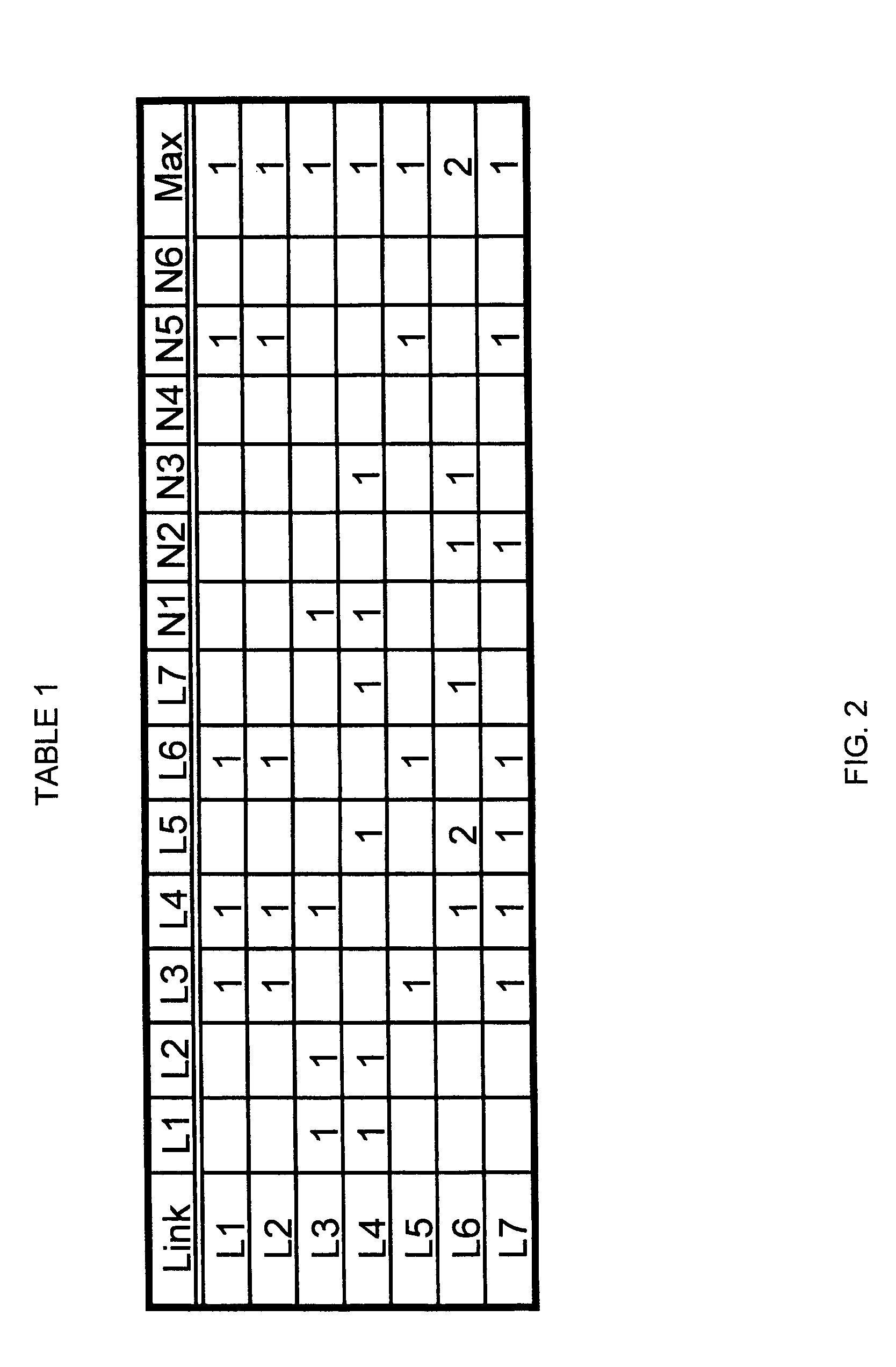
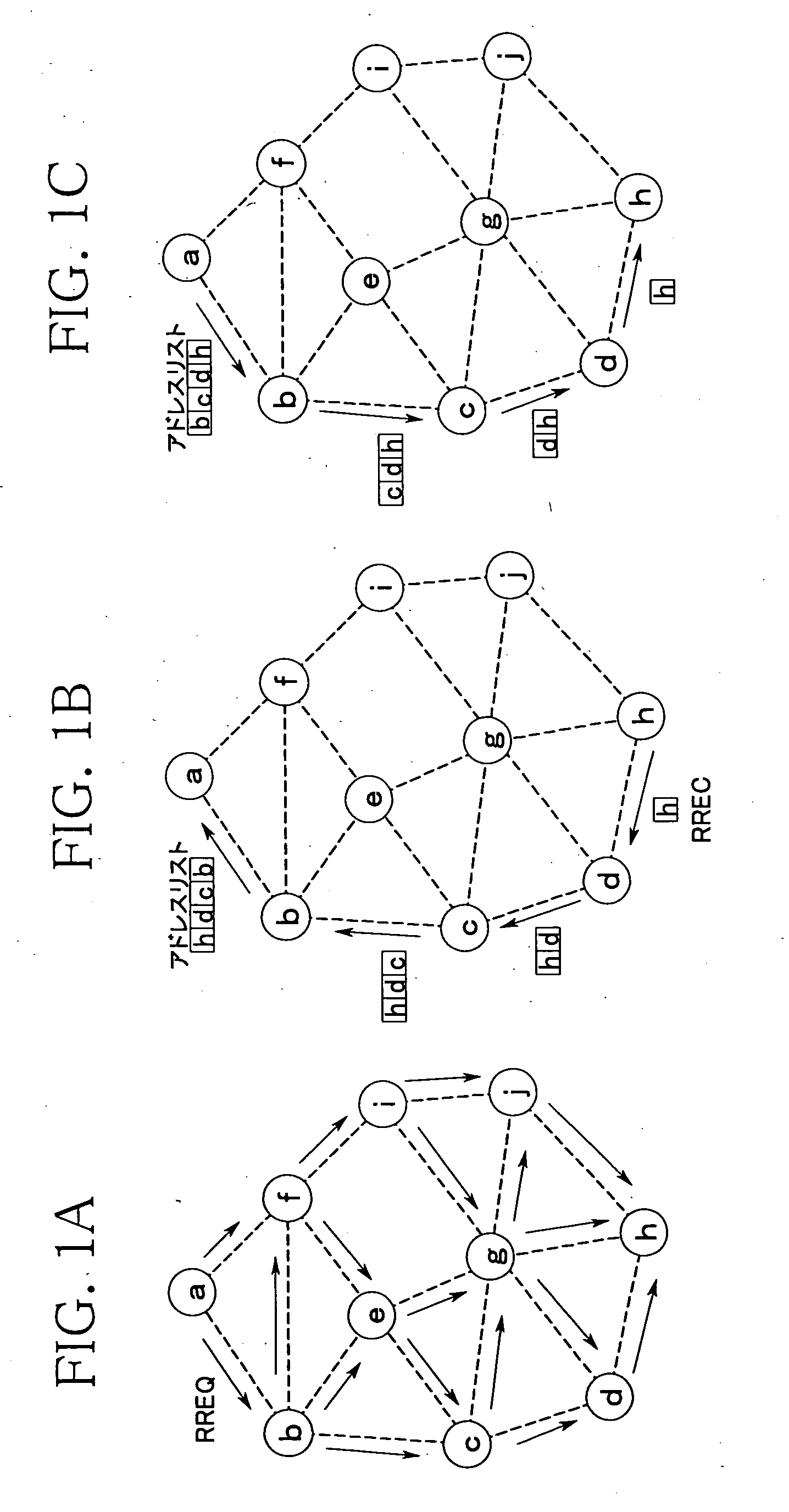
Patents
Literature
136 results about "Path cost" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
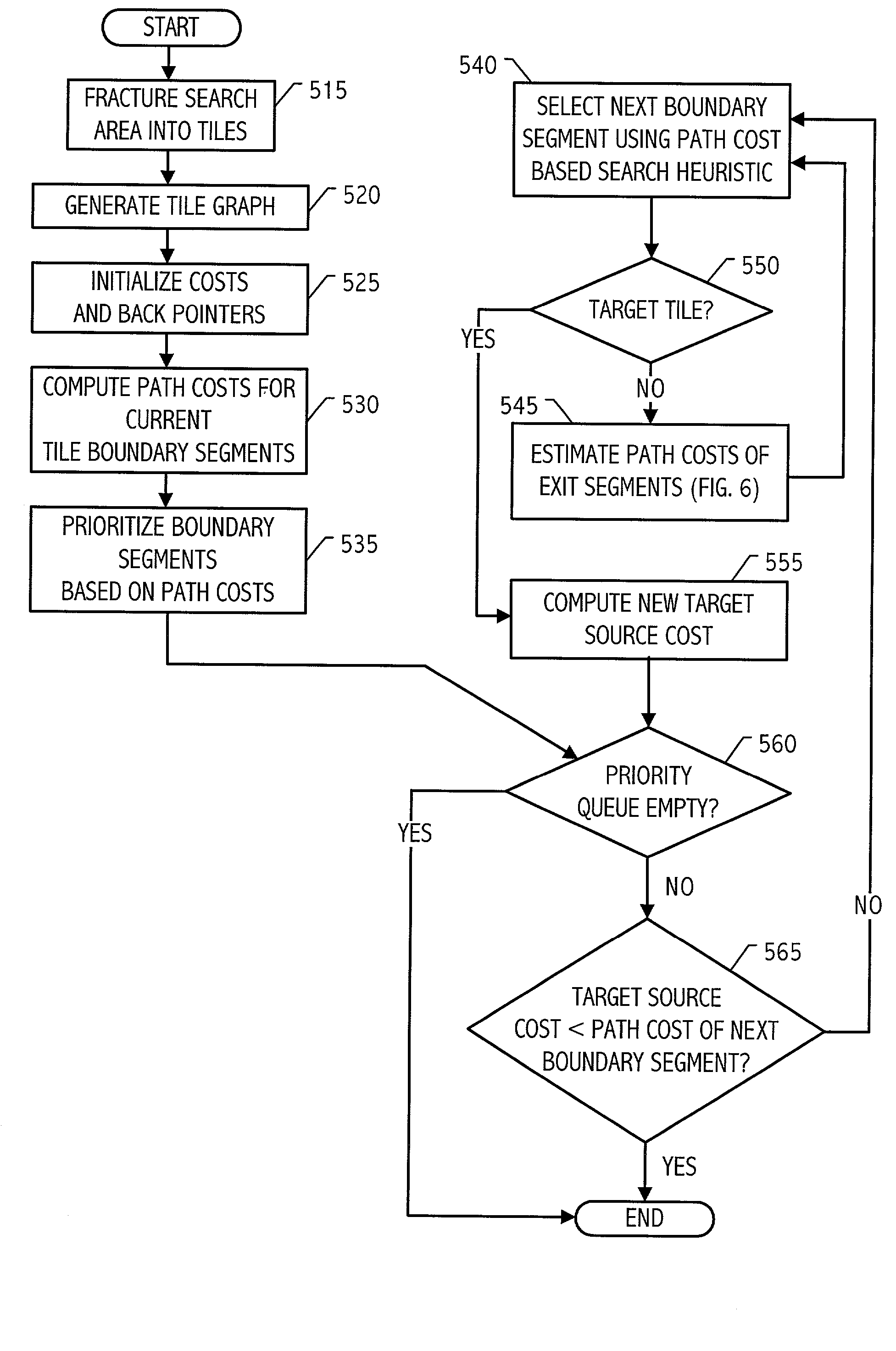
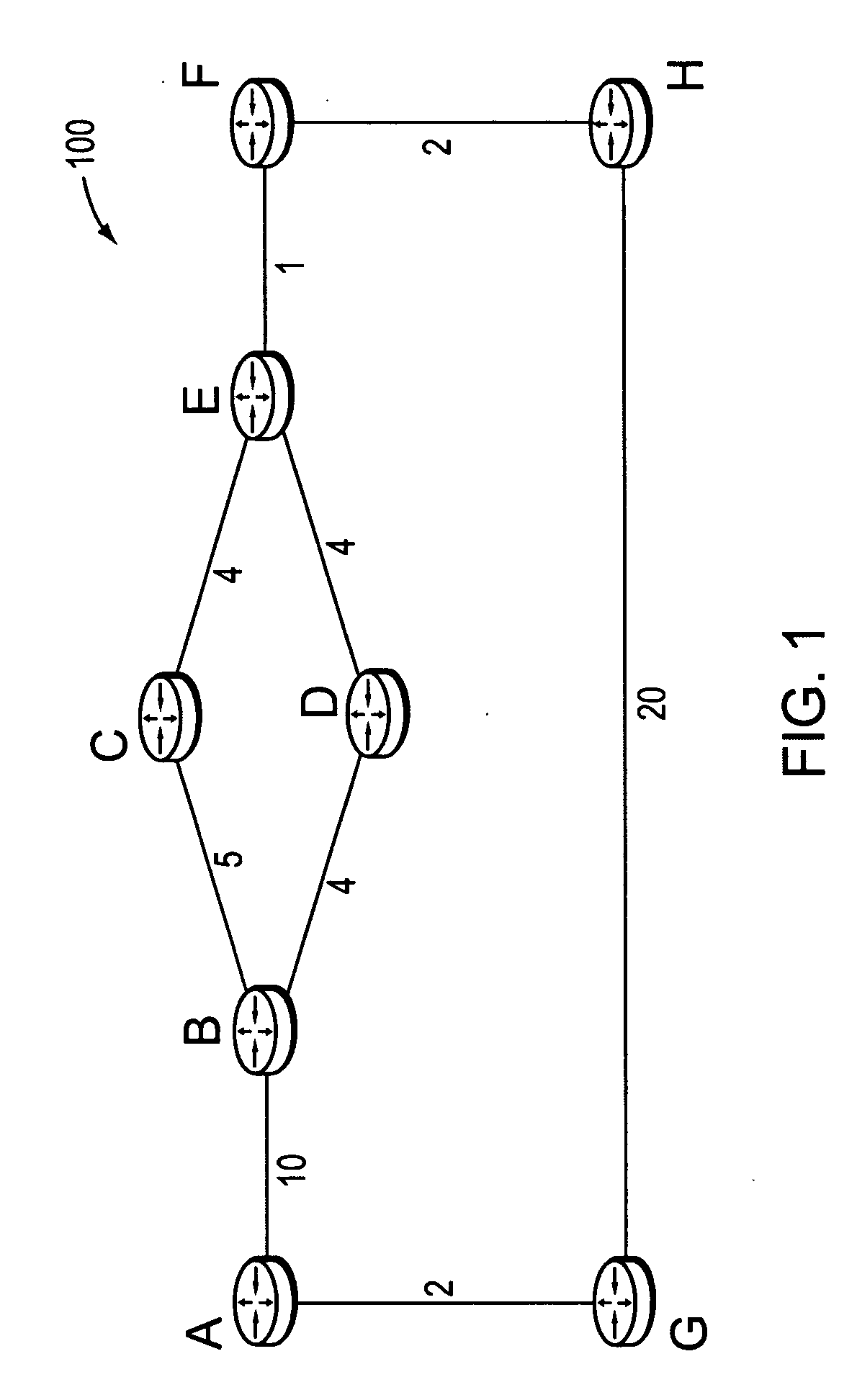
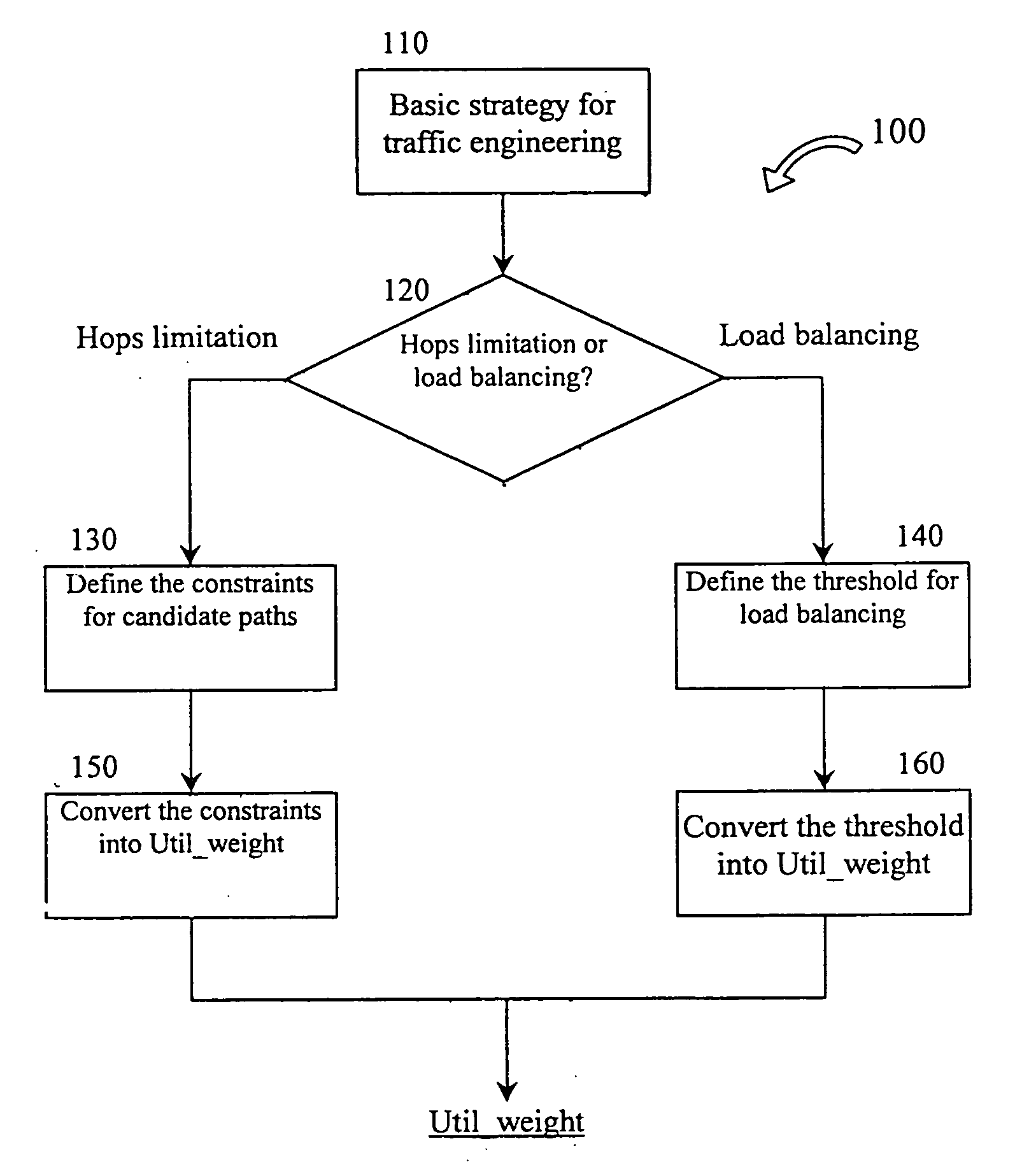
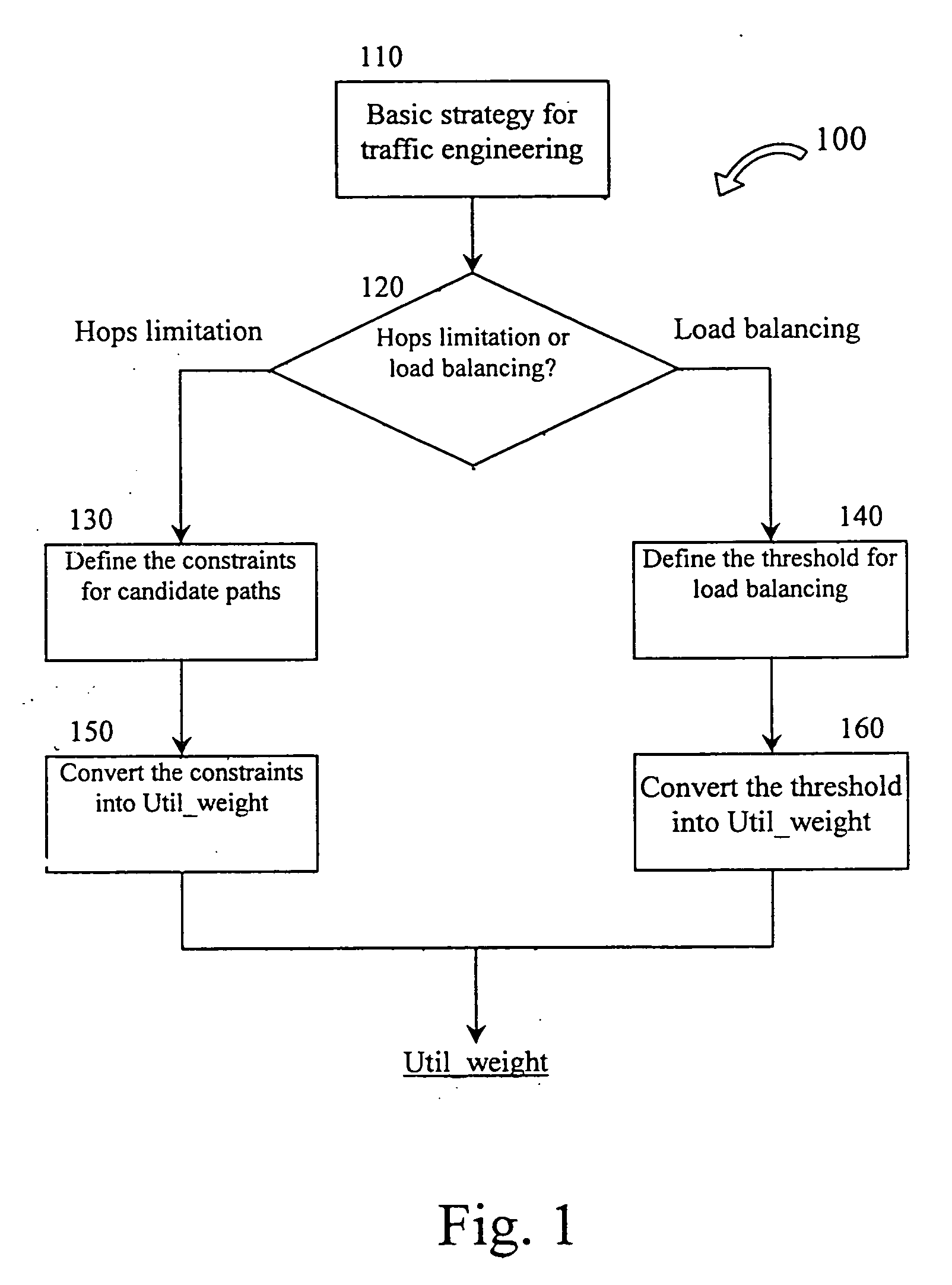
Cost Path is one of a series of algorithms and tools that analyze such costs, collectively known as Cost Distance Analysis. Its most common application is for planning corridors for constructing linear infrastructure such as roads and utilities.
