Patents
Literature
857 results about "Network domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
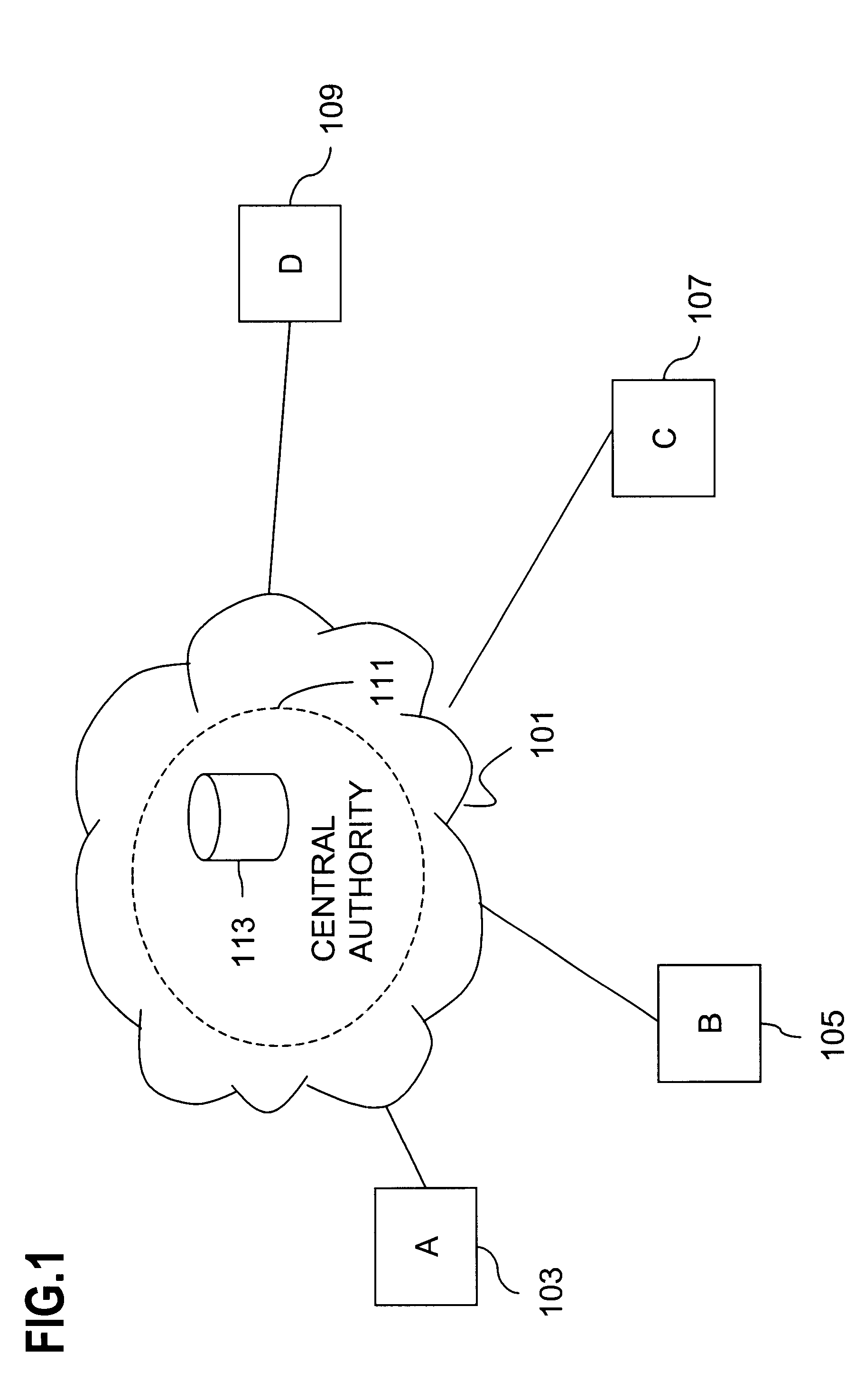
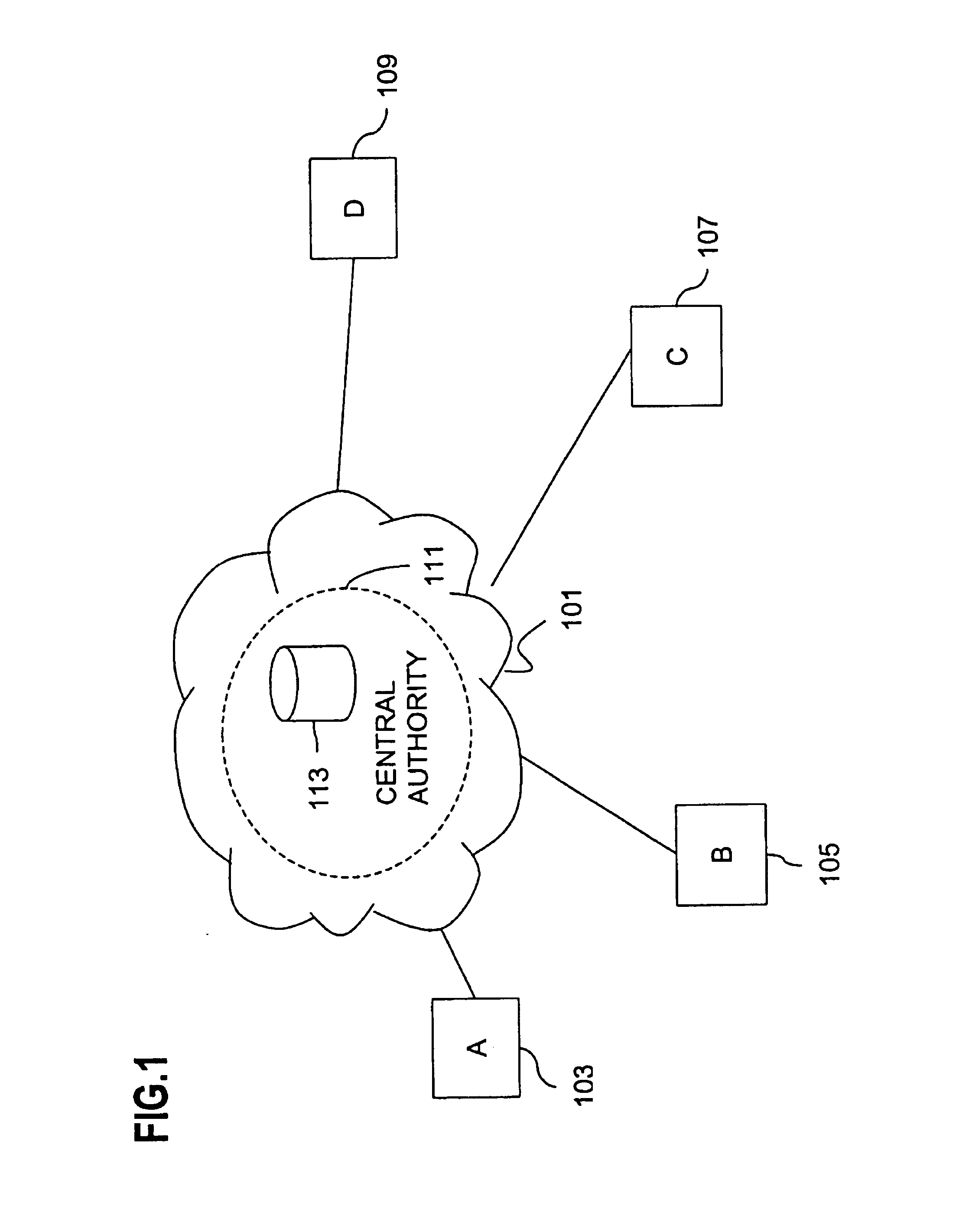
A network domain is an administrative grouping of multiple private computer networks or hosts within the same infrastructure. Domains can be identified using a domain name; domains which need to be accessible from the public Internet can be assigned a globally unique name within the Domain Name System (DNS).
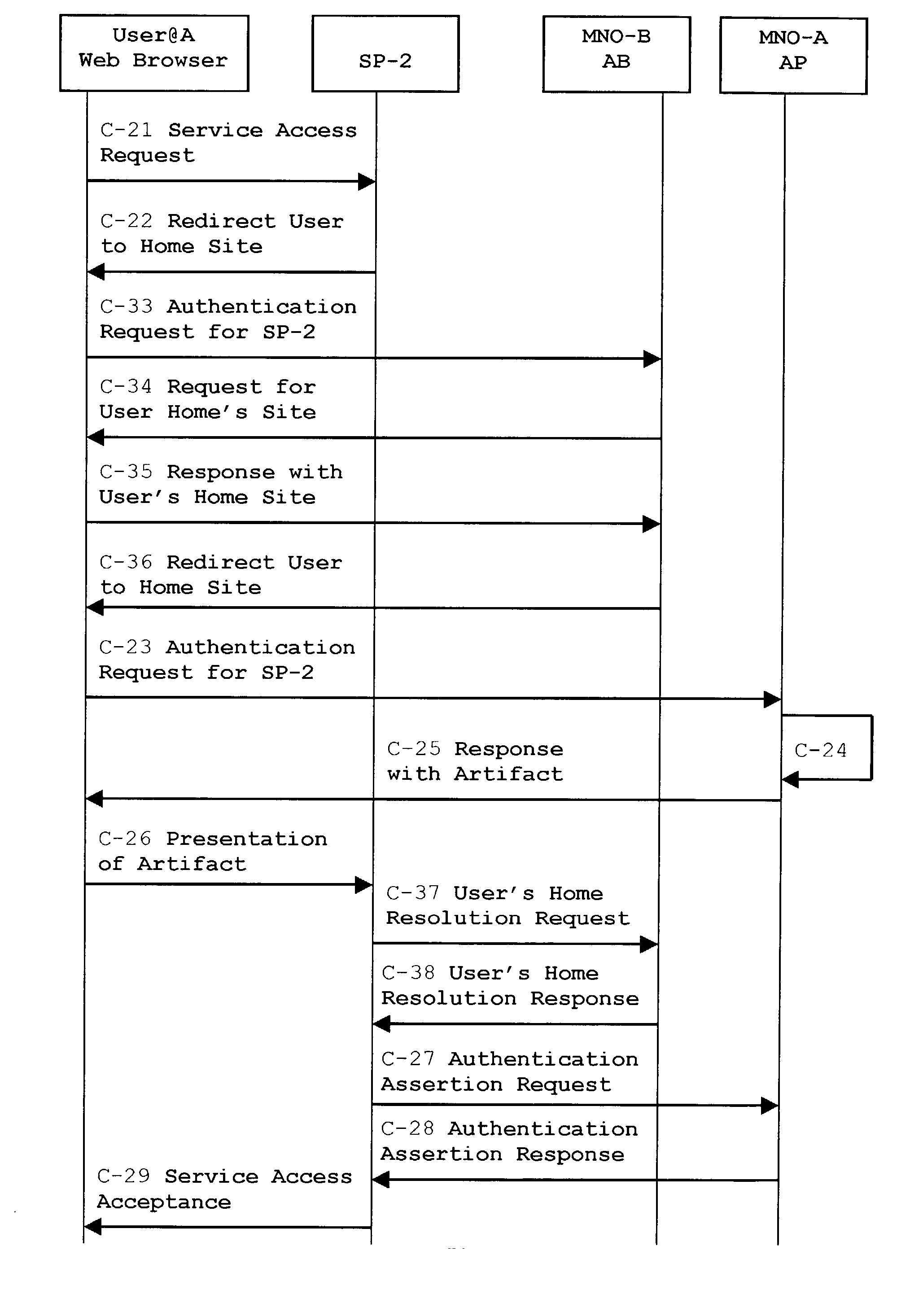
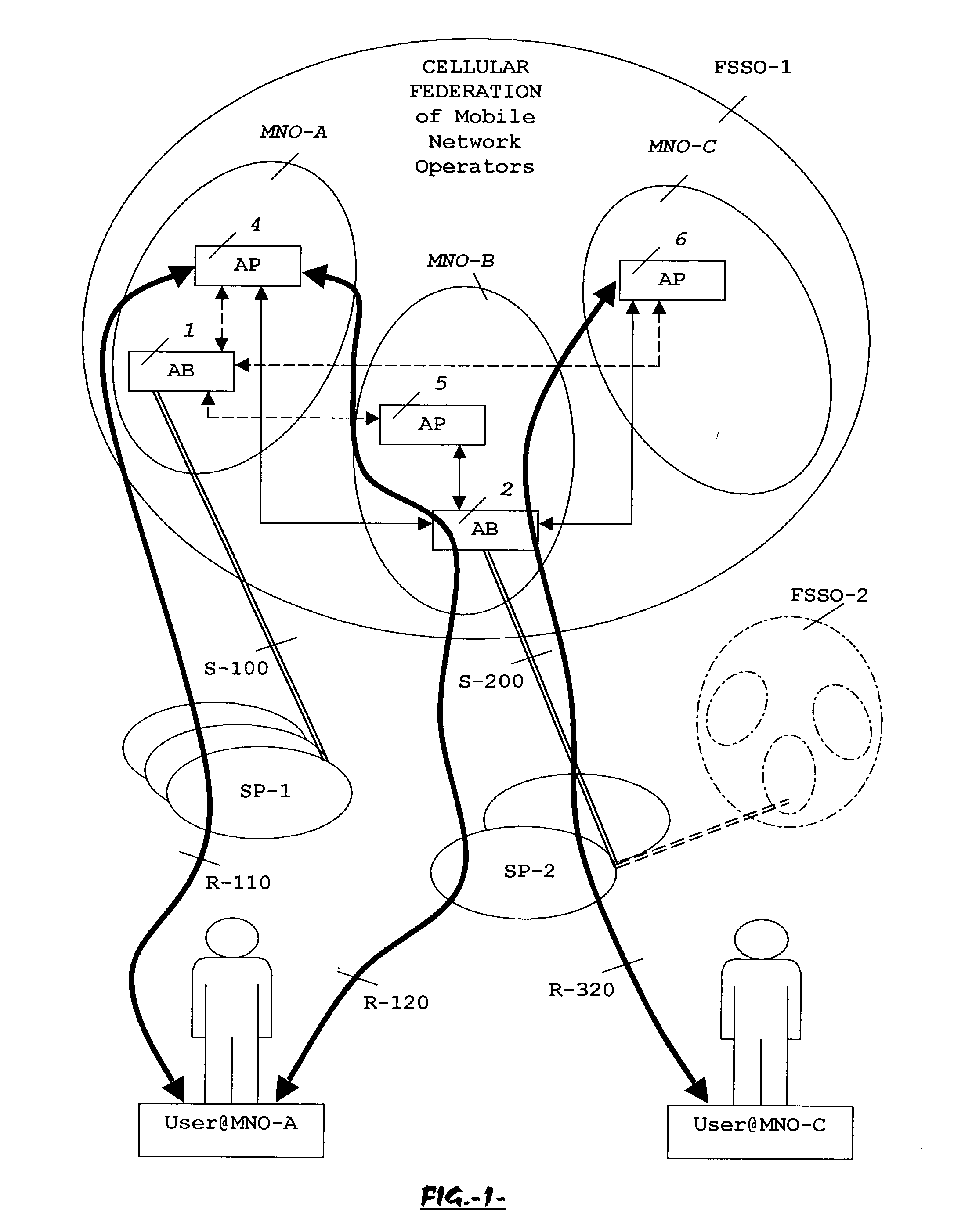
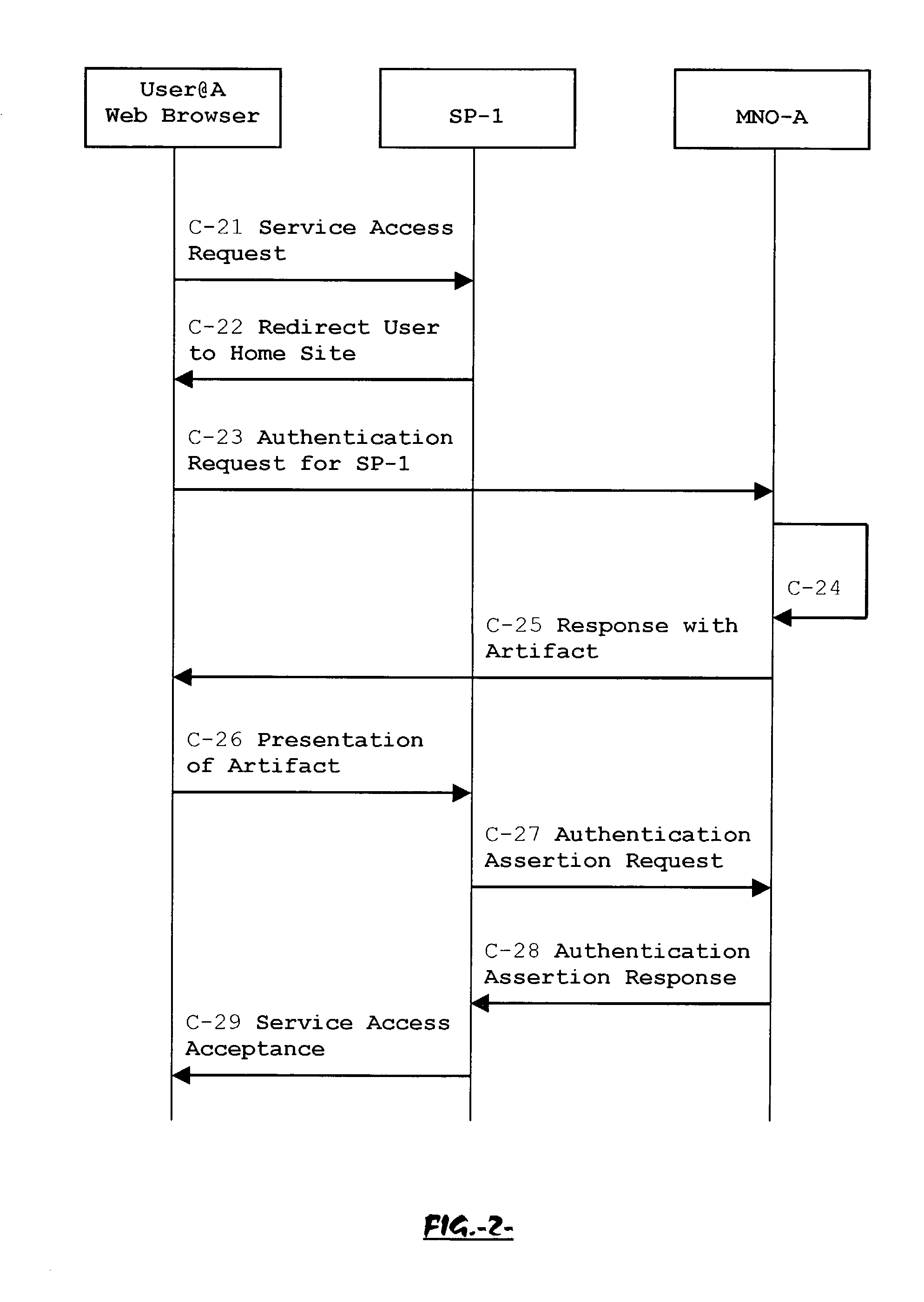
System, method and apparatus for federated single sign-on services
ActiveUS20030163733A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionDigital data processing detailsCyber operationsService domain
The advent of new and sophisticated web services provided by Service Providers to users, services that individually require authentication of user and authorization of access, brings the needs for a new service to facilitate such authentication and access, a service referred to as Single Sign-On (SSO). The basic principle behind SSO is that users are authenticated once at a particular level, and then access all their subscribed services accepting that level of authentication. The present invention provides a system, method and apparatus wherein a cellular Federation of mobile network operators becomes an SSO authentication authority for subscribers of this Federation accessing Service Providers having such agreement with a mobile network operator of the Federation. In accordance with this invention, mobile network operators can leverage their operator-subscriber trust relationship in order to act as SSO authentication authority for those subscribers accessing Service Providers in a service domain other than the mobile network domain.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and apparatus for creating a secure communication channel among multiple event service nodes
InactiveUS7013389B1Easy to scaleUser identity/authority verificationSecure communicationGroup session
An approach for establishing secure multicast communication among multiple event service nodes is disclosed. The event service nodes, which can be distributed throughout an enterprise domain, are organized in a logical tree that mimics the logical tree arrangement of domains in a directory server system. The attributes of the event service nodes include the group session key and the private keys of the event service nodes that are members of the multicast or broadcast groups. The private keys provide unique identification values for the event service nodes, thereby facilitating distribution of such keys. Because keys as well as key version information are housed in the directory, multicast security can readily be achieved over any number of network domains across the entire enterprise. Key information is stored in, and the logical tree is supported by, a directory service. Replication of the directory accomplishes distribution of keys. Event service nodes may obtain current key information from a local copy of the replicated directory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for secure electronic communication services
