Patents
Literature
135 results about "Link rate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
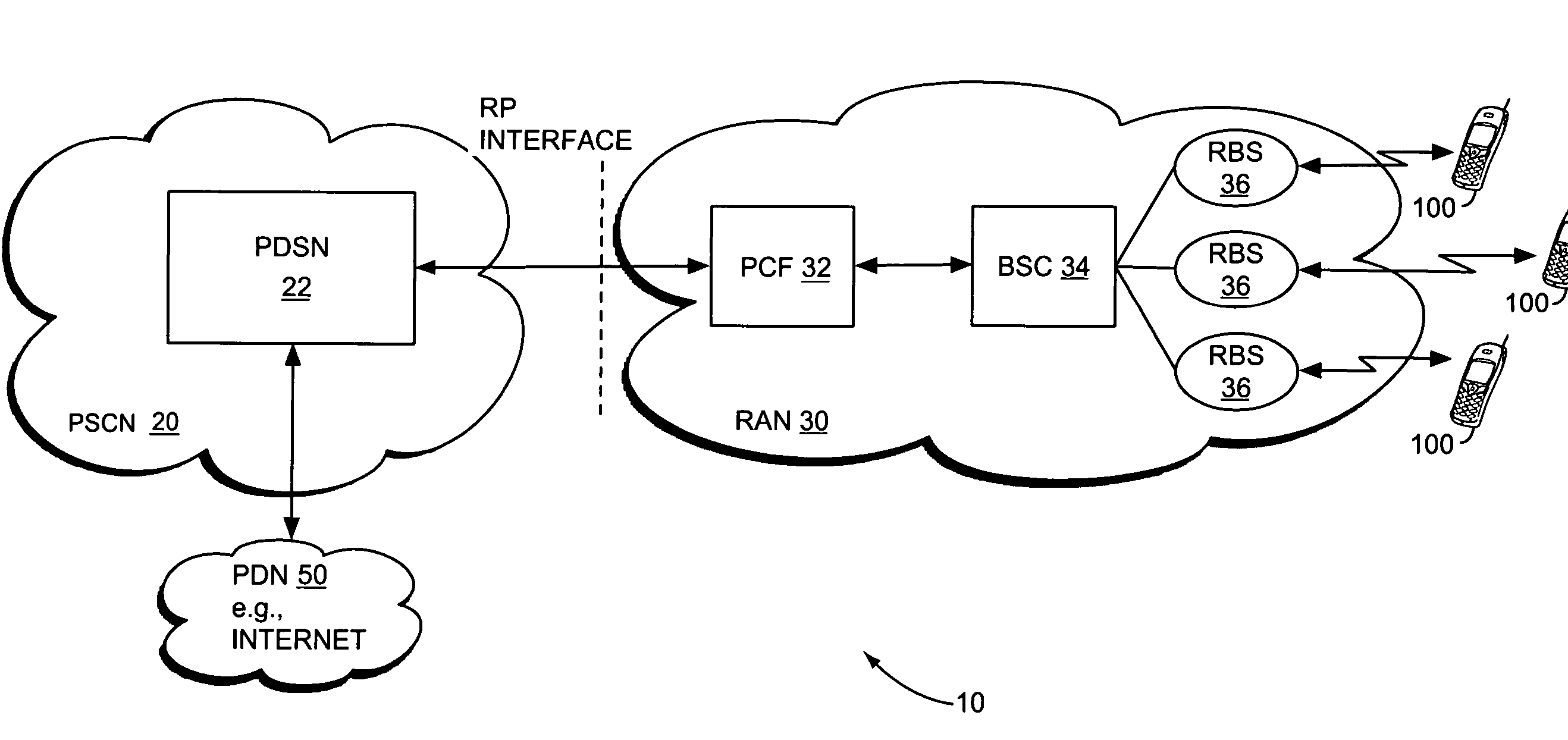
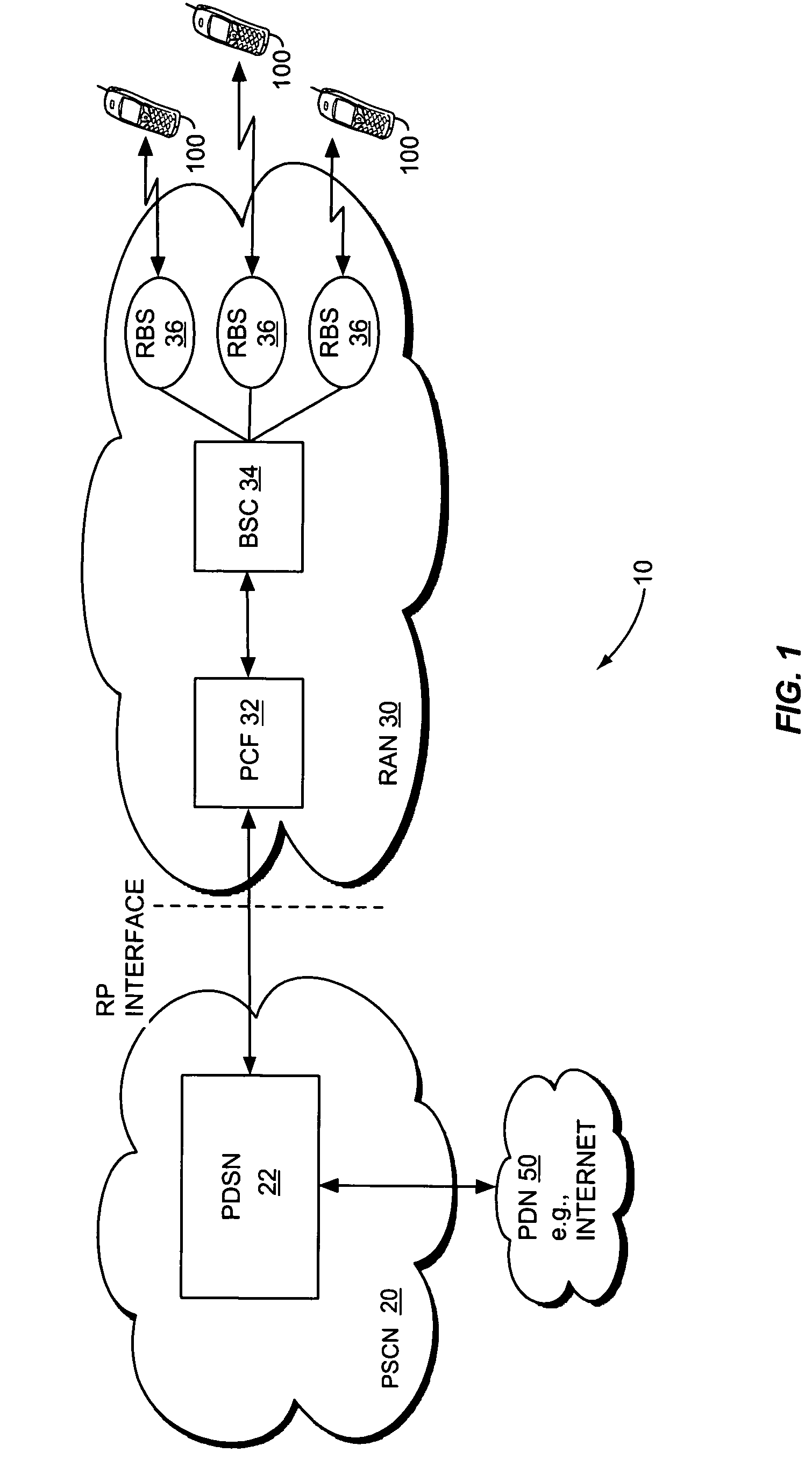
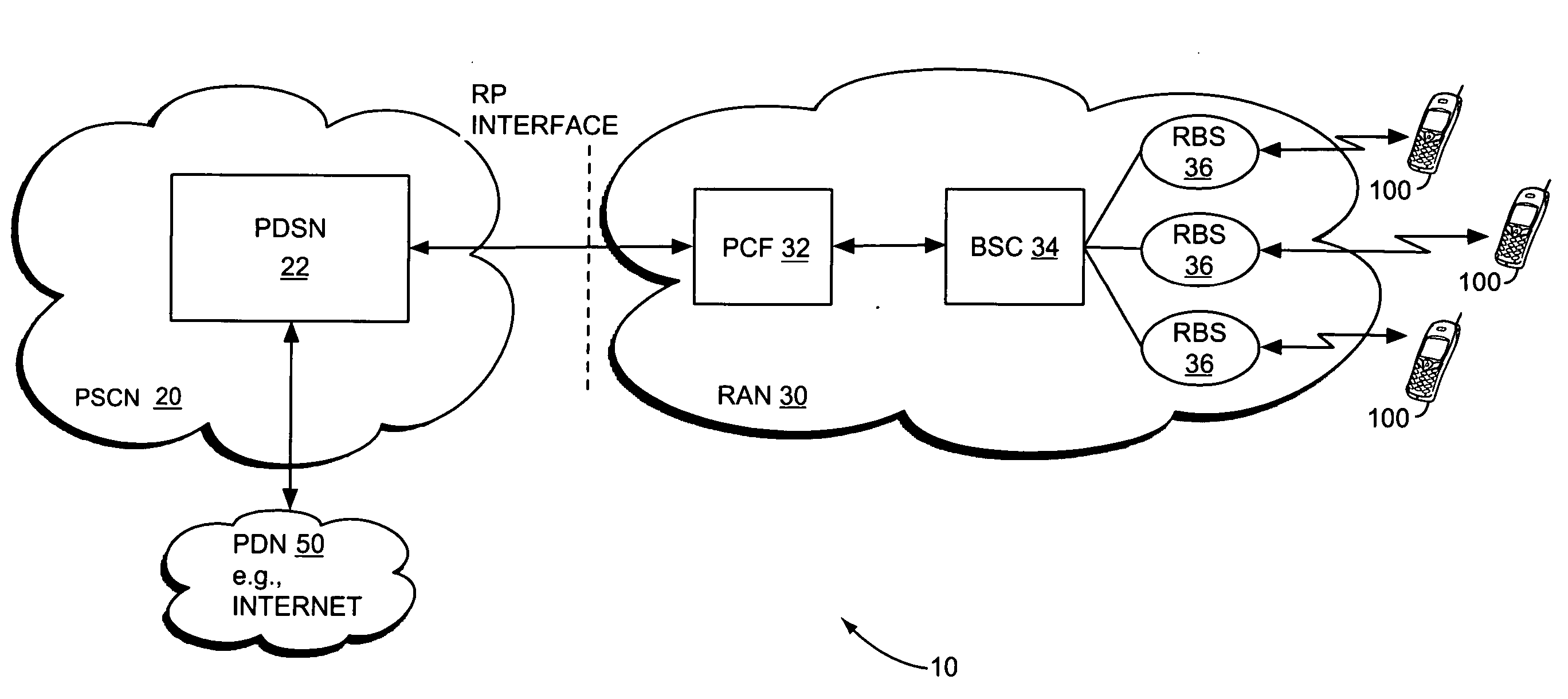
The link rate is directly related to wireless signal strength. The signal strength is at its maximum (100% or close to 100%) when the wireless client is close to the wireless router. In this location, the client would get the optimal link rate.
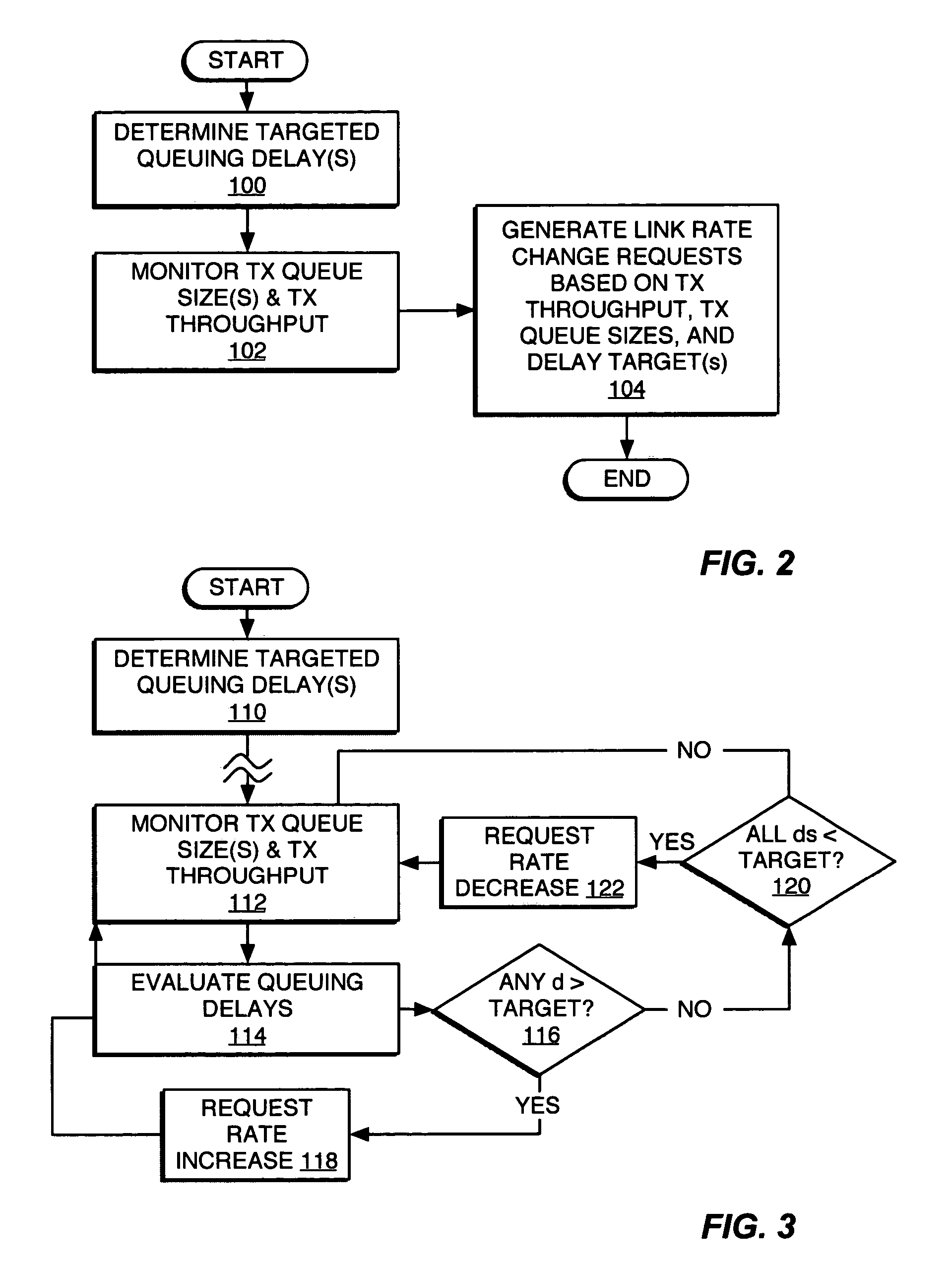
Queuing delay based rate control
InactiveUS20050111361A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementQuality of serviceTelecommunications link
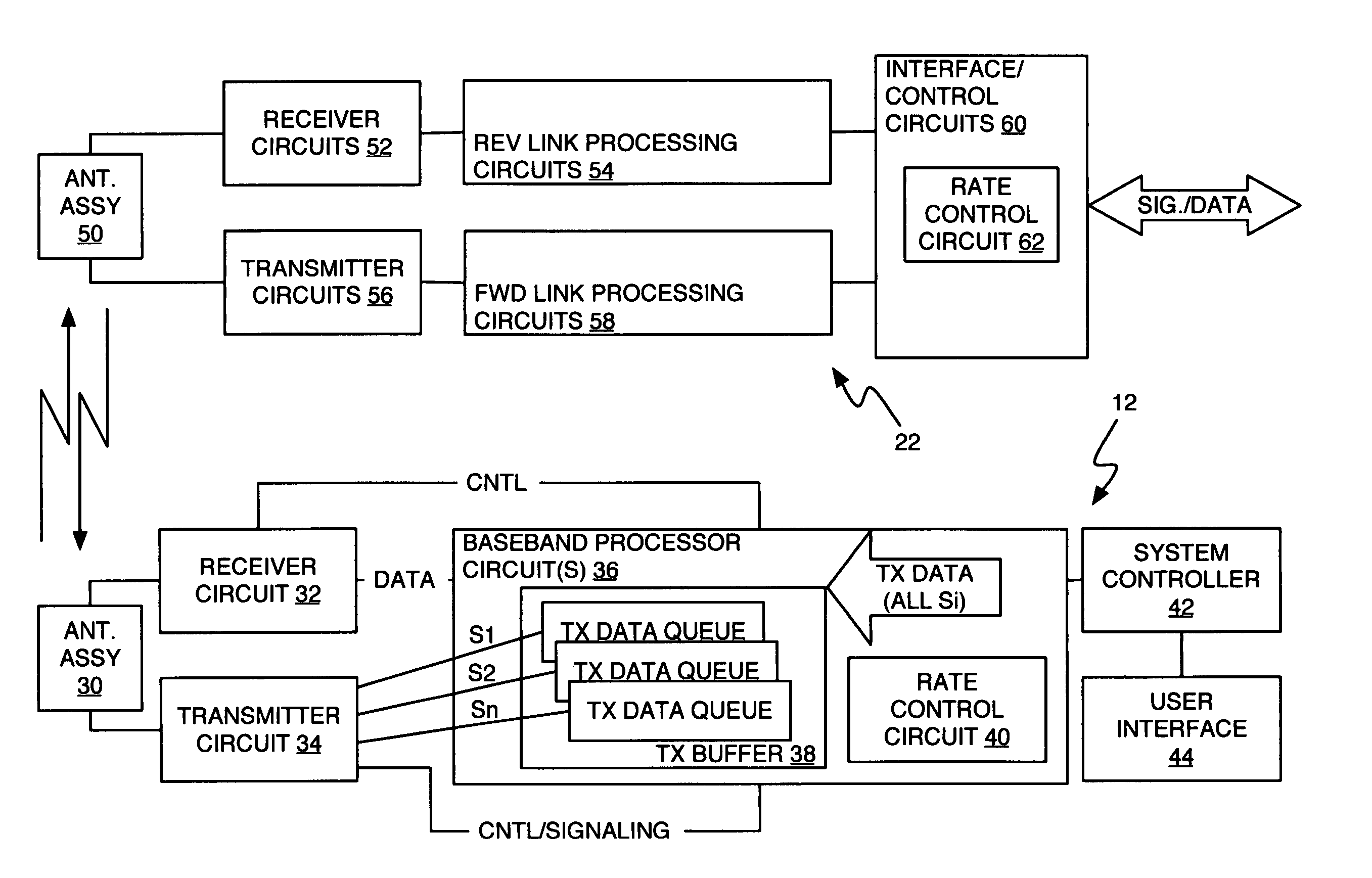
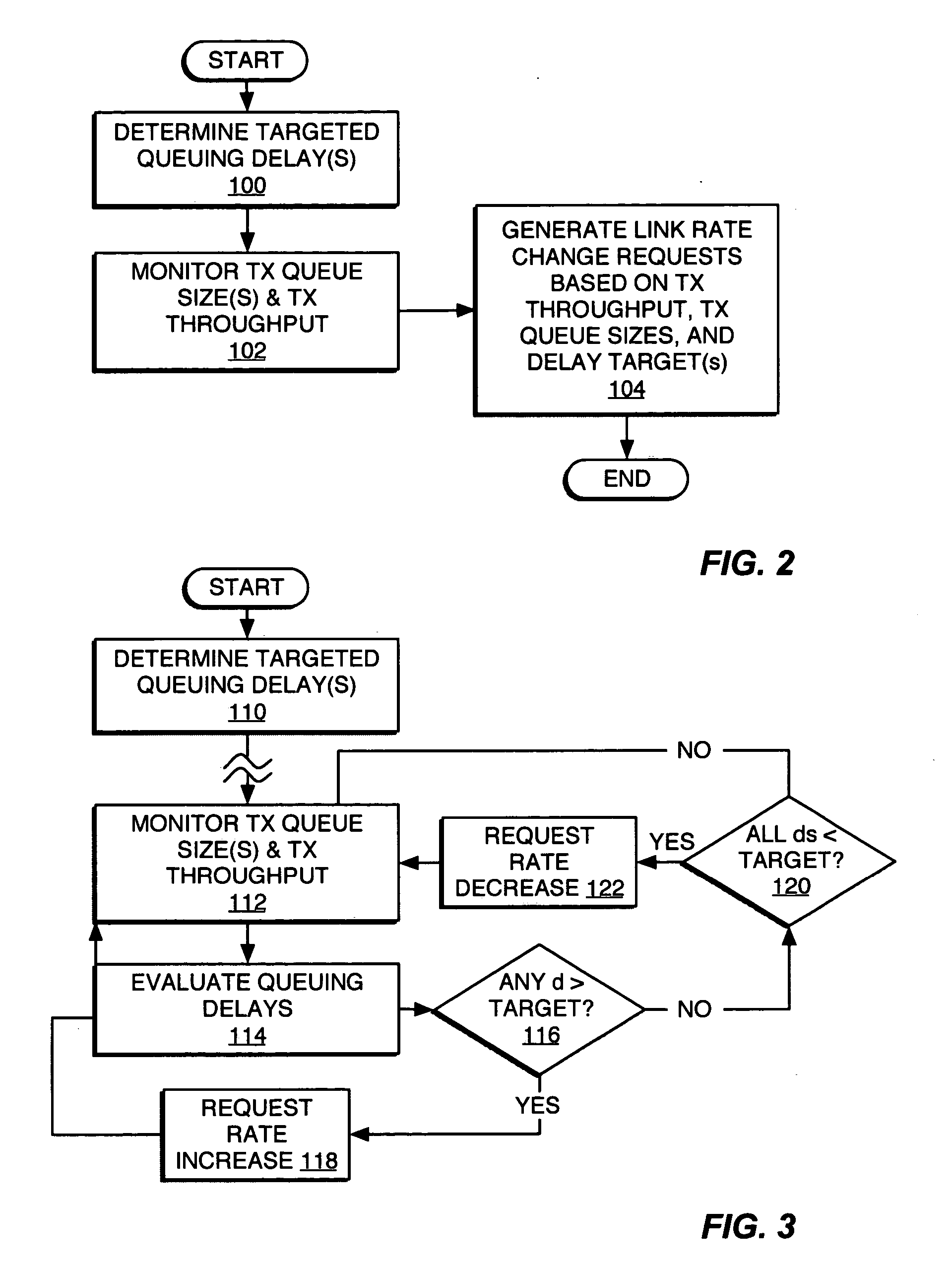
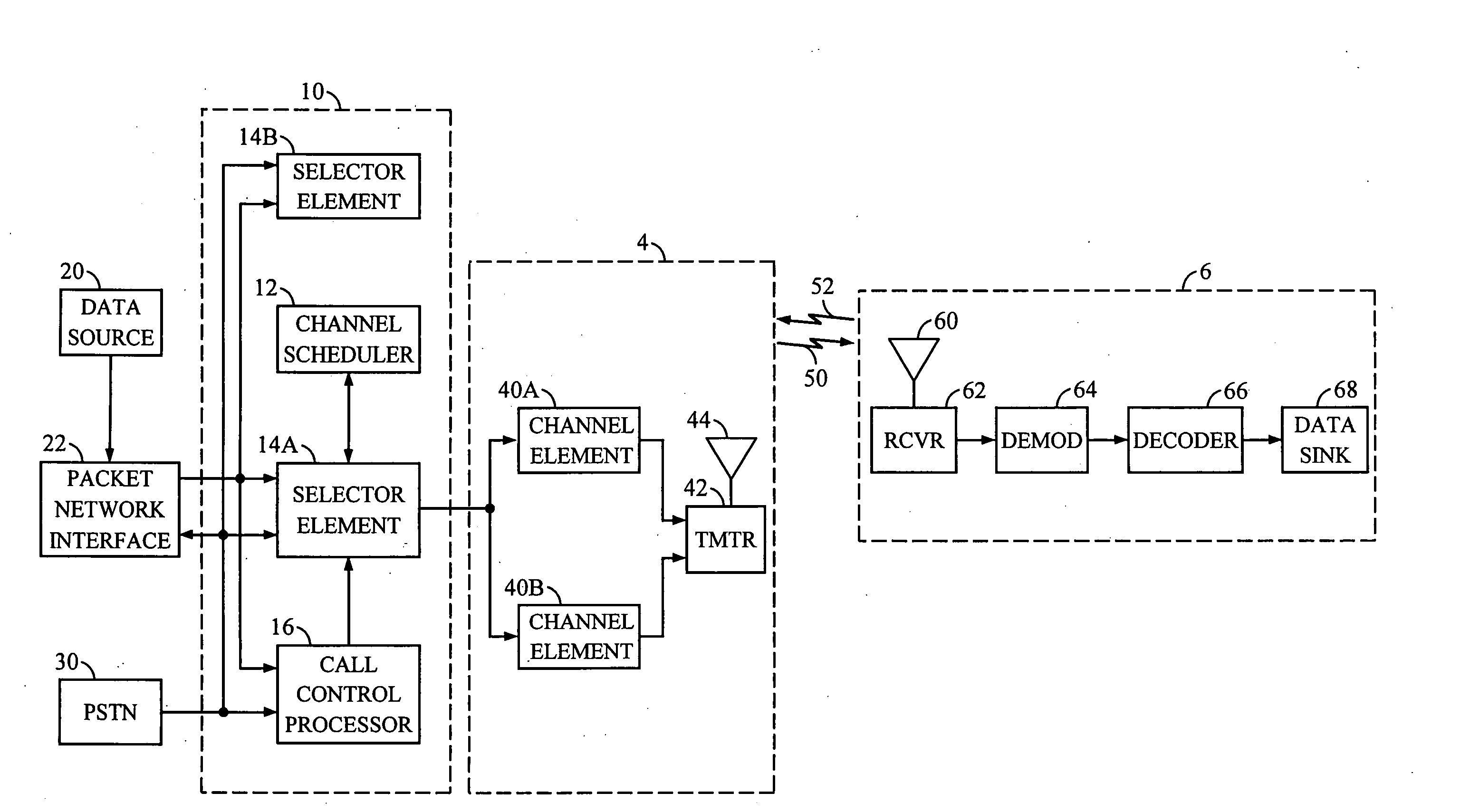
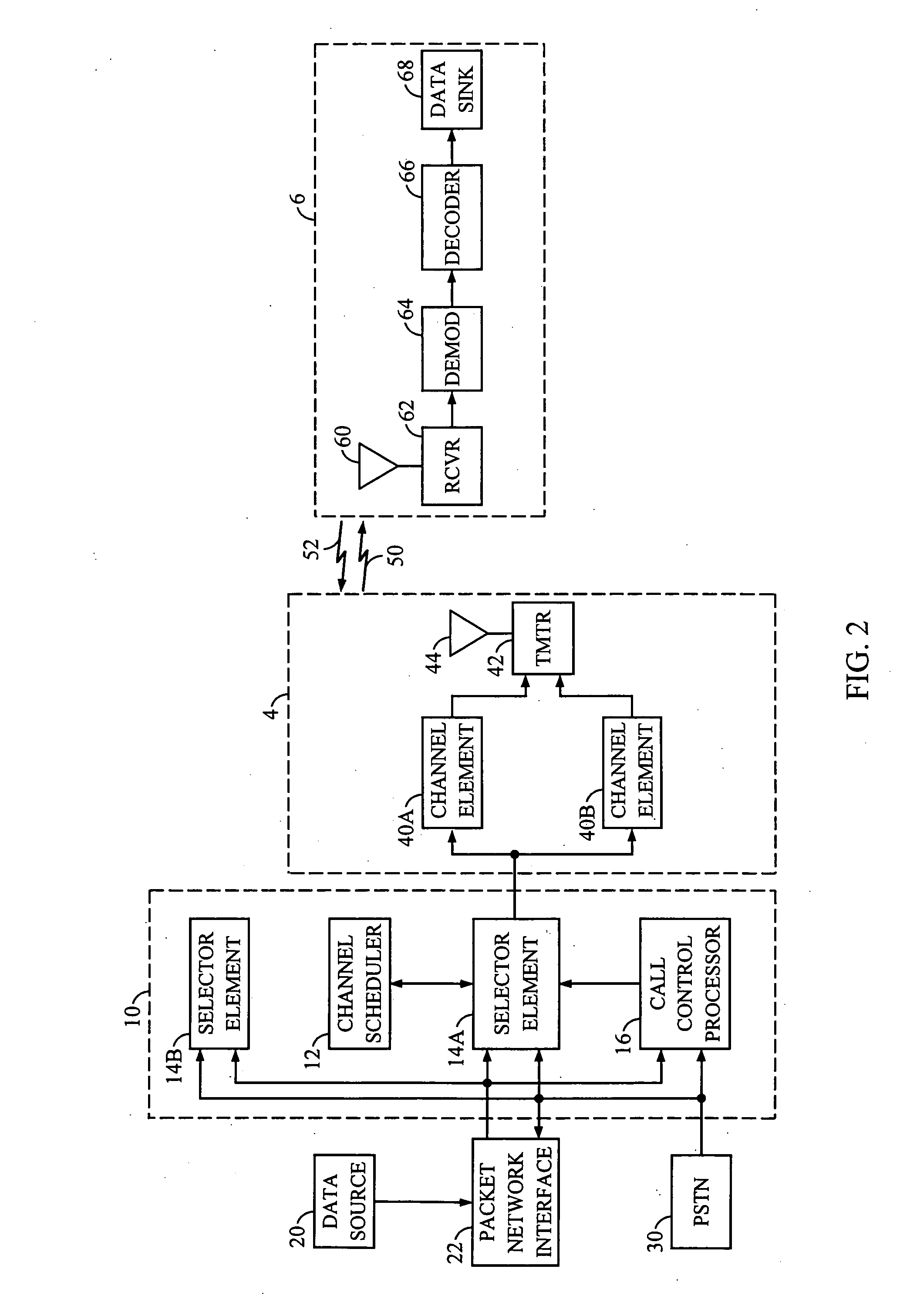
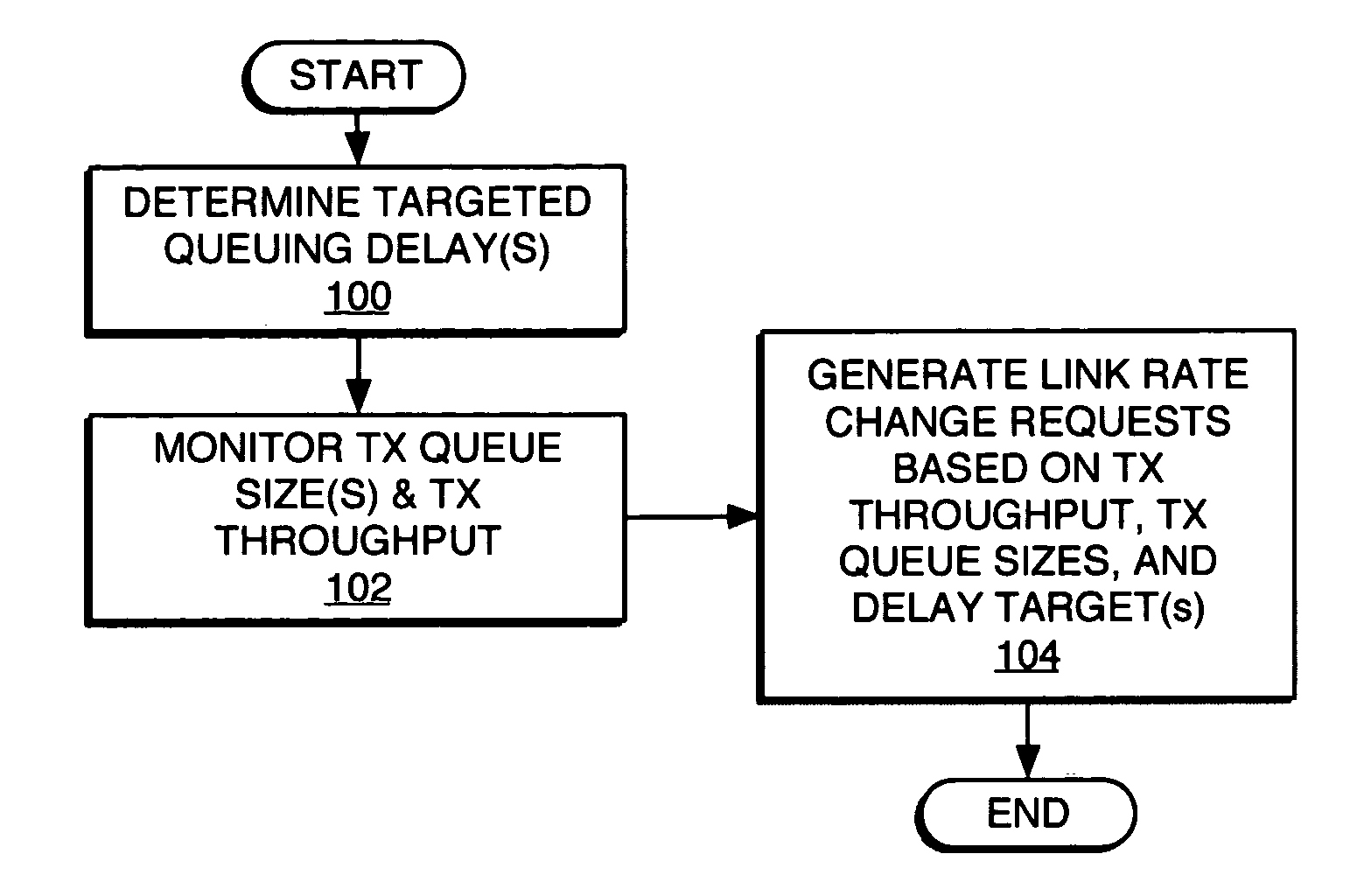
A method and apparatus for rate control adjusts or otherwise requests adjustment of a communication link data rate based on transmit queuing delays. For example, a mobile station may monitor expected transmit queuing delays relative to one or more delay targets or other Quality-of-Service constraints, and request reverse link rate increases or decreases accordingly. Similarly, the mobile station may be configured periodically to request reverse link rate changes based on determining the rate needed to meet targeted queuing delays for one or more service instances being supported by the mobile station in each of a succession of ongoing rate control intervals. Requested rates may be defined data rates or may be virtual rates that can be achieved by using combinations of defined data rates. Queuing-based rate control also can be applied to the base station's forward link, and, more broadly, to essentially any rate controlled communication link.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Delay sensitive adaptive quality control loop for rate adaptation
InactiveUS6915477B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelMultiple-port networksCommunications systemRate adaptation
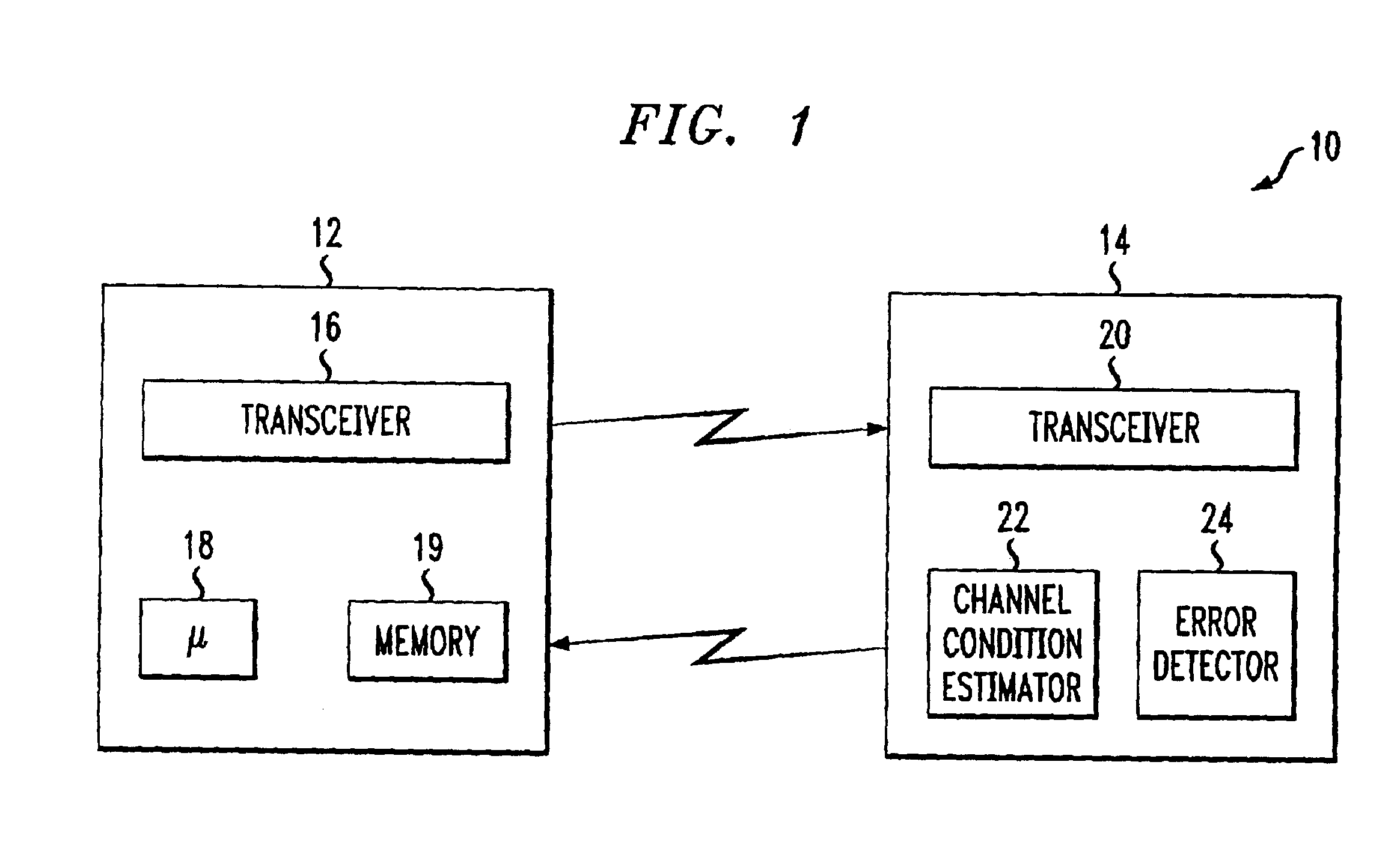
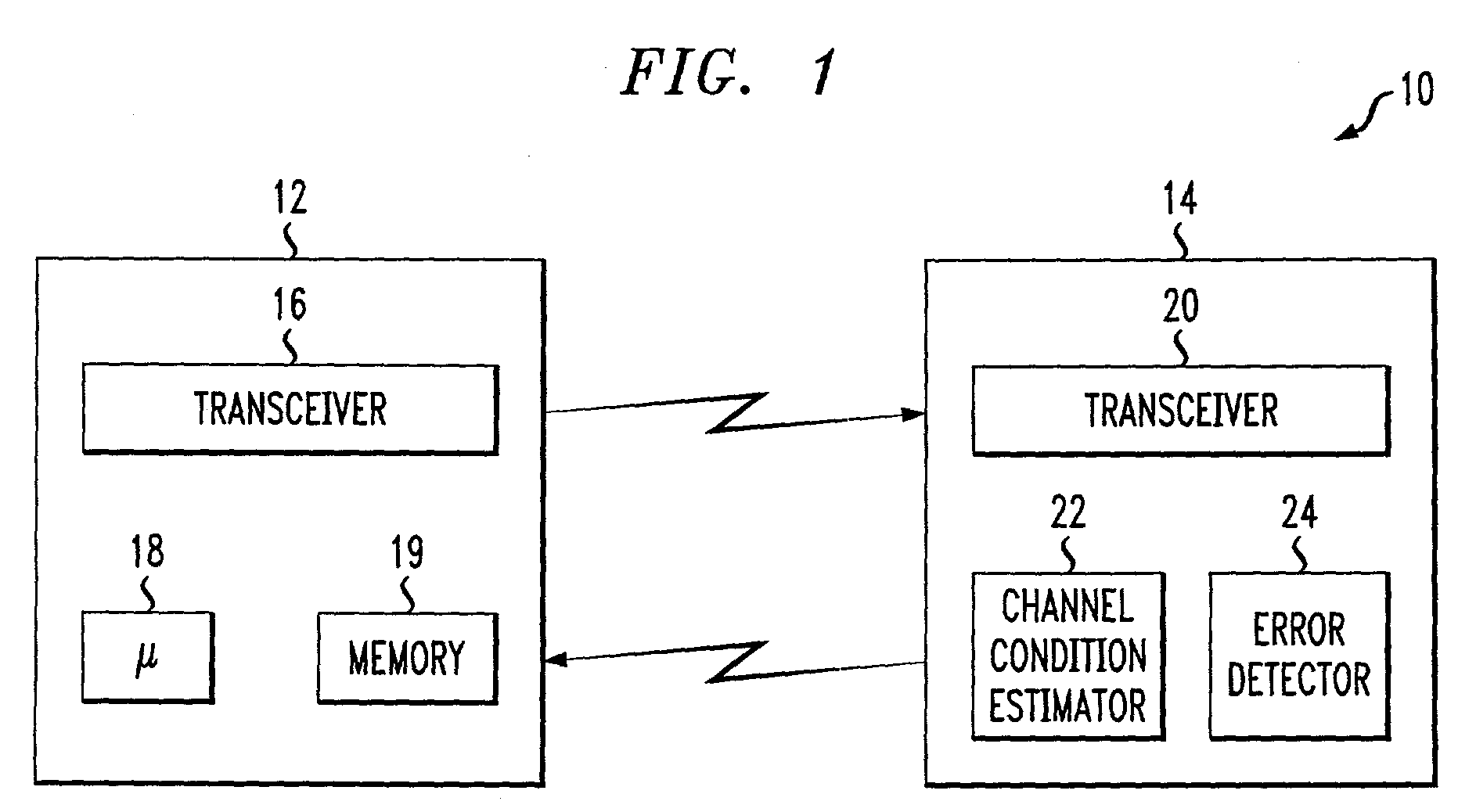
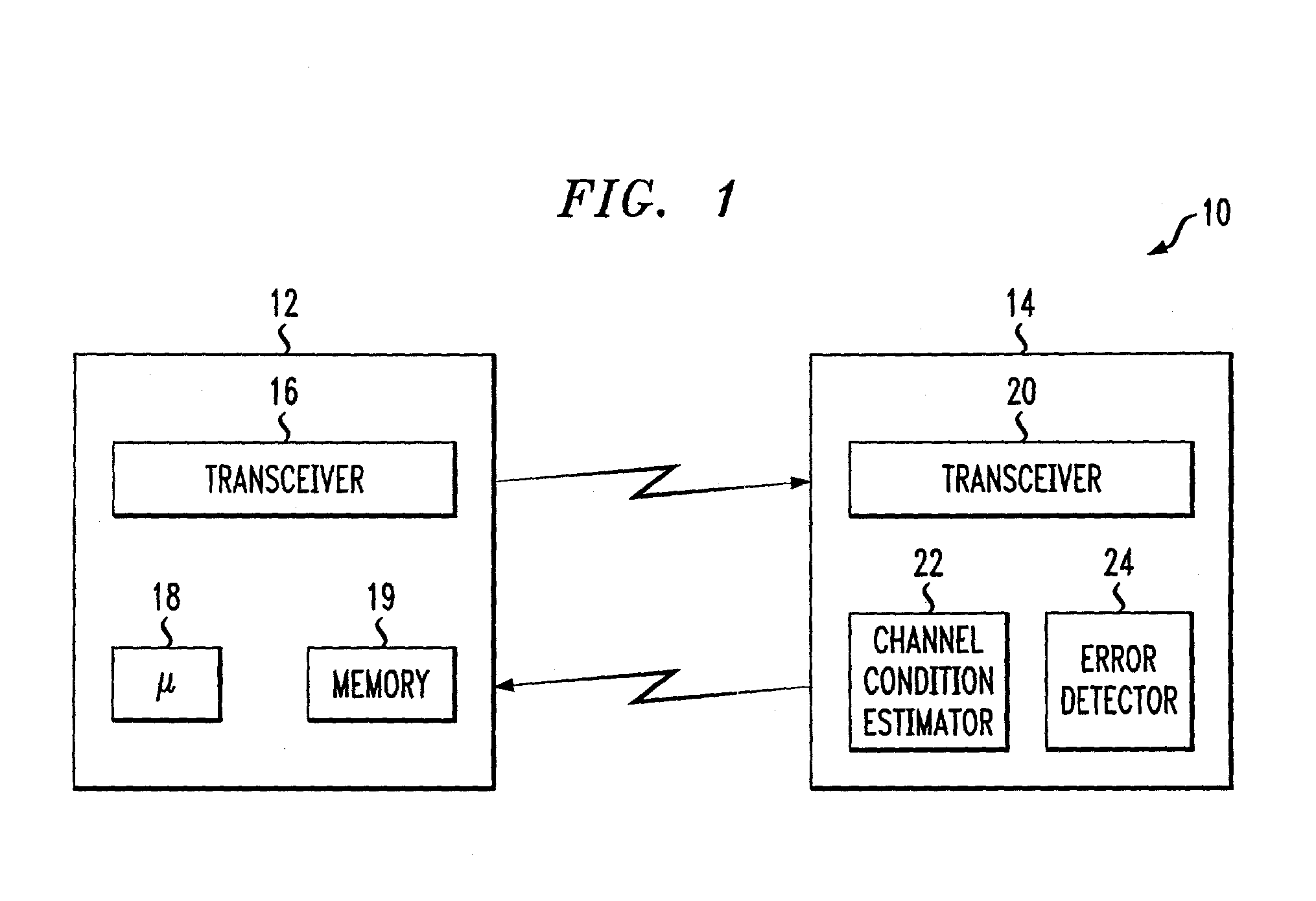
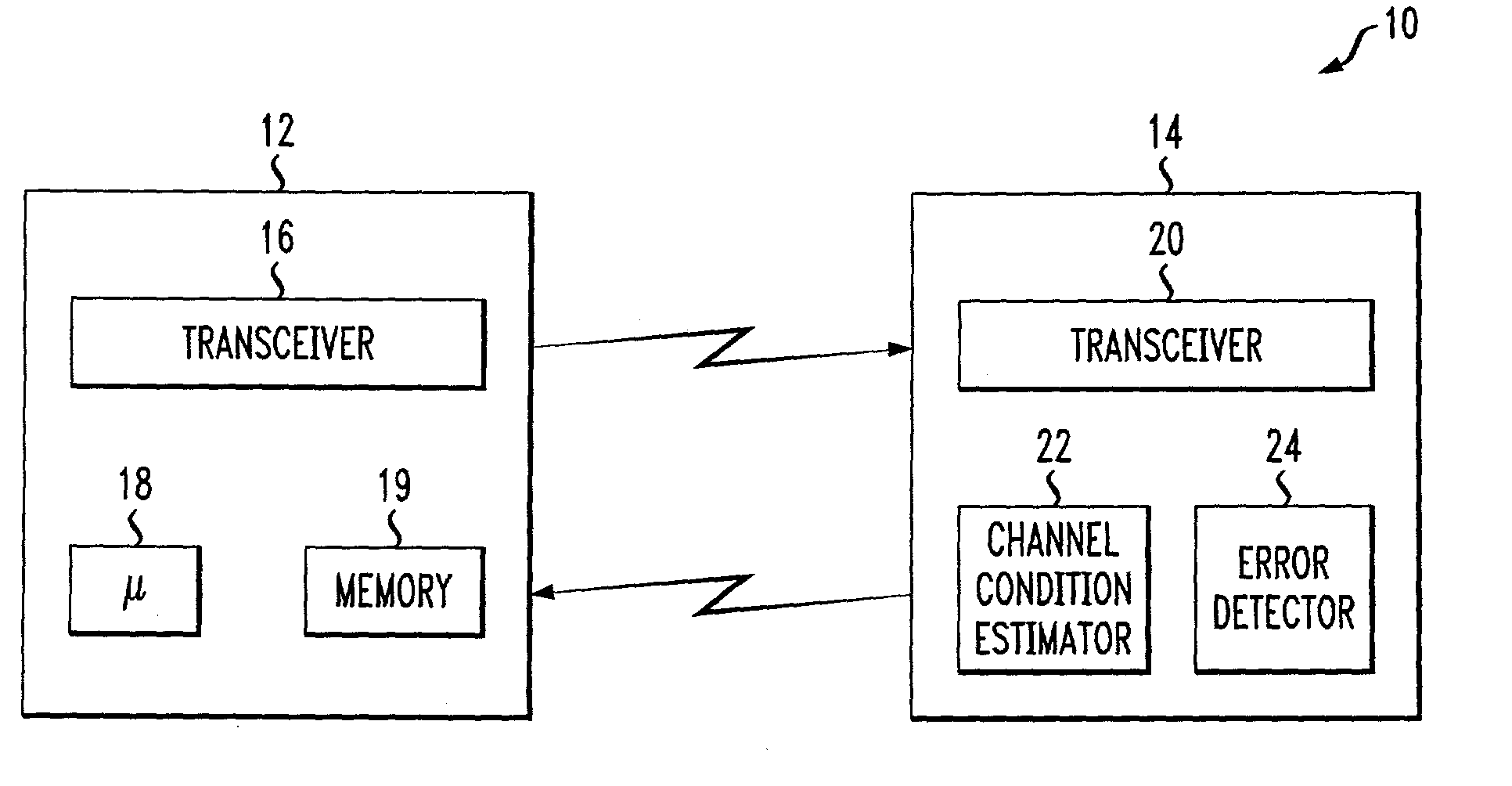
An adaptive quality control loop for link rate adaptation that selectively adjusts channel condition thresholds based on delay sensitivity of data packets being transmitted. For wireless communication systems incorporating an error correction scheme using re-transmissions, the quality control loop adaptively adjusts channel condition thresholds more frequently for delay sensitive data packets, such as video, and less frequently for delay insensitive data packets, such as text messaging. Channel condition thresholds may be adjusted using fixed or variable steps based on error detection results.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
