Patents
Literature
3104 results about "Datagram" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
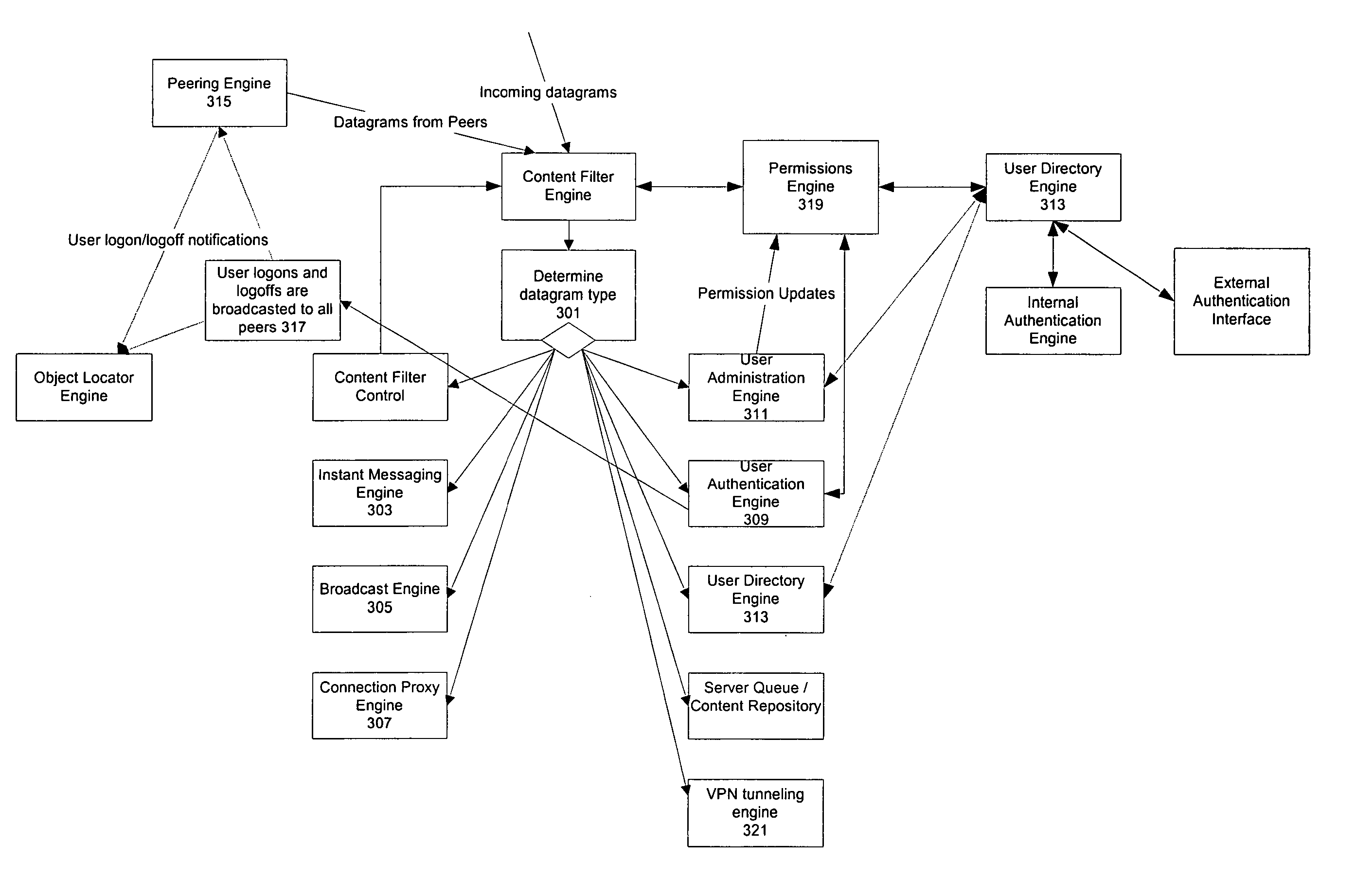
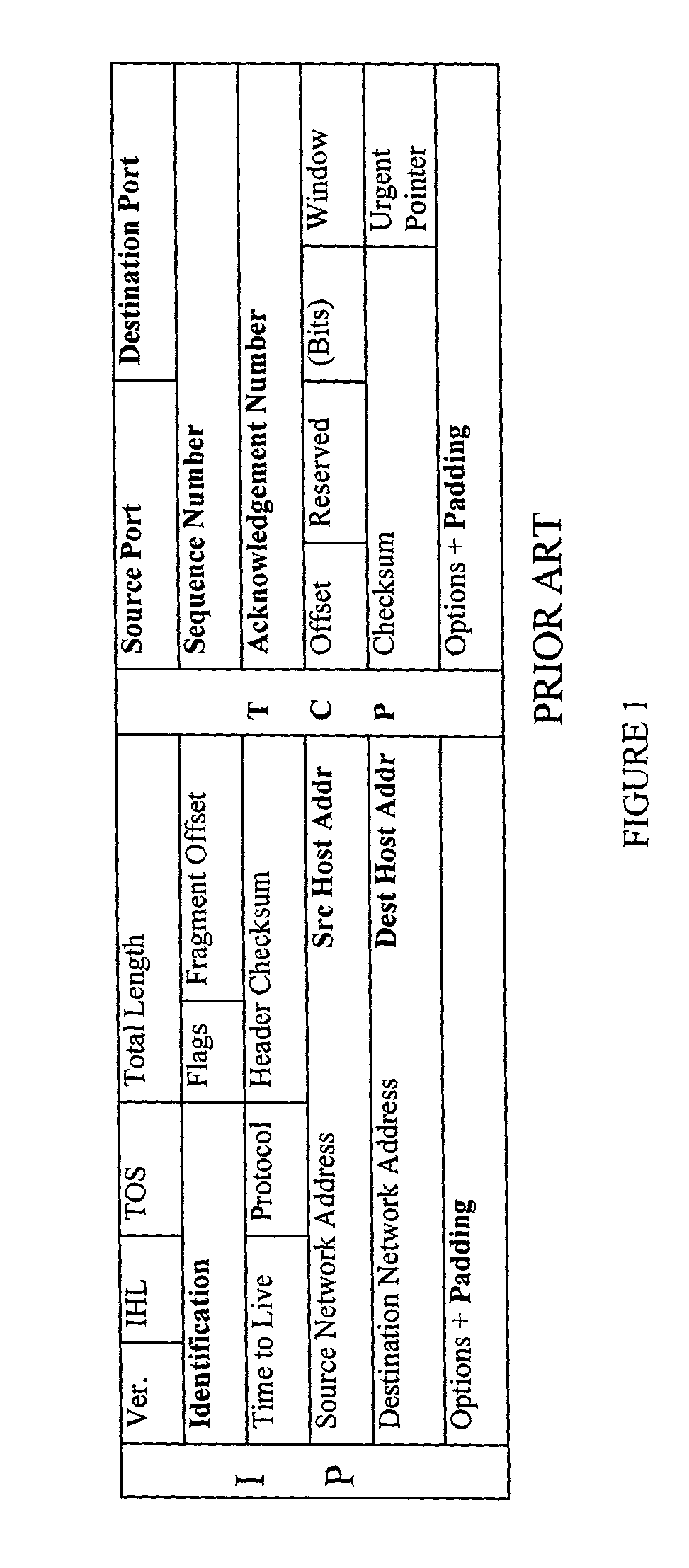
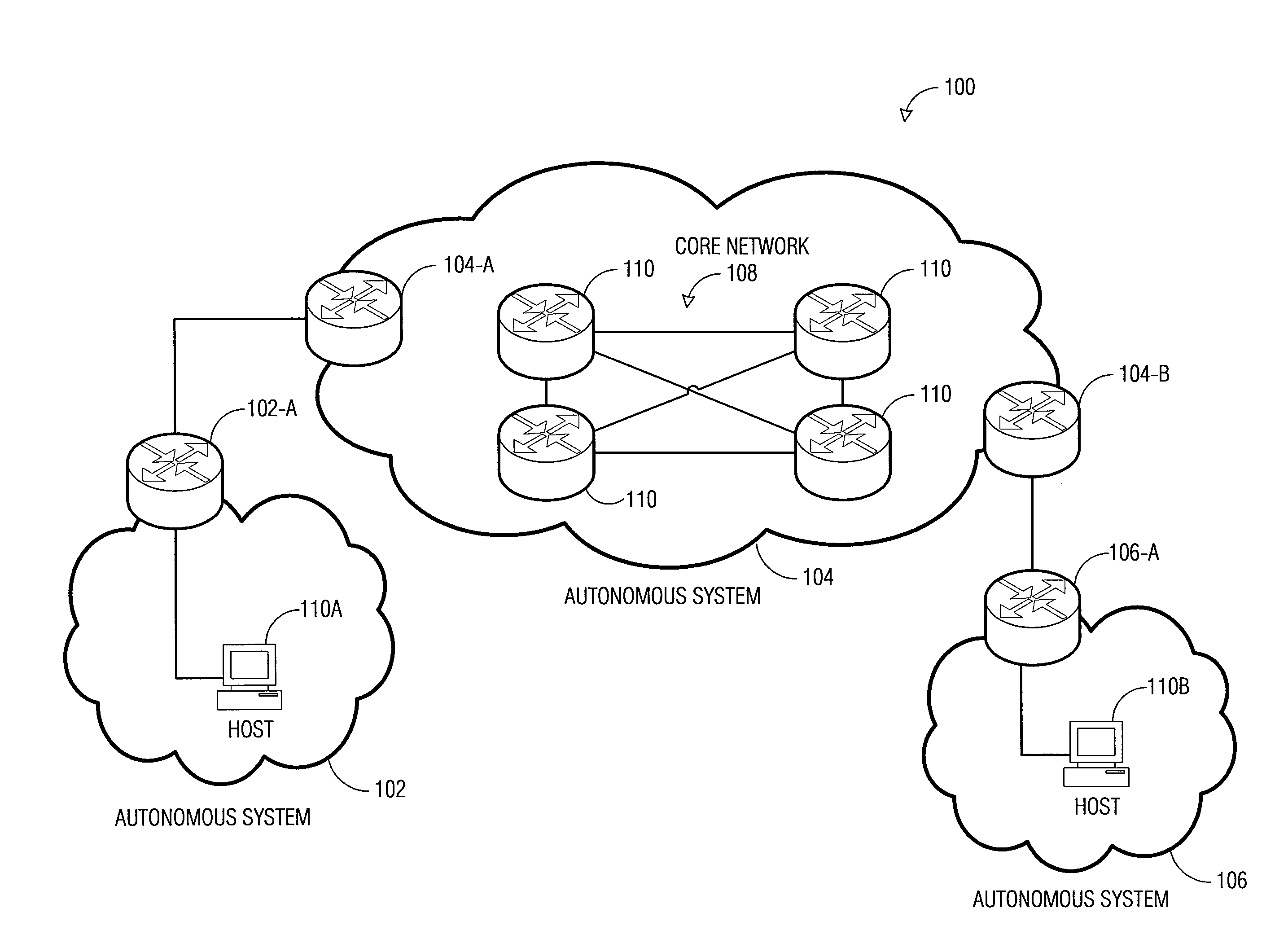
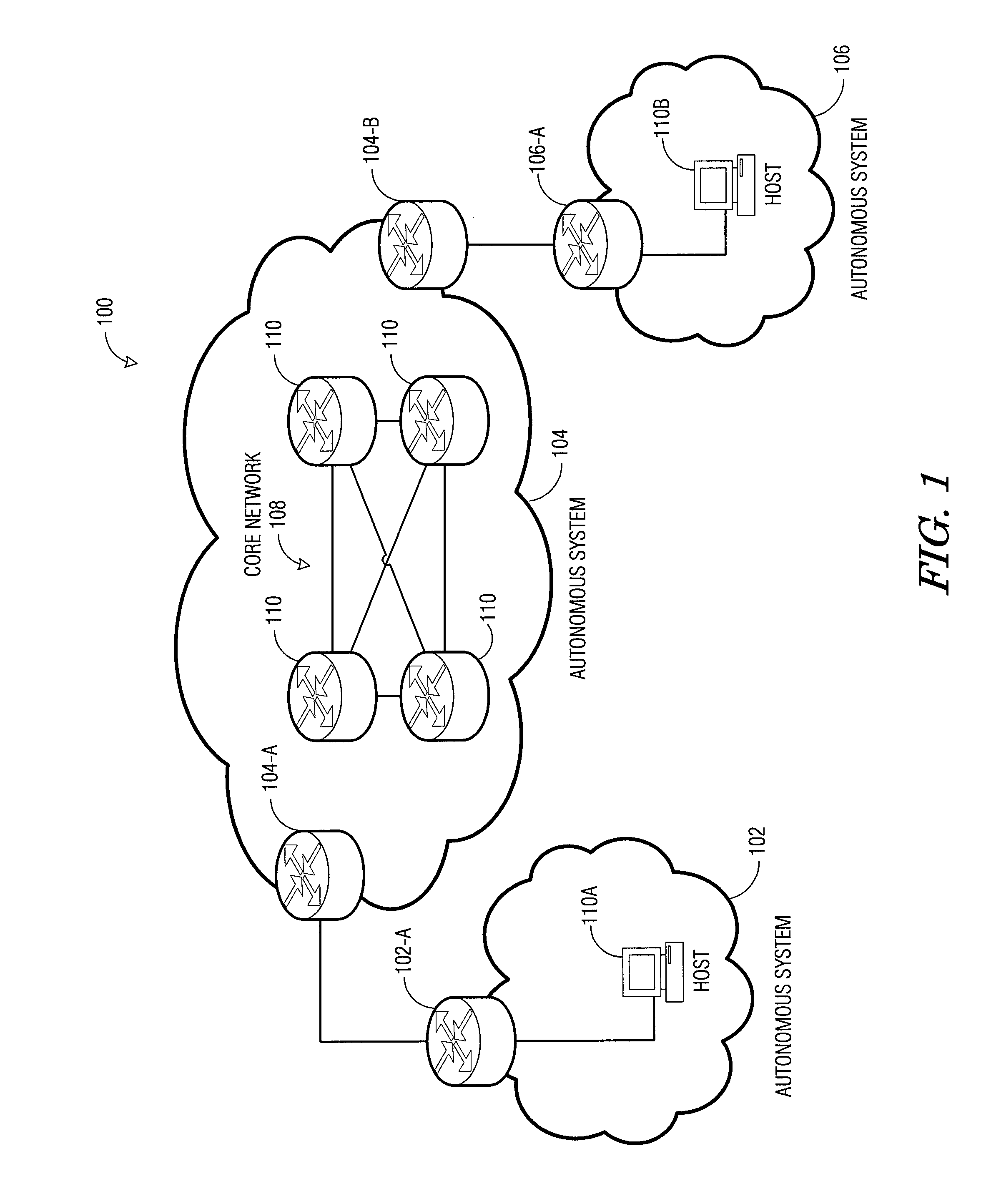
A datagram is a basic transfer unit associated with a packet-switched network. Datagrams are typically structured in header and payload sections. Datagrams provide a connectionless communication service across a packet-switched network. The delivery, arrival time, and order of arrival of datagrams need not be guaranteed by the network.
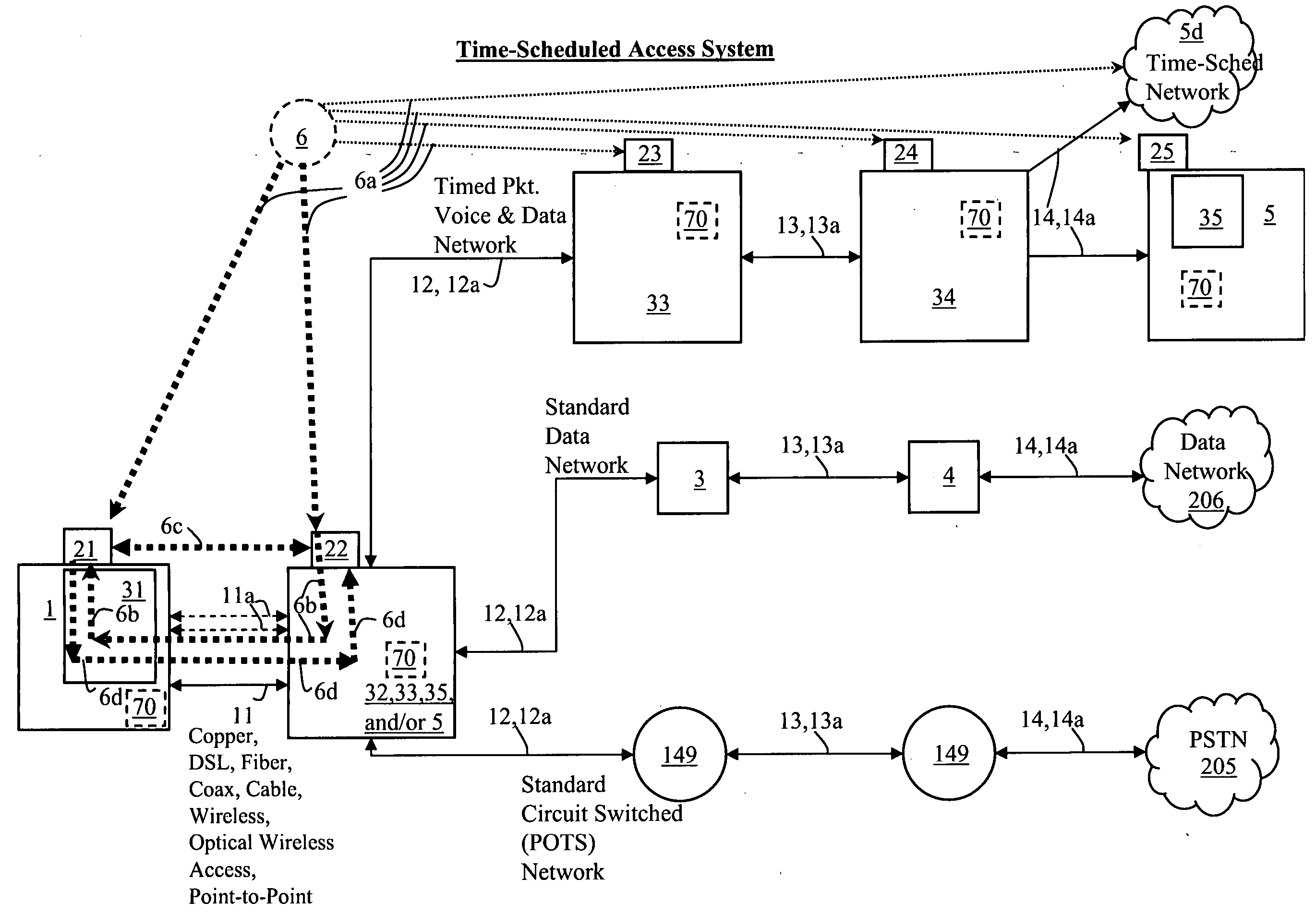
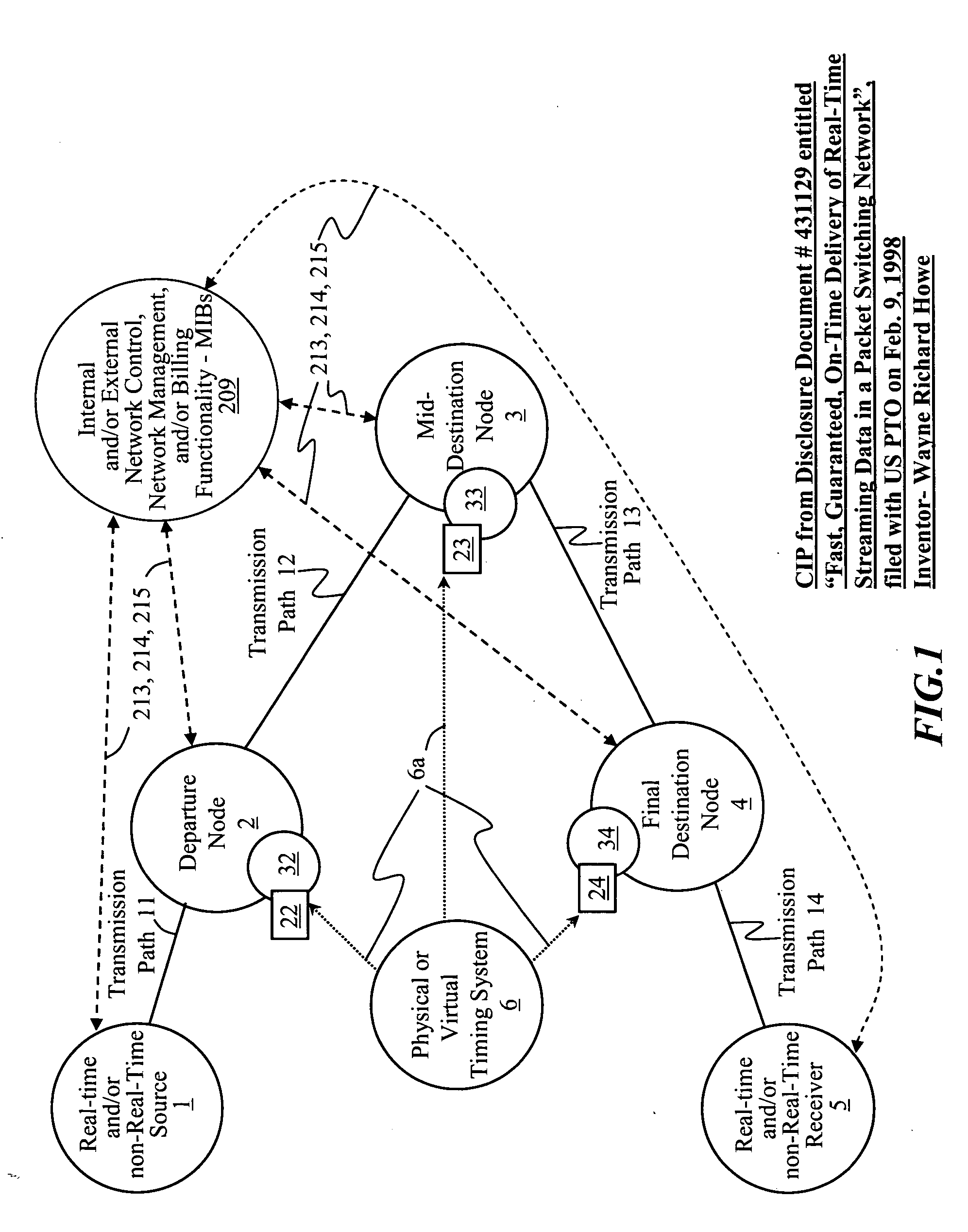
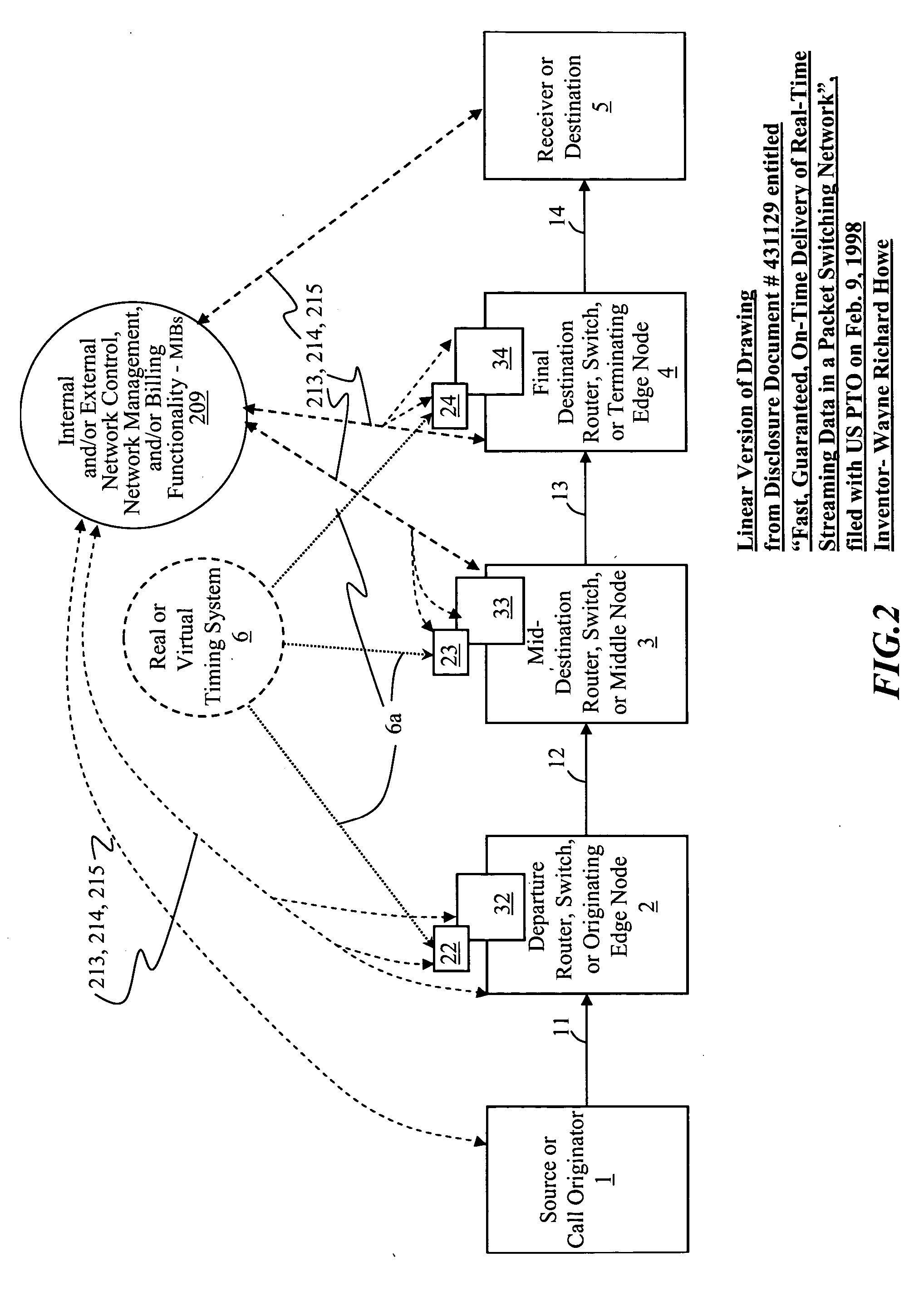
Time-scheduled and time-reservation packet switching
InactiveUS20050058149A1Optimum advantage and efficiencyImprove accuracyMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexData packTime schedule
Systems, methods, devices, processes, procedures, algorithms, networks, and network elements are described for time-scheduled and / or time-reserved dat networks. Invention provides capabilities for synchronizing data networks and / or data network links; for establishing time-schedules, time-reservations, time-schedule reservations, and / or reservation time-slots for packets, cells, frames, and / or datagrams; and for transferring, transmitting, switching, routing, and / or receiving time-sensitive, high-reliability, urgent, and / or other time-scheduled, time-reserved, time-allocated, and / or time-scheduled-reservation packets, cells, frames, and / or datagrams, such as real-time and high-priority messages over these networks. The invention(s) enables packet-, cell-, datagram- and / or frame-based networks to thereby efficiently, reliably, and in guaranteed real-time, to switch and / or route data such as voice, video, streaming, and other real-time, high-priority, high-reliability, and / or expedited data with guaranteed delivery and guaranteed quality of service. Networks may be fixed, point-to-point, mobile, ad-hoc, optical, electrical, and / or wireless.