InactiveUS20090198997A1Easy accessSecure transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageScalable systemEmail address
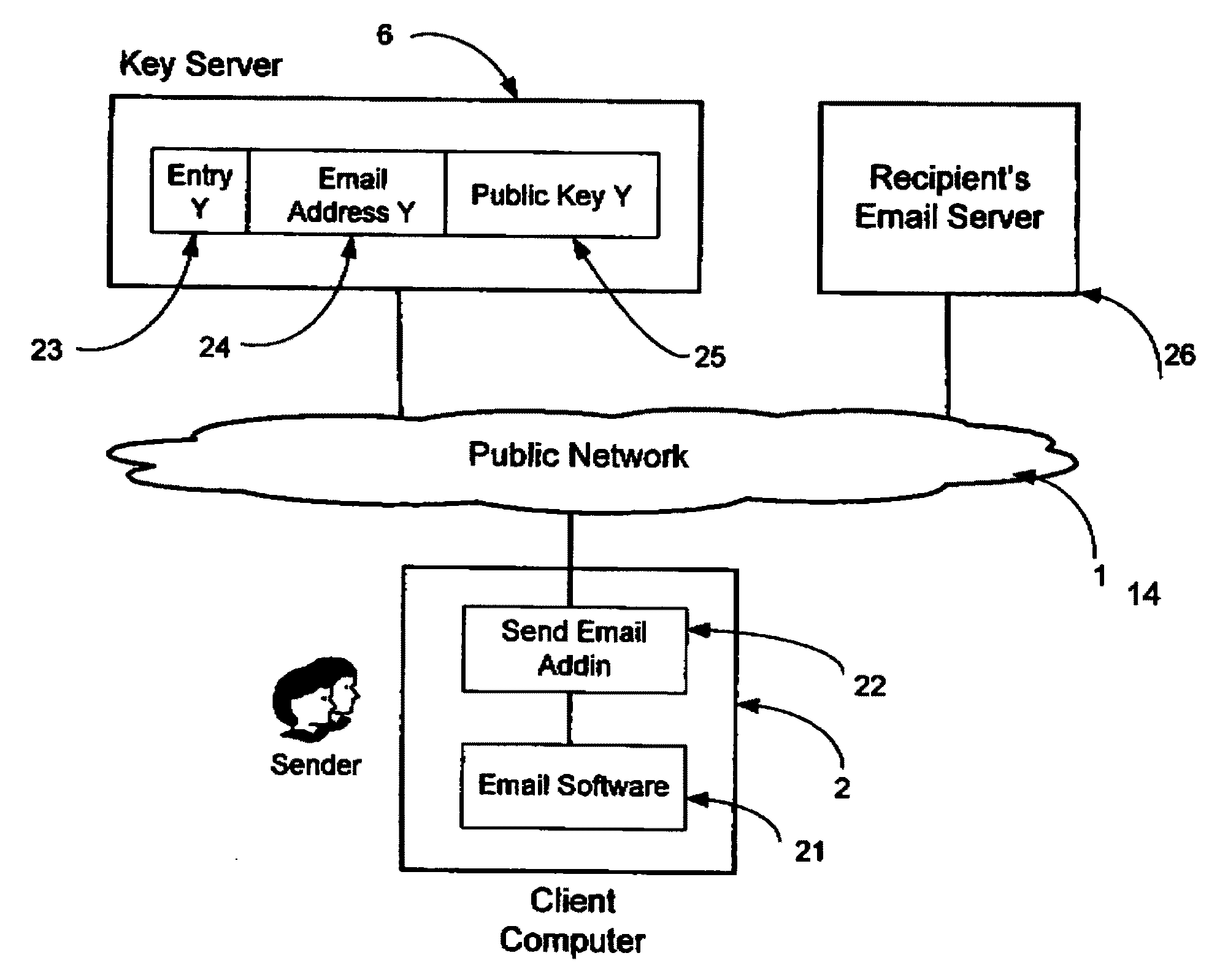
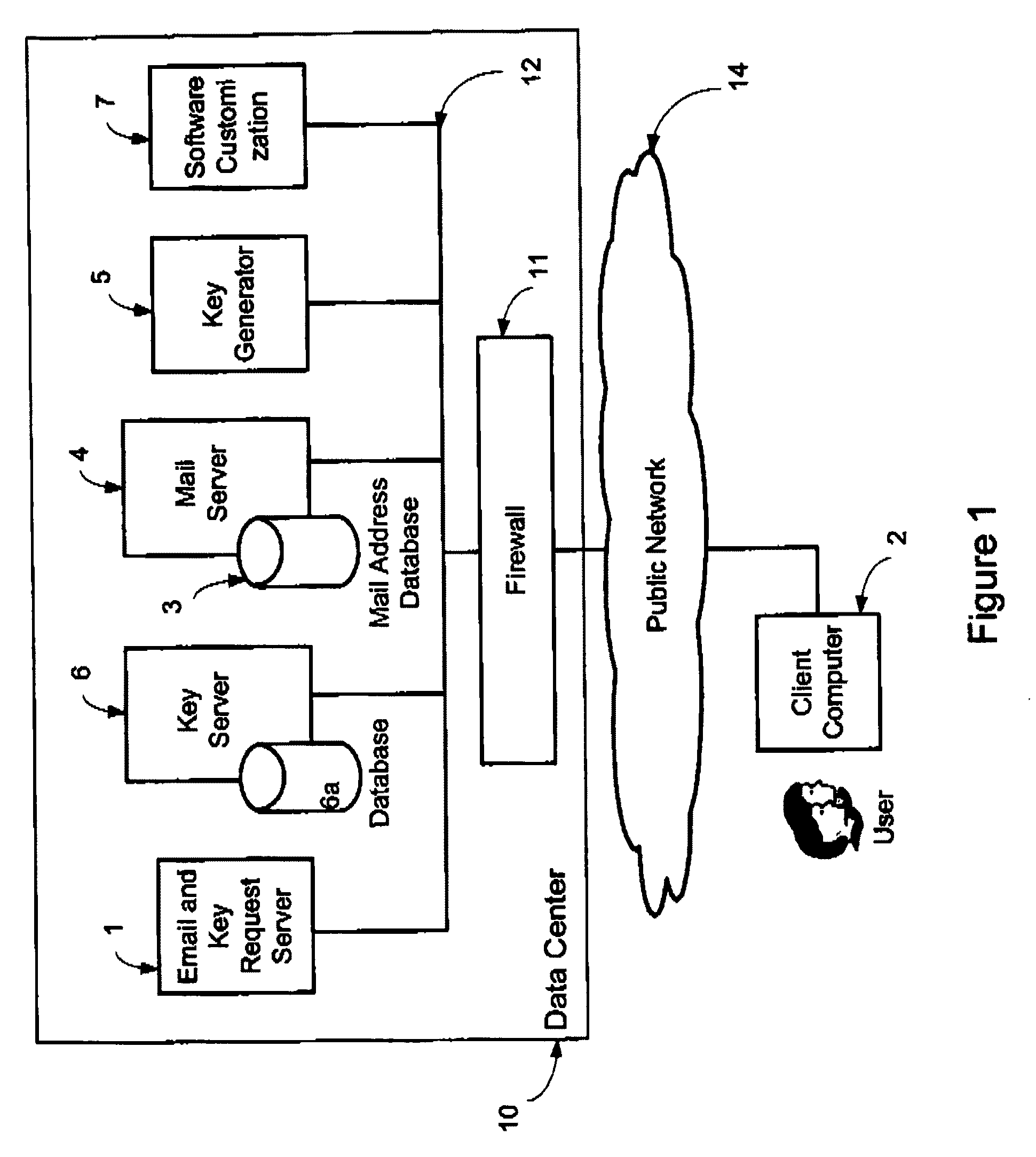
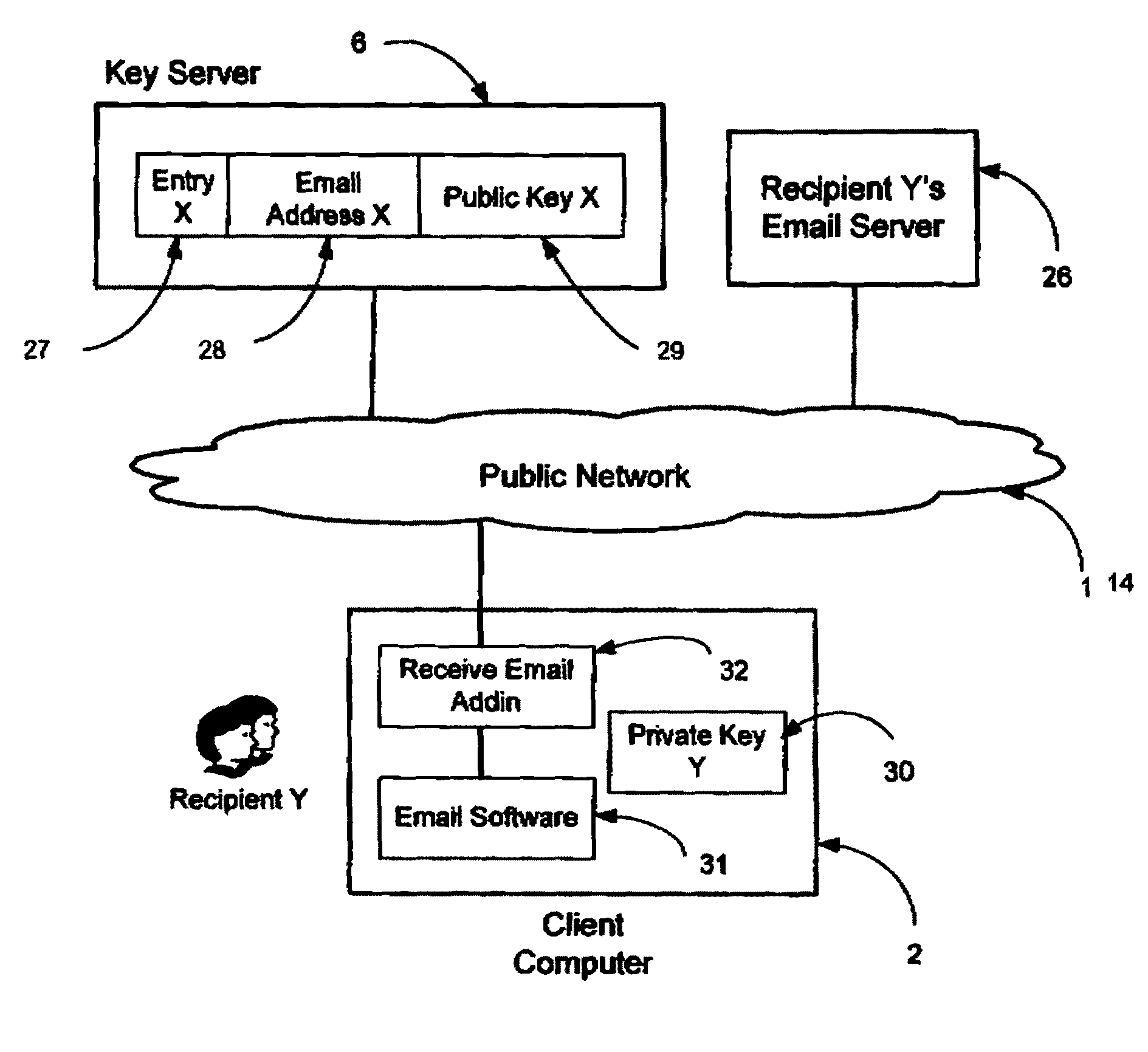
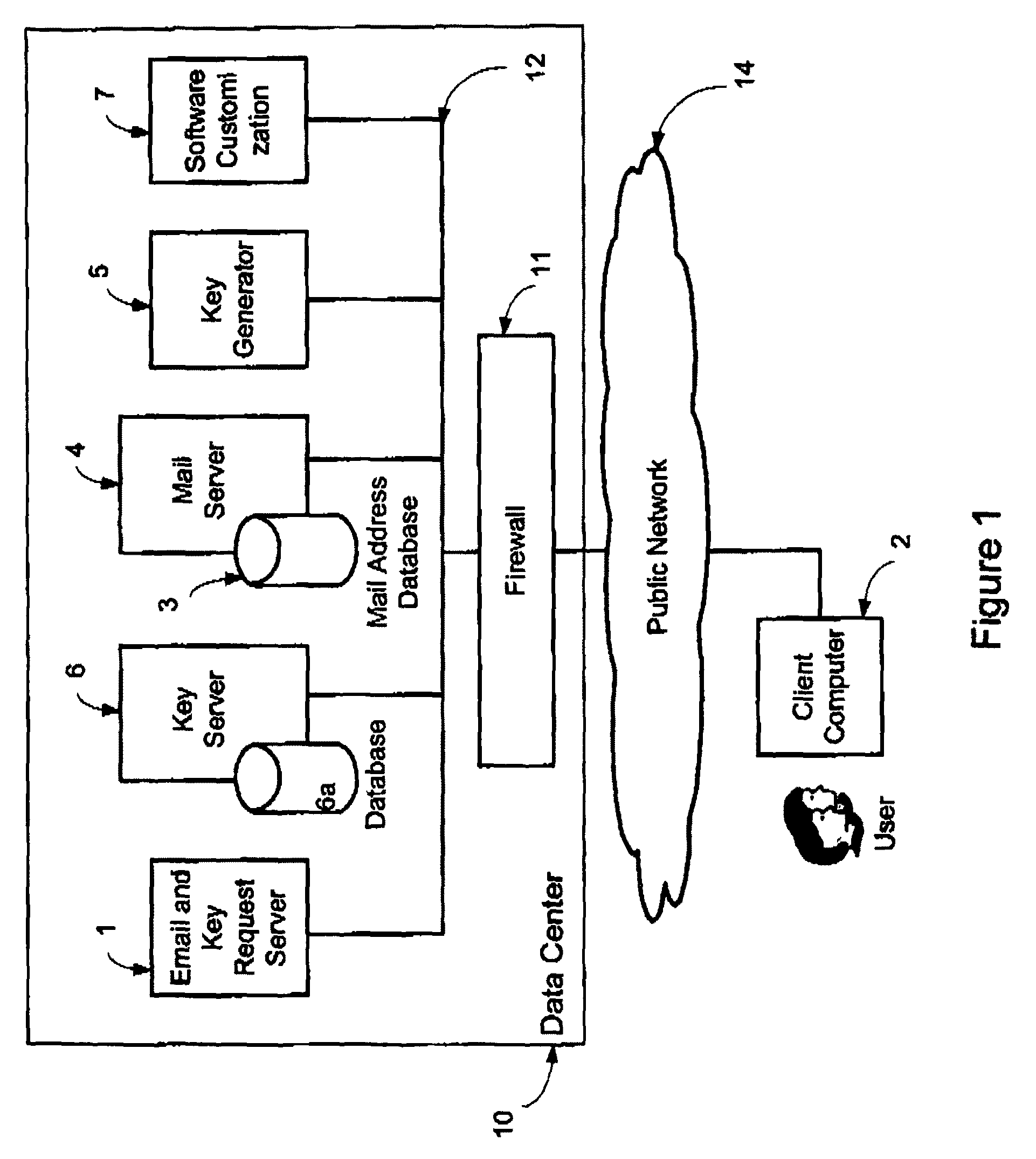
A system, method and software module for secure electronic communication services, wherein a public key (25) of private-public-key pair (30,25) is associated with an email address (24), internet name or other registered unique identifier; the registered user of the unique identifier holds the private-key (30) securely, and the respective public-key (25) is made accessible on a key server (6) for look-up and retrieval by other users, for encryption of communications to be sent to the holder of the private-key, and optionally for message confidentiality, message integrity and authentication of sender and recipient, without requiring certificates. A distributed and scalable system is provided by a server network (600; 401, 501) for registration, key distribution and management preferably using a kDNS server hierarchy (601,602,603) or a key-DNS server hierarchy (701,702,) and associated protocols so that public-keys of recipients can be searched and retrieved over the internet based on the recipients email address or other unique identifier, thus facilitating secure communication between users in different network domains and organizations.
Owner:TOPOSIS CORP
Shared resources in a multi manager environment
ActiveUS20060026225A1Reduce network element performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionInformation repositoryManagement information base
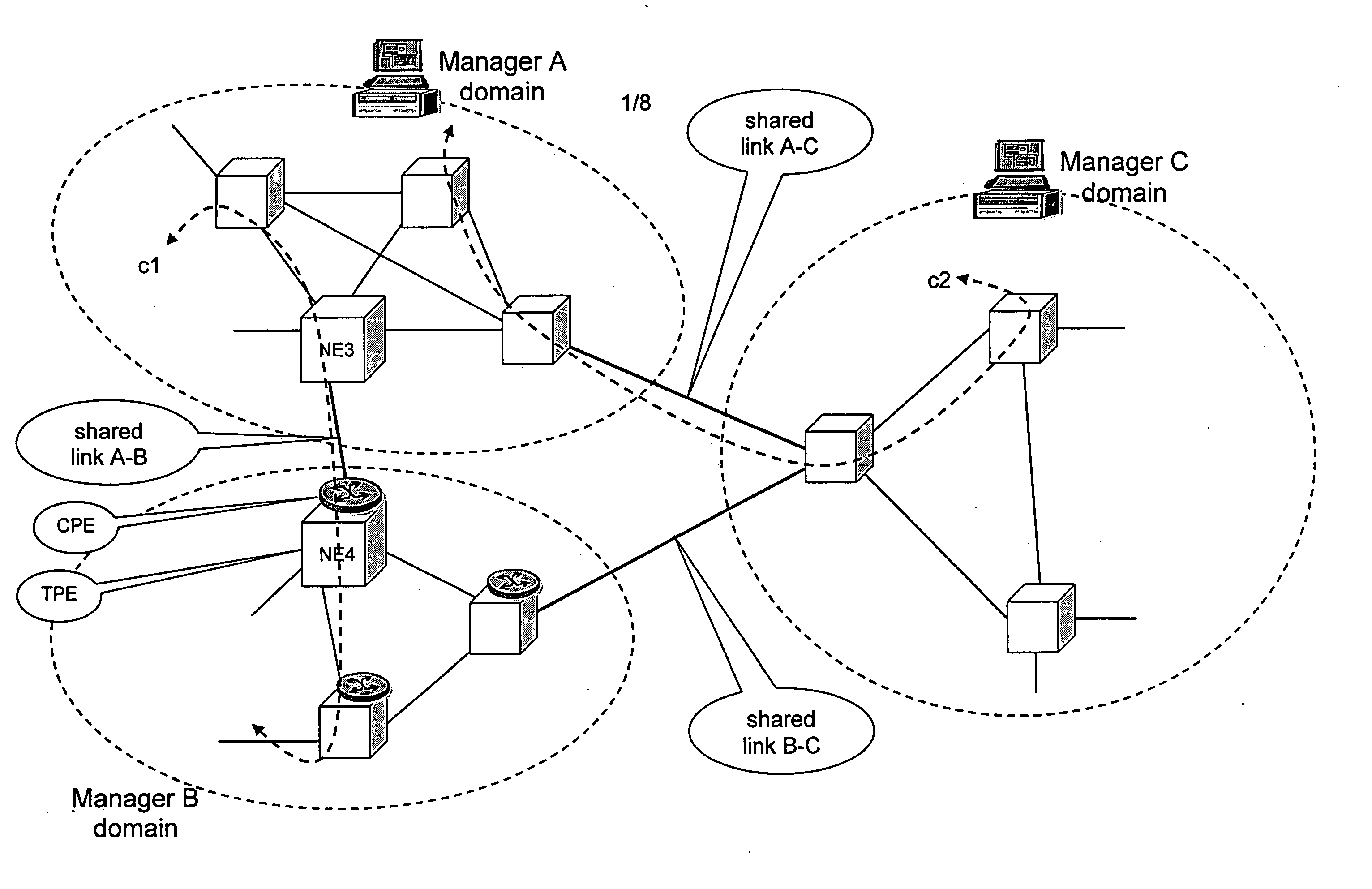
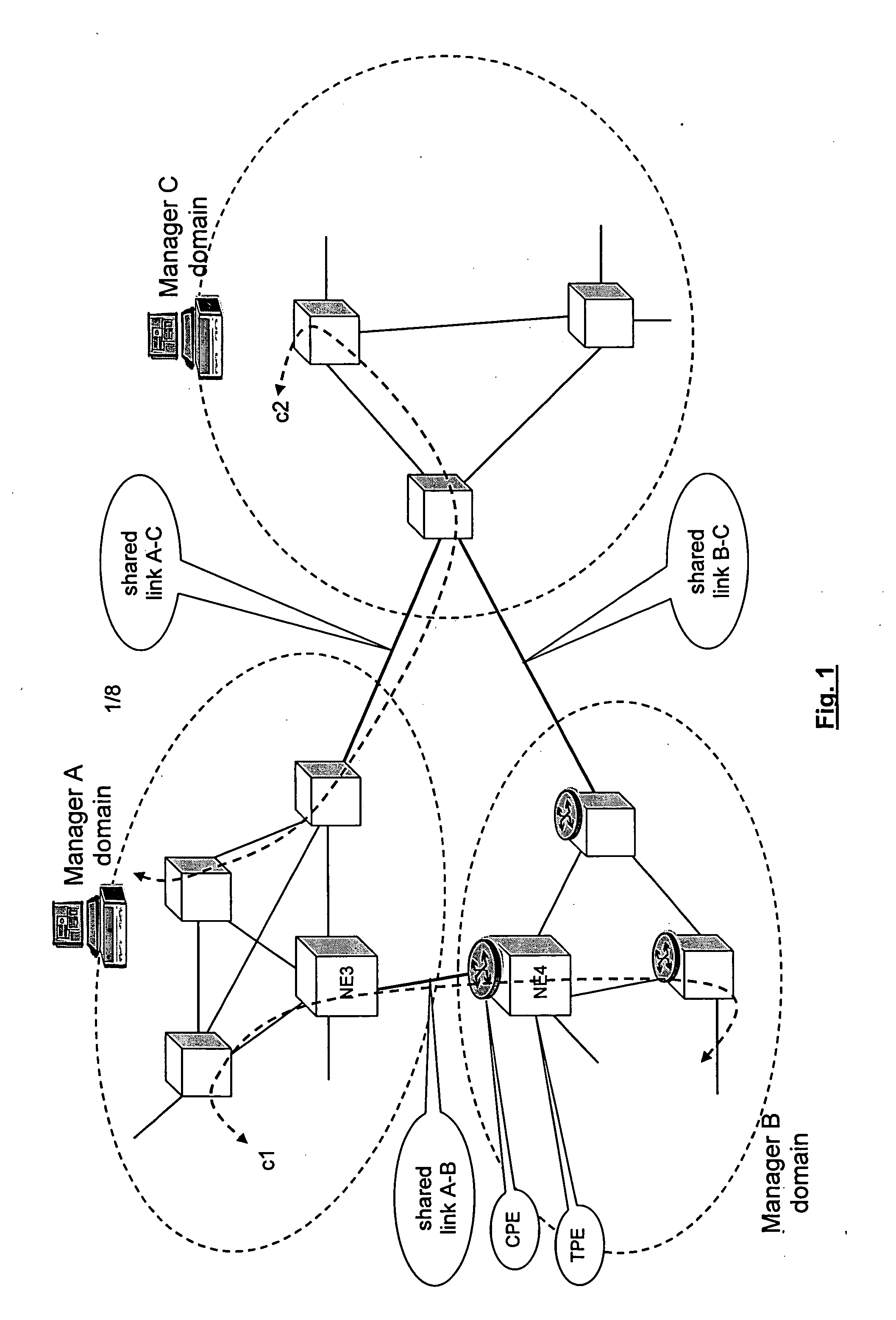
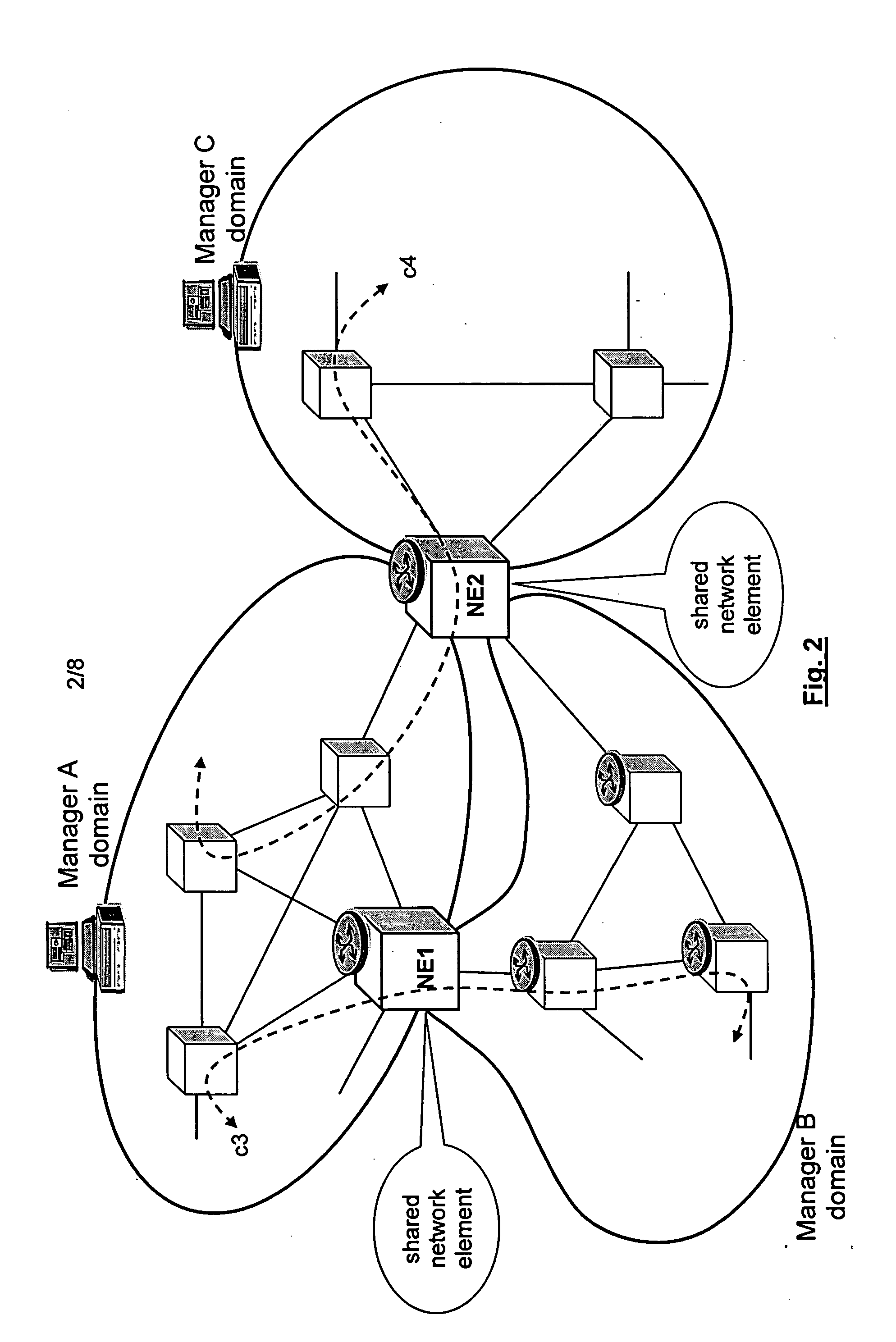
A method is described for controlling a shared resource for interconnecting two or more network domains being controlled by different Managers. Multiple Managers control the shared resource for the configuration of a segment of a connection between two different domains and the Managers cooperate in order to control dynamically the shared resource. Different network domains can be connected by a network element or by a link between different network elements belonging to the different network domains. In the first case the shared resource is a connection matrix of the network element, in the second case the shared resource includes the connection matrixes of the different network elements and the link between the network elements. A shared connection matrix includes some connection points for performing the cross-connections within the matrix: some connection points are controlled by one Manager, other connection points are controlled by another Manager and some shared connection points are controlled by both Managers. Multiple Managers control the shared resource by reading and writing information stored into a management information base, according to an explicit or implicit mode, or alternatevely by transmitting messages in the network directly between the Managers, according to a signalling protocol.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
