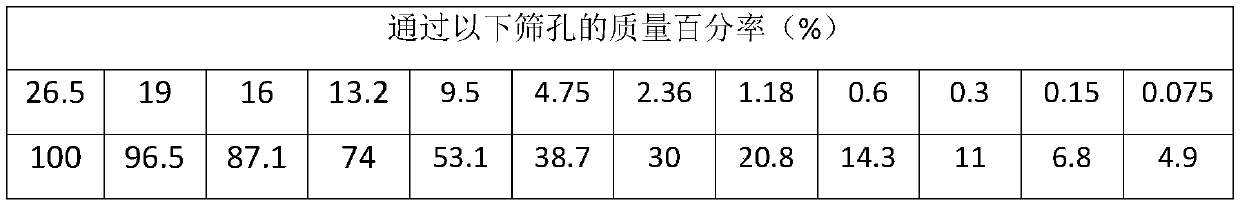
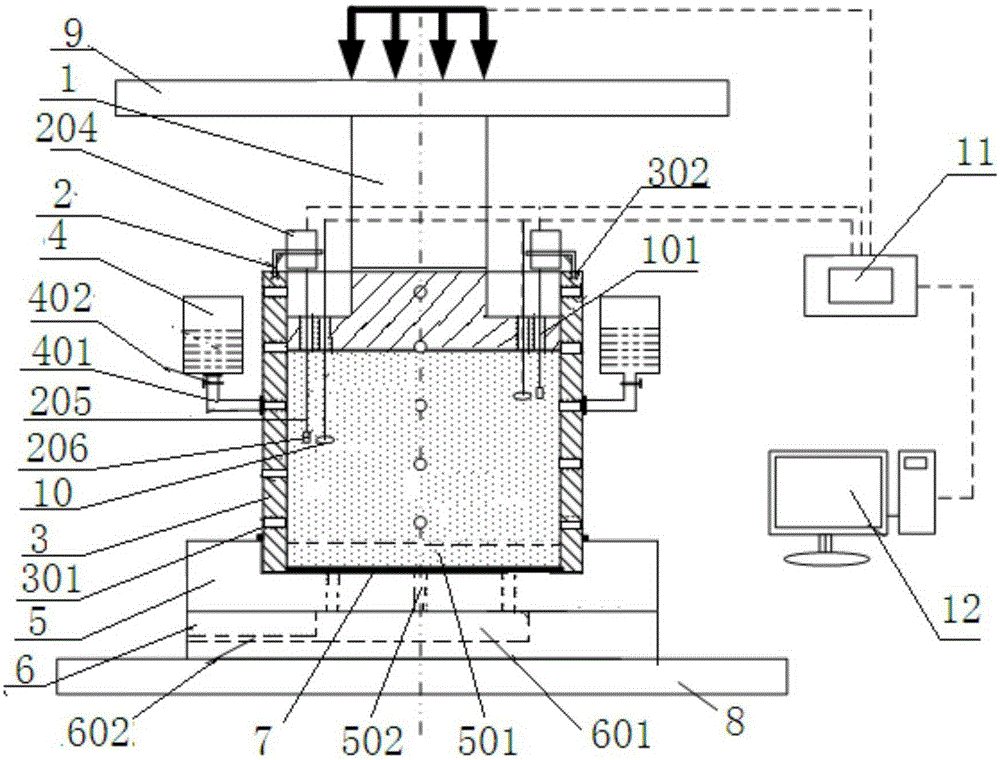
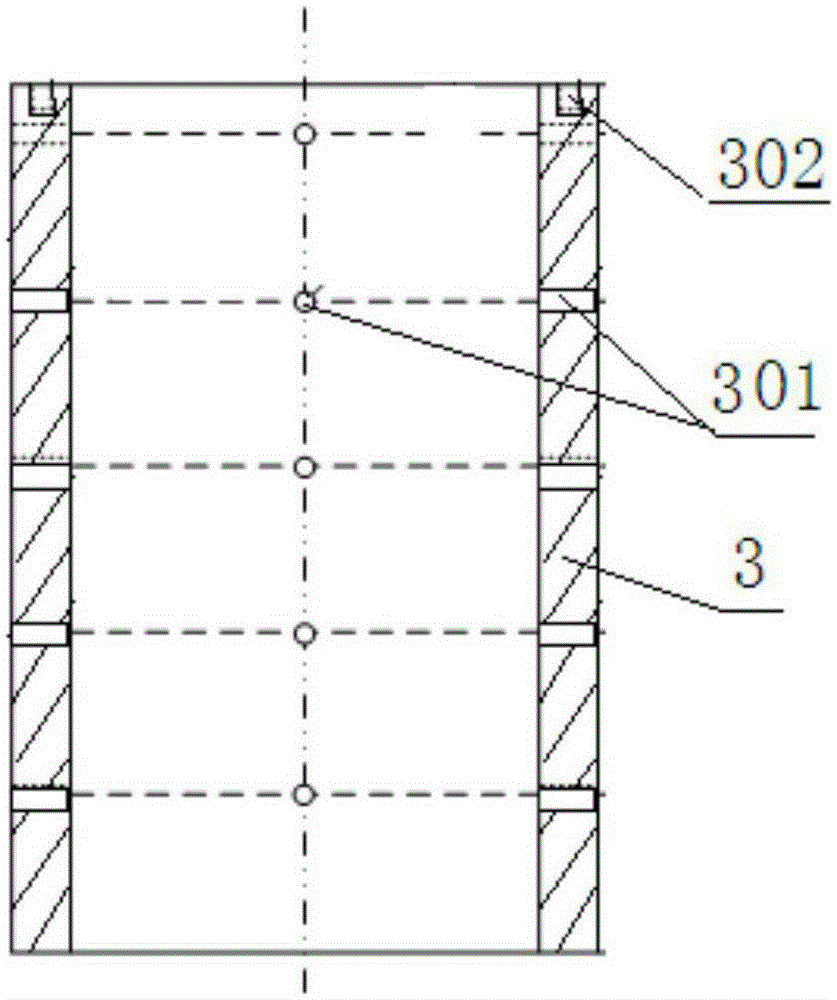
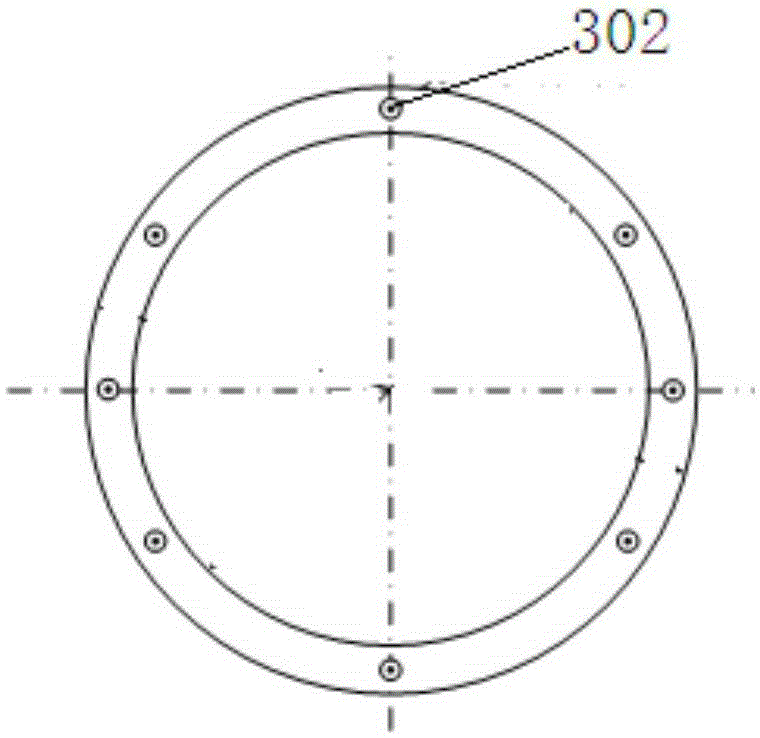
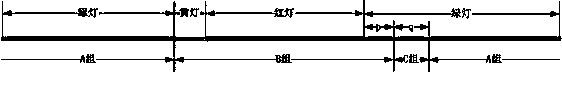Patents
Literature
474 results about "Traffic engineering" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Traffic engineering is a branch of civil engineering that uses engineering techniques to achieve the safe and efficient movement of people and goods on roadways. It focuses mainly on research for safe and efficient traffic flow, such as road geometry, sidewalks and crosswalks, cycling infrastructure, traffic signs, road surface markings and traffic lights. Traffic engineering deals with the functional part of transportation system, except the infrastructures provided.
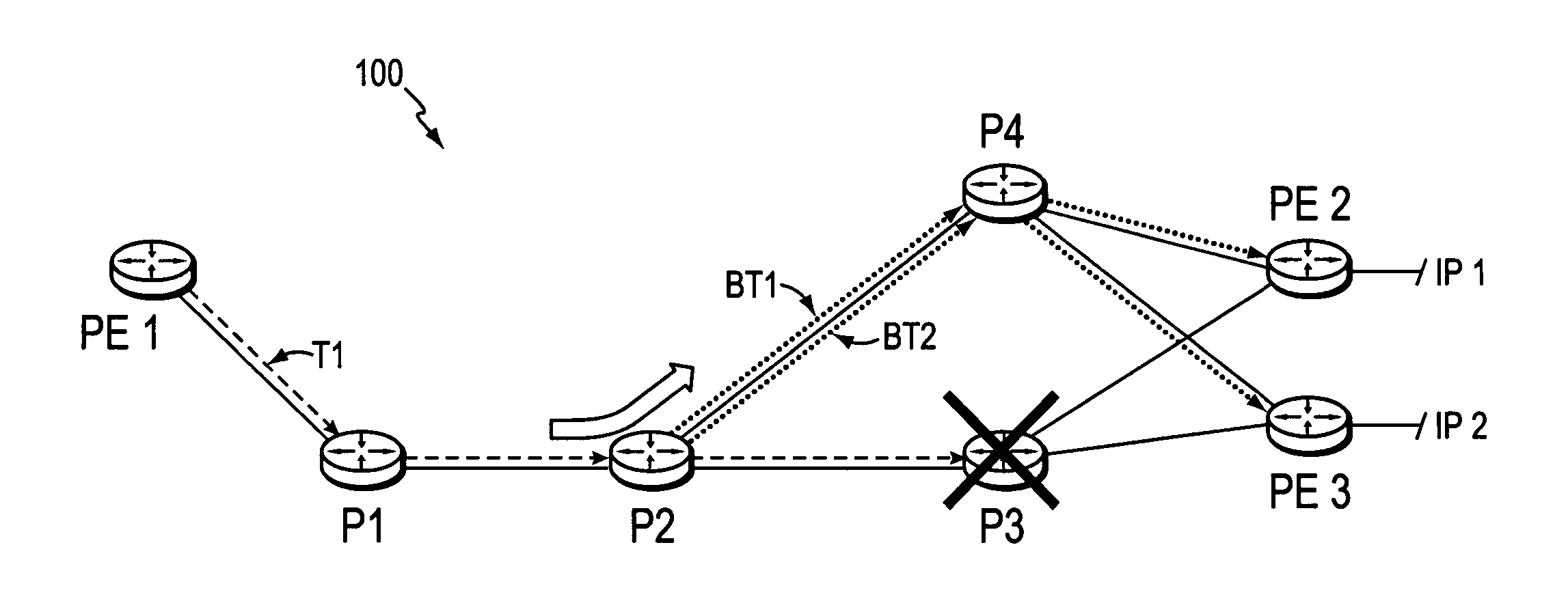
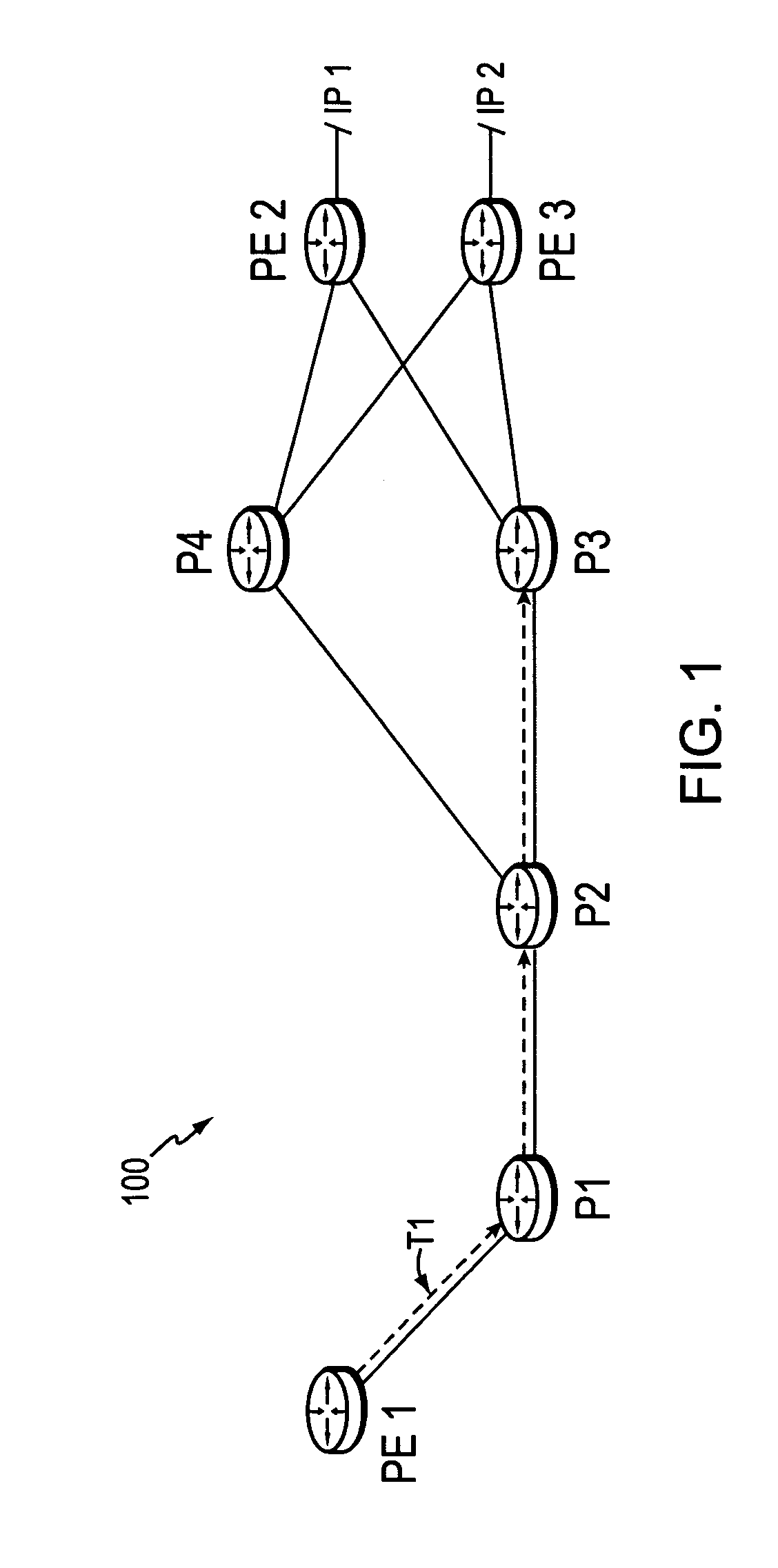
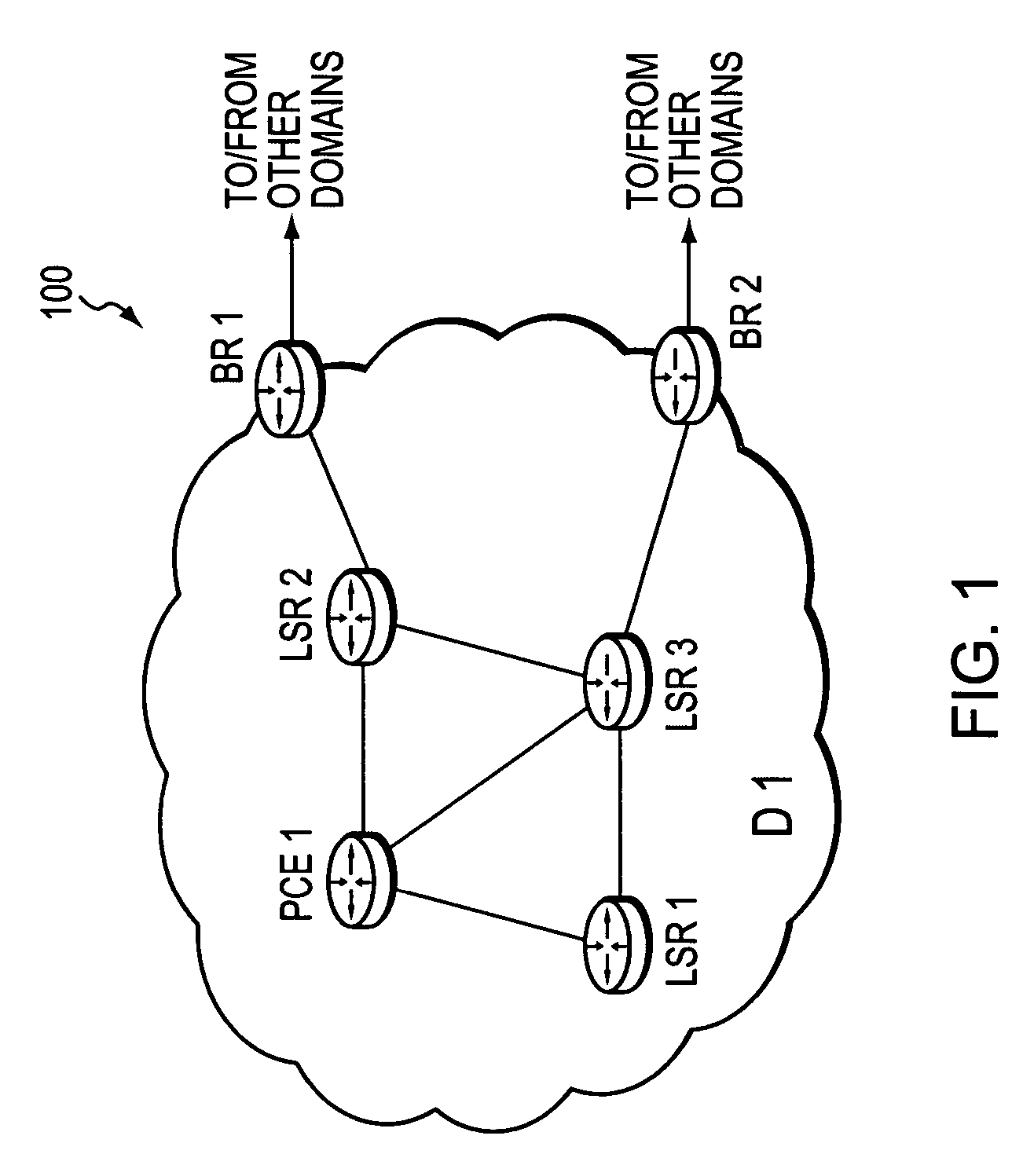
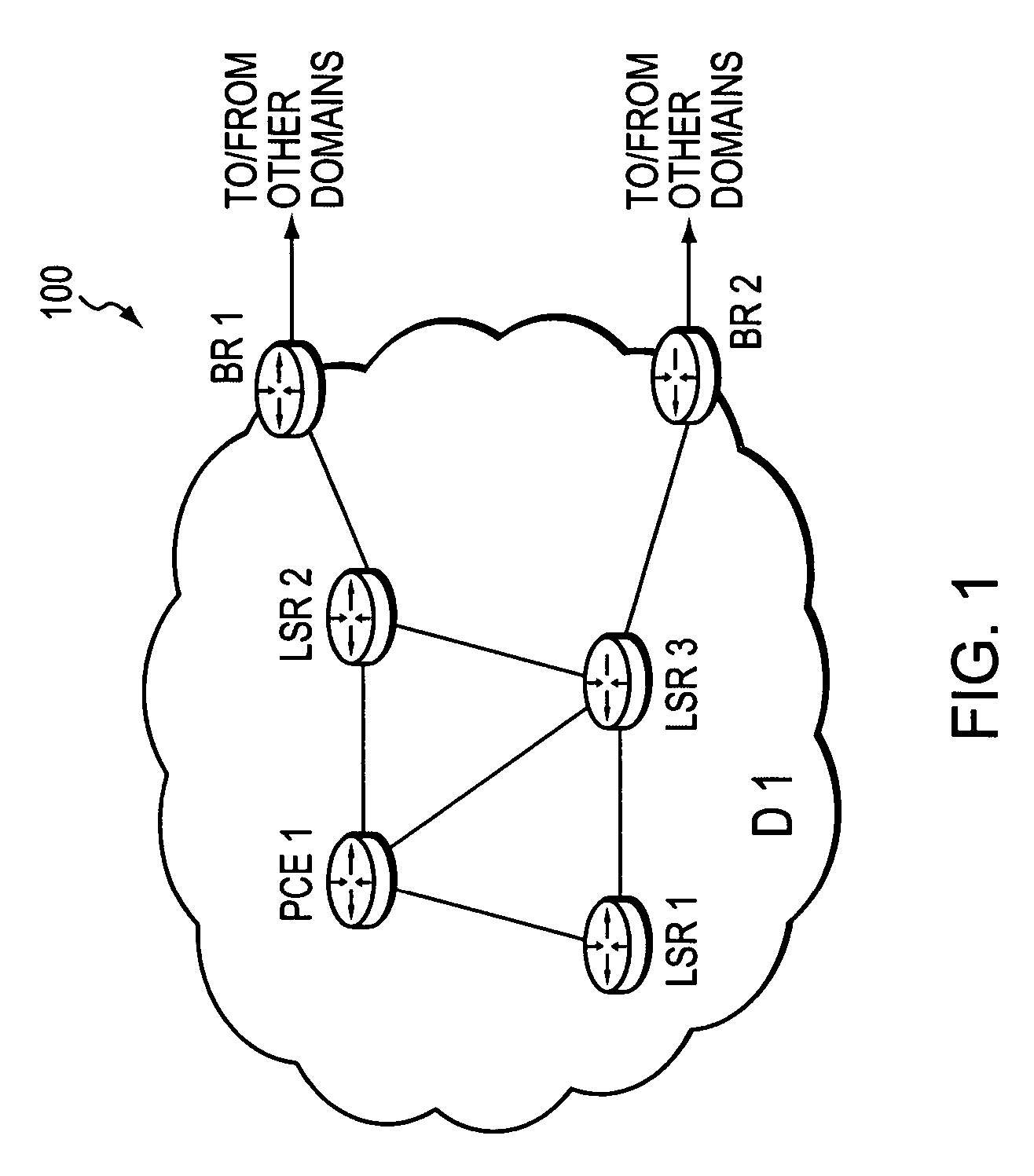
Technique for enabling traffic engineering on CE-CE paths across a provider network
ActiveUS20070133406A1Create efficientlyReduce needError preventionTransmission systemsPrivate networkDistributed computing
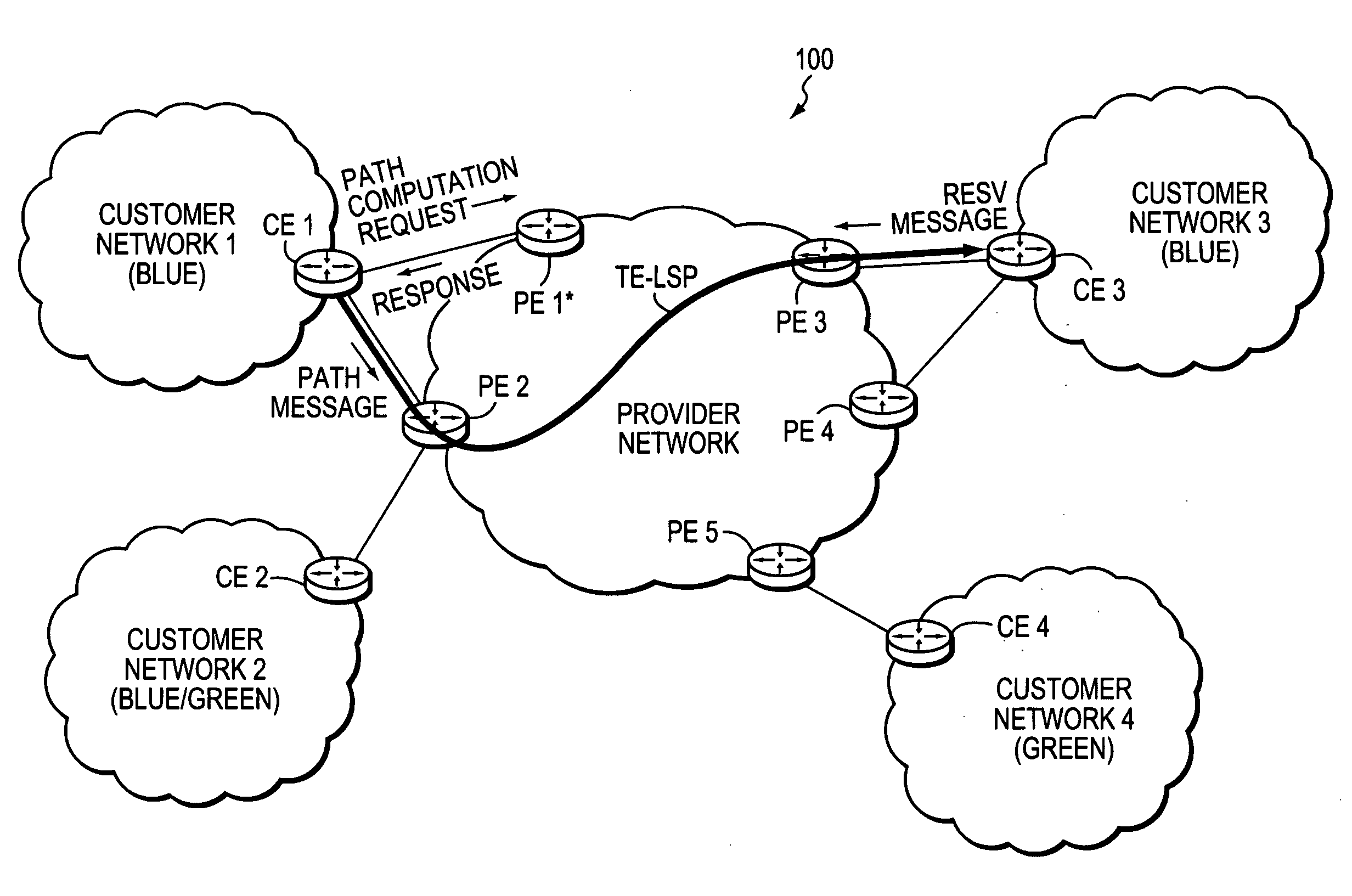
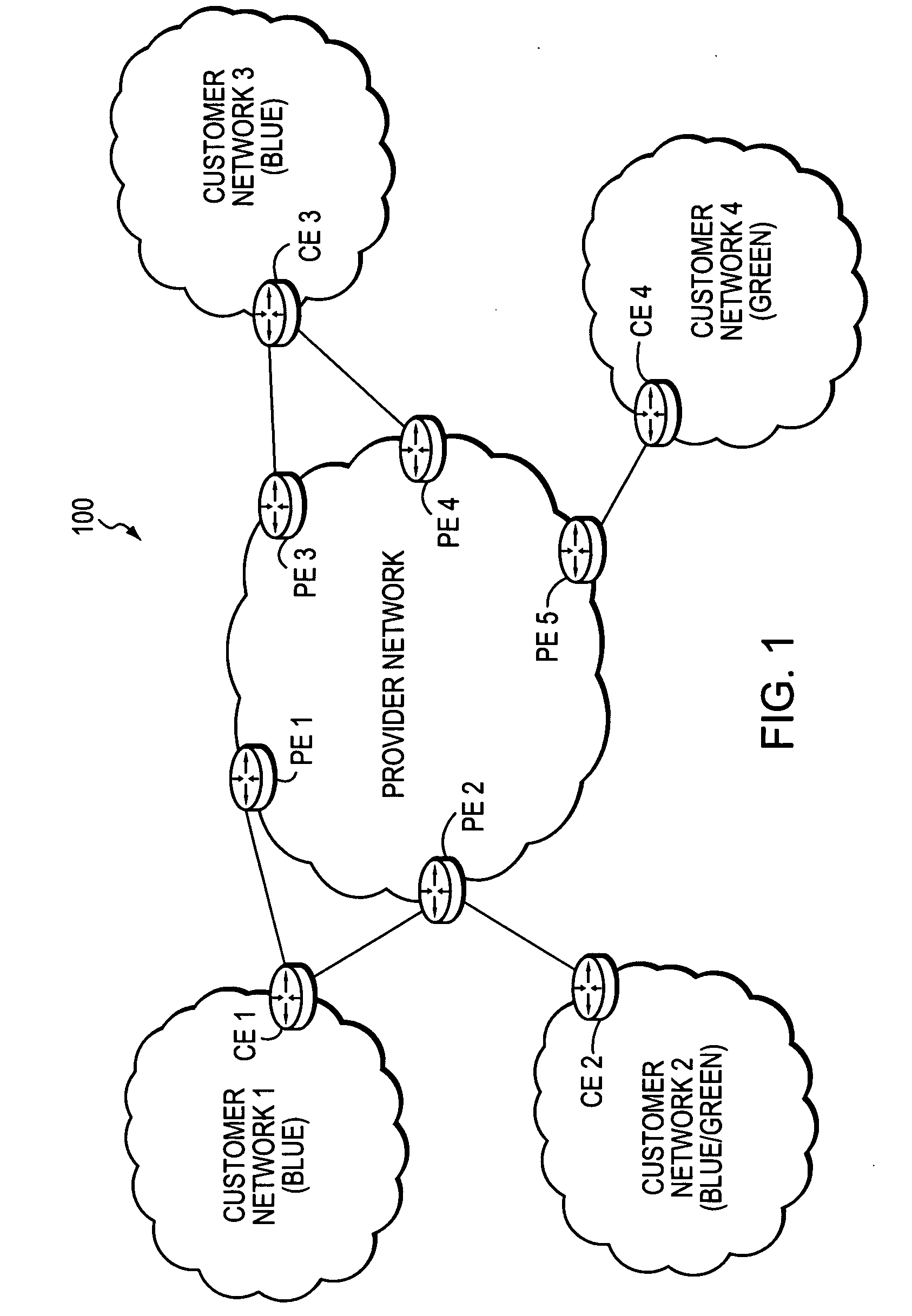
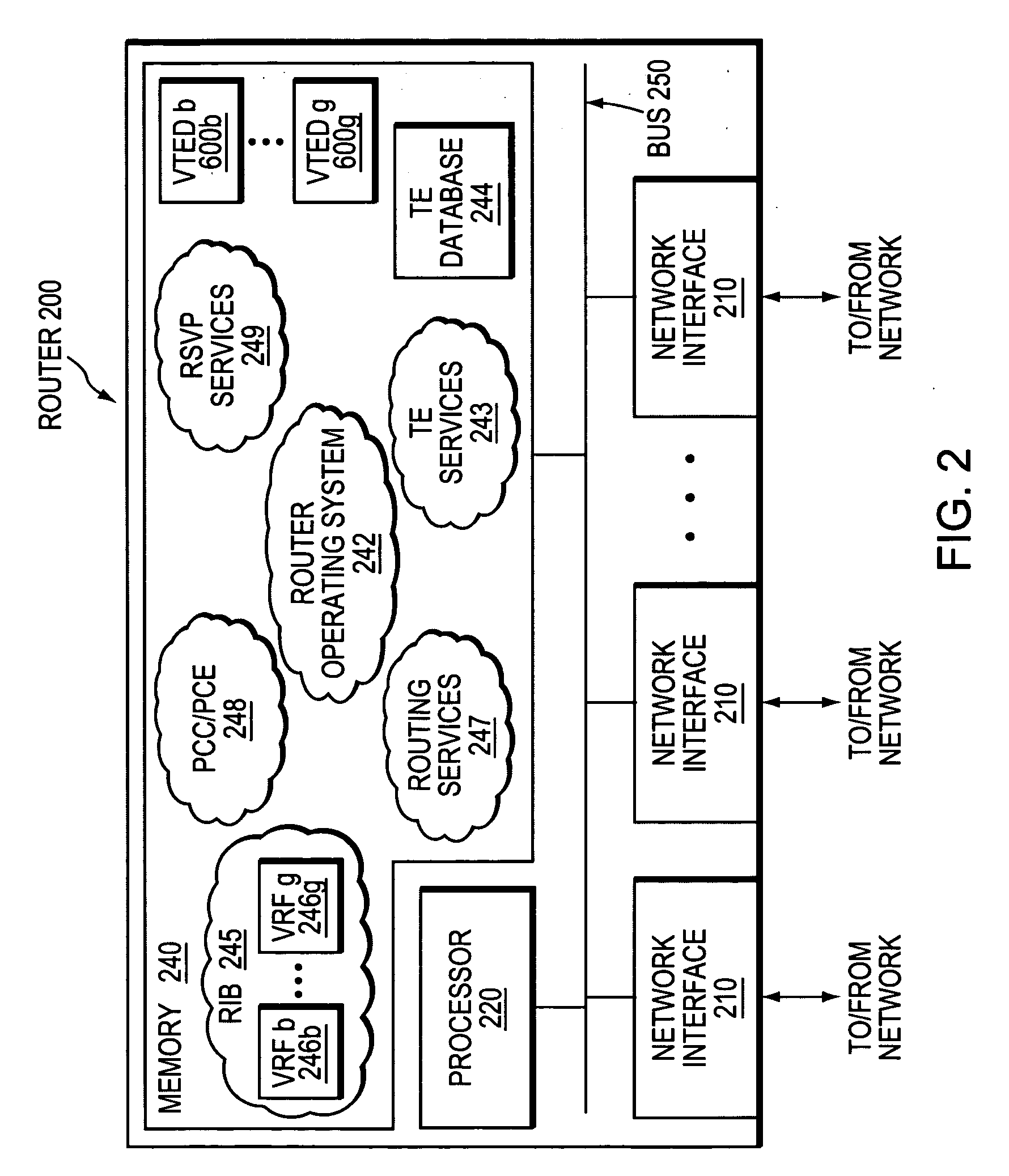
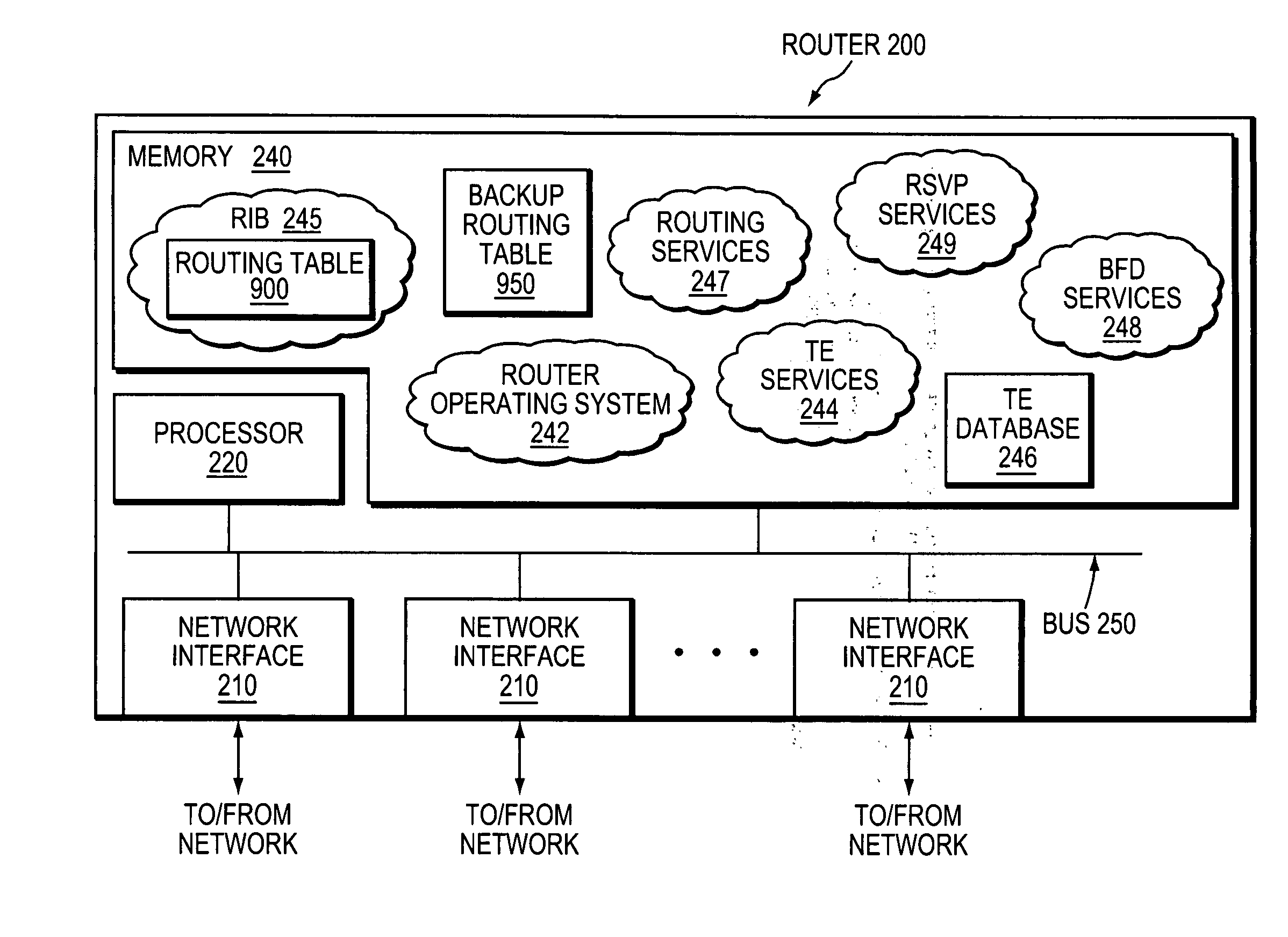
A technique enables Traffic Engineering (TE) on paths between customer edge devices (CEs) across a provider network (“CE-CE paths”) in a computer network. According to the novel technique, TE is configured on a link from a sending provider edge device (PE) to a first CE (“PE-CE link”), e.g., a CE of one or more virtual private networks (VPNs). The sending PE conveys TE information of the PE-CE link to one or more receiving PEs in the provider network. Upon receiving the TE information, each receiving PE expands a TE database (TED) for information regarding the provider network (i.e., a “core TED”) to include TE-configured PE-CE links, e.g., by updating one or more corresponding VPN TEDs (VTEDs) for each VPN maintained by the receiving PE. Once the receiving PEs have the TE information for configured PE-CE links from the provider network, one or more TE techniques may be applied to paths from a second CE of the receiving PE to the first CE (a CE-CE path) to thereby facilitate, e.g., establishment of TE-LSPs along CE-CE paths.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
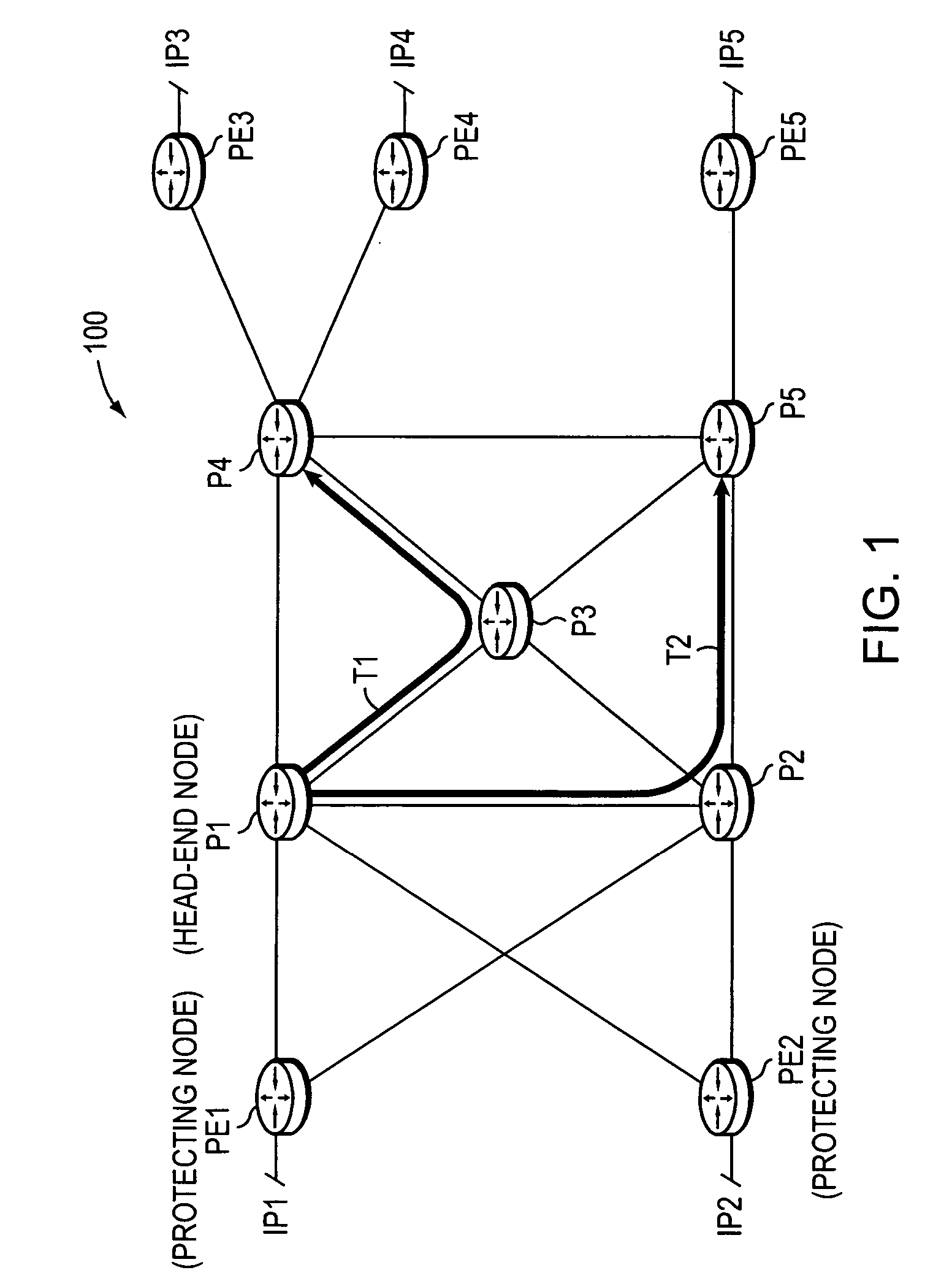
Dynamic protection against failure of a head-end node of one or more TE-LSPs
ActiveUS20070165515A1Preserving scalabilityReduce needError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityLabel switching
A technique dynamically protects against failure of a head-end node of one or more primary Traffic Engineering Label Switched Paths (TE-LSPs) in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a neighboring upstream node (“protecting node”) of the head-end node learns of the primary TE-LSPs (and their respective state control blocks) extending from the head-end node to one or more address prefixes. The protecting node establishes a repair TE-LSP for each of the primary TE-LSPs to a corresponding downstream neighboring node of the head-end node (a “next-next-hop”). In response to detecting a failure of the head-end node, the protecting node locally reroutes traffic destined for the address prefixes to an appropriate repair TE-LSP. Due to the failure of the head-end node, the protecting node then refreshes the states of the primary TE-LSPs using replicated state control blocks accordingly, until the repair TE-LSPs are no longer needed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
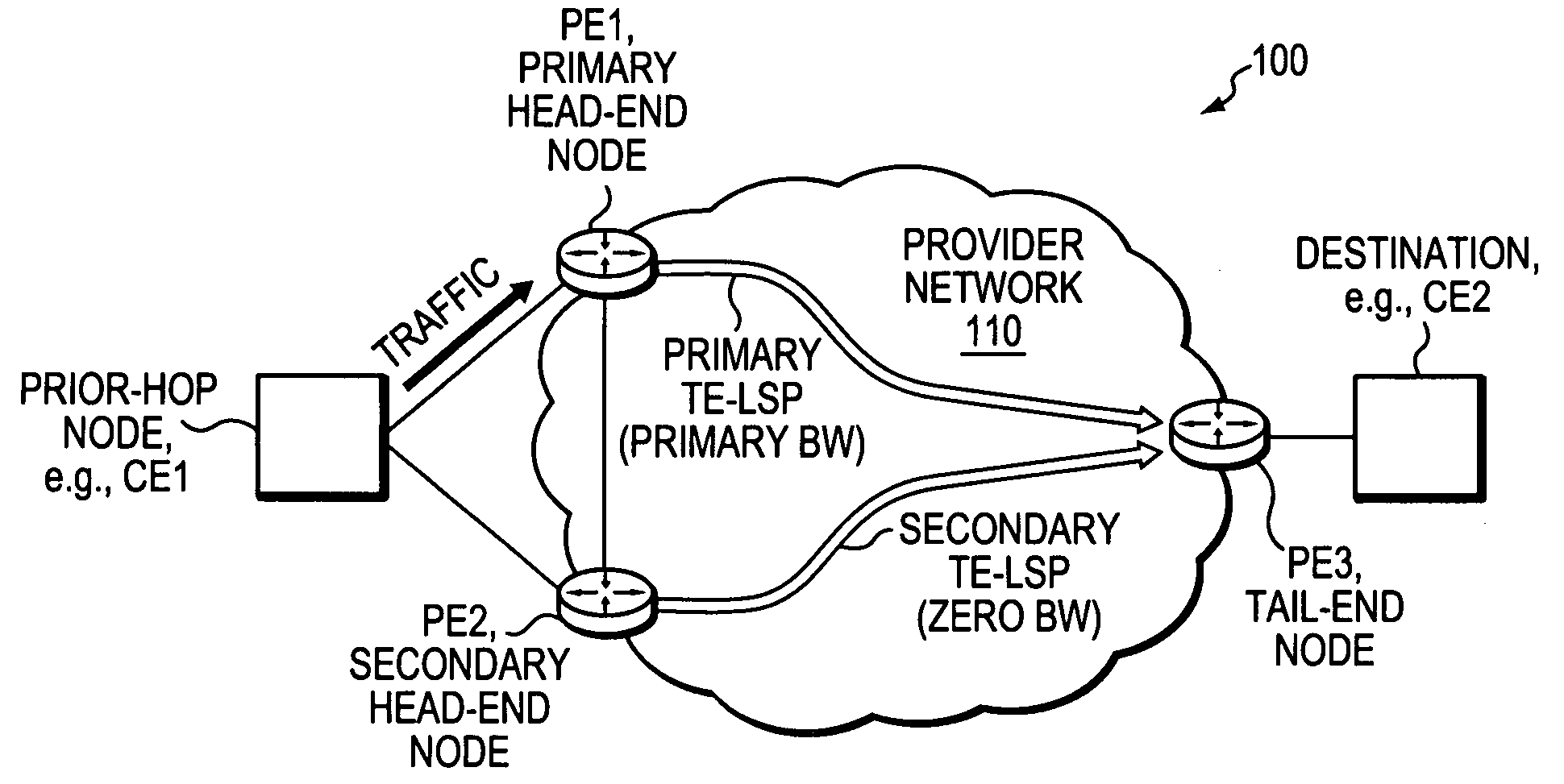
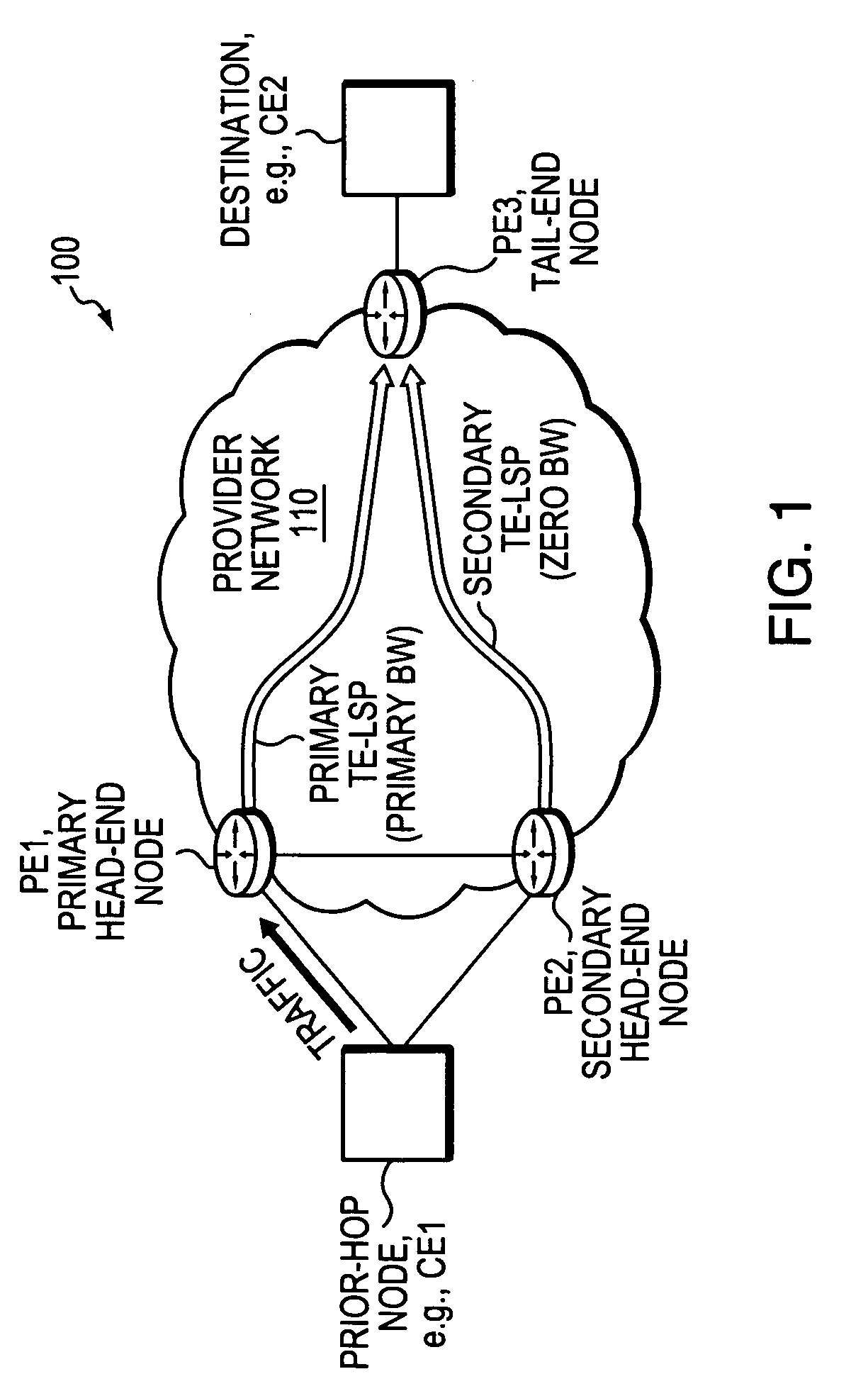
Technique for fast activation of a secondary head-end node TE-LSP upon failure of a primary head-end node TE-LSP
