Patents
Literature
157 results about "Multiprotocol Label Switching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
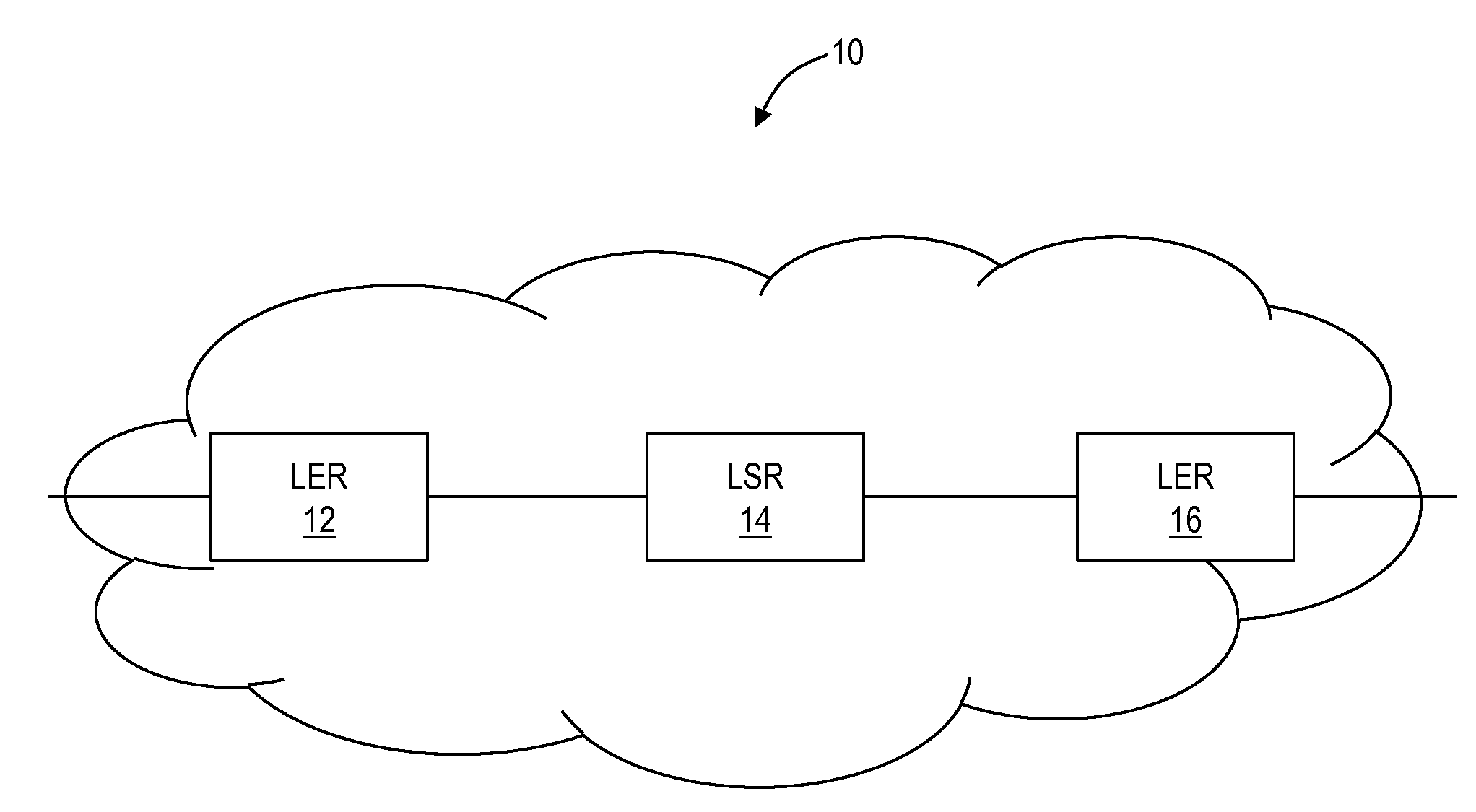
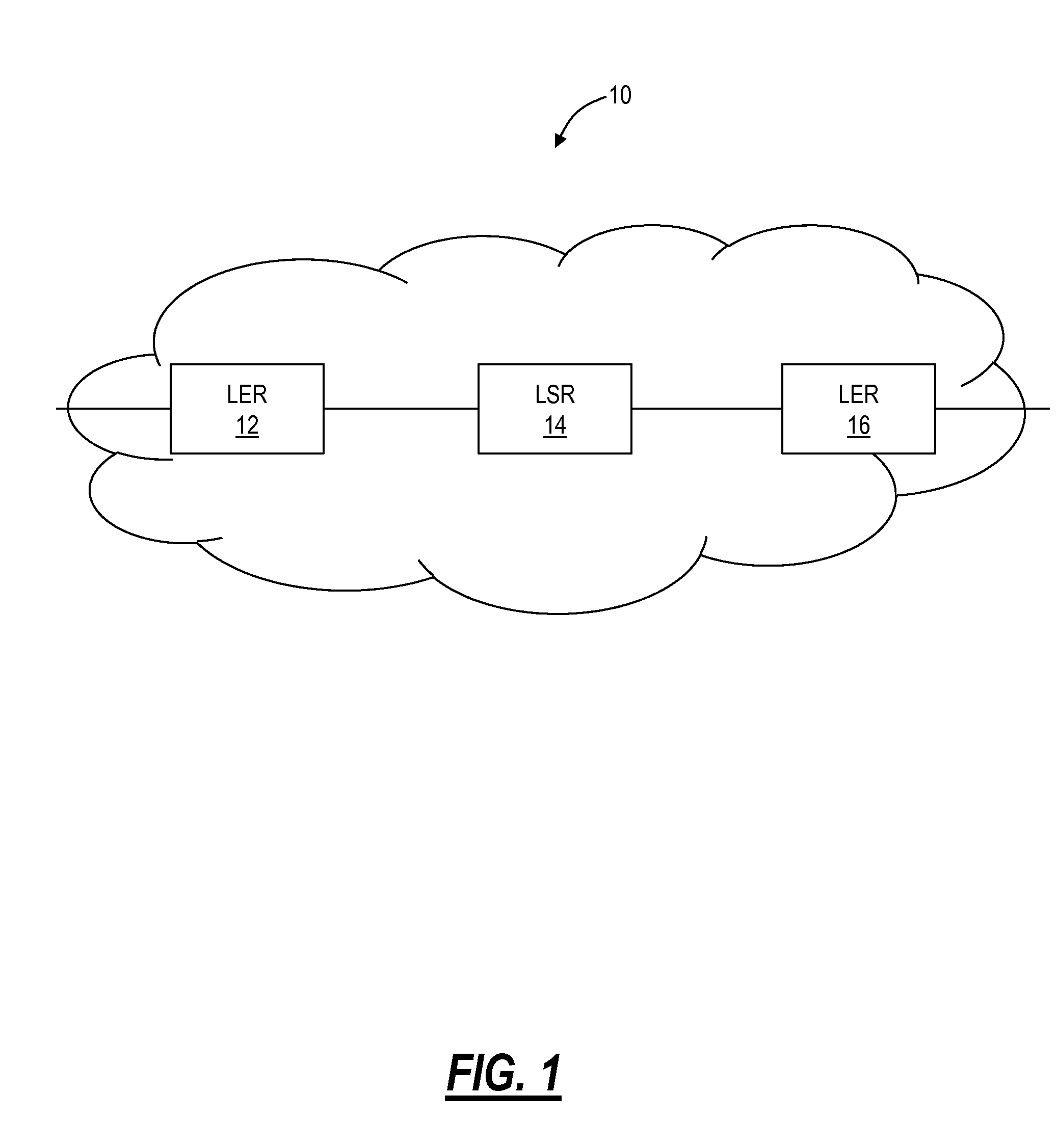
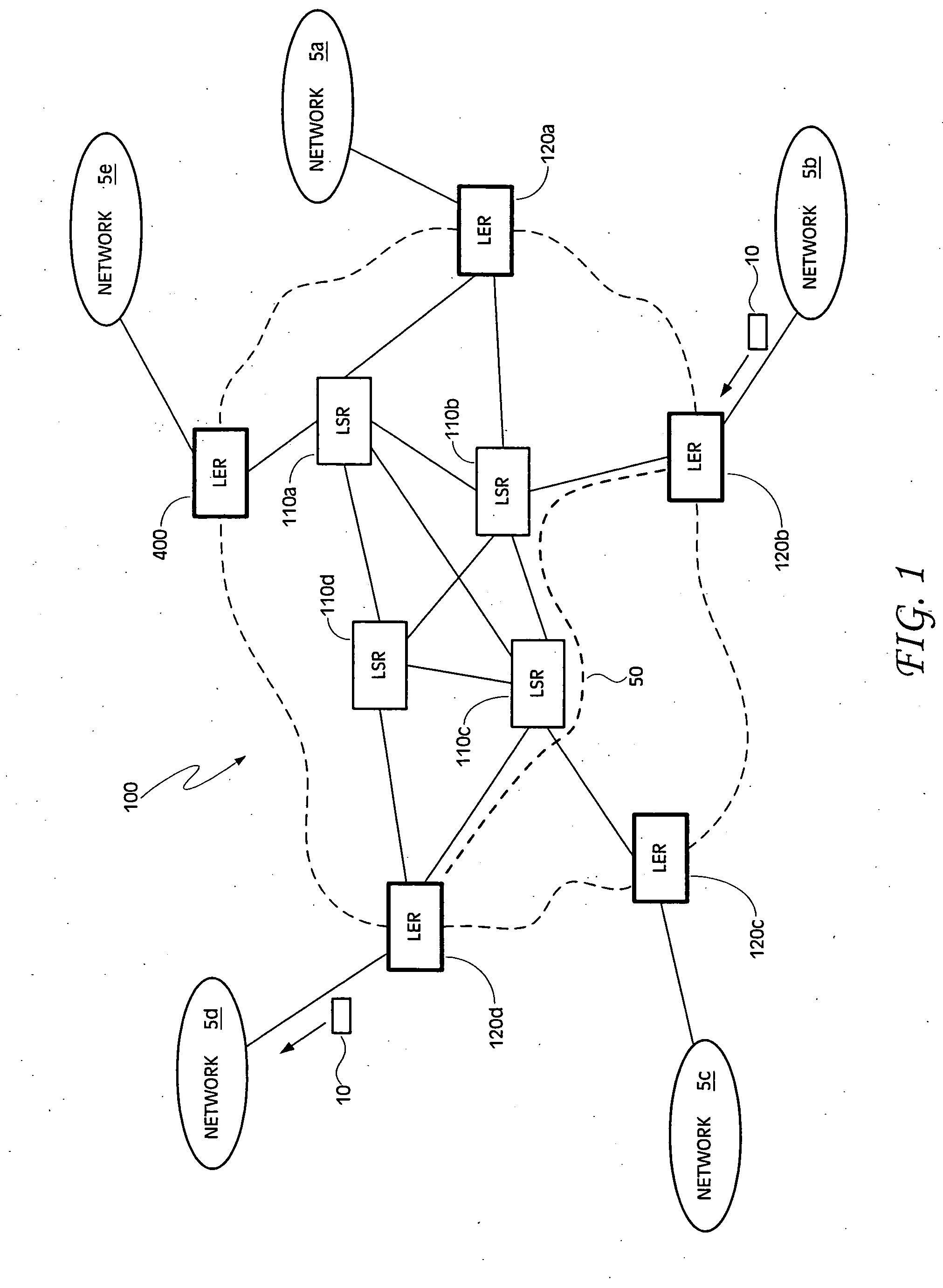
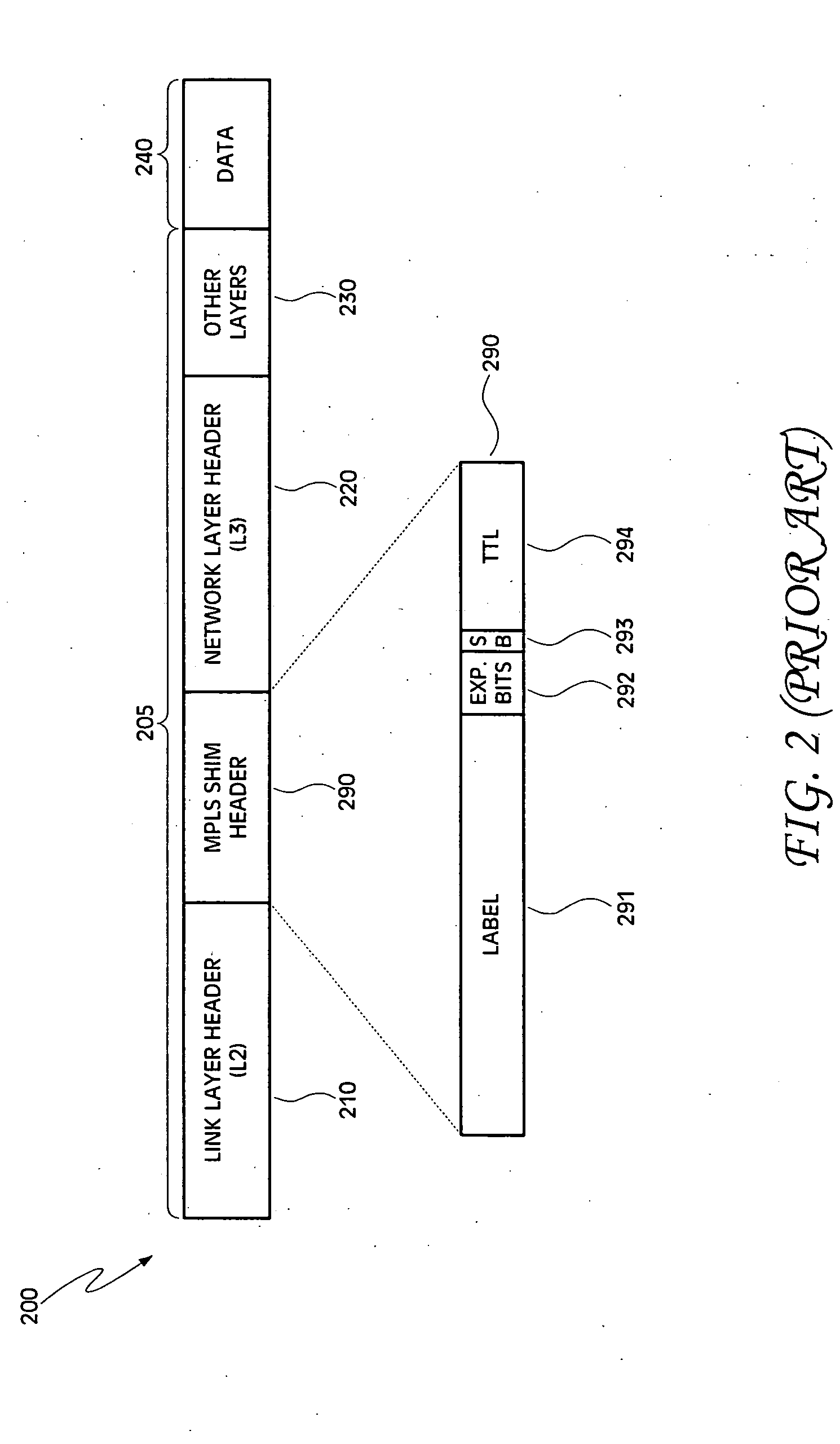
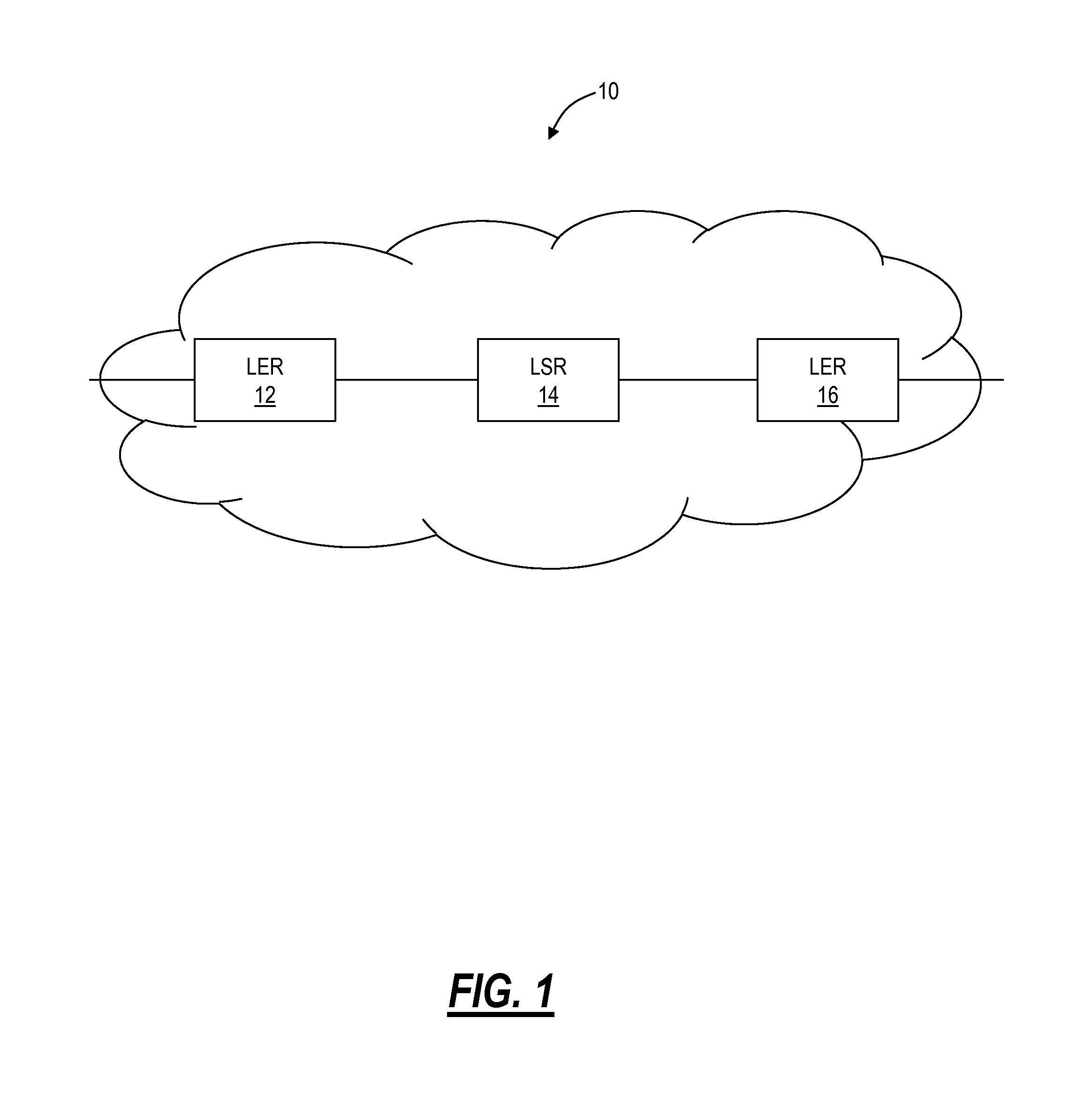
Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a routing technique in telecommunications networks that directs data from one node to the next based on short path labels rather than long network addresses, thus avoiding complex lookups in a routing table and speeding traffic flows. The labels identify virtual links (paths) between distant nodes rather than endpoints. MPLS can encapsulate packets of various network protocols, hence the "multiprotocol" reference on its name. MPLS supports a range of access technologies, including T1/E1, ATM, Frame Relay, and DSL.
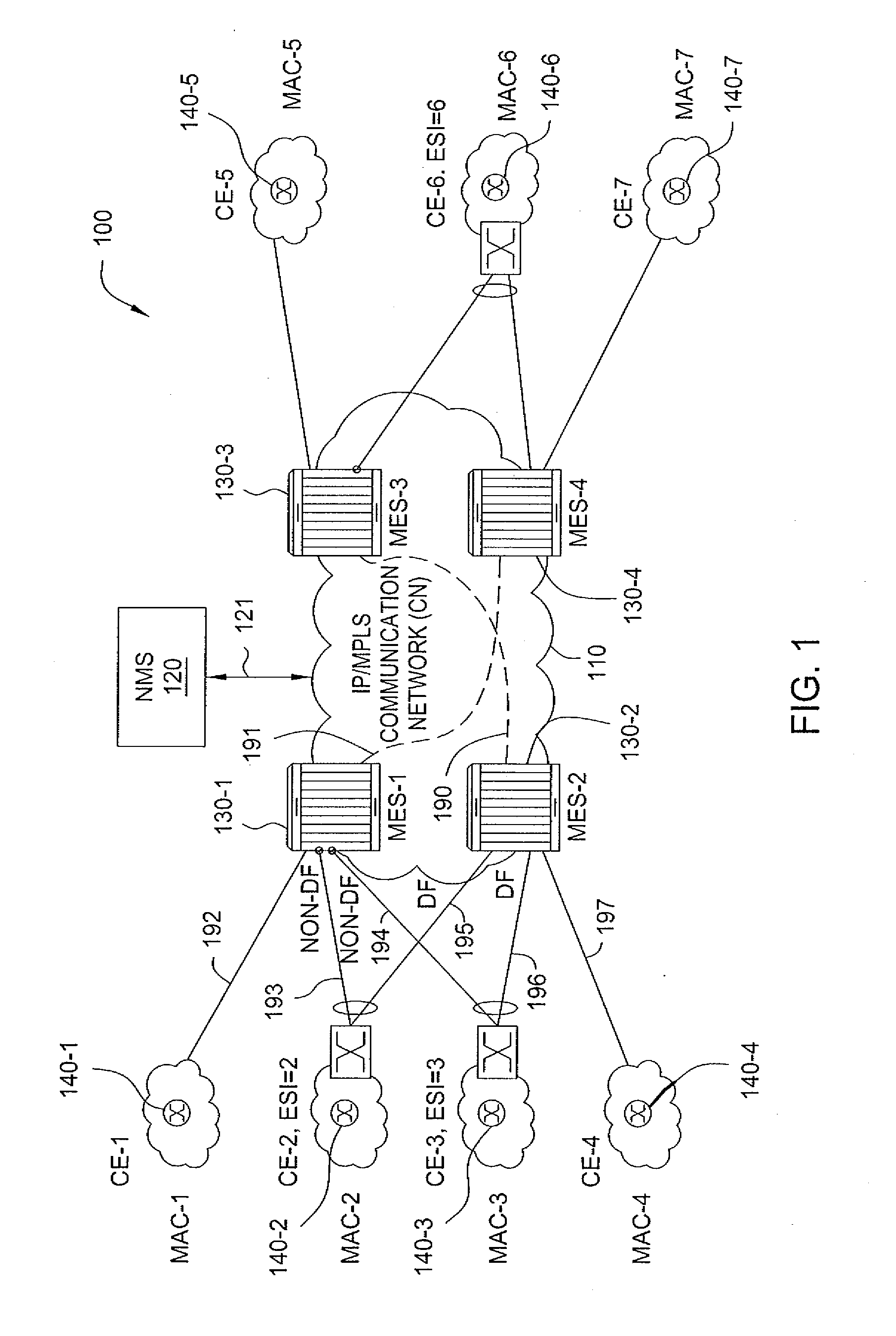
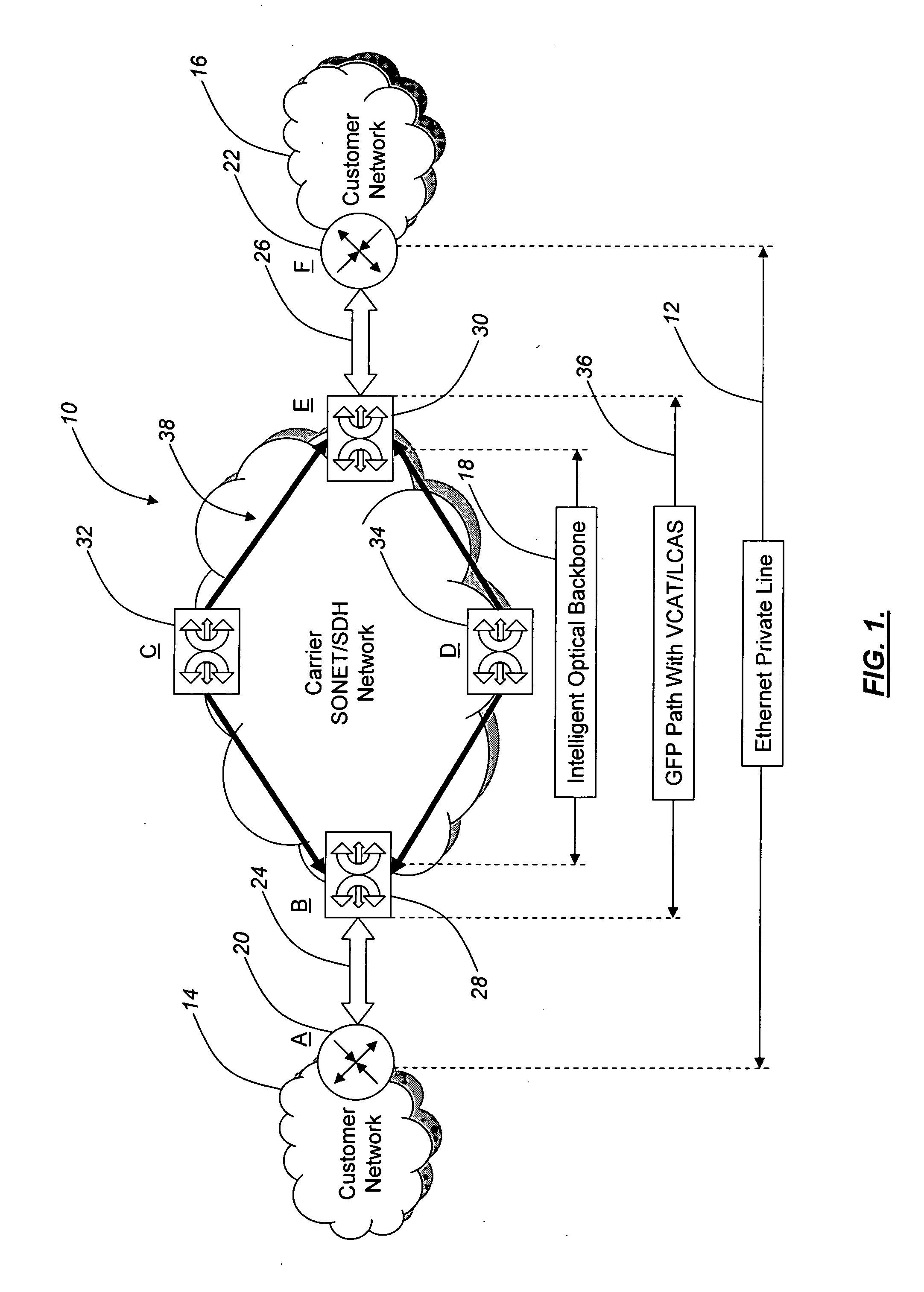
Source identification preservation in multiprotocol label switching networks
ActiveUS20140177638A1Simplify operating proceduresReduce complexityData switching by path configurationMultiprotocol Label SwitchingProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
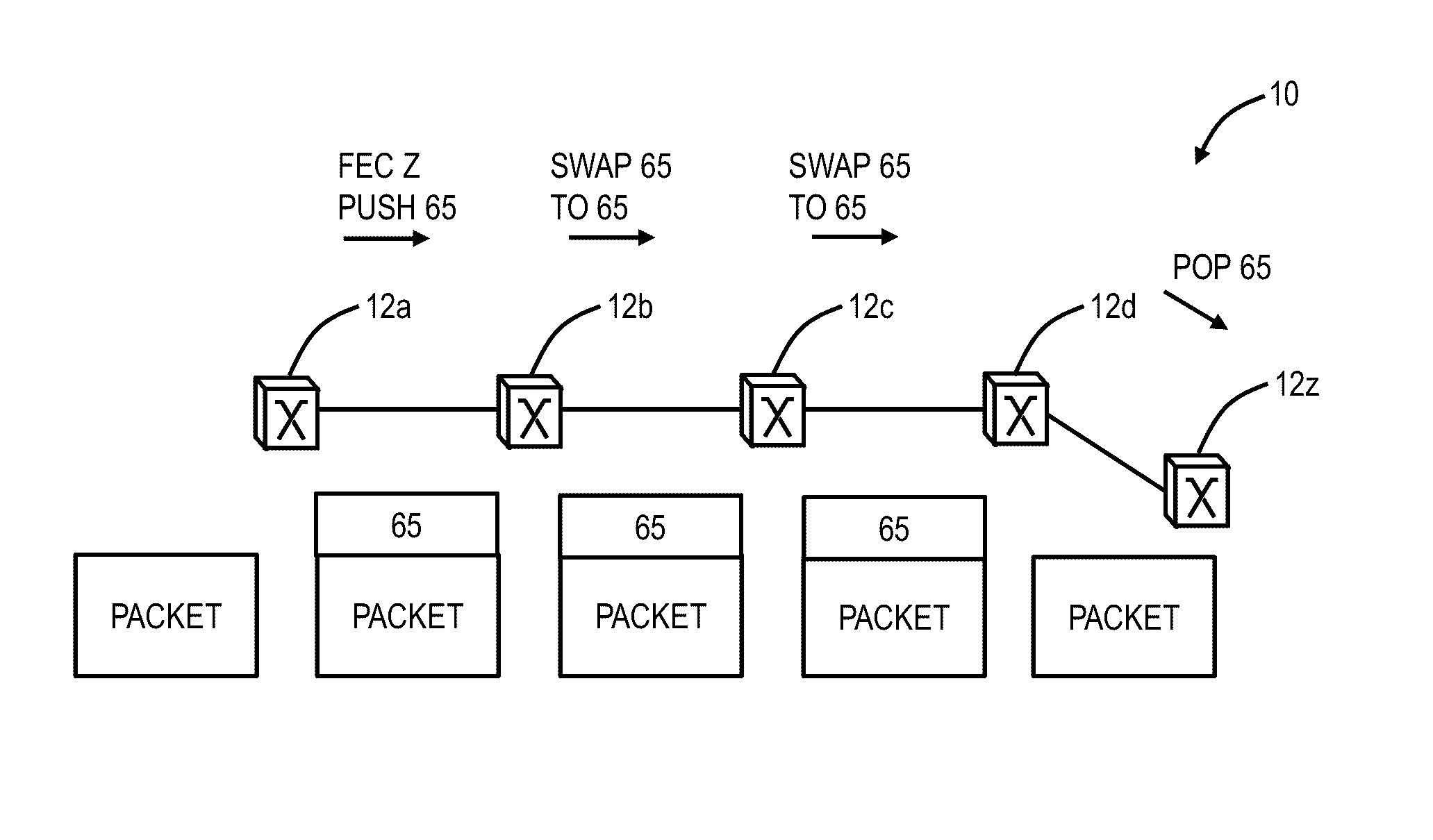
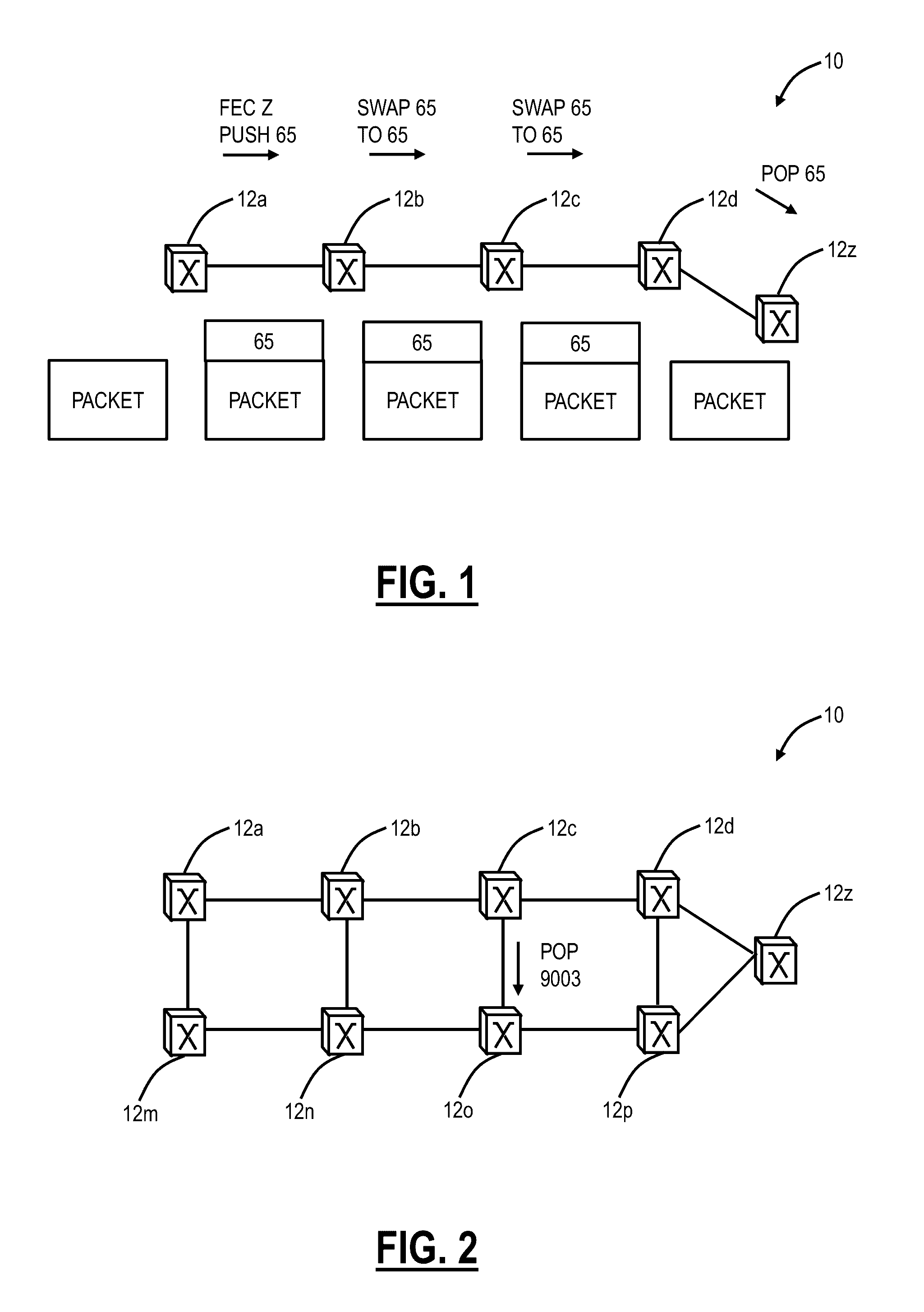
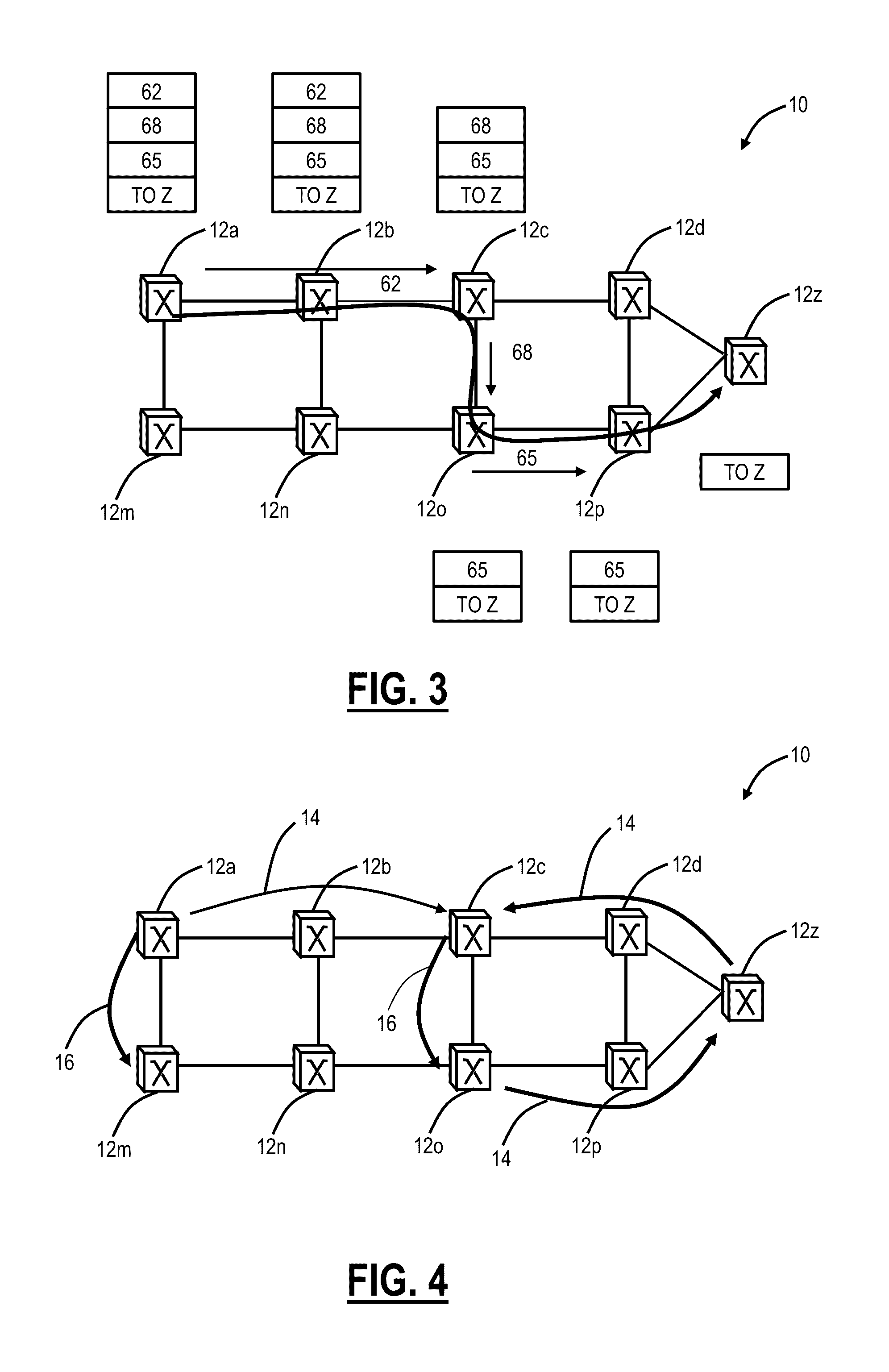
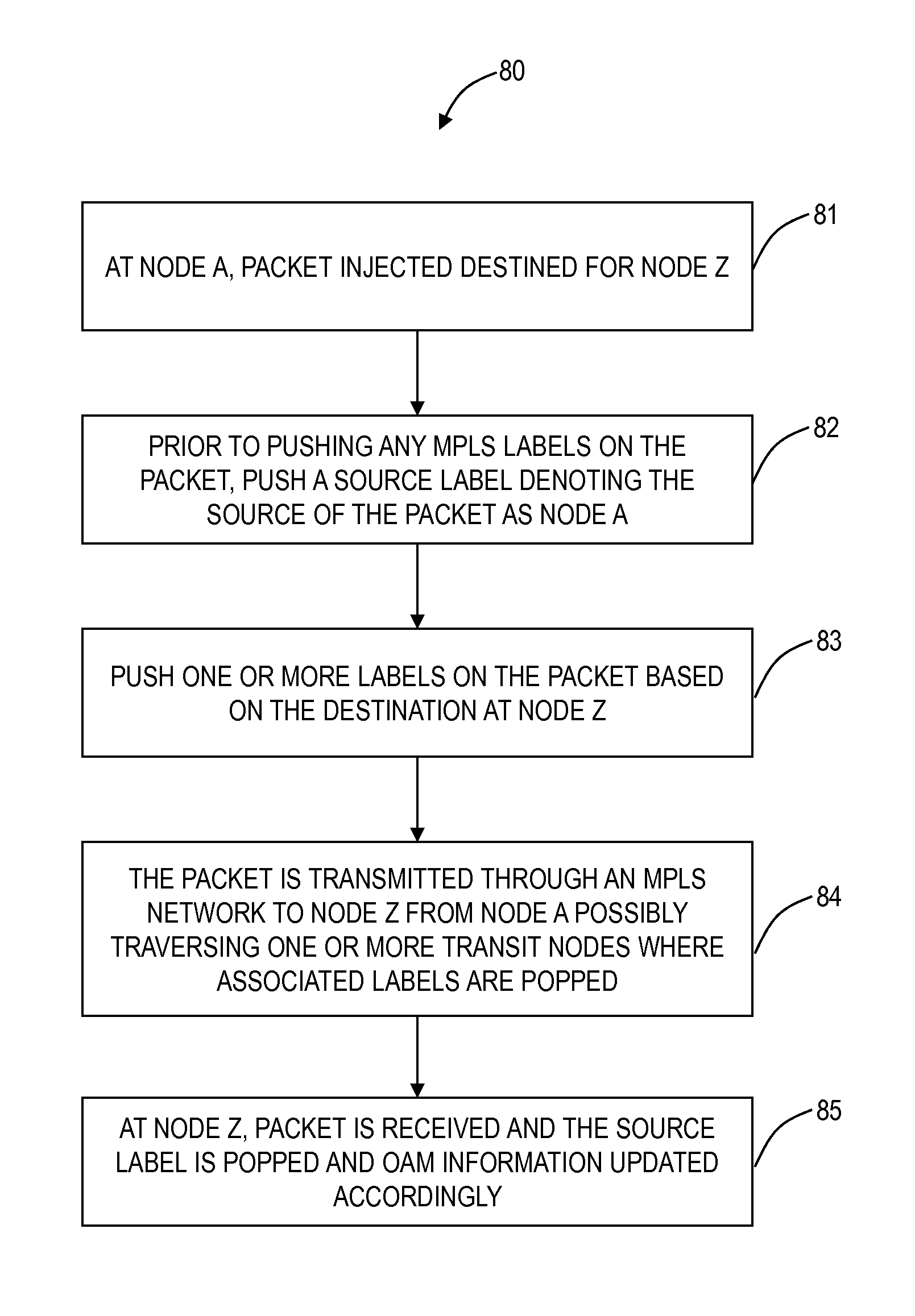
A Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) method, a MPLS network element, and a MPLS network include receiving a packet destined for a destination node at a source node in an MPLS network; pushing an identifier in an MPLS label on an MPLS label stack associated with the packet, wherein the identifier denotes the source node as the source of the packet and is pushed prior to any other MPLS labels on the MPLS stack; pushing one or more labels on the MPLS stack indicative of a route of the packet to the destination node; and transmitting the packet from the source node into the MPLS network. The identifier is located at the bottom of the MPLS stack thereby being a last item popped in the MPLS stack at the destination node, and the identifier can be used for updating OAM data efficiently without requiring deep packet inspection.
Owner:CIENA
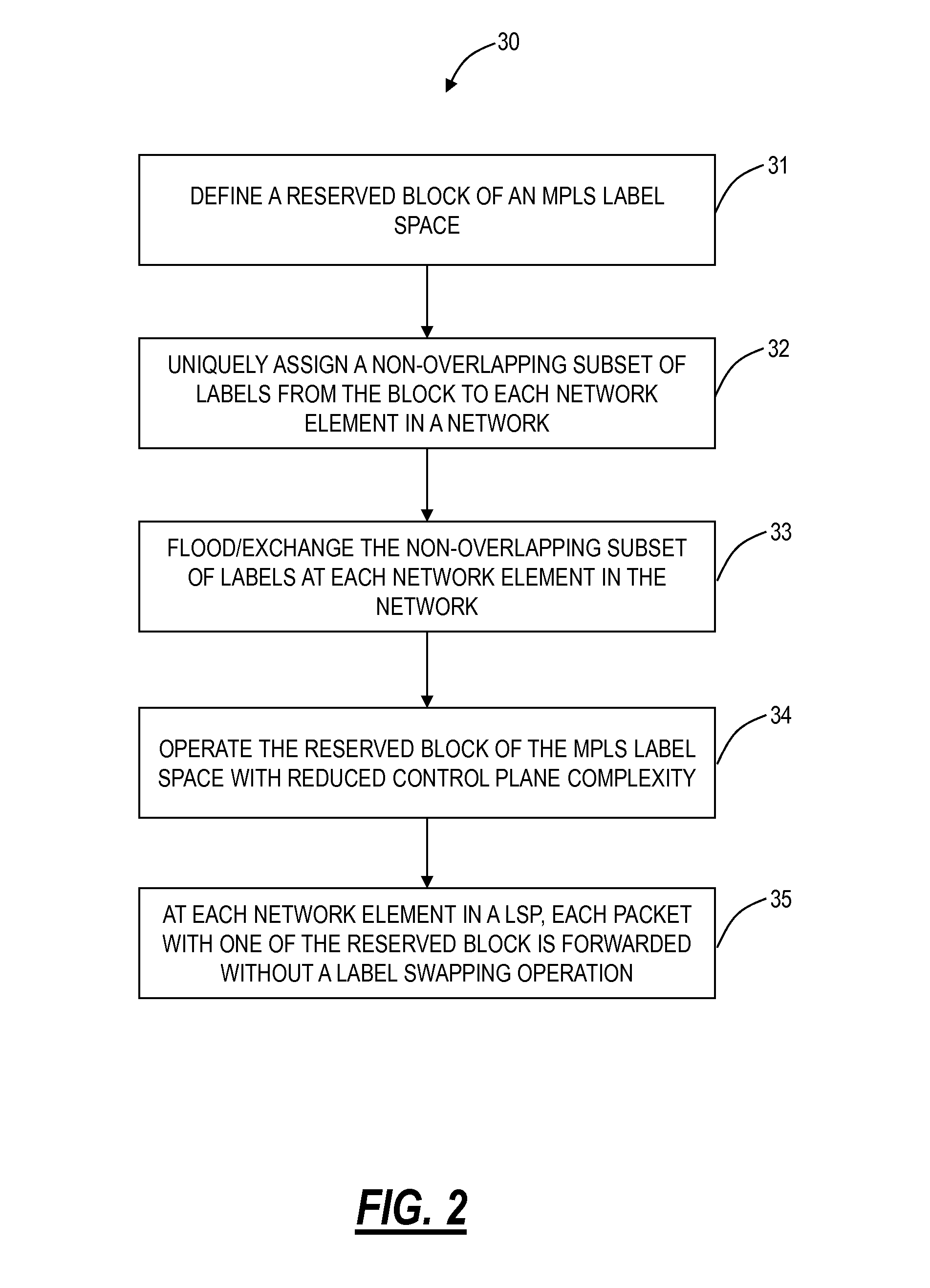
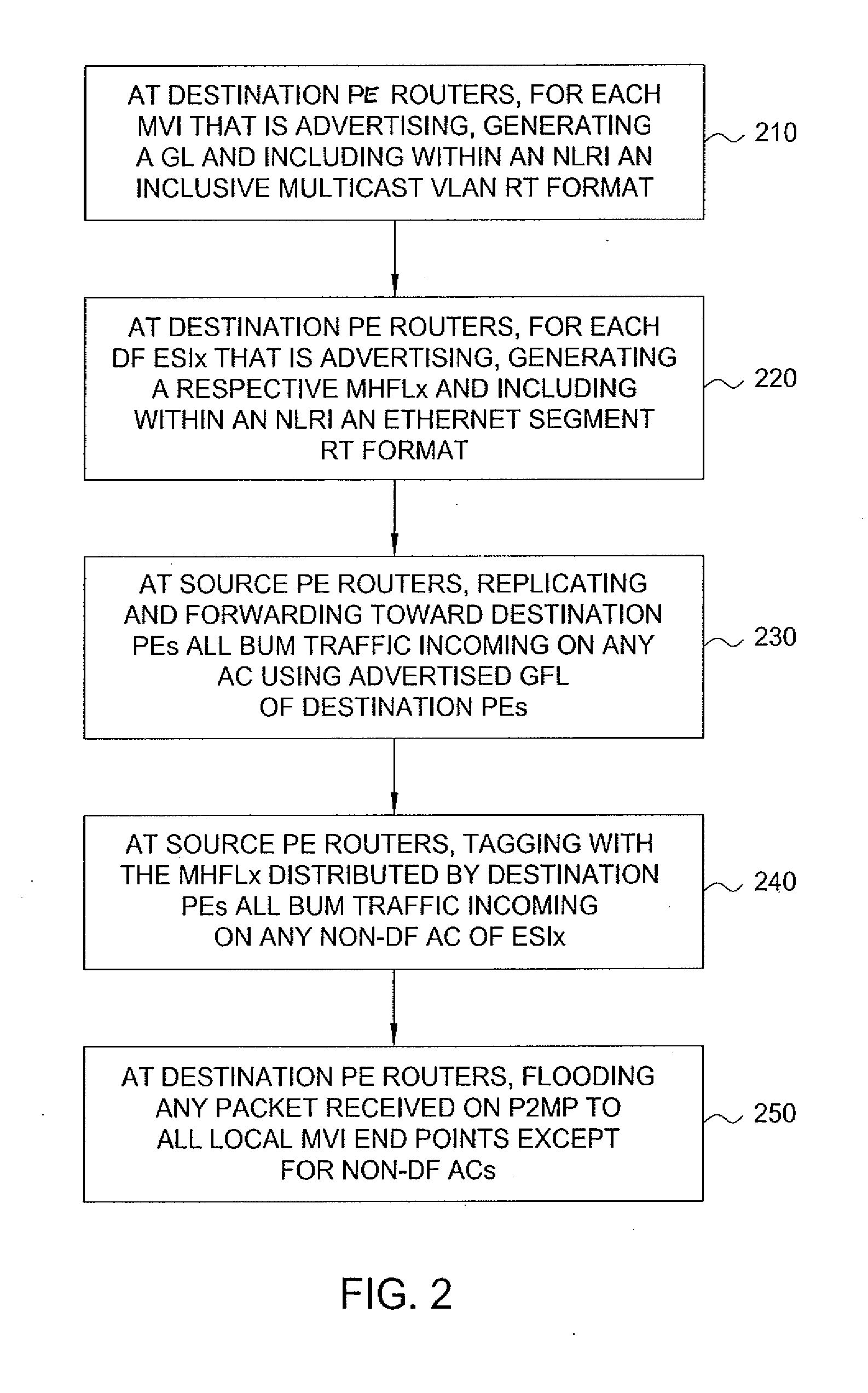
Method and apparatus for mpls label allocation for a bgp mac-vpn
ActiveUS20110286452A1Data switching by path configurationBorder Gateway ProtocolMultiprotocol Label Switching
The invention includes a method and apparatus for distributing flooding labels within a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) infrastructure supporting Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Media Access Control (MAC) Virtual Private Networking (VPN).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Boarder Gateway Protocol Signaling to Support a Very Large Number of Virtual Private Networks
InactiveUS20150003458A1Data switching switchboardsNetworks interconnectionBorder Gateway Protocol24-bit
Disclosed herein are example embodiments for Boarder Gateway Protocol (BGP) signaling in virtual private network (VPN) communications. For example, a first network element may encode Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) information in a Network Layer Reachability Information (NLRI) label field that is longer than 24 bits, and transmit a BGP update message comprising a BGP attribute to a second network element. The BGP attribute comprises the NLRI and a specific Subsequent Address Family Identifier (SAFI) value. The specific SAFI value signals to the second network element, upon reception of the BGP update message by the second network element, that the NLRI label field is more than 24 bits long.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Method and apparatus for multiprotocol switching and routing
InactiveUS6876654B1Low implementation costPartly effectiveTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionMultiprotocol Label SwitchingWire speed
