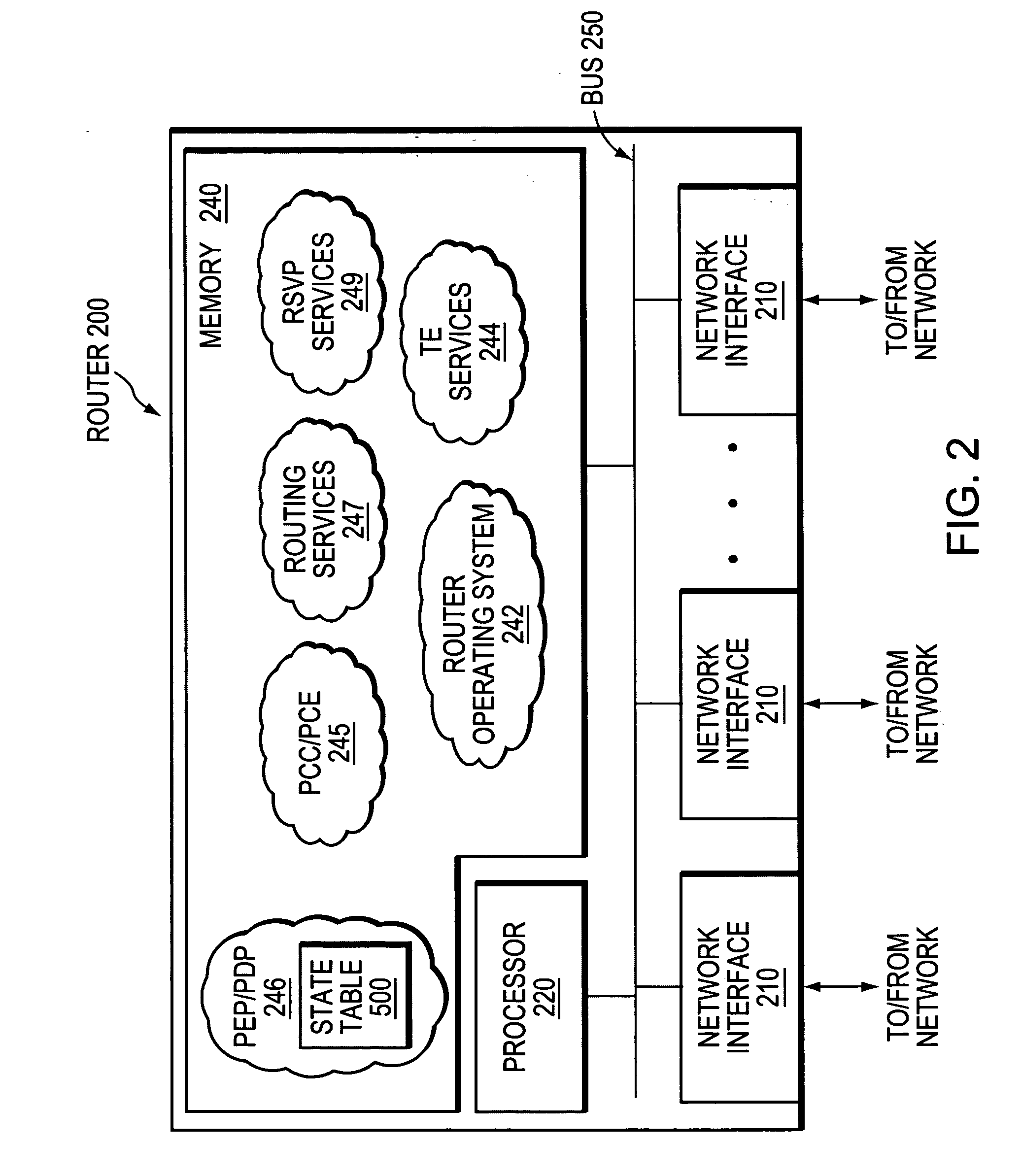
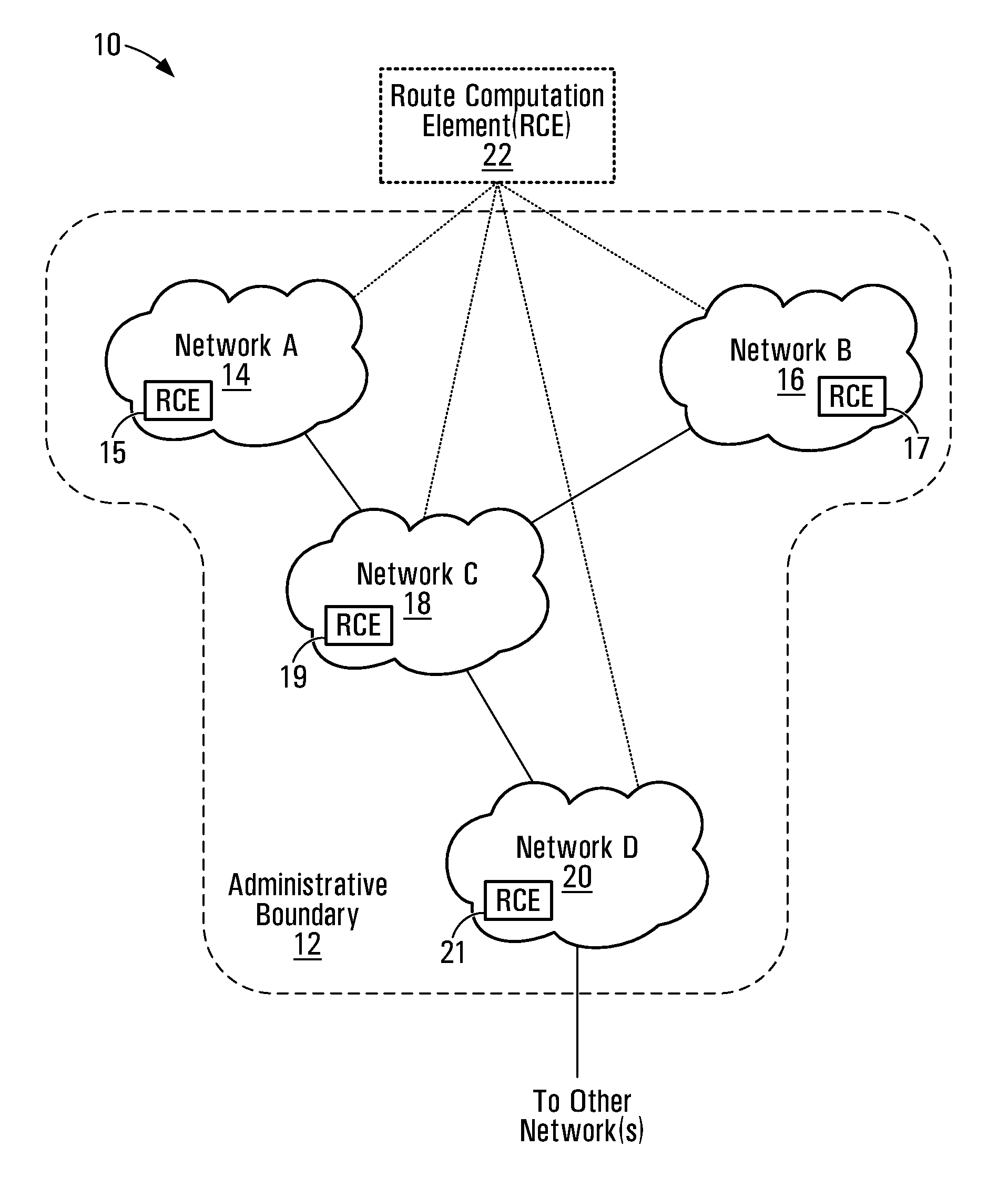
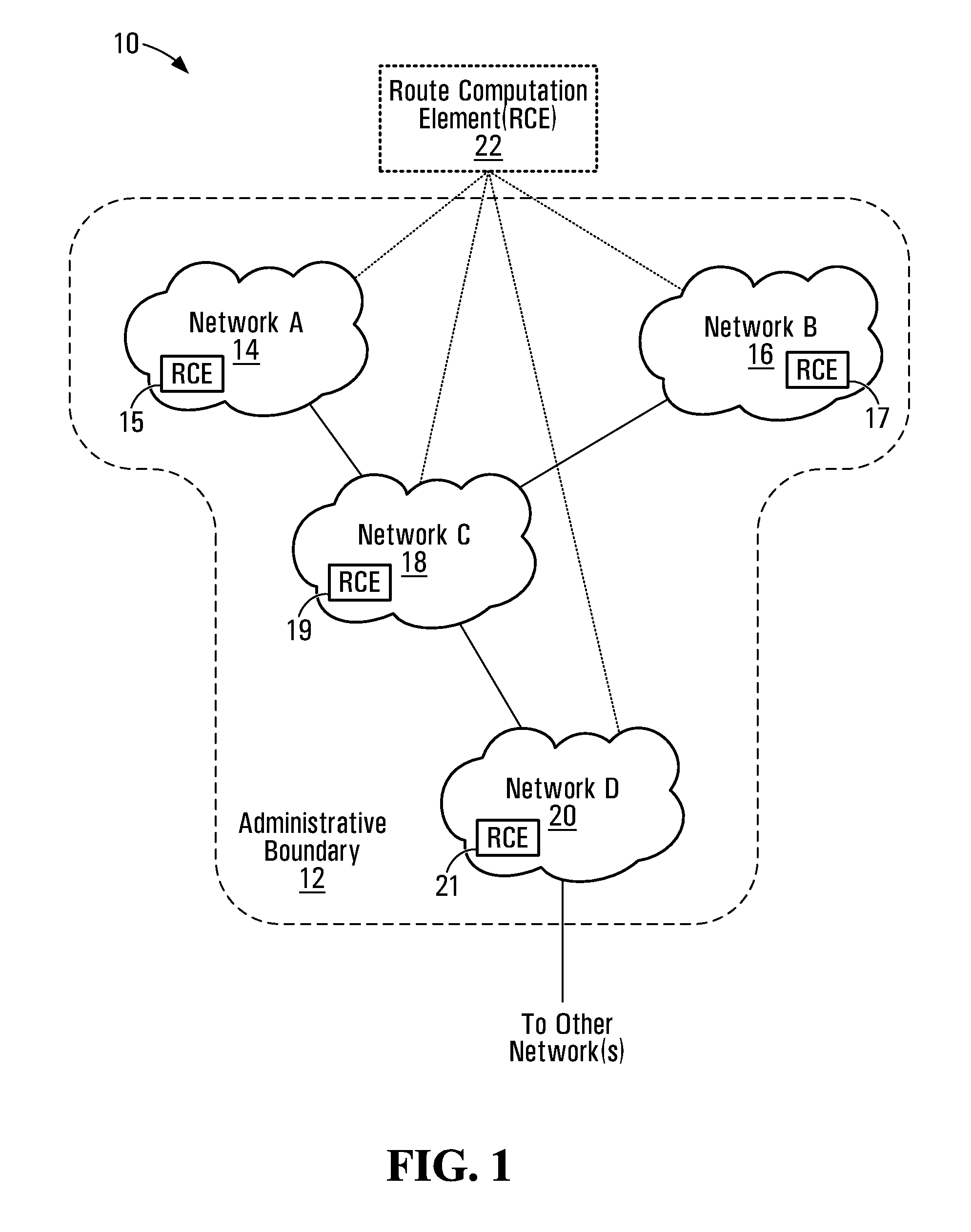
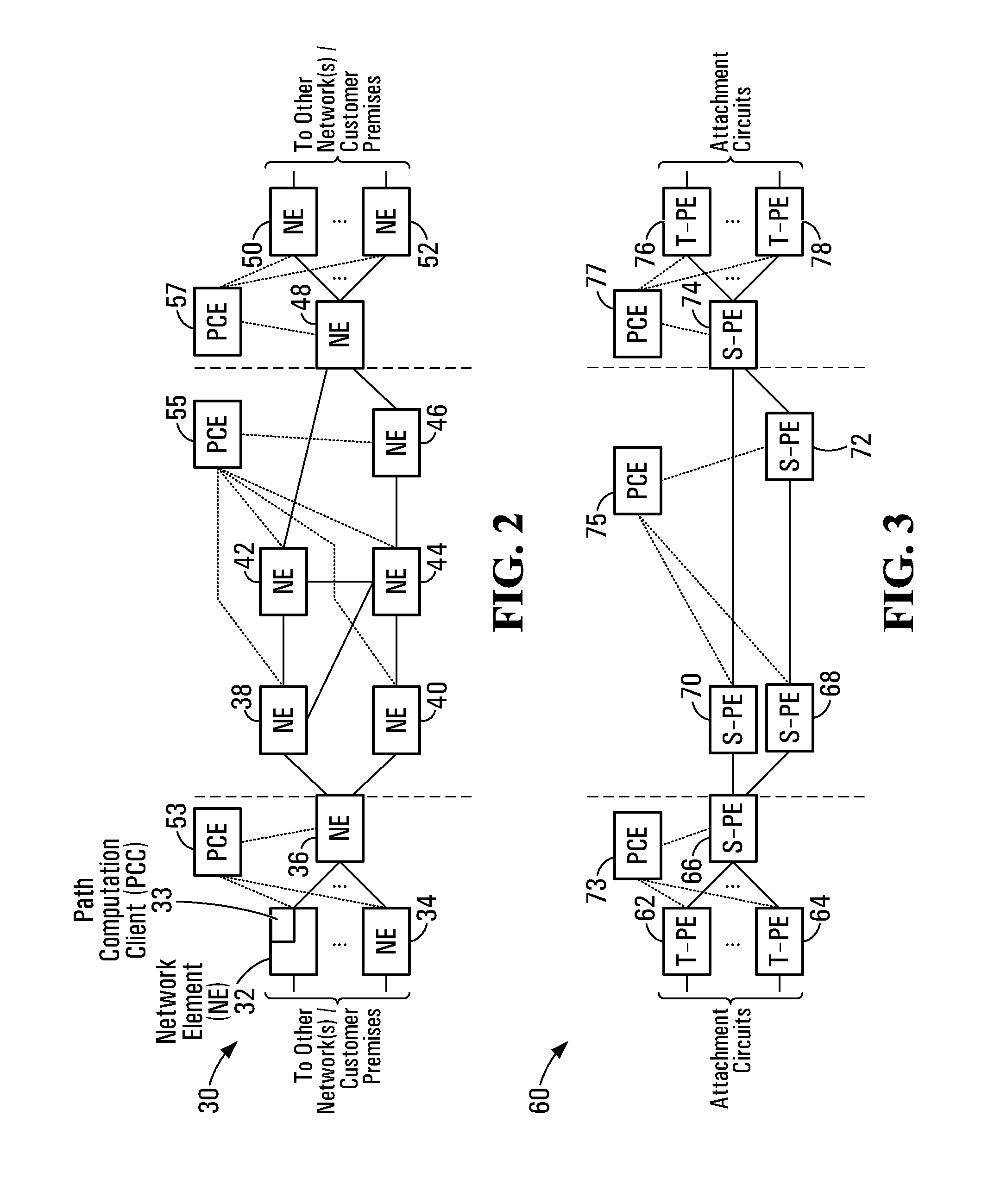
Patents
Literature
243 results about "Path computation element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
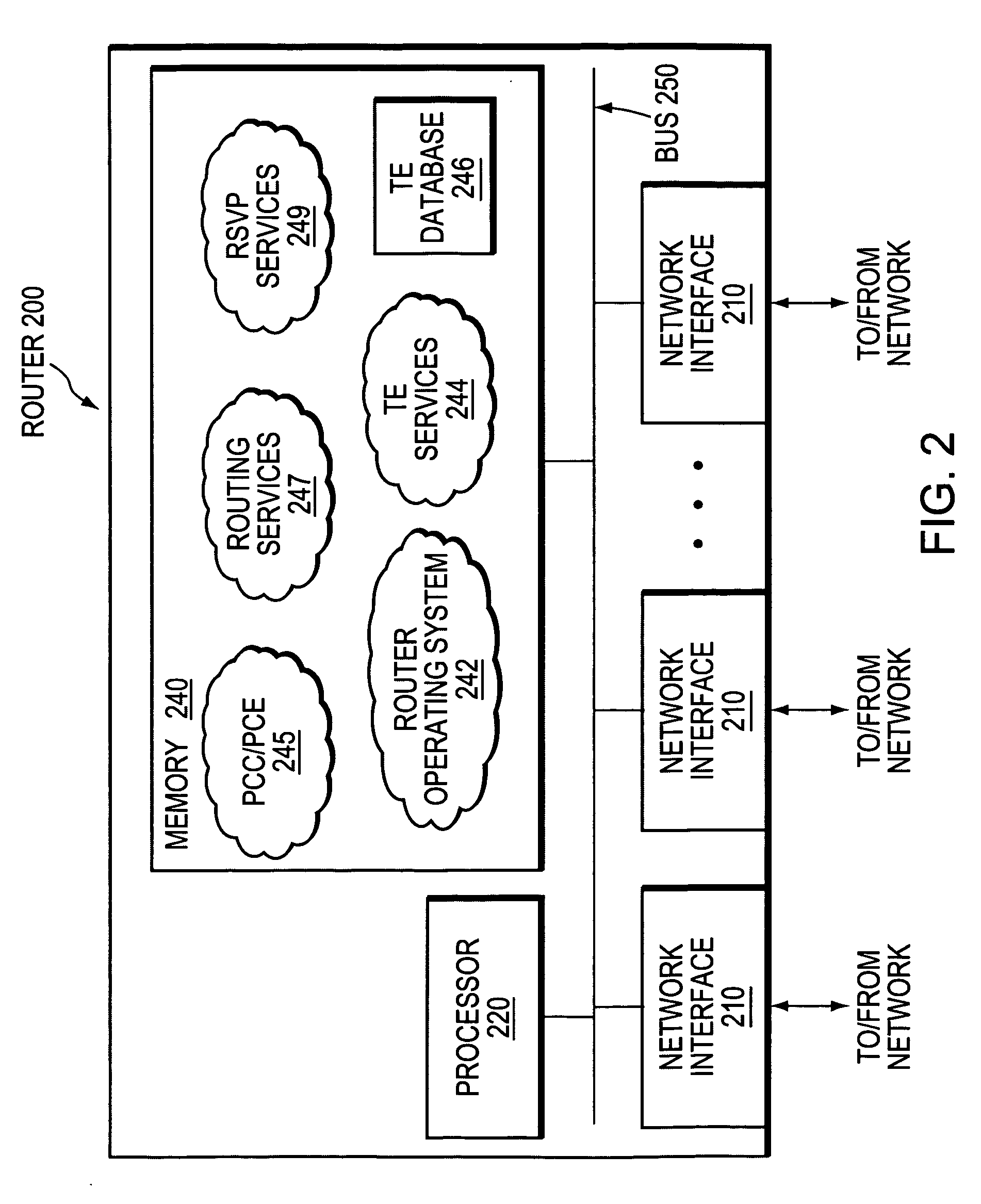
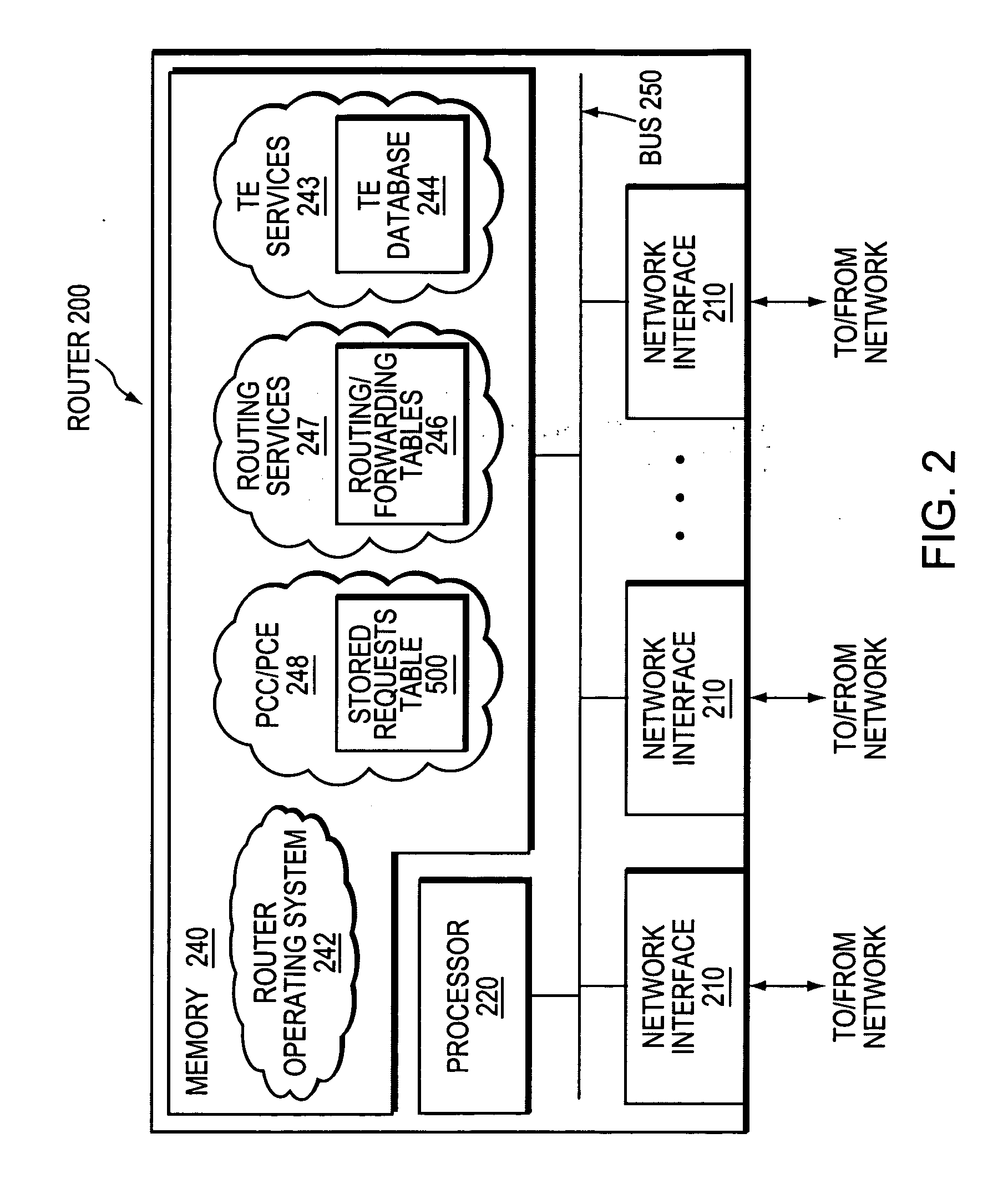
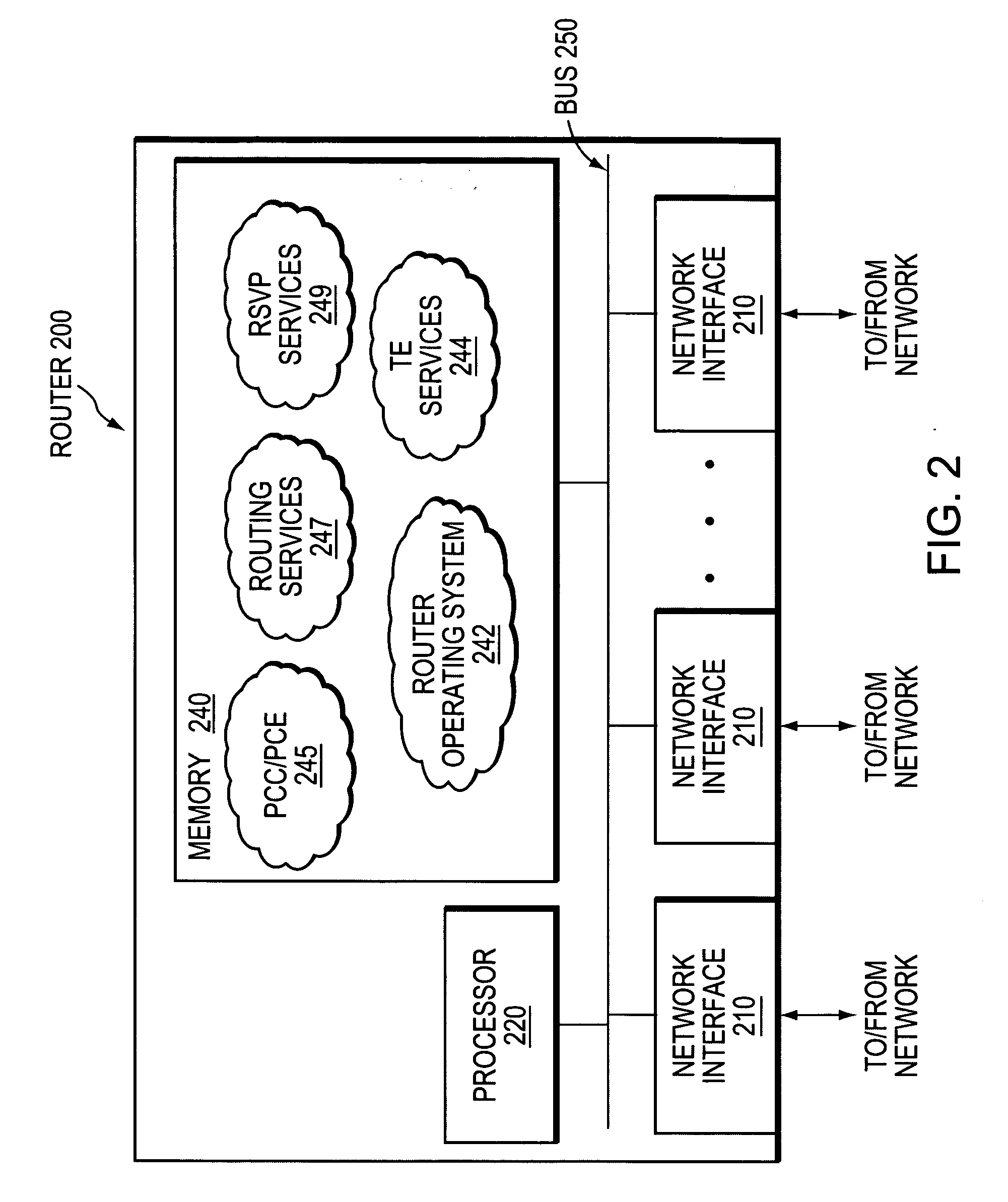
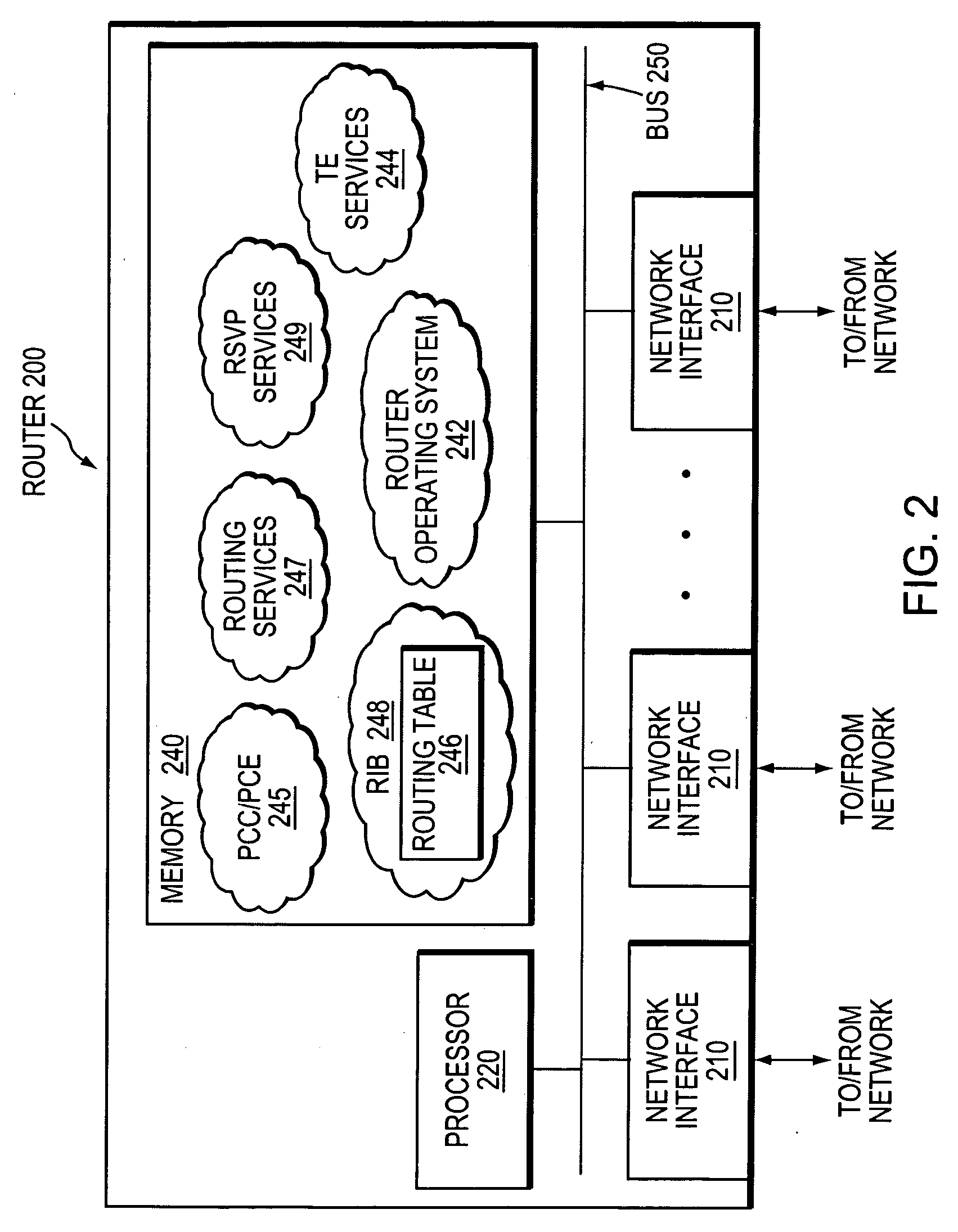
In computer networks, a Path Computation Element (PCE) is a system component, application, or network node that is capable of determining and finding a suitable route for conveying data between a source and a destination.