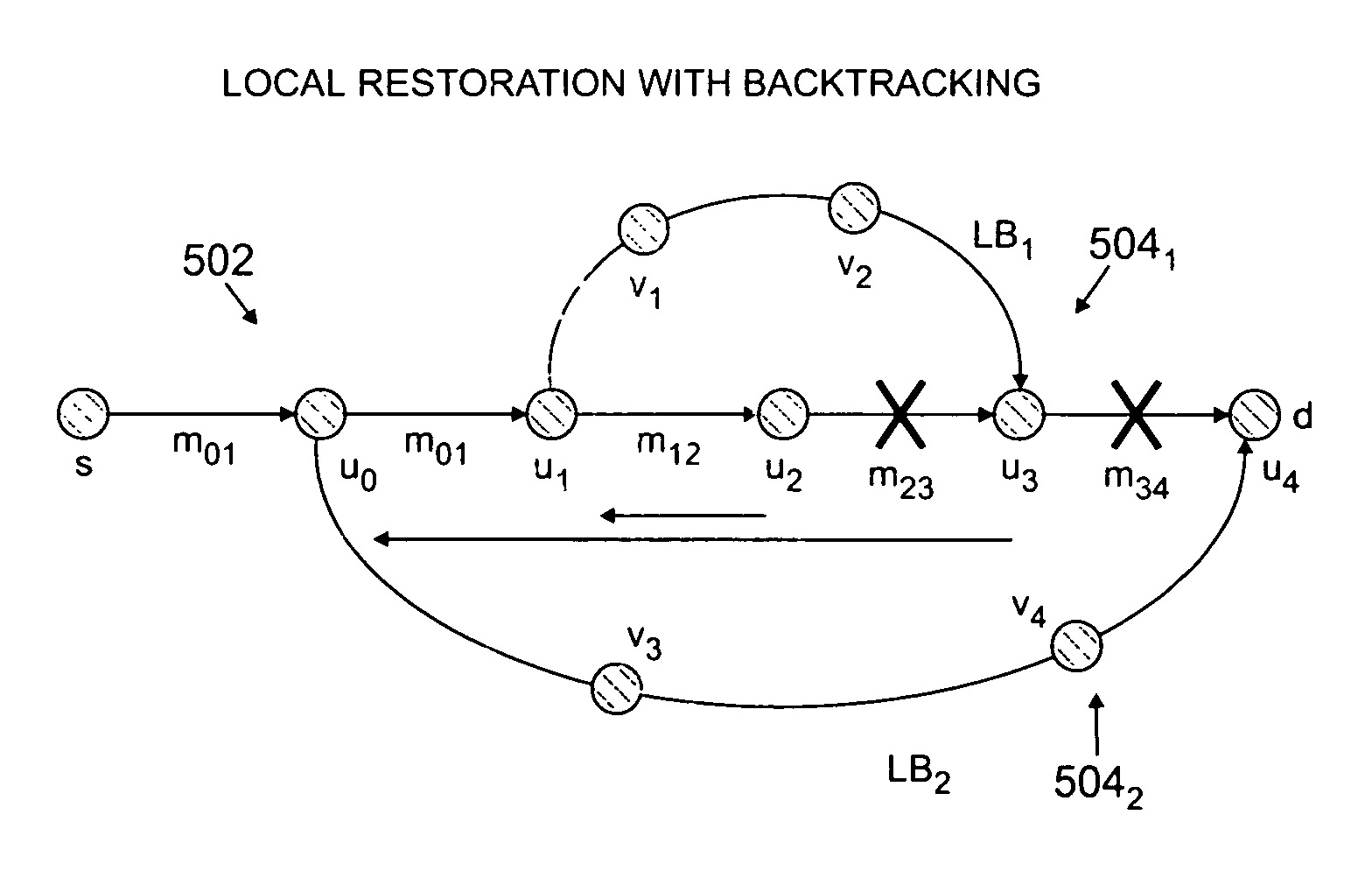
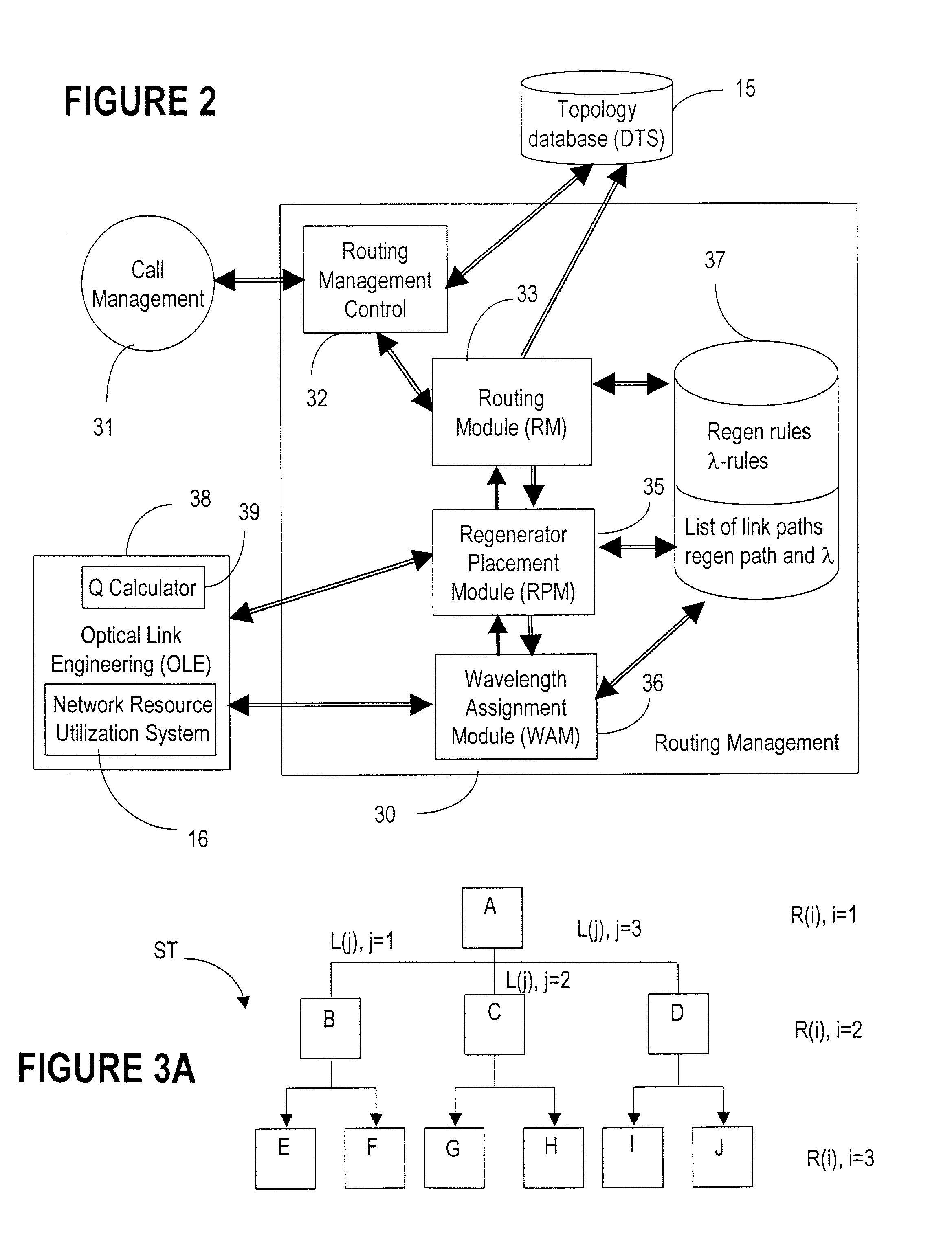
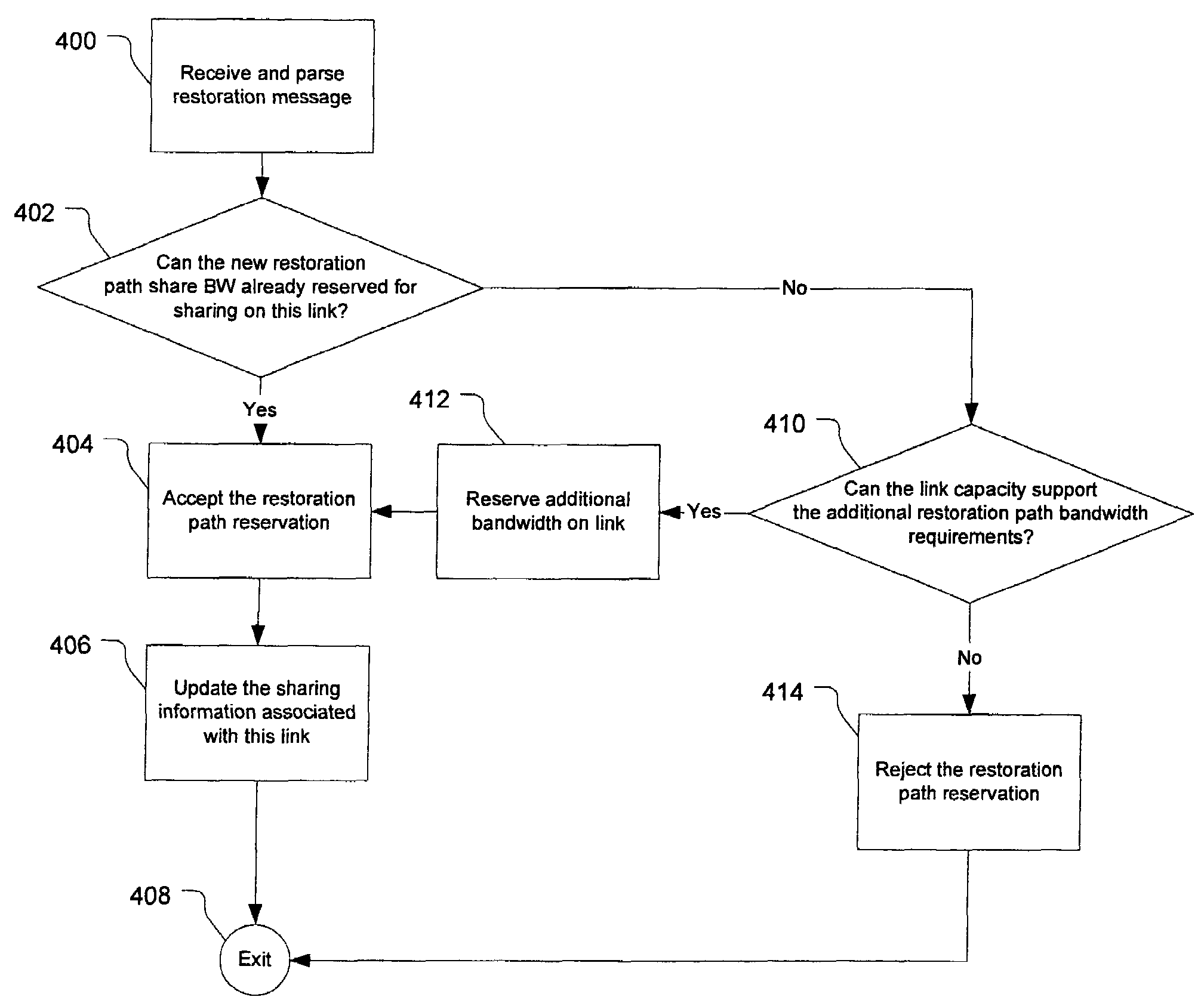
Routing bandwidth guaranteed paths with local restoration in label switched networks
ActiveUS8675493B2Free excess bandwidthMinimize bandwidth usageError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPath costLabel switching
A method of providing at least one restoration path for a primary routing path in a network. The method includes receiving a customer connection request to route information. Costs are assigned for the primary routing path, and the primary routing path is computed based upon the primary routing path costs. A backtracking distance over the primary routing path is determined, and costs for at least one restoration path are assigned. The at least one restoration path may then be computed based upon the at least one restoration path costs.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Targeted Marching
ActiveUS20080091340A1Minimize cost functionSmooth pathImage enhancementInstruments for road network navigationPhysical spaceAlgorithm
A method of finding a path from a start point to a target point, in multi-dimensional space, including: (a) determining a plurality of points in a physical space, including a start point and an target point; (b) computing, using a cost function, for said points an accumulated path cost from the start point to a point; representing a minimal cost path from the start point to the point with respect to an optimization criteria; (c) computing for at least some of said points an estimated-cost-to-target from a point to the target point; and (d) after computing said costs, determining at least one of a minimal path or a minimal path cost of a path from the start point to the target point in the physical space, wherein the determination is based on said accumulated path costs, and is minimal with respect to the optimization criteria.
Owner:PHILIPS MEDICAL SYST TECH
Method and Arrangement for Route Cost Determination and Selection with Link Cost Interaction
ActiveUS20090175172A1Easy to useExtended routeError preventionTransmission systemsData streamShort path algorithm
This invention extends routing mechanisms that use link metrics for route selection so that: A link metric cross correlation vector is determined for all links, where each element in the vector corresponds to some other link, and reflects the change in the link metric value if a data flow would already use this other link. The invention further describes a specific embodiment where all cross-correlating links are adjacent to each other, i.e., they terminate or originate in a common node. A mechanism is described to create an extended routing graph. This extended graph permits the use of standard polynomial time algorithms that simultaneously construct the optimal route and find the optimal route metric (such as shortest-path algorithms) also for the adjacent link cross-correlating case.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Robot path planning method and device in indoor dynamic environment and robot
InactiveCN106774347ANot easy to lose targetNot easy to lose into deadlockPosition/course control in two dimensionsVehiclesEngineeringObstacle avoidance
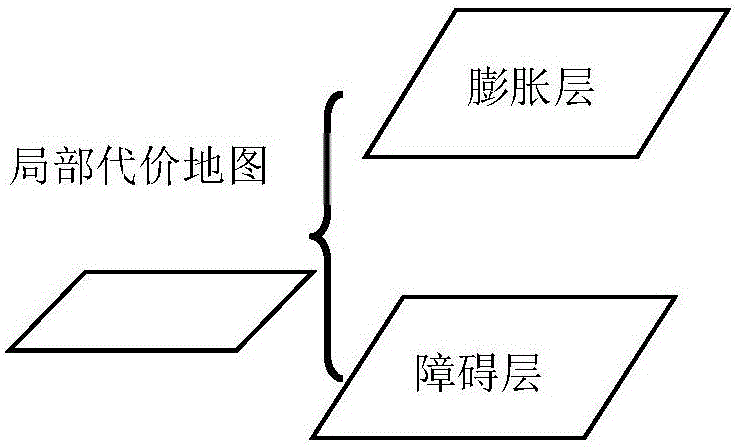
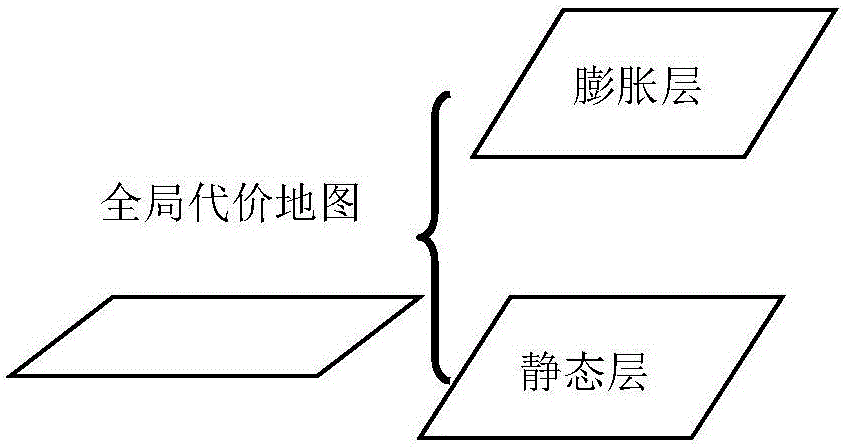
The invention relates to the technical field of robots, in particular to a robot path planning method and device in an indoor dynamic environment and a robot. Known obstacle environment information and obstacle expansion information are taken as reference in global path planning, a local path is generated according to dynamic obstacle information and obstacle expansion information in local path planning, is spliced with a global path with the minimum path cost value sum and replaces the global path with the minimum path cost value sum in a local window to obtain a target obstacle avoidance path, and the robot is controlled with a path fitting control algorithm to move along the target obstacle avoidance path so as to avoid dynamic obstacles. The obstacle environment information acquired in the global path planning is more complete, global environment is taken into consideration in the global path with the minimum path cost value sum, and the local path is generated according to the dynamic obstacle information and the obstacle expansion information in the local path planning, so that the robot can adapt to the changing environment during operating in the local window and is enabled to walk along the finally planned target obstacle avoidance path.
