Patents
Literature
237results about How to "Effective division" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
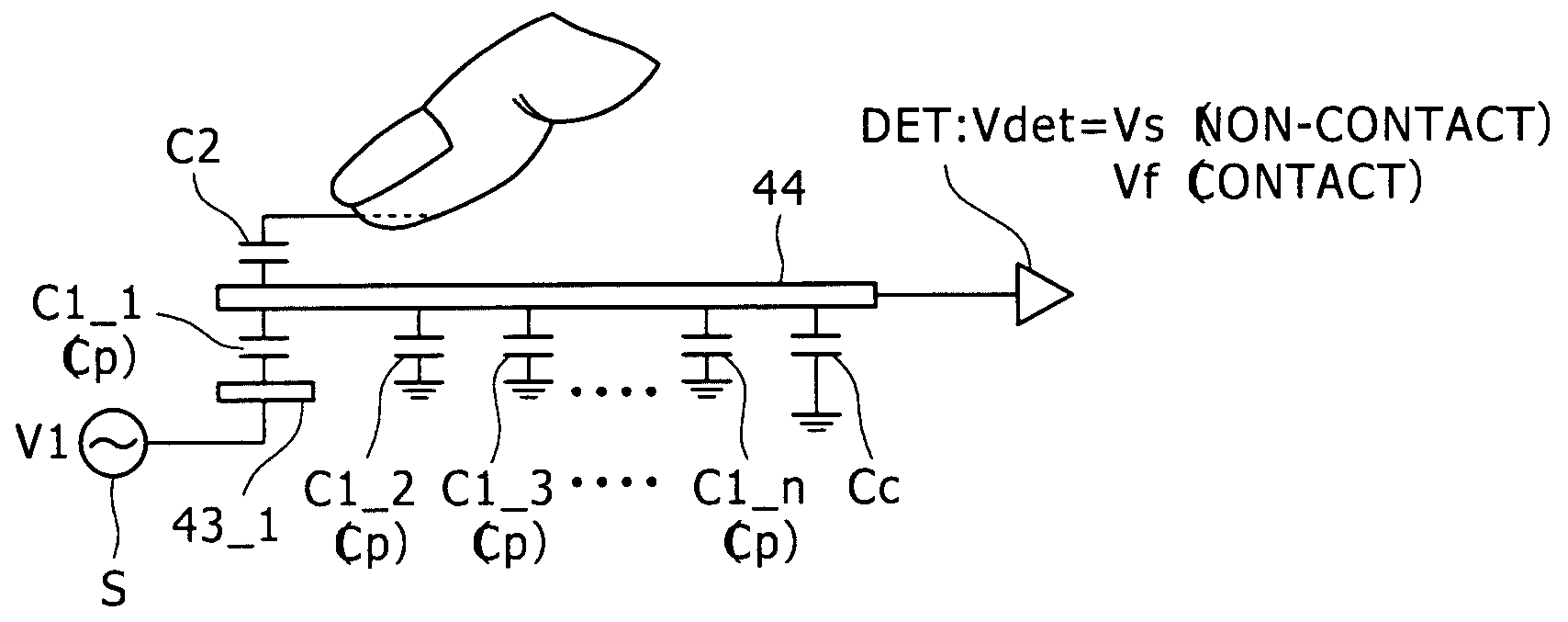
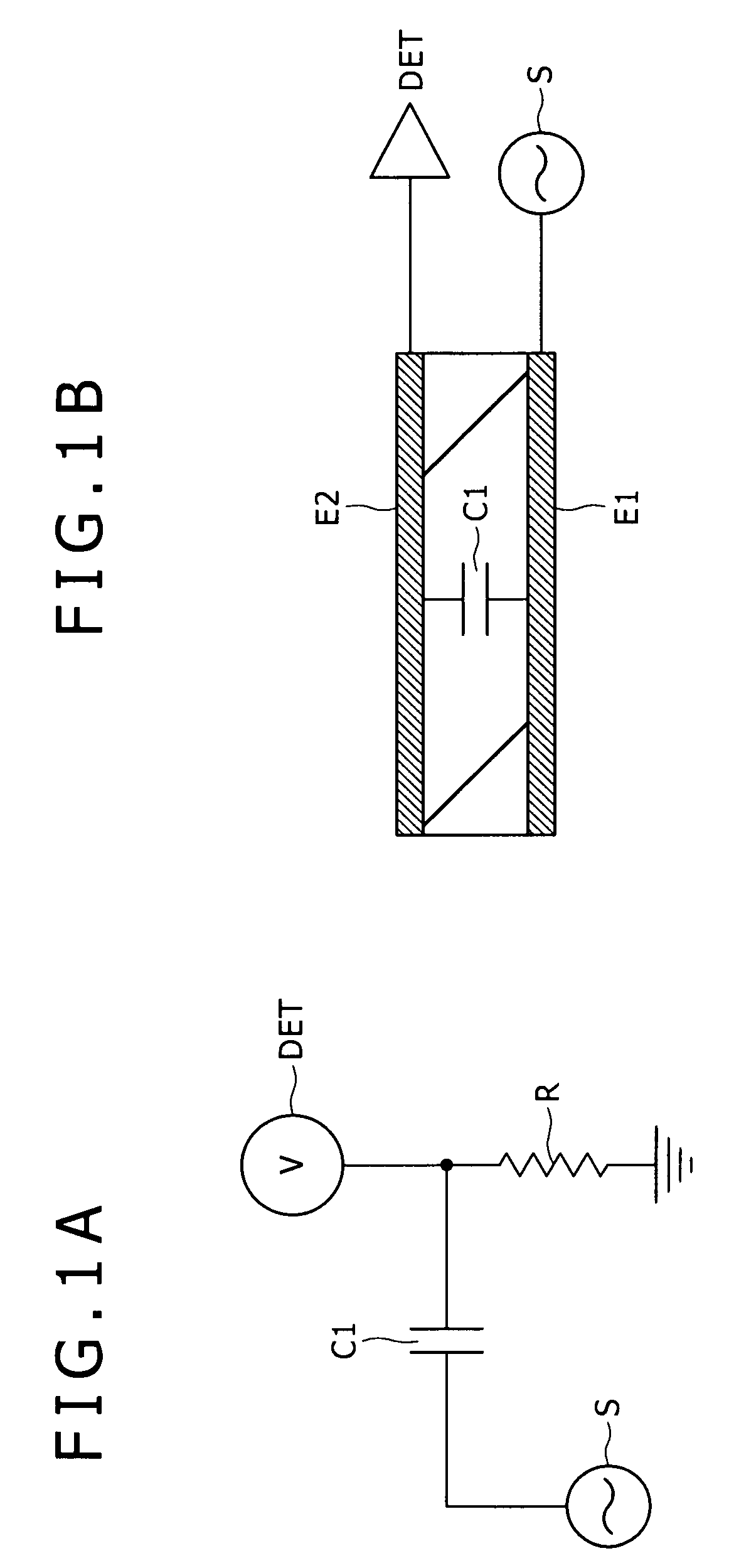
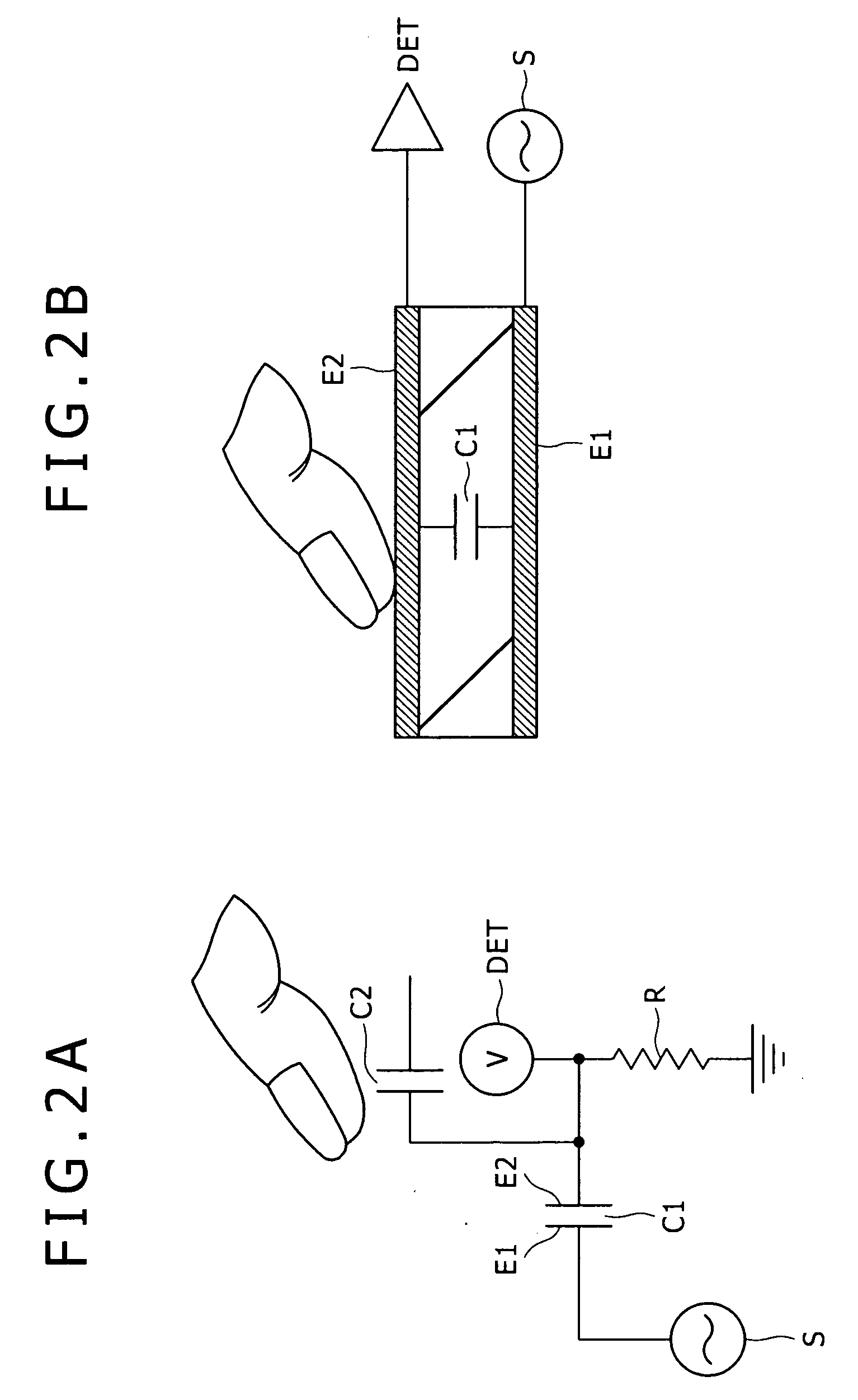
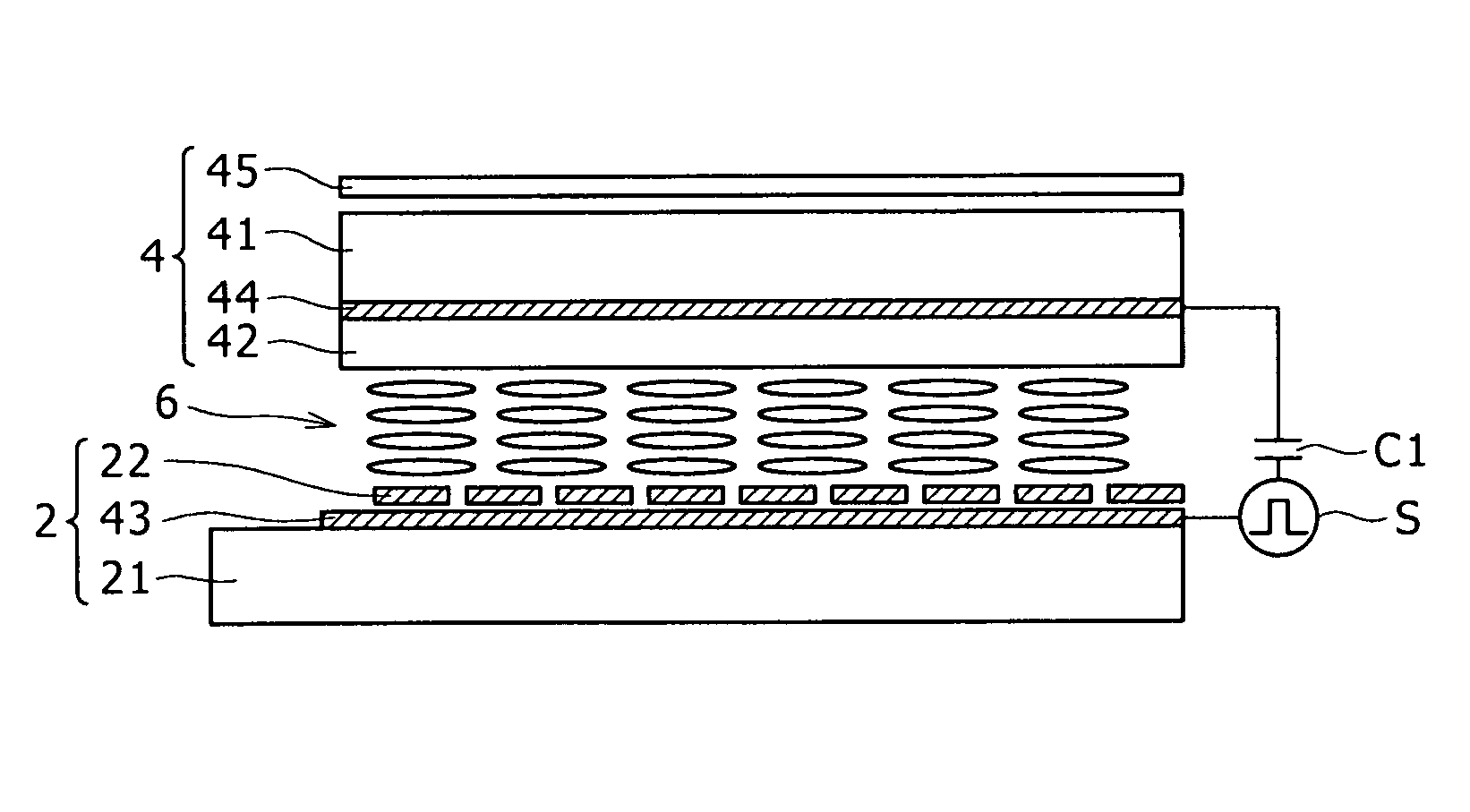
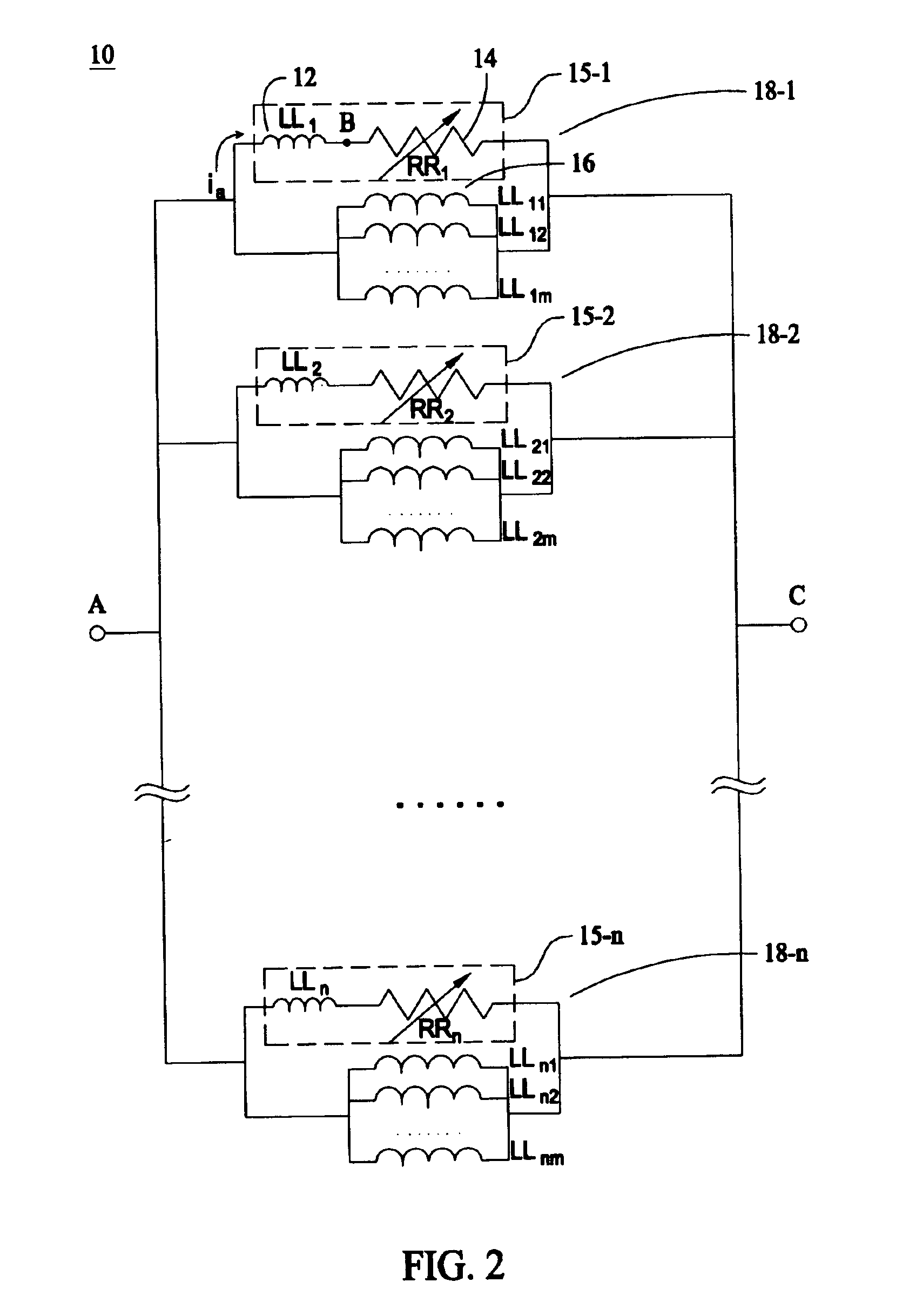
Display device and a method of driving the same
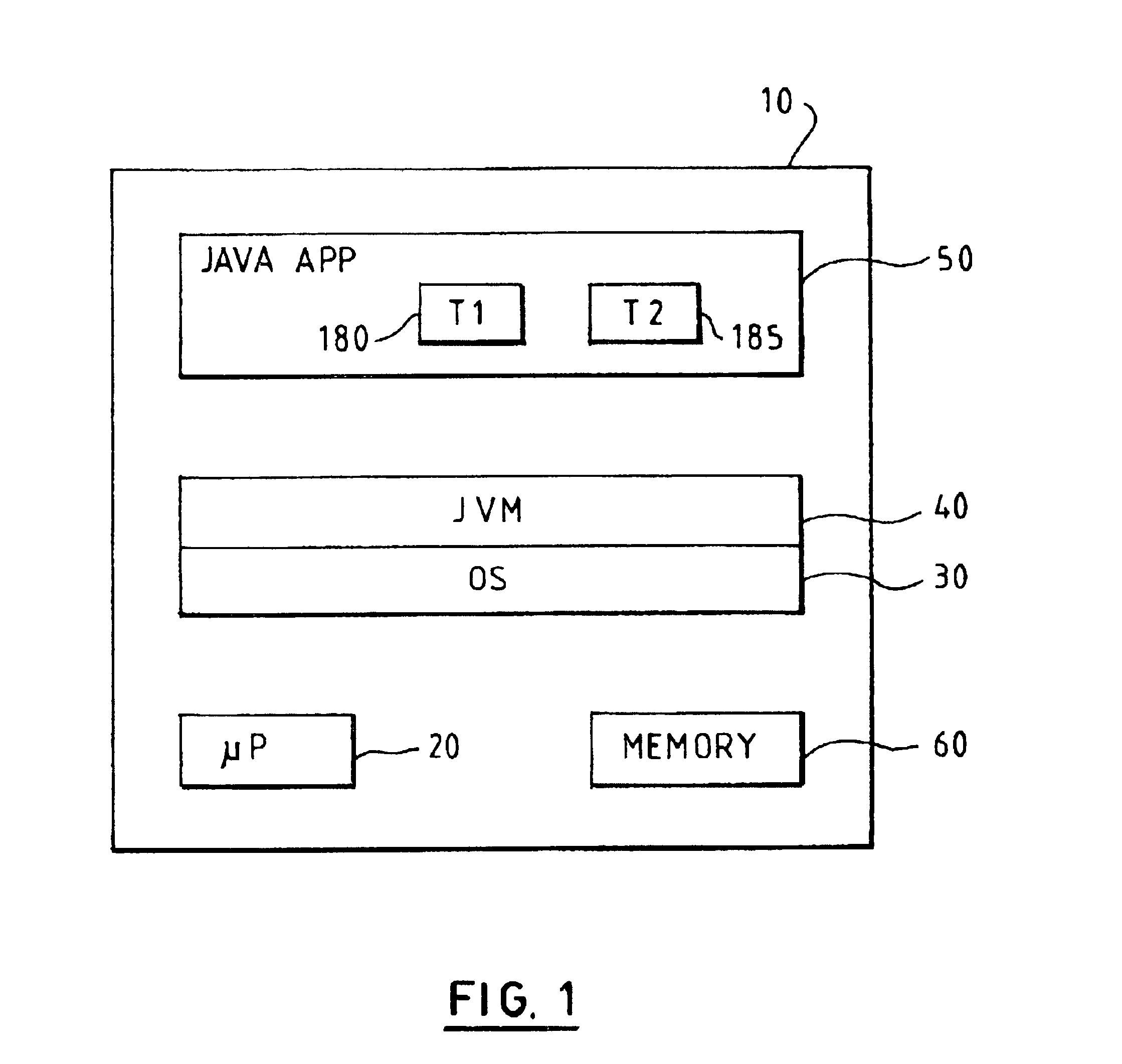
ActiveUS20090256818A1Reduce stepsEffective divisionEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsAC - Alternating currentDisplay device
A display device including: a plurality of pixels; pixel electrodes; n (n≧2) counter electrodes; a display functional layer; a write drive scanning portion; detection electrodes; an alternate current drive scanning portion; and a detecting portion.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
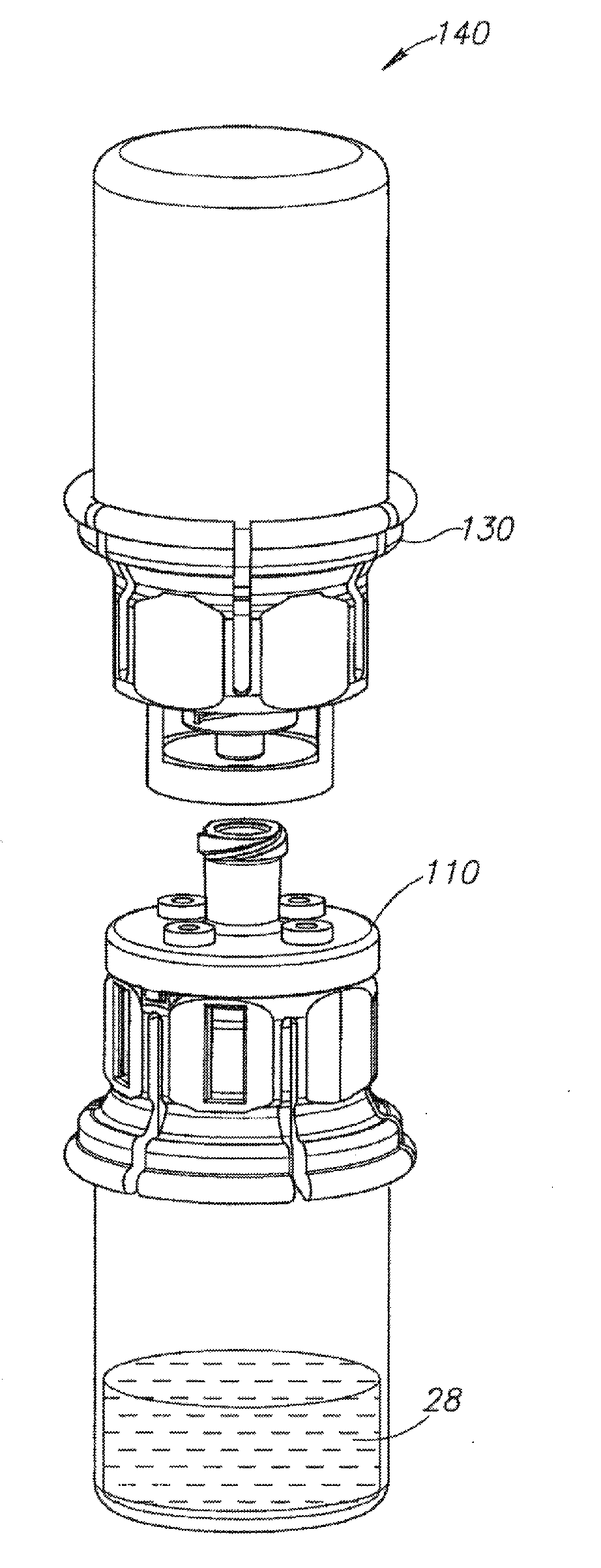
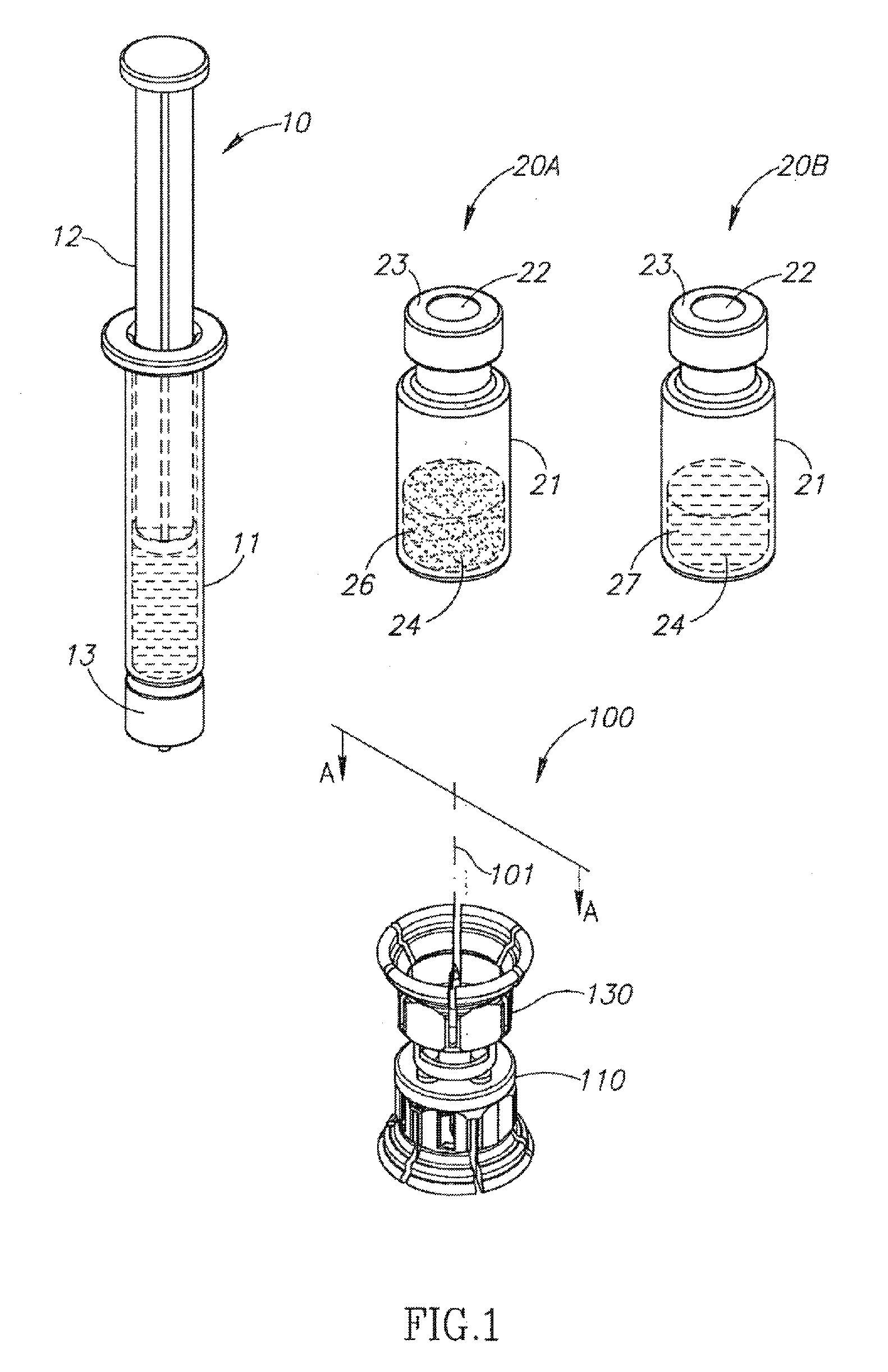
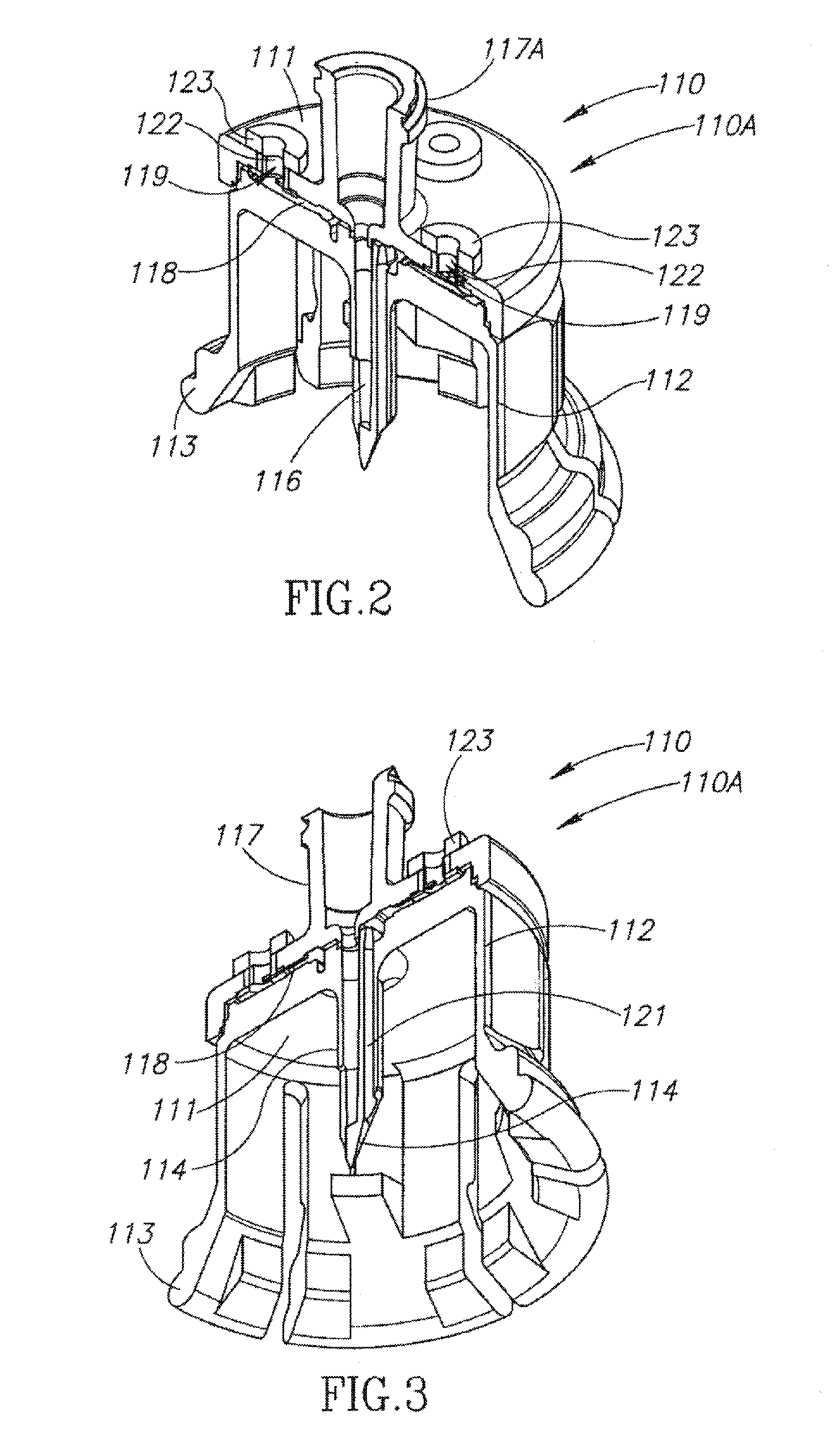
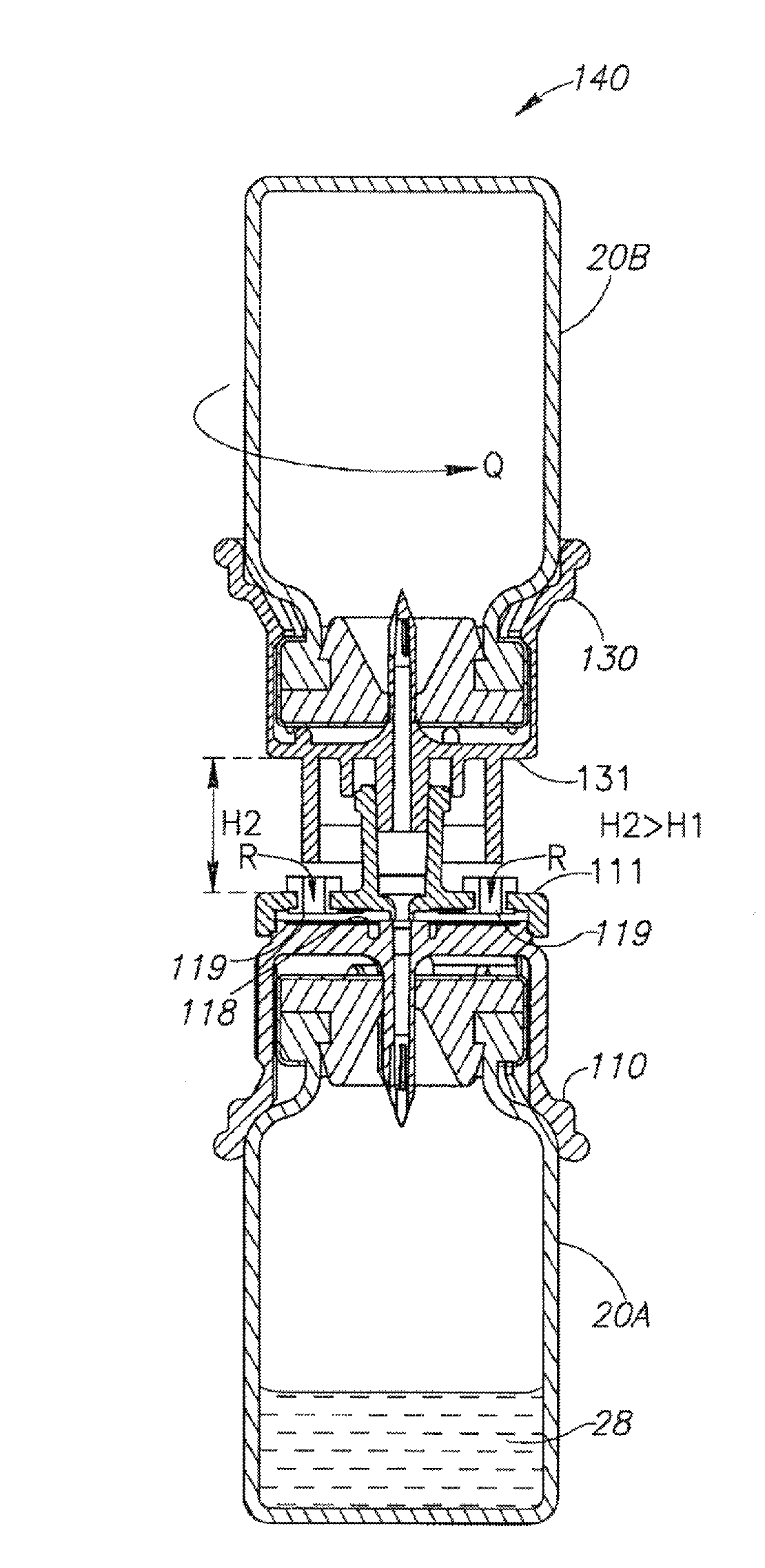
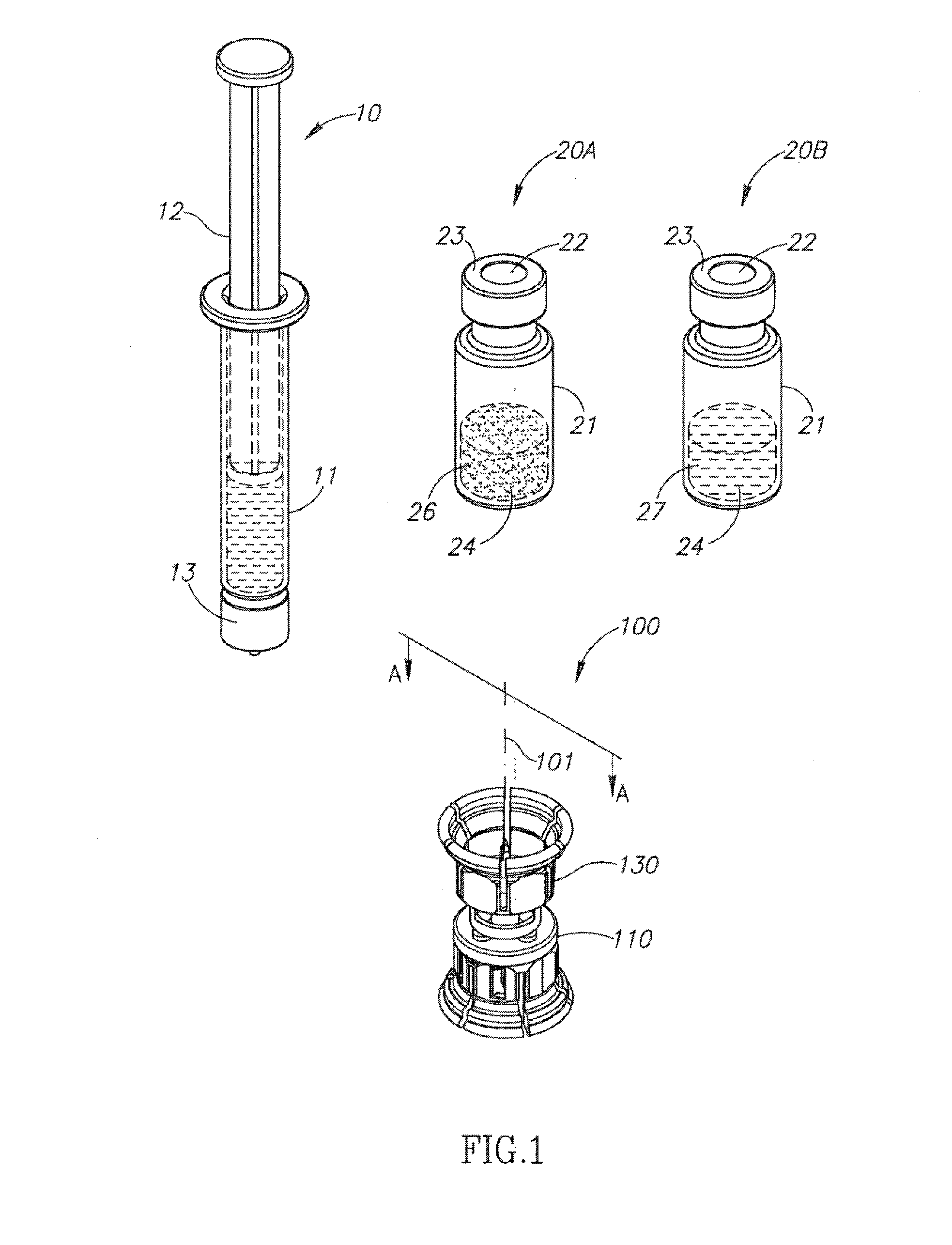
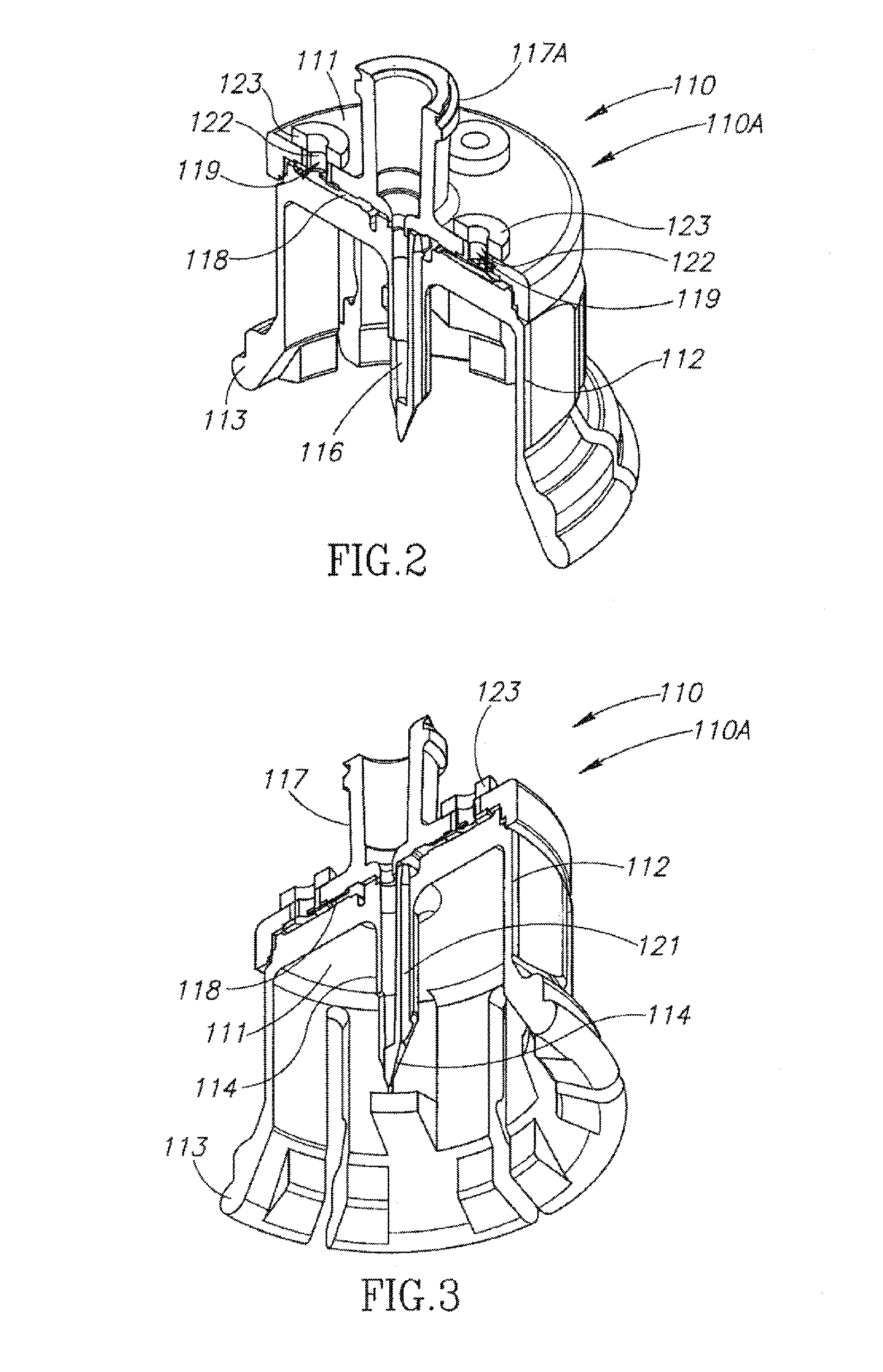
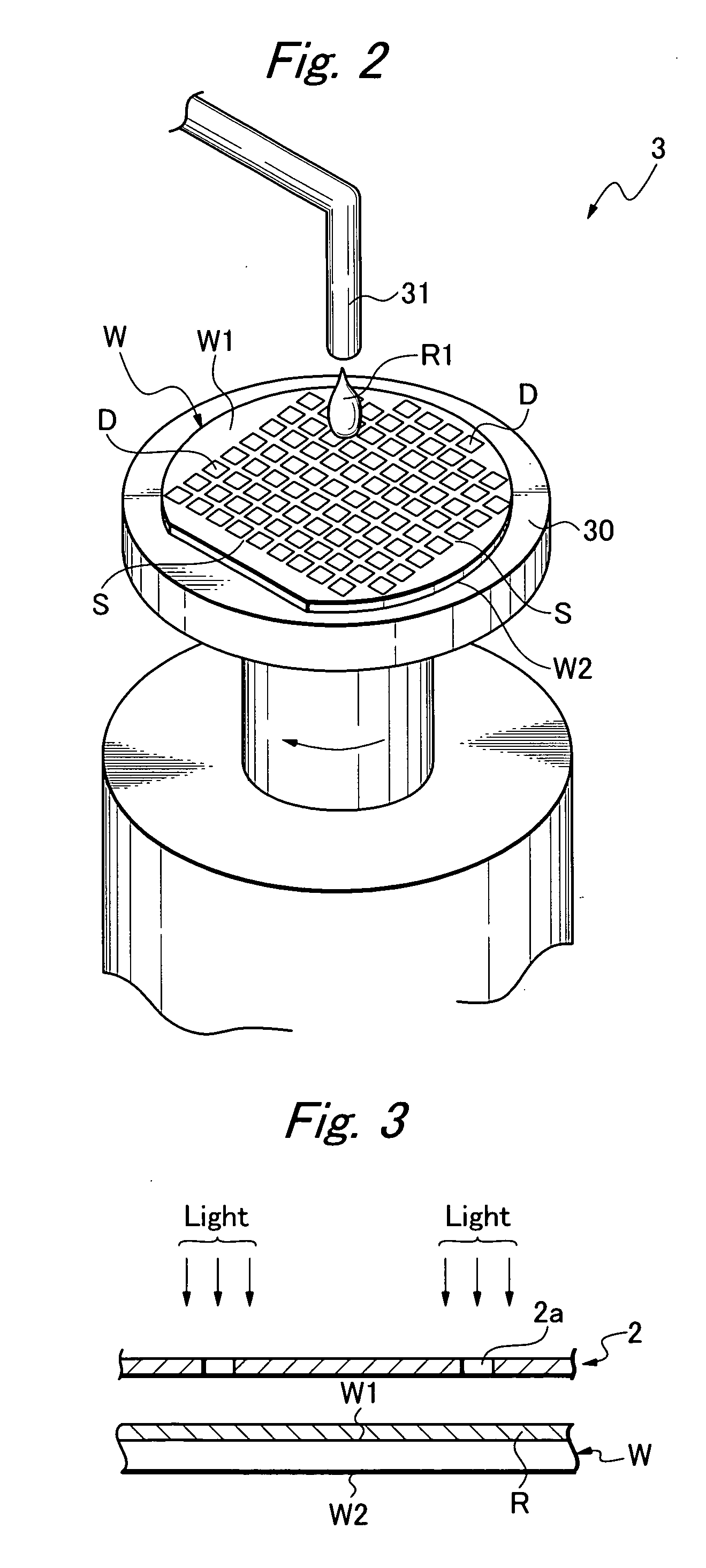
Fluid transfer assembly with venting arrangement
Owner:WEST PHARM SERVICES IL LTD
Fluid transfer assembly with venting arrangement
A fluid transfer assembly including a vented female vial adapter and male vial adapter for use with a pair of vials including a vial with contents under negative pressure for liquid drug reconstitution and administration purposes. The vented female vial adapter includes a venting arrangement and the male vial adapter includes a sealing arrangement for selectively sealing the venting arrangement. The fluid transfer assembly is designed such that only filtered air is drawn into the vial under negative pressure subsequent to reconstitution of liquid drug contents to ensure sterile conditions.
Owner:WEST PHARM SERVICES IL LTD
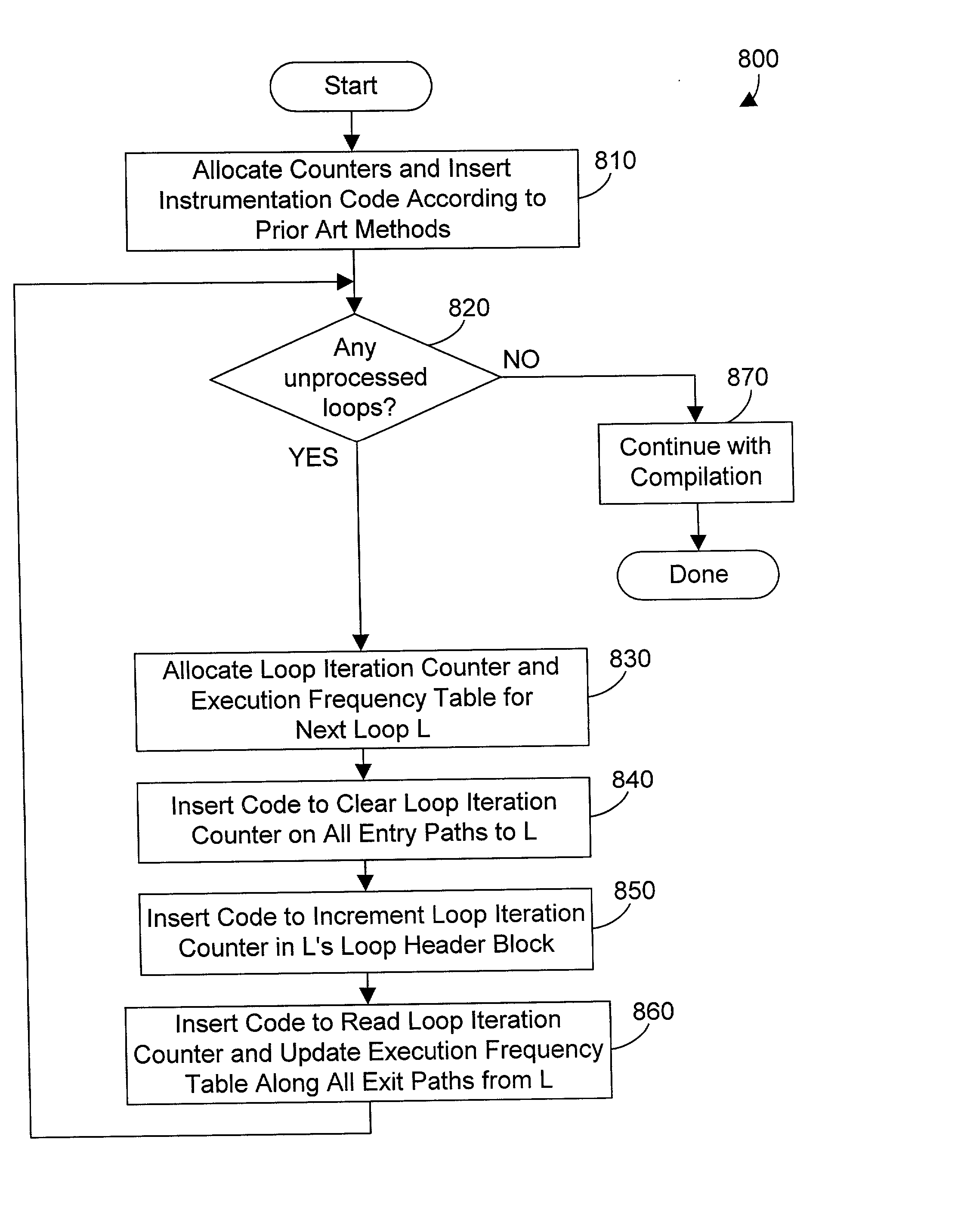
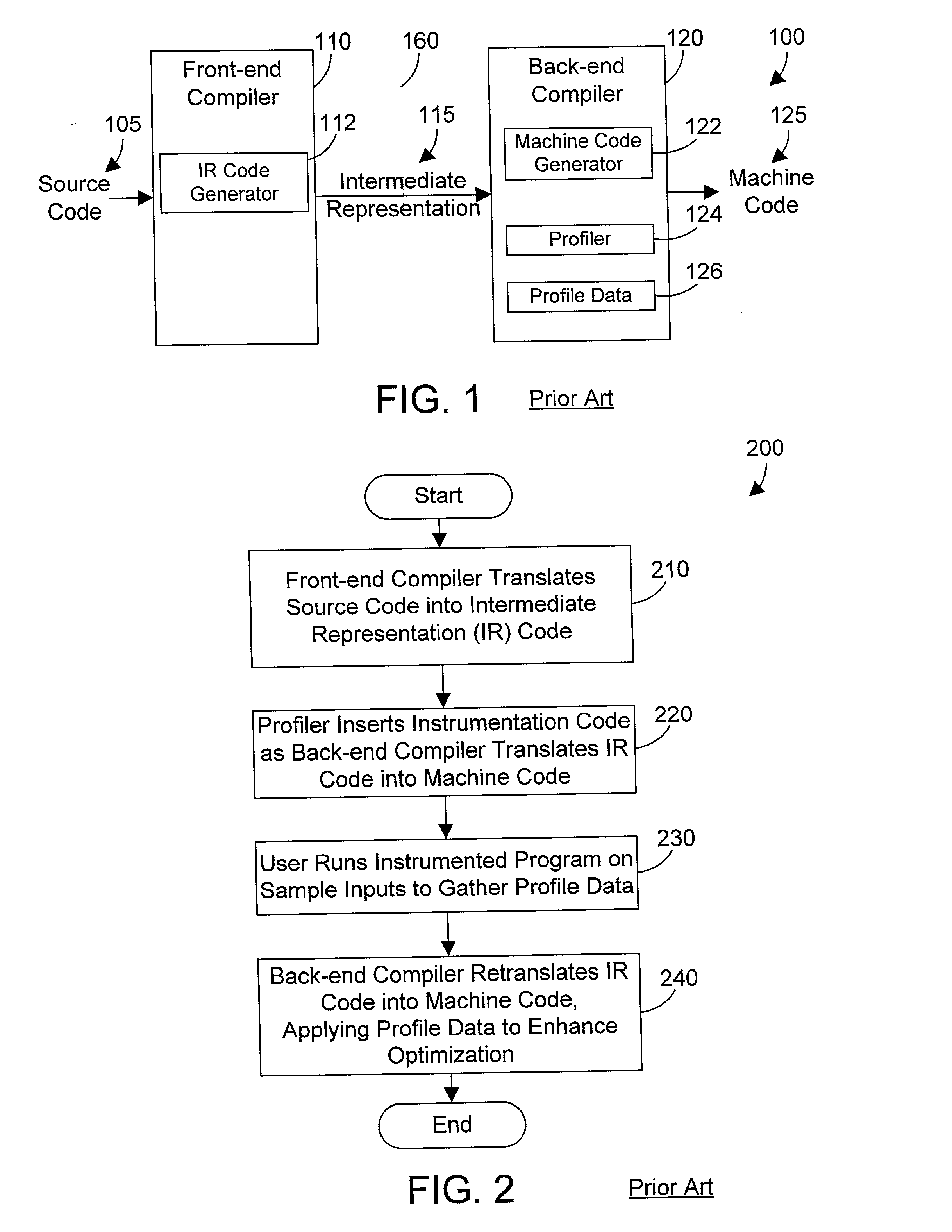
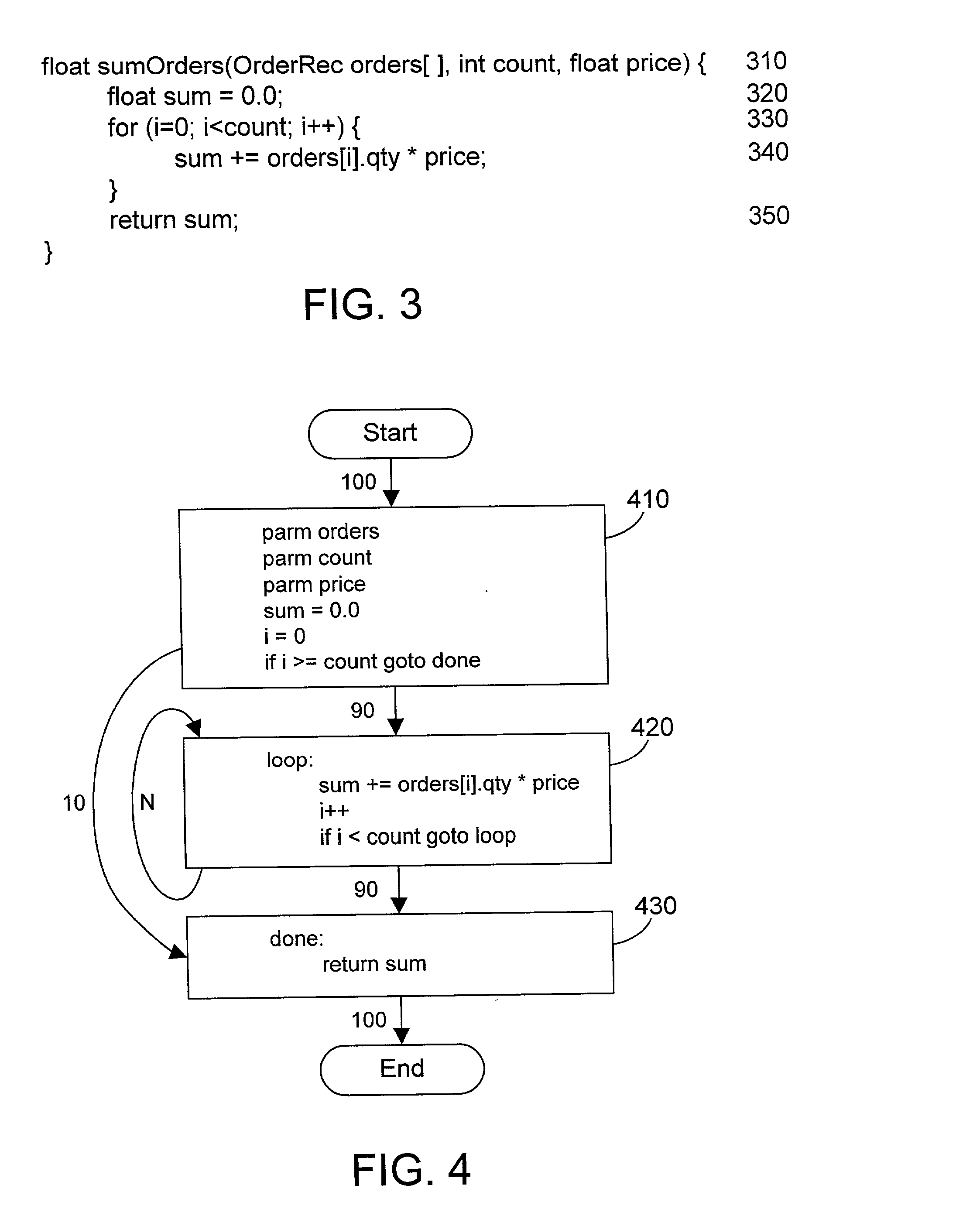
Compiler apparatus and method for optimizing loops in a computer program
ActiveUS20030097652A1Intelligent decisionMinimize total execution timeSoftware engineeringHardware monitoringTheoretical computer scienceLoop optimization