Technique for efficient load balancing of TE-LSPs
ActiveUS20060182035A1Efficient load balancingEqual-cost pathError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPath computation elementLabel switching
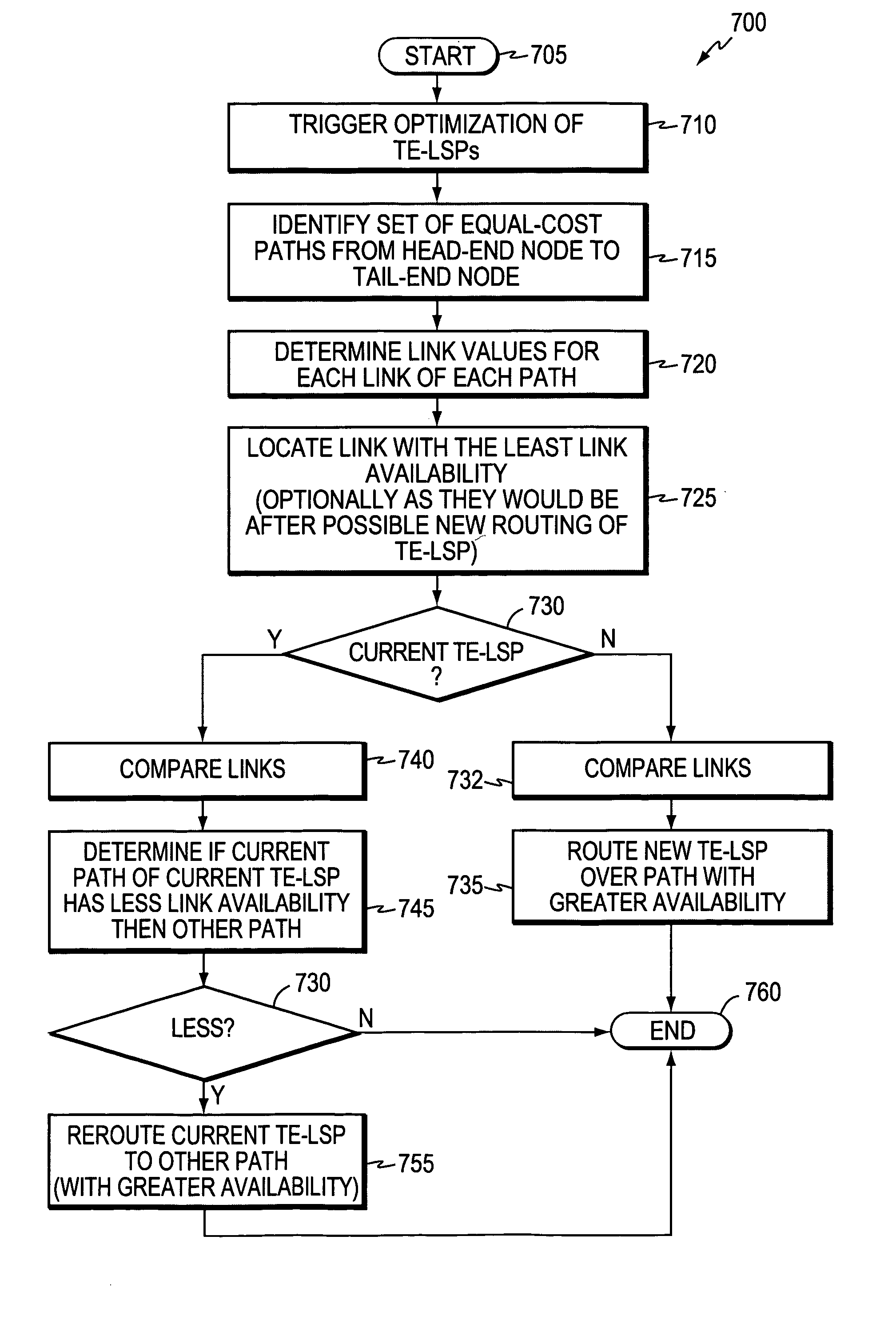
A technique efficiently load balances traffic engineering (TE) label switched paths (LSPs) from a head-end node to a tail-end node of a computer network. The novel load balancing technique identifies (e.g., at the head-end node or a path computation element, PCE) a set of paths with equal costs from the head-end node to the tail-end node, where each path of the set is composed of one or more associated links. “Link values” such as, e.g., the number of unconstrained TE-LSPs on the link, the amount of available bandwidth on the link, or the percent of total available bandwidth already in use on the link, are applied to each link of each path. The most restrictive link values (link availability) of each path of the set, such as, e.g., the link with the lowest amount of available bandwidth, etc., are then compared. Upon comparing the link availability, the novel technique load balances established and / or new TE-LSPs from the head-end node to the tail-end node over the set of paths accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
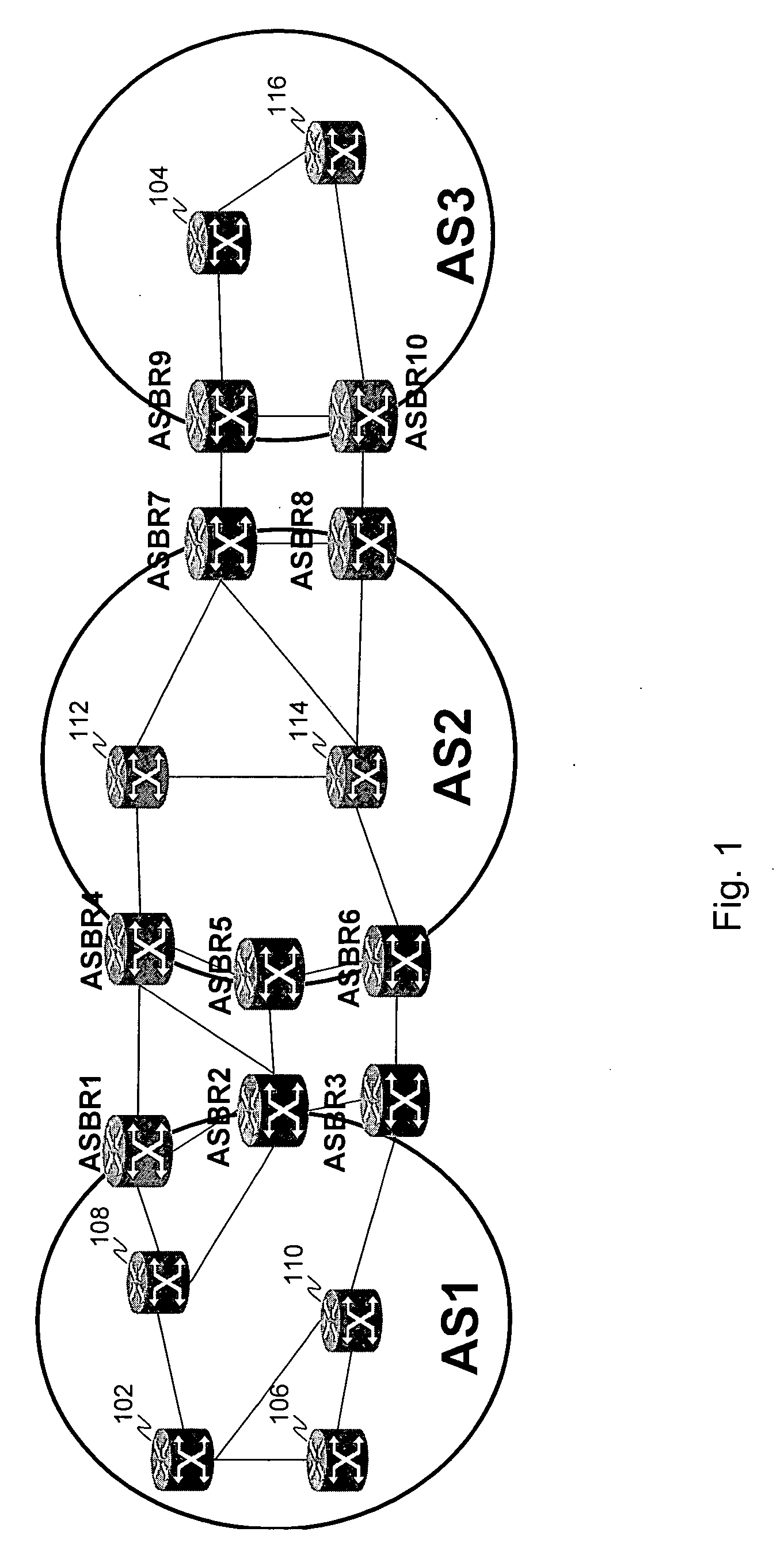
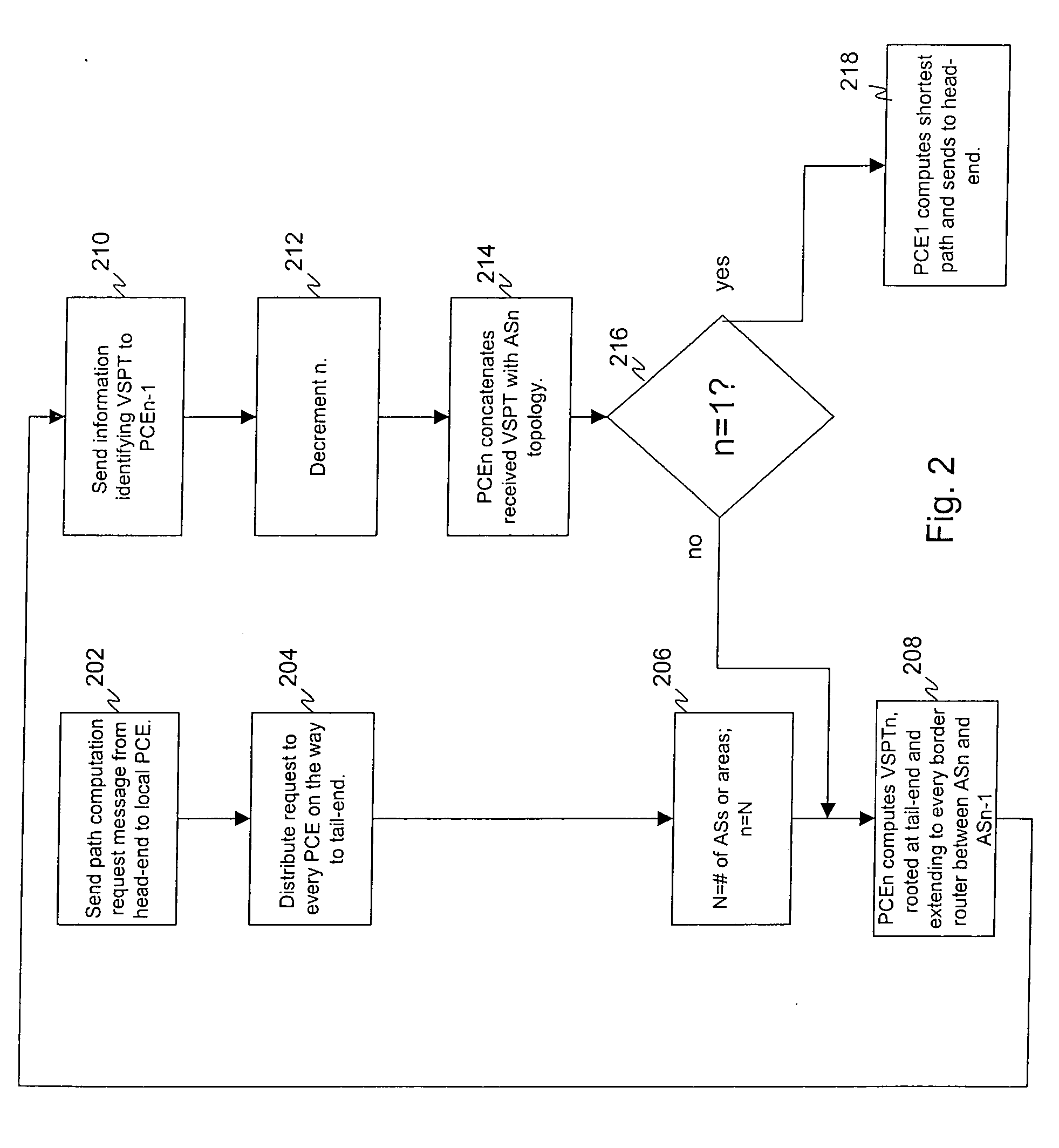
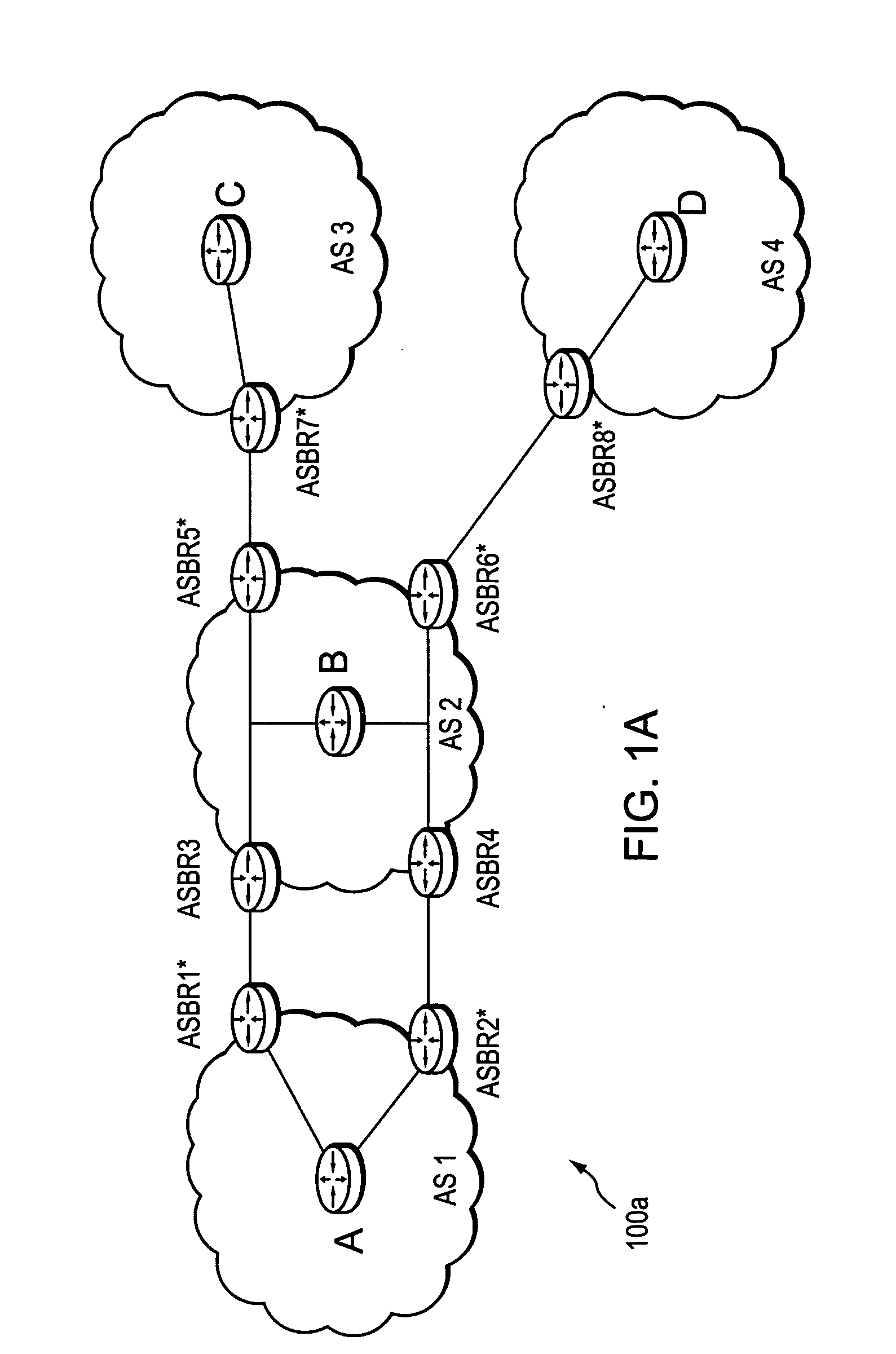
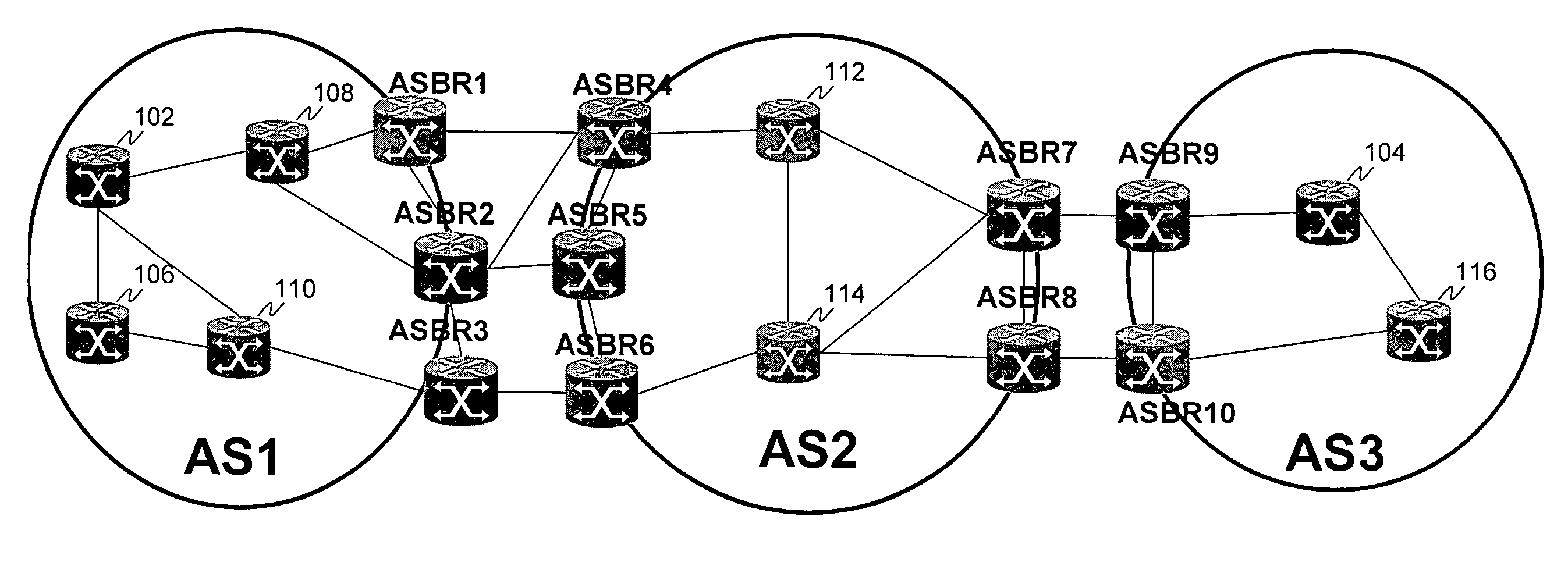
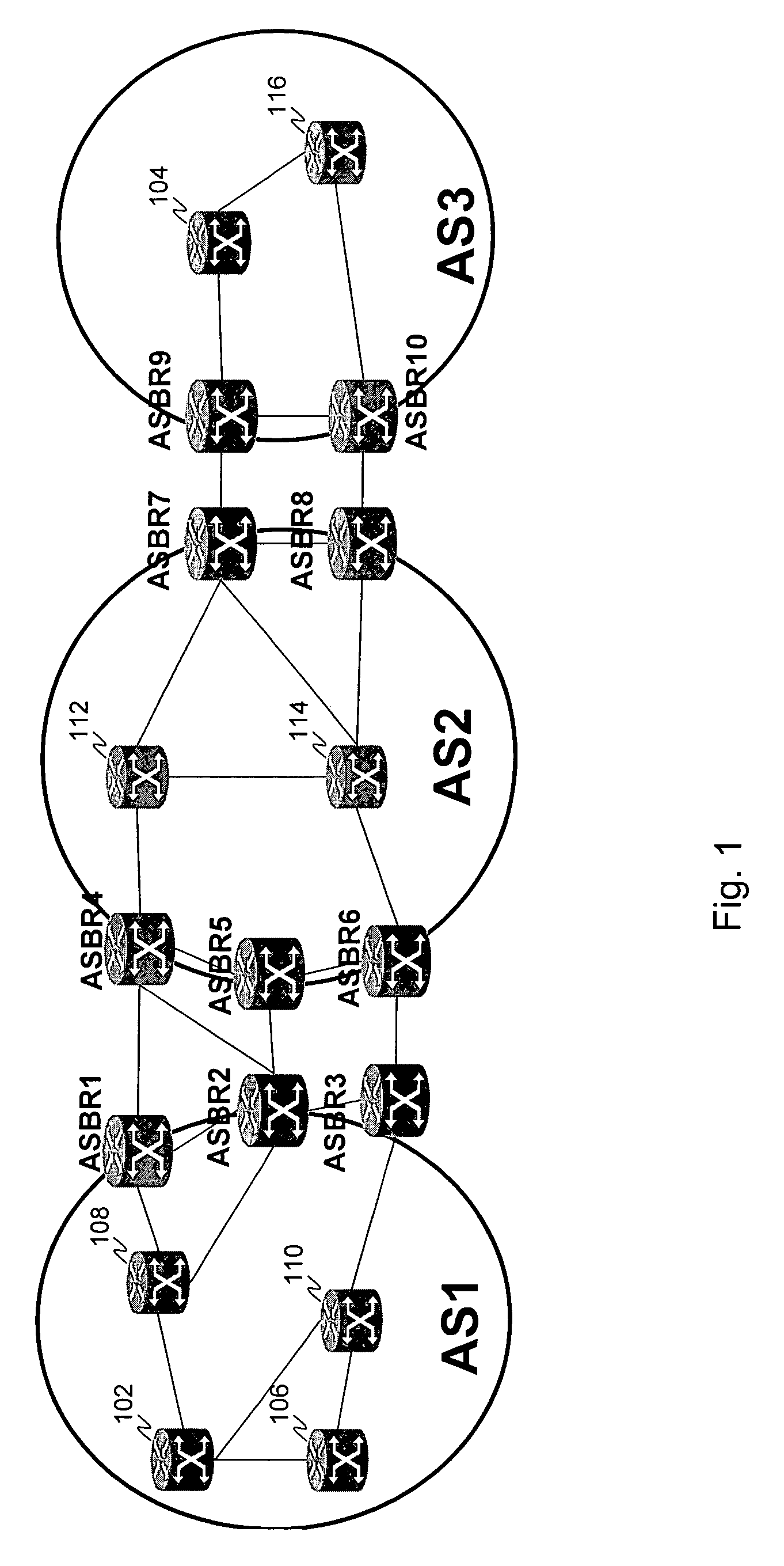
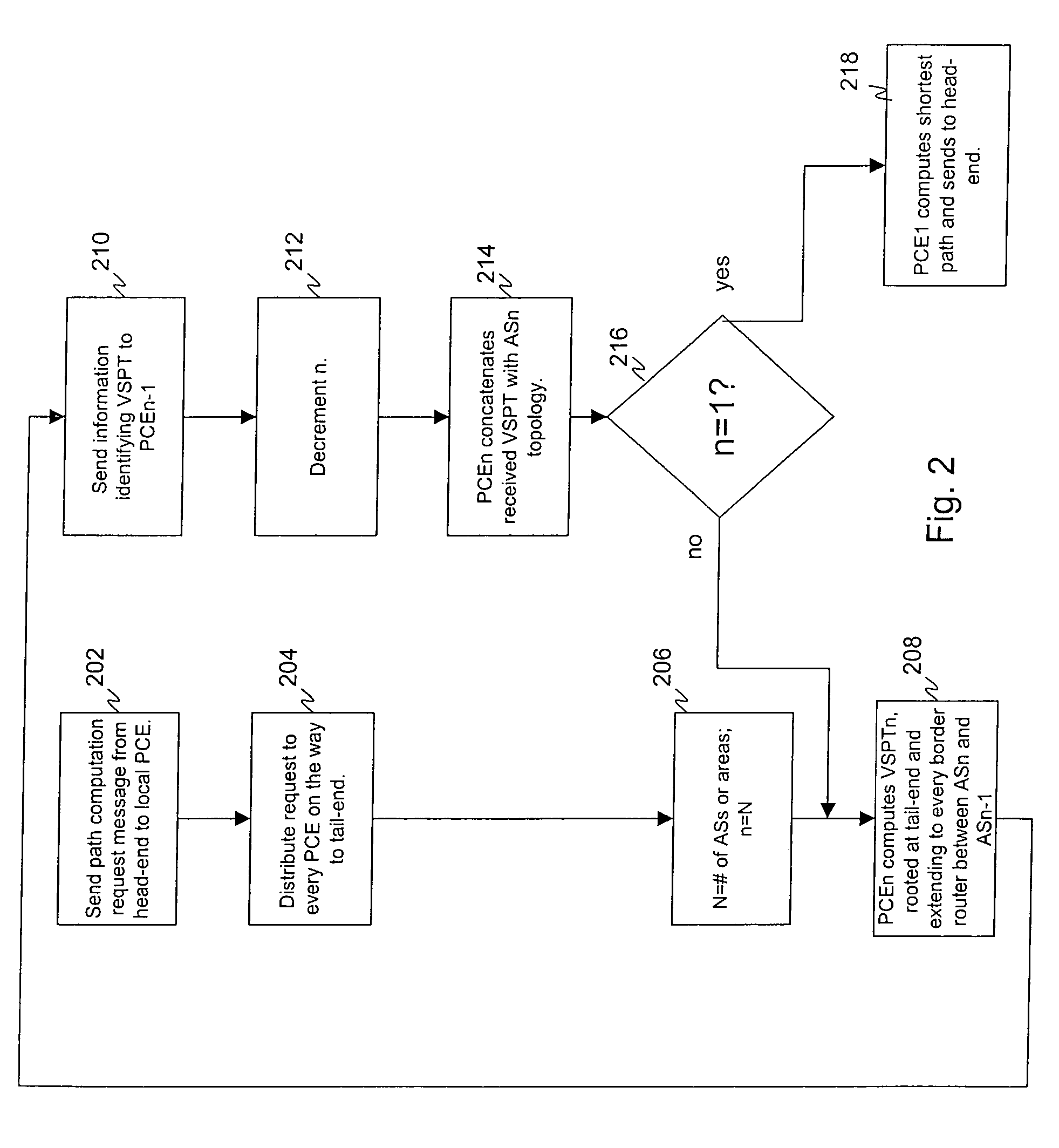
Computing inter-autonomous system MPLS traffic engineering LSP paths
InactiveUS20060039391A1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsPath computation elementMpls traffic engineering
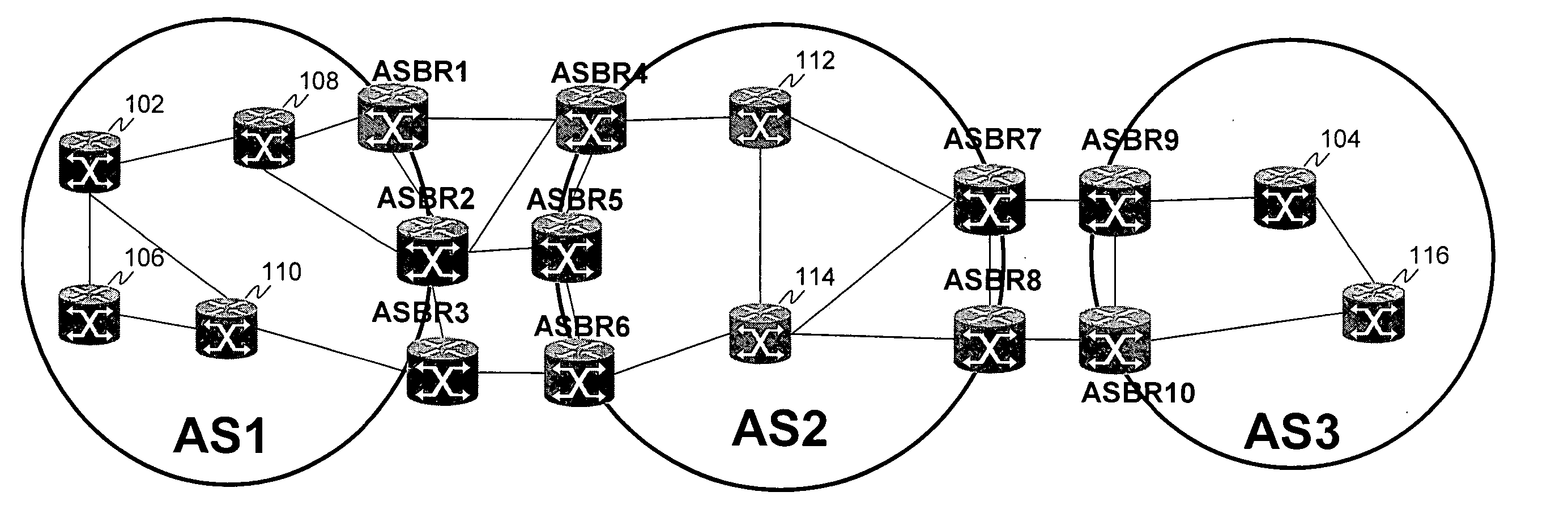
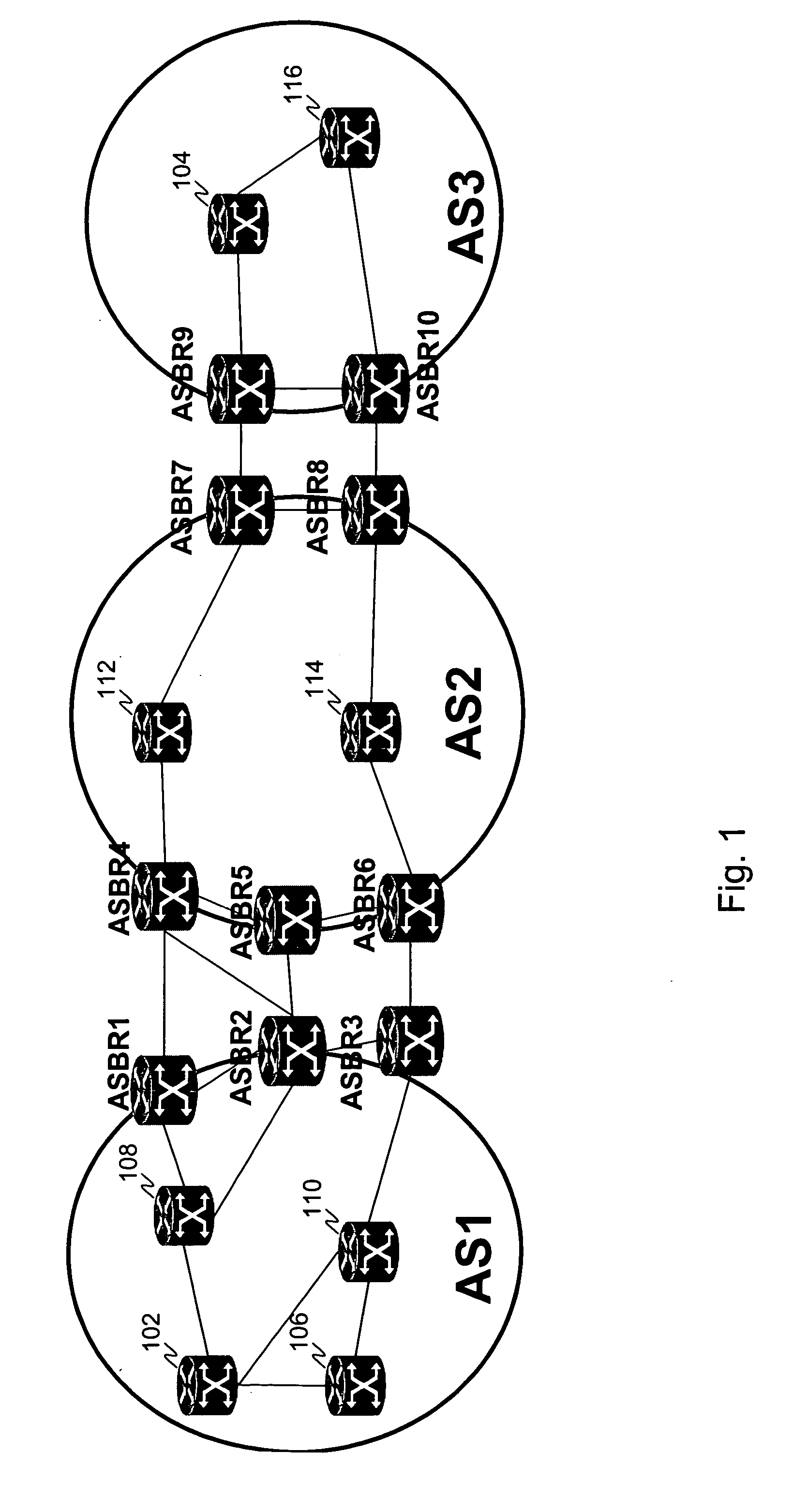
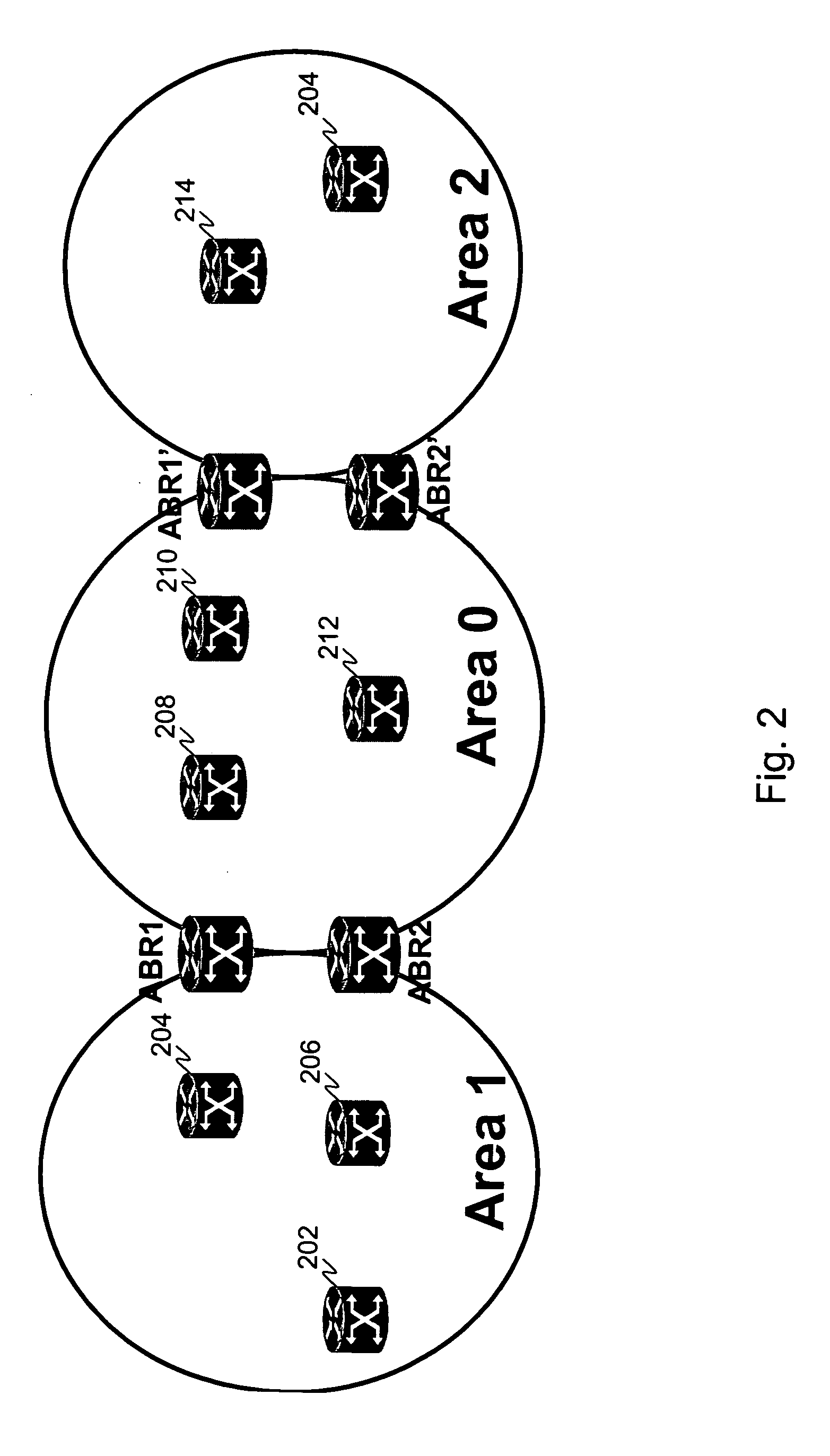
Systems and methods for computing the paths of MPLS Traffic Engineering LSPs across Autonomous System and / or area boundaries. A distributed path computation algorithm exploits multiple path computation elements (PCEs) to develop a virtual shortest path tree (VSPT) resulting in computation of an end-to-end optimal (shortest) path. In some implementations, the VSPT is computed recursively across all the Autonomous Systems and / or areas between the head-end and tail-end of the Traffic Engineering LSP.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
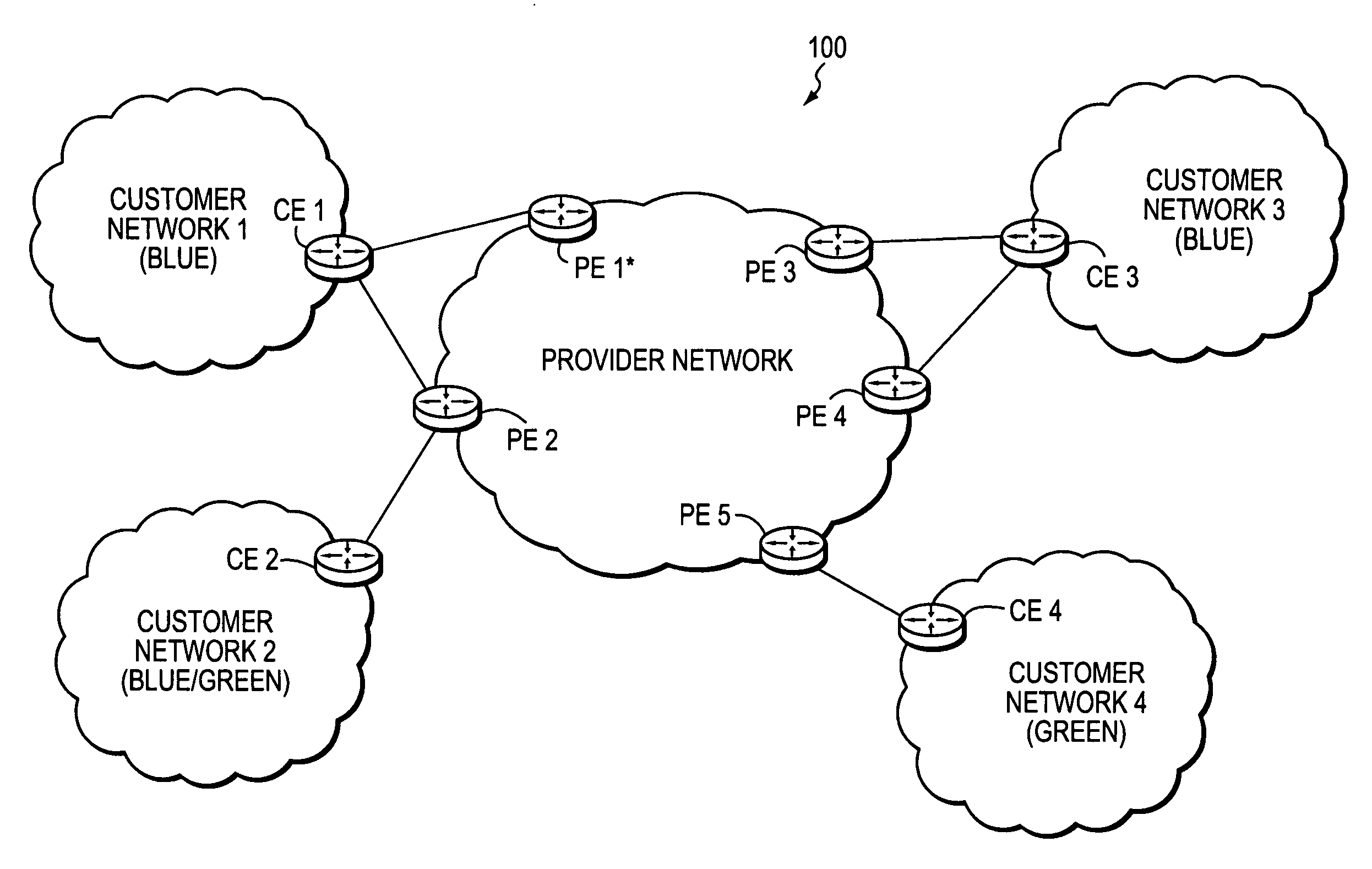
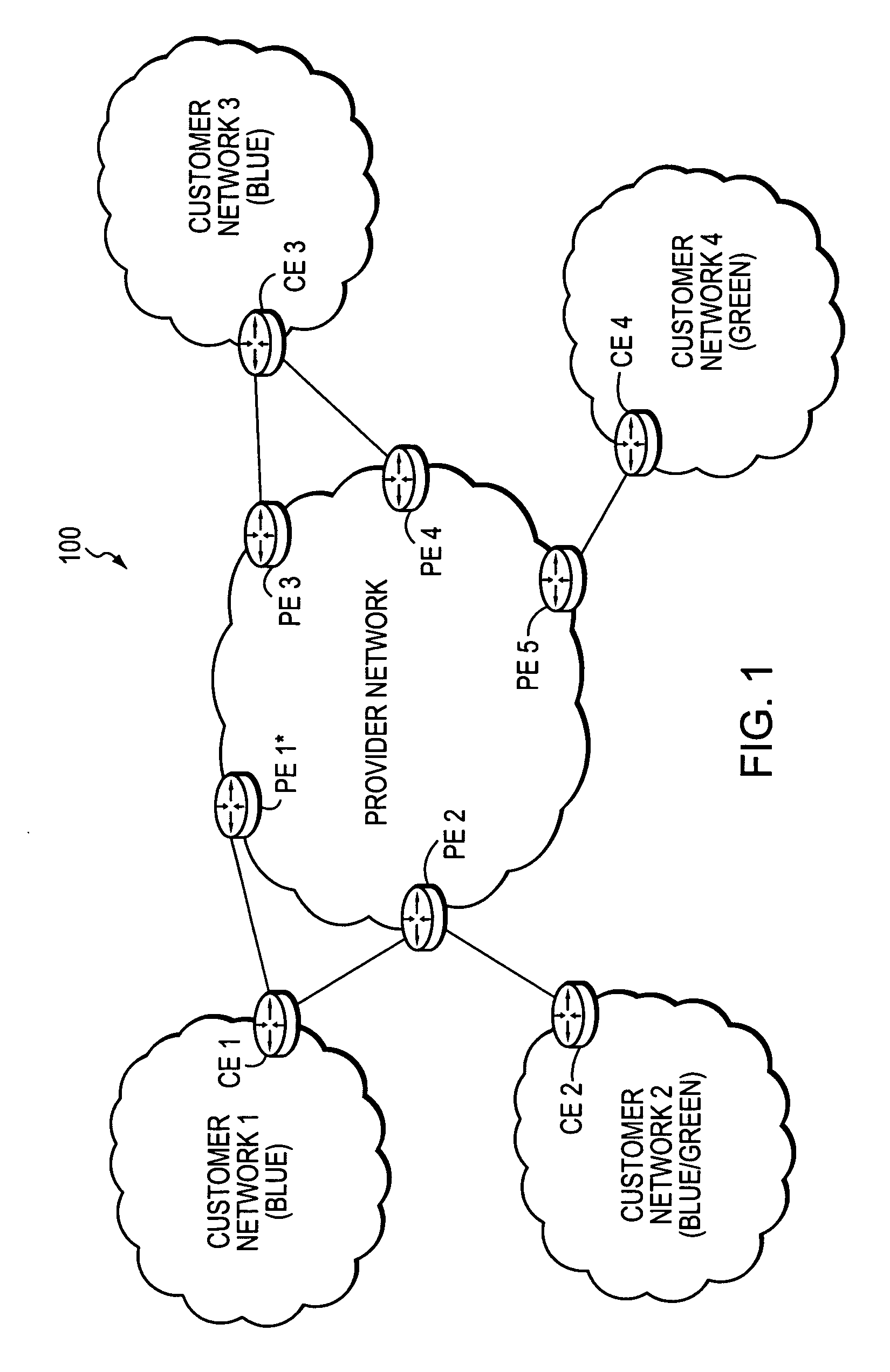
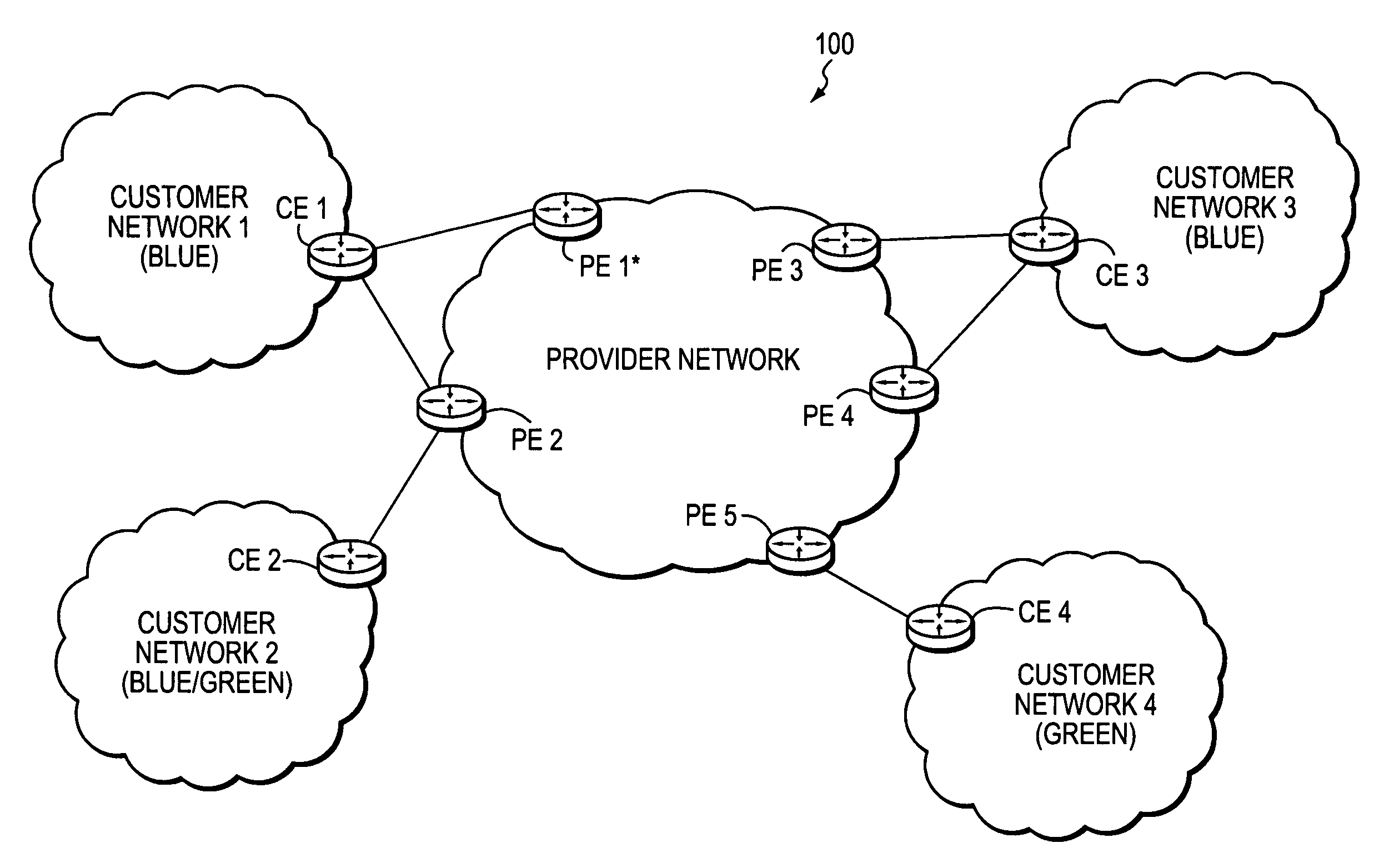
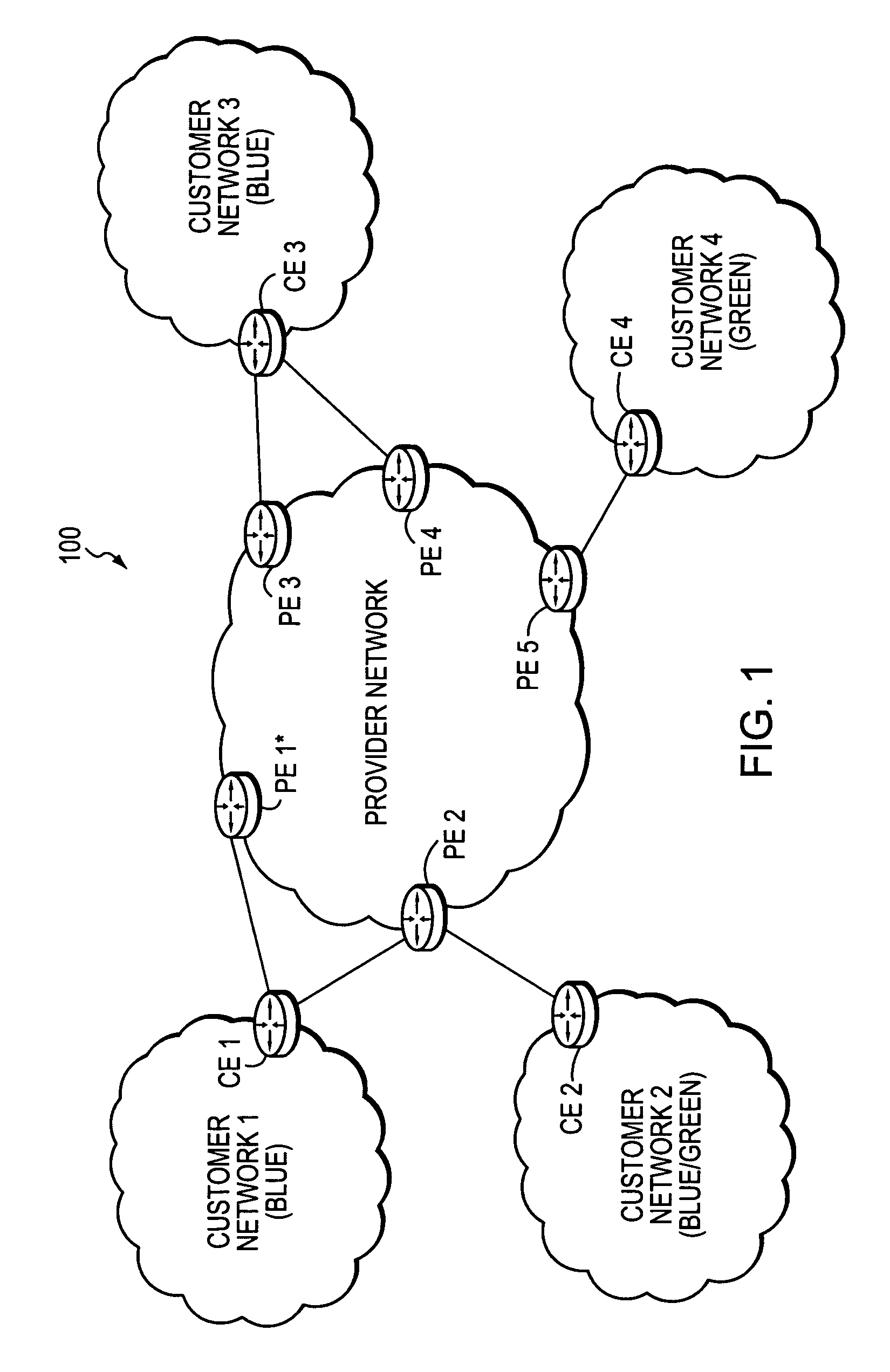
Technique for efficiently routing IP traffic on CE-CE paths across a provider network
InactiveUS20070217419A1Efficient routingImprove overall utilizationError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityPath computation element
A technique efficiently routes Internet Protocol (IP) traffic on paths between customer edge devices (CEs) across a provider network (“CE-CE paths”) in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a path computation element (PCE), e.g., a provider edge device (PE), may learn dynamic link attribute information of remote links from the provider network to one or more remote CEs (e.g., “PE-CE links” or “CE-PE links”). A multi-homed requesting CE requests from the PCE a set of CE-CE path metrics (e.g., costs) to one or more remote destination address prefixes, e.g., via each multihomed CE-PE link from the requesting CE. In response to the request, the PCE computes the set of available CE-CE paths and current metrics to the remote destination address prefixes and returns the corresponding CE-CE path metrics to the requesting CE. The requesting CE modifies its IP forwarding entries accordingly in order to perform IP traffic routing corresponding to the CE-CE path metrics (e.g., asymmetrical load balancing) across its multi-homed CE-PE links.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
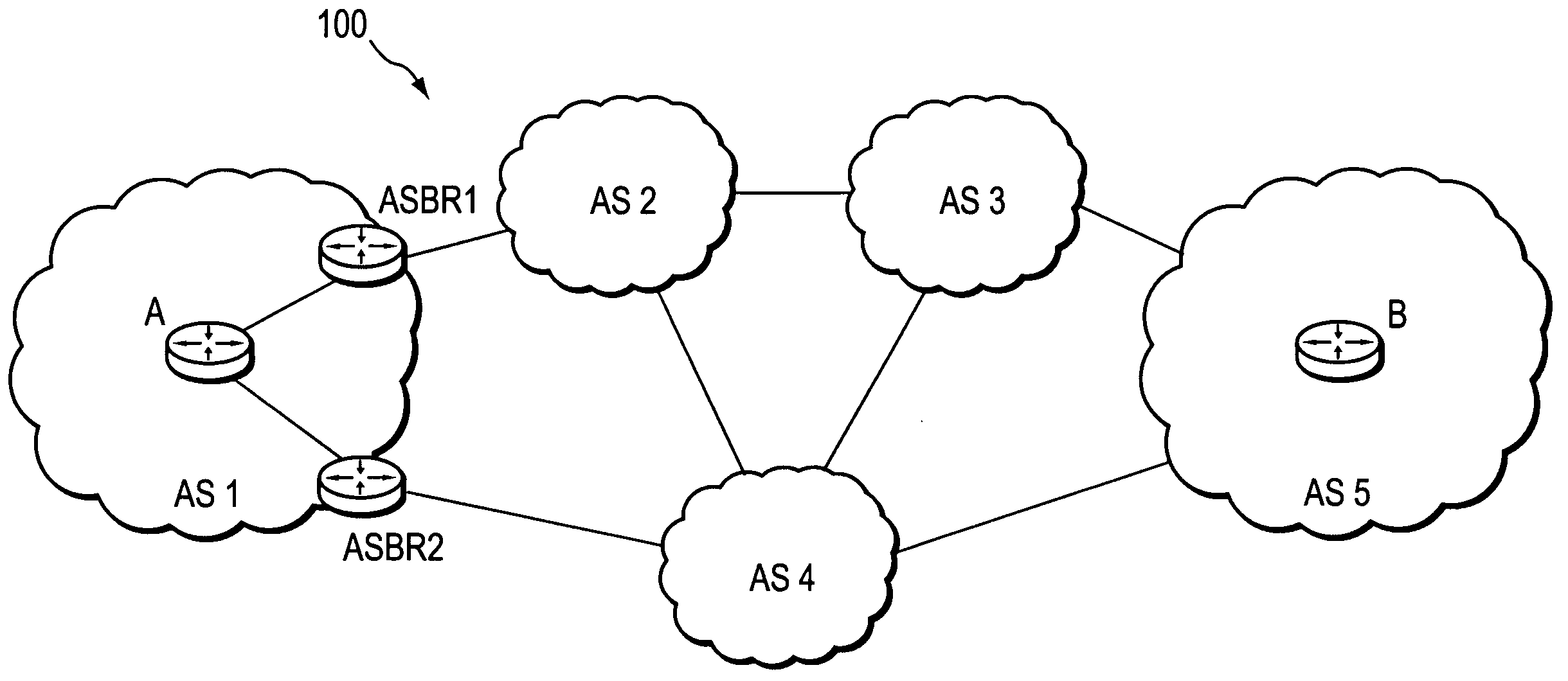
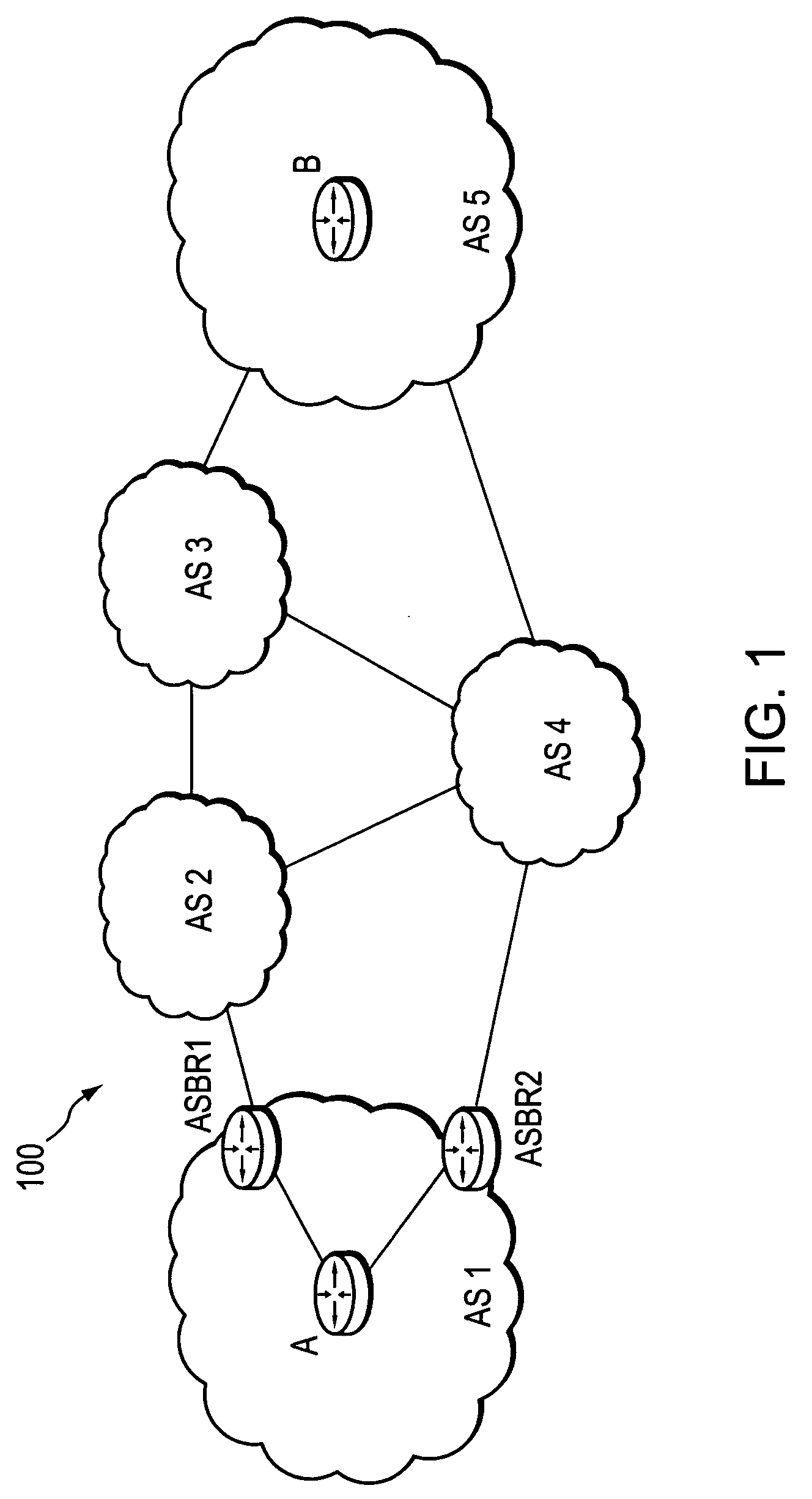
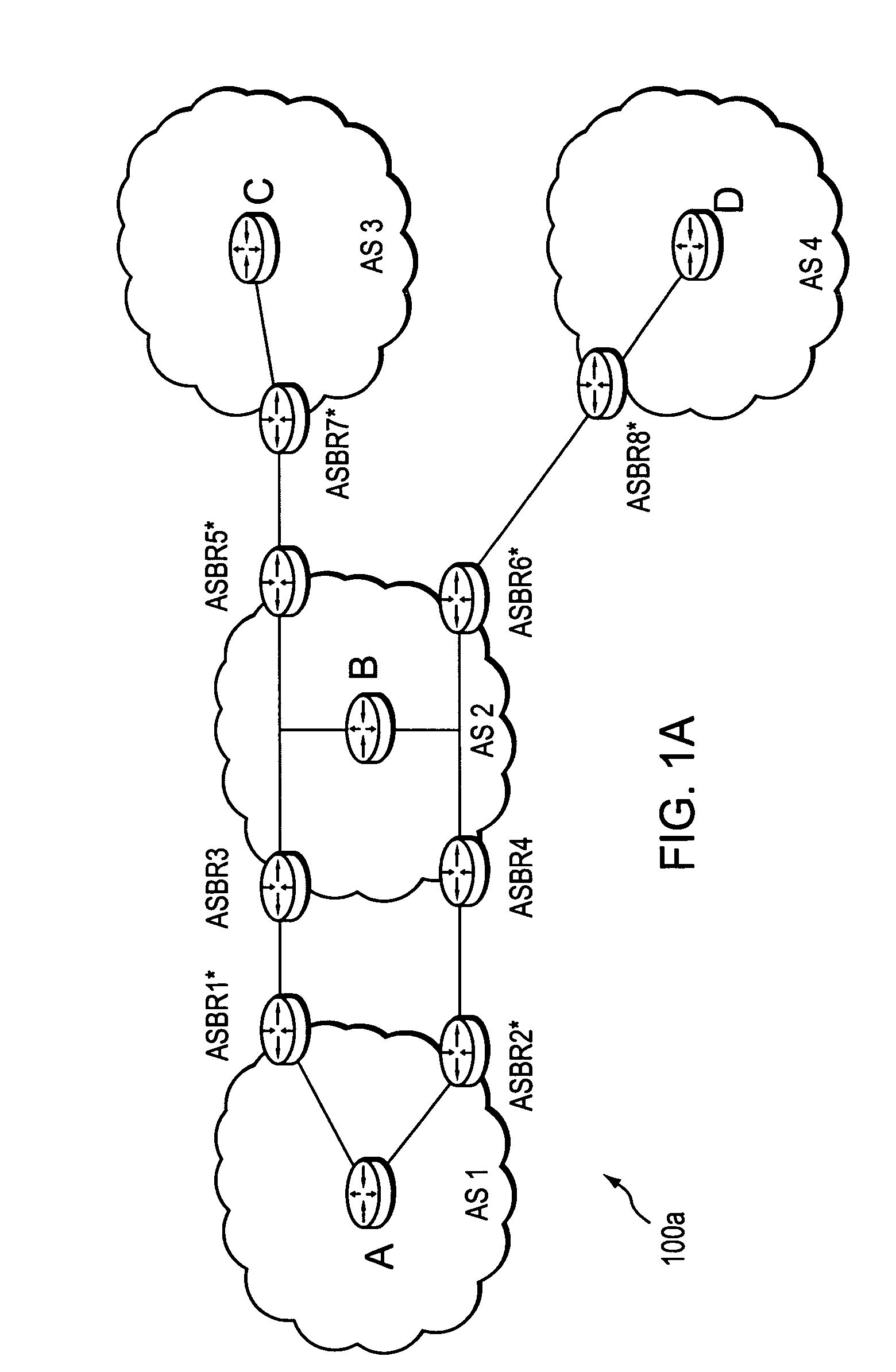
Computation of a shortest inter-domain TE-LSP across a set of autonomous systems
A technique calculates a shortest path for a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) from a head-end node in a local domain to a tail-end node of a remote domain in a computer network. The novel path calculation technique determines a set of different remote domains through which the TE-LSP may traverse to reach the tail-end node (e.g., along “domain routes”). Once the set of possible routes is determined, the head-end node sends a path computation request to one or more path computation elements (PCEs) of its local domain requesting a computed path for each domain route. Upon receiving path responses for each possible domain route, the head-end node selects the optimal (shortest) path, and establishes the TE-LSP accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Inter-domain path computation technique