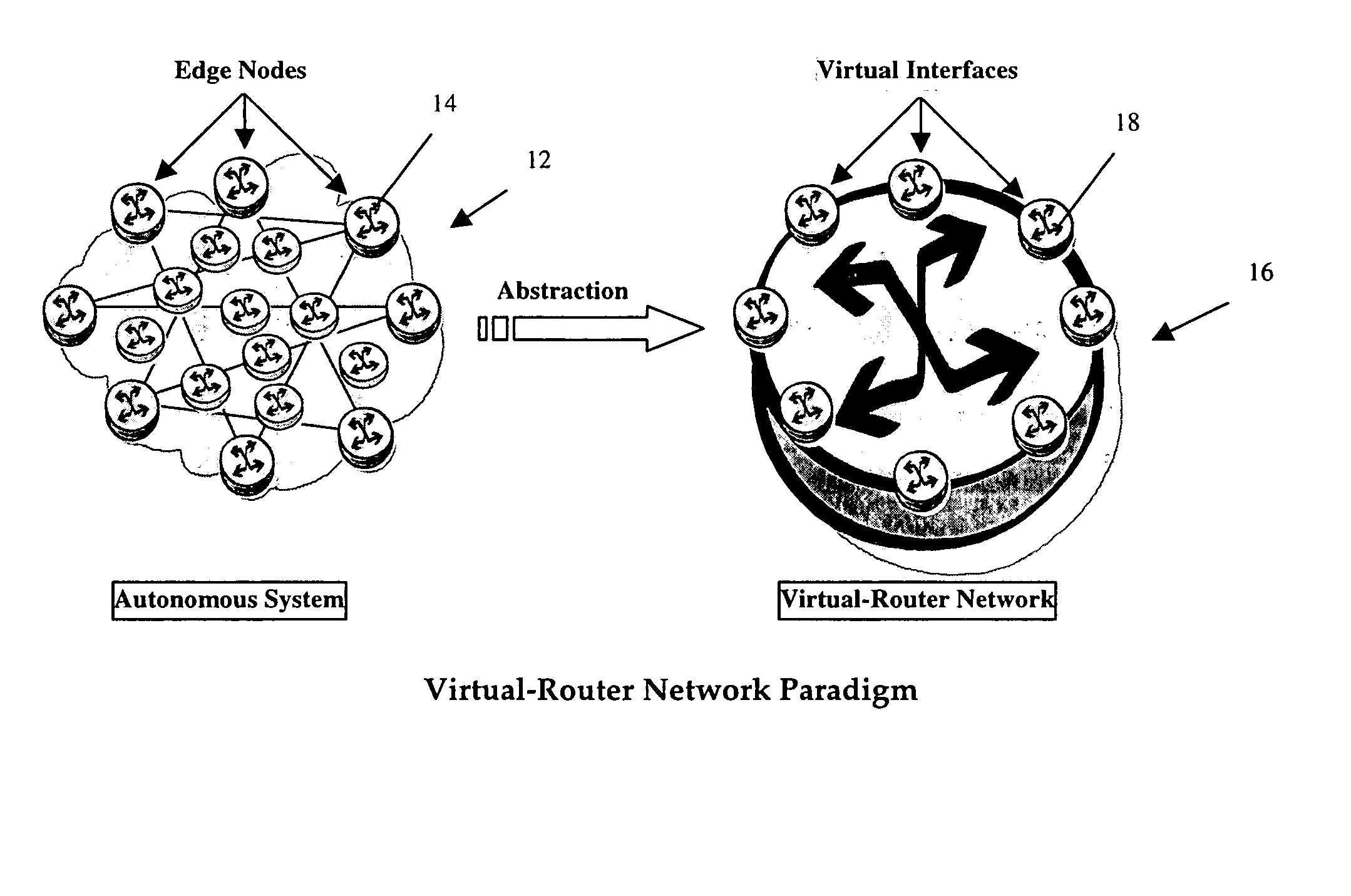
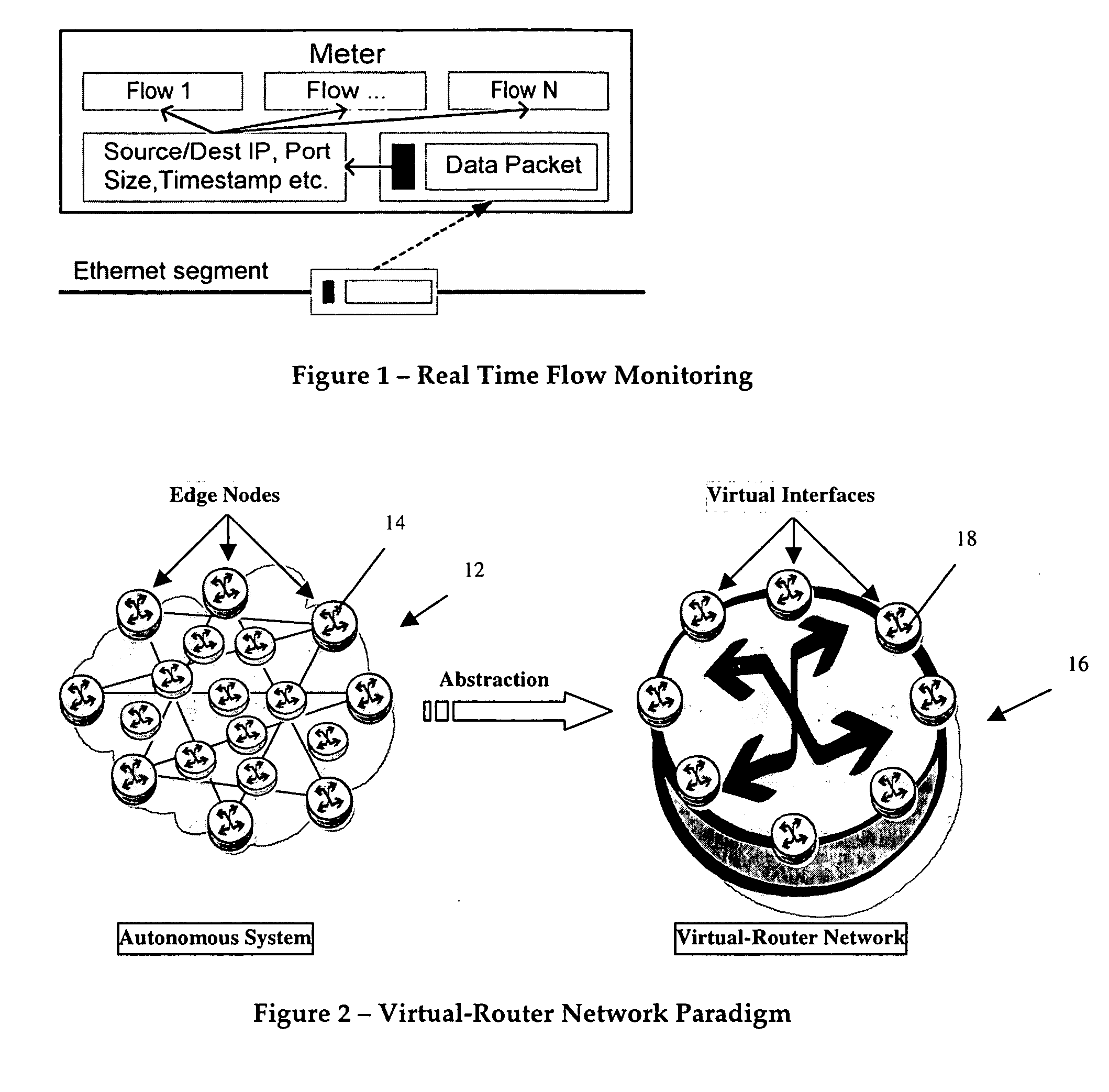
Distributed architecture for real-time flow measurement at the network domain level
ActiveUS20050132044A1Energy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsRelevant informationCommunications system
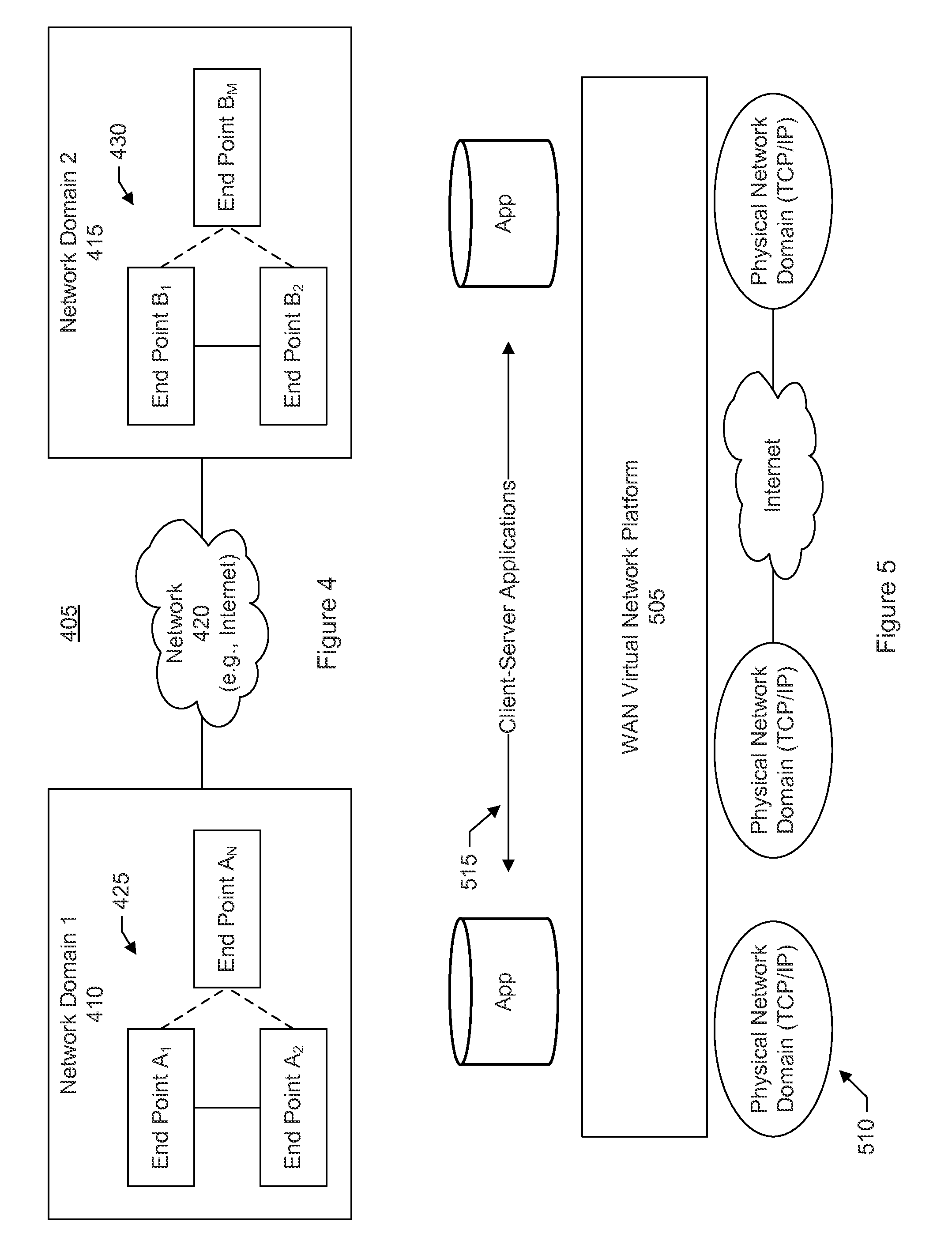
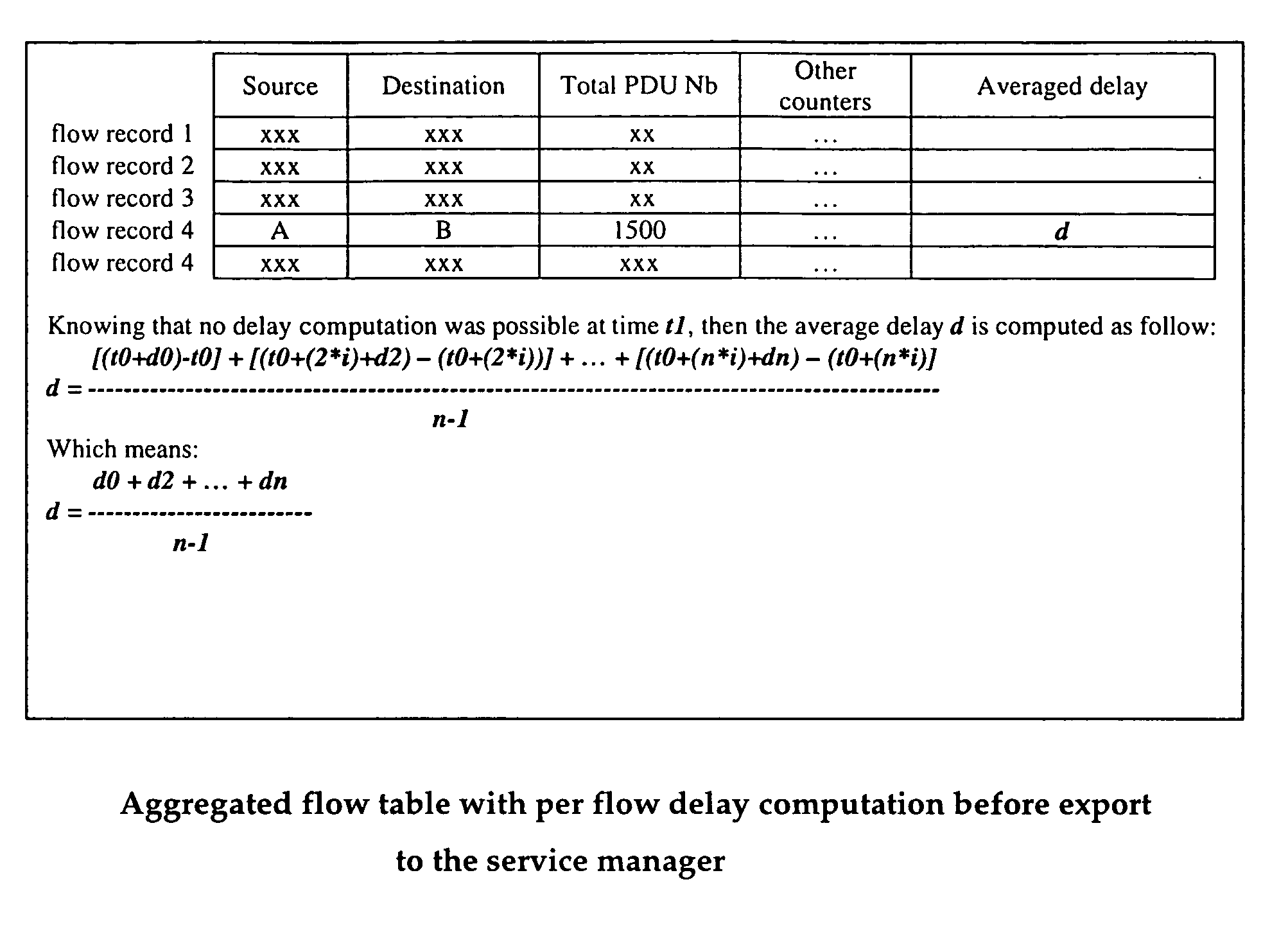
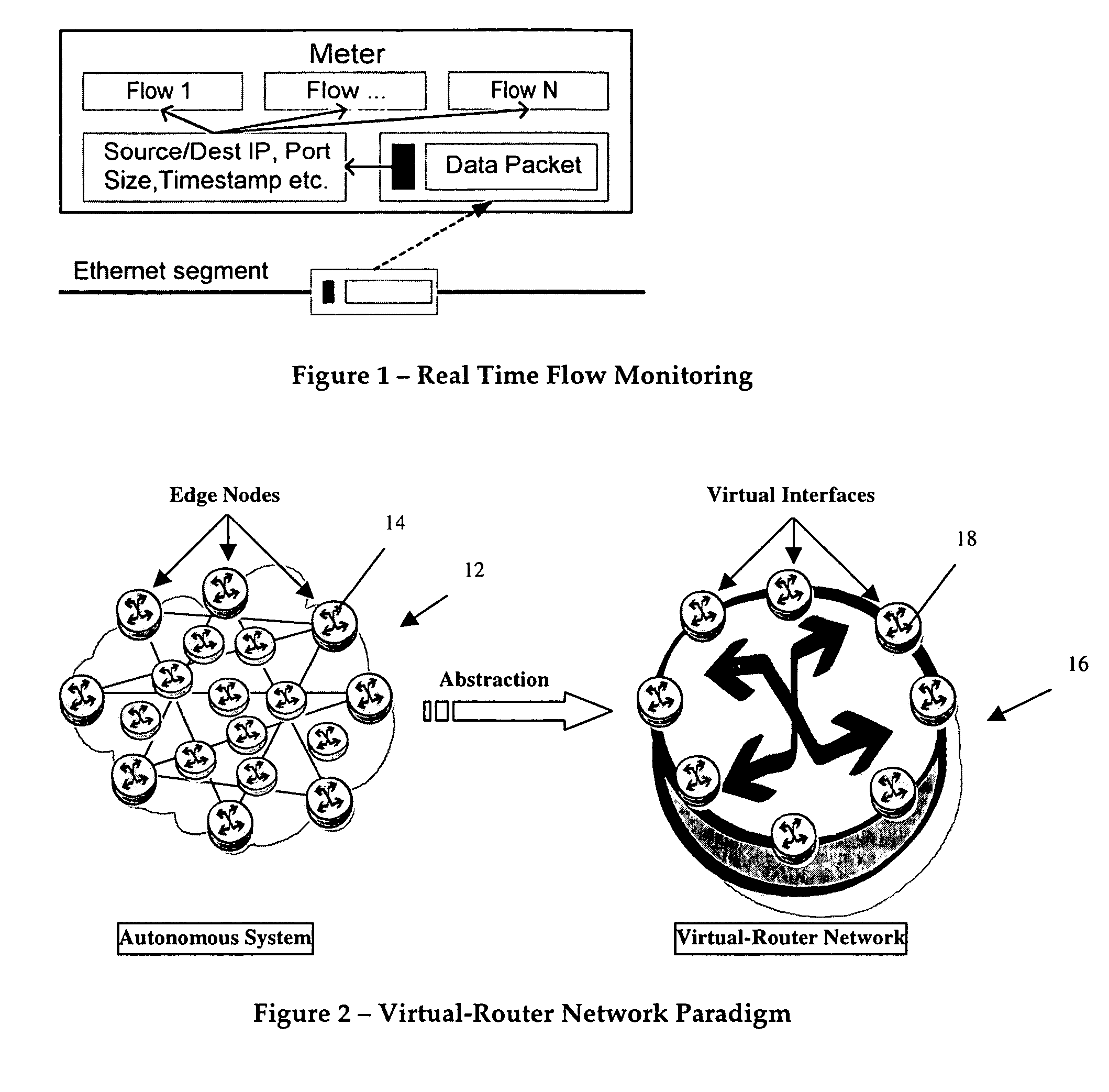
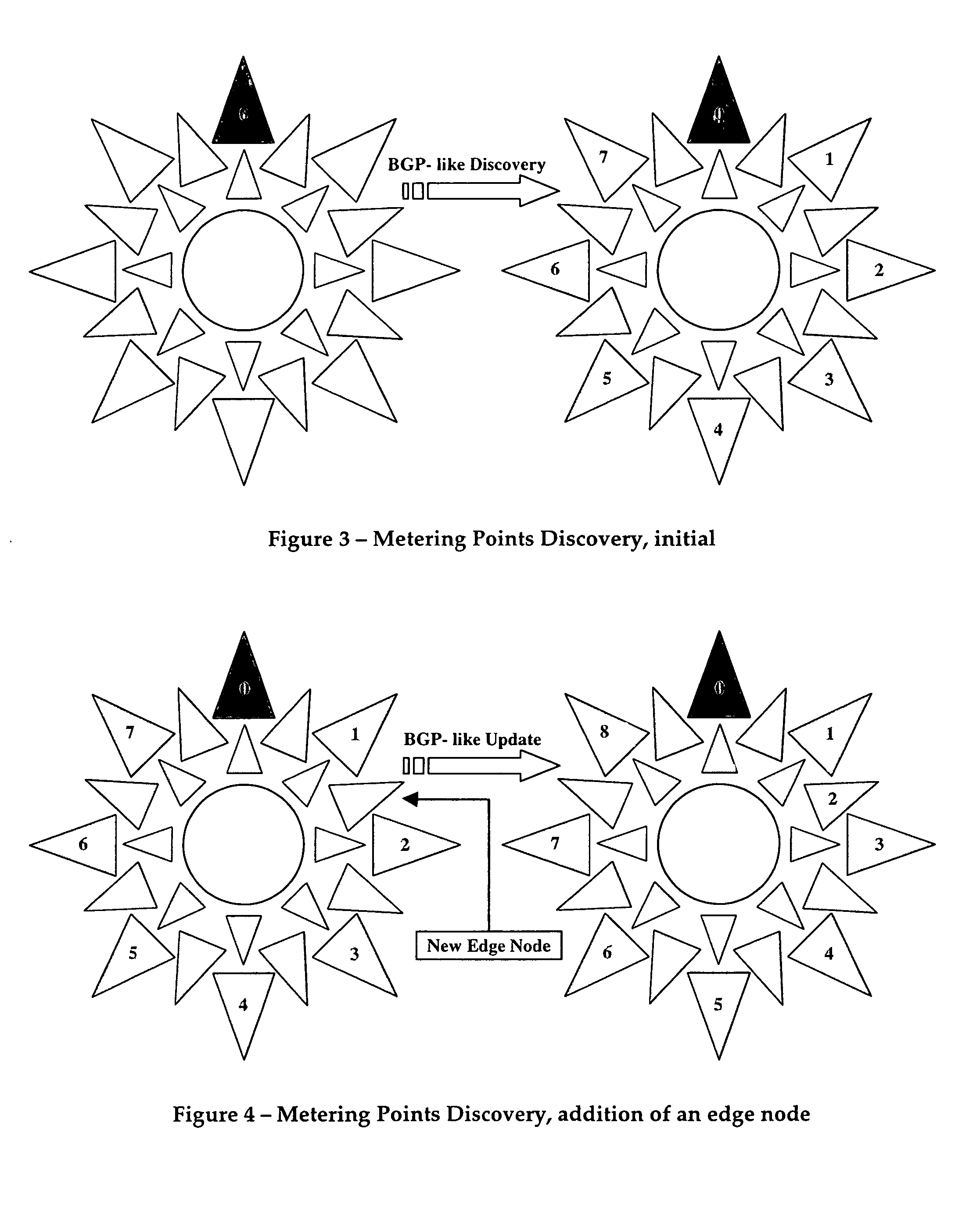
A virtual router network (VRN) for performing real-time flow measurements (RTFM) is provided. The VRN effectively reduces the number of traffic metering points required thereby simplifying the aggregation and exportation of flow records to a collector. The collector may be service manager in a network management system. The metering points, in a preferred embodiment, are at virtual interfaces (VI) which are edge nodes in VRN. One of the virtual interfaces is selected as a master virtual interface and act as a collector and distributor of flow related information. In one aspect of the invention the VRN is used to provide, non-invasively, per-flow delay monitoring in a communication system.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Secure virtual network platform for enterprise hybrid cloud computing environments
ActiveUS20140244851A1Broaden applicationEasy to deployMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksVirtual platformCloud computing
A secure virtual network platform connects two or more different or separate network domains. When a data packet is received at an end point in one network domain, a determination is made as to whether the data packet should be forwarded outside the virtual network platform, or transmitted via the virtual network to a destination in another network domain connected by the virtual network platform.
Owner:ZENTERA SYST
Secure cloud fabric to connect subnets in different network domains
ActiveUS20140337500A1Digital computer detailsData switching networksStructure of Management InformationNetwork topology
A secure virtual network platform connects two or more subnets in different or separate network domains. The secure virtual network can use the under layer physical networks in various domains as an IP forwarding fabric without changing any existing firewalls, security settings, or network topology. A first type of connection across the virtual network involves connecting server groups. A second type of connection across the virtual network involves connecting a server group to a physical network. A third type of connection across the virtual network involves connecting a physical network to another physical network.
