Patents
Literature
4139 results about "Routing table" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
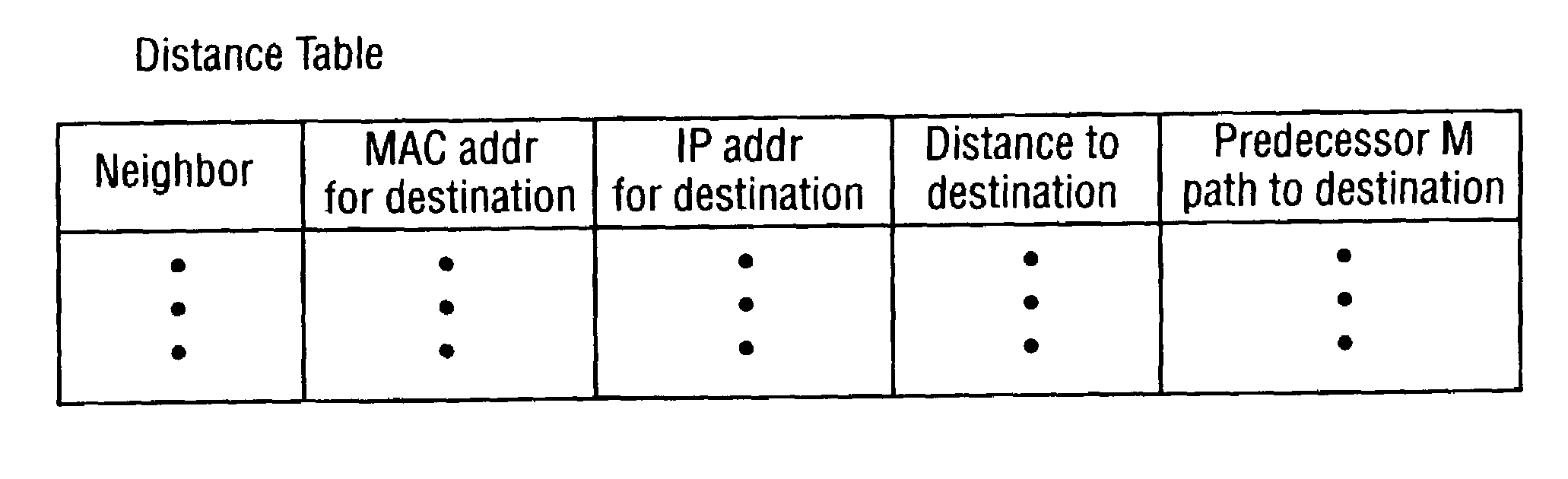
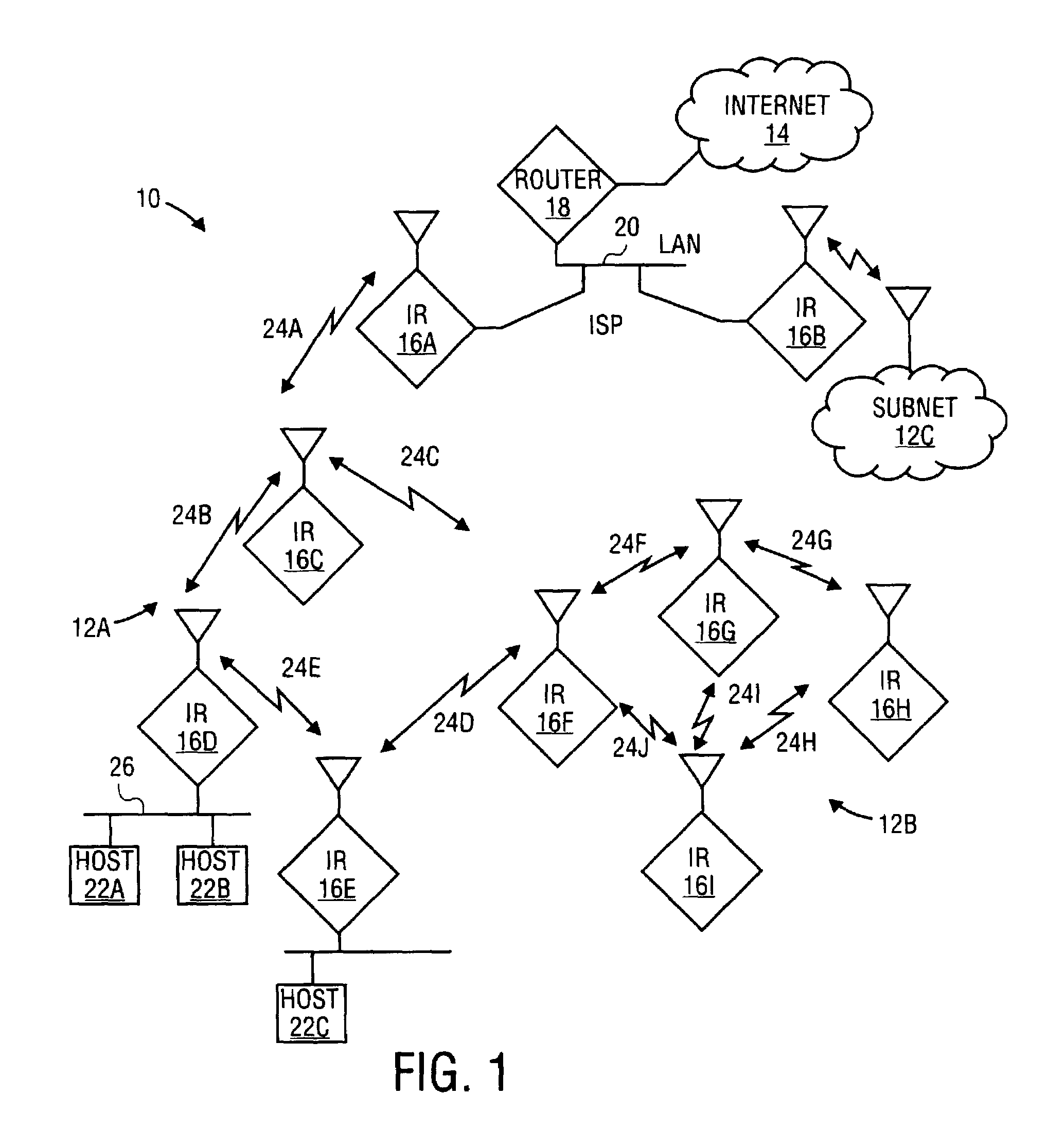
In computer networking a routing table, or routing information base (RIB), is a data table stored in a router or a network host that lists the routes to particular network destinations, and in some cases, metrics (distances) associated with those routes. The routing table contains information about the topology of the network immediately around it. The construction of routing tables is the primary goal of routing protocols. Static routes are entries made in a routing table by non-automatic means and which are fixed rather than being the result of some network topology "discovery" procedure.
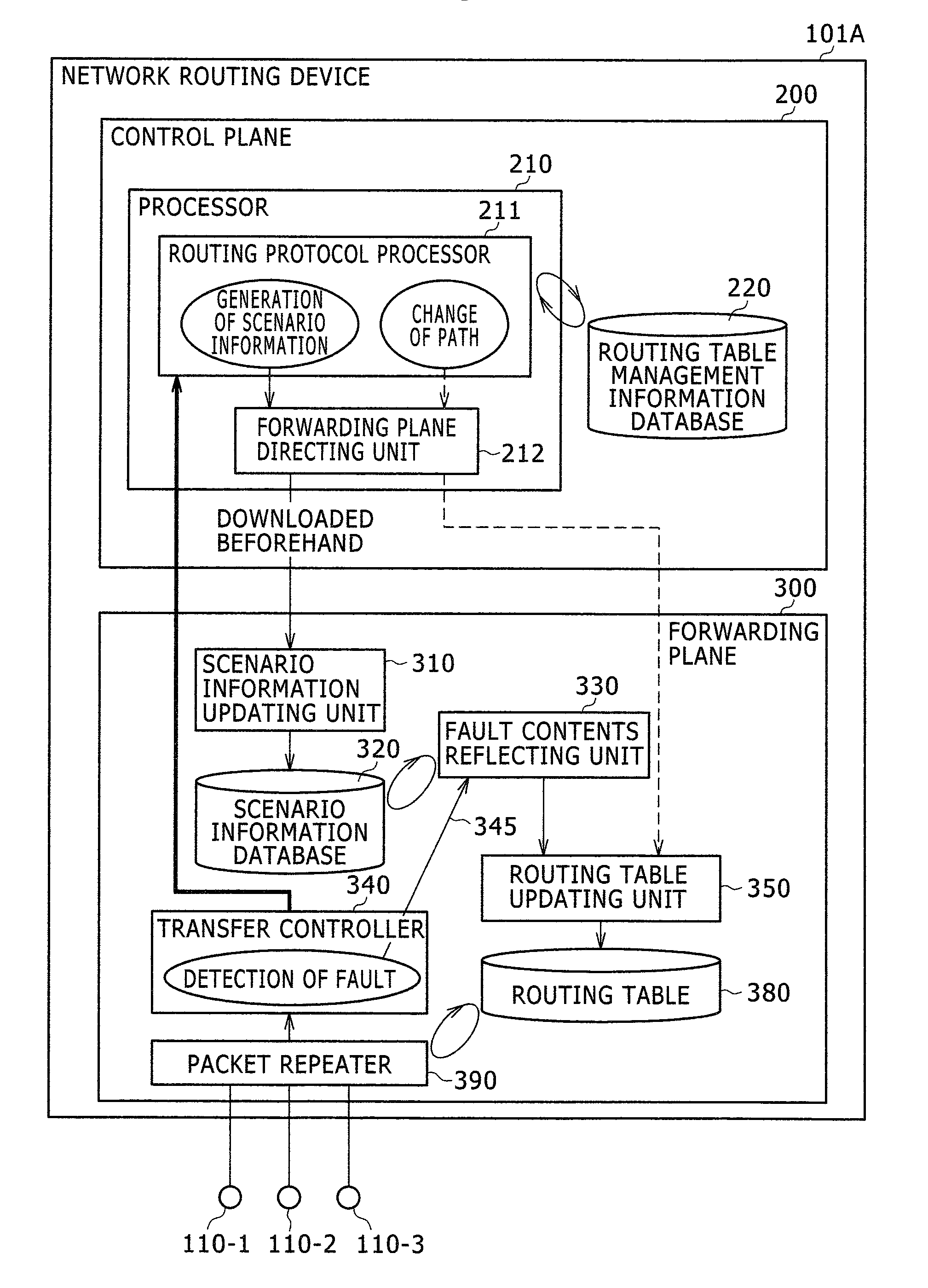
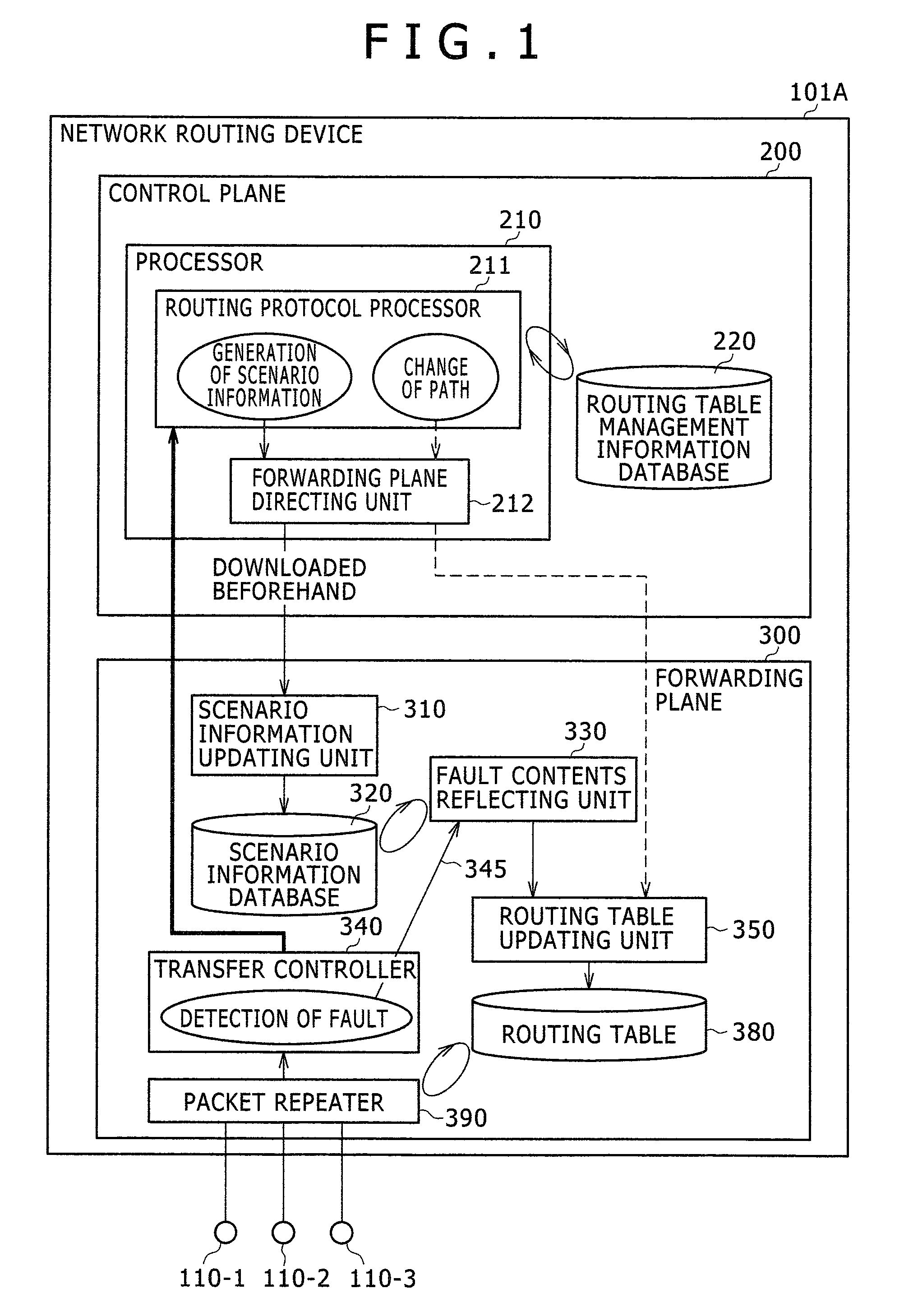
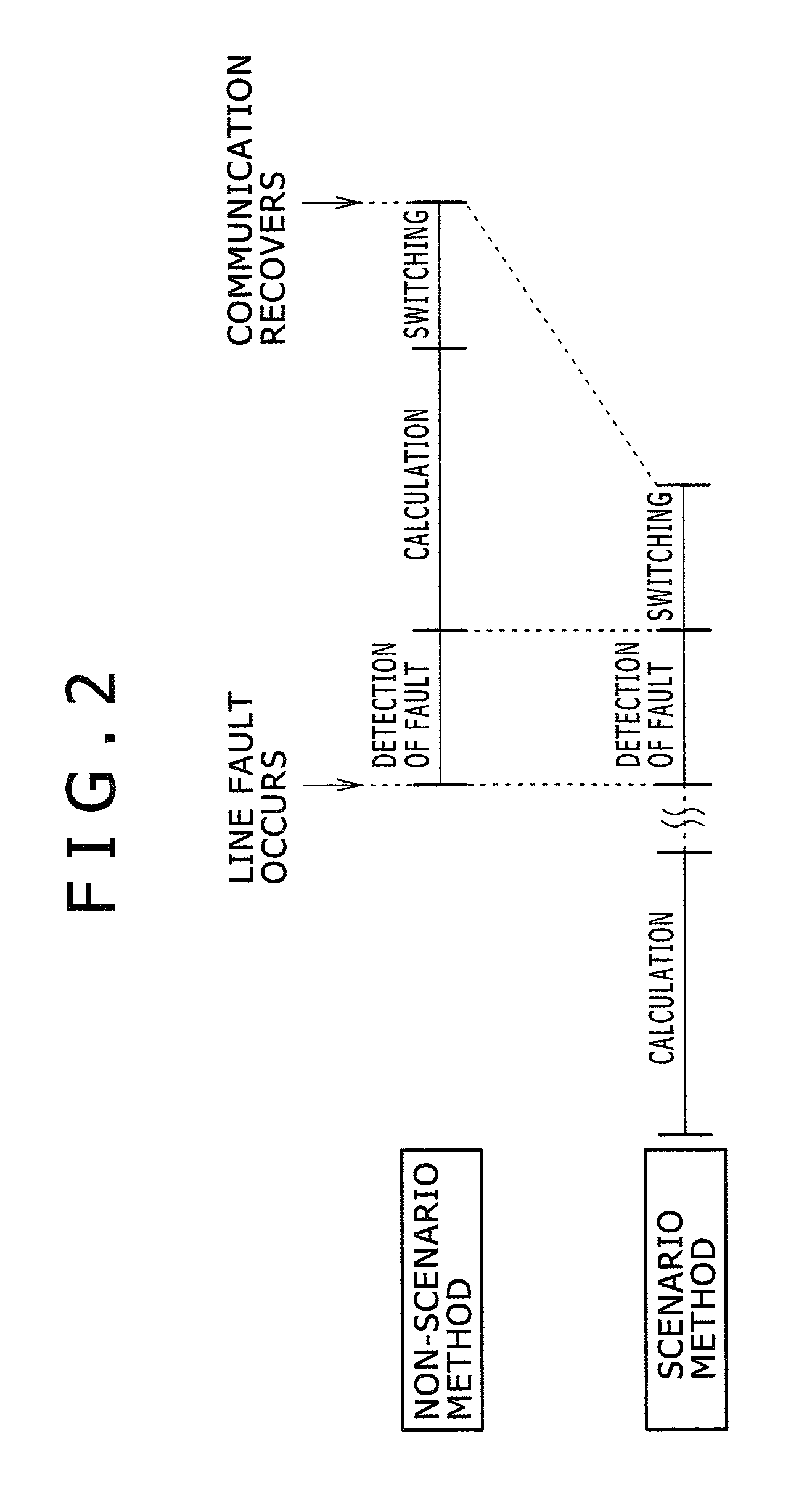
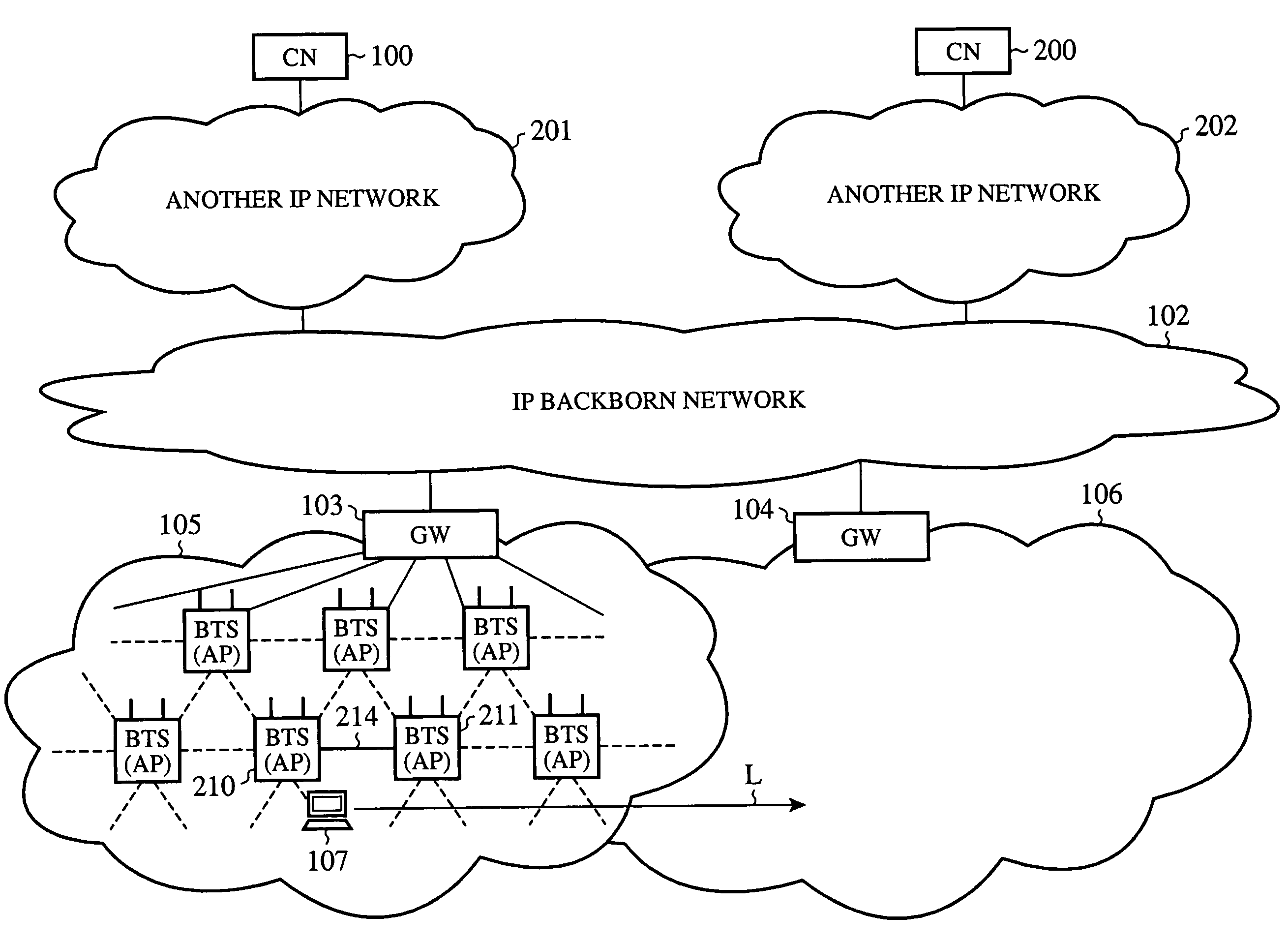
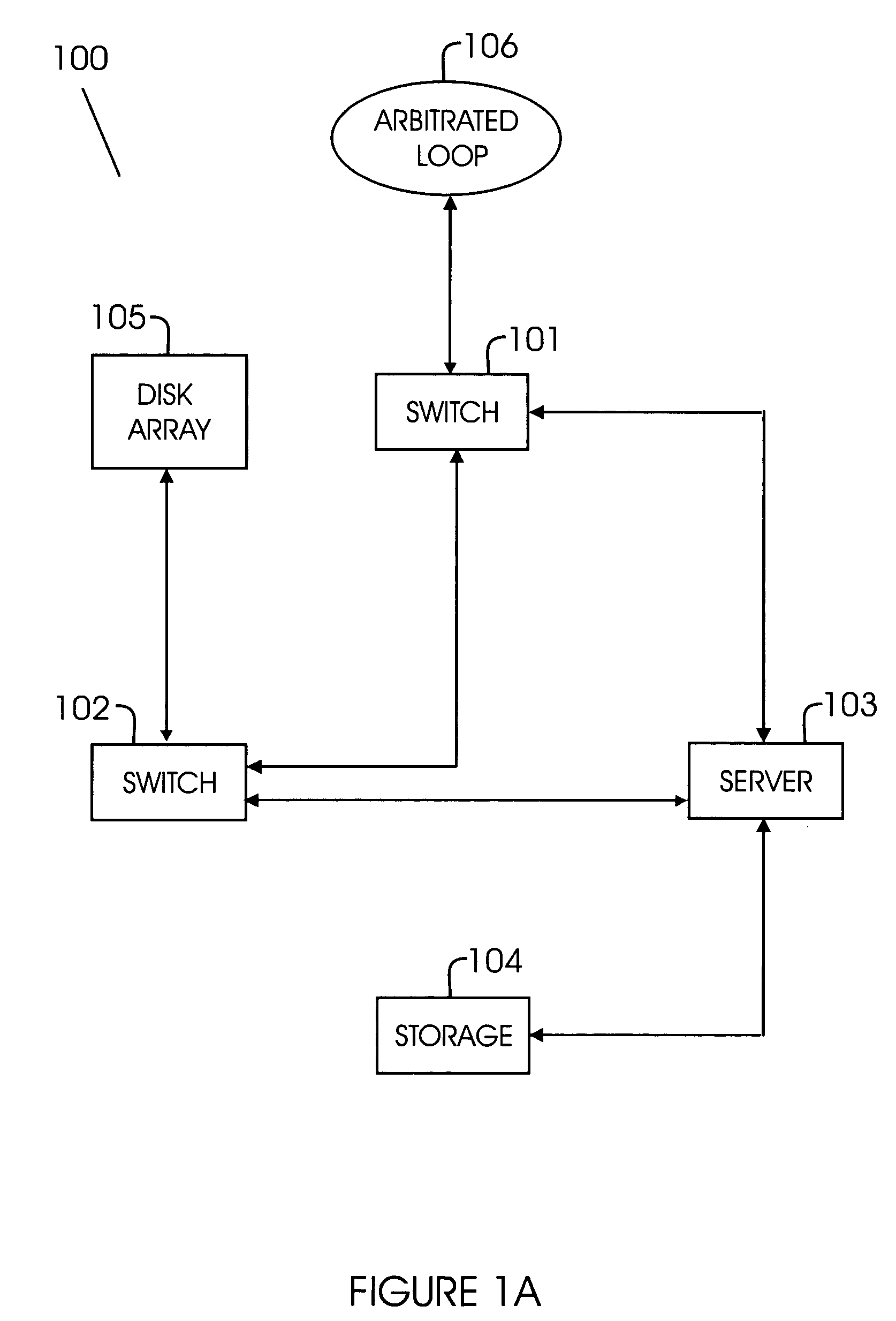
Network routing device and network routing method
A network routing device according to the invention transmits a packet via a second port based upon destination information included in the packet received via a first port referring to a routing table. In addition, the network routing device calculates beforehand a third port which is a transfer destination when a fault occurs in a destination connected to the second port. Further, the network routing device holds scenario information including a combination of the second port and the third port and updates the routing table based upon the scenario information when a fault is detected in either of the ports.
