Patents
Literature
918 results about "Address bus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
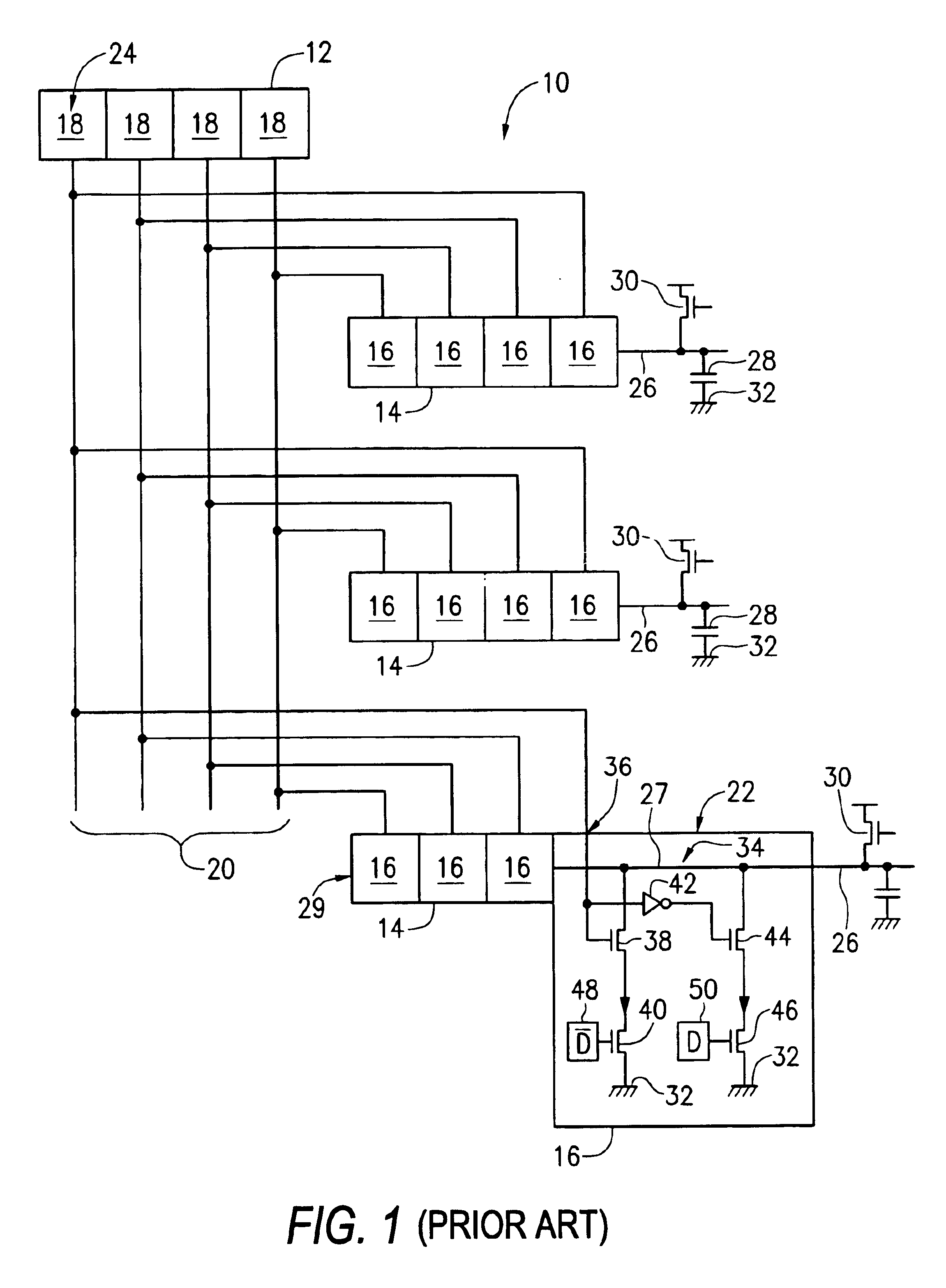
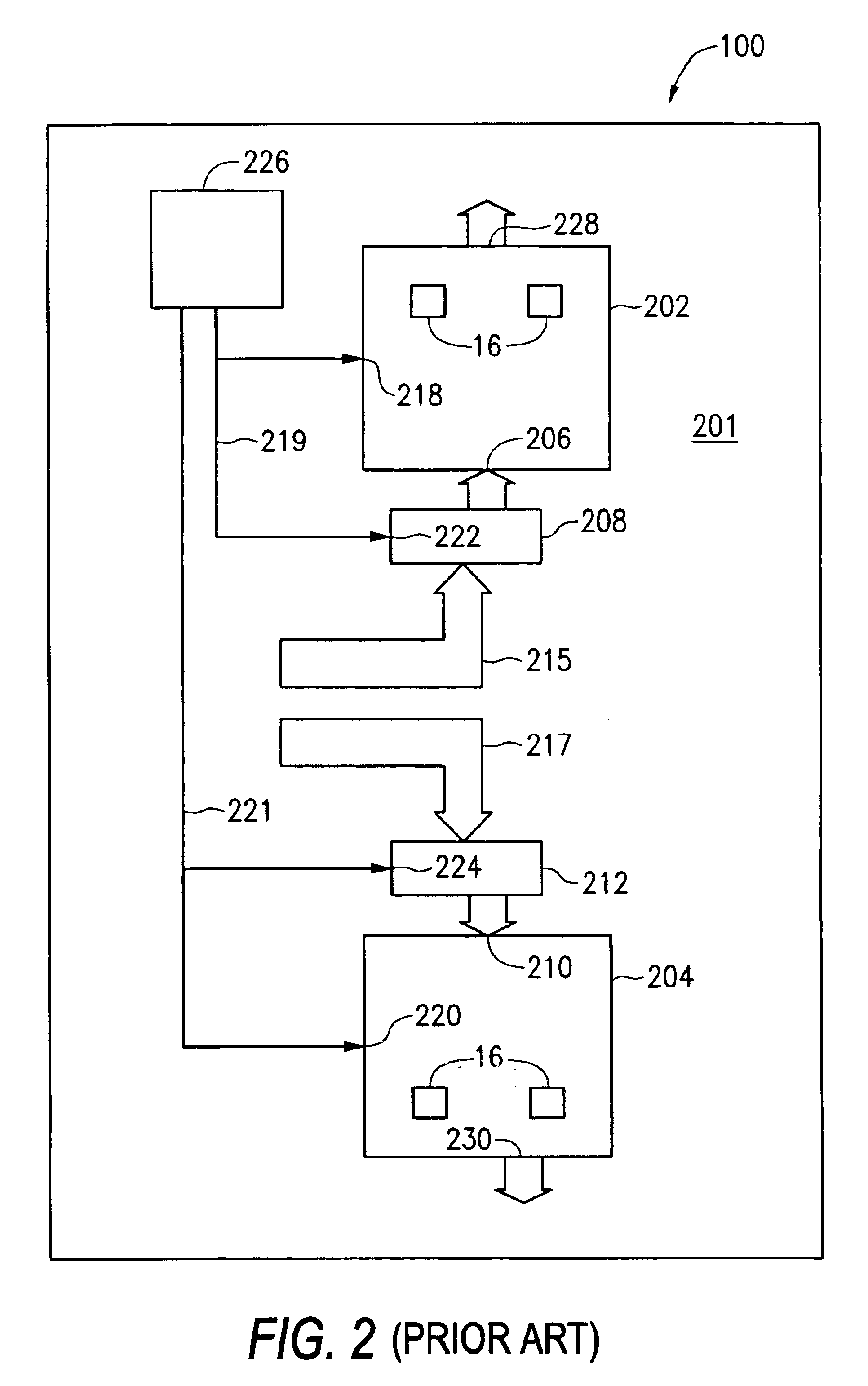
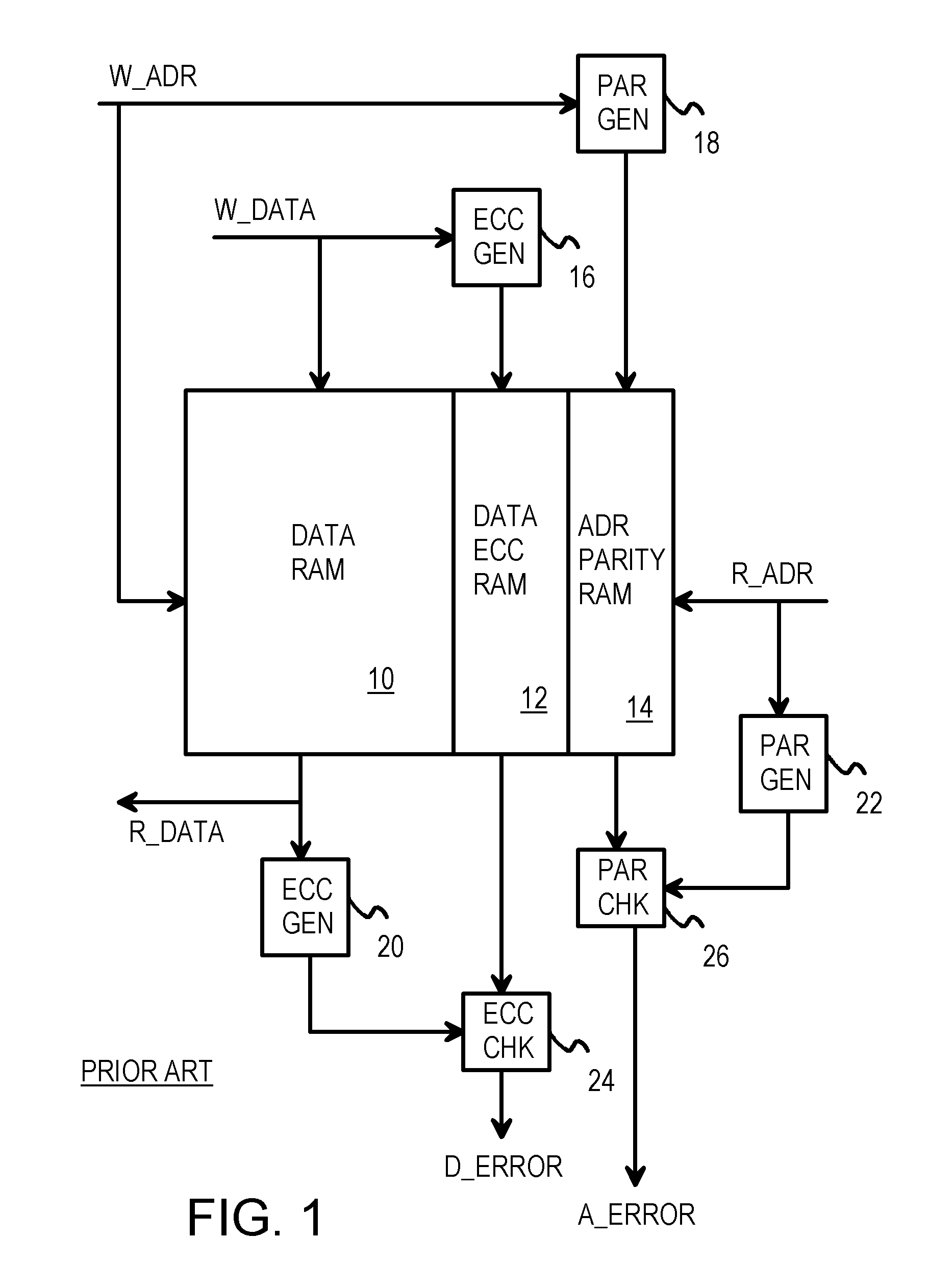
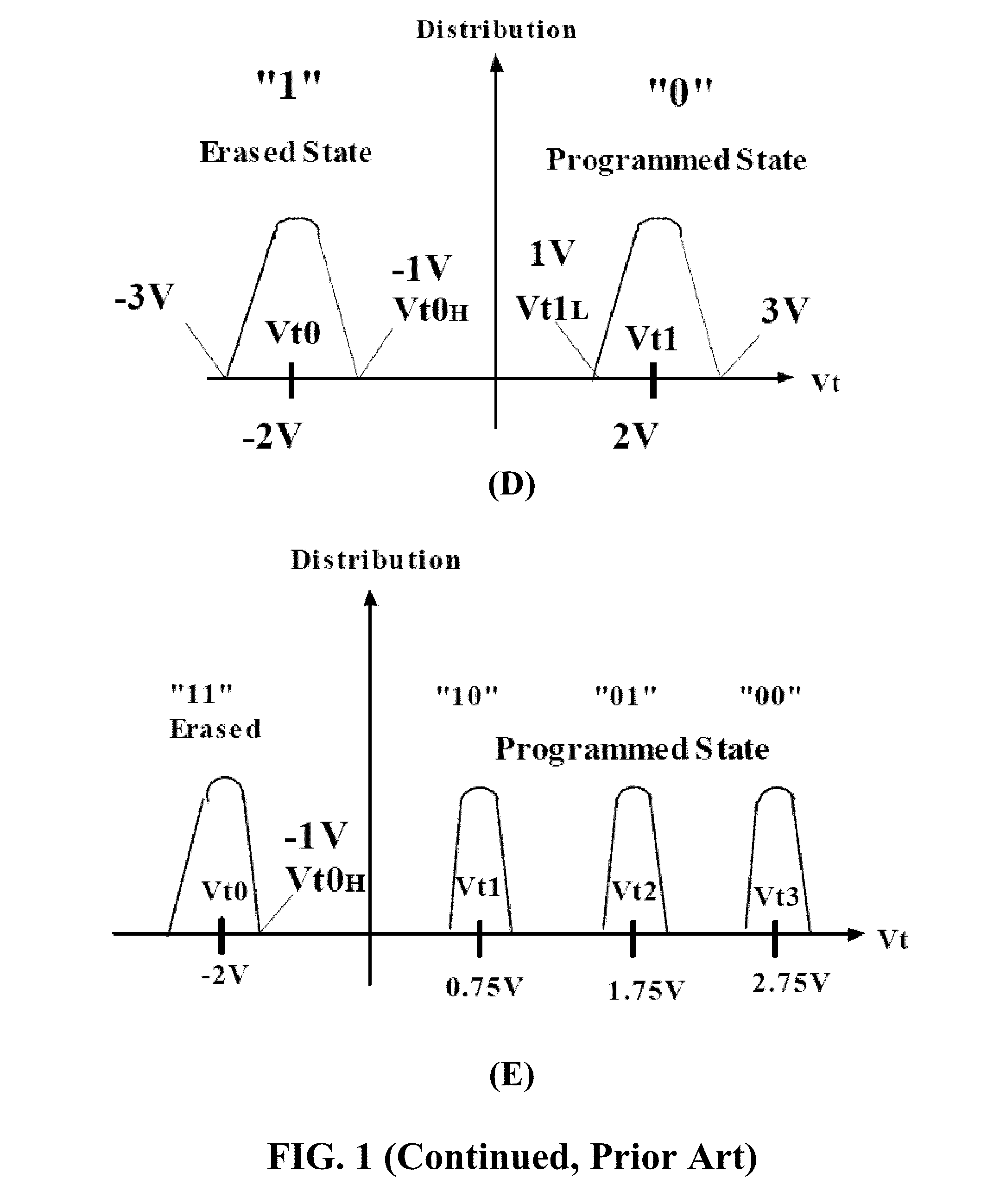
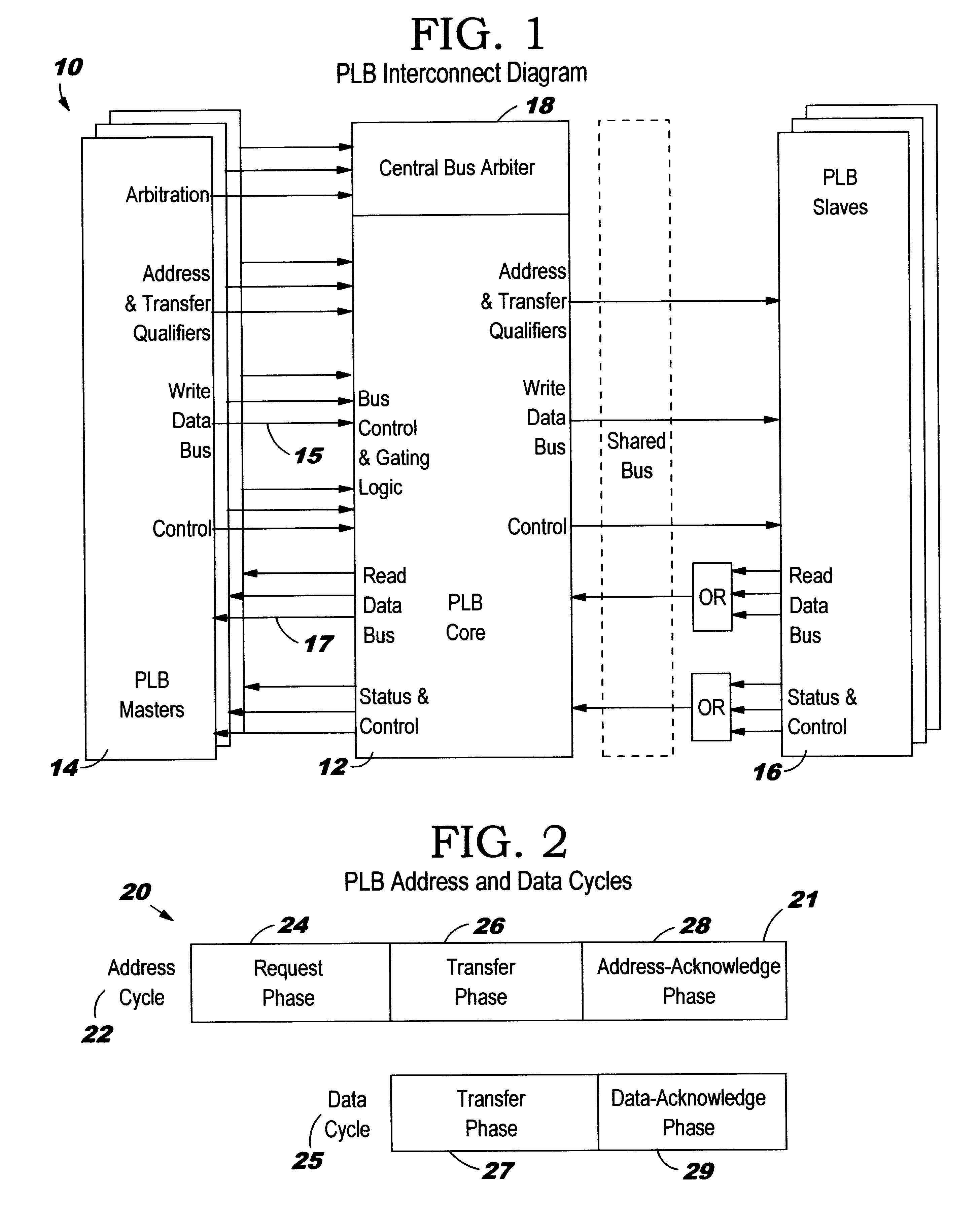
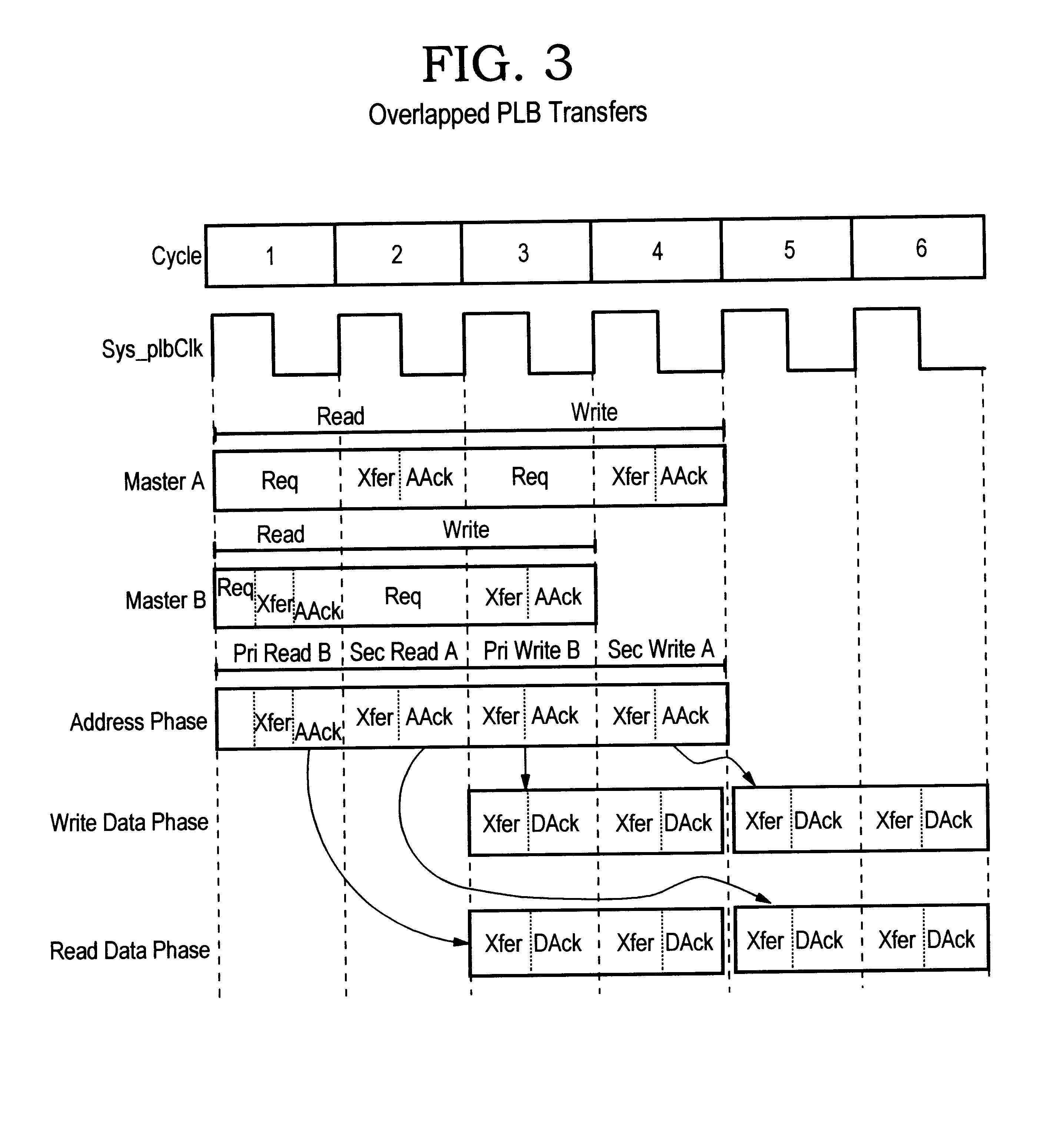
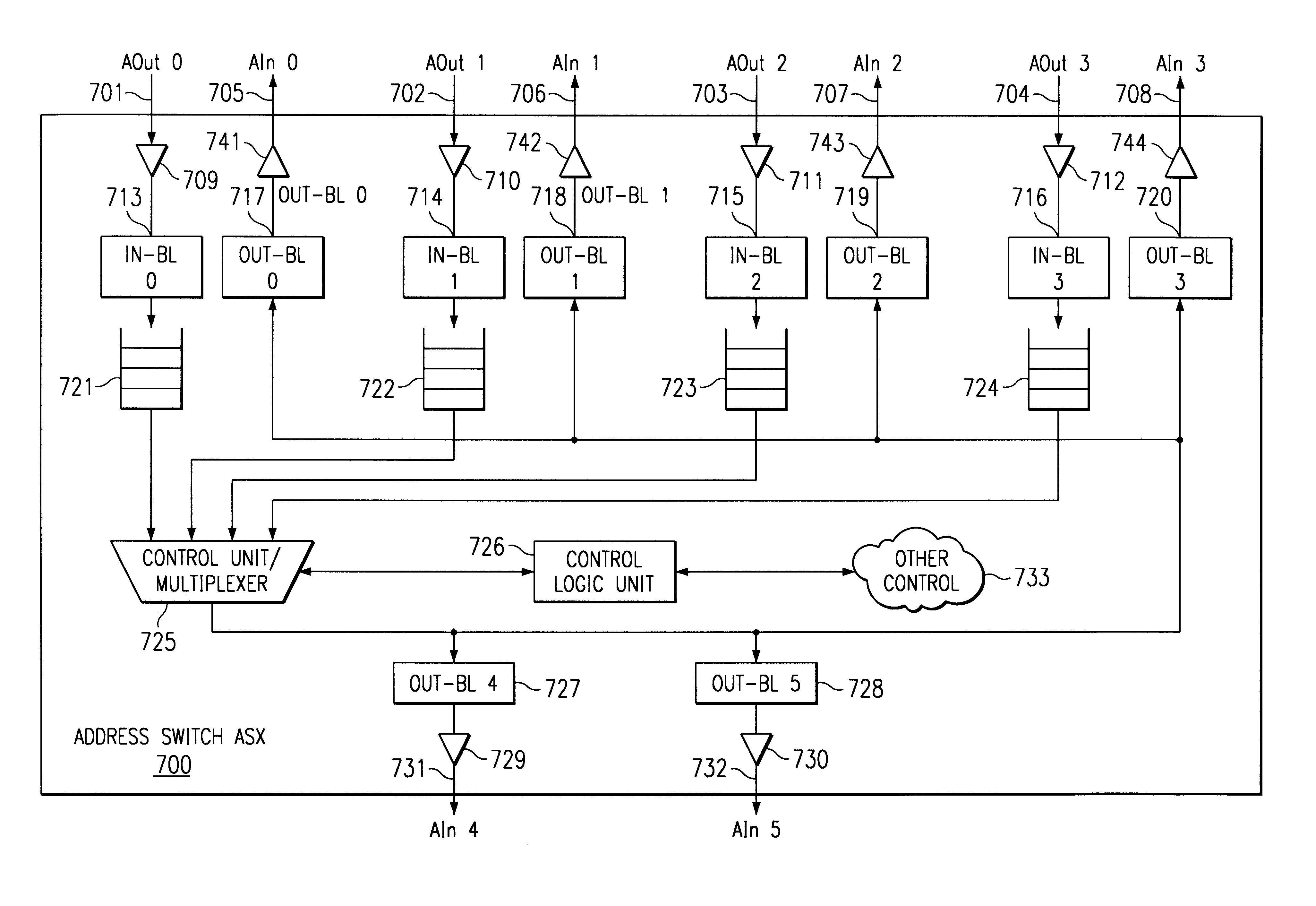
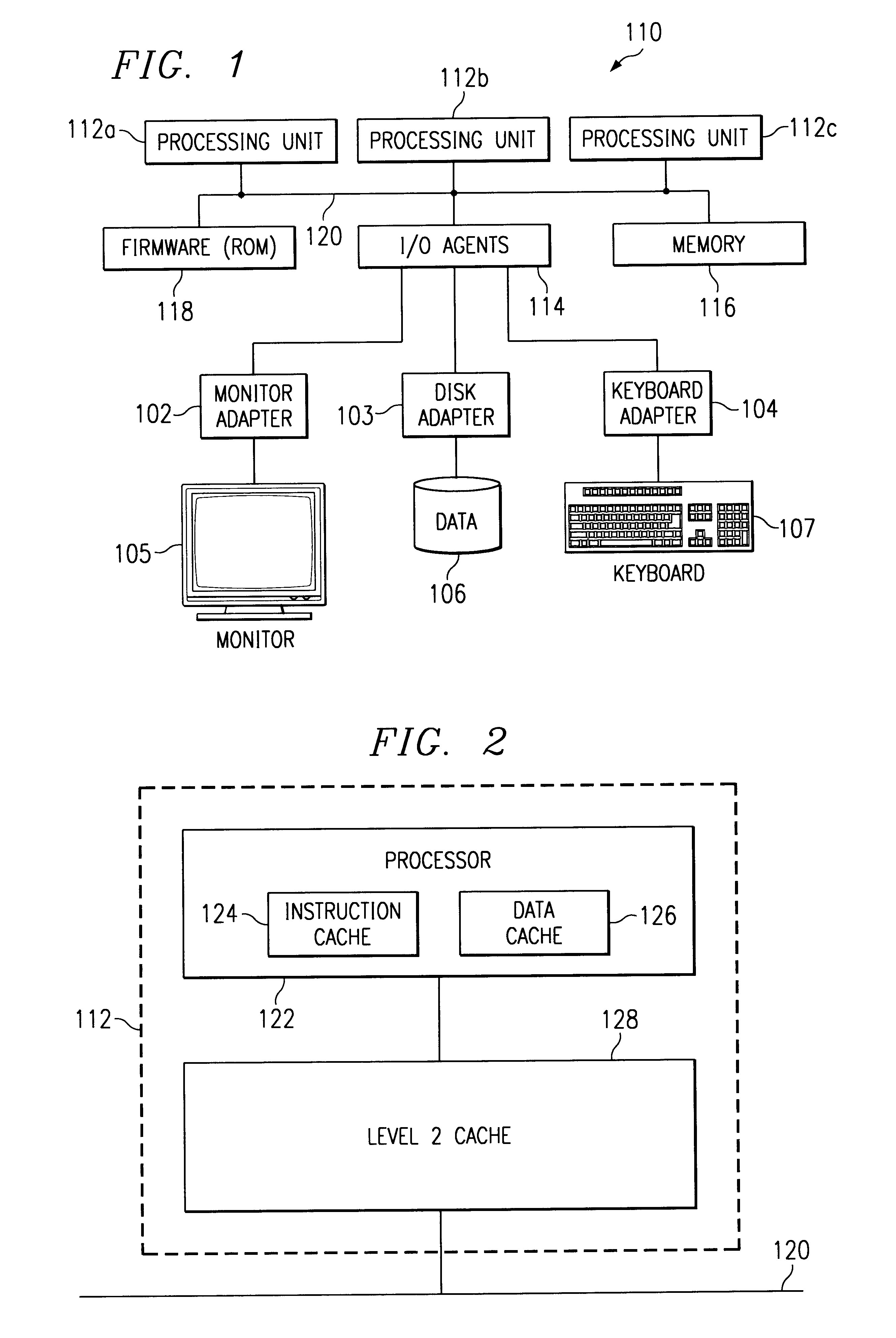
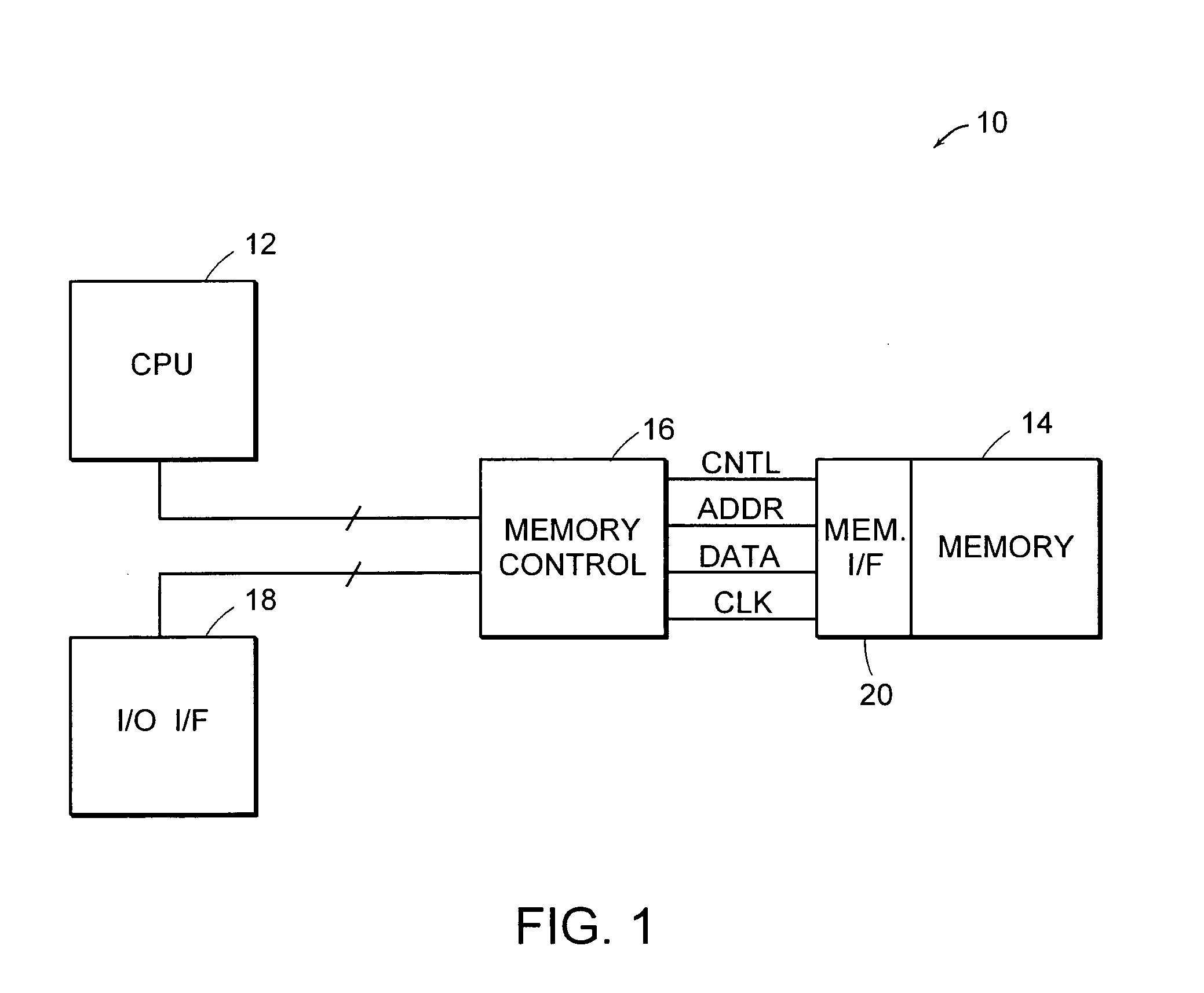
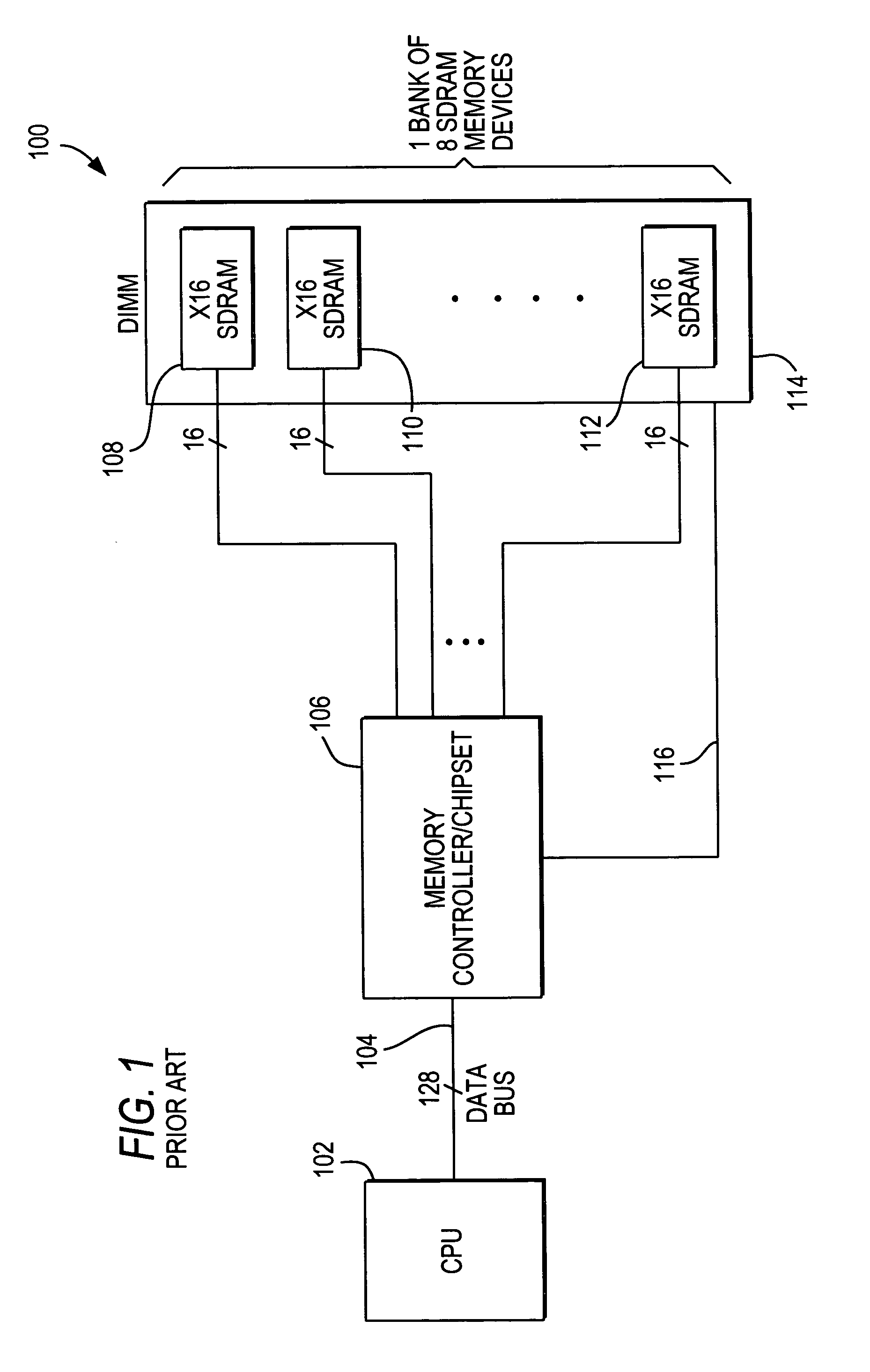
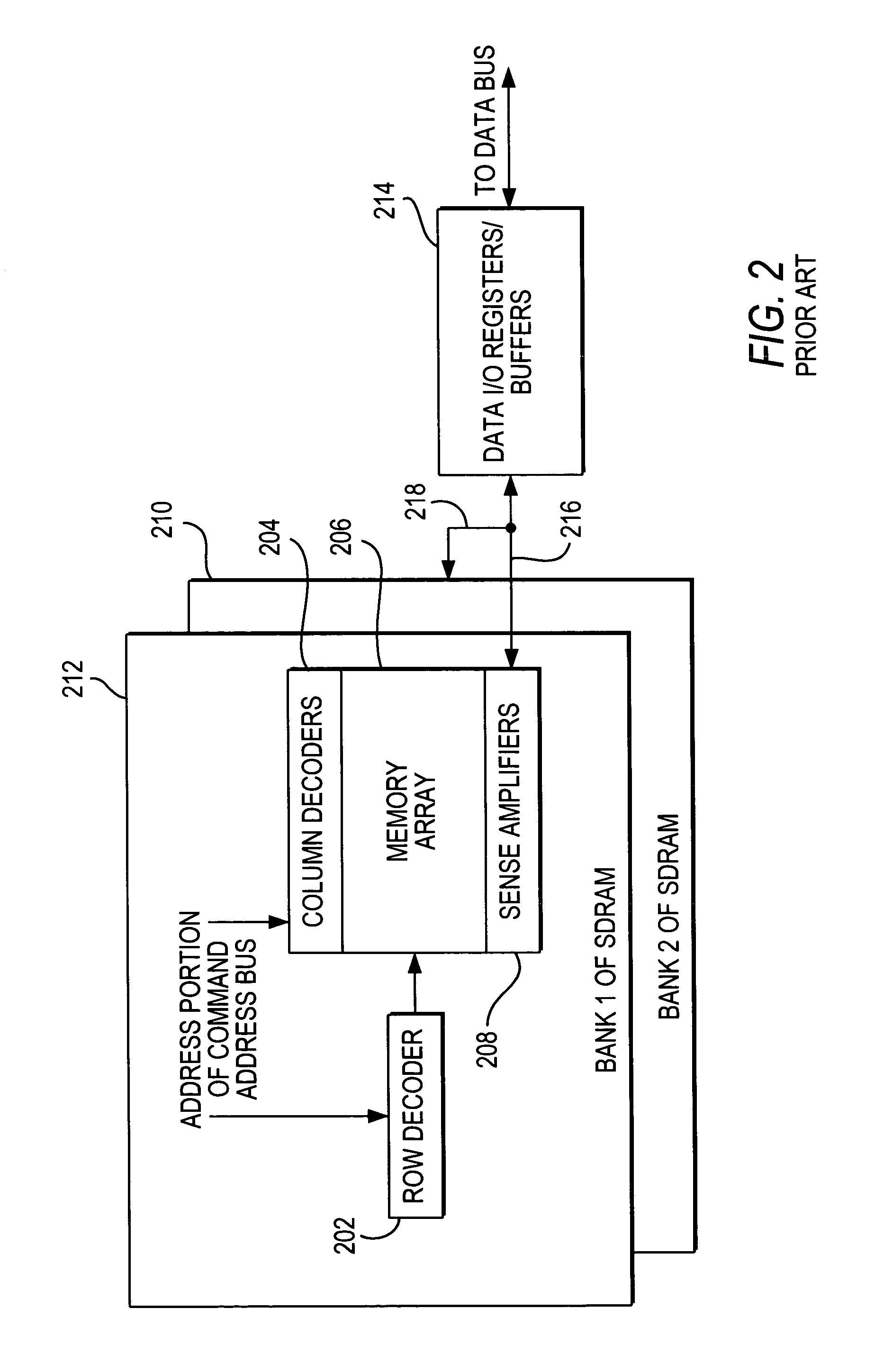
An address bus is a computer bus that is used to specify a physical address. When a processor or DMA-enabled device needs to read or write to a memory location, it specifies that memory location on the address bus. The width of the address bus determines the amount of memory a system can address. For example, a system with a 32-bit address bus can address 2³² memory locations. If each memory address holds one byte, the addressable memory space is 4 GB.
