Patents
Literature
716 results about "Double data rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
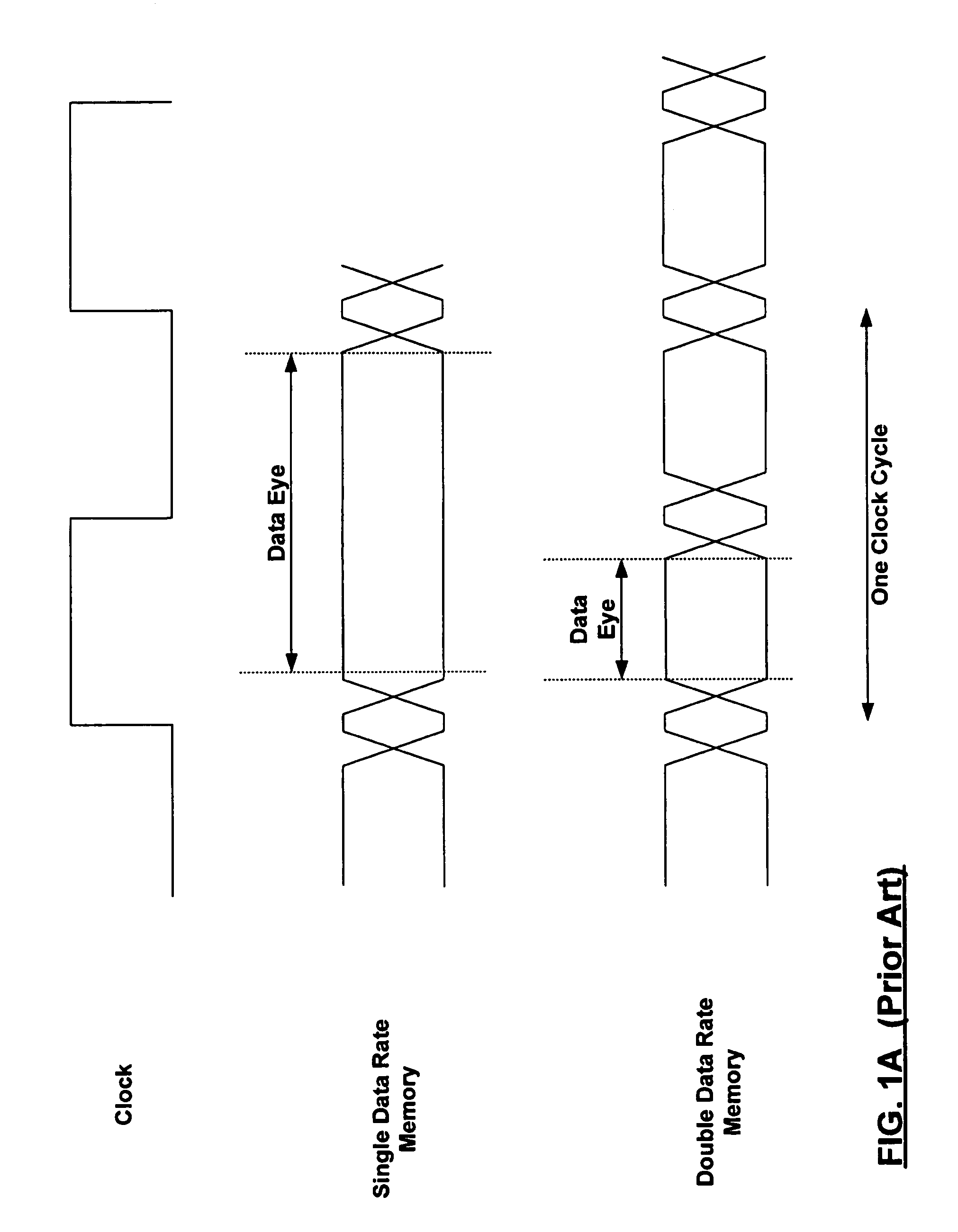
In computing, a computer bus operating with double data rate (DDR) transfers data on both the rising and falling edges of the clock signal. This is also known as double pumped, dual-pumped, and double transition. The term toggle mode is used in the context of NAND flash memory.
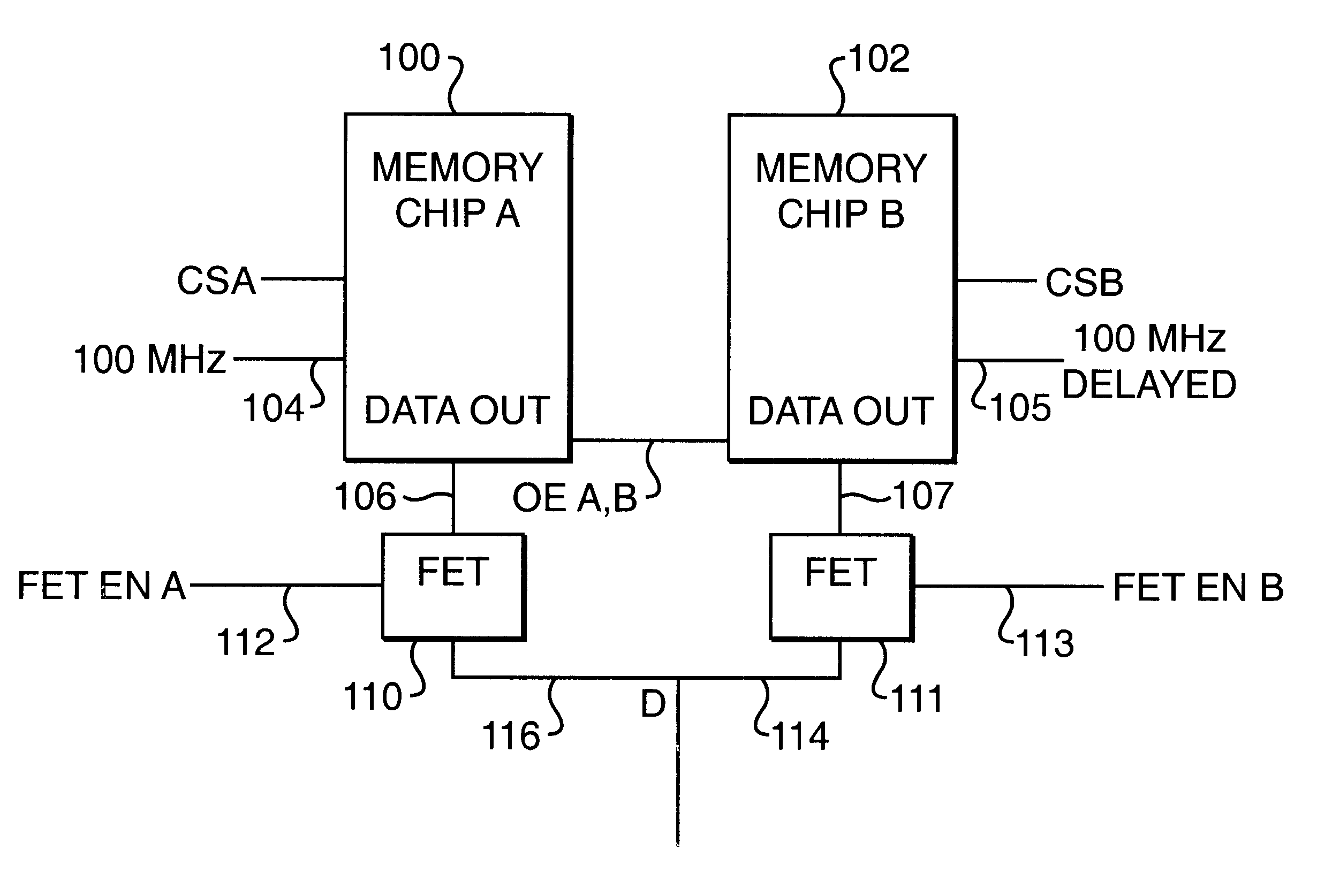
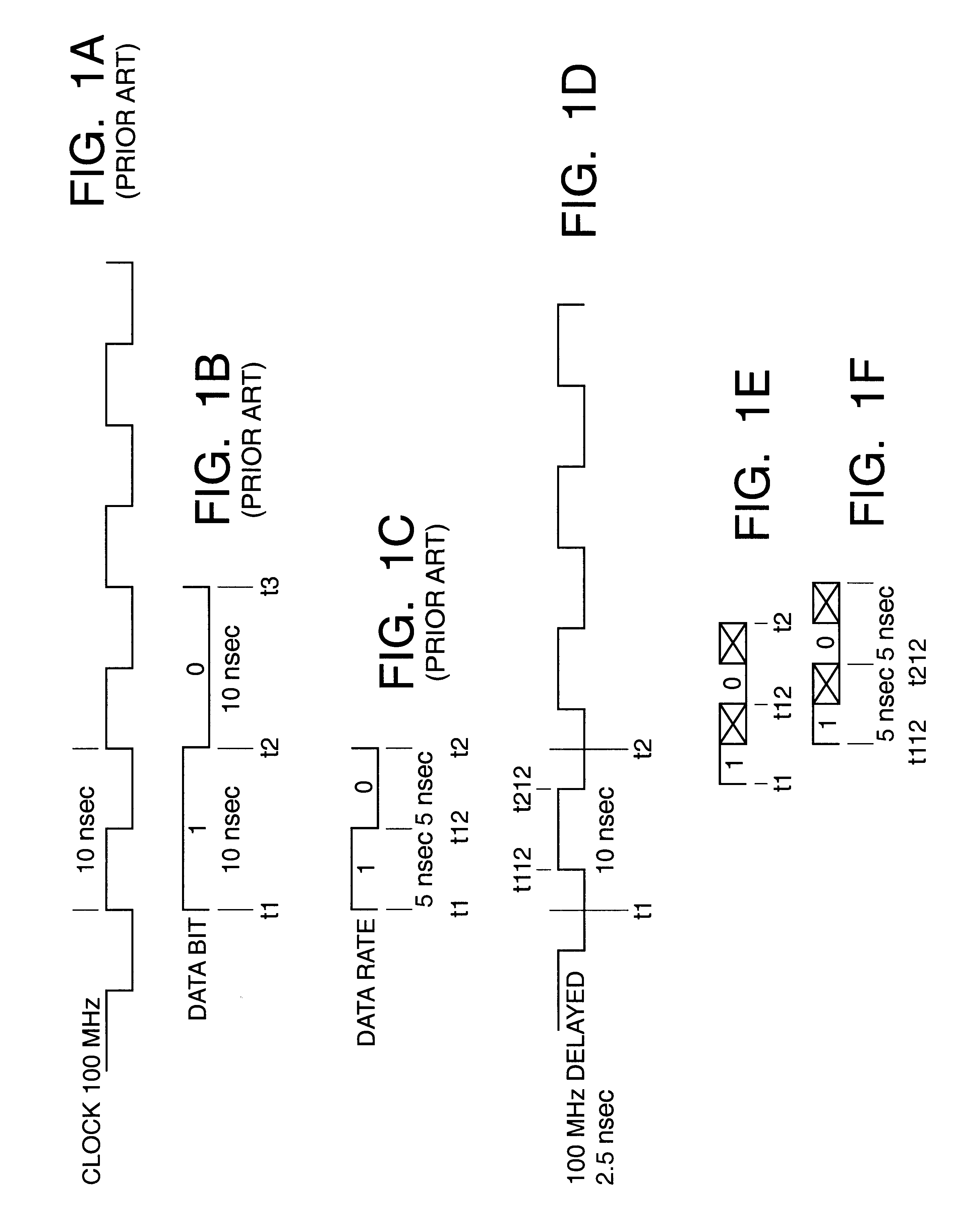
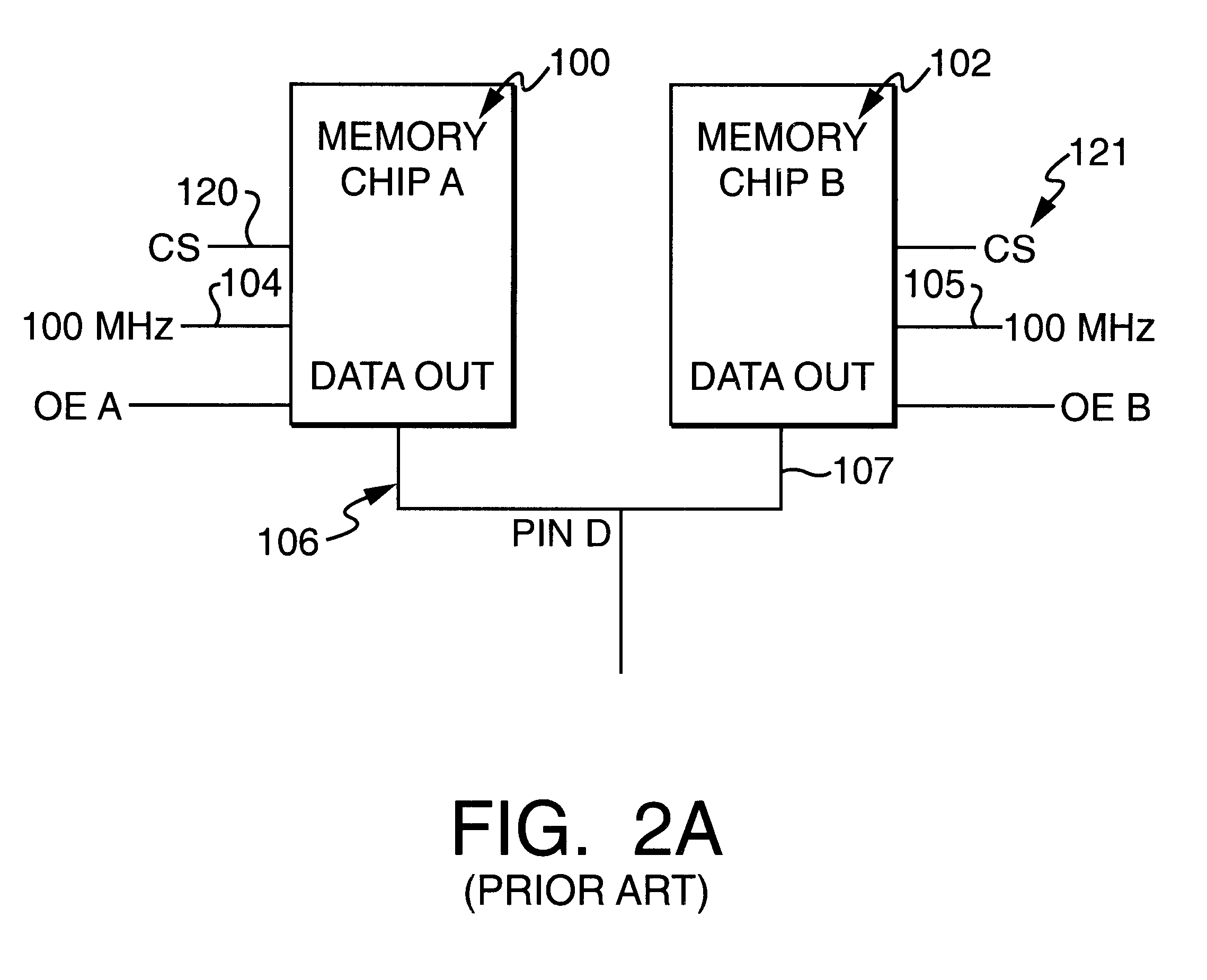
Memory system using FET switches to select memory banks
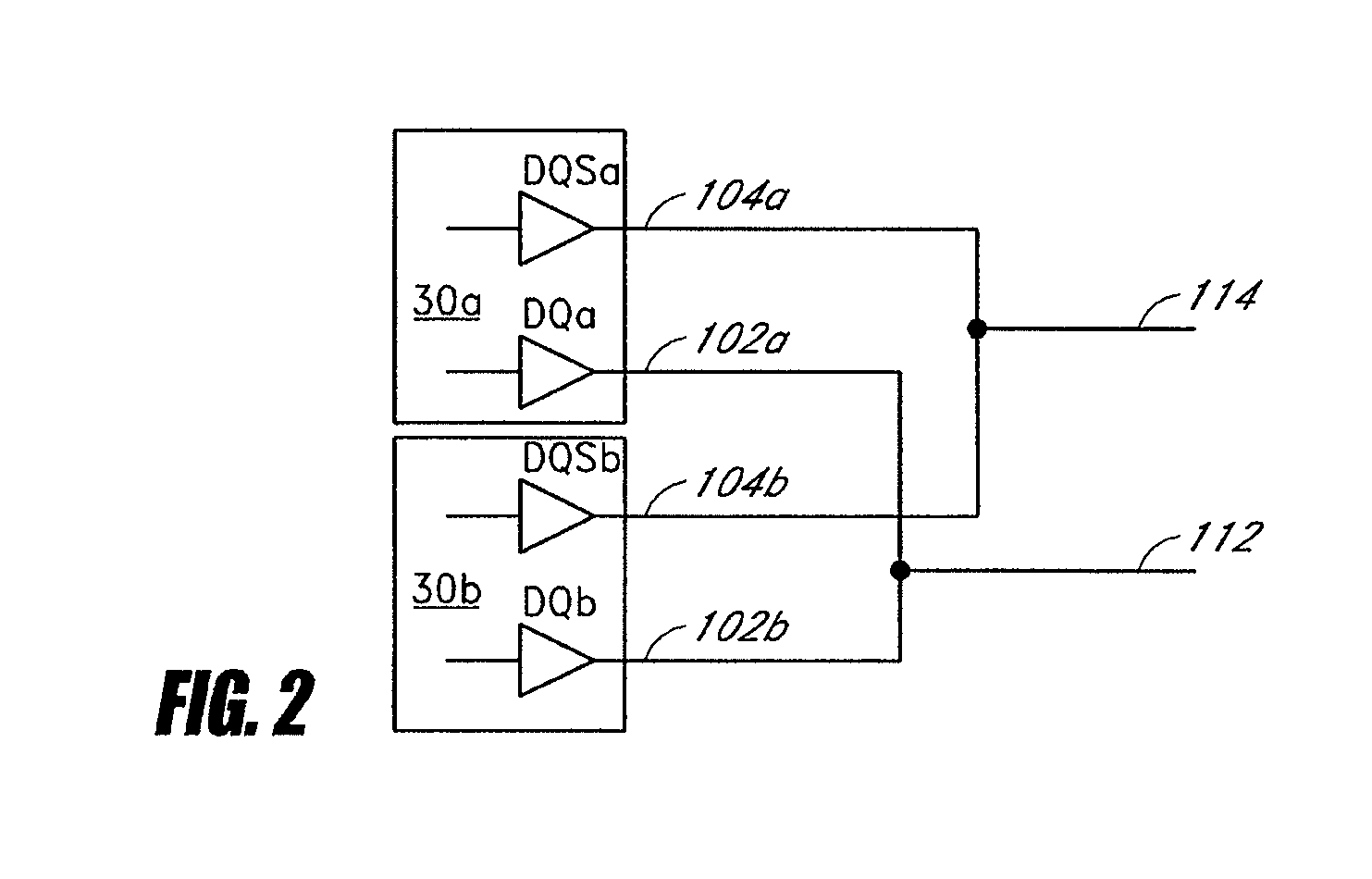
A computer memory system provides a double data rate (DDR) memory output while requiring memory chips with only half the frequency limit of the prior art DDR memory chips. The system contains a first memory bank having data lines and a second memory bank having data lines. The first and second memory banks are associated with first and second clock signals, respectively, where the second clock signal is delayed from the first clock signal such that the data lines of the first memory bank are connected to a data bus in synchronism with the first clock signal while the data lines of the second memory bank are connected with the data bus in synchronism with the second clock signal. In one embodiment, a first FET switch connects the data lines of the first memory bank with the data bus and a second FET switch connects the data lines of the second memory bank with the data bus. The second FET switch is connected to the data bus at a time delayed from the beginning after the start of each clock cycle of the second clock signal. As a result, the data bus is never connected to the data lines of both memory banks at the same time, but rather, the data bus is alternately connected with the first memory bank and then the second memory bank.
Owner:FOOTHILLS IP LLC
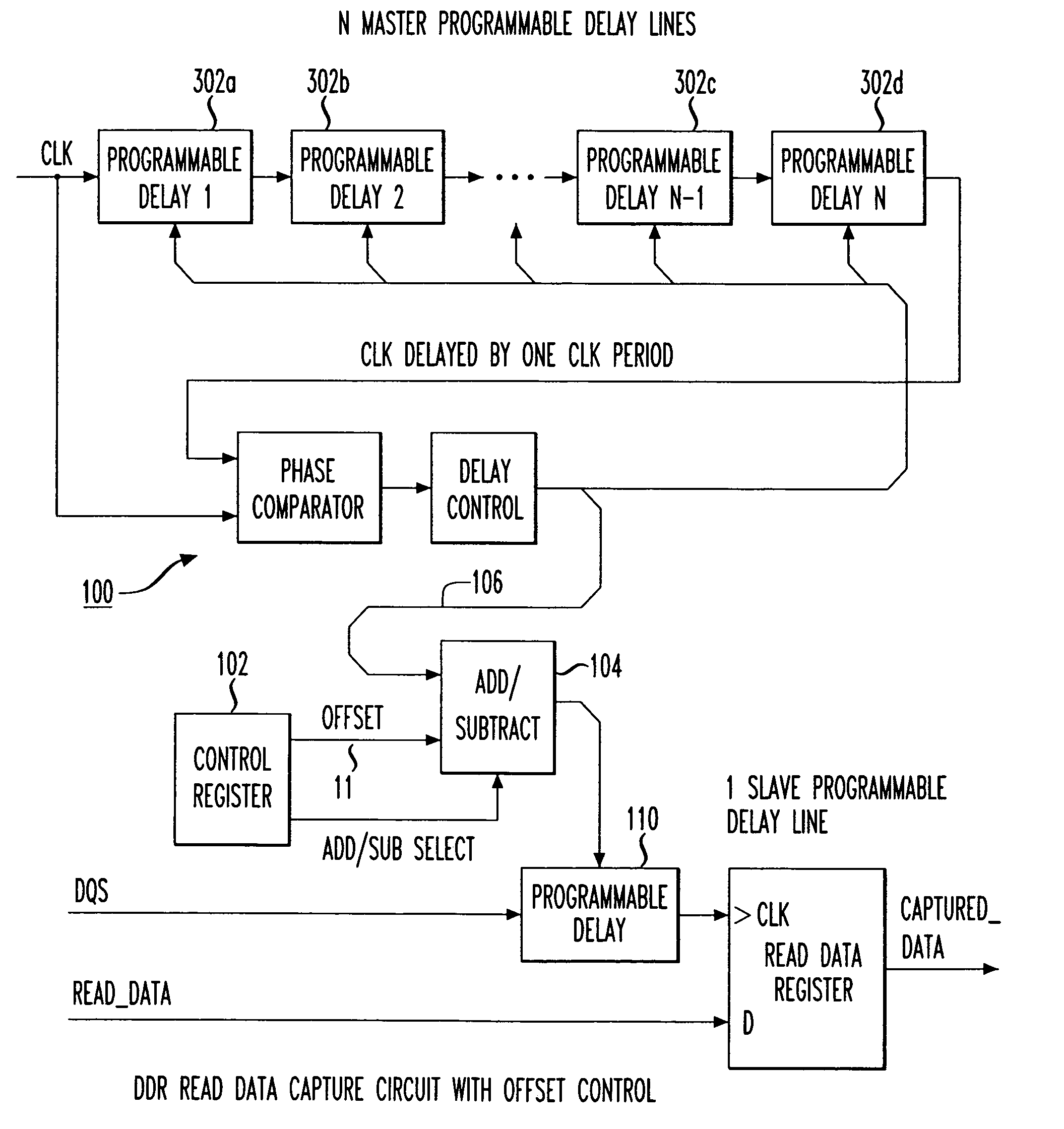
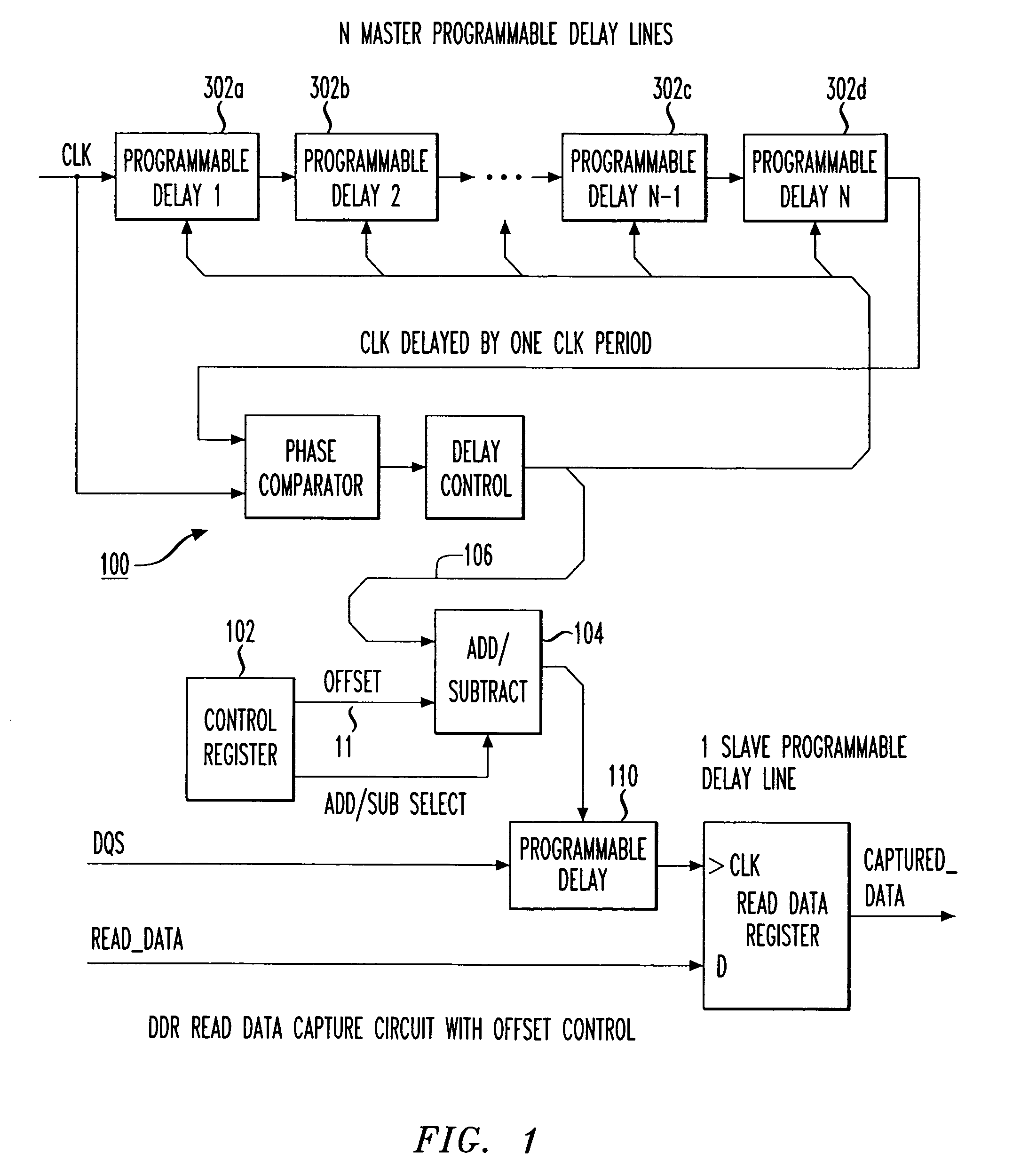
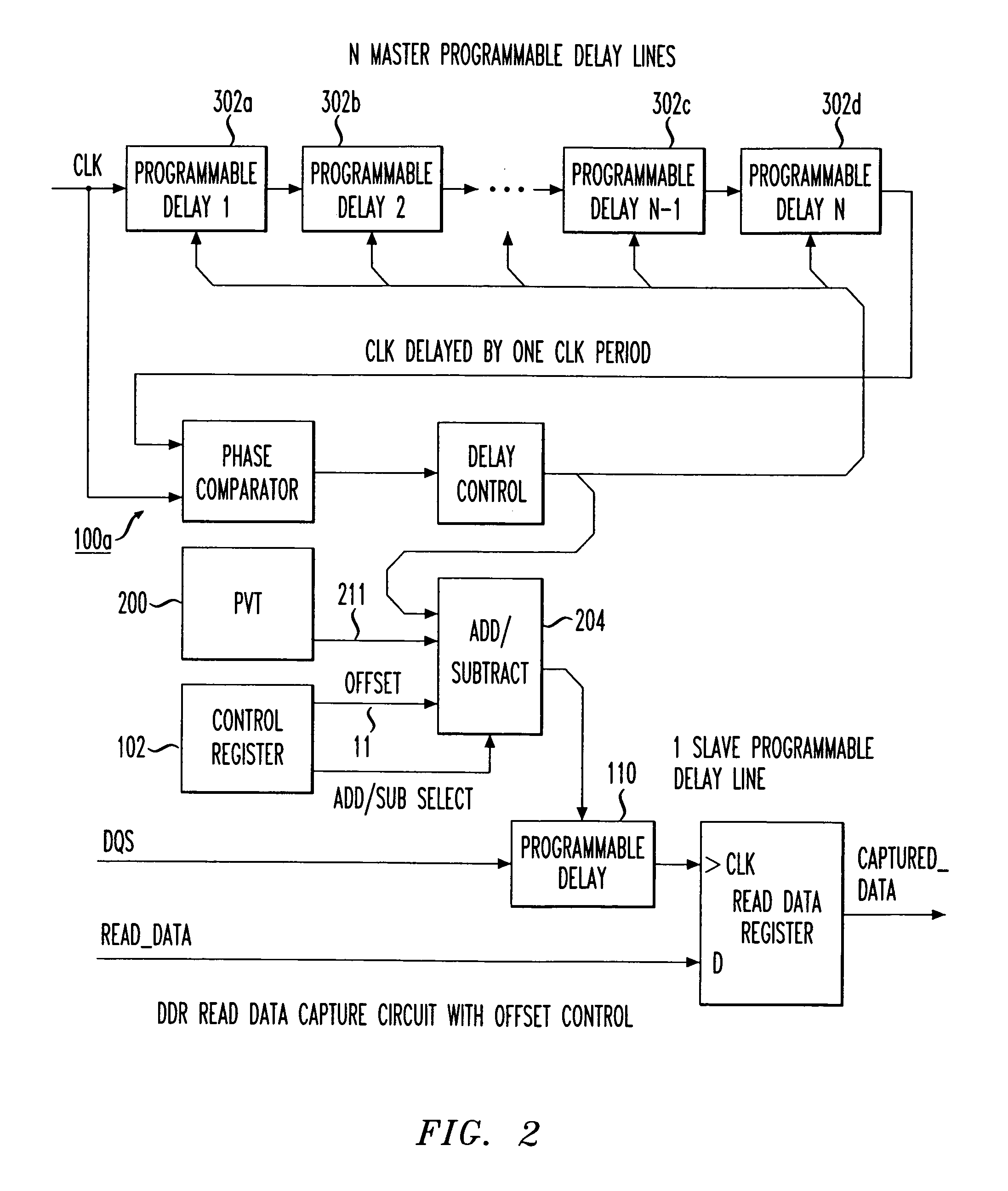
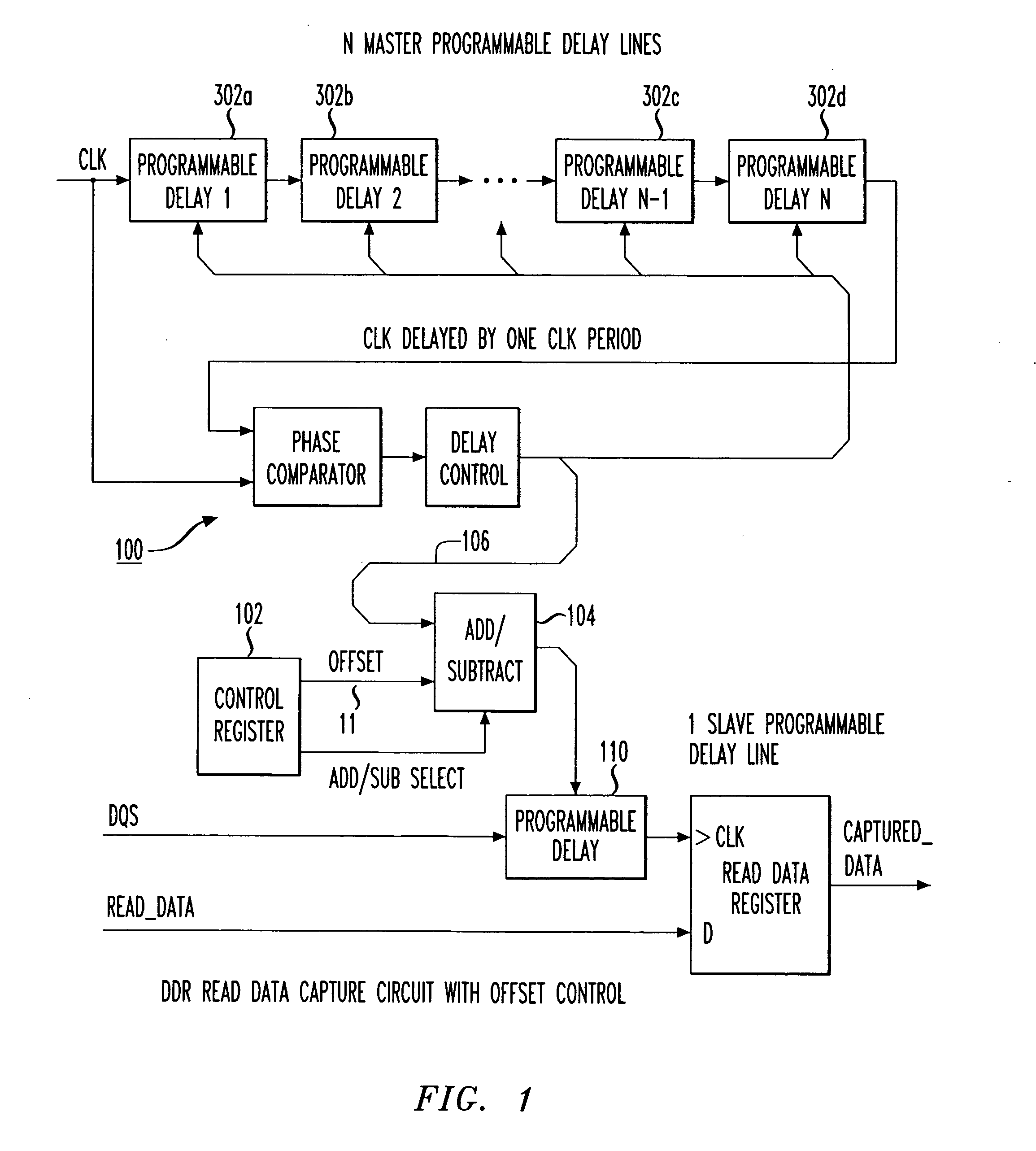
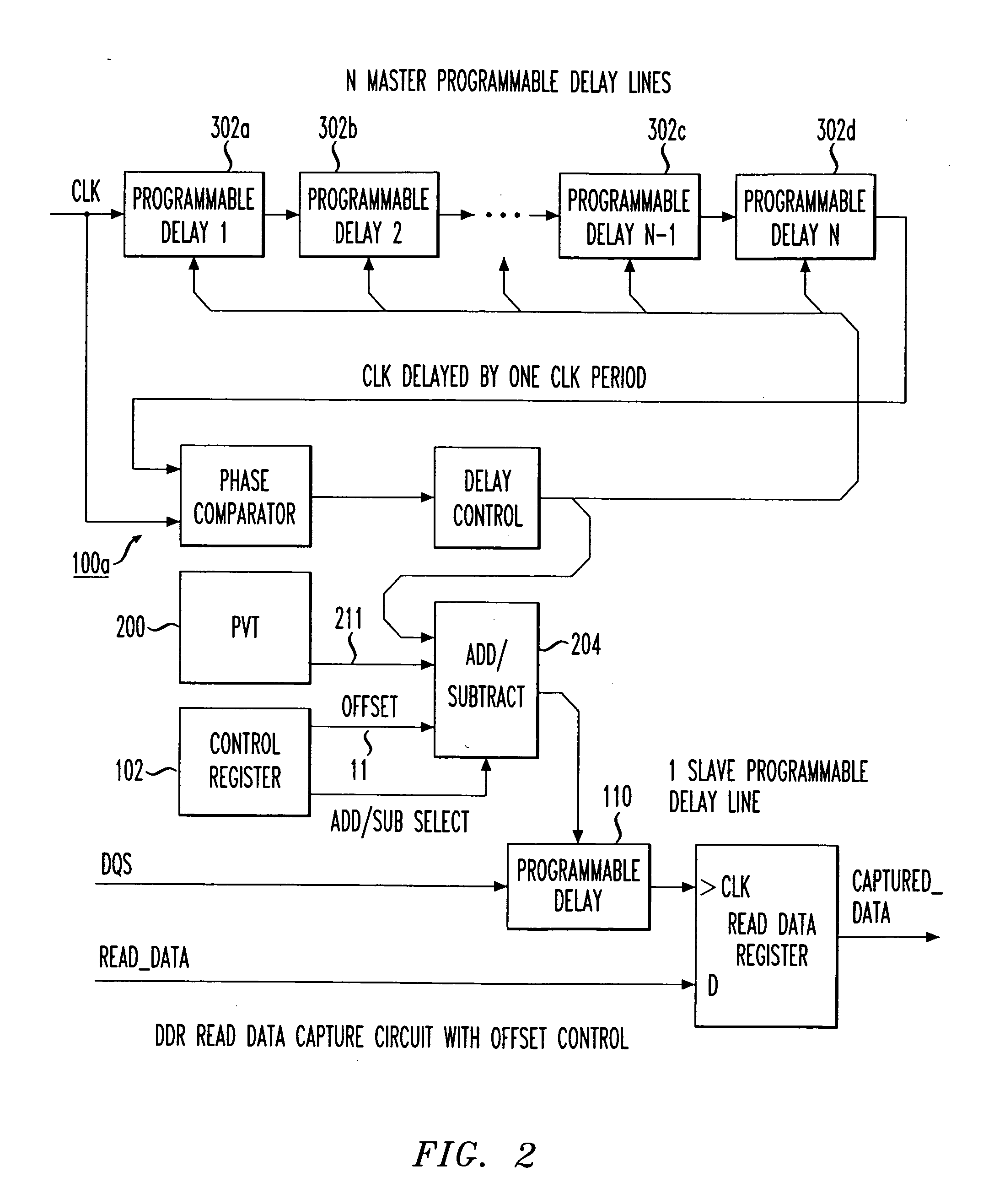
Programmable data strobe offset with DLL for double data rate (DDR) RAM memory
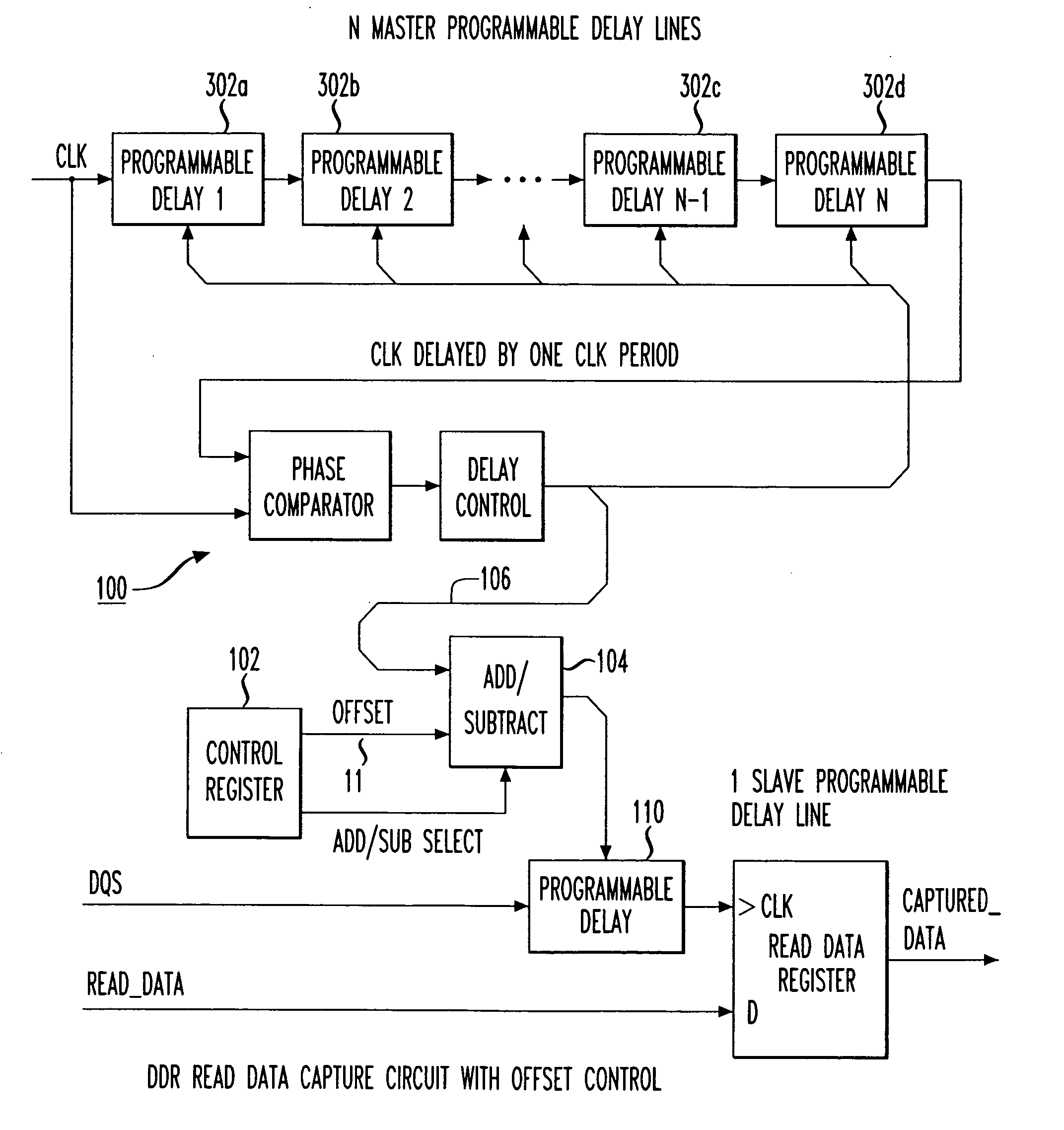
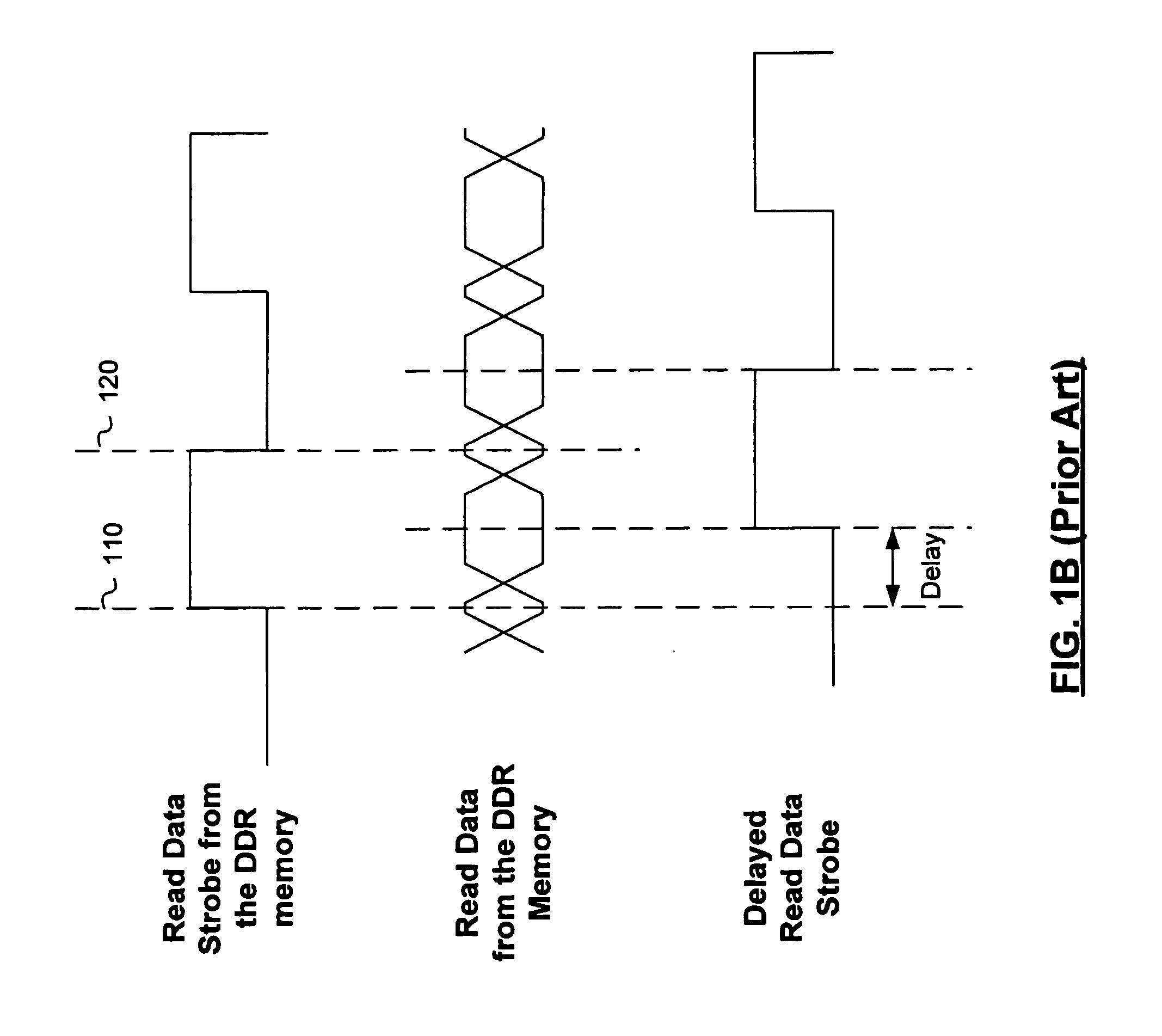
A double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic RAM (SDRAM), or DDR-SDRAM, memory controller employing a delay locked loop (DLL) circuit to delay an SDRAM data strobe (DQS) signal to the center, or ‘eye’ of the read data window. However, in distinction from conventional techniques, the initial delay determined by the DLL is fine tuned with an offset determined by a memory test. Moreover, in an additional embodiment, the delay may be further adjusted during operation to compensate for environmental conditions by a PVT (process, value, temperature) circuit.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