ActiveUS20070280102A1Avoid wastingMinimal delayError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic volumeLabel switching
A technique dynamically activates a secondary Traffic Engineering Label Switched Path (TE-LPs) at a secondary head-end node upon failure of a primary TE-LPs in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a primary head-end node establishes the primary TE-LPs having a primary bandwidth (BW) amount to a primary tail-end node. Also, the secondary head-end node establishes the secondary TE-LPS having zero BW to a secondary tail-end node (e.g., the same as the primary tail-end node). The secondary head-end node monitors the state of the primary TE-LPS, and in response to a failure (e.g., or other state change) substantially immediately adjusts the BW of the secondary TE-LPS to the primary BW amount (“activating” the TE-LPS). A “prior-hop” node to the primary and secondary head-end nodes originally forwarding traffic to the primary head-end node, may then begin forwarding traffic to the secondary head-end node, and thus onto the adjusted secondary TE-LPS.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
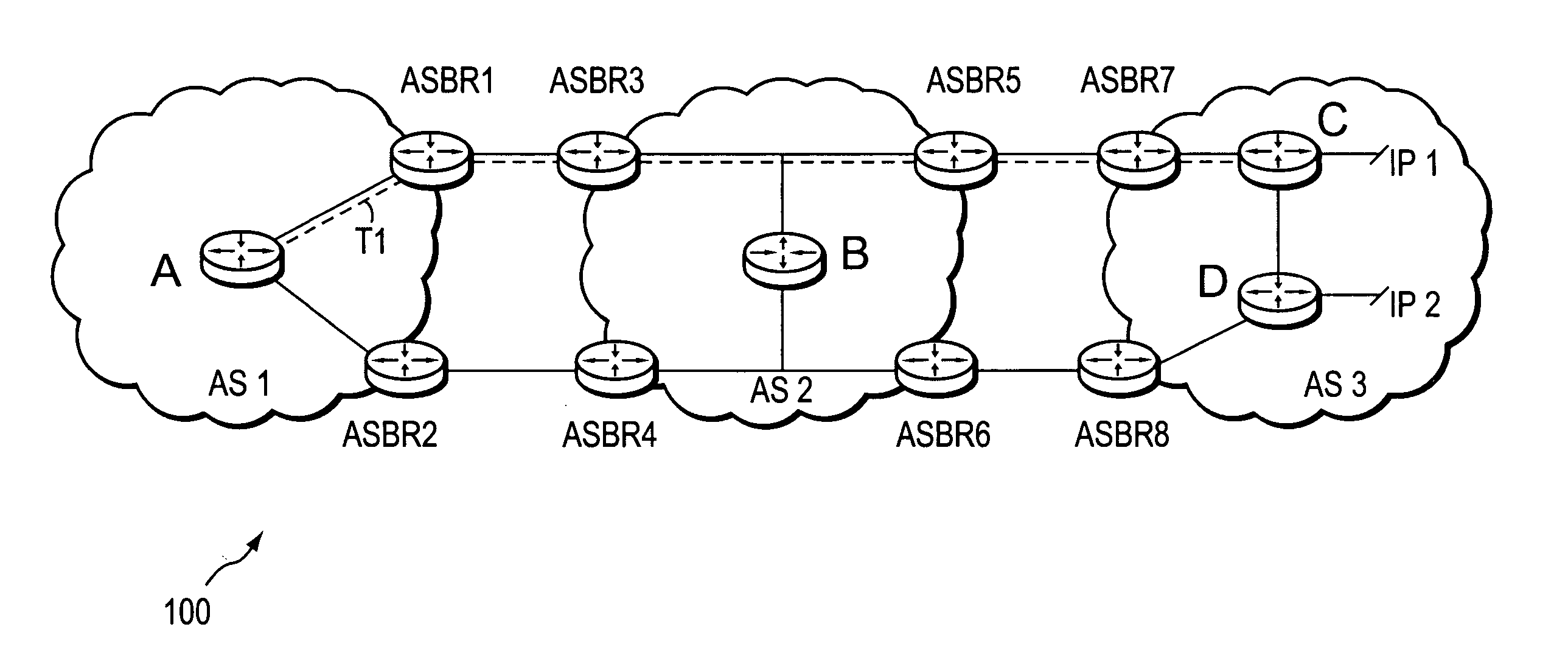
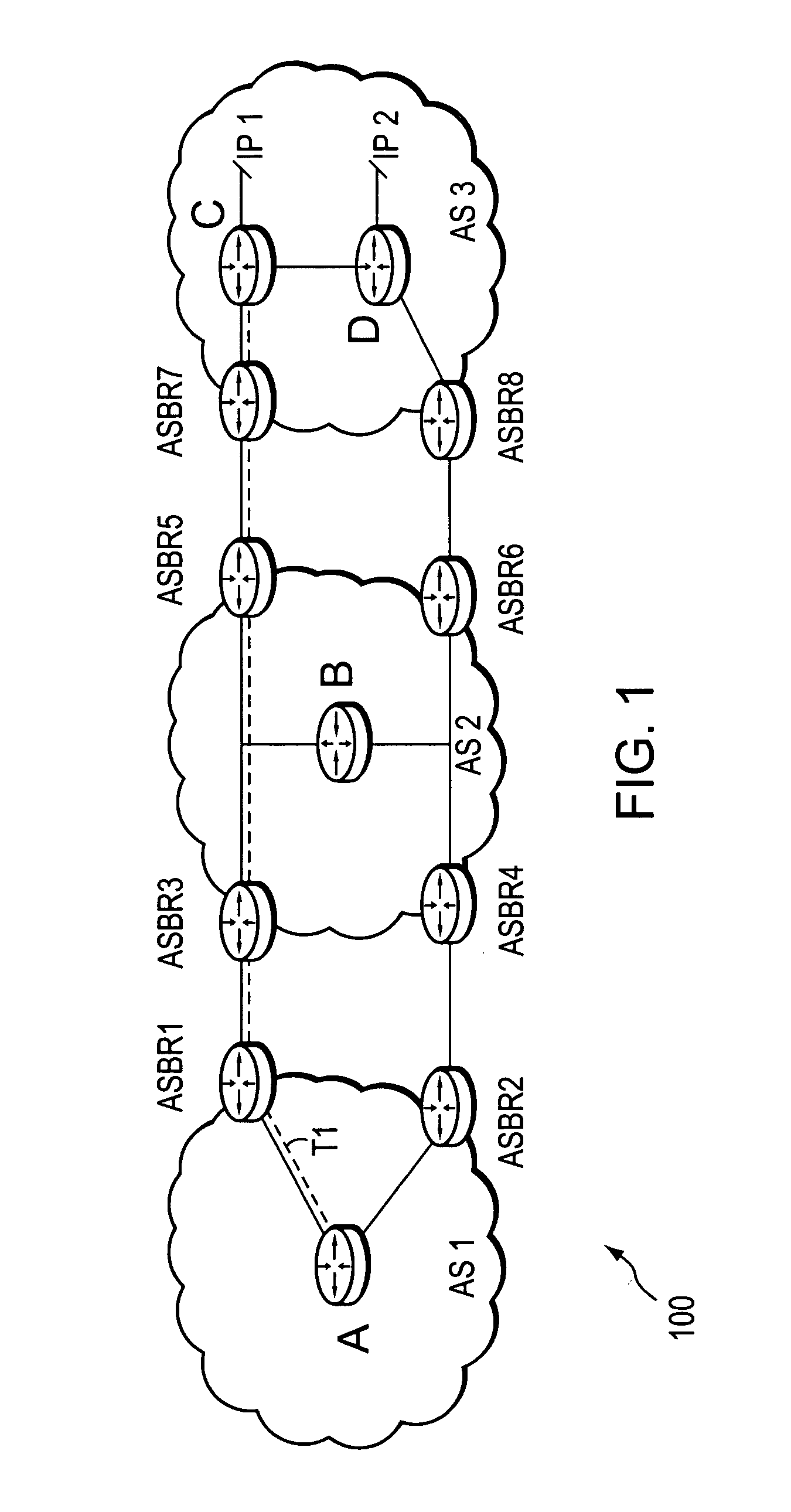
Dynamic retrieval of routing information for inter-AS TE-LSPs
A technique dynamically triggers an exchange of reachability information between a tail-end (remote) domain target node (e.g., a tail-end node) of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) and a local domain head-end node of the TE-LSP in a computer network. The inter-domain information retrieval technique is illustratively based on triggering a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) session whereby at least a portion of the reachability, i.e., routing, information of the tail-end node is transmitted to the head-end node of the TE-LSP in accordance with BGP. Specifically, once a TE-LSP is established between the head-end node and the tail-end node, the head-end node triggers the tail-end node, e.g., through extensions to a request / response signaling exchange, to establish the BGP session. Establishment of the BGP session enables transmission of the routing information from the tail-end node to the head-end node. The head-end node uses the routing information to calculate routes, i.e., address prefixes and associated attributes, reachable from the tail-end node for insertion into its routing table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for protecting against failure of a TE-LSP tail-end node
InactiveUS7586841B2Quick protectionAvoid deploymentError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsPathPingEngineering
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
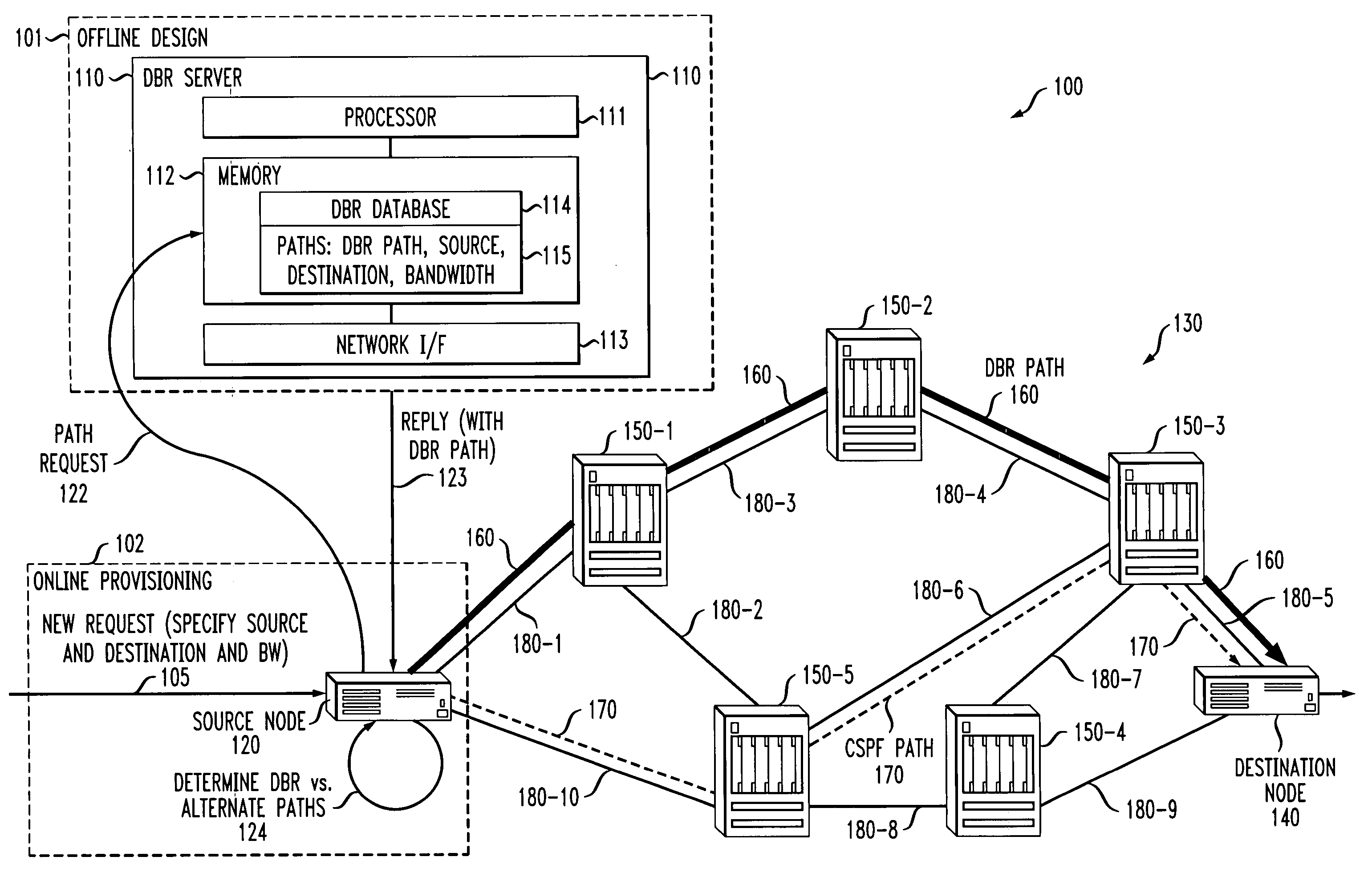
Techniques for network traffic engineering
InactiveUS20050008014A1Carried demand isDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationPathPingInternet traffic
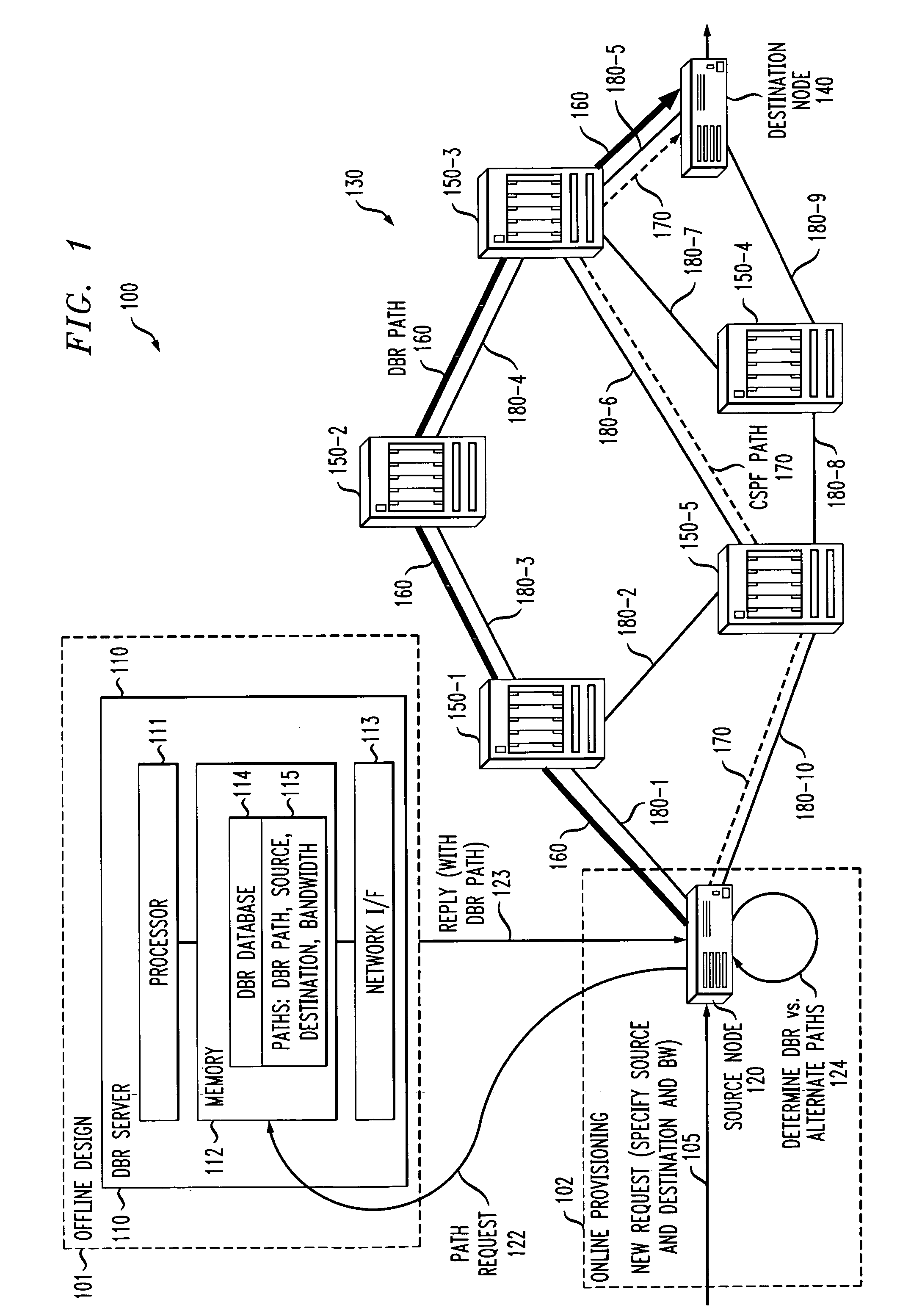
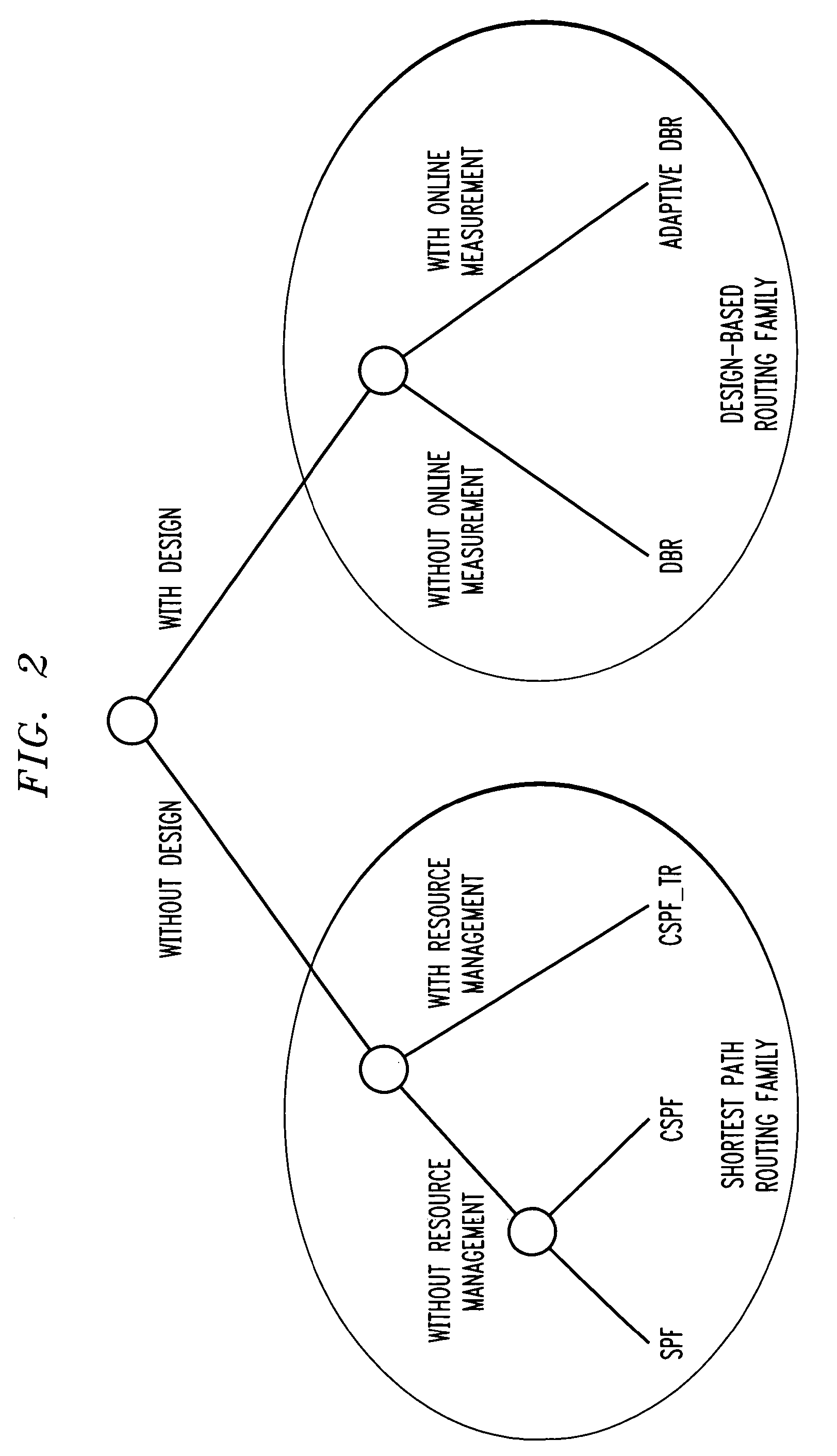
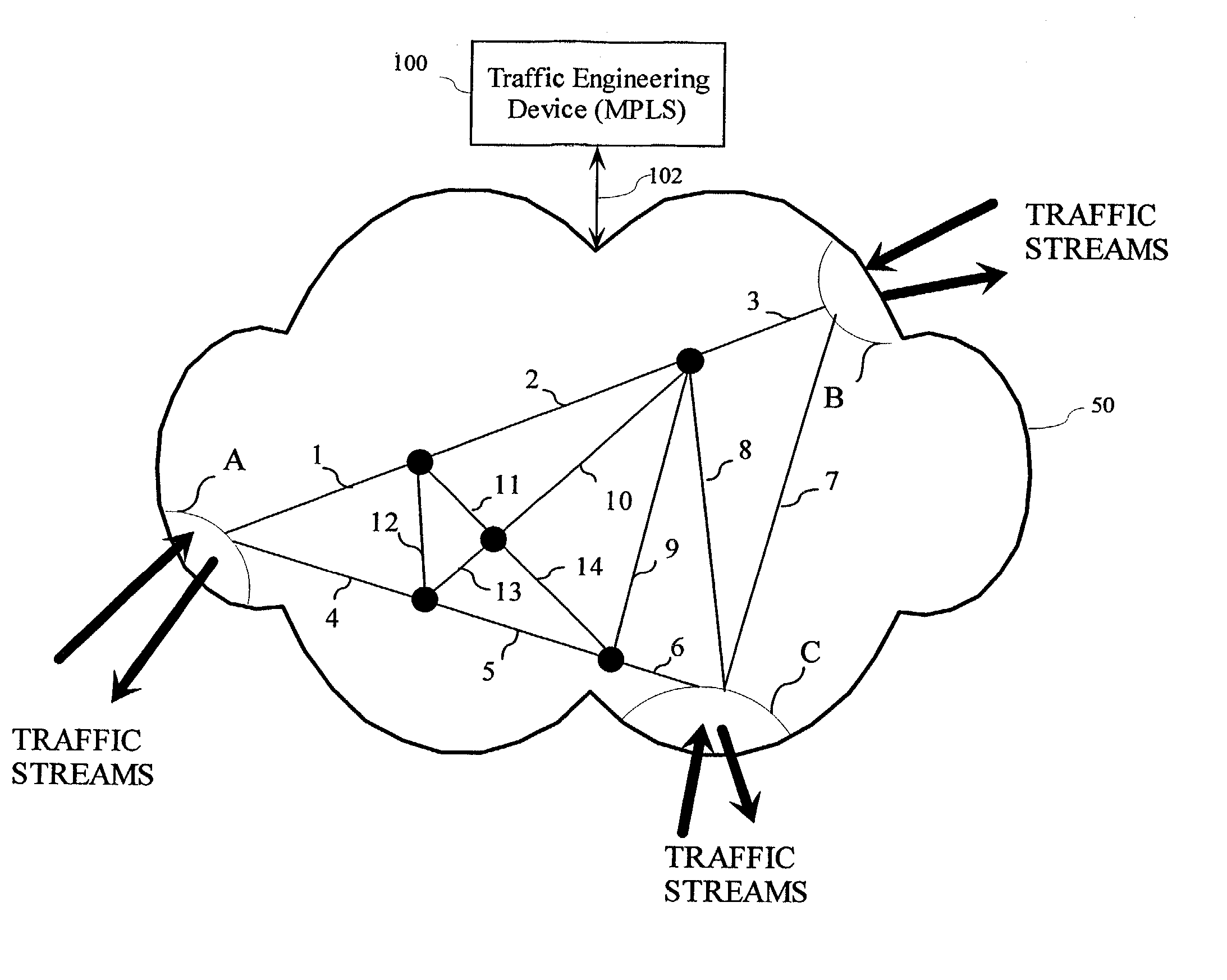
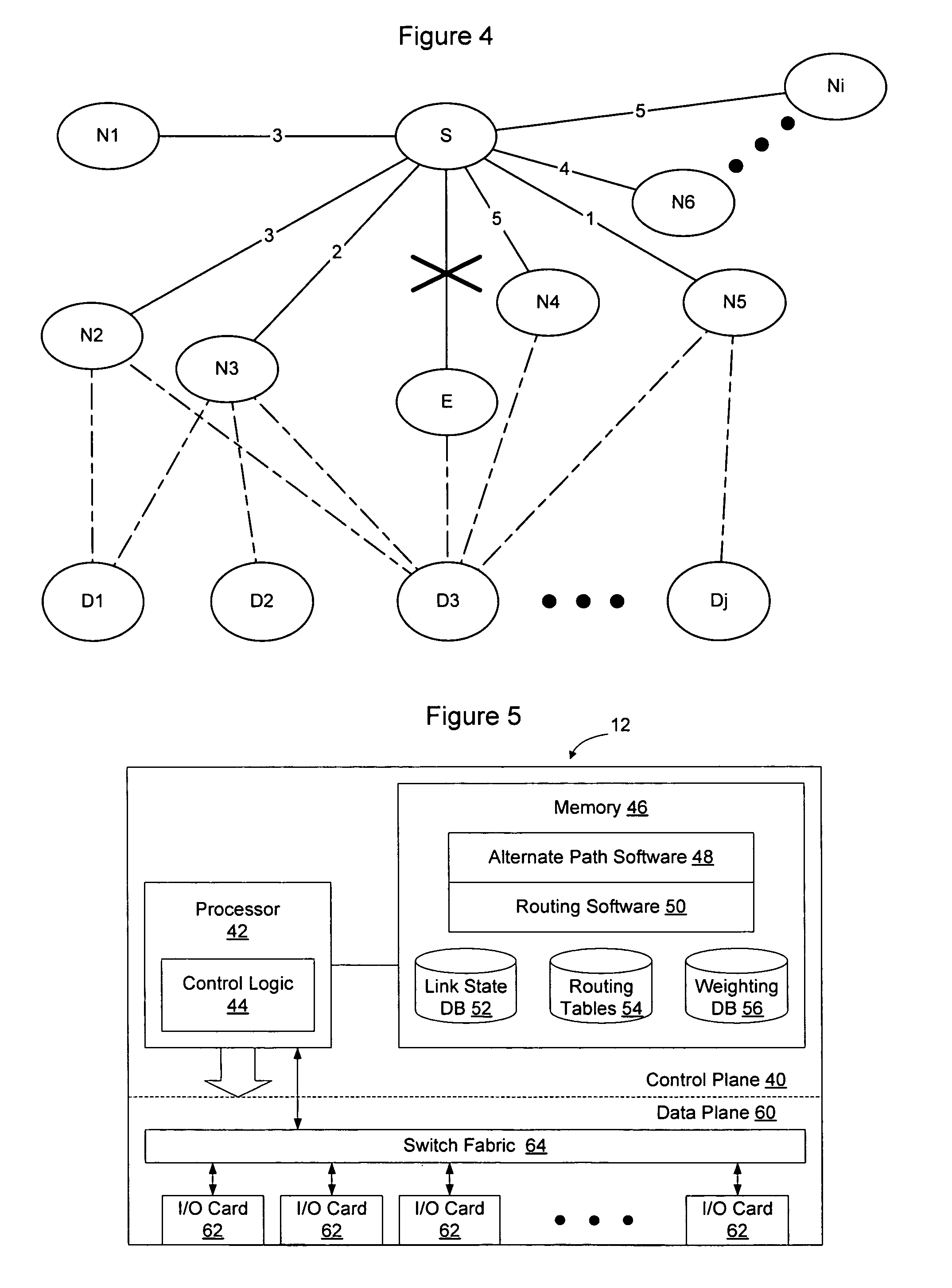
In a traffic engineering technique, a determination is made as to whether any path of a number of predetermined paths meets requirements corresponding to a request. The predetermined paths are determined by substantially maximizing carried demand using at least traffic demand estimates and network topology information and by performing routing for the substantially maximized carried demand. If a given path meeting the requirements is found, a connection on the given path is created, if possible. The predetermined paths are determined through offline TE techniques referred to herein as offline design-based routing (DBR). The requirements for the path may include a destination address and a bandwidth. The offline DBR techniques can include uncertain static demand information or dynamic connections. The offline DBR techniques may be used with adaptive DBR techniques, such that paths are determined offline if possible but can also use shortest path first (SPF), constrained SPF (CSPF) or other techniques during an online path determination. An improvement to a conventional CSPF technique is also presented.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