Audio and video decoder circuit and system
InactiveUS6369855B1Accelerates memory block moveAvoid confictTelevision system detailsPulse modulation television signal transmissionCoprocessorNetwork packet
An improved audio-visual circuit is provided that includes a transport packet parsing circuit for receiving a transport data packet stream, a CPU circuit for initializing said integrated circuit and for processing portions of said data packet stream, a ROM circuit for storing data, a RAM circuit for storing data, an audio decoder circuit for decoding audio portions of said data packet stream, a video decoder circuit for decoding video portions of said data packet stream, an NTSC / PAL encoding circuit for encoding video portions of said data packet stream, an OSD coprocessor circuit for processing OSD portions of said data packets, a traffic controller circuit moving portions of said data packet stream between portions of said integrated circuit, an extension bus interface circuit, a P1394 interface circuit, a communication coprocessors circuit, an address bus connected to said circuits, and a data bus connected to said circuits.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
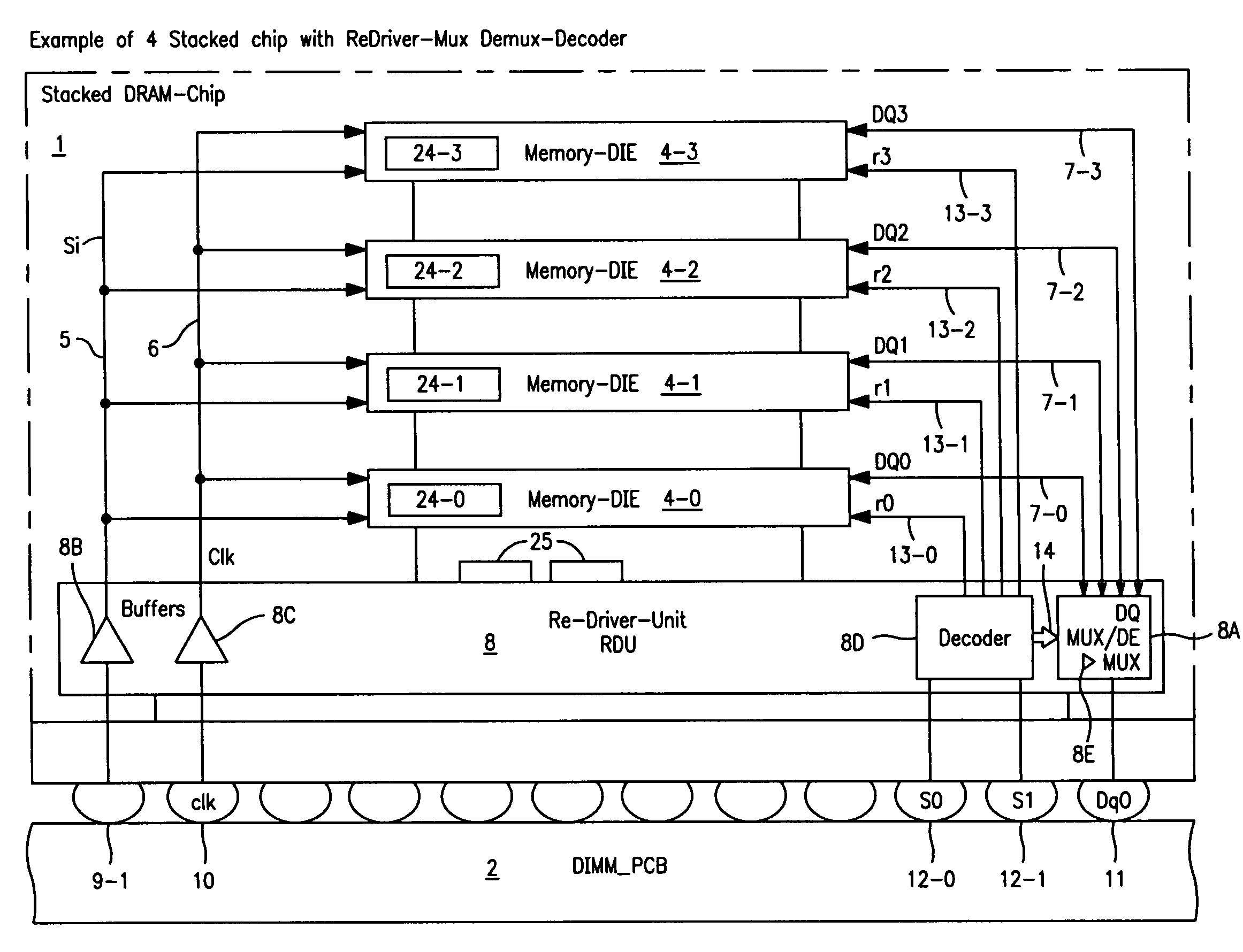
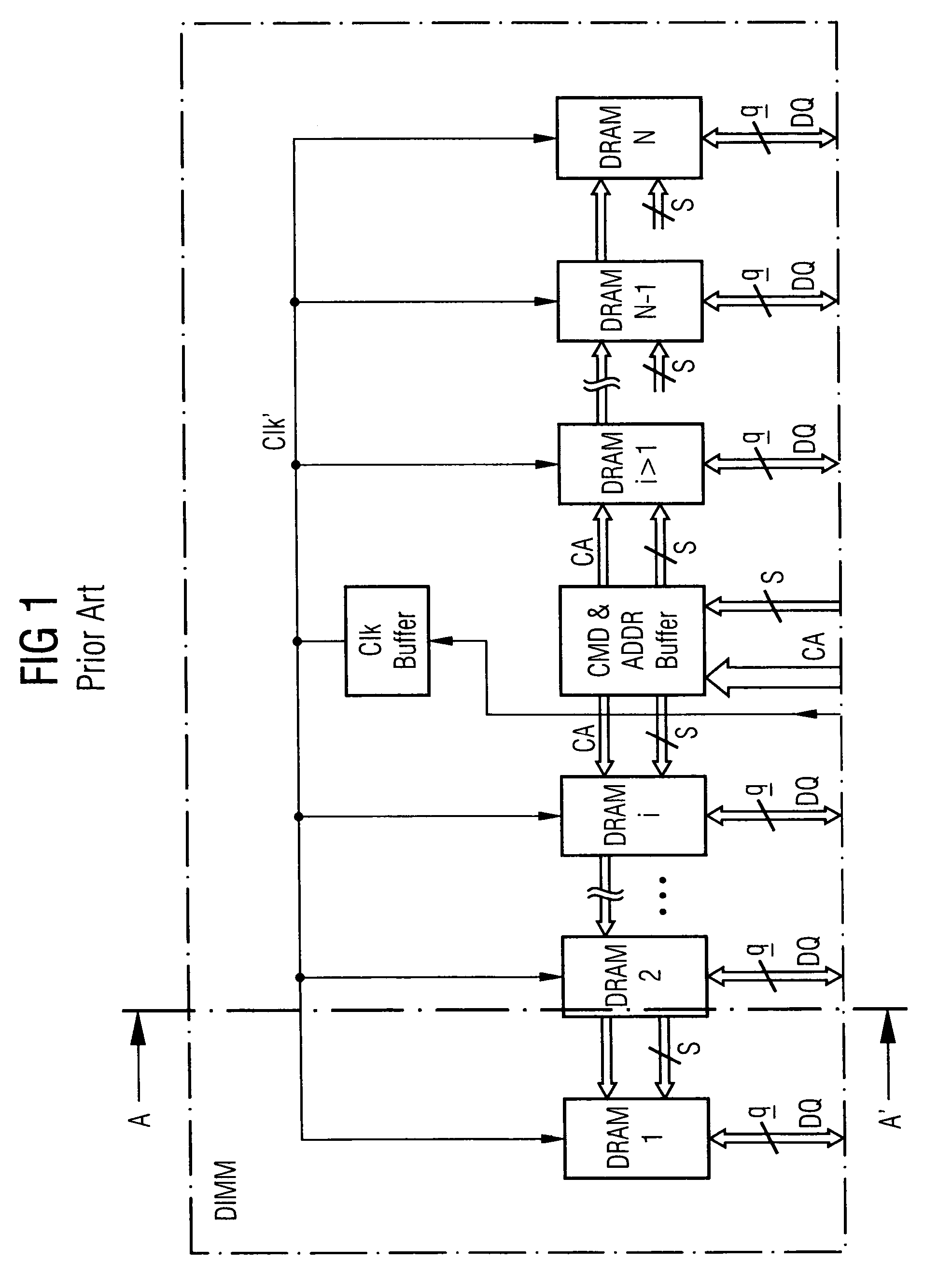
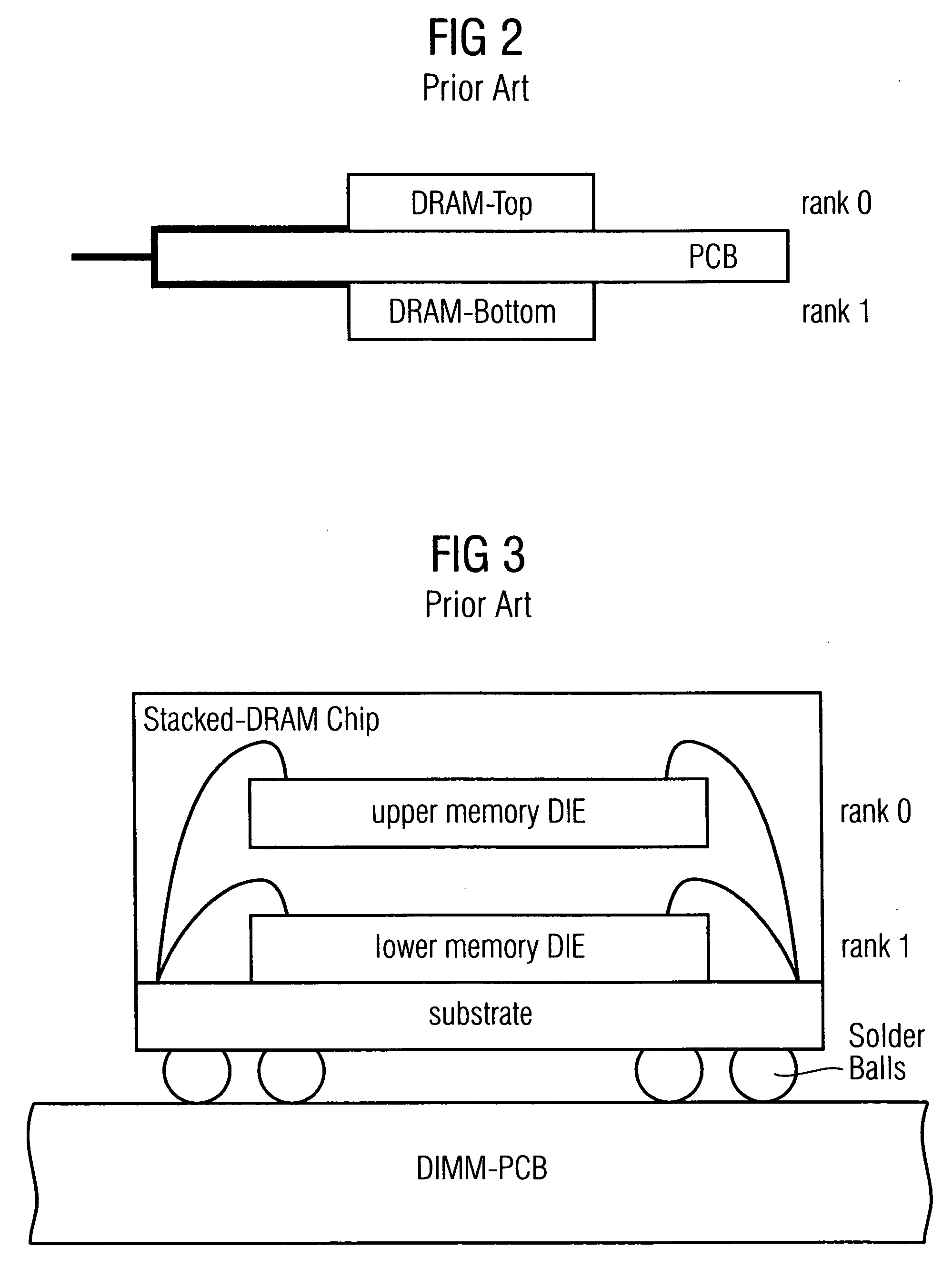
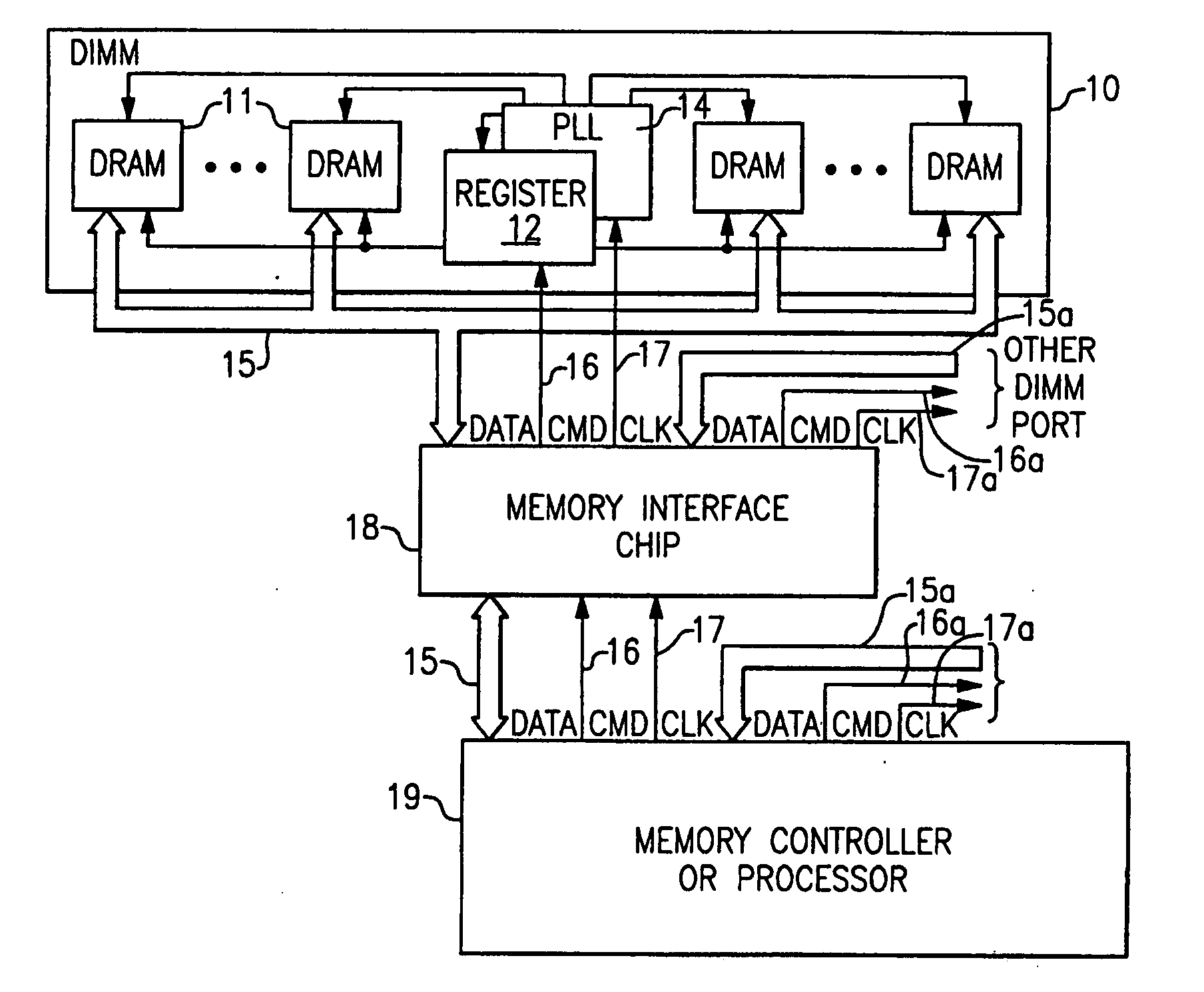
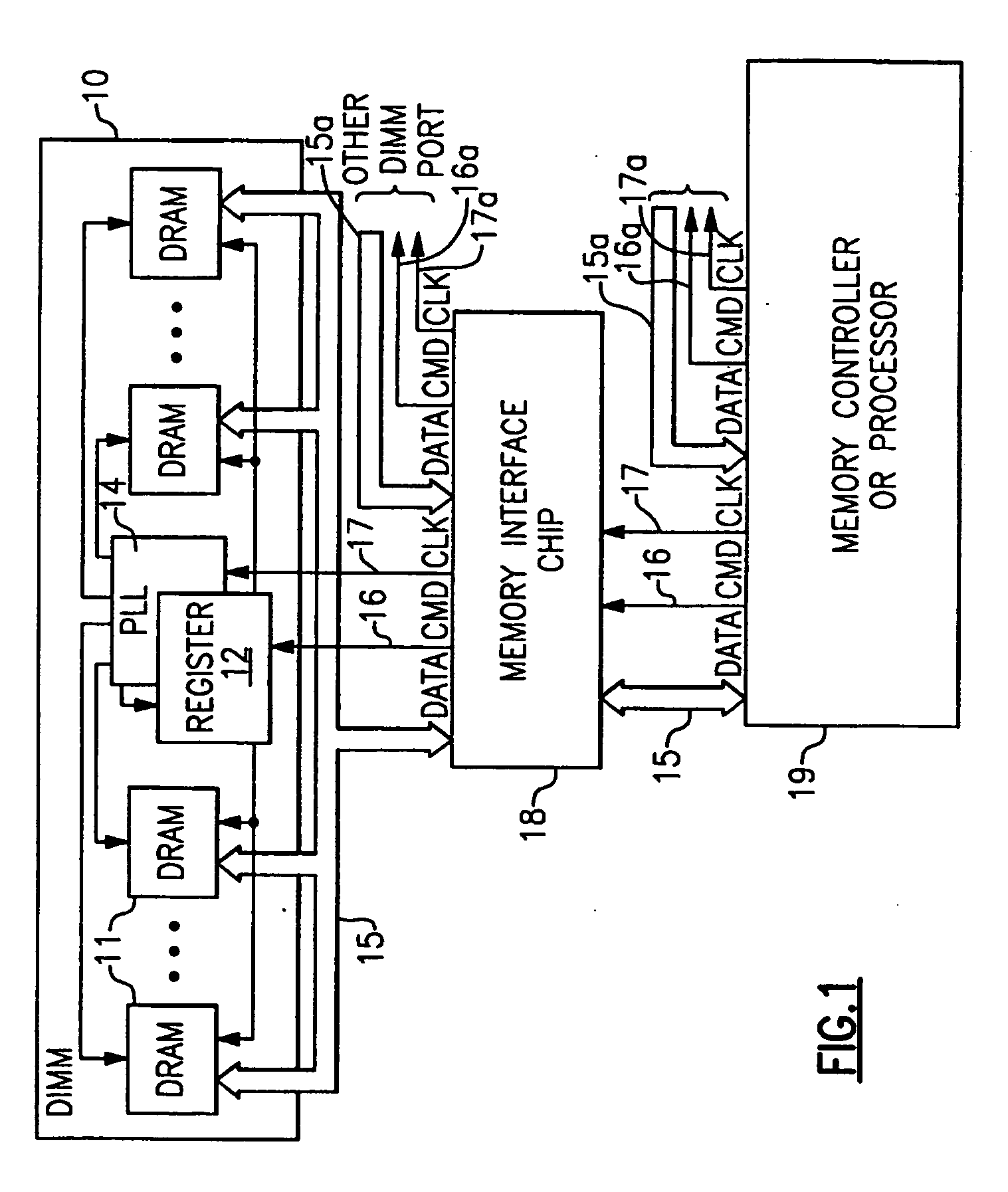
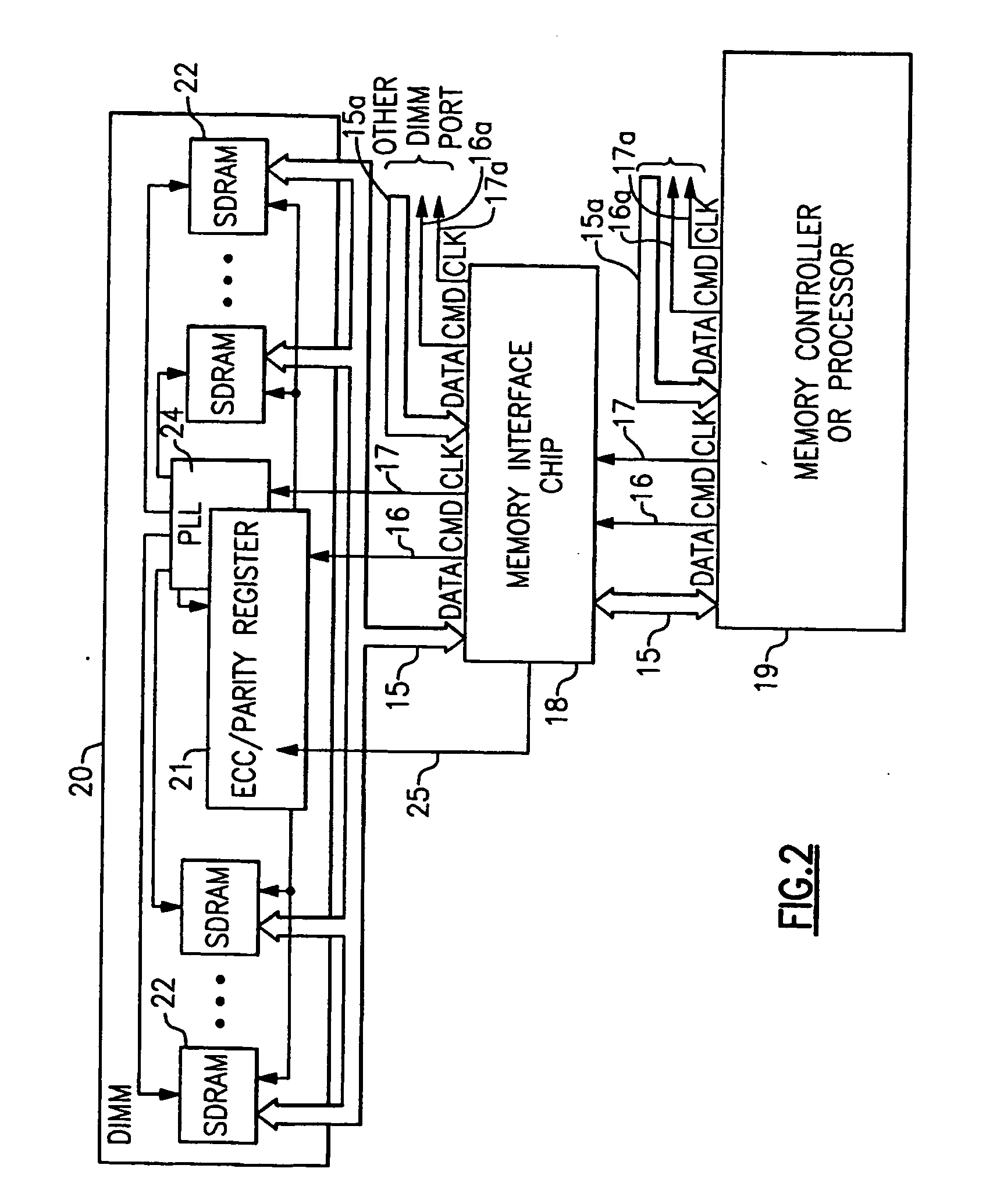
Stacked DRAM memory chip for a dual inline memory module (DIMM)
ActiveUS7200021B2Increase the number ofSmall sizeSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNanoinformaticsInternal memoryMemory chip
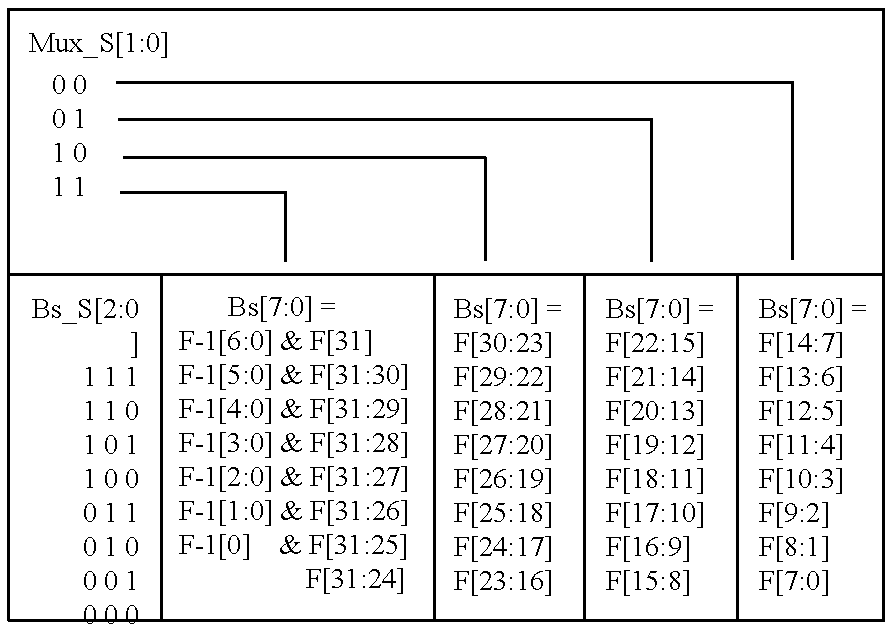
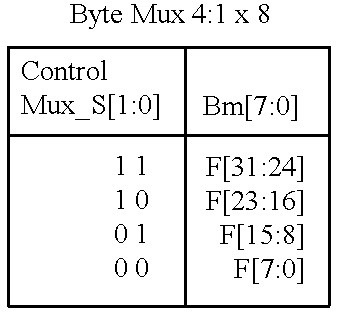
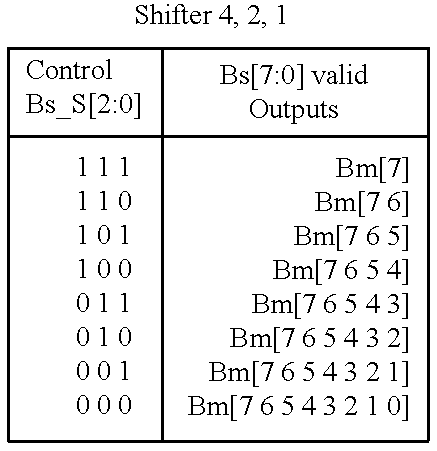
A stacked DRAM memory chip for a Dual In Line Memory Module (DIMM) is disclosed. According to one aspect, the DRAM memory chip comprises at least four stacked DRAM memory dies. Further, the memory dies are each selectable by a corresponding internal memory rank signal. Each memory die comprises an array of memory cells. A common internal address bus is provided for addressing the memory cells and is connected to all stacked DRAM memory dies. Internal data buses are provided for writing data into the memory cells and reading data out of the memory cells of the DRAM memory dies. An integrated redriving unit comprises buffers for all internal address lines provided for driving external address signals applied to address pads of the DRAM memory chip. A multiplexer / demultiplexer switches the internal data lines of the selected DRAM memory die. A memory rank decoder selects a corresponding memory die.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
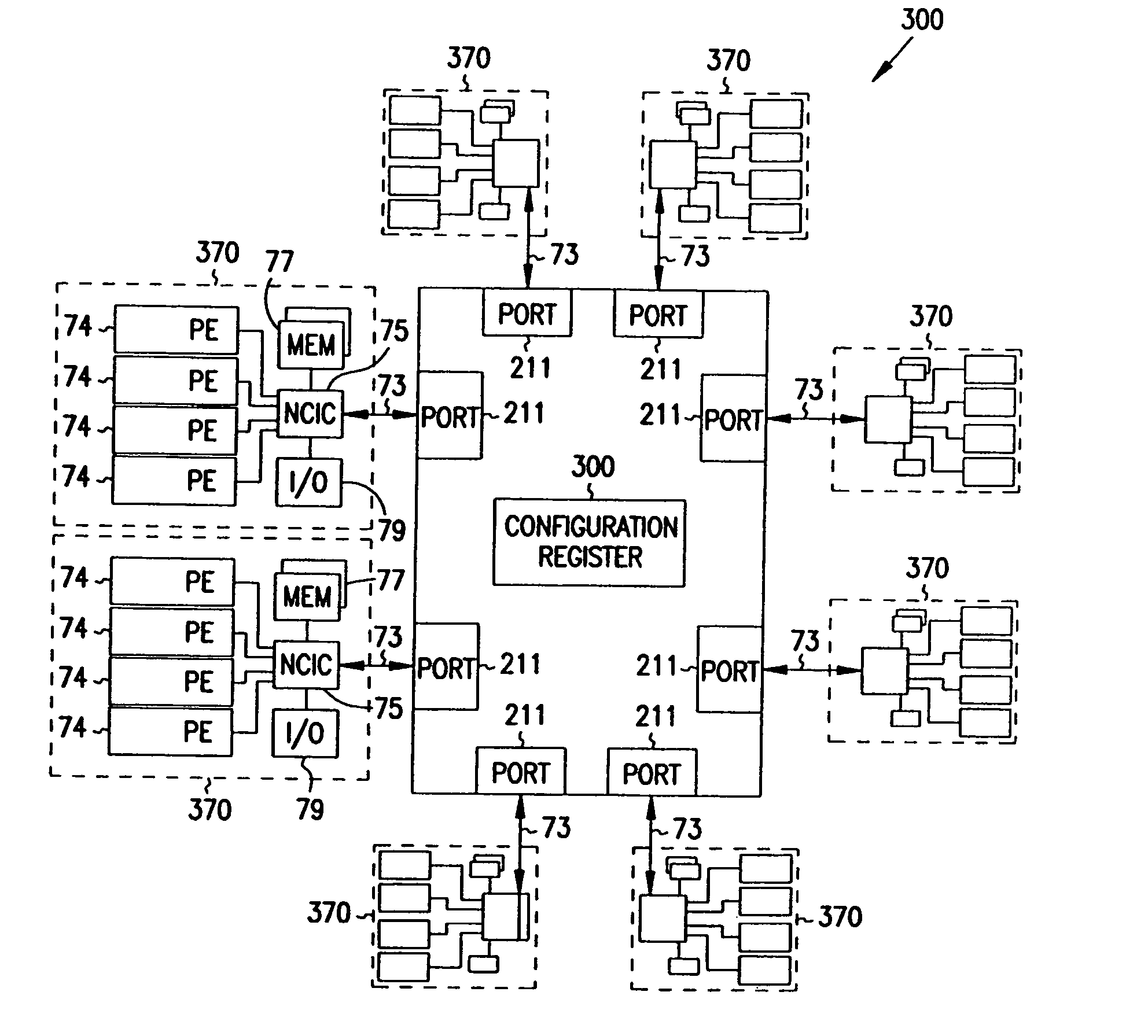
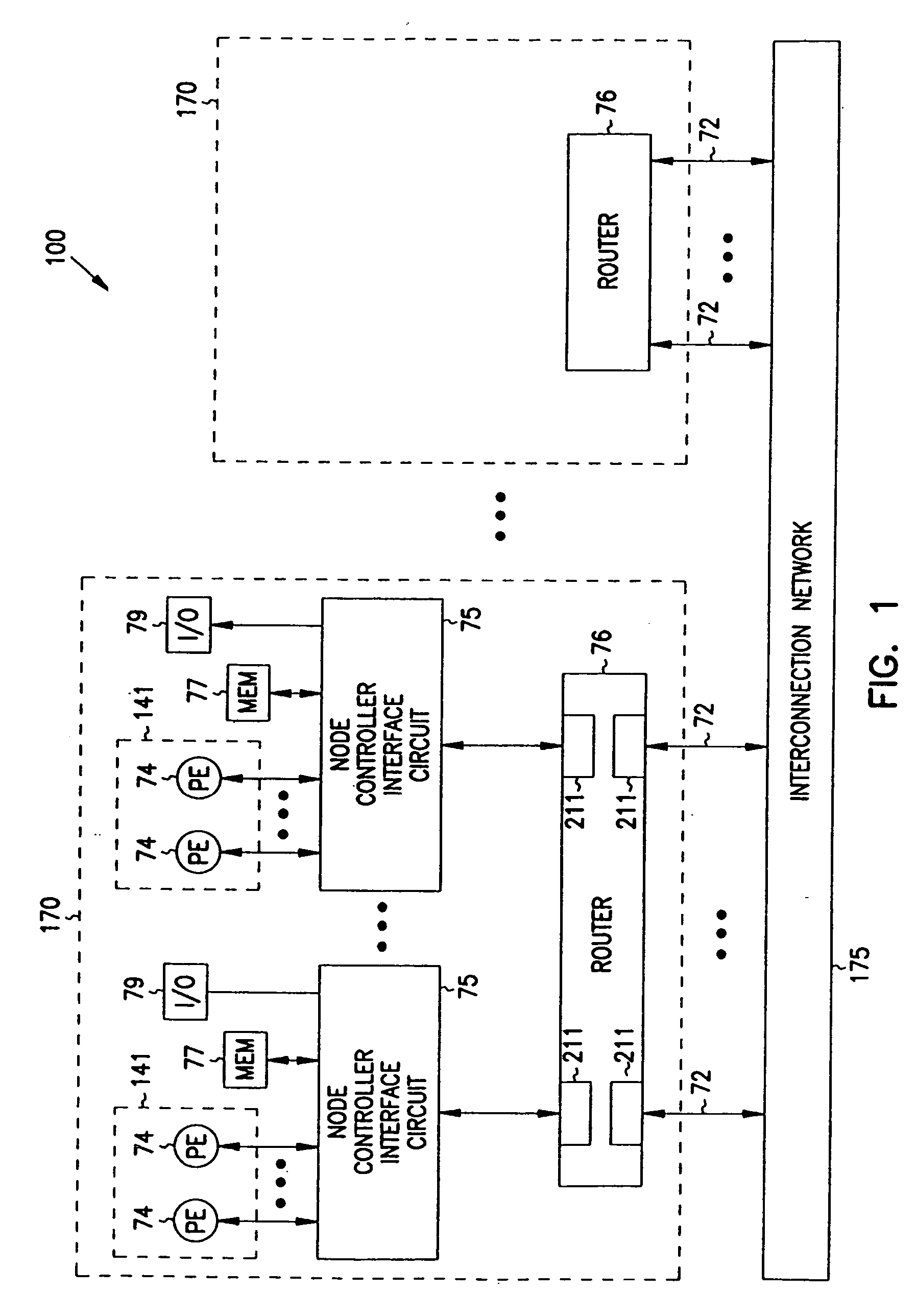
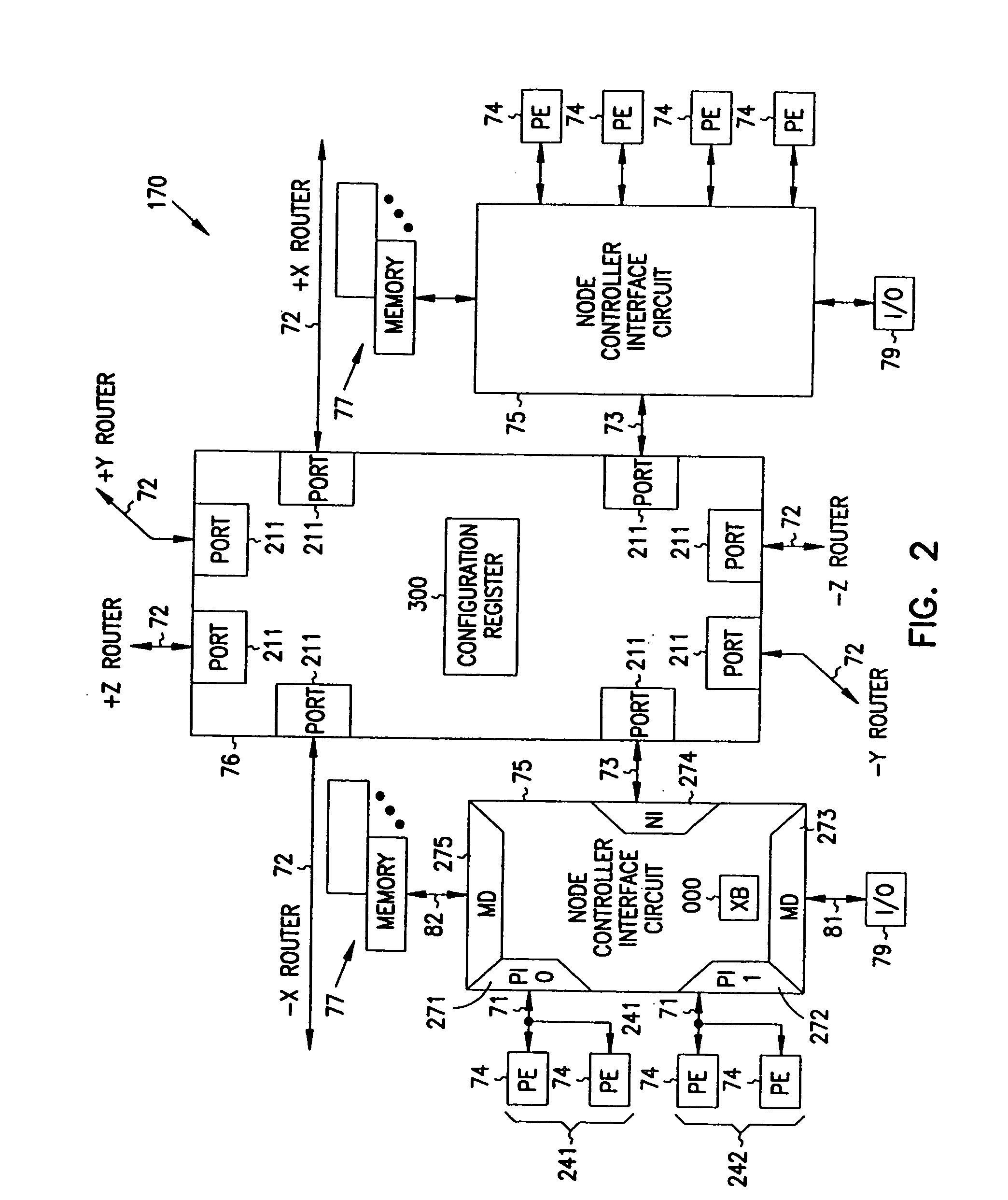