Owner:ALAXALA NETWORKS
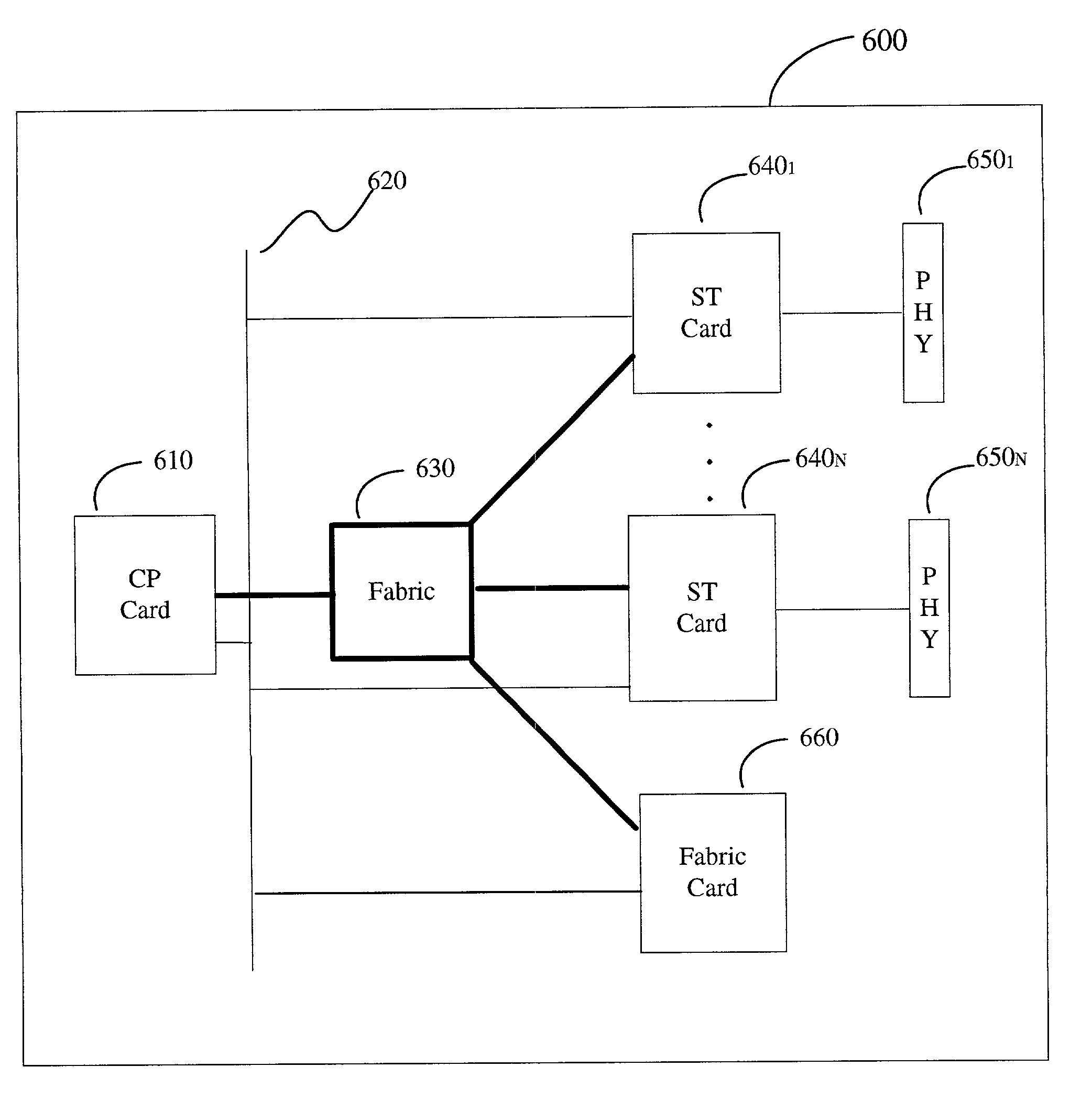
Information routing system and apparatus
ActiveUS6999454B1Time-division multiplexGeneral purpose stored program computerTraffic capacityRouting table
An information routing system and apparatus includes separate control and forwarding planes. The control plane is split into box management control functions and routing control functions. The box management control functions are isolated to a single processing card, while the routing control functions are distributed across multiple processing cards. The routing table is also distributed across multiple processing cards. The multiple processing cards are interconnected via a high-speed backplane bus for control plane traffic and by a fabric for forwarding plane traffic.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
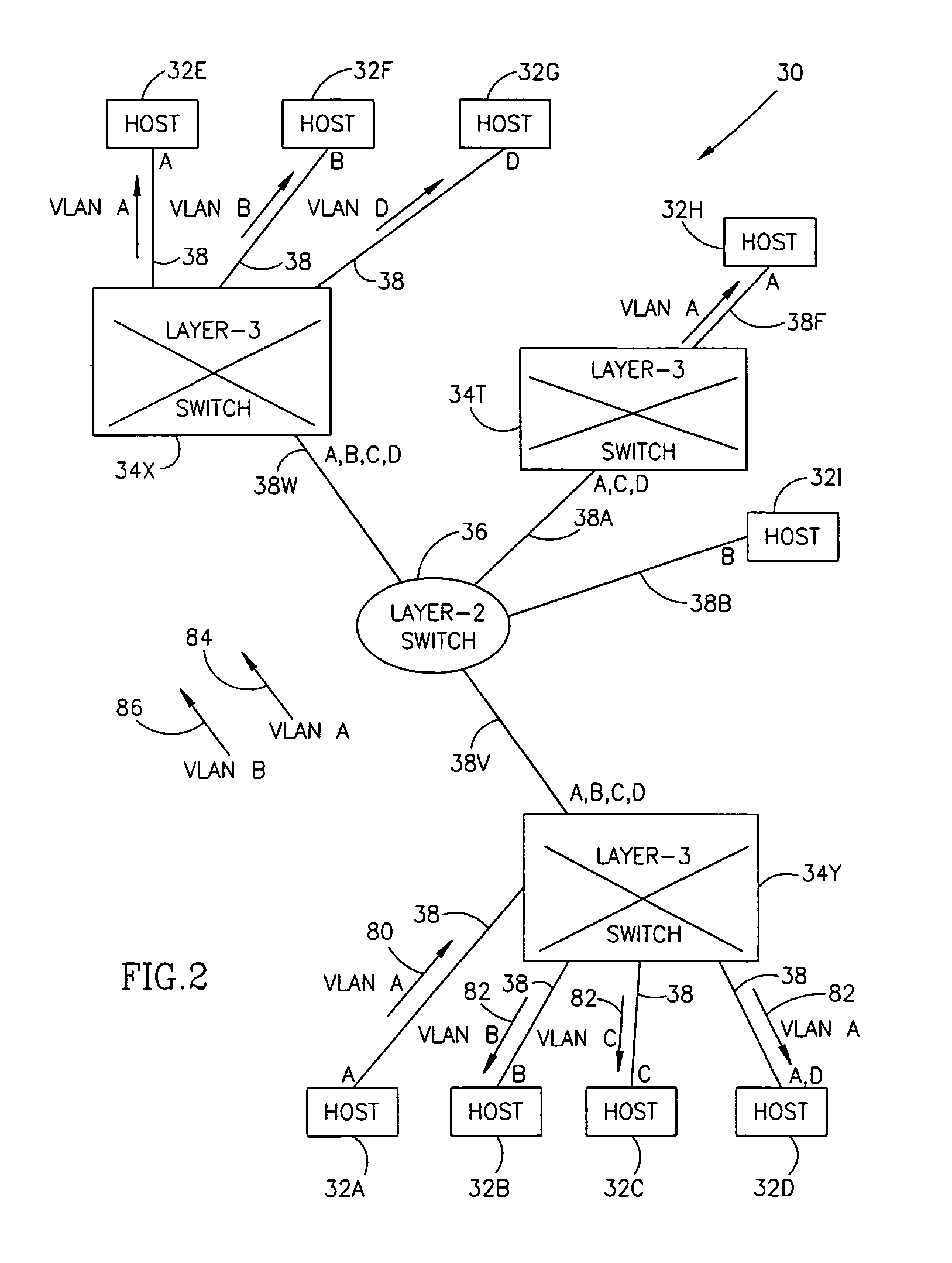
IP multicast in VLAN environment
ActiveUS7924837B1Avoid layeringEasy to implementError preventionTransmission systemsRouting tableVirtual LAN
A method of determining local multicast information of a local area network (LAN), comprising dividing the LAN to a number of segments larger than the number of virtual LANs (VLANs) in the network and creating a layer-3 multicast routing table, which relates to each of the segments separately.
Owner:AVAYA TECH CORP +1
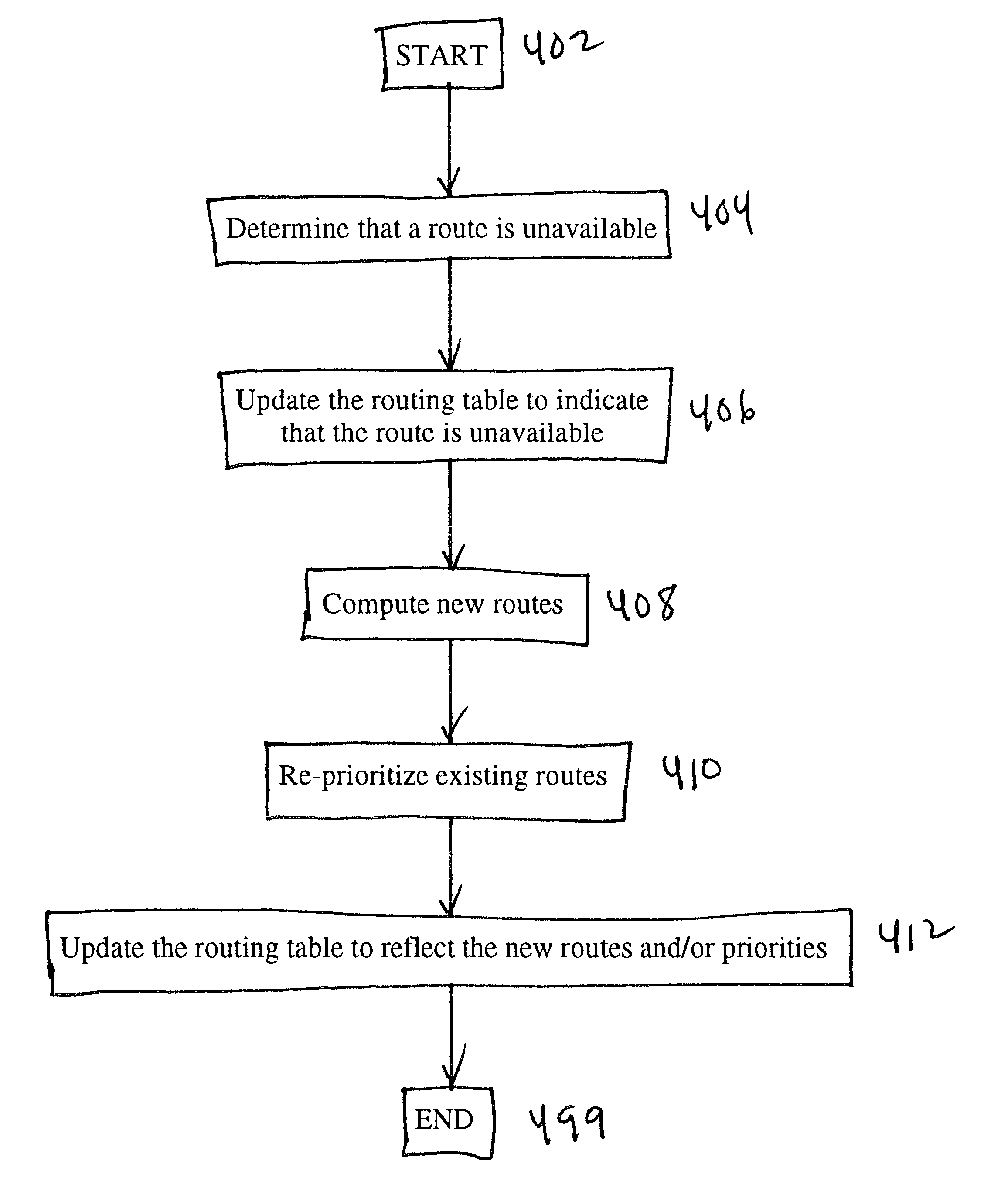
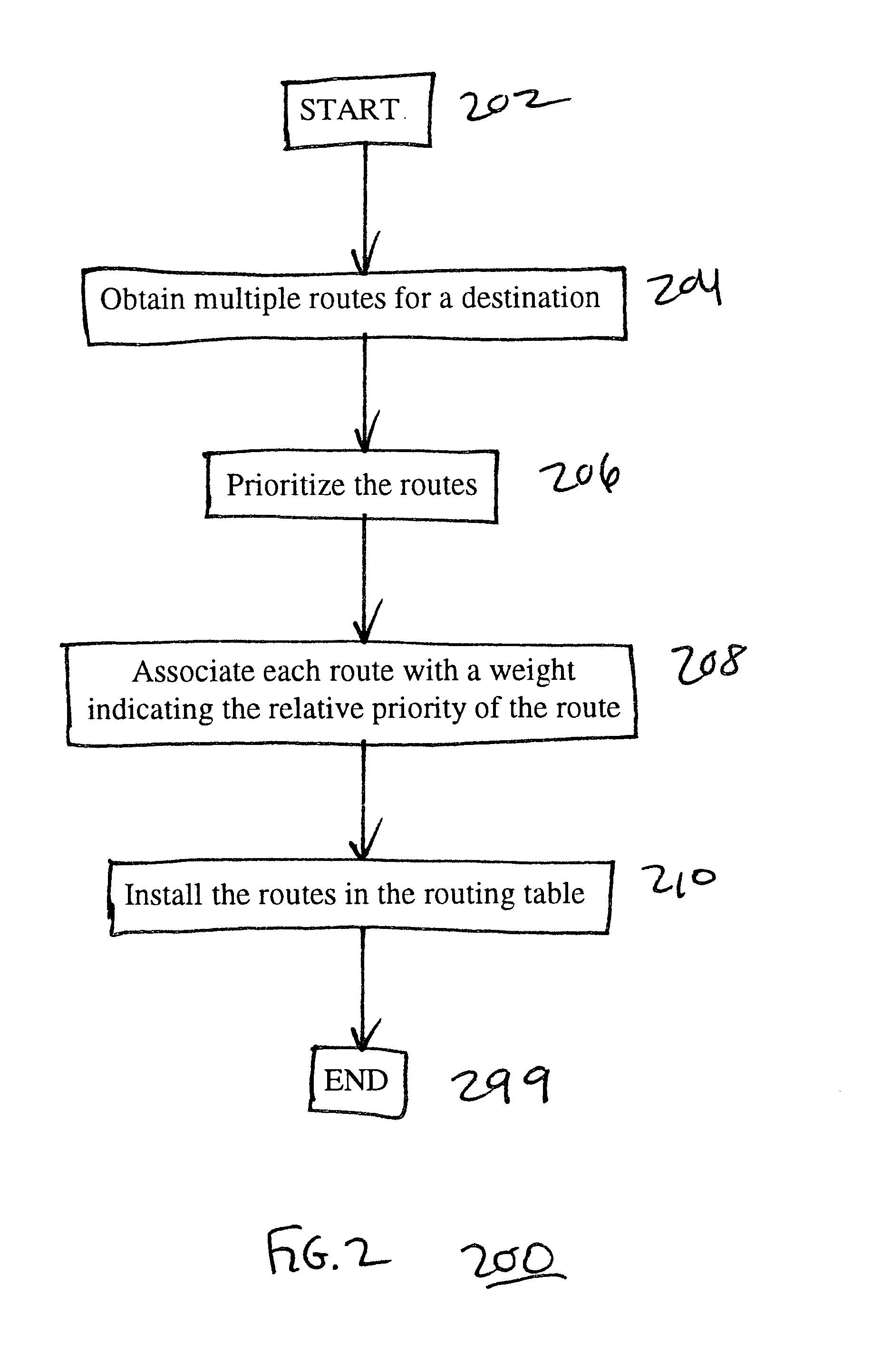
Using alternate routes for fail-over in a communication network
InactiveUS6857026B1Error detection/correctionData switching by path configurationFailoverRouting table
Using alternate routes for fail-over in a communication network involves maintaining a preferred route and an alternate route in a routing table and routing protocol messages according to the alternate route when the preferred route is unavailable. A node obtains multiple routes for a destination, prioritizes the routes, and installs multiple routes in the routing table, including at least the preferred route and the alternate route. When the node receives a protocol message, the node searches the routing table for a highest priority route that is available for routing the protocol message, and routes the protocol message according to the highest priority route that is available for routing the protocol message. When a route becomes unavailable, the node updates the routing table to indicate that the route is unavailable, and may compute new routes and / or re-prioritize existing routes.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Methods and systems for securing access to private networks using encryption and authentication technology built in to peripheral devices
A method for routing packets from a peripheral device to a Virtual Private Network (VPN) gateway includes the step of implementing, by a peripheral device, a change to a routing table. The peripheral device receives an outbound packet. The peripheral device transmits information about the outbound packet to a VPN client application. The peripheral device modifies address information on the outbound packet with address information associated with the VPN client application. The peripheral device transmits the modified outbound packet to the VPN client application.
Owner:CITRIX SYST INC
Method for network-aware clustering of clients in a network
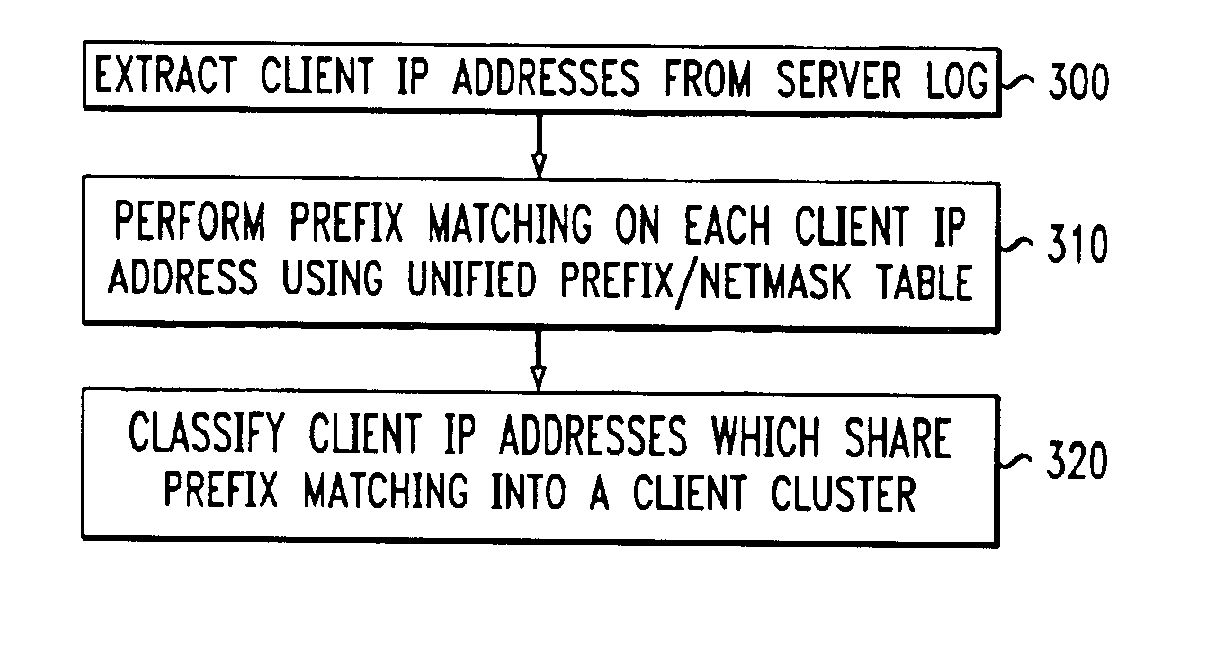
InactiveUS6928485B1Relational databasesMultiple digital computer combinationsServer logContent distribution
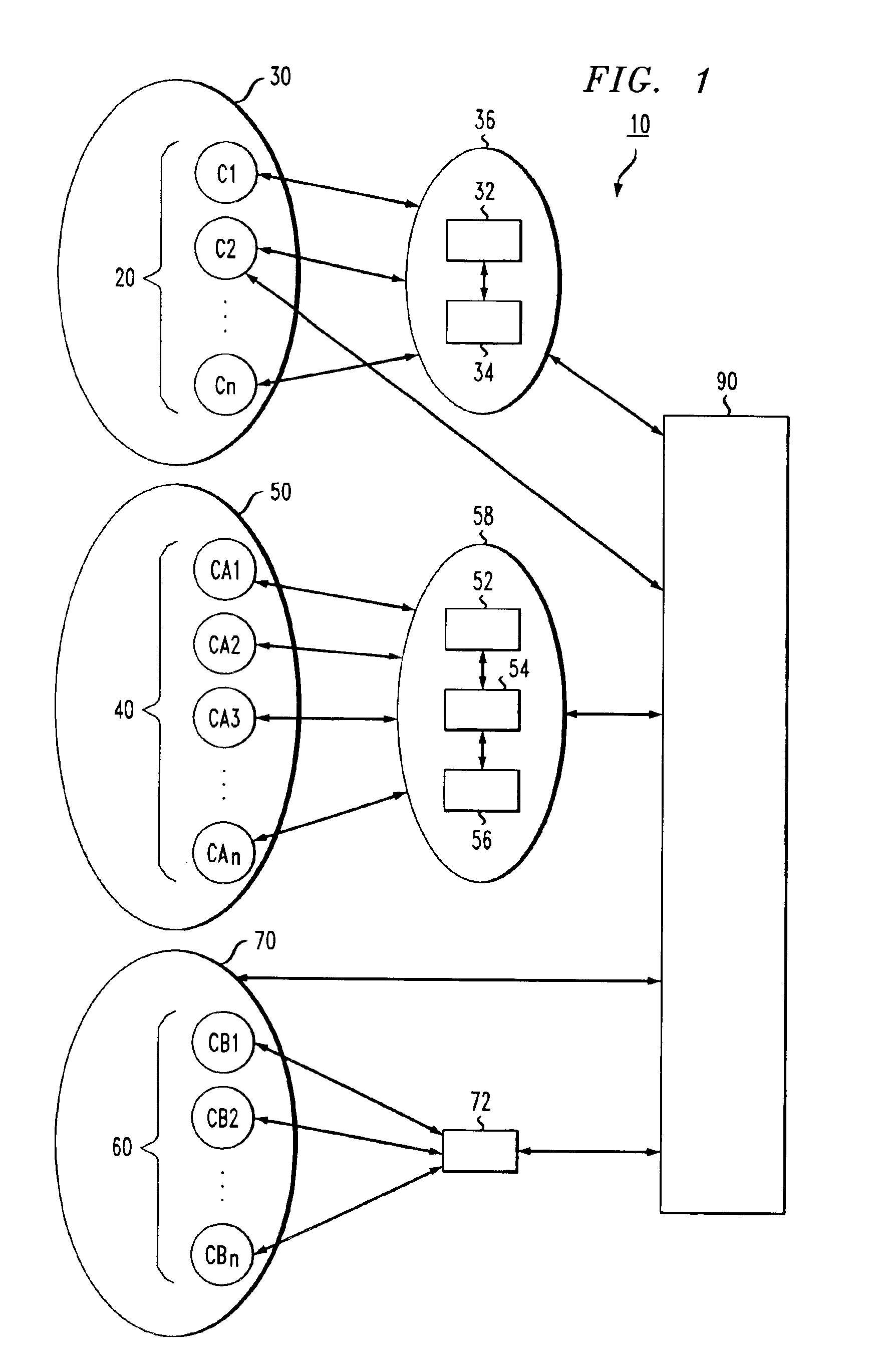
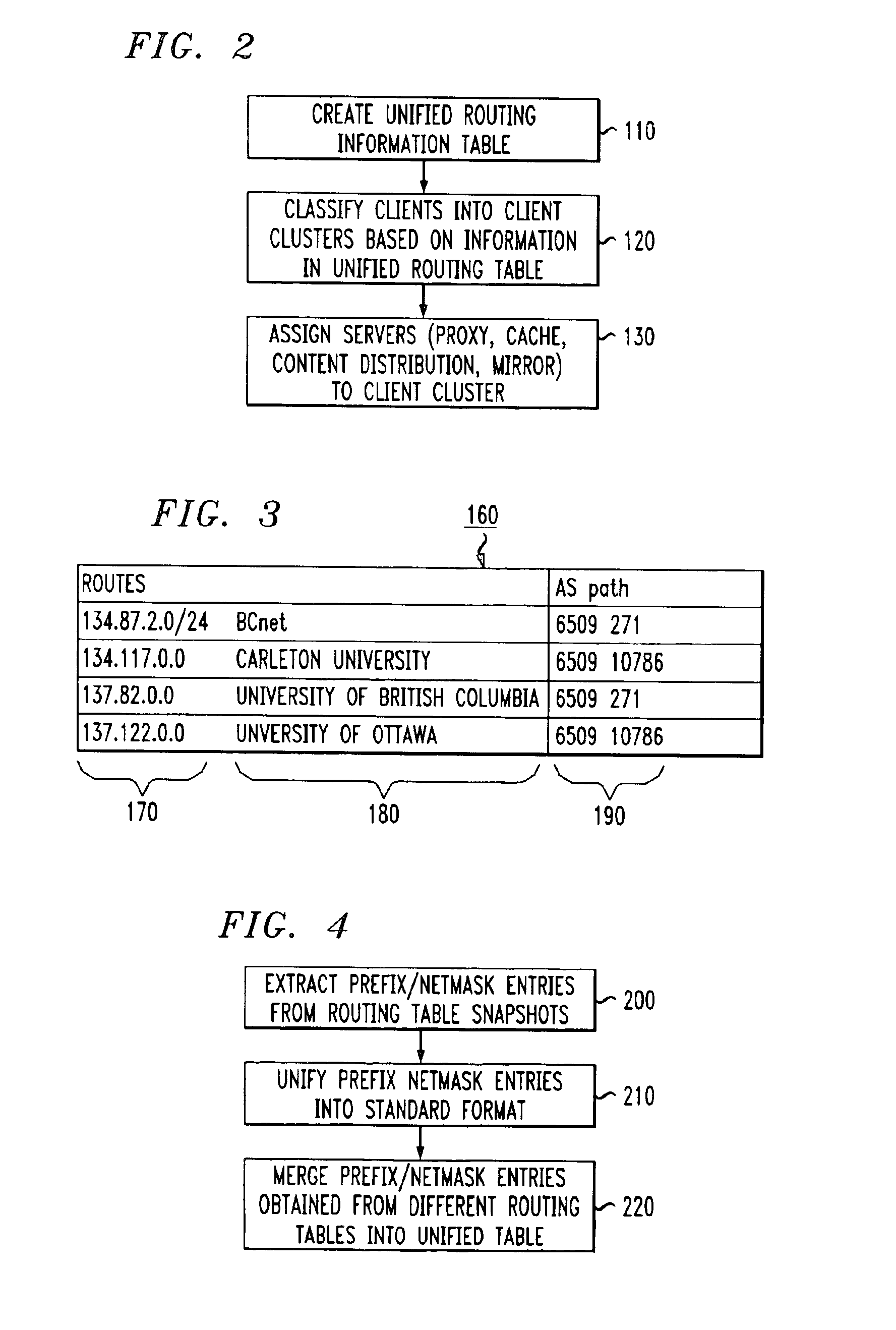
