Patents
Literature
266 results about "Deep brain stimulation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
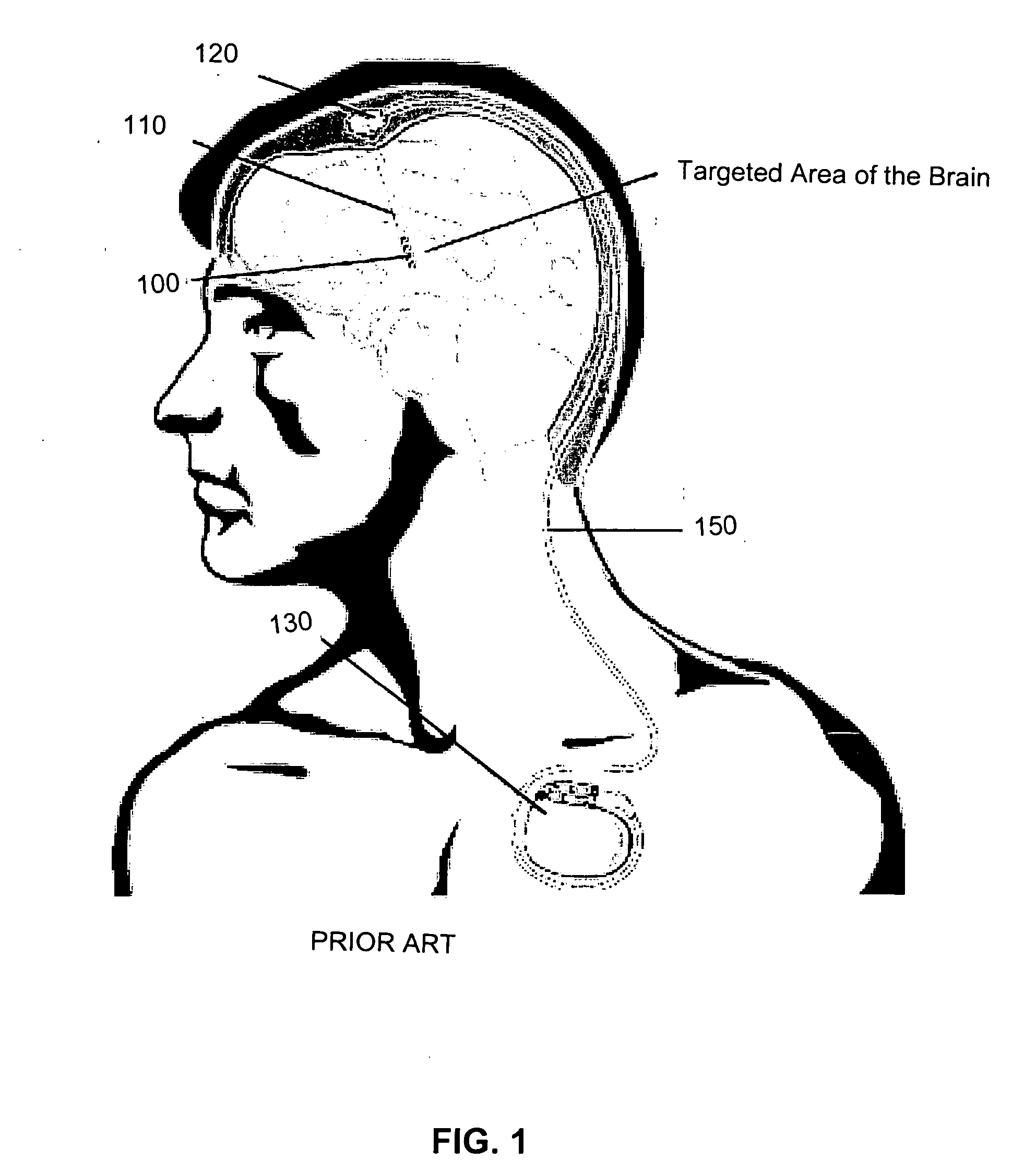
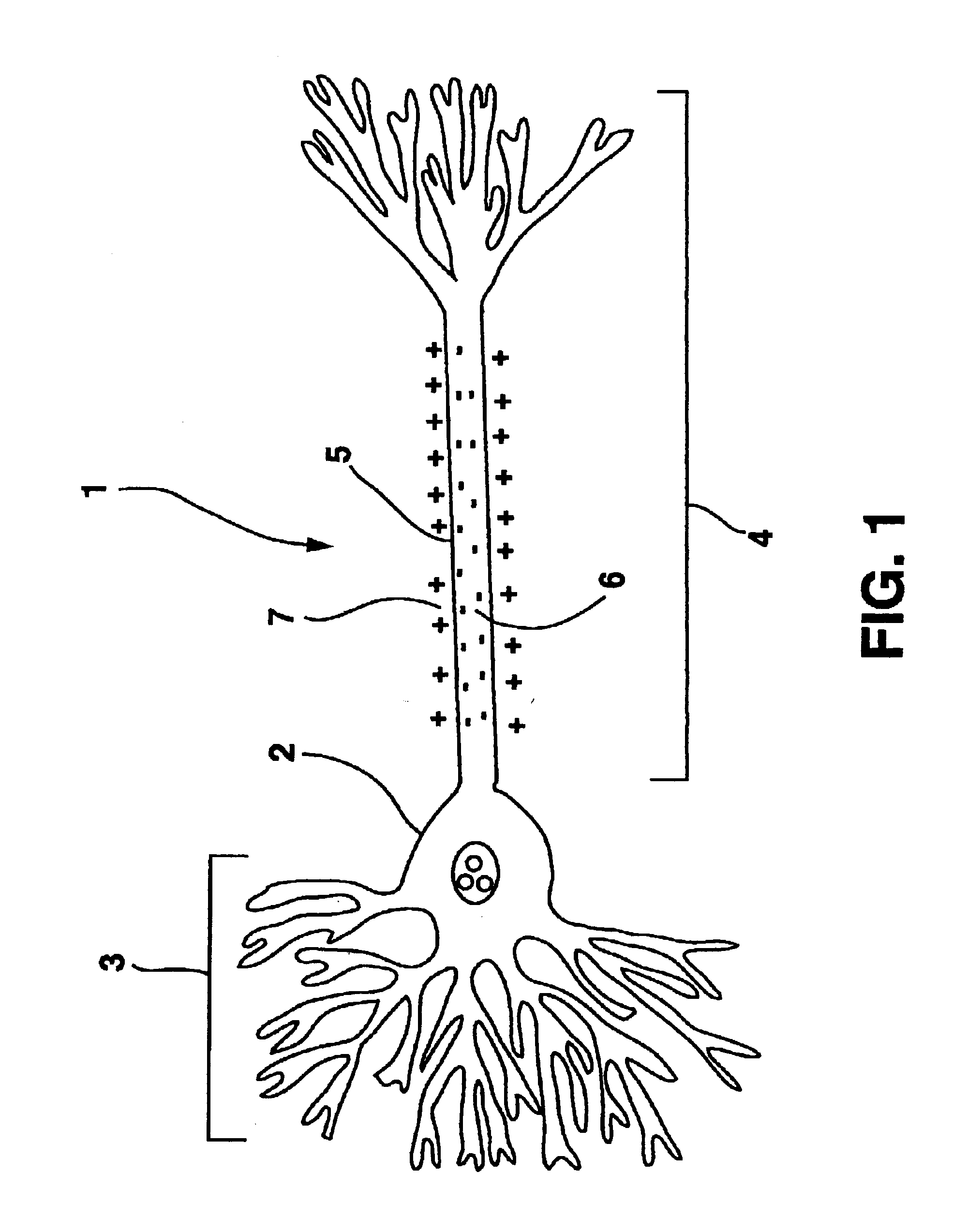
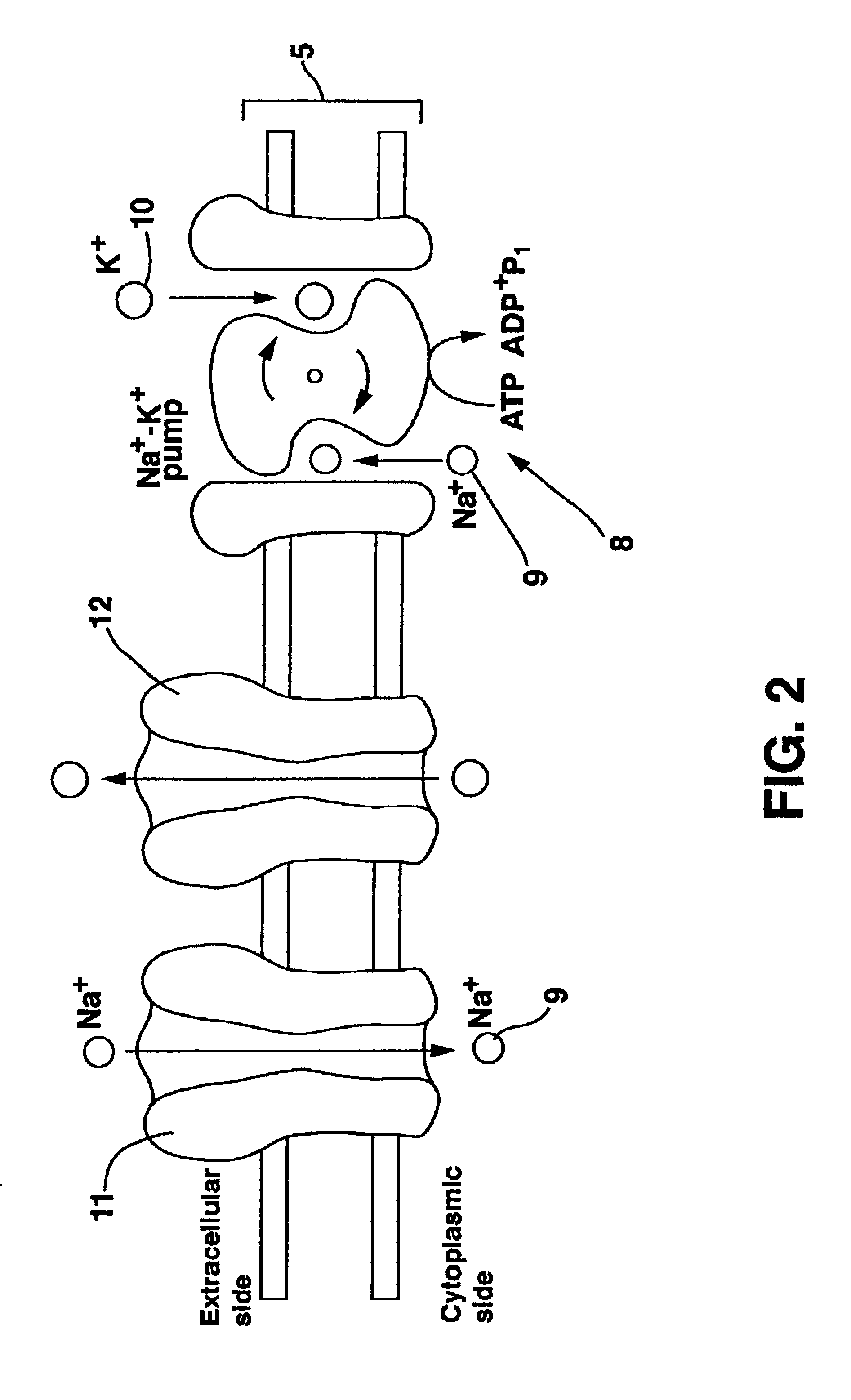
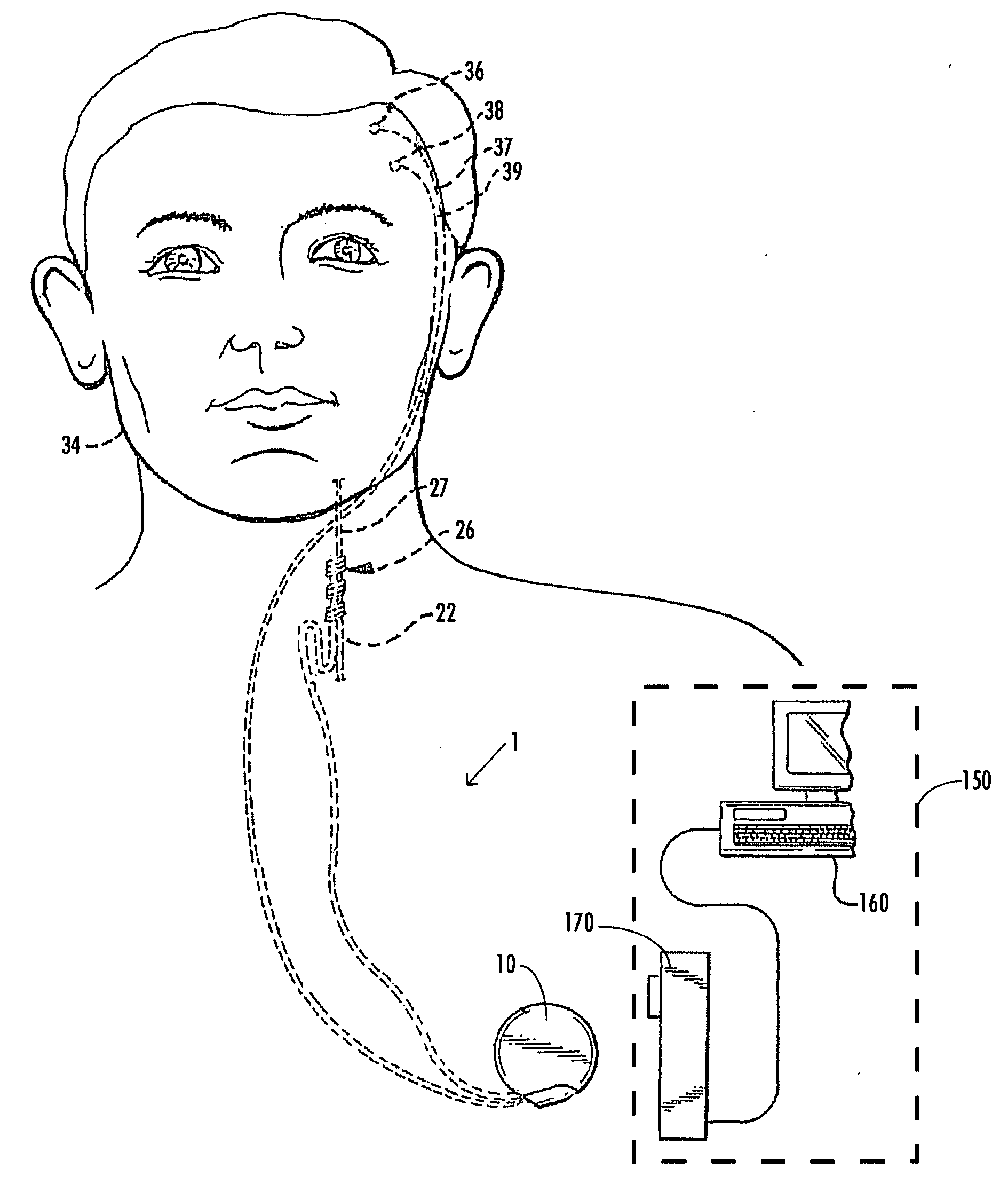
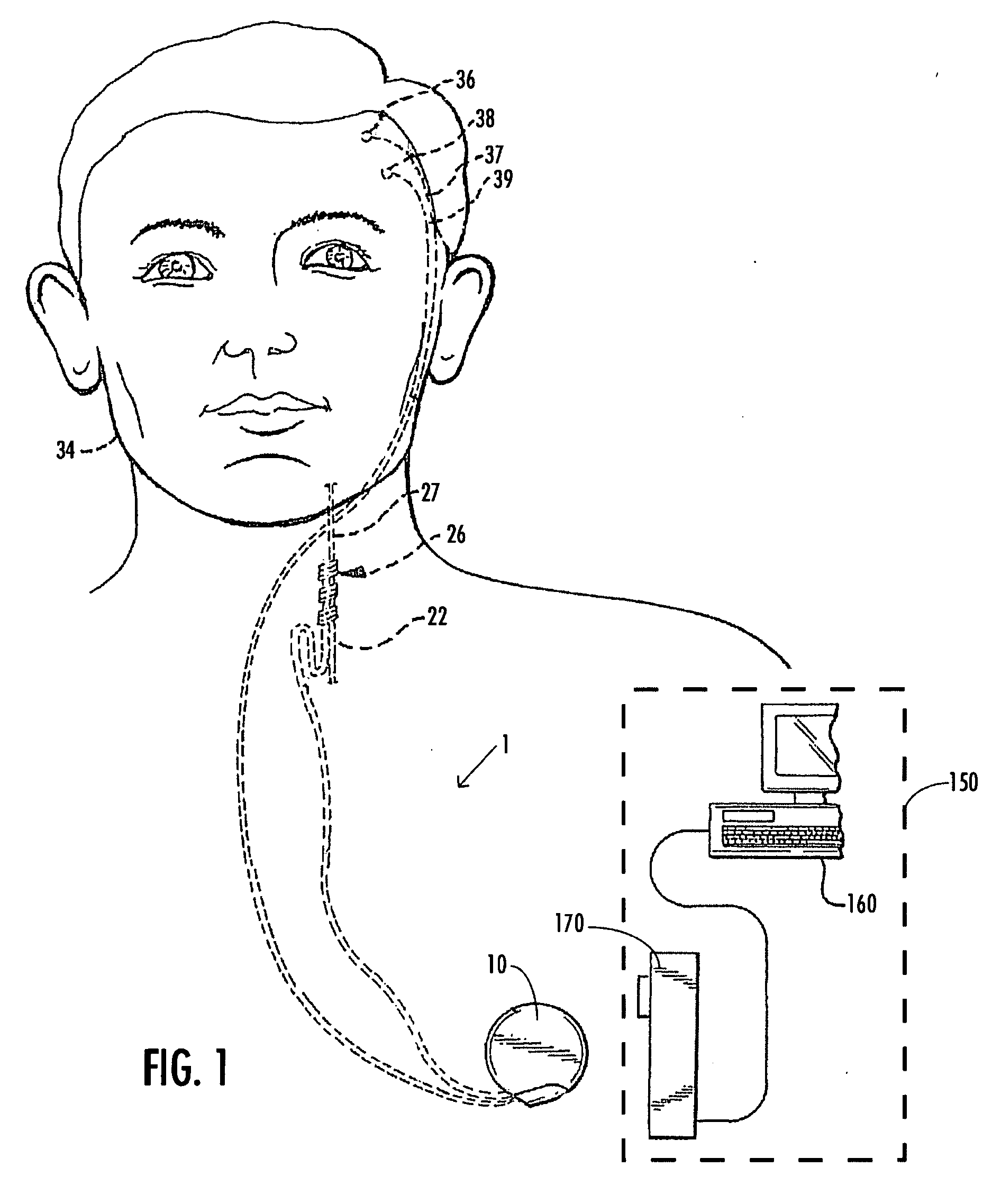
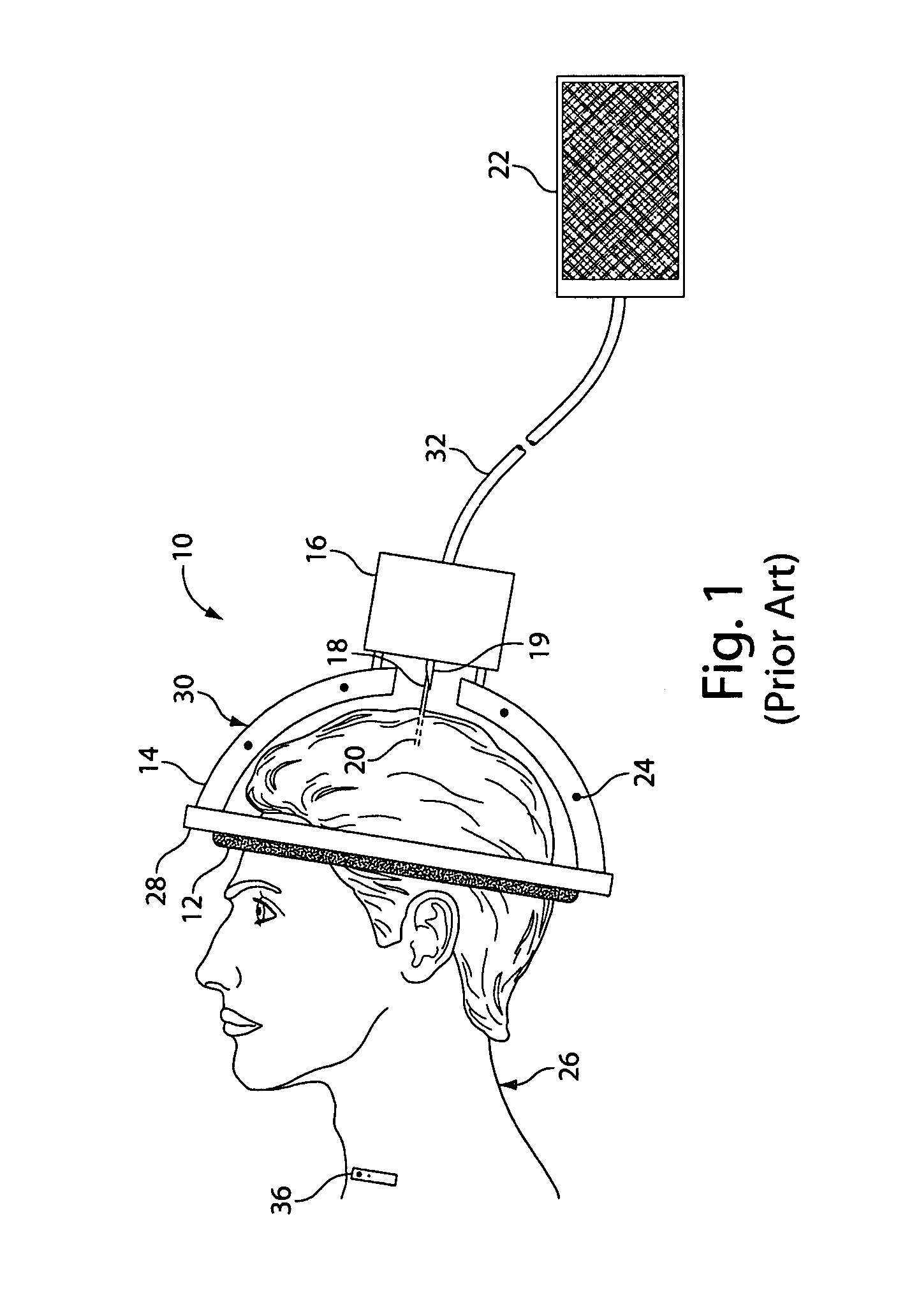
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a neurosurgical procedure involving the placement of a medical device called a neurostimulator (sometimes referred to as a 'brain pacemaker'), which sends electrical impulses, through implanted electrodes, to specific targets in the brain (brain nuclei) for the treatment of movement disorders, including Parkinson's disease, essential tremor, and dystonia. While its underlying principles and mechanisms are not fully understood, DBS directly changes brain activity in a controlled manner.
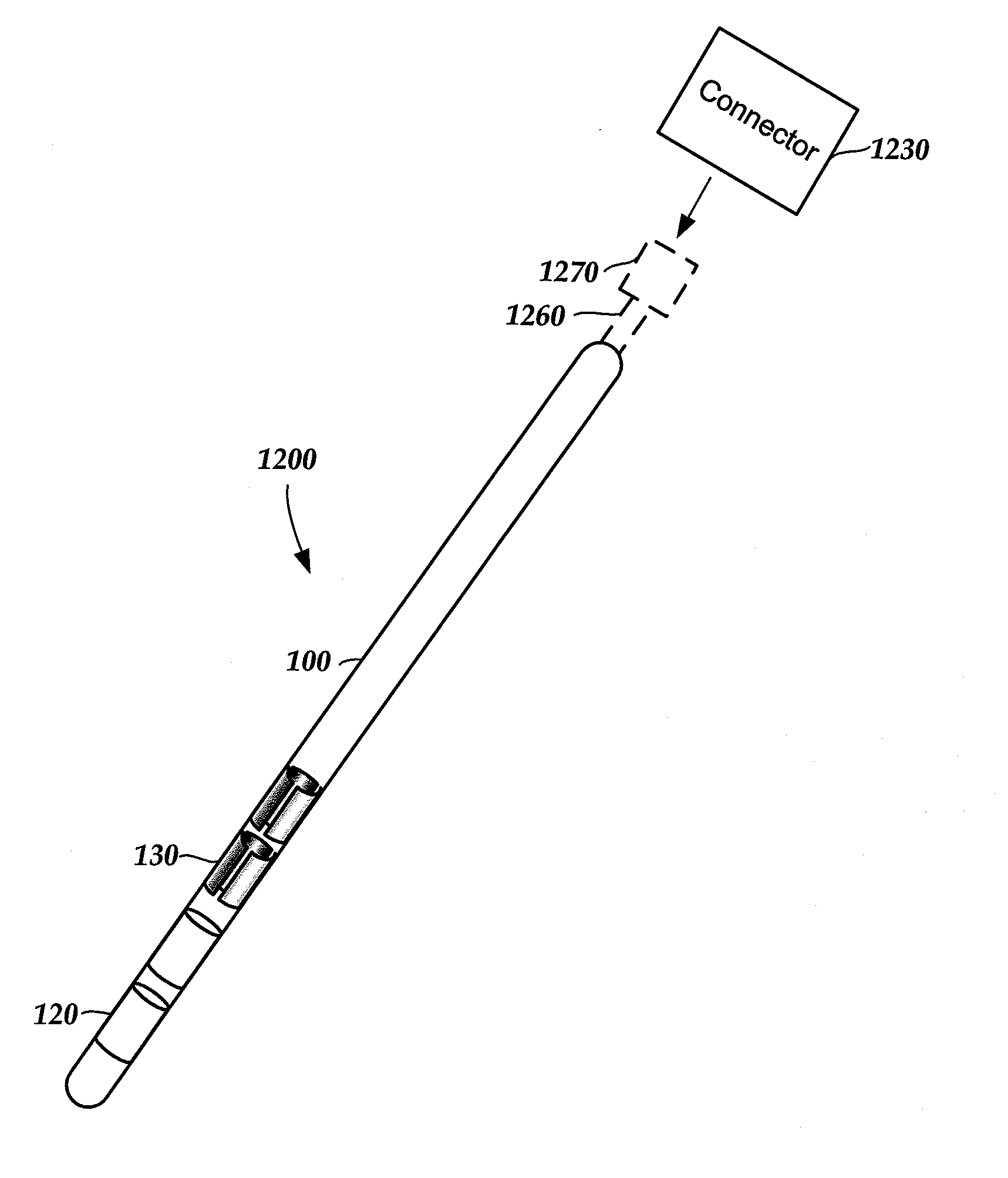
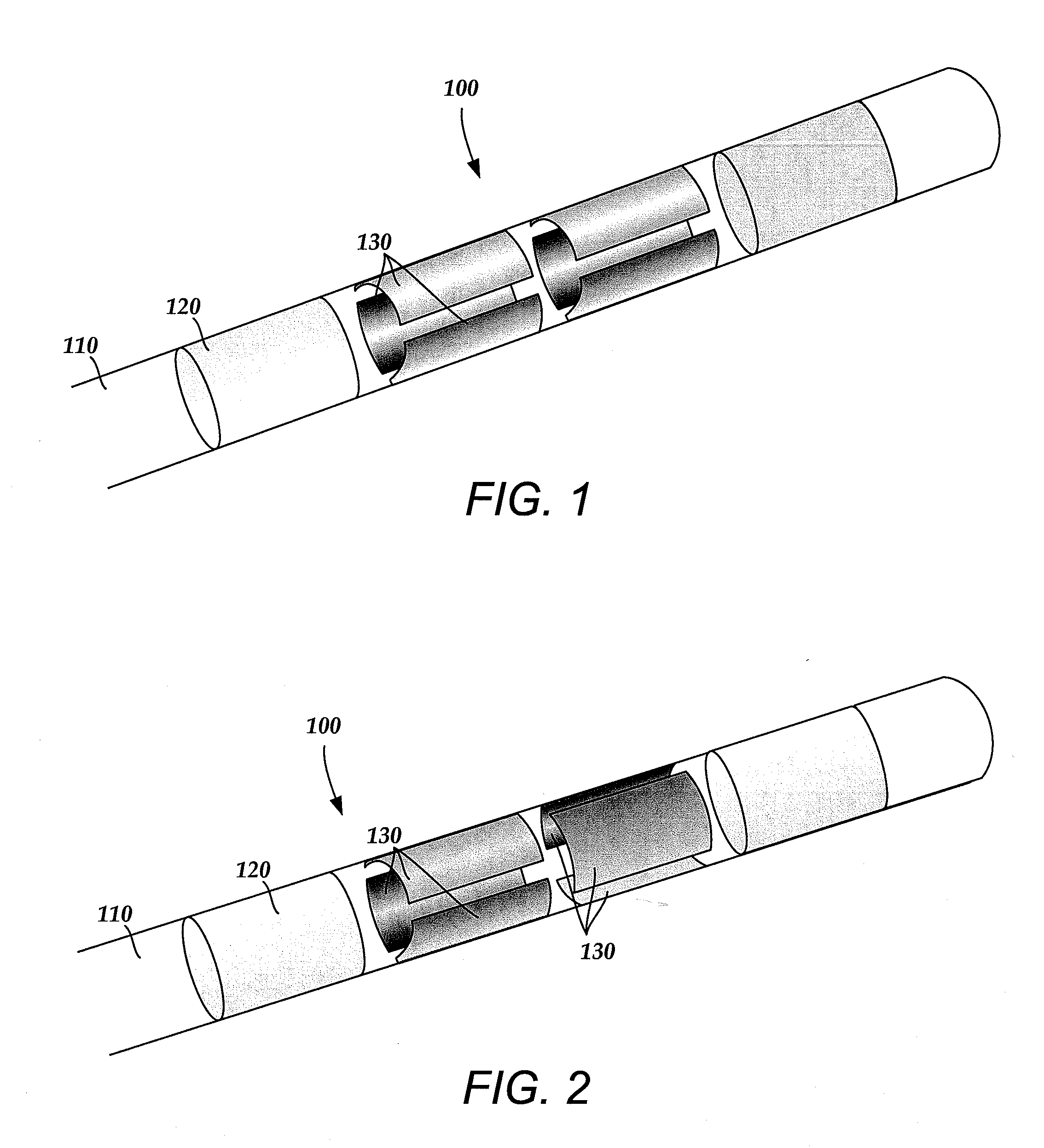
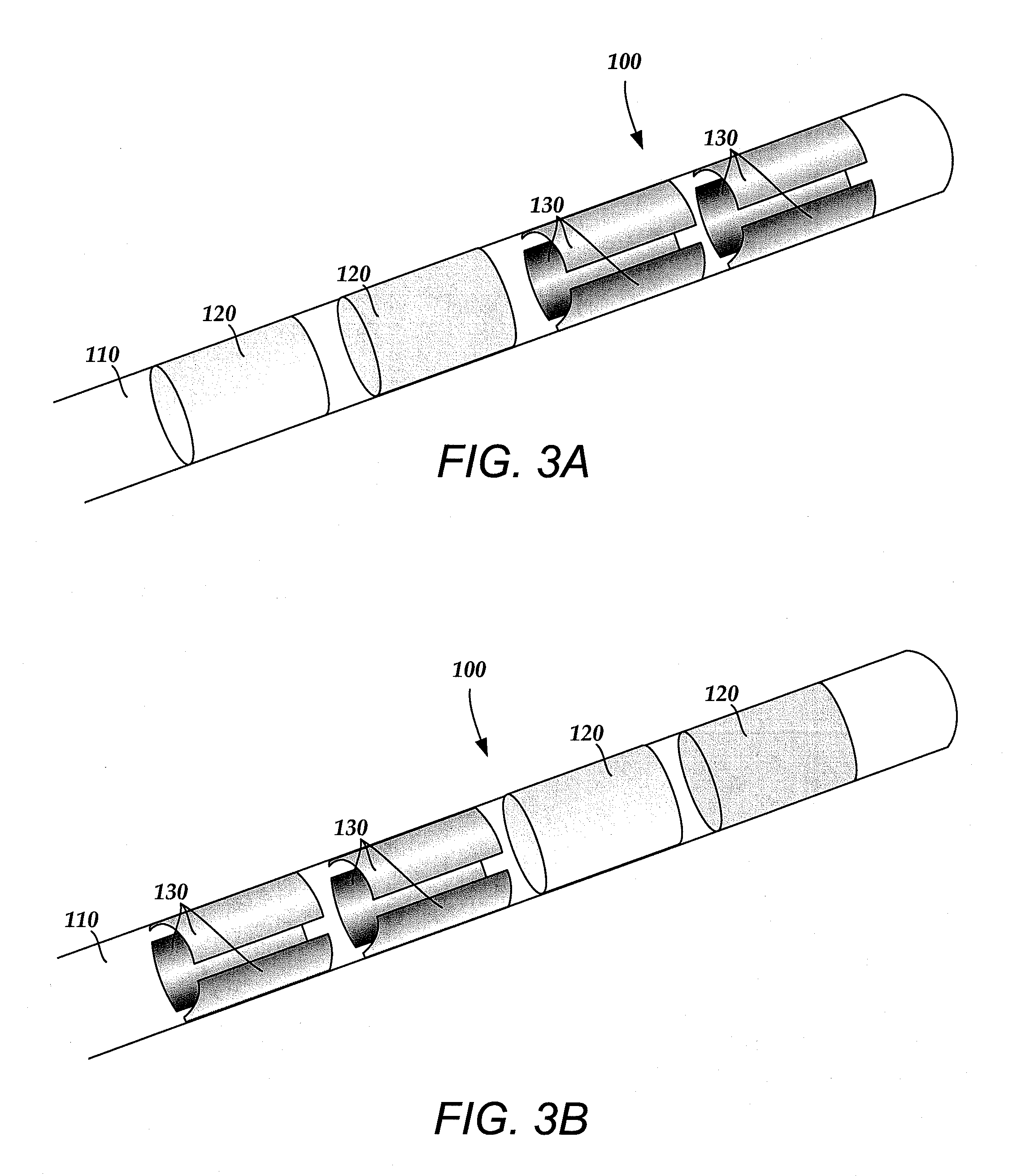
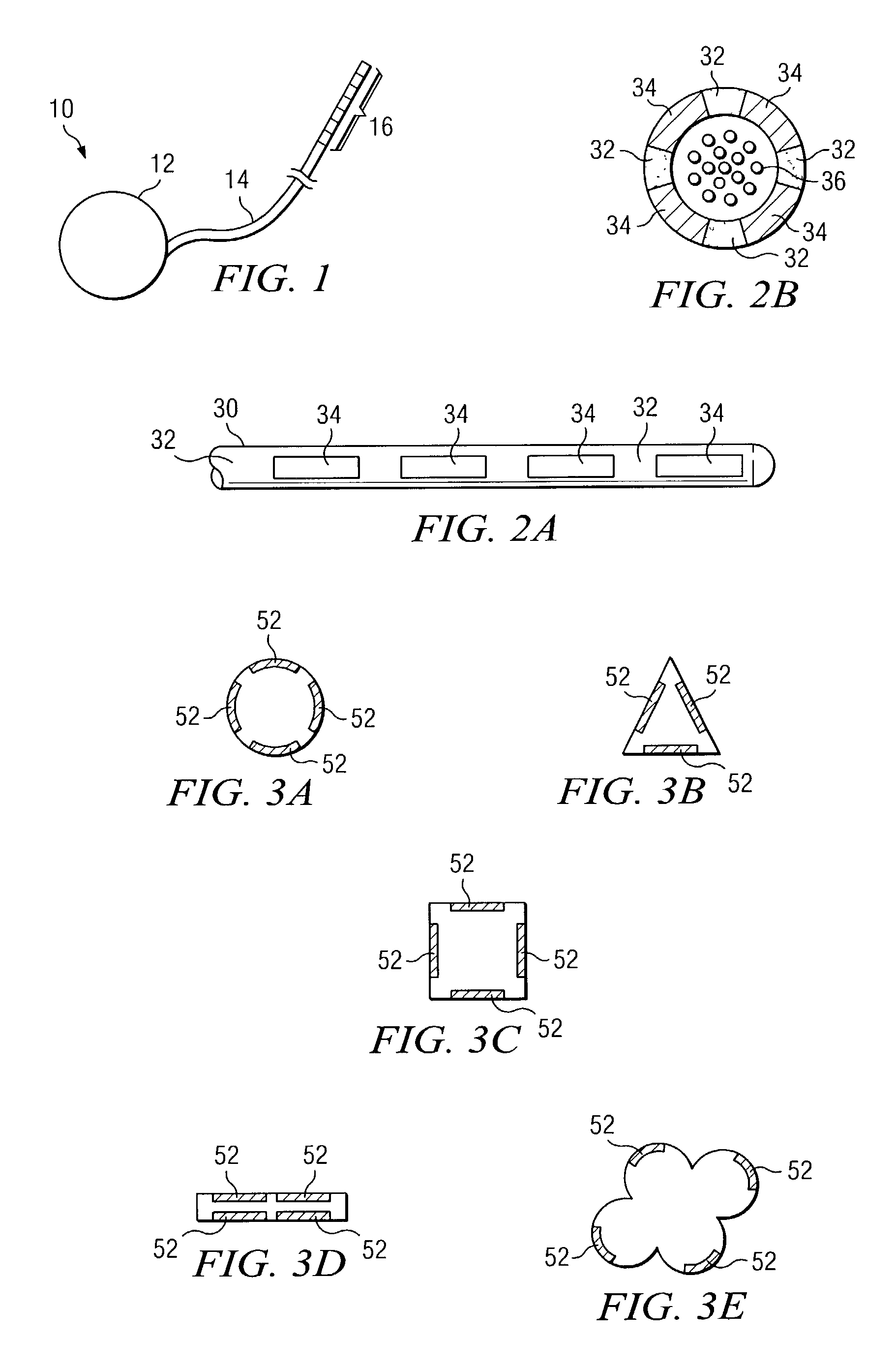
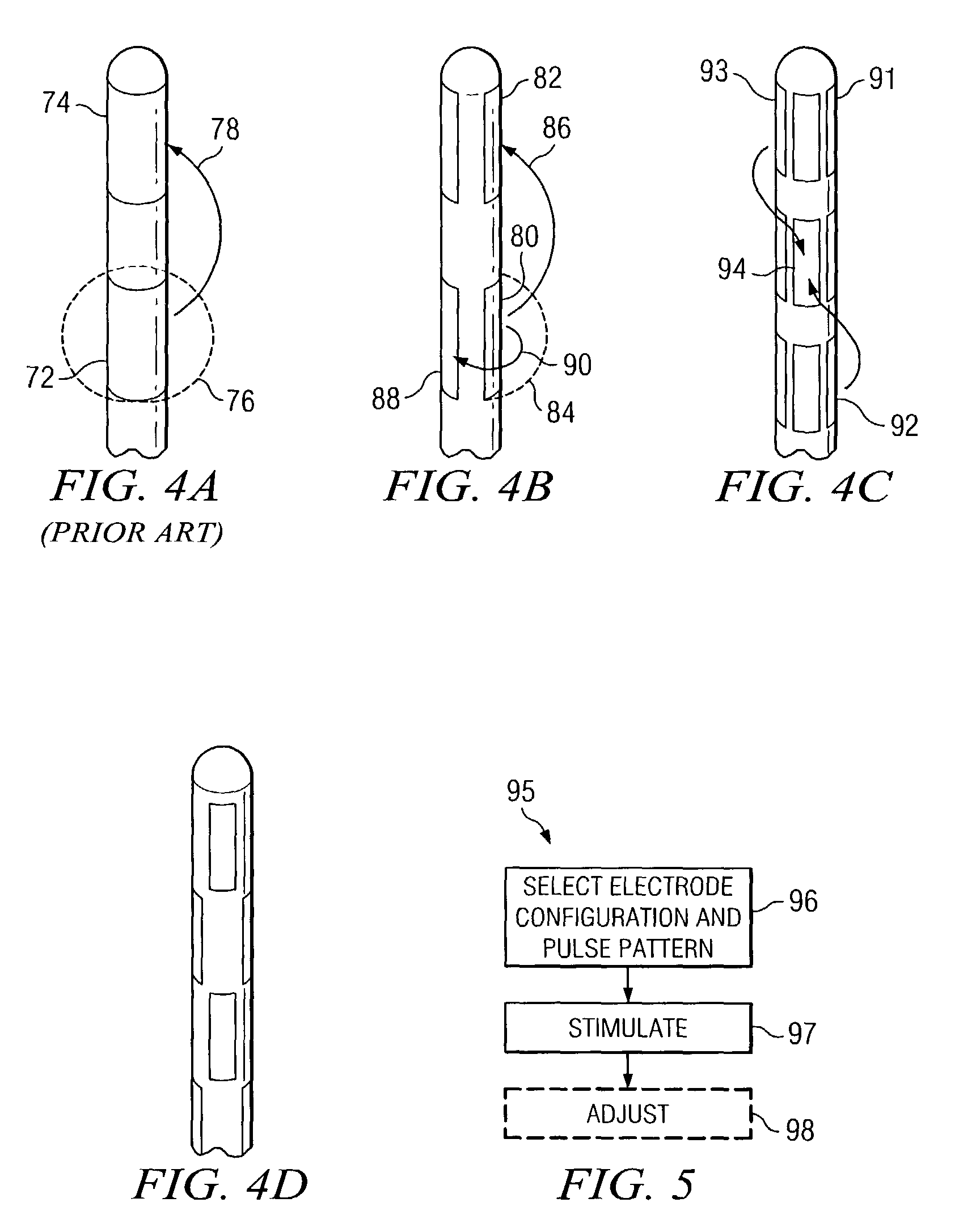
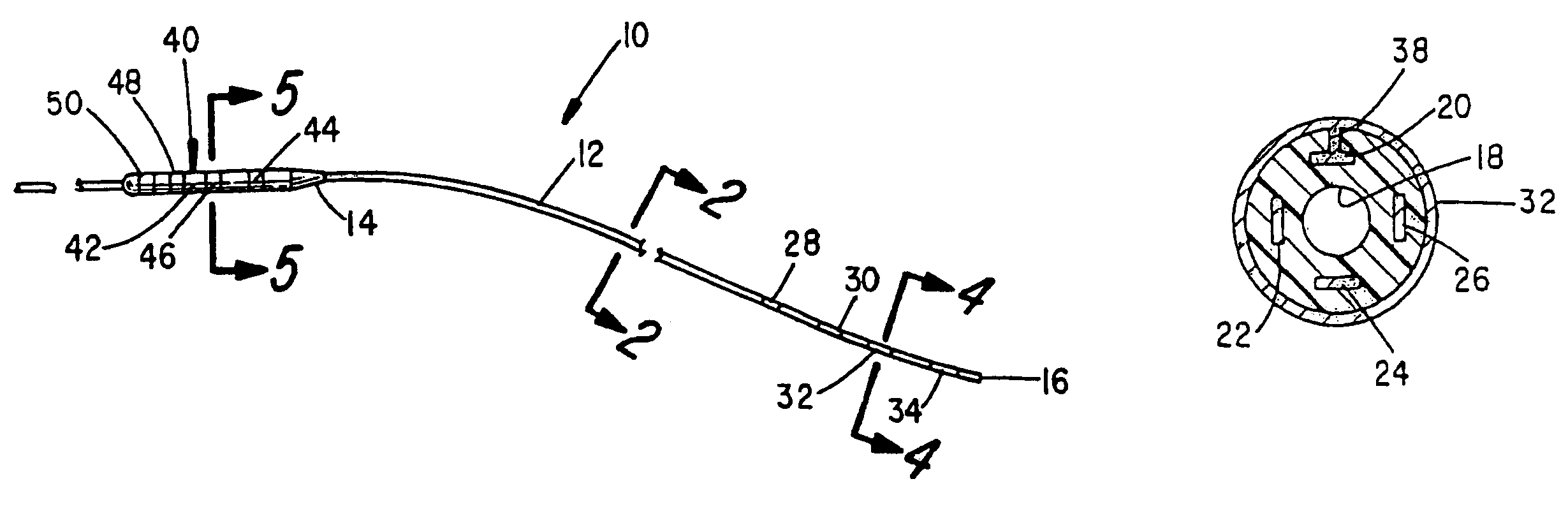
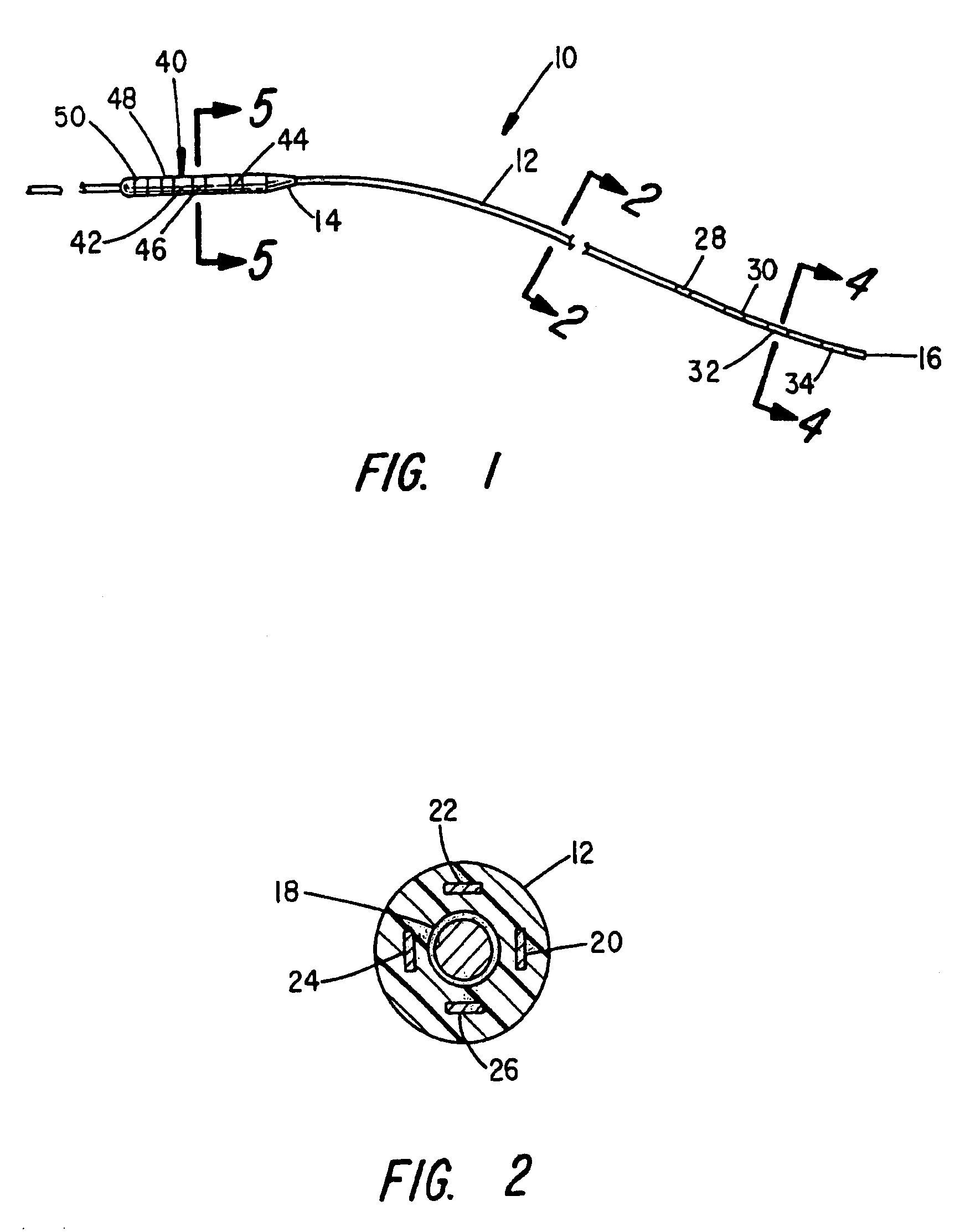
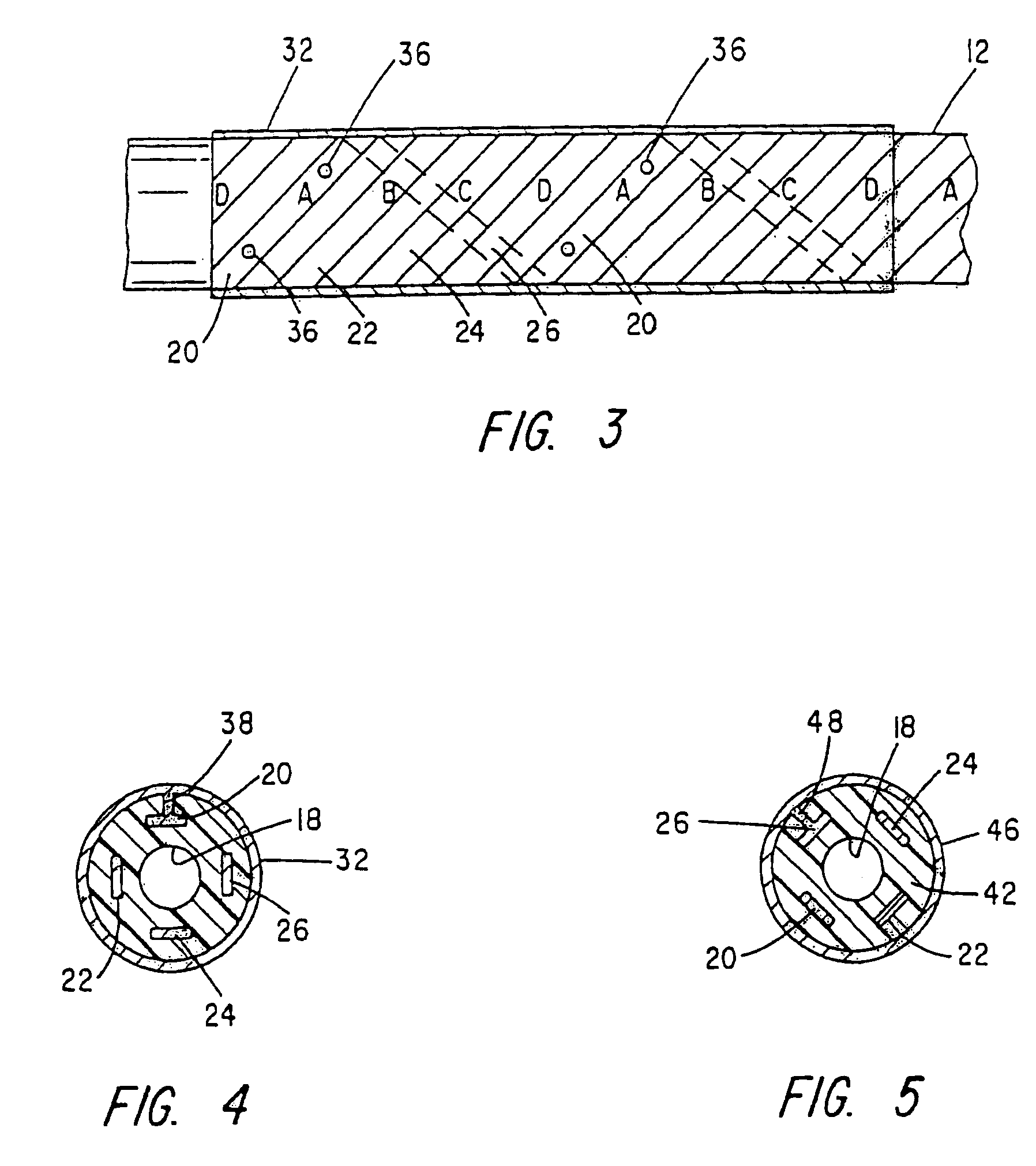
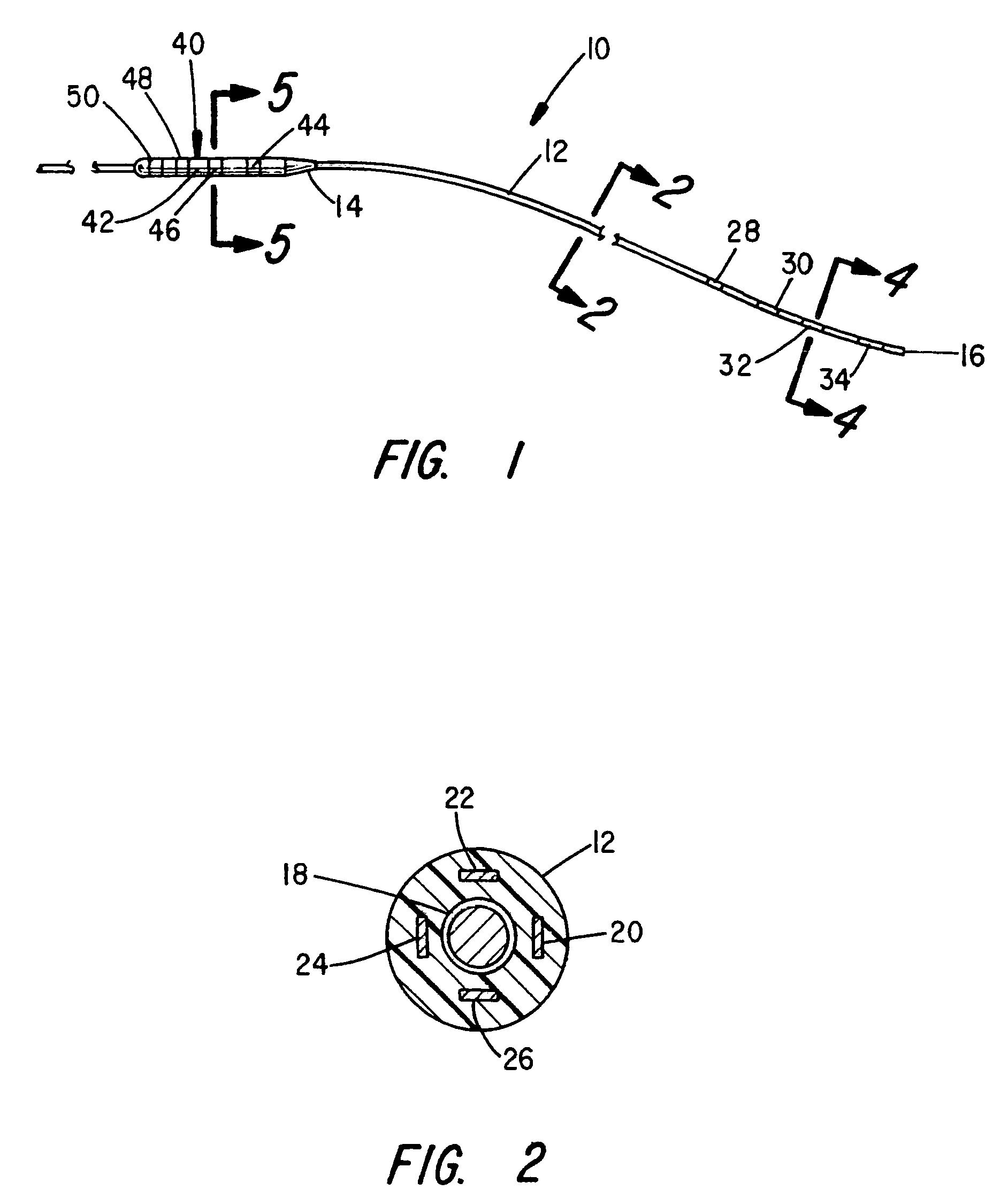
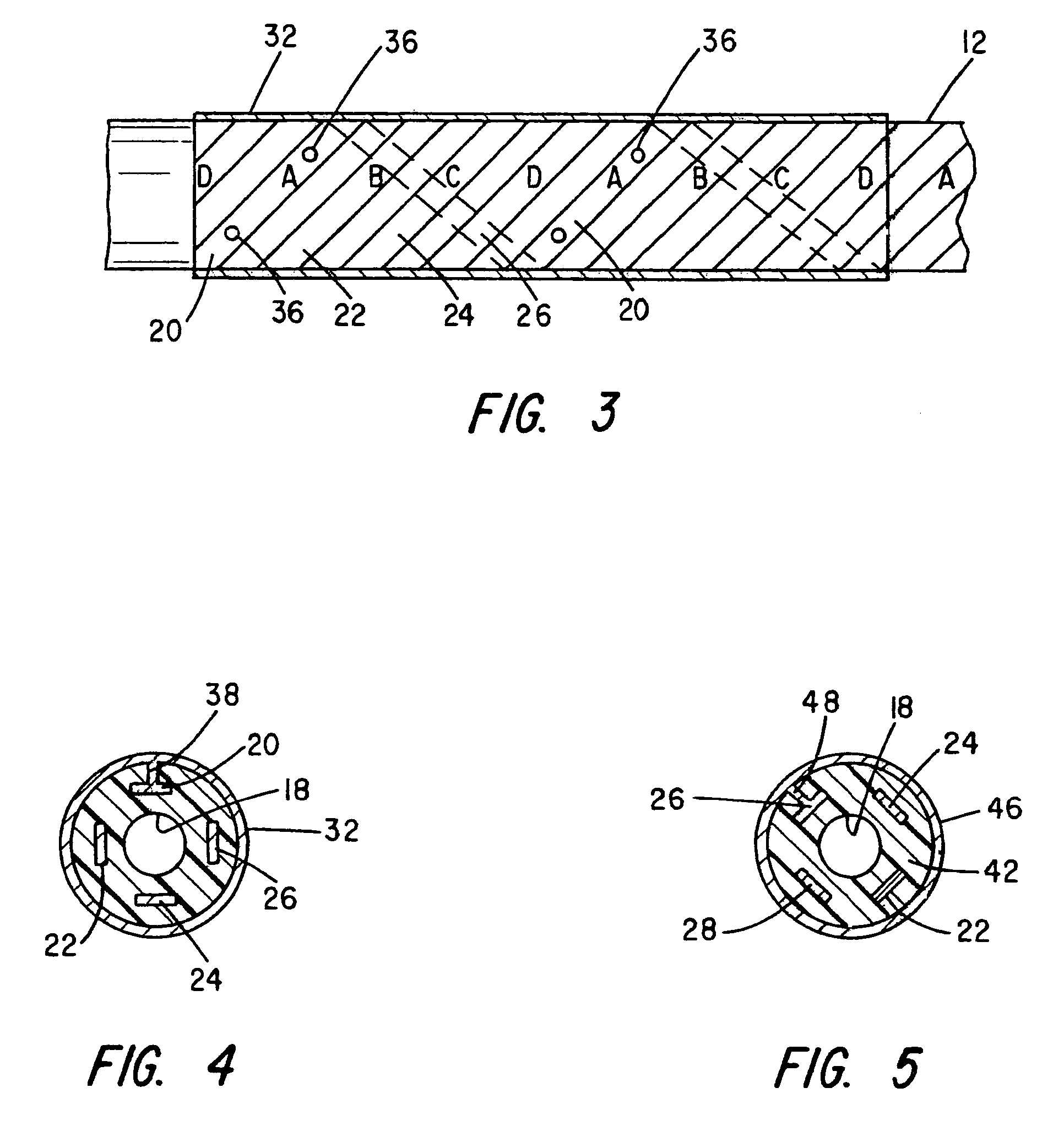
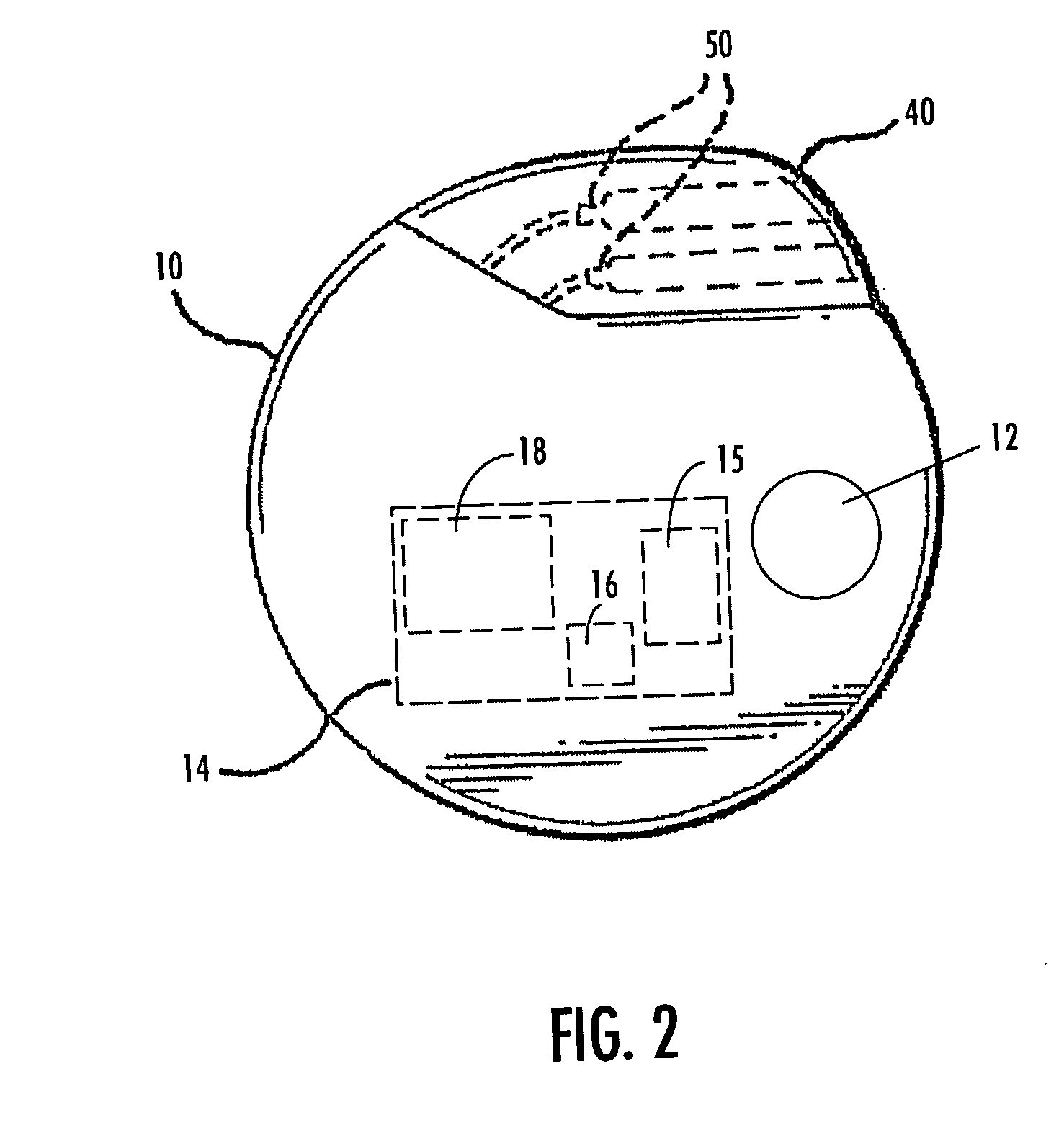
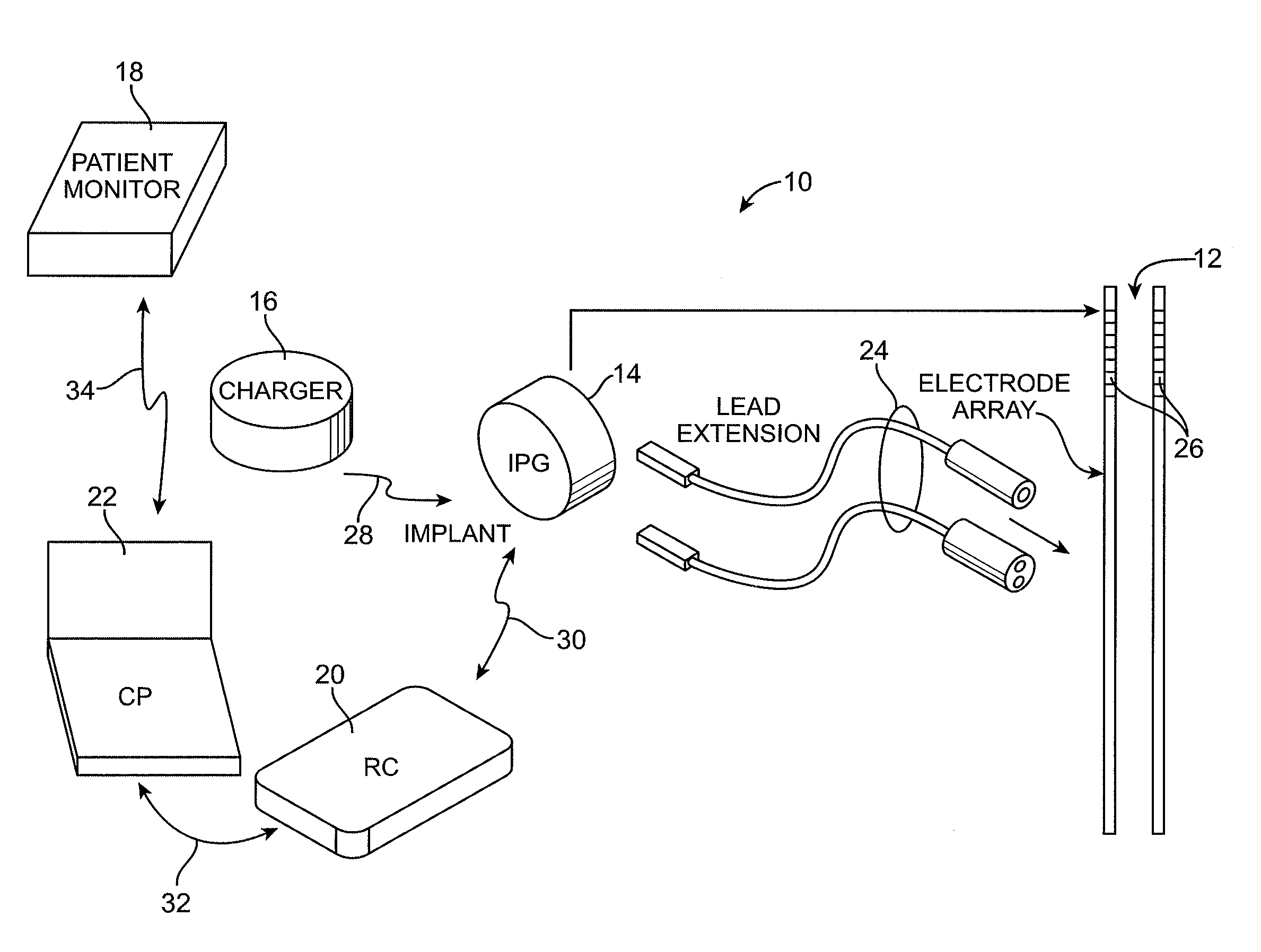
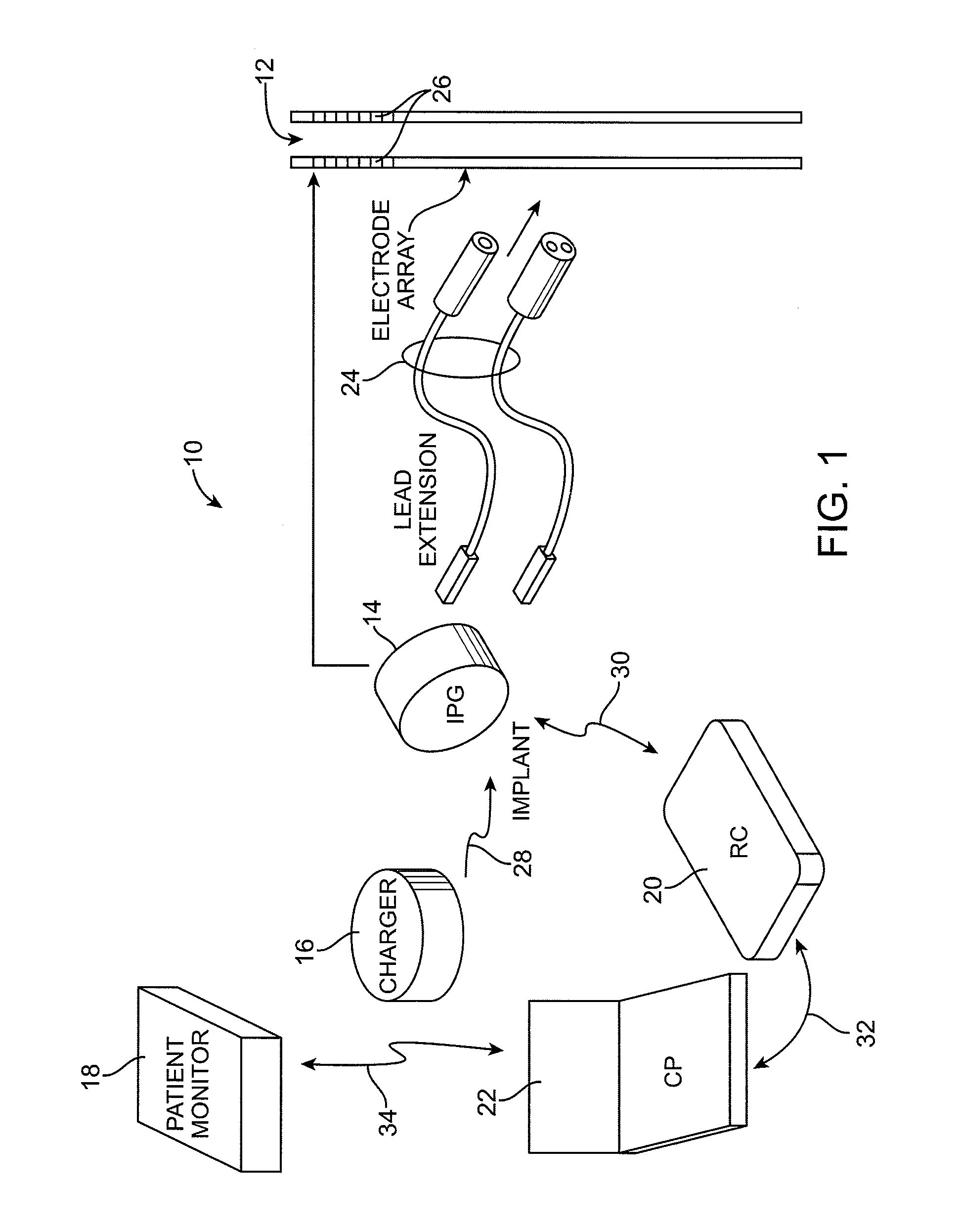
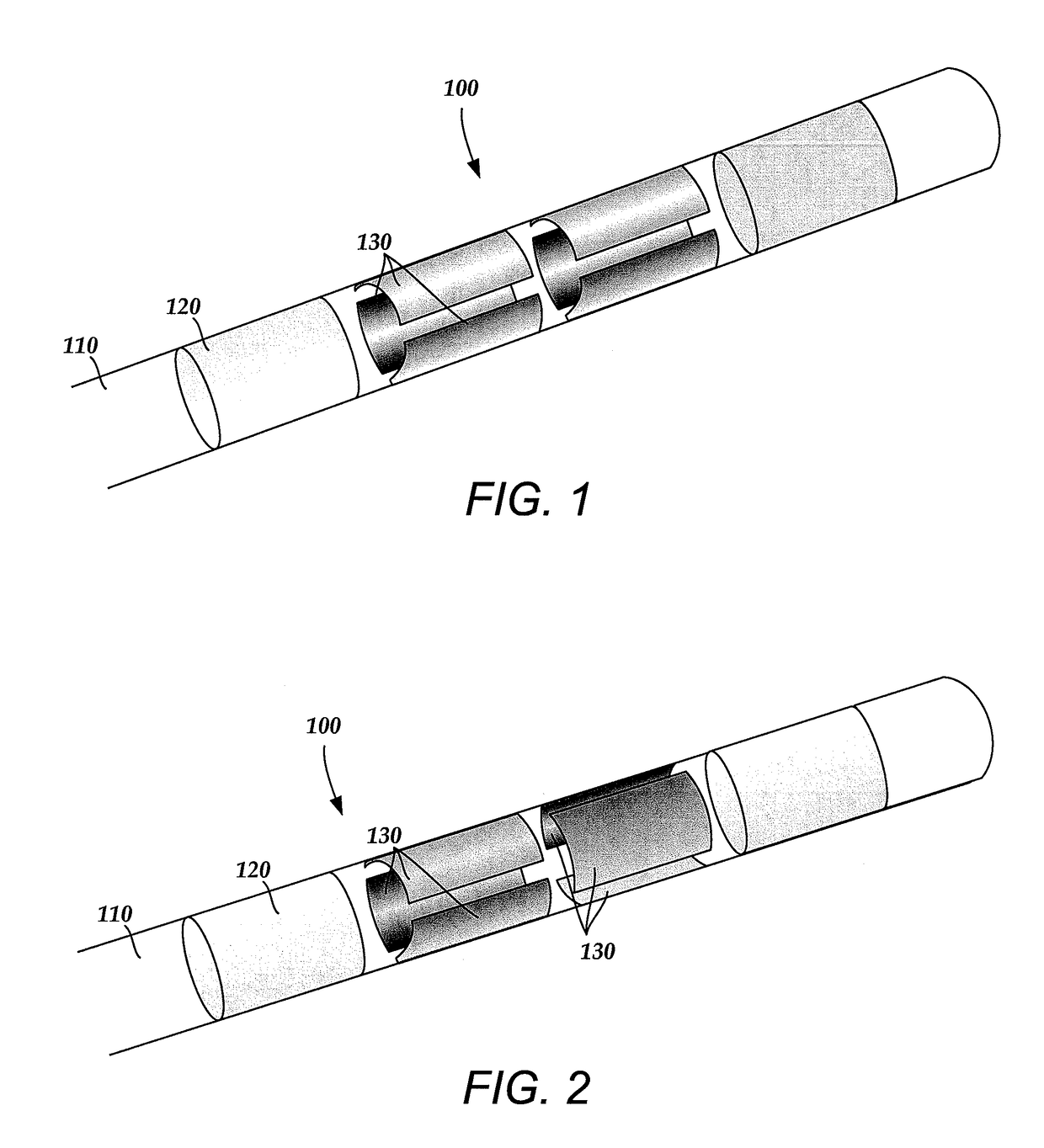
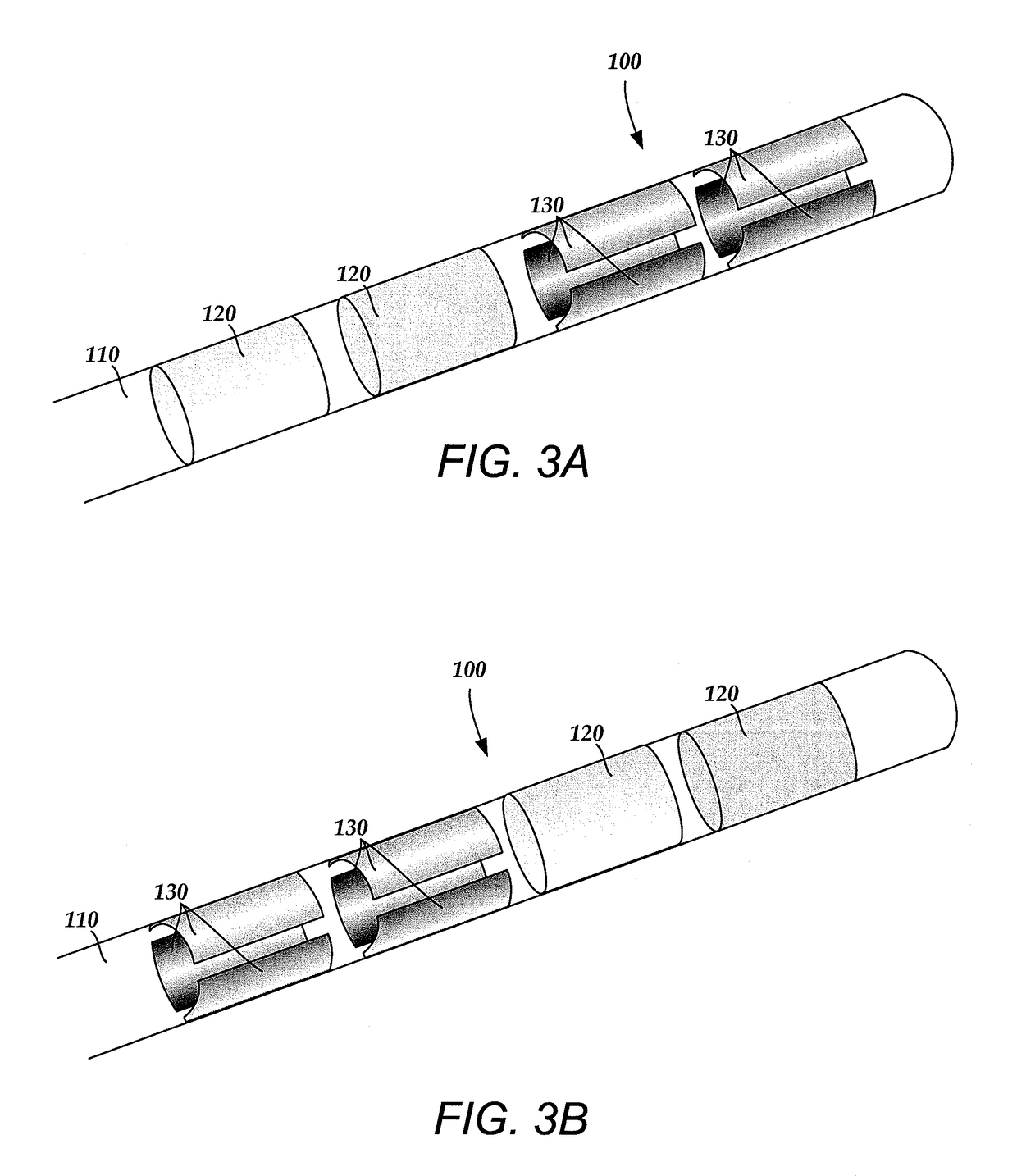
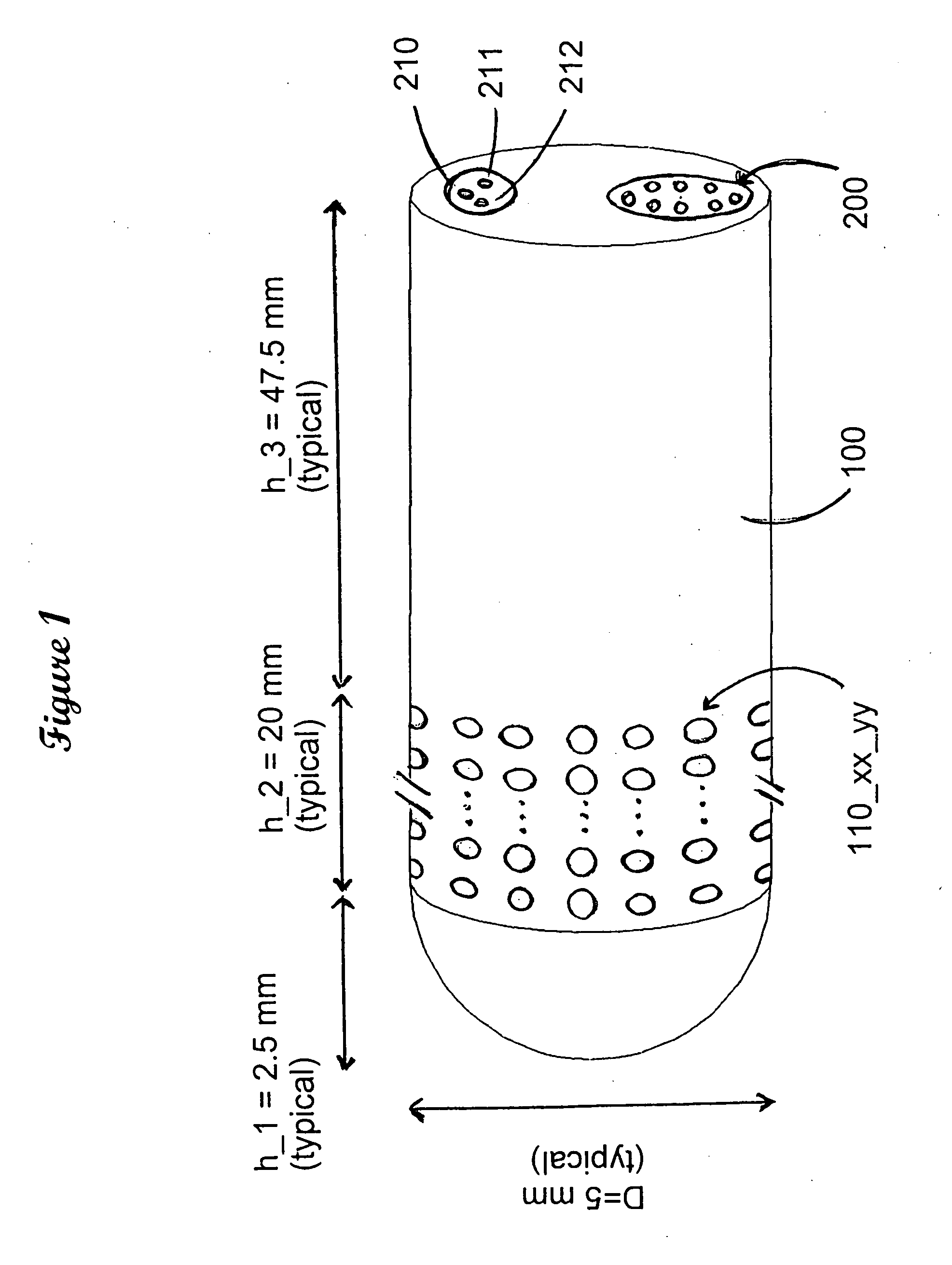
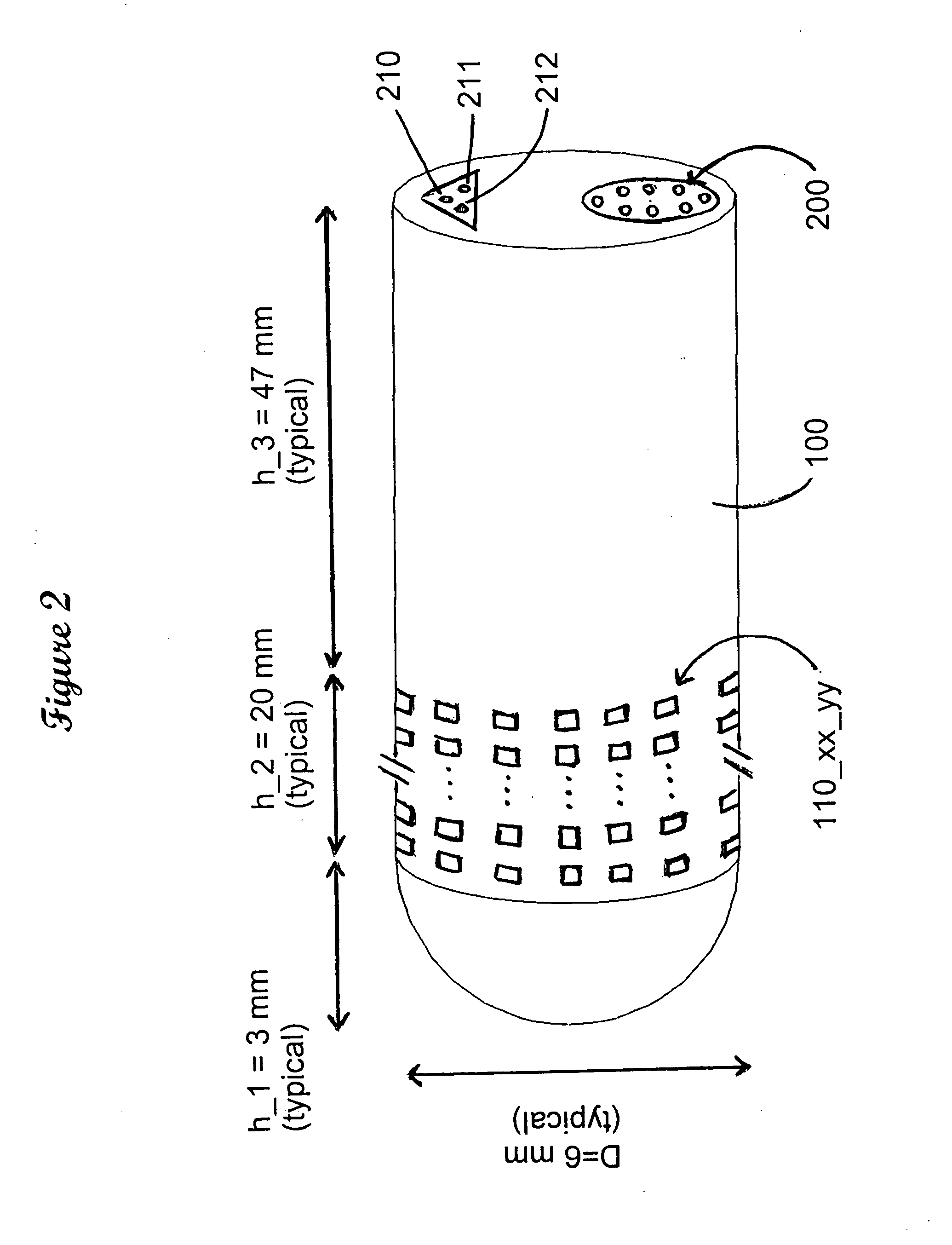
Deep brain stimulation current steering with split electrodes
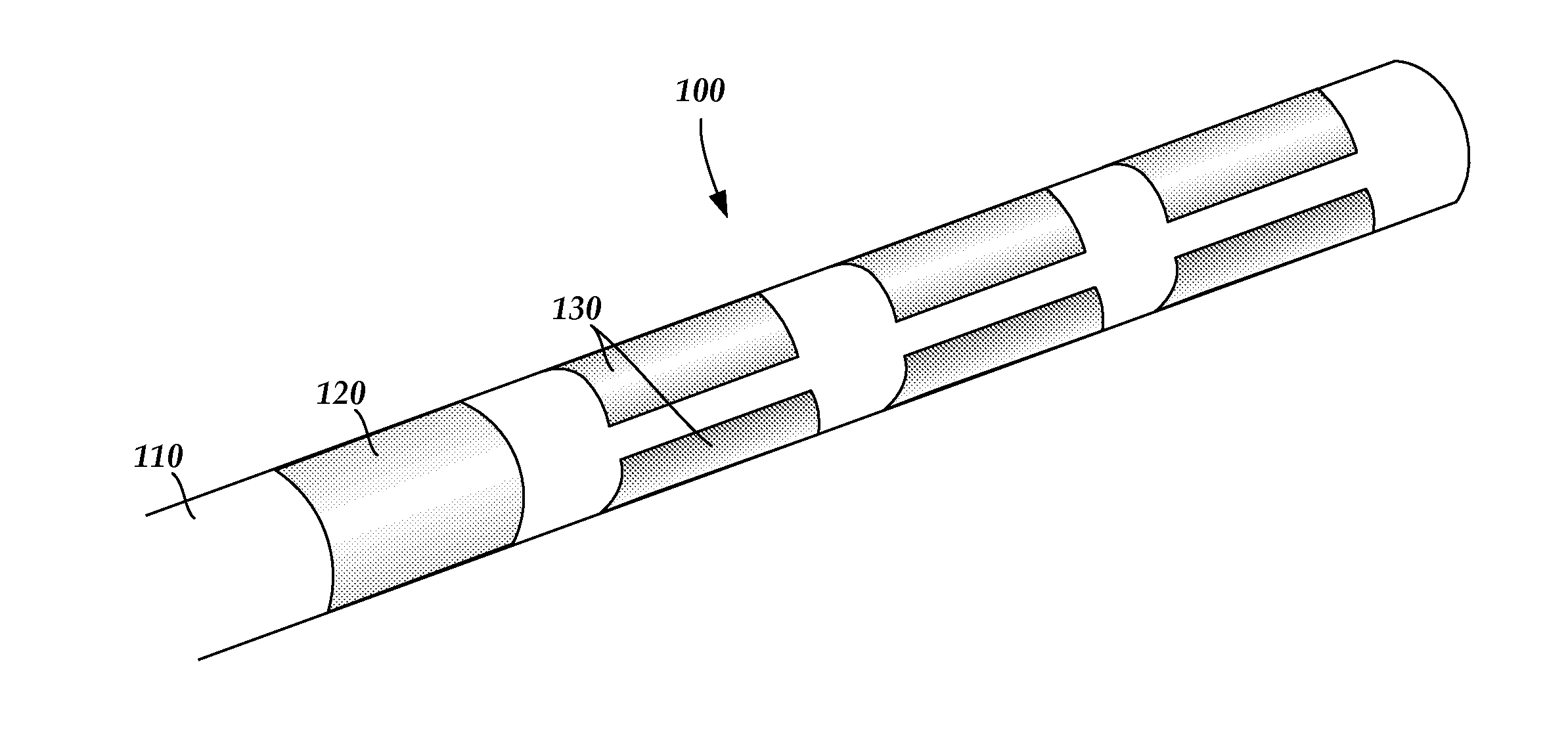
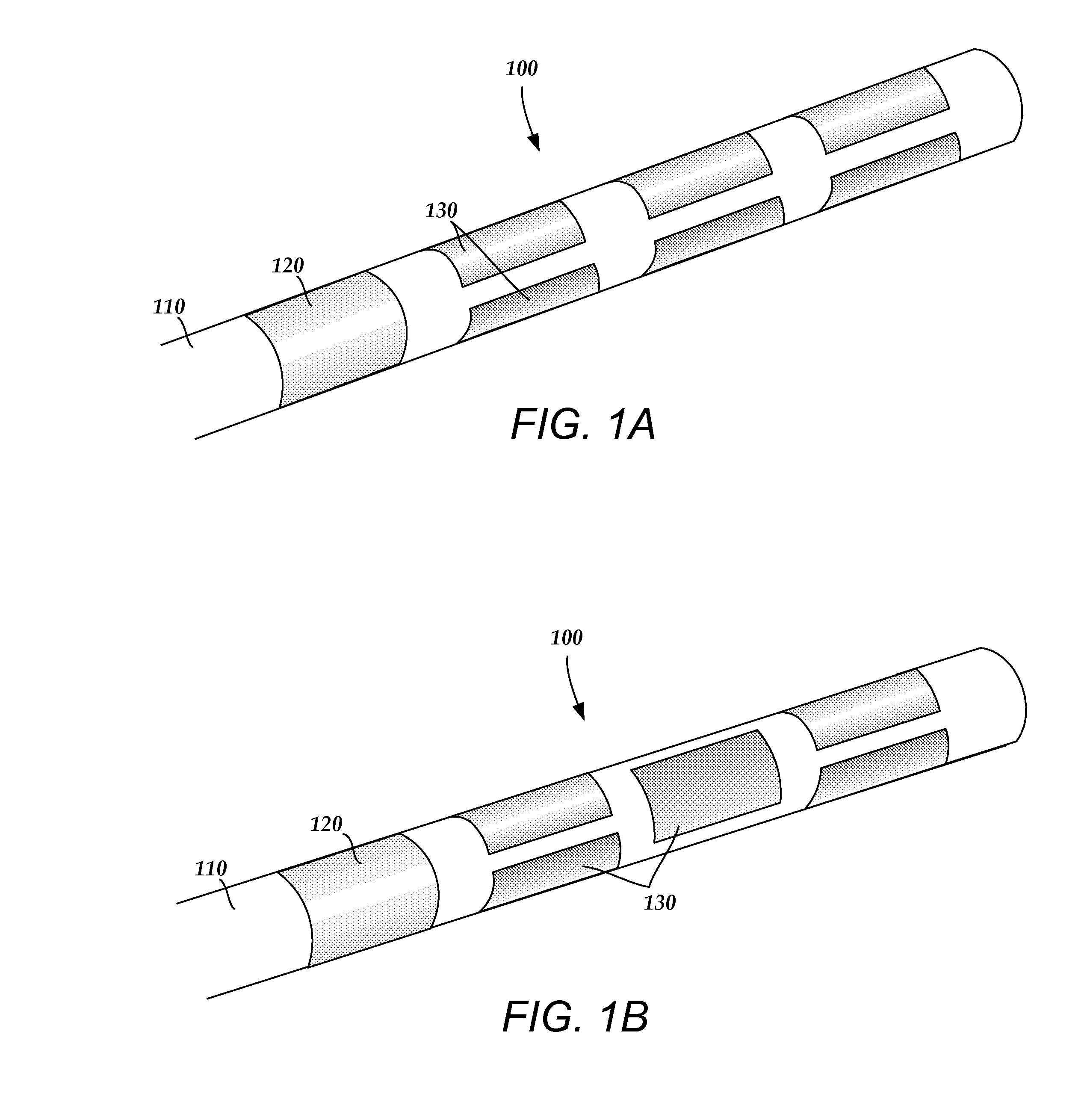
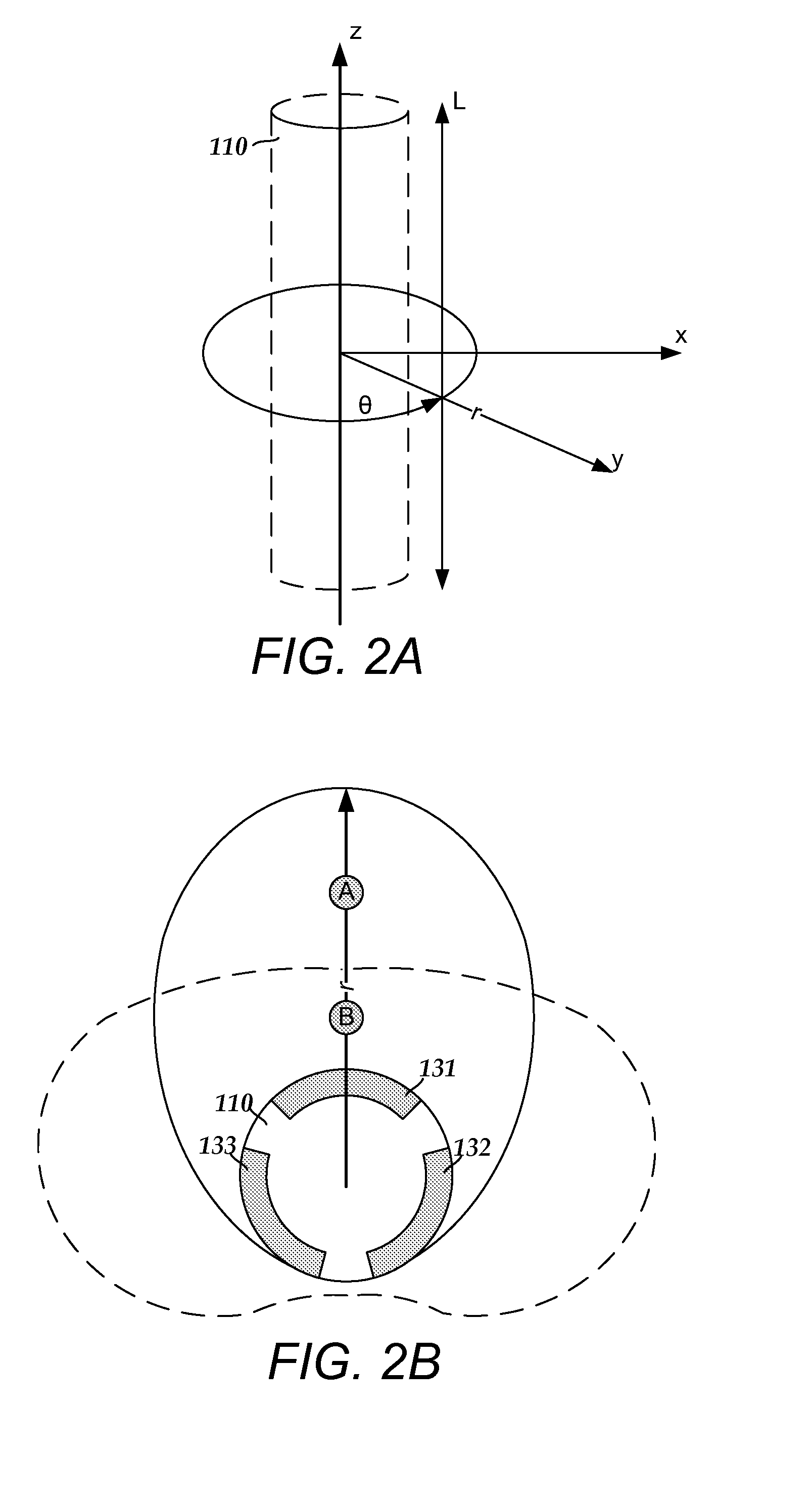
A device for brain stimulation includes a lead having a longitudinal surface, a proximal end, a distal end and a lead body. The device also includes a plurality of electrodes disposed along the longitudinal surface of the lead near the distal end of the lead. The plurality of electrodes includes a first set of segmented electrodes comprising at least two segmented electrodes disposed around a circumference of the lead at a first longitudinal position along the lead; and a second set of segmented electrodes comprising at least two segmented electrodes disposed around a circumference of the lead at a second longitudinal position along the lead. The device further includes one or more conductors that electrically couple together all of the segmented electrodes of the first set of segmented electrodes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Systems and methods for treatment of obesity and eating disorders by electrical brain stimulation and/or drug infusion
InactiveUS6950707B2Reduced activityIncrease excitementHead electrodesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismElectricityMedicine
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Apparatus for directionally stimulating nerve tissue