ActiveUS20060171320A1Computationally efficientOptimization pathError preventionTransmission systemsPath computation elementLabel switching
A technique computes a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) that spans multiple domains of a computer network from a head-end node of a local domain to a tail-end node of a remote domain. The novel inter-domain TE-LSP computation technique comprises a computation algorithm executed by the head-end node, which utilizes Path Computation Elements (PCEs) located within the remote domains (i.e., other than the local domain). Specifically, the head-end node requests path segments from a PCE in each of the remote domains, in which the path segments represent paths between all entry border routers to either all exit border routers of the particular remote domain (i.e., through the domain), or to the tail-end node. Upon receiving path segments from each remote domain, the head-end node combines the path segments with local domain information, and performs a forward path computation from the head-end node to the tail-end node to find the best (i.e., “shortest”) path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
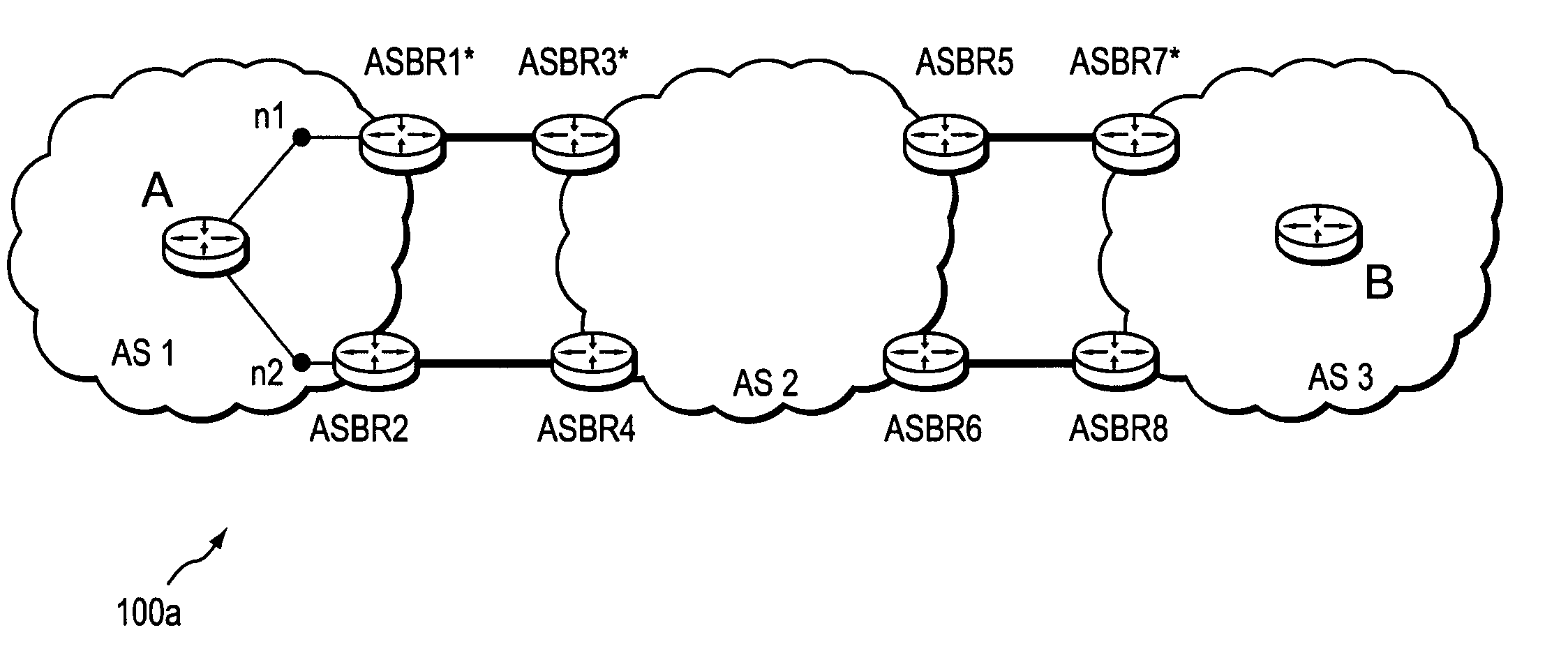
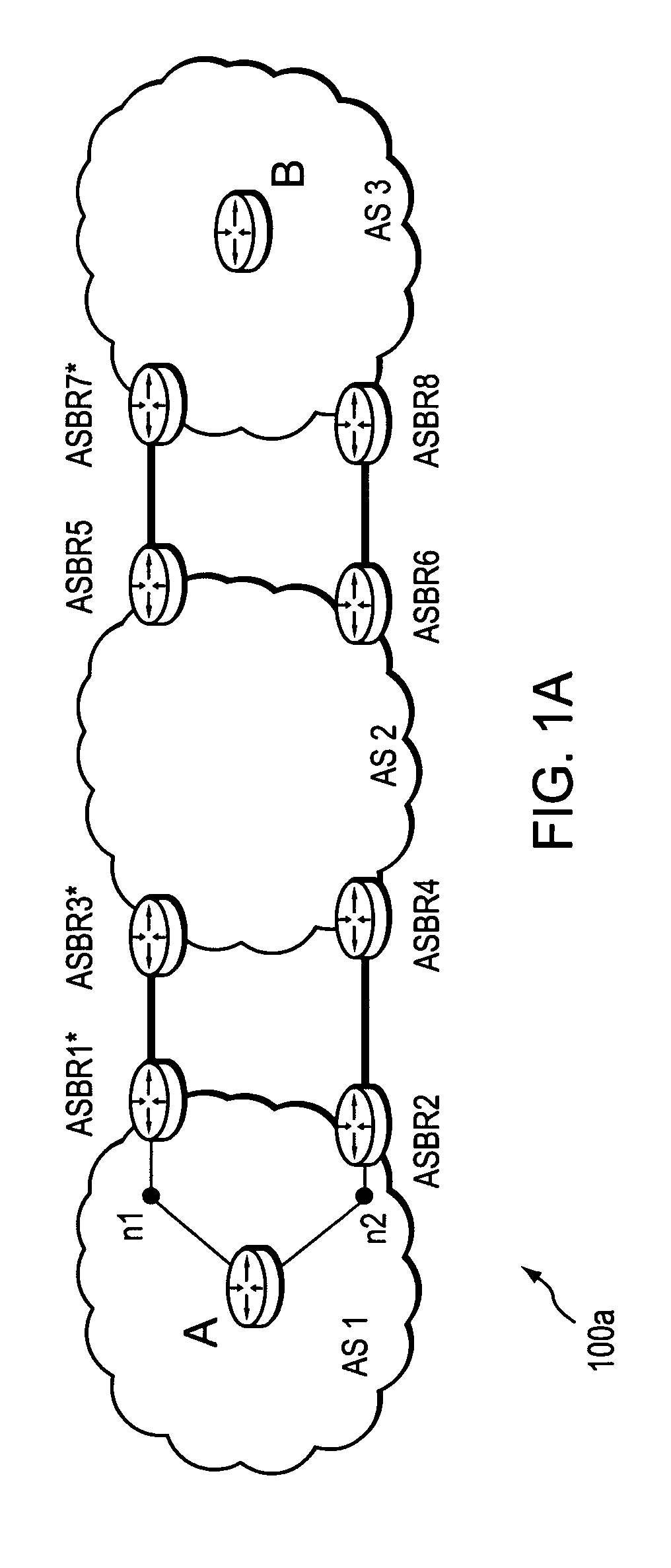
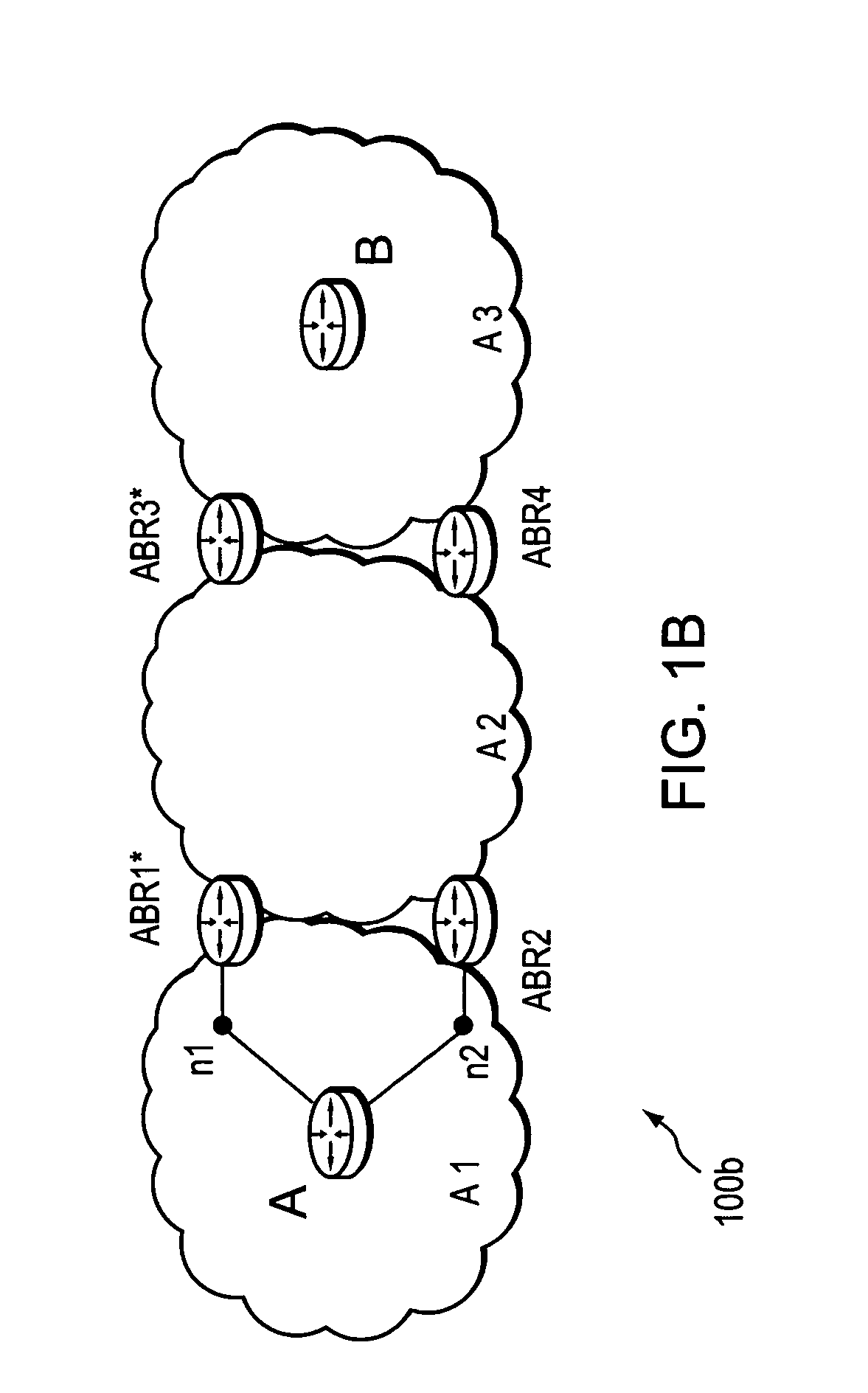
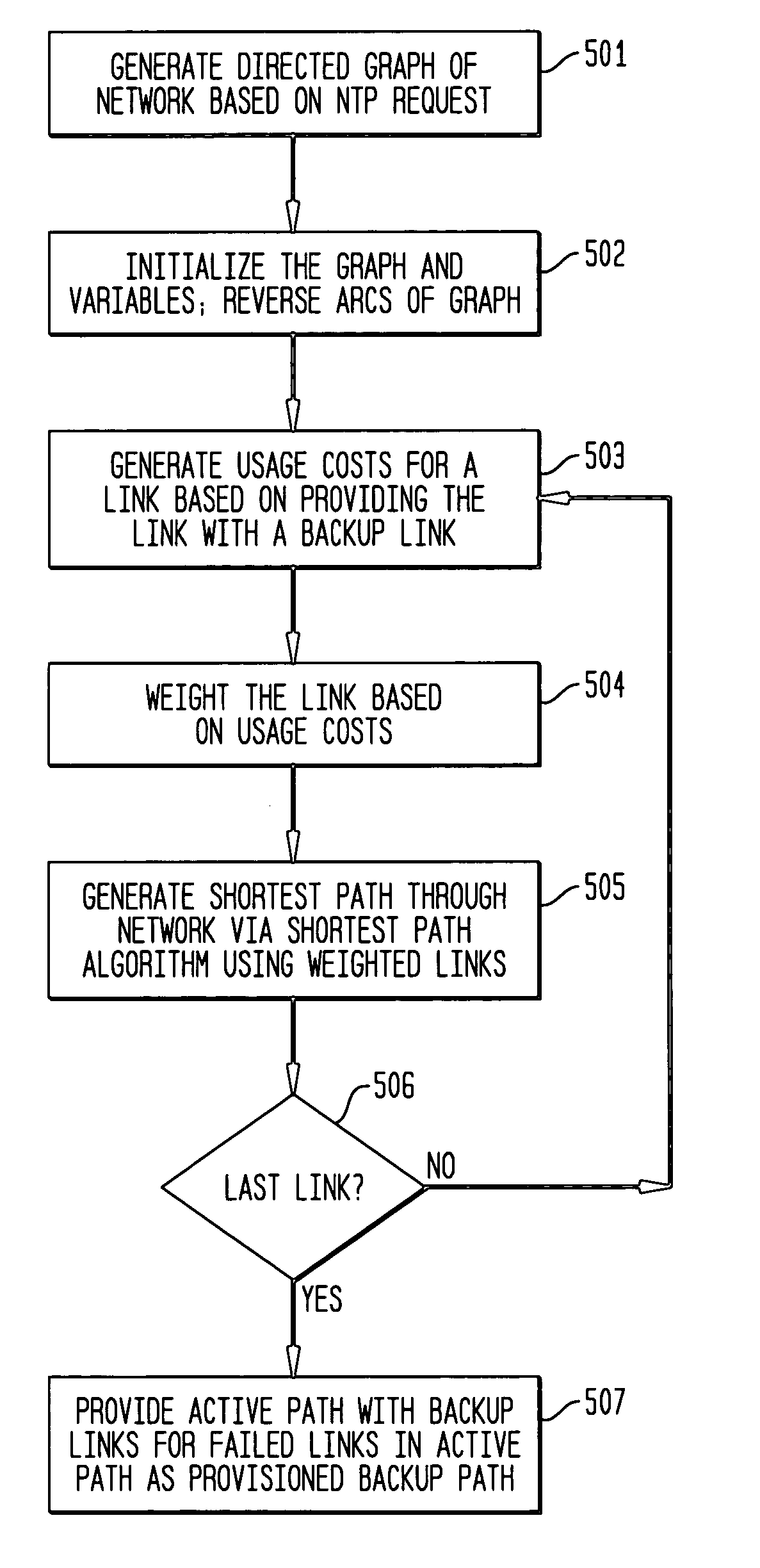
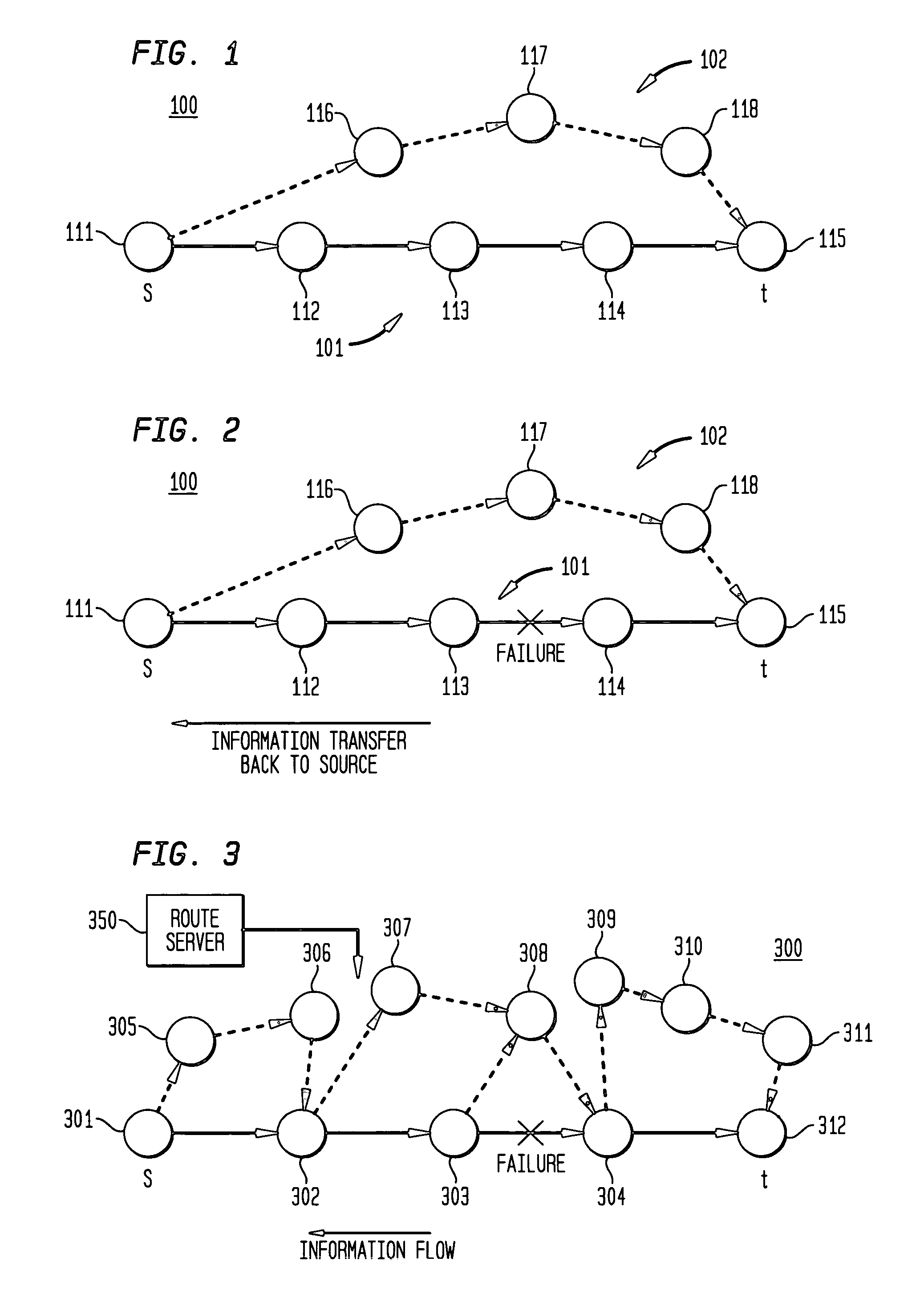
Dynamic backup routing of network tunnel paths for local restoration in a packet network
A packet network of interconnected nodes employing dynamic backup routing of a Network Tunnel Path (NTP) allocates an active and backup path to the NTP based upon detection of a network failure. Dynamic backup routing employs local restoration to determine the allocation of, and, in operation, to switch between, a primary / active path and a secondary / backup path. Switching from the active path is based on a backup path determined with iterative shortest-path computations with link weights assigned based on the cost of using a link to backup a given link. Costs may be assigned based on single-link failure or single element (node or link) failure. Link weights are derived by assigning usage costs to links for inclusion in a backup path, and minimizing the costs with respect to a predefined criterion.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
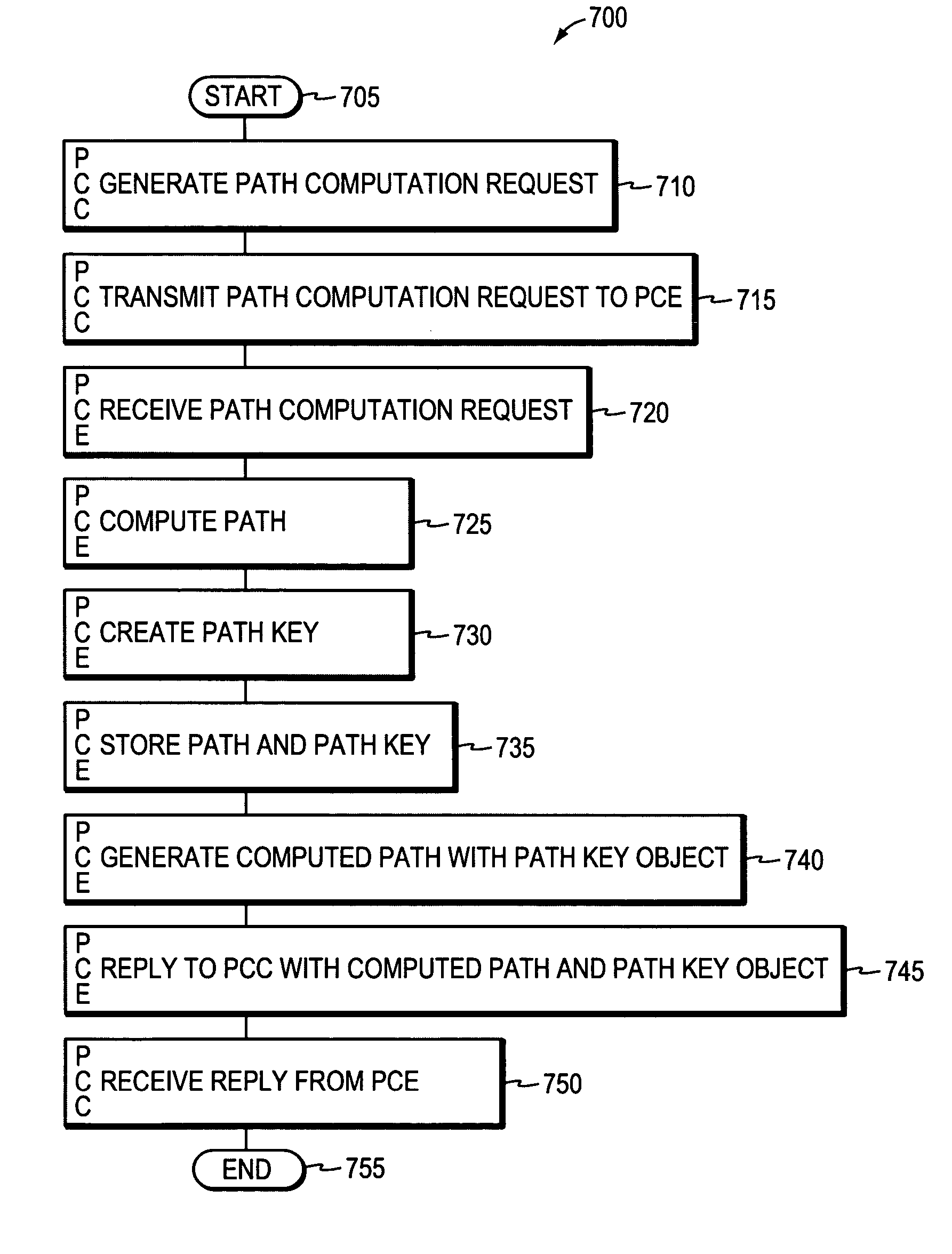
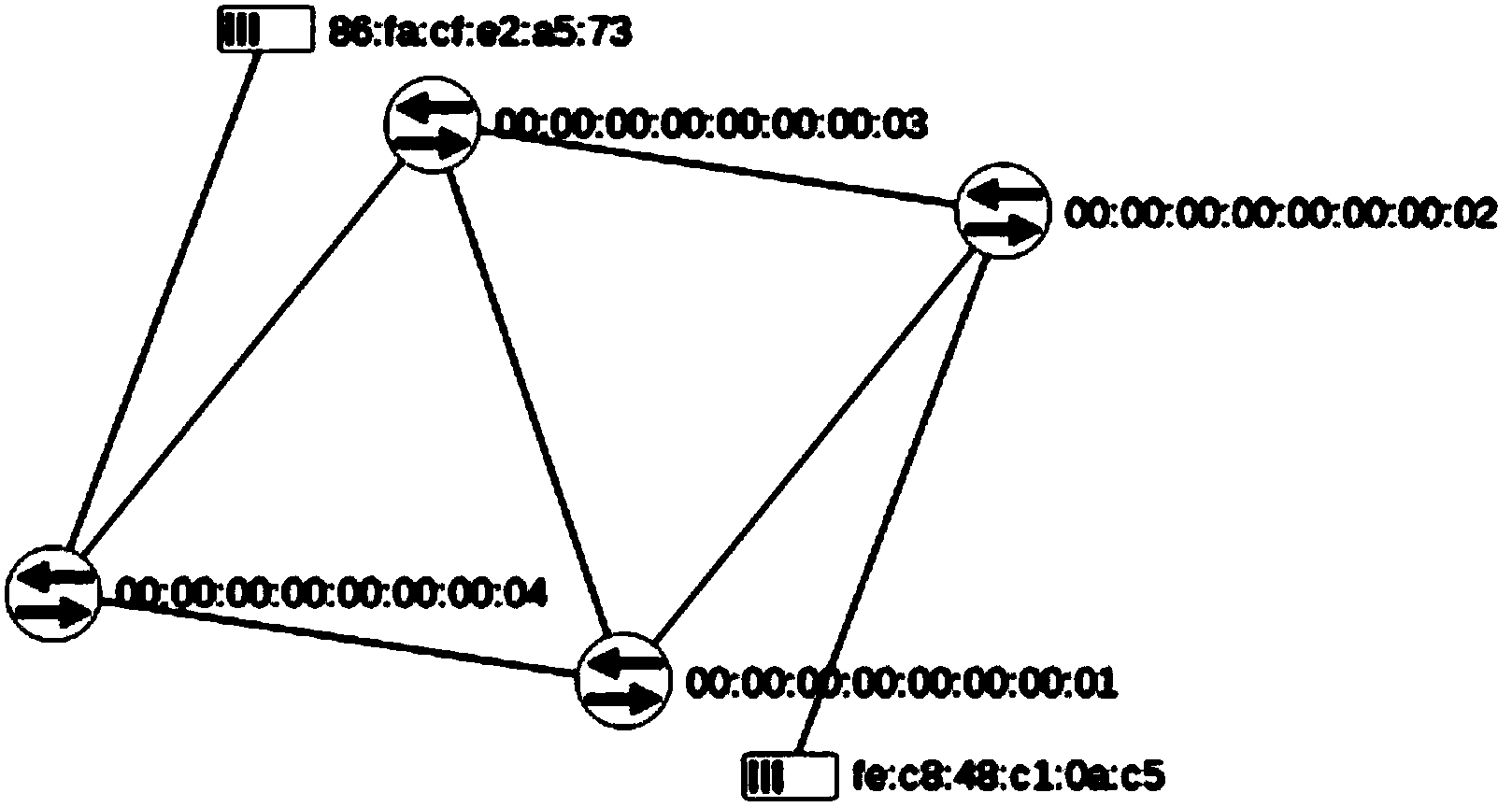
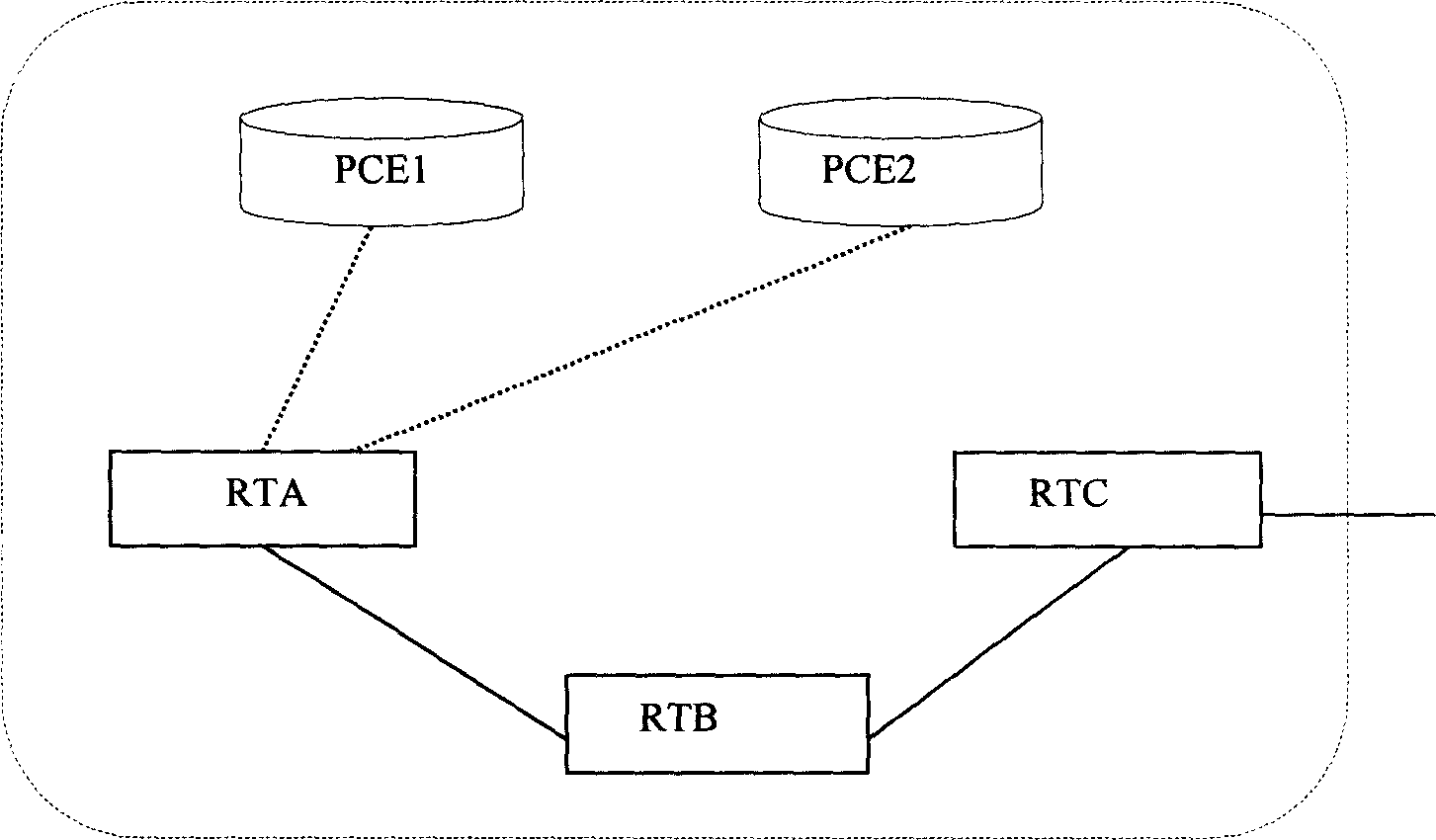
System and method for retrieving computed paths from a path computation element using a path key
ActiveUS20060098657A1Computationally efficientPreserving confidentialityError preventionTransmission systemsTime segmentPath computation element
A technique retrieves computed path segments across one or more domains of a computer network in accordance with a stateful (“semi-stateful”) path computation element (PCE) model. The stateful PCE model includes a data structure configured to store one or more path segments computed by a PCE in response to a path computation request issued by a Path Computation Client (PCC). Notably, each computed path segment stored in the data structure is identified by an associated path-key value (“path key”). The path segment and path key contents of the data structure are temporarily saved (“cached”) at a predetermined location in the network for a configurable period of time.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
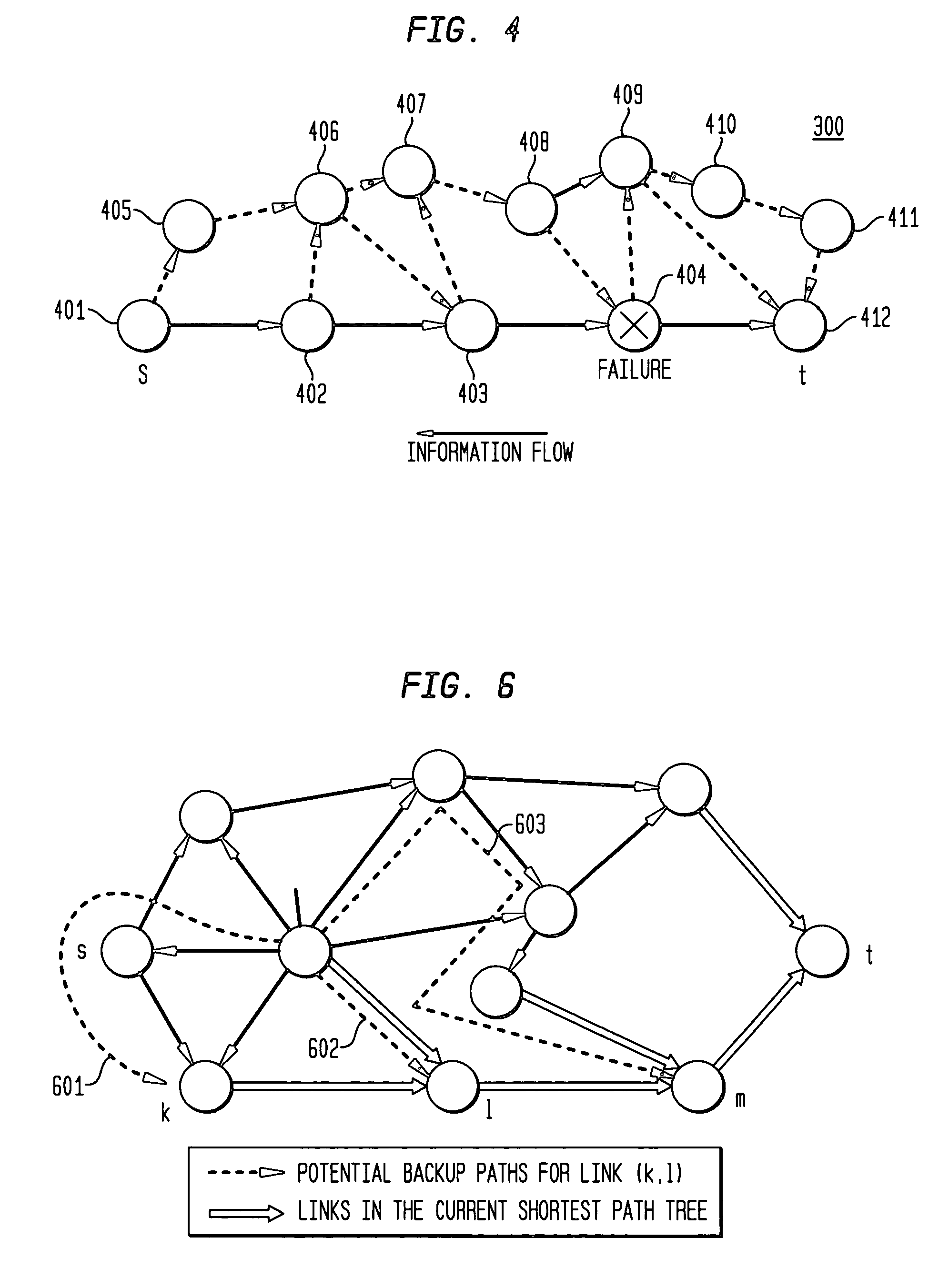
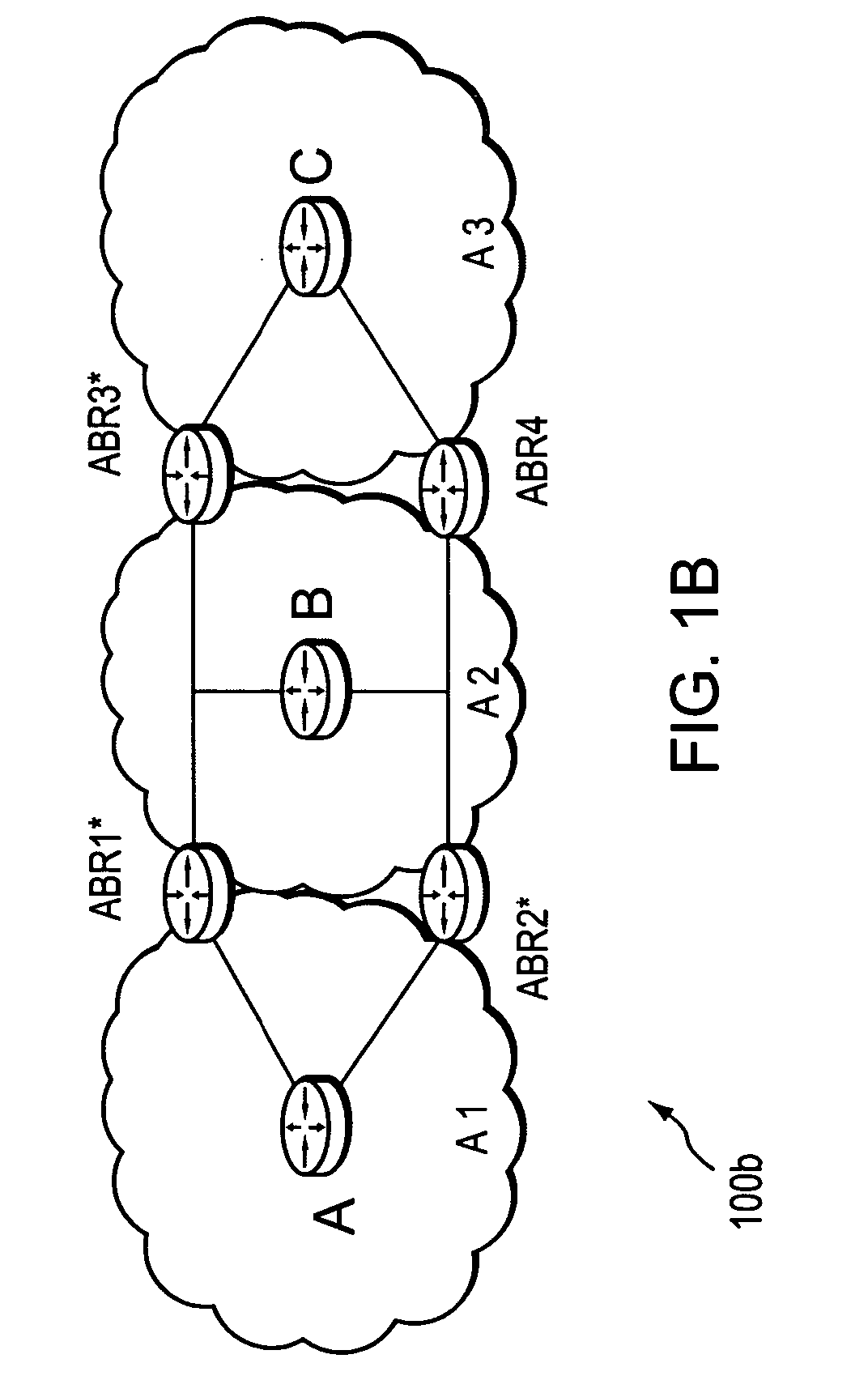
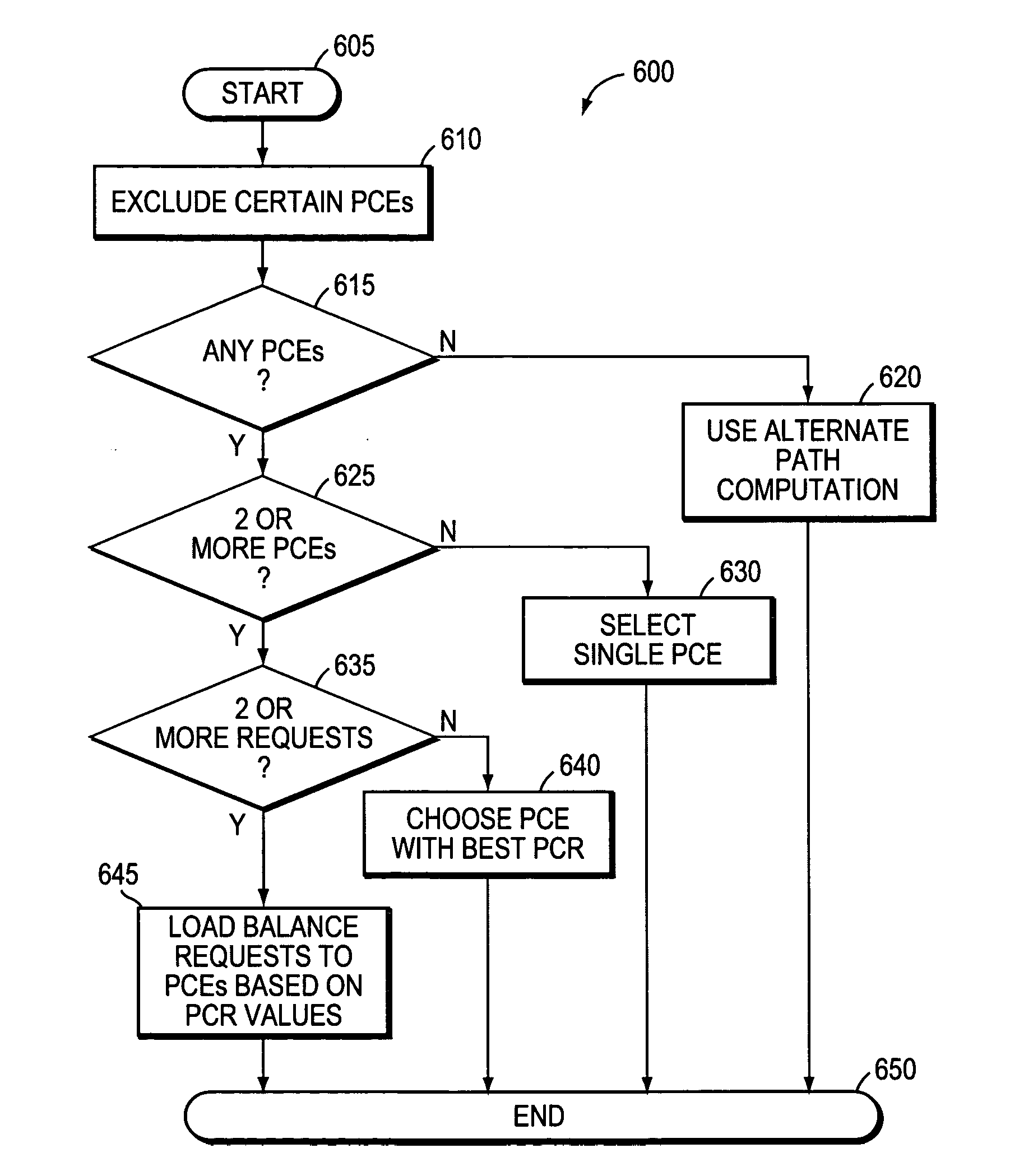
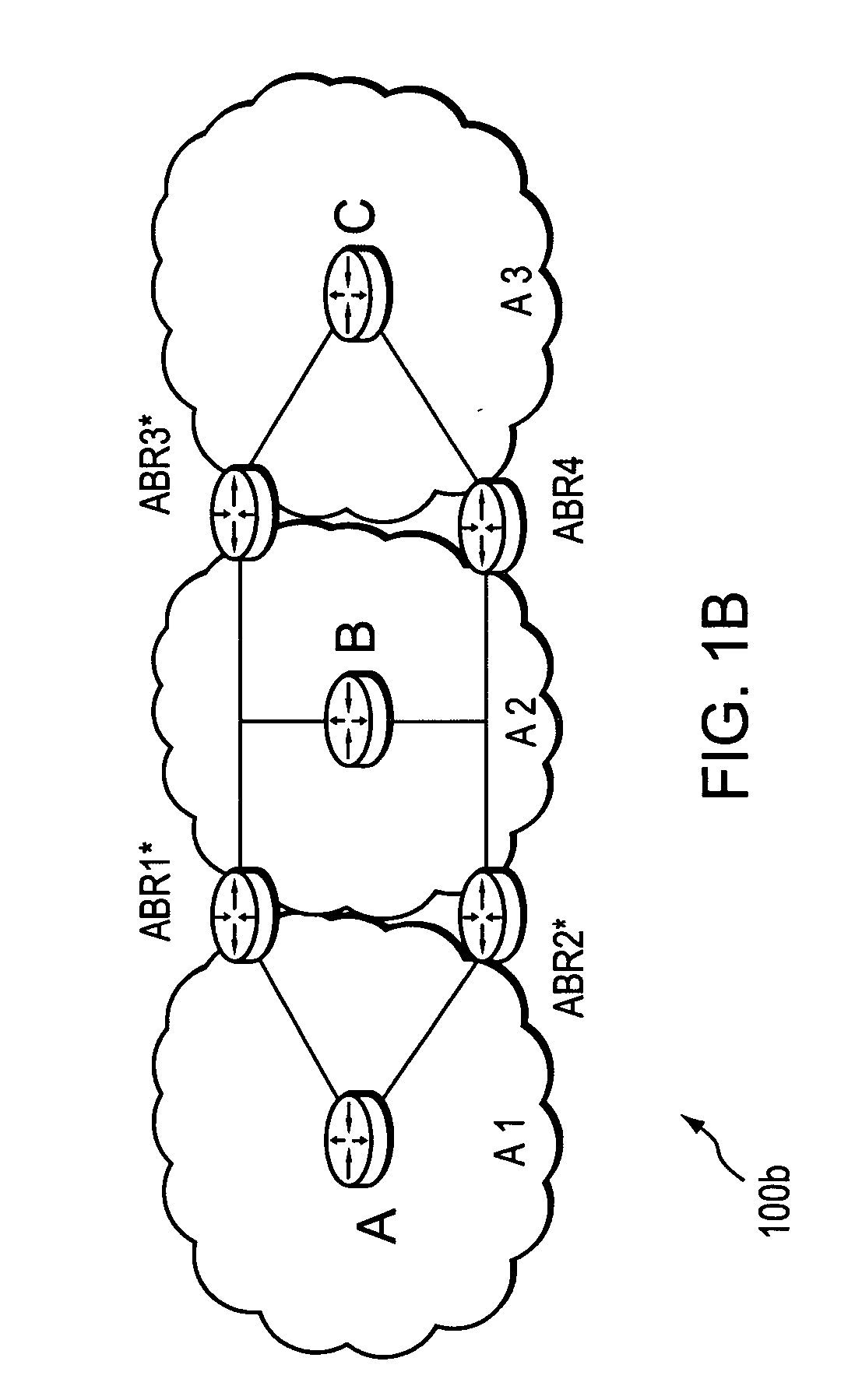
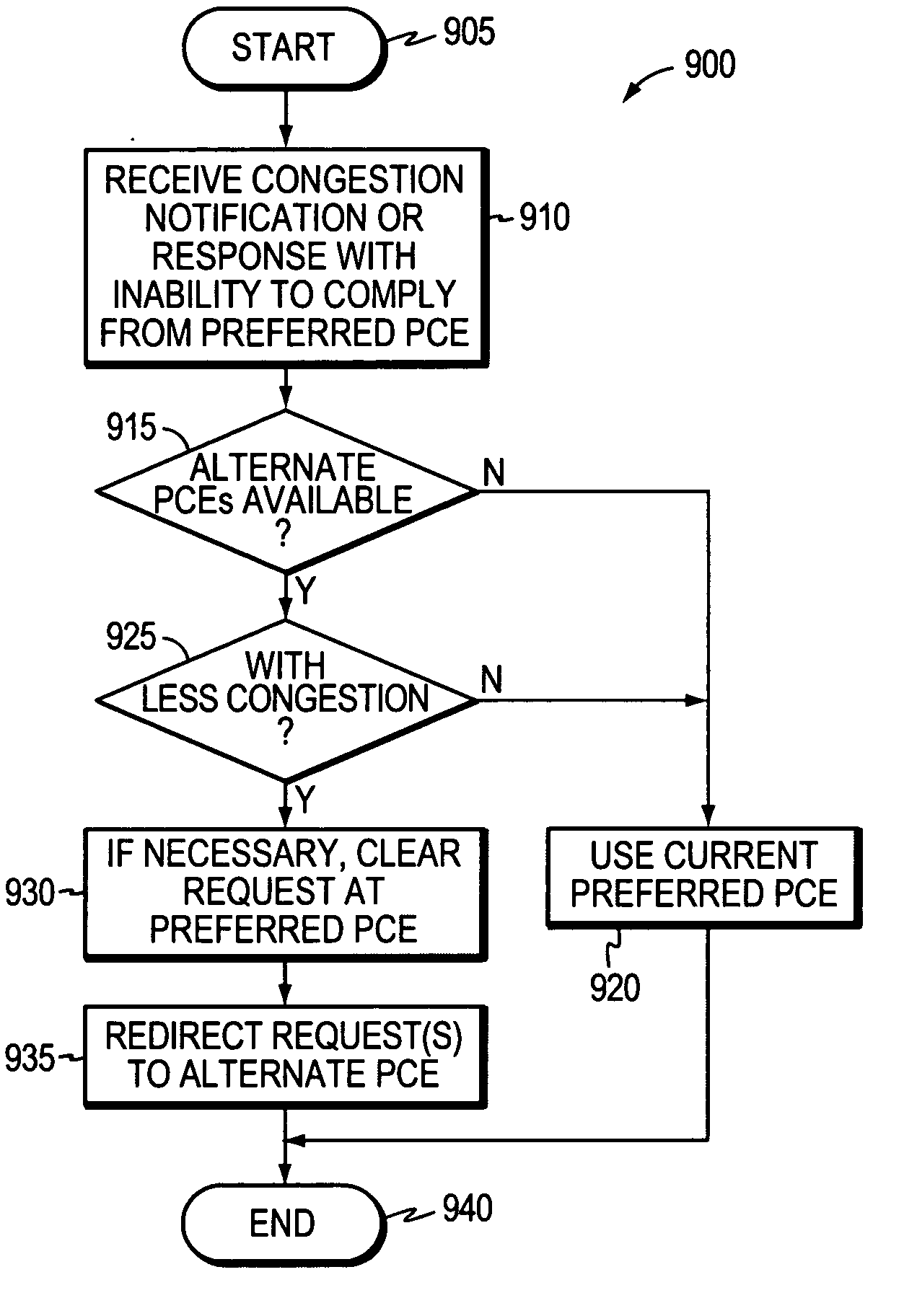
Technique for selecting a path computation element
ActiveUS20060101142A1Valid choiceEfficient load balancingDigital computer detailsTransmissionLow-pass filterPath computation element
A technique efficiently selects a Path Computation Element (PCE) to compute a path between nodes of a computer network. The PCE selection technique is illustratively based on dynamic advertisements of the PCE's available path computation resources, using (i) a low-pass filter algorithm to compute such resources, and (ii) threshold determinations to control distribution of those advertisements. To that end, the novel technique enables one or more PCEs to dynamically send (advertise) their available path computation resources to a Path Computation Client (PCC) by way of the controlled advertisements. In addition, the technique enables the PCC to efficiently select a PCE (or set of PCEs) to service a path computation request based upon those available resources.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Technique for selecting a path computation element based on response time delay
ActiveUS20060198308A1EfficientlyReduce setup timeError preventionTransmission systemsPath computation elementReal-time computing
