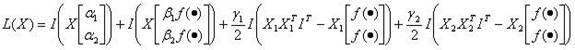Patents
Literature
315 results about "Network Load Balancing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
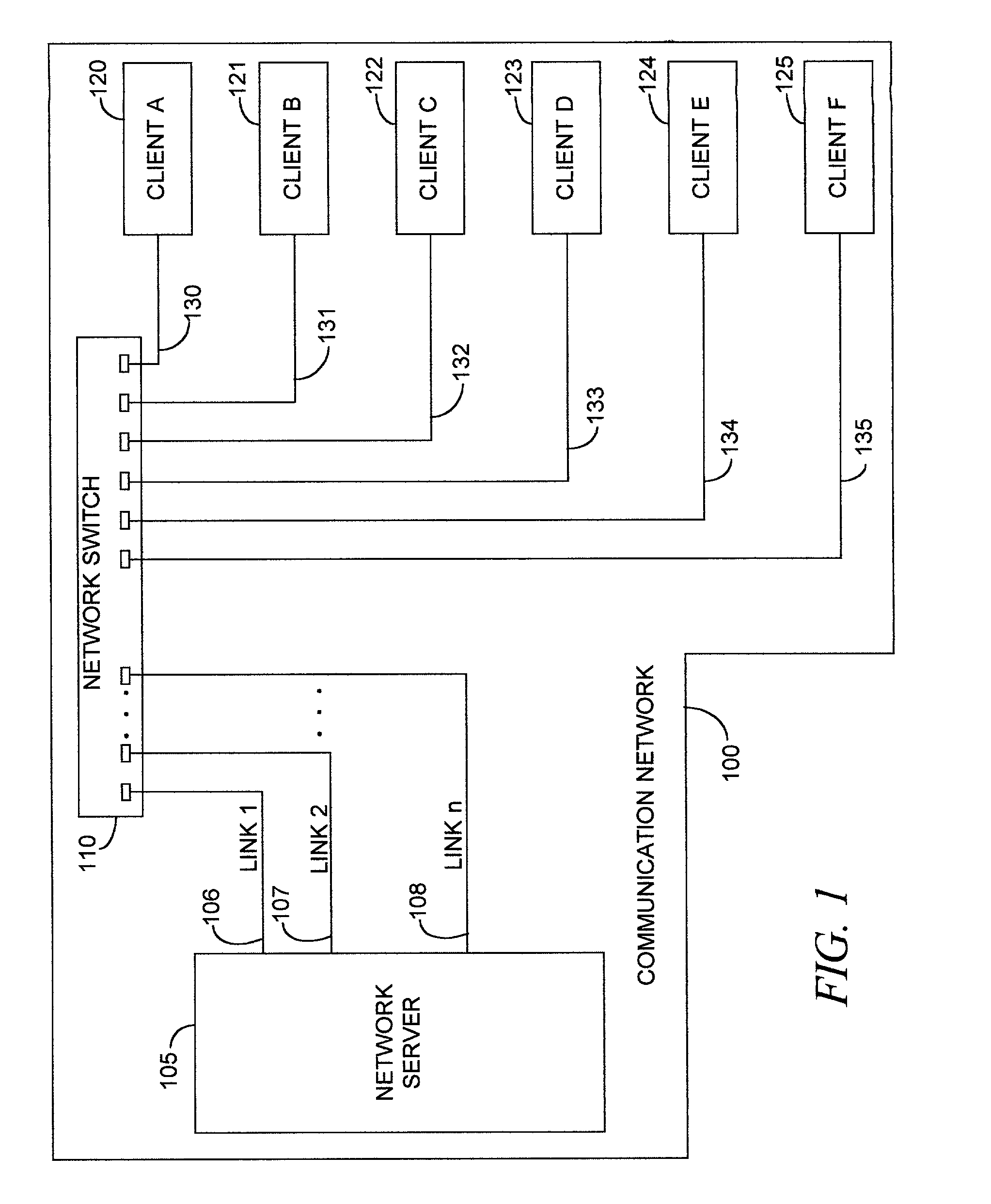
Network load balancing (commonly referred to as dual-WAN routing or multihoming) is the ability to balance traffic across two or more WAN links without using complex routing protocols like BGP. This capability balances is network sessions like Web, email, etc. over multiple connections in order to spread out the amount of bandwidth used by each LAN user, thus increasing the total amount of bandwidth available. For example, a user has a single WAN connection to the Internet operating at 1.5Mbit/s. They wish to add a second broadband (cable, DSL, wireless, etc.) connection operating at 2.5Mbit/s. This would provide them with a total of 4Mbit/s of bandwidth when balancing sessions.
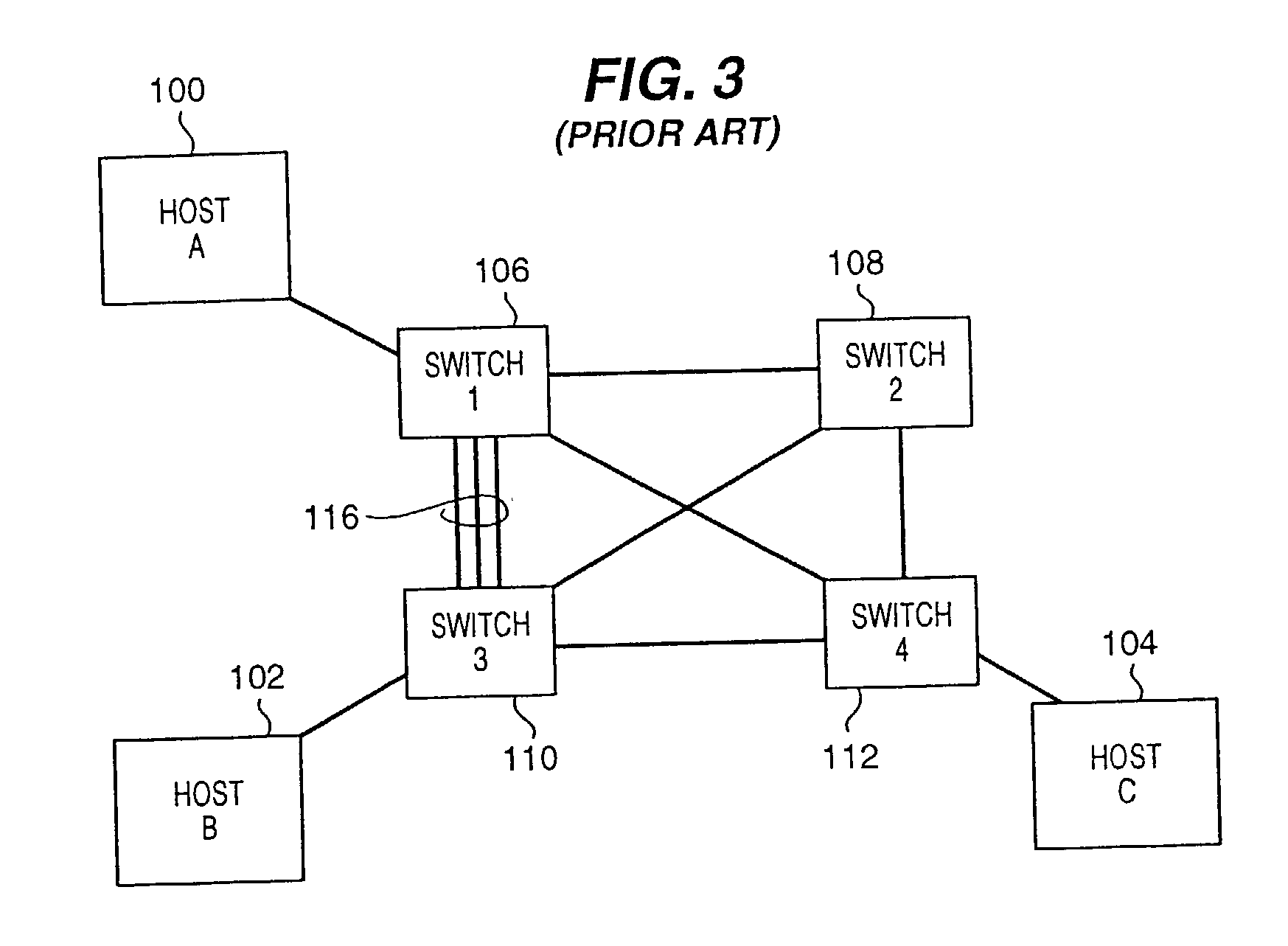
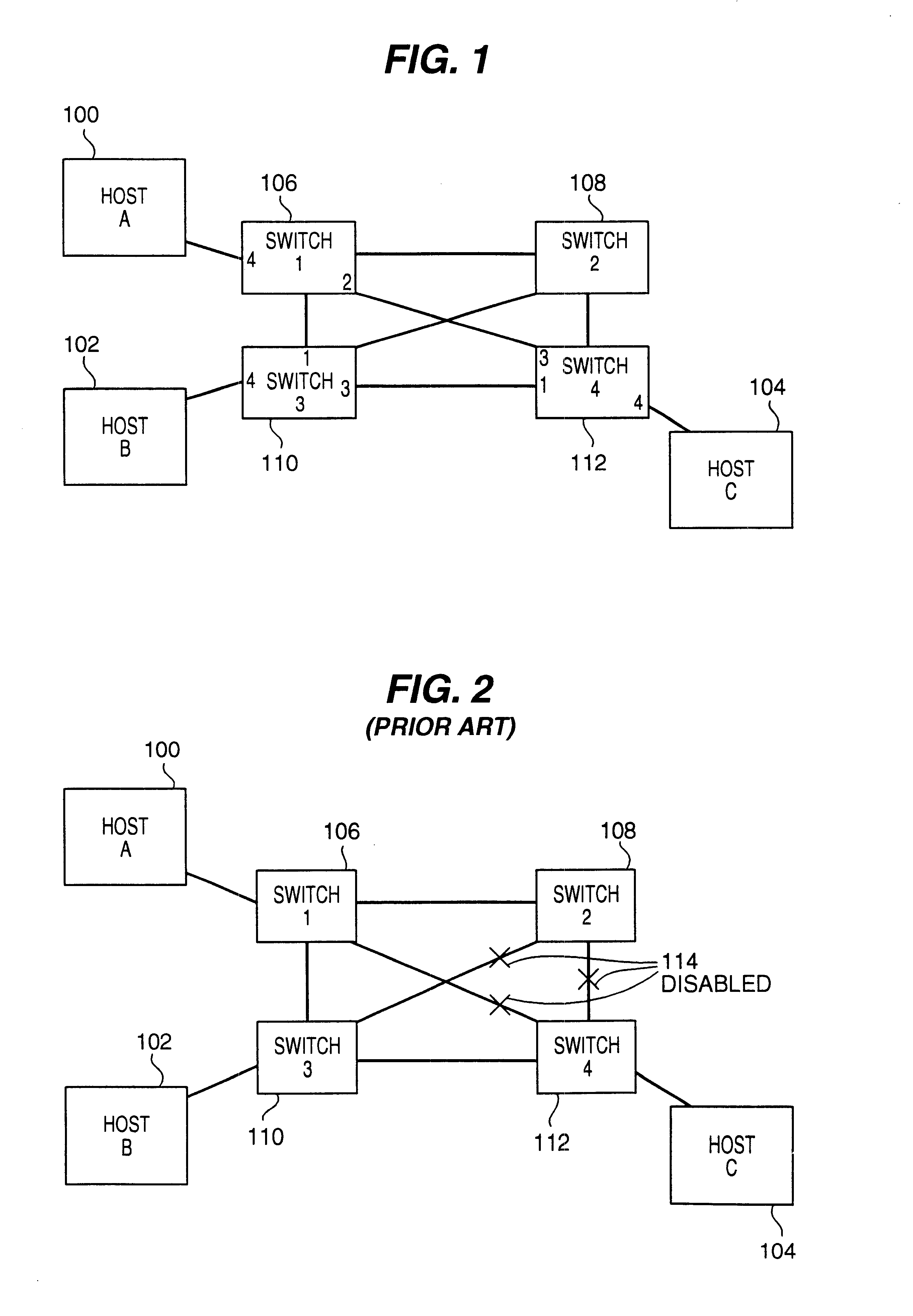
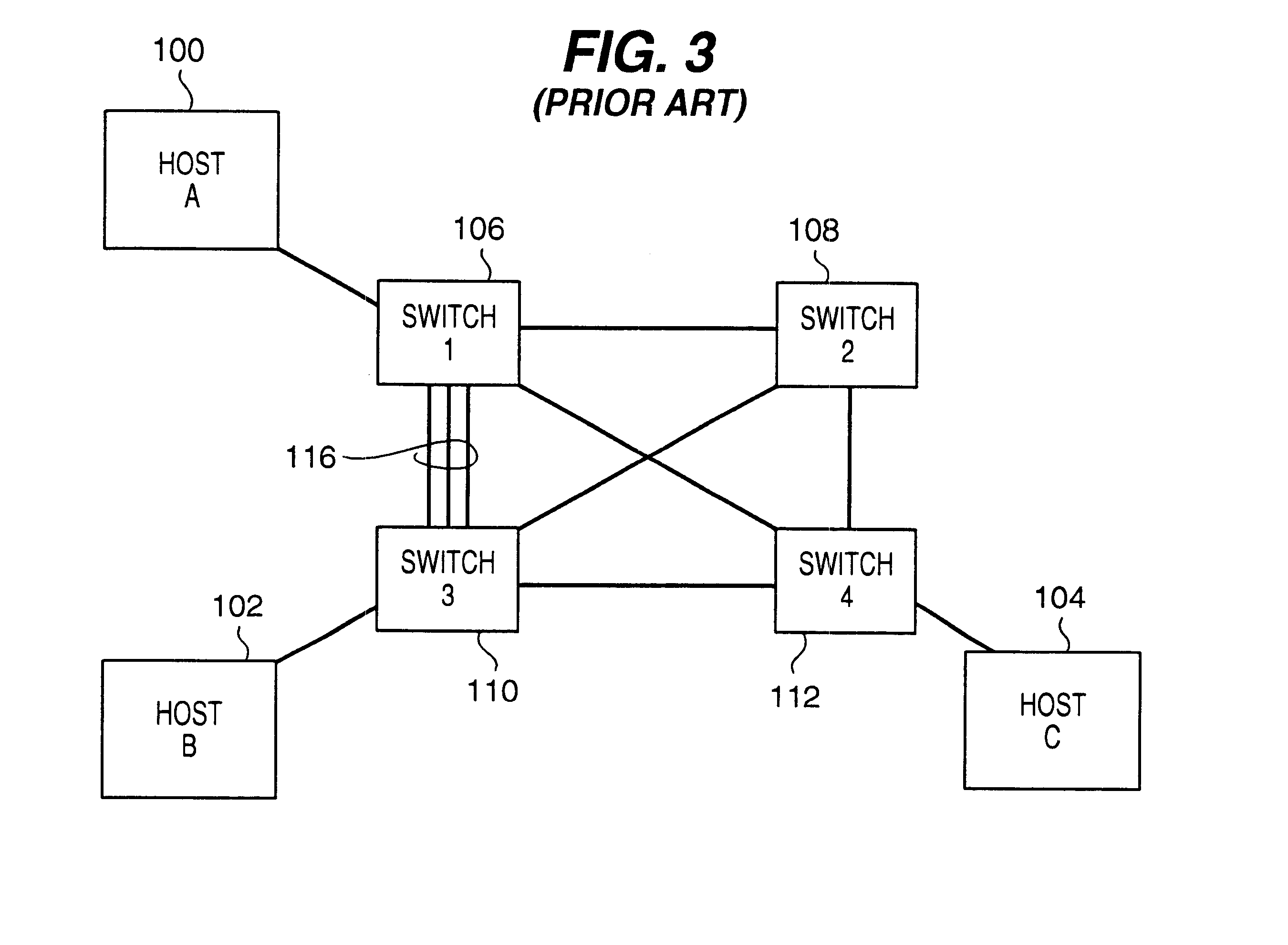
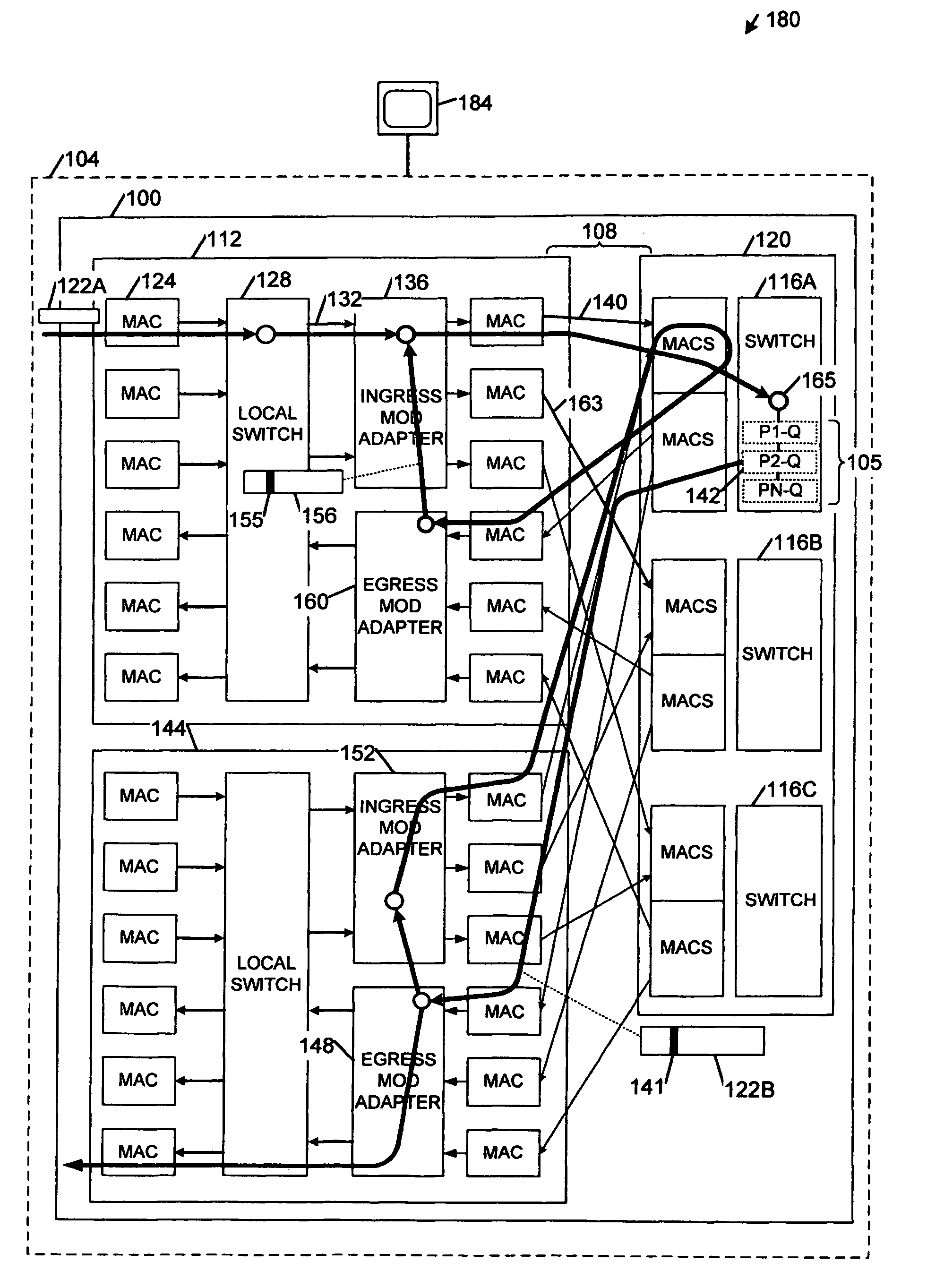
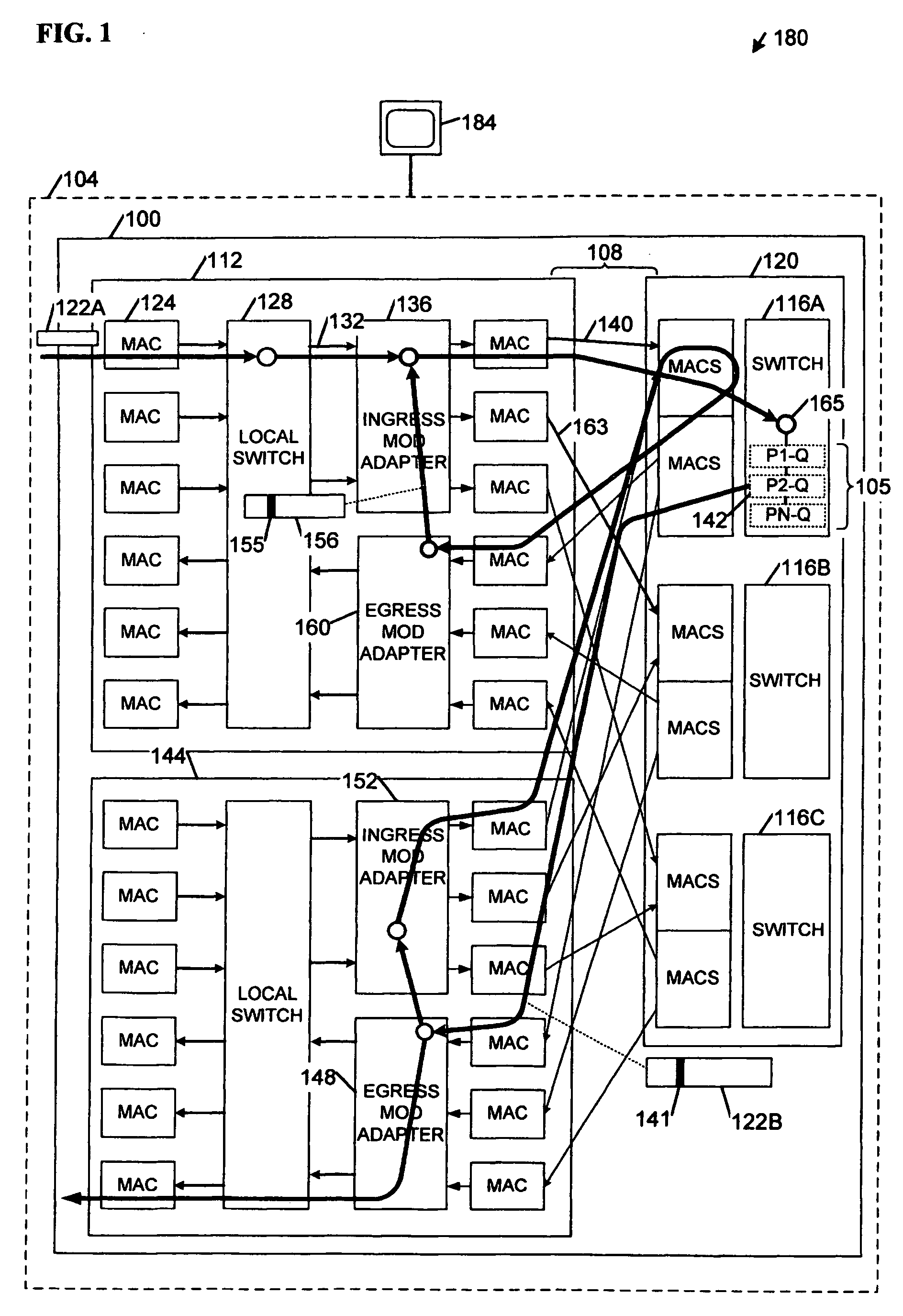
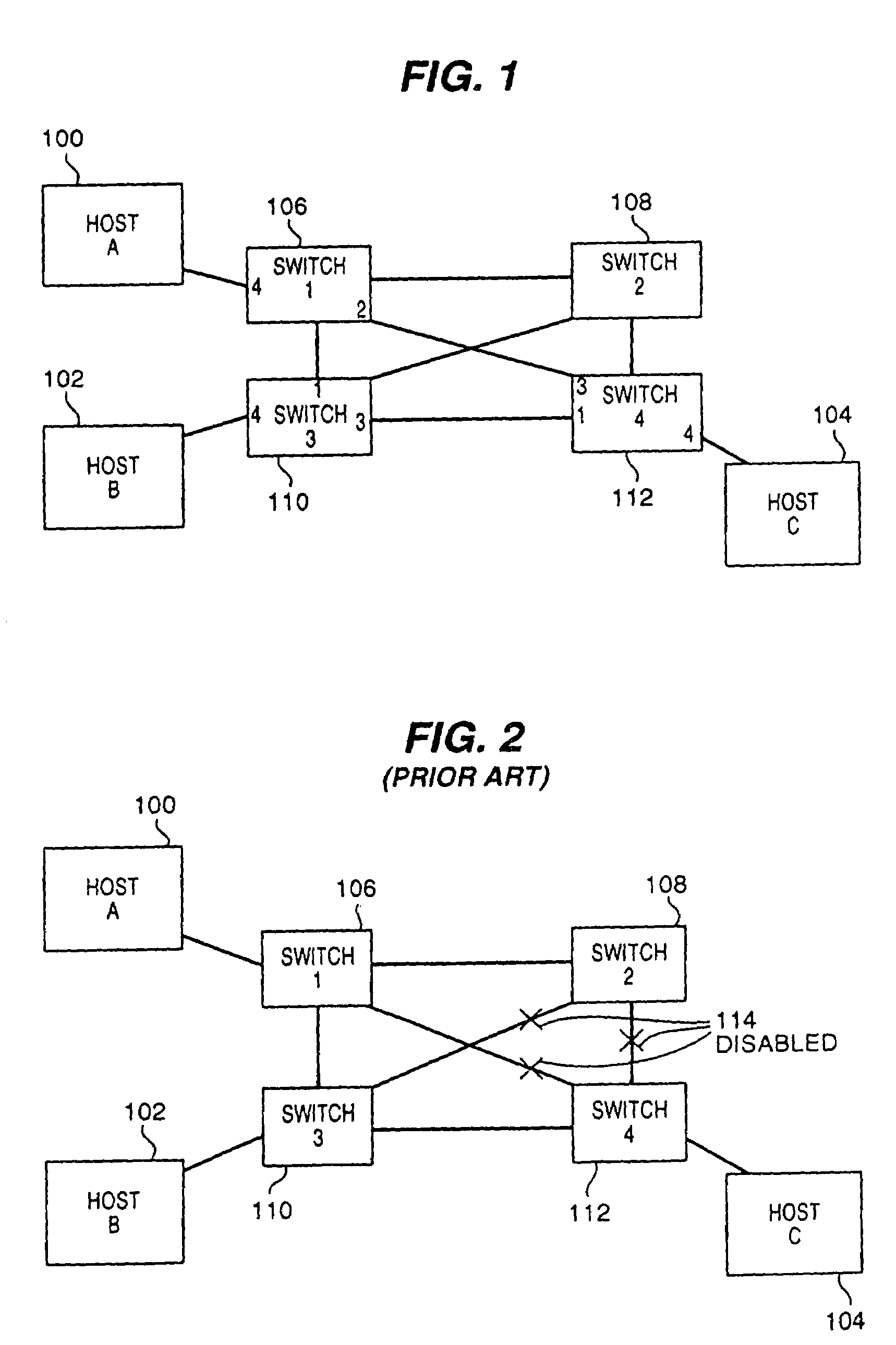
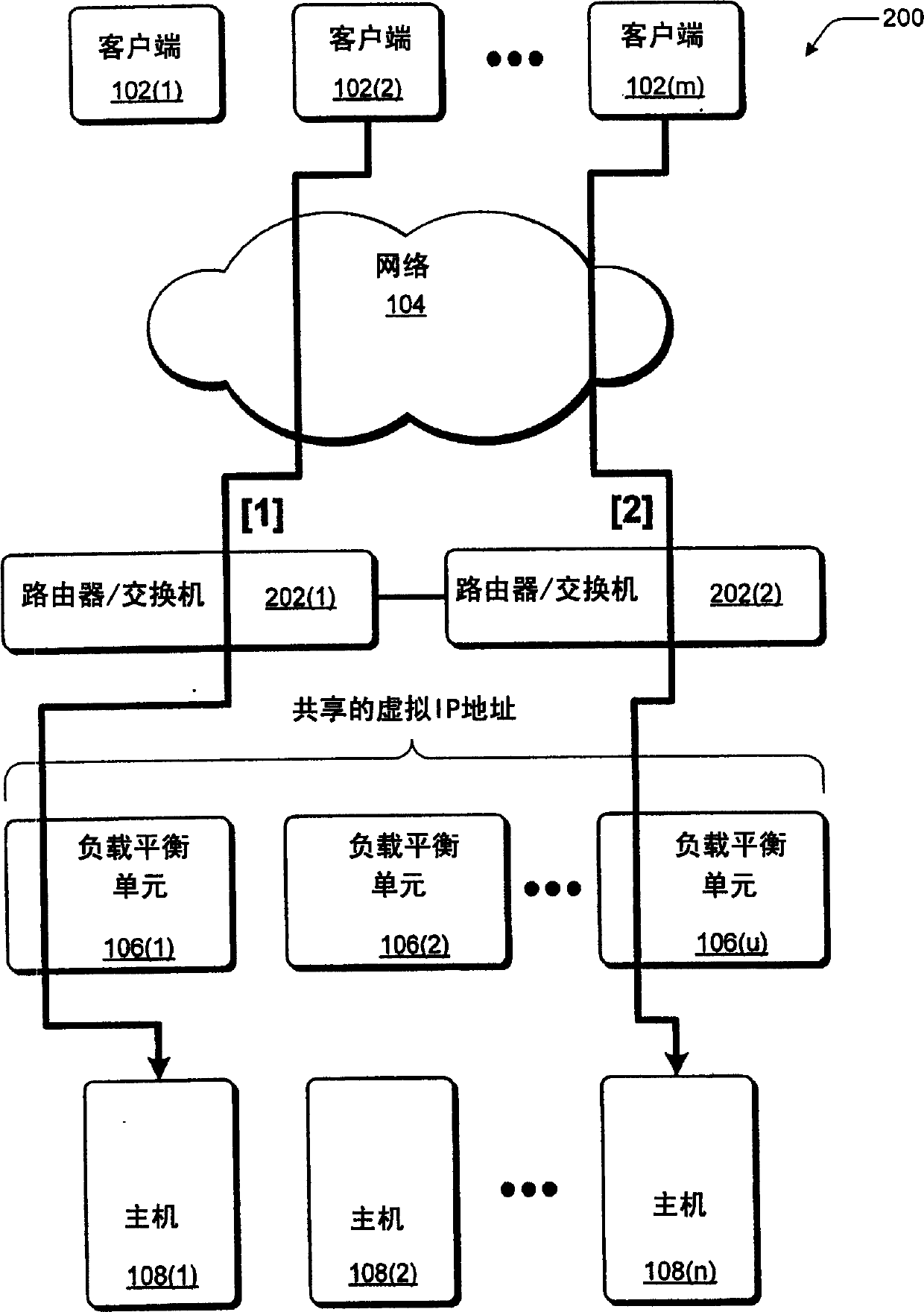
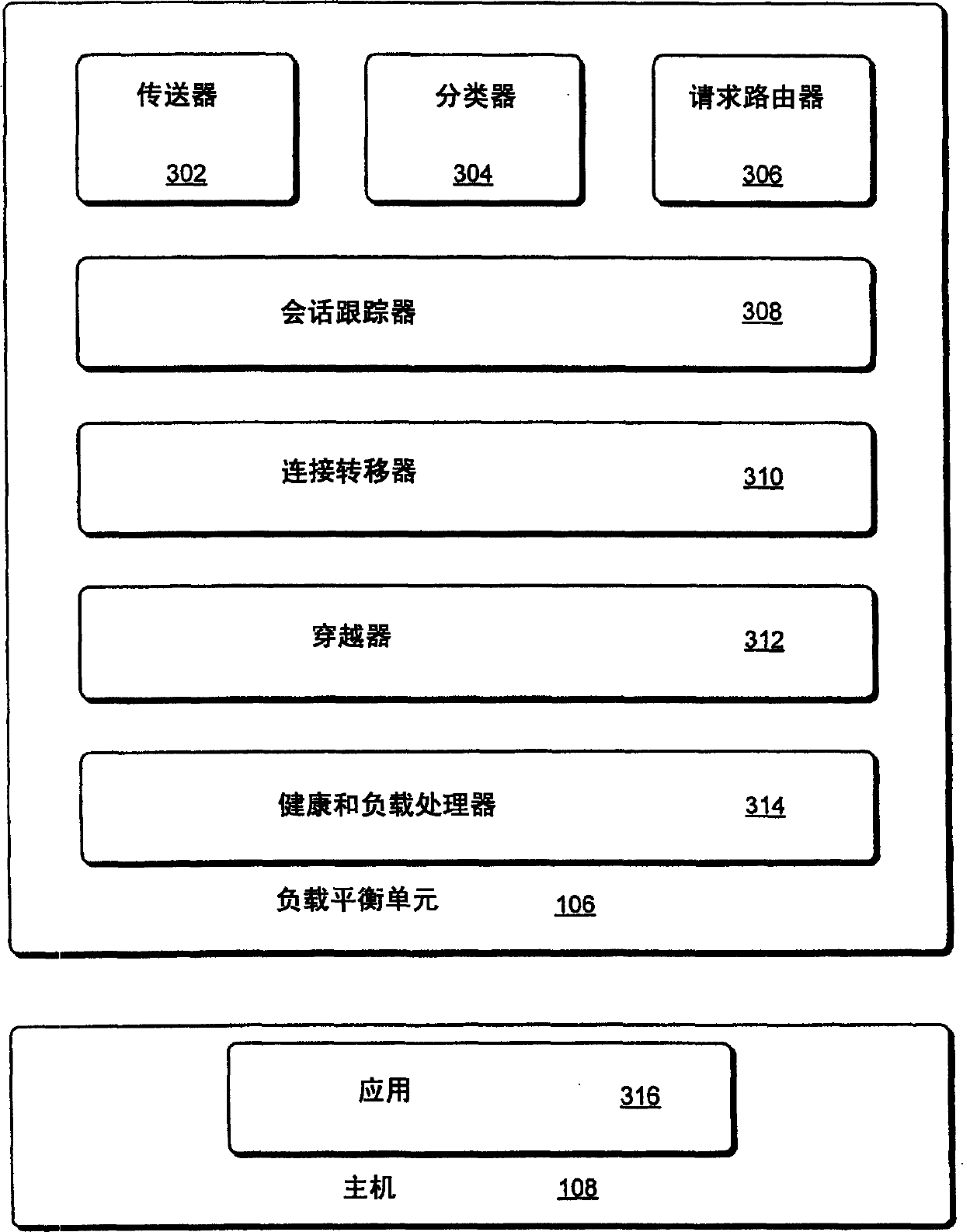
Network load balancing with connection manipulation
ActiveUS20050055435A1Multiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksEncapsulated dataProtocol stack
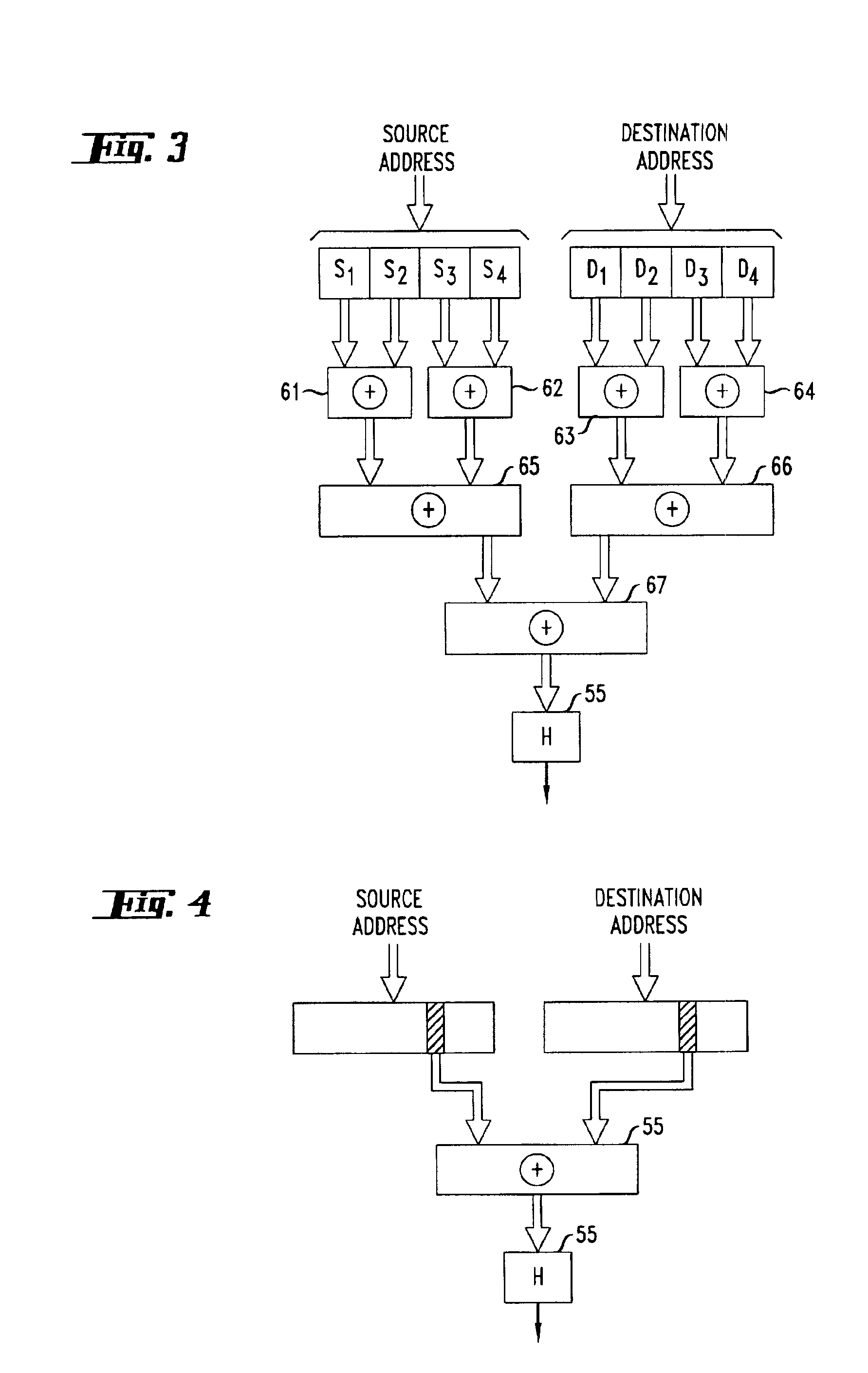
In an exemplary device implementation, a device includes: a connection migrator that is configured to migrate connections away from the device; the connection migrator capable of precipitating a compilation of protocol state for a connection across a protocol stack; the connection migrator adapted to aggregate the compiled protocol state with data for the connection into an aggregated connection state; the connection migrator further capable of causing the aggregated connection state to be sent toward a target device. In an exemplary media implementation, processor-executable instructions direct a device to perform actions including: obtaining at least a portion of a source / destination pair from a packet; accessing an encapsulation mapping table using the at least a portion of the source / destination pair to locate an encapsulation mapping entry; extracting a flow identifier from the encapsulation mapping entry; and replacing part of the packet with the flow identifier to produce an encapsulated packet.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
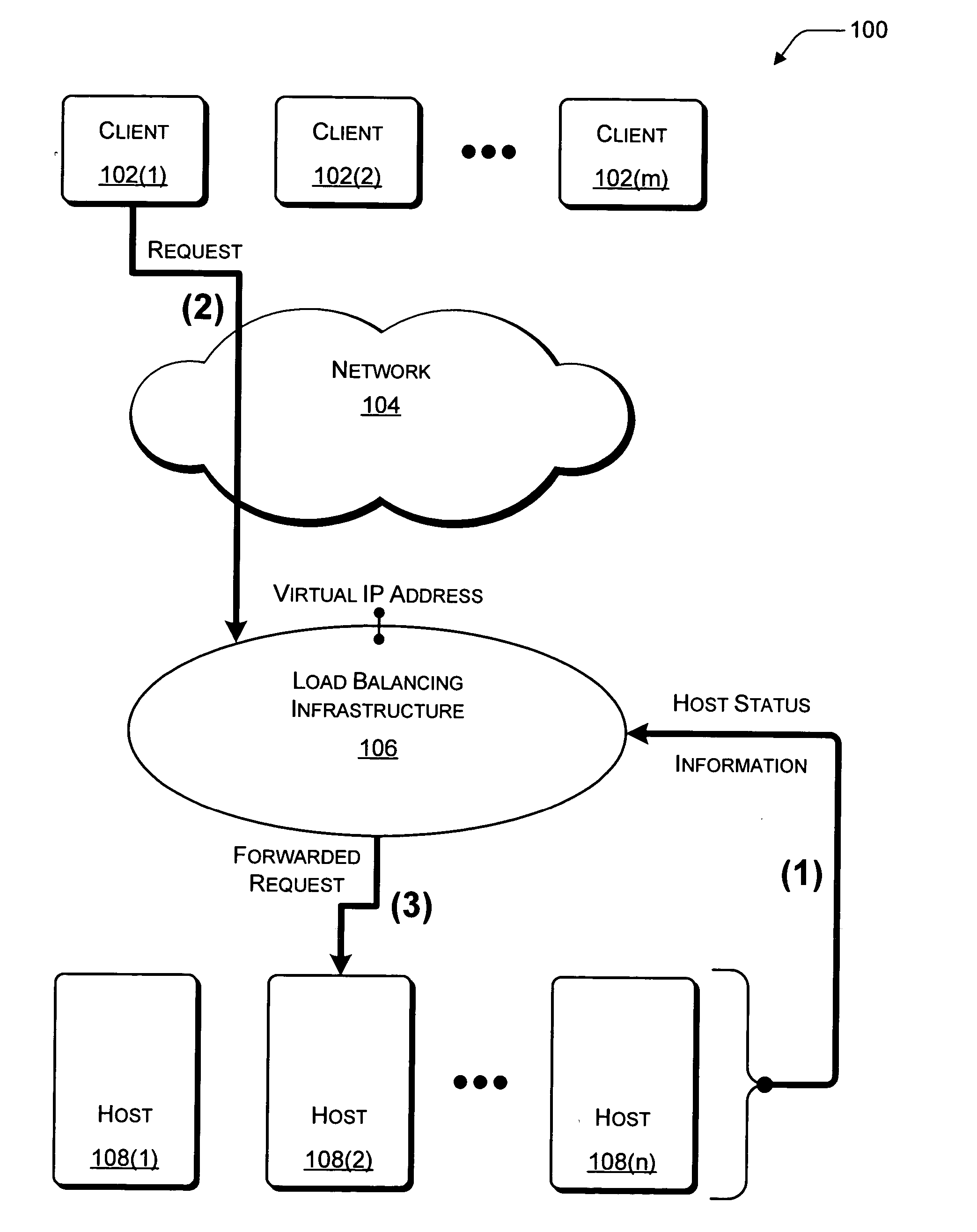
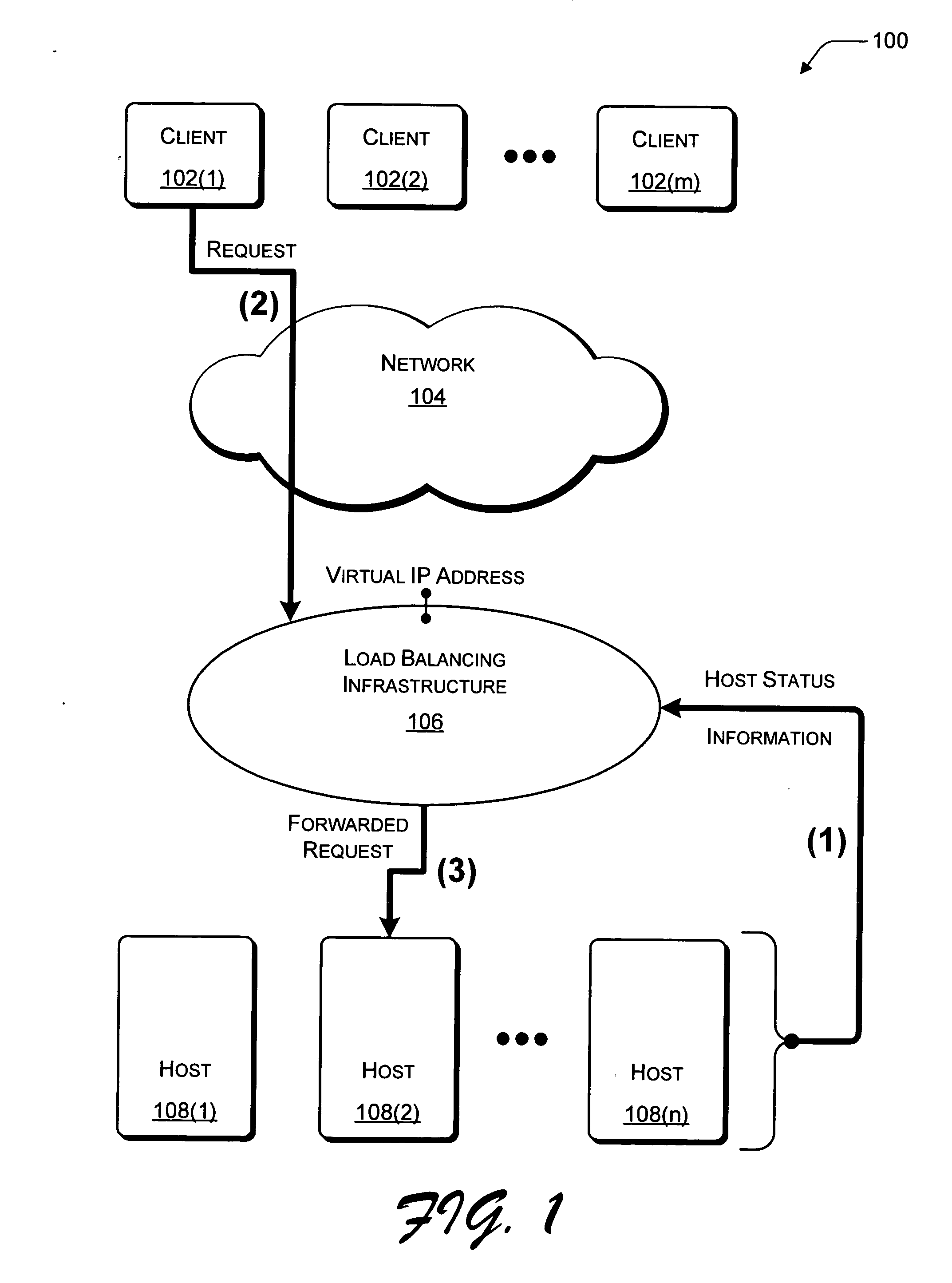
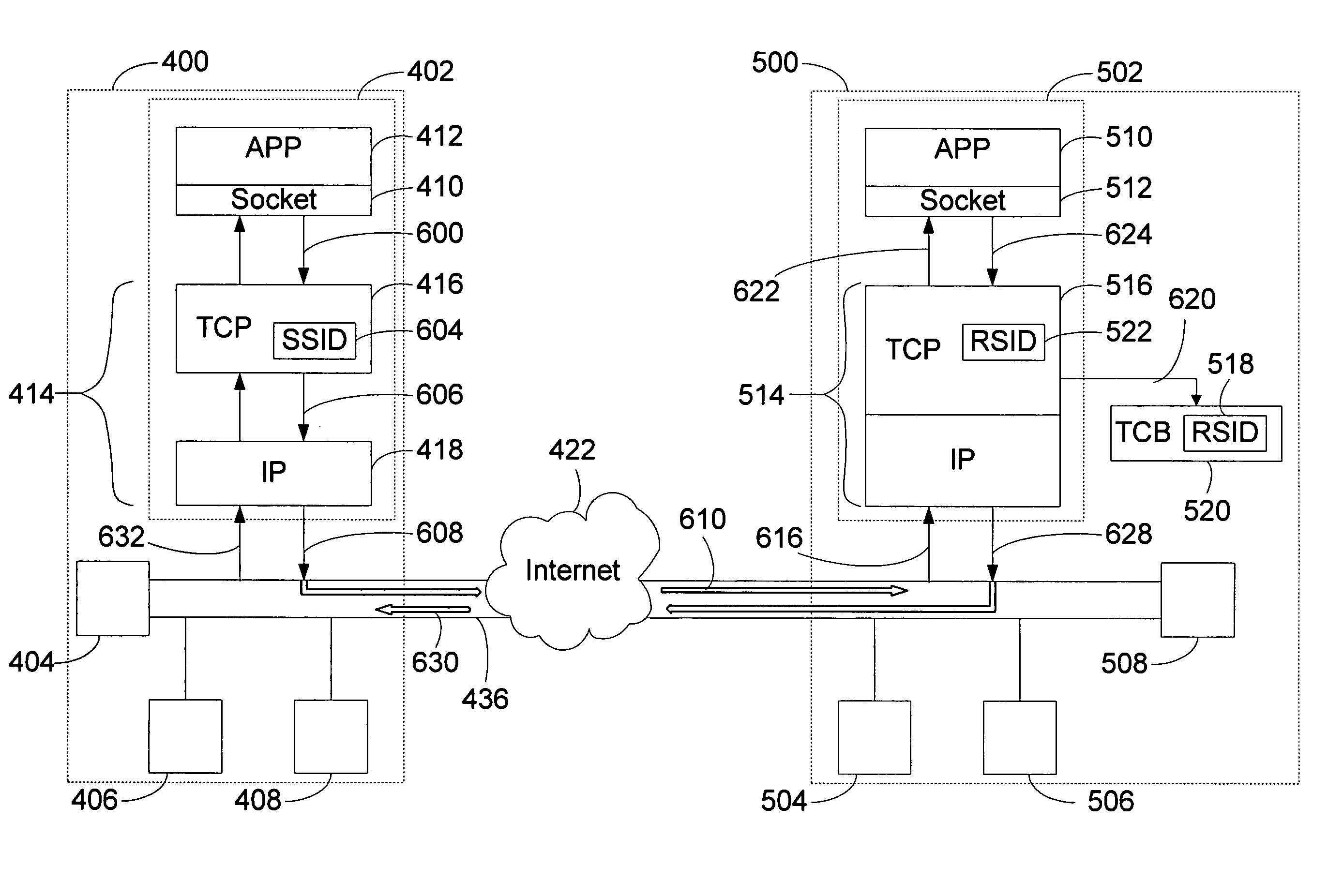
Session load balancing and use of VIP as source address for inter-cluster traffic through the use of a session identifier
InactiveUS7003574B1Improve the level ofCurrent is limitedMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlTraffic capacityIp address