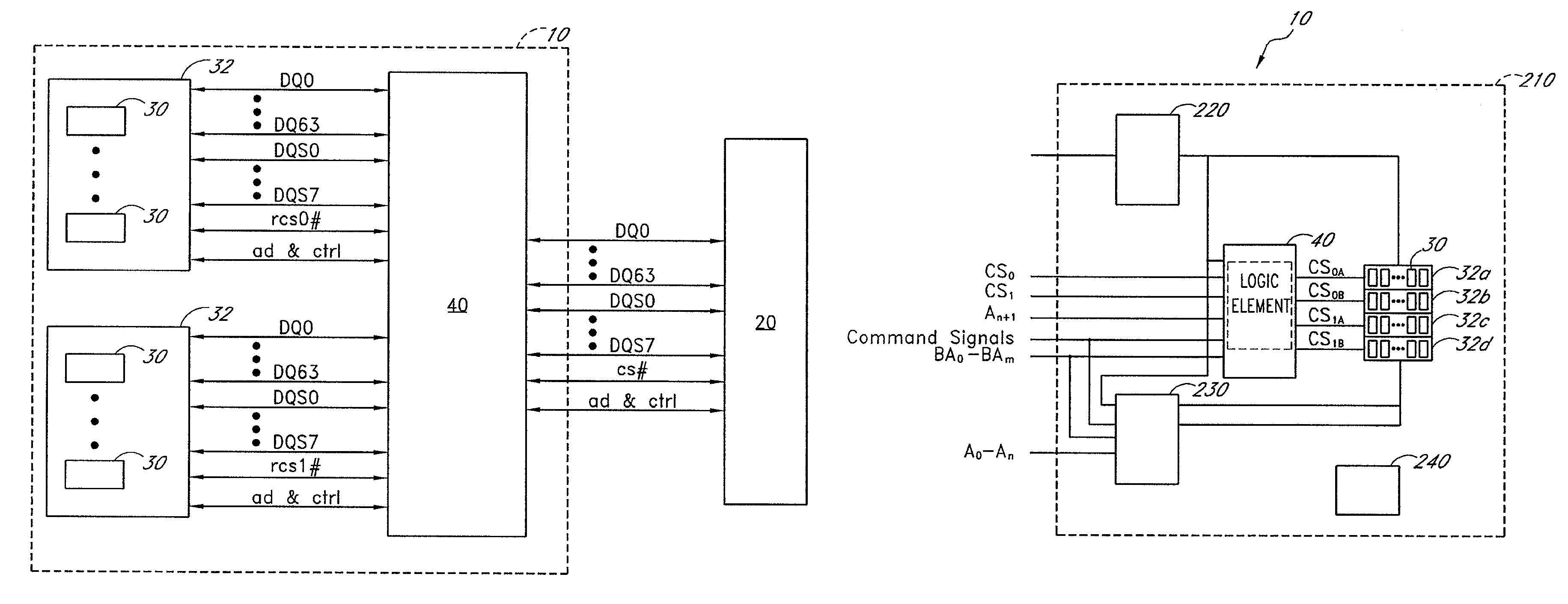
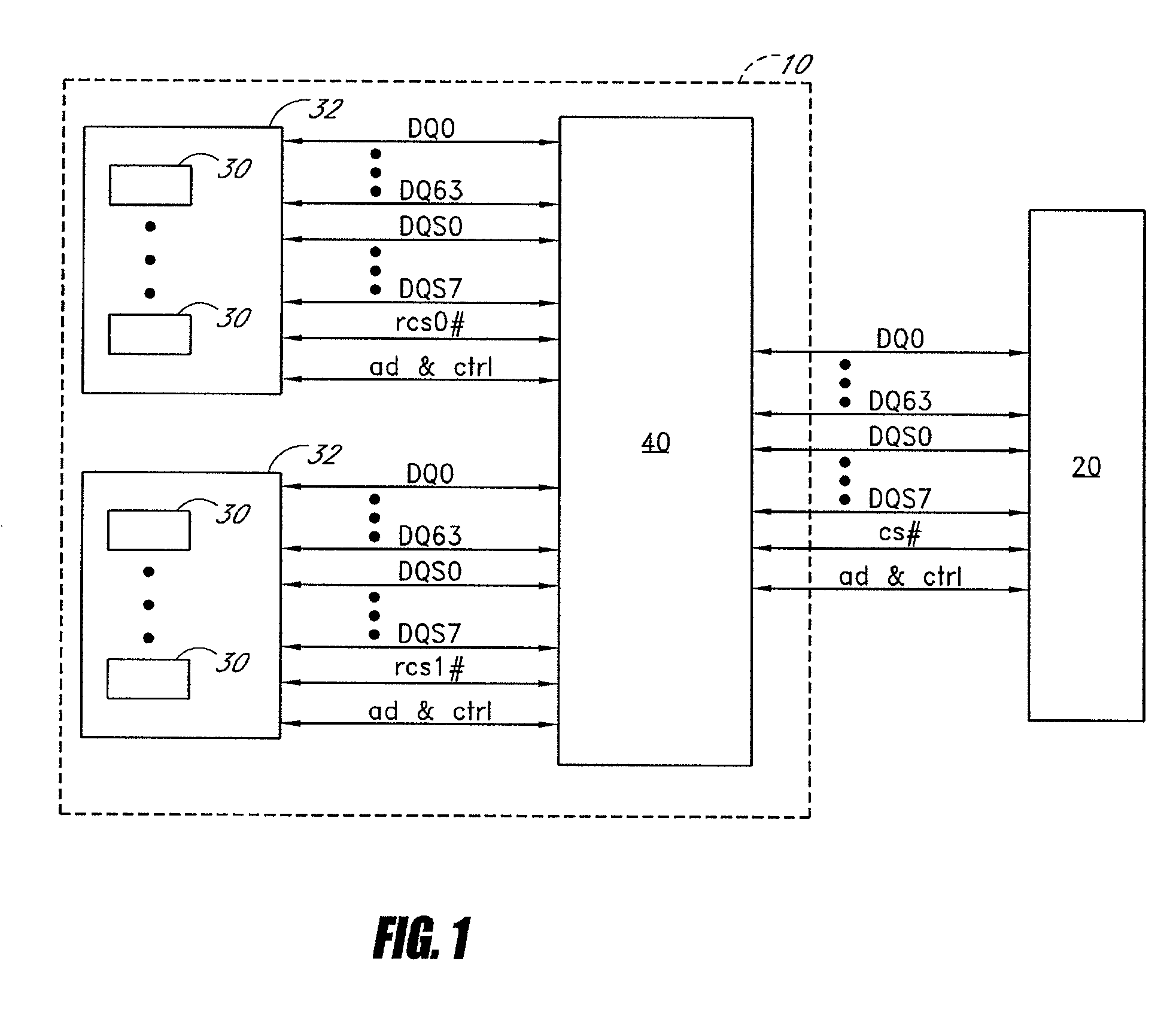
Circuit providing load isolation and memory domain translation for memory module
A circuit is configured to be mounted on a memory module connectable to a computer system so as to be electrically coupled to a plurality of memory devices on the memory module. The memory module has a first number of ranks of double-data-rate (DDR) memory devices activated by a first number of chip-select signals. The circuit is configurable to receive bank address signals, a second number of chip-select signals, and row / column address signals from the computer system. The circuit is further configurable to generate phase-locked clock signals in response to clock signals received from the computer system, to selectively isolate one or more loads of the first number of ranks from the computer system, and to translate between a system memory domain and a physical memory domain of the memory module.
Owner:NETLIST INC
Dynamic switching of parallel termination for power management with DDR memory
InactiveUS6894691B2Attenuation bandwidthReduce resolutionReliability increasing modificationsVolume/mass flow measurementDouble data rateHandling system
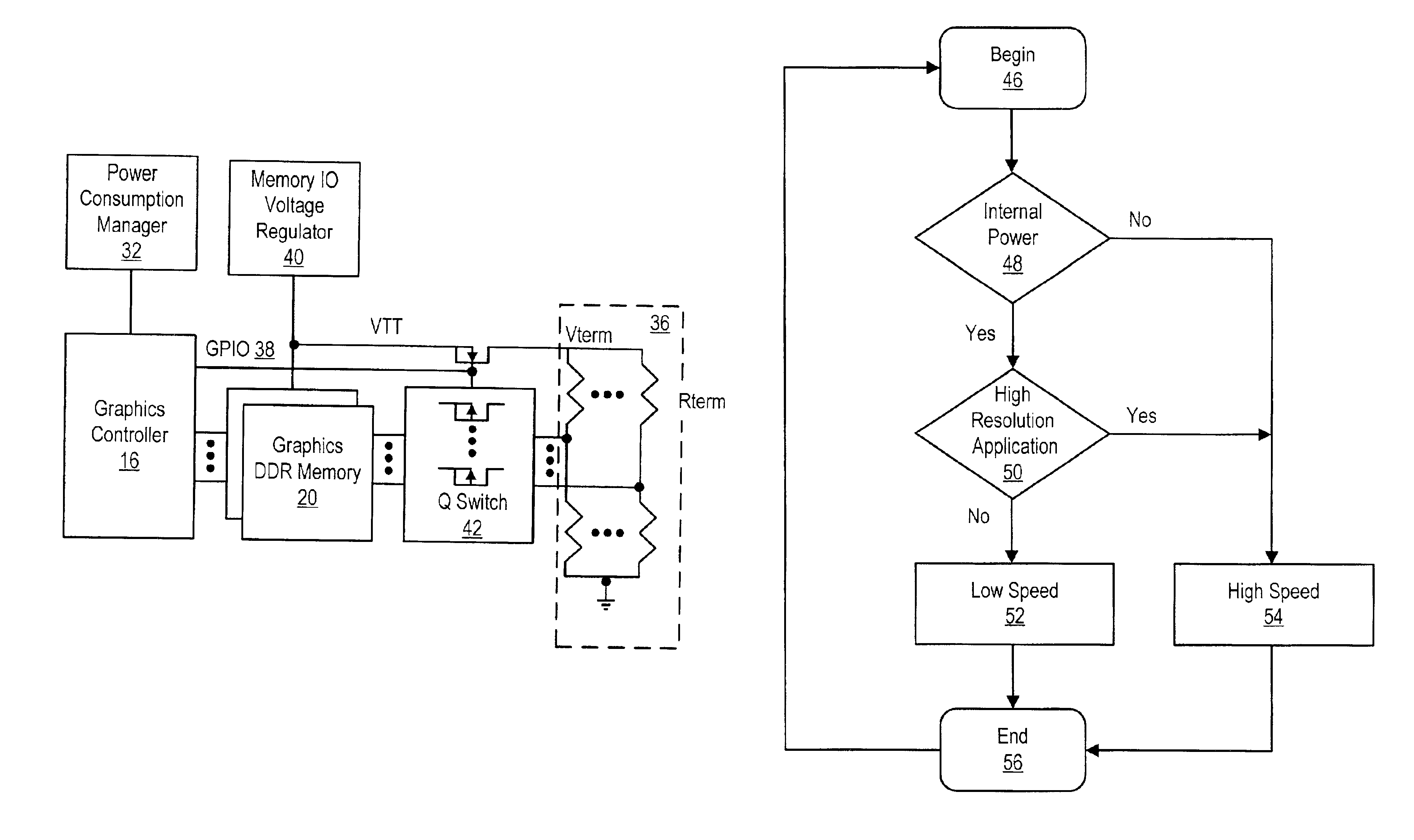
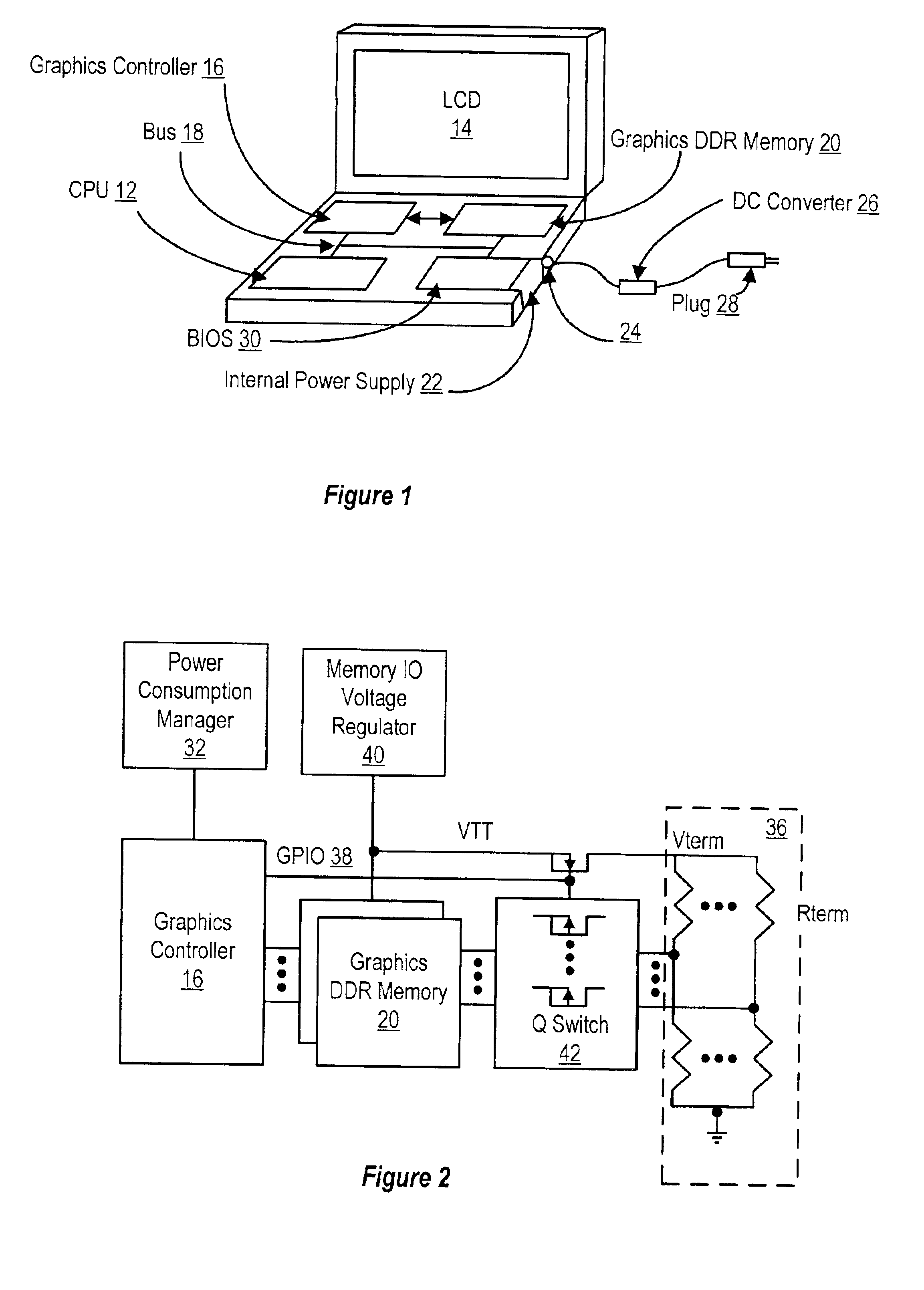
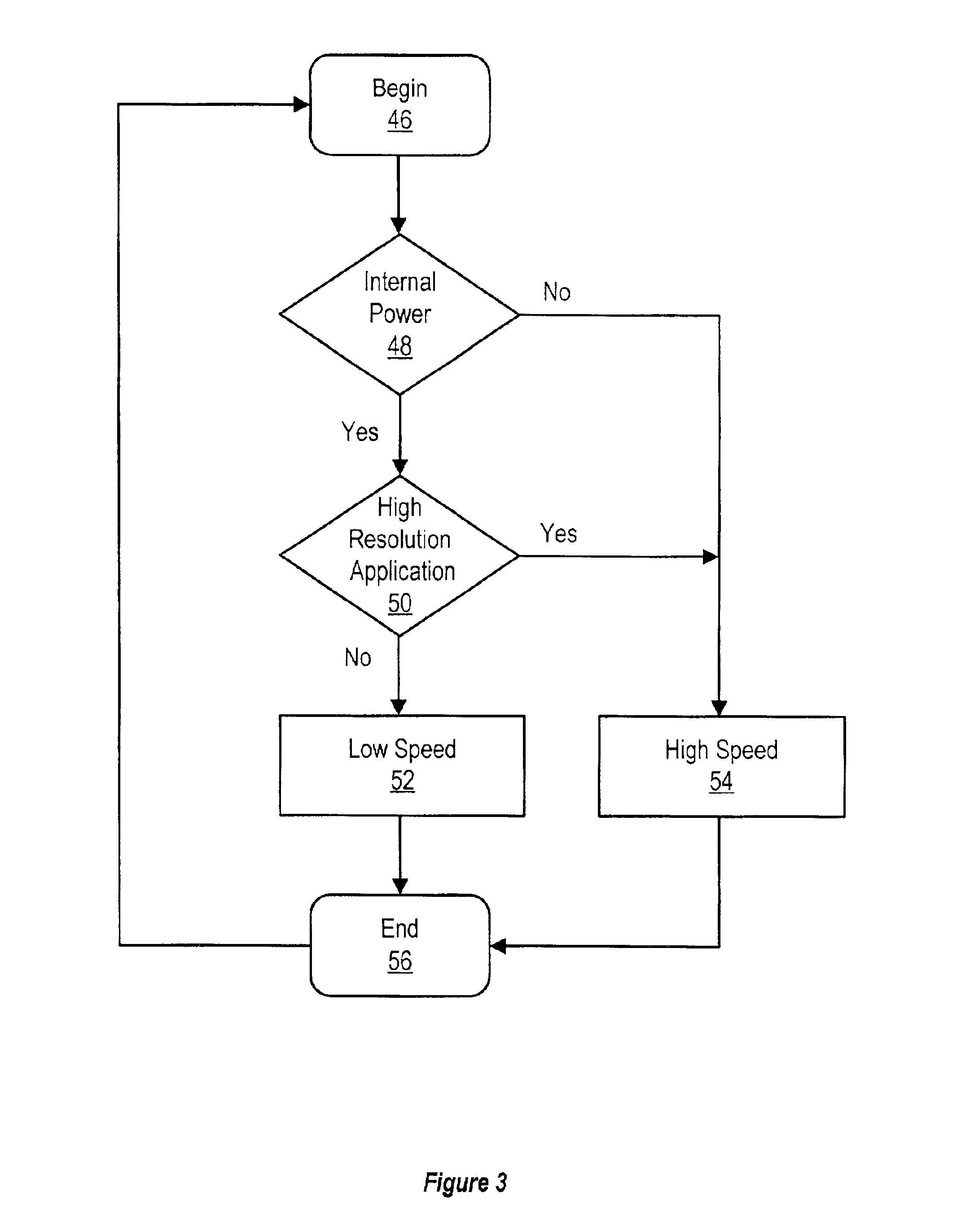
A system and method for managing power consumption of an information handling system dynamically switches between high and low clock speed data transfers with double data rate (DDR) memory. The selection of a high clock speed dynamically switches the DDR memory to connect to a parallel termination for more rapid data transfers with increased power consumption. The selection of a low clock speed dynamically switches the DDR memory to disconnect the parallel termination for slower data transfers with reduced power consumption. In one embodiment, portable computer graphics DDR memory reduces power consumption by selecting low clock speed transfers without parallel termination when operating on internal power. The portable computer graphics DDR memory provides improved display resolution by selecting high clock speed transfers with parallel termination when operating on external power or when displaying information from high resolution applications.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
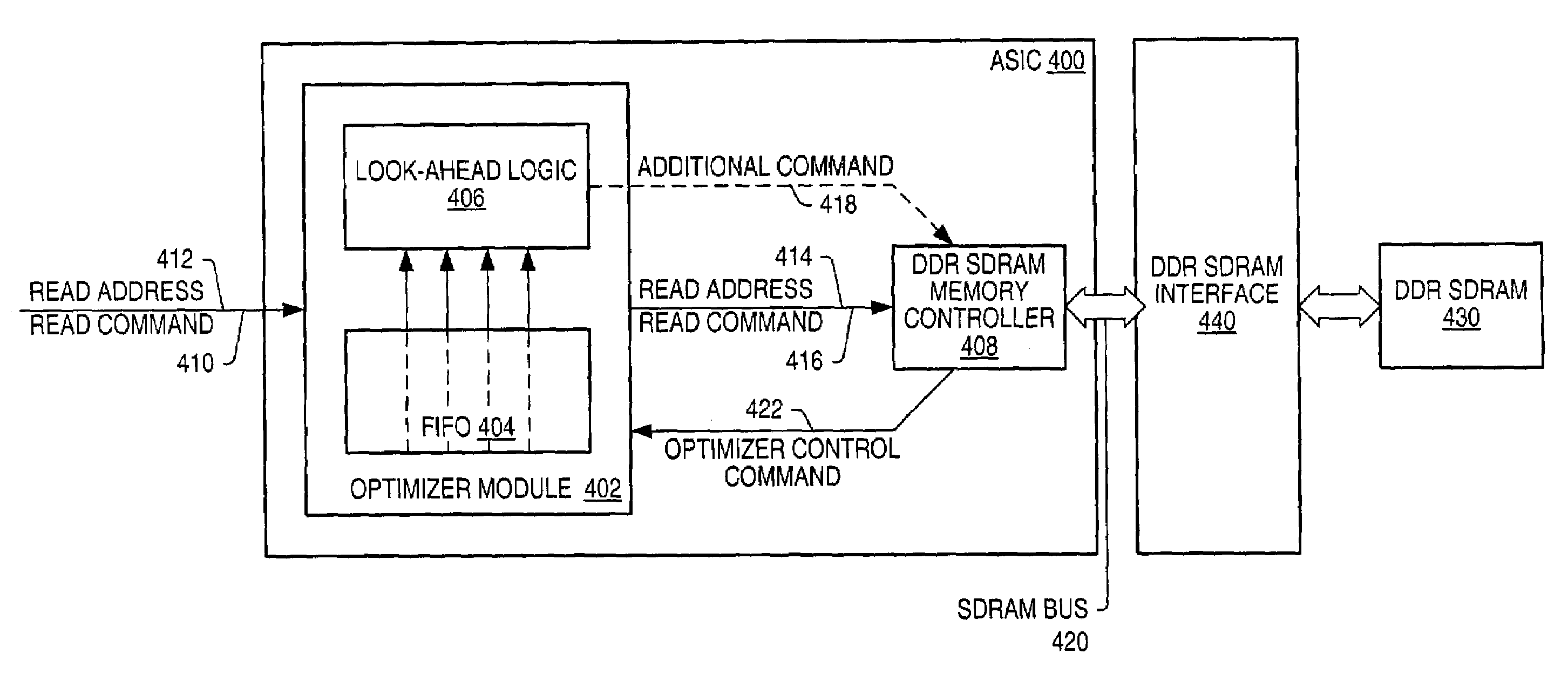
Method for optimizing utilization of a double-data-rate-SDRAM memory system
ActiveUS7089369B2Reduce in quantityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital storageDouble data rateInterleaved memory