This invention relates to an apparatus and method for making such apparatus for providing controlled and directional stimulation patterns for tissue stimulation. The apparatus may be useful in stimulation nervous tissue in the brain, about the spinal cord, on nerve roots, about peripheral nerves, and in muscles, among others. The apparatus includes a implantable pulse generator connected to a lead. The lead has electrodes placed about a perimeter. In addition, the lead may include electrodes placed longitudinally along the axis of the lead. By applying charge differences between circumferentially distributed electrodes, a smaller stimulation field may be established. In addition, by stimulating between electrodes distributed longitudinally on the same side, a directional flow field may be established. Such leads are especially useful in deep brain stimulation as the region in which a stimulation field is strong enough to produce tissue stimulation is directional and minimized.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Methods, systems, and devices for deep brain stimulation using helical movement of the centroid of stimulation
A method of treating a target region in the brain includes a) contacting tissue to be stimulated with a lead of a stimulation device, the stimulation device comprising a pulse generator coupled to the lead, the lead having a plurality of segmented electrodes disposed at a distal end of the lead, the stimulation device being configured and arranged to stimulate a target region using a positionable centroid of stimulation; b) providing stimulation current to at least one of the segmented electrodes of the lead to generate a centroid of stimulation at a location and stimulate tissue around the location of the centroid of stimulation; c) repositioning the centroid of stimulation to a next location along a helical path by altering the provision of stimulation current to the plurality of electrodes and stimulating tissue around the location of the repositioned centroid of stimulation; and d) repeating c) for each location along the helical path. The method may optionally include collecting data associated with each of the locations of the centroid of stimulation; and displaying at least a portion of the collected data.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
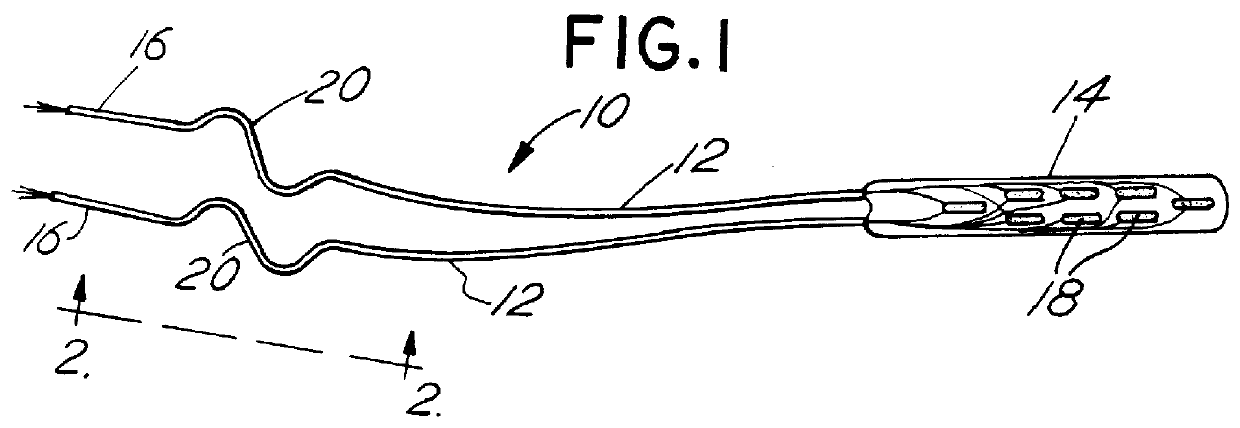
Neurostimulating lead
A neurostimulating lead is provided for use in stimulating the spinal chord, spinal nerves, or peripheral nerves or for use in deep brain stimulation that comprises an elongated, flexible lead having improved steerability properties. The lead includes a plurality of thin-film metal electrodes connected by conductors embedded within the wall of the lead to electrical contacts at the proximal end of the lead. The lead is further designed to include an internal lumen for use with a guidewire in an over-the-wire lead placement.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Treatment of epilepsy by brain stimulation
InactiveUS7003352B1Small sizeInhibition amountElectrotherapyPressure infusionMedicineElectrical stimulations