A method and system for enhancing a load balancing network's ability to load balance sessions is presented. A session identifier is placed within the TCP packet to enable a new mechanism of load distribution and connection grouping within a load balancing system. Specifically, TCP is invoked by a user application to obtain a unique session identifier value. On receiving such a packet, the destination load balancing system hashes over at least the session identifier value, and the node corresponding to the results of the hash algorithm acquires the packet. This method of hashing ensures that the same node acquires all subsequently received TCP packets possessing the same session identifier regardless of the source IP address or source port information. The node then places an identical session identifier value in the form of a response session identifier in its TCP response packet. When the TCP packet with response session identifier is received at a load balancing system, the node whose session identifier matches the response session identifier acquires it.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
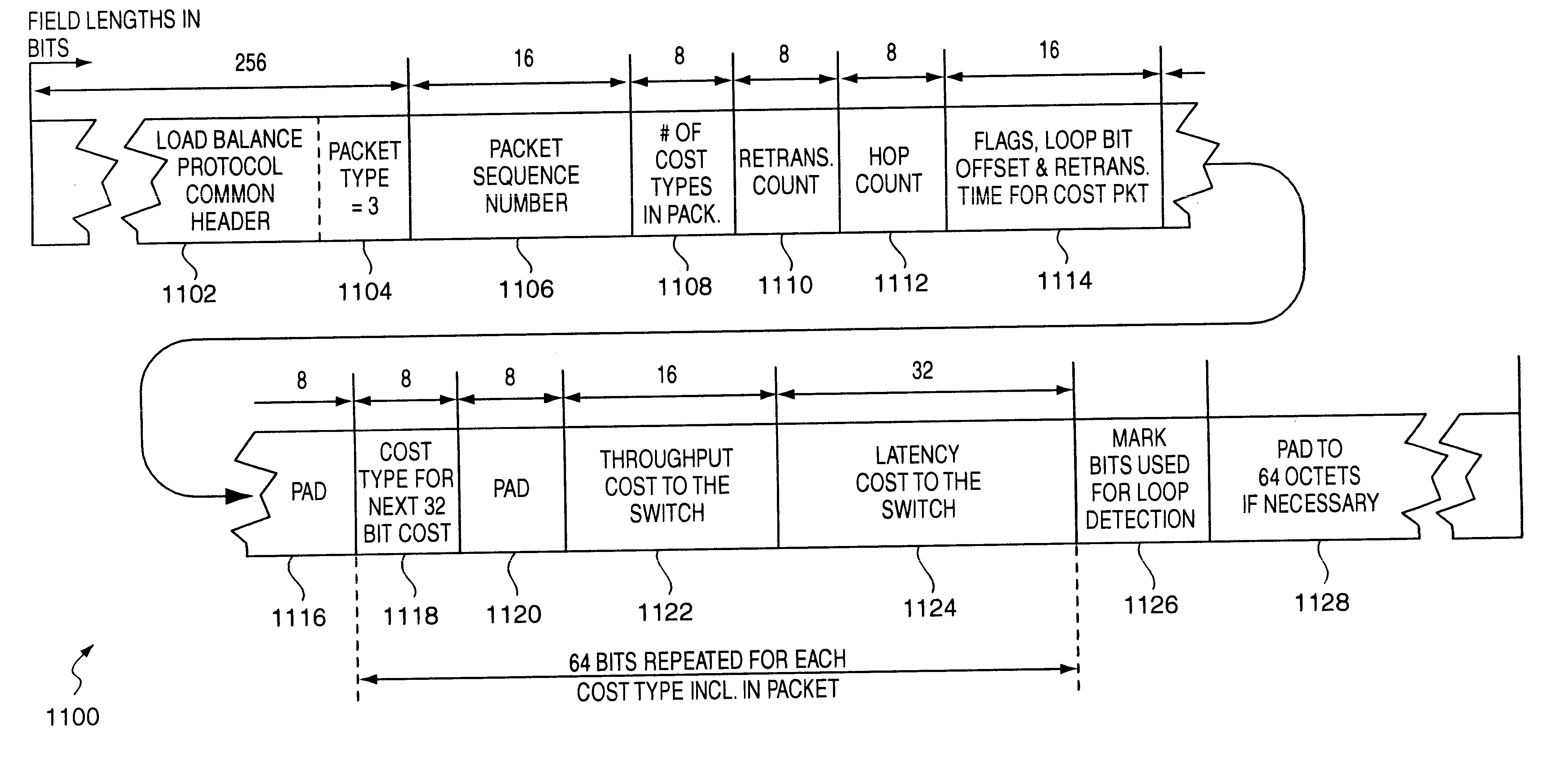
Identity negotiation switch protocols
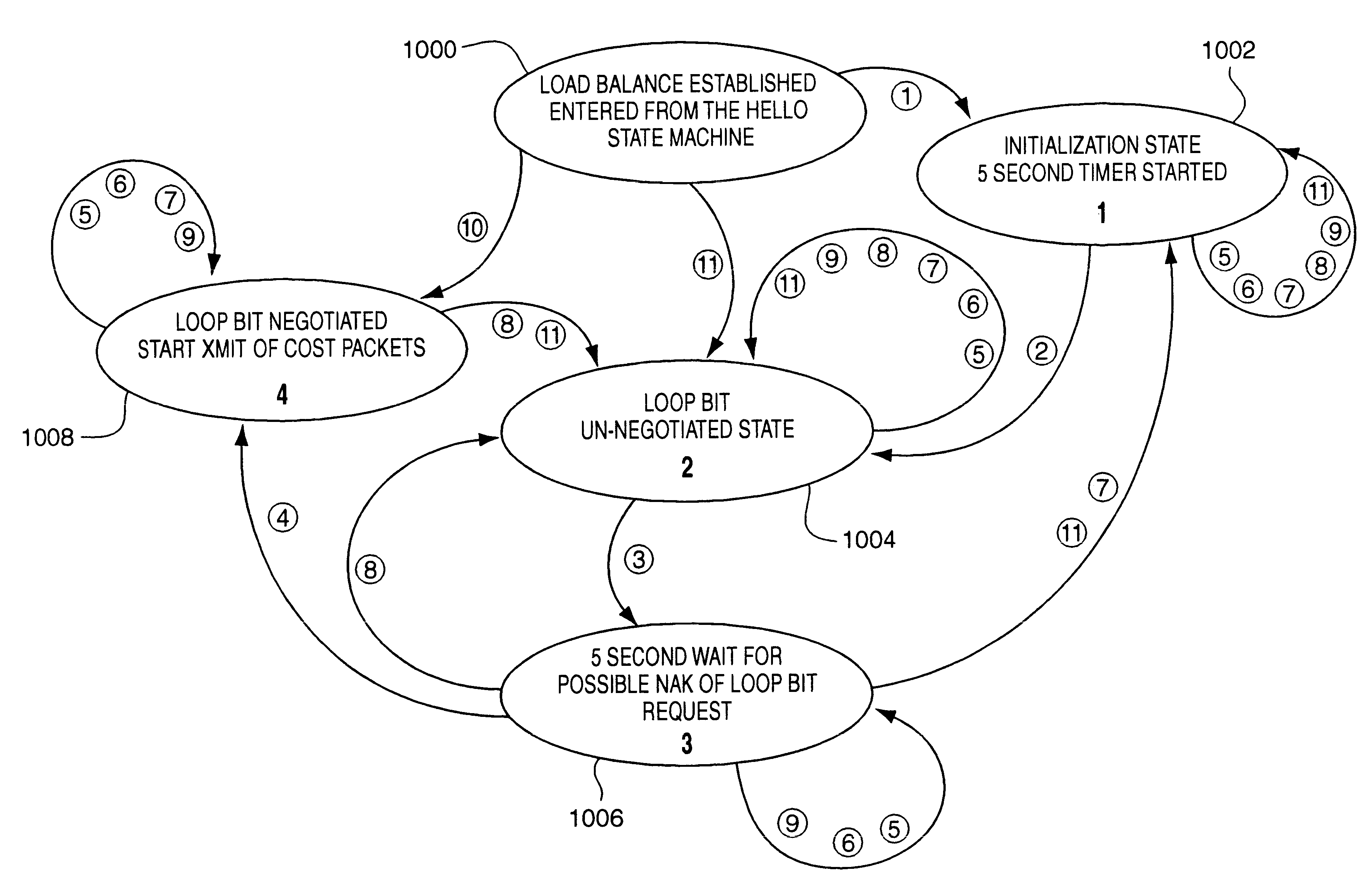
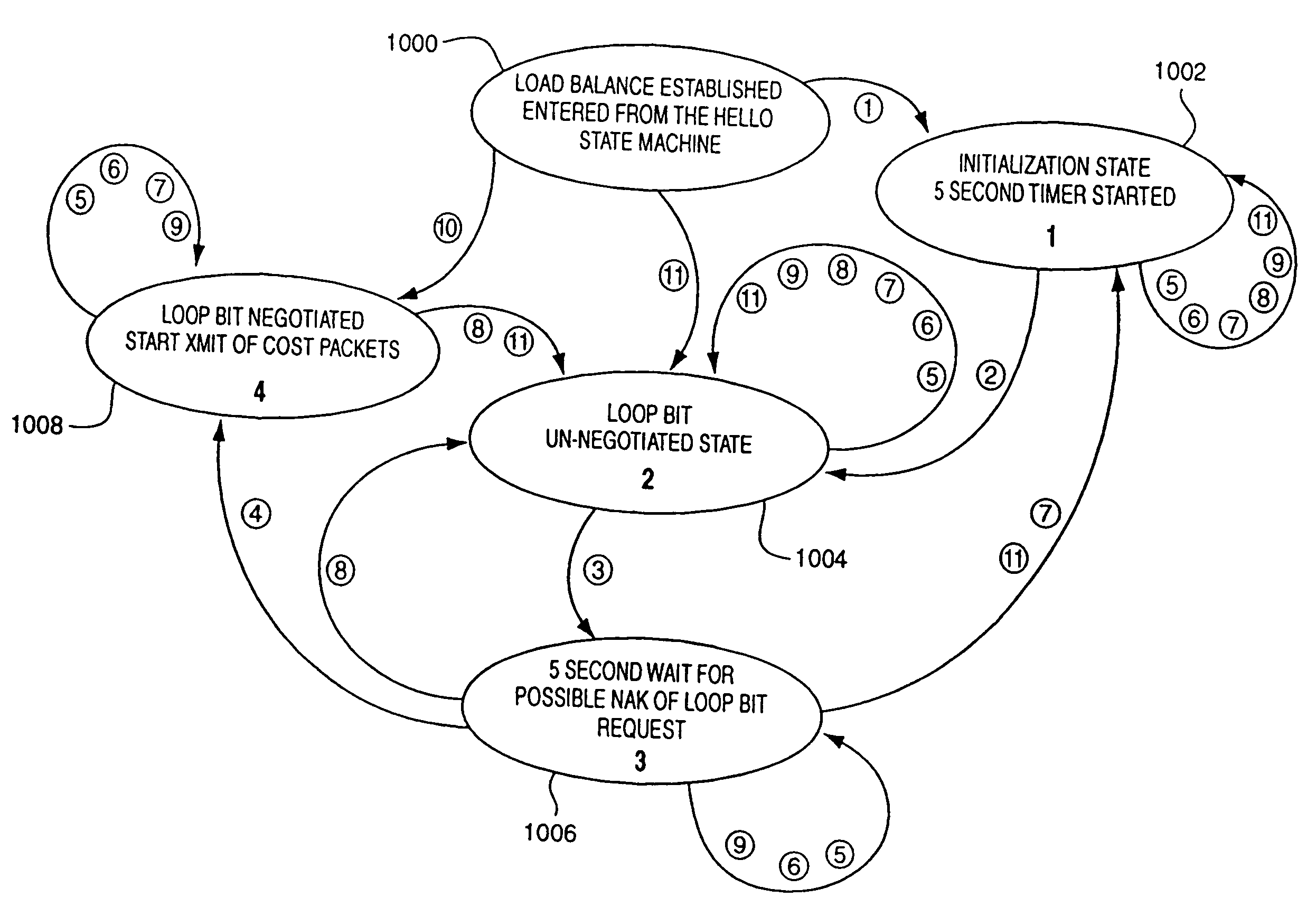
A switch to switch protocol for network load balancing which negotiates among switches operable in accordance with the invention to assign a unique loop bit offset identifier value to each switch. Various other load balancing protocols associated with the switches then utilize the loop bit offset value as an identifier field when determining loops in the network of switches and costs associated with non-looped paths in the switches. A loop bit offset identifier requires less switch processing overhead than techniques which utilize an entire address value (i.e., MAC address value) for such protocols. Further, the loop bit offset identifier assigned by the present invention reduces the size of load balancing related packets. Specifically, cost computation related packets are reduced in size to the minimum 64 byte packet size through use of the loop bit offset identifier value of the present invention.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
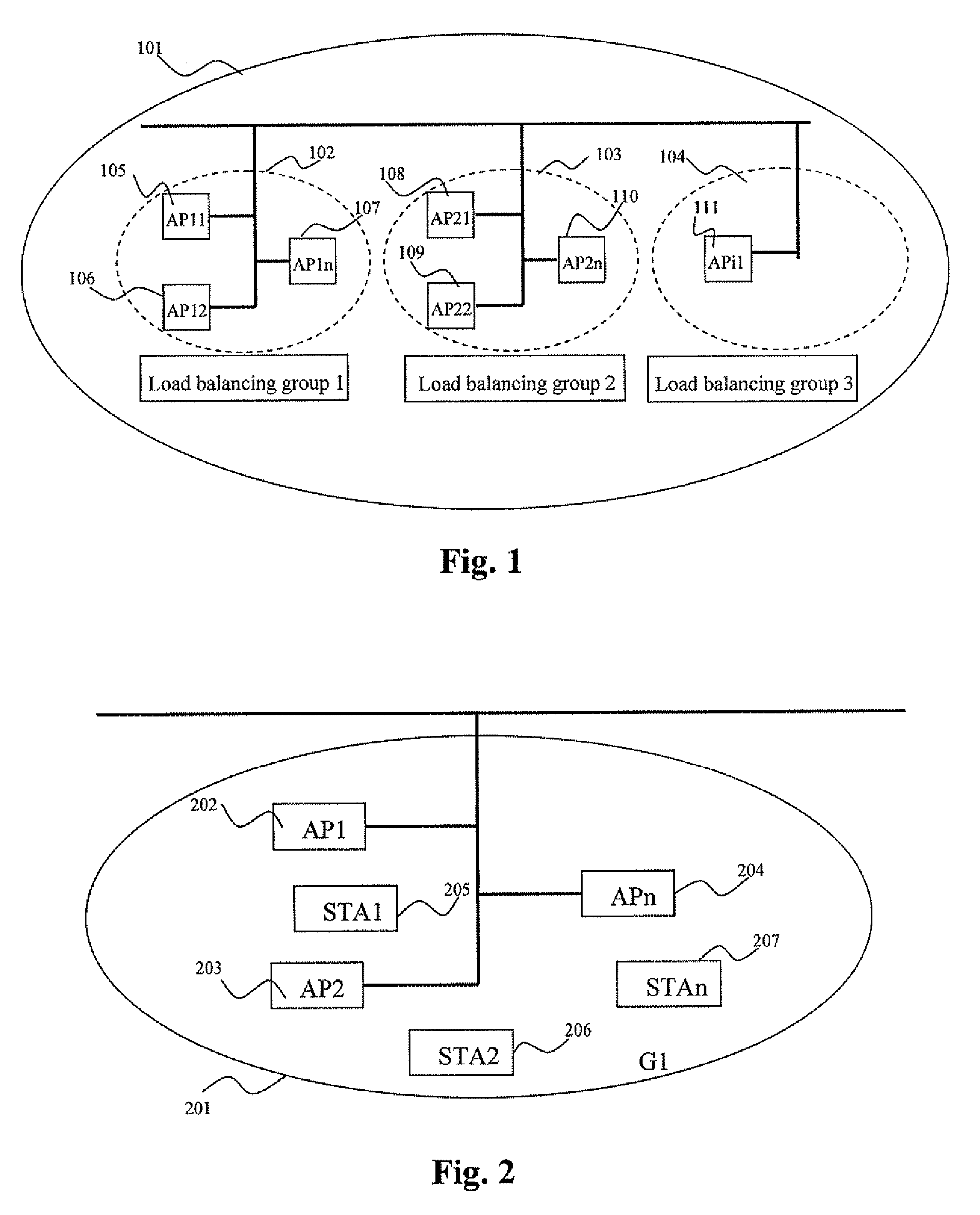
Load balancing method for a wireless area network
InactiveUS7940731B2Improve reliabilityIncrease overheadNetwork traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionWireless mesh networkArea network
The present invention relates to a load balancing method for a wireless local area network, which includes the following steps: initializing the load balancing group, self-organizing to select an online access point from the load balancing group as a load balancing agent center, each access point of the said balancing group managing and processing the load balance in accordance with the load level and balance optimizing policy, therefore implements the network load balance. The method of the invention improves reliability of the network load information, presents the load information from invalidly broadcasting in the wireless local area network, therefore reduces the additional overhead for managing the load balance of the wireless network, particularly in the network that having three layers switching equipment, self-organizing to select the agent center can utilize the network resource in effect, therefore managing the dynamic load balance information much more effectively, reducing the dependence on the upper server, and managing the network much more flexibly.