A predictive memory performance optimizing unit for use with an interleaved memory, for example a DDR SDRAM memory, and suitable for use in a computer graphics system, among others, is described. The unit maintains a queue of pending requests for data from the memory, and prioritizes precharging and activating interleaves with pending requests. Interleaves which are in a ready state may be accessed independently of the precharging and activation of non-ready interleaves. The unit utilizes idle cycles occurring between consecutive requests to activate interleaves with pending requests.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
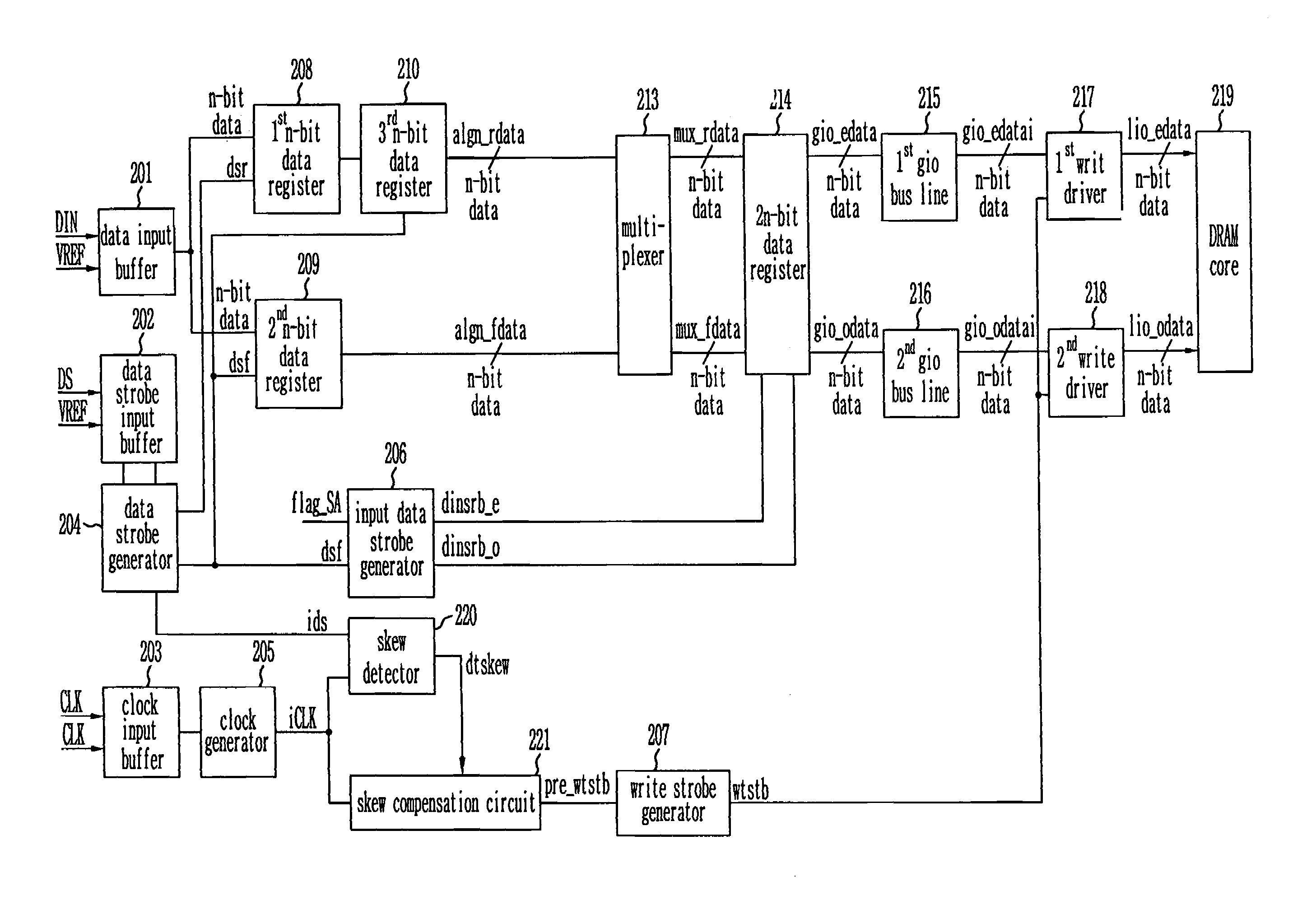
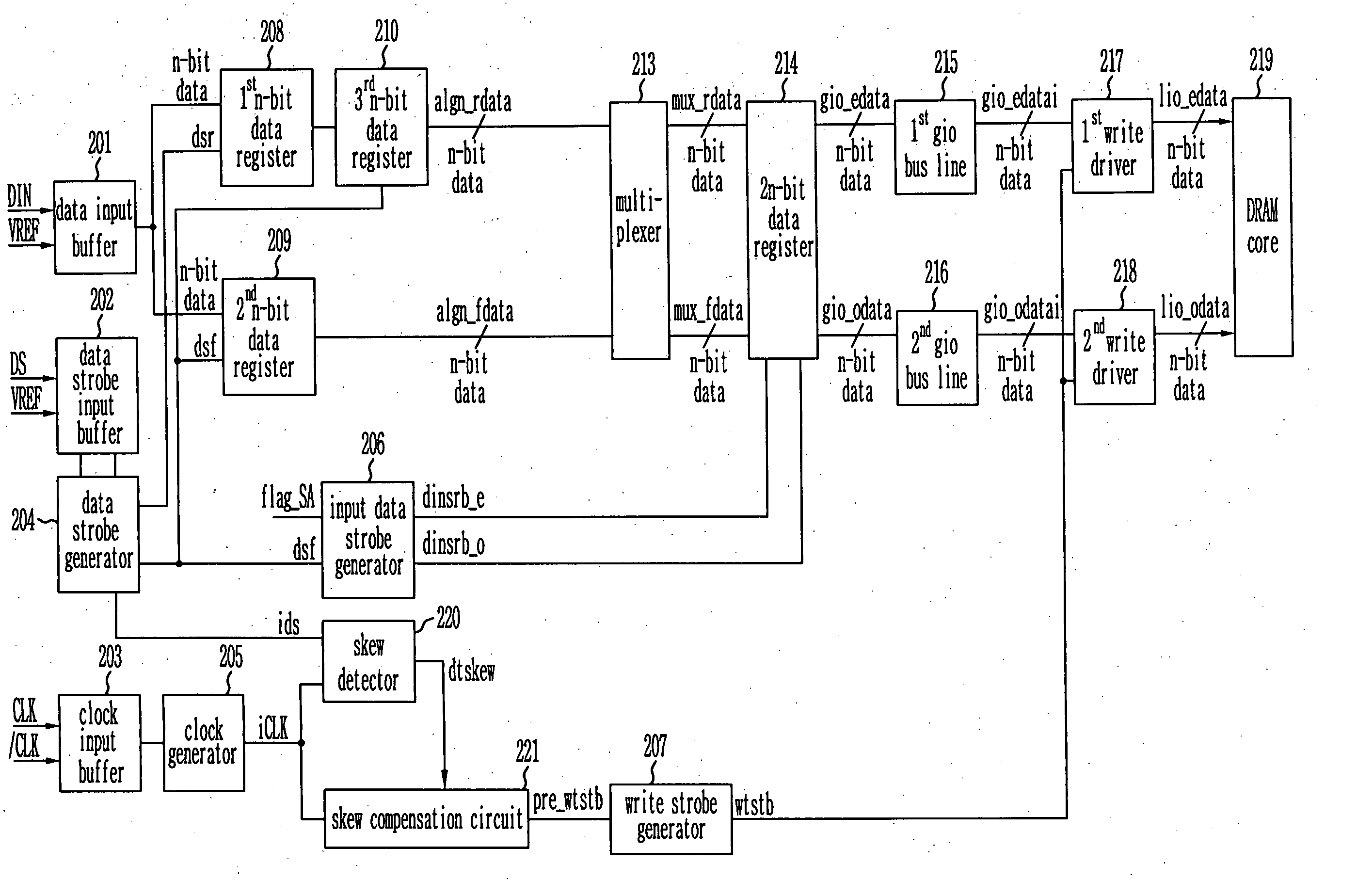
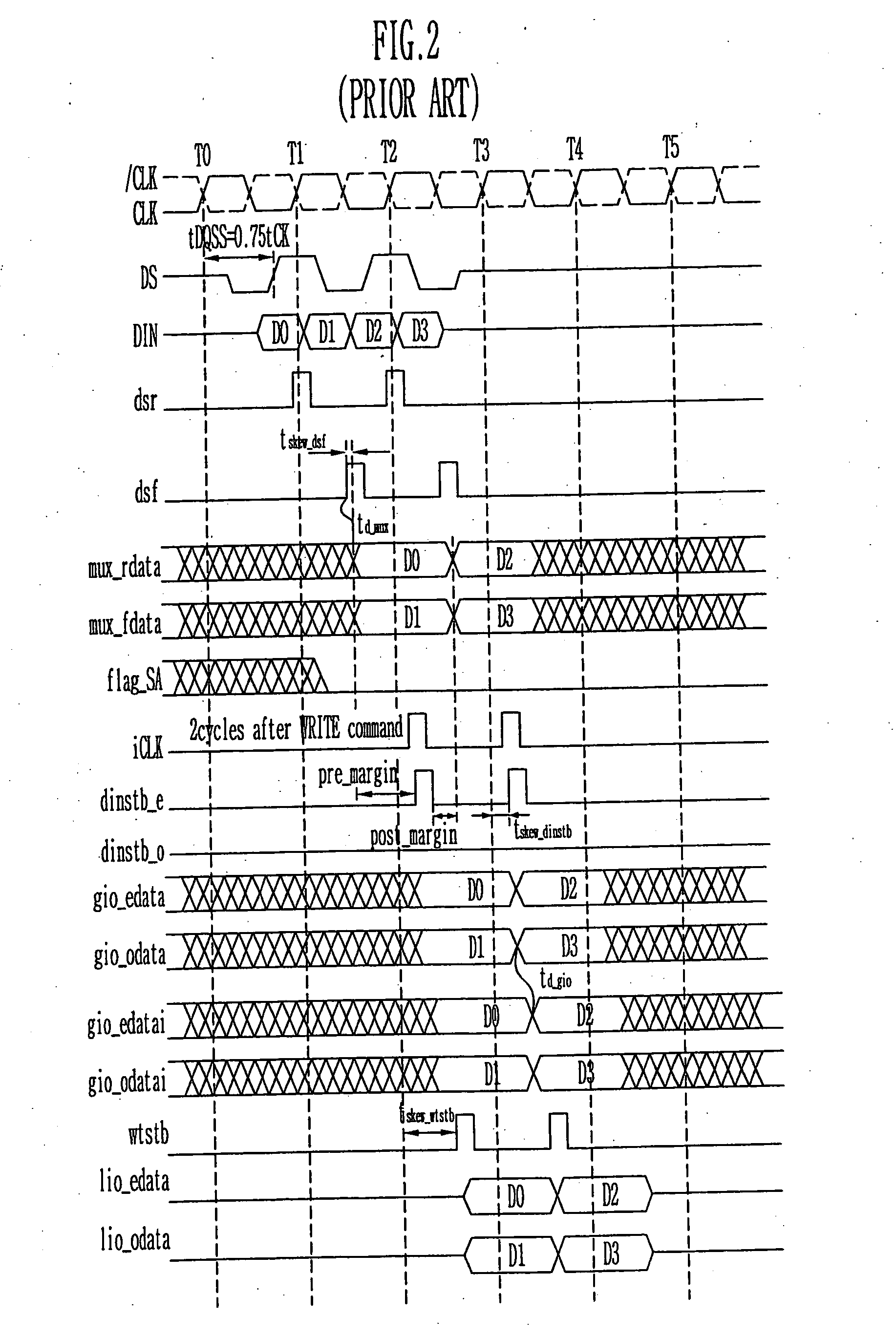
Write circuit of double data rate synchronous DRAM
ActiveUS7042799B2Guaranteed uptimeTiming marginRead-only memoriesDigital storageTiming marginDouble data rate
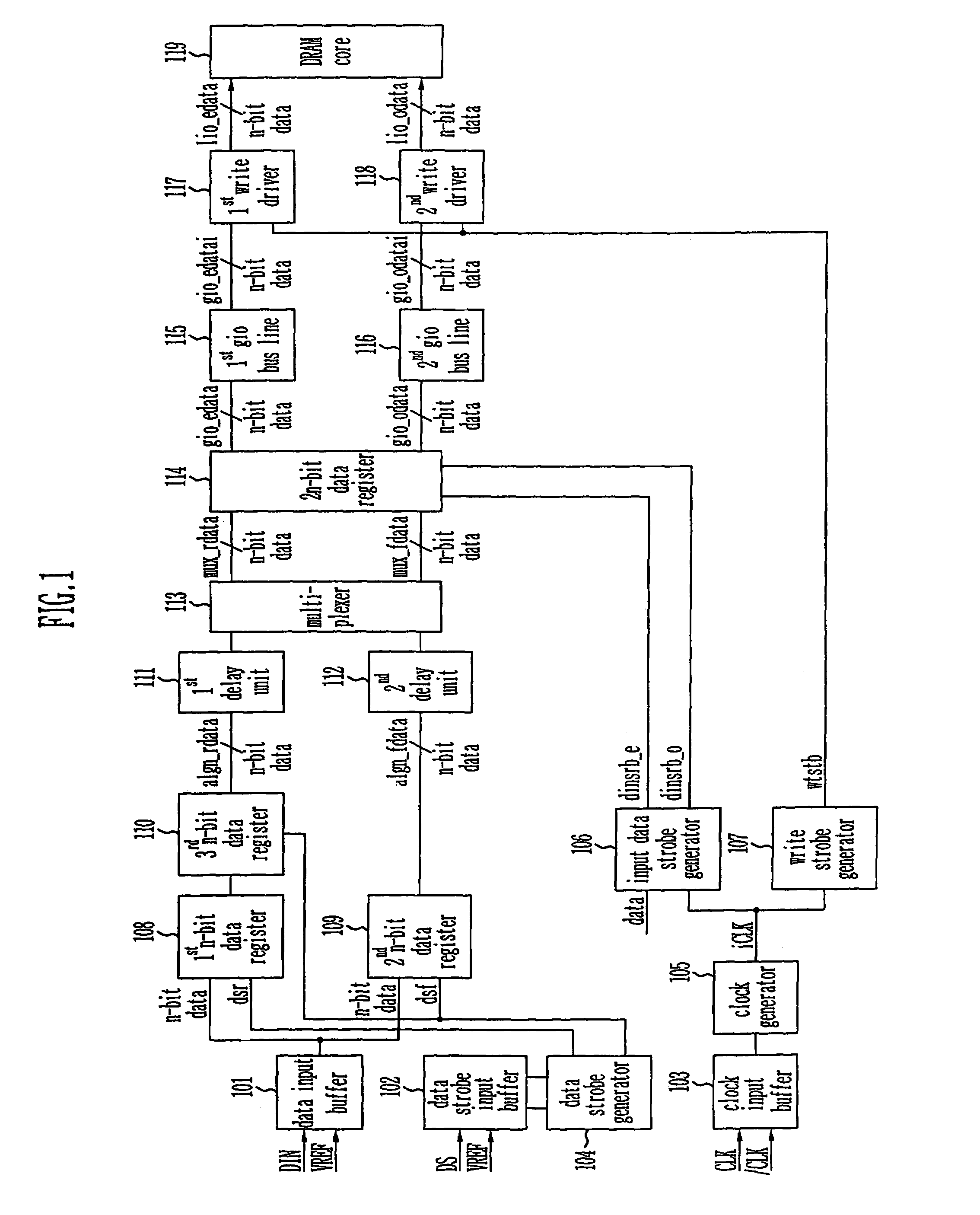
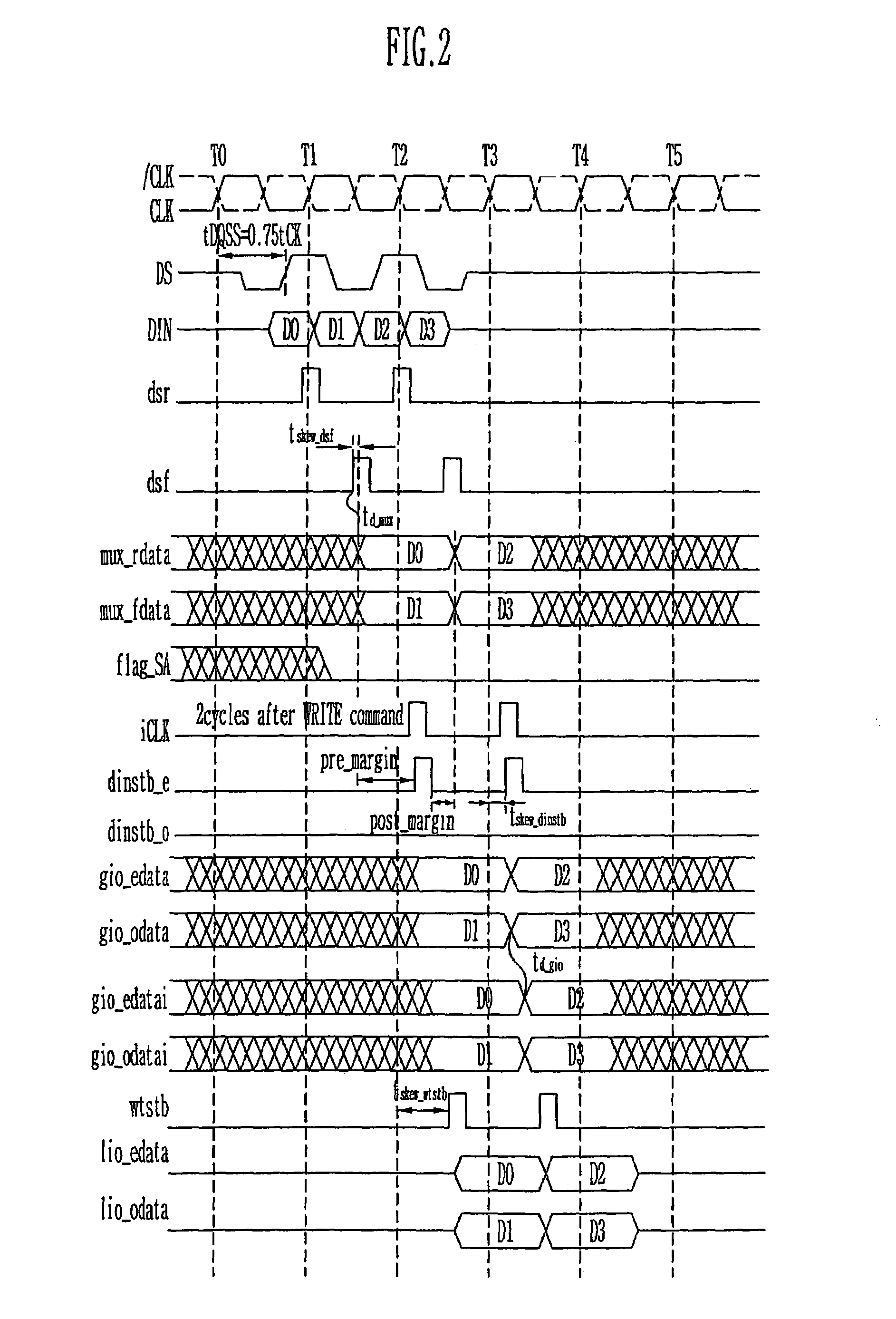
Provided is a write circuit of a DDR SDRAM, in which a clock domain crossing is generated from a writing driver during a data write operation and a proper data is always transferred to a gio bus line by using the delay of an internal data strobe signal's falling for a certain amount of time as an input data strobe bar signal. Moreover, by using a skew detection circuit, it is possible to detect a skew tDQSS between a clock and a data strobe, and the skew tDQSS is automatically compensated by the skew compensation circuit. From the perspective of a timing error between the clock and the data strobe, therefore, the write operation of the DDR SDRAM has twice the timing margin (0.5tCK) compared to that of the related art. This means that a stable, high-speed write operation of the DDR SDRAM can be made possible.
Owner:MOSAID TECH
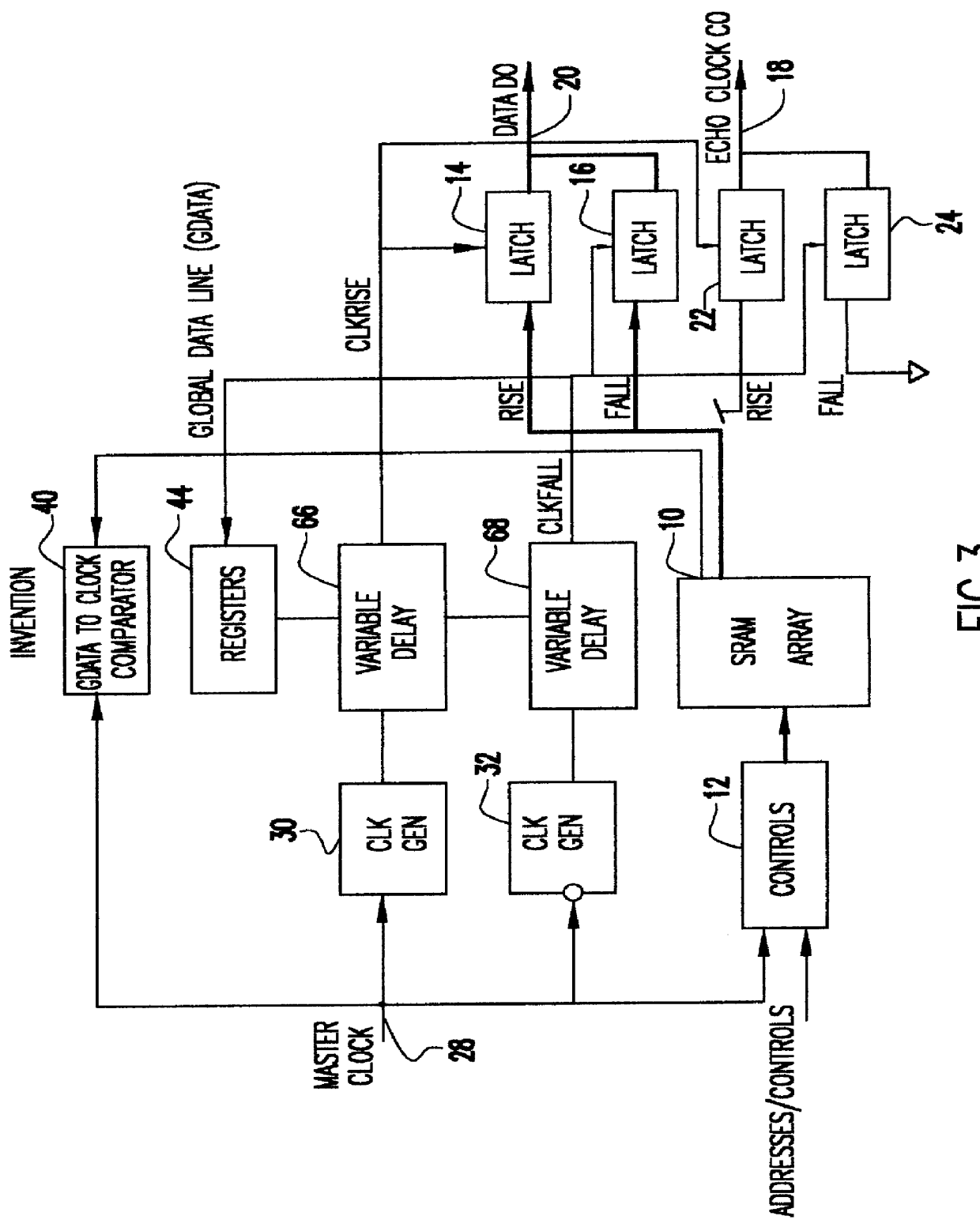
Cycle independent data to echo clock tracking circuit
InactiveUS6134182AAvoid dataDigital storageGenerating/distributing signalsDouble data rateData signal
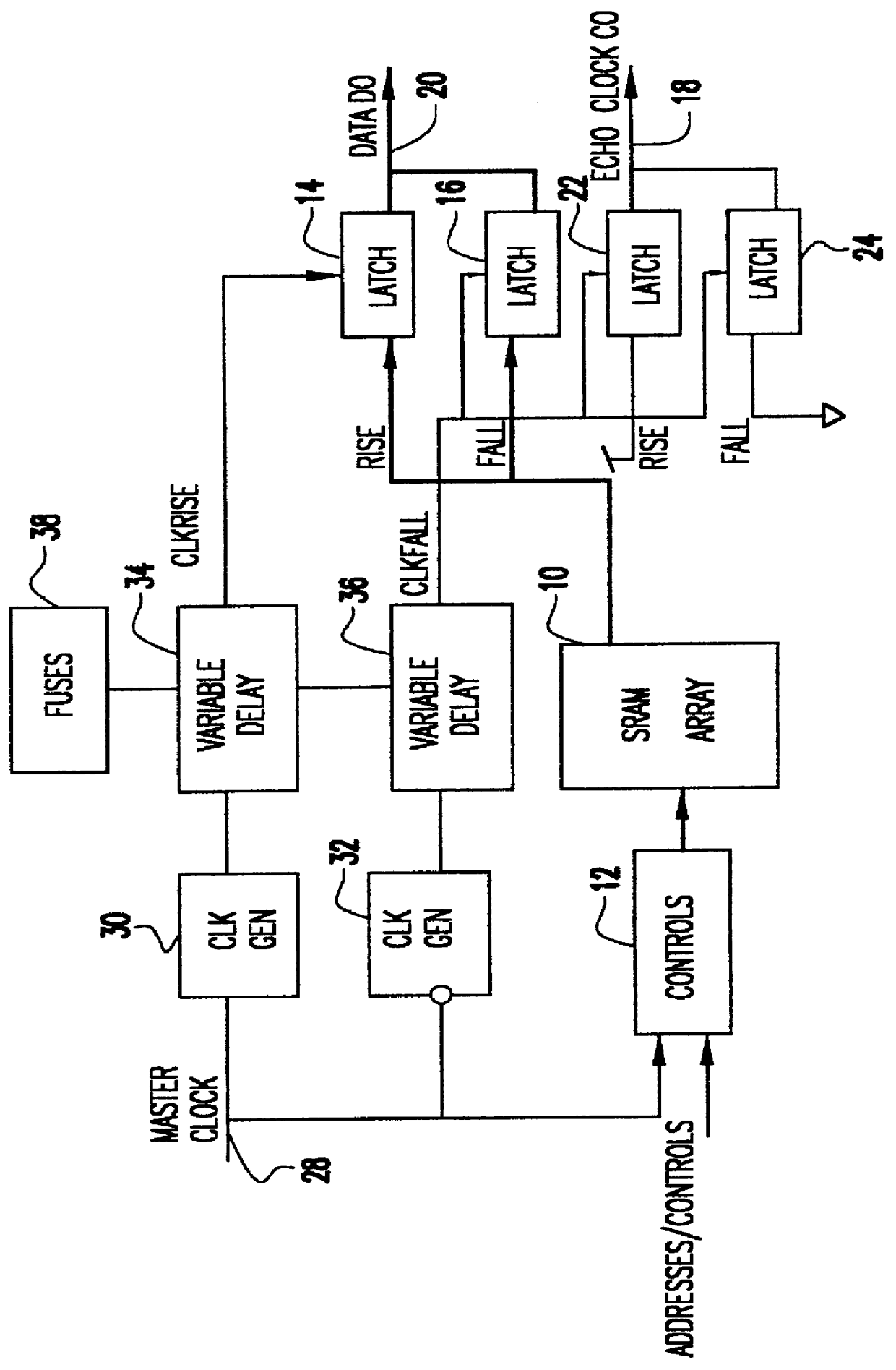
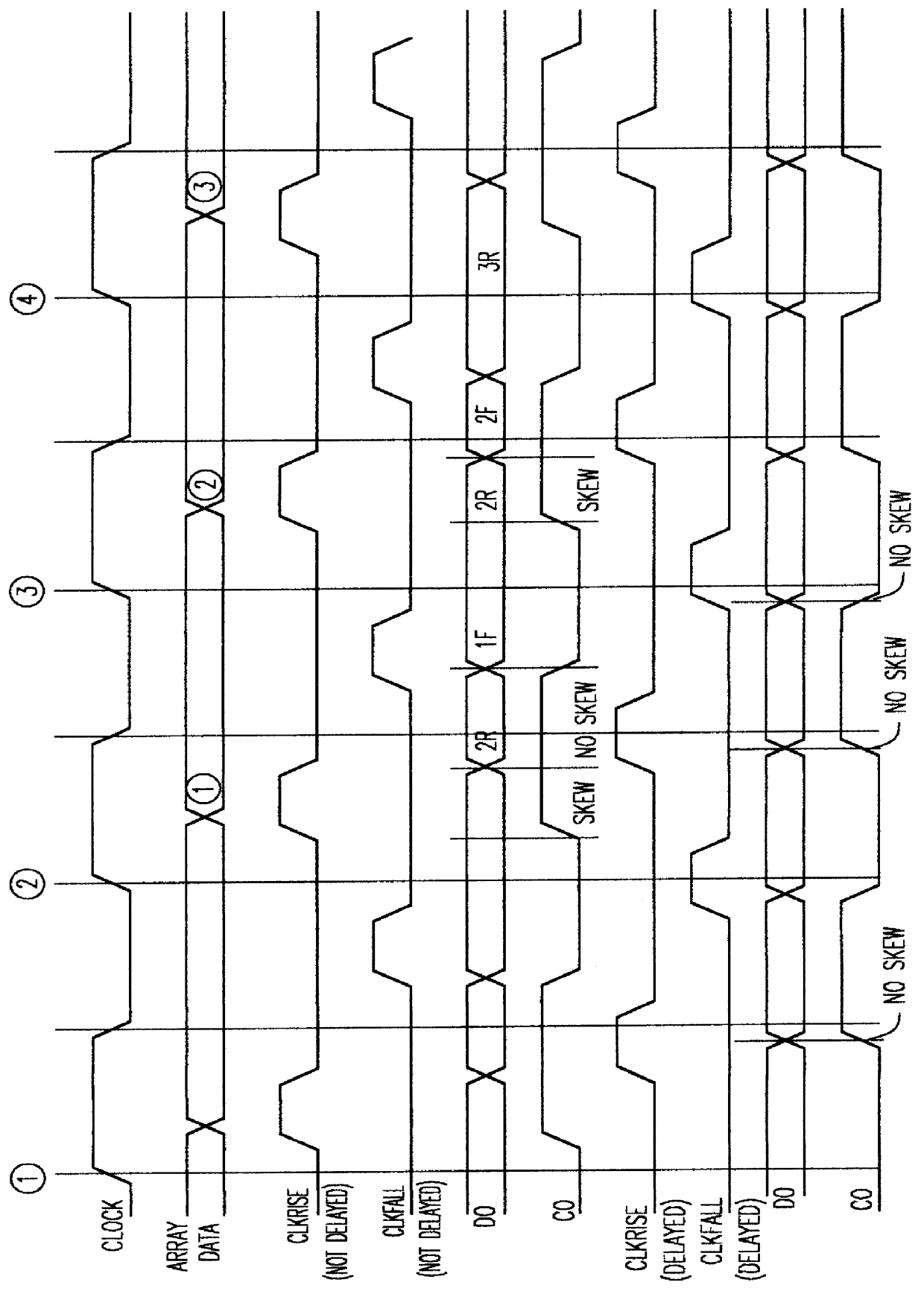
A comparator and variable delay circuit are provided to maintain the tracking between data and echo clocks in a double data rate (DDR)RAM device. This is accomplished by providing a global data signal (dummy data signal) that tracks with the actual memory array data. This global data signal is compared to the timing of the RAM clock (CLOCK) to determine a delay time between the two by which the pipeline clocks (CLKRISE / CLKFALL) must be delayed. As a result, the pipeline clocks are pushed out as needed so that they always transition after the array data arrives at the output latch. Therefore, as cycle time decreases, both echo clocks and data are pushed out identically and maintain their required tracking.