A packet forwarding method and apparatus performs multiprotocol routing (for IP and IPX protocols) and switching. Incoming data packets are examined and the flow (i.e., source and destination addresses and source and destination socket numbers) with which they are associated is determined. A flow table contains forwarding information that can be applied to the flow. If an entry is not present in the table for the particular flow, the packet is forwarded to the CPU to be processed. The CPU can then update the table with new forwarding information to be applied to all future packets belonging to the same flow. When the forwarding information is already present in the table, packets can thus be forwarded at wire speed. A dedicated ASIC is preferably employed to contain the table, as well as the engine for examining the packets and forwarding them according to the stored information. Decision-making tasks are thus more efficiently partitioned between the switch and the CPU so as to minimize processing overhead.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Multicast systems and methods for segment routing
ActiveUS20170033939A1Special service provision for substationNetwork connectionsMultiprotocol Label SwitchingBroadcasting
Multicast systems and methods for Segment Routing include receiving, at a node, a multicast packet including an outer label comprising a Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) source node identifier defining a source-rooted broadcast tree and an inner label including a service identifier defining a service specific multicast tree; responsive to the node including a branch point on the source-rooted broadcast tree, popping the outer label, analyzing the inner label to identify active egress ports, pushing back the outer label, and forwarding the multicast packet to the active egress ports; and responsive to the node including point-to-point transit for the source-rooted broadcast tree, forwarding the multicast packet on the source-rooted broadcast tree.
Owner:CIENA
Device and method for handling MPLS labels
InactiveUS20050125490A1Data switching networksMemory systemsComputer hardwareMultiprotocol Label Switching
A device and method for handling Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) label stacks. An incoming label mapping (ILM) table is stored in a first memory. A received packet's label stack is accessed, and an entry corresponding to a top label of the stack is read from the ILM table. A number of other entries are also read from the ILM table, and these other entries are cached in a second memory.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Defining a static path through a communications network to provide wiretap law compliance
InactiveUS20060018255A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsEnforcementMultiprotocol Label Switching
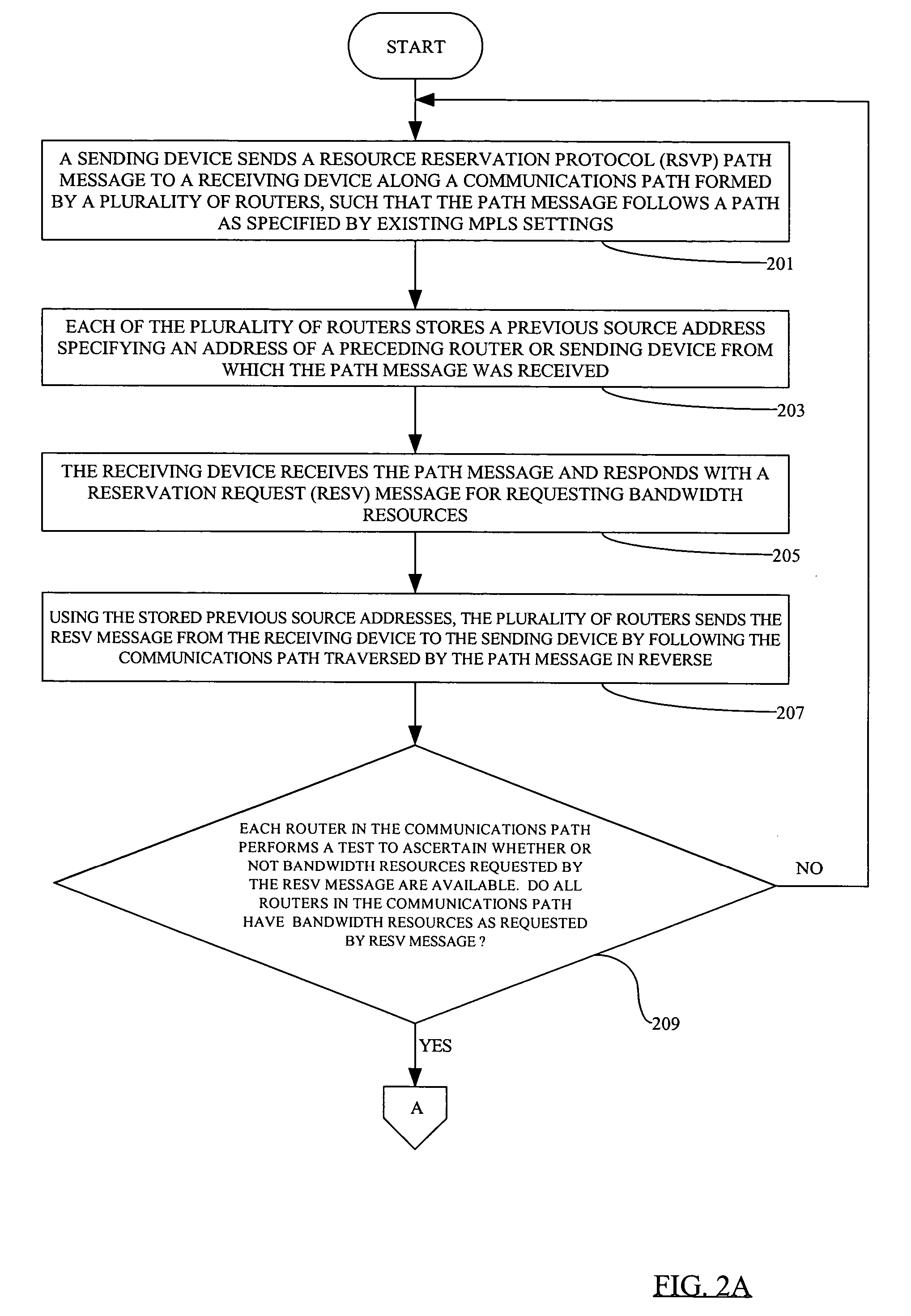
By defining a static path through a communications network for a call placed by an IP-based telephonic device, stream of packets representing the call are rendered available for wiretapping on a communications network that includes a first and a second switching / routing element. The static path is defined using Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) and Resource Reservation Protocol (RSVP). The first switching / routing element responds to a call initiation request received from the telephonic device by sending an RSVP PATH message to the second switching / routing element. The first switching / routing element marks packets sent by the telephonic device with an identical MPLS Forwarding Equivalence Class (FEC) label, so that the plurality of packets will traverse a predesignated IP address in the communications path, and so as to allow law enforcement officials to monitor packets originating from an IP-based telephonic device using a monitoring mechanism situated at the predesignated IP address.
