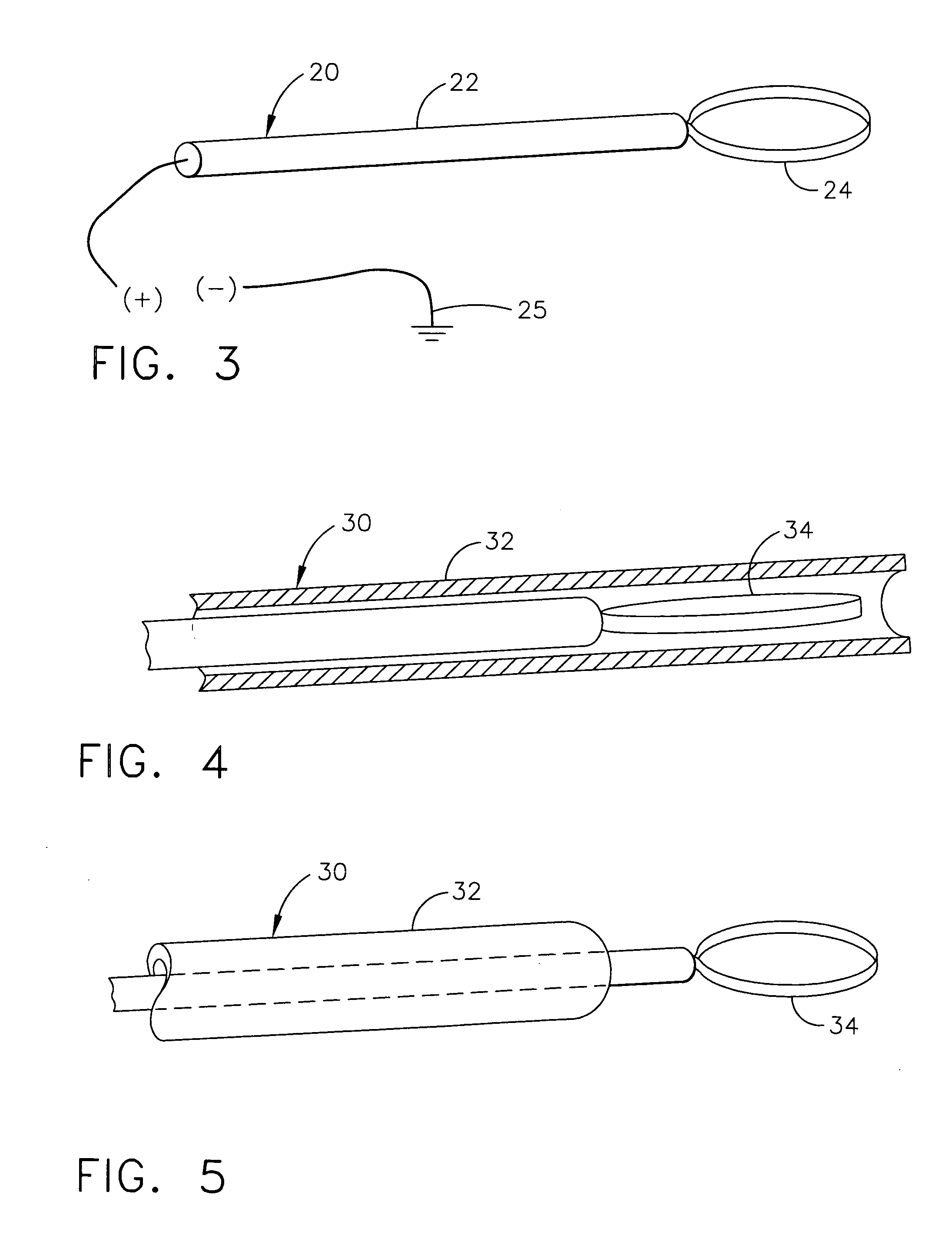
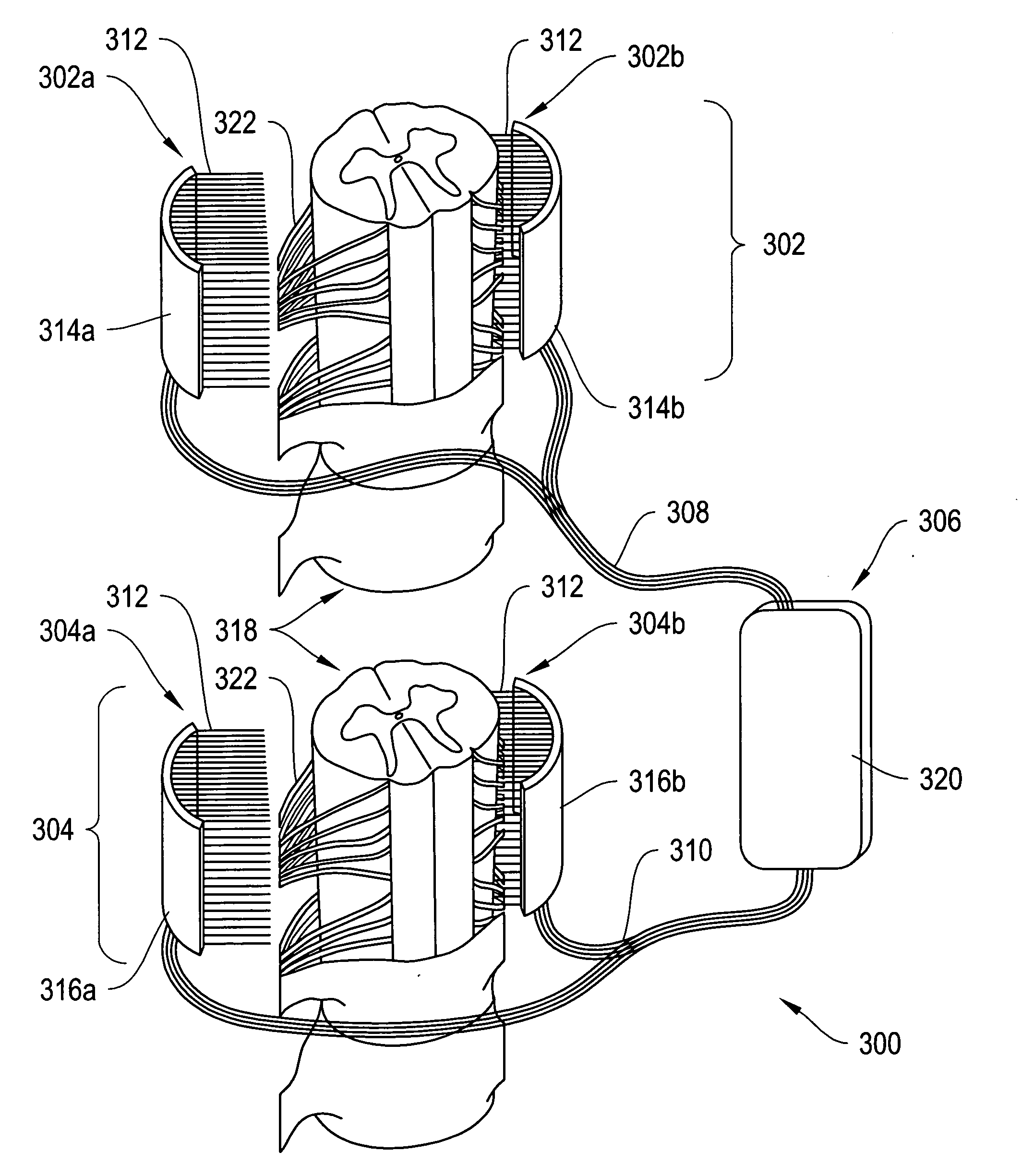
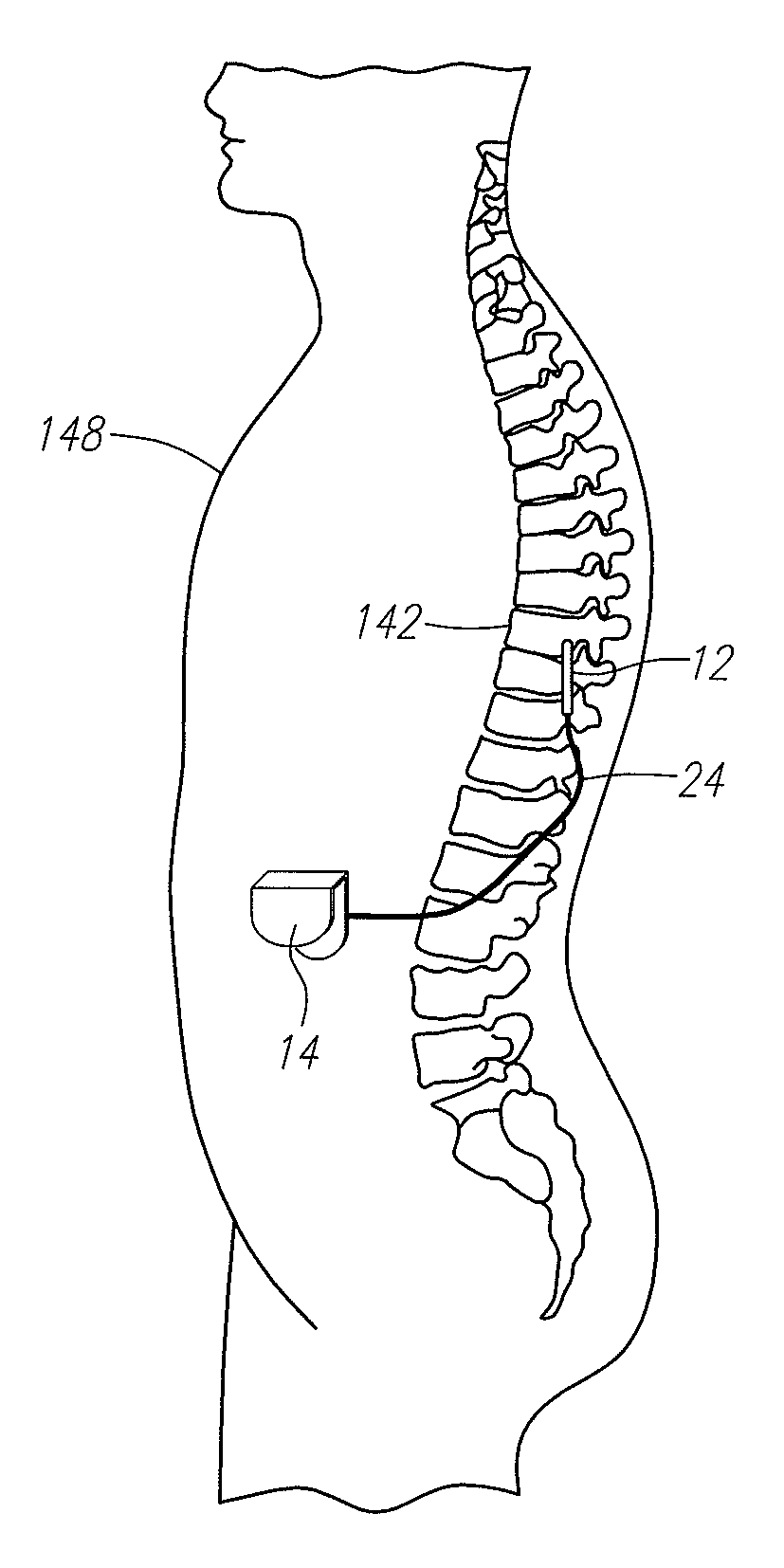
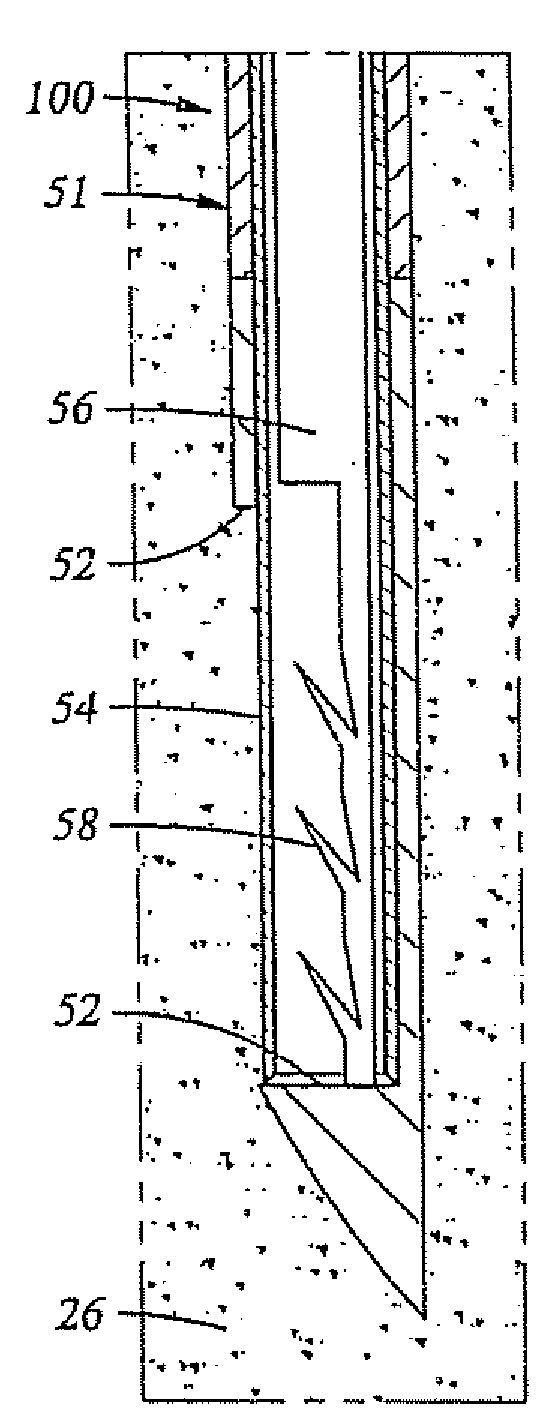
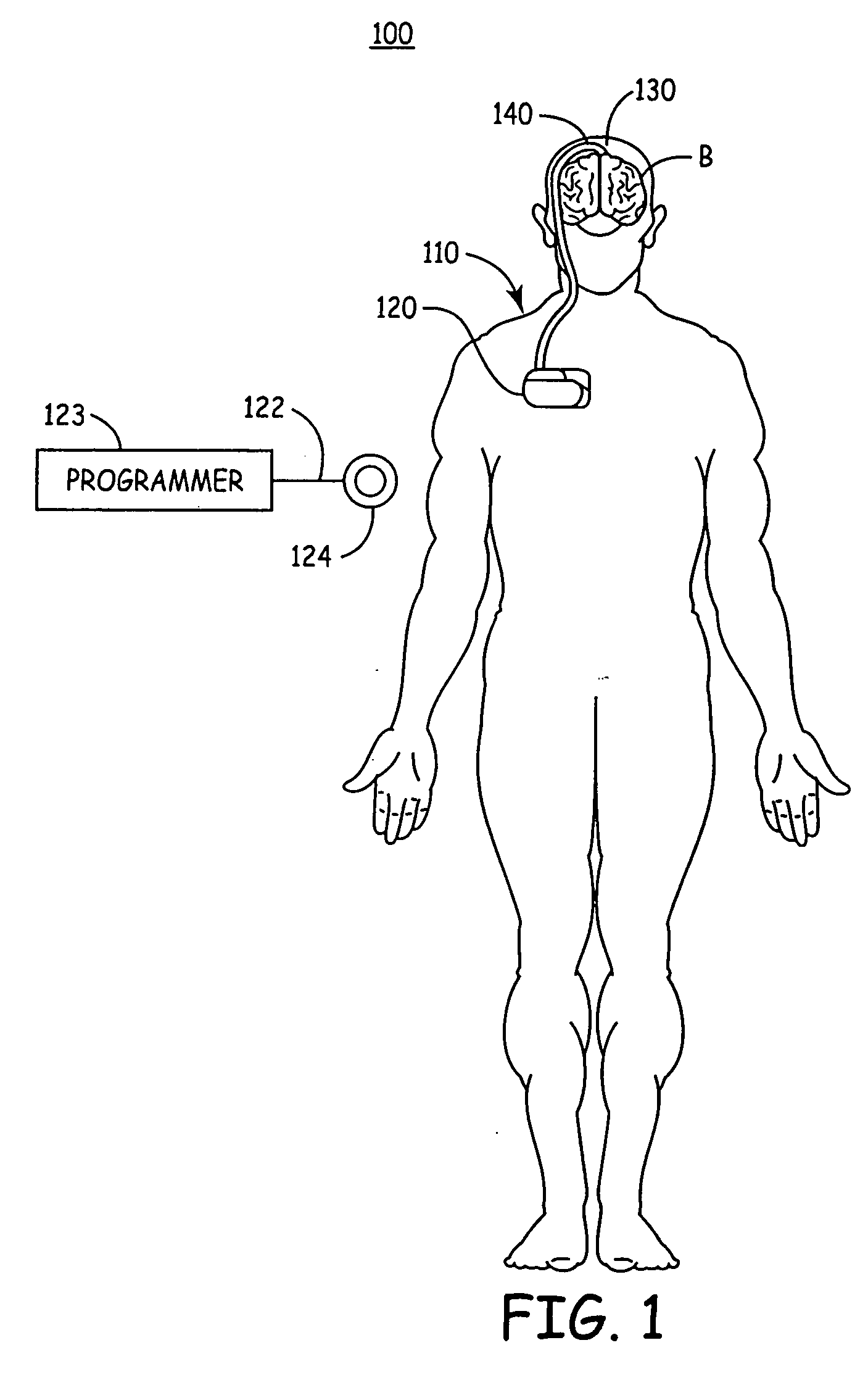
Spinal cord implant systems and methods
InactiveUS20080234791A1Enhances and restores motor functionSpinal electrodesElectromyographyMedicineSpinal cord
A system for transferring spinal cord signals comprises a superior electrode and an inferior electrode. The superior electrode interfaces with a first portion of a spinal cord of a human body; and the inferior electrode interfaces with a second portion of the spinal cord. The superior electrode has at least one superior contact for receiving signals from the first portion of the spinal cord to transmit to the inferior electrode; and the inferior electrode has at least one inferior contact for transmitting signals received from the superior electrode to the second portion of the spinal cord.