Owner:ZTE CORP
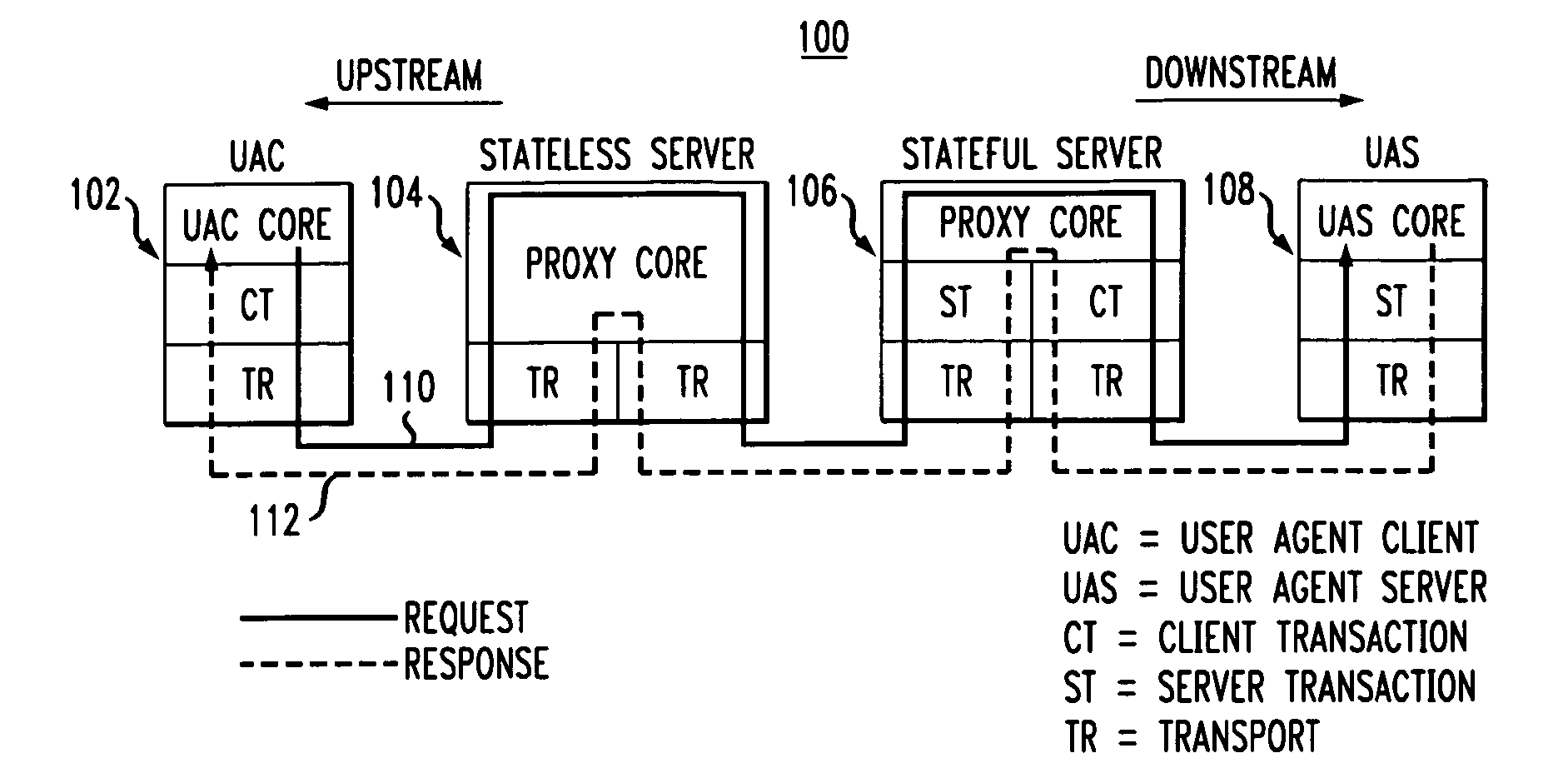
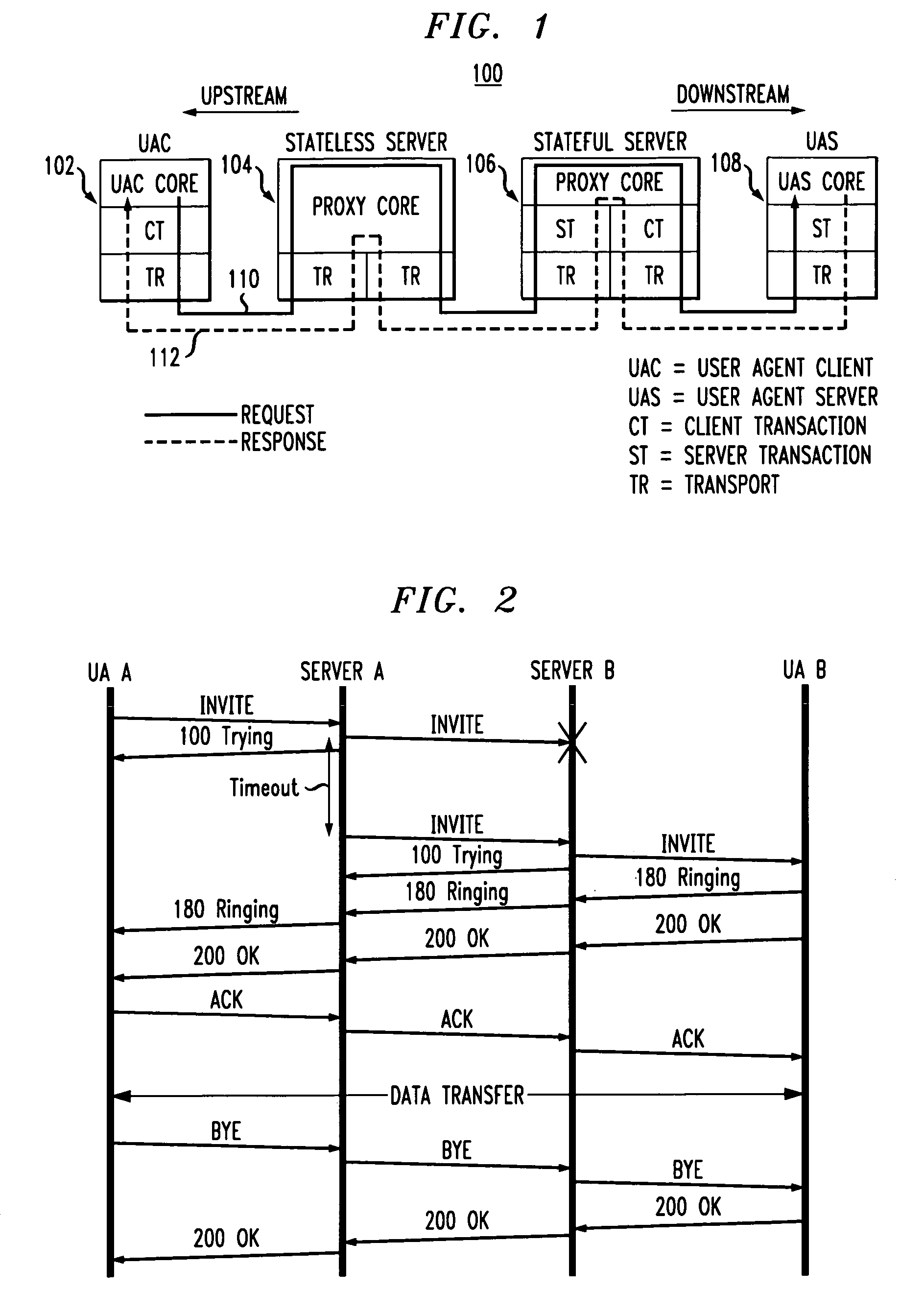
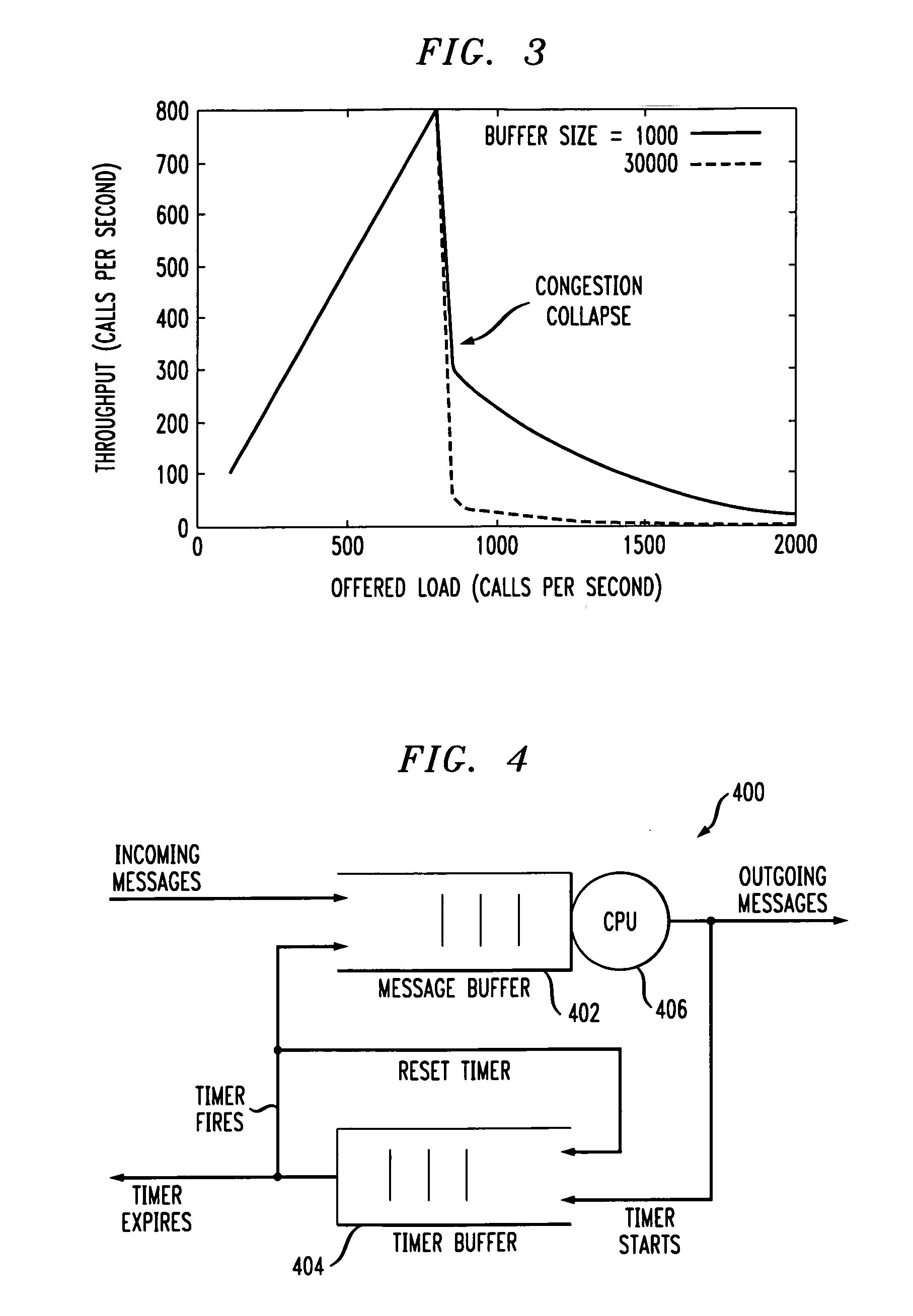
Network load balancing and overload control
ActiveUS20070233896A1Avoid problemsLarge capacityDigital computer detailsTransmissionLoad SheddingOverload control
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Cost propagation switch protocols
A switch to switch protocol for network load balancing which exchanges cost information among all switches in a load balance domain. As compared to prior techniques, the protocol of the present invention updates all switches in the load balance domain periodically. All switches in the load balance domain are thereby assured of having consistent cost information regarding all switches in the load balance domain. Further, the protocol of the present invention reduces the volume of cost messaging traffic as exemplified by techniques which generate updates to the information any time a cost parameter of a switch changed. The preferred embodiment of he protocol of the present invention exchanges messages describing the switch latency for each switch in the load balance domain. A bit mask field in the transmitted cost packets indicates which switches have already received the cost information. Receipt of the same packet a second time by a switch which already received the cost packet is indicative of a loop in the network and the propagation of that packet is terminated.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
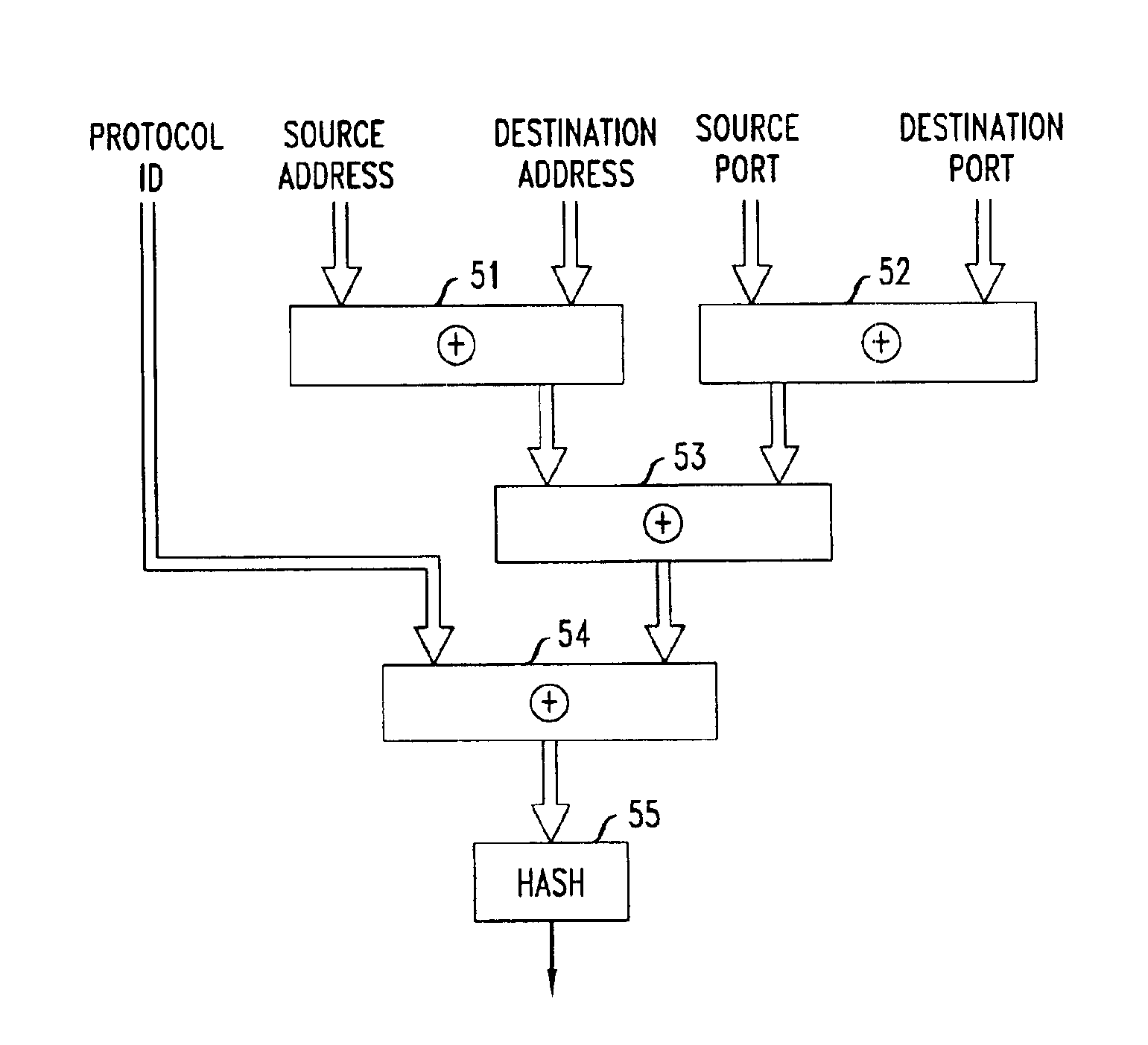
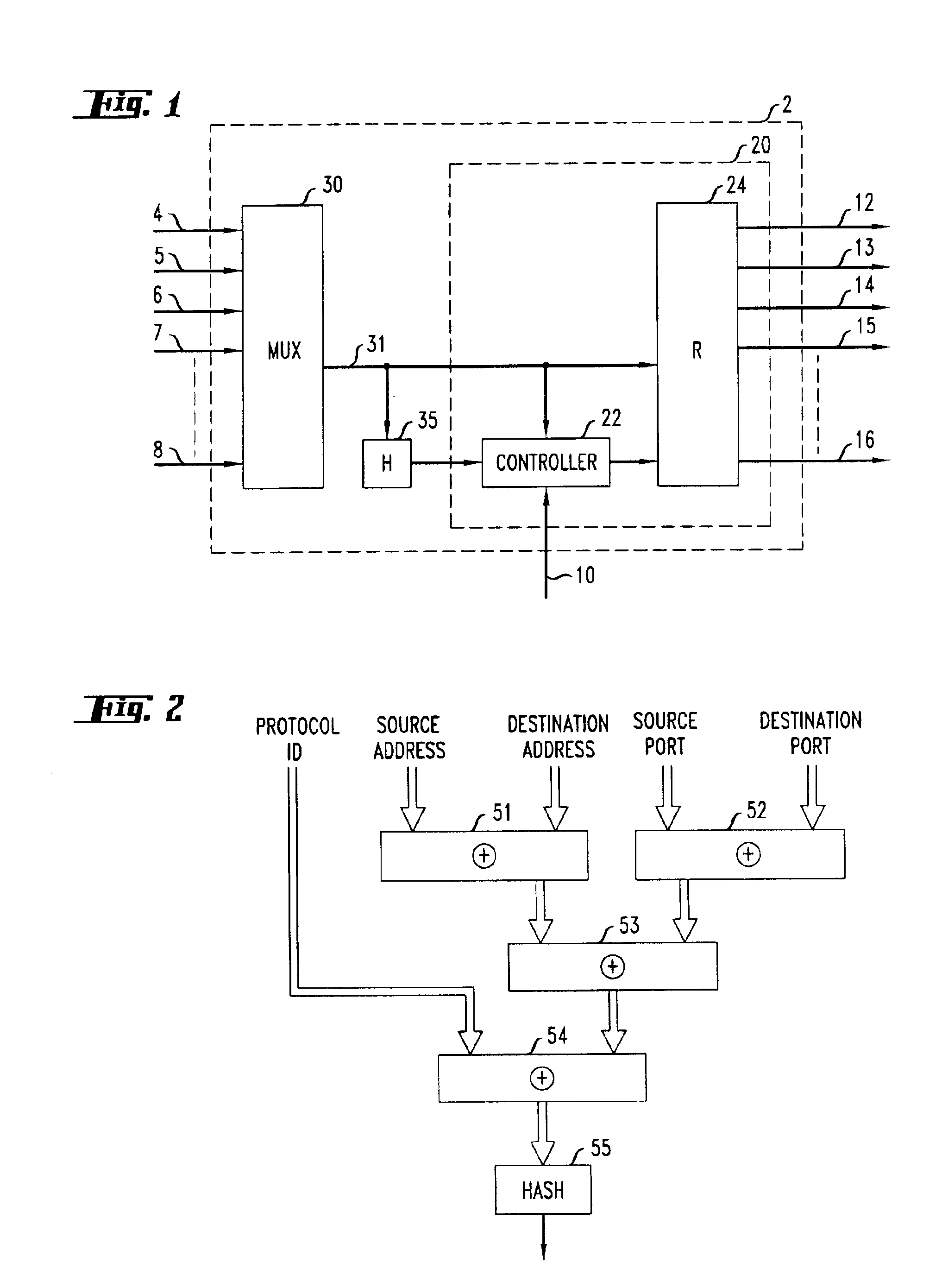
Hashing-based network load balancing
InactiveUS6888797B1Overcome deficienciesError preventionTransmission systemsComputer networkHash table
A hashing-based router and method for network load balancing includes calculating a hash value from header data of incoming data packets and routing incoming packets based on the calculated hash values to permissible output links in desired loading proportions.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
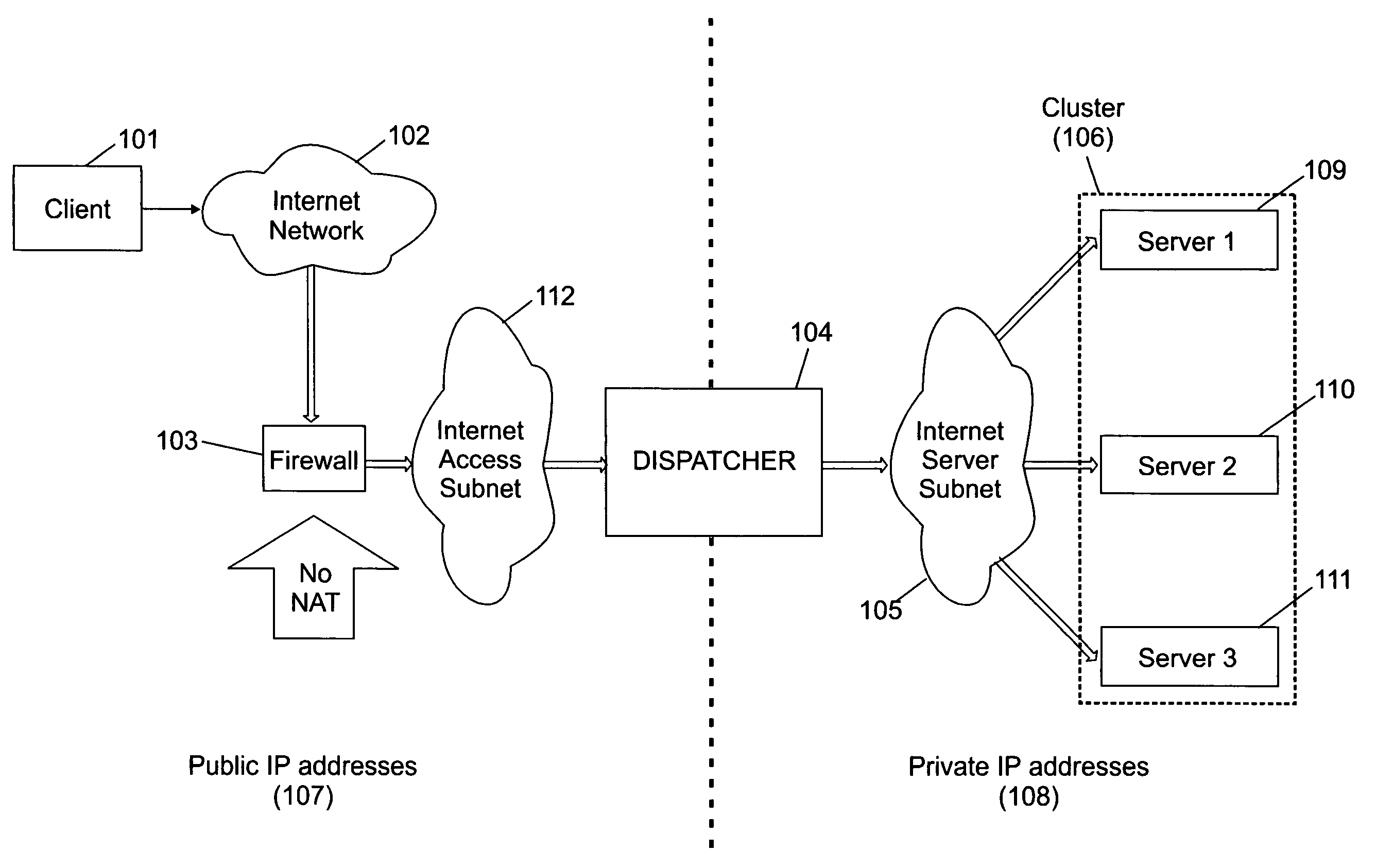
Technique for addressing a cluster of network servers
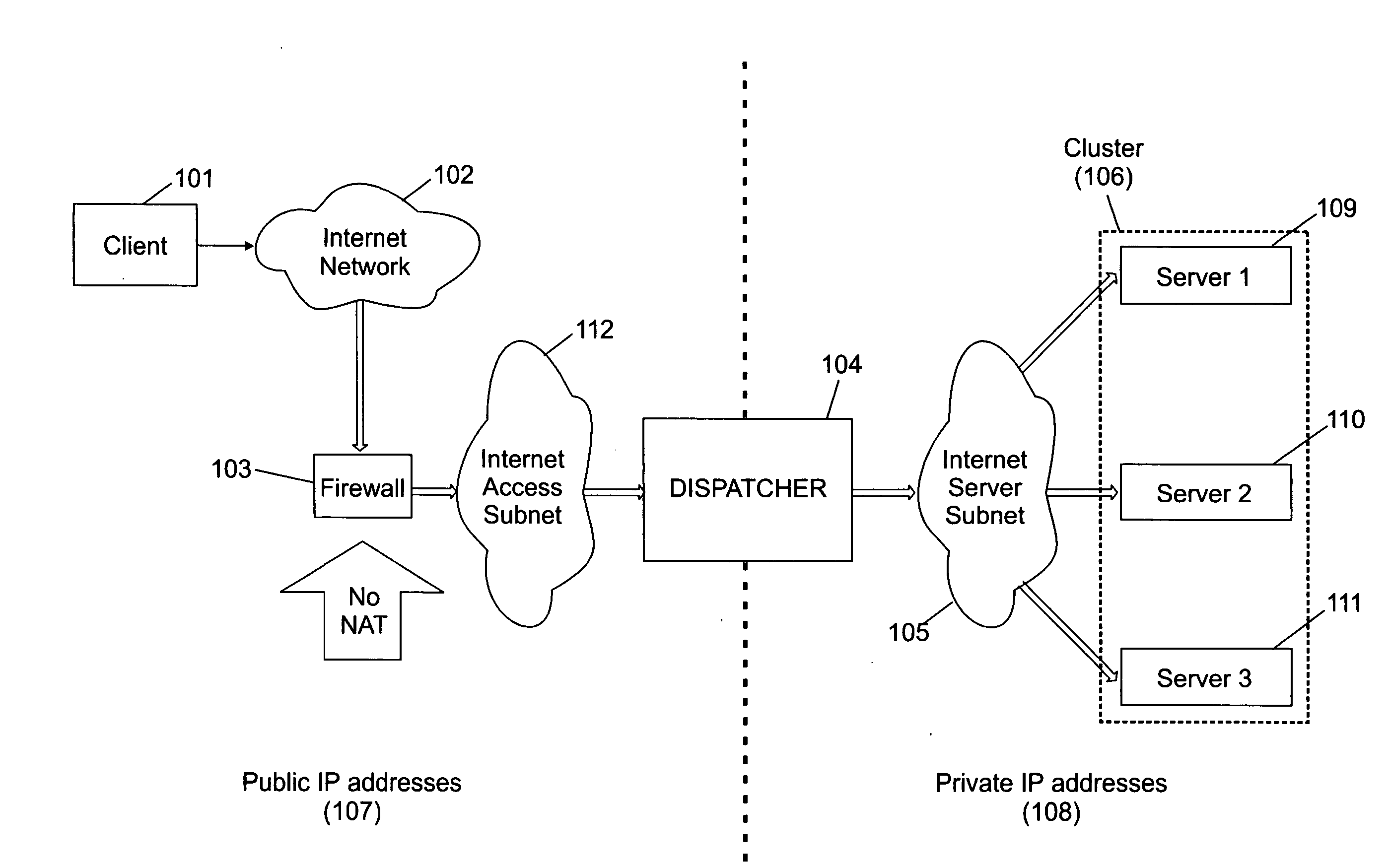
InactiveUS7480737B2Multiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingPrivate IPIp address
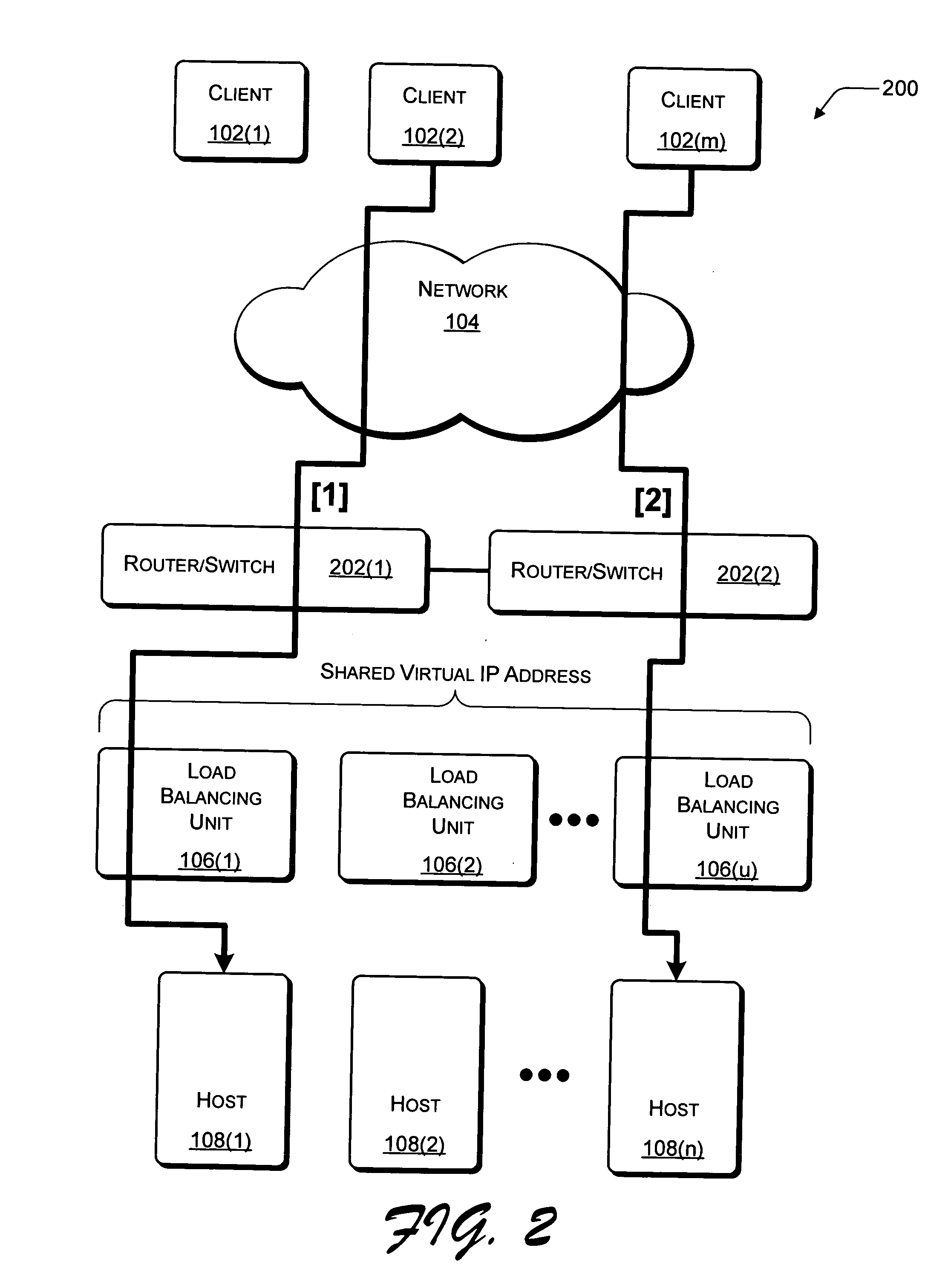
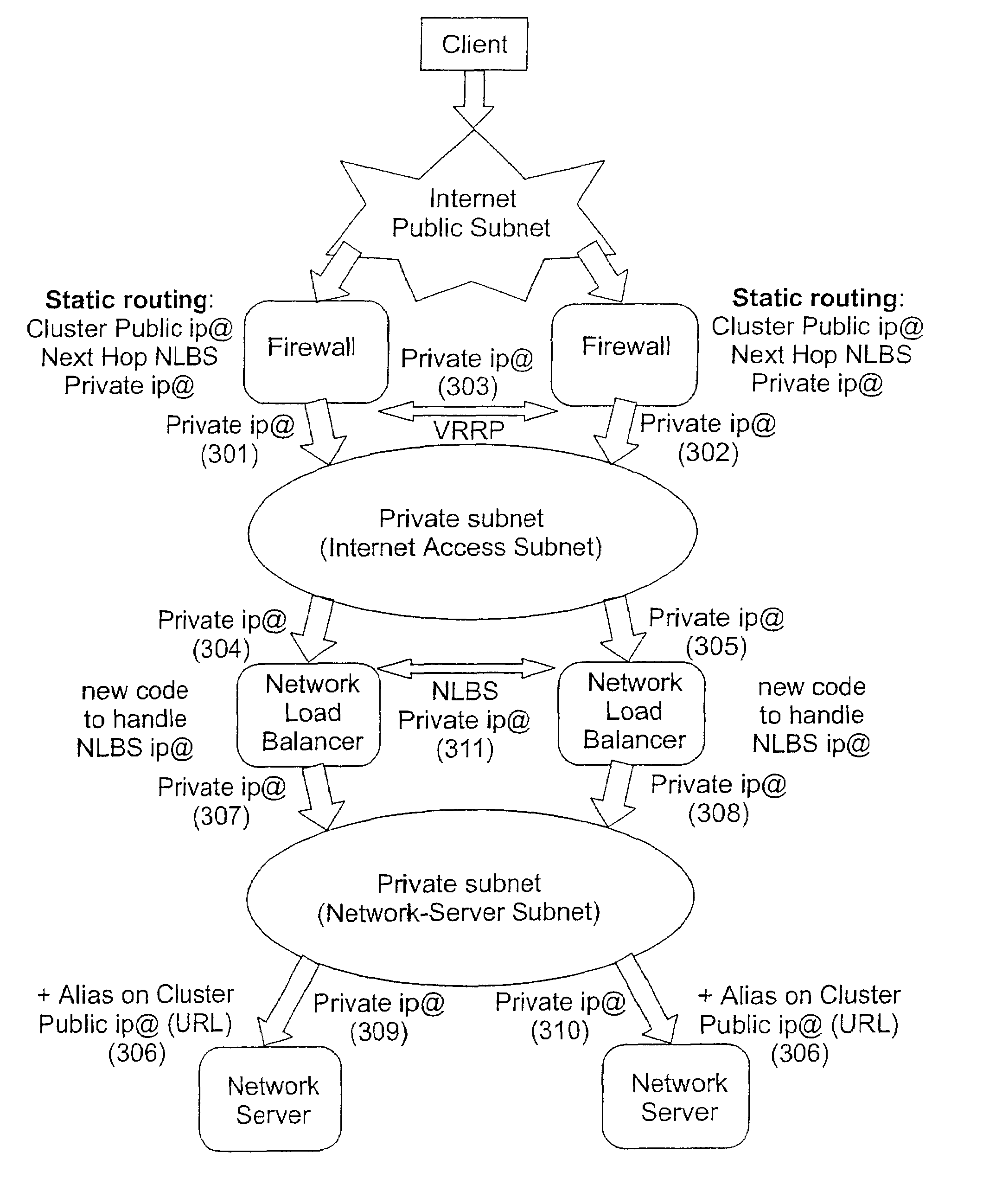
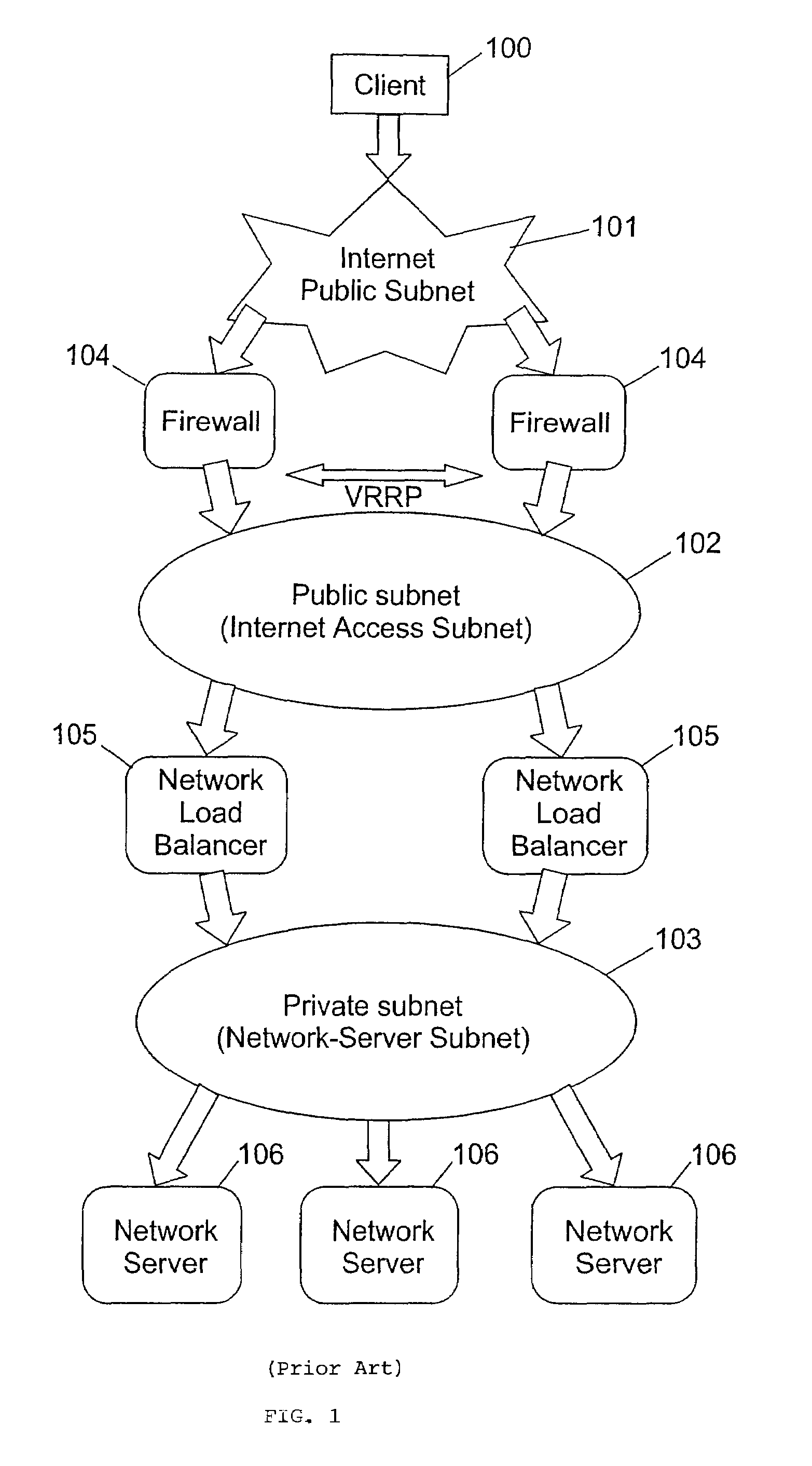
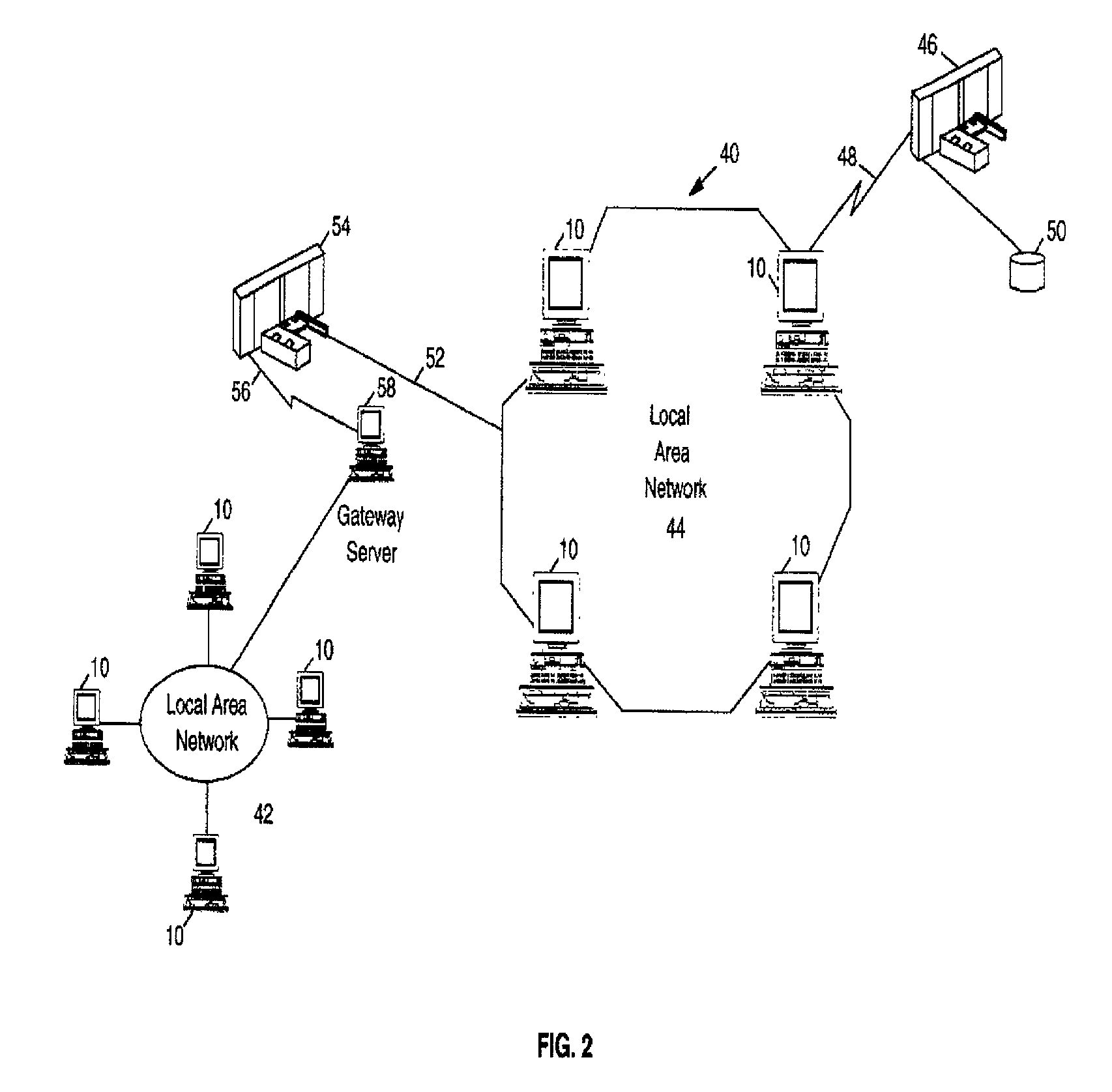
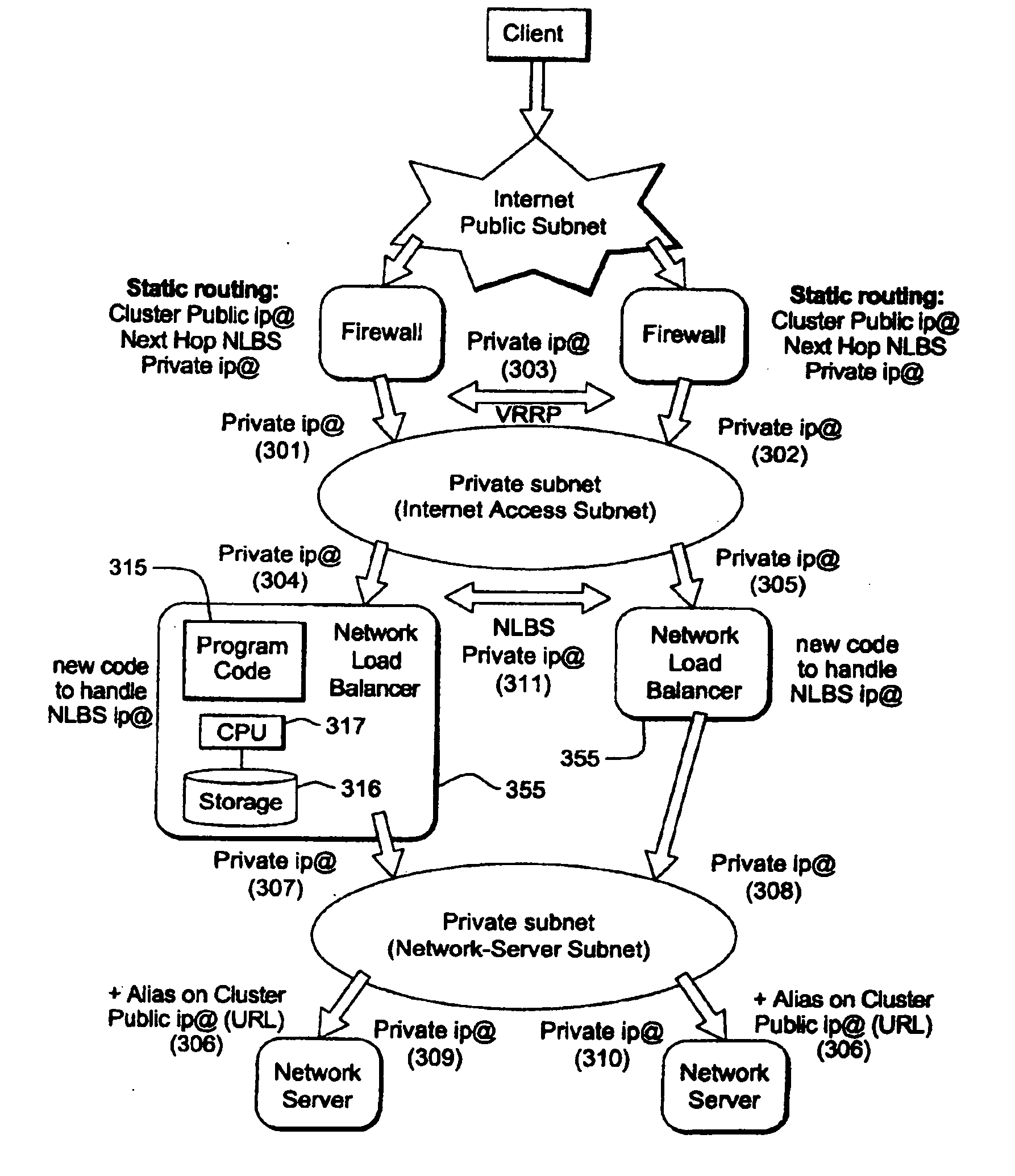
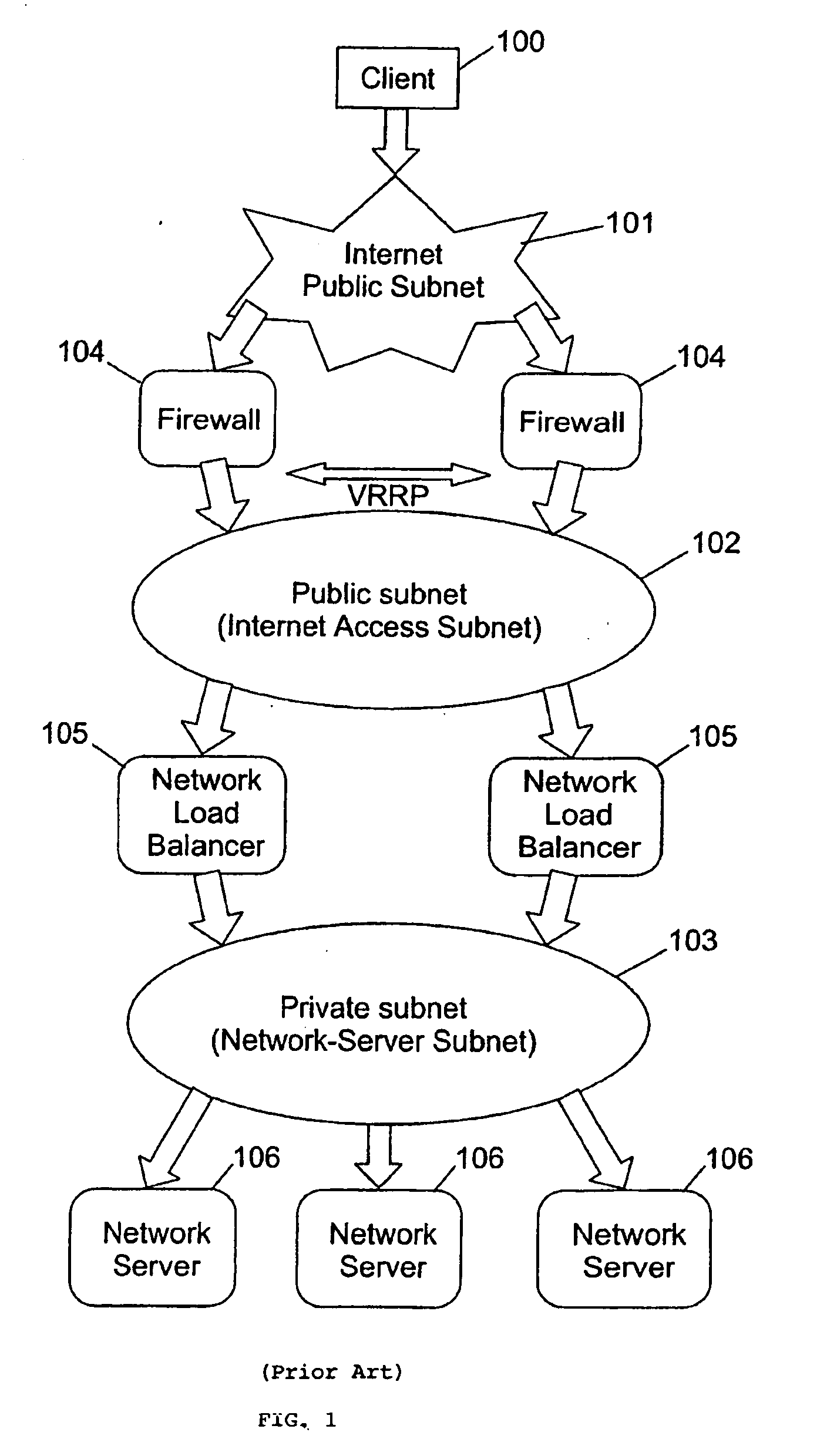
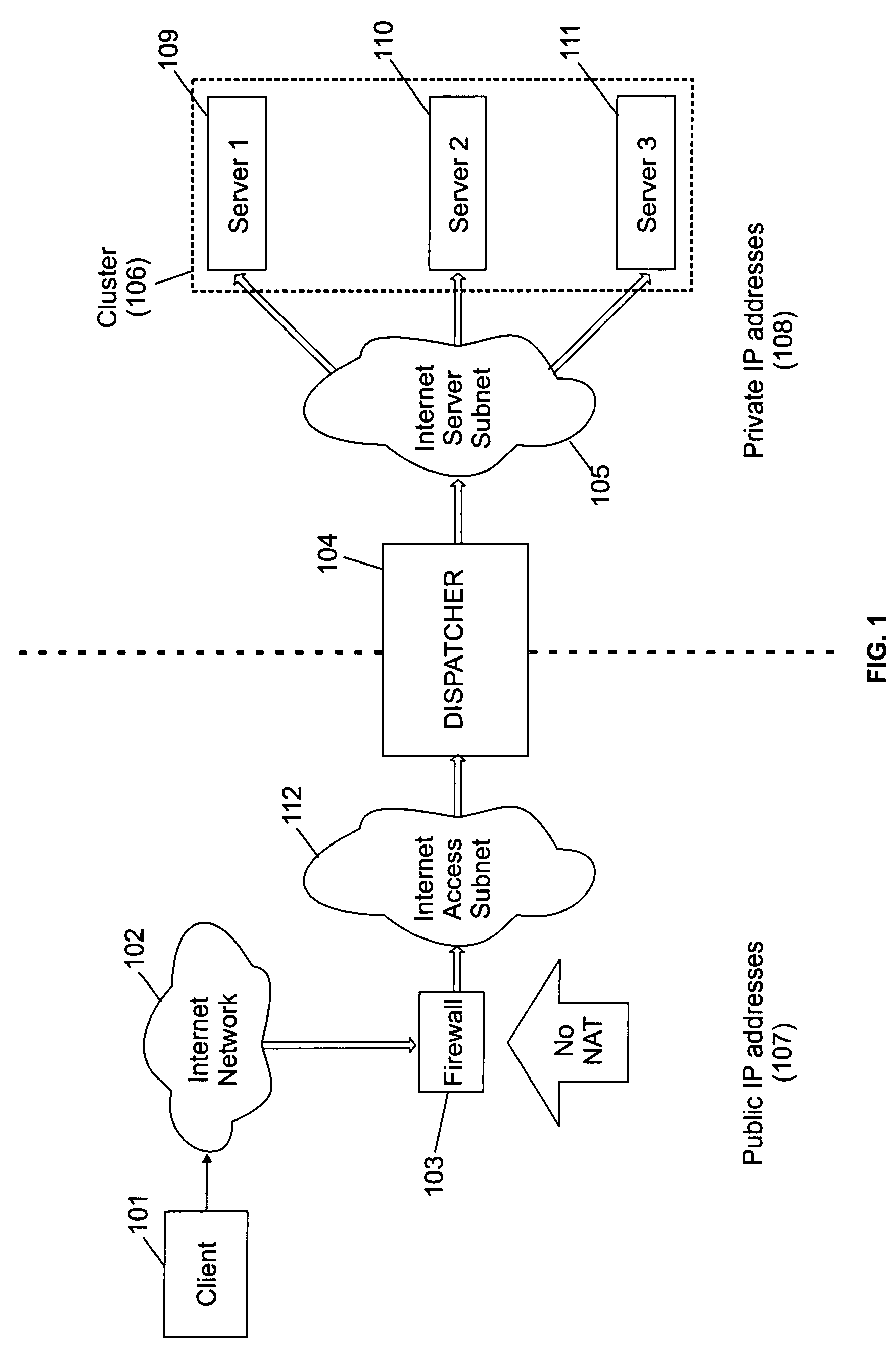
A single firewall or cluster of firewalls with a public IP address is interfaced to an internet public subnet to receive service requests for a cluster of network servers. A first private subnet with a plurality of private IP addresses is interfaced to the single firewall or cluster of firewalls to receive the service requests after passing through a firewall. A plurality of redundant load balancers with a respective plurality of private IP addresses are interfaced to the first private subnet to receive the service requests after passing through the first private subnet. The load balancers are interfaced to a second private subnet. The network servers with respective private IP addresses are interfaced to the second private subnet to receive the service requests from the load balancers. At an initialization time, a private IP address is defined for the network load balancer system within the internet access subnet. When one of the load balancers becomes primary at the initialization time or switches from a standby state to an active state, the network load balancer system private IP address is defined as an alias in an interface table to be recognized by the one load balancer. When the one network load balancer switches from the active state to a standby state, the network load balancer system private IP address previously defined as the alias is released from the interface table.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
System and method for accessing clusters of servers from the internet network
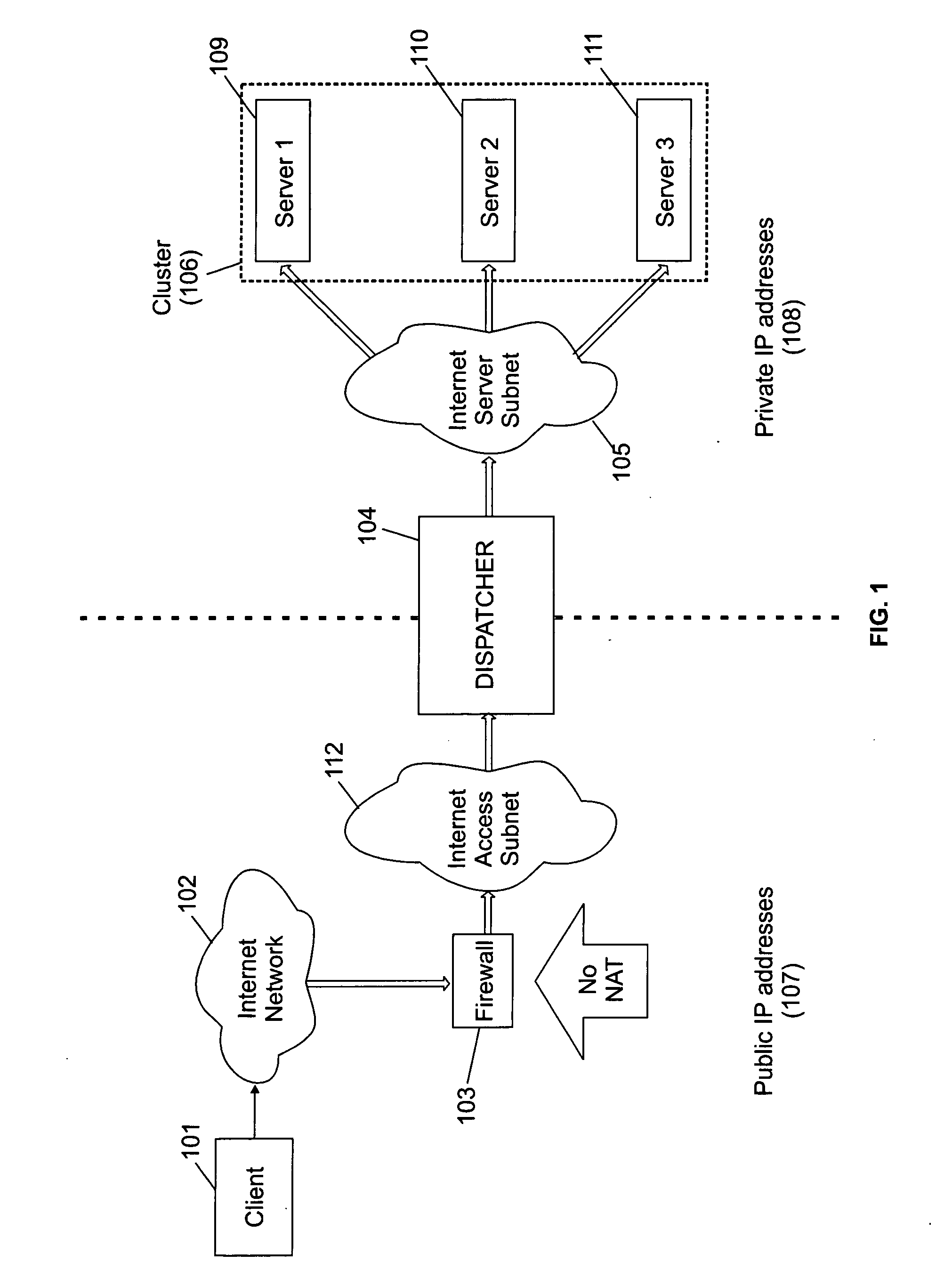
InactiveUS20050005006A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsAccess routePrivate network
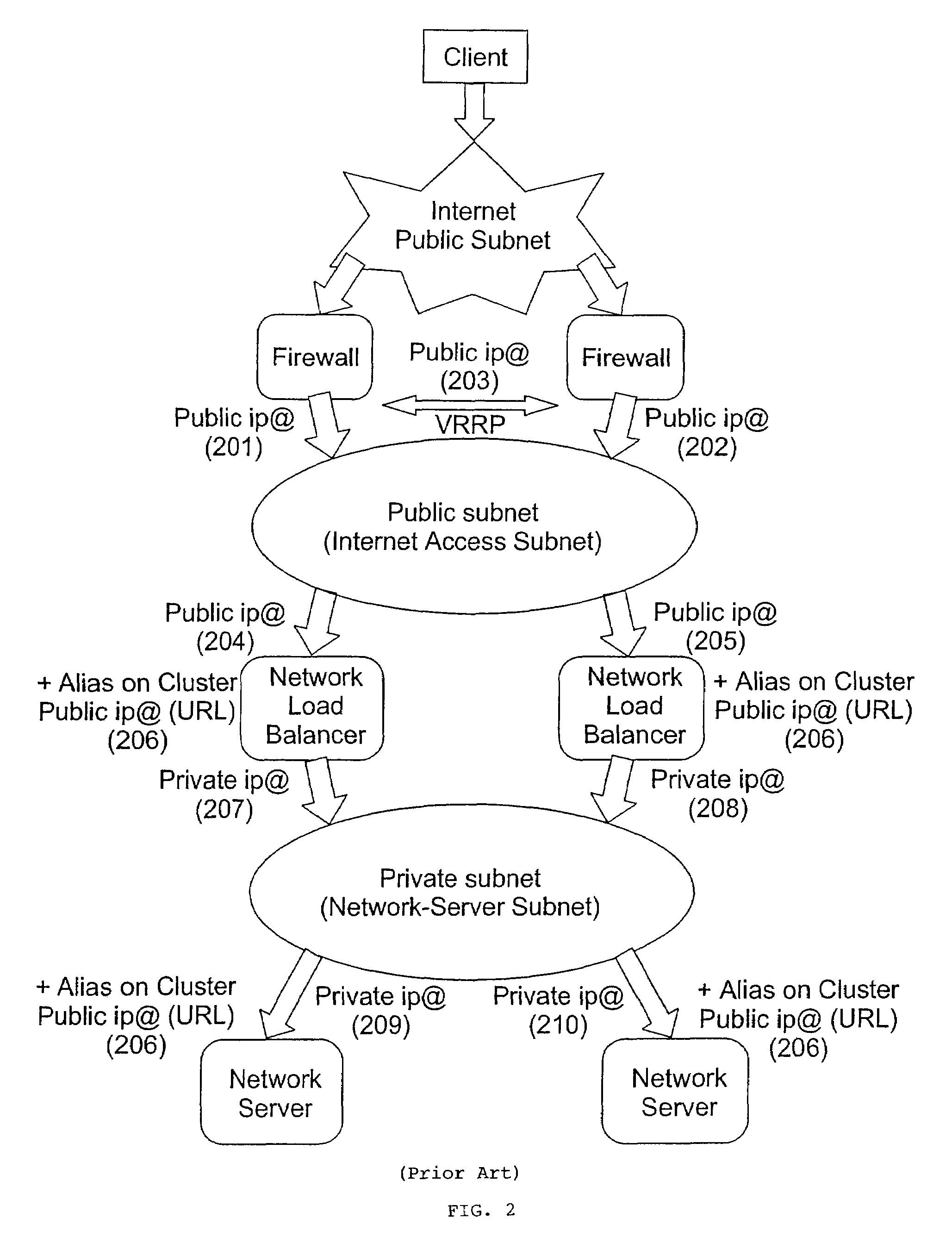
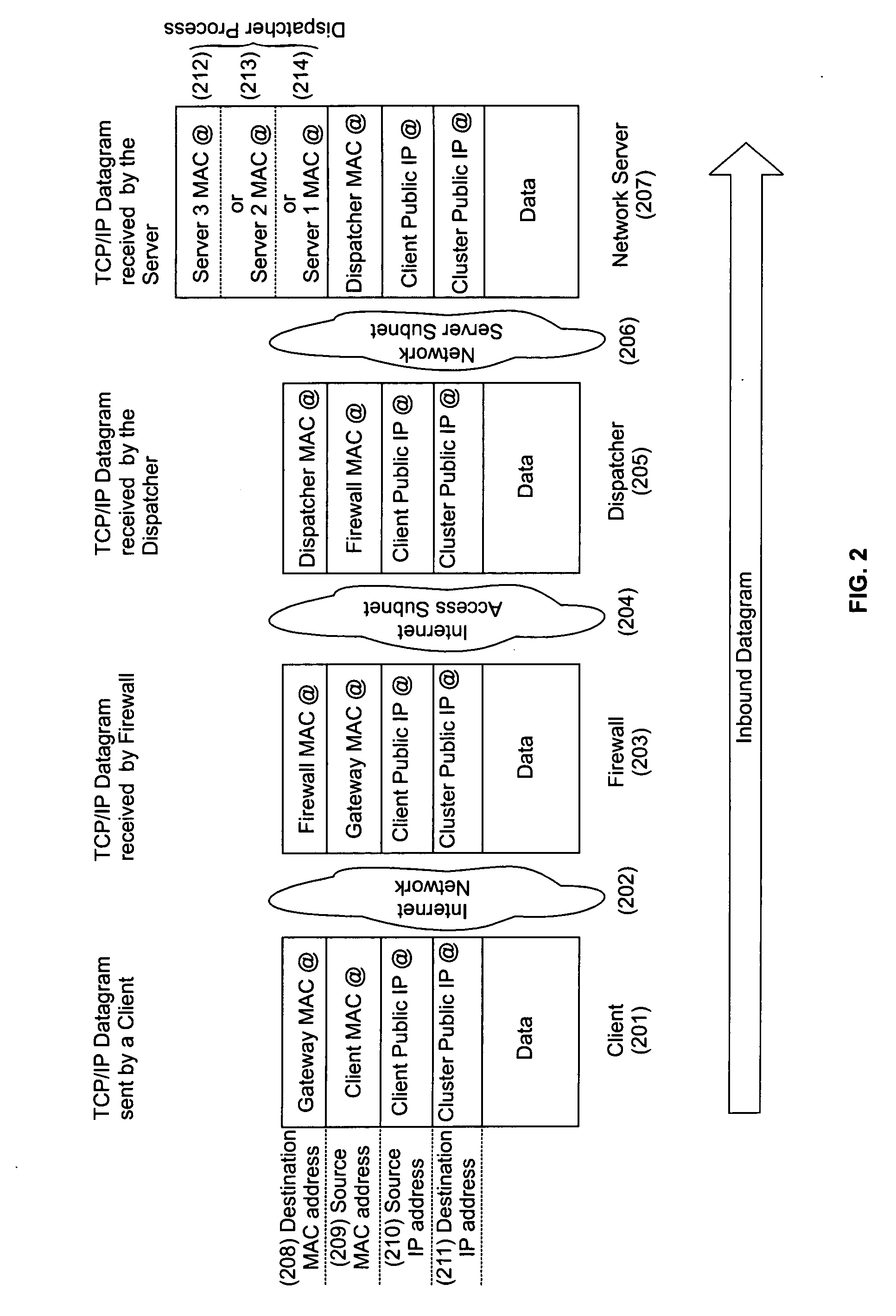
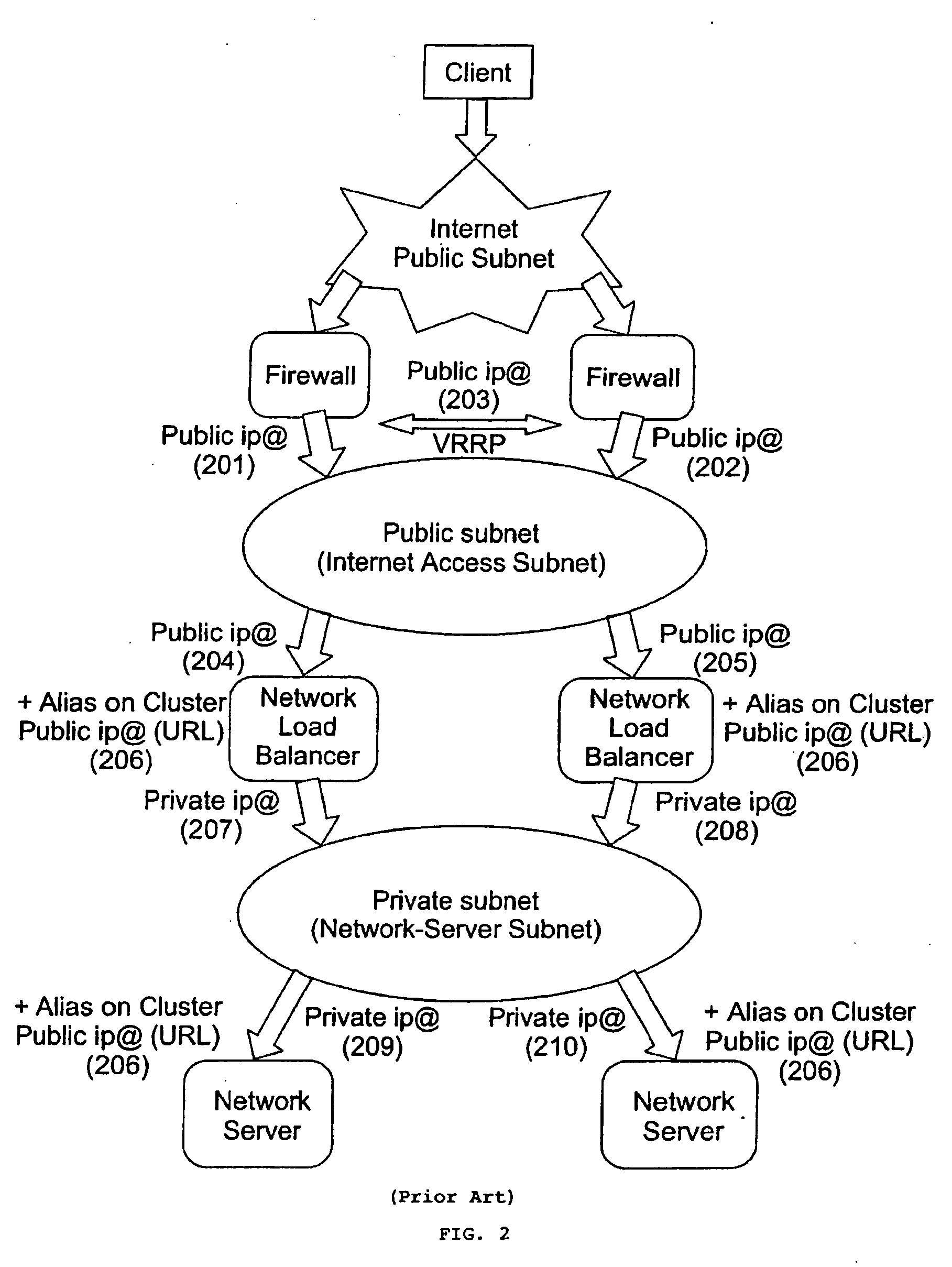
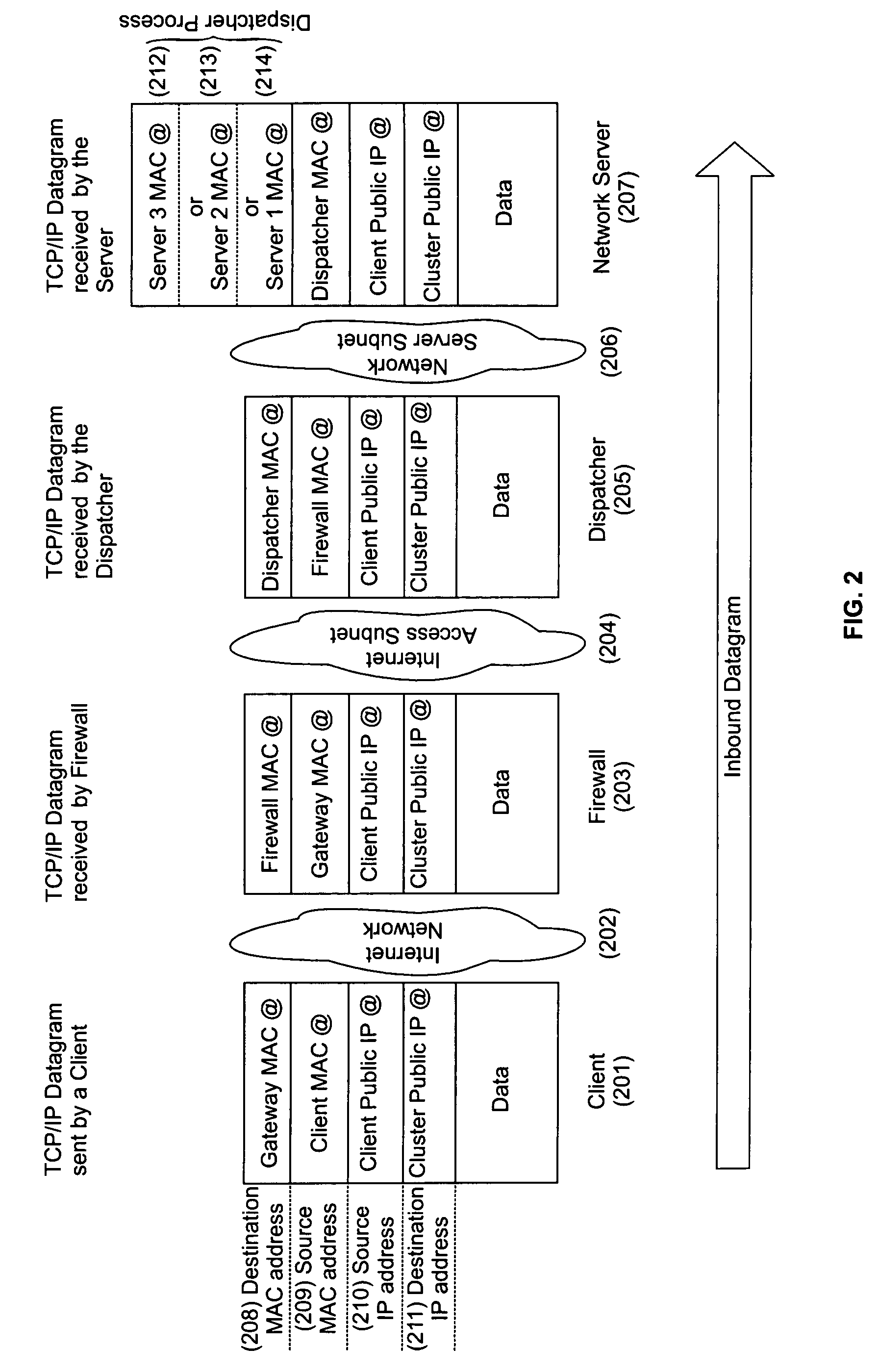
A cluster system and method accesses from an internet network, a network server within one or a plurality of clusters, each cluster being identified by a single cluster public Internet Protocol (IP) address. The cluster system has a plurality of network servers organized in one of a plurality of clusters and a network load balancer system for selecting a destination network server in a cluster. Each cluster has one or a plurality of identical network servers, the network load balancer system being connected on one hand to an access routing device and on another hand to the plurality of network servers through a private network server subnet. The method includes the steps of at initialization time, on each network server defining, as a non-advertising alias, in an interface table, the public IP address of each cluster to which the network server belongs, and upon reception, by the network load balancing system, of a datagram having an IP