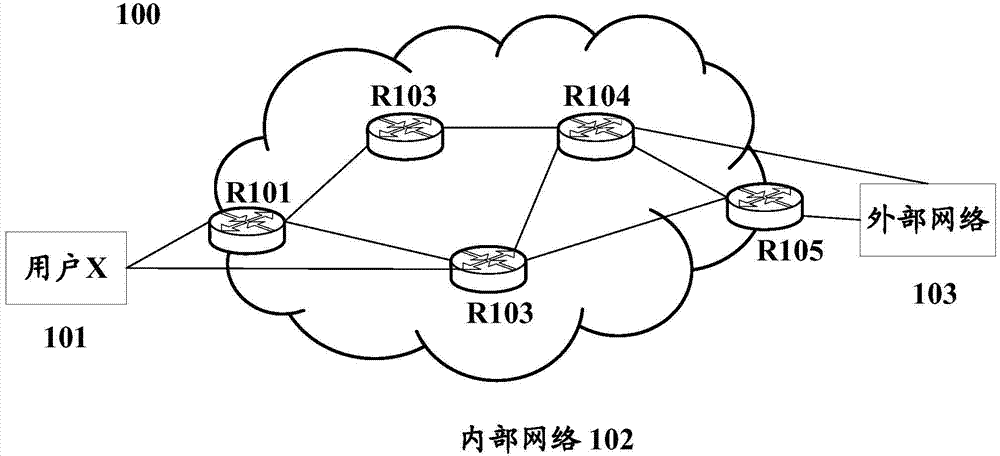
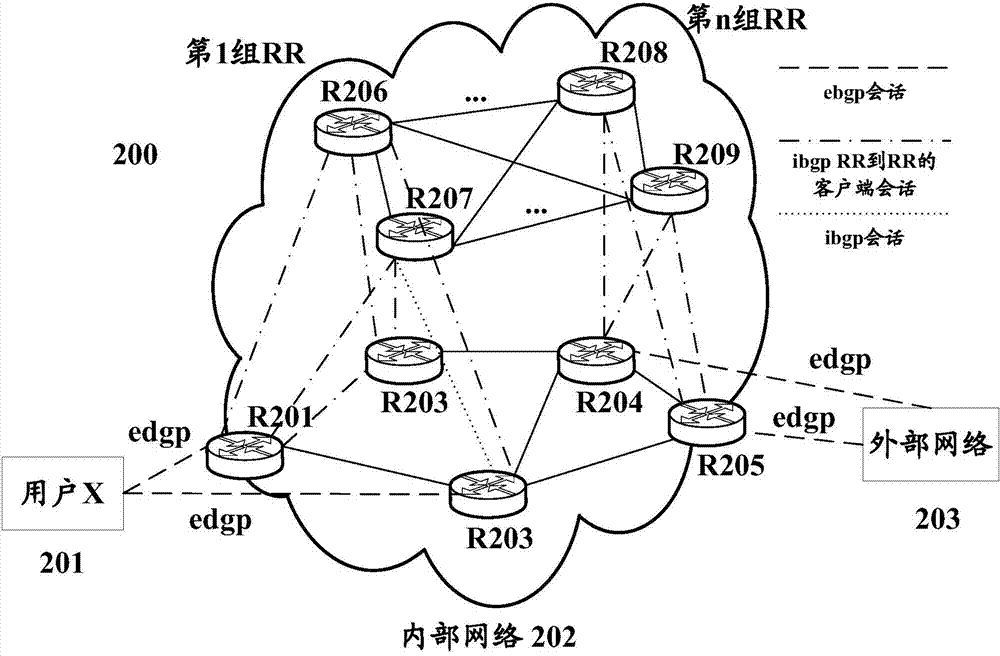
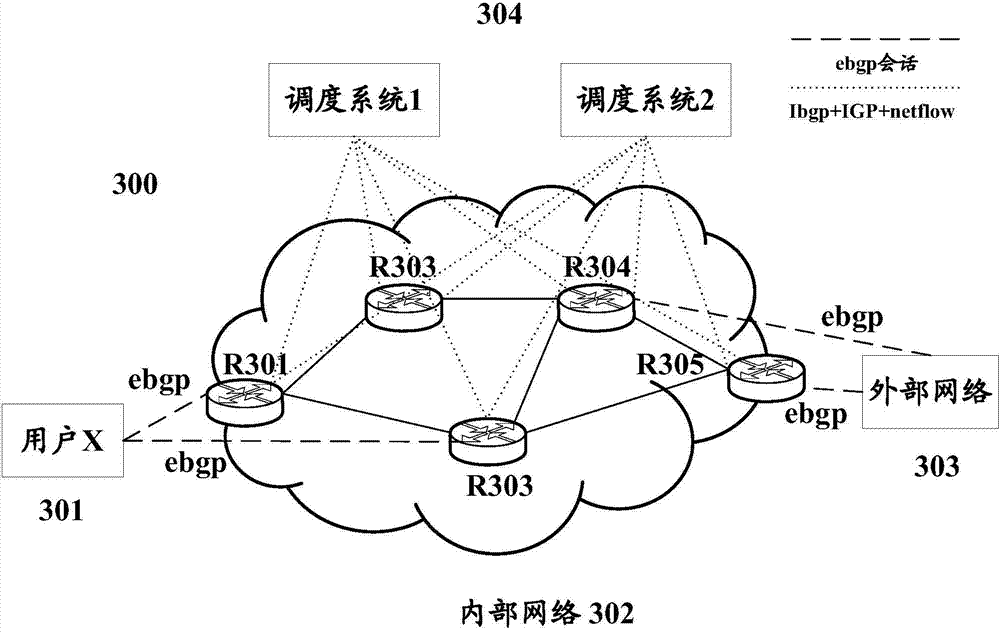
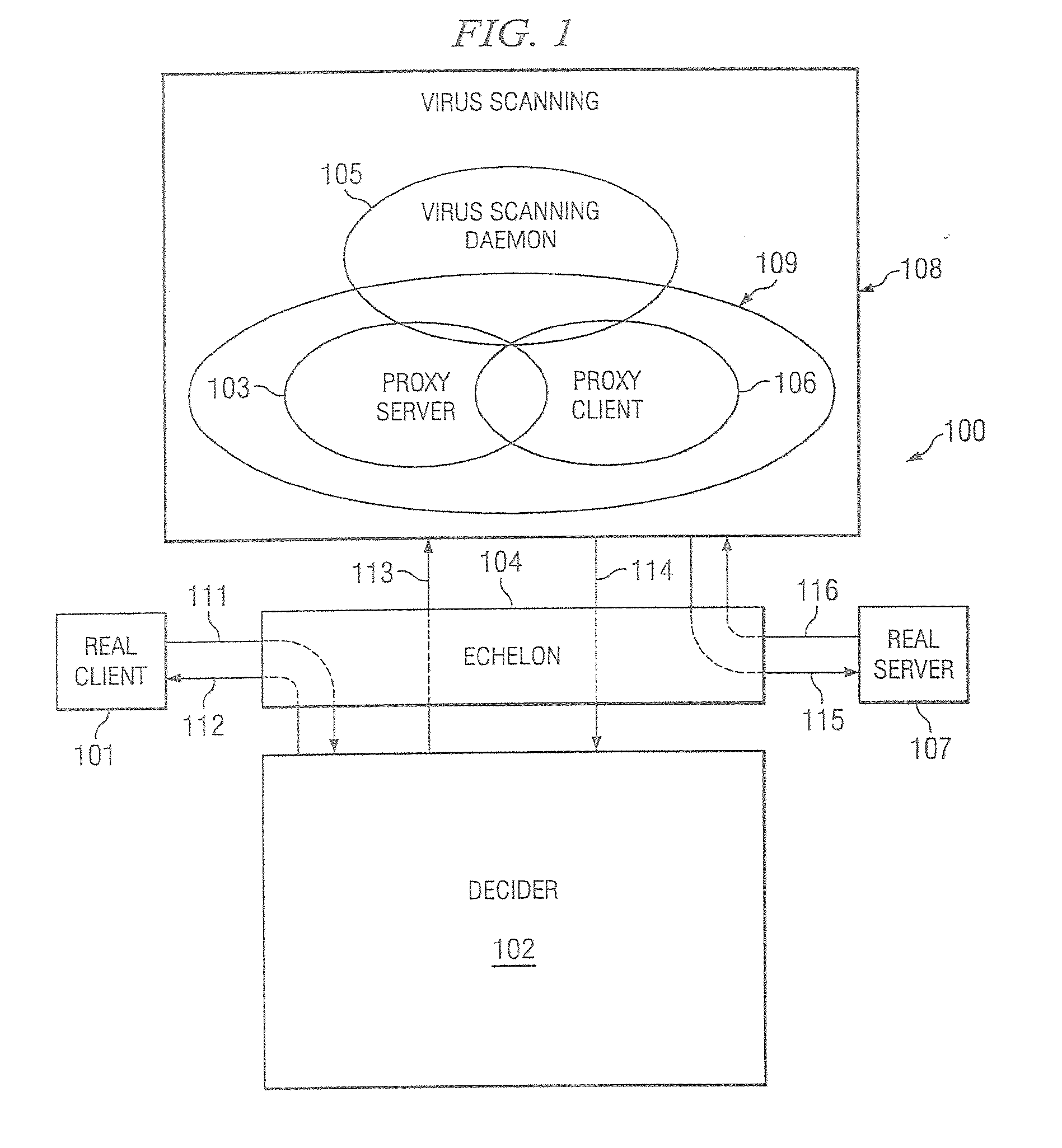
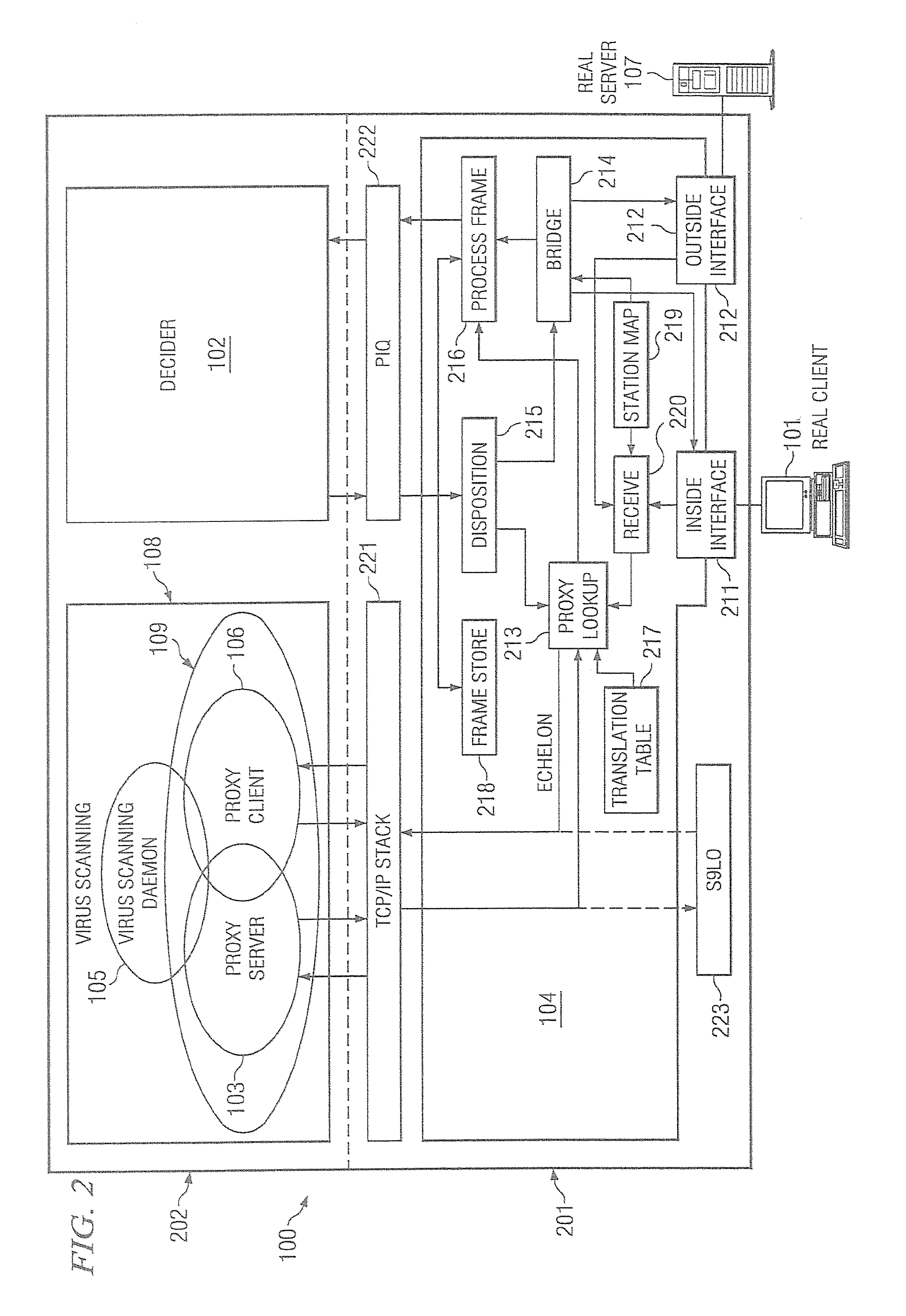
Patents
Literature
141 results about "Interior gateway protocol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
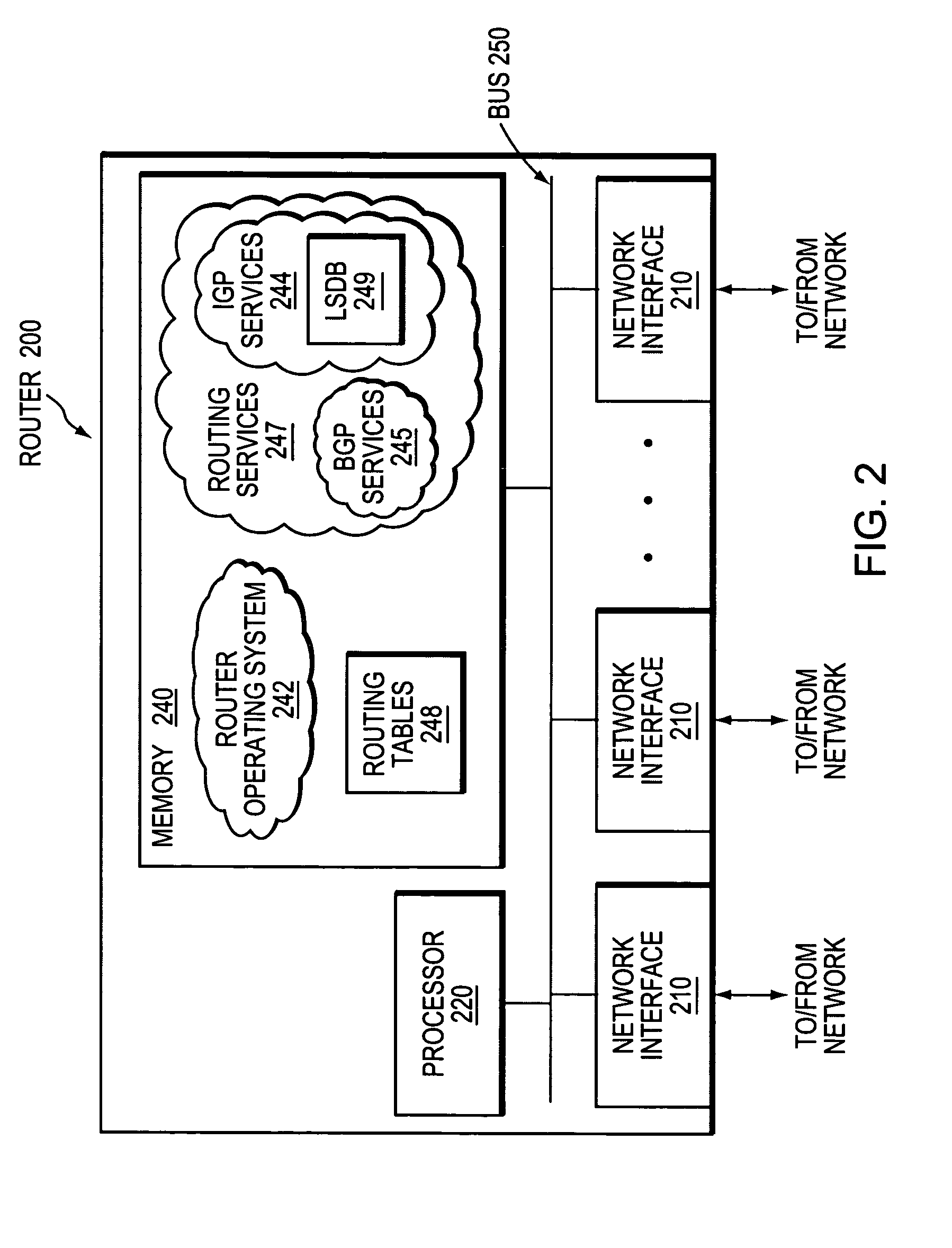
An interior gateway protocol (IGP) is a type of protocol used for exchanging routing information between gateways (commonly routers) within an autonomous system (for example, a system of corporate local area networks). This routing information can then be used to route network-layer protocols like IP.
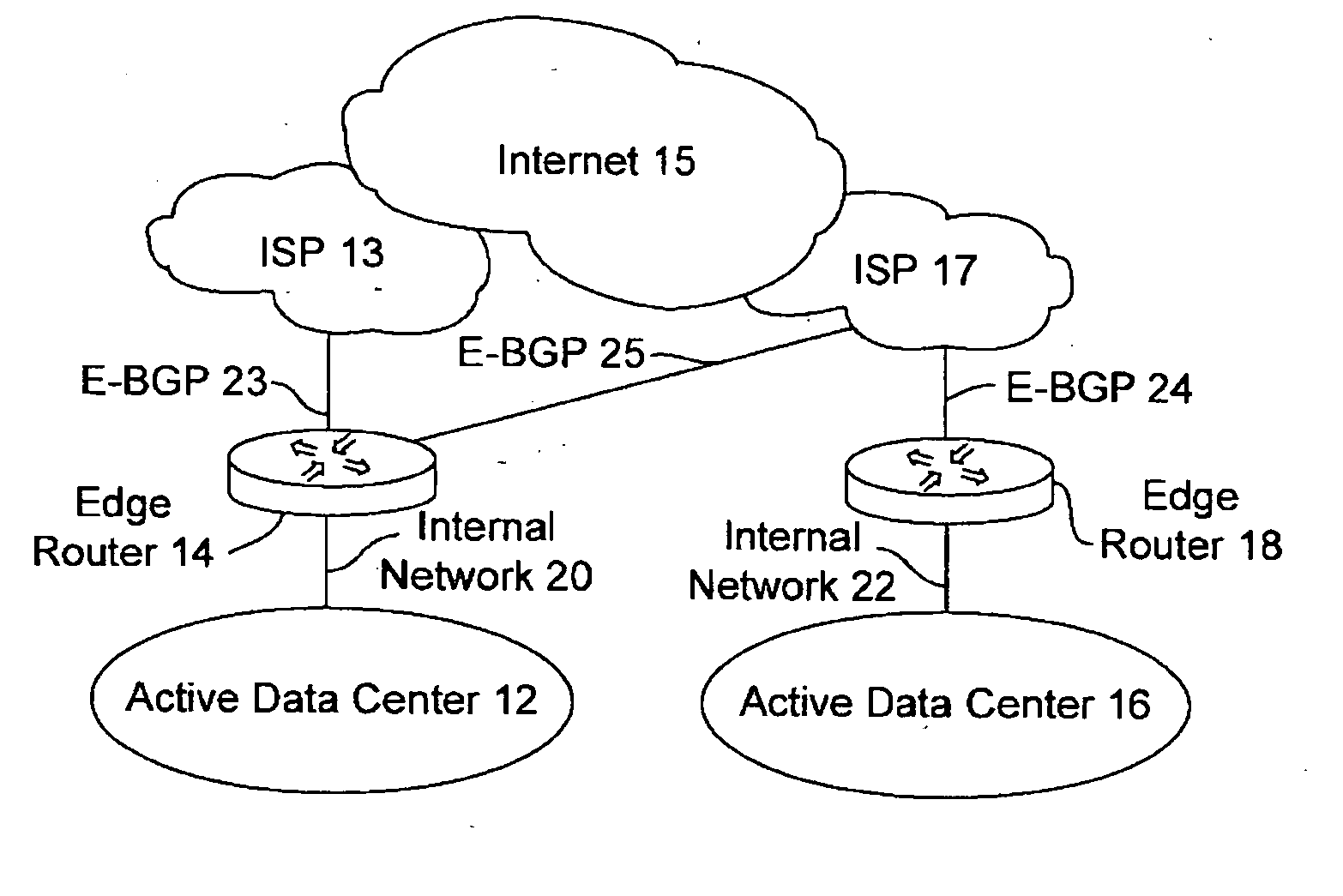
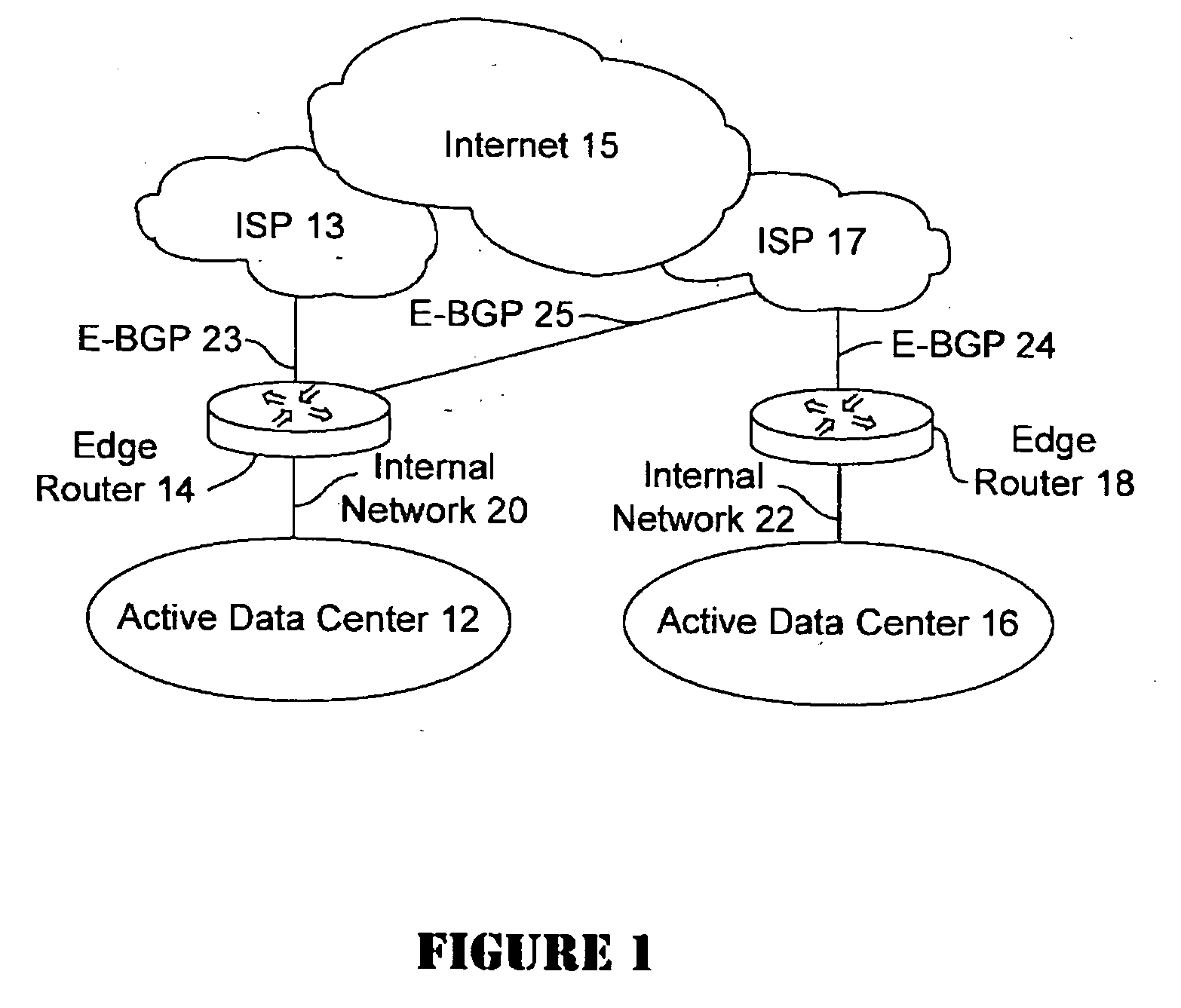
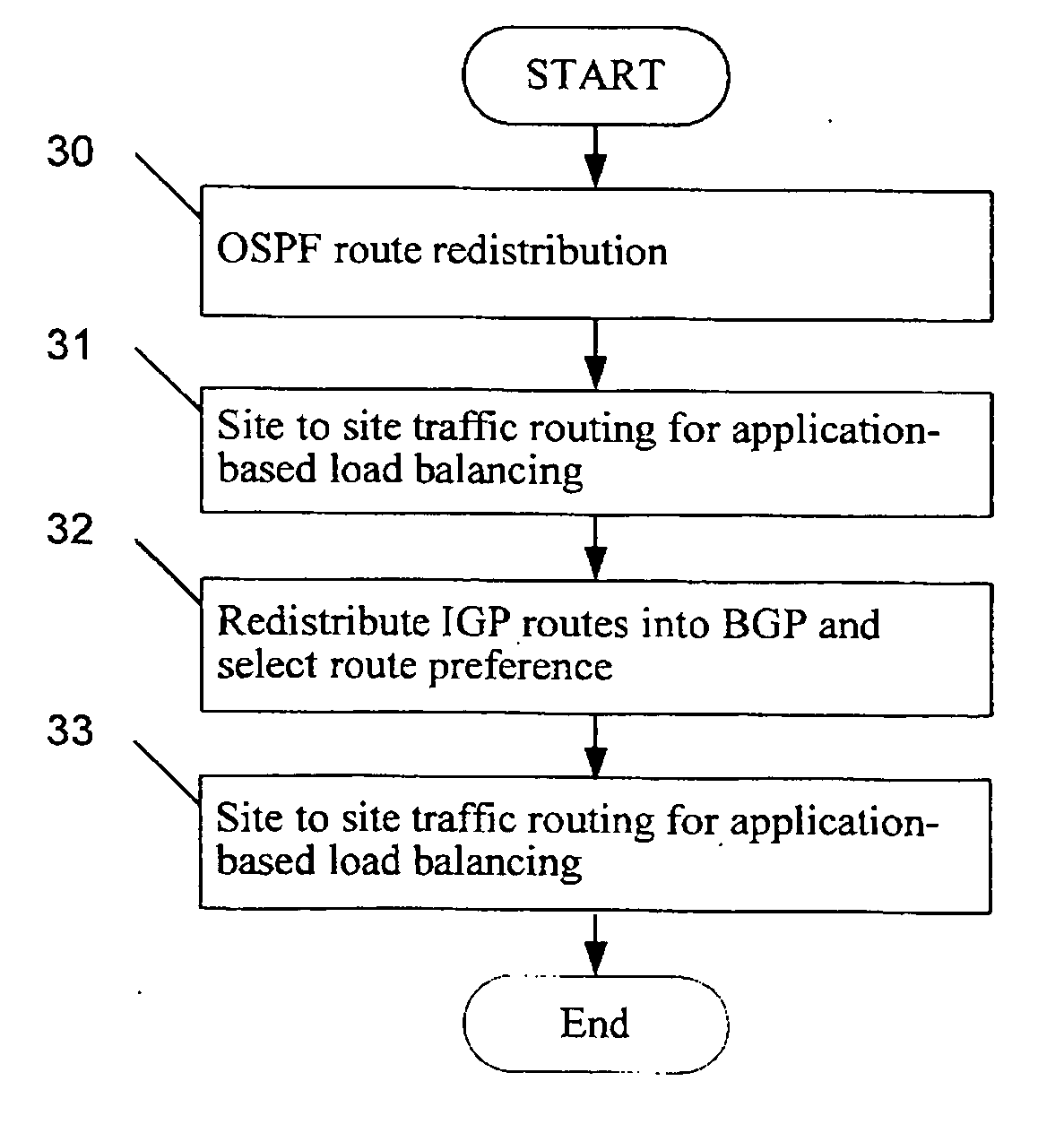
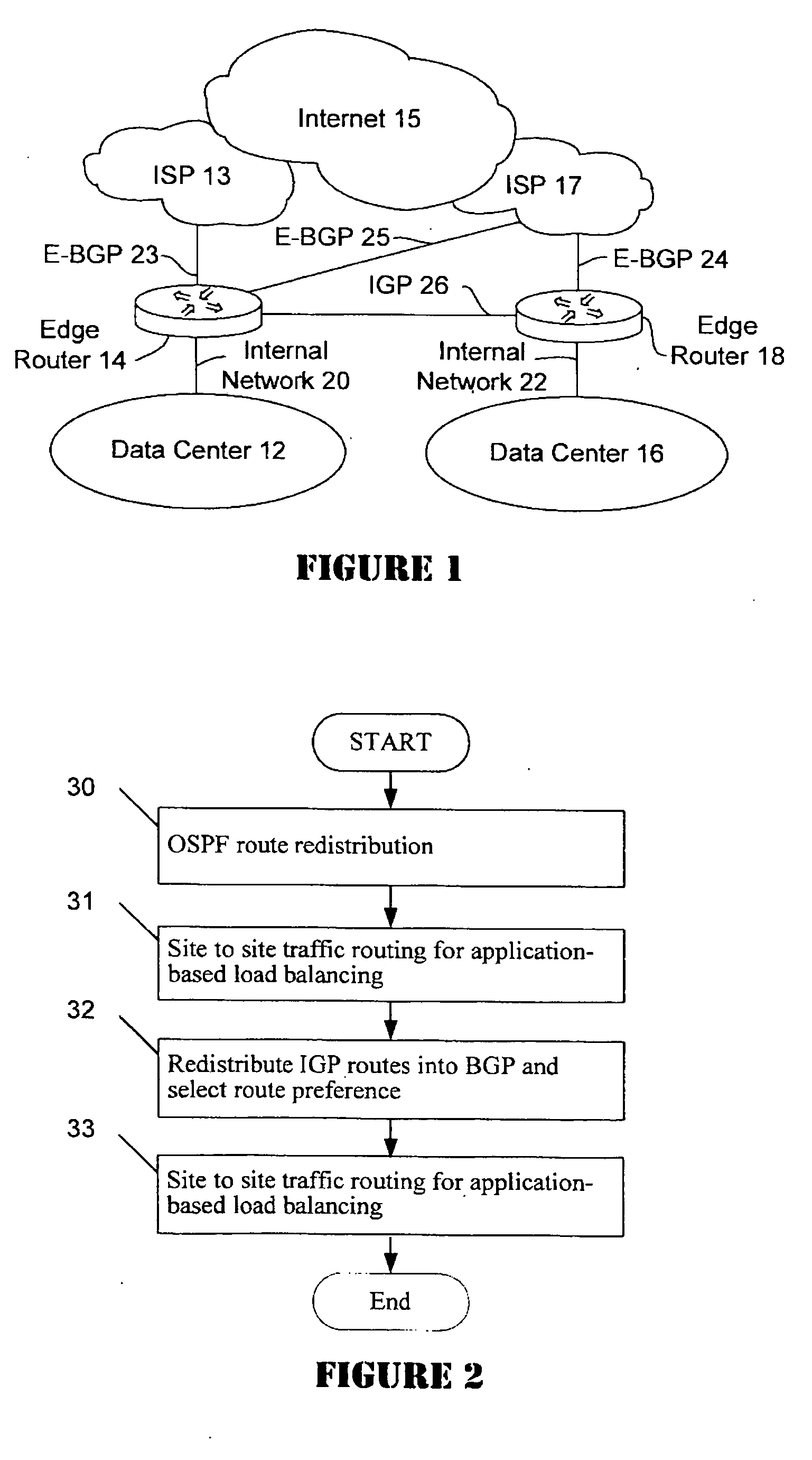
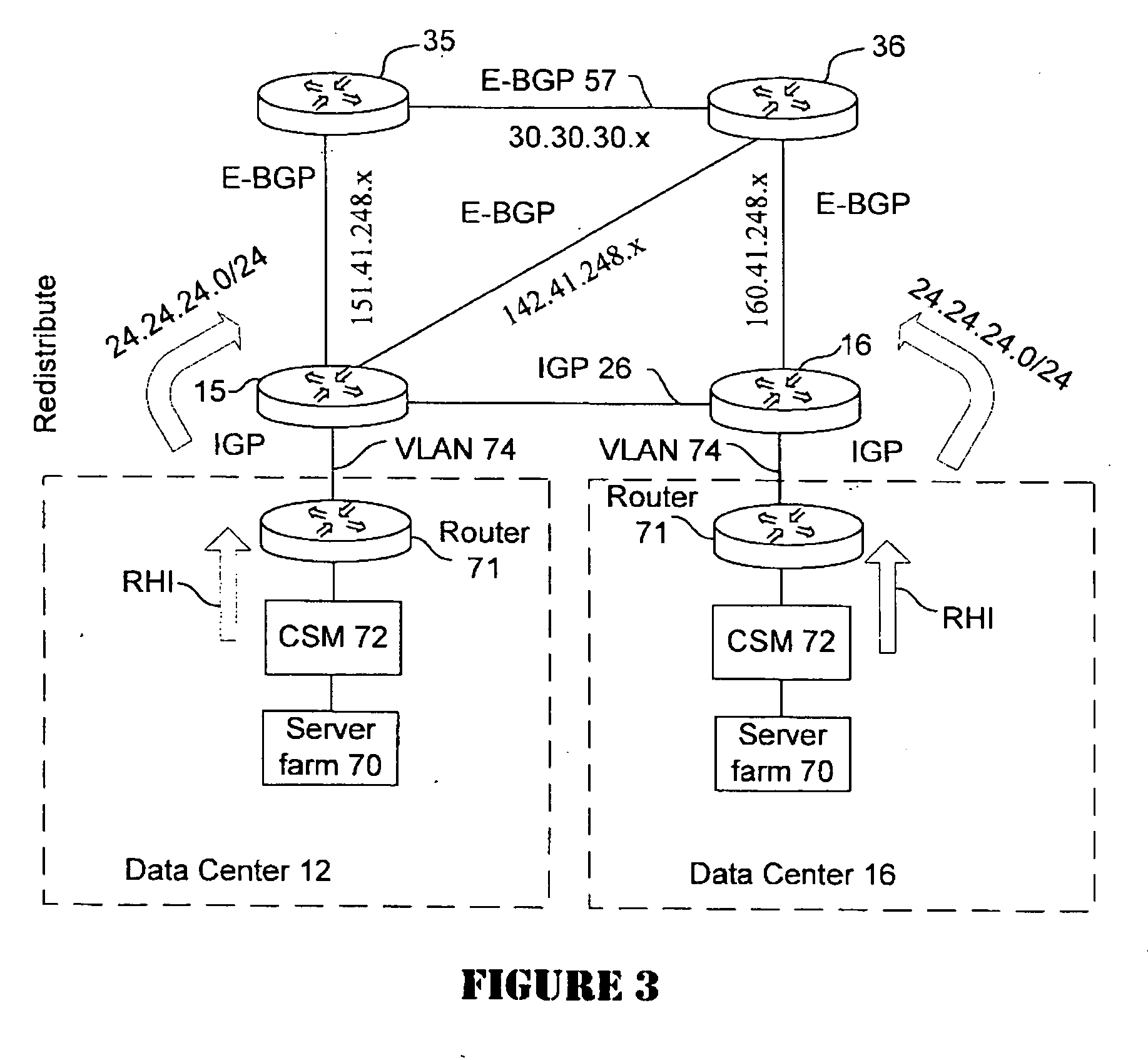
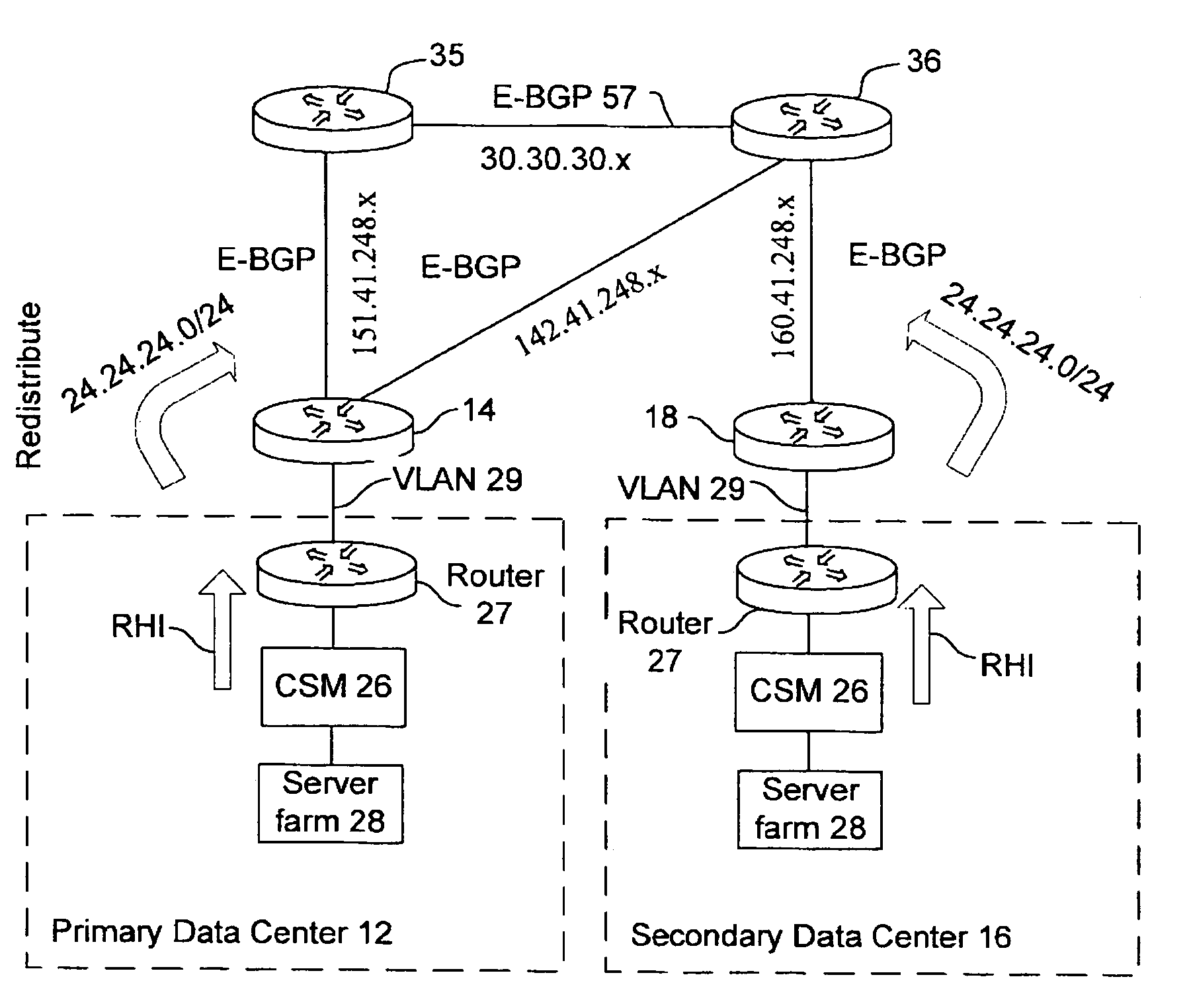
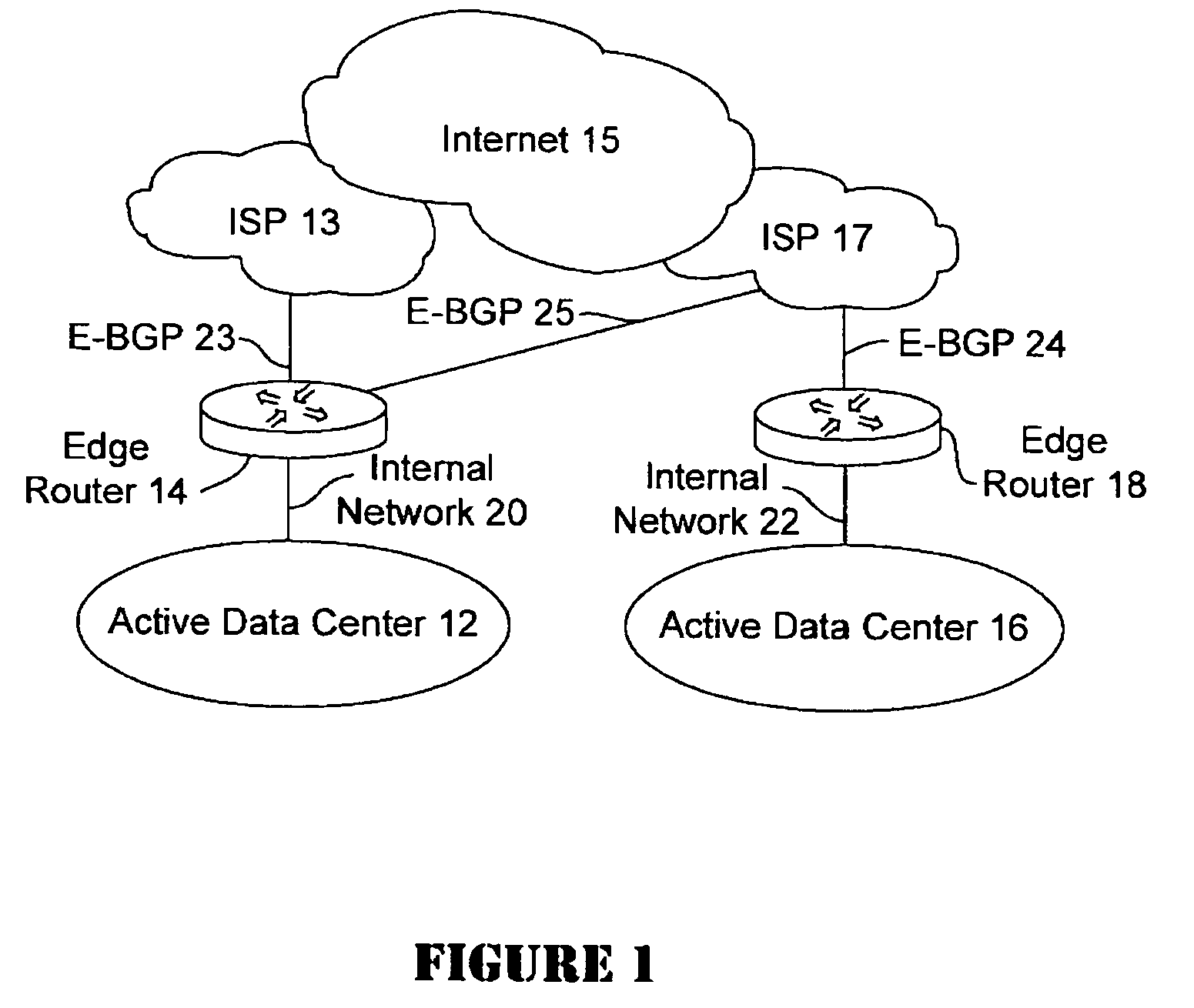
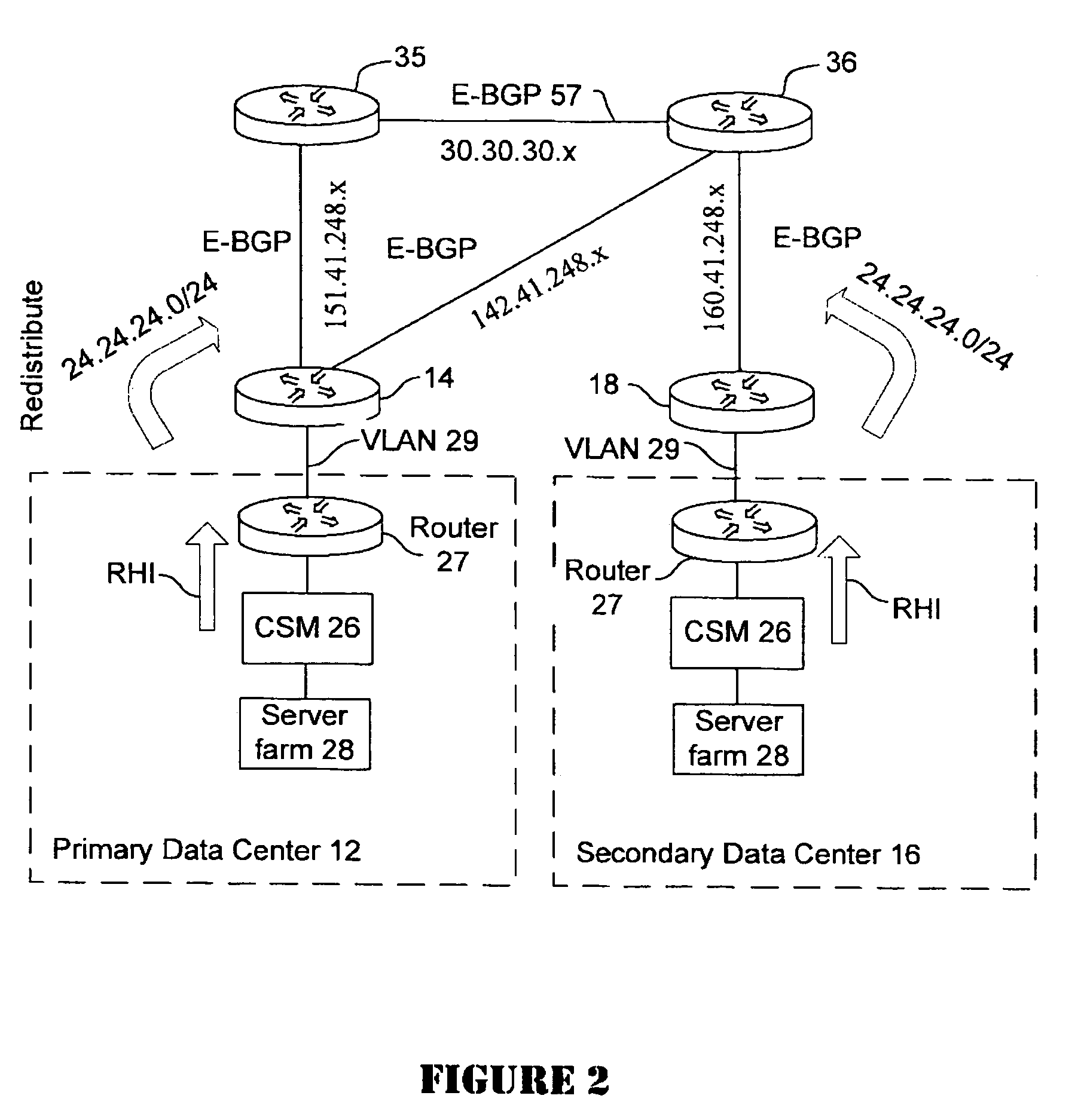
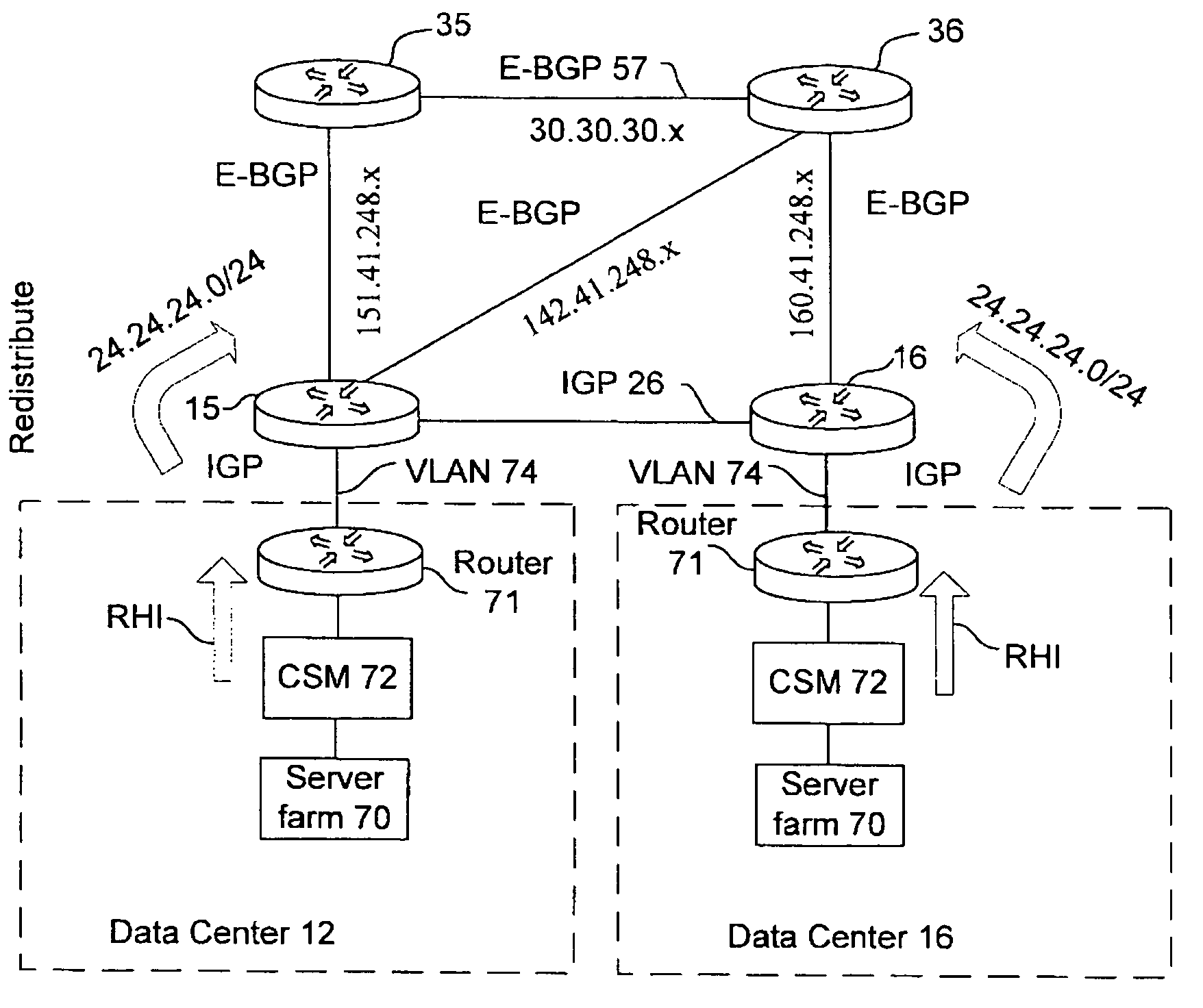
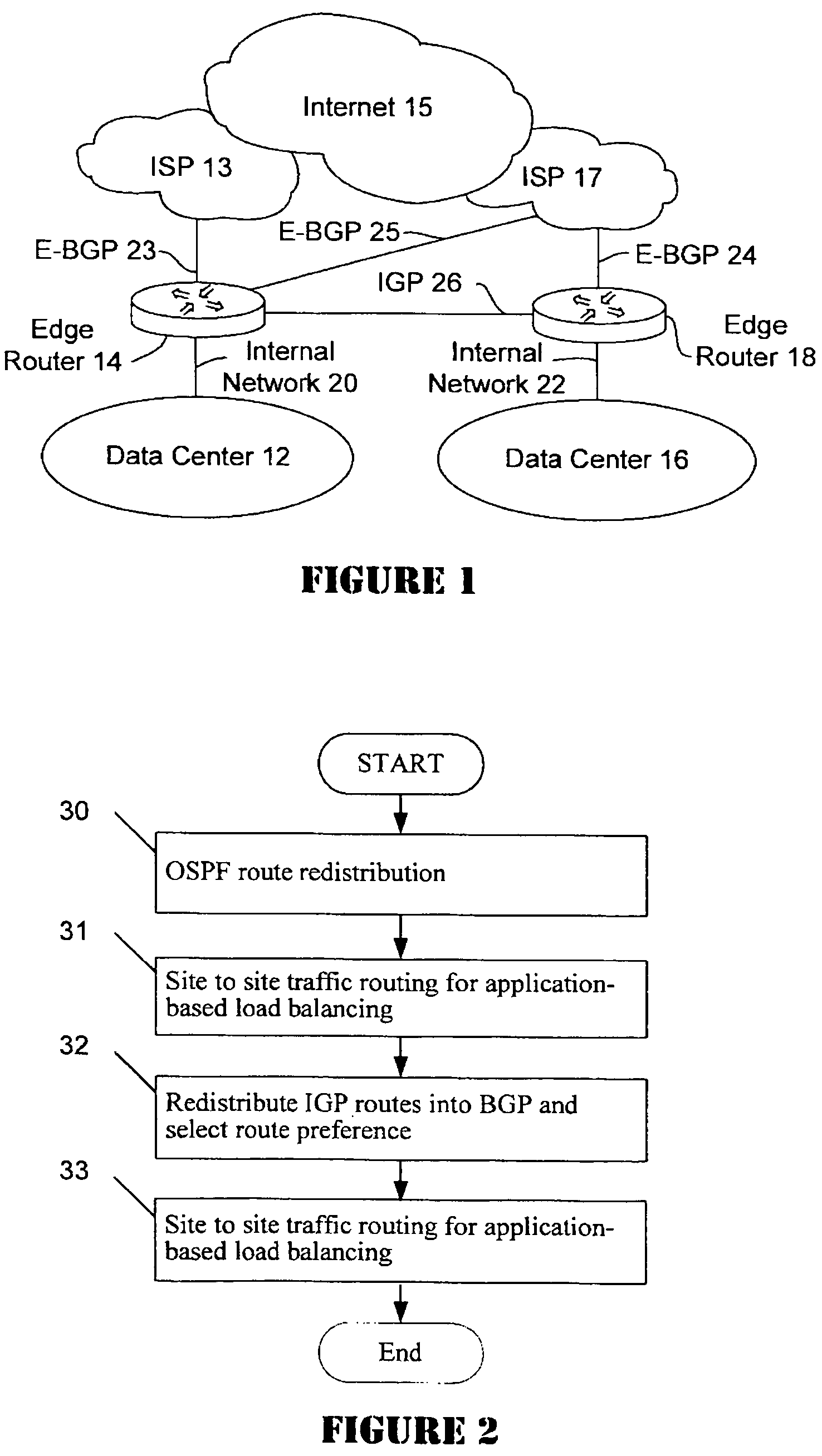
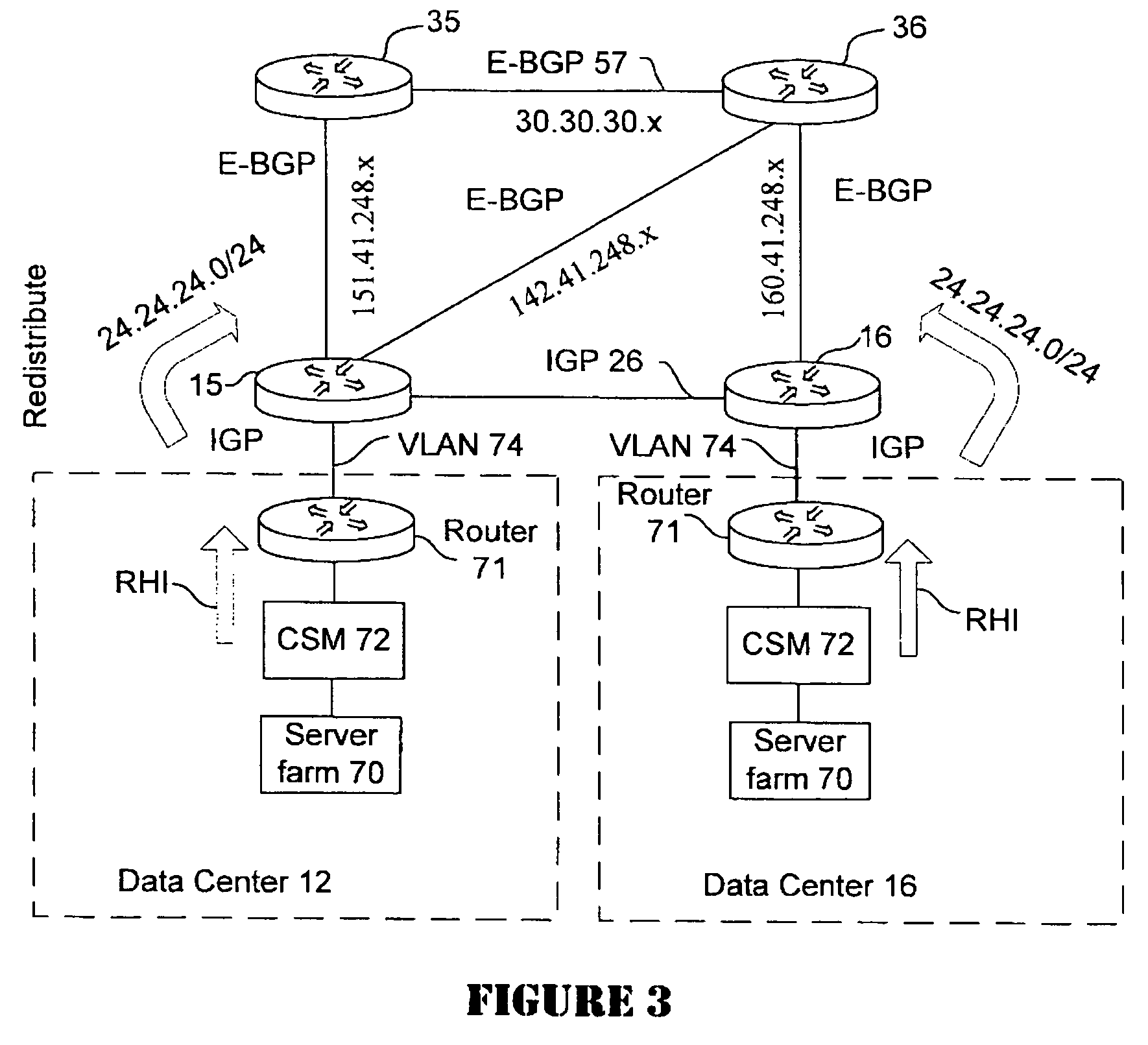
Active-active data center using RHI, BGP, and IGP anycast for disaster recovery and load distribution
A distributed data center topology having at least a pair of active data centers that can recover from a disaster at one of the data centers and achieves load balancing using IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) between data centers. The distributed data centers use virtual IP addresses, route health injection and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) for business continuance, disaster recovery and load balancing. The active / active topology supports load balancing where each site concurrently hosts active applications or applications can be hosted in a logical active / standby mode. IGP and RHI (Route Health Injection) are used to propagate routes to an edge router and BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) and IP Anycast are used for site-to-site recovery and load balancing between data center sites.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
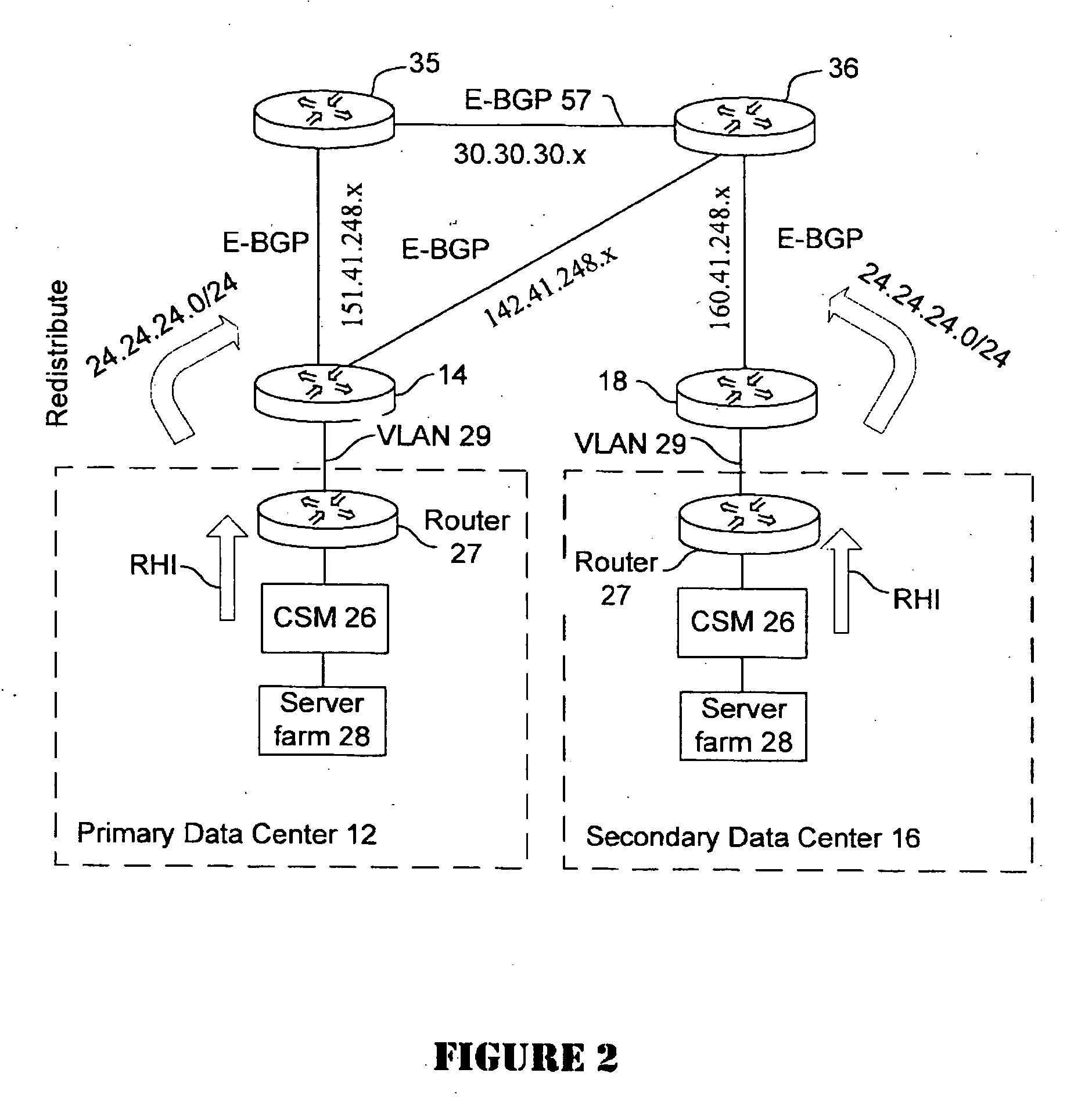
Application based active-active data center network using route health injection and IGP
A distributed data center topology having at least a pair of active data centers that can recover from a disaster at one of the data centers and achieves load balancing using IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) between data centers. The distributed data centers use virtual IP addresses, route health injection and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) for business continuance, disaster recovery and load balancing. Active applications are deployed at each data center to provide a logical active / standby configuration for certain applications. Alternatively, active applications are deployed at both sites and BGP routes traffic to the closest data center edge router. Load balancing occurs over an internal IGP link between sites.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