Owner:LAHEY CLINIC FOUND
Posterior prosthetic spinal disc replacement and methods thereof
The present invention relates generally to a prosthetic spinal disc for replacing a damaged disc between two vertebrae of a spine. The present invention also relates to a method for implanting a prosthetic spinal disc via posterior or posterior lateral implantation. Other surgical approaches for implanting the prosthetic disc may also be used. The present invention also involves a method for implanting the prosthetic spinal disc while either avoiding or minimizing contact with the spinal cord and nerve rootlets, or reducing the time and extent that they need to be repositioned during implantation.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
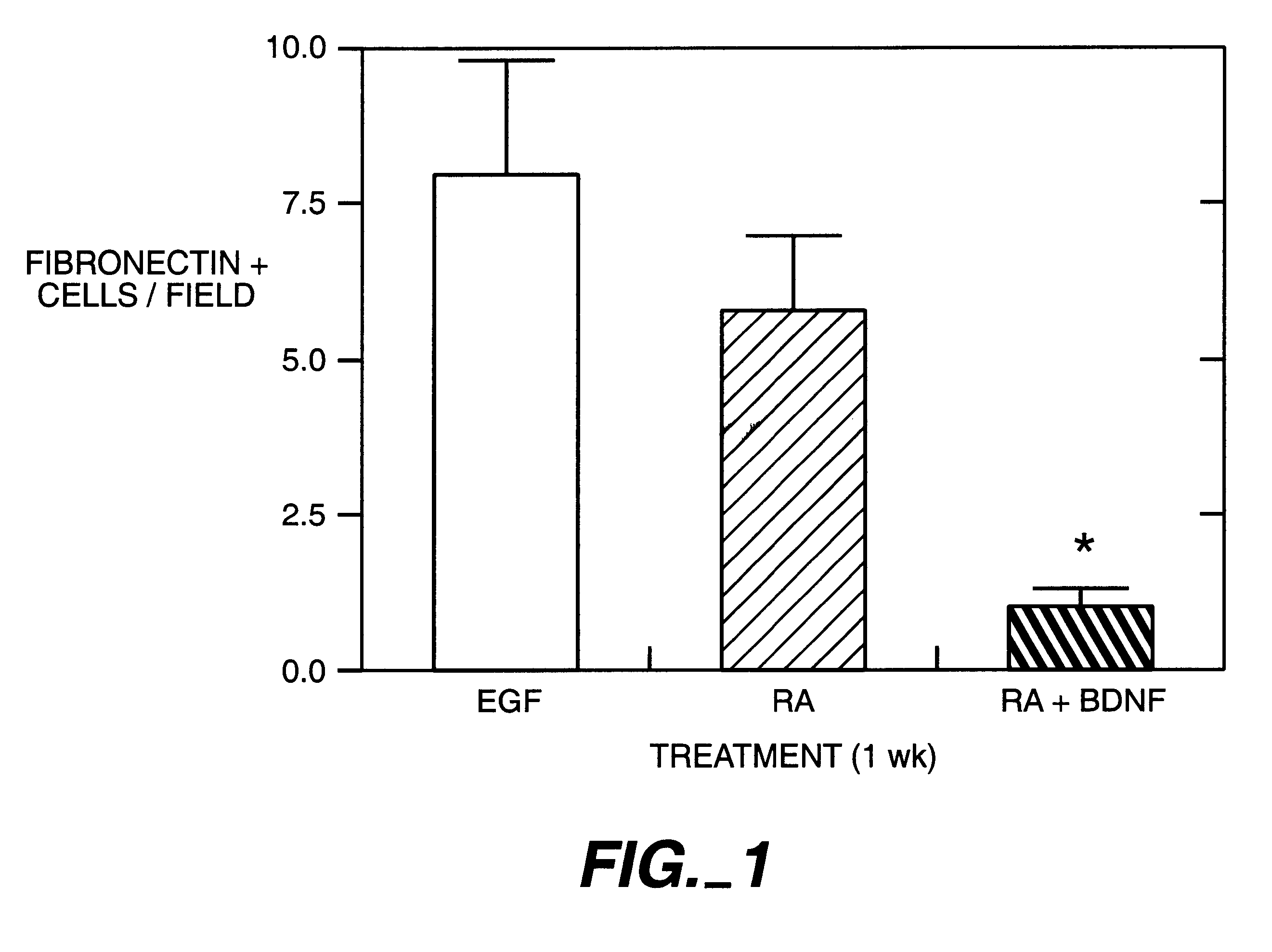
Human cord blood as a source of neural tissue for repair of the brain and spinal cord
InactiveUS20020028510A1Easy to distinguishImprove neurological dysfunctionNervous disorderCell differentiationDiseaseCord blood stem cell
The present invention relates to the use of umbilical cord blood cells from a donor or patient to provide neural cells which may be used in transplantation. The isolated cells according to the present invention may be used to effect autologous and allogeneic transplantation and repair of neural tissue, in particular, tissue of the brain and spinal cord and to treat neurodegenerative diseases of the brain and spinal cord.
Owner:SANERON CCEL THERAPEUTICS +1
Inter-cervical facet joint implant with locking screw system
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
Inter-cervical facet implant and method
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
Inter-cervical facet implant with multiple direction articulation joint and method for implanting
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
Bone marrow cells as a source of neurons for brain and spinal cord repair
Owner:SOUTH FLORIDA UNIVESITY OF
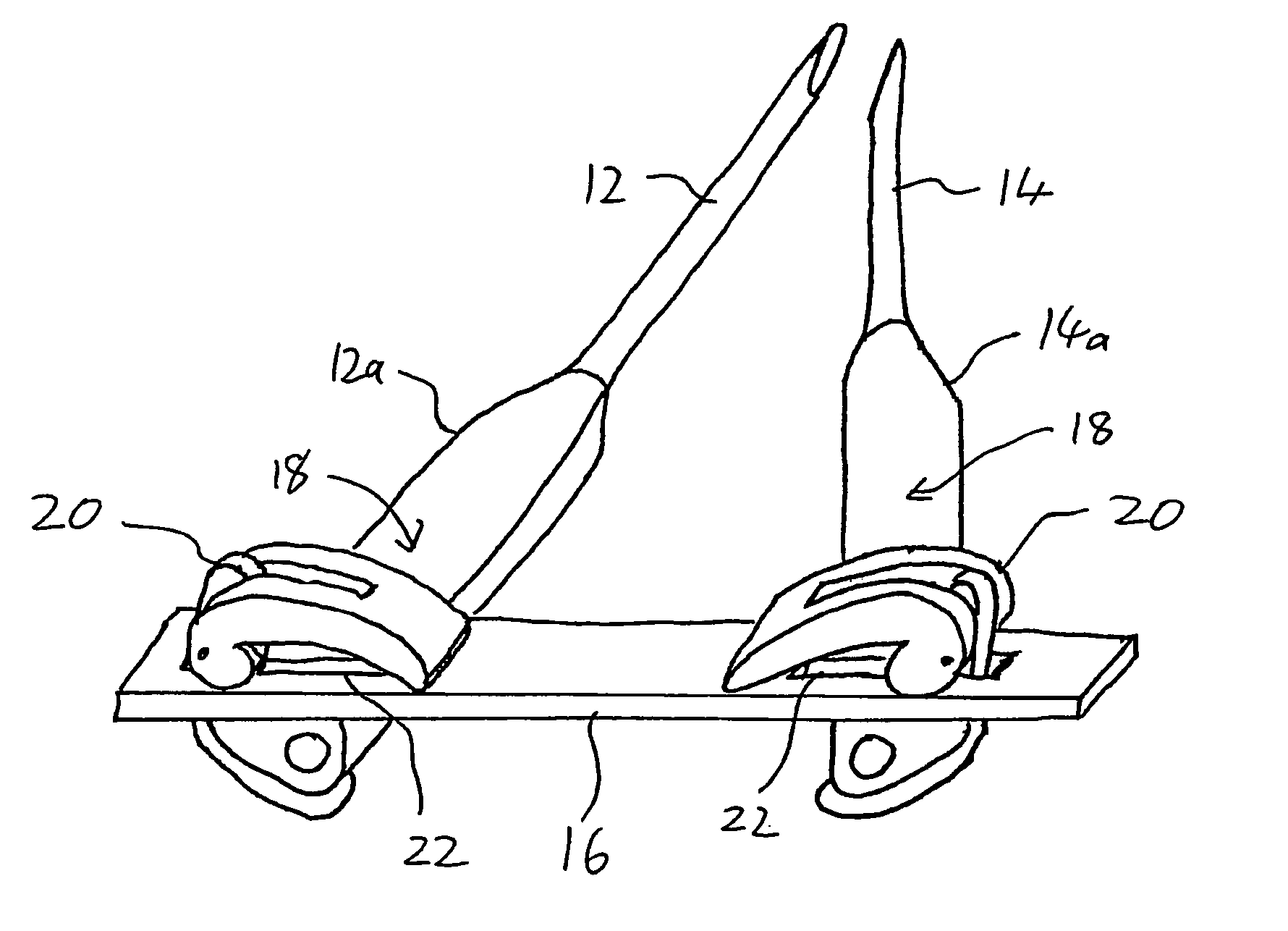
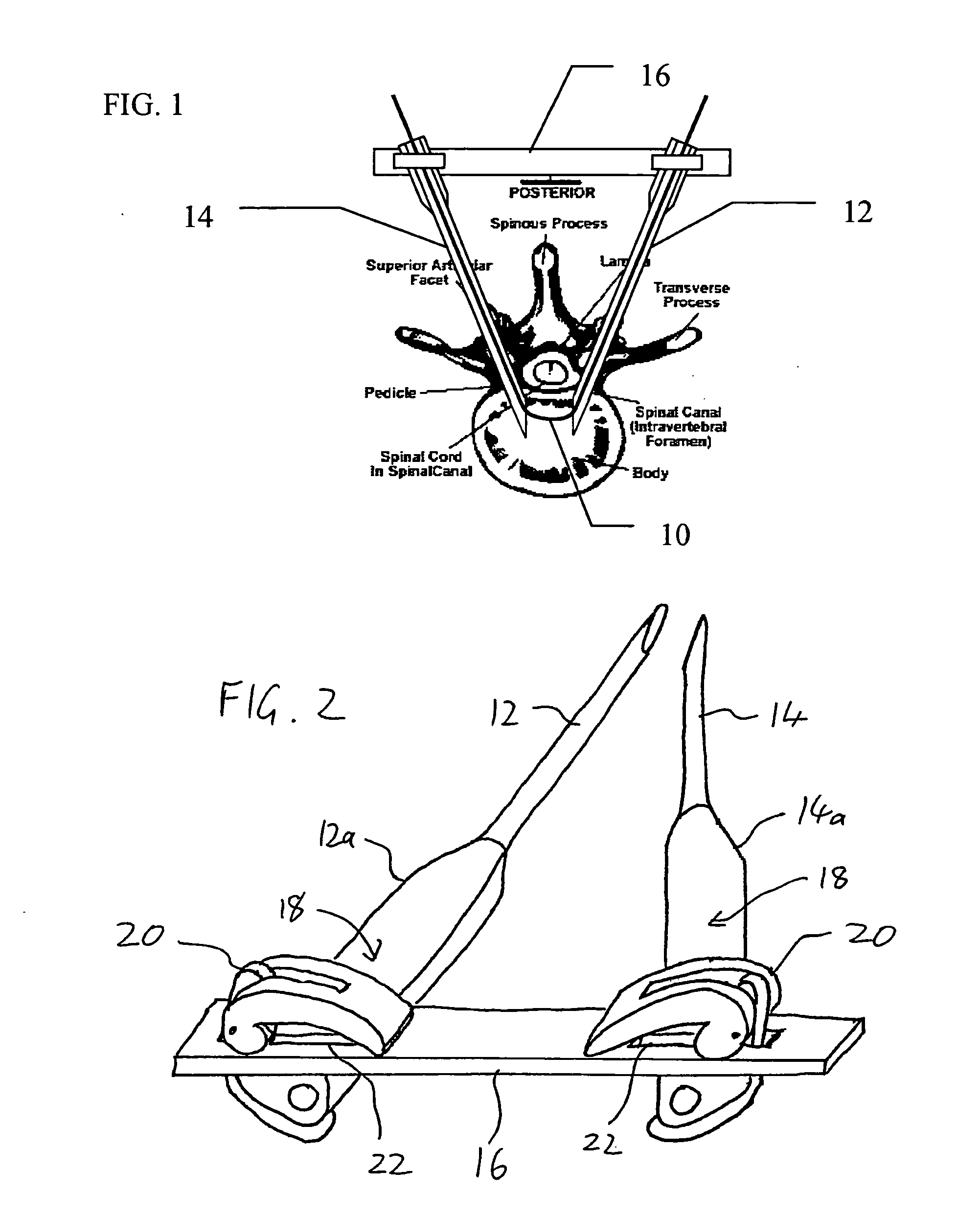
Spinal surgery system and method
InactiveUS20060036241A1Small sizeEasy to fixInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSpinal cord
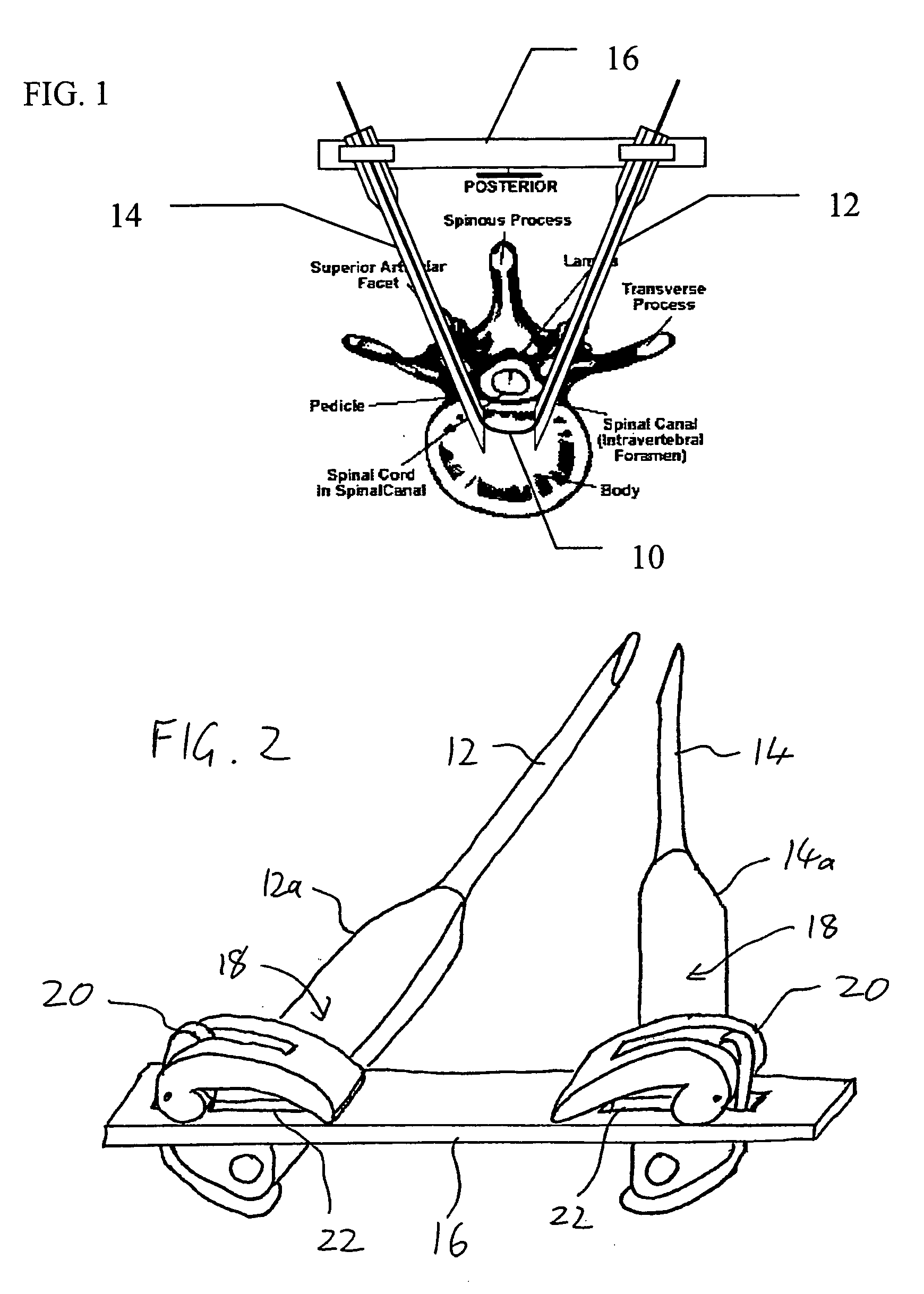
Apparatus and method for minimally invasive spinal surgery employs an elongated flexible guide element inserted so as to pass in through a first lateral posterior incision, through the spinal column anterior to the spinal cord, and out through a second lateral posterior incision contralateral to said first incision. The guide element is used to guide various elements to a desired position within the spinal column as part of the surgical procedure. Preferably, two hollow rigid tubes rigidly coupled outside the body in converging relation are used to define a working gap within the spinal column through which the guide element passes. This provides a platform for manipulation of tissues and introduction of implants anterior to the spinal cord. Procedures described include reinforcement of a degenerative intervertebral disc and restoration of a damaged vertebral body.