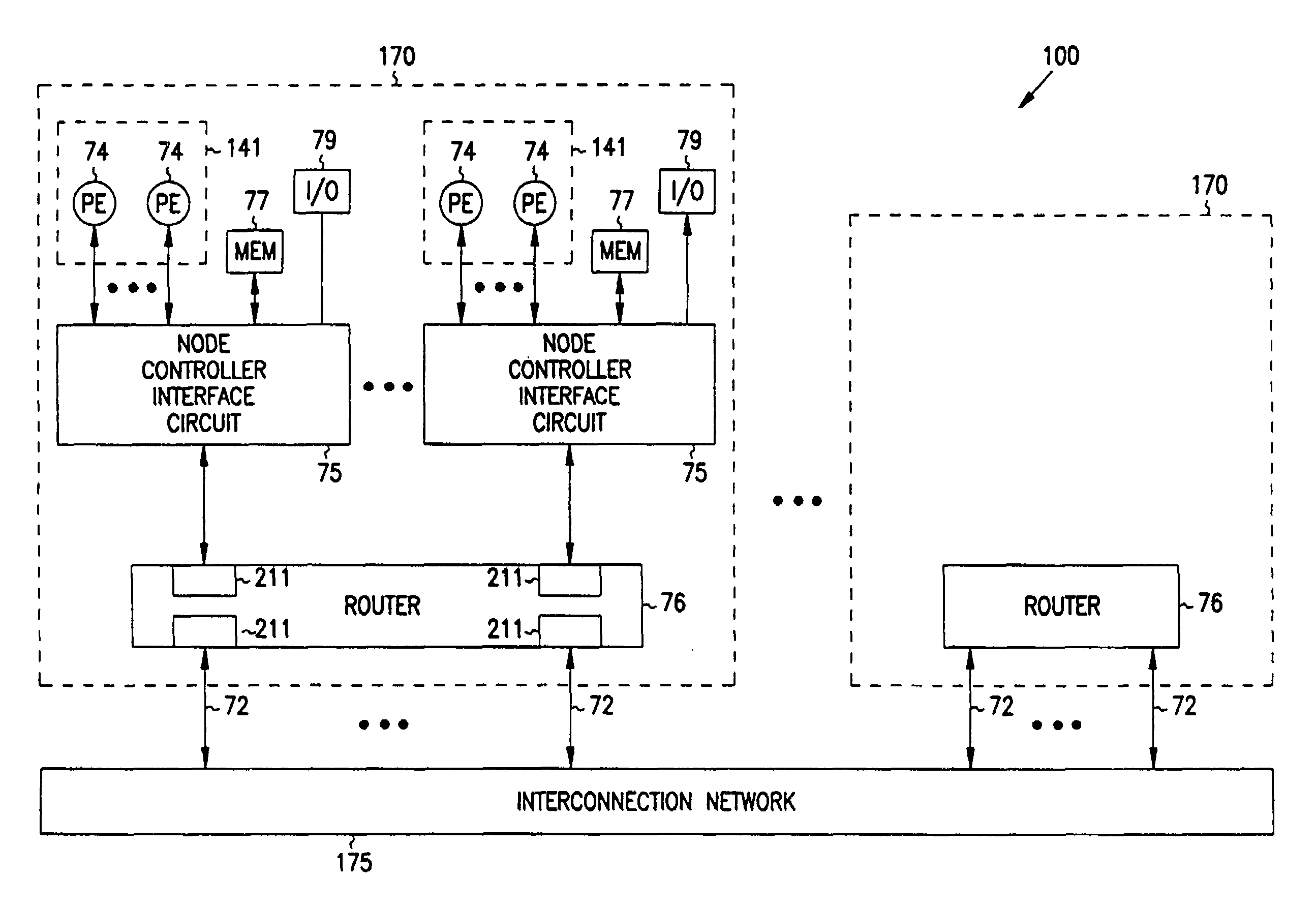
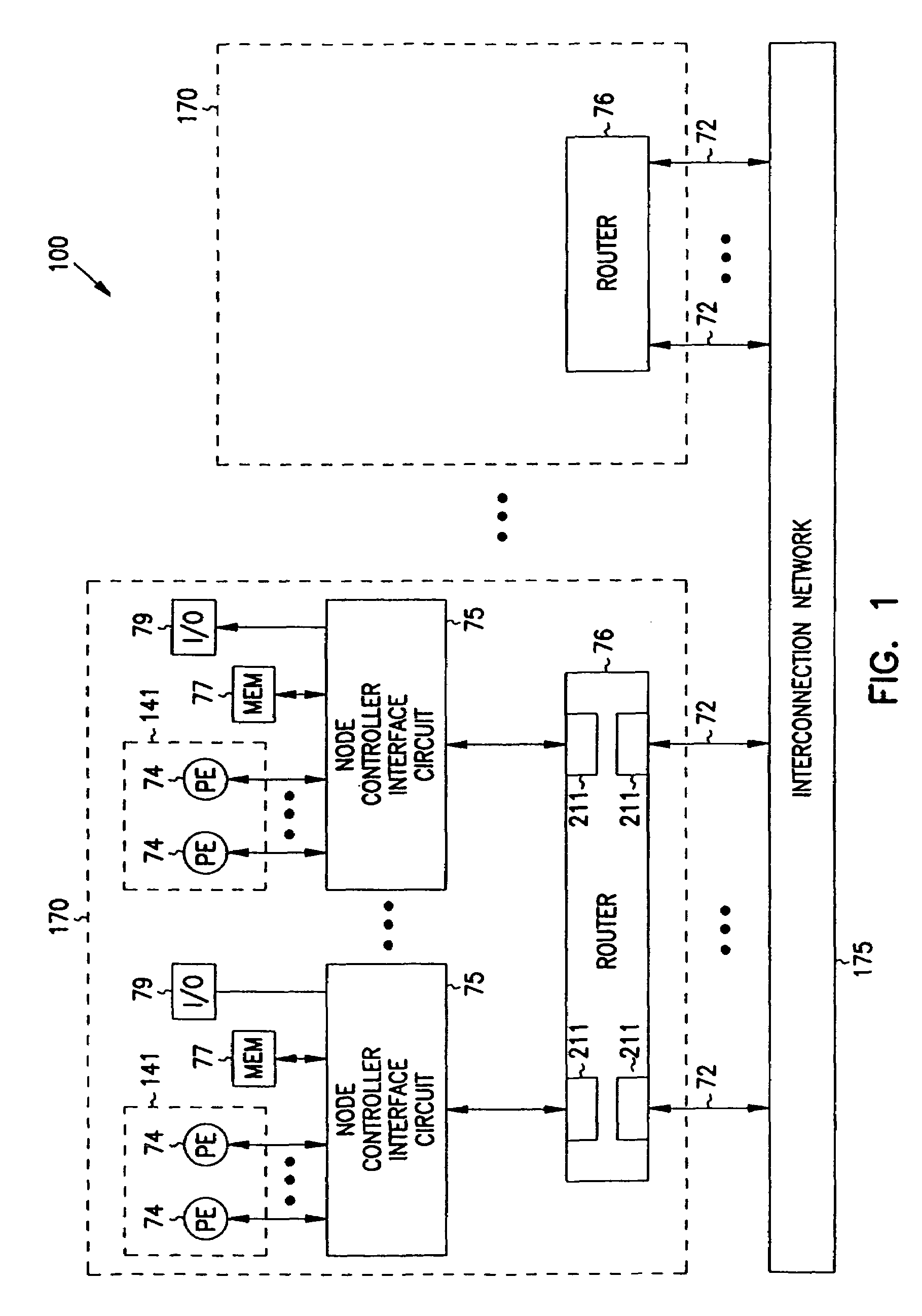
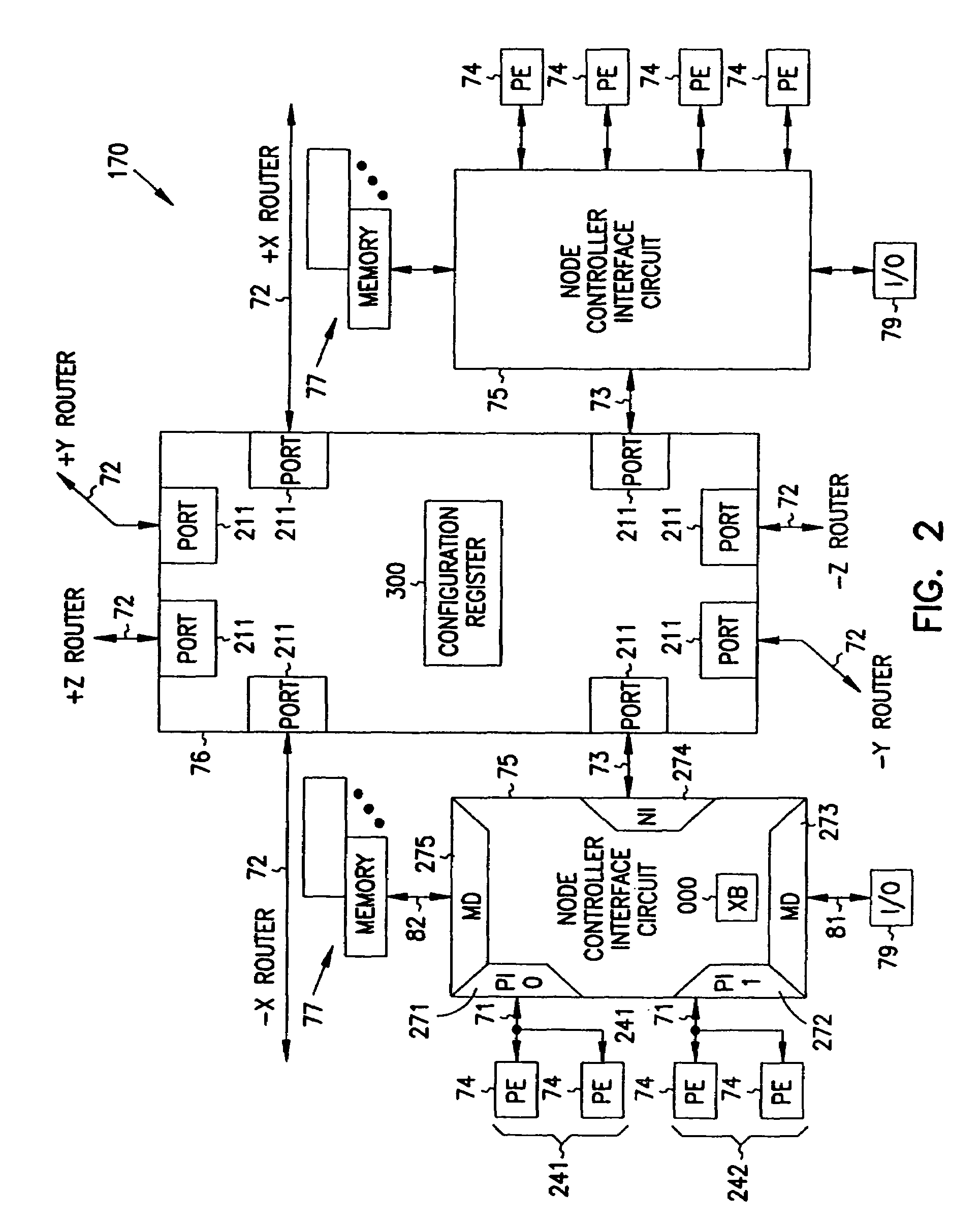
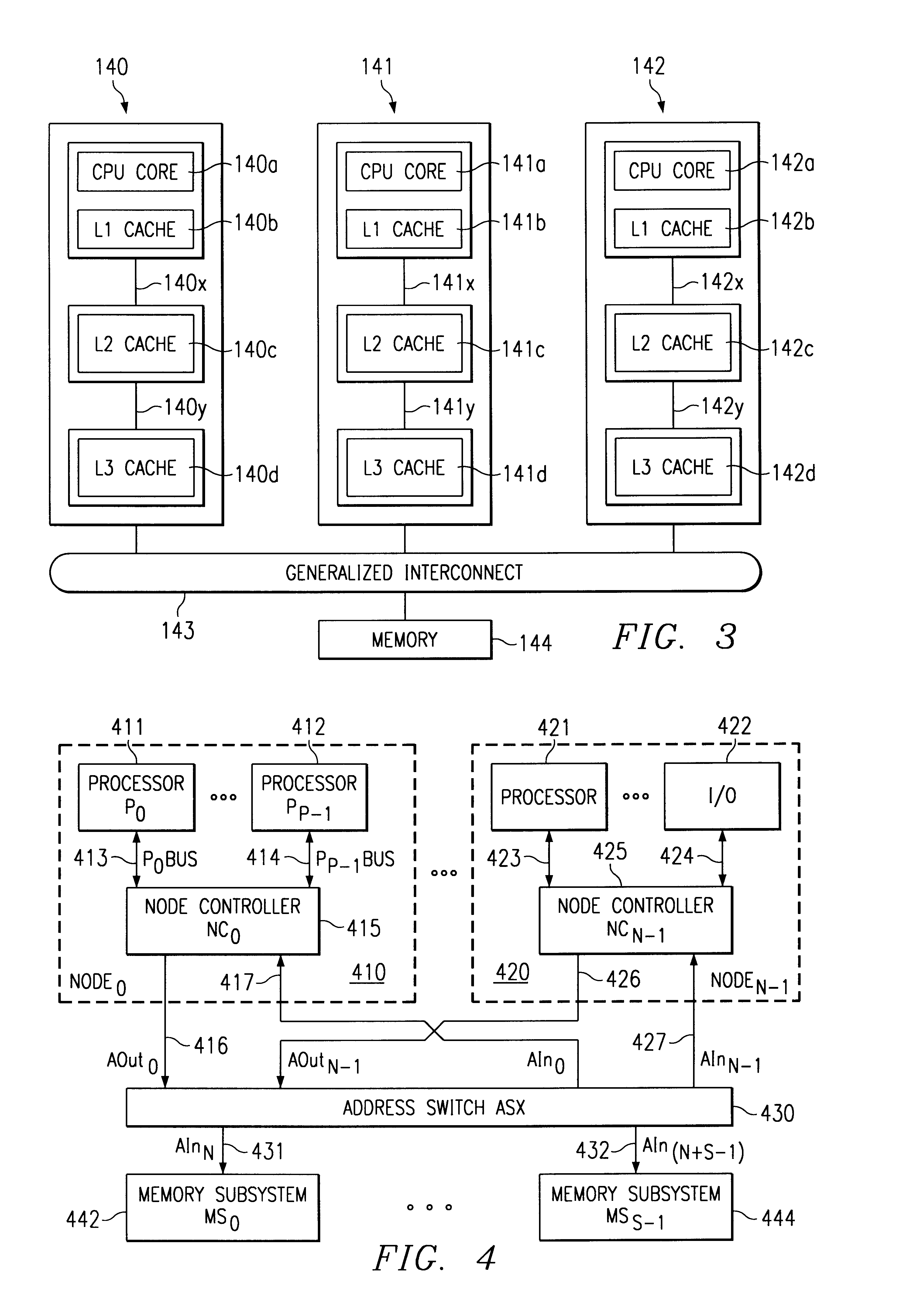
Multiprocessor node controller circuit and method
InactiveUS20050053057A1Ease of parallel processingImprove welfareMultiplex system selection arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressCrossbar switch
Improved method and apparatus for parallel processing. One embodiment provides a multiprocessor computer system that includes a first and second node controller, a number of processors being connected to each node controller, a memory connected to each controller, a first input / output system connected to the first node controller, and a communications network connected between the node controllers. The first node controller includes: a crossbar unit to which are connected a memory port, an input / output port, a network port, and a plurality of independent processor ports. A first and a second processor port connected between the crossbar unit and a first subset and a second subset, respectively, of the processors. In some embodiments of the system, the first node controller is fabricated onto a single integrated-circuit chip. Optionally, the memory is packaged on plugable memory / directory cards wherein each card includes a plurality of memory chips including a first subset dedicated to holding memory data and a second subset dedicated to holding directory data. Further, the memory port includes a memory data port including a memory data bus and a memory address bus coupled to the first subset of memory chips, and a directory data port including a directory data bus and a directory address bus coupled to the second subset of memory chips. In some such embodiments, the ratio of (memory data space) to (directory data space) on each card is set to a value that is based on a size of the multiprocessor computer system.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Pseudo-concurrency between a volatile memory and a non-volatile memory on a same data bus
A system provides pseudo-concurrency for a volatile memory and a non-volatile memory on a same data bus. In one system embodiment, the volatile memory is coupled to its own address bus, and the non-volatile memory is coupled to its own address bus. In another system embodiment, the volatile memory and non-volatile memory are coupled to a multiplexed address bus. Concurrent with an access cycle to the volatile memory, the non-volatile memory may be precharged. After the access cycle to the volatile memory, a data cycle to a non-volatile memory may be executed. Concurrent with an access cycle to the non-volatile memory, the volatile memory may be precharged. After the access cycle to the non-volatile memory, a data cycle to the volatile memory may be executed.