Owner:AVAYA INC
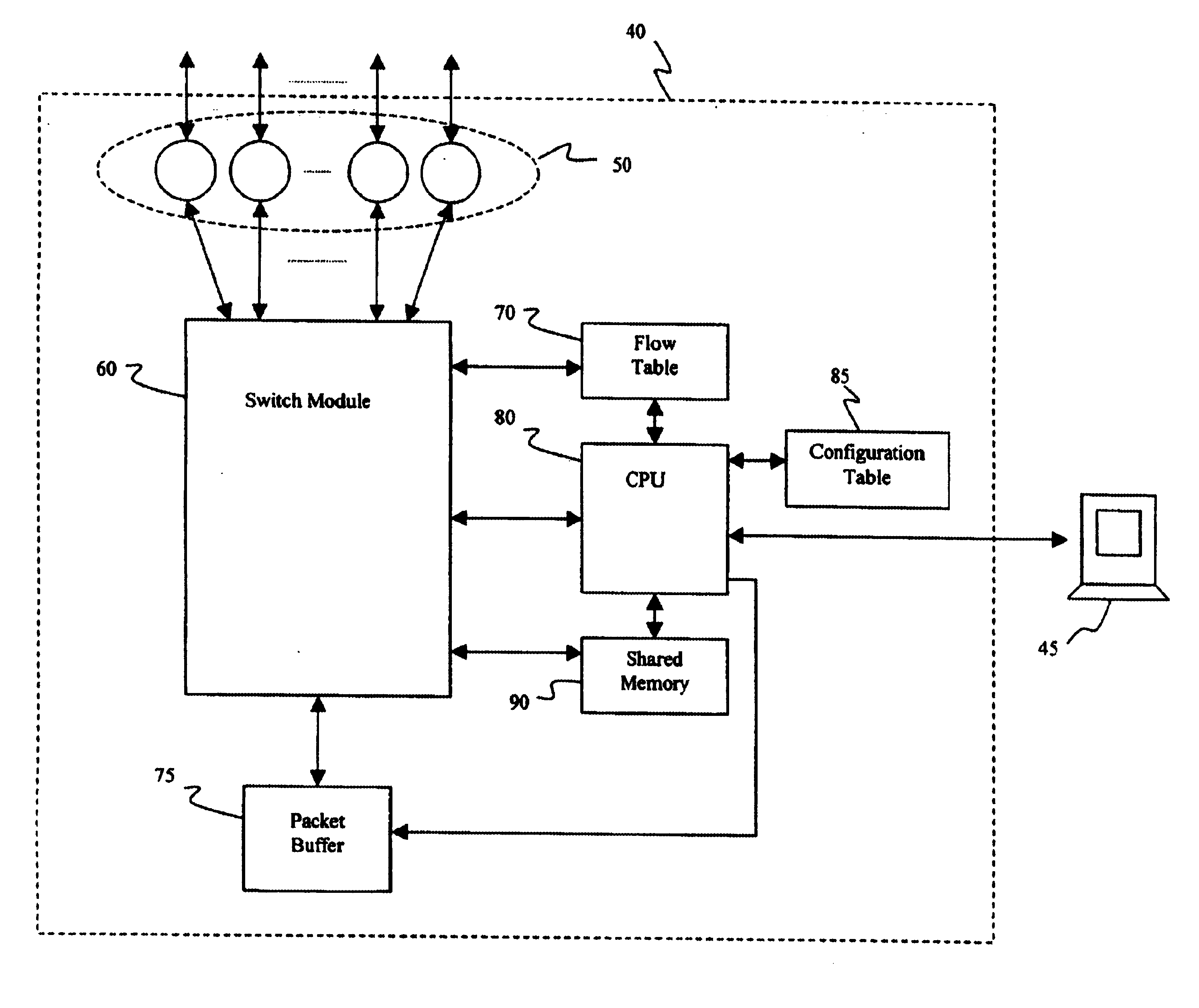
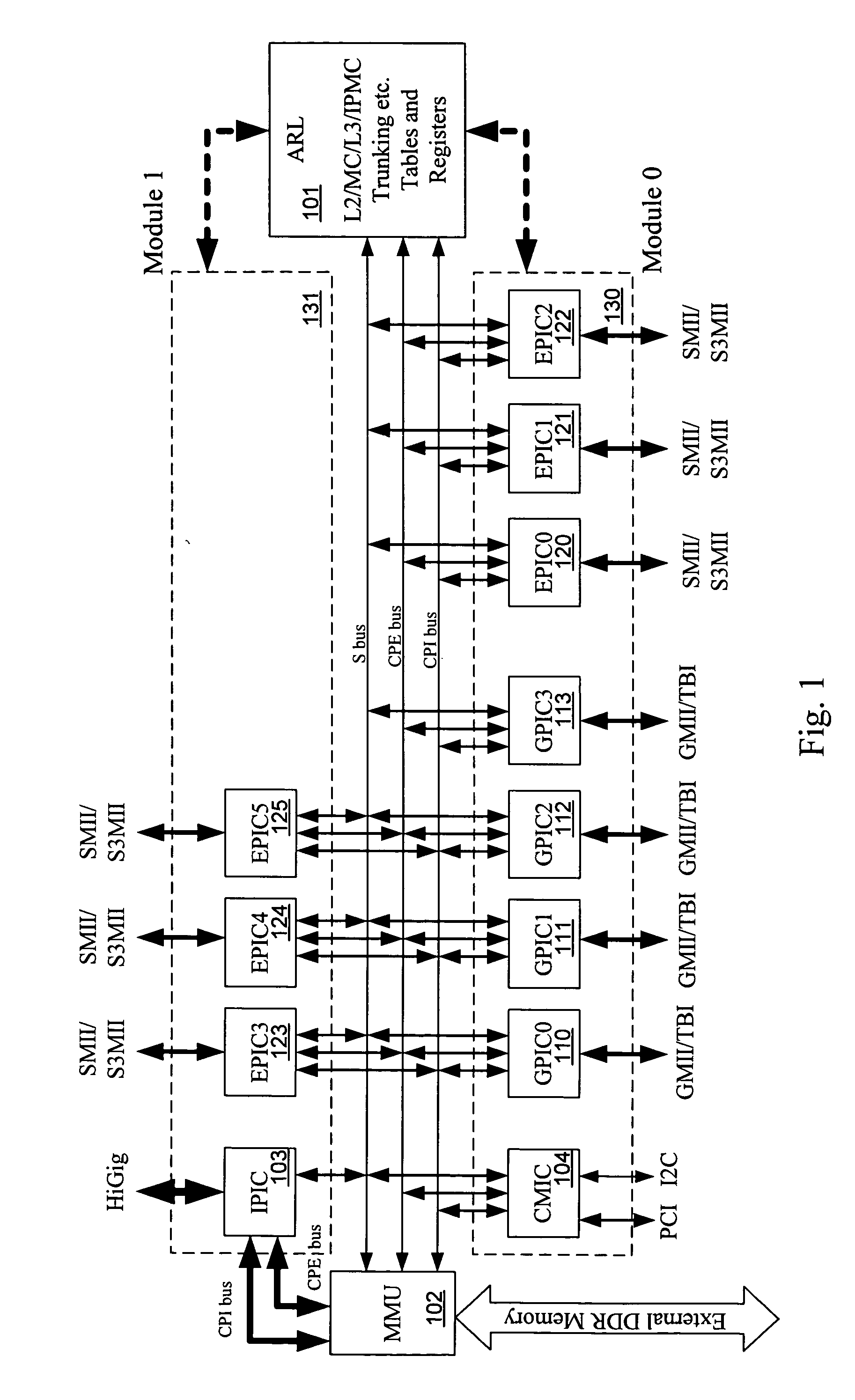
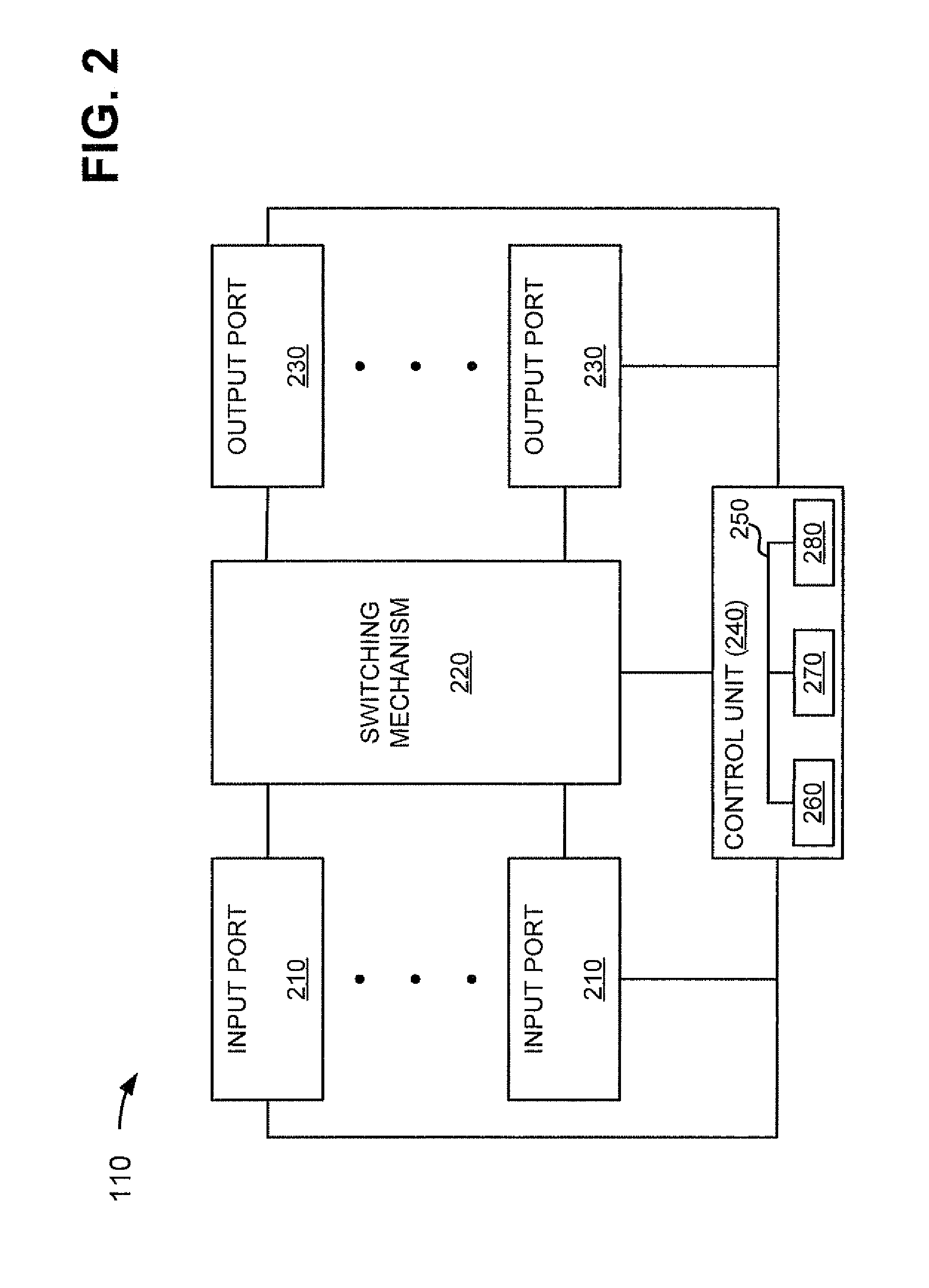
Distributed control of data flow in a network switch
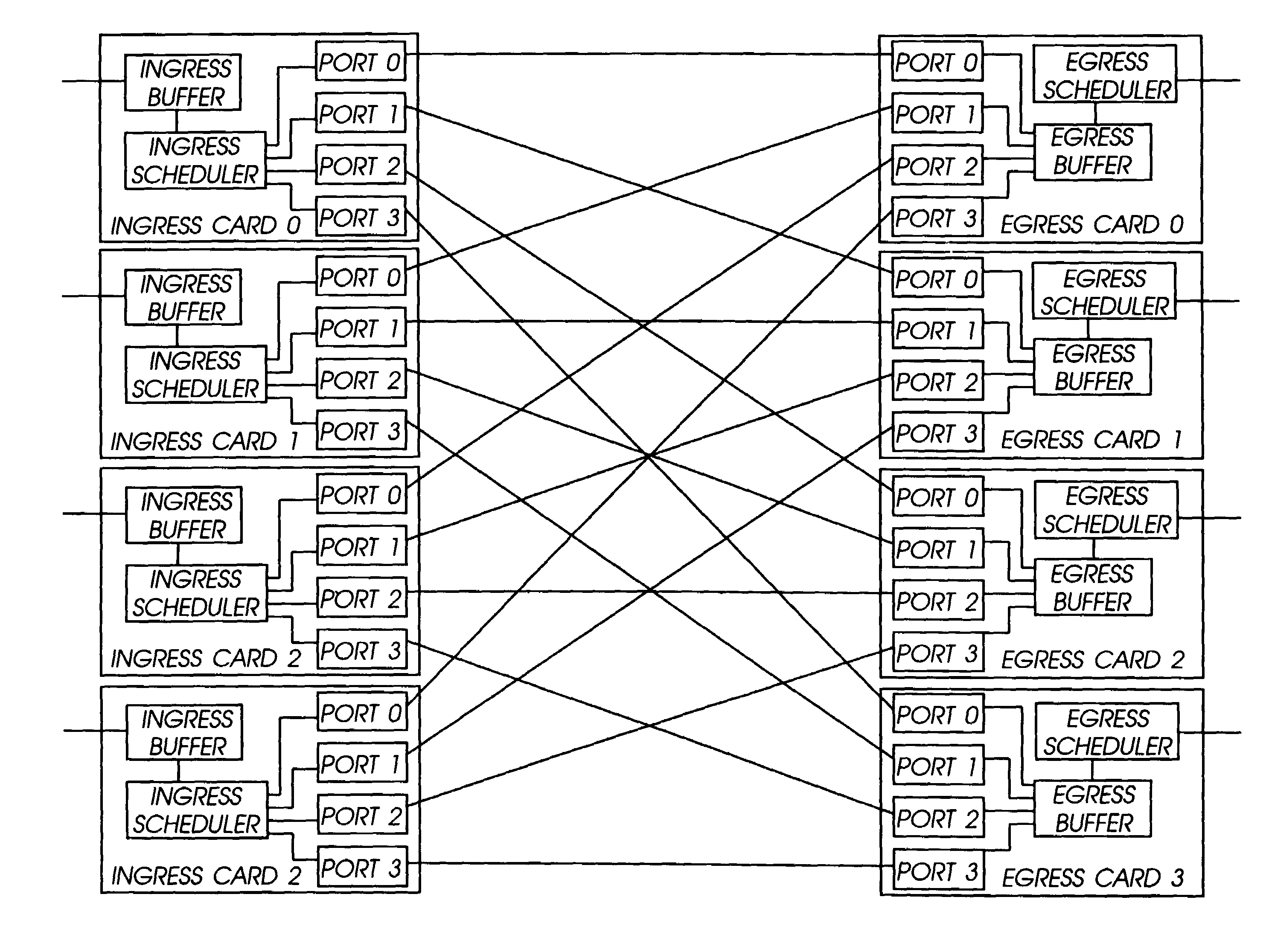
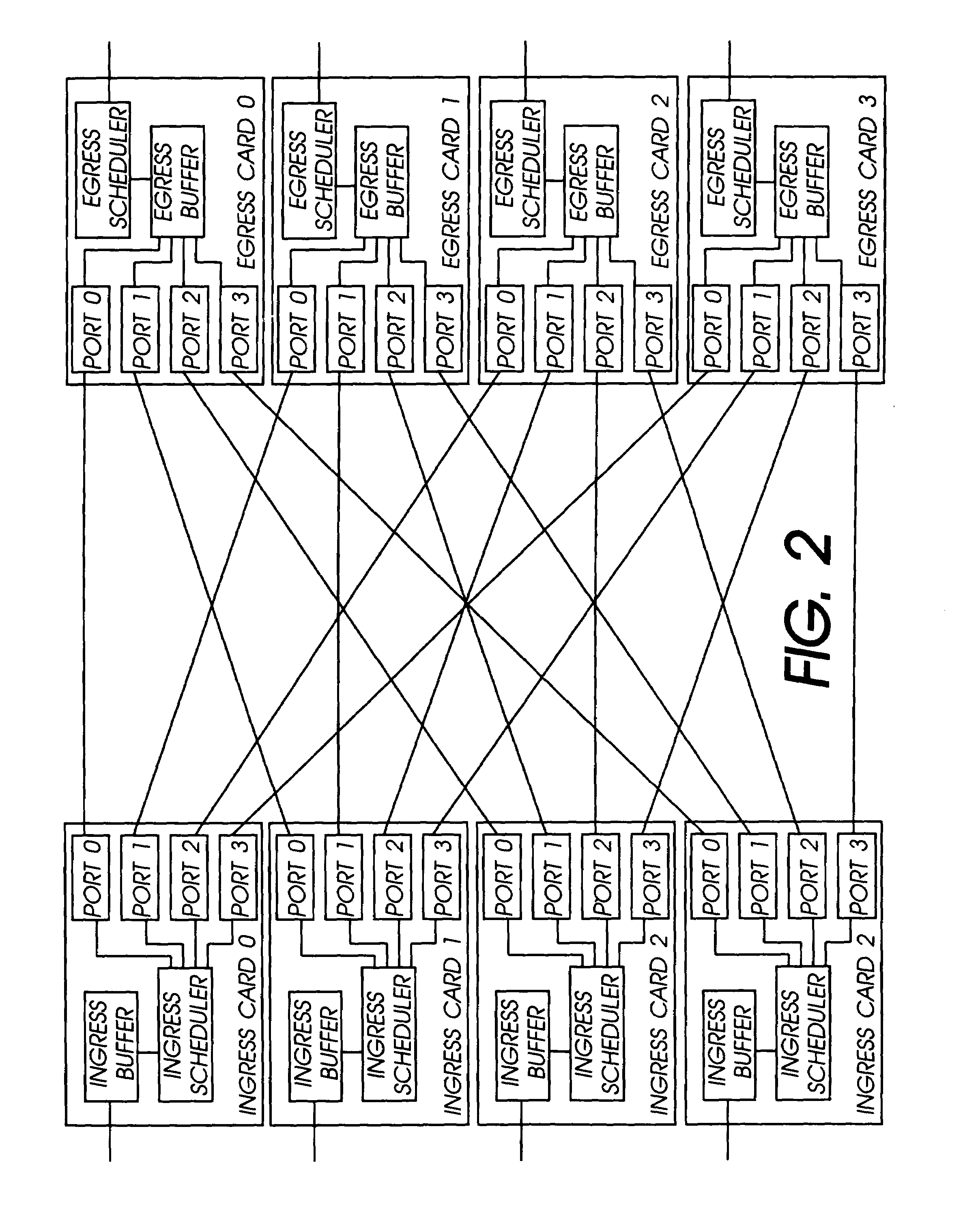
The network switch described herein provides a cell / packet switching architecture that switches between line interface cards across a meshed backplane. In one embodiment, the switching can be accomplished at, or near, line speed in a protocol independent manner. The protocol independent switching provides support for various applications including Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) switching, Internet Protocol (IP) switching, Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) switching, Ethernet switching and frame relay switching. The architecture allows the network switch to provision service on a per port basis. In one embodiment, the network switch provides a non-blocking topology with both input and output queuing and per flow queuing at both ingress and egress. Per flow flow-control can be provided between ingress and egress scheduling. Strict priority, round robin, weighted round robin and earliest deadline first scheduling can be provided.
Owner:FORCE10
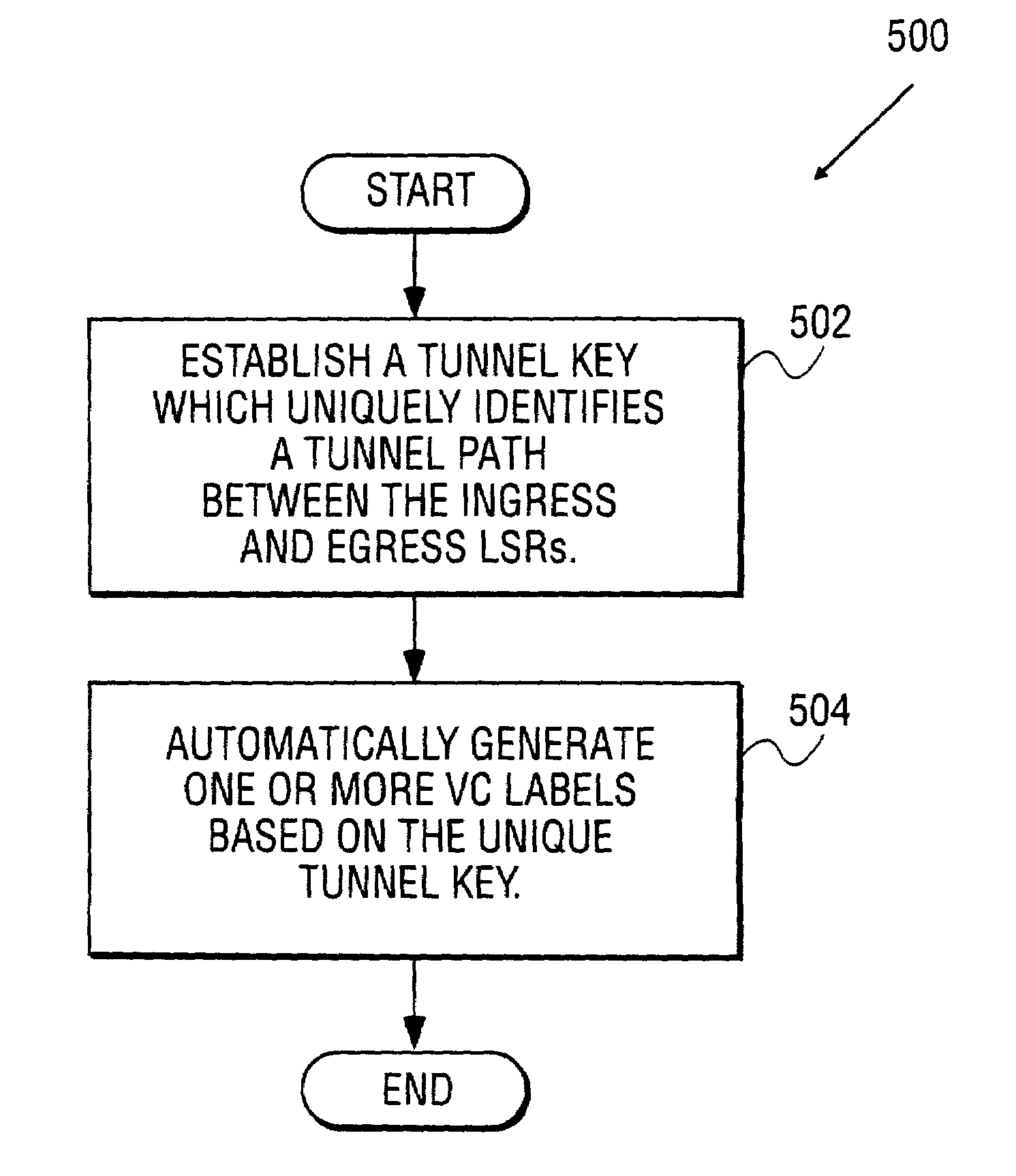
Method and system for assigning multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) VC (VC) labels when transporting asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) data over MPLS network
A first and a second switching node establish a tunnel to transport a packet through a multiprotocol label-switching (MPLS) network. The tunnel is associated with a unique tunnel key. One or more virtual ciruit (VC) labels are automatically generated using the tunnel key.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
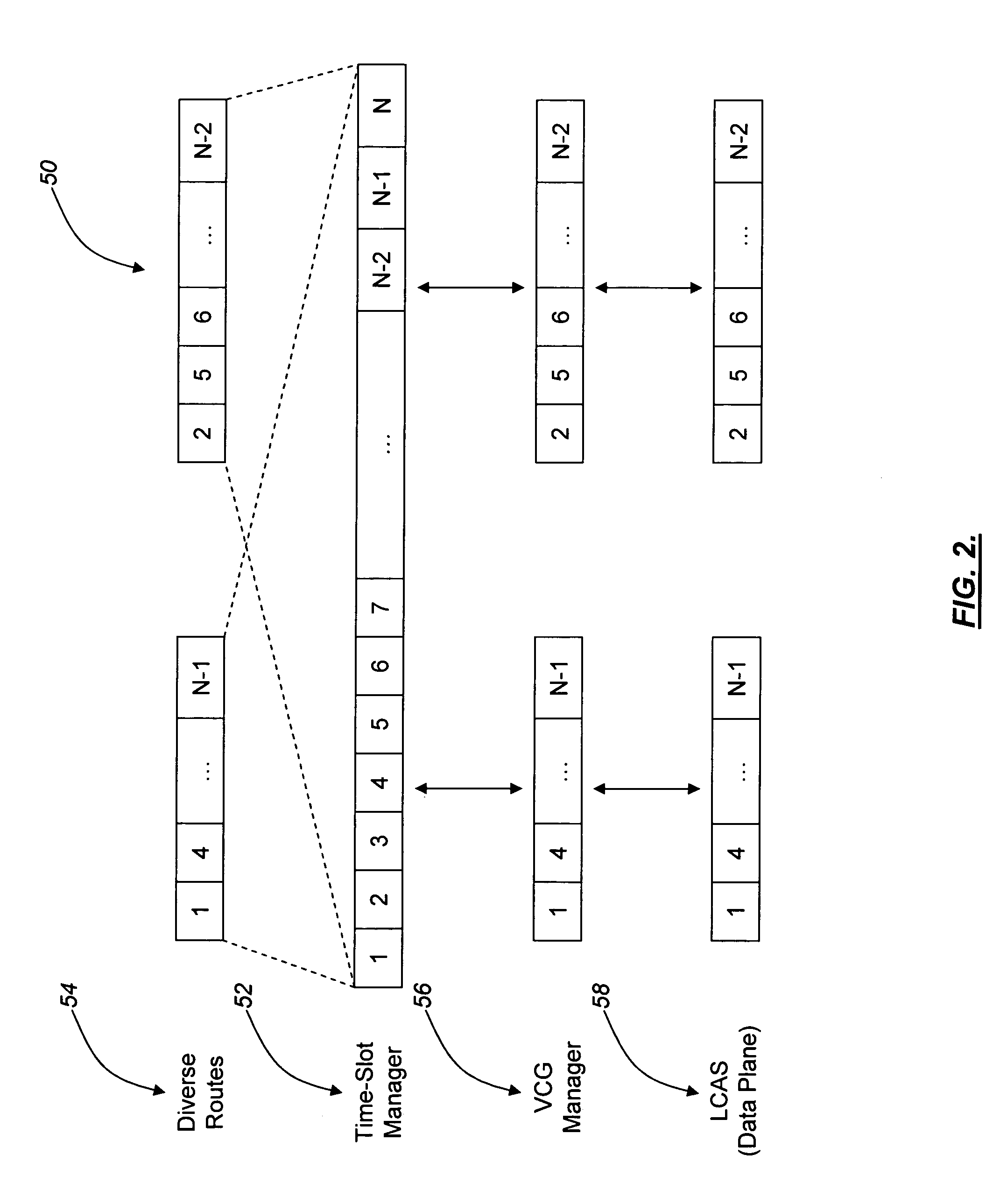
Method and apparatus for interfacing applications to LCAS for efficient SONET traffic flow control
InactiveUS20060018324A1Efficient interfaceError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMultiprotocol Label SwitchingCross connection
The present invention provides methods and apparatuses for interfacing high-layer applications to Link Capacity Adjustment Scheme (LCAS) on Synchronous Optical Network / Synchronous Digital Hierarchy (SONET / SDH) edge nodes. These applications include high-level control protocols, such as Generalized Multiprotocol Label Switching (GMPLS) and Optical Switching and Routing Protocol (OSRP), and user-initiated cross-connect creation and termination. The present invention provides a mechanism that is capable of mapping SONET / SDH connections to Virtual Concatenated Groups (VCGs), thus enabling an efficient interface for operators to control and manage the connections via LCAS. As part of the mechanism, the existing LCAS protocol state machine is enhanced such that the operators can shut down bi-directional SONET / SDH flows from a single edge node, as opposed to from both source and sink nodes, as provided for by existing specifications.
Owner:CIENA
Source identification preservation in multiprotocol label switching networks
ActiveUS9094337B2Simplify operating proceduresReduce complexityData switching networksMultiprotocol Label SwitchingReal-time computing
A Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) method, a MPLS network element, and a MPLS network include receiving a packet destined for a destination node at a source node in an MPLS network; pushing an identifier in an MPLS label on an MPLS label stack associated with the packet, wherein the identifier denotes the source node as the source of the packet and is pushed prior to any other MPLS labels on the MPLS stack; pushing one or more labels on the MPLS stack indicative of a route of the packet to the destination node; and transmitting the packet from the source node into the MPLS network. The identifier is located at the bottom of the MPLS stack thereby being a last item popped in the MPLS stack at the destination node, and the identifier can be used for updating OAM data efficiently without requiring deep packet inspection.