header including a destination IP address field and a medium access control (MAC) header including a destination MAC address field, selecting a destination network server within the cluster corresponding to the cluster public IP address identified in the destination IP address field of the datagram IP header, replacing the destination medium access control (MAC) address field of the datagram MAC header by the MAC address of the selected destination network server, and sending the datagram through the private network server subnet, using the MAC address of the selected destination network server. Upon reception, by the destination network server, of the datagram sent by the network load balancing system, the MAC address in the destination MAC address field of the datagram MAC header is identified as being the MAC address of the selected destination network server, and the IP datagram is processed if the identified cluster public IP address in the destination IP address field of the datagram IP header, is defined as a non-advertising alias in the interface table of the destination network server.
Owner:IBM CORP
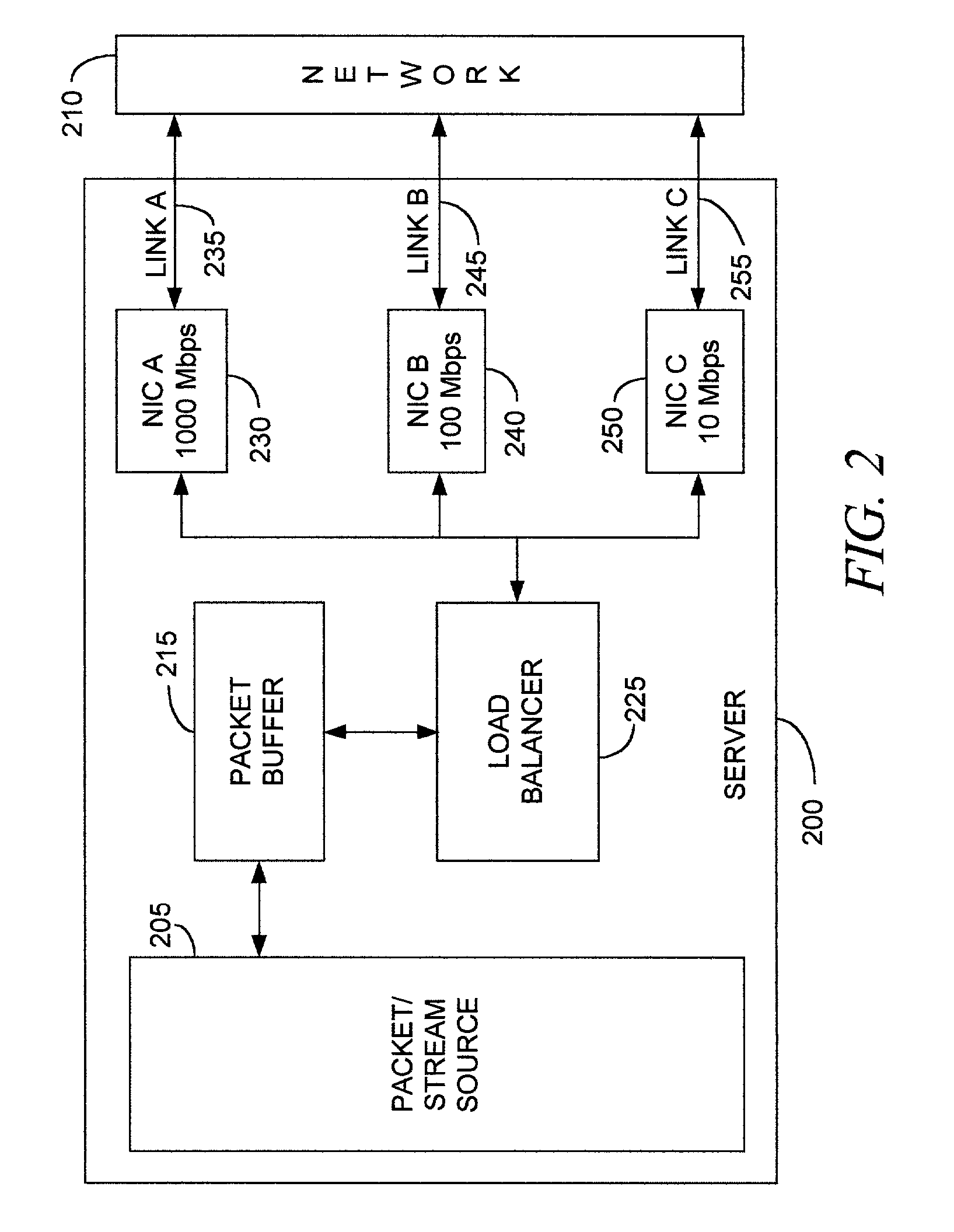
Dynamic network load balancing over heterogeneous link speed
ActiveUS20020054567A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsBalancing networkNetwork link
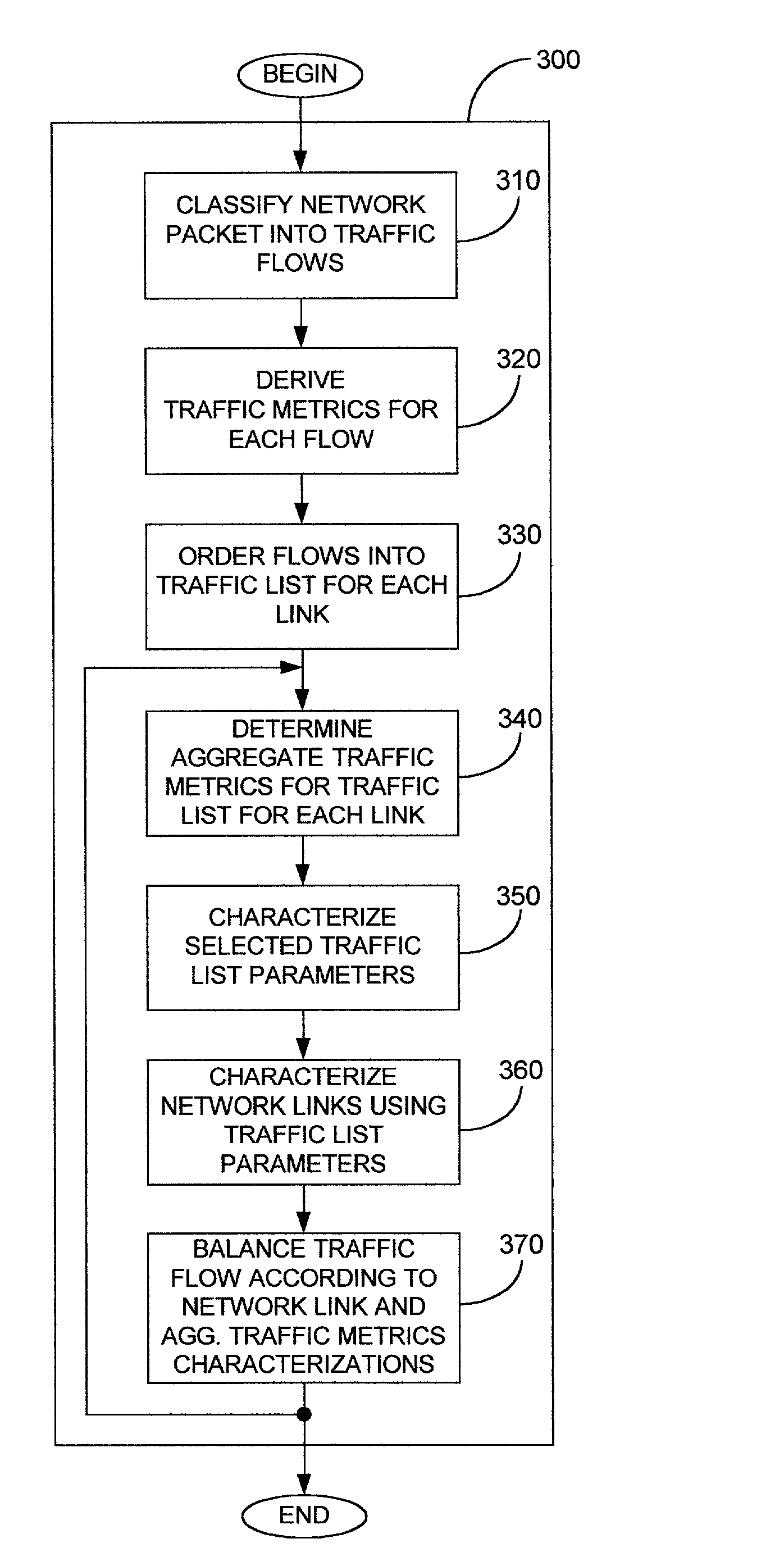
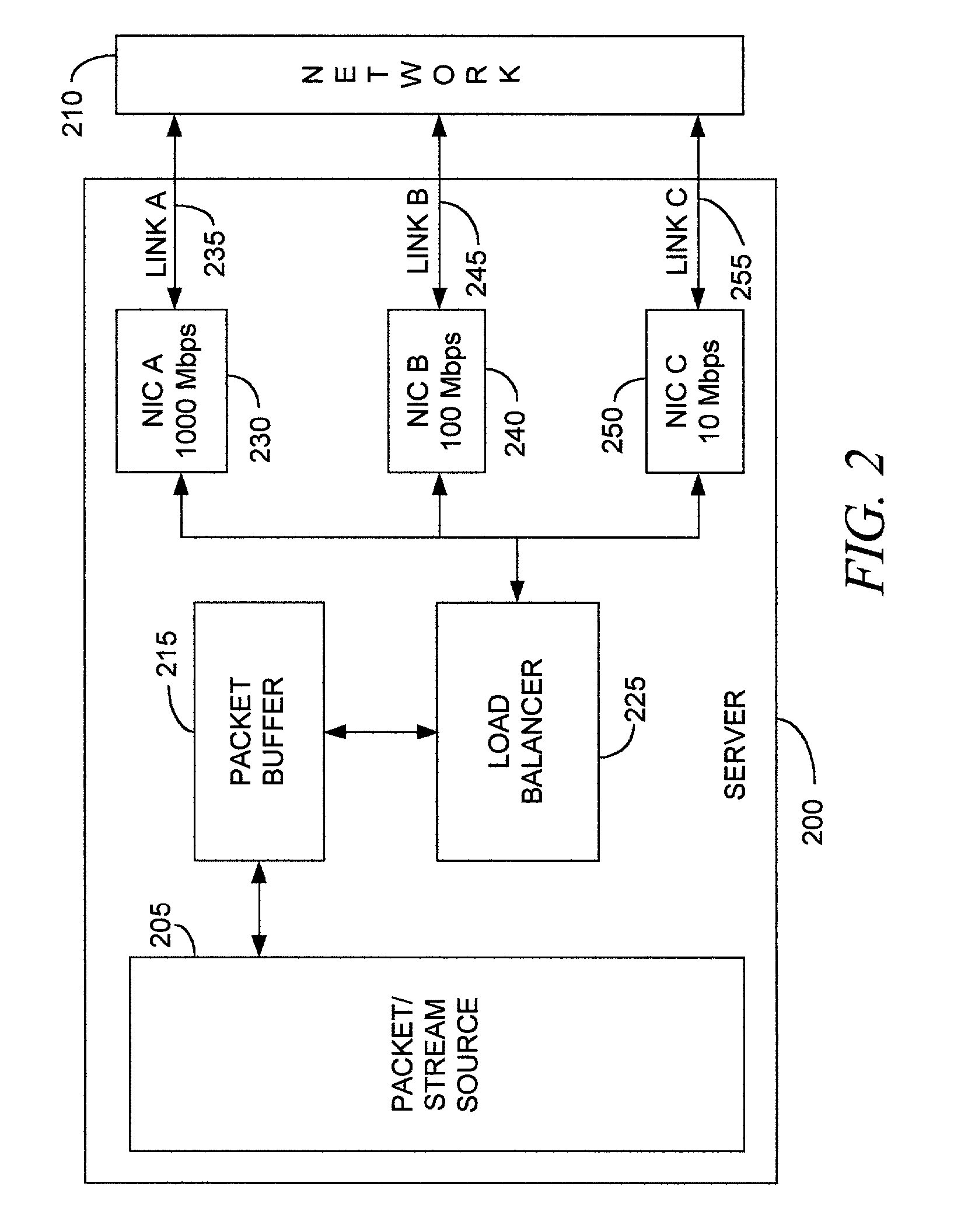
A method, apparatus, and computer program product for balancing transmission unit traffic over network links, including disposing transmission units into flows; grouping flows into first flow lists, each corresponding to a selected network link; determining a traffic metric representative of a traffic load on the selected network link; responsive to the traffic metric, regrouping flows into second flow lists corresponding to the selected network link, the regrouping balancing the transmission unit traffic among the network links; and transmitting the respective second flow list over the respective selected network link. The invention also can include a method for transmitting transmission units through a network, including receiving a transmission unit from a transmission unit source; classifying the transmission unit according to a predetermined flow characteristic; selecting a preselected network link over which the transmission unit is to be transmitted; and transmitting the transmission unit over the preselected network link.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
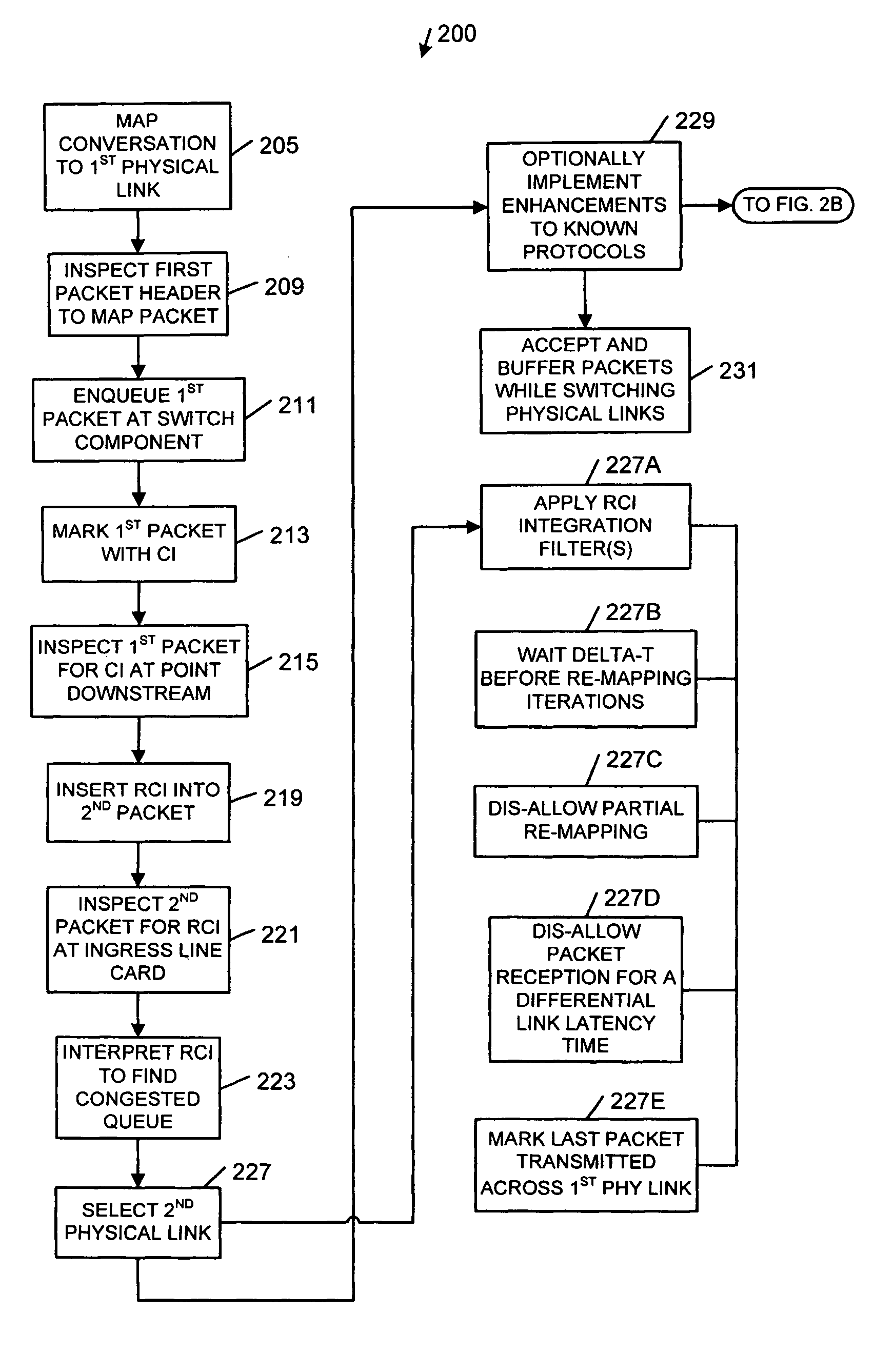
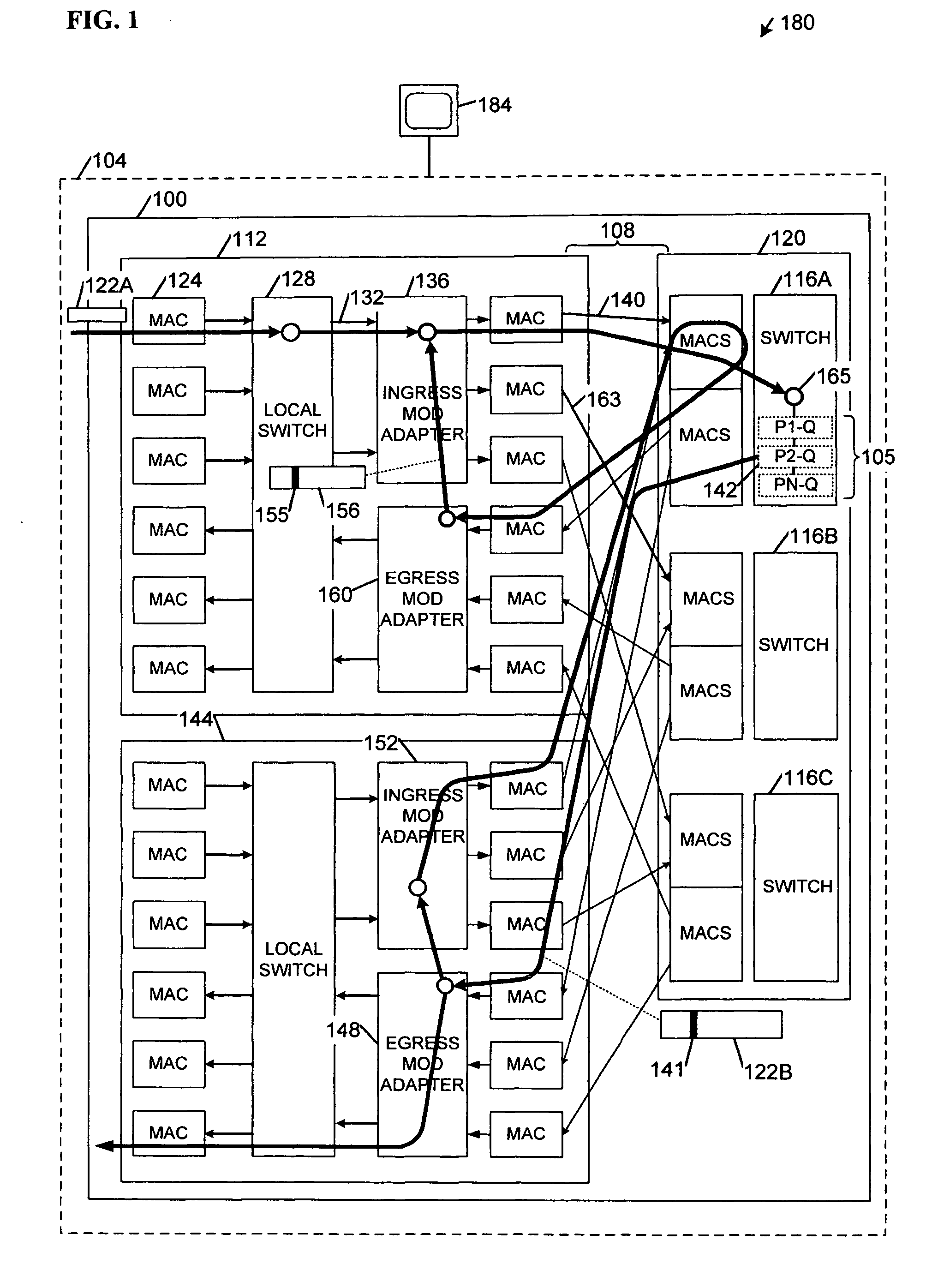
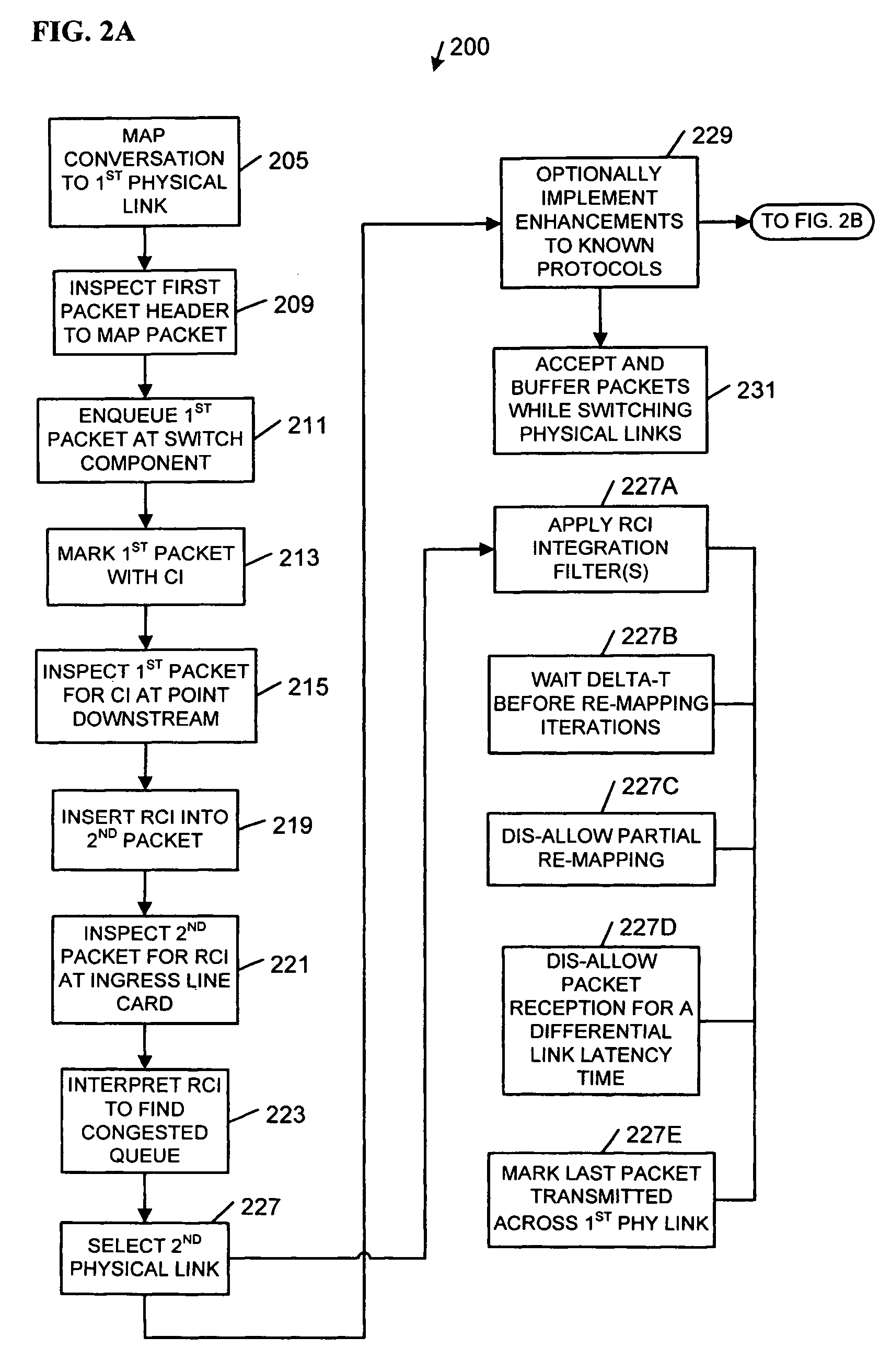
Network load balancing apparatus, systems, and methods
InactiveUS20070053294A1Error preventionTransmission systemsDistributed computingNetwork Load Balancing
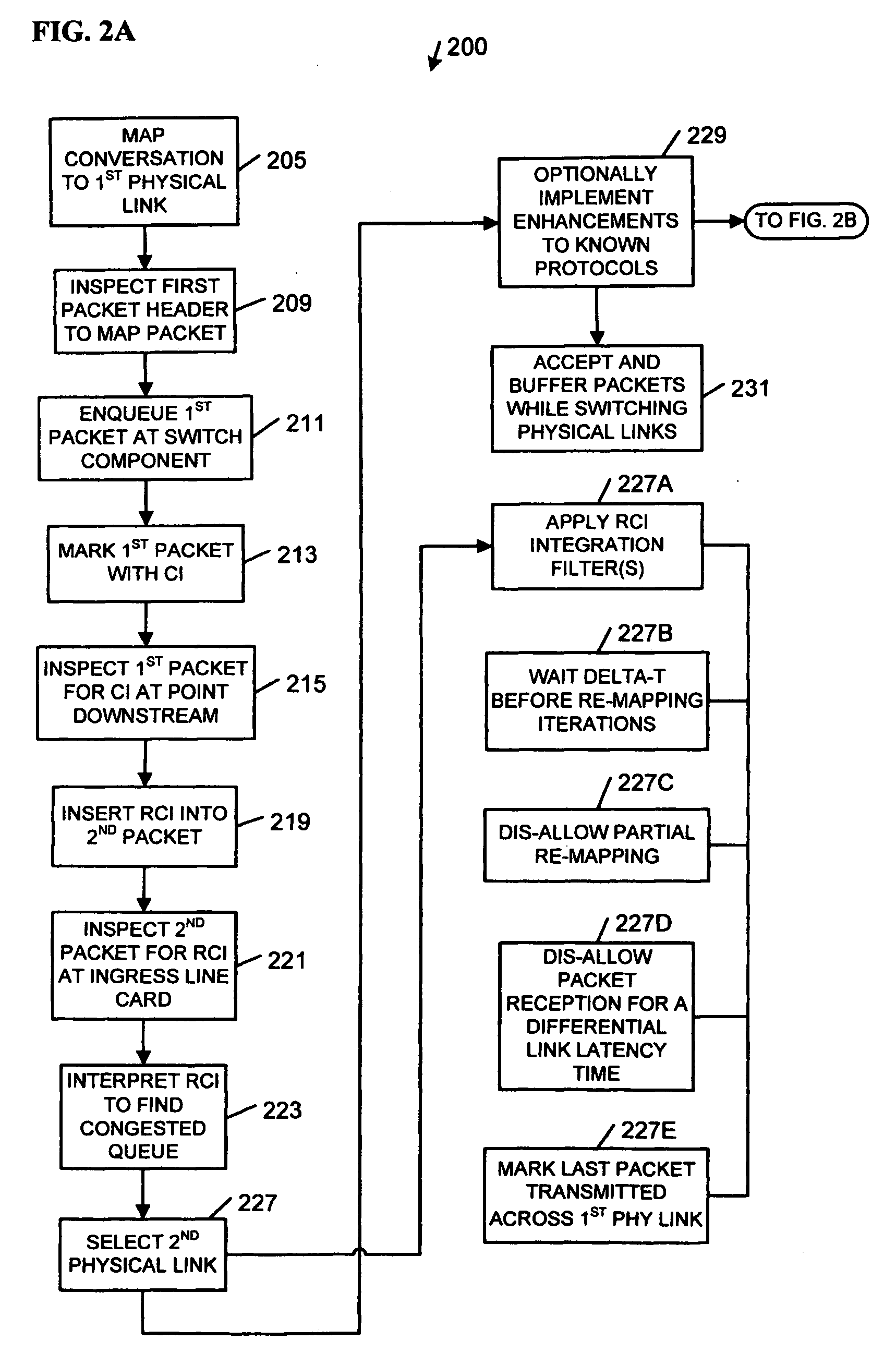
Apparatus, systems, methods, and articles described generally herein may receive a first packet marked with a congestion indicator (CI). Upon receipt of the CI, a load-balancing operation may be performed among a plurality of physical links upstream from a point of congestion to alleviate the congestion. Other embodiments may be described and claimed.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Identify negotiation switch protocols
A switch to switch protocol for network load balancing which negotiates among switches operable in accordance with the invention to assign a unique loop bit offset identifier value to each switch. Various other load balancing protocols associated with the switches then utilize the loop bit offset value as an identifier field when determining loops in the network of switches and costs associated with non-looped paths in the switches. A loop bit offset identifier requires less switch processing overhead than techniques which utilize an entire address value (i.e., MAC address value) for such protocols. Further, the loop bit offset identifier assigned by the present invention reduces the size of load balancing related packets. Specifically, cost computation related packets are reduced in size to the minimum 64 byte packet size through use of the loop bit offset identifier value of the present invention.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Network load balancing and overload control
ActiveUS9219686B2Simple technologyImprove capacity utilizationData switching networksOverload controlMessage routing
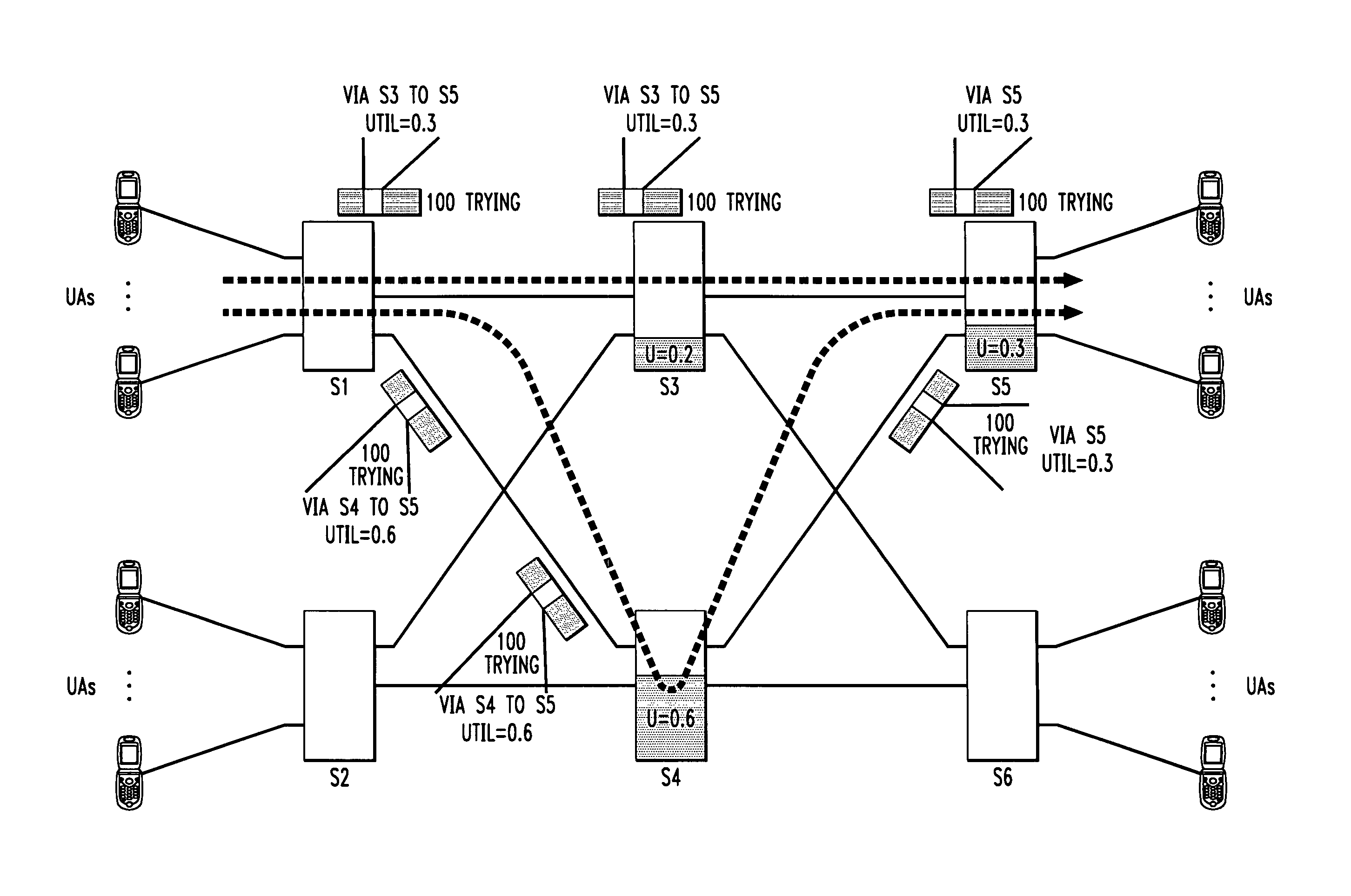
Load balancing and overload control techniques are disclosed for use in a SIP-based network or other type of network comprising a plurality of servers. In a load balancing technique, a first server receives feedback information from at least first and second downstream servers associated with respective first and second paths between the first server and a target server, the feedback information comprising congestion measures for the respective downstream servers. The first server dynamically adjusts a message routing process based on the received feedback information to compensate for imbalance among the congestion measures of the downstream servers. In an overload control technique, the first server utilizes feedback information received from at least one downstream server to generate a blocking message for delivery to a user agent.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Data network information distribution