Owner:ANKE SMART CITY TECH PRC
Primary/restoration path calculation in mesh networks based on multiple-cost criteria
A method for determining primary and restoration paths for a new service in a mesh network involves (1) for each of a plurality of candidate primary / restoration path pairs for the new service, generating a path cost for each candidate pair, where the path cost for each restoration path is a function of the sum of the cost of links within the restoration path, and (2) selecting the primary and restoration paths for the new service from the plurality of candidate path pairs based on the path cost. If no sharing is possible, for low utilization links, the cost of links is a function of the administrative weight of the link, whereas for high utilization links, the link cost is a function of the inverse of the available capacity on the link. If sharing is possible, the cost is a function of the inverse of a sharing degree for the link.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
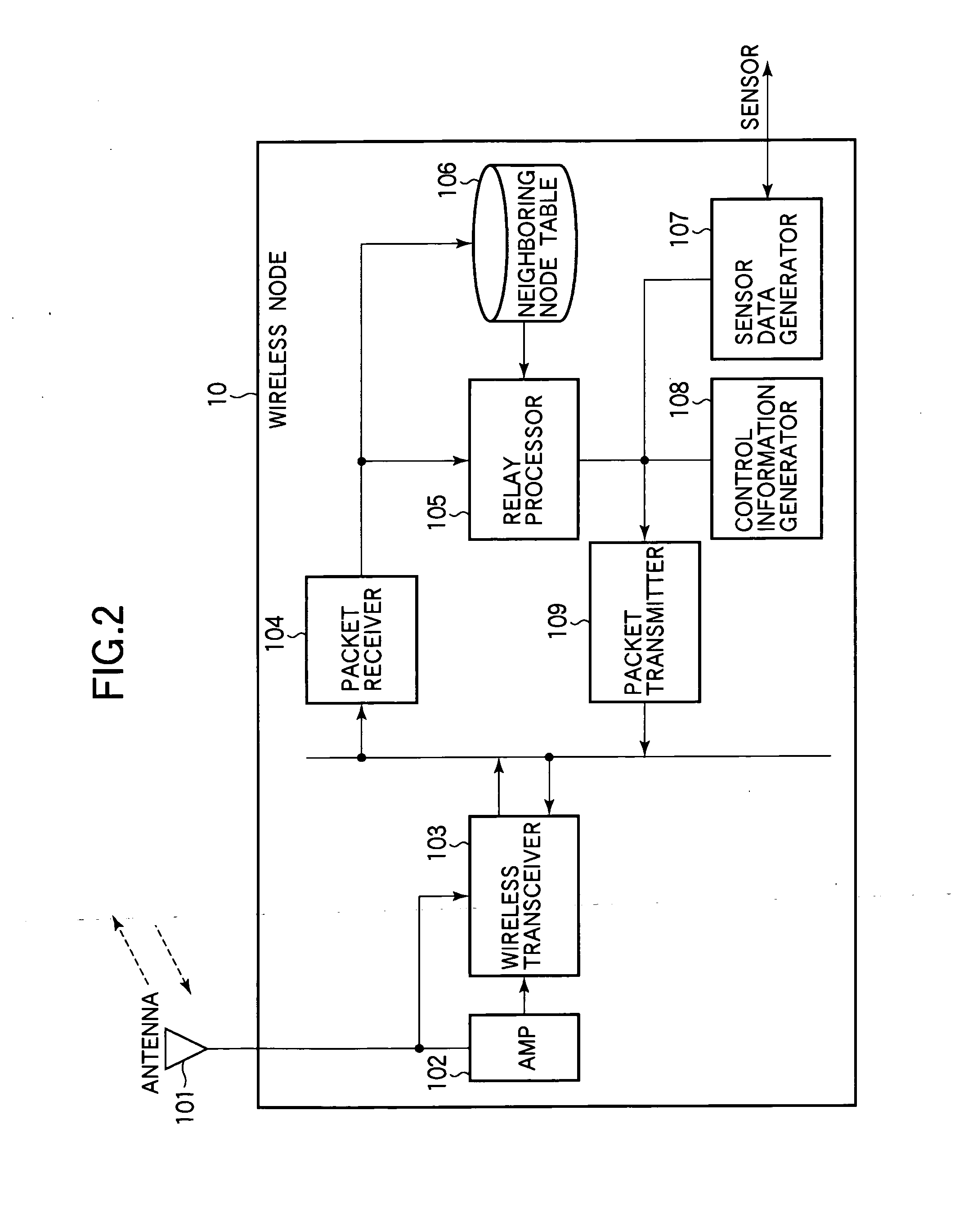
Packet relay system and wireless node
ActiveUS20100195560A1Reduce in quantityAppropriate link costFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexPath costDistributed computing
A packet relay system in which each node calculates a link cost of each adjacent node based on an arrival rate of a packet from each adjacent node, acquires an accumulated value of a link cost calculated by each node in a range of nodes from a sink node for each adjacent node, calculates, for each adjacent node, a path cost of the one adjacent node by adding the link cost calculated to the accumulated value, and relays a data packet to one adjacent node selected from among nodes adjacent to the node based on a path cost of each adjacent node. This enables establishment of an upstream path to a sink node without increasing the amount of communication in a network.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Piecewise linear cost propagation for path searching
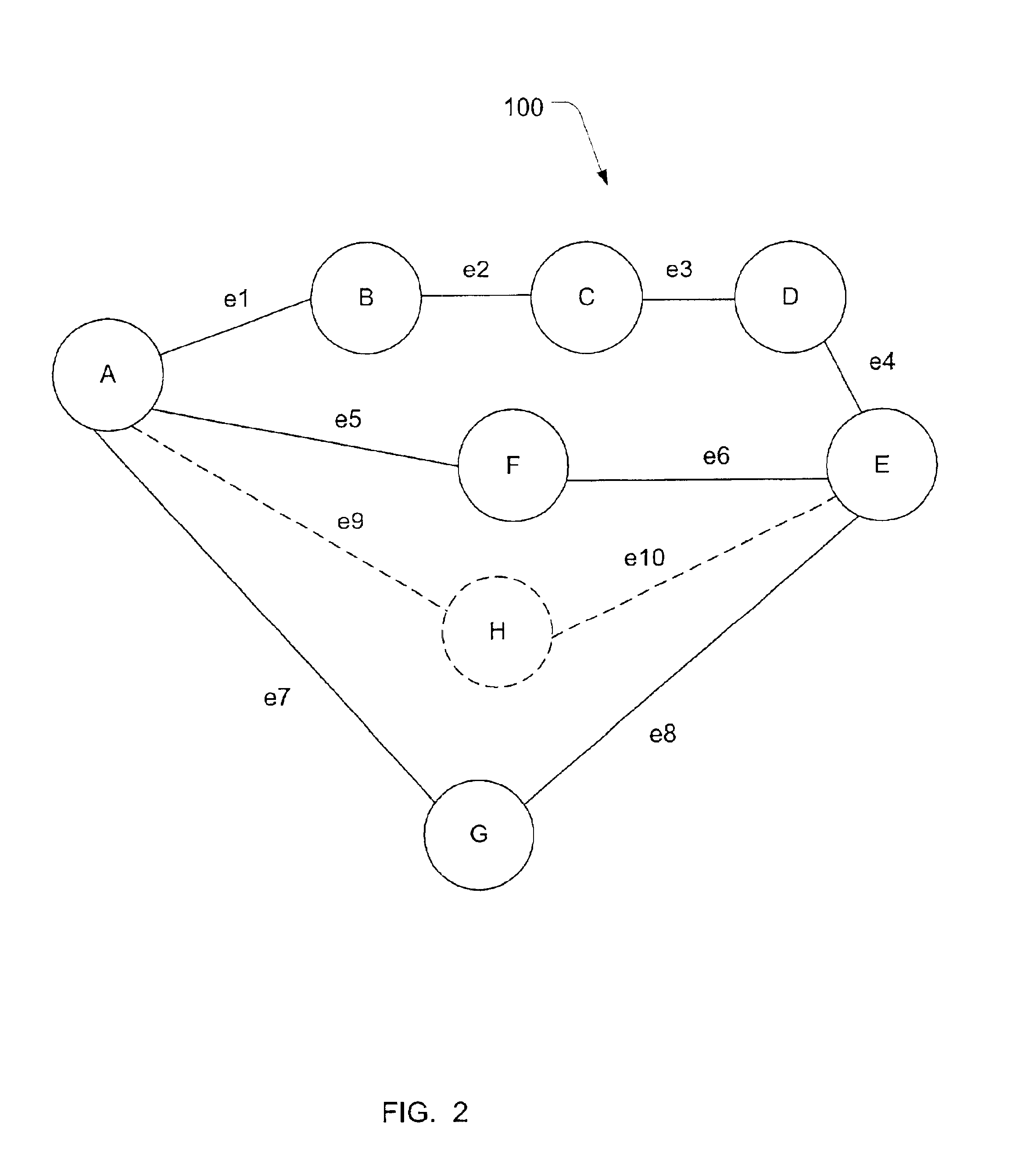
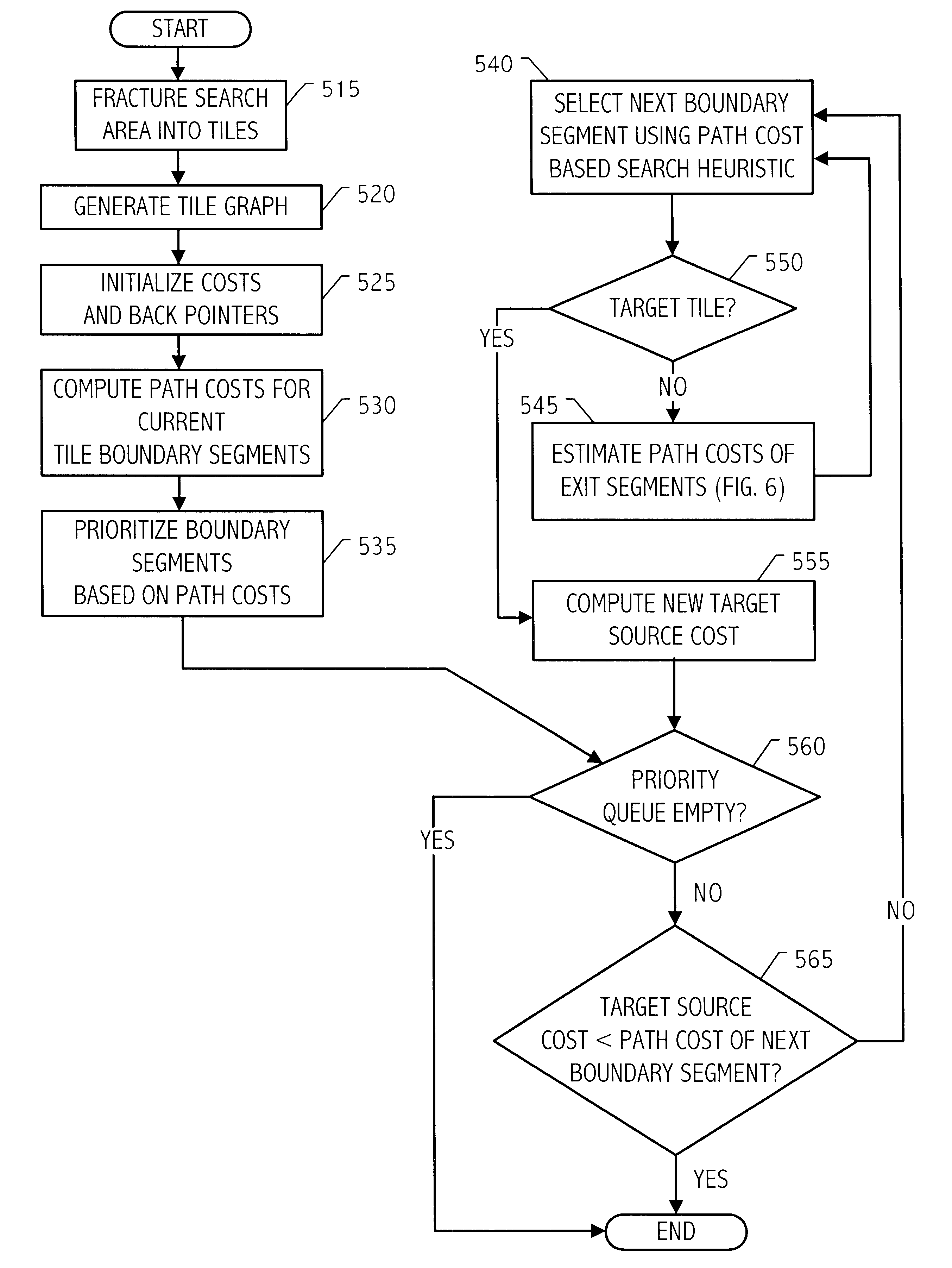
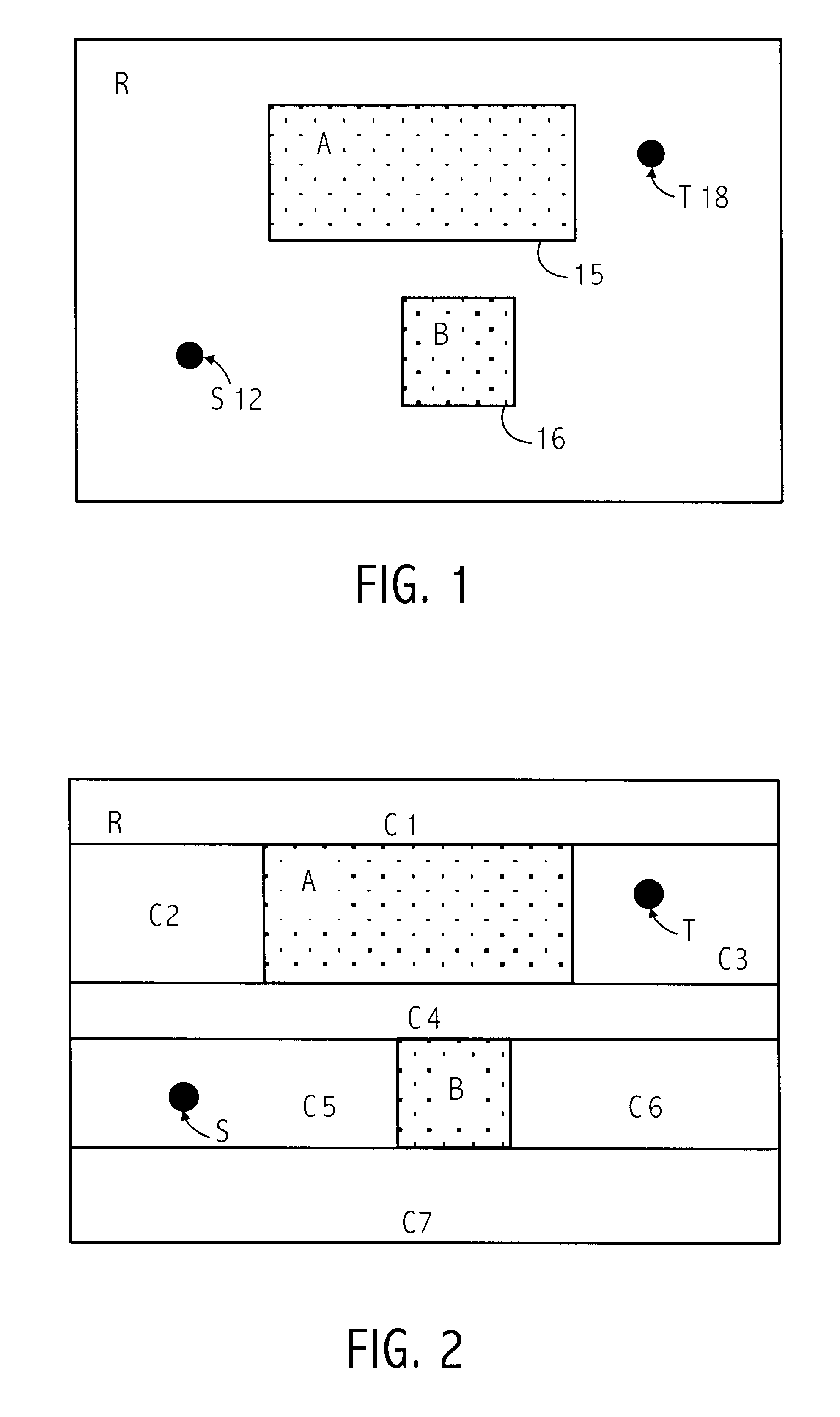
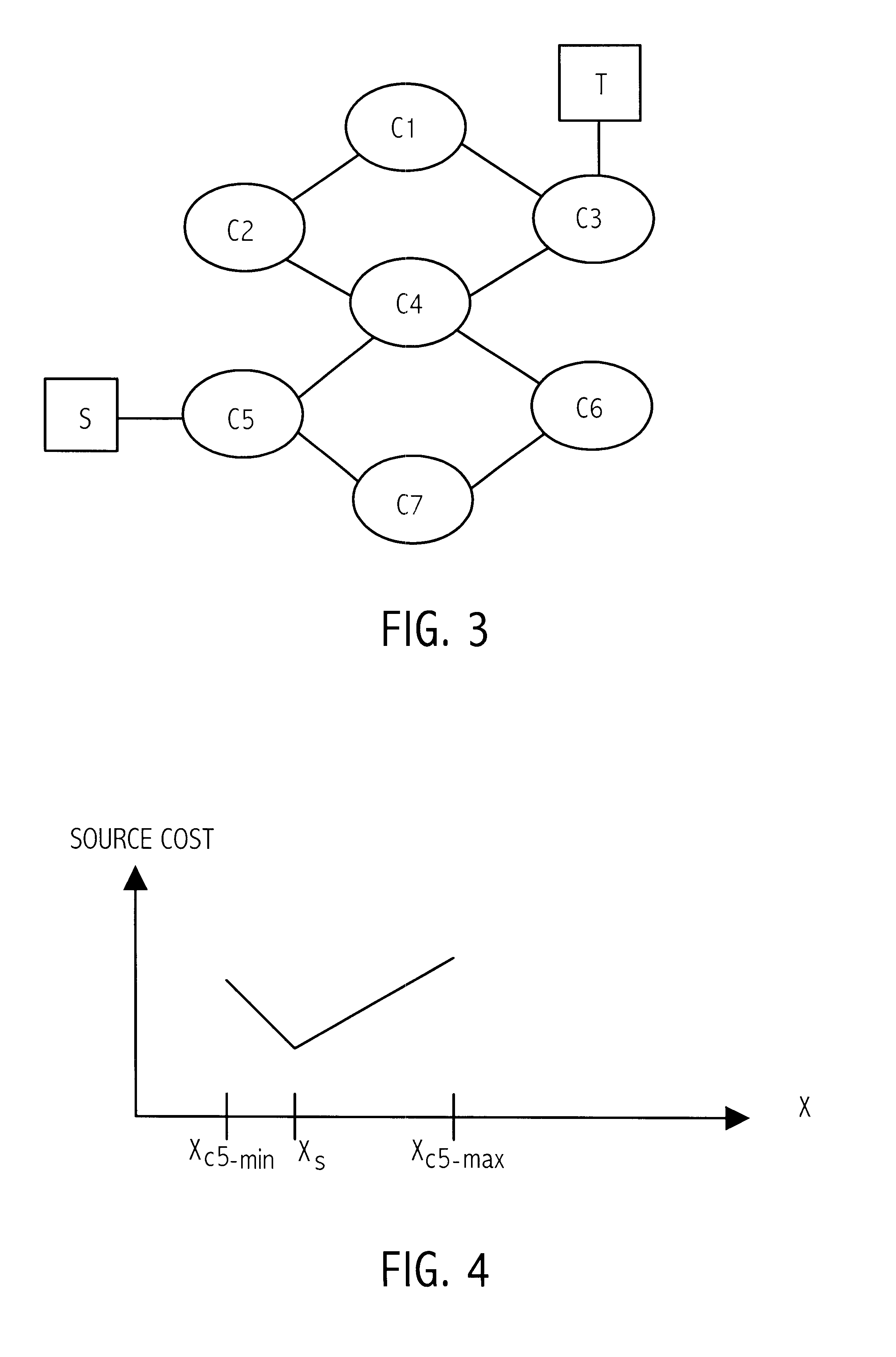
InactiveUS20020100009A1Computer aided designSpecial data processing applicationsMultiple formsPath cost
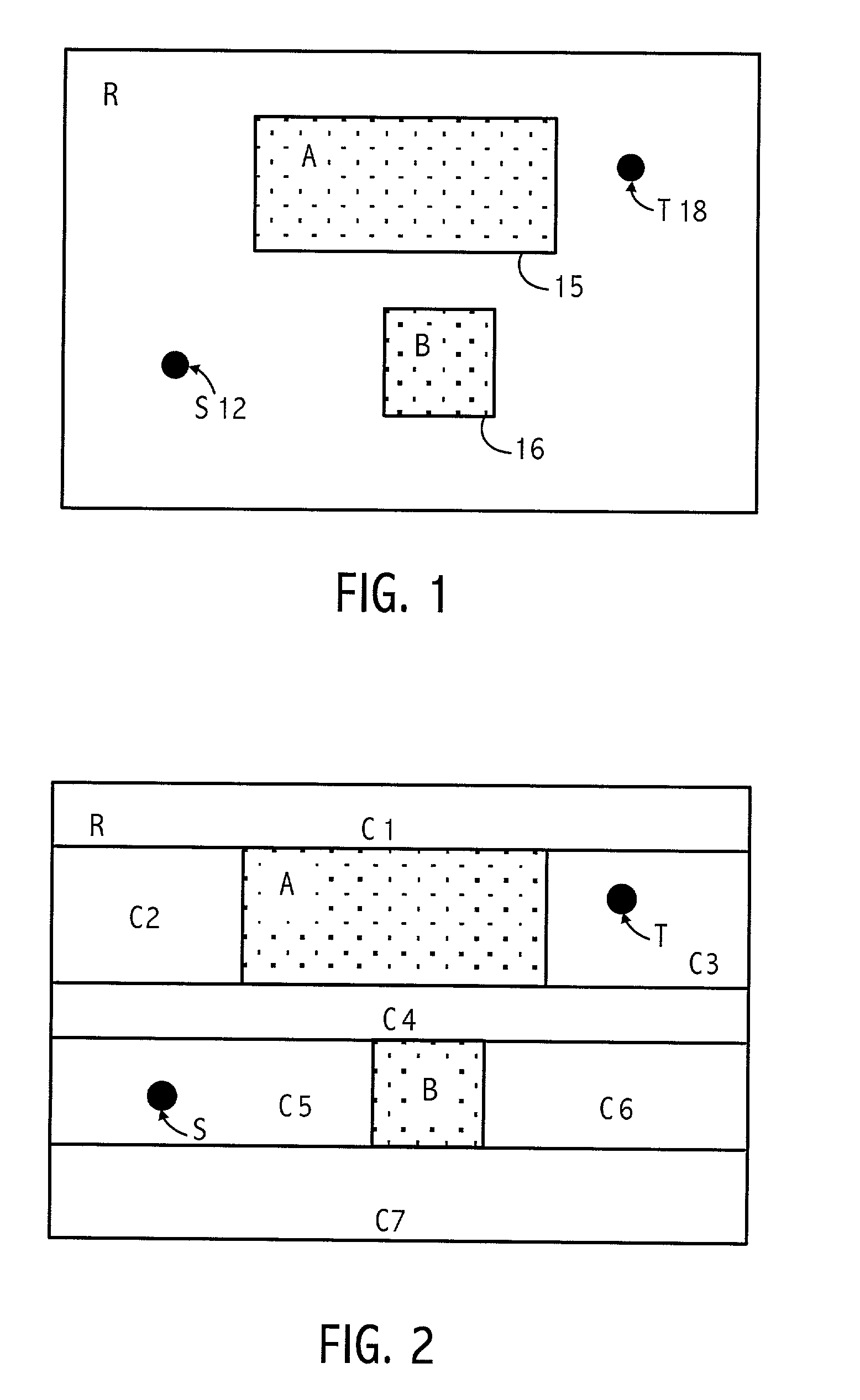
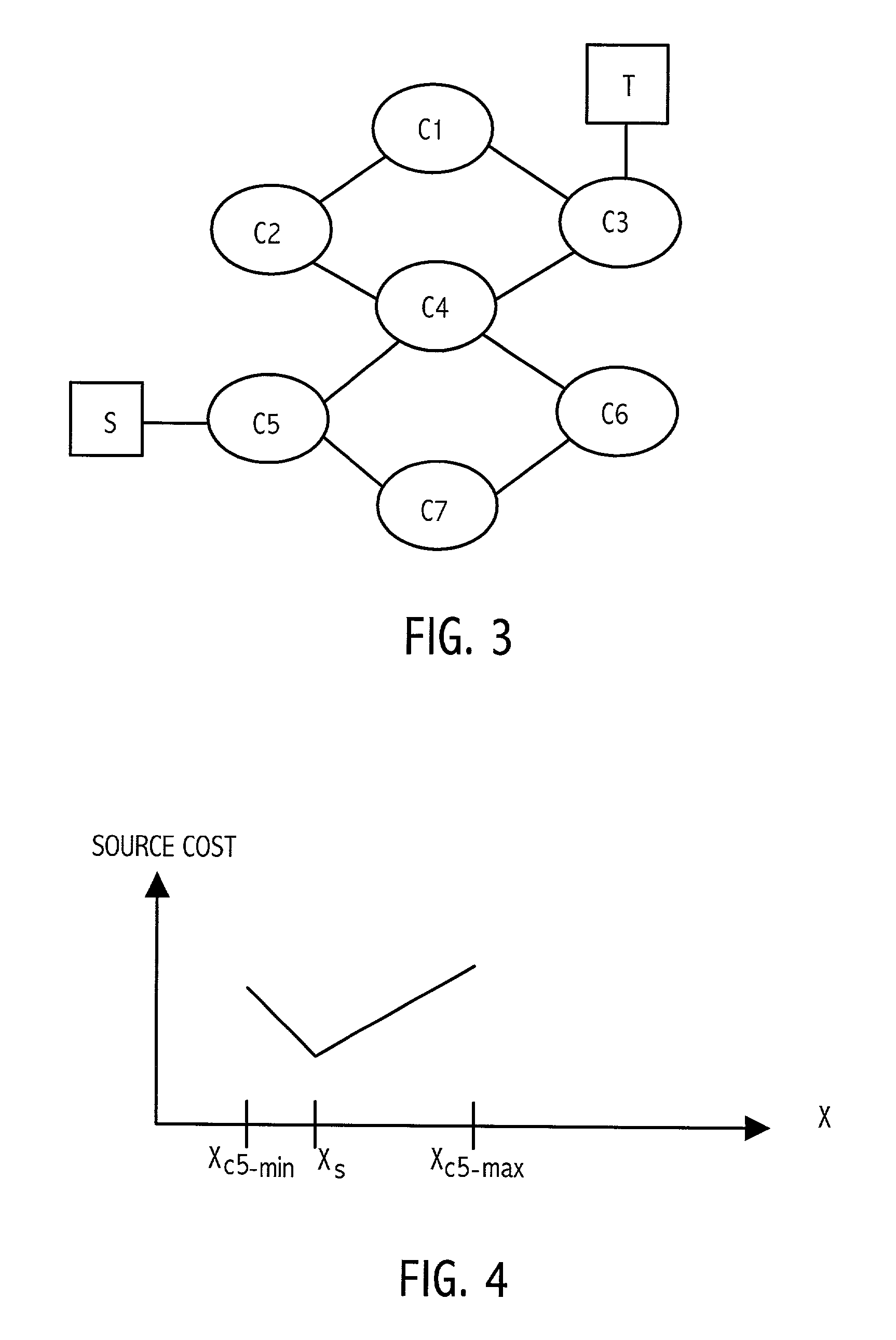
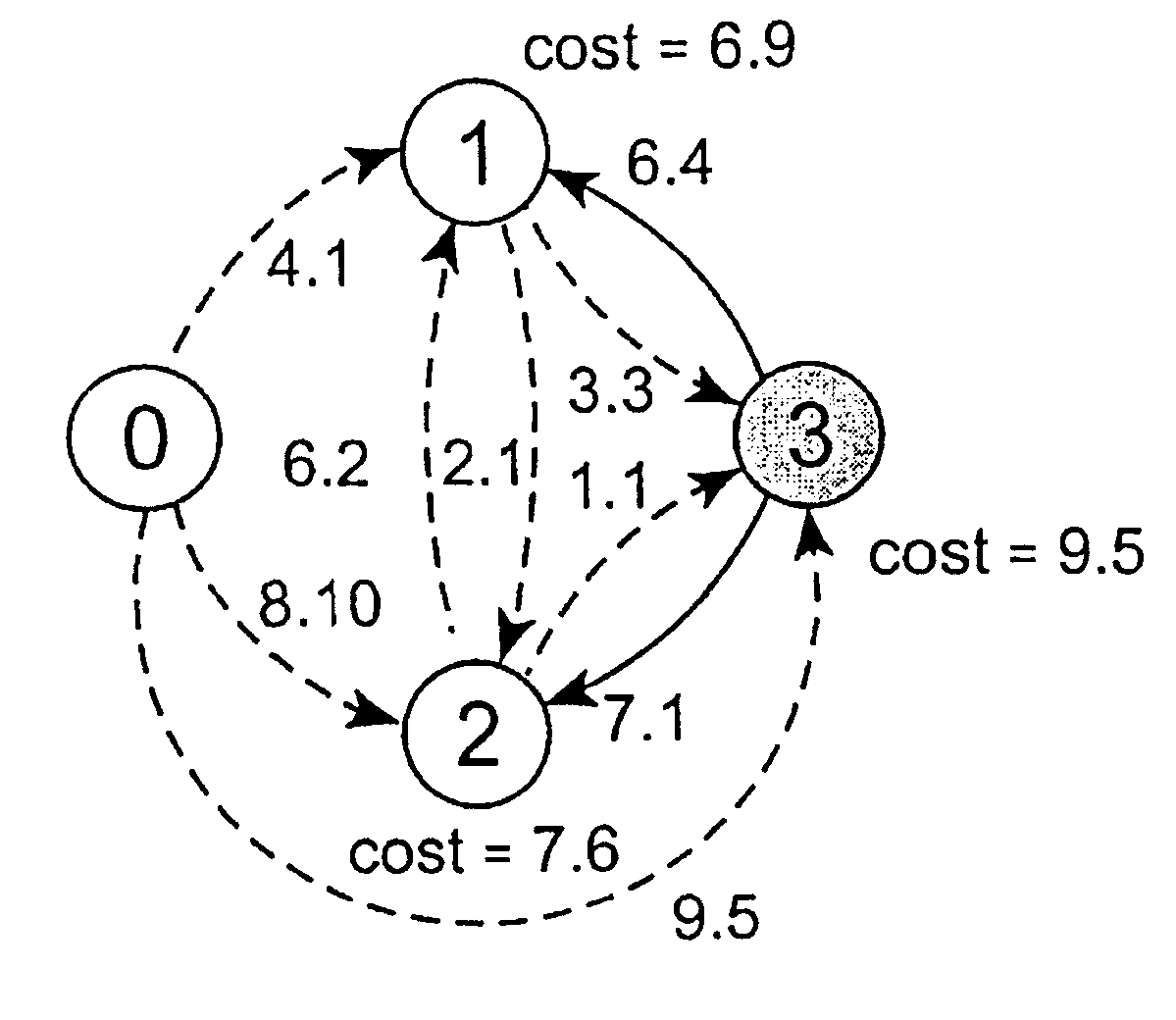
The problem of searching for a low cost path from a source location to a target location through a traversable region partitioned into a plurality of tiles is solved using source and target cost functions. Each tile in the traversable region is defined by boundary segments. The source cost function provides a cost for traversing from the source location to the boundary segment in question. The target cost function provides a cost for traversing from the boundary segment in question to the target location. The target cost function is estimated, and the source cost function is calculated. A path cost function is determined by adding the source and target cost functions. If the target location is a tile, then the target cost may be estimated using a convex hull of the target tile and the boundary segment in question. To facilitate the cost function calculations, multiple forms of cost function propagation between segments are disclosed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
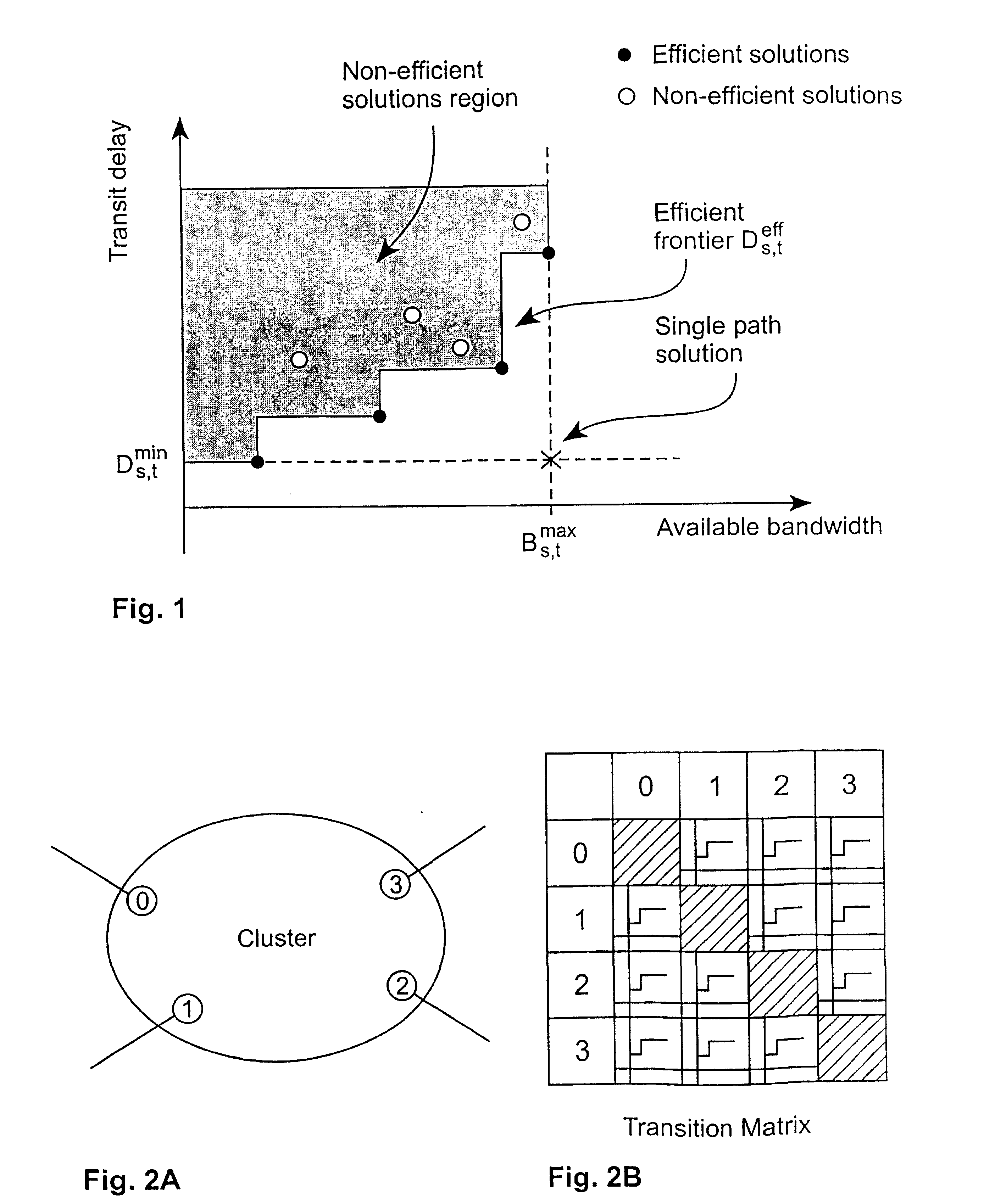
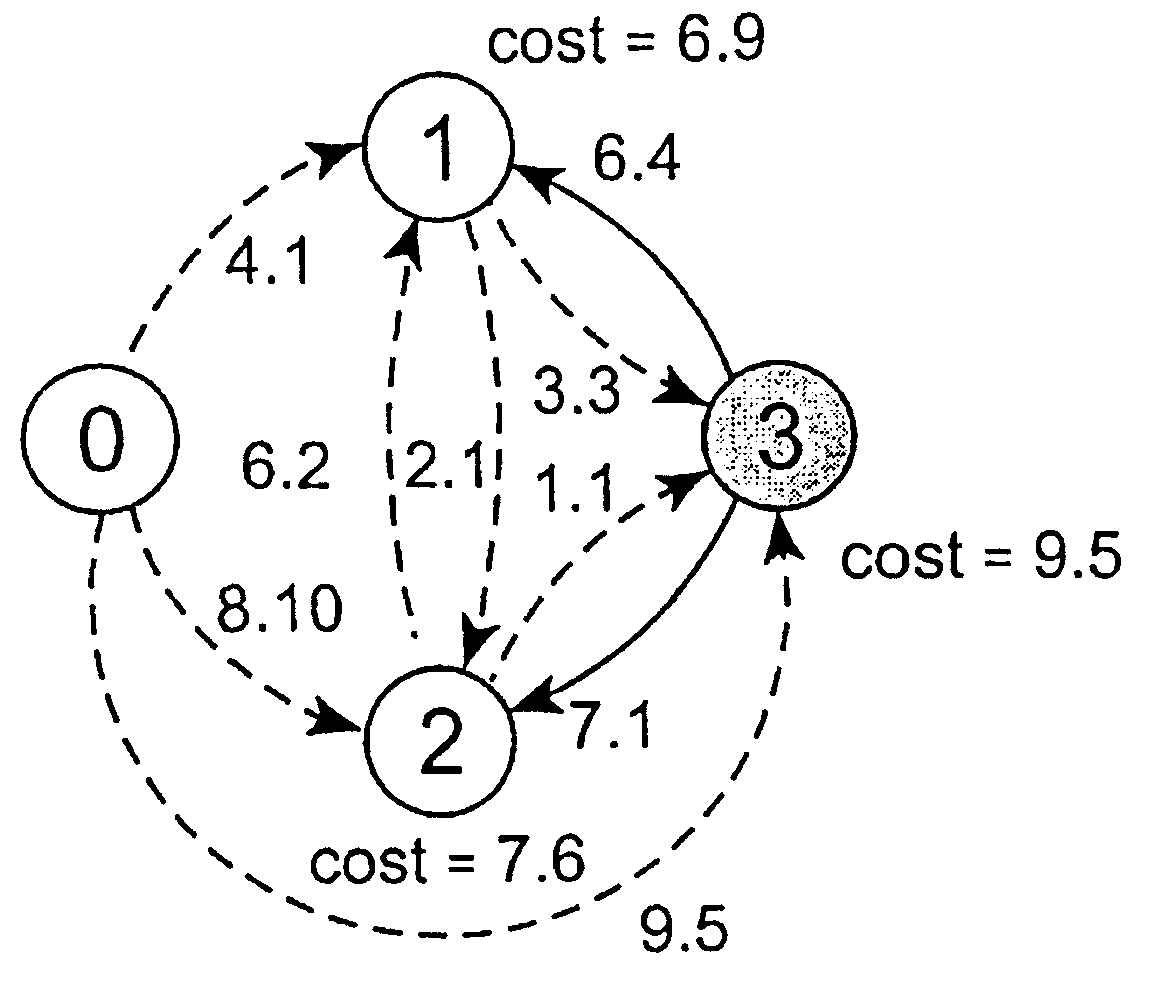
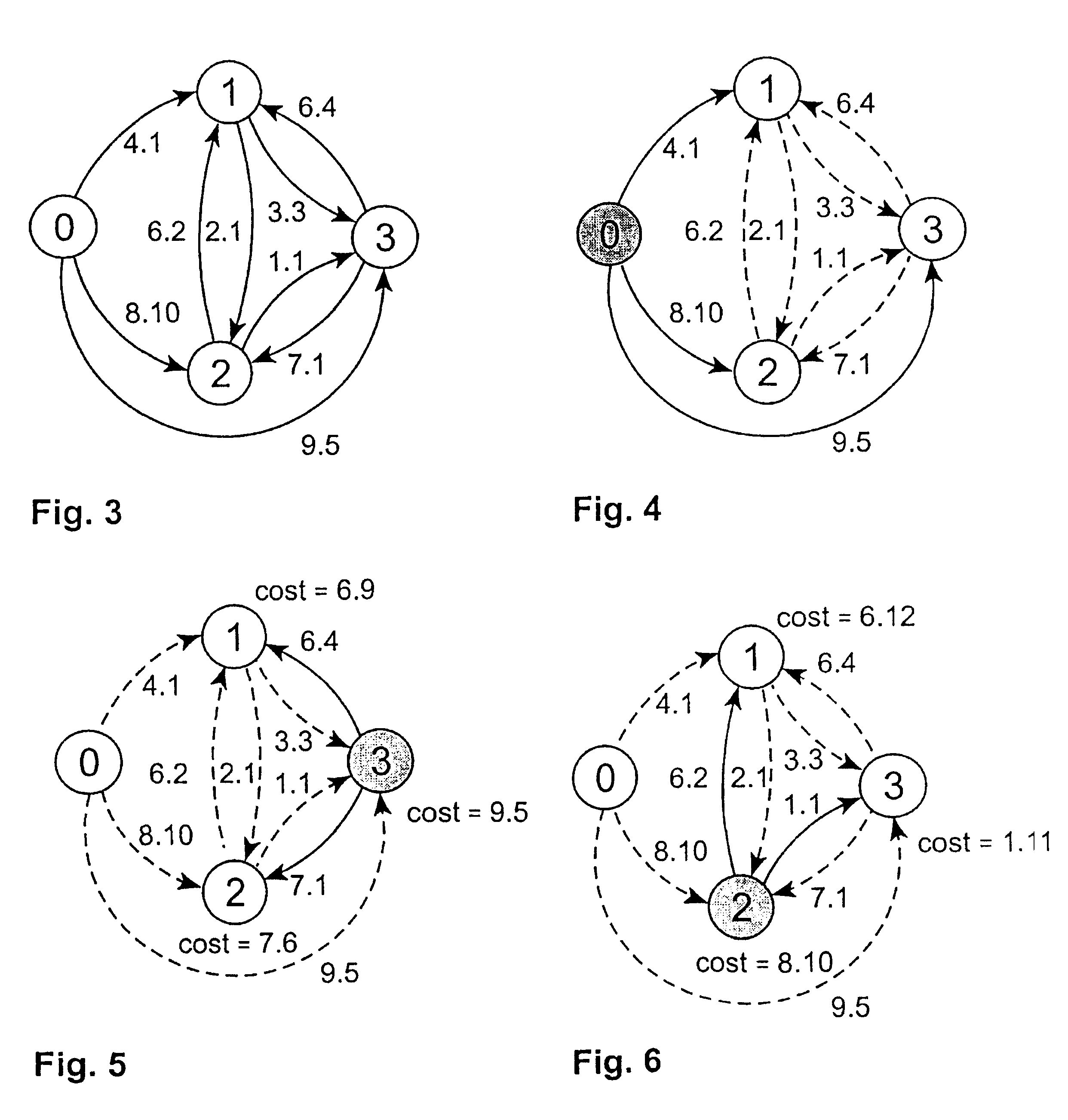
Costs in data networks
InactiveUS20040071089A1Special service provision for substationError preventionPathPingHigh bandwidth
A method for deriving a set of efficient path costs for a group of nodes comprising a source node and a plurality of destination nodes in a data communications networks, wherein the path costs for paths between nodes in the group are defined in the network and each path cost comprises a restrictive cost and an additive cost, comprises iteratively identifying the paths of higher bandwidth first and, when two or more paths of equal bandwidth are encountered, selecting the path having a lower transit delay associated therewith.