Owner:IBM CORP
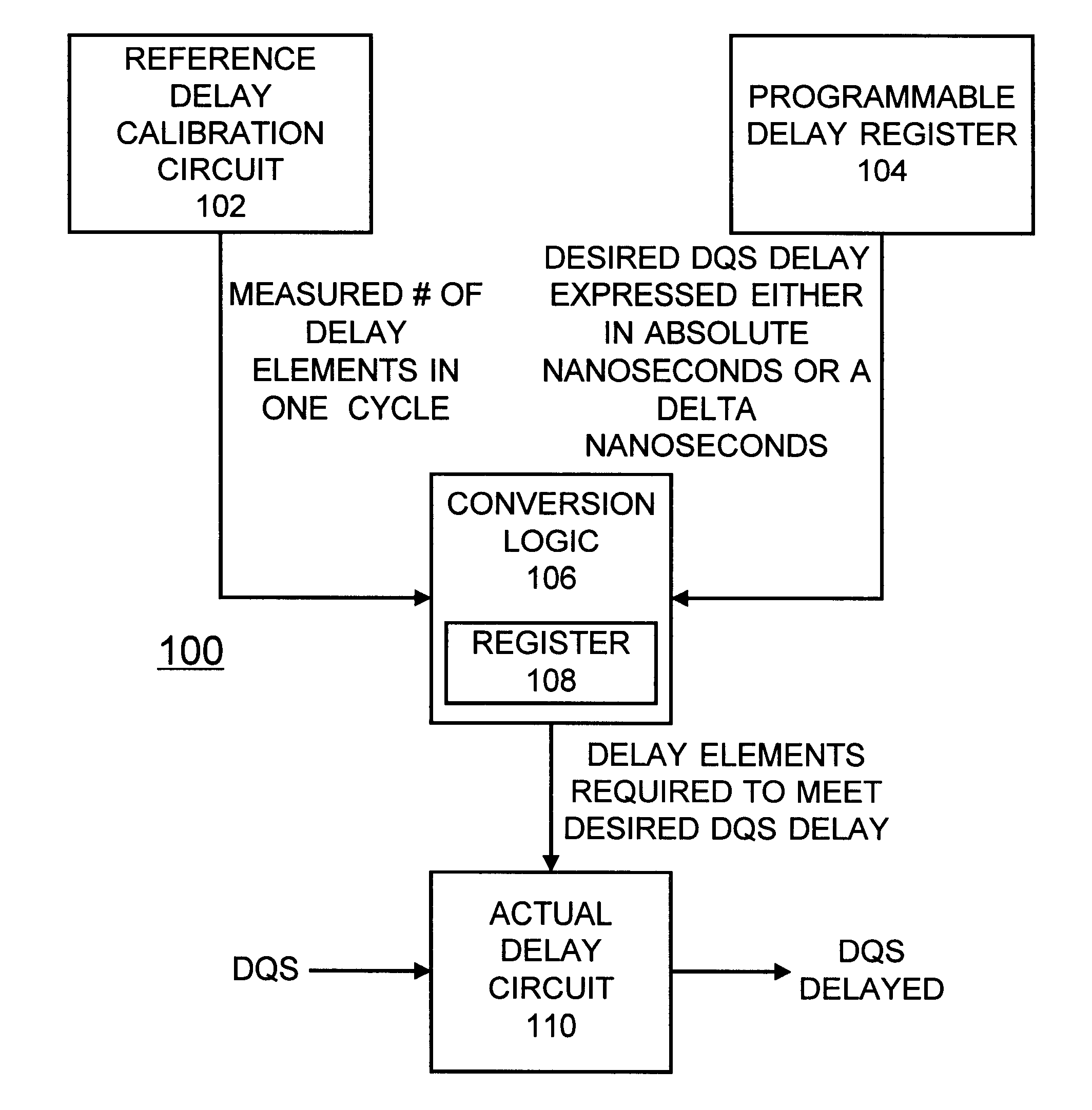
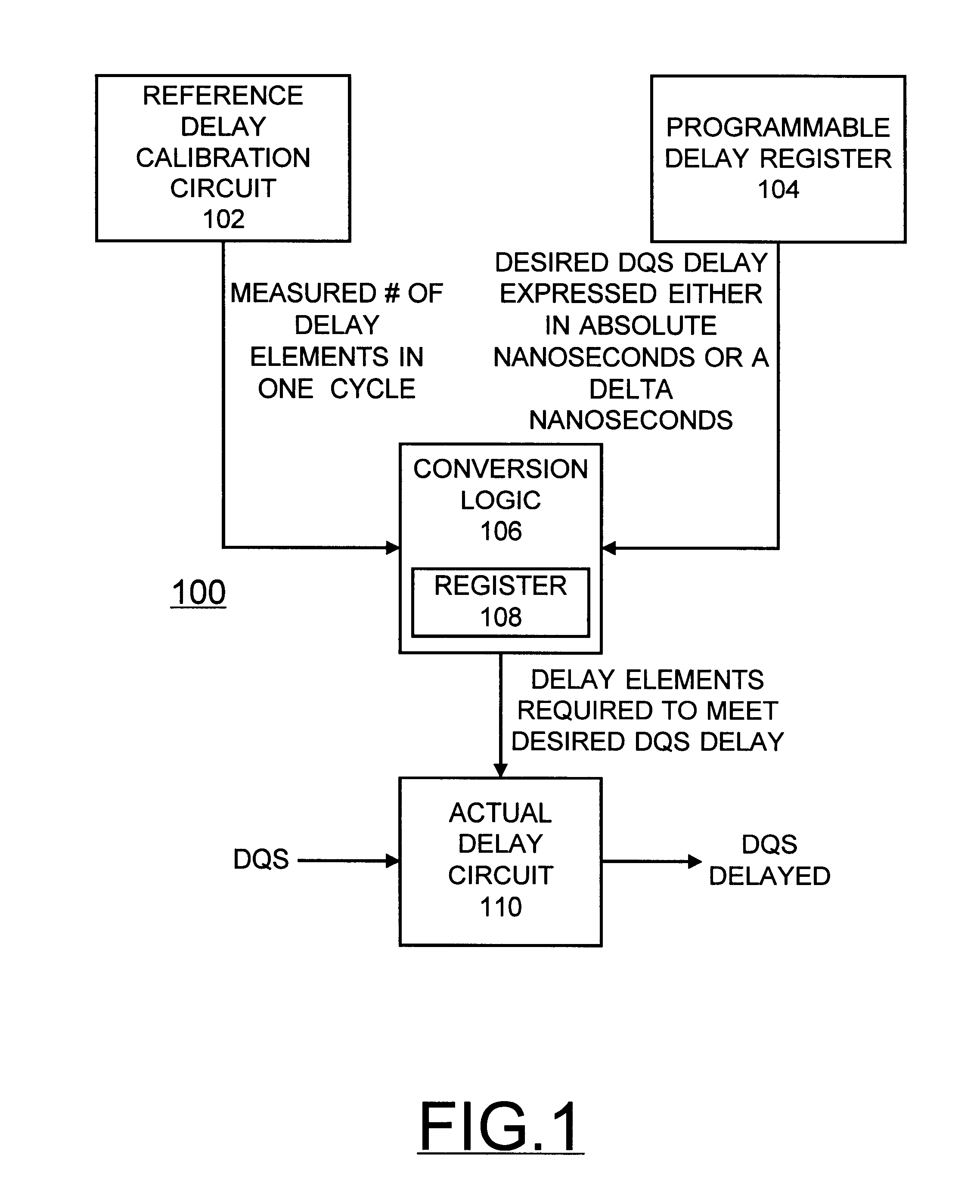
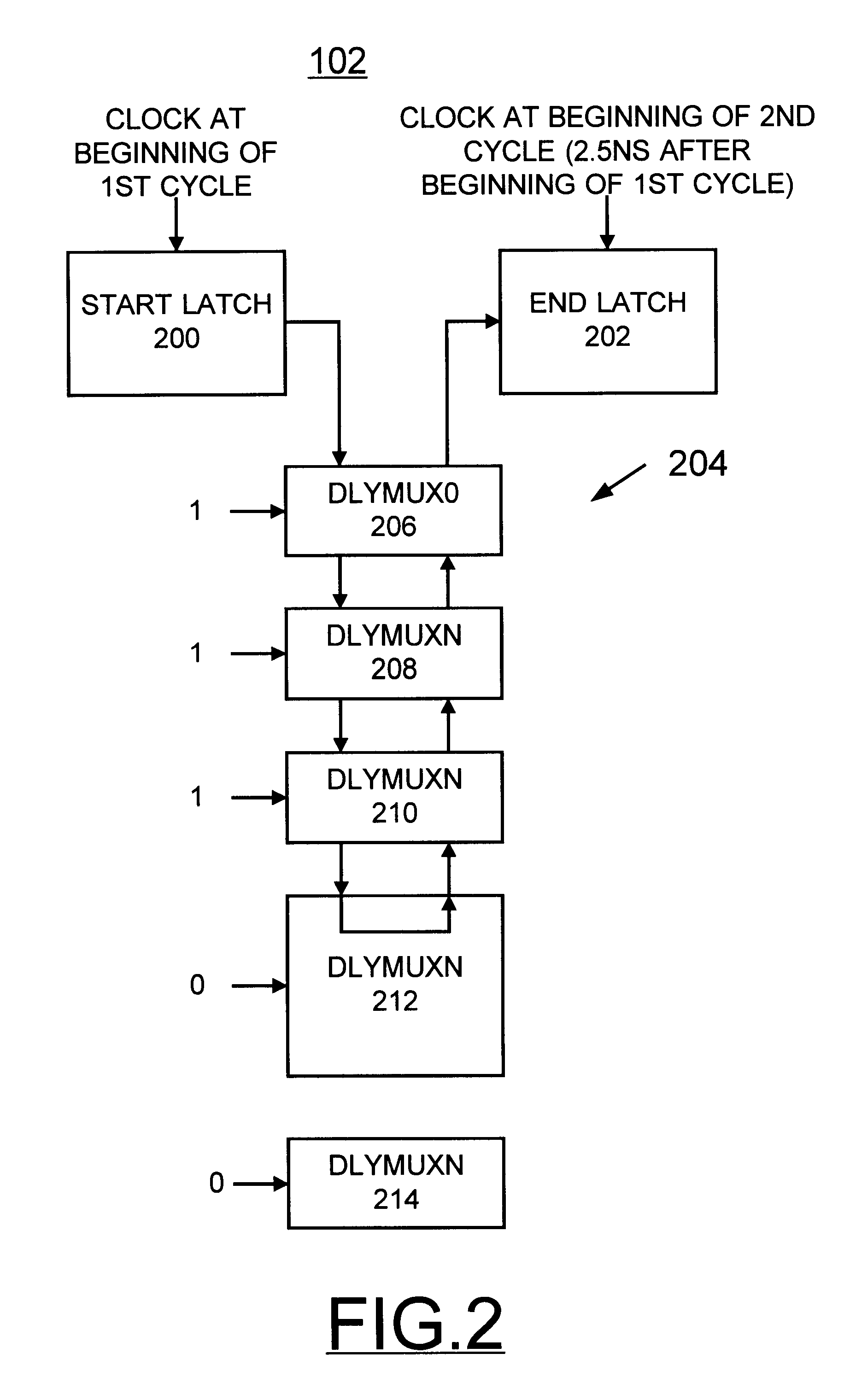
Programmable compensated delay for DDR SDRAM interface using programmable delay loop for reference calibration
A programmable compensated delay for a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) interface is provided. A programmable compensated delay apparatus includes a reference delay calibration circuit for providing a measured number of delay elements in one cycle. A programmable delay register provides a desired delay value. A conversion logic is coupled to the reference delay calibration circuit and the programmable delay register for receiving both the measured number of delay elements in one cycle and the desired delay value. The conversion logic provides a number of required delay elements. A delay circuit is coupled to the conversion logic for receiving the number of required delay elements and providing the desired delay. A SDRAM control logic provides a refresh start signal to the reference delay calibration circuit for updating the delay circuit during each DRAM refresh. The DQS clock strobe on the DDR SDRAM is applied to the delay circuit and is delayed by the desired delay.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
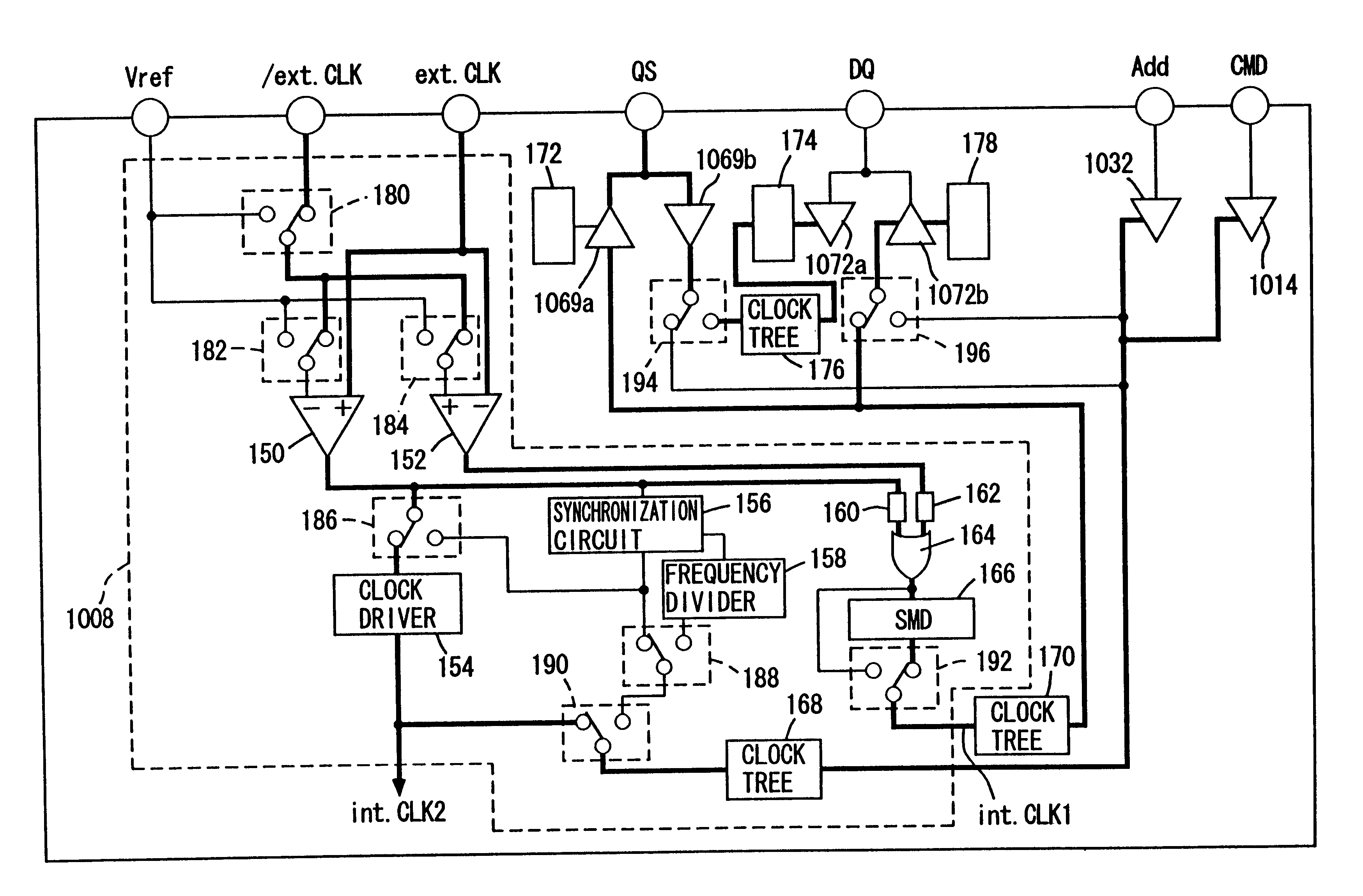
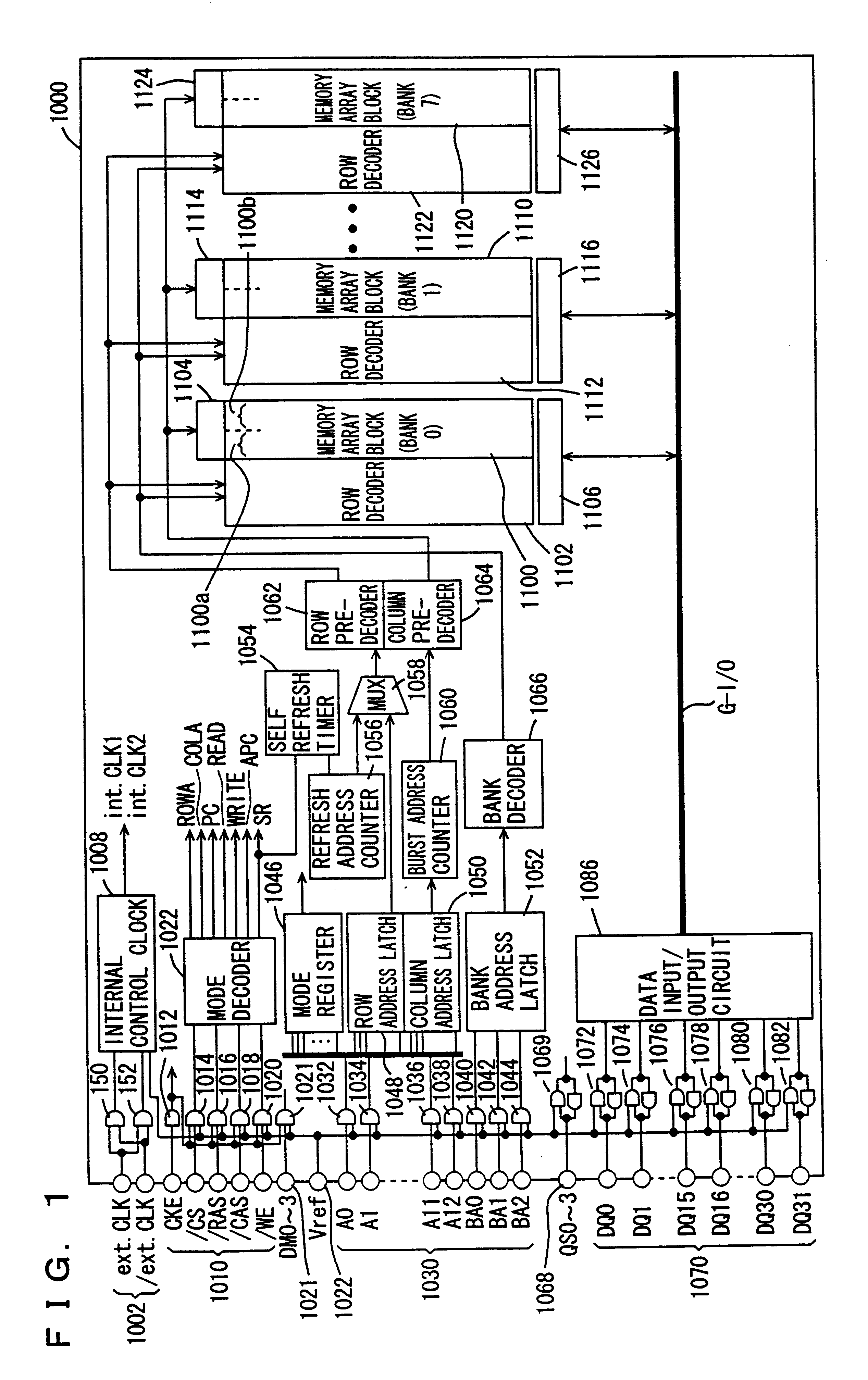
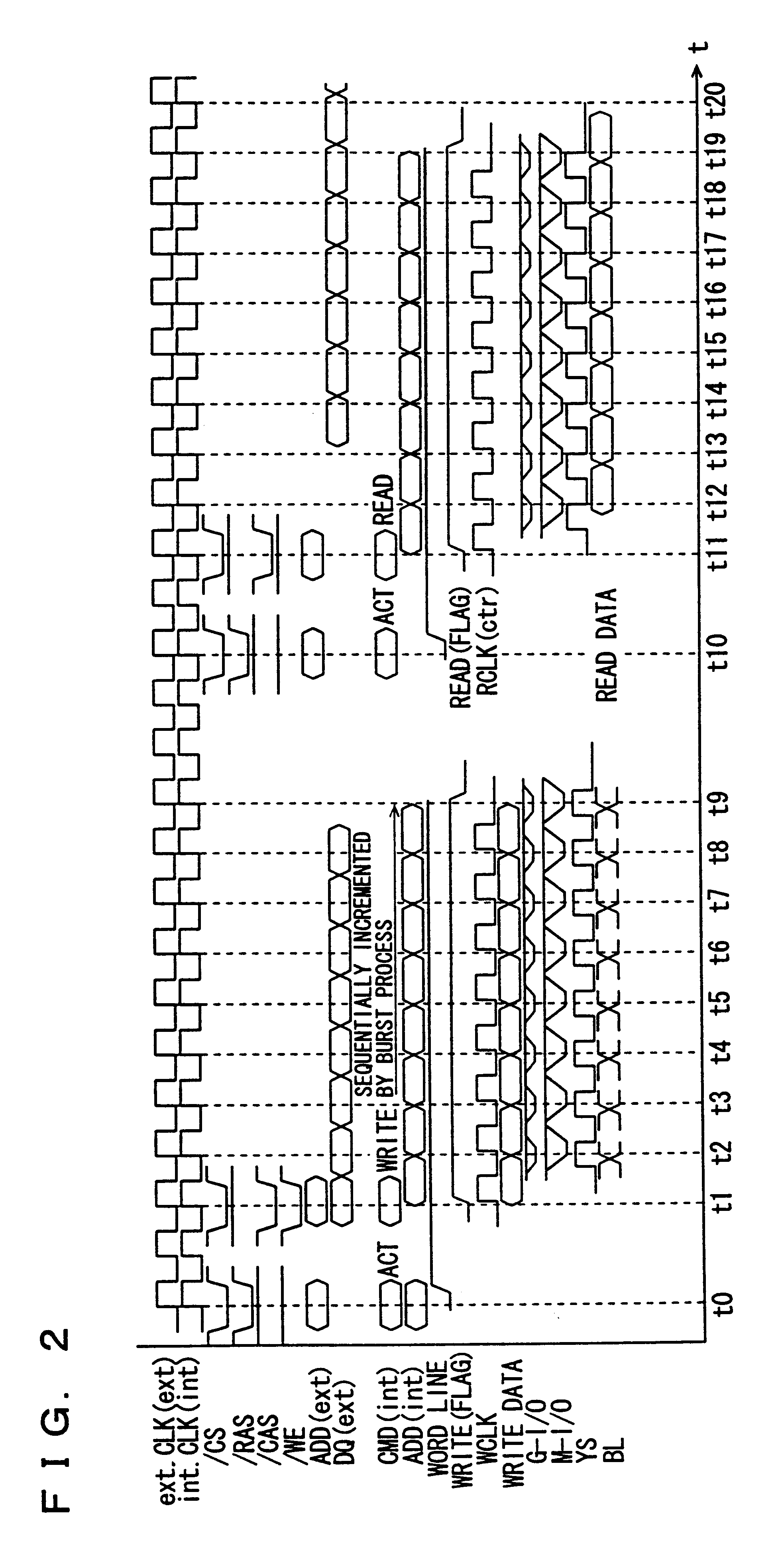
Synchronous double data rate DRAM
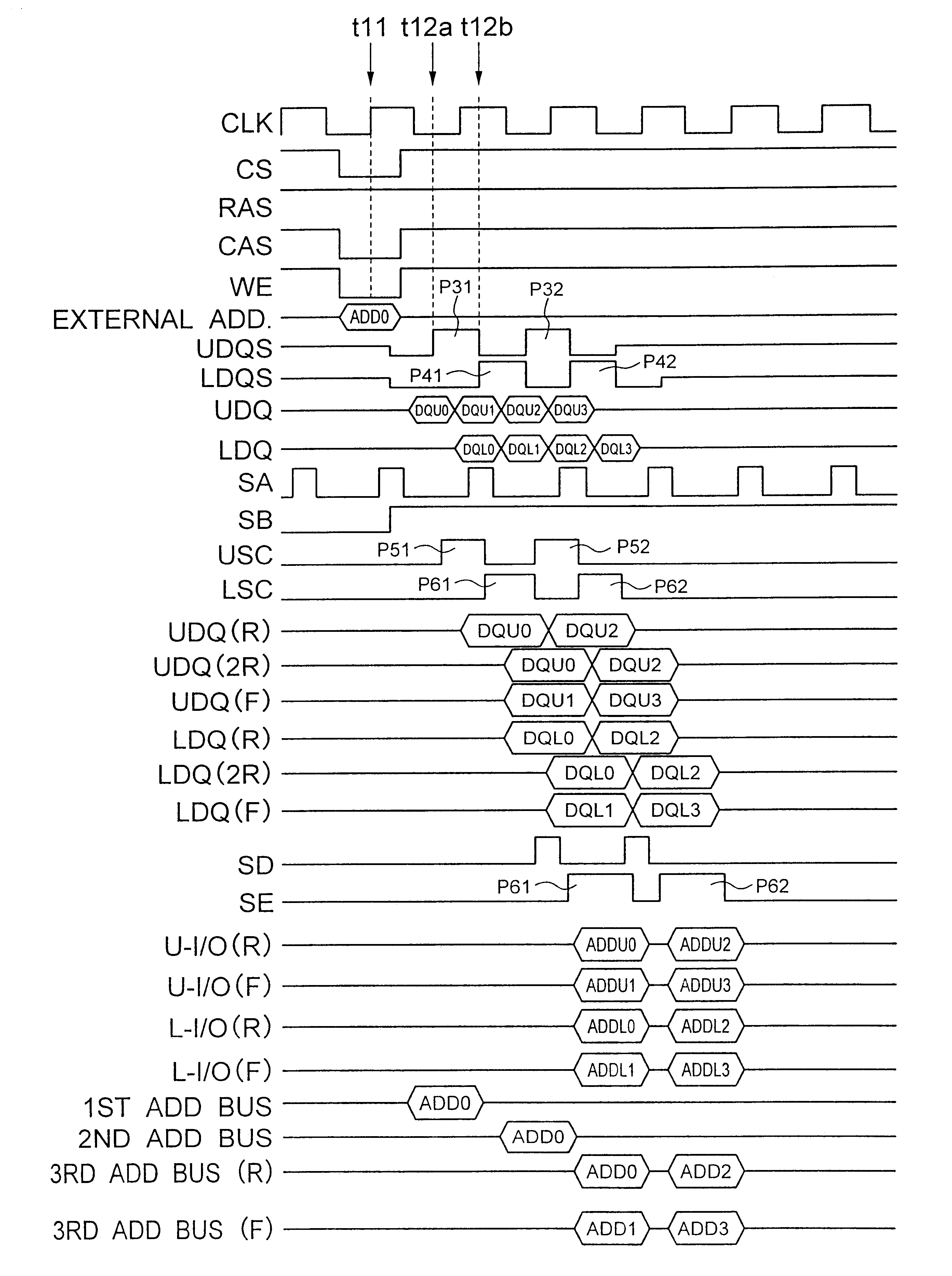
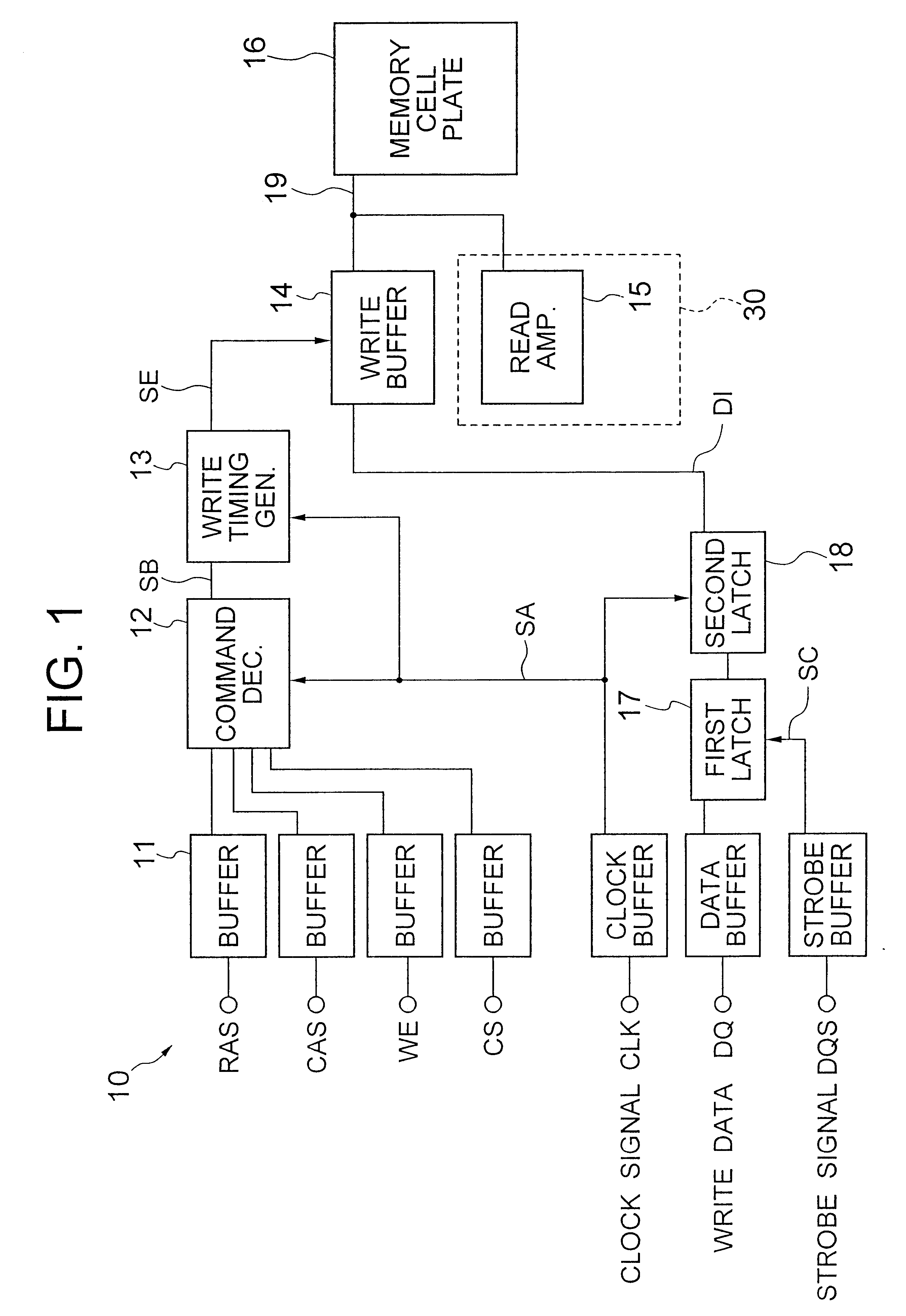
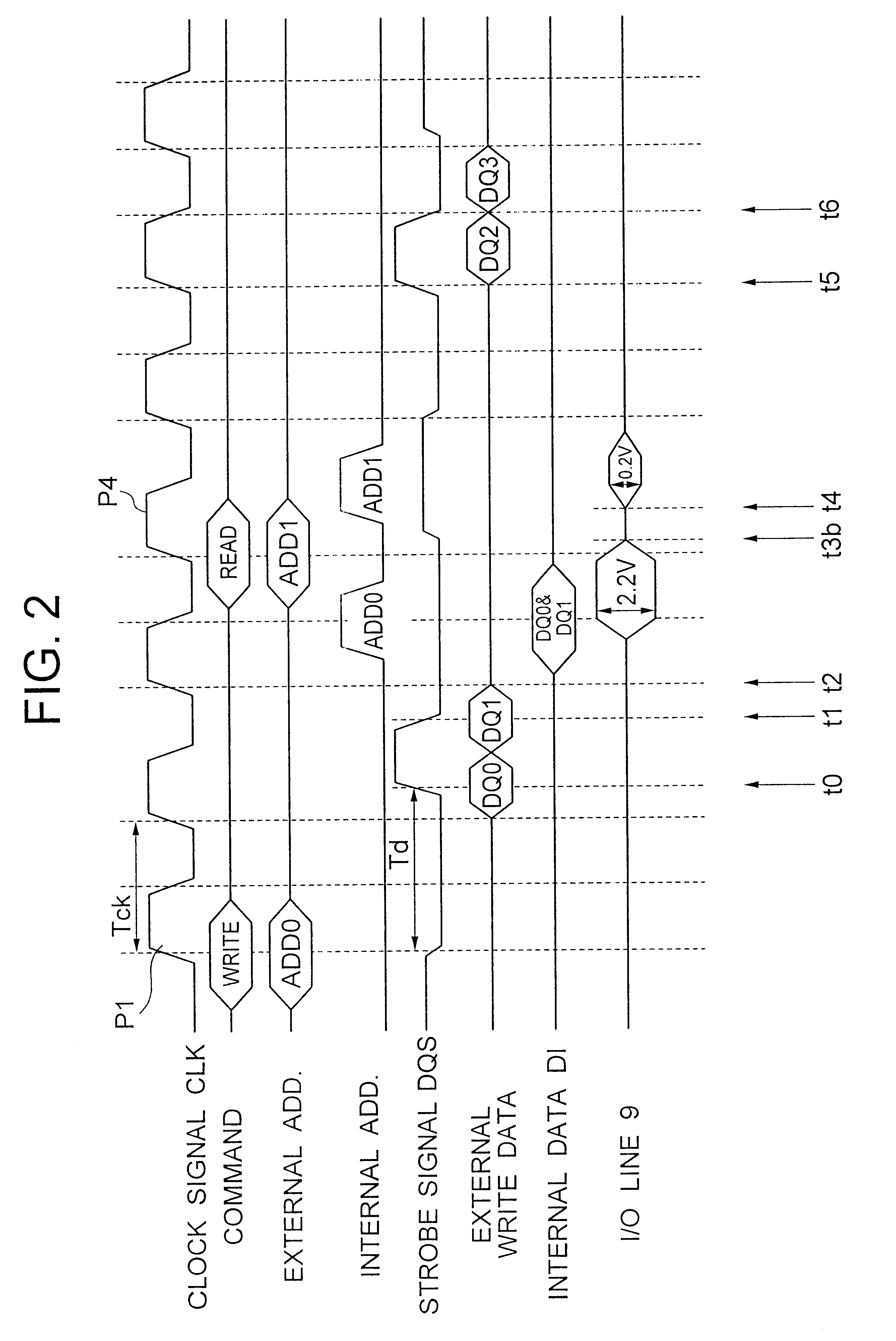
A DDR-SDRM includes a data write section including a latch section for latching first write data at a rising edge of a data strobe signal and second write data at a falling edge of the data strobe signal, and a write buffer section for writing the first write data and the second write data at a time based on the signals generated from the data strobe signal. A read operation is conducted based on the system clock signal.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
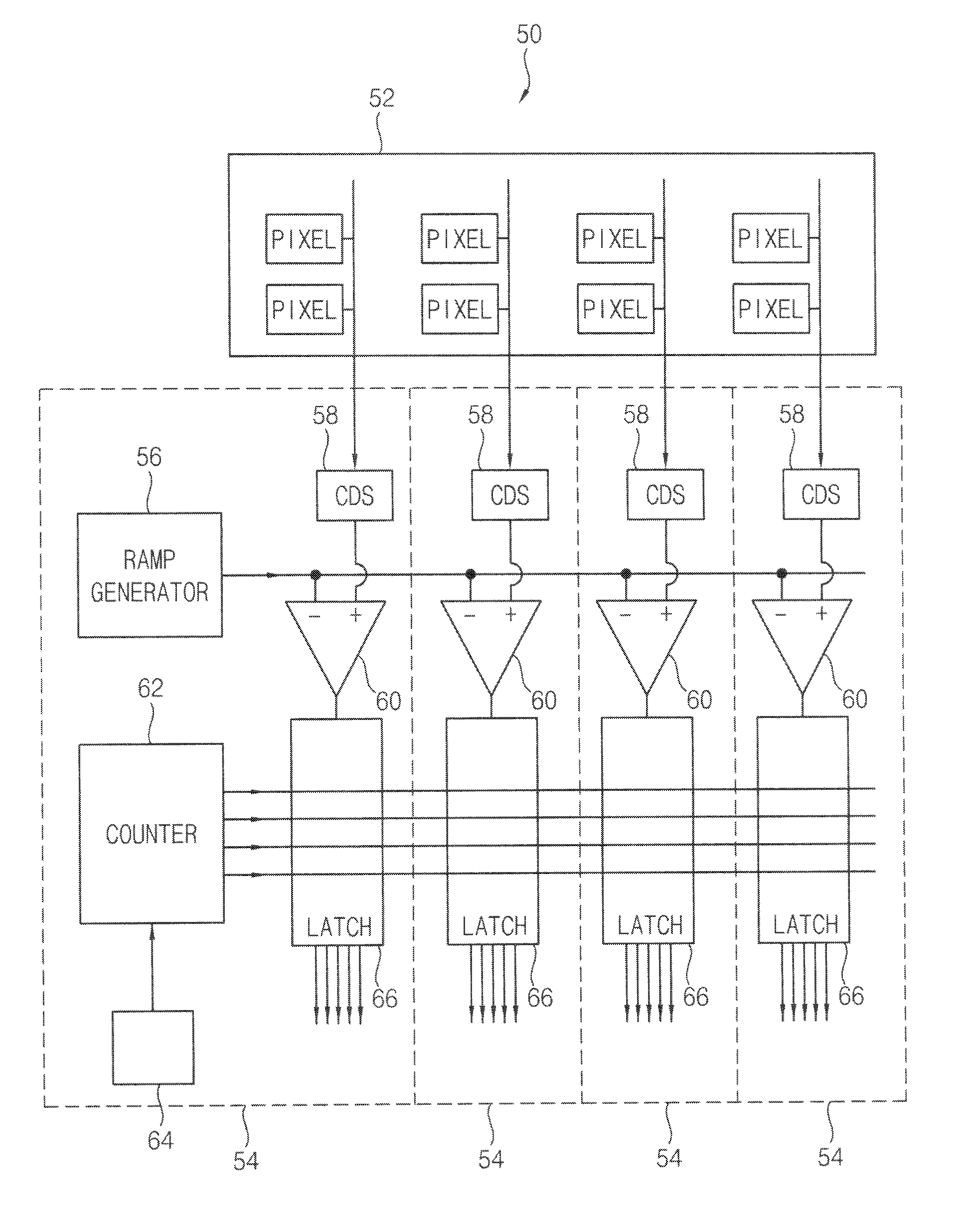
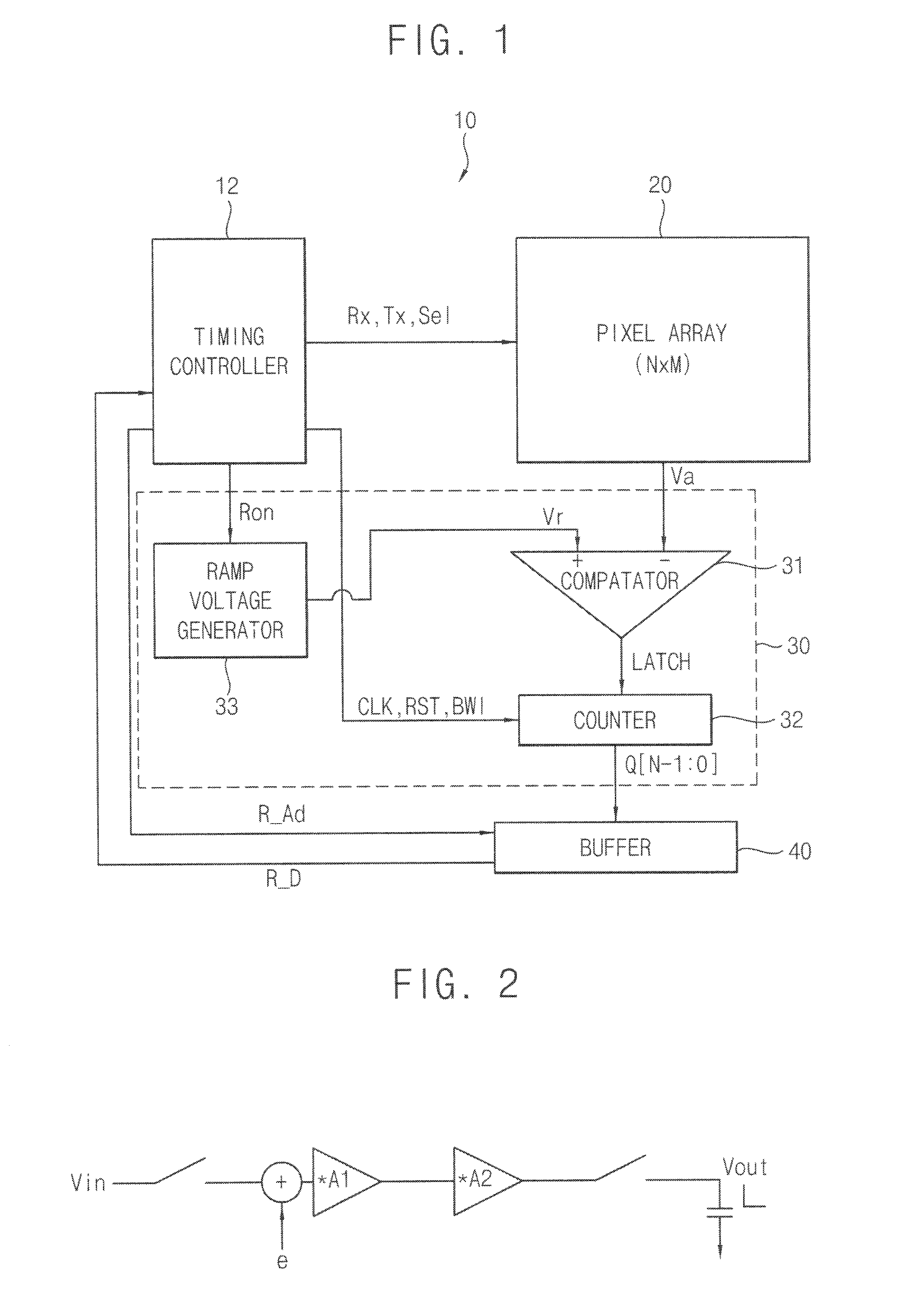
Double data rate (DDR) counter, analog-to-digital converter (ADC) using the same, CMOS image sensor using the same and methods in DDR counter, ADC and CMOS image sensor
InactiveUS20100225796A1Television system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsCMOSDouble data rate
In a double data rate (DDR) counter and counting method used in, for example, an analog-to-digital conversion in, for example, a CMOS image sensor and method, a first stage of the counter generates a least significant bit (LSB) of the value in the counter. The counter includes at least one second stage for generating another bit of the value in the counter. An input clock signal is applied to a data input of the first stage and a clock input of the second stage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
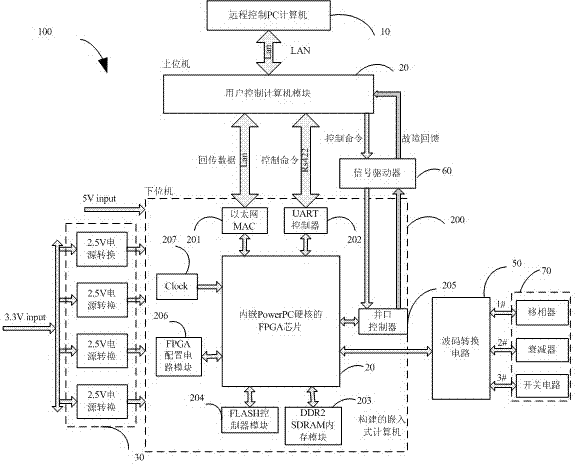
Phased array radar antenna beam control device
ActiveCN102495565AImprove reliabilityMeet developmentProgramme controlWave based measurement systemsDouble data rateUniversal asynchronous receiver/transmitter
The invention relates to a phased array radar antenna beam control device. The phased array radar antenna beam control device comprises a remote control PC (Personal Computer) computer, a user control computer module, a power supply management module, a FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) chip, a signal driver, a wave control conversion circuit and a controlled device which is electrically connected with the wave control conversion circuit, wherein the user control computer module remotely communicates with the remote control PC computer and are electrically connected with the FPGA chip, thepower supply management module and the wave control conversion circuit, respectively. The FPGA chip is embedded with a PowerPC hardcore and used for constructing an embedded computer; the embedded computer also comprises an Ethernet (Media Access Control), a UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) controller, a DDR2SDRAM (Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory) memory module, a FLASH controller module, a parallel controller, a FPGA configuration circuit module and a clock generating circuit module. The phased array radar antenna beam control device provided by the invention has the advantage of high reliability.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIC TECH GRP CORP NO 38 RES INST