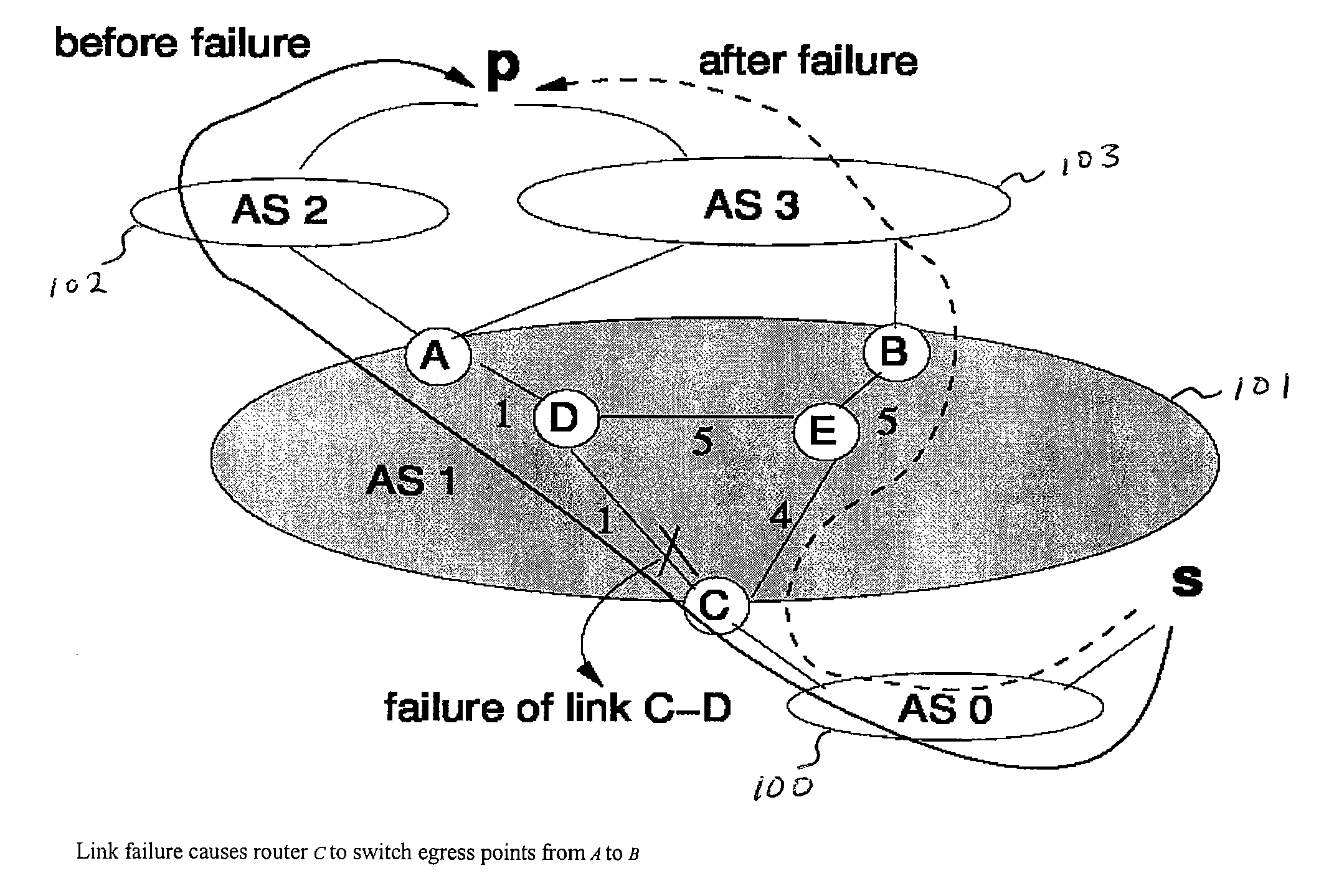
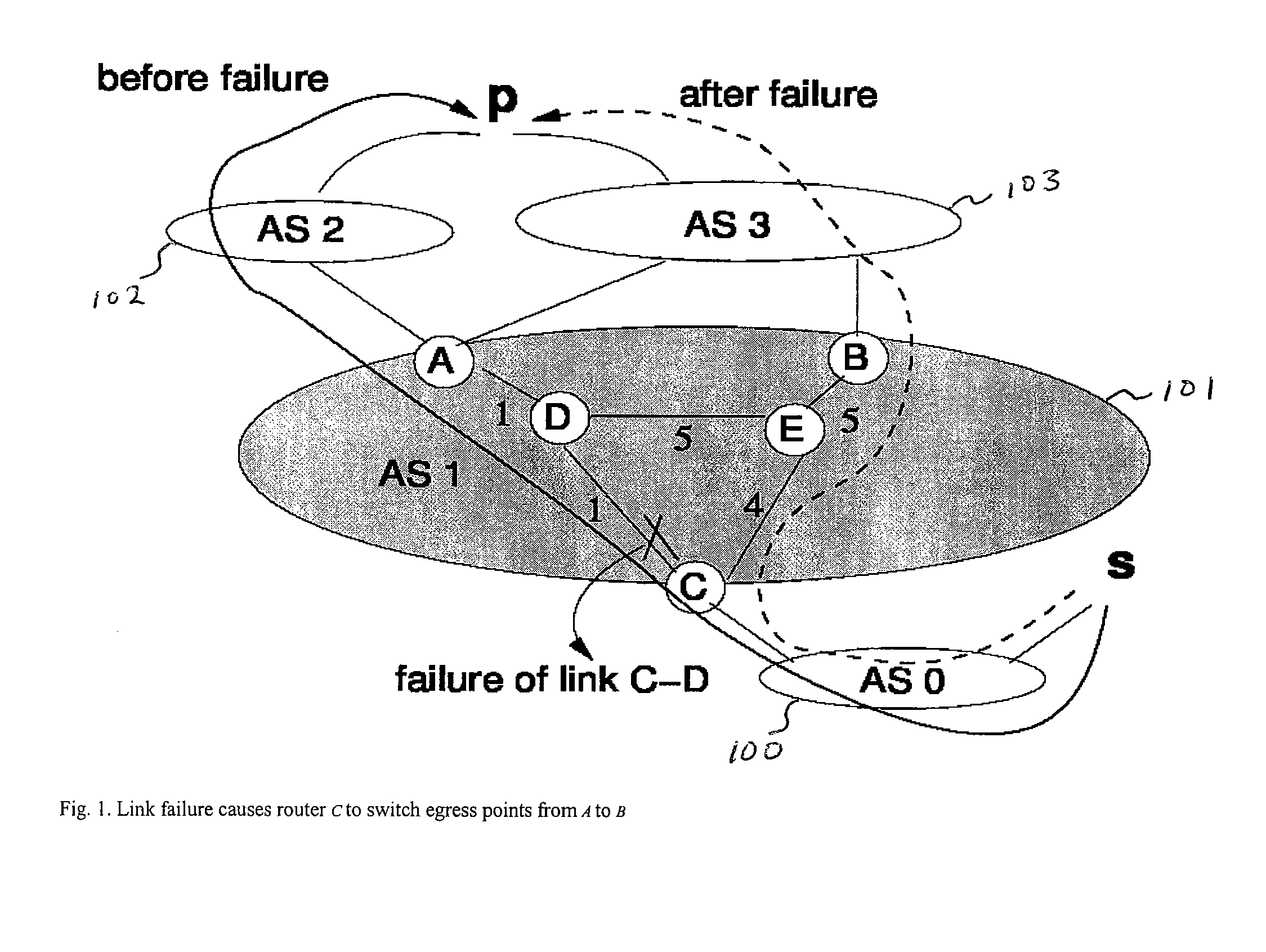
Method for tunable inter domain egress selection
InactiveUS7581022B1Simple to executeError preventionTransmission systemsFlexible MechanismsInter-domain
A flexible mechanism and method for routers to select the egress point for each destination comprises identifying a plurality of points of egress from an autonomous system, ranking the plurality of points of egress according to a metric having variable and fixed terms, selecting a point of egress having the smallest rank, and transmitting packets from a point of ingress via a path to the selected point of egress. The metric is across a plurality of destinations and respective possible points of egress from the autonomous system and the metric is m(i, p, e) equaling α(i, p, e)·d(G,i,e)+β(i, p, e) where a and β are configurable values, i is the identity of the router, p is the destination, G is an undirected weighted graph, the d function is the interior gateway protocol distance and e is a point of egress.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
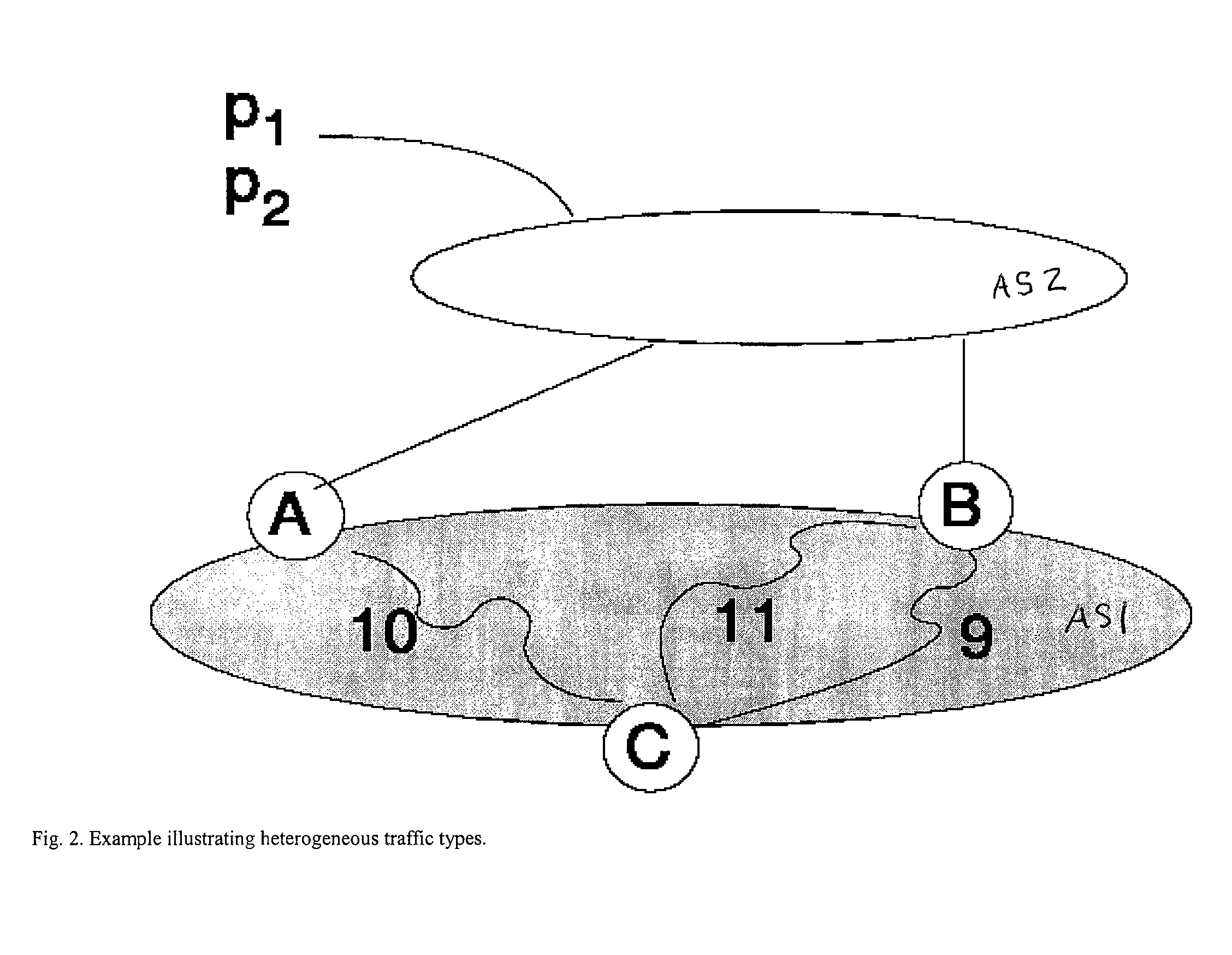
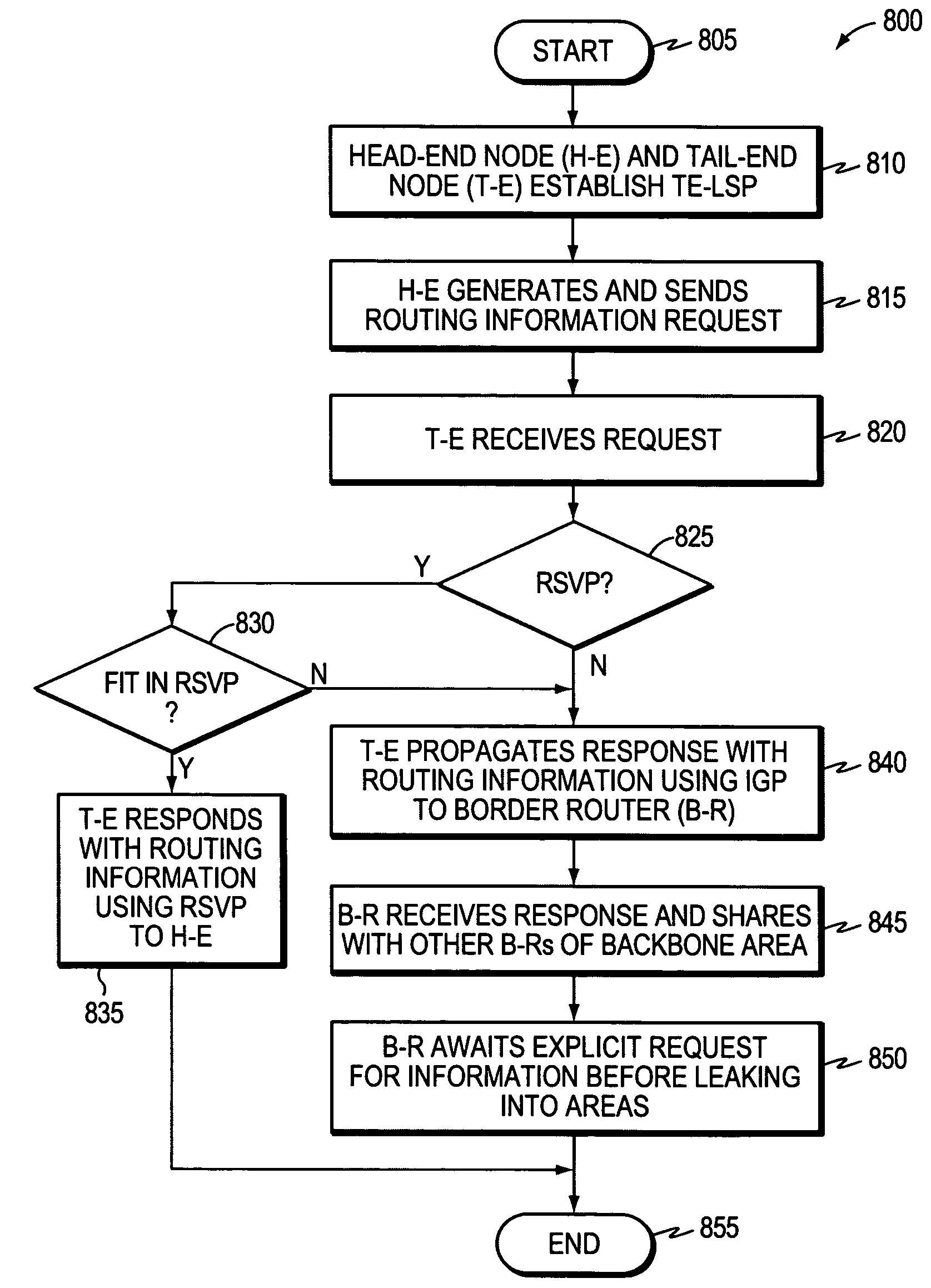
Controlled distribution of inter-area routing information
InactiveUS20070058568A1Limit excess distributionData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityRouting table
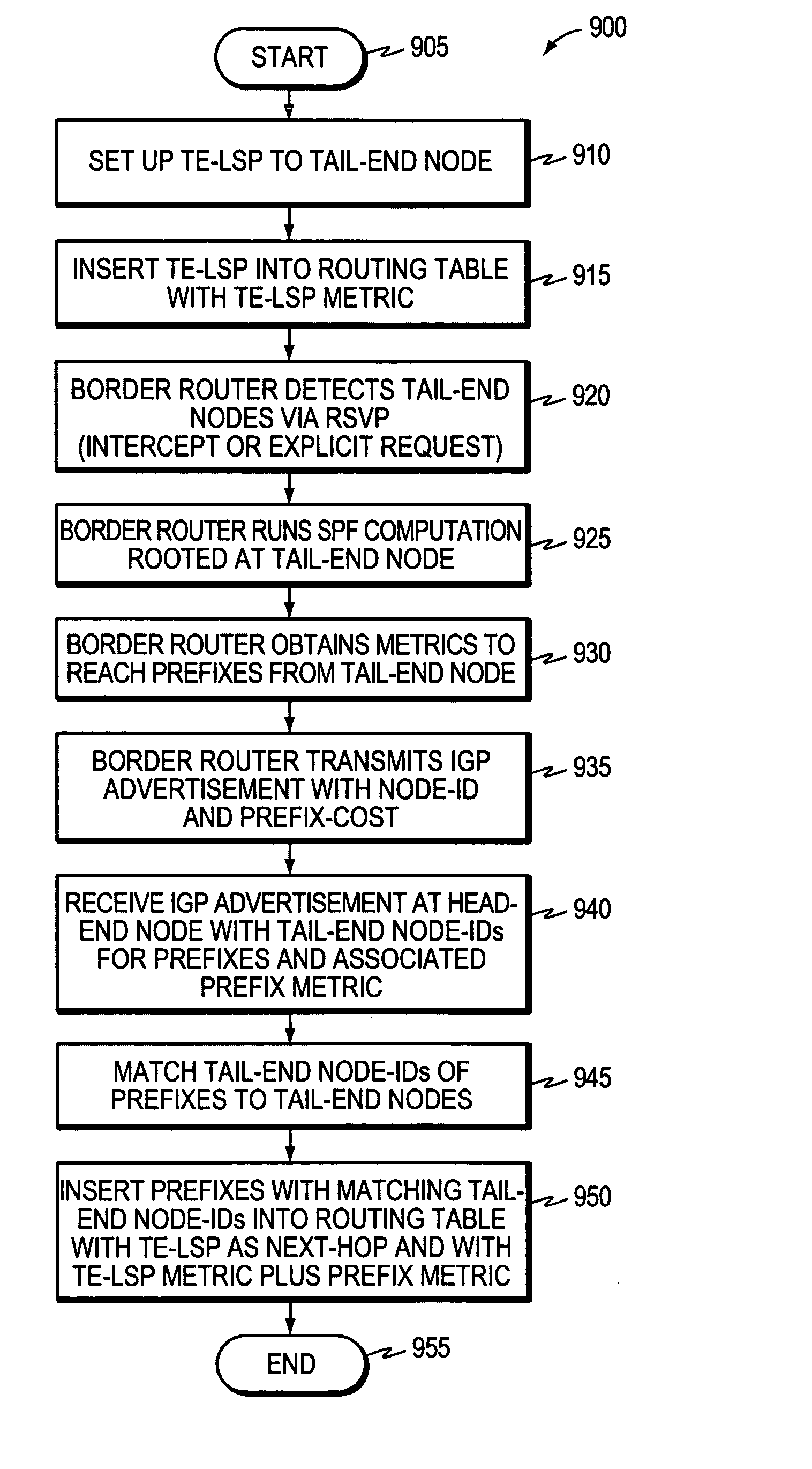
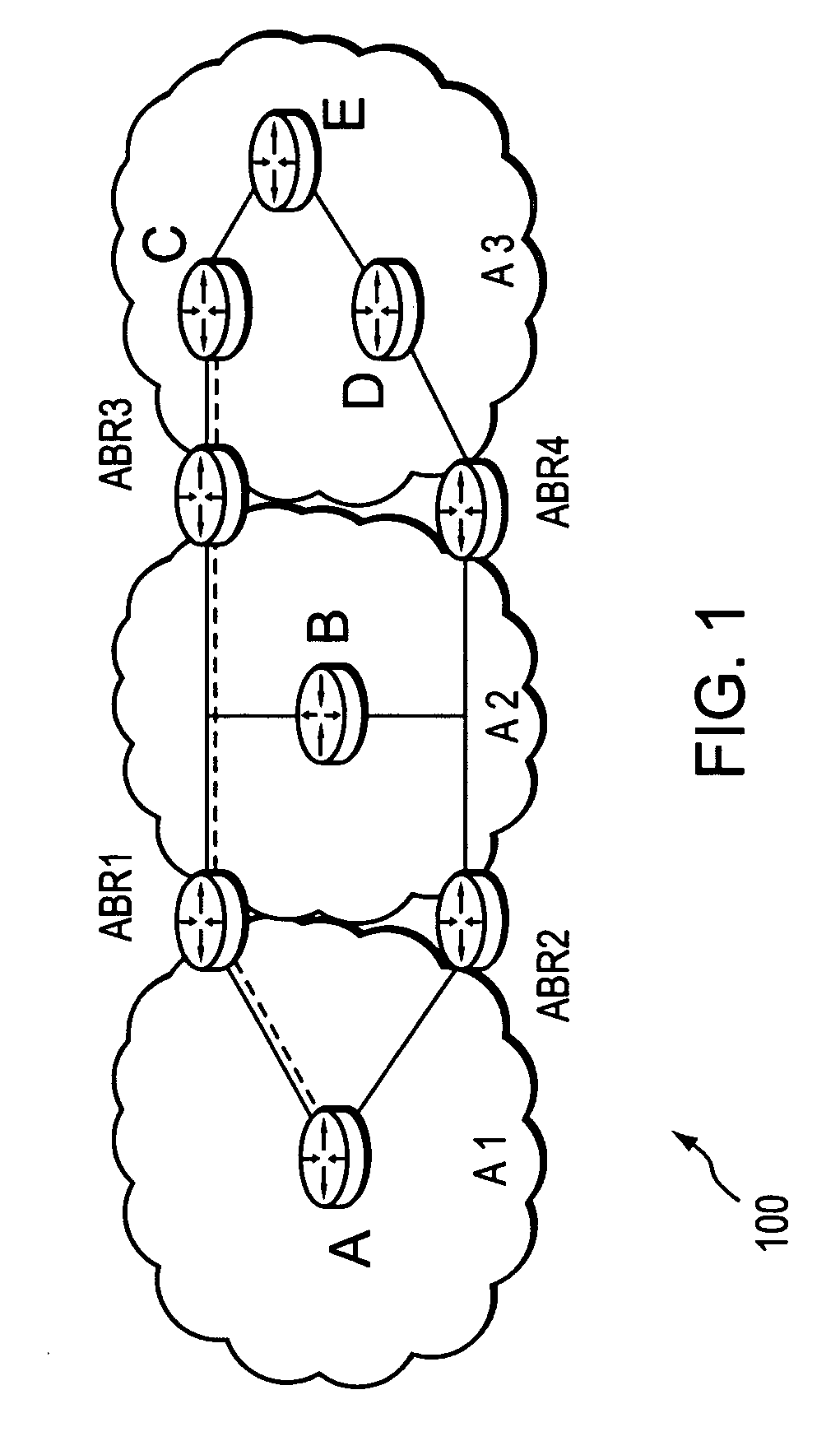
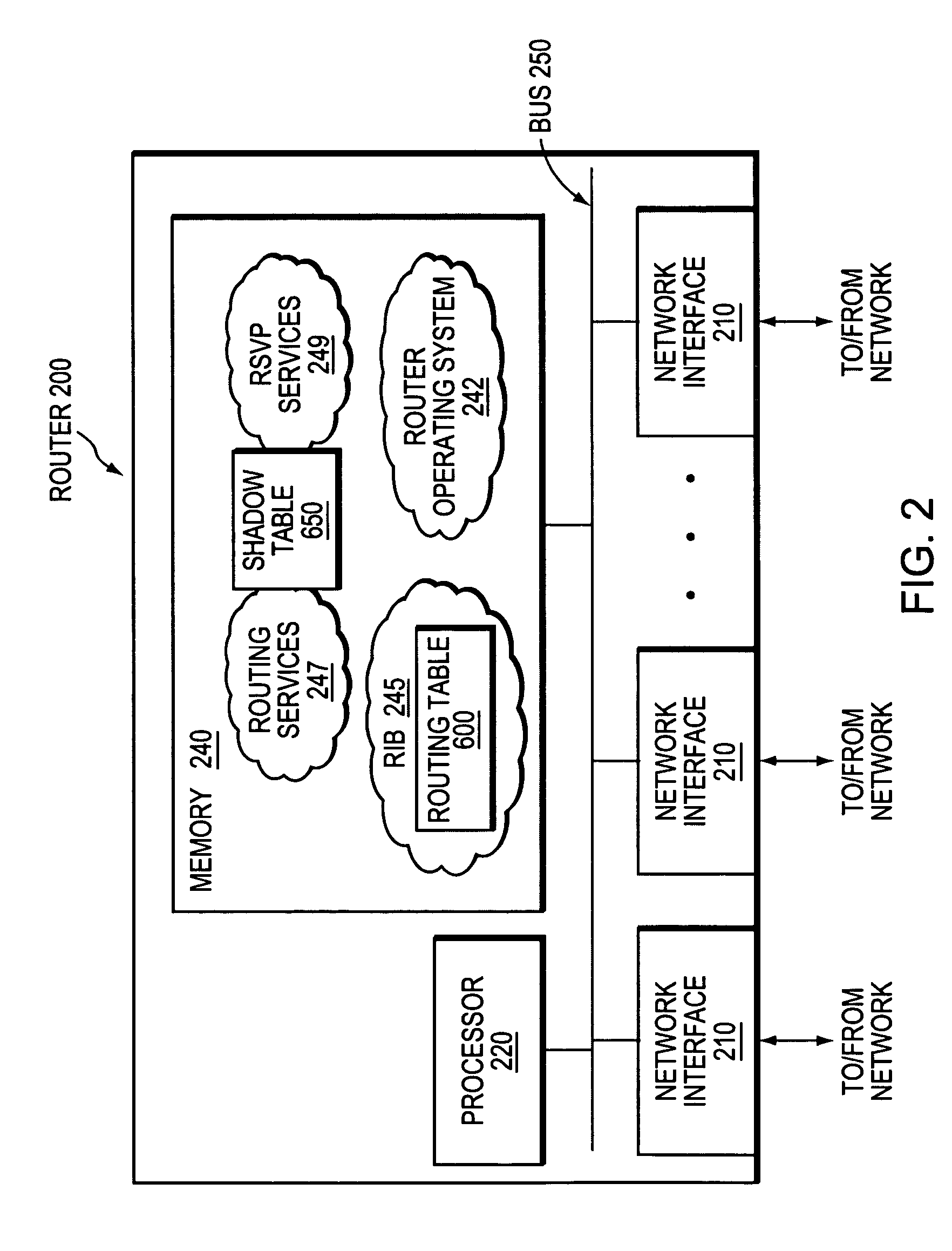
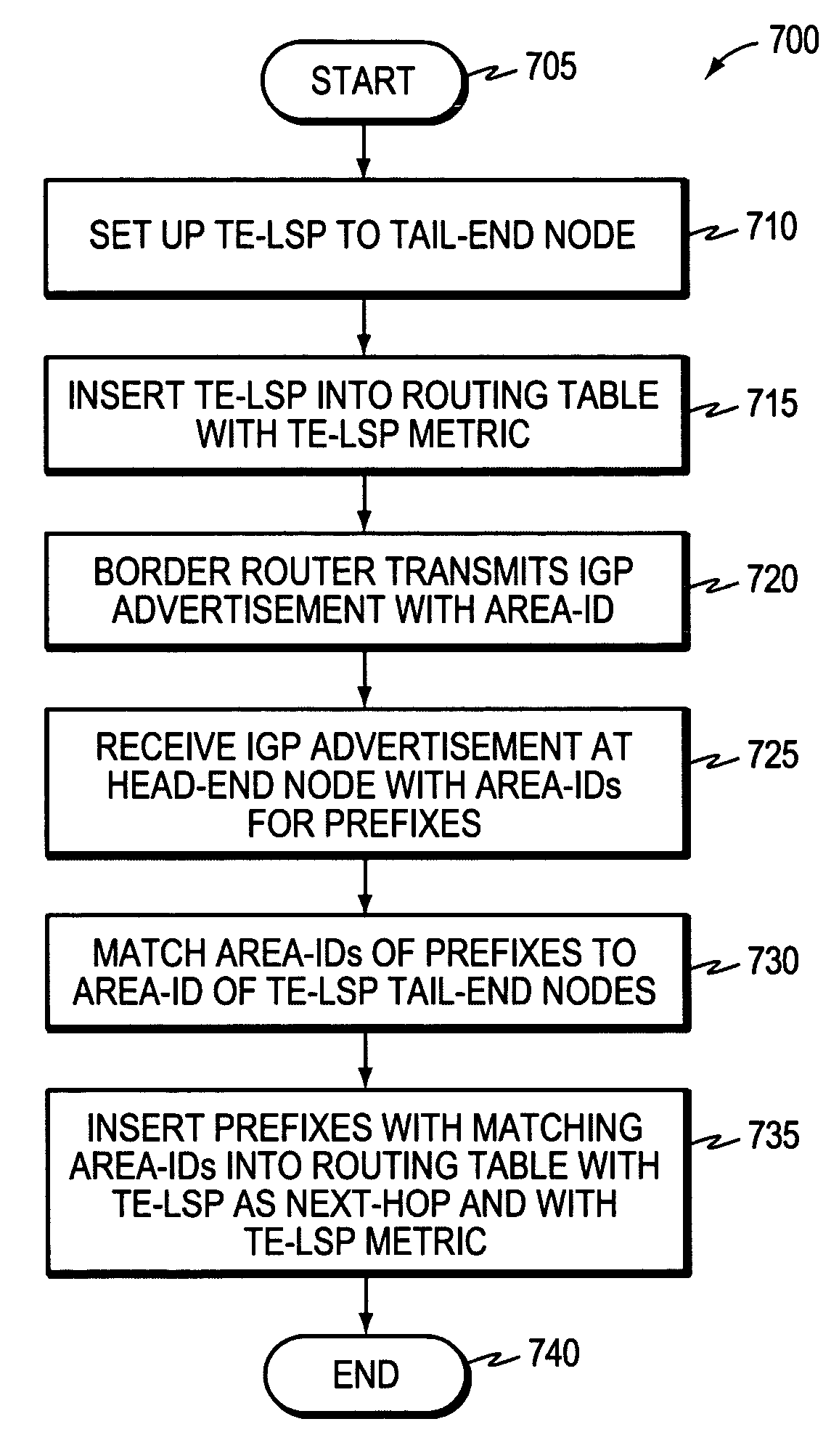
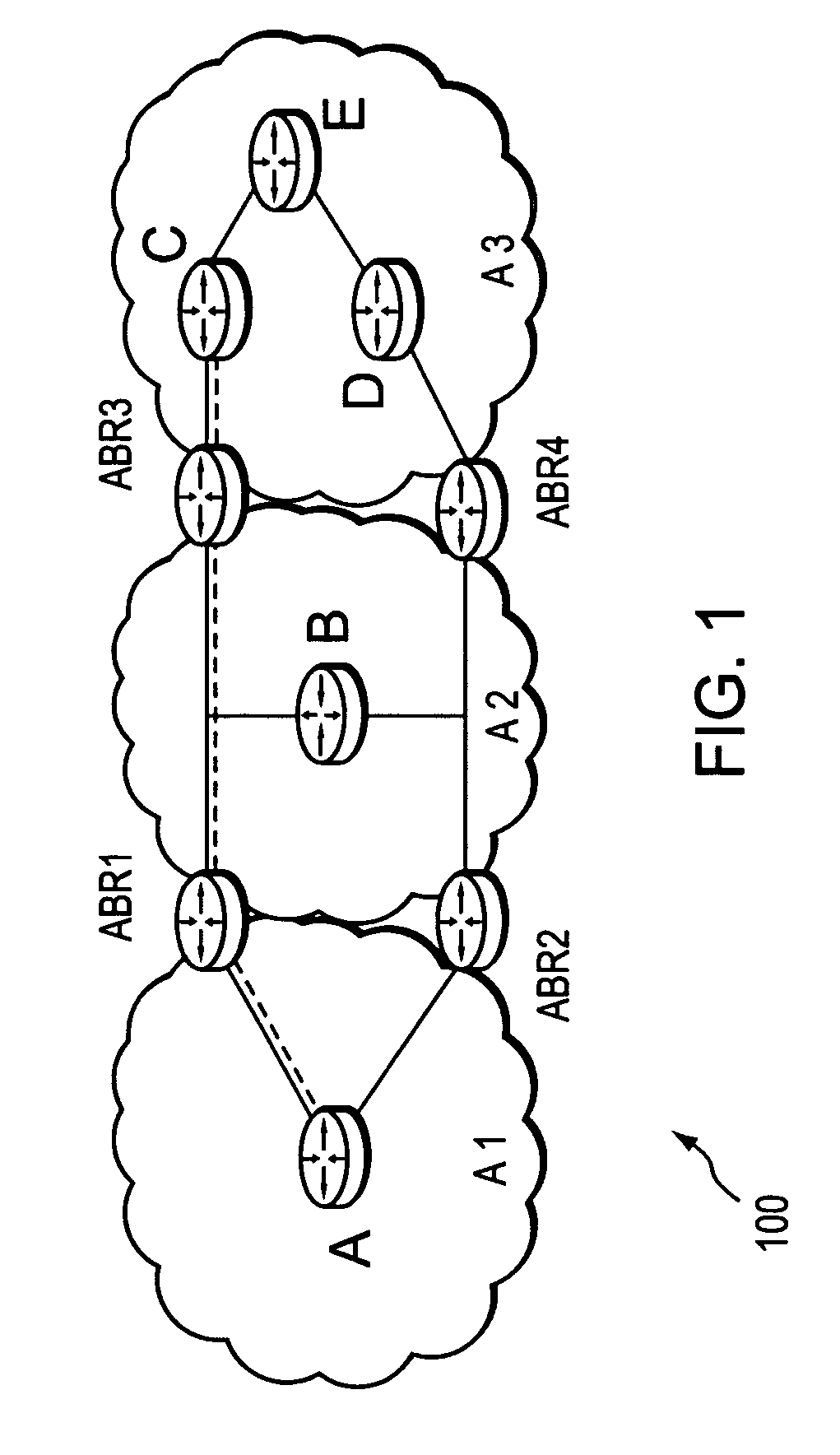
A technique controls distribution of reachability information for a tail-end node of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) to a head-end node of the TE-LSP in a computer network. The TE-LSP preferably spans multiple domains of the network such that the tail-end node resides in a domain (“tail-end domain”) that is different (remote) from the domain of the head-end node (“head-end domain”). According to the inter-domain information distribution technique, the head-end node requests the remote reachability information from the tail-end node, which may employ an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) to transmit the information to a border router of the tail-end domain. The tail-end domain border router then shares this information with at least a head-end domain border router. The head-end node thereafter requests that the head-end domain border router release the reachability information into the head-end domain. The head-end node uses the remote information to calculate routes, i.e., address prefixes and associated attributes, reachable from the tail-end node for insertion into its routing table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