Owner:SIEGAL TZONY
Method and apparatus for spinal procedures
InactiveUS7189240B1Assist in removeExcision instrumentsEndoscopic cutting instrumentsSpinal columnSpinal stenosis
A method of treating spinal stenosis, in which a rasp is brought through a part of a spinal channel and then axially moved so that the rasp removes a stenosis in the spinal channel. Optionally, a shield protects a spinal cord or other sensitive tissues in the spinal channel.
Owner:KYPHON
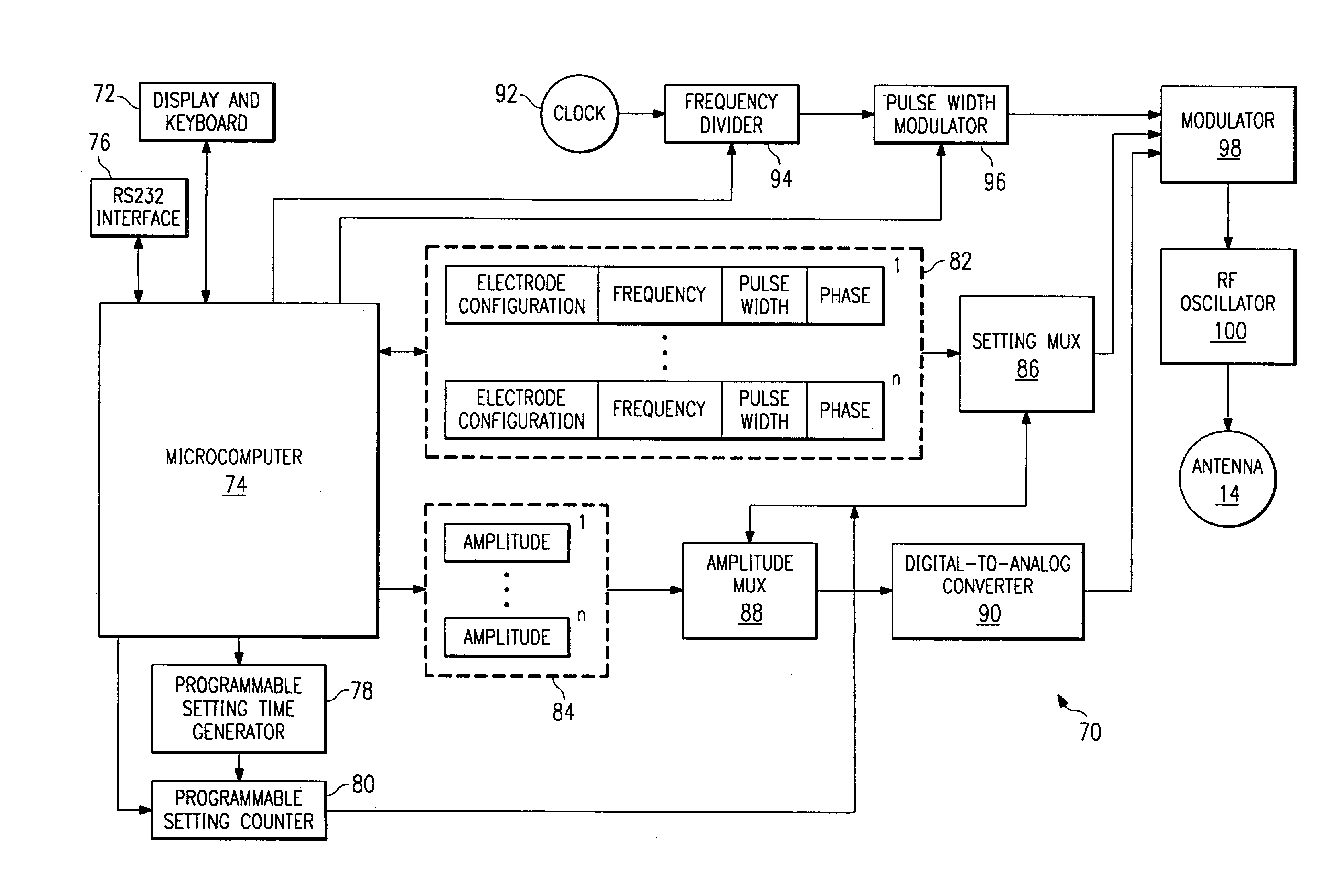
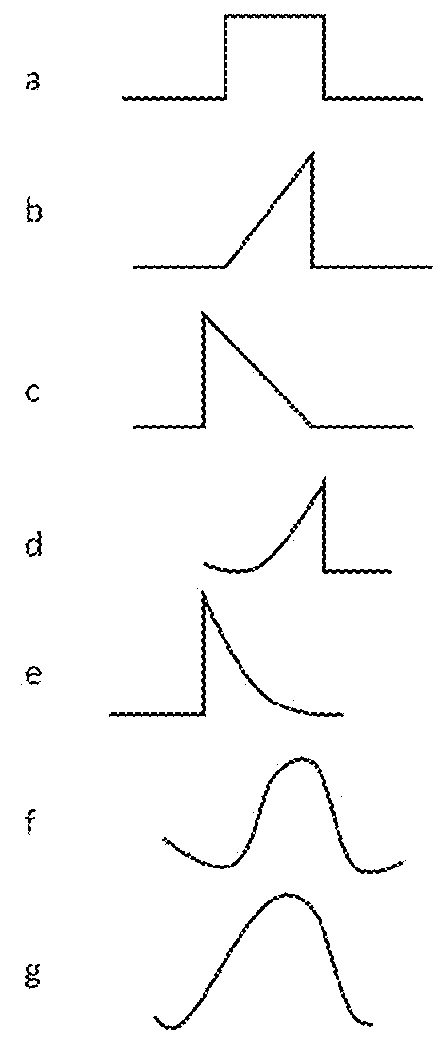
Use of stimulation pulse shape to control neural recruitment order and clinical effect
ActiveUS20090024189A1Uniform chargeImplantable neurostimulatorsArtificial respirationElectricityWave shape
A method, electrical tissue stimulation system, and programmer for providing therapy to a patient are provided. Electrodes are placed adjacent tissue (e.g., spinal cord tissue) of the patient, electrical stimulation energy is delivered from the electrodes to the tissue in accordance with a defined waveform, and a pulse shape of the defined waveform is modified, thereby changing the characteristics of the electrical stimulation energy delivered from the electrode(s) to the tissue. The pulse shape may be modified by selecting one of a plurality of different pulse shape types or by adjusting a time constant of the pulse shape.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Inter-cervical facet implant and method
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
Spinal surgery system and method
ActiveUS20060036273A1Easy to insertInternal osteosythesisNon-surgical orthopedic devicesSpinal columnSpinal cord
Apparatus and method for minimally invasive spinal surgery employs an elongated flexible guide element inserted so as to pass in through a first lateral posterior incision, through the spinal column anterior to the spinal cord, and out through a second lateral posterior incision contralateral to said first incision. The guide element is used to guide various elements to a desired