A profile-based loop optimizer generates an execution frequency table for each loop that gives more detailed profile data that allows making a more intelligent decision regarding if and how to optimize each loop in the computer program. The execution frequency table contains entries that correlate a number of times a loop is executed each time the loop is entered with a count of the occurrences of each number during the execution of an instrumented instruction stream. The execution frequency table is used to determine whether there is one dominant mode that appears in the profile data, and if so, optimizes the loop according to the dominant mode. The optimizer may perform optimizations by peeling a loop, by unrolling a loop, and by performing both peeling and unrolling on a loop according to the profile data in the execution frequency table for the loop. In this manner the execution time of the resulting code is minimized according to the detailed profile data in the execution frequency tables, resulting in a computer program with loops that are more fully optimized.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY INC
High resolution encoding and transmission of traffic information
ActiveUS20160104377A1Increasing geospatial resolutionValid encodingAnalogue computers for vehiclesArrangements for variable traffic instructionsData streamDriver/operator
Systems and methods are provided for increasing the geospatial resolution of traffic information by dividing known location intervals into a fixed number of sub-segments not tied to any one map providers format, efficient coding of the traffic information, and distribution of the traffic information to end-user consuming devices over one or more of a satellite based broadcast transport medium and a data communications network. Exemplary embodiments of the present invention detail a nationwide traffic service which can be encoded and distributed through a single broadcast service, such as, for example, an SDARS service, or a broadcast over a data network. Exemplary embodiments include aggregating the traffic data from segments of multiple location intervals, into predefined and predetermined flow vectors, and sending the flow vectors within a data stream to users. Confidence levels obtained from raw traffic data can both (I) be disclosed to drivers / users to supplement a very low signal (or no signal) speed and congestion report, and (ii) can also be used in various system algorithms that decide what local anomalies or aberrations to filter out as noise, or to disclose as accurate information and thus more granularly depict the roadway in question (and use additional bits to do so) as an actual highly localized traffic condition.