Owner:ZENTERA SYST
Transparant non-disruptable ATM network
InactiveUS6011780AIncrease probabilityIncrease spare capacityError preventionTransmission systemsManagement unitTime switching
A method and apparatus for the transparent, non-disruptable transfer of data, particularly multimedia data, through any packet-based network, such as an ATM network is provided. The method of the present invention includes the step of setting a primary path and a secondary path between nodes of a network, or of a network domain. Accordingly, when a switch or node establishes a Virtual Path (VP) to another switch with specified effective bandwidth, it also has an alternate VP that is available, although no bandwidth is actually used. The method of the present invention further includes the step of optimizing the available capacity of the system through management actions. For handling congestion and resource failures, the total effective bandwidth on each physical link is categorized in terms of idle capacity (unused or available), used capacity (for existing VPs), and spare capacity. When a resource failure occurs, the idle capacity is used for real-time switching of the VP and service is not disrupted. This is accomplished by an alarm indication management cell which is delivered when a resource problem is encountered. This management cell sets forth the secondary path and the bandwidth associated therewith. On the other hand, if idle capacity does not exist, the spare capacity is used, while the bandwidth of all other VPs is reconfigured using virtual bandwidth optimization. Therefore, service disruption does not occur. In a wireless, mobile network, the present invention monitors node movement and takes management actions on the basis of such node movement to prevent service disruption.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
Distributed architecture for real-time flow measurement at the network domain level
ActiveUS8095640B2Energy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsCommunications systemRelevant information
A virtual router network (VRN) for performing real-time flow measurements (RTFM) is provided. The VRN effectively reduces the number of traffic metering points required thereby simplifying the aggregation and exportation of flow records to a collector. The collector may be service manager in a network management system. The metering points, in a preferred embodiment, are at virtual interfaces (VI) which are edge nodes in VRN. One of the virtual interfaces is selected as a master virtual interface and act as a collector and distributor of flow related information. In one aspect of the invention the VRN is used to provide, non-invasively, per-flow delay monitoring in a communication system.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
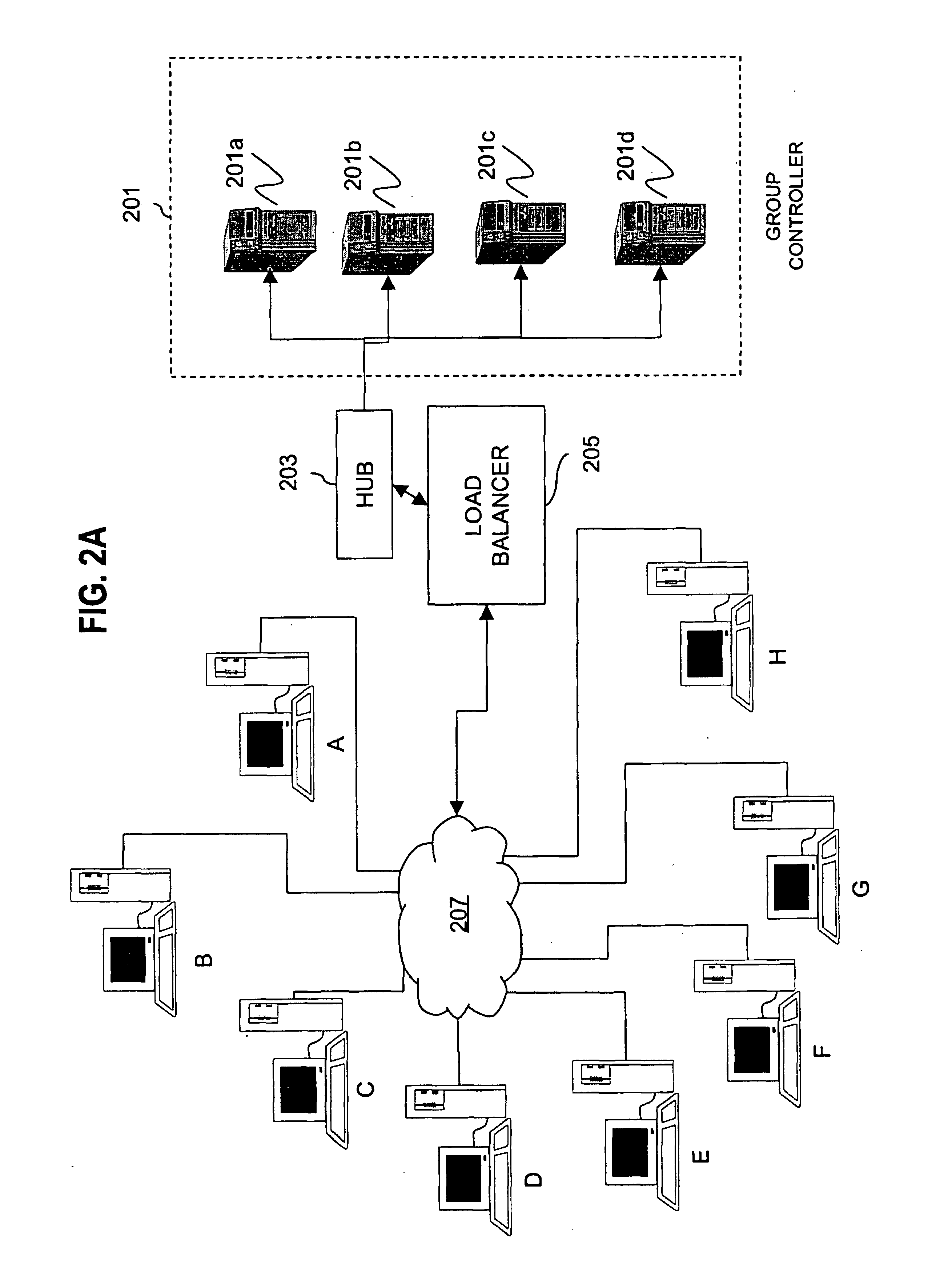
Extensible resource messaging between user applications and network elements in a communication network
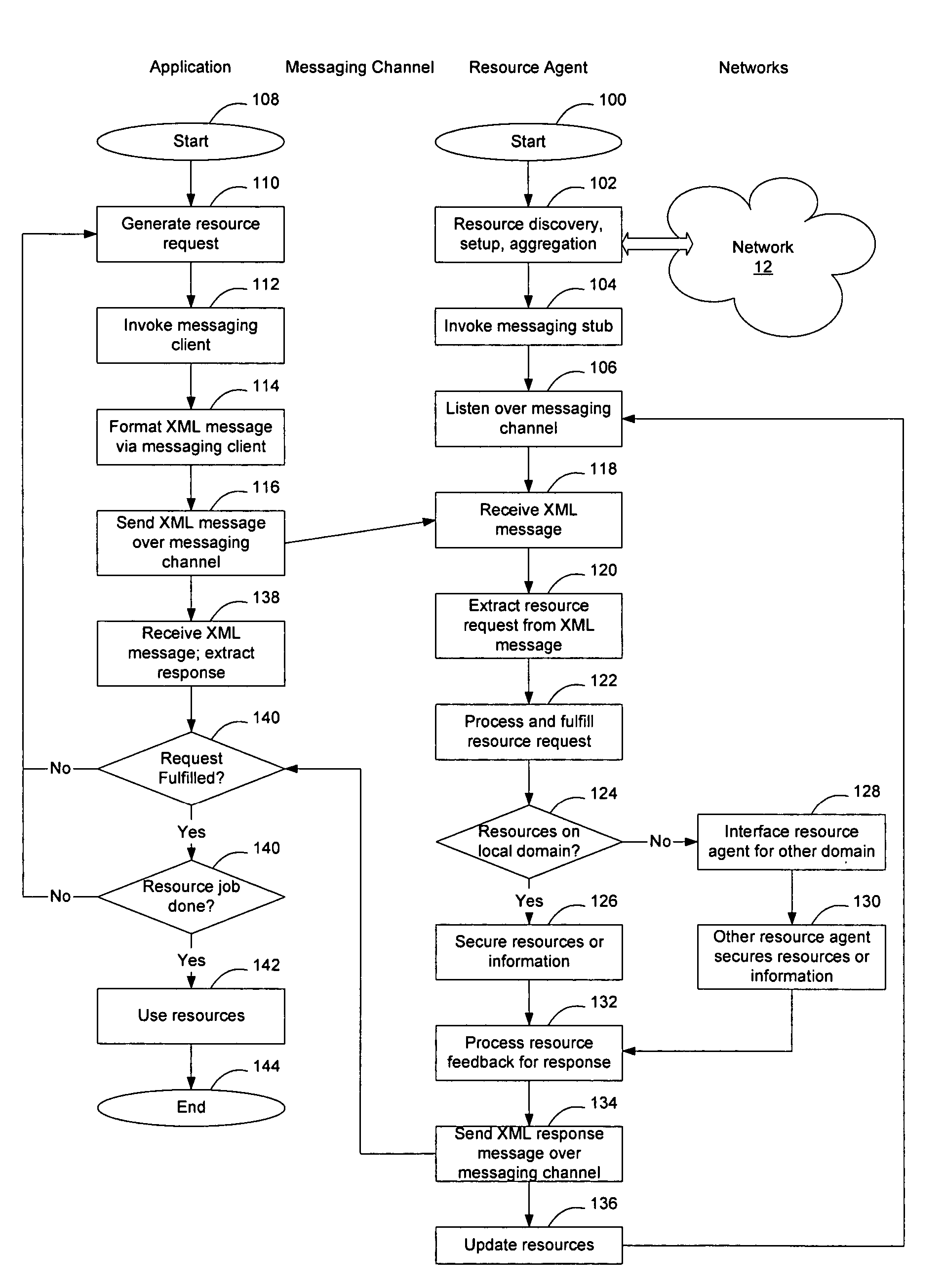
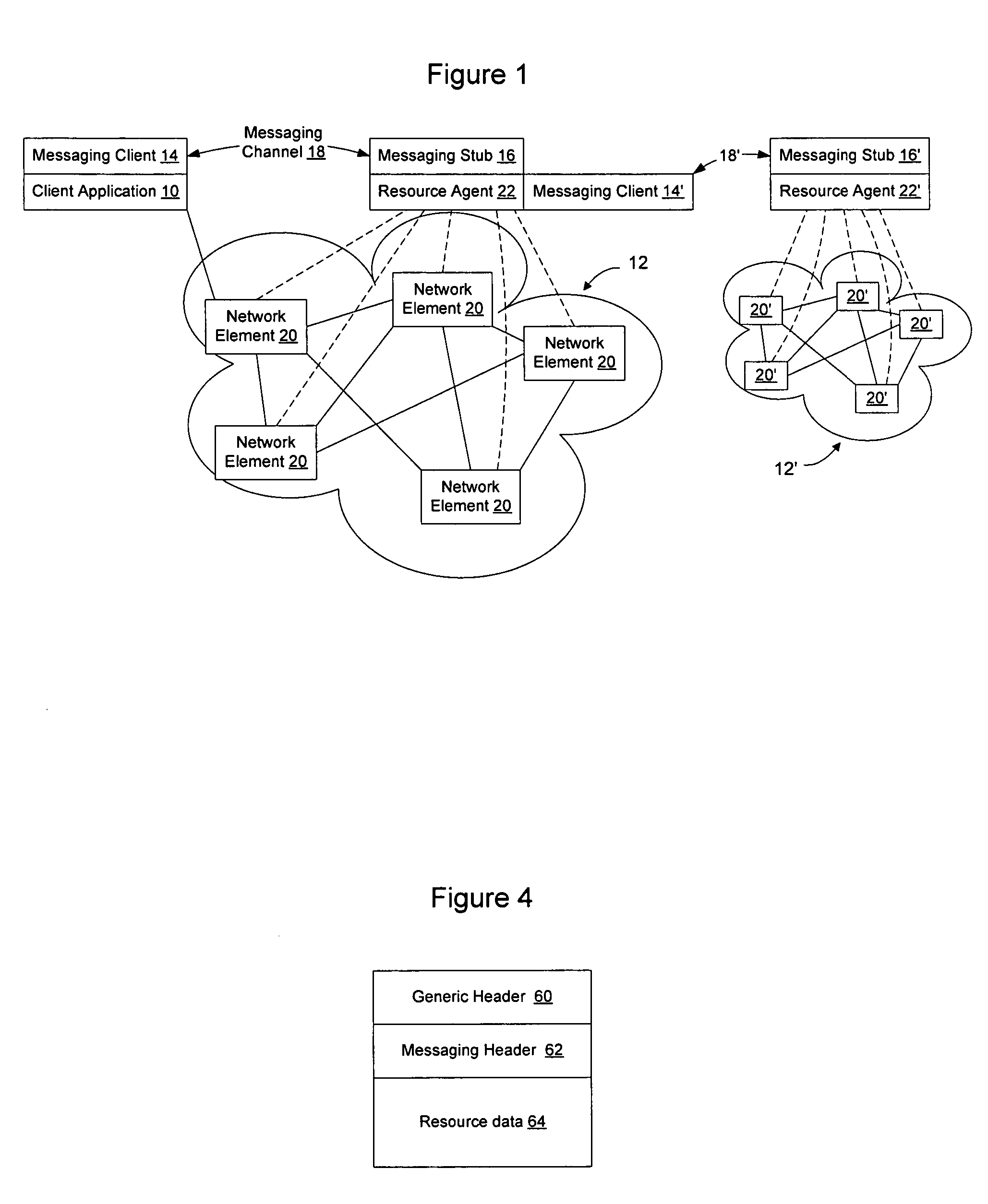
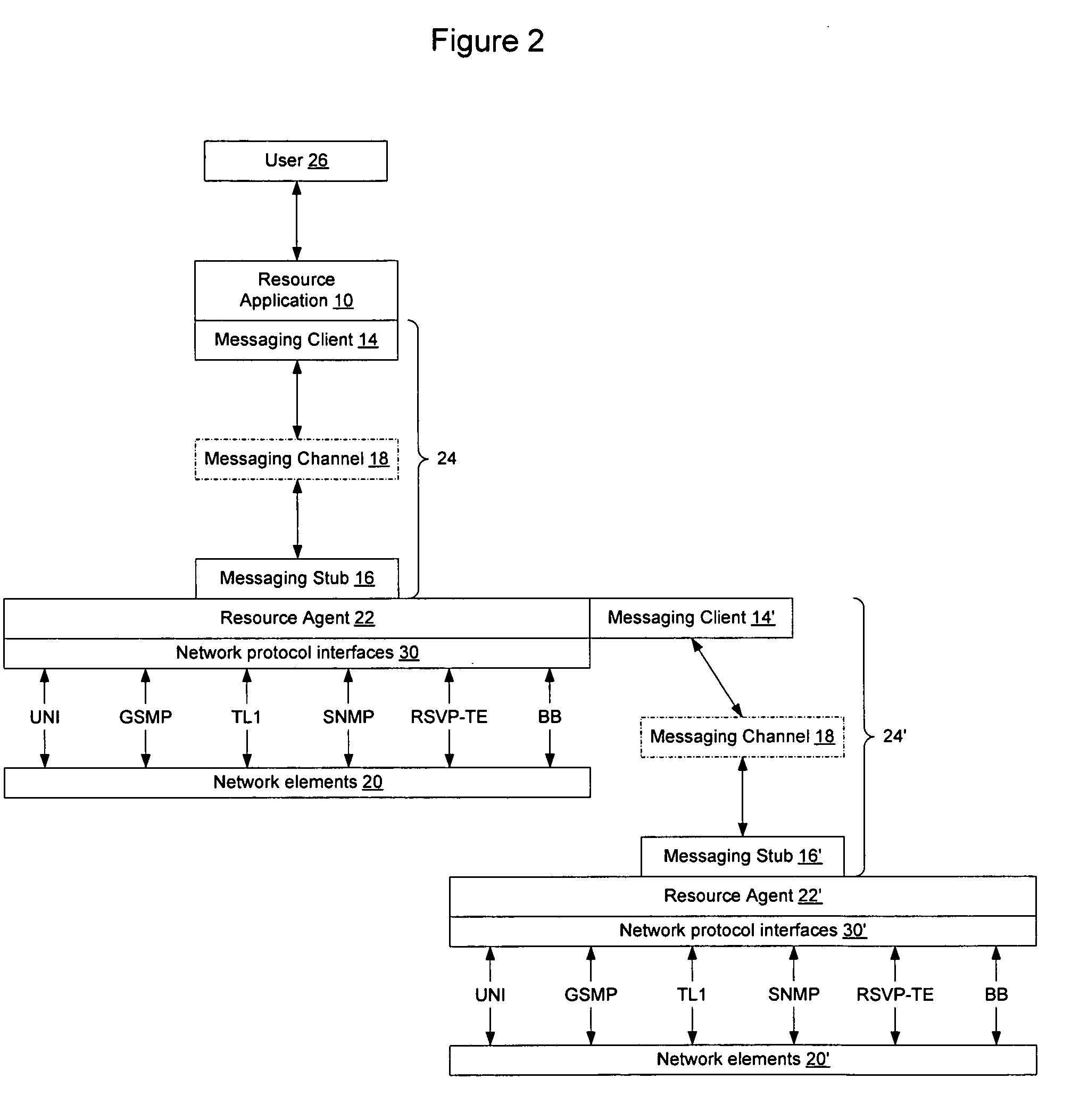
InactiveUS20060075042A1Easily use new network resourceAvoid resourcesMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionXML schemaMessage passing
Extensible resource messaging in a communication network is provided through creation of a flexible, extensible, and secure messaging environment. A client-server architecture may be implemented in which user applications employ messaging clients to send resource requests for network information, allocation and other operations and receive resource responses, and in which network elements, through resource agents, may use messaging servers to accept resource requests and return resource responses. Resource agents in different network domains may interact through the messaging environment and work together to fulfill resource requests. An XML-based messaging mechanism may be built with a defined message format that can provide flexible message contexts. Network resource semantics may be specified using XML schemas so that network resources are expressed as resource-specific XML elements and network updates can be implemented by updating the XML resource schemas. Secure enhancements may be realized by secure transport, message verification and other means.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
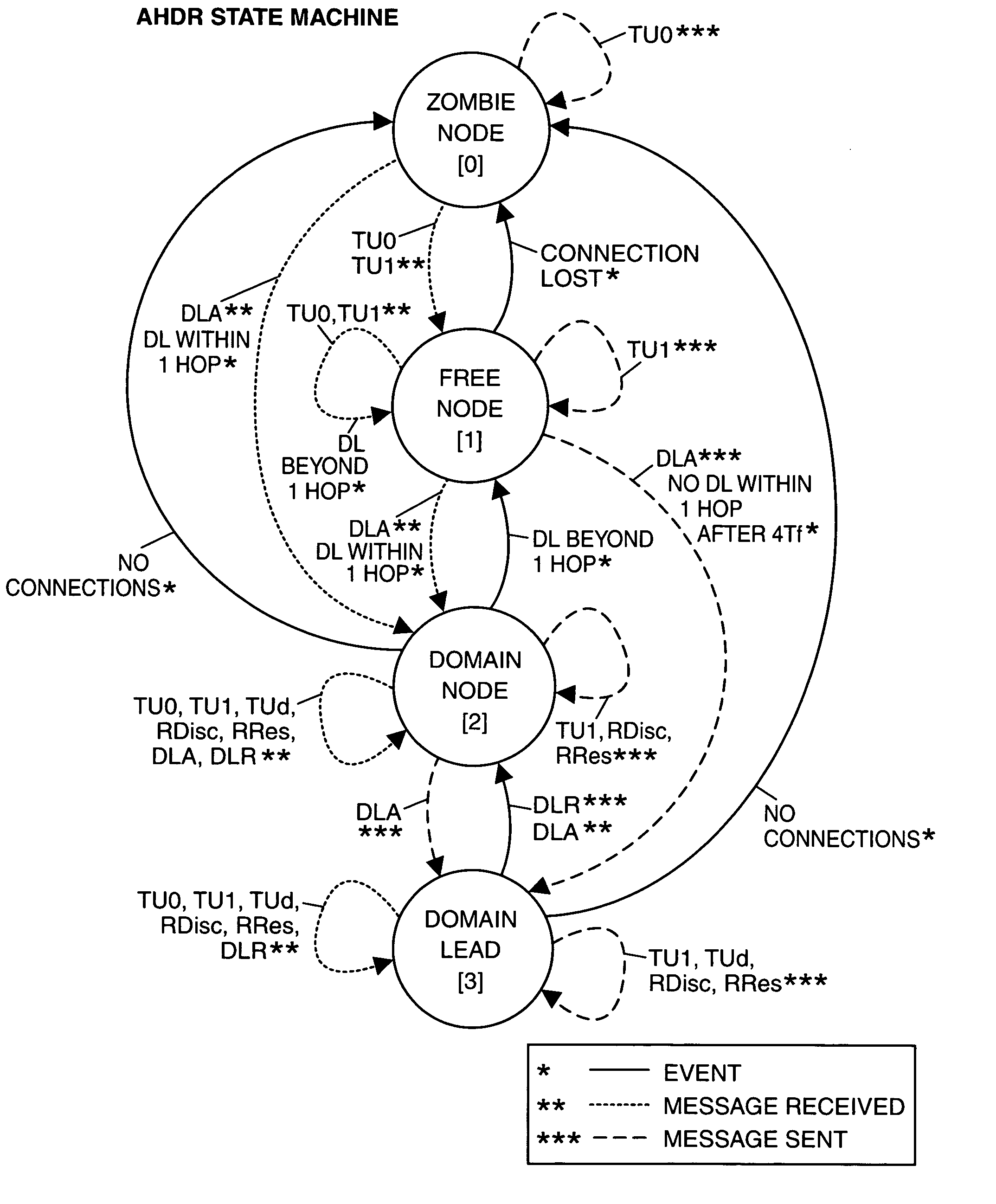
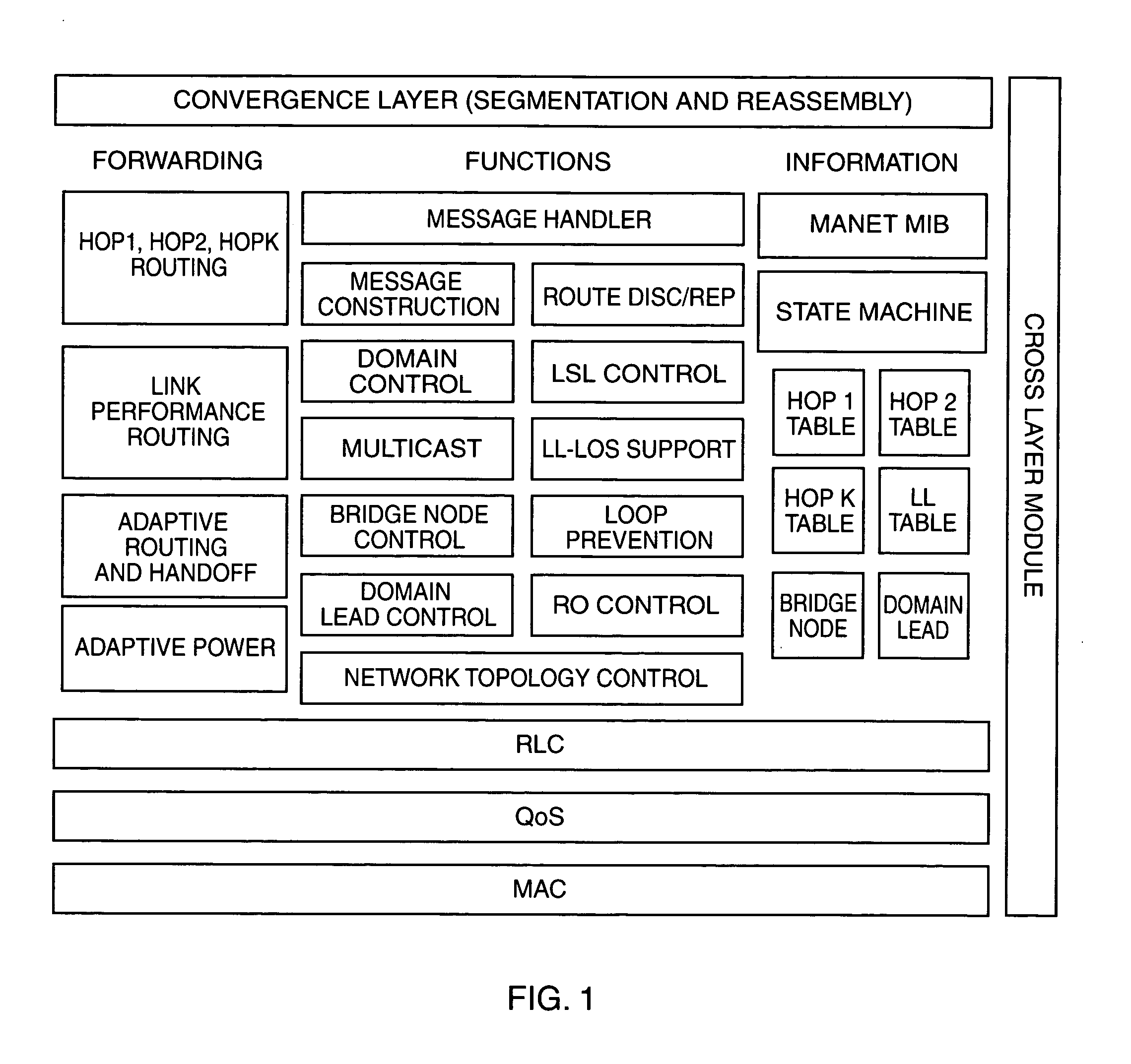
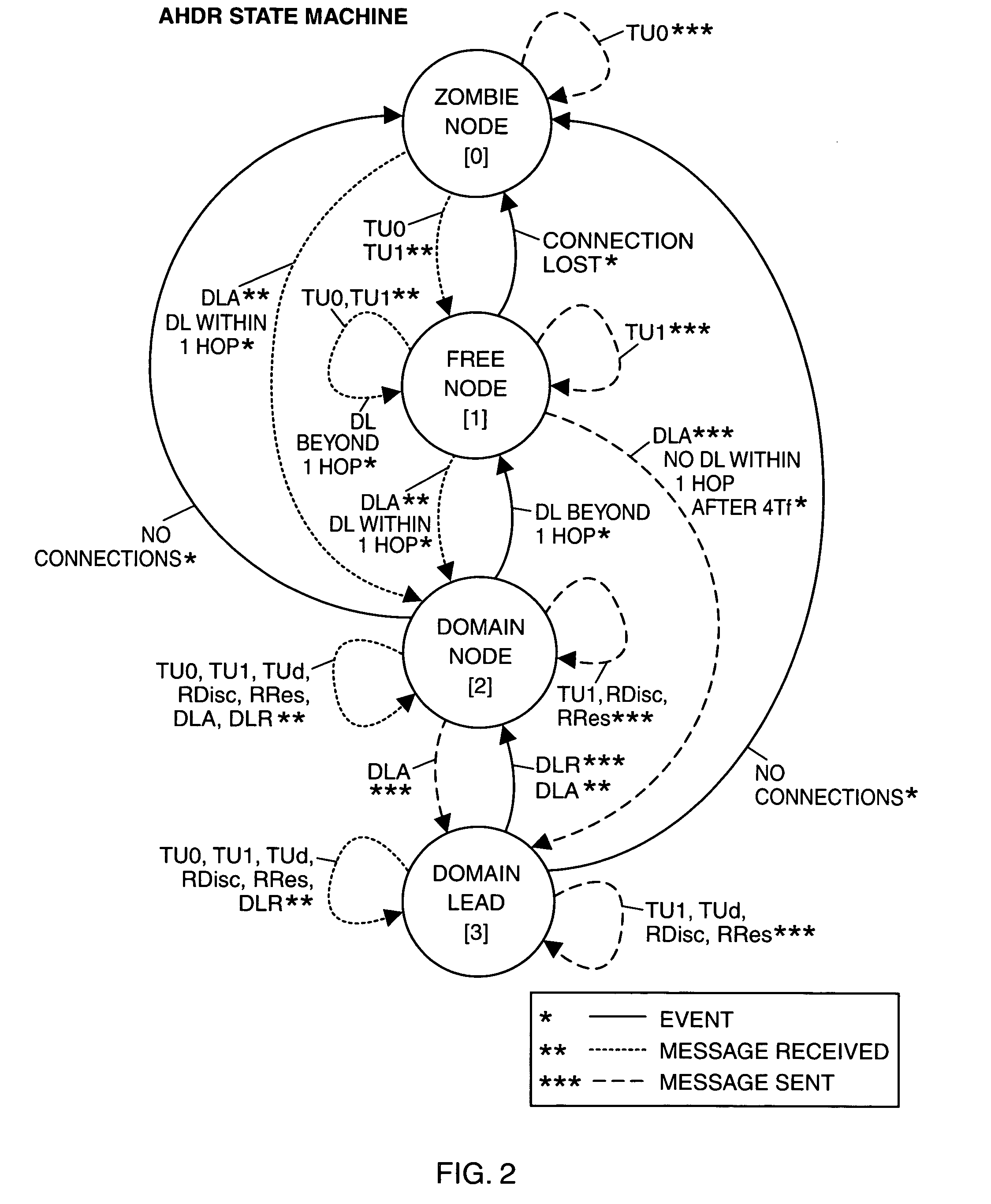
Adaptive message routing for mobile ad hoc networks
Domains are formed in a mobile ad hoc network by exchanging topology update messages among neighboring nodes, each message including the node coverage of the originating node. The node having an optimum coverage of its neighbors becomes a domain lead (DL) node, and nodes within hearing distance or range of the DL node form a network domain. Each domain node, including the DL, selects a set of bridge nodes (BNs) that can link the domain node to nodes in corresponding neighboring domains. All domain lead nodes in the network exchange messages to inform one another of the nodes contained in their respective domains. A node in one domain seeking a route for a message destined to a node in another domain, may send a route discovery (RDisc) message to the DL node of the inquiring node's domain. A responsive route resolution (RRes) message is returned to the inquiring node.