A method for clustering together network clients for guiding of placement of network servers is disclosed. A number of routing table prefix / netmask entries are aggregated and unified into a tubular format. The routing table entries may be converted into a singular format. A network server log is used to extract a number of client IP addresses which are compared to the entries within the unified routing table. A common prefix shared by a number of the client IP addresses and an entry in the unified routing table is determined and used to cluster the clients together in a client cluster. Network servers, such as proxy server, cache servers, content distribution servers and mirror server may be placed in the network according to the client clusters.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Peer-to-peer collaboration system with edge routing
ActiveUS20080288580A1Reduce congestionReduce loadMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionRouting tableNAT traversal
A peer-to-peer collaboration system in which changes to a shared space may be broadcast to all of the peers in a collaboration session using messages sent with a combination of addressing techniques. Messages may be addressed for direct peer-to-peer transmission, indirect transmission through another peer or indirect transmission through a server. The type of addressing used to communicate with each peer is determined through the use of a routing table. The routing table defines interconnected groups of peers and may be used to select one or more peers in each group as the initial recipients of the message. The initial recipients may forward the message to other peers within their groups, such that all peers receive the message. For peers behind a NAT, one or more NAT traversal techniques may be used to obtain information to construct the routing table.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
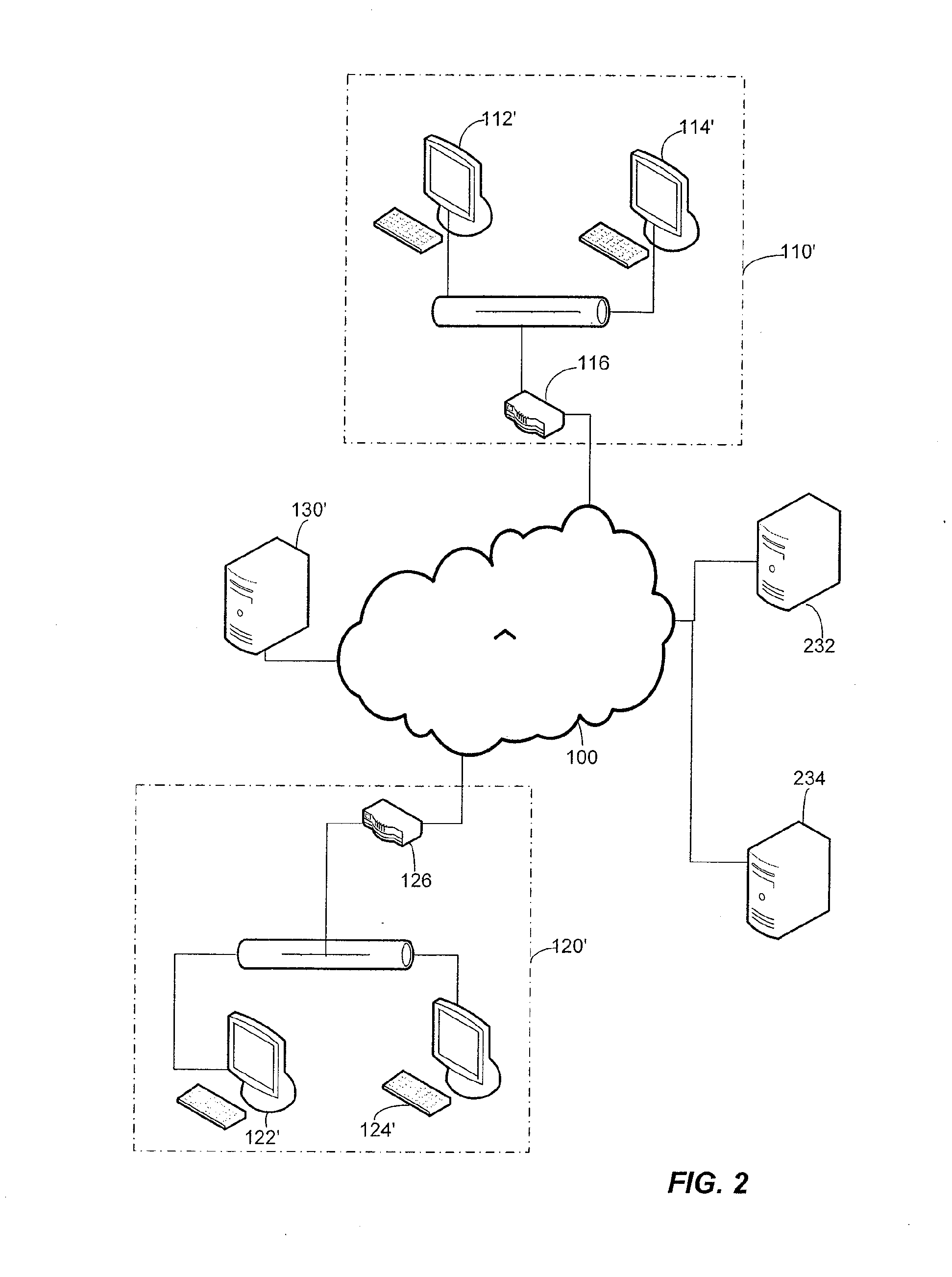
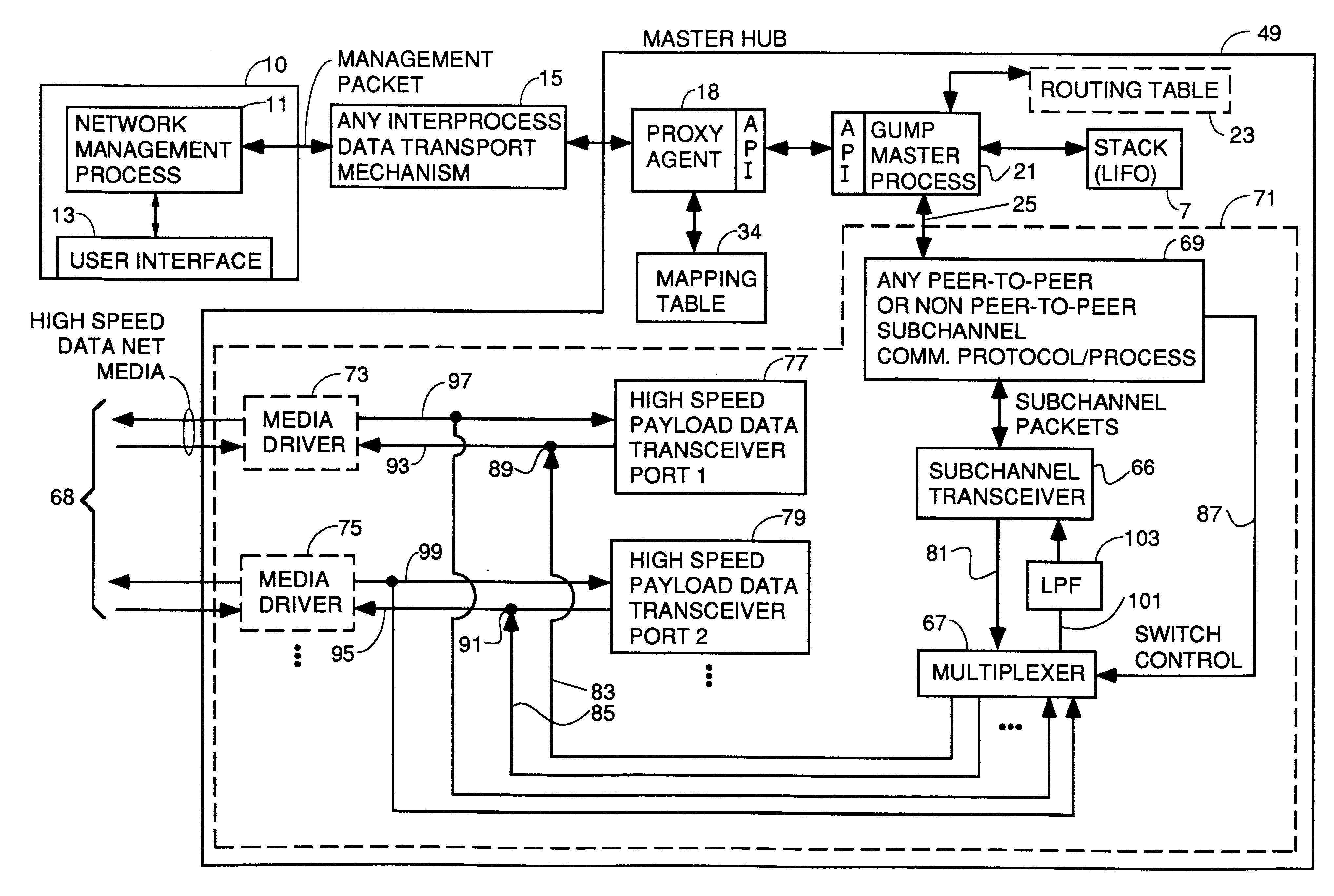
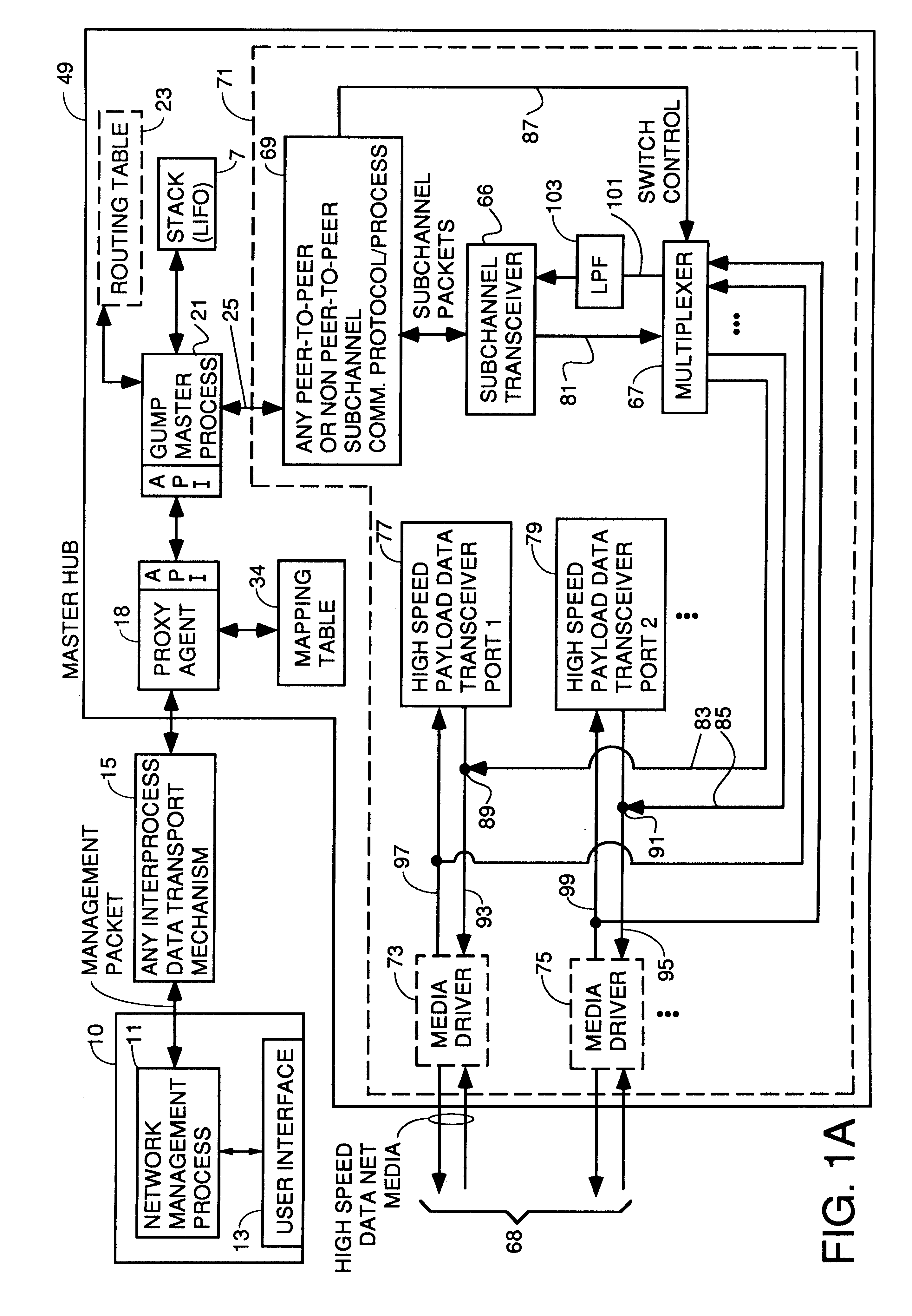
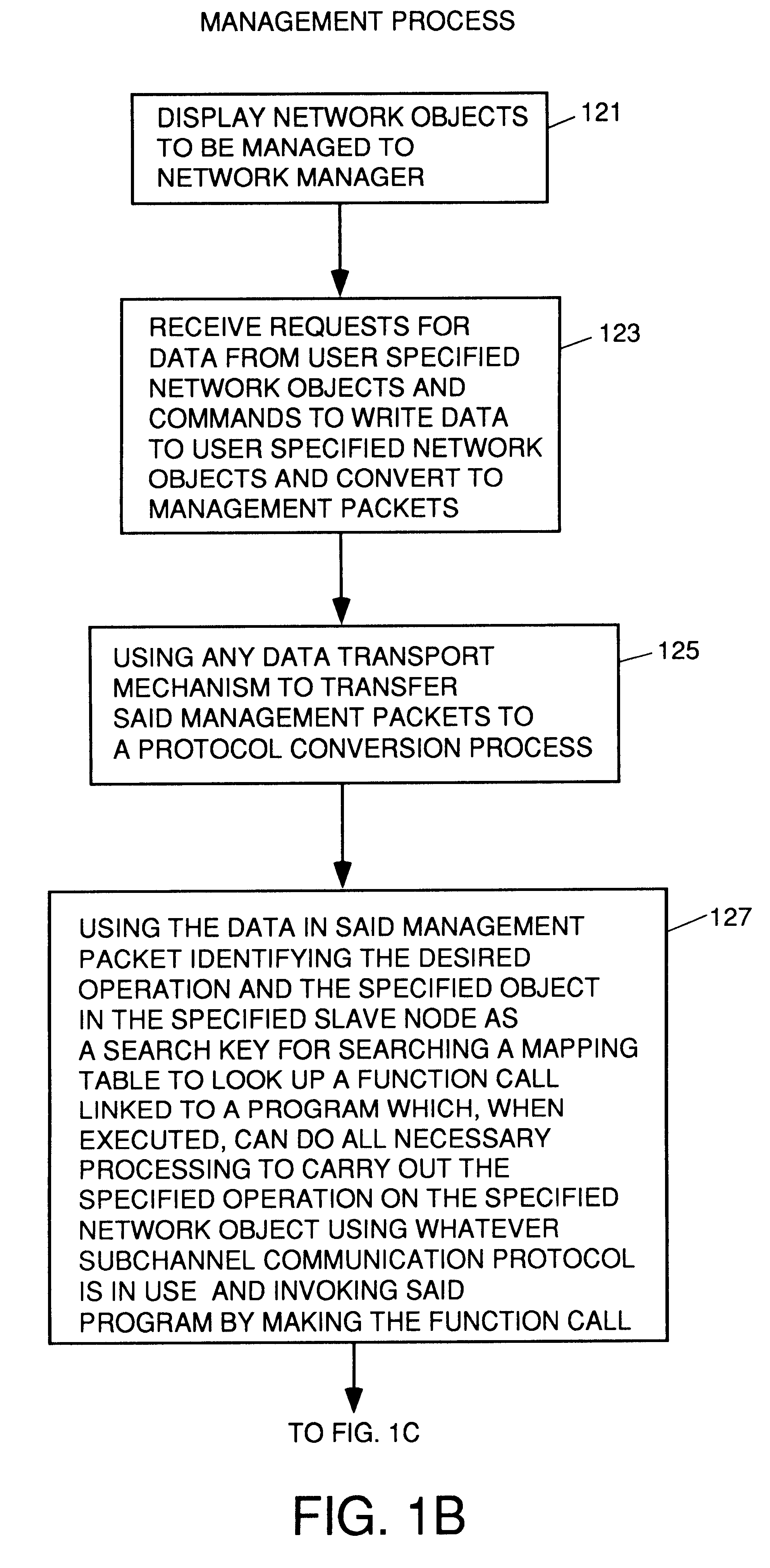
Apparatus and method for unilateral topology discovery in network management
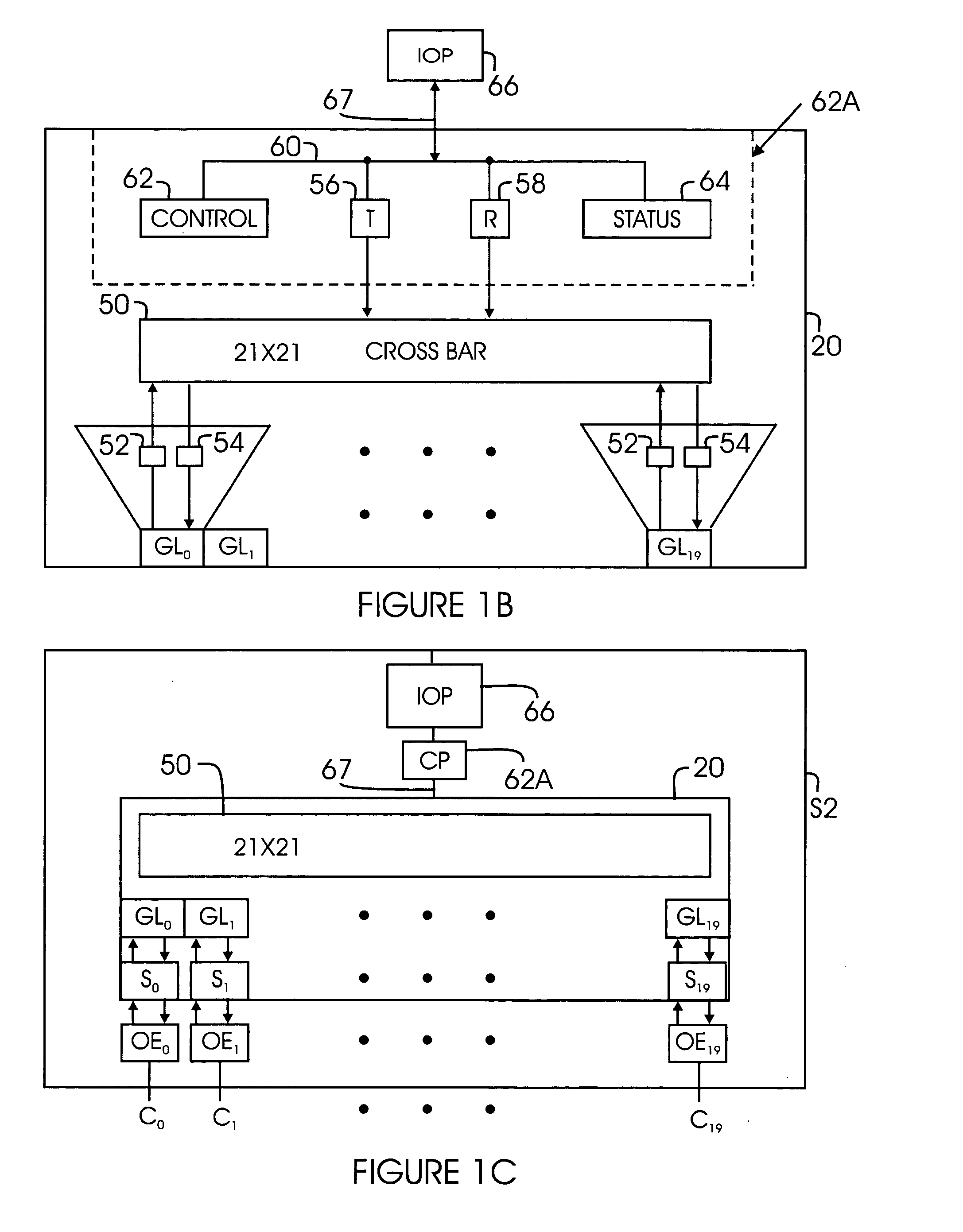
A system for reducing the cost of network managment by using a proxy agent and subchannel communications so fewer SNMP licenses and fewer protocol stacks are needed. Subchannel communication is achieved in a plurality of different embodiments. Embodiments having single subchannel transceivers, multiple transceivers, single multiplexer and multiple multiplexers are disclosed. An NMS process using routing table CRC to automatically detect when the NMS topology information is incorrect and automated topology discovery is disclosed. A process for automated discovery of redundant cables during automated topology discovery is disclosed.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
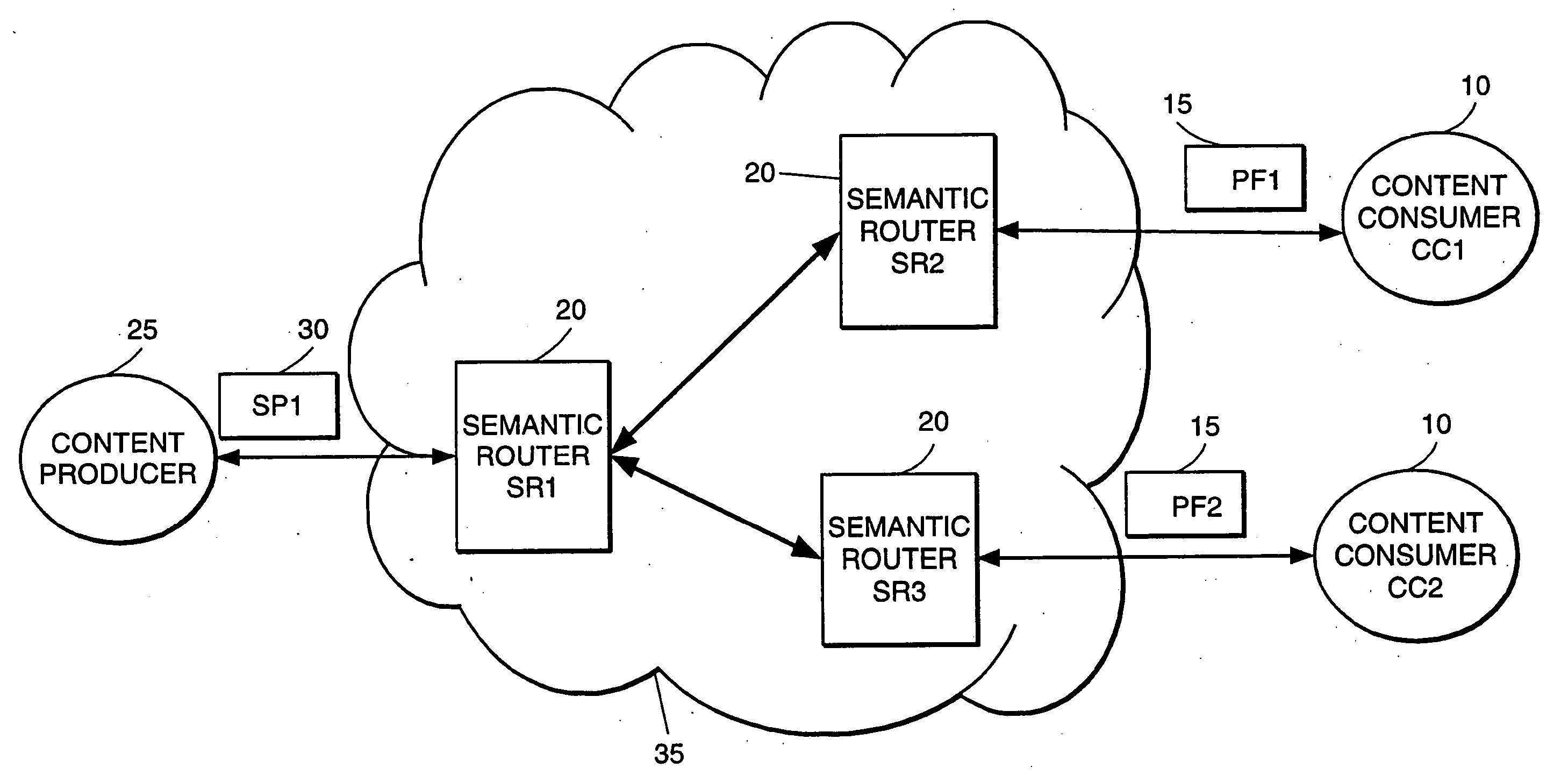
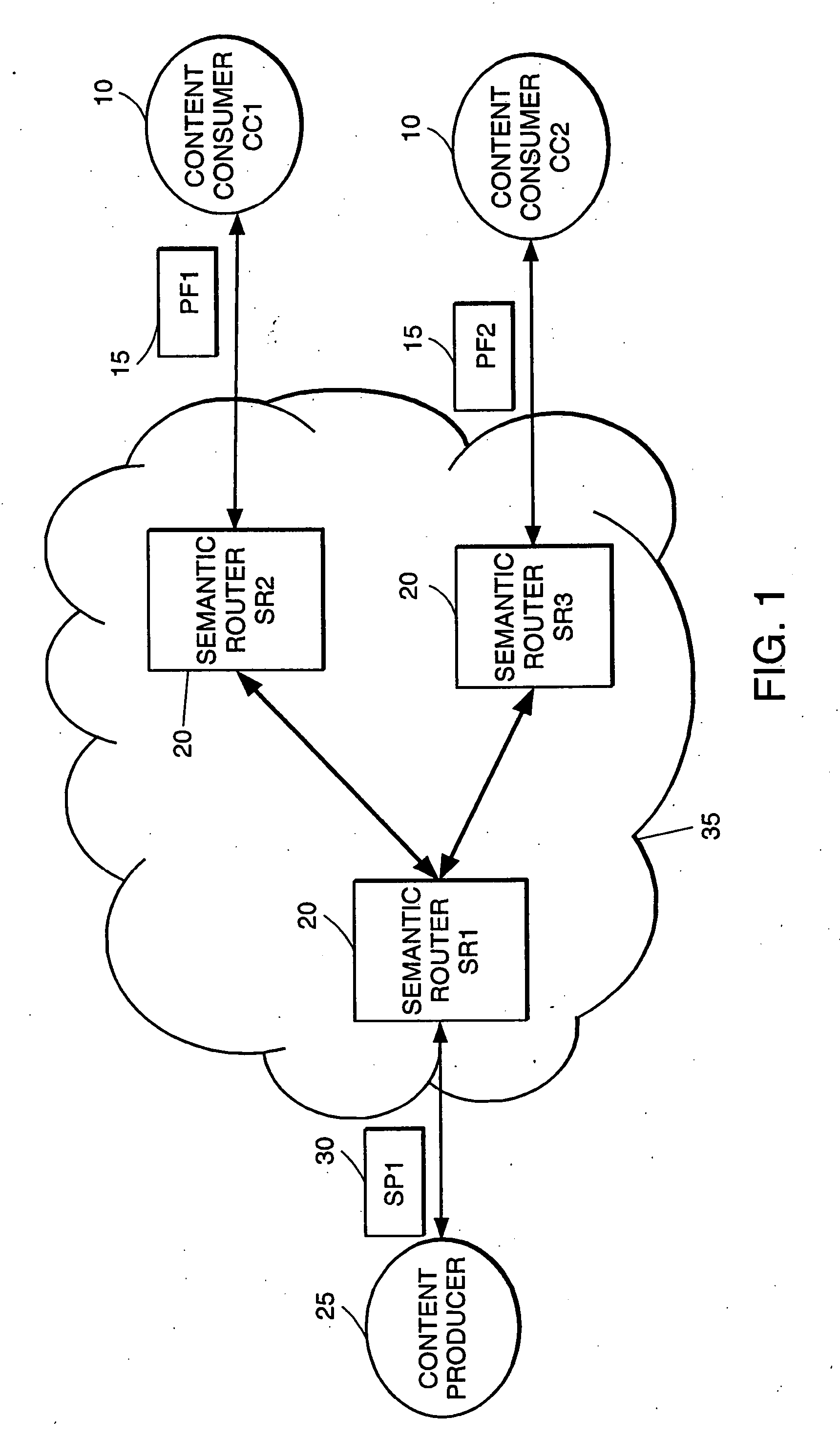
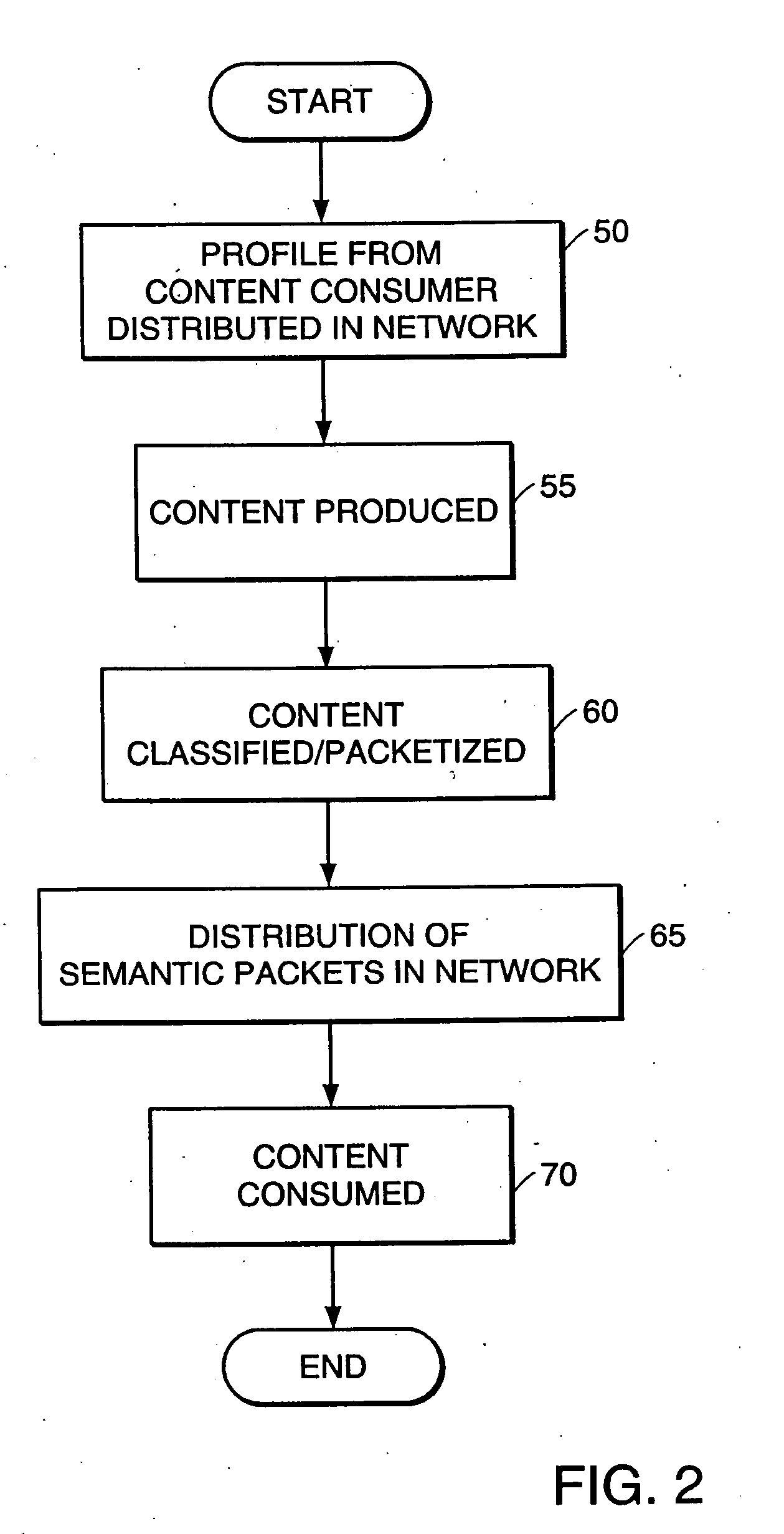
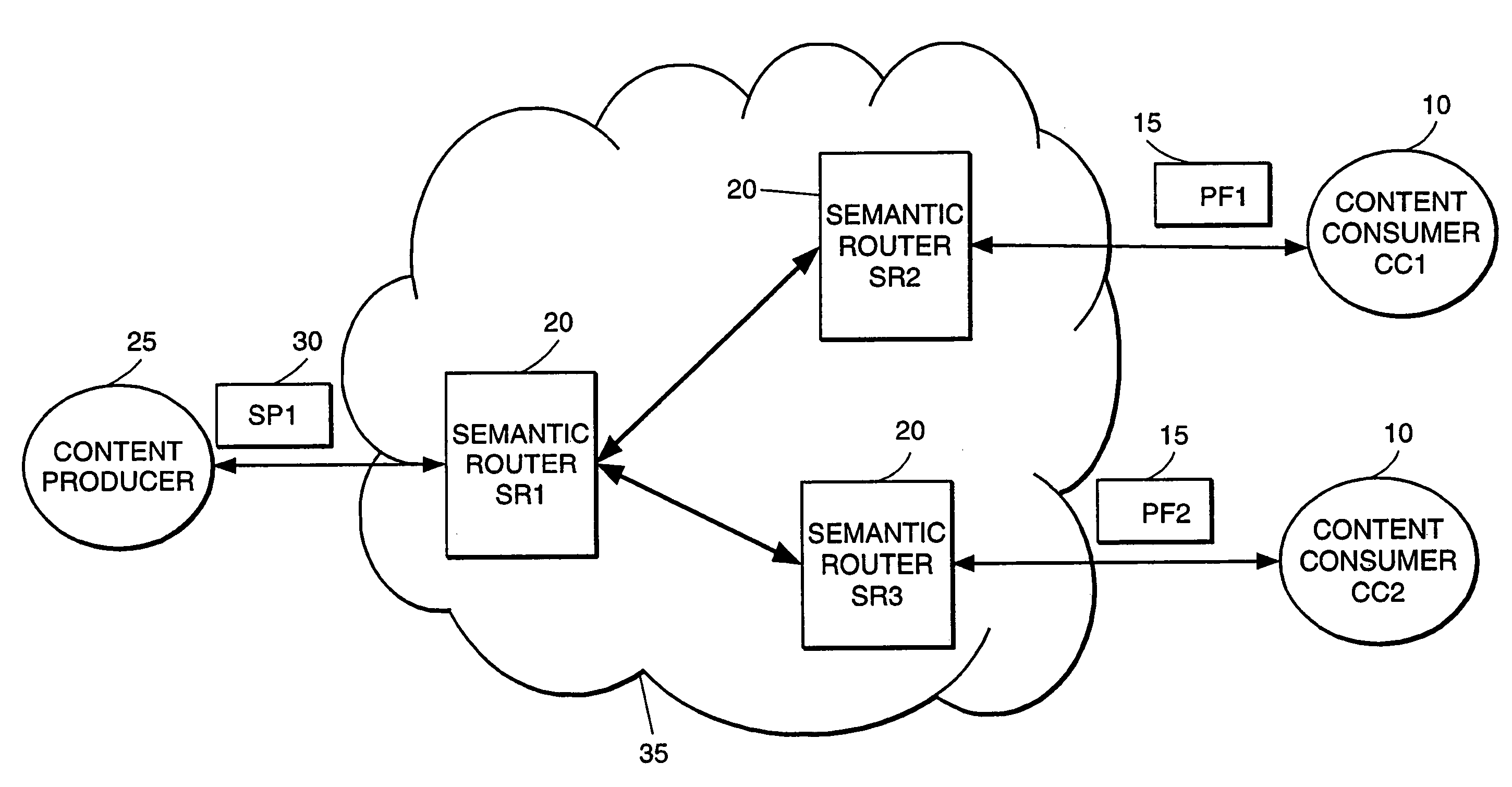
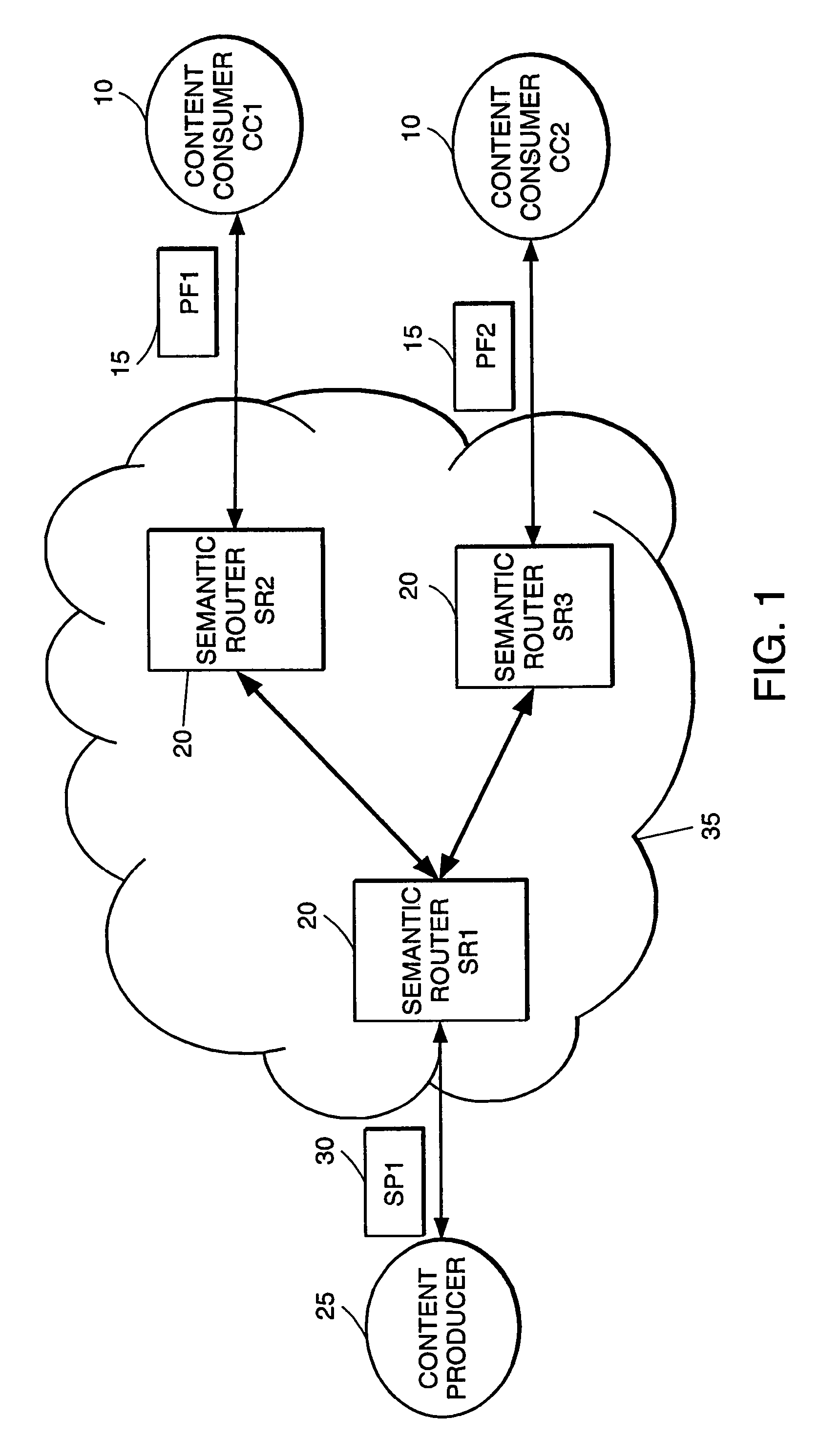
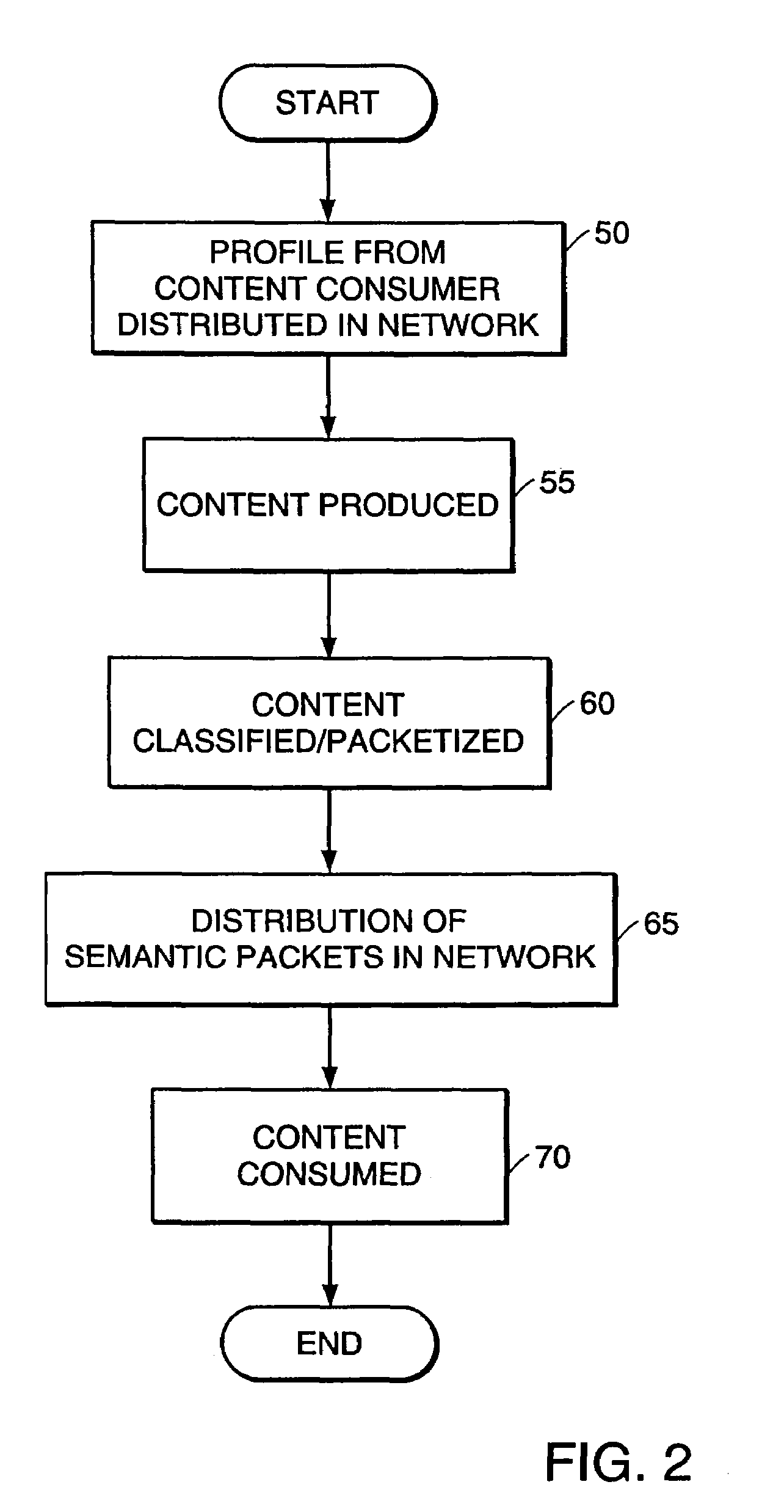
High-performance addressing and routing of data packets with semantically descriptive labels in a computer network
InactiveUS20070239892A1Reduce storageEasy to operateDigital computer detailsData switching networksRouting tableNetwork packet
A method, system and apparatus for routing data through a network based on the content or semantics of the data. Semantic routing engines route the data through the network based upon information maintained in routing tables. The routing tables used to route the content through the network are derived by aggregating information about either content consumers or content producers into ontological
Owner:SEMANDEX NETWORKS
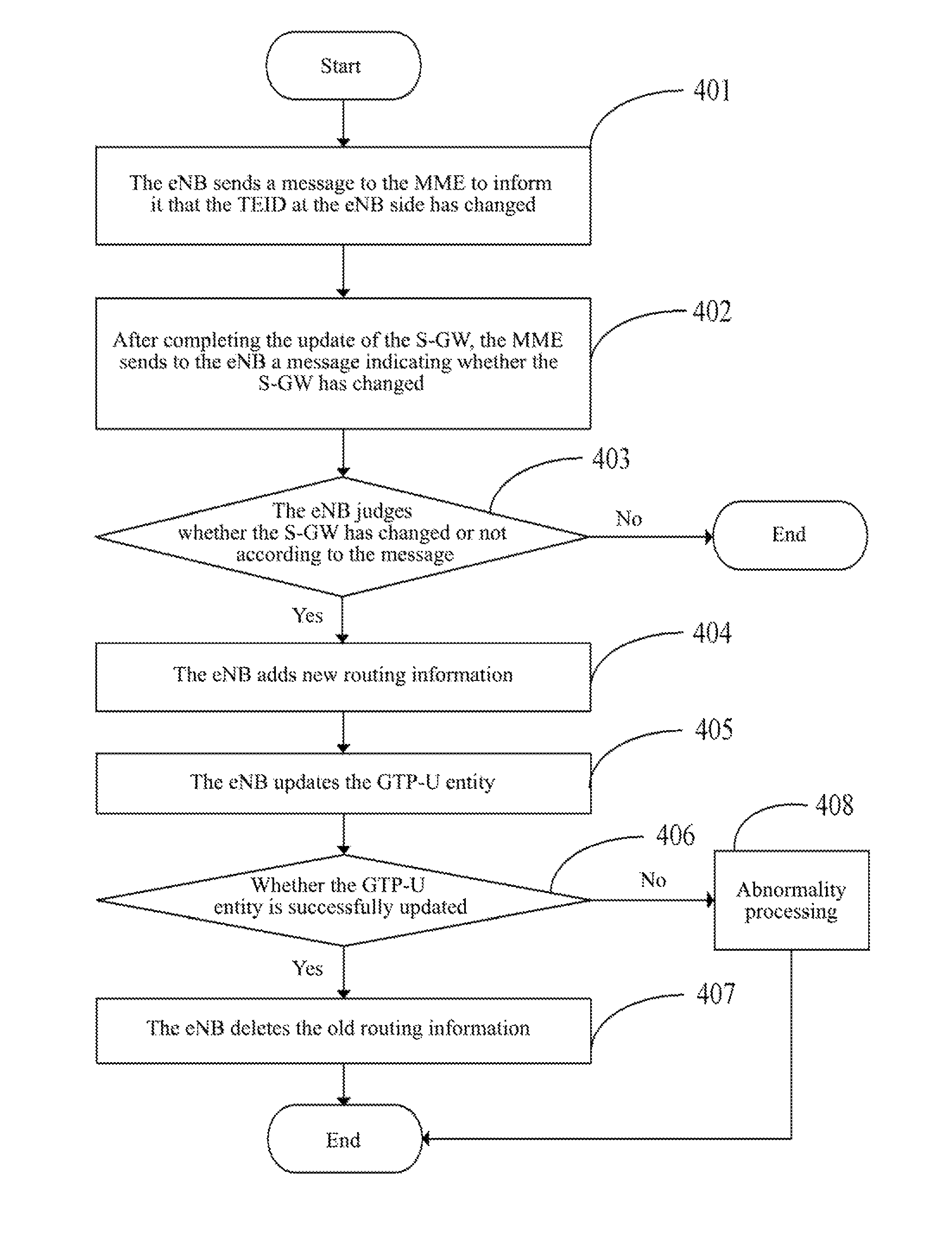
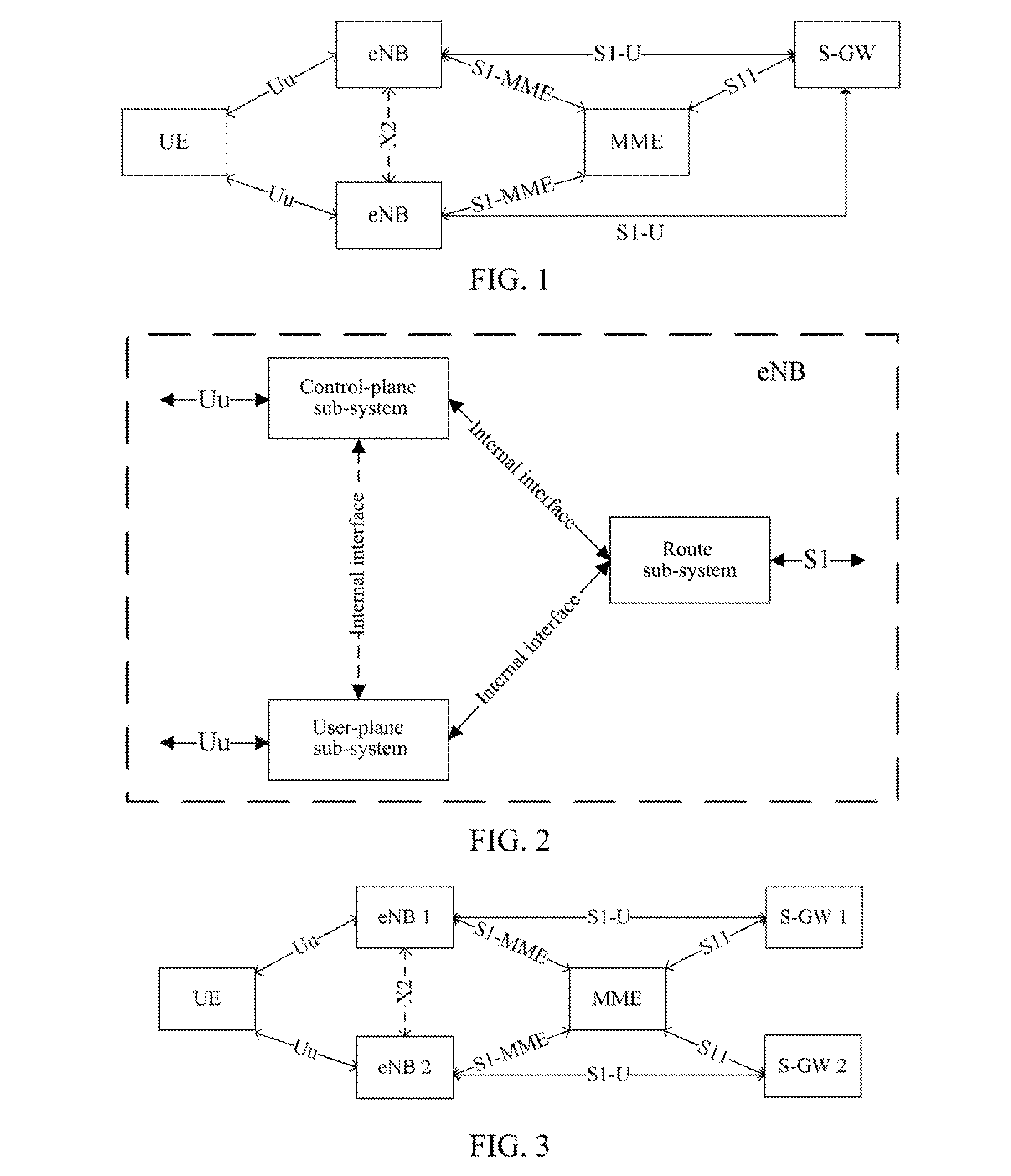
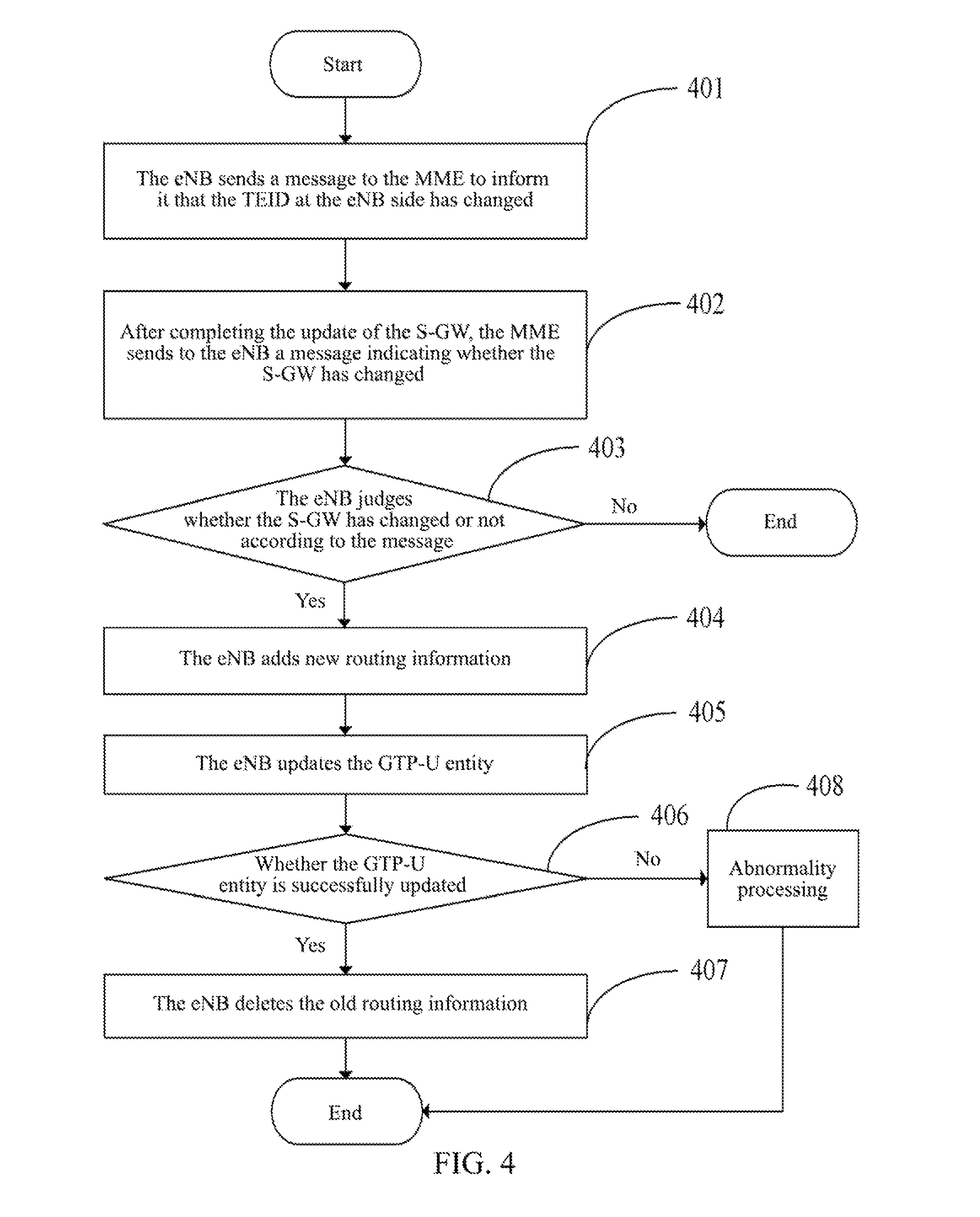
Method, system and evolved NodeB apparatus for implementing inter-evolved NodeB handover
ActiveUS8804667B2Avoid it happening againConnection managementData switching by path configurationGeneral Packet Radio ServiceRouting table