A mobile terminal and its method for adaptively increasing the download rate
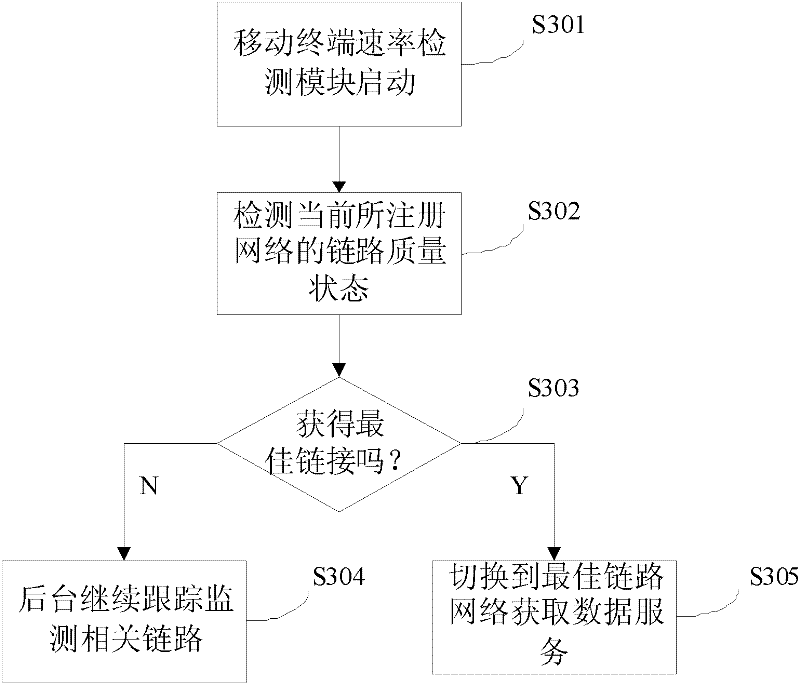
InactiveCN102264063AShorten development timeImprove versatilityAssess restrictionNetwork data managementDownload rateWireless data services
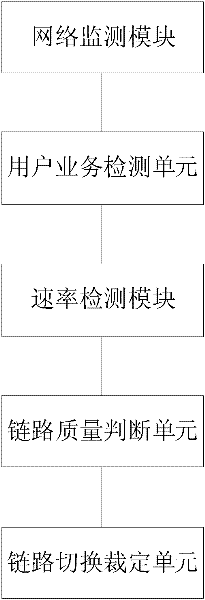
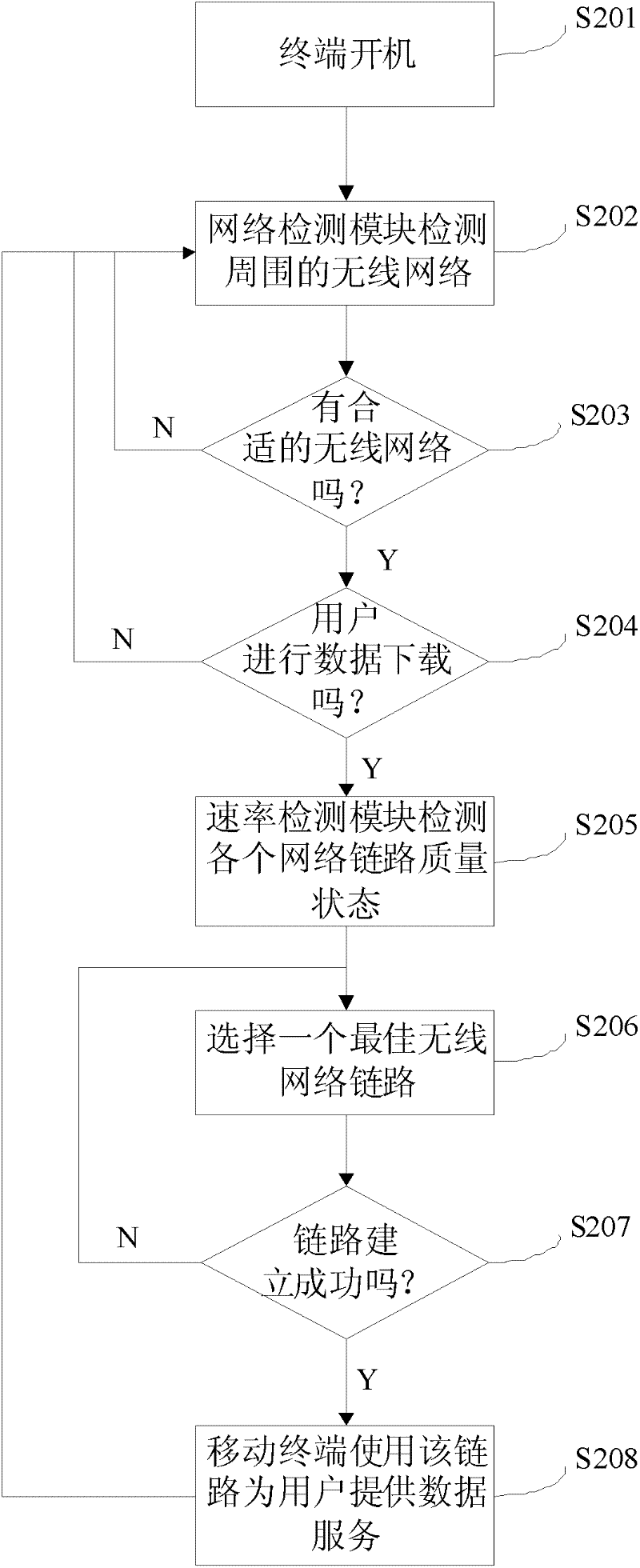
The invention provides a mobile terminal and a method for self-adaptively increasing the download rate thereof. The mobile terminal includes a network monitoring module, a rate detection module and a link switching arbitration unit; the network detection module detects wireless network signals around the mobile terminal; the rate detection module detects the network rate; the link switching The arbitrating unit switches the link for the mobile communication terminal to provide wireless data services to the best link according to the above detection results. The technical solution of the present invention does not require additional protocol development on mobile devices, saves development time, and has better versatility and standardization, and can be widely used in mobile devices with universal access functions, such as mobile phones, data Network cards and other products.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method and apparatus for forward link rate scheduling
InactiveUS7054293B2Increase profitReduce transmission delayPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementHigh rateCommunications system
In a communication system capable of variable rate transmission, scheduling of high speed data transmission improves utilization of the forward link and decreases the transmission delay in data communication. Each remote station is assigned one primary code channel for the duration of the communication with a cell. Secondary code channels of various types and transmission capabilities can be assigned by a channel scheduler for scheduled transmission of data traffic at high rates. Secondary code channels are assigned in accordance with a set of system goals, a list of parameters, and collected information on the status of the communication network. Secondary code channels can be grouped into sets of secondary code channels. Data is partitioned in data frames and transmitted over the primary and secondary code channels which have been assigned to the scheduled user.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Packet based stream transport scheduler and methods of use thereof