position within the spinal column as part of the surgical procedure. Preferably, two hollow rigid tubes rigidly coupled outside the body in converging relation are used to define a working gap within the spinal column through which the guide element passes. This provides a platform for manipulation of tissues and introduction of implants anterior to the spinal cord. Procedures described include reinforcement of a degenerative intervertebral disc and restoration of a damaged vertebral body.
Owner:SEASPINE
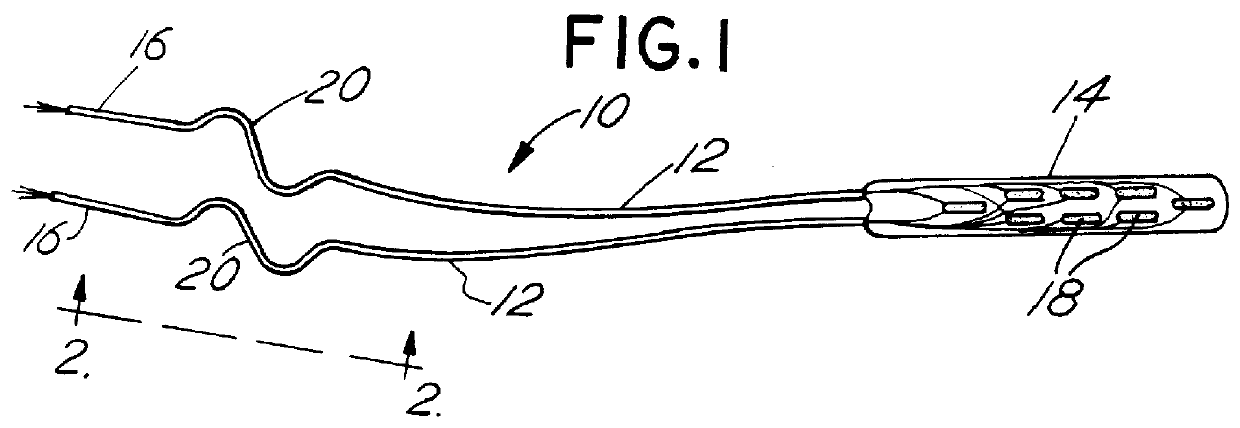
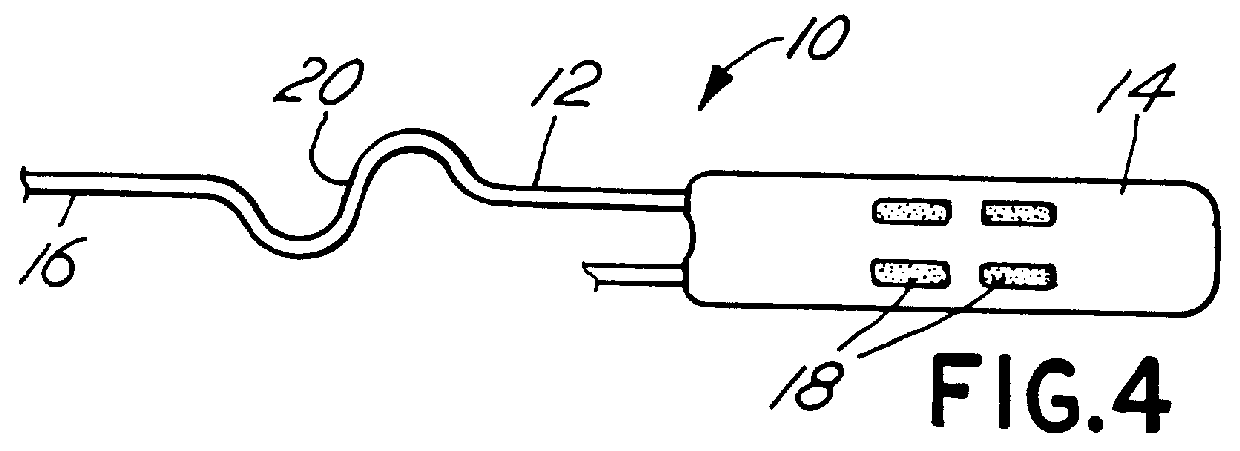
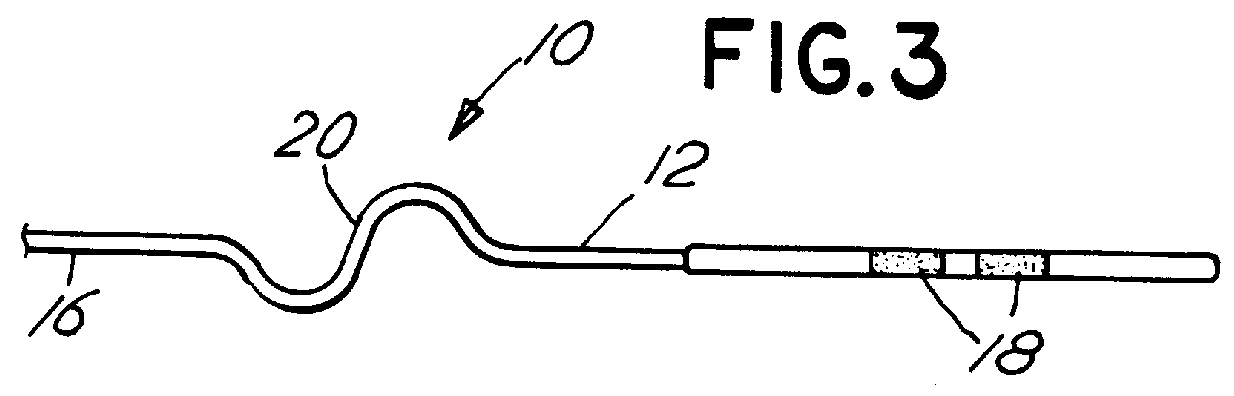
Medical lead with sigma feature
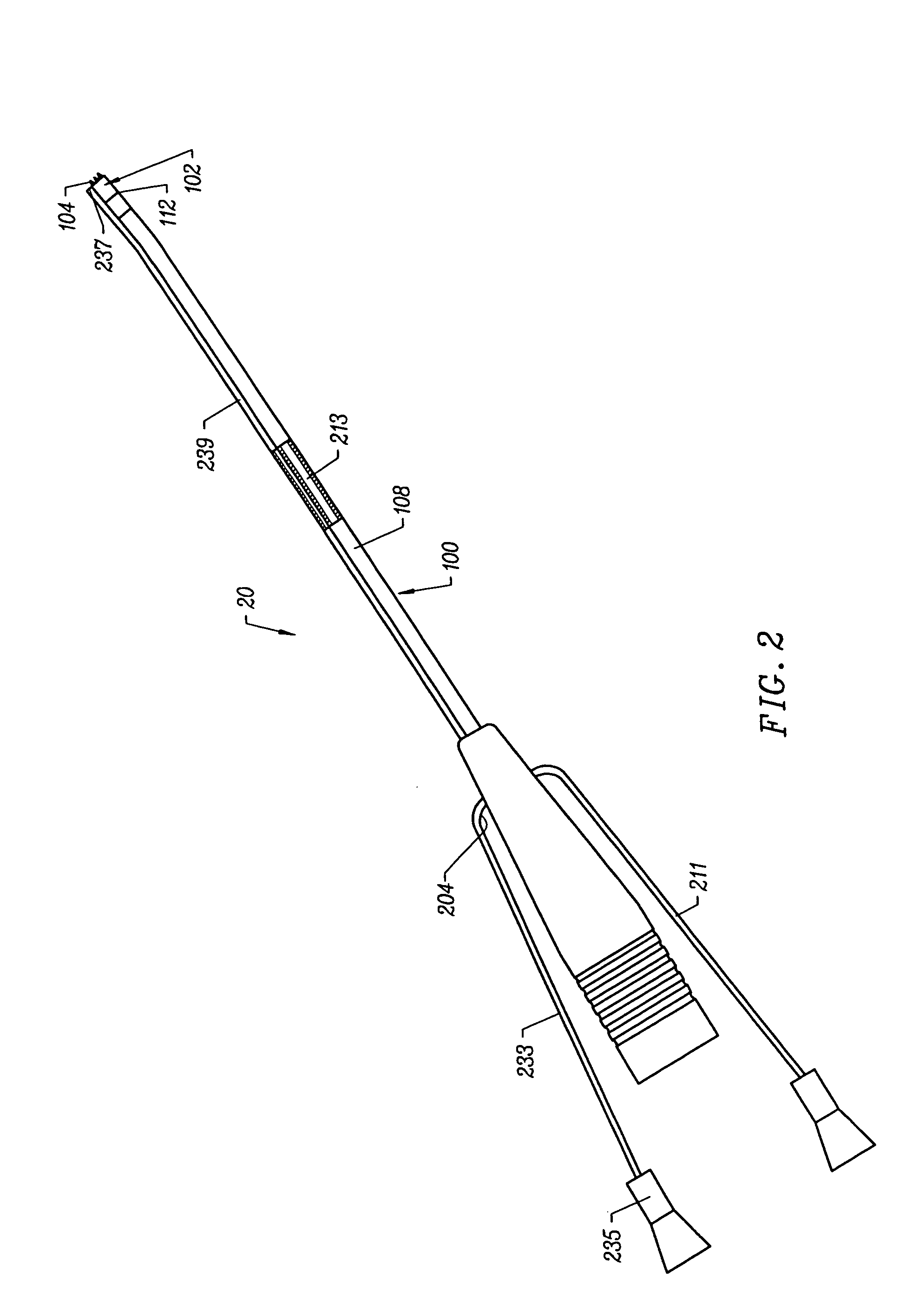
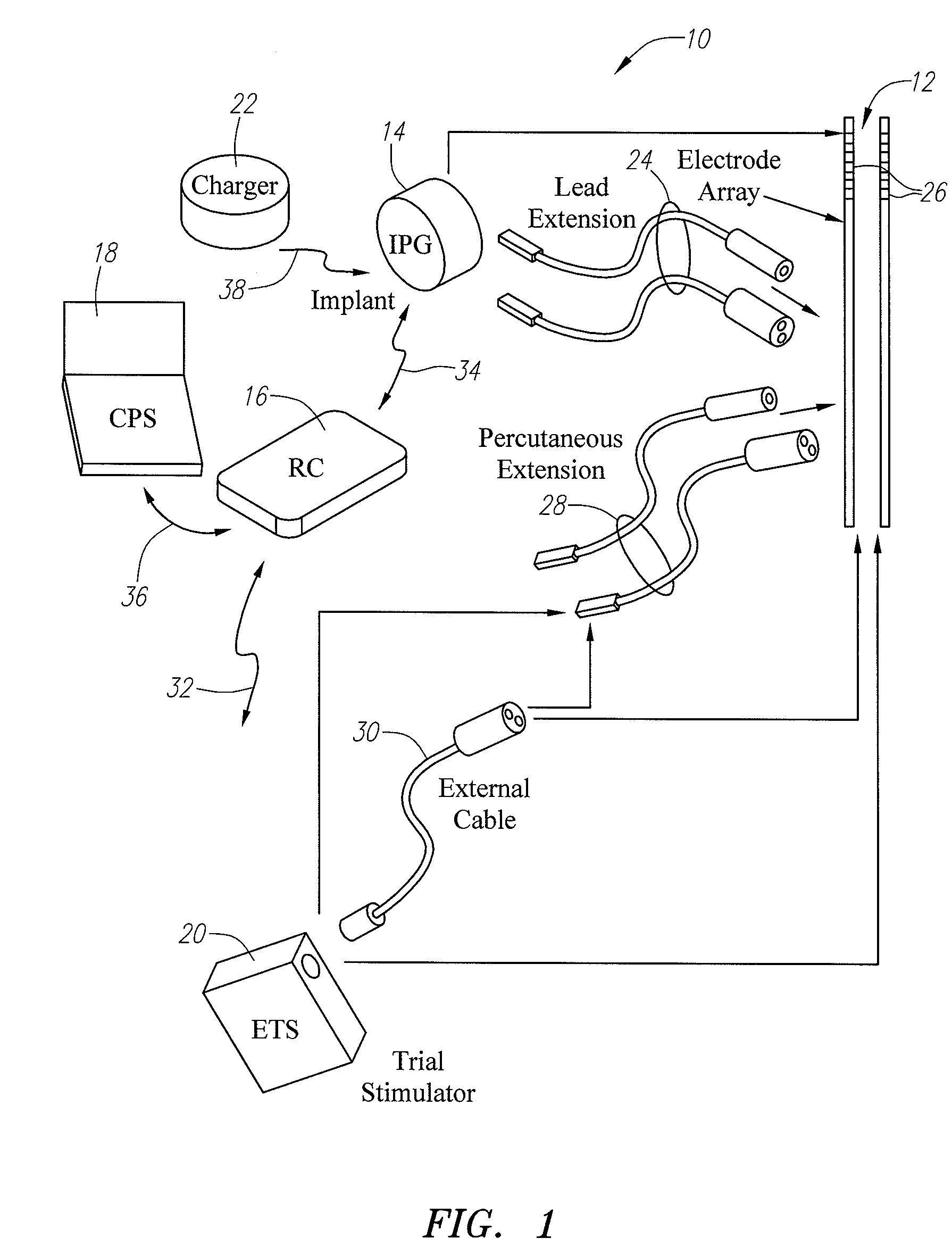
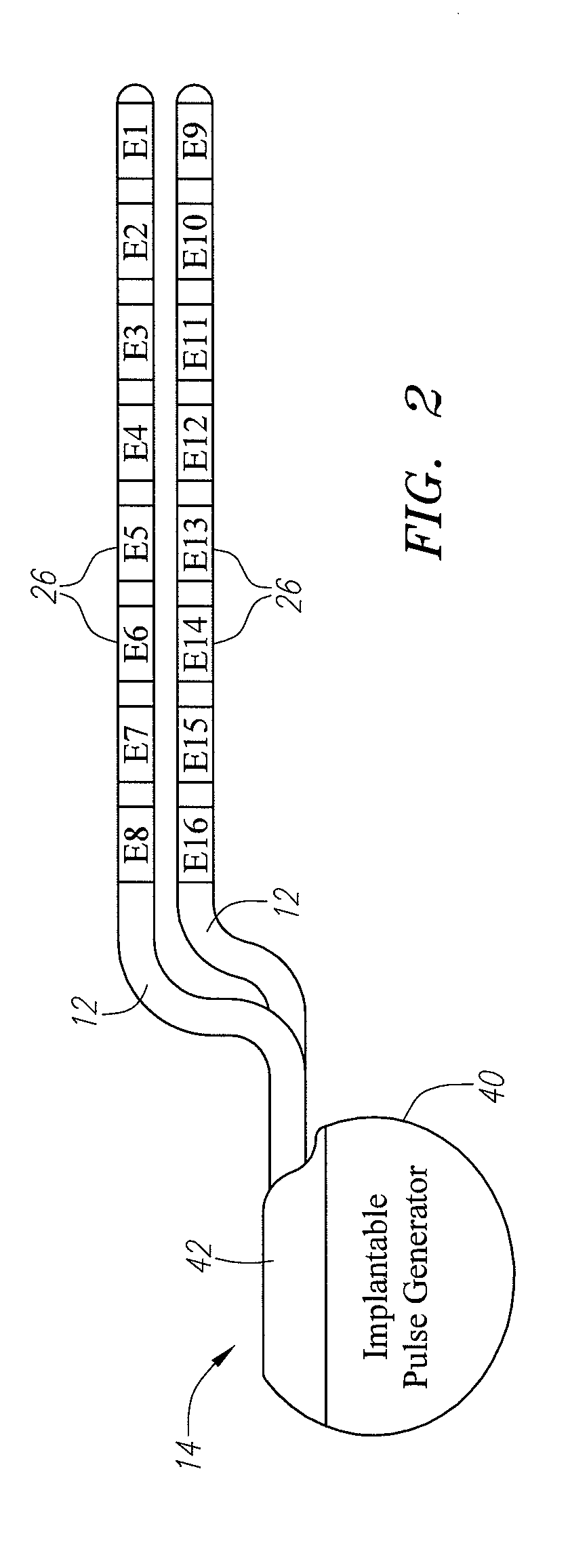
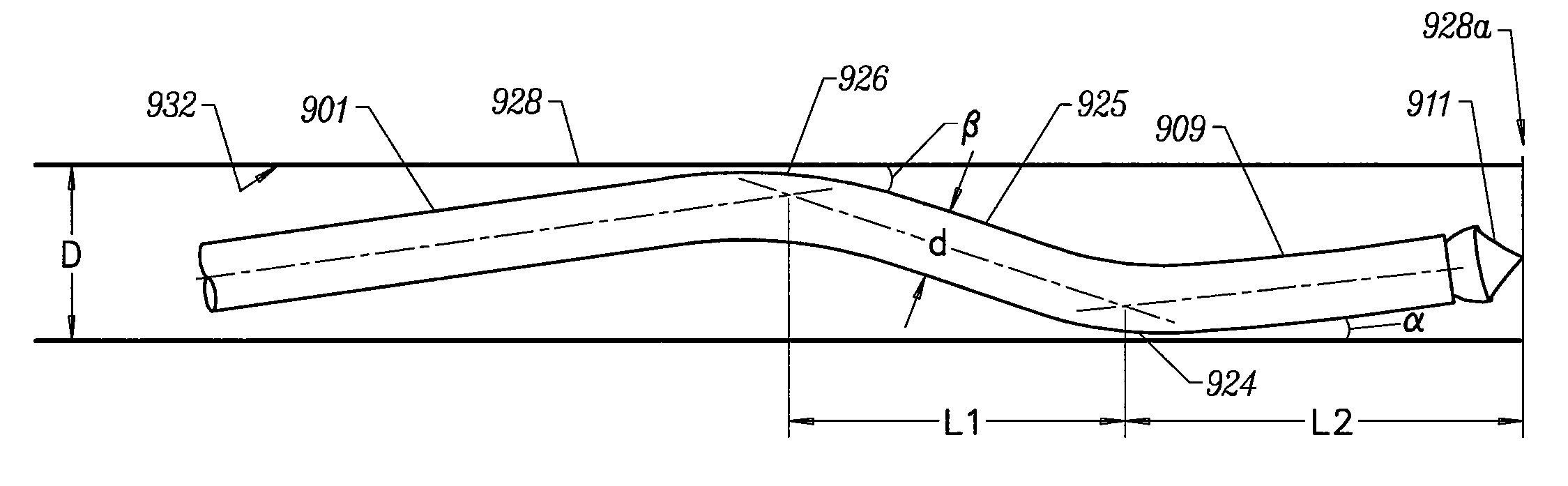
An implantable medical lead for spinal cord, peripheral nerve or deep brain stimulation comprises a lead body which includes a deformable sigma segment preferably in the shape of a sine wave and a lead paddle coupled to the lead body at the distal end thereof. The lead body at its proximal end may be coupled to an implantable pulse generator, additional, intermediate wiring or other stimulation device. The lead paddle may comprise a plurality of electrode contacts for providing electrical stimulation to targeted human tissue. The lead body, which defines the sigma segment, in a plane, couples the lead paddle and pulse generator. The sigma segment provides flexing and bending of the wire when a patient shifts or moves, and especially provides longitudinal extension between the pulse generator and lead paddle.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
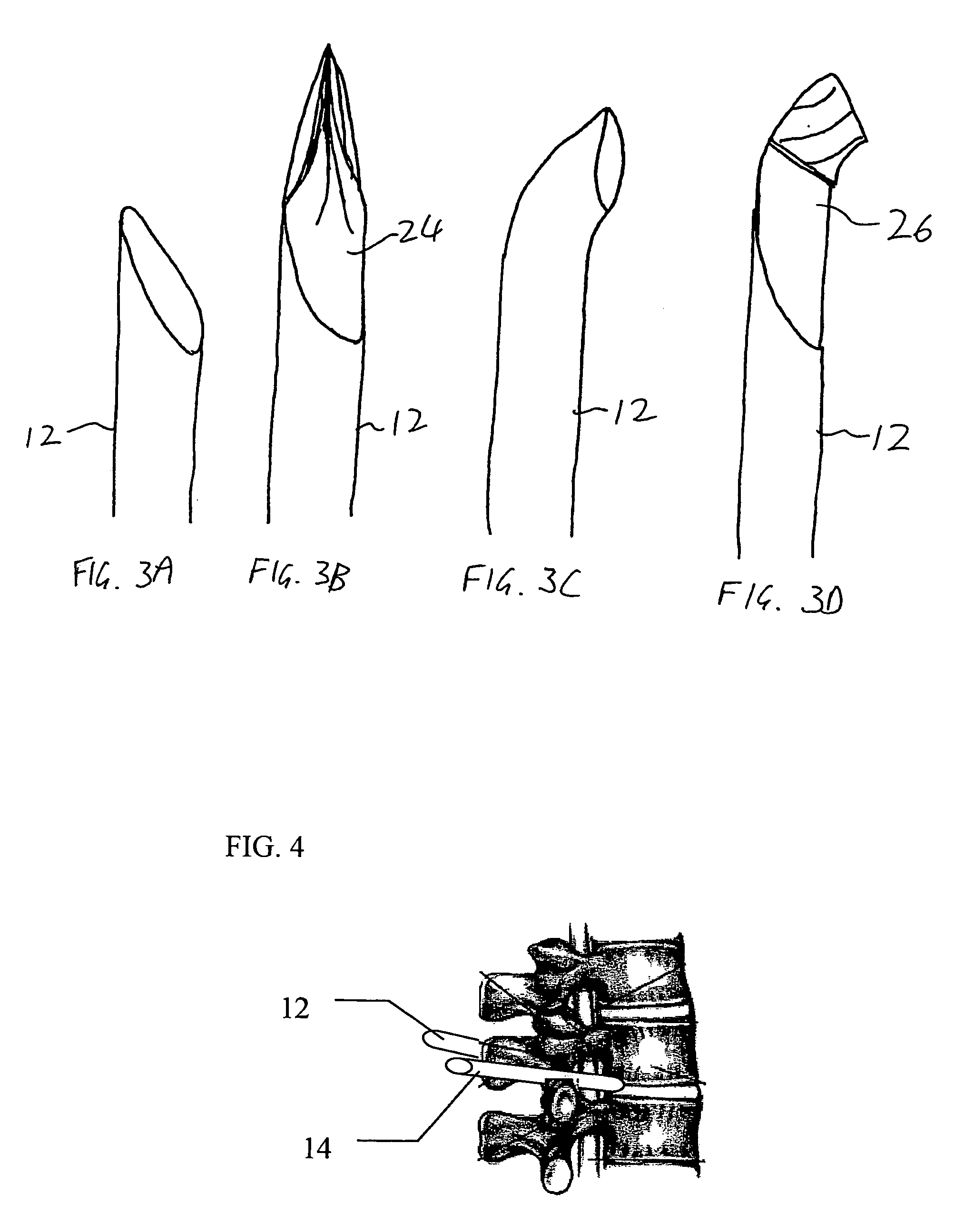
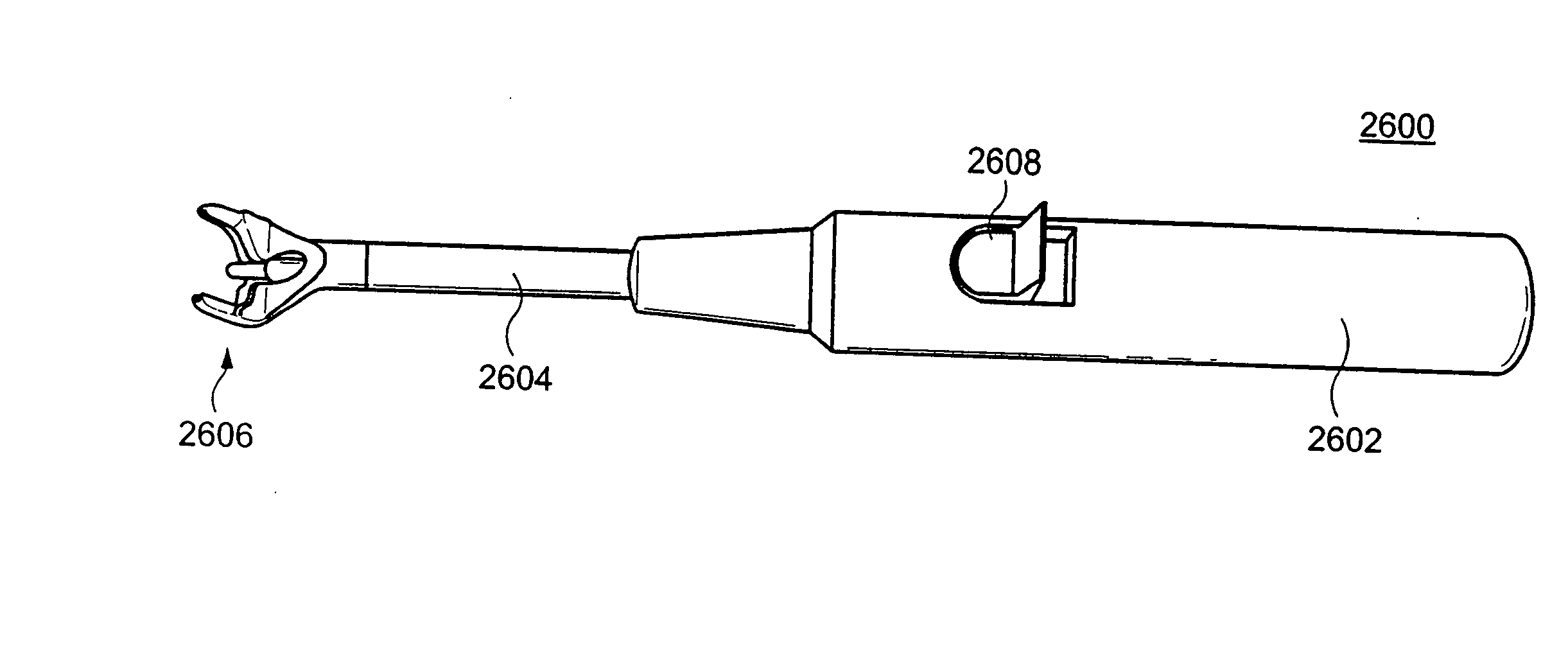
Tools for Percutaneous Spinal Ligament Decompression and Device for Supporting Same
InactiveUS20070055263A1Reduce stenosisVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsExcision instrumentsSpinal ligamentsSpinal column