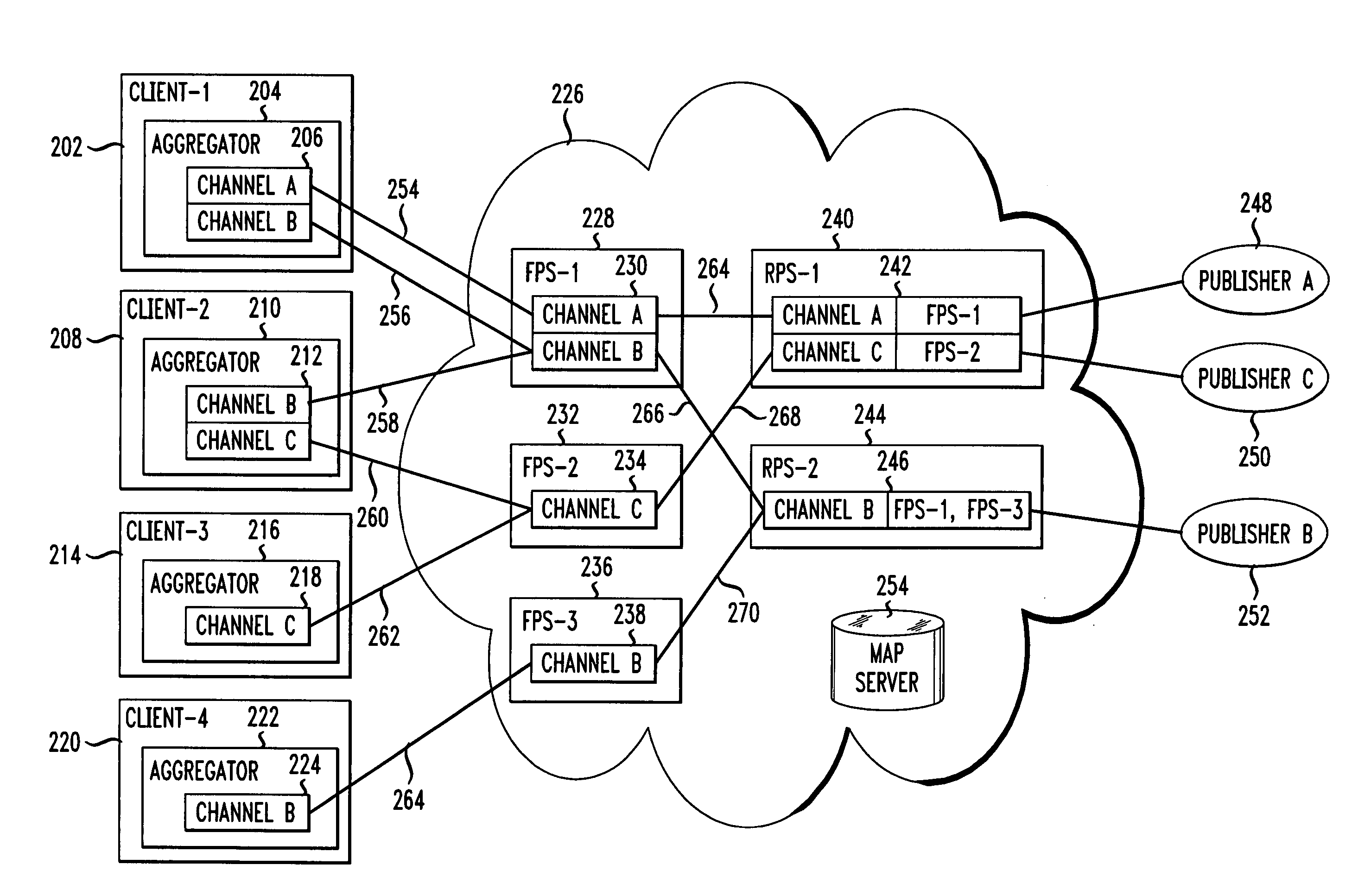
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for delivering information of interests from content providers to clients via a data network. A network architecture includes two types of edge servers, referred to as forward proxy servers and reverse proxy servers. The forward proxy servers are assigned to serve particular clients with respect to particular information and the reverse proxy servers are assigned to serve particular forward proxy servers with respect to particular information. Each of the forward proxy servers stores information identifiers associated with information for which the forward proxy server is assigned to serve to at least one client. Each of the reverse proxy servers stores information identifiers and the associated forward proxy servers that the reverse proxy server is assigned to serve with respect to information associated with the information identifiers. Upon receipt of updated content, the reverse proxy servers send the updated content to those forward proxy servers that the reverse proxy server is assigned to serve with respect to the received updated content. The forward proxy servers then provide the updated content to the clients to which they are assigned, either by responding to a request from those clients or by pushing the information to those clients. Network load balancing is provided by a controller network node for controlling the assignments of clients to forward proxy servers and the assignments of forward proxy servers to reverse proxy servers.
Owner:NEC CORP +1
Automatic network load balancing using self-replicating resources
InactiveUS20030167295A1Reduce in quantityMinimize deletionProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationLoad SheddingParallel computing
The present invention provides a method, system and computer program to balance the computational and network load in networked computers using self-replicating programs, referred to as symbionts. The method presented here reduces hotspots by encapsulating a resource in a symbiont, and having a user access that symbiont through programs that host symbionts, referred to as hosts. When a host accesses a symbiont, it may replicate a copy of that symbiont resource on itself or may be redirected to some other replicate of the same symbiont. The host then offers the replicated resource on the network to alleviate the load experienced by the original symbiont's computer. If the load on a symbiont falls below a threshold, it is removed from the host on which it was hosted.
Owner:VERITY INC
Technique for addressing a cluster of network servers
InactiveUS20090144444A1Multiple digital computer combinationsSecuring communicationPrivate IPIp address
A single firewall or cluster of firewalls with a public IP address is interfaced to an internet public subnet to receive service requests for a cluster of network servers. A first private subnet with a plurality of private IP addresses is interfaced to the single firewall or cluster of firewalls to receive the service requests after passing through a firewall. A plurality of redundant load balancers with a respective plurality of private IP addresses are interfaced to the first private subnet to receive the service requests after passing through the first private subnet. The load balancers are interfaced to a second private subnet. The network servers with respective private IP addresses are interfaced to the second private subnet to receive the service requests from the load balancers. At an initialization time, a private IP address is defined for the network load balancer system within the internet access subnet. When one of the load balancers becomes primary at the initialization time or switches from a standby state to an active state, the network load balancer system private IP address is defined as an alias in an interface table to be recognized by the one load balancer. When the one network load balancer switches from the active state to a standby state, the network load balancer system private IP address previously defined as the alias is released from the interface table.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Identity negotiation switch protocols
InactiveUS7283476B2Increase profitSimpler decoding and comparison techniqueError preventionTransmission systemsByteComputer science
A switch to switch protocol for network load balancing which negotiates among switches operable in accordance with the invention to assign a unique loop bit offset identifier value to each switch. Various other load balancing protocols associated with the switches then utilize the loop bit offset value as an identifier field when determining loops in the network of switches and costs associated with non-looped paths in the switches. A loop bit offset identifier requires less switch processing overhead than techniques which utilize an entire address value (i.e., MAC address value) for such protocols. Further, the loop bit offset identifier assigned by the present invention reduces the size of load balancing related packets. Specifically, cost computation related packets are reduced in size to the minimum 64 byte packet size through use of the loop bit offset identifier value of the present invention.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