A technique efficiently selects a path computation element (PCE) to compute a path between nodes of a computer network. The PCE selection technique is illustratively based on dynamic advertisements of the PCE's available path computation resources, namely a predictive response time (PRT). To that end, the novel technique enables one or more PCEs to dynamically send (advertise) their available path computation resources to one or more path computation clients (PCCs). In addition, the technique enables the PCC to efficiently select a PCE (or set of PCEs) to service a path computation request based upon those available resources.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Efficient constrained shortest path first optimization technique
ActiveUS20070047469A1Efficient CSPF optimization of TE-LSPsEfficient triggerData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityPath computation element
A technique performs an efficient constrained shortest path first (CSPF) optimization of Traffic Engineering (TE) Label Switched Paths (LSPs) in a computer network. The novel CSPF technique is triggered upon the detection of an event in the computer network that could create a more optimal path, such as, e.g., a new or restored network element or increased path resources. Once the novel CSPF technique is triggered, the computing node (e.g., a head-end node of the TE-LSP or a Path Computation Element, PCE) determines the set of nodes adjacent to the event, and further determines which of those adjacent nodes are within the TE-LSP (“attached nodes”). The computing node performs a CSPF computation rooted at the closest attached node to determine whether a new computed path cost is less than a current path cost (e.g., by a configurable amount), and if so, triggers optimization of the TE-LSP along the new path.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Route computation method and system, and path computation element
InactiveUS20100265943A1Efficient executionData switching by path configurationWireless communicationRouting domainPath computation element
A route computation method includes: receiving, by a first bottom-level PCE, a path computation command, performing a route computation on a routing domain managed thereby, obtaining and sending a path segment set with a first node to an upper-level PCE thereof; sending, by the upper-level PCE receiving the path segment set sent by a lower-level PCE, the path computation command to another lower-level PCE according to routing domains that a path to be established between the first node and a second node sequentially passes through, receiving path segment sets sent by all lower-level PCEs, and combining and sending all the received path segment sets to an upper-level PCE thereof, until a top-level PCE receives path segment sets sent by all lower-level PCEs thereof; and combining, by the top-level PCE, all the received path segment sets to generate a set of paths between the first node and the second node.
Owner:MASON LICENSING LLC
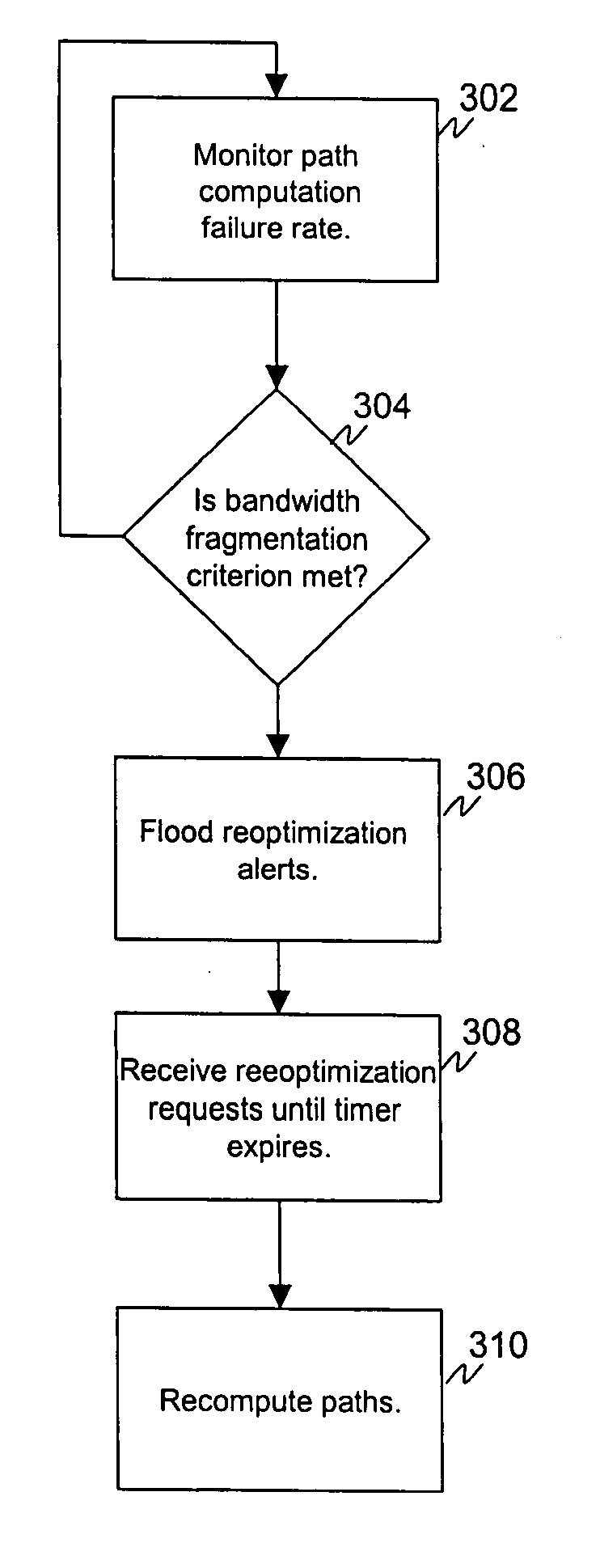
Reoptimization triggering by path computation elements
ActiveUS7031262B2Reduce fragmentationRaise the possibilityError preventionTransmission systemsBandwidth constraintTraffic capacity
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
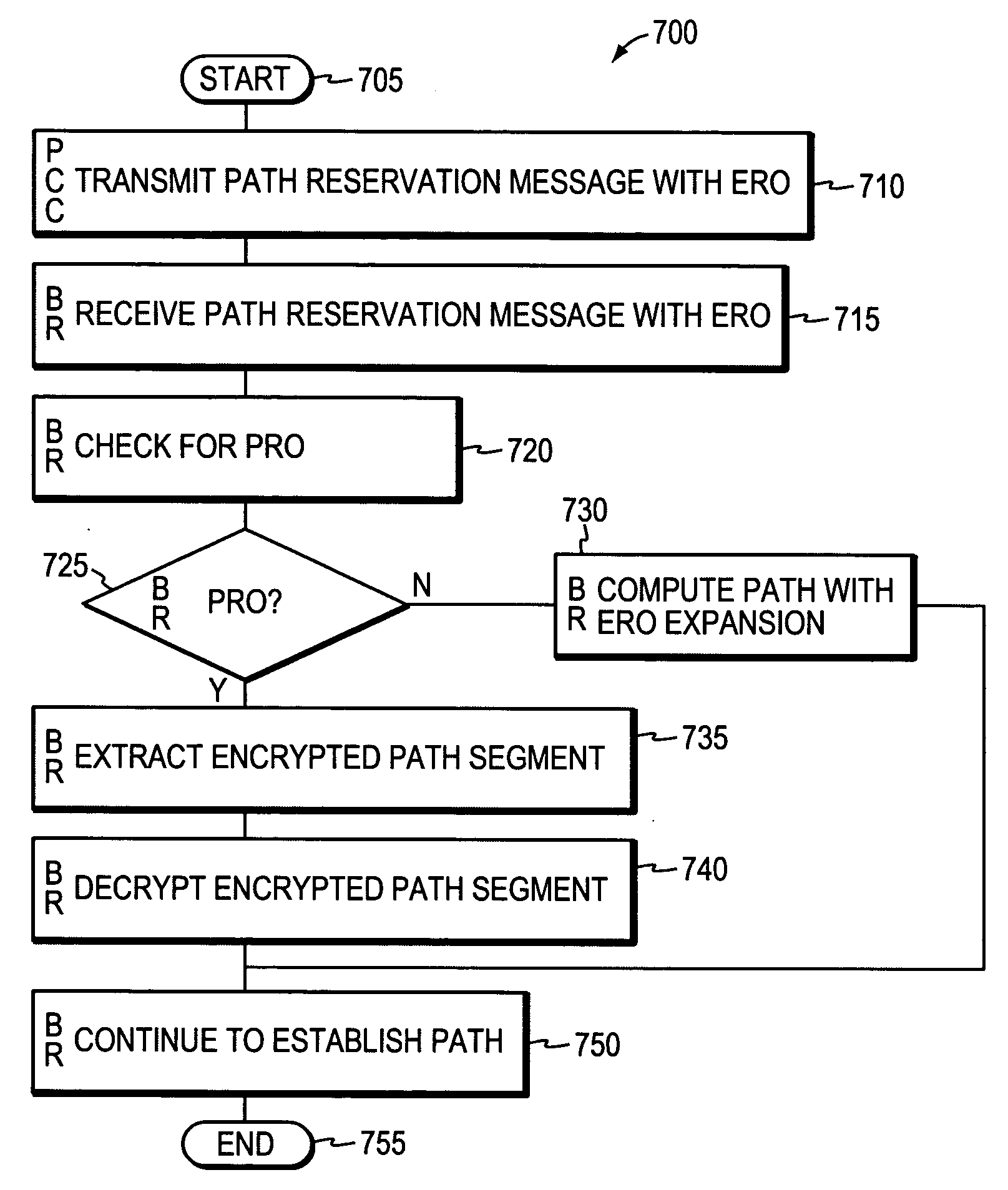
System and method for retrieving computed paths from a path computation element using encrypted objects
InactiveUS20060098587A1Computationally efficientPreserving confidentialityError preventionTransmission systemsConfidentialityPath computation element
A technique retrieves computed path segments across one or more domains of a computer network in accordance with a stateless Path Computation Element (PCE) model. The stateless PCE model includes one or more PCEs configured to compute one or more path segments through the domains in response to a path computation request issued by, e.g., a Path Computation Client (PCC). Notably, each computed path segment is encrypted as a data structure to preserve confidentiality across the domains. Each PCE then cooperates to return a path computation response, including the encrypted path segments and an explicit route object (ERO) containing compressed path descriptions of the computed path segments, to the PCC.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Reoptimization triggering by path computation elements
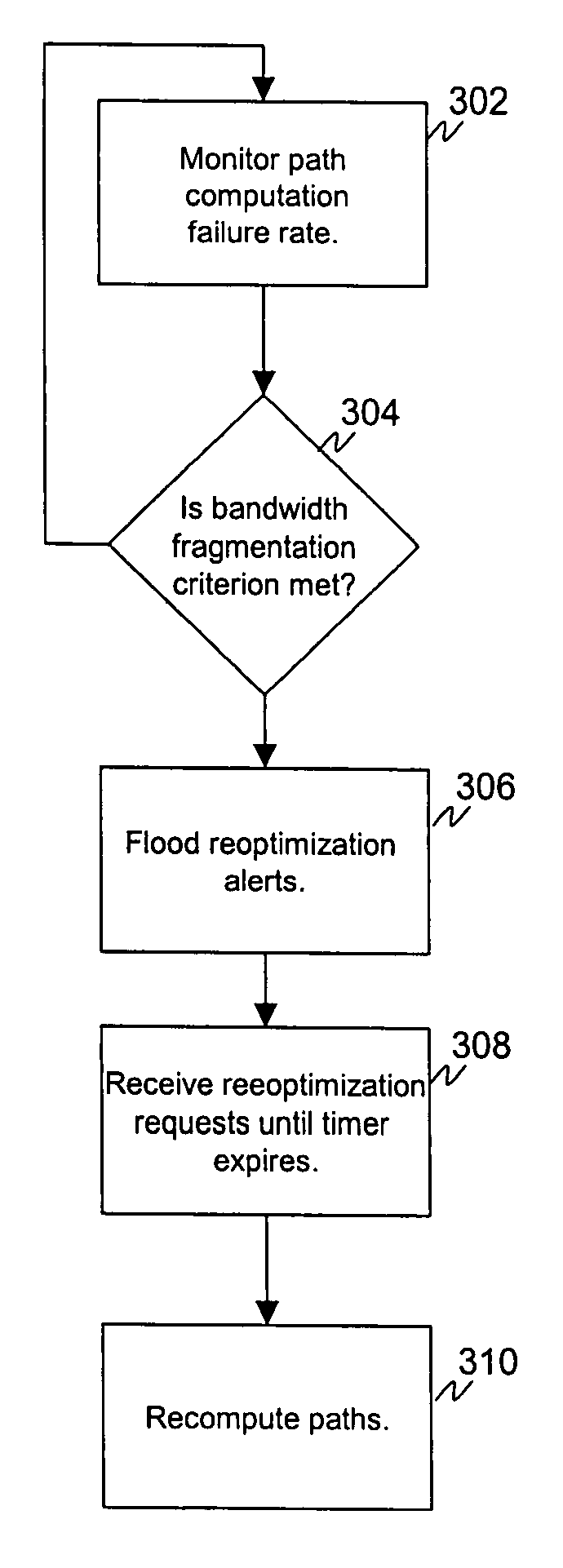
ActiveUS20050259664A1Alleviate bandwidth fragmentationReduce fragmentationError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityBandwidth constraint