A device for providing percutaneous access to a surgical site. In an embodiment, the device comprises a handle. In addition, the device comprises a bone-cutting member extending from the handle, wherein the bone-cutting member includes a handle end fixed to the handle and a cutting end. Further, the device comprises a portal including a first end, a second end, and a through bore extending therebetween, wherein the bone-cutting member is disposed within the through bore and concentric with the portal Still further, the portal has a first position with the second end releasably coupled to the handle and a second position with the second end released from the handle and the bone-cutting member.
Owner:VERTOS MEDICAL
Inter-cervical facet implant with implantation tool
Systems and method in accordance with the embodiments of the present invention can include an implant for positioning within a cervical facet joint for distracting the cervical spine, thereby increasing the area of the canals and openings through which the spinal cord and nerves must pass, and decreasing pressure on the spinal cord and / or nerve roots. The implant can be inserted laterally or posteriorly.
Owner:KYPHON
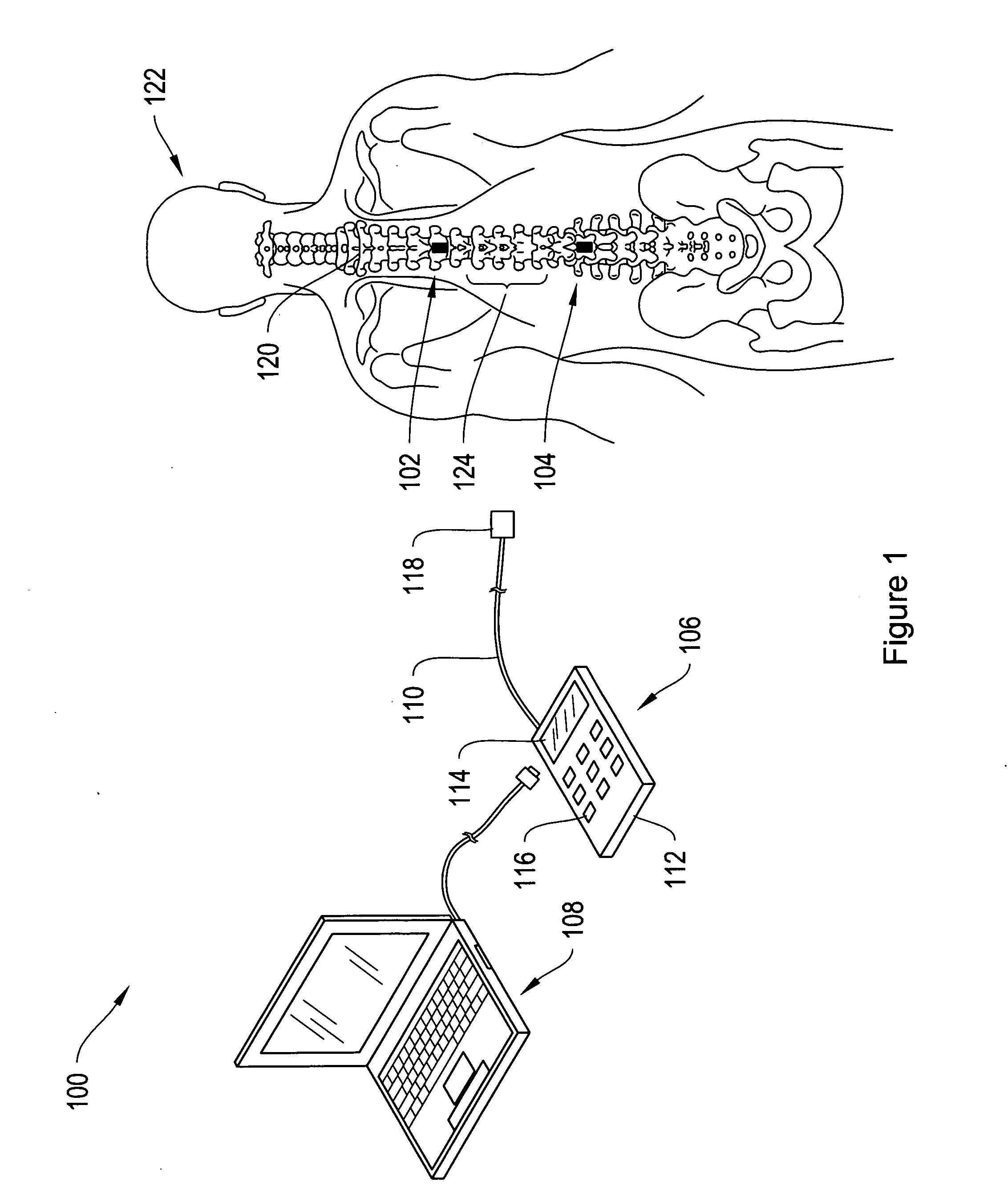
Method and apparatus for controlling a neural stimulus
ActiveUS20140236257A1Avoid misalignmentControlled levelSpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringMedicineSpinal cord
An implantable device applies and controls a neural stimulus. The device has a plurality of electrodes, and a stimulus source for providing a stimulus to be delivered from the electrodes to a neural pathway in order to evoke an action potential on the neural pathway, such as the spinal cord. A control unit controls application of a neural stimulus as defined by a set of parameter values and measures via measurement circuitry an evoked neural compound action potential response. The control unit determines from the measured evoked response a feedback variable, and compares it to a therapy map. The therapy map defines a therapeutic relationship of control variable to feedback variable. One or more of the stimulus parameter values are altered to effect the required change in the control variable. This process is performed iteratively to improve alignment of the feedback variable with the therapy map over time.