Owner:IBM CORP
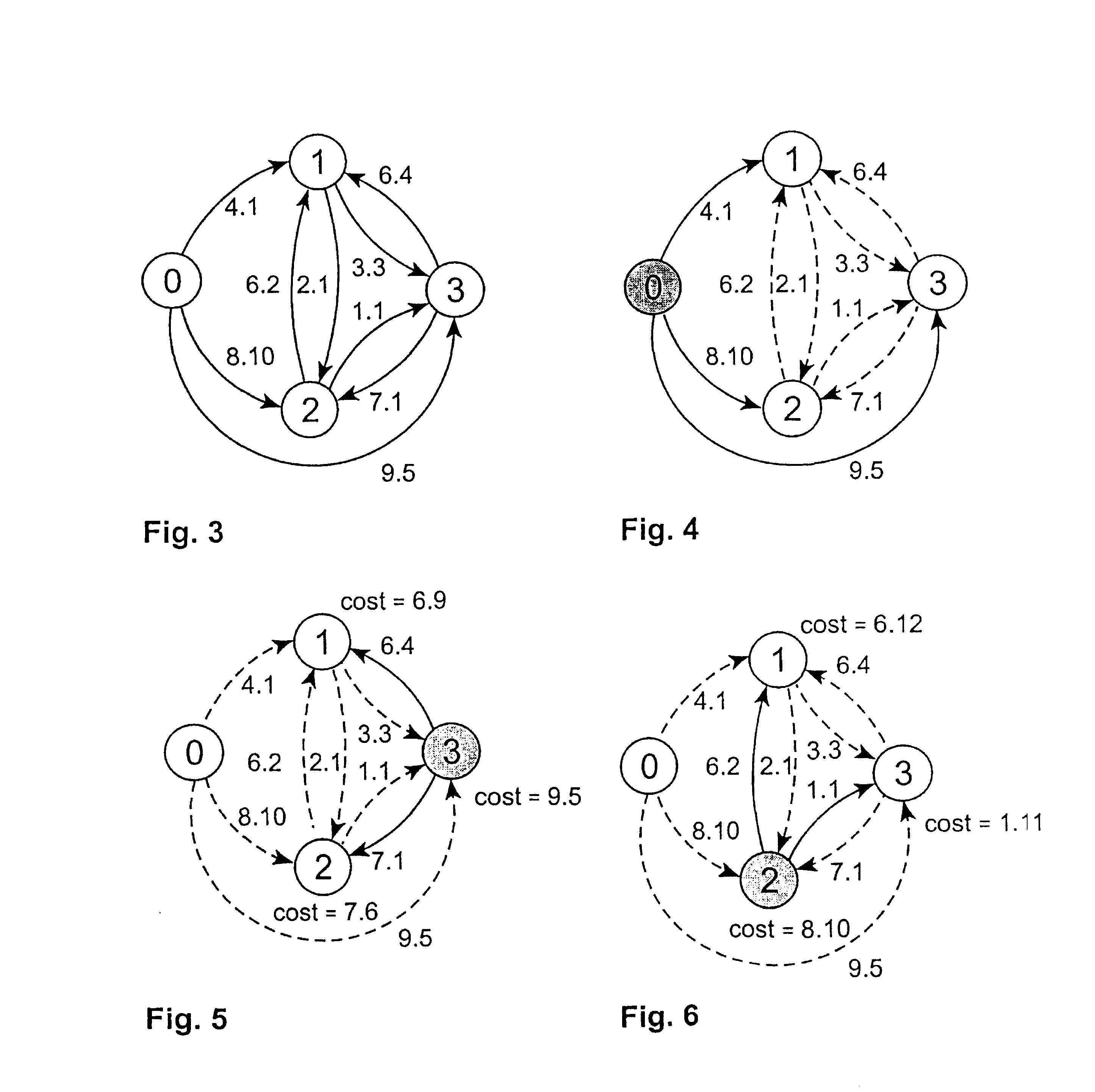
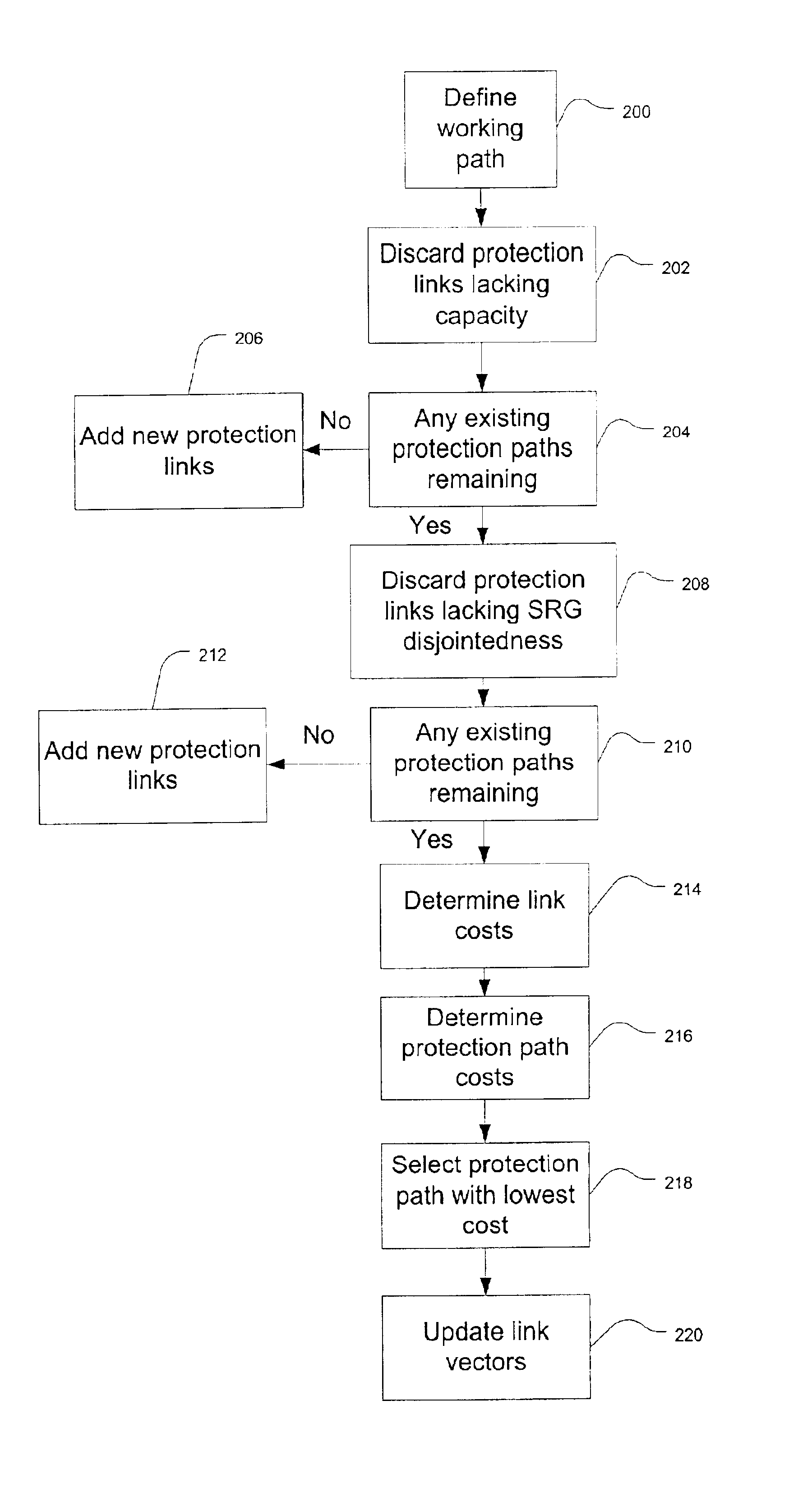
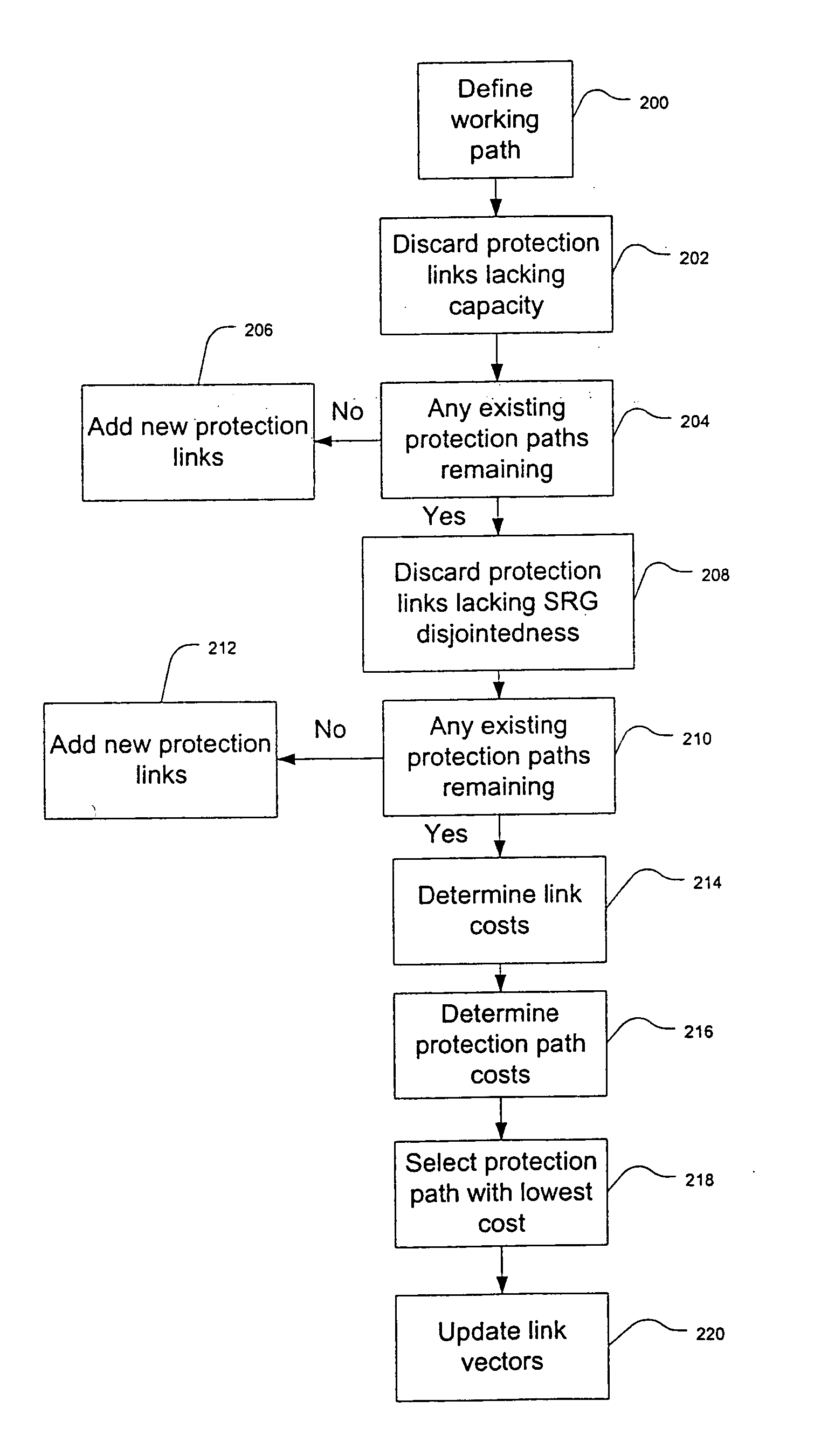
Method and system for allocating protection path resources
An embodiment of the invention is a method of allocating protection path resources including defining a working path and obtaining a link vector for each of a plurality of protection paths. The link vector includes a plurality of link vector elements. A proposed link vector is determined for each of the protection paths. The proposed link vector includes a plurality of proposed link vector elements and is indicative of allocating a respective protection path to the working path. A maximum link vector element is determined and a maximum proposed link vector element is determined. A link cost is determined based on a difference between the maximum proposed link vector element and the maximum link vector element. A path cost is determined for at least two protection paths based on a sum of link costs associated with a respective protection path. One of the at least two protection paths having the minimum path cost is selected to provide protection for the working path.
Owner:CIENA
Piecewise linear cost propagation for path searching
The problem of searching for a low cost path from a source location to a target location through a traversable region partitioned into a plurality of tiles is solved using source and target cost functions. Each tile in the traversable region is defined by boundary segments. The source cost function provides a cost for traversing from the source location to the boundary segment in question. The target cost function provides a cost for traversing from the boundary segment in question to the target location. The target cost function is estimated, and the source cost function is calculated. A path cost function is determined by adding the source and target cost functions. If the target location is a tile, then the target cost may be estimated using a convex hull of the target tile and the boundary segment in question. To facilitate the cost function calculations, multiple forms of cost function propagation between segments are disclosed.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Costs in data networks
InactiveUS7355980B2The method is simple and fastAccelerated settlementSpecial service provision for substationError preventionHigh bandwidthPath cost
A method for deriving a set of efficient path costs for a group of nodes comprising a source node and a plurality of destination nodes in a data communications networks, wherein the path costs for paths between nodes in the group are defined in the network and each path cost comprises a restrictive cost and an additive cost, comprises iteratively identifying the paths of higher bandwidth first and, when two or more paths of equal bandwidth are encountered, selecting the path having a lower transit delay associated therewith.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
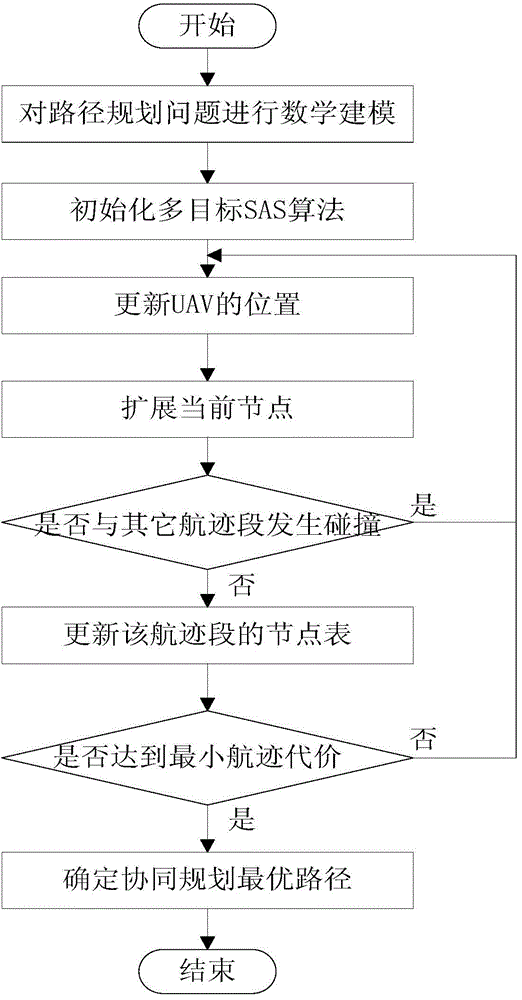
Three-dimensional multi-UAV coordinated path planning method based on sparse A-star search (SAS)
InactiveCN103557867ASolving Multi-Objective Optimization ProblemsVersatilityNavigational calculation instrumentsSpecial data processing applicationsNODALPath cost
The invention belongs to the field of path planning technology and specifically relates to a three-dimensional multi-UAV coordinated path planning method based on SAS. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out modeling on a path planning environment; initializing multi-target SAS calculation parameters consisting of the length of a minimum path section, a maximum turning angle, a maximum angle of climb / glide, a minimum safe distance of UAVs and a minimum flight altitude of UAVs; initializing the positions of the UAVs, wherein each UAV represents a path; updating the positions of the UAVs; expanding a current node; determining whether a path section collides with other path sections; updating a node table of the path section; executing a step (8) if minimum path cost set in the step (2) is met, and otherwise, executing the step (3); determining a cooperated planned optimal path so as to complete path planning. The method overcomes multi-objective optimization problems, has versatility, provides a reasonable optimal solution for a decision maker and better accords with practical needs.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Multi-target route planning and united searching method of drone in urban low-altitude environment
ActiveCN106970648AReduce storage capacityLower requirementRemote controlled aircraftTarget-seeking controlUncrewed vehiclePath cost
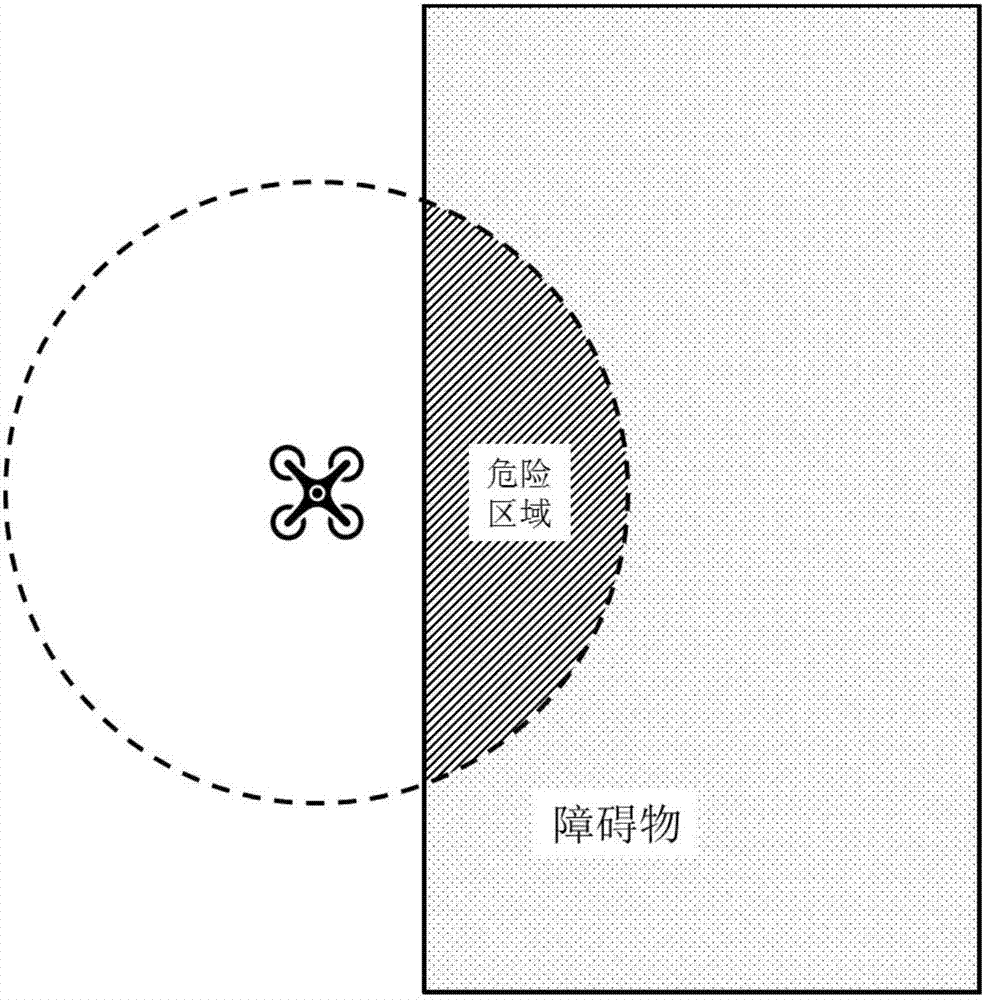
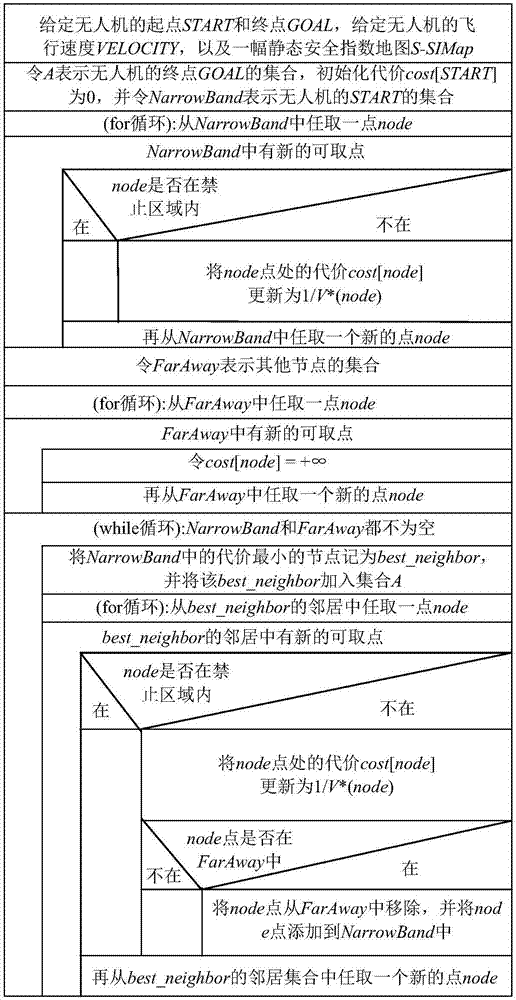