Owner:SIRIUS XM RADIO INC
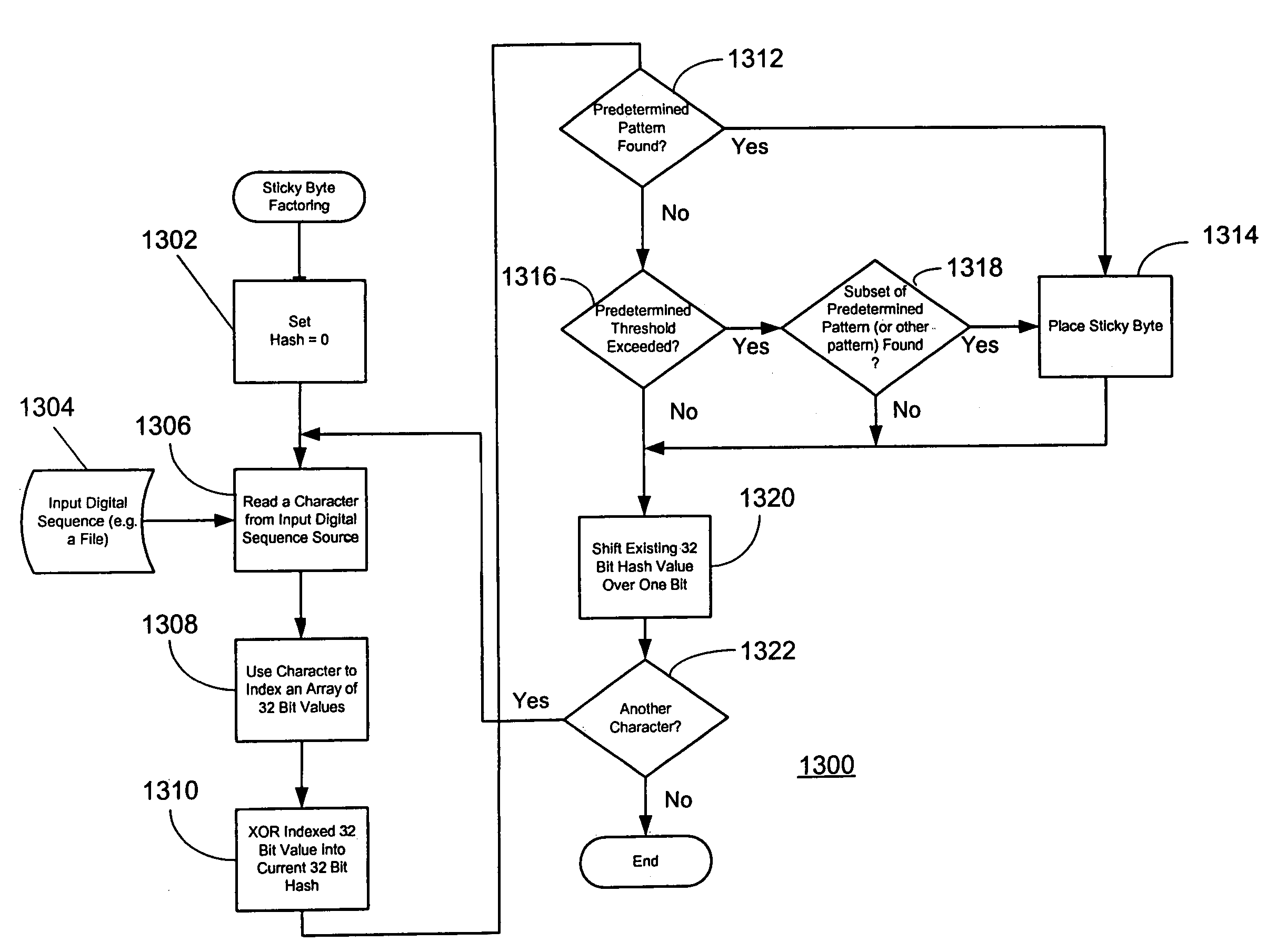
System and method for unorchestrated determination of data sequences using sticky byte factoring to determine breakpoints in digital sequences
InactiveUS7272602B2Near optimal commonalityMinimal computationData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData setRolling hash
A system and method for unorchestrated determination of data sequences using “sticky byte” factoring to determine breakpoints in digital sequences such that common sequences can be identified. Sticky byte factoring provides an efficient method of dividing a data set into pieces that generally yields near optimal commonality. This is effectuated by employing a rolling hashsum and, in an exemplary embodiment disclosed herein, a threshold function to deterministically set divisions in a sequence of data. Both the rolling hash and the threshold function are designed to require minimal computation. This low overhead makes it possible to rapidly partition a data sequence for presentation to a factoring engine or other applications that prefer subsequent synchronization across the data set.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Method of dividing wafer
InactiveUS20060088983A1Improve productivityDie strength of does not decreaseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringPlasma etching
In order to efficiently divide the wafer into individual devices in dicing the wafer without deteriorating the quality of the devices, the front surface of the wafer is coated with a resist film except the regions corresponding to the streets, grooves of a depth corresponding to the finished thickness of the devices are formed by plasma etching in the regions corresponding to the streets, and the back surface of the wafer is ground so that the grooves are exposed from the side of the back surface and that the wafer is divided into individual devices.
Owner:DISCO CORP
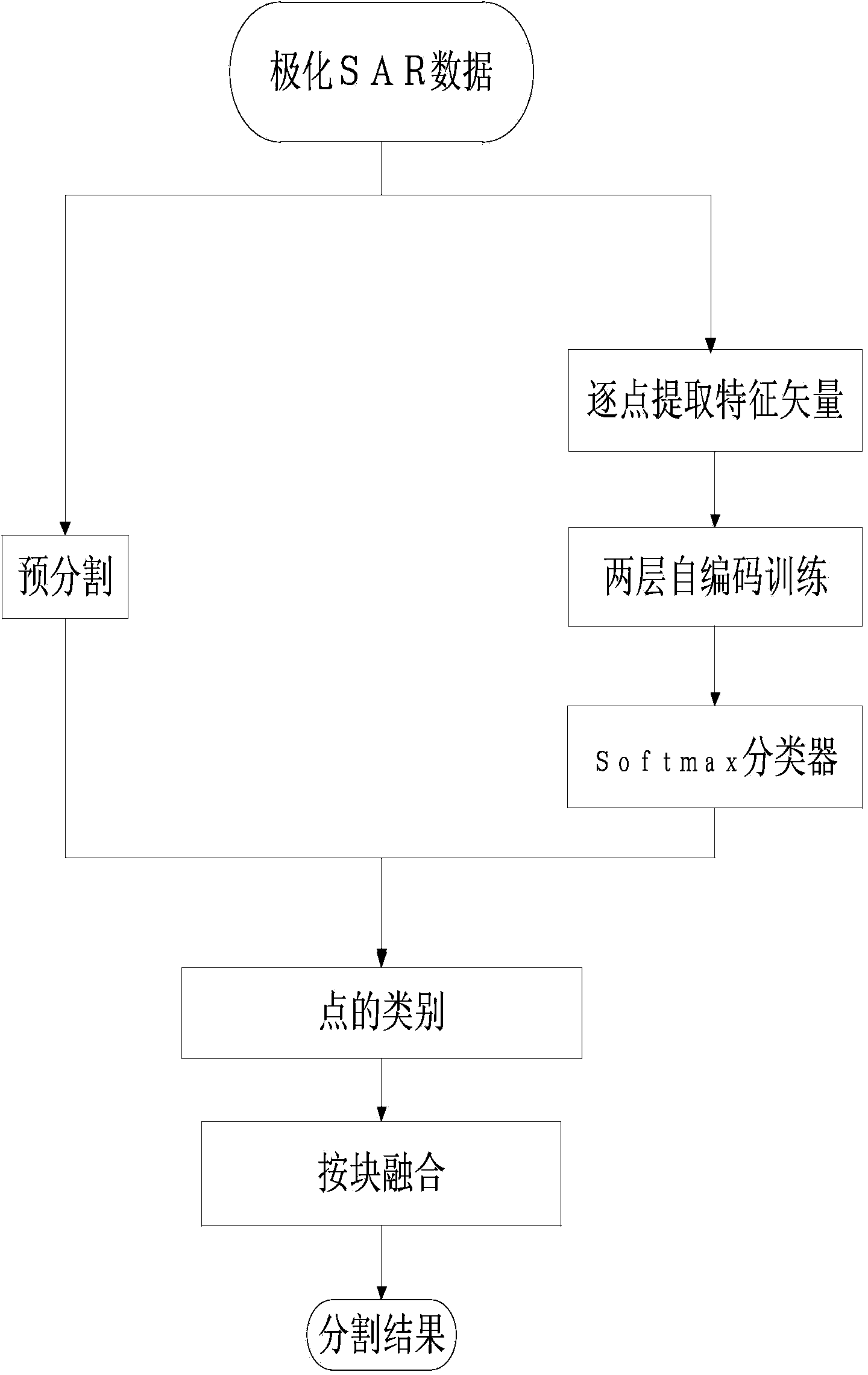
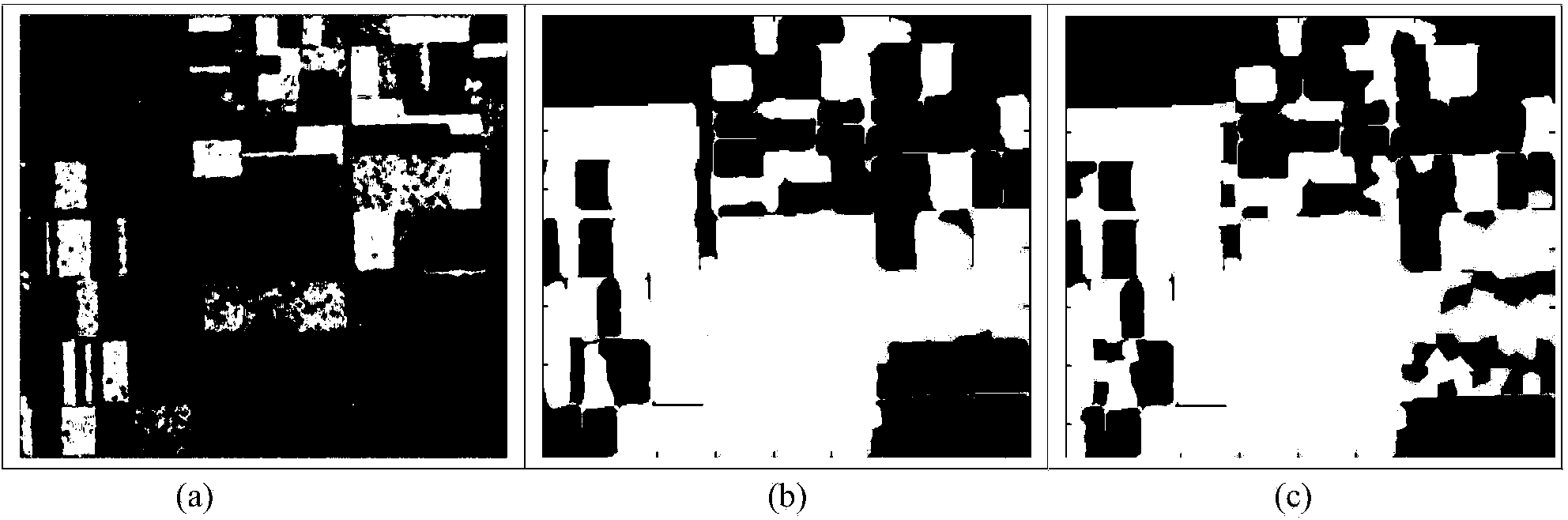
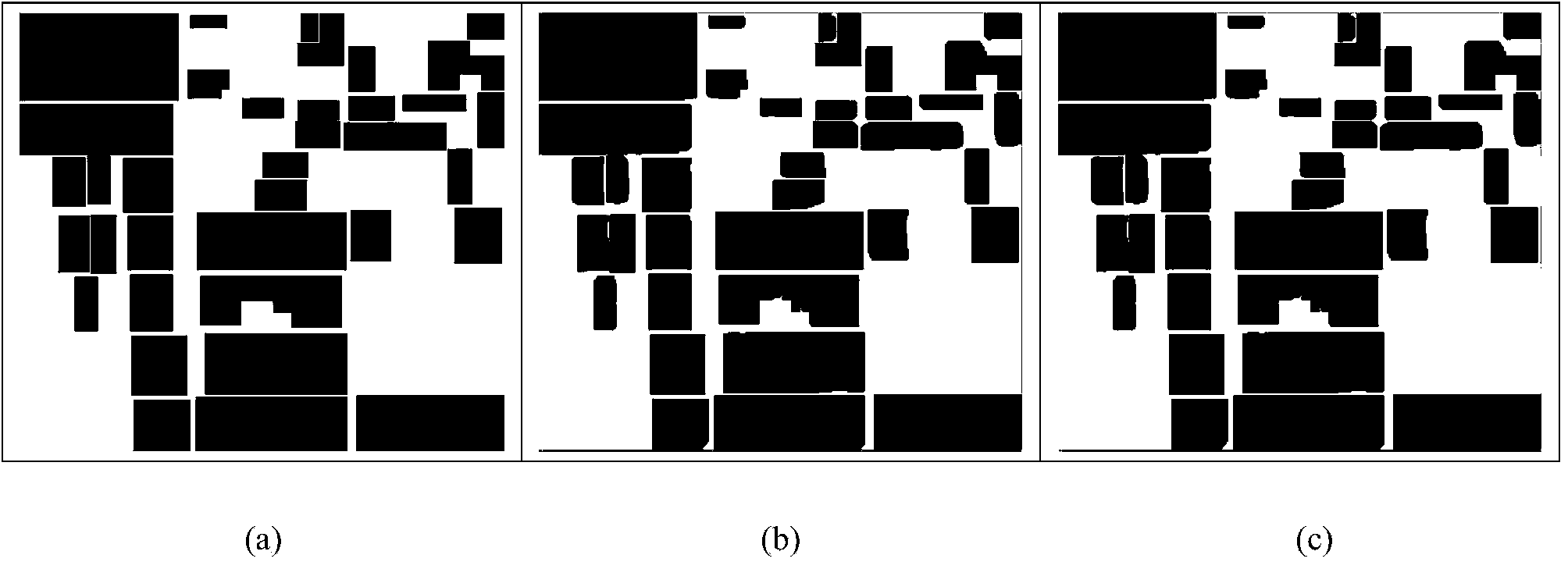
Polarization SAR image classification method based on deep neural network
ActiveCN104077599AEfficient extractionFeature validImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionPower diagramData set
The invention discloses a polarization SAR image classification method based on a deep neural network. The method mainly solves the problems that traditional polarization SAR image classification accuracy is low and boundaries are disorderly. The method includes the classification steps that a power diagram I is acquired from polarization SAR data through Pauli decomposition, the power diagram I is segmented in advance, and then a plurality of small blocks are acquired; a training data set U is selected from a polarization SAR image, input into a two-layer self-coding structure for training and then classified through a Softmax classifier; a test data set V is selected from the polarization SAR image and input into the trained two-layer self-coding structure, and then classification labels are acquired through the Softmax classifier; in the pre-segmented small blocks, the classification labels and channel information of the power diagram I are combined, and then small block labels are acquired. The polarization SAR image classification method has the advantages that the recognition rate is high, result region consistency is good, and the method can be used for polarization SAR homogeneous region terrain classification.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Near infrared imaging
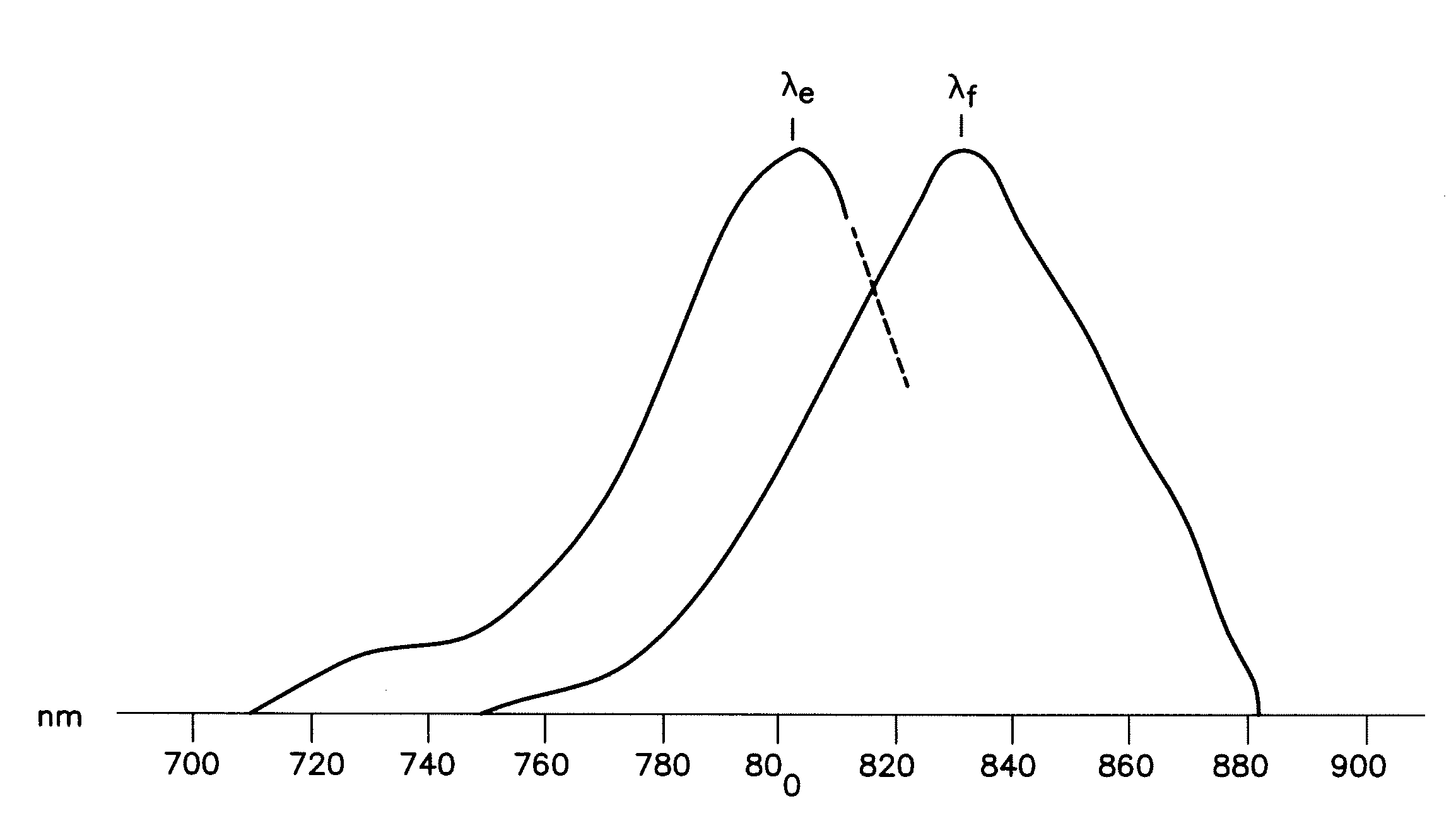
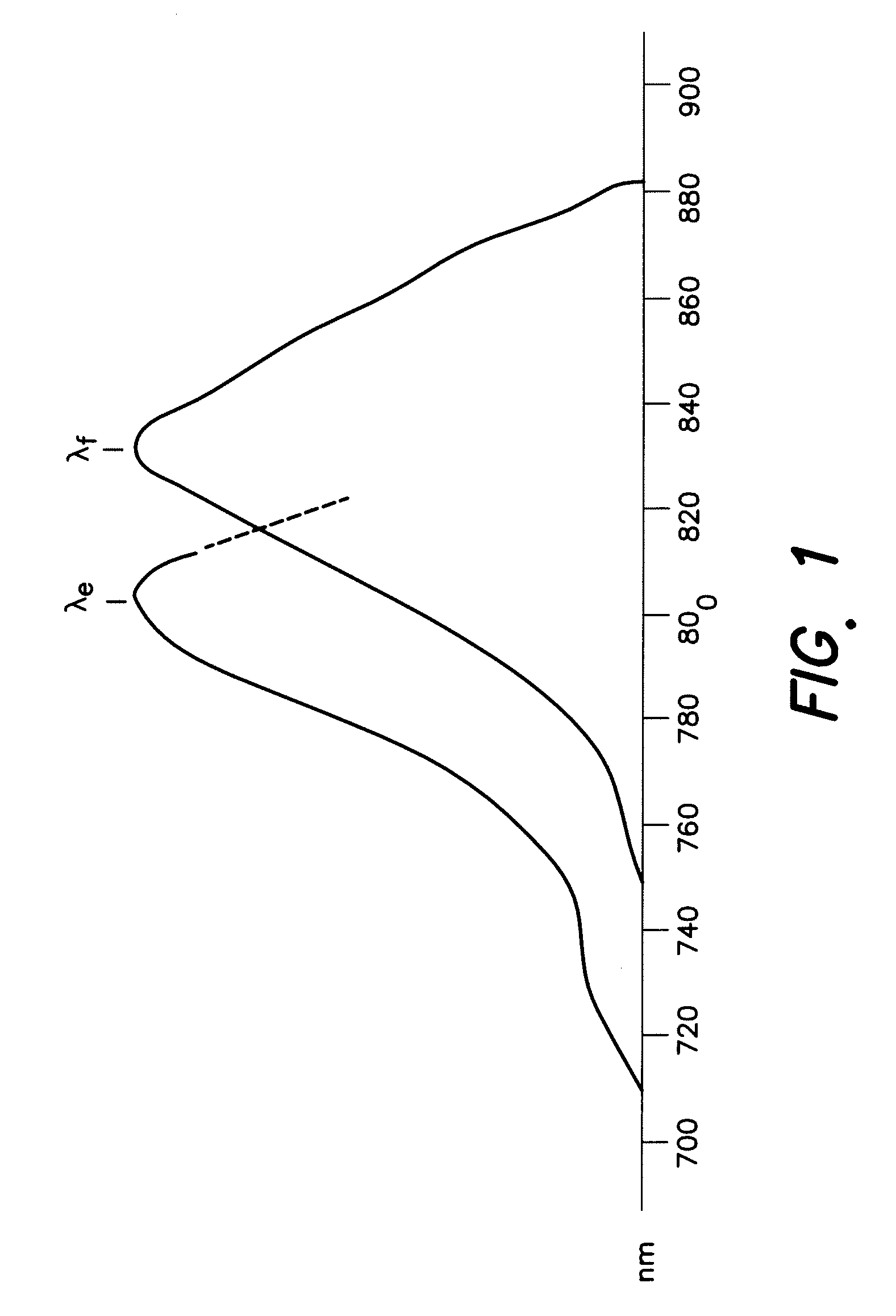
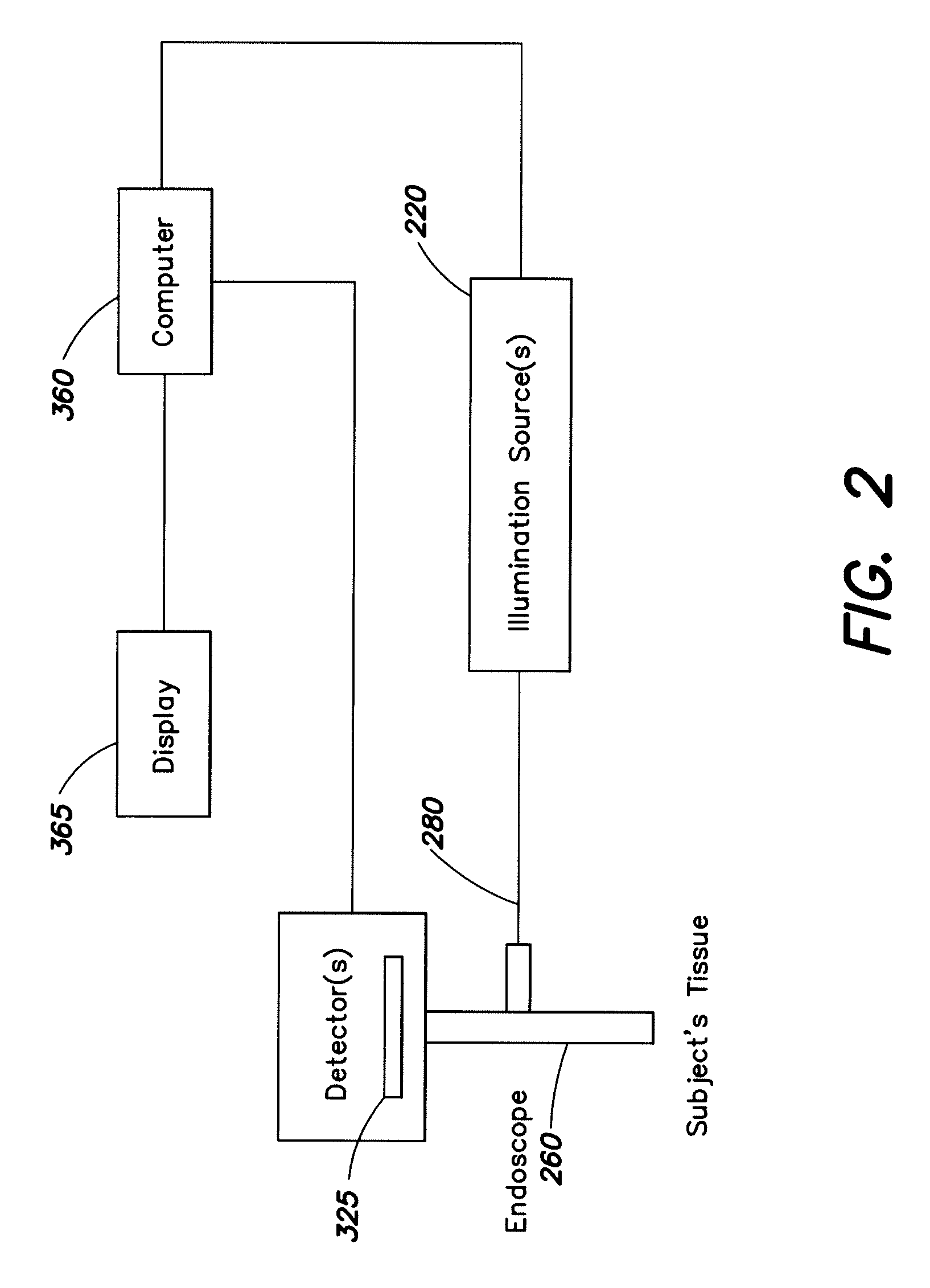
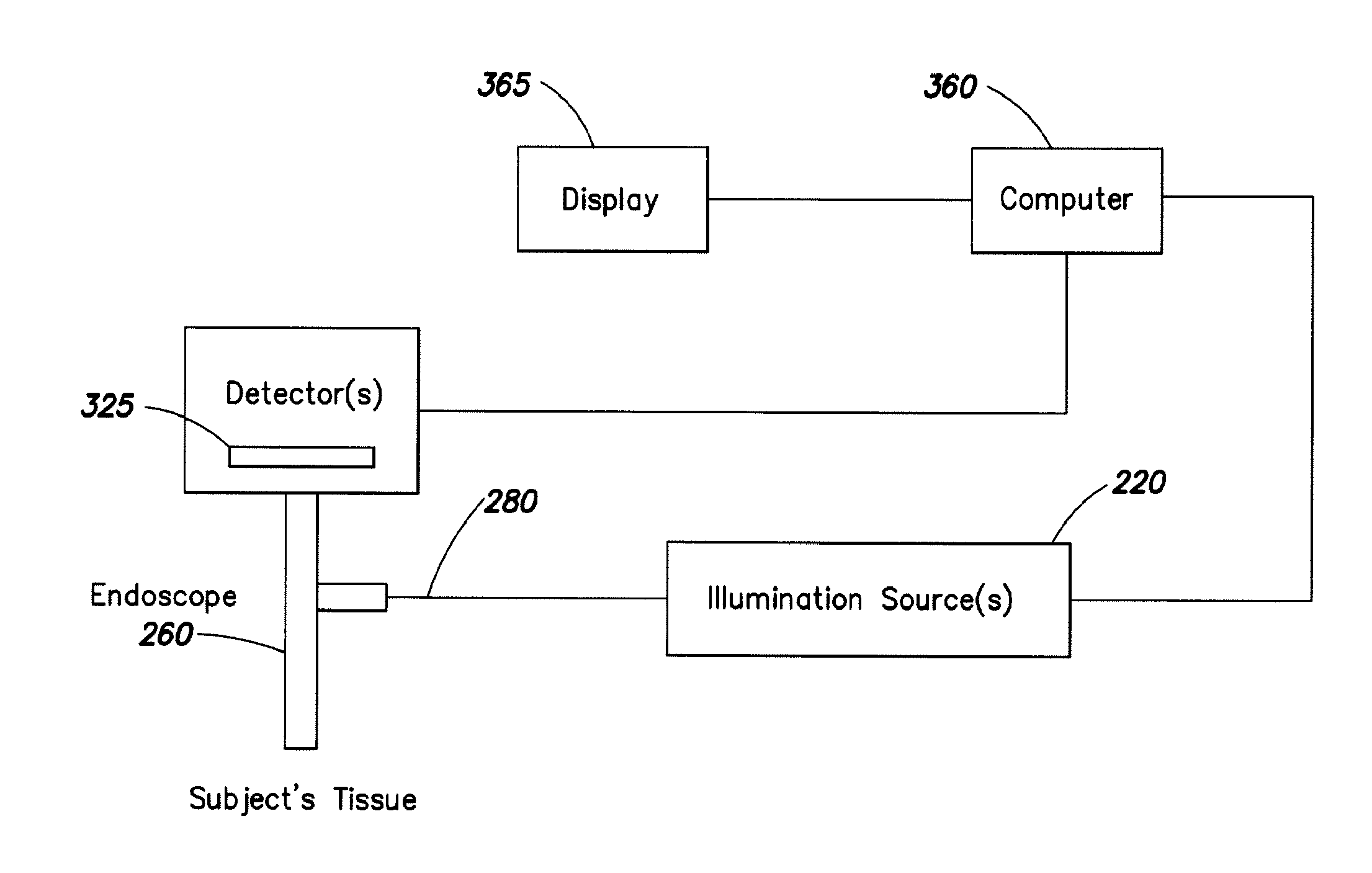
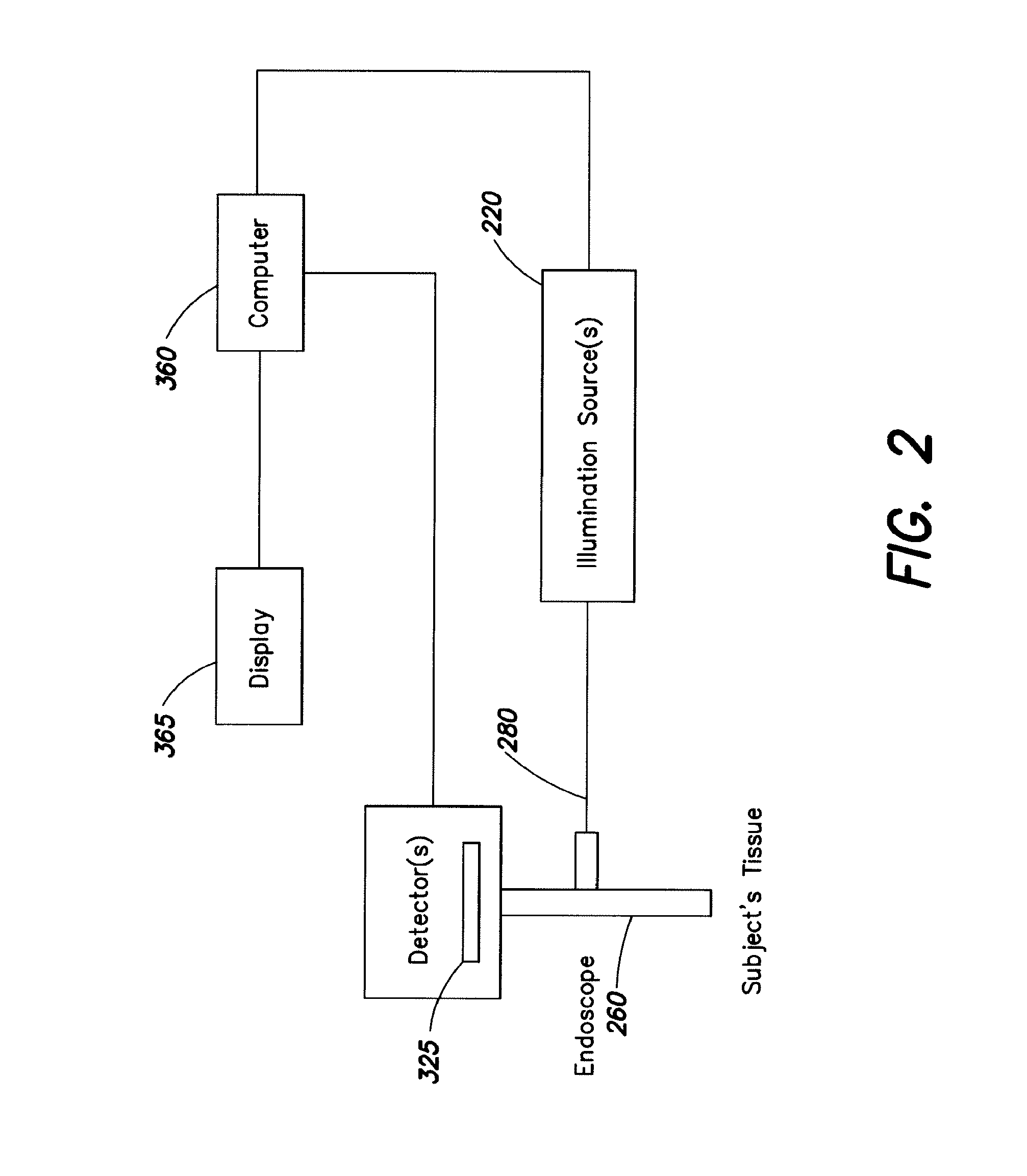
InactiveUS20090303317A1Improve efficiencyImprove throughputTelevision system detailsPrismsLength waveEndoscope
An endoscope or wand device comprising transmitting members, in which the transmitting members comprise a coating that transmits between about 95% and about 99.5% of energy at a wavelength within the infra red spectrum.