System and method for accessing clusters of servers from the internet network
InactiveUS7454489B2Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsAccess routePrivate network
A cluster system and method accesses from an internet network, a network server within one or a plurality of clusters, each cluster being identified by a single cluster public Internet Protocol (IP) address. The cluster system has a plurality of network servers organized in one of a plurality of clusters and a network load balancer system for selecting a destination network server in a cluster. Each cluster has one or a plurality of identical network servers, the network load balancer system being connected on one hand to an access routing device and on another hand to the plurality of network servers through a private network server subnet. The method includes the steps of at initialization time, on each network server defining, as a non-advertising alias, in an interface table, the public IP address of each cluster to which the network server belongs, and upon reception, by the network load balancing system, of a datagram having an IP header including a destination IP address field and a medium access control (MAC) header including a destination MAC address field, selecting a destination network server within the cluster corresponding to the cluster public IP address identified in the destination IP address field of the datagram IP header, replacing the destination medium access control (MAC) address field of the datagram MAC header by the MAC address of the selected destination network server, and sending the datagram through the private network server subnet, using the MAC address of the selected destination network server. Upon reception, by the destination network server, of the datagram sent by the network load balancing system, the MAC address in the destination MAC address field of the datagram MAC header is identified as being the MAC address of the selected destination network server, and the IP datagram is processed if the identified cluster public IP address in the destination IP address field of the datagram IP header, is defined as a non-advertising alias in the interface table of the destination network server.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
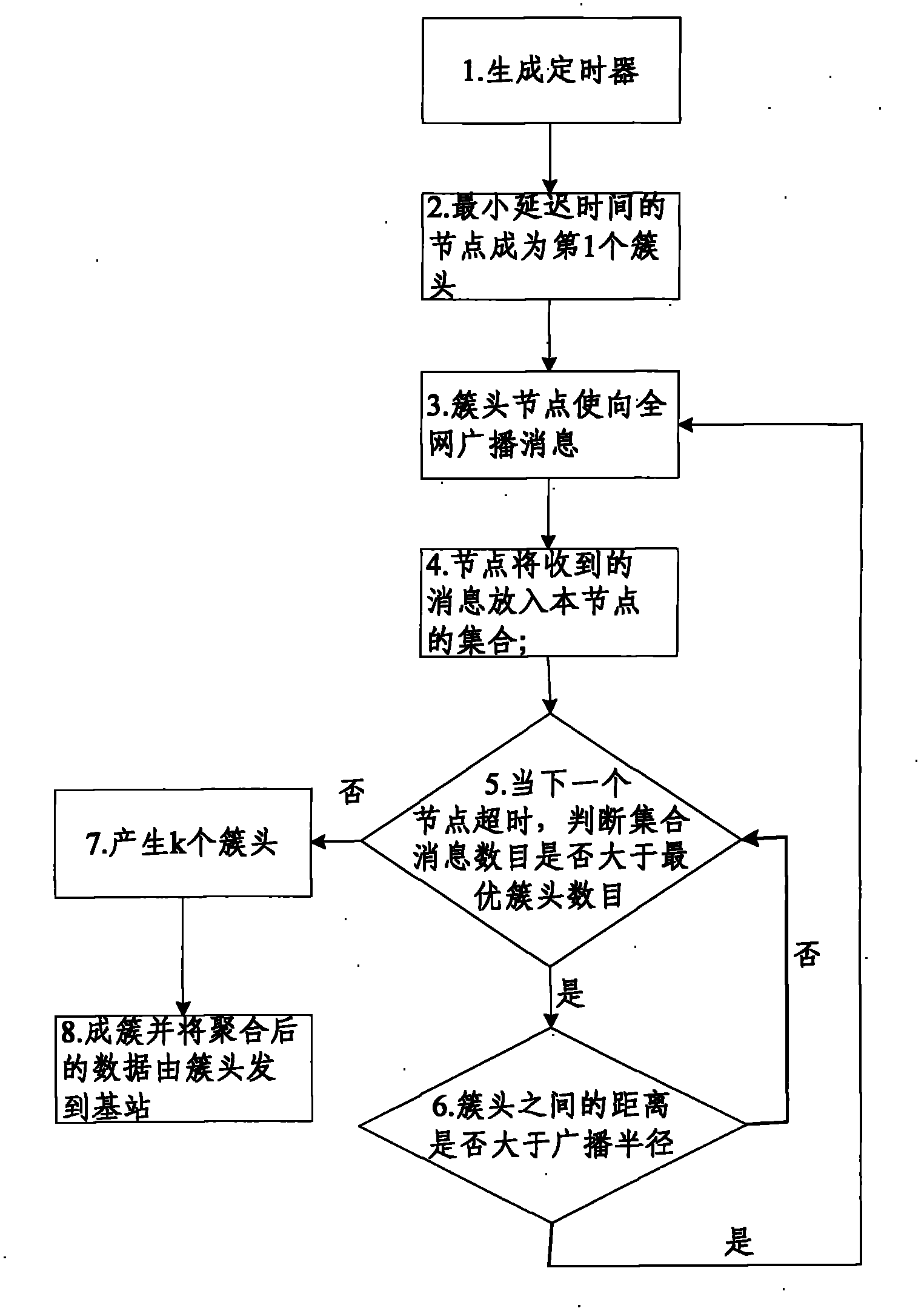
Radio sensor network data collection method based on multi-agent negotiation
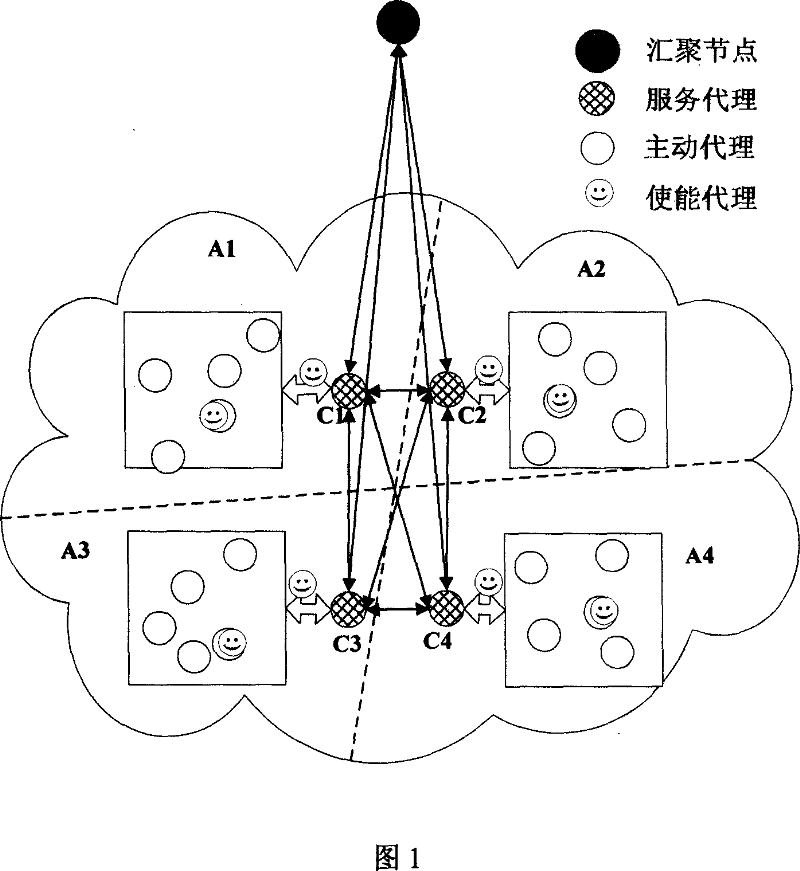
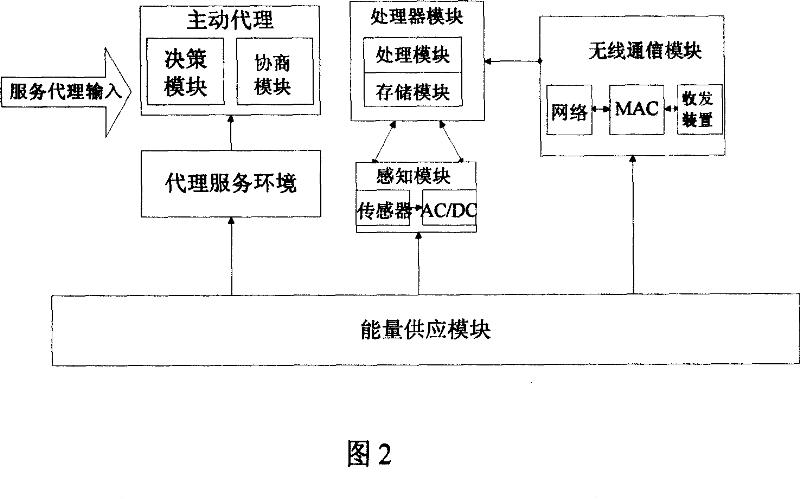
InactiveCN101035040ASolve resource problemsReduce node energy consumptionEnergy efficient ICTStar/tree networksActive agentData aggregator
Based on Multi-Agent consultations wireless sensor network data collection methods, according to the network layer structure of clusters distributed tasks agents, active agents through consultations within the cluster and the cluster service agents consultations to determine the cluster so that agents within the cluster of data collection between the data path and the return path, users interested in the data Distributed processing within the network, access to the information. One form of software services agents and enable agents, the combination of hardware and software initiatives agents, agents and active agents switching, consultation and Acting Regional memory so that it can increase the network's live dynamic performance, multi-agent collaborative completion of a combination of timing of data collection. Compared to traditional data, polymerization method takes place of data transmission network to short the Acting interactive information in the network, data from the main polymerization processing model into the network, such as computing model.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for balancing network load based on wireless sensor energy information
InactiveCN101355517AEven consumptionExtended lifespanNetwork traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationBalancing networkSensing data
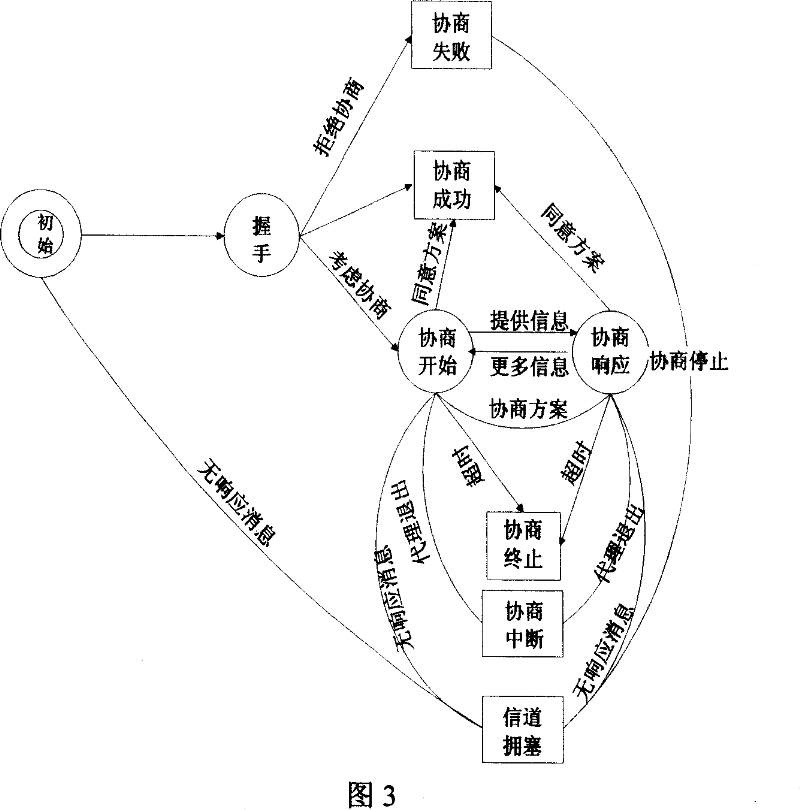
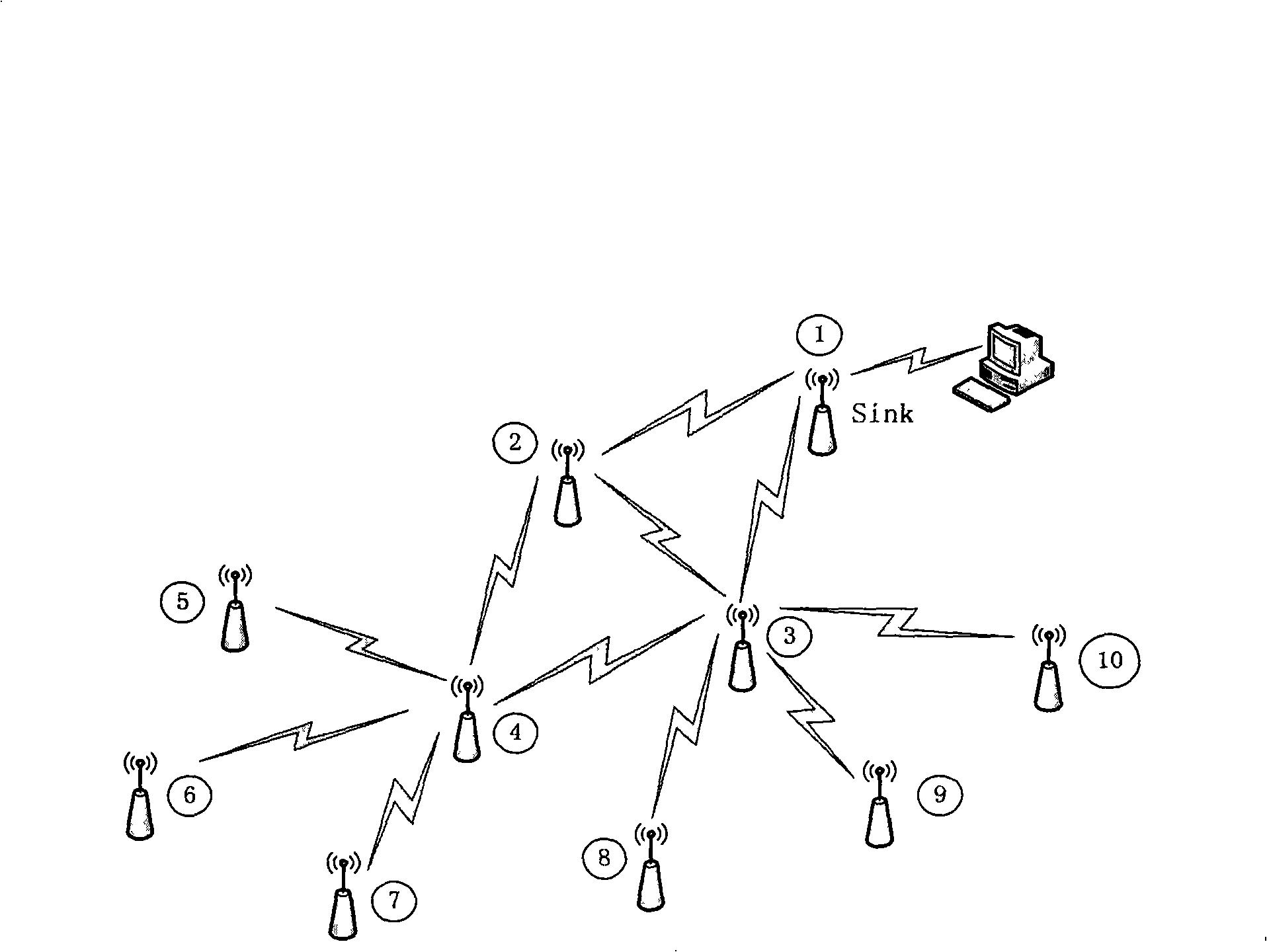
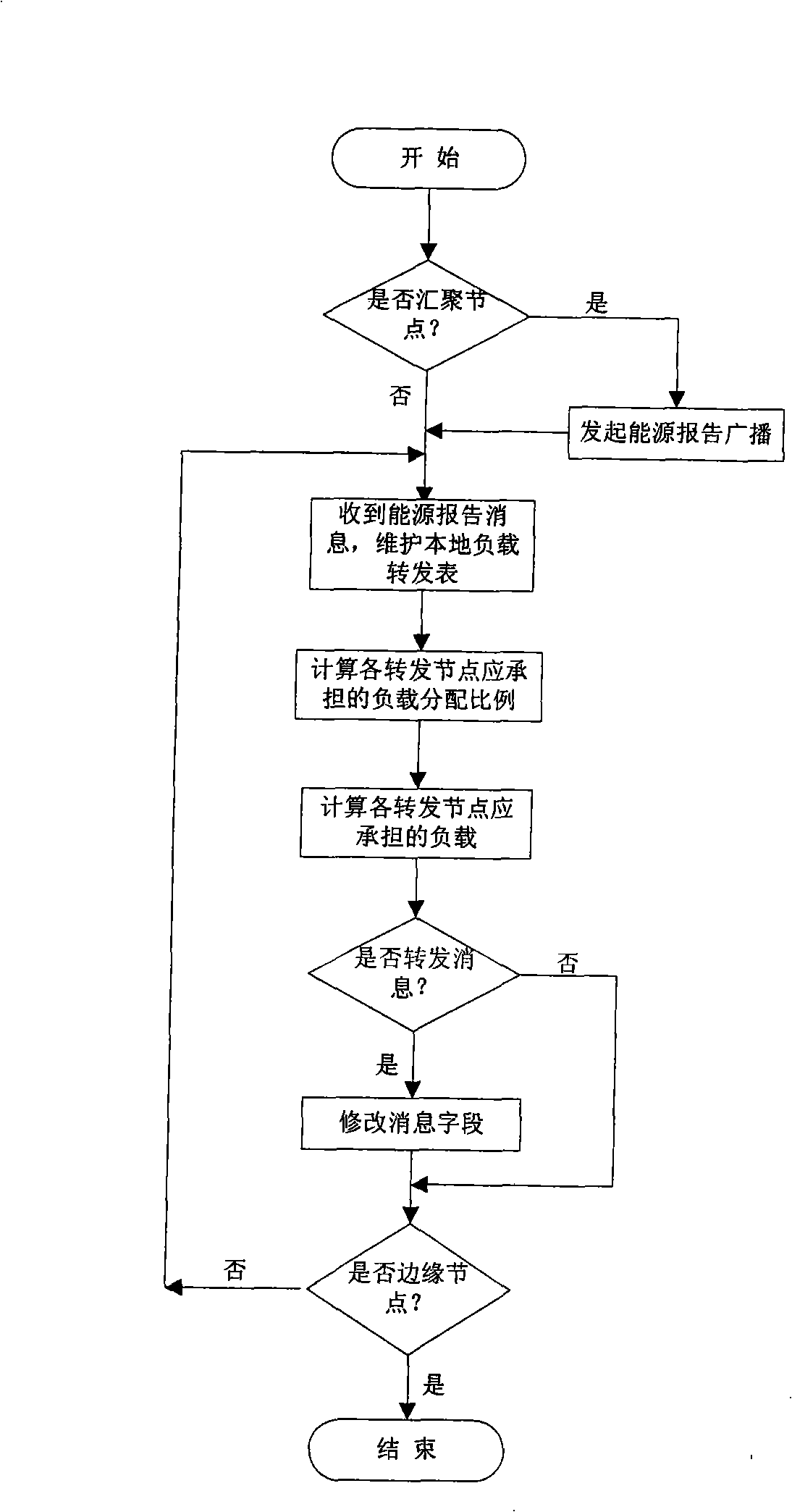
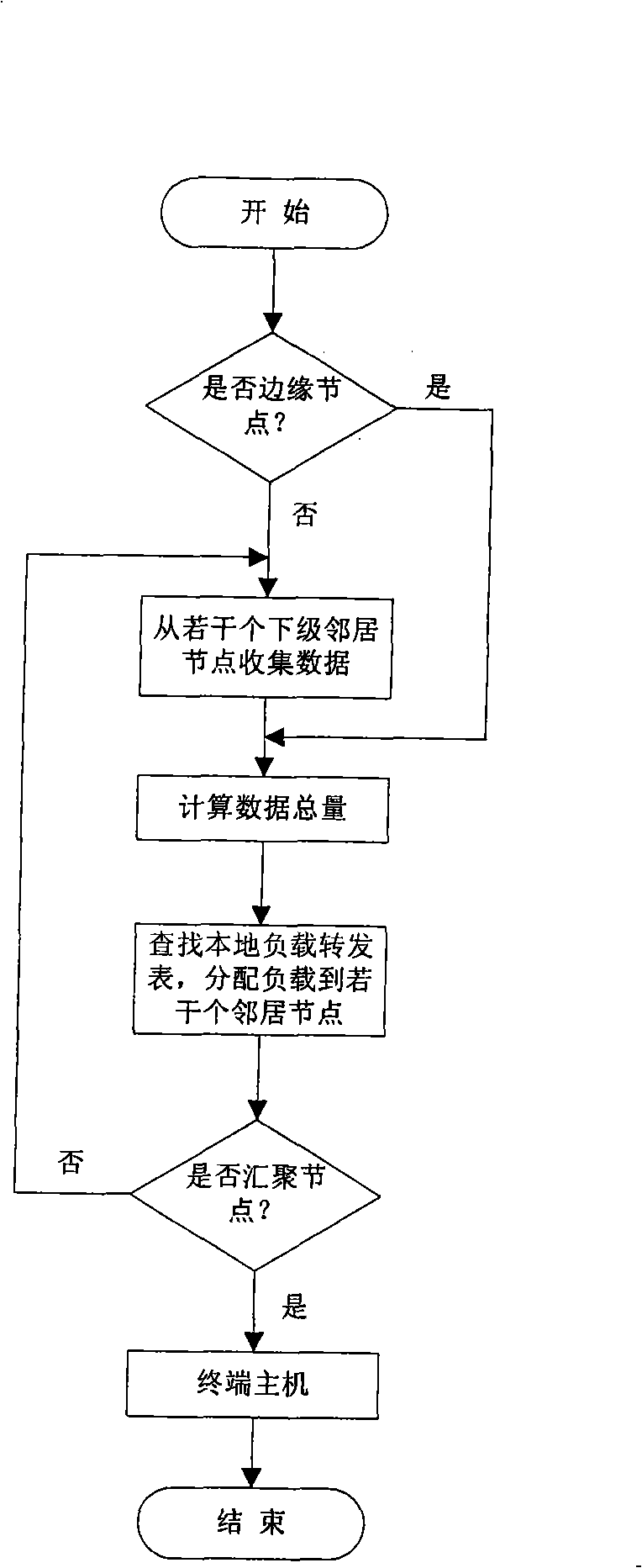
The invention relates to a network load balancing method based on energy information of a wireless sensor, comprising the following steps: (1) Sink broadcasts an energy report message; (2) nodes receive an energy report of the Sink and then update and maintain local load forwarding tables; (3) the load allocation proportion born by various forwarding nodes and the load born by the various nodes are calculated; (4) the message is forwarded when local nodes are far away from convergent nodes compared with the forwarding nodes or are brother nodes of the same layer with the forwarding nodes; (5) various field values in the message are modified by self energy information and the message is forwarded to all the lower-level neighboring nodes or all the brother nodes of the same layer except the forwarding nodes; (6) when all the nodes receive the energy report message, the message forwarding is stopped; (7) after the energy report message is forwarded within a single period, propagation paths which reversely use the energy report message establish a load convergent route from sensing nodes to the convergent node Sink hop by hop; and (8) the convergent node Sink periodically sends out the energy report message and completes allocation and convergence of sensing data. The method solves the problems of network load balancing and network life cycle of a large-scale wireless sensor.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Dynamic network load balancing over heterogeneous link speed