Owner:HOWE WAYNE RICHARD
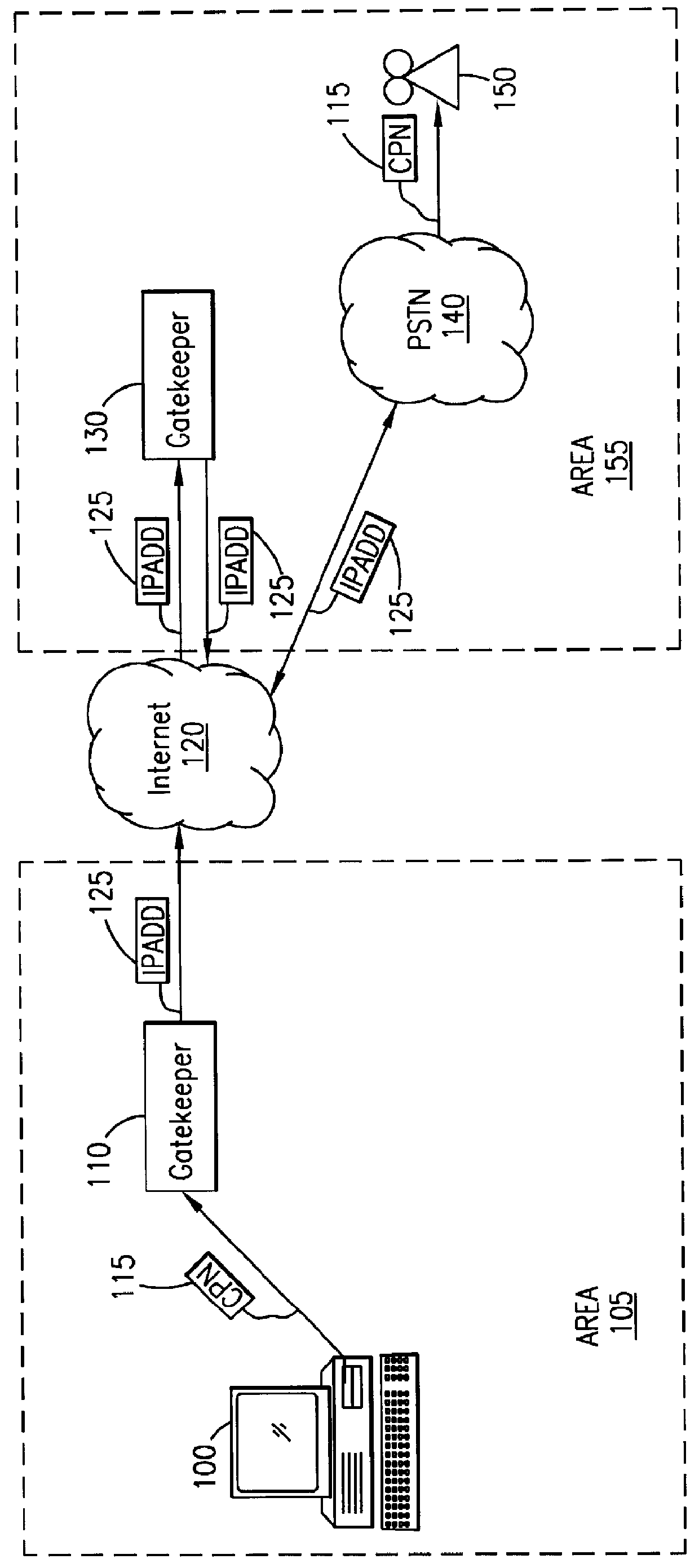
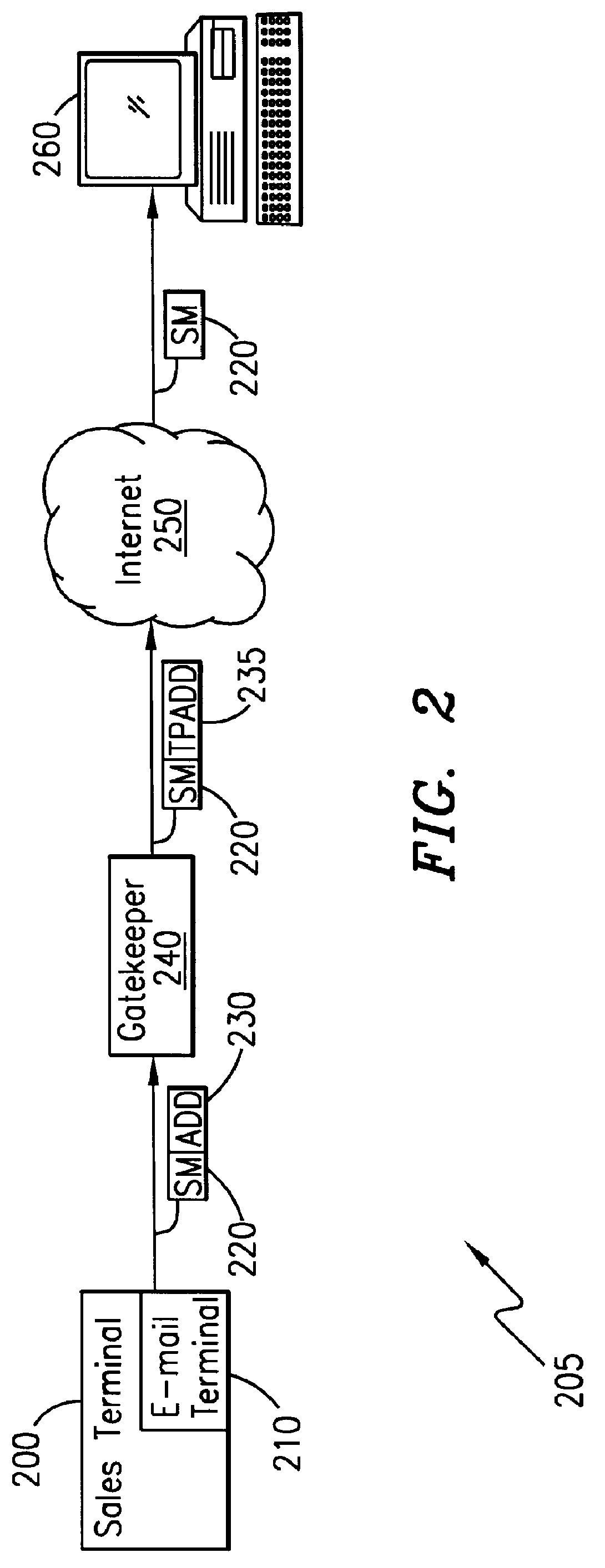
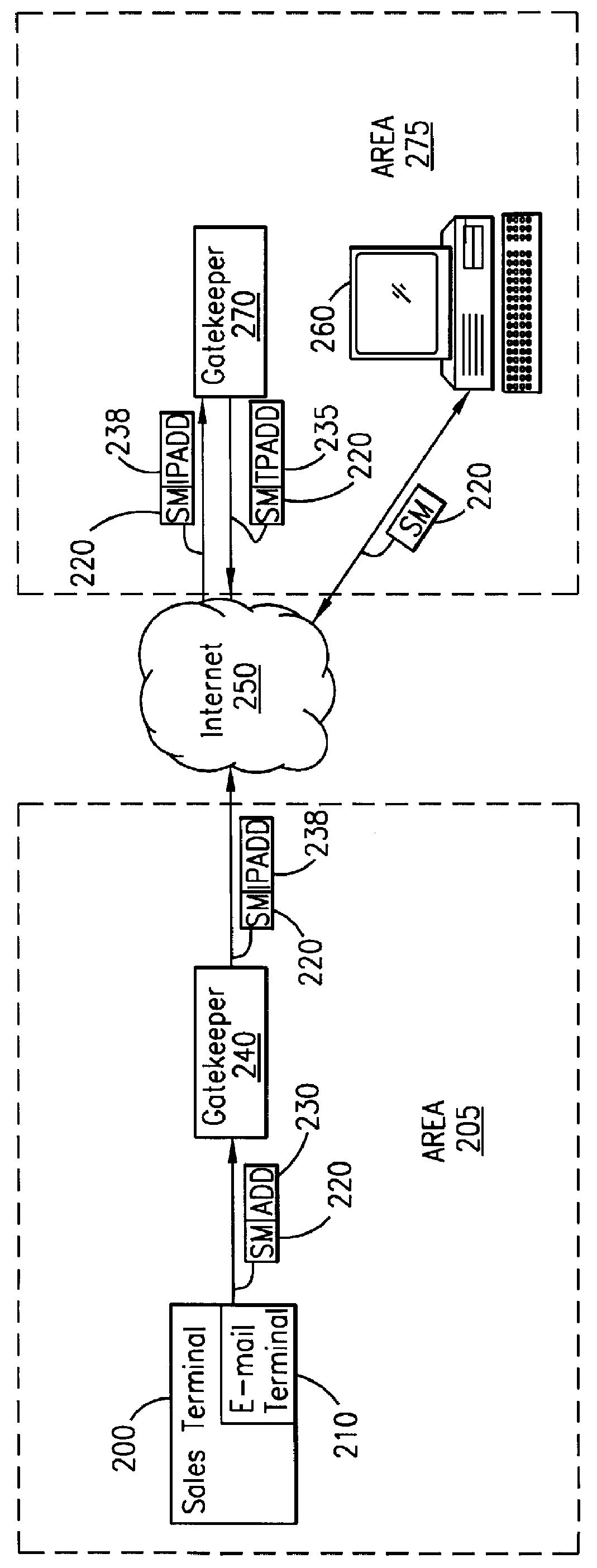
System and method for sending a short message containing purchase information to a destination terminal
InactiveUS6067529AEfficient and cost-effectiveReliable deliveryComplete banking machinesCash registersMulticast addressComputer terminal
A telecommunications system and method is disclosed for providing a substantially immediate electronic receipt after a consumer has made a purchase. When a consumer makes a purchase, the sales terminal, which is attached with a short message / e-mail sending capable terminal, can generate and route a short message along with the detailed purchase information to a transport address or alias address associated with the consumer via a Gatekeeper for the Internet for the area that the sales terminal is located in. Upon receipt of the short message, the Gatekeeper can then convert the alias address to the transport address, if the alias address is given and the consumer does not want the short message sent to the alias address, and forward the short message through the Internet to that transport address (or alias address) as an Internet Protocol datagram for storage and retrieval of the short message by the consumer either immediately or at a later time.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
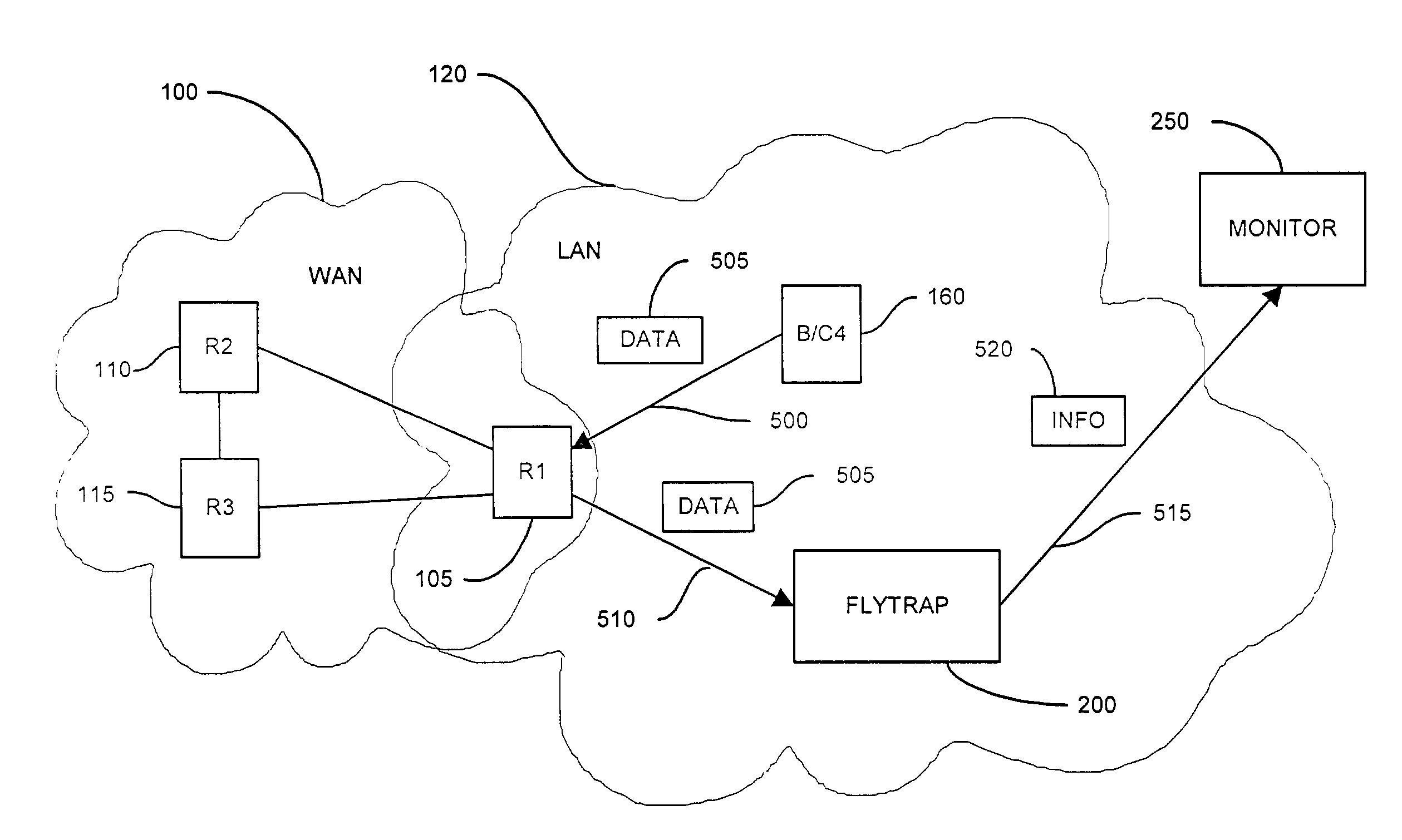
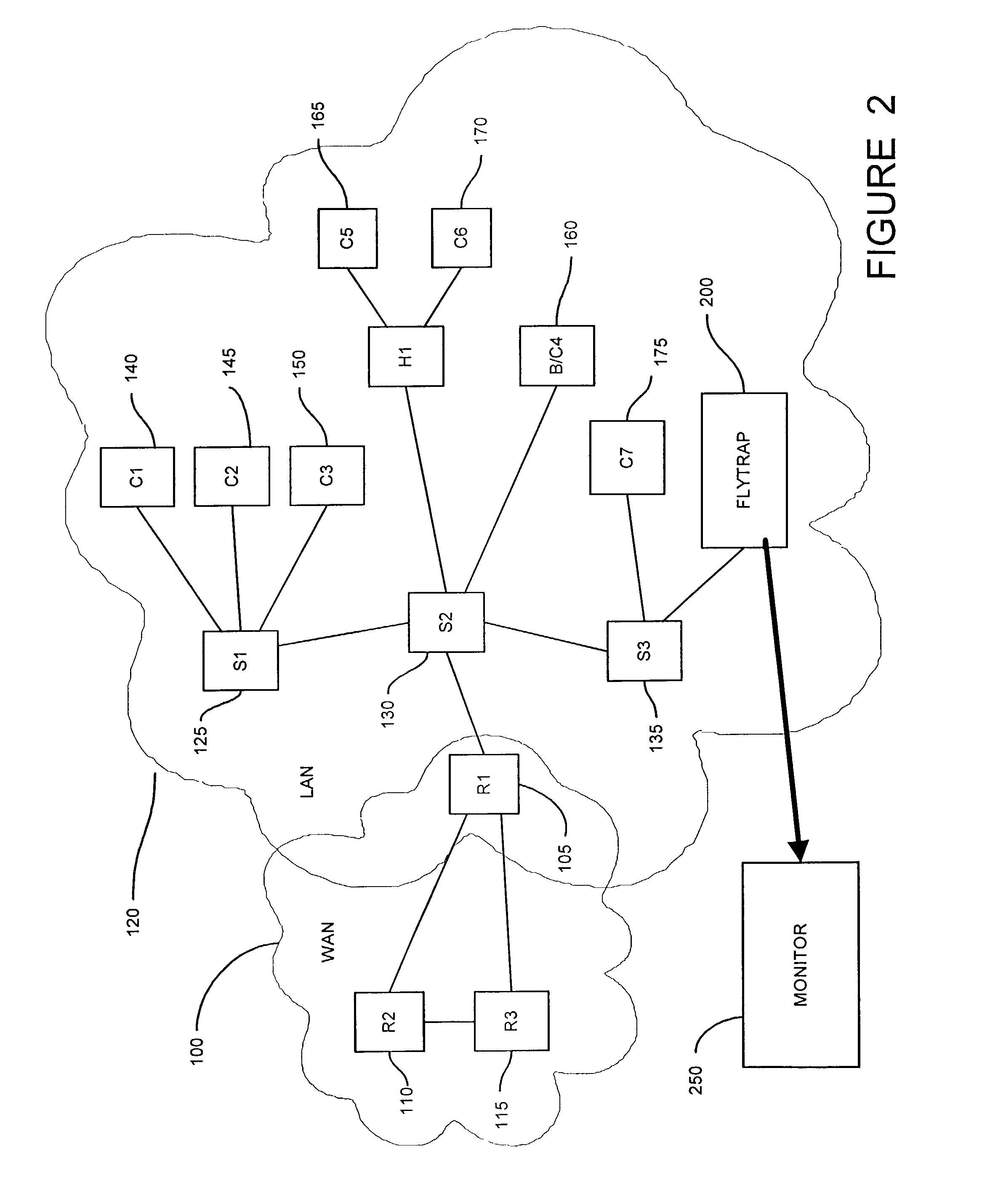
Method and apparatus for capturing and filtering datagrams for network security monitoring
ActiveUS7467408B1Improve network securityReduce network trafficMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionTraffic capacitySecurity monitoring
A method and system for security monitoring in a computer network has a packet sink with filtering and data analysis capabilities. The packet sink is a default destination for data packets having an address unrecognized by the network routers. At the packet sink, the packets are filtered and statistical summaries about the data traffic are created. The packet sink then forwards the data to a monitor, the information content depending on the level of traffic in the network.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
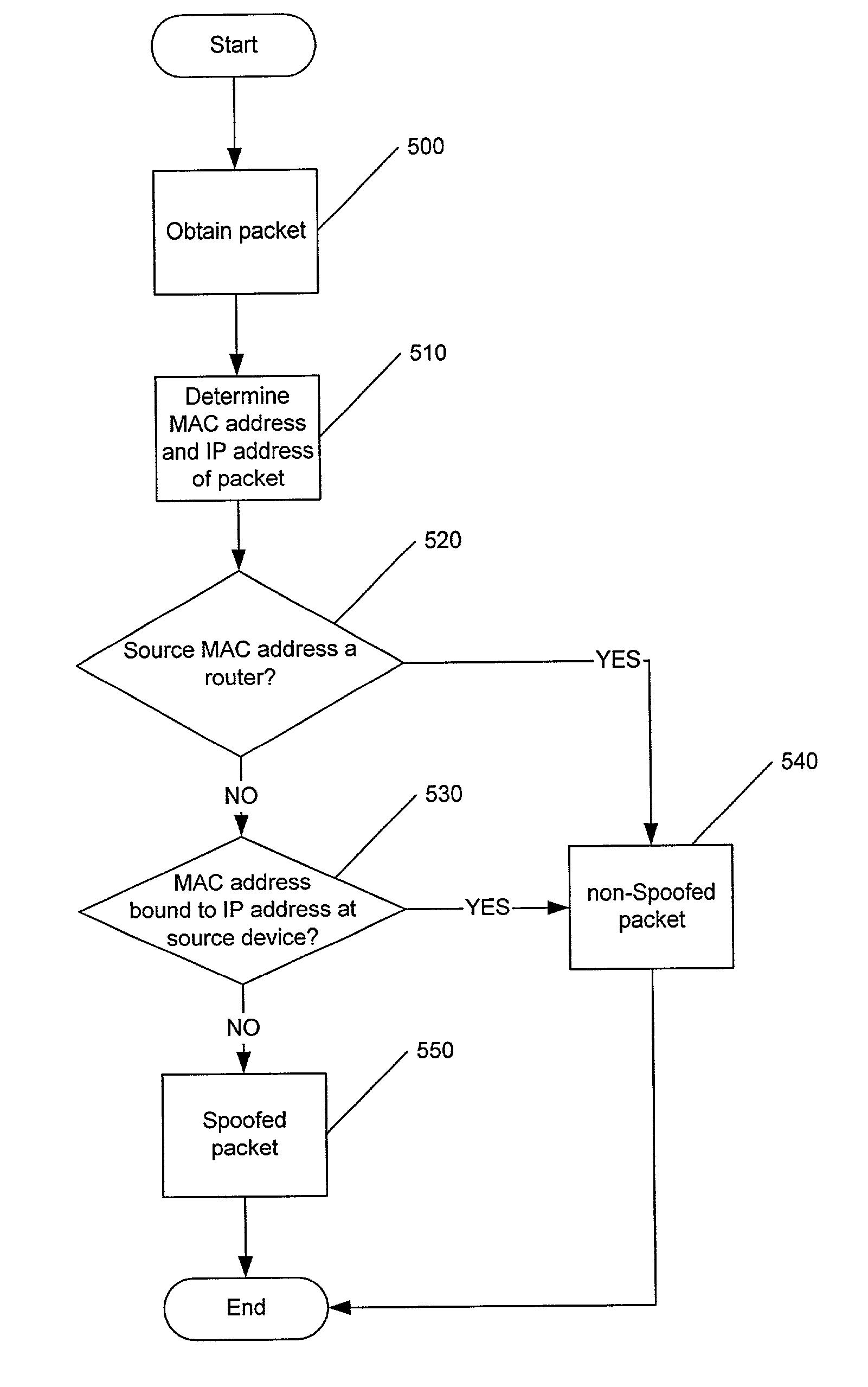
Methods, systems and computer program products for detecting a spoofed source address in IP datagrams
InactiveUS7134012B2Improve usabilityFrequency-division multiplexData switching by path configurationIp addressMedia access control
Methods, systems and computer program products are provided for determining if a packet has a spoofed source Internet Protocol (IP) address. A source media access control (MAC) address of the packet and the source IP address are evaluated to determine if the source IP address of the packet has been bound to the source MAC address at a source device of the packet. The packet is determined to have a spoofed source IP address if the evaluation indicates that the source IP address is not bound to the source MAC address. Such an evaluation may be made for packets having a subnet of the source IP address which matches a subnet from which the packet originated.
Owner:IBM CORP
Pervasive, user-centric network security enabled by dynamic datagram switch and an on-demand authentication and encryption scheme through mobile intelligent data carriers
InactiveUS20040221163A1Improve reliabilityIncrease flexibilityKey distribution for secure communicationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionNetwork connectionEngineering
Methods and systems are provided for improving access control, administrative monitoring, reliability, as well as flexibility of data transmission and remote application sharing over a network. Secure, stable network connections and efficient network transactions among multiple users are supported by an open and distributed client-server architecture. A datagram schema is adapted to enable dynamic datagram switching in support of a multitude of applications and network services. Mobile intelligent data carriers are provided that allow for the implementation of an authentication and encryption scheme. The intelligent data carriers are adapted to target deliver applications to authorized users, thereby achieving access control to not only data but also applications. The authentication and encryption scheme in one embodiment is based on physical or performance biometrics. The methods and systems of this disclosure may be advantageously deployed in an enterprise network environment to support a wide spectrum of business, research, and administrative operations.
Owner:GIRITECH APS
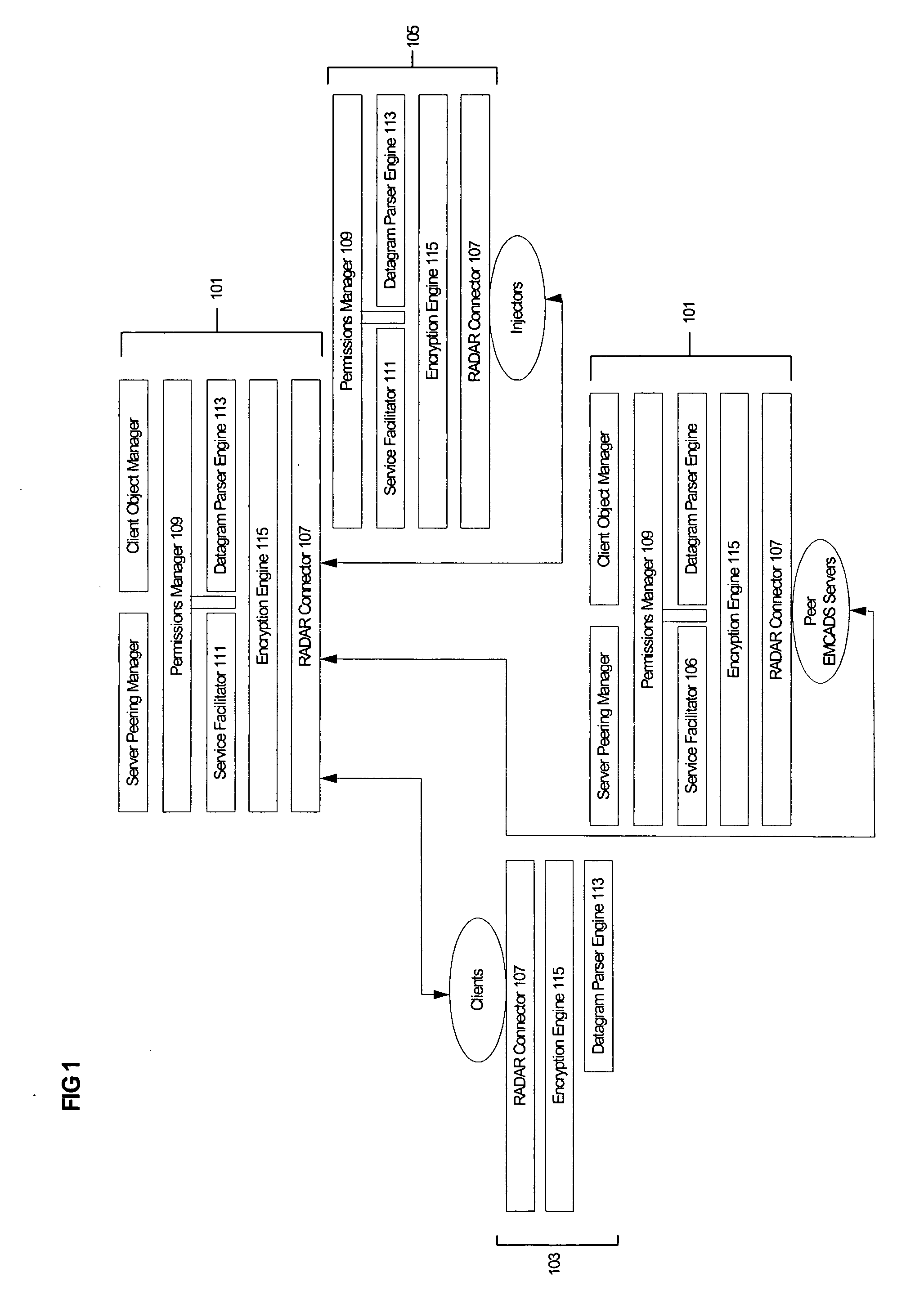
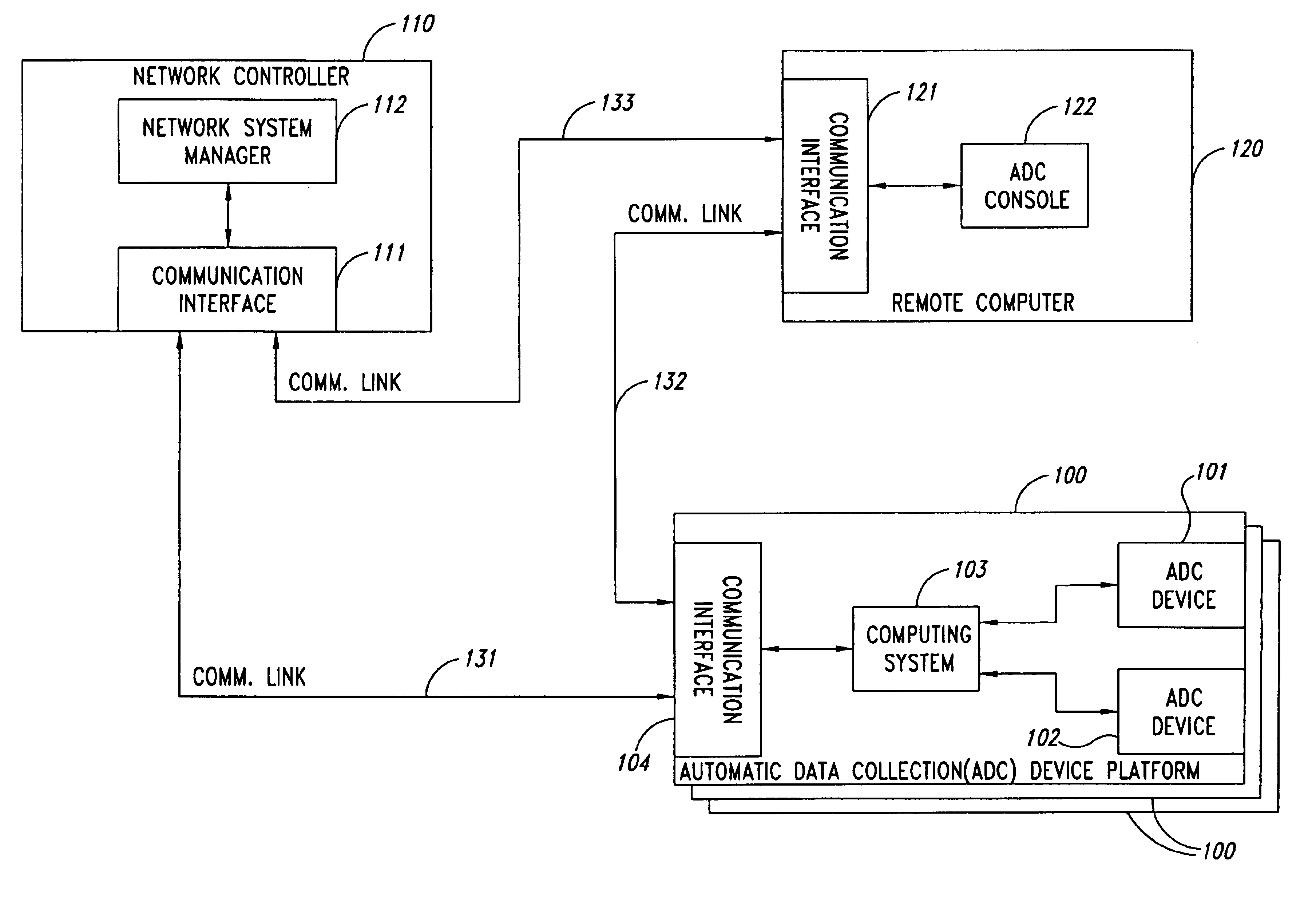
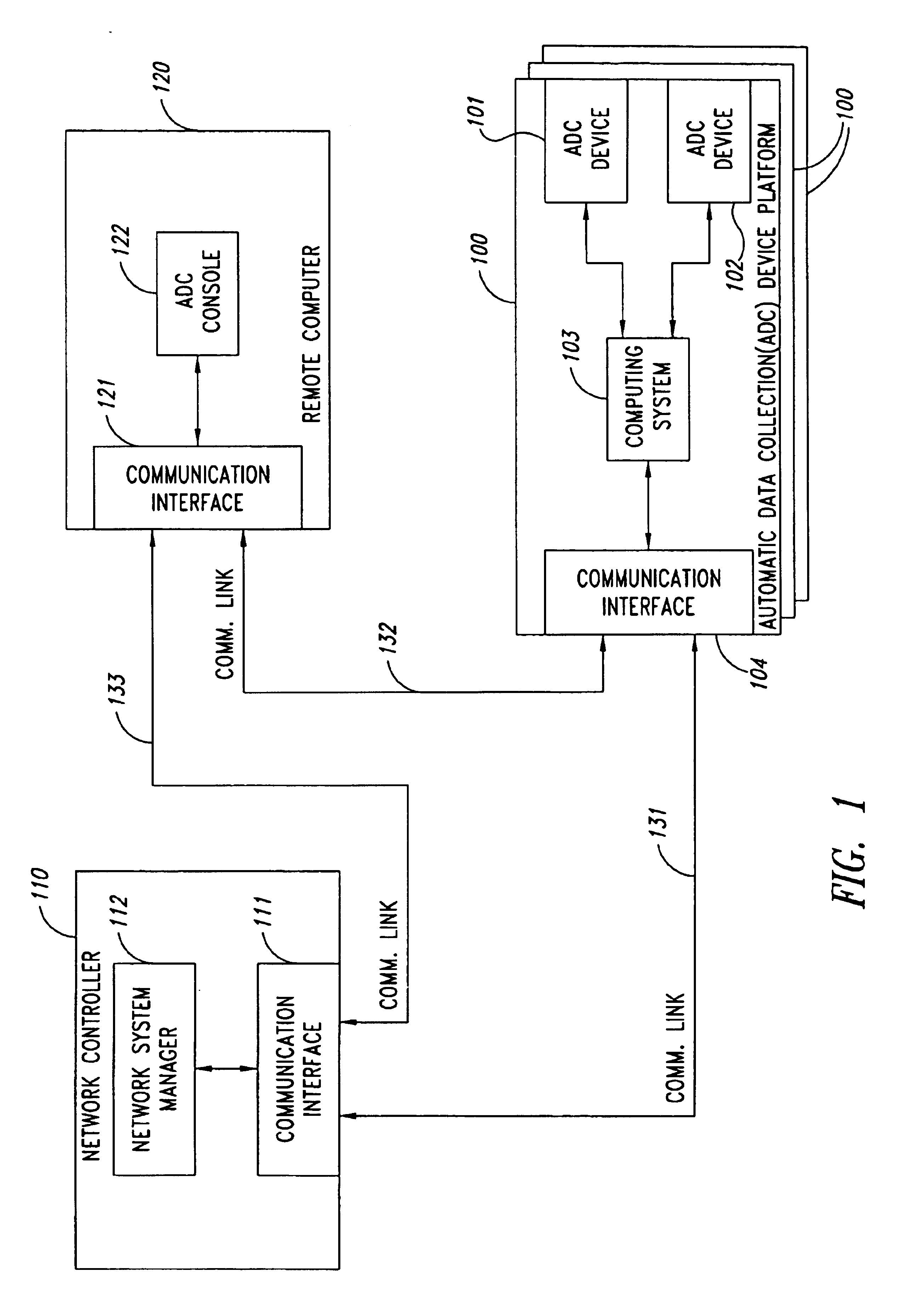
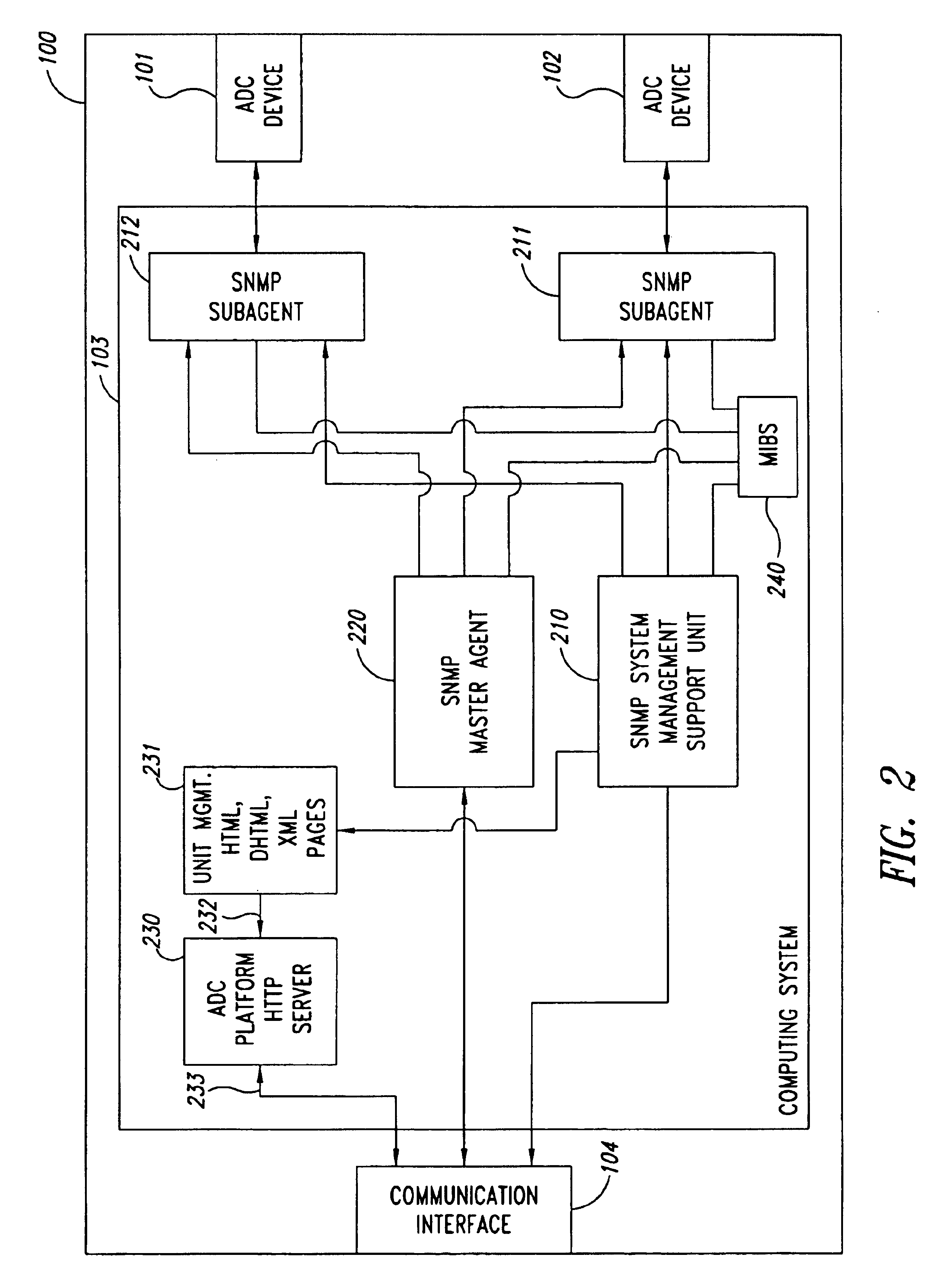
Remote anomaly diagnosis and reconfiguration of an automatic data collection device platform over a telecommunications network
InactiveUS6857013B2Detecting faulty hardware by remote testDigital computer detailsTelecommunications linkExtensible markup
Owner:INTERMEC IP CORP
Pervasive, user-centric network security enabled by dynamic datagram switch and an on-demand authentication and encryption scheme through mobile intelligent data carriers
InactiveUS7103772B2Improve reliabilityIncrease flexibilityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationNetwork connectionApplication software
Owner:GIRITECH APS
Method and system for end-to-end communication between a universal integrated circuit card and a remote entity over an IP-based wireless wide area network and the internet
InactiveUS20050259673A1Data switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsBrick and mortarWide area network
End-to-end communication between a UICC and a remote node on a network without requiring implementation of special purpose protocols at the remote node. The UICC operates to transmit a command using a first protocol from the UICC to the terminal to request the terminal to open a data channel to the network. The wireless terminal operates to, in response to the request to open a data channel, attempt to open a channel to the network. Upon indication that a data channel has successfully been opened: the UICC operates to transmit datagrams of a second protocol to the wireless terminal using the first protocol. The wireless terminal operates to receive the datagrams from the UICC and to transmit the datagrams received from the UICC to the network using the second protocol. The wireless terminal operates to receive datagrams of the second protocol from the remote entity and to transmit the datagrams from the remote entity to the UICC using the first protocol.