Owner:NOVADAG TECH INC
Method and system for detecting and locating network anomaly
ActiveCN108667816AGuaranteed continuityConvenient expression calculationPlatform integrity maintainanceNeural architecturesNerve networkAlgorithm
The invention discloses a method and system for detecting and locating network anomaly, which relates to the fields of Internet security, deep learning and neural network. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, dividing the URL according to special characters; secondly, performing word vector encoding on the divided URL with word2vec; putting word vectors into a convolution layer for automatic feature processing; combining a convolution layer result with an attention layer which possesses a sequential attention mechanism; and finally, performing maximum pooling and full-connectionon an attention layer result to obtain a final anomaly detection result, and at the same time, using the output of the attention layer to locate the malicious code in the URL. The invention has an excellent detection effect, not only is the detection rate high, but also the malicious code fragment in the URL can be located and visualized, thus effectively avoiding the drawbacks of the artificial feature engineering and the expert knowledge method.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
System for providing flow-targeted ventilation synchronized to a patient's breathing cycle
ActiveUS20140238398A1Smoothly and safely transitionReducing exposure to further riskTracheal tubesOperating means/releasing devices for valvesOxygenEndotracheal tube
A system selectively delivers either breath-synchronized, flow-targeted ventilation (BSFTV) or closed-system positive pressure ventilation (CSPPV) to augment respiration of a patient with a standard tracheal tube. A removable adaptor has a cap that can be removably attached to the proximal connector of the tracheal tube in BSFTV mode, and an inner cannula that extends within the tracheal tube to effectively divide it into two lumens. The adaptor includes a ventilator connector for removably engaging a ventilator hose to deliver air / oxygen through the adaptor and one lumen of the tracheal tube with a flow rate varying over each respiratory cycle in a predetermined waveform synchronized with the patient's respiratory cycle to augment the patient's spontaneous respiration. The adaptor also includes a port allowing the spontaneously-breathing patient to freely inhale and exhale in open exchange with the atmosphere through the other lumen.
Owner:FISHER & PAYKEL HEALTHCARE LTD
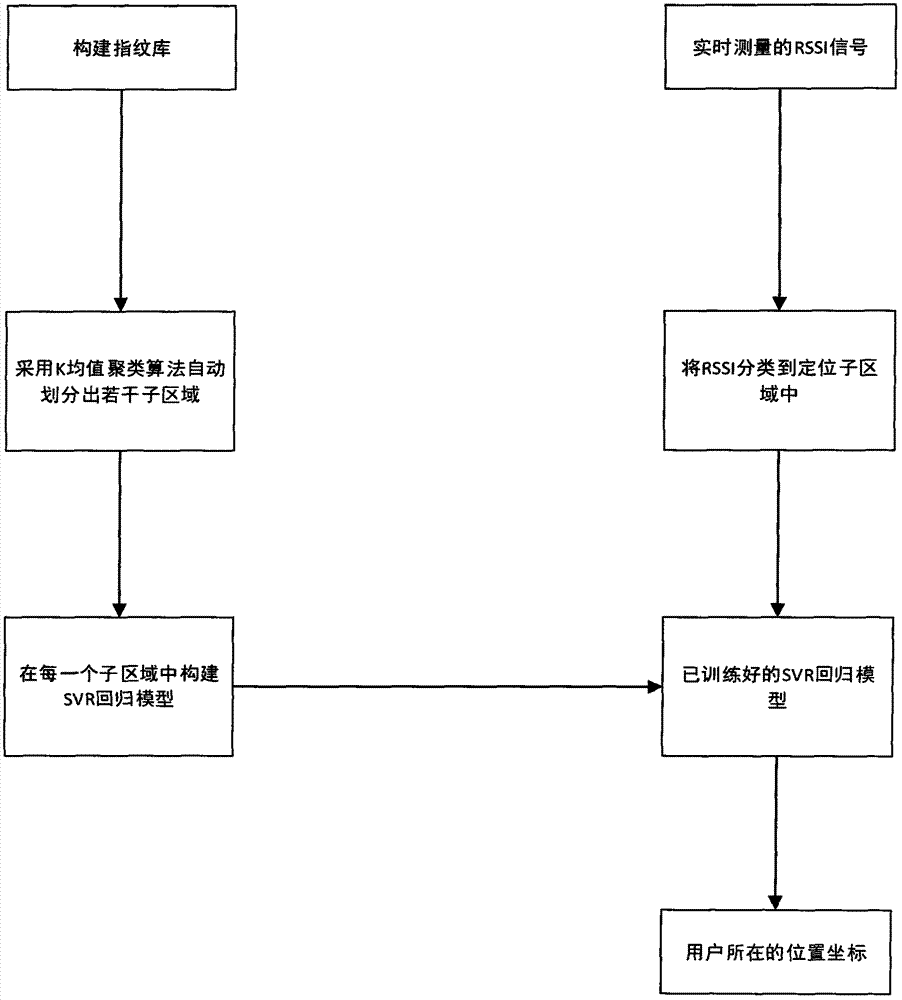
Indoor positioning method based on SVM and K mean value clustering algorithm
InactiveCN104853434AReduce fingerprint libraryThe mapping mode is simpleLocation information based serviceCluster algorithmSupport vector machine
The invention adopts a method based on a SVM (Support Vector Machine) and a K mean value clustering algorithm for realizing indoor positioning and aims to improve positioning precision and stability of indoor positioning and to reduce complexity of a positioning algorithm. The main positioning process includes a first step of selecting a plurality of reference points uniformly in a positioning area and collecting RSSI samples on the points, and forming fingerprints based on the RSSI samples and the position coordinates of the reference points, wherein the fingerprints form a fingerprint database; a second step of adopting a K mean value clustering algorithm for the fingerprint database and dividing the positioning area into a plurality of sub areas with smaller ranges automatically; a third step of adopting an SVM algorithm for the positioning sub areas and constructing positioning sub models for each sub area; a fourth step of calculating the mean value of RSSI in each sub area and determining the mean value as the clustering center of said sub area; a fifth step of calculating Eucidean distance between a real time RSSI signal and all the clustering centers of the sub areas, determining the nearest sub area and realizing precise positioning by utilizing the positioning model constructed in the third step.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +3