A mechanism to alleviate bandwidth fragmentation in a network employing path computation element(s) to place MPLS Traffic Engineering tunnels. One application is a multiple Autonomous System or multiple area network employing distributed computation of MPLS Traffic Engineering LSPs. A particular path computation element may determine that bandwidth fragmentation is present based on monitoring of path computation failures where desired paths are blocked due to bandwidth constraints. In response to the detected bandwidth fragmentation condition, the path computation element floods a routing notification within its Autonomous System or area. Nodes respond to the routing notification by requesting reoptimization of their own previously requested Traffic Engineering LSPs allowing the path computation element an opportunity to alleviate bandwidth fragmentation.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Dynamic enforcement of MPLS-TE inter-domain policy and QoS
InactiveUS20070019558A1Efficient mechanismError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of servicePolicy decision
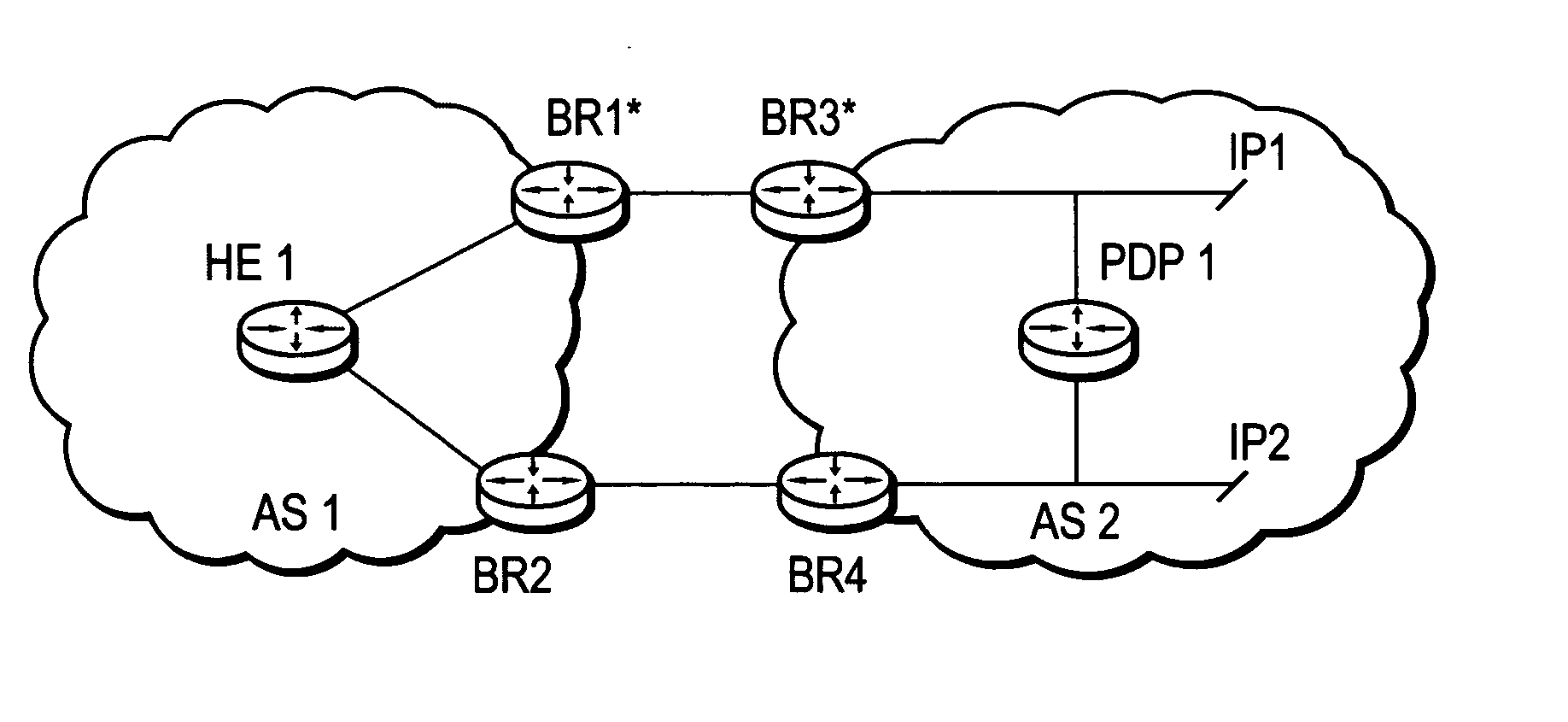
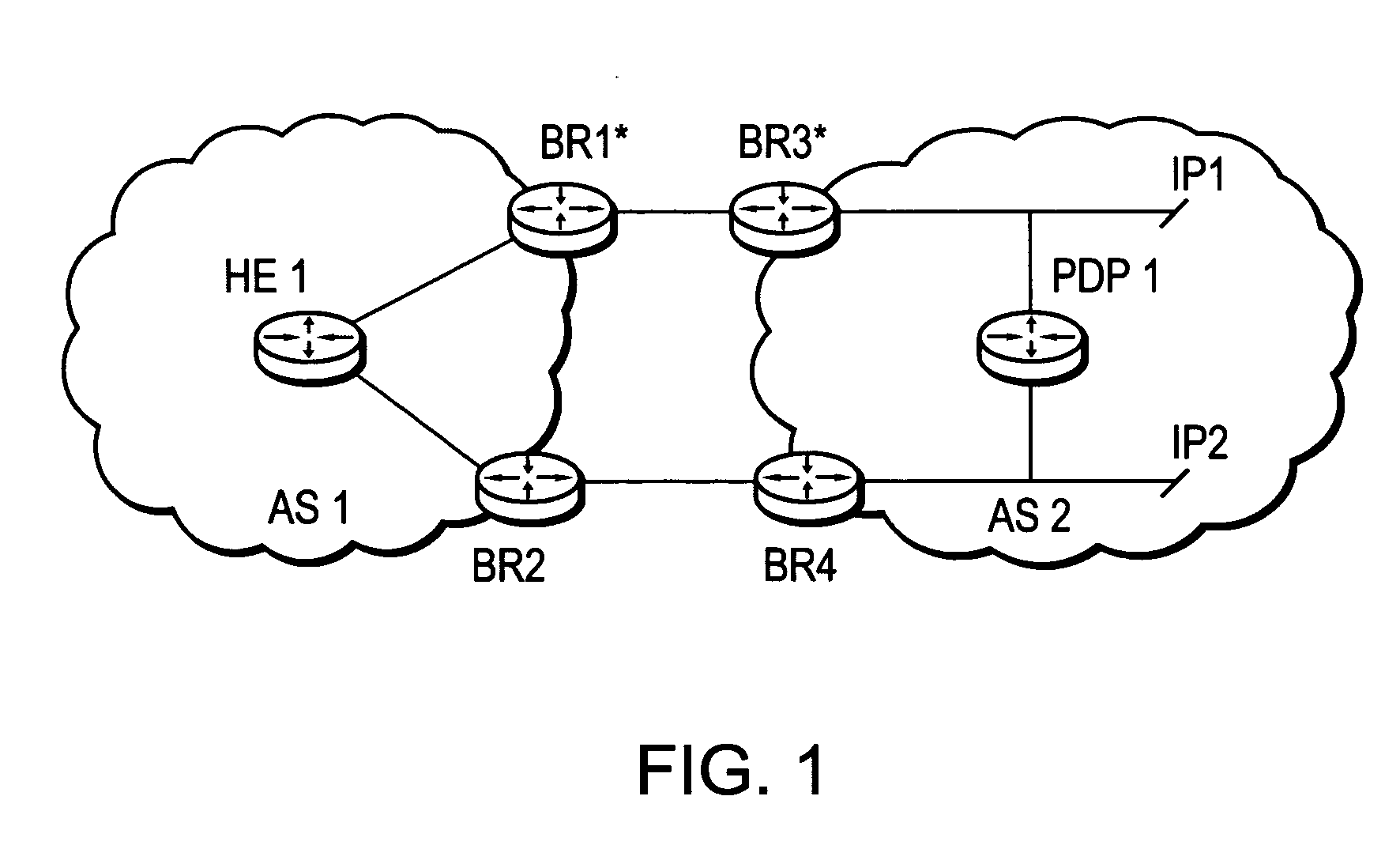
A technique dynamically enforces inter-domain policy and quality of service (QoS) for Traffic Engineering (TE) Label Switched Paths (LSPs) between a local domain and a remote domain in a computer network. According to the enforcement technique, a Path Computation Element (PCE) of the local domain receives a path computation request for an inter-domain TE-LSP from the remote domain, and triggers a policy verification procedure at a Policy Decision Point (PDP) of the local domain. The PDP determines whether the requested TE-LSP is allowed based on configured policy for the remote domain and previously established TE-LSPs from the remote domain. In the event the requested TE-LSP is allowed and subsequently established, a Policy Enforcement Point (PEP) along the TE-LSP, e.g., a border router of the local domain or a dedicated server, updates the PDP with the state of the TE-LSP. In response to the update, the PDP returns a QoS template indicating configured QoS guidelines the PEP must enforce for that TE-LSP. If the TE-LSP is eventually torn down, the PEP again updates the PDP with the state of the TE-LSP.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Virtual connection route selection apparatus and techniques
ActiveUS20080205271A1Error preventionTransmission systemsCommunications systemPath computation element
Virtual connection route selection apparatus and techniques are disclosed. At a communication traffic routing apparatus, metric information associated with multiple different routes for a virtual connection, such as a PseudoWire, toward a destination is collected. The metric information may be collected from one or more remote route computation elements capable of computing routes for virtual connections between the routing apparatus and other routing apparatus over an underlying communication system, or during actual establishment of the virtual connections, for example. An initial or re-optimized route for a virtual connection can then be selected at the routing apparatus based on the collected metric information. In some embodiments, although the virtual connection routes are paths computed by Path Computation Elements (PCEs), actual path selection decisions are distributed to routers.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Technique for efficiently routing IP traffic on CE-CE paths across a provider network
InactiveUS7522603B2Efficiently routedEfficient routingError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityPath computation element
A technique efficiently routes Internet Protocol (IP) traffic on paths between customer edge devices (CEs) across a provider network (“CE-CE paths”) in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a path computation element (PCE), e.g., a provider edge device (PE), may learn dynamic link attribute information of remote links from the provider network to one or more remote CEs (e.g., “PE-CE links” or “CE-PE links”). A multi-homed requesting CE requests from the PCE a set of CE-CE path metrics (e.g., costs) to one or more remote destination address prefixes, e.g., via each multi-homed CE-PE link from the requesting CE. In response to the request, the PCE computes the set of available CE-CE paths and current metrics to the remote destination address prefixes and returns the corresponding CE-CE path metrics to the requesting CE. The requesting CE modifies its IP forwarding entries accordingly in order to perform IP traffic routing corresponding to the CE-CE path metrics (e.g., asymmetrical load balancing) across its multi-homed CE-PE links.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
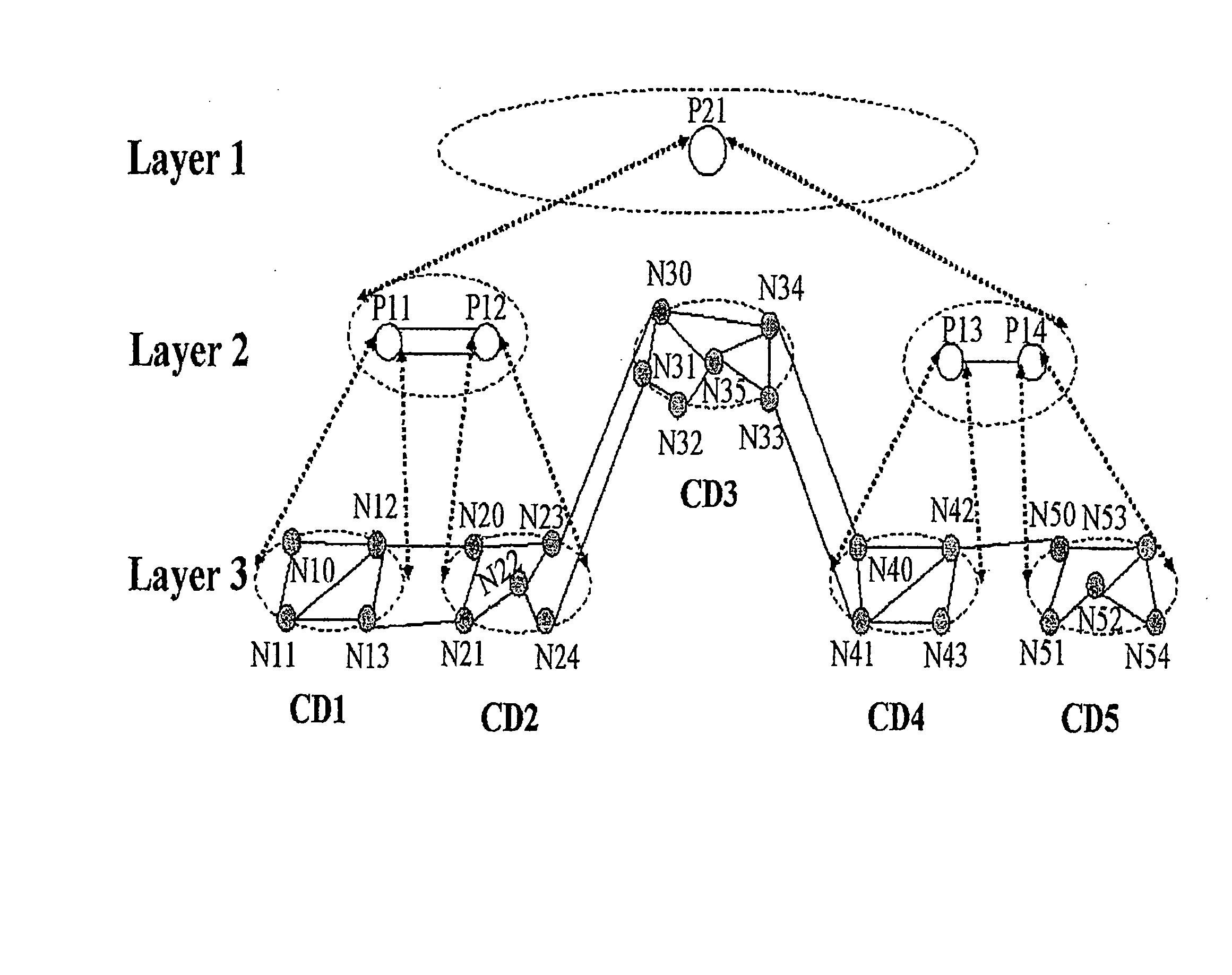
Method and system for multi-domain route computation
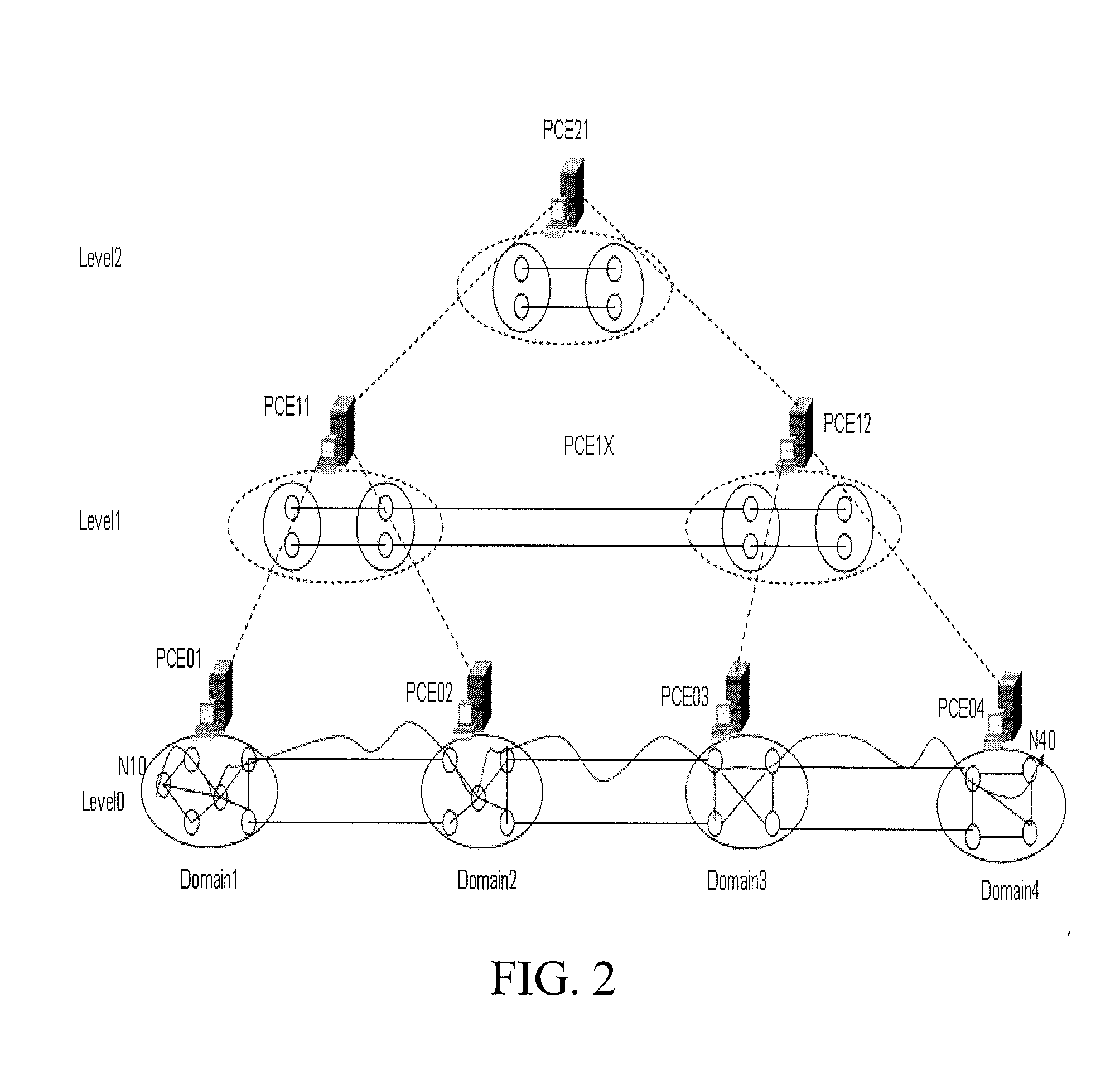
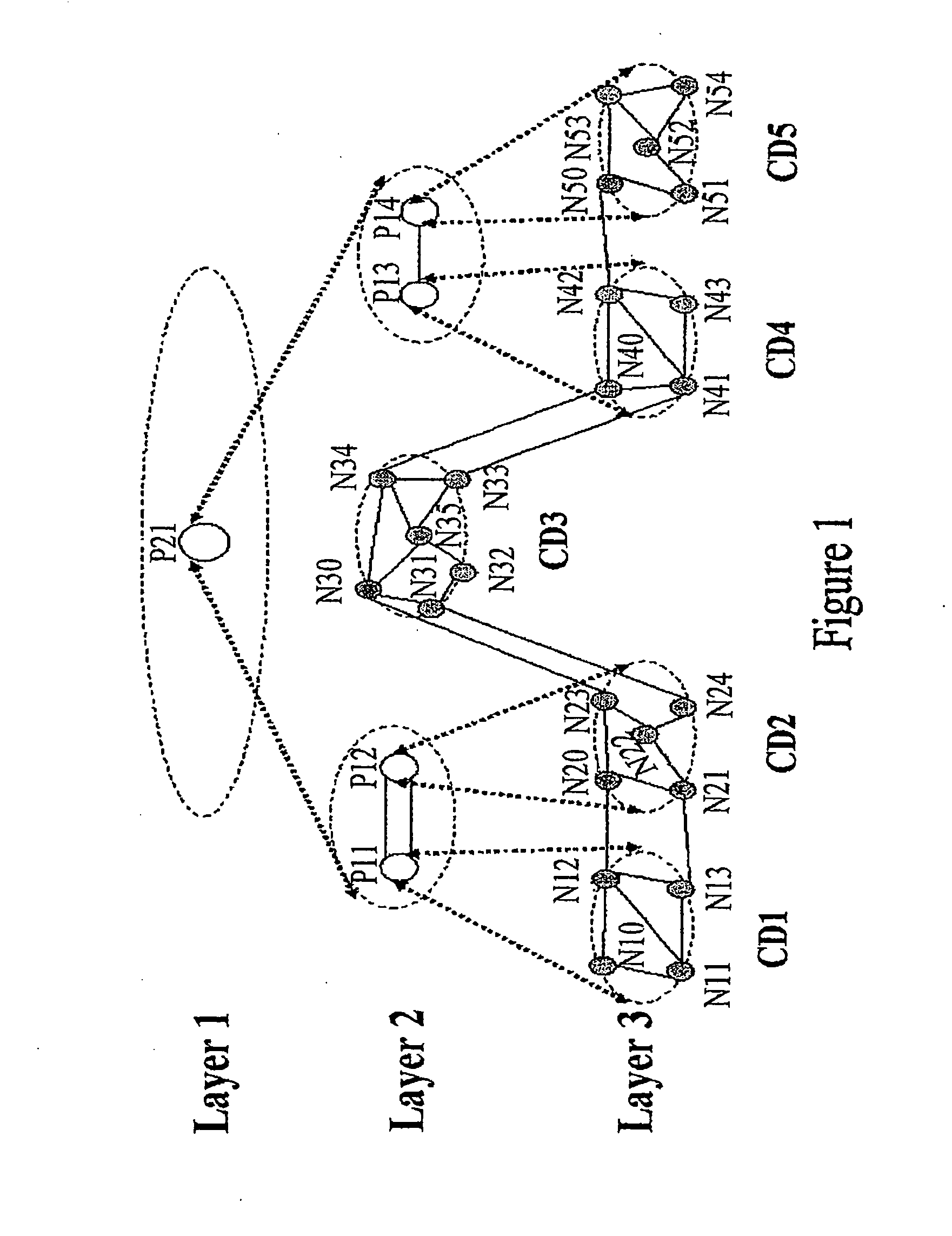
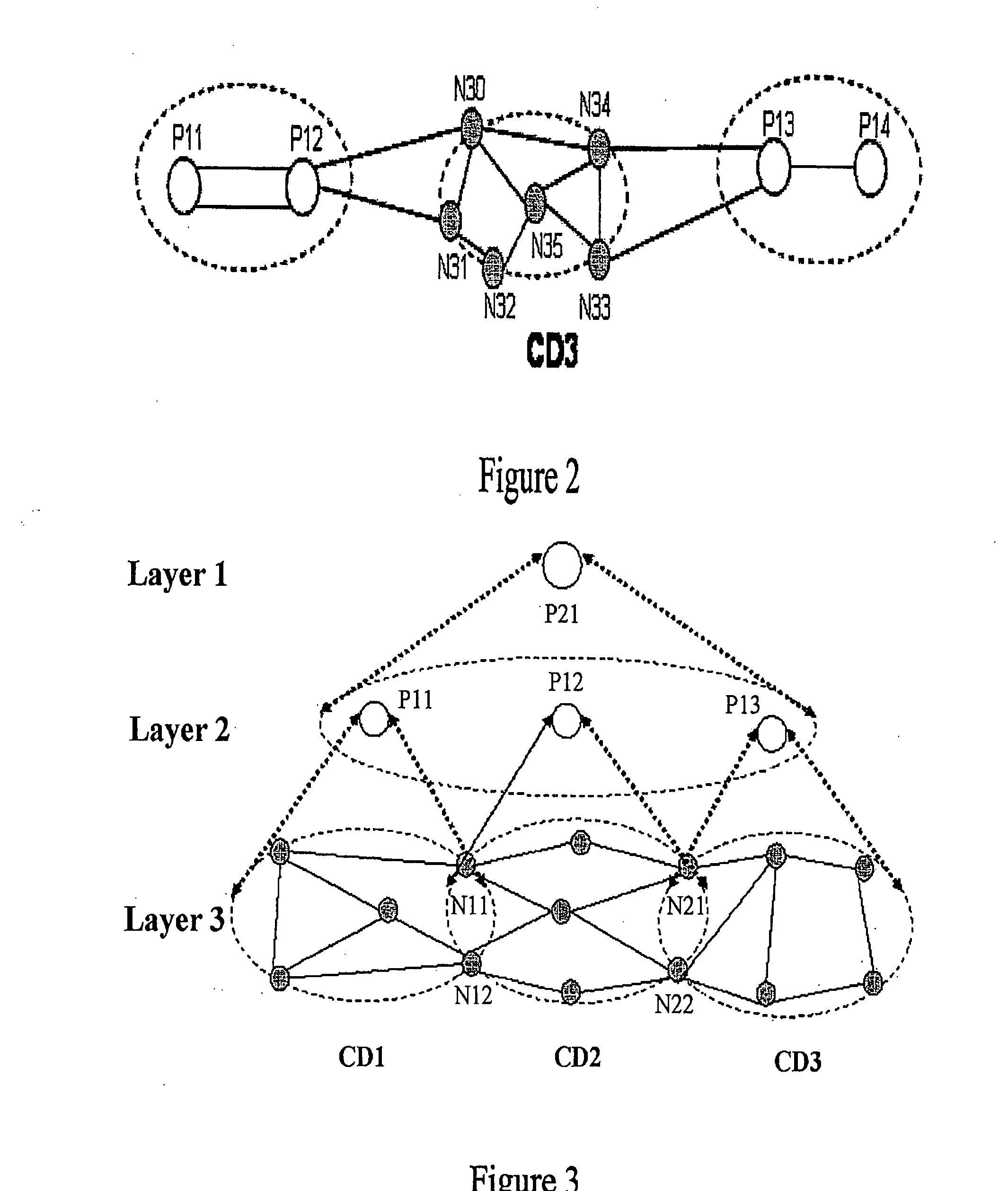
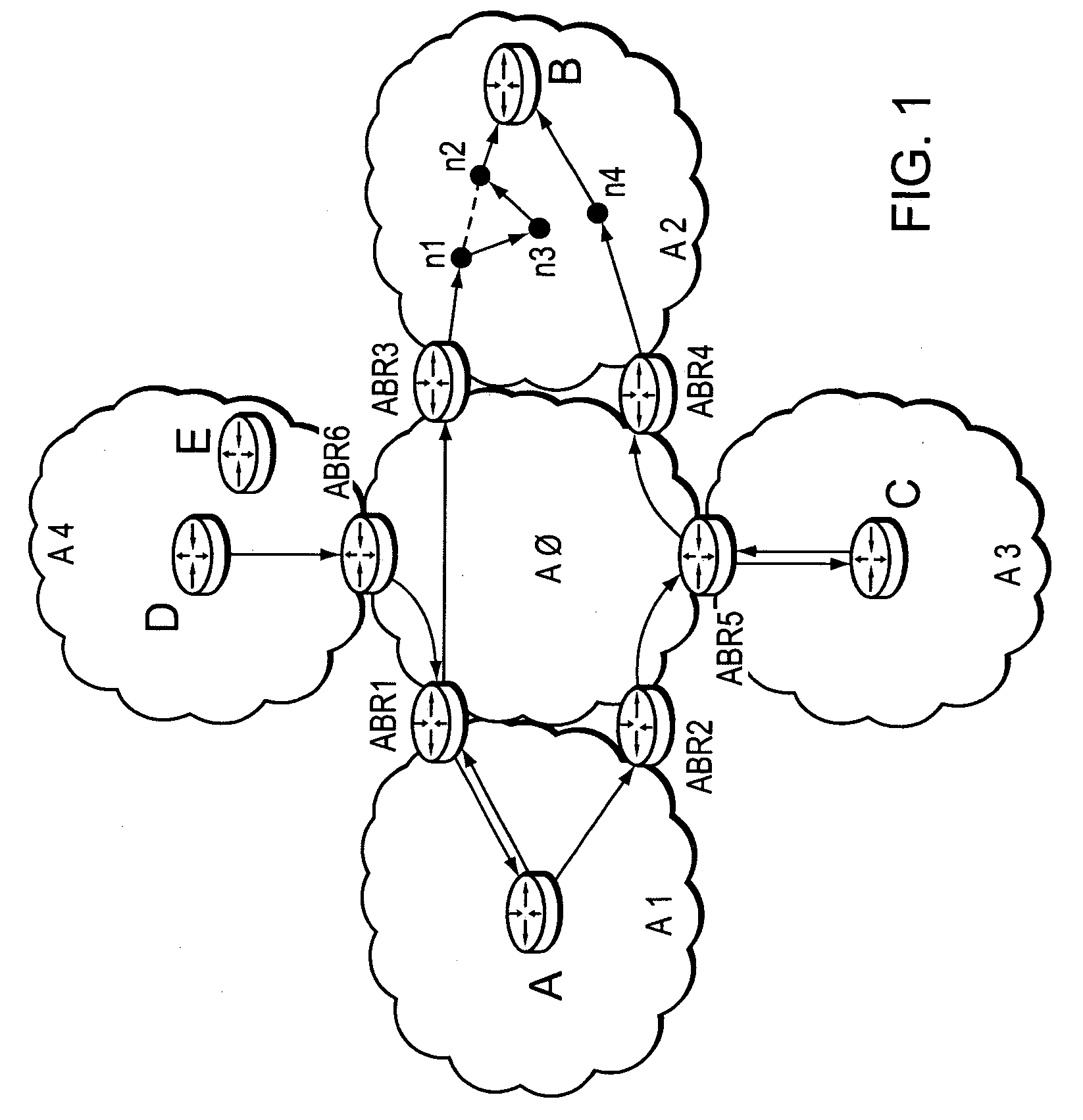