System and method for deriving traffic demands for a packet-switched network
The present invention is directed to a method and system for deriving traffic demands for a packet-switched network. A novel model of defining traffic demands as a volume of load originating from an ingress link and destined to a set of egress links enables support for traffic engineering and performance debugging of large operational packet-switched networks.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Dynamic enforcement of MPLS-TE inter-domain policy and QoS
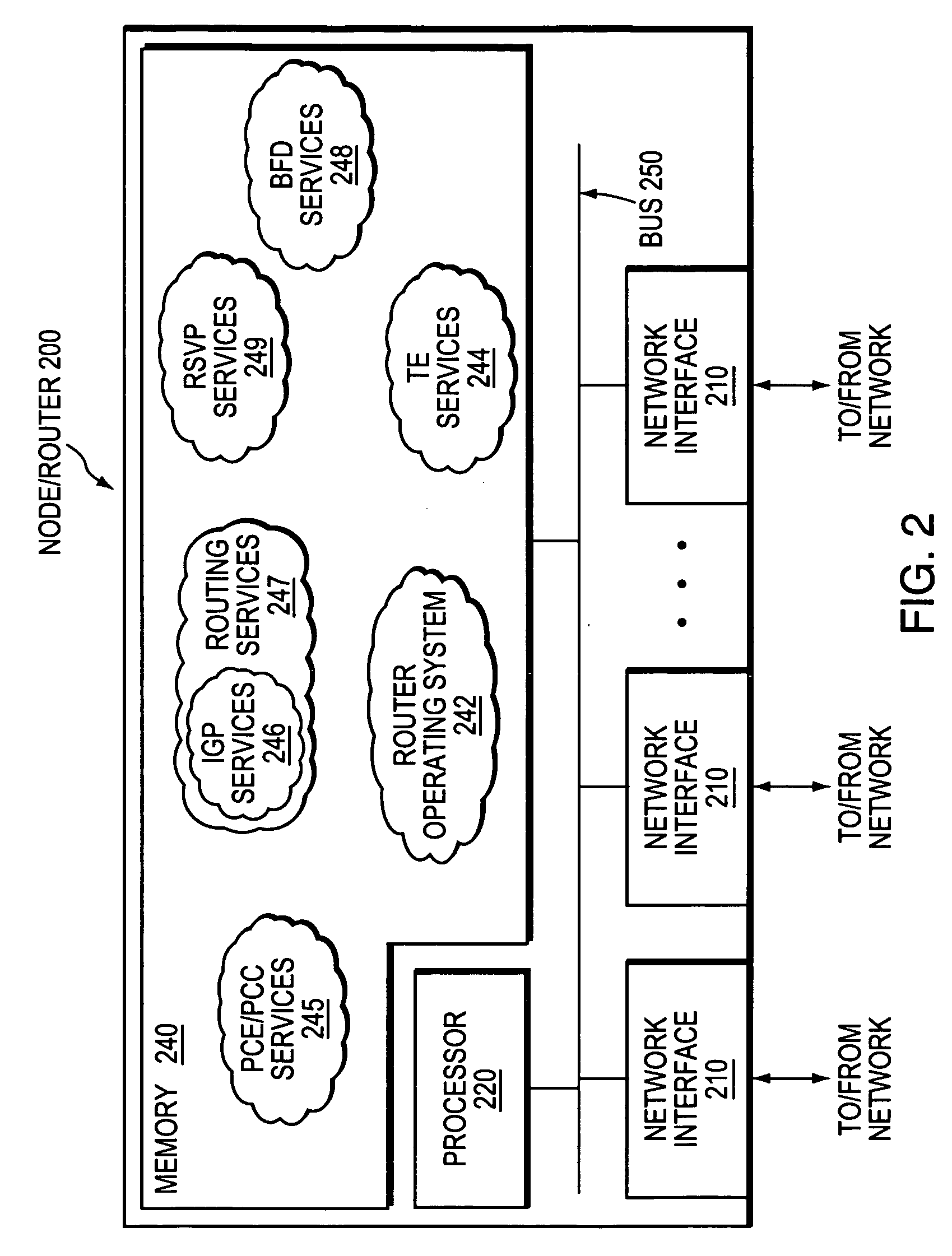
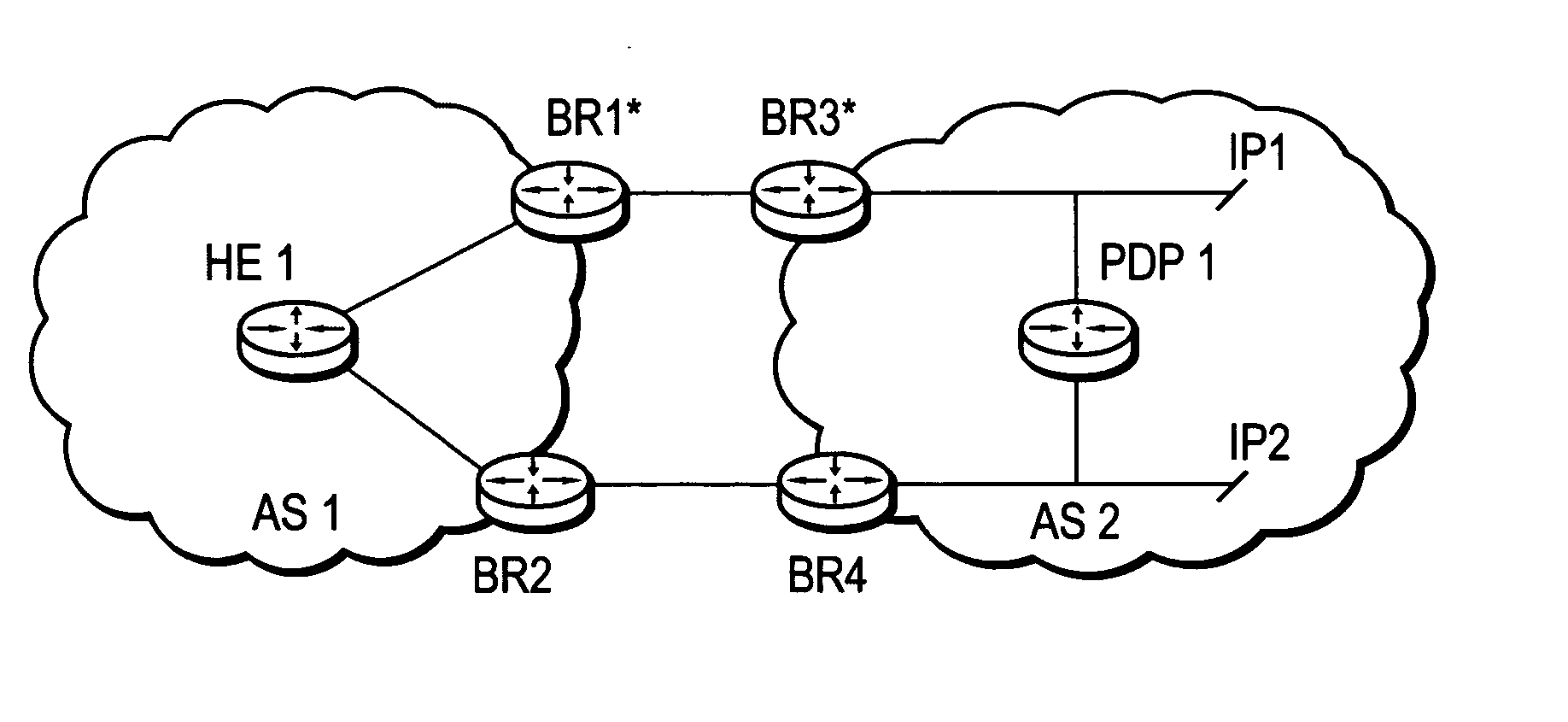
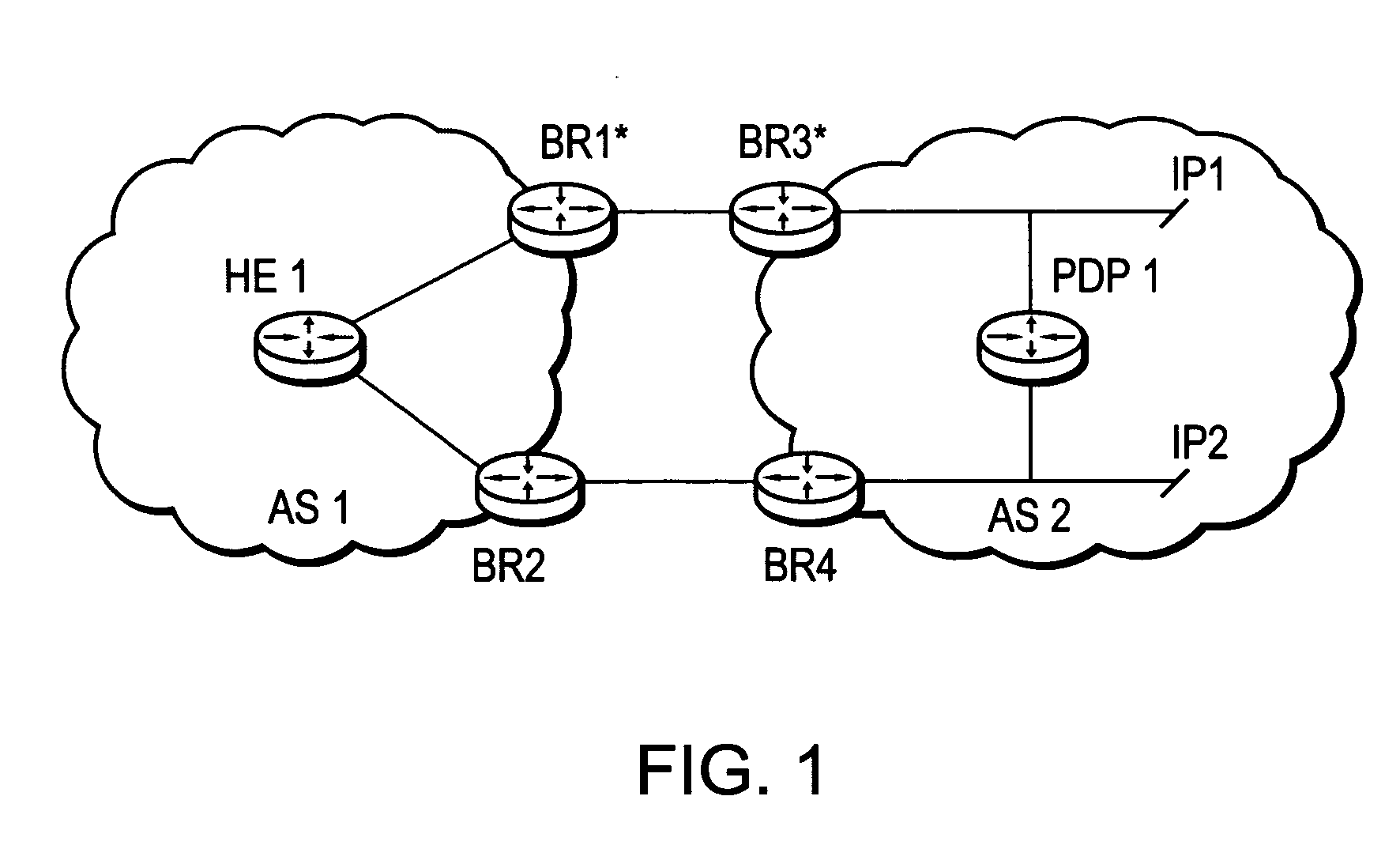
InactiveUS20070019558A1Efficient mechanismError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsQuality of servicePolicy decision
A technique dynamically enforces inter-domain policy and quality of service (QoS) for Traffic Engineering (TE) Label Switched Paths (LSPs) between a local domain and a remote domain in a computer network. According to the enforcement technique, a Path Computation Element (PCE) of the local domain receives a path computation request for an inter-domain TE-LSP from the remote domain, and triggers a policy verification procedure at a Policy Decision Point (PDP) of the local domain. The PDP determines whether the requested TE-LSP is allowed based on configured policy for the remote domain and previously established TE-LSPs from the remote domain. In the event the requested TE-LSP is allowed and subsequently established, a Policy Enforcement Point (PEP) along the TE-LSP, e.g., a border router of the local domain or a dedicated server, updates the PDP with the state of the TE-LSP. In response to the update, the PDP returns a QoS template indicating configured QoS guidelines the PEP must enforce for that TE-LSP. If the TE-LSP is eventually torn down, the PEP again updates the PDP with the state of the TE-LSP.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method and apparatus for communications traffic engineering
InactiveUS20020186658A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityLabel switching
This invention provides for a technique for selectively off-loading traffic from congested sub-regions of a network to more lightly-loaded regions by making use of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS). For each network element, an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) routing is employed to provide re-routing and to identify congested links caused by re-routed trunks for each single failure. The re-routed traffic is then analyzed and alternate Label Switched Paths (LSPs) are identified for such traffic trunks so that the traffic is directed to the alternate LSPs during the single failure event.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
System, device and method for limiting tunnel traffic in an information communication network
ActiveUS7123587B1Avoid destabilizationAvoid congestion problemsError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityForwarding equivalence class
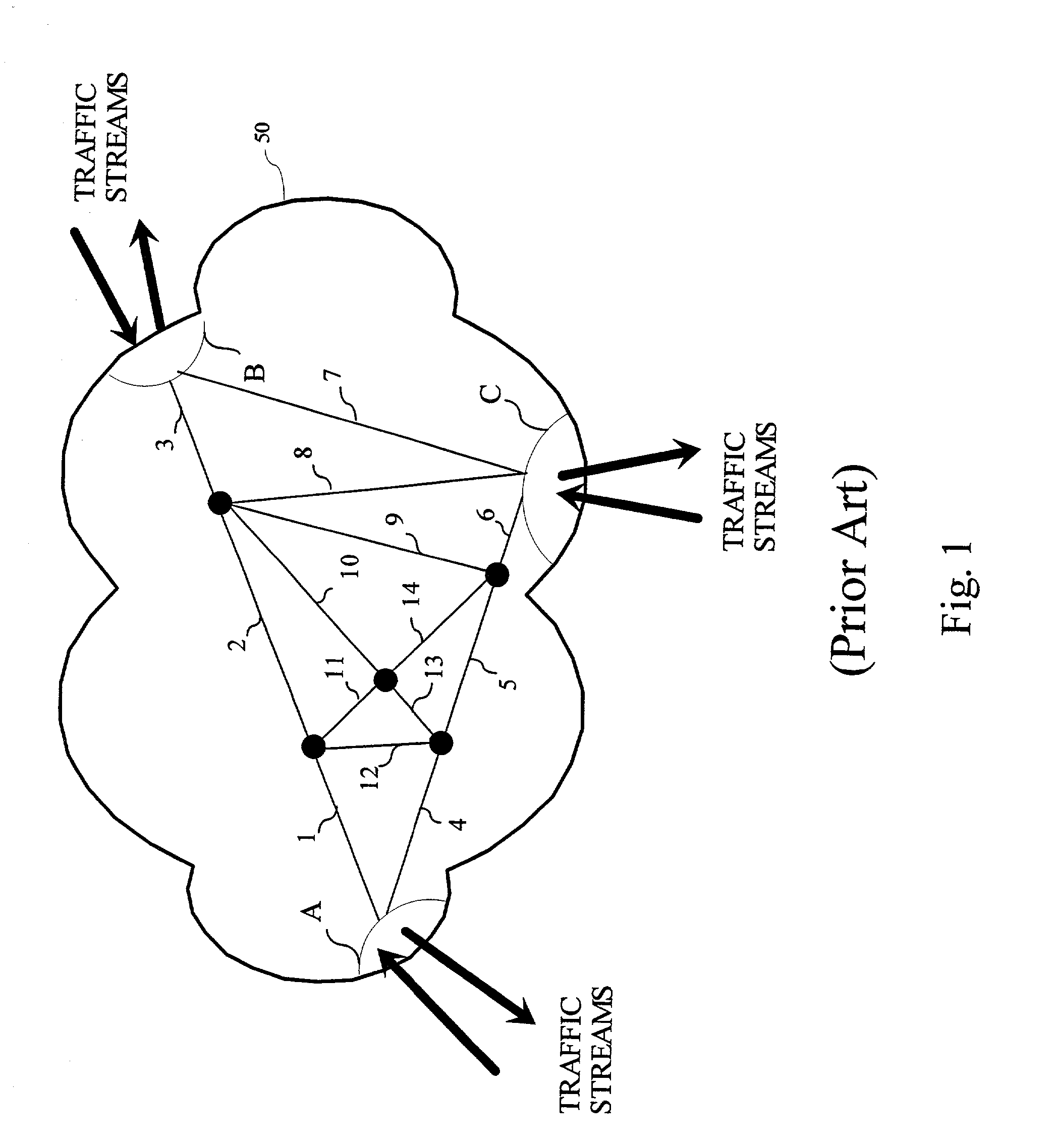
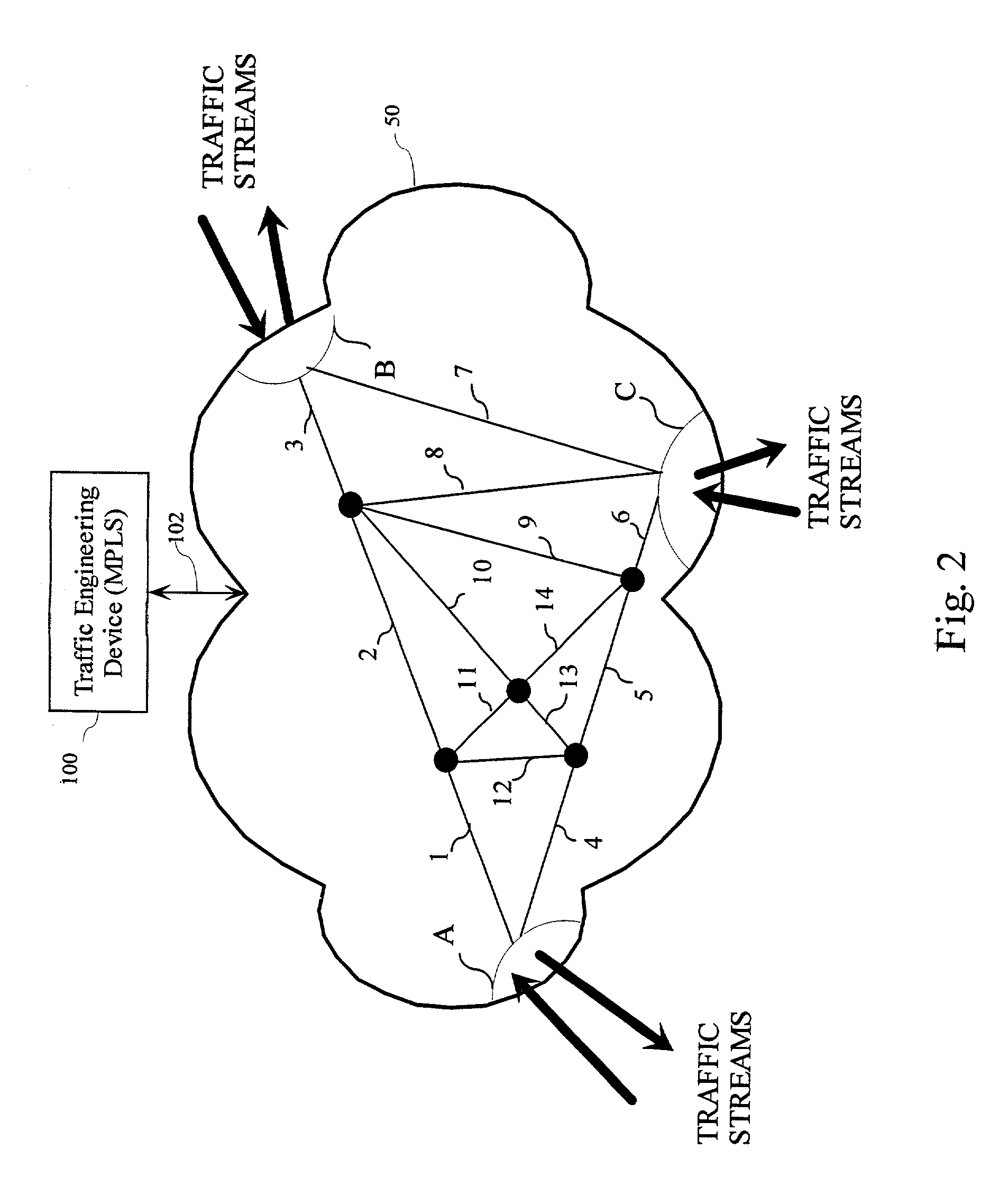
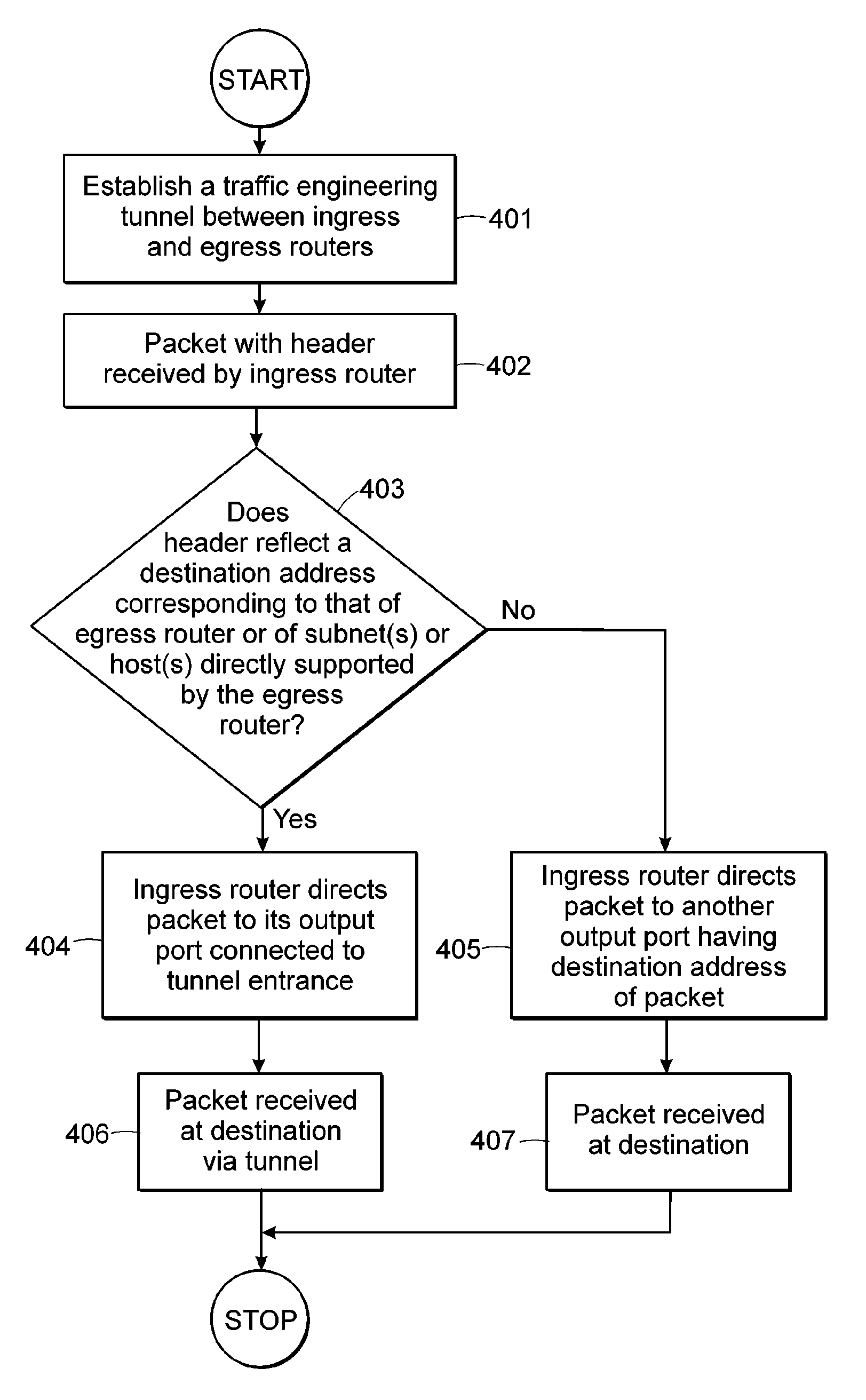
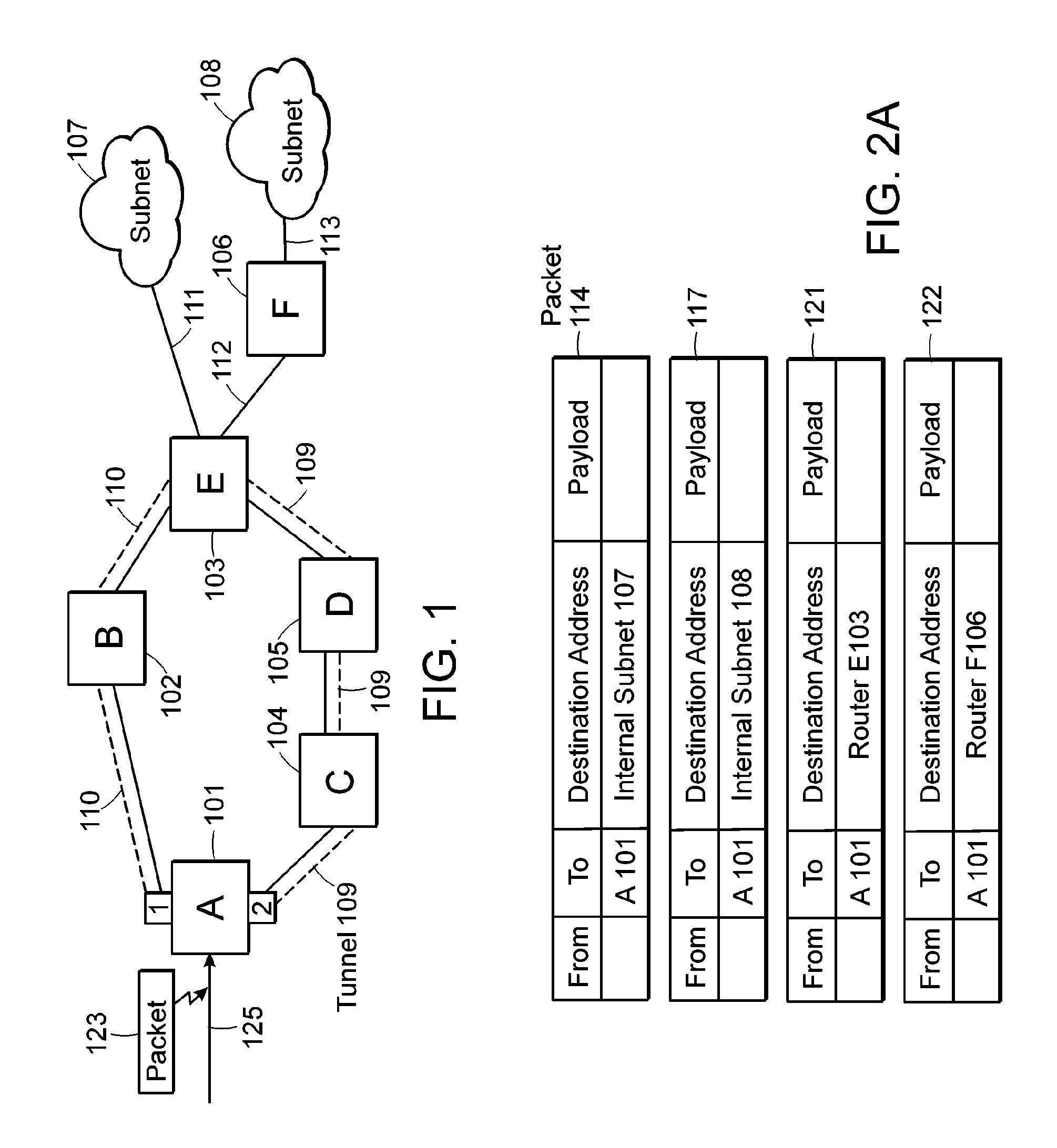
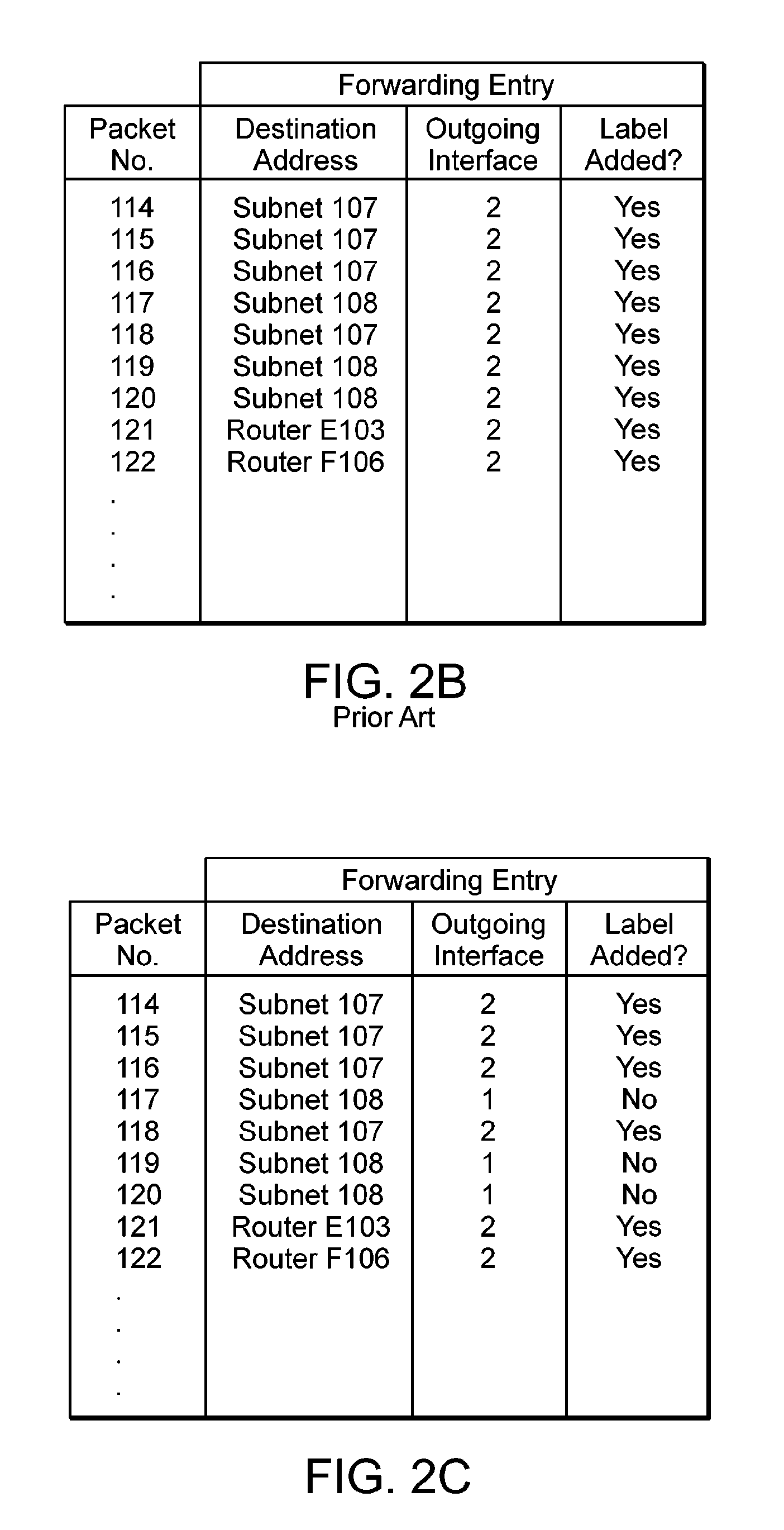