Laser processing method
ActiveUS20140334511A1Improve productivityQuality improvementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLaser processingOptical axis
A laser processing method of applying a pulsed laser beam to a single crystal substrate to thereby process the single crystal substrate. The laser processing method includes a numerical aperture setting step of setting the numerical aperture (NA) of a focusing lens for focusing the pulsed laser beam so that the value obtained by dividing the numerical aperture (NA) of the focusing lens by the refractive index (N) of the single crystal substrate falls within the range of 0.05 to 0.2, a positioning step of relatively positioning the focusing lens and the single crystal substrate in the direction along the optical axis of the focusing lens so that the focal point of the pulsed laser beam is set at a desired position in the direction along the thickness of the single crystal substrate, and a shield tunnel forming step of applying the pulsed laser beam to the single crystal substrate so as to focus the pulsed laser beam at the focal point set in the single crystal substrate thereby forming a shield tunnel extending between the focal point and a beam incident surface to which the pulsed laser beam is applied.
Owner:DISCO CORP
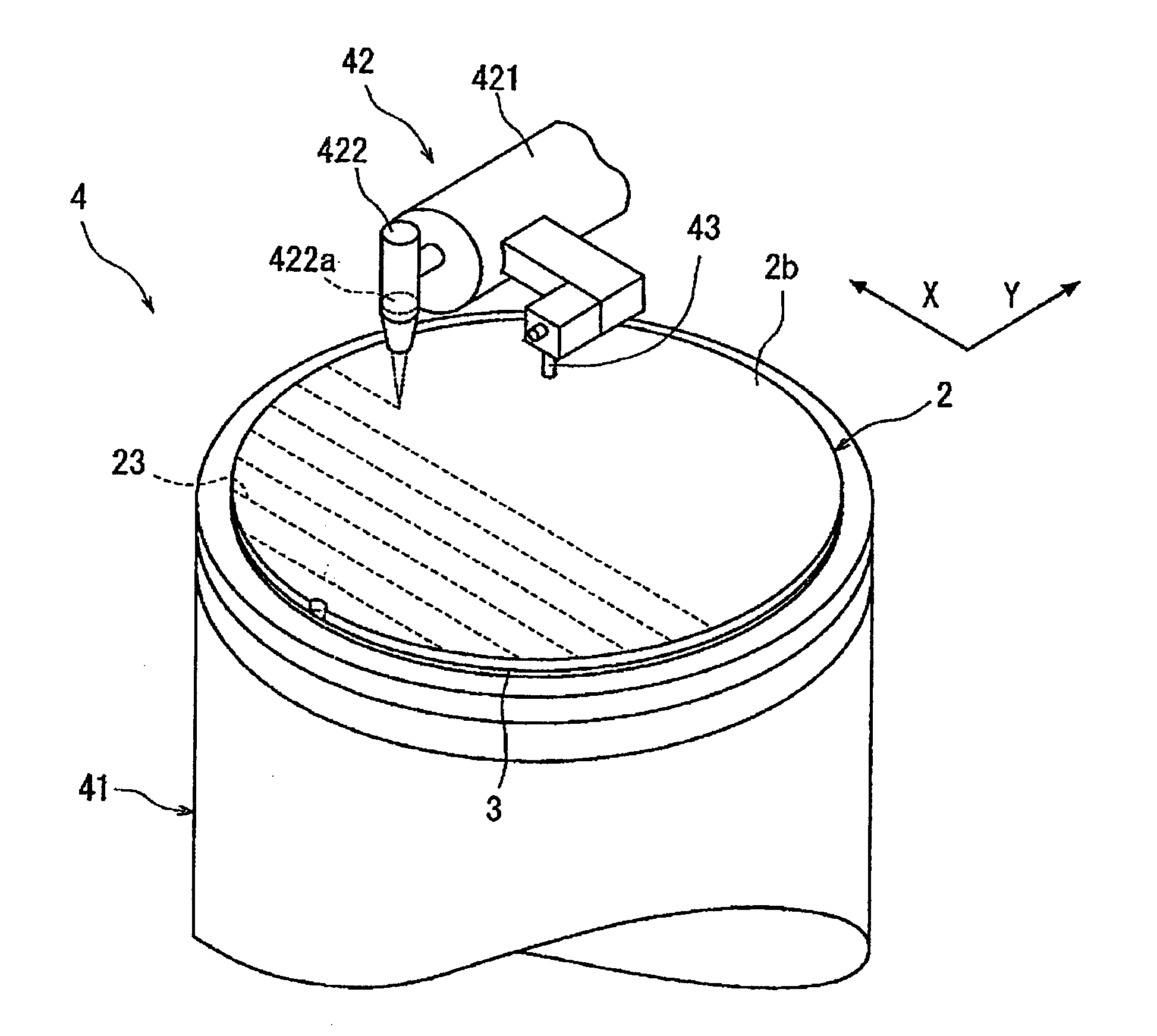
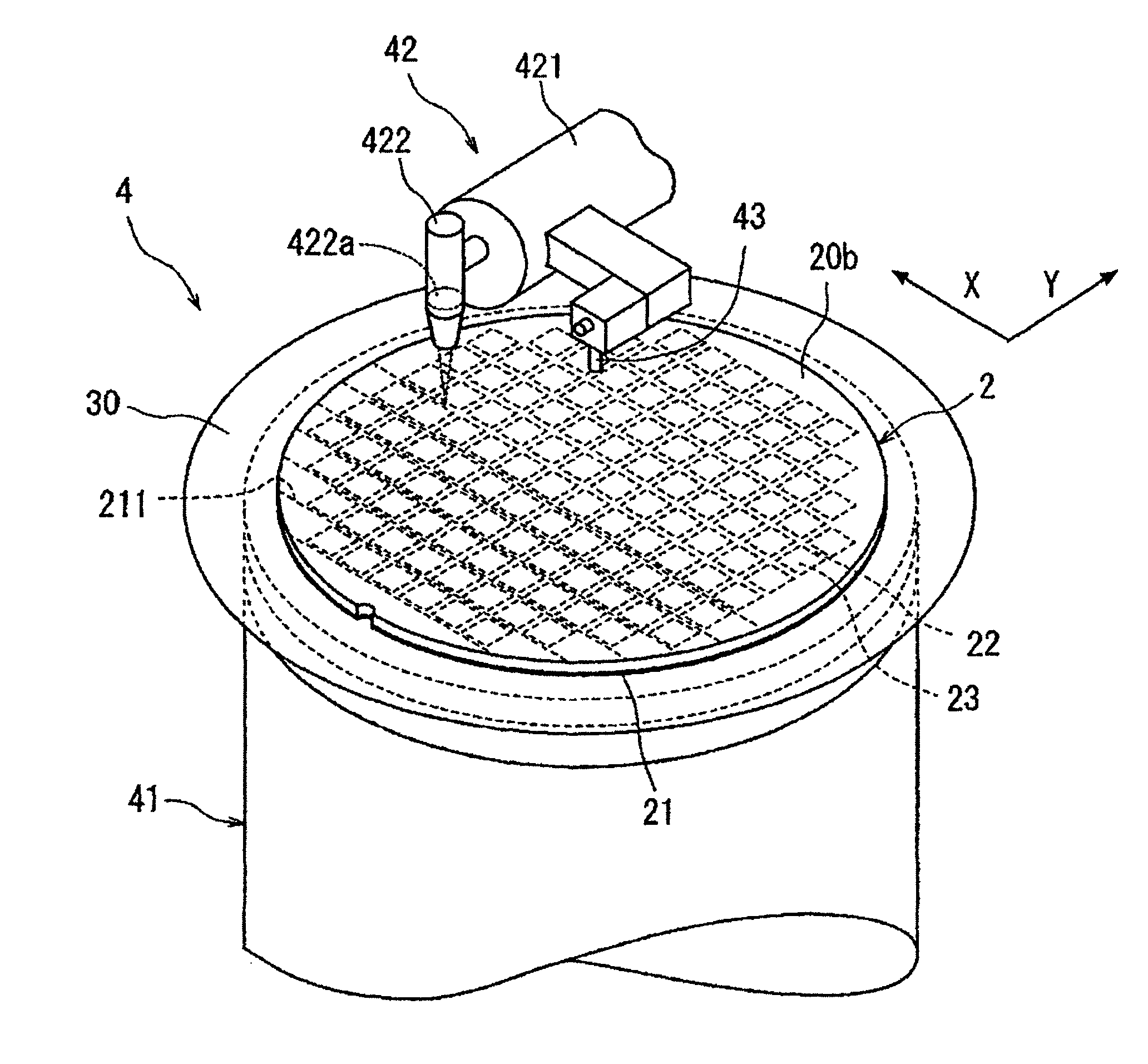
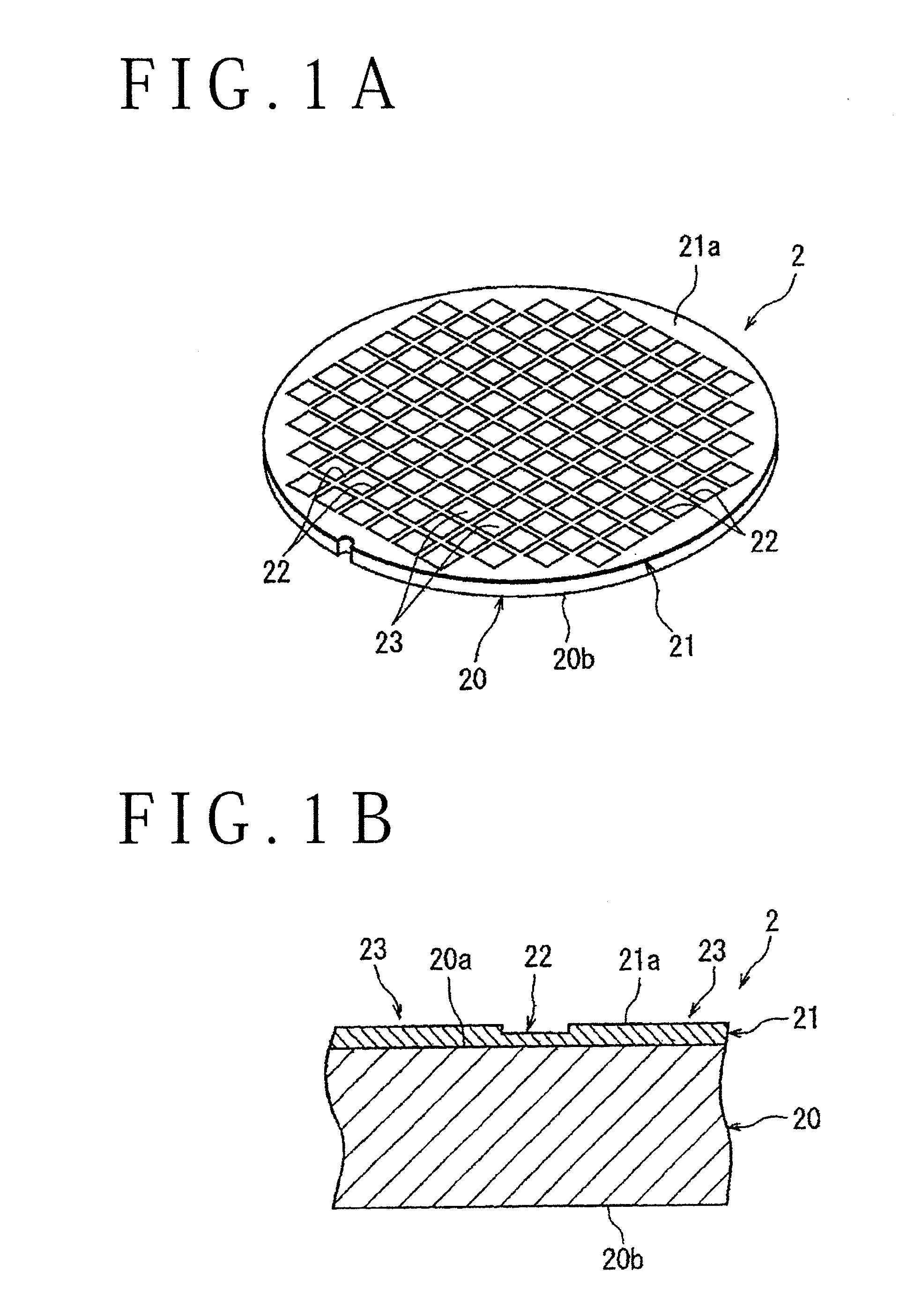
Wafer dividing method
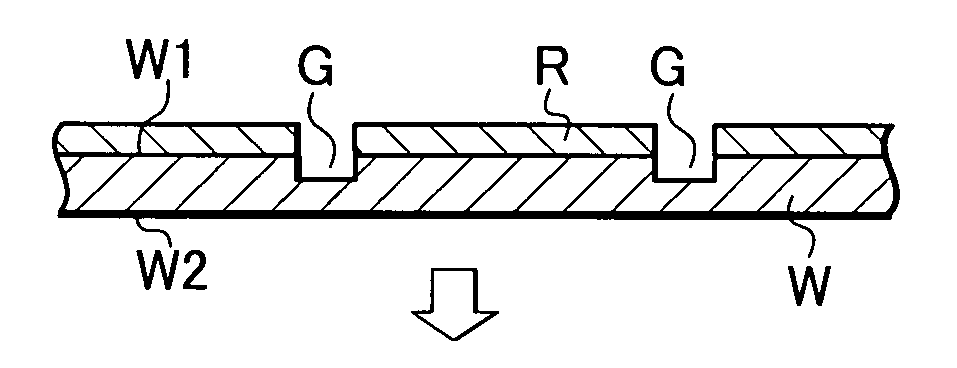
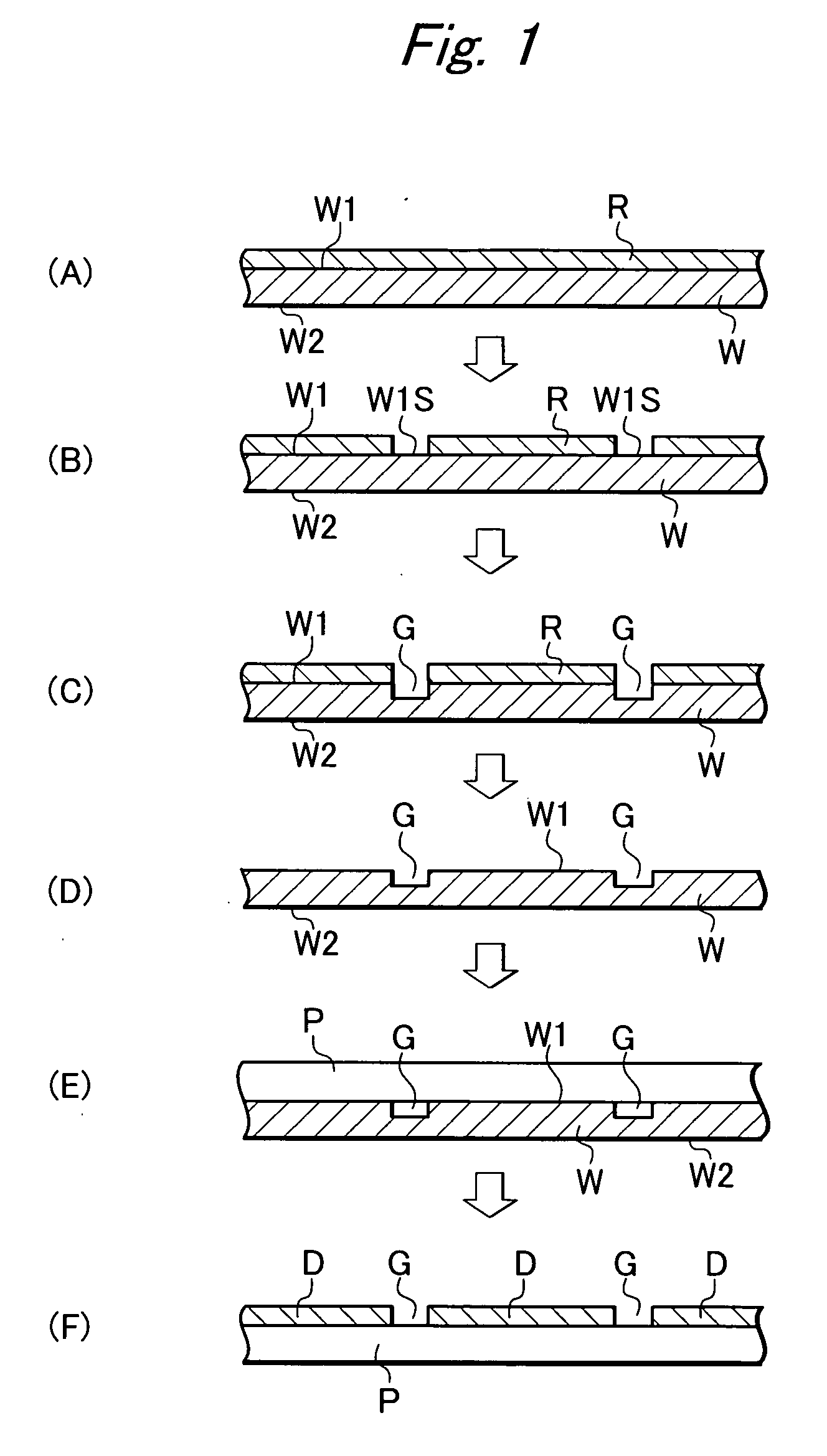
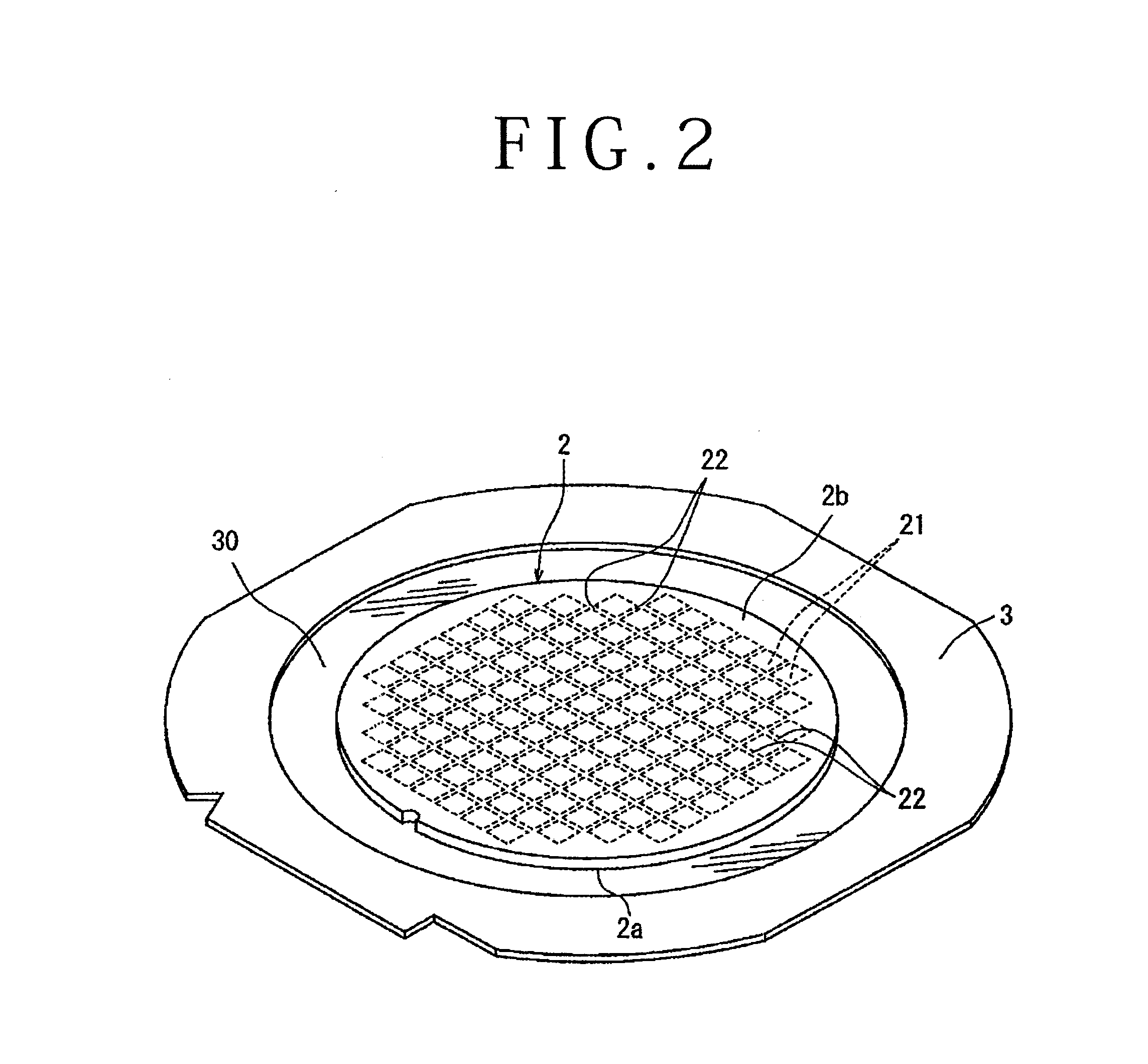
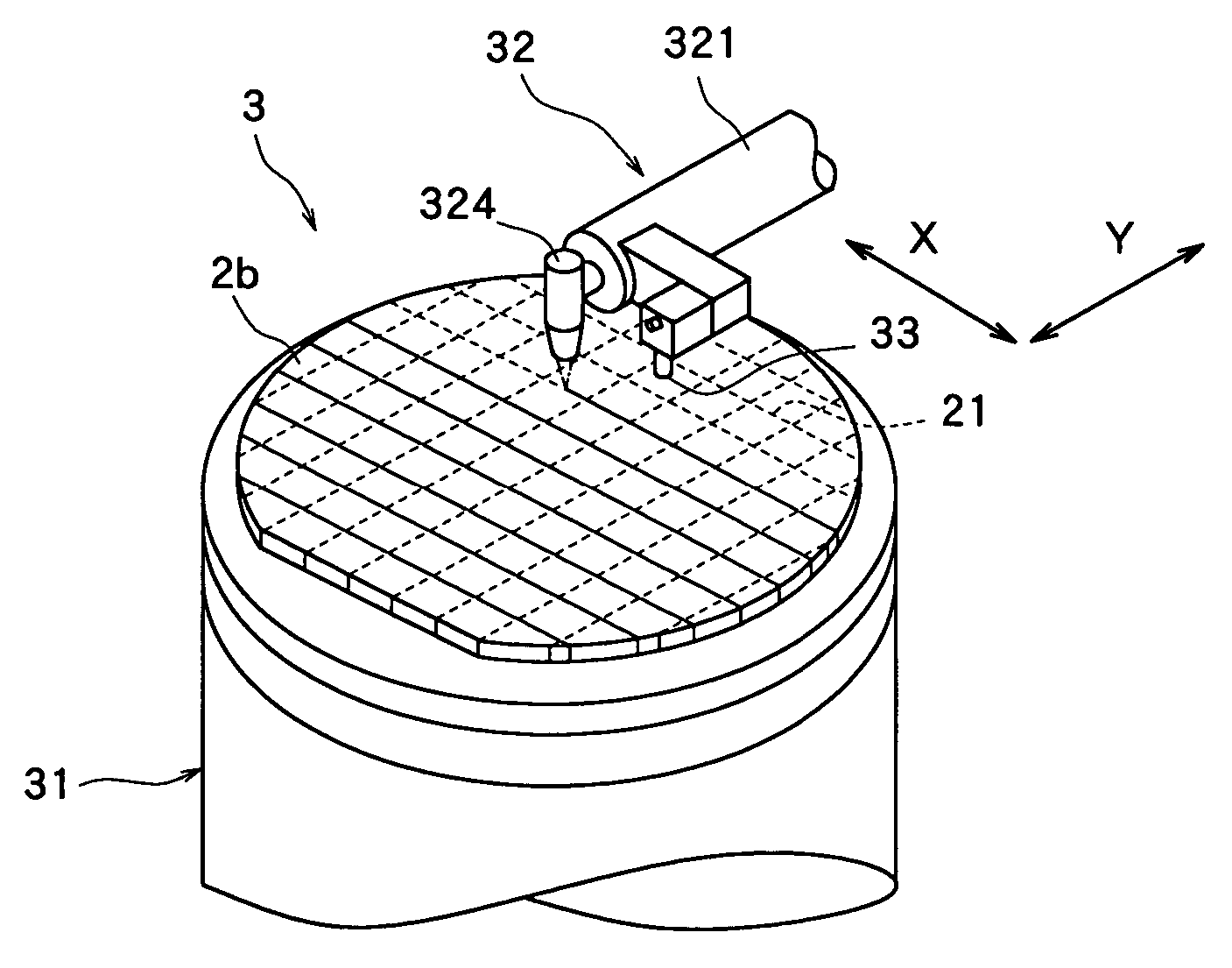
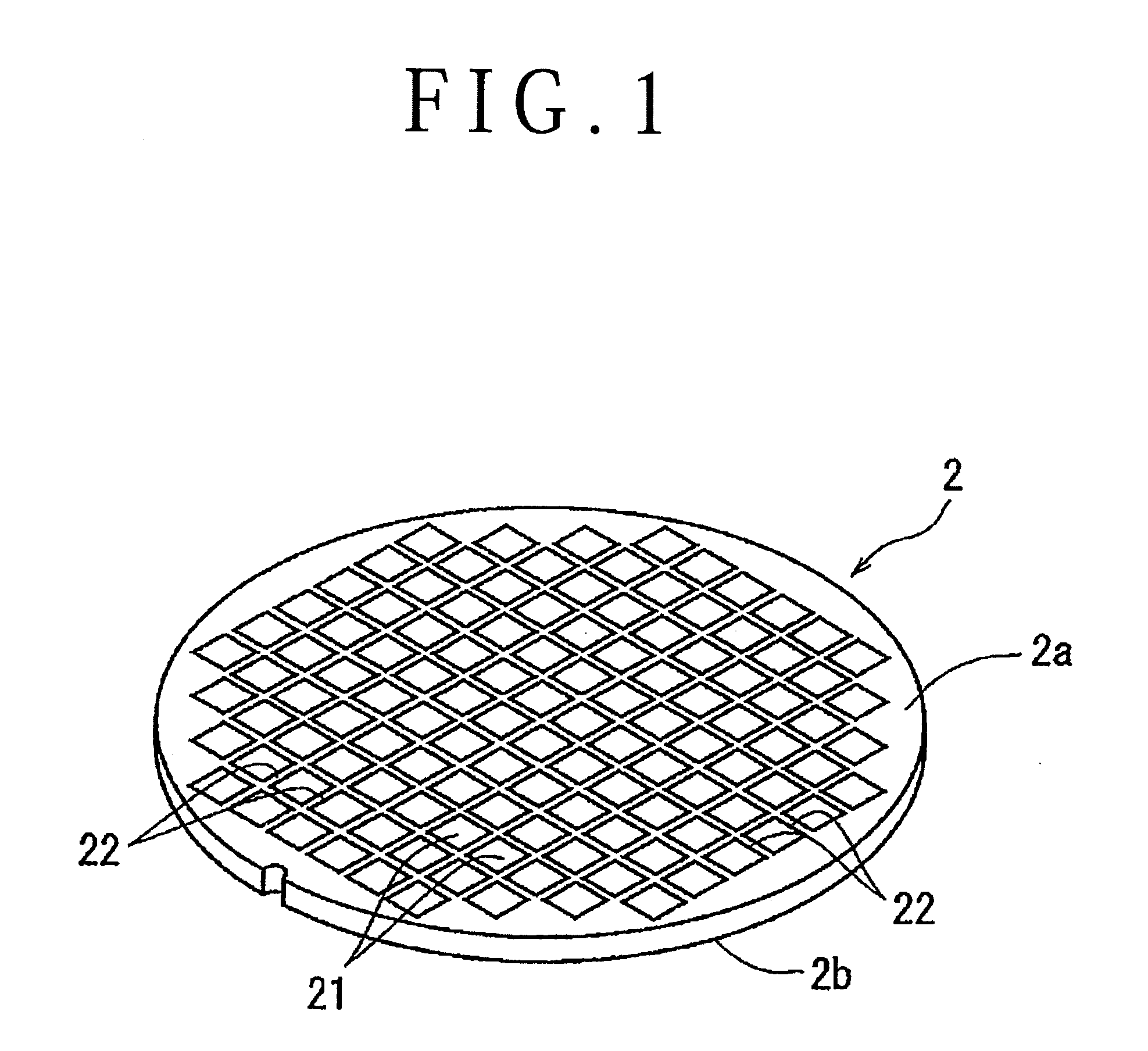
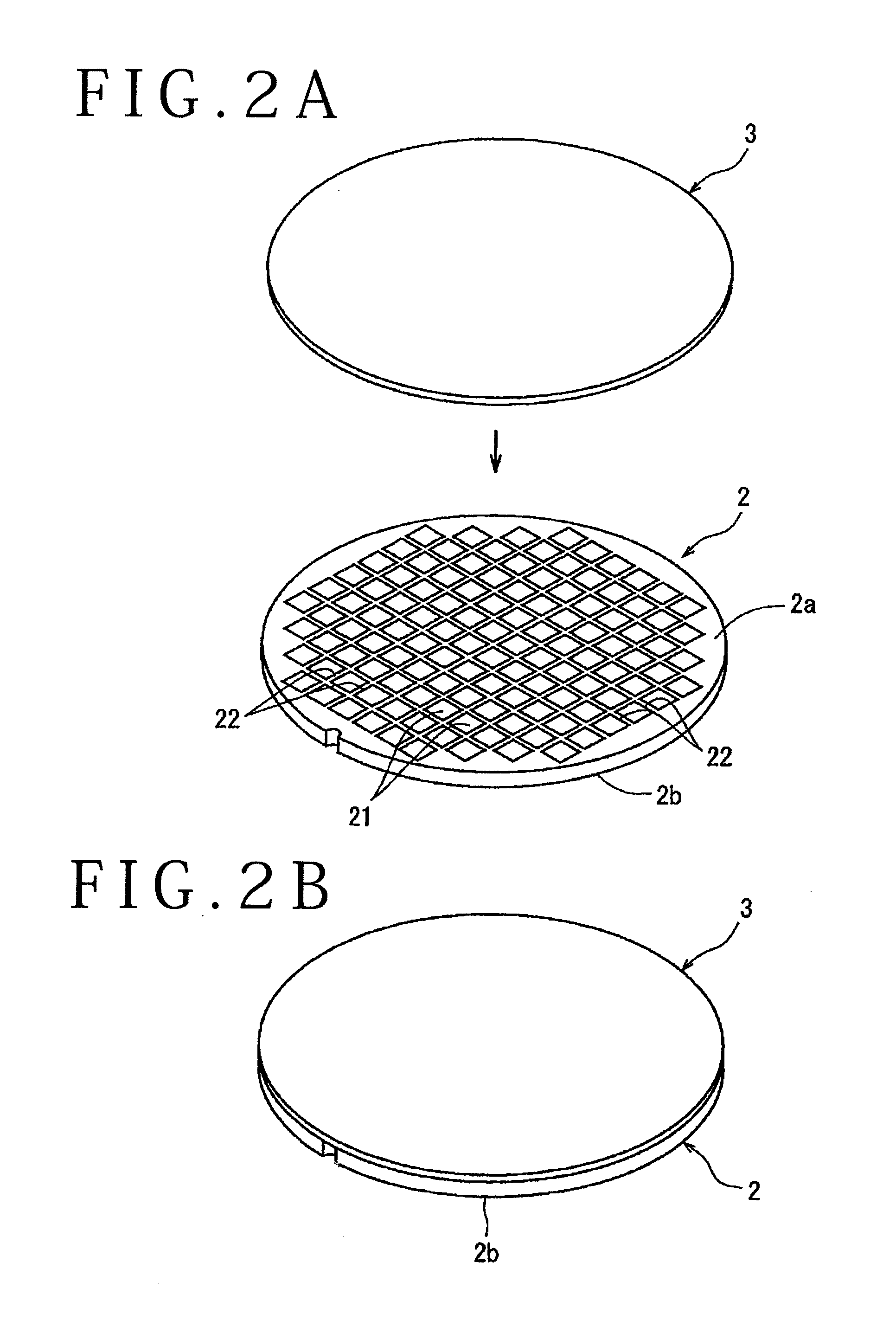
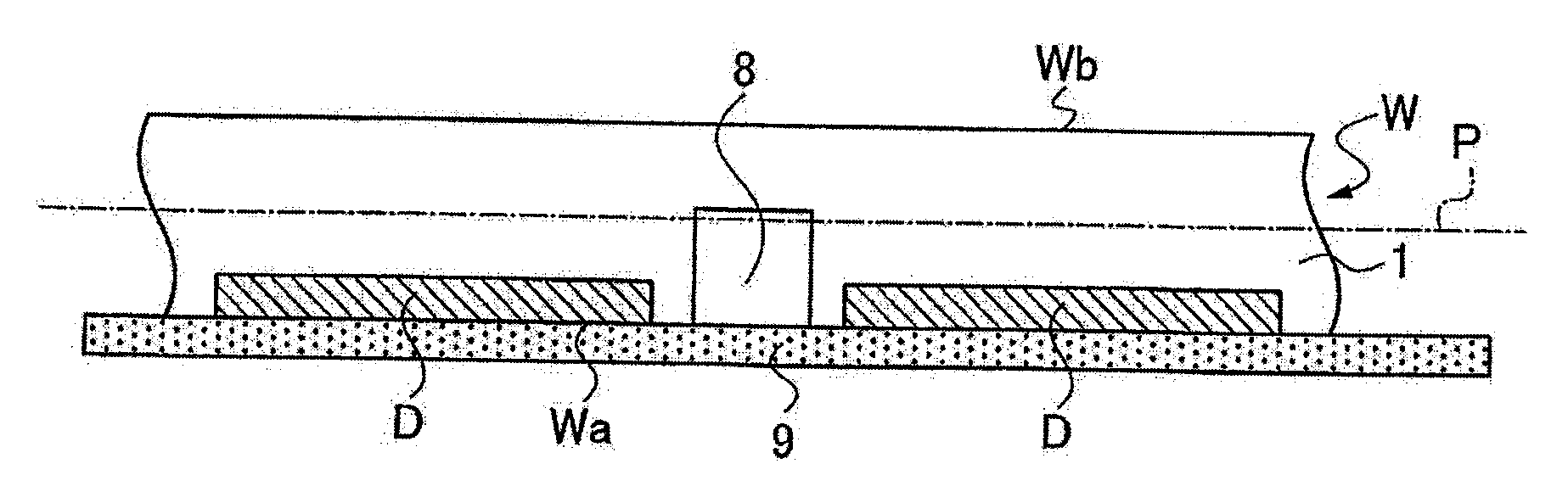
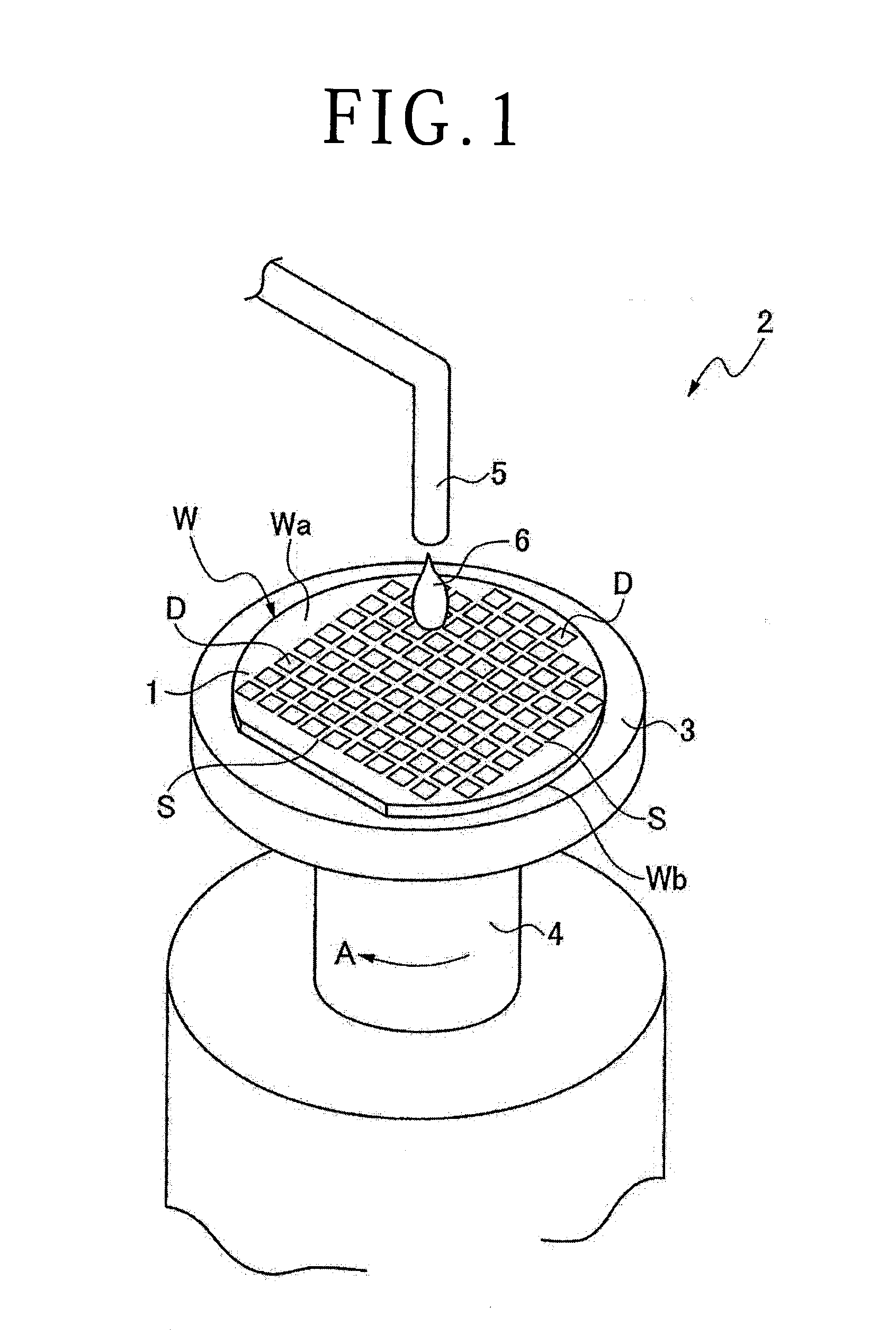
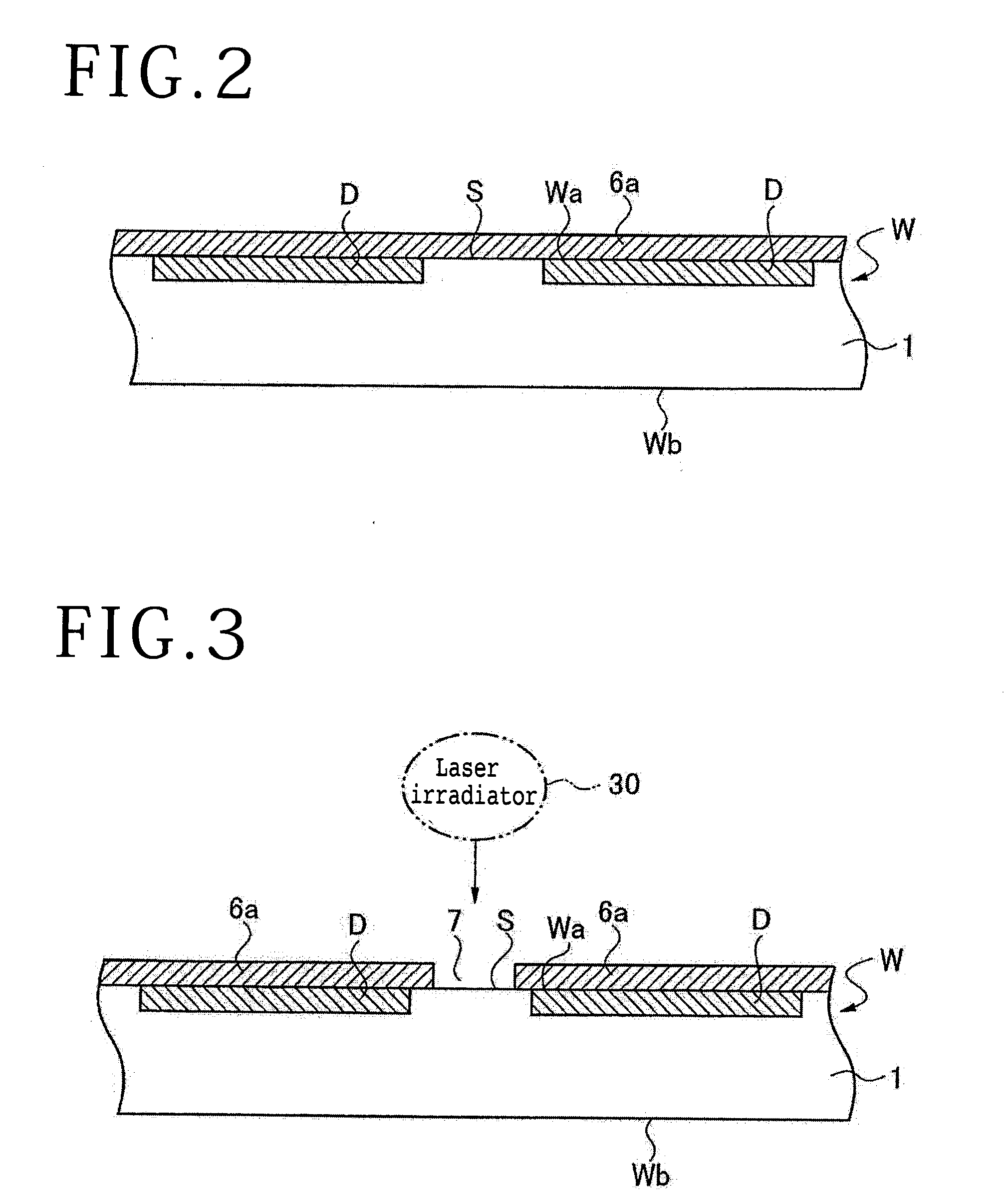
ActiveUS20050090077A1Effective divisionWafer can be divided efficientlySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFine working devicesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of dividing a wafer along predetermined dividing lines, comprising the steps of a deteriorated layer forming step for applying a pulse laser beam capable of passing through the wafer along the dividing lines to form deteriorated layers in the inside of the wafer along the dividing lines; an extensible protective tape affixing step for affixing an extensible protective tape to one side of the wafer before or after the deteriorated layer forming step; and a dividing step for dividing the wafer along the deteriorated layers by expanding the protective tape affixed to the wafer after the deteriorated layer forming step.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Near Infrared Imaging
ActiveUS20130184591A1Improve efficiencyImprove throughputTelevision system detailsPrismsLength waveEndoscope
Endoscopes and wands, useful for near infrared imaging, particularly for medical purposes, have transmitting members that transmit between about 95% and 99.9% of the energy at a wavelength within the infrared spectrum. The wands and endoscopes have at least one channel for transmitting and receiving light in the visible spectrum and at least one channel for transmitting and receiving light in the infrared spectrum.