ActiveUS20080002664A1Improve efficiencyReduce riskError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPath computation elementAutomatically switched optical network
A method and system for multi-domain route computation. In the invention, Path Computation Elements (PCEs) are placed in different layers and computation domains between upper and lower layer PCEs are mapped so that a computation task is divided into multiple computation tasks layer by layer and that the multi-domain route computation is finally fulfilled. The invention separates route computation from signaling and runs route computation tasks in parallel. Route establishment is done by signaling after route computation. The present invention may realize route computation based on complex Traffic Engineering (TE) constraints and enable end-to-end diverse route computation. The invention places PCEs in layers, allowing good scalability and high computation efficiency. The present invention is applicable to the Automatically Switched Optical Network (ASON) and the Multi-Protocol Label Switched Network Traffic Engineering (MPLS-TE) network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Client distributed path computation method based on software defined network architecture
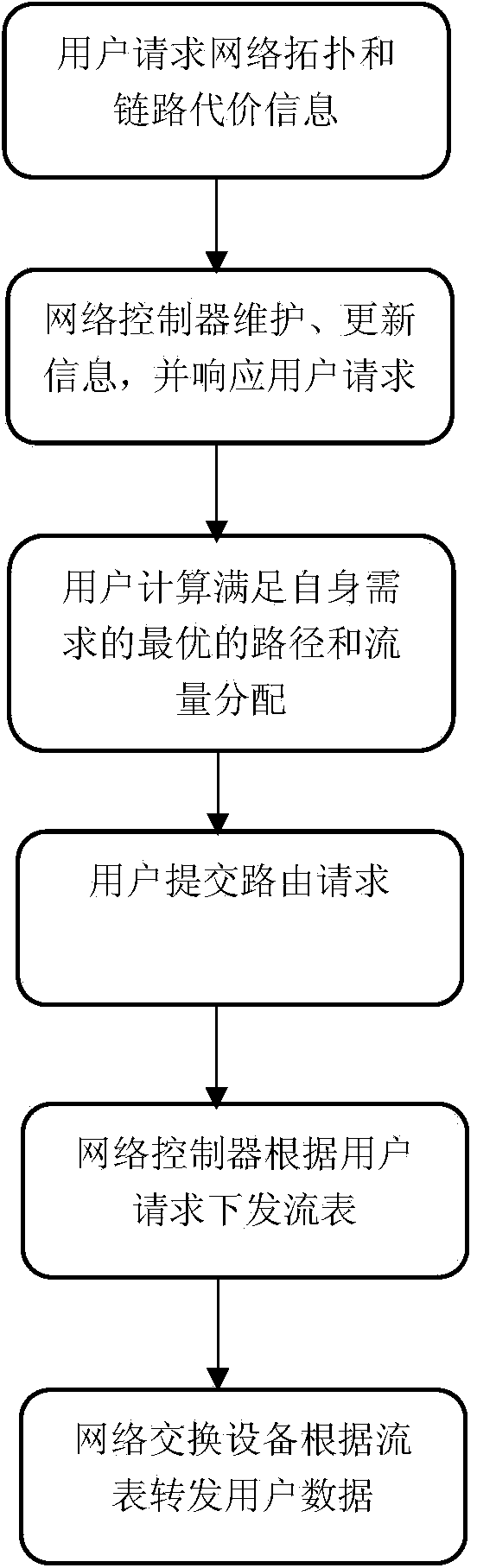
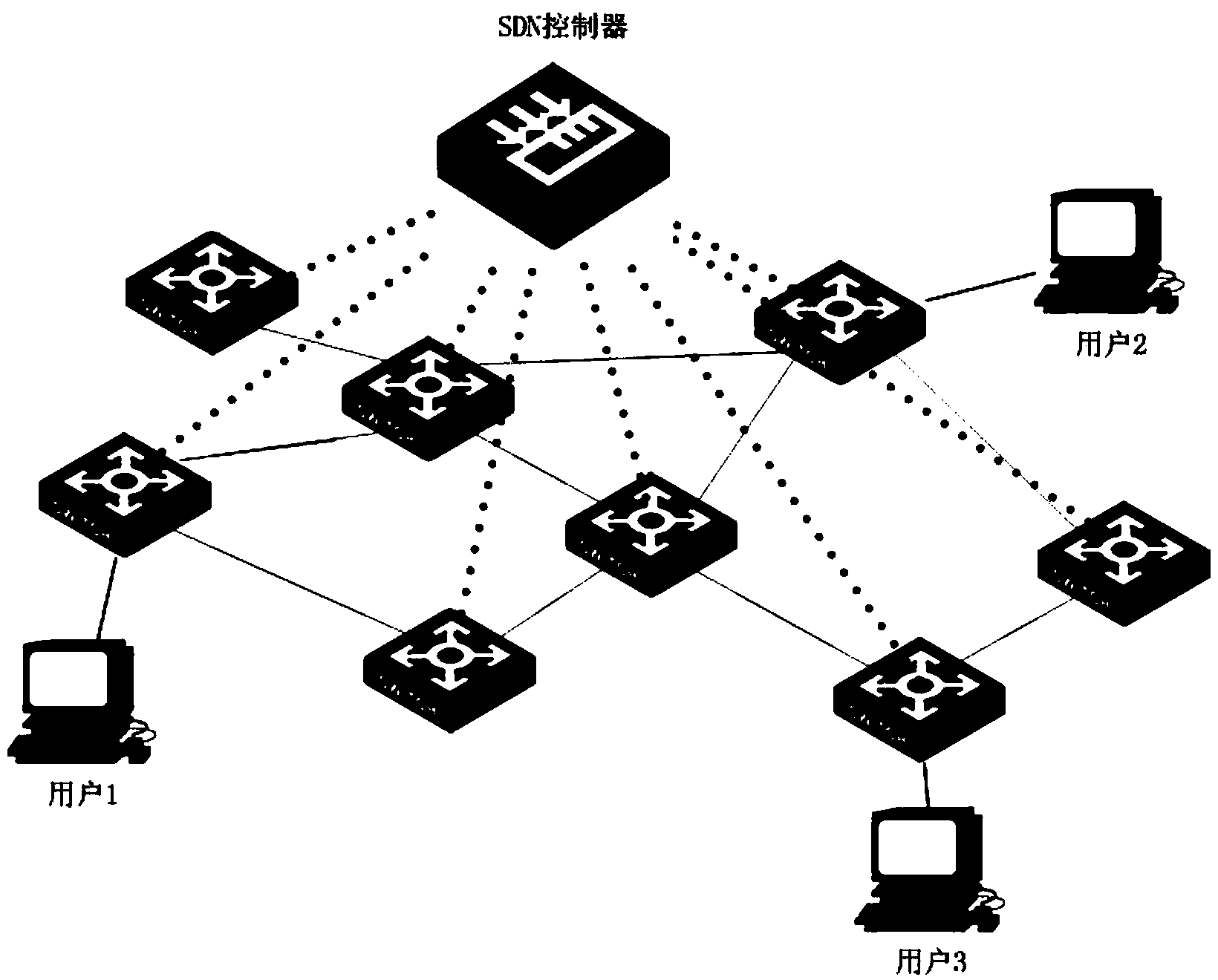
ActiveCN104253749AChange limitationsHigh transparencyData switching networksPath computation elementNetwork architecture
The invention discloses a client distributed path computation method based on a software defined network architecture. The client distributed path computation method comprises the following steps: a user obtains network topology and linkcost information from a network controller through a northbound interface of a controller, calculates the path on the basis, determines route and flow distribution, and submits a route request to the controller; the network controller is responsible for updating the network topology and link state, and issuing a flow statement to data forwarding equipment according to the route selection of the user. Through the route calculation, the user participates in the network control to achieve the distributed optimization during the use process of network resources; meanwhile, the controller provides network topology information for the user, and can achieve the virtualization of the network resources and functions for the user and the optimal configuration and the integrated use of the network resources. Through the application of the method, the user can get great rights within a network safety range, the network transparency is improved, and an SDN frame serves for the user.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Computing inter-autonomous system MPLS traffic engineering LSP paths
Systems and methods for computing the paths of MPLS Traffic Engineering LSPs across Autonomous System and / or area boundaries. A distributed path computation algorithm exploits multiple path computation elements (PCEs) to develop a virtual shortest path tree (VSPT) resulting in computation of an end-to-end optimal (shortest) path. In some implementations, the VSPT is computed recursively across all the Autonomous Systems and / or areas between the head-end and tail-end of the Traffic Engineering LSP.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for realizing path computation in network domain
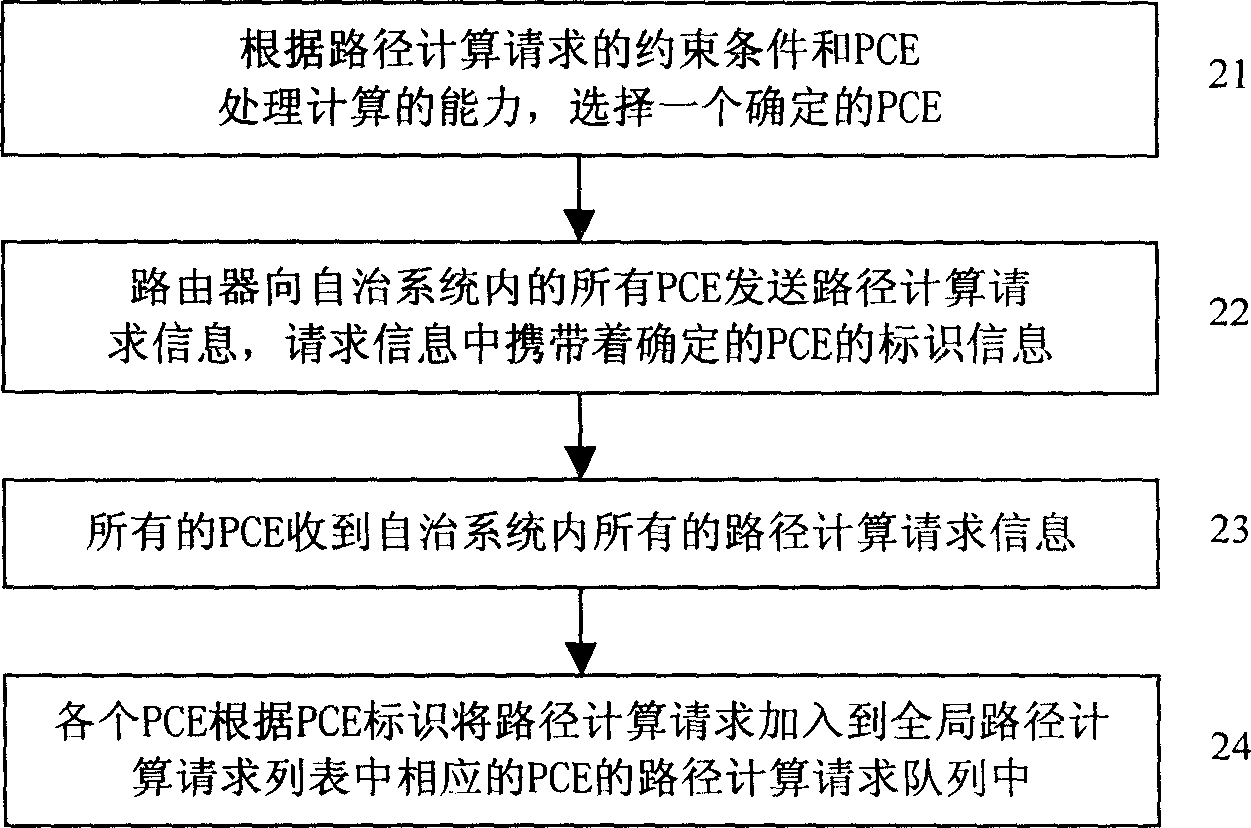
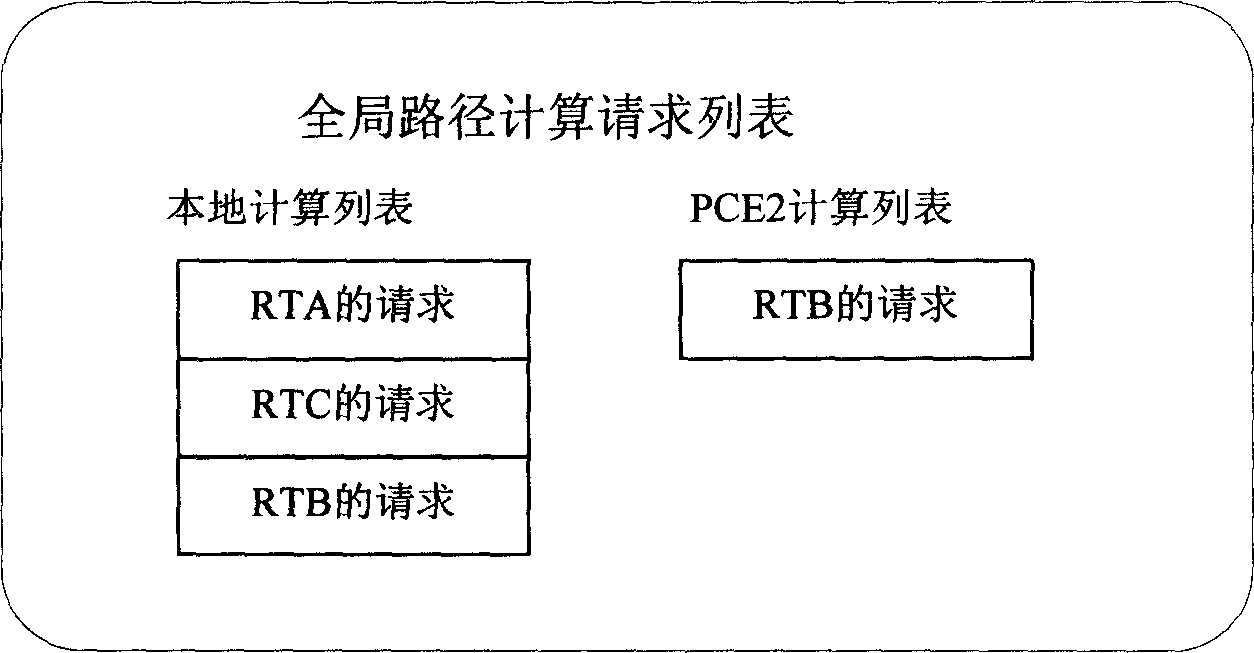
ActiveCN1866852AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracyData switching networksResource informationPath computation element
The invention discloses a route calculating method of network area, which is characterized by the following: the route calculation network entity saves global route calculating information for route calculating in the network area; the global route calculating information is composed of the following information: all current route calculating request information, current network resource information for distributing and current occupying resource;the route calculation network entity calculates the route according to the saved global route calculation information. The invention improves the efficiency and correctness of treating route calculation task, which improves the whole protocol operation efficiency.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Inter-domain optimization trigger in PCE-based environment
ActiveUS20060176820A1Improve efficiencyOptimization pathError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPath computation elementDistributed computing