Introducing one or more stimulating drugs to the brain and / or applying electrical stimulation to the brain is used to treat epilepsy. At least one implantable system control unit (SCU) produces electrical pulses delivered via electrodes implanted in the brain and / or drug infusion pulses delivered via a catheter implanted in the brain. The stimulation is delivered to targeted brain structures to adjust the activity of those structures. The small size of the SCUs of the invention allow SCU implantation directly and entirely within the skull and / or brain. Simplicity of the preferred systems and methods and compactness of the preferred system are enabled by the modest control parameter set of these SCU, which do not require or include a sensing feature.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
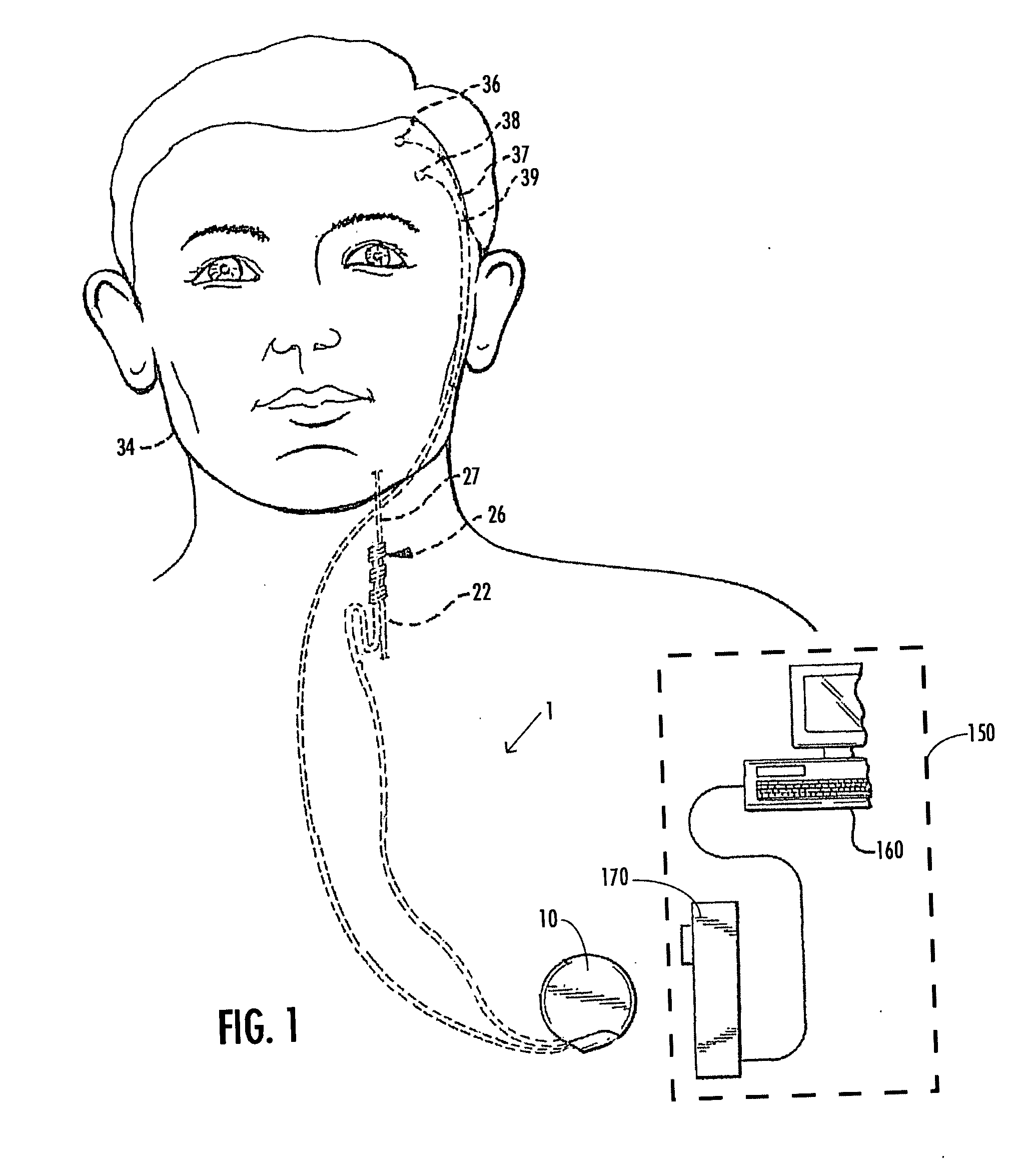
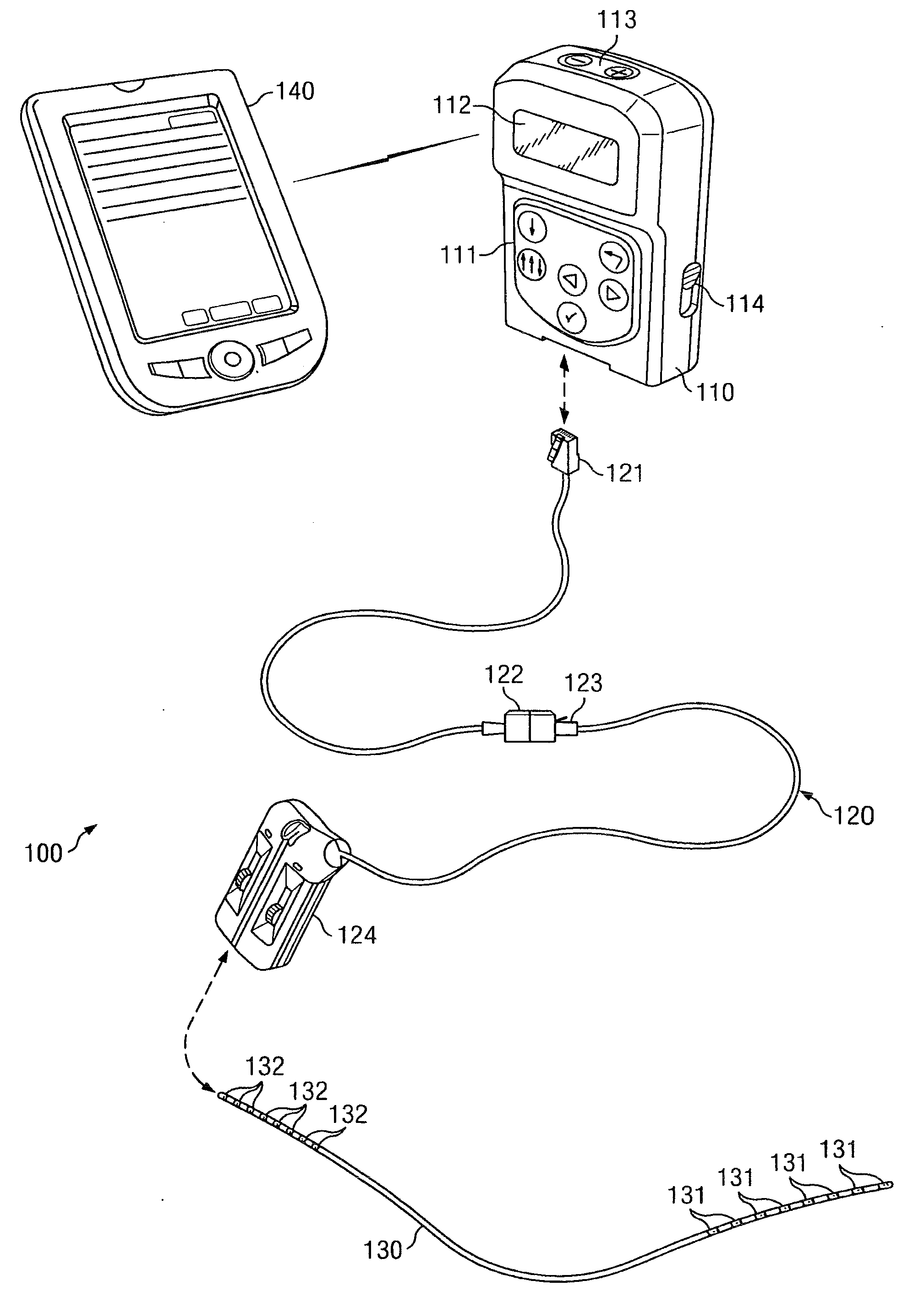
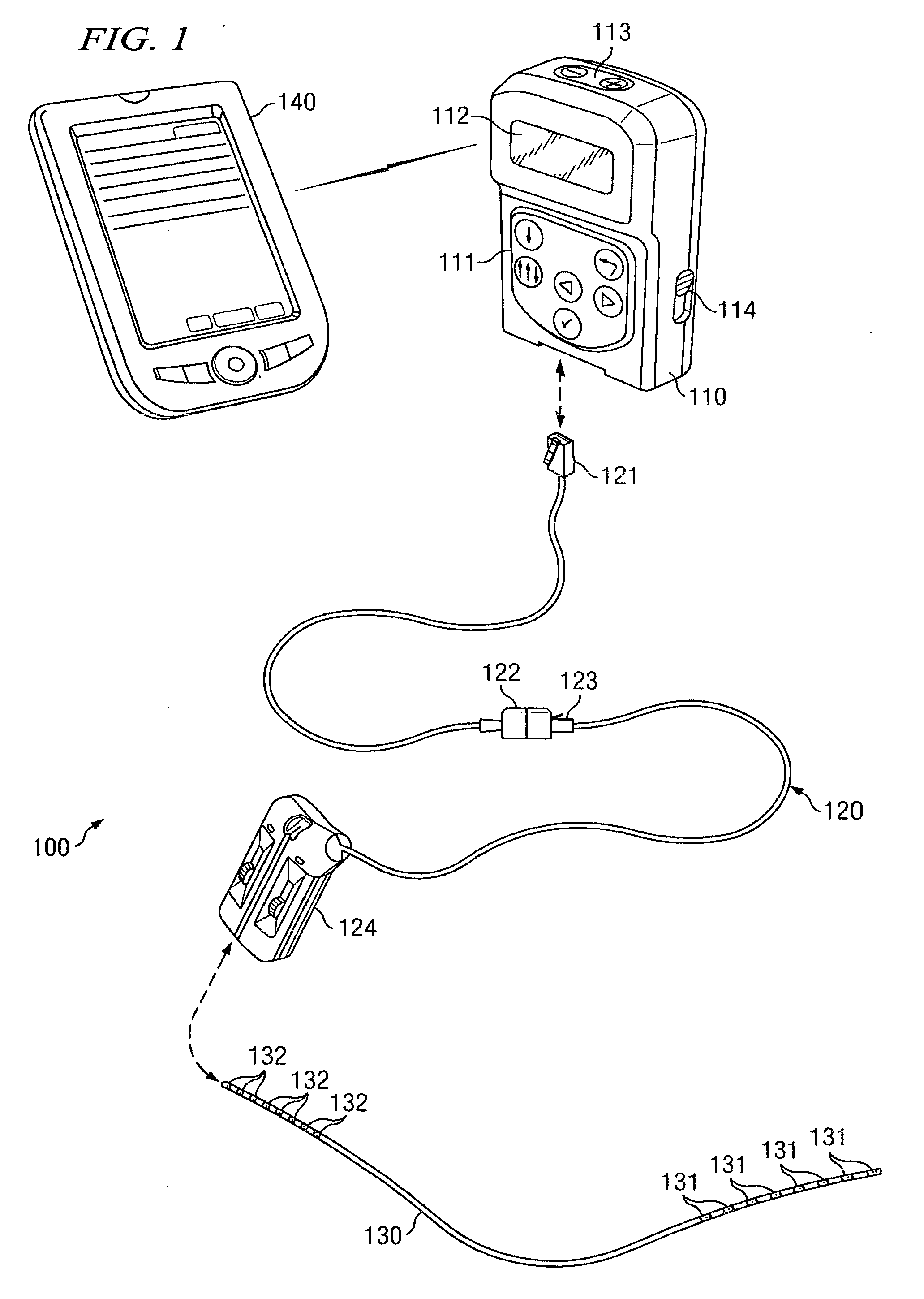
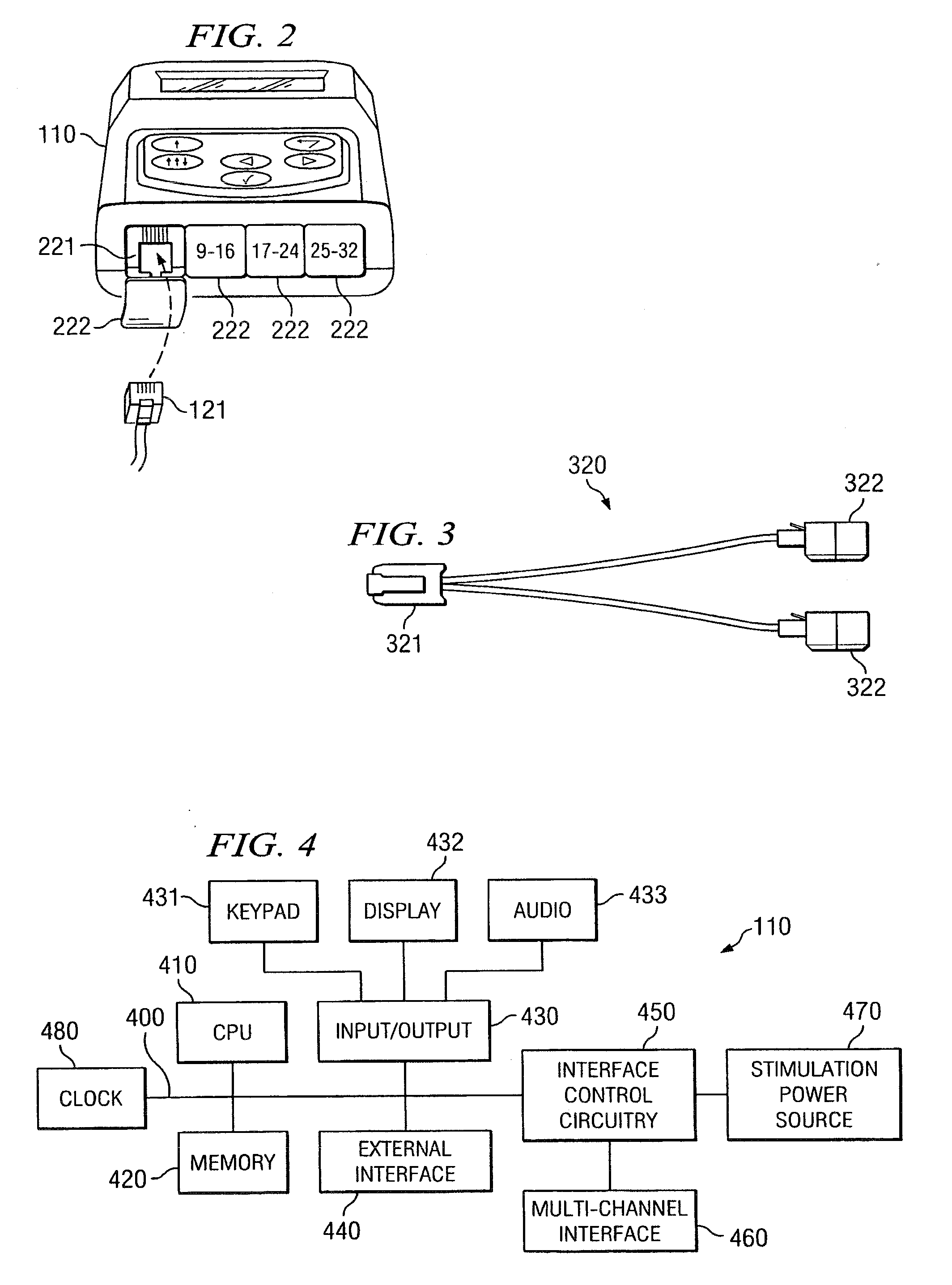
Clinician programmer for use with trial stimulator
Disclosed are systems and methods which provide an external clinician interface, such as through the use of a laptop computer or a personal digital assistant (PDA). The foregoing clinician interface may be used with trial stimulators well suited for use interoperatively and during patient trial. Stimulators of embodiments are adapted for use in providing stimulation to a plurality of tissues and / or areas of the body, such as spinal cord stimulation, deep brain stimulation, etcetera.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
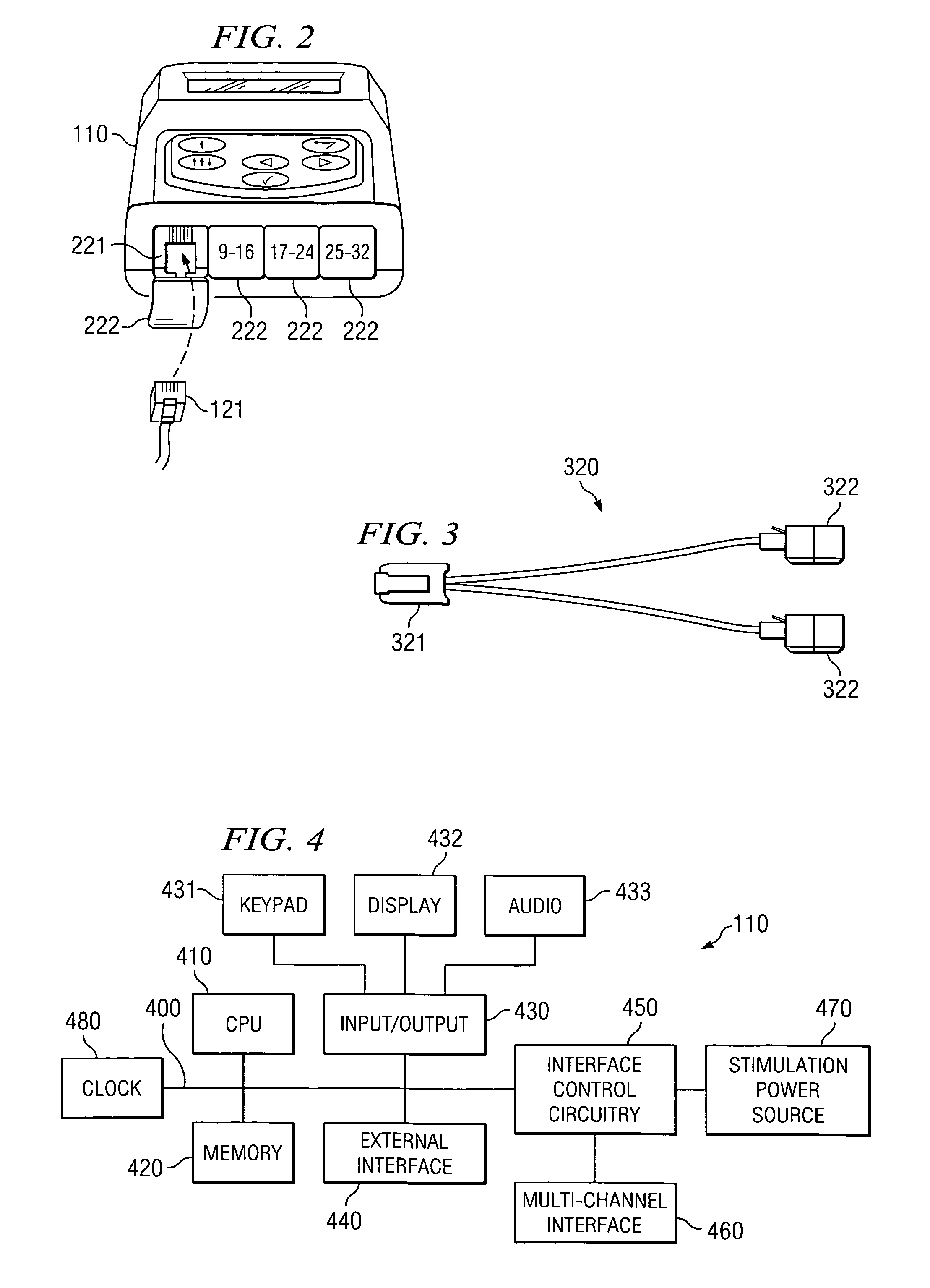
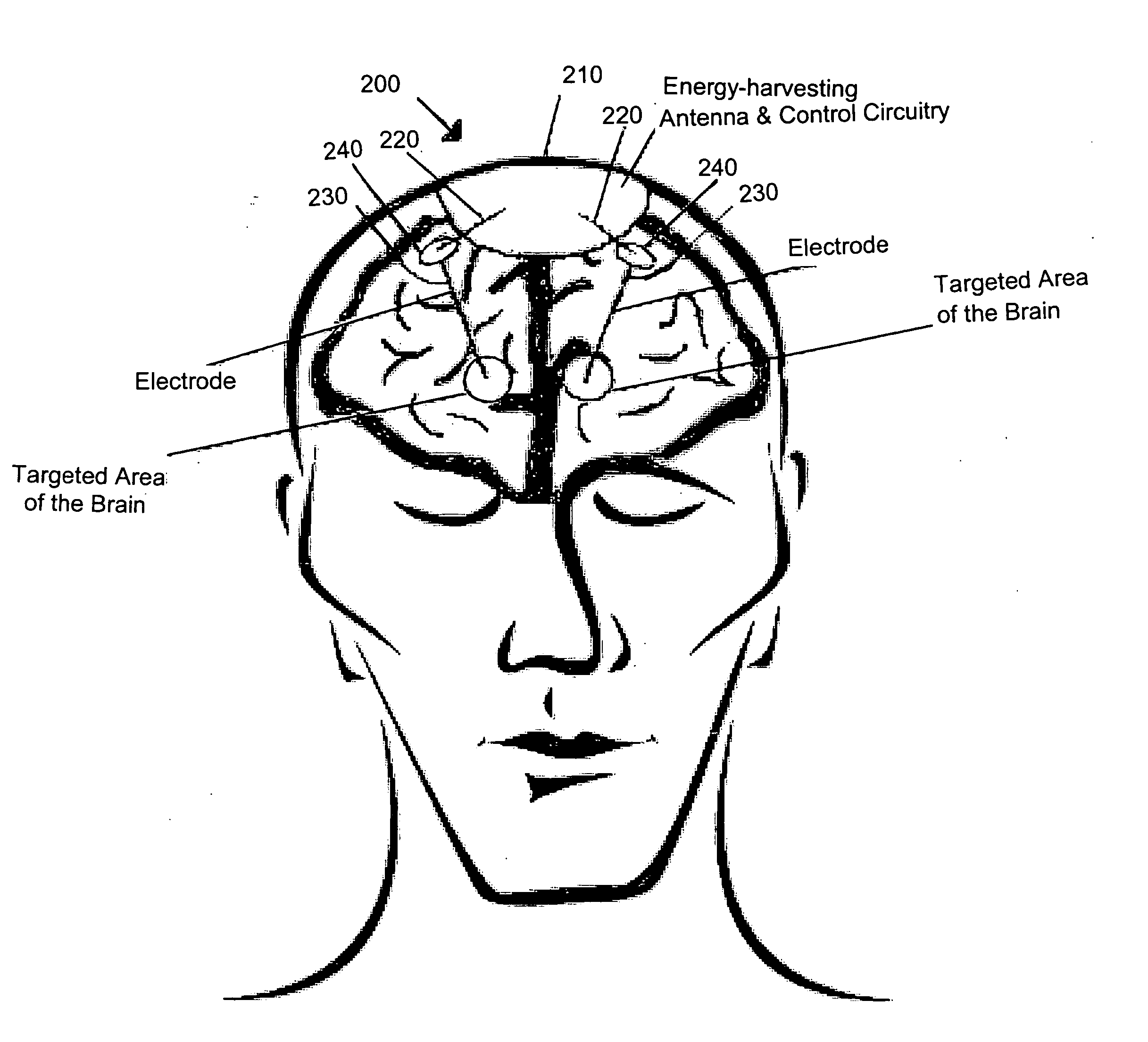
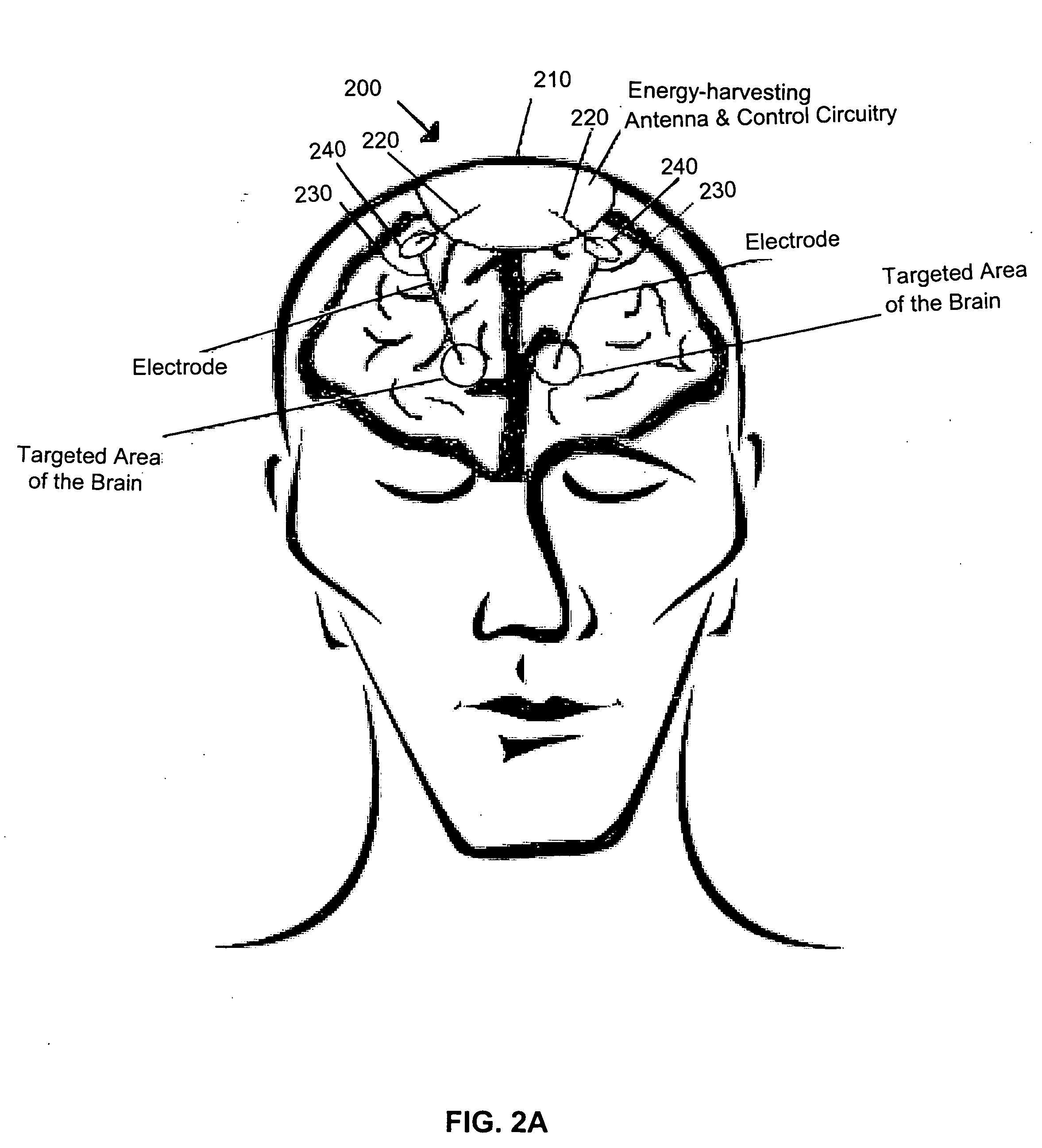
Device for brain stimulation using RF energy harvesting
A device for brain stimulation using radio frequency harvesting is disclosed. The device includes a circuit implantable under a scalp of a patient, the circuit comprising a radio frequency harvesting power circuit and a stimulation circuit, and a plurality of electrodes coupled to the circuit, the plurality of electrodes providing brain stimulation to targeted areas of the brain. The electrodes may provide stimulation to targeted areas of the brain including deep brain stimulation for the treatment of Parkinson's disease and cortical stimulation for the treatment of stroke victims.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Selective neurostimulation for treating epilepsy
A method and device for treating epilepsy are disclosed which provide for electrical, chemical or magnetic stimulation of certain areas of the brain to modulate neuronal activity of areas associated with symptoms of epilepsy. Deep brain stimulation is combined with vagus nerve stimulation to enhance symptomatic relief of the disorder. Some embodiments also employ a sensing capability to optimize the therapeutic treatment regimen.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Selective brain stimulation using conditioning pulses
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Selective neurostimulation for treating mood disorders
ActiveUS20070027500A1Relieve symptomsAlter modulation of neuronal activityHead electrodesDiseaseRegimen
A method and device for treating a mood and / or anxiety disorder are disclosed which comprise electrical, chemical or magnetic stimulation of certain areas of the brain to modulate neuronal activity of areas associated with symptoms of mood disorders. In certain embodiments, deep brain stimulation is combined with cranial nerve stimulation to enhance symptomatic relief of the disorder. Certain embodiments also employ a sensing capability to optimize the therapeutic treatment regimen.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