Owner:CIENA
Detection method and device of service path
ActiveCN102437931AImprove fault location efficiencyLow technical requirementsData switching networksMultiprotocol Label SwitchingInternet Protocol
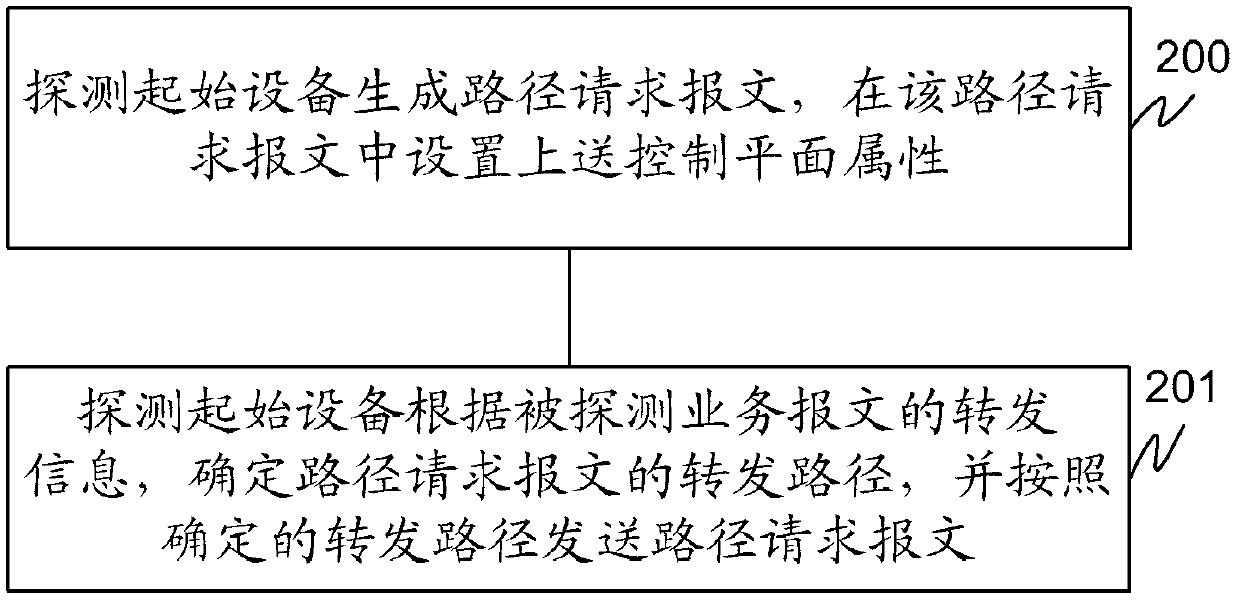
The invention discloses a detection method and device of a service path. The method comprises the following steps of: generating a path request message by a detection starting device; configuring an upper control panel attribute in the path request message, wherein forwarded information of a detected service message is carried by the path request message; according to the forwarded information of the detected service message, determining a forwarding path of the path request message by the detection starting device and sending the path request message according to the determined forwarding path. By realizing the technical scheme provided by the invention, the path of the path request message is the same as an actual path of the detected service message, so that the technical problem in the existing scheme that the actual service path cannot be obtained in a multi-service loading network is solved, the fault location efficiency of an IP / MPLS (Internet Protocol / Multiprotocol Label Switch) loading network is improved and the technical requirements on operation and maintenance personnel are reduced.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) edge service extraction
ActiveUS7411904B2Flexible and efficient networkError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityMultiprotocol Label Switching
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
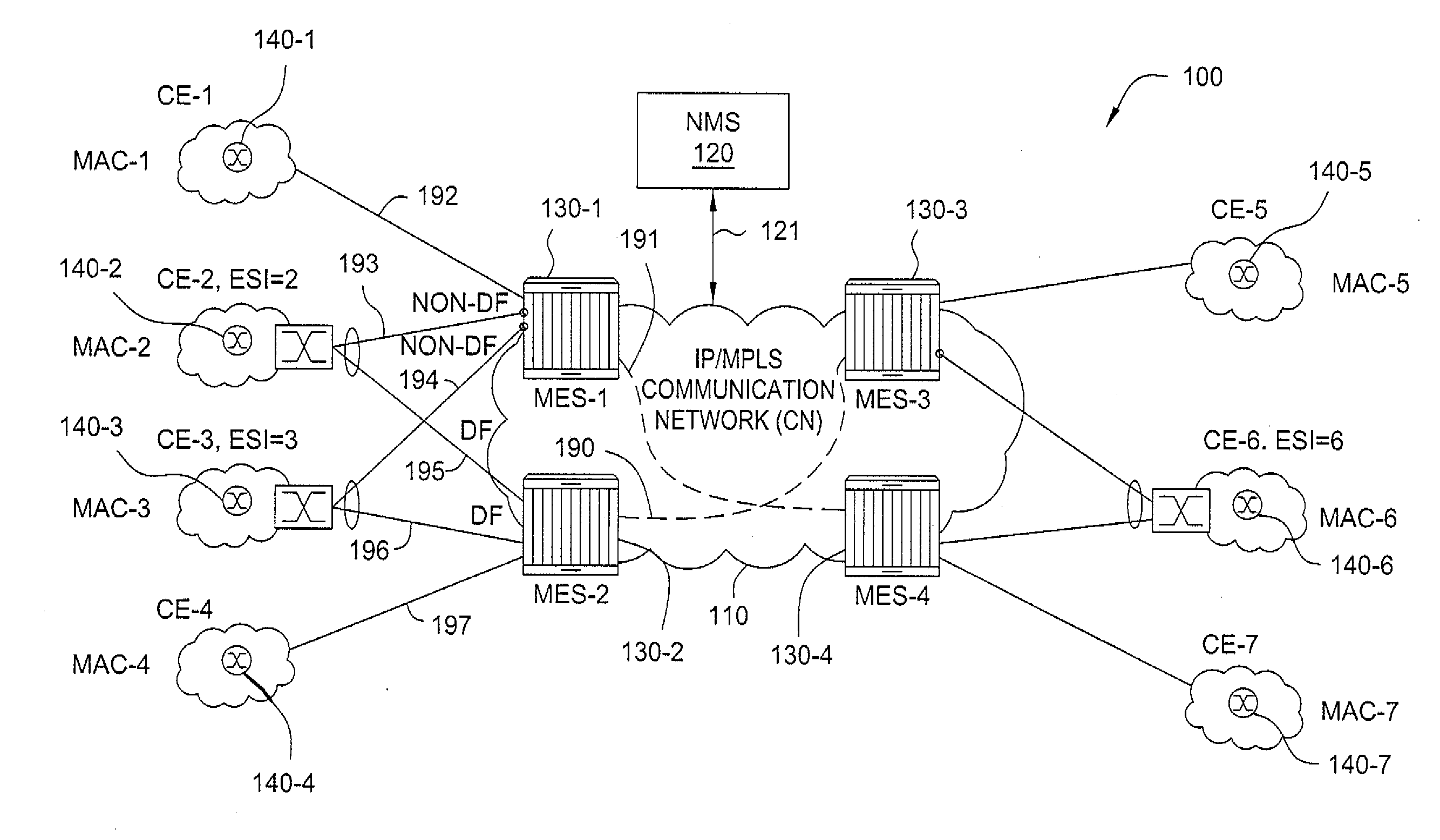
Method and system for realizing multicast protection
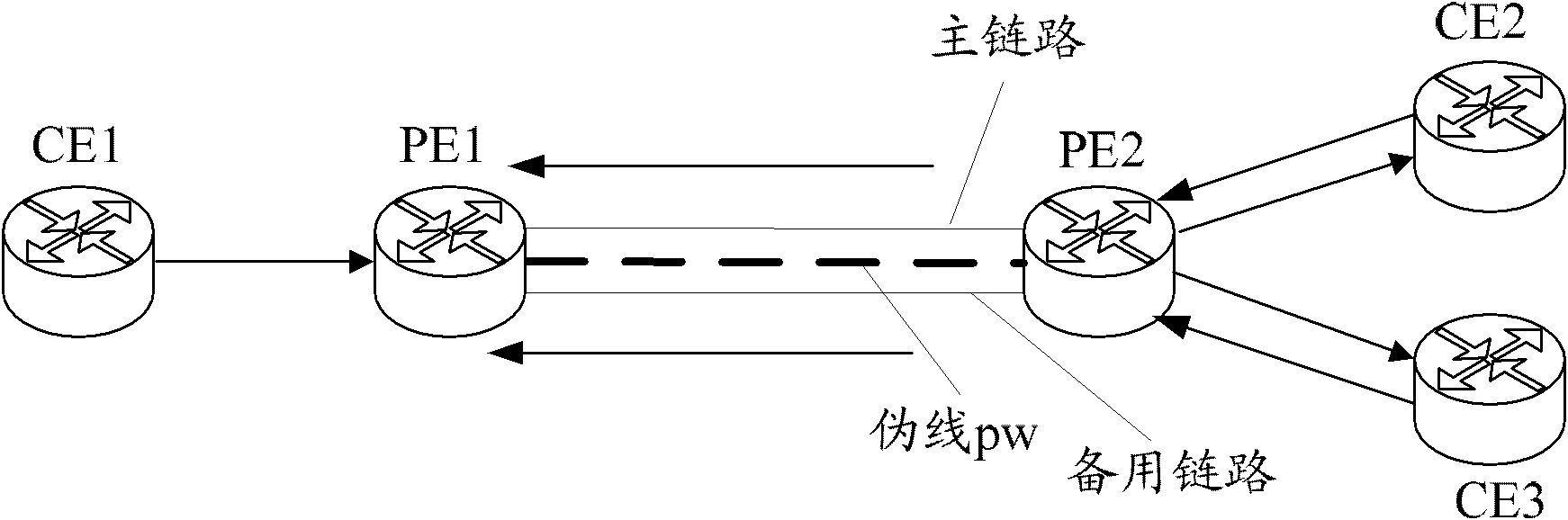
ActiveCN102025541AQuick switchMeet protection switching requirementsSpecial service provision for substationMultiprotocol Label SwitchingPseudo-wire
The invention discloses a method for realizing multicast protection. The method comprises the following steps: a main link and a backup link are configured for a PW (pseudo wire) between uplink PE (provider edge) and downlink PE; the downlink PE and the uplink PE establish a T-MPLS (transmission-multiprotocol label switching) multicast forwarding table respectively; the uplink PE sends an acquired multicast data message to the downlink PE through the master / slave links simultaneously; the downlink PE forwards the multicast data message received from the main link to corresponding CE (customer edge) according to the T-MPLS multicast forwarding table, and discards the multicast data message received from the backup link; and when the main link fails, the main link is switched to the backup link, and the downlink PE forwards the multicast data message received from the backup link to the CE. The invention also provides a system for realizing multicast protection. Through the technical scheme of the invention, normal transmission of multicast services can be guaranteed when a link in the T-MPLS network fails.
Owner:ZTE CORP
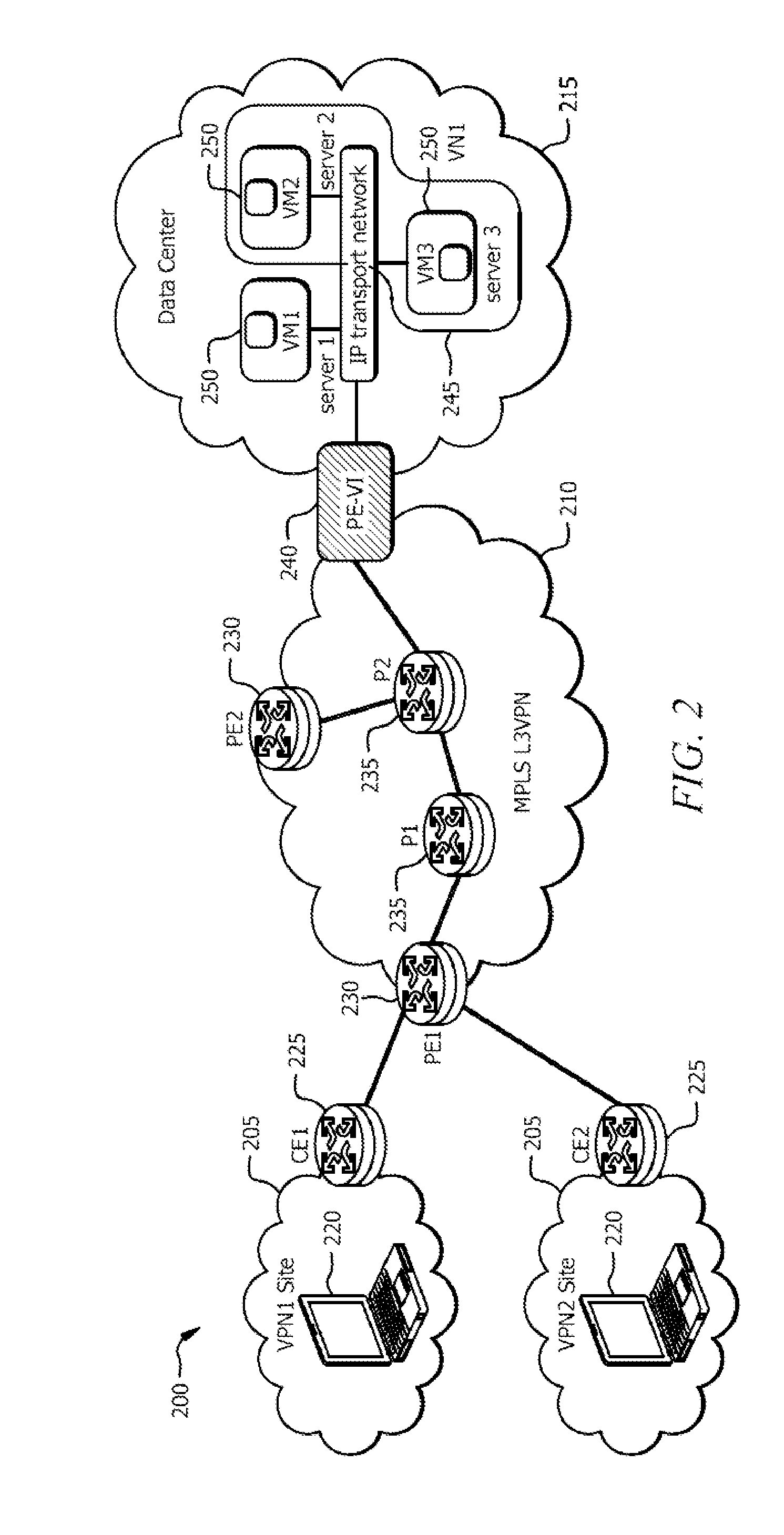
Multiprotocol label switching routers
InactiveUS6885677B1Equipment is cheapMinimize complexityTime-division multiplexData switching networksMultiprotocol Label SwitchingGeneral purpose computer
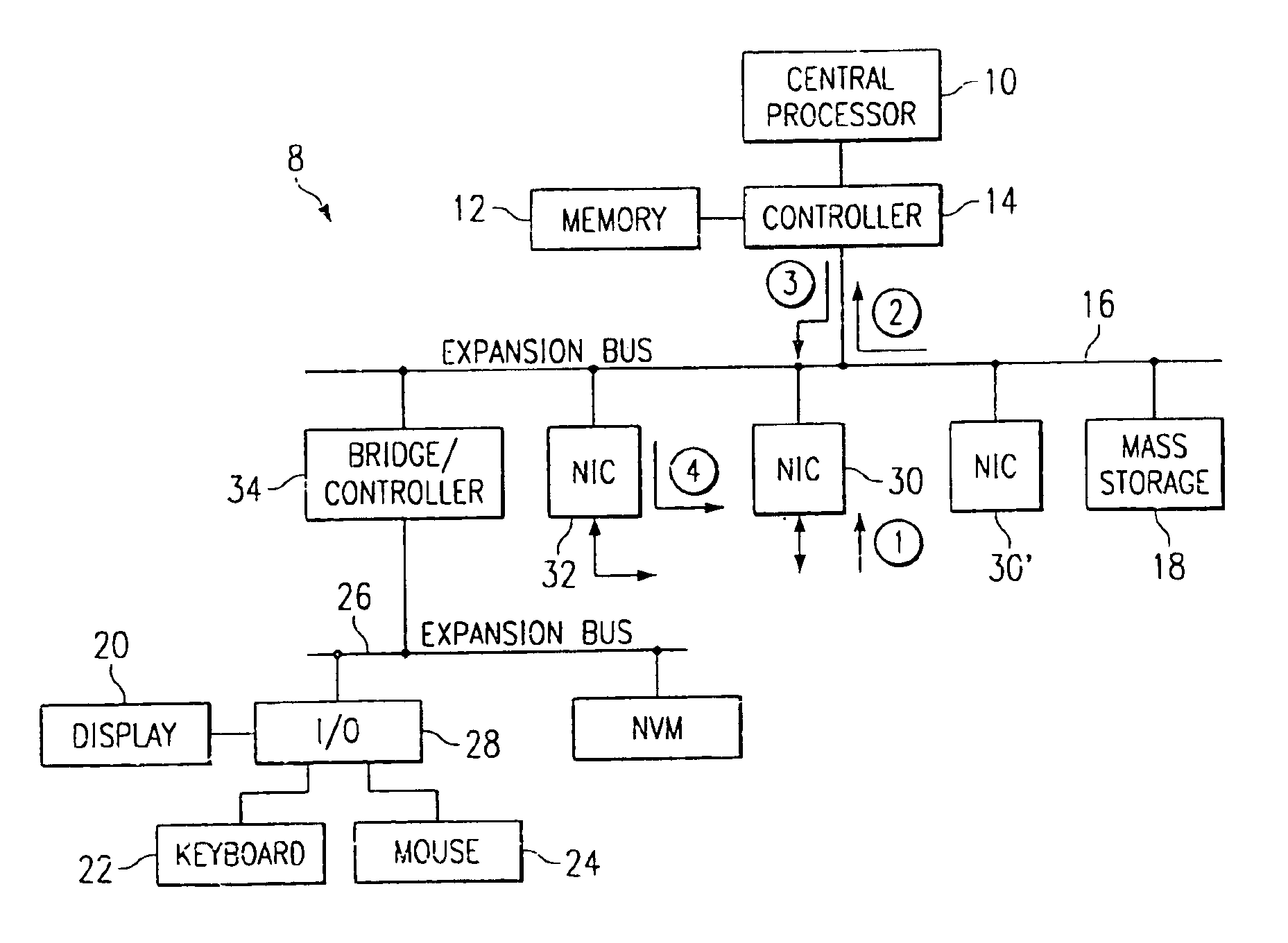
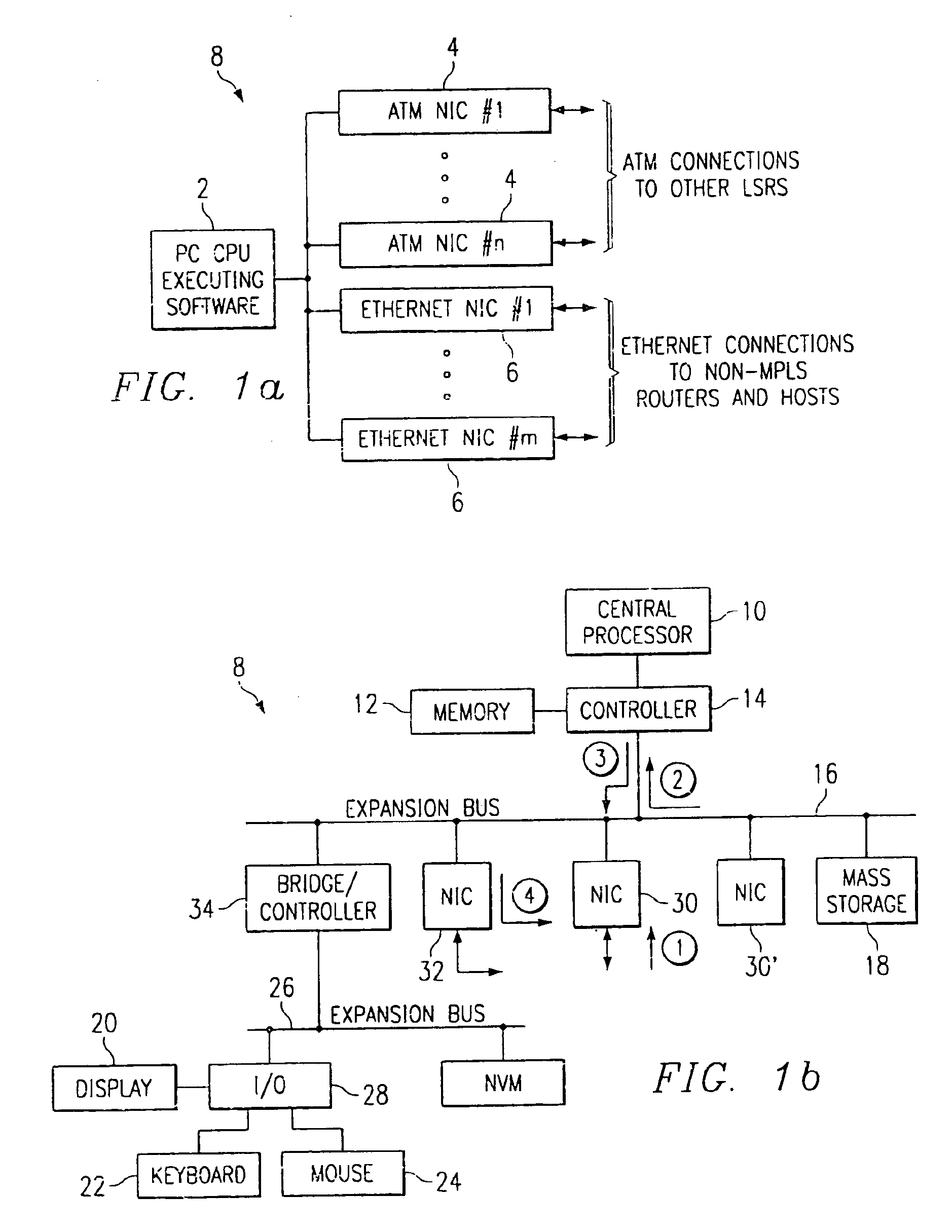
In one aspect, a method of using a general purpose computer 8 as an MPLS-enabled label switched router includes executing software on the general purpose computer 8 that allows it to communicate with other label switched routers using label distribution protocol. The general purpose computer 8 includes a central processor 10, a memory 12, network interface cards 30 and 32 and also typically includes local I / O such as a keyboard 22, a mouse 24 and a display device 20 for communicating with a local user.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
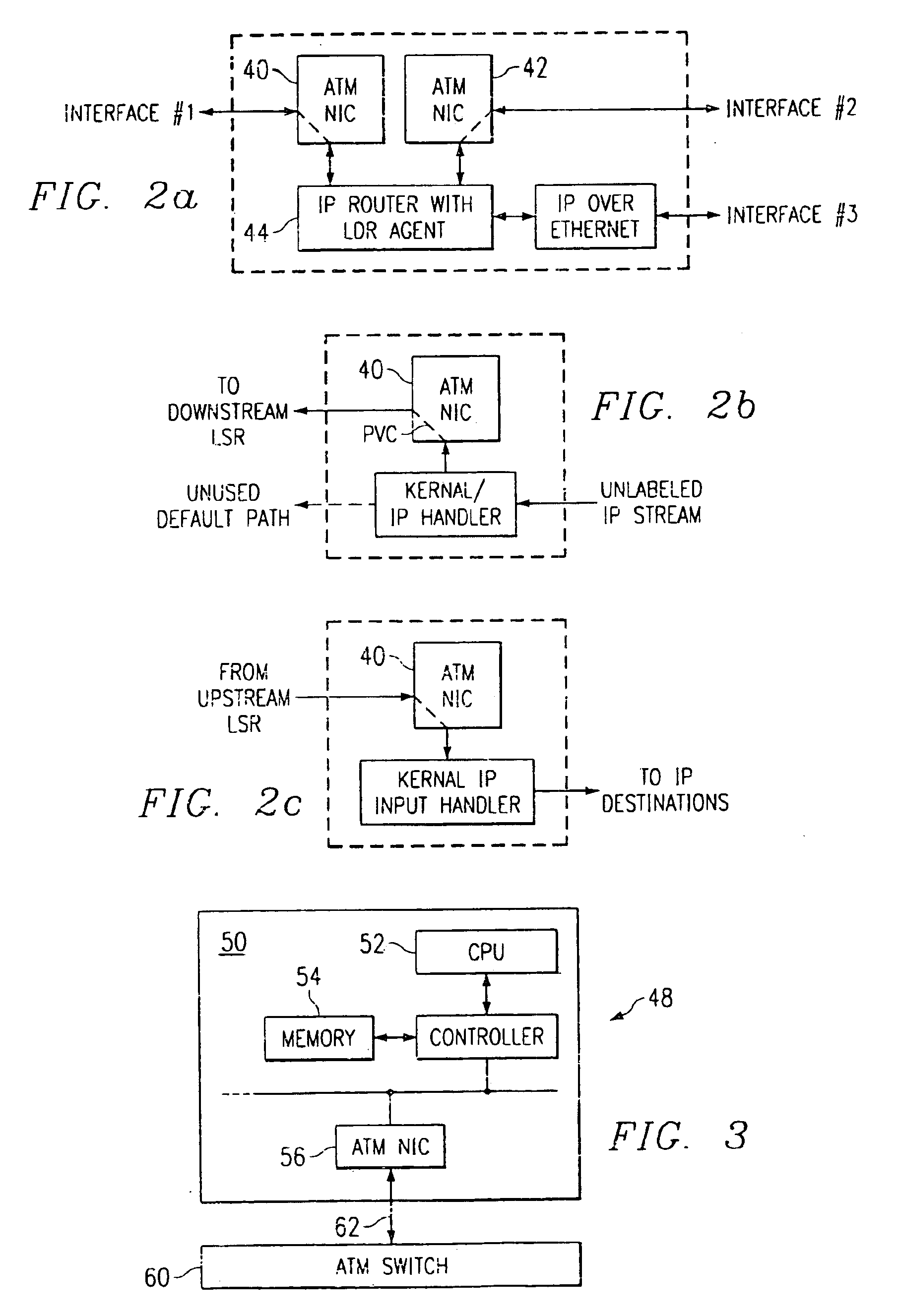
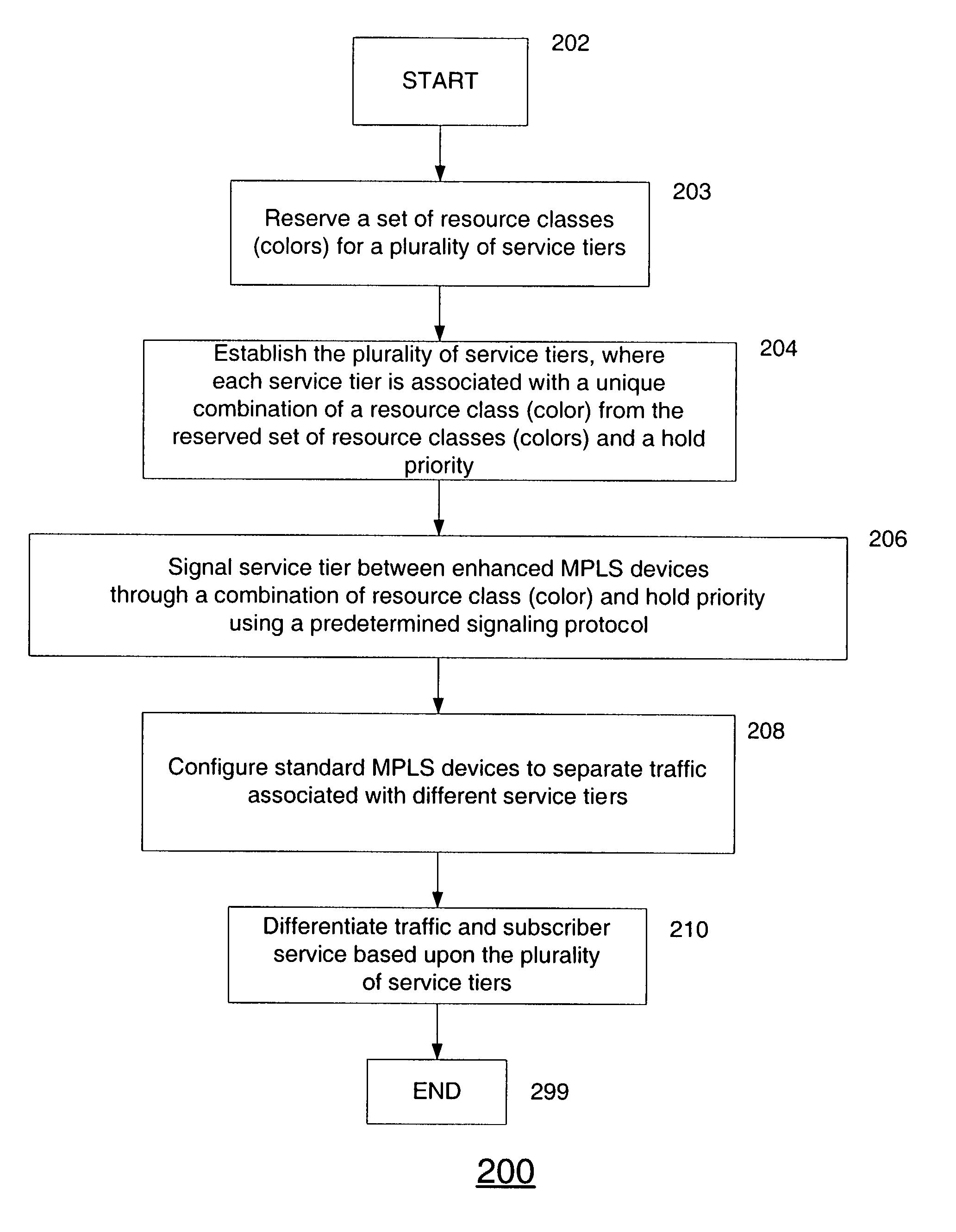
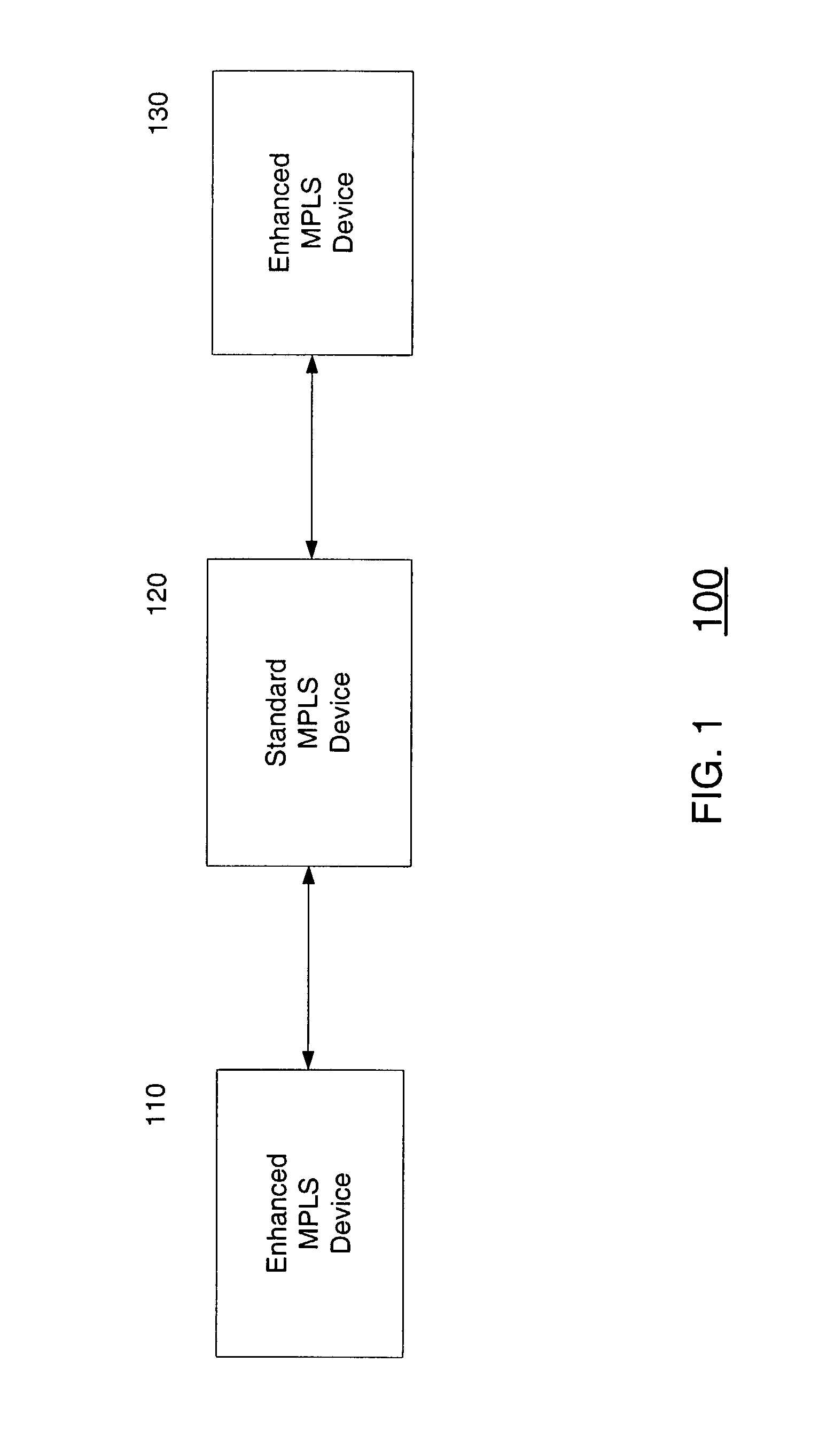