A technique triggers optimization of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) that spans multiple domains of a computer network from a head-end node of a local domain to a tail-end node of a remote domain. The technique is based on the detection of an event in the remote domain (“event domain”) that could create a more optimal TE-LSP, such as, e.g., restoration of a network element or increased available bandwidth. Specifically, a path computation element (PCE) in the event domain learns of the event and notifies other PCEs of the event through an event notification. These PCEs then flood an event notification to label switched routers (LSRs) in their respective domain. Upon receiving the notification, if an LSR has one or more TE-LSPs (or pending TE-LSPs), it responds to the PCE with an optimization request for the TE-LSPs. The PCE determines whether a particular TE-LSP may benefit from optimization based on the event domain (i.e., whether the TE-LSP uses the event domain), and processes the request accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Routing and spectrum resource allocation method and system for resource awareness in elastic optical path network
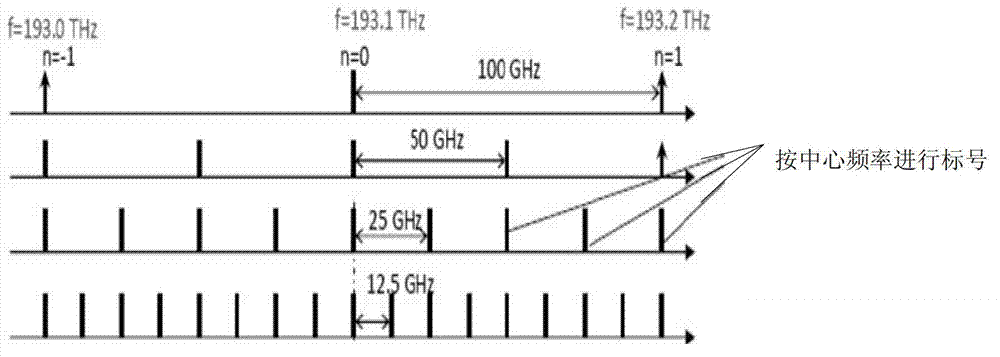
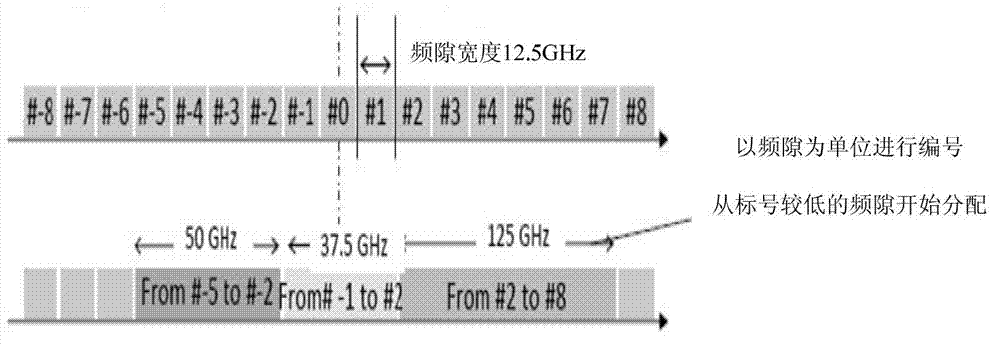
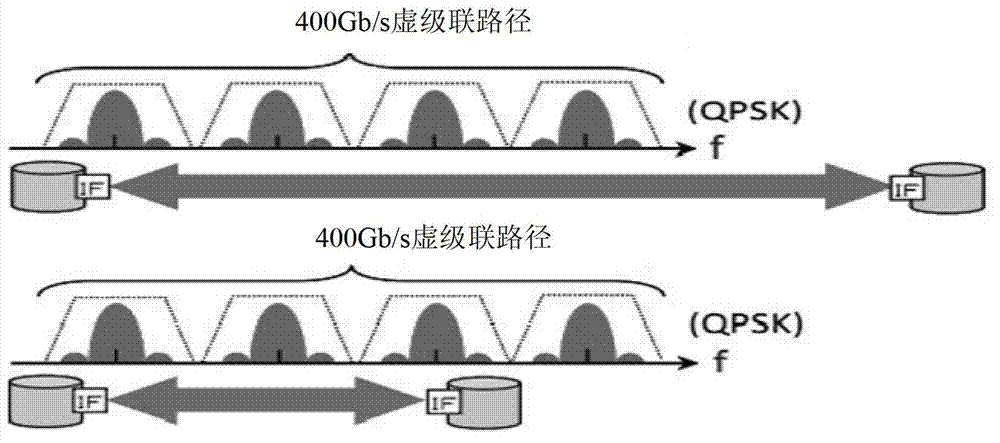
InactiveCN103051547AMake full use ofFull and reasonable useData switching networksFrequency spectrumPath computation element
The invention discloses a routing and spectrum resource allocation method and a system for resource awareness in an elastic optical path network. The method comprises the following steps that when a request for communication service between an originating node and a destination node arrives, firstly whether the established idle optical paths in the current network can carry the communication service or not is judged, if so, the idle optical paths are directly used for communication, and if not, a PCE (Path Computation Element) generates an auxiliary list of candidate optical paths, wherein the auxiliary list contains link hops of each candidate optical path; a modulation method is determined according to the link hops and frequency slots required by the corresponding candidate optical path for carrying the communication service are computed; the PCE selects a working path according to the required frequency slots and the available frequency slots for the optical path; frequency slot distribution is conducted in the working path to establish a new optical path; and communication is conducted between the originating node and the destination node. After the communication is completed, the new optical path is temporarily not removed, a timer is started up and the steps are repeated within fixed time to realize the resource awareness in the optical path network and solve the problem of high network service blocking rate caused by blockage of the shortest path.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Network path selection using bandwidth prediction
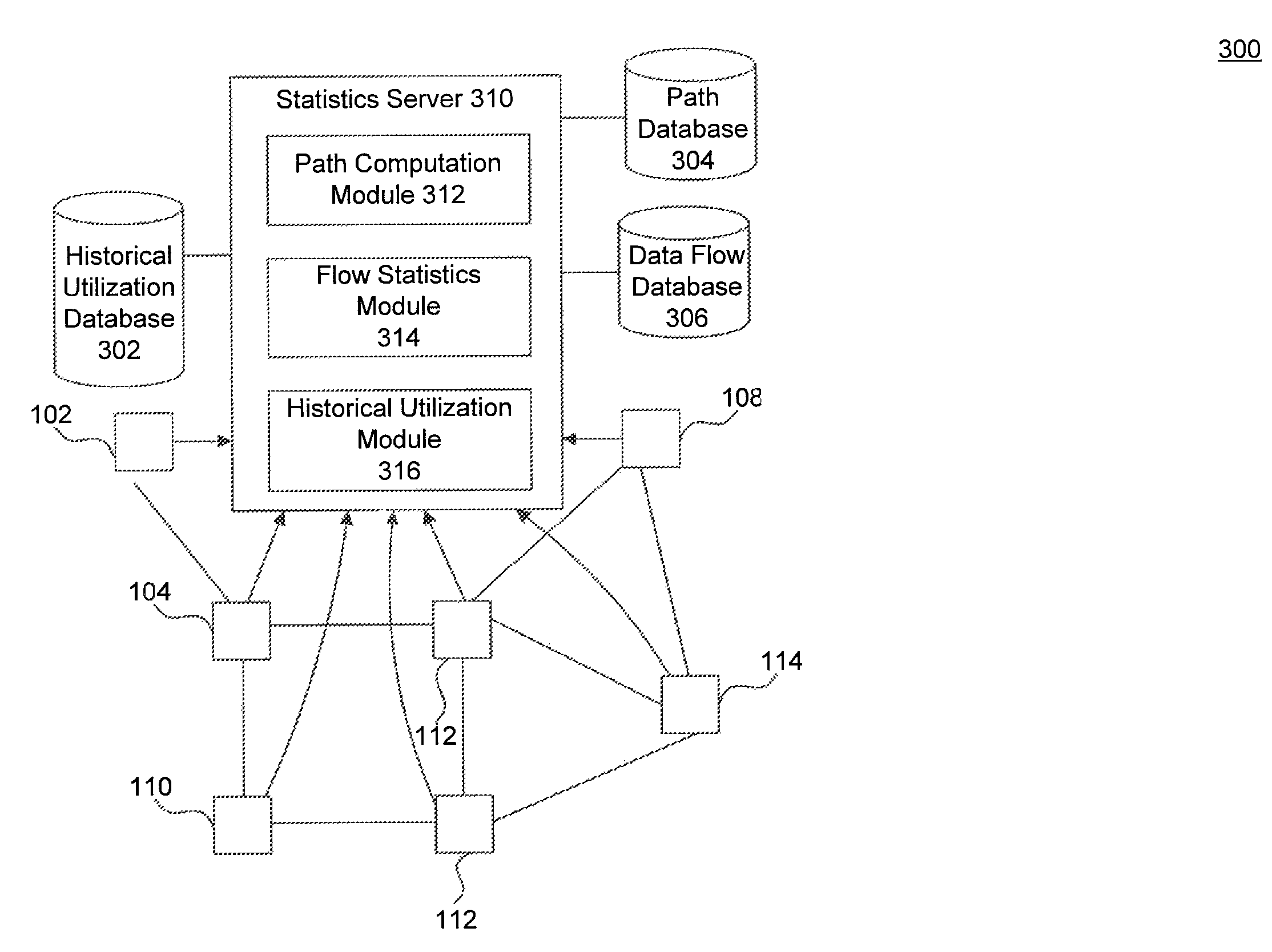
ActiveUS8811172B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData streamPath computation element
In an embodiment, a system routes a new data stream from a source to a destination through a plurality of forwarding devices interconnected with links. The system includes a control device that receives a request to create a path through the plurality of interconnected forwarding devices for a new data stream and determines a type of the new data stream. A data flow database stores historical usage characteristics of data streams having the determined type. A path computation module determines, based on the historical usage characteristics of data streams having the determined type, the requested path through plurality of interconnected forwarding devices from the source to the destination.
Owner:LEVEL 3 COMM LLC
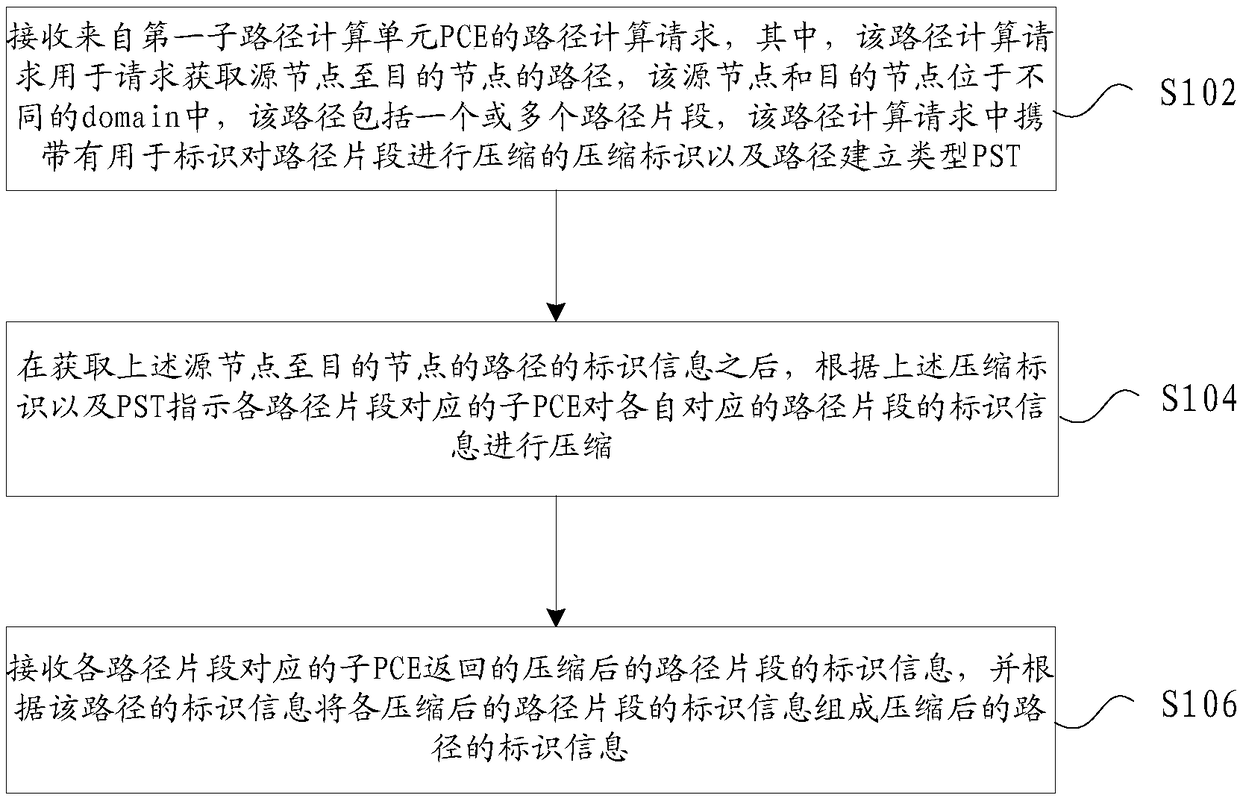
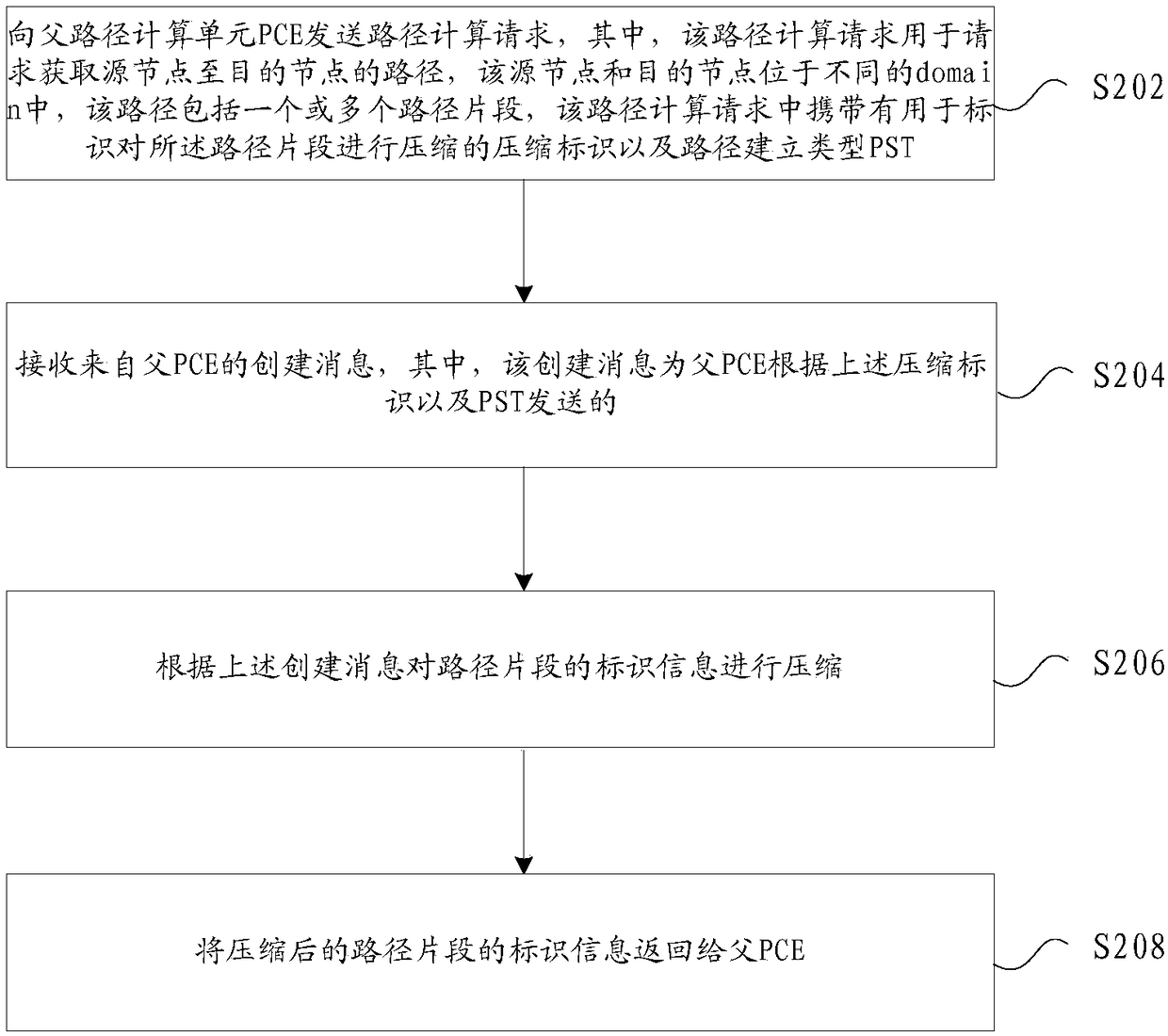
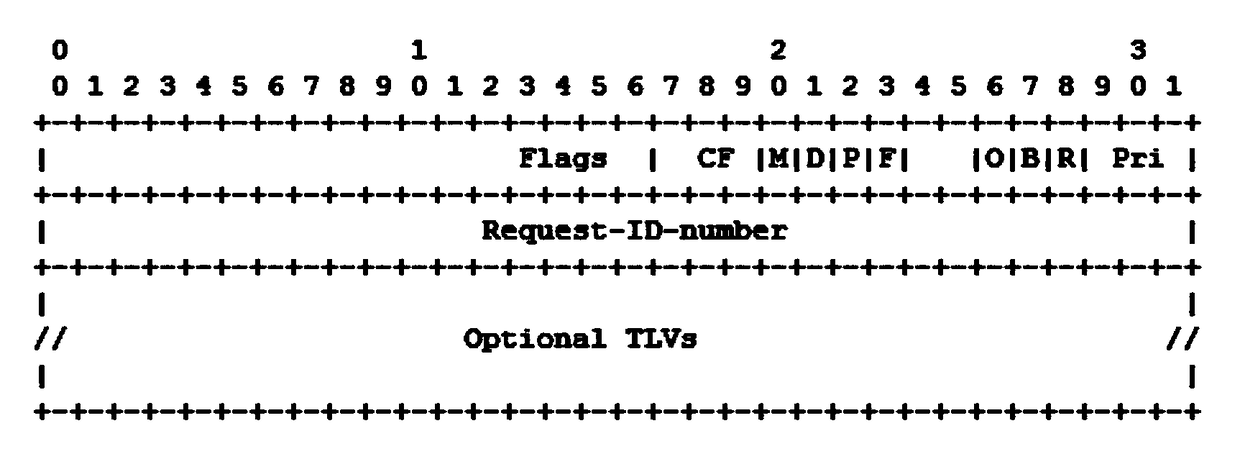
Method and device for determining identification information of cross-domain path, and storage medium
ActiveCN109218189AShorten the lengthSolve long problemsData switching networksPath computation elementComputer science
The present invention provides a method and device for determining the identification information of a cross-domain path, and a storage medium. The method includes: receiving a path computation request from a first sub-path computation element (PCE), wherein the path computation request carries a compression identifier that identifies the compression of path segments and a path setup type (PST); after the identification information of a path from a source node to a destination node is received, instructing sub PCEs corresponding to respective path segments to compress the identification information of respective path segments according to the compression identifier and the PST; receiving the compressed identification information of the path segments returned by the sub-PCEs corresponding to respective path segments, and forming the compressed identification information of respective path segments into the compressed identification information of the path according to the identificationinformation of the path. The method effectively reduces the length of the identification information of the path, thereby solving the excessively long path identification information in the prior art.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Path computation and network topological method, structure, system, entity and router