Neurostimulating lead
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Selective nerve stimulation for the treatment of eating disorders
ActiveUS20070027498A1Avoid problemsConvenient treatmentHead electrodesMedical devicesRegimenMedicine
A method and apparatus for treating persons suffering from an eating disorder includes direct or indirect stimulation of selected areas of the brain associated with a symptom of the eating disorder. The stimulation regimen is programmable to enable physician optimization of stimulation signal parameters to ameliorate at least one symptom of bulimia or another eating disorder. Certain embodiments employ deep brain stimulation and / or sensing together with cranial nerve stimulation and / or sensing.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
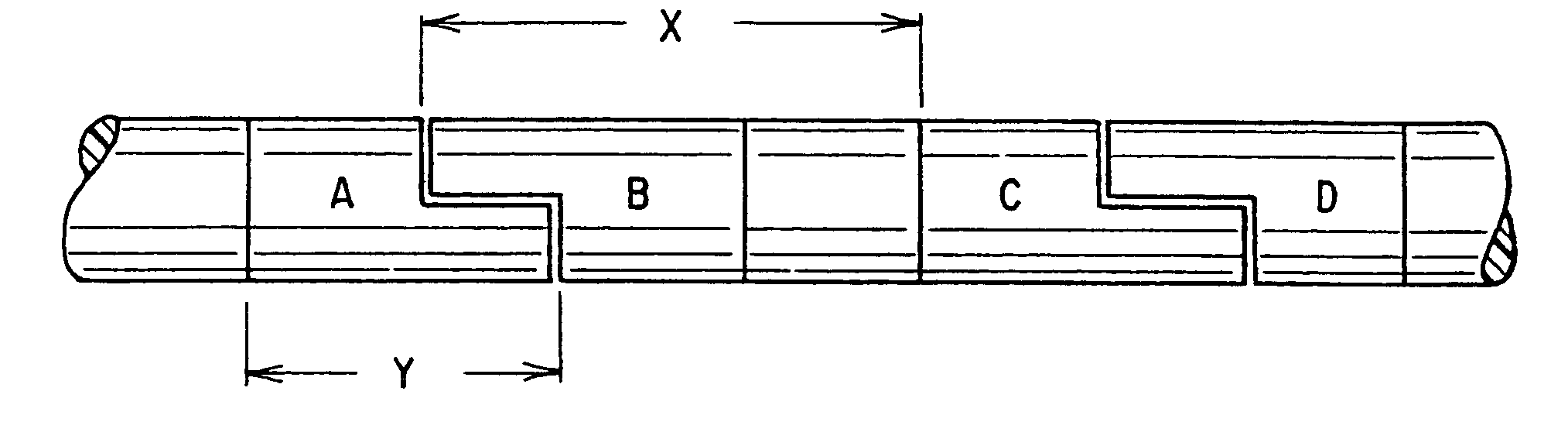
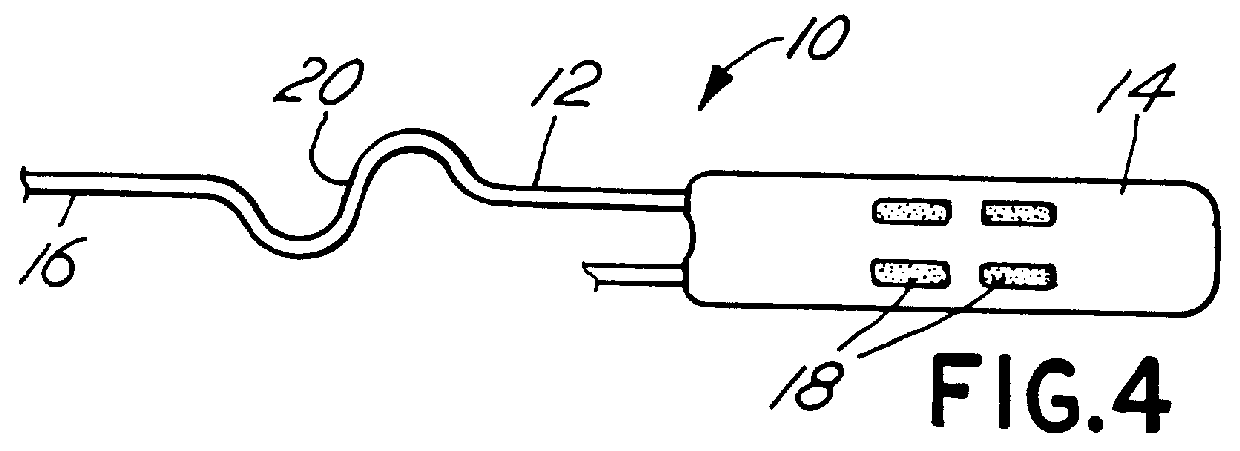
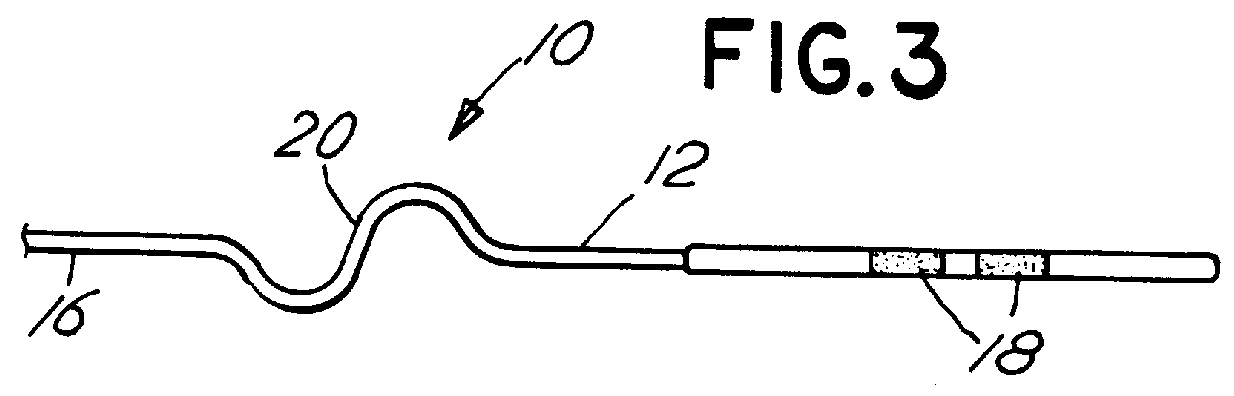
Medical lead with sigma feature
An implantable medical lead for spinal cord, peripheral nerve or deep brain stimulation comprises a lead body which includes a deformable sigma segment preferably in the shape of a sine wave and a lead paddle coupled to the lead body at the distal end thereof. The lead body at its proximal end may be coupled to an implantable pulse generator, additional, intermediate wiring or other stimulation device. The lead paddle may comprise a plurality of electrode contacts for providing electrical stimulation to targeted human tissue. The lead body, which defines the sigma segment, in a plane, couples the lead paddle and pulse generator. The sigma segment provides flexing and bending of the wire when a patient shifts or moves, and especially provides longitudinal extension between the pulse generator and lead paddle.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
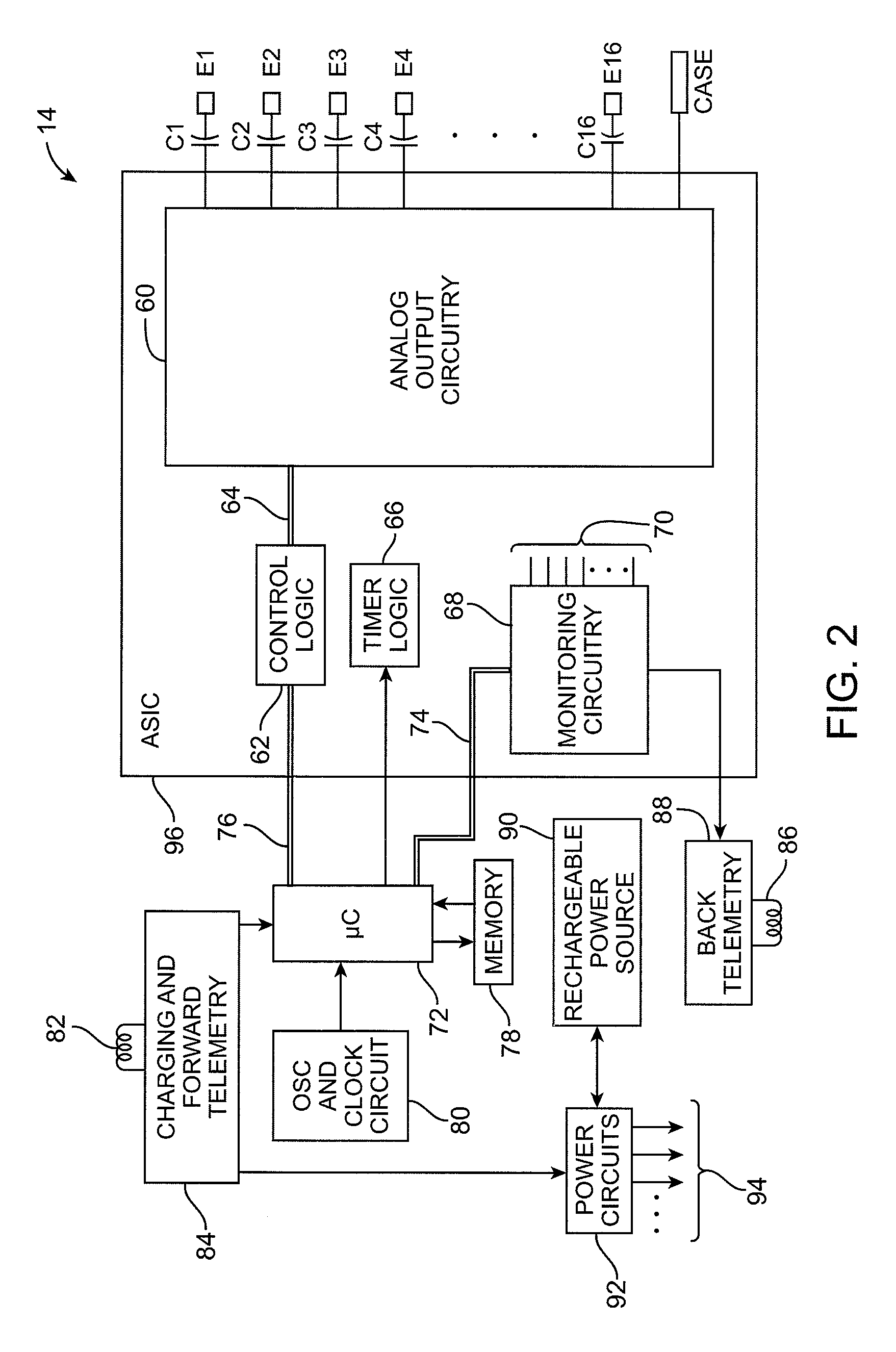
Mulit-programmable trial stimulator
ActiveUS20090024187A1Simple inputEasy to explainImplantable neurostimulatorsArtificial respirationMedicineElectrode impedance
Disclosed are systems and methods which provide trial stimulators suited for use interoperatively and during patient trial. Trial stimulator embodiments provide a patient interface and / or clinician interface which appears and functions substantially the same as an interface of a pulse generator controller which will be used after a trial period. A compliance monitor feature may be provided to facilitate verifying the proper use of the trial stimulator during a trial period. A diagnostic feature may be provided to facilitate verifying proper operation of various aspects of a trial stimulator, such as electrode impedance analysis. Trial stimulators of embodiments provide stimulation to a plurality of tissues and / or areas of the body, such as spinal cord stimulation, deep brain stimulation, etcetera. Embodiments provide for multi-electrode stimulation and multi-stimulation programs. Embodiments are configured to provide active discharge of stimulation pulses as well as to utilize constant current sources in providing the stimulation pulses.