Owner:AXALTO SA
Secure PKI Communications for "Machine-to-Machine" Modules, including Key Derivation by Modules and Authenticating Public Keys
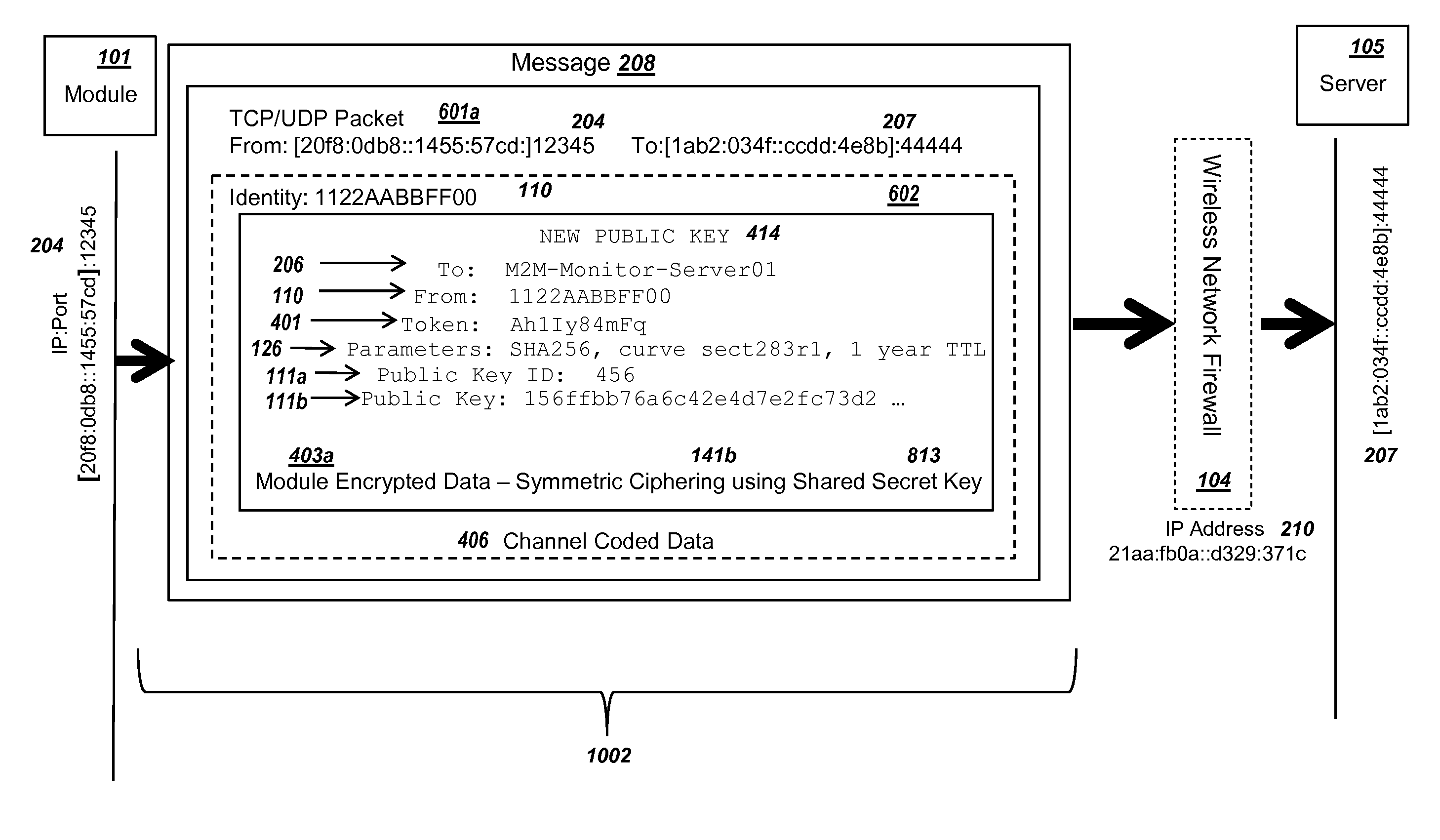
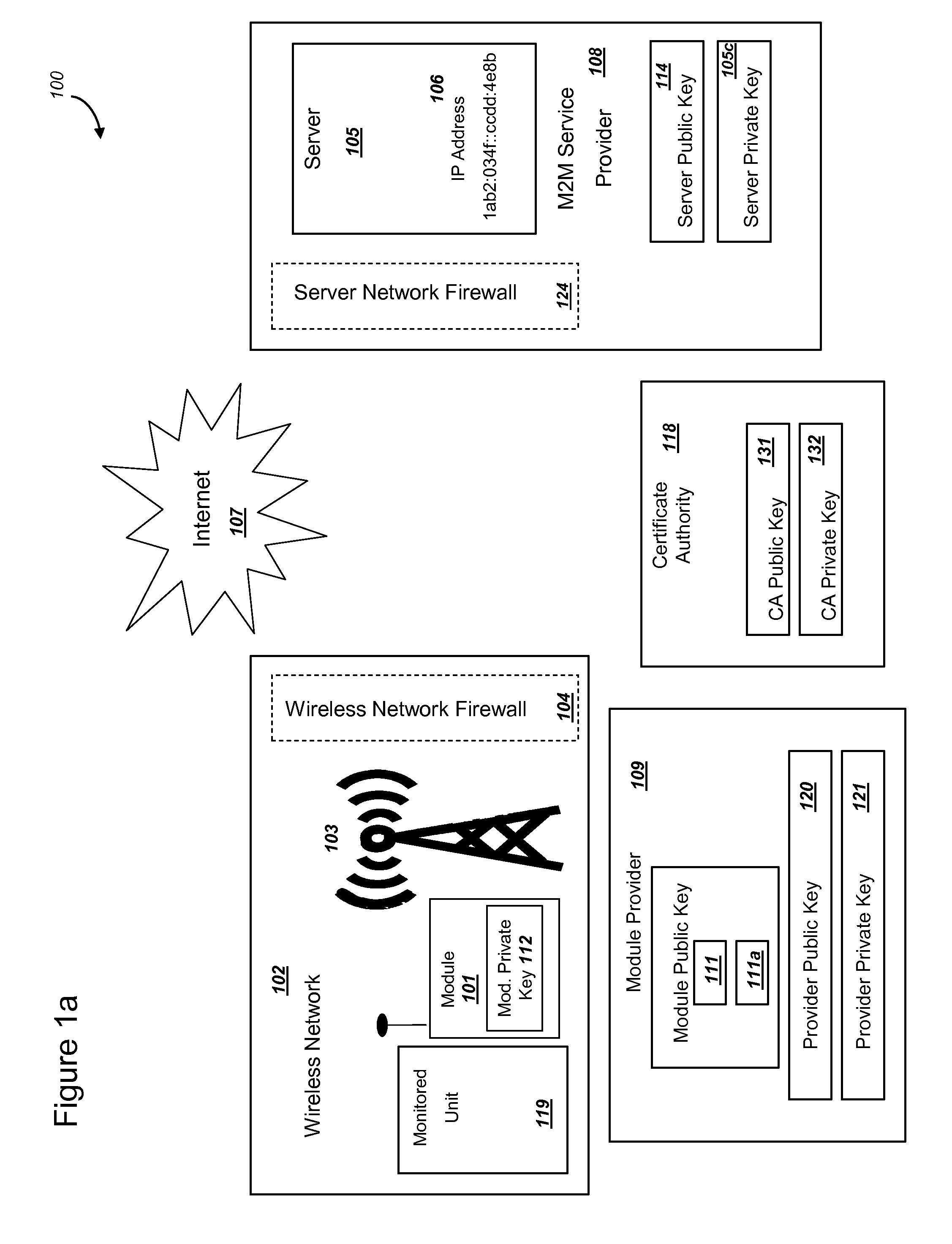
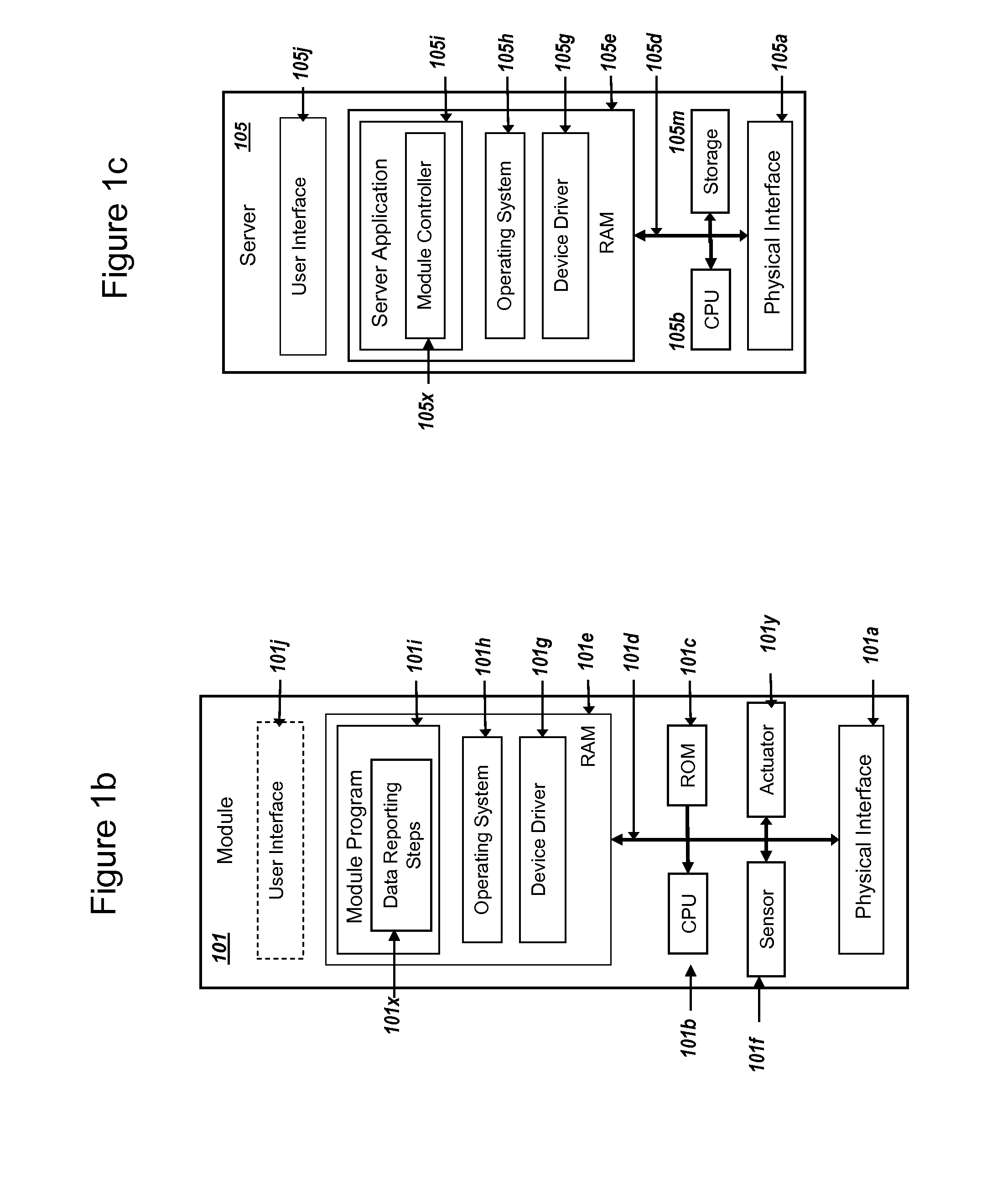
ActiveUS20150095648A1Extend battery lifeImprove efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageComputer hardwareDigital signature
Methods and systems are provided for efficient and secure “Machine-to-Machine” (M2M) between modules and servers. A module can communicate with a server by accessing the Internet, and the module can include a sensor and / or actuator. The module and server can utilize public key infrastructure (PKI) such as public keys to encrypt messages. The module and server can use private keys to generate digital signatures for datagrams sent and decrypt messages received. The module can internally derive pairs of private / public keys using cryptographic algorithms and a set of parameters. A server can use a shared secret key to authenticate the submission of derived public keys with an associated module identity. For the very first submission of a public key derived the module, the shared secret key can comprise a pre-shared secret key which can be loaded into the module using a pre-shared secret key code.
Owner:NETWORK 1 TECH +1
Establishing consistent, end-to-end protection for a user datagram
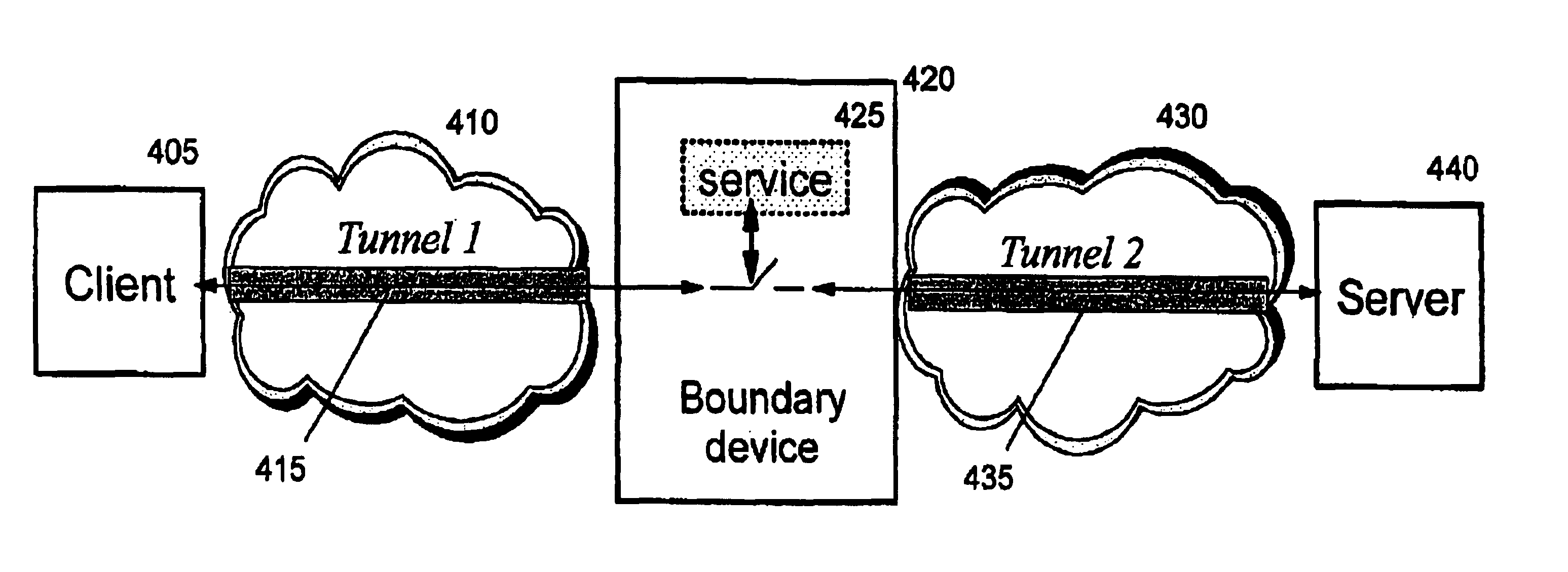
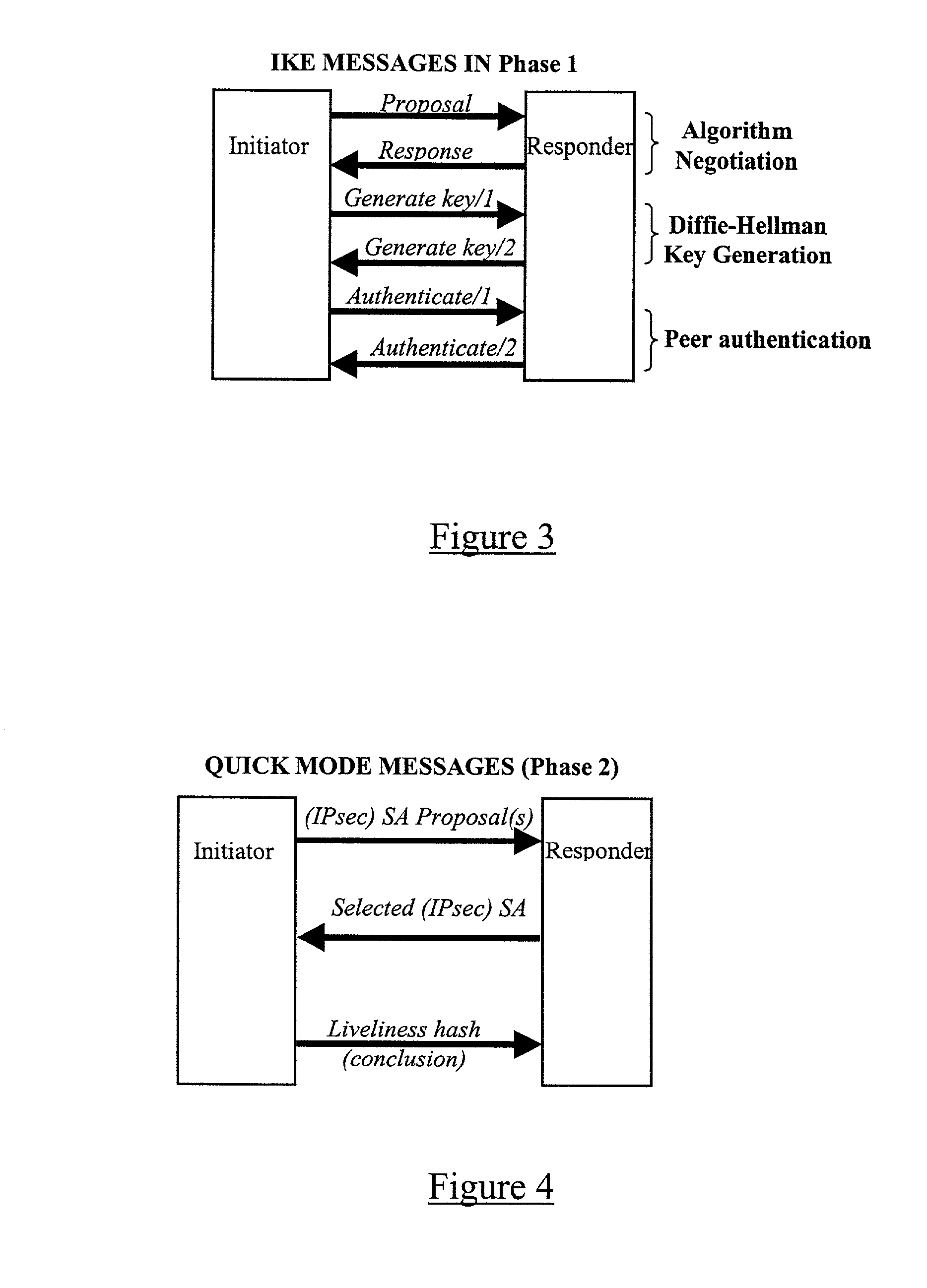
A method, system, and computer program product for providing consistent, end-to-end protection within a computer network for user datagrams (i.e. packets) traveling through the network. The network may comprise network segments that are conventionally assumed to be secure (such as those found in a corporate intranet) as well as network segments in non-secure networks (such as the public Internet or corporate extranets). Because security breaches may in fact happen in any network segment when datagrams are unprotected, the present invention discloses a technique for protecting datagrams throughout the entire network path by establishing cascaded tunnels. The datagrams may be exposed in cleartext at the endpoints of each tunnel, thereby enabling security gateways to perform services that require content inspection (such as network address translation, access control and authorization, and so forth). The preferred embodiment is used with the “IPSec” (Internet Protocol Security Protocol) and “IKE” (Internet Key Exchange) protocols, thus providing a standards-based solution.
Owner:IBM CORP
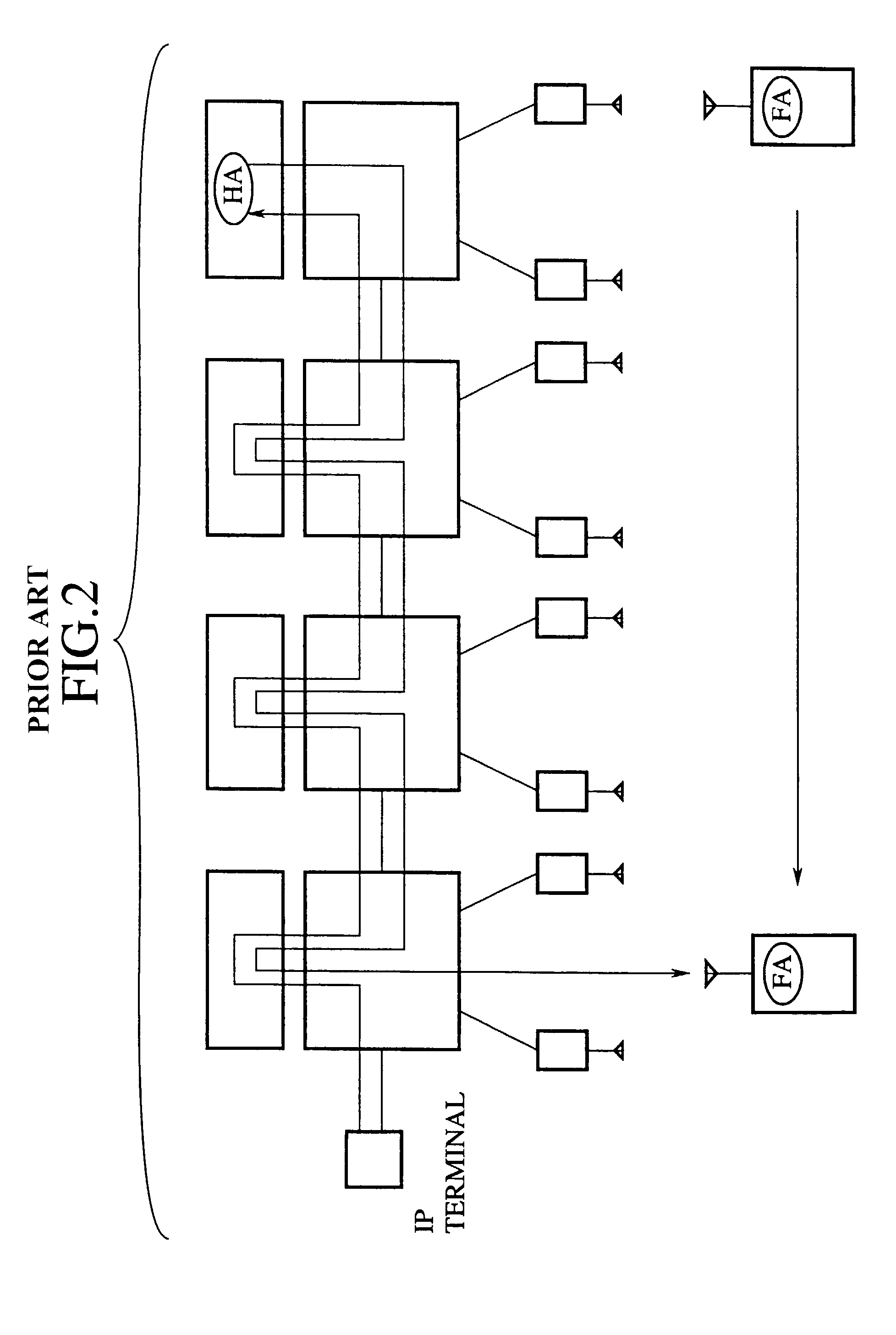
Router device, datagram transfer method and communication system realizing handoff control for mobile terminals
InactiveUS7151758B2Increase speedEasy to controlData switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsCommunications systemHandoff control
A mobile supporting router device for realizing the handoff control associated with the moving in high speed is forms by at least one first interface connected with radio base stations, each capable of accommodating at least one mobile terminal; at least one second interface connected with a wire network; an information exchanging unit for exchanging a routing protocol on a network layer, through the second interface; a memory unit for storing information regarding a routing on the network layer based on the routing protocol exchanged by the information exchanging unit; a transfer unit for transferring datagram through the first interface according to the information regarding the routing on the network layer stored in the memory unit; a moving detection unit for detecting a moving of the mobile terminal among the radio base stations; and an information updating unit for updating the information regarding the routing on the network layer stored in the memory unit when the moving of the mobile terminal is detected by the moving detection unit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
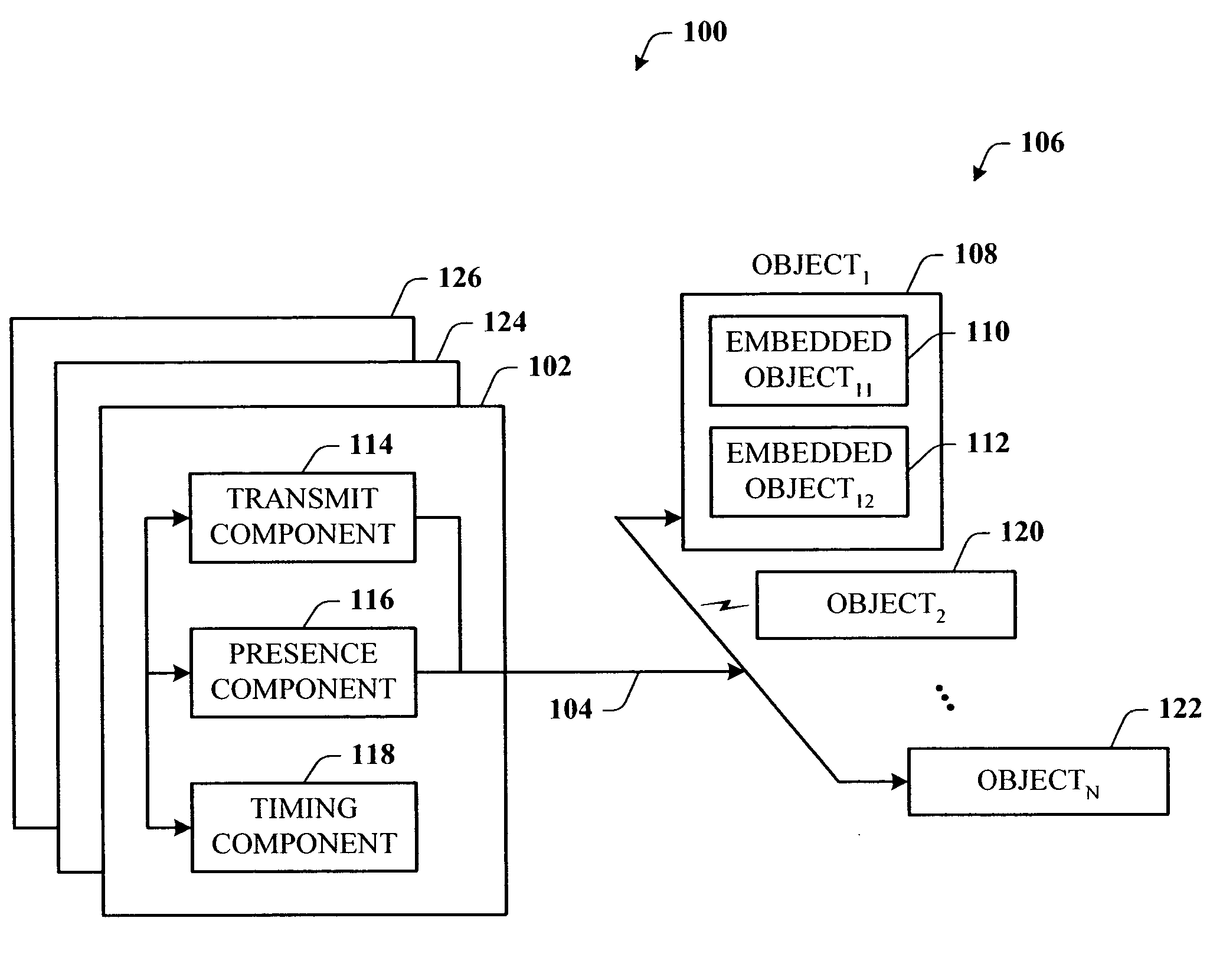
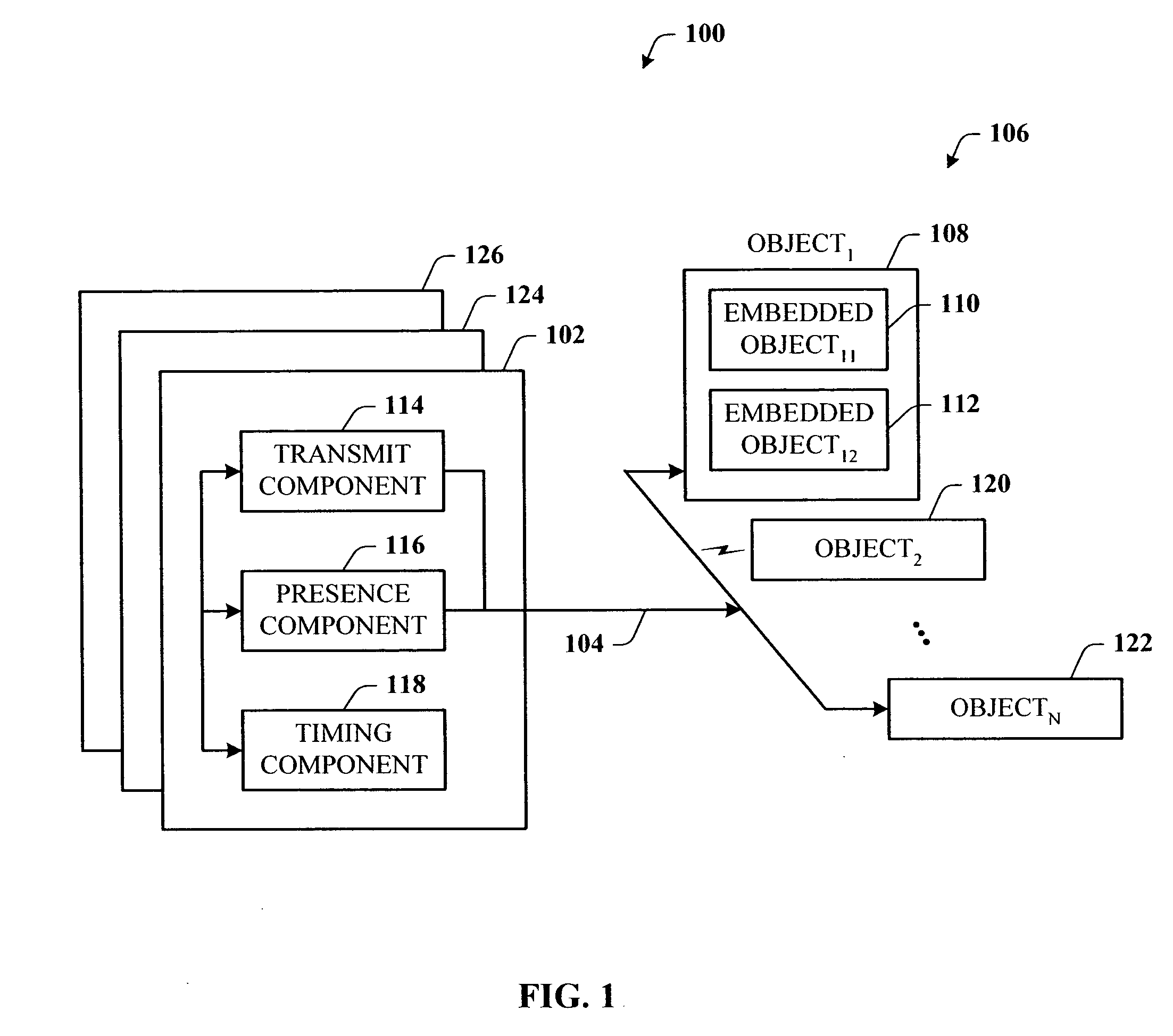
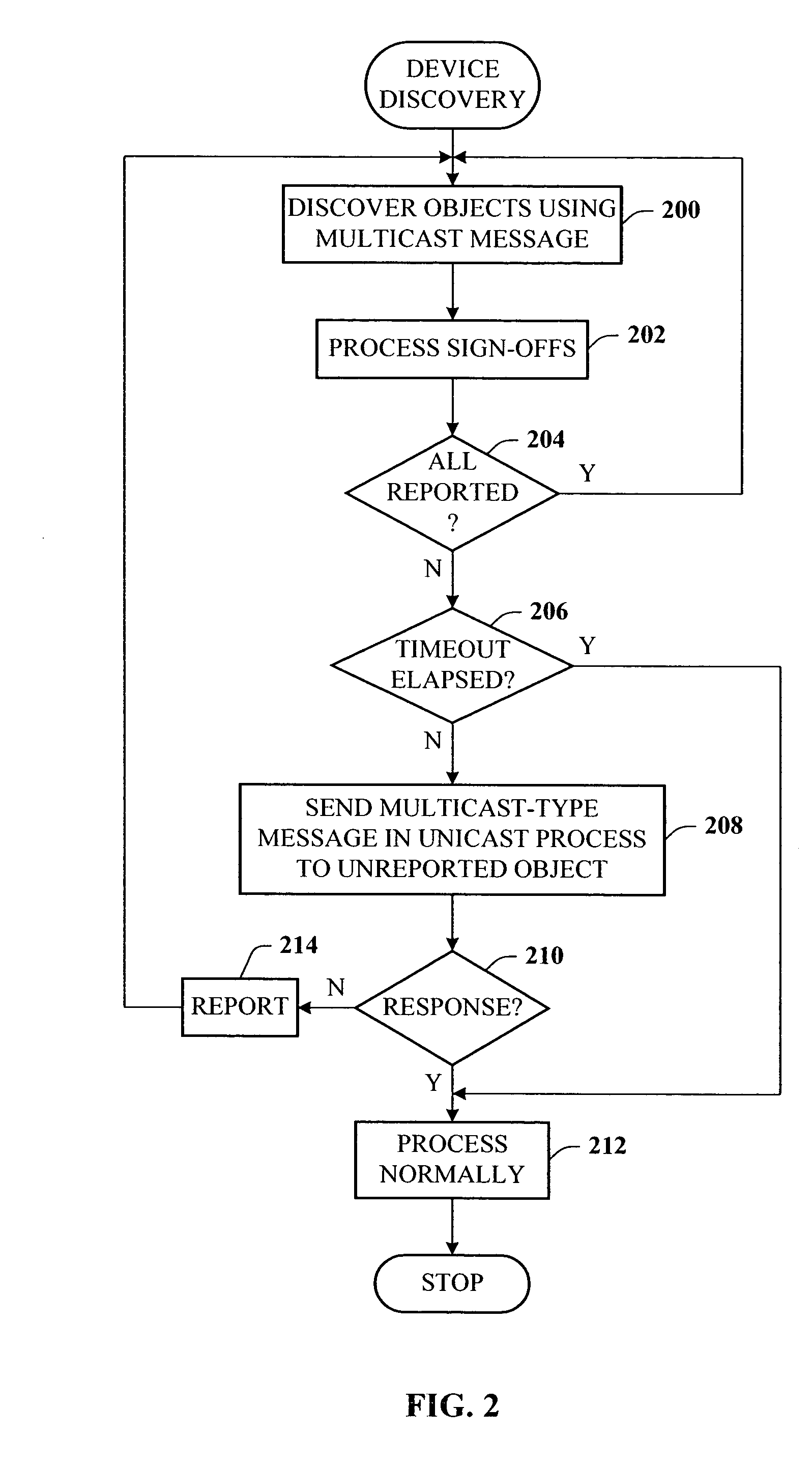
Presence tracking for datagram based protocols with search
InactiveUS20050108331A1Reduce network trafficEasy searchMultiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationClient-sideBroadcast multicast