Owner:STRYKER EUROPEAN OPERATIONS LIMITED
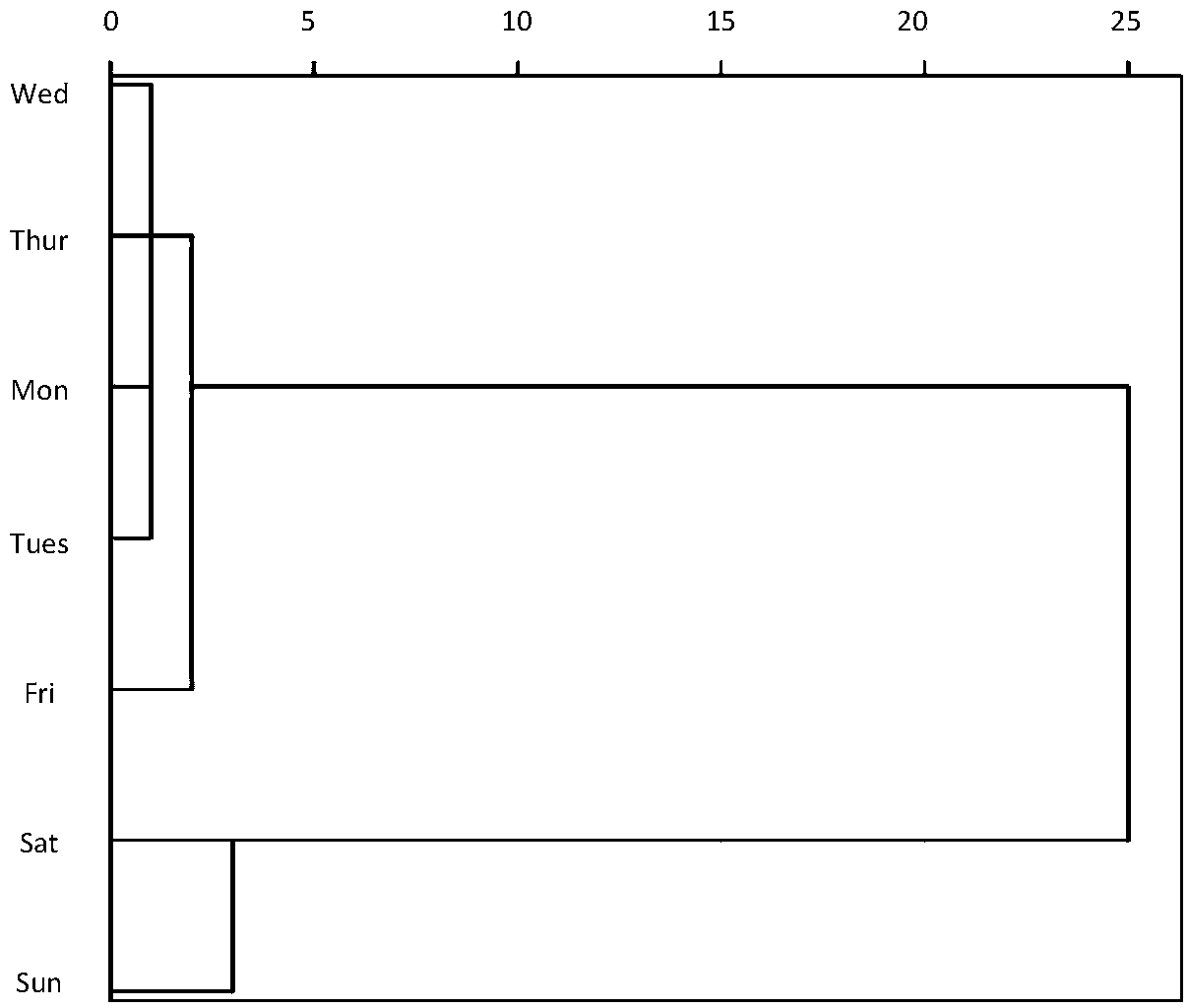
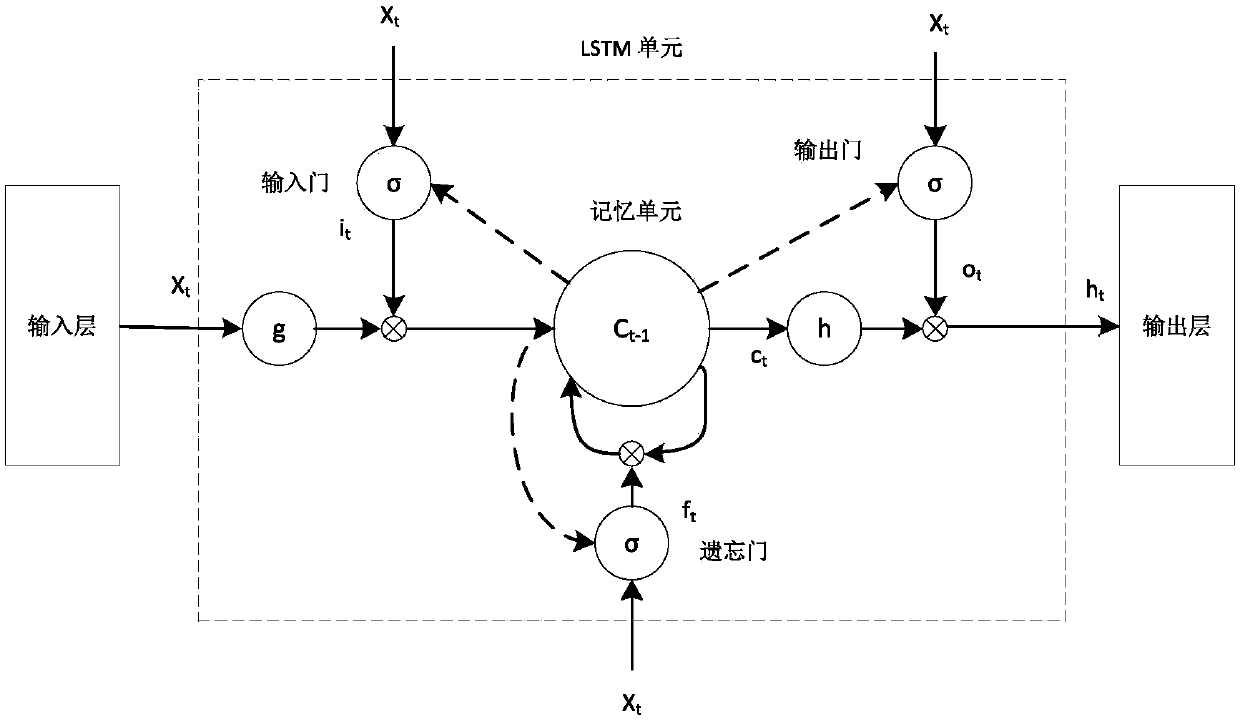
An urban rail transit passenger flow volume prediction method based on A-LSTM
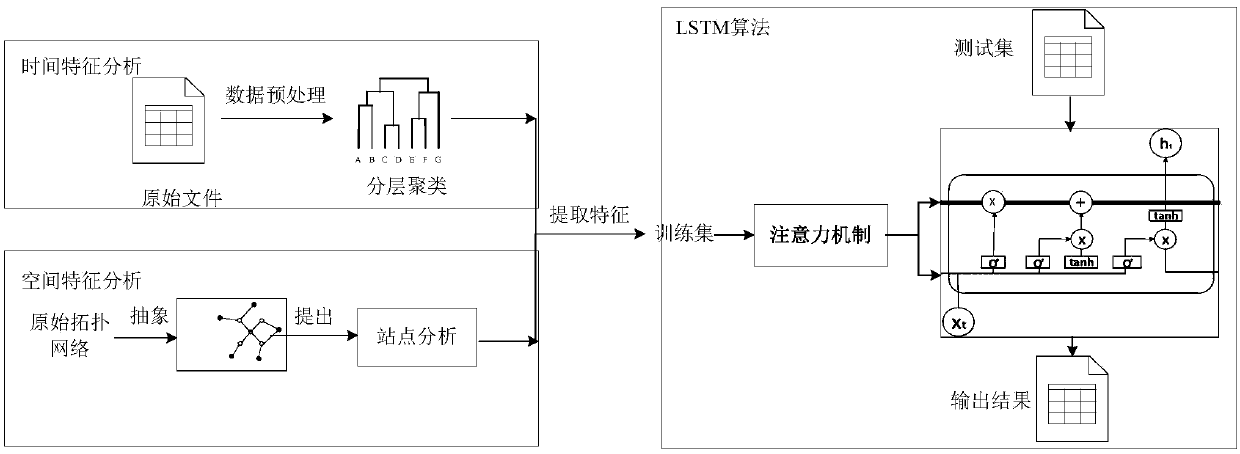
ActiveCN109583656AEffective divisionImprove forecast accuracyForecastingNeural architecturesTraffic predictionPrediction algorithms
The invention belongs to the field of machine learning, and discloses an urban rail transit passenger flow volume prediction method based on A-LSTM. The method relates to three parts of time feature extraction, spatial feature extraction and prediction algorithm design. Wherein the time characteristics are mainly characterized in that clustering analysis is carried out on the week factors througha hierarchical clustering method, and relationships among the weeks are searched; Wherein the spatial characteristics refer to passenger flow distribution characteristics of different subway stations,and the spatial passenger flow distribution relation is searched by analyzing the different stations; The prediction algorithm is mainly based on an improved LSTM neural network, and an attention mechanism is added, so that the LSTM network pays more attention to input characteristics with greater influence on prediction by a model, and passenger flow data can be predicted more accurately.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
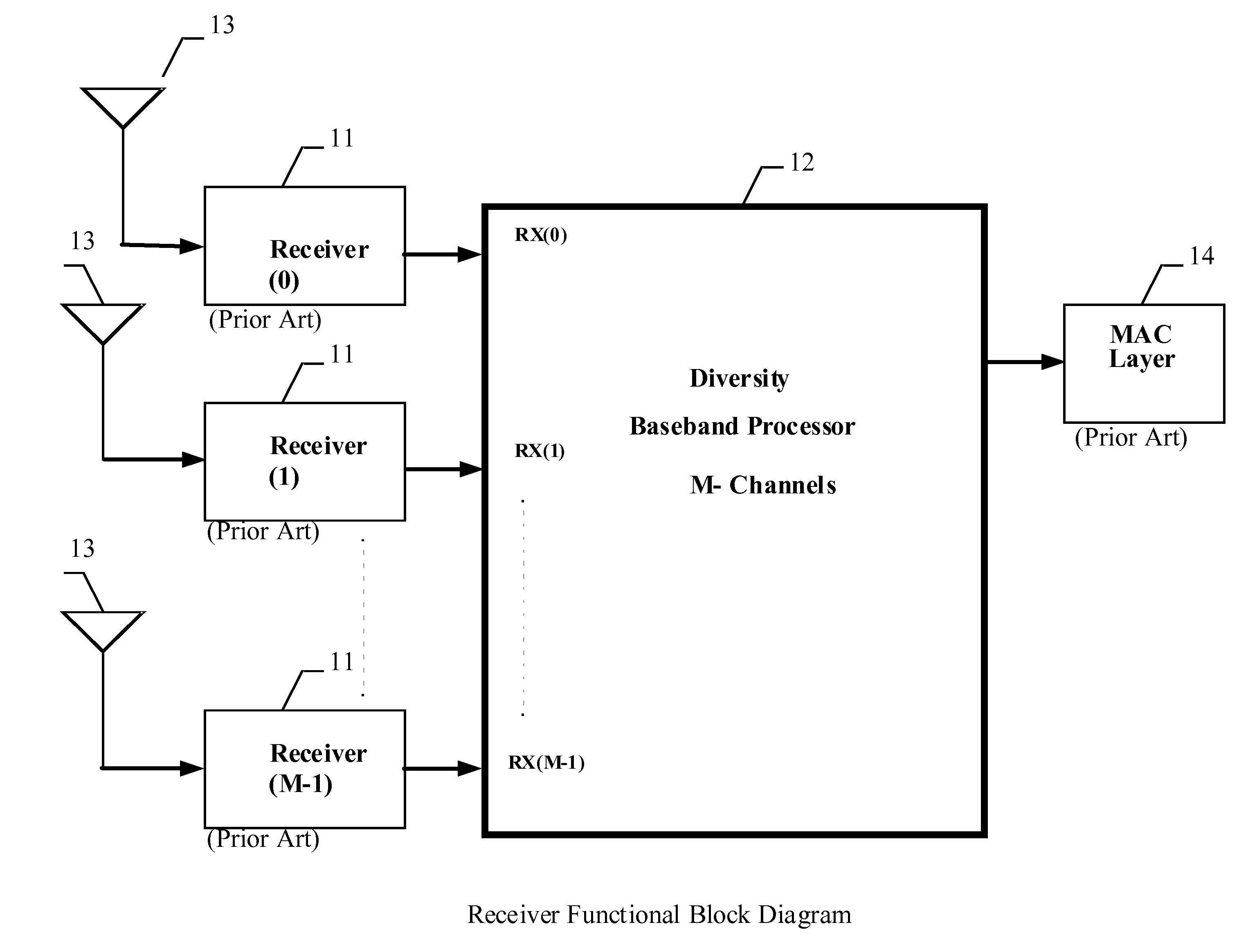
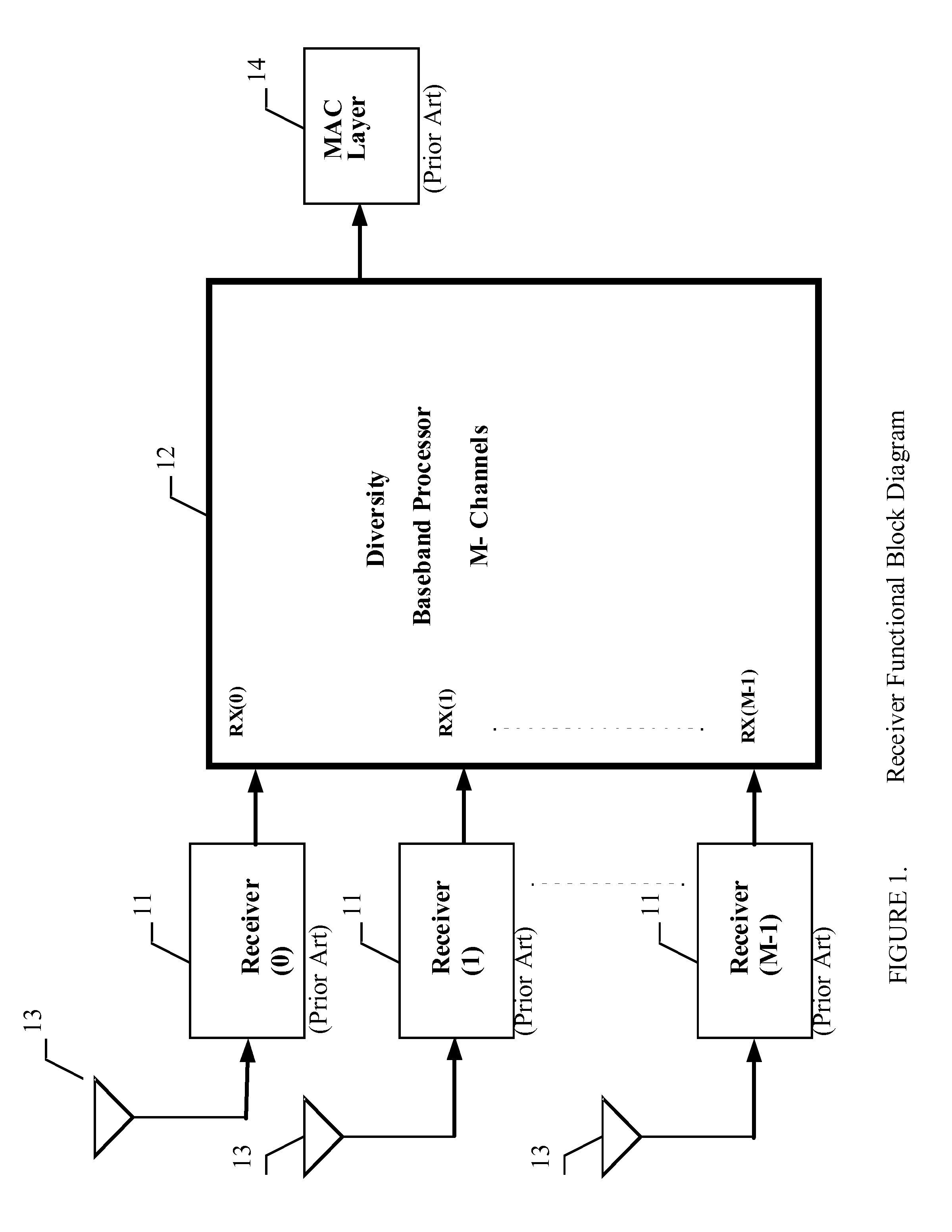
MIMO wireless system with diversity processing
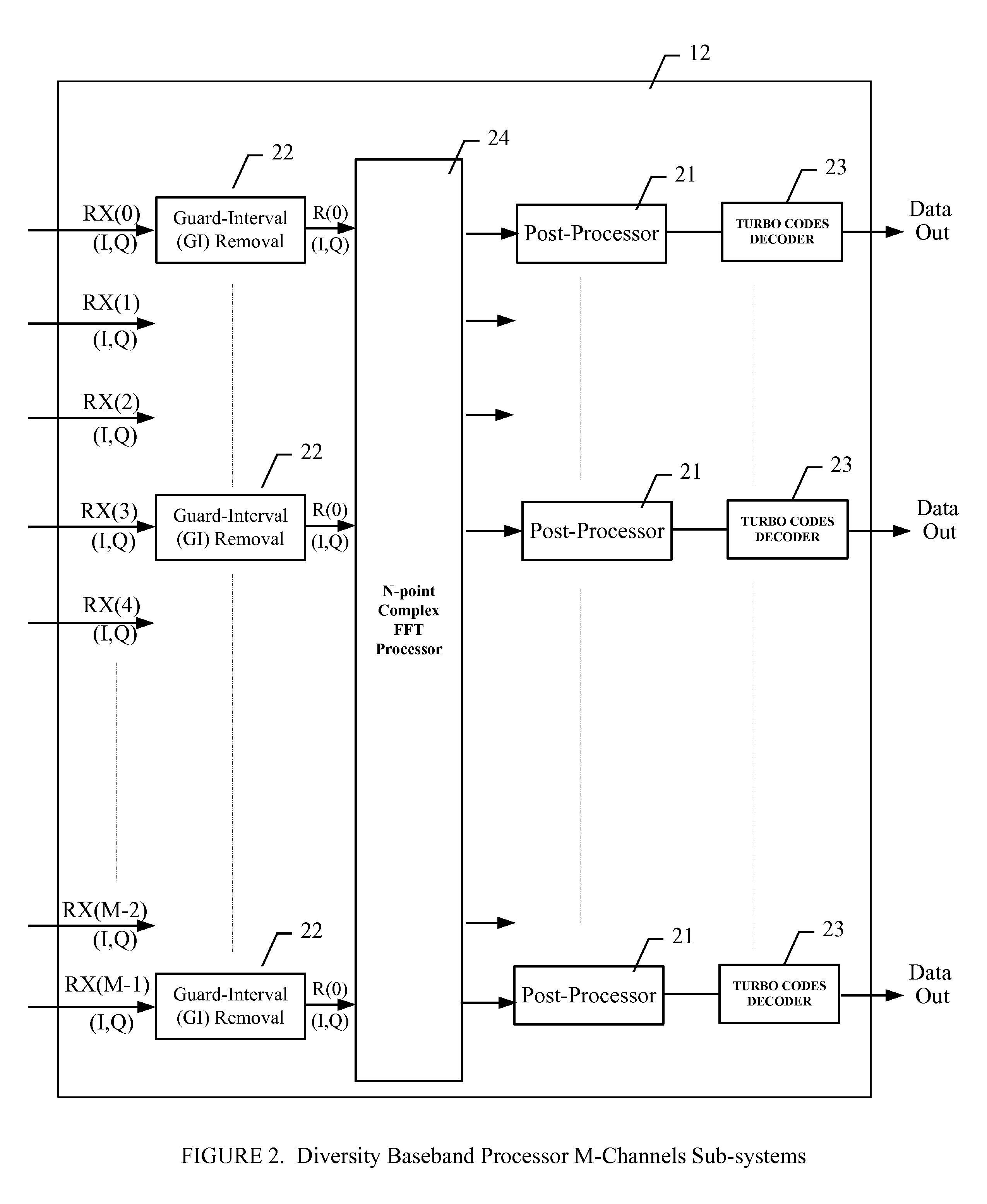
InactiveUS20120057660A1Increased error-rateImprove signal-to-noise ratioPolarisation/directional diversityCode conversionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Wireless systems
A MIMO wireless system with Diversity processing is provided having Turbo Codes Decoders for computing orthogonal multipath signals from multiple separate antennas. The invention decodes multipath signals that have arrived at the terminal via different routes after being reflected from buildings, trees or hills. The Turbo Codes Decoder with Diversity processing increases the signal to noise ratio (SNR) more than 6 dB which enables the Wireless system to deliver data rates from up to 600 Mbit / s. A Turbo Codes Decoder block is provided to compute baseband signals from multiple different receiver paths. Several pipelined max-Log-MAP decoders are used for iterative decoding of received data. A Sliding Window of Block N data is used for pipeline operations.
Owner:TURBOCODE LLC
Energy Storage and Retrieval Systems
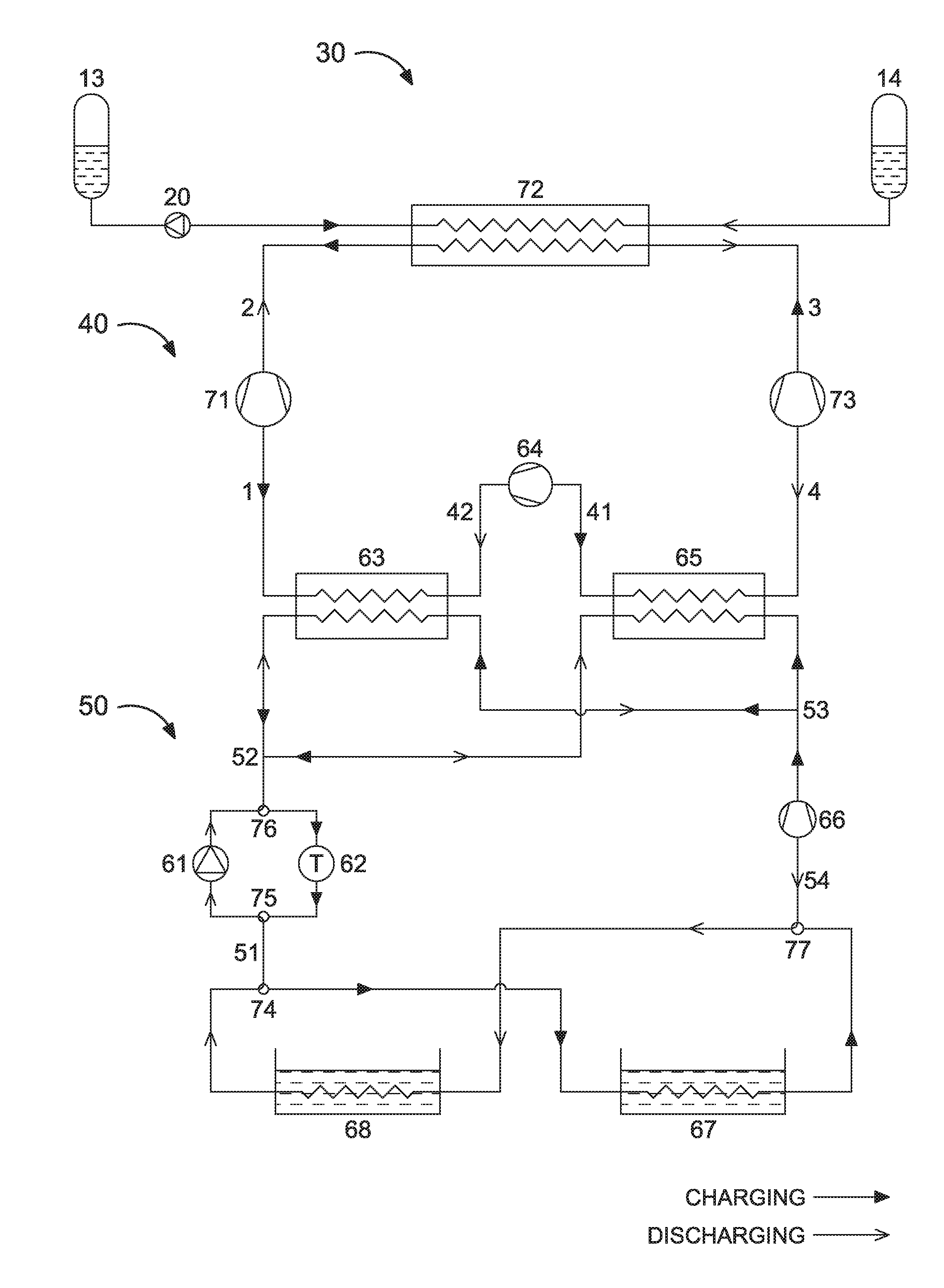
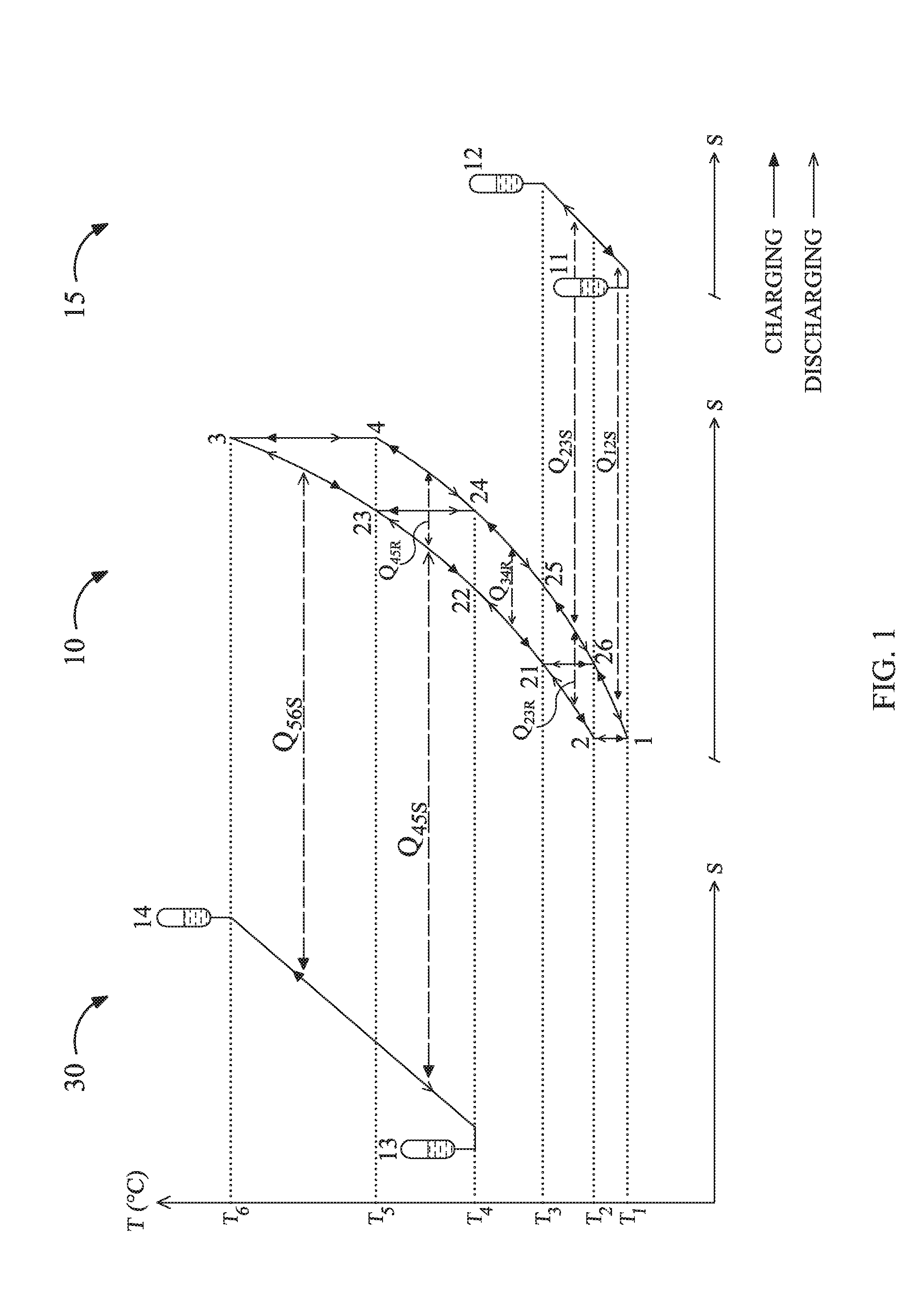
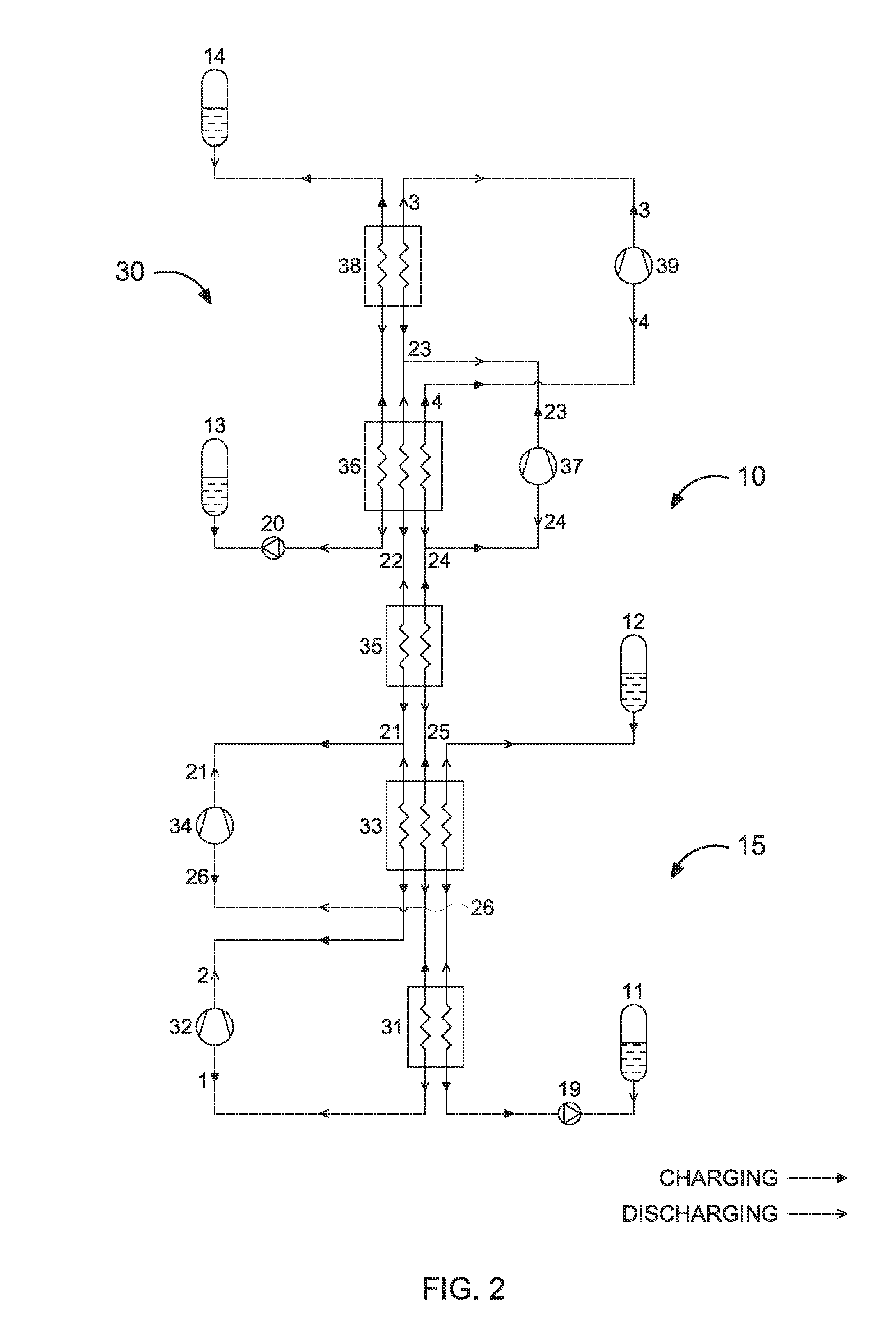
ActiveUS20160298498A1Fast chargingExtend under-water speed and rangeFrom solar energyEngine fuctionsWorking fluidMechanical energy
Systems and methods for storing and retrieving thermo-mechanical energy are disclosed. The systems and methods include a thermodynamic cycle (e.g., a reversible transcritical, trilateral, Brayton or Rankine / vapor compression cycle) that includes a plurality of loops and works as a heat pump in charging mode and as a heat engine in discharging mode. Each loop in the thermodynamic cycle includes pressure increasing and decreasing devices, high and low pressure heat exchanging devices, and the same or different working fluid. The system further includes one or more heat storage chains with hot and cold storage reservoirs and a heat storage fluid. At least one of the high and low pressure heat exchanging devices is a gradient heat exchanging device that exchanges heat with the heat storage chain. Also, at least one other high or low pressure heat exchanging device exchanges heat with a separate heat storage device or a heat source or sink.