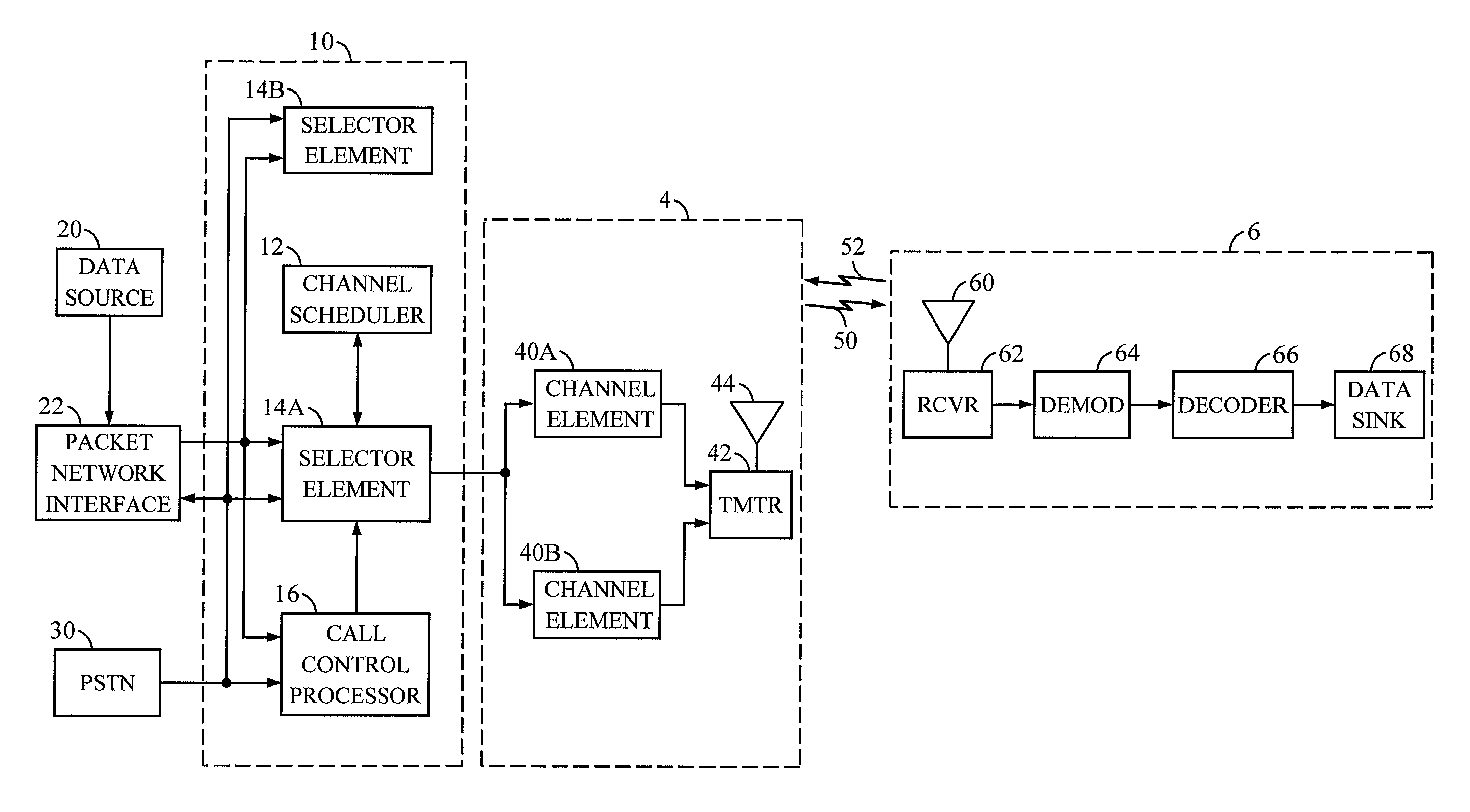
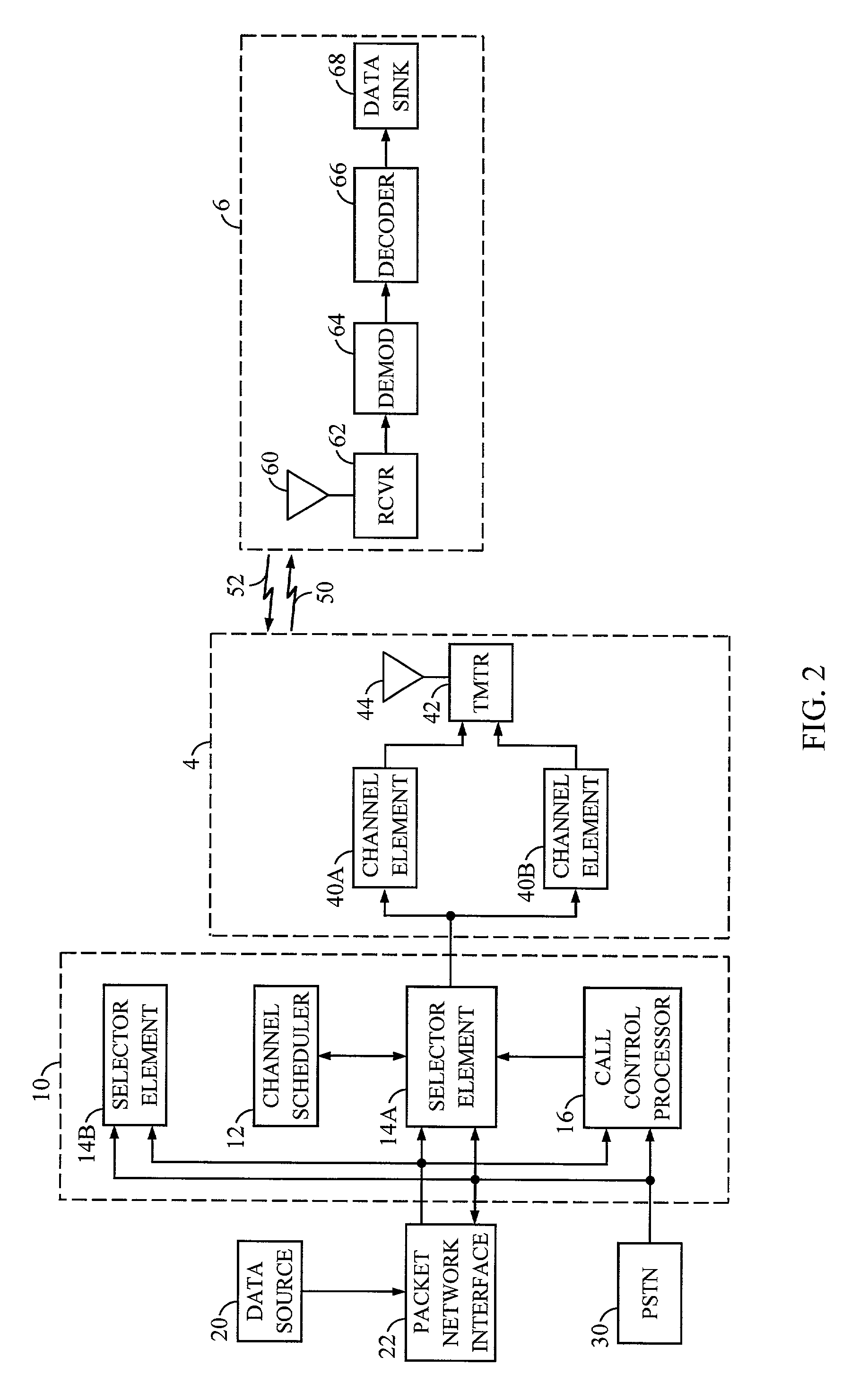
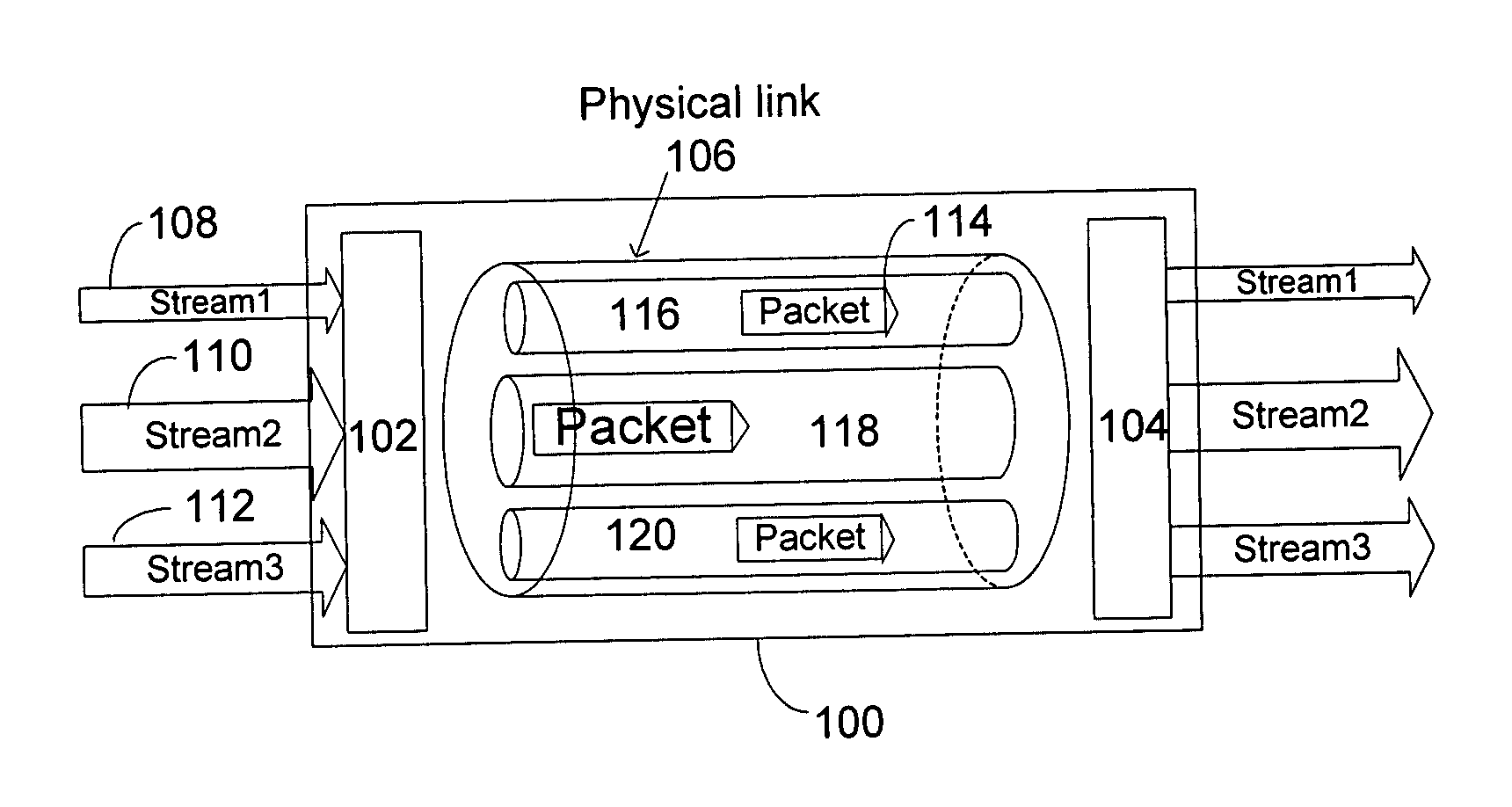
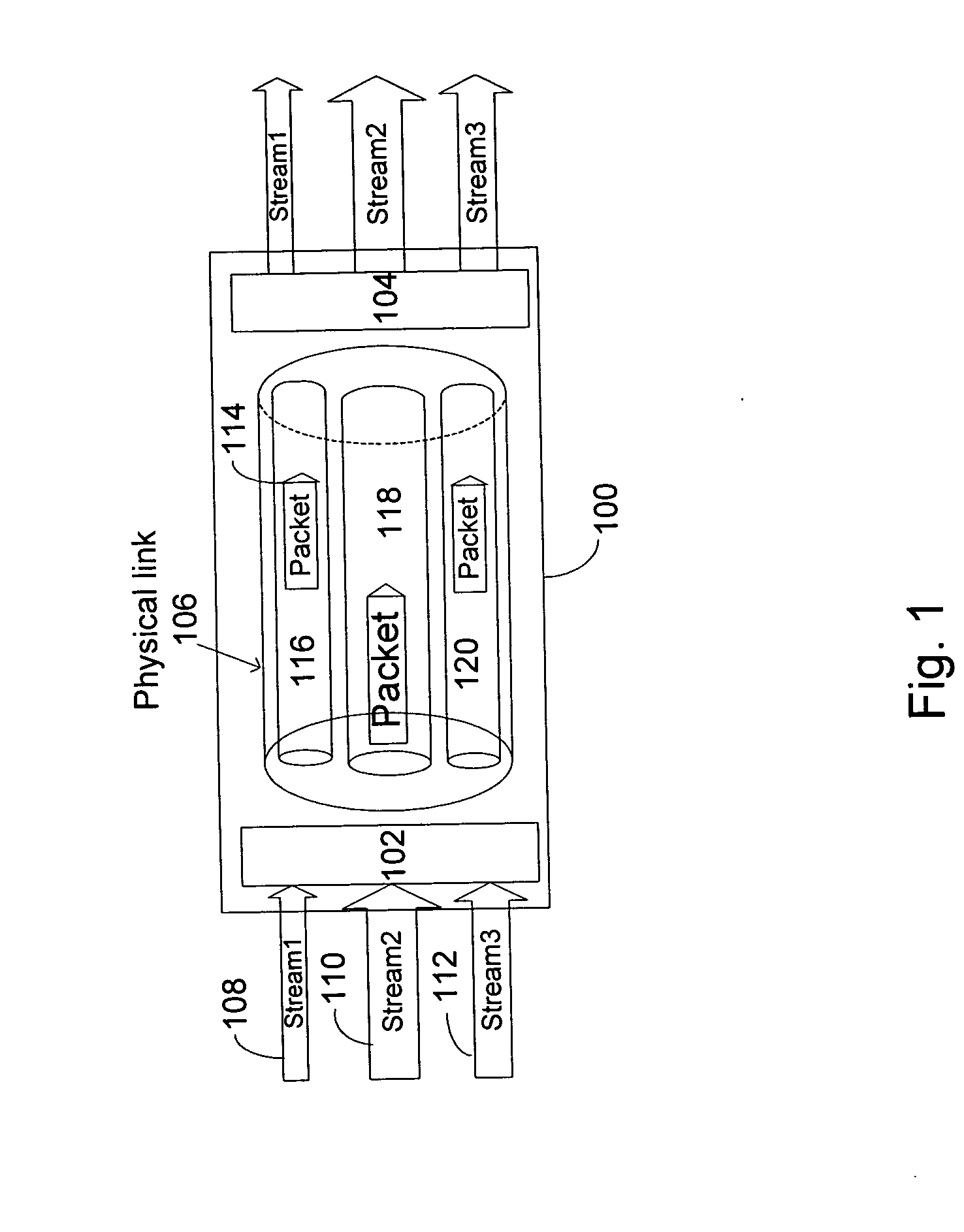
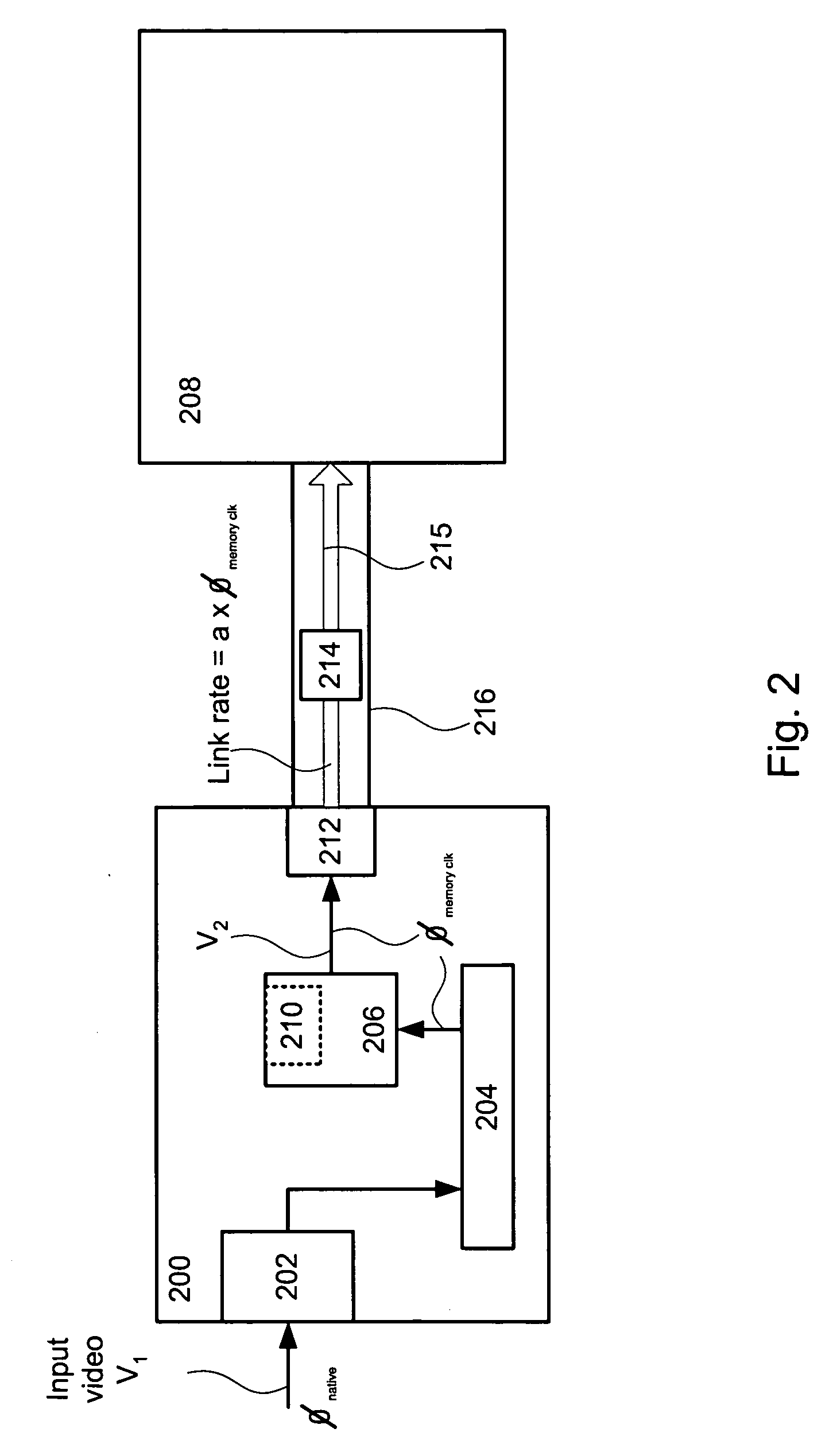
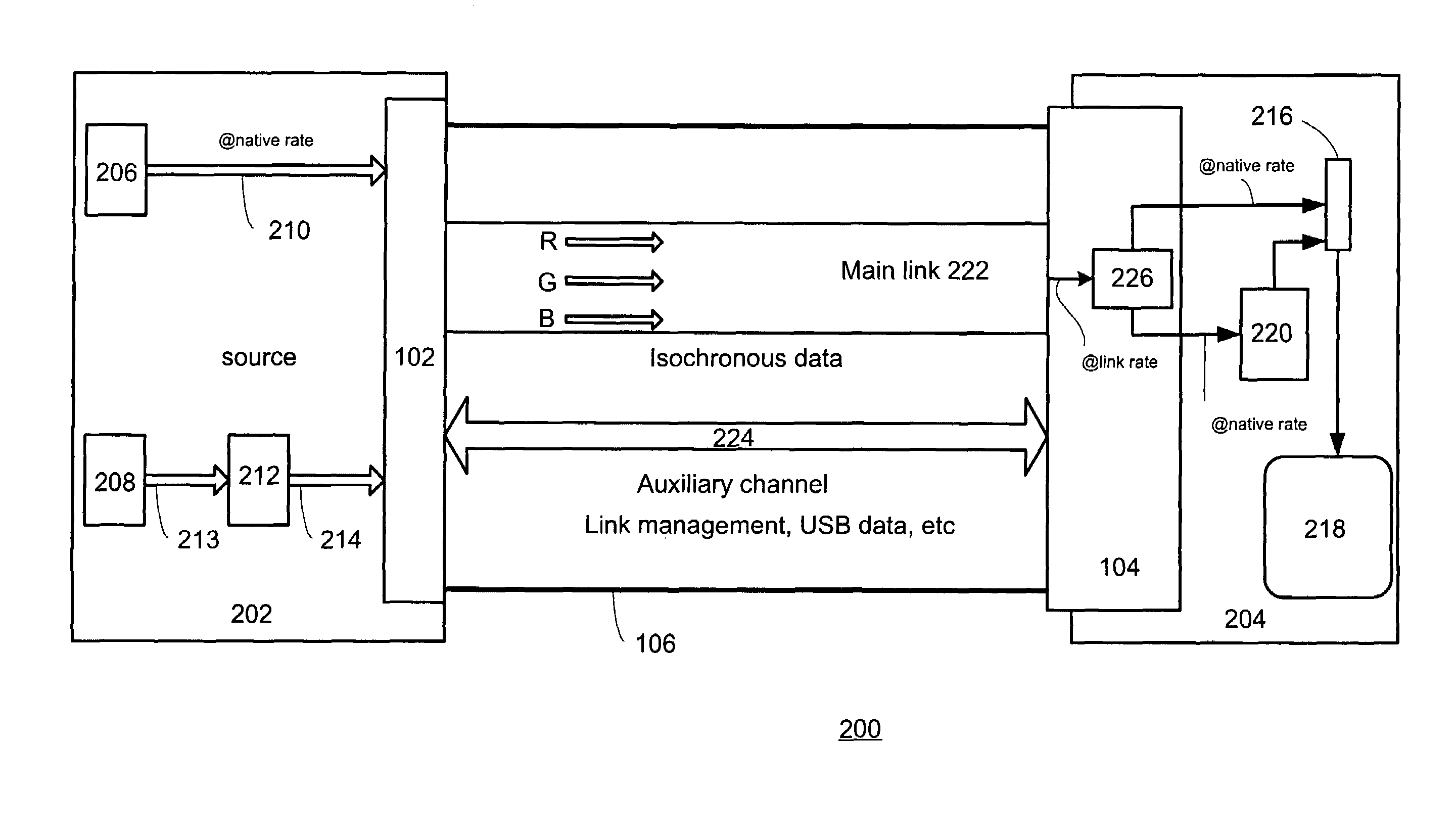
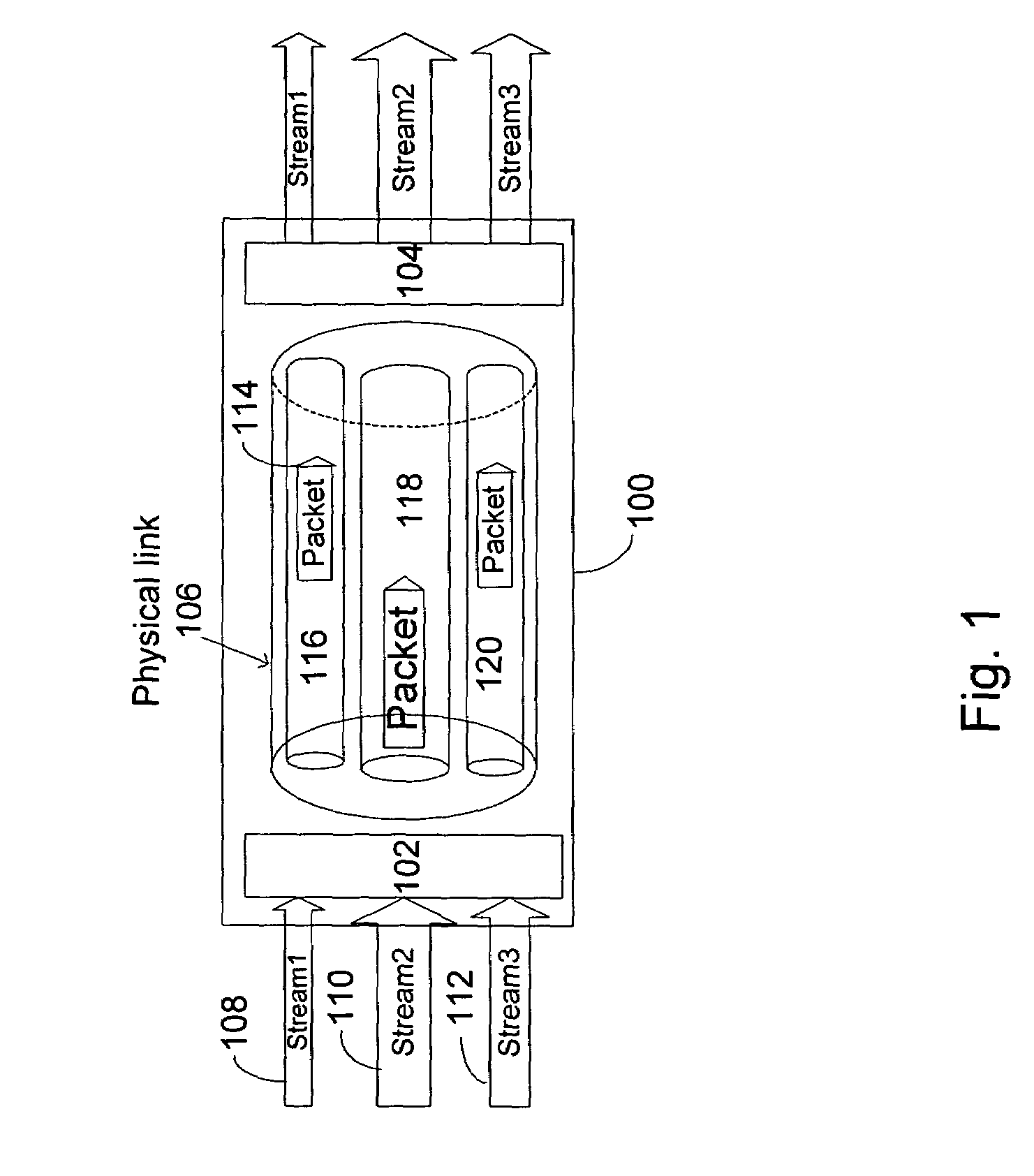
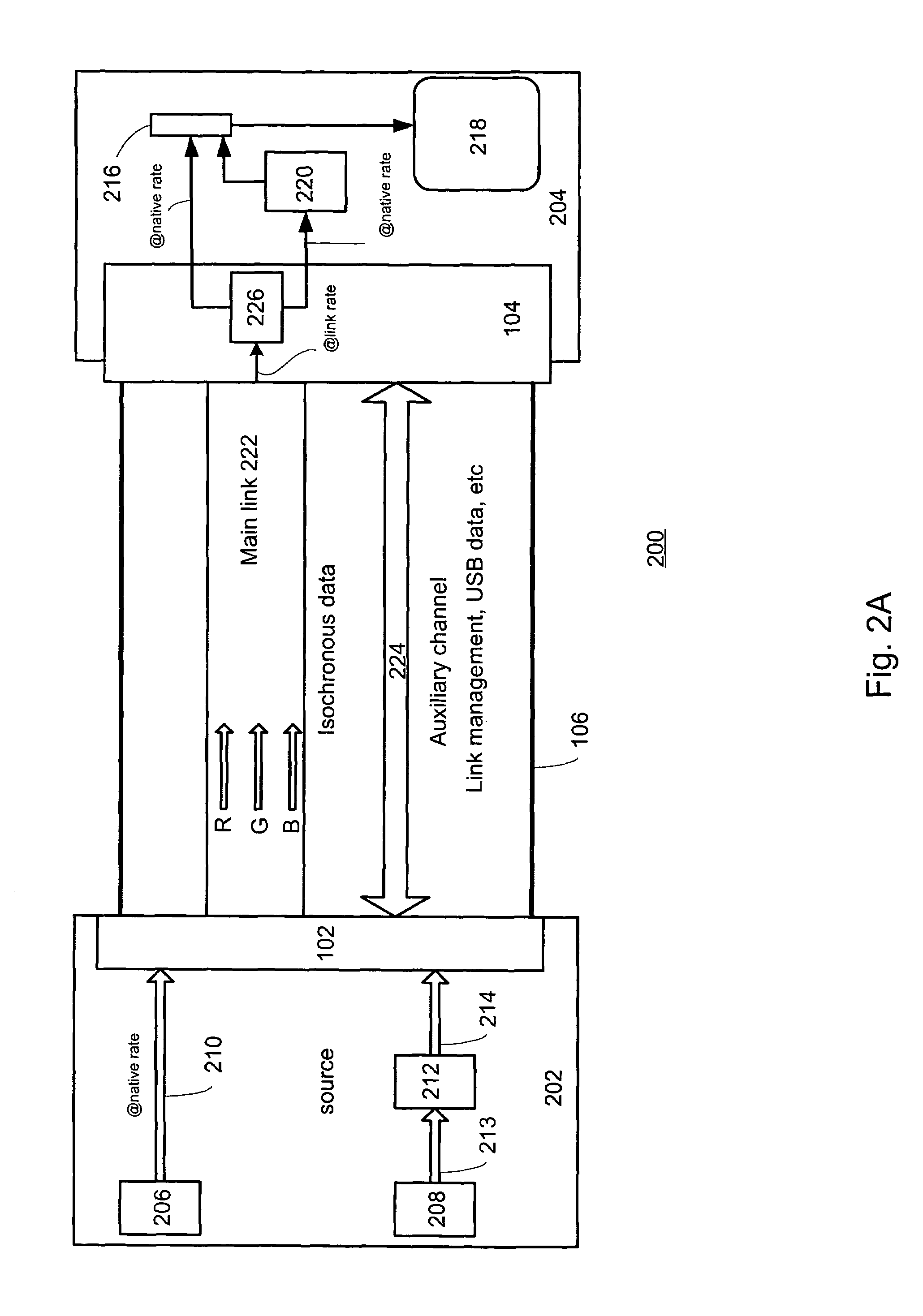
A method of coupling a multimedia source device to a multimedia sink device by providing a source device having a transmitter unit coupled thereto, providing sink device having a receiver unit coupled thereto, receiving a source data stream in accordance with a native stream rate by the transmitter unit, coupling the transmitter unit and the receiver unit by way of a linking unit, forming a multimedia data packet stream formed of a number of multimedia data packets and generating a transport schedule for transferring the multimedia data packet stream in accordance with a link rate between the transmitter unit and the receiver unit wherein the multimedia data
Owner:GENESIS MICROCHIP
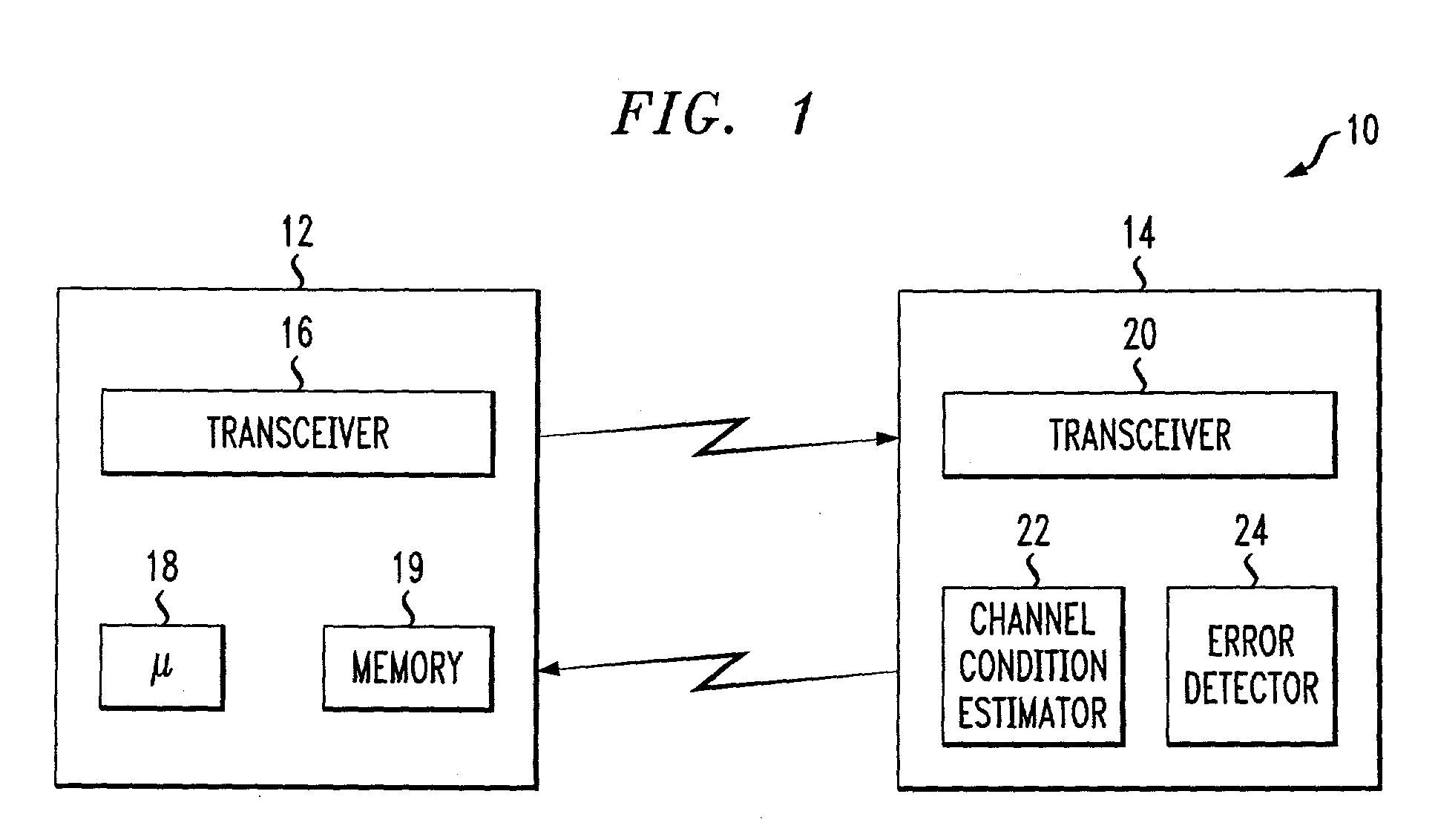
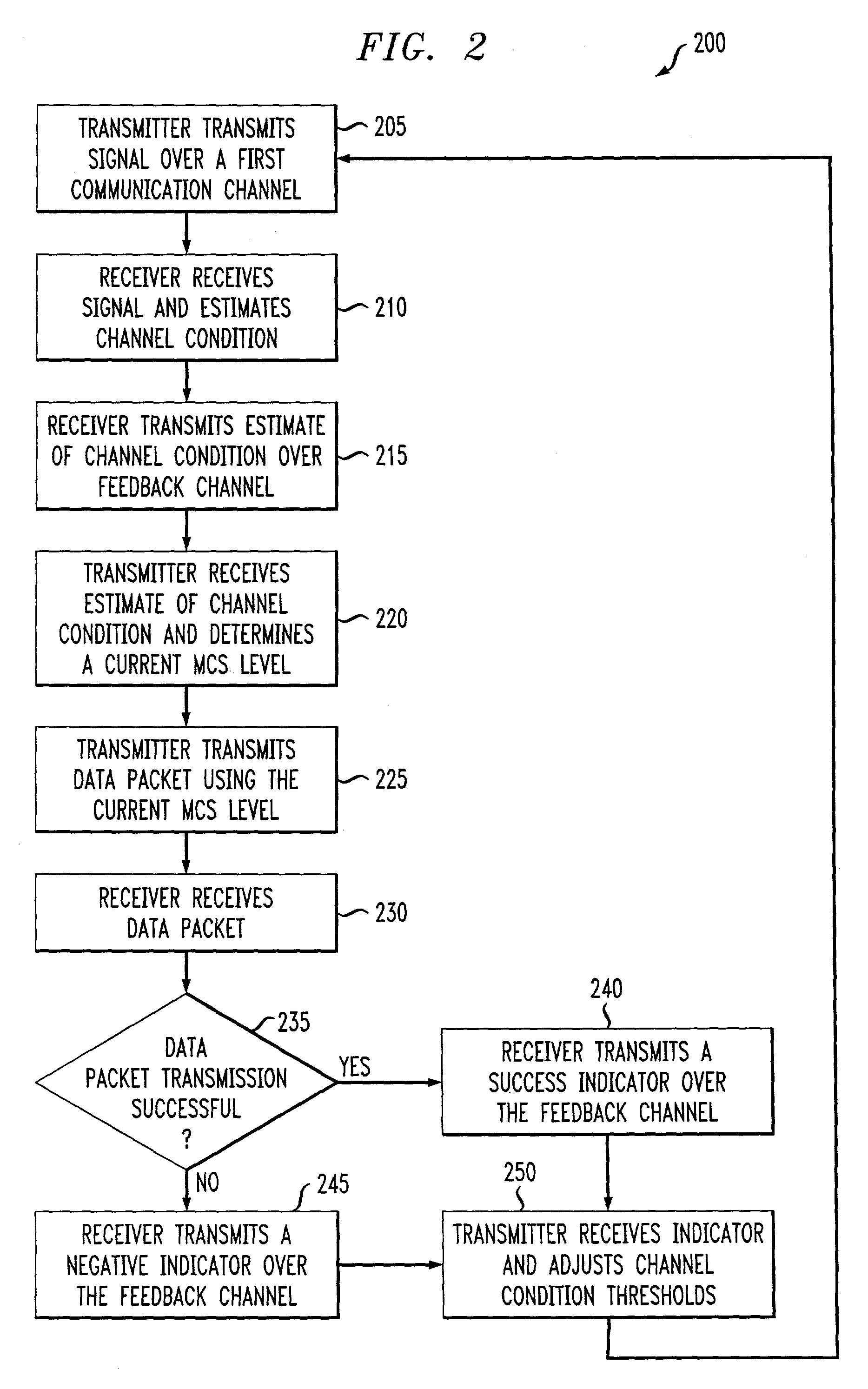
Multi-channel adapative quality control loop for link rate adaptation in data packet communications
InactiveUS20030123598A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission monitoringPacket communicationRate adaptation
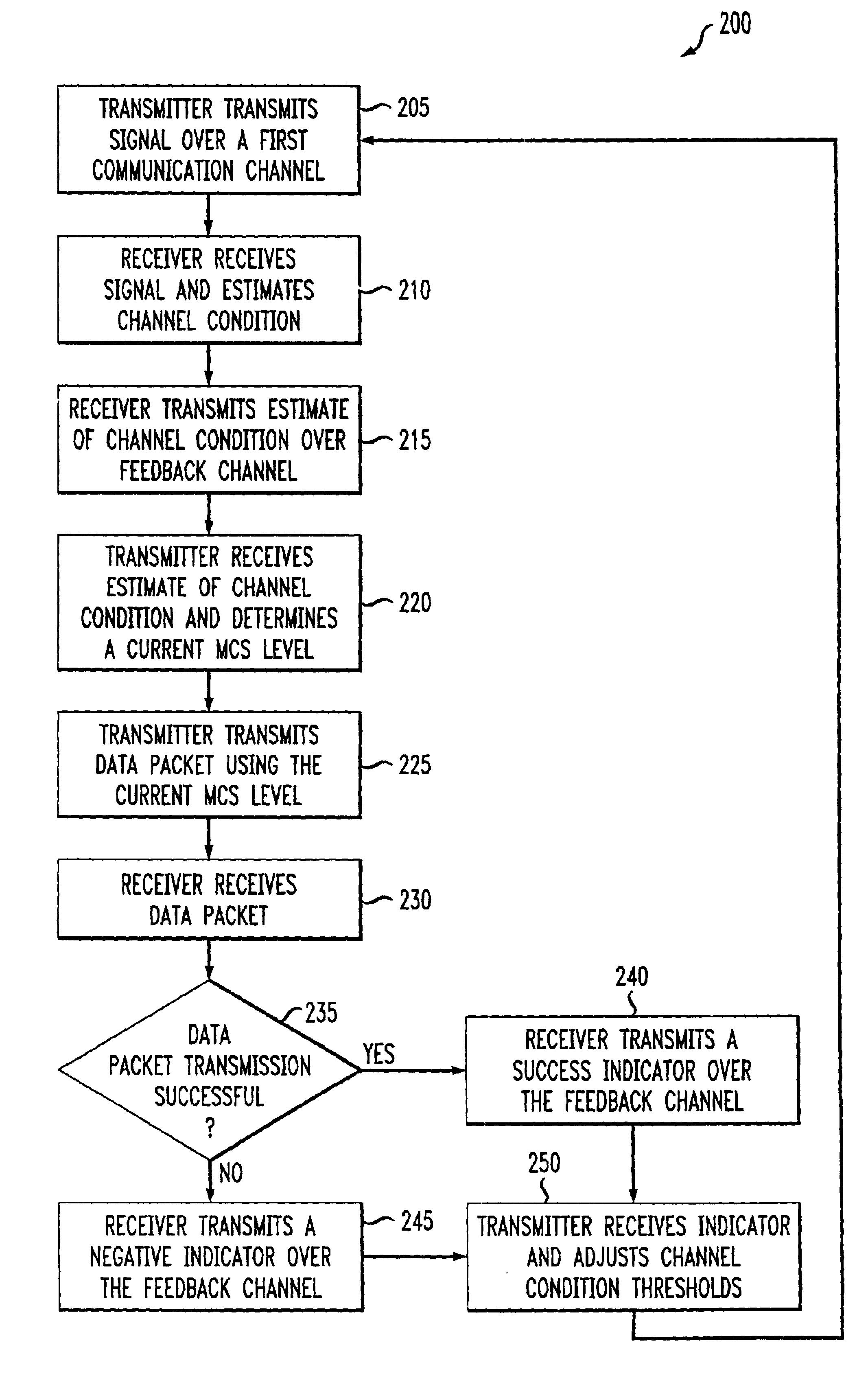
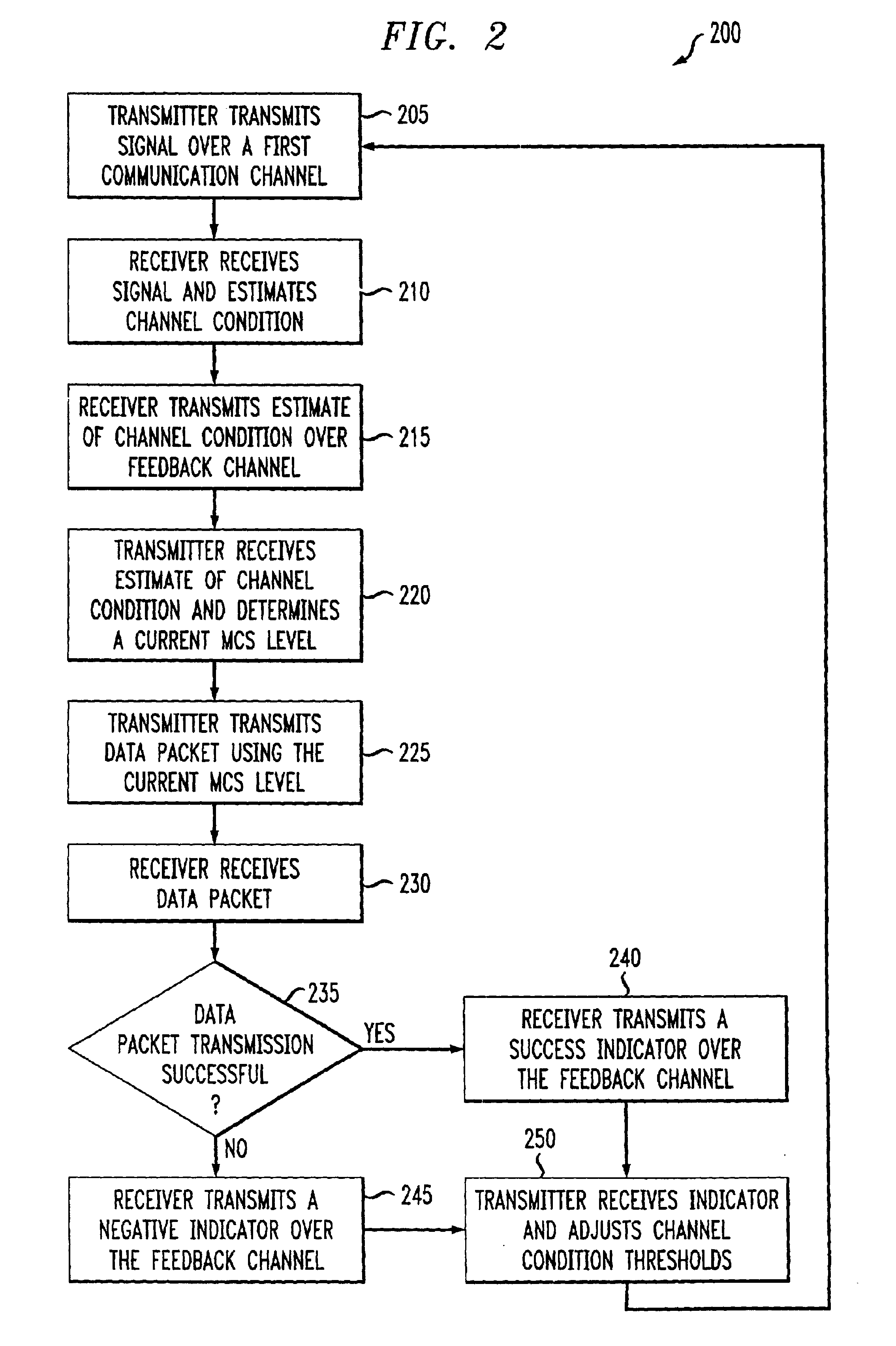
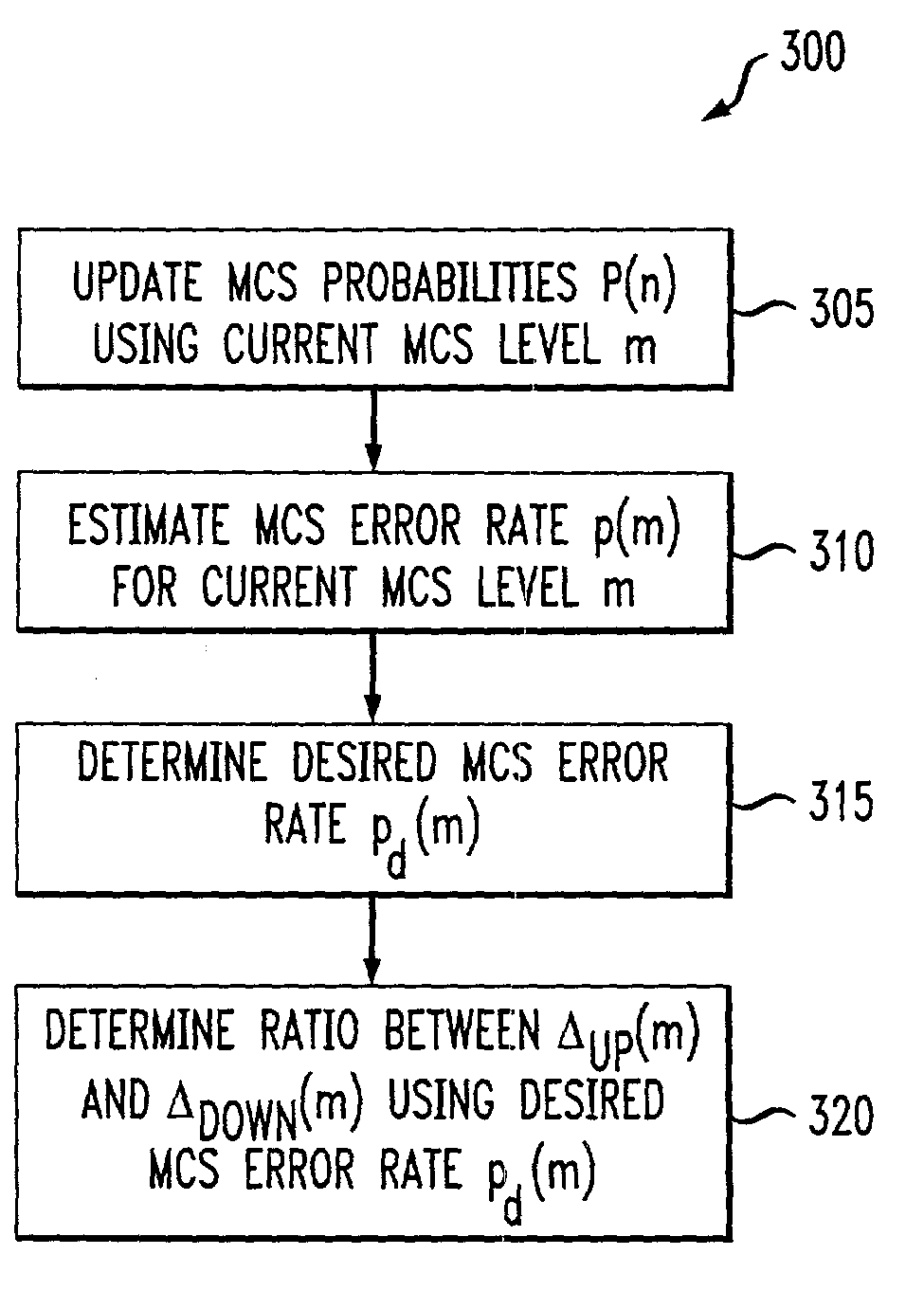
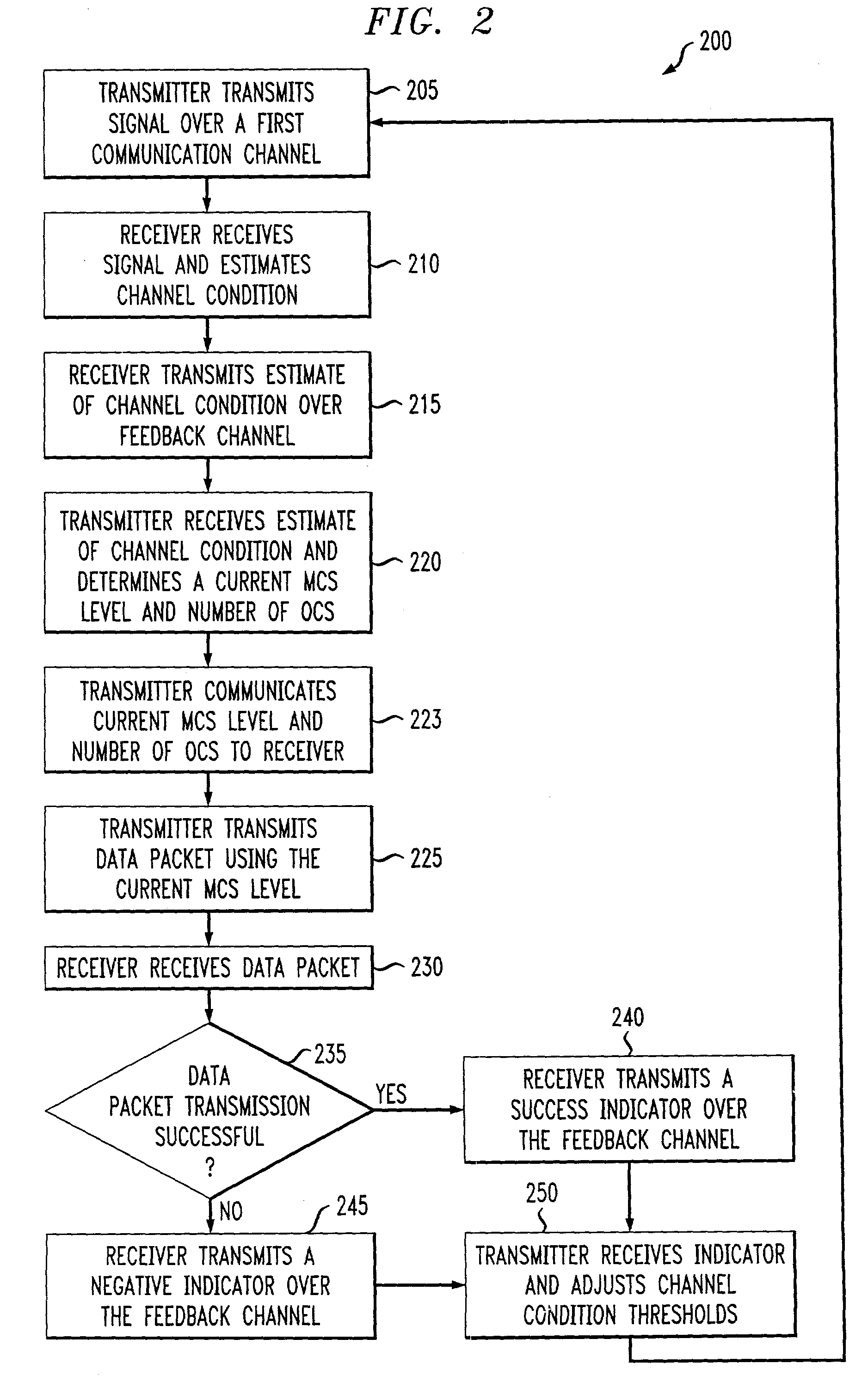
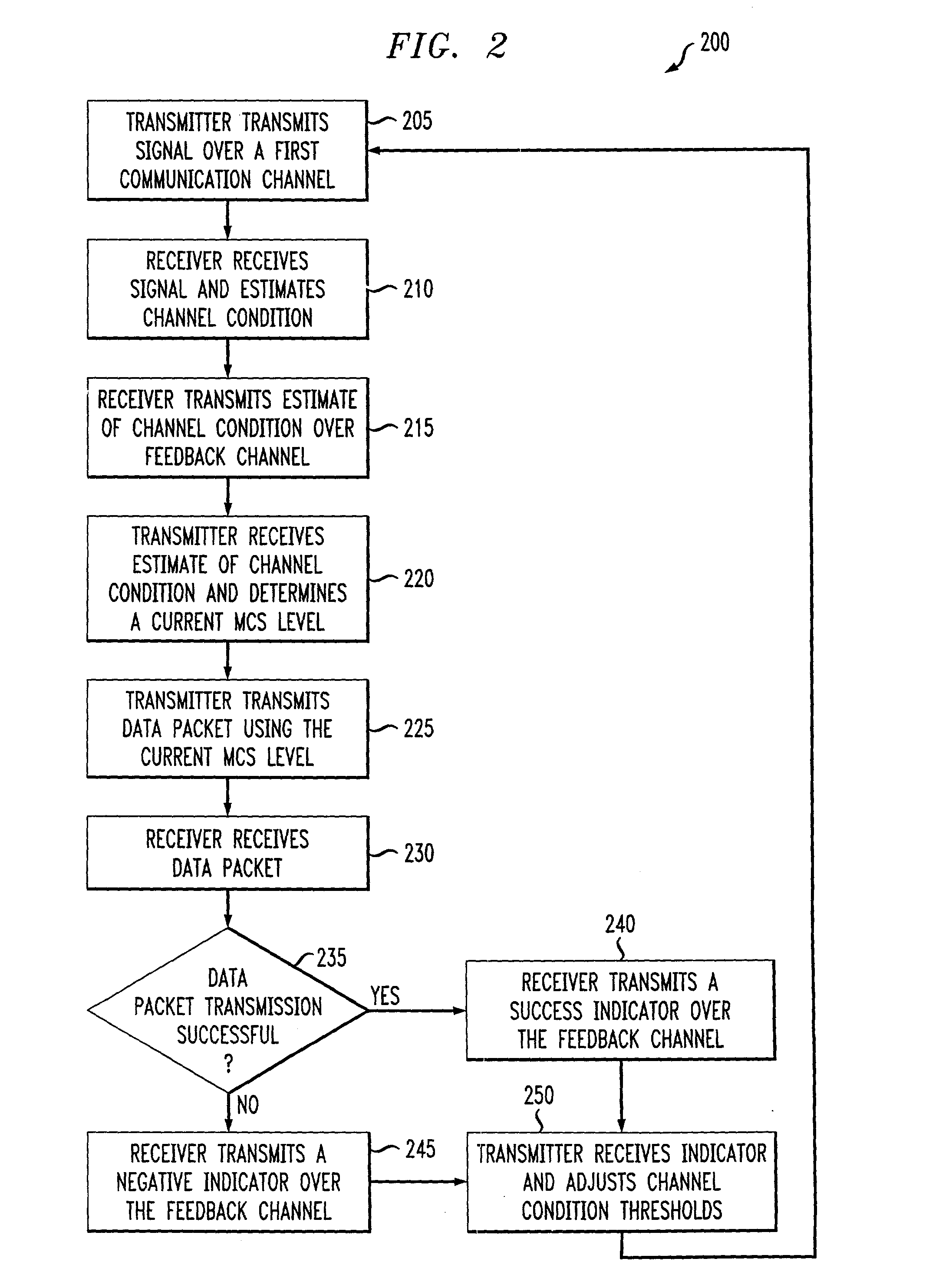
An adaptive quality control loop for link rate adaptation based on modulation and / or coding schemes (also referred to as "MCS levels") and one or more spreading codes that adaptively selects channel condition thresholds in real-time without measuring all the factors that affect selecting optimal channel condition thresholds. The adaptive quality control loop involves adjusting the channel condition thresholds with variable up and down steps based on target quality metrics along with measurements such as error detection results, relative frequencies of visiting each MCS level, and transmitted data rates, wherein the target quality metrics can be a block error rate or bit error rate target criterion. If the target quality metric is a block error rate target criterion, the variable step is determined using a desired MCS error rate based on MCS probabilities, MCS error rates and the block error rate target criterion. If the target quality metric is a bit error rate target criterion, the variable step is determined using a desired MCS error rate based on MCS probabilities, MCS error rates, average rate of bit errors, data rate, and the bit error rate target criterion.