The invention provides a multi-target route planning and united searching method of a drone in an urban low-altitude environment, and belongs to the technical field of drone route planning. The method comprises steps of firstly, based on a static-state known obstacle, constructing a static-state safe index map, and based on an obstacle which is actively detected by the drone in a flight process and is not marked in a geographical map, constructing a dynamic state safe index map on an airborne platform; and then, based on offline searching and online searching, solving and optimizing a multi-target route planning problem of flight time and flight safety of the drone in an united manner. According to the invention, a path costing little from a start point to a termination point is planned in an offline manner; when an unknown obstacle is detected, a changed flight track is planned in an online manner through online searching, so a dynamic obstacle is avoided; and there is a quite small searching space in the online searching, so a safe route can be planned again from the drone rapidly, so requirements on real-time planning of routes for drones are met.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Efficient constrained shortest path first optimization technique
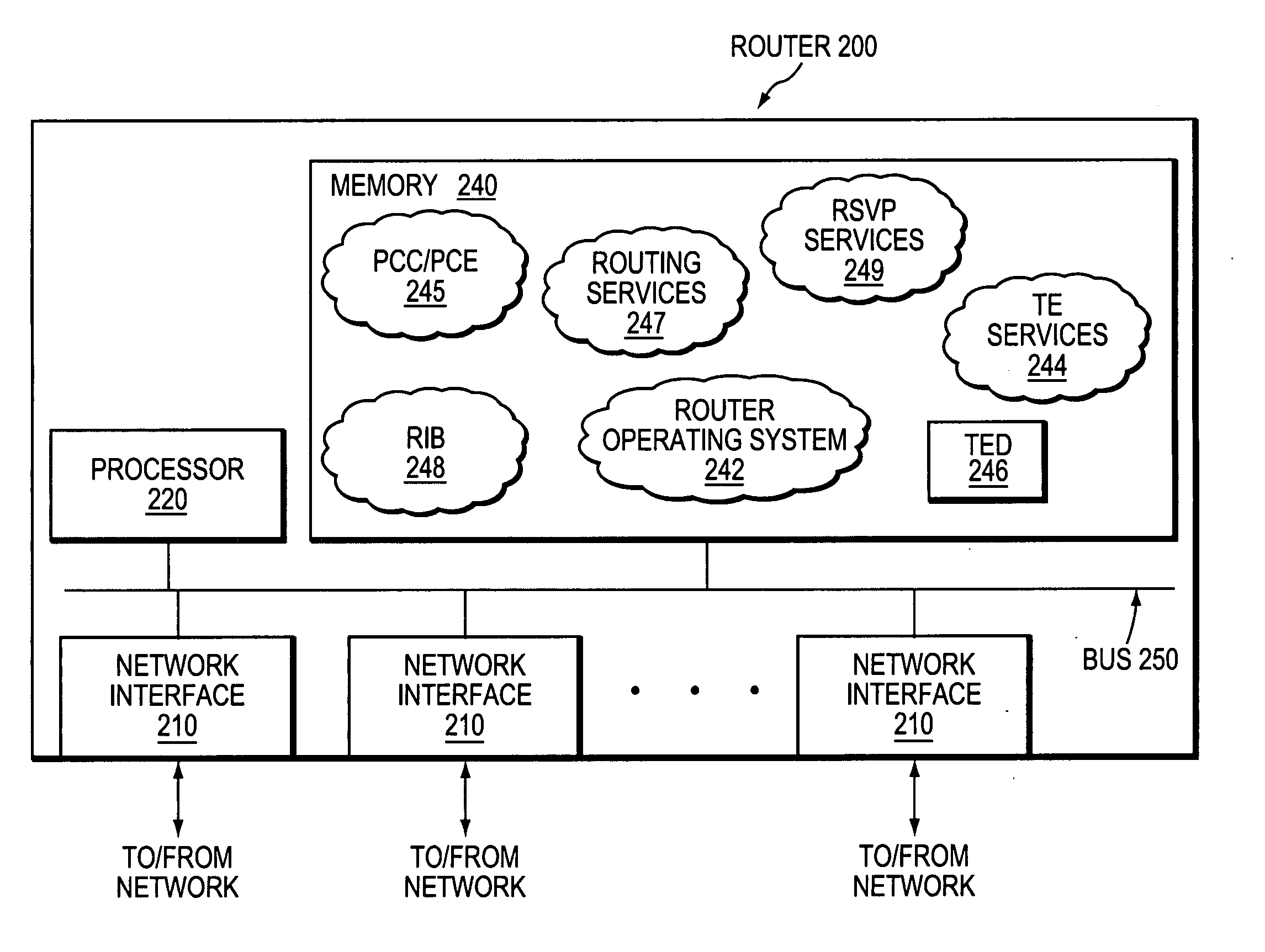
ActiveUS20070047469A1Efficient CSPF optimization of TE-LSPsEfficient triggerData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityPath computation element
A technique performs an efficient constrained shortest path first (CSPF) optimization of Traffic Engineering (TE) Label Switched Paths (LSPs) in a computer network. The novel CSPF technique is triggered upon the detection of an event in the computer network that could create a more optimal path, such as, e.g., a new or restored network element or increased path resources. Once the novel CSPF technique is triggered, the computing node (e.g., a head-end node of the TE-LSP or a Path Computation Element, PCE) determines the set of nodes adjacent to the event, and further determines which of those adjacent nodes are within the TE-LSP (“attached nodes”). The computing node performs a CSPF computation rooted at the closest attached node to determine whether a new computed path cost is less than a current path cost (e.g., by a configurable amount), and if so, triggers optimization of the TE-LSP along the new path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
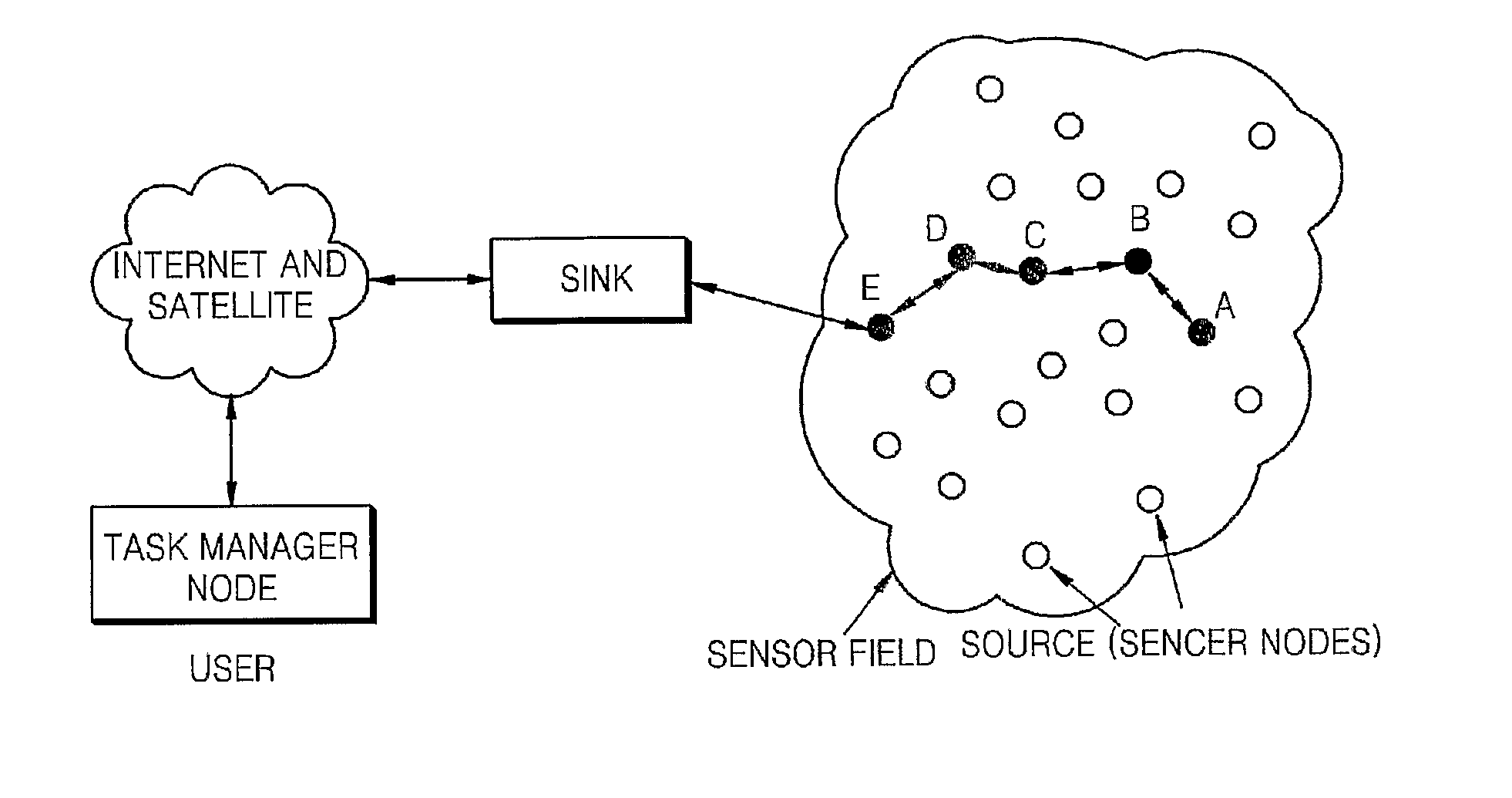
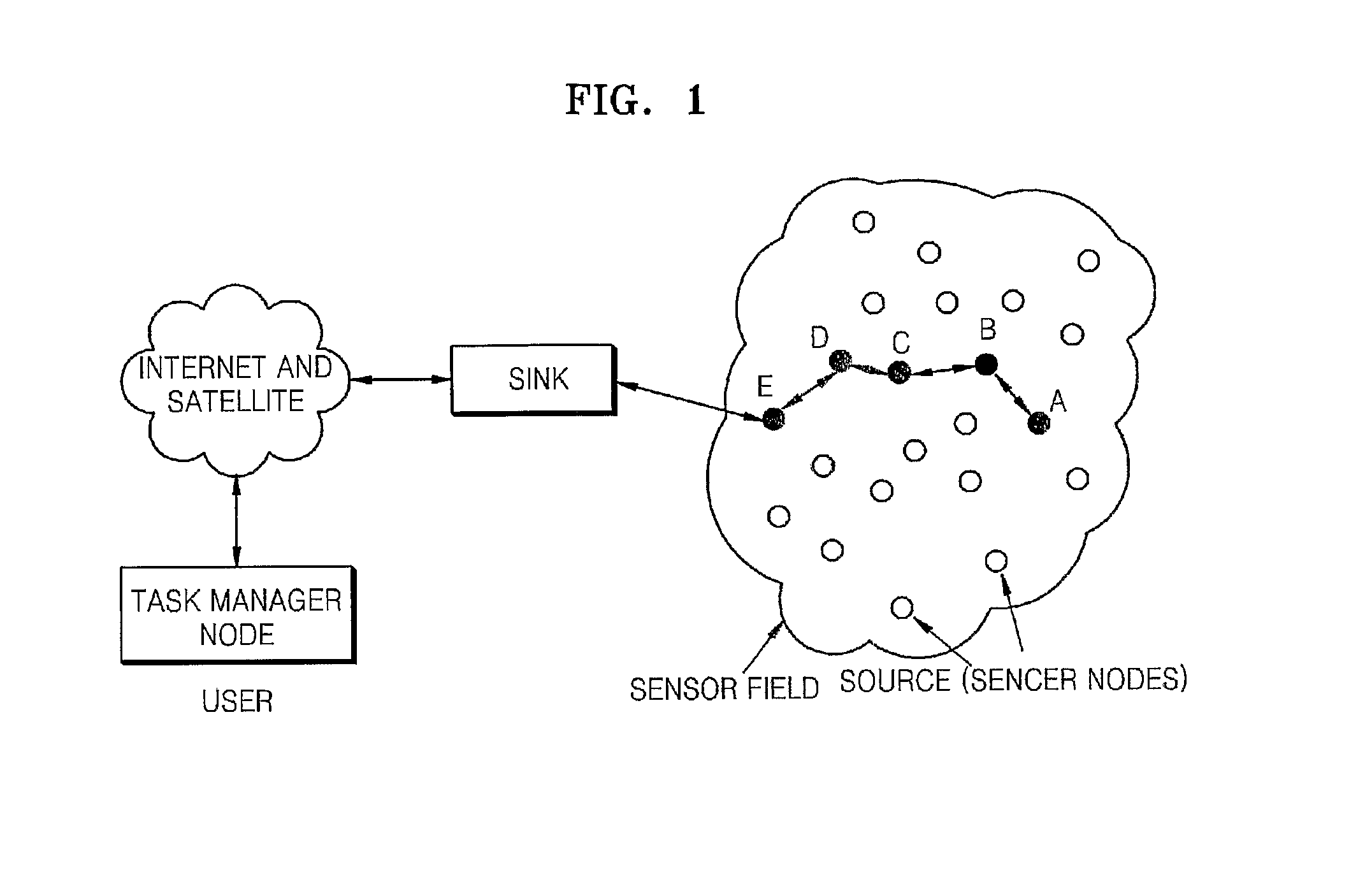
Multi-path routing method in wireless sensor network
InactiveUS20100220653A1Connection managementWireless commuication servicesWireless mesh networkWireless sensor networking
A multi-path routing method is provided a multi-path routing method for selecting appropriate multiple paths when information sensed from a source node is transmitted to a sink node in wireless sensor networks. The source node for transmitting the sensed information first transmits a Hello message to the sink node to identify the existence and position of the sink node. The sink node receives the Hello message and then re-transmits the Hello message with respect to all the received Hello messages. Respective middle nodes accumulate distances between the middle nodes while the Hello message is transmitted to the source node through a reverse path of the Hello message, and all the middle nodes maintain a real distance from the sink node. The source node receiving all the Hello messages can rout a plurality of appropriate paths through Hop-by-hop to the sink node by providing respective weights to an energy remaining amount, an appropriate transmission radius and a real distance from the sink node. Accordingly, priorities can be provided to lifetime of the source node, average energy consumption and the shortest path by adjusting the respective weights when routing the plurality of paths. In addition, appropriate paths can be routed considering the transmission success rate of a path, and a load balancing effect can be obtained using path cost.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
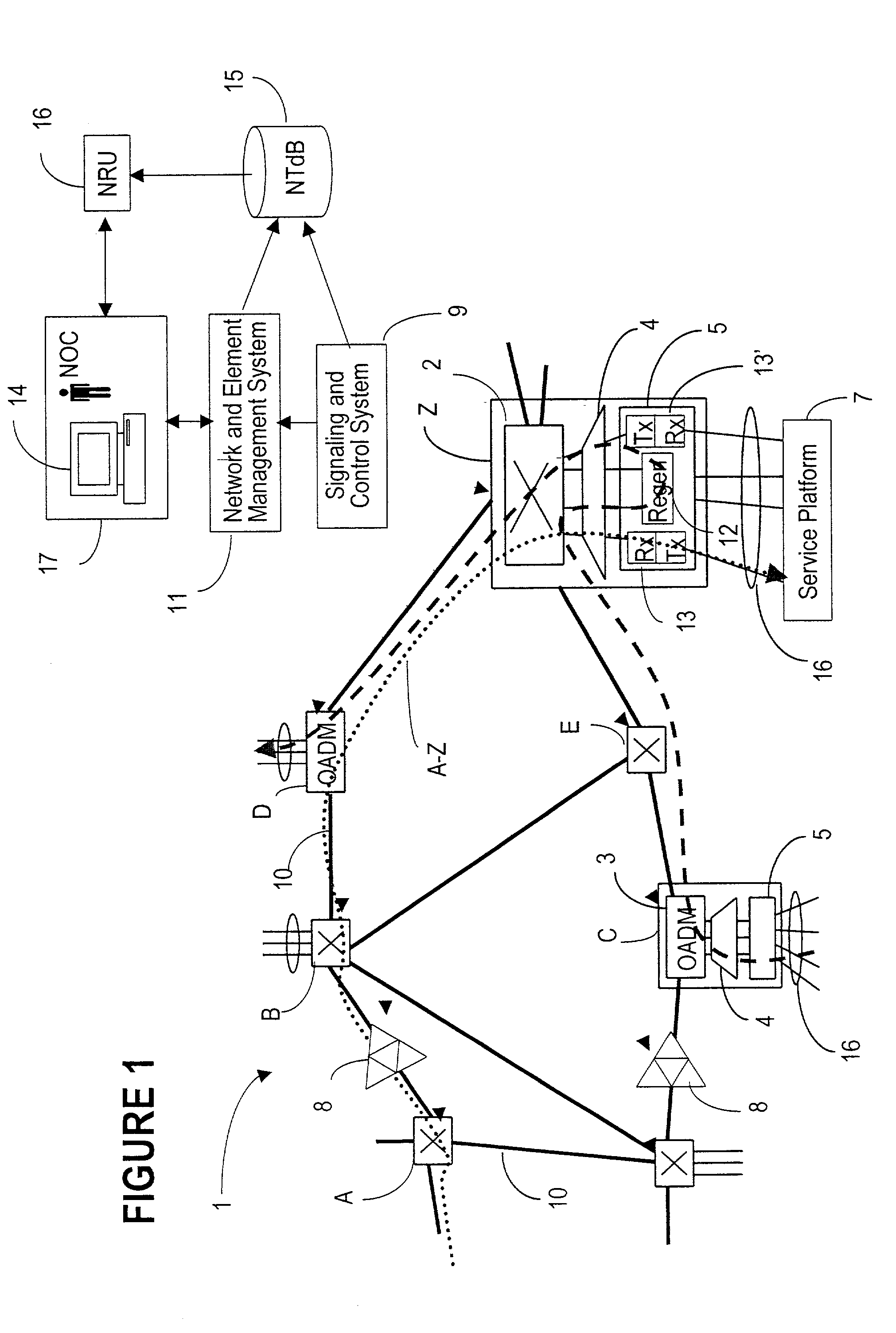
Wavelength routing and switching mechanism for a photonic transport network
InactiveUS7171124B2Flexibility of provisioningLow costLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsPhoton transmissionAutomatic routing
A connection between a source node and a destination node is automatically routed and switched in a WDM photonic network, on receipt of a connection request. A switching and routing mechanism selects a plurality of valid link paths using a path tree, where invalid branches are eliminated based on constraints received in the connection request, and on a link and path cost functions. A regenerator placement tree is used for determining a plurality of viable regenerator paths for each valid link path. On the regenerator placement tree, non-viable branches are eliminated based on constraints received with the request and on regenerator availability at the intermediate nodes along the respective path, and on the specification of these available regenerators. Next, the switching and routing mechanism assigns a set of wavelengths to each viable regenerator path, and estimates the performance of the path using a Q estimator. The regenerator paths are ordered according to their performance and the switching and routing mechanism attempts to setup a paths to serve the request, starting with the best path.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
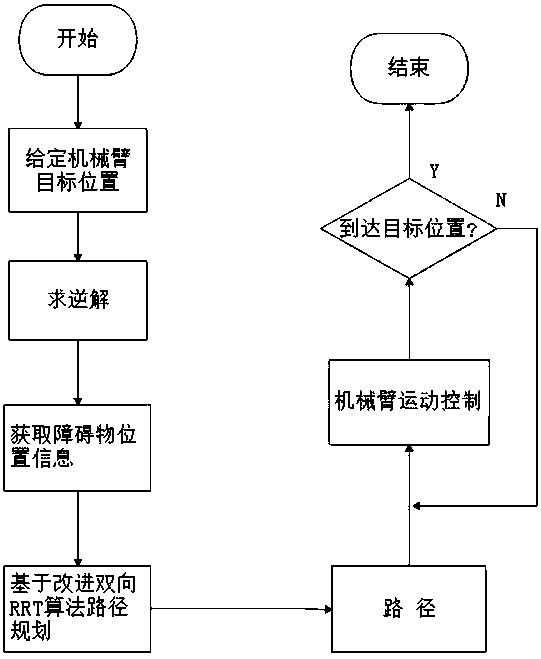
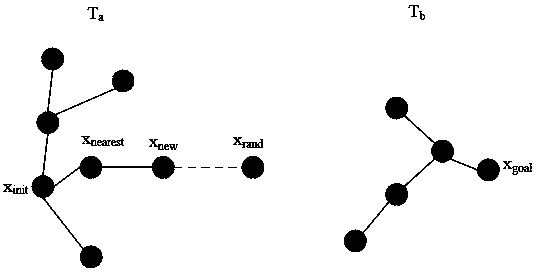
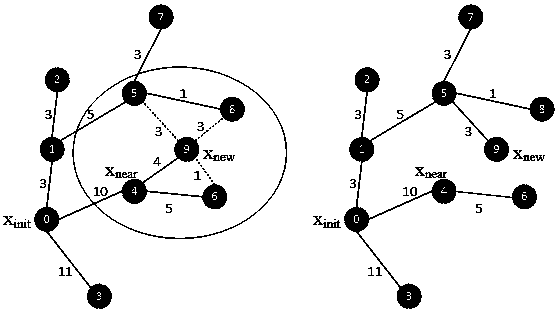
Mechanical arm motion planning method for improving bidirectional RRT algorithm
PendingCN110497403AReduce computational complexitySolve the problem that the motion path is not optimalProgramme-controlled manipulatorPath costComputer science