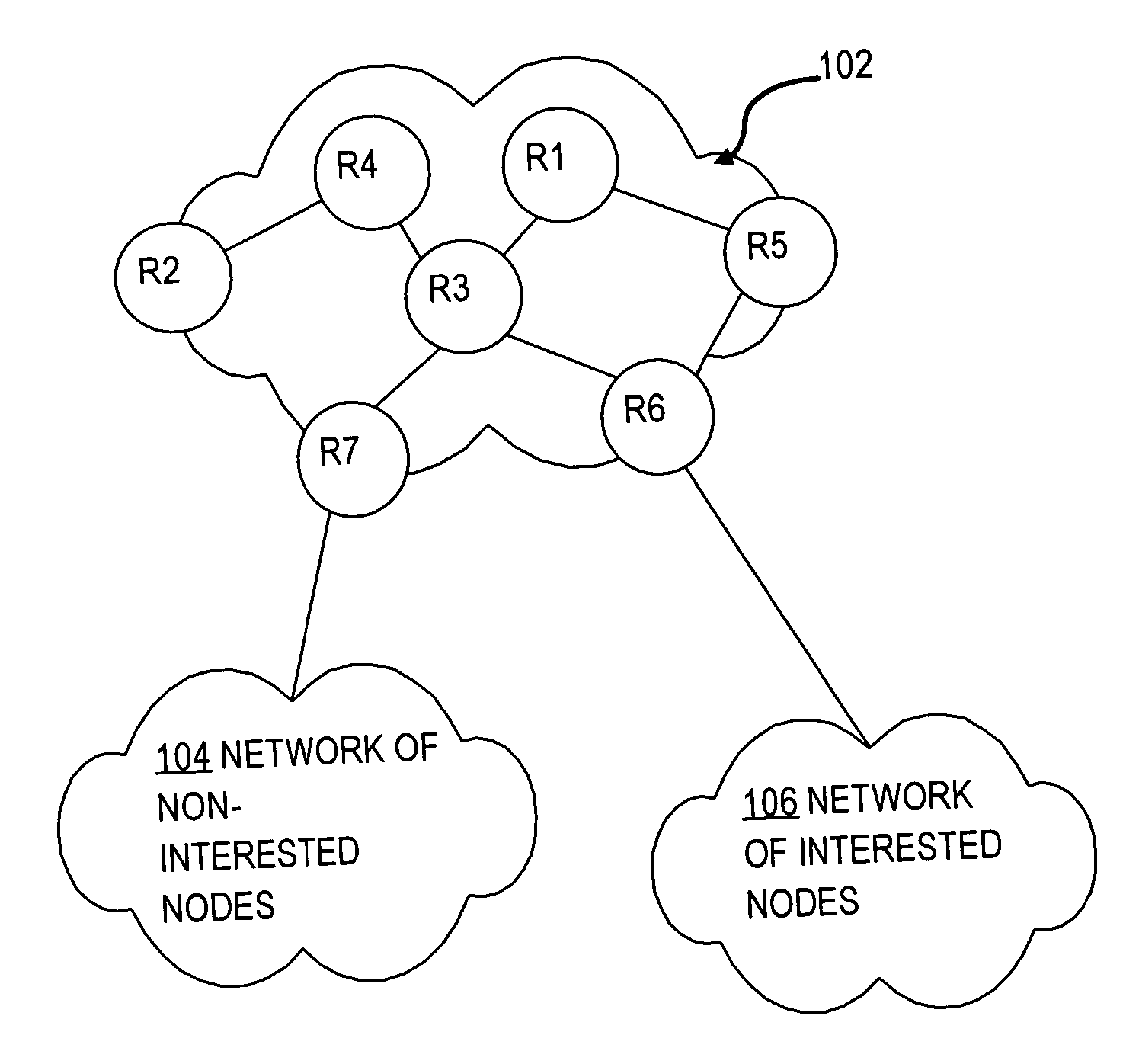
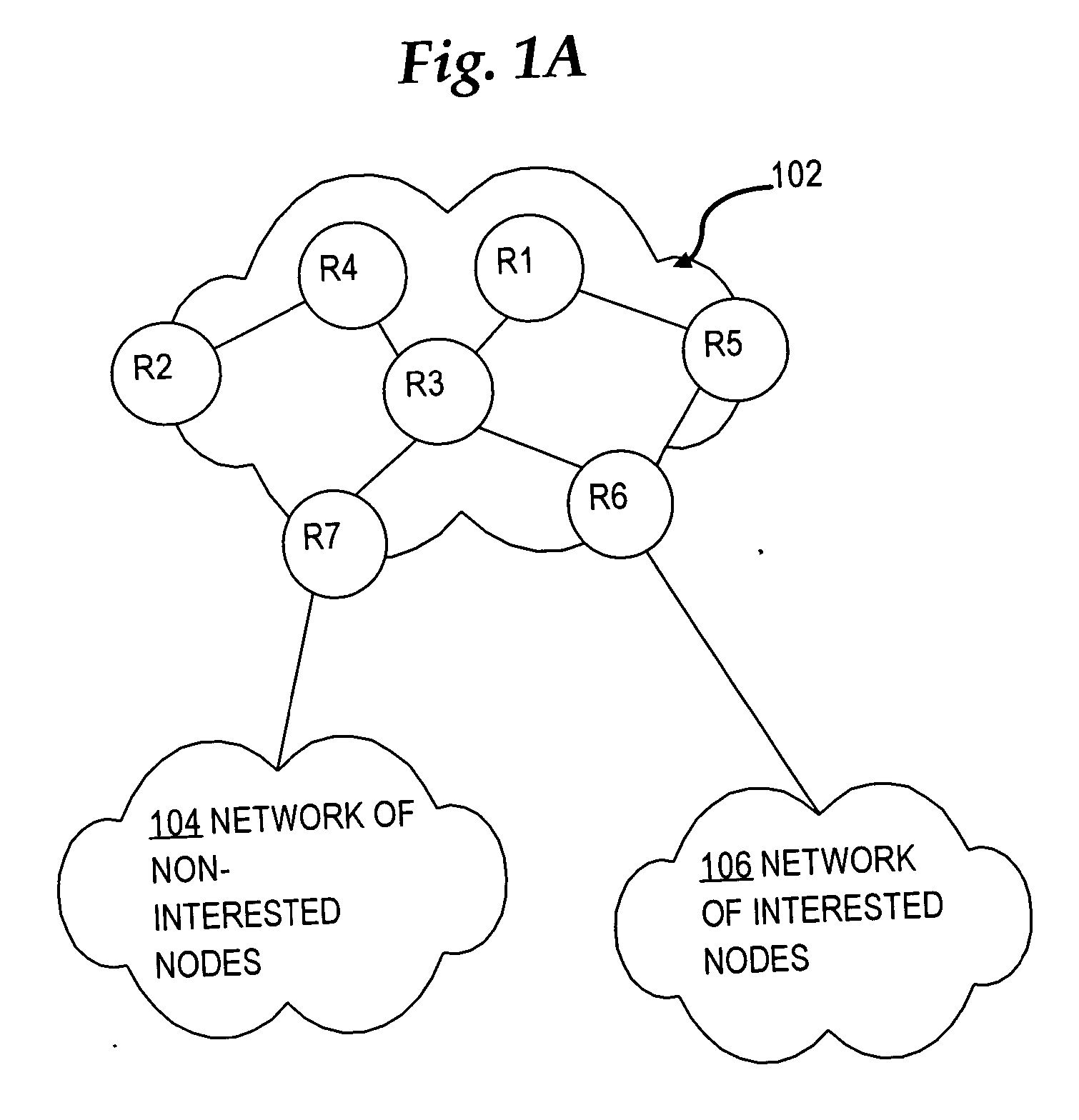
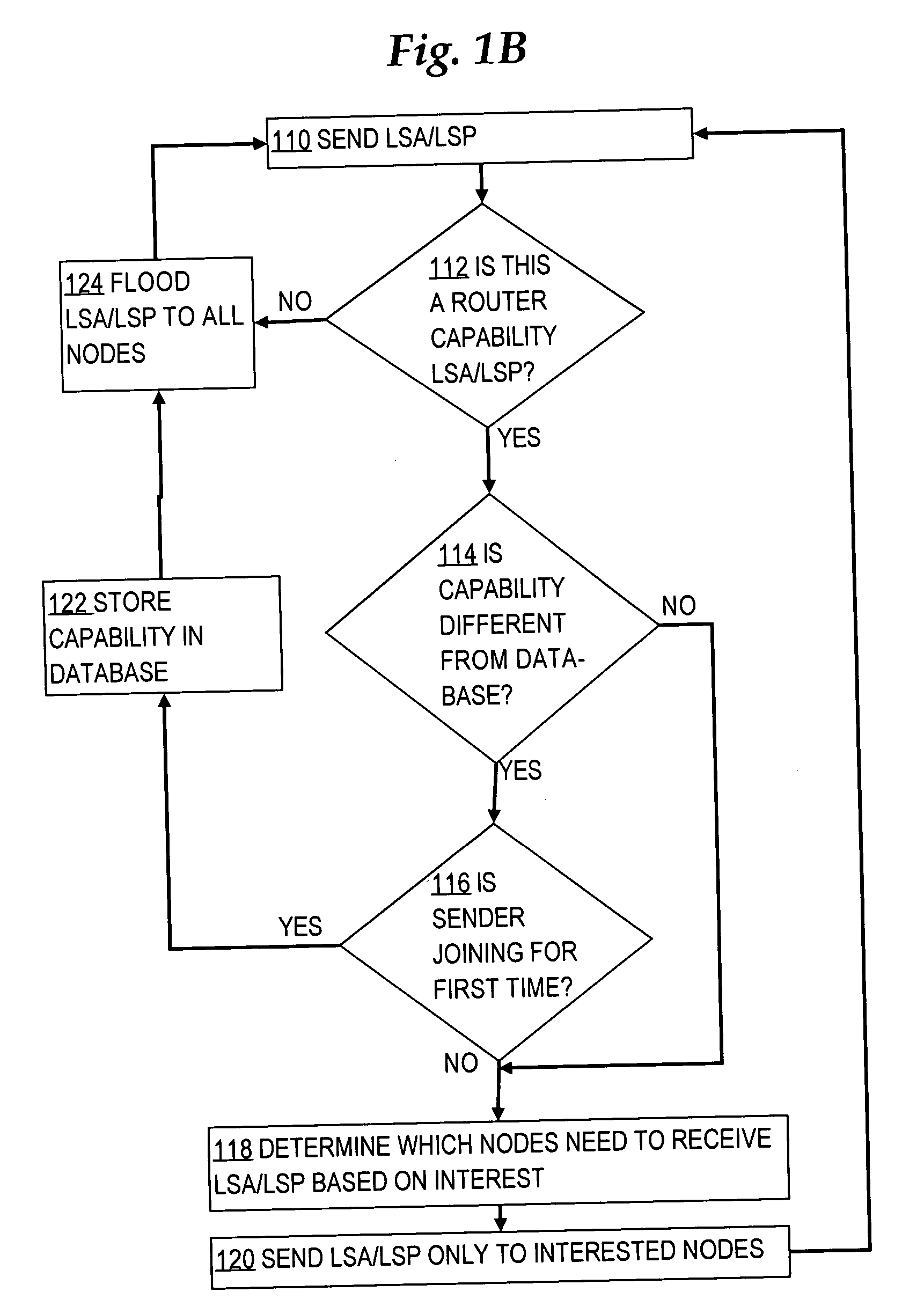
Selectively sending link state messages in a network link state protocol based on interest of network nodes
In a link state protocol such as an interior gateway protocol (IGP), link state advertisements or link state packets (LSA / LSPs) are sent only to network nodes that have expressed interest in them, rather than always flooding them.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
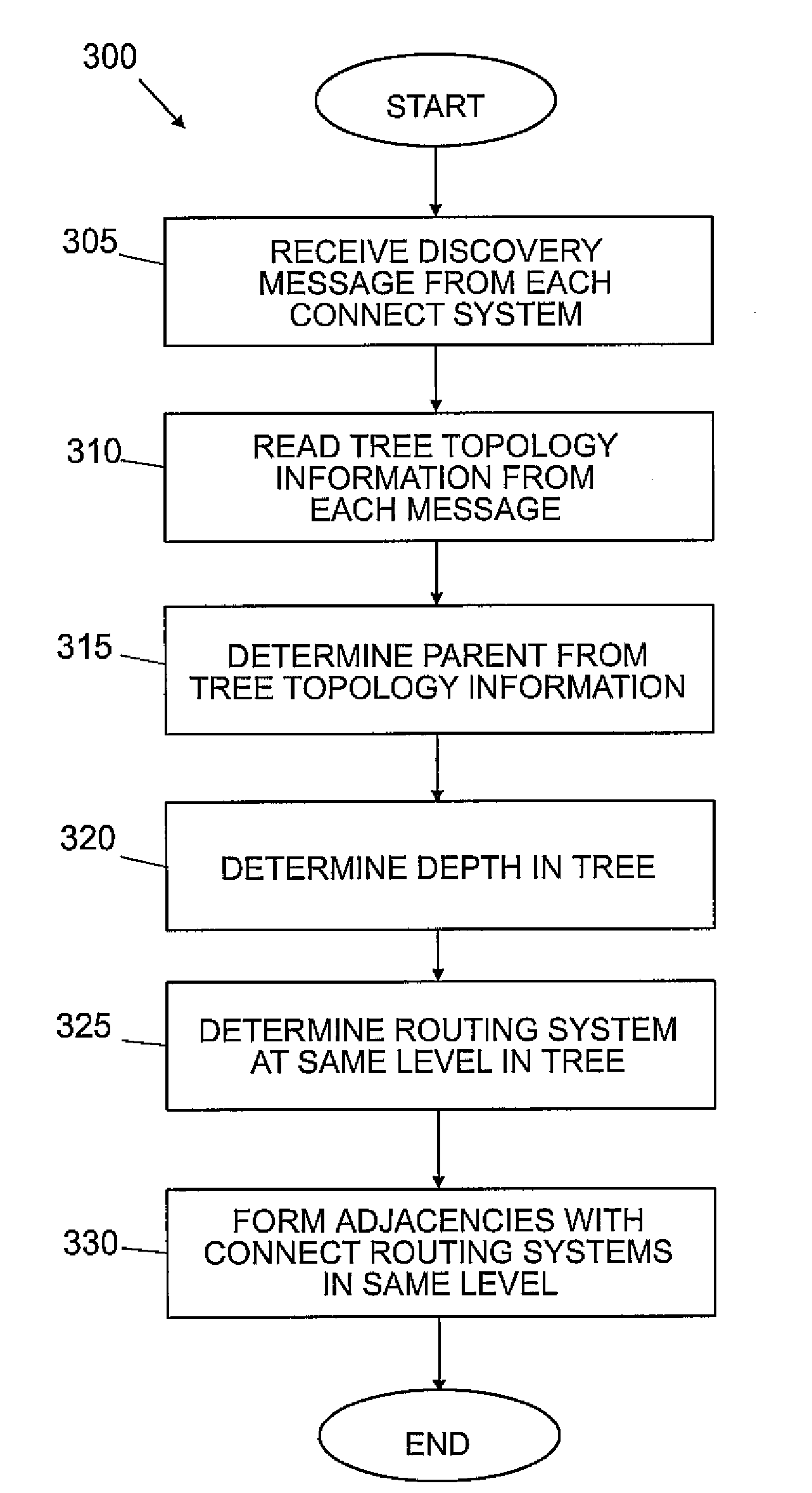
Tree based wireless mesh for an ospf network with intra-tree communication optimization
ActiveUS20080080401A1Shorten convergence timeReduce floodingAssess restrictionConnection managementTopology informationDevice Grid
A system for providing a tree topology for a network having an interior gateway protocol. A first router receives a hello message from all connected routers in the network. The hello messages include tree topology information. The first router then uses the tree topology information to determine a parent of the router. The first router then establishes connections with directly connected routers at the same level in the tree topology. The first router also generates link messages that include all of the prefixes for children of the first router and broadcasts the link messages.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
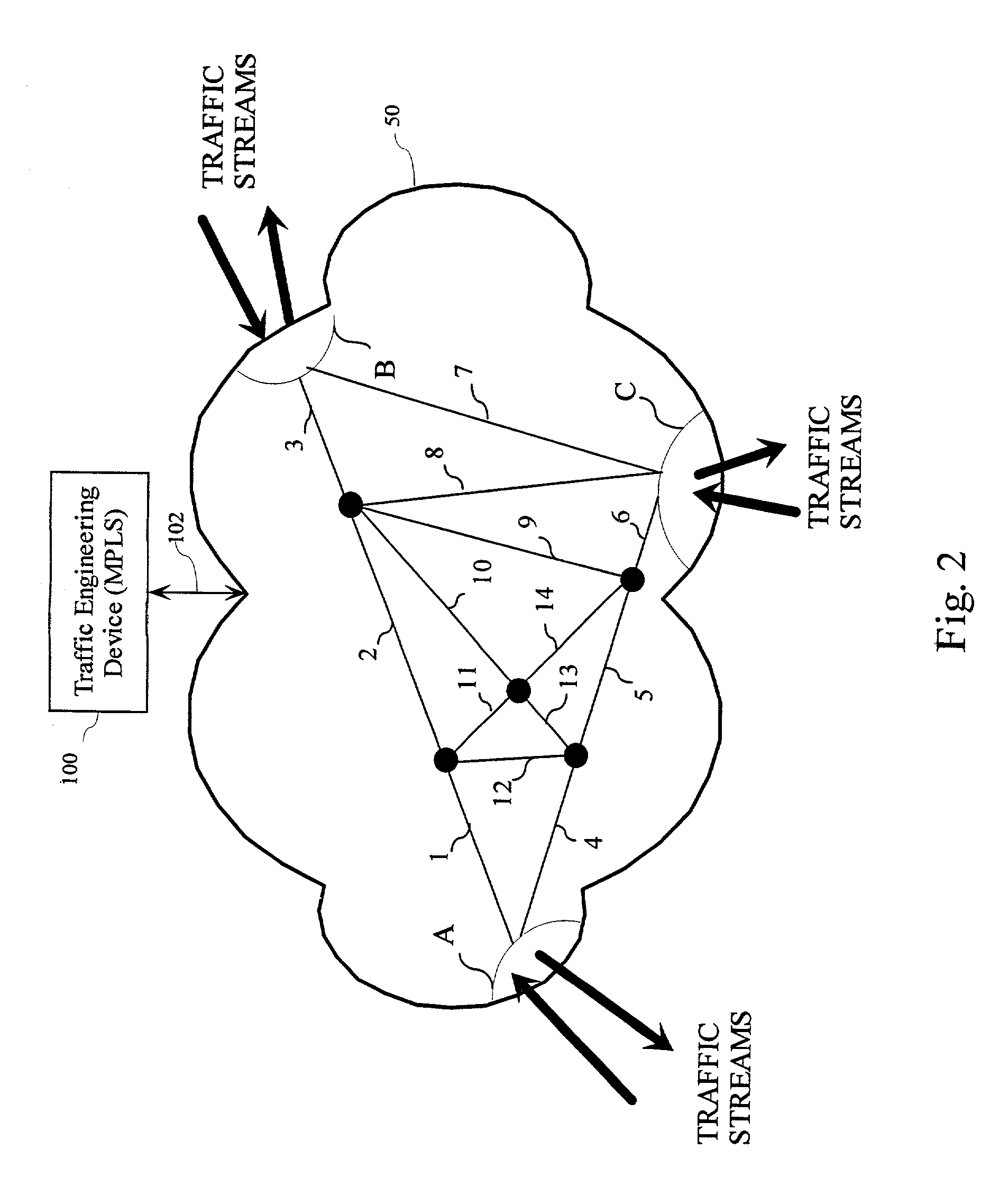
Method and apparatus for communications traffic engineering
InactiveUS20020186658A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTraffic capacityLabel switching
This invention provides for a technique for selectively off-loading traffic from congested sub-regions of a network to more lightly-loaded regions by making use of Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS). For each network element, an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) routing is employed to provide re-routing and to identify congested links caused by re-routed trunks for each single failure. The re-routed traffic is then analyzed and alternate Label Switched Paths (LSPs) are identified for such traffic trunks so that the traffic is directed to the alternate LSPs during the single failure event.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Active-active data center using RHI, BGP, and IGP anycast for disaster recovery and load distribution