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
CAM memory architecture and a method of forming and operating a device according to a CAM memory architecture
InactiveUS6906938B2Lower requirementOptimized areaDigital storageMemory systemsControl signalControl data
A method for a content addressable memory that includes receiving a first data value for evaluation at a first memory block during a first time interval, receiving a second data value for evaluation at a second memory block during a second time interval and evaluating said both the first and second data values during a third time interval. According to one embodiment of the invention the first and second time intervals are separate so that the first and second data blocks receive unique data out of phase with one another from a single address bus. Evaluation of both data values takes place substantially simultaneously in the respective memory blocks. Also included is a device architecture and a device adapted to control data transfer to two CAM memory blocks in response to alternate phase transitions of a control signal.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
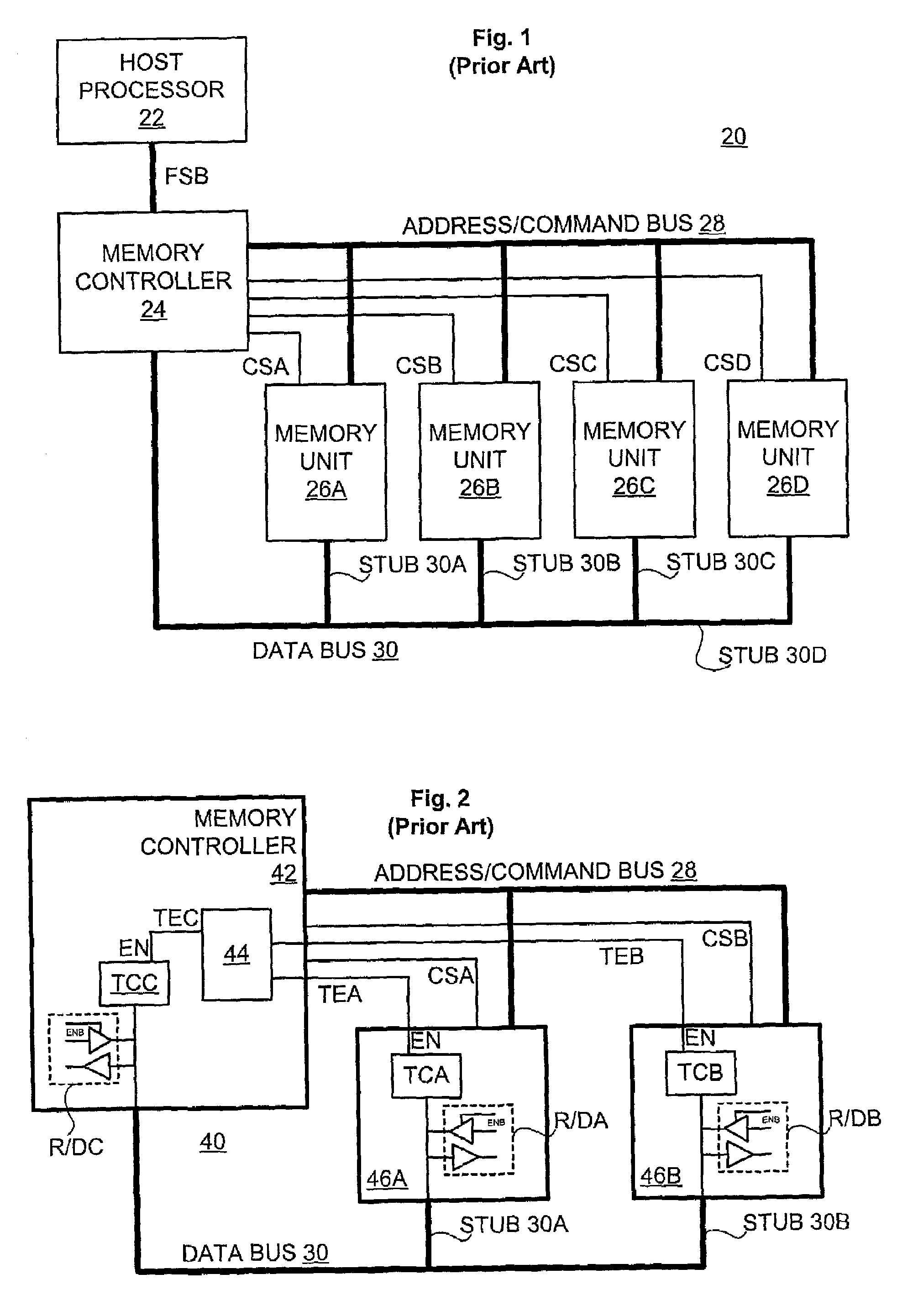
Memory bus termination with memory unit having termination control
Methods and apparatus for a memory system using line termination circuits in each memory unit (e.g., integrated circuit memory device) are disclosed. The memory unit contains termination control logic that sets the state of a controllable termination circuit to control reflections on the data bus. The termination control logic determines the proper state for the termination circuit from the state of its memory unit, and in some cases, from the approximate state of the data bus as gleaned from commands decoded from the command / address bus. A termination configuration register on the unit can be used to define the appropriate termination state for each unit state and / or data bus state.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
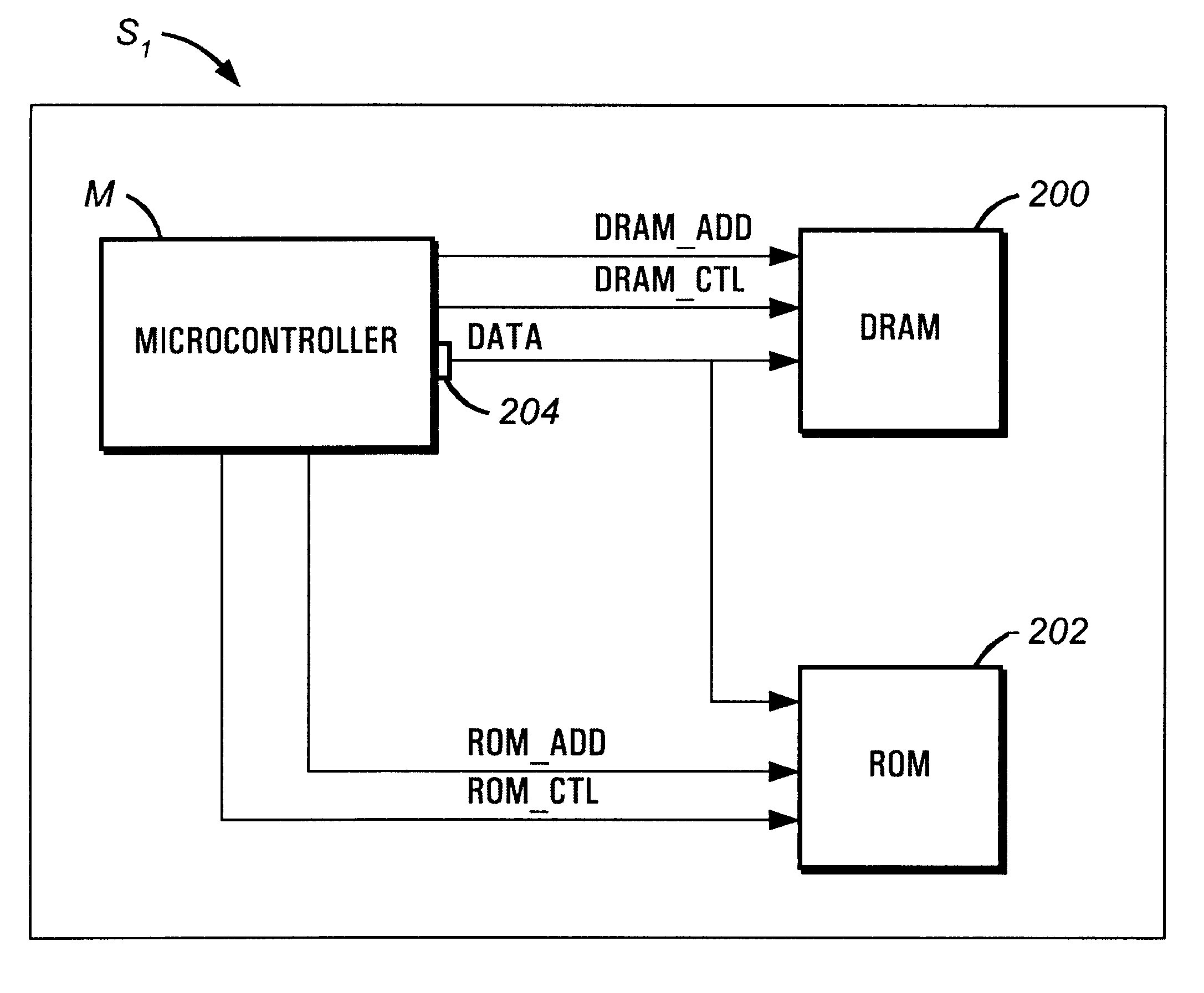
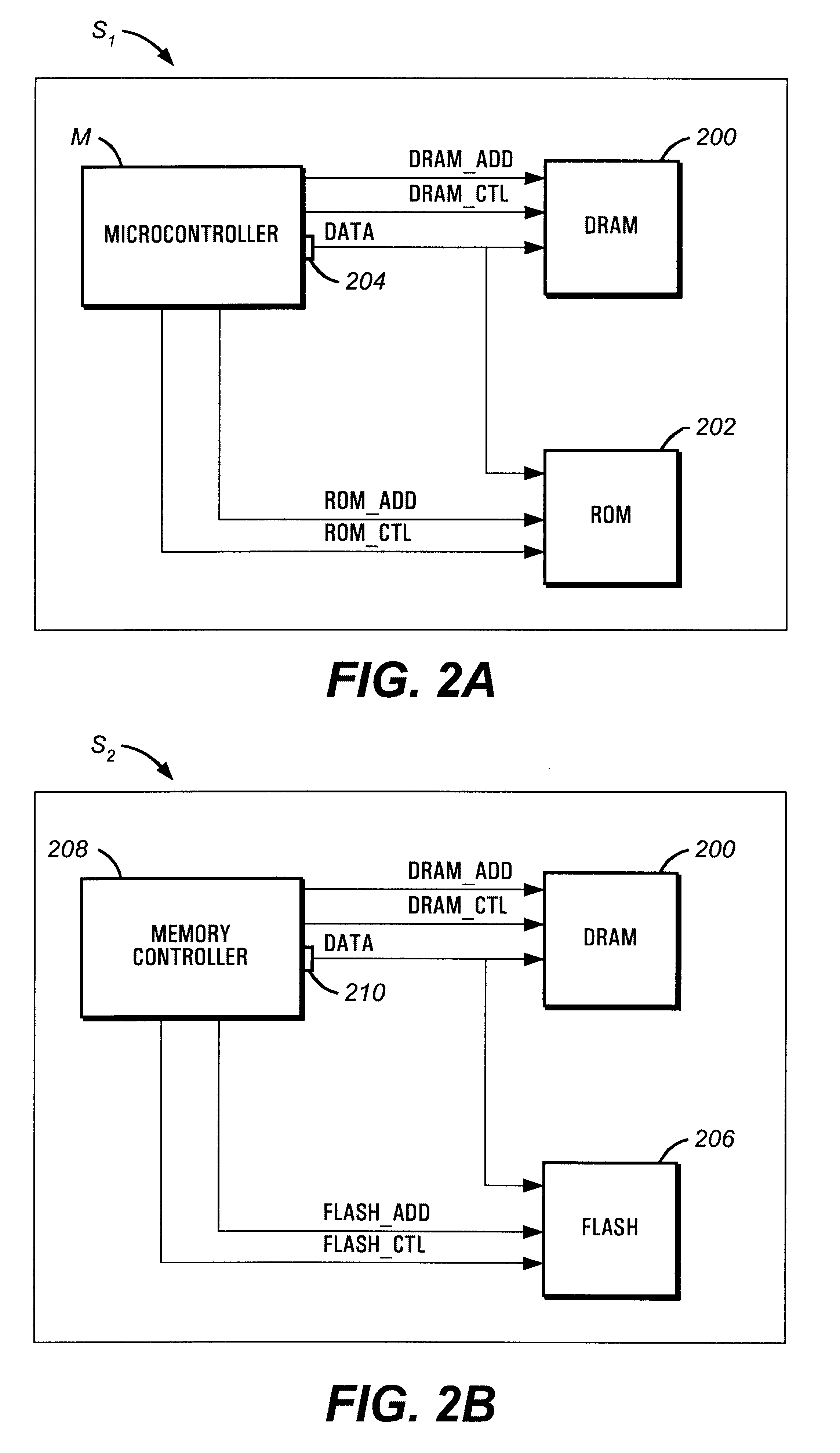
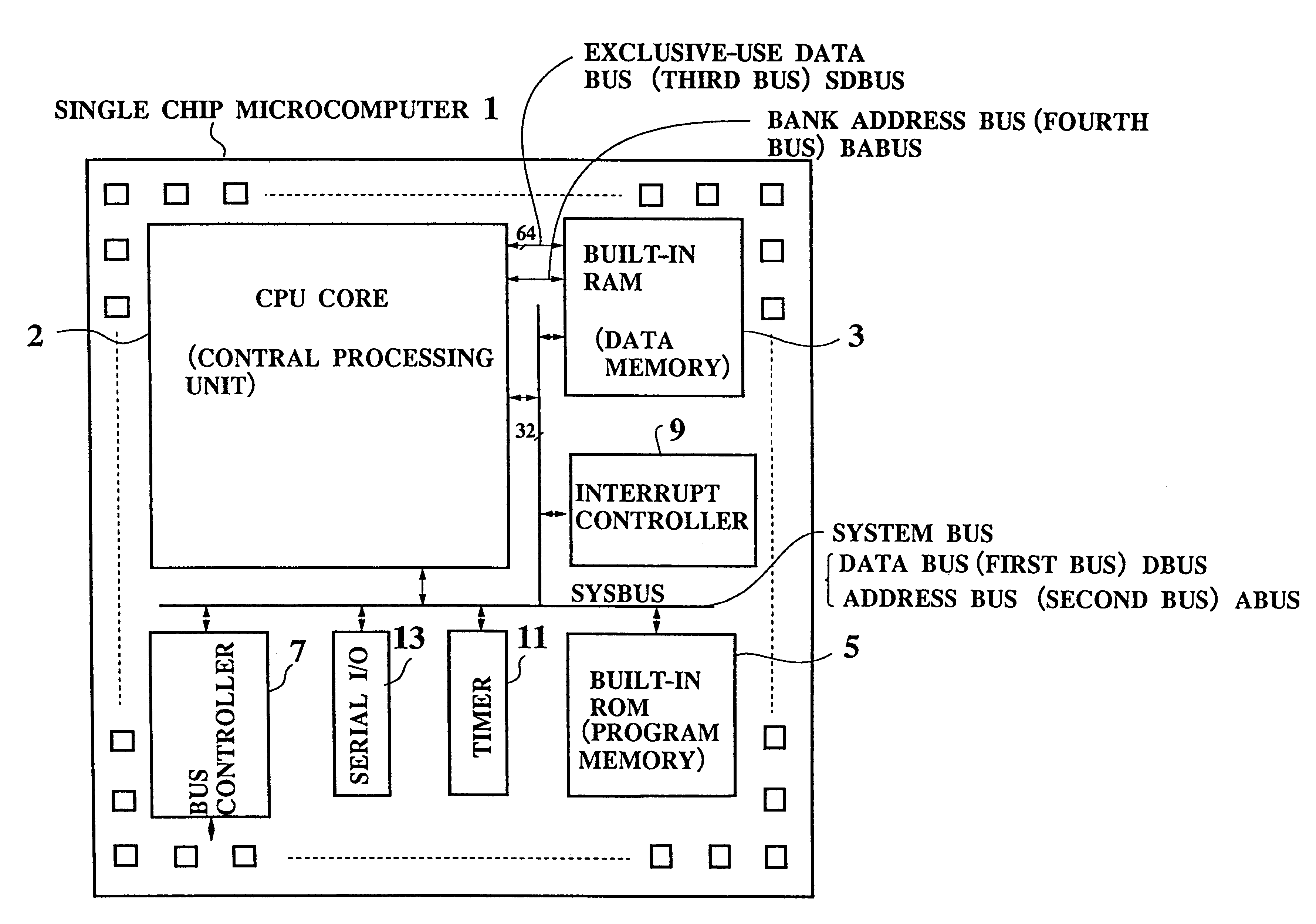
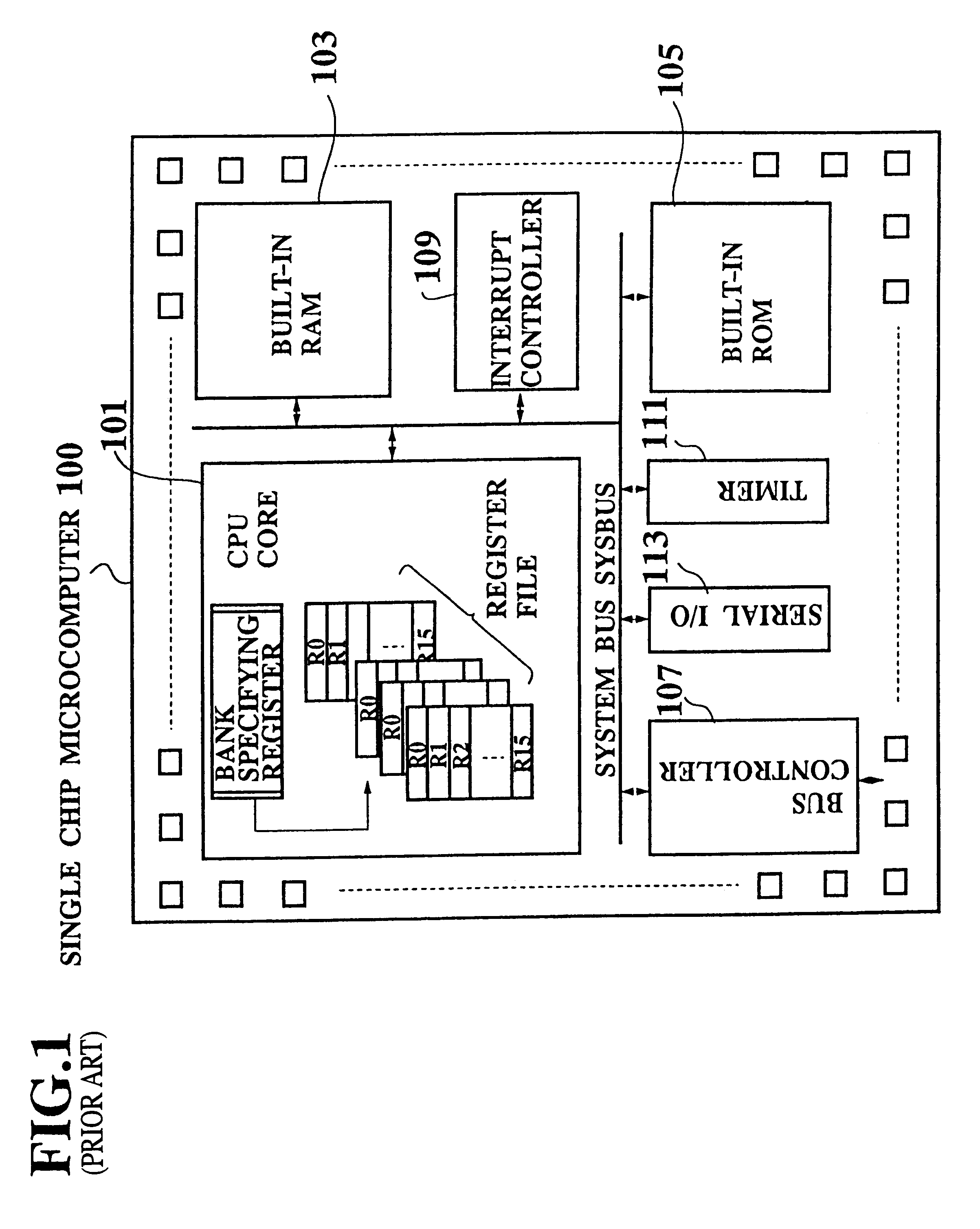
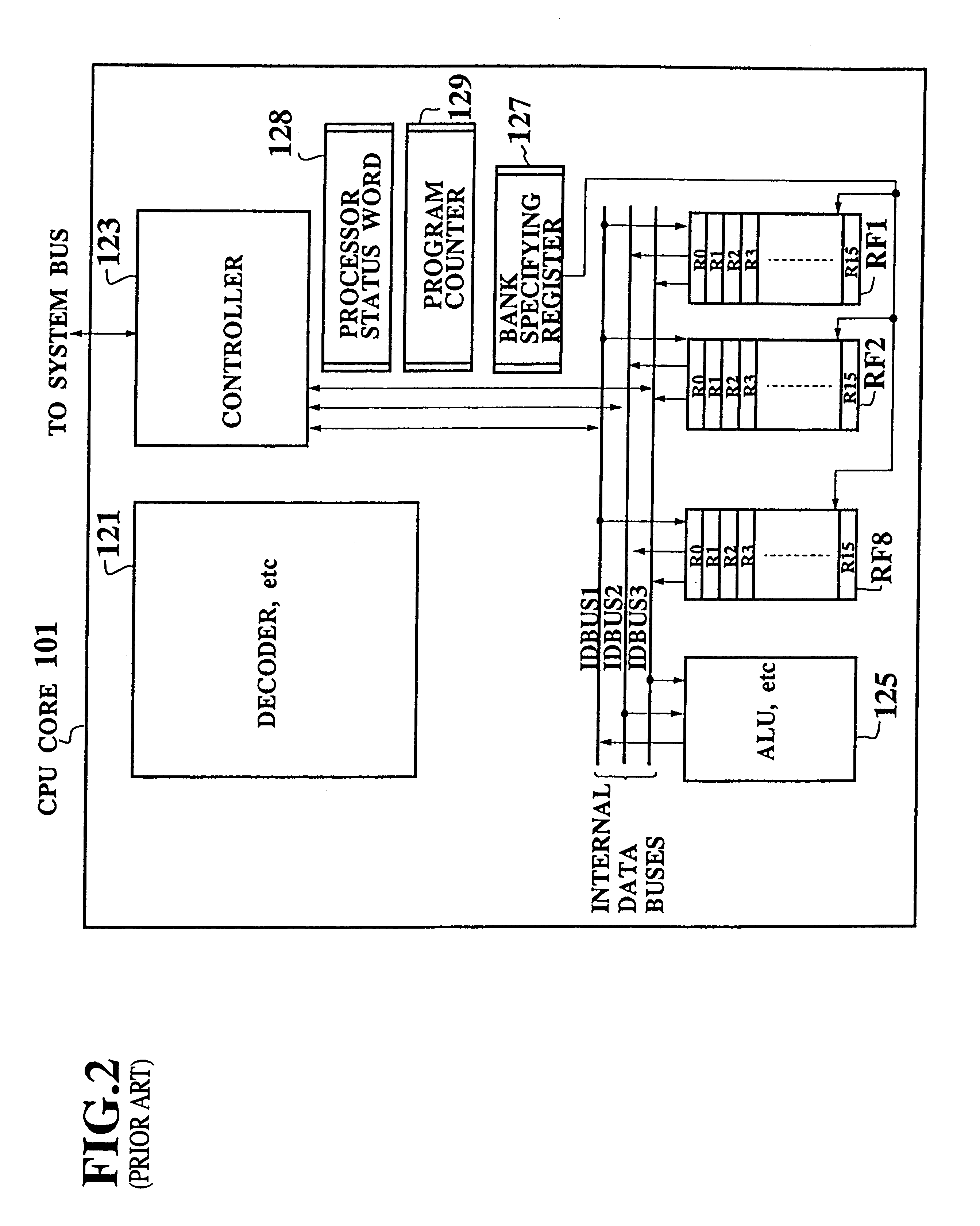
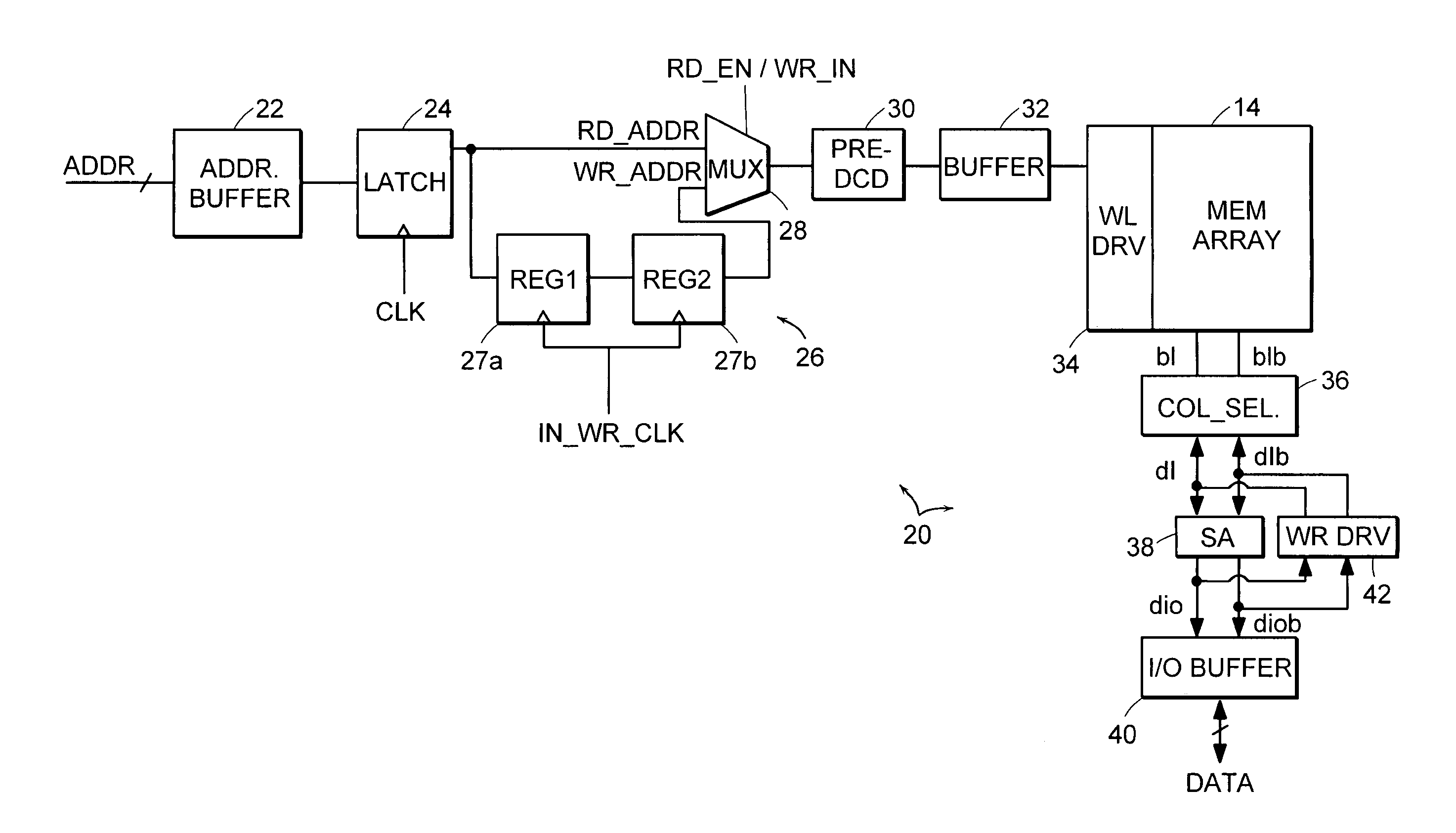
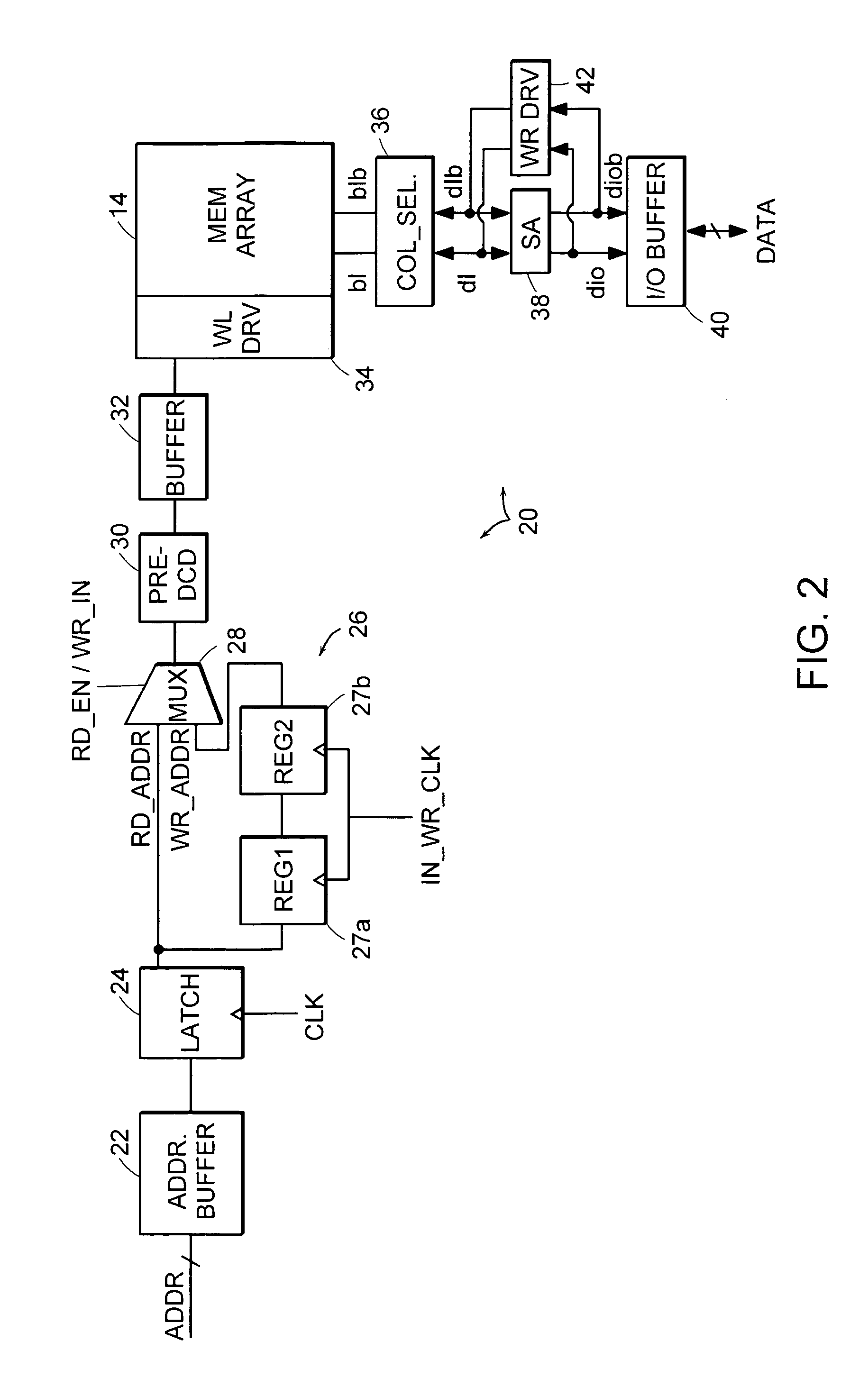
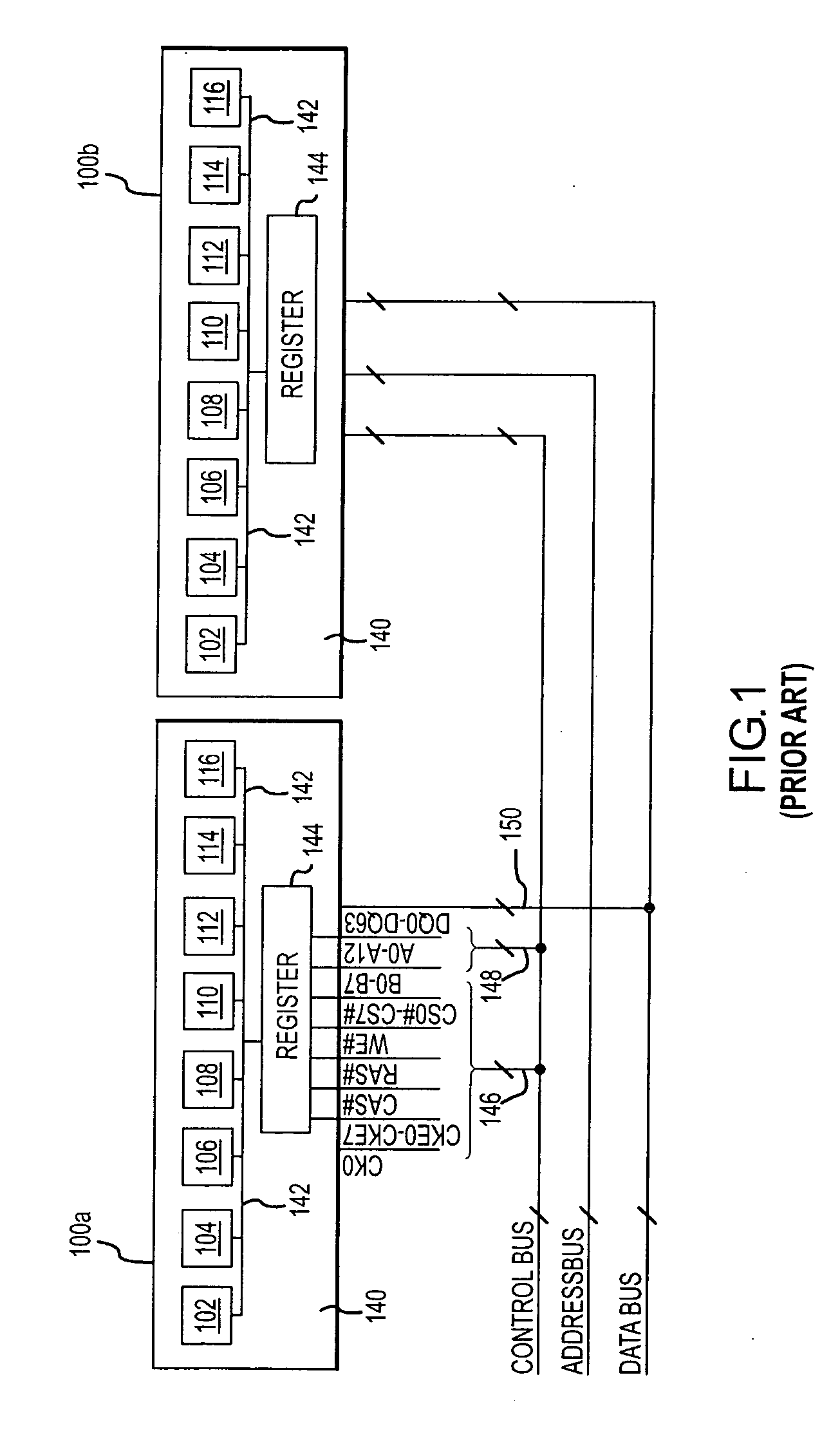
Single chip microcomputer having a dedicated address bus and dedicated data bus for transferring register bank data to and from an on-line RAM
InactiveUS6223279B1Efficiently chip spaceData transferArchitecture with single central processing unitSpecial data processing applicationsGeneral purposeProcessor register
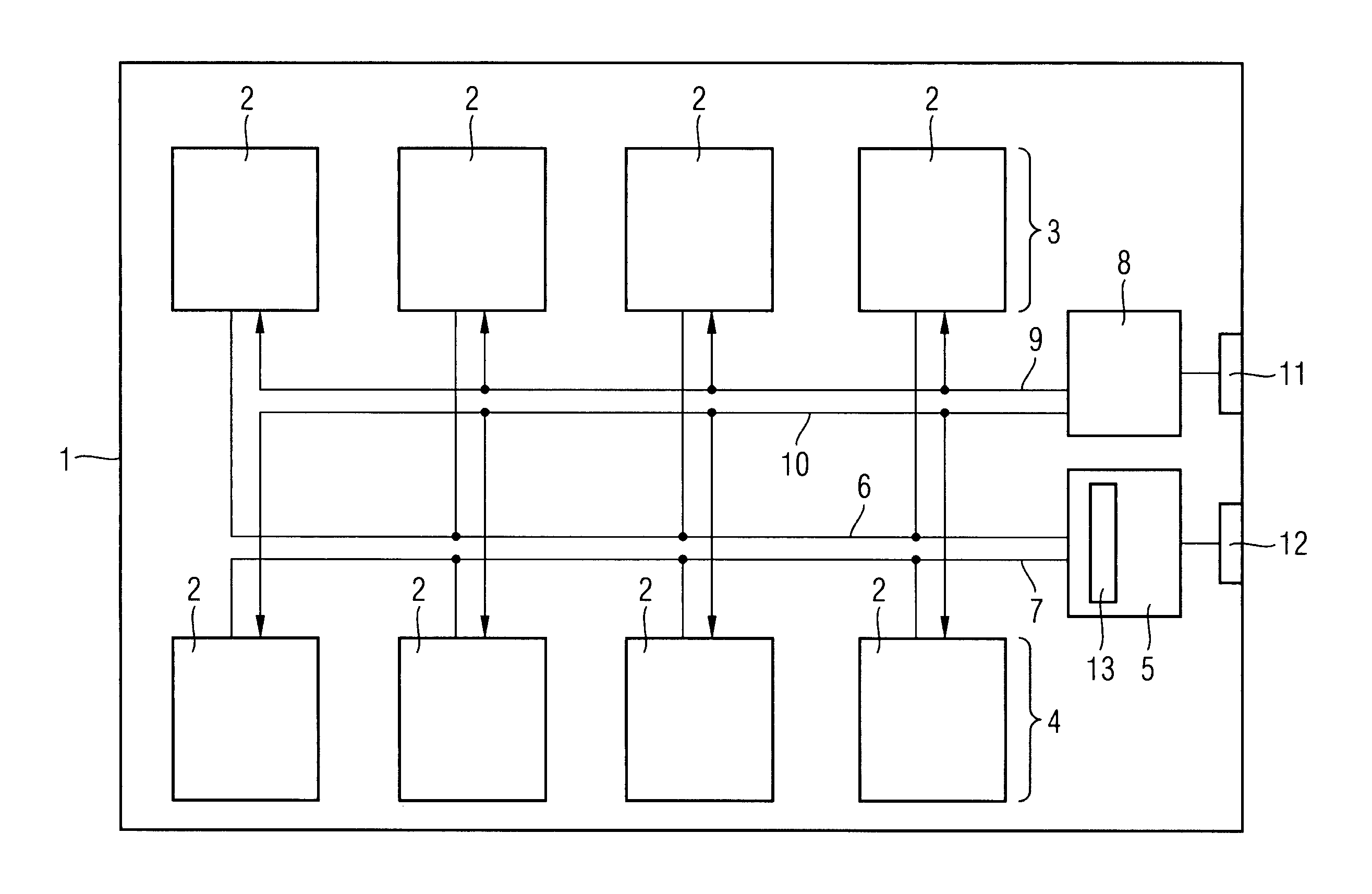
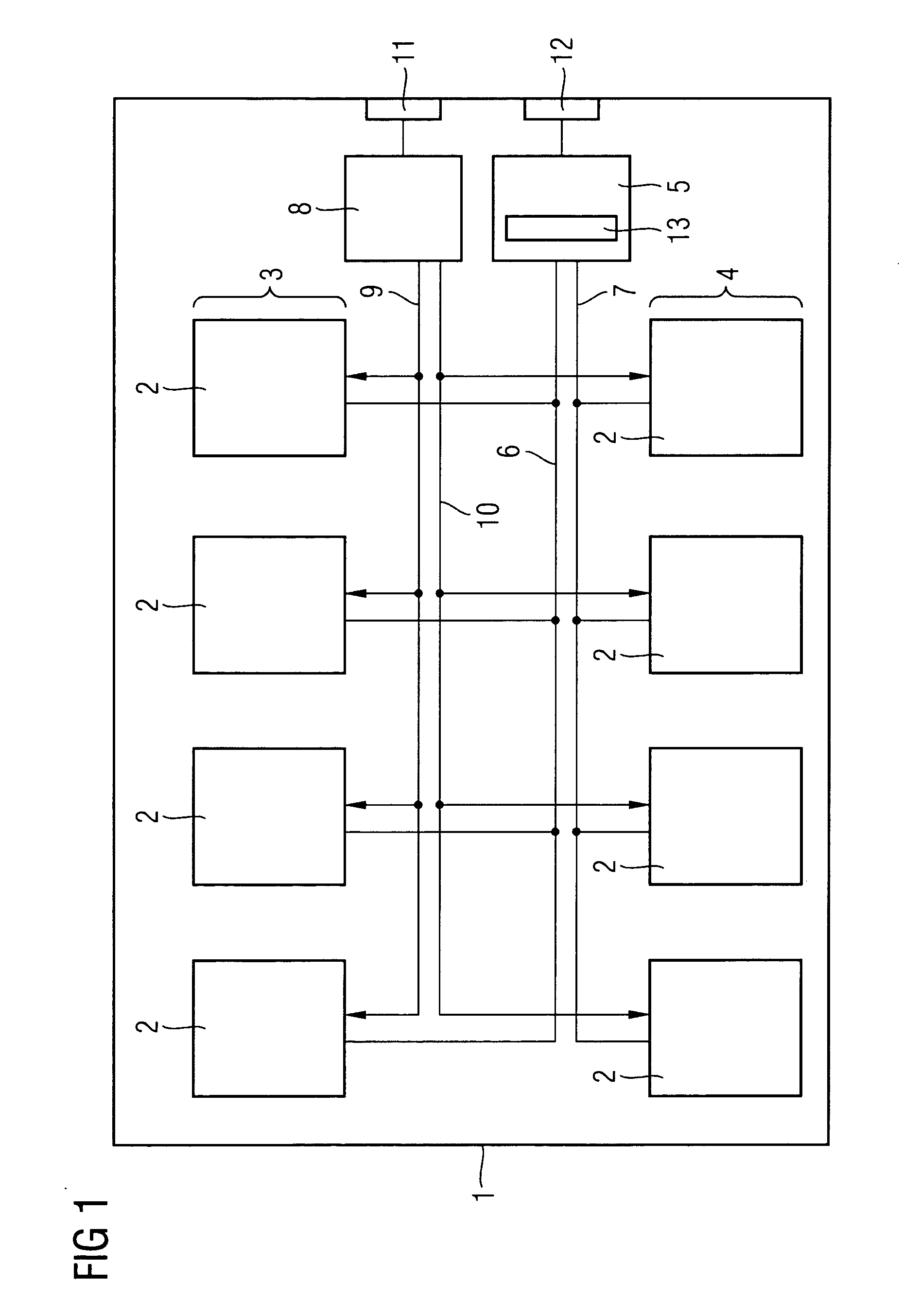
A single chip microcomputer comprises a central processing unit (CPU) 2, a on-chip RAM 3, a on-chip ROM 5, a first bus DBUS for connecting the CPU, RAM, and ROM with one another and transferring data between them, a second bus ABUS for passing address data corresponding to the data passed through the first bus, a third bus SDBUS for connecting the CPU 2 with the RAM 3 and transferring data between them, the number of bits of the third bus SDBUS being larger than that of the first bus DBUS, and a fourth bus BABUS for connecting the CPU 2 with the RAM 3 and passing address data corresponding to the data passed through the third bus SDBUS. The CPU 2 has a data memory RF serving as general purpose registers for providing internal data to the third bus SDBUS, and a bank specifying register BP for holding positional data of a mapping region in the RAM 3 where the contents of the data memory RF are mapped and providing the positional data to the fourth bus BABUS. The RAM 3 has a memory cell array 31, a bank address control circuit 35 connected to the fourth bus BABUS, for generating a real address according to the contents of the bank specifying register BP (BP0, BP1), and a selection circuit 37 for selecting the real address generated by the bank address control circuit 35, or the address provided through the second bus ABUS.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
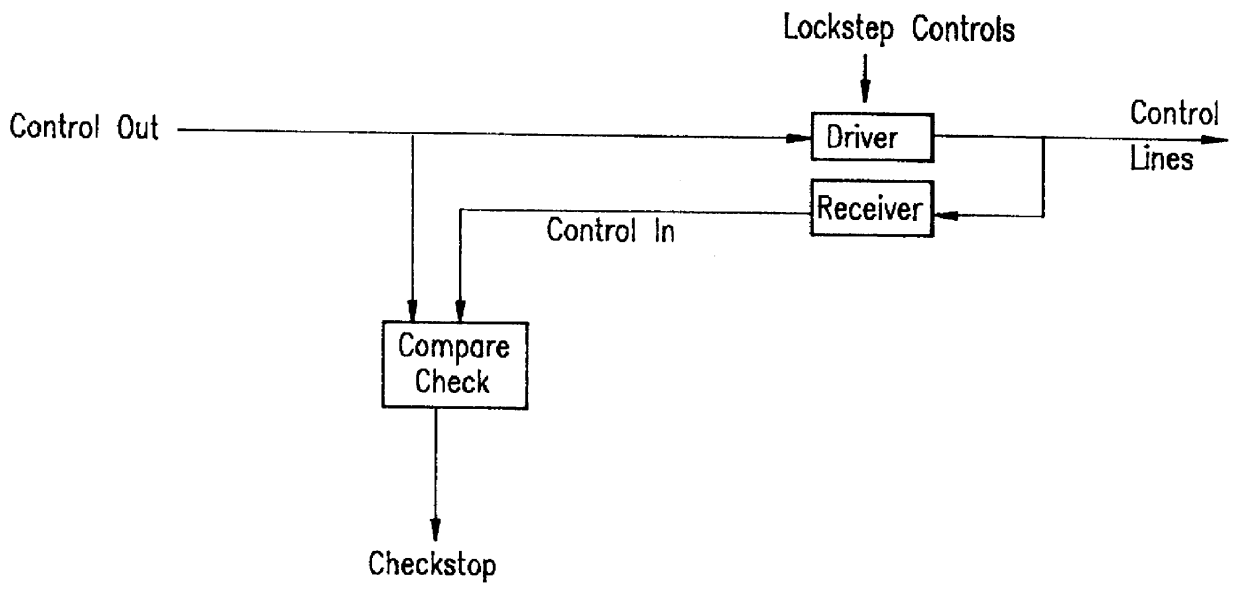
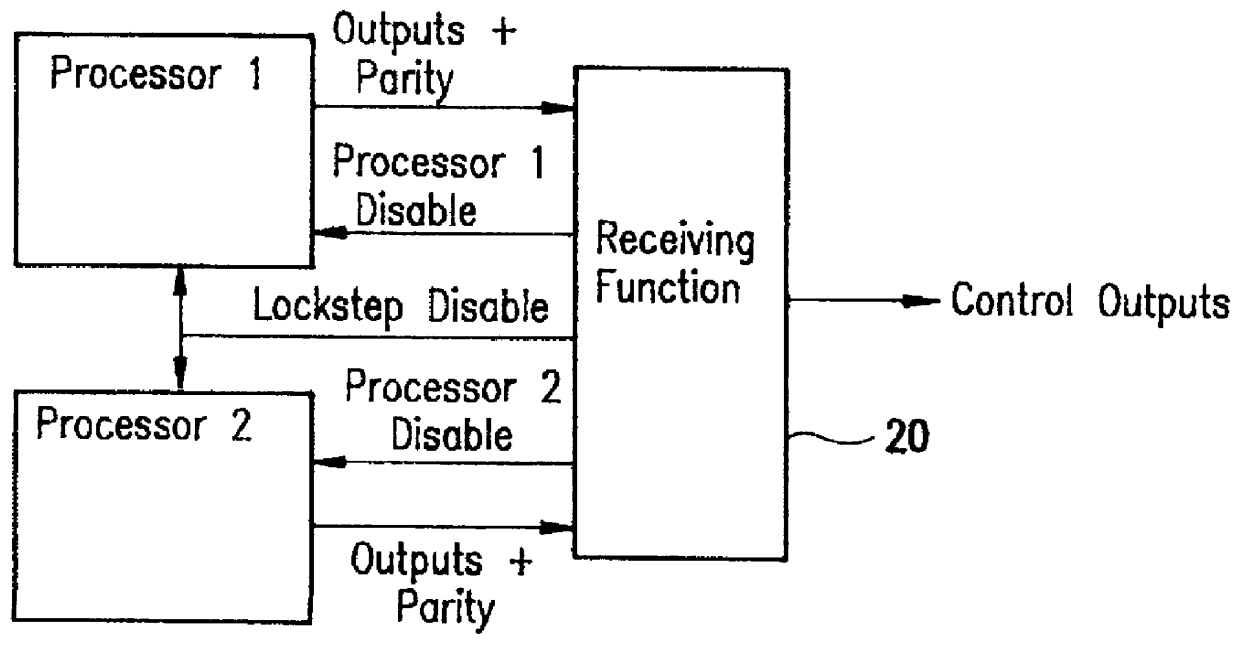
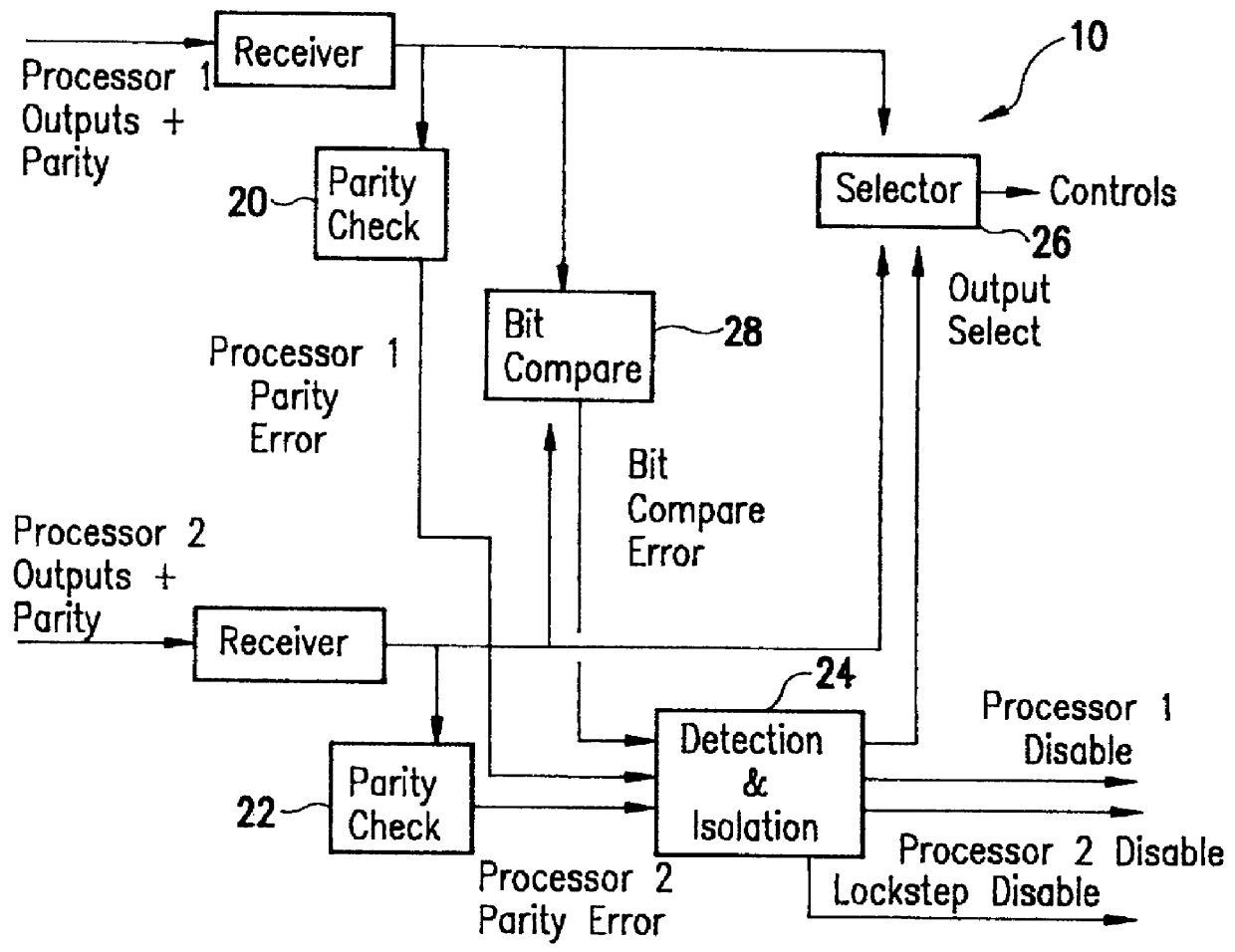
Error detection and fault isolation for lockstep processor systems
InactiveUS6065135ARedundant data error correctionRedundant hardware error correctionMemory addressAddress bus
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
Address error detection by merging a polynomial-based CRC code of address bits with two nibbles of data or data ECC bits
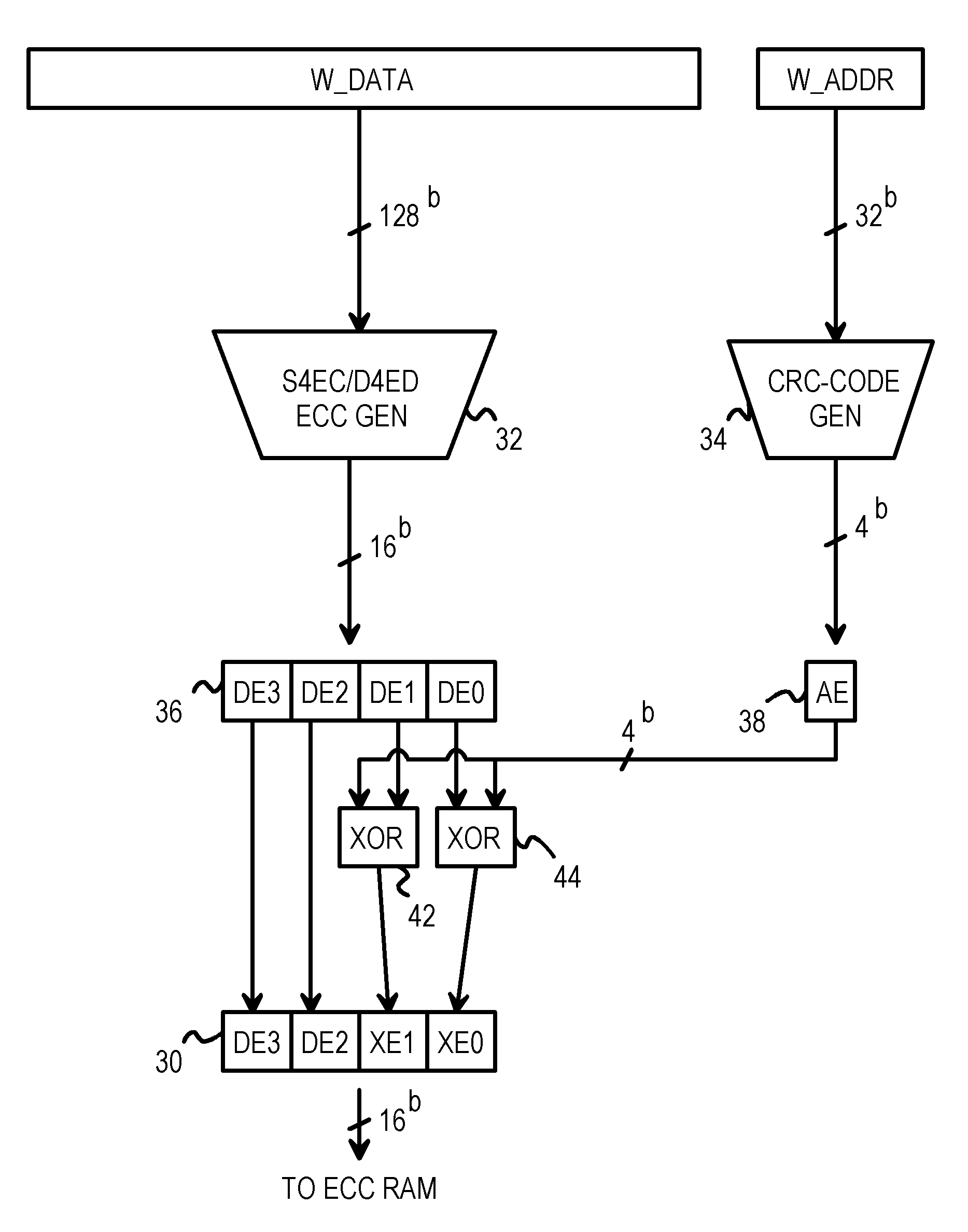
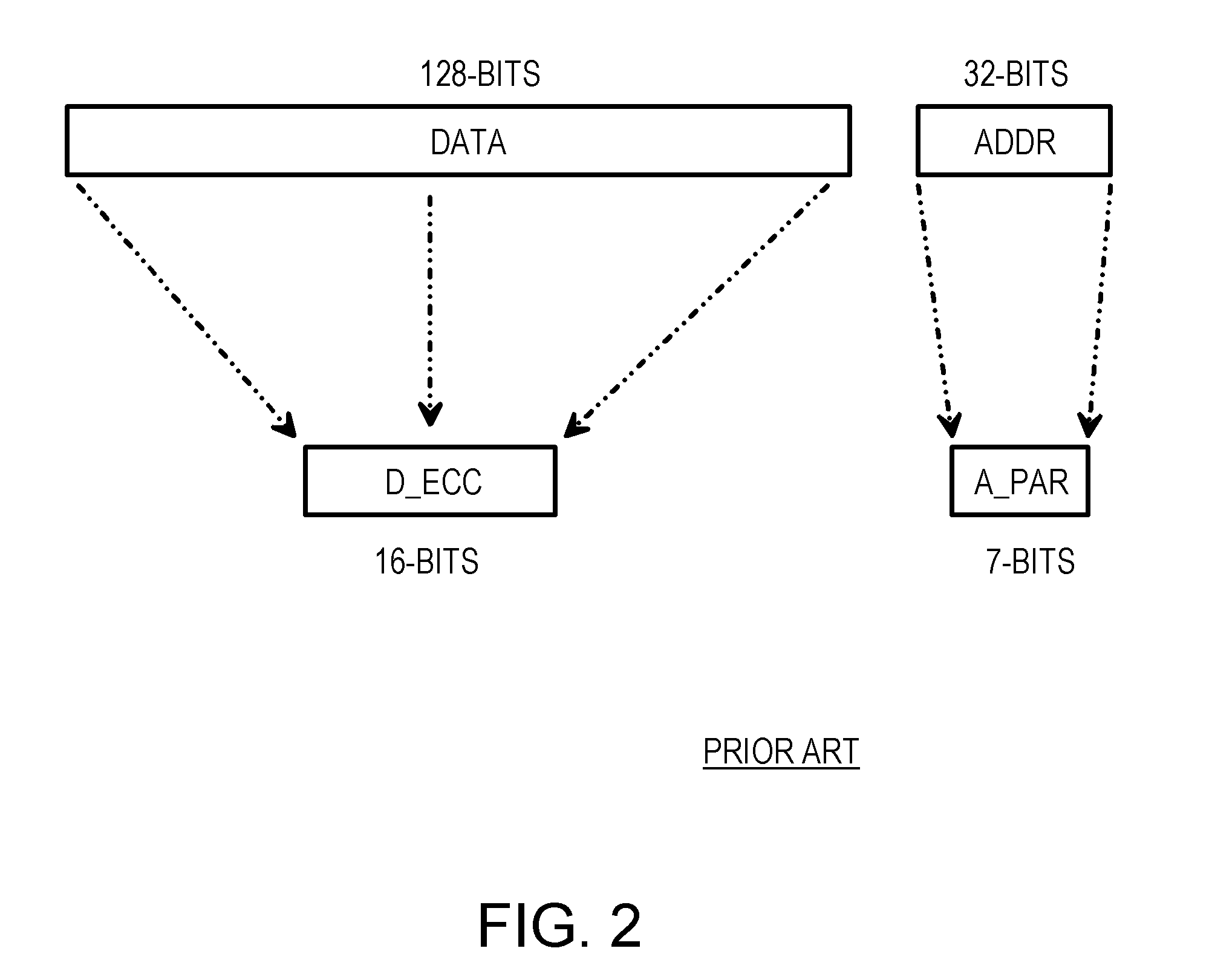
A memory system provides data error detection and correction and address error detection. A Single-byte Error-Correcting / Double-byte Error-Detecting (SbEC / DbED) code with the byte being a 4-bit nibble is used to detect up to 8-bit errors and correct data errors of 4 bits or less. Rather than generating address parity, which is poor at detecting even numbers of errors, a cyclical-redundancy-check (CRC) code generates address check bits. A 32-bit address is compressed to just 4 address check bits using the CRC code. The 4 address check bits are merged (XOR'ed) with two 4-bit nibbles of the data SbEC / DbED code to generate a merged ECC codeword that is stored in memory. An address error causes a 2-nibble mis-match due to the redundant merging of the 4 address check bits with 2 nibbles of data correction code. The CRC code is ideal for detecting even numbers of errors common with multiplexed-address DRAMs.
Owner:AZUL SYSTEMS
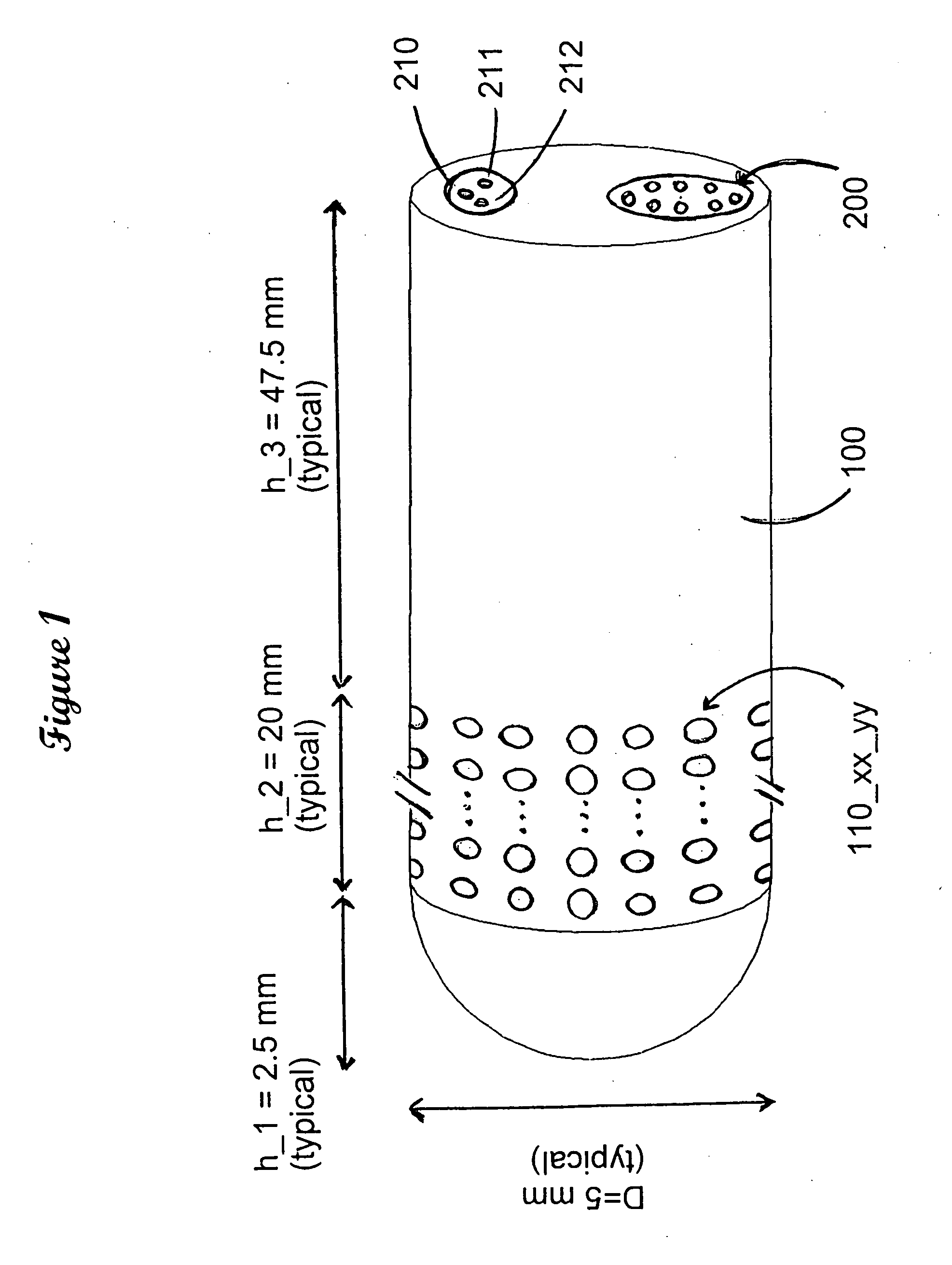
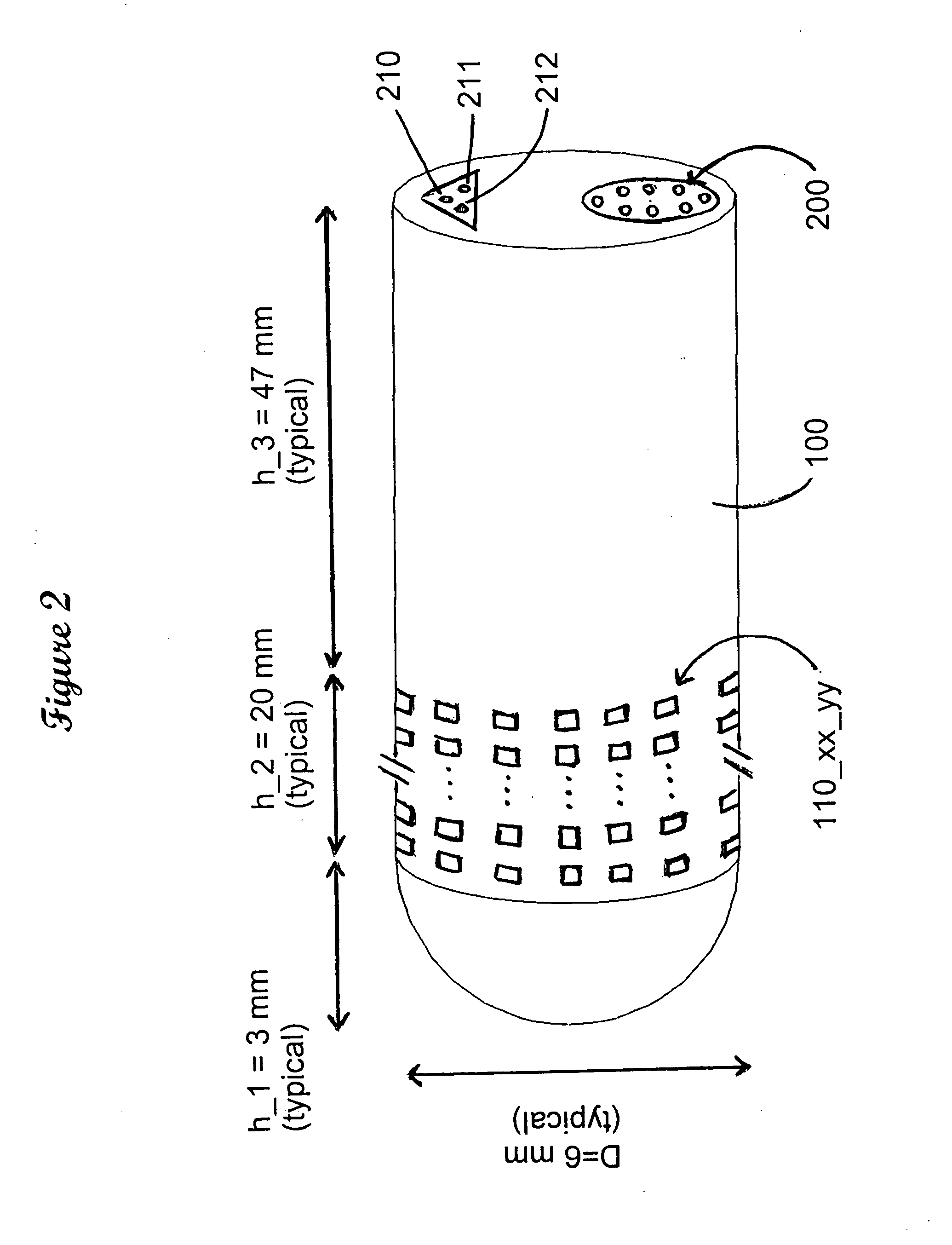
Method and means for connecting and controlling a large number of contacts for electrical cell stimulation in living organisms
ActiveUS20100082076A1High voltageUndesirable side-effectHead electrodesElectrical measurement instrument detailsAddress busEngineering