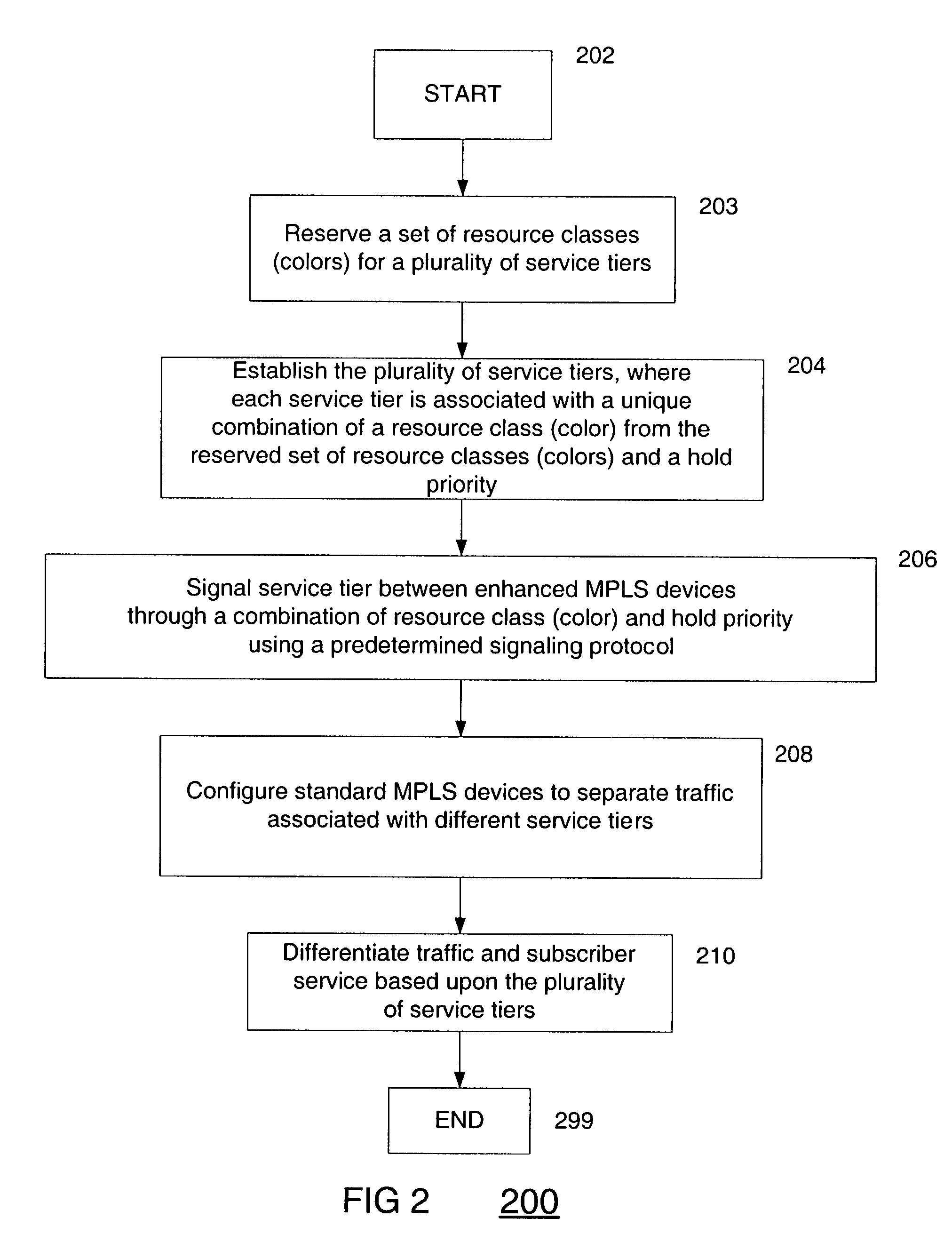
System, device, and method for traffic and subscriber service differentiation using multiprotocol label switching
InactiveUS7020150B2Less provisioningReduce management costsTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityMultiprotocol Label Switching
A system, device, and method for traffic and subscriber service differentiation using multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) creates different service tiers, where each service tier is associated with a unique combination of resource class (color) and hold priority. Enhanced MPLS devices separate traffic into separate queues based upon service tier. Standard MPLS devices are typically configured to separate traffic for different service tiers under normal operating conditions. Enhanced MPLS devices signal service tier using a predetermined signaling protocol such as RSVP-TE or CR-LDP.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
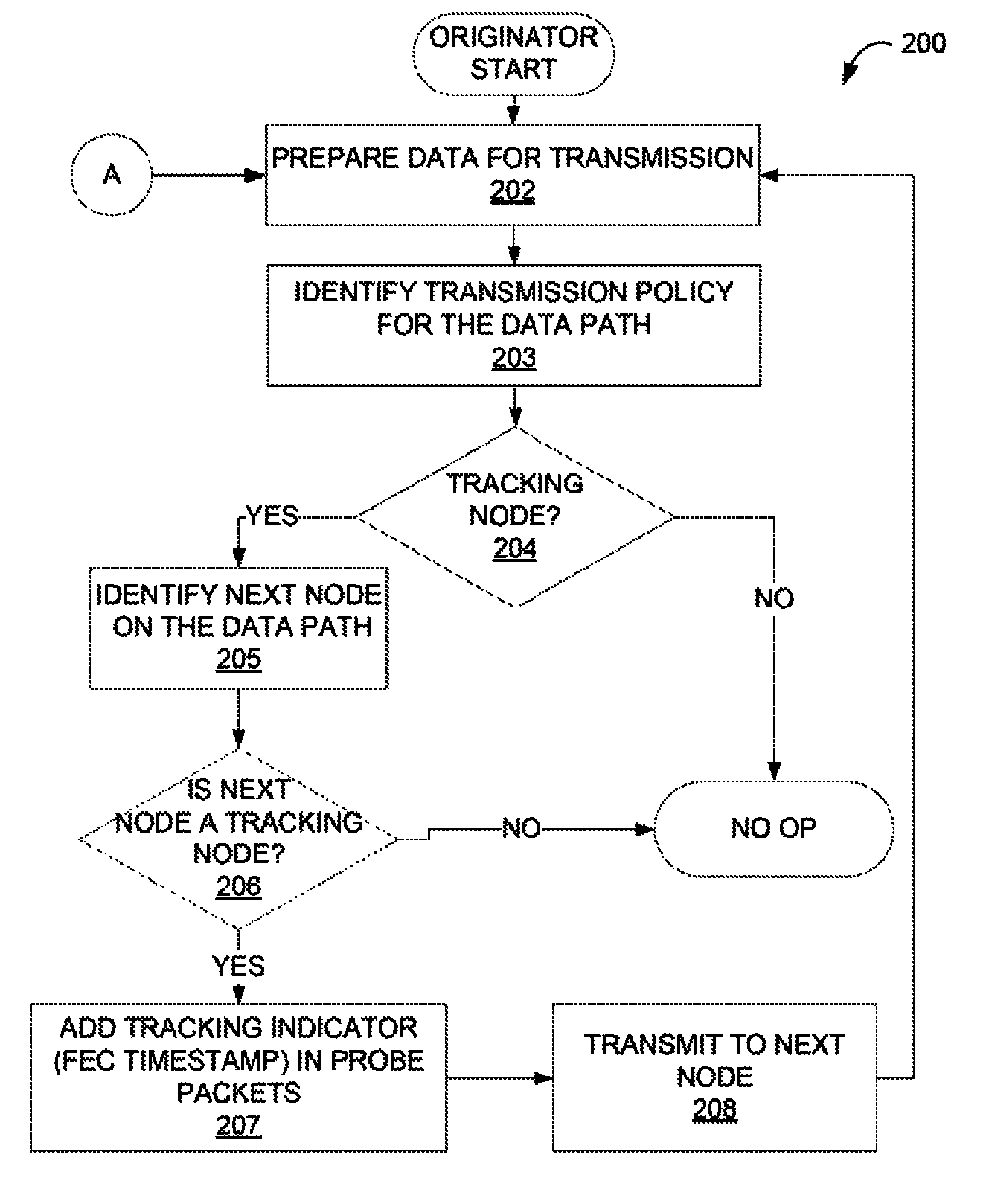
Performance measurement in a network supporting multiprotocol label switching (MPLS)
A method and apparatus to provide hop-by-hop tracking for a communication network is described. In one embodiment, a router verifies that a next downstream router supports tracking and in response, adds a tracking indicator and a timestamp to the data packet. An end router provides a compilation of all the timestamps back to the originating router.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
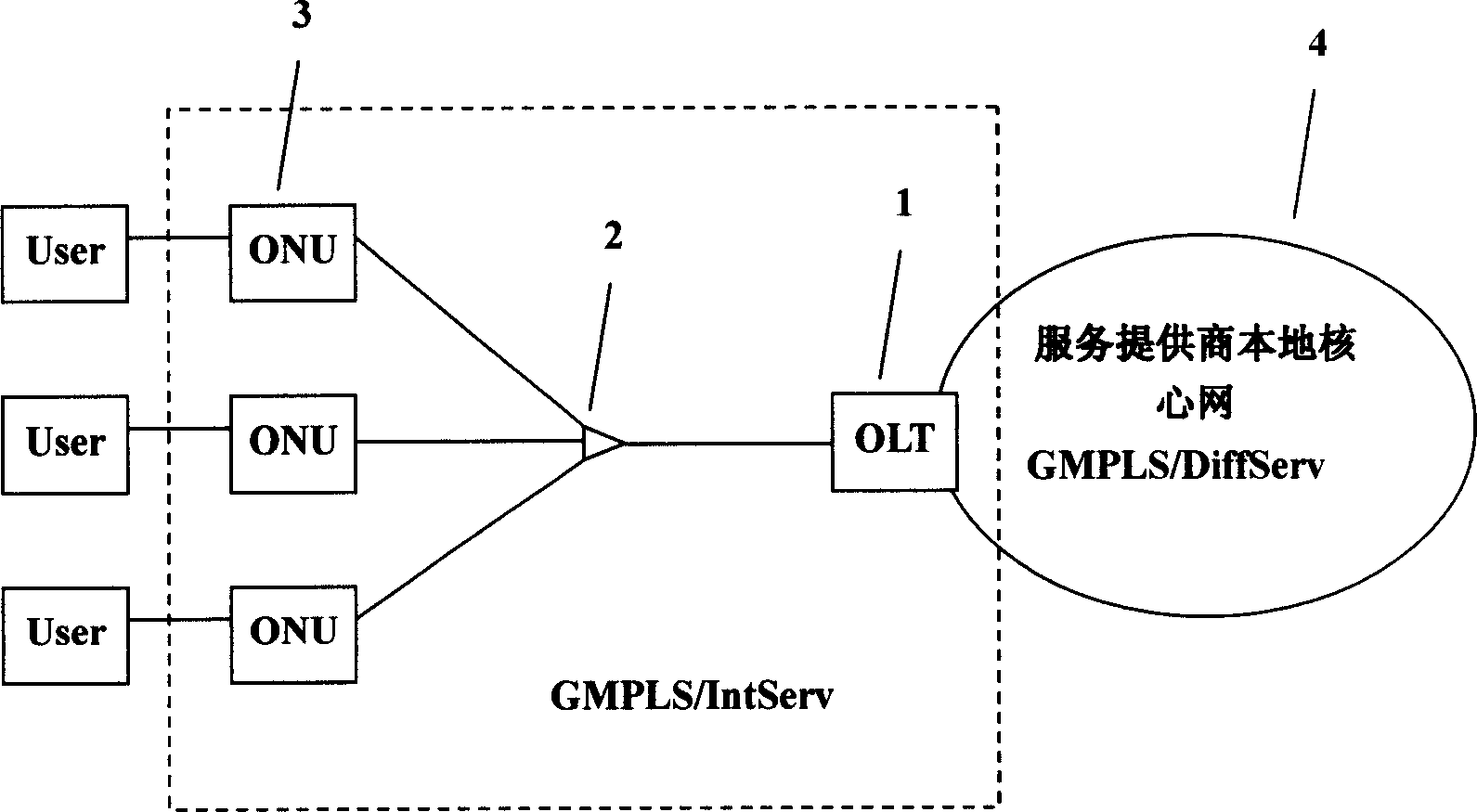
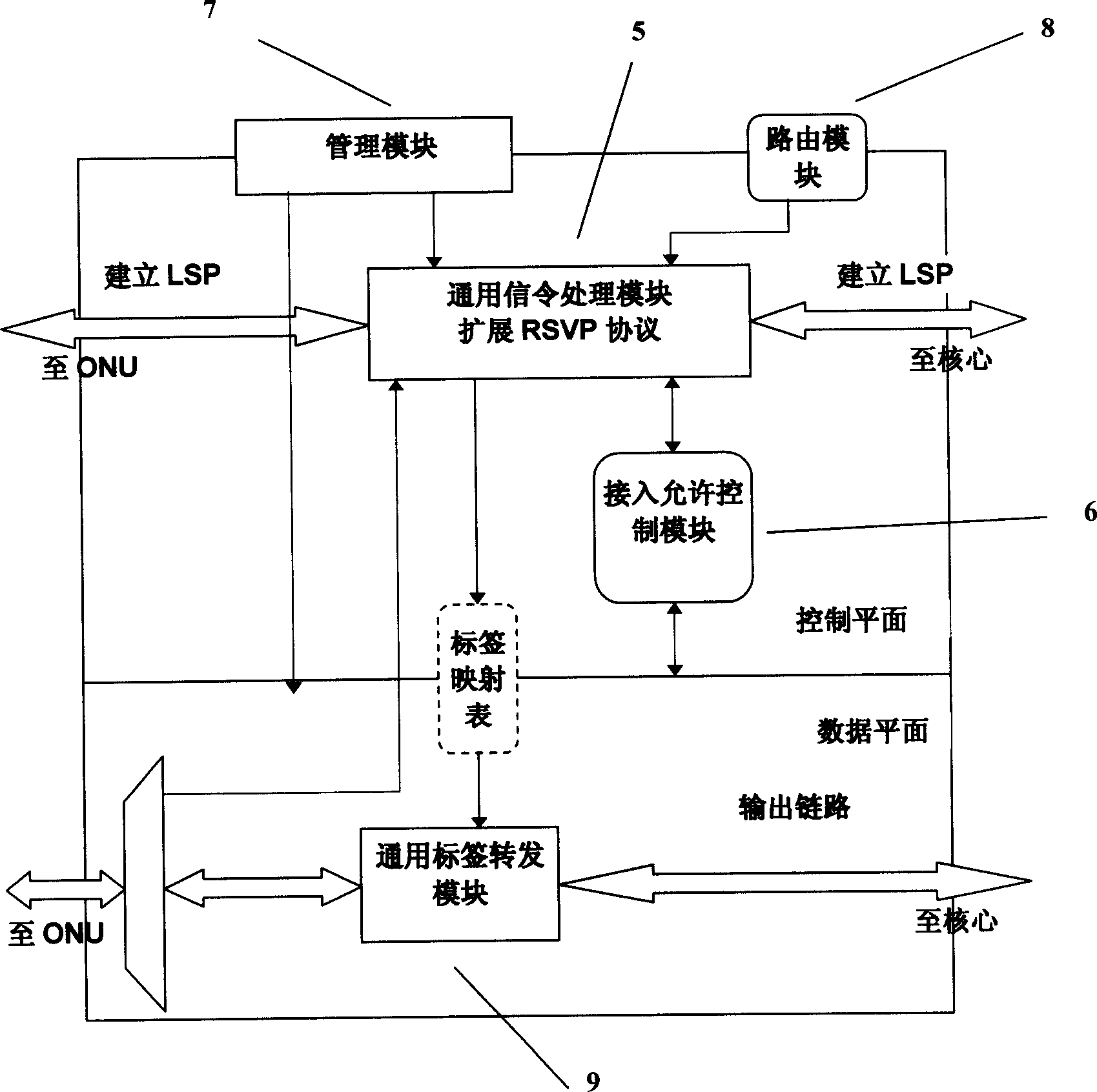
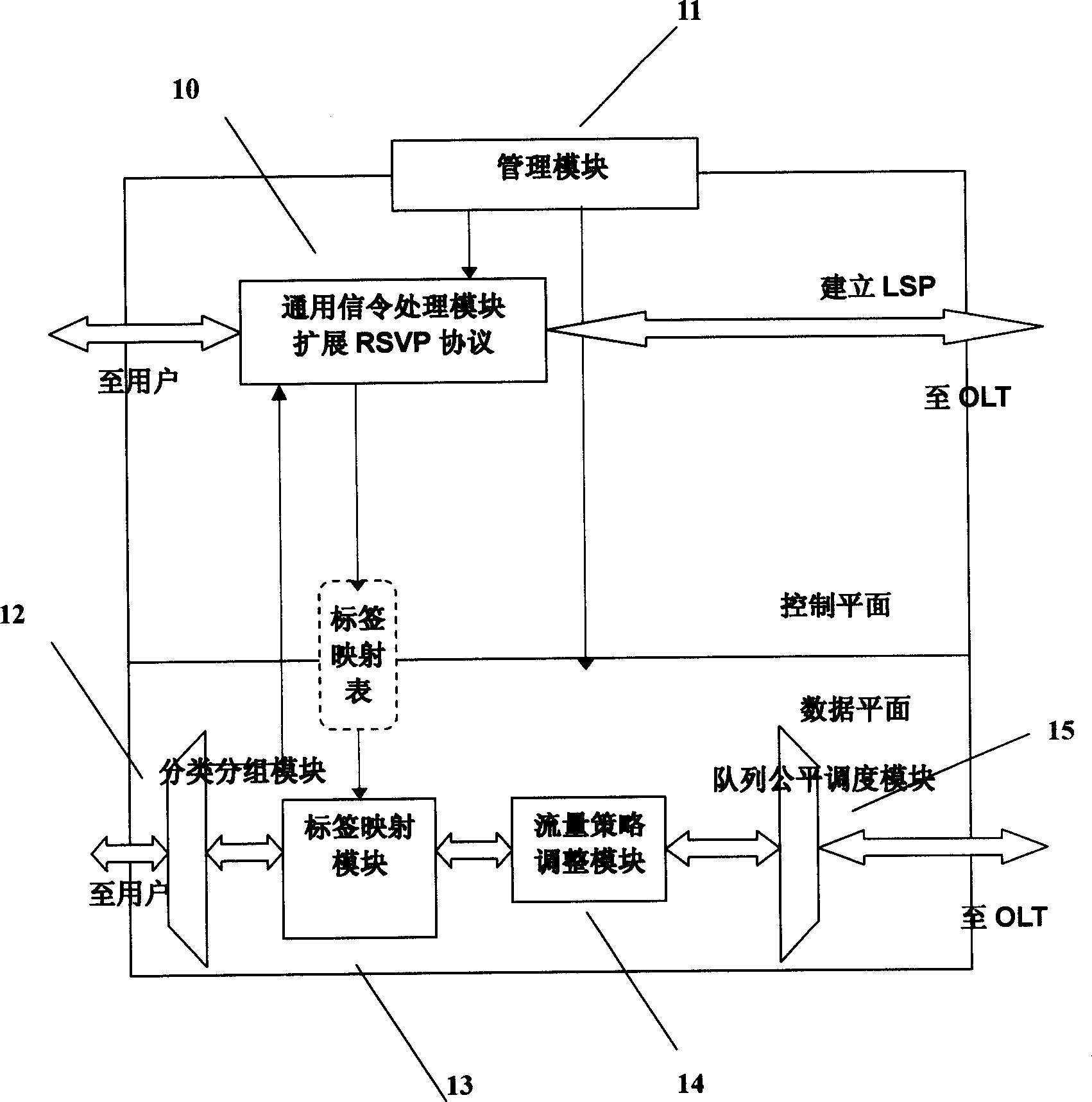
Passive optical network system based on generalized multiprotocol label switching (GMPLS) protocol
InactiveCN1725756ARealize intelligenceRealize intelligent controlTransmissionTelecommunications linkMultiprotocol Label Switching
A passive optical network system based on label exchanging protocol of universal multi-protocol is prepared as connecting optical line terminal OLT to multiple optical network unit ONU by wideband passive optical distribution network , using OLT and ONU as edge router and GMPLS domain of said exchanging protocol for being connected to the other GMPLS router in said multi-protocol by communication link , using OLT as intermediate router of integrated service in system individually for controlling all communication activities , using ONU as inlet router of integrated service in system for executing command of OLT .
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for sharing backup path in MPLS network, label switching router for setting up backup in MPLS network, and system therefor
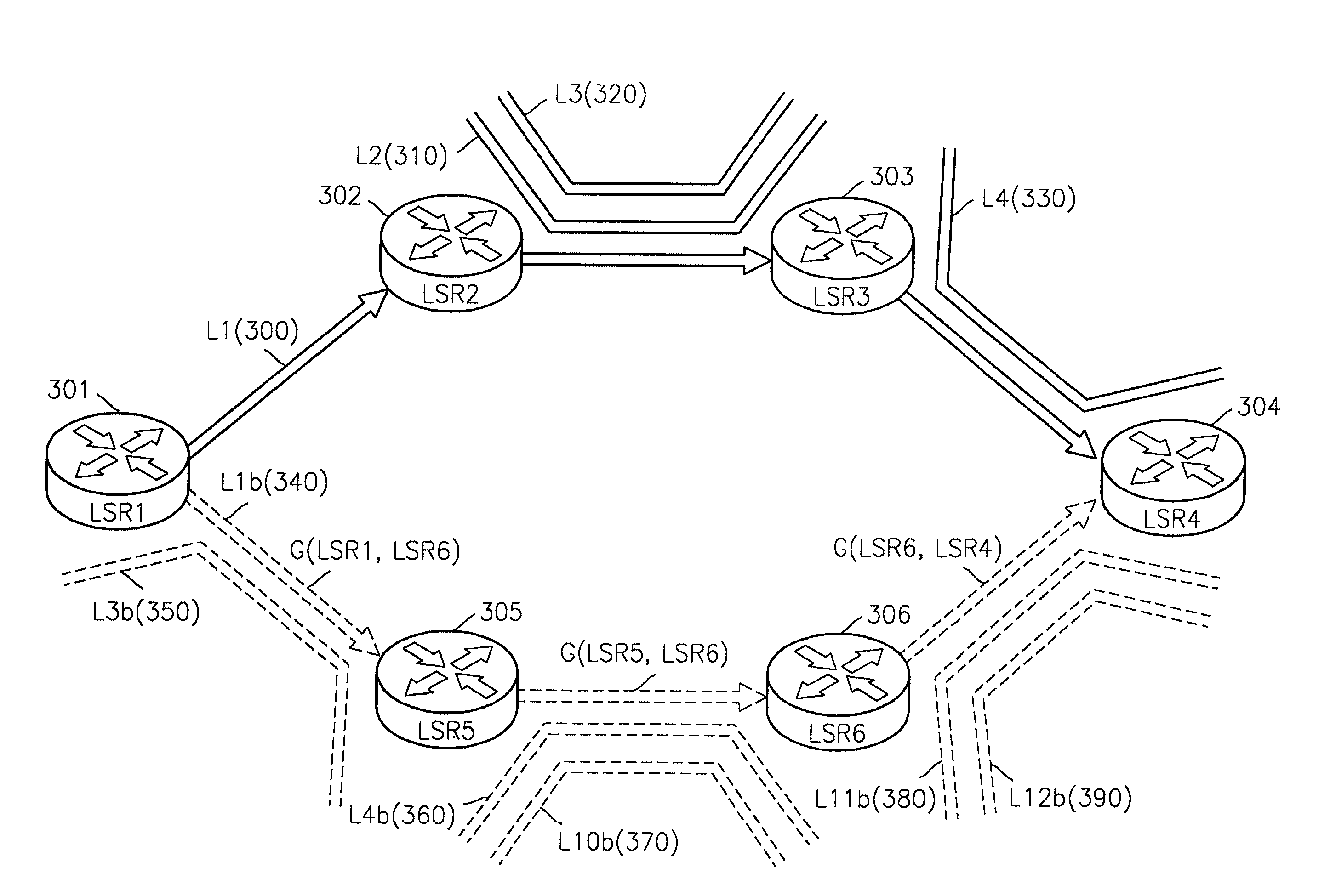
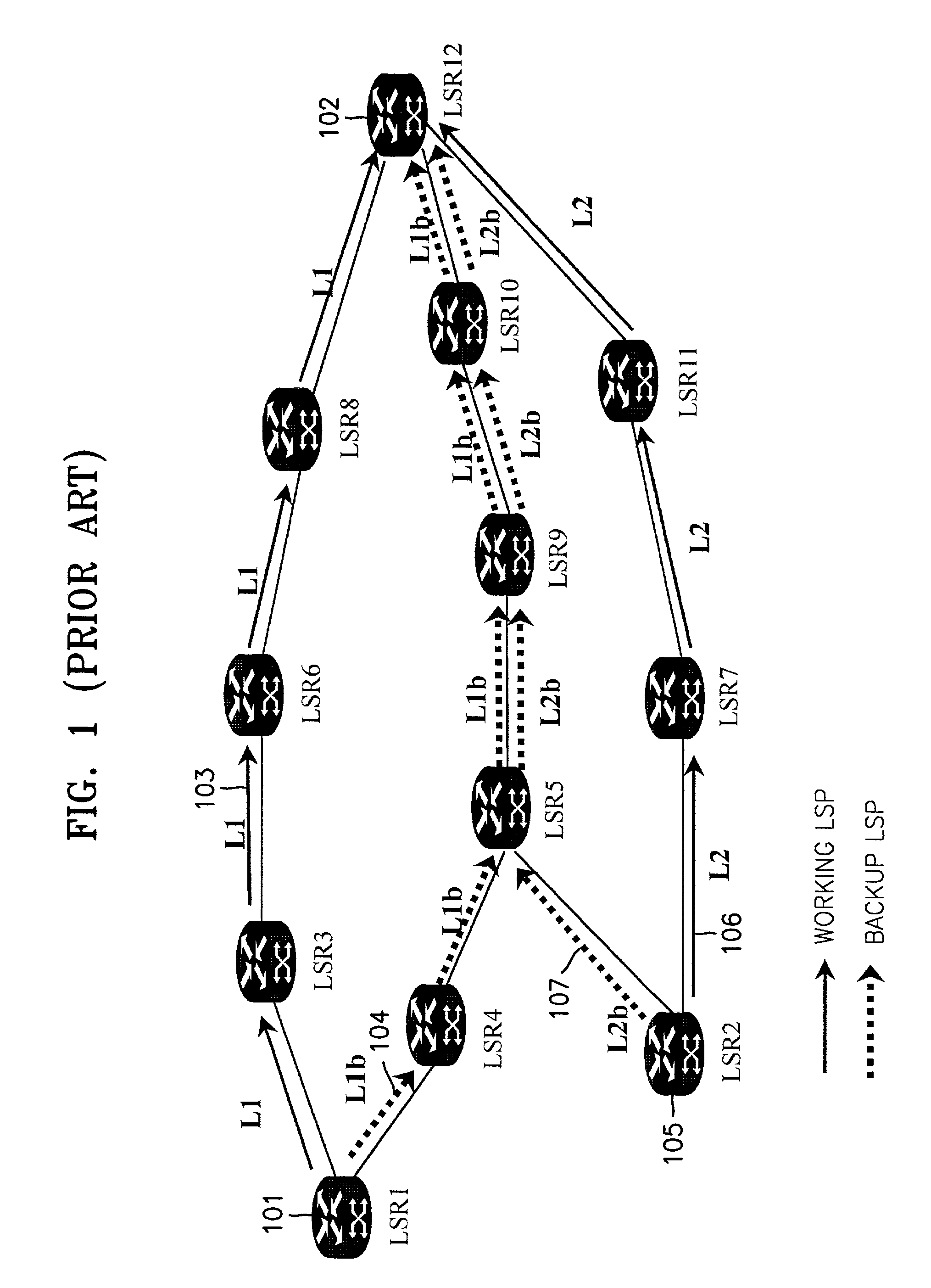
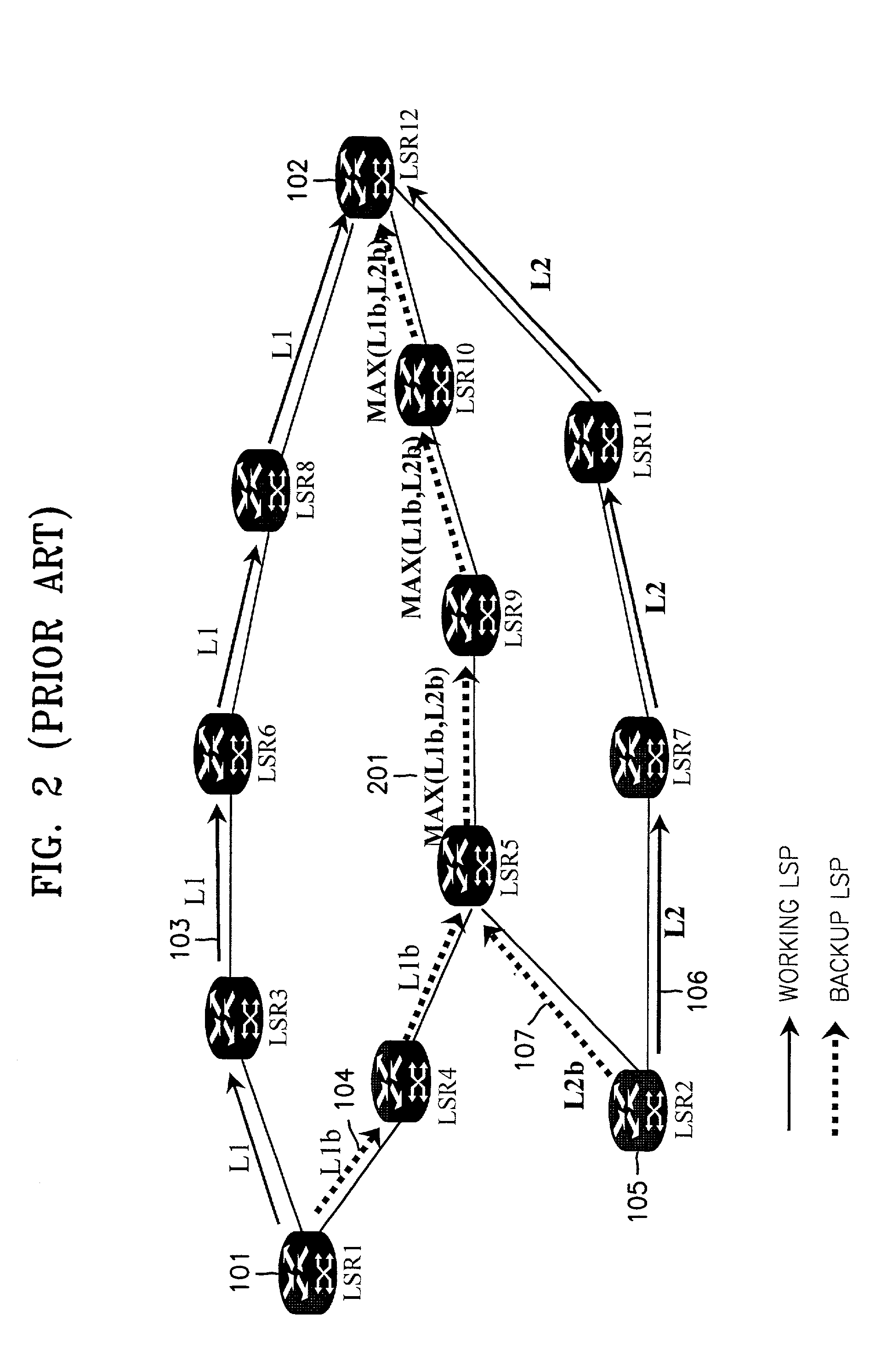
A method for sharing a backup path in a MultiProtocol Label Switching (MPLS) network, a label switching router (LSR) for setting a backup path in an MPLS network, a system for setting a backup path in an MPLS network, and a recording medium therefor are provided. The method includes the steps of acquiring link configuration information of links included in a working path when the working path is set between a source node and a destination node, and allocating bands for a backup path using the link configuration information when the backup path is set between the source node and the destination node. In the method, an optimal band is allocated to each of links included in a backup path by calculating a band using information, which is obtained during setting of a working path, about at least one other working path sharing links with the working path when the backup path is set, thereby efficiently managing network resources without wasting them.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST +1
Apparatus and methods for intelligent deployment of network infrastructure based on tunneling of ethernet ring protection
ActiveUS20150036483A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsMultiprotocol Label SwitchingCarrier Ethernet
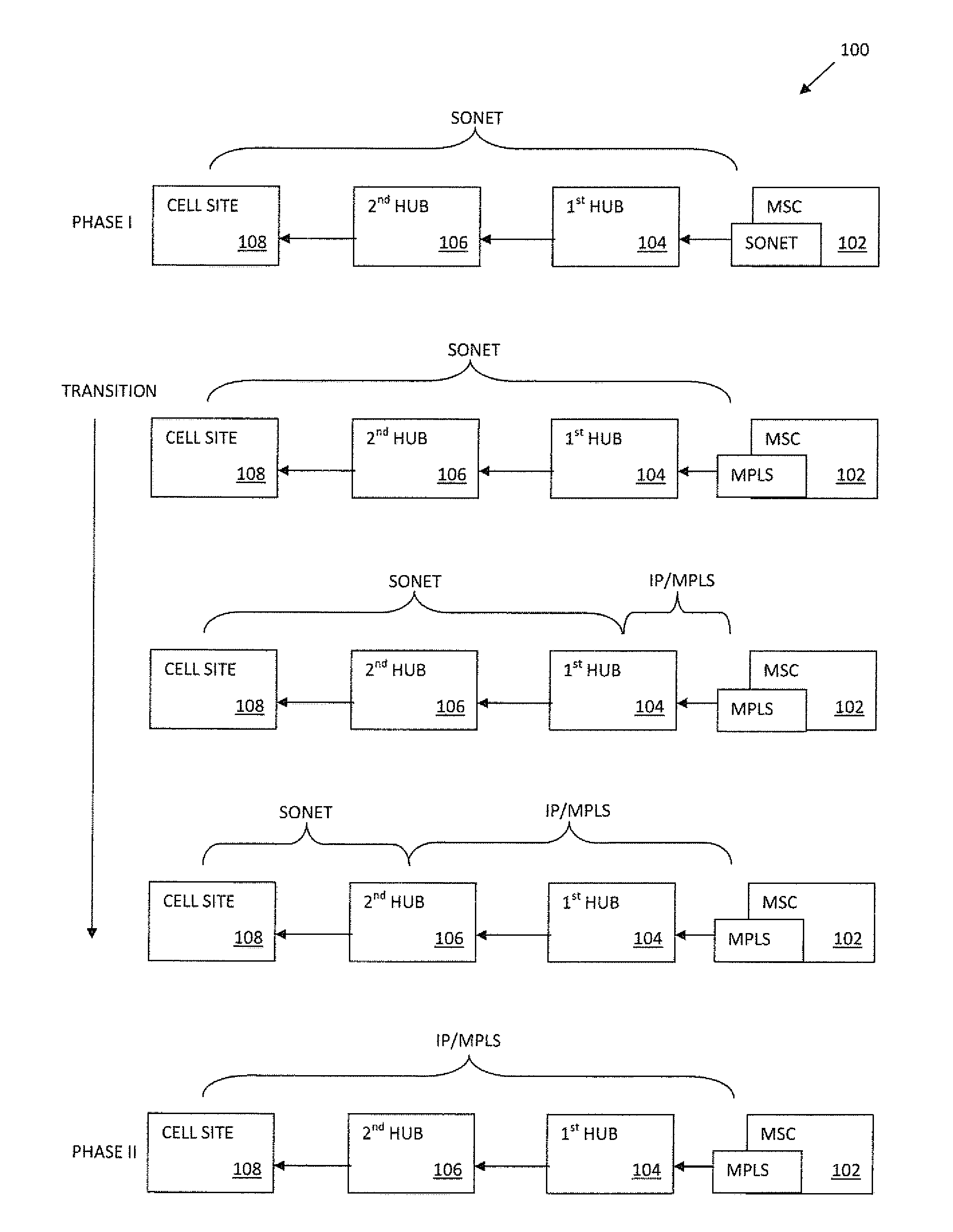
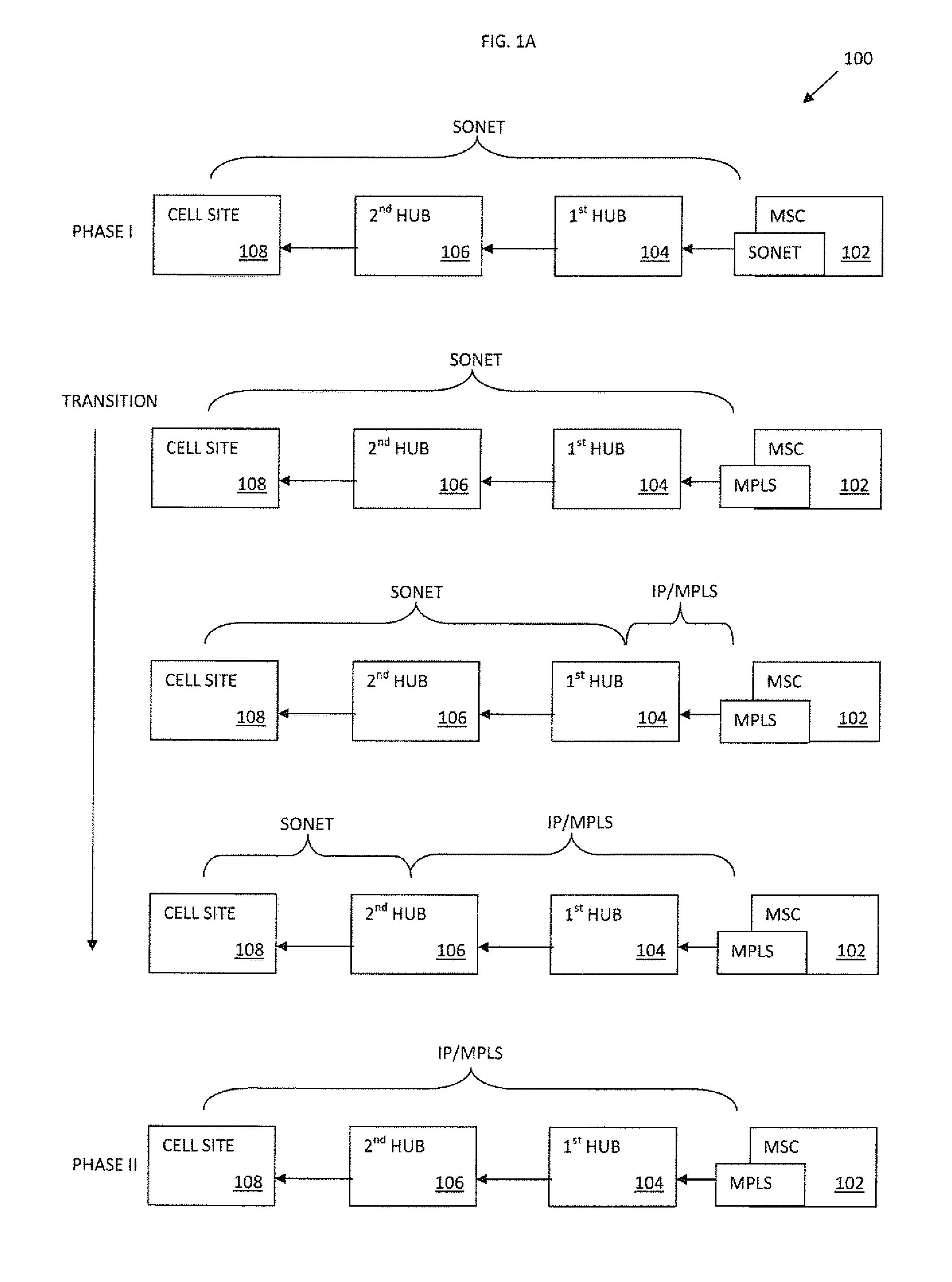