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Delay sensitive adapative quality control loop for rate adaptation
InactiveUS20030126536A1Multiple-port networksError prevention/detection by using return channelRate adaptationCommunications system
An adaptive quality control loop for link rate adaptation that selectively adjusts channel condition thresholds based on delay sensitivity of data packets being transmitted. For wireless communication systems incorporating an error correction scheme using retransmissions, the quality control loop adaptively adjusts channel condition thresholds more frequently for delay sensitive data packets, such as video, and less frequently for delay insensitive data packets, such as text messaging. Channel condition thresholds may be adjusted using fixed or variable steps based on error detection results.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Using packet transfer for driving LCD panel driver electronics
ActiveUS20050062711A1Increase speedImprove the display effectTelevision system detailsColor television detailsData packDisplay device
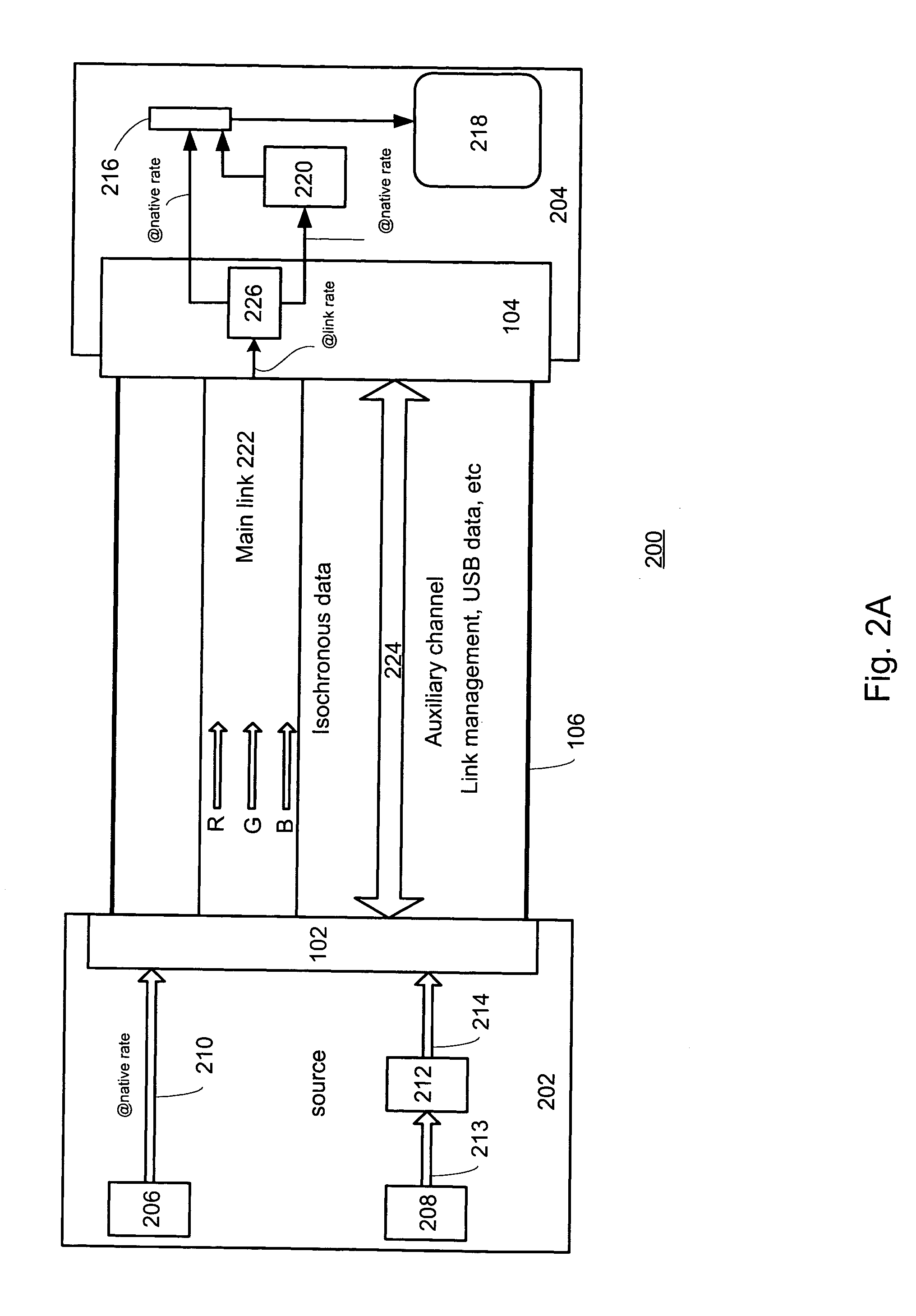
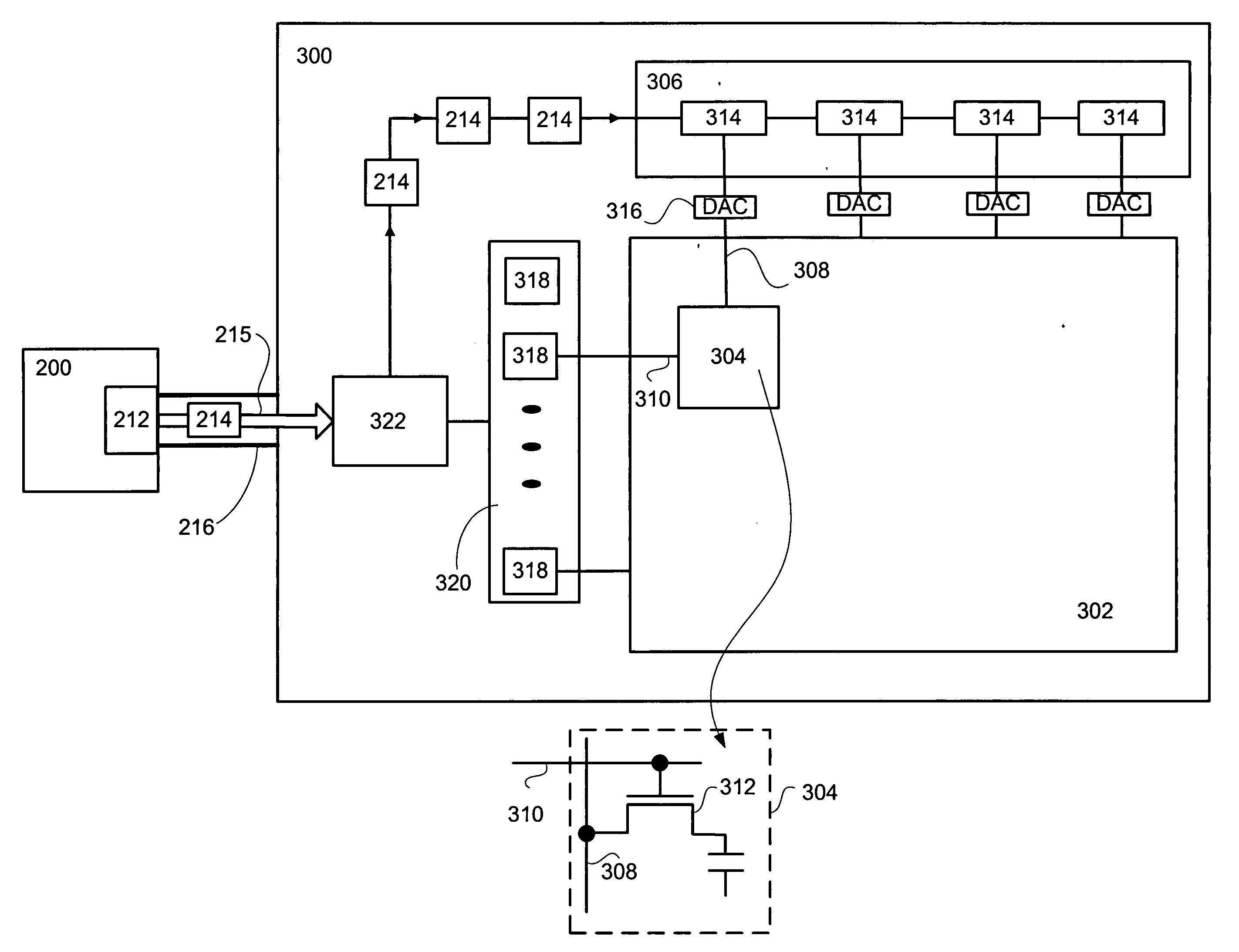
In a digital display device, a packet based method of driving selected pixel elements by way of associated data latches included in a column driver is disclosed. For each frame lines in a video frame, a number of video data packets are provided directly to the column driver at a link rate and each of the number of data latches are populated with appropriate video data based upon video data packets within a line period τ. Selected pixel elements are driven based upon the video data.
Owner:GENESIS MICROCHIP
Bypassing pixel clock generation and CRTC circuits in a graphics controller chip
In a video processor unit, a method of providing a video data stream at a clock rate that is independent of a pixel clock rate. Receiving native video data from a video source at a native clock rate, storing the video data in a memory unit, reading selected portions of the video data at a memory clock rate, rasterizing the selected video data, packetizing the rasterized video data, sending the packetized video data to a display unit by way of a link at a link rate, wherein the link rate is directly related to the memory clock rate.