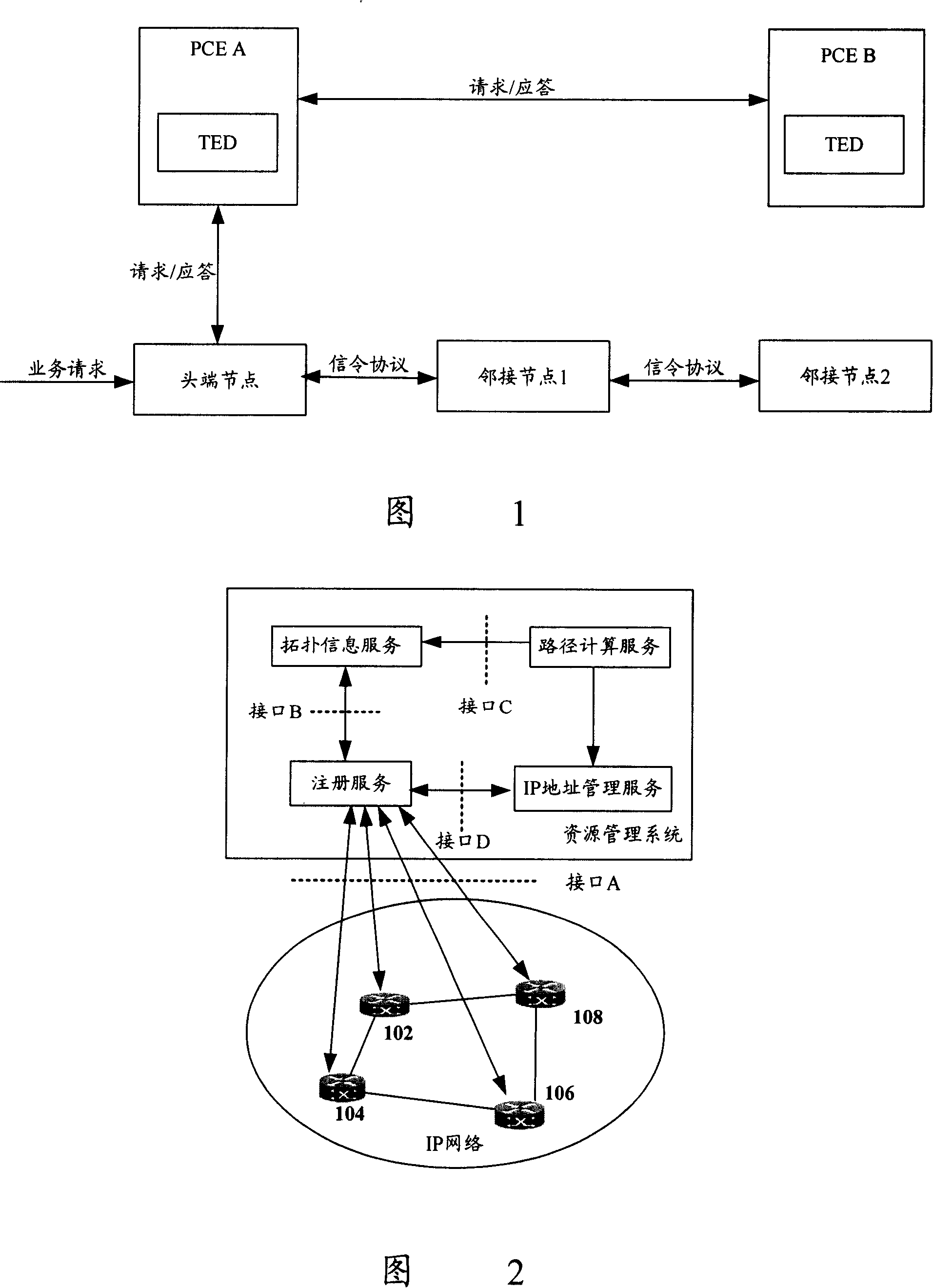
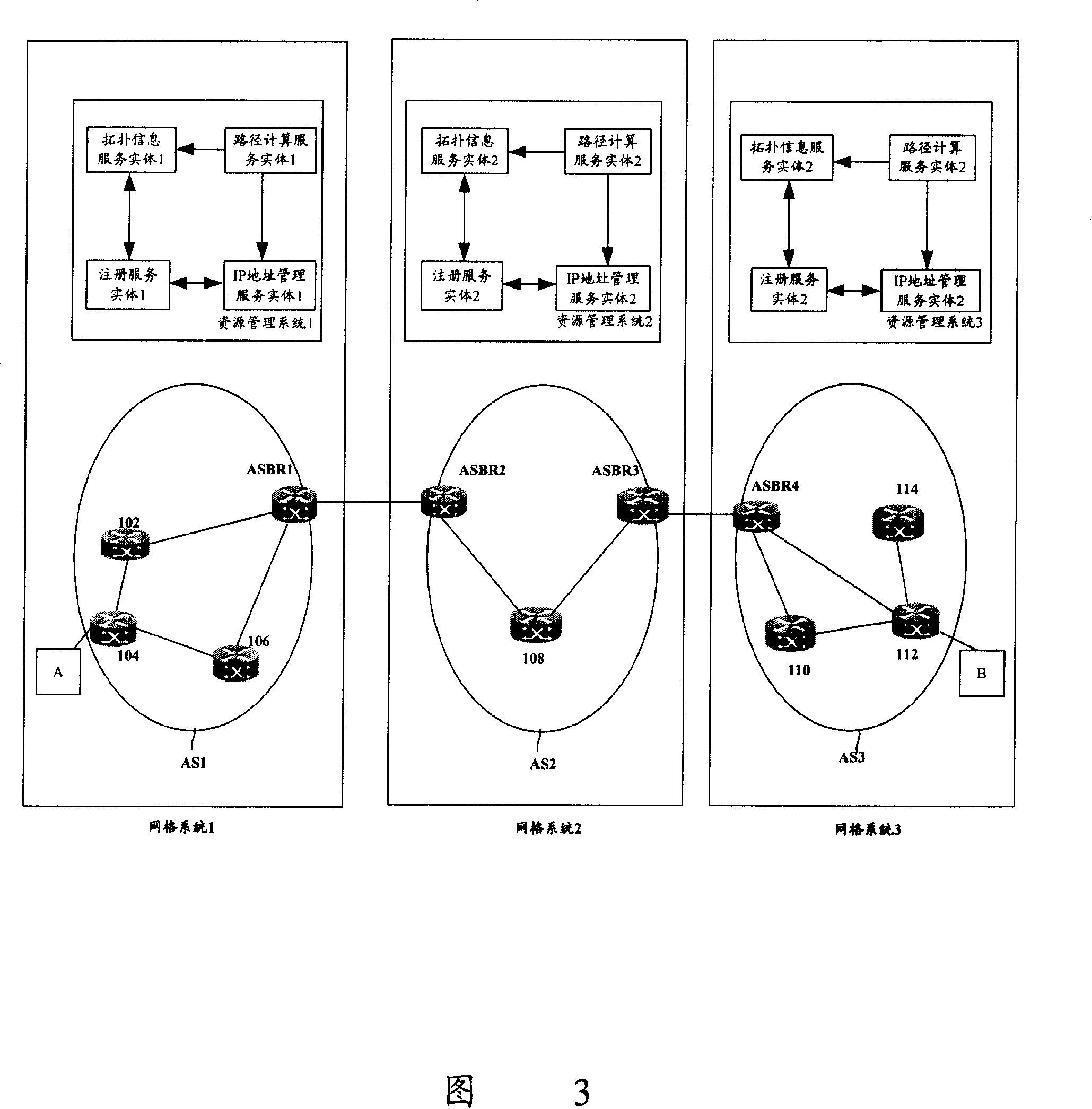
InactiveCN101155134AQuick response to changesData switching networksPath computation elementResource Management System
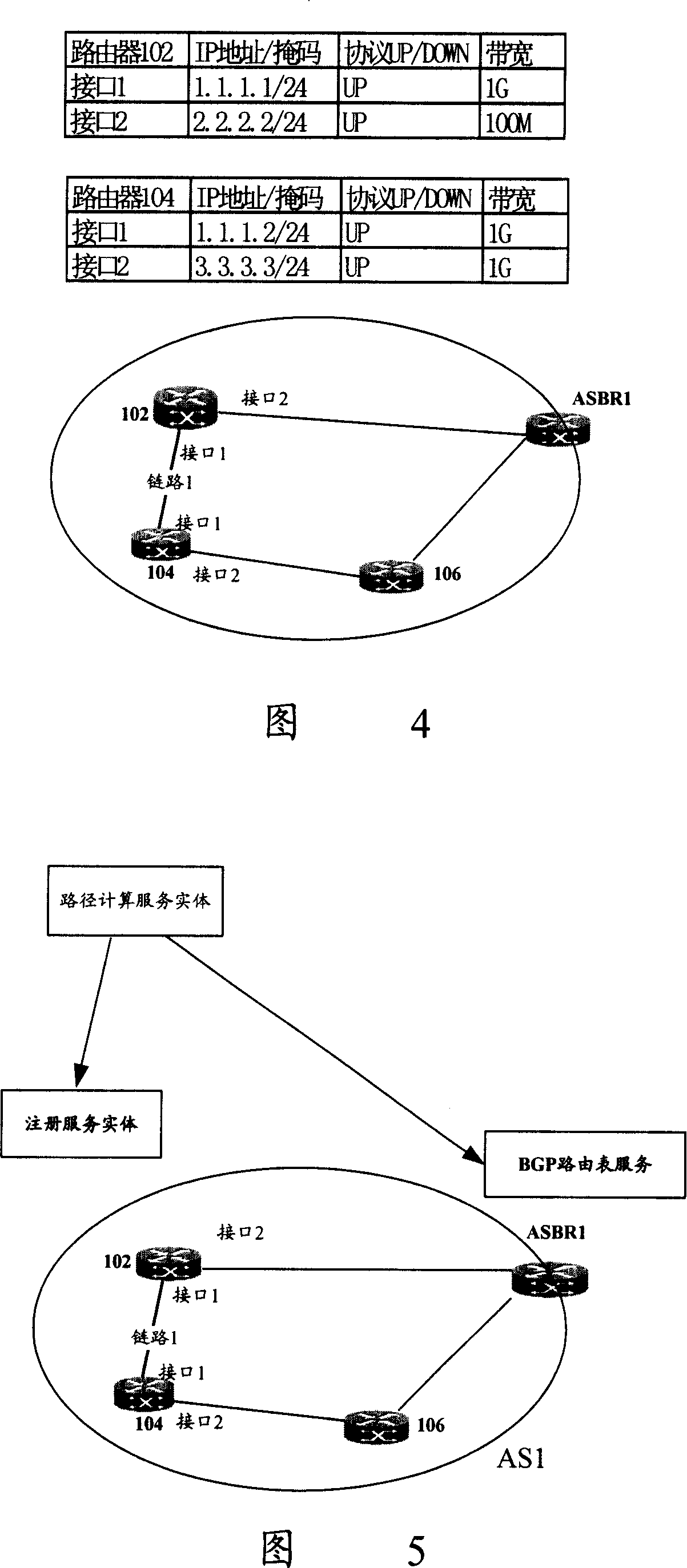
The invention discloses a path computing method. A router forming IP network is divided to form at least one grid. Each grid comprises at least one router, each grid collects the router resource of each router in the said grid. Each grid establishes network topology based on the collected router resource and the path computing is performed based on the network topology and IP address resource of router. The invention also discloses a network topology method, grid frame, resource management system, enrollment service body, autonomous system and router, to increase the efficiency of resource management of network and path calculation.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
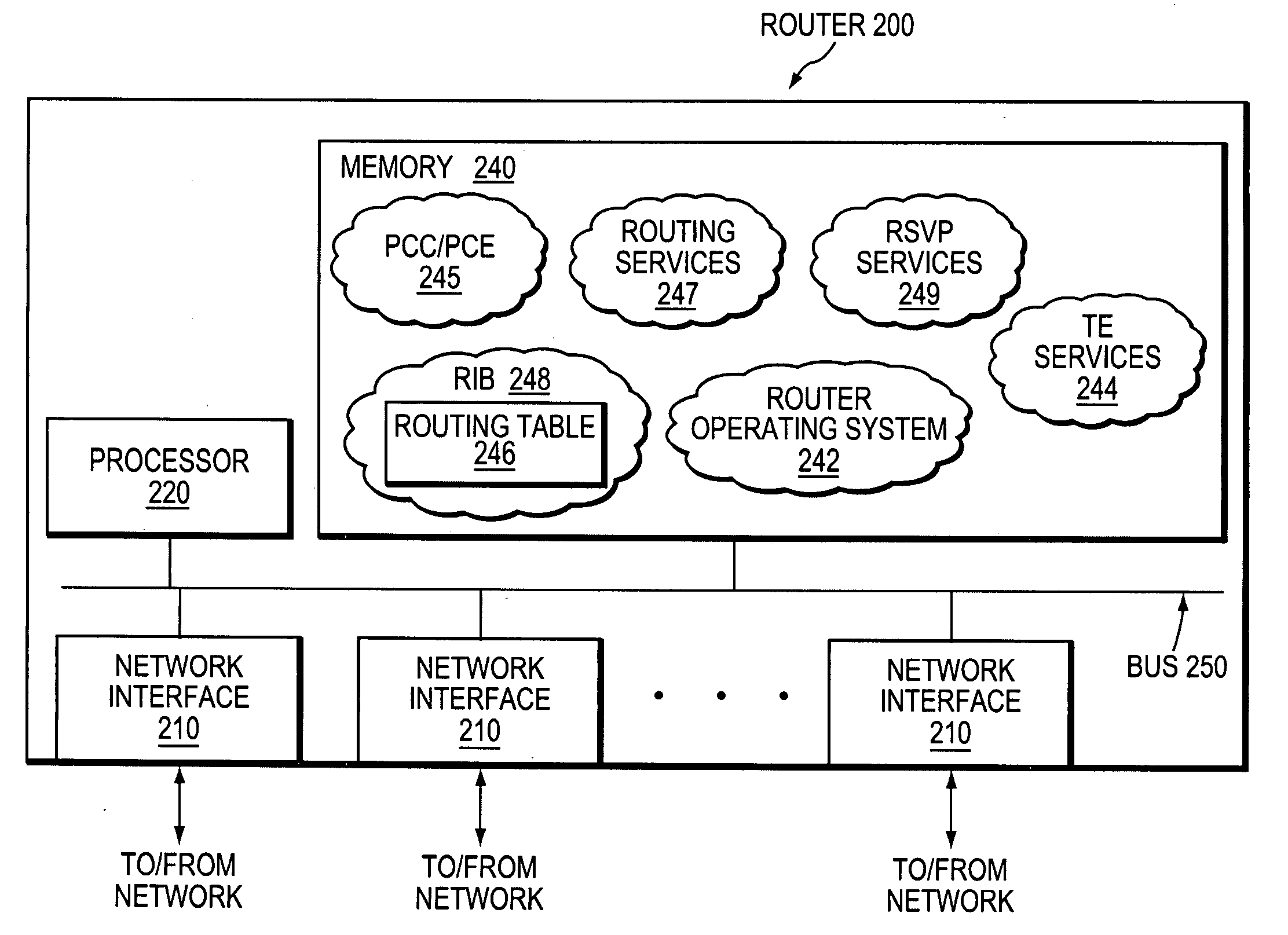
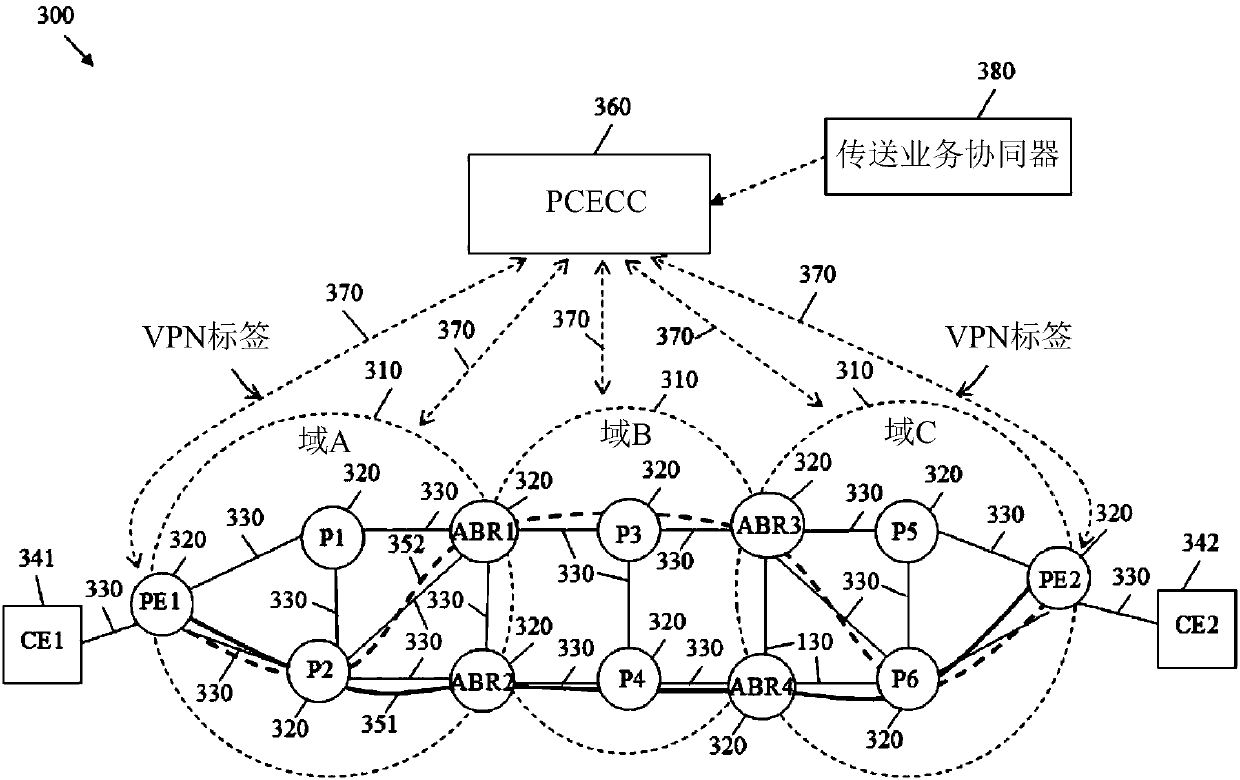
Path computation element central controllers (pceccs) for network services
The invention discloses path computation element central controllers (PCECCS) for network services. According to the invention, a method implemented by a path computation element centralized controller (PCECC), the method comprises: receiving a service request to provision for a service from a first edge node and a second edge node in a network; computing a path for a label switched path (LSP) from the first edge node to the second edge node in response to the service request; reserving label information for forwarding traffic of the service on the LSP; and sending a label update message to athird node on the path to facilitate forwarding of the traffic of the service on the path, wherein the label update message comprises the label information.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Device and method for service recovery
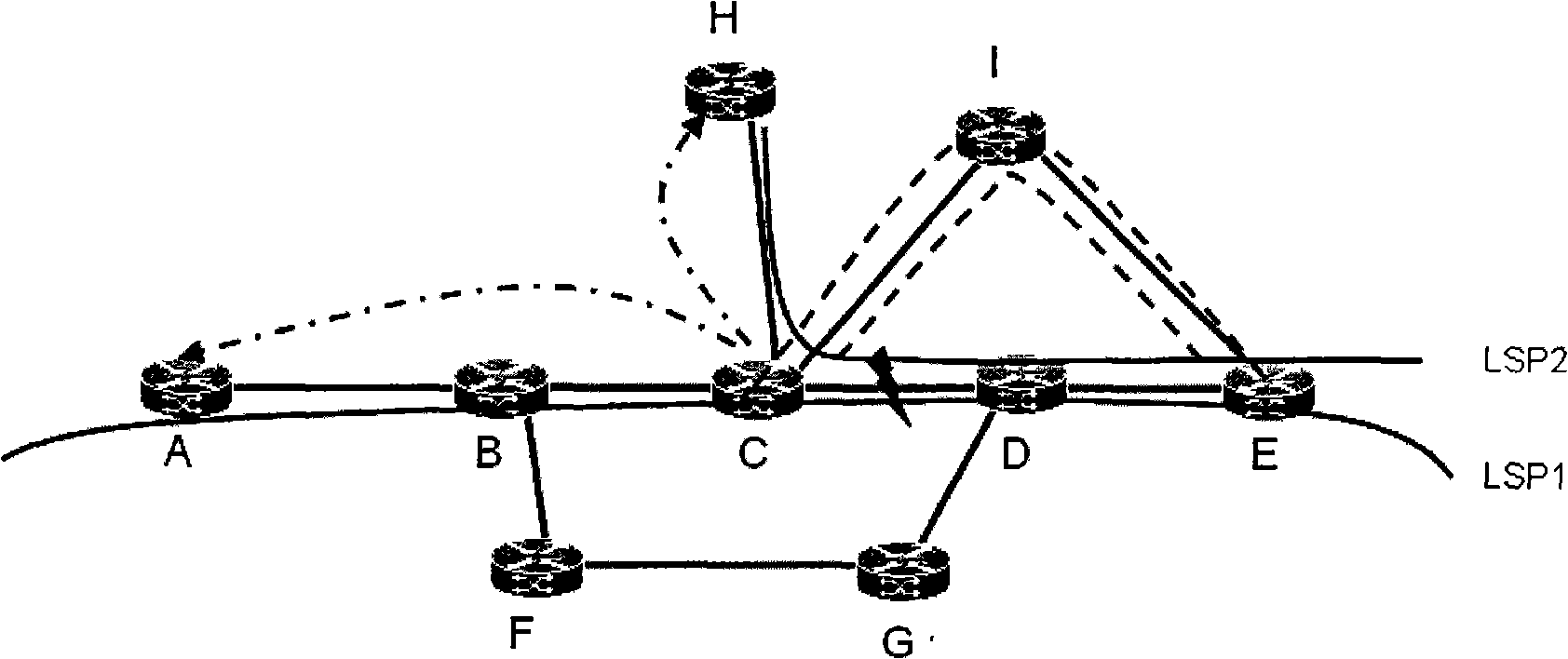
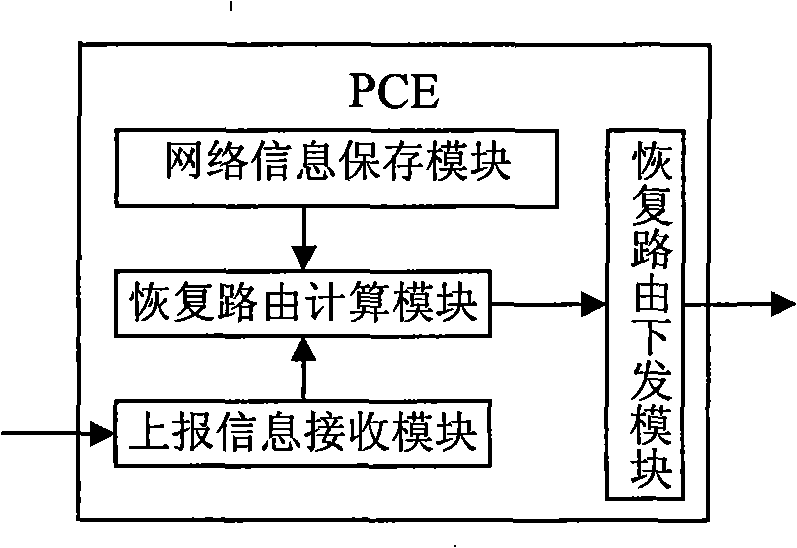
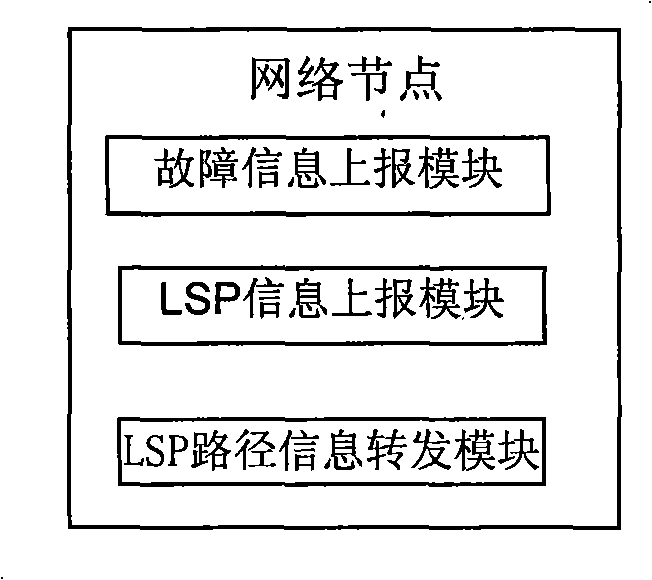
ActiveCN101286892AOptimal Restoration ReroutingData switching by path configurationPath computation elementLabel switching
The invention relates to a device and a method for recovering service. The device essentially comprises a path computation element (PCE) and network nodes. The method essentially comprises the steps that: the nodes reports network failure information to the PCE; the PEC calculates LSP route of recovered rerouting according to the saved network information, obtained failure information and the information of label switching path (LSP) influenced by the failure; according to the LSP route of the recovered rerouting, corresponding recovered LSP is established so as to realize the recovery of the service. Utilization of the method of the invention can ensures that when failure occurs to the network, the PCE establishes the optimal recovered rerouting and shortens the time of rerouting according to the obtained network topology information of the whole network, the link information, the LSP information and the failure information reported by the nodes.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
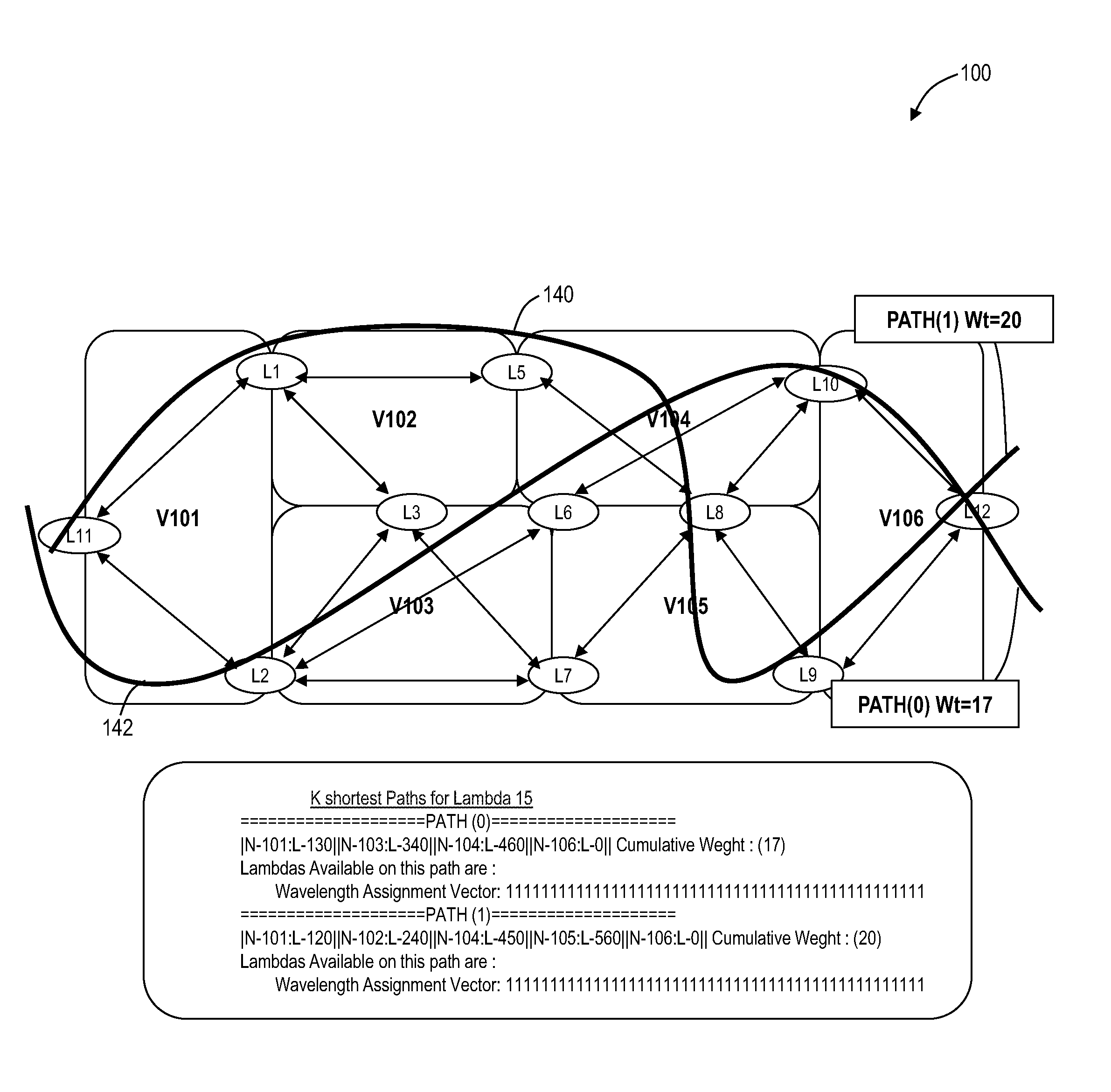
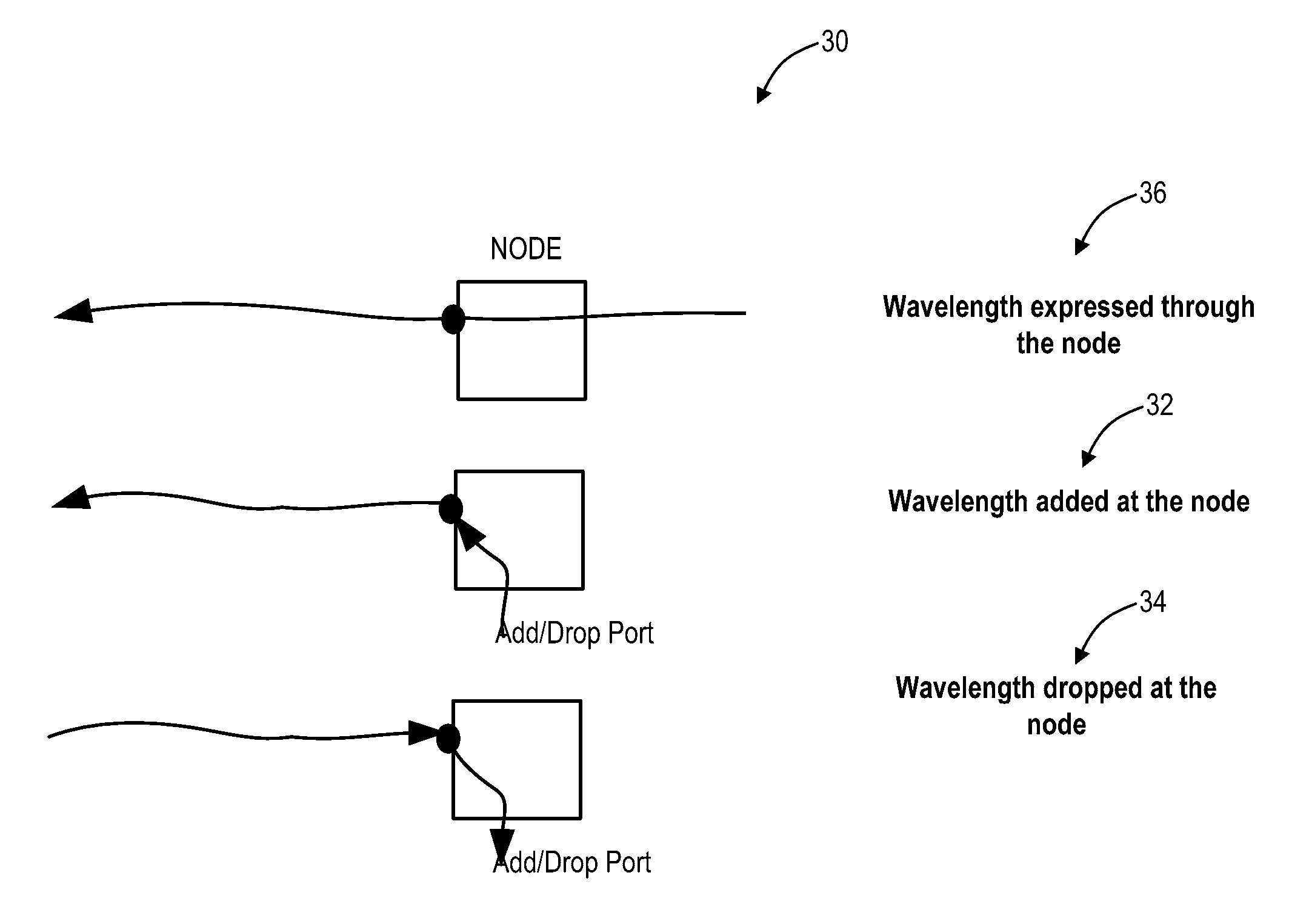
Path computation systems and methods in optical networks
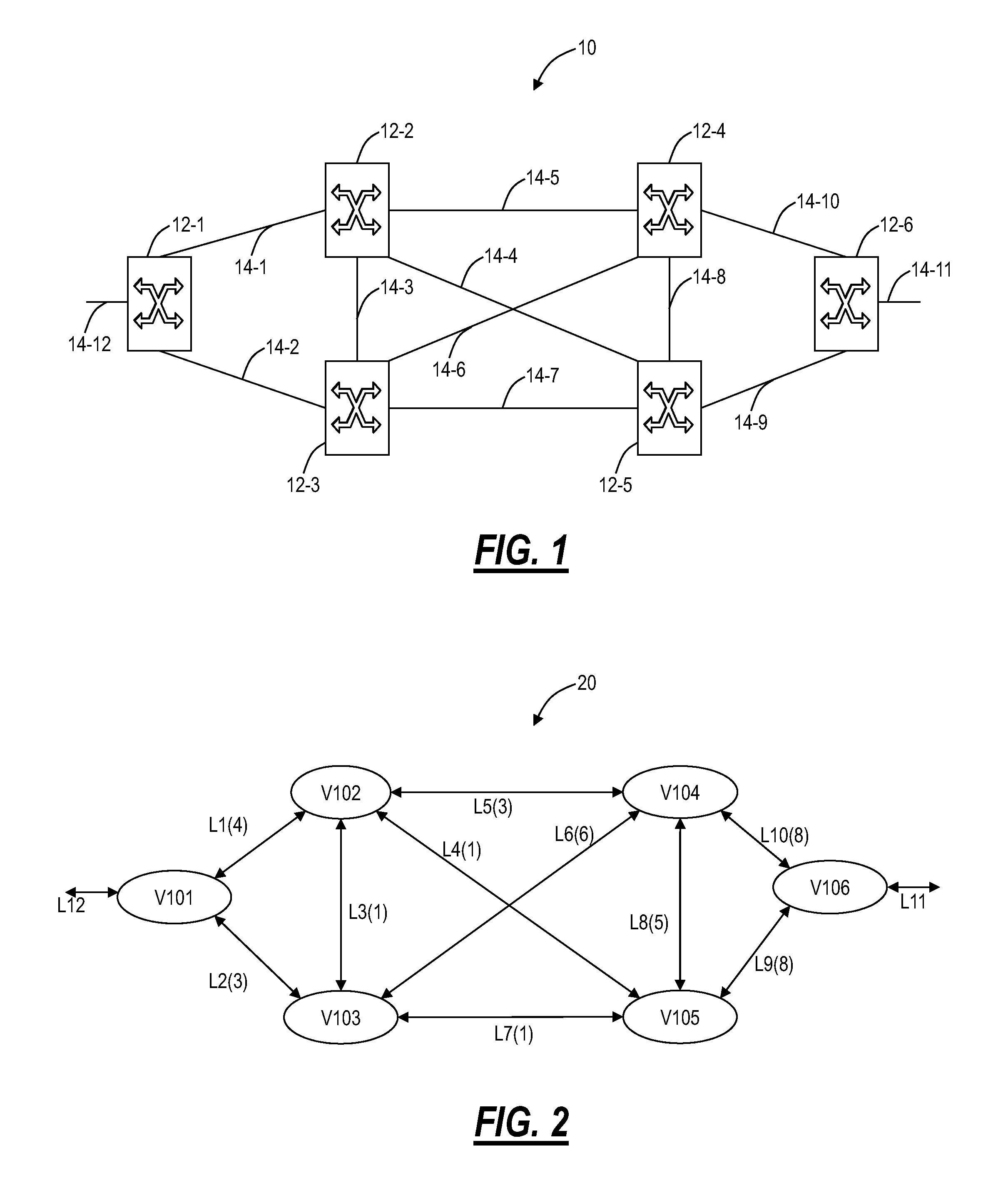
A path computation method includes defining photonic constraints associated with a network, wherein the photonic constraints include wavelength capability constraints at each node in the network, wavelength availability constraints at each node in the network, and nodal connectivity constraints of each node in the network, and performing a constrained path computation in the network using Dijkstra's algorithm on a graph model of the network with the photonic constraints considered therein. An optical network includes a plurality of interconnected nodes each including wavelength capability constraints, wavelength availability constraints, and nodal connectivity constraints, and a path computation element associated with the plurality of interconnected photonic nodes, wherein the path computation element is configured to perform a constrained path computation through the plurality of interconnected nodes using Dijkstra's algorithm on a graph model with the photonic constraints considered therein.
Owner:CIENA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com