There is disclosed an apparatus and method for limiting tunnel traffic in a network. Traffic engineering tunnels are used to direct traffic along a predefined path, which may differ from the path that internet protocol (IP) routing would determine. Interior gateway protocol (IGP) cut through will allow the forwarding of all destinations downstream of a tunnel through the tunnel, without the operator needing to specify a forwarding equivalence class (FEC). But congestion in the tunnel and network instability may result from this approach. A solution to these problems is disclosed which limits the traffic in the tunnel to only that with destination addresses of the tunnel's egress router or nodes directly supported thereby. Other solutions are disclosed which allow tunnel traffic to nodes having destination addresses other than those being directly supported by the tunnel's egress router. All of these solutions are achieved in both pre-determined forwarding entry and dynamic packet-by packet embodiments.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Method for constructing double-arch tunnel by rebuilding and expanding existing single-hole tunnel
InactiveCN101737061AIncrease the construction work areaImprove construction efficiency and construction safetyUnderground chambersTunnel liningSingle holeEngineering
The invention relates to a method for constructing a double-arch tunnel by rebuilding and expanding an existing single-hole tunnel. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide a method for constructing the double-arch tunnel by rebuilding and expanding the existing single-hole tunnel, which adopts a ' middle pilot hole, the existing tunnel and a right hole' three pilot pit construction scheme, enlarges construction face and reduce excavation face and surrounding rock disturbed zone. To solve the technical problem, the invention adopts a technical scheme that the method for constructing the double-arch tunnel by rebuilding and expanding the existing single-hole tunnel comprises the following steps: 1.1 constructing the middle pilot hole parallel to the existing single-hole tunnel on one side of the existing single-hole tunnel and completing supporting construction; 1.2, constructing a left hole by sequence and zone on the basis of the existing single-hole tunnel and communicating the left hole and the middle pilot hole; and 1.3, after excavating the left hole to a certain size, constructing the right hole by sequence and zone and communicating the right hole with the middle pilot hole. The method is mainly used in highway traffic engineering and municipal traffic engineering.
Owner:POWERCHINA HUADONG ENG COPORATION LTD
Programmable switching engine with storage, analytic and processing capabilities
InactiveUS20150063349A1Good varietyEasy to manageMultiplex system selection arrangementsCircuit switching systemsStructure of Management InformationMulti dimensional
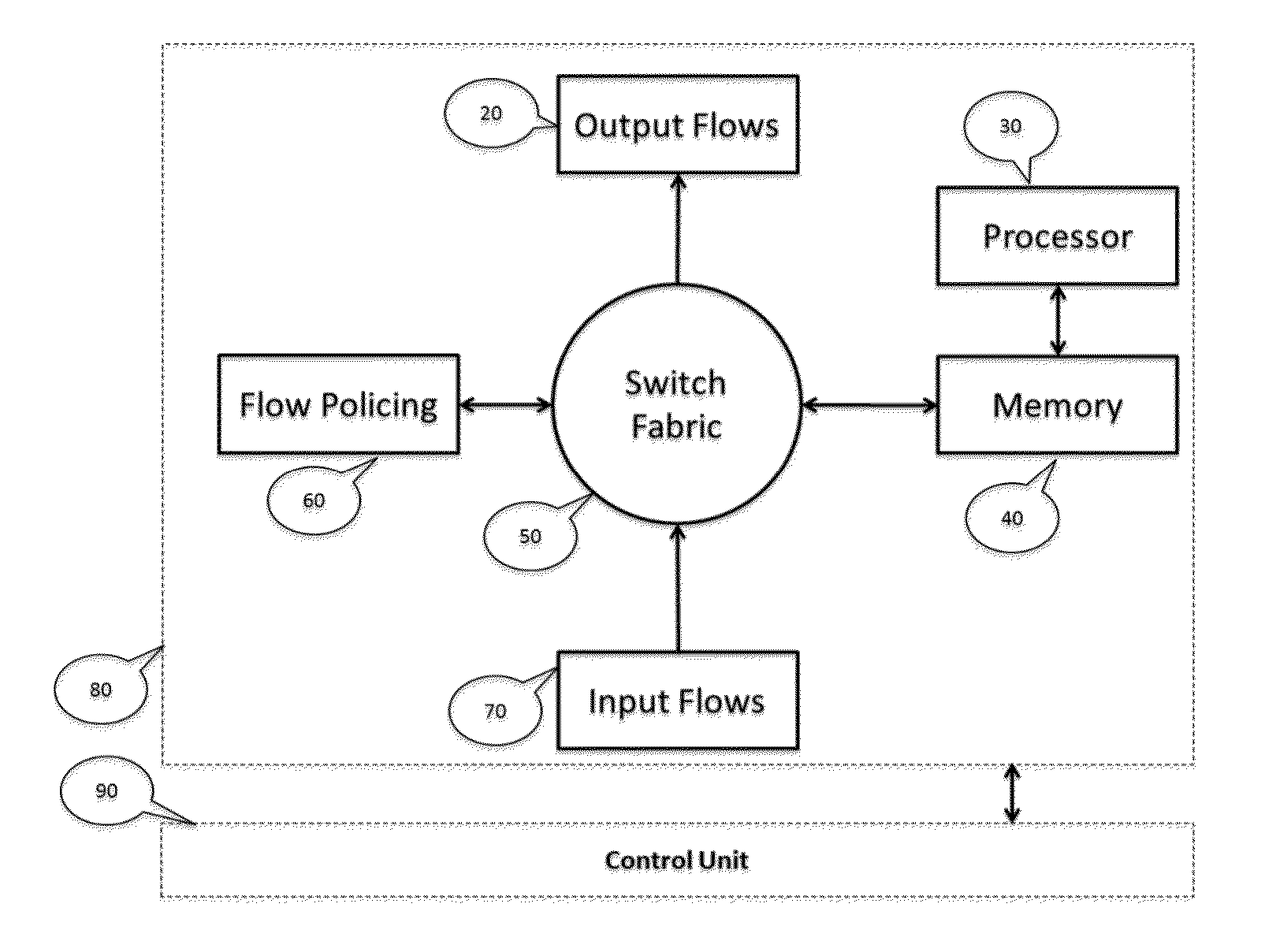
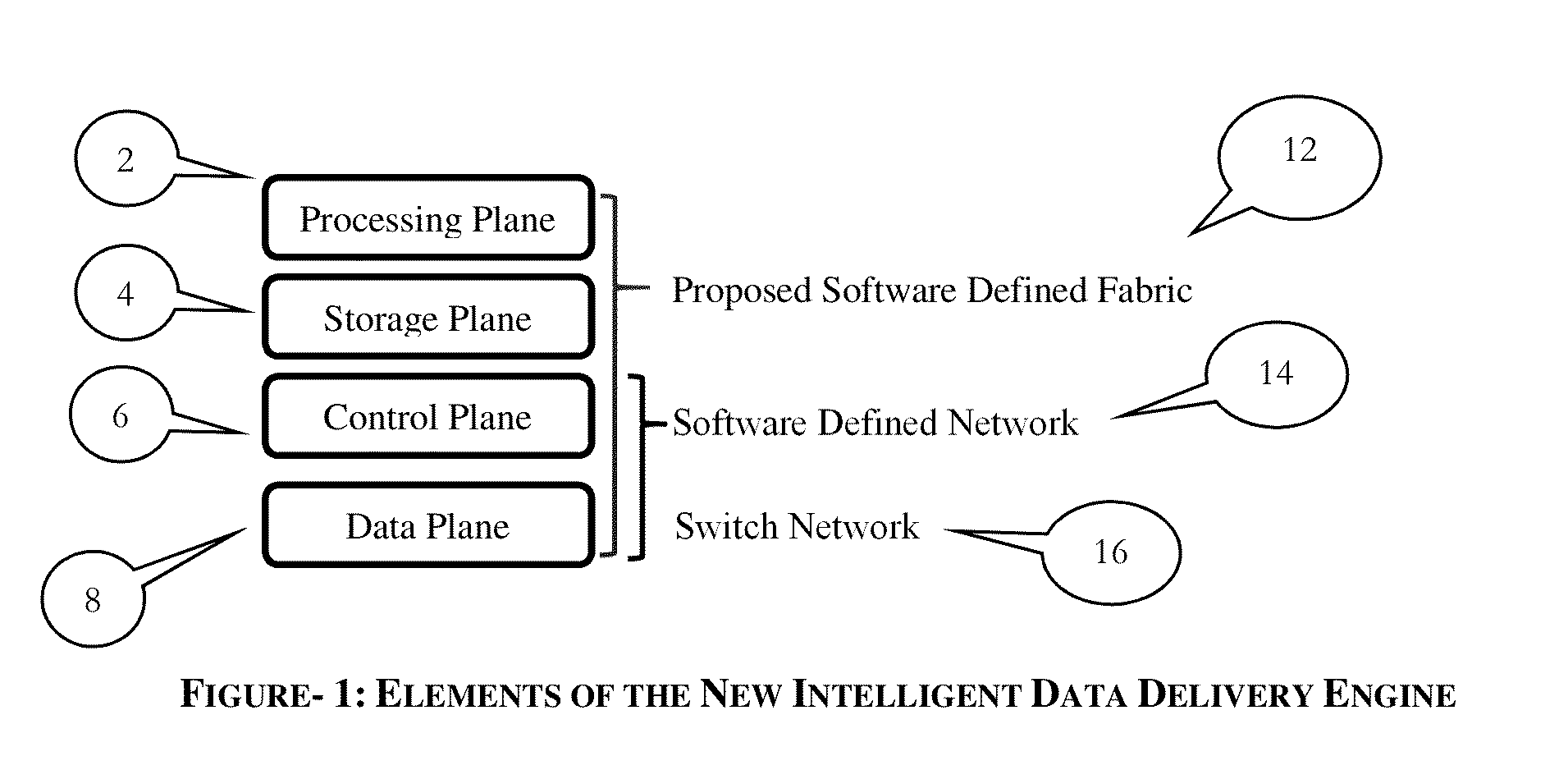
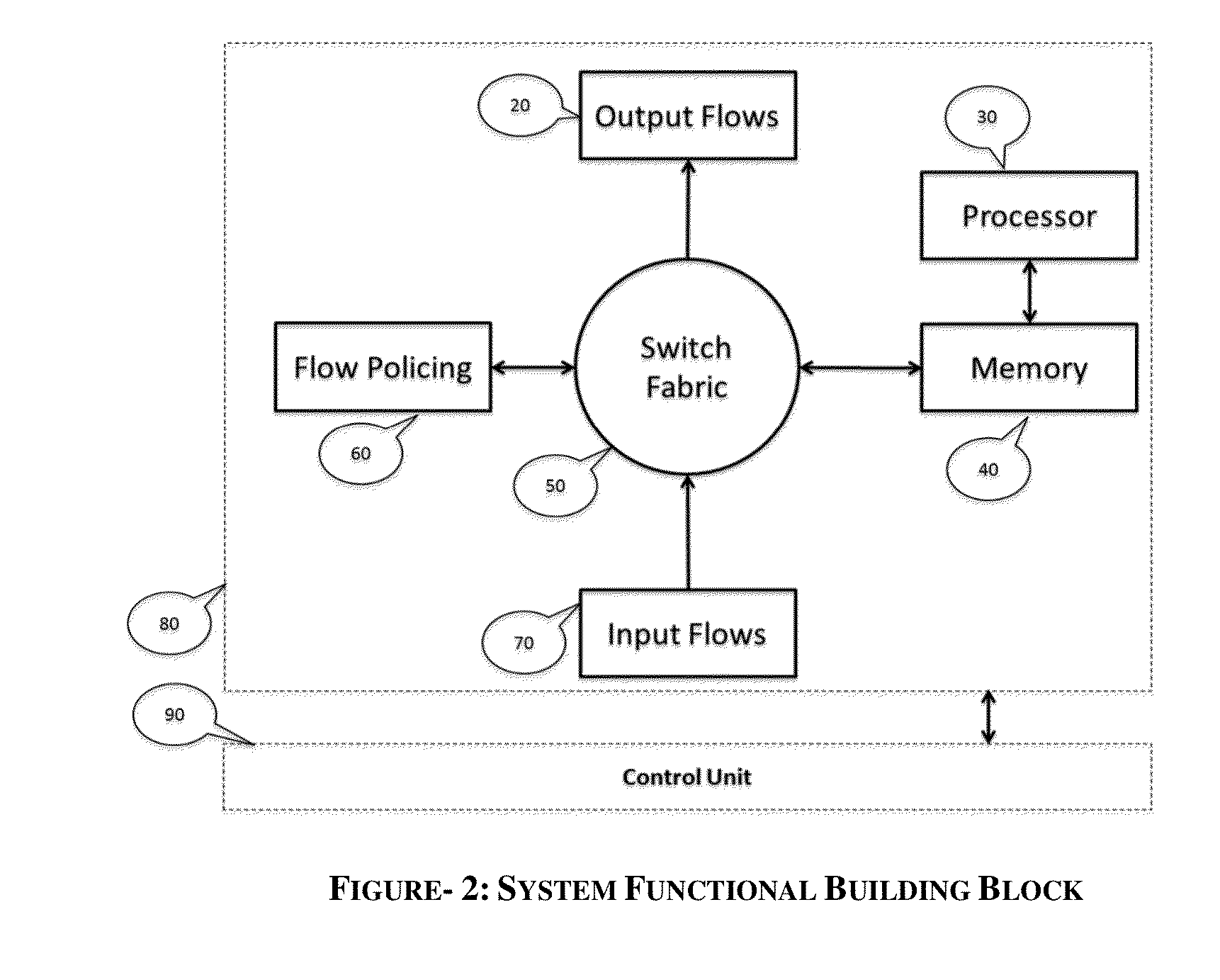
An improvement to the prior-art extends an intelligent solution beyond simple IP packet switching. It intersects with computing, analytics, storage and performs delivery diversity in an efficient intelligent manner. A flexible programmable network is enabled that can store, time shift, deliver, process, analyze, map, optimize and switch flows at hardware speed. Multi-layer functions are enabled in the same node by scaling for diversified data delivery, scheduling, storing, and processing at much lower cost to enable multi-dimensional optimization options and time shift delivery, protocol optimization, traffic profiling, load balancing, and traffic classification and traffic engineering. An integrated high performance flexible switching fabric has integrated computing, memory storage, programmable control, integrated self-organizing flow control and switching.