Low output skew double data rate serial encoder
ActiveUS20080036631A1Reduce complexitySmall sizeParallel/series conversionDouble data rateMultiplexer
A Double Data Rate (DDR) serial encoder is provided. In one aspect, the DDR serial encoder includes a non-glitchless multiplexer and digital logic for ensuring a glitch-free encoder output. By using a non-glitchless multiplexer, the size and complexity of the encoder is significantly reduced. In another aspect, the DDR serial encoder has a single layer of logic between the final register stage and the encoder output and a reduced number of paths from the final register stage to the encoder output, thereby resulting in reduced output skew and increased link rate.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
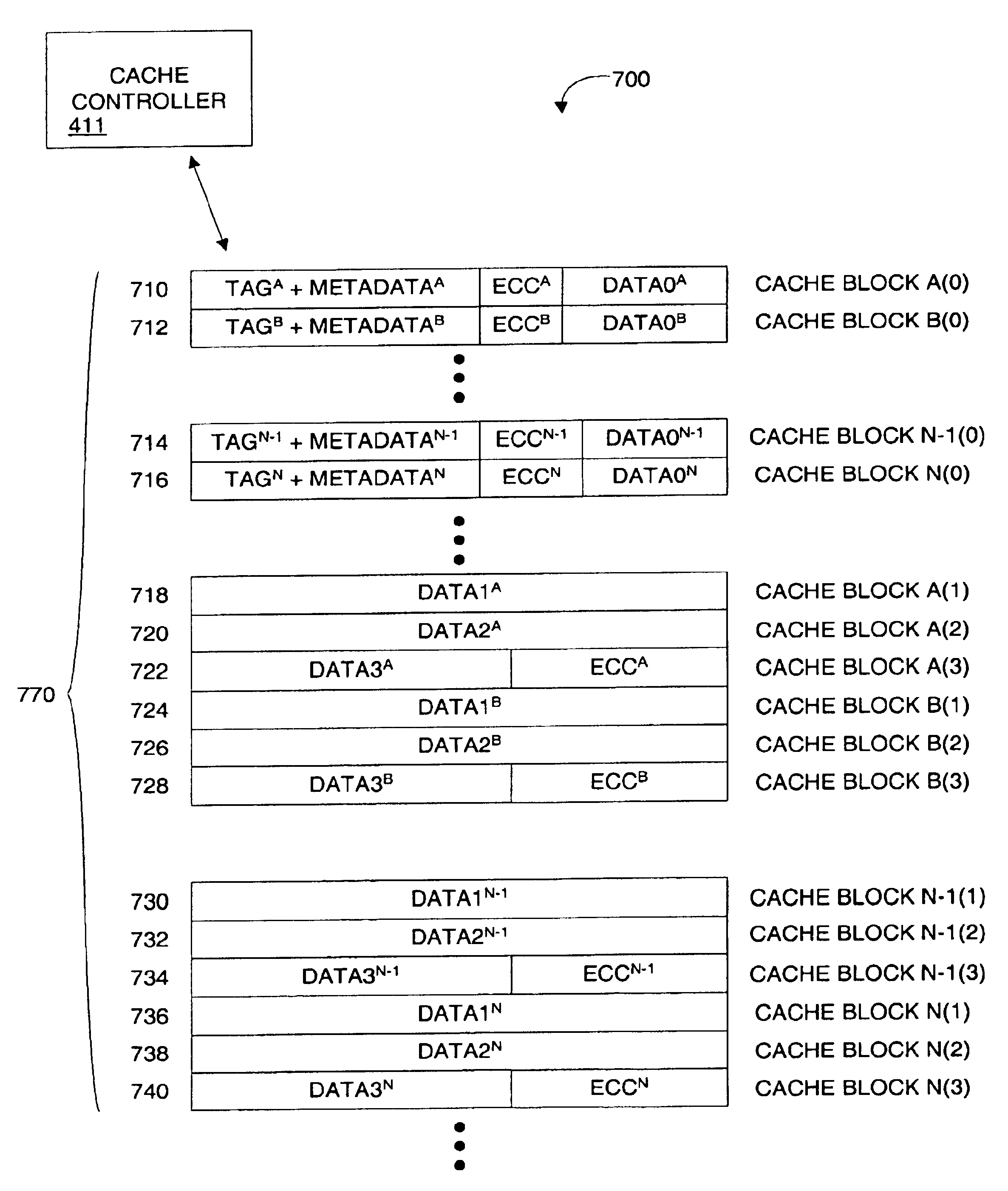
N-way set-associative external cache with standard DDR memory devices
InactiveUS6912628B2Increasing snoop bandwidthHigh bandwidthMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDouble data rateBurst transmission
A method, cache system, and cache controller are provided. A two-way and n-way cache organization scheme are presented as at least two embodiments of a set-associative external cache that utilizes standard burst memory devices such as DDR (double data rate) memory devices. The set-associative cache organization scheme is designed to fully utilize burst efficiencies during snoop and invalidation operations. Cache lines are interleaved in such a way that a first burst transfer from the cache to the cache controller brings in a plurality of tags.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
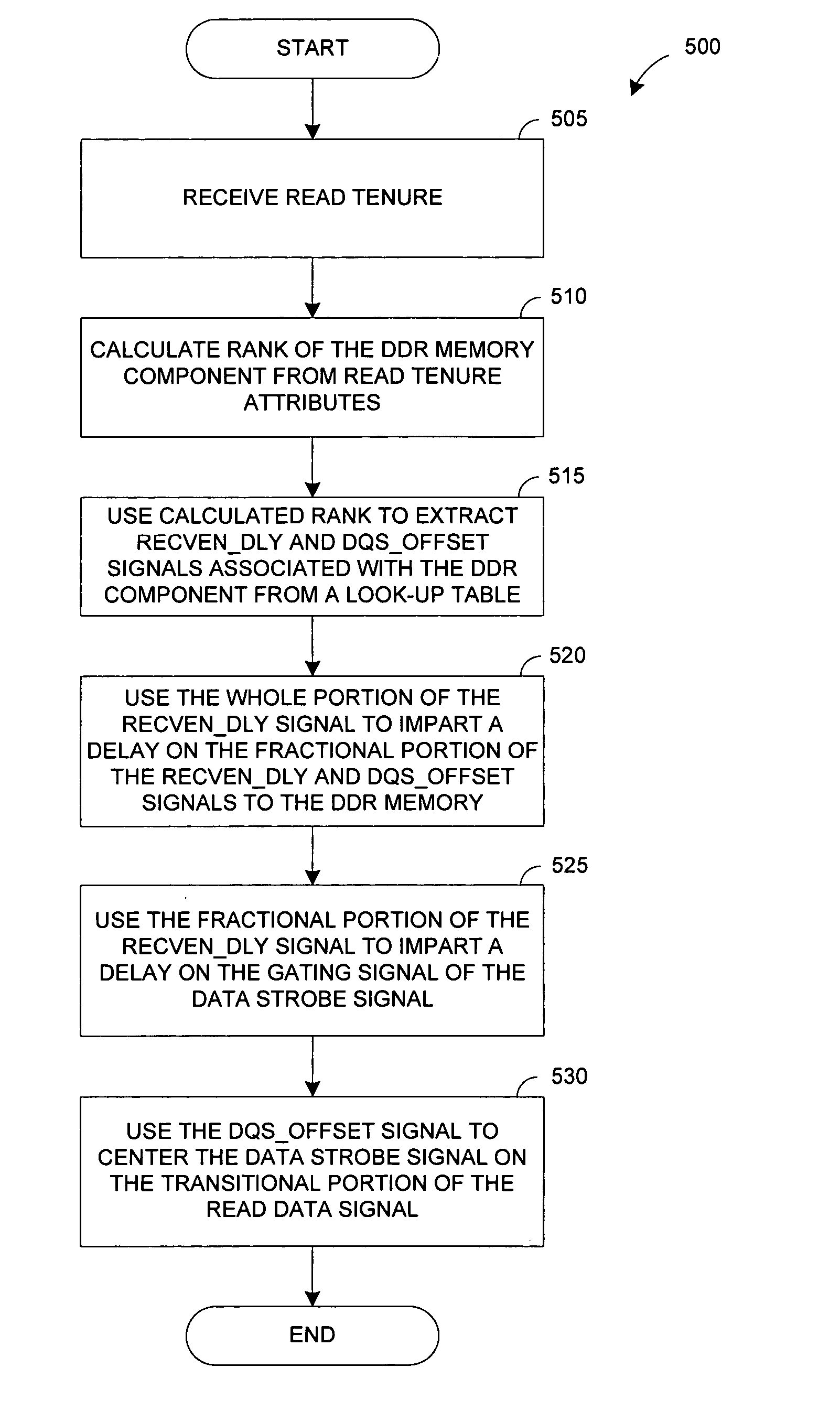
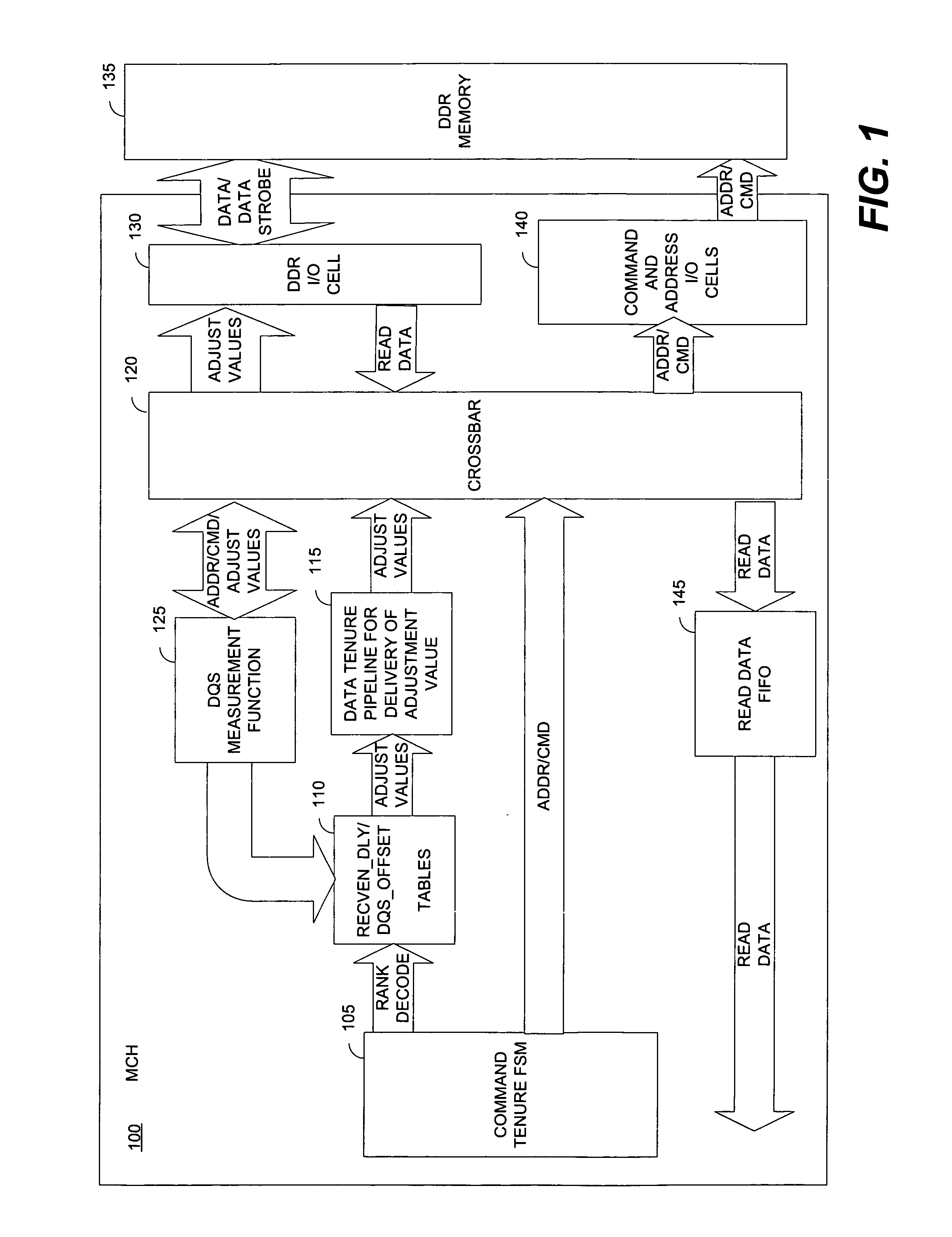
System and method for dynamic rank specific timing adjustments for double data rate (DDR) components
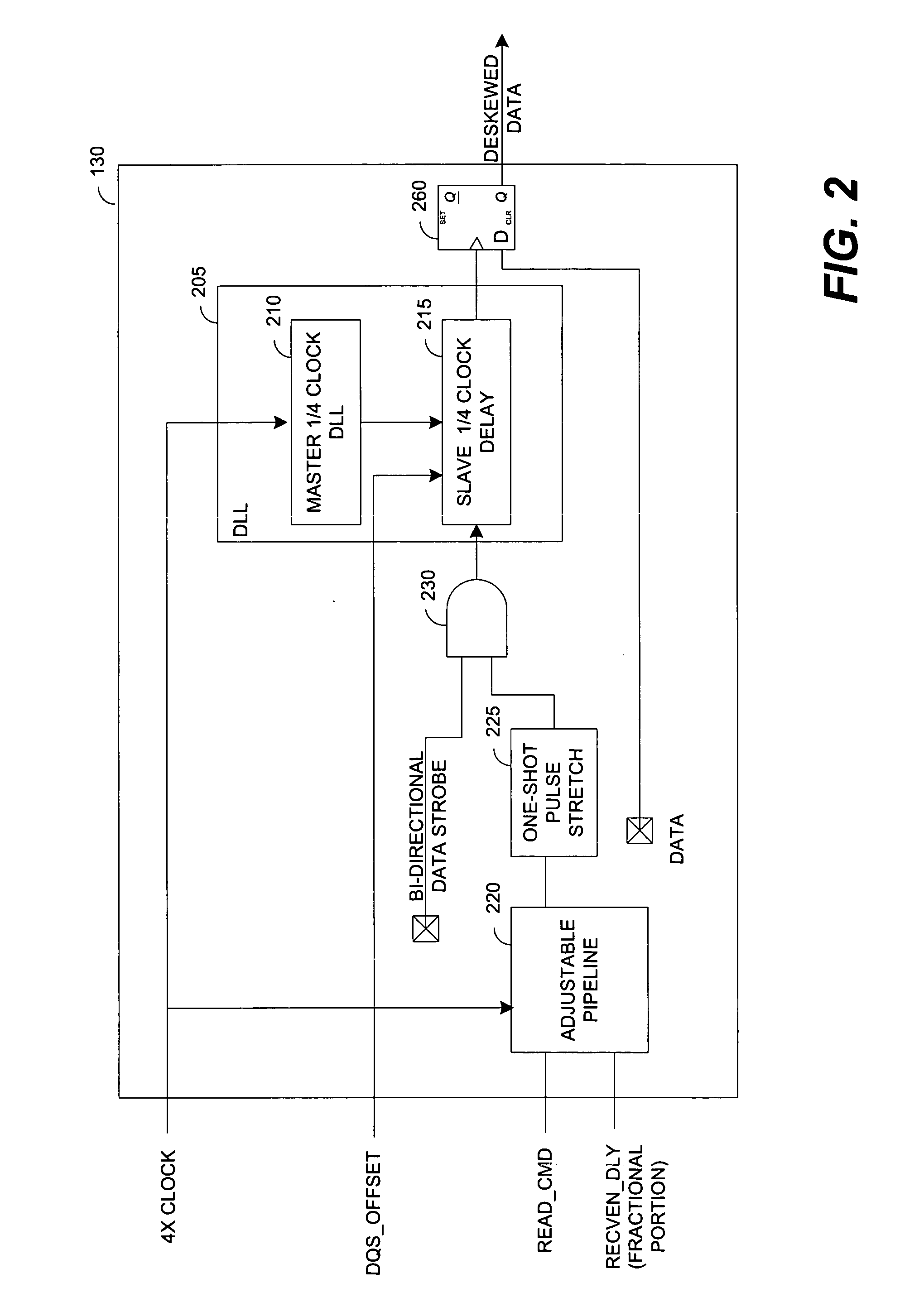
In some embodiments, a system and method for making rank-specific adjustments to the READ tenure parameters of a double data-rate (DDR) memory component to improve the DDR bus timing margins. When a READ tenure is encountered for the DDR memory component, the rank of the DDR memory component is calculated and the value is used to retrieve two adjustment signals, which are specific to the DDR memory component, from the look up table. One of the adjustment signals is used to adjust a gating signal for the data strobe signal of the component. The other adjustment signal is used to fine tune a required ¼ clock delay for the data strobe signal to read the data from the DDR memory component while adjusting for the inherent latency of the DDR memory component. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Memory interface system and method for reducing cycle time of sequential read and write accesses using separate address and data buses
ActiveUS7142477B1Improve data throughputImprove throughputDigital storageDouble data rateMemory interface
A memory interface system and method are provided for transferring data between a memory controller and an array of storage elements. The storage elements are preferably SRAM elements, and the memory interface is preferably one having separate address bus paths and separate data bus paths. One address bus path is reserved for receiving read addresses and the other address bus path is reserved for receiving write addresses. One of the data bus paths is reserved for receiving read data from the array, and the other data bus path is reserved for receiving data written to the array. While bifurcating the address and data bus paths within the interface is transparent to the memory controller, the separate paths afford addressing phases of a read and write address operation to be partially overlapped, as well as the data transfer phases. This will essentially reduce the cycle time between a read and write memory access, and proves useful when maximizing the data throughput across the data bus when implementing double data rate (QDR) mechanisms.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
Operable synchronous semiconductor memory device switching between single data rate mode and double data rate mode
A synchronous semiconductor memory device operates an input / output buffer circuit in synchronization with an external clock signal in a single data rate SDRAM operation mode. In a double data rate SDRAM operation mode, an internal clock signal of a frequency two times that of the external clock signal is generated. The input / output buffer circuit is operated in synchronization with the internal clock signal.