Owner:GENESIS MICROCHIP
Dynamic reverse link rate limit algorithm for high data rate system
InactiveUS6999425B2Minimize irregularityNetwork traffic/resource managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsRate limitingMoving average
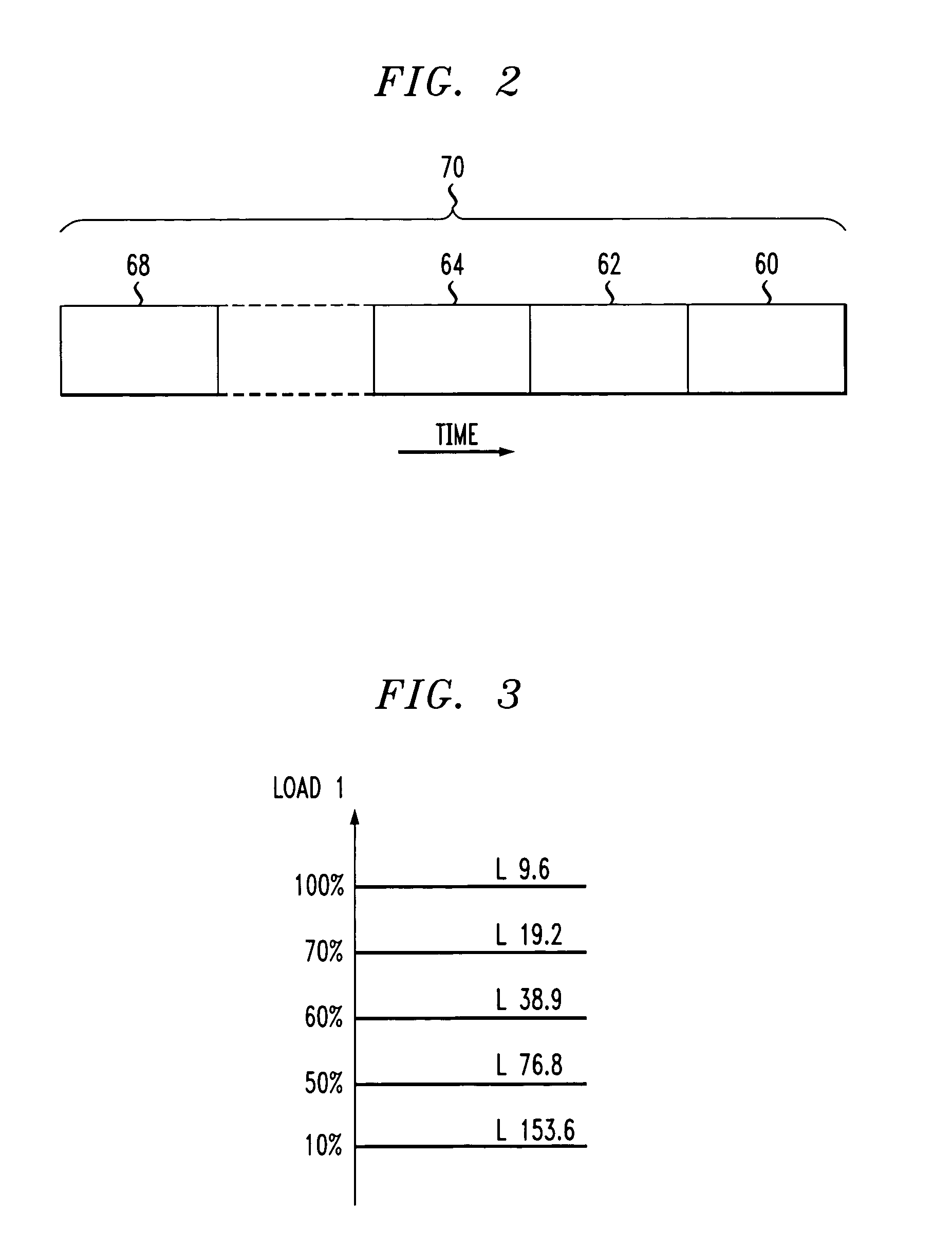
A method for determining the reverse link data Rate Limit for mobile stations active on the reverse link of a High Data Rate system is disclosed. In the ideal case, the Rate Limit is based on only the number of mobile stations located in a common sector that are actually active on the reverse link. Currently, the Rate Limit is determined from the total number of mobile stations in a common sector where the total includes mobiles that are transmitting and receiving. Thus, the current method includes mobile stations that are active on the forward link and may not be active on the reverse link. In this invention, a more optimum method of estimating the reverse link loading is obtained from calculations which includes only the mobile stations which are active on the reverse link. An estimate of the reverse link loading of the mobile stations in a common cell is obtained by adding together the data rates of the data sent from each mobile in a common sector during a common frame. This aggregate rate of data during the frame is filtered to minimize irregularities by using the moving average of an infinite impulse response filter and then normalized. The normalized result is a percentage of the maximum achievable aggregate reverse link rate. The final result is compared with a set of threshold values to obtain the maximum Rate Limit that is then set for each mobile station.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Dynamic Feedback For Outbound Link Rate Adjustment In Multi-Rate Downstream
InactiveUS20080181108A1Adjust robustnessIncrease modulation orderError preventionTransmission systemsTransport layerSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
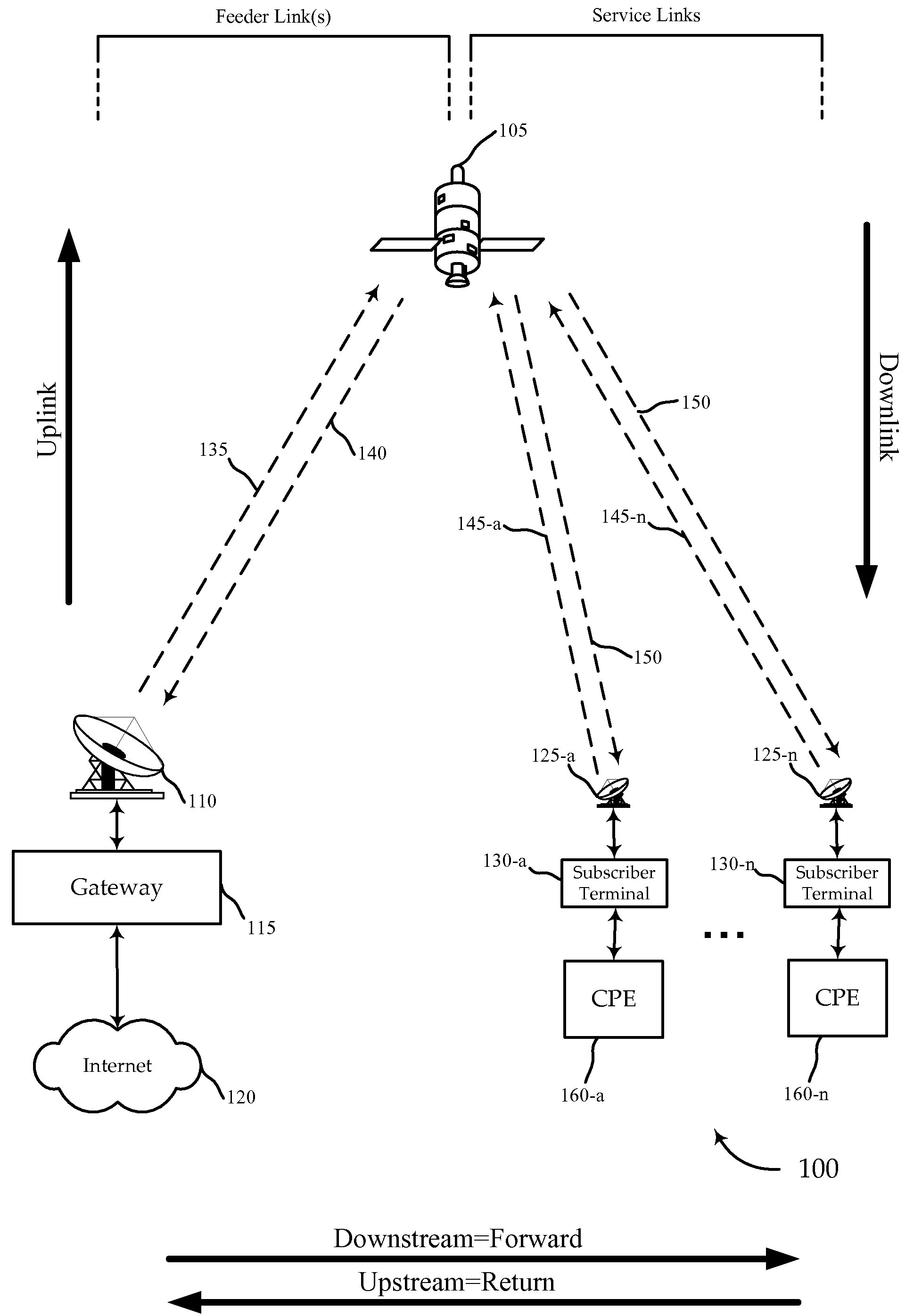
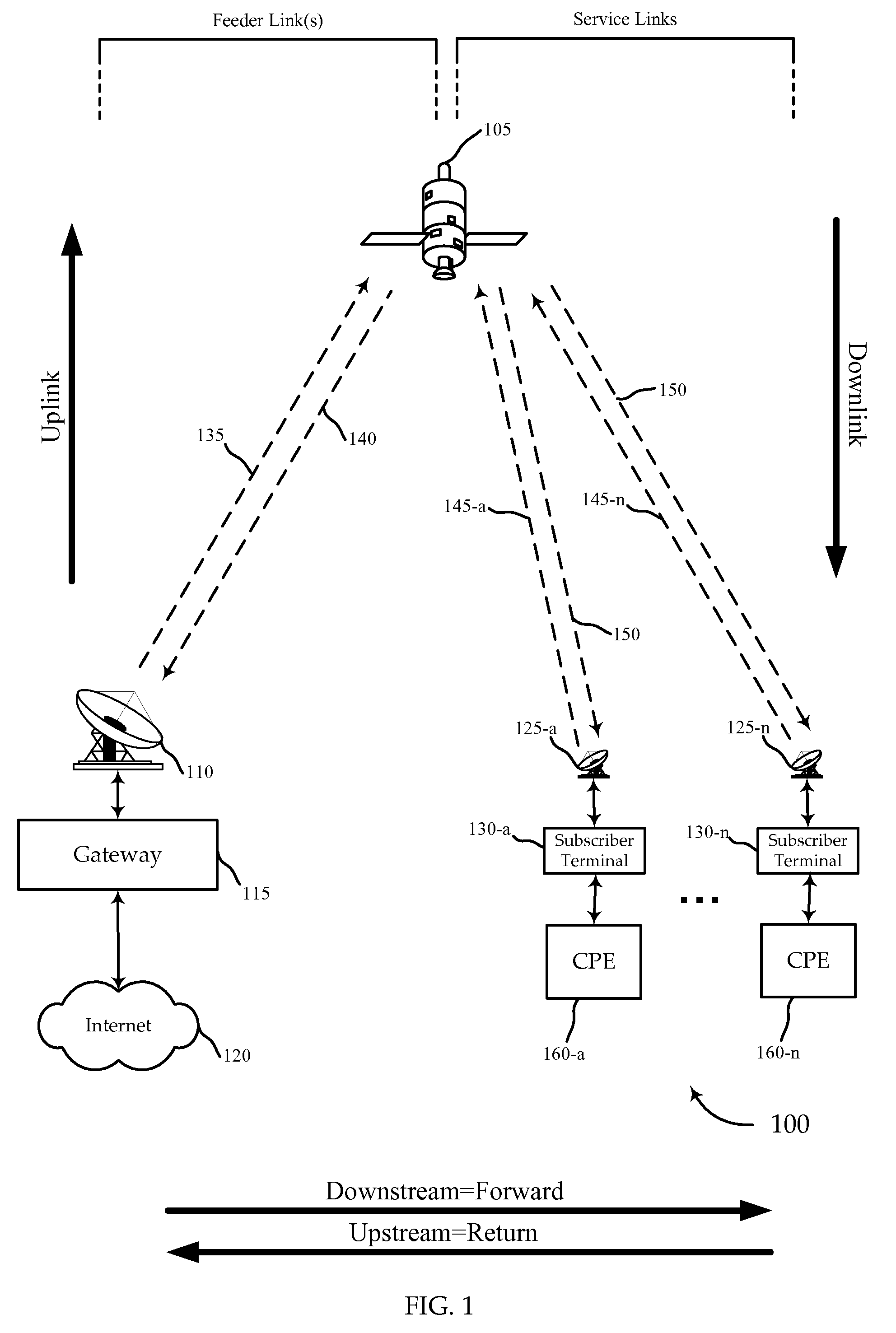
Systems and methods for regulating the throughput of a channel between a gateway and one or more subscriber terminals are disclosed. Various embodiments of the invention provide for monitoring link utilization between a gateway and a subscriber terminal at, for example, the physical layer of the OSI model. Based in part on the link utilization the link throughput may be throttled at a layer higher than, for example, the transport layer. Regulating may occur by advertising a decreased TCP window size or intelligently dropping packets. In another embodiment, a subscriber terminal may estimate the signal to noise ratio of a forward link channel and communicate this SNR to the gateway. The gateway may adjust the modulation and / or coding of the signal in response to the SNR. The gateway may also throttle deliver of packets in response to changes these changes in the modulation and / or coding of the signal.
Owner:VIASAT INC
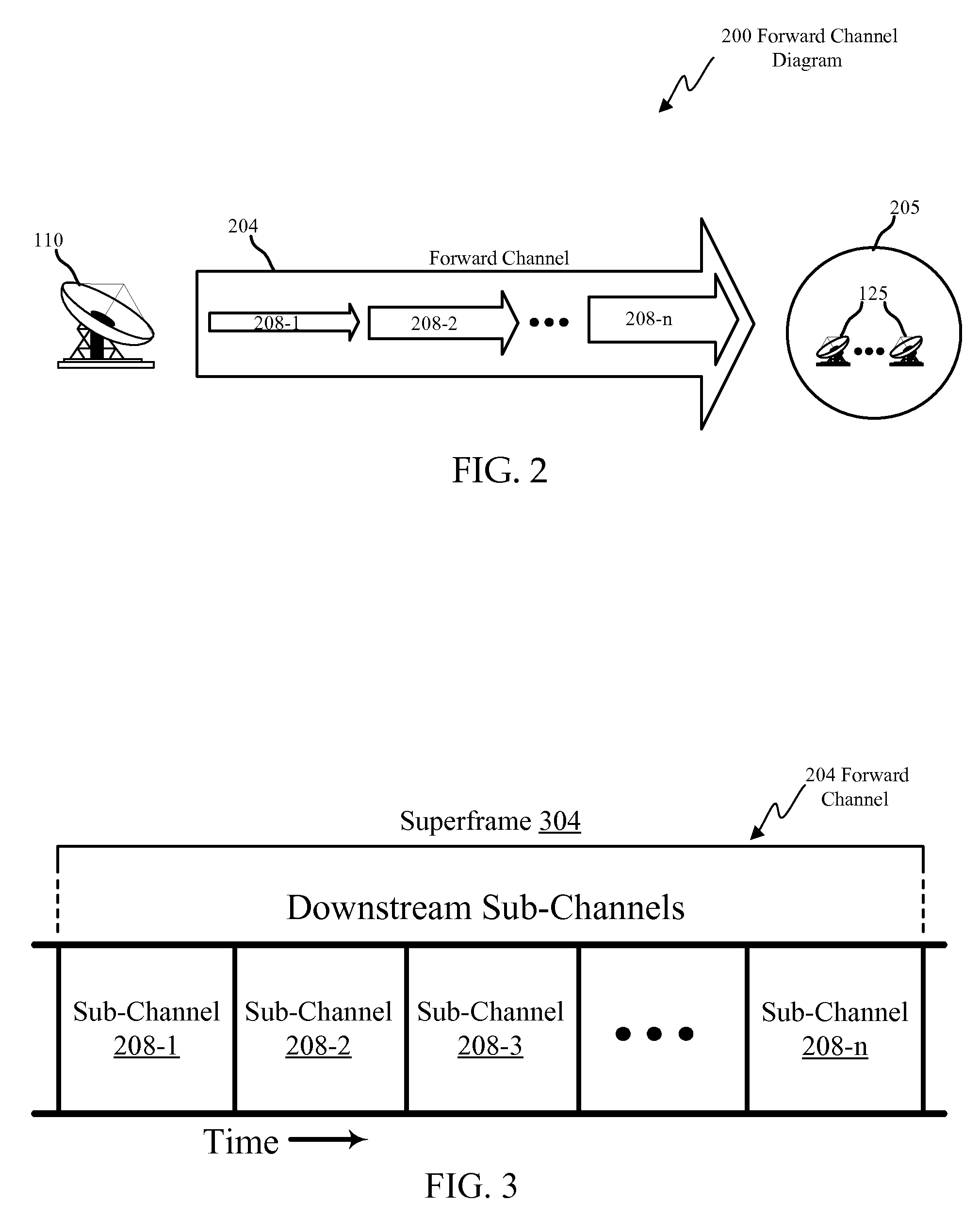
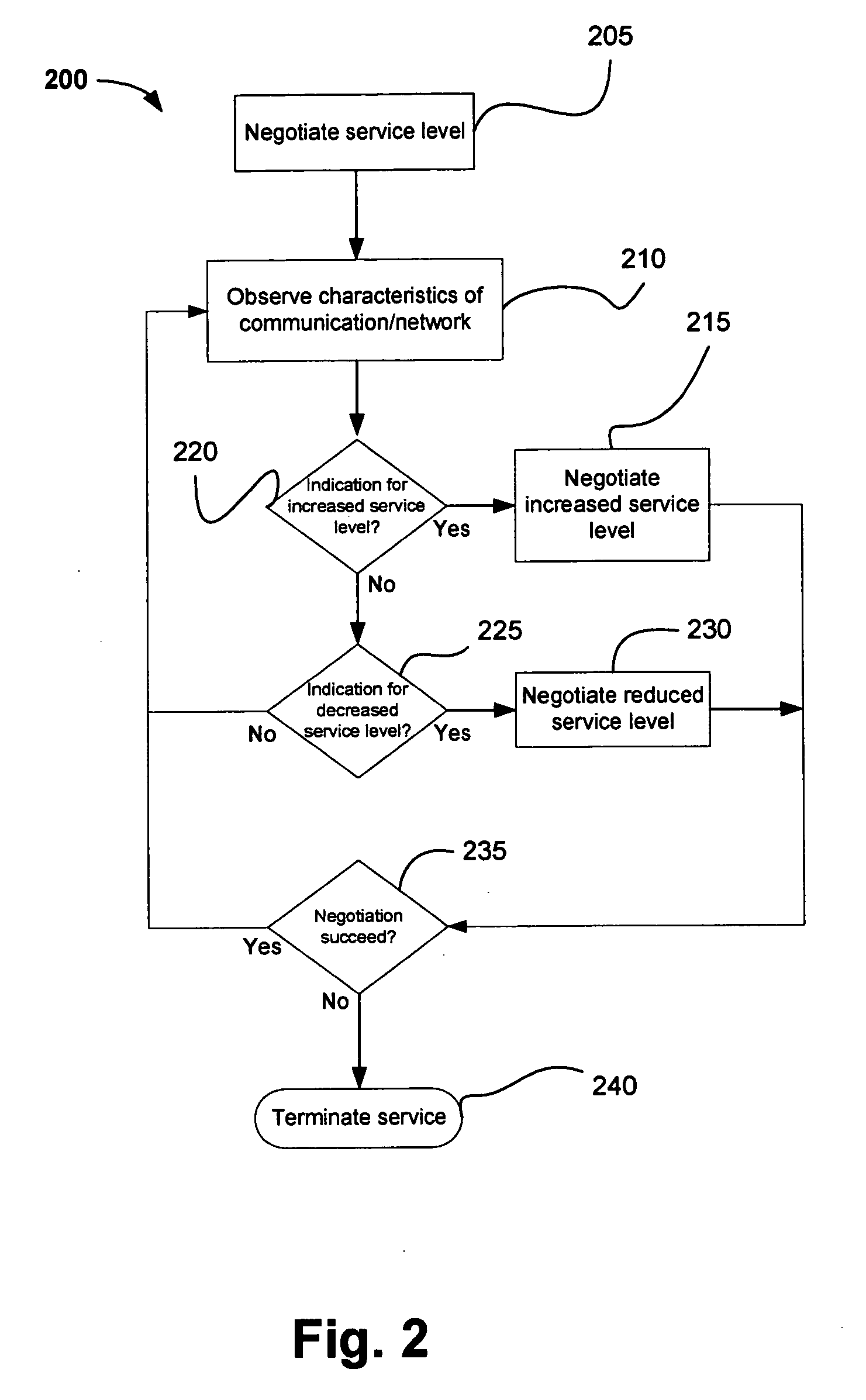
Method and system for adapting wireless network service level
InactiveUS20050243755A1Network traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesTelecommunications linkData stream
Methods and systems for communicating in a wireless network negotiate a level of service for a data stream between peers of the wireless network. The level of service may be modified based on one or more characteristics of a communication link or the wireless network such as channel load, channel free time, physical (PHY) link rate, data rate and / or overall channel capacity. Various specific embodiments and variations are also disclosed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Method and apparatus for forward link rate scheduling
InactiveUS20060203731A1Increase profitReduce transmission delayError preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemHigh rate
In a communication system capable of variable rate transmission, scheduling of high speed data transmission improves utilization of the forward link and decreases the transmission delay in data communication. Each remote station is assigned one primary code channel for the duration of the communication with a cell. Secondary code channels of various types and transmission capabilities can be assigned by a channel scheduler for scheduled transmission of data traffic at high rates. Secondary code channels are assigned in accordance with a set of system goals, a list of parameters, and collected information on the status of the communication network. Secondary code channels can be grouped into sets of secondary code channels. Data is partitioned in data frames and transmitted over the primary and secondary code channels which have been assigned to the scheduled user.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Adapative quality control loop for link rate adaptation in data packet communications
InactiveUS20030123477A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCode conversionPacket communicationRate adaptation
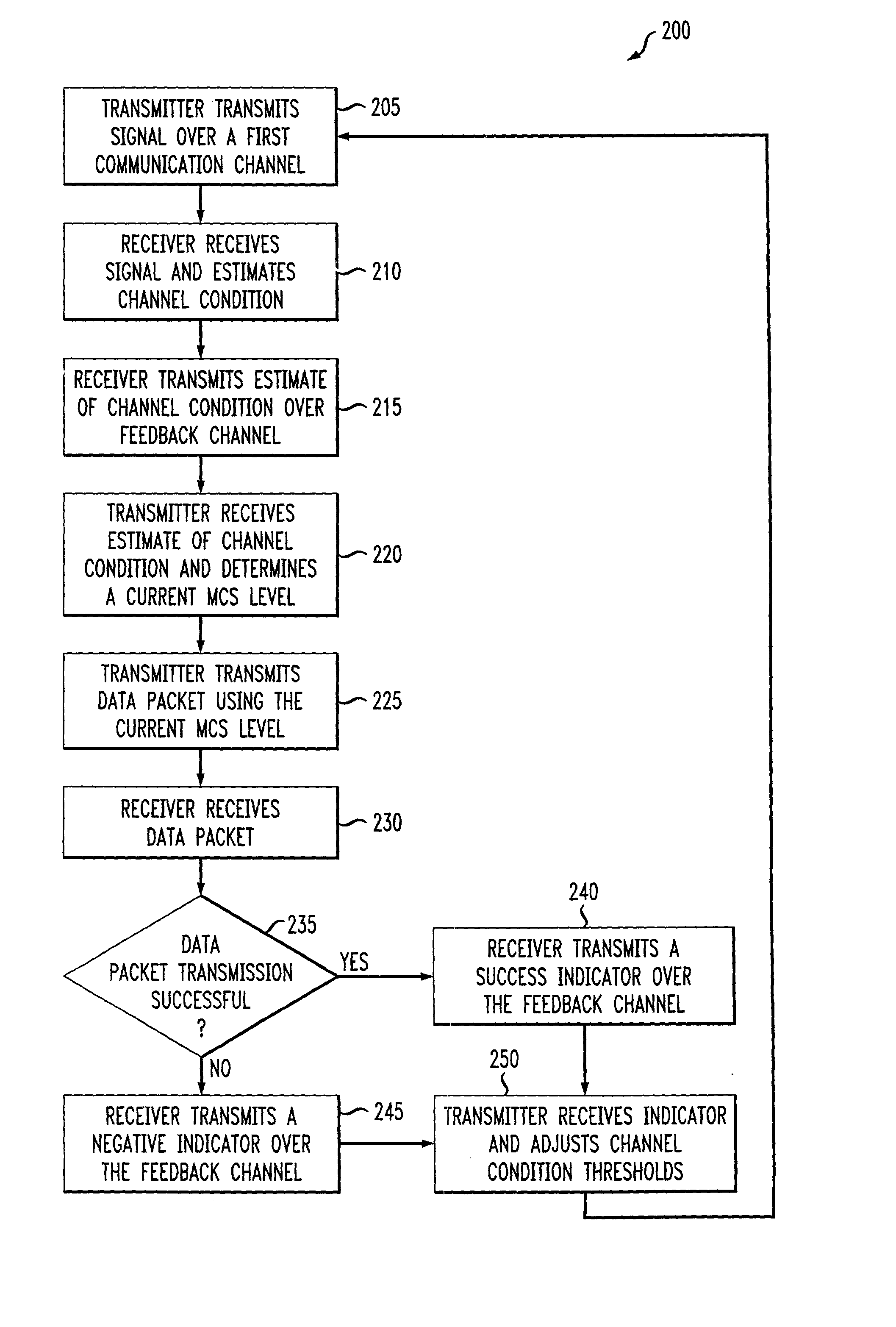
An adaptive quality control loop for link rate adaptation that adaptively selects optimal channel condition thresholds in real-time without measuring all the factors that affect selecting channel condition thresholds. The adaptive quality control loop involves adjusting the channel condition thresholds with variable up and down steps based on target quality metrics along with measurements such as error detection results, relative frequencies of visiting each modulation and / or coding schemes (also referred to as "MCS levels") and transmitted data rates. In one embodiment, the adaptive quality control loop comprises the step of adjusting a channel condition threshold based on a error detection result for a data packet transmission using a variable step. The channel condition threshold is associated with an MCS level used in the data packet transmission.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
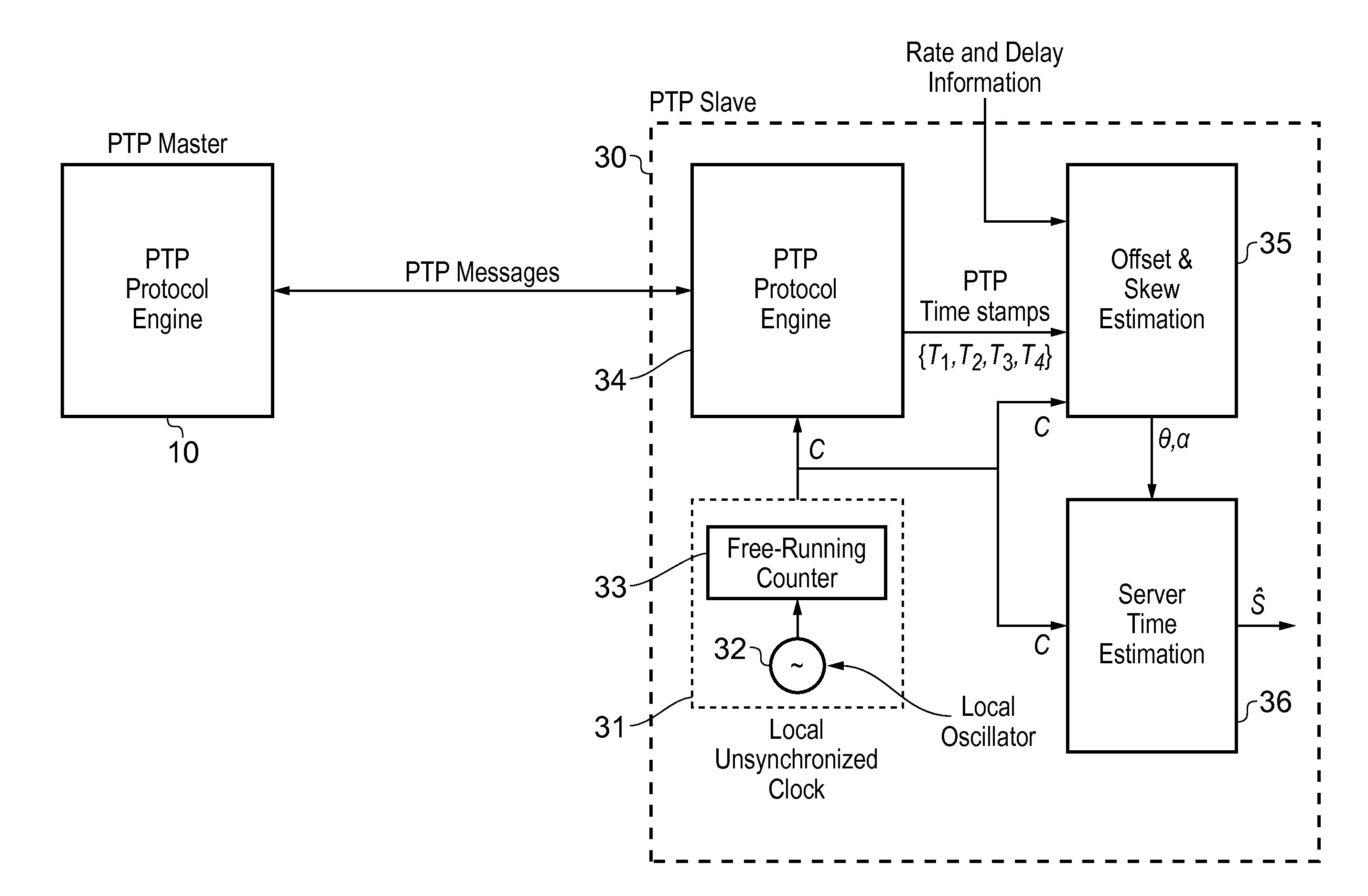
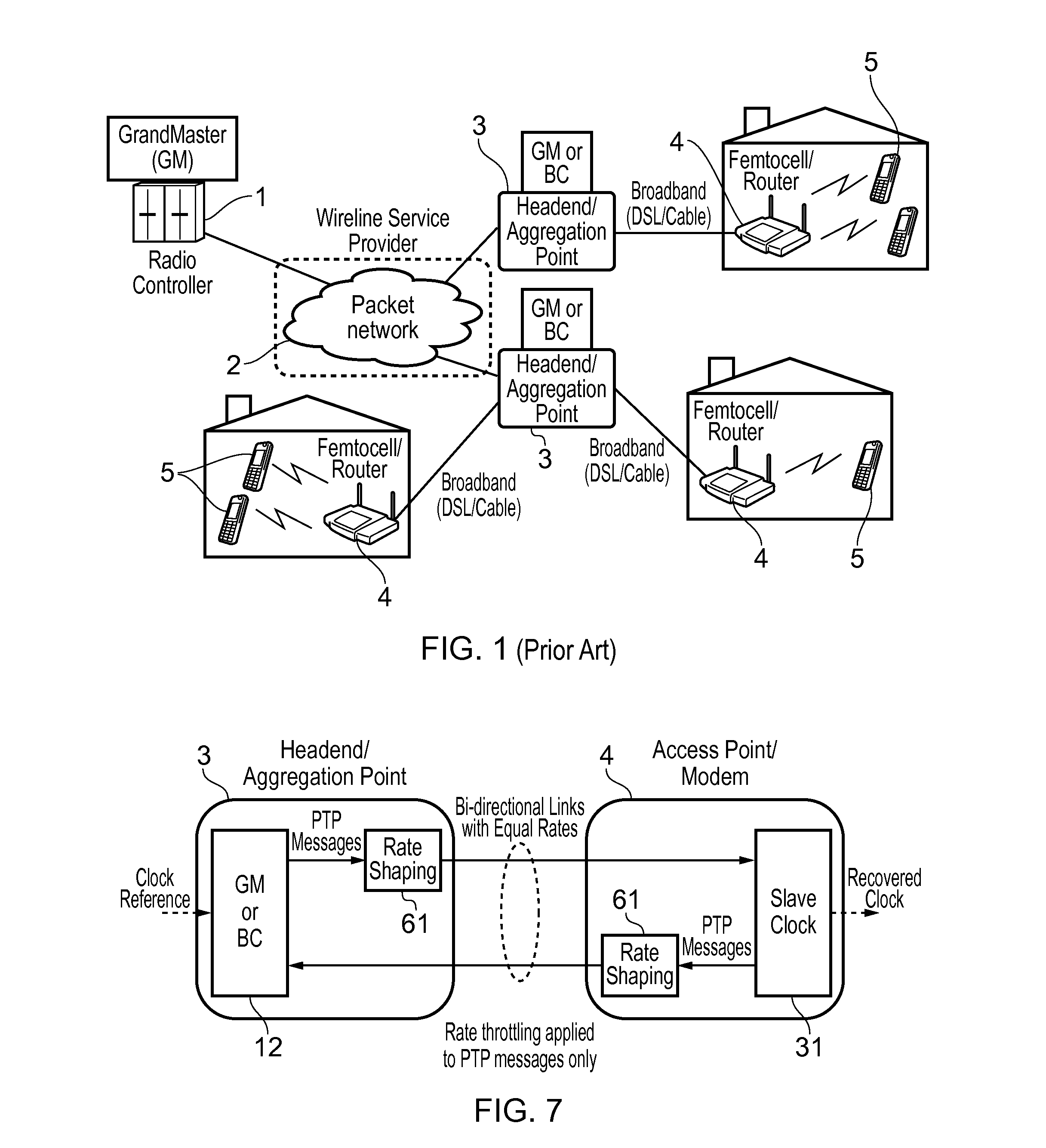
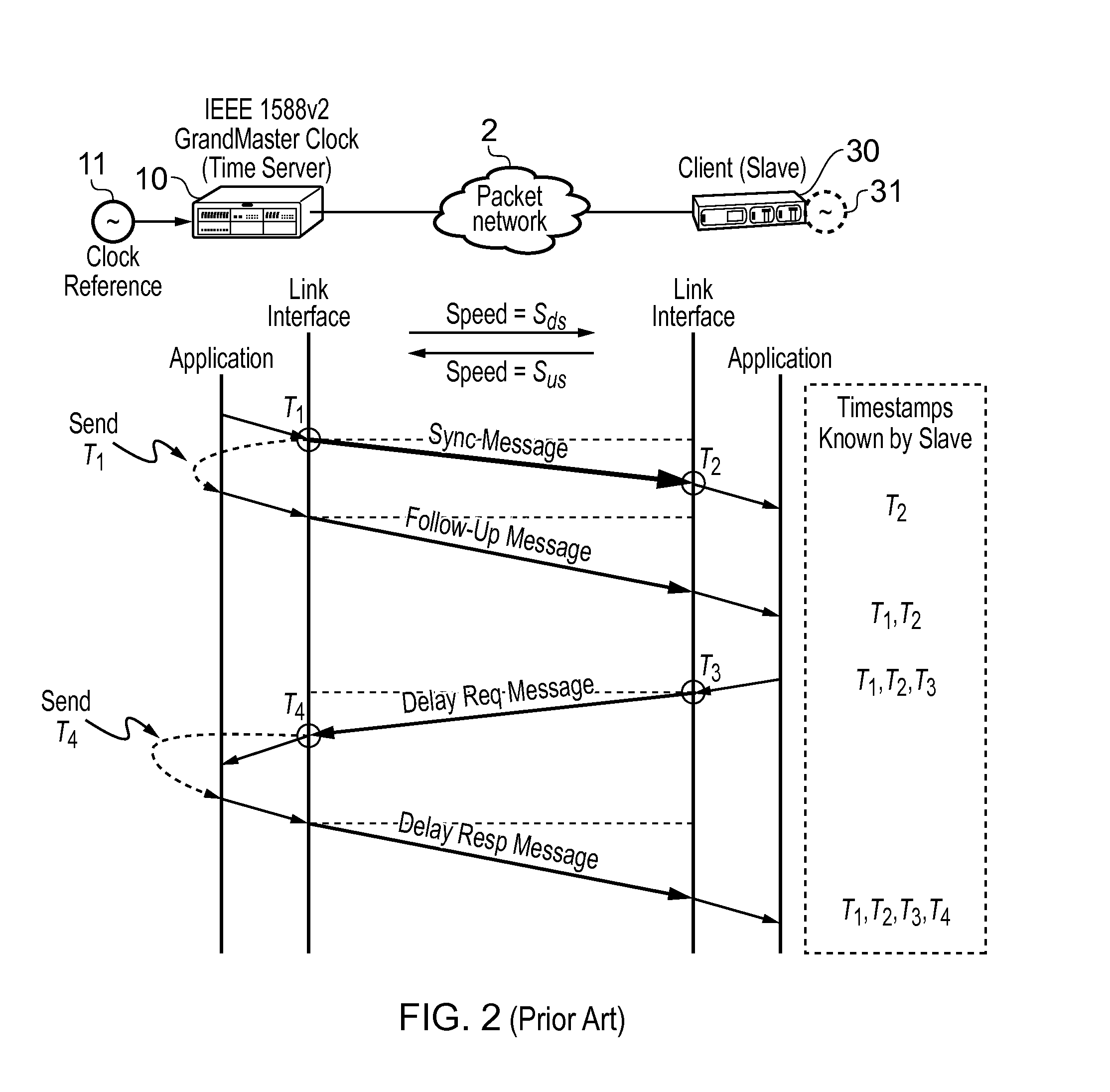
Method and devices for clock synchronization over links with asymmetric transmission rates
This invention relates to methods and devices for clock synchronization. The invention has particular application in the alignment of slave clocks to a master clock and in dealing with transmission delay asymmetries where the forward and reverse communication paths between the master and slave clocks have asymmetric transmission rates. Such methods and devices have particular application in small cell backhaul solutions for 4G / LTE deployments. In embodiments of the invention, the slave clock uses link rate information to estimate the transmission delay asymmetry and thus estimate the offset and skew of the slave clock. Embodiments provide a simple linear approximation technique and a Kalman filter-based technique for estimating offset and skew of the slave clock.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC +2
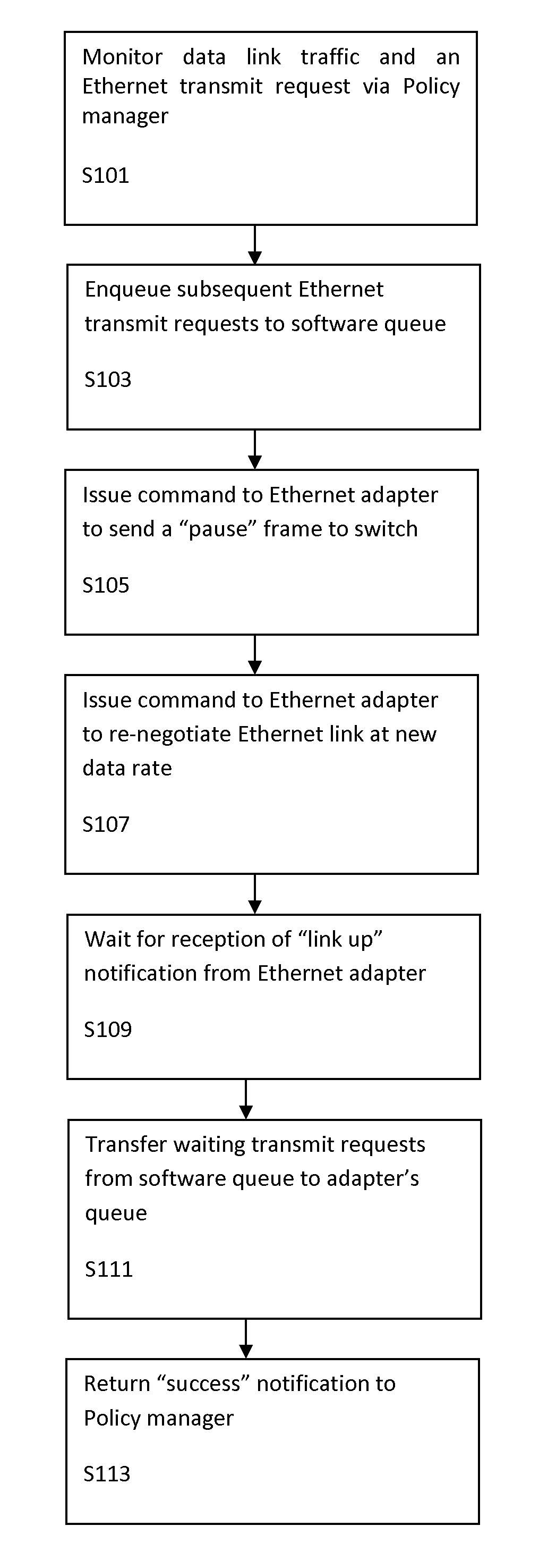
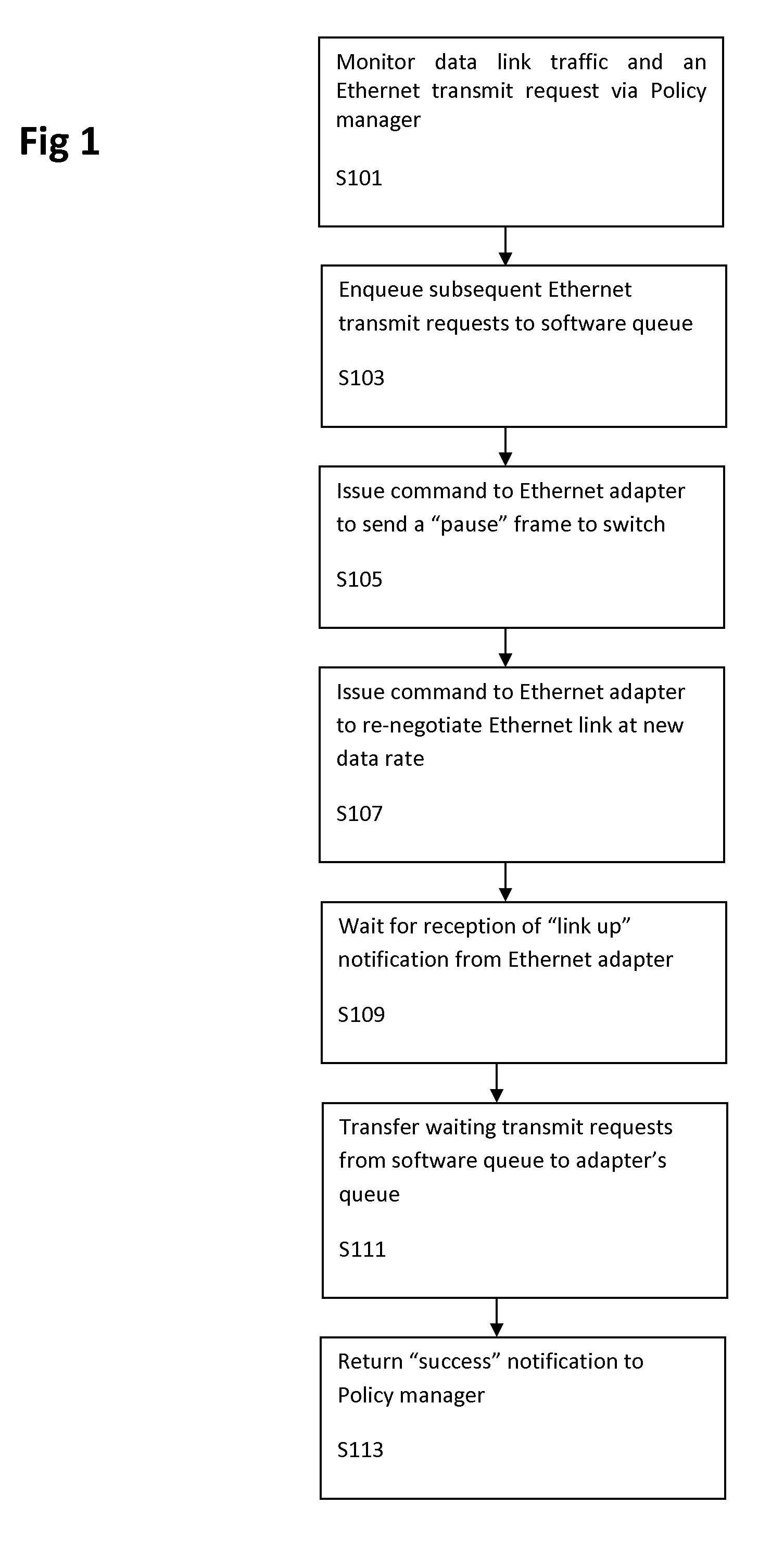
Energy efficient ethernet via dynamic adapter driver link speed negotiation
InactiveUS7558874B1Reducing Ethernet power consumptionReduce power consumptionVolume/mass flow measurementMultiple digital computer combinationsTraffic capacityOperational system
A method of reducing Ethernet power consumption in a network having an operating system by reducing an Ethernet link speed to a minimum rate required for current data link traffic, and automatically commanding an Ethernet adapter / cable to decrease or increase a link rate by dynamically auto-negotiating an Ethernet port by IEEE standards to a lower or higher link rate without user intervention.