Owner:BAE SYST INFORMATION & ELECTRONICS SYST INTERGRATION INC
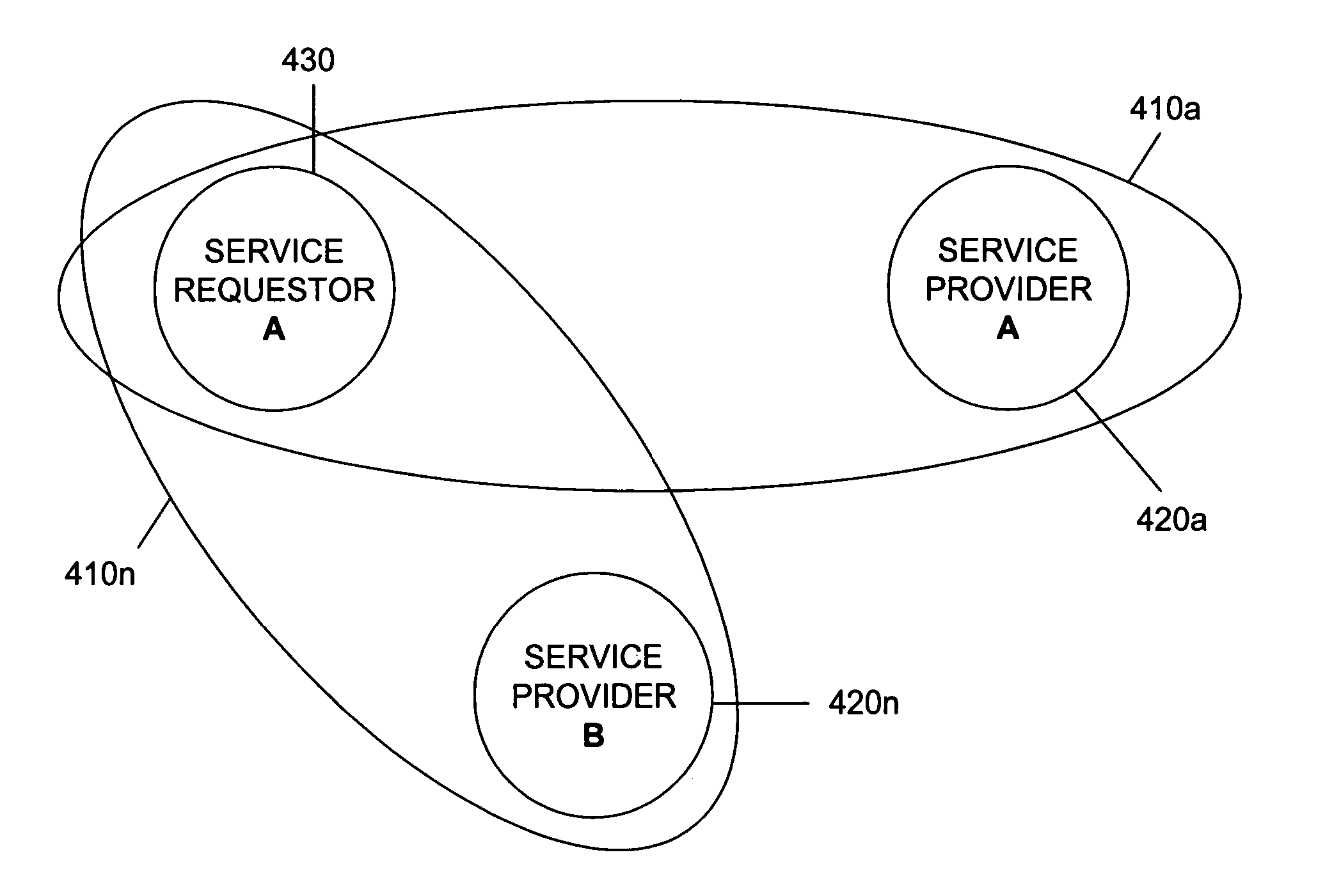
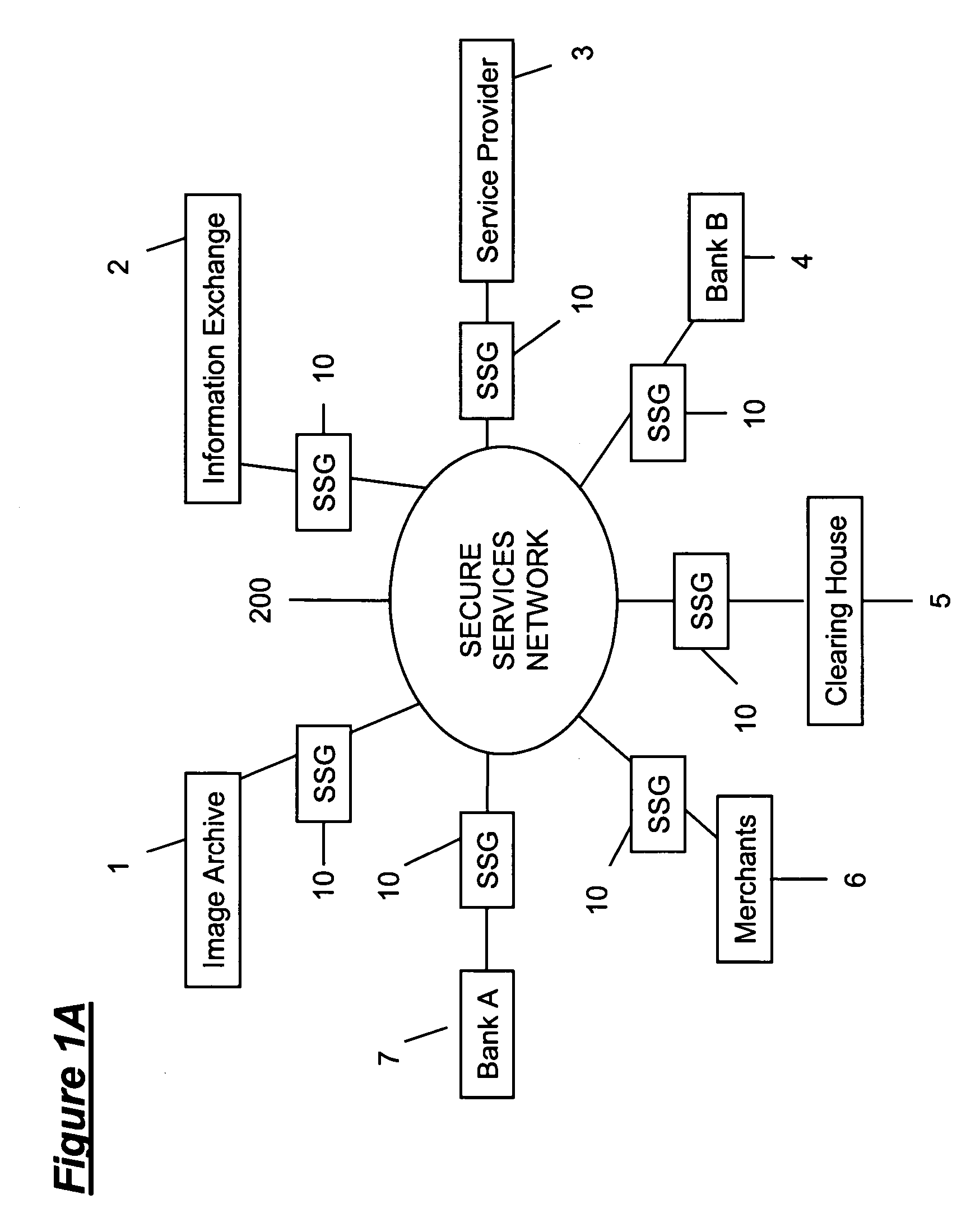
Secure service network and user gateway
ActiveUS20060107036A1Limited in functionally and participant reach and flexibilityLow costFinanceBilling/invoicingEngineeringPeer-to-peer
A secure service network (SSN) comprising an IP network infrastructure wherein the access of one participant to another participant in the network is controlled by a secure service gateway (SSG) in which a point of origination universal identifier (PoUID) represents a unique identifier for the participant within a participant's internal network domain and the interconnection of the SSGs within the SSN as a precondition of access creates a bilaterally secure peer to peer service connection. Participants in the network are service providers, service requesters, or both. A global secure service gateway (GSSG) may be interconnected in the SSN to provide a central access authority and management services.
Owner:WMR E PIN
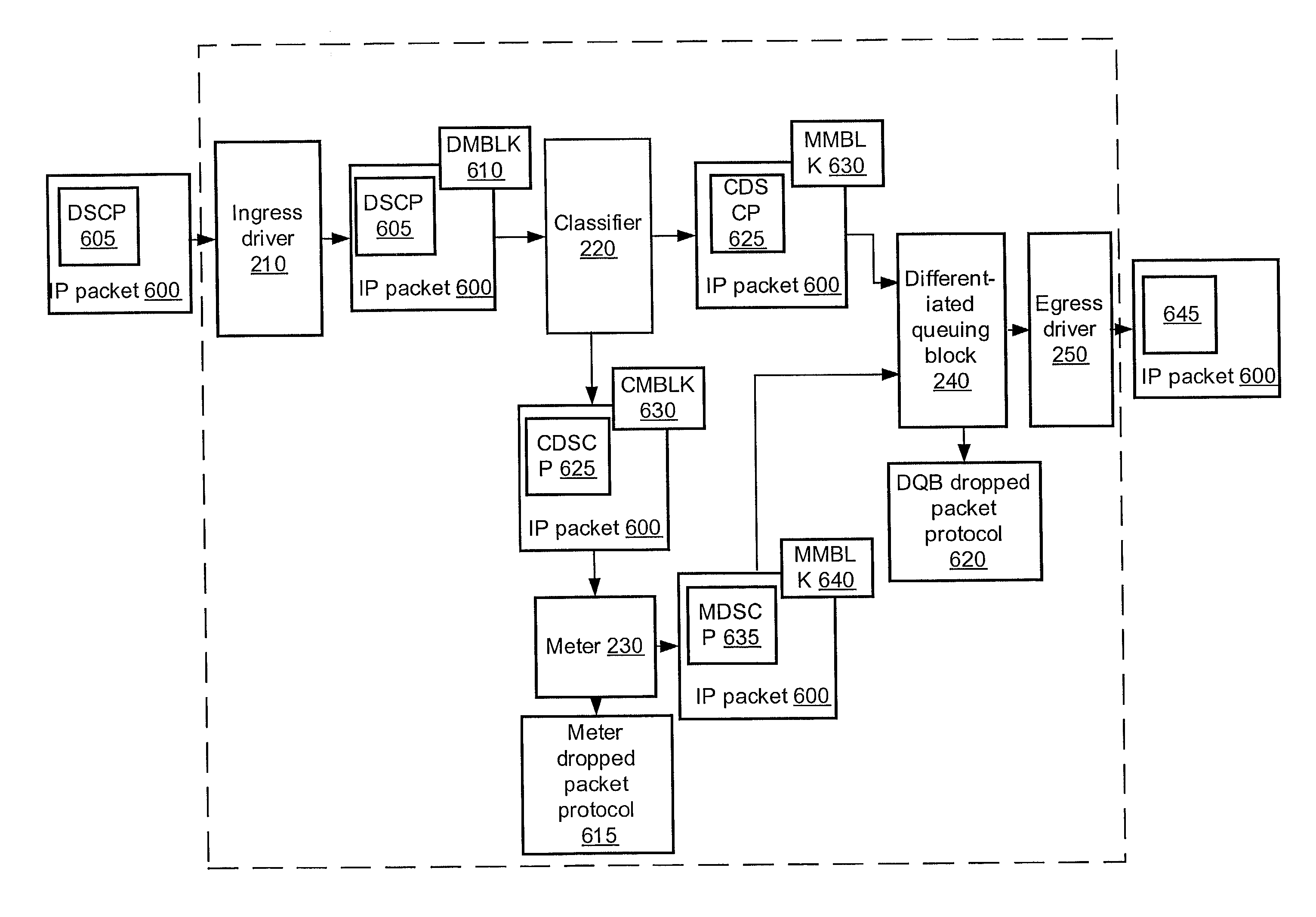
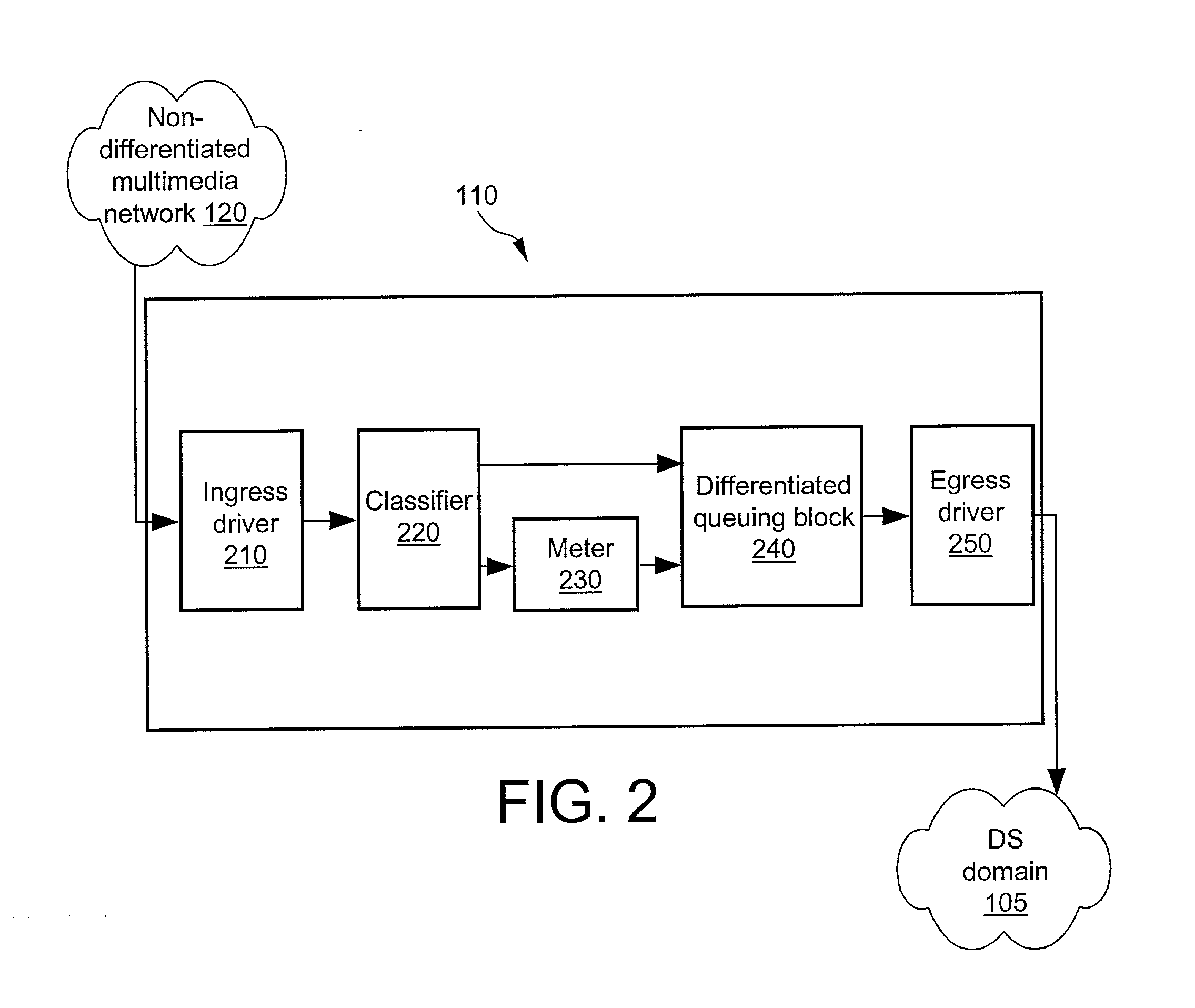
System for and method of differentiated queuing in a routing system
ActiveUS7020143B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsDifferentiated servicesTraffic capacity
The invention relates to a method for routing Internet traffic. The method generally includes the steps of receiving a packet from multimedia network, allocating a message block header for the packet, wherein the header is used to hold behavior aggregate values for internal router mapping, and queuing and routing the packet to a differentiated services network domain in a manner that ensures a specific QoS.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
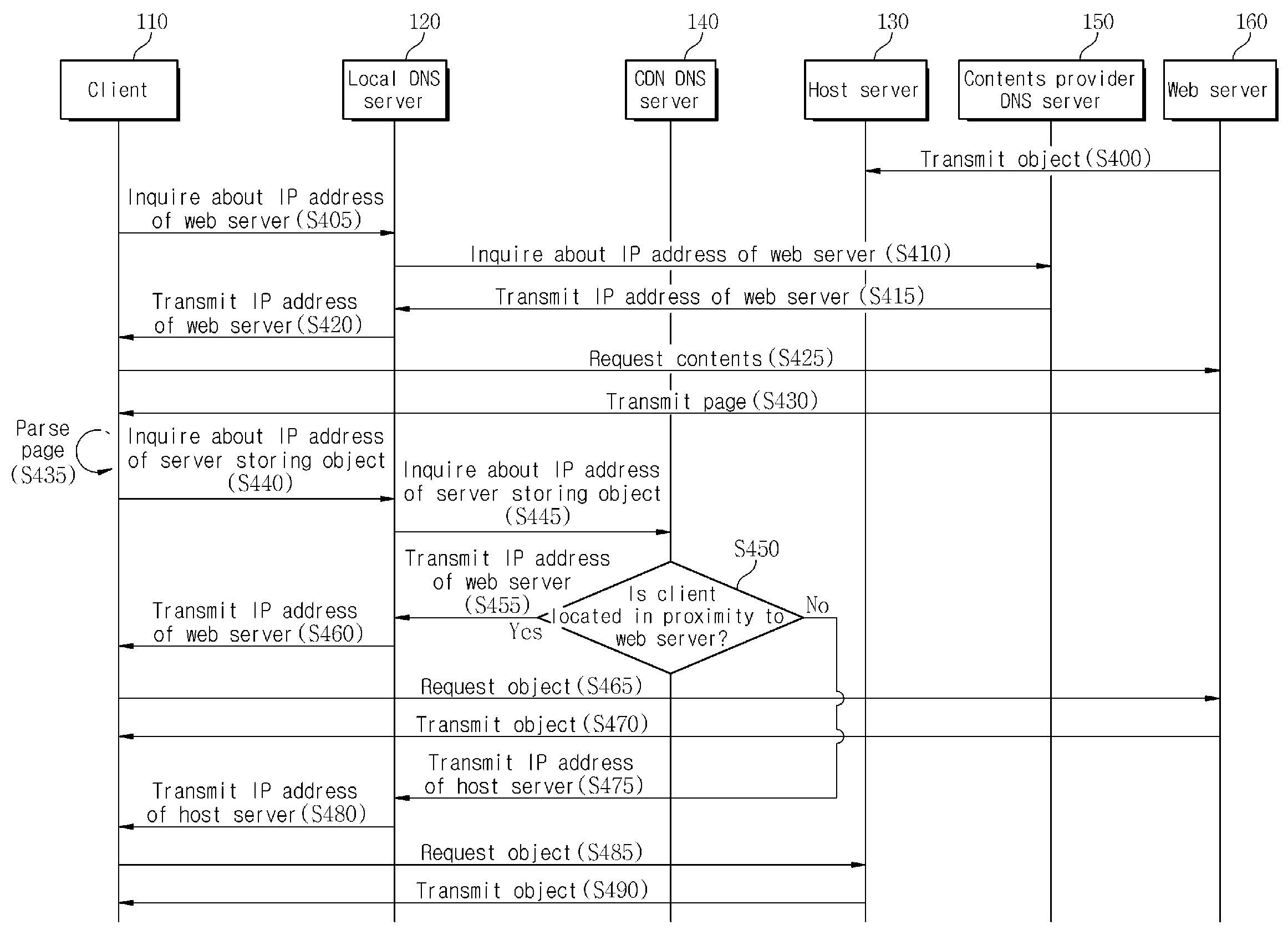
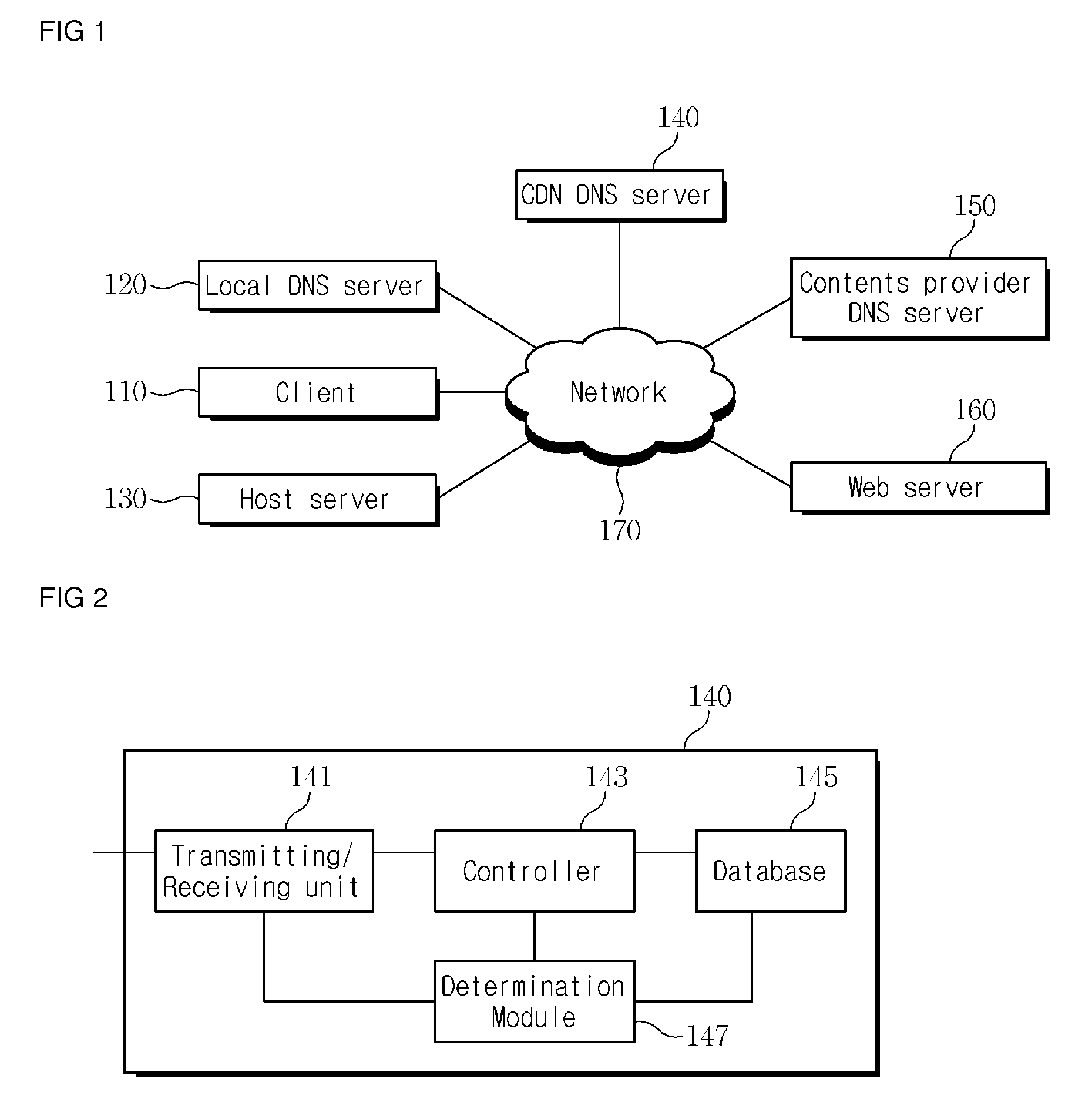
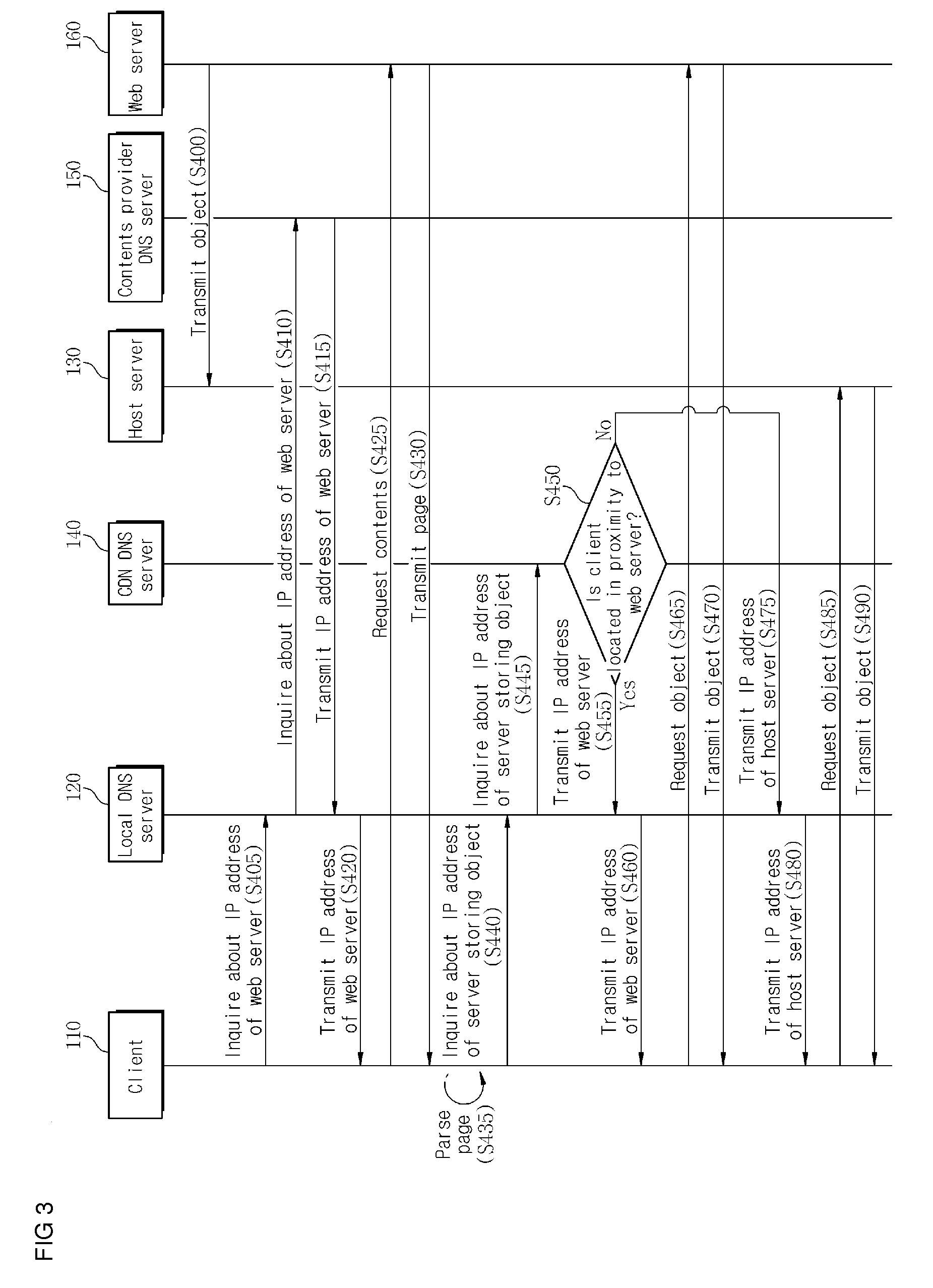
Contents provider participation type contents delivery system and method, and contents delivery network domain name system server thereof
InactiveUS20100042725A1Improve service qualityDecrease useless network loadMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDomain nameService improvement
A CP participated contents delivery system and method, and a CDN DNS server of the system are provided. When a client detects an embedded object while parsing a page received from a web server, the client inquires of a local DNS server about the IP address of a server storing the object. The local DNS server receives the inquiry of the client and inquires of a CDN DNS server about the IP address of the server storing the object. The CDN DNS server selects a server located in proximity to the client from a host server of a CDN provider, which stores the object, and the web server. The selected server transmits the object to the client. Accordingly, the client can rapidly receive the object and a contents provider can promote qualitative contents providing service improvement.