A presence tracking architecture for datagram-based protocols. A client application seeking to know the presence or lack thereof of a device and / or service utilizes a standard protocol in a non-intuitive way to trigger notification of the device and / or service before any associated timeout expires. At first presence, a multicast message is broadcast to notify all devices. Subsequently, on-demand notification may be requested by a client application by sending directly (e.g., in unicast) to the device before its timeout has expired a message that is normally only sent in multicast. If capable, the device can then respond normally with a unicast message indicating it is on-line. If the response is not received, the device and / or service is determined to be off-line.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Simple multicast extension for mobile IP SMM
InactiveUS6988146B1Multiple digital computer combinationsWireless network protocolsComputer networkForeign agent
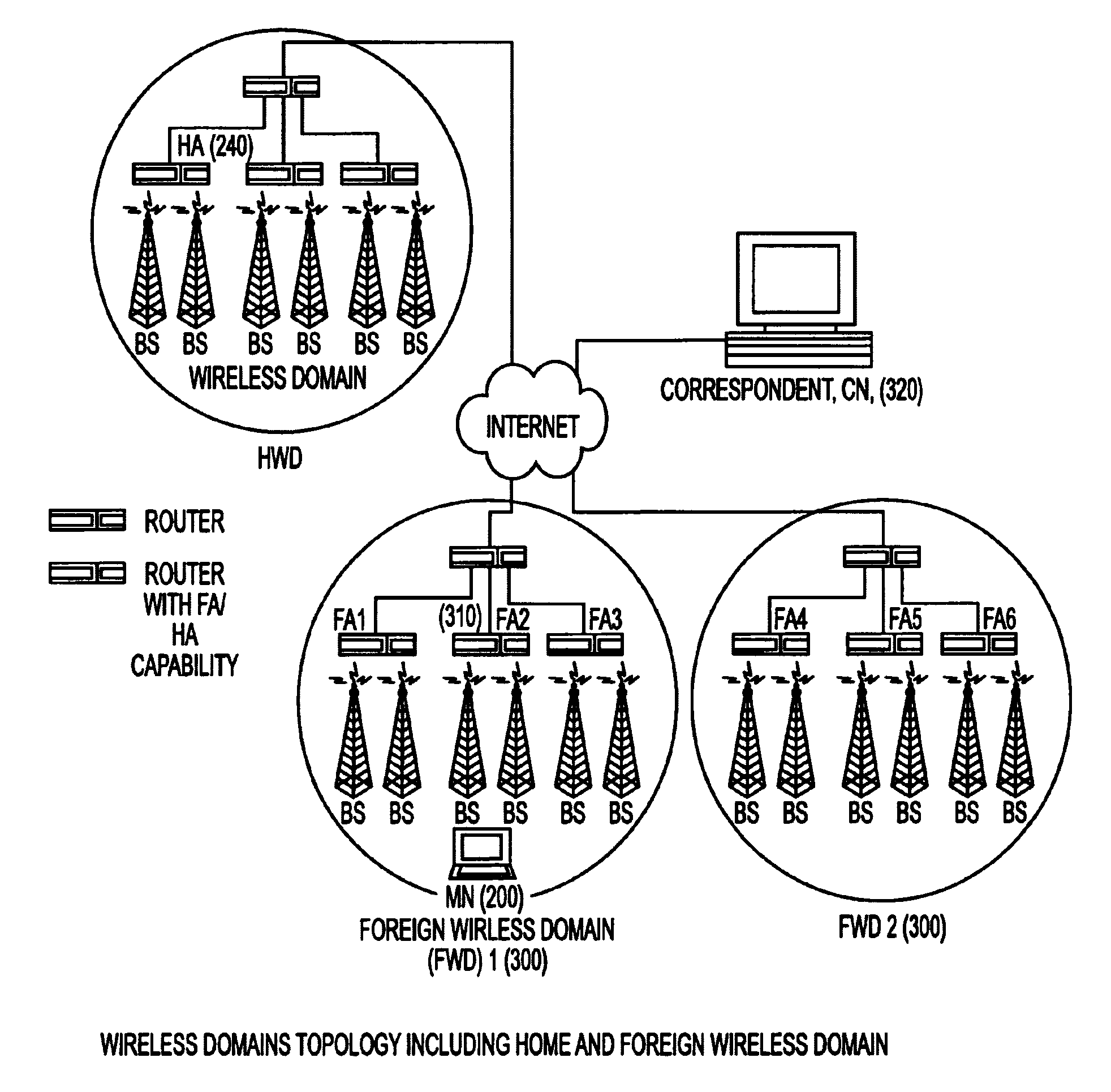
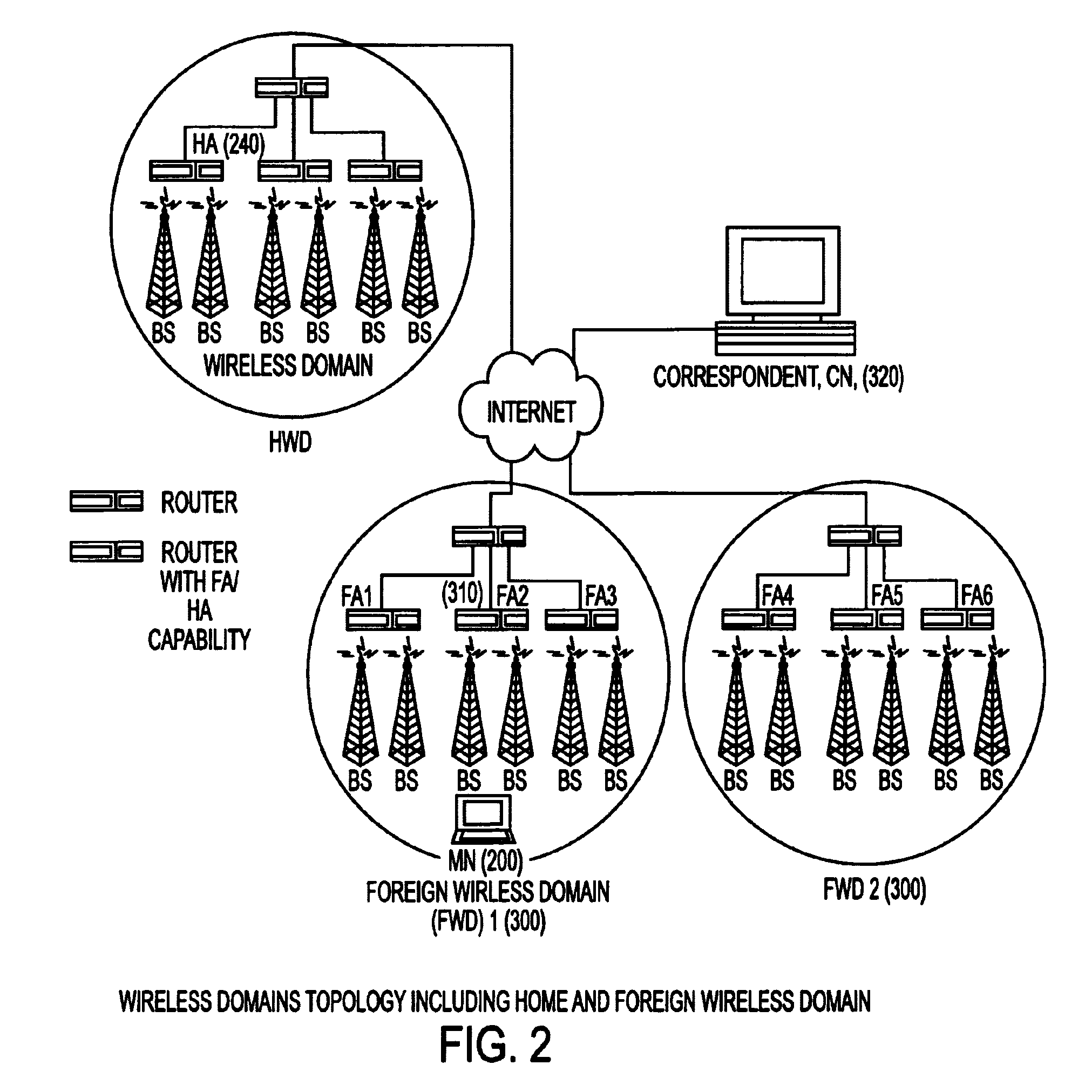
Under Simple Multicast Extension for Mobile IP, when a mobile node arrives at a foreign wireless domain, it listens for an agent advertisement sent by a foreign agent. The foreign agent attaches a network access identifier (NAI) extension to the agent advertisement. The mobile node uses the NAI extension to decide which action to take. If the mobile node determines that it is receiving an agent advertisement message from the same foreign agent it previously was in communication with, no action is required. If the mobile node discovers that it has entered a new foreign domain, it sends a registration request to the foreign agent. If the mobile node identifies that it is still in the same domain but has moved from a previous foreign agent to a new one, it sends a multicast subscription request to the new foreign agent.If a home agent supports the Simple Multicast Extension for Mobile IP, it allocates a source specific multicast address and inserts the address in a source specific multicast address extension after the registration reply. In addition, tunneling is used to route datagrams from correspondent nodes to the mobile node while the mobile node is in a foreign domain. The destination address of the tunnel is set to the source specific multicast previously allocated. Finally, update messages are used to inform correspondent nodes of a mobile nodes' new location.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
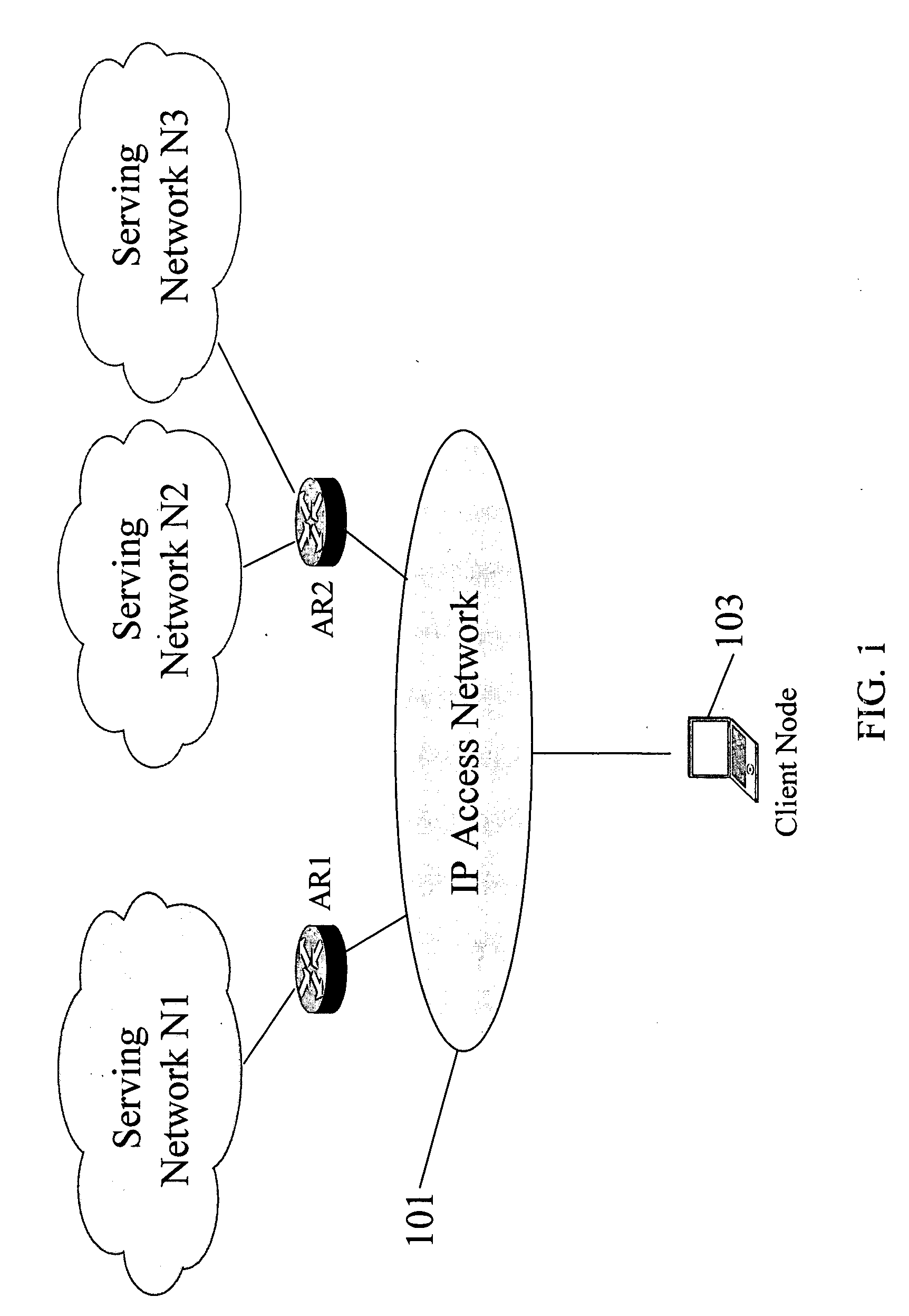
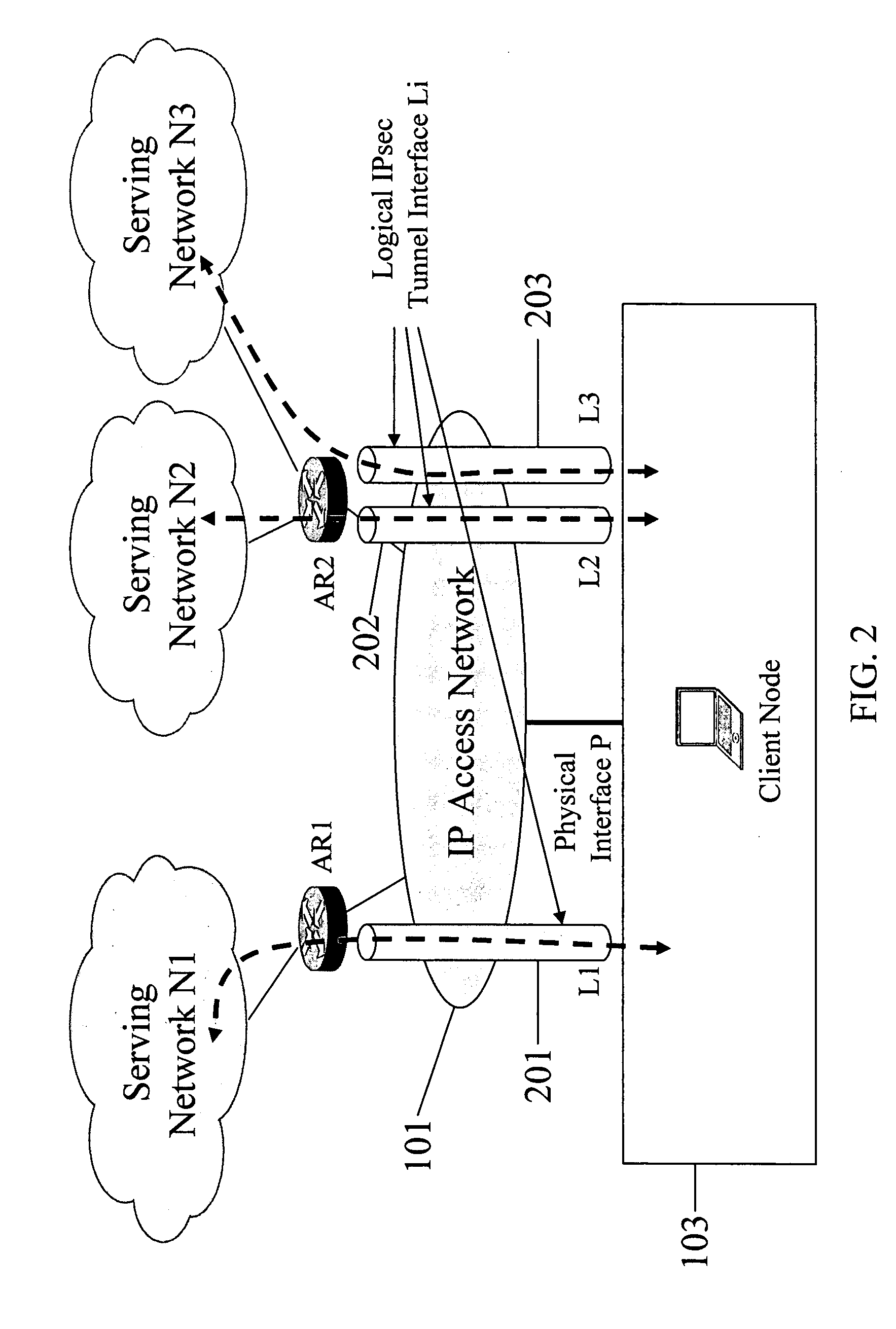
Serving network selection and multihoming using IP access network
InactiveUS20050165953A1Simple methodAssess restrictionMultiple digital computer combinationsAccess networkClient-side
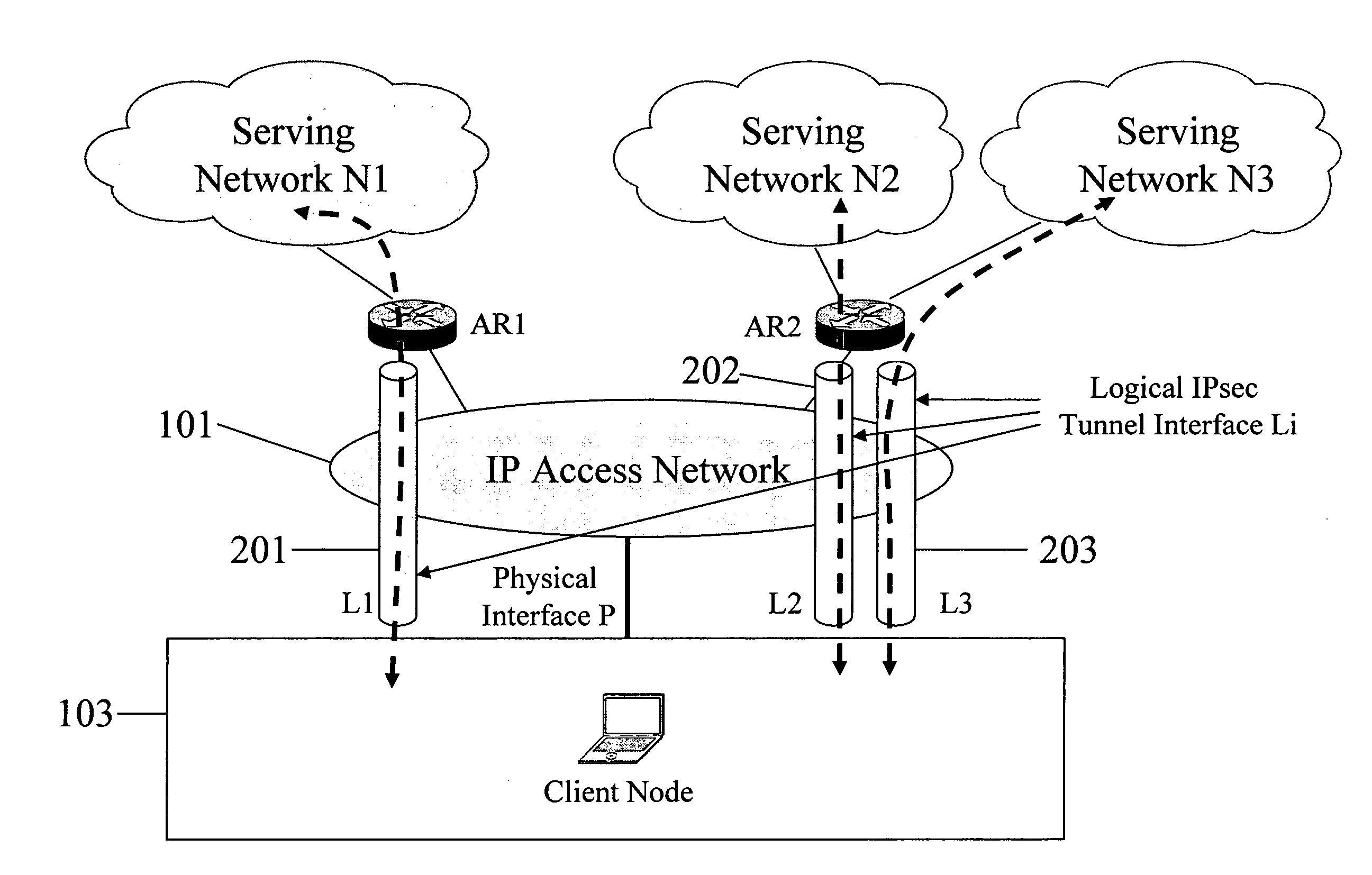
In some illustrative embodiments, an IP-layer based network selection and multihoming method is provided that enables a flexible and secure dynamic selection of one or more serving networks for use by a client node. The method is independent of any link-layer technology. A serving network can be an ISP network, a NAP network exchange facility, a VLAN, or the like. Network information is advertised to a client node, the client node is authenticated and authorized for use of an access router, and a secure tunnel is established between the client node and the access router. The method can be implemented by using standard protocols, and can work over any existing or future link-layer technologies that are able to carry IP datagrams, without any modification.
Owner:TELCORDIA TECHNOLOGIES INC +2
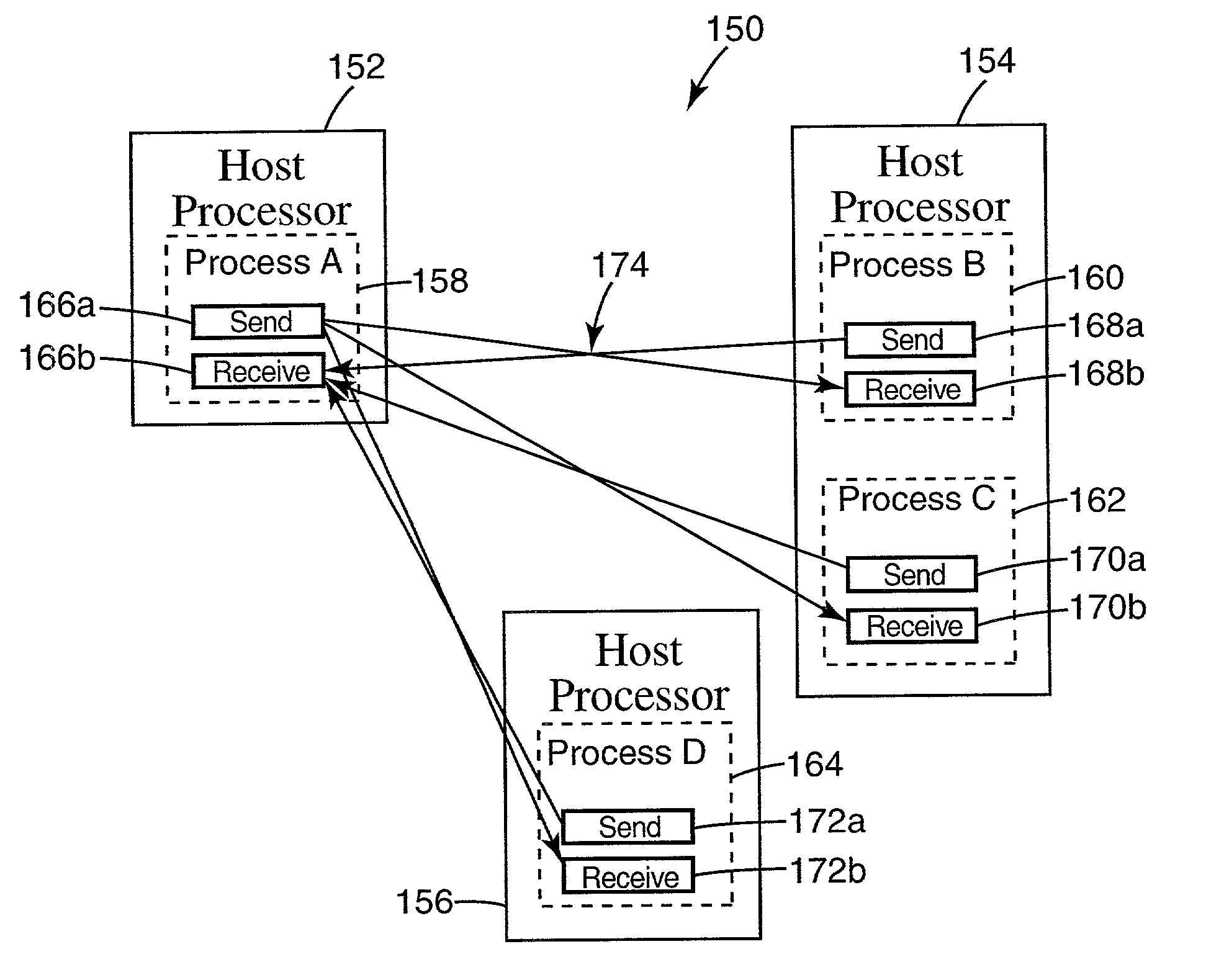
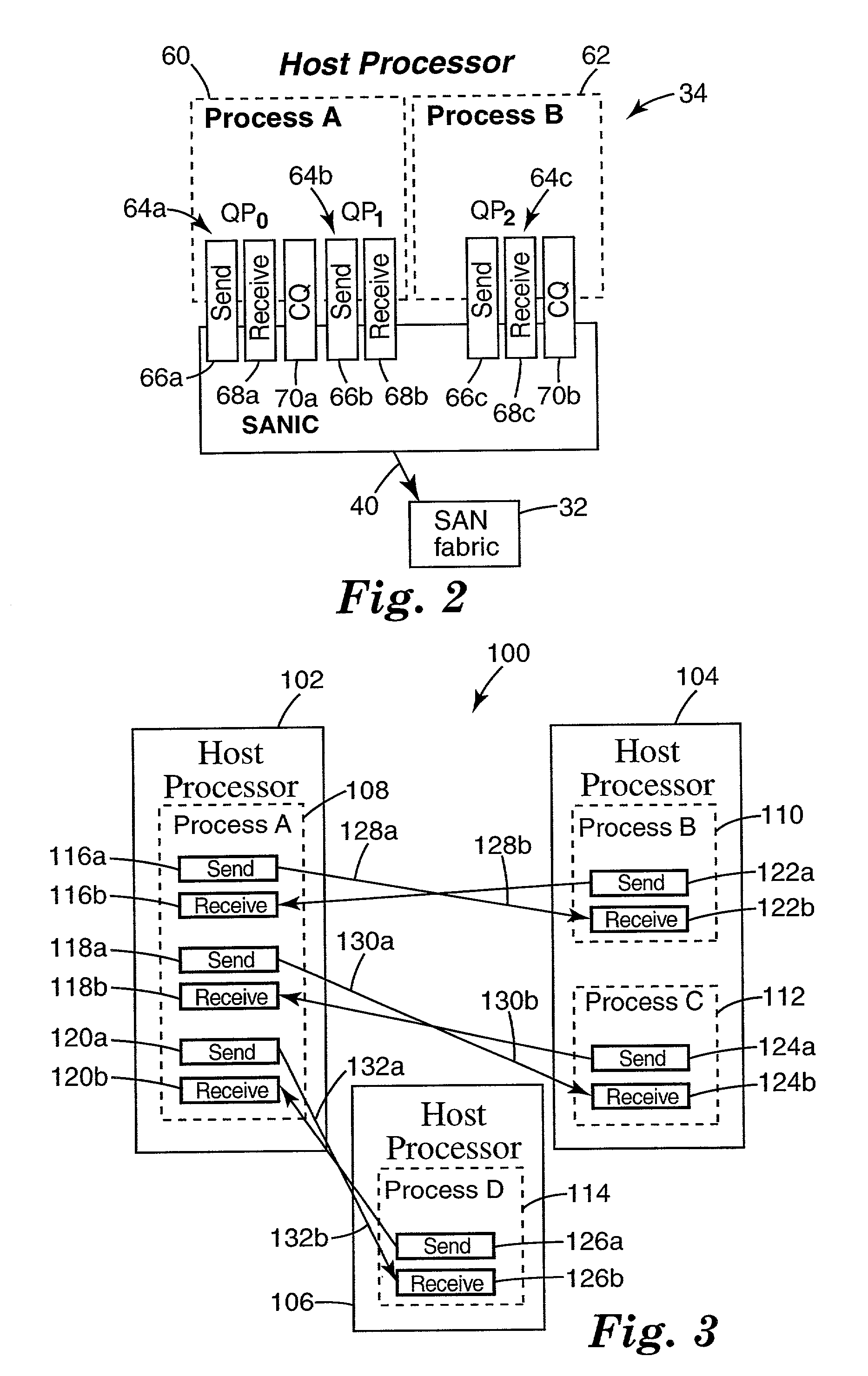
Reliable datagram transport service
InactiveUS7171484B1Multiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlComputerized systemDistributed computing
A distributed computer system includes a source endnode including a source process which produces message data and a send work queue having work queue elements that describe the message data for sending. A destination endnode includes a destination process and a receive work queue having work queue elements that describe where to place incoming message data. A communication fabric provides communication between the source endnode and the destination endnode. An end-to-end context is provided at the source endnode and the destination endnode storing state information to ensure the reception and sequencing of message data sent from the source endnode to the destination endnode permitting reliable datagram service between the source endnode and the destination endnode.