A distributed data center topology having at least a pair of active data centers that can recover from a disaster at one of the data centers and achieves load balancing using IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) between data centers. The distributed data centers use virtual IP addresses, route health injection and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) for business continuance, disaster recovery and load balancing. The active / active topology supports load balancing where each site concurrently hosts active applications or applications can be hosted in a logical active / standby mode. IGP and RHI (Route Health Injection) are used to propagate routes to an edge router and BGP (Border Gateway Protocol) and IP Anycast are used for site-to-site recovery and load balancing between data center sites.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
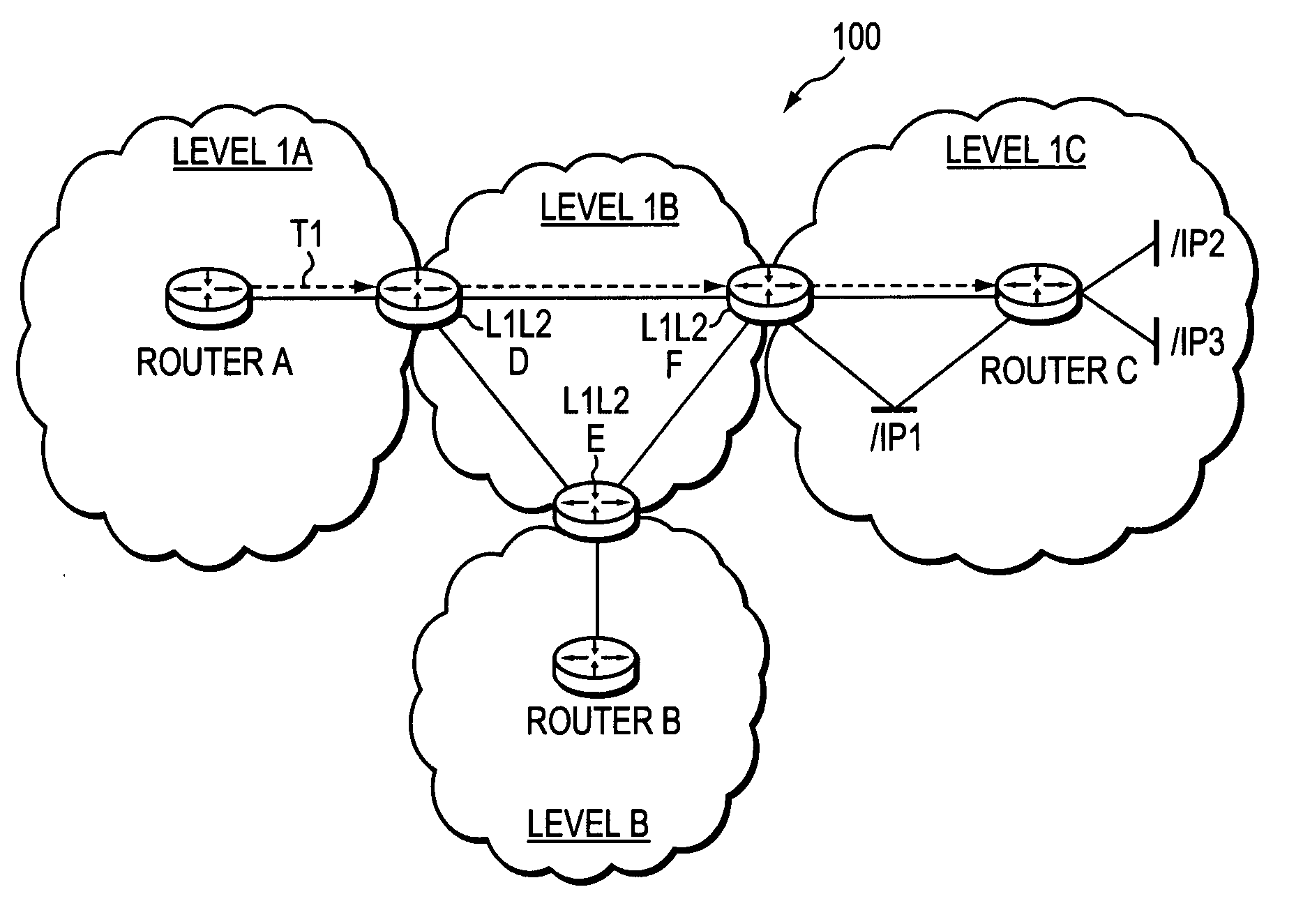
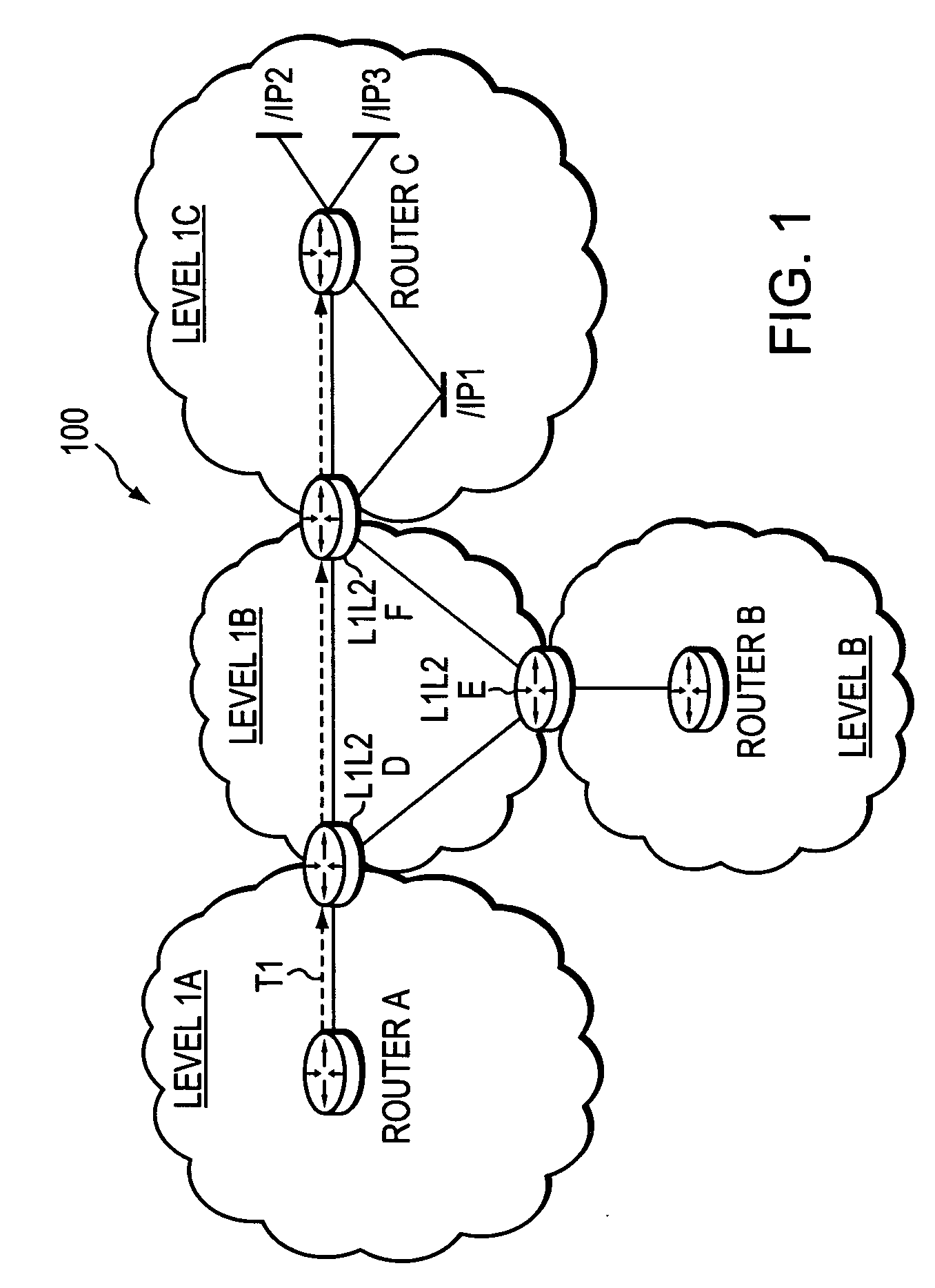
Inter-domain TE-LSP with IGP extensions
ActiveUS20060114916A1Avoid errorsReduce riskData switching by path configurationRouting tableInformation propagation
A technique propagates reachability information for a tail-end node of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) to a head-end node of the TE-LSP in a computer network. The TE-LSP preferably spans multiple domains of the network such that the tail-end node resides in a domain that is different (remote) from the domain of the head-end node. The inter-domain information propagation technique employs an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) to transmit the remote reachability information from a target node residing in the same domain as the tail-end node to the head-end node. The head-end node uses the remote information to calculate routes, i.e., address prefixes and associated attributes, reachable from the tail-end node for insertion into its routing table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Multicast systems and methods for Segment Routing
ActiveUS20180324090A1Special service provision for substationNetwork connectionsRouting domainComputer science
A multicast method for Segment Routing includes, in a Segment Routing network with a plurality of nodes, wherein Segment Routing utilizes globally significant labels as node identifiers such that path state installation is only required at an ingress node of a Segment Routing domain, advertising a multicast flow by a source node; determining roles in the multicast flow for the plurality of nodes; and installing appropriate forwarding behavior for the multicast flow at the plurality of nodes based on the determined roles. The advertising can utilize Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). For the multicast flow, source node segments are used to construct source routed trees rather than destination-based paths, wherein the source routed trees define broadcast paths, versus destination-based paths which are used in Segment Routing to define a node segment.