Owner:SK PLANET CO LTD
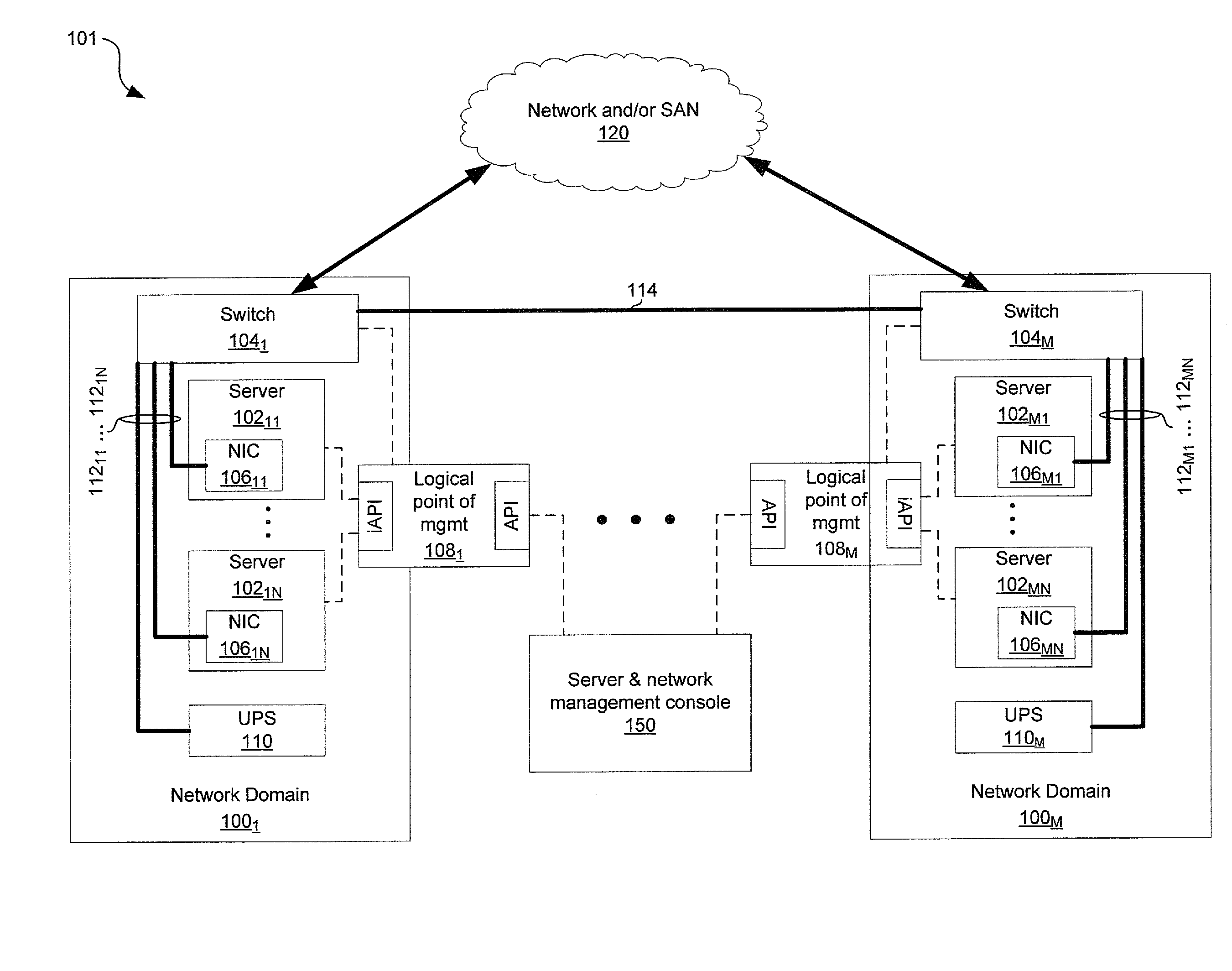
Method and system for managing network power policy and configuration of data center bridging
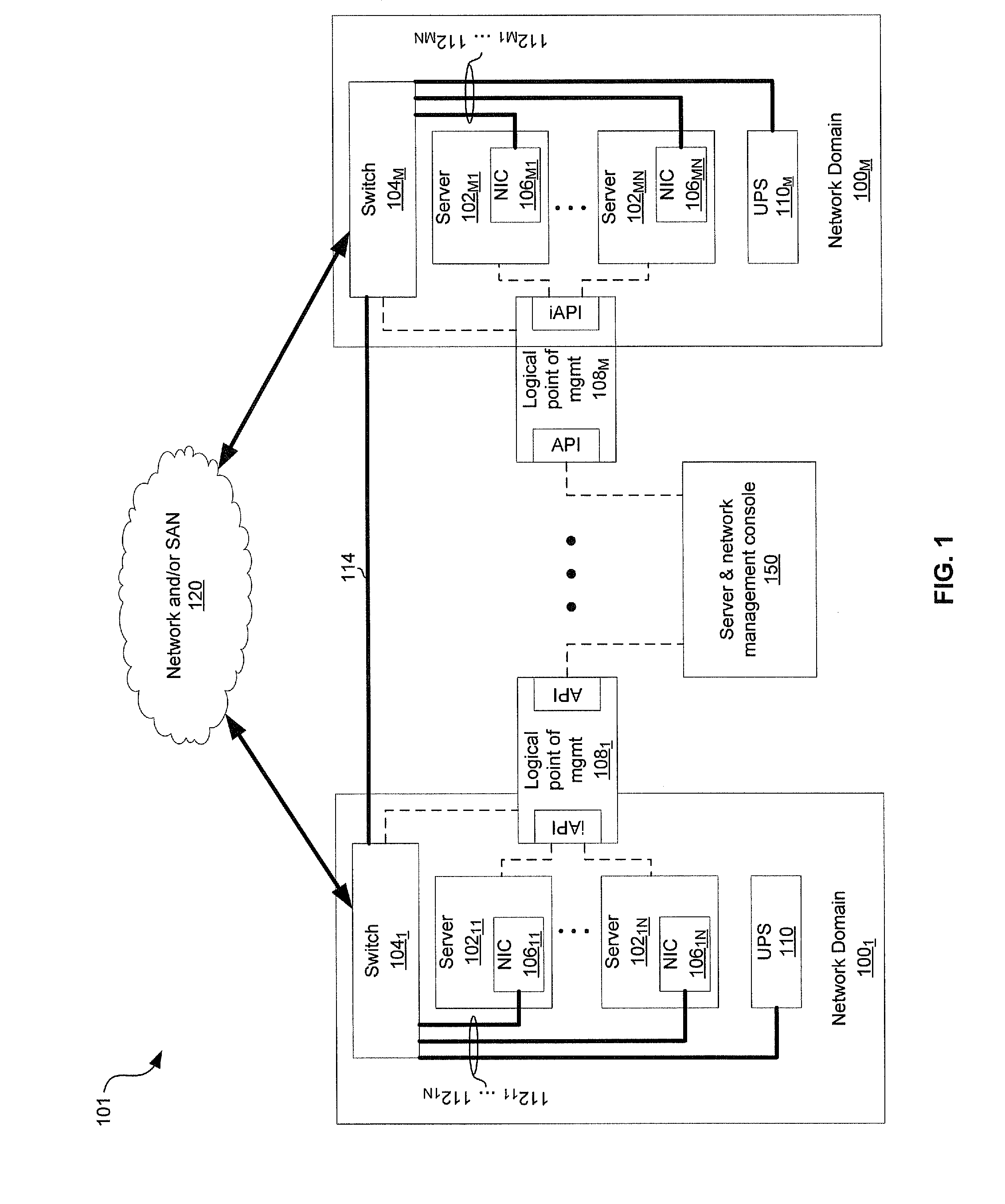
Certain aspects of a method and system for managing network power policy and configuration of data center bridging may include a network domain that comprises a single logical point of management (LPM) that coordinates operation of one or more devices, such as network interface controllers (NICs), switches, and / or servers in the network domain: The single LPM may be operable to manage one or both of a network power policy and / or a data center bridging (DCB) configuration policy for the network domain.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
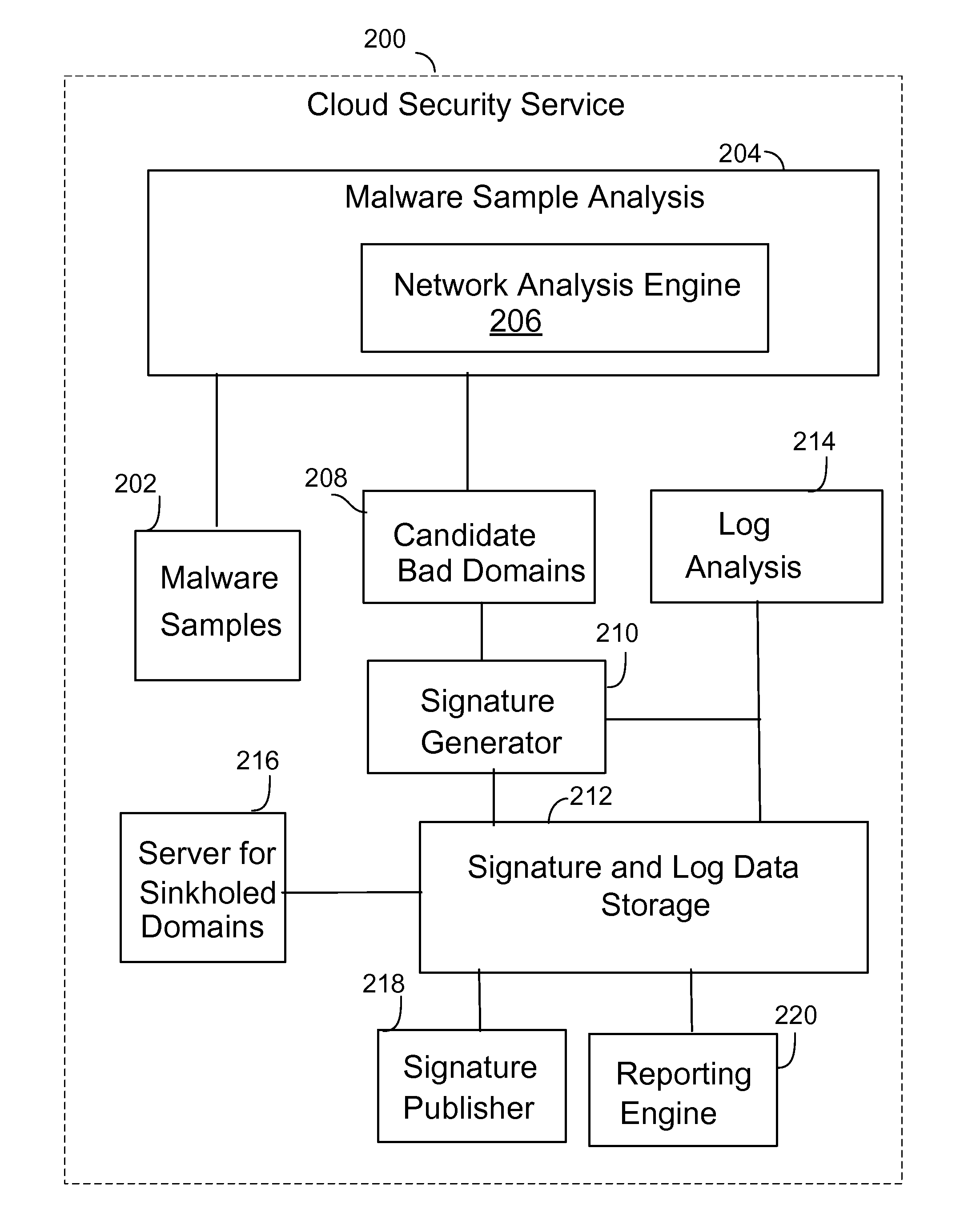
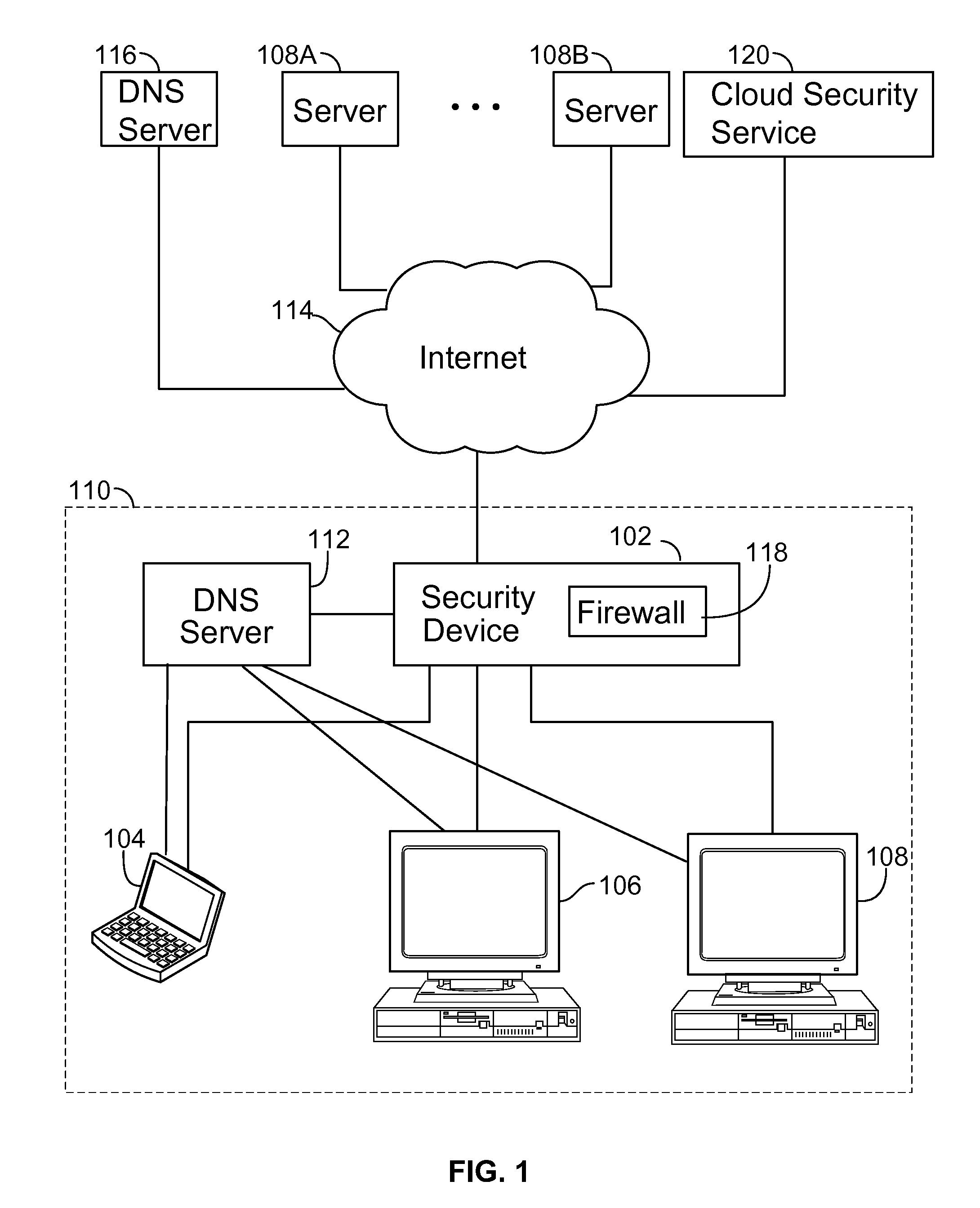
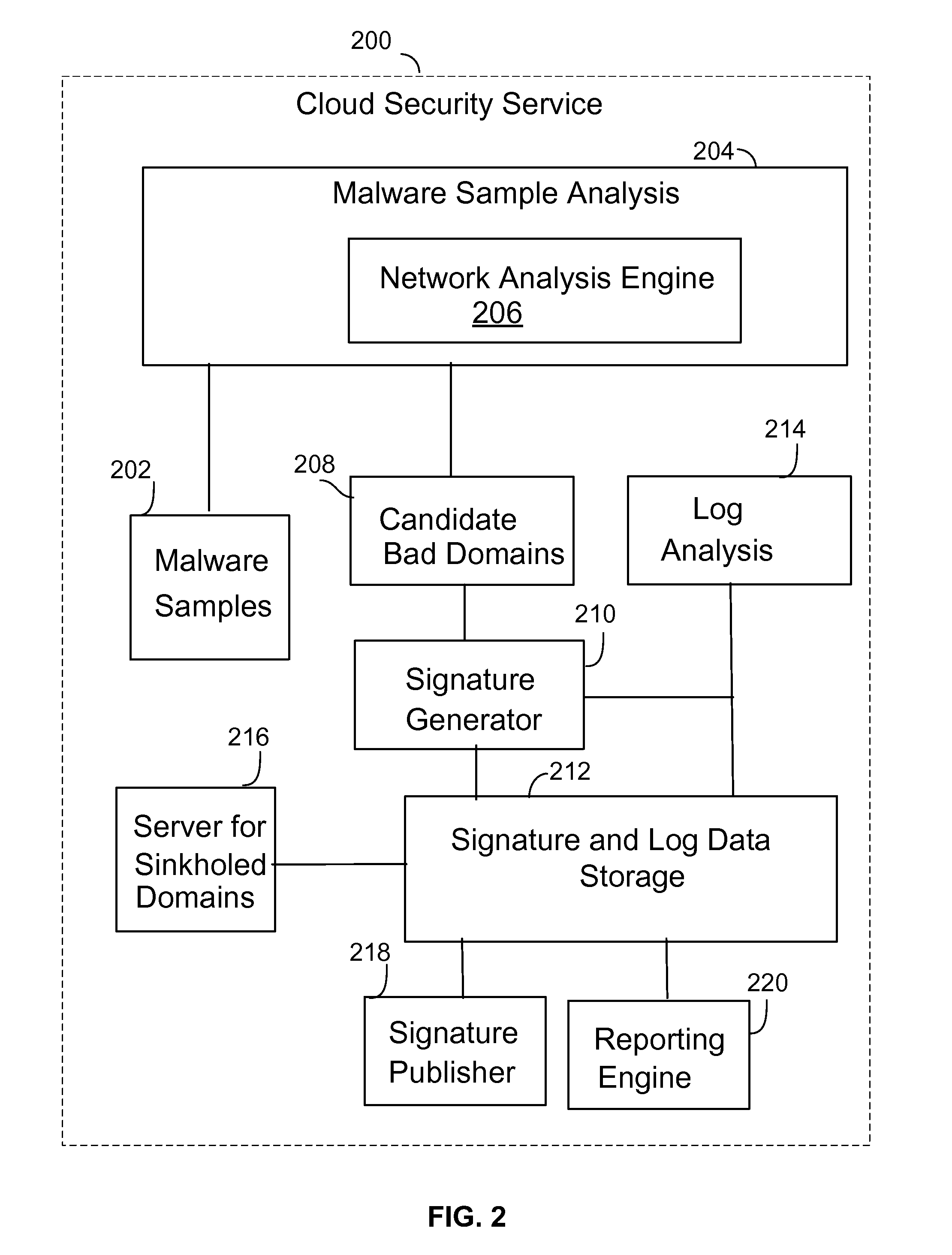
Sinkholing bad network domains by registering the bad network domains on the internet
Techniques for sinkholing bad network domains by registering the bad network domains on the Internet are provided. In some embodiments, sinkholing bad network domains by registering the bad network domains on the Internet includes determining a network domain is a bad network domain, in which the bad network domain is determined to be associated with an identified malware (e.g., malware that has been identified and has been determined to be associated with the bad domain), and the bad network domain is sinkholed by registering the bad network domain with a sinkholed IP address; and identifying a host that is infected with the identified malware based on an attempt by the host to connect to the sinkholed IP address.