Owner:KRAUSE MICHAEL R +4
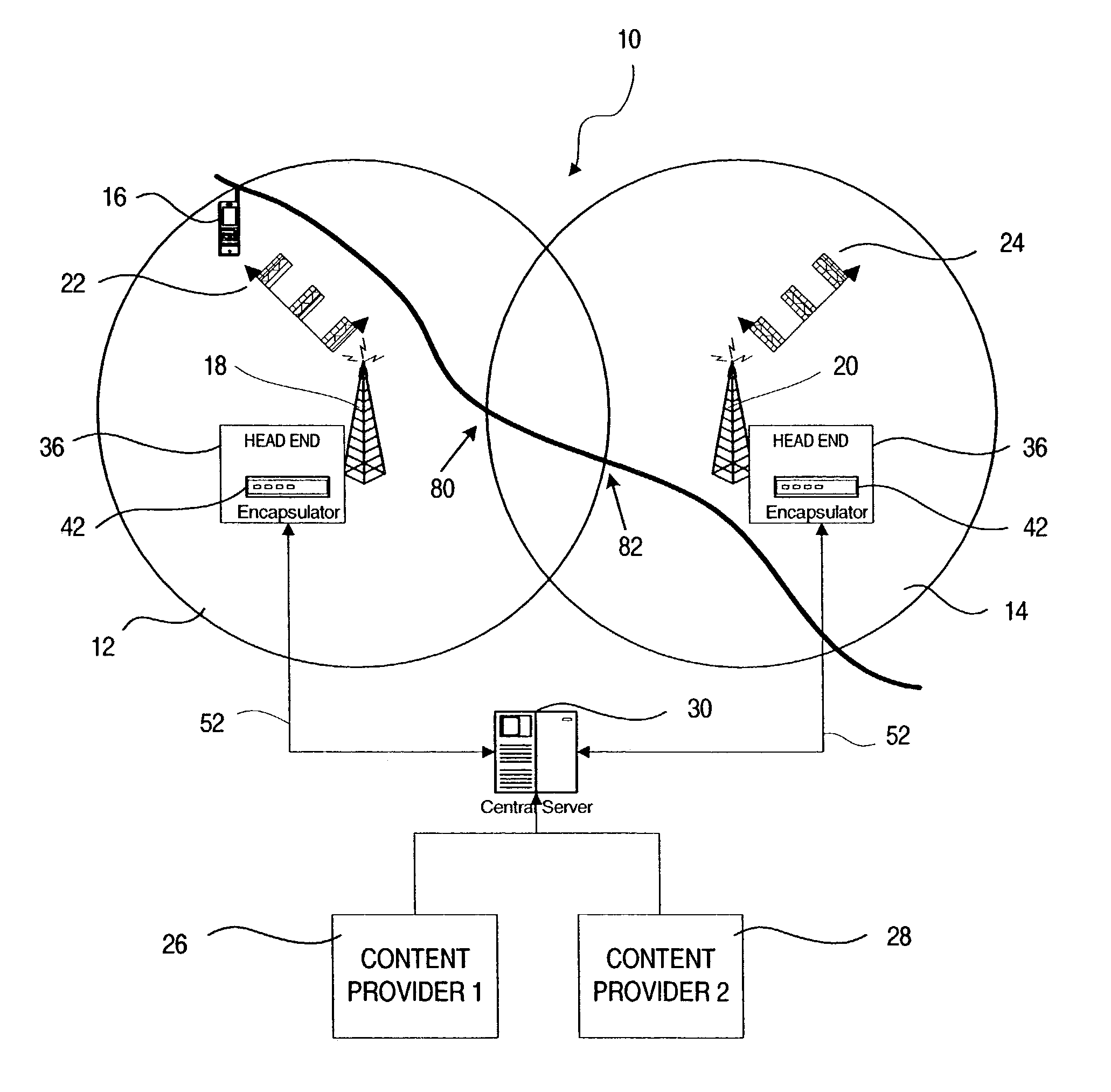
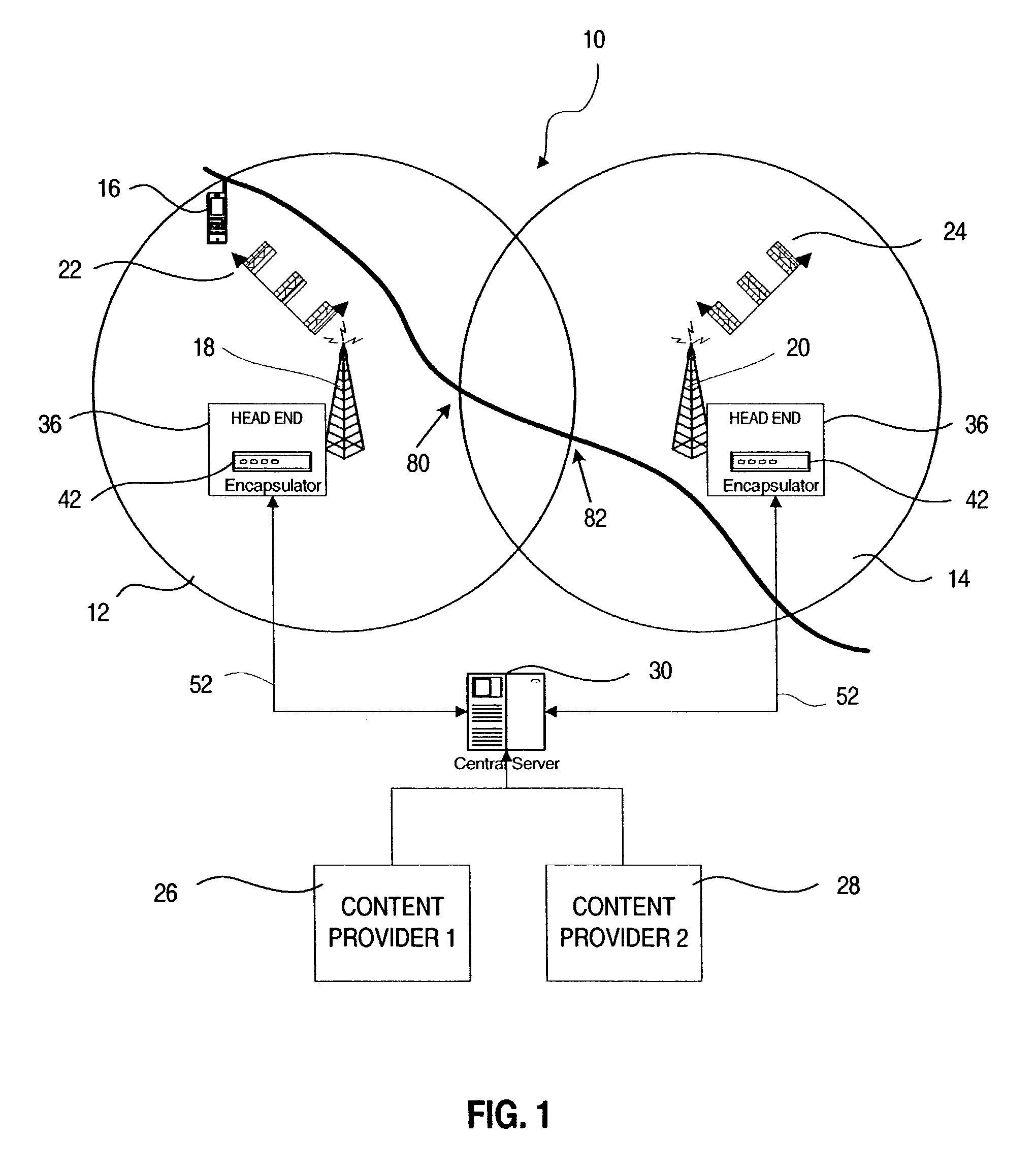
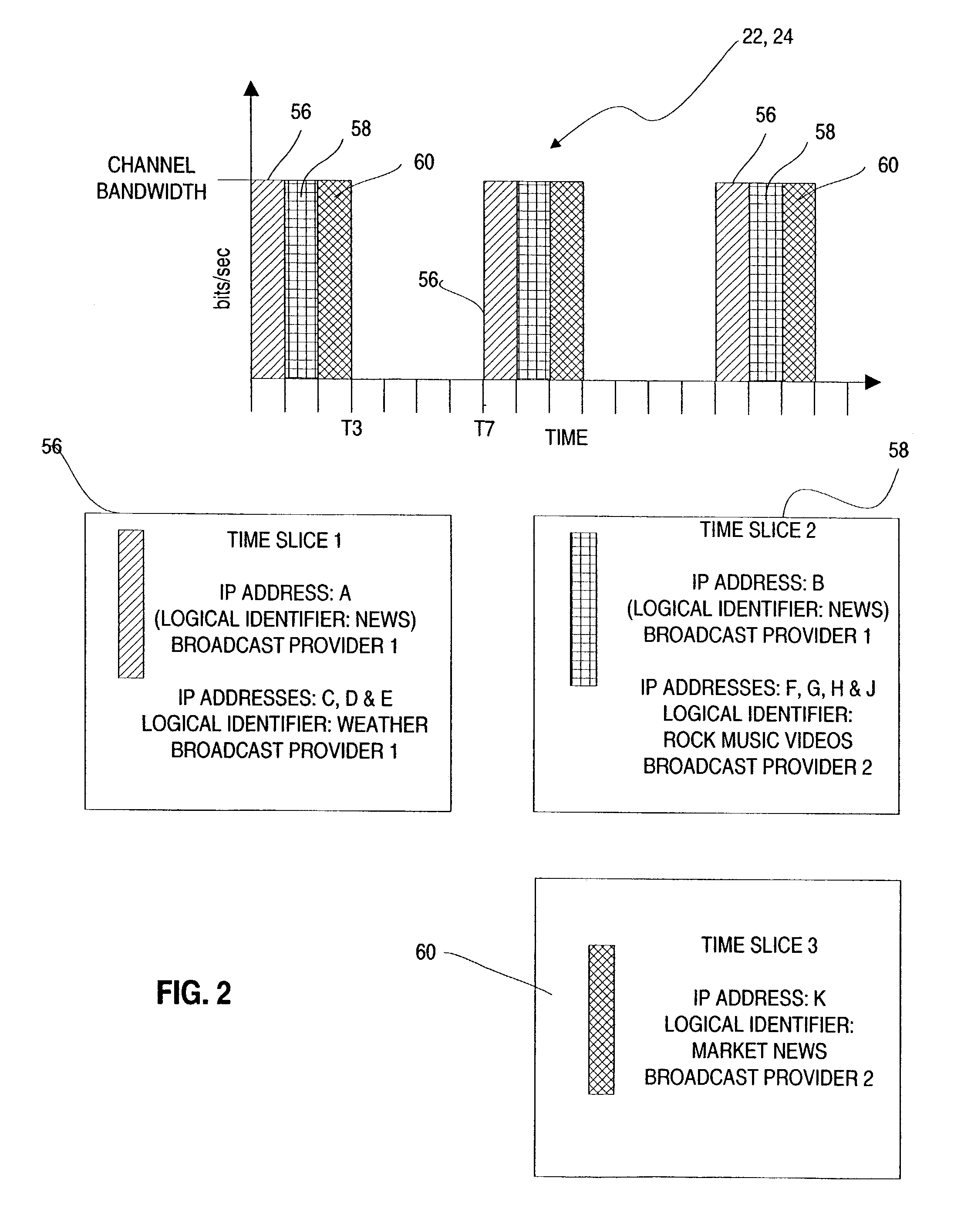
Broadcast hand-over in a wireless network
ActiveUS6977914B2Reduce resolutionBroadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexBurst transmissionBroadcasting
A system and method are disclosed for providing multicast channel handover in a mobile device within a mobile network. First and second transmitters within first and second cells broadcast datagrams associated with a logical identifier according to link-level access parameters common to the first and second transmitters. A mobile device receives the broadcast datagrams for the logical identifier from the first transmitter by configuring the common link-level access parameters. As part of handover from the first cell to the second cell, the mobile device continues receiving the broadcast datagrams from the second transmitter by maintaining the common link-level access parameters. In one embodiment, the datagrams are IP datagrams transmitted in an MPEG2 transport stream. The link-level access parameters may include time slice parameters associated with burst transmissions from the first and second transmitters according to an embodiment of the invention.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
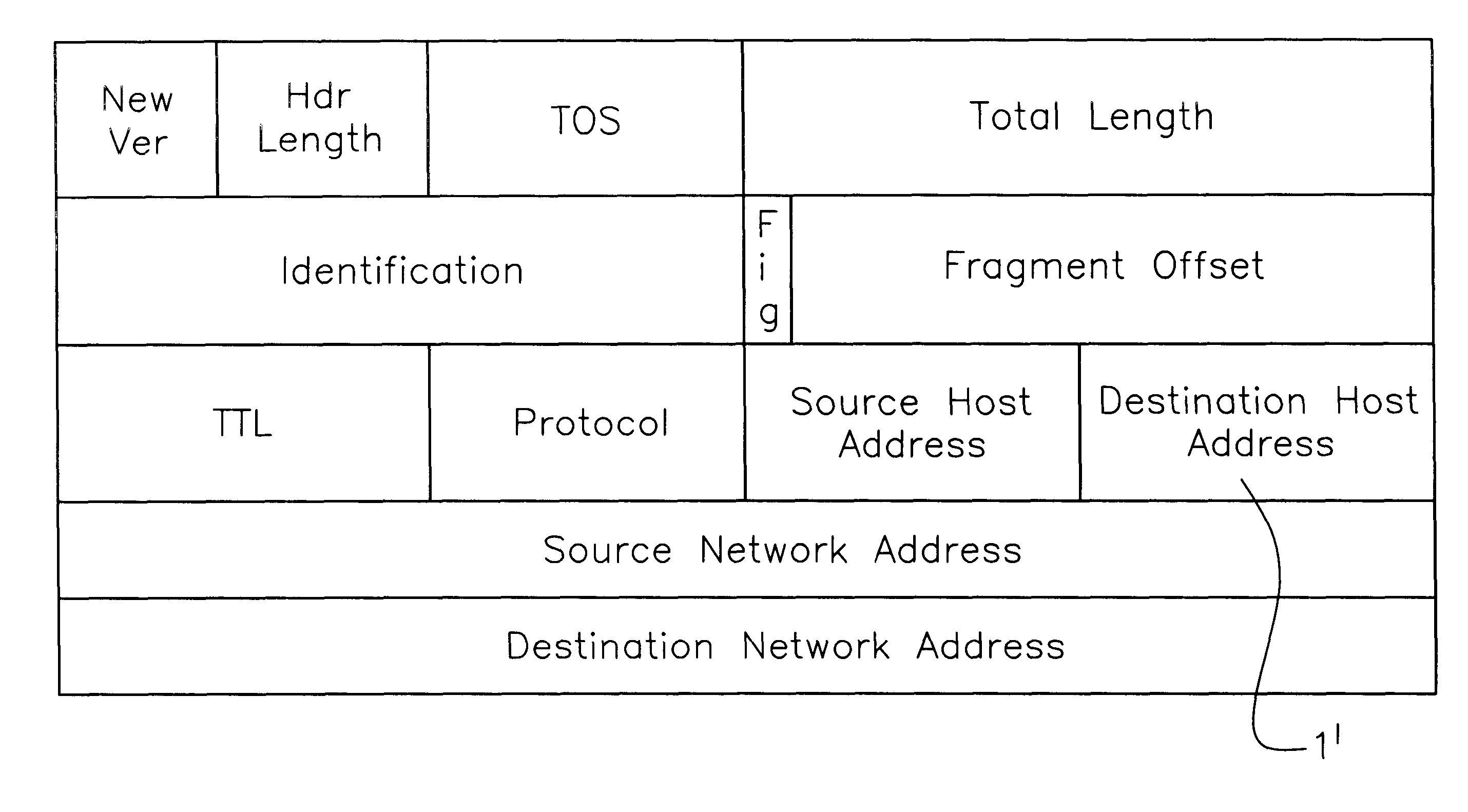
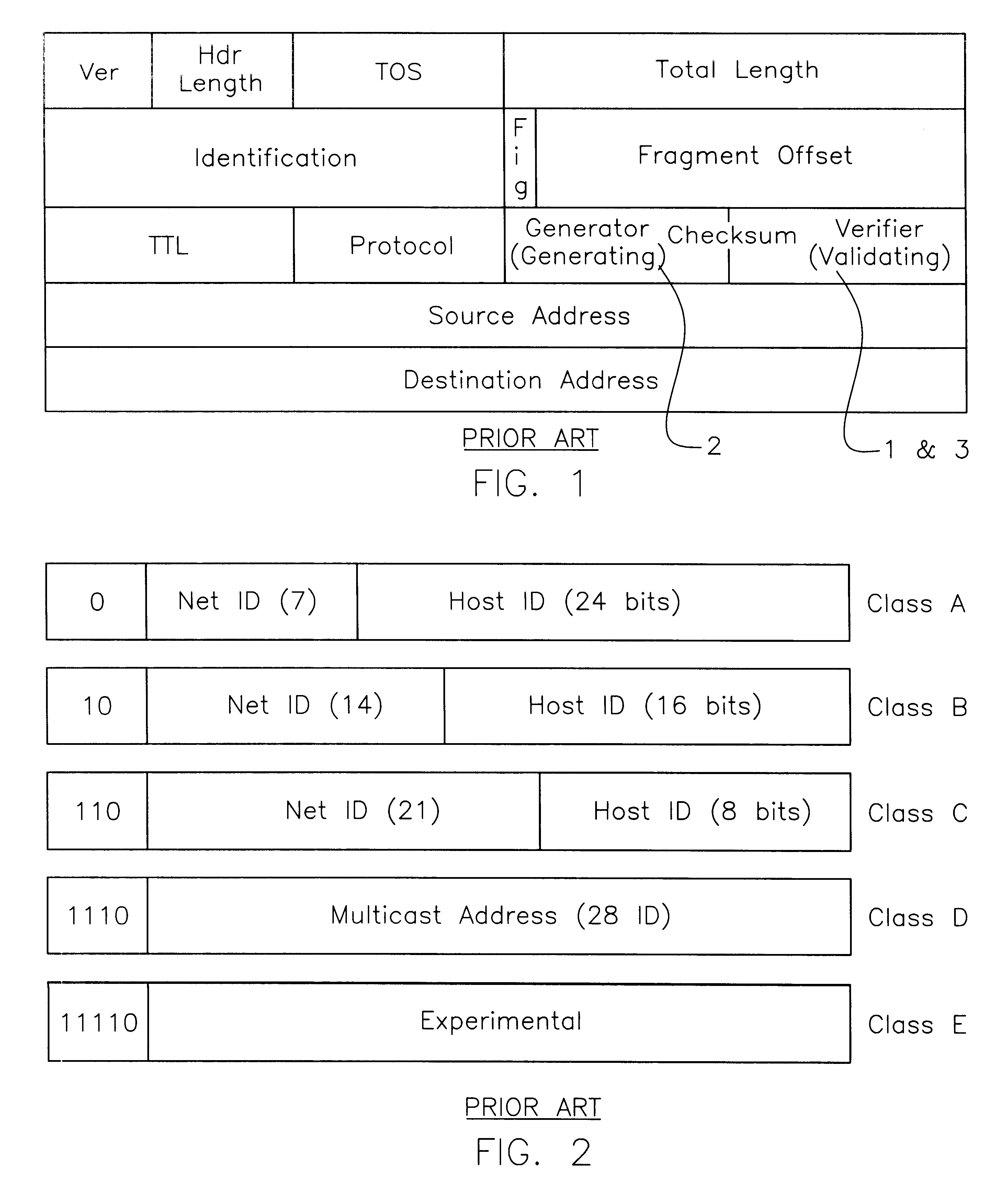
Internet and related networks, a method of and system for substitute use of checksum field space in information processing datagram headers for obviating processing speed and addressing space limitations and providing other features
InactiveUS6330614B1Add featureIncrease internet speedElectric signal transmission systemsTime-division multiplexInformation processingPrivate network
In Internet and related networks, a method of and system for substitute use of the normal checksum field space in information processing (IP) datagram headers for obviating current processing time and addressing space limitations, involving replacing the current checksum usage in the checksum field with its attendant processing time with further source host and destination host addresses of lesser processing time, thereby increasing the address space for the network and decreasing the require header processing time, and / or providing space for autonomous system numbers, a higher layer protocol-based routing information (including of the MPLS type) or for Virtual Private Networks Indentifiers in the header.
Owner:NEXABIT NETWORKS
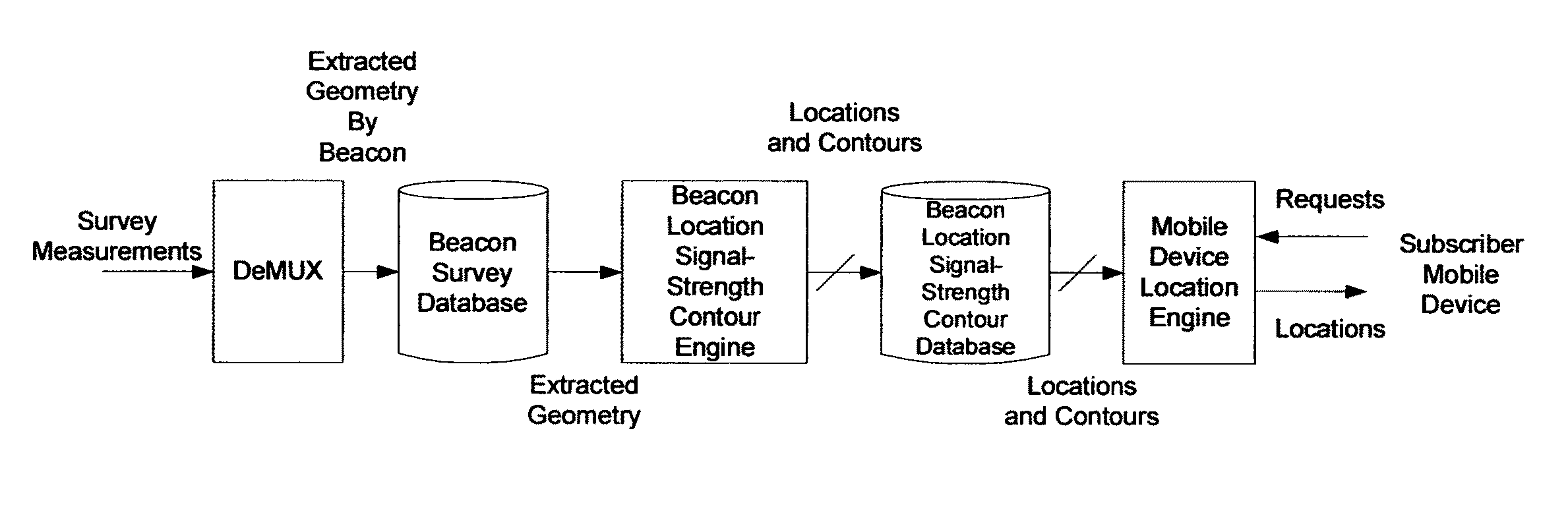
System framework for mobile device location
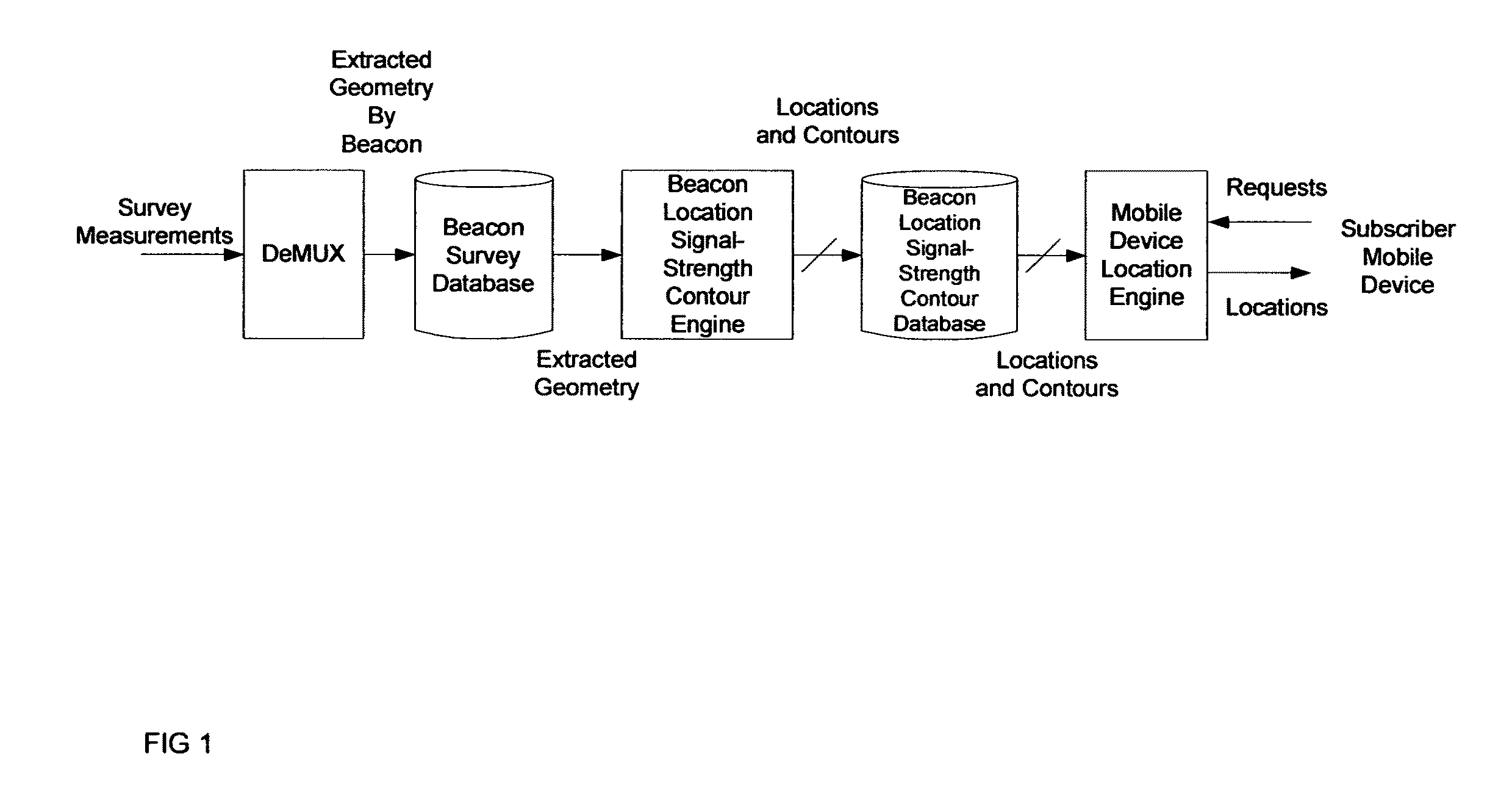
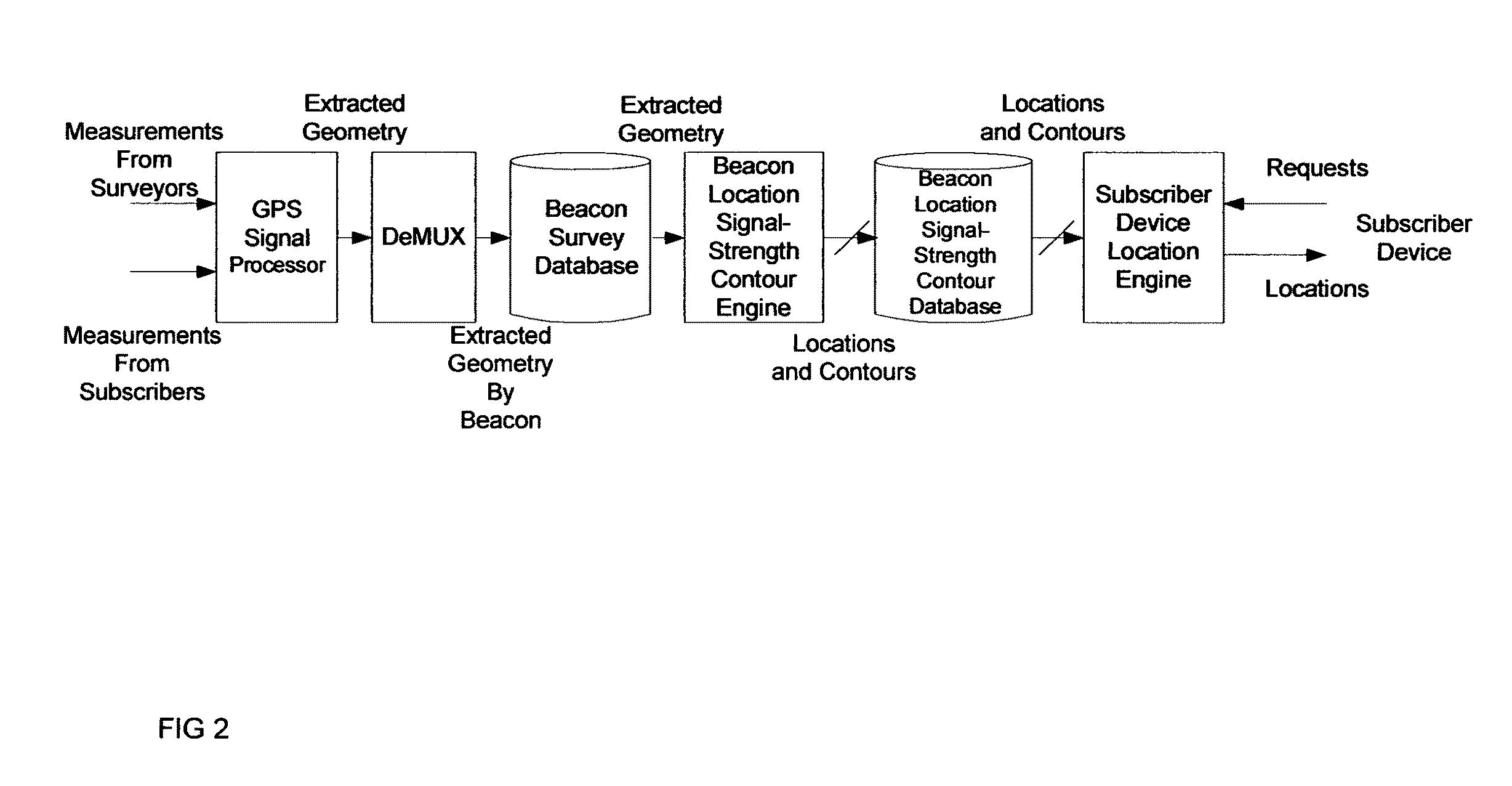
ActiveUS7994981B1Rapid and inexpensive compilationRapid and inexpensive and maintenanceBeacon systems using radio wavesPosition fixationMobile deviceUltimate tensile strength
A method for estimating the location of a beacon from an ensemble of measurements associated with said beacon, where, contained in each measurement, are GPS data from which surfaces of location may be extracted, together with the ID's of beacons detectable at the point of measurement, is disclosed. The method comprises extracting the canonical set of surfaces of location implicit in each of the associated measurements, and determining the estimate of the location of the beacon as the point for which the sum of the squares of the distances to each of the surfaces so extracted is minimized. A system for the compilation of a database of beacon locations from measurements containing a time-stamped recording of the composite GPS signal (which recording is referred to as a datagram), together with the ID's and associated signal strengths of beacons detectable at the point of measurement, is also disclosed. The system comprises GPS signal processing means for extracting, from each time-stamped datagram, the canonic set of surfaces of location, and beacon location estimation means for estimating the location of a beacon from an ensemble of surfaces of location associated with said beacon.
Owner:ETHERWHERE CORP
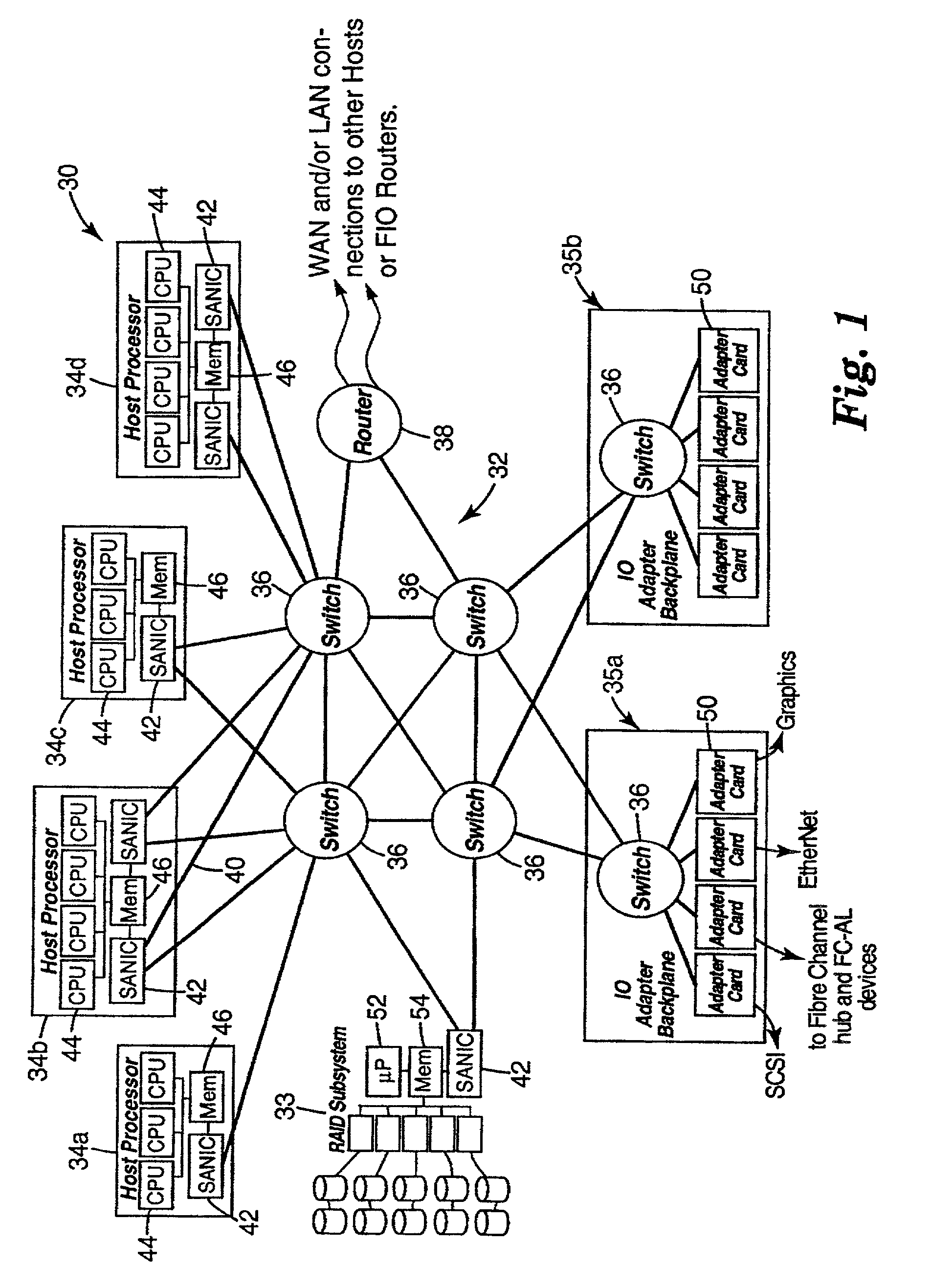
Remote direct memory access with striping over an unreliable datagram transport
In a multinode data processing system in which nodes exchange information over a network or through a switch, a structure and mechanism are provided which enables data packets to be sent and received in any order. Normally, if in-order transmission and receipt are required, then transmission over a single path is essential to insure proper reassembly. However, the present mechanism avoids this necessity and permits Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) operations to be carried out simultaneously over multiple paths. This provides a data striping mode of operation in which data transfers can be carried out much faster since packets of single or multiple RDMA messages can be portioned and transferred over several paths simultaneously, thus providing the ability to utilize the full system bandwidth that is available.