A method, a system and an evolved NodeB (eNB) apparatus for implementing inter-eNB switch are disclosed in the present invention. The method includes: when a user equipment switches from a source-side eNB to a target-side eNB, if the target-side eNB acquires via the Mobility Management Entity (MME) that the Serving Gateway (S-GW) has changed, the target-side eNB adds the new route relation of the S-GW and then updates the General Packet Radio Service (GPRS) Tunnelling Protocol User Plane (GTP-U) entity. The present invention can effectively solve the problem of the uplink data packet loss due to the time difference existing between the update to the Tunnel Endpoint Identifier (TEID) and the routing table by the eNB when inter-eNB switch is performed via X2 and the S-GW has changed, thus enhancing the user experience during the switch.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Fault tolerant shared system resource with communications passthrough providing high availability communications
InactiveUS6865157B1Improve usabilityError preventionTransmission systemsRouting tableHigh availability
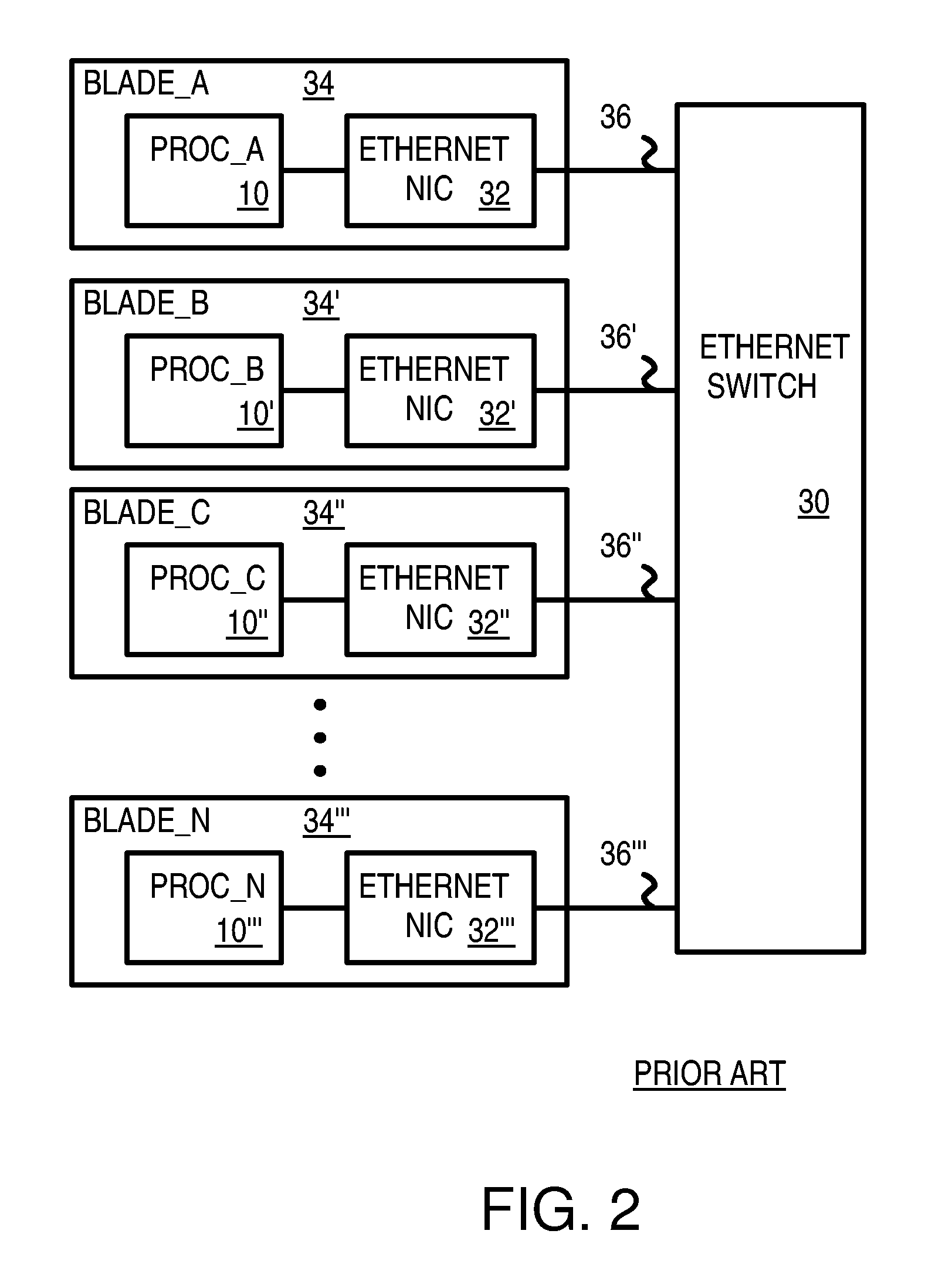
A communications passthrough mechanism for high availability network communications between a shared system resource and clients of the system resource. The system resource includes a control / processing sub-system including multiple peer blade processors. A port of each blade processor is connected to each client / server network path and each client is connected to a corresponding port of each blade processor. Each blade processor includes a network fault detector exchanging beacon transmissions with other blade processors through corresponding blade processor ports and network paths. Each blade processor includes response generator responsive to a failure to receive a beacon transmission from a failed port of an other blade processor for redirecting the client communications to the failed port on the other blade processor to the corresponding port of the blade processor. A path manager in the blade processor is responsive to operation of the response generator for modifying the communications routing table to correspond with the redirection message to route the client communications to the failed port of the other blade processor to the other blade processor through the inter-processor communications link. Each blade processor may also include an inter-blade communications monitor for detecting a failure in the inter-processor communications link between the blade processor and another blade processor, reading the communications routing table to select a functional network communications path to a port of the other blade processor, and modifying the communications routing table to redirect inter-processor communications to the selected functional network communications path.
Owner:EMC CORP
Method and communication device for routing unicast and multicast messages in an ad-hoc wireless network
ActiveUS20080095163A1Network topologiesBroadcast transmission systemsWireless mesh networkRouting table
A method and communication device for routing unicast and multicast messages. The method for routing a unicast message includes receiving a first control packet including routing parameters from a group header node, updating a routing table based upon the routing parameters, receiving a second control packet including additional routing parameters from a group node, updating the routing table based upon the additional routing parameters and generating a forwarding table from the routing table when both of the updated steps are completed. The unicast message is routed based upon the forwarding table. A method for routing a multicast message comprises receiving the multicast message, determining if a multicast group destination for the multicast message is in a multicast forwarding table (MFT), determining if the multicast message has been previously forwarded and forwarding the multicast message if the message was not previously forwarded and the multicast group destination is in the MFT.