An improved electrode for neural stimulation, including deep brain stimulation, cortical stimulation, muscle stimulation and other similar applications. The improvement of our invention over prior art consisting of the possibility of a larger number of electrode pads from where to originate the electrical stimulation, thereby offering the possibility of fine control of the location of the stimulating signal. Our invention discloses a system of address wires which controls switches and demultiplexers to select one of a plurality of wires and one of a plurality of electrode pads from where the electric stimulation starts, and latches that maintain some selected choices after the address buses go on to select other wires and other electrode tips. Our invention also discloses time delay lines which are used to keep the stimulating pulses for a pre-assigned time, after which the stimulating pulses stop until further instruction to start again.
Owner:LEE CHONG IL +1
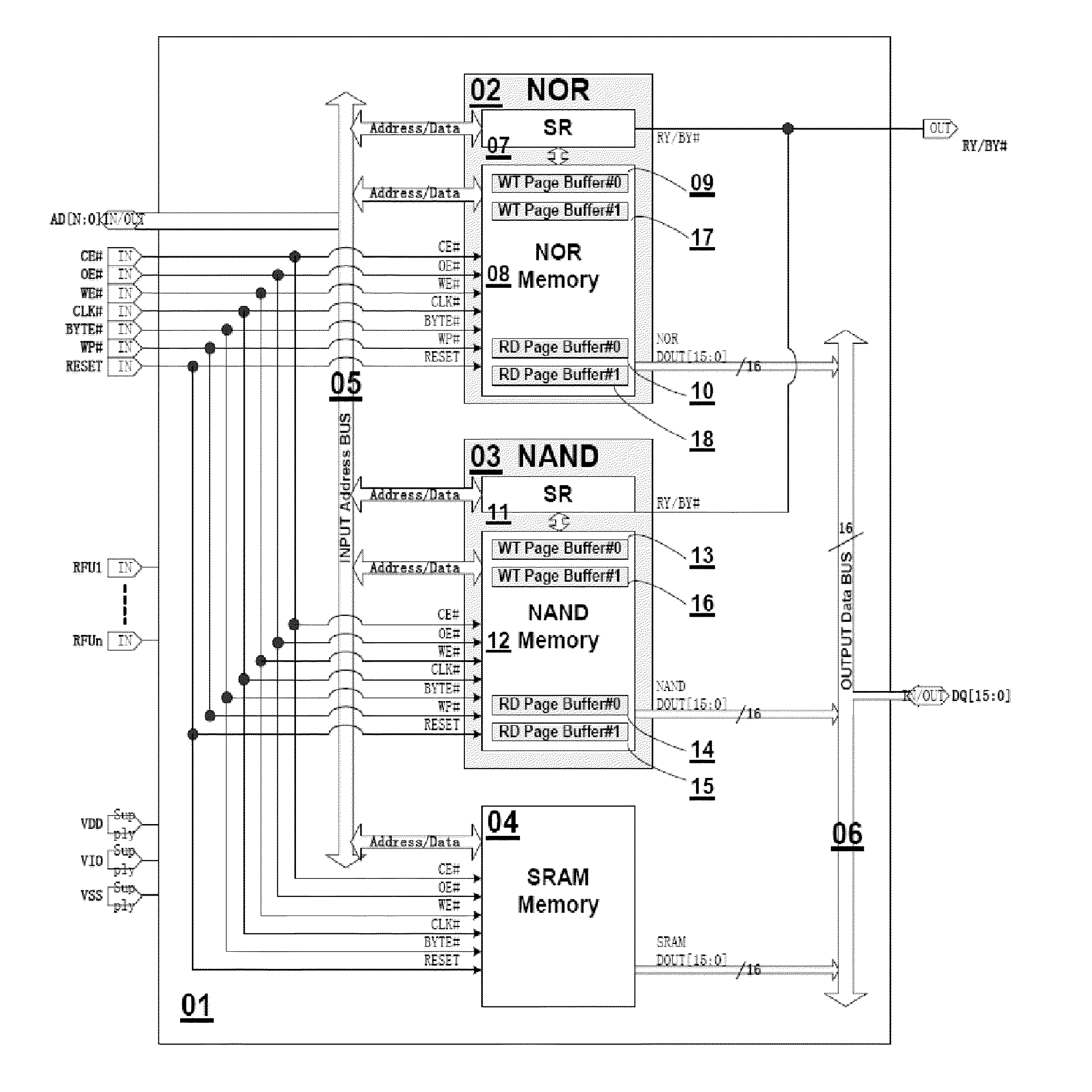
Memory system having NAND-based nor and NAND flashes and SRAM integrated in one chip for hybrid data, code and cache storage
InactiveUS20100329011A1Faster and improved read and write operation of memoryEasy to operateMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRead-only memoriesAddress busMemory map
A memory system includes a NAND flash memory, a NOR flash memory and a SRAM manufactured on a single chip. Both NAND and NOR memories are manufactured by the same NAND manufacturing process and NAND cells. The three memories share the same address bus, data bus, and pins of the single chip. The address bus is bi-directional for receiving codes, data and addresses and transmitting output. The data bus is also bi-directional for receiving and transmitting data. One external chip enable pin and one external output enable pin are shared by the three memories to reduce the number of pins required for the single chip. Both NAND and NOR memories have dual read page buffers and dual write page buffers for Read-While-Load and Write-While-Program operations to accelerate the read and write operations respectively. A memory-mapped method is used to select different memories, status registers and dual read or write page buffers.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Memory device, memory controller and method for operating the same
InactiveUS20060129740A1Send quicklyMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageMemory bankData access
One embodiment of the present invention provides a memory device comprising a plurality of sets of memory banks, wherein each memory bank includes a memory array and is adapted to be read out in a data access; a plurality of internal data buses and a plurality of internal command and address buses connected to the plurality of sets of memory banks, respectively, such that each set of memory banks is associated with one of the internal data buses and one of the internal command and address buses; a command and address port for receiving command and address data from outside; and a command and address unit to direct the received command and address data to one of the sets of memory banks via the associated command and address bus, depending on the address data; and a data output unit for receiving data read out from one set of memory banks via the respective internal data bus in the data access and for serially outputting the received data.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Individually accessible macrocell
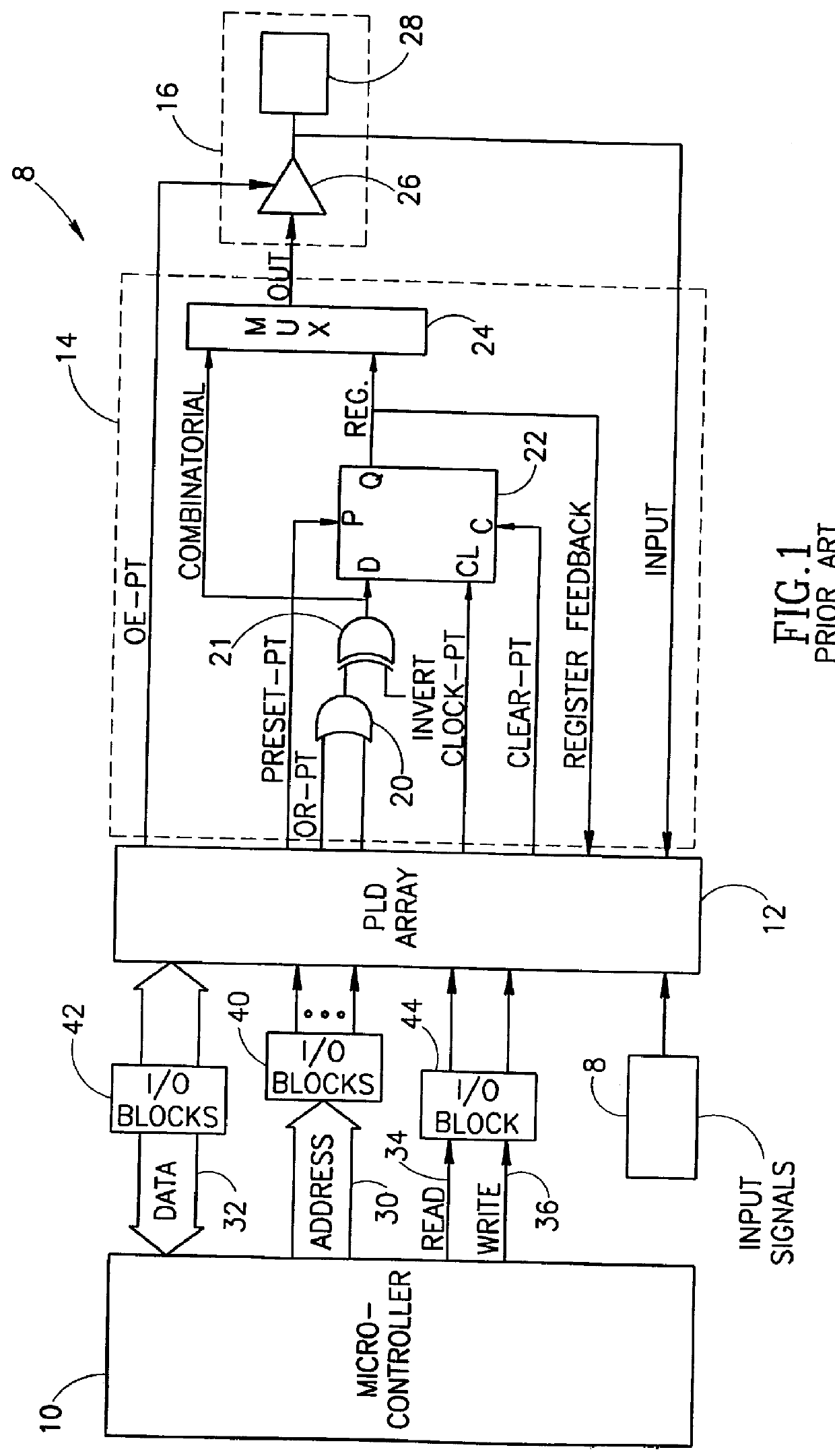
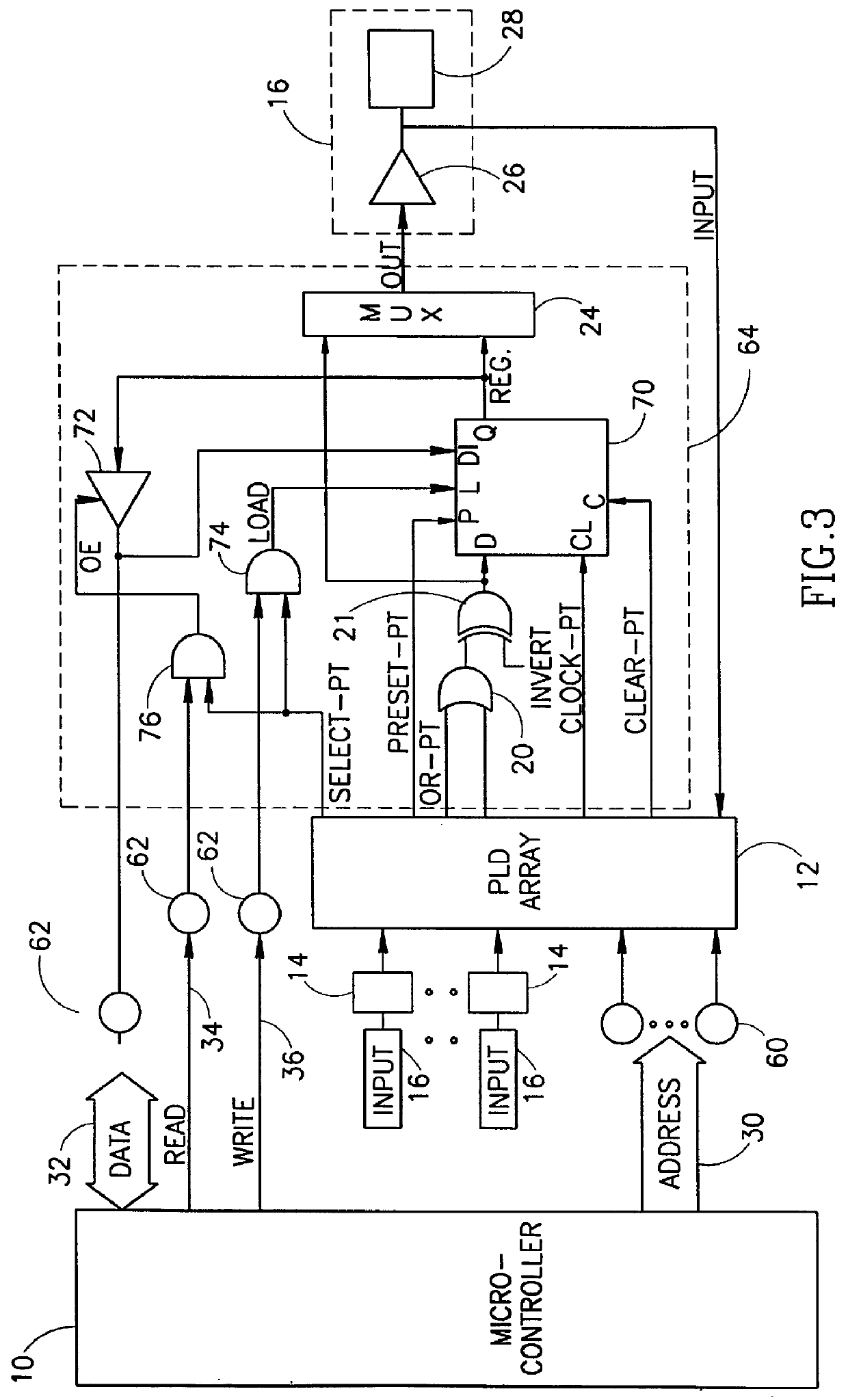
InactiveUS6066961ASolid-state devicesArchitecture with single central processing unitMicrocontrollerProgrammable logic device
A circuit connectable to a microcontroller having an address bus, a data bus, a read line and a write line include a programmable logic device (PLD) array, at least one input pin, at least two databus macrocells and a bit mask register. The input pin is connected to the PLD array and is connectable to the address bus. The databus macrocell is connected to the PLD array and to an external unit and is also connectable to the data bus, the read line and the write line. The bit mask register has at least two bits, each associated with one of the at least two macrocells. The databus can directly access the databus macrocell only if its associated bit in the bit mask register is of the correct state. In another embodiment, the write line carries an edge write signal and the databus accesses the databus macrocell on one edge of the edge write signal.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
High reliability memory module with a fault tolerant address and command bus
ActiveUS20060236201A1Improve compatibilityEasy to solveElectronic circuit testingPrinted circuit aspectsFault toleranceTime error
Owner:IBM CORP
Multiprocessor node controller circuit and method
InactiveUS7406086B2Ease of parallel processingImprove welfareMultiplex system selection arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressMemory chip
Improved method and apparatus for parallel processing. One embodiment provides a multiprocessor computer system that includes a first and second node controller, a number of processors being connected to each node controller, a memory connected to each controller, a first input / output system connected to the first node controller, and a communications network connected between the node controllers. The first node controller includes: a crossbar unit to which are connected a memory port, an input / output port, a network port, and a plurality of independent processor ports. A first and a second processor port connected between the crossbar unit and a first subset and a second subset, respectively, of the processors. In some embodiments of the system, the first node controller is fabricated onto a single integrated-circuit chip. Optionally, the memory is packaged on plugable memory / directory cards wherein each card includes a plurality of memory chips including a first subset dedicated to holding memory data and a second subset dedicated to holding directory data. Further, the memory port includes a memory data port including a memory data bus and a memory address bus coupled to the first subset of memory chips, and a directory data port including a directory data bus and a directory address bus coupled to the second subset of memory chips. In some such embodiments, the ratio of (memory data space) to (directory data space) on each card is set to a value that is based on a size of the multiprocessor computer system.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
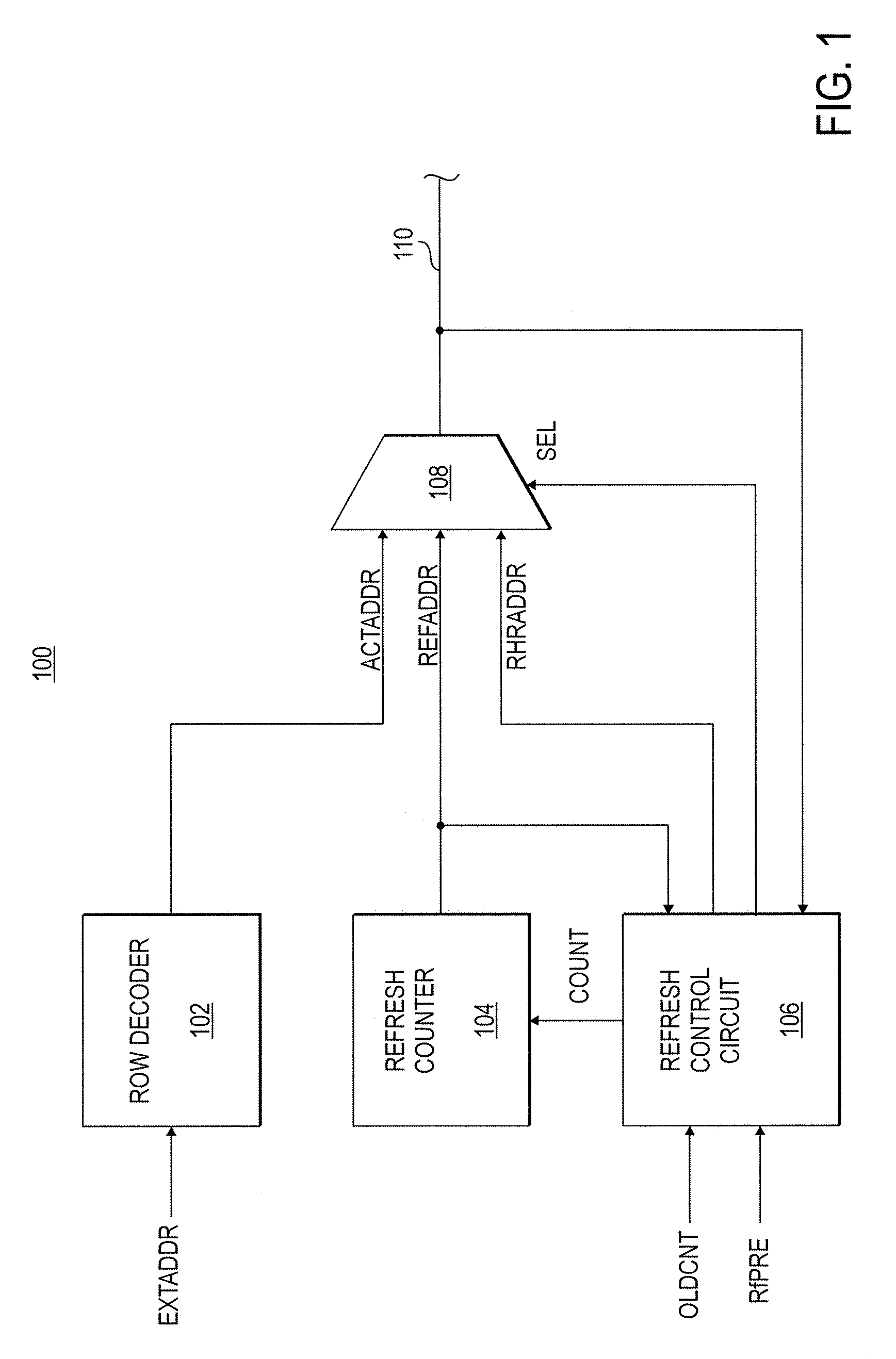
Apparatuses and methods for selective row refreshes