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL
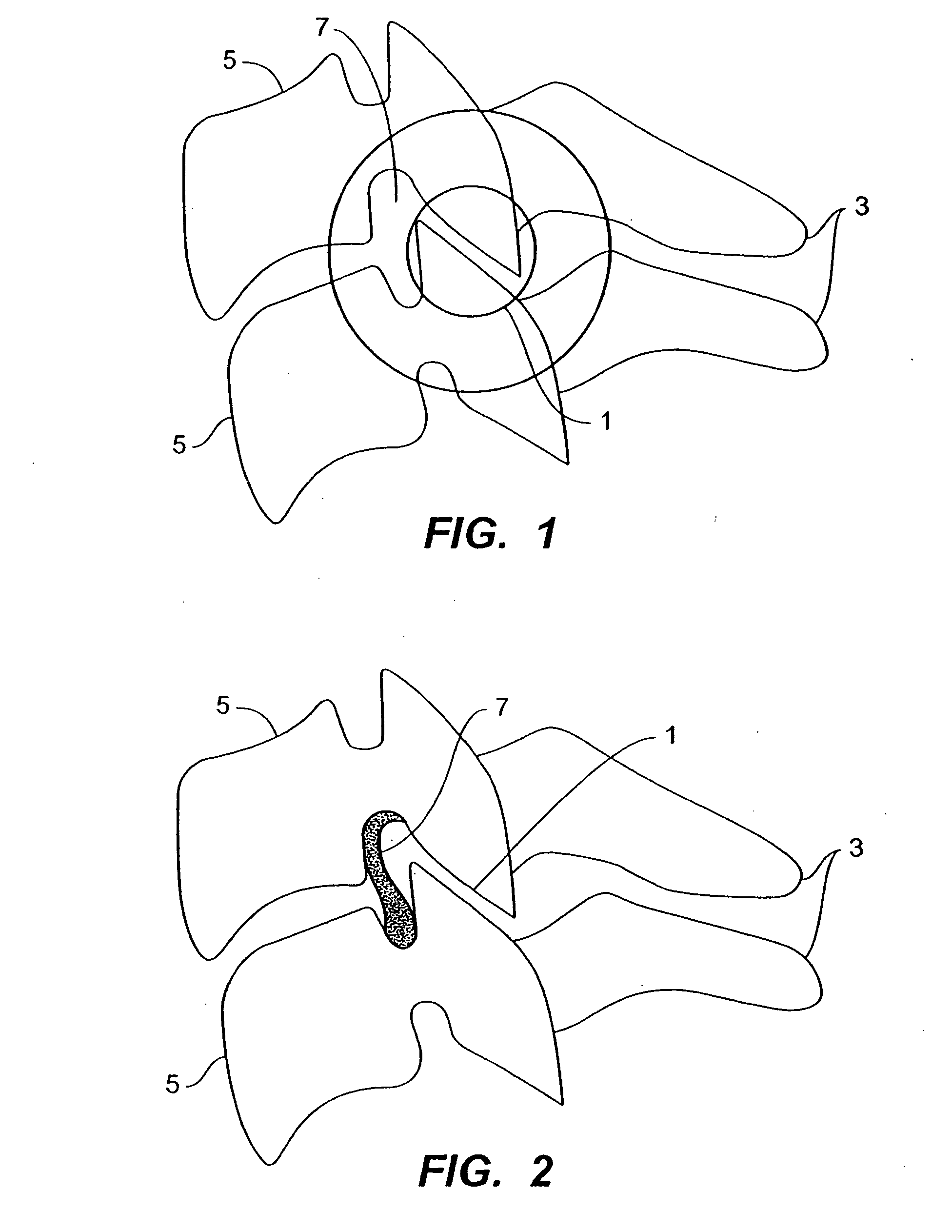
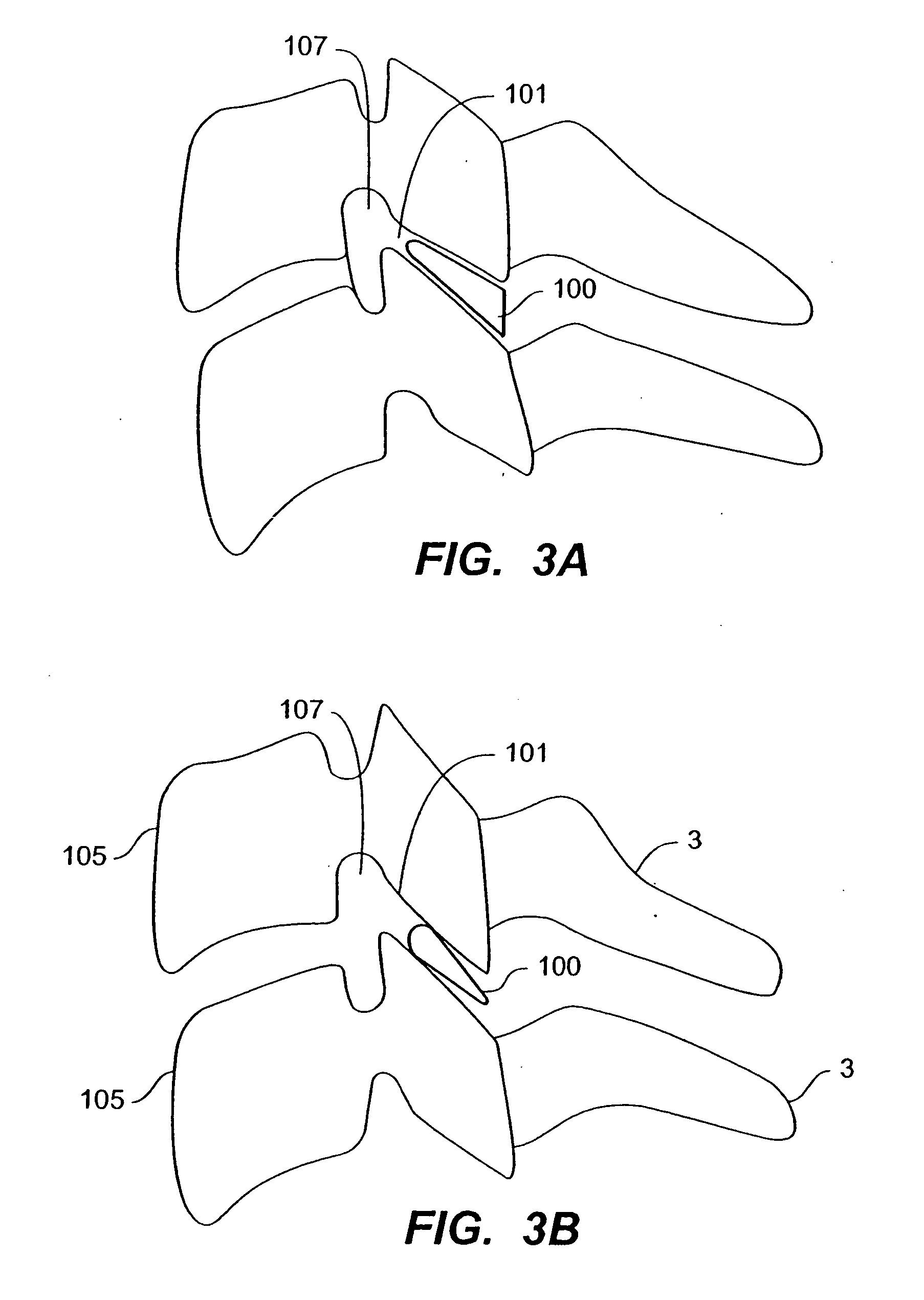
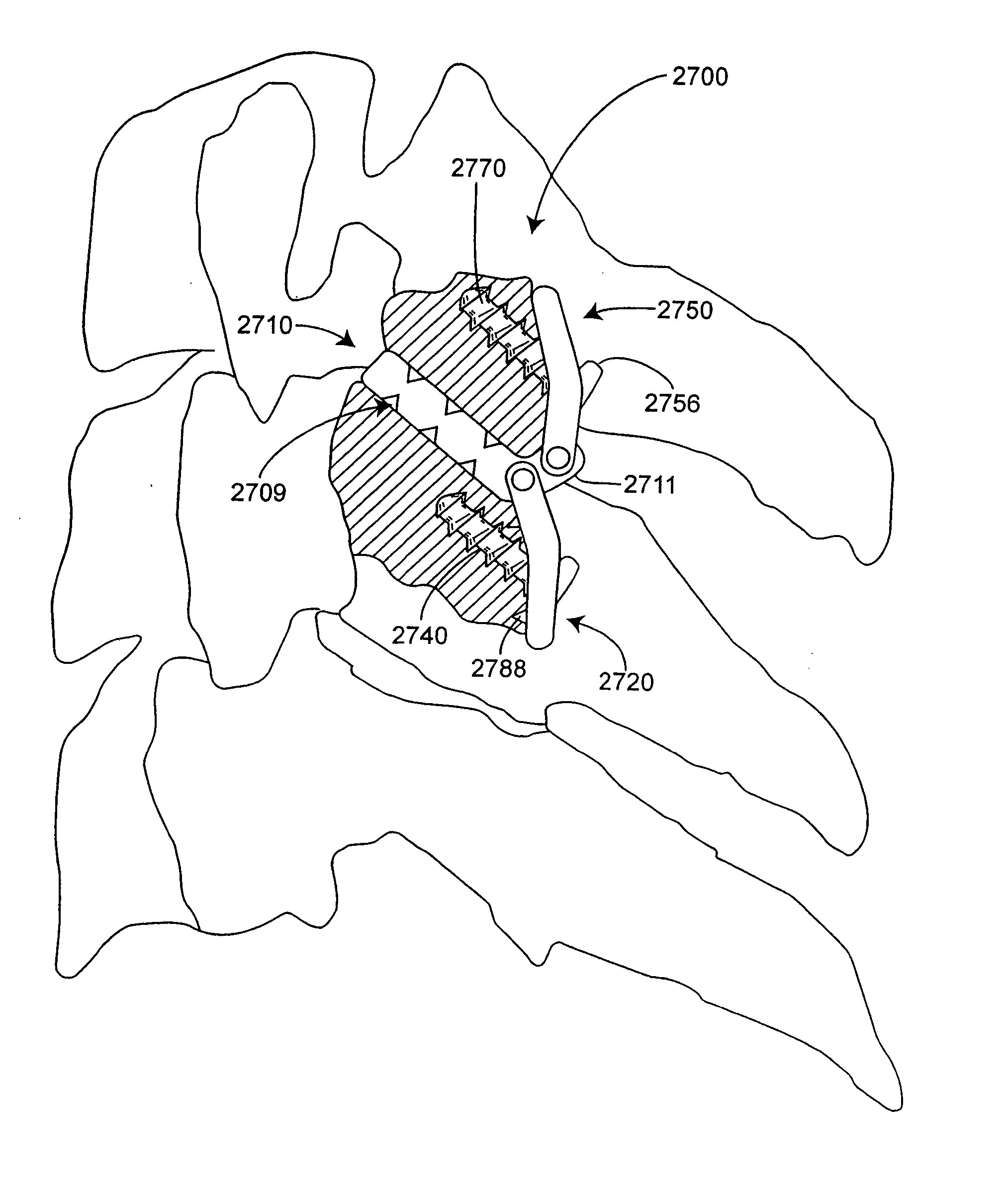
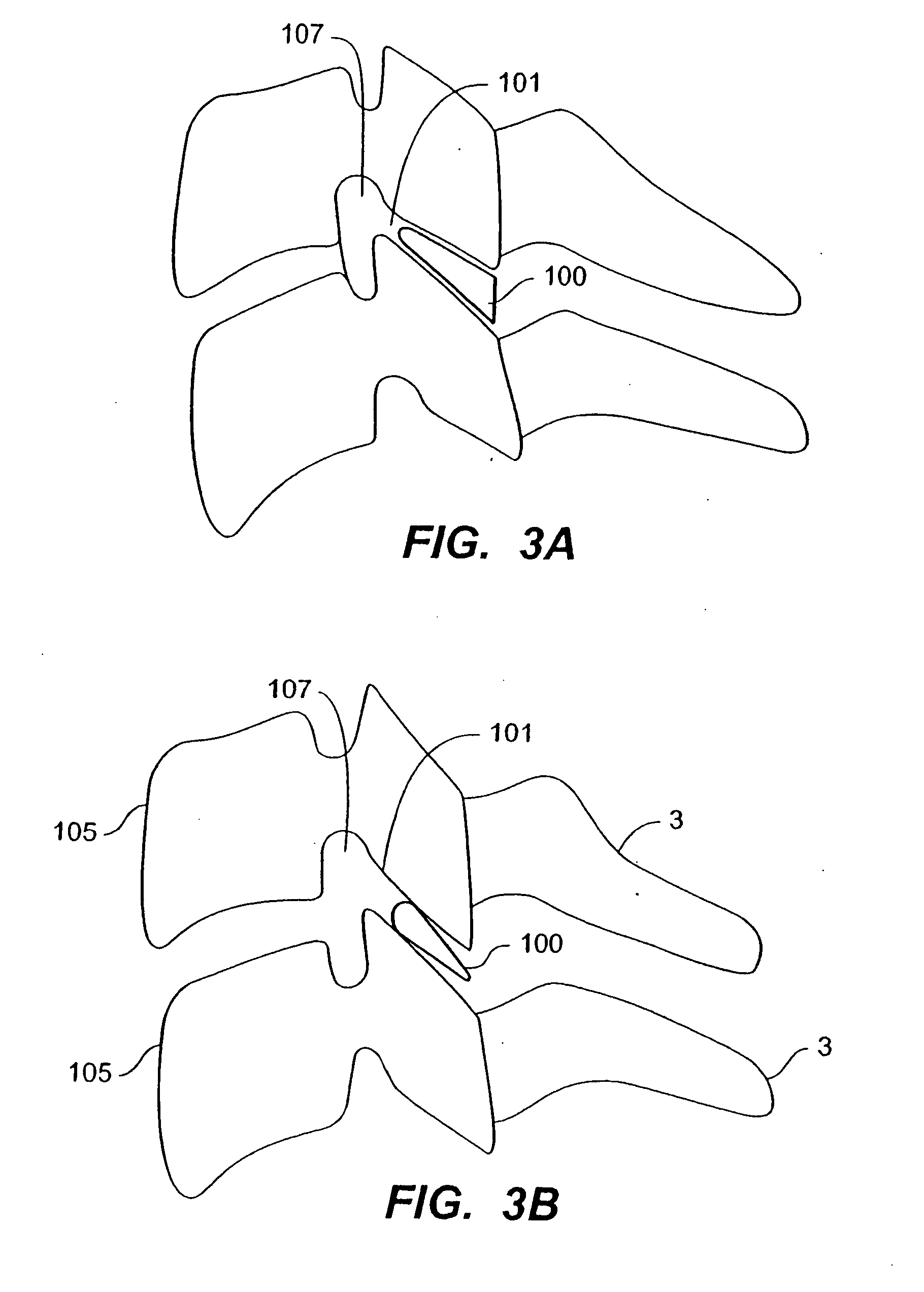
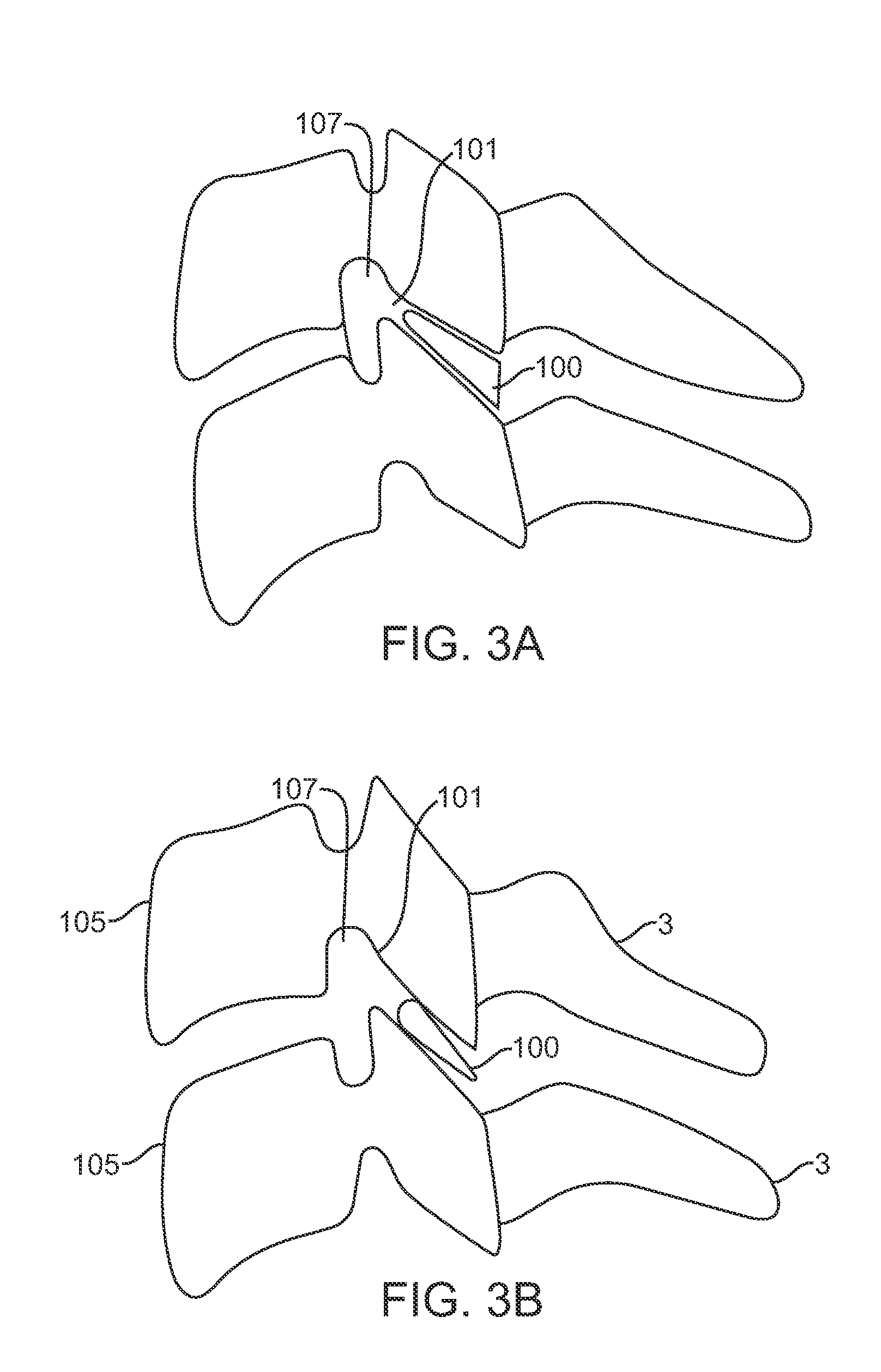
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion cage
InactiveUS20070260314A1Easy to insertShrink the necessary spaceSpinal implantsSpinal cordEngineering
A cage to separate and support adjacent vertebrae in the spine that have undergone orthopedic spinal fusion procedures. The cage has first and second spacer members for insertion between adjacent vertebrae with a hinge located between the spacers. An advancing mechanism is located between the first and second spacer members that pivotally moves the first and second spacer members relative to each other at an angle which facilitates the insertion of the cage around the spinal cord. After insertion, the advancing mechanism is operable to position the first and second spacer members in the desired position between the two adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:BIYANI ASHOK
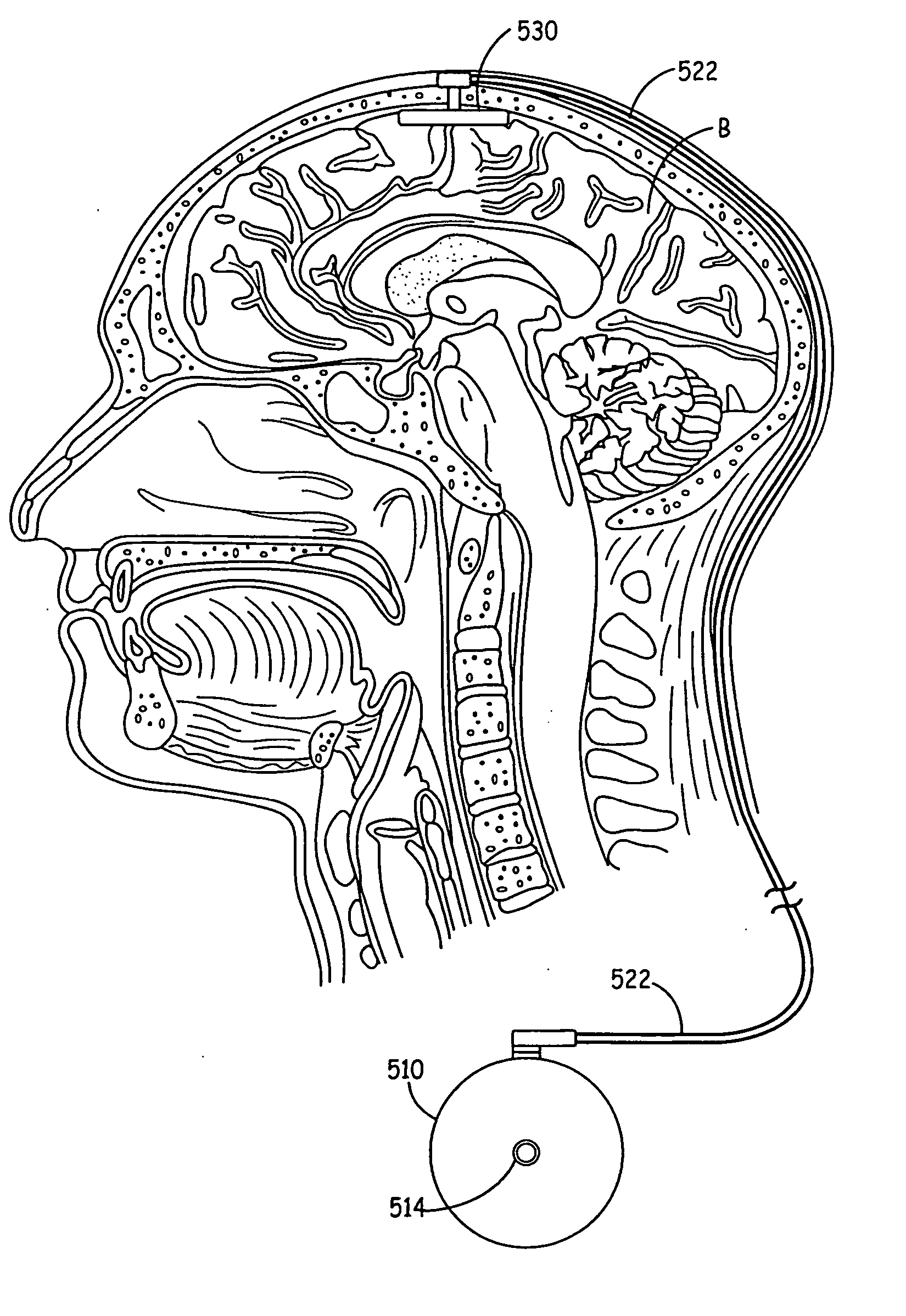
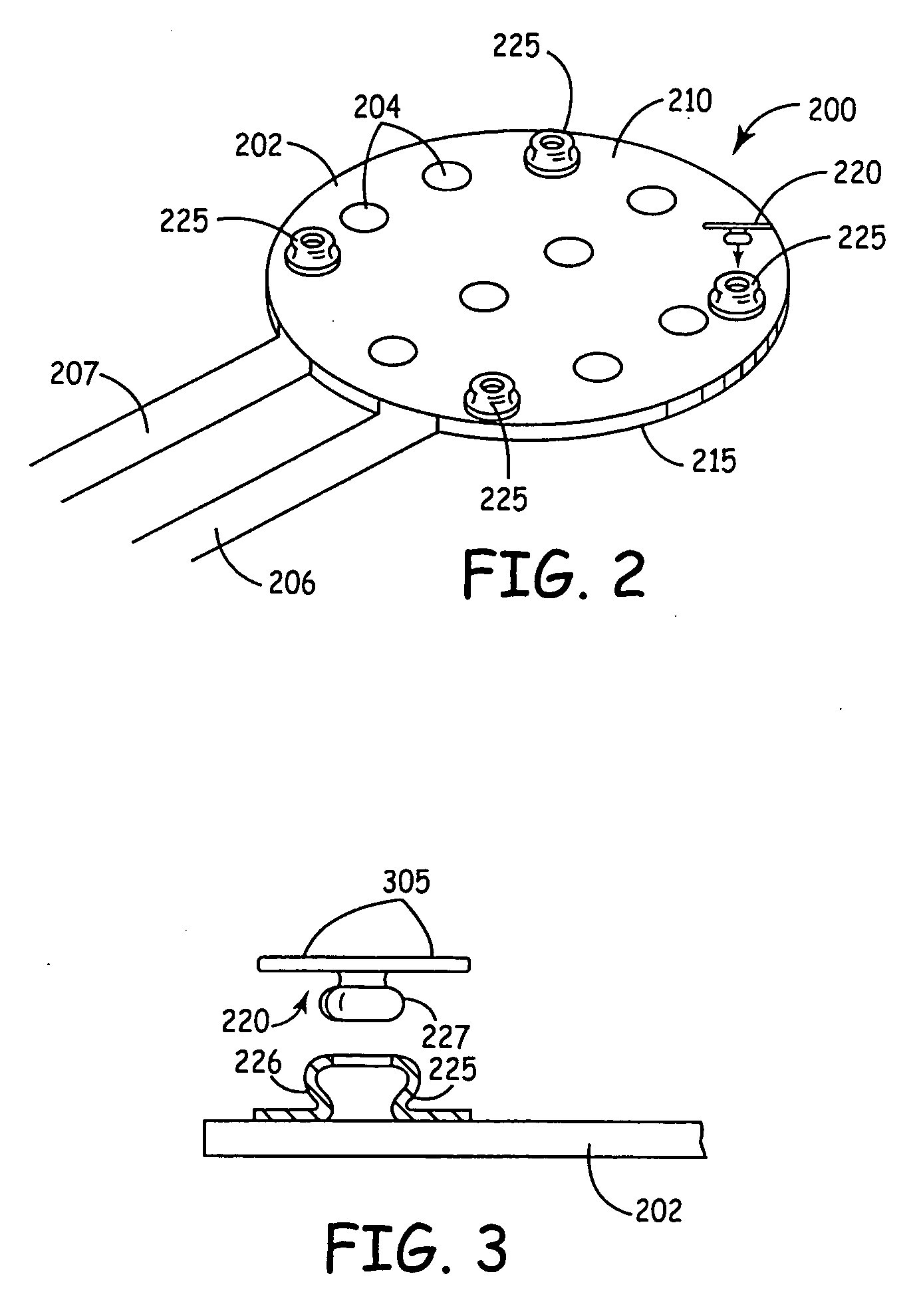
Anchoring of a medical device component adjacent a dura of the brain or spinal cord
A method and implantable medical device system capable of being anchored in a head or spinal cord of a patient. During implant, the dura of the patient is partially removed and the medical device component is placed on one side of the dura. The medical device component contains one or more anchors that mate with one or more nuts placed on the other side of the dura. The medical device component is thereby attached to the dura in a substantially fixed position relative to the head or spinal cord.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