Owner:TOYOTA INFOTECH CENT U S A +1
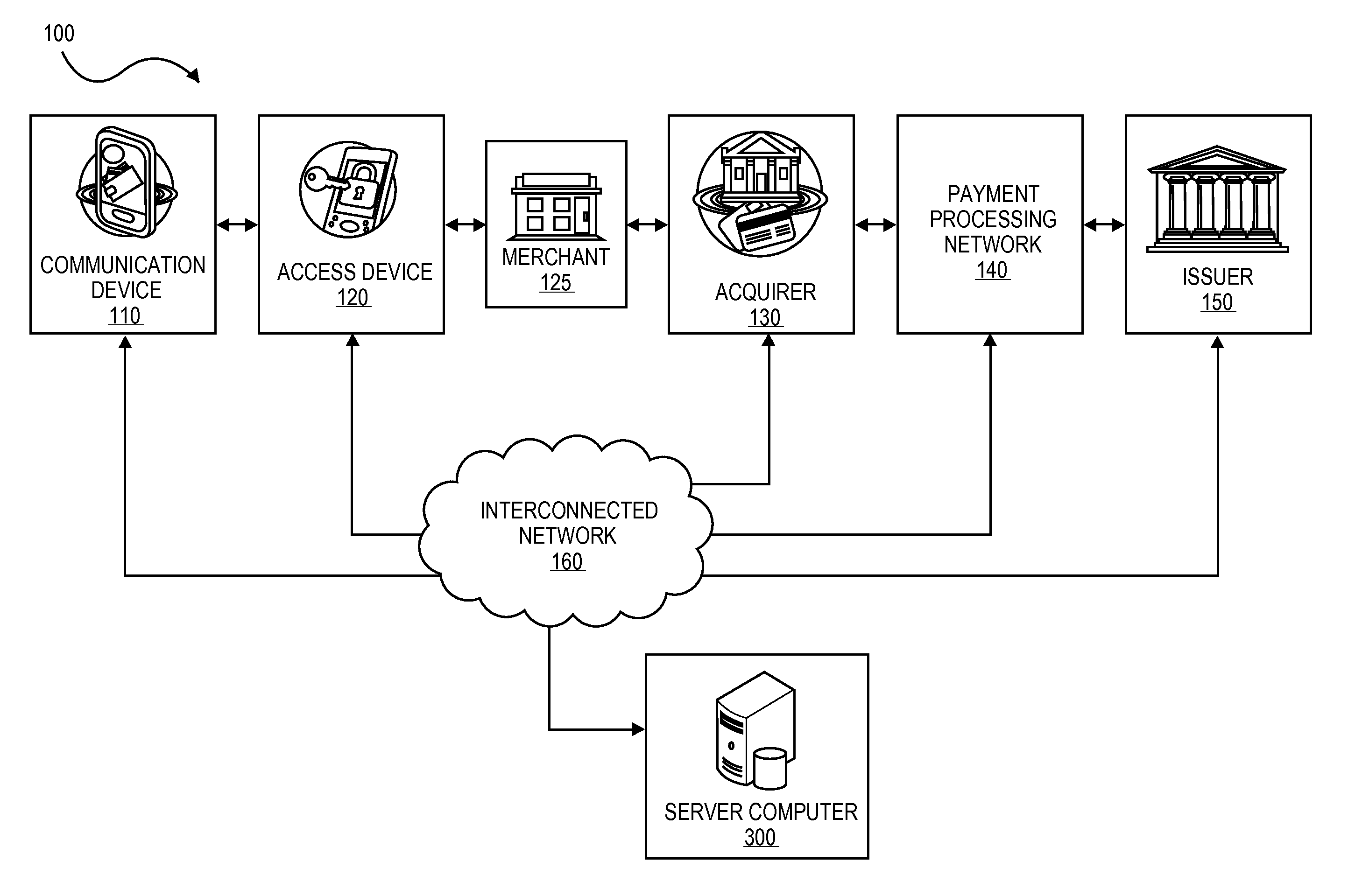
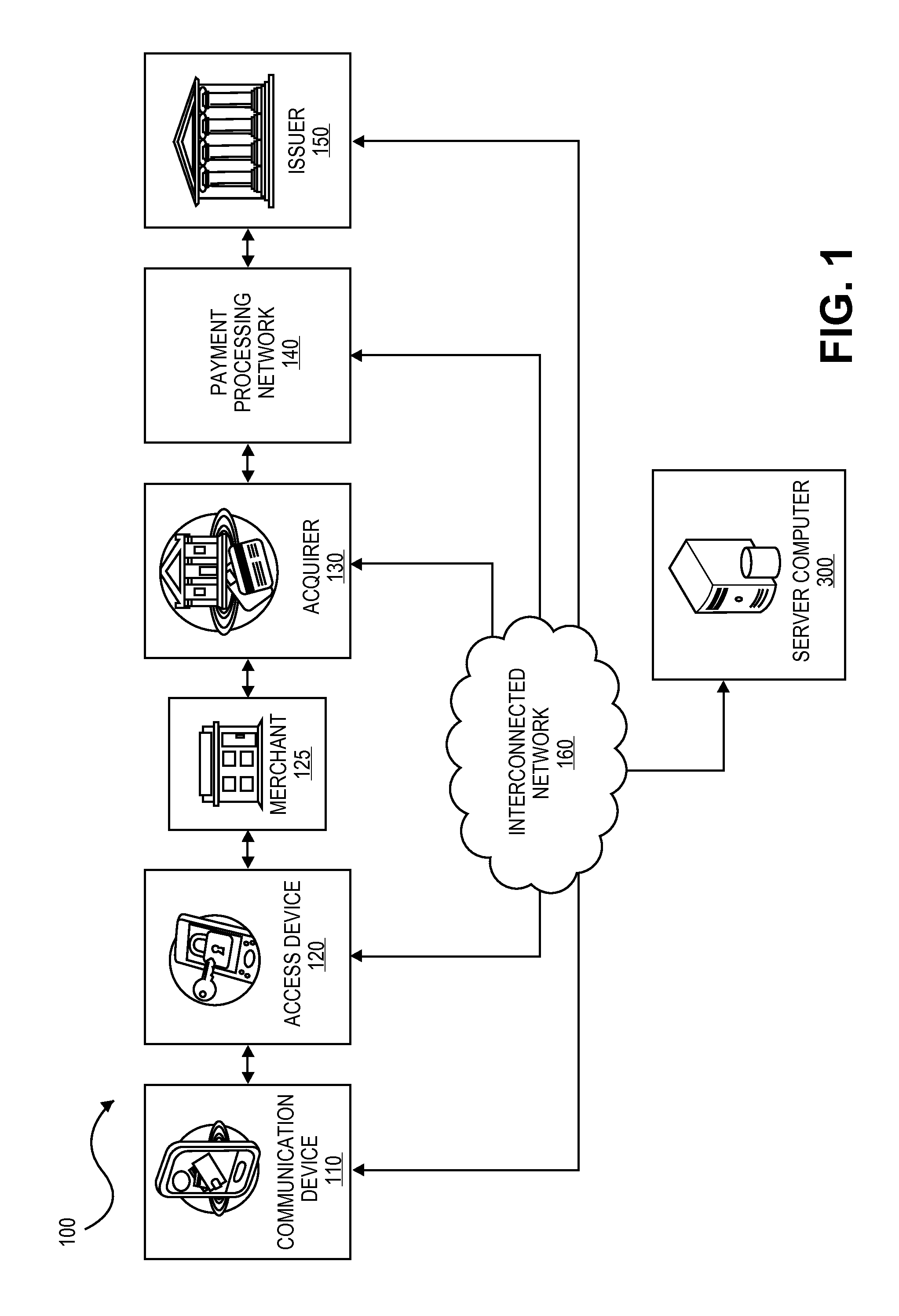
Transactions using temporary credential data
A method is disclosed. The method includes receiving a credential request message requesting a temporary credential associated with a payment account, and then determining, by a server computer, using a routing table and data associated with the payment card, a third-party computer associated with the payment account. The method also includes transmitting the credential request message to the third-party computer, and receiving, by the server computer, the temporary credential from the third-party computer. The method also includes determining, by the server computer, the communication device associated with the requested temporary credential and transmitting, by the server computer, the temporary credential to the communication device.
Owner:VISA INT SERVICE ASSOC
Scheme of sending email to mobile devices
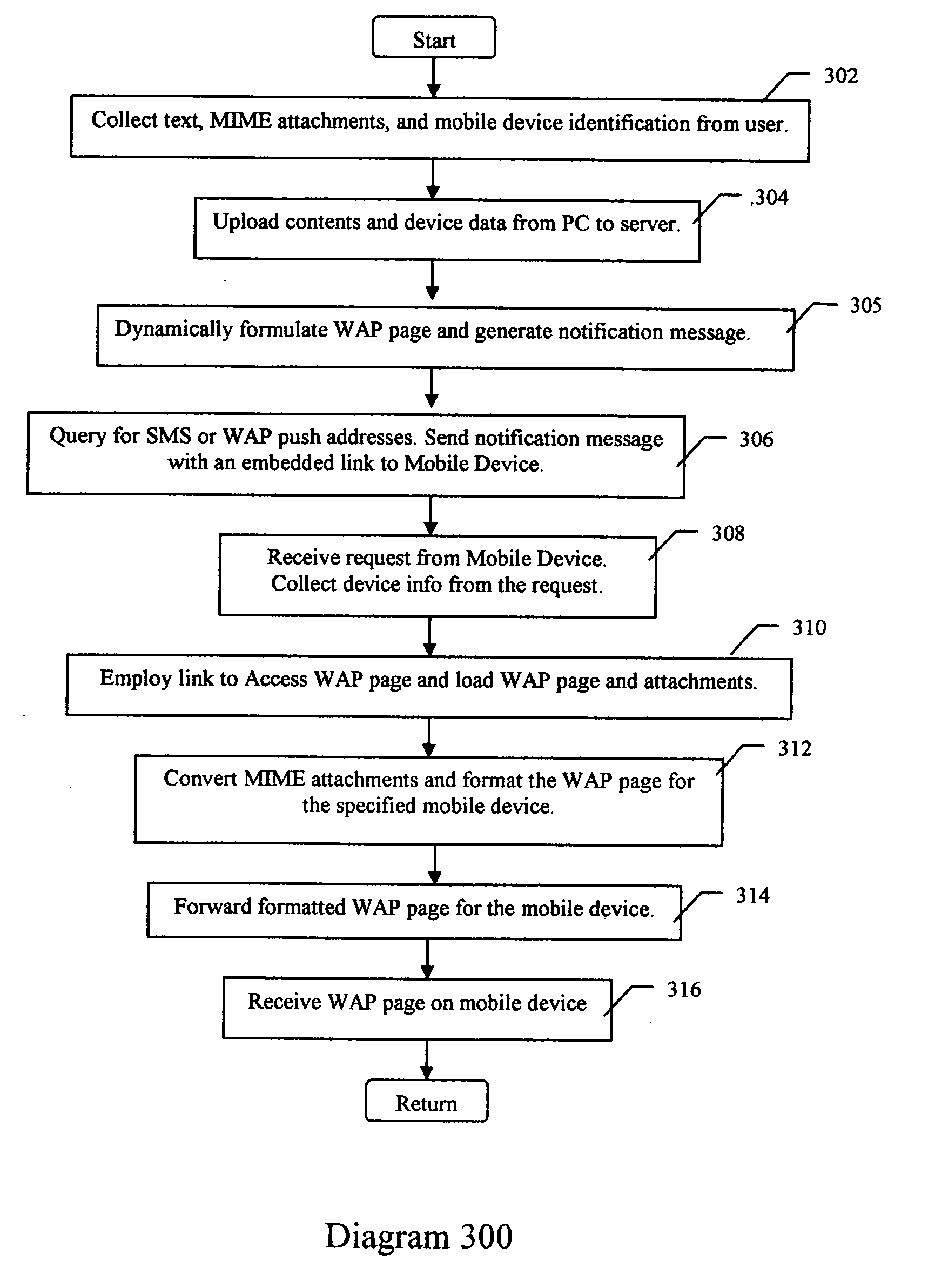
InactiveUS20060218234A1Multiple digital computer combinationsMessaging/mailboxes/announcementsMessage lengthRouting table
A method, apparatus, client and server are directed at providing a simplified scheme to deliver email messages that include text message body, and / or MIME attachments from desktop computing devices to messaging (such as SMS) and wireless internet capable phones. A web form is provided for users to compose messages and / or adding MIME attachments from their PC. Also provided in the form are input fields for users to enter device numbers for recipients. Upon submitting the form, message body and MIME attachments are uploaded and stored on the server. An email WAP page that contains the message body and the links to all the MIME attachments is created dynamically and stored on the server. The server then queries a service database and looks up a domain routing table to build the email like messaging addresses for recipients. The server sends a notification message with an embedded link to the email like messaging addresses. The link, such as a URL, a script, an executable, a program, and the like, pointing to the email WAP page, can be invoked from mobile devices. When the link is invoked on the mobile device, it sends a request to the server for the email WAP page. Upon receiving the request from the mobile device, the server collects the information about the mobile device; queries a device database for formats, display and capabilities; locates and loads the email WAP page; converts the MIME attachments to the formats supported by the mobile device; formats the email WAP page for display on the mobile device; delivers the formatted email WAP page to the mobile device. The email WAP page can be viewed, downloaded, and played on the mobile device. The scheme of the present invention supports a device number based authentication. The scheme of the present invention can also be implemented to deliver email messages to multiple mobile devices. The scheme of the present invention can expand the PC to SMS capabilities by enabling text messaging with arbitrary message length.
Owner:DENG LI +1
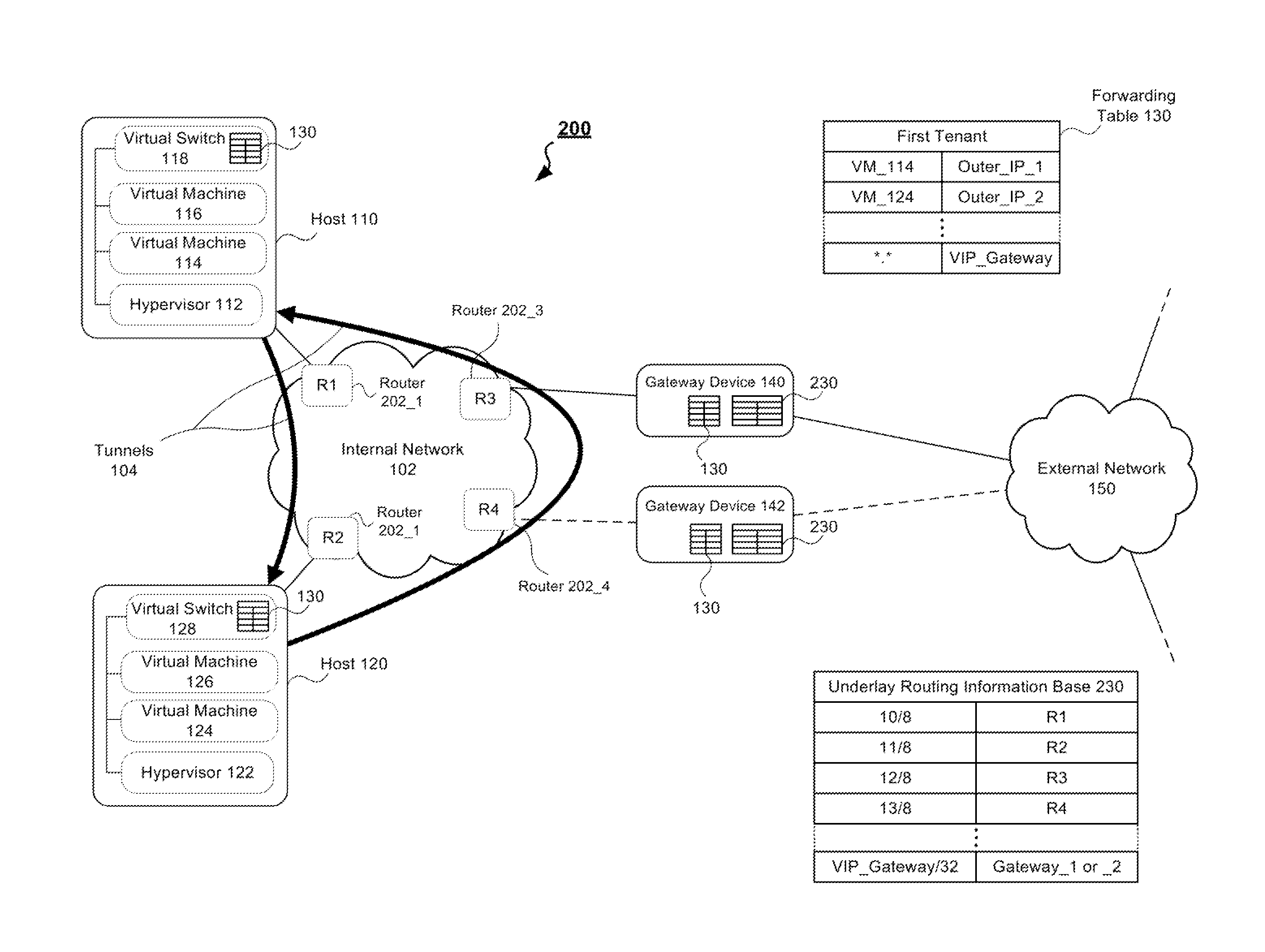
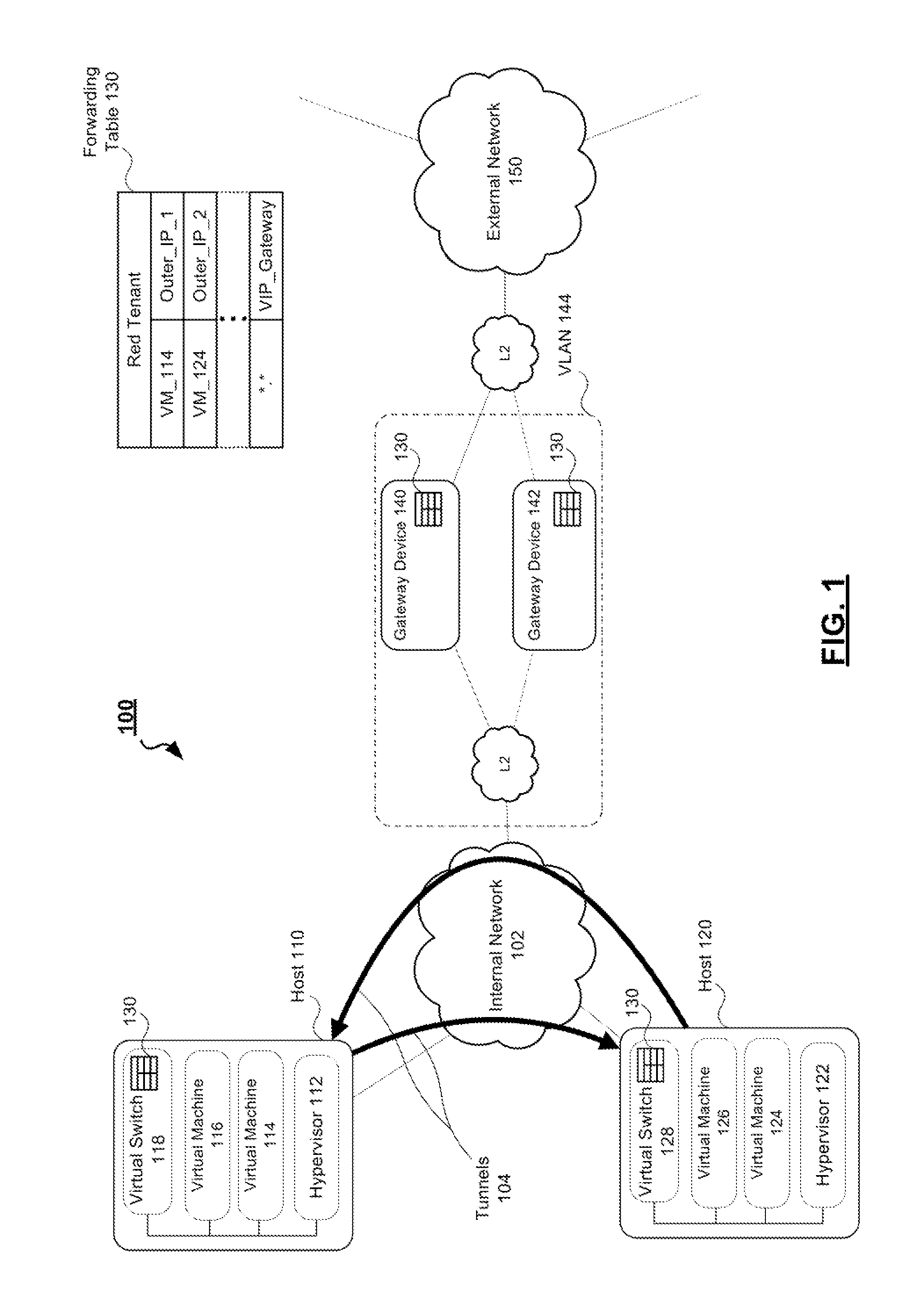
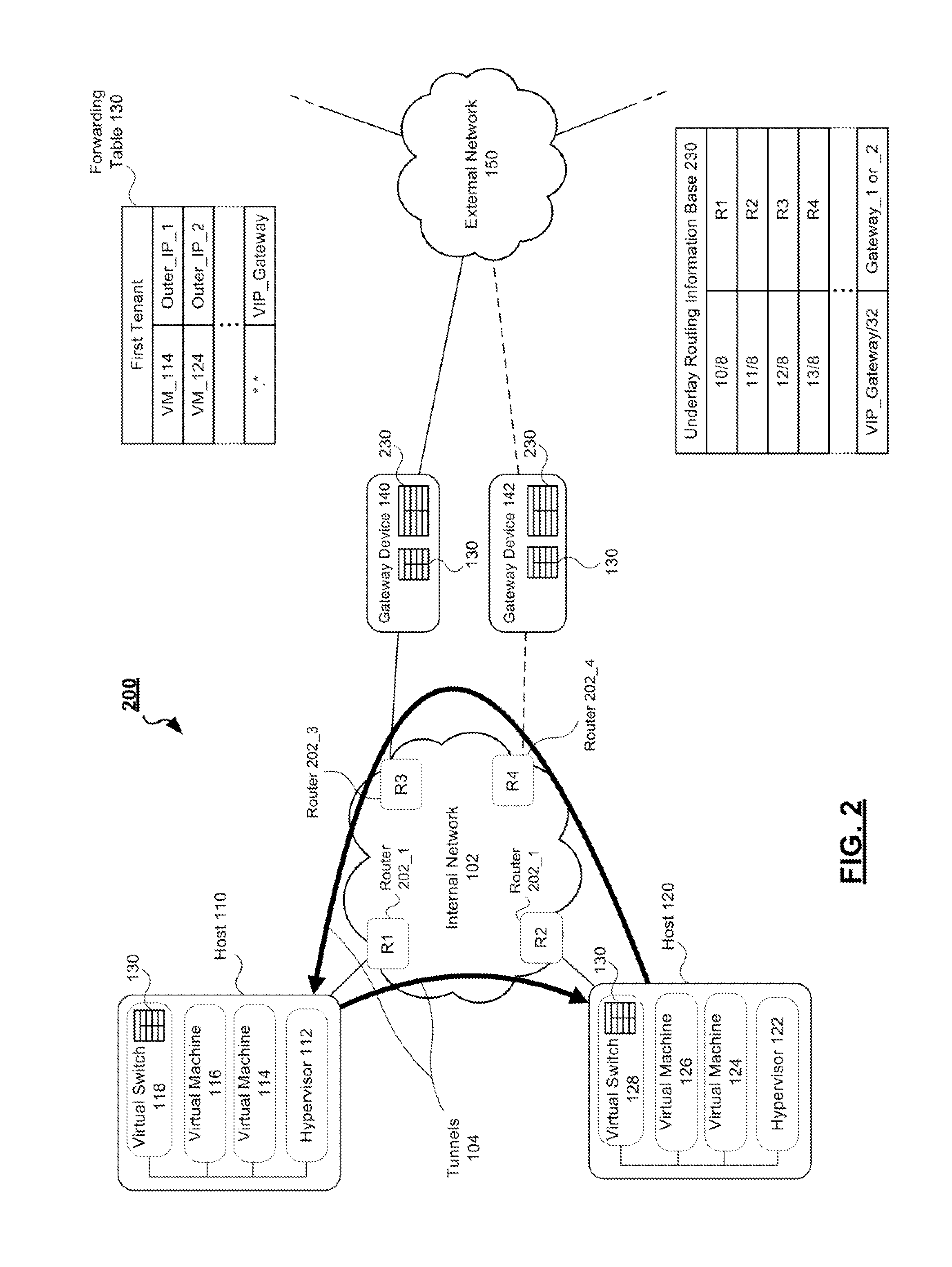
Systems and methods for providing vlan-independent gateways in a network virtualization overlay implementation
An information handling system is provided. The information handling system includes a first hypervisor running on a first server and a second hypervisor running on a second server. The first hypervisor manages a first virtual switch and has an overlay forwarding table in memory supporting at least one virtual machine, while the second hypervisor manages a second virtual switch and also has the overlay forwarding table in memory and supports at least one other VM. The information handling system further includes a plurality of gateway devices coupled to the hypervisors. The gateway devices share a floating address and are configured to export a host route, associated with the address, into a corresponding entry in an underlay routing table to redirect network traffic from a first gateway device to a second gateway device.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
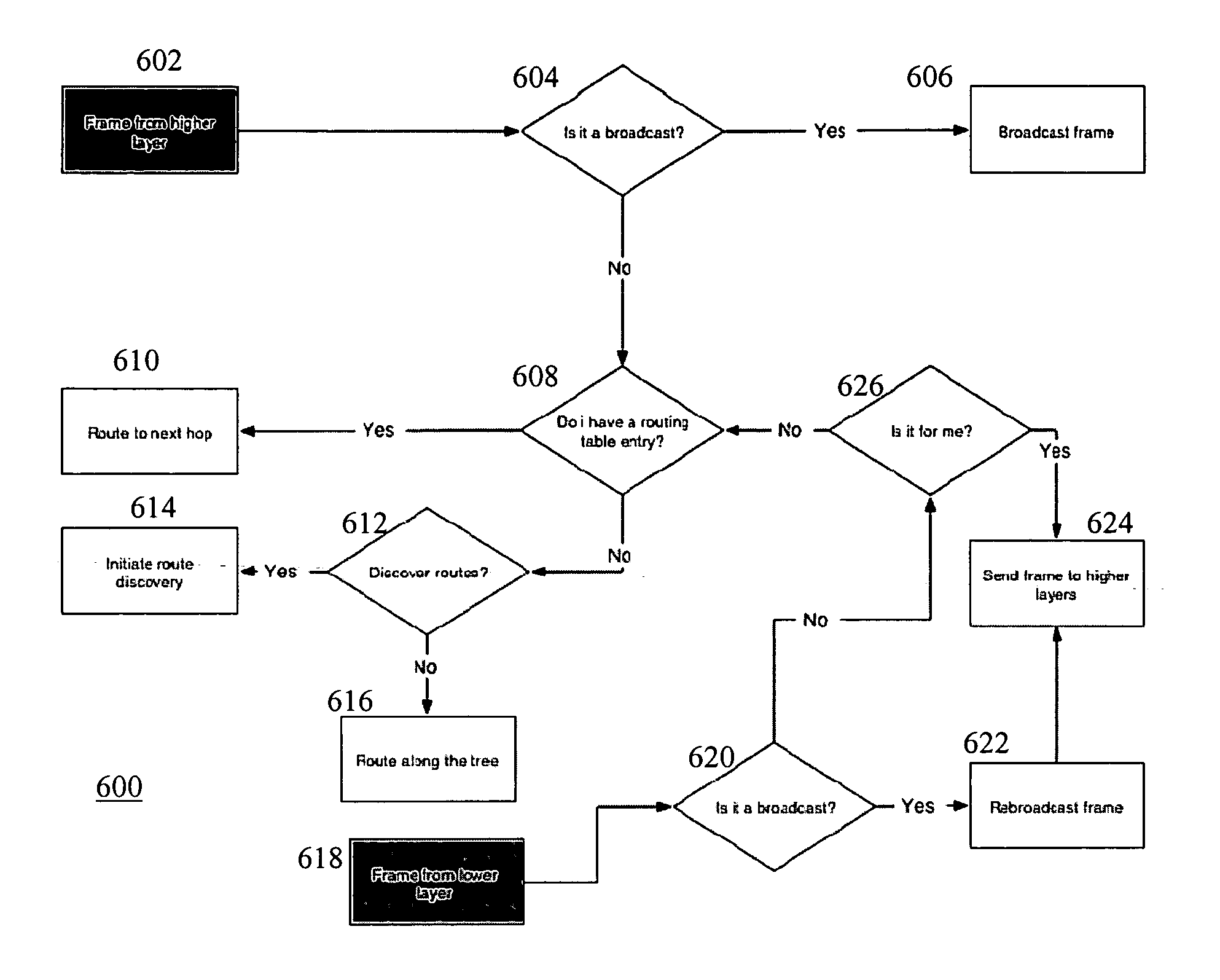
Methods and apparatuses for routing data in a personal area network
The invention is a routing method for data in a personal area network. The personal area network includes a plurality of nodes. The method includes receiving a frame at a node, determining whether the node contains a routing table entry for the frame destination, and when the node contains a routing table entry, determining a route for the frame based on a first routing protocol. The method further includes, when the node does not contain a routing table entry for the frame destination, determining whether a route should be discovered for the frame destination, and when a route should not be discovered, determining a route for the frame based on a second routing protocol.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +4