Owner:IBM CORP
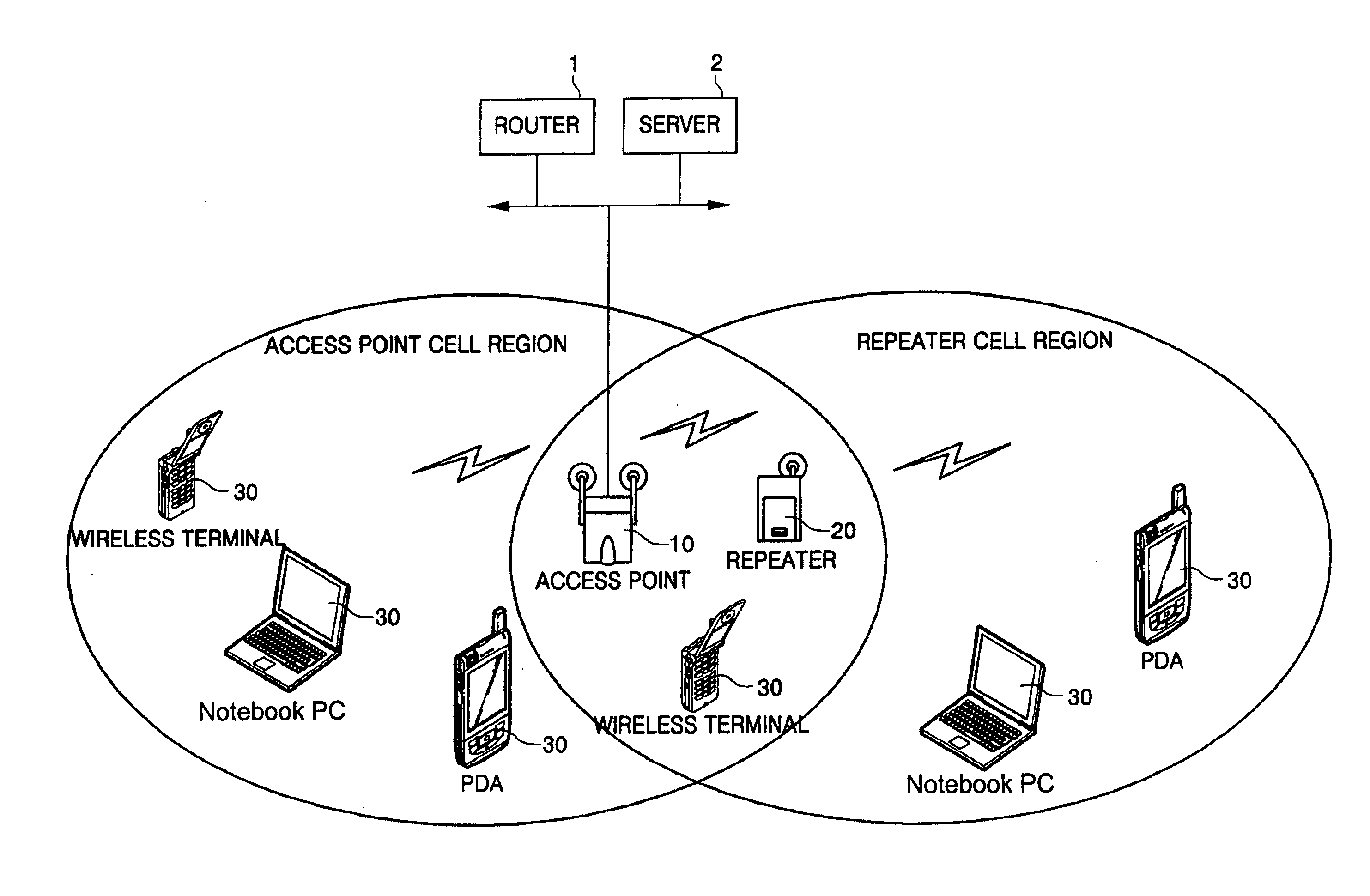
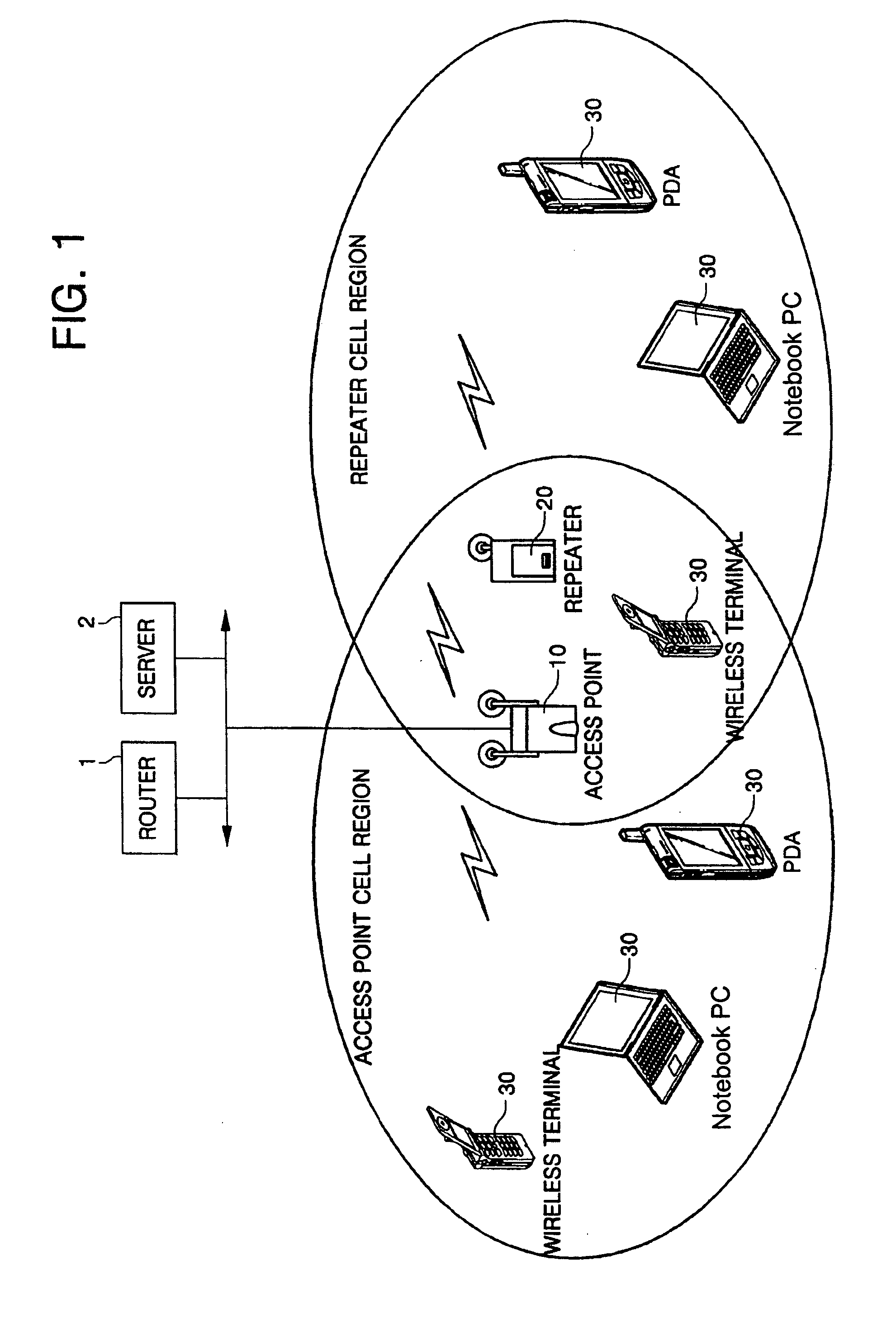
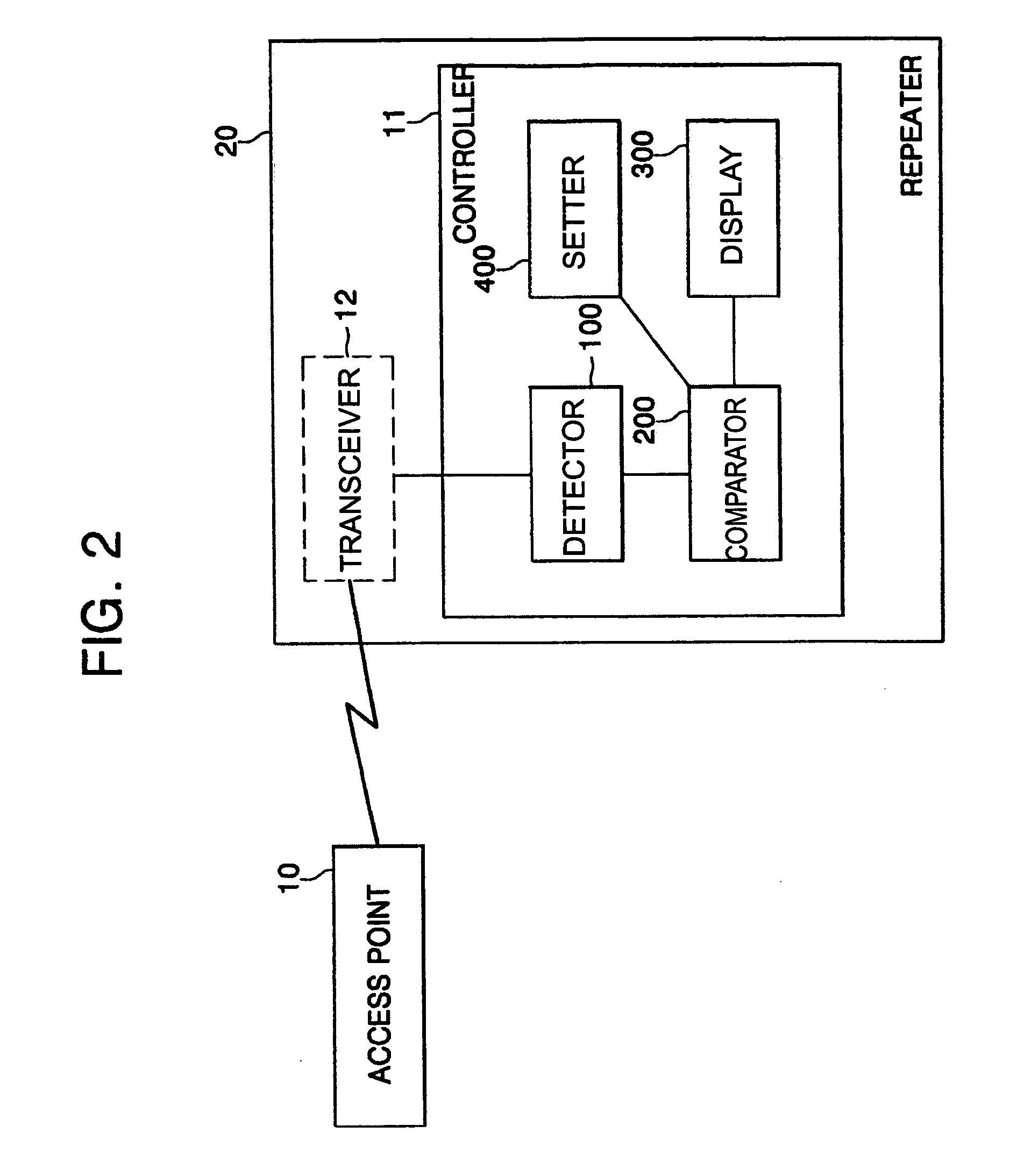
Wireless distribution system (WDS) repeater in wireless local area network (WLAN) and its control method
A Wireless Distribution System (WDS) repeater in a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN), the WDS repeater includes: a controller adapted to compare a wireless link rate of a WLAN signal received from an Access Point (AP) of the WLAN to a wireless link rate threshold registered in a wireless link rate table, and to display a connectability status of the wireless link according to the comparison result. A method of displaying a WDS link status in a wireless LAN system includes: detecting a wireless link rate of a WLAN signal received from an AP; comparing the detected wireless link rate to a wireless link rate threshold registered in a wireless link rate table; and displaying an ability to establish a connection when the detected wireless link rate is equal to or greater than the wireless link rate threshold.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Queuing delay based rate control
InactiveUS7706403B2Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexQuality of serviceTelecommunications link
A method and apparatus for rate control adjusts or otherwise requests adjustment of a communication link data rate based on transmit queuing delays. For example, a mobile station may monitor expected transmit queuing delays relative to one or more delay targets or other Quality-of-Service constraints, and request reverse link rate increases or decreases accordingly. Similarly, the mobile station may be configured periodically to request reverse link rate changes based on determining the rate needed to meet targeted queuing delays for one or more service instances being supported by the mobile station in each of a succession of ongoing rate control intervals. Requested rates may be defined data rates or may be virtual rates that can be achieved by using combinations of defined data rates. Queuing-based rate control also can be applied to the base station's forward link, and, more broadly, to essentially any rate controlled communication link.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Reverse link rate control mechanism for QoS
InactiveUS20050025077A1Network traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionQuality of serviceMobile station
A reverse link rate control method and apparatus provide first rate control commands as the primary rate control for general, ongoing control of the reverse link rates of one or more mobile stations. These first rate control commands comprise, for example, periodically transmitted common rate control commands that are generated as a function of reverse link loading and are used to control the reverse link rates of mobile stations whose service requirements currently do not require targeted reverse link rate control. The exemplary method and apparatus further provide second rate control commands on an as needed basis, that are sent to targeted ones of the mobile stations to meet the specific Quality-of-Service requirements at individual mobile stations, or groups of mobile stations. Supplemental rate control channels can be assigned and released dynamically to targeted mobile stations to provide supplemental rate control on an as-needed basis.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Data packet based stream transport scheduler wherein transport data link does not include a clock line
A method of coupling a multimedia source device to a multimedia sink device by providing a source device having a transmitter unit coupled thereto, providing sink device having a receiver unit coupled thereto, receiving a source data stream in accordance with a native stream rate by the transmitter unit, coupling the transmitter unit and the receiver unit by way of a linking unit, forming a multimedia data packet stream formed of a number of multimedia data packets and generating a transport schedule for transferring the multimedia data packet stream in accordance with a link rate between the transmitter unit and the receiver unit wherein the multimedia data.