Owner:ADVANCED NEUROMODULATION SYST INC
Cranial sealing plug
Various embodiments of a burr hole plug assembly offer significant improvements for allowing lead and / or cannula access through a burr hole drilled through a patient's skull in connection with a Deep Brain Stimulation system, and subsequent sealing of such burr hole. The various burr hole plug assemblies described: (a) accommodate various burr hole sizes and provide a secure fit in the burr hole; (b) accommodate various locations for lead positioning and adjustment; (c) allow the lead to remain in a static position when the burr hole plug assembly is placed; (d) protect the lead from fracture at the exit location of the plug; (e) remain flush with the skull to avoid skin erosion and to eliminate unsightly flange protrusion from the patients' skull; (f) adequately hold the lead in place over time; and (g) provide a selection of various types of burr hole plug assemblies and sizes for use by the implanting surgeon, thereby eliminating the need for surgeons to resort to custom plugs and plug assemblies made in the operating room specifically to fit a given patient.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
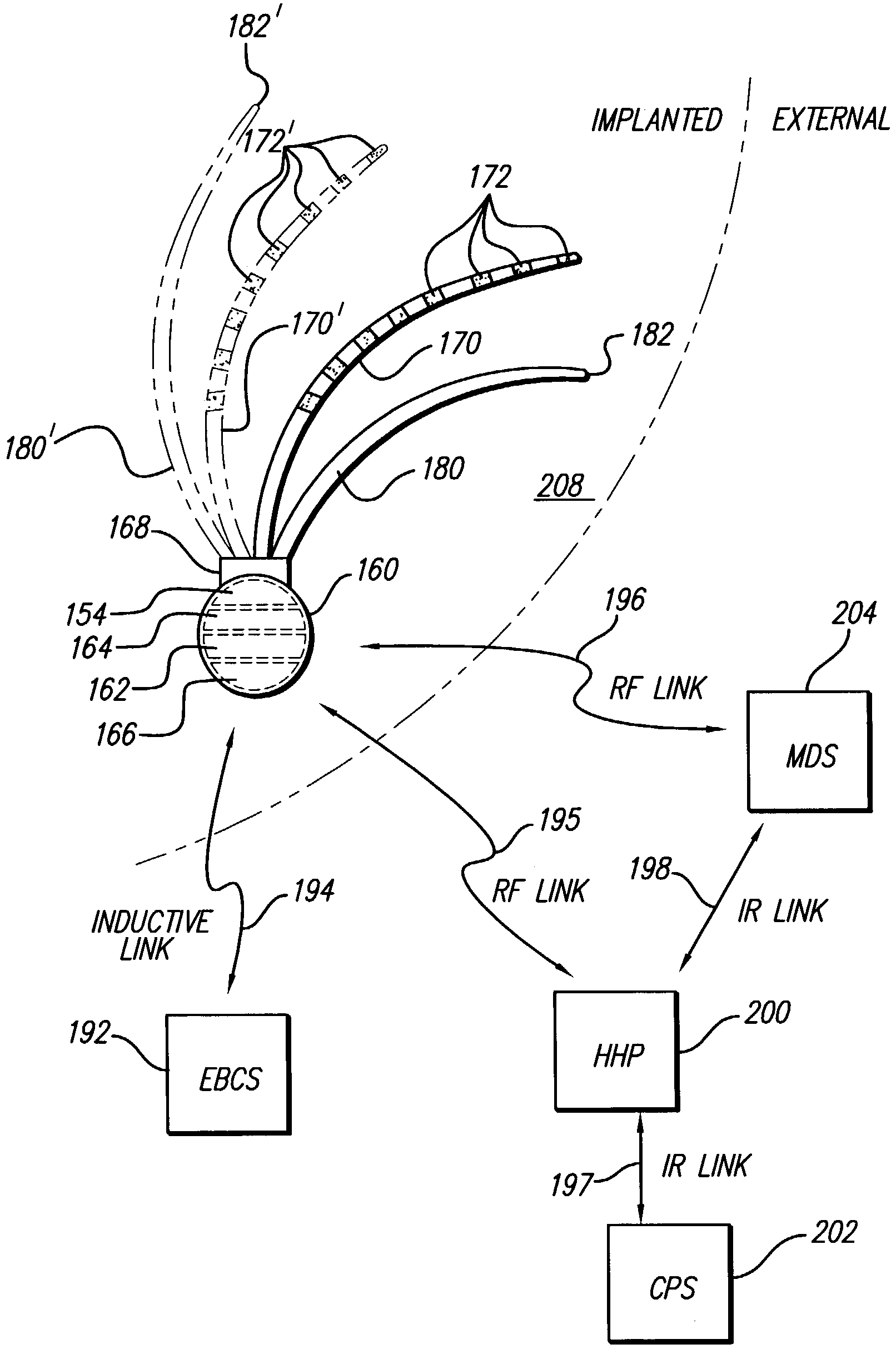
Automated fitting system for deep brain stimulation
Methods, systems, and external programmers provide therapy to a patient having a dysfunction. In one aspect, stimulation energy is conveyed from a neurostimulator to electrodes located within a tissue region of the patient, thereby changing the status of the dysfunction. A physiological end-function of the patient indicative of the changed status of the dysfunction is measured, and stimulation parameters are programmed into the neurostimulator based on the measured physiological end-function. In another aspect, electrodes are placed adjacent to a tissue region of the patient, and stimulation energy is conveyed from the electrodes to the tissue region in accordance with the stimulation parameters, thereby changing the status of the dysfunction. A physiological end-function of the patient indicative of the changed status of the dysfunction is measured, and the stimulation parameters are adjusted based on the measured physiological end-function.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Devices and methods for optimized neuromodulation and their application
InactiveUS20160001096A1Reduce image distortionLow costUltrasound therapyDiagnosticsDiagnostic Radiology ModalitySpinal cord
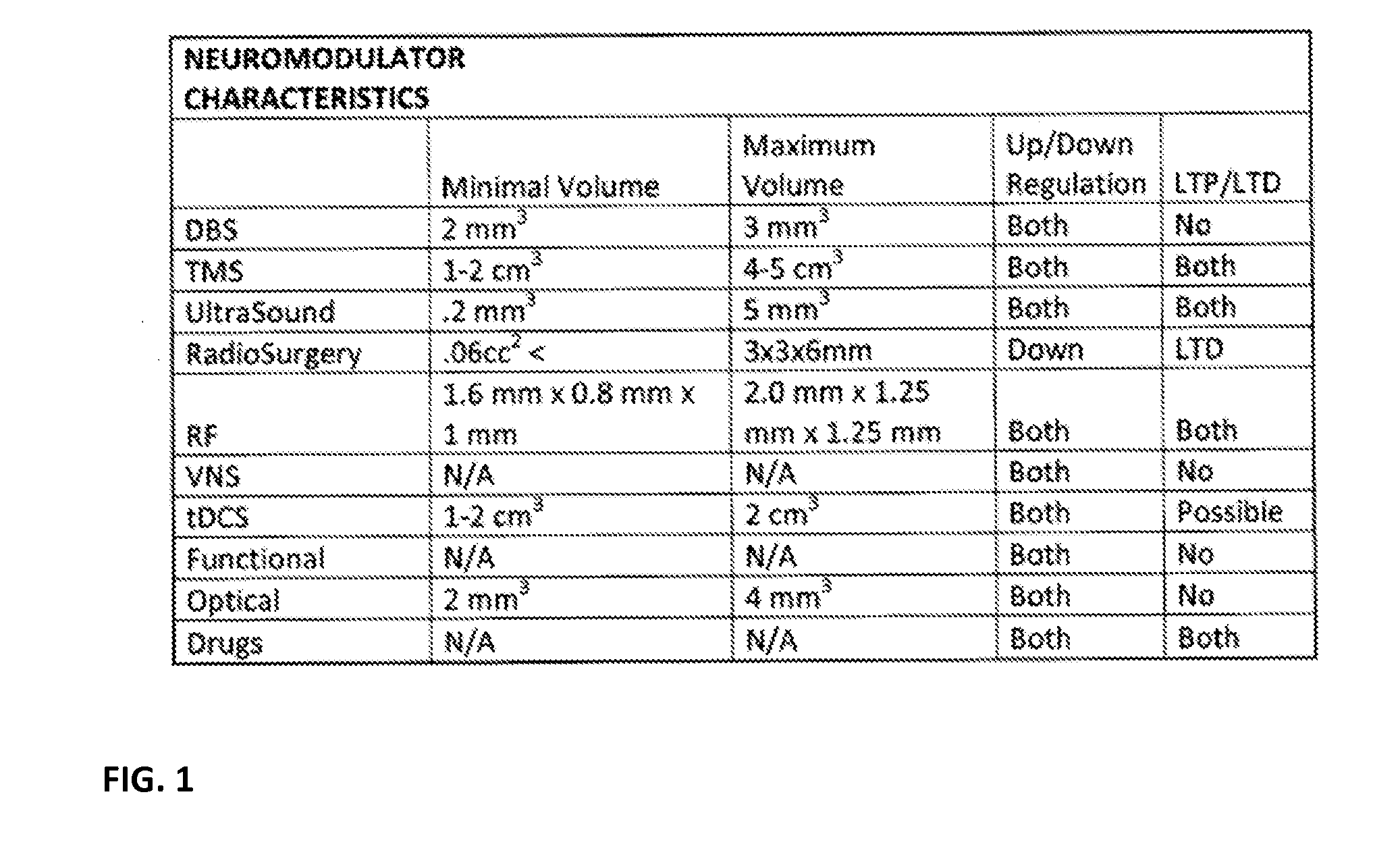
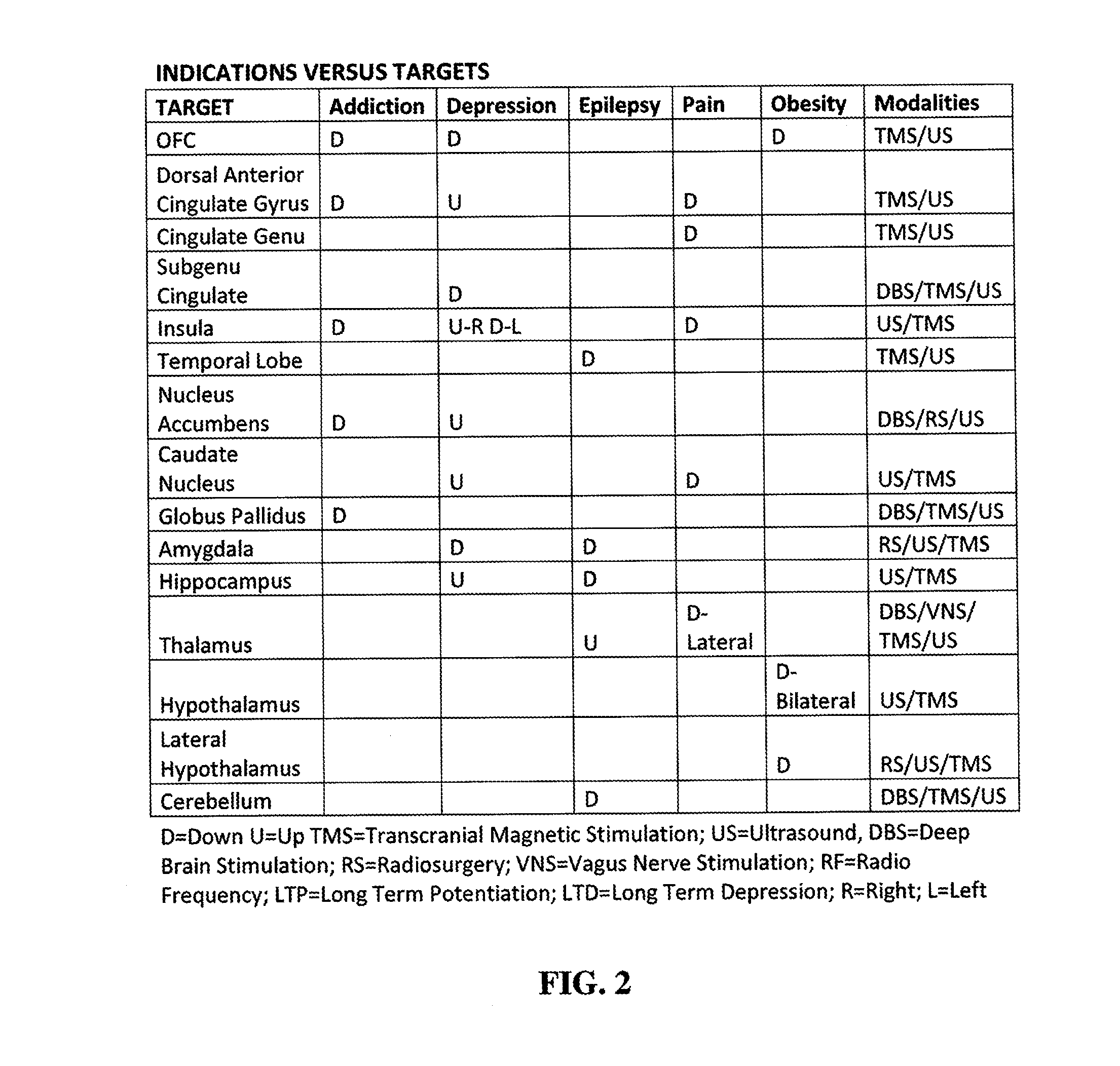
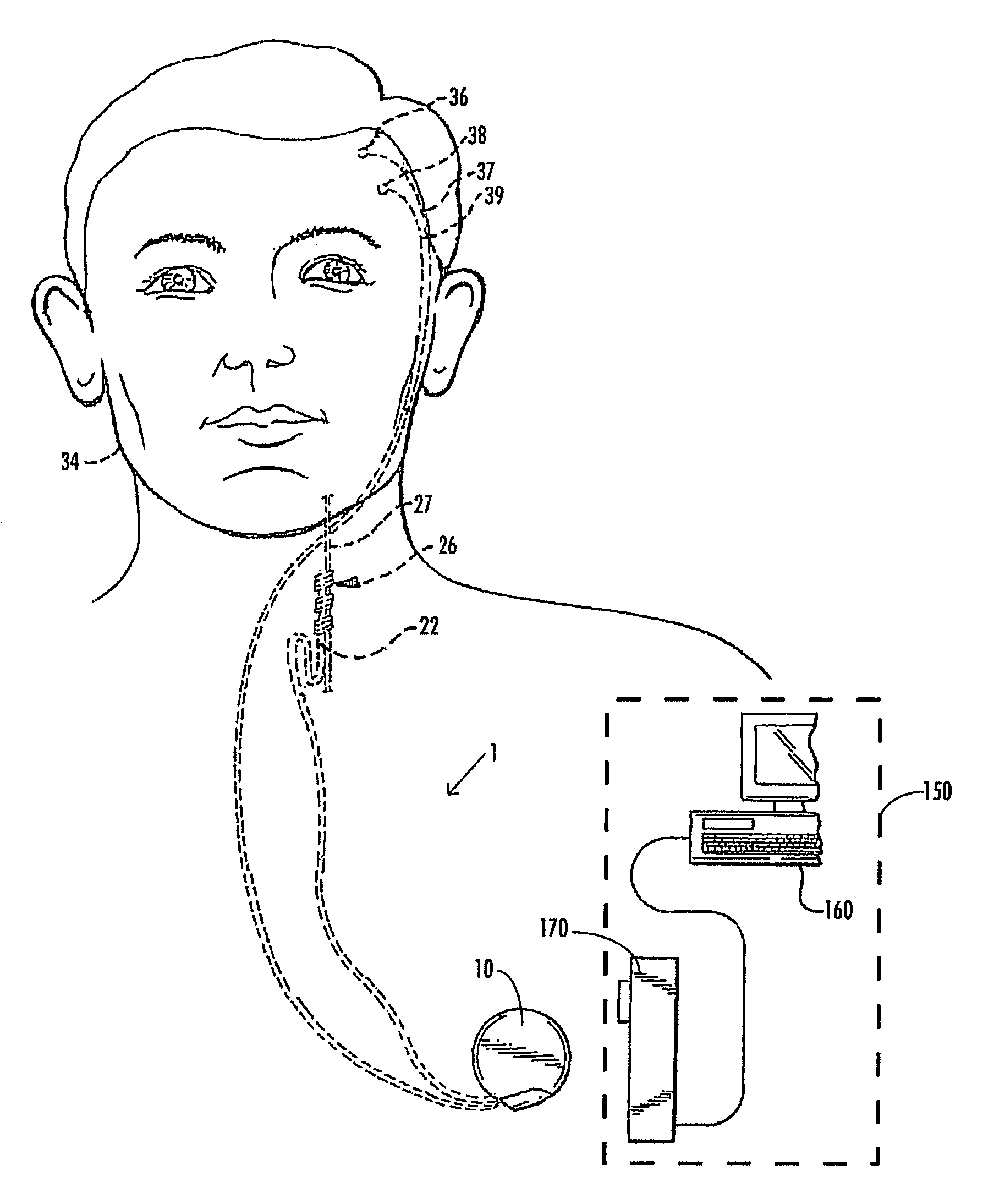