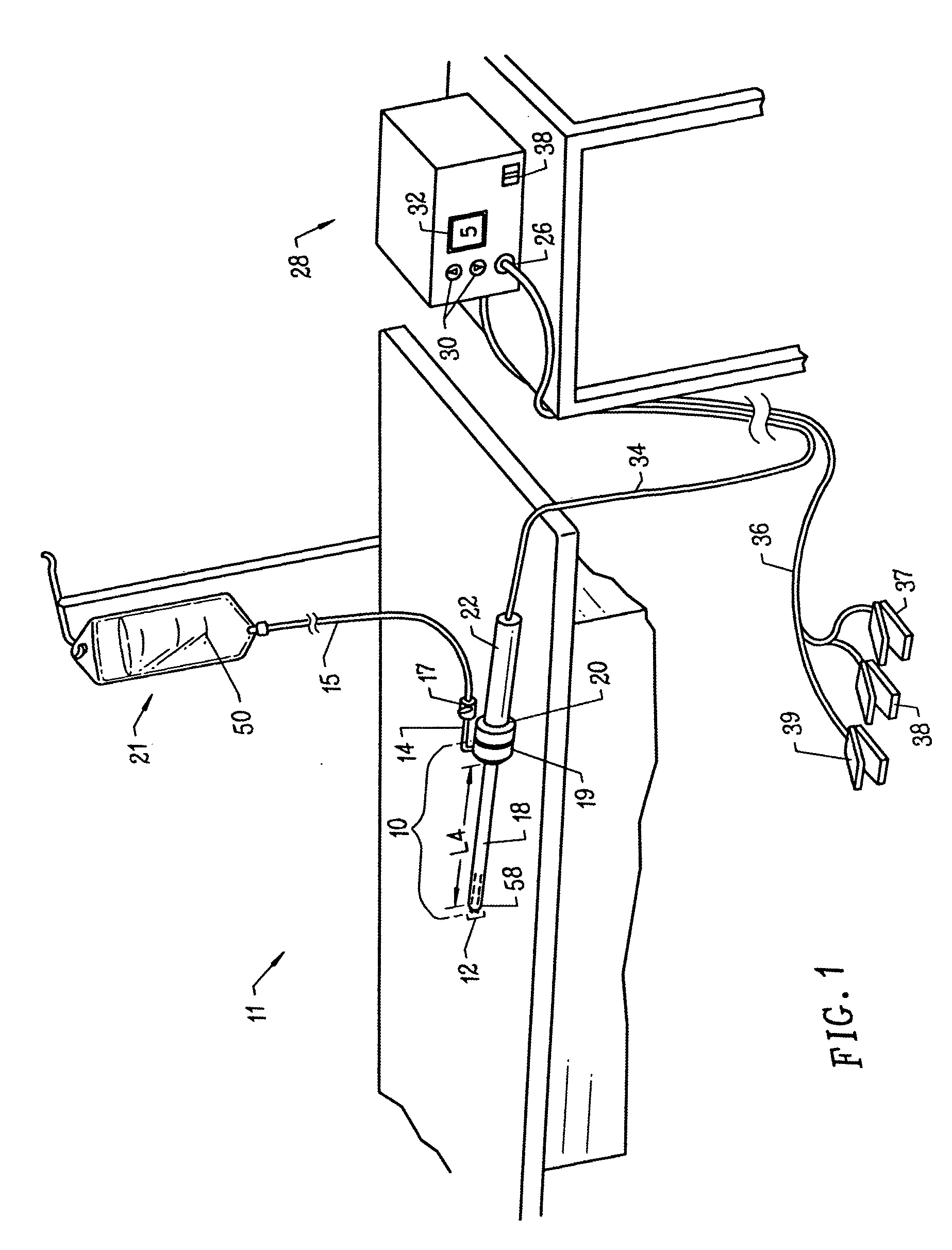
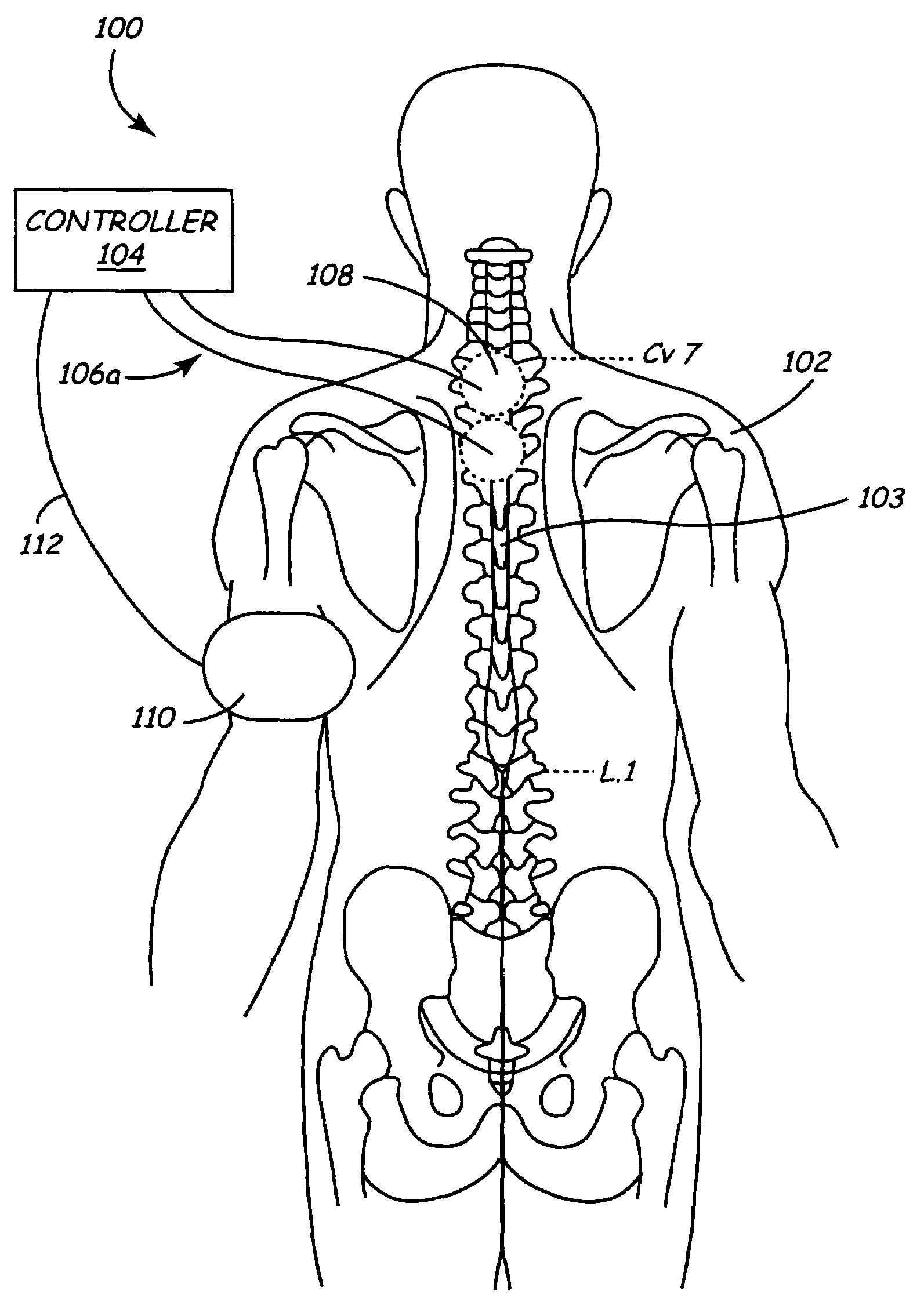
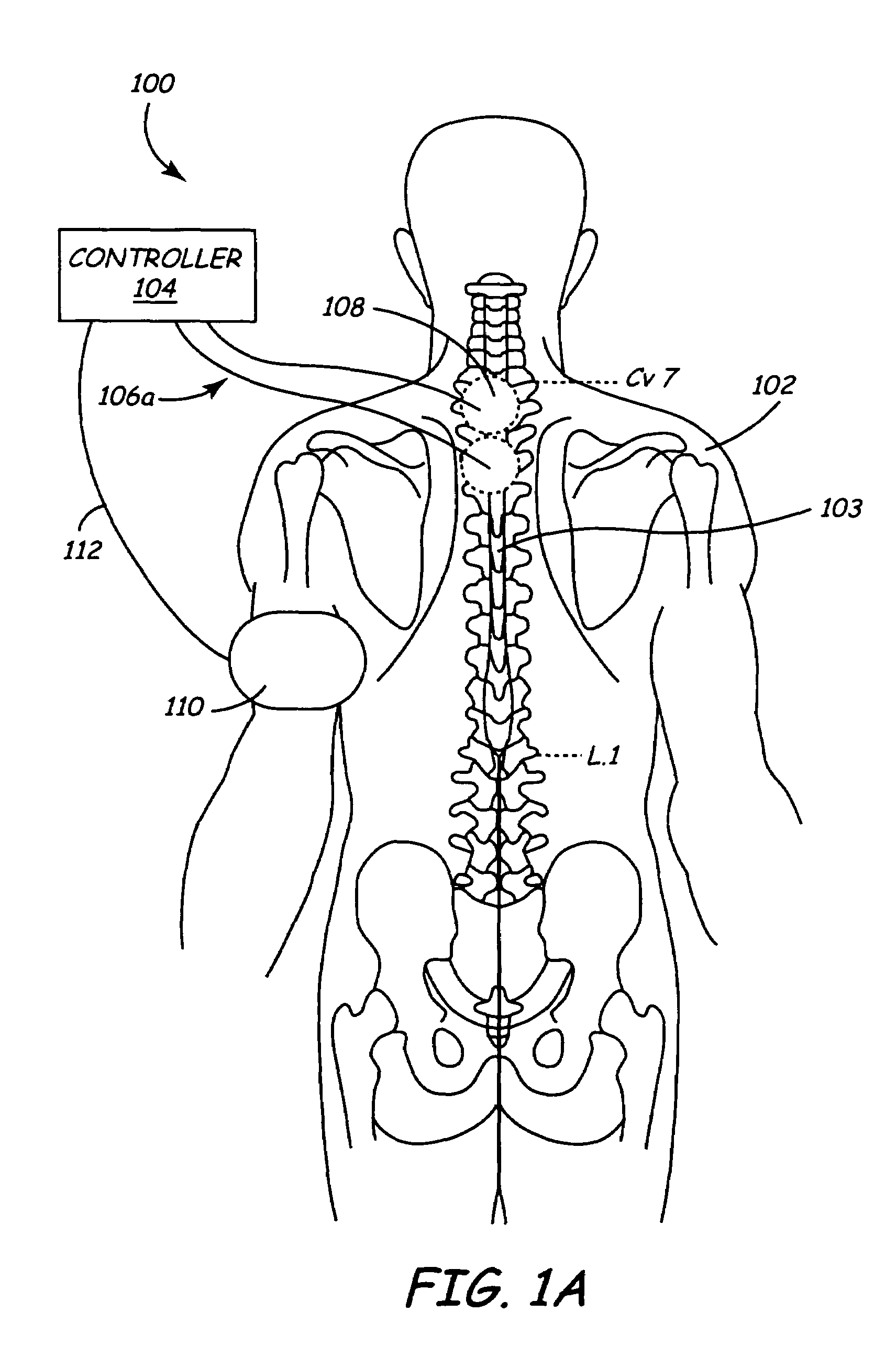
Multiprogrammable tissue stimulator and method
An electronic stimulation system is used to control pain over multiple regions of a patient's body. The system has one or more percutaneous leads, each having multiple electrodes, implanted within the patient's epidural space parallel to the axis of the spinal cord. The leads are connected to either a totally implanted system or a radio frequency system. The system is able to treat pain over different regions of a patient's body by “simultaneously” stimulating the patient with at least three different stimulation settings. “Simultaneous” stimulation involves sequentially stimulating the patient with the multiple stimulation settings such that the patient receives the cumulative effect of each stimulation setting, while not perceiving the transition from one stimulation setting to another.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Method and apparatus for controlling a neural stimulus
Owner:SALUDA MEDICAL PTY LTD
Devices and methods for optimized neuromodulation and their application
InactiveUS20160001096A1Reduce image distortionLow costUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySpinal cord
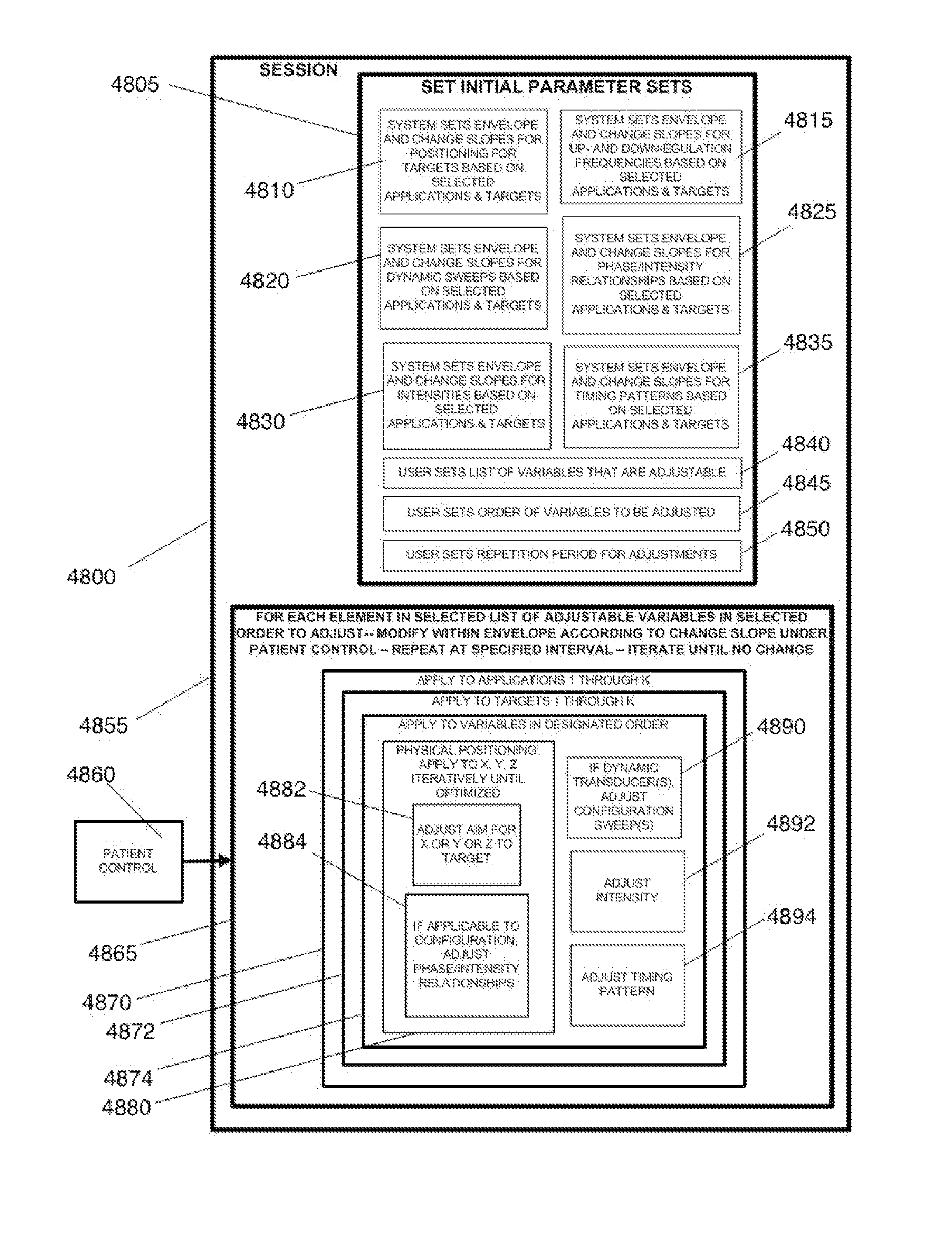
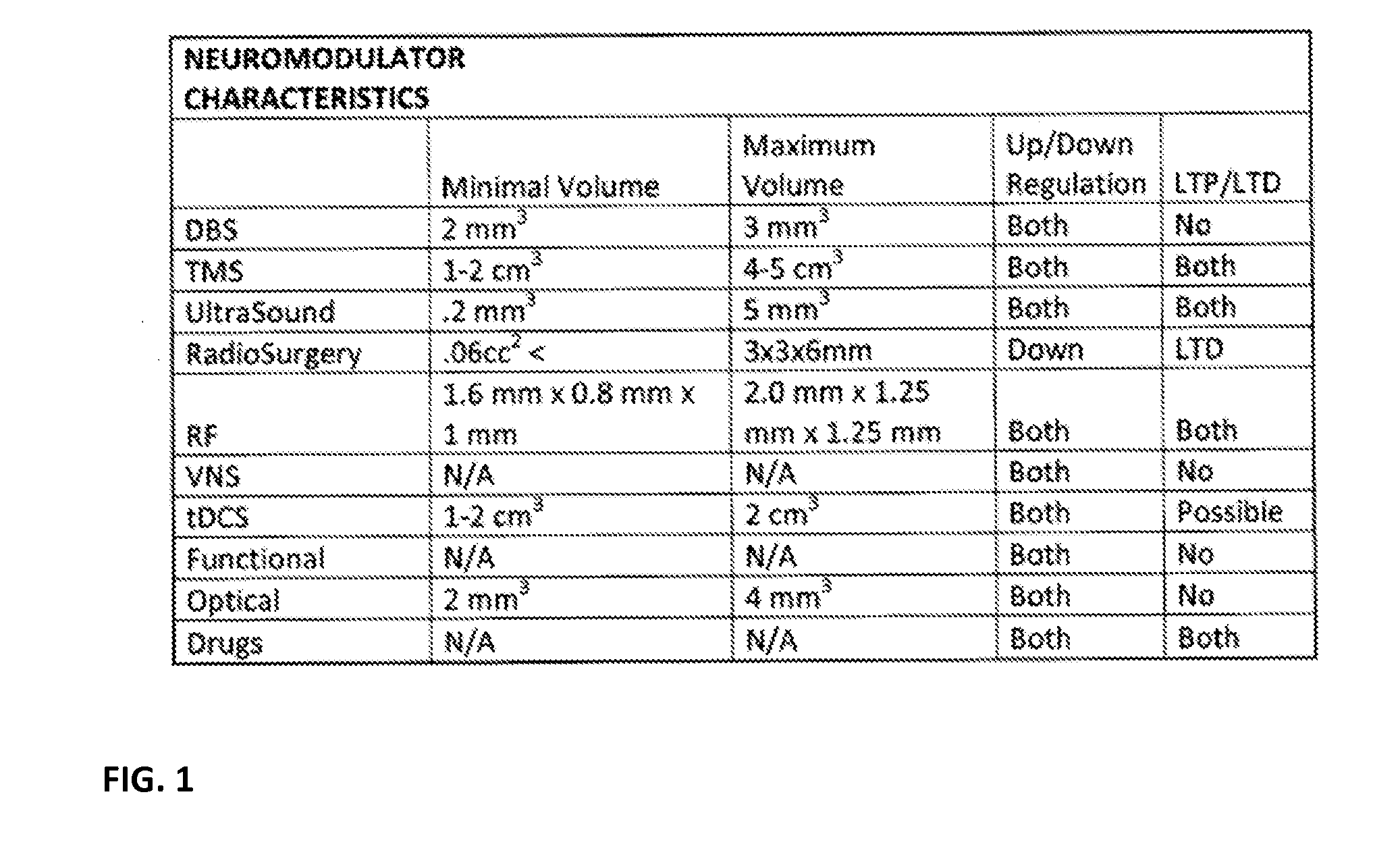
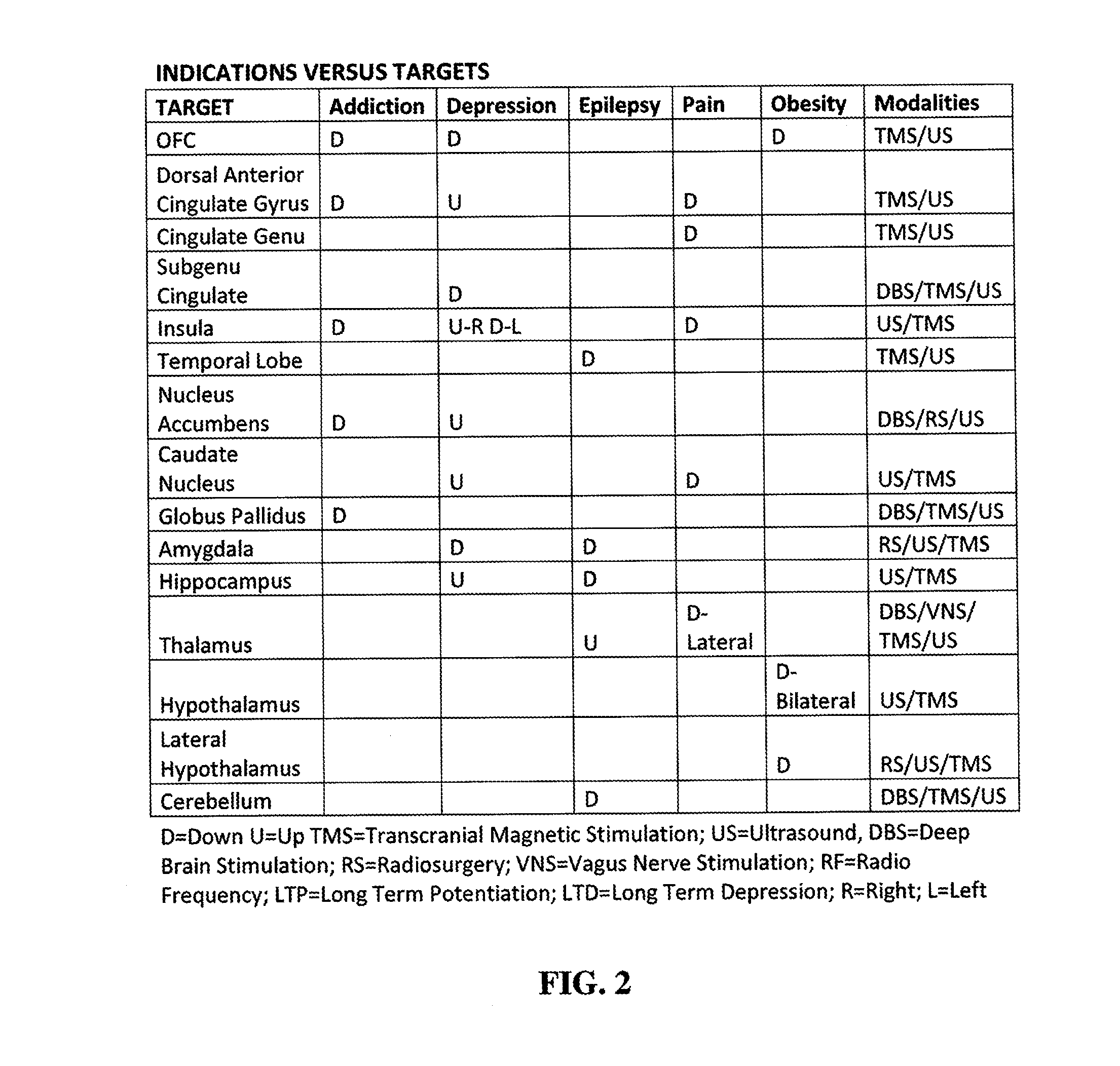
Disclosed are methods and systems for optimized deep or superficial deep-brain stimulation using multiple therapeutic modalities impacting one or multiple points in a neural circuit to produce Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD). Also disclosed are methods for treatment of clinical conditions and obtaining physiological impacts. Also disclosed are: methods and systems for Guided Feedback control of non-invasive deep brain or superficial neuromodulation; patterned neuromodulation, ancillary stimulation, treatment planning, focused