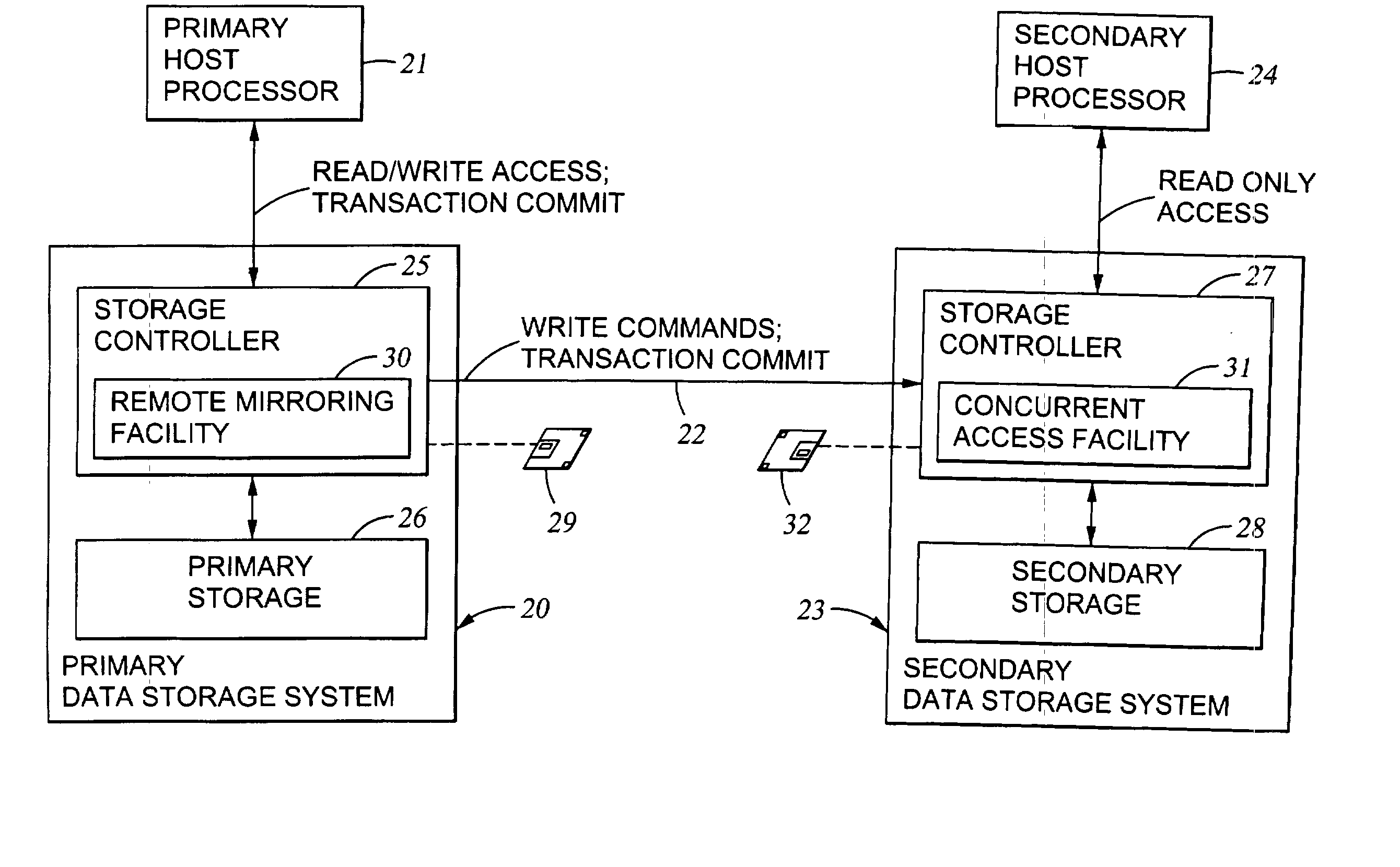
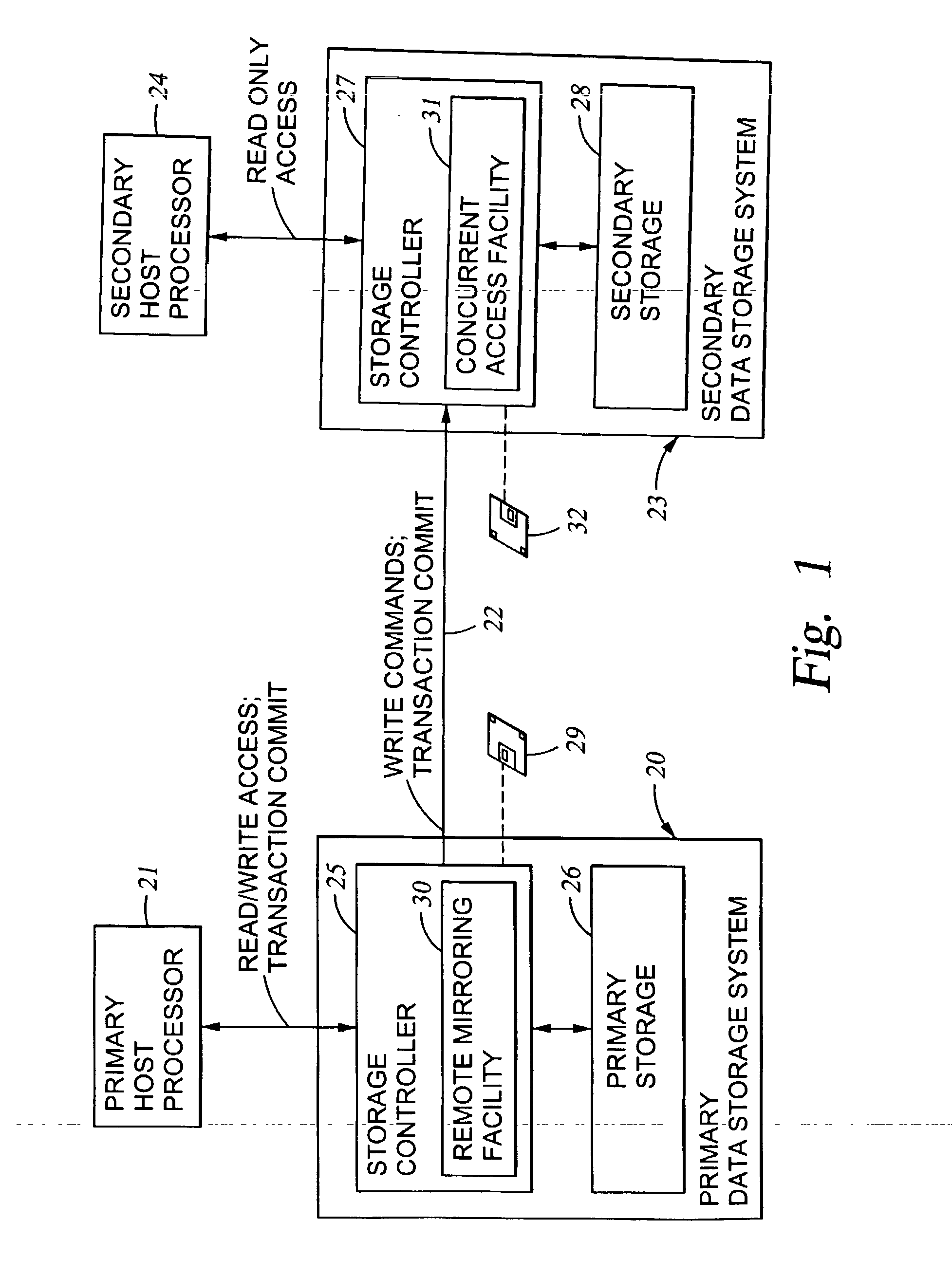
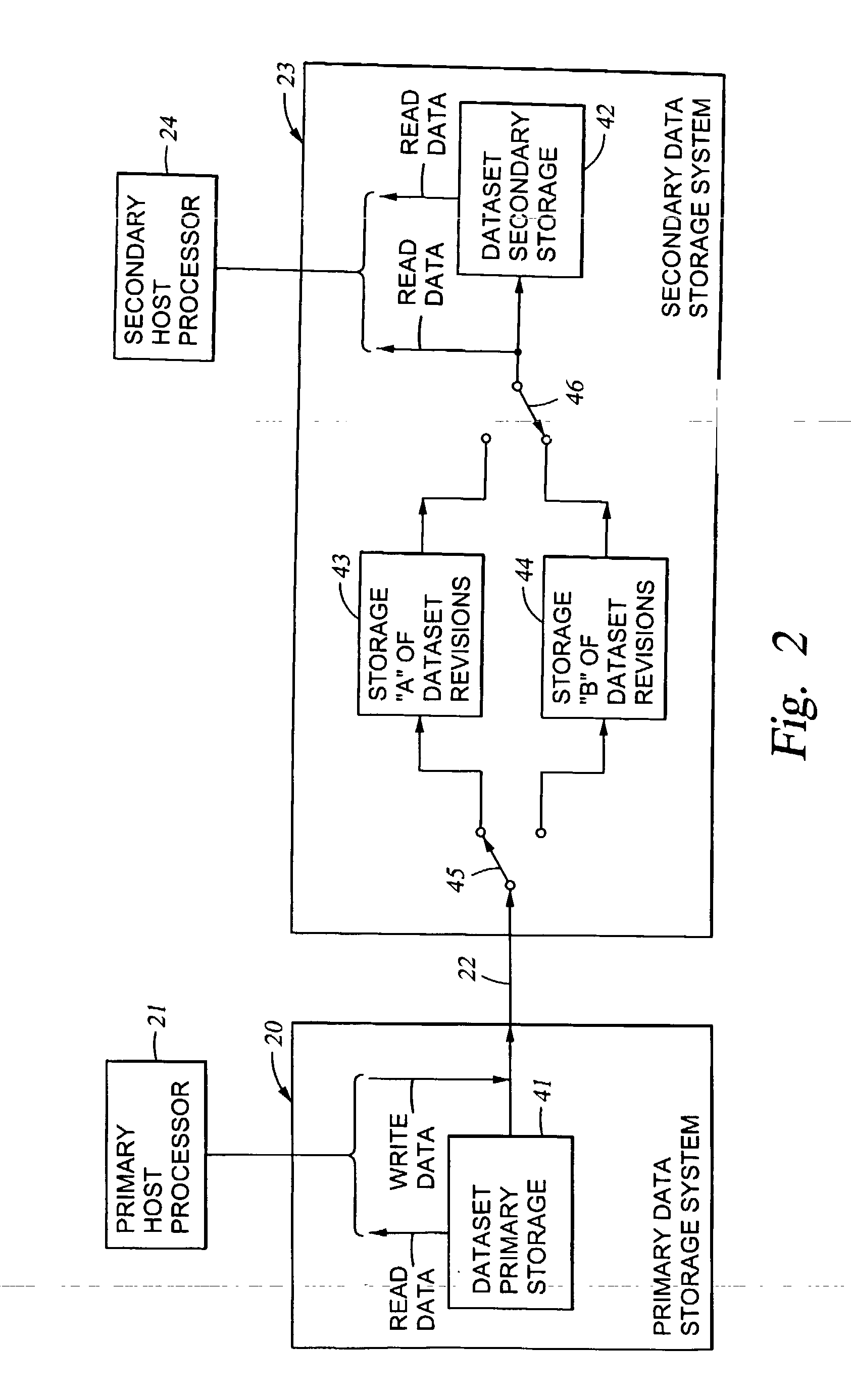
Replication of remote copy data for internet protocol (IP) transmission
ActiveUS20030217119A1Special service provision for substationError detection/correctionInternet protocol suiteRouting table
Consistent updates are made automatically over a wide-area IP network, concurrently with read-only access to the remote copies. A replication control protocol (RCP) is layered over TCP / IP providing the capability for a remote site to replicate and rebroadcast blocks of the remote copy data to specified groups of destinations, as configured in a routing table. A volume multicast layer over RCP provides for multicasting to specified volume extents of the blocks. The blocks are copied at the logical level, so that it does not matter what physical structure is used for storing the remote copies. Save volumes buffer the remote copy data transmitted between the primary or secondary file system volume and the IP network, in order to ensure independence between the replication process, the IP transport method, and the primary file system being replicated.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
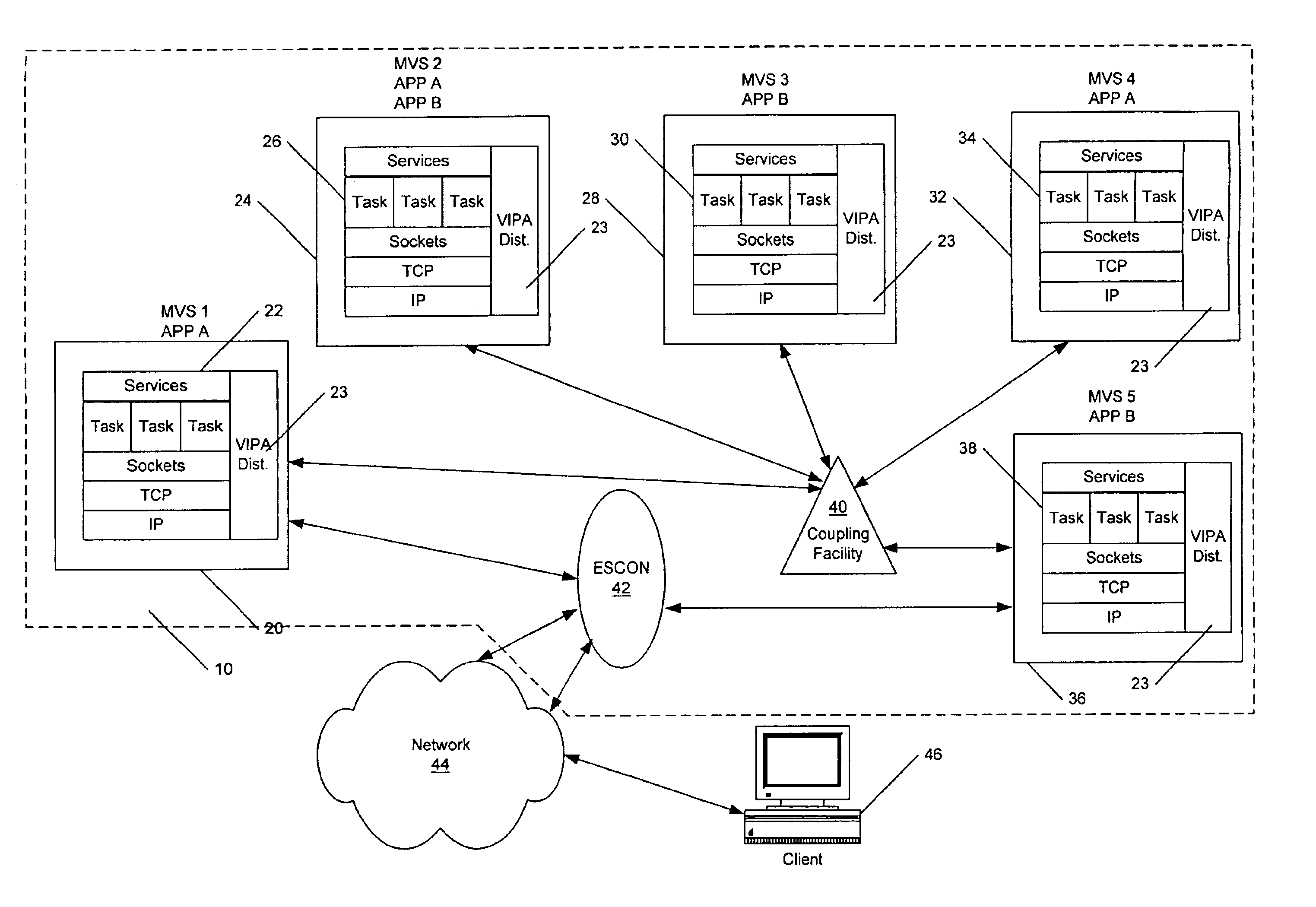
System having a single IP address associated with communication protocol stacks in a cluster of processing systems
Methods, systems and computer program products provide communications with a plurality of application instances using a plurality of communication protocol stacks and a single Internet Protocol (IP) address. A stack is established as a routing stack associated with the single IP address. Other stacks which are associated with the single IP address are defined as candidate target stacks and an identification of candidate target stacks and the routing stack is distributed to the stacks. The routing stack is notified when an application associated with a candidate target stack listens to a port of the IP address to establish a current actual target stack. A request to establish a connection to the IP address and the port of the IP address is received and a routing table entry corresponding to the current actual target stack is created to provide a routing path from the routing stack to the current actual target stack. Communications to the port of the IP address received by the routing stack are routed based on the routing table.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
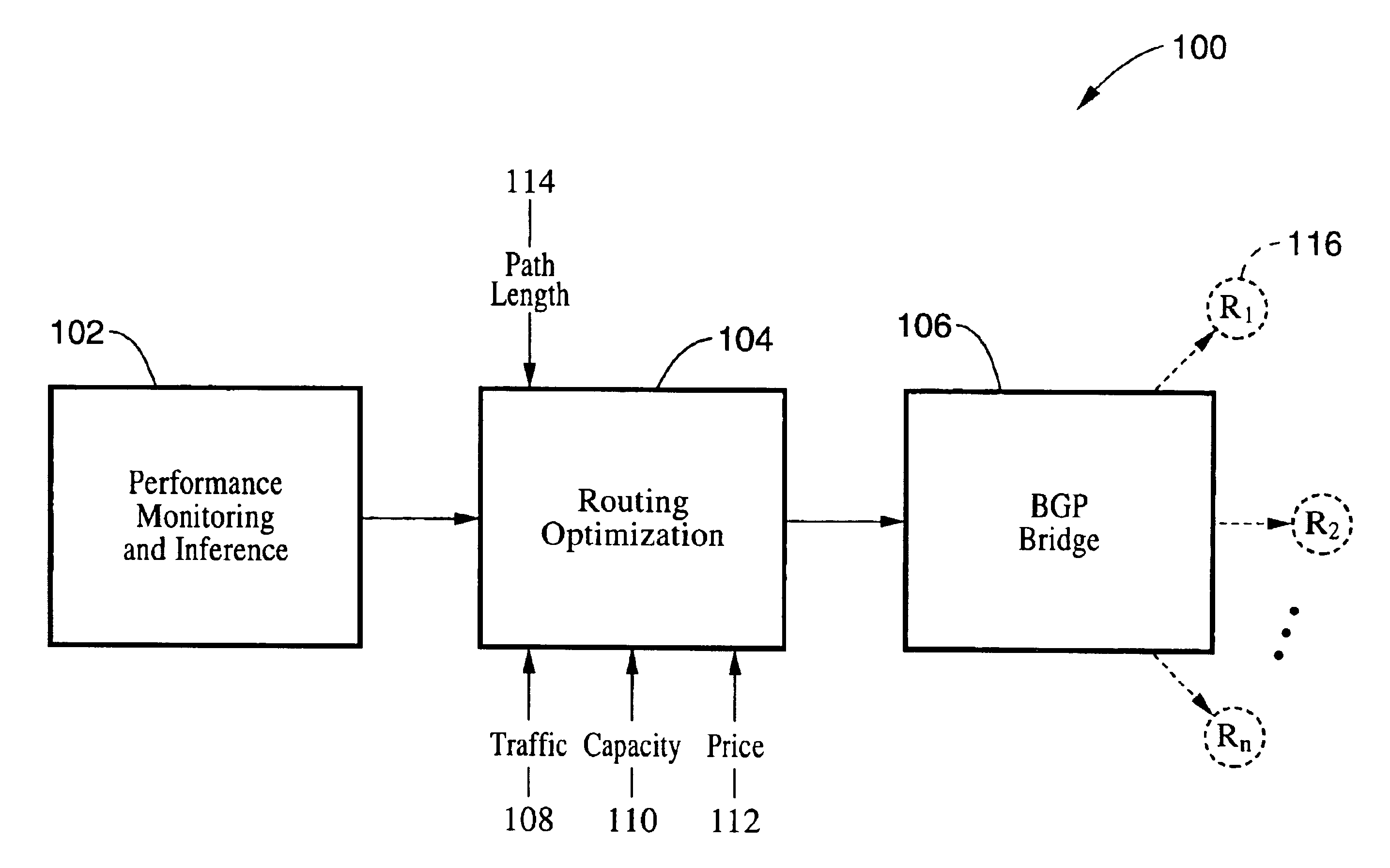
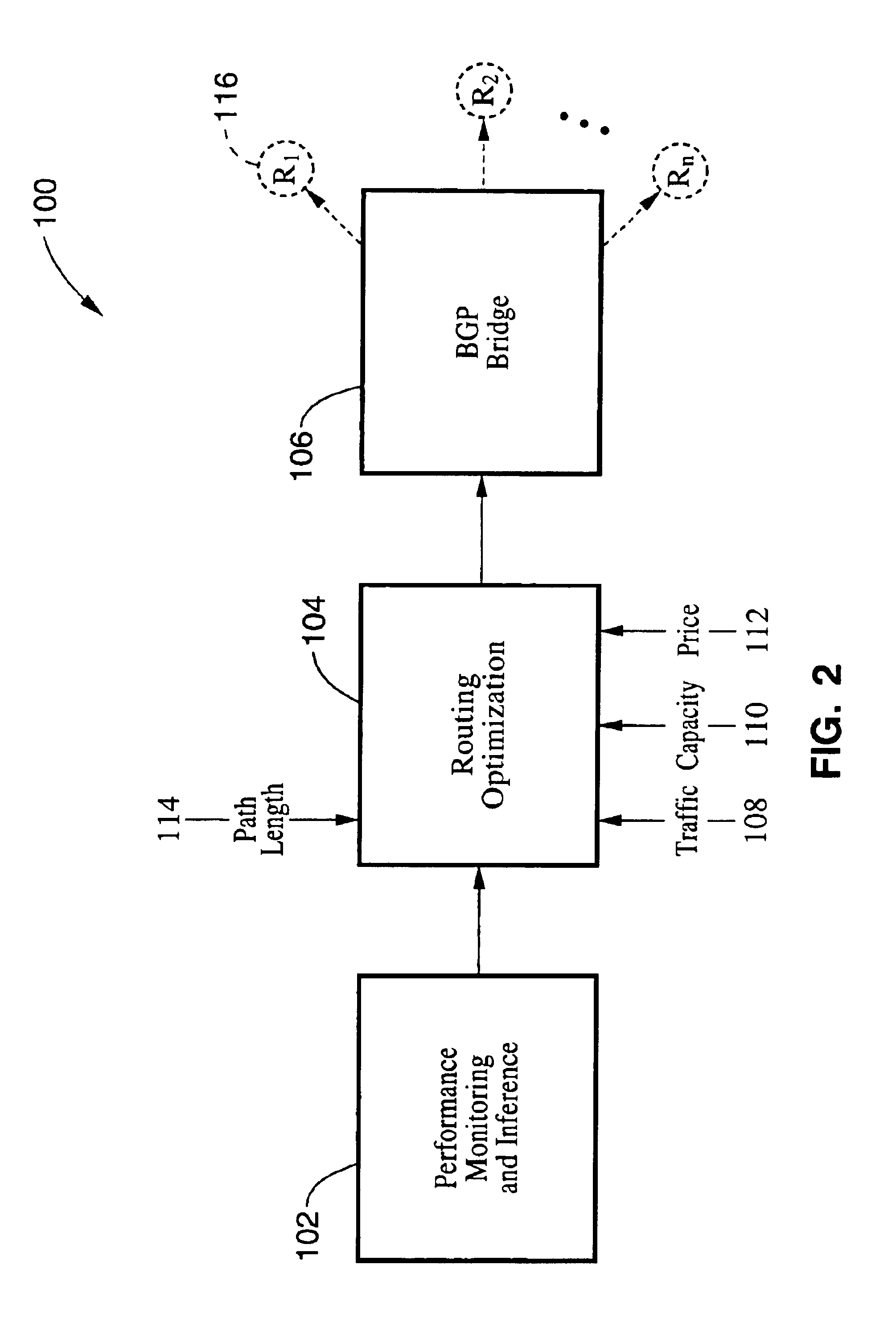
Method and system for optimizing routing through multiple available internet route providers
InactiveUS6981055B1Optimize route selectionInability to overcomeDigital computer detailsData switching by path configurationTraffic capacityRouting table
A method and system for optimizing routing traffic to a destination when multiple routes are available. A performance monitoring and inference component measures the performance of the available paths to a large set of subnetworks, and uses those measurements to infer the performance of all available paths to an even larger set of subnetworks. A routing optimization component uses a cost function that assigns a cost to a routing table based on information from the performance monitoring and inference component, as well as other path characteristics, and further uses a minimization methodology to find a routing table with a very low cost, as defined by the cost function. A BGP bridge takes the routing table generated by the routing optimization component and communicates that information to the routers using BGP, thereby ensuring that the routers will route traffic in accordance with the routing table.
Owner:INTERNAP HLDG LLC
System and method for developing and interpreting e-commerce metrics by utilizing a list of rules wherein each rule contain at least one of entity-specific criteria
InactiveUS7013323B1Quick and efficientImprove throughputMultiple digital computer combinationsMarketingRouting tableExternal data
A system, method and computer program product for developing and interpreting e-commerce metrics is disclosed. The method involves collecting pages that are commonly transmitted over a computer network (e.g., the Internet, an institutional intranet, etc.), where the pages are relevant to the business operations of an entity, collecting external data, which may or may not be available on the computer network, but that is highly relevant to the entity, processing the collected pages with additional information such as contact information, routing tables, financial information, and other data which does not need to be collected more than once, and scoring the pages based on all the information collected to determine statistics. The statistics are analyzed for business information which may be important to the operations of the entity. The method then produces a report to deliver a continuous stream of e-commerce intelligence for the entity.