Owner:PALO ALTO NETWORKS INC
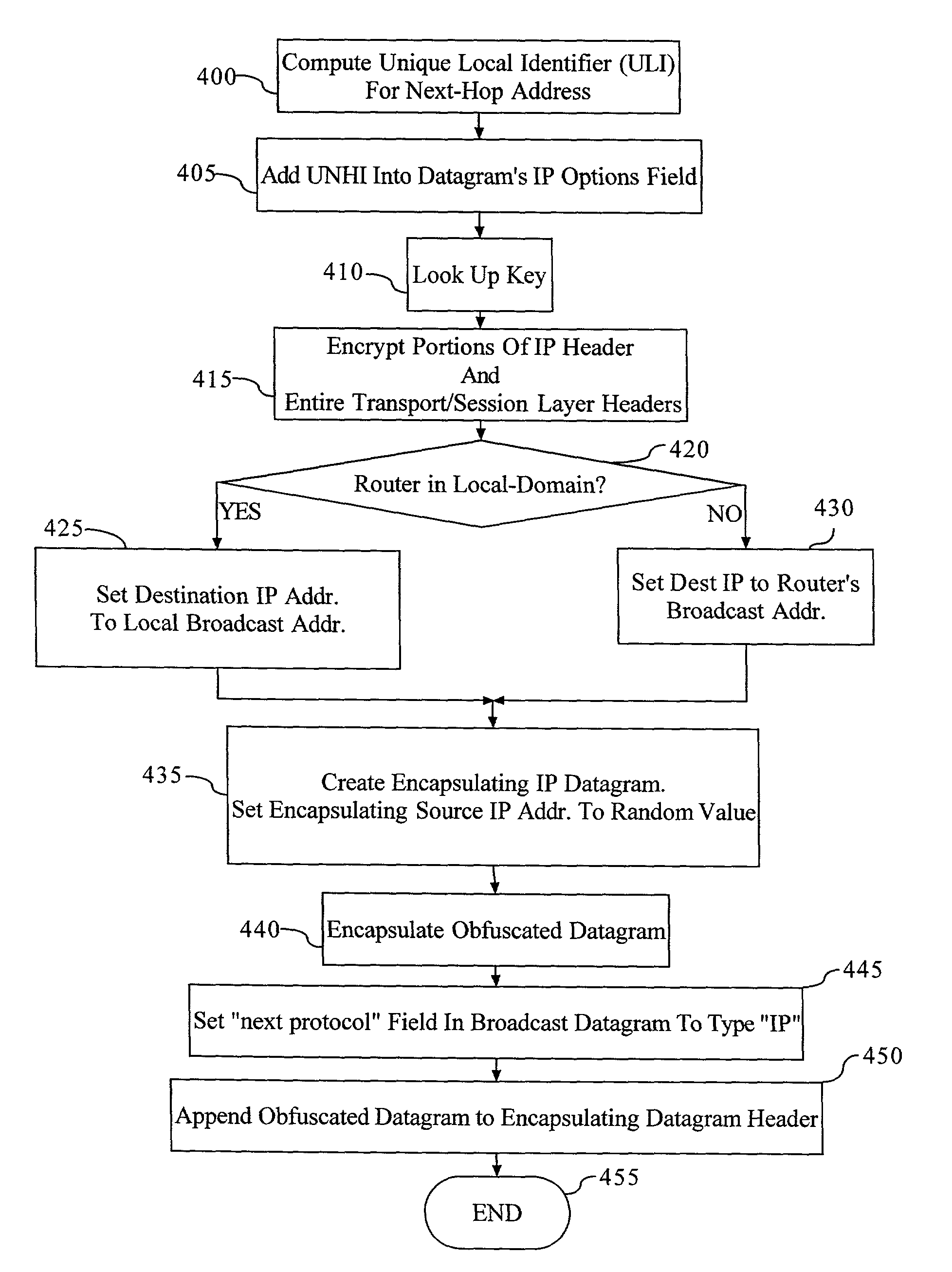
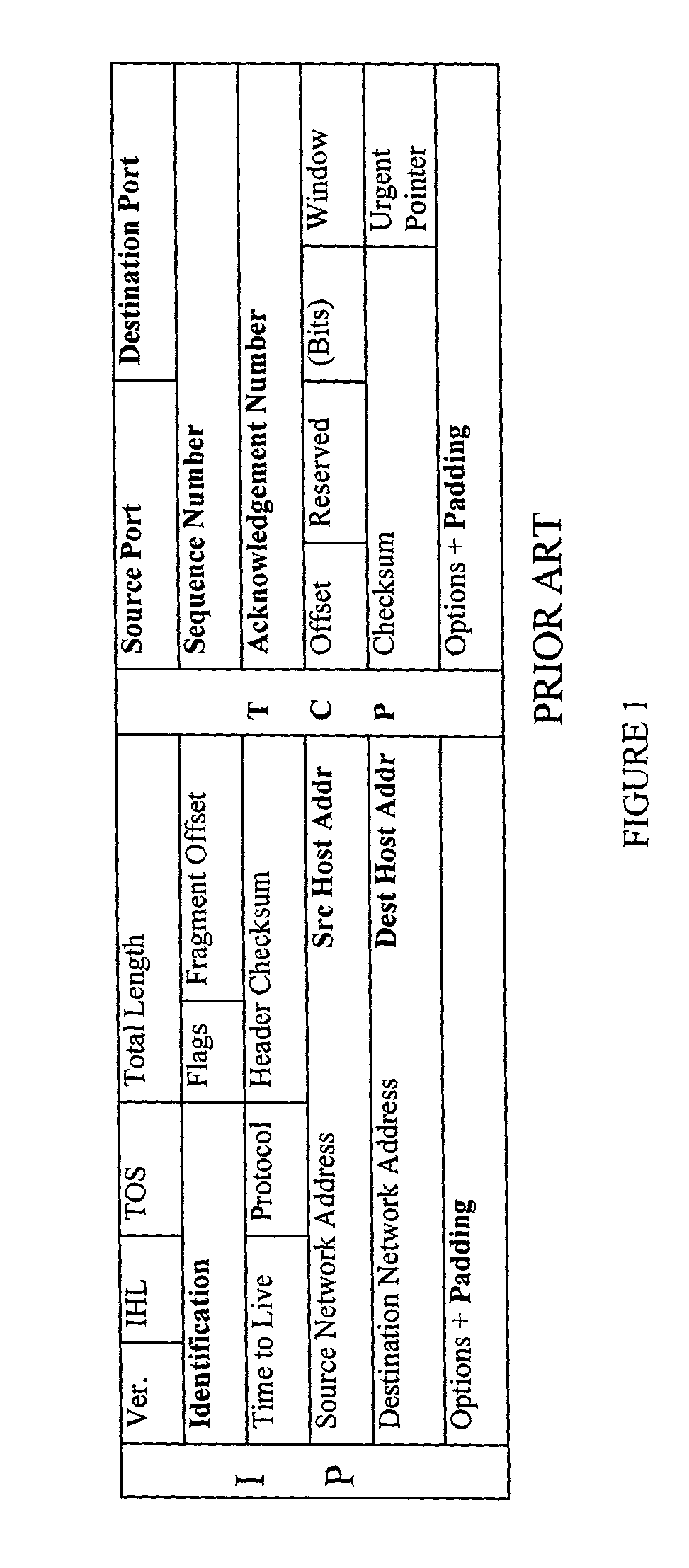
Method and apparatus for anonymous IP datagram exchange using dynamic network address translation
Methods, apparatus, system and computer program are provided for concealing the identity of a network device transmitting a datagram having a network layer header. A unique local identifier and broadcast address are determined in accordance with a next-hop address. A partially encrypted network layer header is determined by encrypting a plurality of identifying portions of the network layer header, where one portion of the network layer header is the unique local identifier. The datagram is encapsulated with another network layer header whose address is set to the broadcast address. The encapsulated datagram can be received and detunneled, and an address of a recipient can be extracted from the network layer header. The datagram is then admitted into a network domain.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC +1
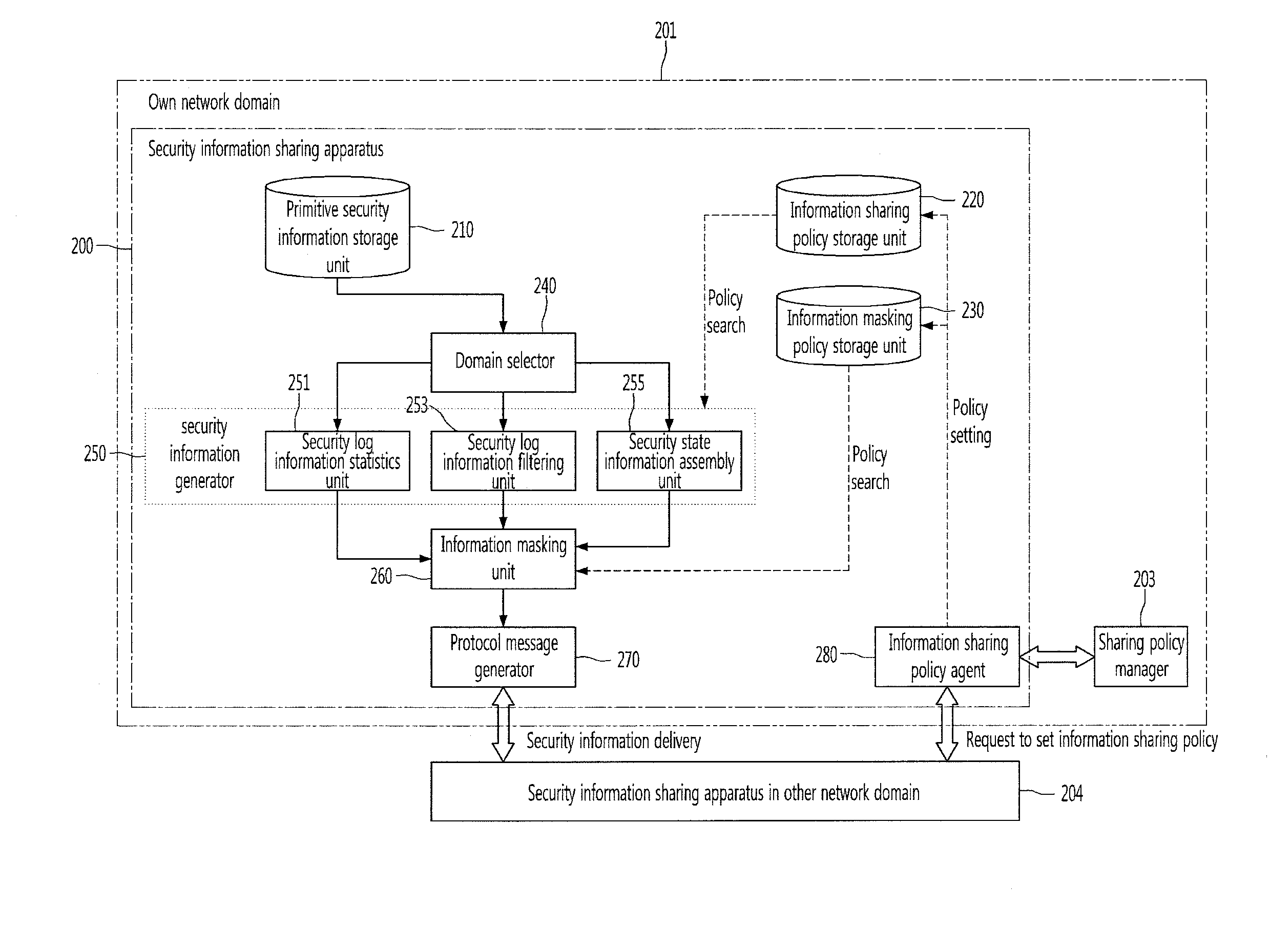
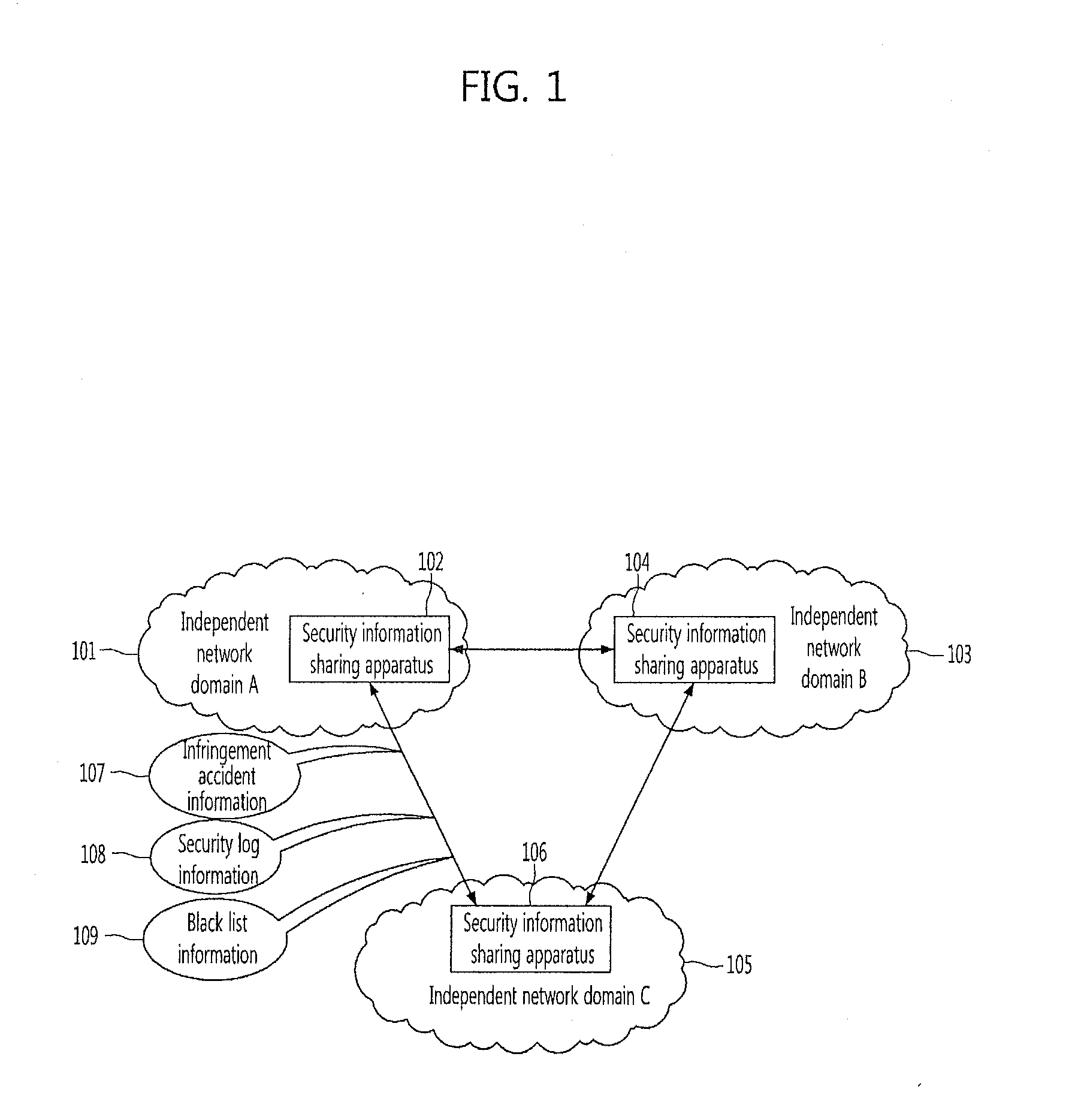
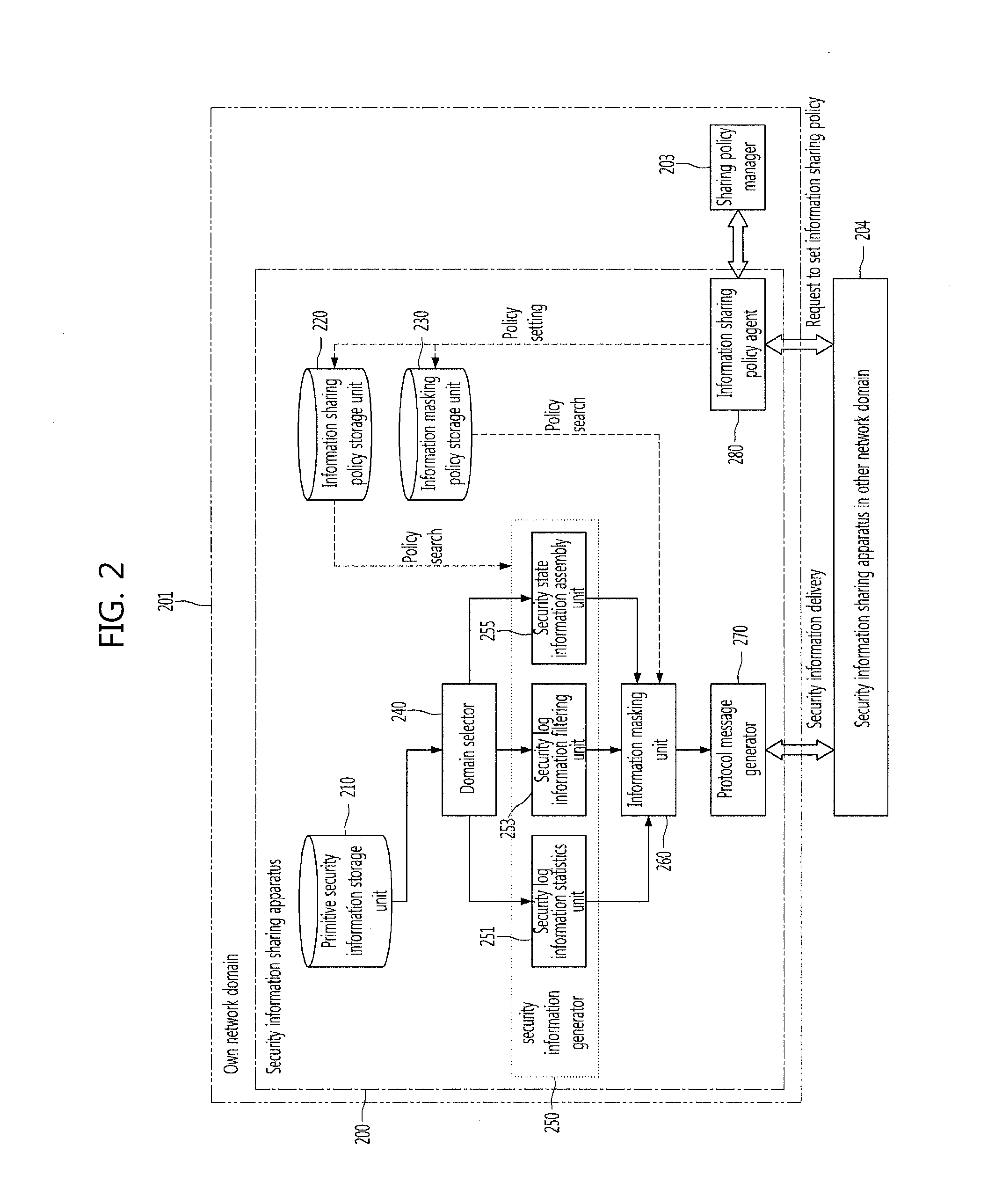
Apparatus for sharing security information among network domains and method thereof
InactiveUS20120110633A1Blocking in networkTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsInformation sharingInternet privacy
Provided are a security information sharing apparatus capable of sharing security information among network domains and a method thereof. The security information sharing apparatus includes a primitive security information storage unit configured to store primitive security information to be shared with other network domains, an information sharing policy storage unit configured to store an information sharing policy for information to be shared, an information masking policy storage unit configured to store an information masking policy for information not to be opened to the other network domain, a domain selector configured to select the other network domain to receive the shared security information, a shared security information generator configured to generate shared security information for the selected other network domain by applying the information sharing policy to the primitive security information, an information masking unit configured to mask information not to be opened in the generated security information according to the information masking policy, a protocol message generator configured to generate a protocol message for the shared security information subjected to the information masking, to be transmitted, and a protocol message transmitter configured to transmit the protocol message to the selected other network domain.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
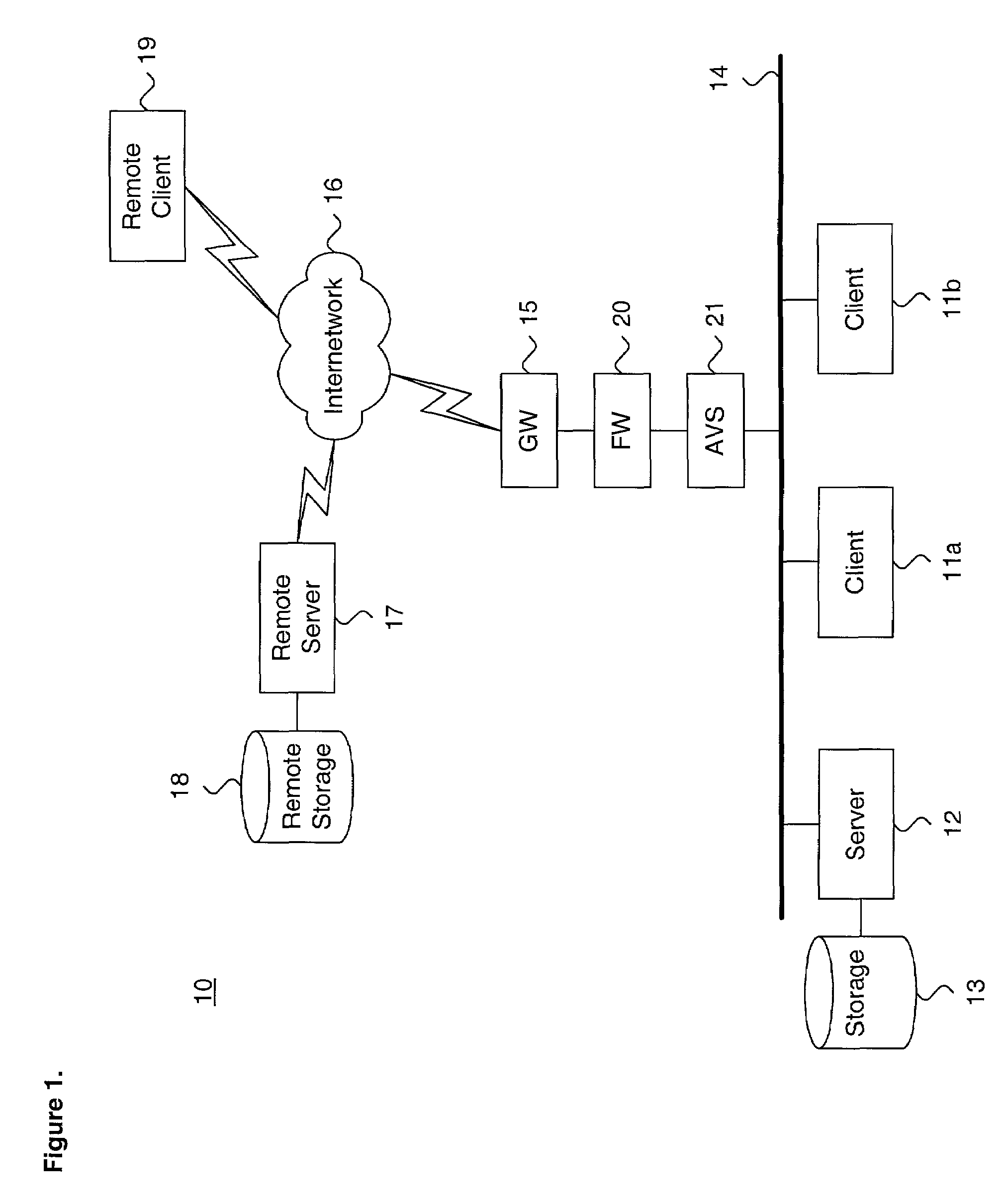
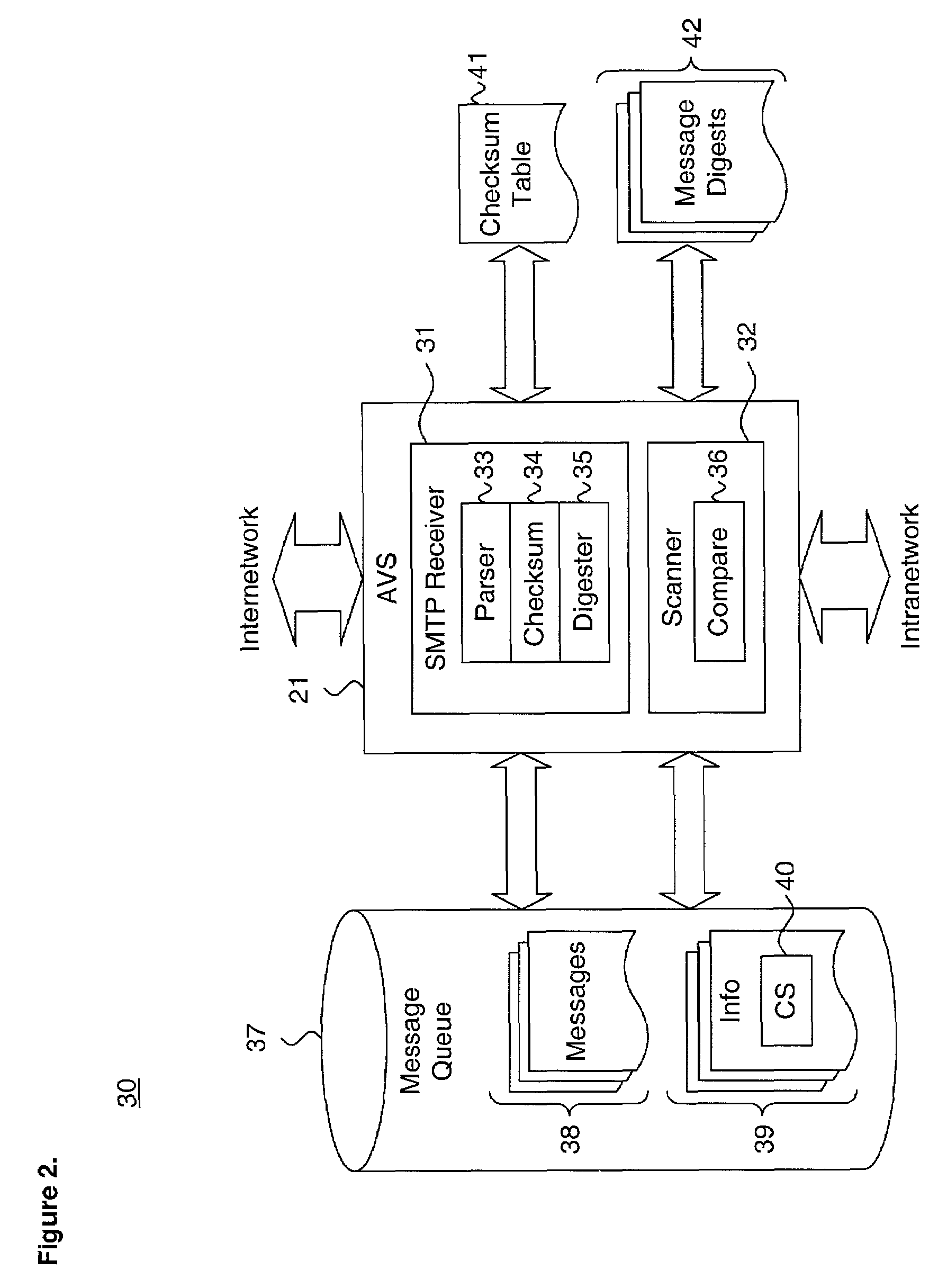
System and method for performing efficient computer virus scanning of transient messages using checksums in a distributed computing environment
ActiveUS6993660B1Efficient detectionMemory loss protectionUser identity/authority verificationDistributed Computing EnvironmentChecksum
A system and method for performing efficient computer virus scanning of transient messages using checksums in a distributed computing environment is described. An incoming message is intercepted at a network domain boundary. The incoming message includes a body storing message content. The message content is parsed from the body and a checksum is calculated over the parsed message content. The checksum is stored in an information file associated with the incoming message in a transient message store. The incoming message is scanned for a presence of at least one of a computer virus and malware to identify infected message contents. The checksum corresponding to each infected message content and an infection indicator is recorded.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
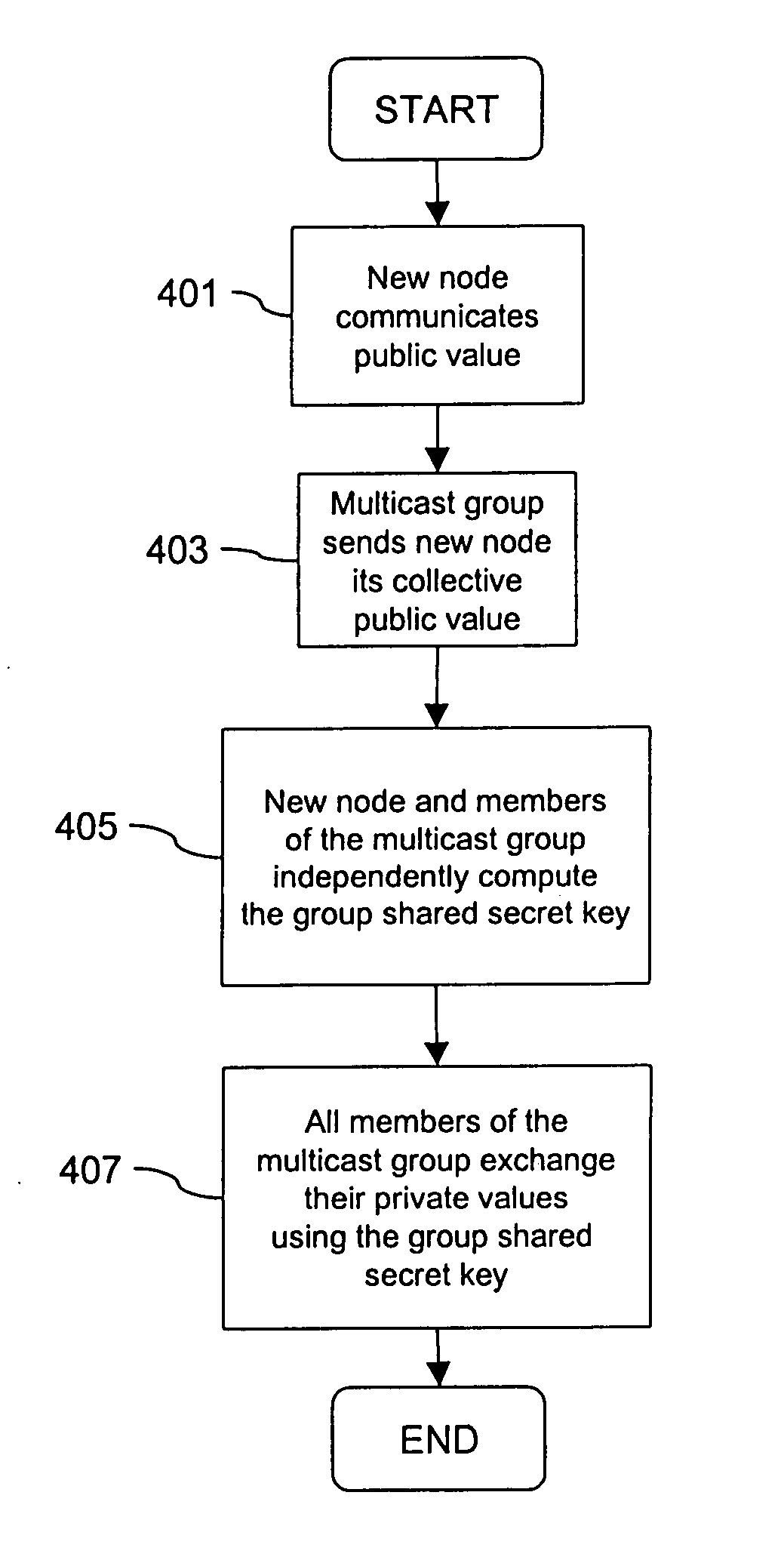
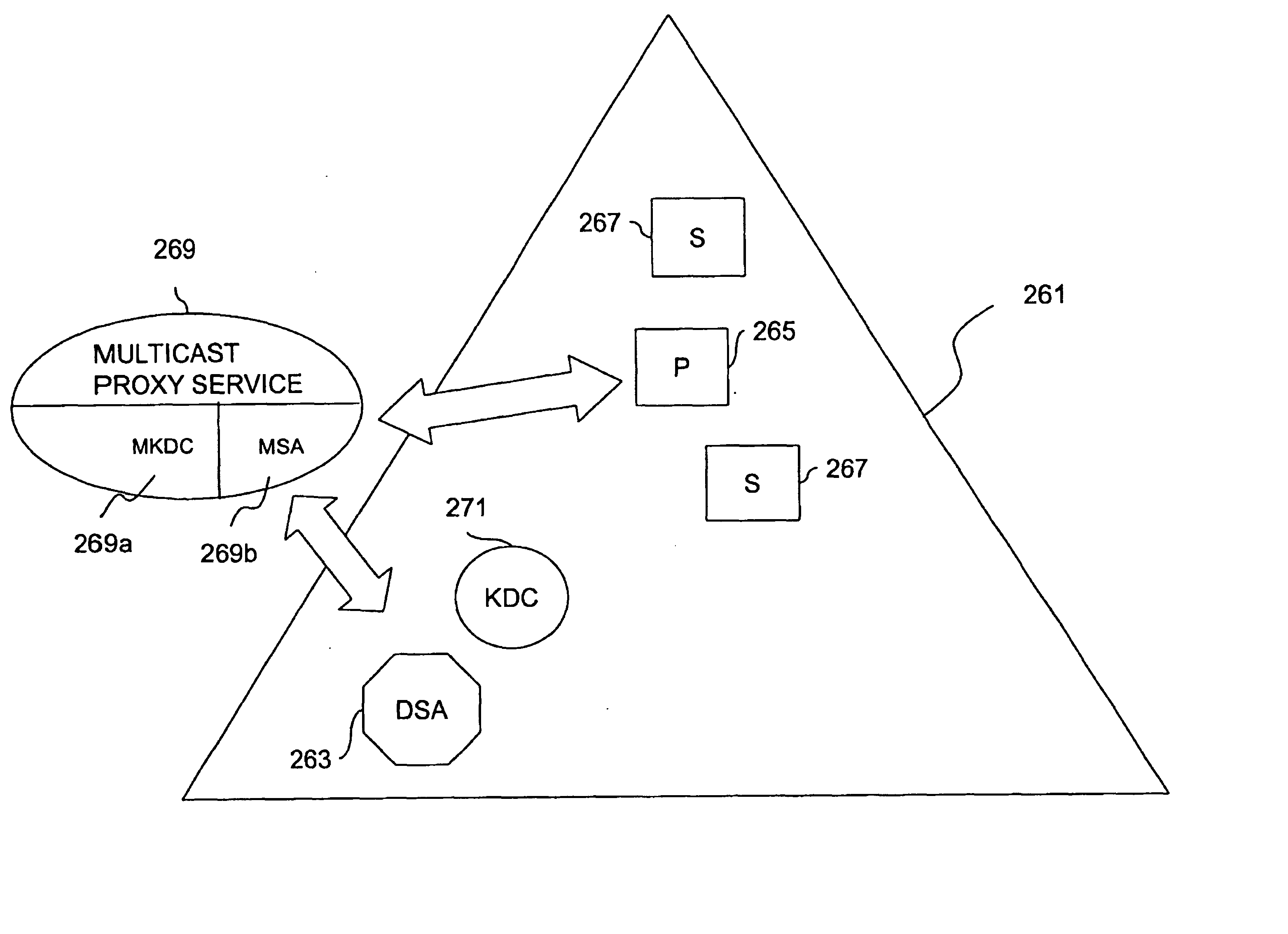