Apparatuses and methods for selective row refreshes are disclosed herein. An example apparatus may include a refresh control circuit. The refresh control circuit may be configured to receive a target address associated with a target plurality of memory cells from an address bus. The refresh control circuit may further be configured to provide a proximate address to the address bus responsive, at least in part, to determining that a number of refresh operations have occurred. In some examples, a plurality of memory cells associated with the proximate address may be a plurality of memory cells adjacent the target plurality of memory cells.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
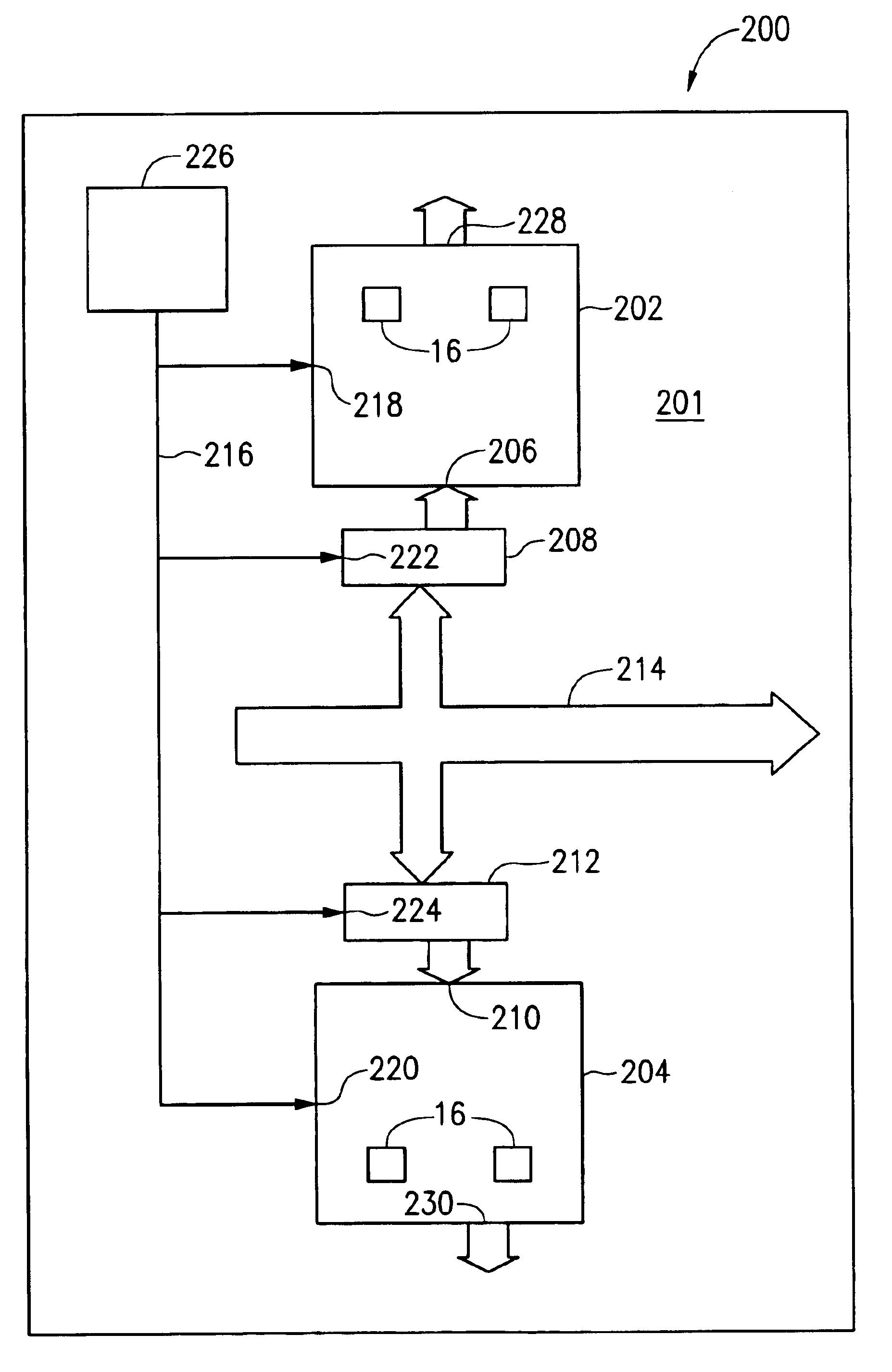
Routability for memory devices
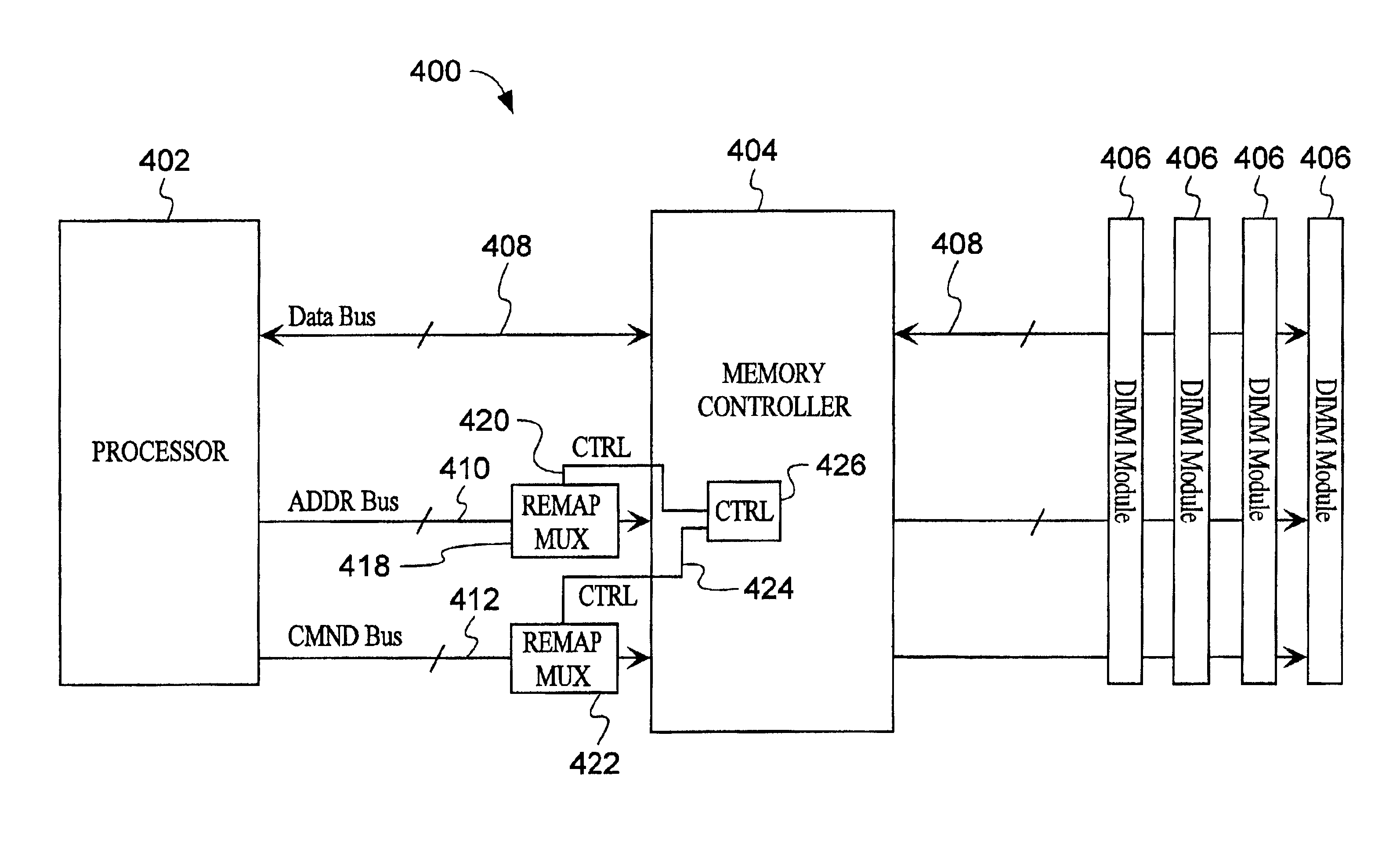
A computer system provides improved routability for memory modules. Chips are placed on the back side of the module directly behind the chips on the front side, and vias connects destination pins on the front side to the back side. Internal assignments are routed to the pins so as to be bilaterally symmetrical. These functions can include any of the pins used on the memory chip, including the address bus and the command bus. The bit positions of the internal assignments routed to pins connected together need not be identical. Where bit positions are coupled together, a remap multiplexer is used to perform rerouting of logical information onto different physical bus lines. The remap multiplexer may be implemented in the system BIOS, in the memory controller, or altematively on the memory module. Further, the rerouting may be accomplished through any combination of hardware or software.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Method and apparatus for verifying the integrity of control module operation
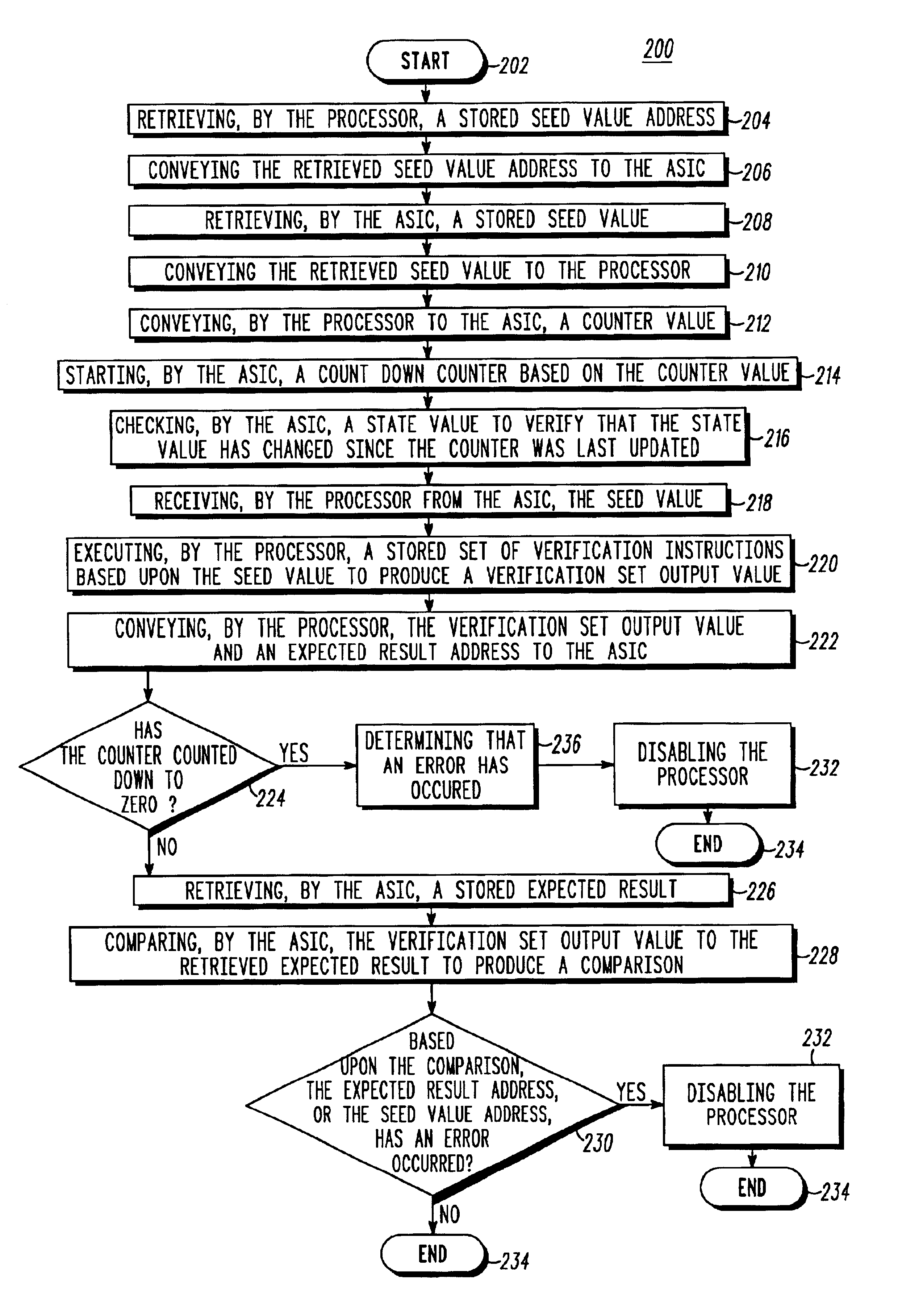
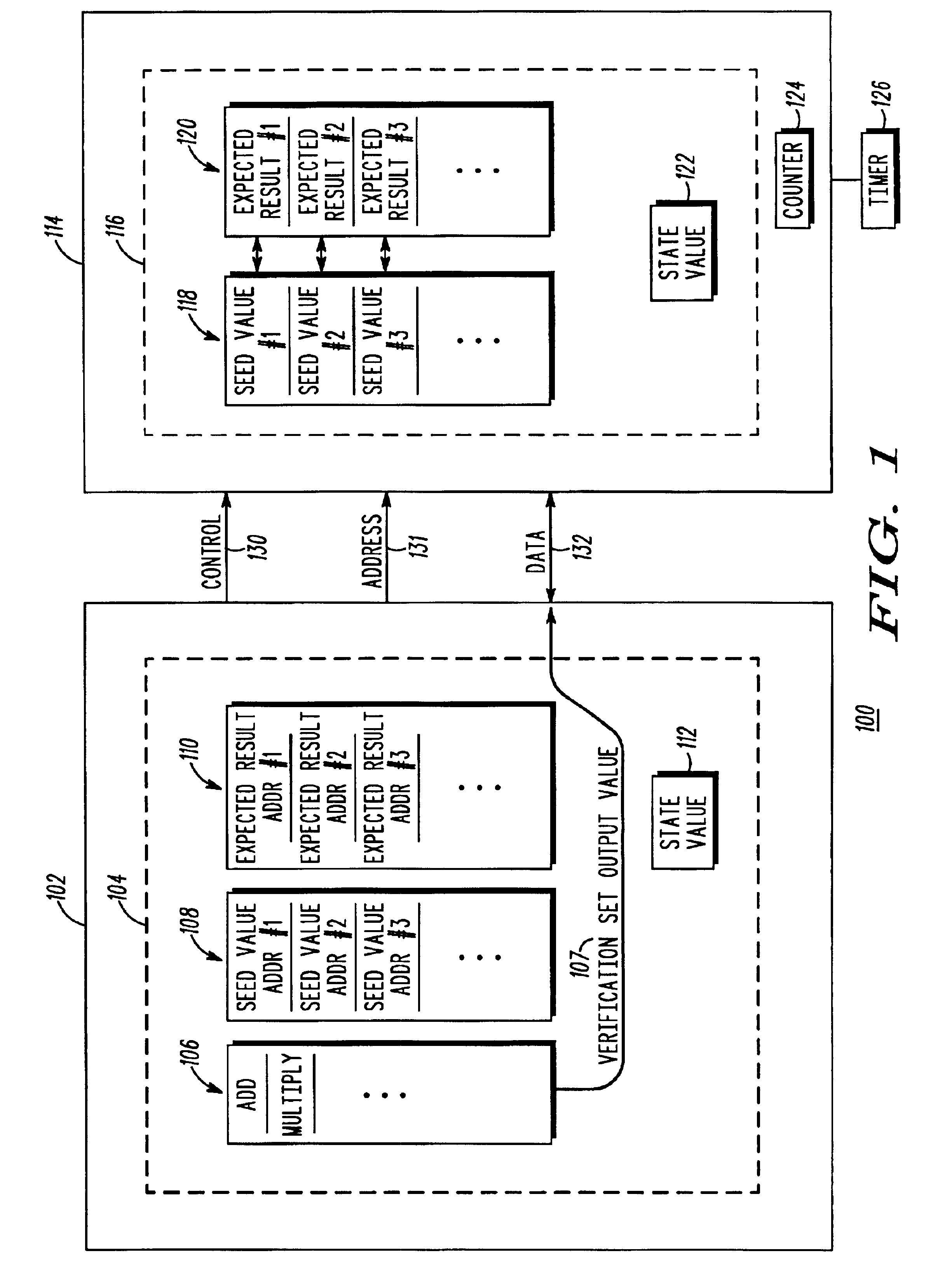
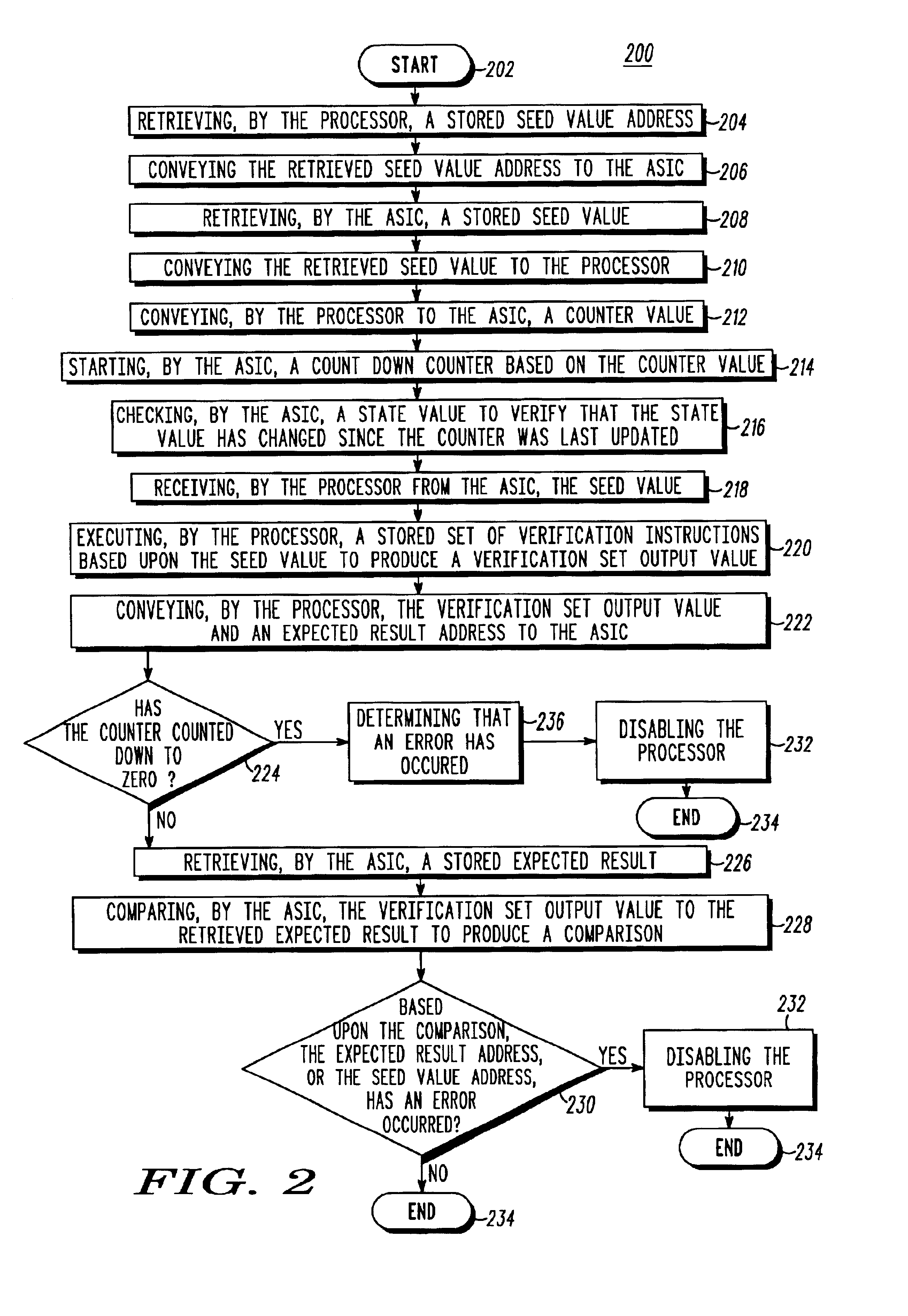
A control module (100) includes a first signal processing unit (102) that is coupled to a second signal processing unit (114) by a control bus (130), an address bus (131) and a data bus (132). The control module conveys seed value addresses (108) and expected result addresses (110) over the address bus, seed values (118) and verification set output values (107) over the data bus, and compares each verification set output value to an expected result (120), thereby allowing the control module to determine whether the first signal processing unit, the control bus, the address bus, and the data bus are collectively functioning correctly. By properly selecting the seed value addresses, expected result addresses, seed values, and expected results (and correspondingly, verification set output values), proper operation of each line of the address bus and control bus may be individually verified.
Owner:TEMIC AUTOMOTIVE OF NORTH AMERICA
Method and apparatus for storing and distributing memory repair information
ActiveUS20080065929A1Easy to integrateConvenient to accommodateElectronic circuit testingStatic storageDistributed memoryControl signal
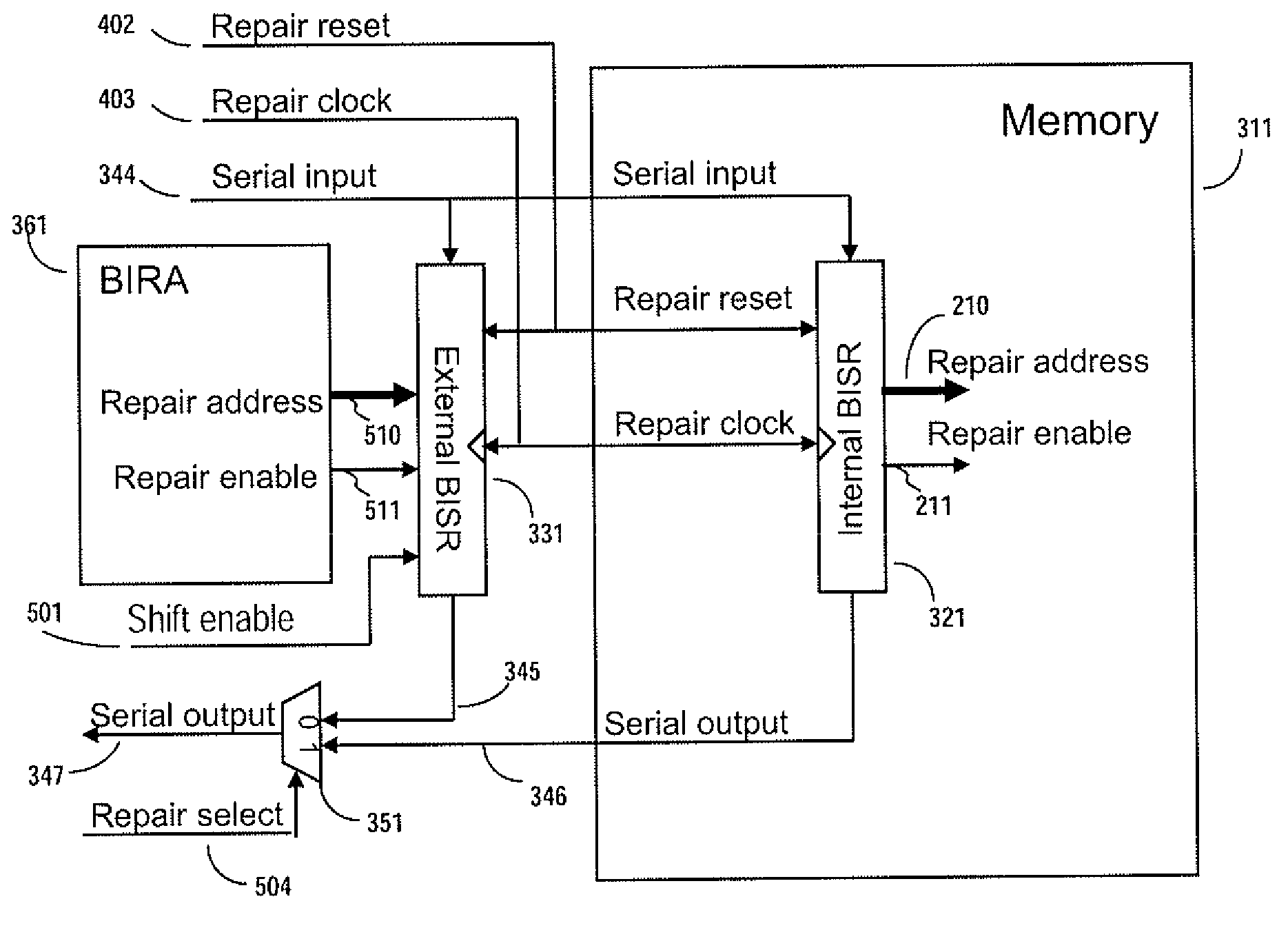
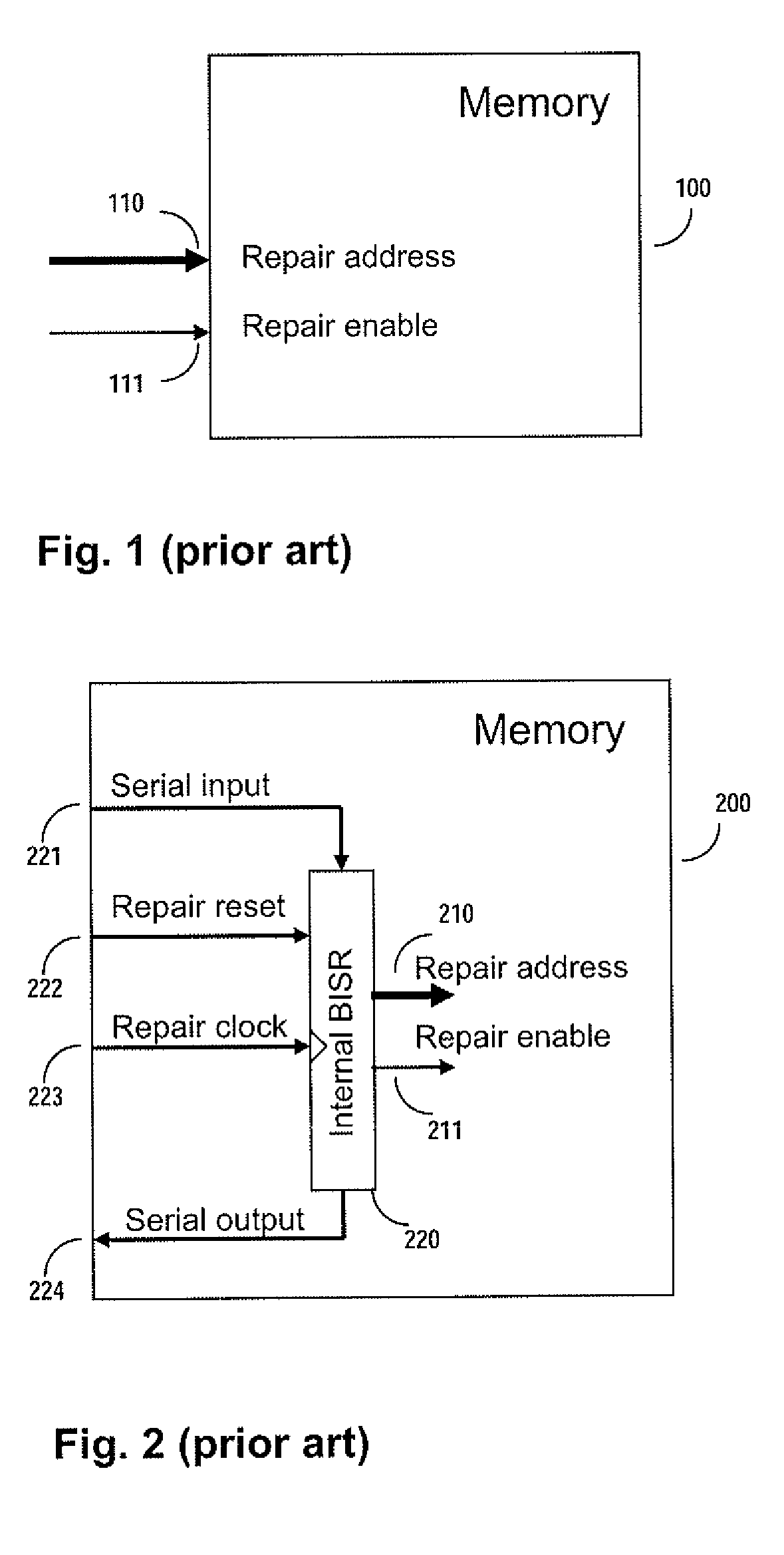
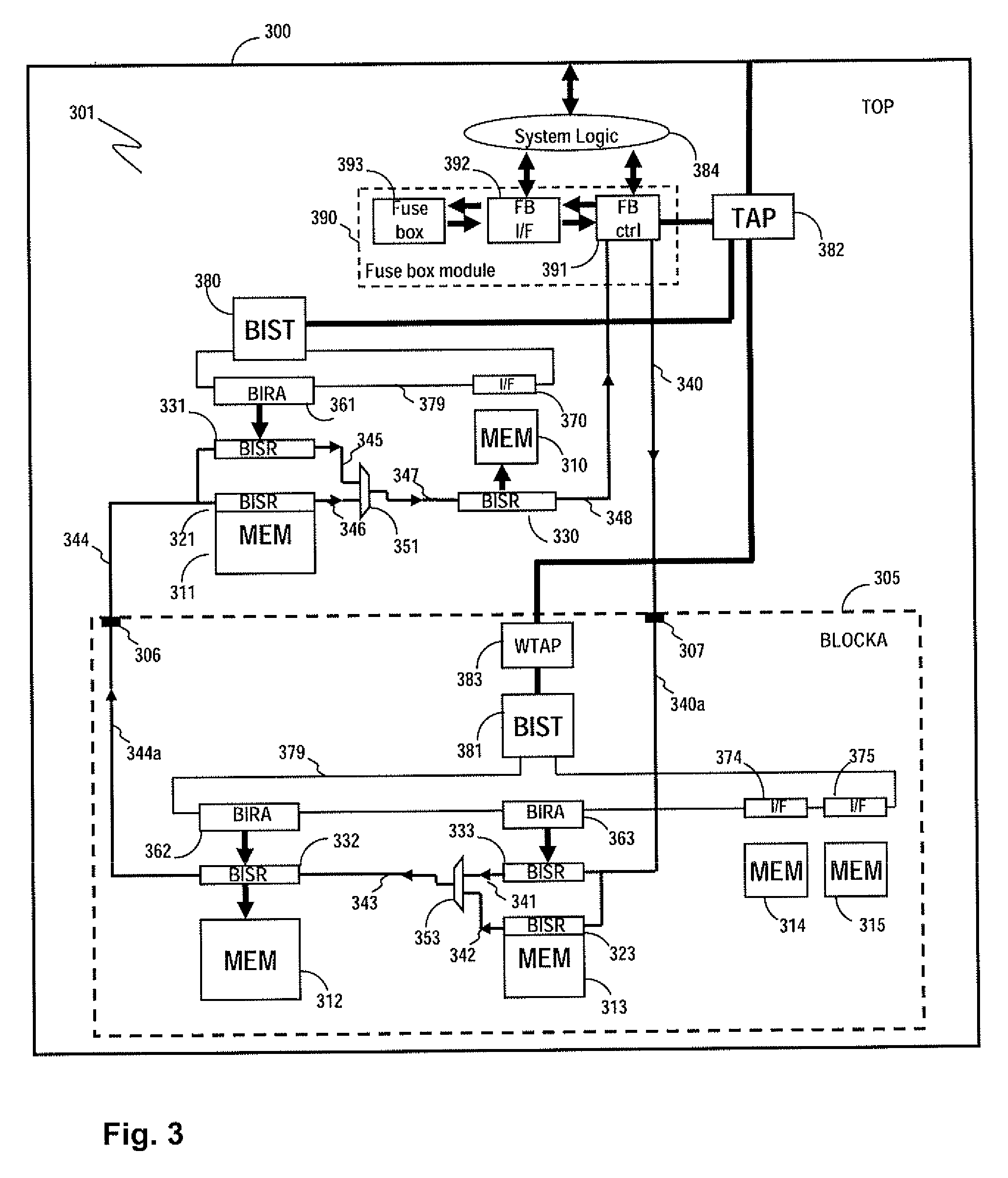
A system for repairing embedded memories on an integrated circuit is disclosed. The system comprises an external Built-In Self-repair Register (BISR) associated with every reparable memory on the circuit. Each BISR is configured to accept a serial input from a daisy chain connection and to generate a serial output to a daisy chain connection, so that a plurality of BISRs are connected in a daisy chain with a fuse box controller. The fuse box controller has no information as to the number, configuration or size of the embedded memories, but determines, upon power up, the length of the daisy chain. With this information, the fuse box controller may perform a corresponding number of serial shift operations to move repair data to and from the BISRs and into and out of a fuse box associated with the controller. Memories having a parallel repair interface are supported by a parallel address bus and enable control signal on the BISR, while those having a serial repair interface are supported by a parallel daisy chain path that may be selectively cycled to shift the contents of the BISR to an internal serial register in the memory. Preferably, each of the BISRs has an associated repair analysis facility having a parallel address bus and enable control signal by which fuse data may be dumped in parallel into the BISR and from there, either uploaded to the fuse box through the controller or downloaded into the memory to effect repairs. Advantageously, pre-designed circuit blocks may provide daisy chain inputs and access ports to effect the inventive system therealong or to permit the circuit block to be bypassed for testing purposes.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
Interactive IR electronic white board
InactiveUS7429706B2Durable surfaceReduce complexityTransmission systemsGraph readingAddress busLinearity
The present invention discloses an interactive IR electronic white board, around which is an infrared emitting and receiving array. An output port of a column driver of emitting array is connected to high frequency modulating signal generator, and an output port of a column driver of the receiving array is connected to a microprocessor through a signal receiving circuit and an analog-digital converter A / D. The emitting array and the receiving array are connected to emitting and the receiving driver through emitting and receiving driver lines, and the emitting driver and the receiving driver are connected with the microprocessor through address bus. The present invention utilizes the Inverse Square Law of optical theory and the linear direct ratio relation between the quantity change of light particles received by an infrared receiving diode and the output voltage of the receiving diode to associate the output voltage of the receiving diode with the interrupted width of the infrared light path, so that it can calculate the coordinate of interrupter accurately and improve the resolution of infrared scanning. The present invention can not only distribute pens or erase, but can be used by plurality of users at the same time as well.