Owner:IBM CORP
Virtual machine operating system LAN
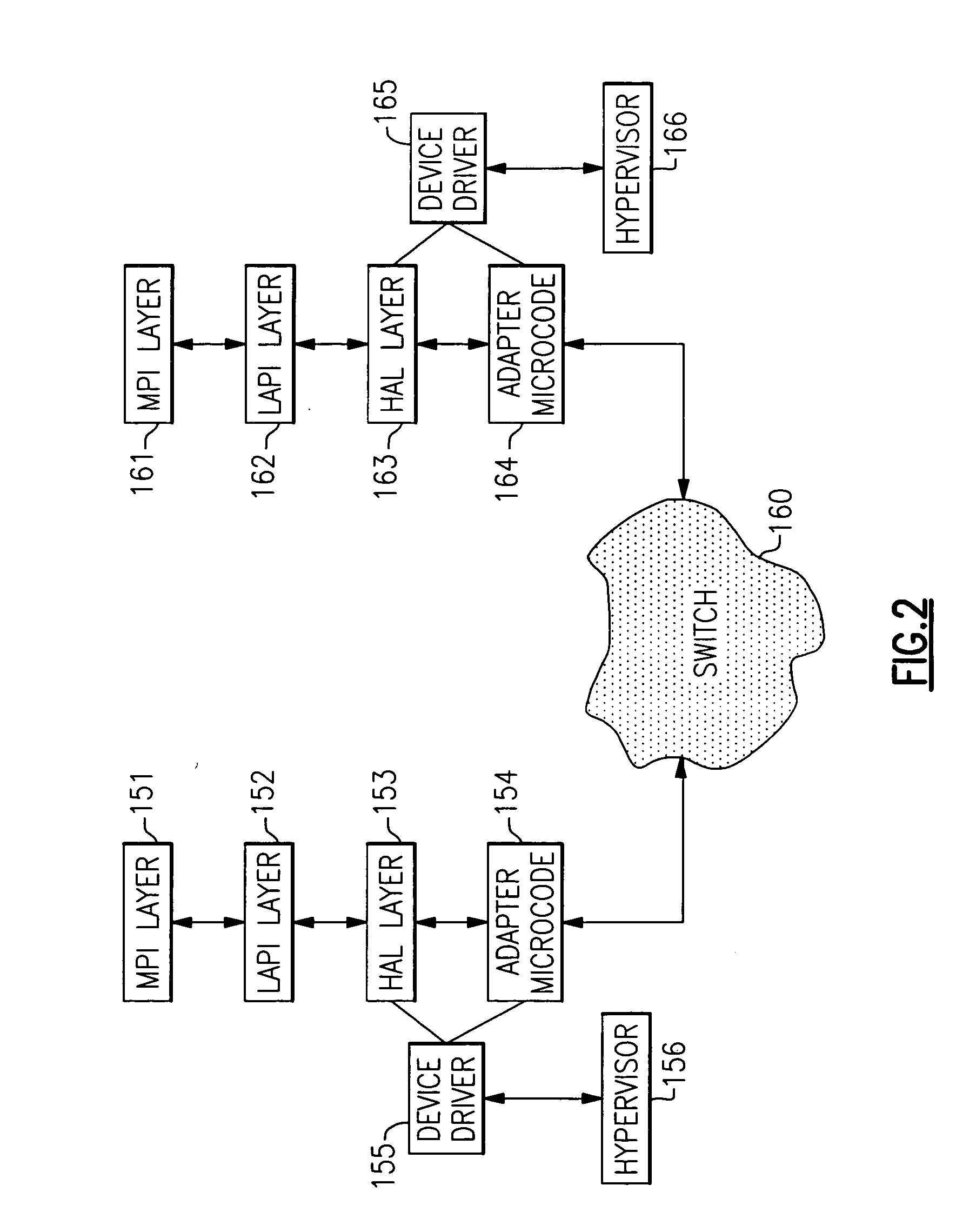
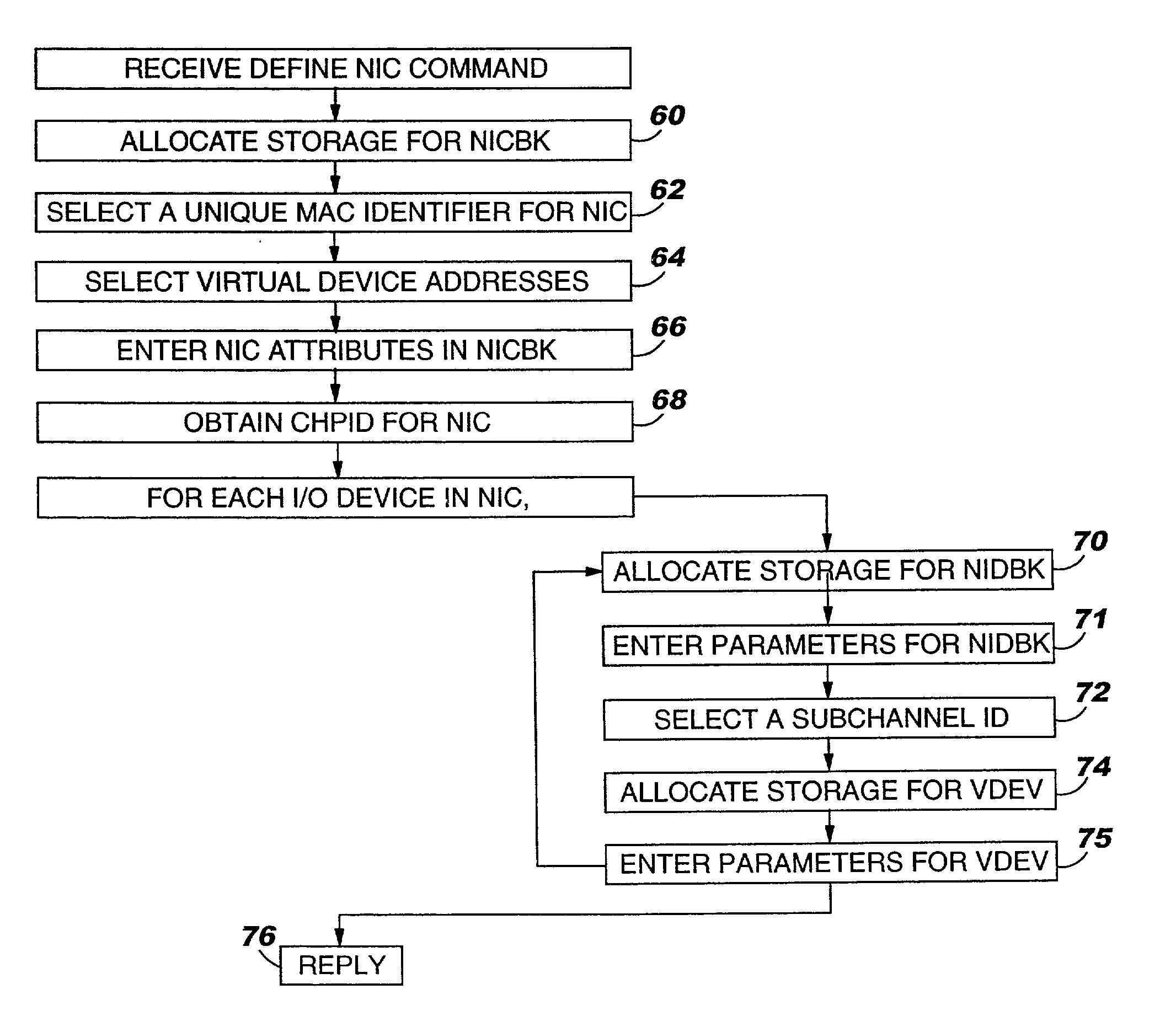
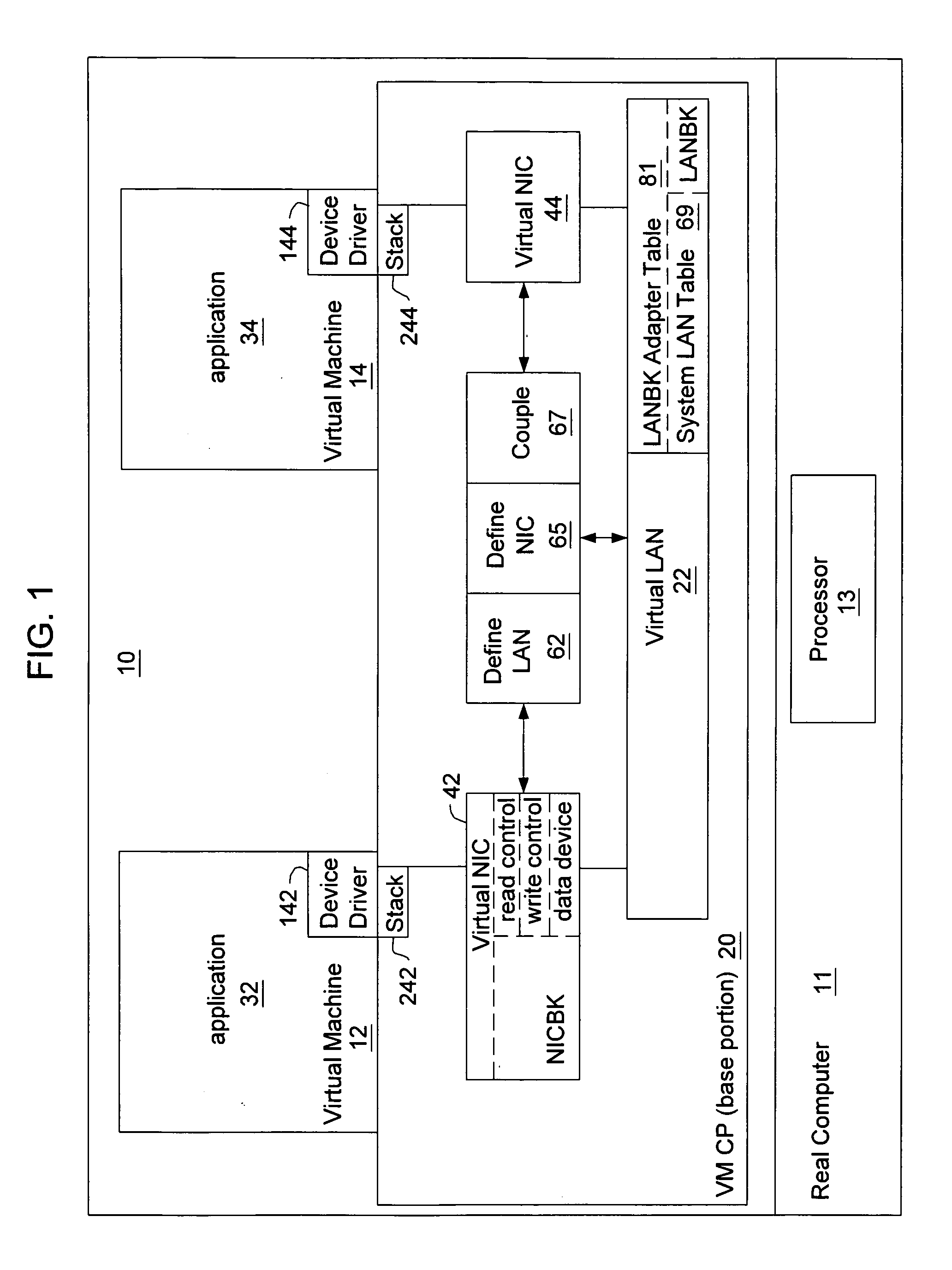
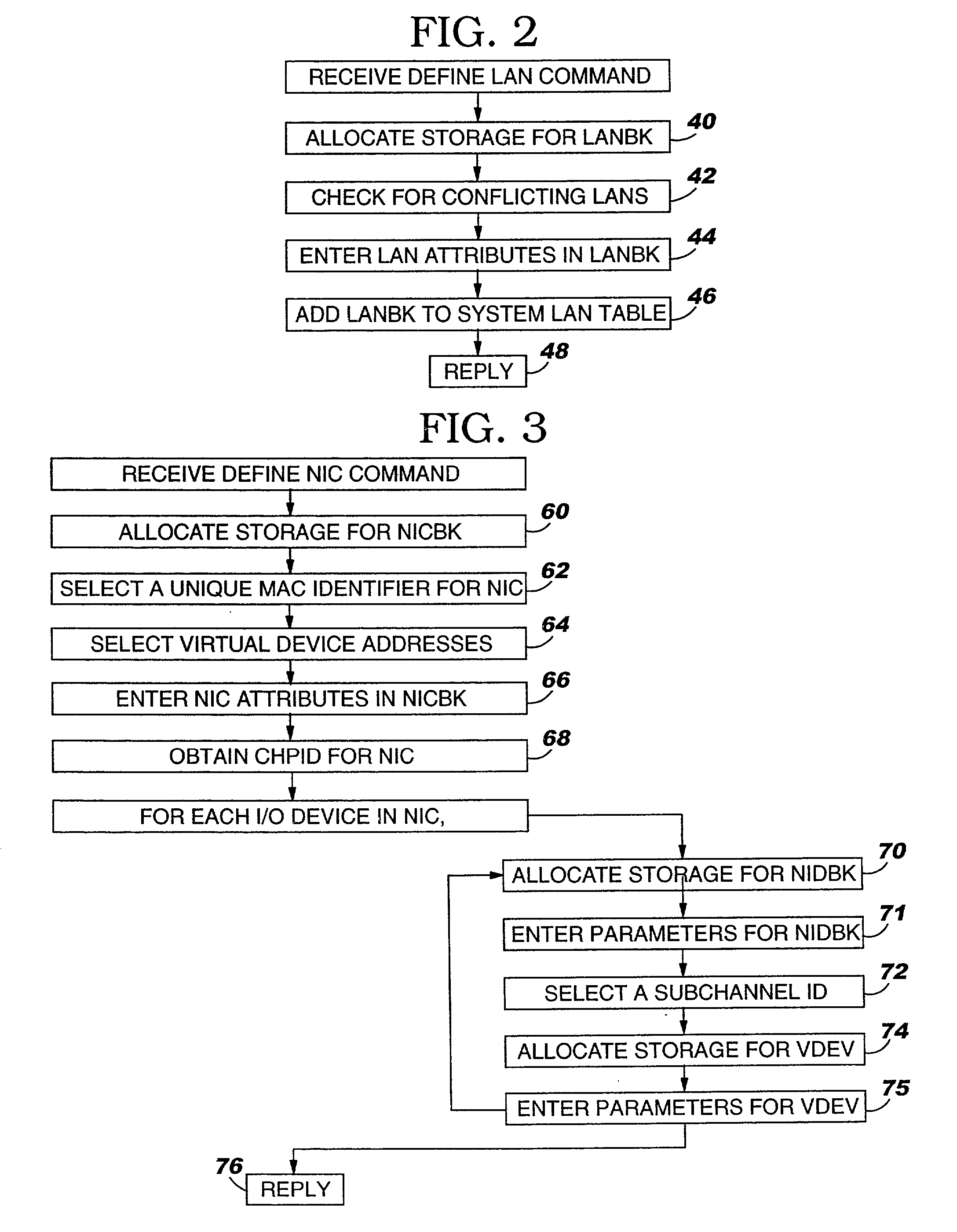
ActiveUS7111303B2Simple methodMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsOperational systemIp address
A virtual machine operating system for communication between first and second applications which execute in different user portions of the virtual machine operating system and use Internet Protocol (IP). The virtual machine operating system comprises a first user portion, a second user portion and a base portion. The first user portion executes the first application and includes a first device driver for a first virtual network interface card (NIC). The second user portion executes the second application and includes a second device driver for a second virtual NIC. The base portion is shared by the first and second user portions and includes the first and second virtual NICs. The base portion maintains a table of IP addresses by which each device driver addresses its respective NIC and other, corresponding addresses by which the base portion addresses the virtual NIC. The first device driver is programmed to receive an IP datagram from the first application and pass it to the first NIC using IP. The datagram includes an IP address of the second virtual NIC and an indication that the second application should receive the datagram. The base portion is programmed to determine the other address of the second NIC based on the table and transfer the datagram to a storage location associated with the second virtual NIC or the second device driver.
Owner:IBM CORP
Securing Voice over IP traffic
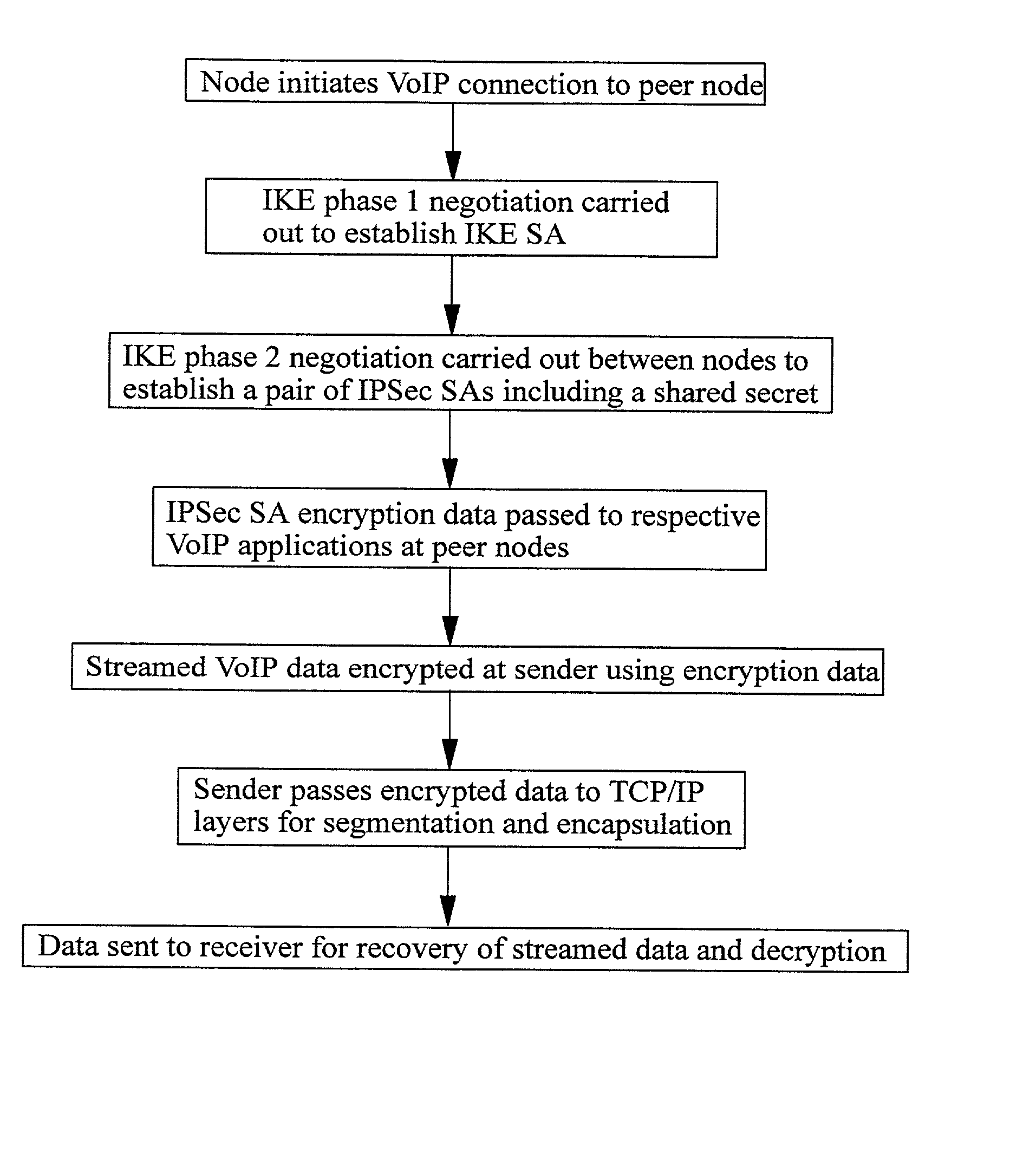
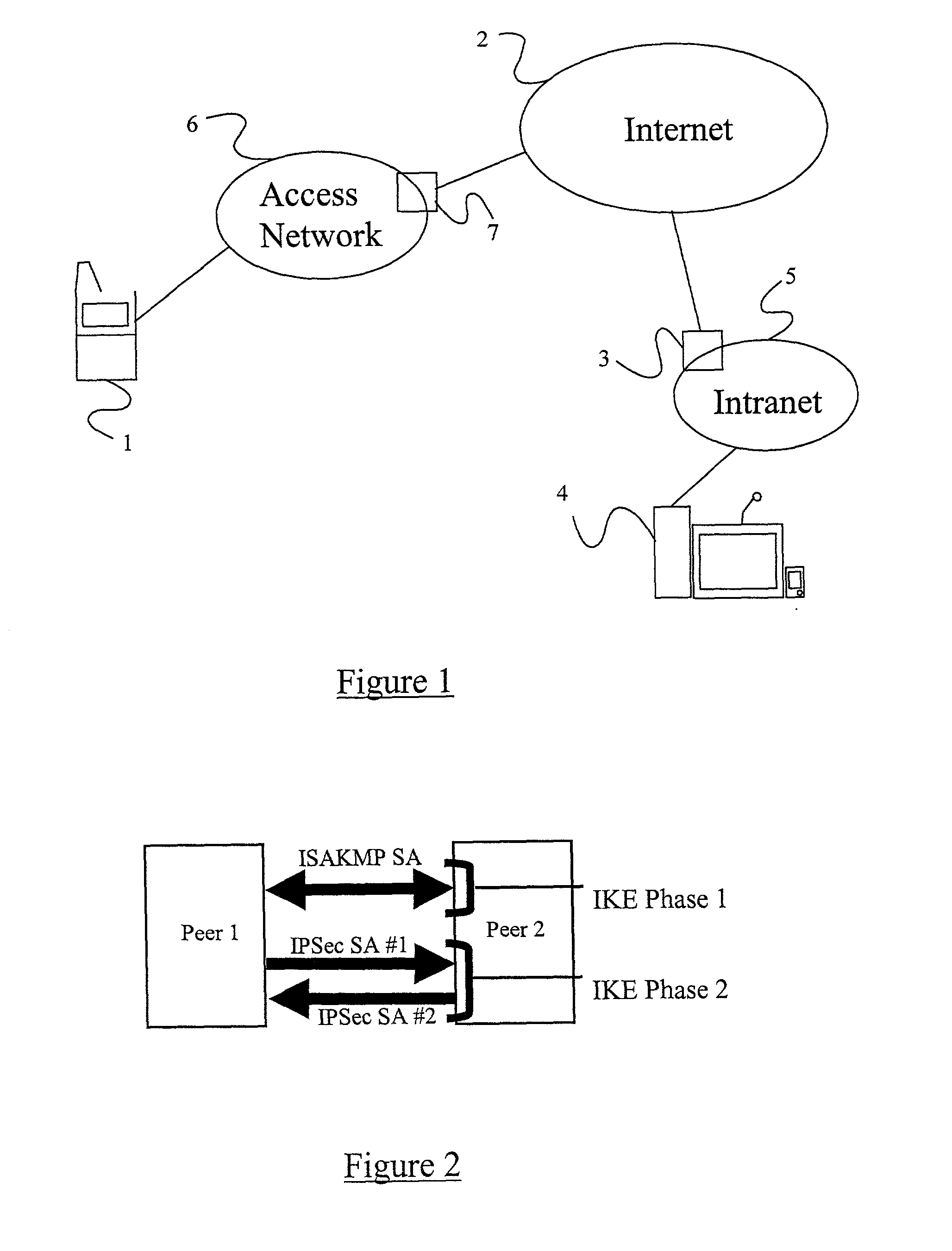
A method of sending streamed data over an IP network from a first node 1 to a second node 4, the method comprising using Internet Key Exchange (IKE) to establish an IKE security association (SA) between the first and second nodes 1,4. A shared secret is established between the first and second nodes using the IKE SA, and the streamed data encrypted at the first node 1 with a cipher using the shared secret or a key derived using the shared secret. IP datagrams are constructed containing in their payload, segments of the encrypted streamed data, the datagrams not including an IPSec header or headers. The IP datagrams are then sent from the first node 1 to the second node 4.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and apparatus for anonymous IP datagram exchange using dynamic network address translation
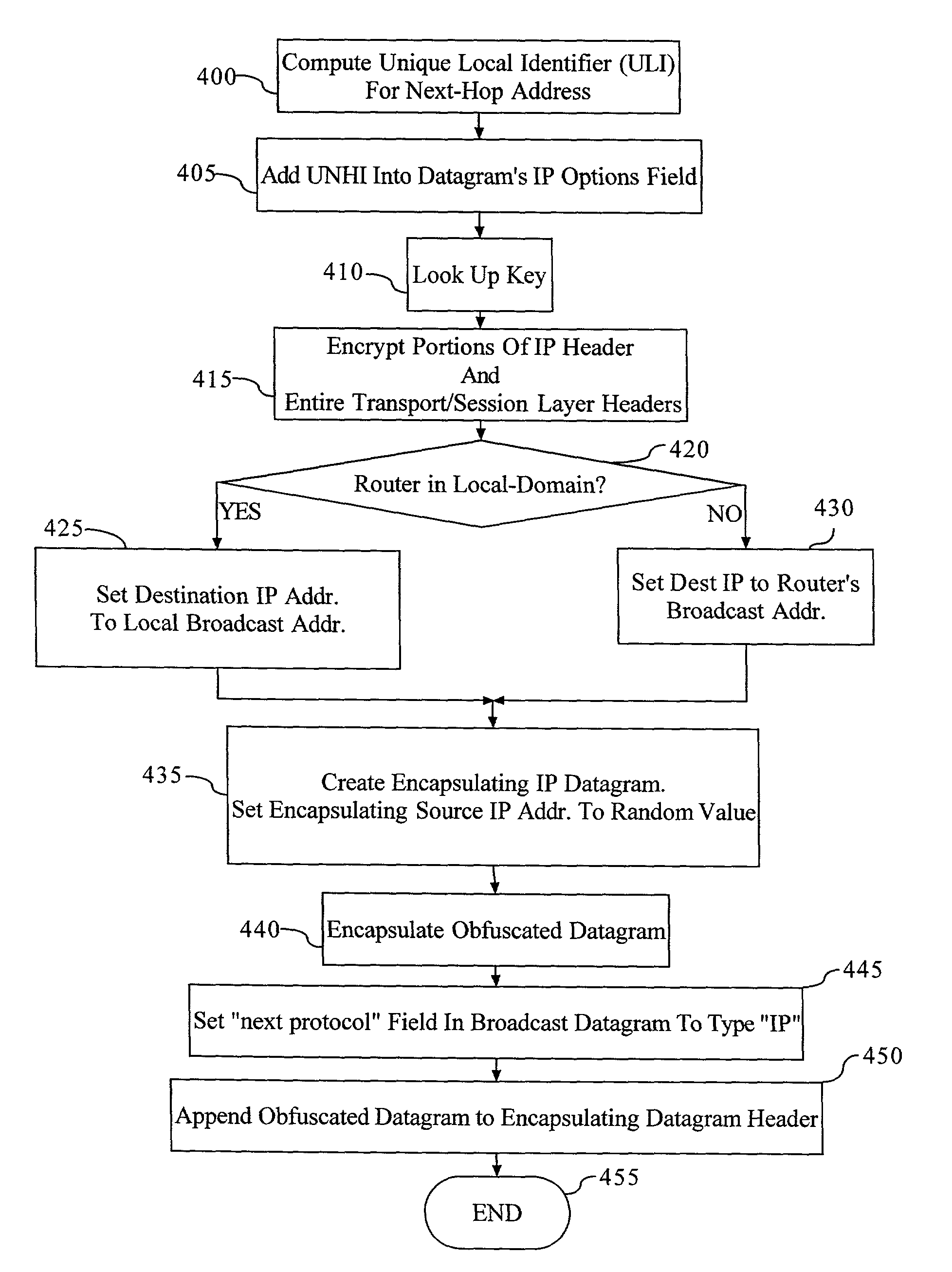
Methods, apparatus, system and computer program are provided for concealing the identity of a network device transmitting a datagram having a network layer header. A unique local identifier and broadcast address are determined in accordance with a next-hop address. A partially encrypted network layer header is determined by encrypting a plurality of identifying portions of the network layer header, where one portion of the network layer header is the unique local identifier. The datagram is encapsulated with another network layer header whose address is set to the broadcast address. The encapsulated datagram can be received and detunneled, and an address of a recipient can be extracted from the network layer header. The datagram is then admitted into a network domain.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC +1
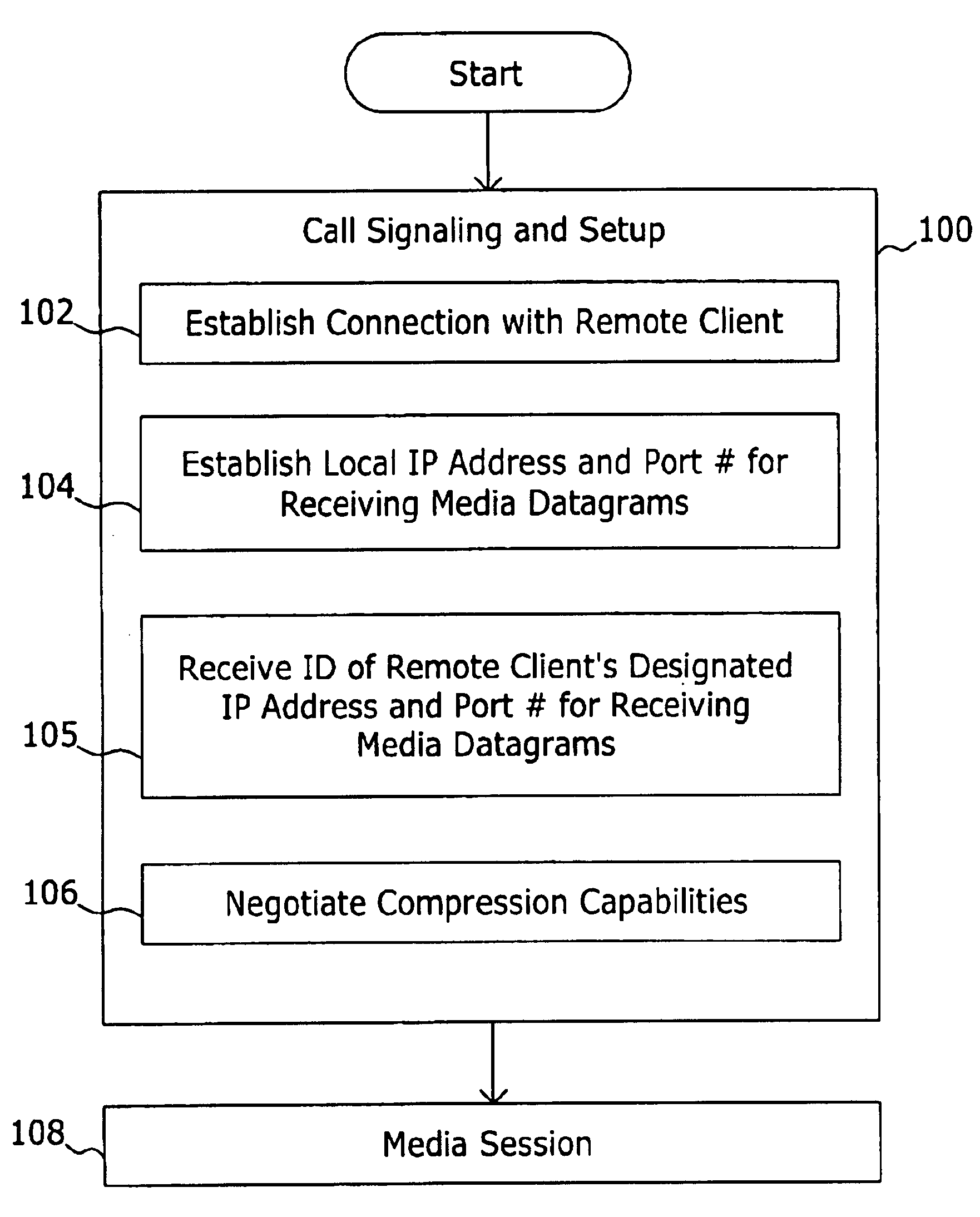
System and method for determining a connectionless communication path for communicating audio data through an address and port translation device
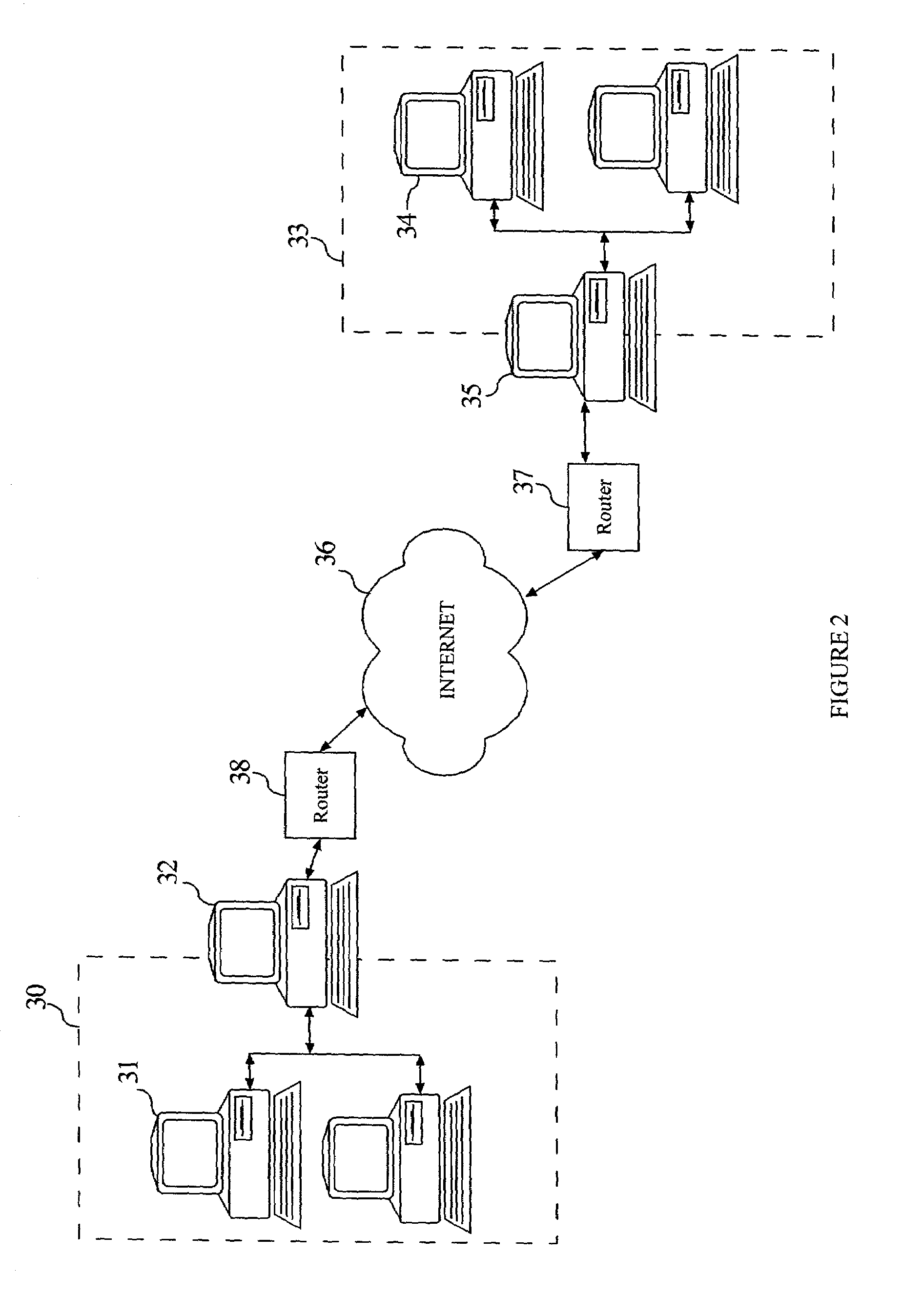
ActiveUS6928082B2Digital computer detailsData switching by path configurationConnectionless communicationIp address
A method of audio communication utilizing media datagrams between a first telephony client located behind a network address translation (NAT) server and a remote second telephony client is disclosed. Each client utilizes a single port number for both sending and receiving media datagrams. A media datagram is sent from the first telephony client to the second telephony client on a UDP / IP channel utilizing a destination IP address and port number provided by the second telephony client. The second telephony client extracts the source IP address and source port number from the received media datagram to determine if the first telephony client is located behind a NAT server. If the first telephony client is located behind a NAT server, the extracted source IP address and port number are stored and used to send media datagrams to the first telephony client located behind the NAT server.