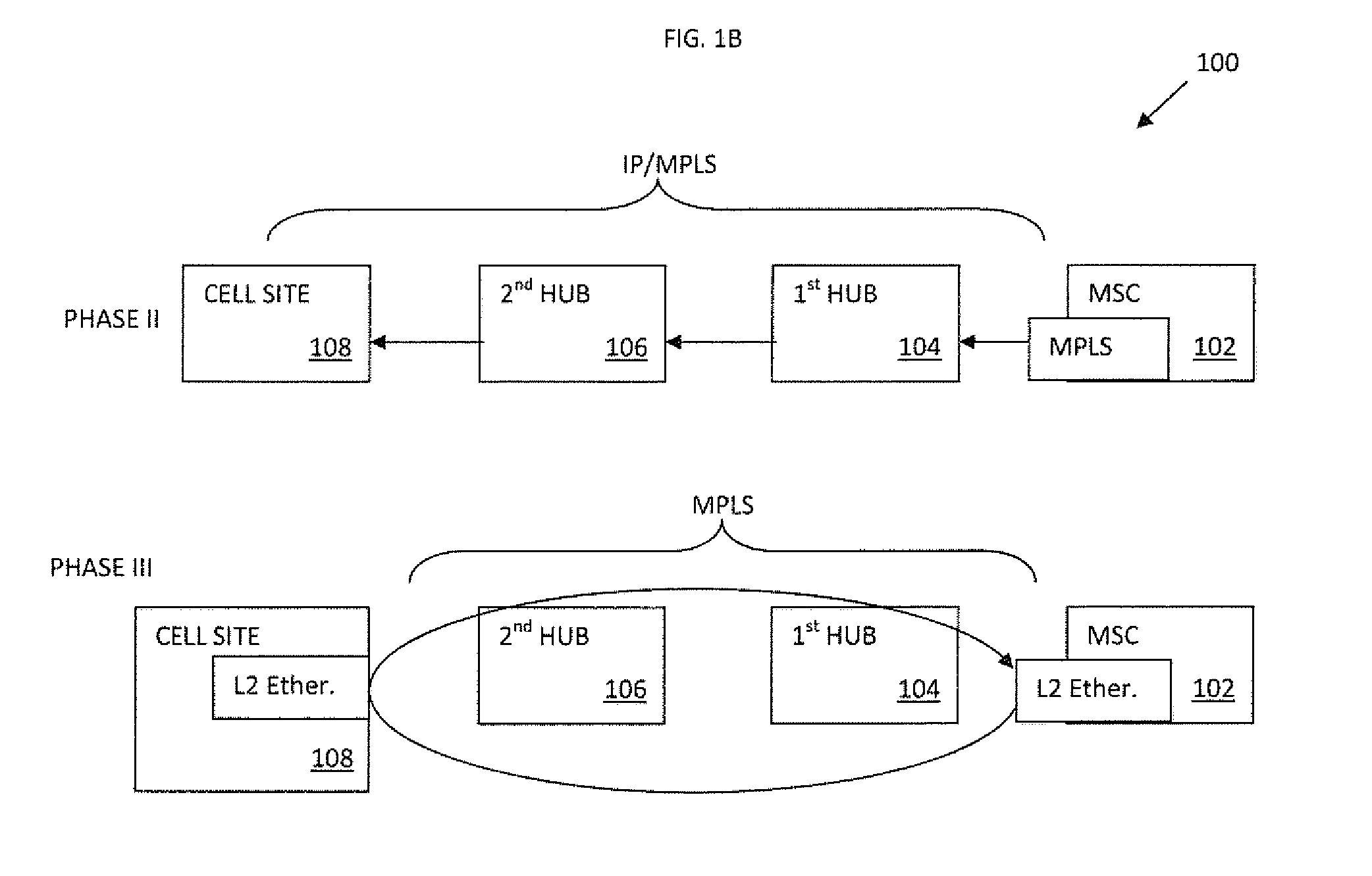
Apparatus and methods for intelligent deployment and transition from a first network infrastructure to a second network infrastructure. Various embodiments of the present disclosure are directed to, among other things, methods and apparatus that leverage tunneling of Ethernet ring network technologies. In one exemplary embodiment, a modified implementation of the ITU-T G.8032 data link protocol is combined with Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) transport networks to provide Carrier Ethernet and Retail Ethernet services. Unlike existing network infrastructure, the exemplary MPLS network aggregates traffic between the base station (BS) and mobile switching center (MSC) within a logical ring network topology.
Owner:TIME WARNER CABLE ENTERPRISES LLC
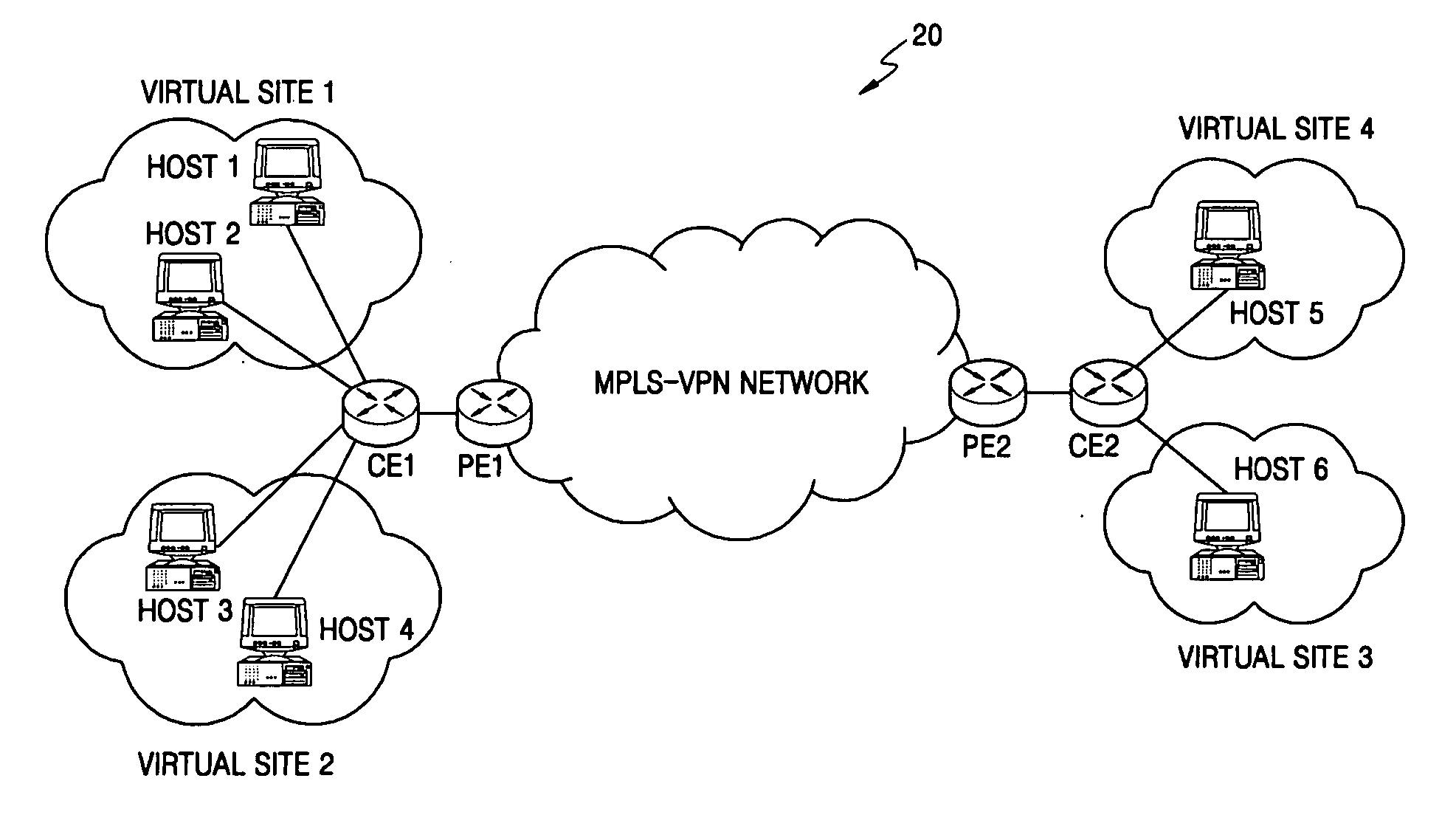
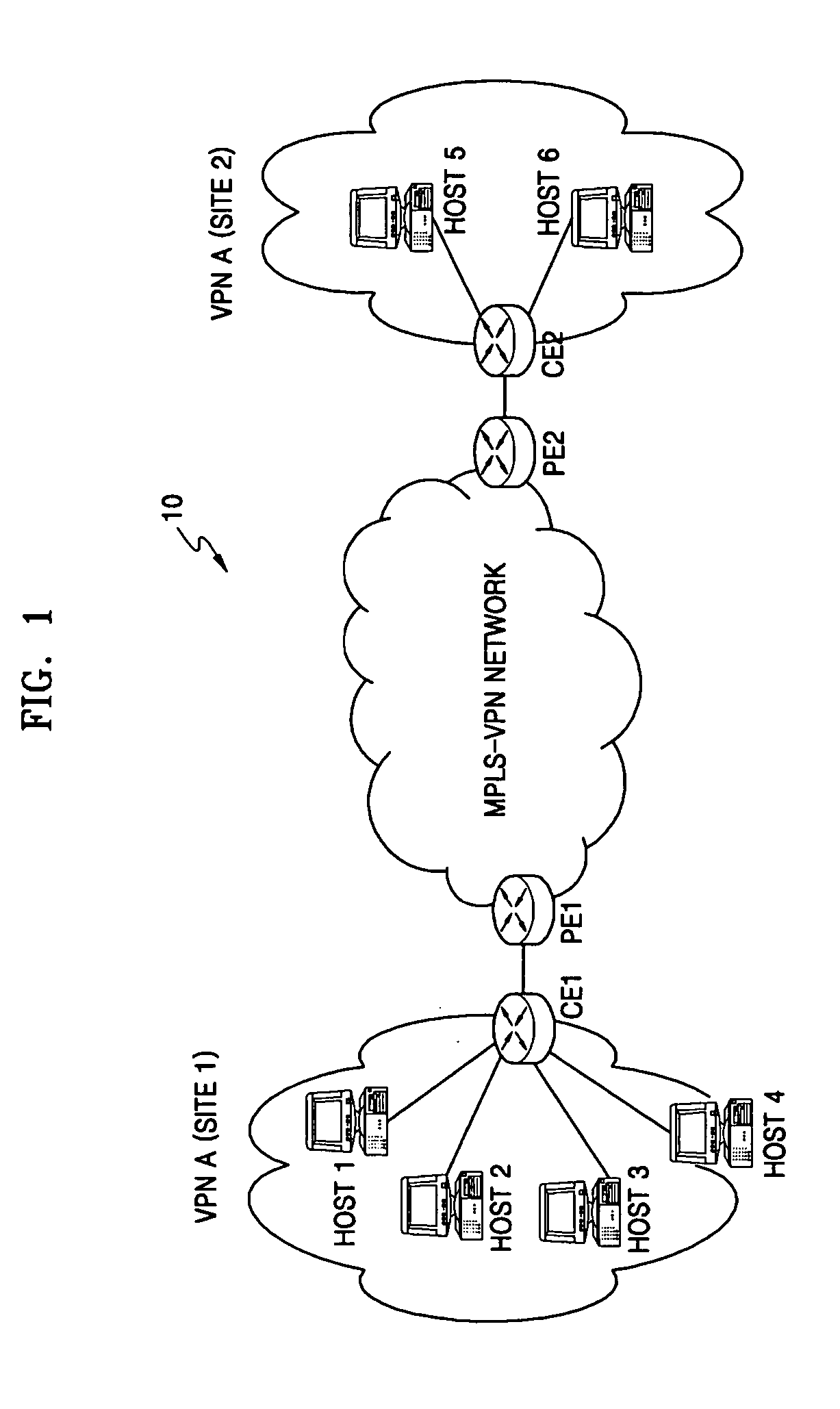
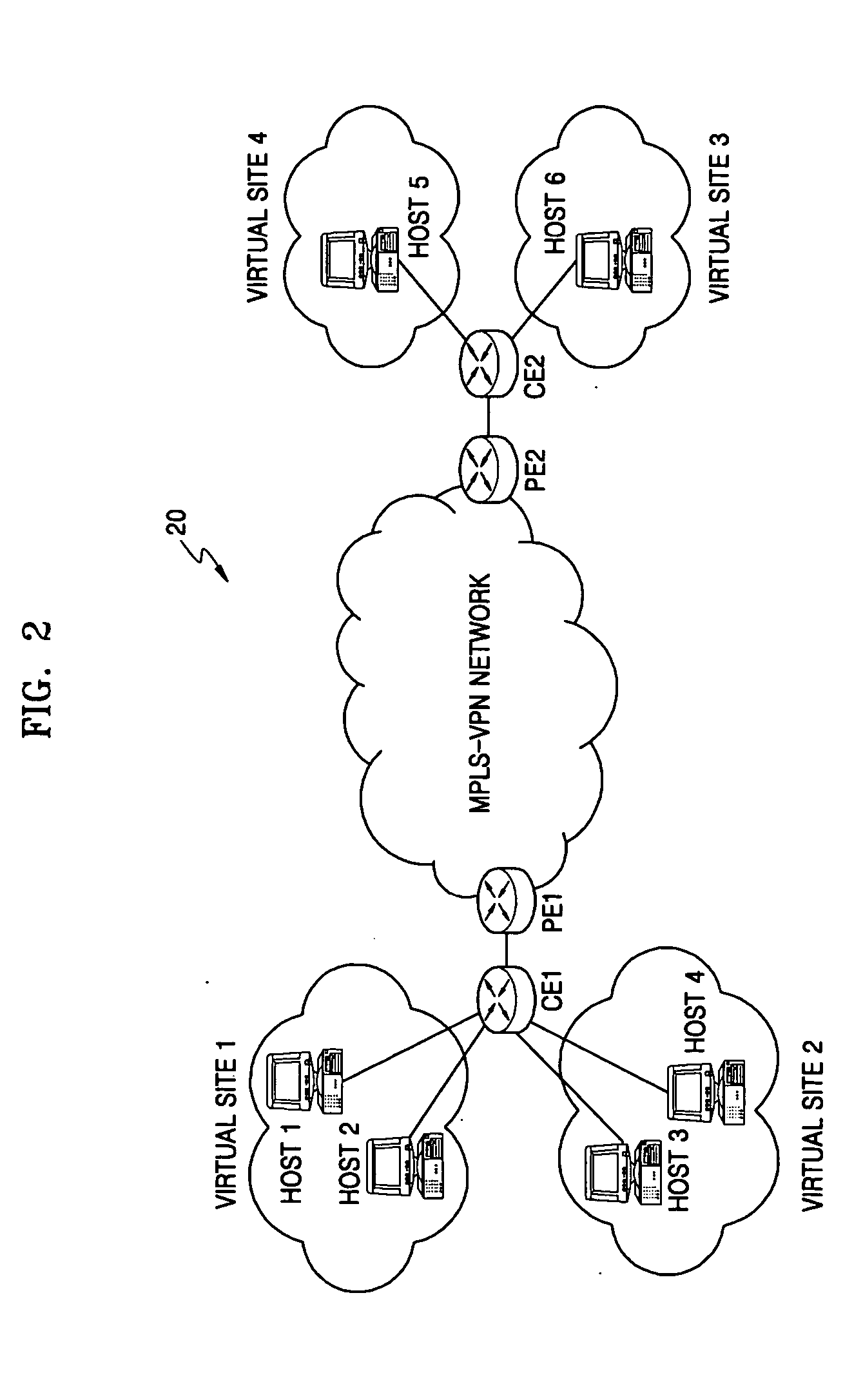
Apparatus and method of designating virtual sites using policy informations in multiprotocol label switching networks
InactiveUS20050120089A1Effective divisionDigital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionDifferentiated servicesMultiprotocol Label Switching
Provided are an apparatus and method of dividing virtual sites using policy properties in multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) networks. In this method, when multiple virtual sites are selected with respect to one interface, not only usually used source IP addresses and VLAN tags but also TOS fields and MPLS labels are used so that more various kinds of virtual sites can be selected. Also, since the TOS fields and MPLS labels can express additional QoS-related information, differentiated services can be provided by selecting a wider variety of kinds of virtual sites.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
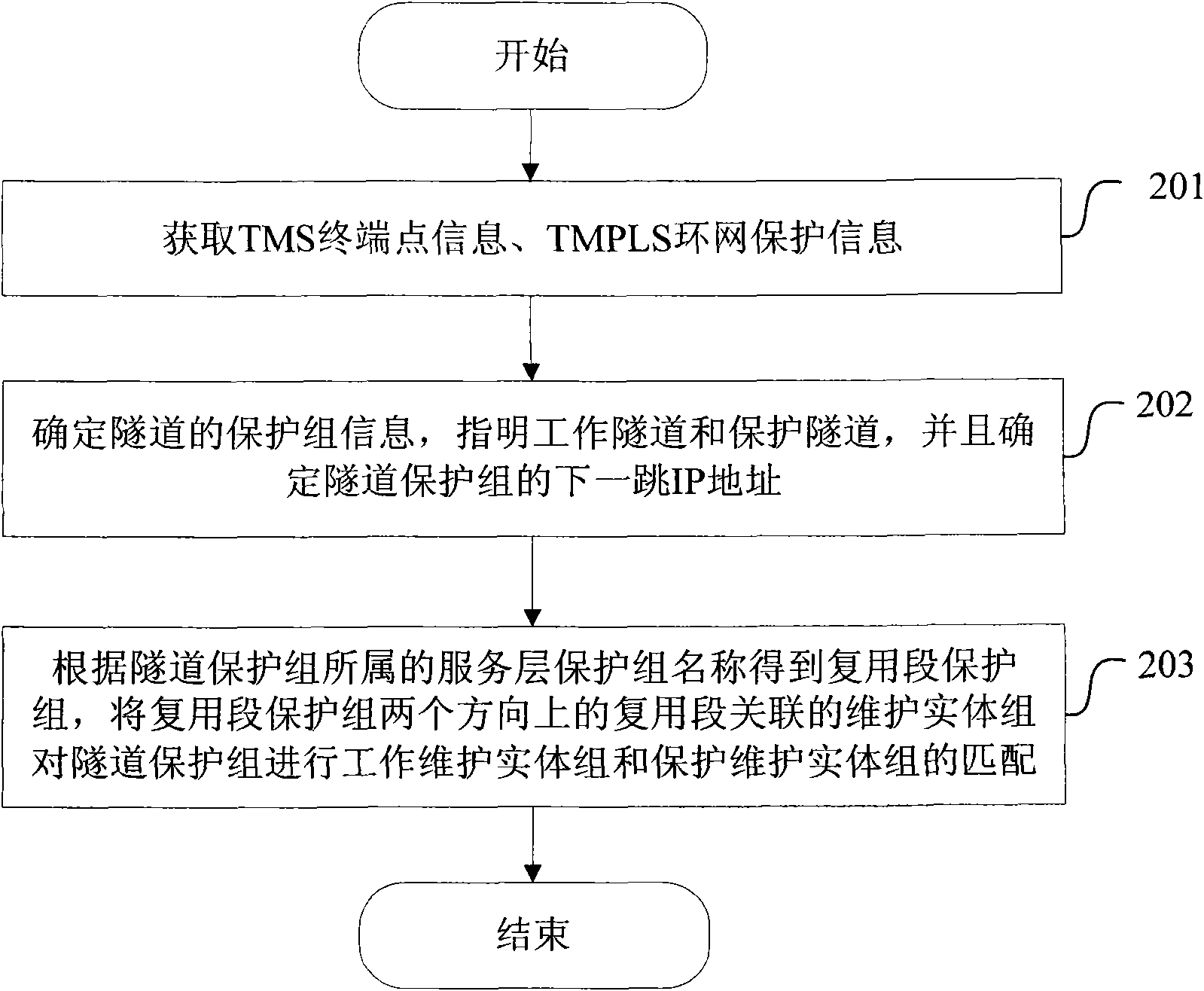
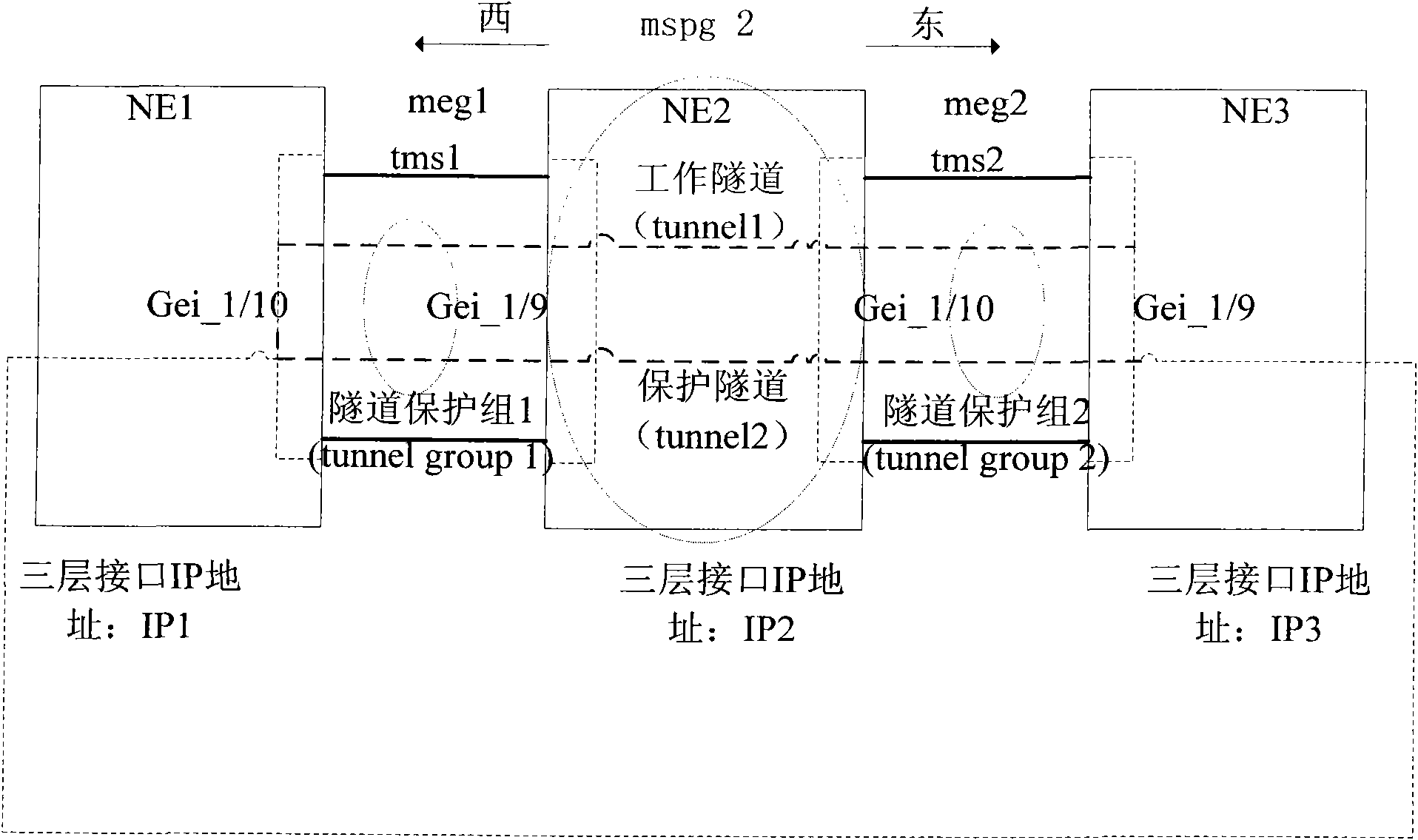
Method and device for allocating transport-multiprotocol label switching and ring network protecting maintenance entity groups
ActiveCN101599862ASimple data entryImprove configuration accuracyNetworks interconnectionMultiprotocol Label SwitchingRing network
The invention provides a method for allocating transport-multiprotocol label switching and ring network protecting maintenance entity groups, which comprises the following steps: establishing a tunnel protecting group, and determining a working tunnel and a protecting tunnel of the tunnel protecting group, and an address of a next hop of the tunnel protecting group; and selecting a multiplex section protecting group to which the tunnel protecting group belongs, obtaining addresses of a next hop of a multiplex section of the multiplex section protecting group in two directions, comparing the addresses of the next hop of the multiplex section in the two directions and the address of the next hop of the tunnel protecting group, and if the address of the next hop of the multiplex section in one direction is the same as the address of the next hop of the tunnel protecting group, allocating maintenance entity groups corresponding to the multiplex section in the direction as working maintenance entity groups, and maintenance entity groups corresponding to the multiplex section in the other direction as protecting maintenance entity groups. The invention also provides a device for allocating transport-multiprotocol label switching and ring network protecting maintenance entity groups. When allocating the tunnel protecting group, the method and the device have simple input data and high allocation accuracy.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Performance measurement in a network supporting multiprotocol label switching (MPLS)
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
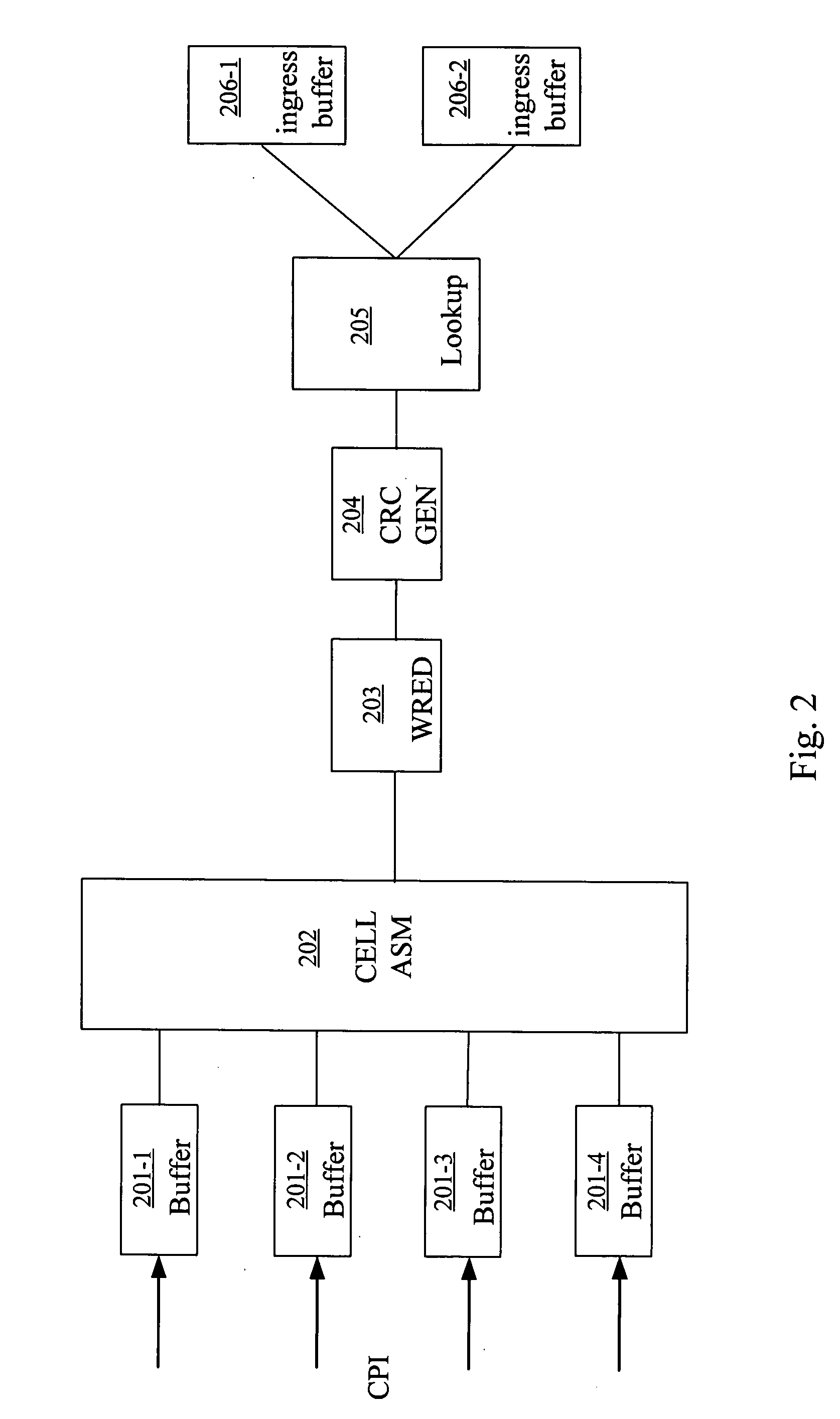
Single and double tagging schemes for packet processing in a network device
ActiveUS20050008009A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexPacket processingMultiprotocol Label Switching