A method, apparatus, and computer program product for balancing transmission unit traffic over network links, including disposing transmission units into flows; grouping flows into first flow lists, each corresponding to a selected network link; determining a traffic metric representative of a traffic load on the selected network link; responsive to the traffic metric, regrouping flows into second flow lists corresponding to the selected network link, the regrouping balancing the transmission unit traffic among the network links; and transmitting the respective second flow list over the respective selected network link. The invention also can include a method for transmitting transmission units through a network, including receiving a transmission unit from a transmission unit source; classifying the transmission unit according to a predetermined flow characteristic; selecting a preselected network link over which the transmission unit is to be transmitted; and transmitting the transmission unit over the preselected network link.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
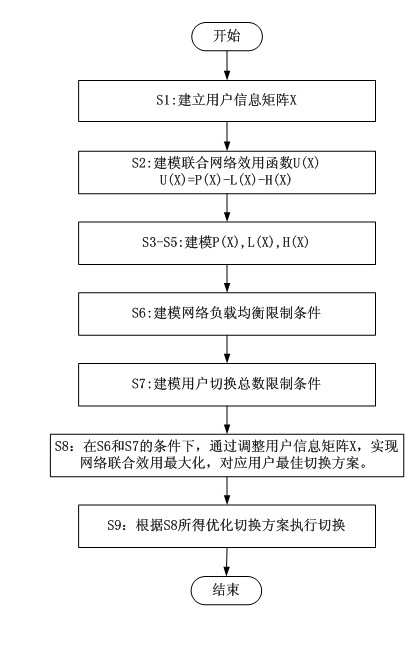
Heterogeneous network vertical handover method based on network joint effect optimization and load balancing
InactiveCN102625370AVertical Toggle MaximizationJoint utility optimizationNetwork traffic/resource managementAccess networkQuality of service
The invention discloses a heterogeneous network vertical handover method based on network joint effect optimization and load balancing and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. According to the invention, load balancing and network joint effect maximization between access networks are realized through optimized vertical handover and access network selection of users of a commonly covered area of heterogeneous access networks. A user information matrix is established, a network joint effect function is modeled, and under the conditions of giving access network load balancing, joint network user handover times and the like, optimized user vertical handover and network election schemes are obtained through maximizing the network joint effect.According to the heterogeneous integration realizing network, user vertical handover and network selection schemes of access network load, user handover times, user business characteristics and other factors are comprehensively considered, the maximization of network comprehensive benefits and the enhancement of quality of service (QoS) for users are realized.
Owner:SHENZHEN TINNO WIRELESS TECH
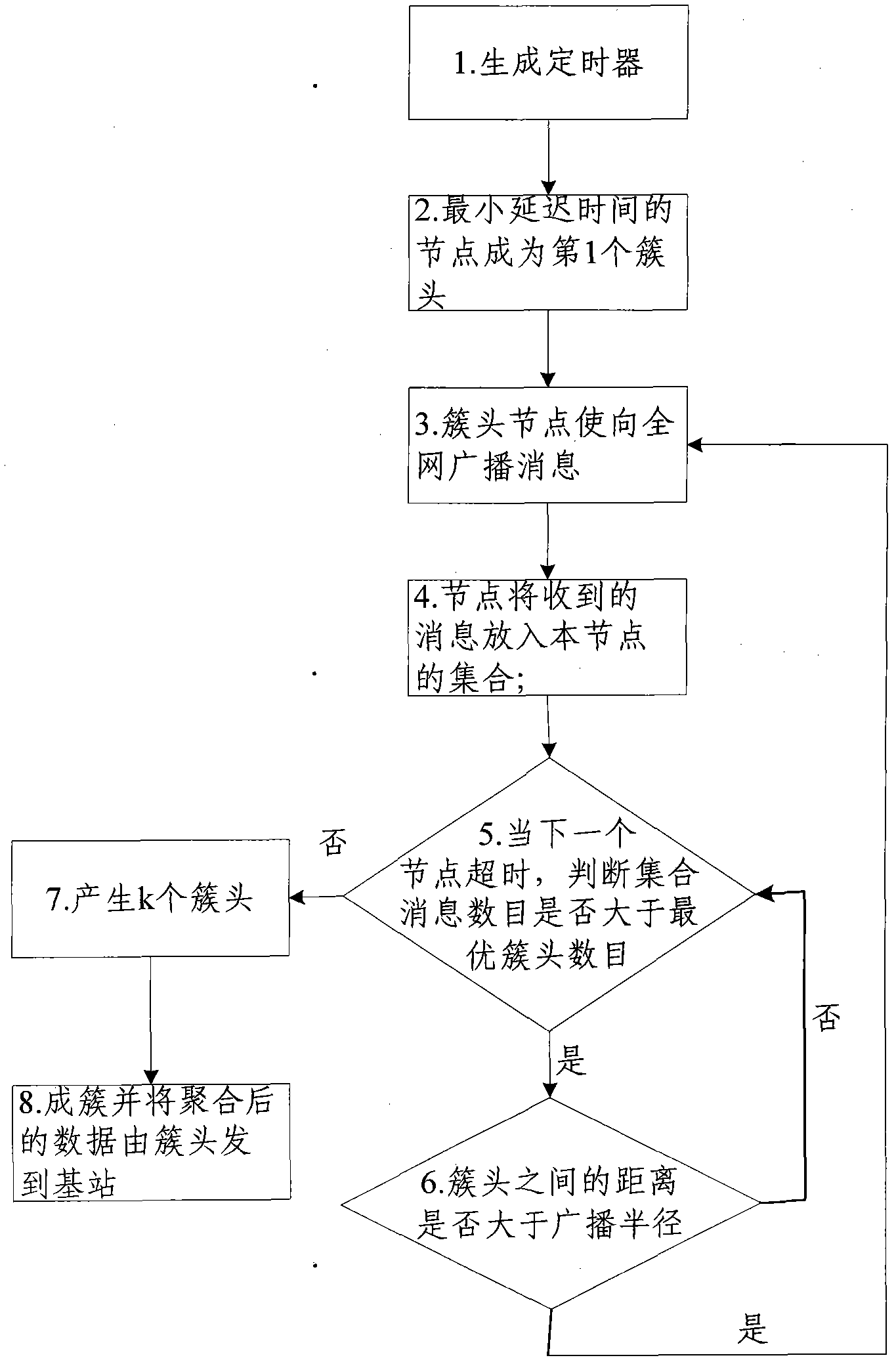
Distributed multi-jump energy-saving communication method in wireless sensor network
ActiveCN102026331AAvoid confictLower energy billsPower managementEnergy efficient ICTWireless sensor networkingEnergy consumption
The invention relates to a method for carrying out distributed multi-jump energy-saving communication in a wireless sensor network. In a process of cluster head selection, a node with large energy is preferentially used as a cluster head, and cluster heads with the same energy can not collide in a process of cluster head competition, thereby the cluster heads are uniformly distributed. In a process of transmitting data to a base station from the cluster heads, the cluster heads uniformly distributed in the network constitute a route tree, and the quantity of cluster head nodes directly communicating with the base station is reduced in the mode of multi-jump transmission, thereby energy consumption is further reduced. Simultaneously, the method also limits the shortest transmitting distance of a multi-jump route, lowers the circuit consumption of a middle node, reduces the transmission times of multi-jump data, saves the energy consumption of the network, weakens the hot problems in the network, saves network energy, keeps network load balanced and prolongs the life cycle of the network.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
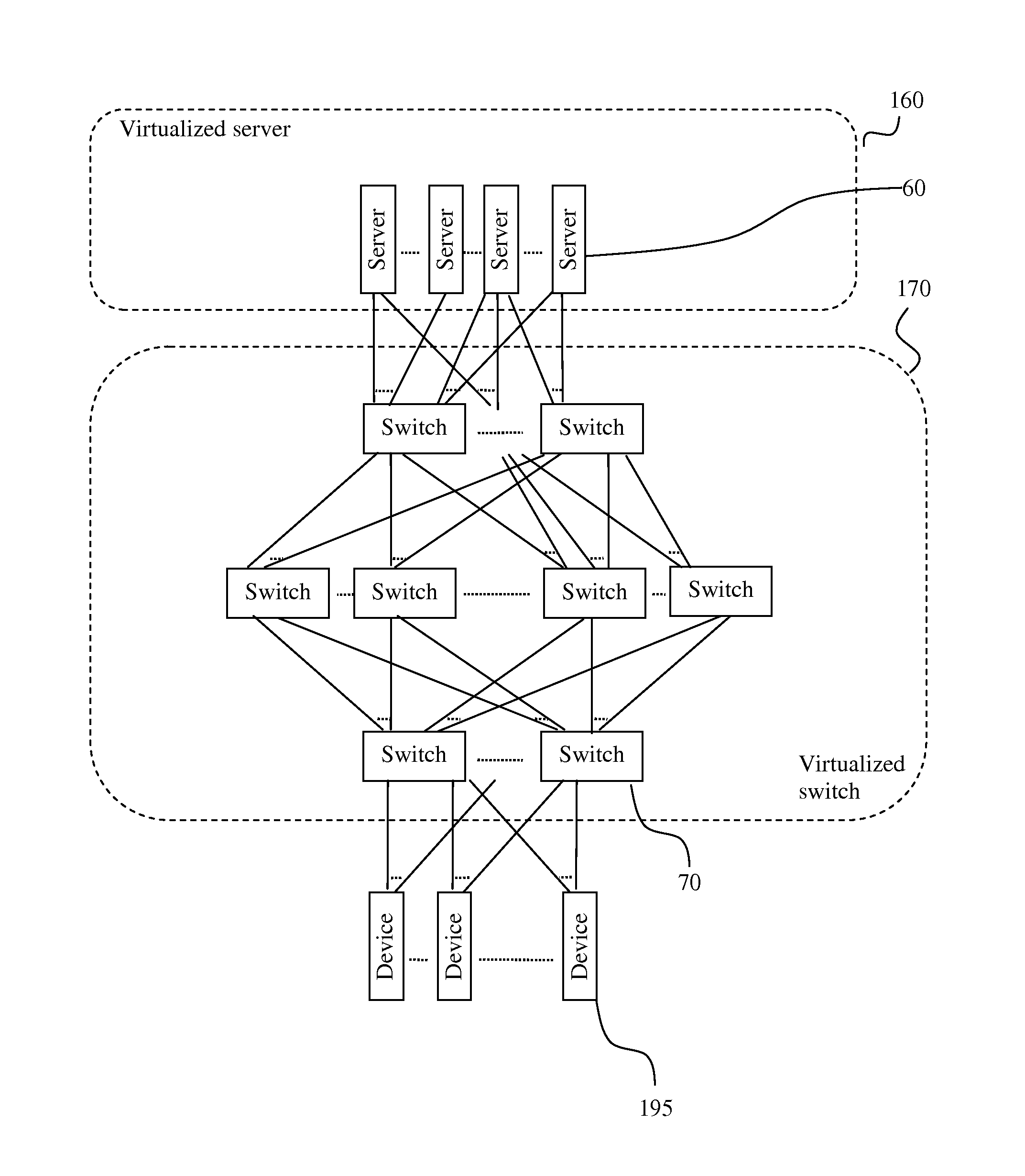
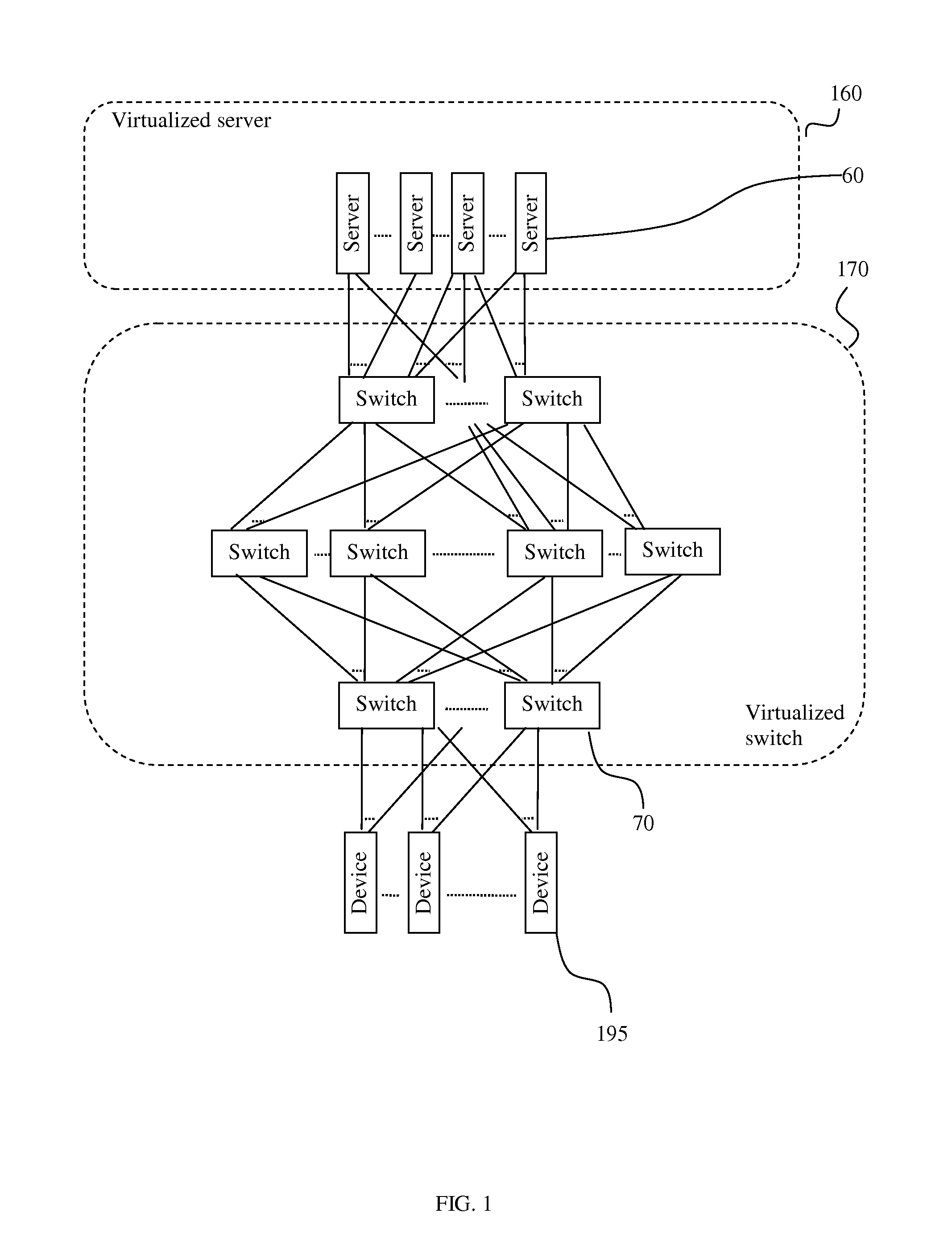
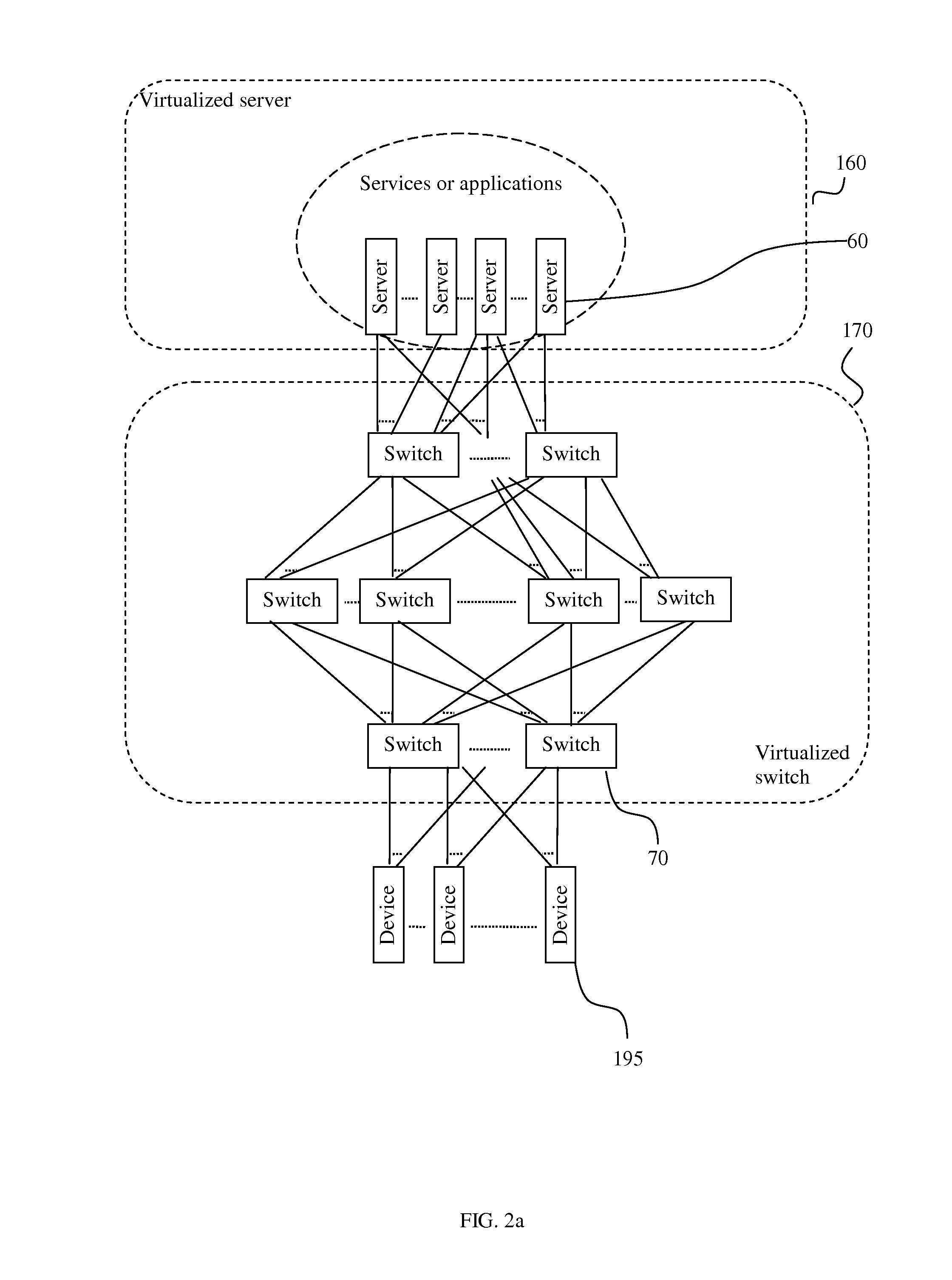
Network traffic load balancing
InactiveUS20140307553A1Large capacityReduce failureError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityTelecommunications
A system and methods of using commodity switches and commodity servers to produce a load-balanced, highly-available network for a computing cloud are disclosed. The system comprises switches and servers. The switches are organized in tiers. The switches in the highest tier are connected to the servers via uplink switch ports. The switches in the lowest tier are connected to devices external to the system via downlink switch ports. A packet received from any downlink switch port is forwarded to one of the at least one link aggregation of uplink switch ports. A packet received from any uplink switch port is forwarded according to the first label in the packet. A server is configured to insert one or more labels in a packet to be sent out via the switches. A value in a label indicates the switch port to be selected to send out the packet received at a switch.