Disclosed are methods and systems for optimized deep or superficial deep-brain stimulation using multiple therapeutic modalities impacting one or multiple points in a neural circuit to produce Long-Term Potentiation (LTP) or Long-Term Depression (LTD). Also disclosed are methods for treatment of clinical conditions and obtaining physiological impacts. Also disclosed are: methods and systems for Guided Feedback control of non-invasive deep brain or superficial neuromodulation; patterned neuromodulation, ancillary stimulation, treatment planning, focused shaped or steered ultrasound; methods and systems using intersecting ultrasound beams; non-invasive ultrasound-neuromodulation techniques to control the permeability of the blood-brain barrier; non-invasive neuromodulation of the spinal cord by ultrasound energy; methods and systems for non-invasive neuromodulation using ultrasound for evaluating the feasibility of neuromodulation treatment using non-ultrasound / ultrasound modalities; neuromodulation of the whole head, treatment of multiple conditions, and method and systems for neuromodulation using ultrasound delivered in sessions.
Owner:MISHELEVICH DAVID J
Selective neurostimulation for treating epilepsy
A method and device for treating epilepsy are disclosed which provide for electrical, chemical or magnetic stimulation of certain areas of the brain to modulate neuronal activity of areas associated with symptoms of epilepsy. Deep brain stimulation is combined with vagus nerve stimulation to enhance symptomatic relief of the disorder. Some embodiments also employ a sensing capability to optimize the therapeutic treatment regimen.
Owner:LIVANOVA USA INC
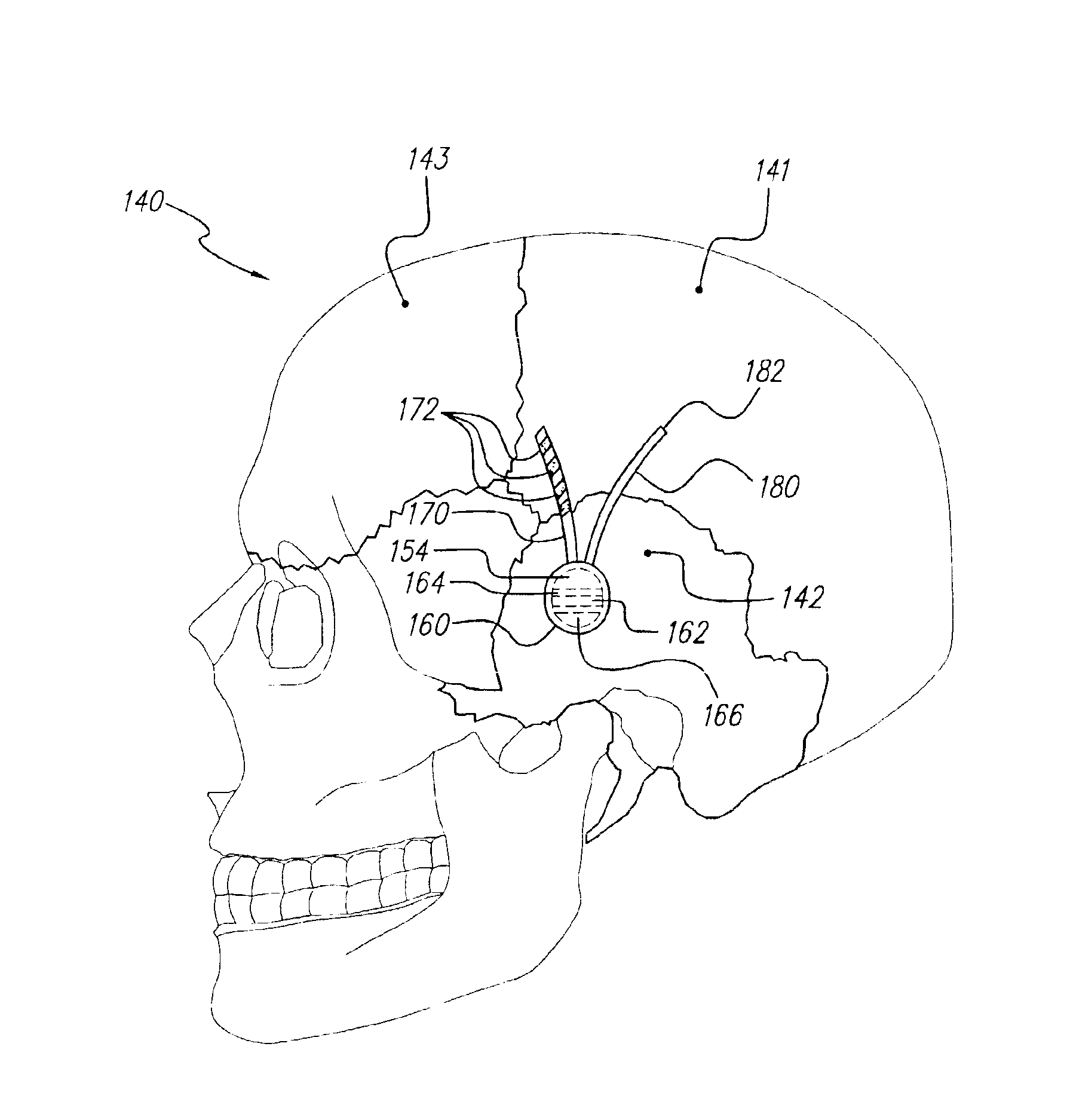
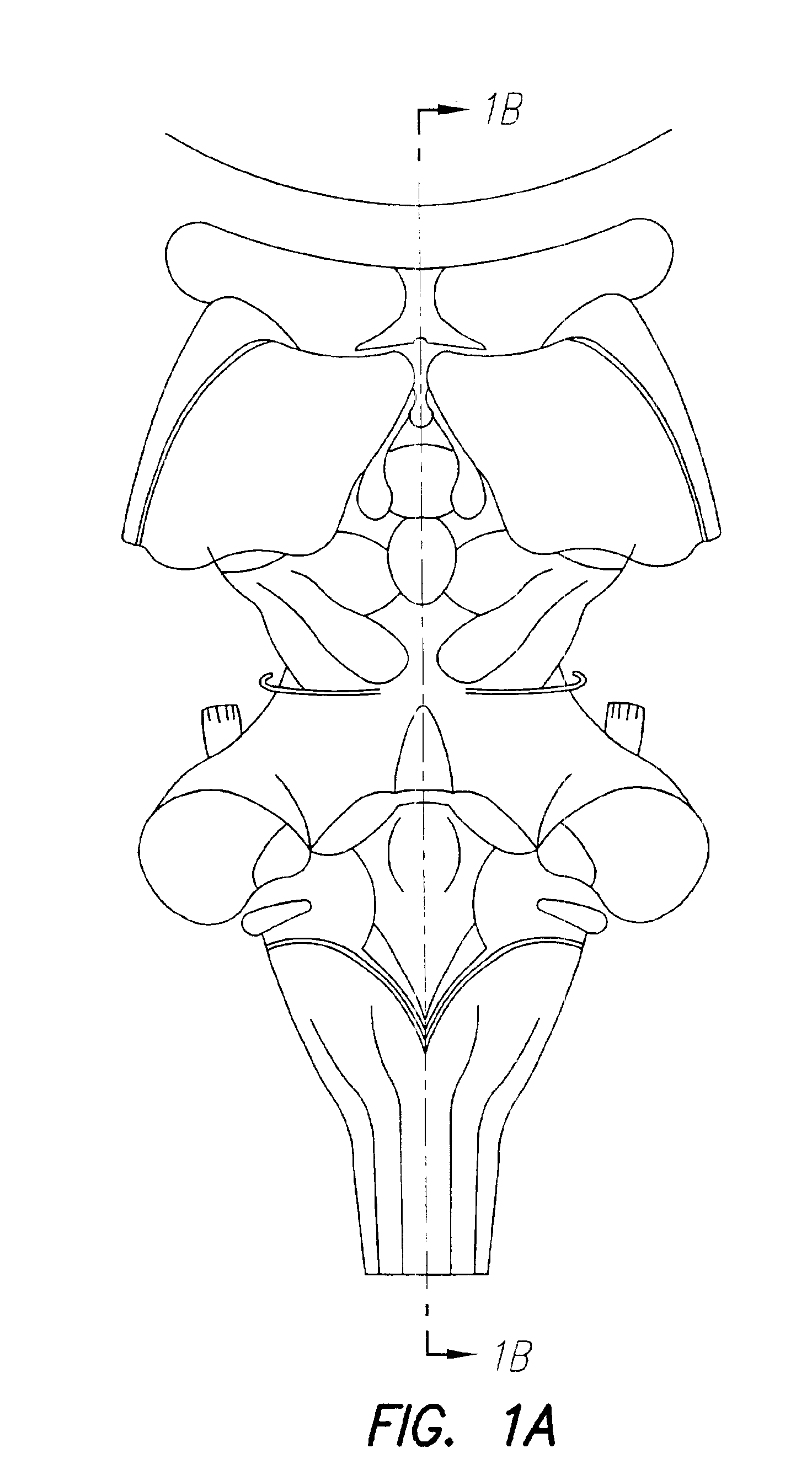
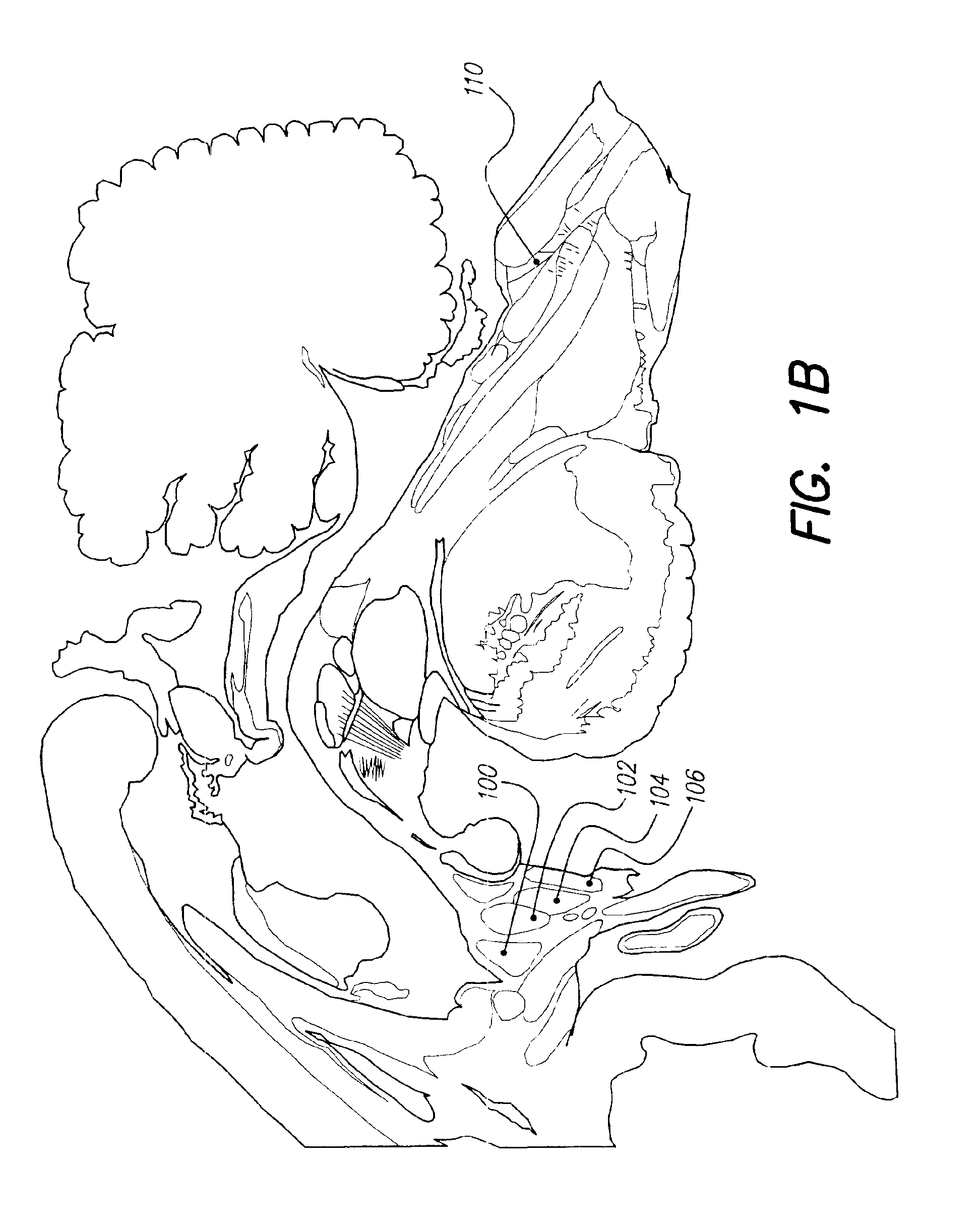
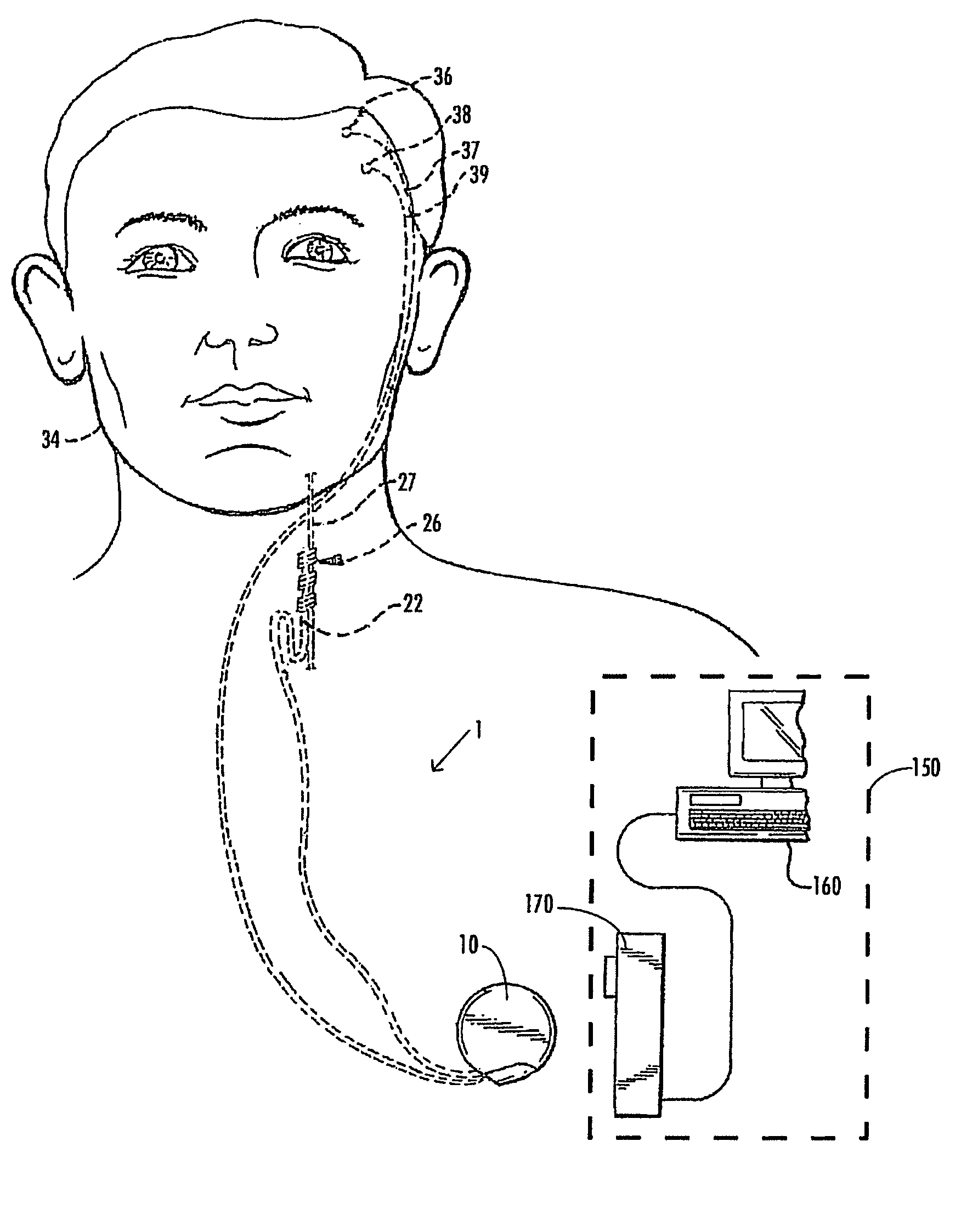
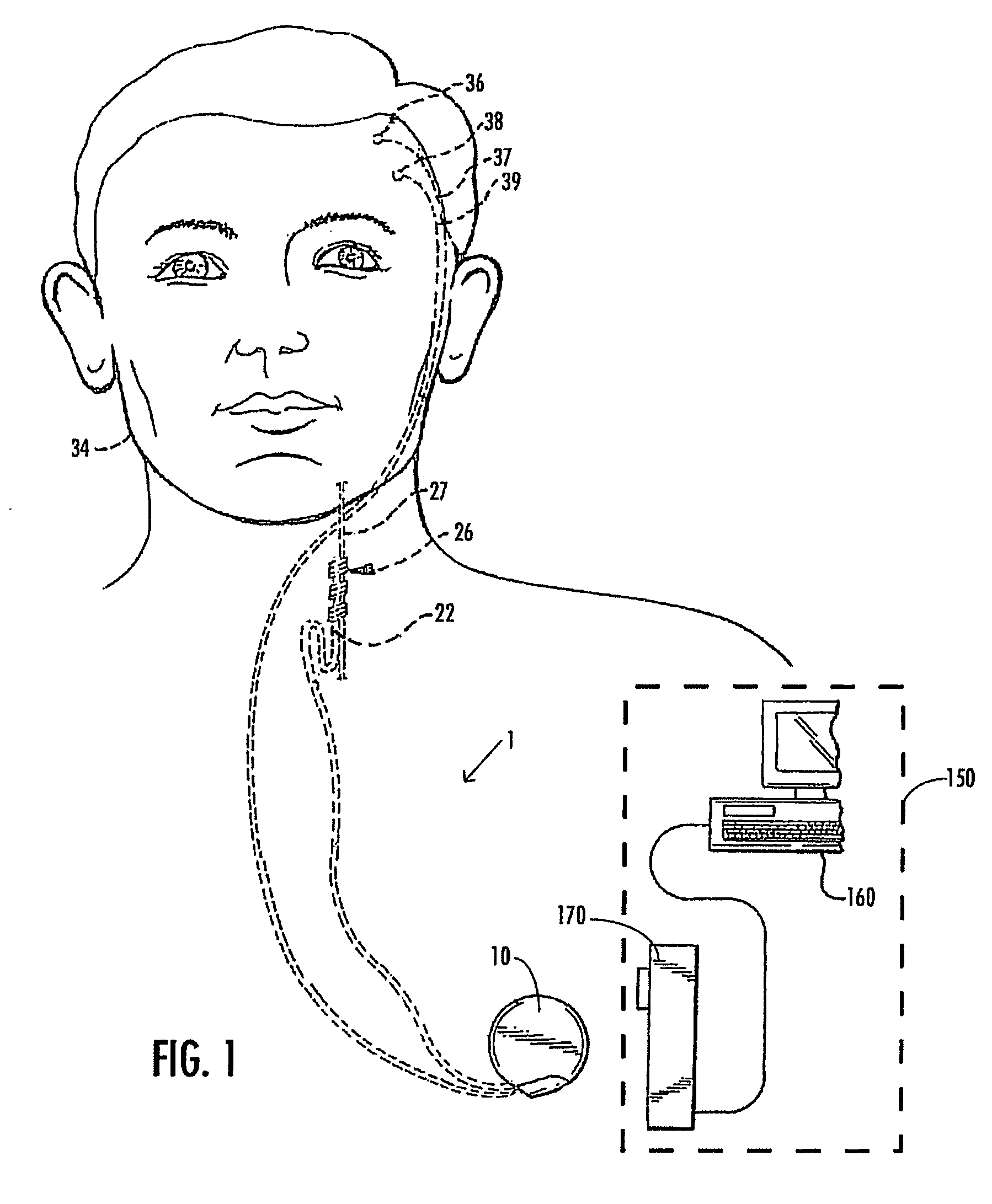
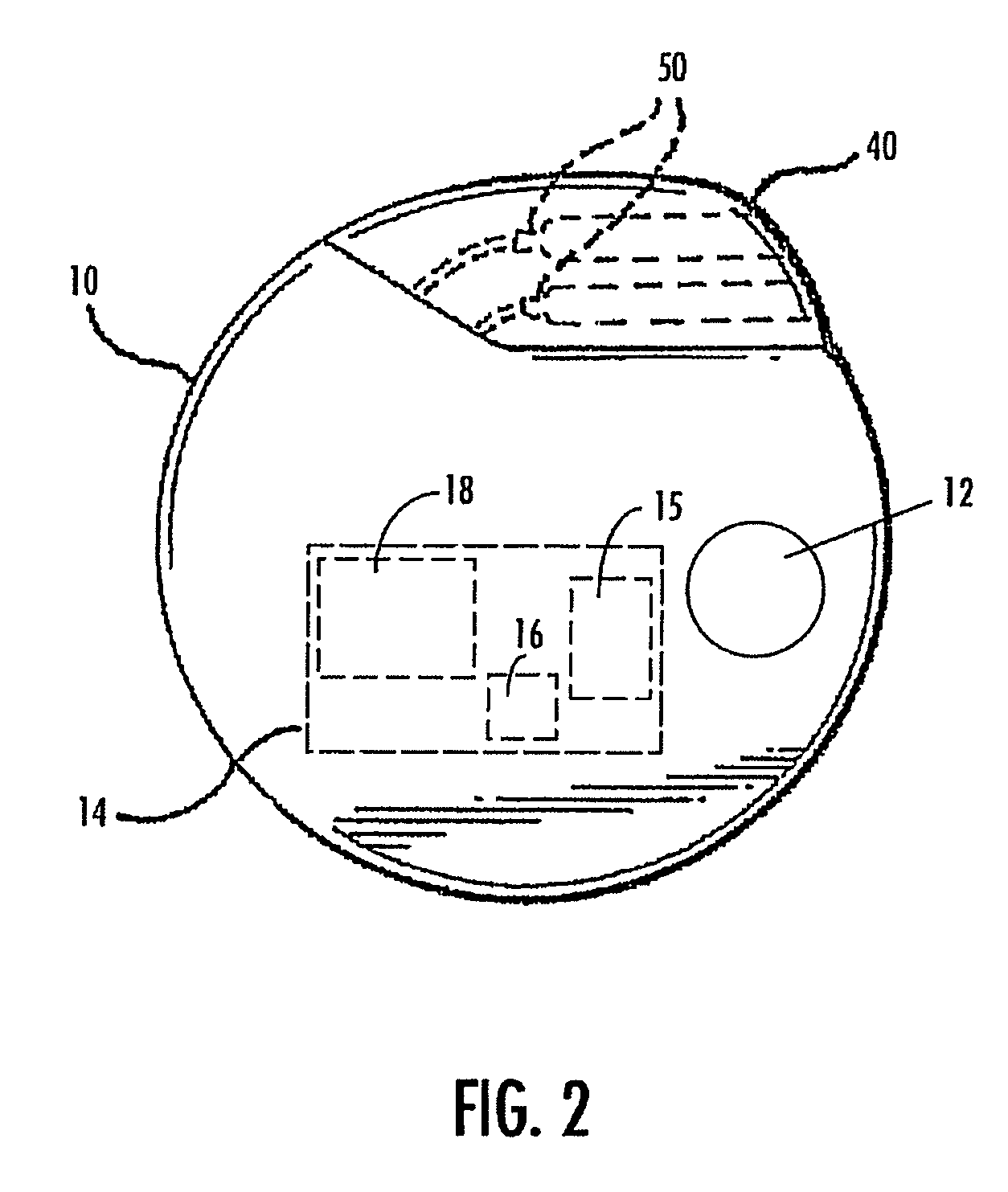
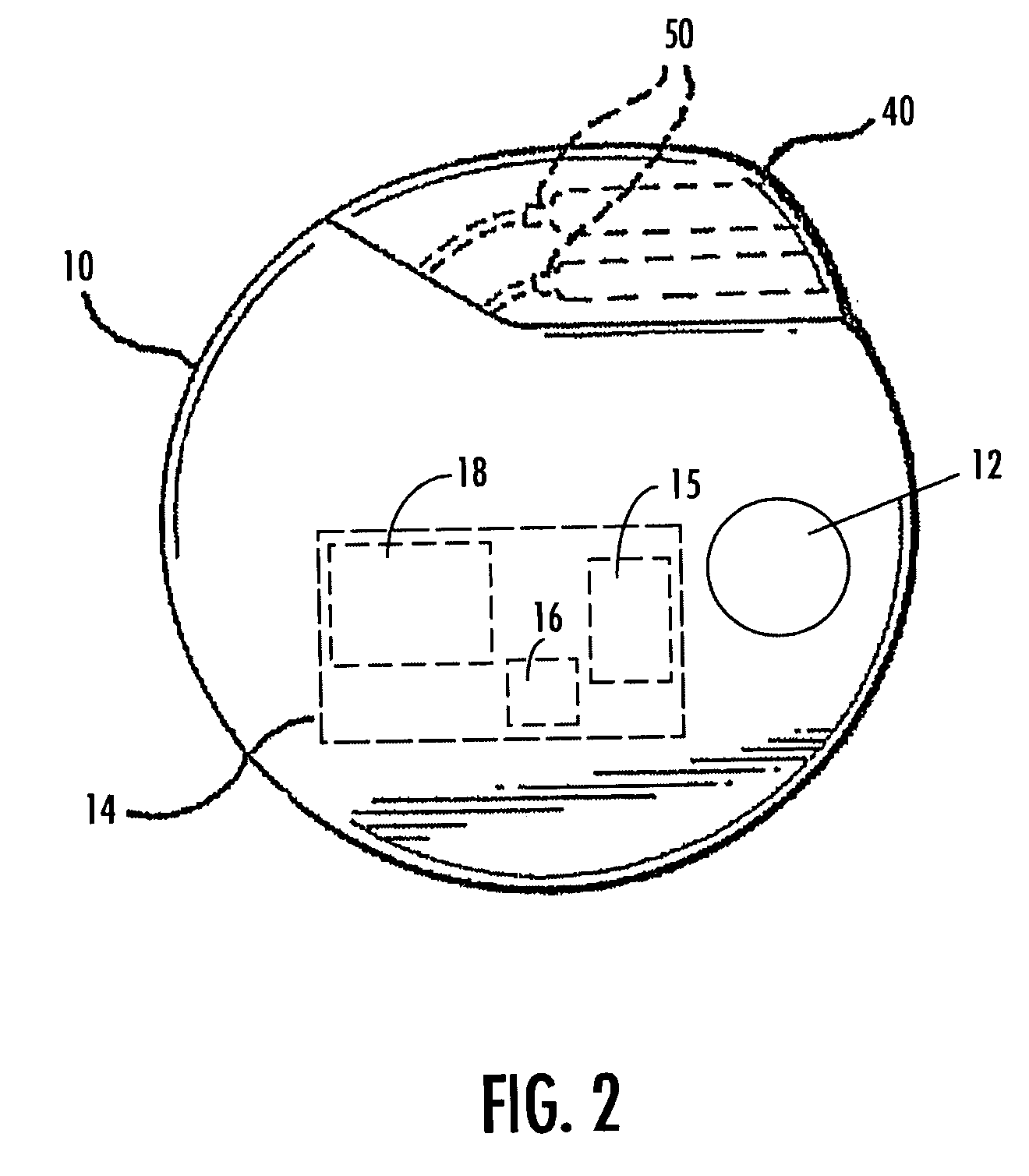
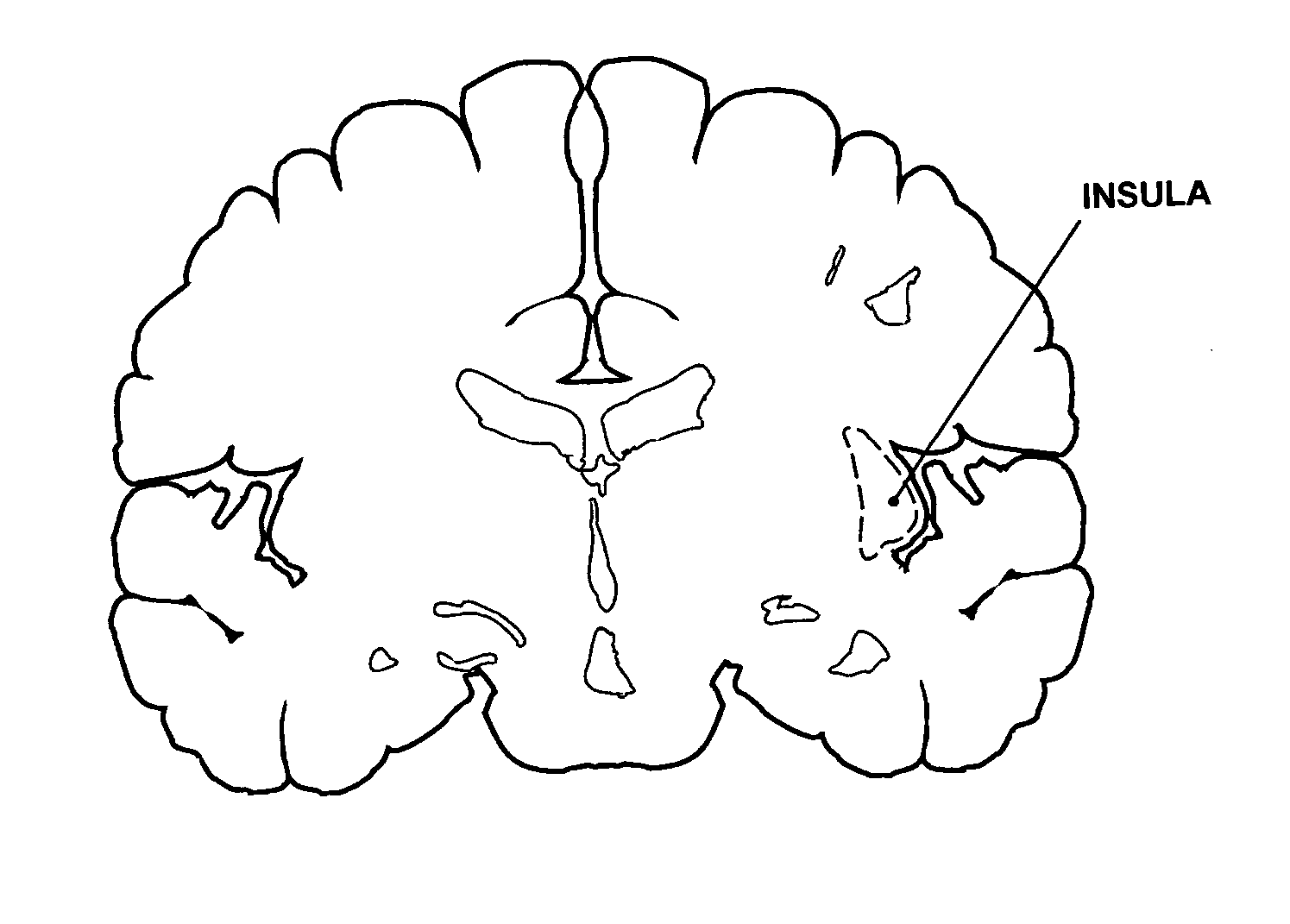
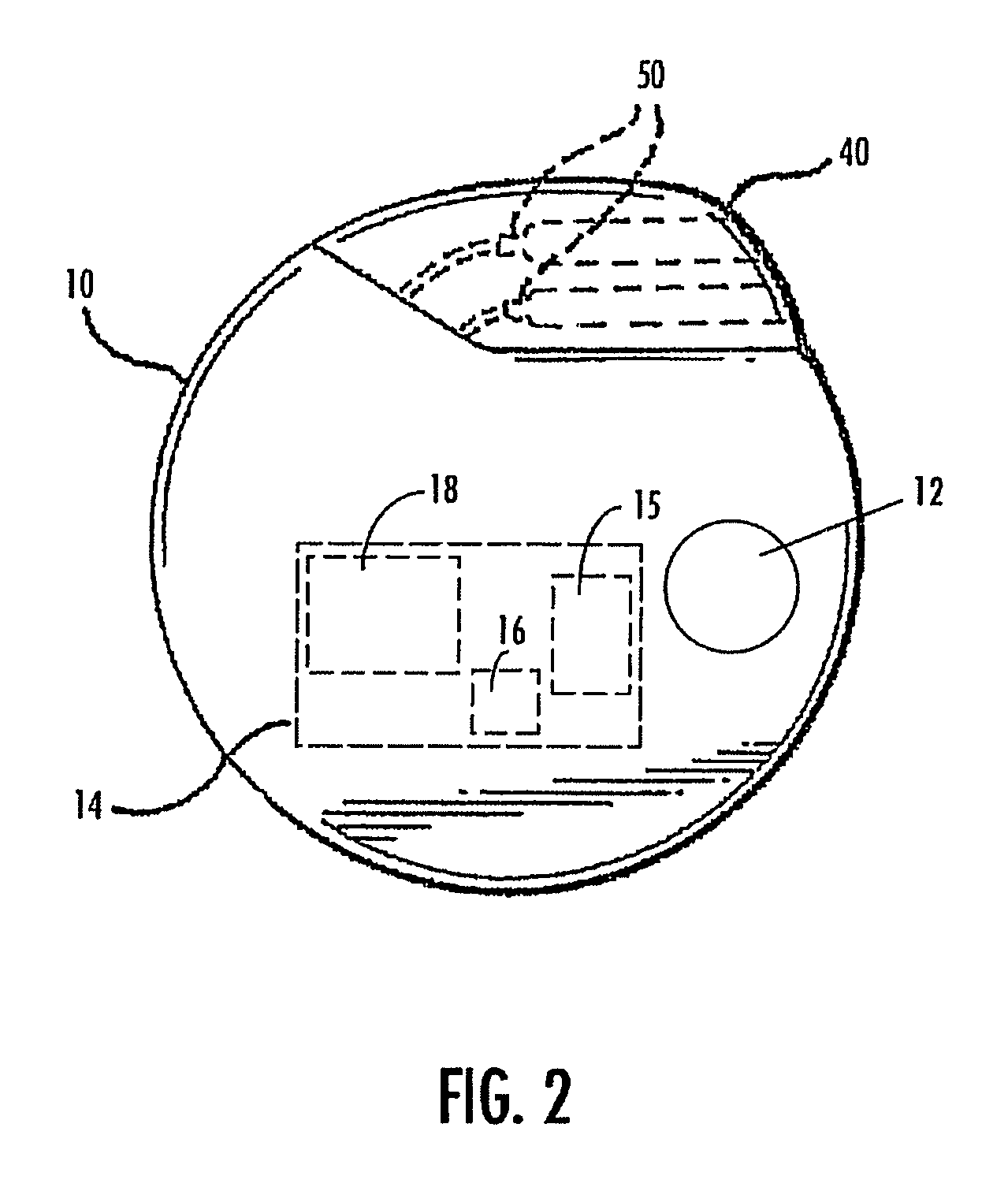
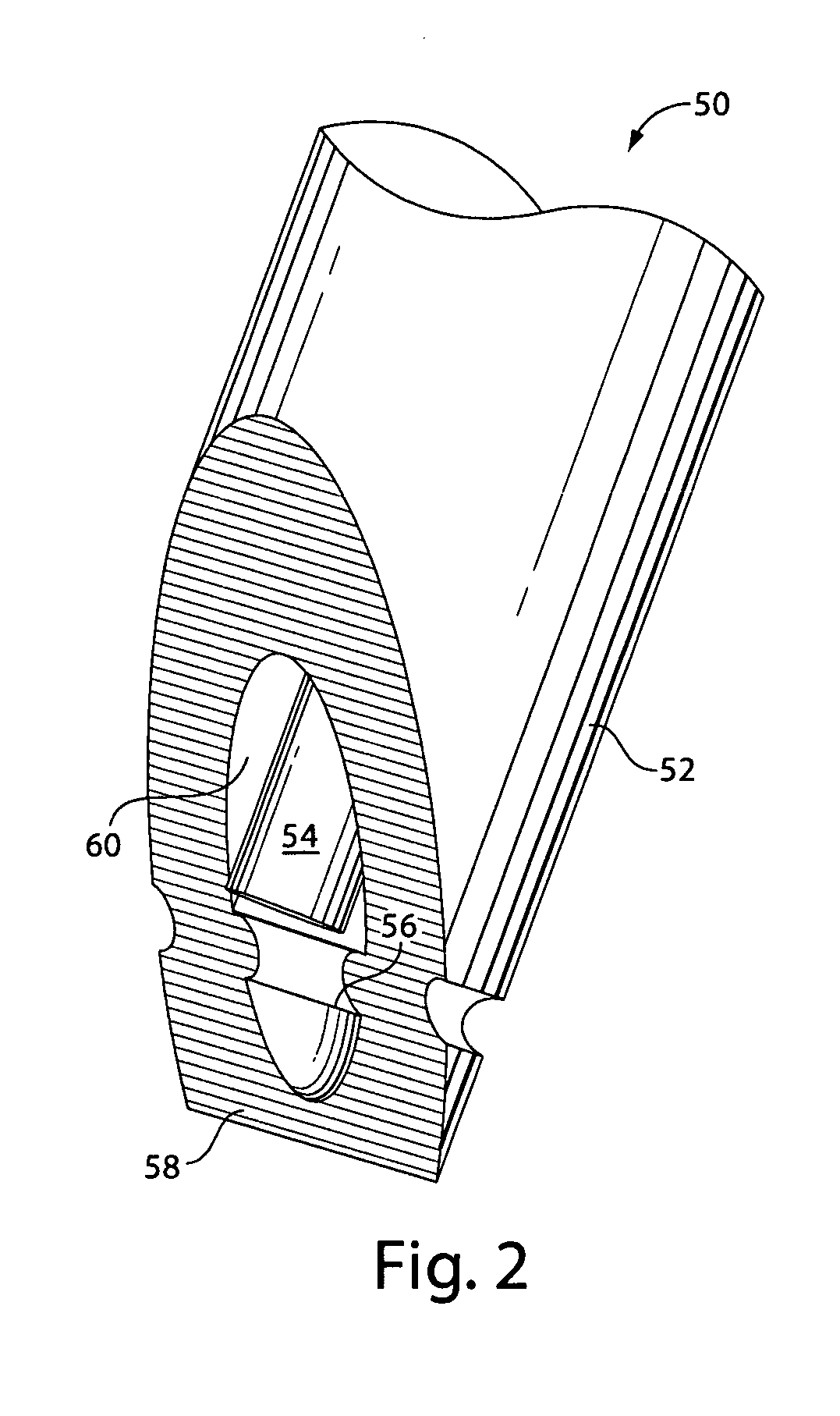
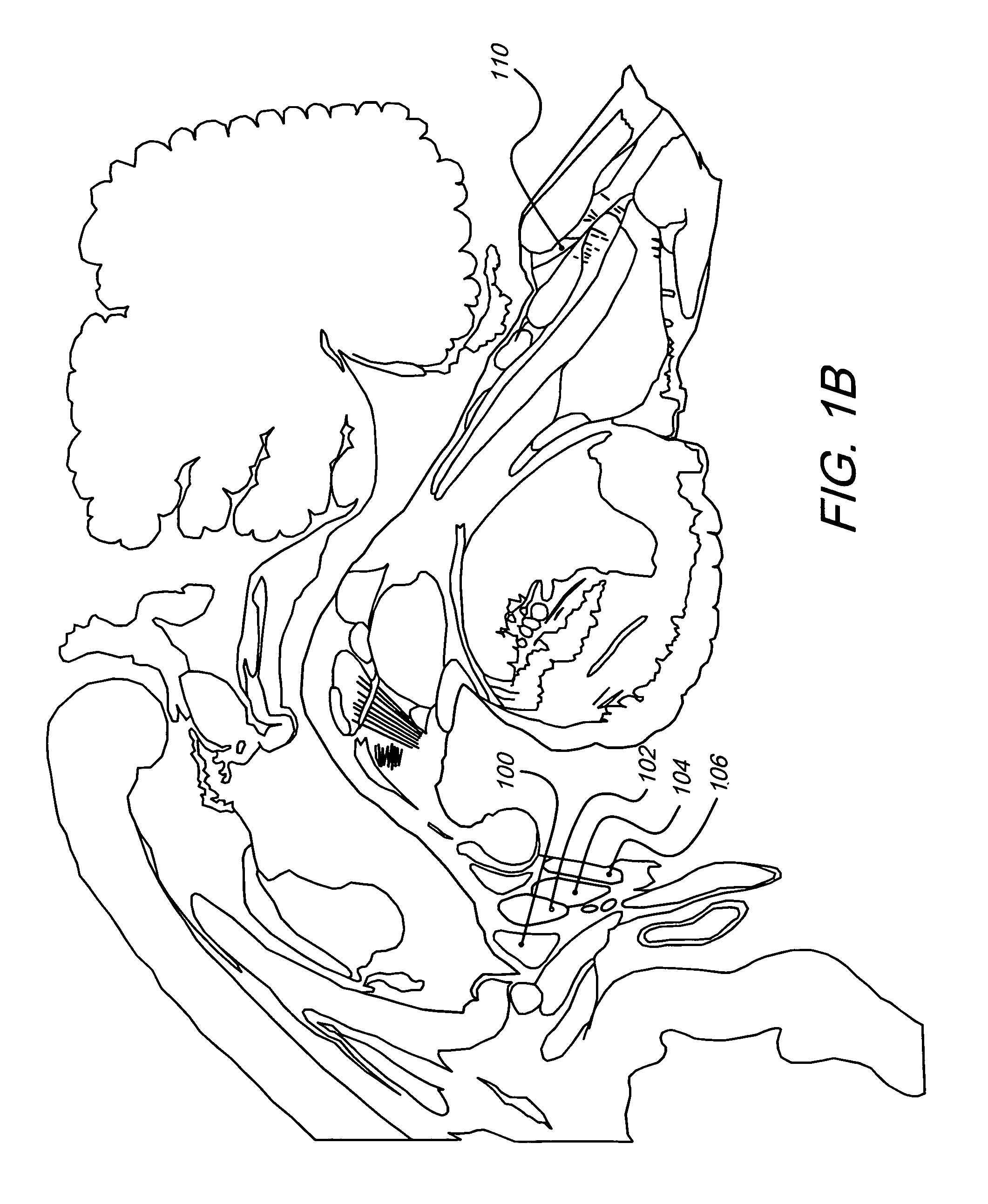
Deep brain stimulation
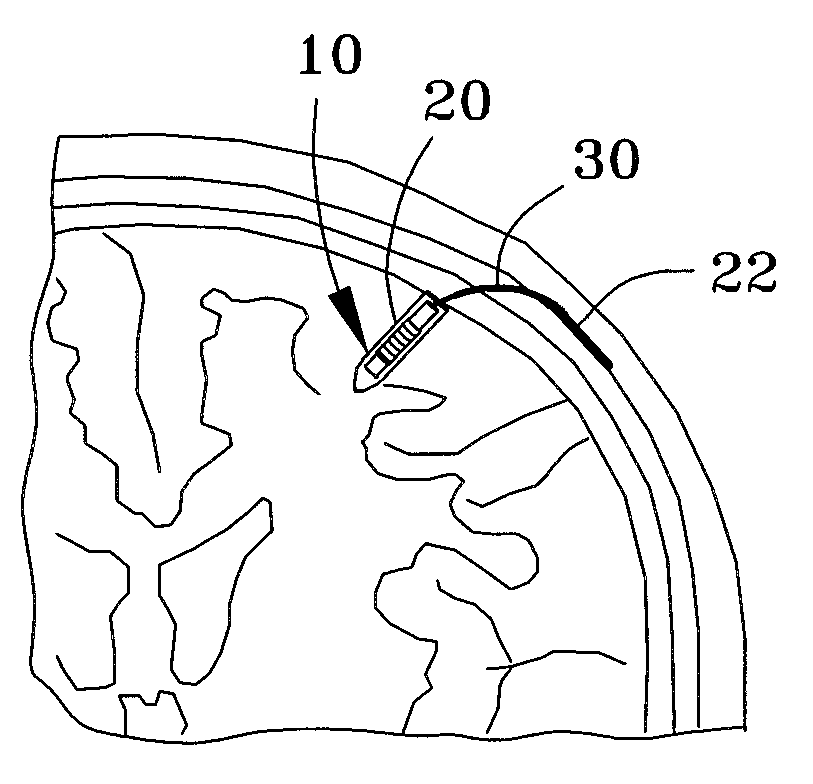
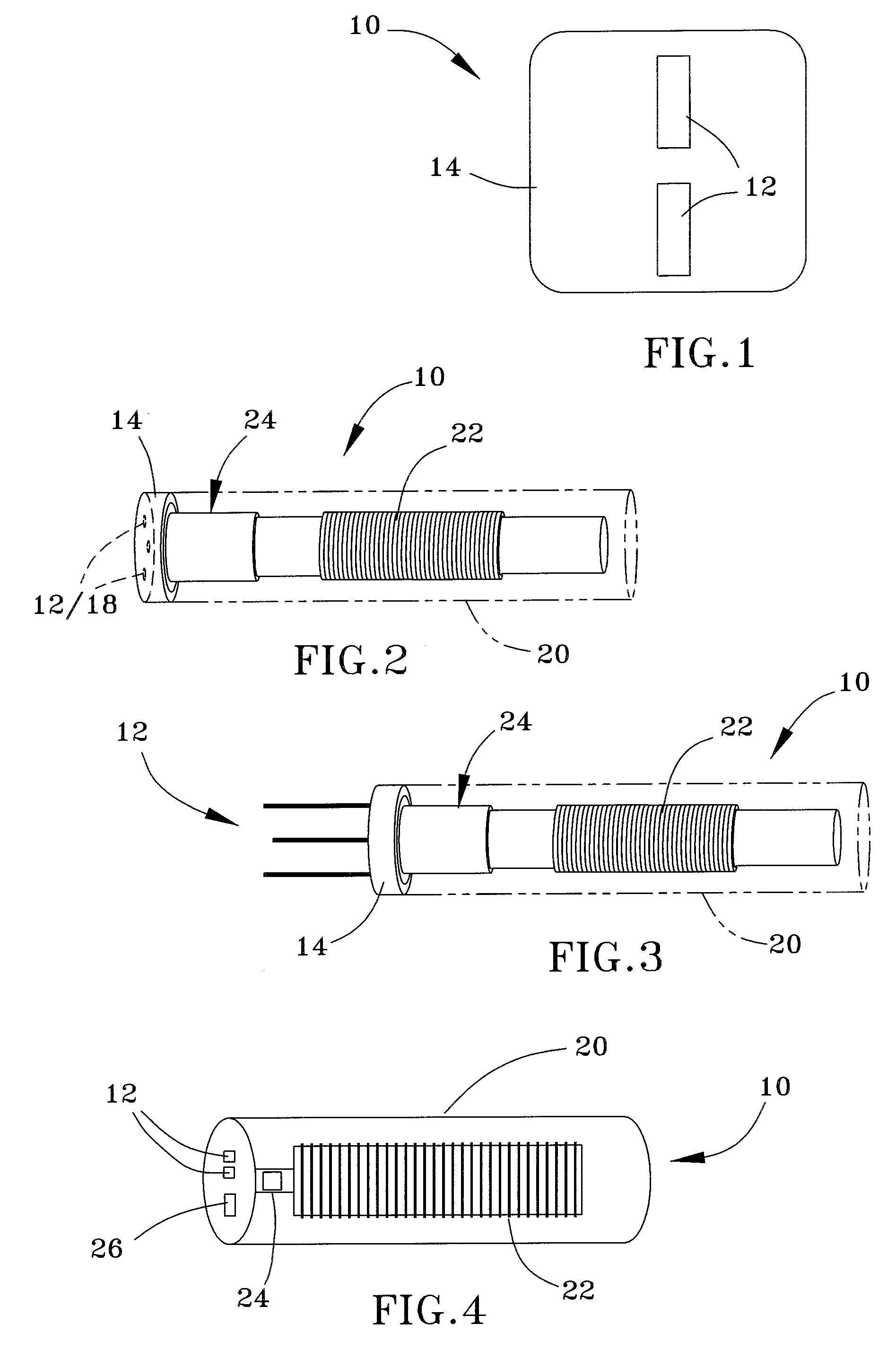
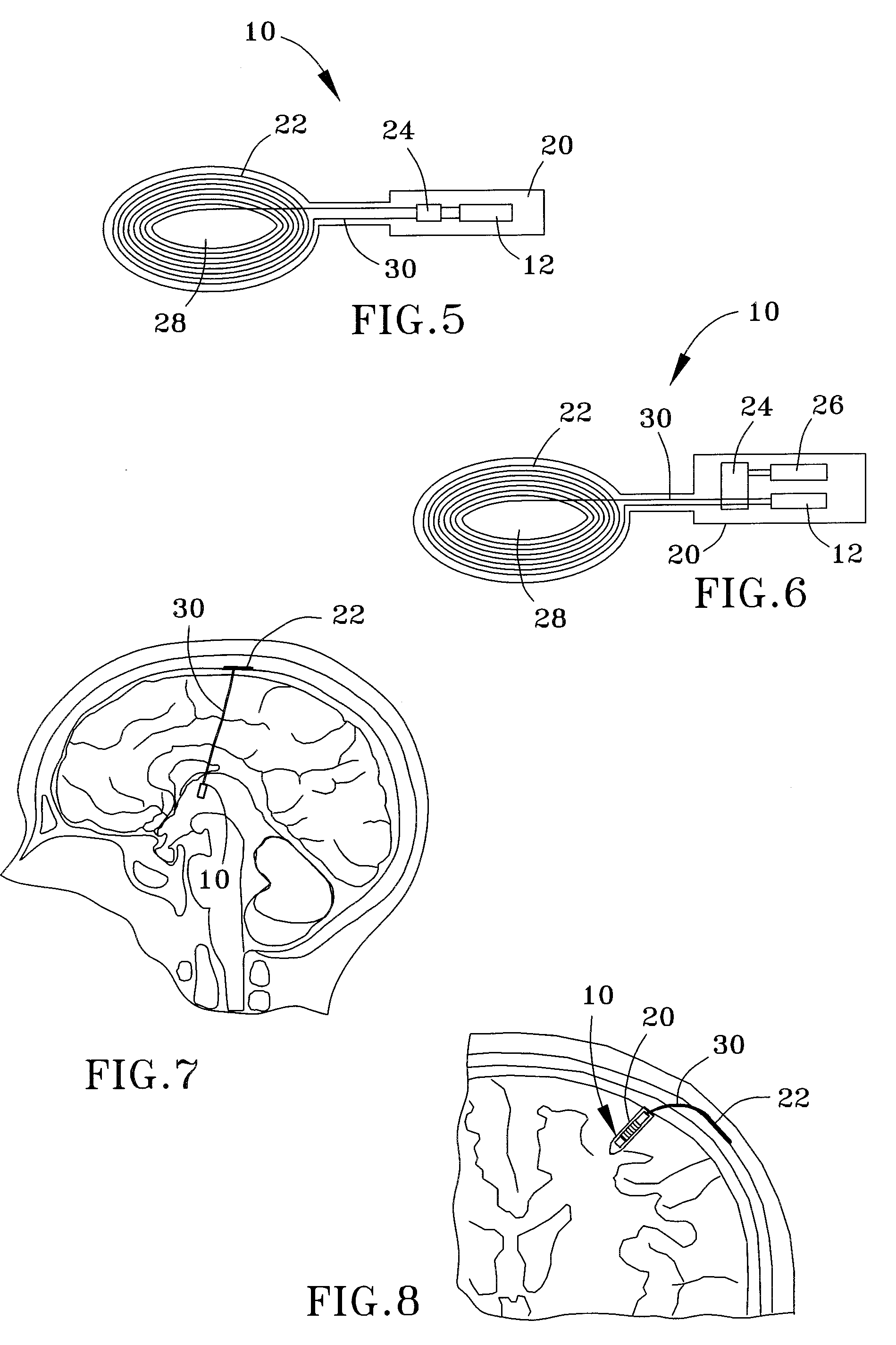
InactiveUS20050267347A1Less invasiveLess time-consumingHead electrodesSensorsSurgeryDeep brain stimulation
A probe used in deep brain stimulation includes a cannula comprising an elongated housing defining an internal aperture and having a base portion with a notch, the housing having a longitudinal axis, and an electrode configured to be inserted through the aperture of the cannula. The electrode and notch are configured such that the electrode will contact the notch when inserted in the cannula and be directed out of the cannula at a non-zero angle relative to the longitudinal axis of the housing.