Owner:GENESIS MICROCHIP
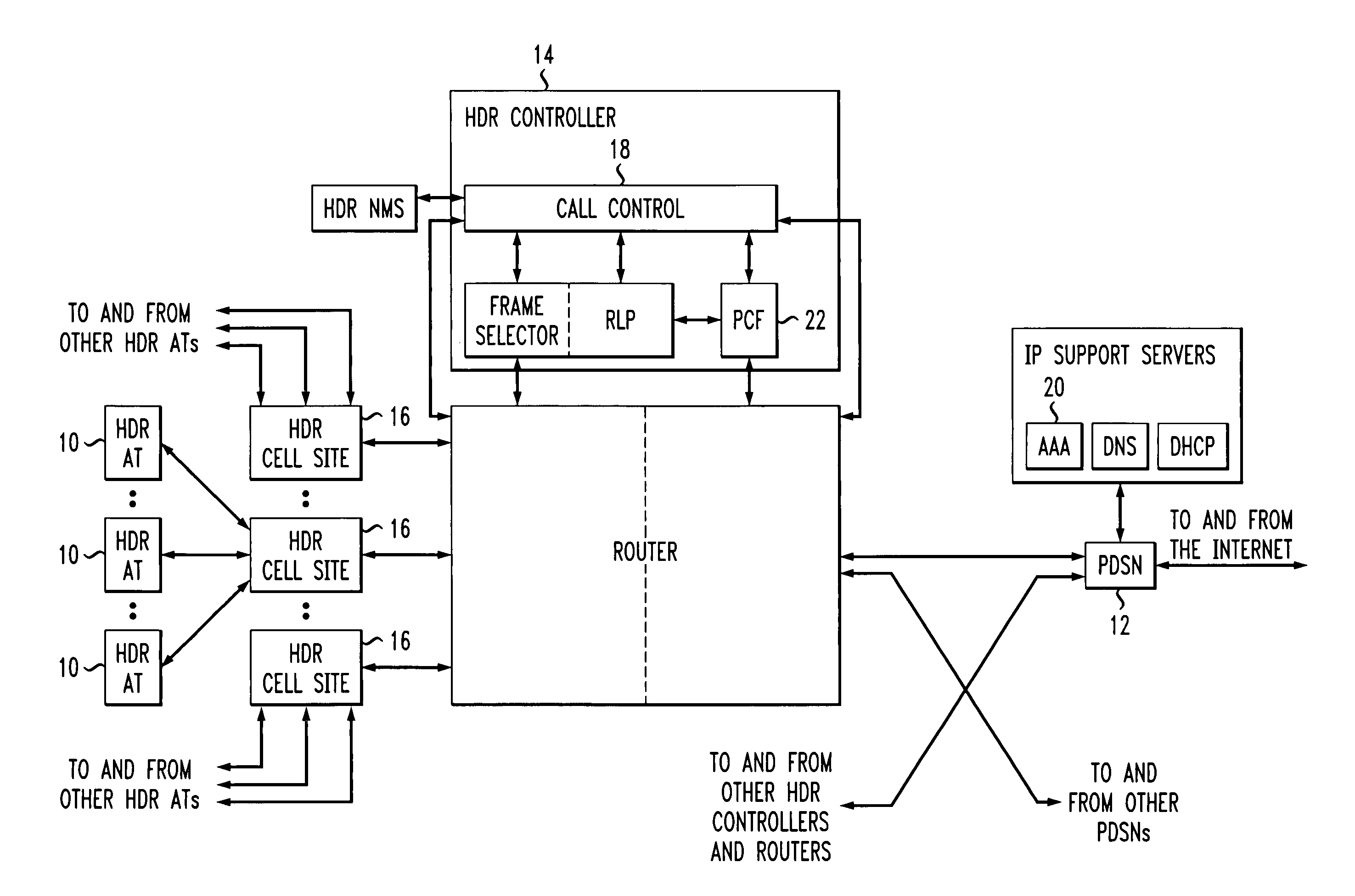
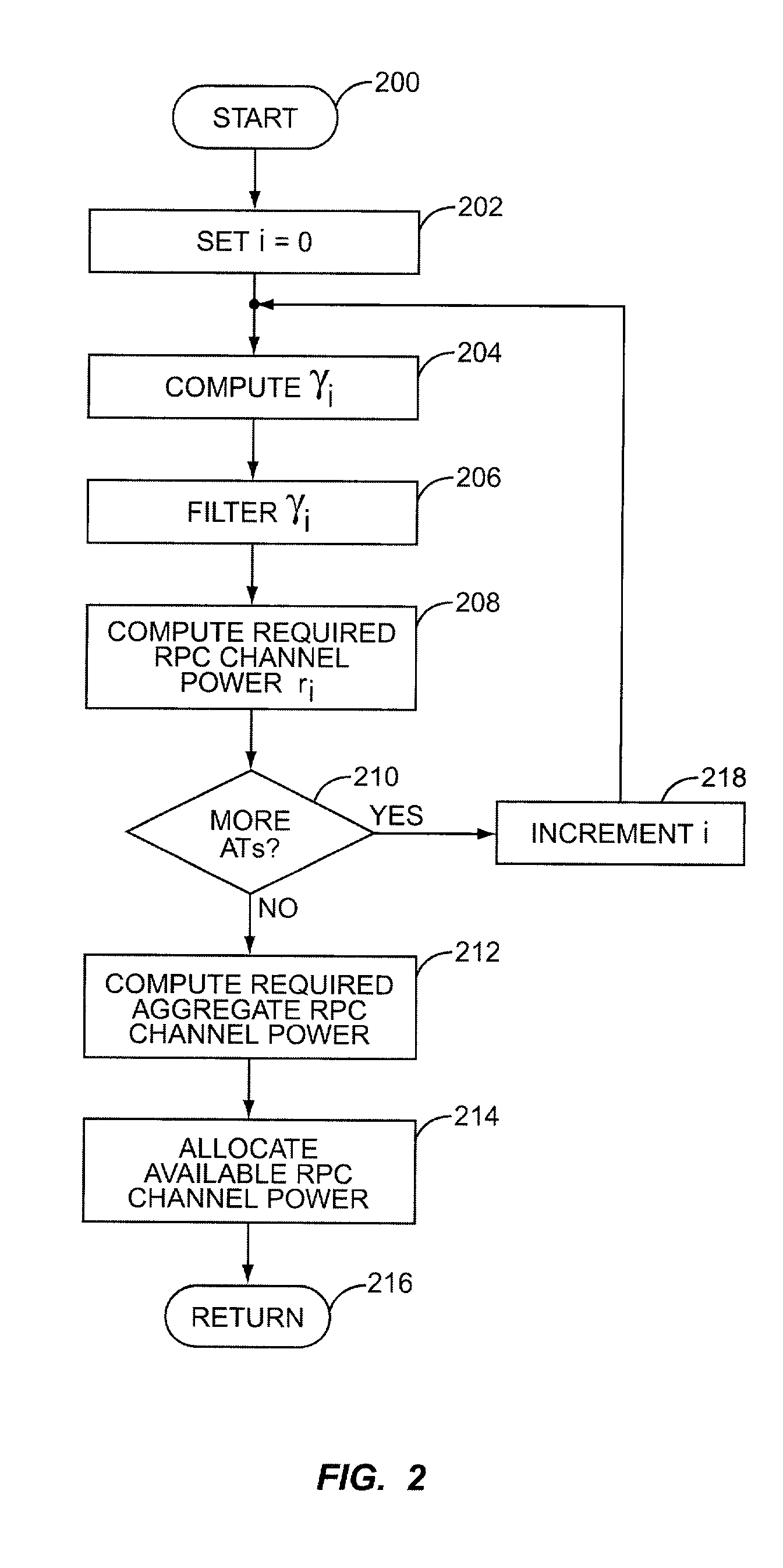
RPC channel power control in a HDR network
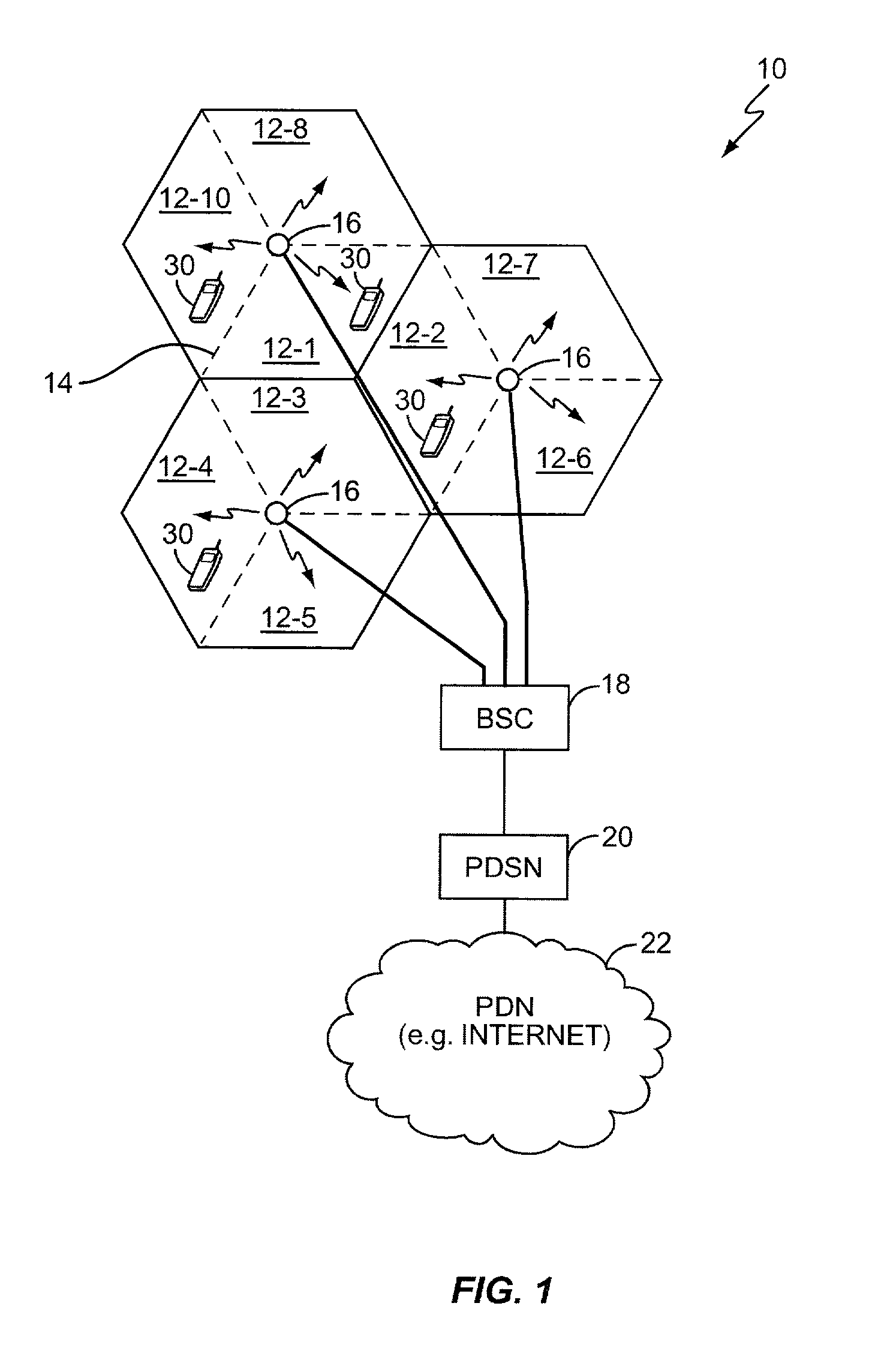
In a communication network based on the TIA / EIA / IS-856 standard, or in other network types where forward link power control is desirable but where no reverse link channel or sub-channel to direct such power control is available, forward link rate request information from an access terminal may be used to infer carrier-to-interference (C / I) ratios at the access terminal. Such information allows the network to control power for the forward link channel of interest. In a TIA / EIA / IS-856 setting, the network uses DRC channel information from the access terminal to set RPC channel power transmitted to the access terminal from one or more sectors in the network. That is, radio base stations within the network may determine C / I or like values for active access terminals using DRC channel information from those terminals and calculated needed RPC channel power accordingly. This process may be extended to include access control procedures.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
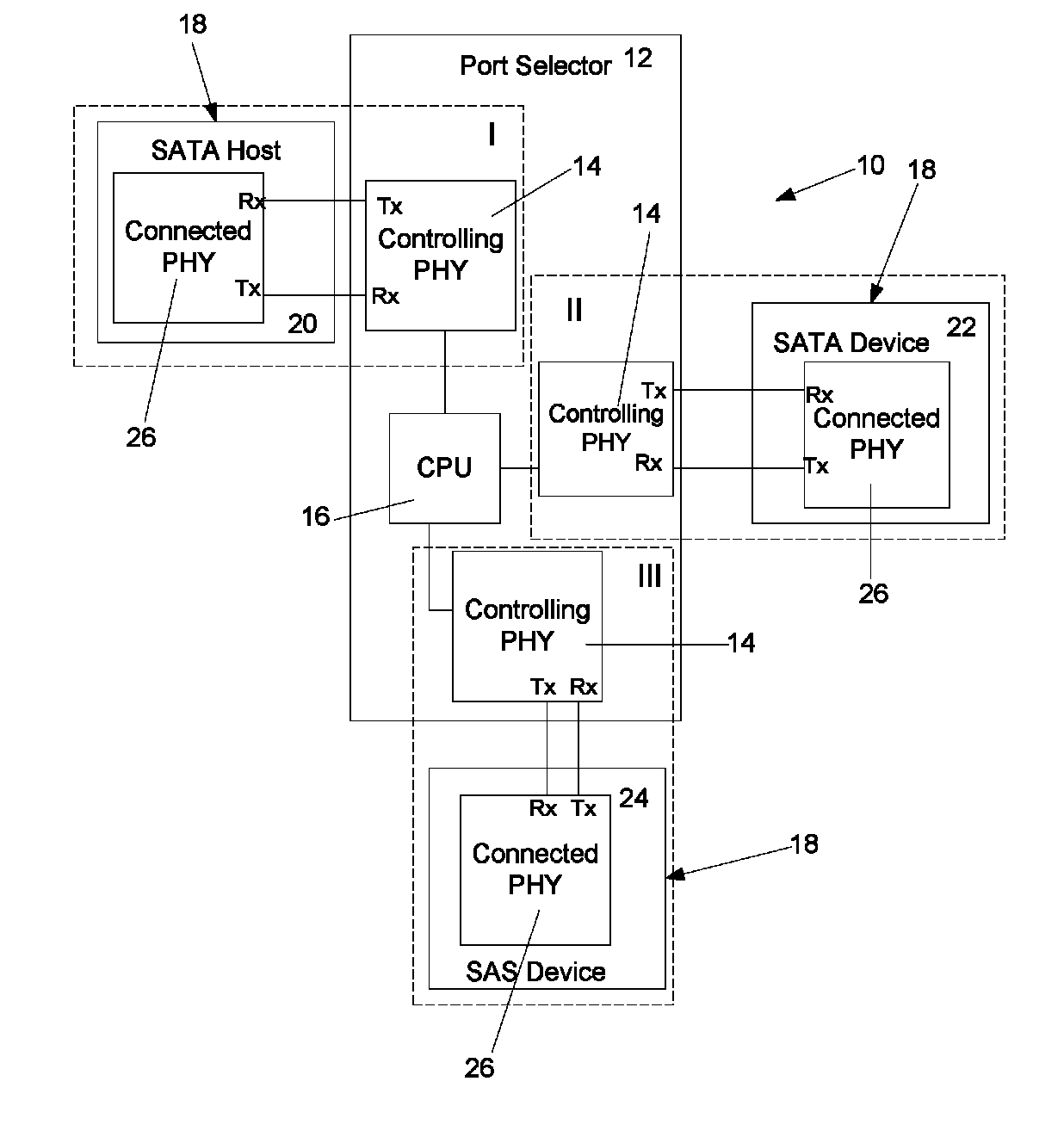
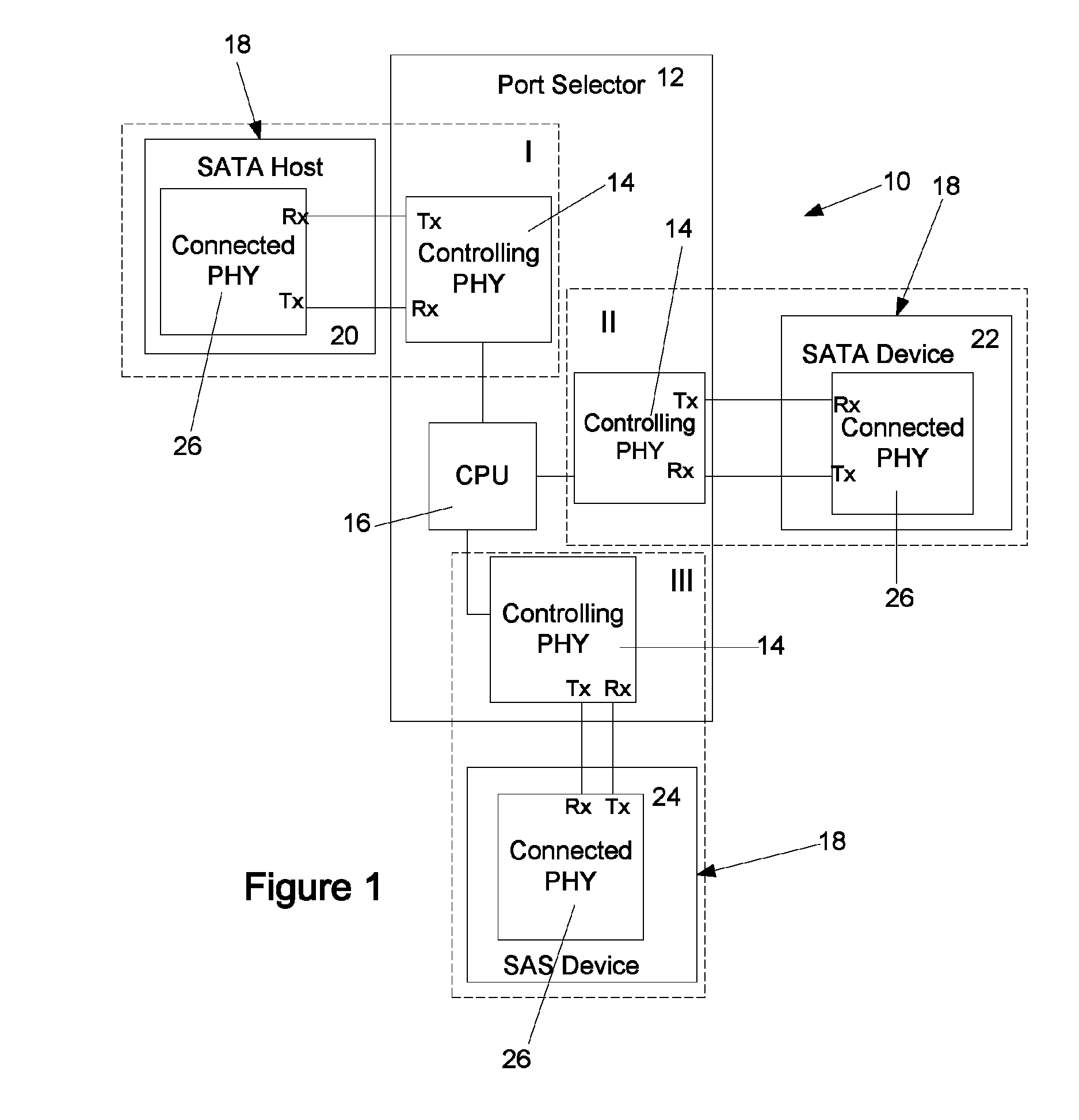
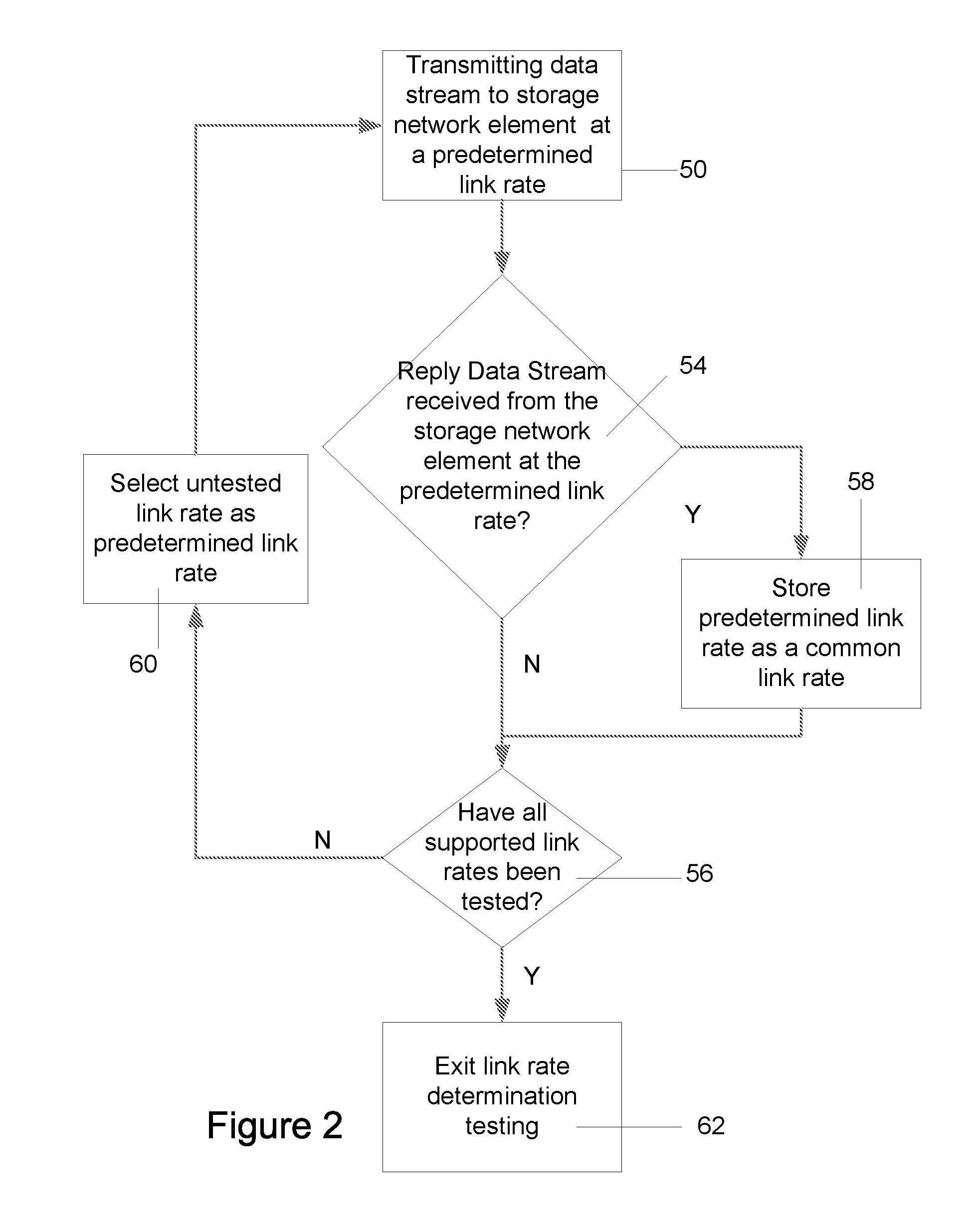
Method of rate snooping in a SAS/SATA environment
ActiveUS7774424B1Reduce/prevent rate thrashingMultiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingDistributed computingNetwork element
A method and apparatus for determining a set of common link rates for communication between two storage network elements in a storage network system. During the speed negotiation process, a controlling storage network element receives supported link rate information from a connected storage network element without providing any information in return. By not providing such information, although the speed negotiation process may not be completed, the controlling storage network element is still able to determine the supported link rates of the connected storage network element.
Owner:MICROSEMI STORAGE SOLUTIONS
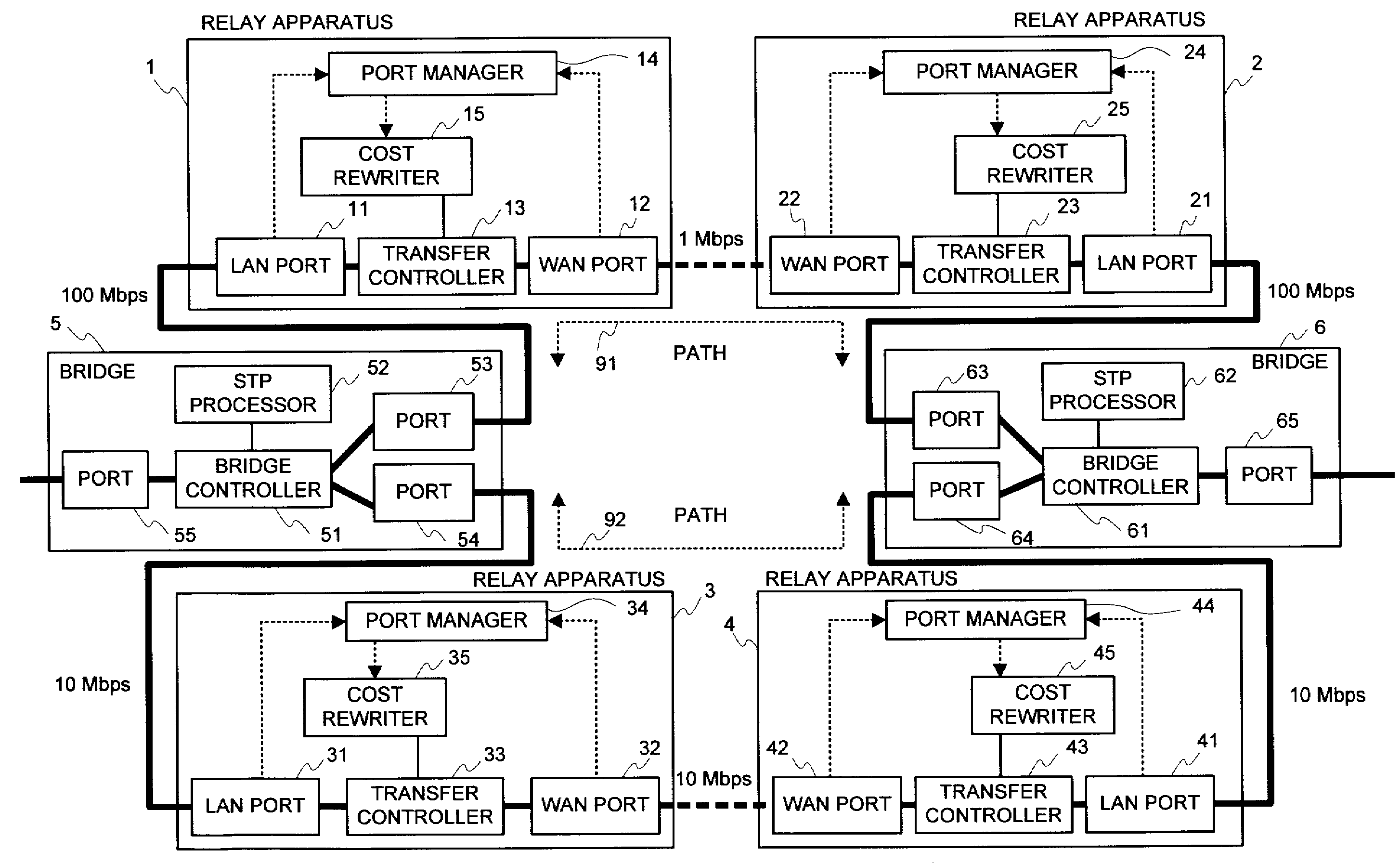
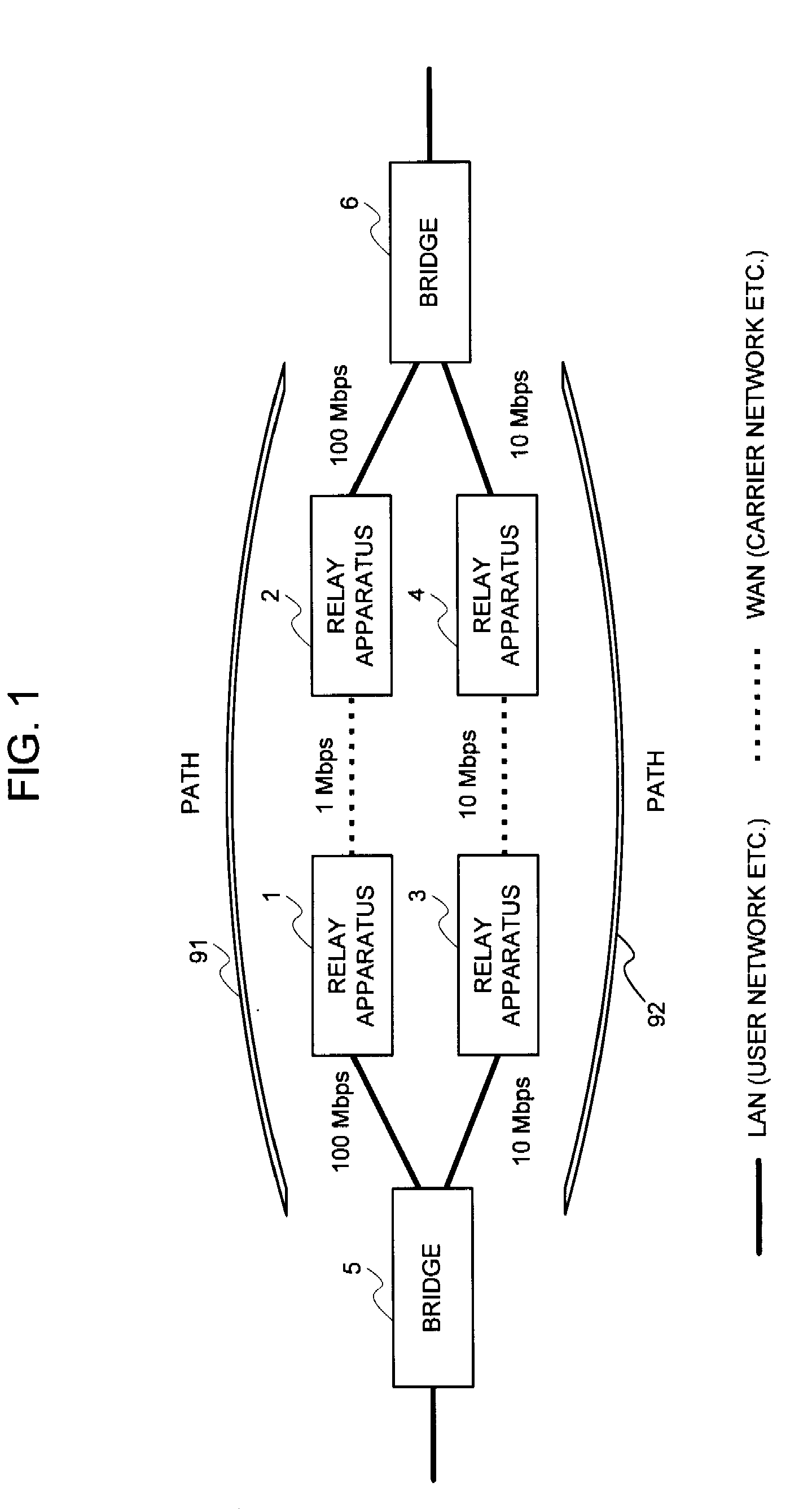
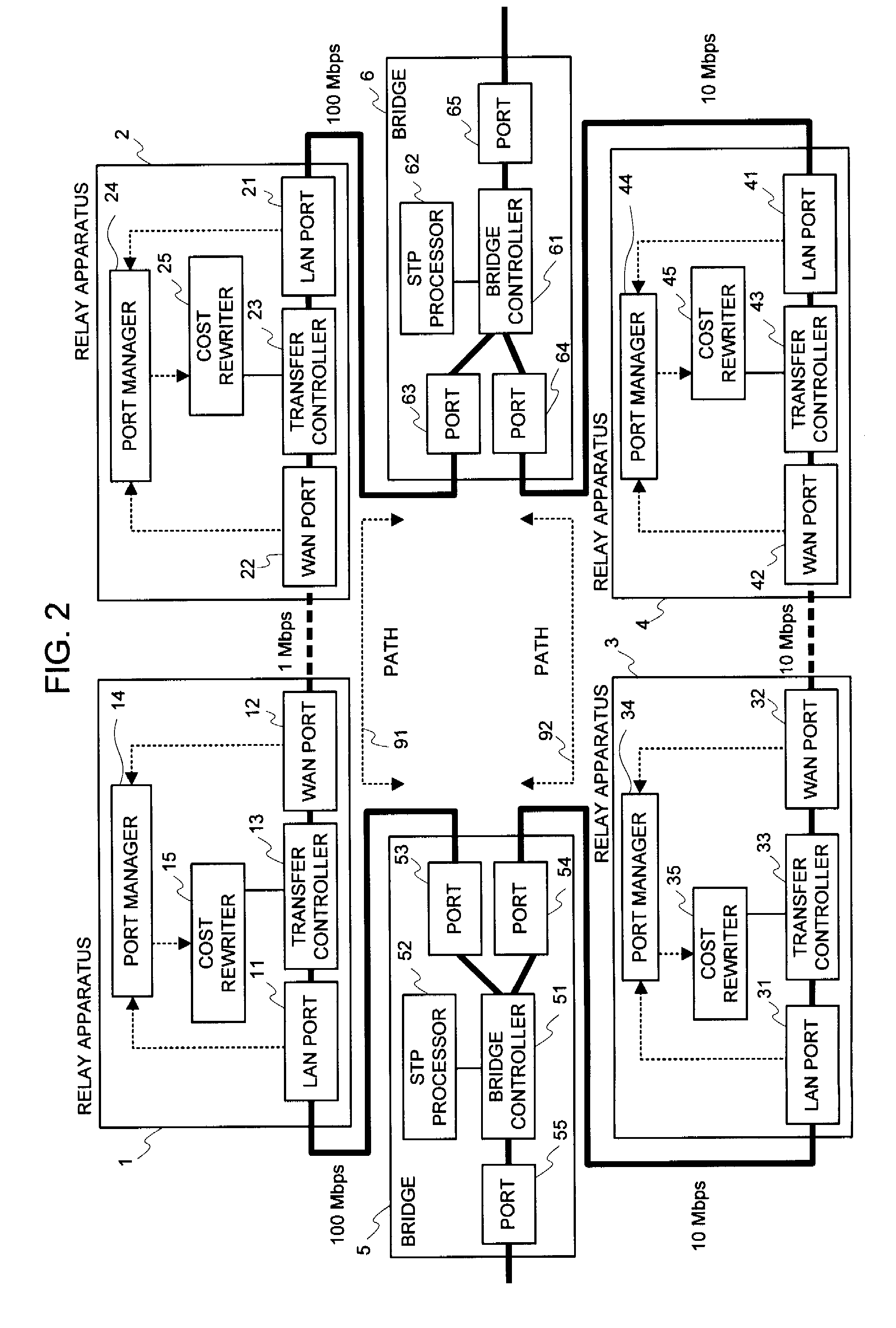
Relay apparatus, path selection system, path selection method and program
InactiveUS20080219168A1Improve efficiencyIncrease net efficiencyError preventionTransmission systemsSelection systemPath cost
An object of the present invention is to reflect a band of the bottleneck into the cost, to select an optimal path, and to enhance an efficiency of the net utilization without making a setting or a modification to the apparatus (bridge etc.) in which the path control protocol operates in a case where a difference exists between an actually utilizable rate (a band of the bottleneck) in the path between the bridges etc. and a link rate of the connection link such as the bridge etc. in a net in which the apparatus (bridge etc.), in which the path control protocol (STP etc.) for automatically computing a cost of a link by a physical band of the connection link operates, exists. In the system of the present invention, the port manager within the relay apparatus, upon receipt of a notification of the link rate from the port, investigates which side, out of the WAN side and the LAN side, becomes a bottleneck, and the cost rewriter within the relay apparatus rewrites the root path cost field within the BPDU in conformity to the rate of the bottleneck.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method of rate control
A radio base station performs reverse link rate control in a wireless communication network by “stealing” bits on a forward common power control channel. The forward common power control channel is divided into a plurality of frames, with each frame including a plurality of power control groups and each power control group including a plurality of power control slots. The radio base station may dynamically select power control slots depending on user demand to be used for reverse link rate control.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method of rate control
A radio base station performs reverse link rate control in a wireless communication network by “stealing” bits on a forward common power control channel. The forward common power control channel is divided into a plurality of frames, with each frame including a plurality of power control groups and each power control group including a plurality of power control slots. The radio base station may dynamically select power control slots depending on user demand to be used for reverse link rate control.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
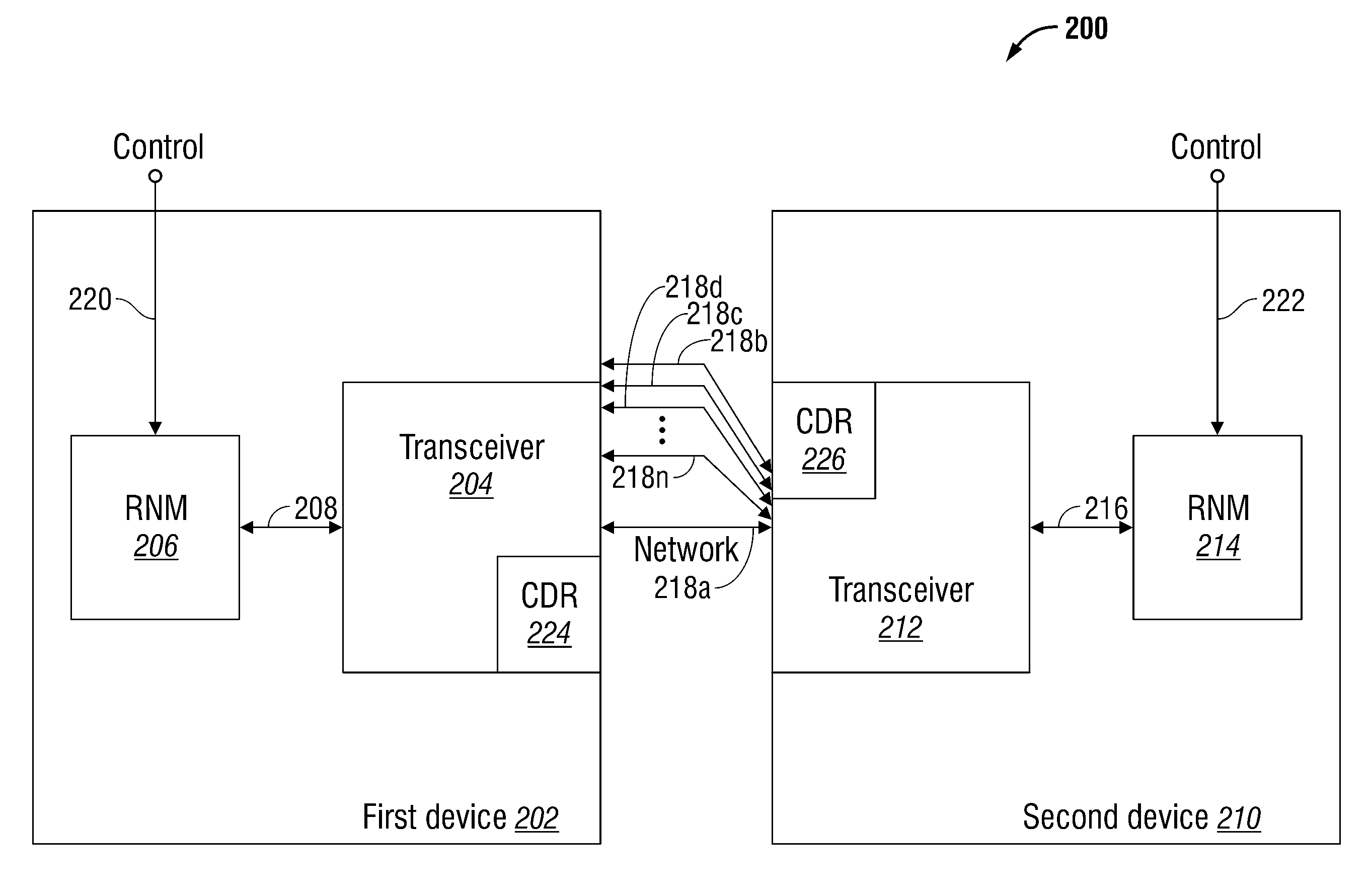
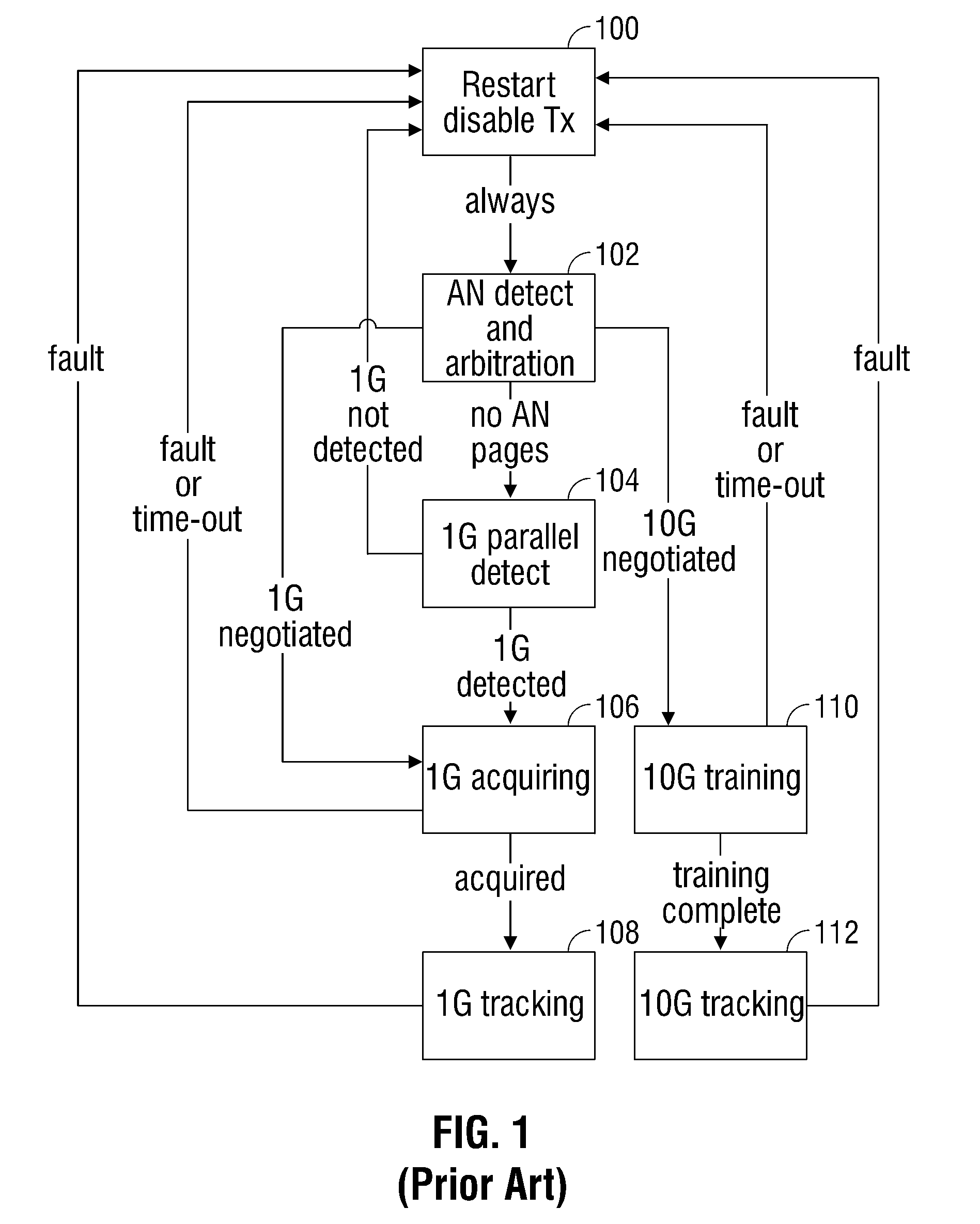
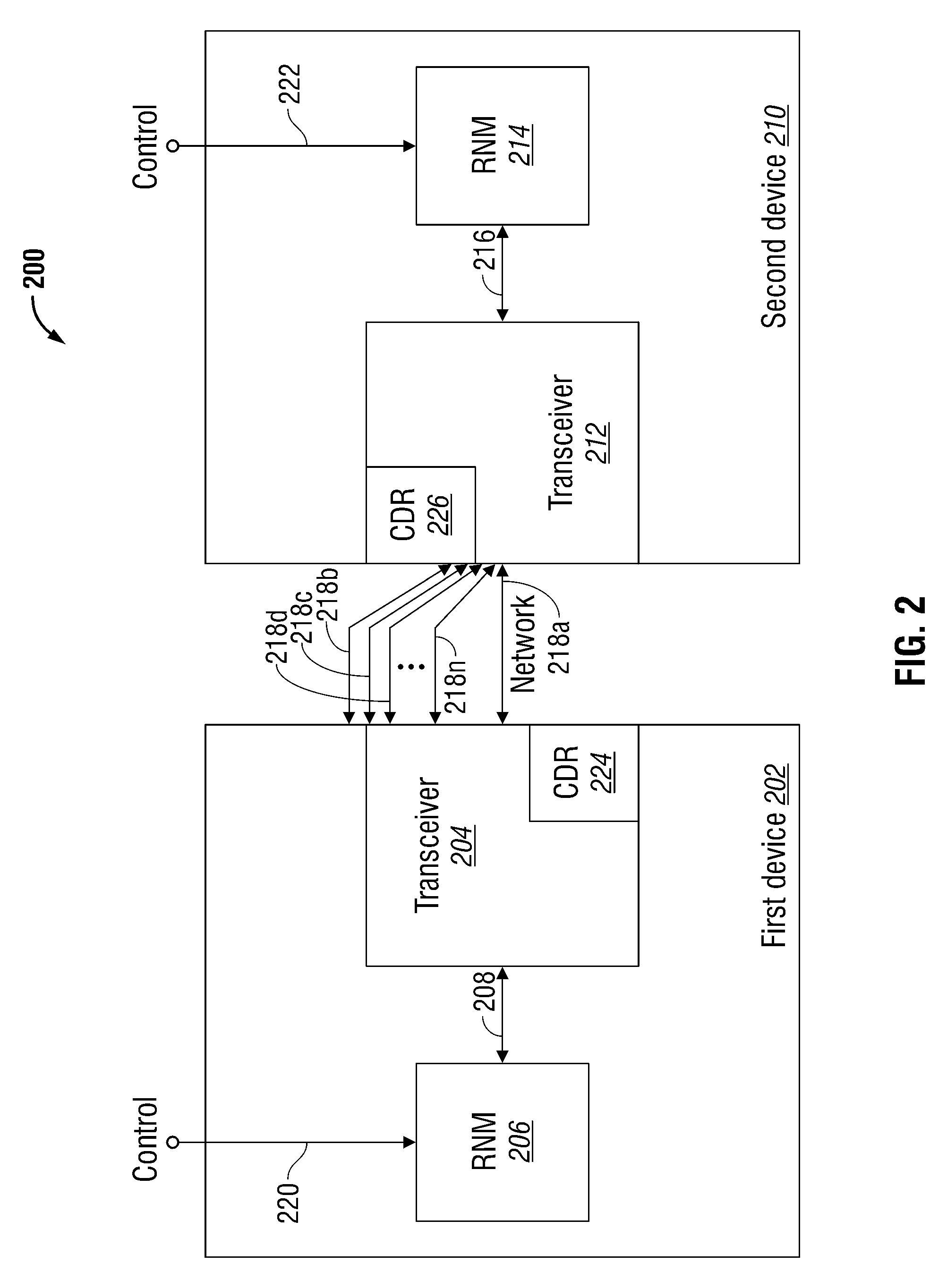
System and Method for Multilane Link Rate Negotiation
ActiveUS20100077097A1Improve performanceMore powerEnergy efficient ICTMultiple digital computer combinationsCommunications systemNetwork connection
A system and method are provided for negotiating a link data rate in a communication system using a plurality of data rates. In a system including a first device network-connected to a second device, auto-negotiation (AN) messages are mutually transmitted. The AN messages indicate rate information such as preferred data rate capabilities, if the device has a dual-rate capability, single data rate capabilities, or is capable of communicating over a plurality of physical medium lanes. If the AN messages are mutually transmitted, a negotiated link data rate is established. However, if one of the devices cannot send AN messages, the other device times-out, and a link data rate is established at the data rate transmitted by the device that is not AN-capable.