Owner:FUNG HEI TAO
System, method and program product for streamlined virtual machine desktop display
InactiveUS20130132971A1Lower latencyImprove responsivenessStatic indicating devicesMultiprogramming arrangementsOperating systemNetwork Load Balancing
A shared resource system, method of updating client displays and computer program products therefor. At least one client device locally displays activity with resources shared with the client device. A management system on provider computers that is providing resources shared by the client devices selectively generates prioritized display updates. The management system provides updates to respective client devices according to update priority. Updates may also be ordered for network load balancing.
Owner:IBM CORP
Network load balancing with connection manipulation
ActiveCN1607781AData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsComputer scienceProtocol stack
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
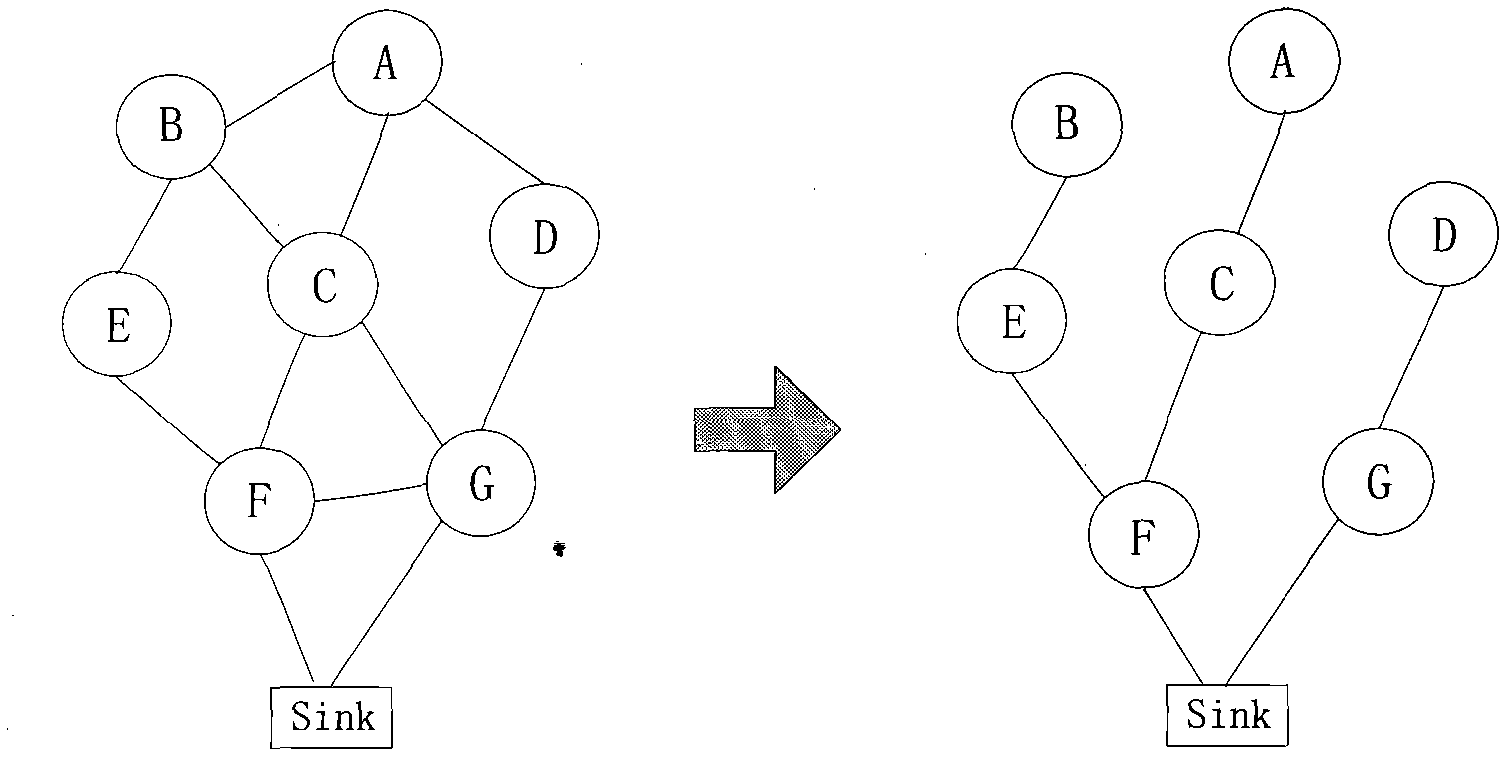
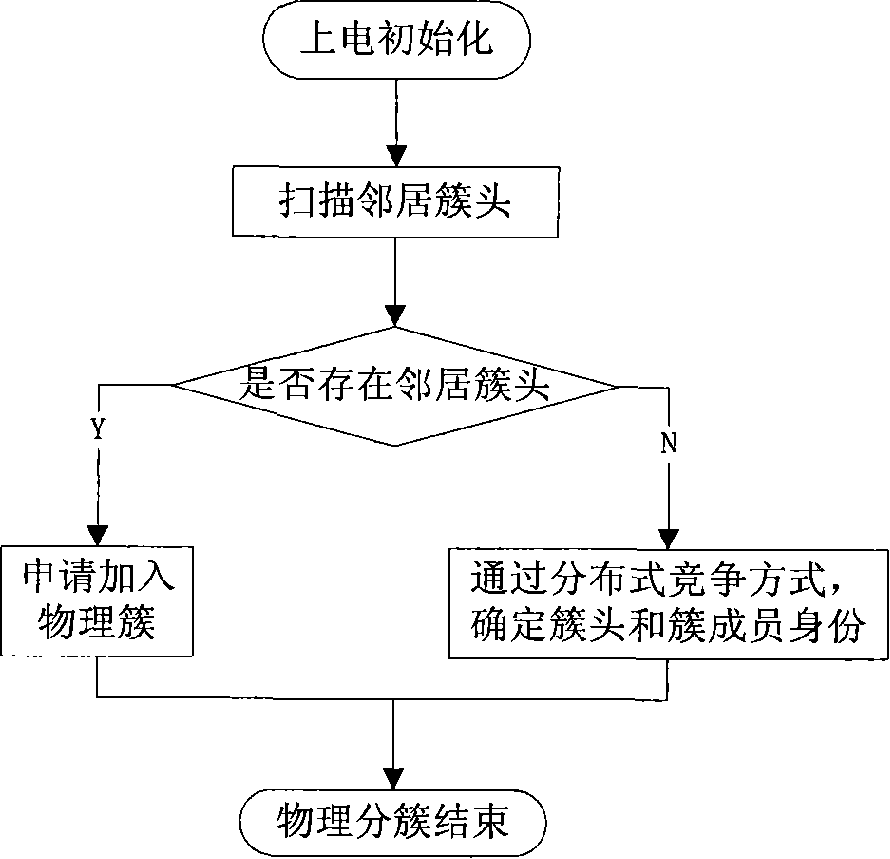
Double cluster based wireless sensor network distributed topology control method
InactiveCN101184004ALoad balancingImprove energy efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTData switching by path configurationWireless sensor networkingLife time
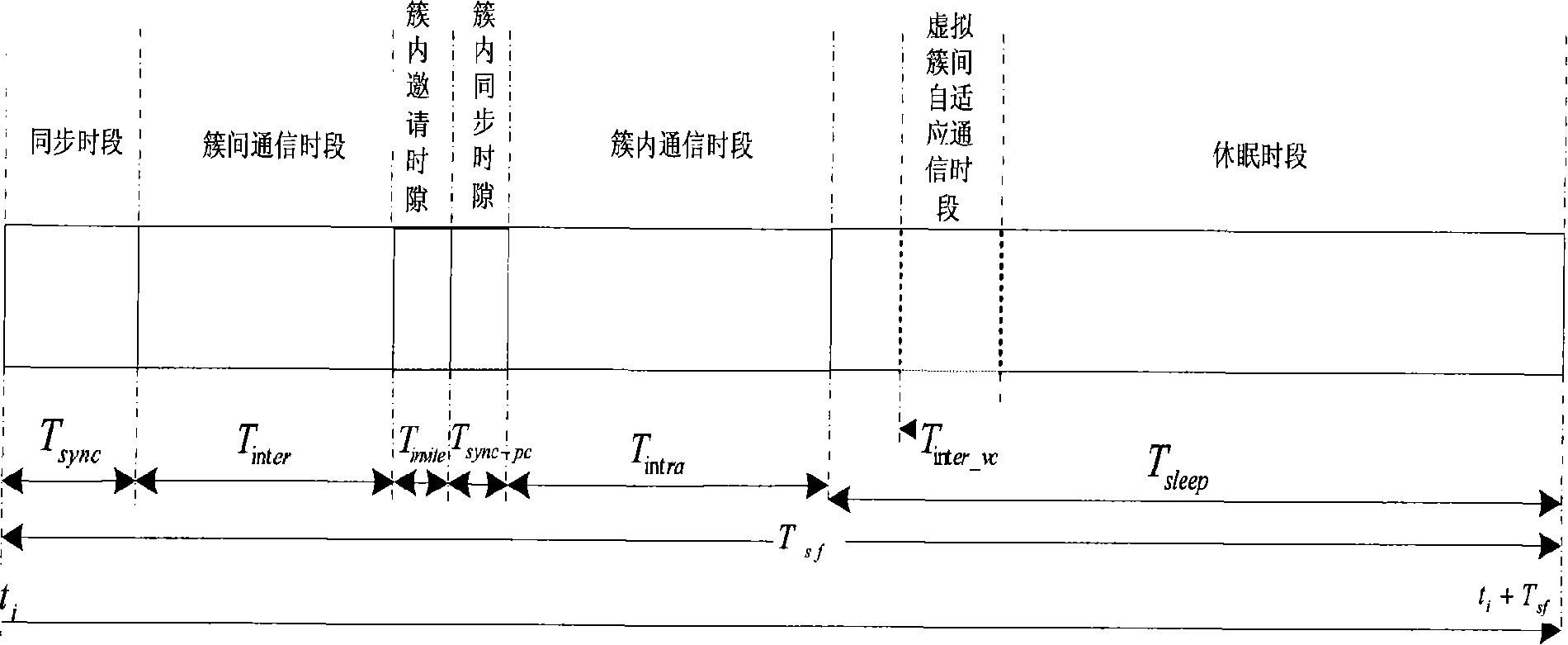
The invention relates to a distributed topology control realization method for wireless sensor network based on double clustering, which comprises a physical clustering step and a virtual clustering step, wherein, the physical clustering step is determining the cluster head or cluster member status of each node, so as to form a physical cluster; the virtual clustering step adopts distributed competitive mode; the cluster head of the physical cluster can generate own cycle dispatch table or follow the cycle dispatch table which is generated by the adjacent cluster head, so that the cluster heads of the adjacent physical clusters can form a virtual clustering which is run periodically and slept synchronously, and the communication between the cluster heads can be realized through an adaptivecommunication mechanism. The invention aims at the characteristics of the wireless sensor network on energy limitation, application specificity, and random dense distribution of nodes; on the basis of meeting the specific QoS requirement, the network load balancing can be realized effectively; the network energy consumption efficiency can be enhanced and the life time of network system can be extended.
Owner:JIAXING WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS CENT CAS
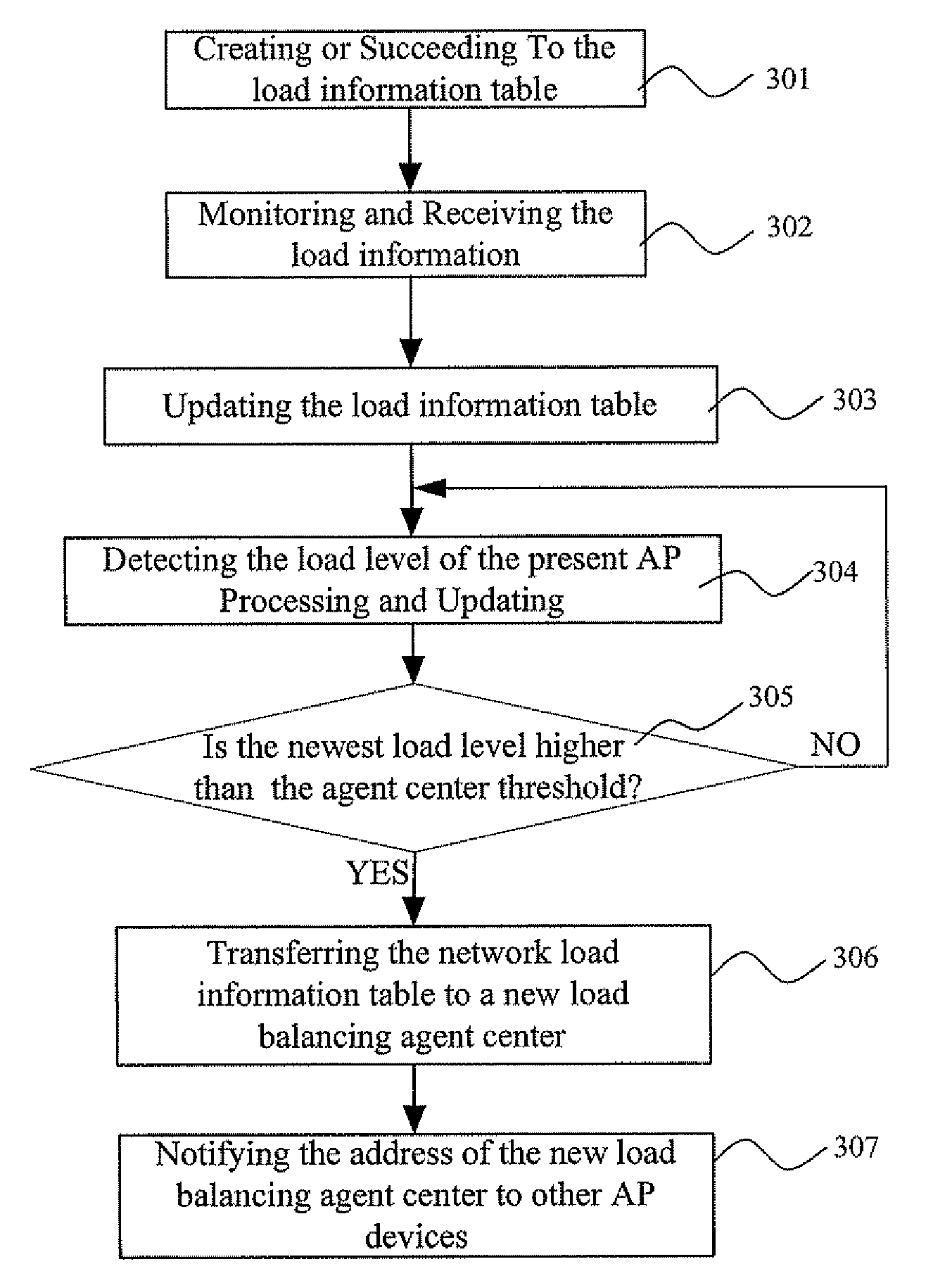
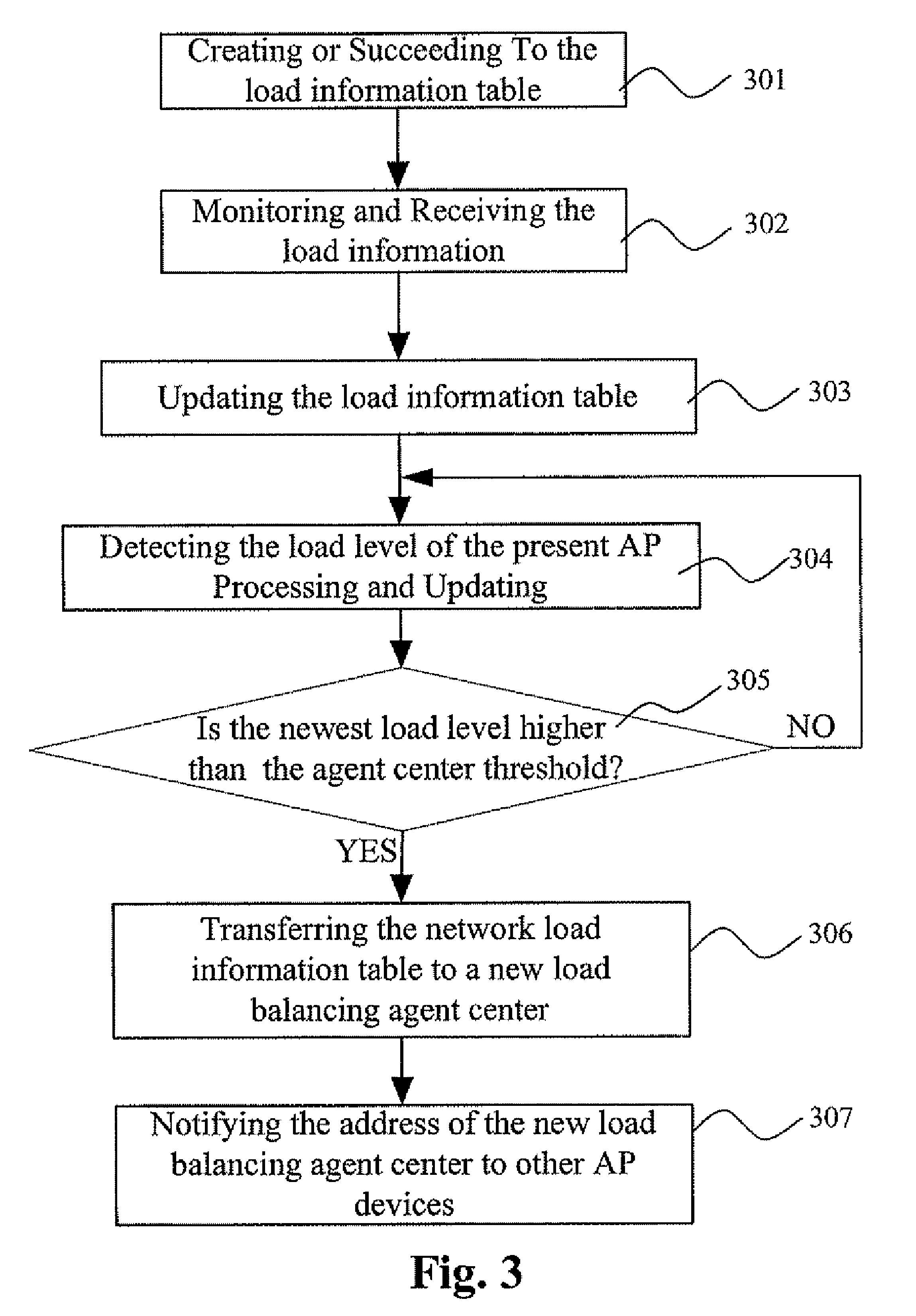
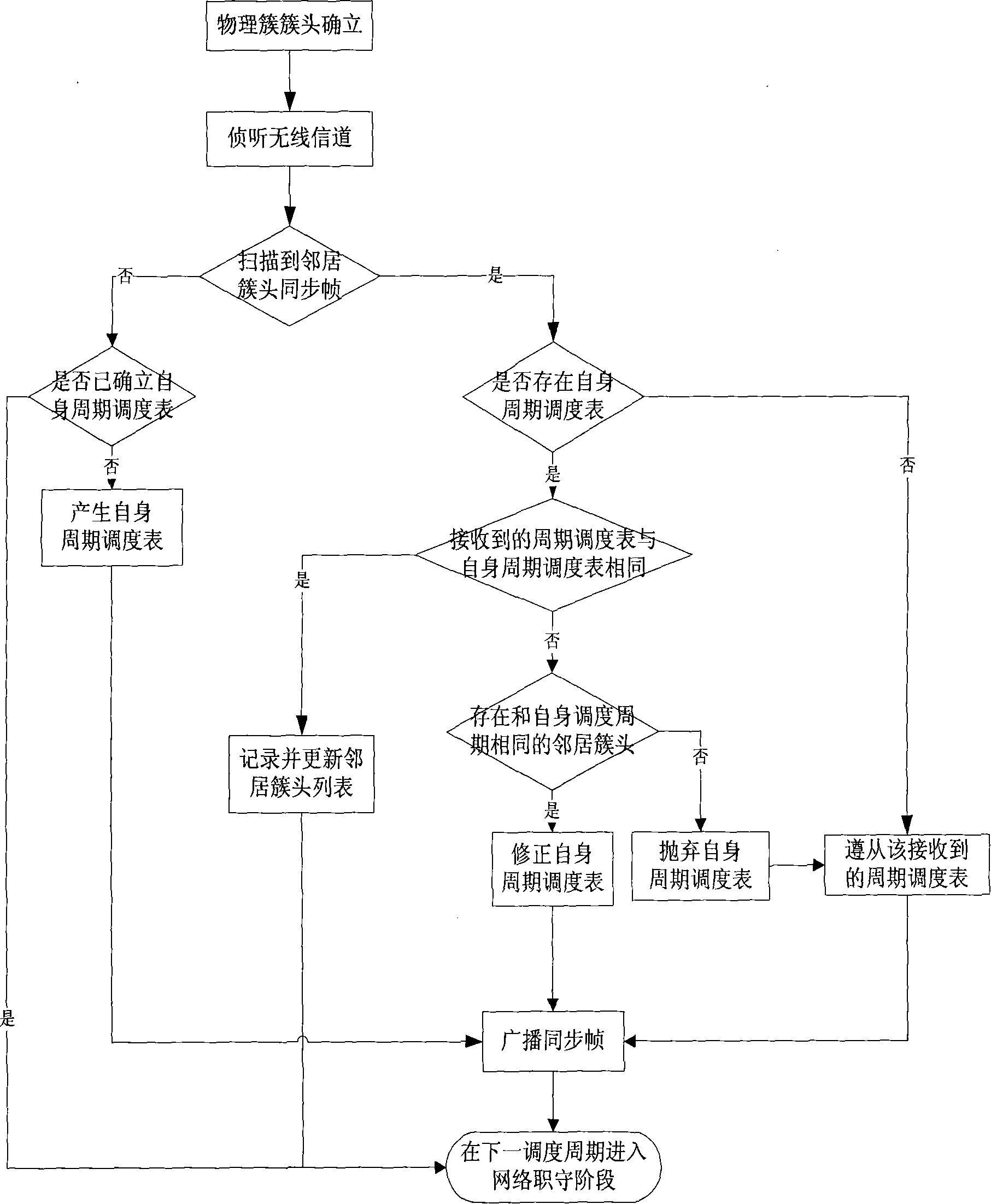
Dynamic network load balancing method and system
InactiveUS20050169294A1Solve the low efficiency of data transmissionGuaranteed normal transmissionNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexData transmissionSystem dynamics
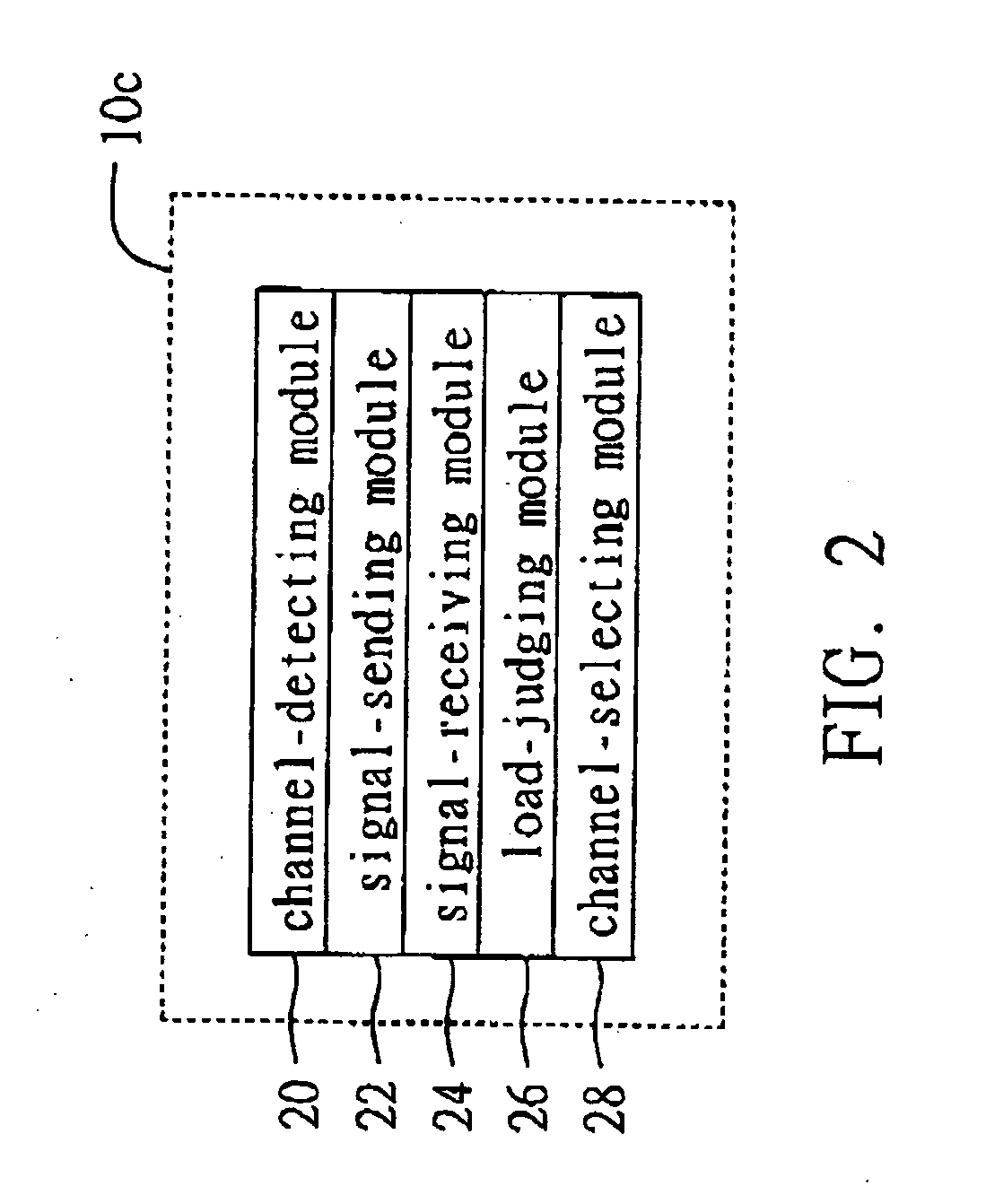
Dynamic network load balancing method and system are applicable to a wireless communication network. A channel-detecting module detects channels that provide wireless communications between network stations and a plurality of access points. A signal-sending module sends a probing data packet to each of the access points in a predetermined period via the channels detected by the channel-detecting module. A signal-receiving module receives a response data packet from each of the access points after receiving the probing data packets. A load-judging module calculates a response time between sending the probing data packet by the signal-sending module and receiving the response data packet by the signal-receiving module. A channel-selecting module selects a channel with the shortest response time for data transmission based on the response time for each of the channels calculated by the load-judging module. The channel-selecting module also can switch channels according to a predetermined threshold value for switching.
Owner:RDC SEMICON CO LTD
A network load balancing system and a balancing method based on deep reinforcement learning
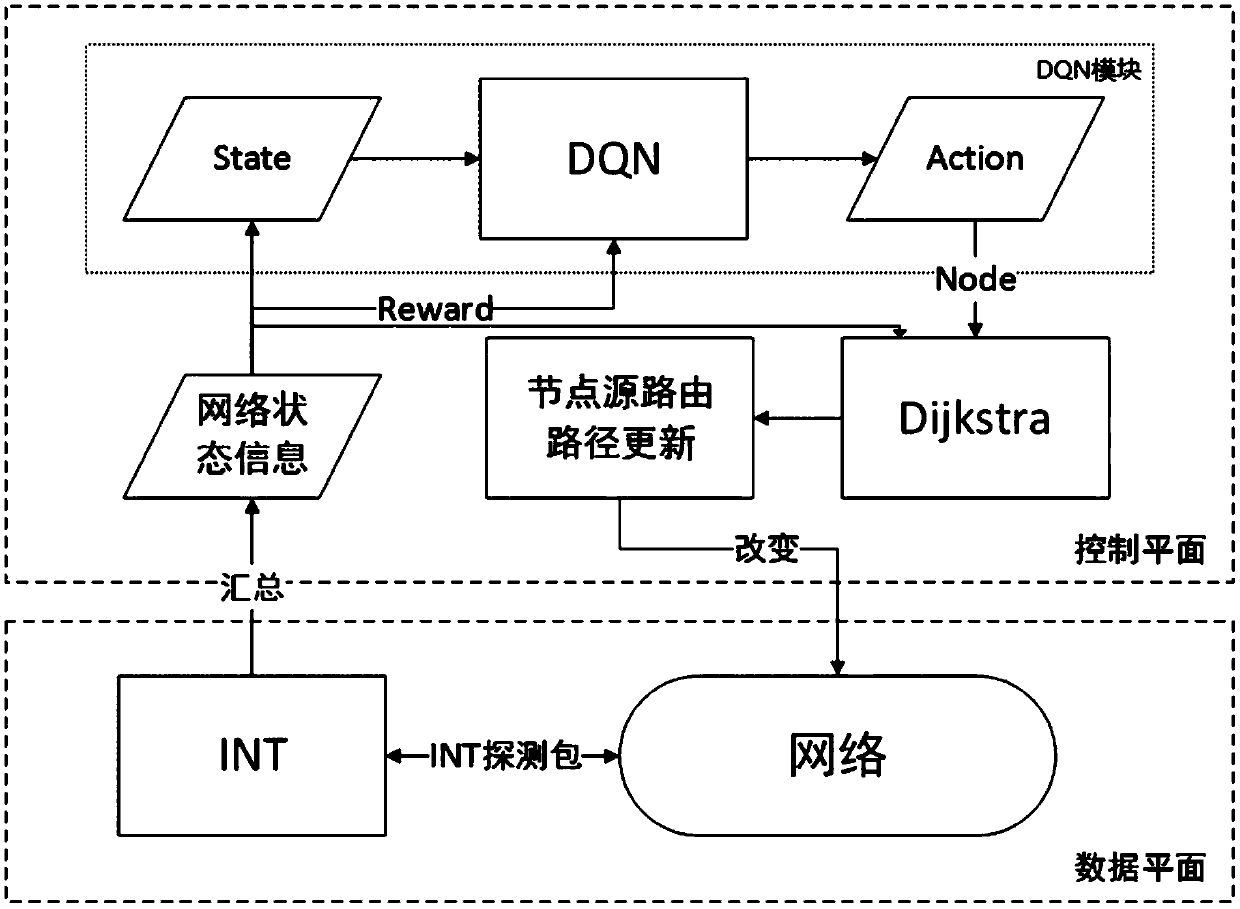
ActiveCN109039942ASimple structureLoad balancingComputing modelsData switching networksNetwork modelRouting algorithm
The invention discloses a network load balancing system and a balancing method based on depth reinforcement learning. The balancing system comprises a control plane and a data plane. The control planecomprises an INT module and a network module. The INT module obtains network information on each node in the network module by sending a detection packet and sends the network information to the control plane. The control plane comprises a DQN module, a network state information module, a shortest path routing algorithm module and a node source route path update module. The network state information module receives the network information sent by the control plane and sends the network information to the DQN module. The output action of DQN module calls dijkstra algorithm module to calculatethe optimal path, and transmits the update result of node flow table to the corresponding node equipment in the network. This scheme is based on P4's INT technology and Deep Q Network model in artificial intelligence to achieve intelligent load balancing of SDN network, so as to realize the rational utilization of network resources, effectively improve network efficiency and reduce network congestion.
Owner:NANJING ZHAOSHICHANG NETWORK TECH
Network load balancing apparatus, systems, and methods
Apparatus, systems, methods, and articles described generally herein may receive a first packet marked with a congestion indicator (CI). Upon receipt of the CI, a load-balancing operation may be performed among a plurality of physical links upstream from a point of congestion to alleviate the congestion. Other embodiments may be described and claimed.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com