Owner:DRAM MEMORY TECH
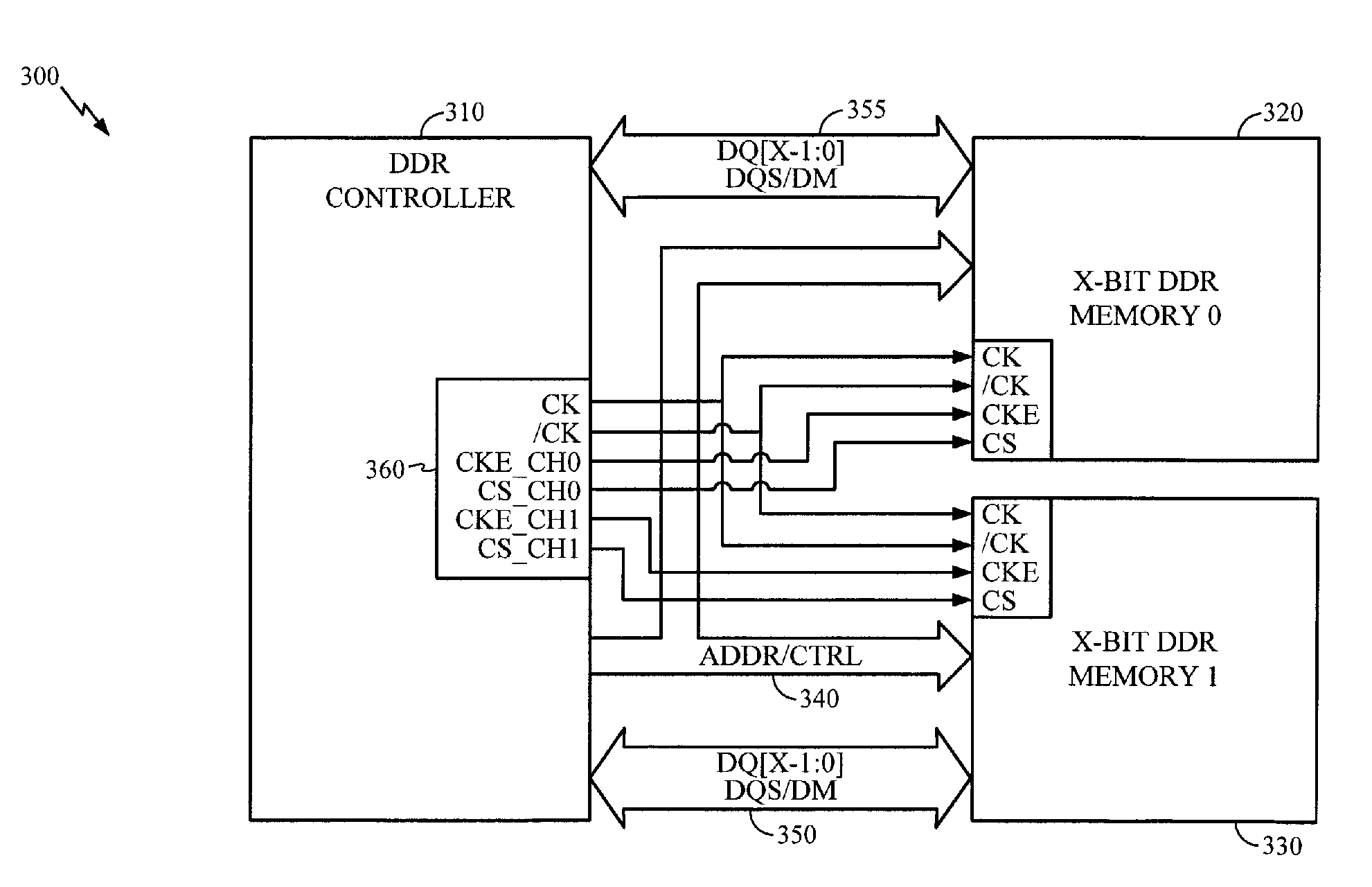
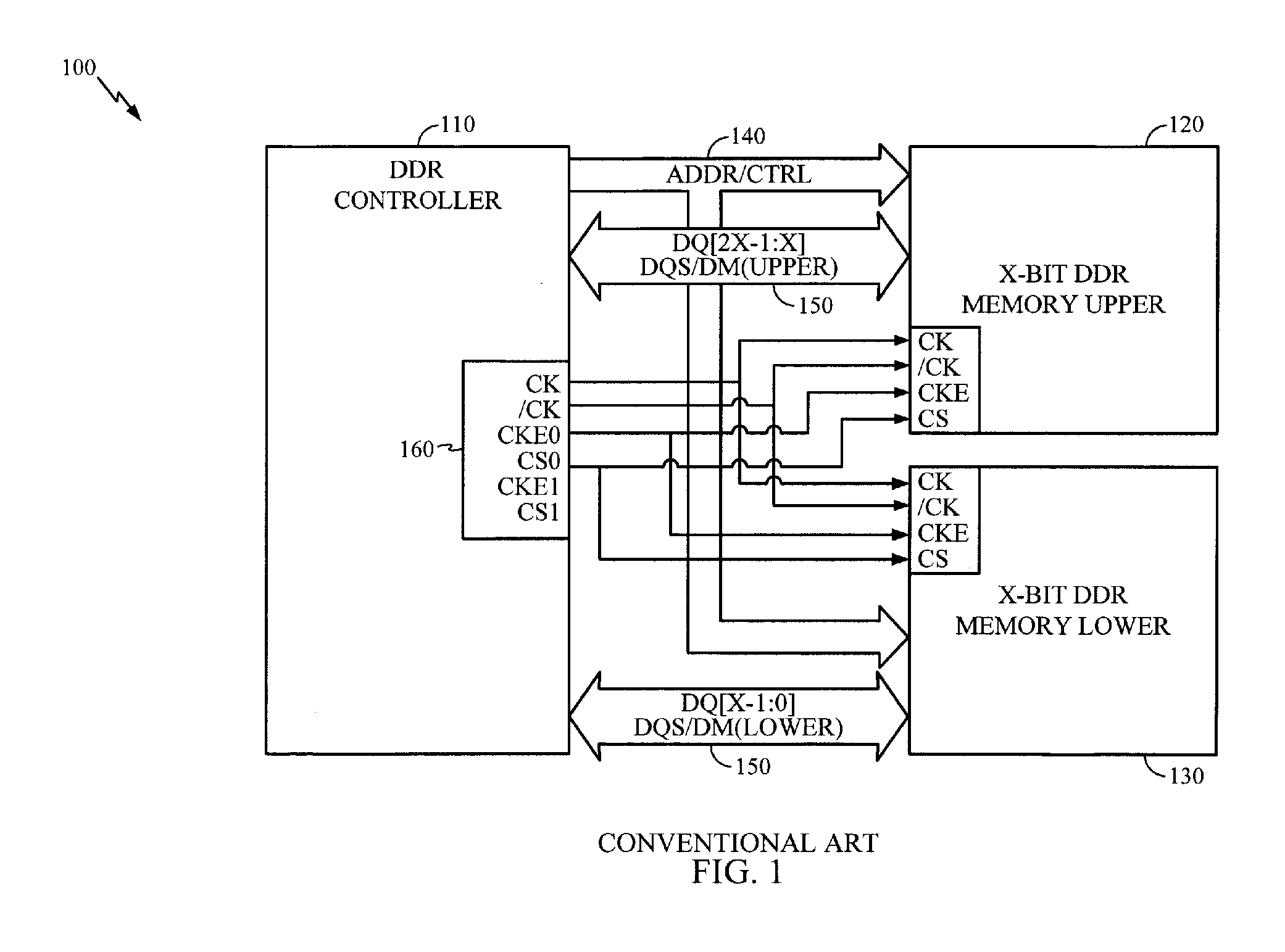
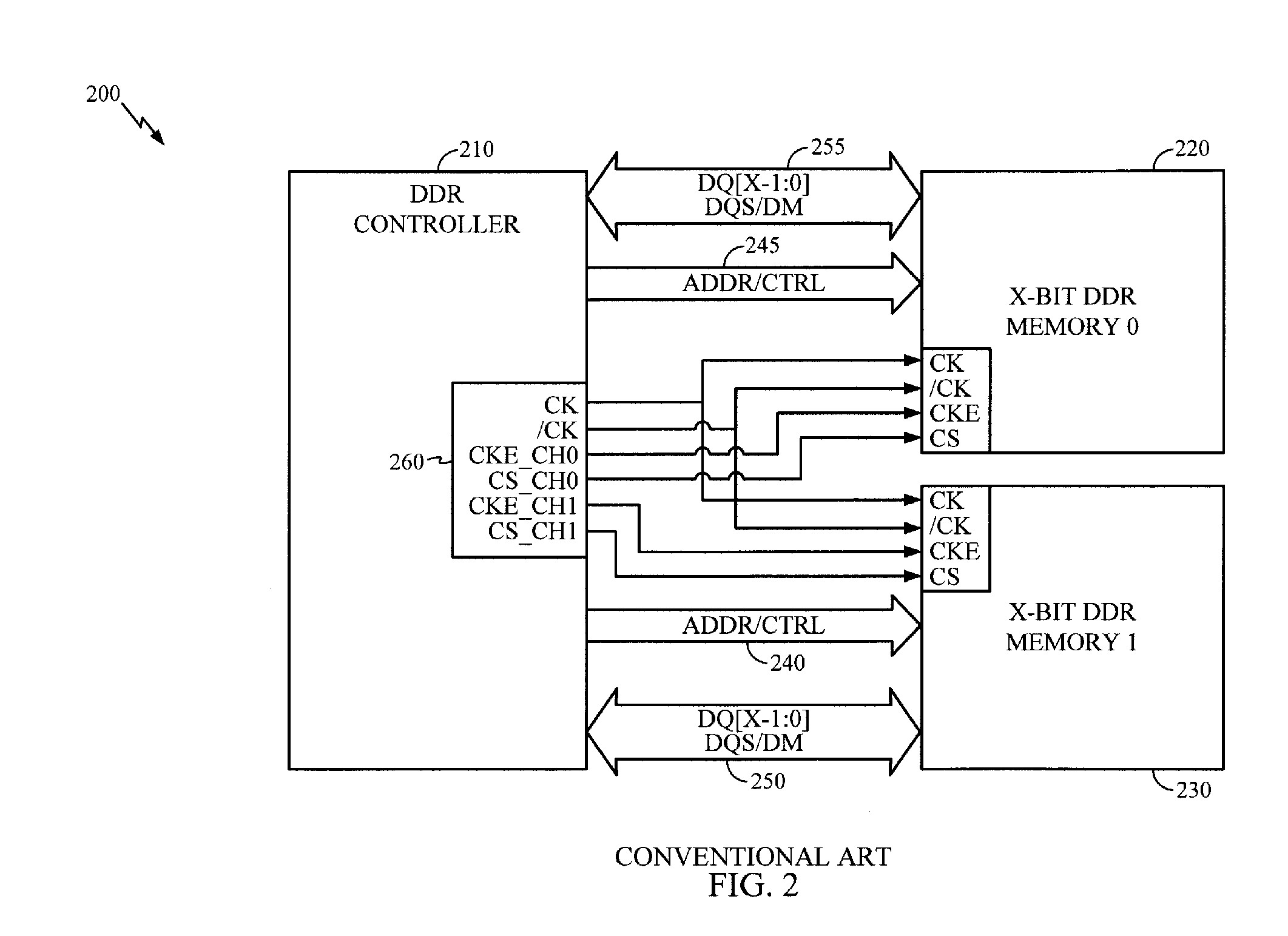
Dual Channel Memory Architecture Having a Reduced Interface Pin Requirements Using a Double Data Rate Scheme for the Address/Control Signals
Apparatuses and methods for dual channel memory architecture with reduced interface pin requirements are presented. One memory architecture includes a memory controller, a first memory device coupled to the memory controller by a shared address bus and a first clock signal, and a second memory device coupled to the memory controller by the shared address bus and a second clock signal, where the polarity of the second clock signal is opposite of the first clock signal. A method for performing data transactions is presented. The method includes providing addressing signals over a shared address bus to a first memory device and a second memory device, providing clock signals to the memory devices which are reversed in polarity, where the clock signals are derived from a common clock signal, and transferring data to the memory devices over separate narrow data buses in an alternating manner based upon the clock signals.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
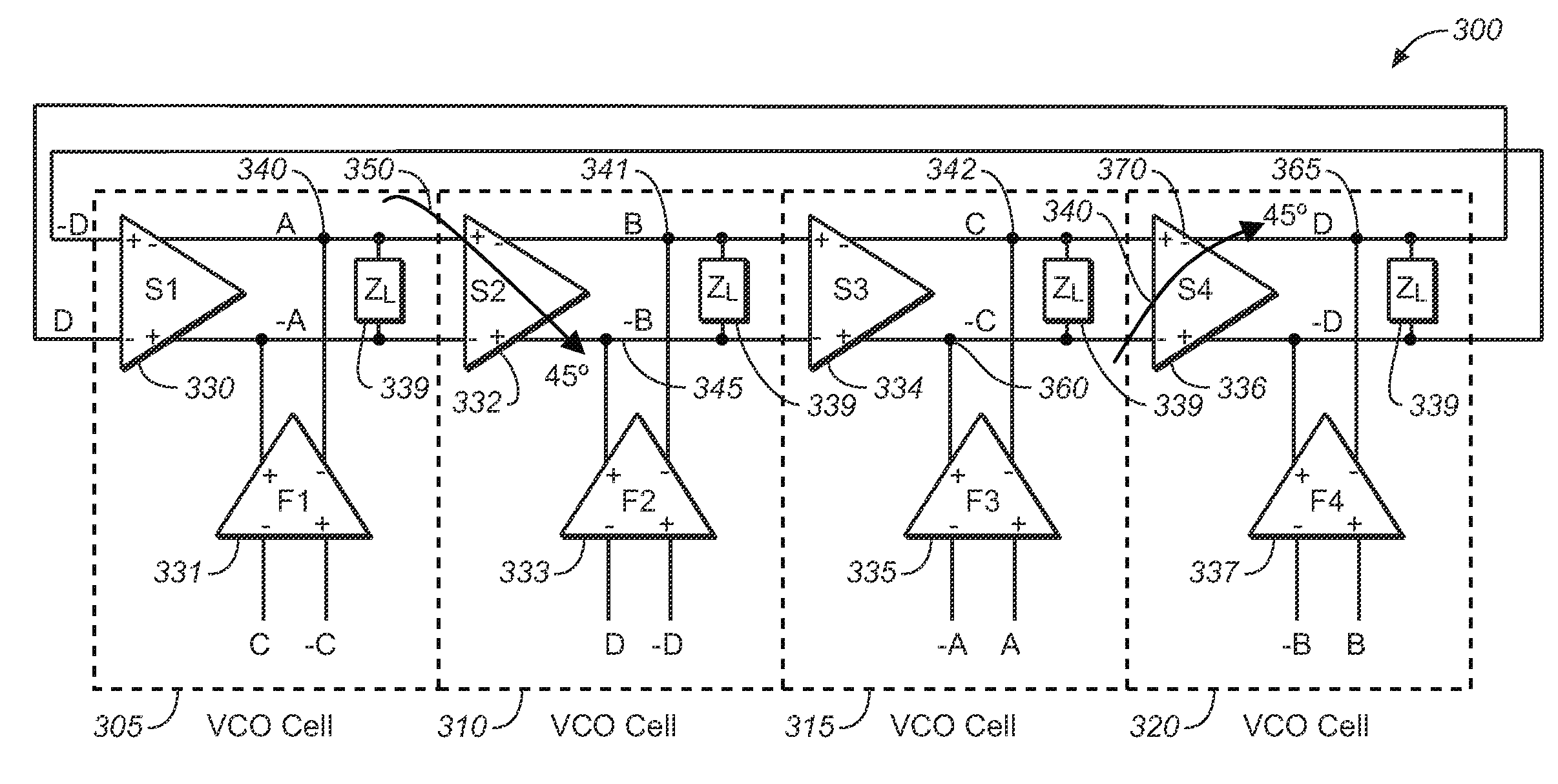
System and method for phase-locked loop (PLL) for high-speed memory interface (HSMI)
ActiveUS7659783B2Optimize allocationMeet the blocking requirementsPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationLoop filterDouble data rate
A phase-locked loop (PLL) to provide clock generation for high-speed memory interface is presented as the innovate PLL (IPLL). The IPLL architecture is able to tolerate external long loop delay without deteriorating jitter performance. The IPLL comprises in part a common mode feedback circuit with a current mode approach, so as to minimize the effects of mismatch in charge-pump circuit, for instance. The voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) of the IPLL is designed using a mutually interpolating technique generating a 50% duty clock output, beneficial to high-speed double data rate applications. The IPLL further comprises loop filter voltages that are directly connected to each VCO cell of the IPLL. Conventional voltage-to-current (V-I) converter between loop filter and VCO is hence not required. A tight distribution of VCO gain curves is therefore obtained for the present invention across process corners and varied temperatures.
Owner:MICREL
Echo clock on memory system having wait information
A method and a circuit configuration for implementing a double data rate feature in a memory device capable of operating in a variable latency mode. The memory device may utilize a WAIT_DQS signal that combines functionality of a WAIT signal indicating when valid data is present on a data bus in Read cycle and the memory is ready to accept data in Write cycle, and a data strobe (DQS) signal.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS LTD
Forward and reverse link channels dynamic processing gain
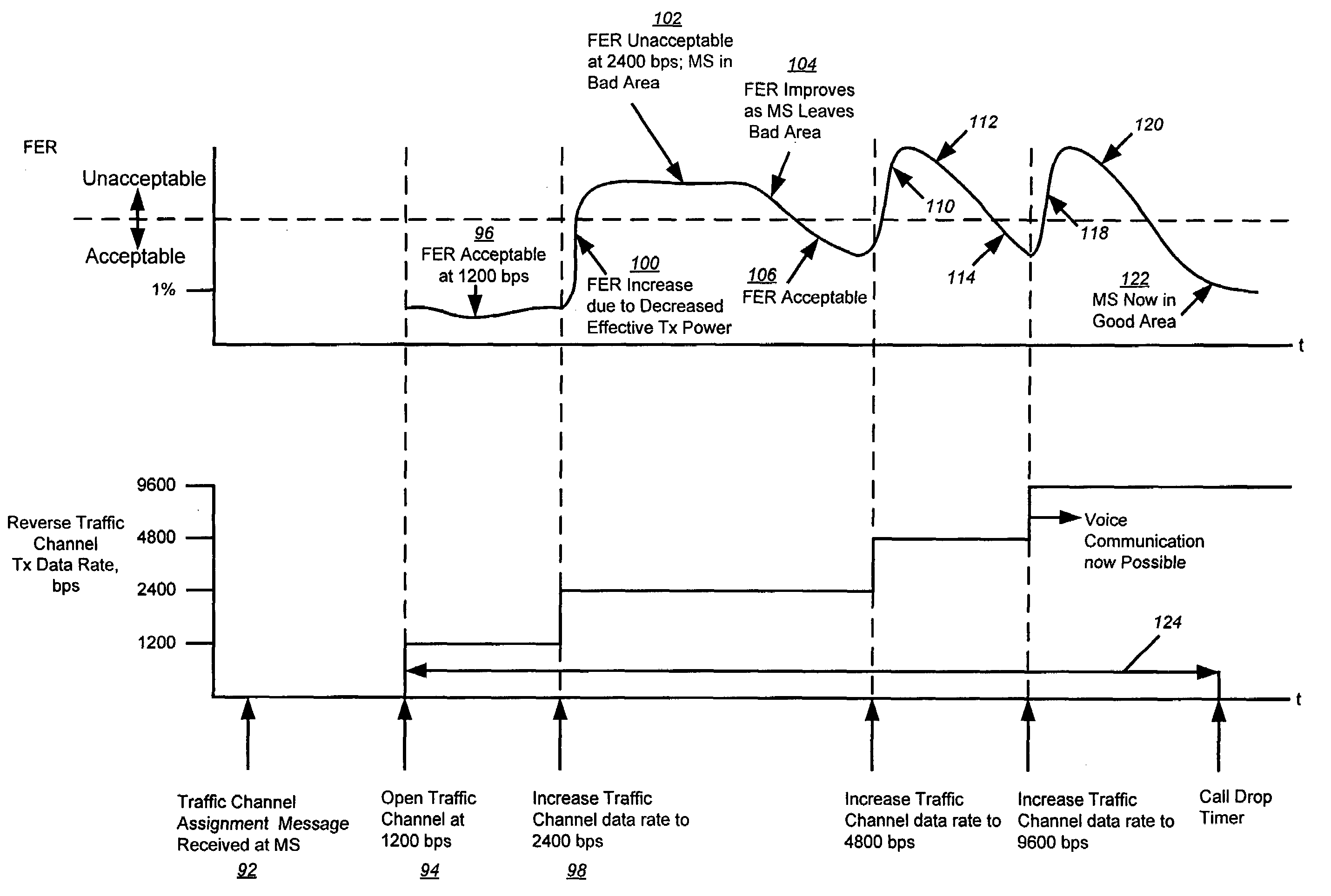
InactiveUS7058400B2Increase probabilityDetrimental to environmentEnergy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementDouble data rateTransmitted power
A method and apparatus for dynamically controlling forward and reverse link channel processing gain to minimize dropped connections and improve the reliability of hard handoffs is disclosed. The transmission bit stream of a forward or reverse link channel is allowed to become dynamic under controlled conditions in such a way as to take advantage of the inherit strengths that the concept of processing gain provides and thereby improve the probability of establishing and maintaining a forward or reverse link traffic channel. Dropped connections due to reverse link fades and dropped connections during call origination are minimized by allowing a MS to transmit reverse traffic channel data using dynamically adjustable data rates to increase the processing gain and the effective transmit power level. In addition, dropped connections during hard handoffs are minimized by using a special code channel and dynamically adjustable data rates to evaluate the proposed new link.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Programmable data strobe offset with DLL for double data rate (DDR) RAM memory
A double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic RAM (SDRAM), or DDR-SDRAM, memory controller employing a delay locked loop (DLL) circuit to delay an SDRAM data strobe (DQS) signal to the center, or ‘eye’ of the read data window. However, in distinction from conventional techniques, the initial delay determined by the DLL is fine tuned with an offset determined by a memory test. Moreover, in an additional embodiment, the delay may be further adjusted during operation to compensate for environmental conditions by a PVT (process, value, temperature) circuit.
Owner:AGERE SYST INC
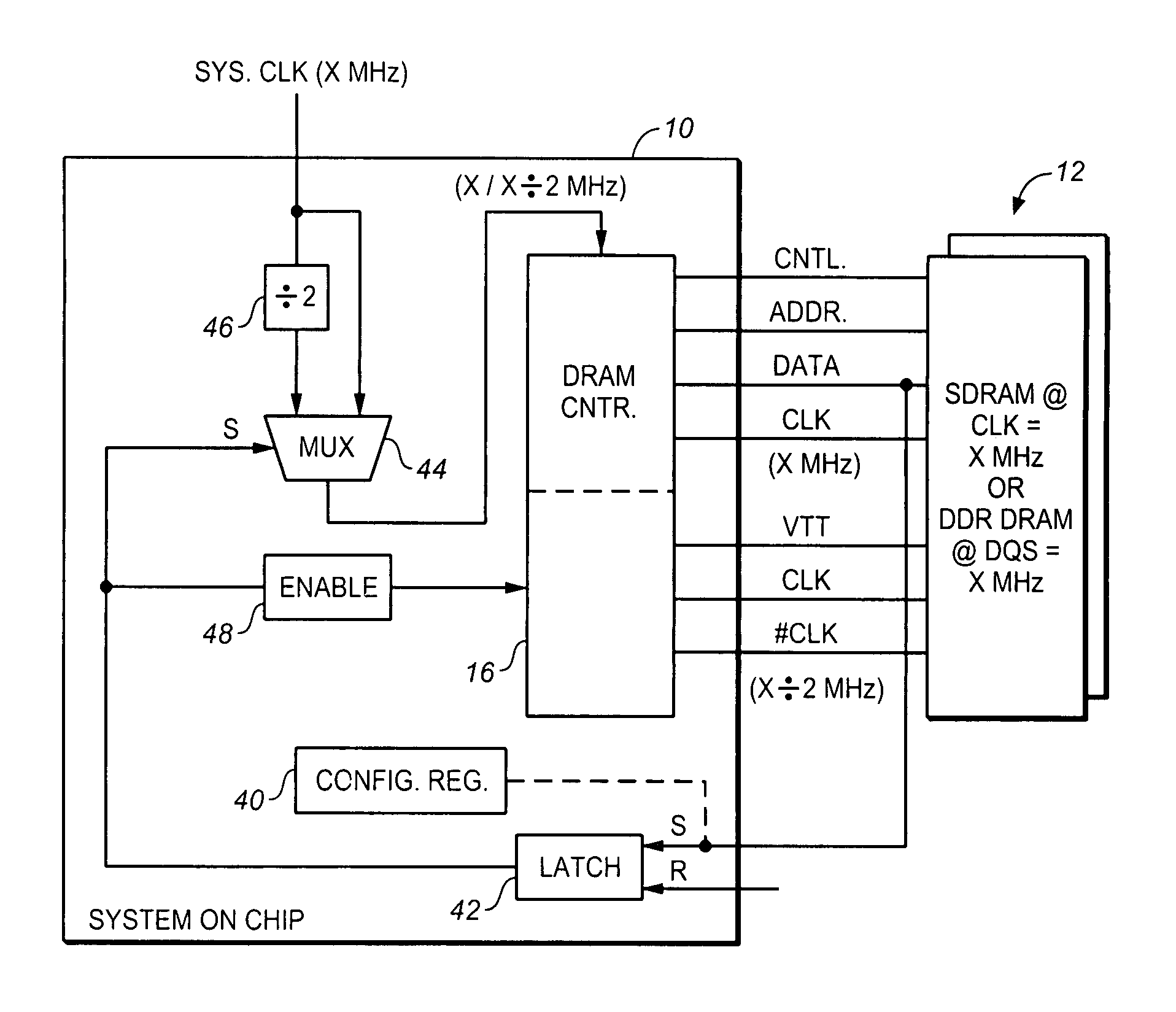
Low power memory controller that is adaptable to either double data rate DRAM or single data rate synchronous DRAM circuits
ActiveUS7243254B1Data transfer rateLess costlyGenerating/distributing signalsMemory systemsPower-on resetElectricity
A memory controller is provided and a method for transferring data between the memory controller and a memory device. The memory controller can be implemented on an integrated circuit that also contains an execution unit. The execution unit can be clocked at a first clock rate, whereas the memory controller can be selectively clocked at either the first clock rate or a second clock rate that is approximately one-half frequency of the first clock rate. By clocking the memory controller at either the first clock rate or the second clock rate, the memory controller can accommodate different types of semiconductor memory. For example, the memory controller can control single data rate (SDR) DRAM memory if it is clocked at a first clock rate. Conversely, the memory controller can control double data rate (DDR) DRAM memory if it is clocked at approximately one-half the first clock rate. By selectively clocking the memory controller at different clocking rates, the memory controller need not be modified in hardware, yet can accommodate different memory devices by allowing a user to simply plug one type of memory into a receptacle rather than another depending on the cost constraints and user application. Therefore, the memory controller is adaptable during a power-on reset in which the computer system is initialized to automatically receive and control different types of memory selected by a user.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
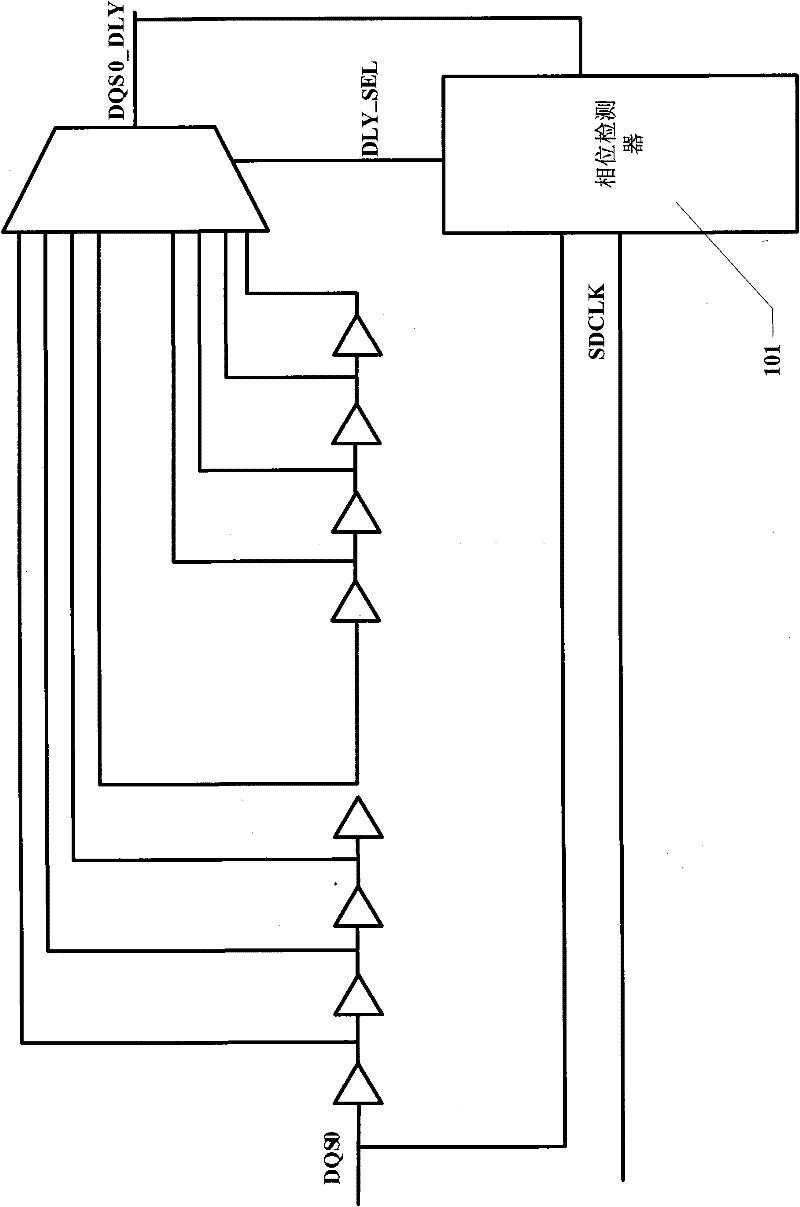
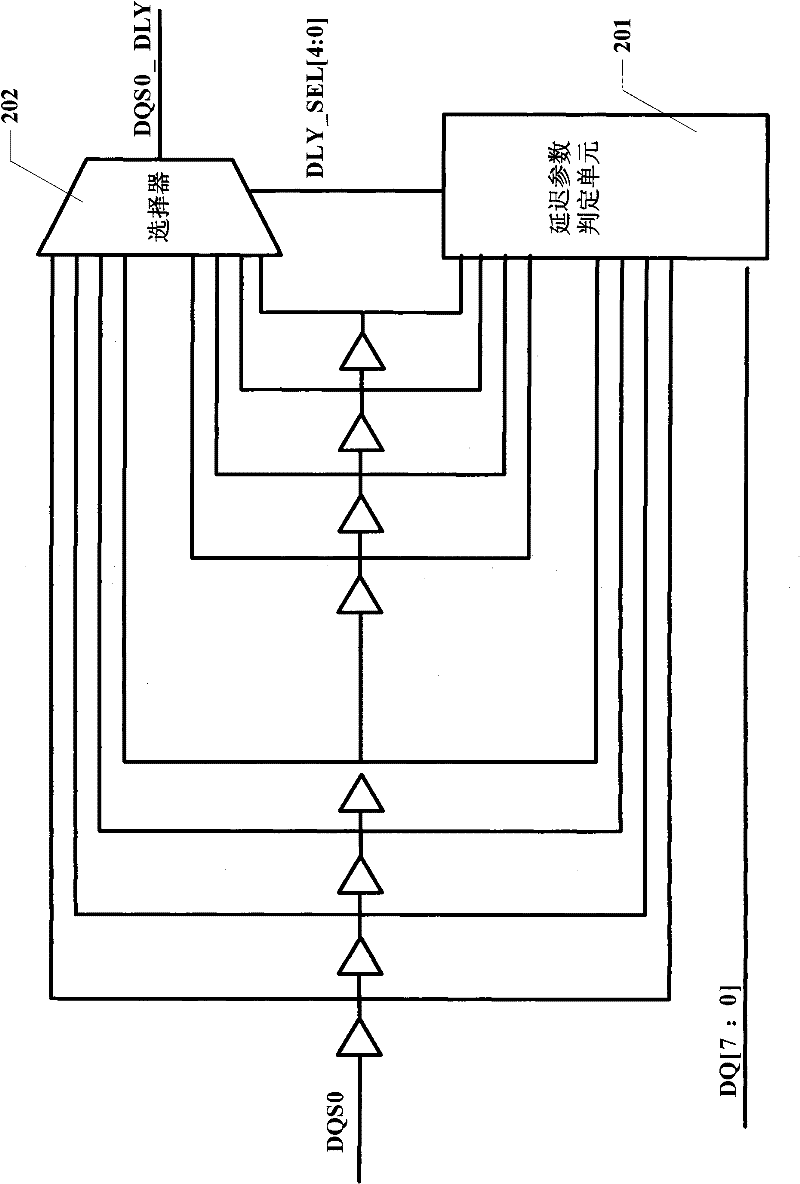
Method for calibrating phase of DQS (bidirectional data strobe) delay for DDR (double data rate) controller and apparatus thereof
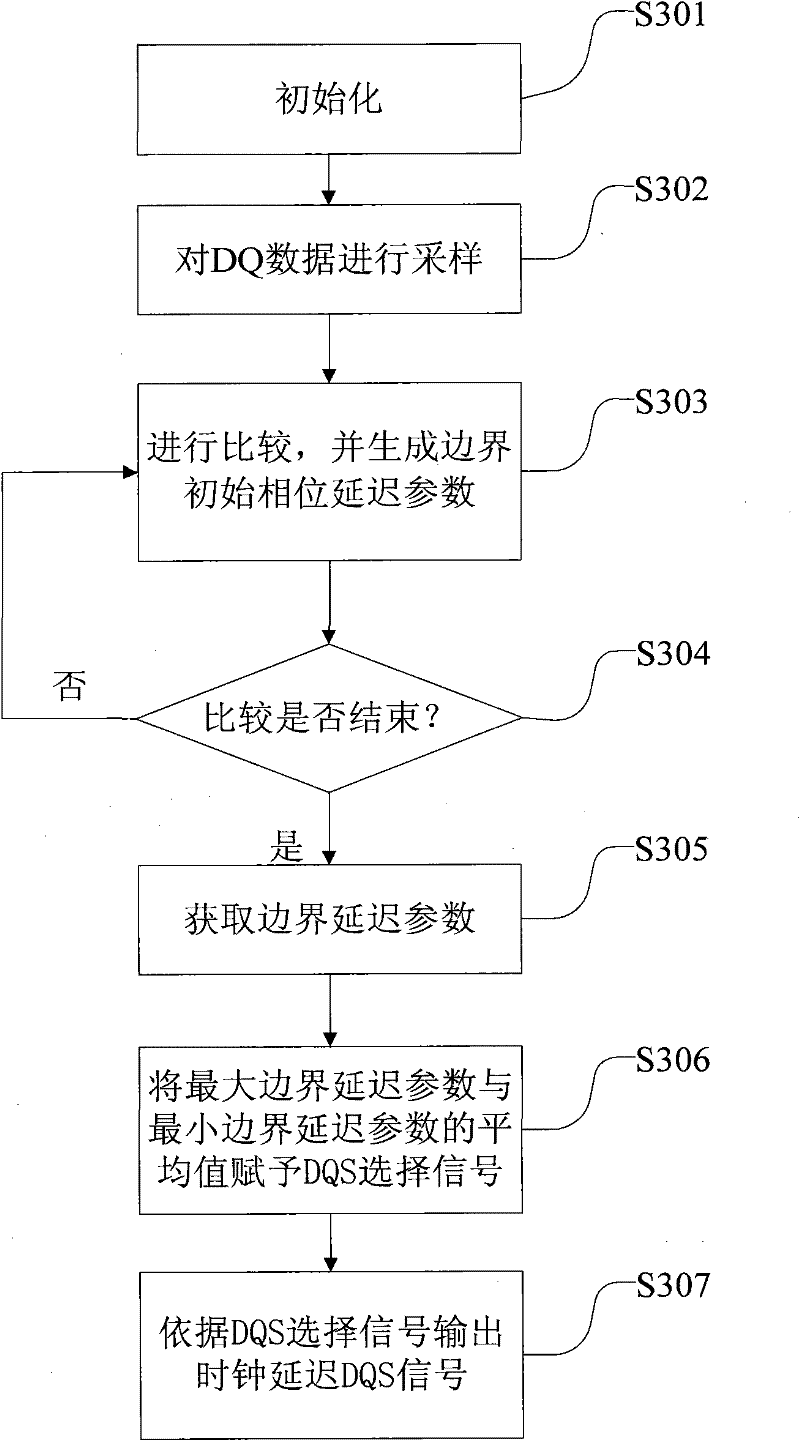
ActiveCN102347081AImprove stabilityImprove anti-interference abilityStatic storageDouble data rateScreening method
The invention discloses a phase calibration method of the DQS delay for a DDR controller and an apparatus thereof. The method comprises the following steps: 1, sampling DDR data DQ according to trigger signals after different grade delays of a DQS signal; 2, comparing the data DQ acquired by sampling with a preset self-check datum in byte, and acquiring a minimum boundary delay parameter and a maximum boundary delay parameter through delaying for two beats; 3, endowing a mean value of the minimum boundary delay parameter and the maximum boundary delay parameter to a DQS selection signal; and 4, delaying the DQS signal according to the output clock of the DQS selection signal to obtain a DQS signal at the center of an effective datum window. According to the invention, the phase calibration of the DQS delay is realized through adopting a delay parameter determination unit and hardware in a delay parameter output circuit, and the delayed DQS can accurately fall on the center of the effective datum window through a datum screening method with the delay parameter determination unit, thereby the stability, the accuracy and the interference immunity of datum sampling are enhanced.