Owner:HO WAI
Mobile wireless communication device architectures and methods therefor
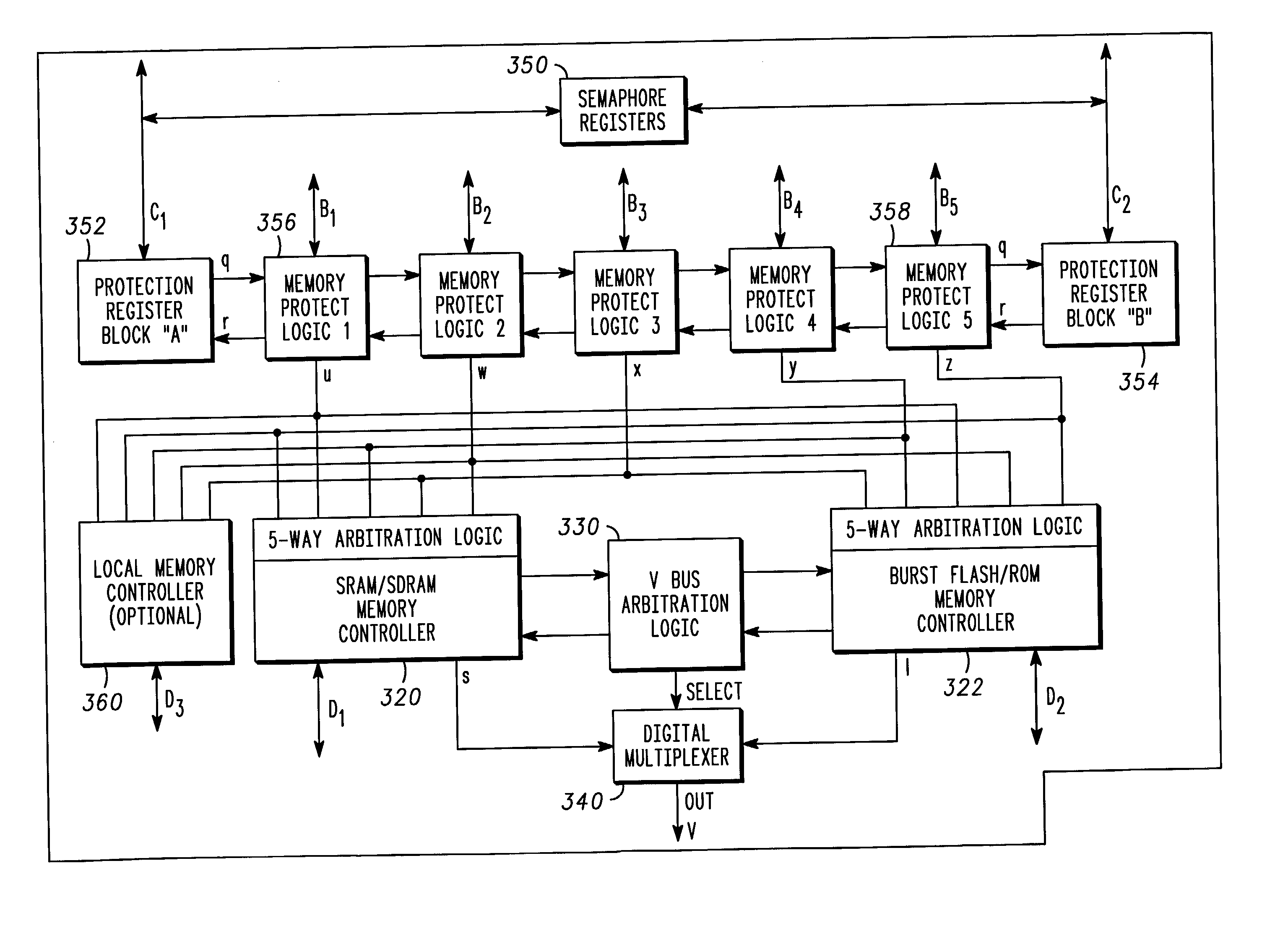
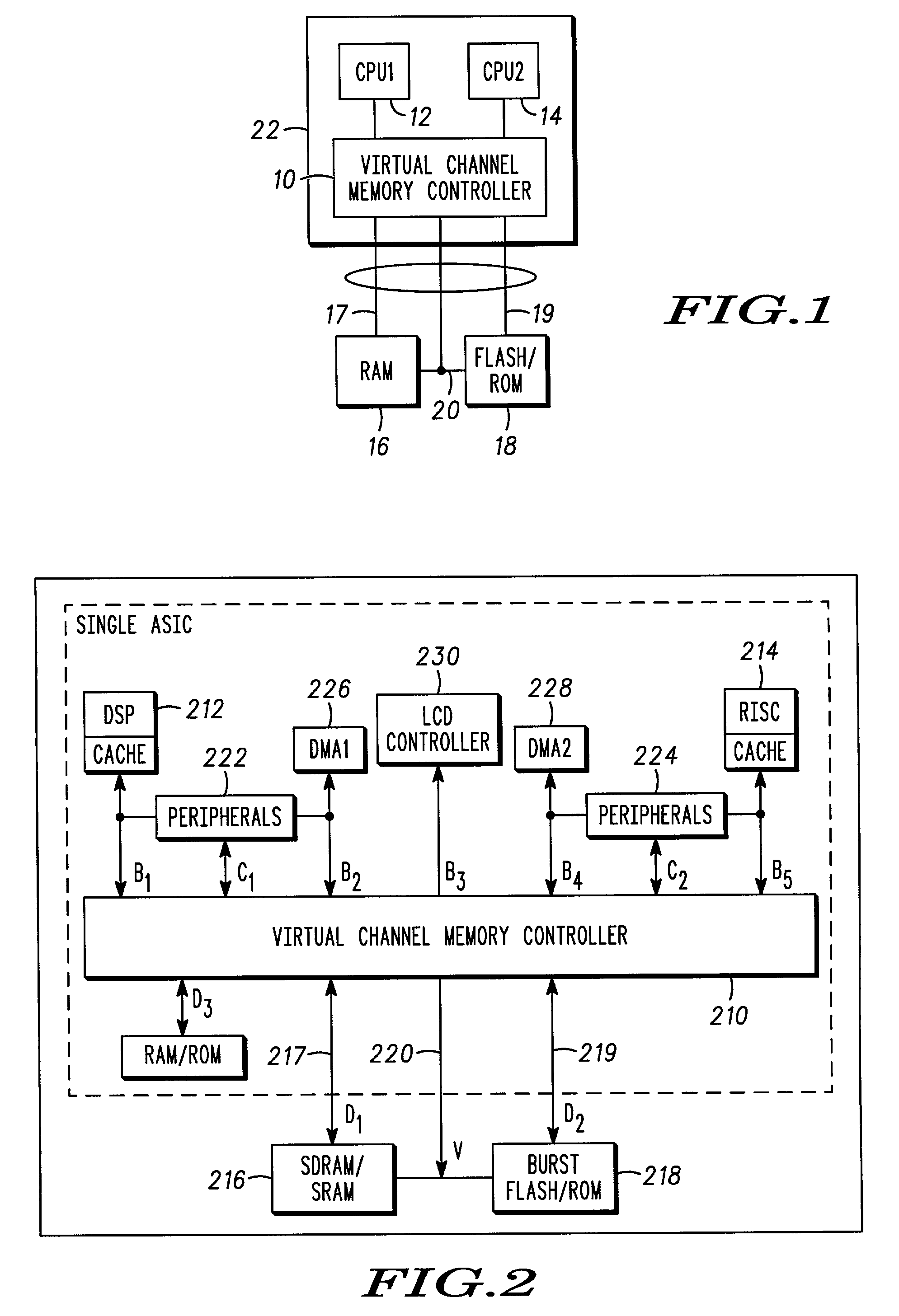
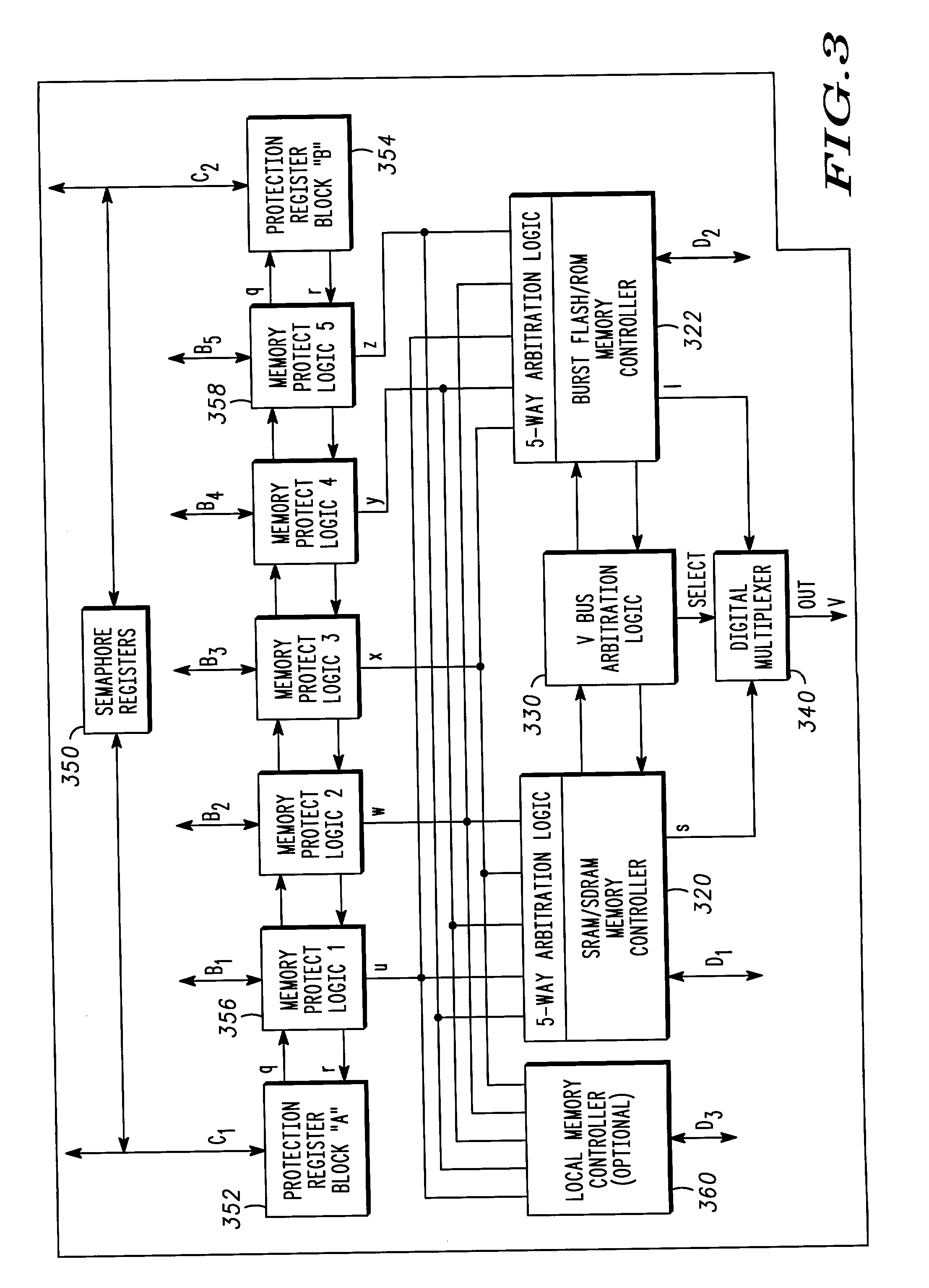
A wireless communications architecture having first and second synchronous memory devices coupled to a virtual channel memory controller by corresponding first and second data buses, and a shared address and control bus interconnecting the virtual channel memory controller and the first and second synchronous memory devices. The first and second synchronous memory devices are addressed with the shared address bus, and the first and second memory locations are accessed via the first and second data buses, respectively.
Owner:APPLE INC
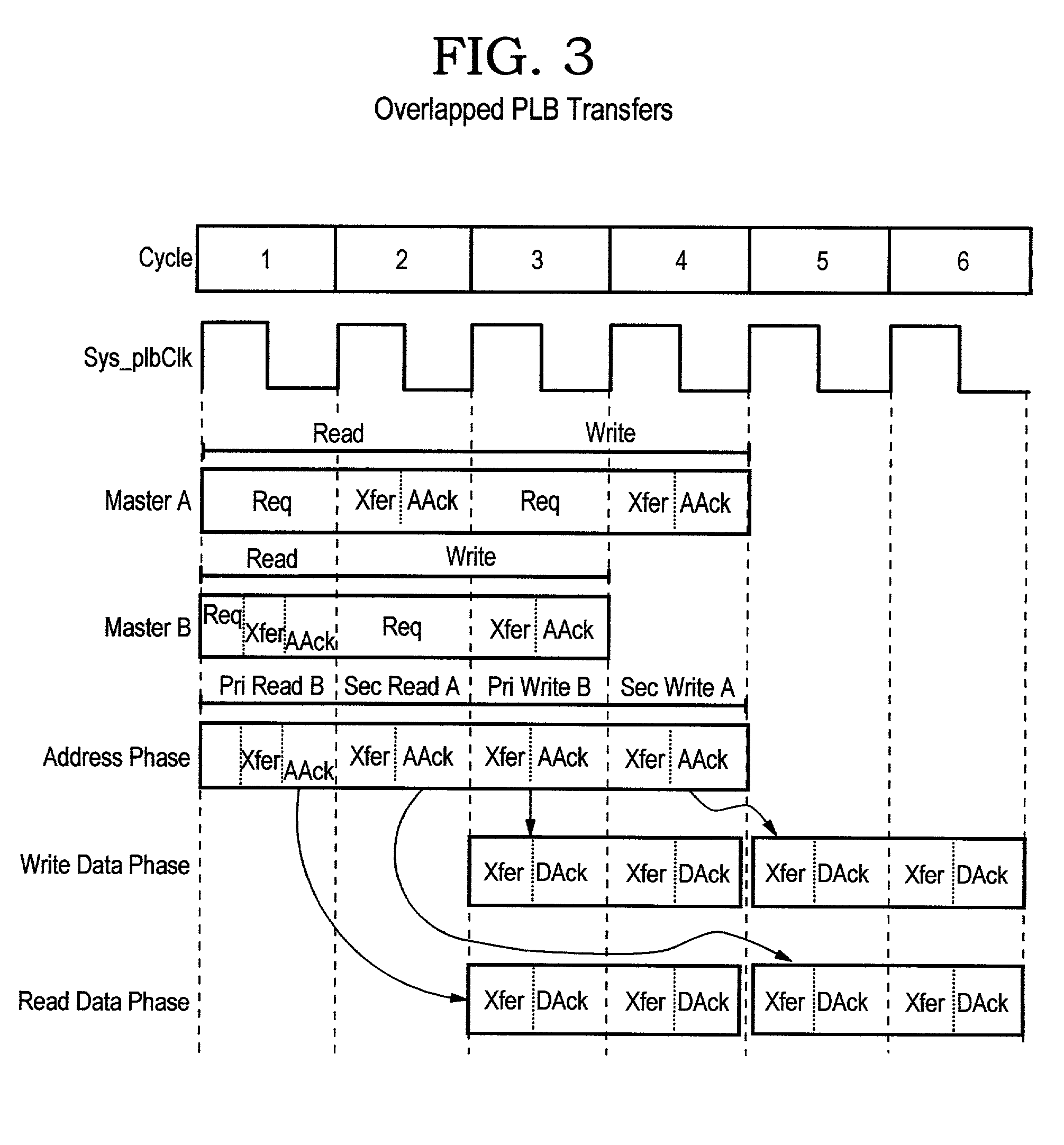
Multi-master computer system with overlapped read and write operations and scalable address pipelining
InactiveUS6772254B2Lower latencyElectric digital data processingComputer hardwareComputerized system
Owner:INTEL CORP
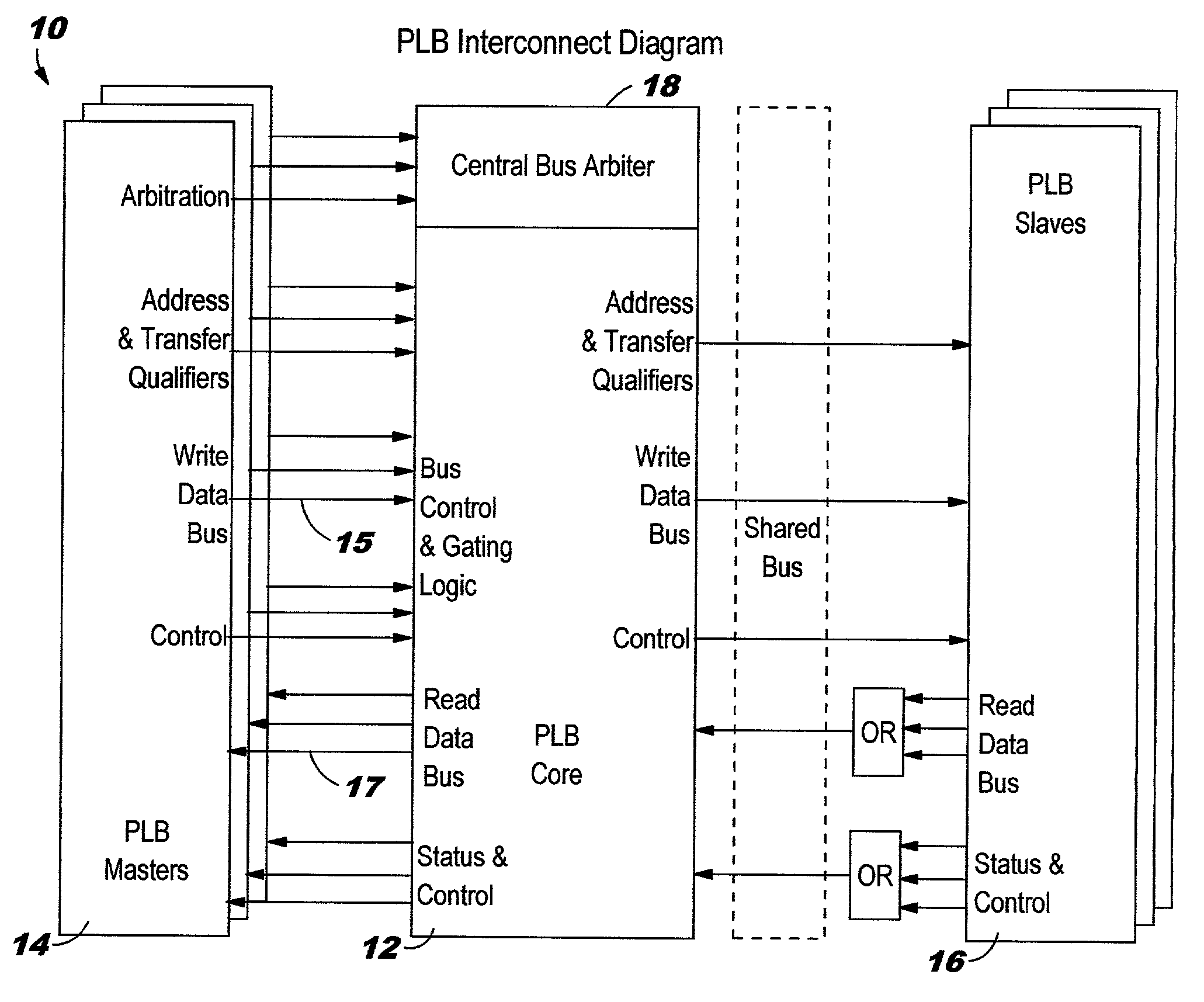
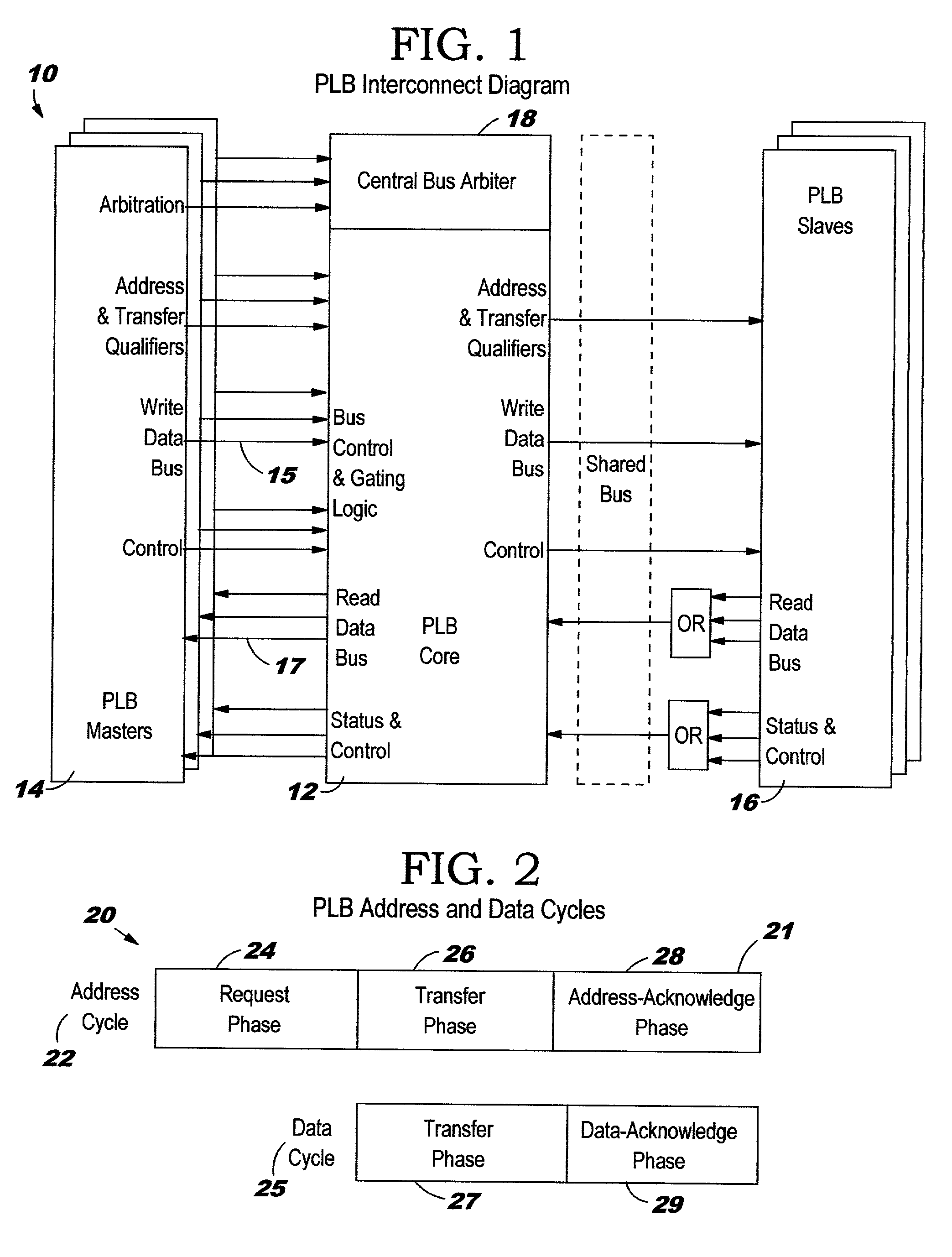
Method and apparatus for avoiding data bus grant starvation in a non-fair, prioritized arbiter for a split bus system with independent address and data bus grants
InactiveUS6535941B1Reduce delaysSpeeding up data bus grant processMemory systemsMulti processorAddress bus
A distributed system structure for a large-way, symmetric multiprocessor system using a bus-based cache-coherence protocol is provided. The distributed system structure contains an address switch, multiple memory subsystems, and multiple master devices, either processors, I / O agents, or coherent memory adapters, organized into a set of nodes supported by a node controller. The node controller receives transactions from a master device, communicates with a master device as another master device or as a slave device, and queues transactions received from a master device. Since the achievement of coherency is distributed in time and space, the node controller helps to maintain cache coherency. In order to reduce the delays in giving address bus grants, a bus arbiter for a bus connected to a processor and a particular port of the node controller parks the address bus towards the processor. A history of address bus grants is kept to determine whether any of the previous address bus grants could be used to satisfy an address bus request associated with a data bus request. If one of them qualifies, the data bus grant is given immediately, speeding up the data bus grant process by anywhere from one to many cycles depending on the requests for the address bus from the higher priority node controller.