Owner:ZEROFOX
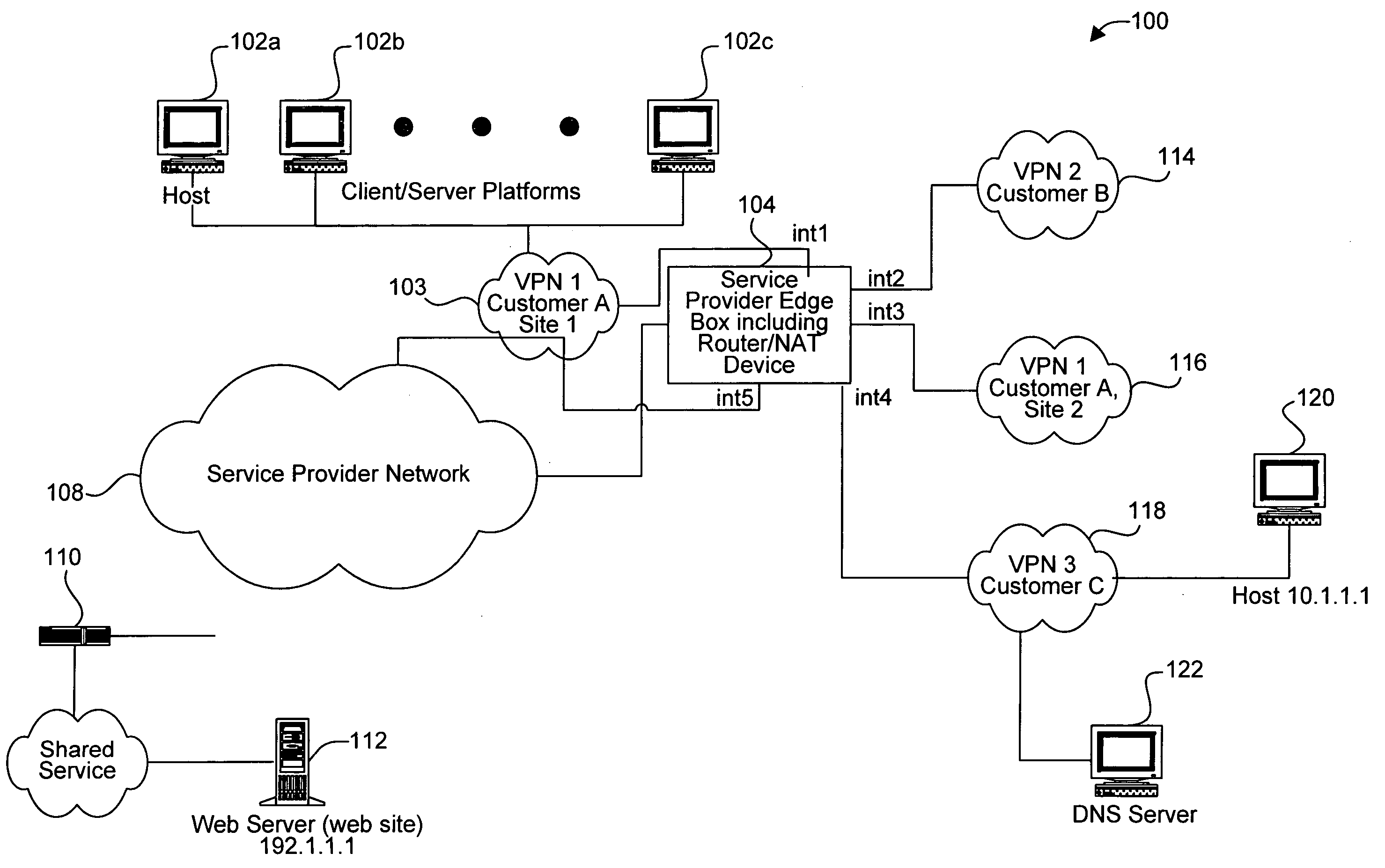
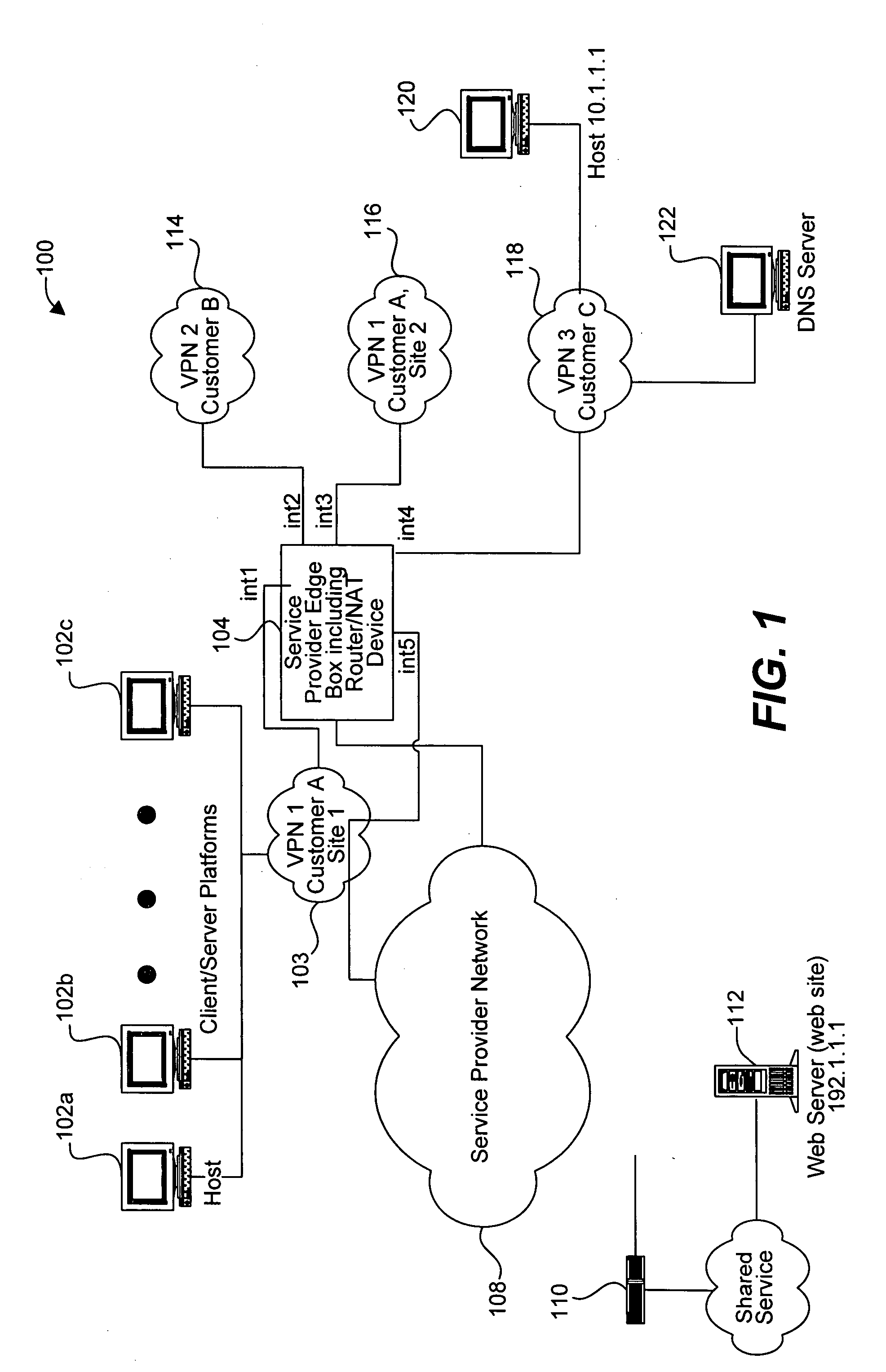
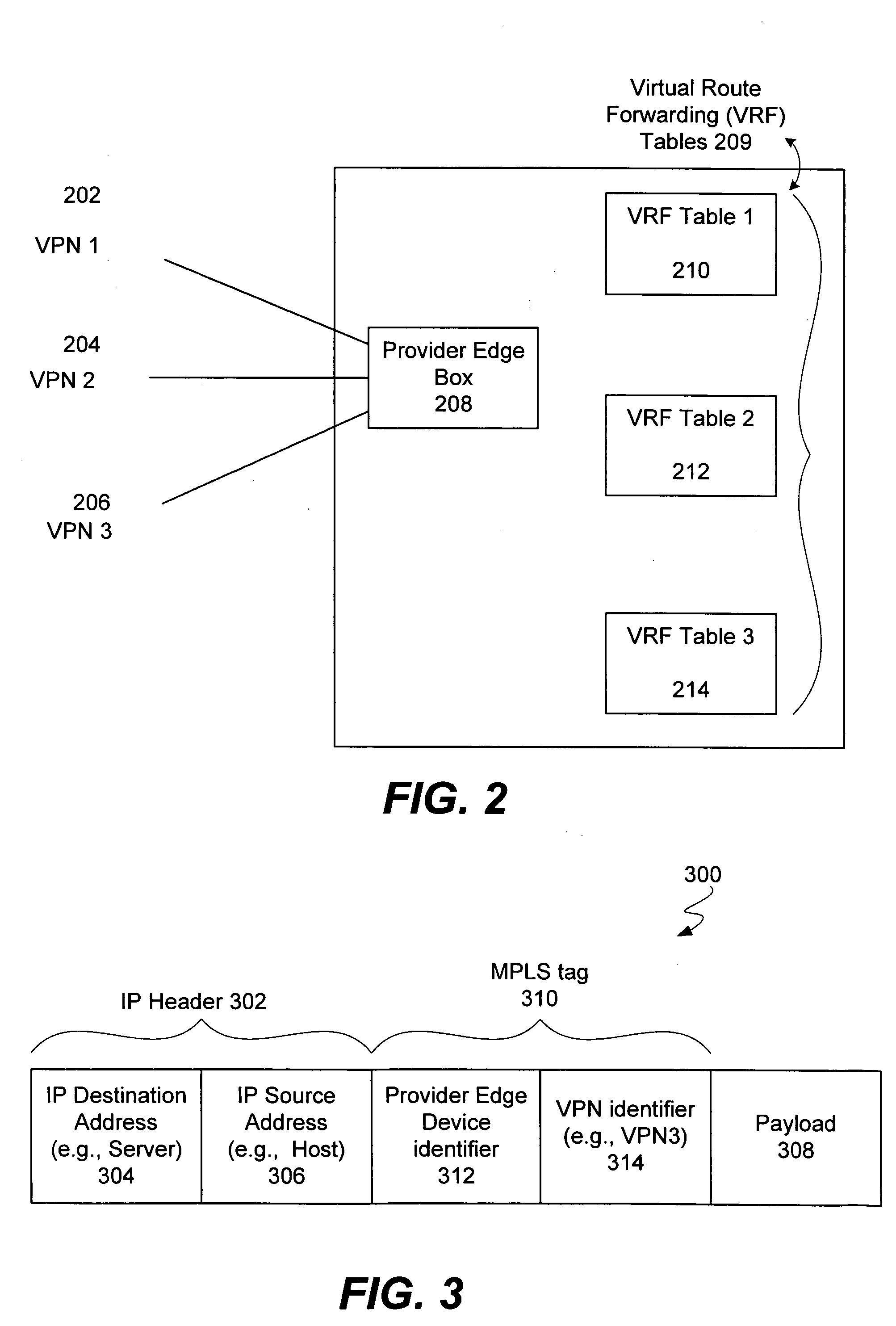
Apparatus and methods for handling shared services through virtual route forwarding(VRF) -aware- NAT
Methods and apparatus for performing NAT are disclosed. Specifically, NAT is performed at a service provider network device associated with an interface of a service provider network. When a packet is sent from a VPN to a node outside the service provider network (e.g., to access a shared service), the packet includes a VPN identifier (or VRF identifier) In accordance with various embodiments, each packet includes an MPLS tag that includes the VPN identifier. The VPN identifier is stored in a translation table entry. The storing of the VPN identifier will enable a reply packet from the shared service network to the customer VPN to be routed using a routing table identified by the VPN identifier.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
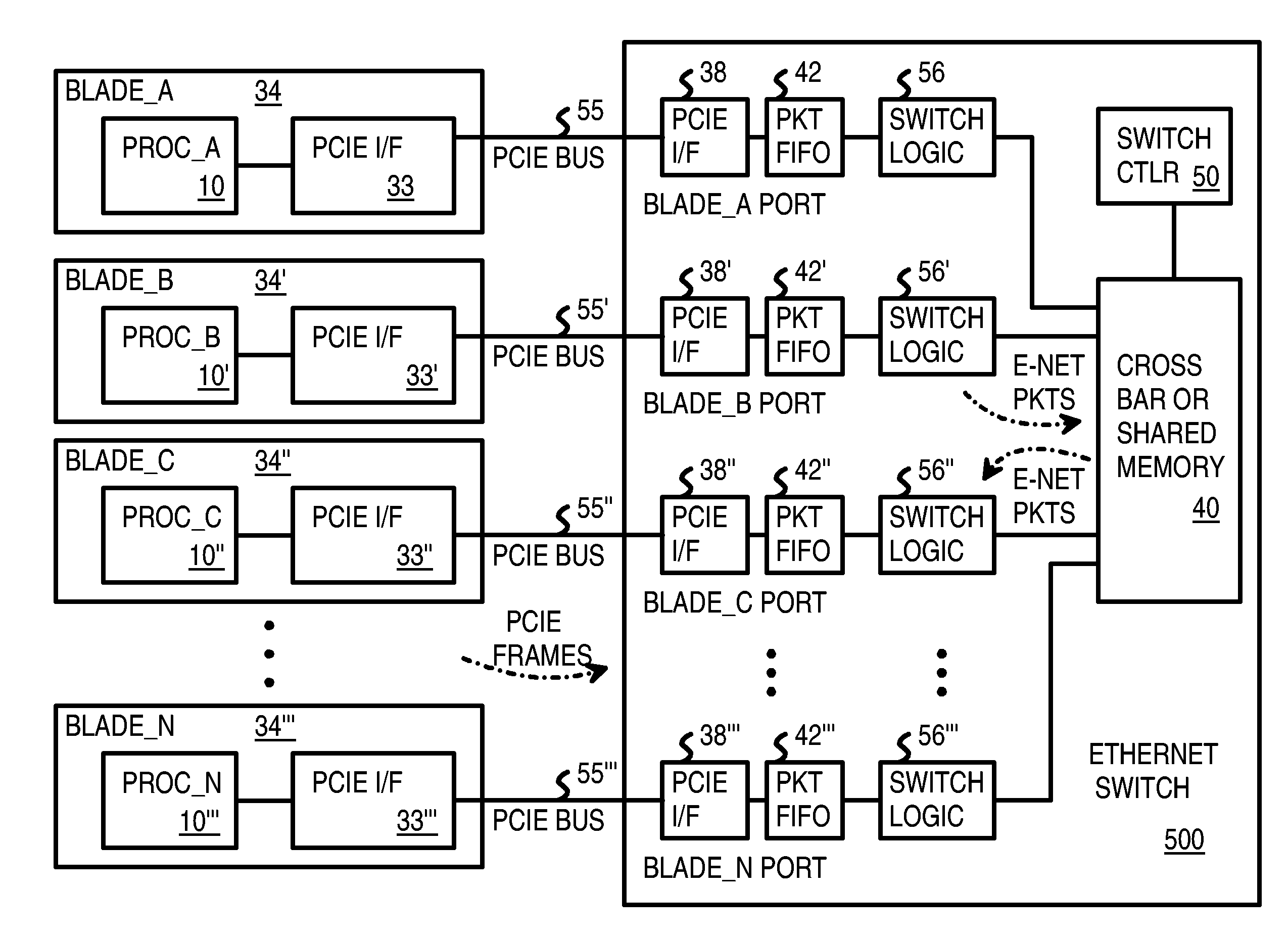
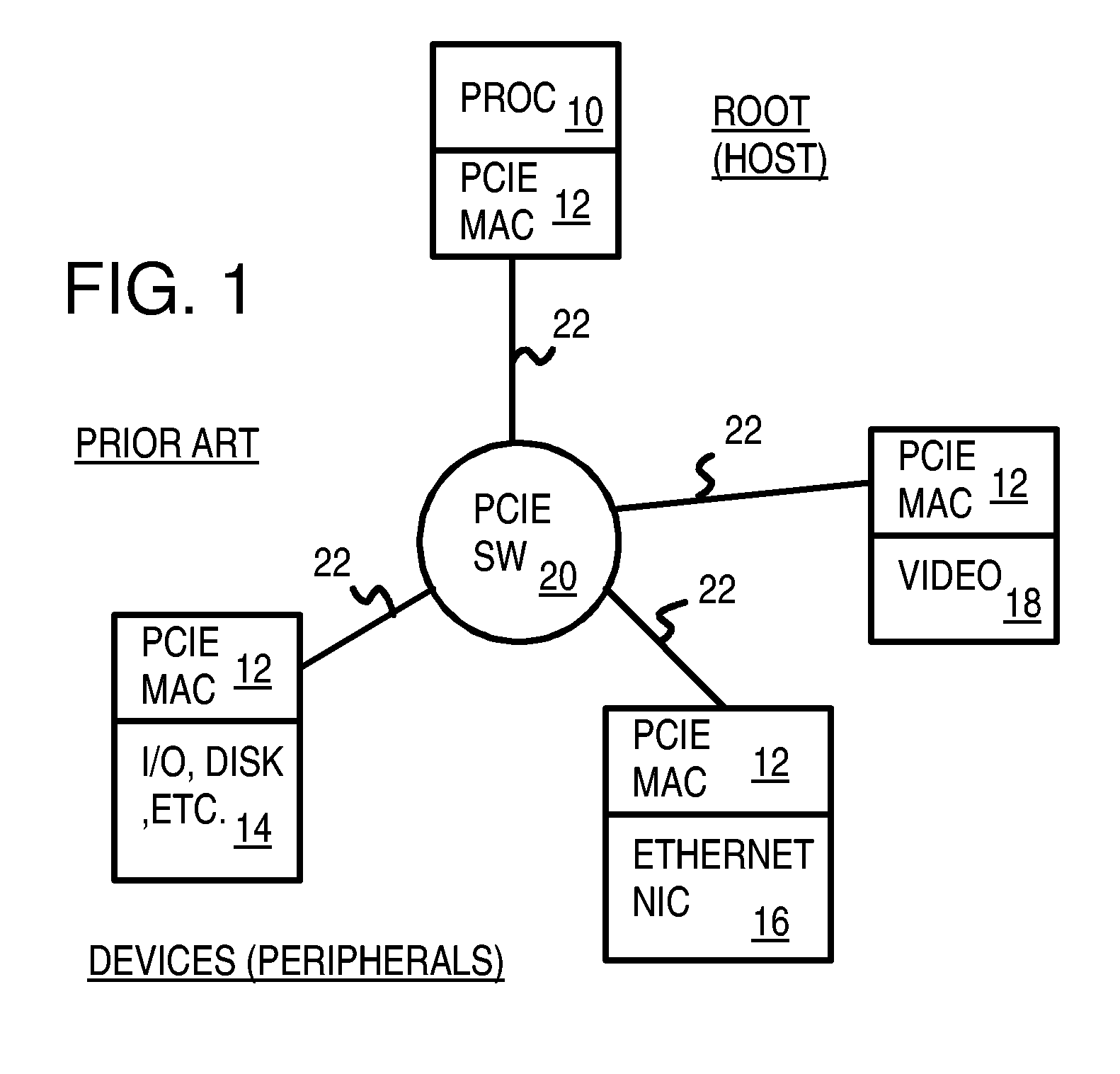
Pseudo-ethernet switch without ethernet media-access-controllers (MAC's) that copies ethernet context registers between PCI-express ports
A Pseudo-Ethernet switch has a routing table that uses Ethernet media-access controller (MAC) addresses to route Ethernet packets through a switch fabric between an input port and an output port. However, the input port and output port have Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIE) interfaces that read and write PCI-Express packets to and from host-processor memories. When used in a blade system, host processor boards have PCIE physical links that connect to the PCIE ports on the Pseudo-Ethernet switch. The Pseudo-Ethernet switch does not have Ethernet MAC and Ethernet physical layers, saving considerable hardware. The switch fabric can be a cross-bar switch or can be a shared memory that stores Ethernet packet data embedded in the PCIE packets. Write and read pointers for a buffer storing an Ethernet packet in the shared memory can be passed from input to output port to perform packet switching.
Owner:DIODES INC
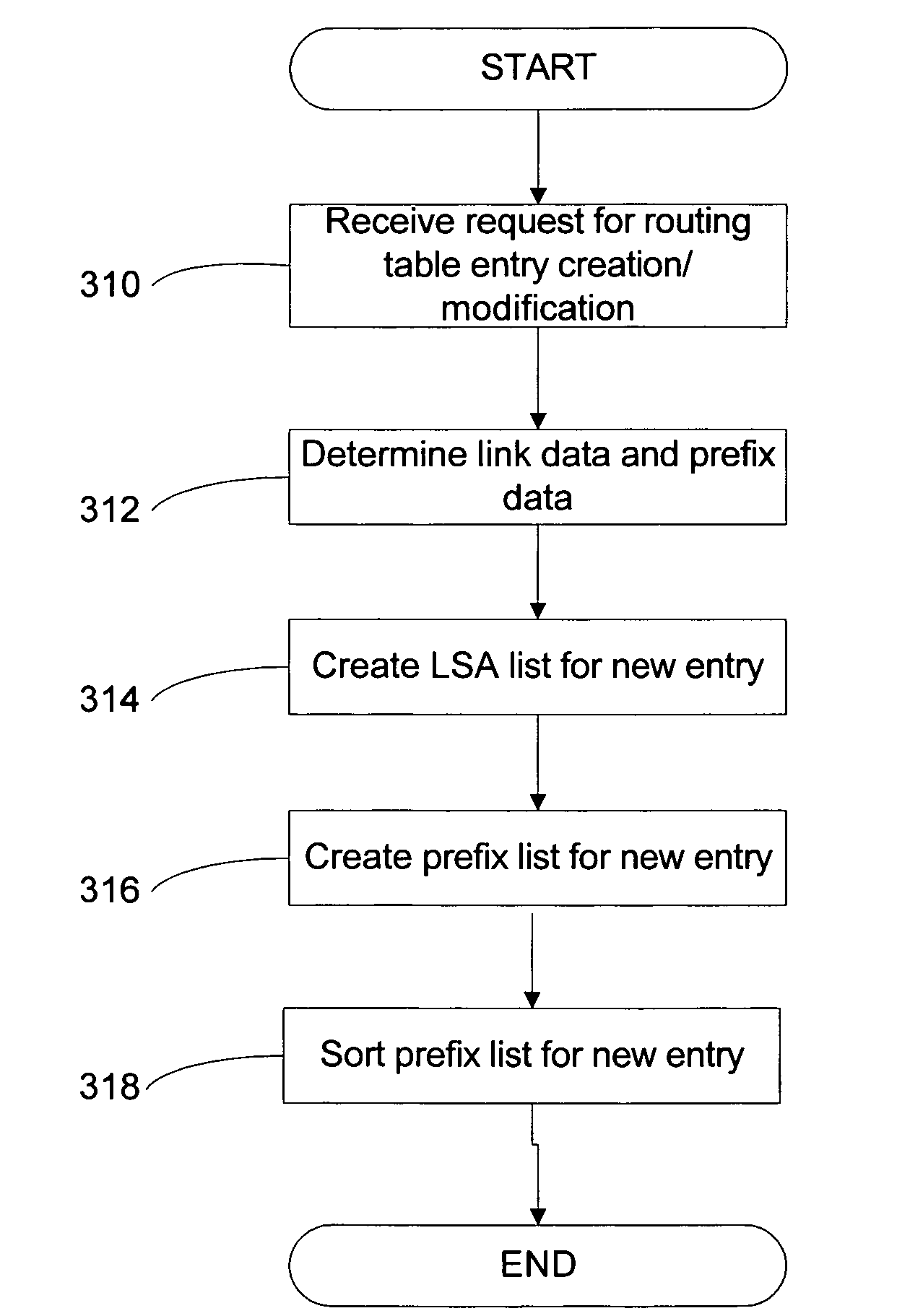
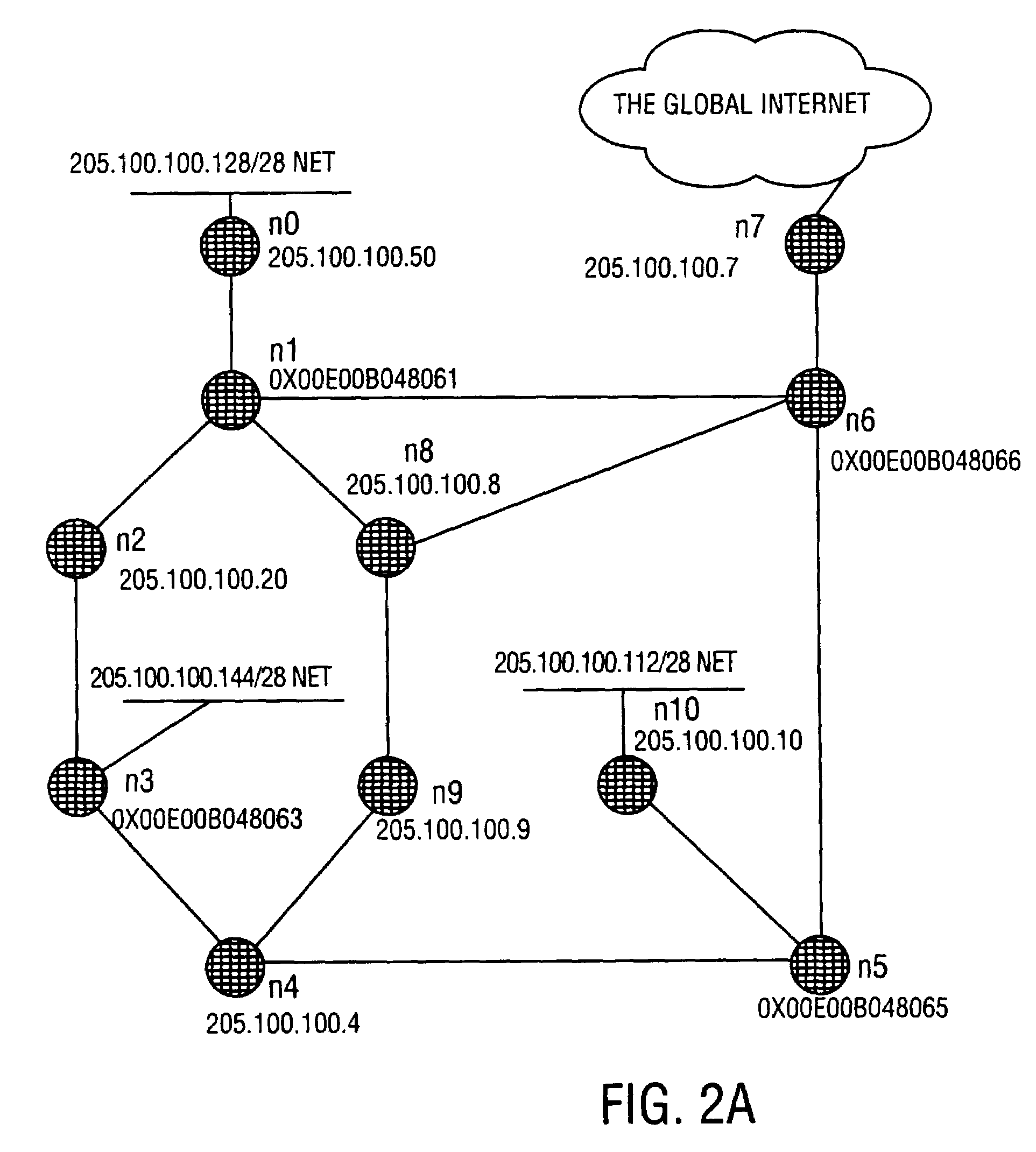
System and method for routing table computation and analysis
InactiveUS20070189284A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsRouting tableNetwork link
Described is a system and method for determining routing information for a network link, the network link including a plurality of subnets, each subnet having the same routing information as the network link, storing the routing information as an entry in a routing table, determining subnet information for each of the plurality of subnets and storing the subnet information for each of the plurality of subnets in the entry. Methods of comparing and searching the subnet information are also described.
Owner:WIND RIVER SYSTEMS
Small group multicast in a computer network
InactiveUS7016351B1RelievingBroadcast transmission systemsTime-division multiplexRouting tableMulticast packets
The invention solves the problem of overloading intermediate routers with state information as the number of multicast groups increases to millions of groups. The invention places multicast delivery tree information in the header of an encapsulated multicast packet, thereby relieving the routers from maintaining any state information about the multicast groups. The encapsulated packet is referred to as a small group multicast packet, or SGM packet. Routers which are neither branch points of the delivery tree nor destination routers will also need to do no additional forwarding processing other than that needed for standard unicast forwarding. A protocol designation field in the Layer 3 header informs the router that the packet is a SGM packet, and that the router is therefore instructed to parse the packet for route information. The router parses the SGM packet header and determines the next hop address of routers in the multicast delivery tree. The standard unicast forwarding tables are then consulted to determine the next packet destination addresses, and the router then rewrites the SGM packet and routes it to the next hop router. The routing tables also instruct the router as to which outbound port to route the packet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
High-performance addressing and routing of data packets with semantically descriptive labels in a computer network
InactiveUS7555563B2Reduce storageEasy to operateDigital computer detailsData switching networksRouting tableNetwork packet
A method, system and apparatus for routing data through a network based on the content or semantics of the data. Semantic routing engines route the data through the network based upon information maintained in routing tables. The routing tables used to route the content through the network are derived by aggregating information about either content consumers or content producers into ontological.