Owner:KREUGER STEN
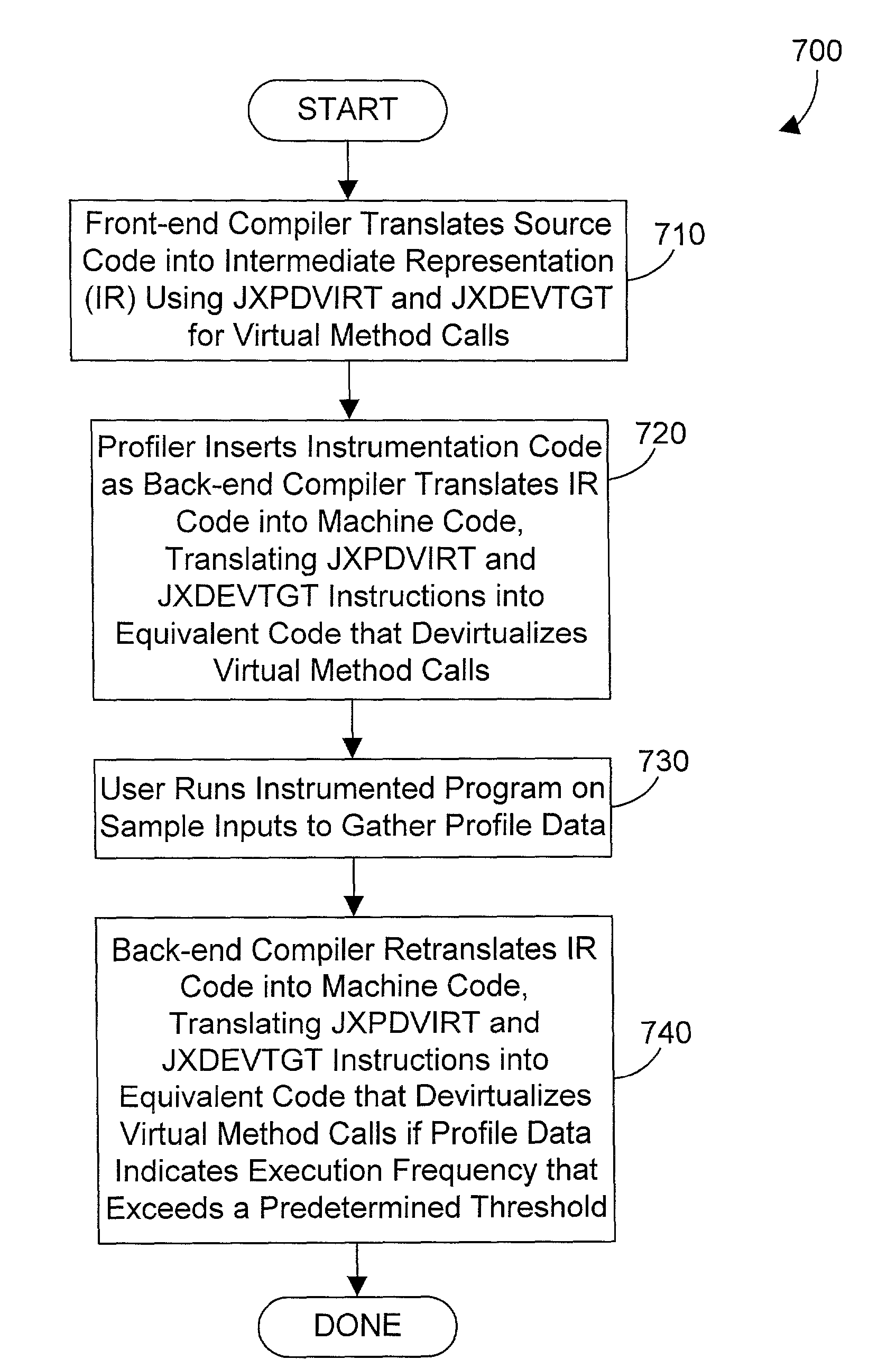
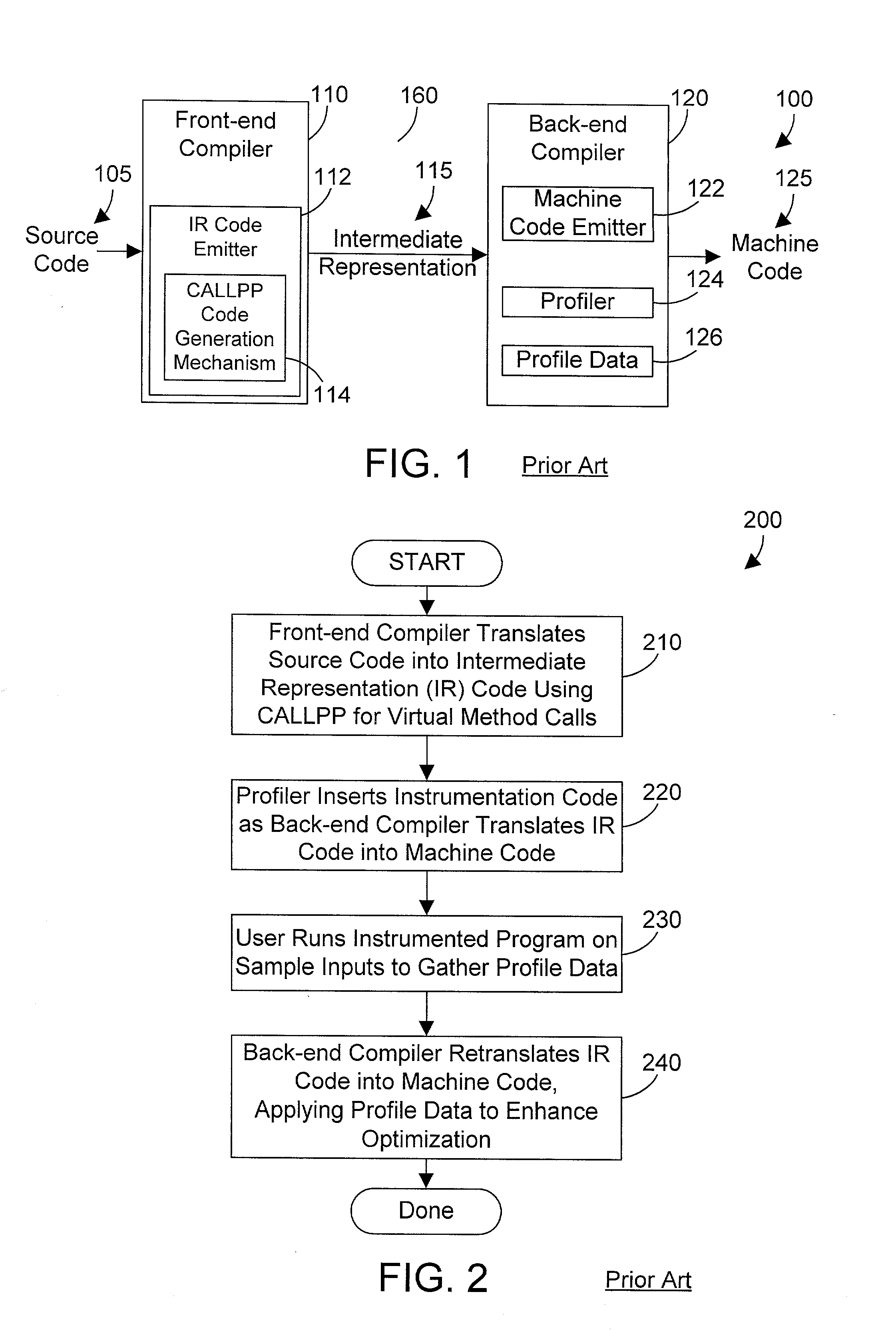
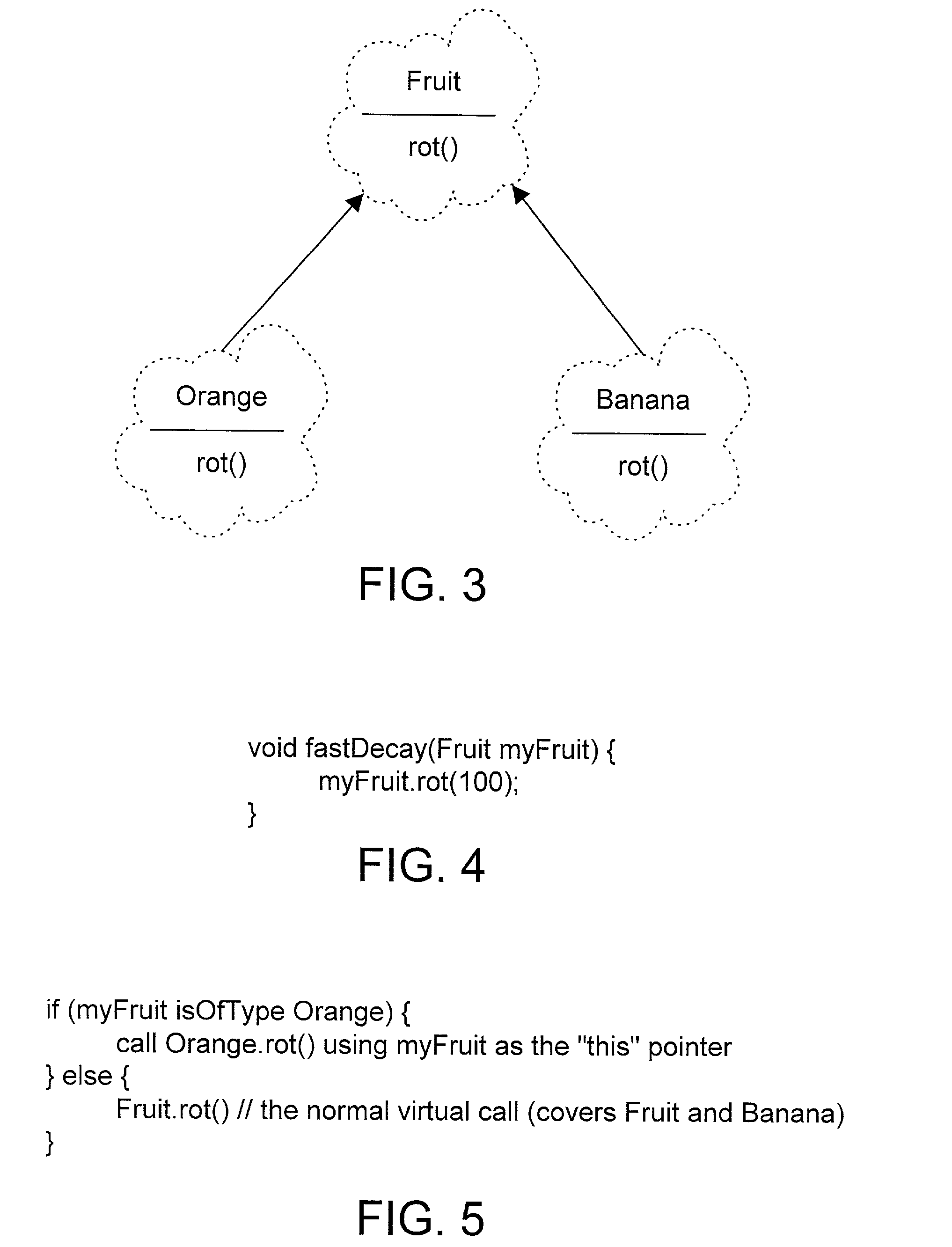
Compiler apparatus and method for devirtualizing virtual method calls
A front-end compiler generates unique instructions for virtual method calls in intermediate representation code that may be passed to a back-end compiler. A back-end compiler in accordance with the preferred embodiments receives the intermediate representation code, and processes the unique instructions to generate therefrom equivalent code with explicit method calls, where possible. The machine code from the back-end compiler is then executed using sample inputs to generate profile data. The profile data and intermediate representation code are fed into the back-end compiler, which then generates code that may devirtualize virtual method calls according to the profile data by providing one or more explicit method calls for target methods that have an execution frequency (as indicated by the profile data) that exceeds a predetermined threshold.
Owner:LINKEDIN
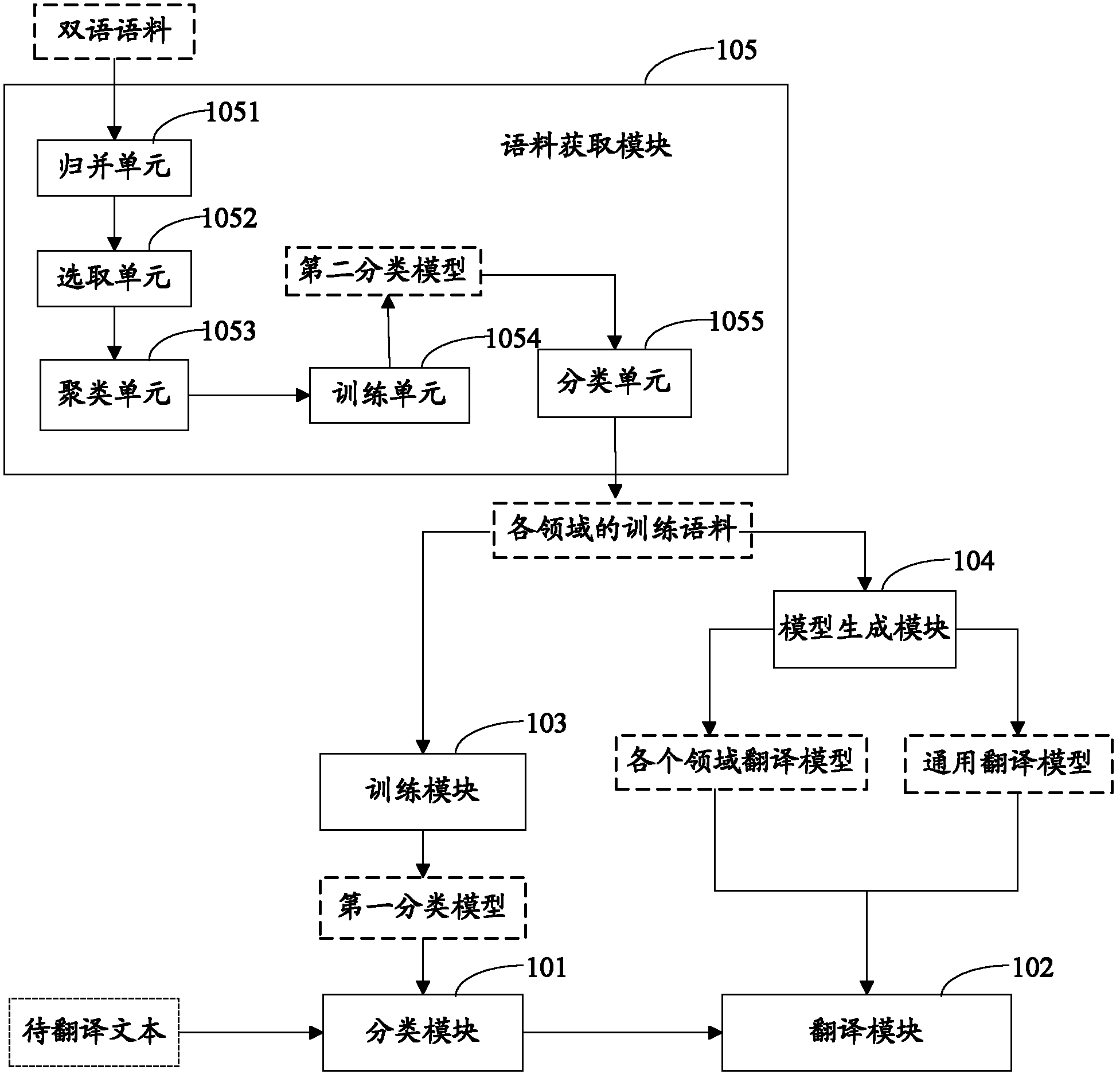
Method and device for obtaining corpus, method and system for generating translation model and method and system for mechanical translation
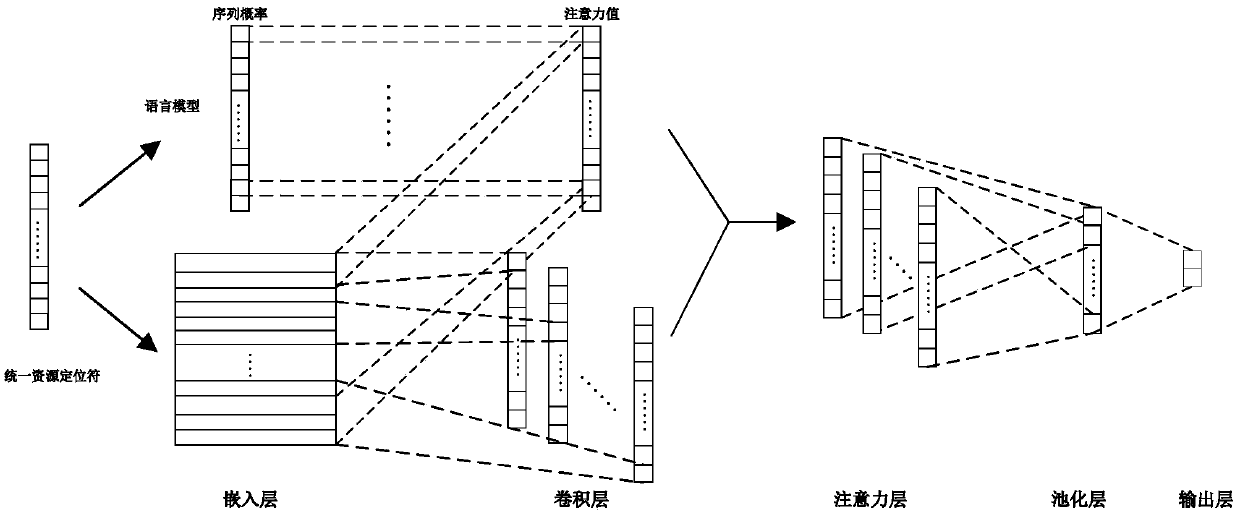
ActiveCN103049436AImprove effectivenessEffective divisionSpecial data processing applicationsMachine translationSpeech recognition
The invention provides a method and device for obtaining corpus, a method and system for generating a translation model and a method and system for mechanical translation. The system for the mechanical translation comprises a classification module and a translation module. The classification module is used for utilizing a first classification module to classify texts to be translated to determine the fields where the texts to be translated belong to, and the first classification model is obtained by training corpus in various fields. The translation module is used for utilizing field translation models corresponding to the fields where the texts to be translated belong to translate the texts to be translated, wherein the field translation models are obtained by training the corpus of the corresponding fields. Through the way, translation accuracy can be improved effectively.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Fibre channel frame batching for IP transmission
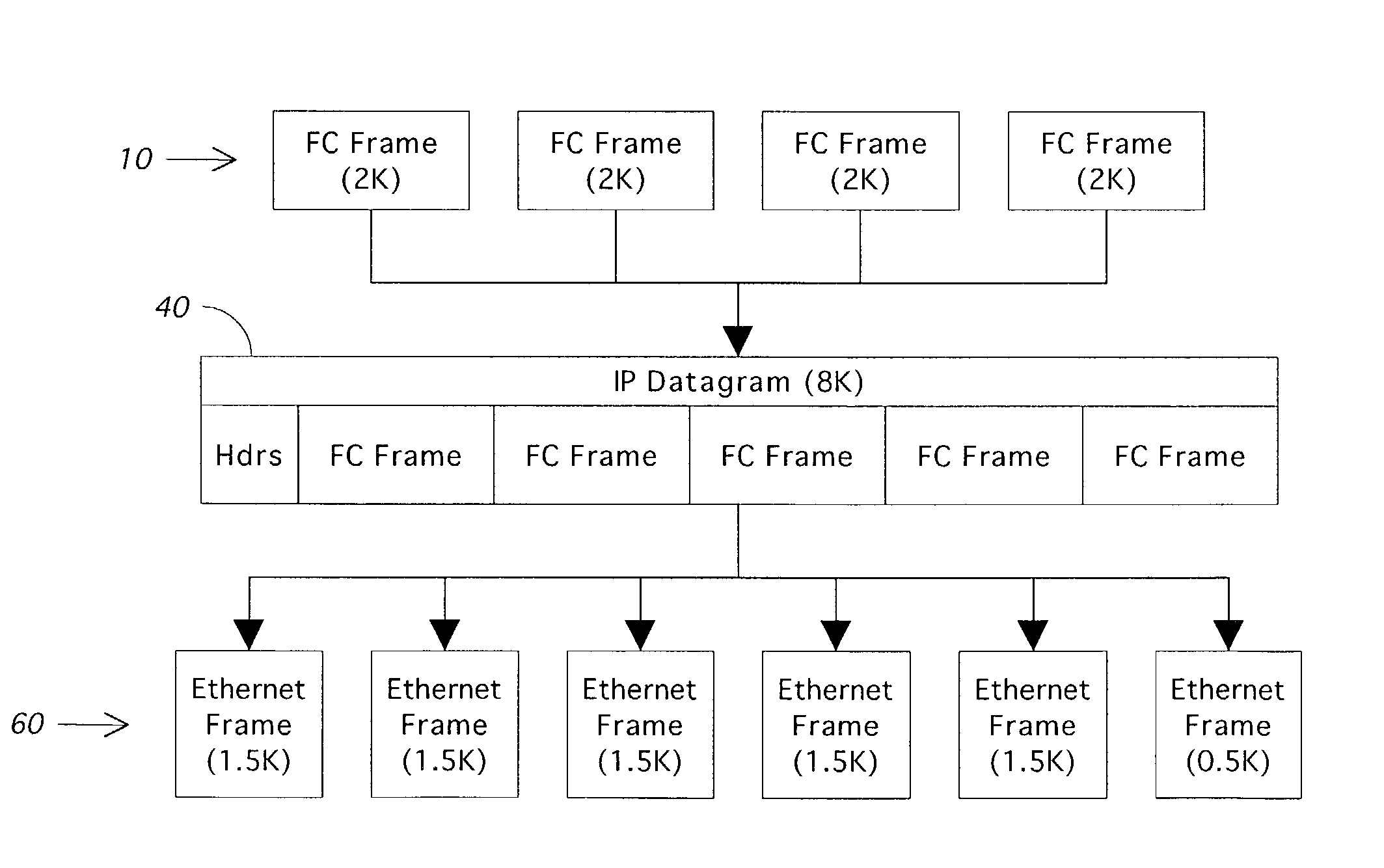
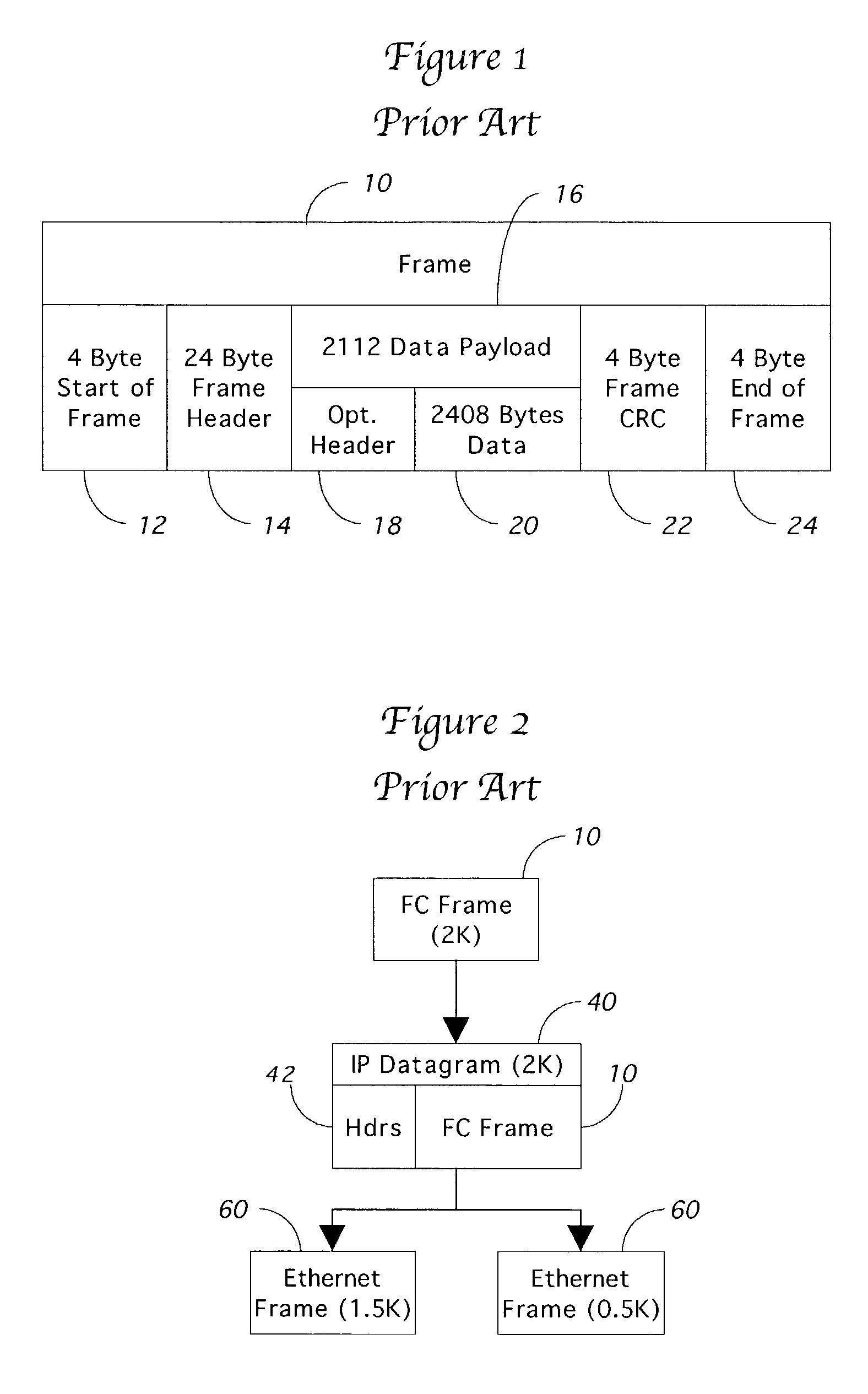
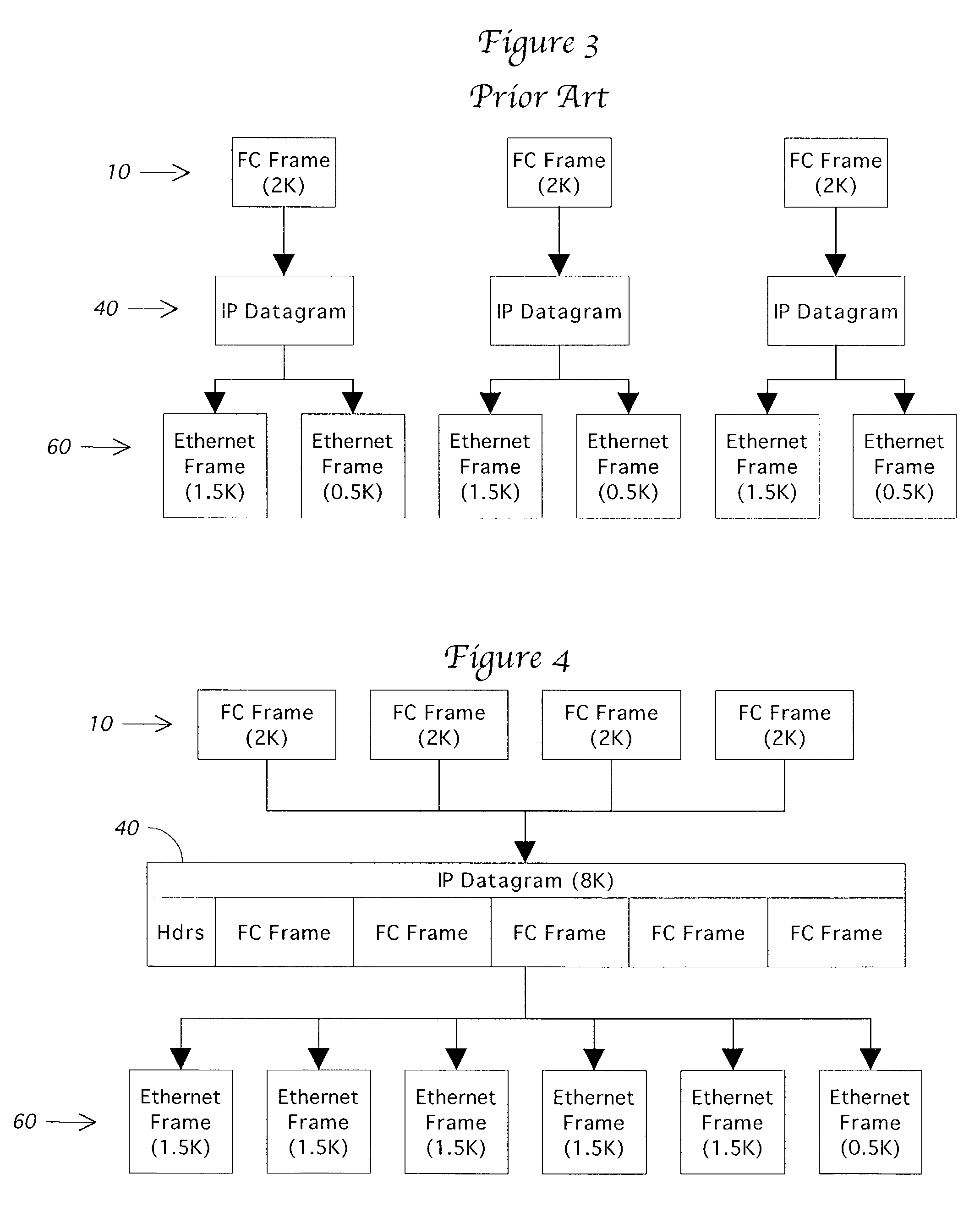
InactiveUS7308001B2Guaranteed normal transmissionOvercome limitationsTime-division multiplexNetworks interconnectionFiberFibre Channel
A storage router and related method are presented for combining multiple Fibre Channel frames together into a single IP datagram for tunneling transmission over an Internet protocol network. The storage router operates by storing incoming Fibre Channel frames in a Fibre Channel frame buffer. When there is sufficient data in the buffer, multiple Fibre Channel frames are taken from the buffer and combined into a single IP datagram. The number of Fibre Channel frames to be combined can be established through a variety of tests, including total bytes of data, number of frames, or through a time-out mechanism. The network layer then fragments the datagram into data link level frames, such as 1500 byte Ethernet frames. When the IP datagram arrives at the final destination, the segmented IP datagram is reconstructed, and the multiple Fibre Channel frames are extracted from the IP datagram and passed on to the recipient Fibre Channel network.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Surface plasmon optic devices and radiating surface plasmon sources for photolithography
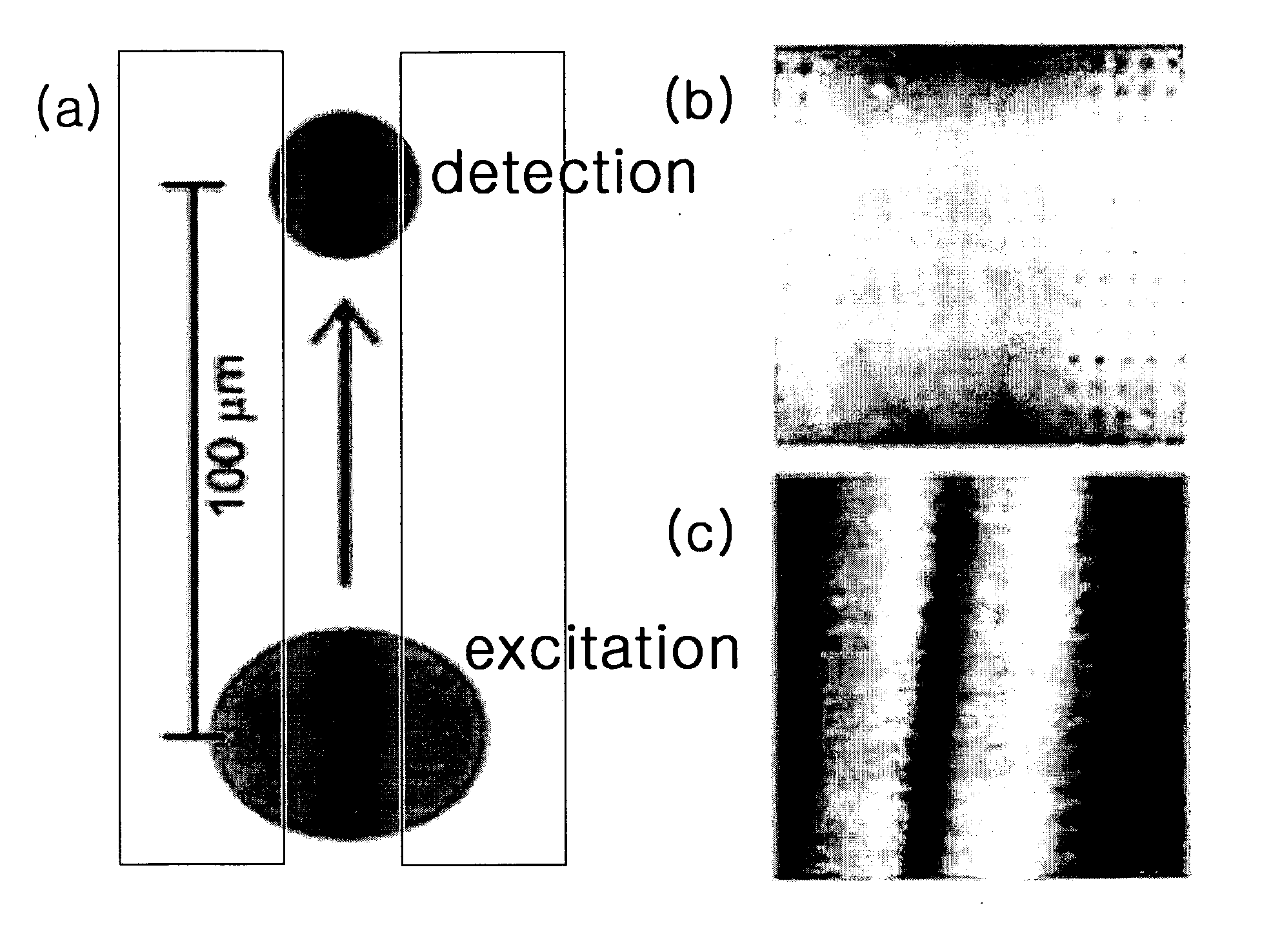
InactiveUS20050062973A1Effective divisionDirection is limitedScattering properties measurementsCoupling light guidesDielectric substrateAir interface
Disclosed is a surface plasmon optic device that has a periodic array of apertures in a dielectric substrate and a metal film formed on the dielectric substrate and emits light from metal-air interface. The surface plasmon optic device includes a surface plasmon generating apparatus, a surface plasmon detecting apparatus, a surface plasmon controlling apparatus, an etching apparatus, etc. if a metal diffraction grating is disposed on the metal film having a well-defined interface, propagation of the surface plasmon can be efficiently reflected, divided and controlled. Further, radiating surface plasmon having a half period of a lattice constant formed at air-metal (1, 0) can be preserved at a distance of at least a few micron.