Owner:IBM CORP
Memory interface system and method for reducing cycle time of sequential read and write accesses using separate address and data buses
ActiveUS7142477B1Improve data throughputImprove throughputDigital storageDouble data rateMemory interface
A memory interface system and method are provided for transferring data between a memory controller and an array of storage elements. The storage elements are preferably SRAM elements, and the memory interface is preferably one having separate address bus paths and separate data bus paths. One address bus path is reserved for receiving read addresses and the other address bus path is reserved for receiving write addresses. One of the data bus paths is reserved for receiving read data from the array, and the other data bus path is reserved for receiving data written to the array. While bifurcating the address and data bus paths within the interface is transparent to the memory controller, the separate paths afford addressing phases of a read and write address operation to be partially overlapped, as well as the data transfer phases. This will essentially reduce the cycle time between a read and write memory access, and proves useful when maximizing the data throughput across the data bus when implementing double data rate (QDR) mechanisms.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
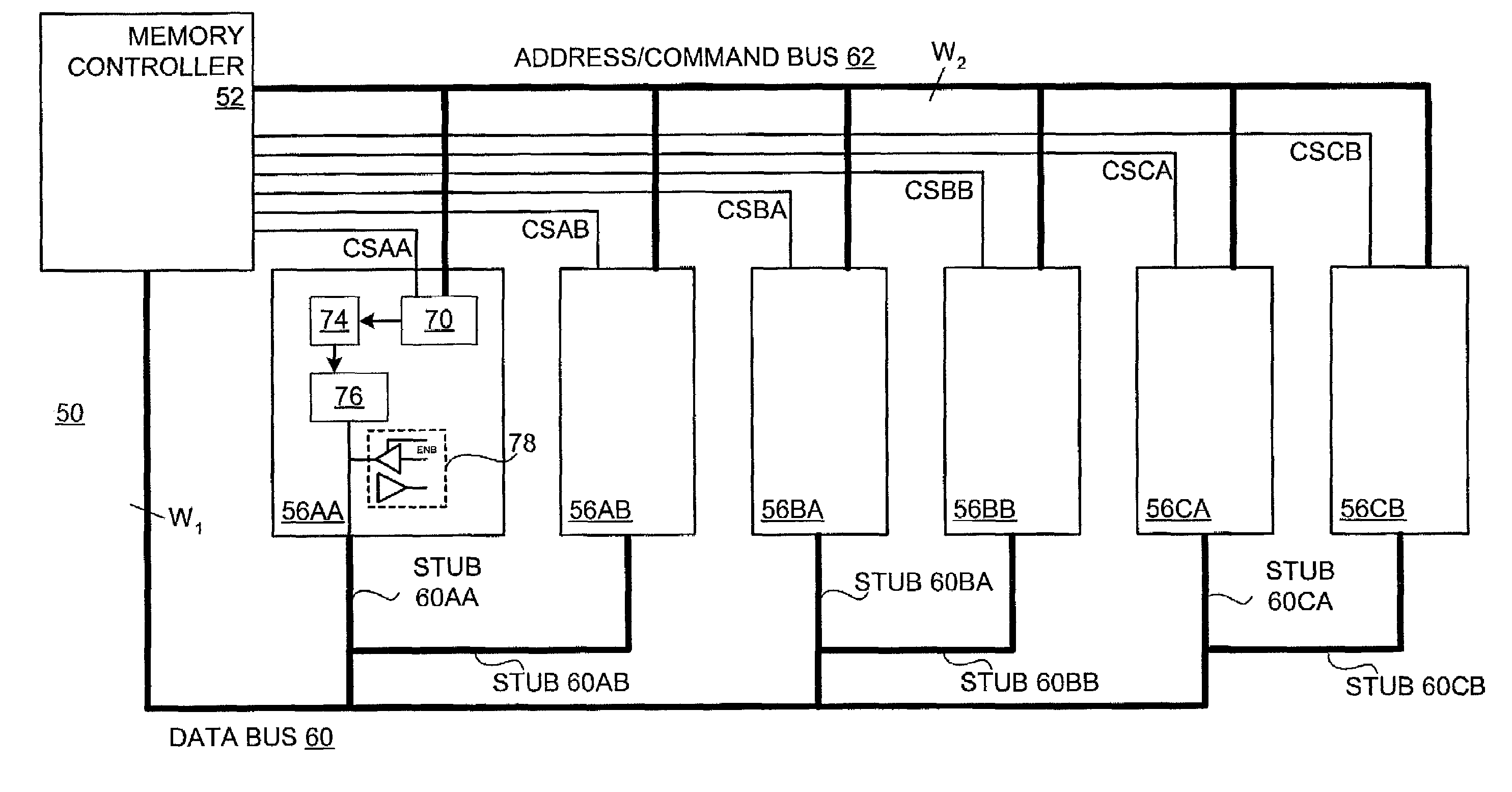
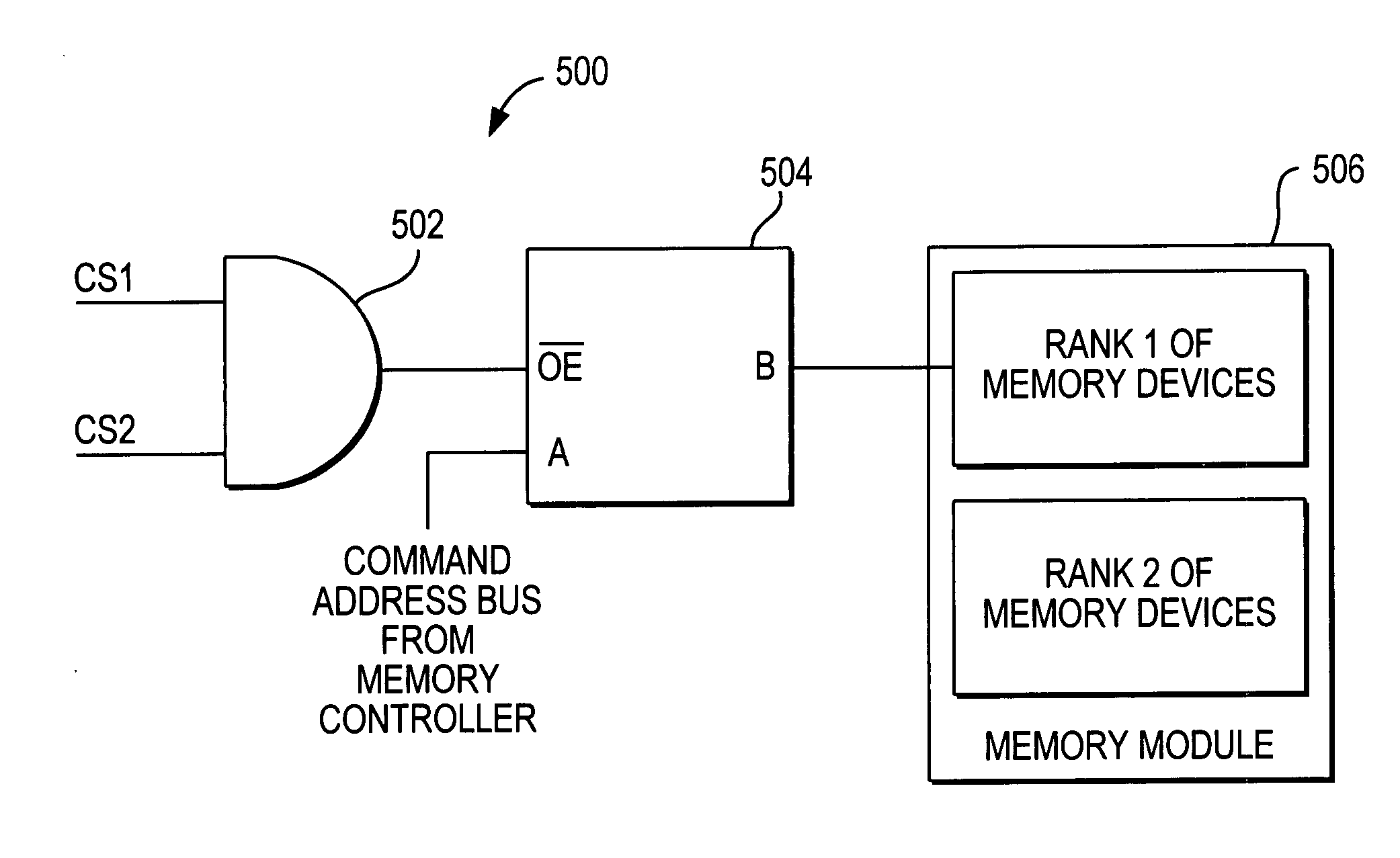
Memory devices with buffered command address bus
InactiveUS7149841B2Increase the number ofReduce overloadEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer moduleComputerized system
Circuits and methods are provided that alleviate overloading of the command address bus and limit decreases in command address bus bandwidth to allow increased numbers of memory modules to be included in a computer system. A plurality of switches is coupled between the command address bus (which is coupled to the memory controller) and a respective plurality of memory modules. Each switch provides command address bus data only to its respective memory module. Preferably, only one switch does so at a time, limiting the loading seen by the memory controller.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
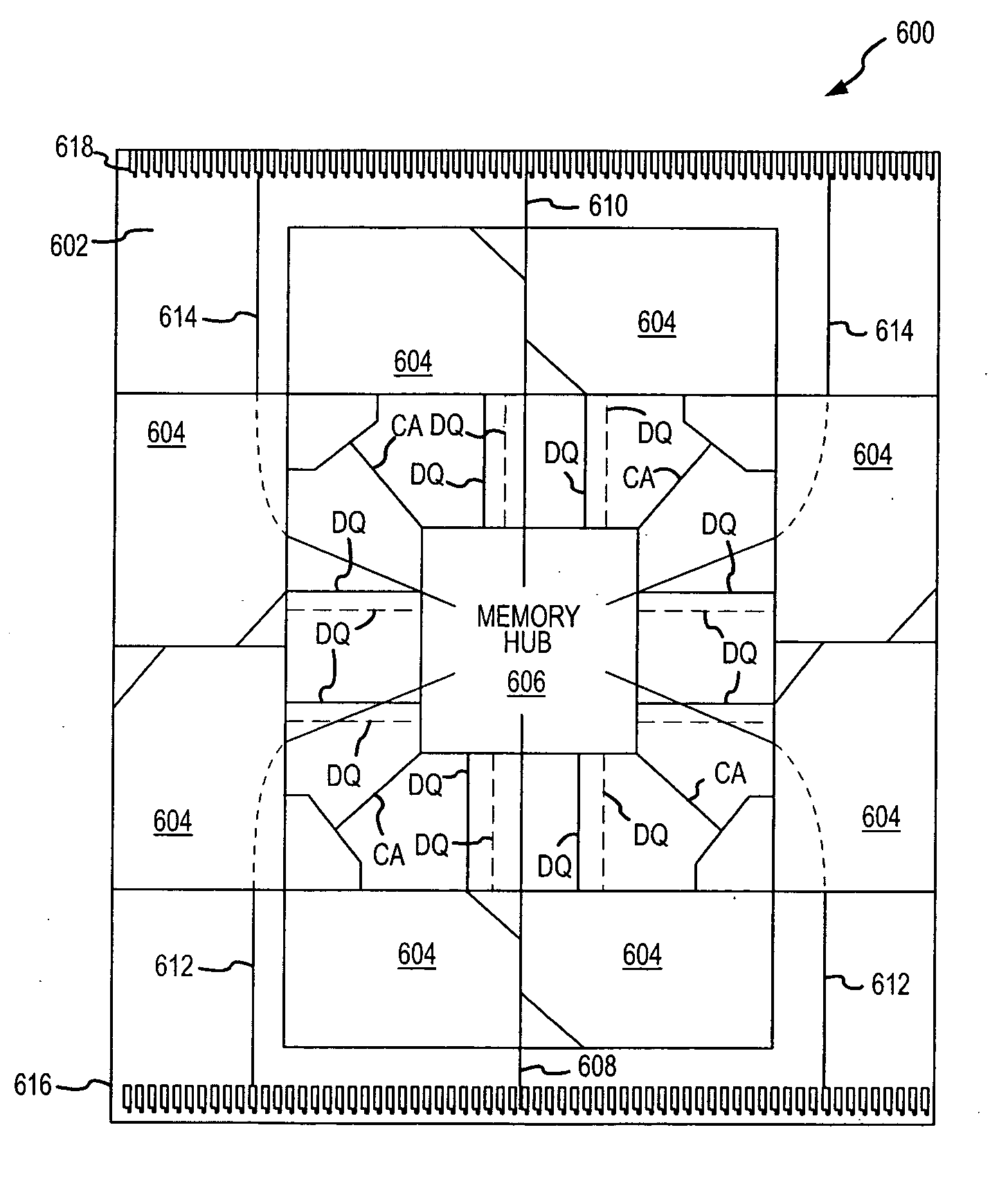
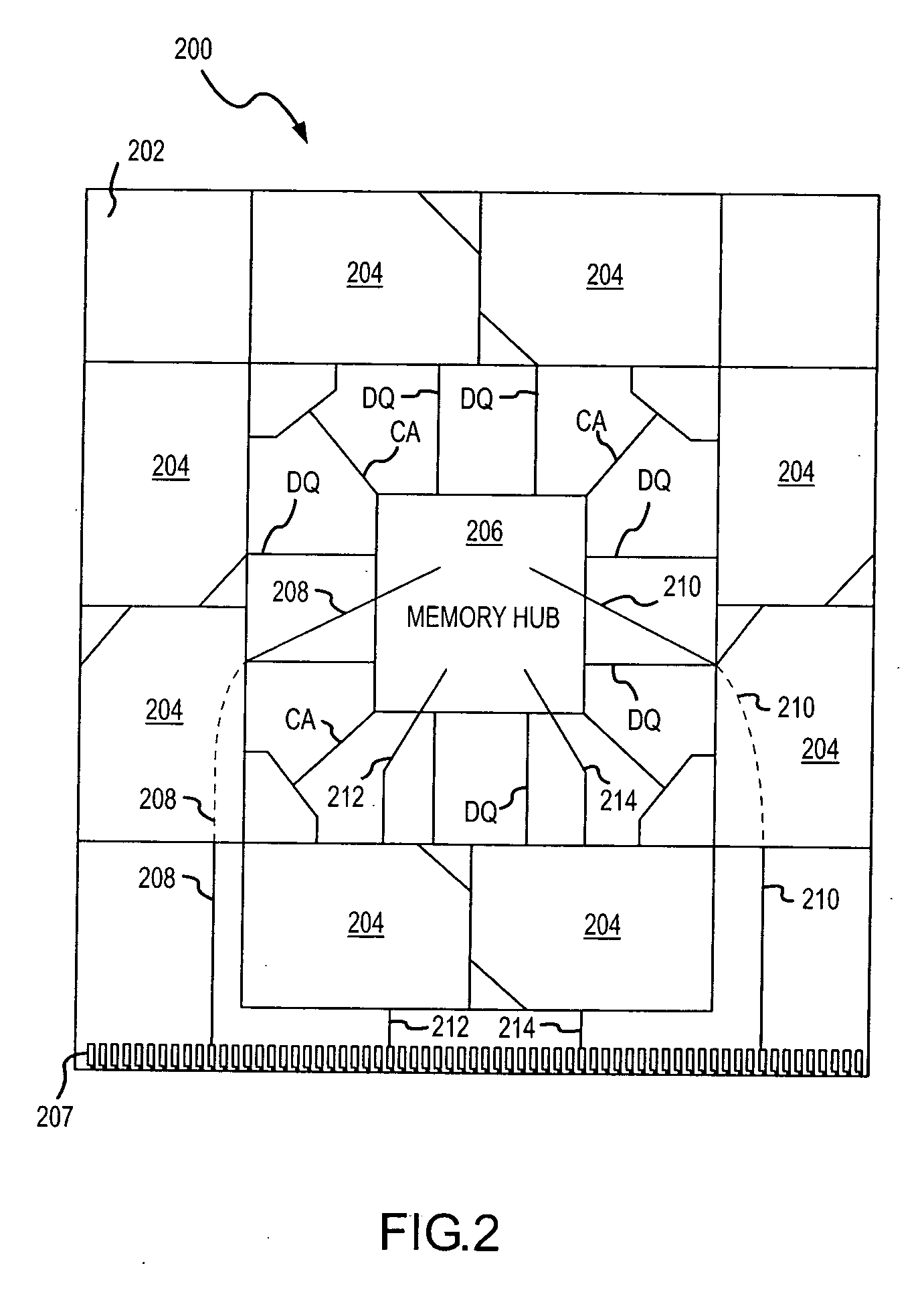
System and method for optimizing interconnections of components in a multichip memory module
An apparatus and method couples memory devices in a memory module to a memory hub on the module such that signals traveling from the hub to the devices have approximately the same propagation time regardless of which device is involved. Specifically, the devices are arranged around the hub in pairs, with each pair of devices being oriented such that a functional group of signals for each device in the pair, such as the data bus signals, are positioned adjacent each other on a circuit board of the module. This allows for a data and control-address busses having approximately the same electrical characteristics to be routed between the hub and each of the devices. This physical arrangement of devices allows high speed operation of the module. In one example, the hub is located in the center of the module and eight devices, four pairs, are positioned around the hub.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Multi-master computer system with overlapped read and write operations and scalable address pipelining
InactiveUS20020062414A1Reduce system latencyLower latencyMemory systemsComputer hardwareComputerized system
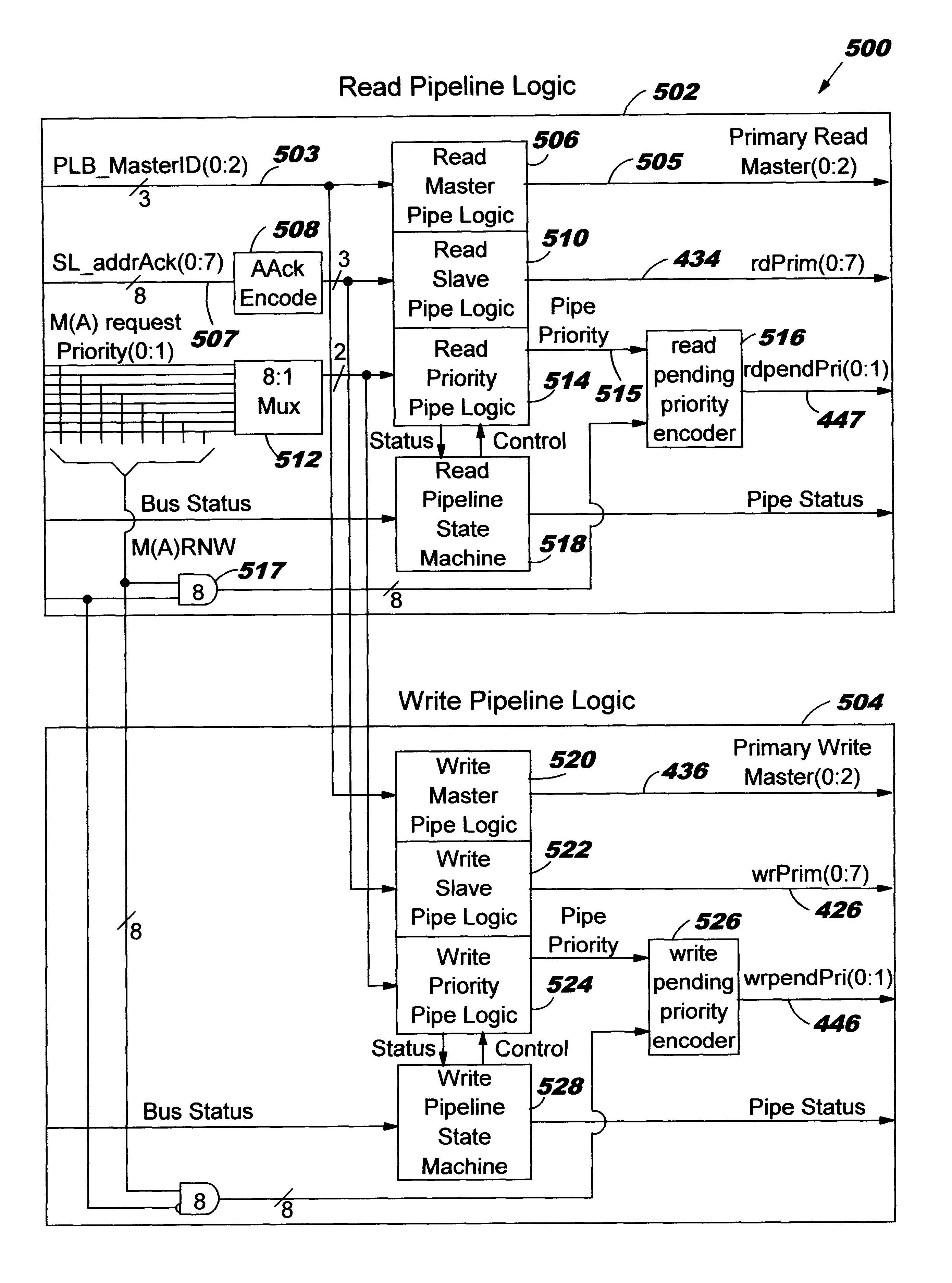
A multi-master computer system having overlapped read and write signal with scalable address pipelining programmable increases the depth of address pipelining independently on two overlapped read and write data busses up to "N" deep requests. The system includes a local bus having an address bus, a read bus, and a write bus. Master devices are coupled to separate address, read data and write data buses. Slave devices are attached to the data busses through shared, but decoupled address, read and write data buses. An arbiter is coupled to the data bus and allows masters to compete for bus ownership. The arbiter includes read and write pipeline logic for processing and priortizing master and slave read and write data transfers across the data bus. Programming apparatus alters the read and write pipeline logic for address pipelining
Owner:INTEL CORP
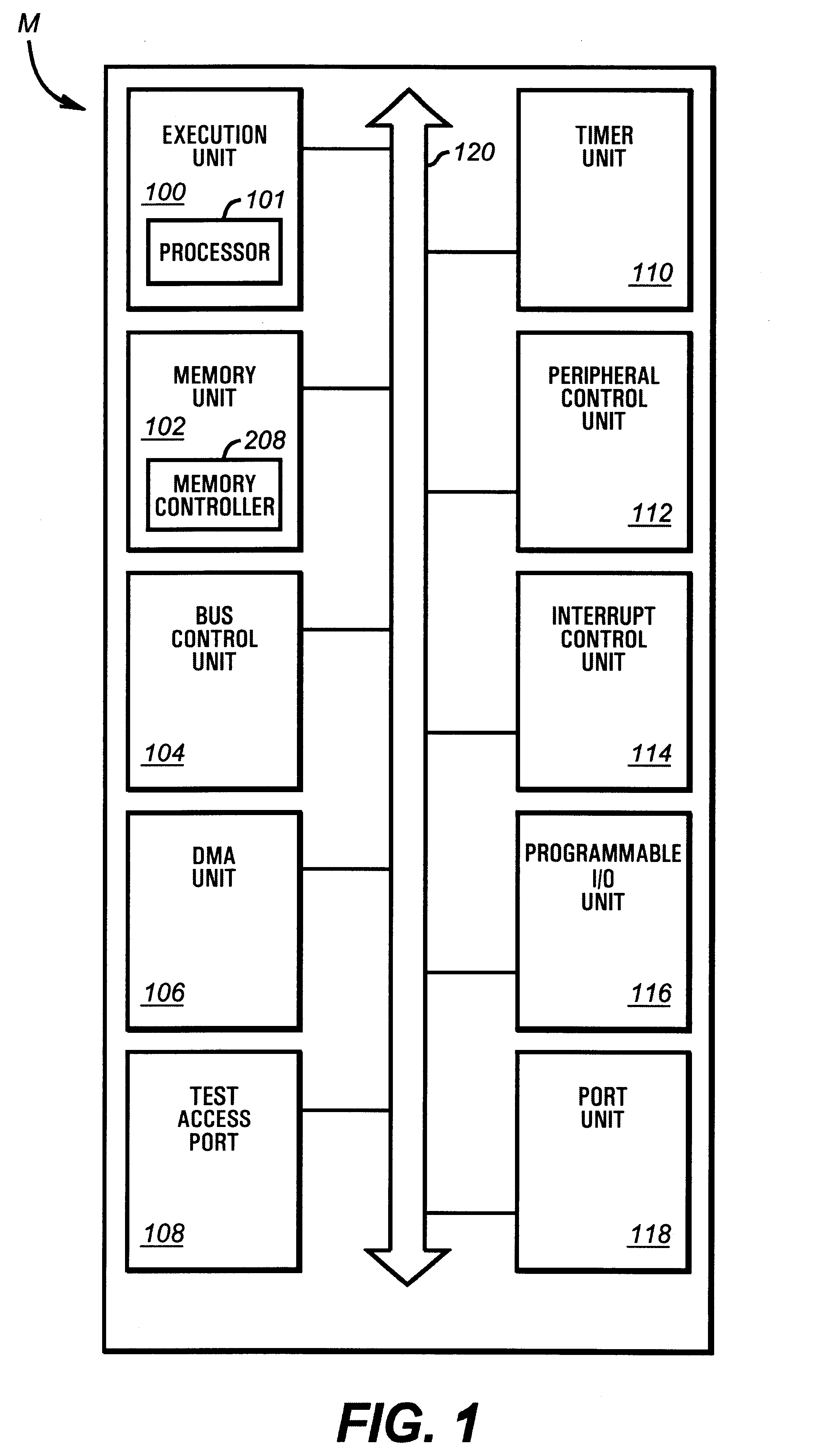
Debugging embedded systems
InactiveUS20020144235A1Software testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsMemory addressMicrocontroller
An embedded system is provided with the capability to be debugged. The embedded system includes a central processing unit (CPU) that is coupled to a bus having certain contents. A register, also with contents, is available for loading by the CPU. Finally, a debug logic circuit is also included. The debug logic circuit is coupled to both the bus and the CPU. The debug circuit itself is composed of a breakpoint detect circuit that is coupled to the bus and to the register. This circuitry enables a breakpoint signal that is produced by the breakpoint detect circuit when the contents of the register equal the contents of the bus. A method is also provided for debugging an embedded system having a microcontroller with a CPU. First, a debug logic circuit that resides on the same chip as the microcontroller is programmed to detect a predetermined condition in the microcontroller. Next, application software is run on the microcontroller. When a predetermined condition is detected, the CPU is interrupted which provides the ability to view the condition of the microcontroller. Programming the debug logic circuit can include the storing of a breakpoint address in a breakpoint address register. Afterward, a program memory address bus is selected for comparison to the contents of the breakpoint address register, upon which time a breakpoint counter is set to zero. The steps of interrupting and detecting are accomplished by comparing the contents of the program memory address bus to the contents of the breakpoint register and, if they are equal, then the CPU is interrupted.
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Interactive ir electronic white board
InactiveUS20060097989A1Durable surfaceReduce complexityCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingAddress busLinearity
The present invention discloses an interactive IR electronic white board, around which is an infrared emitting and receiving array. An output port of a column driver of emitting array is connected to high frequency modulating signal generator, and an output port of a column driver of the receiving array is connected to a microprocessor through a signal receiving circuit and an analog-digital converter A / D. The emitting array and the receiving array are connected to emitting and the receiving driver through emitting and receiving driver lines, and the emitting driver and the receiving driver are connected with the microprocessor through address bus. The present invention utilizes the Inverse Square Law of optical theory and the linear direct ratio relation between the quantity change of light particles received by an infrared receiving diode and the output voltage of the receiving diode to associate the output voltage of the receiving diode with the interrupted width of the infrared light path, so that it can calculate the coordinate of interrupter accurately and improve the resolution of infrared scanning. The present invention can not only distribute pens or erase, but can be used by plurality of users at the same time as well.
Owner:HO WAI
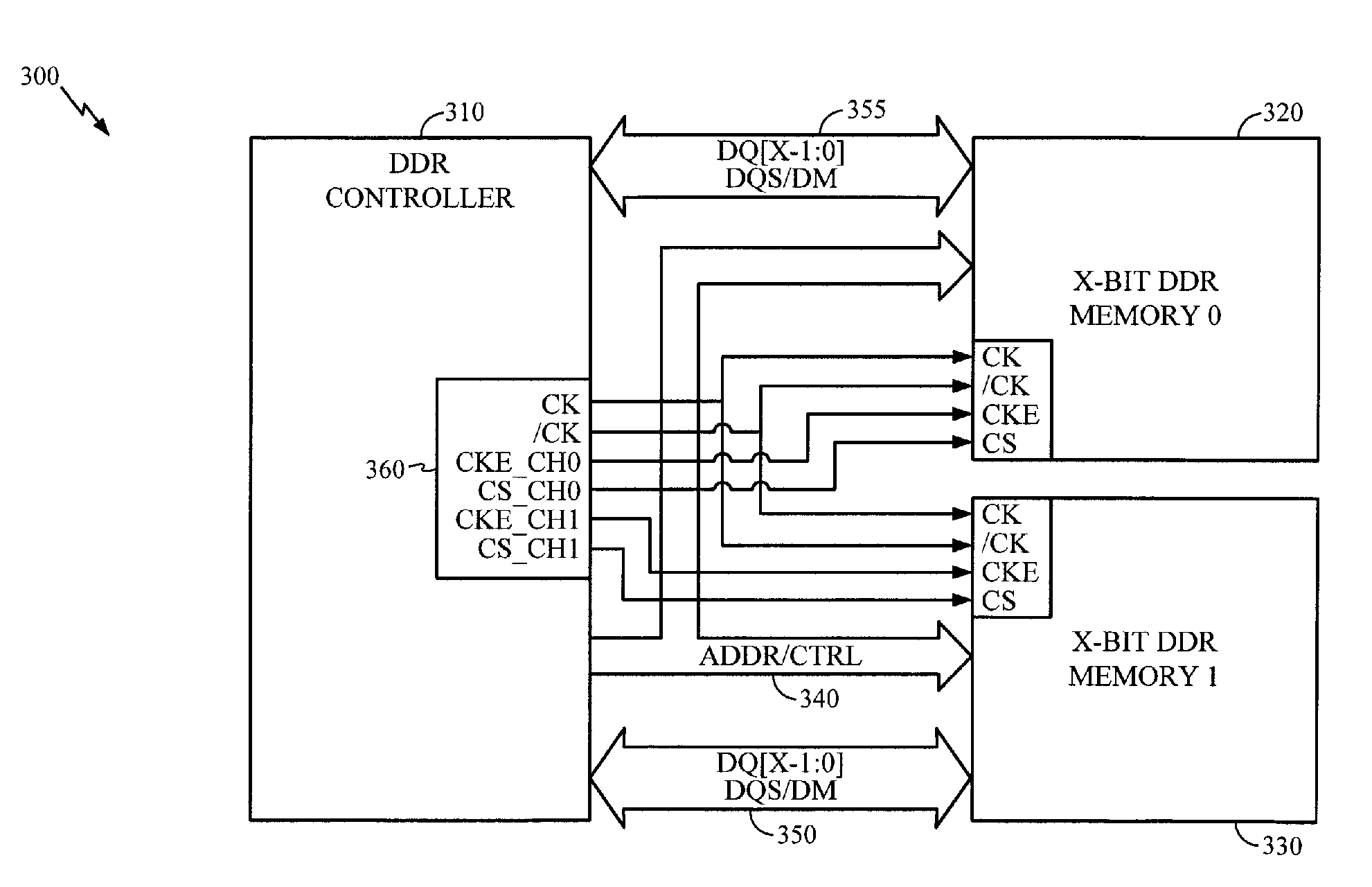
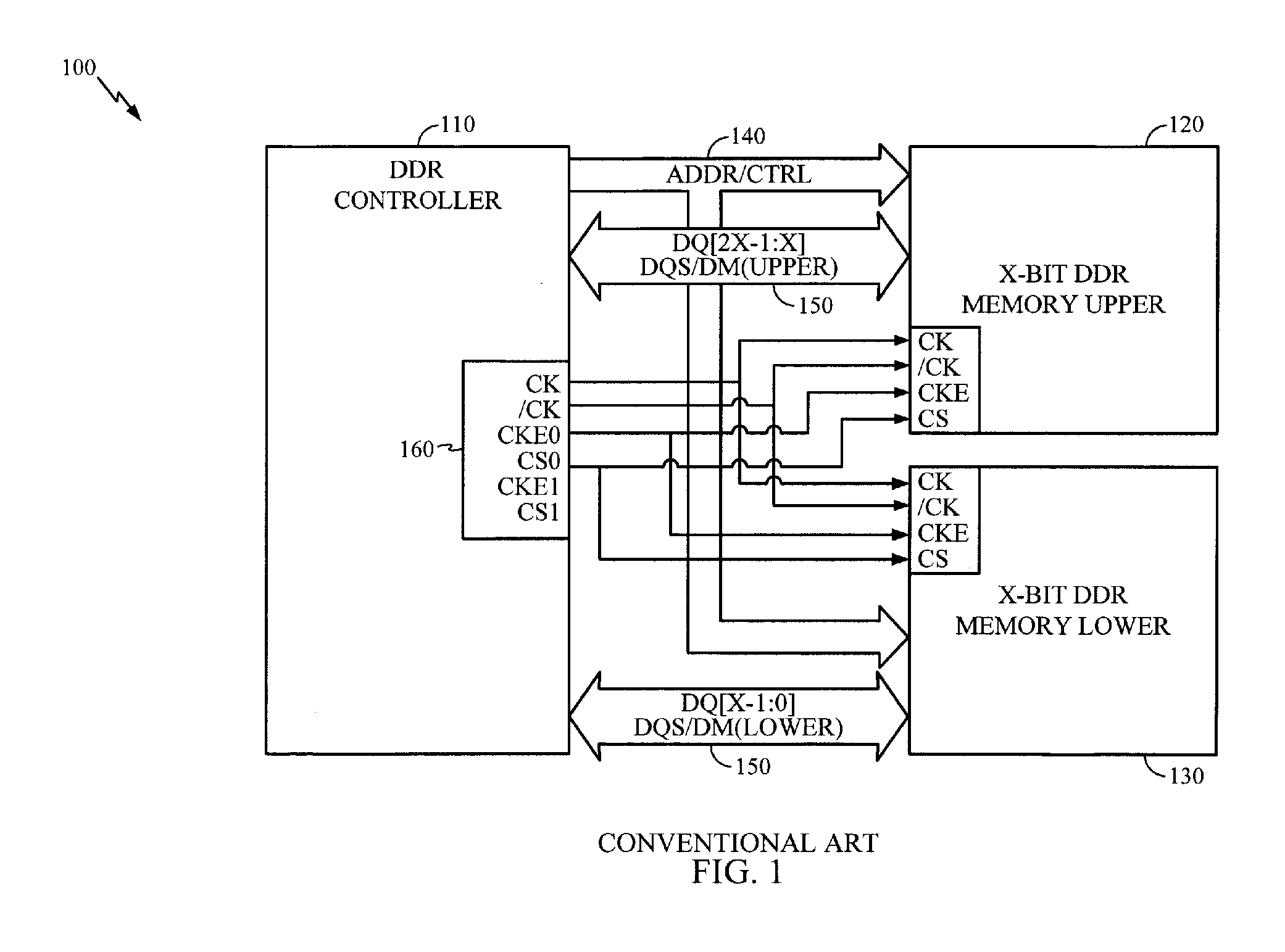
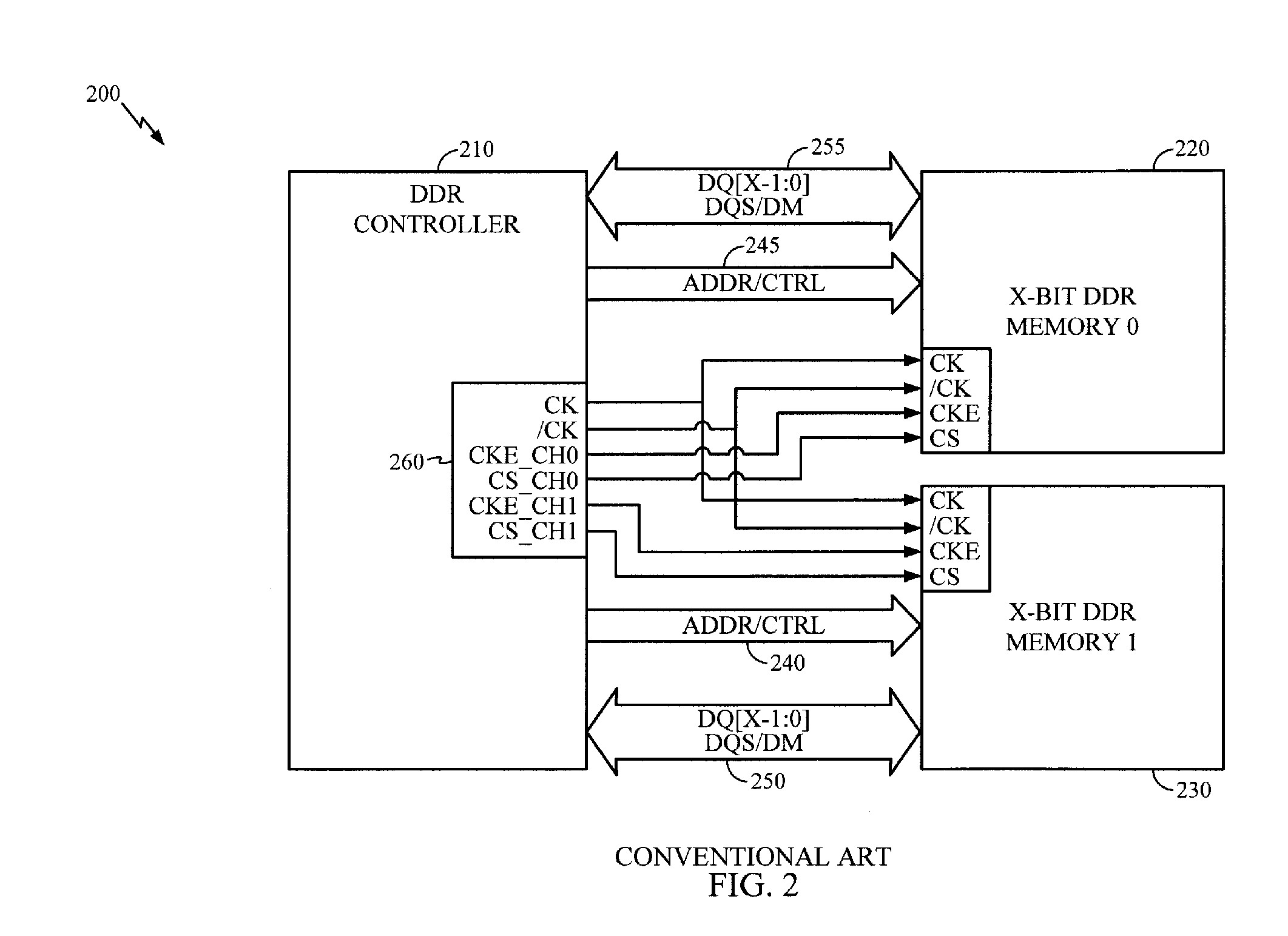
Dual Channel Memory Architecture Having a Reduced Interface Pin Requirements Using a Double Data Rate Scheme for the Address/Control Signals
Apparatuses and methods for dual channel memory architecture with reduced interface pin requirements are presented. One memory architecture includes a memory controller, a first memory device coupled to the memory controller by a shared address bus and a first clock signal, and a second memory device coupled to the memory controller by the shared address bus and a second clock signal, where the polarity of the second clock signal is opposite of the first clock signal. A method for performing data transactions is presented. The method includes providing addressing signals over a shared address bus to a first memory device and a second memory device, providing clock signals to the memory devices which are reversed in polarity, where the clock signals are derived from a common clock signal, and transferring data to the memory devices over separate narrow data buses in an alternating manner based upon the clock signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com