Owner:CIENA
System, device and method for limiting tunnel traffic in an information communication network
ActiveUS7123587B1Avoid destabilizationAvoid congestion problemsError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityForwarding equivalence class
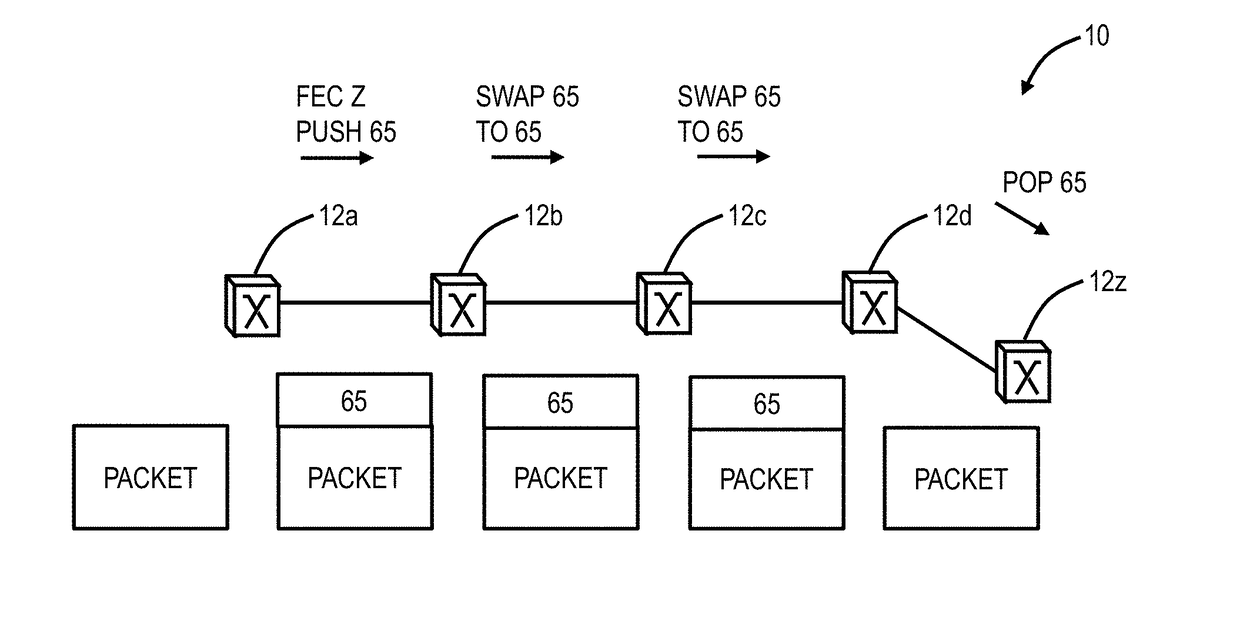
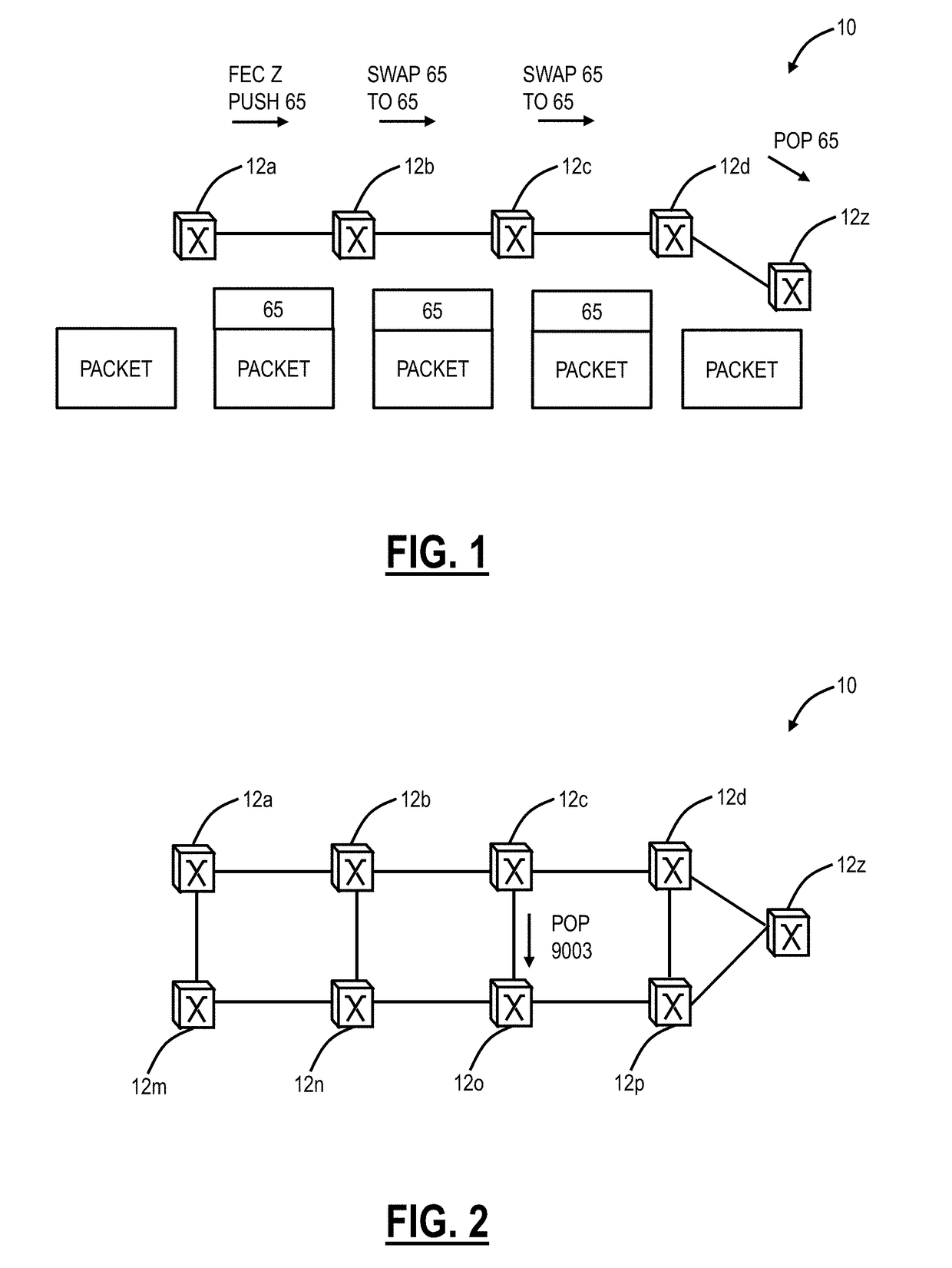
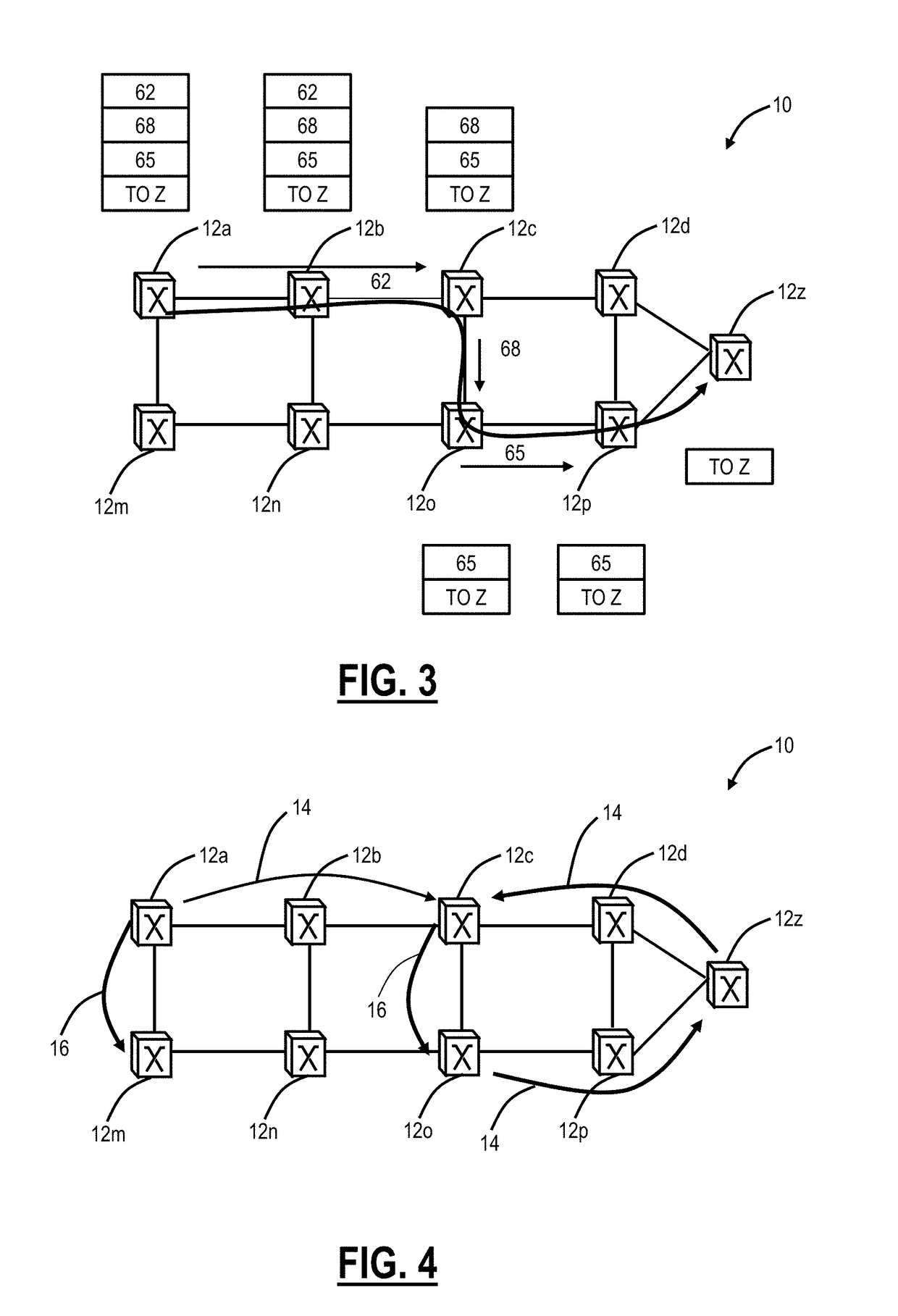
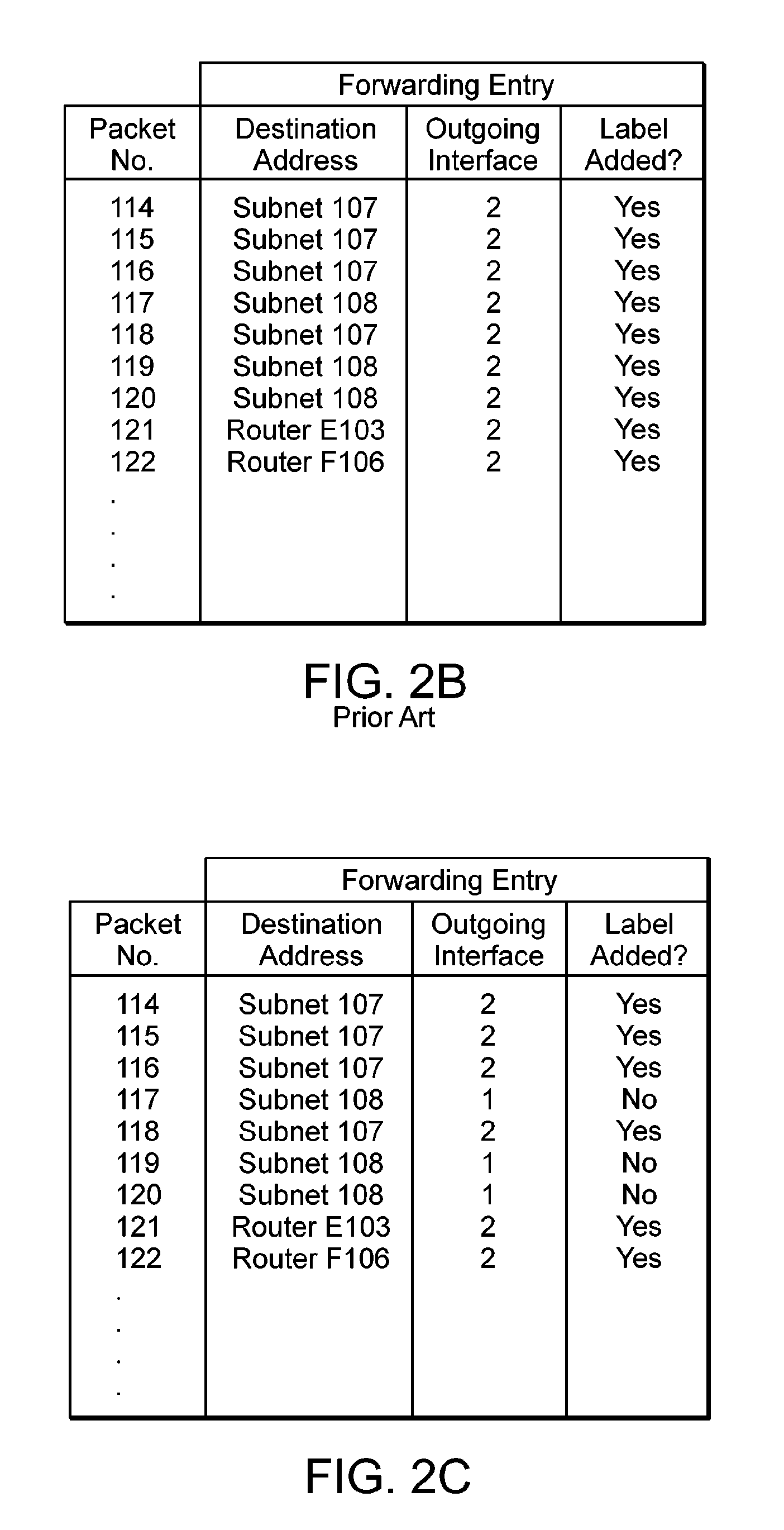
There is disclosed an apparatus and method for limiting tunnel traffic in a network. Traffic engineering tunnels are used to direct traffic along a predefined path, which may differ from the path that internet protocol (IP) routing would determine. Interior gateway protocol (IGP) cut through will allow the forwarding of all destinations downstream of a tunnel through the tunnel, without the operator needing to specify a forwarding equivalence class (FEC). But congestion in the tunnel and network instability may result from this approach. A solution to these problems is disclosed which limits the traffic in the tunnel to only that with destination addresses of the tunnel's egress router or nodes directly supported thereby. Other solutions are disclosed which allow tunnel traffic to nodes having destination addresses other than those being directly supported by the tunnel's egress router. All of these solutions are achieved in both pre-determined forwarding entry and dynamic packet-by packet embodiments.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Application based active-active data center network using route health injection and IGP
A distributed data center topology having at least a pair of active data centers that can recover from a disaster at one of the data centers and achieves load balancing using IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol) between data centers. The distributed data centers use virtual IP addresses, route health injection and Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) for business continuance, disaster recovery and load balancing. Active applications are deployed at each data center to provide a logical active / standby configuration for certain applications. Alternatively, active applications are deployed at both sites and BGP routes traffic to the closest data center edge router. Load balancing occurs over an internal IGP link between sites.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Techniques for decreasing queries to discover routes in an interior gateway protocol
InactiveUS20070183334A1Error preventionTransmission systemsResource consumptionDistributed computing
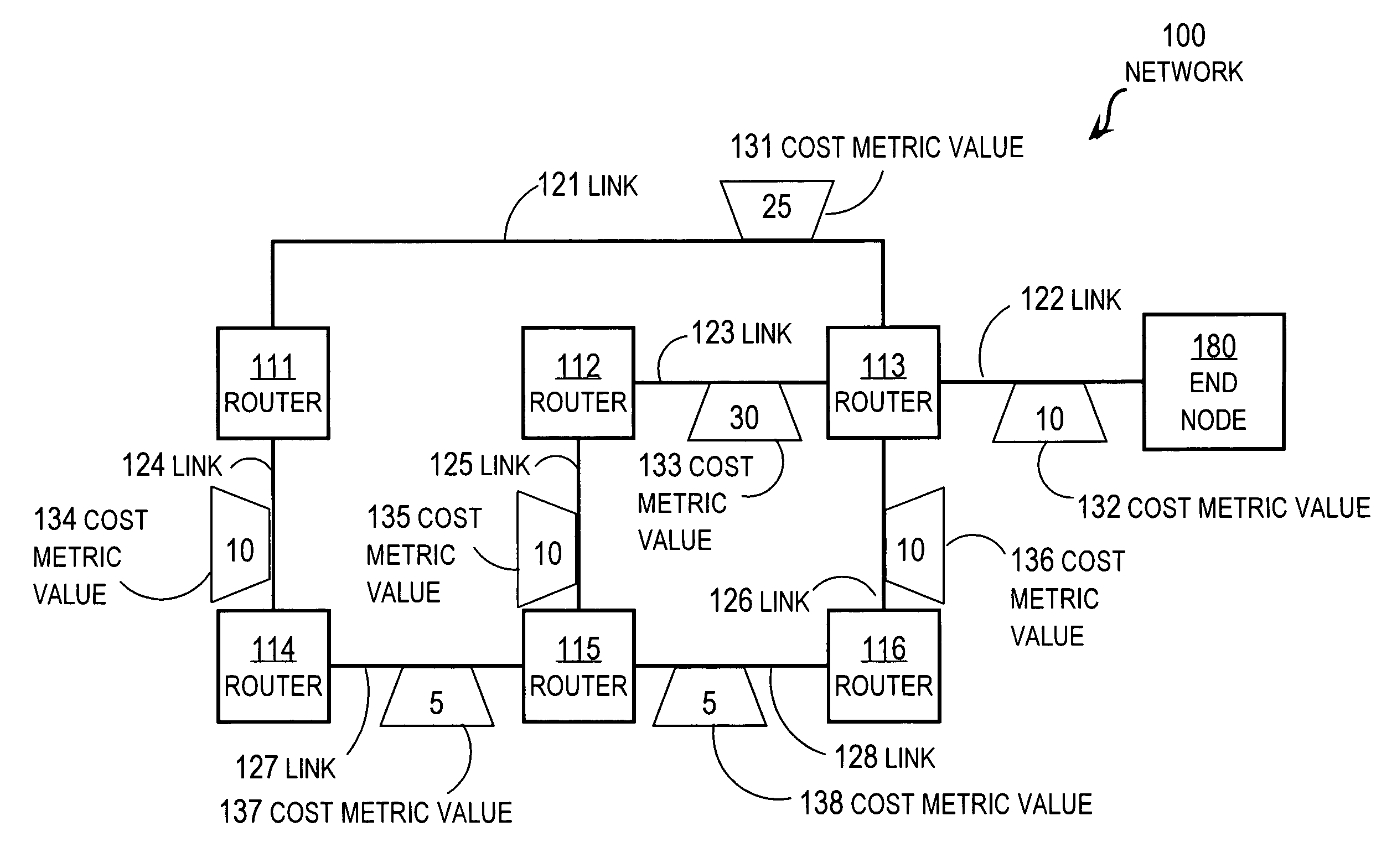
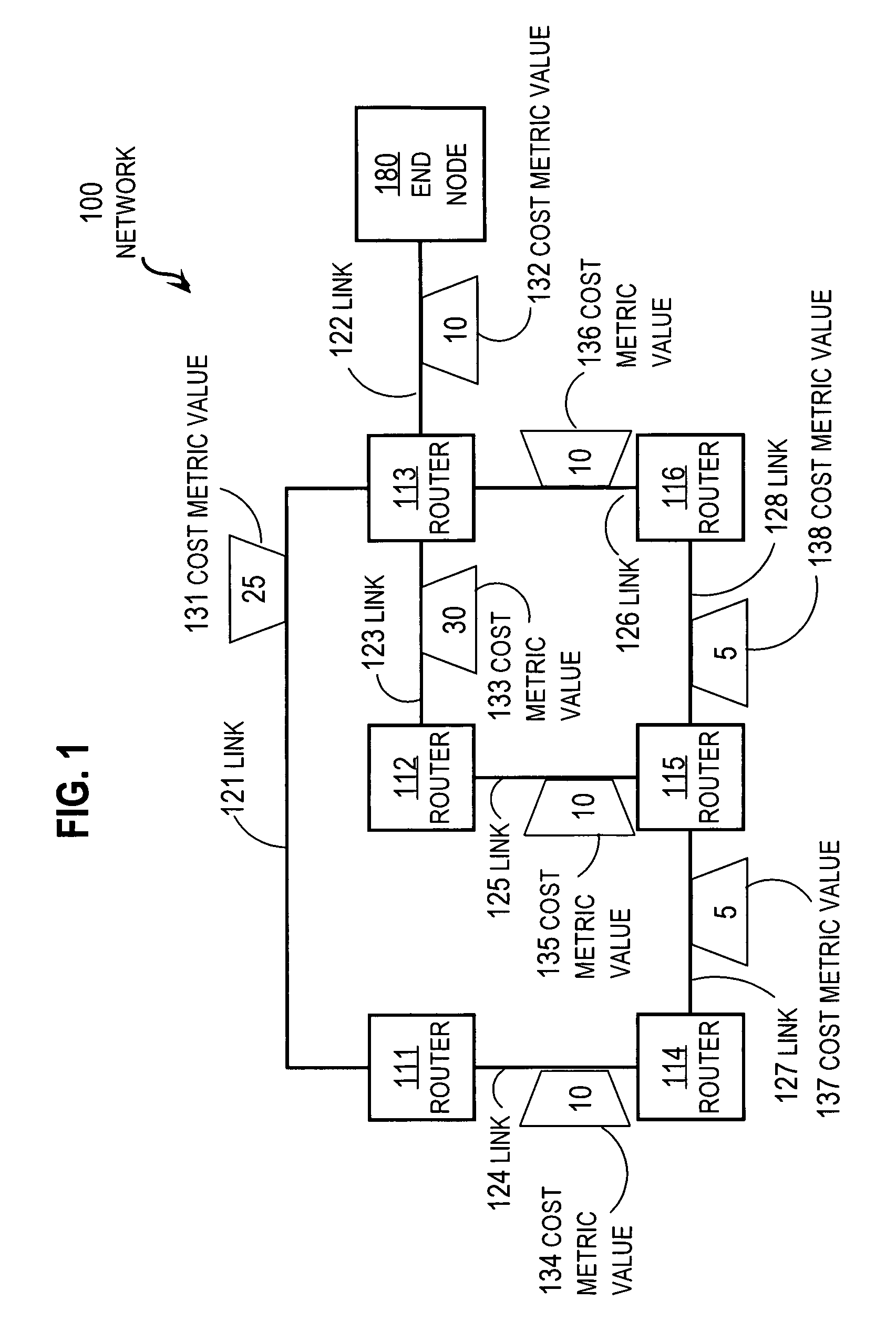
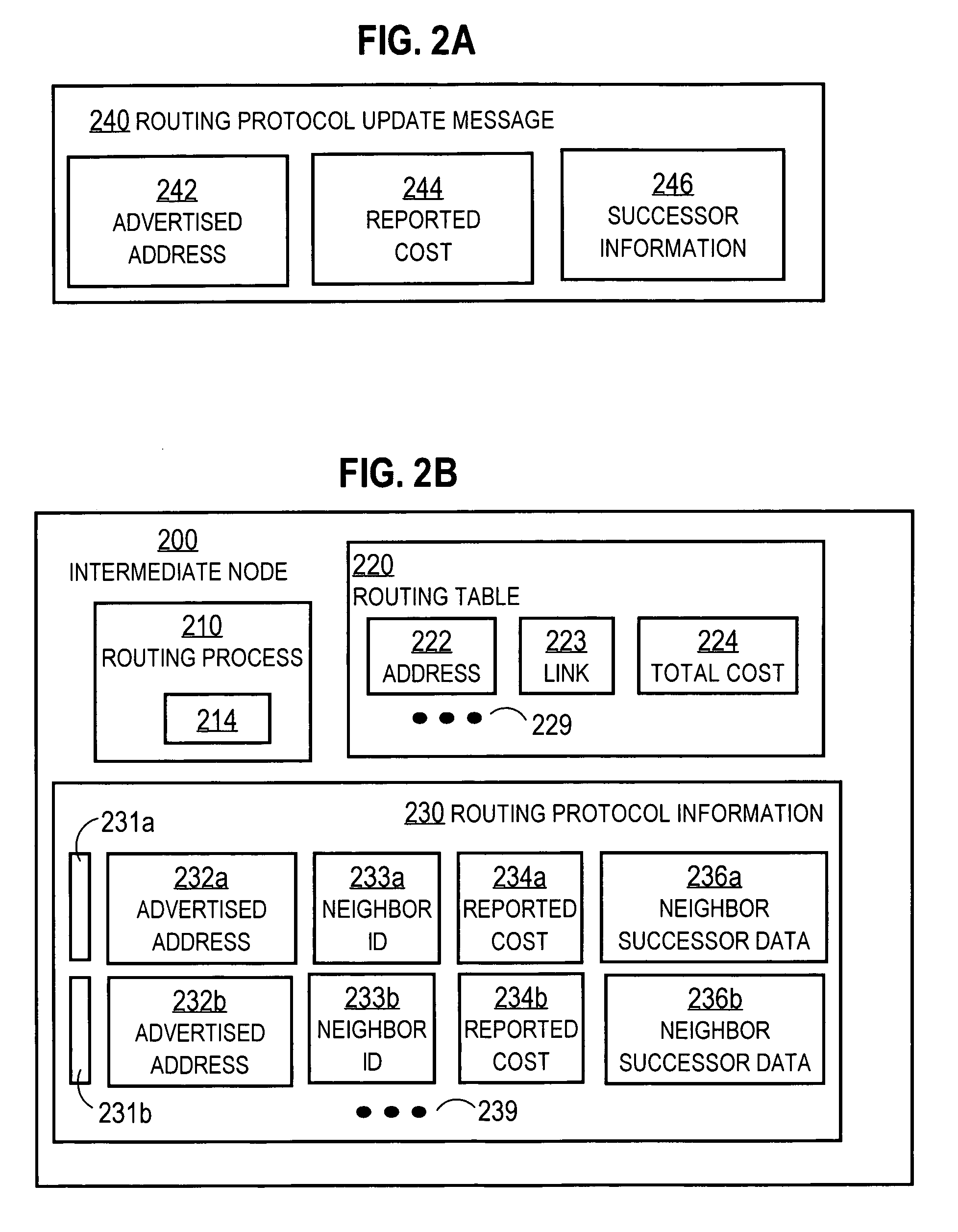
Techniques for recovering lost routes include receiving reported costs for transmitting data to a destination from neighboring nodes; and determining total costs as a sum of costs for transmitting data packets to the neighboring nodes and a corresponding reported cost. A selected neighboring node with a minimum total cost is determined as the next hop for the route to the destination. A feasible successor set of neighboring nodes which have reported costs less than the total cost of the selected neighboring node and excluding the selected neighboring node, and successor data about the feasible successor set, are determined. The successor data is sent to the neighboring nodes. A neighboring node that loses a route to the particular destination node is able to determine whether to query the sending node while recovering a lost route to the destination based on the successor data, thereby reducing network resource consumption.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
BIER (Bit Indexed Explicit Replication) message transmission method and system
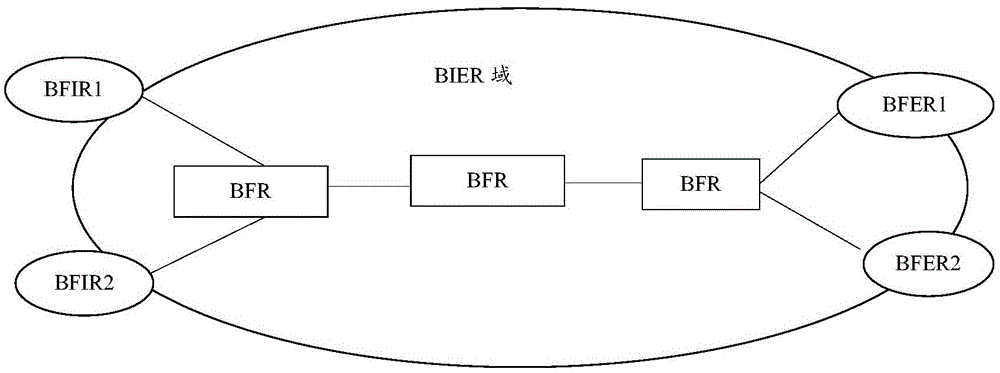
InactiveCN106341327ASolve the problem that the BIER message cannot be transmittedNetworks interconnectionInformation supportDistributed computing
The invention discloses a BIER (Bit Indexed Explicit Replication) message transmission method and system. The method comprises the steps that a BIER node packages a BIER message according to link capability attribute information supported by a non-BIER node carried by an extended IGP (Interior Gateway Protocol); and the BIER node transmits the packaged BIER message to the non-BIER node. The BIER message transmission method and system disclosed by the invention are used for solving a problem that the non-BIER node cannot transmit the BIER message in an existing BIER network.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Method of building control channel, forwarding point (FP) and controller
ActiveCN103067277ASave storage resourcesImprove forwarding performanceEnergy efficient ICTNetwork connectionsVirtual clusterControl channel
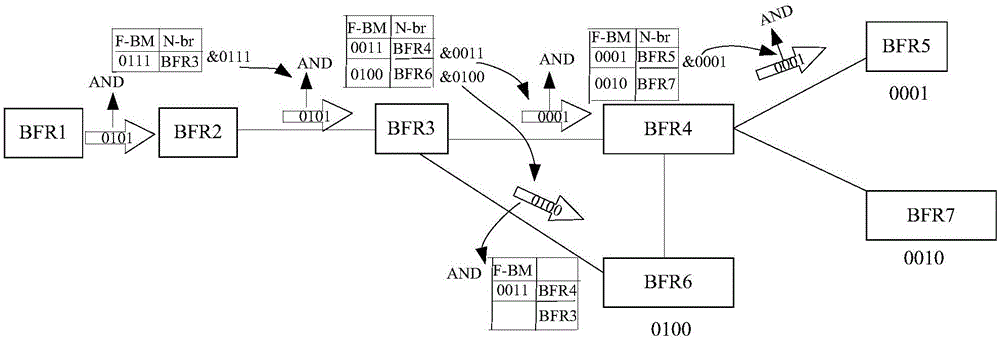
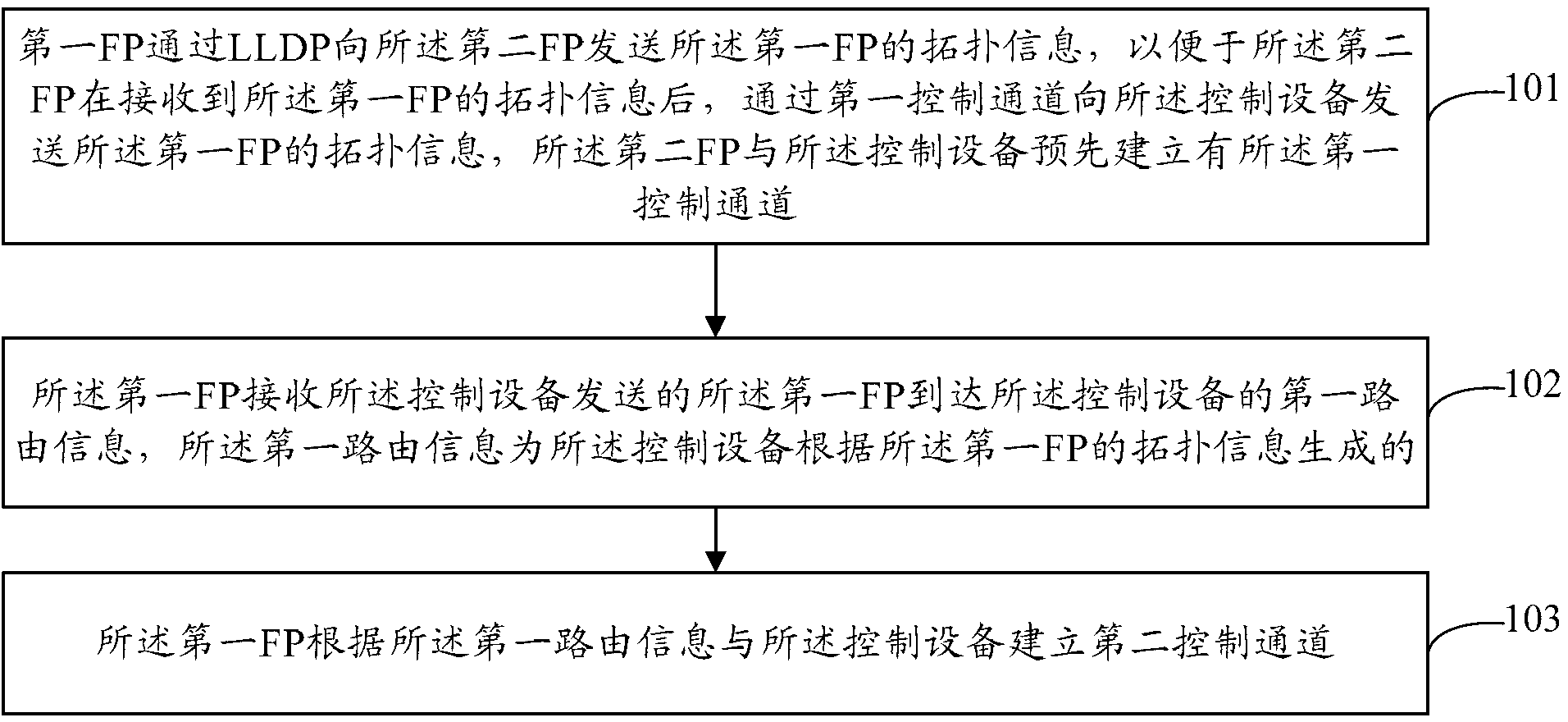
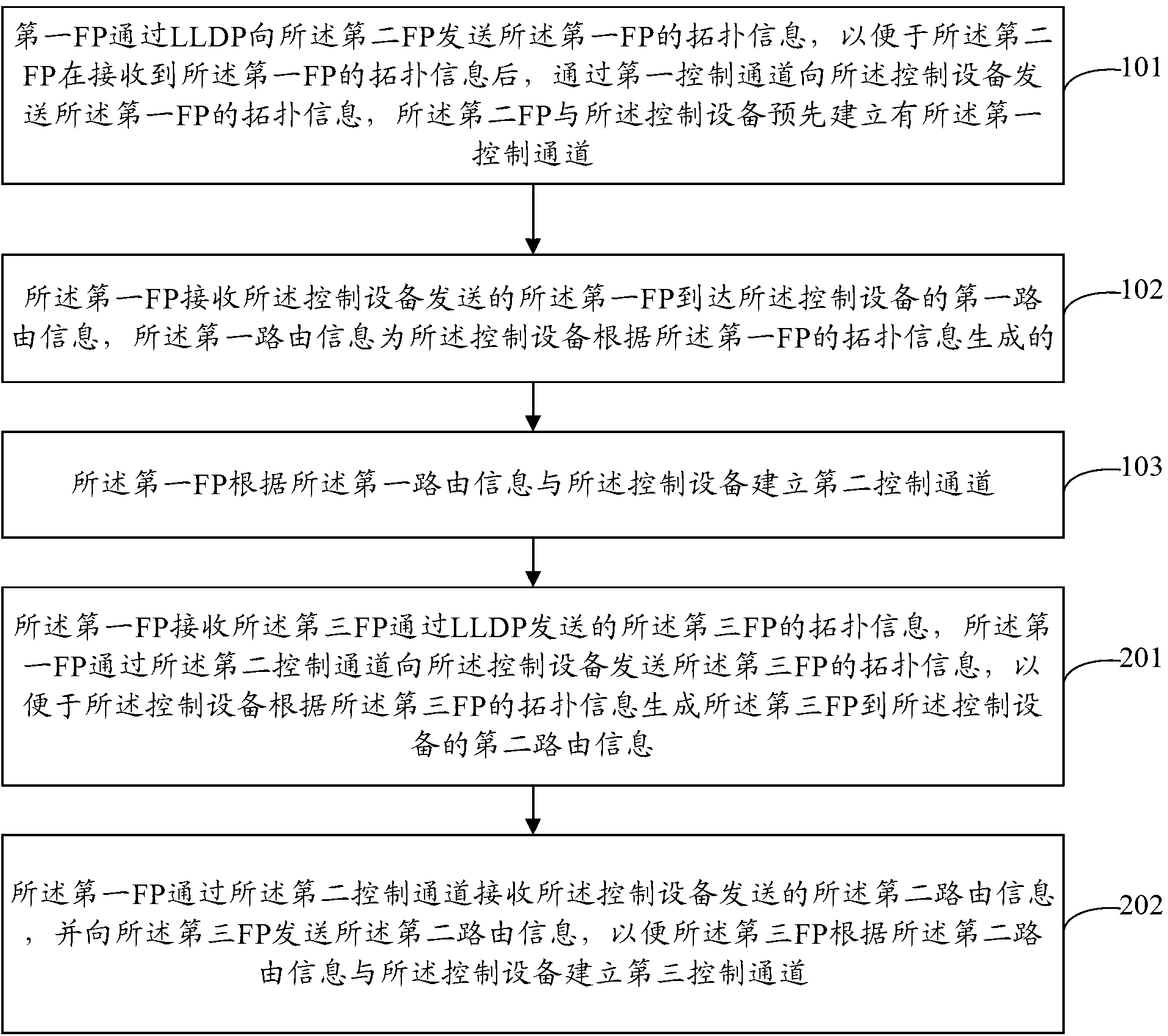
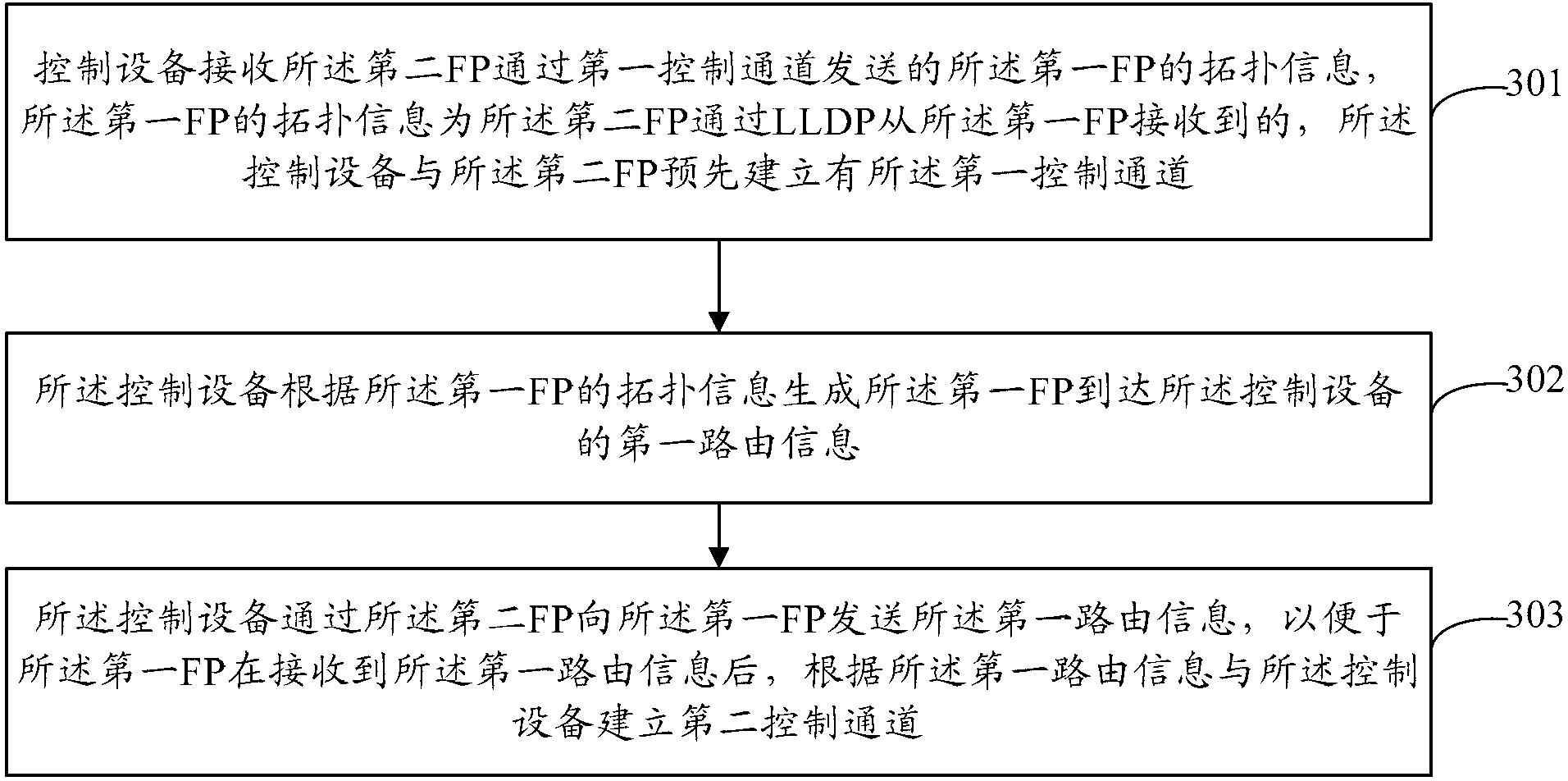
The invention provides a method of building a control channel, a forwarding point (FP) and a controller. The method comprises that a first FP sends the topological information of the first FP to a second FP through a link layer discovery protocol (LLDP), so that the second FP can send the topological information of the first FP to the controller through a first control channel after the second FP receives the topological information of the first FP. The first FP receives first routing information sent by the controller that the first FP reaches the controller, and the first routing information is generated by the controller according to the topological information of the first FP. The first FP builds a second control channel with the controller according to the first routing information. The first FP does not need to run an interior gateway protocol (IGP), the fact that the first FP maintaining the neighbourship of the IGP is avoided, and the first FP does not need to store the routing information of other FPs reach a virtual cluster, the storage resource of the first FP is beneficial to be saved, and the forwarding performance of the first FP is beneficial to be improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Network flow regulation method and system
ActiveCN103618677AEfficient use ofImprove resource utilizationData switching networksTraffic capacityBorder Gateway Protocol
The invention relates to a network flow regulation method and a network flow regulation system. The method comprises the following steps: transmitting an interior gateway protocol (IGP) data packet to a network node in a network and receiving response of the network node on the IGP data packet, and acquiring network topology information of a router; performing periodic polling on each router in the network through a simple network management protocol (SNMP), and determining link utilization information; analyzing routing information transmitted from an external network to the network according to a border gateway protocol (BGP) update message, and determining BGP routing information; collecting network flow information, determining data flow information of a border router according to the related information of the network flow information, wherein the data flow information of the border router comprises flow information and flow direction information, classifying the flow information, and forming a flow matrix; receiving a user scheduling policy input by a user and a BGP scheduling policy determined and optimized according to the information; and transmitting traction routing to a specific router in the network according to the optimized BGP scheduling policy.