Owner:MAX BORN INST FUT NICHTLINEARE OPTIK & KURZZEITSPEKTROSKOPIE +1
Display device and a method of driving the same
ActiveUS8319737B2Reduce stepsEffective divisionEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsDisplay deviceAlternating current
A display device including: a plurality of pixels; pixel electrodes; n (n≧2) counter electrodes; a display functional layer; a write drive scanning portion; detection electrodes; an alternate current drive scanning portion; and a detecting portion.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY WEST
Wafer processing method
ActiveUS20140248757A1High molding strengthImprove productivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusPulsed laser beamSplit lines
A wafer processing method for dividing a wafer along a plurality of division lines to obtain a plurality of individual chips. The wafer processing method includes a filament forming step of applying a pulsed laser beam having a transmission wavelength to the wafer along each division line in the condition where the focal point of the pulsed laser beam is set inside the wafer in a subject area to be divided, thereby forming a plurality of amorphous filaments inside the wafer along each division line, and an etching step of etching the amorphous filaments formed inside the wafer along each division line by using an etching agent to thereby divide the wafer into the individual chips along the division lines.
Owner:DISCO CORP
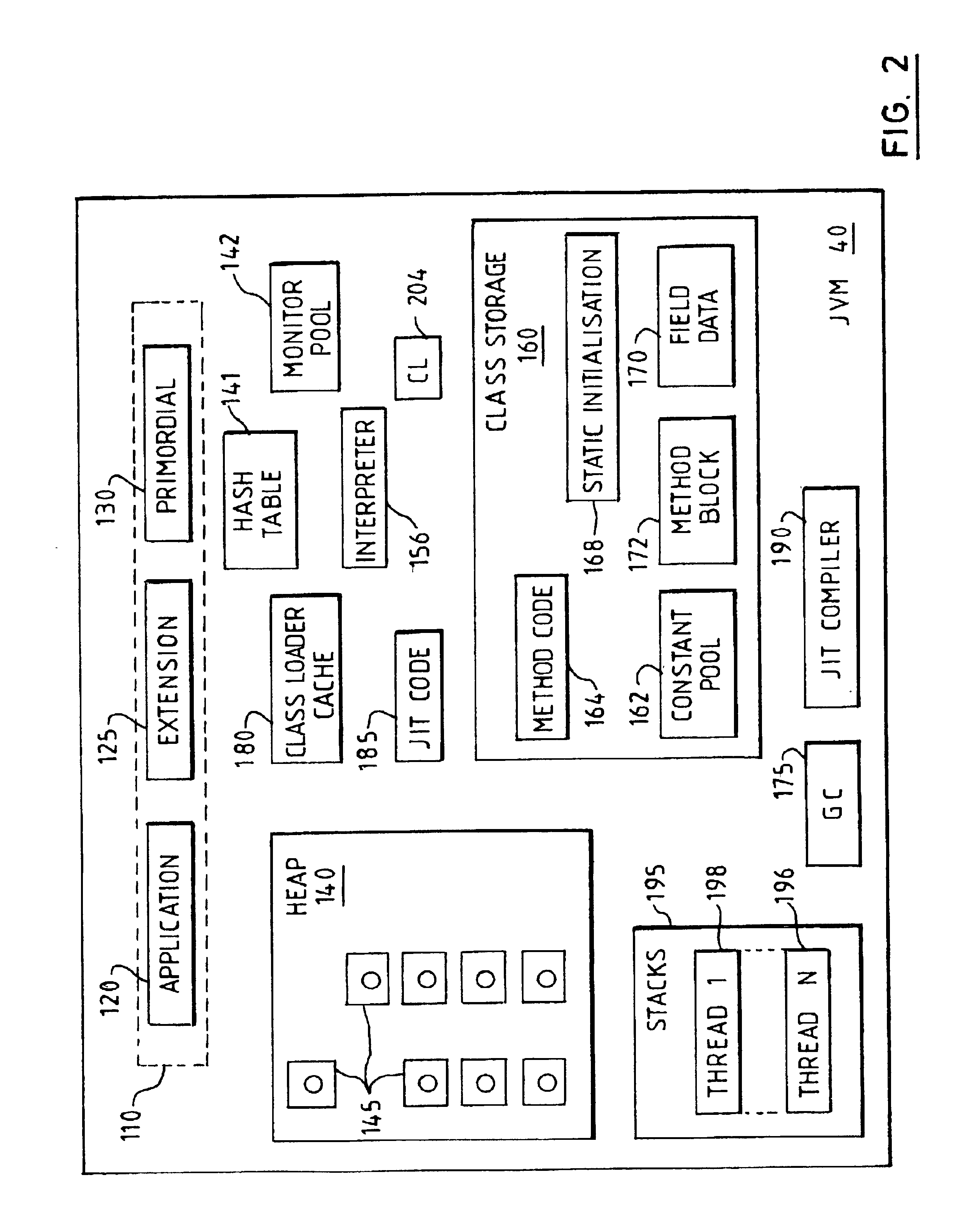
Computer system with heap and card table
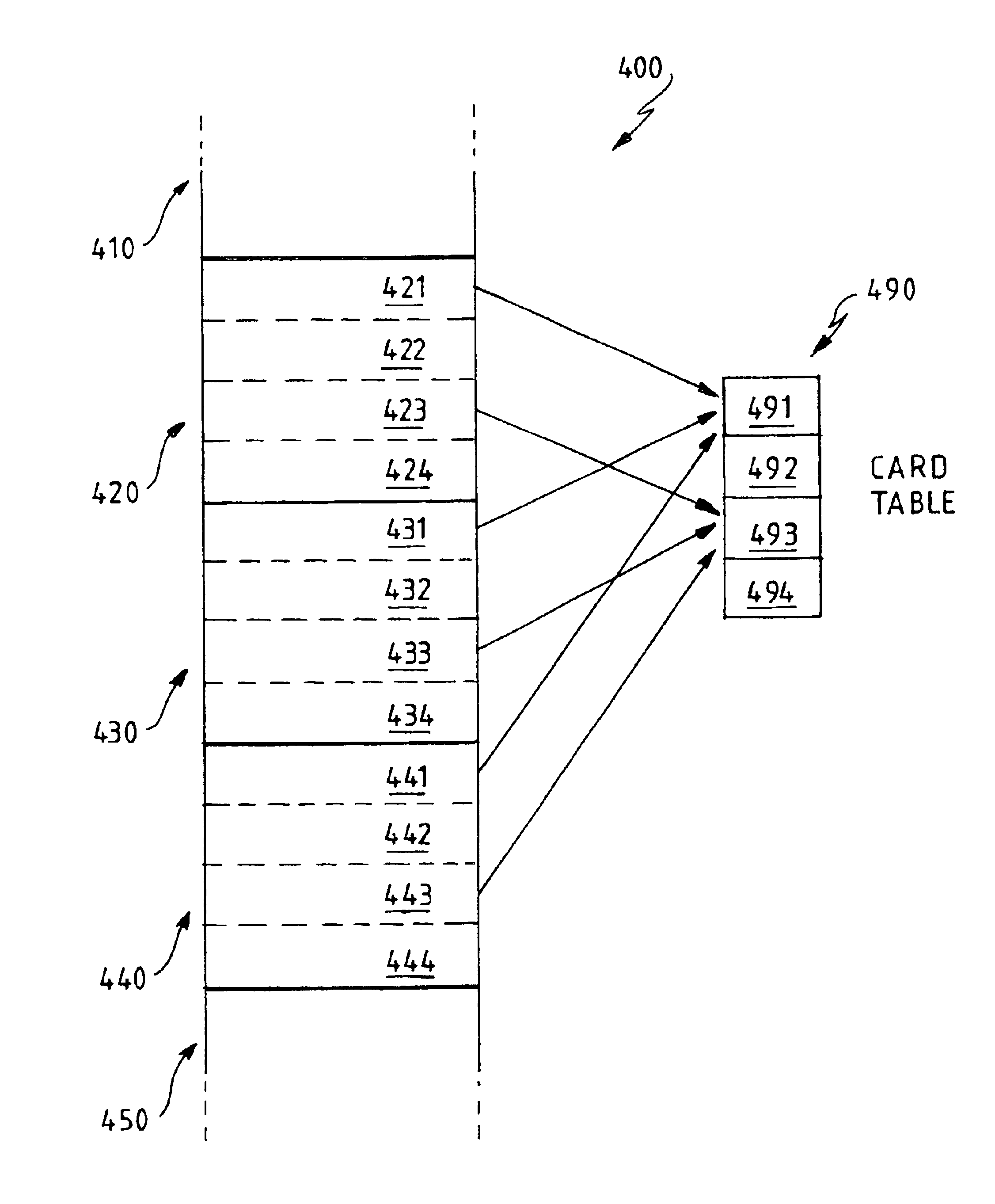
InactiveUS6845437B2Efficient managementEliminate needData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOptimization systemMemory address
A computer system has a heap for storing objects and a card table for tracking updates to objects on the heap, typically for garbage collection purposes. In particular, the heap is divided into segments, each corresponding to a card in the card table, and any update to a segment in the heap triggers a write barrier to mark the corresponding card in the card table. It is important that this write barrier is as efficient as possible to optimize system performance. In some circumstances an object update may be made to an address outside the heap. To ensure that this still properly maps to a card in the card table, the entire memory space is folded cyclically, so that any given memory address corresponds to one, and only one card, in the card table.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of dividing wafer
InactiveUS20160307851A1Effective divisionEasy to disassembleSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringWater soluble
A method of dividing a wafer includes a protective film forming step of forming a water-soluble protective film on a front side of the wafer, a mask forming step of forming an etching mask on the front side of the wafer by partly removing the water-soluble protective film along the streets, a plasma etching step of performing a plasma etching on the wafer along the streets through the etching mask in the form of the water-soluble protective film, and a protective film removing step of removing the water-soluble protective film by supplying cleaning water to the water-soluble protective film. After plasma etching, i.e. in removing the protective film, the water-soluble protective film can easily be removed from the front side of the wafer simply by supplying the cleaning water from a water supply unit to the water-soluble protective film.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Transient electromagnetic detection method for ground-roadway of multi-layer goaf
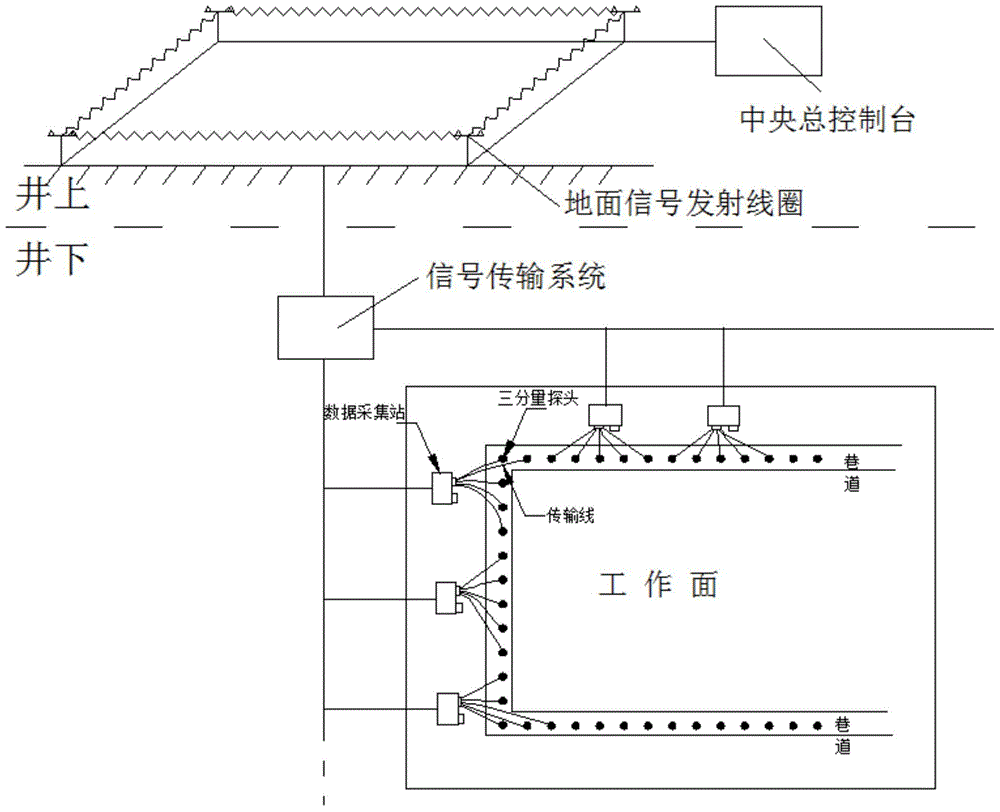
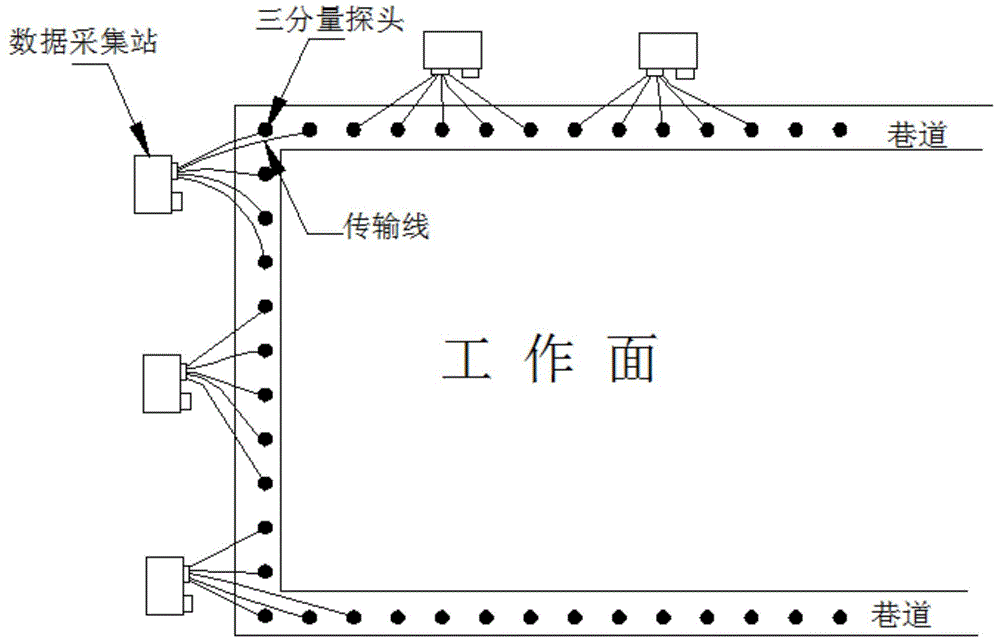
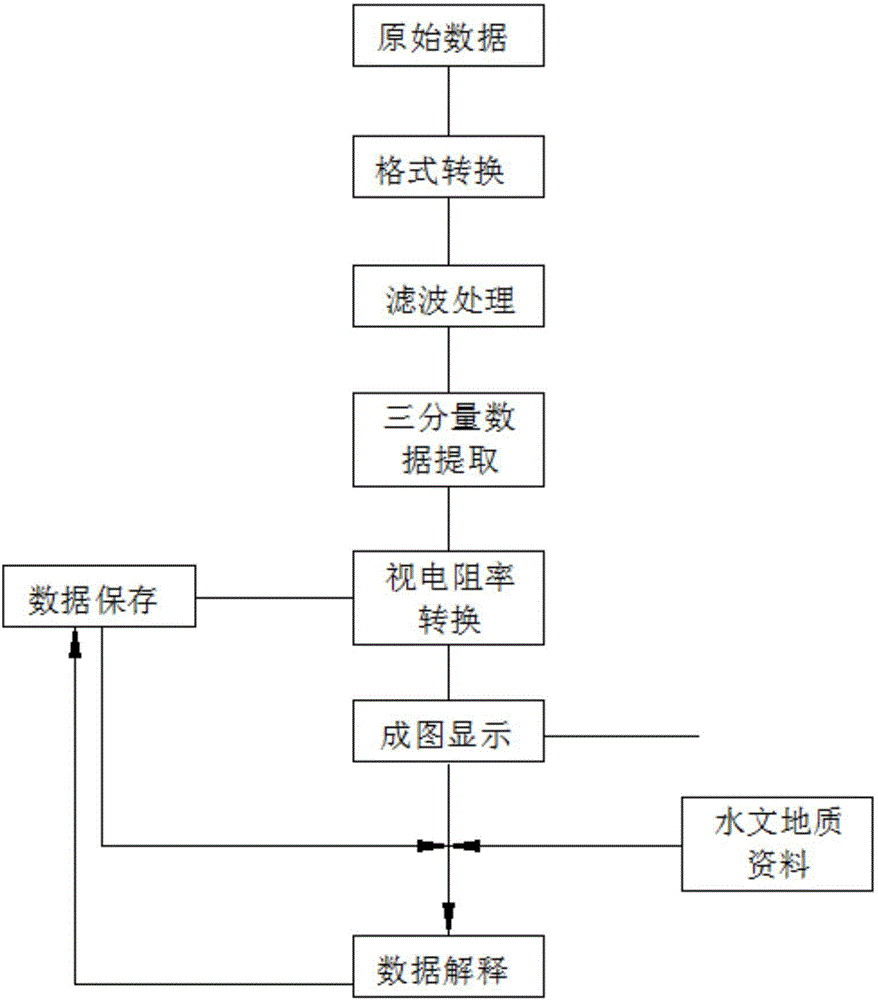
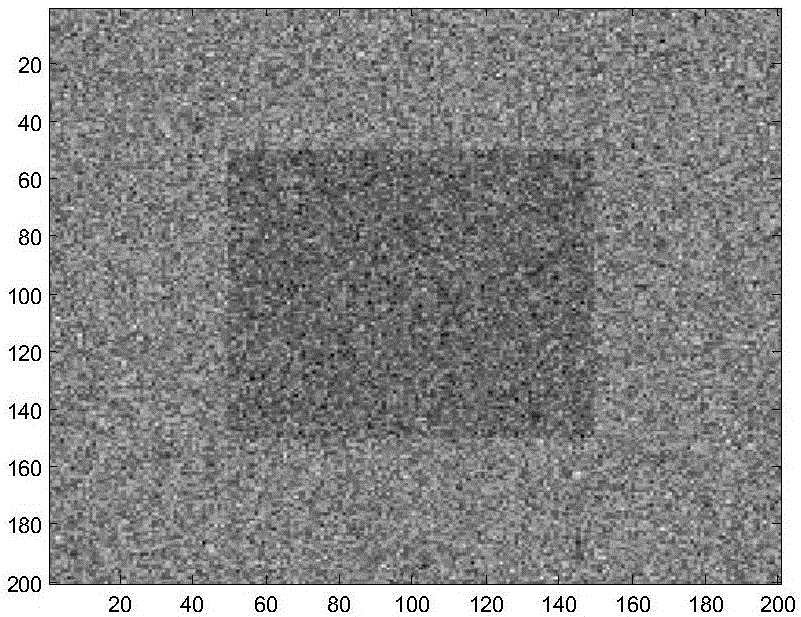
InactiveCN104597511AEffective divisionImprove resolutionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingWater resource assessmentData acquisitionDynamic monitoring
The invention discloses a transient electromagnetic detection method for ground-roadway of a multi-layer goaf. The transient electromagnetic detection method for the ground-roadway of the multi-layer goaf mainly includes data gathering and data processing. The concrete steps include that paving a large emitting coil on the ground to emit electromagnetic signals to the underground, distributing three-component receiving probes at upper and lower gate roadways, cutting holes, connection roadways and the like of the roadway of the underground working surface to gather data, and transmitting the data to a general console desk on the ground through an underground data gathering station and a data transmission system; processing the data, and obtaining the analysis result through the primary processing and apparent resistivity conversion for the data, image display of the data and data comparison. The transient electromagnetic detection method for the ground-roadway of the multi-layer goaf is capable of identifying the water layer position of the multi-layer goaf of the whole mine lot without blind area in a high resolution, realizing dynamic monitoring and effectively dividing the boundaries of each goaf in the mine lot in the vertical direction and horizontal direction to provide guarantee for the safety production of coal; the transient electromagnetic detection method for the ground-roadway of the multi-layer goaf greatly improves the resolution capability of the multi-layer goaf of the mine and realizes careful exploration.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Method for effectively segmenting hyperspectral oil-spill image
InactiveCN106447688AImprove Segmentation AccuracyAccurate segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisBoundary contourEuler–Lagrange equation
Provided is a method for effectively segmenting a hyperspectral oil-spill image. The method comprises steps of: defining an initial level set function and other related functions; acquiring a new fitting item in combination with a Fisher criterion; constructing an edge stop function to obtain a new length item; performing improvement in combination with an end member extraction algorithm; introducing a level set regular item to prevent reinitialization of the level set function; minimizing an energy function to obtain an Euler-Lagrange equation; setting parameters; selecting a display band and an initial contour; displaying a segmentation result graph; calculating various segmentation precision evaluation indexes; comparing and evaluating the accuracy of the segmentation results. The method can classify a target area in a simulated hyperspectral image and a real hyperspectral image, and effectively segments the hyperspectral oil-spill image with boundary blur and noise, improves the segmentation accuracy of the hyperspectral image, obtain a more accurate classification effect, makes the parameter change more stable, makes the contour curve more accurate, obtains the continuous and closed boundary contour, and has higher precision of segmentation.
Owner:DALIAN MARITIME UNIVERSITY
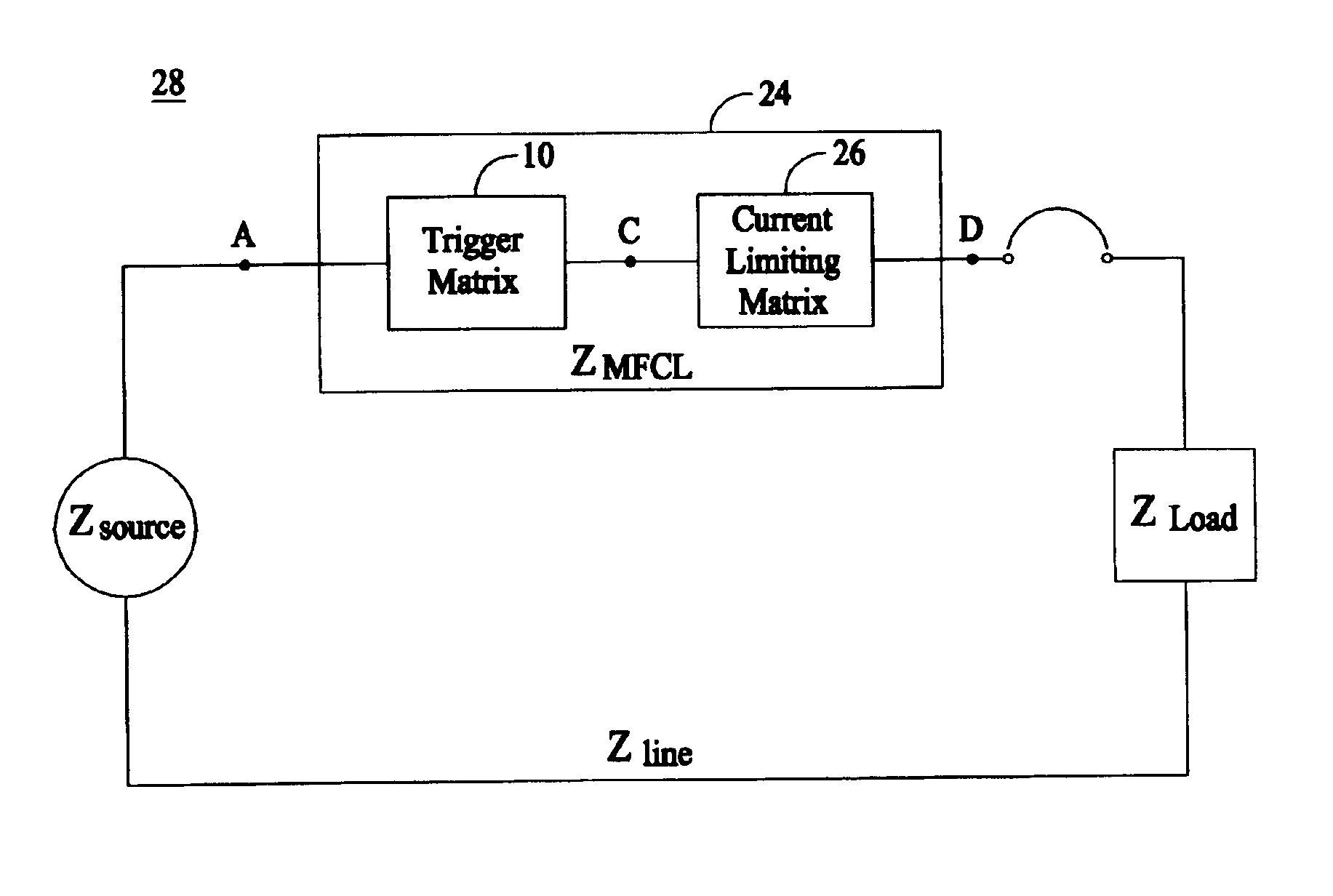
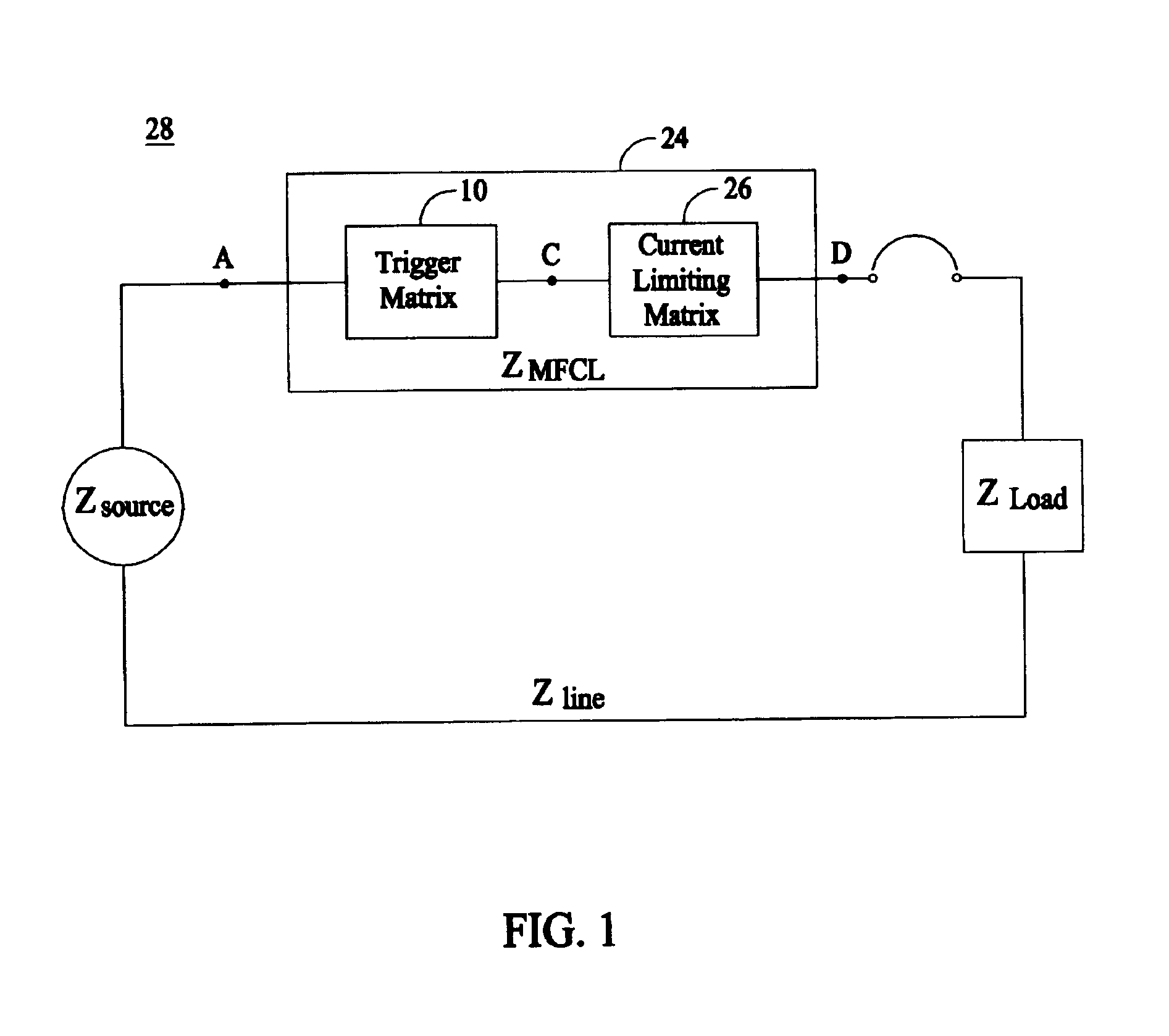
Superconducting matrix fault current limiter with current-driven trigger mechanism
InactiveUS6958893B2Uniform applicationHigh strengthEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentSuperconductor elements usageModularityConductive materials
A modular and scalable Matrix-type Fault Current Limiter (MFCL) that functions as a “variable impedance” device in an electric power network, using components made of superconducting and non-superconducting electrically conductive materials. An inductor is connected in series with the trigger superconductor in the trigger matrix and physically surrounds the superconductor. The current surge during a fault will generate a trigger magnetic field in the series inductor to cause fast and uniform quenching of the trigger superconductor to significantly reduce burnout risk due to superconductor material non-uniformity.
Owner:SUPERPOWER INC
Optical device wafer processing method
ActiveUS20150044799A1Improve productivityNot to damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesLight beamPulsed laser beam
In an optical device wafer processing method, a light emitting layer on the front side of a wafer is removed by applying a pulsed laser beam to the wafer along division lines from the back side of a substrate with the focal point of the beam set near the light emitting layer, thereby partially removing the light emitting layer along the division lines. A shield tunnel is formed by applying the beam to the wafer along the division lines from the back of the substrate with the focal point of the beam set near the front of the substrate. This forms a plurality of shield tunnels arranged along each division line, each shield tunnel extending from the front side of the substrate to the back side thereof. Each shield tunnel has a fine hole and an amorphous region formed around the fine hole for shielding the fine hole.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com