Owner:ARDALAN SHAHAB +1
Method and apparatus for selecting between available neighbors in a rapid alternate path calculation
InactiveUS20080056137A1Reduce computational complexityComputational complexity is reducedError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityRapid processing
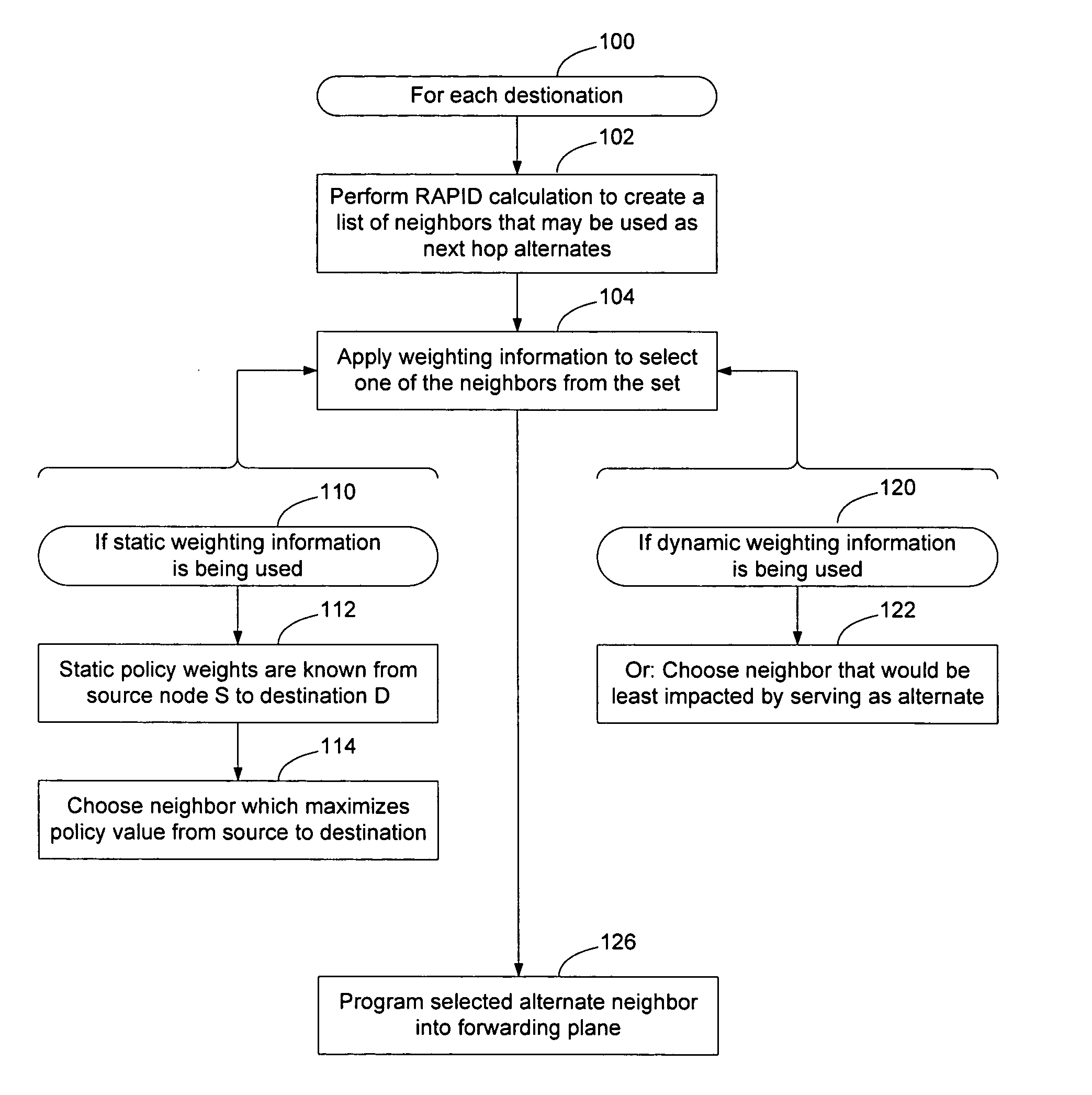
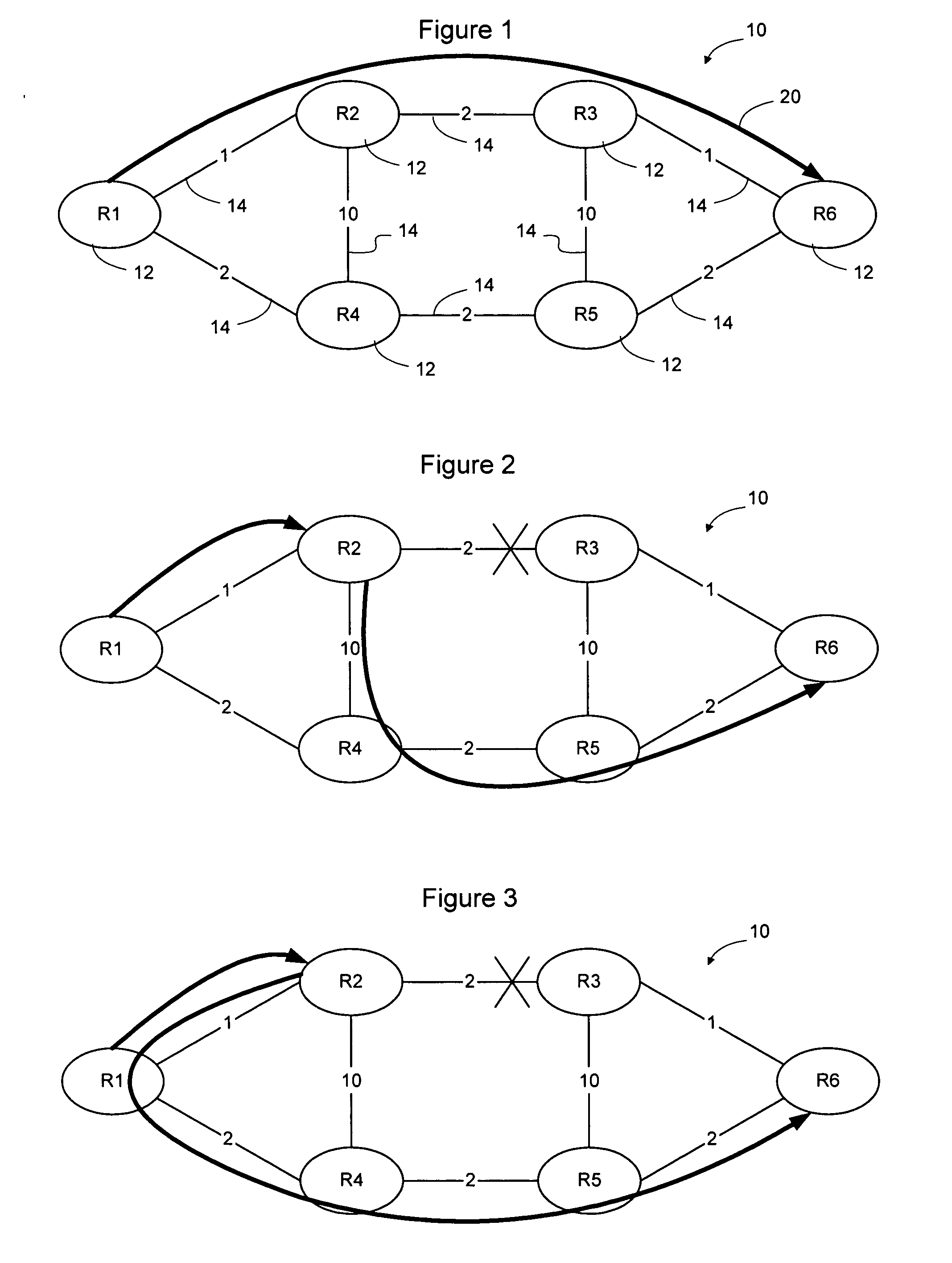
A weighting process may be used to select between alternate neighbors in a RAPID calculation to enable policy and / or traffic engineering considerations to affect the selection of an alternate path through the network. The information used to weight the neighbors may static administratively assigned weighting information or dynamic weighting information such as local statistical traffic condition information. The process may take into account the amount of traffic being handled by the current primary next hop for the destination, the available capacity of the available alternate neighbors, the ability of the alternate neighbors to handle the additional traffic, and other considerations. Weighting may occur after a set of available loop free alternate neighbors has been determined. Alternatively, weighting may occur before the RAPID calculation has been performed to cause the neighbors to be ordered prior to RAPID processing. This may enable RAPID calculation to stop without considering all available neighbors.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
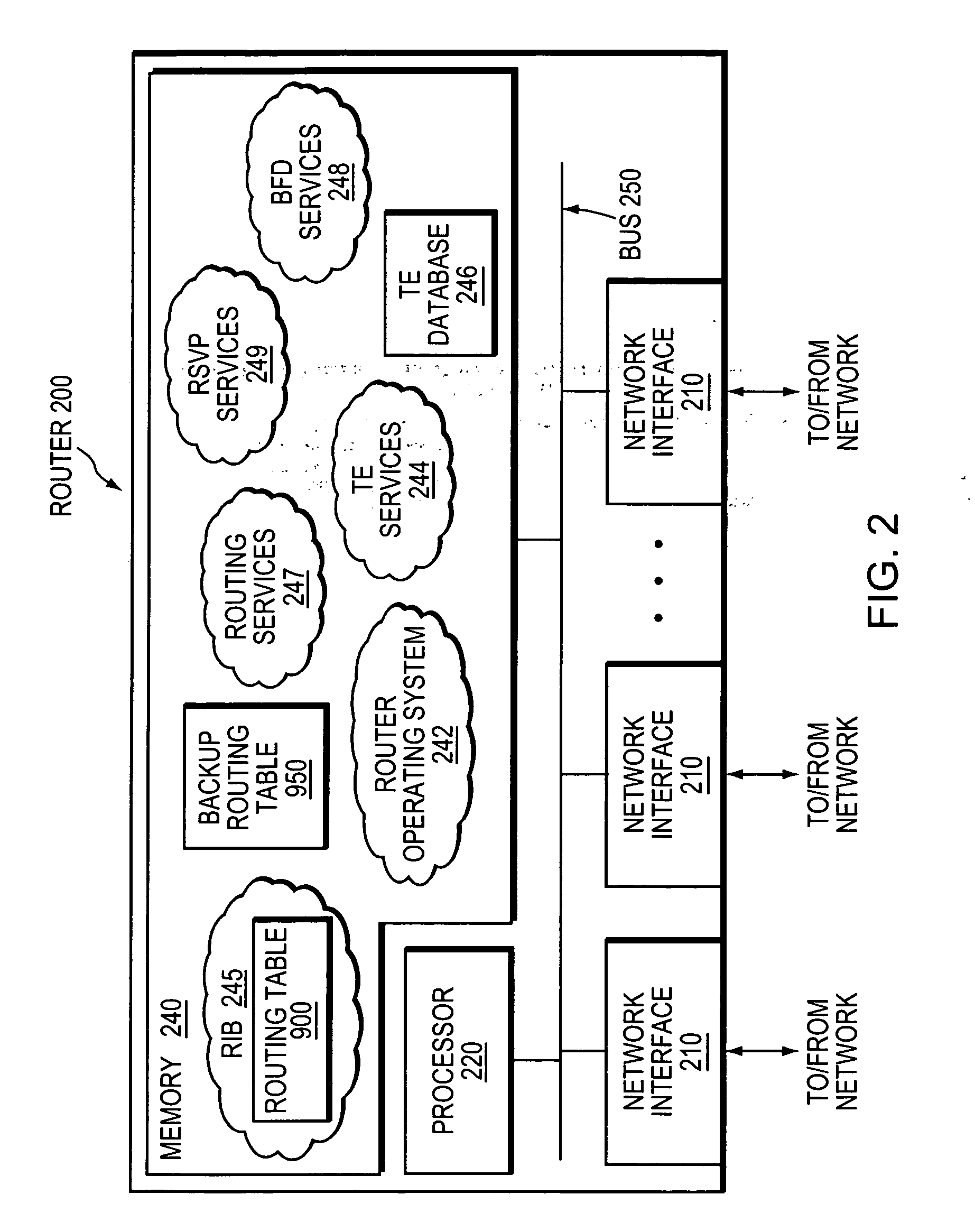
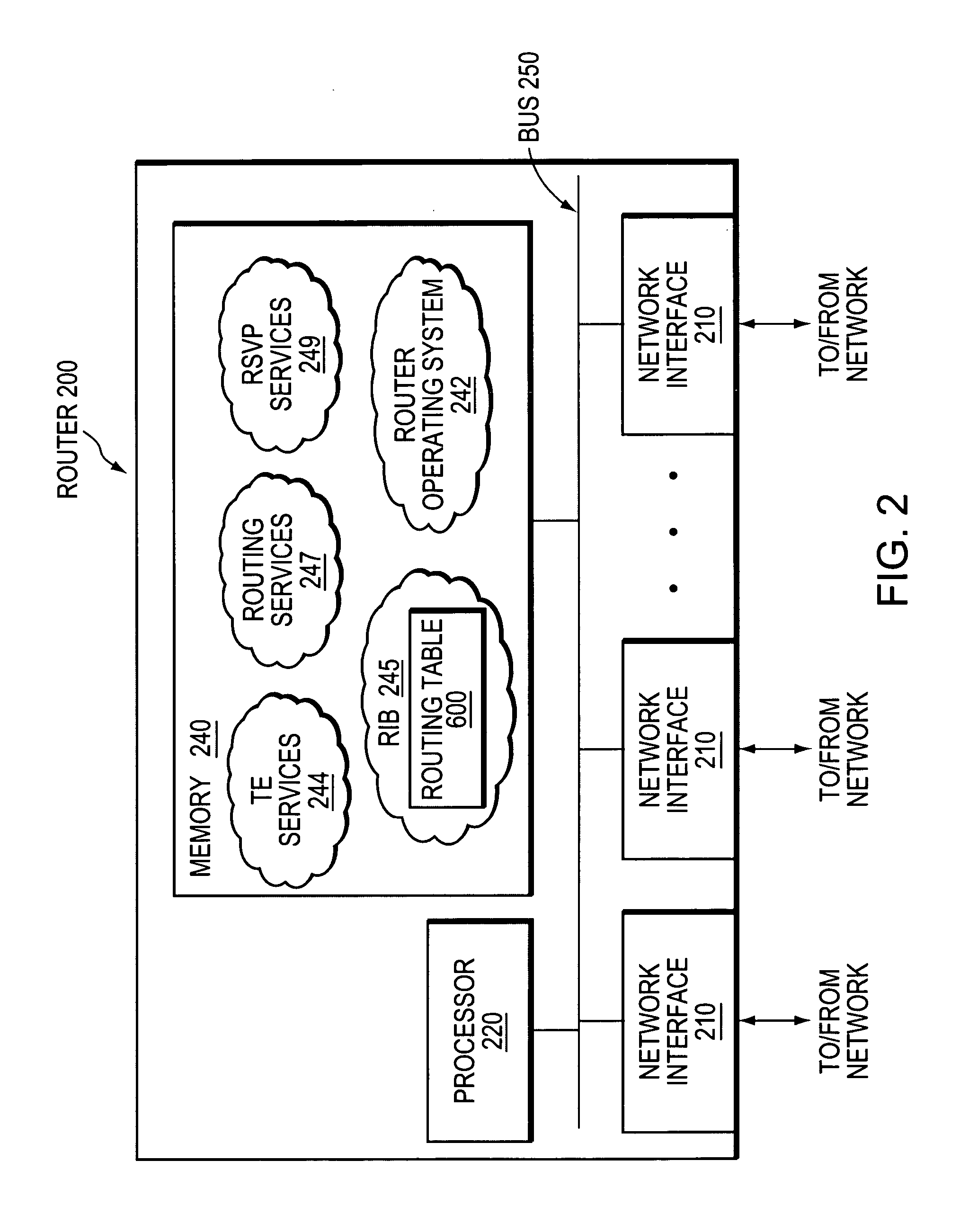
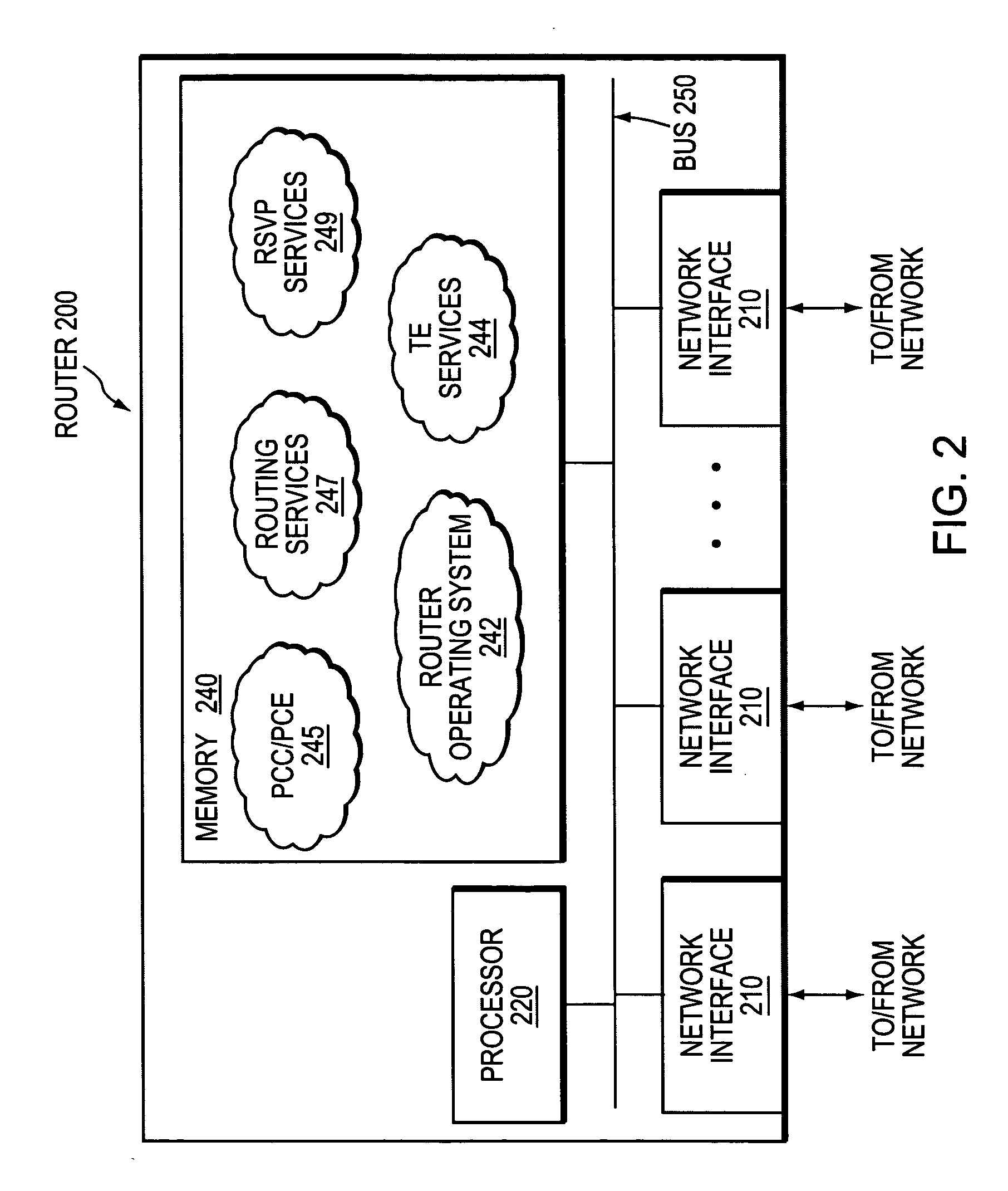
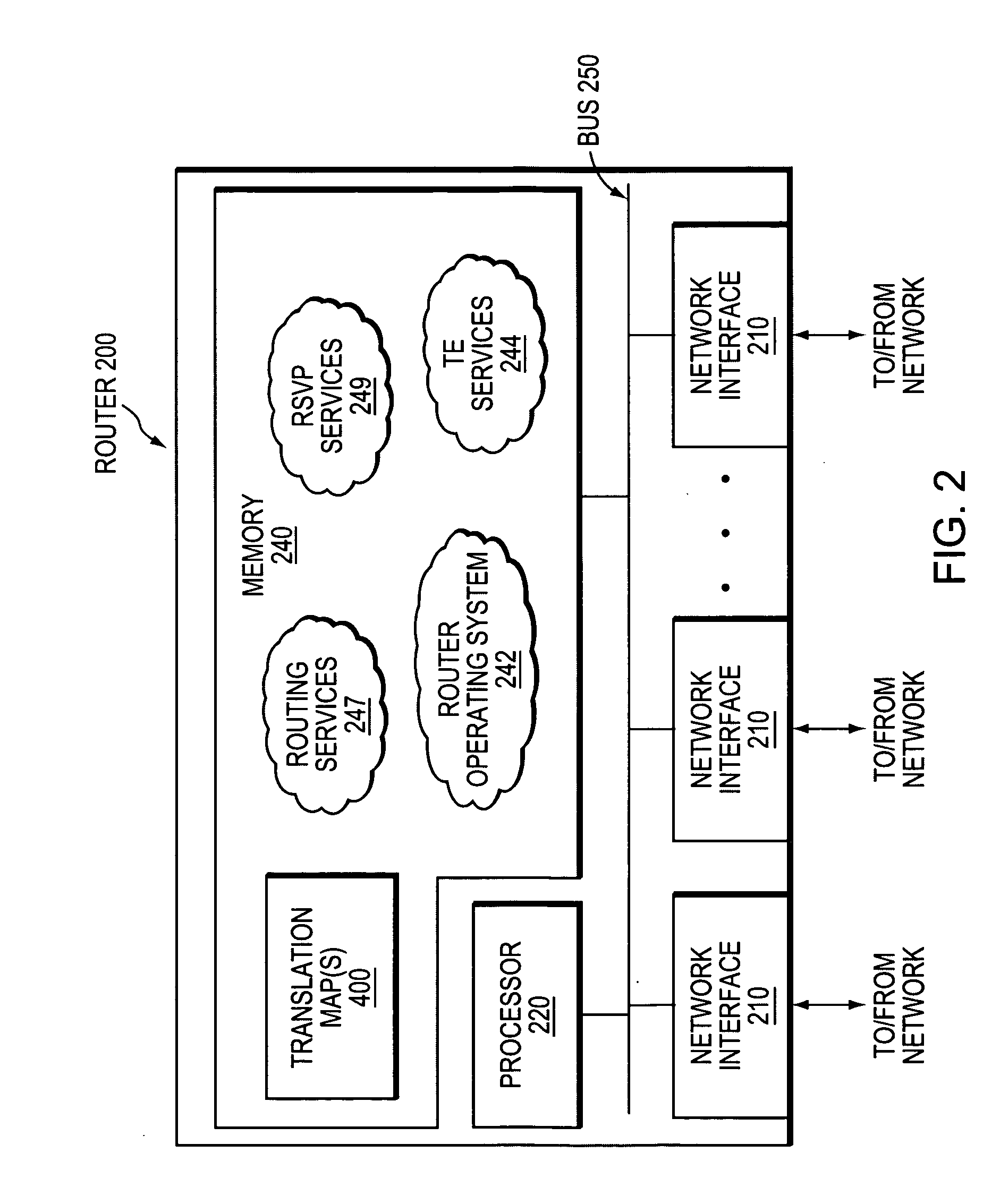
Data structure for implementation of traffic engineering function in multiprotocol label switching system and storage medium for storing the same
InactiveUS7065084B2Easy to manageQuality improvementData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsForwarding equivalence classType-length-value
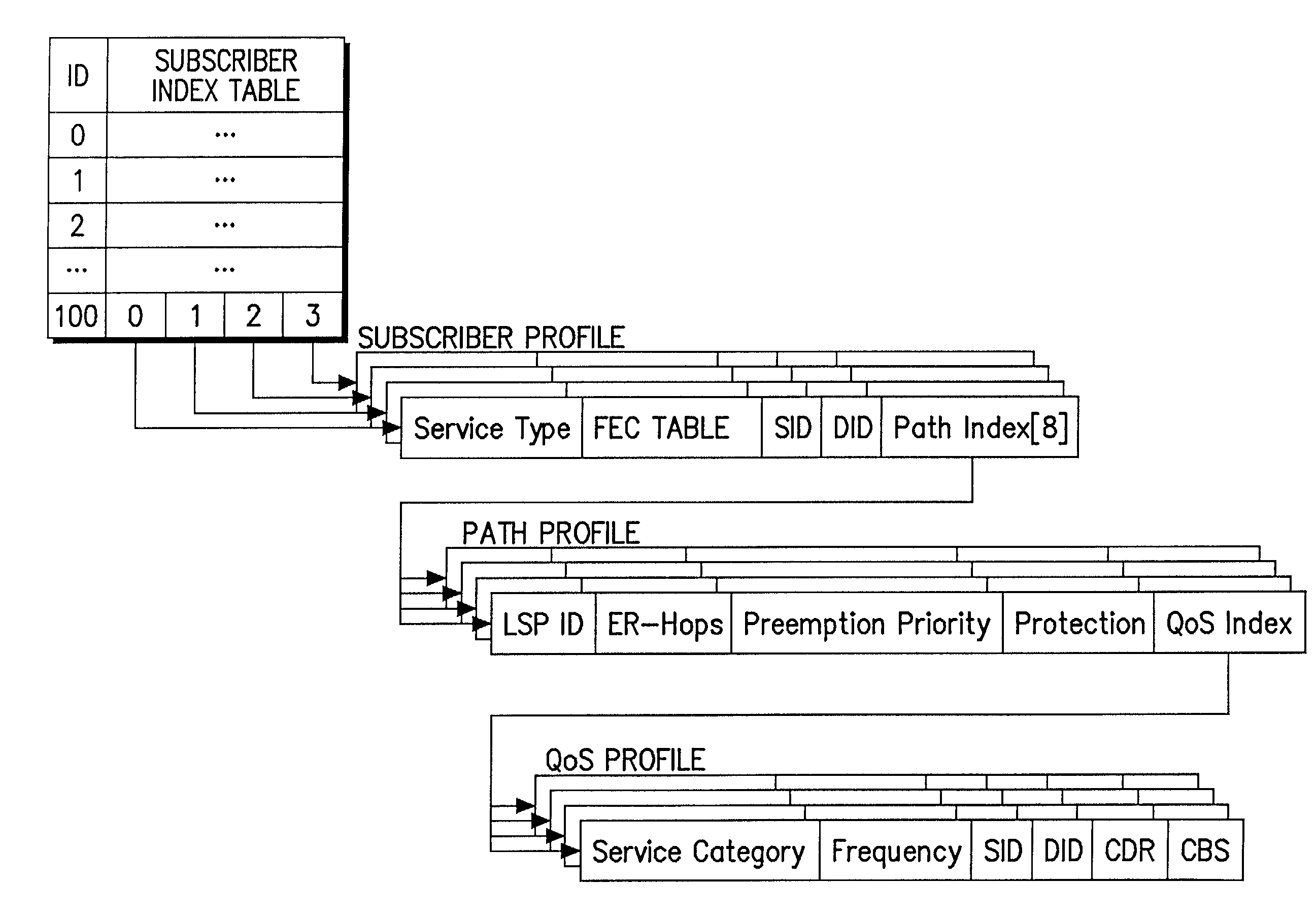
A data structure for implementing a traffic engineering function in a multiprotocol label switching system comprises: a subscriber profile including a plurality of entries for storing forwarding equivalence class (FEC) information required for setup of a label switched path (LSP) based on the traffic engineering function, the entries of the subscriber profile being sequentially assigned indexes corresponding to one traffic engineering service subscriber identification (ID); a path profile including a plurality of entries for storing respective path information items regarding a type length value (TLV) of a signal protocol required for setup of an explicit routed label switched ath (ER-LSP) based on the traffic engineering function, the entries of the path profile being sequentially assigned indexes corresponding to respective path information items; and a quality of service (QoS) profile including a plurality of entries for storing respective QoS information items regarding a TLV of a signal protocol required for setup of a constraint routed label switched path (CR-LSP) based on the traffic engineering function, the entries of the QoS profile being sequentially assigned indexes corresponding to respective QoS information items. The indexes assigned to the profile entries include a plurality of indexes set by an operator for interlinking corresponding ones of the subscriber profile entries, the path profile entries, and the QoS profile entries.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Detecting and evaluating system for controlling traffic state at road cross, implementing method and use thereof
InactiveCN101419750ASimple applicationThe judgment process is simpleArrangements for variable traffic instructionsDetection of traffic movementData transmissionCondition monitoring
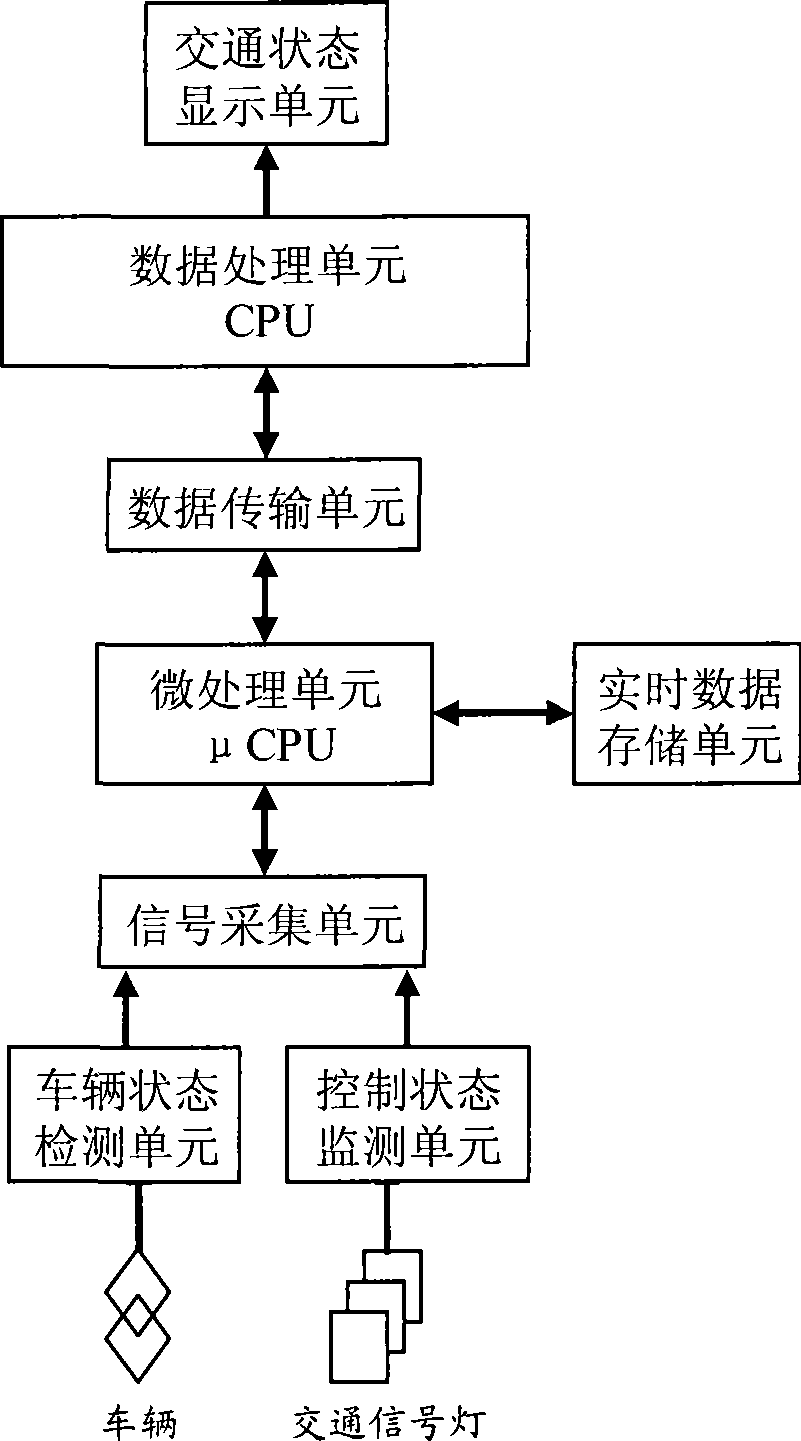