Owner:SEMANDEX NETWORKS
Unified routing scheme for ad-hoc internetworking
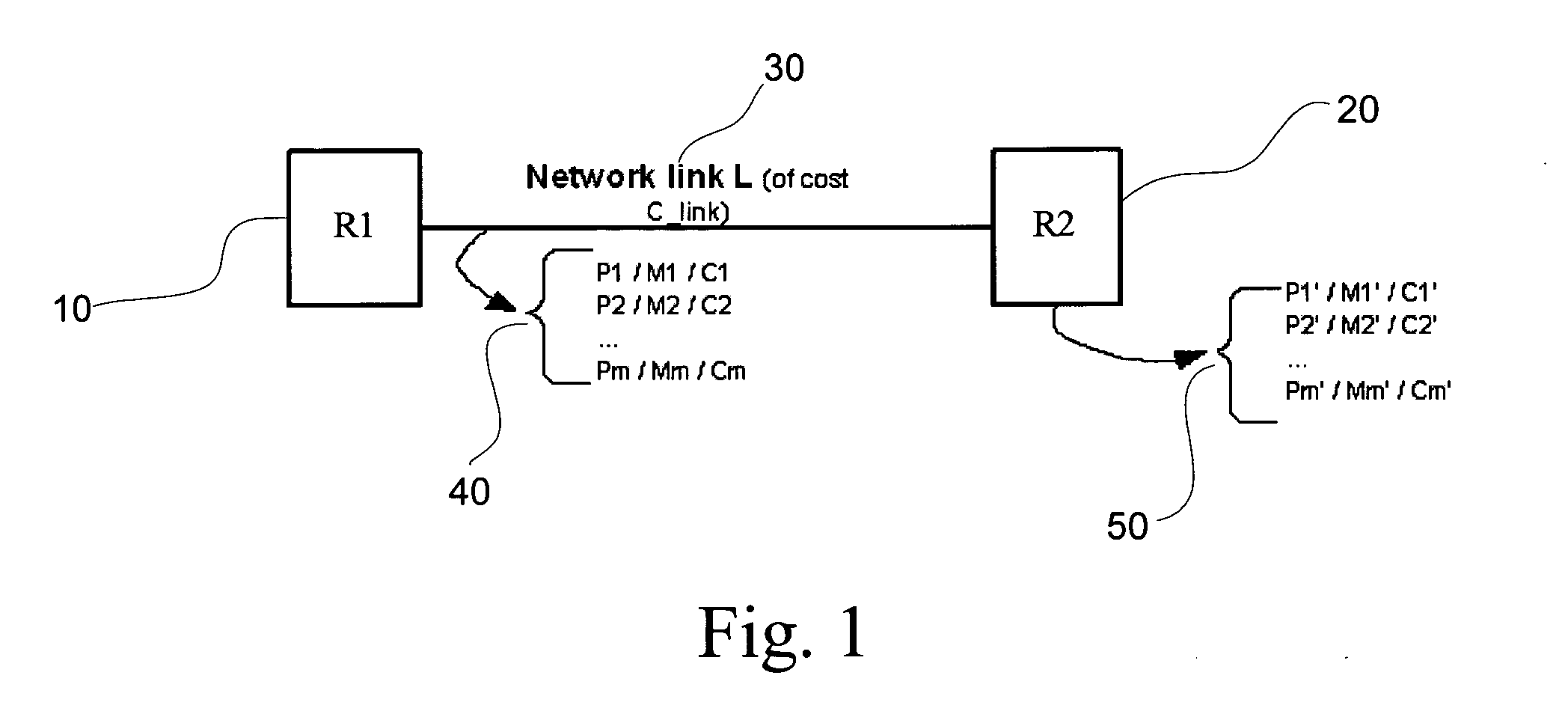
InactiveUS7159035B2Data switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsRouting tableShort path algorithm
Routing table update messages that include both network-level and link-level addresses of nodes of a computer network are exchanged among the nodes of the computer network. Further, a routing table maintained by a first one of the nodes of the computer network may be updated in response to receiving one or more of the update messages. The routing table is preferably updated by selecting a next node to a destination node of the computer network only if every intermediate node in a path from the next node to the destination node satisfies a set of nodal conditions required by the first node for its path to the destination node and the next node offers the shortest distance to the destination node and to every intermediate node along the path from the next node to the destination node. The shortest distance to the destination node may be determined according to one or more link-state and / or node-state metrics regarding communication links and nodes along the path to the destination node. Also, the nodal characteristics of the nodes of the computer system may be exchanged between neighbor nodes, prior to updating the routing table. Preferred paths to one or more destination nodes may be computed according to these nodal characteristics, for example using a Dijkstra shortest-path algorithm.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
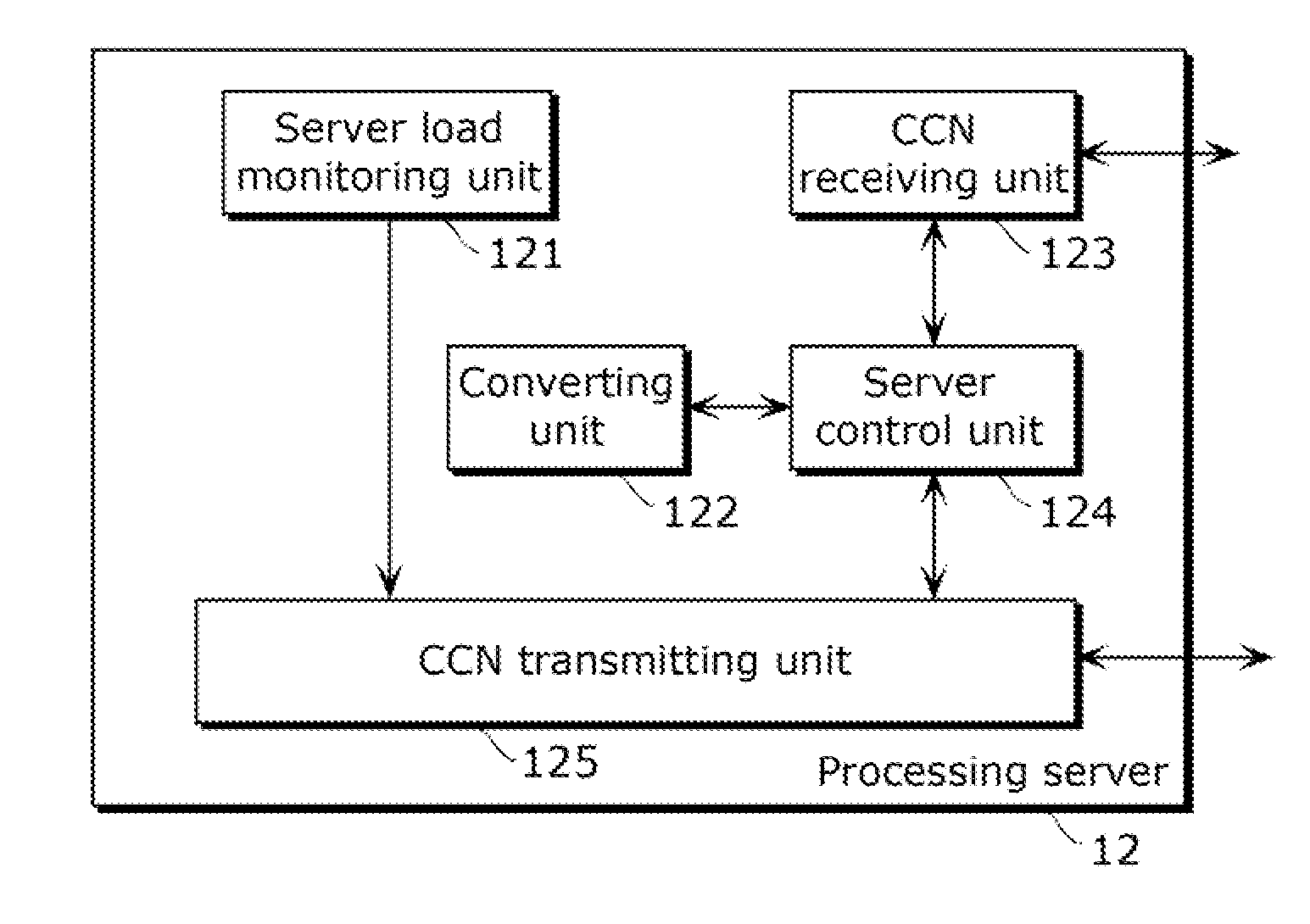
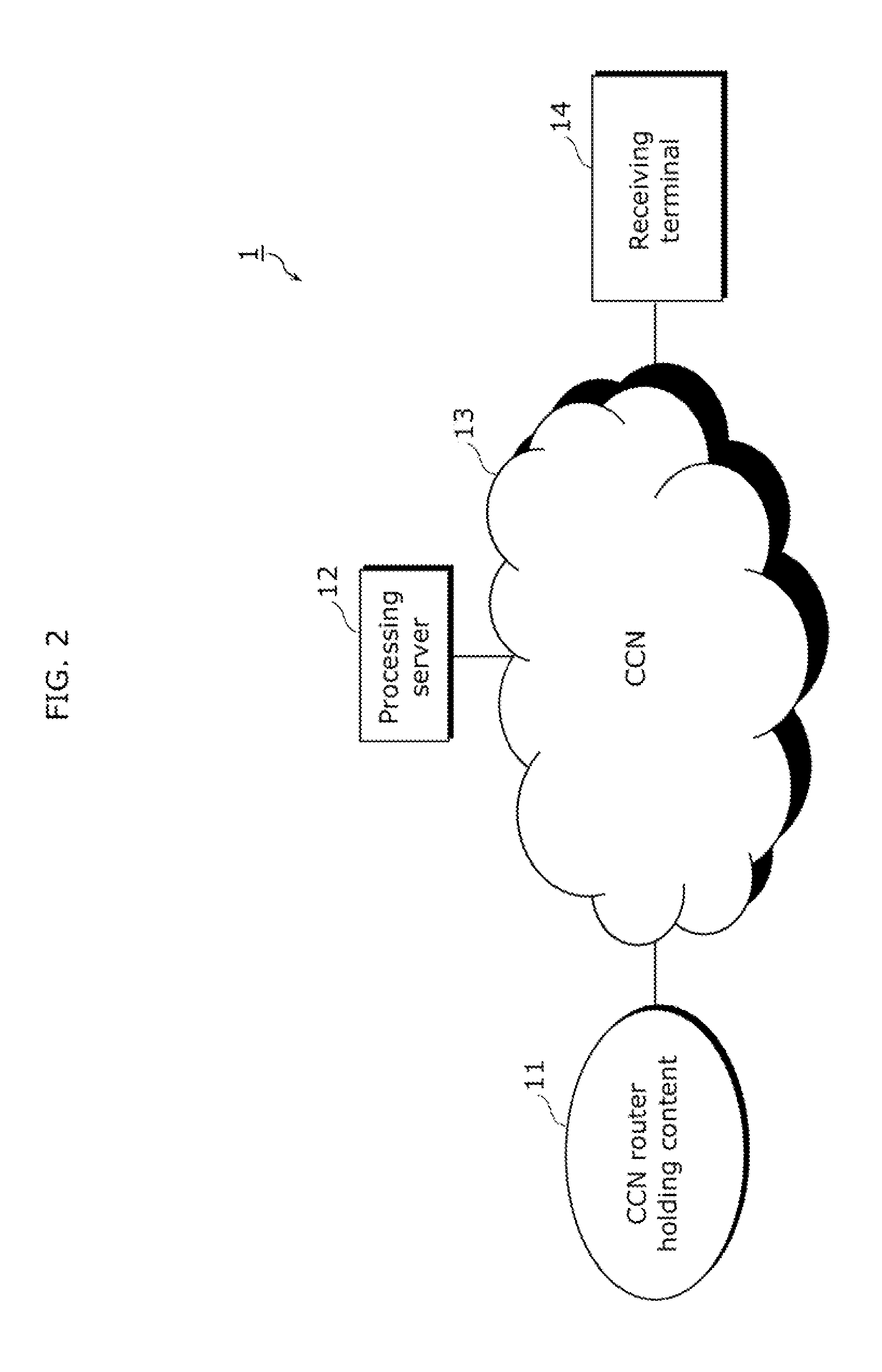
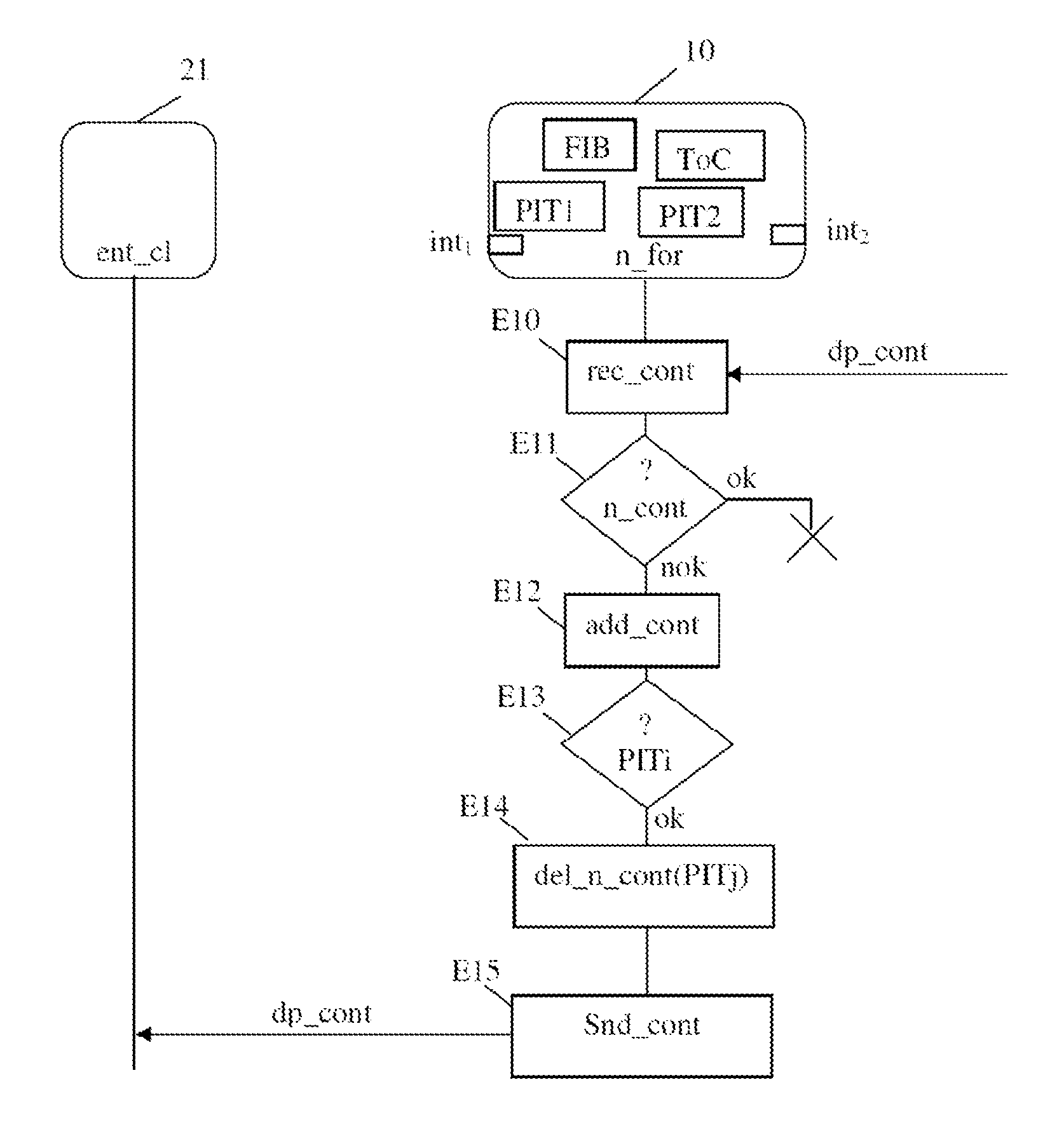
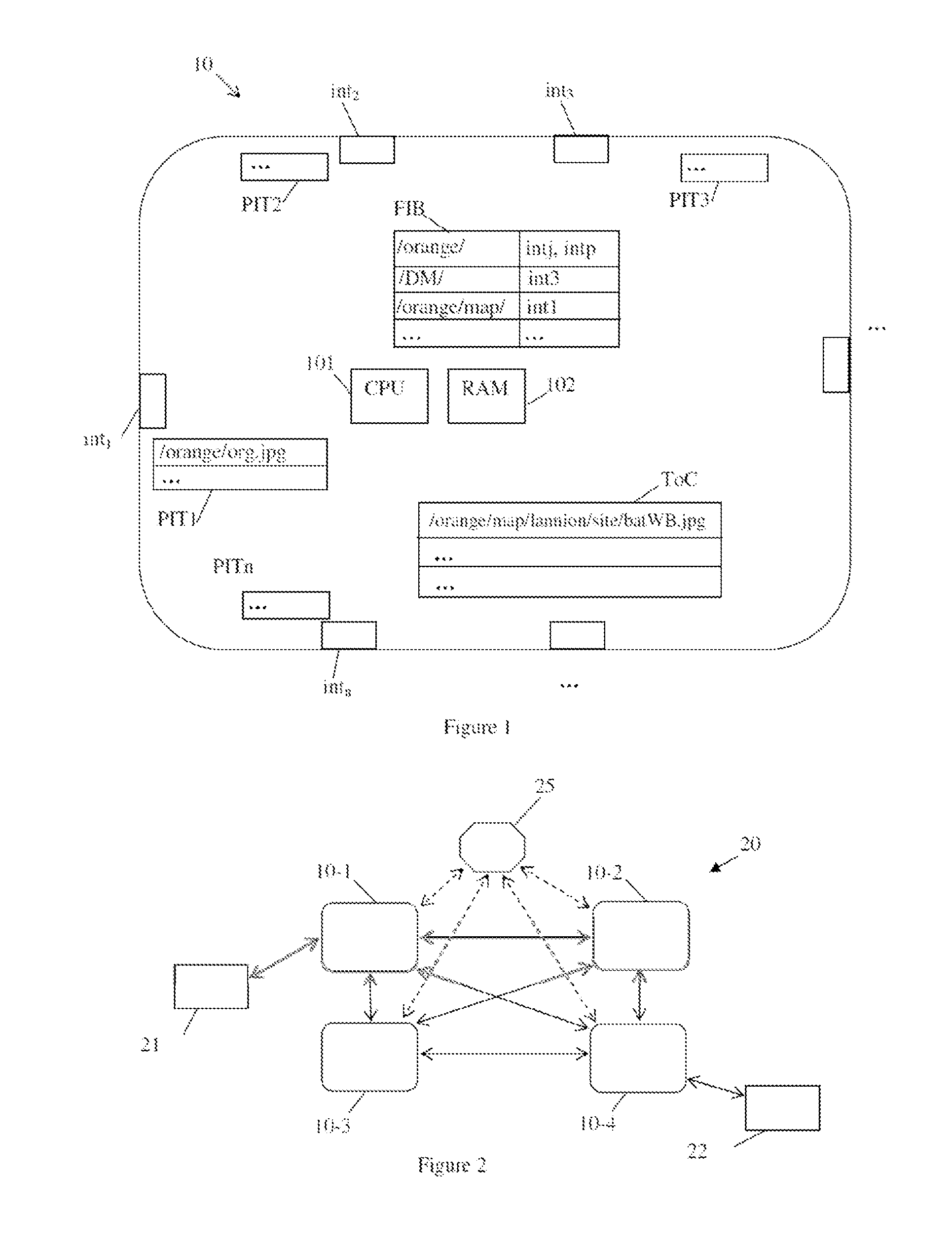
Server, router, receiving terminal, and processing method
ActiveUS20150095481A1Digital computer detailsForward error control useRouting tableComputer terminal
A server according to the present disclosure includes: a converting unit that converts content data to enhance a real-time property, and creates a packet of the converted content data; and a server control unit that updates a routing table that describes processing for an interest packet, wherein when an interest packet for content including converted content data is received, the server control unit performs control of issuing an interest packet for original content data of the content which is to be converted, and when original content data to be processed is received from a CCN, the server control unit performs control of causing the original content data to be converted, a packet of the converted original content data to be created, and the packet of the converted original content data to be transmitted as a response packet for the interest packet for the content including the converted content data.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
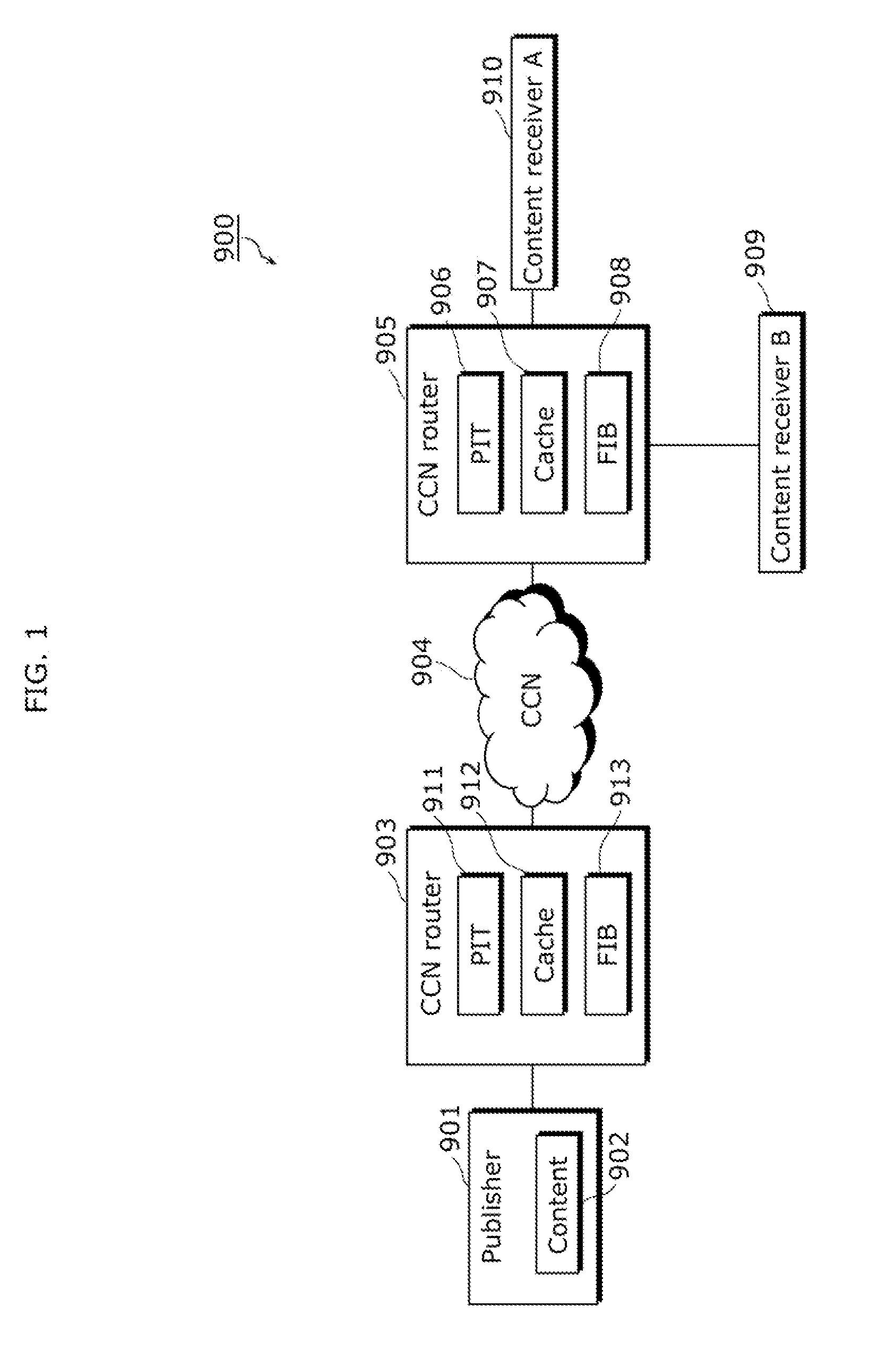
Method for Processing a Request in an Information-Centric Communication Network
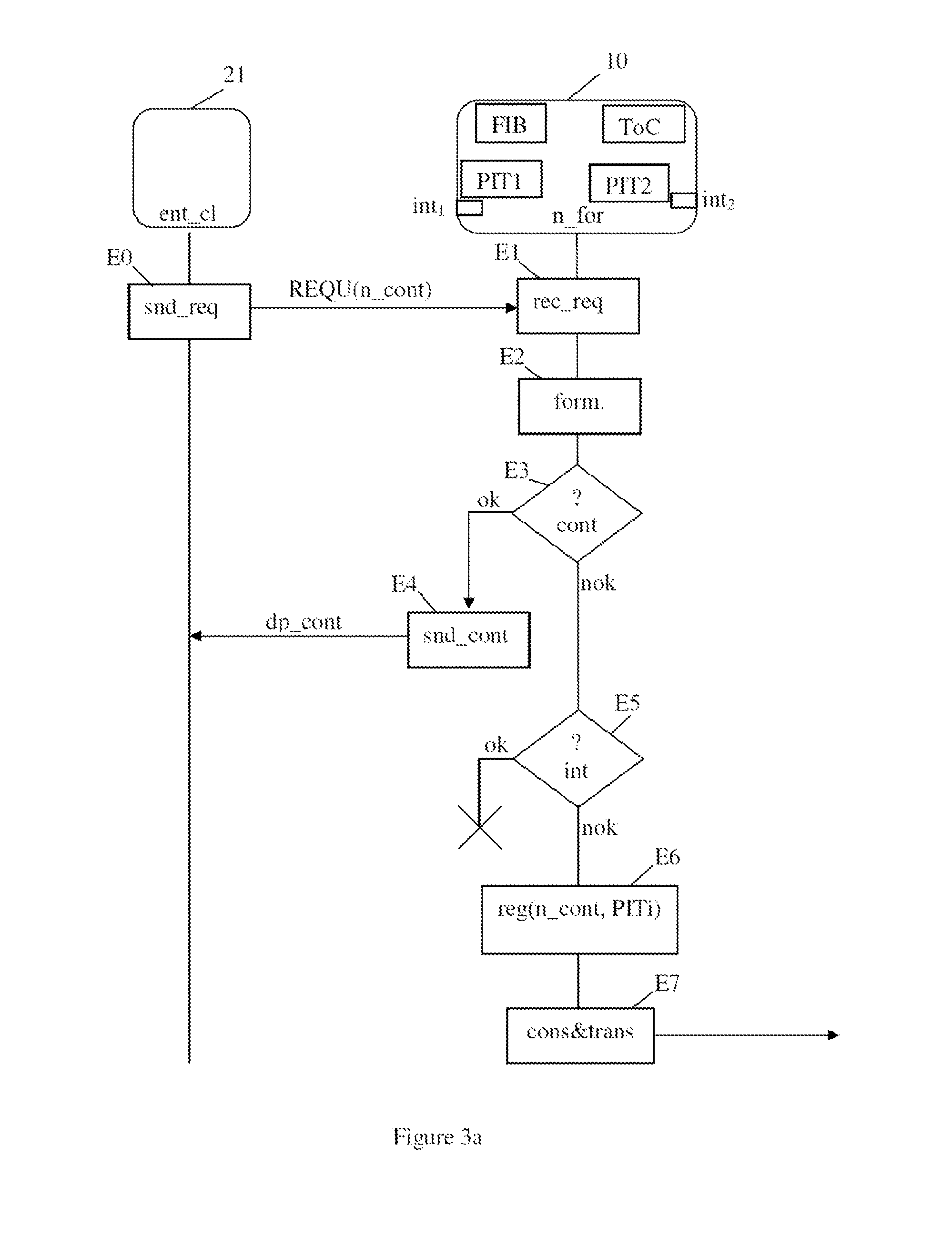
ActiveUS20140314093A1Small sizeOptimize processing timeData switching by path configurationRouting tableNetwork packet
A method for processing a request for content by a routing device in a communication network implementing a name-based routing. The device includes plural interfaces to receive a request for content and a data packet associated with a content, and a routing table adapted to determine, based on a content name, at least one interface to route the request. The method includes: receiving the request through a first interface; if the device is not able to provide said data packet, searching for the name of the content in a table of pending requests associated with the first interface; in case the content name does not appear in the table, storing the name of the content in the table; and transmitting the request through at least one second interface, the second interface being determined as a function of the name of the content on the basis of the routing table.
Owner:ORANGE SA (FR)
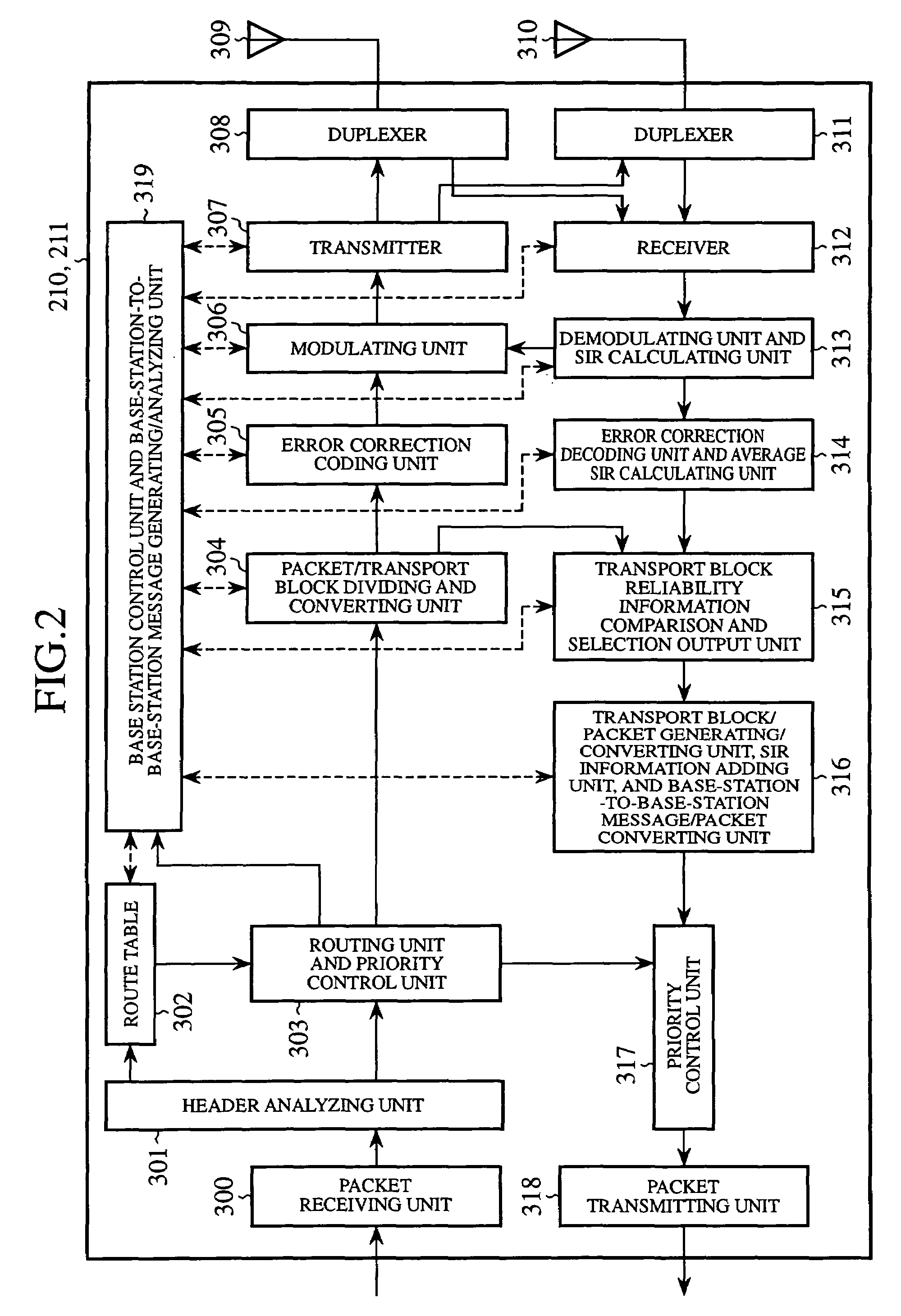
Radio base station device and mobile communication system
InactiveUS7418273B2Avoid congestionAvoid network congestionError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityRouting table
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
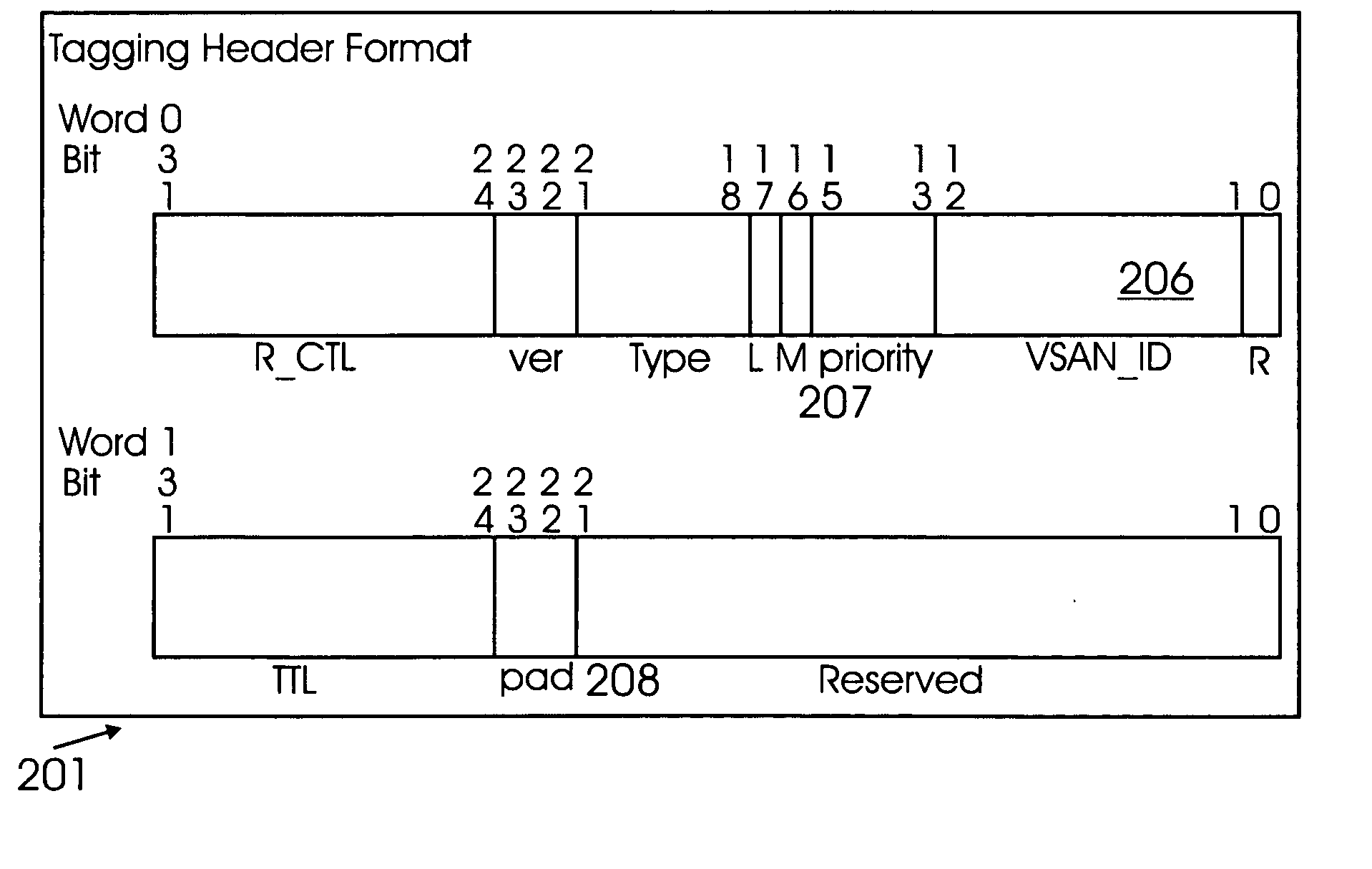
Method and system for using extended fabric features with fibre channel switch elements
A fibre channel switch element and method for routing fibre channel frames is provided. The switch element includes a receive segment that can add a virtual storage area network (“VSAN”) tagging header to frames that are received by the receive segment; and strip the VSAN tagging header before frames are sent to ports that do not support virtual fabric capability. The receive segment includes a table used for matching fabric extension parameters. An incoming frame's VSAN identity value is compared to a control word entry to generate a value used for routing the incoming frame. The table is used to determine if a frame is part of a virtual fabric. The routing table for each port is used to route frames and the routing table includes entries for supported virtual fabrics.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com