A method of handling datagrams in a network device is disclosed. The method includes the steps of receiving an incoming datagram at a port of the network device, determining a type for the incoming datagram based on fields in the incoming datagram and a destination address, adding a tag to the datagram to assist in routing the datagram, obtaining a multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) label when the datagram is a MPLS datagram, processing the datagram based on the MPLS label and the destination address and discarding or forwarding the datagram based upon the processing step. The tag is stripped from the datagram before it is sent from an egress port of the network switch.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
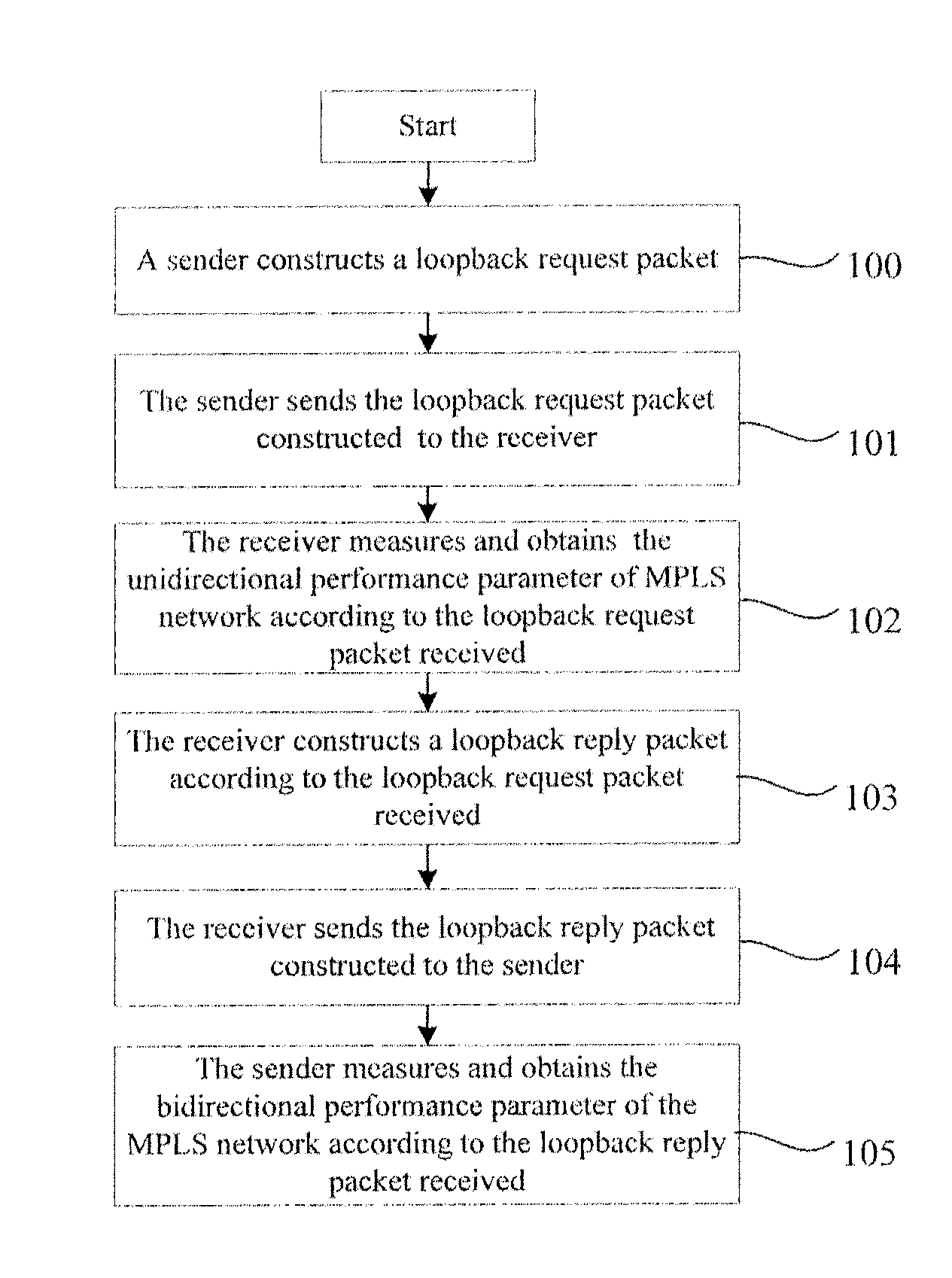
Method, System and Device for Measuring Performance Parameters of Multiprotocol Label Switching Network
InactiveUS20070242620A1Performance parameterError preventionTransmission systemsMultiprotocol Label SwitchingComputer science
Embodiments of the present invention provides a method for measuring performance parameters of MultiProtocol Label Switching (MPLS) network, including: sending a performance parameter measurement packet carrying first information for measuring a performance parameter of the MPLS network to a second party; measuring the performance parameter of the MPLS network according to the first information in the performance parameter measurement packet. The embodiments of the invention also provide a system and a device for measuring performance parameters of the MPLS network.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
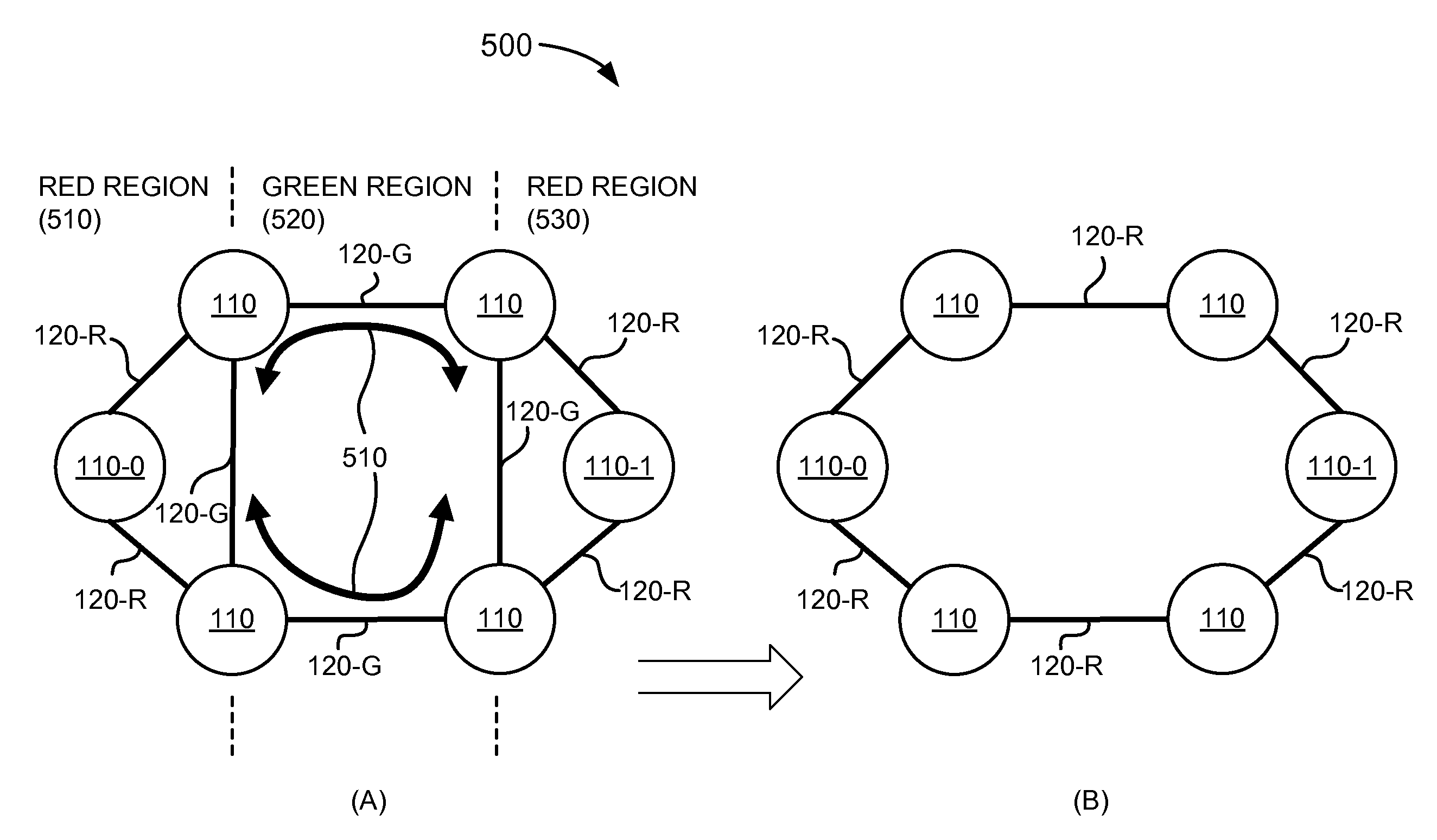
LSP hierarchy for MPLS networks
ActiveUS8451846B1Time-division multiplexData switching by path configurationMultiprotocol Label SwitchingComputer science
A system may define a first region that includes a first colored link of a multiprotocol label switching (MPLS) network, and may define a second region that includes a second colored link of the MPLS network. The system may define a boundary between the first and second regions based on the first colored link and the second colored link.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
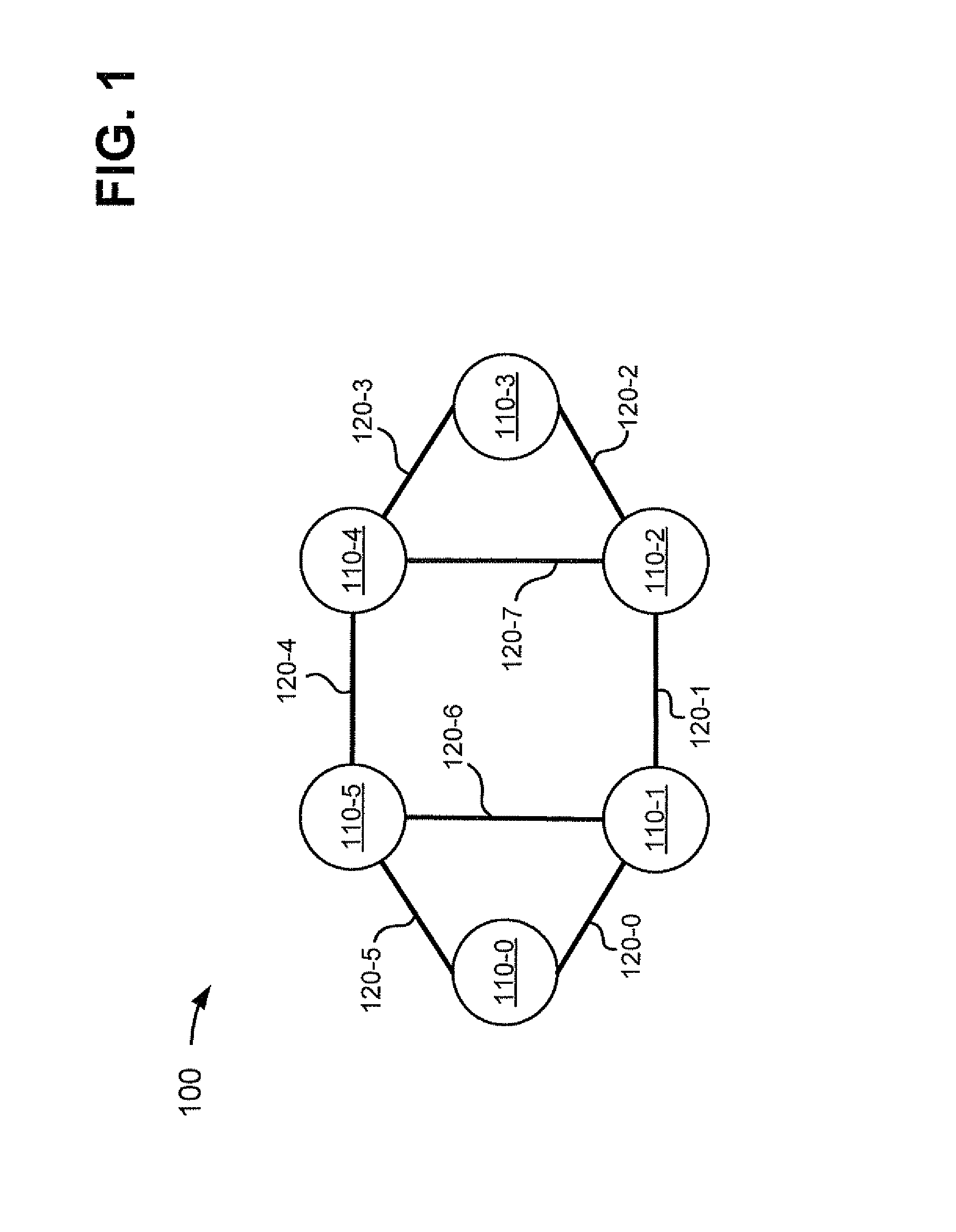
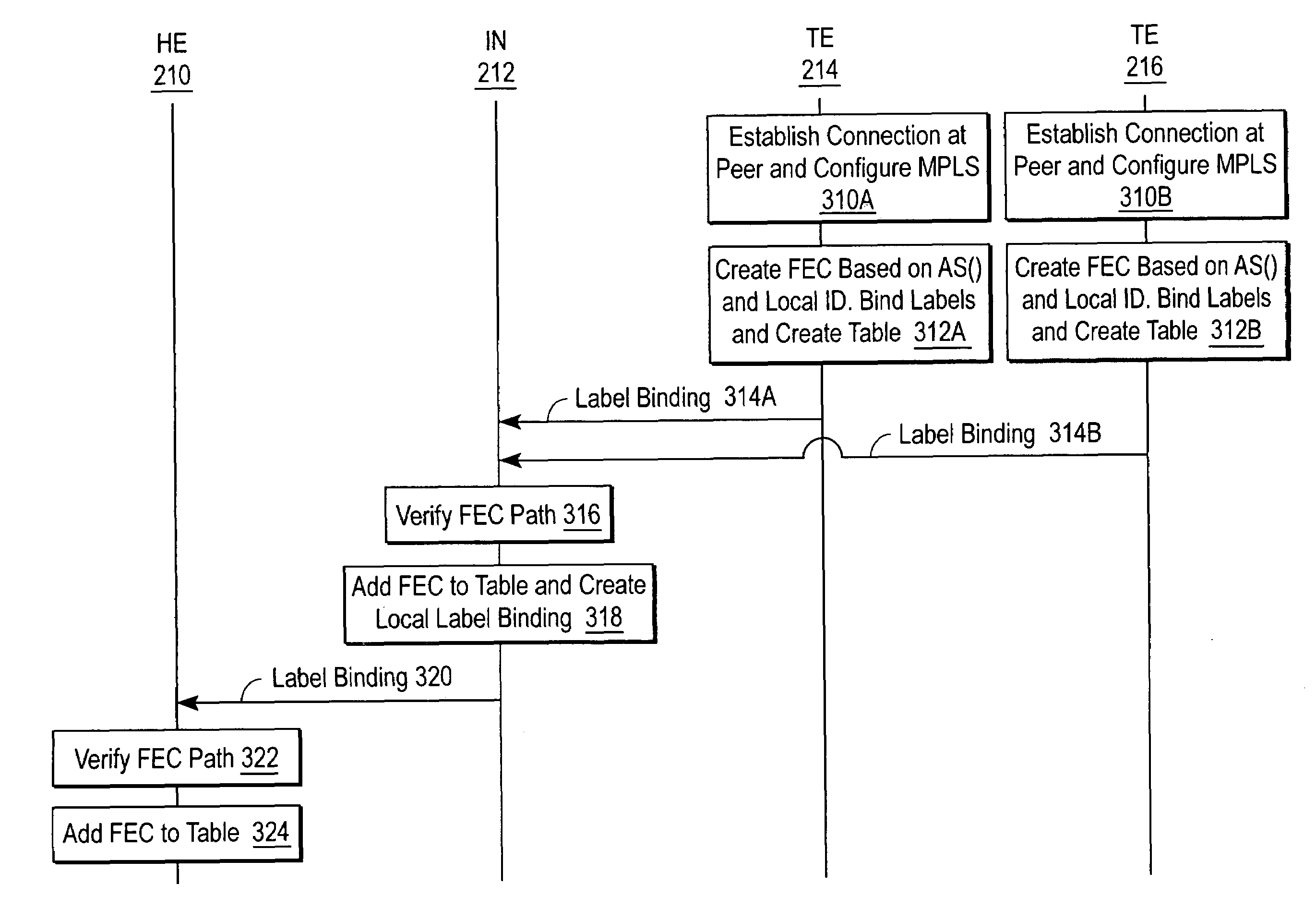
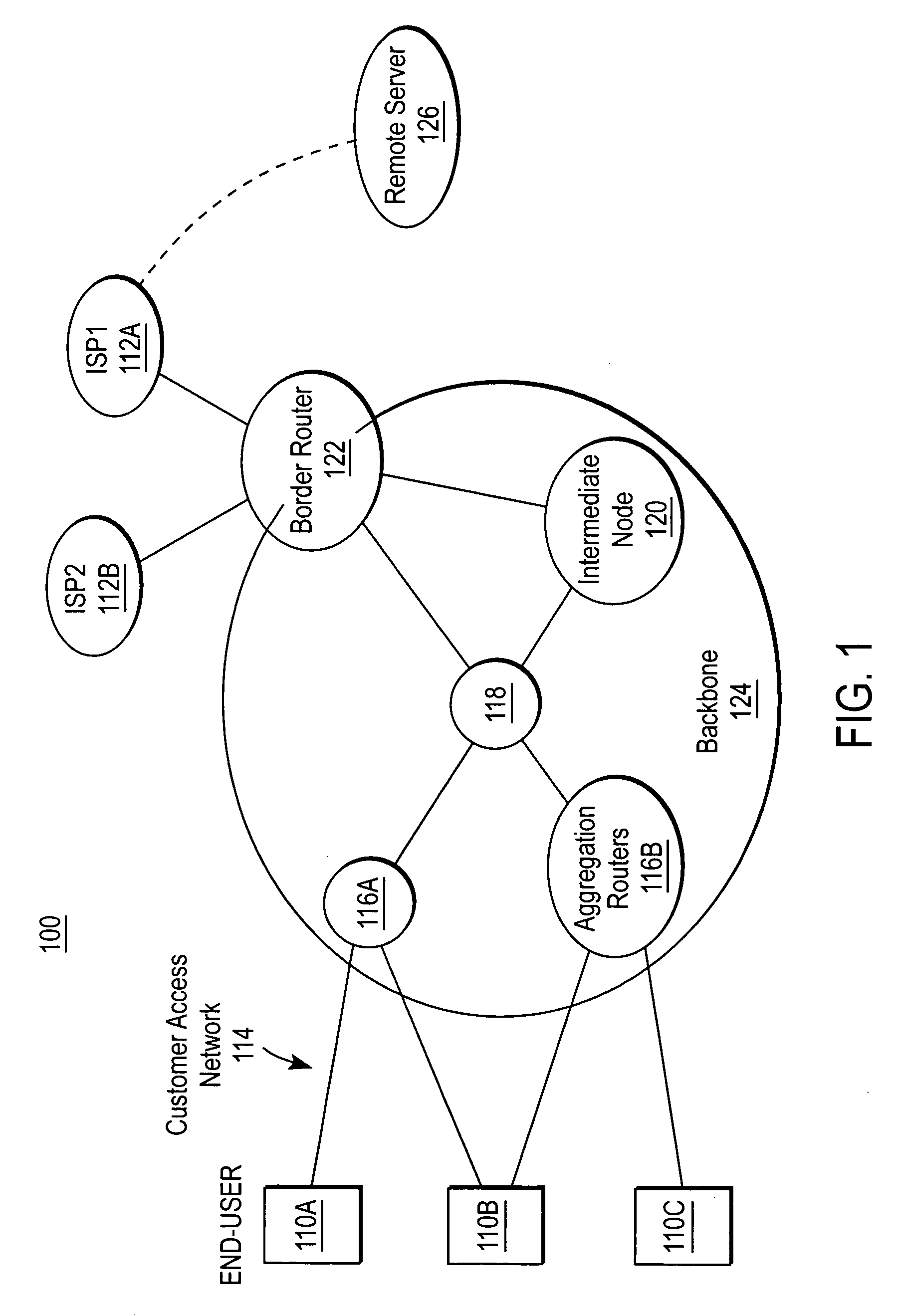
Sharing IP network resources
InactiveUS6985963B1Efficient sharingEnergy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsAccess networkMultiprotocol Label Switching
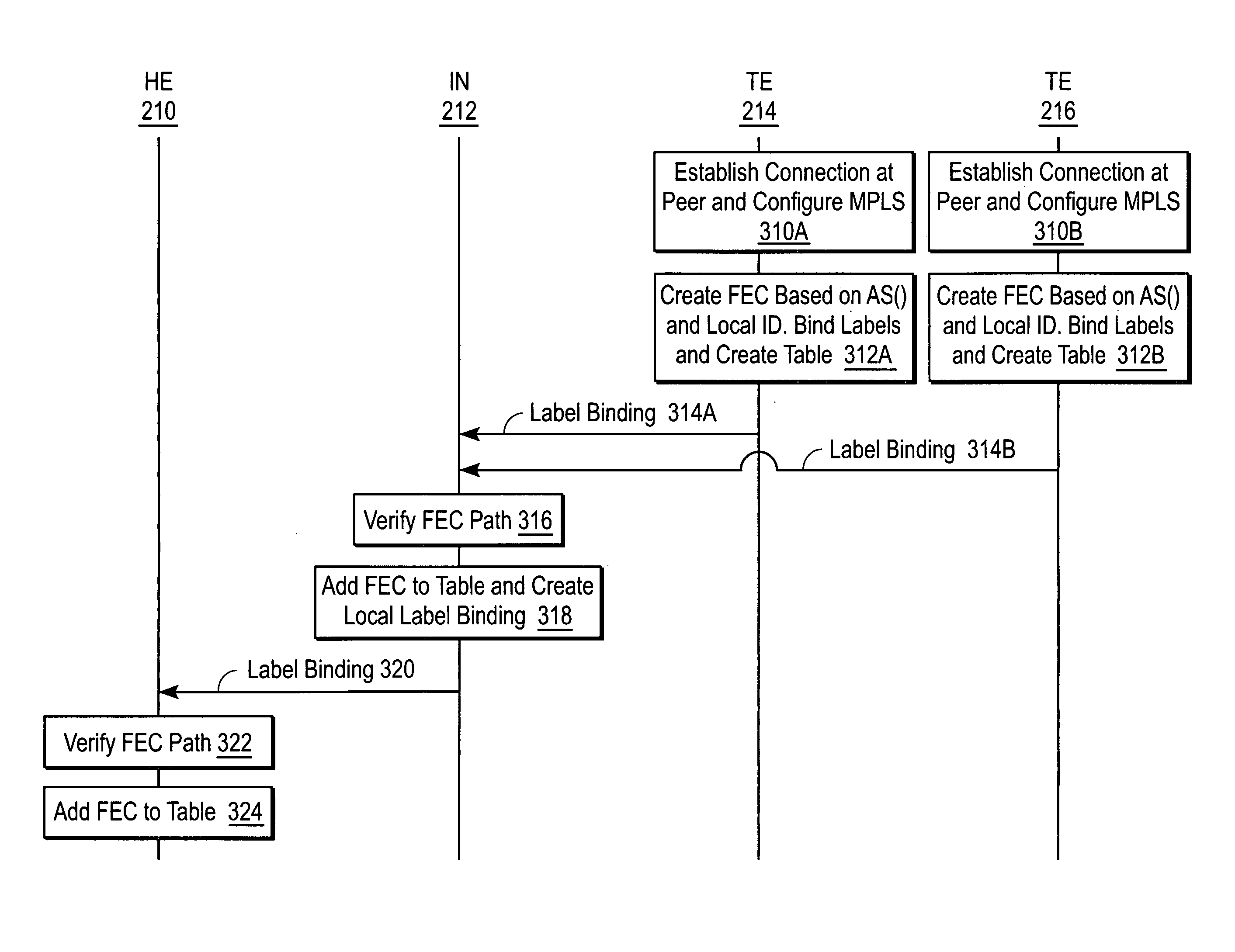
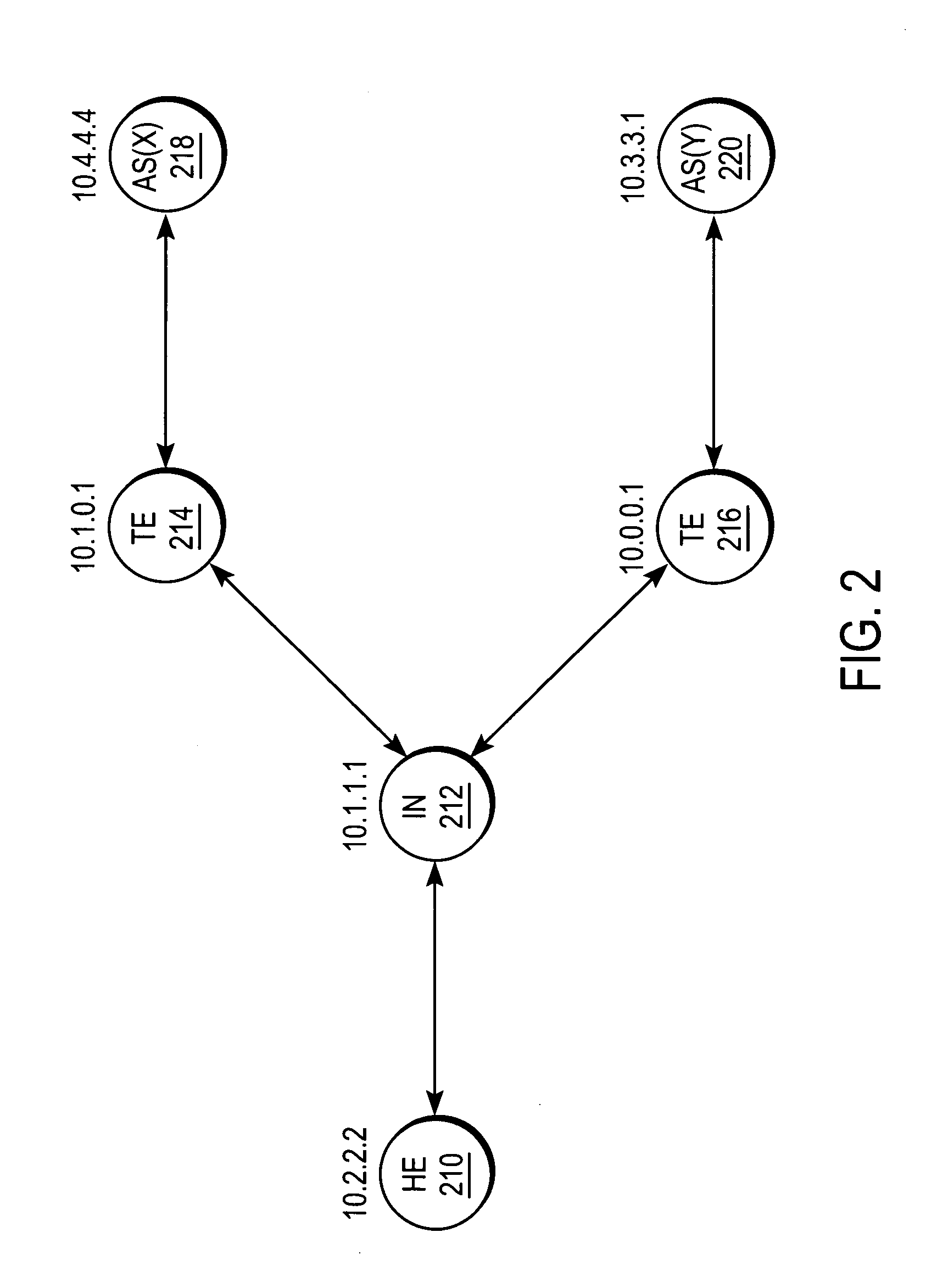
A system and method for sharing access to an internet protocol (IP) network among multiple internet service providers (ISPs) uses multiprotocol label switching (MPLS). End-users are coupled to a broadband customer access network. Each end-user is also associated with at least one of the ISPs. An aggregation router interfaces the customer access network with a network backbone. The network backbone includes a border router for interfacing between the network backbone and the network of an ISP. When the border router is activated, it creates a forwarding equivalency class (FEC) corresponding to the ISP. The border router stores a label for the FEC and the interface for reaching the ISP in an FEC table. The border router advertises the label binding for the FEC to all upstream nodes. An intermediate node receiving the label binding creates its own FEC table, associates a new label with the FEC, and advertises the new label binding to its upstream nodes. The aggregation router receives and builds a FEC table containing the label bindings for all ISPs reachable over the network backbone. When the aggregation router receives a data packet from an end-user, the aggregation router determines the ISP associated with the end-user, labels the data packet with the label corresponding to the FEC for that ISP, and routes the packet on the network backbone. The packet eventually reaches the border router, which pops off the label and passes the packet to the ISP.