Owner:PALO ALTO NETWORKS INC
Border gateway protocol manager and method of managing the selection of communication links
InactiveUS6829221B1Avoid congestionLeast costError preventionTransmission systemsBorder Gateway ProtocolCommunication link
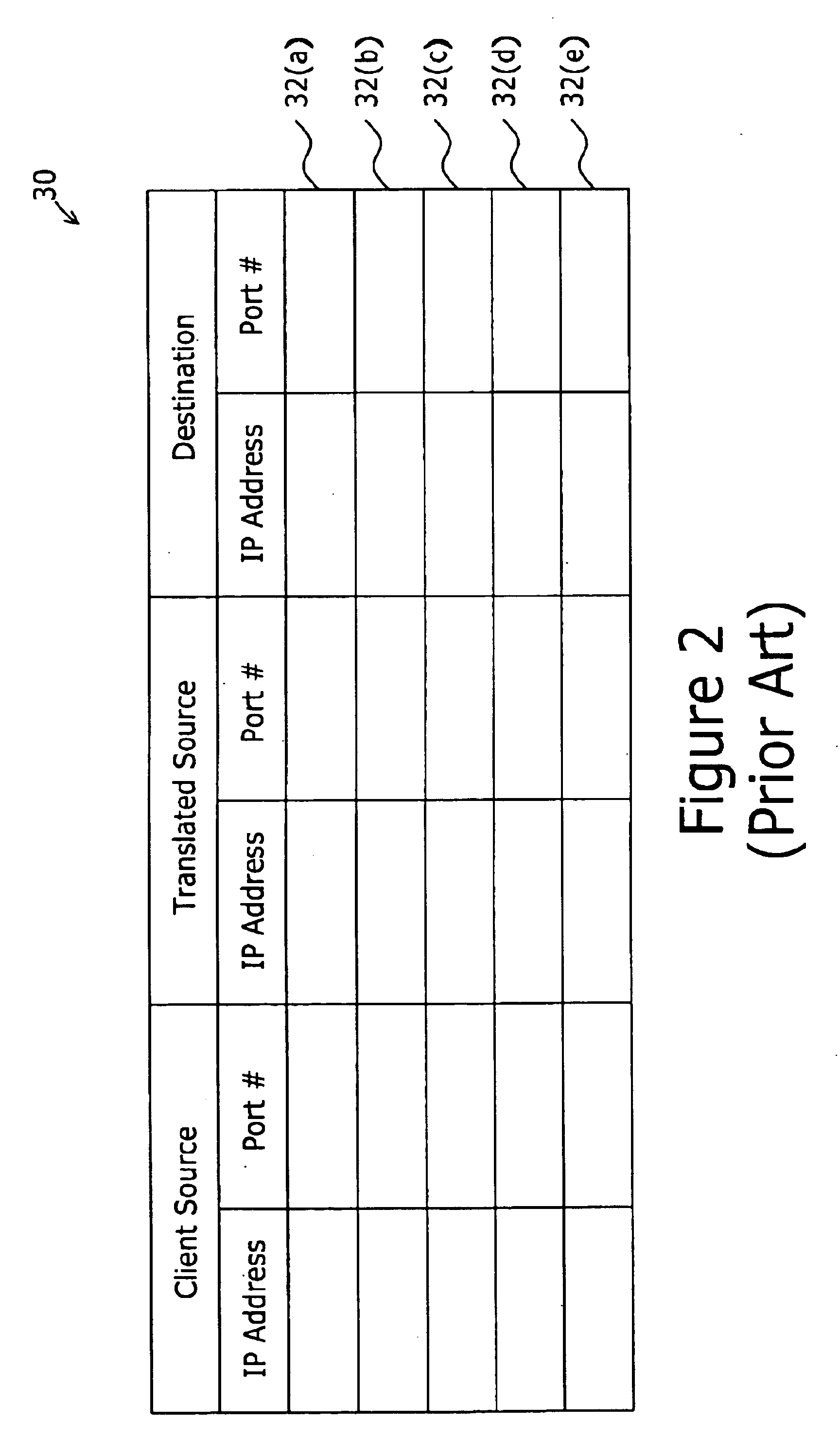
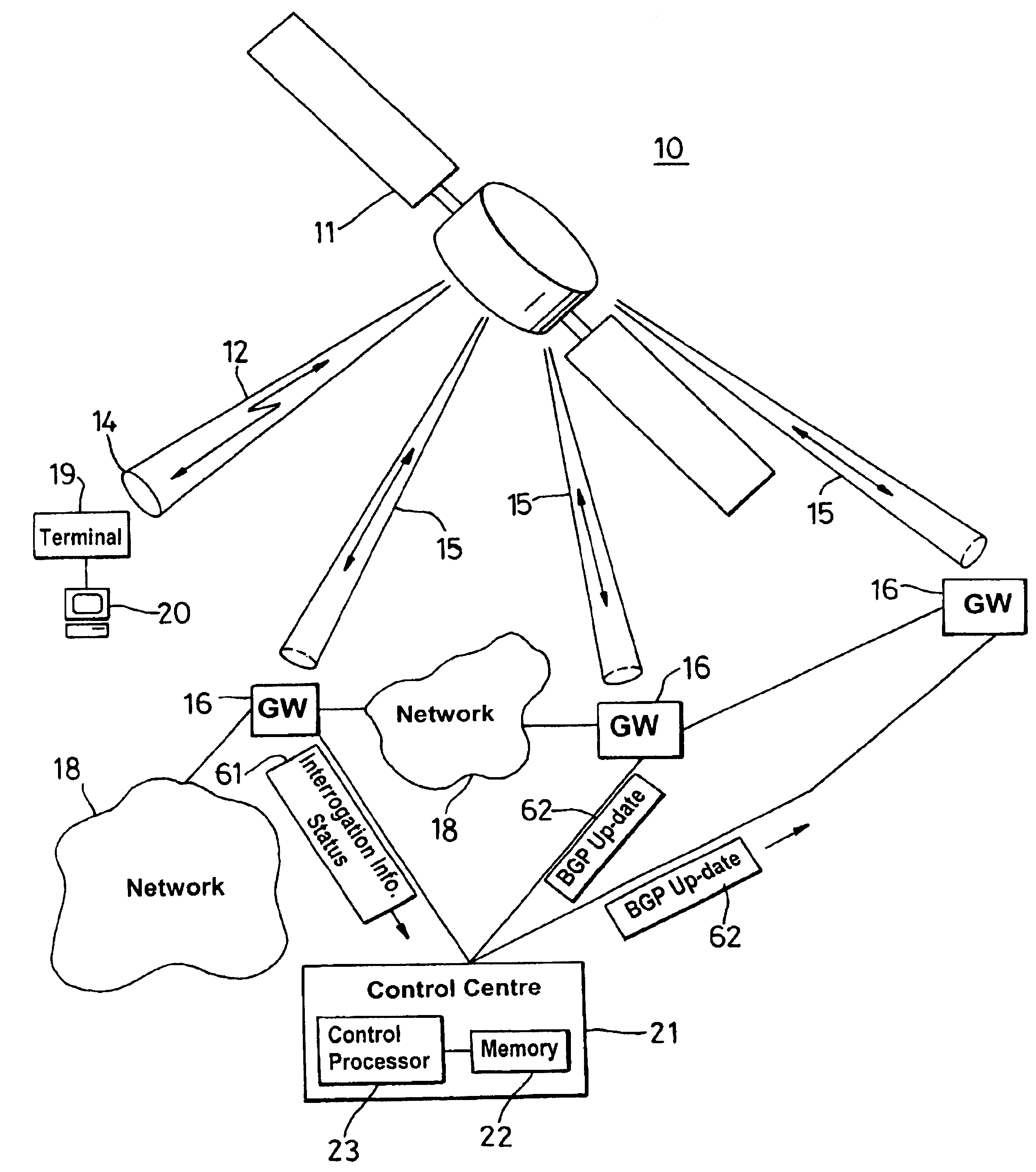
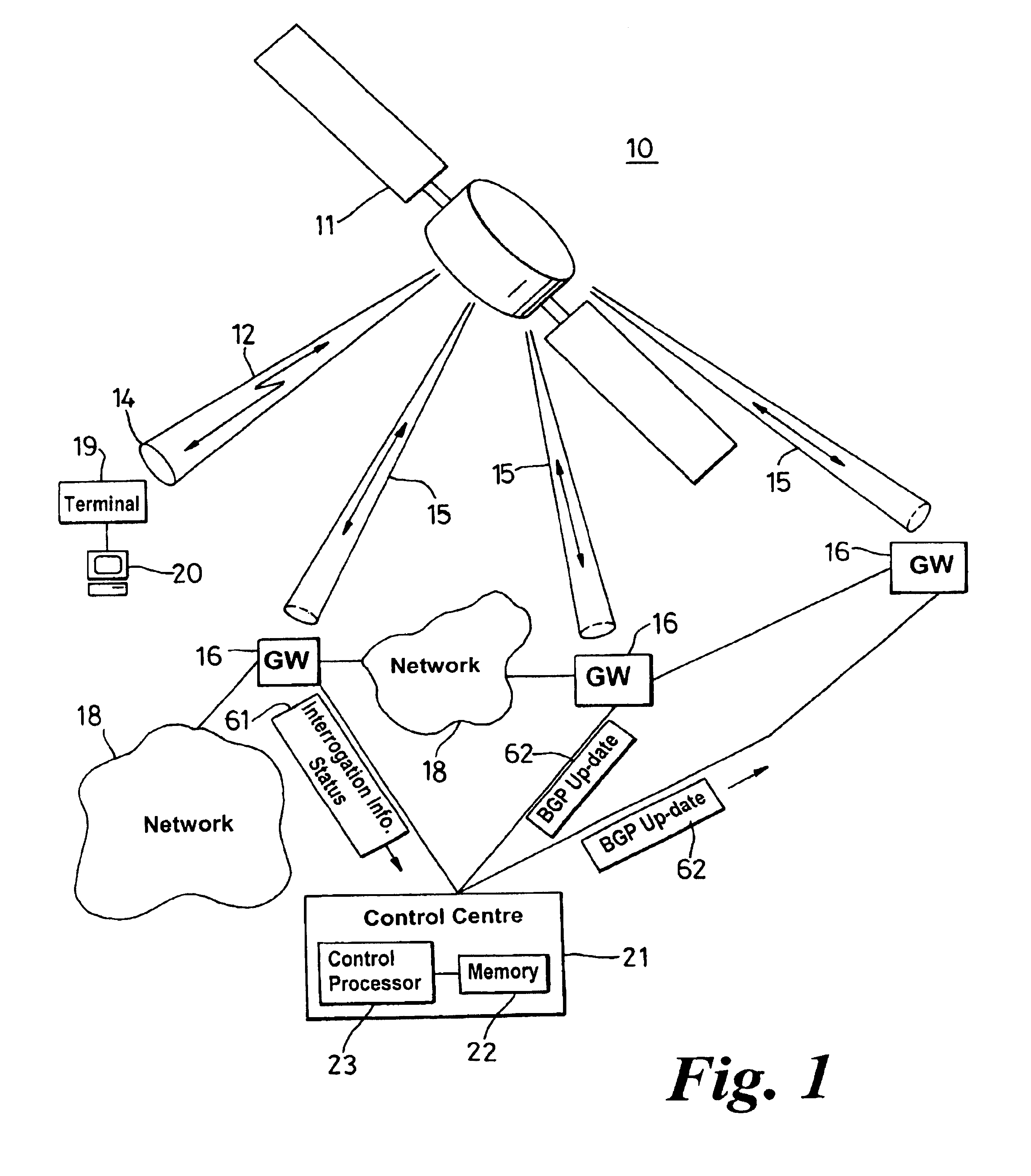
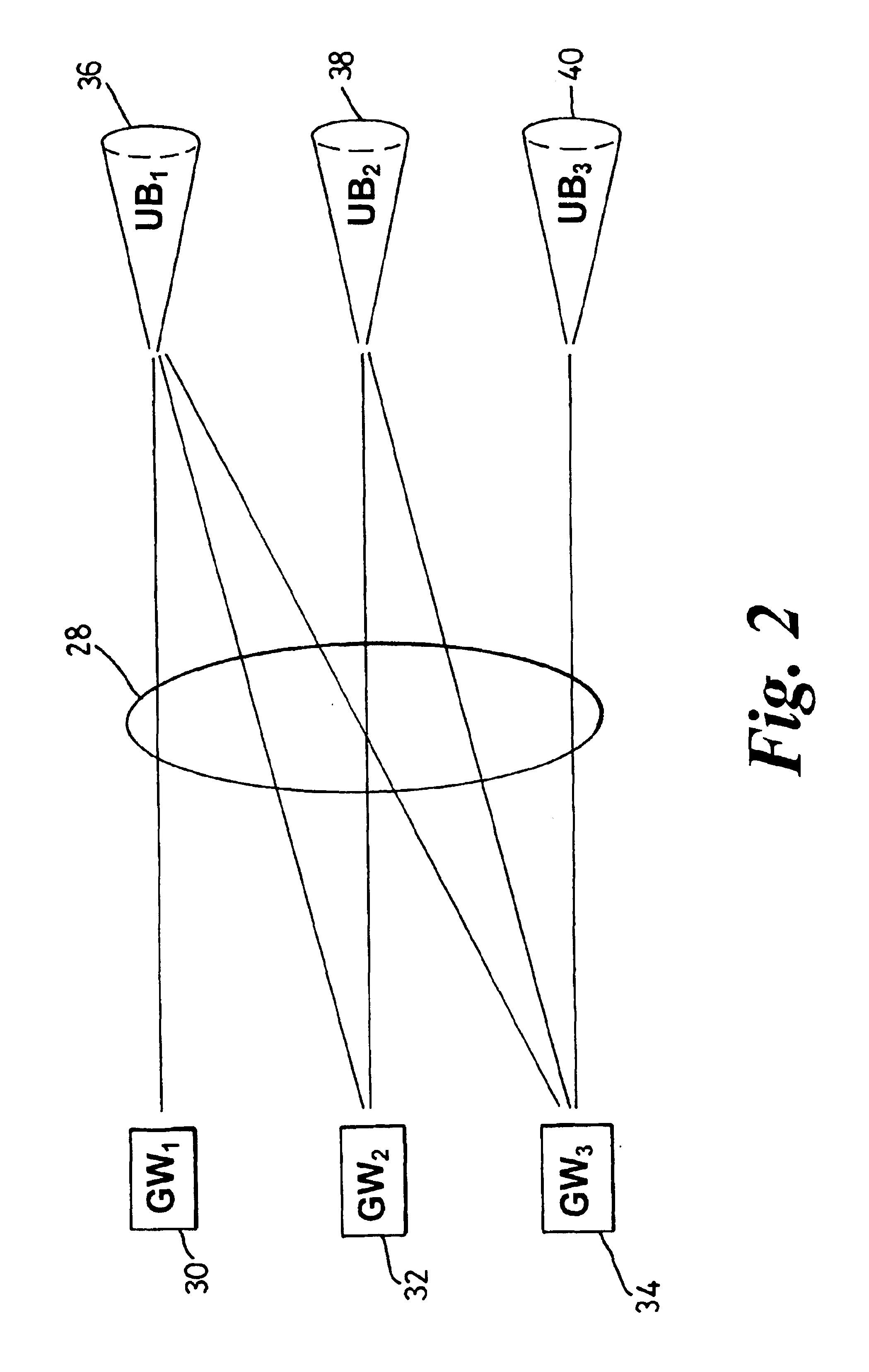
A border gateway protocol (BGP) management system (10) dynamically determines an optimum or preferred data route (12) from wireline networks (18) into a satellite communication system (11). Multiple gateways (16, 30-34) provide access points to the wireline networks. The management system includes a connectivity matrix which processes (74) information, such as bandwidth availability and route congestion, and then generate a BGP update that is communicated (80) into at least one of the gateways. The BGP update promotes preferred gateways and so identifies a preferred access path to the satellite system. Specifically, the BGP update instruction contains a metric altering a weighting of an identified route data route, which metric effects path selection at a gateway receiving IP datagrams. The metric is derived from information pertaining to a connectivity matrix associated with the satellite system.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
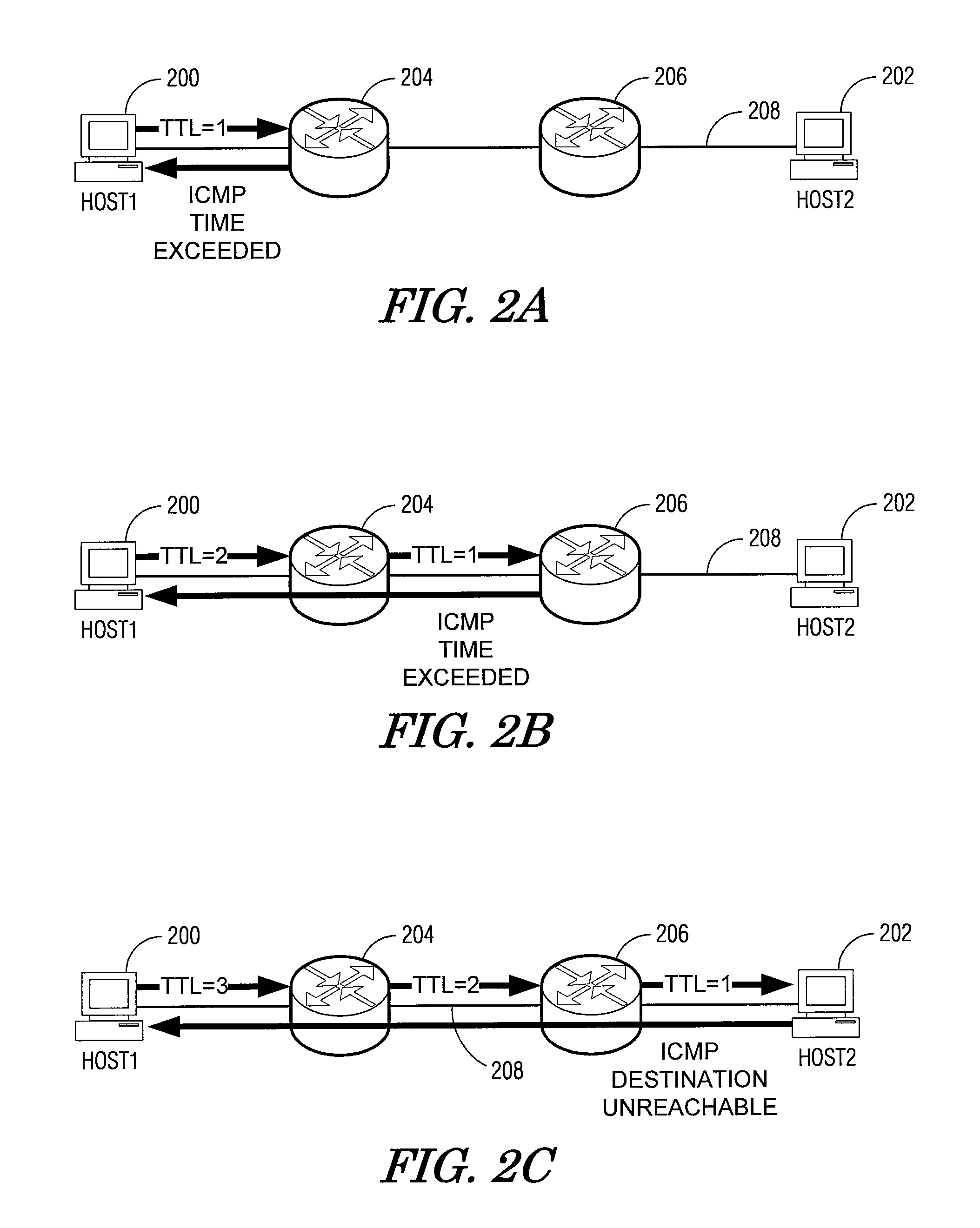
User datagram protocol traceroute probe extension
The embodiments described herein provide methods and apparatuses for implementing a User Datagram Protocol traceroute probe extension. In an example embodiment, a request to transmit a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packet to a remote destination is received. A probe header and a probe data element is then stored in a data field of the UDP packet. The UDP packet is then transmitted toward the remote destination. In an example embodiment, a User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packet is received and it is determined whether the UDP packet includes a probe data structure. When the determination is affirmative, the probe data structure is processed.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
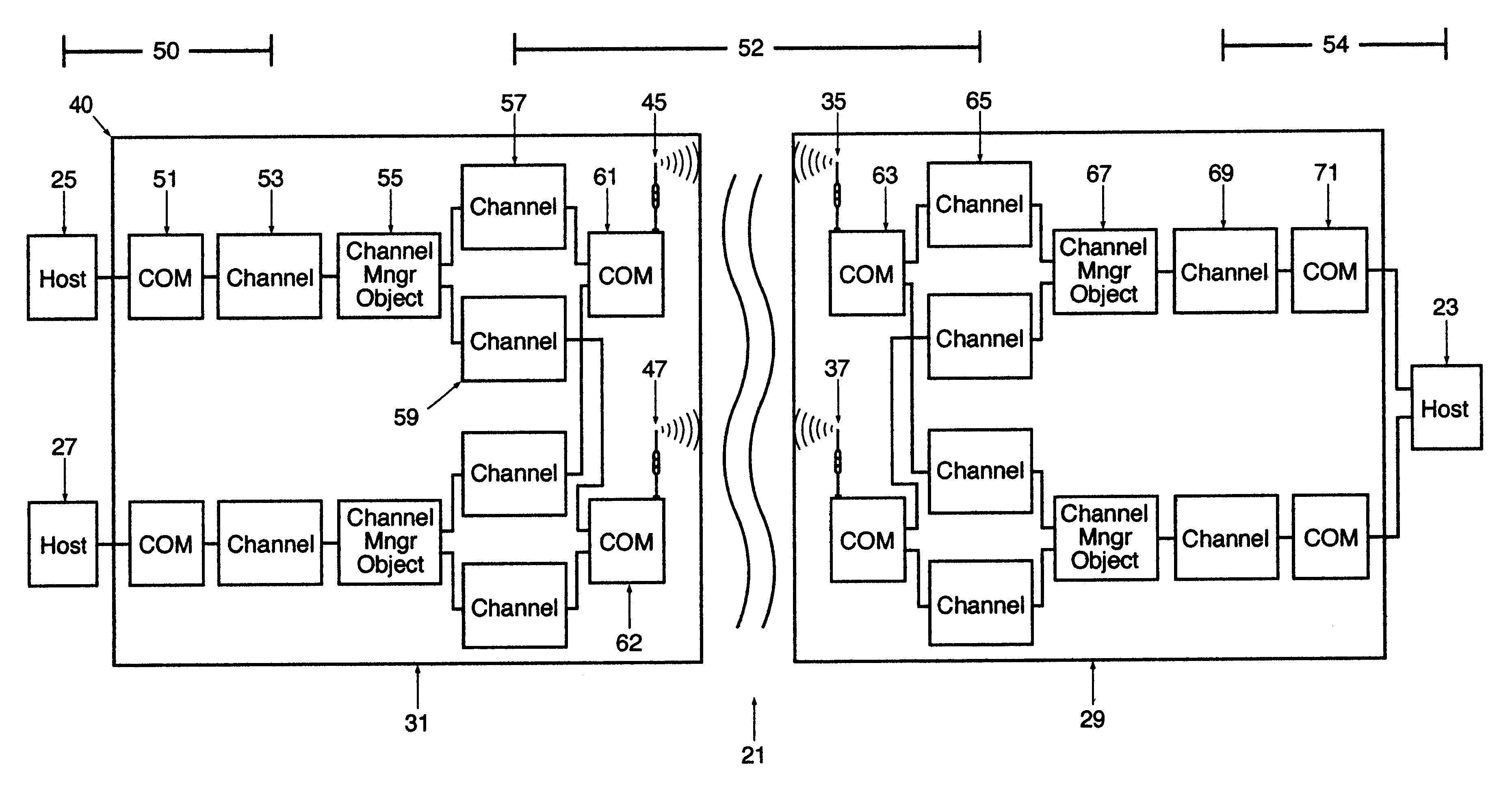
Method and apparatus for transportation of data over a managed wireless network using unique communication protocol
InactiveUS6587441B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsError prevention/detection by using return channelWireless controlWireless mesh network
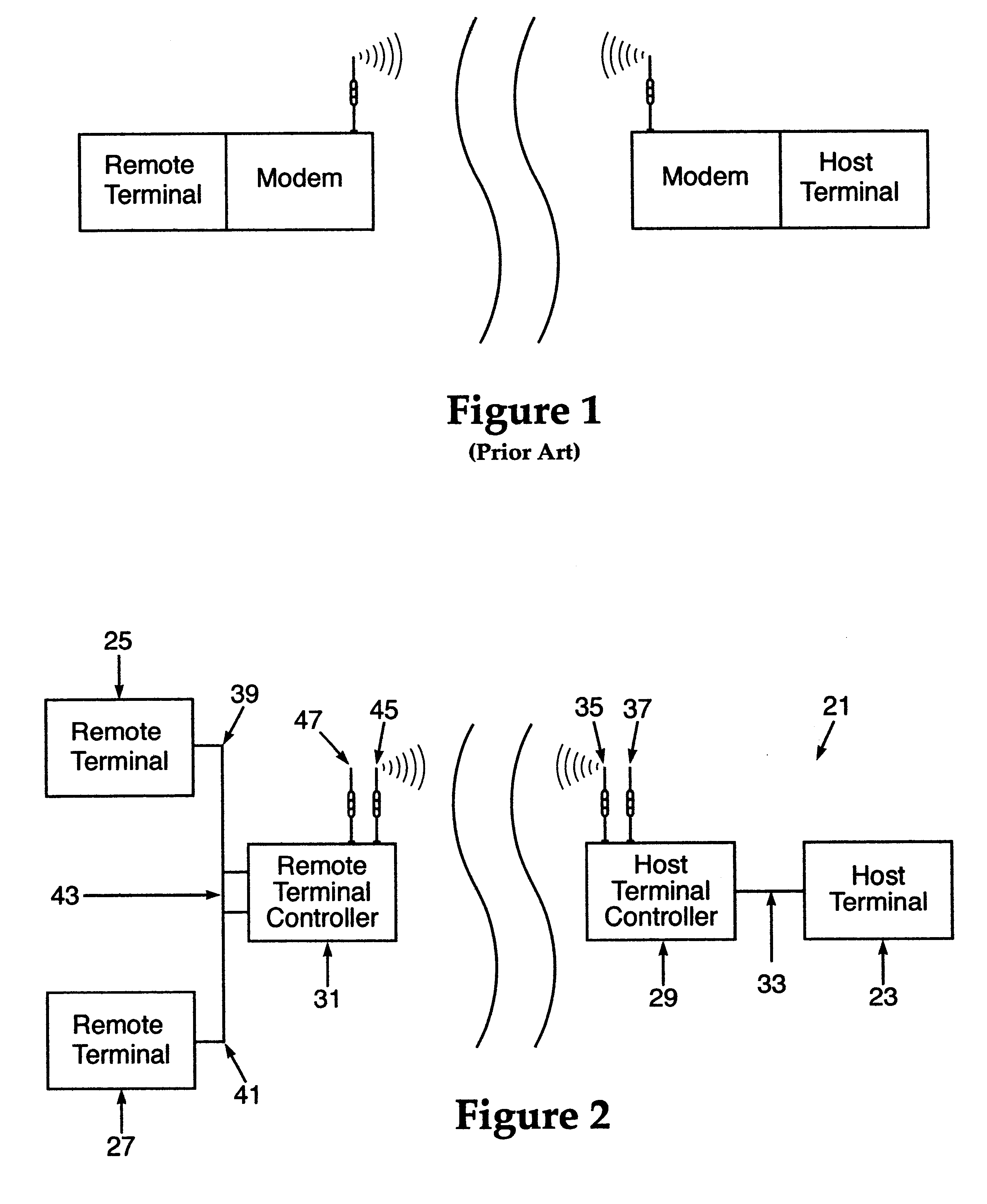
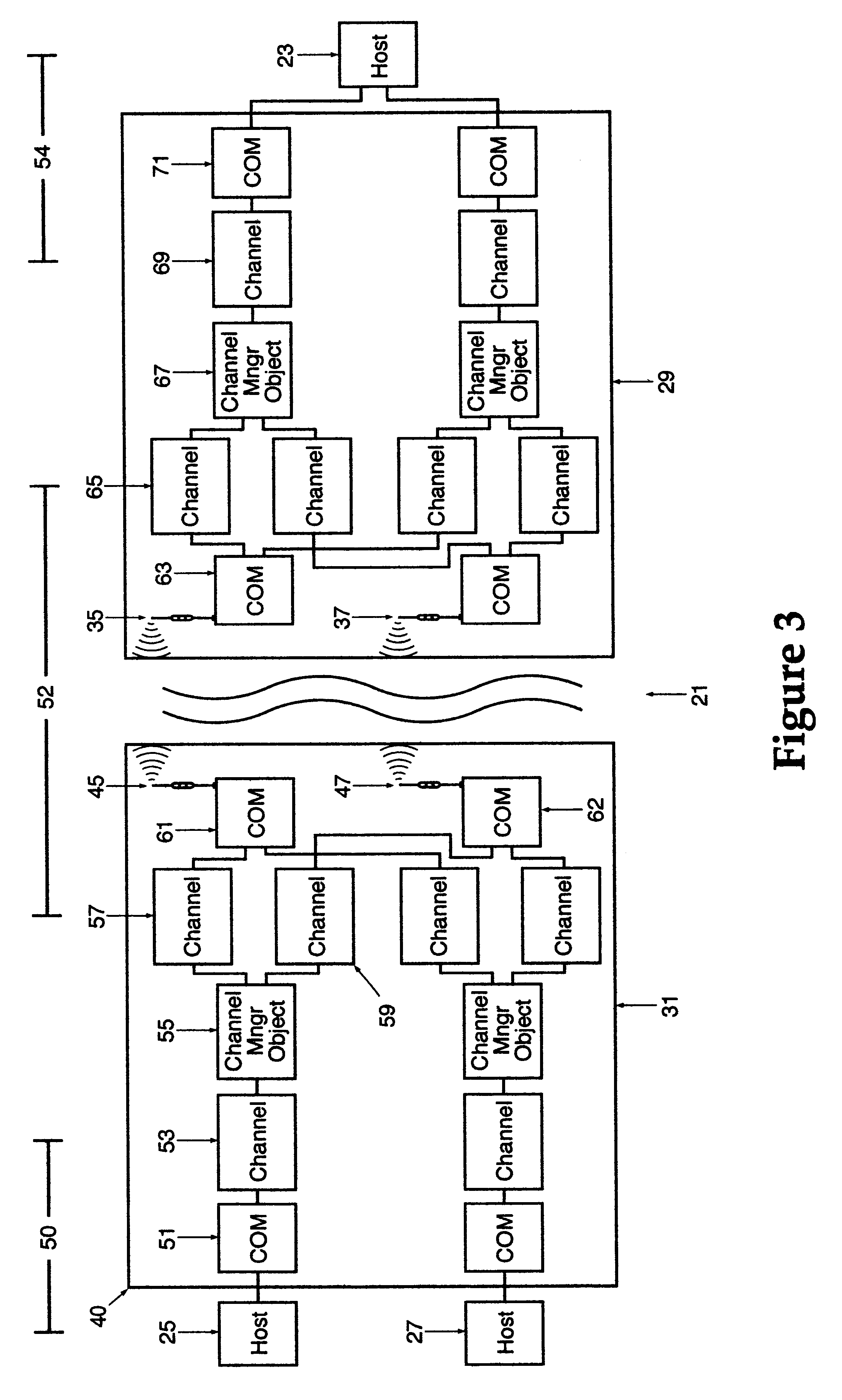
A wireless, redundant, secure, real-time, network for a proprietary interactive data transfer system having a remote terminal and a host data center, such as an automated teller banking system, is disclosed. Controllers for the remote terminal and the host data center receive the proprietary language messages and packetize and encrypt the messages for sending over the best wireless carrier among the plurality of wireless carriers the controllers are connected to. The wireless control protocol monitors the communications to provide for selection of the most reliable communication carrier for any part of a transmission. Each network segment of the signal path has at least one state-controlled gate which reports the status of that signal path. Real time transmission and acknowledgment of securely packetized messages on wireless communications carriers via an object oriented coding control application provides for reliable datagram transfer independent of the reliability of any one signal path.