The invention discloses a mechanical arm motion planning method for improving a bidirectional RRT algorithm. The method integrates the traditional bidirectional RRT algorithm, an optimal searching mode of a parent node is introduced and a connecting mode of a node is updated, the distance of the mechanical arm path planning is greatly reduced, the searching speed of the bidirectional RRT algorithmcan be guaranteed and an optimal path is planned; and the target position of a mechanical arm is given and the obstacle information in the environment is acquired, a collision-free path is planned byadopting an improved bidirectional RRT algorithm, and the mechanical arm moves to the target position according to the planned path, so that the motion planning of the mechanical arm on the basis ofthe improved bidirectional RRT algorithm is completed. According to the mechanical arm motion planning method for improving the bidirectional RRT algorithm, the improved bidirectional RRT algorithm isadopted, so that the planning path cost can be greatly reduced, the optimal path is planned for the mechanical arm, and the problem that the motion path is not optimal is solved; and the method not only is suitable for motion planning research of mechanical arms in a high-dimensional space, but also can be applied to the field of mobile robots, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
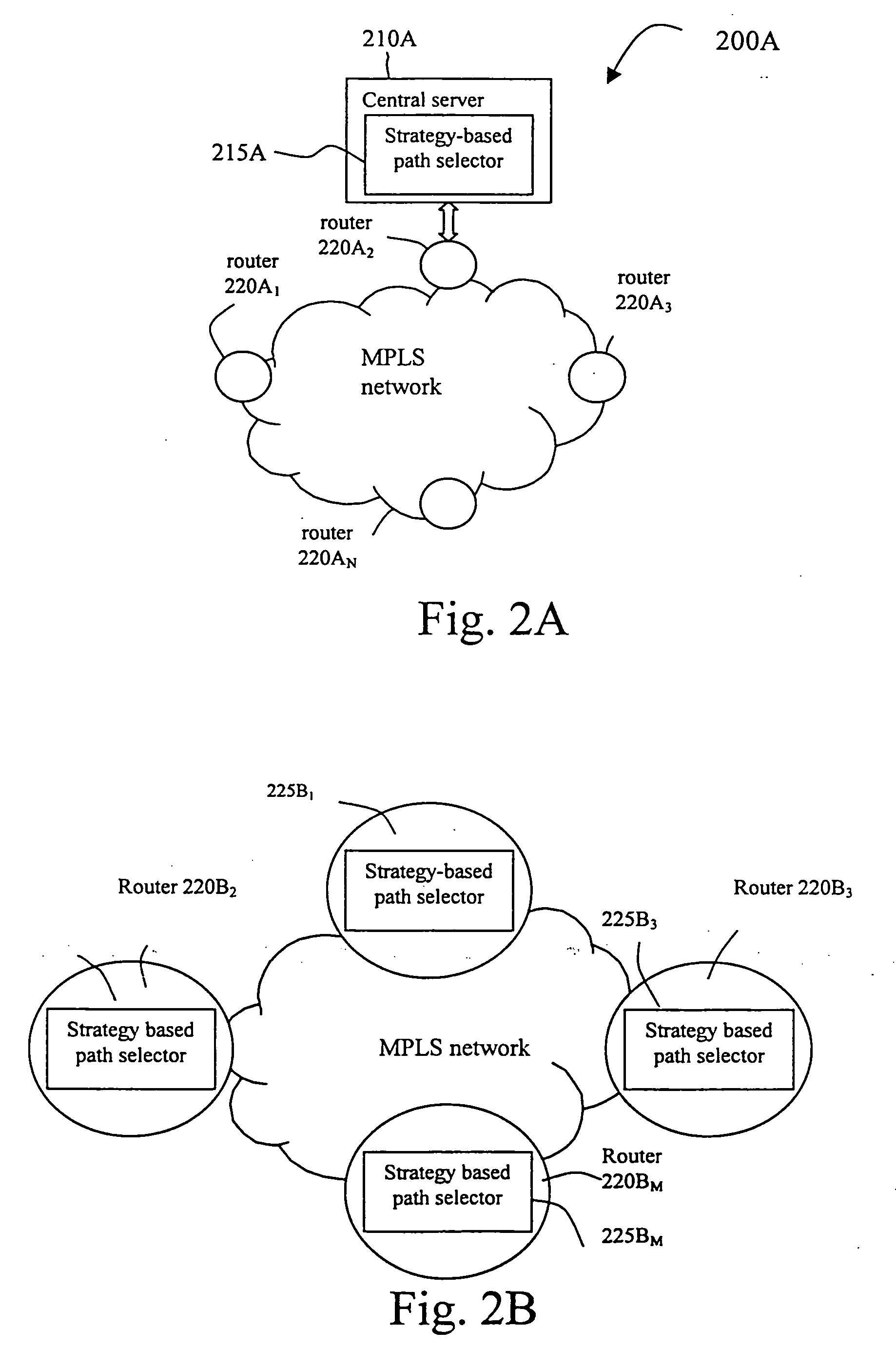
Method and apparatus for path selection in telecommunication networks
InactiveUS20060067217A1SwitchingSimple and efficient path selectionError preventionTransmission systemsTelecommunications networkNetwork conditions
This invention provides a method and an apparatus for selecting path in a telecommunication network. In the invention, a control strategy parameter is generated based on a control strategy, and a network condition parameter is generated based on the condition of the network, a path cost for each of a plurality of candidate paths is calculated based on the control strategy parameter and the network condition parameter, then a path with the minimal path cost is selected from among the candidate paths.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD +1
Method and system for audio/video bridging aware shortest path bridging
InactiveUS20080285459A1Least costEnergy efficient ICTTelevision system detailsQuality of serviceLeast cost
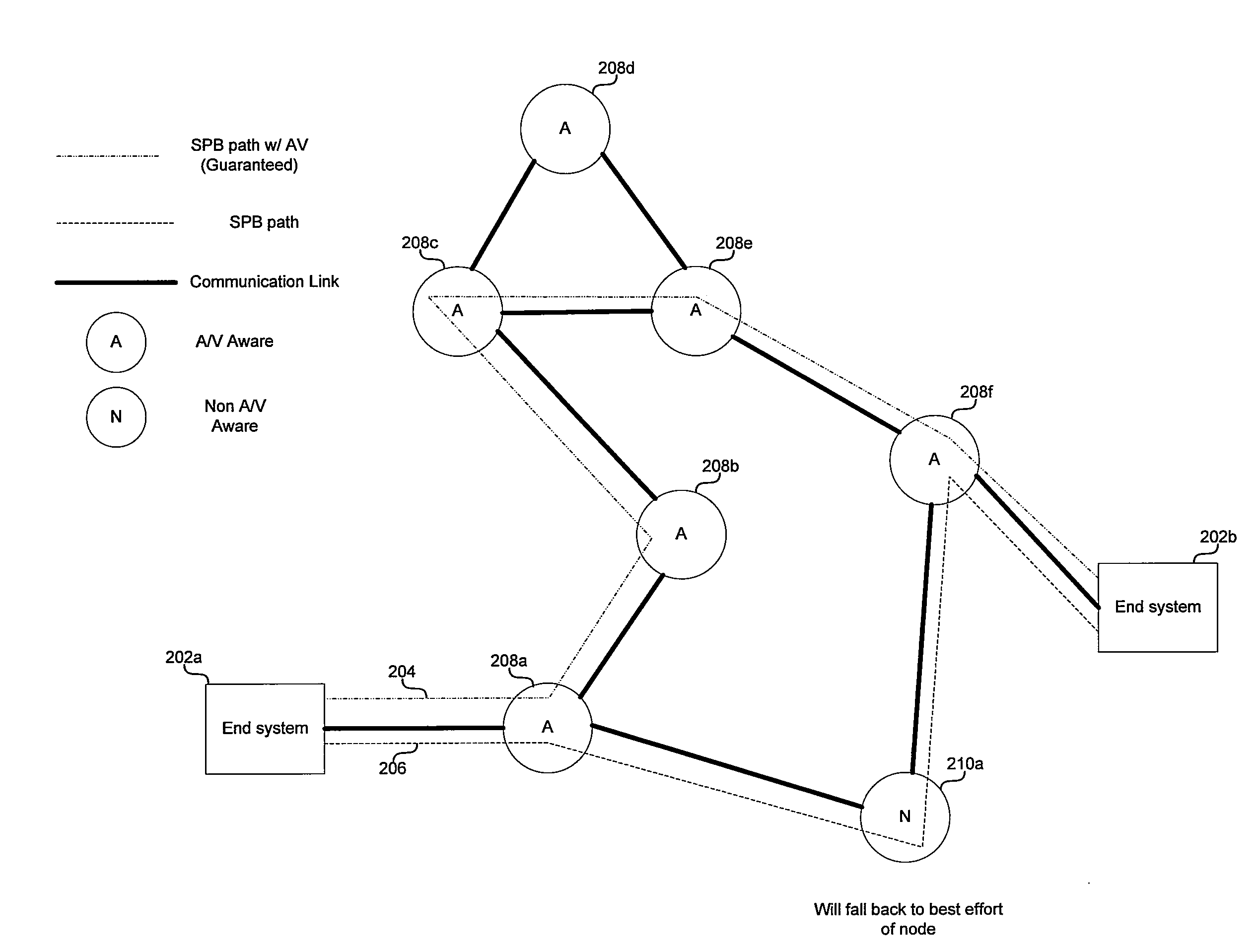
Aspects of a method and system for Audio / Video Bridging aware shortest path bridging are provided. In this regard, network nodes which are AVB enabled and capable of routing information based on a desired path cost and / or a desired quality of service (QoS) may be identified, and an AVB enabled path comprising one or more of the identified nodes may be established for communication over a network. In this regard, the desired cost may be a least cost and may be the “shortest path” between two nodes in a network. Additionally, the nodes maybe identified using Shortest path Bridging protocols and / or Audio Video Bridging protocols and / or extensions thereof. Also, bridge protocol data units may be exchanged to identify the nodes.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Unmanned aerial vehicle route planning method based on improved Salp algorithm
ActiveCN108919641AAvoid enteringImprove search abilityAdaptive controlPosition/course control in three dimensionsLocal optimumPlanning approach
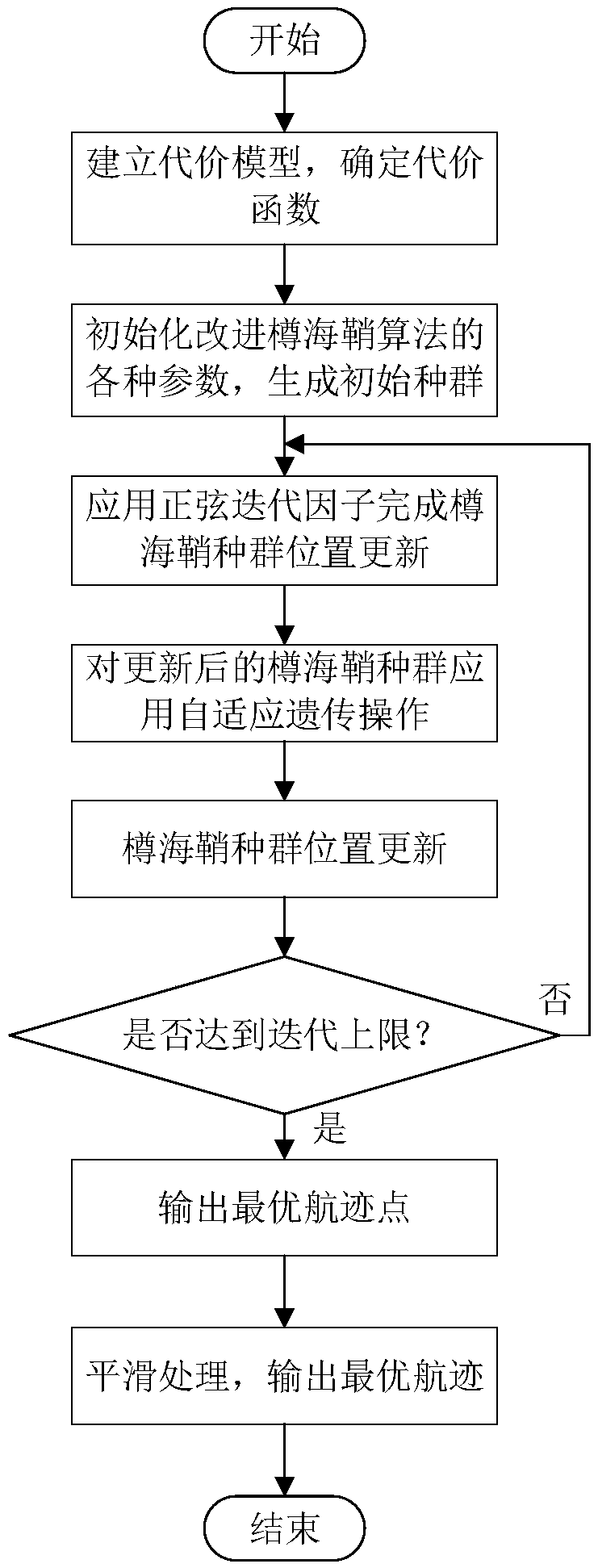
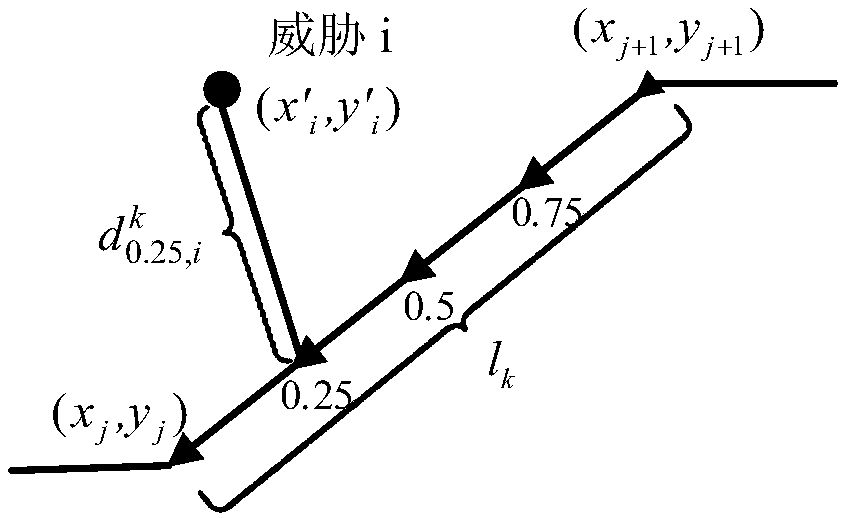
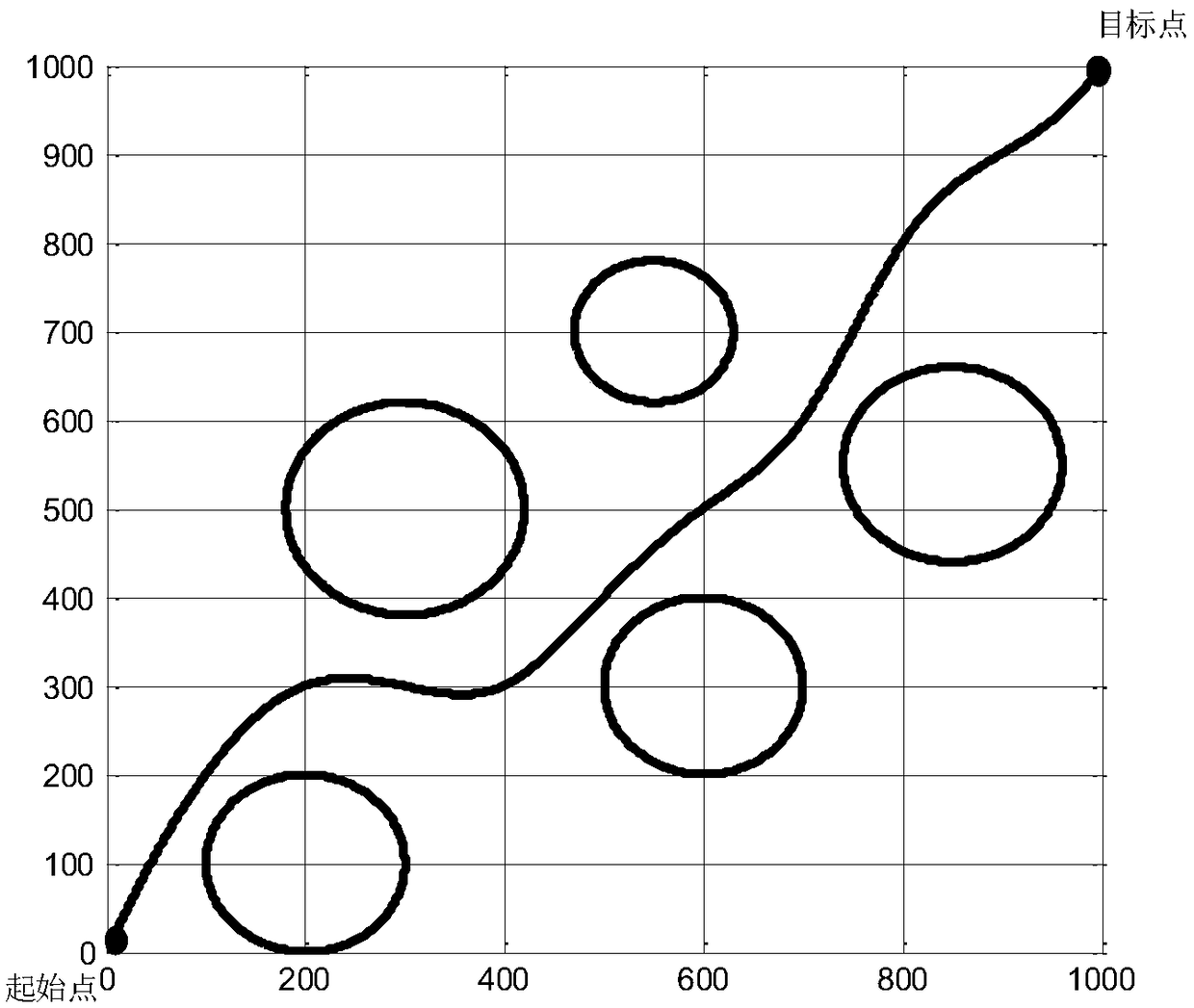
The invention provides an unmanned aerial vehicle route planning method based on an improved Salp algorithm, belonging to the technical field of unmanned aerial vehicle route planning. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, determining a start point position, a destination point position and a threatening area range; establishing a route planning cost model through path cost and threatening cost; performing optimizing for the established cost model, on the basis of a basic Salp algorithm, updating the position of a population with a sinusoidally varying iterative factor, embeddingan adaptive genetic operator to improve optimizing capability of the algorithm; after upper limit of iteration is reached, obtaining an optimal individual position, namely unmanned aerial vehicle optimal route points from the start point to the destination point; smoothening a connection line of the obtained optimal route points, obtaining the optimal route, and realizing route planning. The method provided by the invention can plan the optimal route from the start point to the destination point and avoid that the route is in the threatening area, the method has flexible, simple and fast calculation processes, and the method solves a problem that the existing route planning optimization algorithm has relatively low convergence speed and is very liable to be caught in local optimum.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
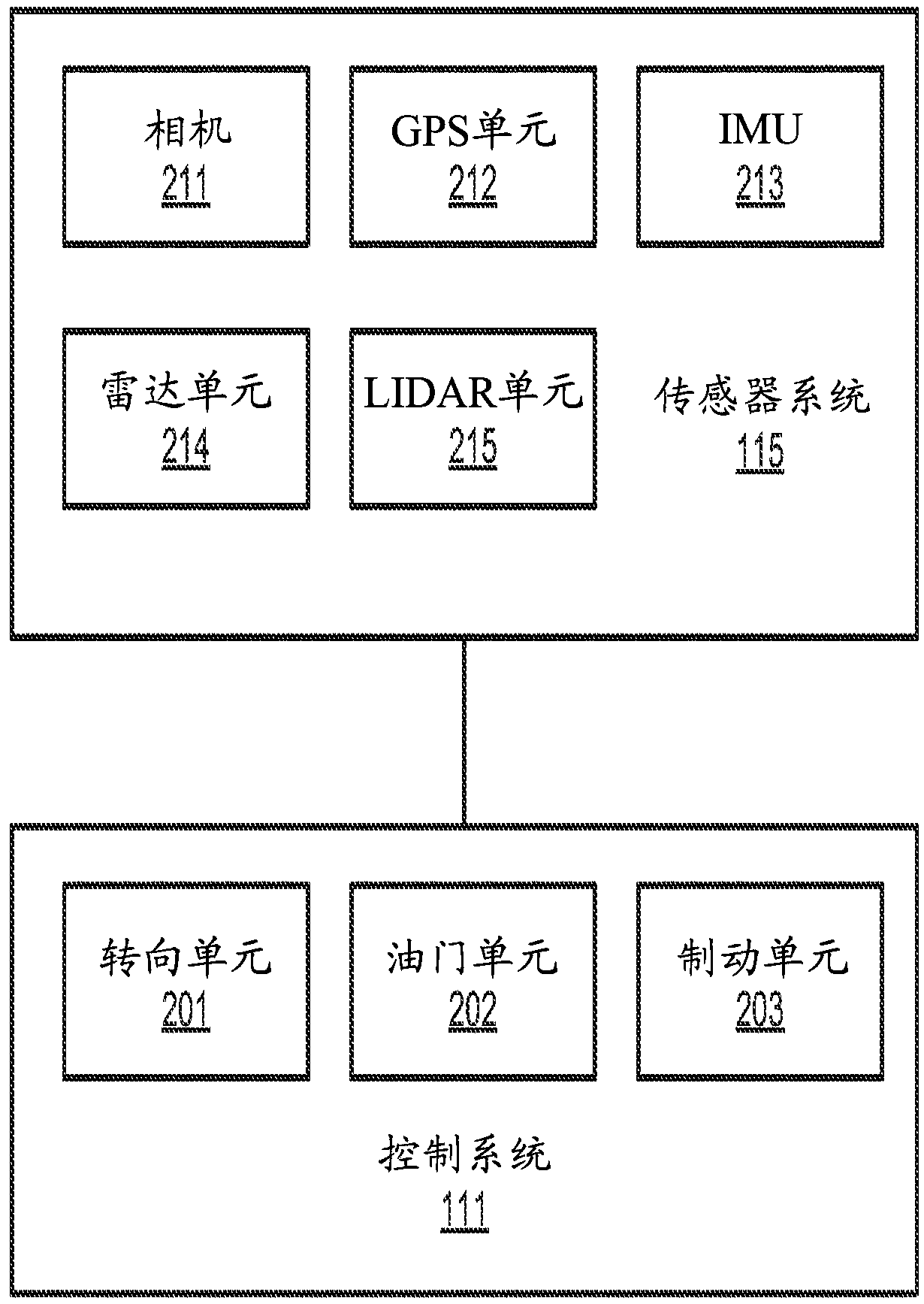
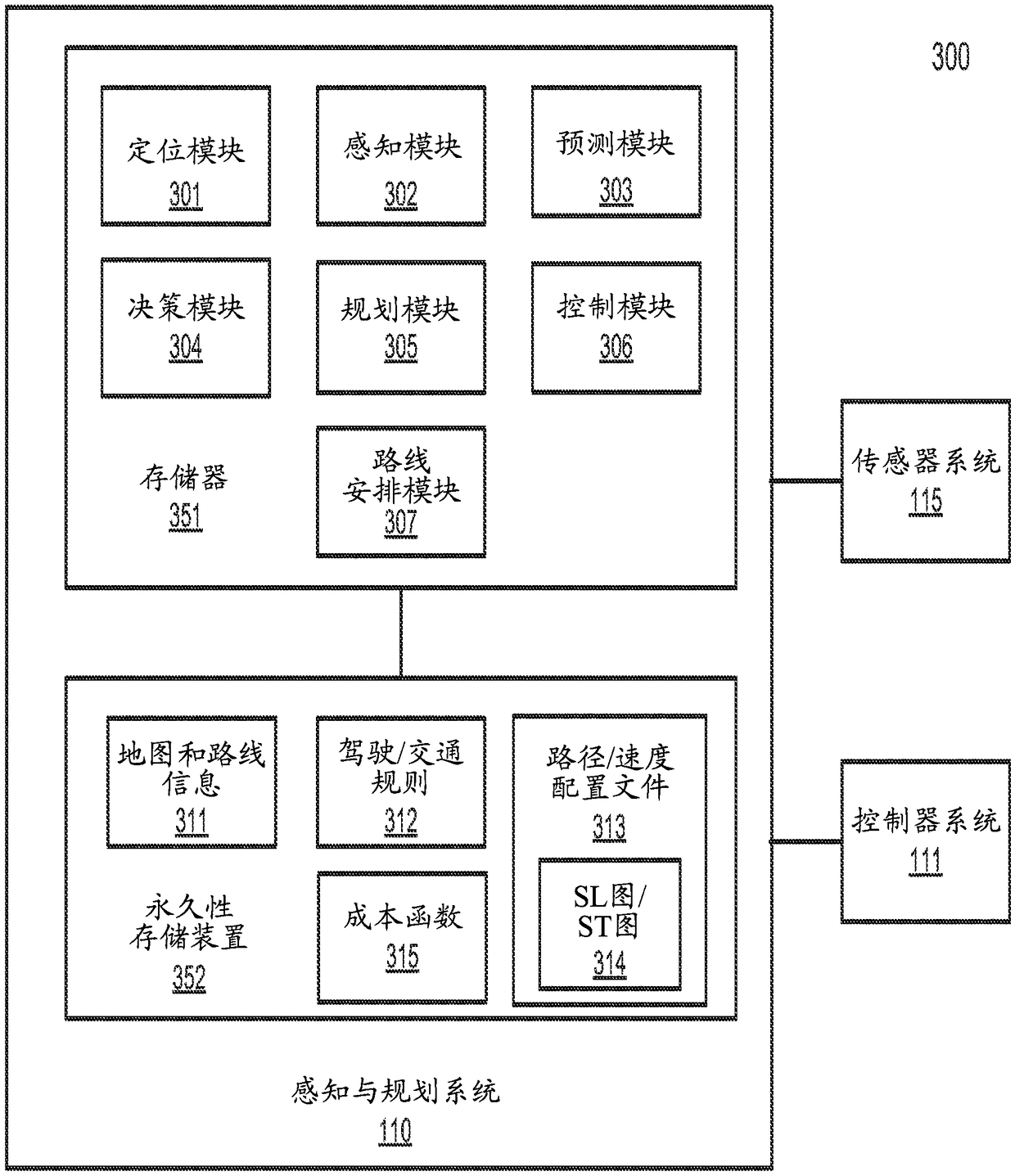
Cost-based path planning for autonomous driving vehicles
PendingCN109489675AInstruments for road network navigationAutonomous decision making processPath costSystem usage