Owner:LEADCORE TECH
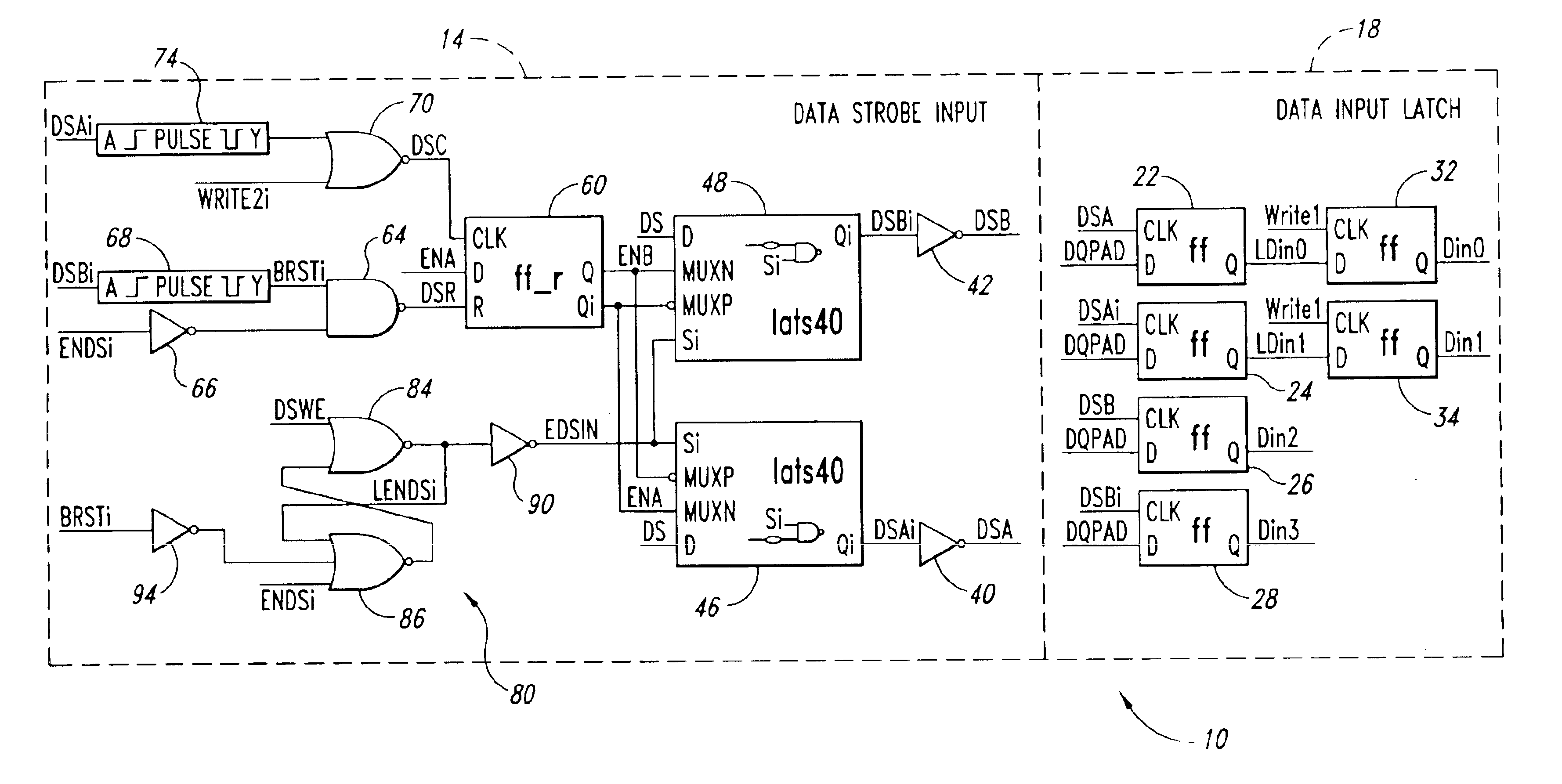
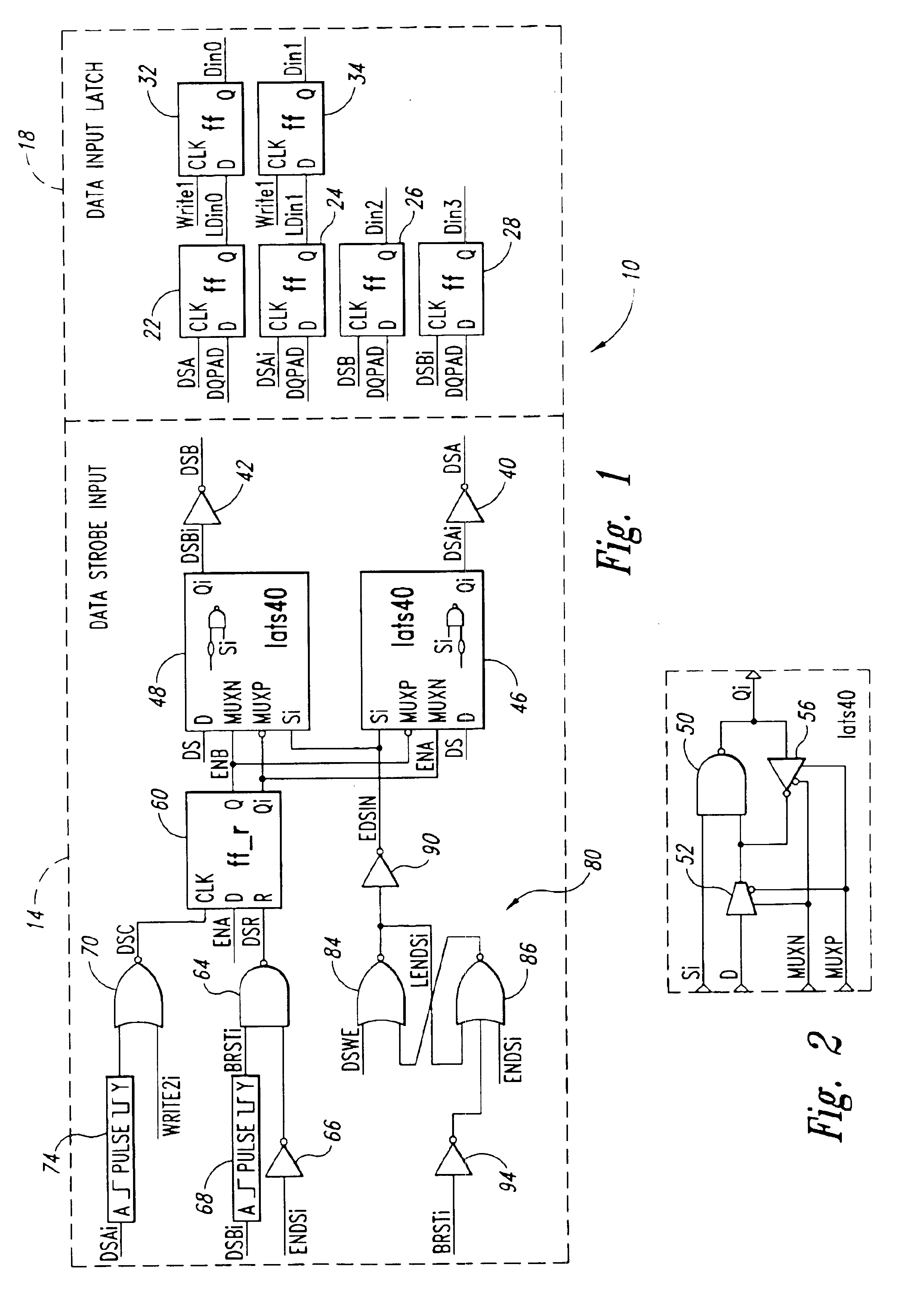
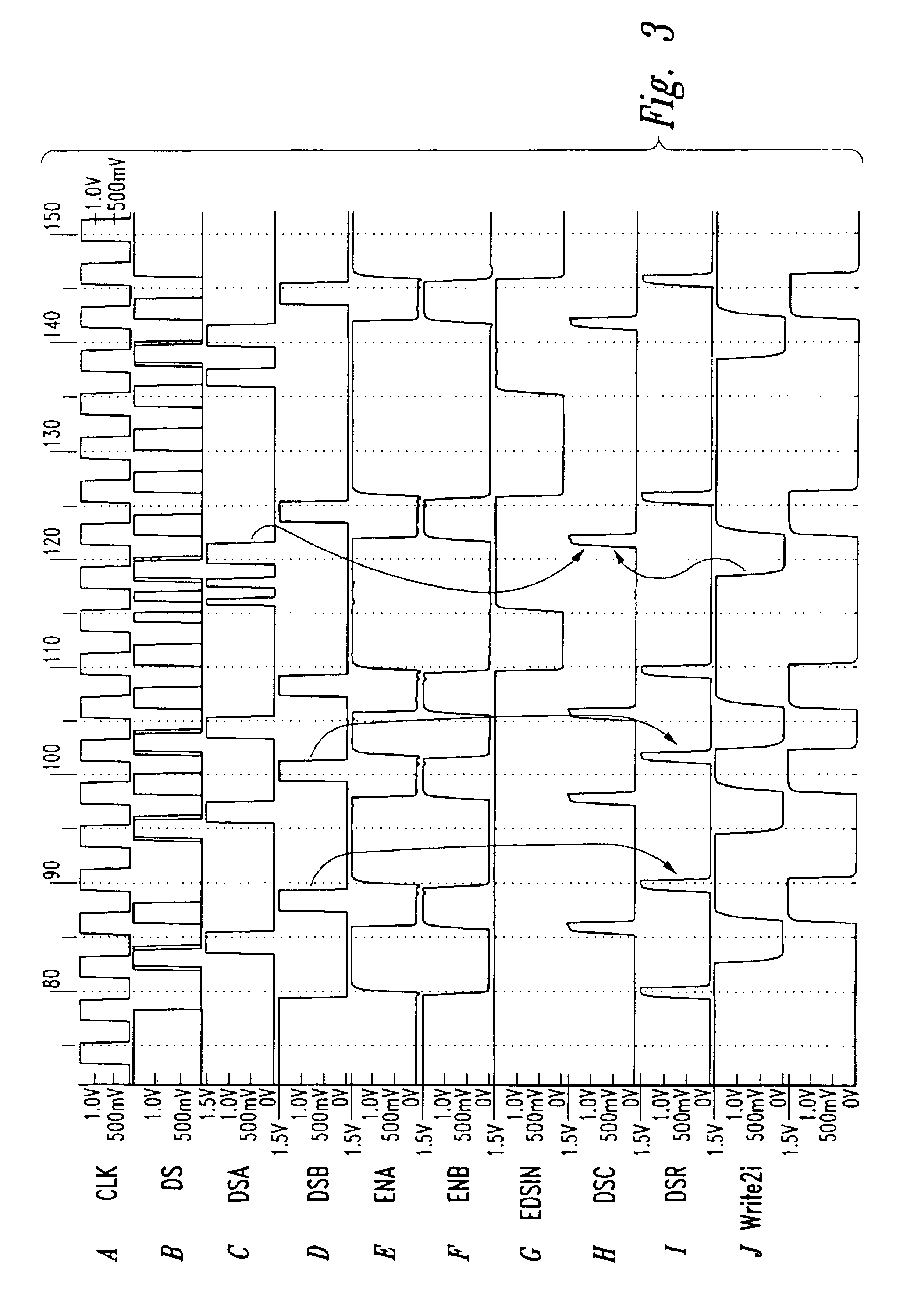
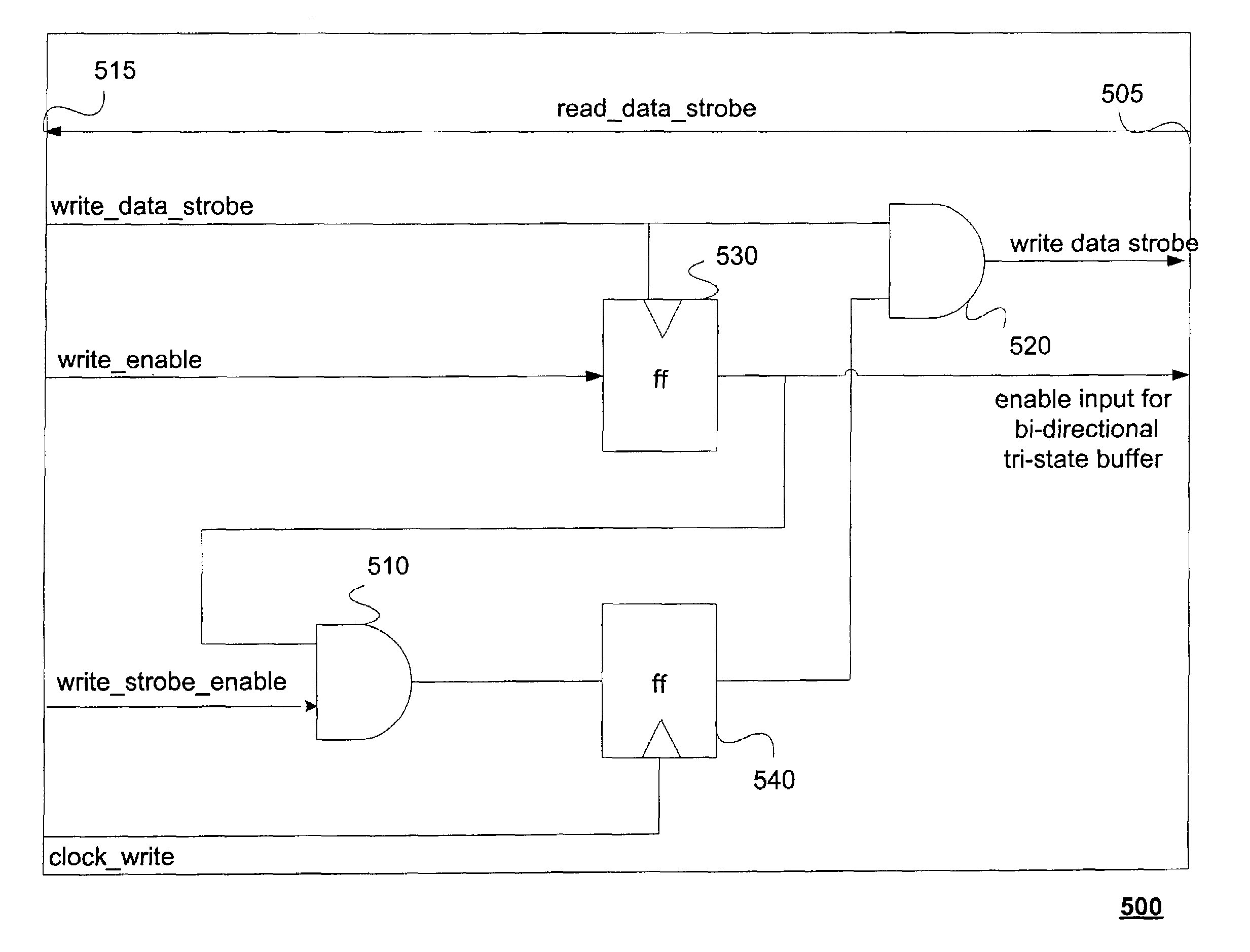
Data strobe synchronization circuit and method for double data rate, multi-bit writes
A data strobe synchronization circuit includes first and second logic circuits receiving global data strobe pulses and respective enable signal. A control circuit initially applies an enable signal to the first logic circuit so that the first logic circuit generates a first data strobe pulse responsive to each global data strobe pulse. The control circuit receives a write control signal. When the write control signal becomes active, the control circuit terminates the enable signal applied to the first logic circuit and applies an enable signal to the second logic circuit. The second logic circuit then generates a second data strobe pulse responsive to the next global data strobe pulse. The first and second data strobe pulses are used to latch a data signal in respective flip-flops. The data strobe pulses may latch the data signal in pairs of flip-flops on the leading and trailing edges of the data strobe pulses.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
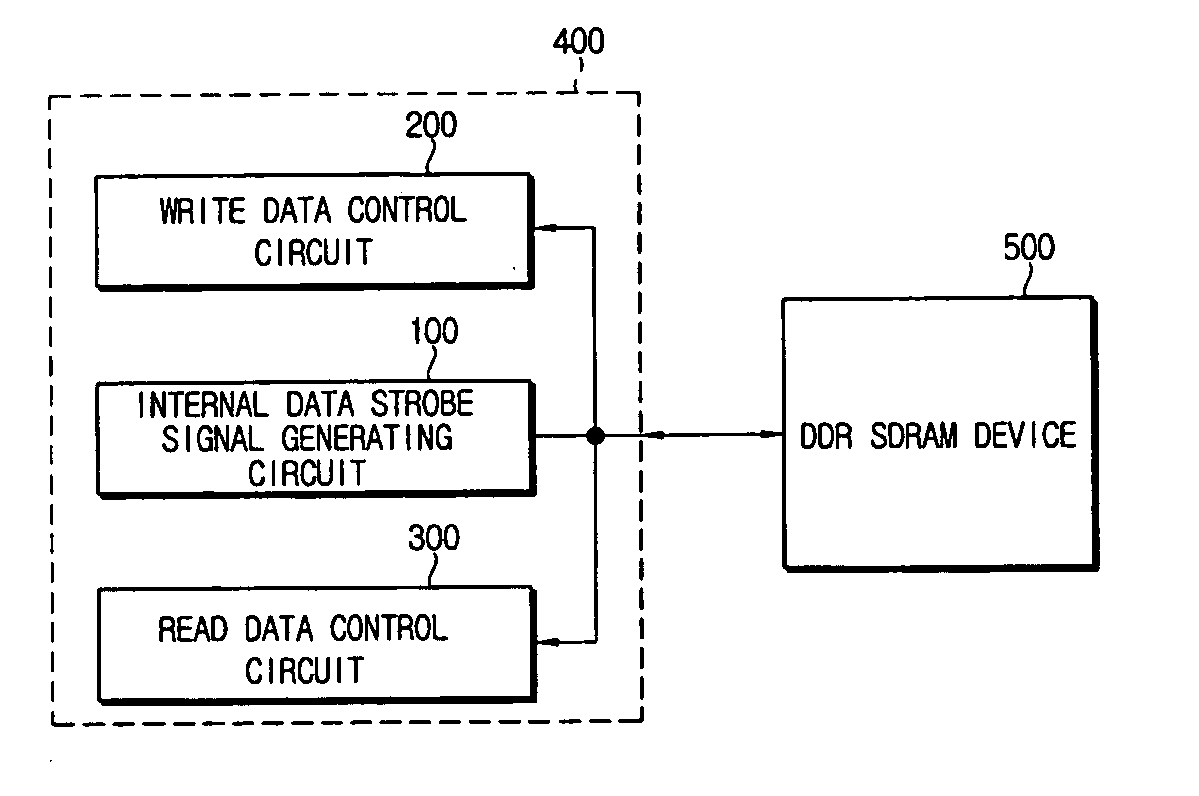
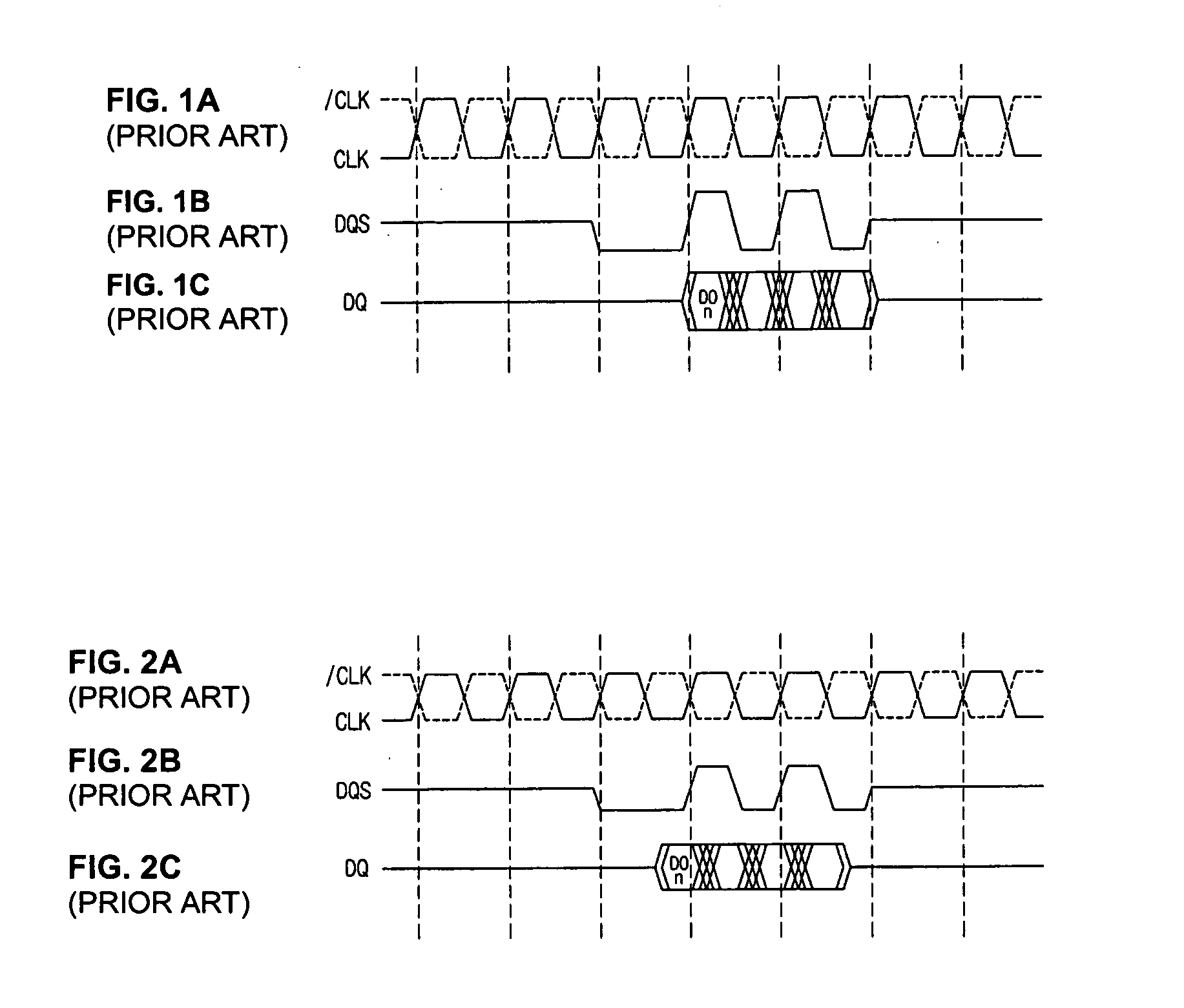
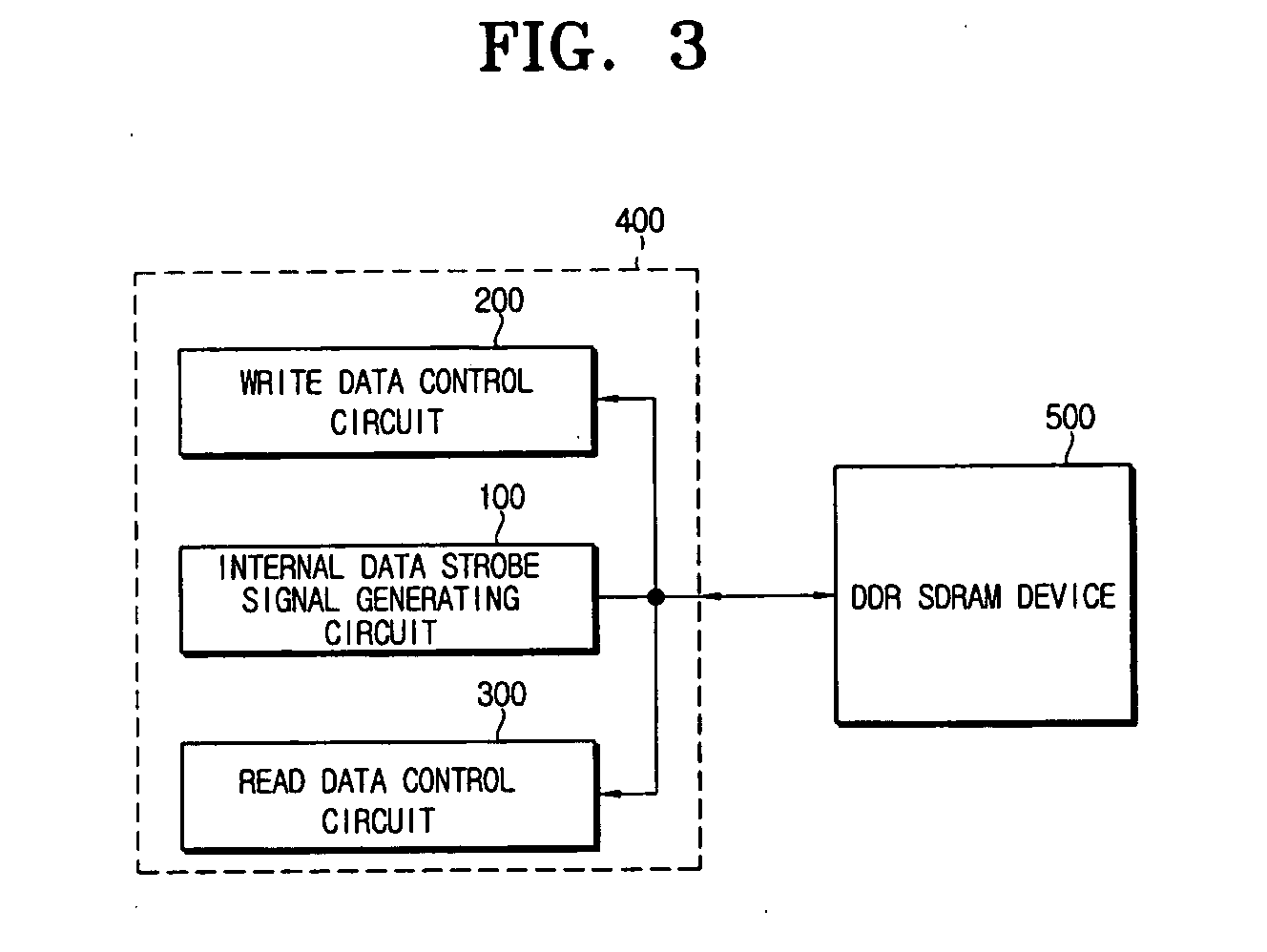
Data control circuit for DDR SDRAM controller
A data control circuit for a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) that secures a stable reading / writing operation of DDR SDRAM data by generating an actively controllable internal data strobe signal. The data control circuit includes an internal data strobe signal generating circuit generating and outputting an internal data strobe signal a rising edge of which is located in a center part of valid DDR SDRAM data; a read data control circuit for receiving the internal data strobe signal, generated from the internal data strobe signal generating circuit as a clock input, dividing captured data into even data and odd data, and transmitting the even data and the odd data to a system bus; and a write data control circuit transmitting the internal data strobe signal input from the internal data strobe signal generating circuit to a DDR SDRAM device as a data strobe signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
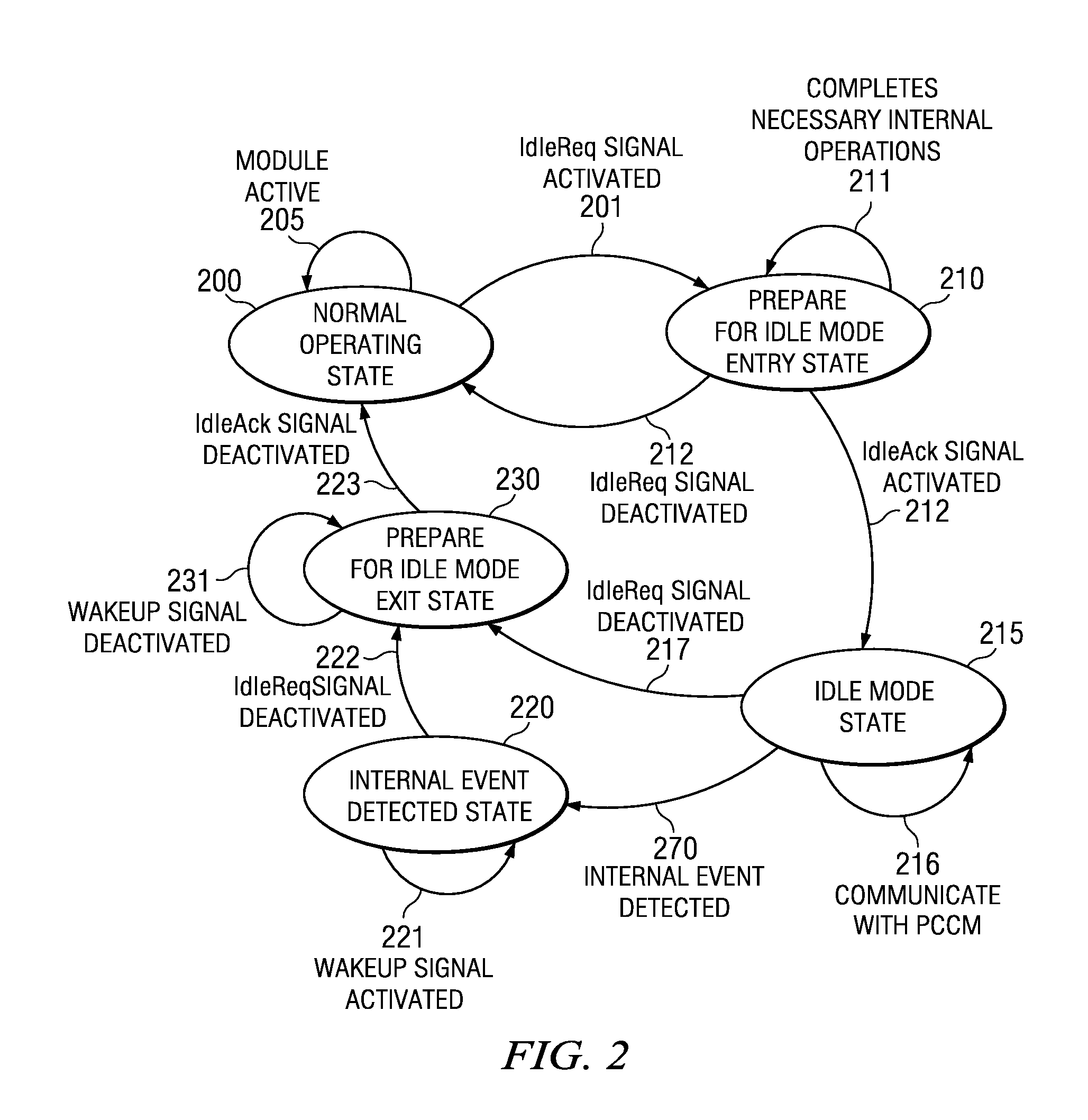
Memory Controller Idle Mode
An apparatus and method for dynamically modifying one or more operating conditions of a memory controller in an electronic device. Operating conditions may comprise clock frequency and power, which may be modified or removed. Dynamic modification of operating conditions may be done for purposes of optimizing a parameter, such as power consumption. A mode, referred to as idle mode, may be used as a transitional or operational mode for the memory controller. The performance of the memory controller may dynamically vary in response to changes in its operating conditions. As such, the memory controller may comprise multiple modes, or submodes, of operation. The performance of the memory controller may depend on the type of memory it controls, for instance Double Data Rate (DDR) Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
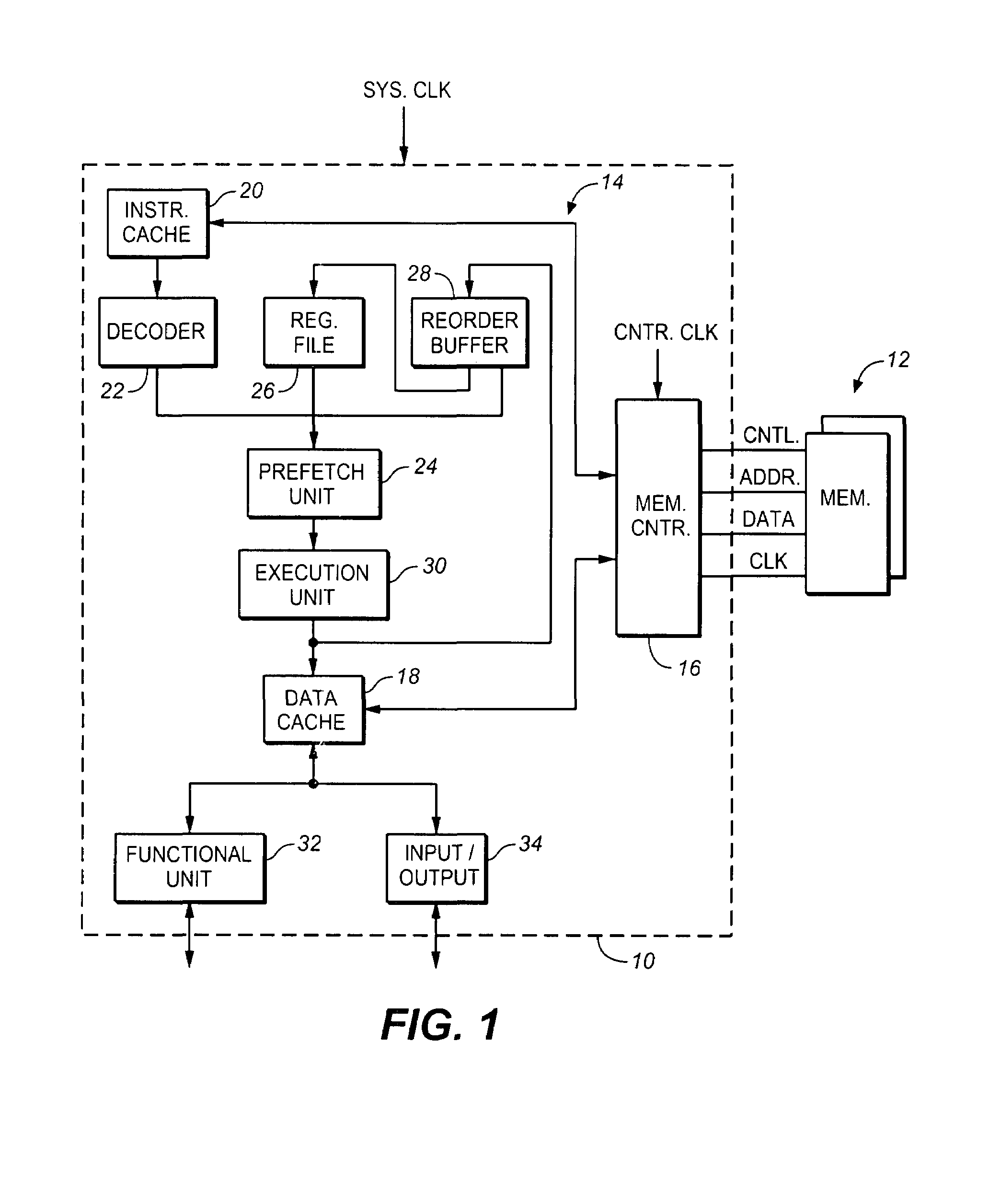
Method and apparatus to enable DRAM to support low-latency access via vertical caching
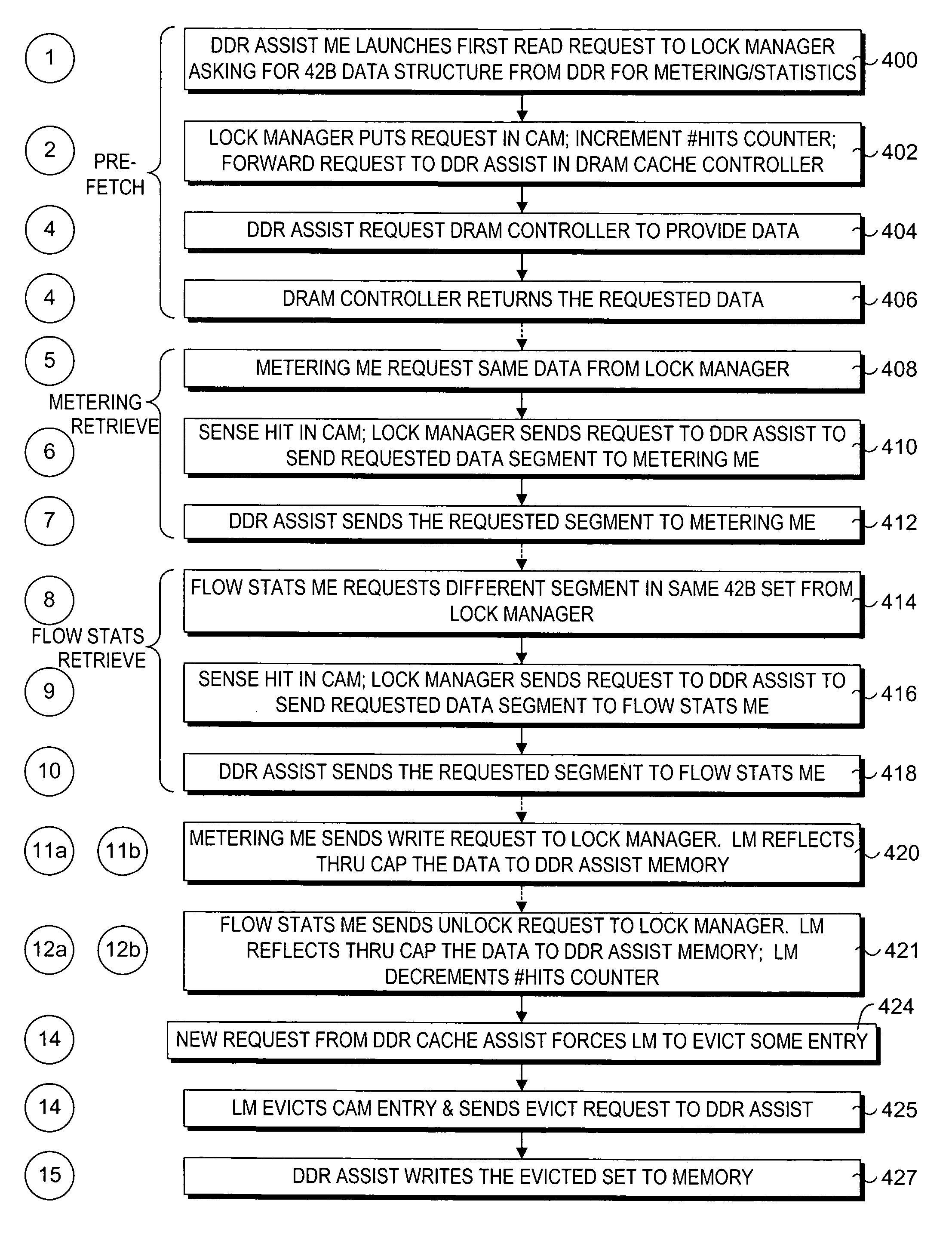
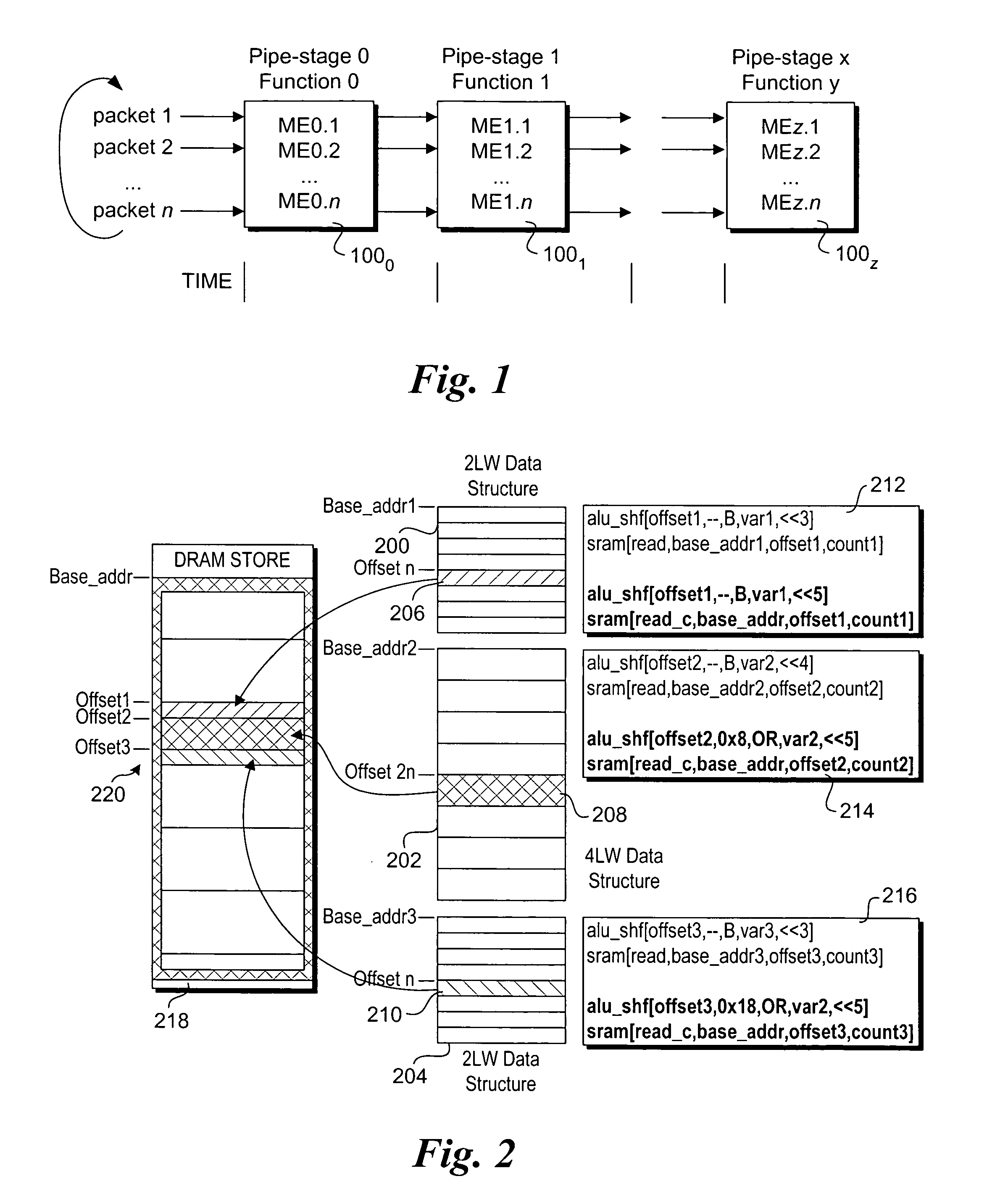
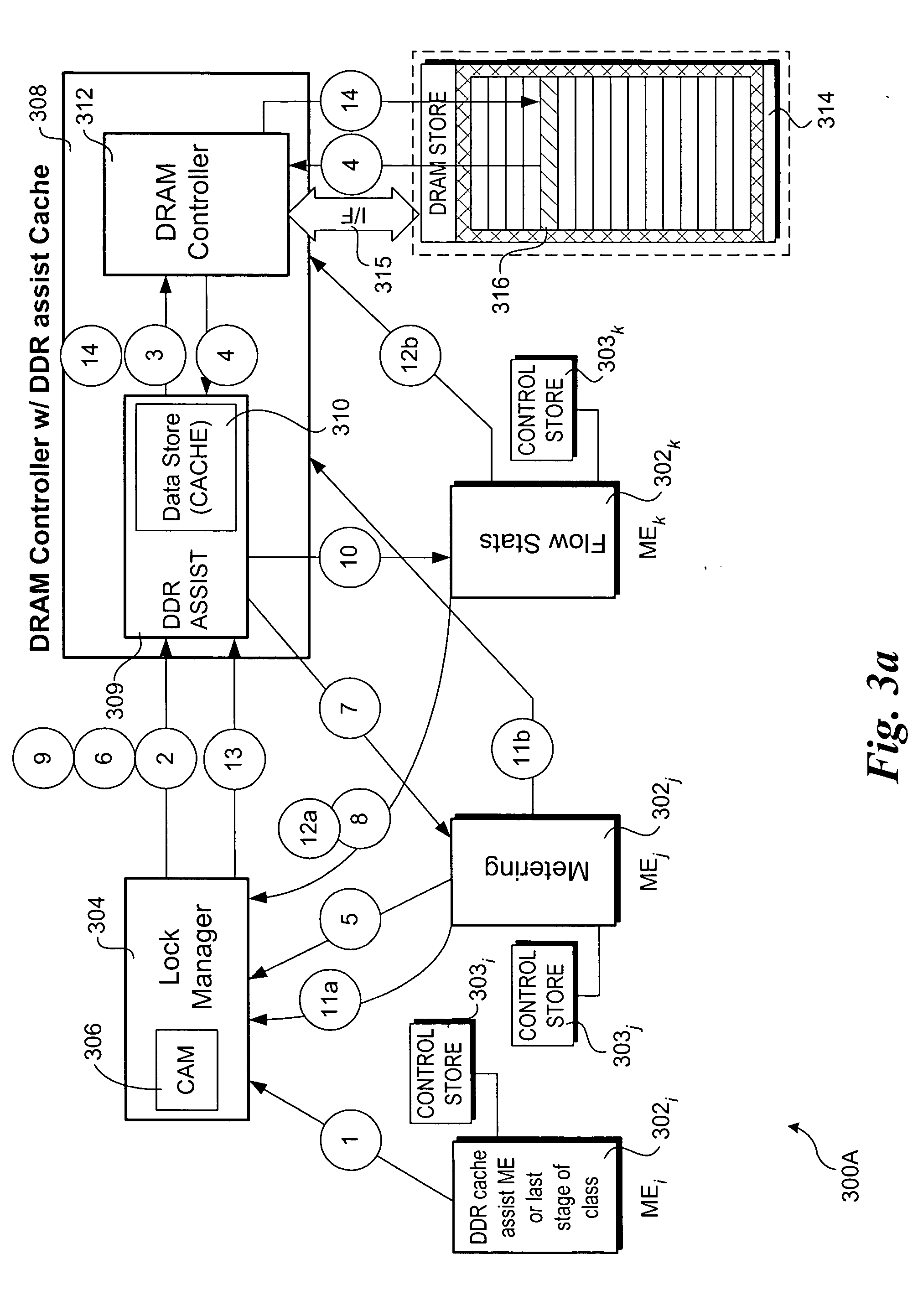