shaped or steered ultrasound; methods and systems using intersecting ultrasound beams; non-invasive ultrasound-neuromodulation techniques to control the permeability of the blood-brain barrier; non-invasive neuromodulation of the spinal cord by ultrasound energy; methods and systems for non-invasive neuromodulation using ultrasound for evaluating the feasibility of neuromodulation treatment using non-ultrasound / ultrasound modalities; neuromodulation of the whole head, treatment of multiple conditions, and method and systems for neuromodulation using ultrasound delivered in sessions.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Systems and methods for electrosurgical spine surgery
InactiveUS7462178B2Lower the volumeUse performanceSurgical needlesEndoscopesSpinal cordSurgical department
Methods and apparatus for selectively applying electrical energy to a target location within a patient's body, particularly including tissue in the spine. In a method of the invention high frequency (RF) electrical energy is applied to one or more active electrodes on an electrosurgical probe in the presence of an electrically conductive fluid to remove, contract or otherwise modify the structure of tissue targeted for treatment. In one aspect, a dura mater and spinal cord are insulated from the electrical energy by an insulator positioned on a non-active side of the probe. In another aspect, a plasma is aggressively formed in the electrically conductive fluid by delivering a conductive fluid to a distal end portion of the probe and aspirating the fluid from a location proximal of the return electrode. In another aspect, a distal end of an electrosurgical probe having at least one electrode on a biased, curved, bent, or steerable shaft is guided or steered to a target site within an intervertebral disc having a disc defect for treatment of tissue to be treated at the target site by the selective application of electrical energy thereto.
Owner:AOL LLC A DELAWARE LLC +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com