Owner:OSTER DORAN
Deep brain stimulation current steering with split electrodes
A device for brain stimulation includes a lead having a longitudinal surface, a proximal end, a distal end and a lead body. The device also includes a plurality of electrodes disposed along the longitudinal surface of the lead near the distal end of the lead. The plurality of electrodes includes a first set of segmented electrodes comprising at least two segmented electrodes disposed around a circumference of the lead at a first longitudinal position along the lead; and a second set of segmented electrodes comprising at least two segmented electrodes disposed around a circumference of the lead at a second longitudinal position along the lead. The device further includes one or more conductors that electrically couple together all of the segmented electrodes of the first set of segmented electrodes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
Method and means for connecting and controlling a large number of contacts for electrical cell stimulation in living organisms
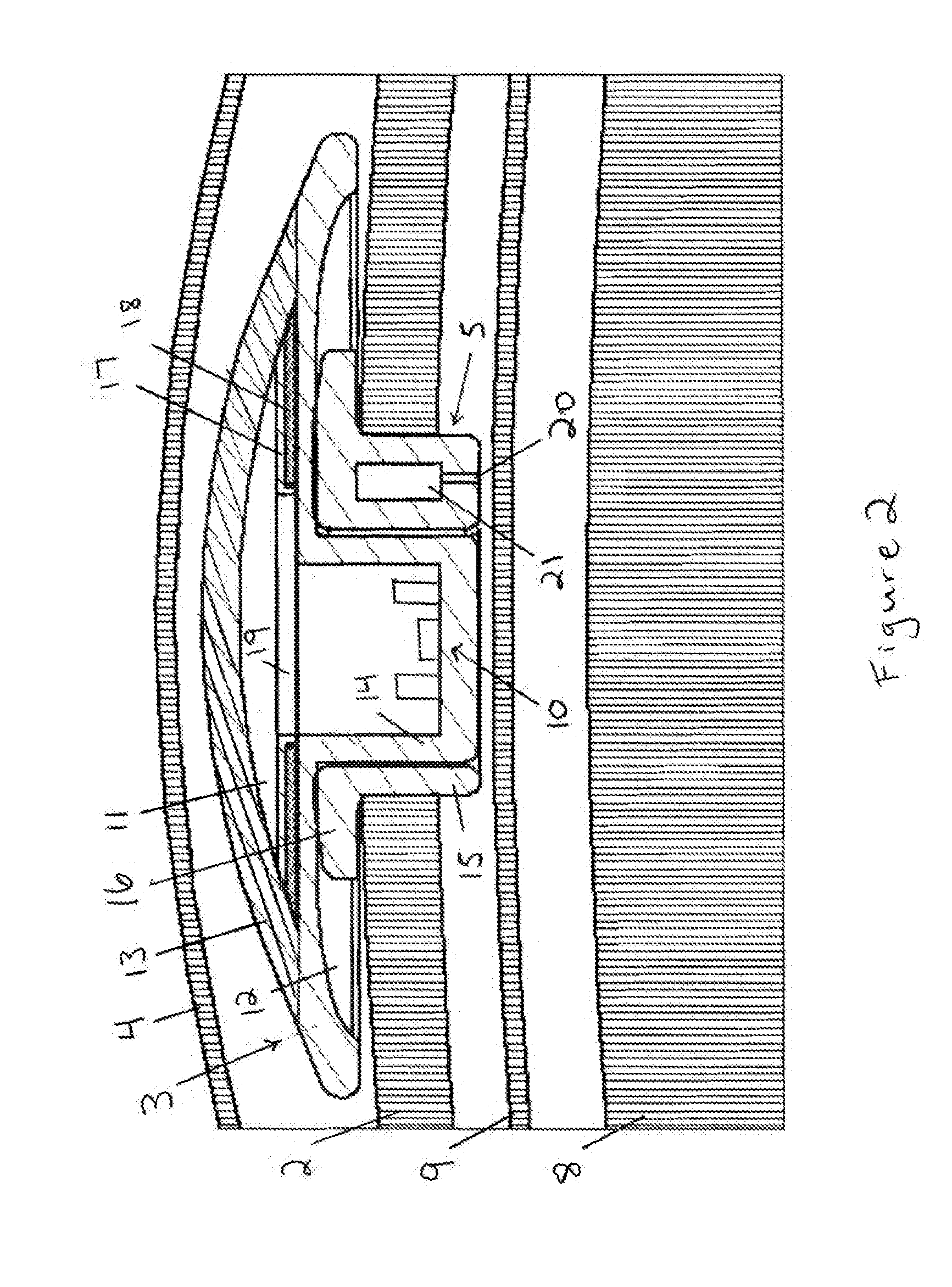
ActiveUS20100082076A1High voltageUndesirable side-effectHead electrodesElectrical measurement instrument detailsAddress busEngineering
An improved electrode for neural stimulation, including deep brain stimulation, cortical stimulation, muscle stimulation and other similar applications. The improvement of our invention over prior art consisting of the possibility of a larger number of electrode pads from where to originate the electrical stimulation, thereby offering the possibility of fine control of the location of the stimulating signal. Our invention discloses a system of address wires which controls switches and demultiplexers to select one of a plurality of wires and one of a plurality of electrode pads from where the electric stimulation starts, and latches that maintain some selected choices after the address buses go on to select other wires and other electrode tips. Our invention also discloses time delay lines which are used to keep the stimulating pulses for a pre-assigned time, after which the stimulating pulses stop until further instruction to start again.
Owner:LEE CHONG IL +1
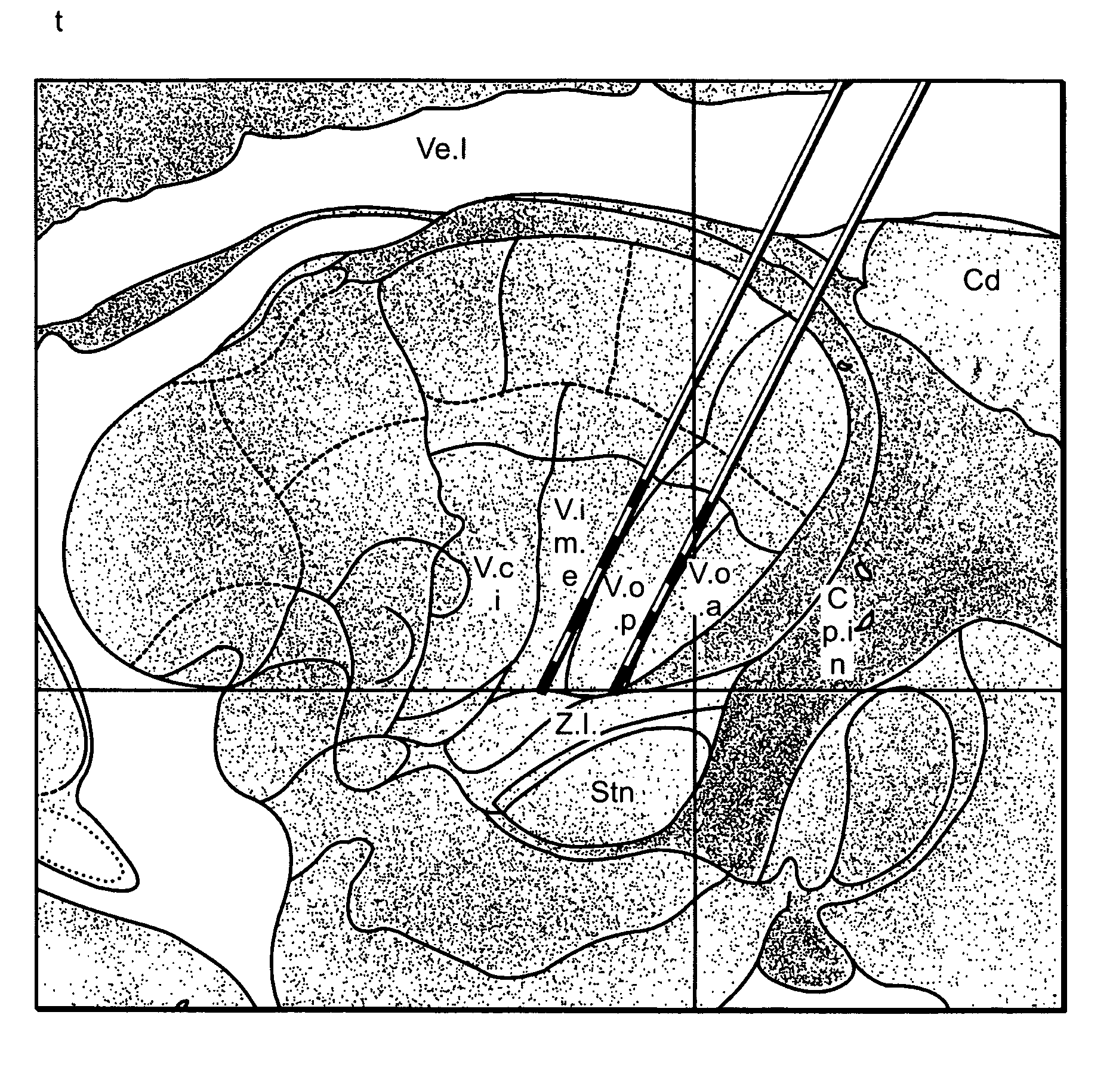
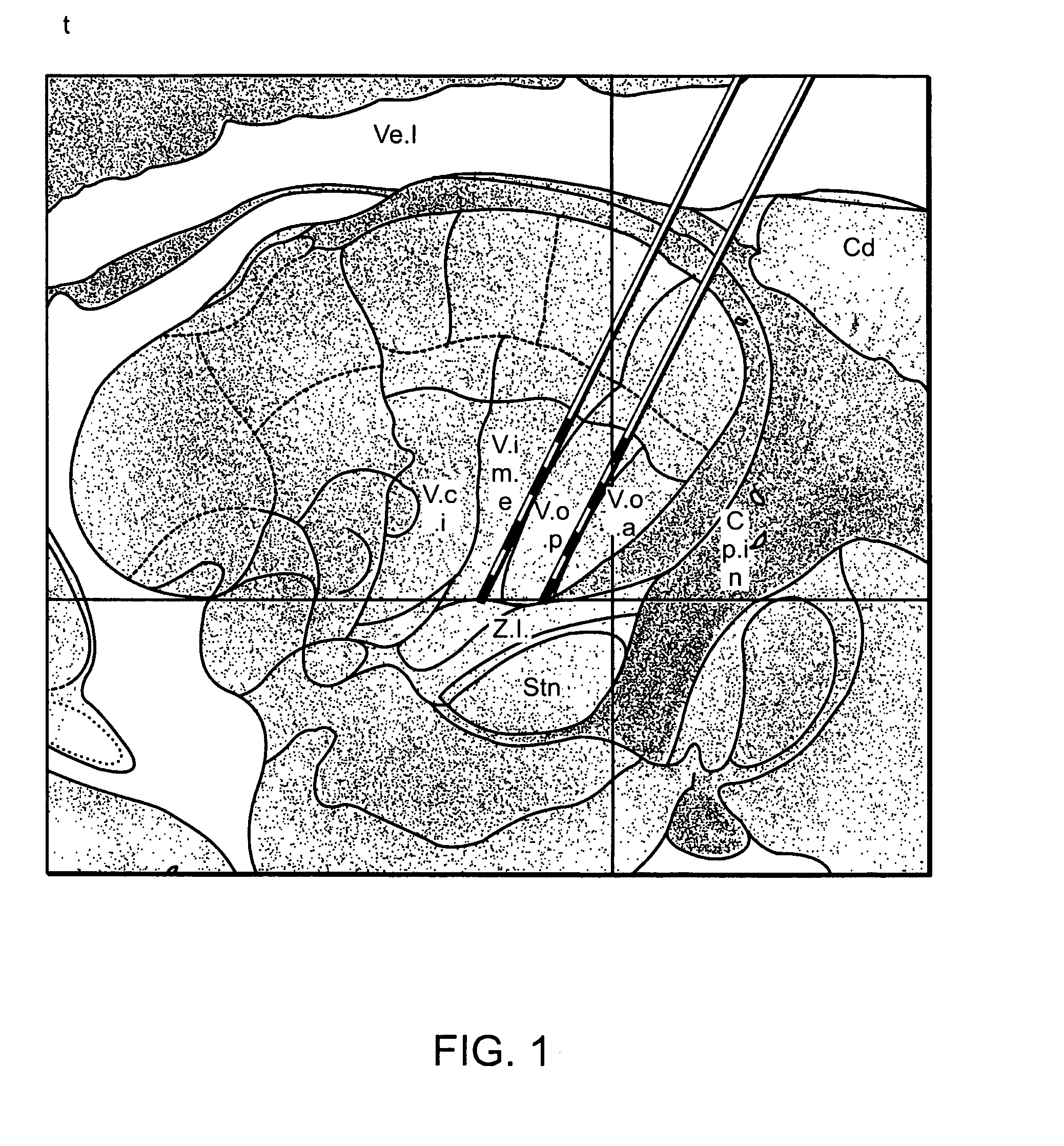
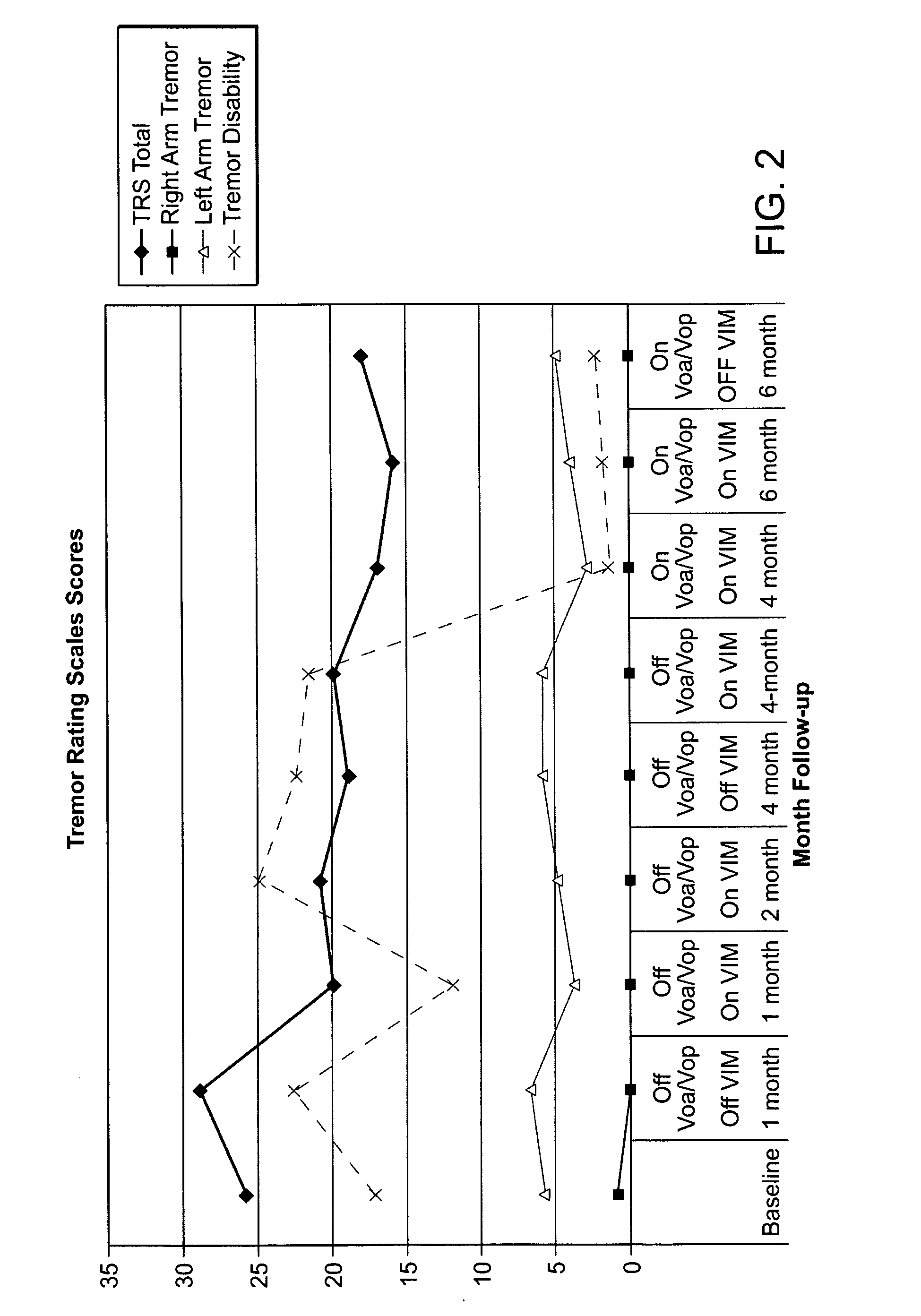
Multiple lead method for deep brain stimulation
ActiveUS20080103547A1Easy to controlGood treatment effectHead electrodesExternal electrodesDiseaseThalamus
New methods for deep brain stimulation (DBS) surgery using two or more electrical leads are provided. The methods are useful for treating a wide variety of brain-associated disorders including movement-related disorders, psychiatric disorders, metabolic / eating disorders, memory disorders, and pain. Methods featuring stimulation of distinct target areas of a subject's brain, such as the thalamic ventralis intermedius (VIM) and the ventralis oralis (VOA / VOP) using multiple electrical leads for treatment of tremor provide superior clinical outcomes to stimulation with single leads implanted in these target areas.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
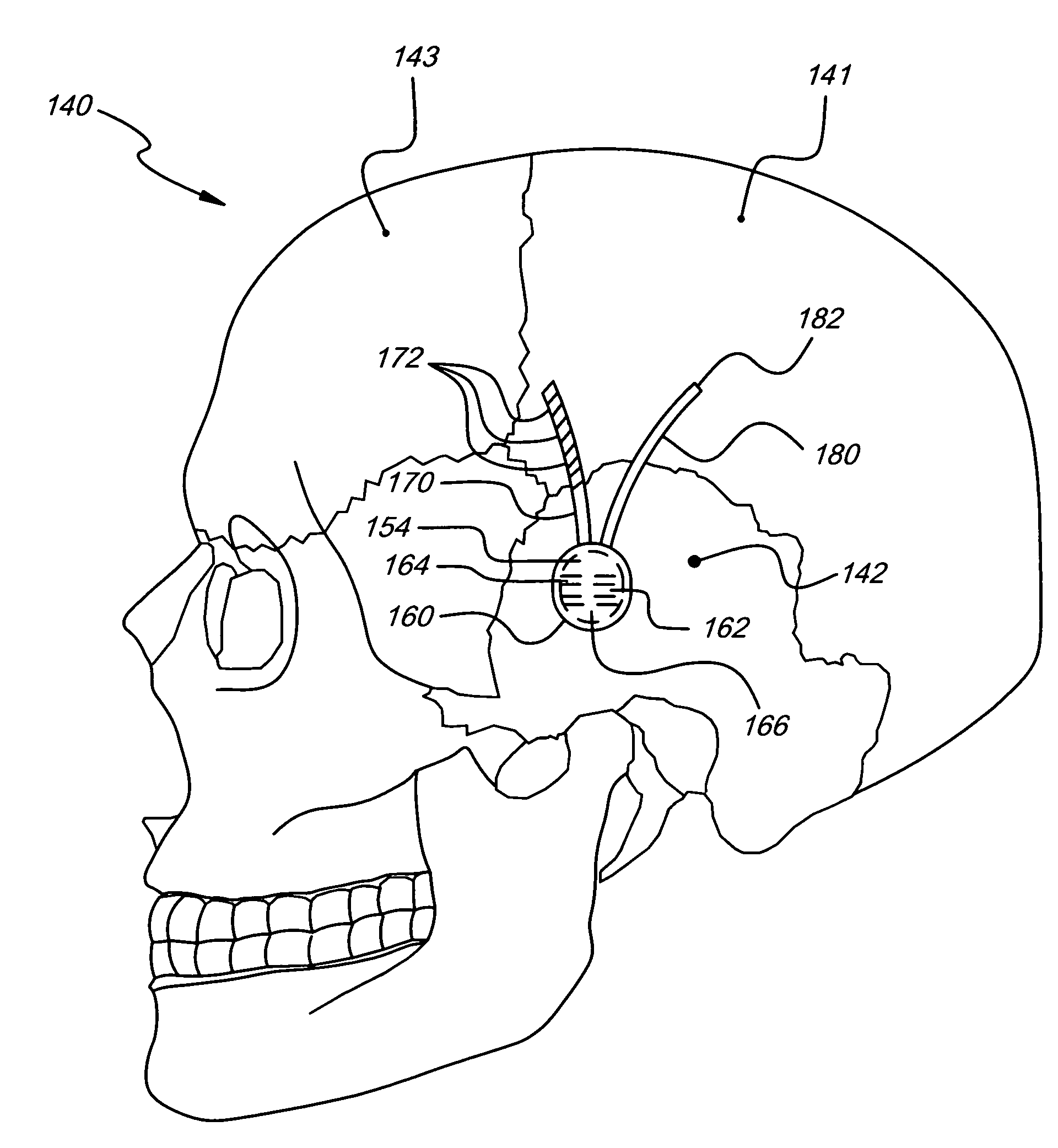
Implantable transcranial pulse generator having a collapsible portion
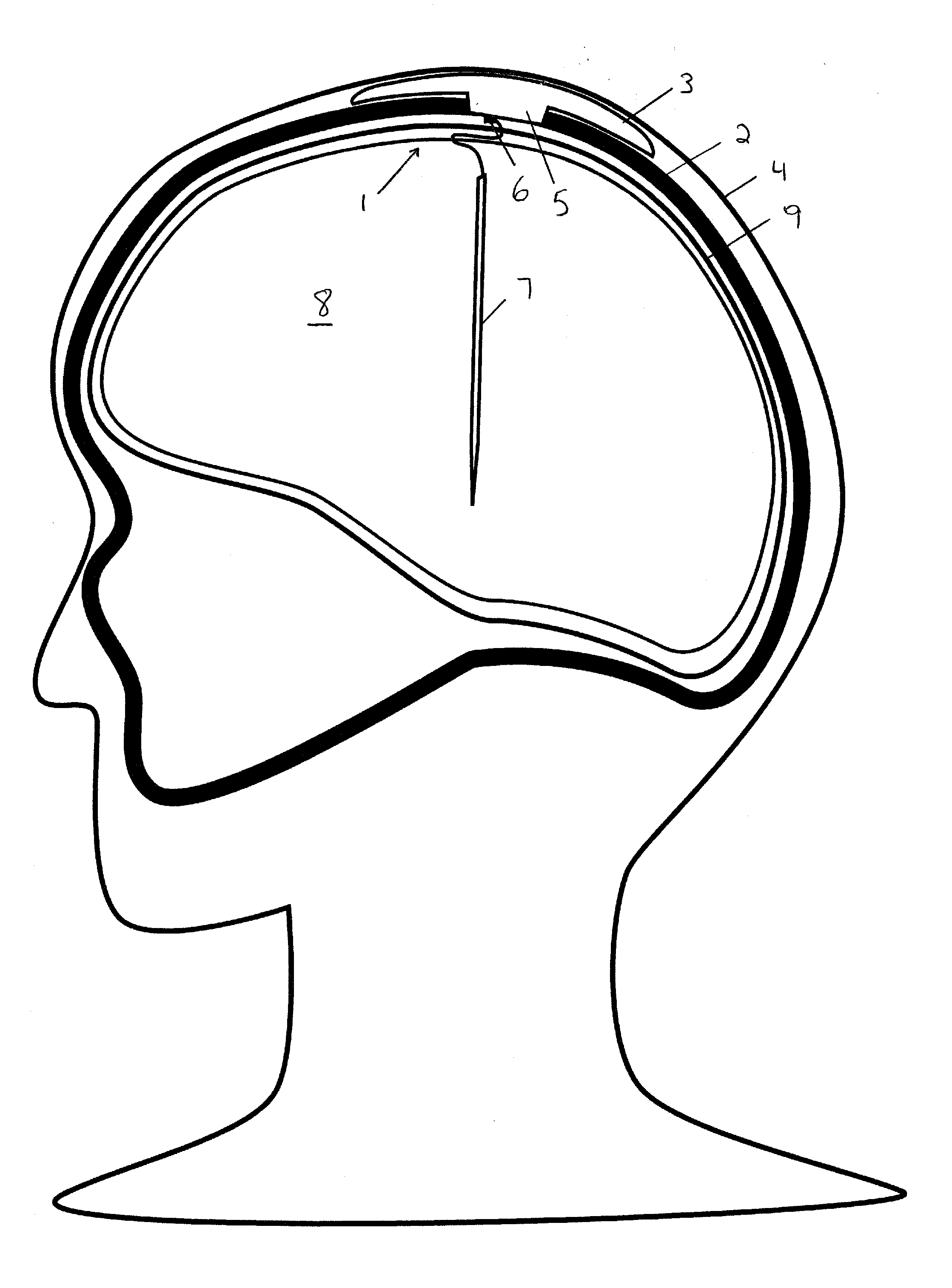
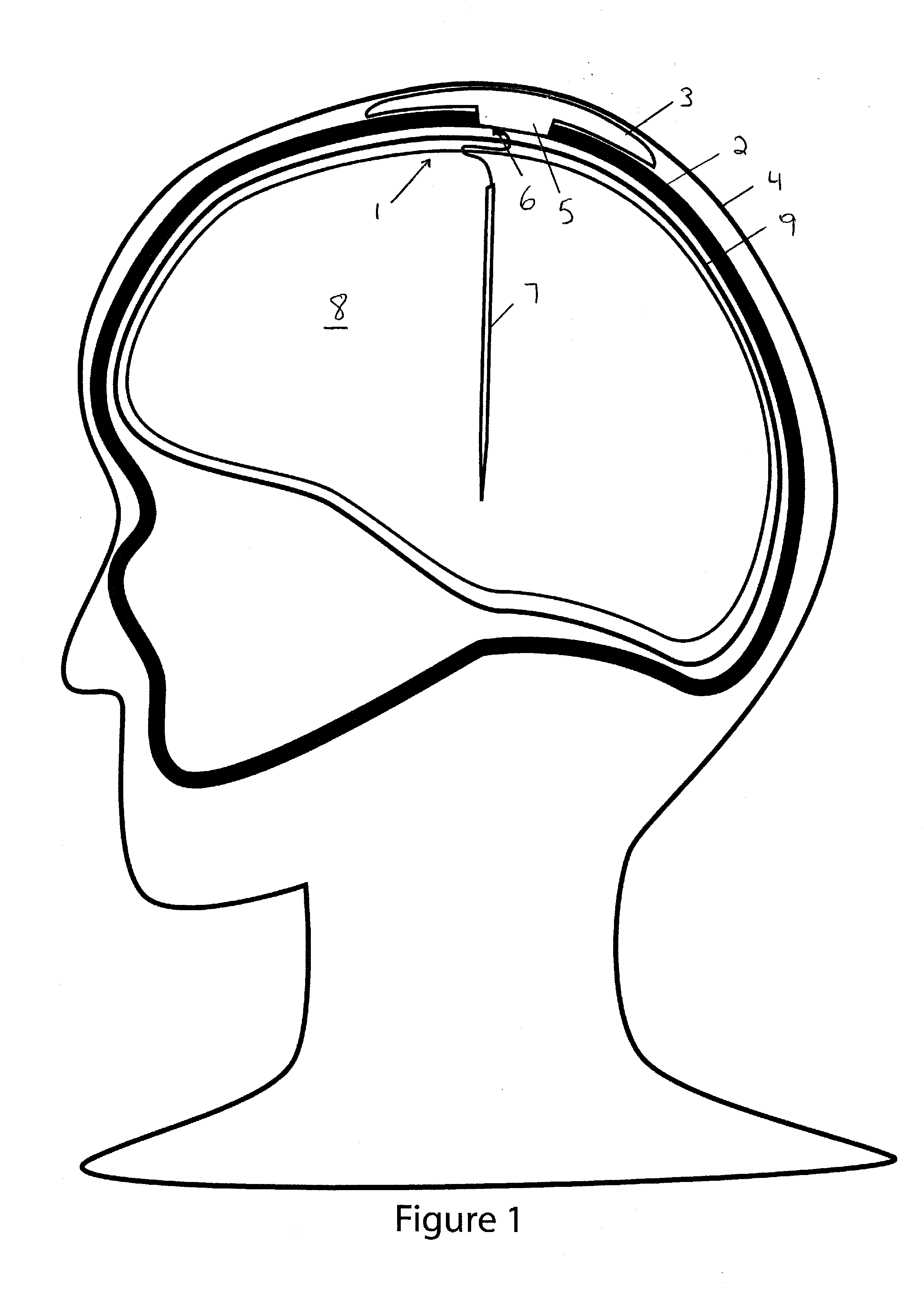
An implantable transcranial pulse generator for generating neuro-modulating electrical signals used, for example, in the treatment of medical conditions through deep brain stimulation (DBS). The implantable pulse generator comprises a collapsible dome portion that deforms upon impact to protect the patient from injury and the pulse generator from being damaged. The dome is removably mounted to a transcranial insert that is secured within a burr hole located in the patient's cranium. Both the dome and the insert contain electronic components and have complementary connectors facilitating direct electrical interconnection. The electronics within the dome are mounted on flexible substrates to permit deformation of the collapsible portion. The dome may include a re-fillable reservoir for supplying controlled dosages of a pharmaceutically active composition to the brain through the transcranial insert.