The invention provides a city signal control intersection traffic state detecting and evaluating system based on data characteristic and a method and an application thereof. The system comprises a vehicle state detection unit, a control state monitoring unit, a signal collecting unit, a microprocessing unit, a data transmitting unit, a data processing unit and a traffic state display unit, wherein, the vehicle state detection unit and the control state monitoring unit are connected with the signal collecting unit in parallel; then the signal collecting unit is also connected with the microprocessing unit, the data transmitting unit, the data processing unit and the traffic state display unit sequentially; the microprocessing unit is also connected with a real time data storage unit signal; and the control state monitoring unit is also connected with a traffic signal lamp signal. The method is applicable to various traffic engineering technology activities carried out by traffic real time data analysis, and the method has the advantages of intuition, easy application, high judgement accuracy and wide application range.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
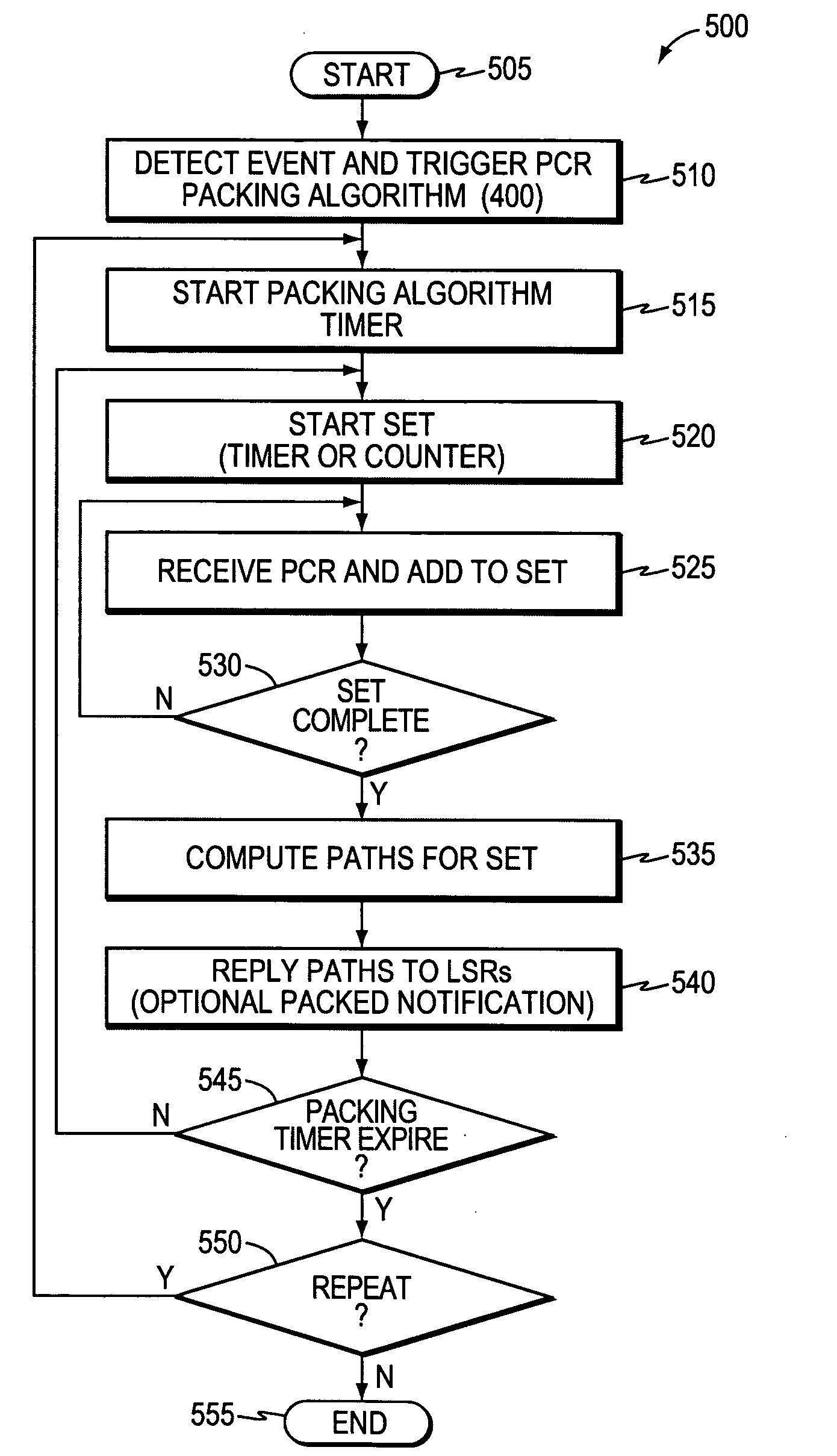
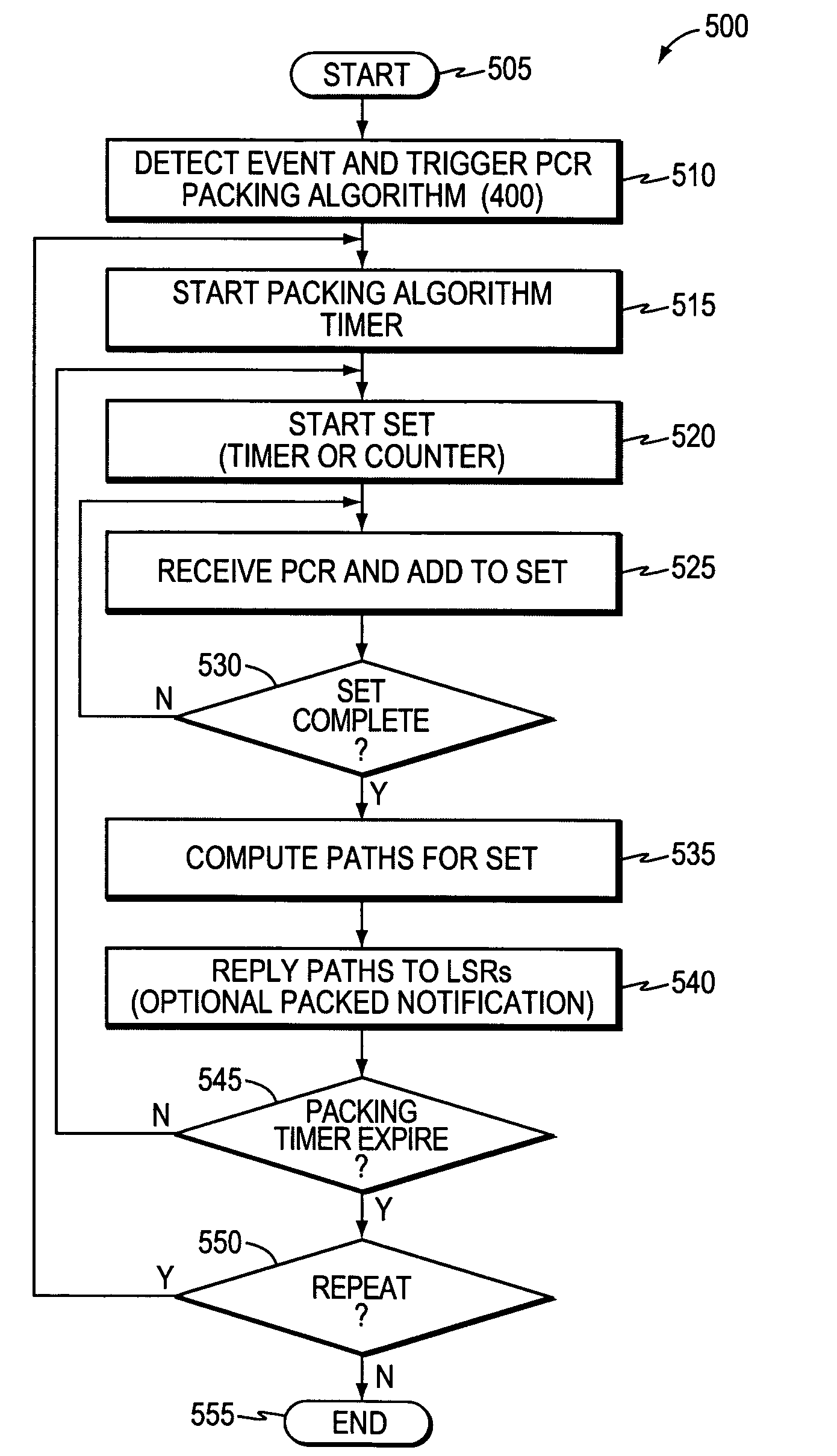
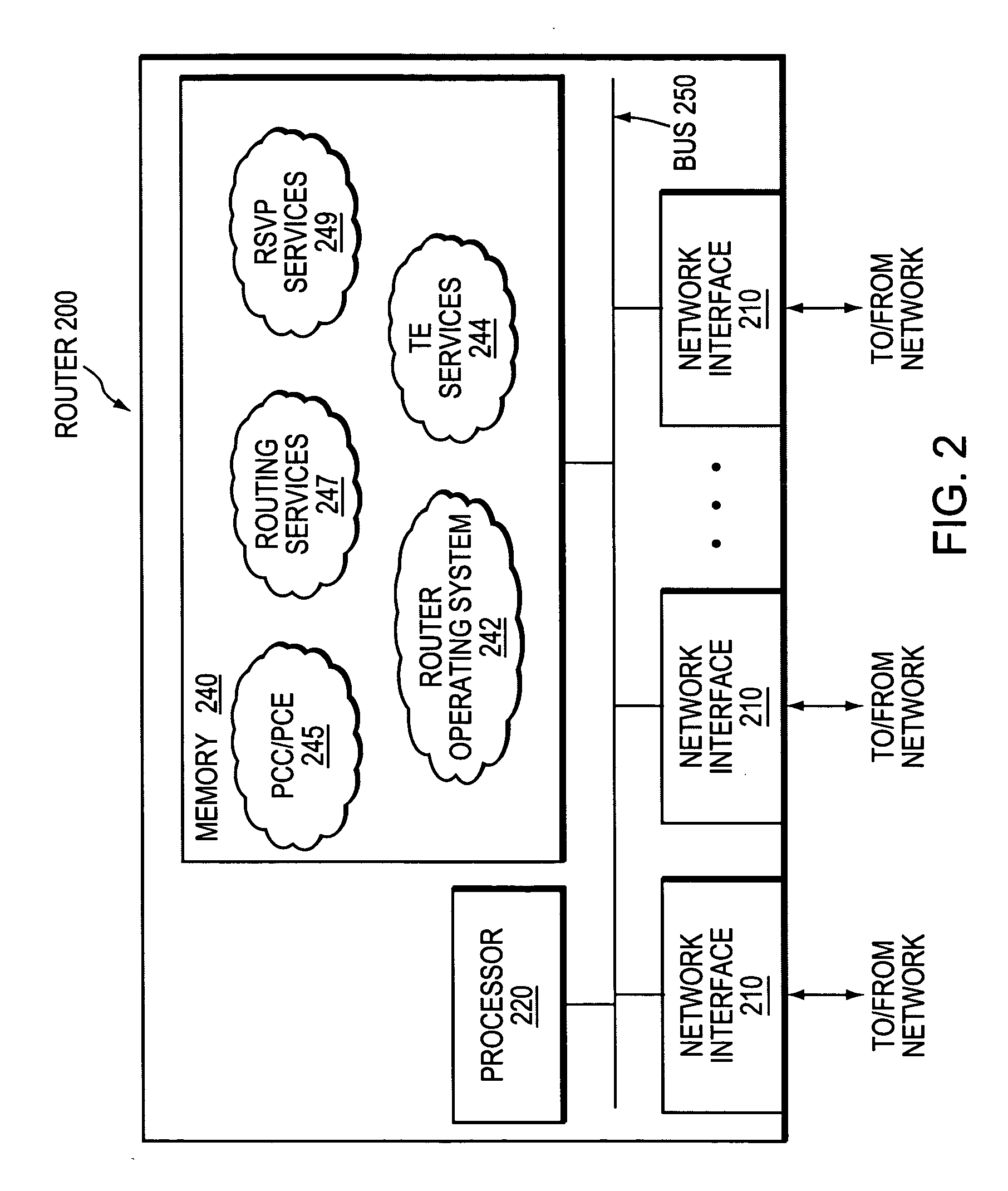
Trigger for packing path computation requests
InactiveUS20060176828A1Alleviate the conditionReduce failureError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic volumeTraffic capacity
A technique triggers packing of path computation requests (PCRs) for traffic engineering (TE) label switched paths (LSPs) that are sent from one or more label-switched routers (LSRs) to a path computation element (PCE) of a computer network. According to the novel technique, incoming PCRs are packed into sets in response to a certain event, and one or more TE-LSPs (paths) are computed for each PCR of a particular set based on the PCRs of that set. Specifically, the PCE detects an event in the network (“network event”) indicating that an increase in the number of incoming PCRs has occurred, or that an increase is likely to occur due to, e.g., a change in a network element. Once the net-work event has been detected, the PCE packs the incoming PCRs into configured-length sets, such as, e.g., for a specified time interval or a certain number of PCRs. The PCE computes paths for each PCR of a particular set while considering the other PCRs of that set, thereby reducing race conditions, signaling overhead, and set-up failures.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Method for calculating delays in intersection based on motorcade following theory
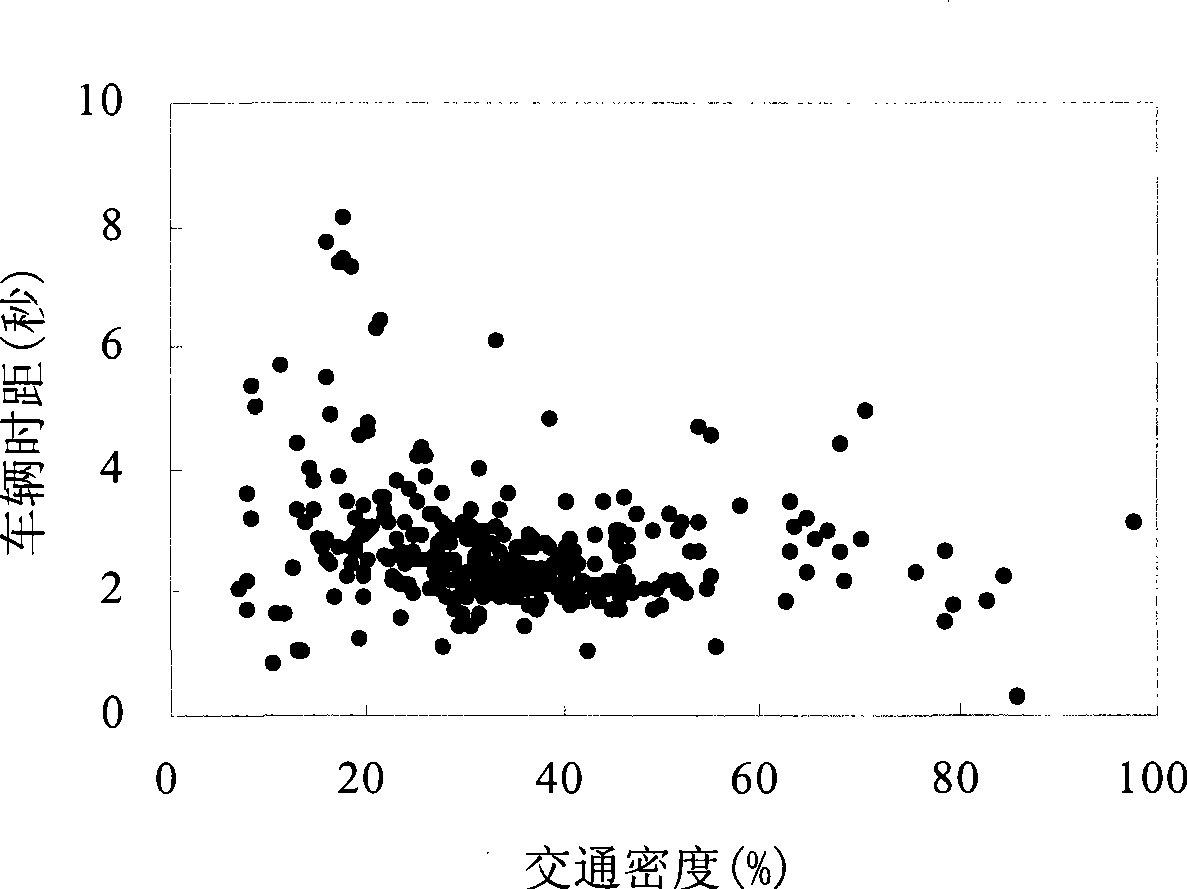
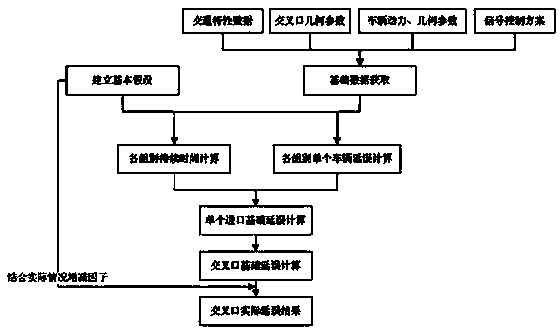
InactiveCN103366574ASolve problems with limited applicabilityImprove regularityDetection of traffic movementTraffic characteristicAlgorithm
The invention discloses a method for calculating delays in an intersection based on the motorcade following theory. The method includes the steps of firstly establishing a basic assumption, then collecting traffic characteristic data, intersection geometrical parameters, vehicle power, geometrical parameters and signal control schemes, marshalling the collected data into parameters needed in an algorithm, dividing vehicles into three sets according to the different states of the vehicles when the vehicles pass the intersection in a period based on the traffic engineering theory, utilizing the input data to judge respective duration of three sets of traffic flow inputs according to discriminant in the algorithm, then further calculating delay time of vehicles belonging to each set, calculating delays in all entrance channels respectively with combination of the distribution of the traffic flow inputs, then obtaining total delay of the intersection, and eventually adding or subtracting factors in the calculation result combining with the practical situation, and modifying the calculation result. The method has the advantages of being high in applicability, clear in parameters, large in calculated amount, suitable for being combined with computer programming, and capable of being further applied to an intersection signal control timing scheme.