According to some embodiments, a system generates a number of possible decisions for routing the ADV from a first location to a second location based on perception information perceiving a driving environment surrounding the ADV, including one or more obstacles in view of a set of traffic rules. The system calculates a number of trajectories based on a combination of one or more of the possible decisions. The system calculates a total cost for each of the trajectories using a number of cost functions and selects one of the trajectories with a minimum total cost as the driving trajectory to control the ADV autonomously. The cost functions include a path cost function, a speed cost function, and an obstacle cost function.
Owner:BAIDU USA LLC
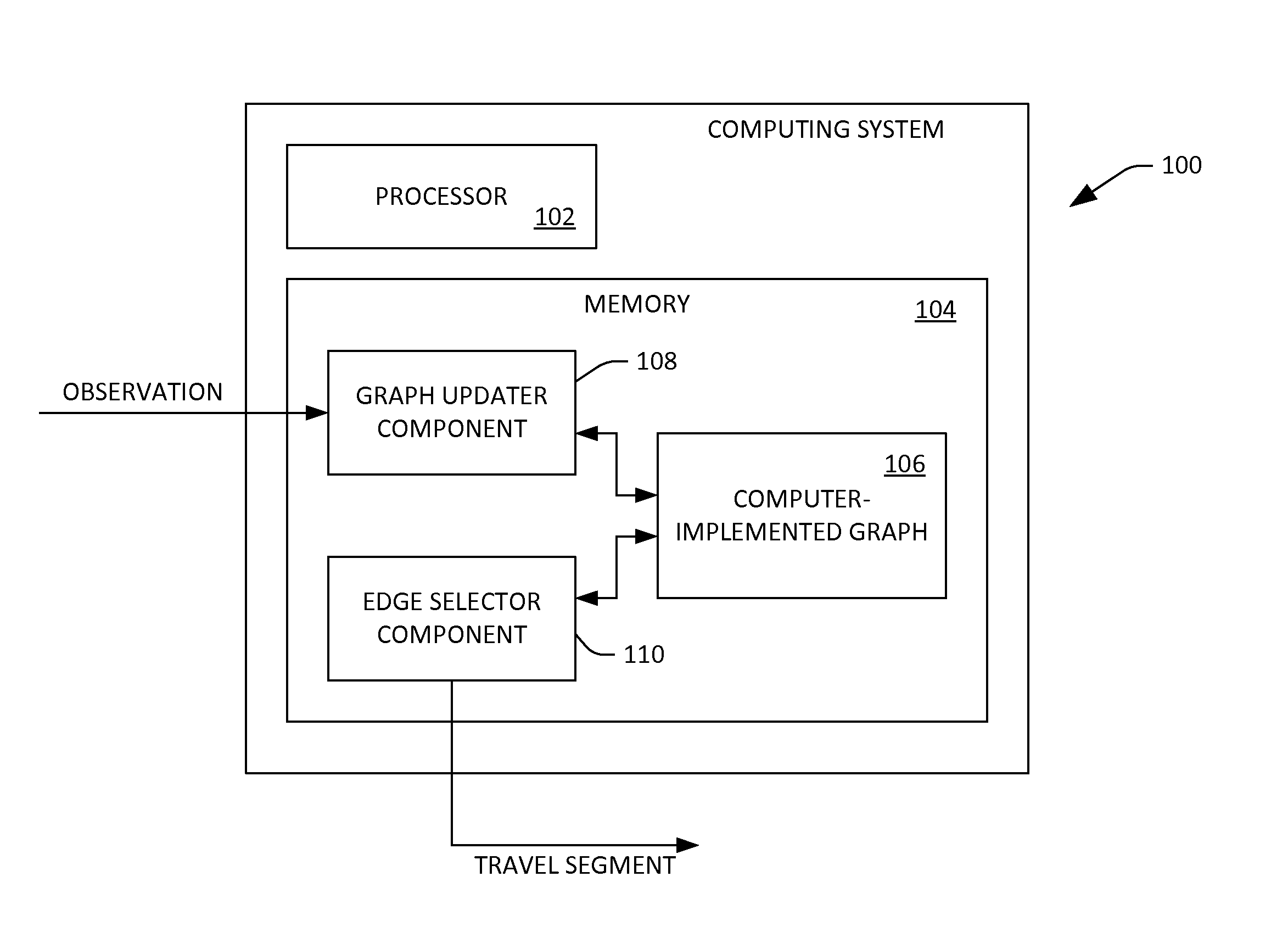
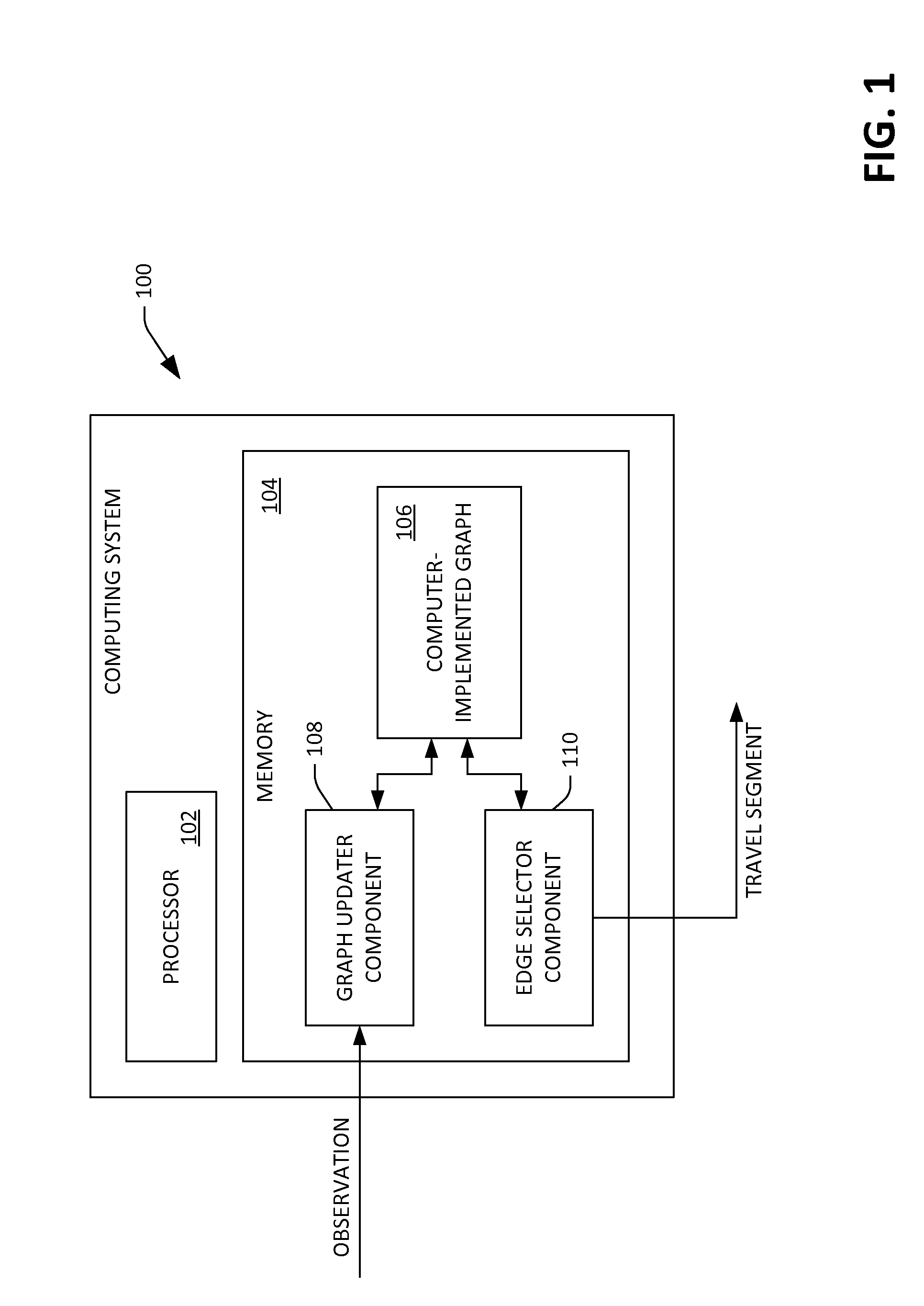
Travel path identification based upon statistical relationships between path costs
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
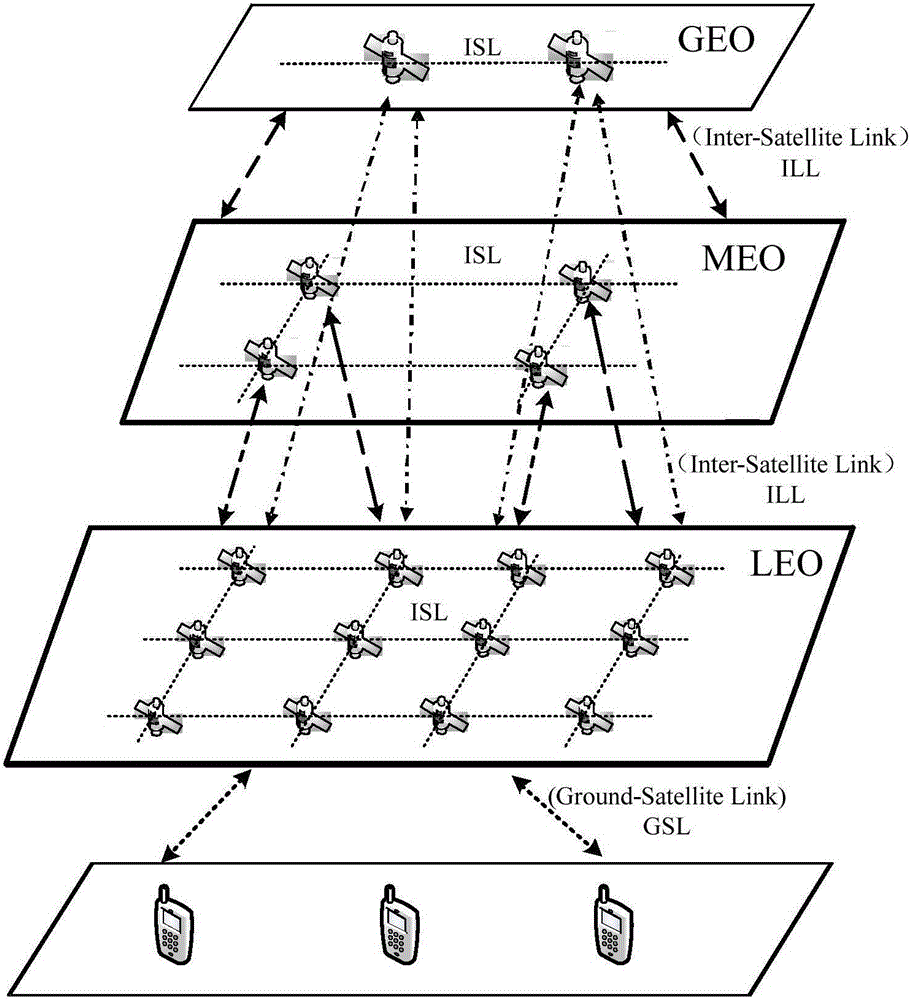
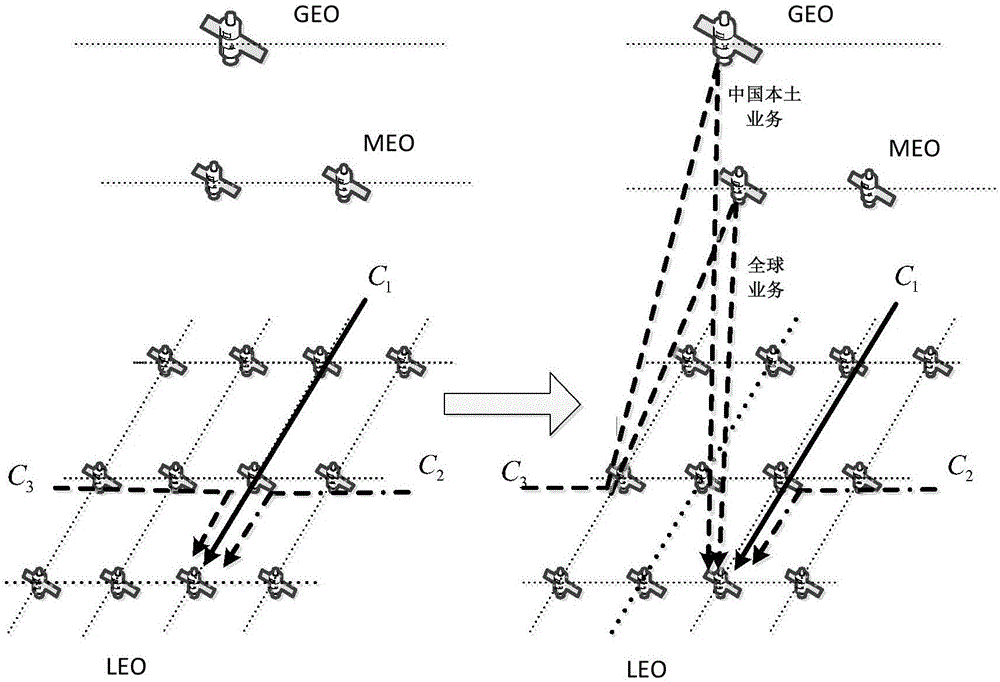
Satellite network routing method based on control point optimization of software-defined network
ActiveCN105959232AAvoid congestionLoad balancingData switching networksQuality of serviceService flow
This invention relates to the technical field of satellite communication, and specifically relates to the satellite network routing method based on control point optimization of software-defined network. The method comprises the following steps: satellite node sets different path cost functions according to different types of communication services; initialize network and maintain basic routing table; real-time monitor self-service and transmit service load; according to the feedback result of load state of a satellite link, judge whether the link is jammed or not; and if so, start a bypassing mechanism for avoiding the jam till the link in the jam area is less than a jam relief threshold. The method provided by the invention combines the characteristic of centralized control of the software-defined network and the prior satellite routing technology, avoids the jam and balances the load of the network by using a lower overhead, considers the QoS (Quality of Service) requirements of different service types, and preferentially bypasses the service with a lower priority; based on the service flow, the bypassing service is realized; and according to the rate of the bypassing service, reasonable hash function is set to select the bypassing service flow ID (Identification), so that the group with same one service flow is arrived according to the order of the sequence.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Node used in photonic network, and photonic network
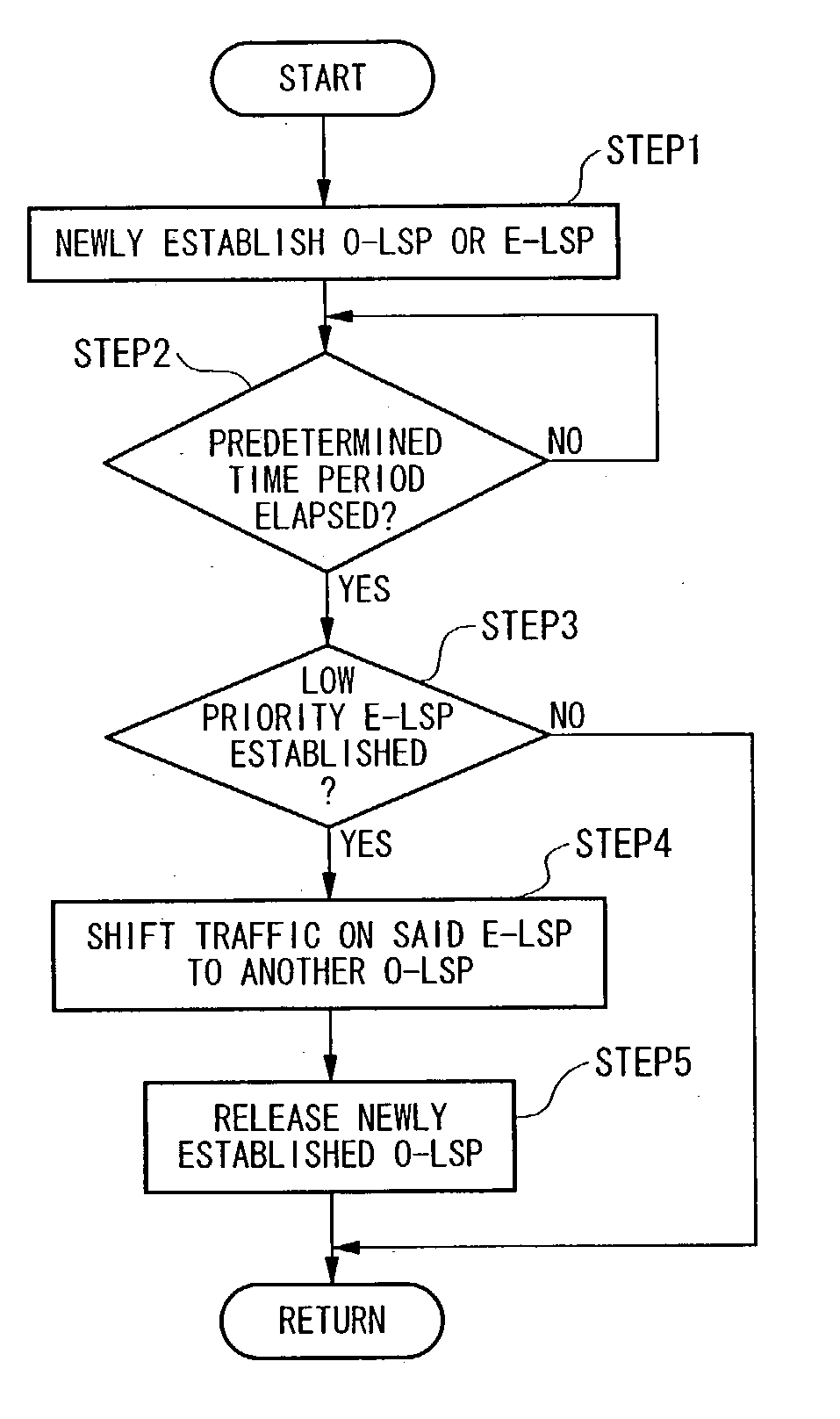
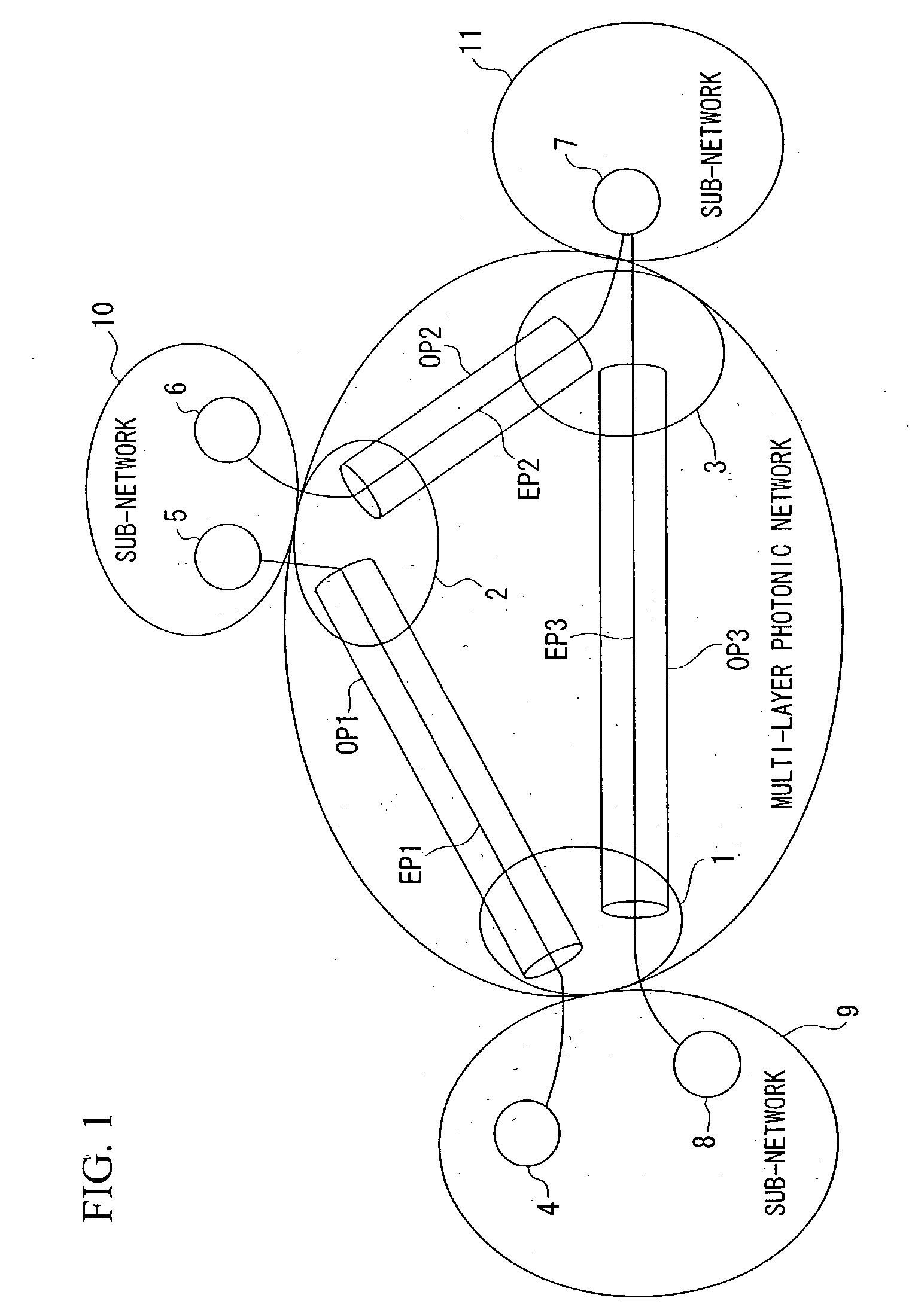
A multi-layer photonic network and nodes used therein are provided. The multi-layer photonic network comprises a packet network which performs switching and transfer in packet units, and a photonic network comprising optical transmission lines and photonic switches, and which accommodates the packet network. The multi-layer photonic network also has a two layer structure of optical wavelength links (O-LSPs) and packet links (E-LSPs). The O-LSPs are constituted by the optical transmission lines and comprise optical wavelength switching capability (LSC) which is capable of switching in optical wavelength units and packet switching capability (PSC) which is capable of switching in packet units at both their ends. The E-LSPs include the O-LSPs and PSCs at both their ends. Each node includes a section for automatically establishing an O-LSP according to an establishment request for an E-LSP while taking account of path information including path cost, resource consumption, and traffic quantity.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
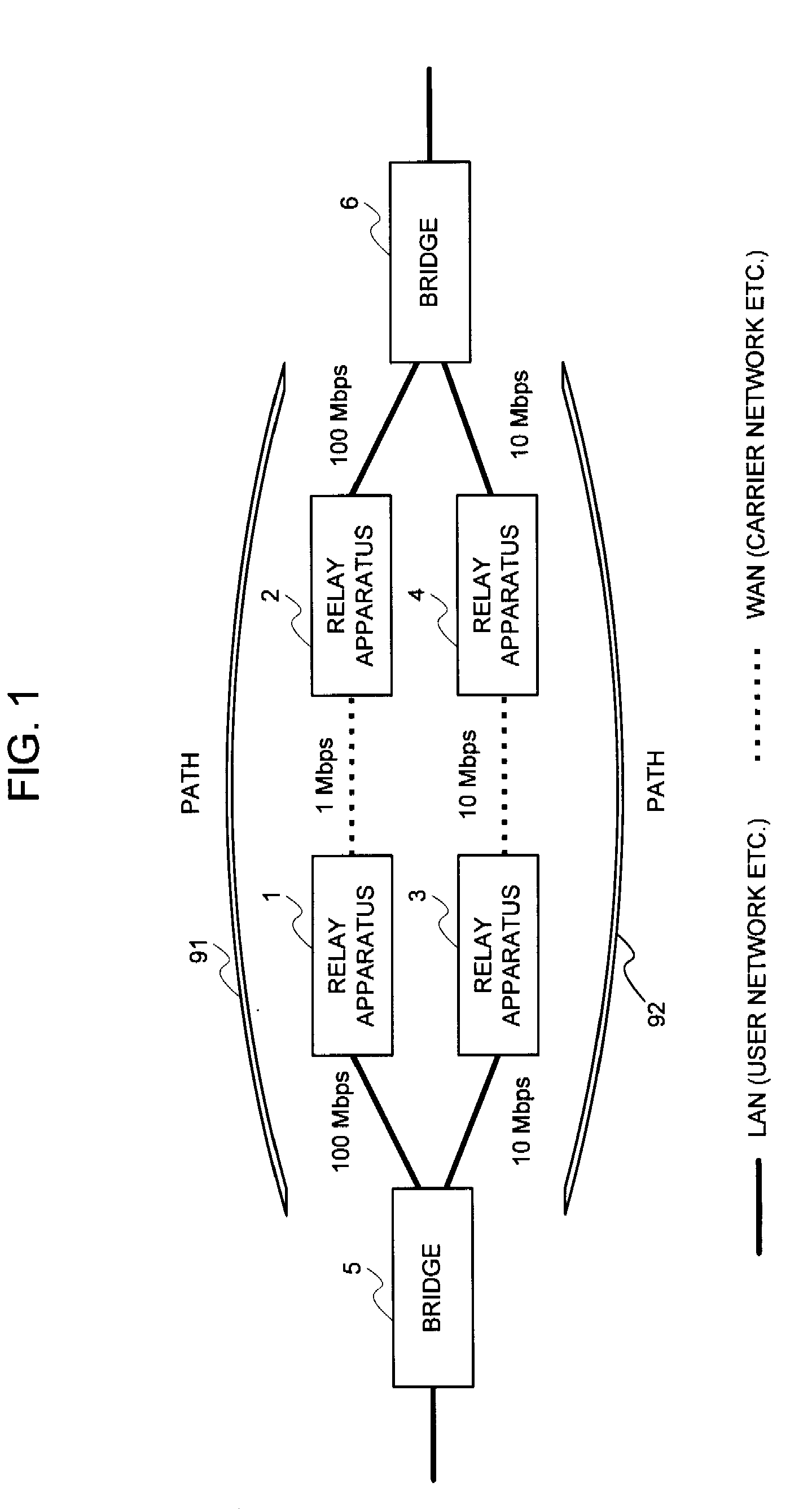
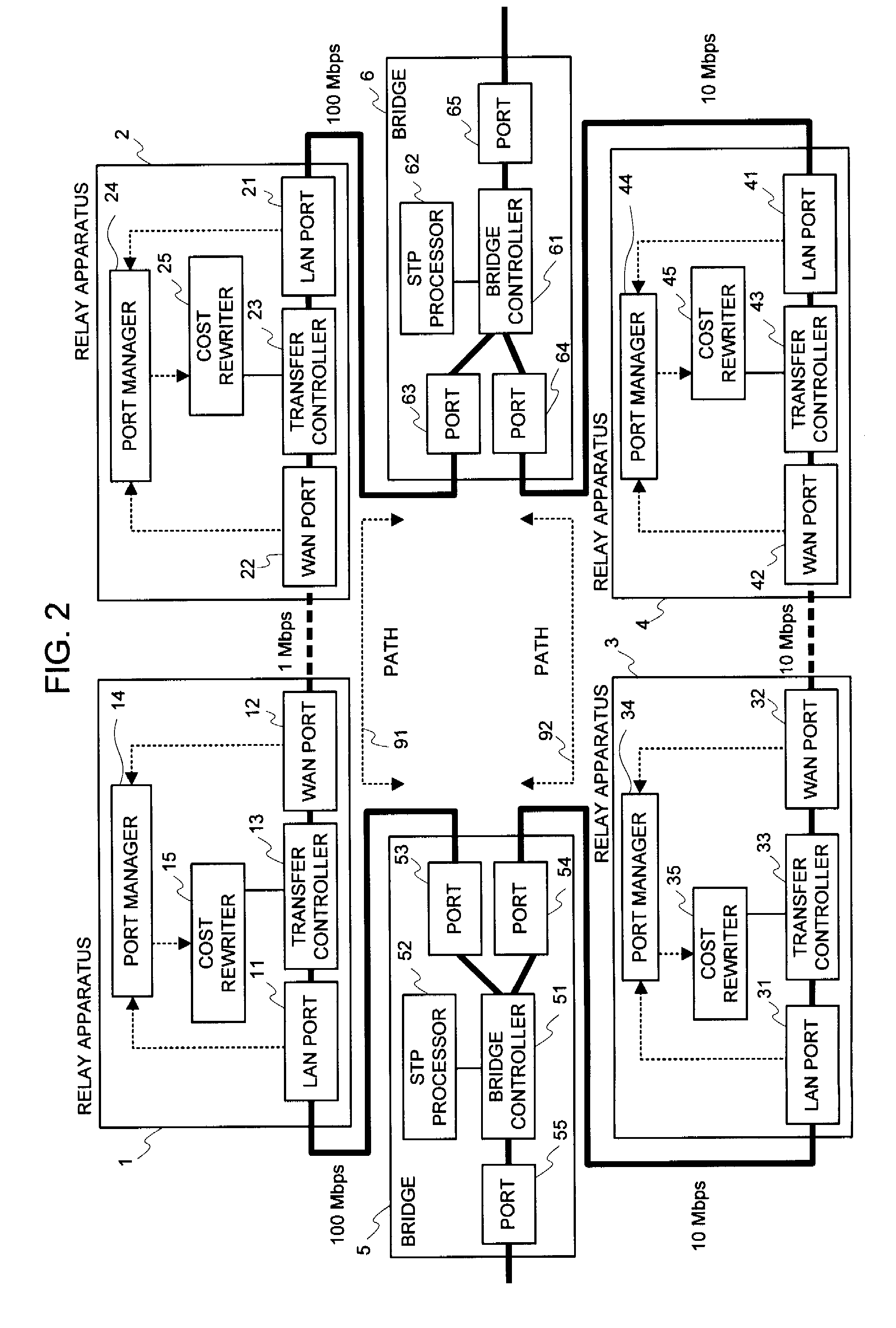
Relay apparatus, path selection system, path selection method and program
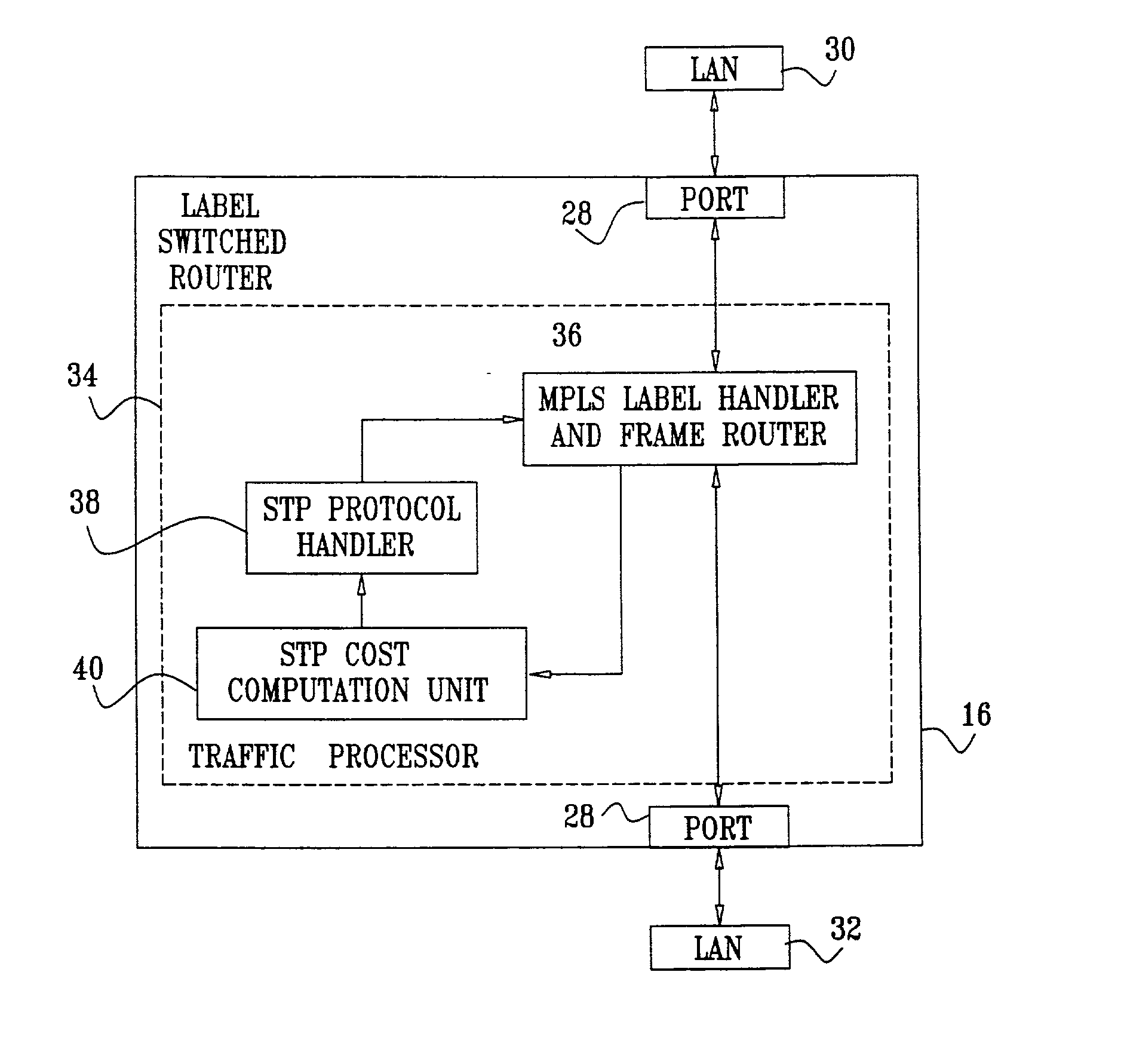
InactiveUS20080219168A1Improve efficiencyIncrease net efficiencyError preventionTransmission systemsSelection systemPath cost
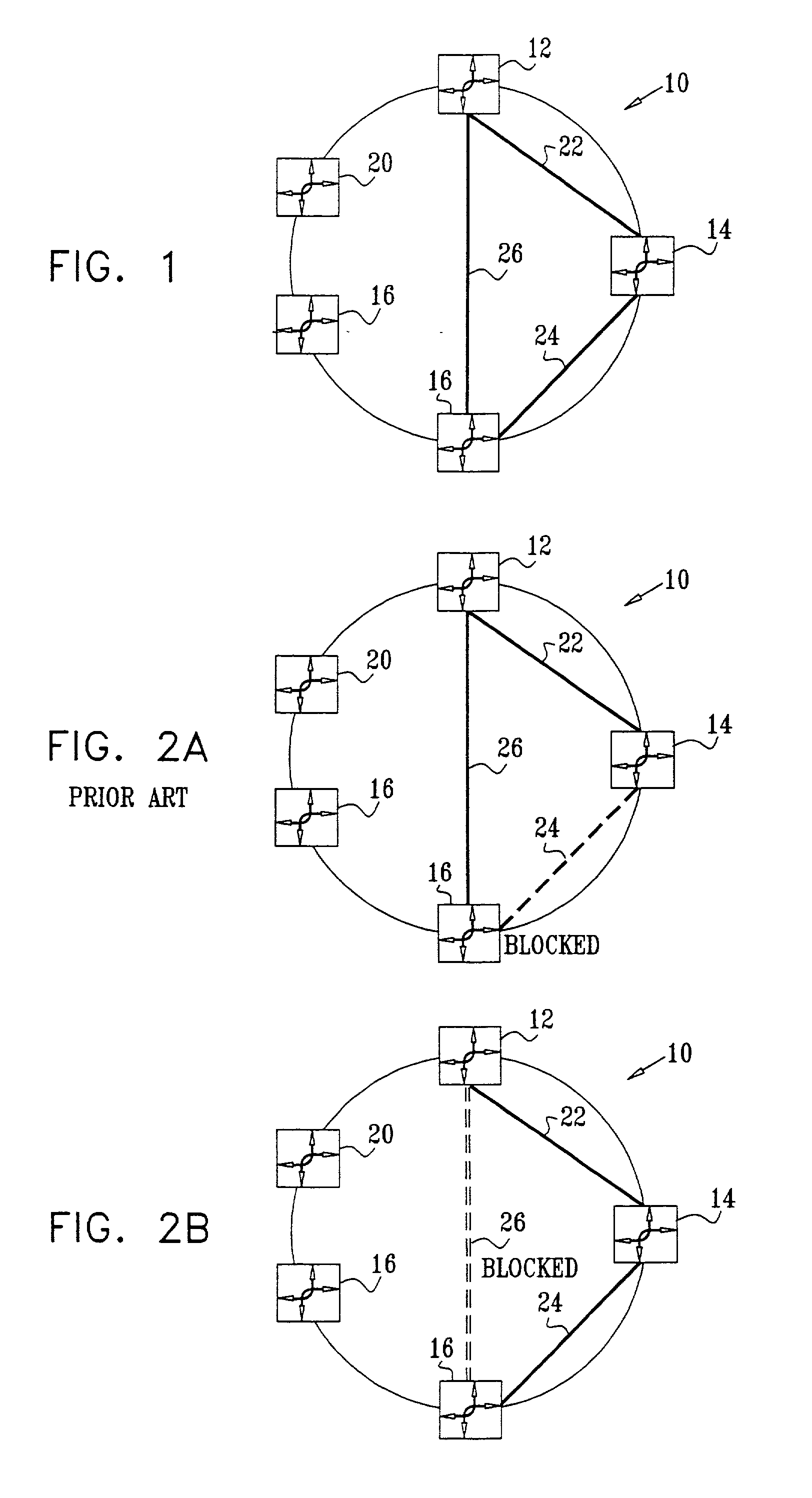
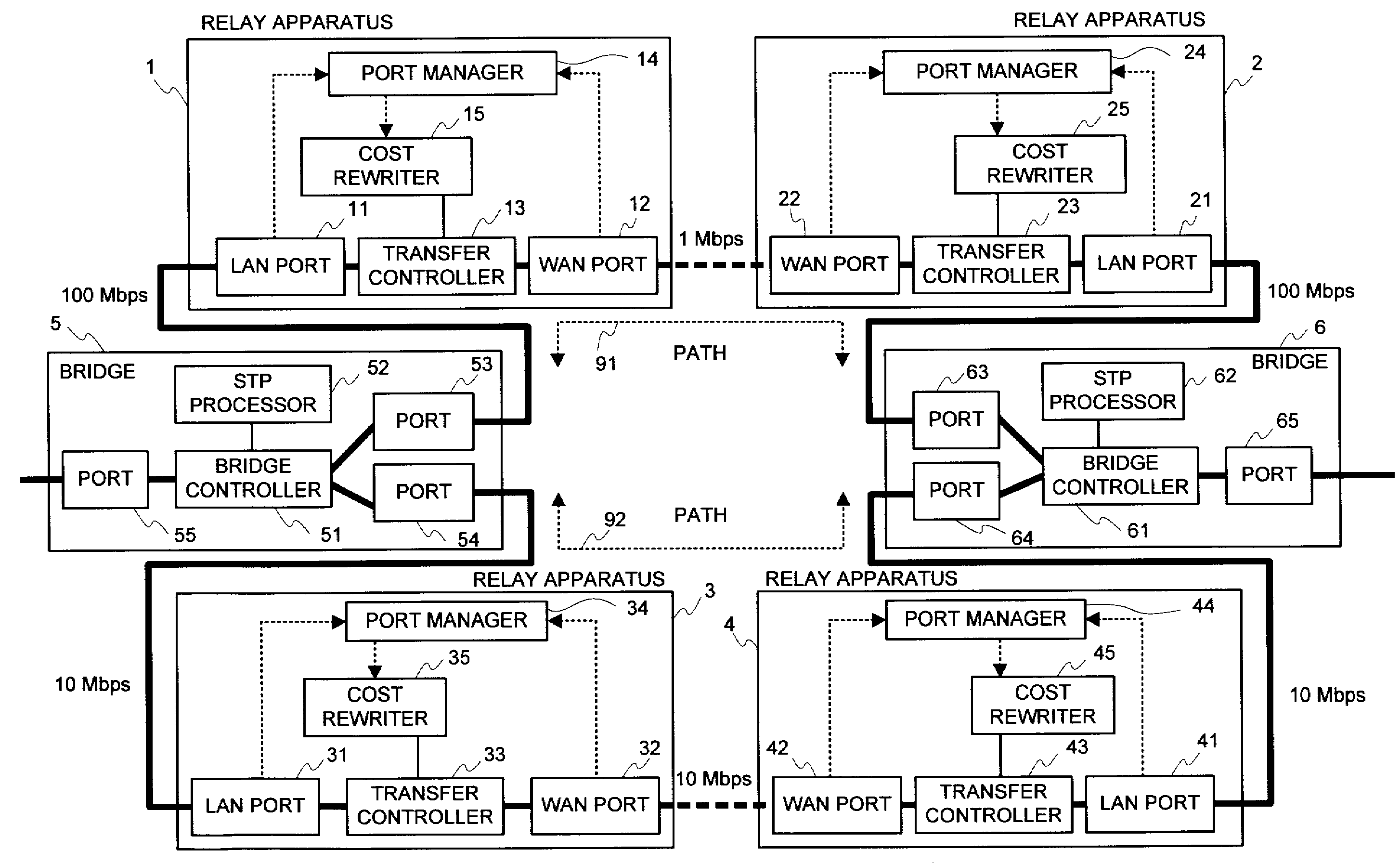
An object of the present invention is to reflect a band of the bottleneck into the cost, to select an optimal path, and to enhance an efficiency of the net utilization without making a setting or a modification to the apparatus (bridge etc.) in which the path control protocol operates in a case where a difference exists between an actually utilizable rate (a band of the bottleneck) in the path between the bridges etc. and a link rate of the connection link such as the bridge etc. in a net in which the apparatus (bridge etc.), in which the path control protocol (STP etc.) for automatically computing a cost of a link by a physical band of the connection link operates, exists. In the system of the present invention, the port manager within the relay apparatus, upon receipt of a notification of the link rate from the port, investigates which side, out of the WAN side and the LAN side, becomes a bottleneck, and the cost rewriter within the relay apparatus rewrites the root path cost field within the BPDU in conformity to the rate of the bottleneck.