Owner:MACOM CONNECTIVITY SOLUTIONS LLC
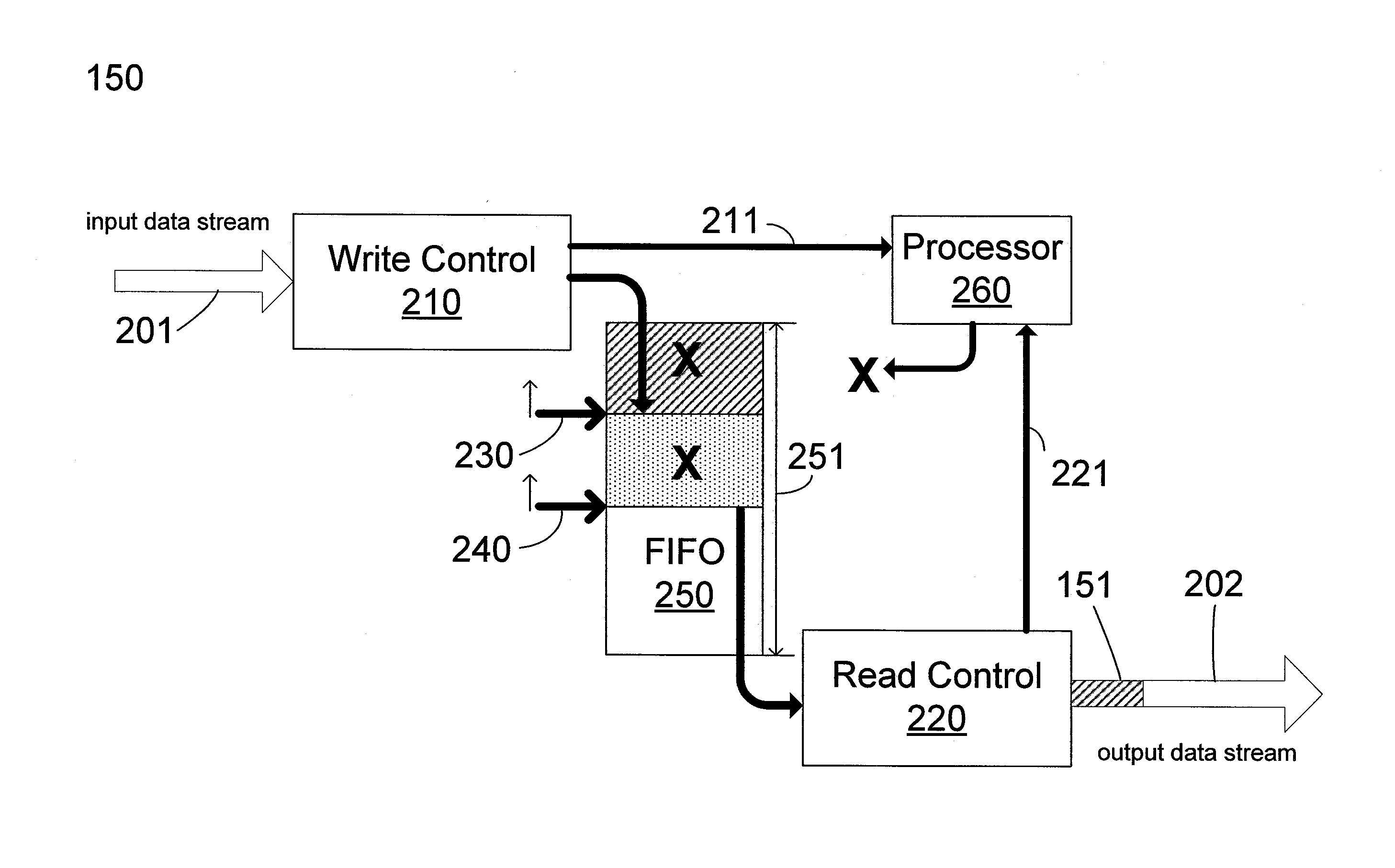
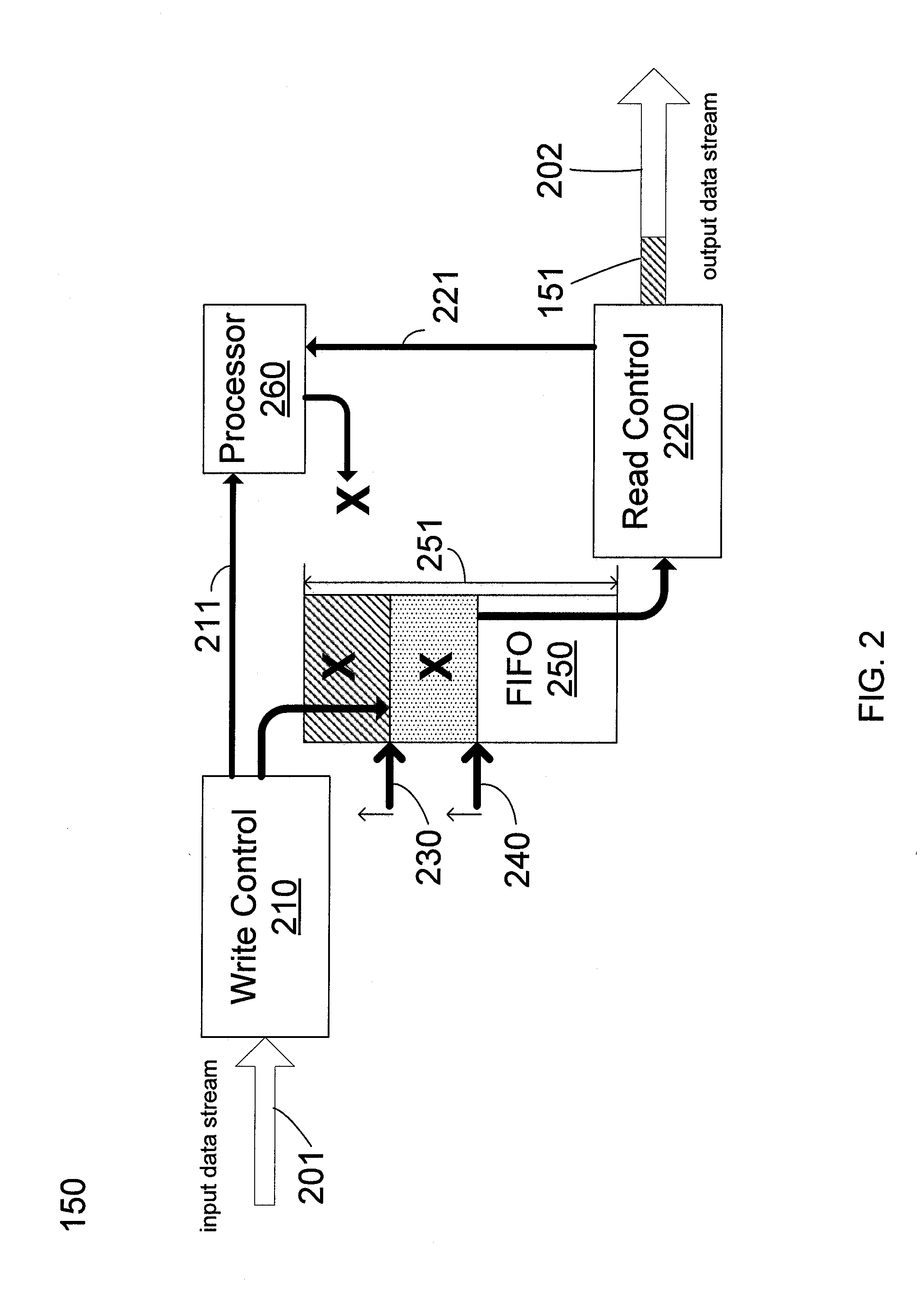
Data rate buffering in display port links
ActiveUS20110249192A1Television system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesData streamData rate
Rate matching for use in data links between a source device and a sink device is provided. A rate matching device includes a first-in-first-out (FIFO) buffer having a write pointer and a read pointer; a write control having a write clock to write an input data stream from the source device onto the FIFO buffer using the write pointer; a read control having a read clock to read data from the FIFO buffer using a read pointer, insert data to an output data stream and transmitting the data stream to the sink device; a processor to provide a bit number based on the write clock period and the read clock period, wherein the read control inserts blanking data into the output data stream while the read pointer is stopped in the FIFO buffer to allow the write pointer to move ahead by the bit number provided by the processor. Some embodiments are thus able to avoid buffer overflow or underflow scenarios.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Dynamic mode selection and energy distribution method in energy capture D2D network
InactiveCN107071914ARealize dynamic usageImprove performancePower managementSignal-to-quantization-noise ratioMode selection
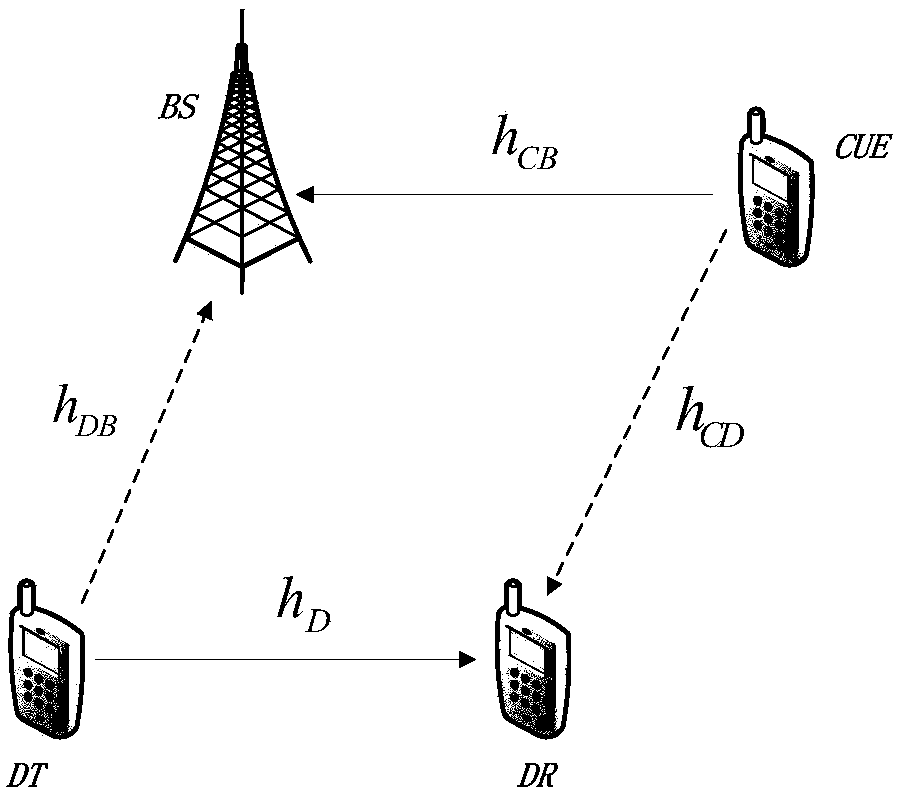
The invention discloses a dynamic mode selection and energy distribution method in an energy capture D2D network. The method comprises the following steps: taking K time slots as one transmission stage in consideration of the time-slot transmission for a cellular system, which is coexisting with a battery powered user, of D2D in energy capture energy supply; dynamically selecting a resource reuse mode for the user under different channel conditions and energy states by use of a signal to noise ratio (SNR) threshold at each time slot of the transmission stage, and constructing a utility index by combining the current channel information with the formerly acquired channel information, performing online energy distribution and power control according to the utility index parameter; when the current time slot channel utility index is greater than the mean value of the previous utility indexes, applying all available energy of the current time slot to the current time slot data sending, otherwise, only using a half of energy and reserving the other half to the later time slots; after determining the energy value used by the current time slot, controlling the user sending power by taking the maximum user transmission rate sum as the target under the limitation of the energy and the cellular link rate.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
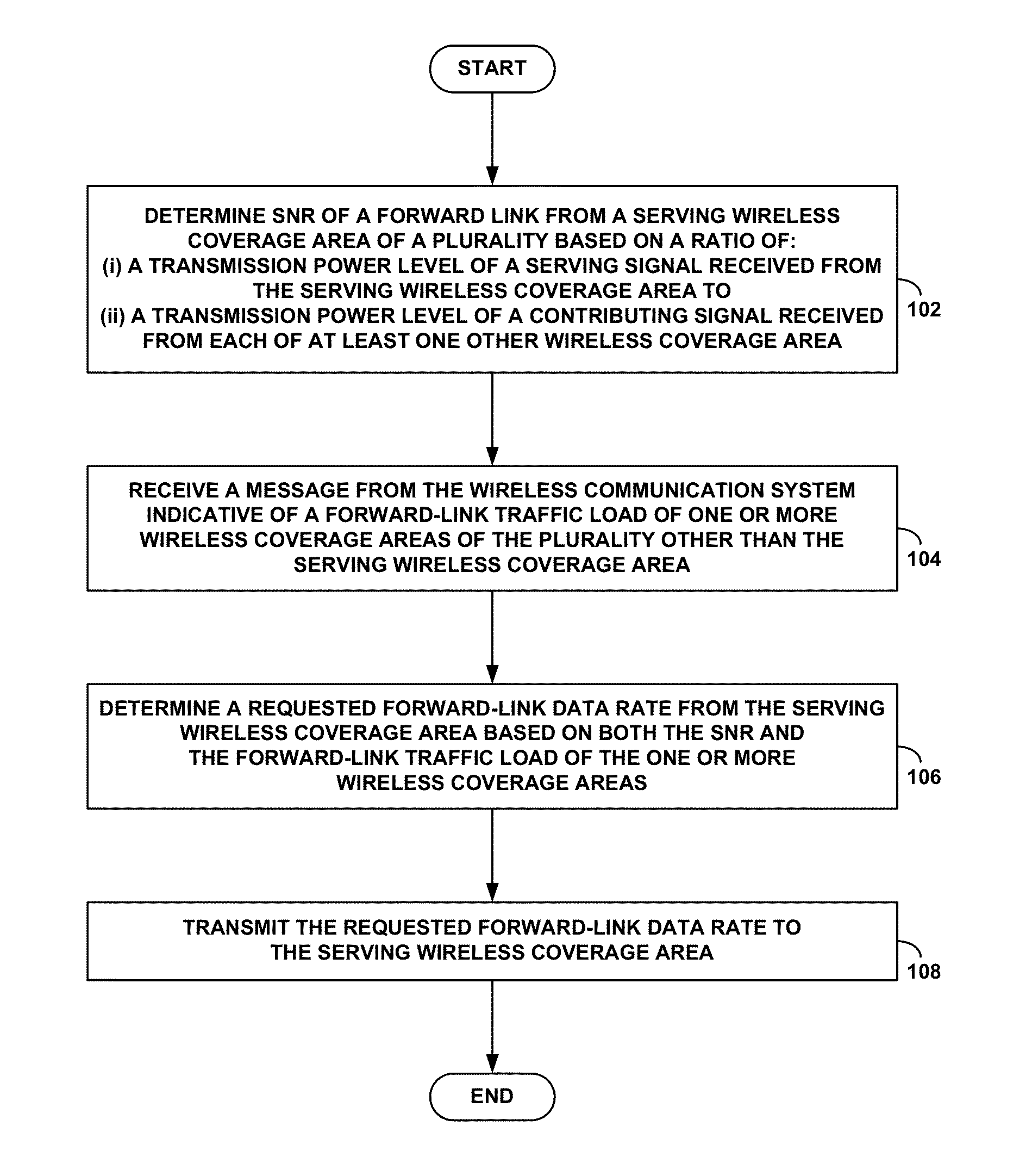
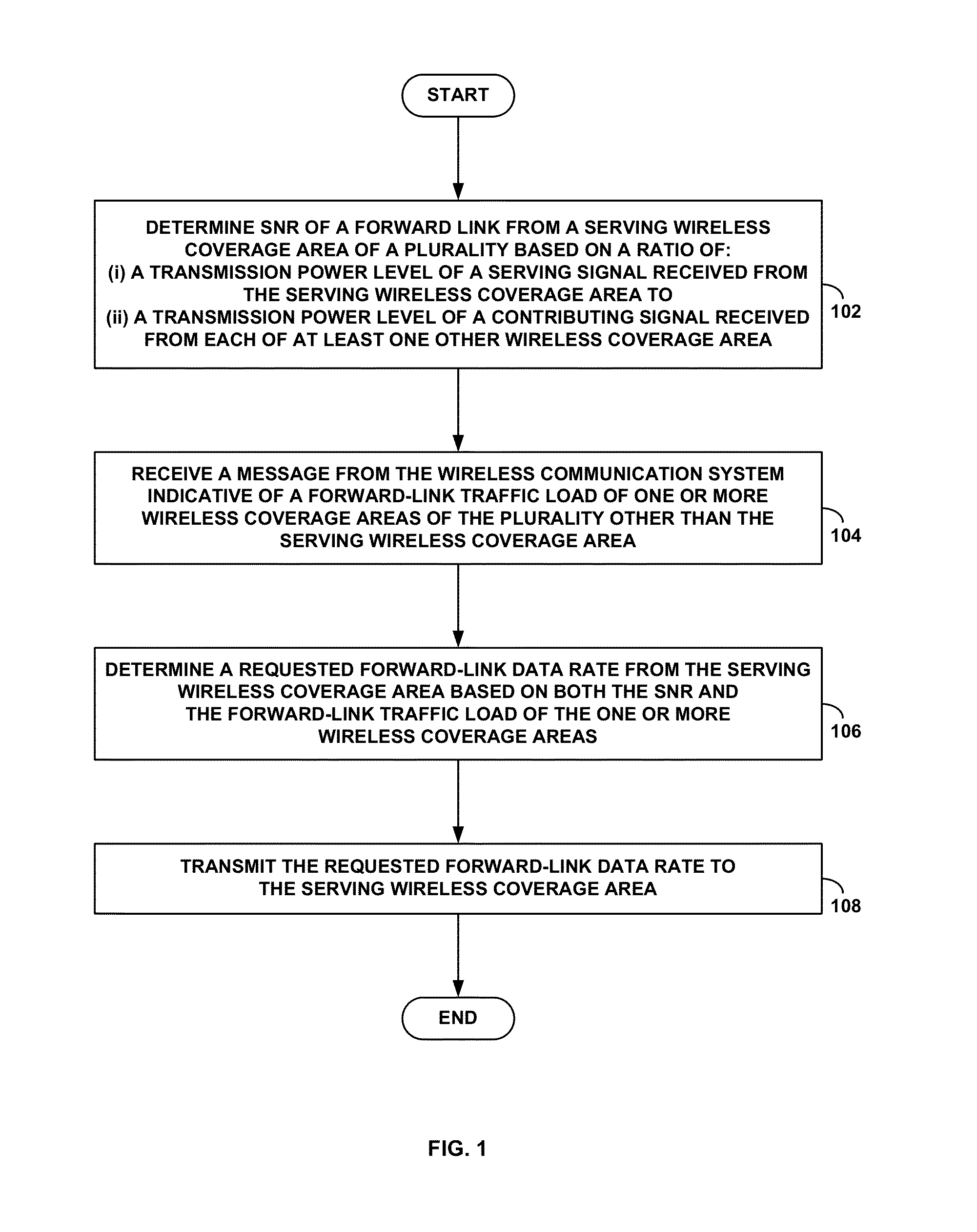
Specification of forward-link rate control based on neighbor load
ActiveUS8614964B1Power managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method and system is disclosed for forward-link data-rate request determination based on neighbor load. An access terminal in a wireless communication system that includes a plurality of base stations will determine an initial requested forward-link data rate by measuring a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) of the forward link from its serving base station. The access terminal will then use information indicative of forward-link traffic load of its neighboring base stations to modify its initial determination, whereby the access terminal will increase its initial determination if the average forward-link traffic load of its neighboring base stations is below a threshold load. The access terminal will then transit its forward-link data-rate request (initial or increased) to its serving base station.
Owner:SPRINT SPECTRUM LLC
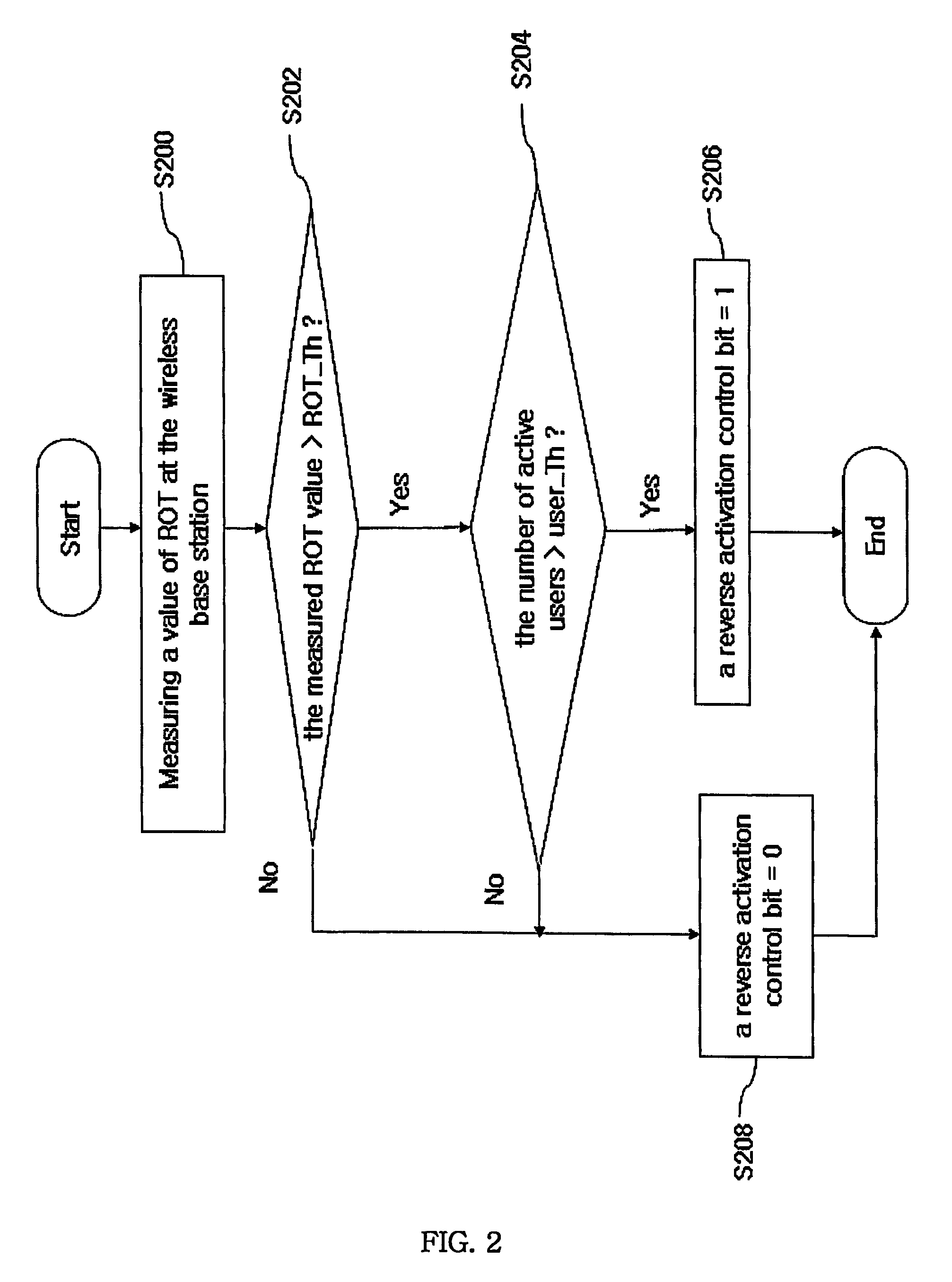
Method and system for controlling reverse link rate in CDMA 1xEV-DO mobile communication system
InactiveUS7689173B2Radio transmission for post communicationTransmission monitoringCommunications systemEngineering
A method and a system for controlling a reverse link rate by using the number of active users who are carrying out communication in a CDMA 1xEV-DO mobile communication system is disclosed. A value of rise-over-thermal (ROT) at each antenna end of a wireless base station is measured and compared with a threshold ROT which defines an allowable limit of the ROT. A reverse activation control bit is set as 0 if the measured ROT value is smaller than or equal to the threshold ROT. The number of the active users is compared with a threshold user number which defines an allowable limit of the active users if the measured ROT value is greater than the threshold ROT. The reverse activation control bit is set as 0 if the number of the active users is smaller than or equal to the threshold user number. The reverse activation control bit is set as 1 if the number of the active users is greater than the threshold user number.
Owner:SK TELECOM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com