Method for balancing network load based on wireless sensor energy information
A wireless sensor, energy information technology, applied in wireless communication, data exchange network, network traffic/resource management, etc., can solve the problems of reducing network lifetime, only considering and so on, achieving strong scalability and prolonging the lifetime effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
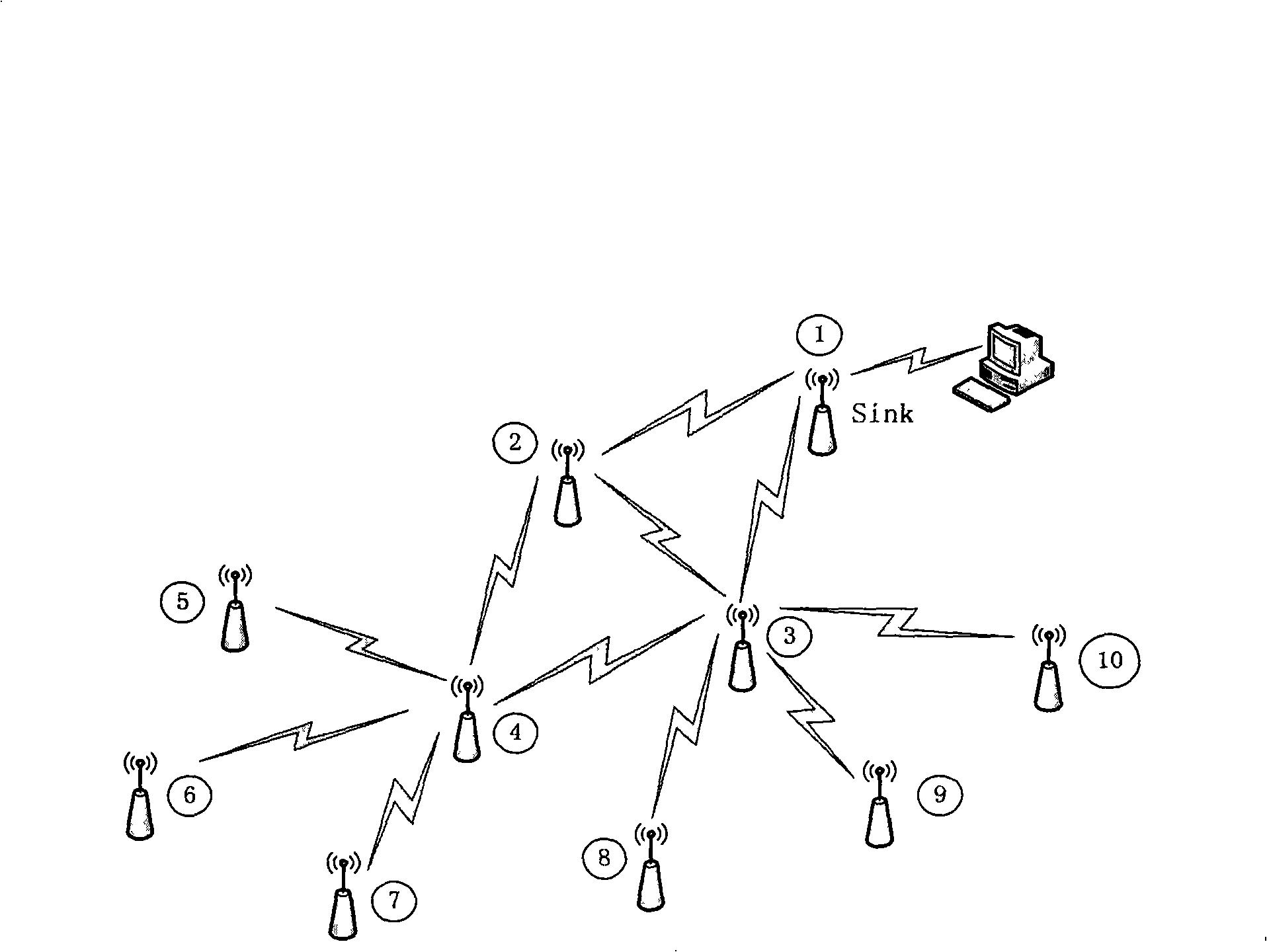
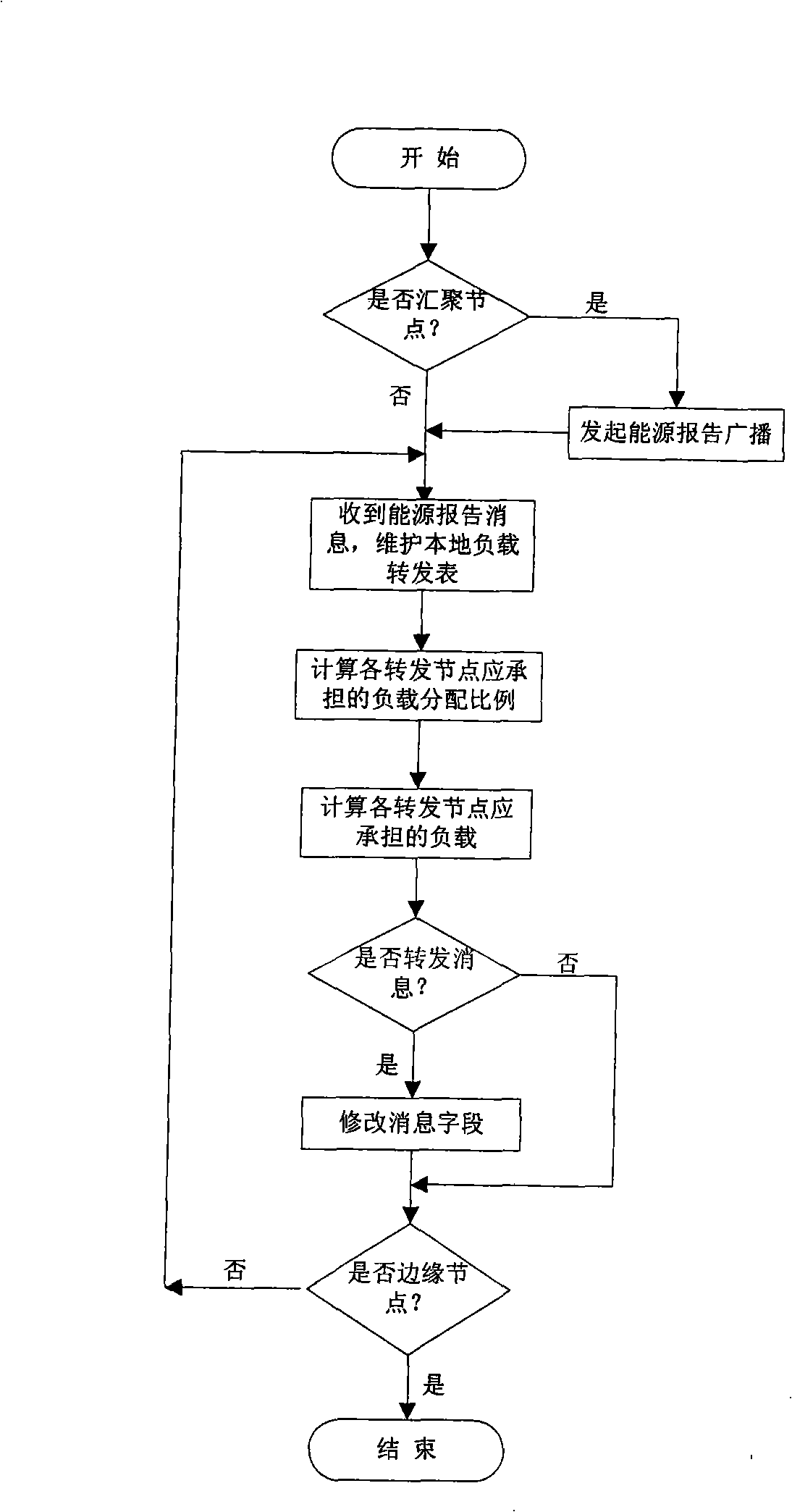