Owner:上海济安交通工程咨询有限公司
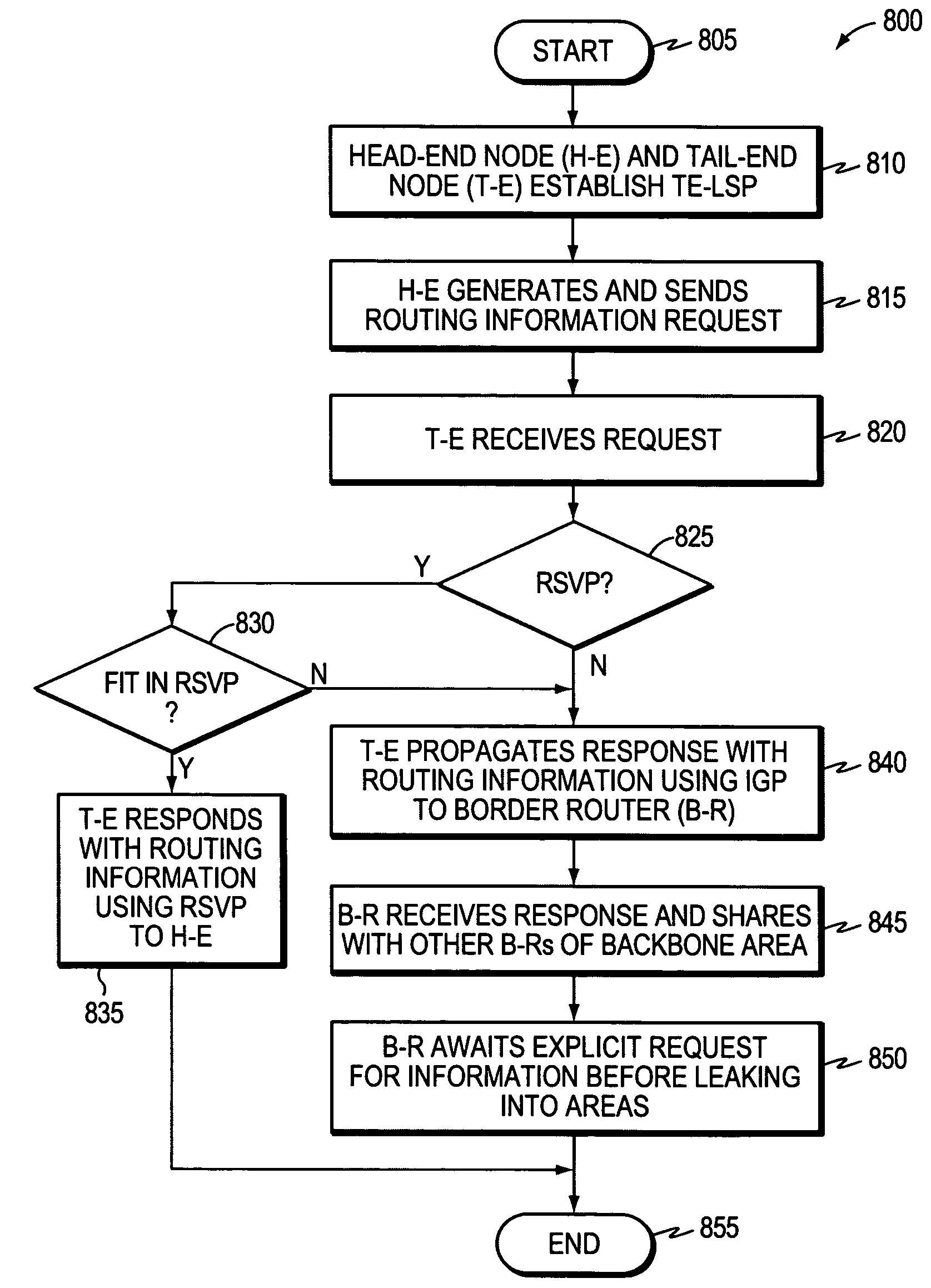
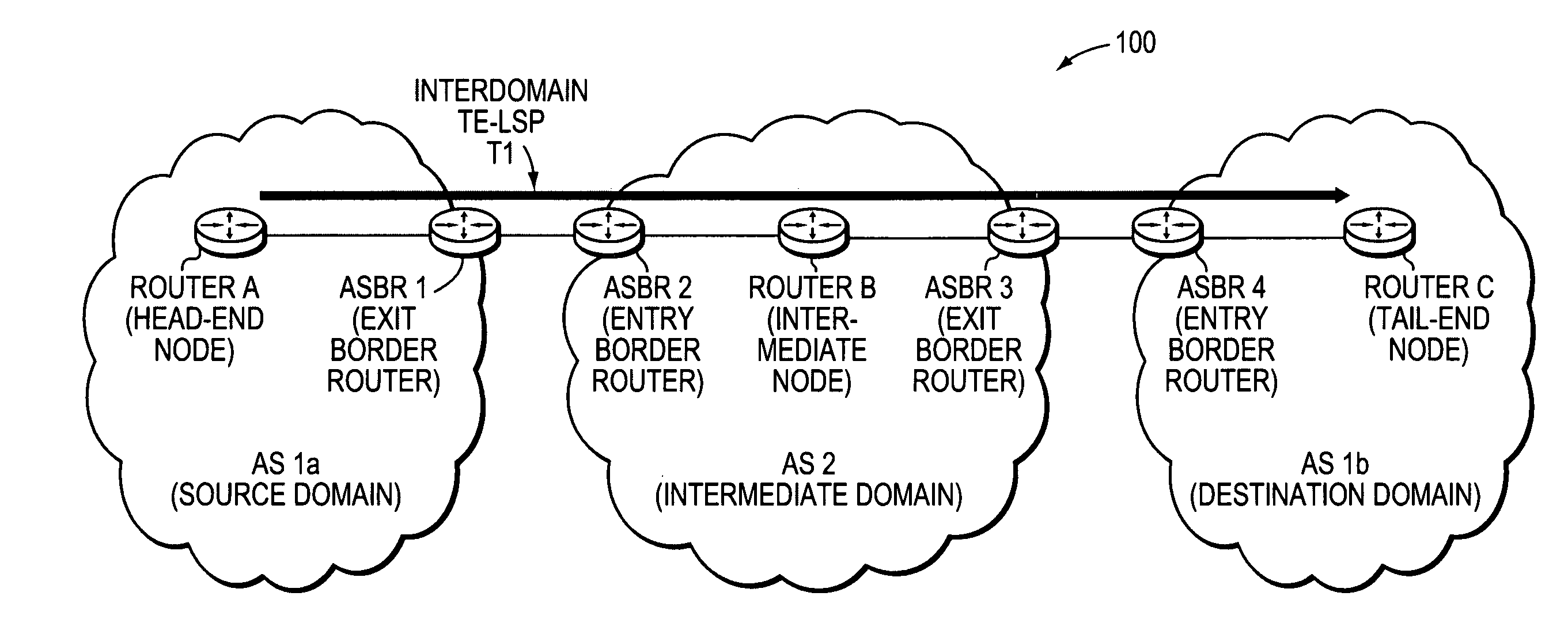
Controlled distribution of inter-area routing information
A technique controls distribution of reachability information for a tail-end node of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) to a head-end node of the TE-LSP in a computer network. The TE-LSP preferably spans multiple domains of the network such that the tail-end node resides in a domain (“tail-end domain”) that is different (remote) from the domain of the head-end node (“head-end domain”). According to the inter-domain information distribution technique, the head-end node requests the remote reachability information from the tail-end node, which may employ an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) to transmit the information to a border router of the tail-end domain. The tail-end domain border router then shares this information with at least a head-end domain border router. The head-end node thereafter requests that the head-end domain border router release the reachability information into the head-end domain. The head-end node uses the remote information to calculate routes, i.e., address prefixes and associated attributes, reachable from the tail-end node for insertion into its routing table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
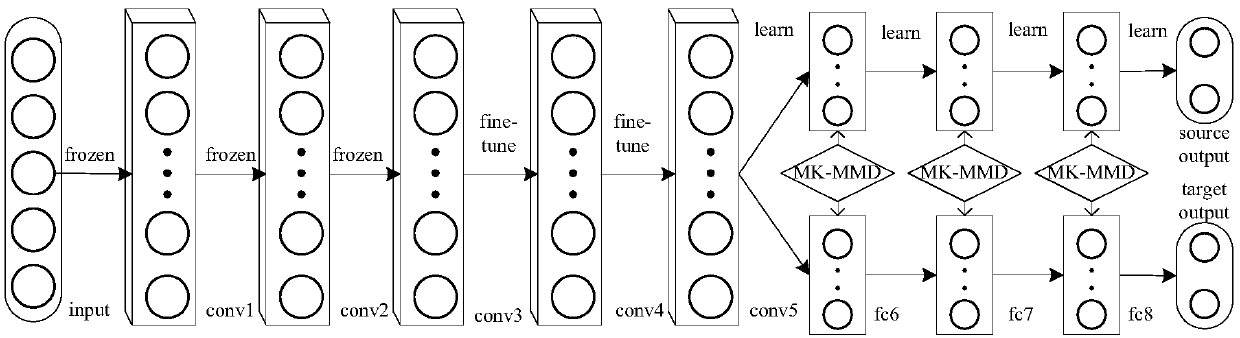
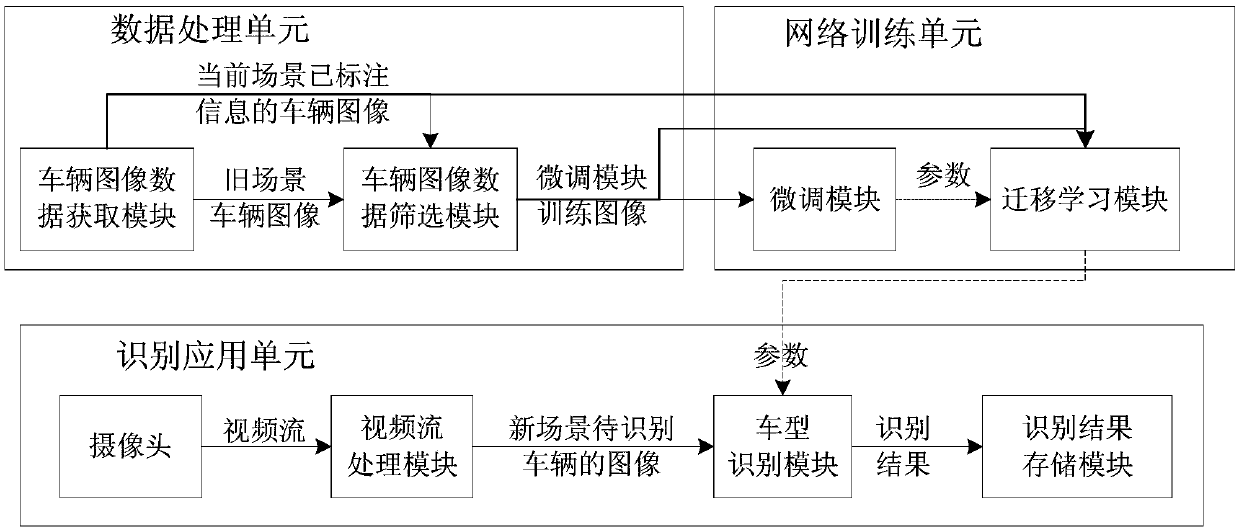
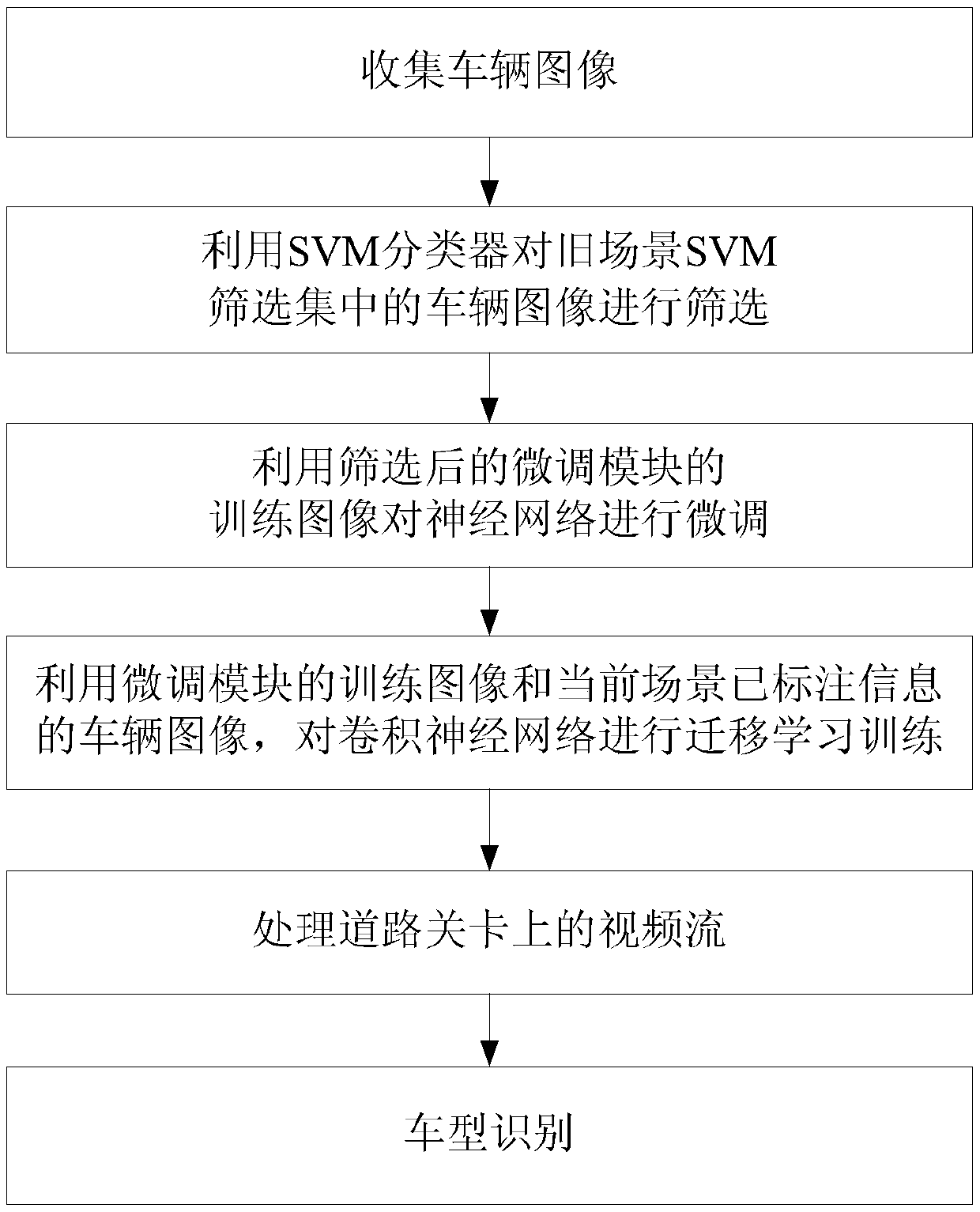
Vehicle type identification device and method for realizing cross-scene cold start based on transfer learning
ActiveCN109657552AReduce varianceReduce the need to manually annotate image dataCharacter and pattern recognitionSimulationIdentification device
The invention discloses a vehicle type identification device and method for realizing cross-scene cold start based on transfer learning. The vehicle type recognition device is provided with three components, namely a first component, a second component and a third component, Data processing unit, a network training unit and an identification application unit, According to the invention, only a small amount of vehicle image data marked with vehicle type information exists in a target domain; A domain adaptation method of transfer learning is adopted. The parameter difference of the vehicle typerecognition convolutional neural network model between the source domain of the old vehicle type recognition scene and the target domain of the new vehicle type recognition scene is reduced, parameter migration of the vehicle type recognition convolutional neural network model from the old vehicle type recognition scene to the new vehicle type recognition scene is achieved, and cross-scene cold start vehicle type recognition is achieved. The method can be used for the initial stage of actual intelligent traffic engineering, enables the convolutional neural network model to achieve a high accuracy rate on a vehicle model identification task under the condition of lacking vehicle image data with marked vehicle model information in an actual vehicle model identification scene, and has a goodapplication prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
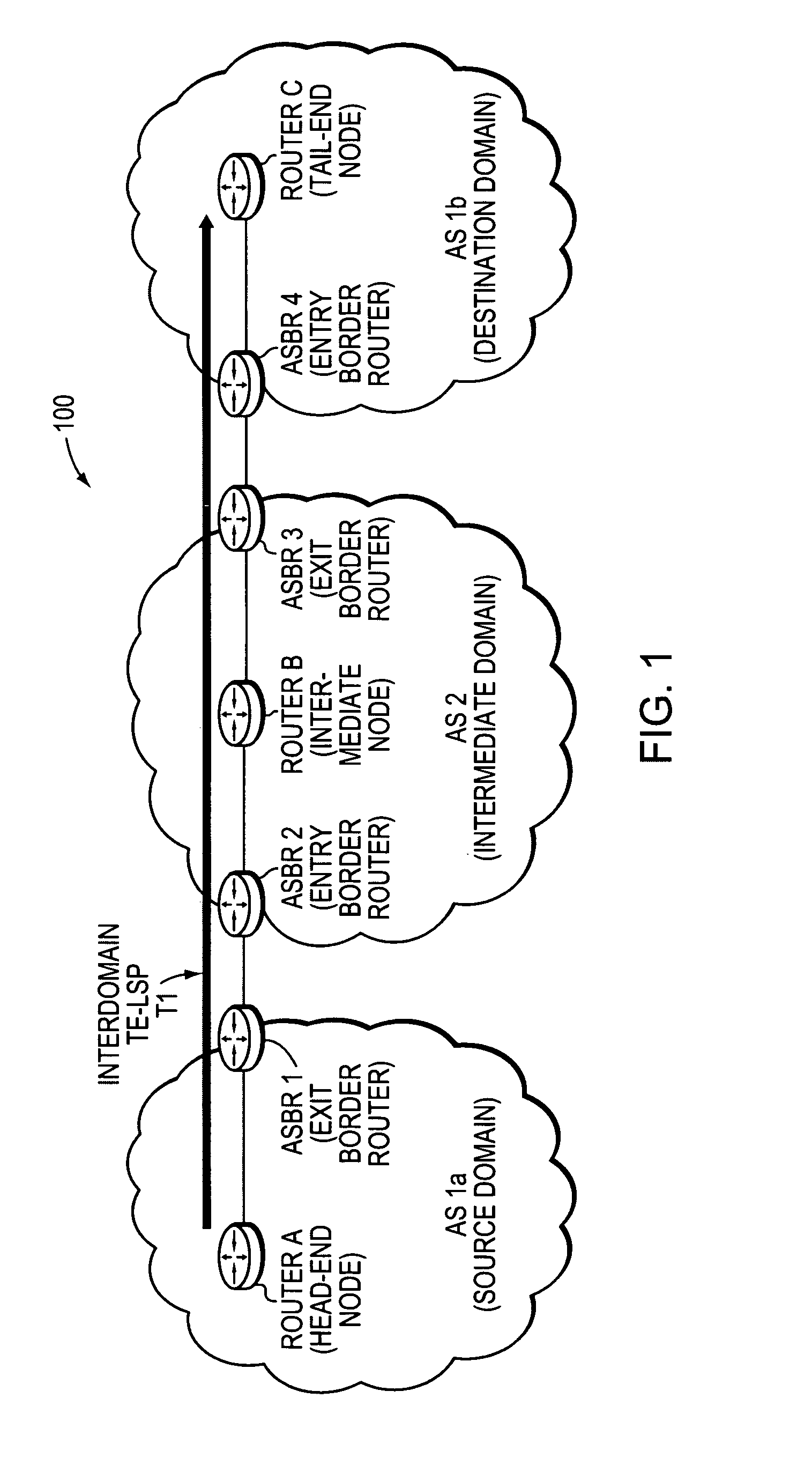
Technique for dynamically restoring original TE-LSP attributes for interdomain TE-LSPs
ActiveUS20070208871A1Reduce needMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDistributed computingTraffic volume
A technique dynamically restores original attributes of a Traffic Engineering La-bel Switched Path (TE-LSP) that are provided in a source domain for a destination domain when traversing one or more intermediate domains that may translate the TE-LSP attributes in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a head-end node requests an interdomain TE-LSP having one or more original TE-LSP attributes (e.g., priority, bandwidth, etc.) using a signaling exchange. The head-end node may also request restoration of the original TE-LSP attributes upon entrance into the destination domain. Intermediate domains (e.g., border routers of the domains) receiving the request may translate the original TE-LSP attributes into corresponding intermediate domain TE-LSP attributes. When the request reaches the destination domain, the intermediate domain TE-LSP attributes of the requested TE-LSP are restored into the original TE-LSP attributes.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Tester and measuring method for structural depth of large-porosity drainage asphalt pavement
The invention relates to a tester and measuring method for the structural depth of a large-porosity drainage asphalt pavement, belonging to the technical field of highway engineering in traffic engineering. The tester and measuring method can accurately measure the structural depth of the surface of the large-porosity drainage asphalt pavement and avoid the phenomenon of sand leaking holes in measurement of the structural depth of the large-porosity drainage asphalt pavement with a sand patch method, so accurate data is provided for evaluation of the macroscopic structure, draining performance and like of the pavement. Moreover, the tester and measuring method can rapidly measure the structural depth of the pavement and enables manpower and material resources to be saved and work efficiency to be improved in practical engineering needing considerable measurement of the structural depth of pavements.
Owner:BROADVISION ENG CONSULTANTS
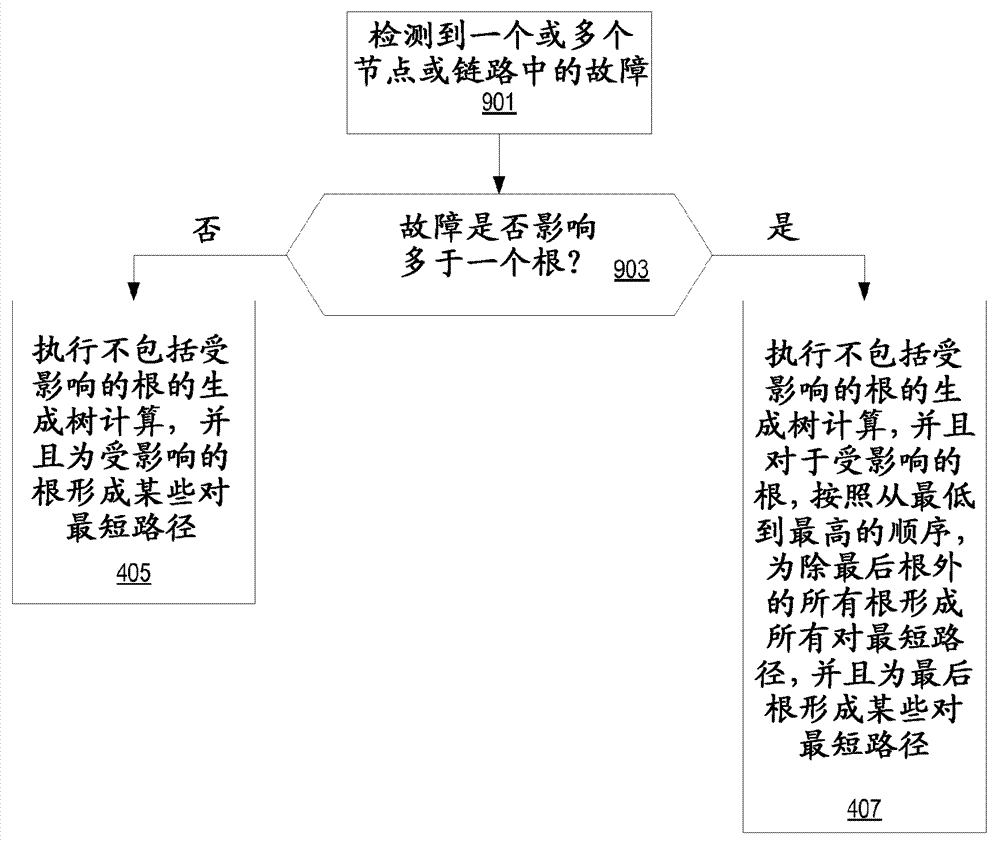
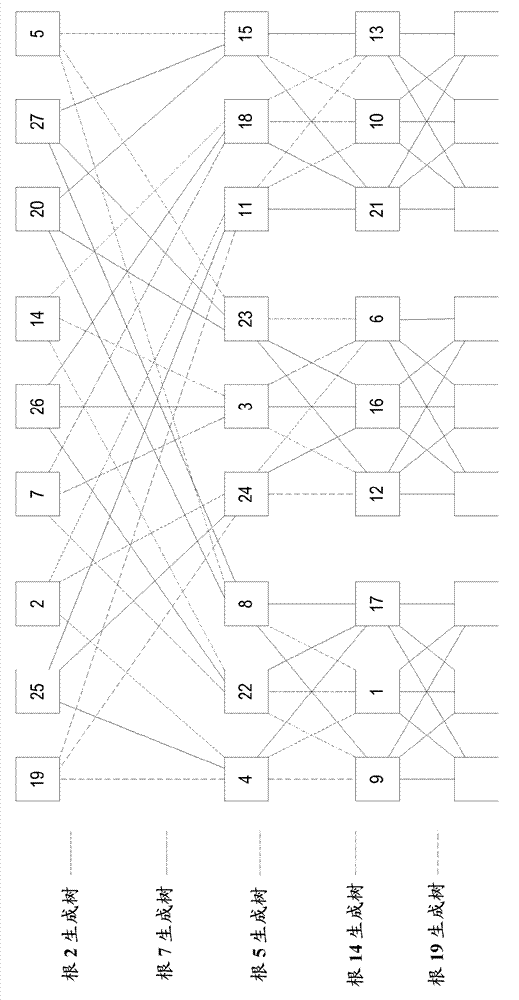
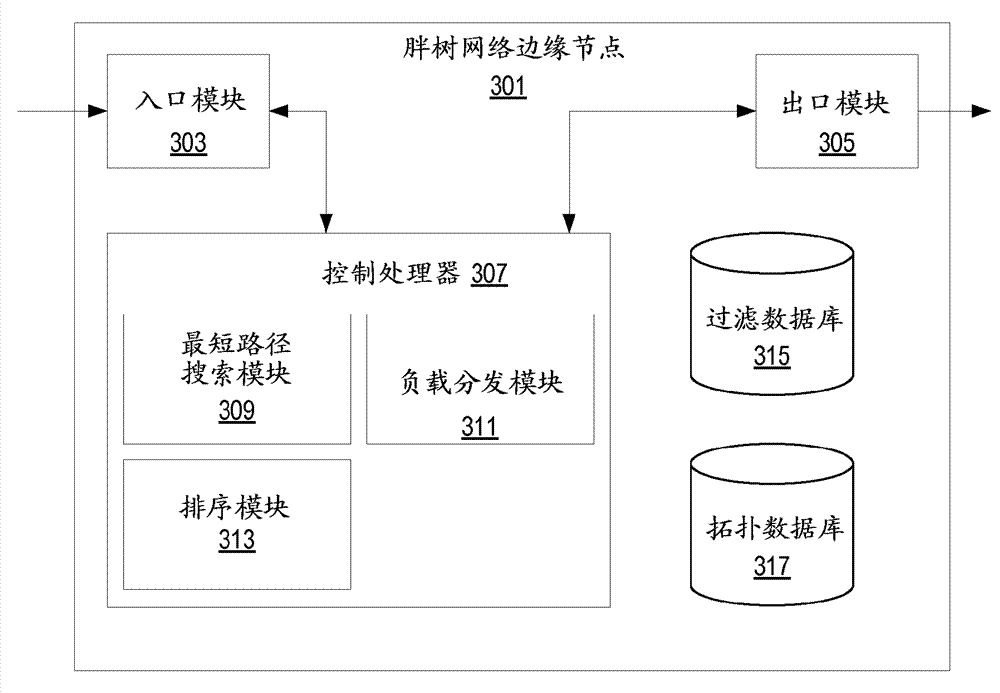
Automated traffic engineering for fat tree networks
ActiveCN103026668AReduce computational complexityDigital computer detailsData switching networksEngineeringMedia access control
Embodiments of a method implemented in at least one fat tree network node for improved load distribution, wherein the node is one of a plurality of fat tree network nodes in a fat tree network each of which implement a tie-breaking process to produce minimum cost trees, is described. In some embodiments, a spanning tree computation for each root node of the fat tree network in order from a lowest ranked root node to a highest ranked node is performed, a filtering database for each root node of the fat tree network, wherein the filtering database includes a set of media access control (MAC) addresses of the leaf nodes of the fat tree network generated, and link utilization for each computed tree to use as a prefix to link identifiers used for at least one tie-breaking algorithm added.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
A high-modulus warm-mix asphalt additive and a preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN109777134AImprove overall performanceGood high temperature performanceClimate change adaptationBuilding insulationsAntioxidantPitch blende
The invention belongs to the field of traffic engineering admixtures, and relates to preparation and application of a high-modulus warm-mix asphalt additive. The additive is prepared mainly from a high modulus warm-mix main agent, a thermoplastic elastomer, vegetable oil, a crosslinking agent, a coupling agent, an antioxidant, an antiager and tackifying resin through single-screw low-temperature extrusion and granulation. The additive prepared can be direly added into a material mixture, and is suitable for high-modulus asphalt pavement engineering and winter low-temperature construction environments having high requirements on environment protection. An asphalt mixture prepared by utilizing the additive has excellent high-temperature performance, high dynamic modulus, good low-temperaturetoughness, excellent resistance to water damage, and the like, can reduce temperature for construction such as material mixture mixing, paving and grinding by 20-30 DEG C, achieves a warm mix effects, and is suitable for promotion and application.