Method and apparatus to enable slower memory, such as dynamic random access memory (DRAM)-based memory, to support low-latency access using vertical caching. Related function metadata used for packet-processing functions, including metering and flow statistics, is stored in an external DRAM-based store. In one embodiment, the DRAM comprises double data-rate (DDR) DRAM. A network processor architecture is disclosed including a DDR assist with data cache coupled to a DRAM controller. The architecture further includes multiple compute engines used to execute various packet-processing functions. One such function is a DDR assist function that is used to pre-fetch a set of function metadata for a current packet and store the function metadata in the data cache. Subsequently, one or more packet-processing functions may operate on the function metadata by accessing it from the cache. After the functions are completed, the function metadata are written back to the DRAM-based store. The scheme provides similar performance to SRAM-based schemes, but uses much cheaper DRAM-type memory.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Configurable high-speed memory interface subsystem
InactiveUS7437500B2Input/output to record carriersDigital storageComputer architectureDouble data rate
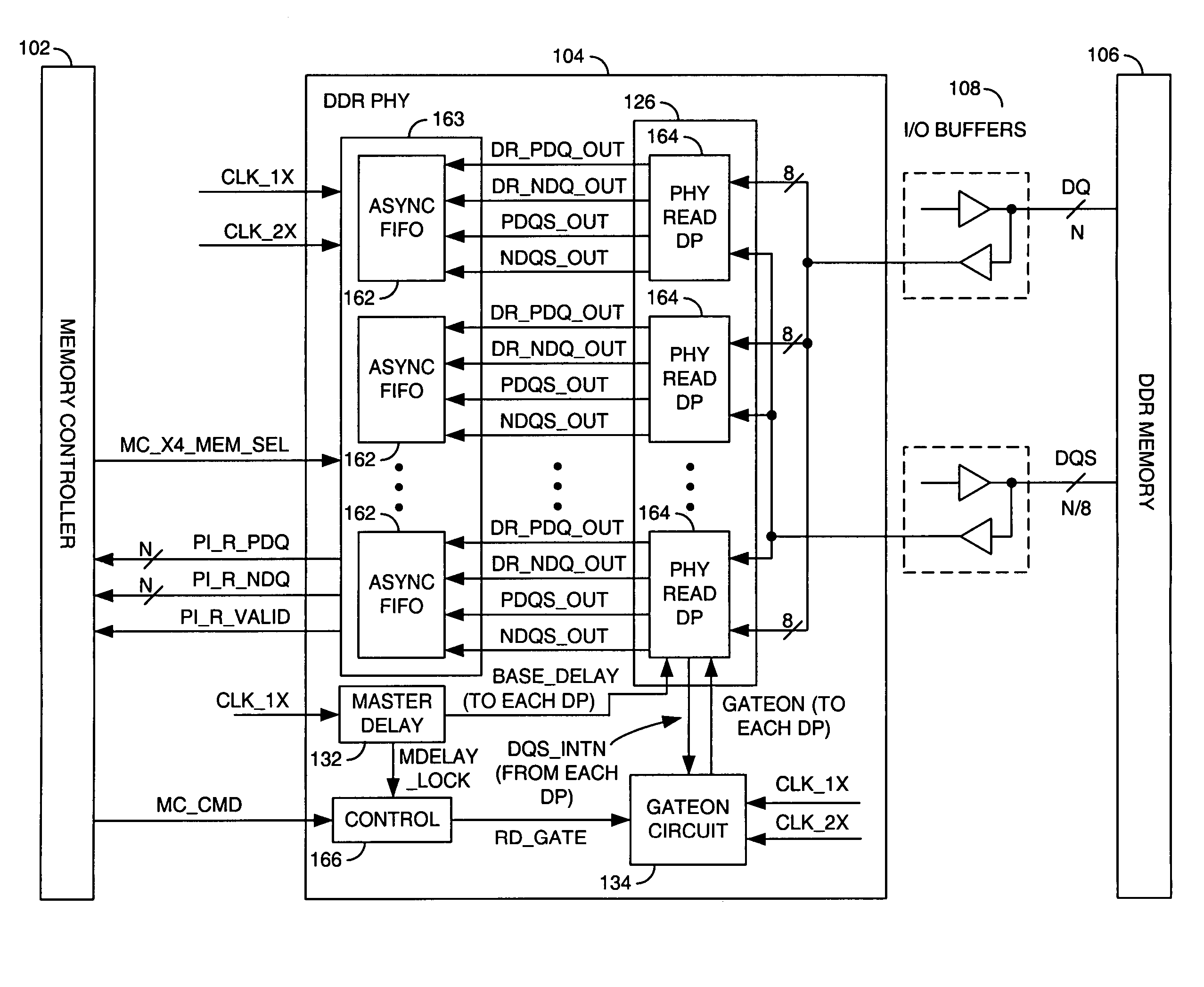
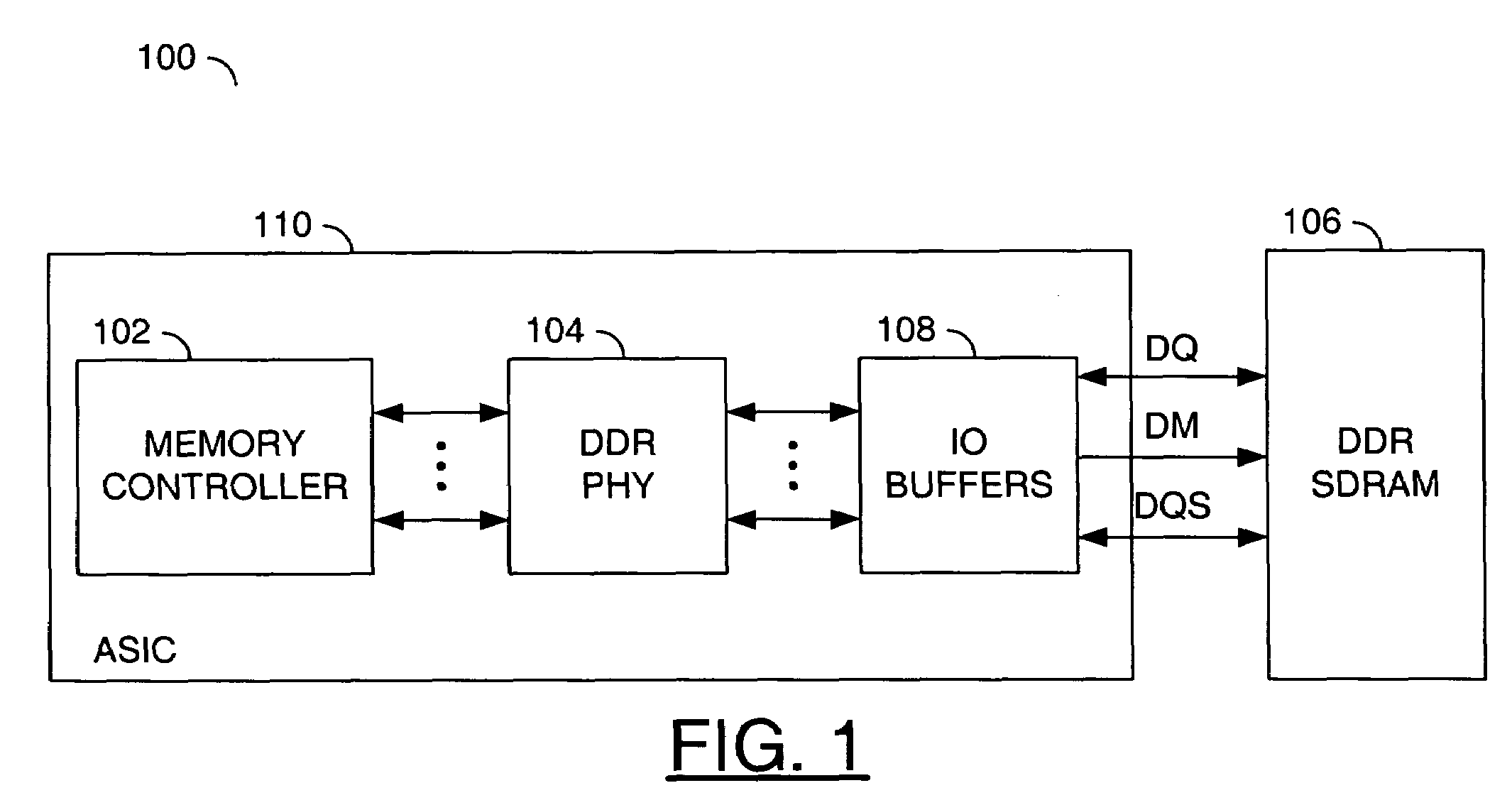
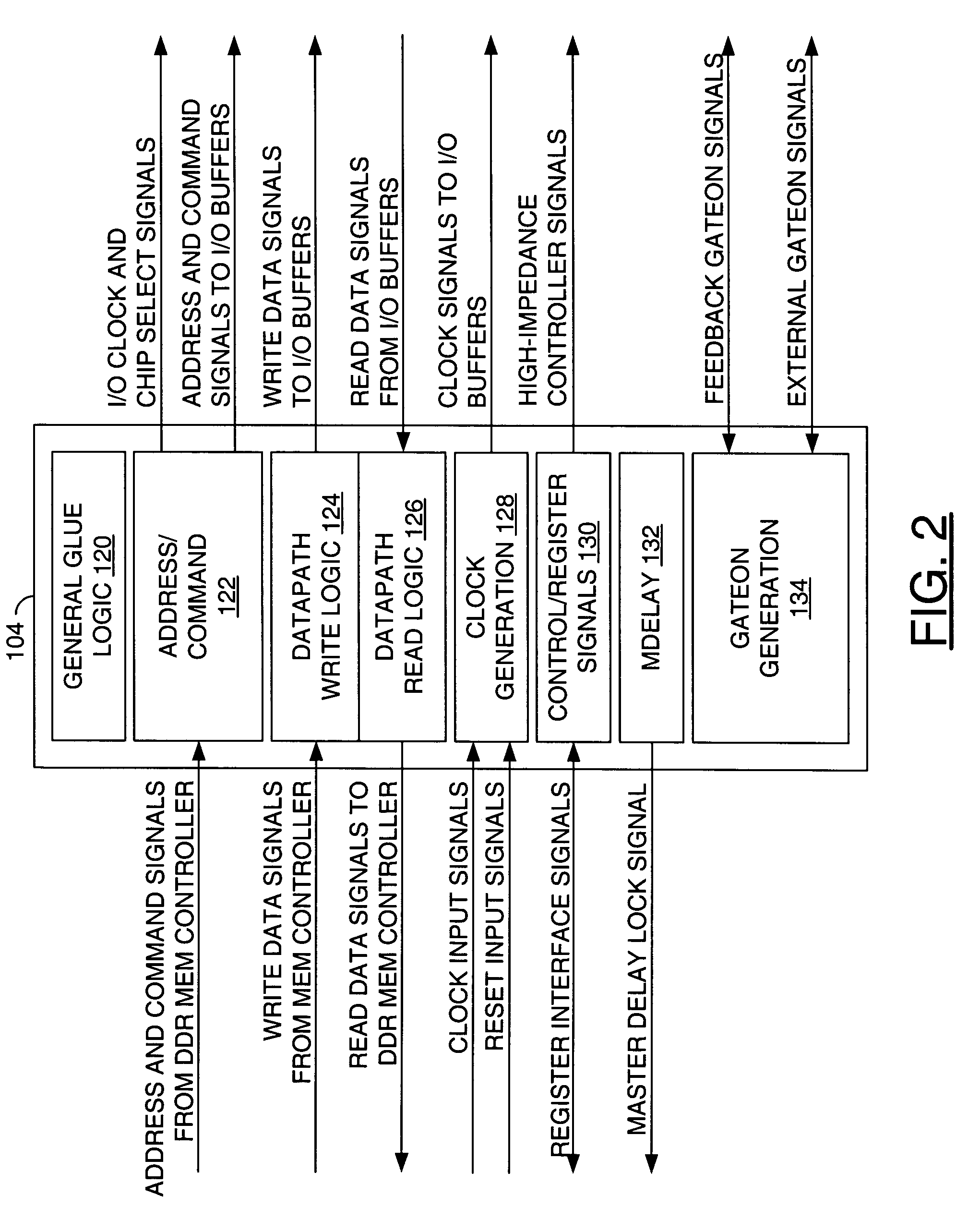
A core including a write logic IP block, a read logic IP block, a master delay IP block and an address and control IP block. The write logic IP block may be configured to communicate data from a memory controller to a double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM). The read logic IP block may be configured to communicate data from the double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) to the memory controller. The master delay IP block may be configured to generate one or more delays for the read logic IP block. The address and control logic IP block may be configured to control the write logic IP block and the read logic IP block. The core is generally configured to couple the double data rate (DDR) synchronous dynamic random access memory (SDRAM) and the memory controller.
Owner:BROADCOM INT PTE LTD
Input/output cells for a double data rate (DDR) memory controller
InactiveUS7062625B1Reliably capture write dataImprove write reliabilityDigital storageMemory systemsDouble data rateControl signal
An interface for sending write data, write control signals and write data between a memory controller and a double data rate (DDR) memory with the appropriate timing relationships so that the write data can be reliably written in the DDR memory. Also, an interface for reliably capturing read data received from the DDR memory during a read operation.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
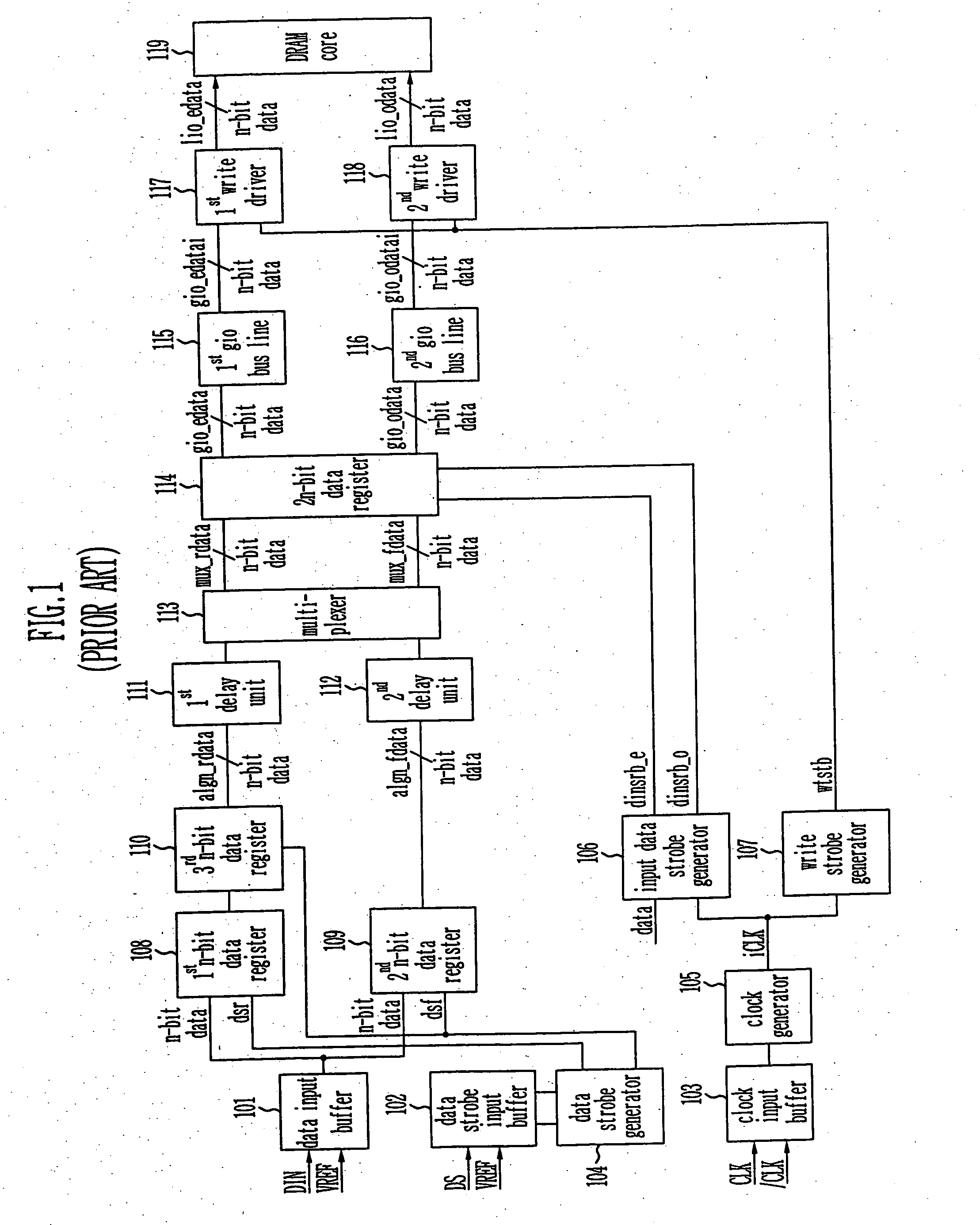
Write circuit of double data rate synchronous DRAM
ActiveUS20050141331A1Stable data write operationGuaranteed uptimeRead-only memoriesDigital storageTiming marginDouble data rate
Provided is a write circuit of a DDR SDRAM, in which a clock domain crossing is generated from a writing driver during a data write operation and a proper data is always transferred to a gio bus line by using the delay of an internal data strobe signal's falling for a certain amount of time as an input data strobe bar signal. Moreover, by using a skew detection circuit, it is possible to detect a skew tDQSS between a clock and a data strobe, and the skew tDQSS is automatically compensated by the skew compensation circuit. From the perspective of a timing error between the clock and the data strobe, therefore, the write operation of the DDR SDRAM has twice the timing margin (0.5tCK) compared to that of the related art. This means that a stable, high-speed write operation of the DDR SDRAM can be made possible.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com