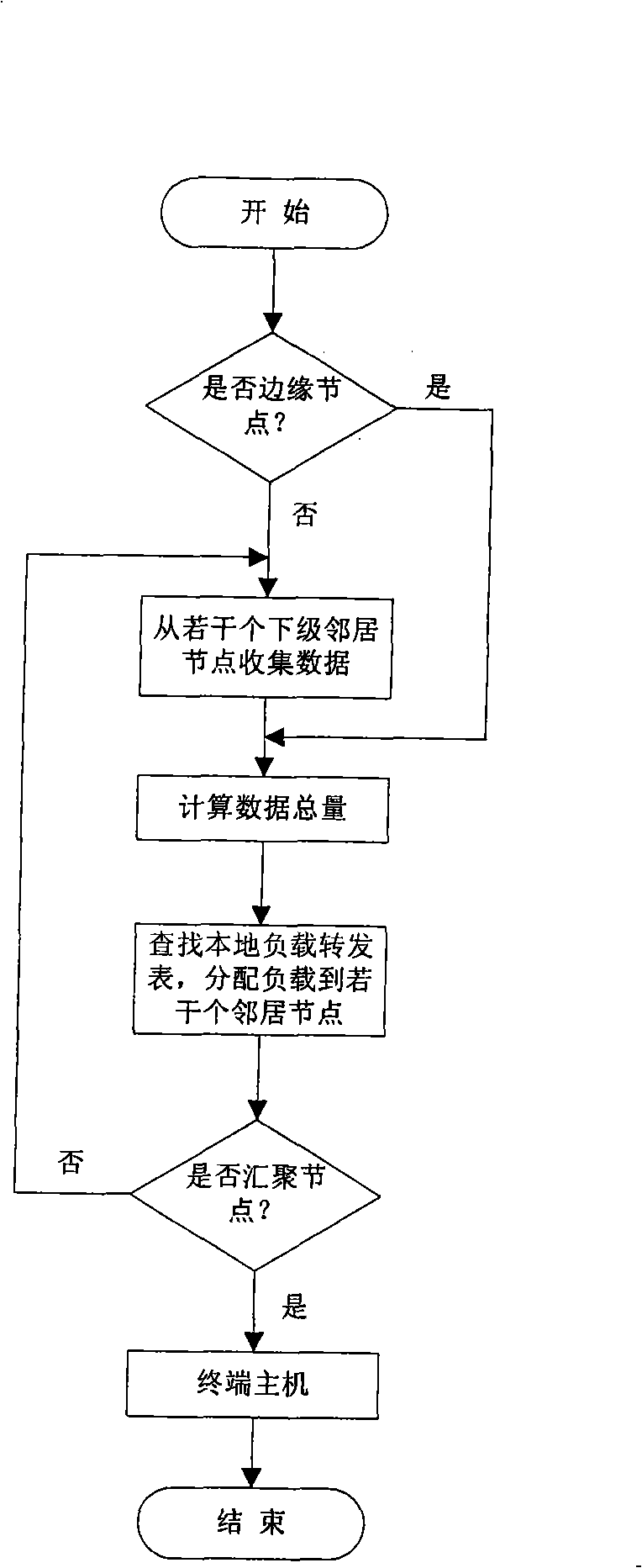
[0037] The present invention needs two prerequisites before concrete implementation:
[0038] First, each node in the wireless sensor network can calculate its own remaining energy and consumed energy.
[0039] The energy consumption model of the node mainly includes the energy consumed by the wireless transceiver and the energy consumed by the power amplifier, which can be expressed by the following formula:
[0040] E. Tx (k,d)=E Tx-elec (k)+E Tx-amp (k,d)=E elec *k+ε amp *k*d 2
[0041] E. Rx (k)=E Rx-elec (k)=E elec *k
[0042] Among them, E Tx (k,d) and E Rx (k) are the sending energy and receiving energy consumed by the node to transmit k-bit data respectively, E Tx-elec (k) and E Tx-amp (k, d) are the energy consumed by the wireless transceiver and power amplifier on the node respectively, d is the distance between the sending node and the receiving node, E elec and ε amp Both are hardware-related parameters, which can be treated as constants in actual use...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com