Owner:NEC CORP
Wireless communication system and nodes
ActiveUS20110235504A1Blocking in networkAvoid transmissionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemPath cost
A wireless communication system includes a first node, multiple second nodes, and multiple third nodes that communicate with the first node through the second nodes. The second and third nodes transmit control information to their neighboring third nodes, which calculate link costs from the reception status of the control information. The control information transmitted by each node includes a path cost indicating the cost of a path between the transmitting node and the first node. From the path costs in received control information, each third node selects a second node through which to communicate with the first node, and selects a parent node as the destination of the first hop on the path through the selected second node to the first node. Routing is thereby accomplished autonomously without having the second nodes flood the system with routing requests.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
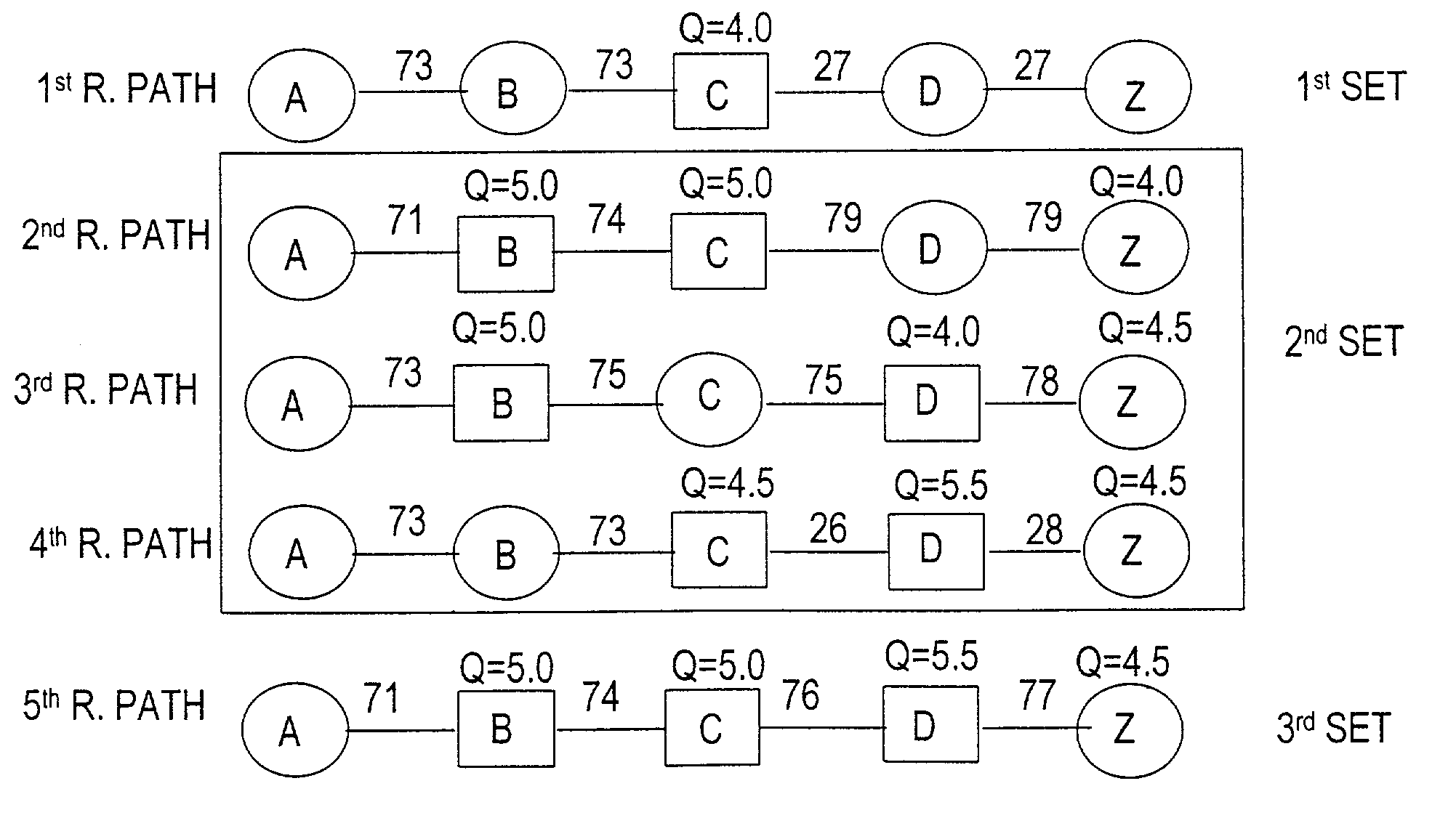
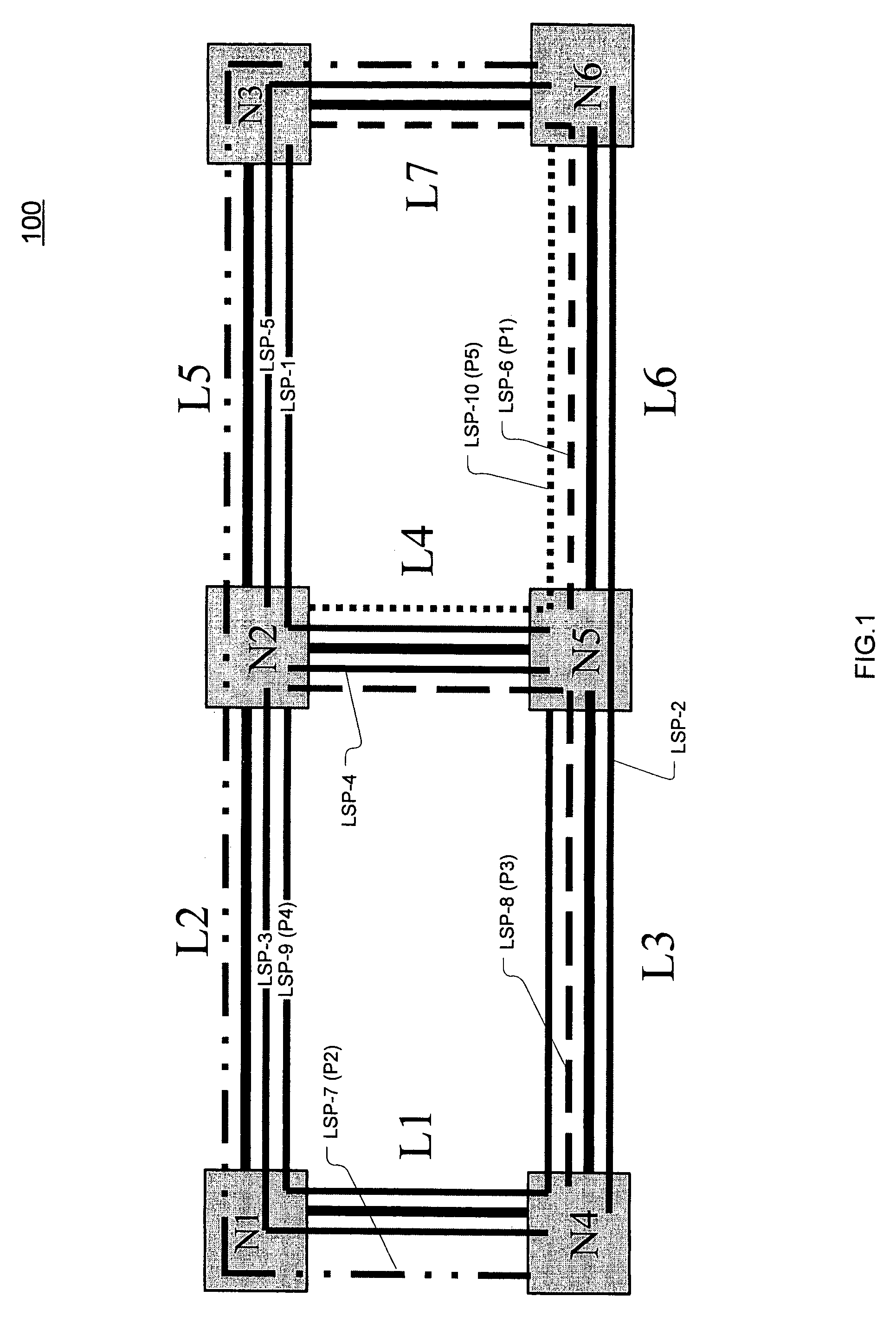
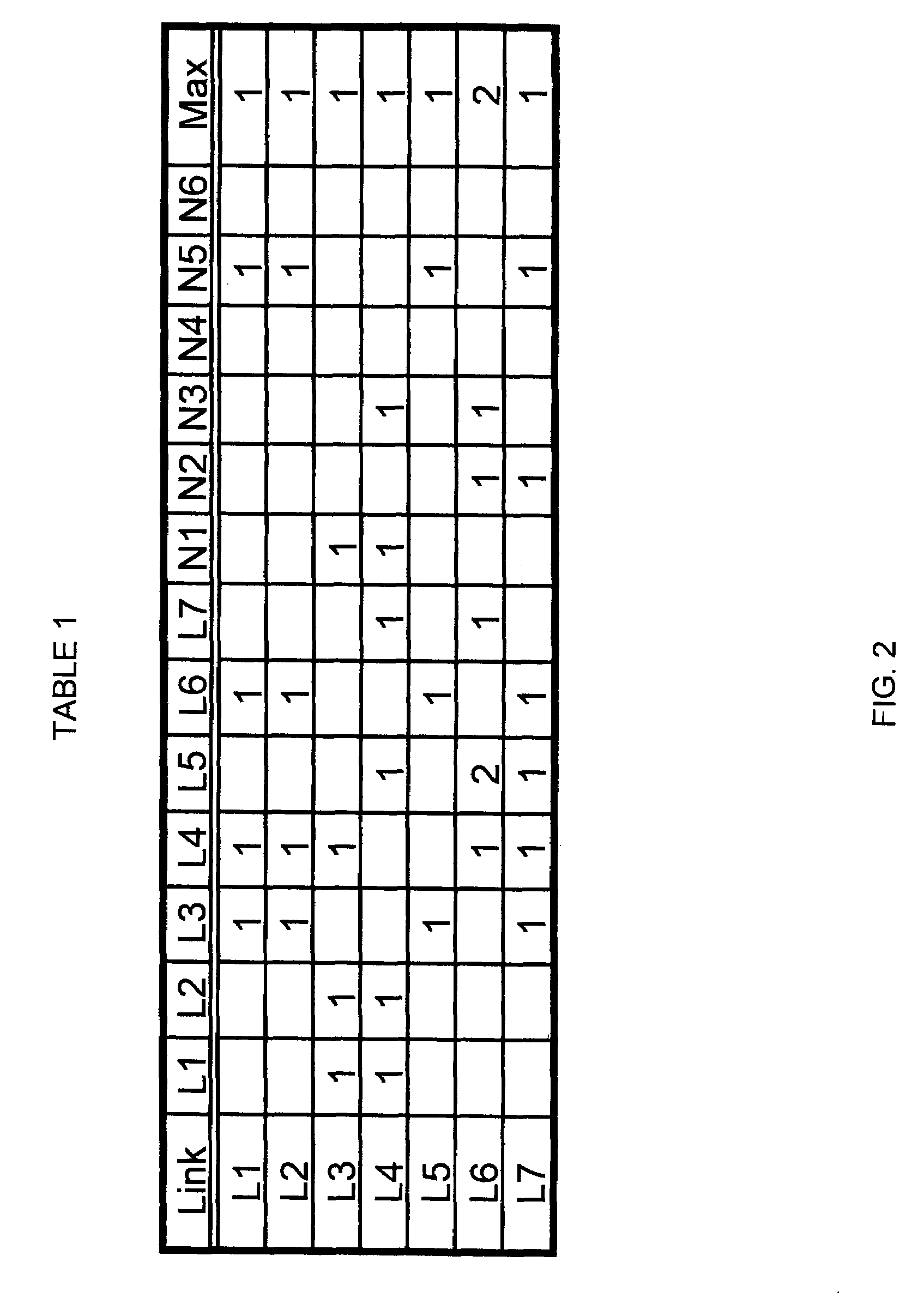
Restoration path calculation in mesh networks
A method for determining a restoration path corresponding to a primary path for a new service in a mesh network involves (1) generating path costs for candidate restoration paths for the new service, and (2) selecting, for the new service, the restoration path with the lowest path cost, where generating the path cost involves (a) determining, for each link Li in the candidate restoration path, a set B-Li-set of links protected by Li (b) determining, for each link Li, a set I-Li-set of links in the set B-Li-set that are also in the primary path (c) calculating, for each link Li, a link cost based on the set B-Li-set and the set I-Li-set, and (d) calculating the path cost based on a sum of the link costs. In some embodiments, the method includes an efficient scheme for representing, disseminating, storing, and updating sharing information in an OSPF-TE protocol context.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Satellite network inter-satellite link failure recovery method based on regional division
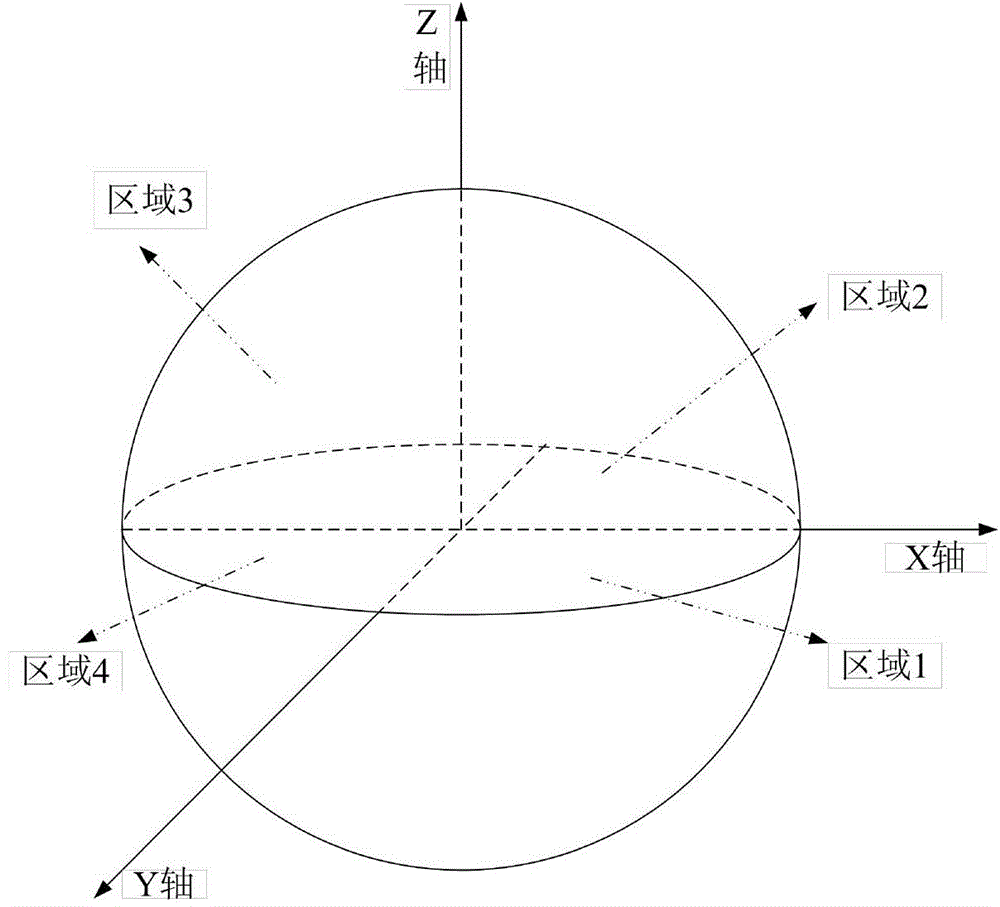
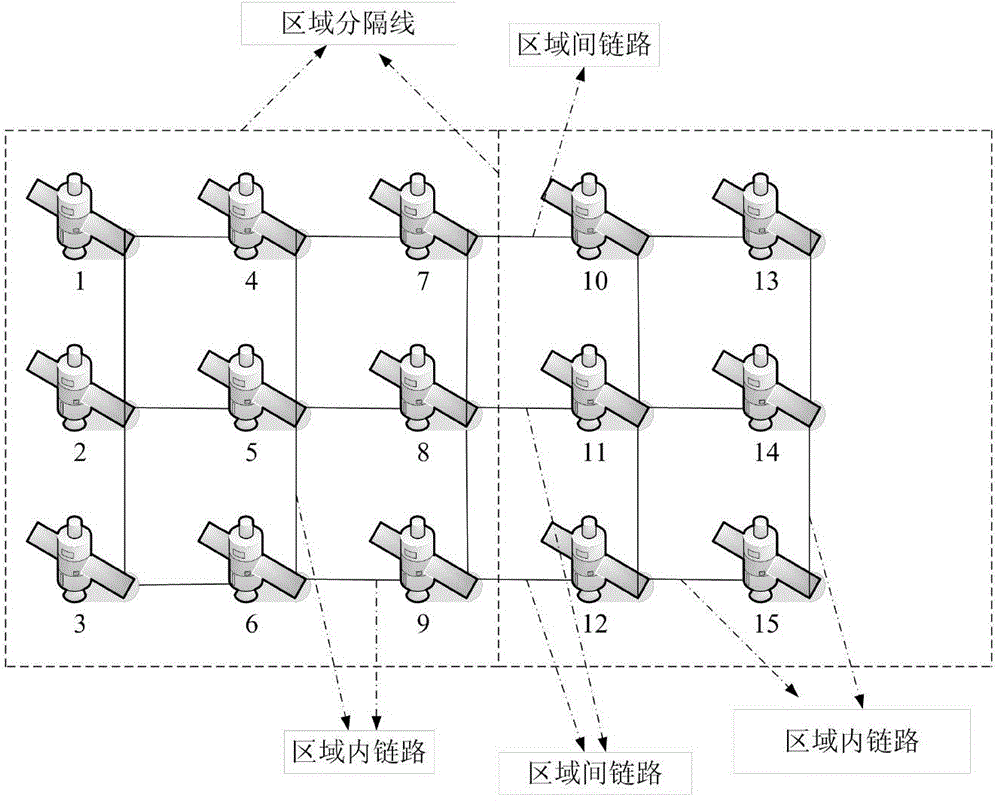
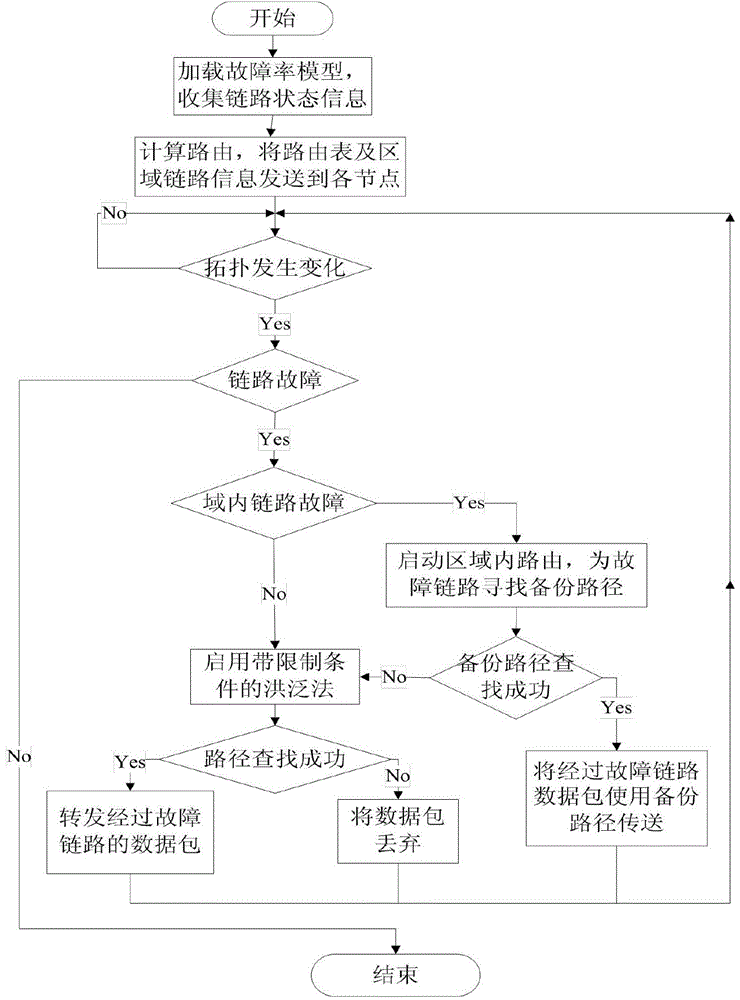
ActiveCN103986512AAvoid troubleSolve the real problemRadio transmissionRelay systems monitoringRecovery methodTime delays
Provided is a satellite network inter-satellite link failure recovery method based on regional division. Firstly, the link failure probability is added to a path cost formula to avoid links high in fault rate, and failures cannot happen to paths selected by services as far as possible; then a satellite network is divided into eight different regions, the topology of the satellite network is monitored, when a link failure occurs in the satellite network, rerouting is carried out in the regions of a small range, proper alternative paths are found for the fault links, and all the services passing through the failure links can be forwarded by the alternative paths; when no proper alternative paths exist in the regions, flooding information is sent by adopting a flooding method with limiting conditions, and proper forwarding paths are found for the services. The services in the satellite network avoid the failure links as far as possible, the alternative paths can be searched for fast after the link failure occurs, time delay needed by link failure recovery is shortened, resource waste is reduced, and therefore the communication efficiency of the satellite network is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com