Owner:王逊
Message processing method and label switching router
ActiveCN104980350AEasy maintenanceEasy to manageNetworks interconnectionMulti protocolMessage processing
The present invention provides a message processing method and a label switching router, so as to solve the problem that a current egress label switching router (LSR) can not learn about the LSRs passed by an IP message forwarded in a multi protocol label switching (MPLS) network. The method is applicable to the MPLS network of segment routing (SR) and includes the following steps: an ingress LSR of a label switching path (LSP) tunnel receives an interior gateway protocol (IGP) based notification message transmitted by an egress LSR of the LSP tunnel, wherein the notification message is used to notify the ingress LSR that the egress LSR has the capability of identifying a label history stack; after the notification message is received, an MPLS label stack is inserted into the IP message which enters into the LSP tunnel and an MPLS message is created, wherein, from the top to the bottom of the stack, the MPLS label stack includes: multiple segments, a label history identifier and a label history stack, wherein multiple segments are used to identify the LSRs passed in turn when the MPLS message is forwarded in the LSP tunnel, the label history identifier is used to identify the label history stack included in the MPLS message, and the label history stack includes multiple segments; the MPLS message is transmitted to the egress LSR through the LSP tunnel.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
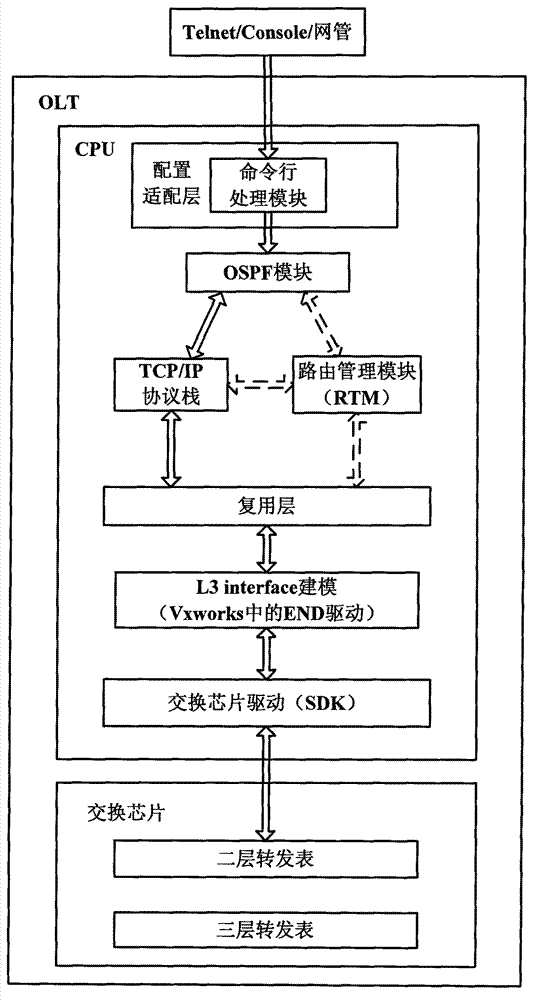
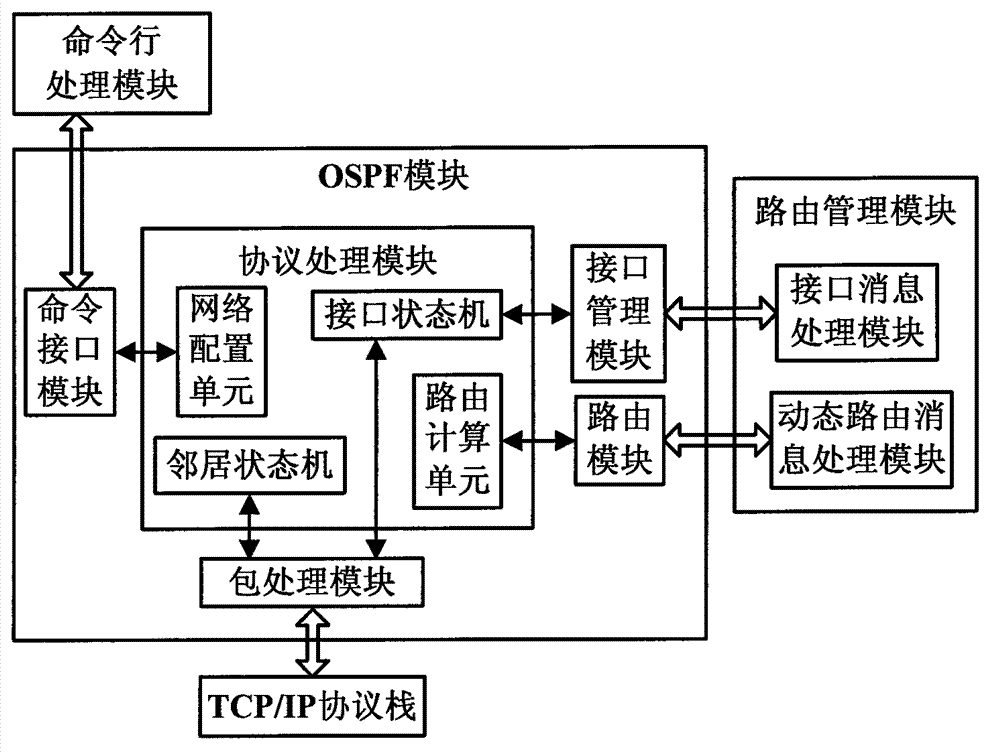
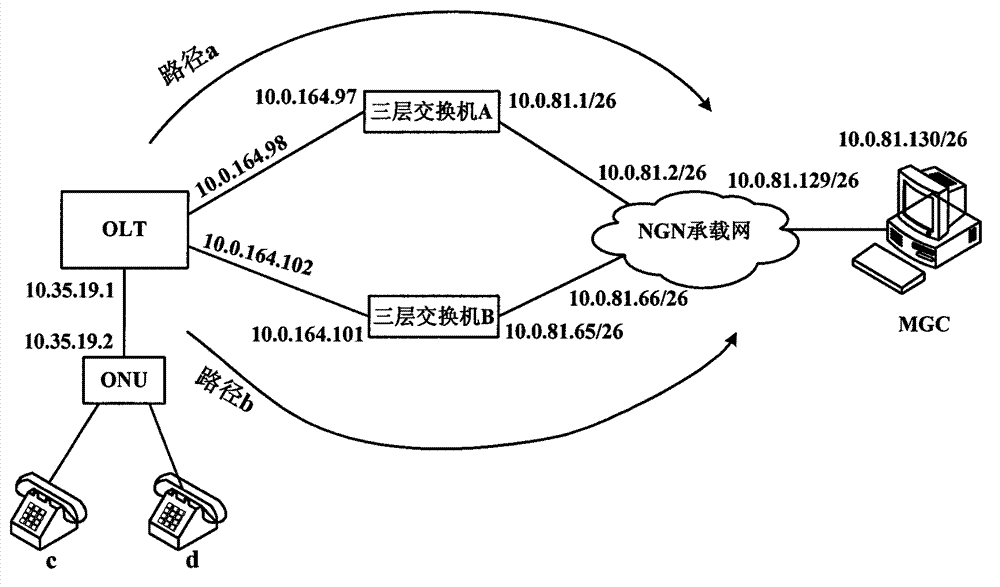
System and method for realizing OLT voice double upper-link protection based on OSPF routing protocol
ActiveCN102857422ARealize dual uplink protectionFast protection switchingData switching networksRouting tableProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
The invention discloses a system and a method for realizing OLT (Optical Line Terminal) voice double upper-link protection based on OSPF (Open Shortest Path First Interior Gateway Protocol) routing protocol, and relates to the field of PON (Passive Optical Network). A CPU of an OLT master control panel in the system comprises an OSPF module and an RTM (Running Timer Meter) module. Two upper-link ports of an OLT are respectively connected with a NGN (Next Generation Network) through three-layer exchangers A and B to connect with a remote-end MGC (Media Gateway Controller) server; paths A and B are formed between the OLT and the MGC server; the OLT and the three-layer exchangers A and B are respectively configured with the OSPF protocols and operate; the OLT learns the routes of all network sections on the paths A and B through the OSPF route protocol; the OSPF module stores the learnt routes in the route table of the OSPF module and announces the learnt routes to the RTM module; and the RTM modules collects the route items and writes the route items in an RIB table. When a main link breaks, the OSPF route protocol learns the route of a backup link and carries out rapid protective rearrangement to the high real-time voice business among internetworking nodes.
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
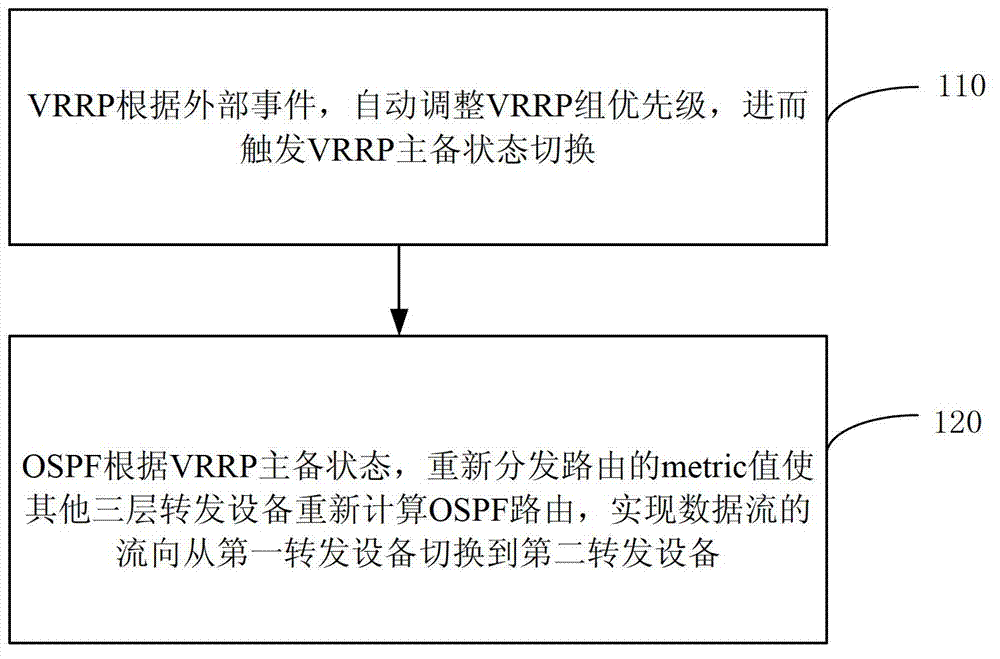
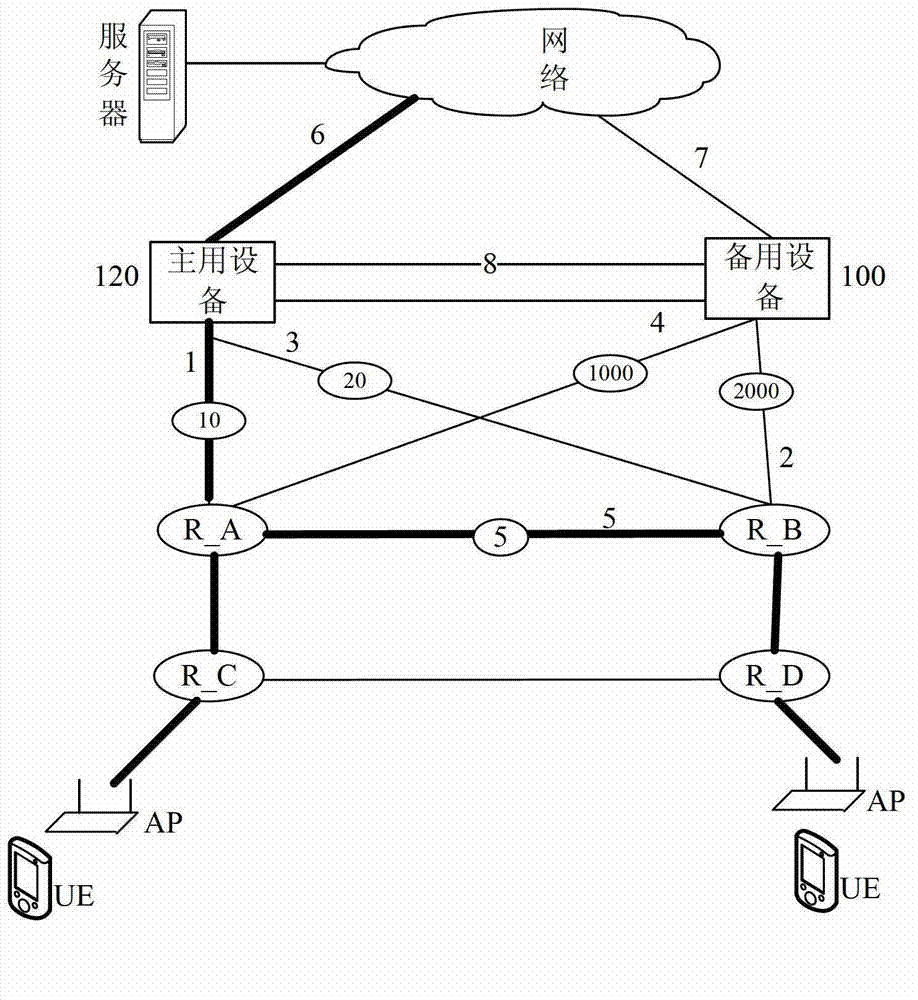
Method and system achieving network redundancy and data flow seamless switching
InactiveCN103095571AProblems affecting useData switching networksData streamVirtual Router Redundancy Protocol
The invention relates to the field of communication technology and discloses a method and a system achieving network redundancy and data flow seamless switching. The method includes the following steps of using a virtual router redundancy protocol (VTRP) to trigger switching of a first transmitting device to a second switching device according to the changes of links, and using an open shortest path first (OSPF) interior gateway protocol to update route information and to switch the flow direction of the data flow. Main and standby switching is achieved through the use of the VRRP, and when the main and standby states of a VRRP group switch, and the OSPF interior gateway protocol is used for updating the route information and switching the flow direction of the data flow, so that after a linkage mechanism of the VRRP and the OSPF interior gateway protocol is used for achieving the switch, the route information is timely updated, the problem that the data flow direction is wrong and therefore the use of a user is affected is avoided, and the data flow seamless switching is ensured.
Owner:CHENGDU SKSPRUCE TECH
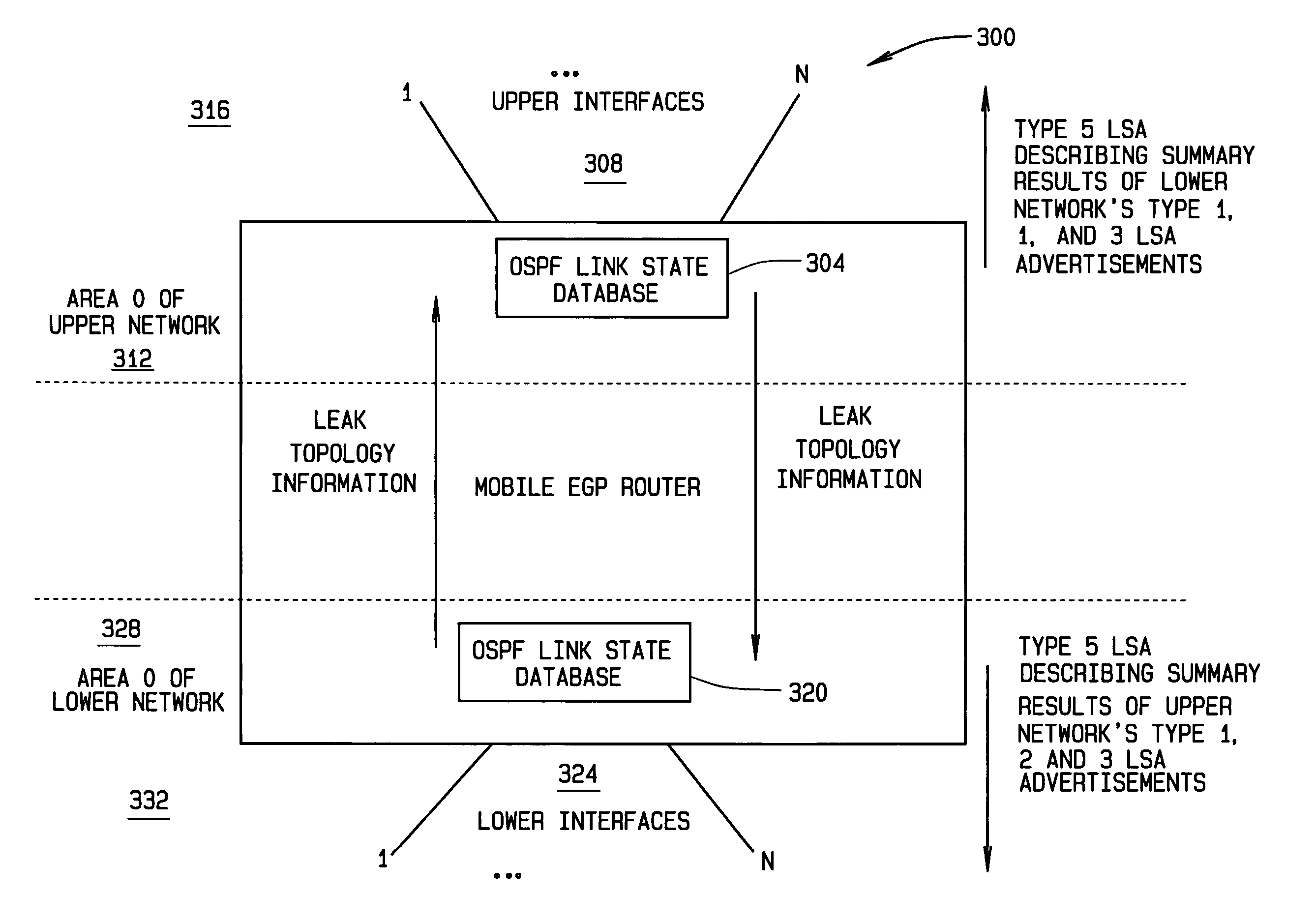
Interior gateway protocol summarization preserving internet protocol reachability information
ActiveUS20090073996A1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsComputer networkTTEthernet
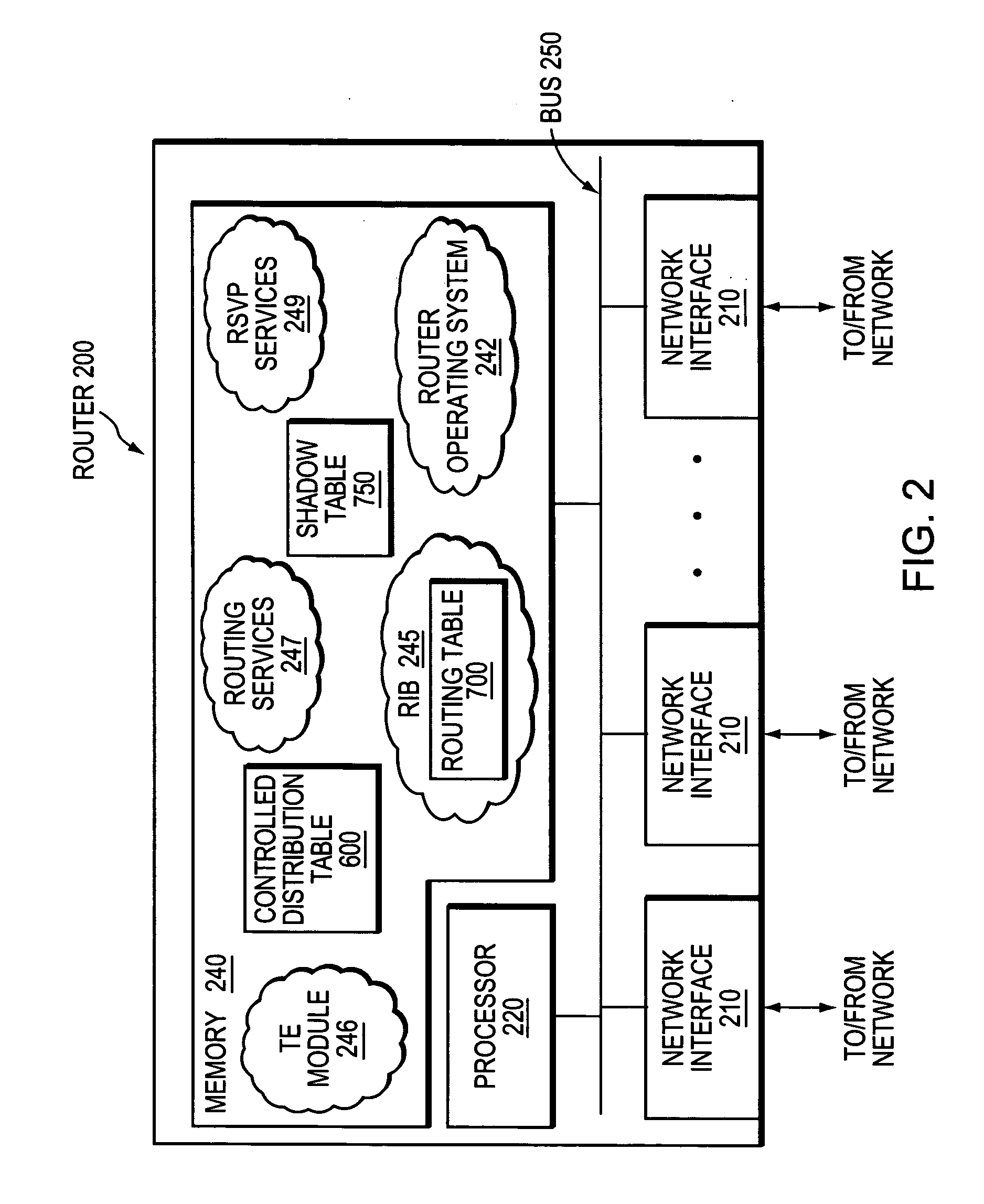
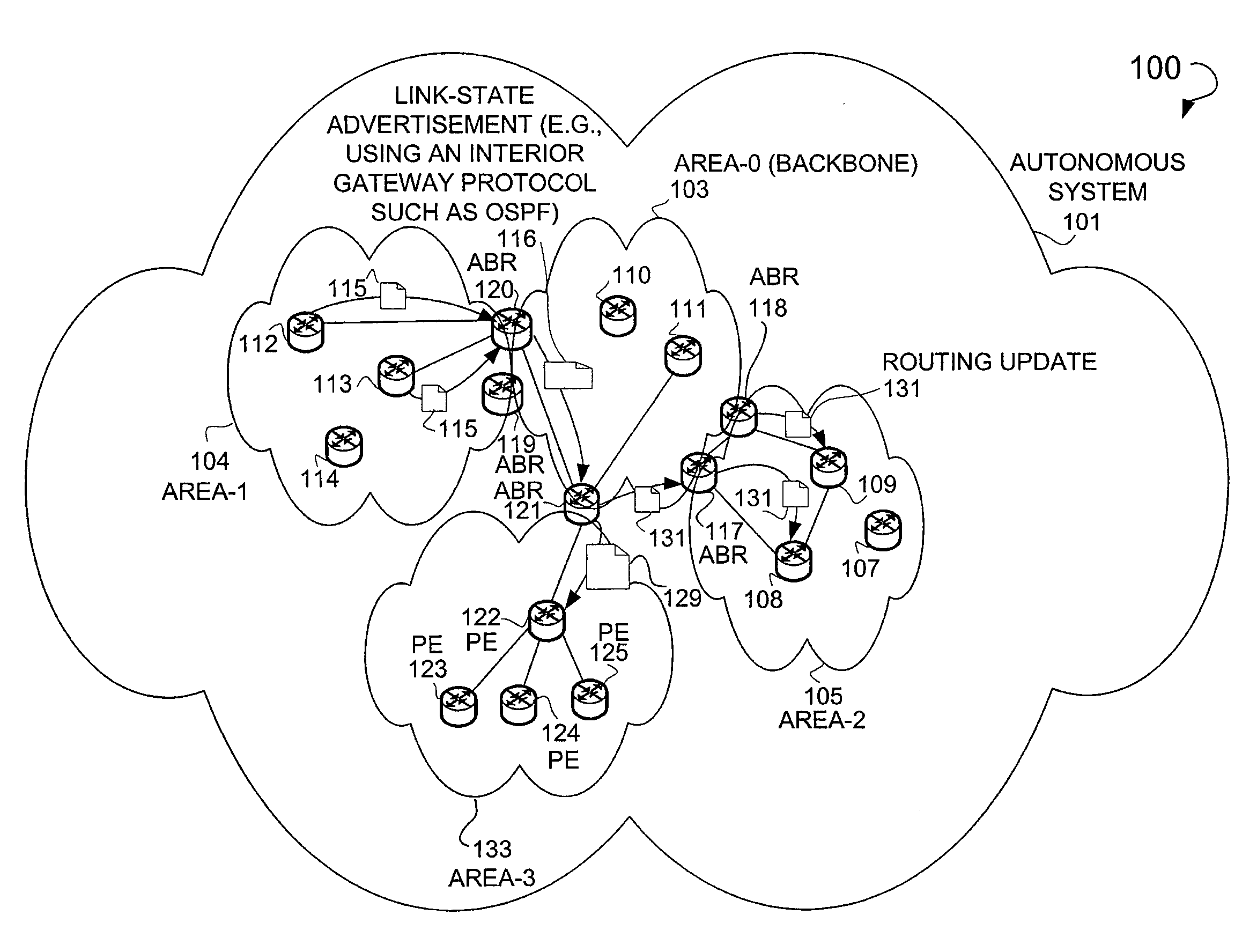
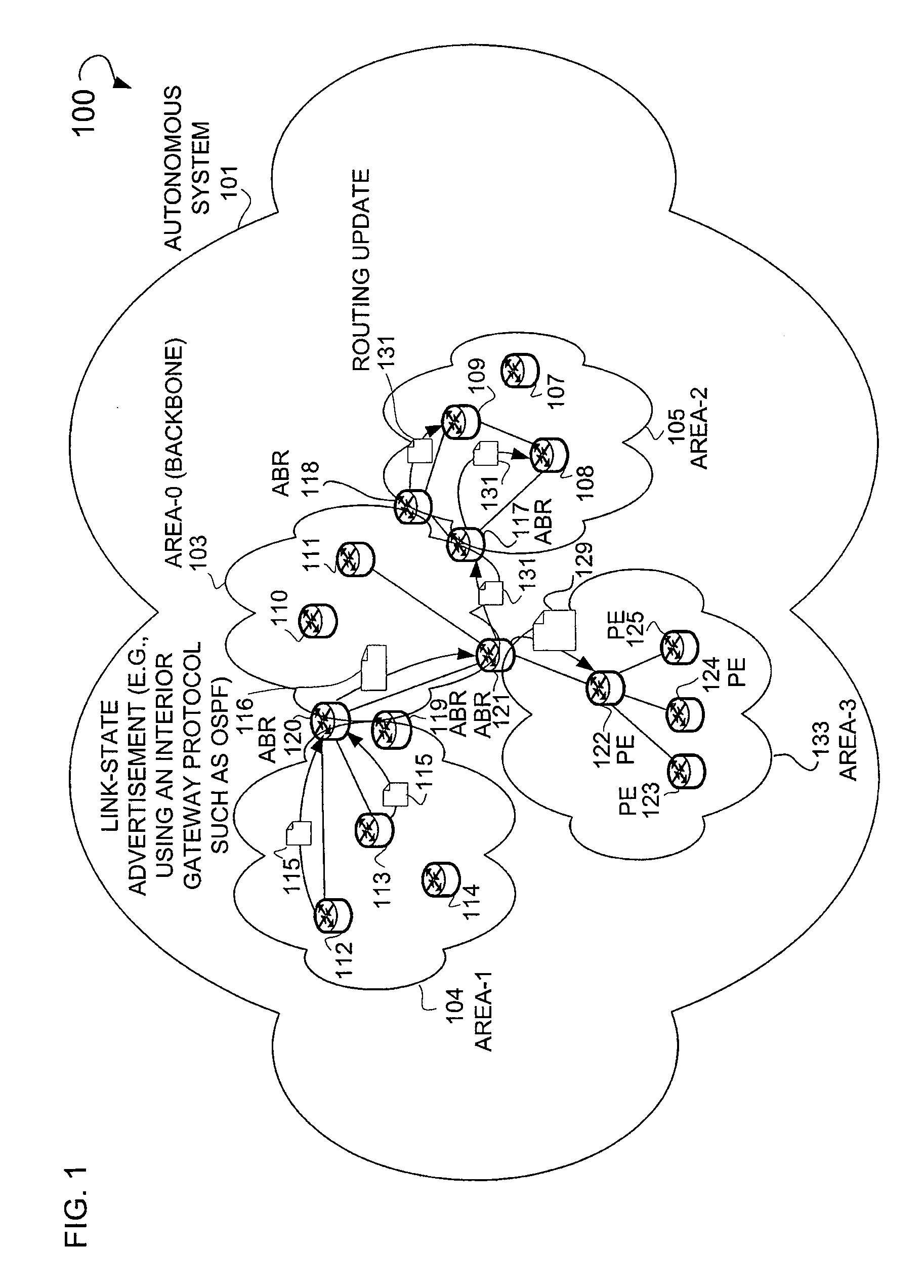
In one example embodiment, a system and method is illustrated that includes receiving connectivity data for at least one network device, the connectivity data describing a connection to the at least one network device within an area. The system and method further includes processing the connectivity data to obtain a routing update for distribution to another network device outside the area. Additionally, the system and method includes a routing summary in the routing update, the routing summary including an address prefix. Further, the system and method includes reachability information in the routing update, the reachability information including an address for the at least one network device.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Controlled distribution of inter-area routing information
A technique controls distribution of reachability information for a tail-end node of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) to a head-end node of the TE-LSP in a computer network. The TE-LSP preferably spans multiple domains of the network such that the tail-end node resides in a domain (“tail-end domain”) that is different (remote) from the domain of the head-end node (“head-end domain”). According to the inter-domain information distribution technique, the head-end node requests the remote reachability information from the tail-end node, which may employ an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) to transmit the information to a border router of the tail-end domain. The tail-end domain border router then shares this information with at least a head-end domain border router. The head-end node thereafter requests that the head-end domain border router release the reachability information into the head-end domain. The head-end node uses the remote information to calculate routes, i.e., address prefixes and associated attributes, reachable from the tail-end node for insertion into its routing table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for network edge data protection
ActiveUS20090320135A1Quick implementationAvoid the needMemory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsDomain nameNetwork Communication Protocols
Disclosed are systems and methods which examine information communication streams to identify and / or eliminate malicious code, while allowing the good code to pass unaffected. Embodiments operate to provide spam filtering, e.g., filtering of unsolicited and / or unwanted communications. Embodiments provide network based or inline devices that scan and scrub information communication in its traffic pattern. Embodiments are adapted to accommodate various information communication protocols, such as simple mail transfer protocol (SMTP), post office protocol (POP), hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP), Internet message access protocol (IMAP), file transfer protocol (FTP), domain name service (DNS), and / or the like, and / or routing protocols, such as hot standby router protocol (HSRP), border gateway protocol (BGP), open shortest path first (OSPF), enhanced interior gateway routing protocol (EIGRP), and / or the like.