Owner:MEDTRODE
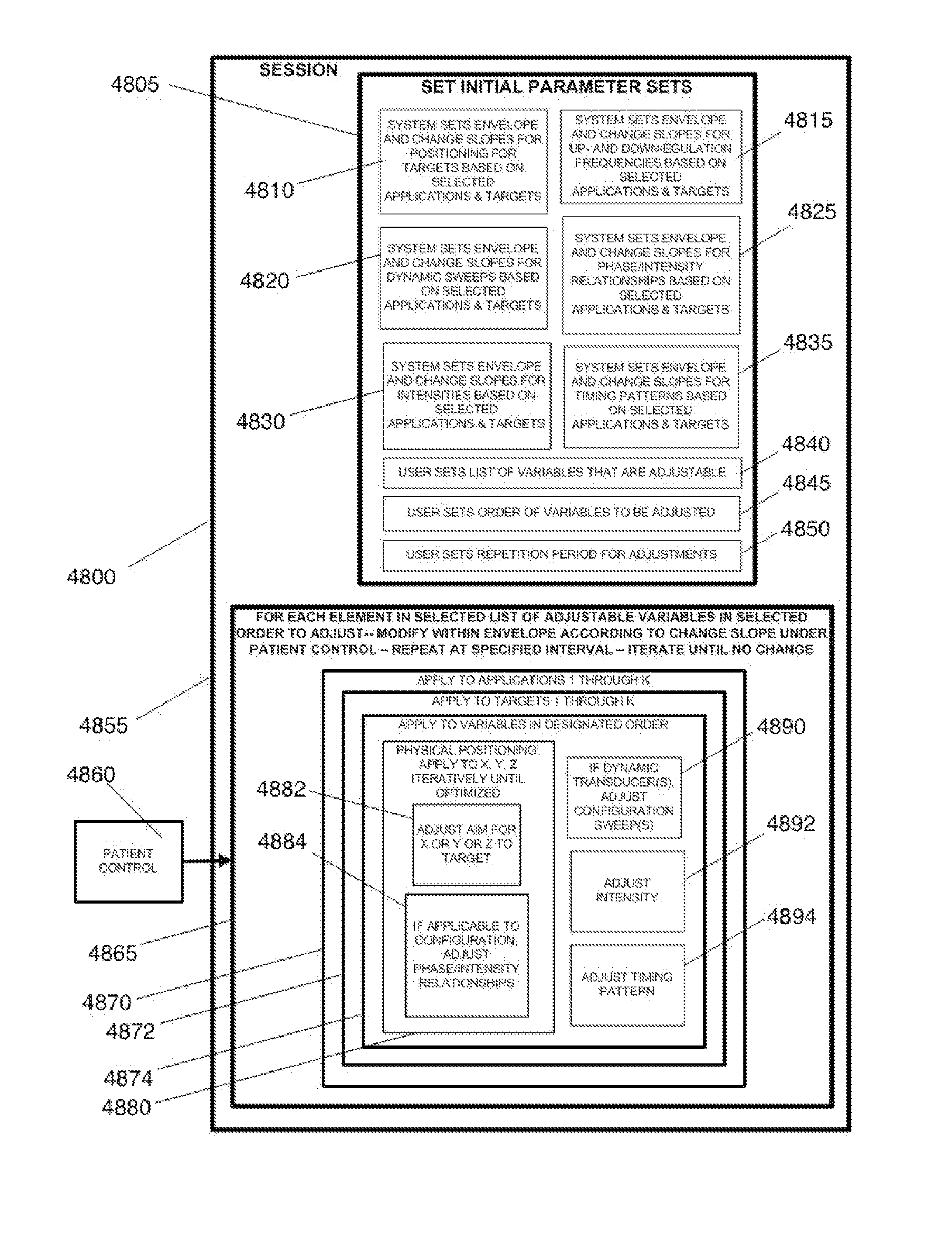
Movement disorder therapy system, devices and methods, and intelligent methods of tuning
ActiveUS20140074179A1Maximize battery lifeImprove the quality of lifeMedical simulationHead electrodesDiagnostic Radiology ModalityHuntingtons chorea
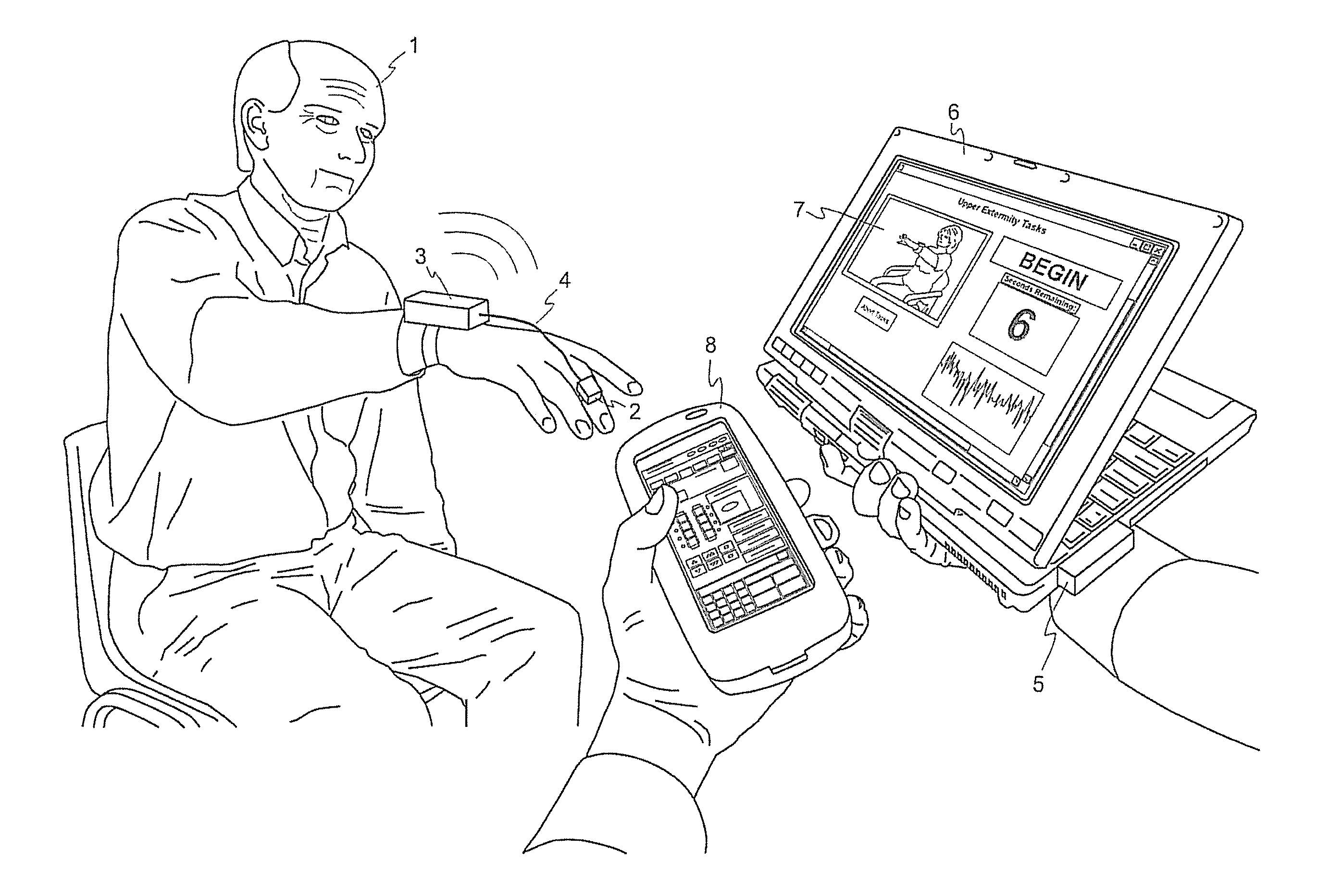
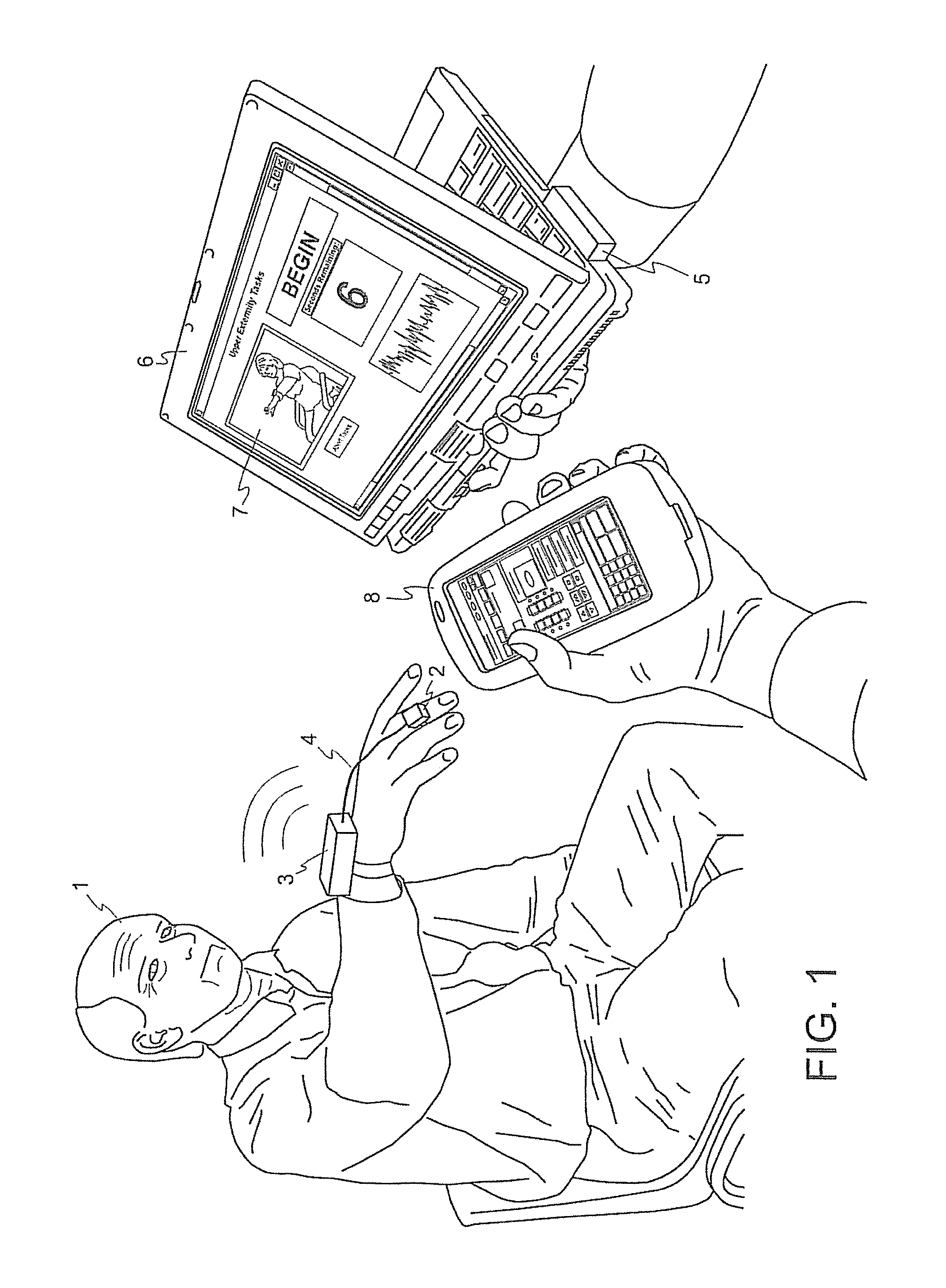
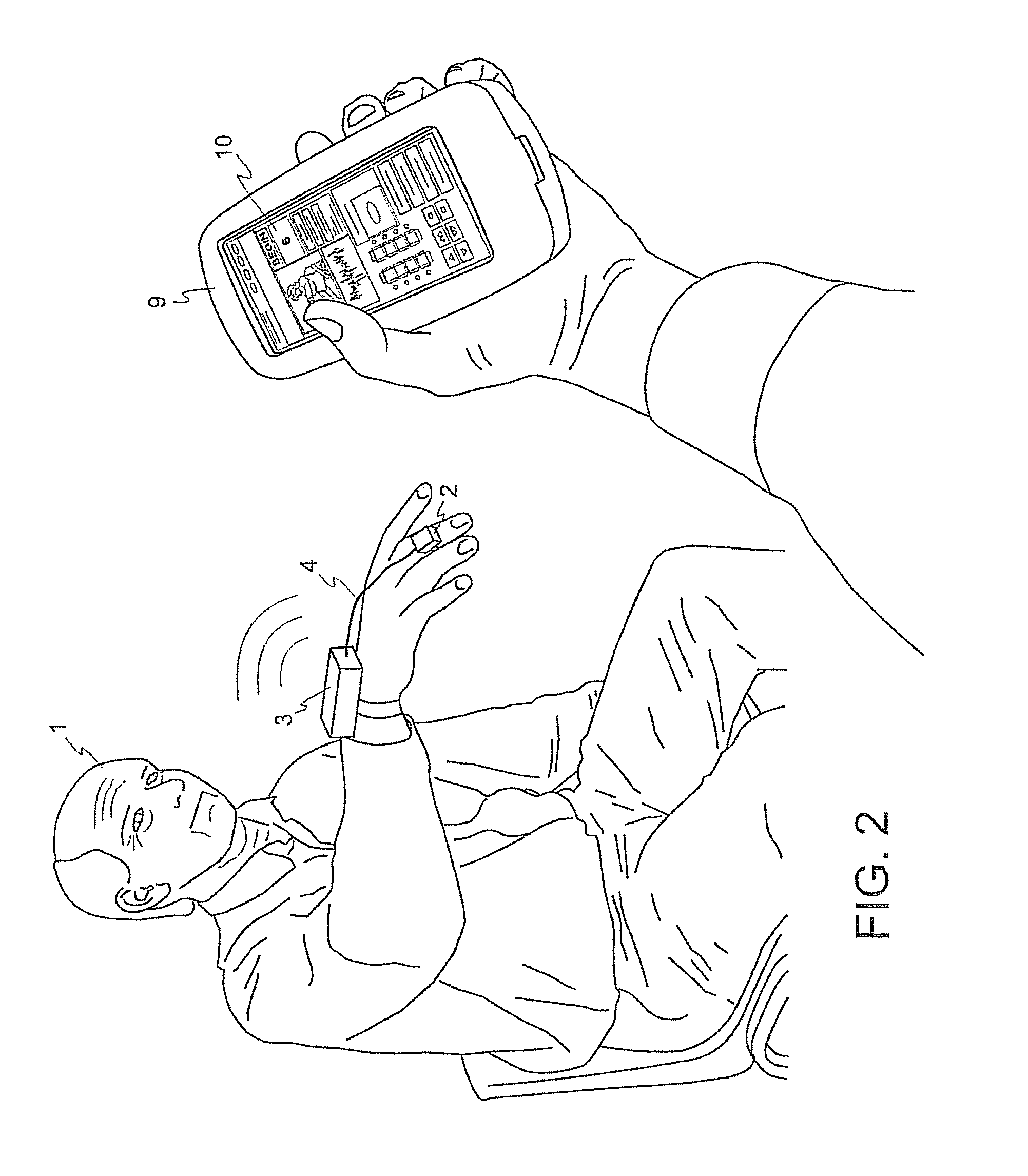
The present invention relates to methods for tuning treatment parameters in movement disorder therapy systems. The present invention further relates to a system for screening patients to determine viability as candidates for certain therapy modalities, such as deep brain stimulation (DBS). The present invention still further provides methods of quantifying movement disorders for the treatment of patients who exhibit symptoms of such movement disorders including, but not limited to, Parkinson's disease and Parkinsonism, Dystonia, Chorea, and Huntington's disease, Ataxia, Tremor and Essential Tremor, Tourette syndrome, stroke, and the like. The present invention yet further relates to methods of tuning a therapy device using objective quantified movement disorder symptom data acquired by a movement disorder diagnostic device to determine the therapy setting or parameters to be provided to the subject via his or her therapy device. The present invention also provides treatment and tuning remotely, allowing for home monitoring of subjects.
Owner:GREAT LAKES NEUROTECH
Miniature wireless system for deep brain stimulation
ActiveUS20090105784A1Meet the blocking requirementsReduce riskElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringElectricityImplanted device
An implantable system and method for deep brain stimulation (DBS) treatments. The implantable system is sufficiently small and self-contained to enable implantation of the entire system within the brain, or optionally within the brain and the surrounding tissue. The system comprises an implantable inductor on which a voltage is induced when subjected to an electromagnetic field, and an implantable device comprising a housing, stimulating elements at an exterior surface of the housing, and electronics within the housing and electrically connected to the implantable inductor. The electronics produces a brain-stimulating current from the voltage induced on the implantable inductor and then delivers the brain-stimulating current to the stimulating elements. Deep brain stimulation is performed by subjecting the inductor to an electromagnetic field to induce a voltage on the inductor that powers the electronics to produce and deliver the brain-stimulating current to the stimulating elements.
Owner:UIM PRESSURE IMPLANT INC
Treatment of pathologic craving and aversion syndromes and eating disorders by electrical brain stimulation and/or drug infusion
InactiveUS7493171B1Reduced activityIncrease excitementHead electrodesDiagnosticsFeeding disabilityFeeding disorder
Systems and methods for introducing one or more stimulating drugs and / or applying electrical stimulation to the brain to at least treat or prevent obesity and / or other eating disorders, as well as drug, nicotine and alcohol addiction, uses at least one system control unit (SCU) producing electrical pulses delivered via electrodes implanted in the brain and / or producing drug infusion pulses, wherein the stimulating drug(s) are delivered to targeted areas in the brain.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
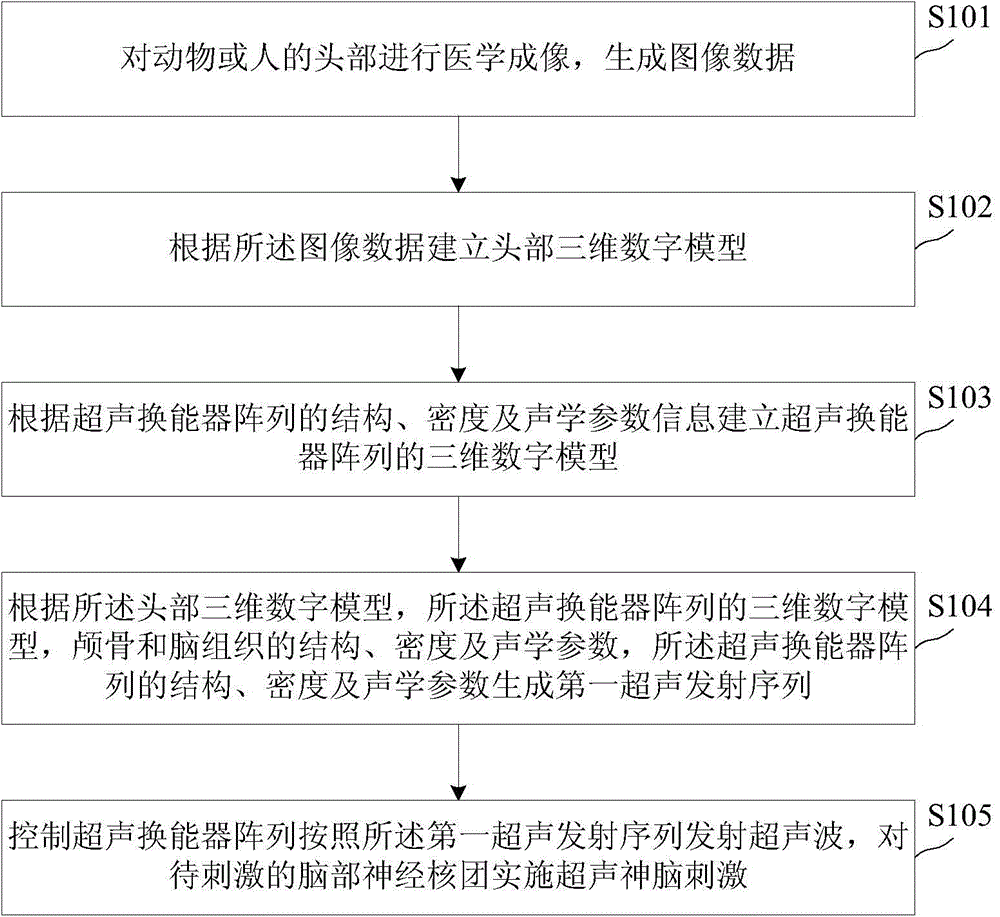
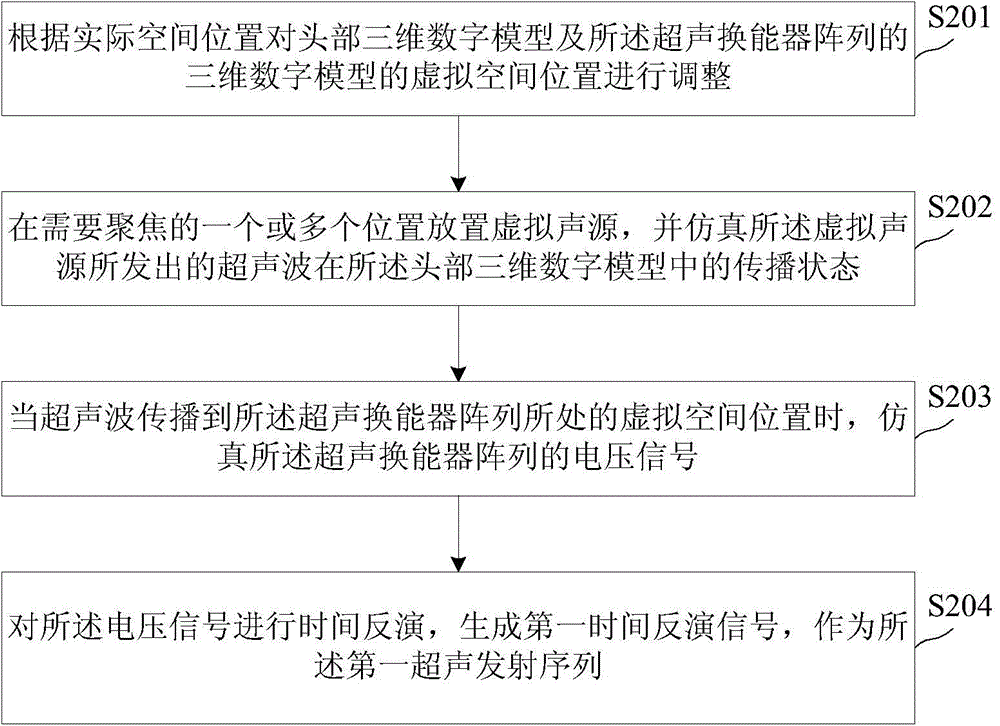
Ultrasound deep brain stimulation method and system
ActiveCN104548390ARealize regulationImprove spatial resolutionMedical simulationUltrasound therapySonificationMedicine
The invention discloses an ultrasound deep brain stimulation method and system. The ultrasound deep brain stimulation method comprises steps as follows: medical imaging is performed on the head of an animal or a human being, and image data are generated; a head three-dimensional digital model is established according to the image data; a three-dimensional digital model of an ultrasound transducer array is established according to structure, density and acoustic parameter information of the ultrasound transducer array; a first ultrasound emission sequence is generated according to the head three-dimensional digital model, the three-dimensional digital model of the ultrasound transducer array, structure, density and acoustic parameters of skull and brain tissue and the structure, density and acoustic parameter information of the ultrasound transducer array; the ultrasound transducer array is controlled to emit ultrasound waves according to the first ultrasound emission sequence, and ultrasound deep brain stimulation is implemented on to-be-stimulated brain nerve nuclei. With adoption of the method and the system, ultrasound can noninvasively penetrate through a skull and is concentrated in a deep brain area; by means of different ultrasound emission sequences, ultrasound nerve regulation can be realized, and an action mechanism can be researched.
Owner:GREEN VALLEY BRAINTECH SHENZHEN MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Monitoring Brain Neural Potentials
ActiveUS20160287126A1Eliminate needElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyMedicineBiomarker (petroleum)
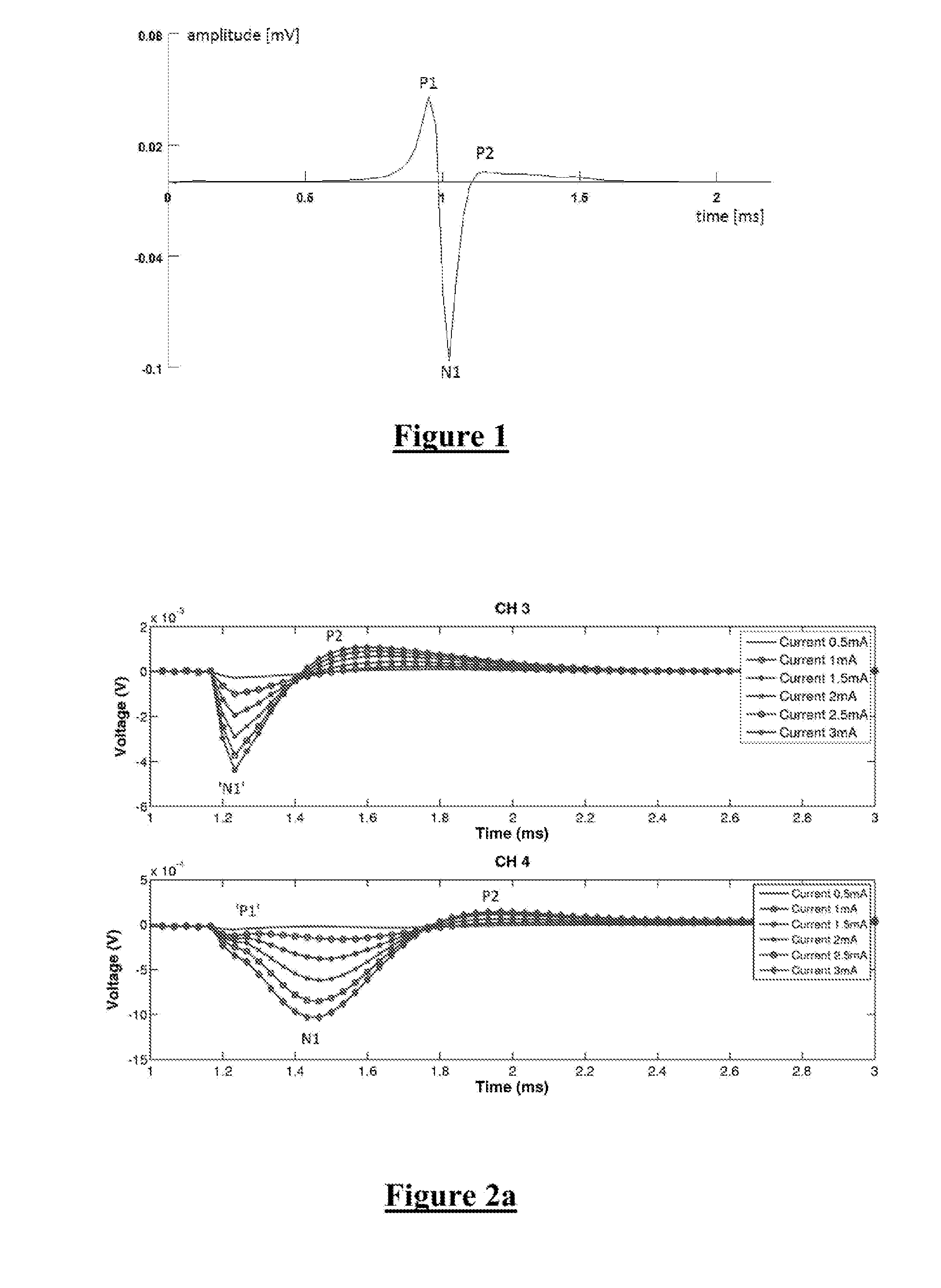
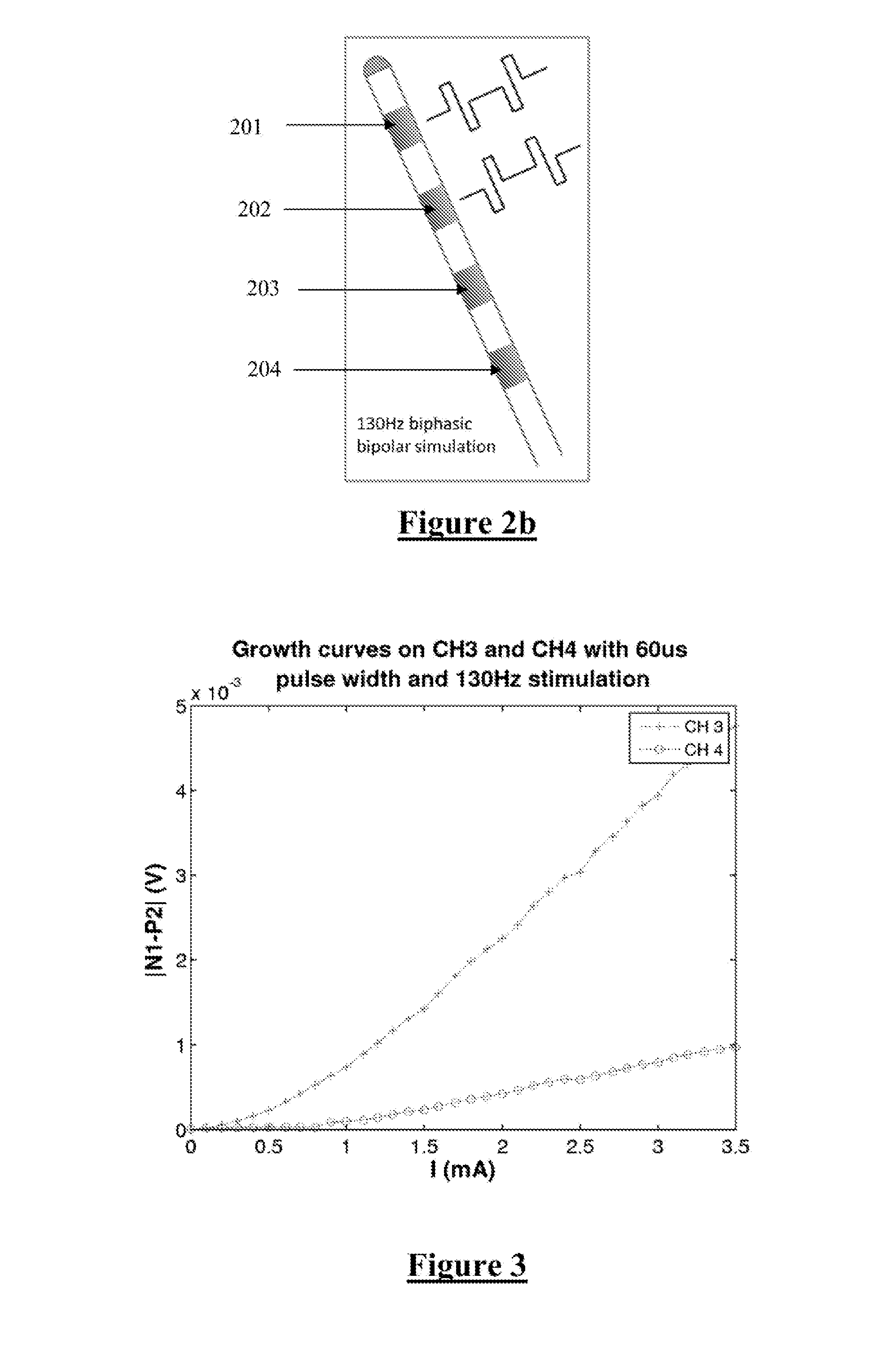
Neural activity in the brain arising from a stimulus is monitored. A stimulus is applied to a target structure of the brain and a neural measurement is obtained from at least one electrode implanted in contact with the target structure. The neural measurement is configured to capture a measure of any late response arising in the target structure, typically being a neural response arising after conclusion of an ECAP, such as in the period 1.5-10 ms after stimulus onset. The late response(s) can be a useful biomarker such as of therapeutic ranges of deep brain stimulation, disease progression, medication efficacy, and intra-operative changes.
Owner:CLOSED LOOP MEDICAL PTY LTD
Movement disorder therapy system, devices and methods, and intelligent methods of tuning
ActiveUS9211417B2Expand accessShorten the timeMedical simulationHead electrodesHuntingtons choreaMovement disorders
The present invention relates to methods for tuning treatment parameters in movement disorder therapy systems. The present invention further relates to a system for screening patients to determine viability as candidates for certain therapy modalities, such as deep brain stimulation (DBS). The present invention still further provides methods of quantifying movement disorders for the treatment of patients who exhibit symptoms of such movement disorders including, but not limited to, Parkinson's disease and Parkinsonism, Dystonia, Chorea, and Huntington's disease, Ataxia, Tremor and Essential Tremor, Tourette syndrome, stroke, and the like. The present invention yet further relates to methods of tuning a therapy device using objective quantified movement disorder symptom data acquired by a movement disorder diagnostic device to determine the therapy setting or parameters to be provided to the subject via his or her therapy device. The present invention also provides treatment and tuning remotely, allowing for home monitoring of subjects.
Owner:GREAT LAKES NEUROTECHNOLOGIES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com