Owner:WUHAN MUNICIPAL CONSTR GROUP +1
Water-containing gangue compression testing device and testing method thereof
InactiveCN105181463AChange wetting methodGet compressionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesWater contentEngineering
The invention discloses a water-containing gangue compression testing device and a testing method thereof. The water-containing gangue compression testing device comprises a steel barrel for storing gangues, wherein the steel barrel is divided into a plurality of layers from the whole height; a pressure sensor and a stay wire displacement sensor are arranged on each layer; the steel barrel is put on a testing machine to be subjected to a compression test so as to obtain a compression ratio and force magnitude relation of gangues on different-height layers; the same batch of gangues are tested again, but the difference is as follows: a fixed amount of water is injected at the height of a certain layer, and a compression test is carried out; the compression ratio and force magnitude relations of the gangues before and after the water is added are compared to obtain the influences on a compression process by the moisture content of the gangues on the certain layers; by that analogy, a plurality of times of tests are carried out to obtain the influences on the compression process by the moisture content of the gangues at different-height positions. The water-containing gangue compression testing device and the testing method thereof, disclosed by the invention, not only can be used for underground engineering of gangue mining with filling and the like, but also can be used for the fields of building and traffic engineering including geotechnical side slope stability analysis, gravel foundation treatment, roadbed deformation calculation and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Anti-dazzle principle based design method for traffic engineering facilities at road tunnel exit
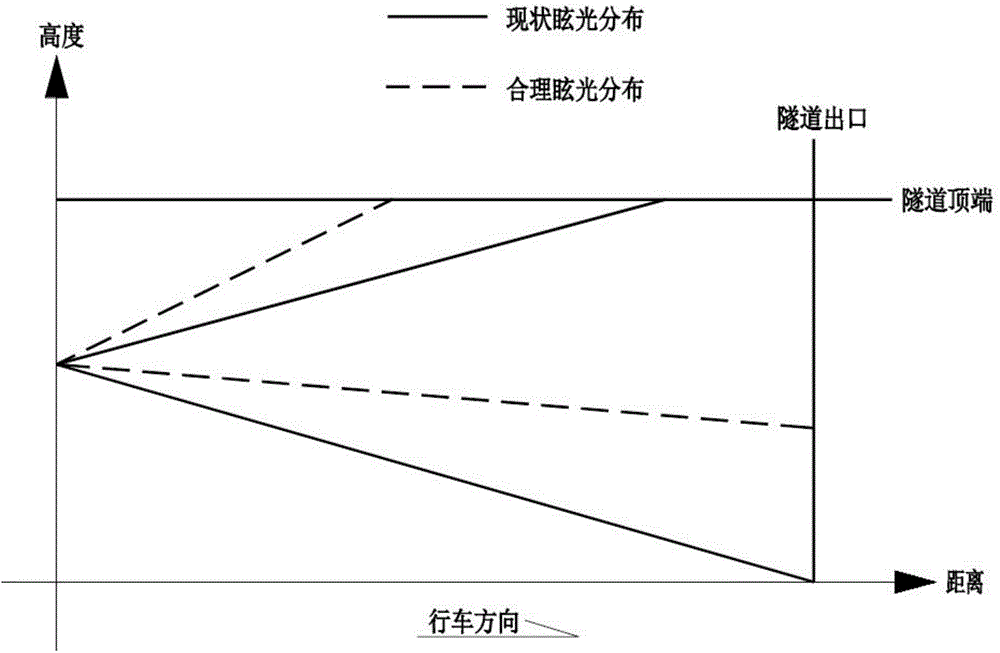
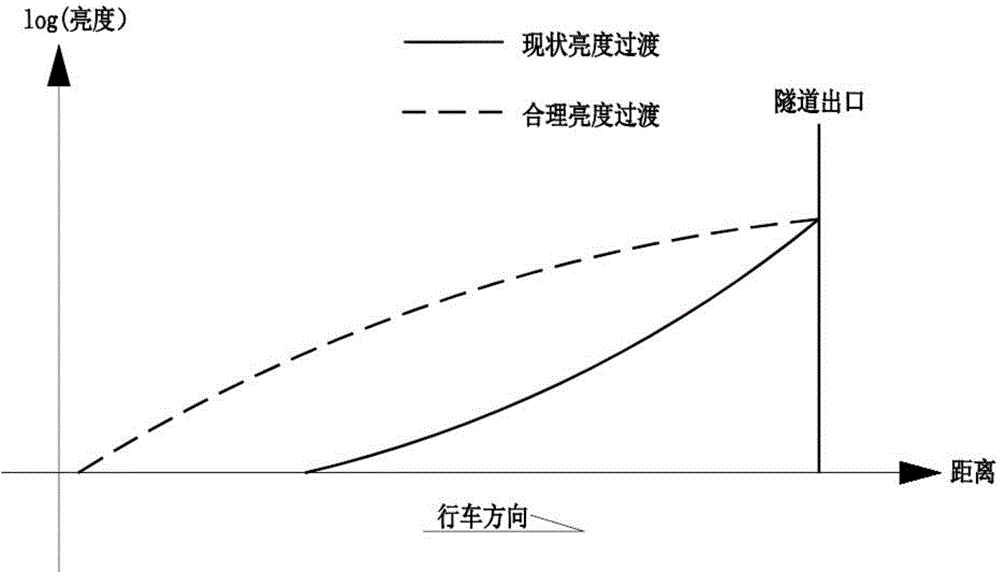
InactiveCN103557005AIncrease visual recognitionReduce glare areaProtective constructionTunnelsDriver/operatorLight energy
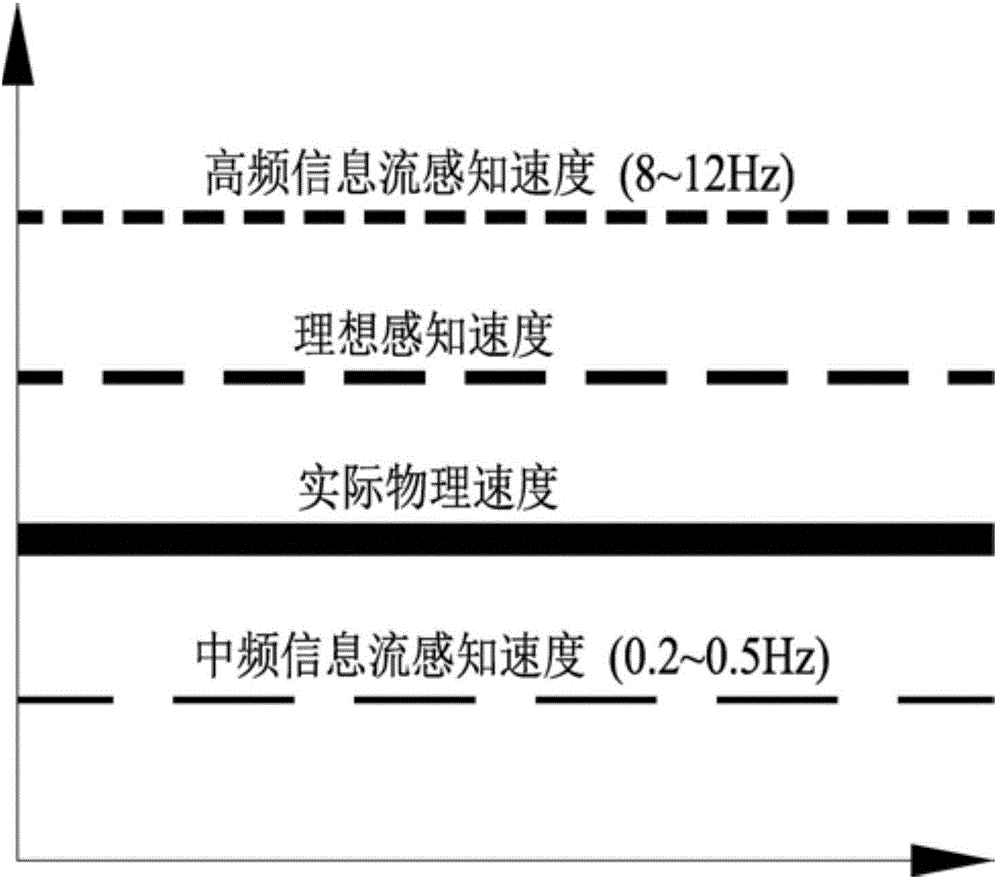
The invention relates to an anti-dazzle principle based design method for traffic engineering facilities at a road tunnel exit. The method is characterized in that tunnel exit anti-dazzle facilities are arranged in front of the tunnel exit to ease intensive brightness transition caused by insufficient illuminating lamps at the tunnel exit; coloured painting materials of which reflection coefficients gradually reduce are arranged on the tunnel ceiling, side walls and roads from the top down to ease brightness transition and beam divergence at the tunnel exit, so as to lift the dazzle area, reduce the dazzle area below the visual line of a driver and increase the visual adaptation time; horizontal road direction lines and road lane keeping lines are arranged on the road, and side wall vertical direction lines and side wall double-layered contour marks are arranged on the side walls, so as to form a closed mid-frequency retroreflective information stream together; high-frequency red and white marked lines arranged on maintenance road edges and road side reflective raised route markers form a high frequency visual information stream to increase the driver's instantaneous velocity sensation, and promote the driver's speed feeling and distance feeling, and accordingly, the coordination and unification of the tunnel lighting energy conservation and tunnel traffic safety are realized.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
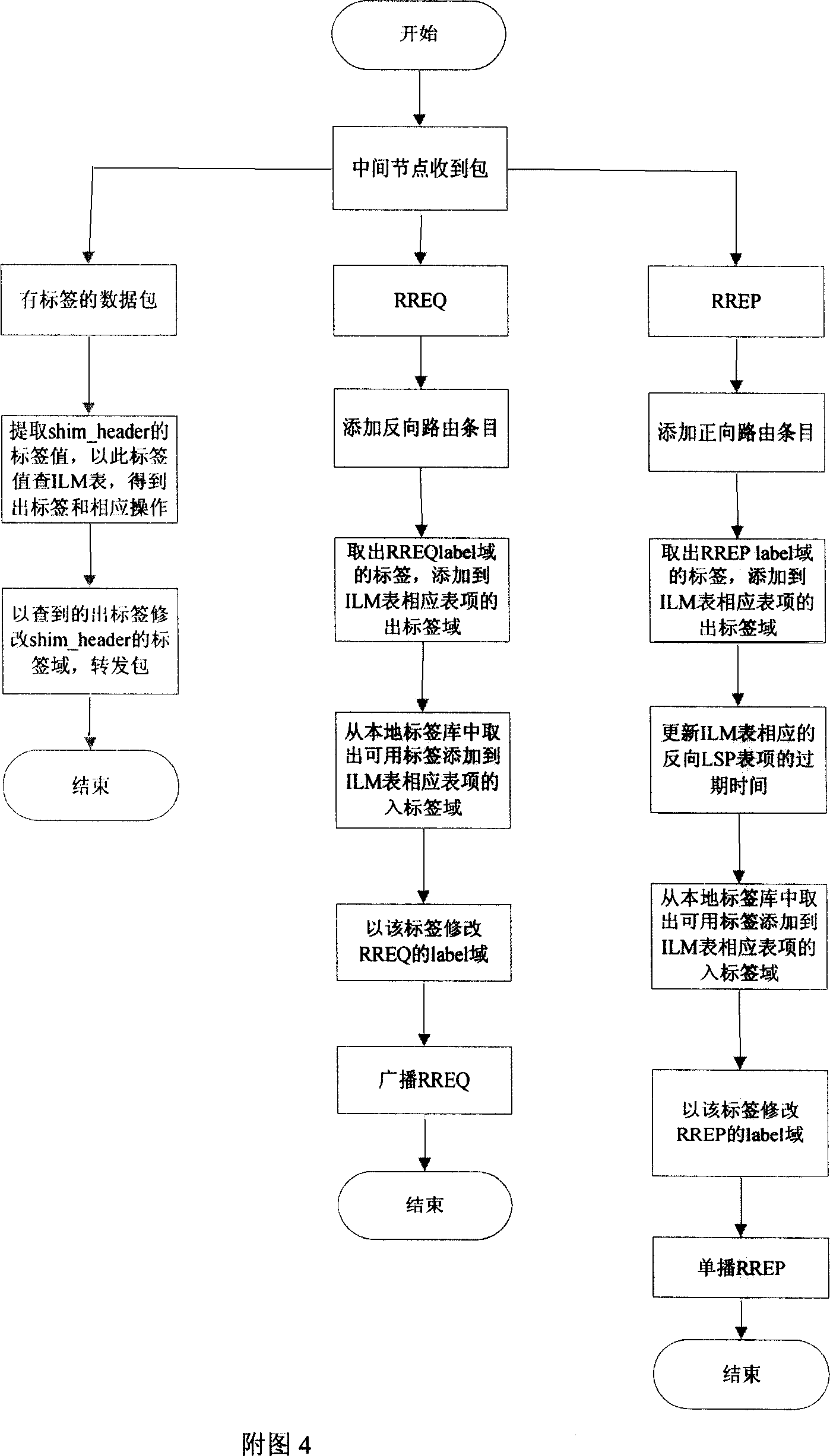
A multi-path routing technology for Ad Hoc network based on tag exchange
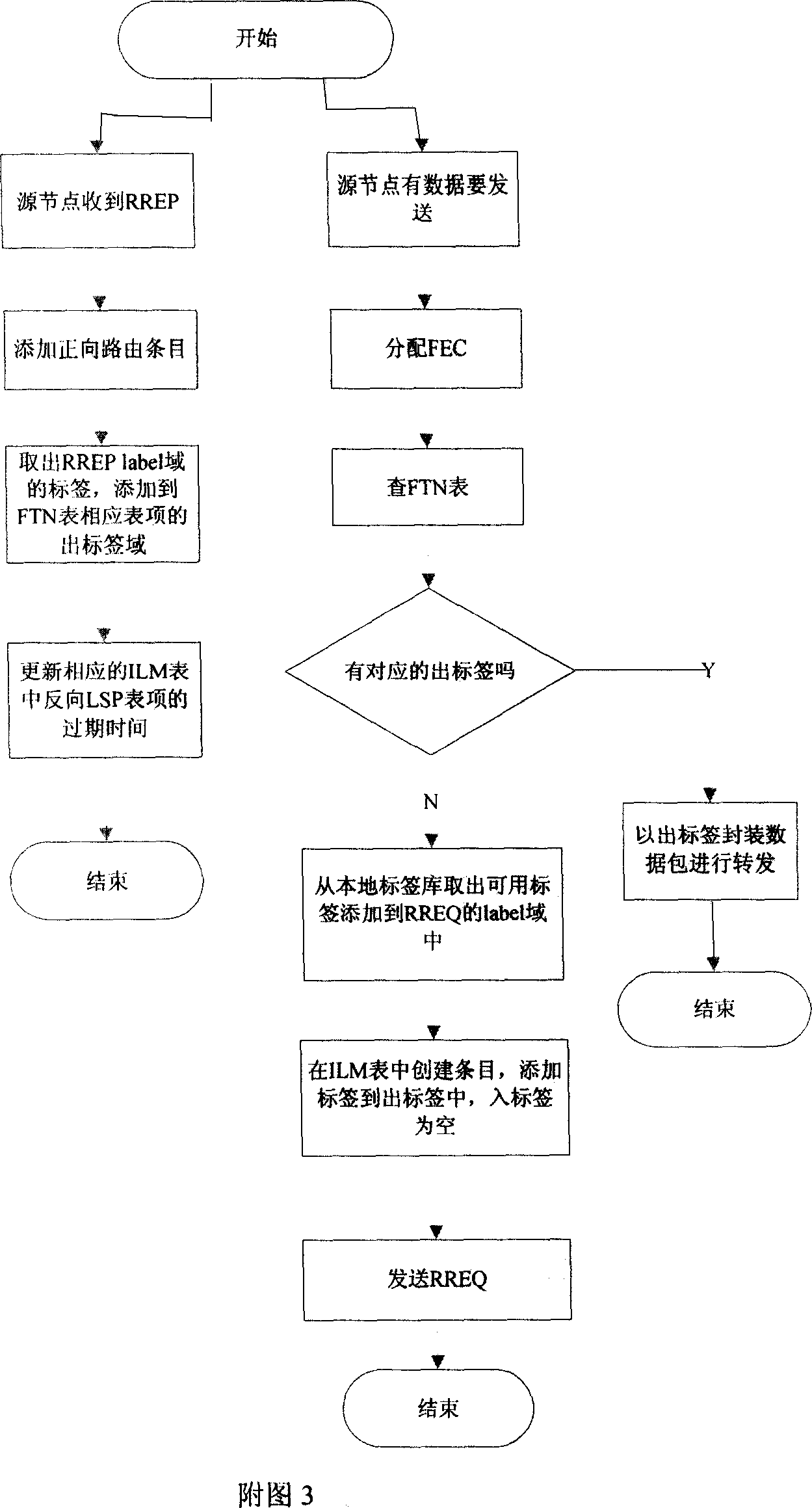
InactiveCN101106522ANetwork topologiesData switching networksQuality of serviceTransmission time delay
The invention designs a Ad Hoc network multipath route technology based on label exchange, which includes sending opposite label when sending route request information, sending positive label when sending route reply information and establishing a plurality of bidirectional label exchange routes and local node repair based on label exchange route. The protocol brings MPLS label exchange technology into Ad Hoc network and can improve the network throughput, transmission time delay and service quality and realize traffic engineering in Ad Hoc network.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for creating post engineering information model for railway and urban railway traffic station
The invention relates to a method for creating a post engineering information model for a railway and urban railway traffic station. Rail traffic engineering construction involves a plurality of fields and has complex links and a large amount of information, the entire process is perfected continuously with the addition and optimization of all engineering information, and the requirement on total planning of the entire process is high. The method comprises the following steps: making a single functional department create an information model of the department and establish a working set of the department; gathering the working sets of all departments onto the same working platform by sharing elevation and a shaft screen to integrate into a project working set; embedding plant feature information, design information and construction information into a system to form completion data for an operator; gradually separating the information, and constructing task flow in real time according operation for loading and outputting; and releasing cache after finishing output, and recording a log file. According to the method, various types of relevant information in a project are integrated reasonably through a parameter information model, and the created information model is shared and transmitted in a full life cycle process, so that the engineering progress is effectively optimized.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY FIRST SURVEY & DESIGN INST GRP
System and method for elastic scaling of virtualized network functions over a software defined network
ActiveUS20190097946A1Network connectionsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationQuality of serviceVirtualization
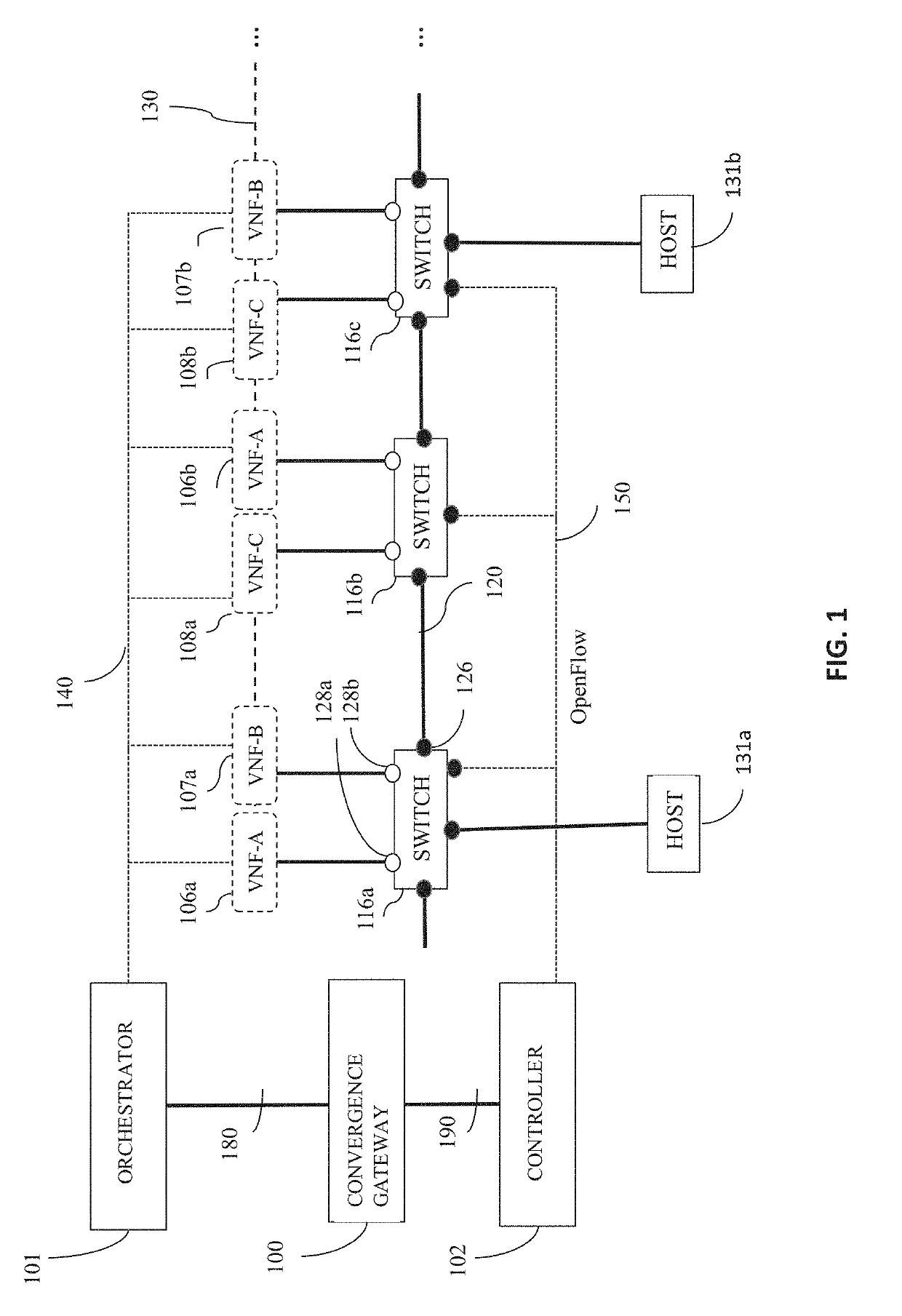
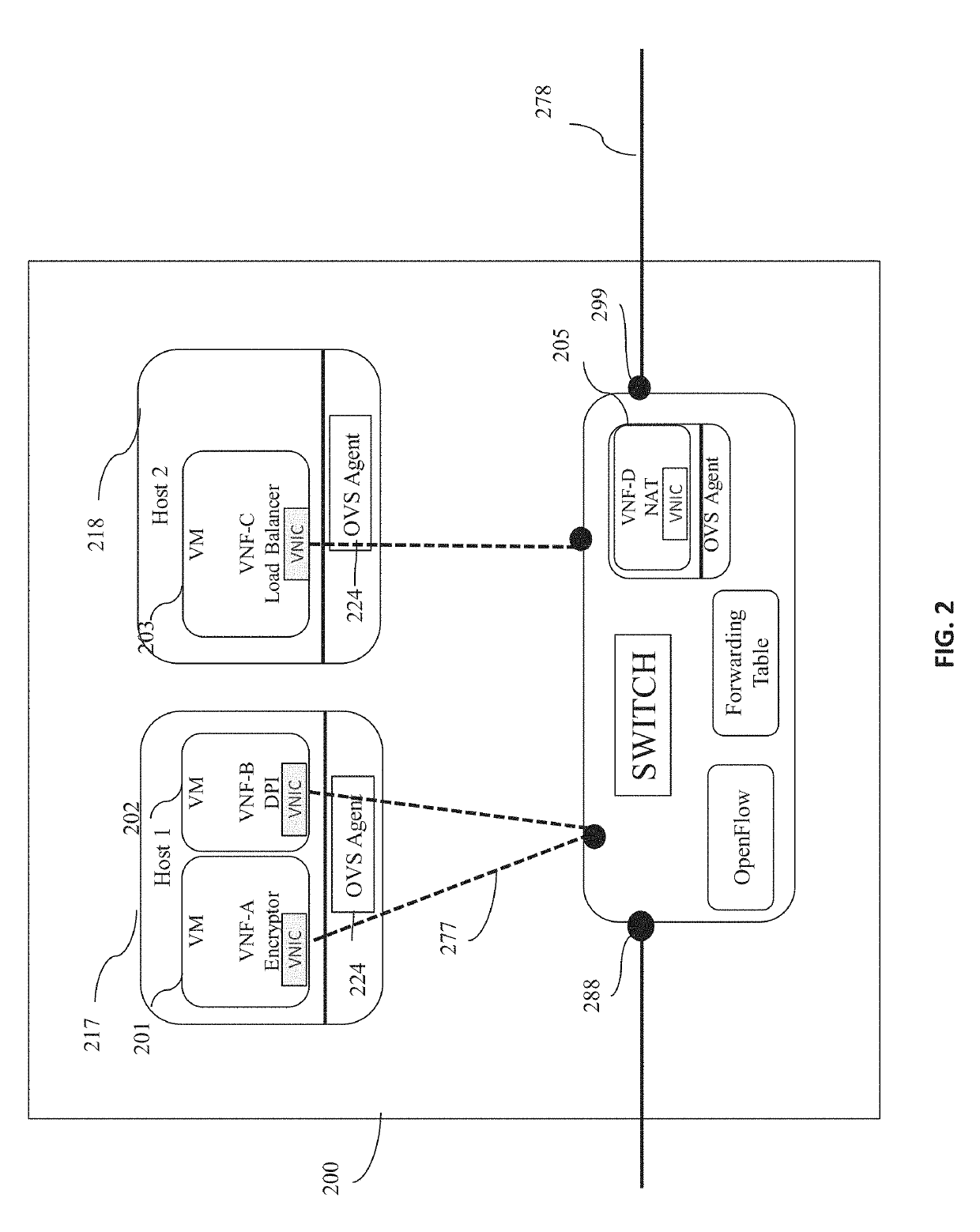
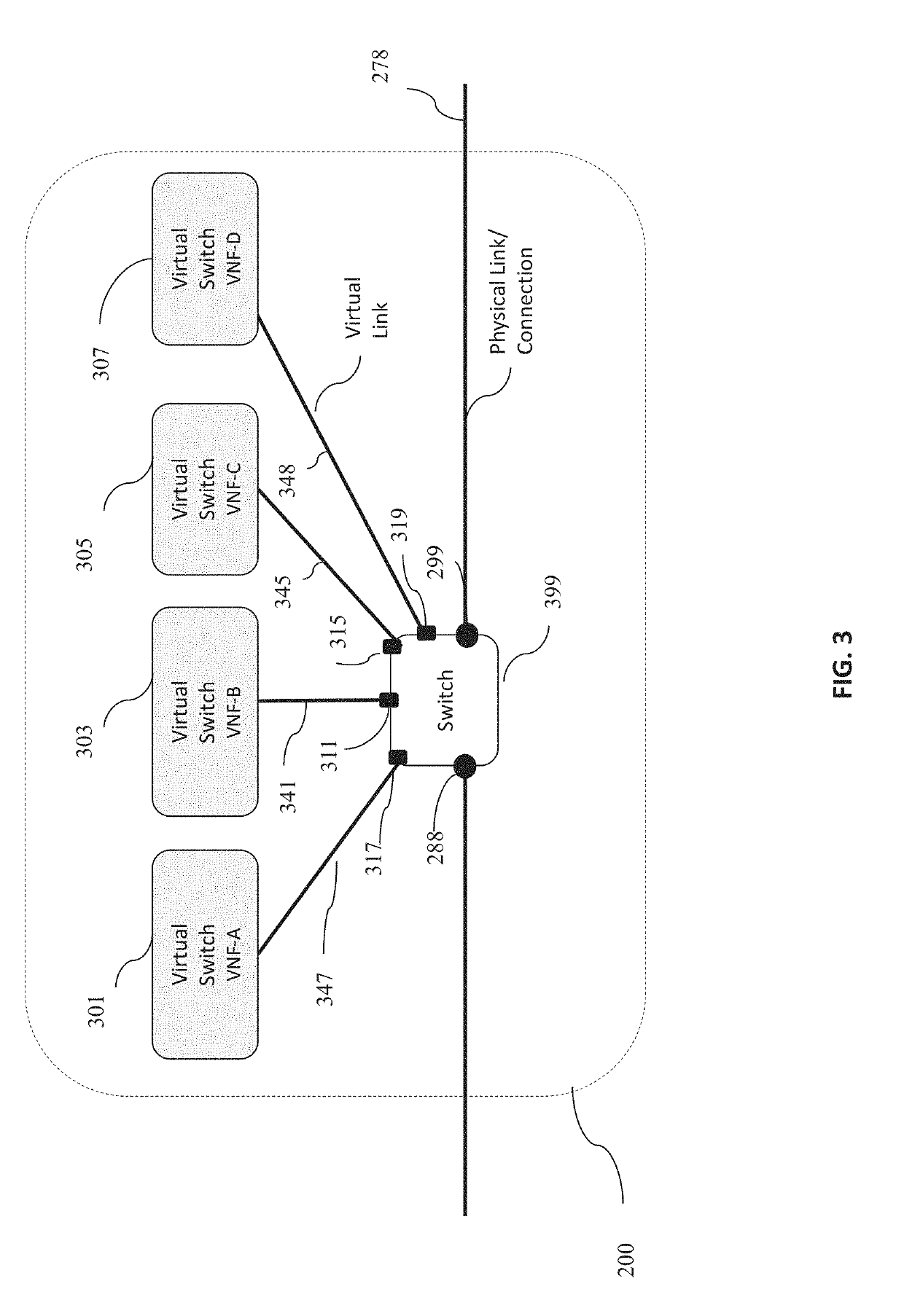
When network function virtualization (NFV) is overlaid on top of a SDN, a convergence gateway mediates between the orchestrator and the SDN controller. The convergence gateway collects from the orchestrator the information on the location, capacity, status, and usage information of all virtualized functions that run on SDN's physical platforms, and passes that information to the controller. The controller decides to optimally route a data flow for service chaining by obeying traffic engineering and quality of service policies of that data flow, choosing from available virtualized functions along that route. An information model based approach is also presented for information sharing across the orchestrator, convergence gateway and controller.
Owner:ARGELA YAZILIM & BILISIM TEKNOLOJILERI SAN & TIC A S
Trigger for packing path computation requests
InactiveUS7623461B2Alleviate the conditionReduce failureError preventionTransmission systemsPathPingPath computation element
A technique triggers packing of path computation requests (PCRs) for traffic engineering (TE) label switched paths (LSPs) that are sent from one or more label-switched routers (LSRs) to a path computation element (PCE) of a computer network. According to the novel technique, incoming PCRs are packed into sets in response to a certain event, and one or more TE-LSPs (paths) are computed for each PCR of a particular set based on the PCRs of that set. Specifically, the PCE detects an event in the network (“network event”) indicating that an increase in the number of incoming PCRs has occurred, or that an increase is likely to occur due to, e.g., a change in a network element. Once the network event has been detected, the PCE packs the incoming PCRs into configured-length sets, such as, e.g., for a specified time interval or a certain number of PCRs. The PCE computes paths for each PCR of a particular set while considering the other PCRs of that set, thereby reducing race conditions, signaling overhead, and set-up failures.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Device for and a method of monitoring service data for automated traffic engineering in a communications network
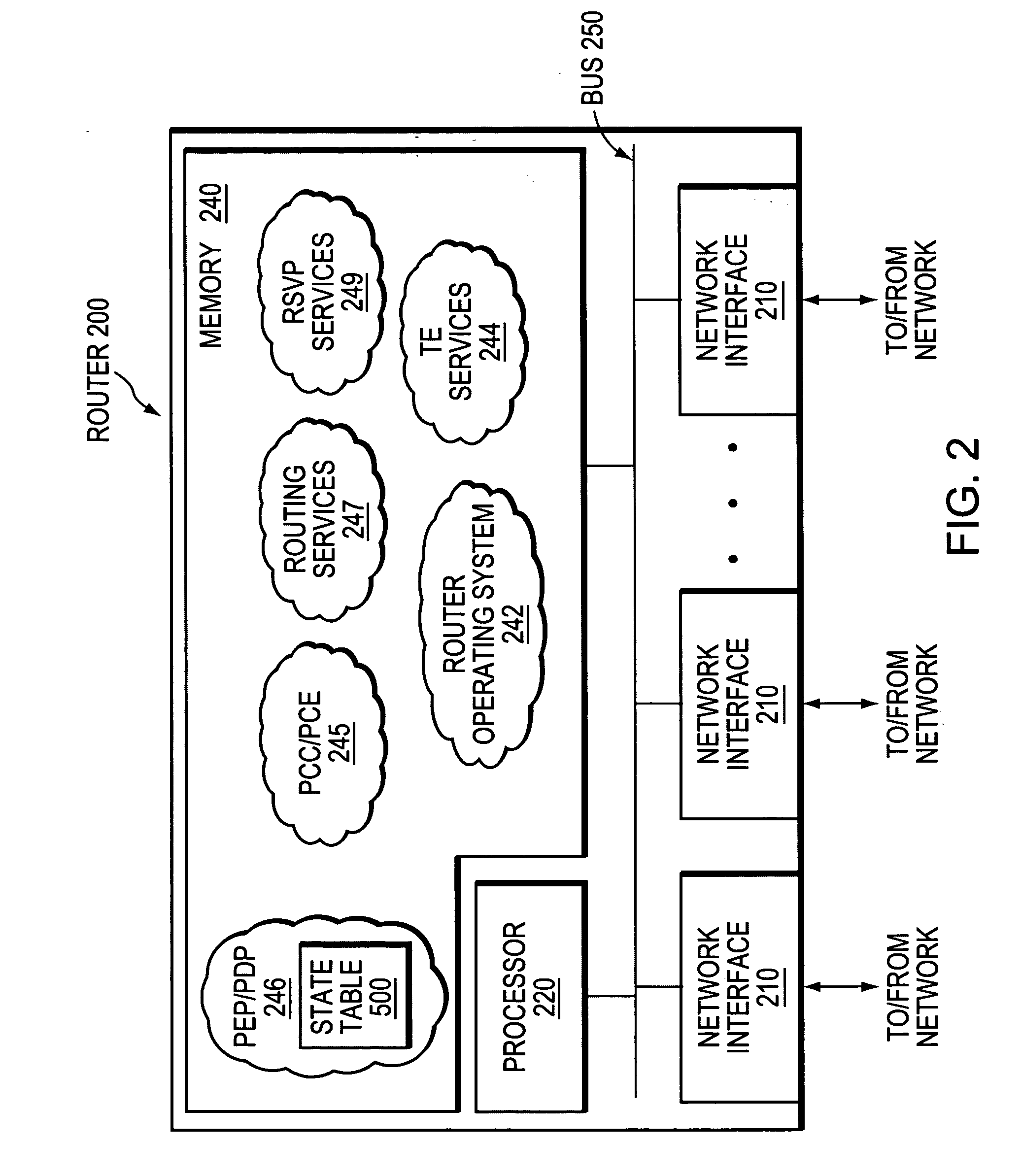
InactiveUS20030220769A1Error detection/correctionDigital computer detailsReliability engineeringReal-time computing
A device for monitoring service data for controlling traffic engineering modules (11, 12) and delivered by management modules (7) of a communications network. The device comprises i) a memory (9) for storing rules each defined by at least one condition representative of an event in the network associated with one of the traffic engineering modules (11, 12) and at least one action representative of at least one command to be executed by the associated module and ii) monitoring means (3) adapted, on receiving service data designating an event, to extract from the memory (9) at least one of the rules corresponding to the event and to deliver each command representative of the action associated with the condition representative of the event to the traffic engineering module (11, 12) associated with that event in the extracted rule.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com