Owner:TREND MICRO INC
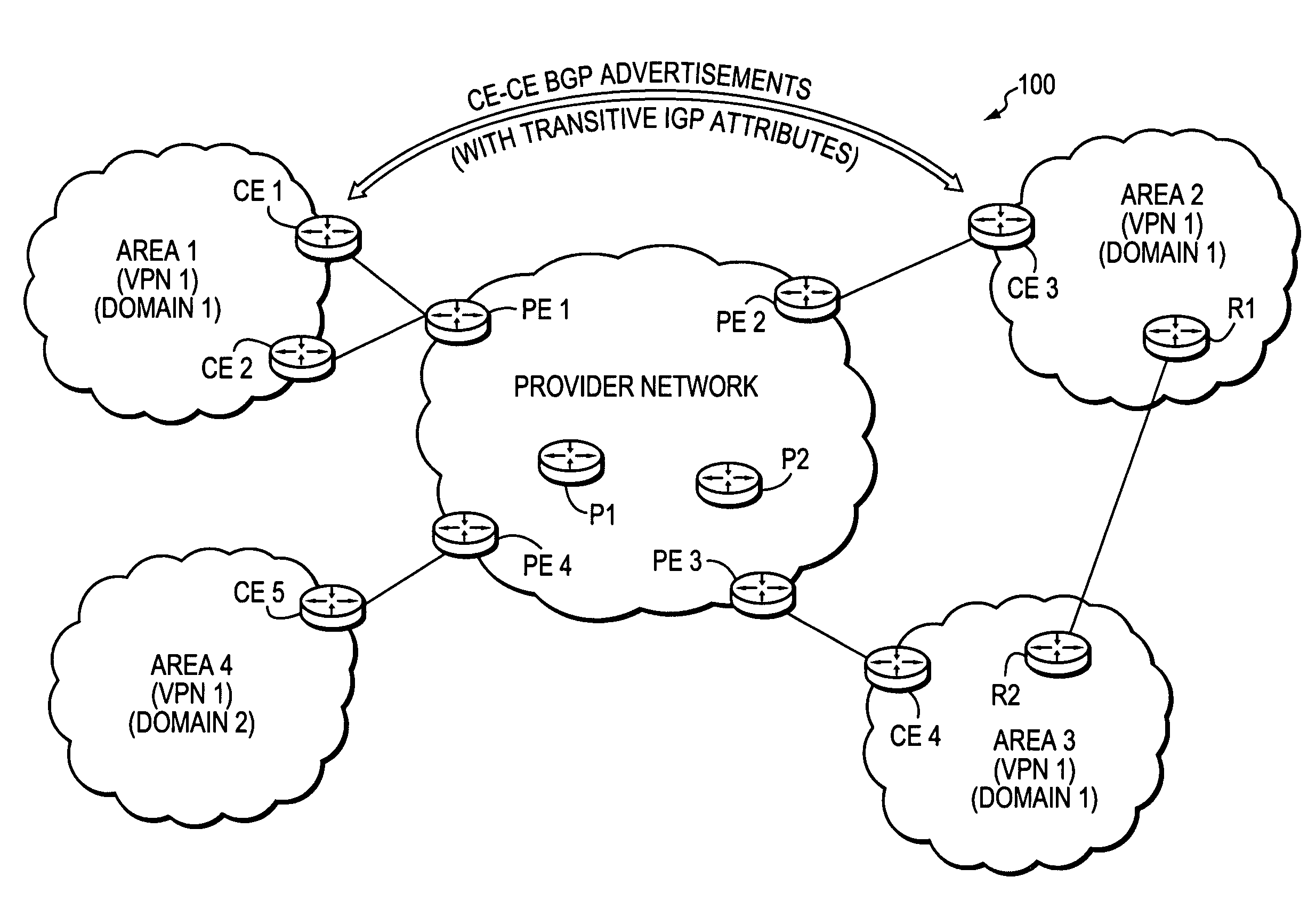
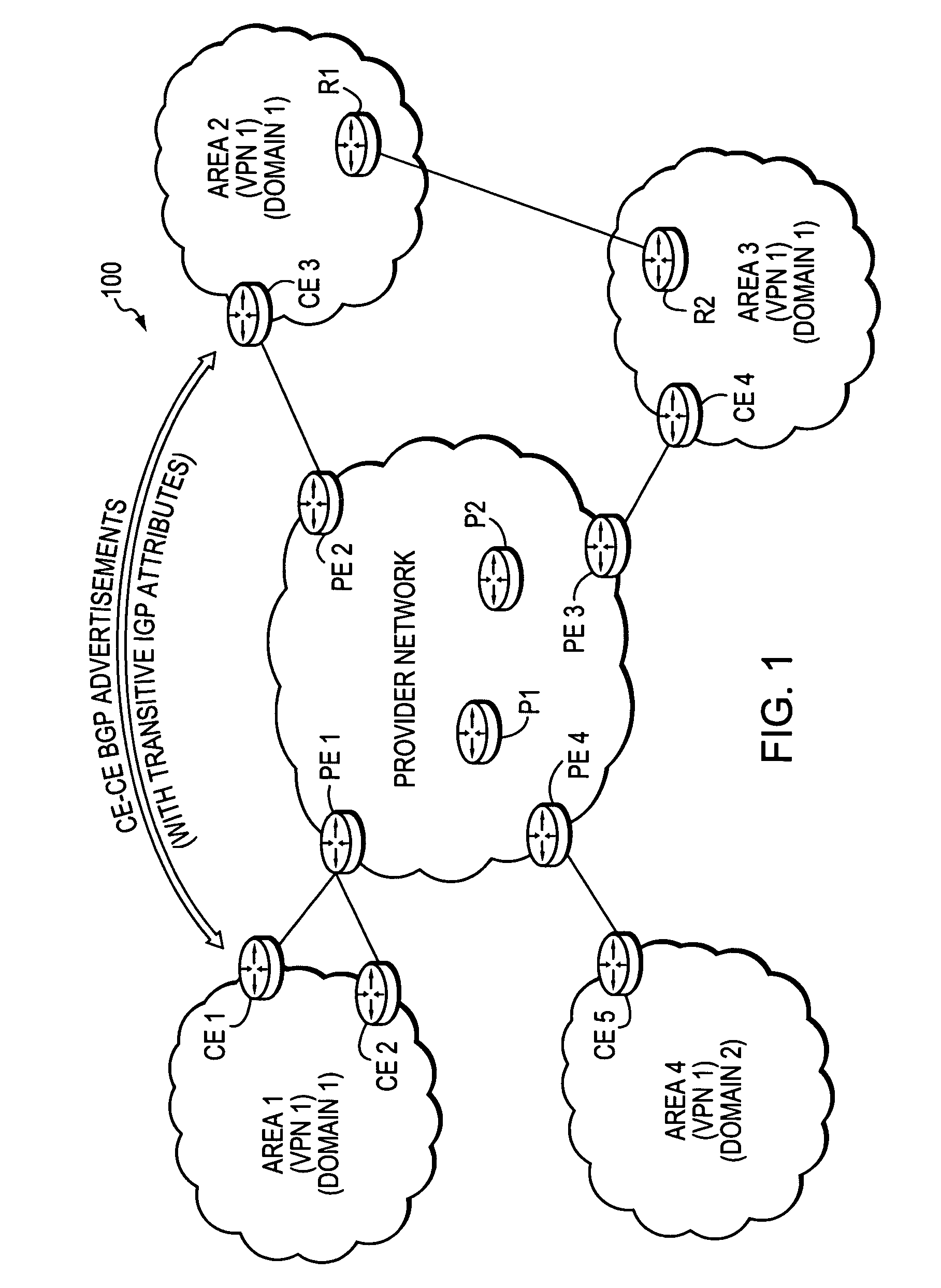
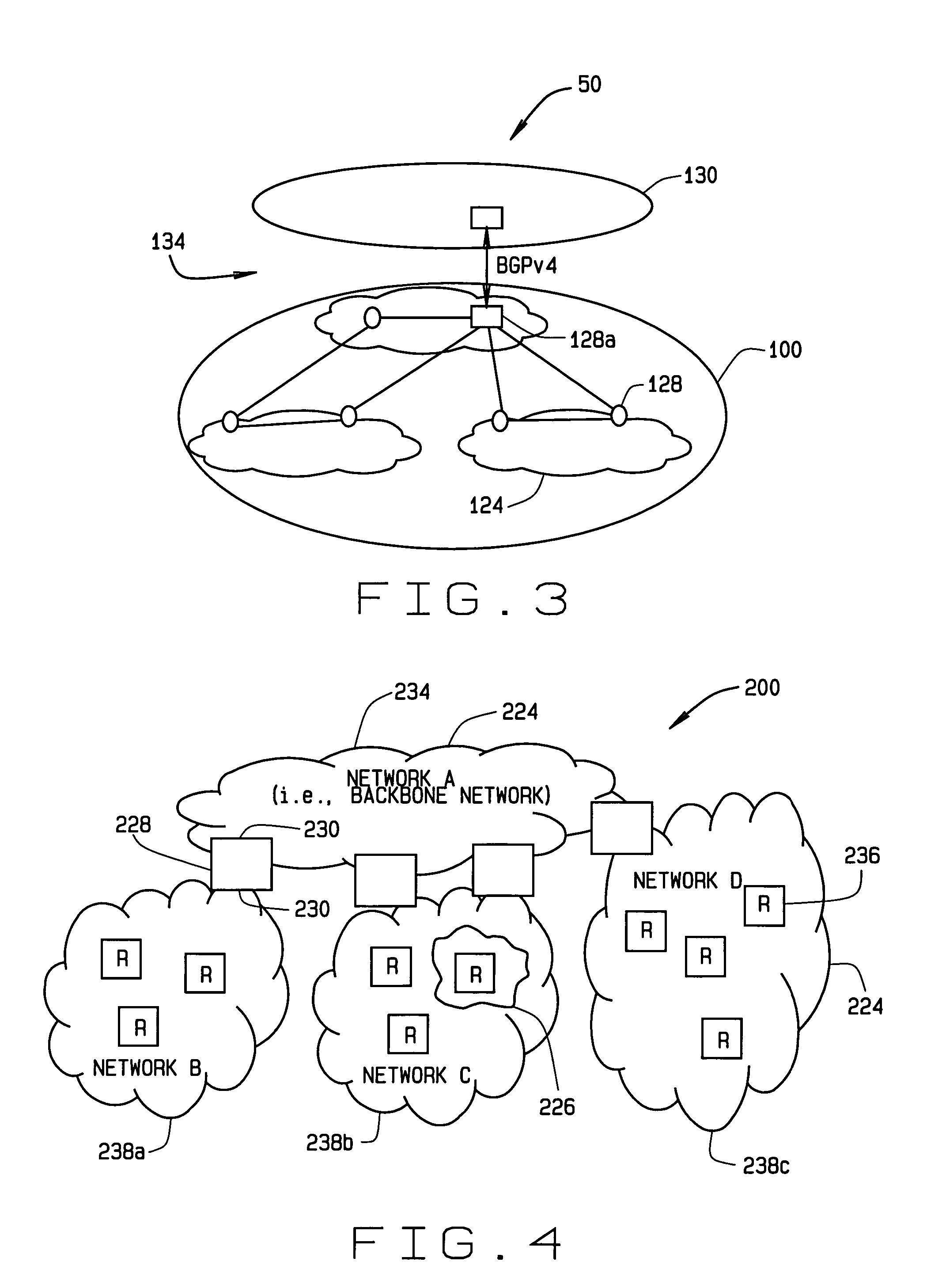
Maintaining IGP transparency of VPN routes when BGP is used as a PE-CE protocol
InactiveUS7865615B2Maintains IGP transparencyReduce needDigital computer detailsNetwork connectionsBorder Gateway ProtocolPrivate network
A technique maintains Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) transparency of Virtual Private Network (VPN) routes when Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is used as a Provider Edge Device (PE) to Customer Edge Device (CE) protocol in a computer network. According to the novel technique, a first CE generates a BGP advertisement to advertise one or more VPN routes of its customer network, the BGP advertisement having one or more transitive IGP attributes for the advertised routes. The first CE sends the BGP advertisement to a first PE, which then propagates the BGP advertisement among devices of a provider network maintaining the transitive IGP attributes. A second PE sends the BGP advertisement to a second CE, along with the transitive IGP attributes. Upon receiving the BGP advertisement, the second CE converts the BGP advertisement and transitive IGP attributes into corresponding IGP advertisements. The second CE may then propagate the IGP advertisements into its customer network as either internal VPN routes or as external routes accordingly.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Inter-domain TE-LSP with IGP extensions
ActiveUS7460481B2Avoid errorsReduce riskError preventionTransmission systemsRouting tableInformation propagation
A technique propagates reachability information for a tail-end node of a traffic engineering (TE) label switched path (LSP) to a head-end node of the TE-LSP in a computer network. The TE-LSP preferably spans multiple domains of the network such that the tail-end node resides in a domain that is different (remote) from the domain of the head-end node. The inter-domain information propagation technique employs an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP) to transmit the remote reachability information from a target node residing in the same domain as the tail-end node to the head-end node. The head-end node uses the remote information to calculate routes, i.e., address prefixes and associated attributes, reachable from the tail-end node for insertion into its routing table.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Controlling the signaling of label-switched paths using a label distribution protocol employing messages which facilitate the use of external prefixes
ActiveUS8176201B1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsType-length-valueForwarding equivalence class
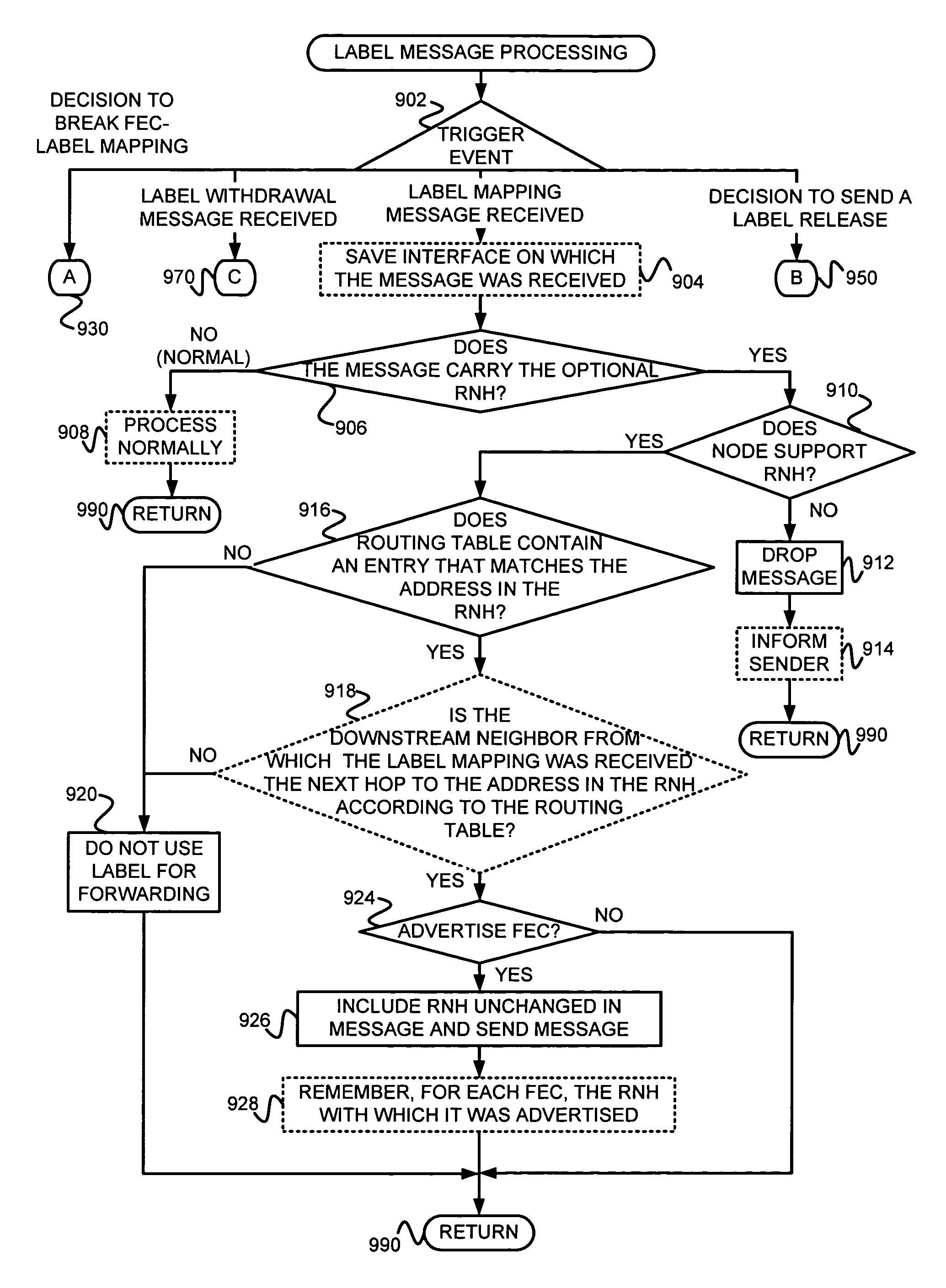
Label distribution protocol (LDP) signaled label-switched paths (LSPs) are supported without requiring information about remote autonomous systems (ASs) to be injected into the local interior gateway protocol (IGP). This may be done by (i) decoupling a forwarding equivalency class (FEC) element from the routing information, and (ii) specifying a next hop on which the FEC relies. An LDP messaging structure (e.g., an LDP type-length-value (TLV)) that includes a label, FEC information (e.g., a host address or prefix of an egress LSR of the LSP) and a next hop (e.g., a host address or prefix of a border node, such as an AS border router (ASBR)) may be provided. This messaging structure may be included in one or more of (a) label mapping messages, (b) label withdraw messages, and (c) label release messages. If an LDP message including the expanded LDP messaging structure is received at a node, the node may determine whether or not to propagate the LSP using the next hop information, rather than the FEC information. If, on the other hand, the LDP message includes a normal LDP messaging structure, the node may determine whether or not to propagate the LSP as usual.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Method, device and system for creating bidirectional multicast distribution trees on basis of interior gateway protocol
ActiveCN103546381ASimple operation and maintenanceSolve complex operation and maintenance problemsData switching networksDistribution treeProtocol Independent Multicast
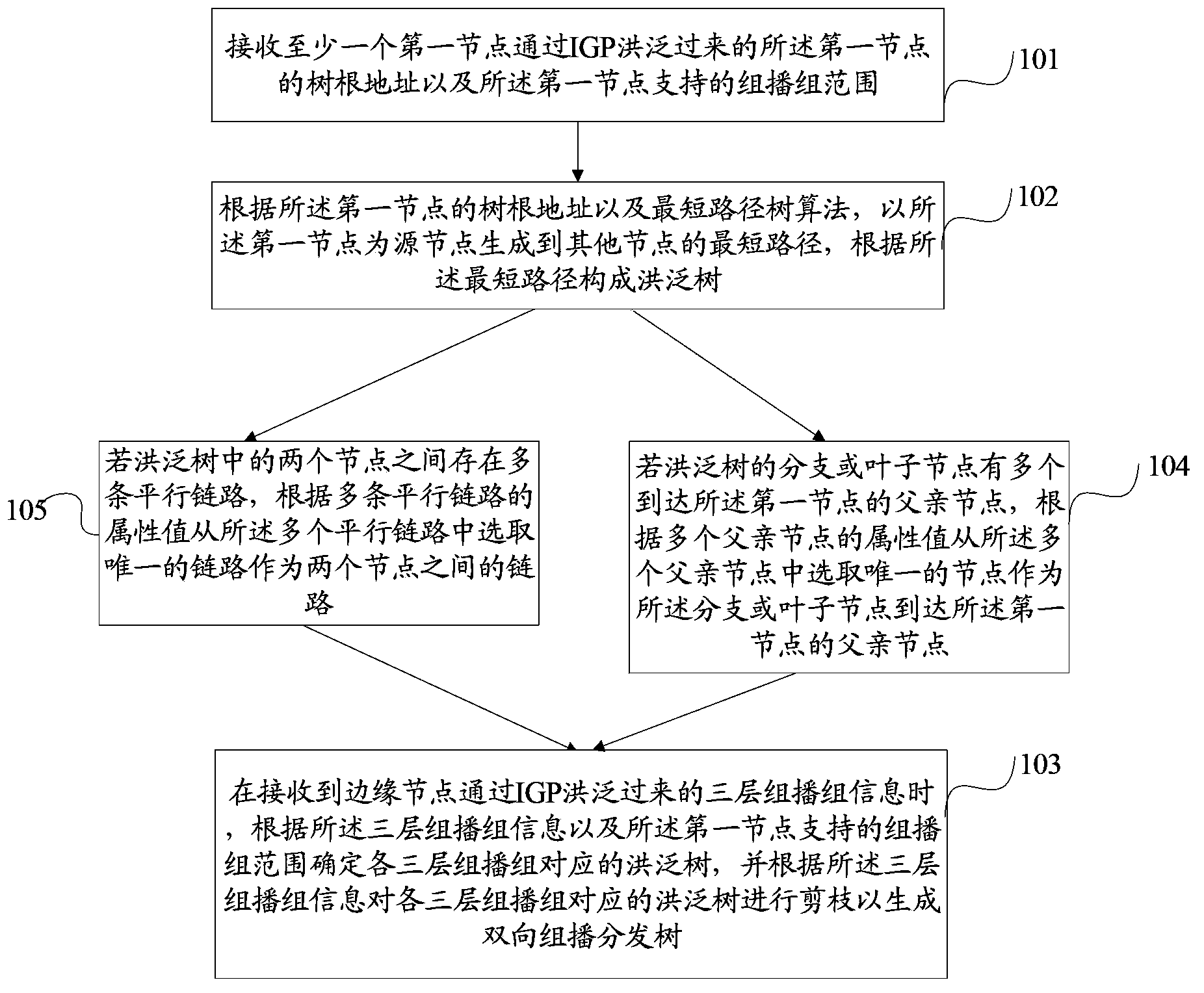
An embodiment of the invention discloses a method, a device and a system for creating bidirectional multicast distribution trees on the basis of an interior gateway protocol, and relates to the technical field of communication. The technical scheme includes that the method comprises receiving a root address of at least one first node and a multicast group range supported by the first node; generating shortest paths from each first node, which is used as a source node, to other nodes according to the corresponding root address and a shortest path tree algorithm, and creating flooding trees according to the shortest paths; determining flooding trees corresponding to various three-layer multicast groups according to three-layer multicast group information and the multicast group ranges supported by the first nodes when the three-layer multicast group information is received, and generating the bidirectional multicast distribution trees for the flooding trees corresponding to the various three-layer multicast groups according to the three-layer multicast group information. The root addresses of the first nodes are transmitted by the first nodes by means of flooding. The three-layer multicast group information is transmitted by edge nodes by means of flooding. The method, the device and the system have the advantage that the problem of complexity in operation and maintenance due to the fact that a PIM (protocol independent multicast) routing protocol and a unicast routing protocol which is an IGP (interior gateway protocol) need to be simultaneously operated and maintained in multipoint-to-multipoint multicast scenes can be solved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Network element equipment configuration and management method and device as well as network element equipment
ActiveCN104579728ARealize the effect of plug and tubeData switching networksHigh level techniquesIp addressNetwork management
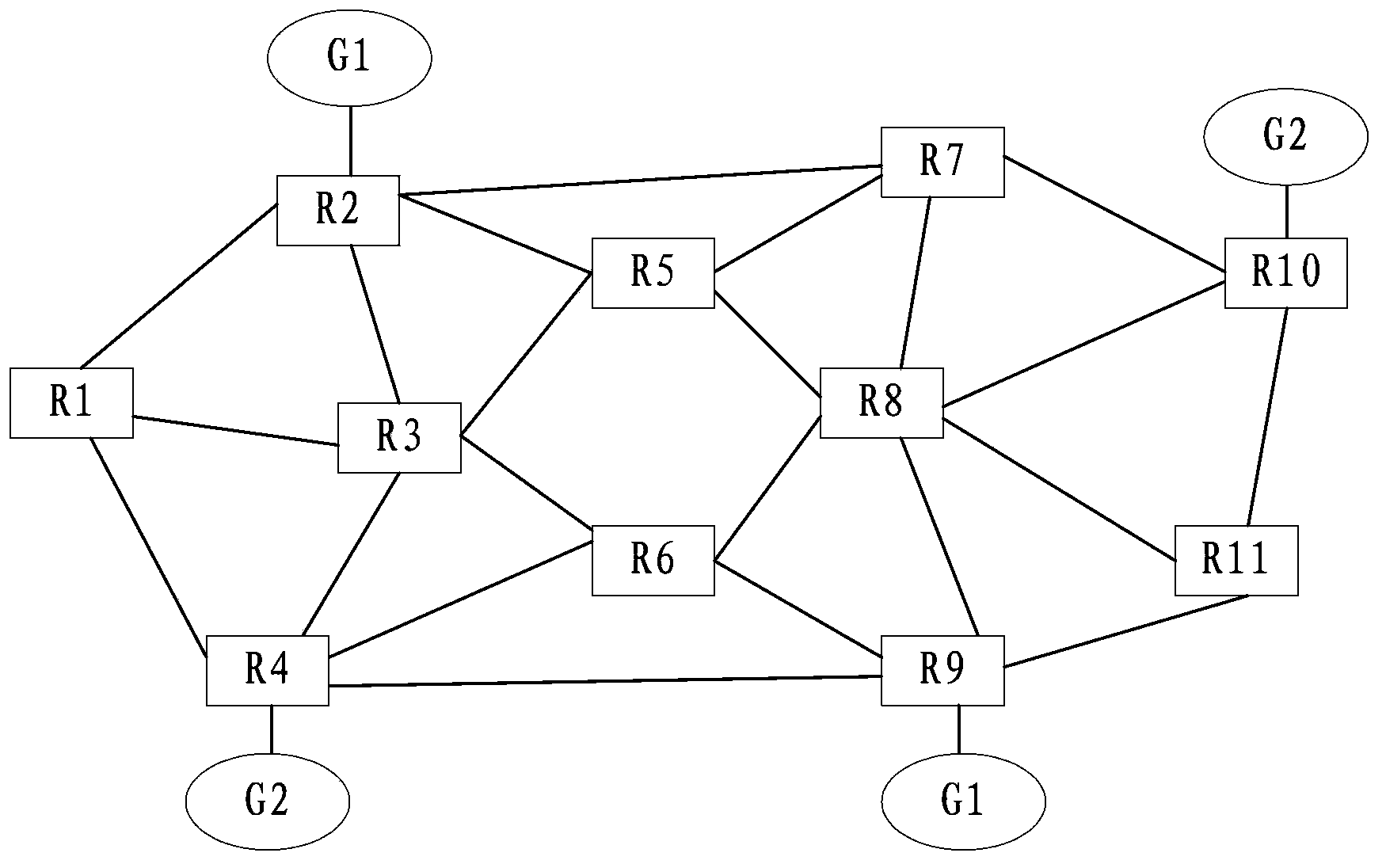
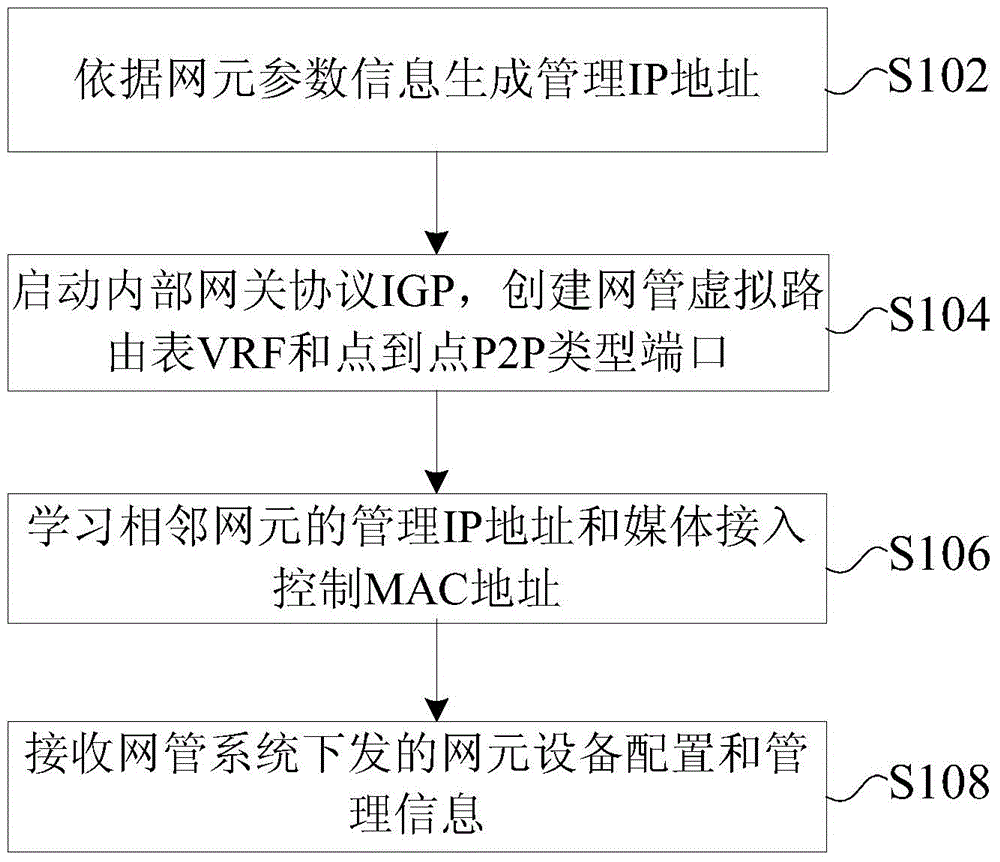
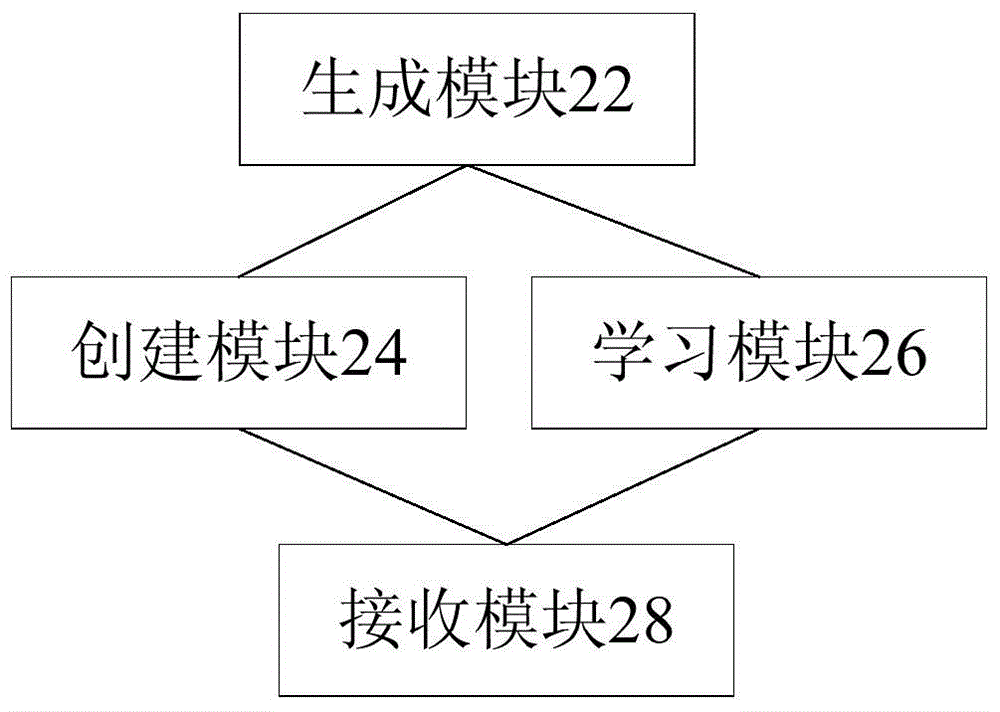
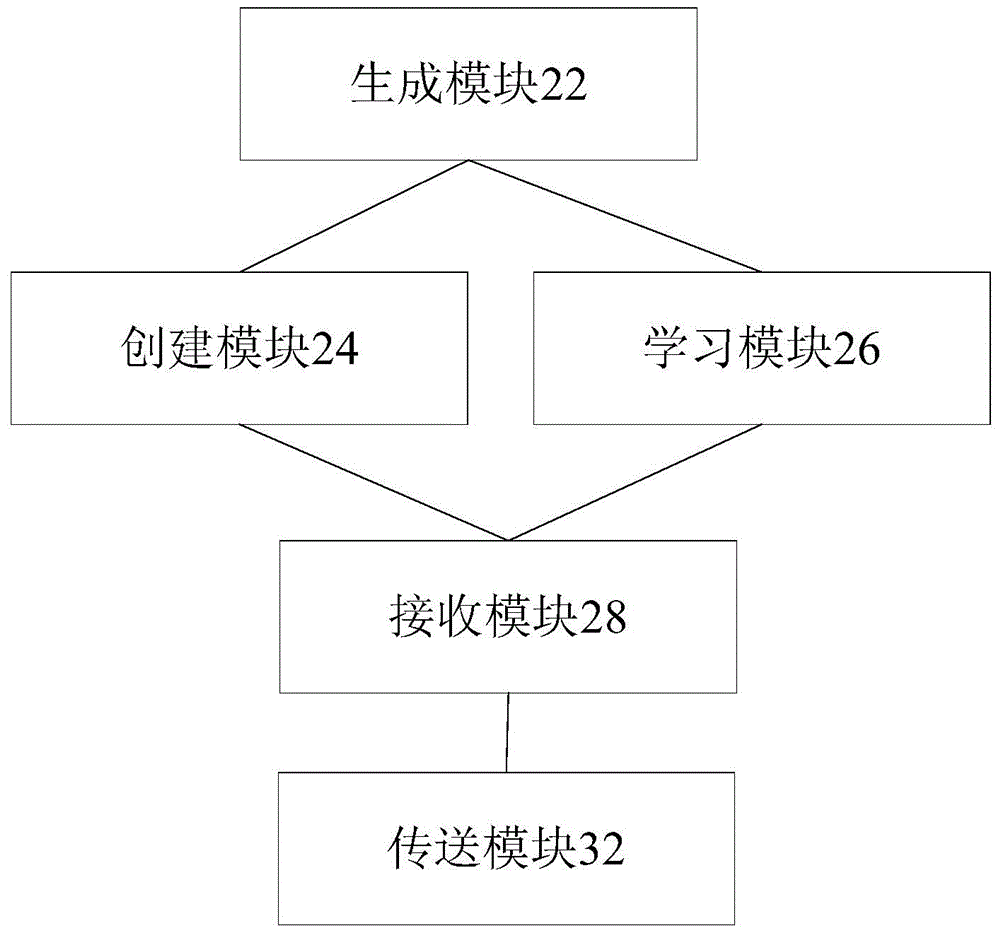
A network element device configuration and management method, device and network element device, the method comprising: generating a management IP address according to network element parameter information; starting an interior gateway protocol (IGP), and creating a network management virtual route forwarding table (VRF) and a point to point (P2P) port; learning the management IP address and media access control (MAC) address of a neighboring network element; and receiving network element device configuration and management information issued by the network management system. The solution solves the problems in the relevant art of heavy workload in manual configuration of nodes, complicated operations, reduced network performance and poor user experience, thus eliminating manual configuration of network devices and realizing the effect of "plug-and-management" of the network element devices.