Owner:MAYFAIR WIRELESS
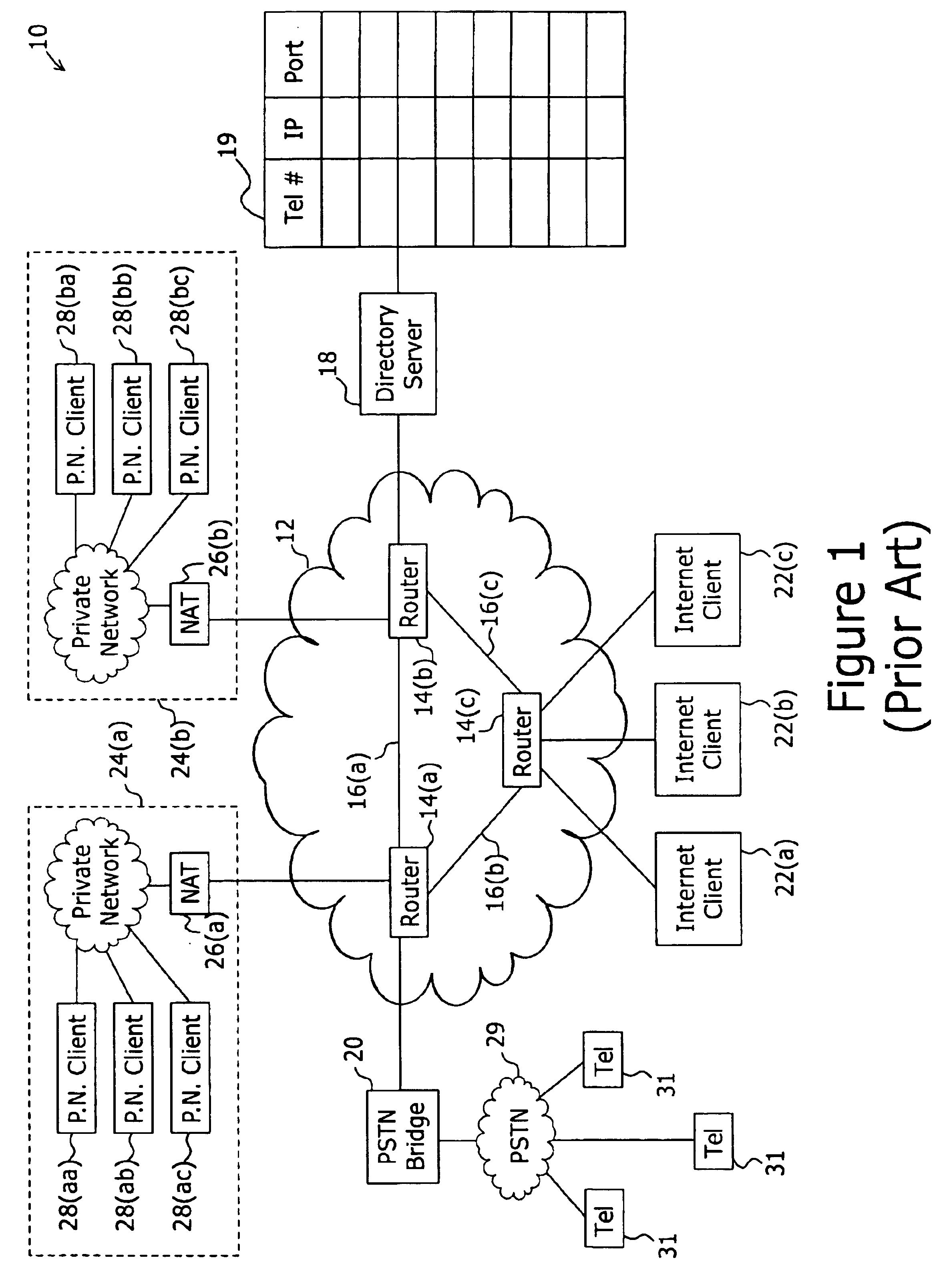
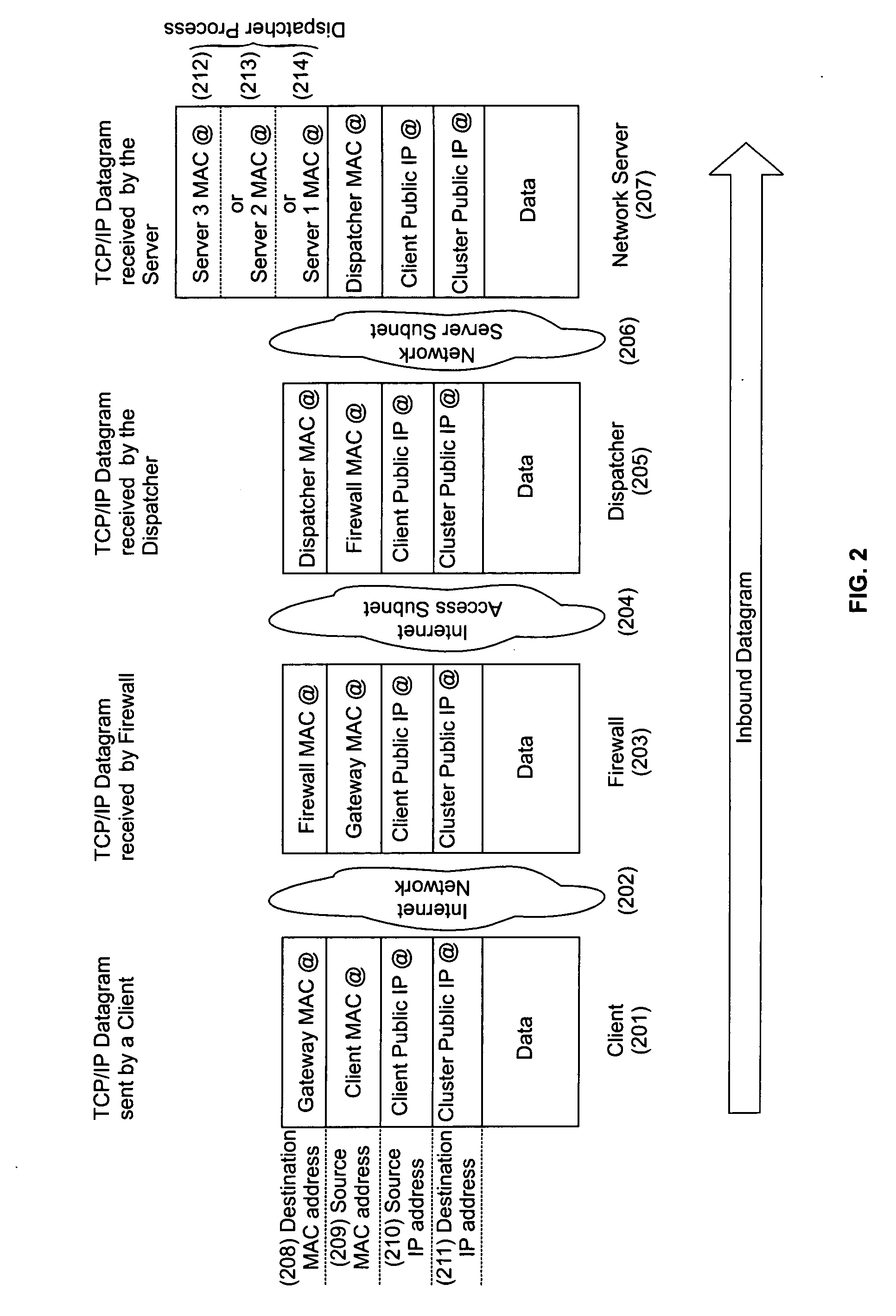
System and method for accessing clusters of servers from the internet network
InactiveUS20050005006A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsAccess routePrivate network
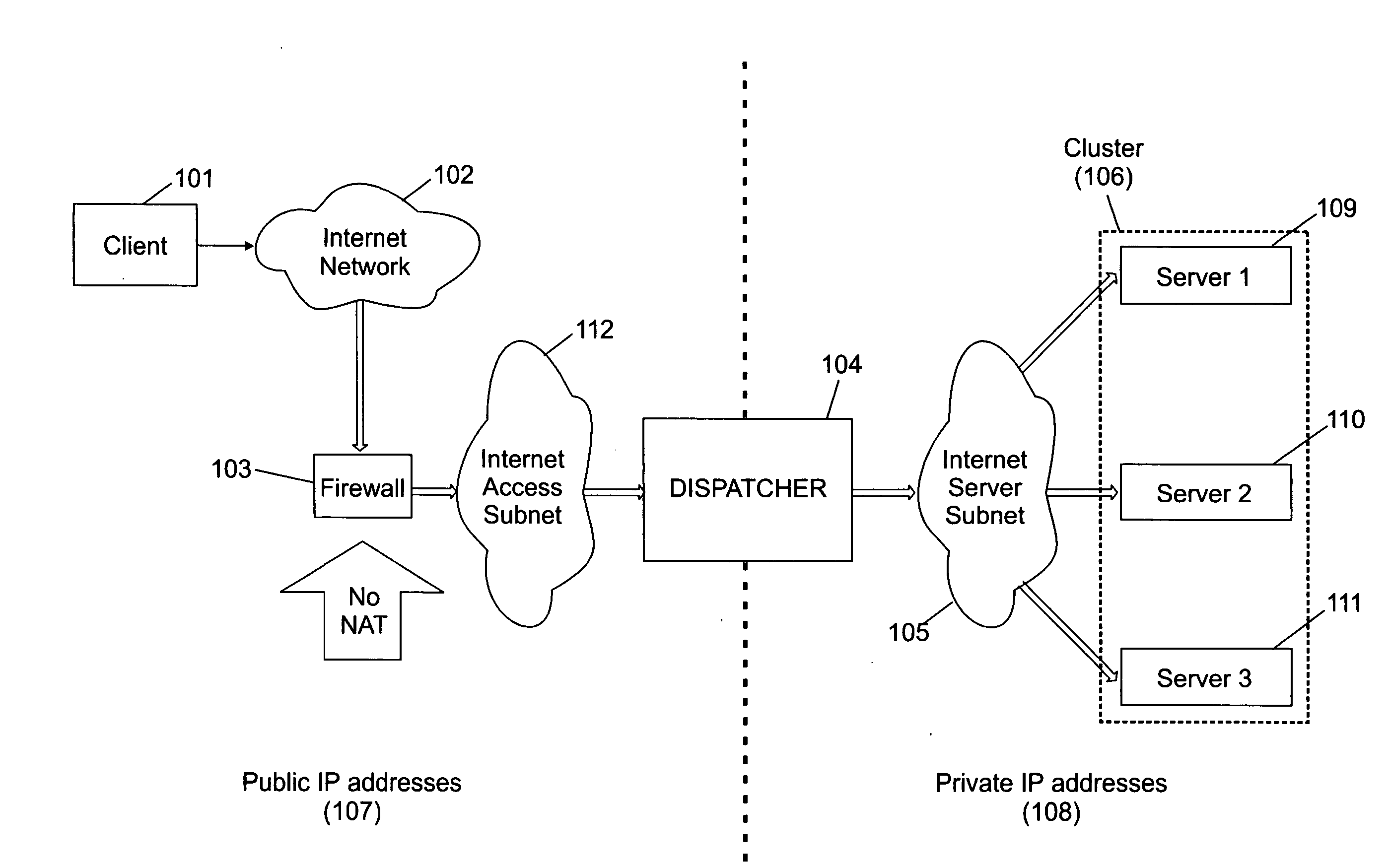
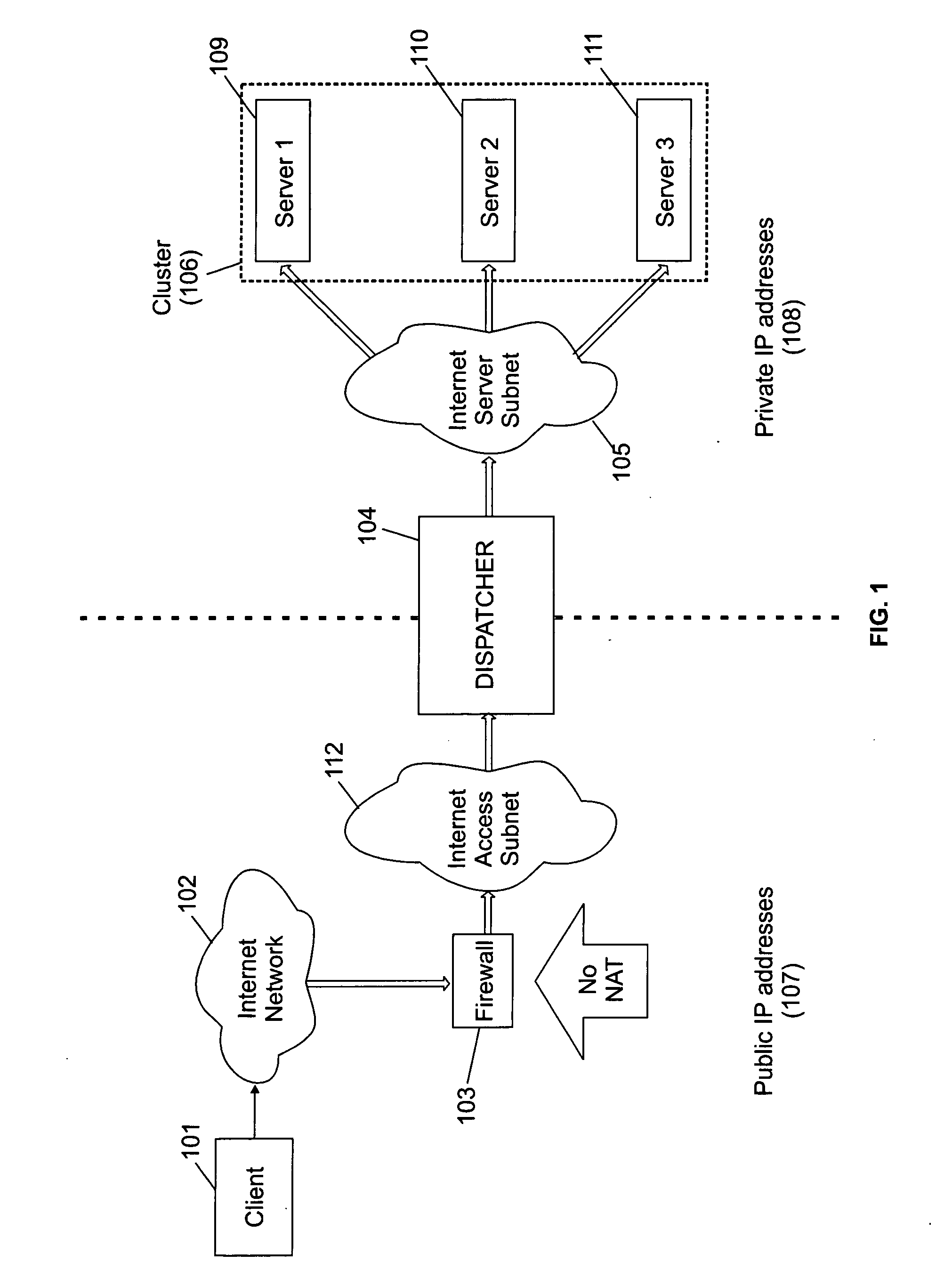
A cluster system and method accesses from an internet network, a network server within one or a plurality of clusters, each cluster being identified by a single cluster public Internet Protocol (IP) address. The cluster system has a plurality of network servers organized in one of a plurality of clusters and a network load balancer system for selecting a destination network server in a cluster. Each cluster has one or a plurality of identical network servers, the network load balancer system being connected on one hand to an access routing device and on another hand to the plurality of network servers through a private network server subnet. The method includes the steps of at initialization time, on each network server defining, as a non-advertising alias, in an interface table, the public IP address of each cluster to which the network server belongs, and upon reception, by the network load balancing system, of a datagram having an IP header including a destination IP address field and a medium access control (MAC) header including a destination MAC address field, selecting a destination network server within the cluster corresponding to the cluster public IP address identified in the destination IP address field of the datagram IP header, replacing the destination medium access control (MAC) address field of the datagram MAC header by the MAC address of the selected destination network server, and sending the datagram through the private network server subnet, using the MAC address of the selected destination network server. Upon reception, by the destination network server, of the datagram sent by the network load balancing system, the MAC address in the destination MAC address field of the datagram MAC header is identified as being the MAC address of the selected destination network server, and the IP datagram is processed if the identified cluster public IP address in the destination IP address field of the datagram IP header, is defined as a non-advertising alias in the interface table of the destination network server.
Owner:IBM CORP
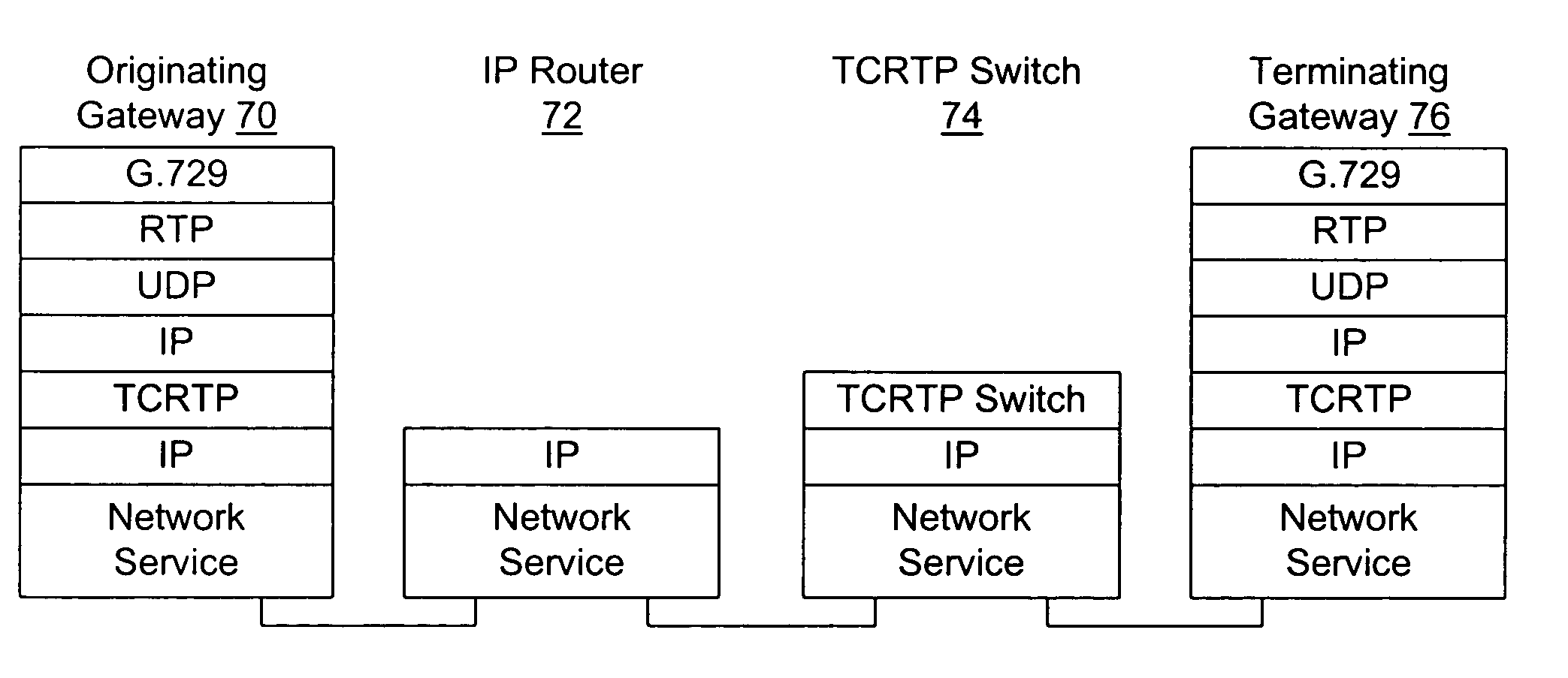
Tunneled datagram switching
InactiveUS7136377B1Improve scalabilityCall control can be simplifiedTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationState dependentReal-time data
A method for transporting real-time data such as voice over a packet-based infrastructure, and a switch for use with that method, are disclosed. In this method, datagrams from multiple data streams are packaged in a single tunnel packet for transport across a network to an intermediate switching point (switch). To reduce bandwidth, each datagram in the tunnel packet (e.g., tunneled datagram) can be sent in a compressed-header format identified by a context identifier (CID) for its data stream. The switch saves context state for each tunnel and CID it is receiving packets for. The switch deaggregates received tunnel packets into tunneled datagrams and associates each datagram with its context state. Based on the destination indicated in its context state, each datagram it re-aggregated in an outgoing tunnel packet bound for a next switch or the destination endpoint itself.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Point-to-multipoint passive optical network that utilizes variable-length packets
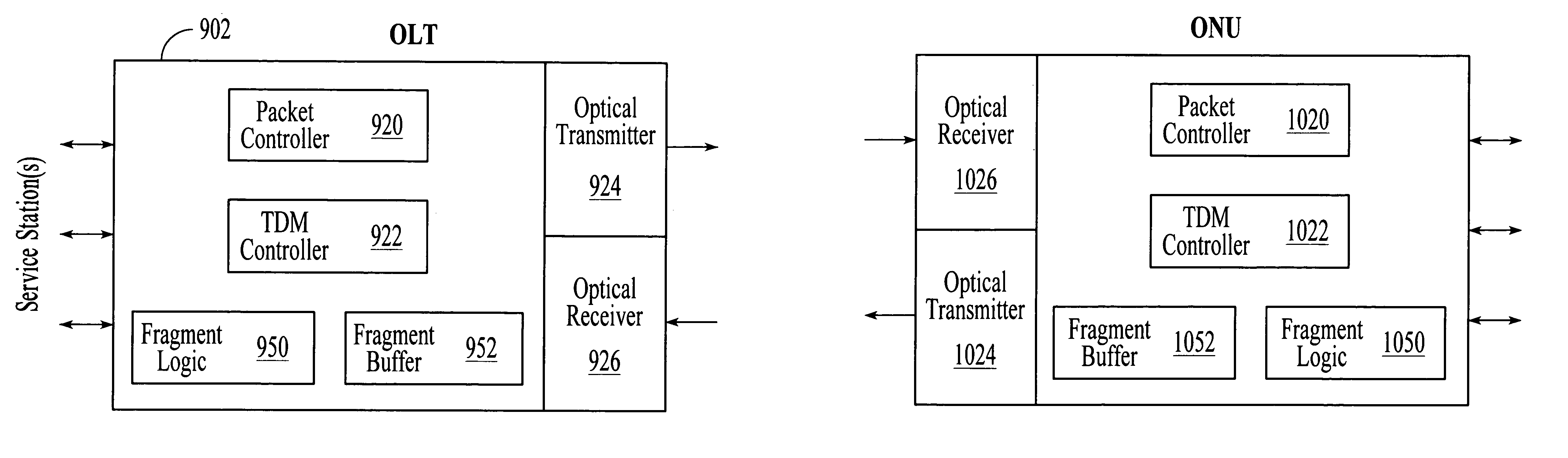
InactiveUS7031343B1Reduce transmission overheadRemoves distance limitationMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexVariable lengthTime-division multiplexing
A point-to-multipoint passive optical network transmits downstream data from an optical line terminal (OLT) to multiple optical network units (ONUs) in variable-length packets and upstream data from the ONUs to the OLT in variable-length packets utilizing time division multiplexing to avoid transmission collisions. In an embodiment, the variable-length downstream packets and the variable-length upstream packets are formatted according to IEEE 802.3. In an embodiment, the length of the variable-length downstream and upstream packets is related to the length of Internet protocol (IP) datagrams carried within the packets.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
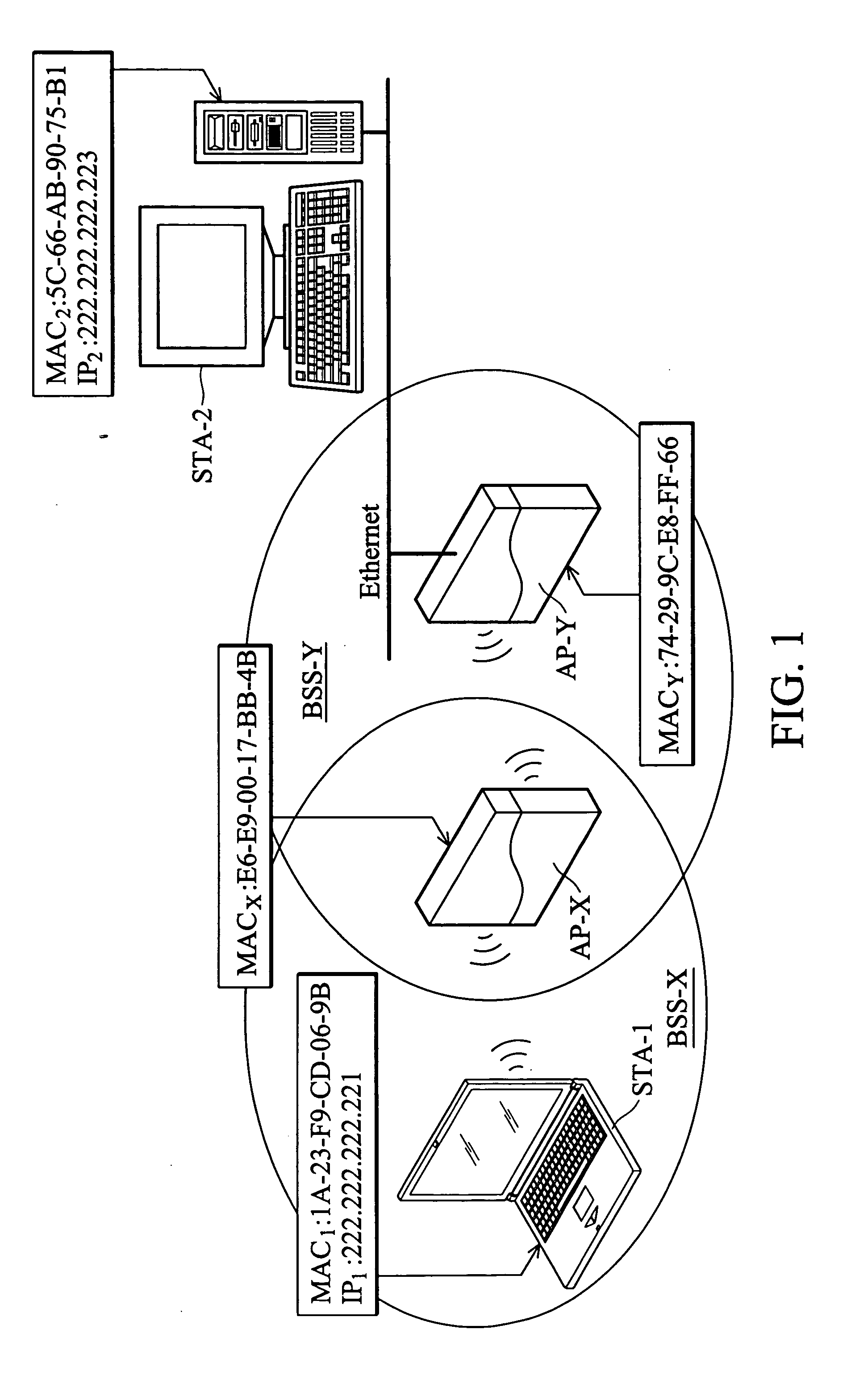
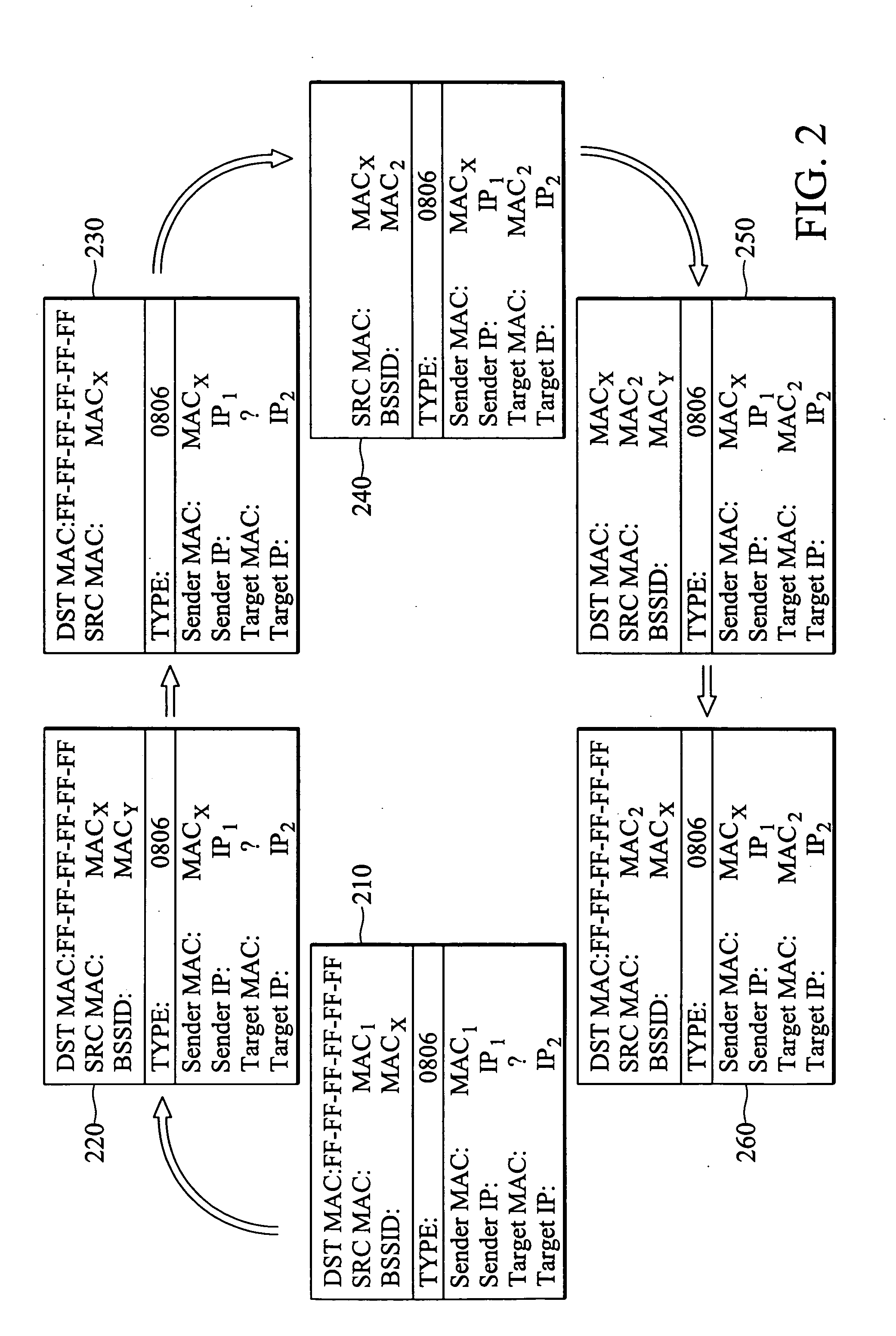
Method and apparatus for wireless relay within a network environment
An apparatus and method for relaying messages via a wireless medium within a network environment having an access point that provides access to a destination station. The apparatus of the invention includes a means for modifying an ARP query packet by substituting a built-in MAC address for a sender address in an ARP datagram of the ARP query packet and a source address in a MAC header of the ARP query packet and further changing a BSSID in the MAC header of the ARP query packet from the built-in MAC address to a MAC address of the access point. Moreover, the apparatus of the invention includes another means for modifying an ARP reply packet issued from the destination station by changing a BSSID in a MAC header of the ARP reply packet from the MAC address of the access point to the built-in MAC address.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com