Owner:AT HOME BONDHOLDERS LIQUIDATING TRUST +1
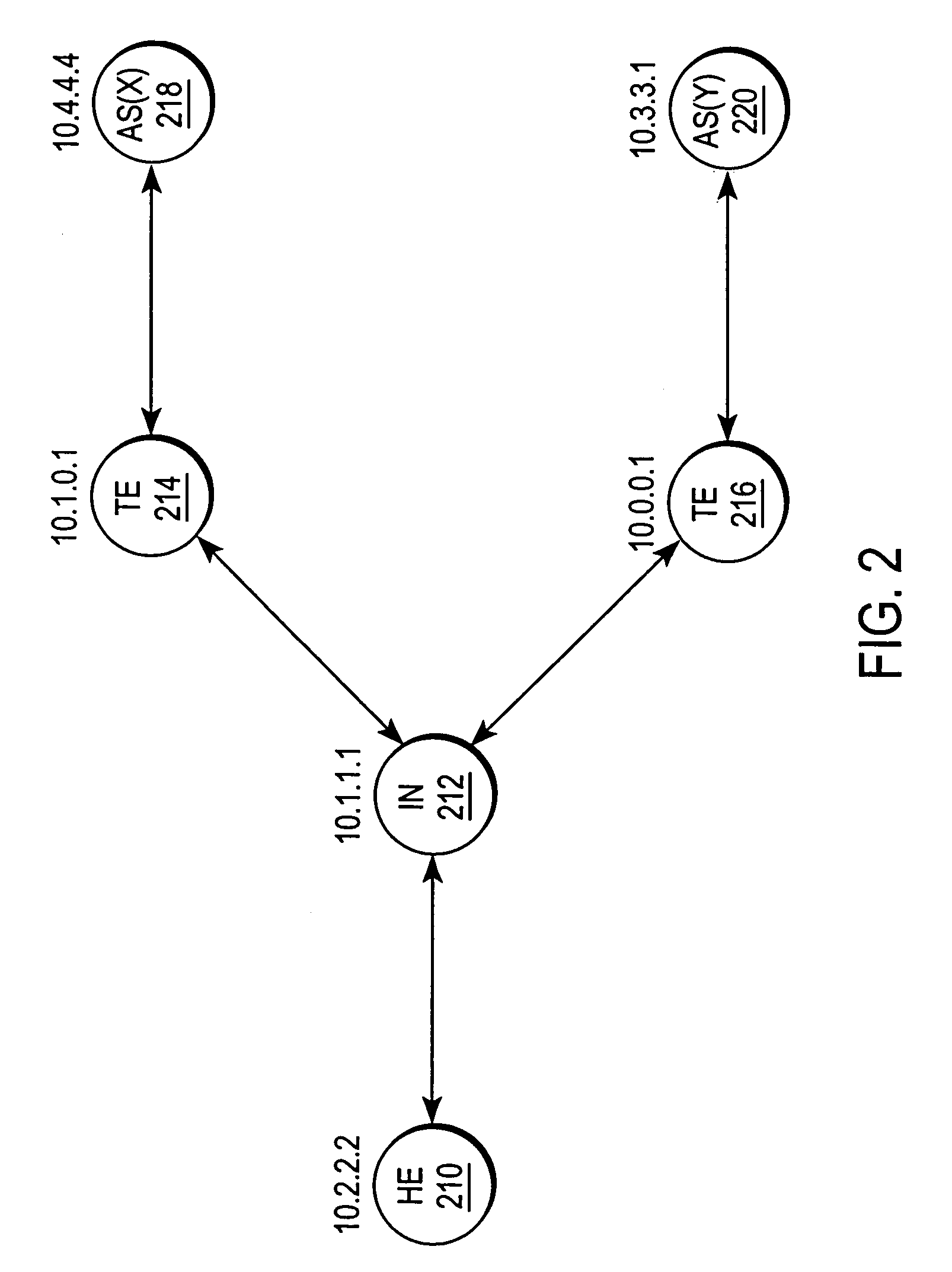
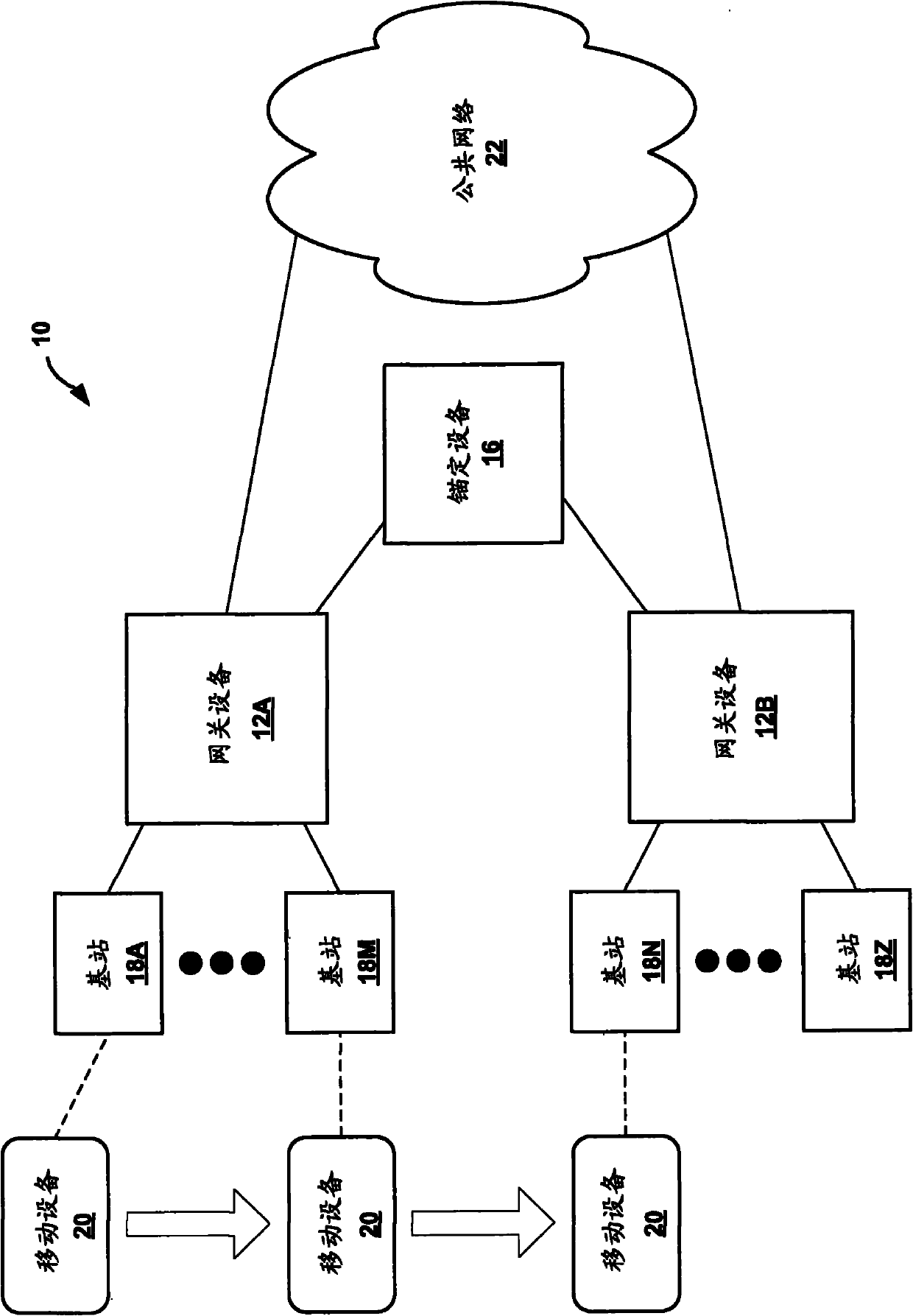
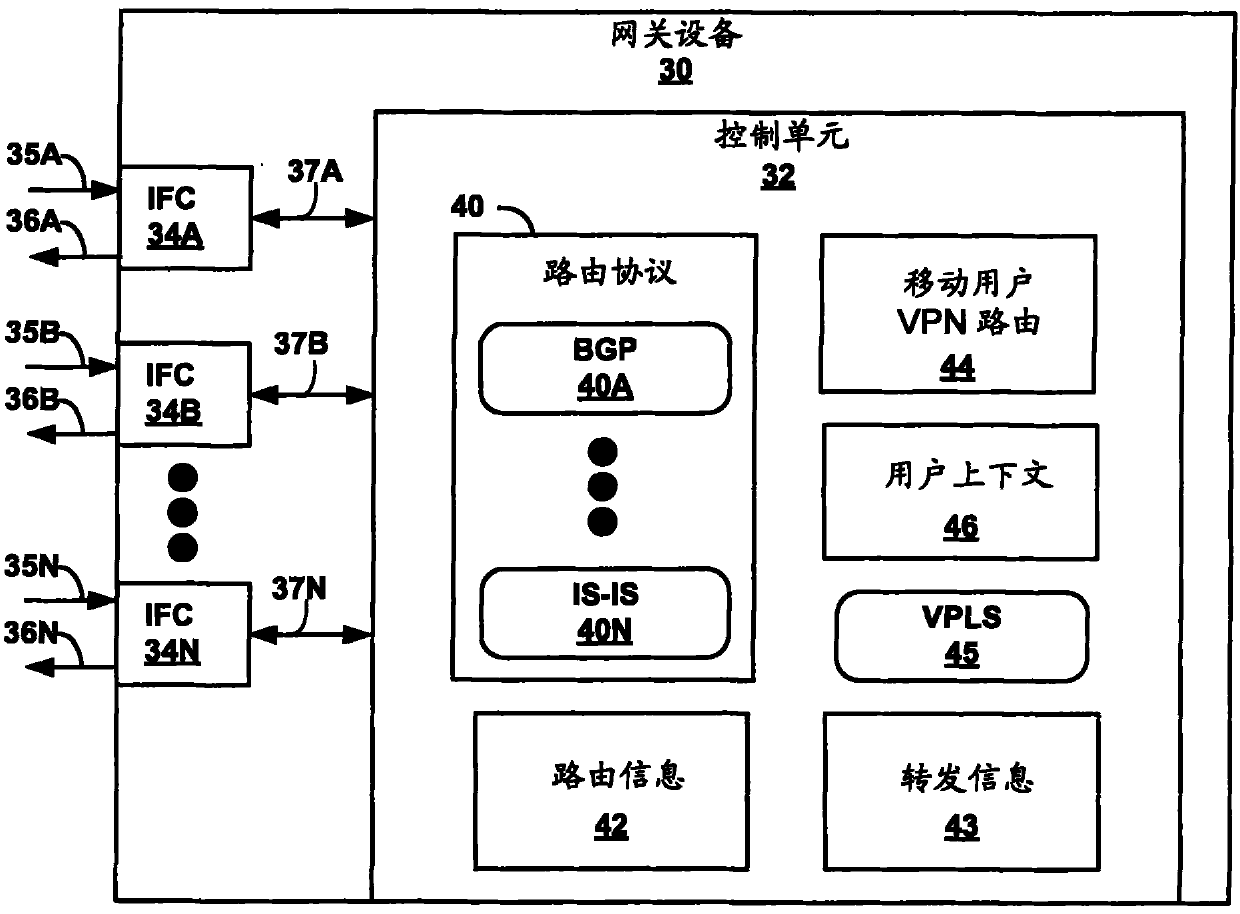
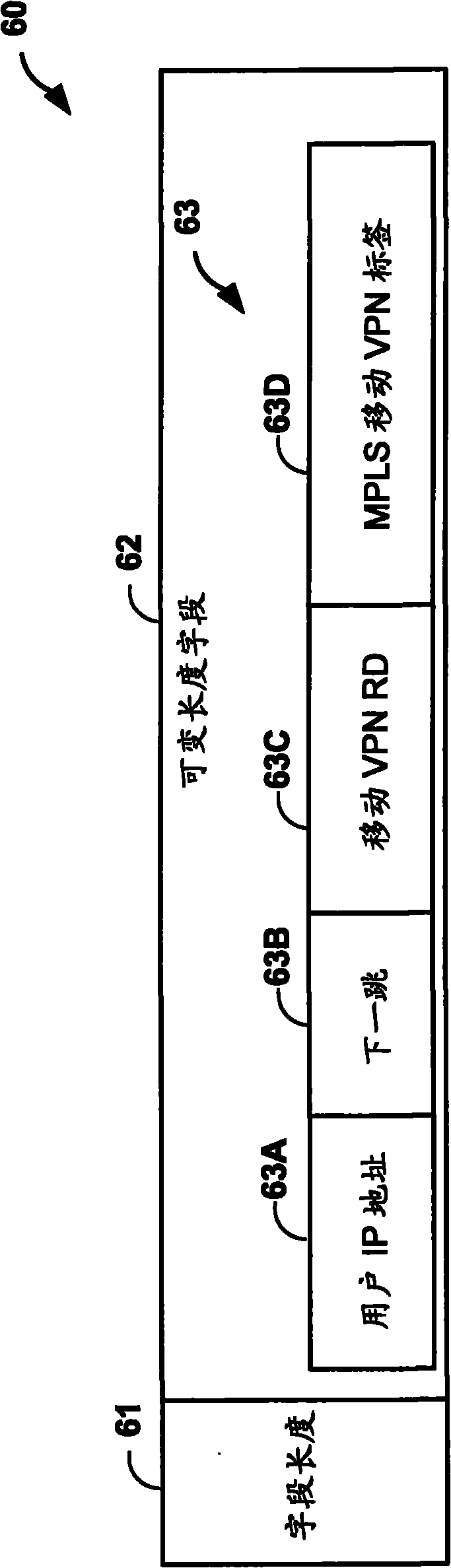
Network-based macro mobility in cellular networks using an extended routing protocol
A new architecture provides network-based mobility in cellular networks that is built on Internet Protocol (IP) / Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) technologies, such as Virtual Private Local Area Network (LAN) Service (VPLS), the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and BGP MPLS Layer 3 Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). The architecture consists of several building blocks that provide functionality for different aspects of cellular network mobility. One building block is network-based macro mobility in IP / MPLS networks. The macro mobility techniques described herein are built on extensions to a routing protocol such as BGP. Another building block relates to transferring subscriber context between network devices while preserving the IP address of the subscriber. The techniques described herein provide a subscriber context transfer mechanism for mobile subscriber management that is built on extensions to a routing protocol such as BGP. Another building block of the mobility architecture is network-based micro mobility based on VPLS.
Owner:JUMIPER NETWORKS INC
Sharing IP network resources
InactiveUS20060041682A1Efficient sharingEnergy efficient ICTMultiprogramming arrangementsAccess networkMultiprotocol Label Switching
A system and method for sharing access to an internet protocol (IP) network among multiple internet service providers (ISPs) uses multiprotocol label switching (MPLS). End-users are coupled to a broadband customer access network. Each end-user is also associated with at least one of the ISPs. An aggregation router interfaces the customer access network with a network backbone. The network backbone includes a border router for interfacing between the network backbone and the network of an ISP. When the border router is activated, it creates a forwarding equivalency class (FEC) corresponding to the ISP. The border router stores a label for the FEC and the interface for reaching the ISP in an FEC table. The border router advertises the label binding for the FEC to all upstream nodes. An intermediate node receiving the label binding creates its own FEC table, associates a new label with the FEC, and advertises the new label binding to its upstream nodes. The aggregation router receives and builds a FEC table containing the label bindings for all ISPs reachable over the network backbone. When the aggregation router receives a data packet from an end-user, the aggregation router determines the ISP associated with the end-user, labels the data packet with the label corresponding to the FEC for that ISP, and routes the packet on the network backbone. The packet eventually reaches the border router, which pops off the label and passes the packet to the ISP.
Owner:AT HOME BONDHOLDERS LIQUIDATING TRUST
Access method and device of multiprotocol label switching double-layer virtual private network
ActiveCN101808042AImprove scalabilityReduce management complexityNetworks interconnectionExtensibilityAccess method
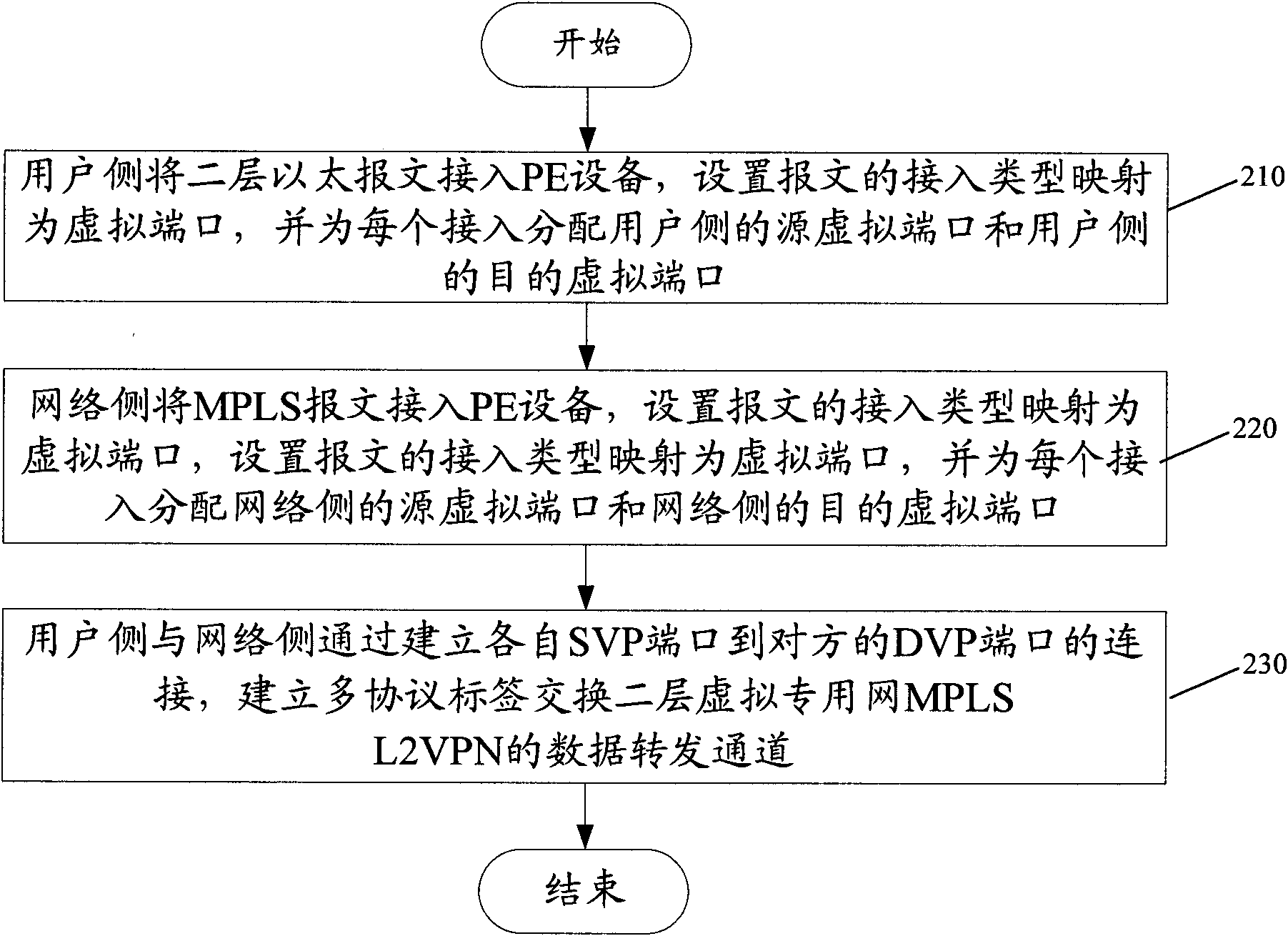
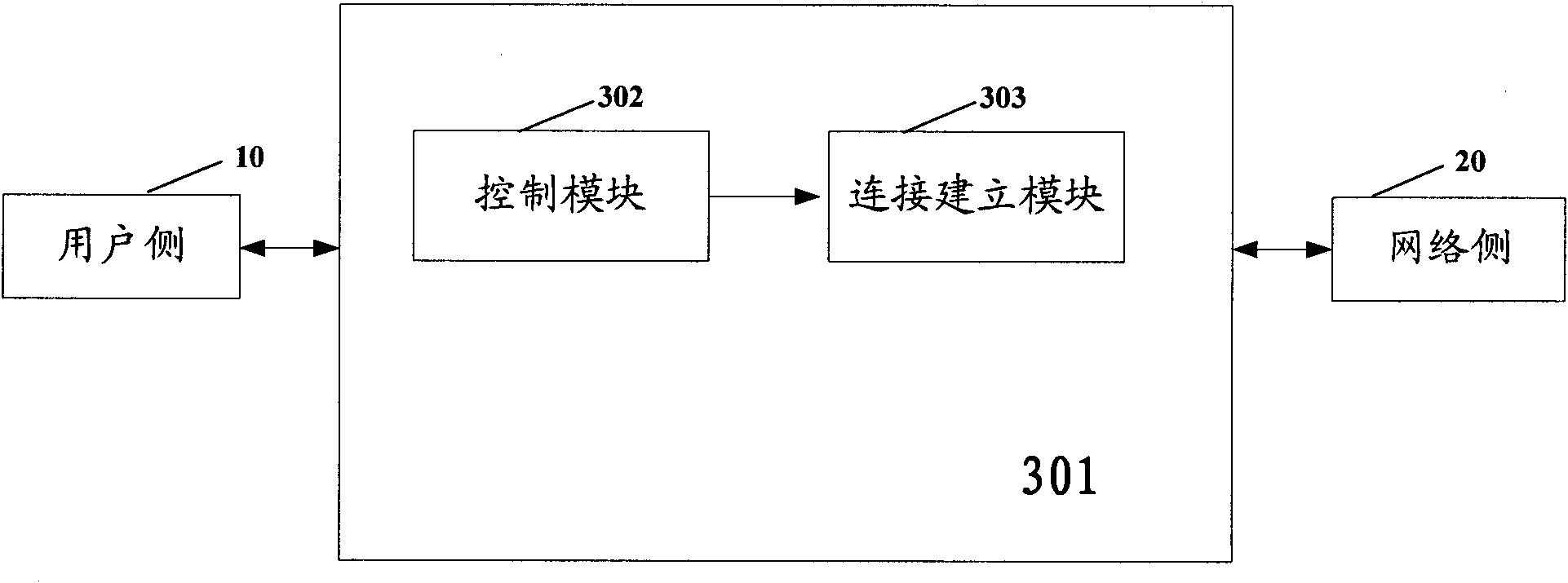
The invention discloses an access method and a device of multiprotocol label switching double-layer virtual private network. The method comprises the following steps: a user side and a network side respectively access respective message into operator route equipment; the access type mapping of the message is a virtual port, and each access is distributed with respective SVP port and DVP port; and the user side and the network side build a data forwarding path of a multiprotocol label switching double-layer virtual private network by building the connection of respective SVP port to opposite side DVP port. The invention maps various access modes into the virtual port in a unified mode, and accesses MPLS L2VPN in and forwards on the basis of VSI and VP. The invention enhances the expandability for user messages to access into L2VPN, lowers L2VPN access management complexity and system development difficulty and improves system reliability.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com