Owner:ZTE CORP
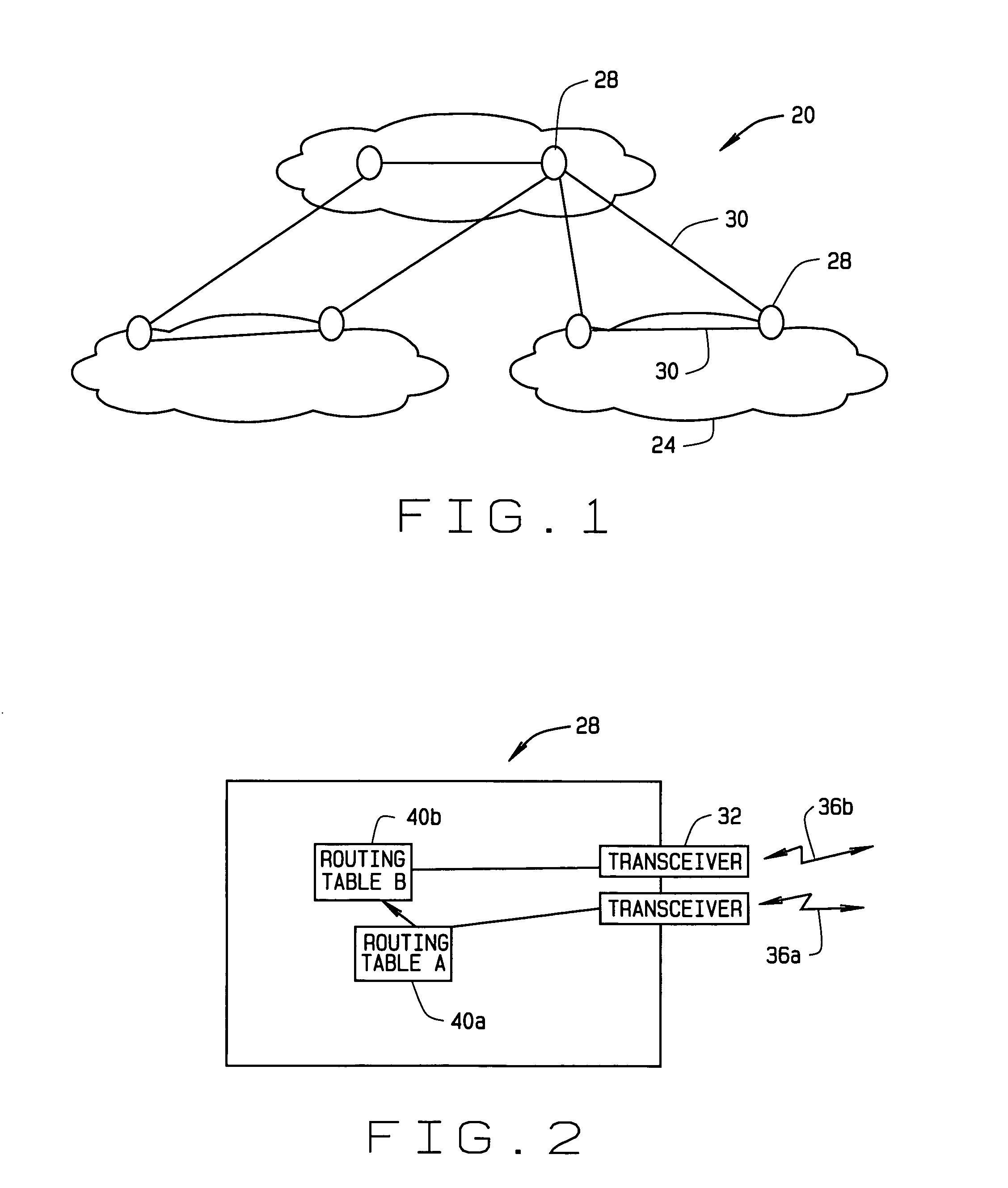
Virtual exterior gateway protocol and related methods
InactiveUS7519009B2Interconnection arrangementsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionInterior gateway protocolExterior Gateway Protocol
An aggregation of a plurality of networks. The aggregation includes a plurality of peer nodes of the networks, each node including a plurality of channels operating at a plurality of interior gateway protocol (IGP) routing levels configured to provide a mesh interface between at least two of the networks. This aggregation makes it possible to configure extremely large aggregated networks. It also supports inter-autonomous system (AS) mobility and movement needs of mobile ad-hoc network (MANET) networks.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
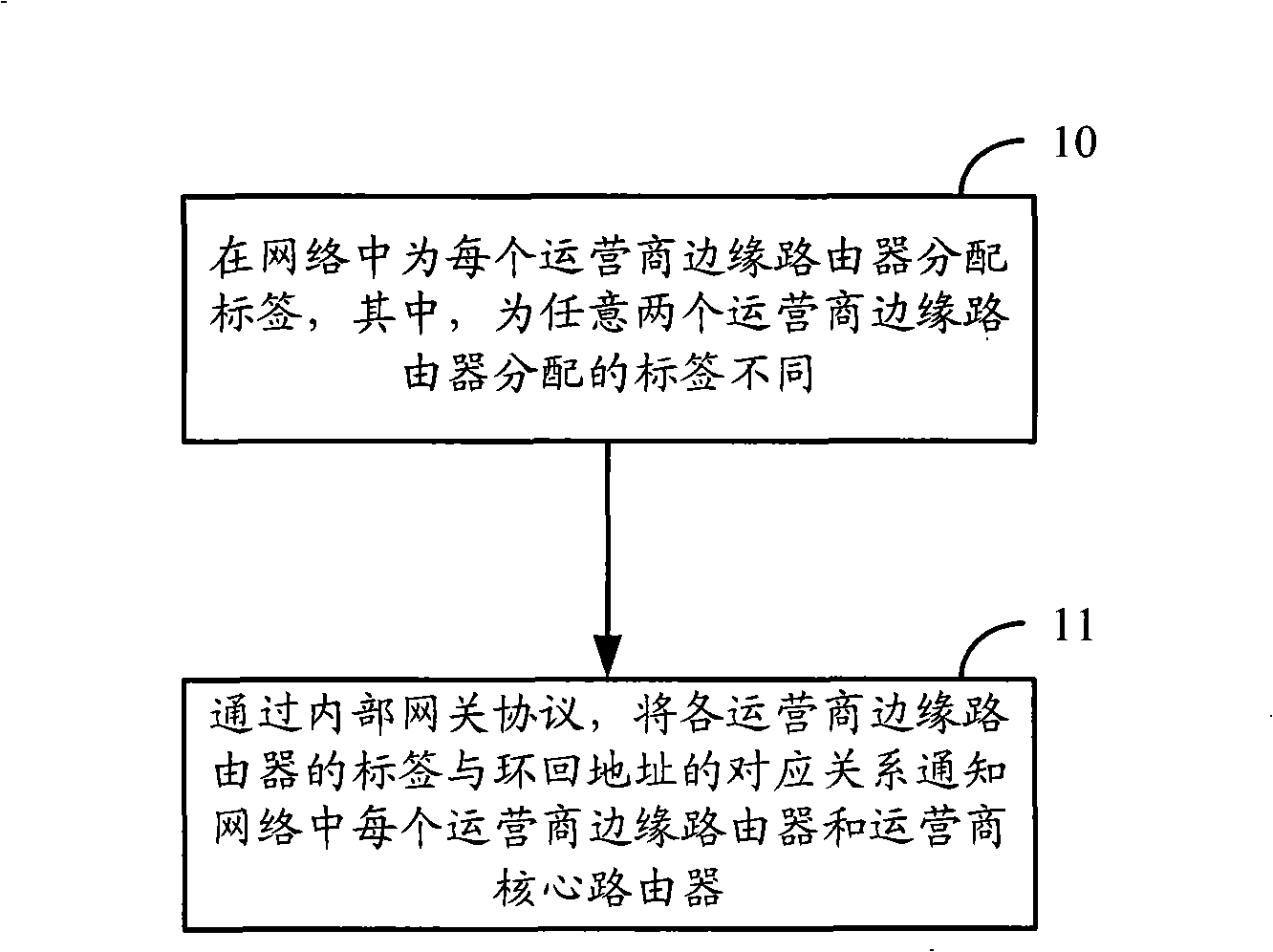
Method and apparatus for distributing label
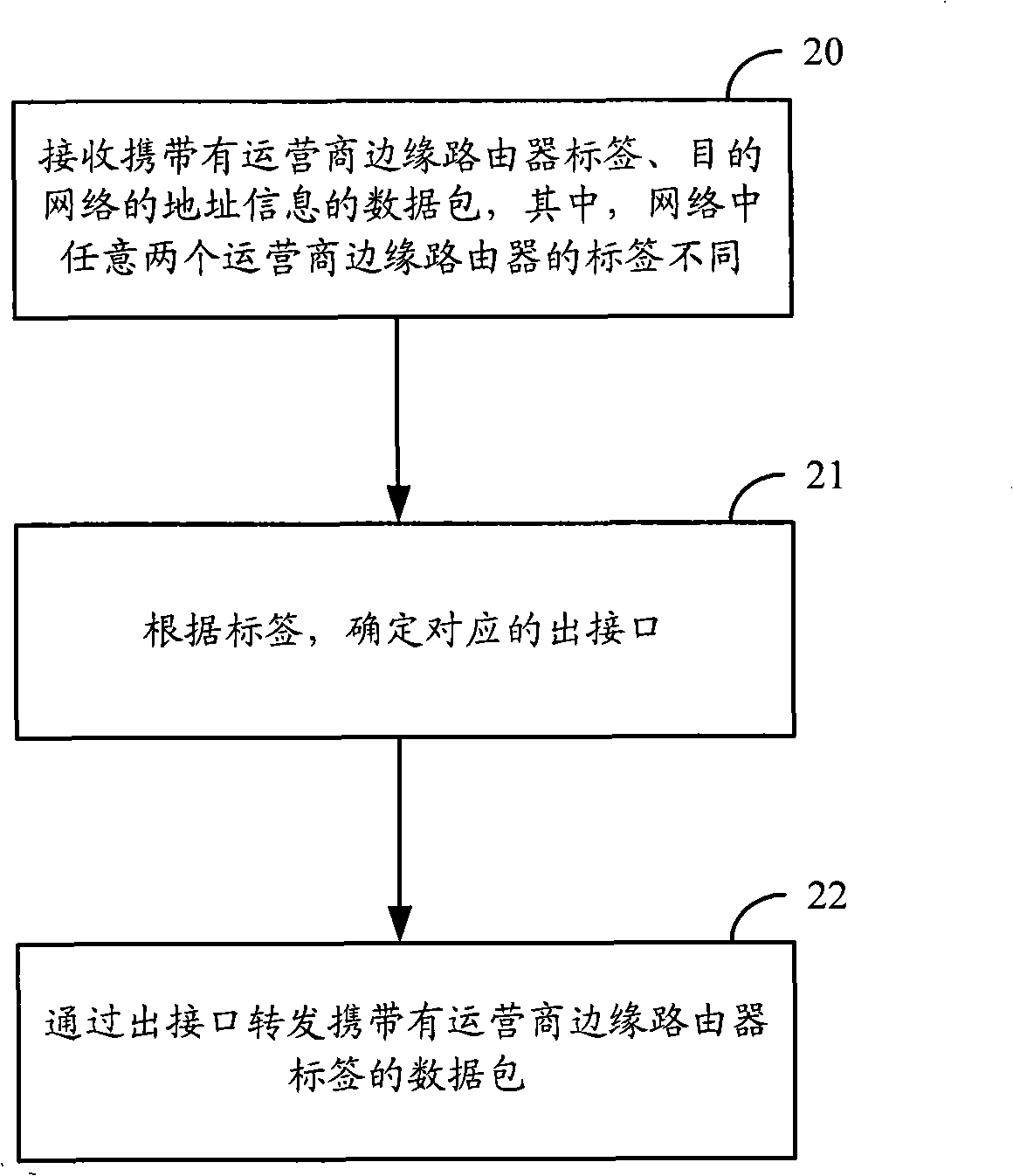
ActiveCN101355487AShorten convergence timeReduce overheadNetworks interconnectionCore routerData mining
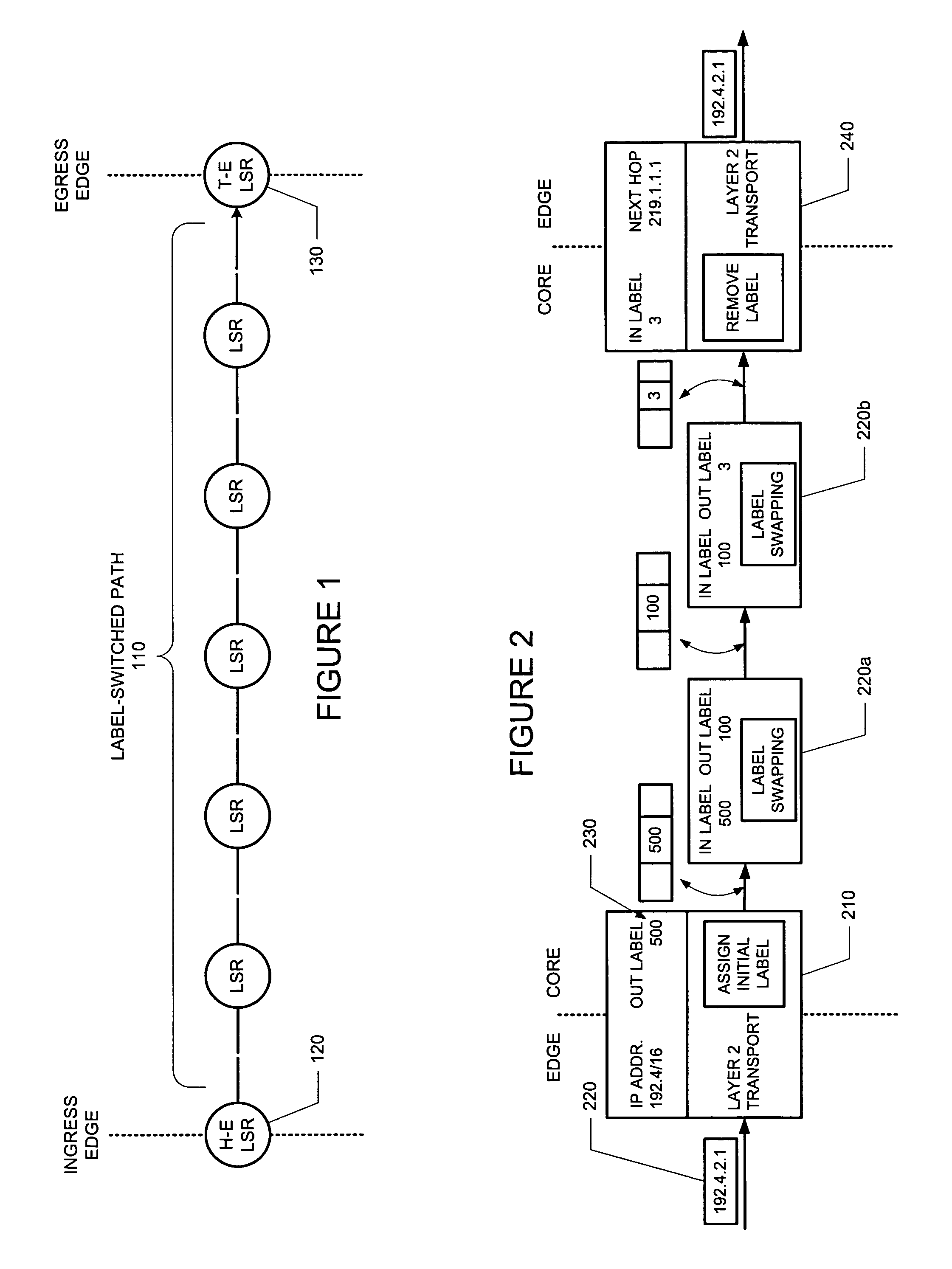
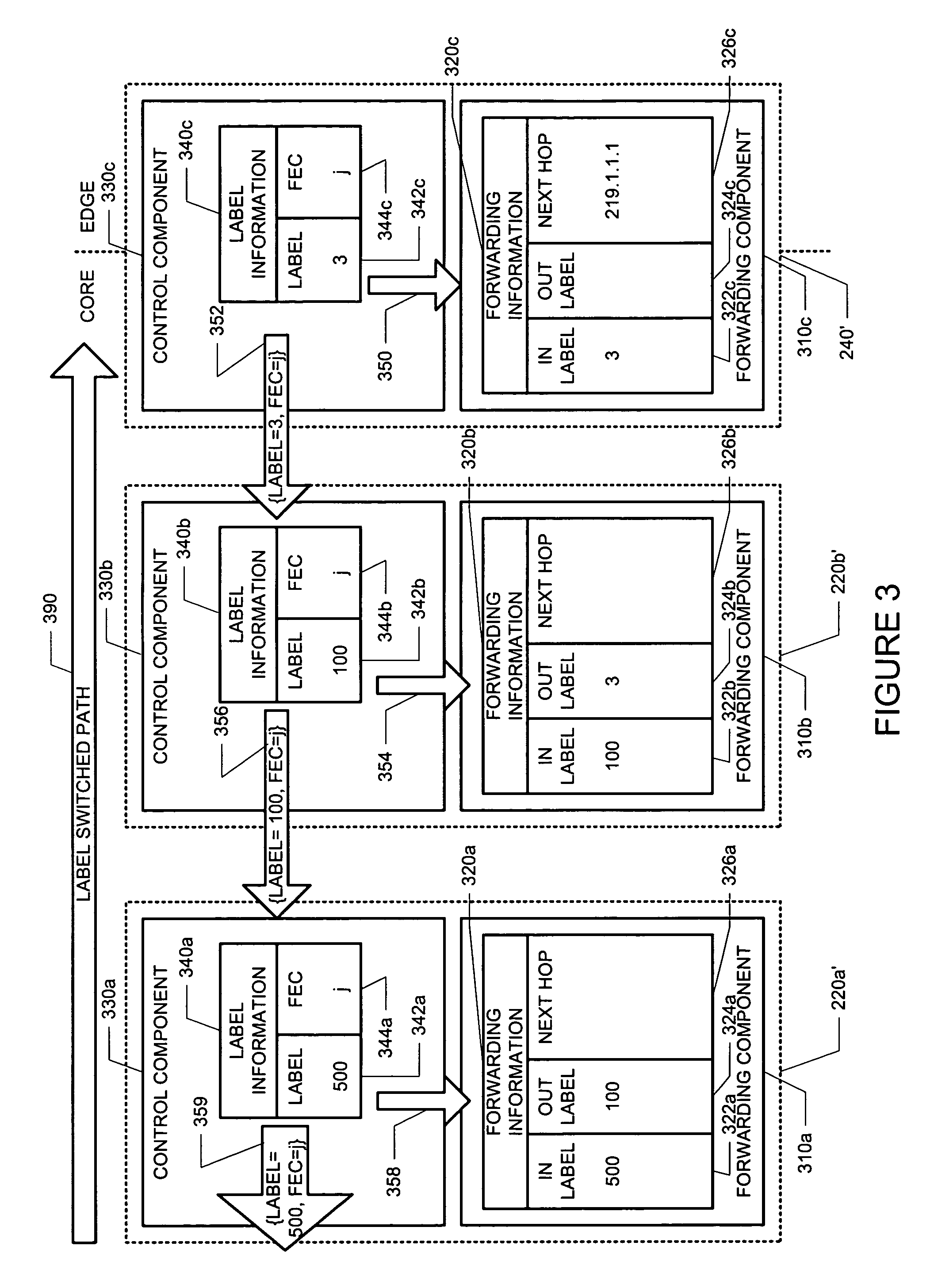
The invention discloses a method for label distribution, comprising the following steps: a label is allocated for each operator edge router in a network, wherein labels allocated for any two operator edge routers are different; and through an inner gateway protocol, the corresponding relation of the label of each operator edge router and a loopback address is notified to each operator edge router and an operator core router. Meanwhile, the invention discloses a label processing method, a label distribution device and a label processing device. The method can realize label distribution without adopting dynamic label distribution protocols such as LDP.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE COMM GRP CO LTD
System and method for routing packet traffic
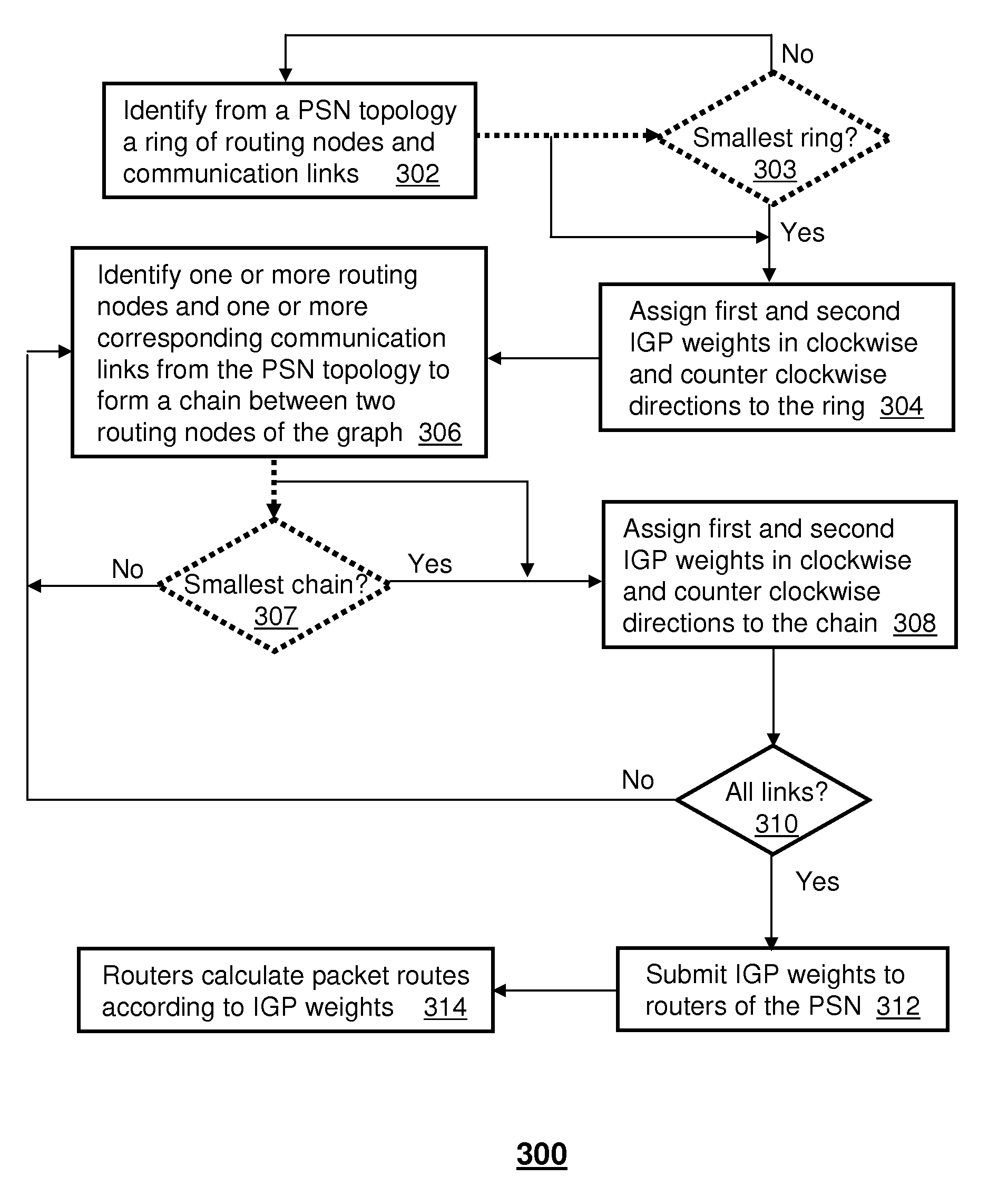
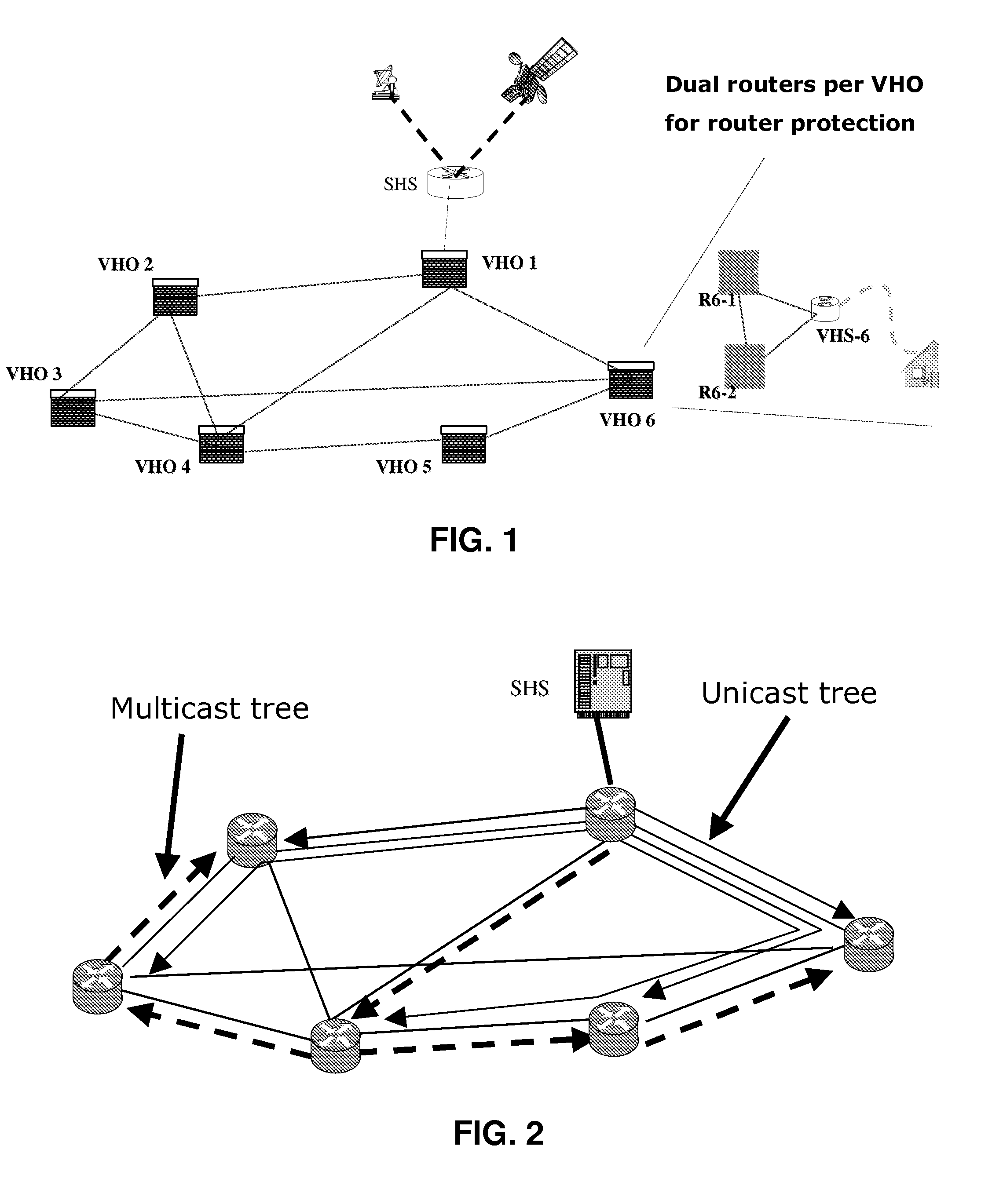
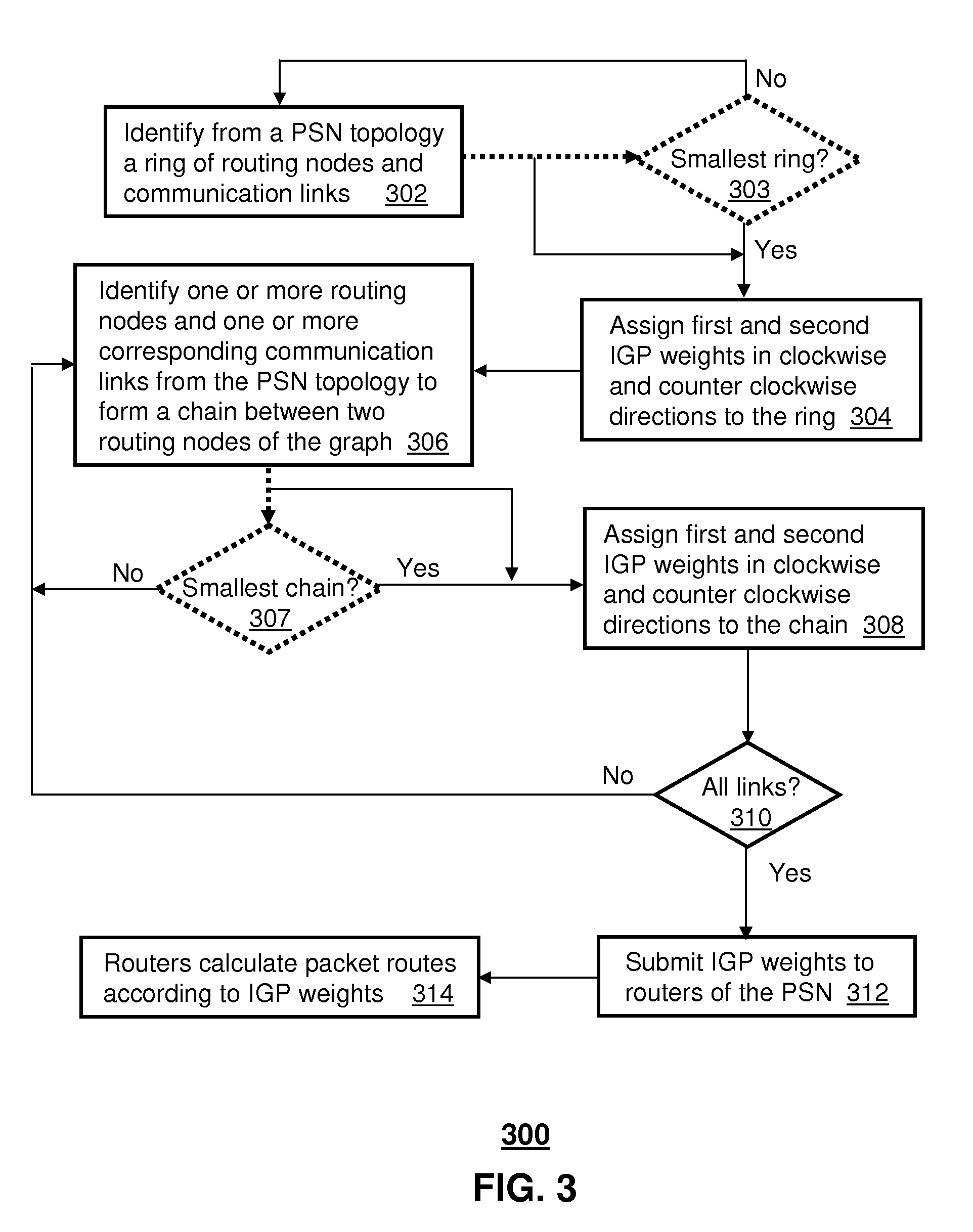
ActiveUS20080089335A1Avoid occupyingSpecial service provision for substationError preventionComputer networkMulticast packets
A system and method for routing packet traffic is disclosed. A system that incorporates teachings of the present disclosure may include, for example, a router having a routing element that routes packet traffic according to Internal Gateway Protocol (IGP) weights that prevent multicast packet traffic and unicast packet traffic from occupying a common unidirectional link. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com