Method and apparatus for distributing and updating private keys of multicast group managers using directory replication
InactiveUS20050044356A1Optimize allocationKey distribution for secure communicationGroup sessionSecure multicast
An approach for establishing secure multicast communication among multiple multicast proxy service nodes is disclosed. The multicast proxy service nodes, which can be distributed throughout an enterprise domain, are organized in a logical tree that mimics the logical tree arrangement of domains in a directory server system. The attributes of the multicast proxy service nodes include the group session keys that are members of the secure multicast or broadcast groups. Because keys as well as key version information are housed in the directory, multicast security can be achieved over any number of network domains across the entire enterprise. Key information is stored in, and the logical tree is supported by, a directory service. Replication of the directory accomplishes distribution of keys. Multicast proxy service nodes may obtain current key information from a local copy of the replicated directory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
System and method for secure electronic communication services
InactiveUS8538028B2Easy accessSecure transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationSecure communicationScalable system
Owner:TOPOSIS CORP
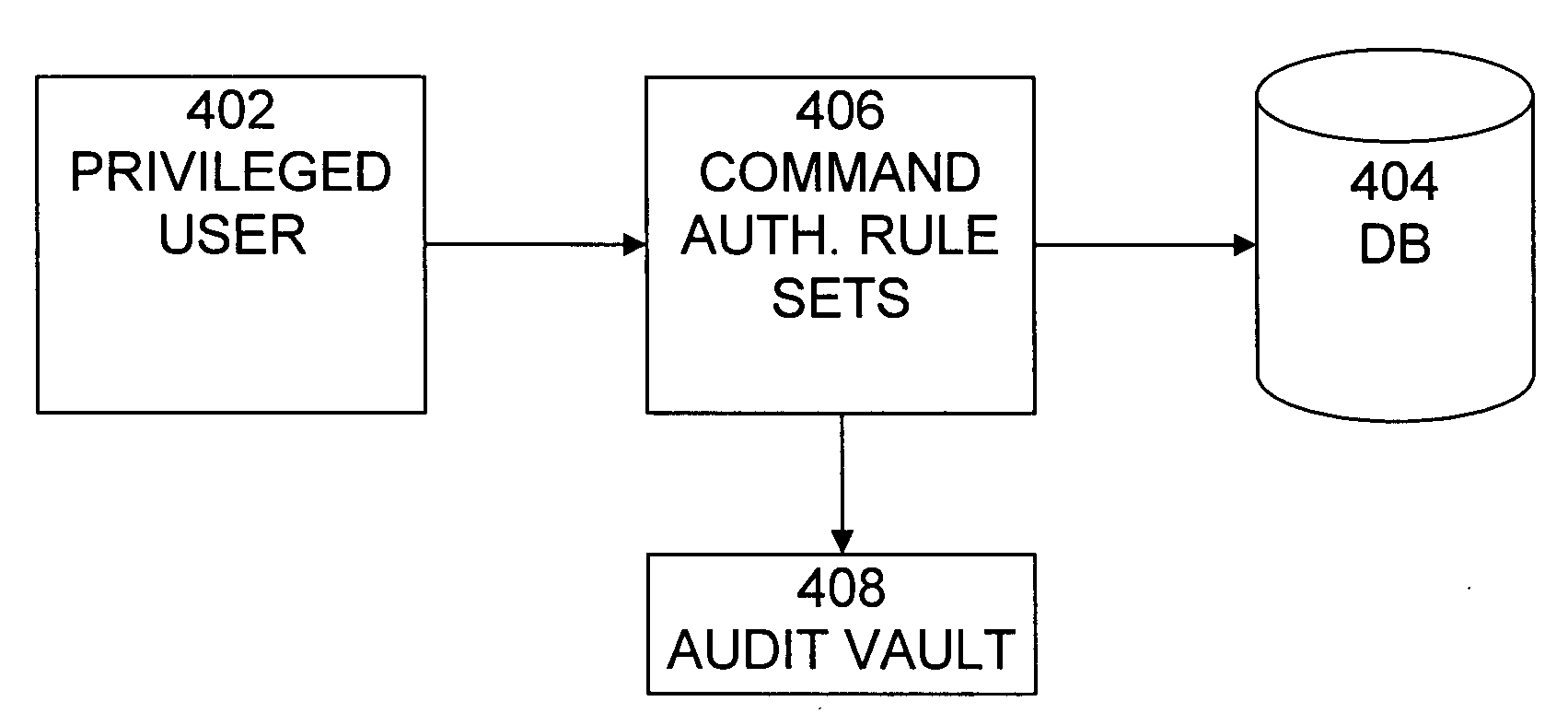
Cross-domain security for data vault
ActiveUS20060248599A1Ease of administrationEnsure effective implementationDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDatabase securitySecurity level
A secure database appliance leverages database security in a consistent framework provides consistent, flexible, and adaptable security using mandatory access controls in addition to user and role based security for access control and accountability. A database system communicatively connected to a plurality of network domains, each network domain having a level of security, the database system comprises at least one database accessible from all of the plurality of network domains, the database comprising data, each unit of data having a level of security and access control security operable to provide access to a unit of data in the database to a network domain based on the level of security of the network domain and based on the level of security of the unit of data.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
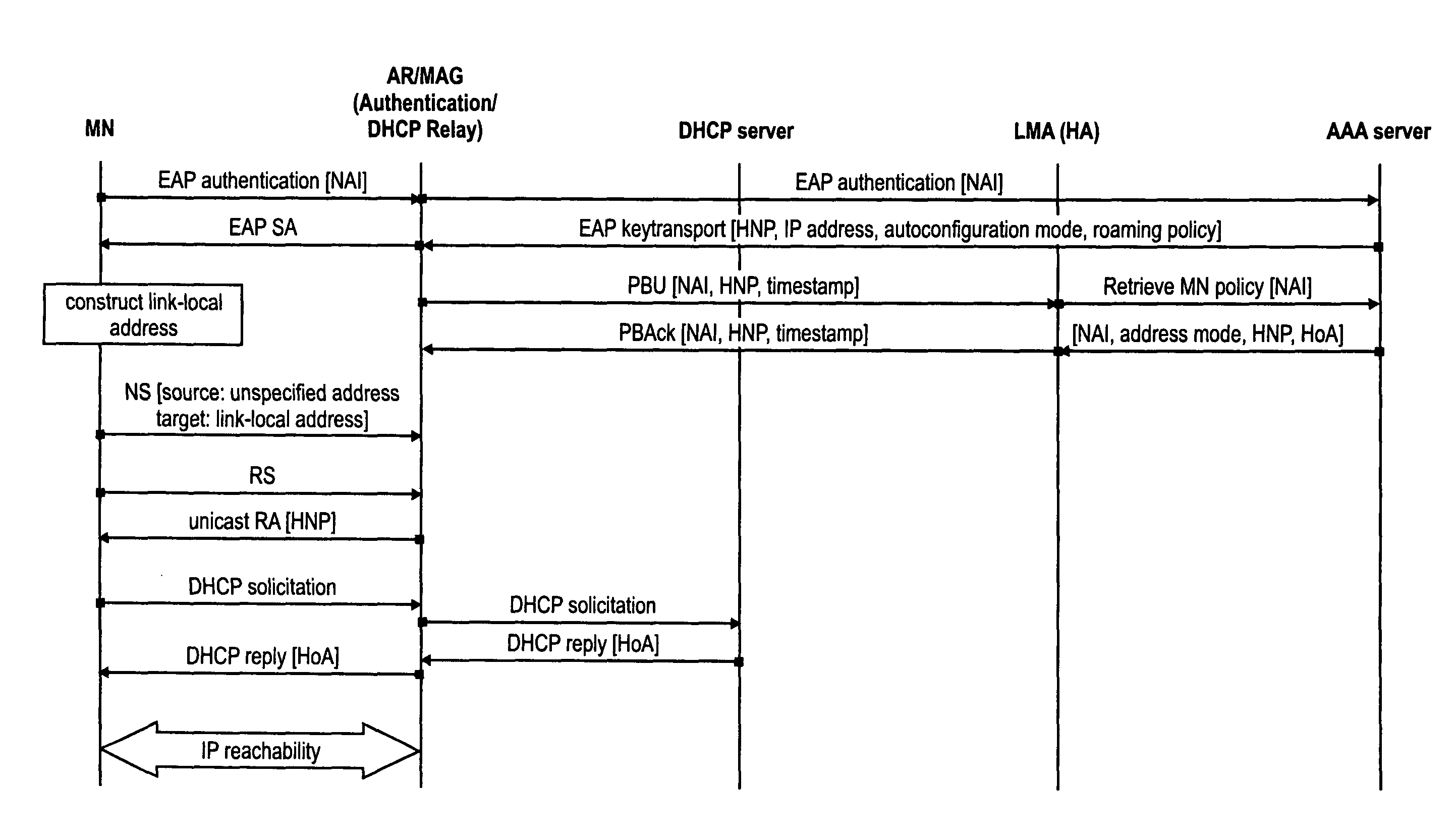
Detection of mobility functions implemented in a mobile node
InactiveUS20100215019A1Easy to detectEasy to operateNetwork topologiesWireless network protocolsAccess networkIp address
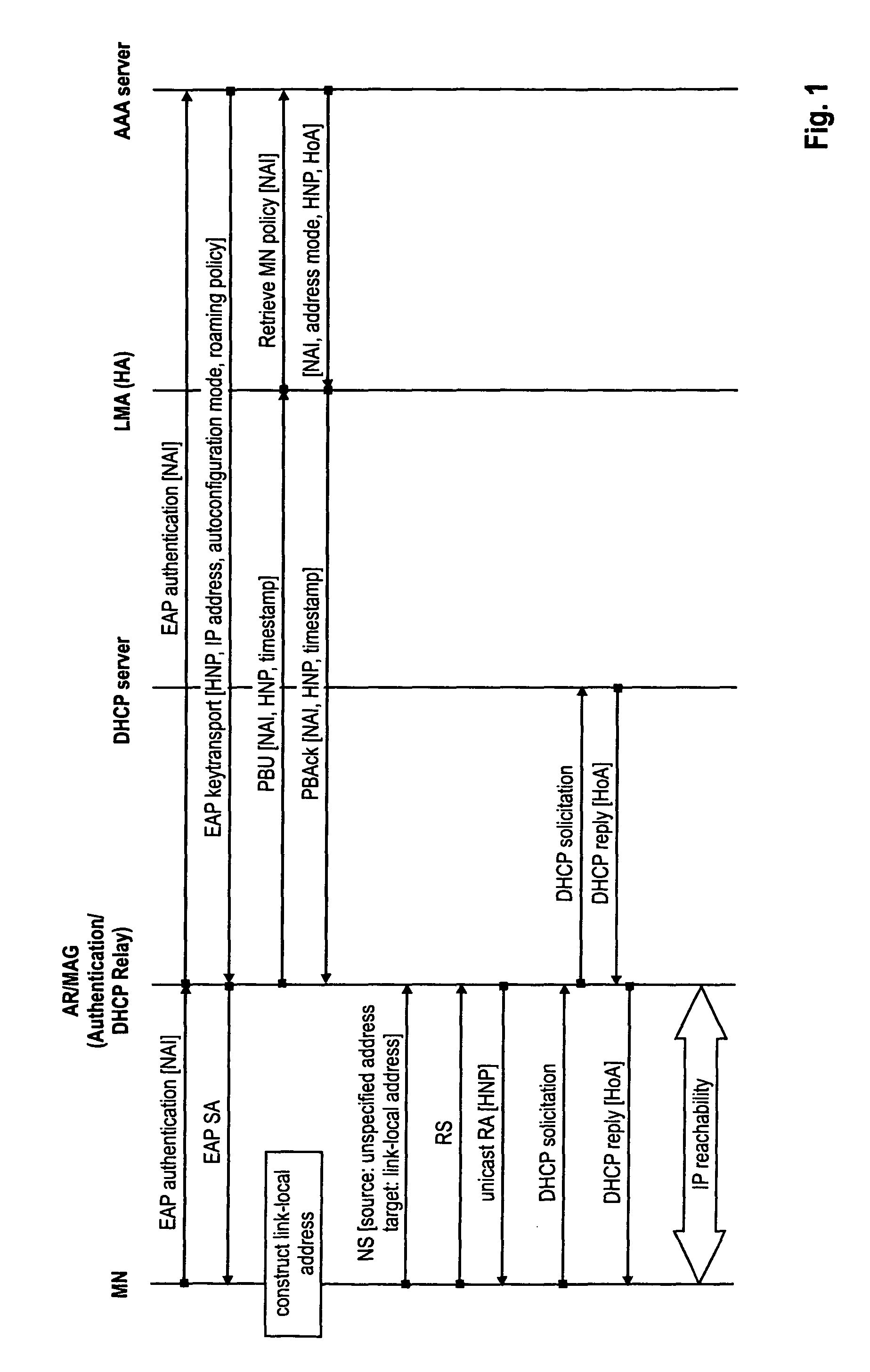
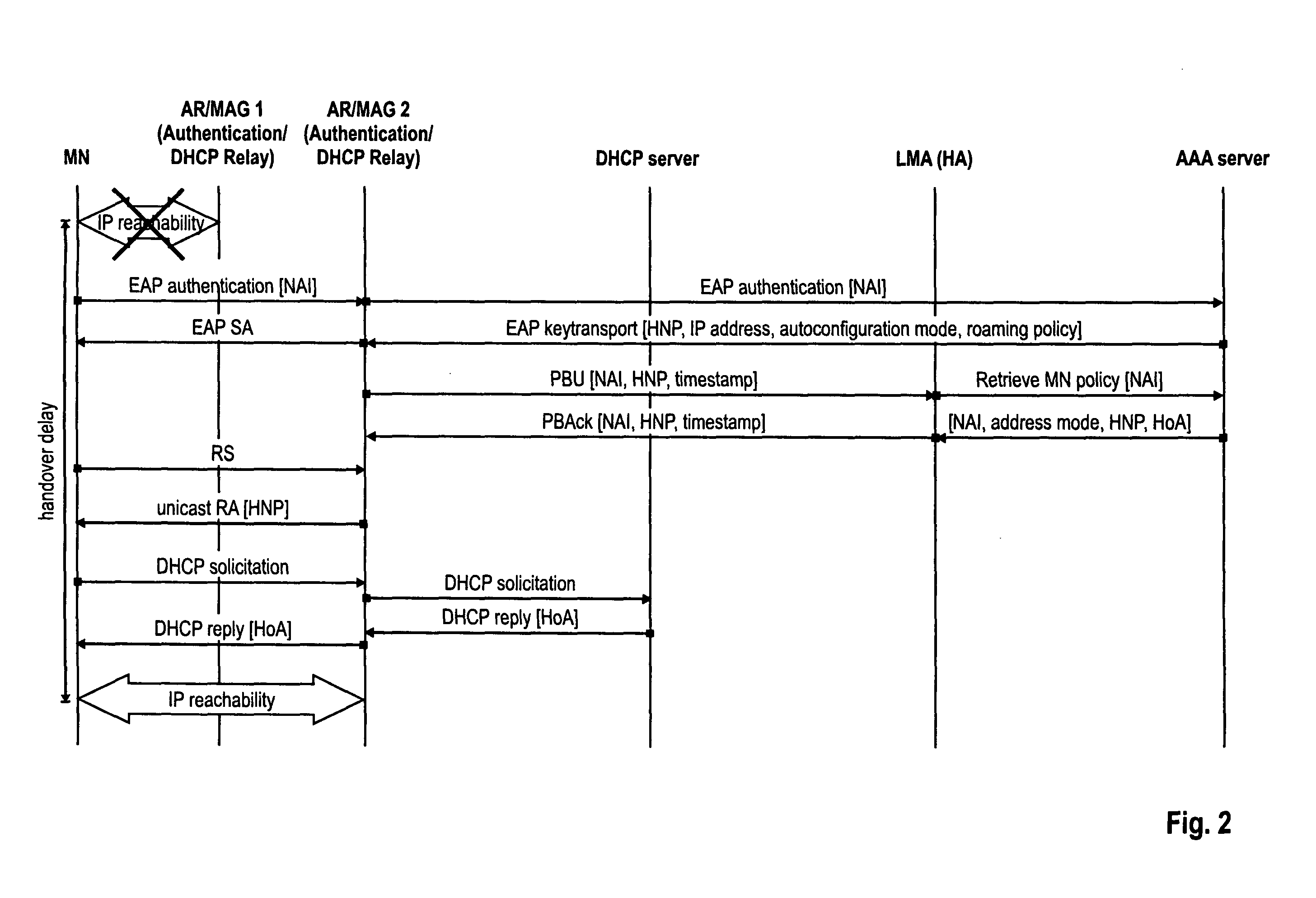
The invention relates to a method for configuring an IP address of a mobile node attaching to a first access network during an inter-access technology handover from another, second access network. Moreover, the invention relates to a mobile access gateway and a mobile node that participate in this method. First and second access network belong to a network domain offering a network-based mobility function. In order to detect whether a mobile node implements a network-based mobility function a virtual interface discovery is performed by checking whether the mobile node also configures the address according to the home network prefix offered to the mobile node before the handover on its interface to the first access network. In parallel, an address configuration is performed. Based on the detection of whether a virtual interface is implemented at the mobile node, the mobile access gateway may decide whether to use network-based mobility or client-based mobility and change the address configuration.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for traversing metadata across multiple network domains at various layers of the protocol stack
InactiveUS20050122979A1Data processing applicationsData switching by path configurationProtocol stackNetwork segment
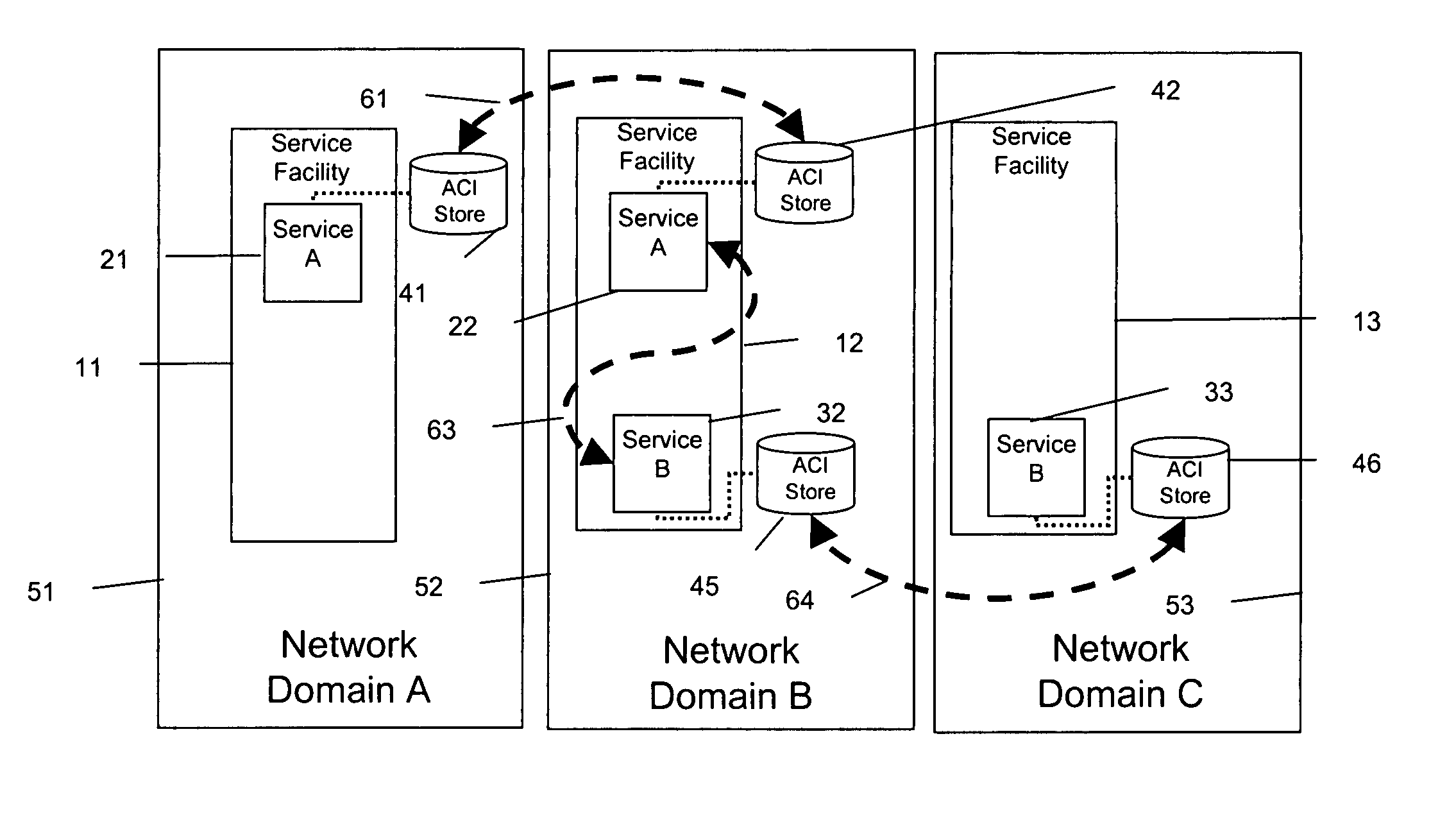
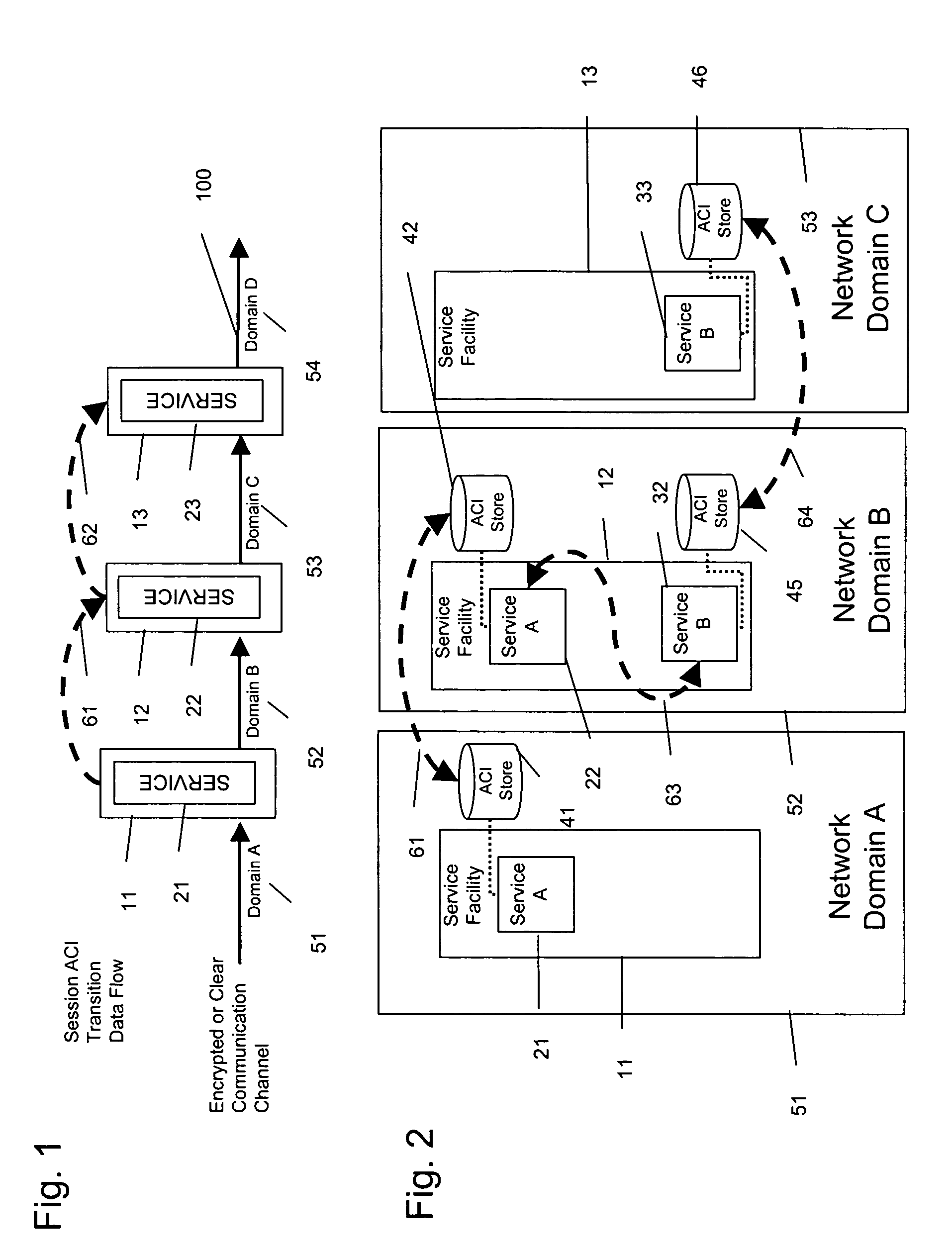
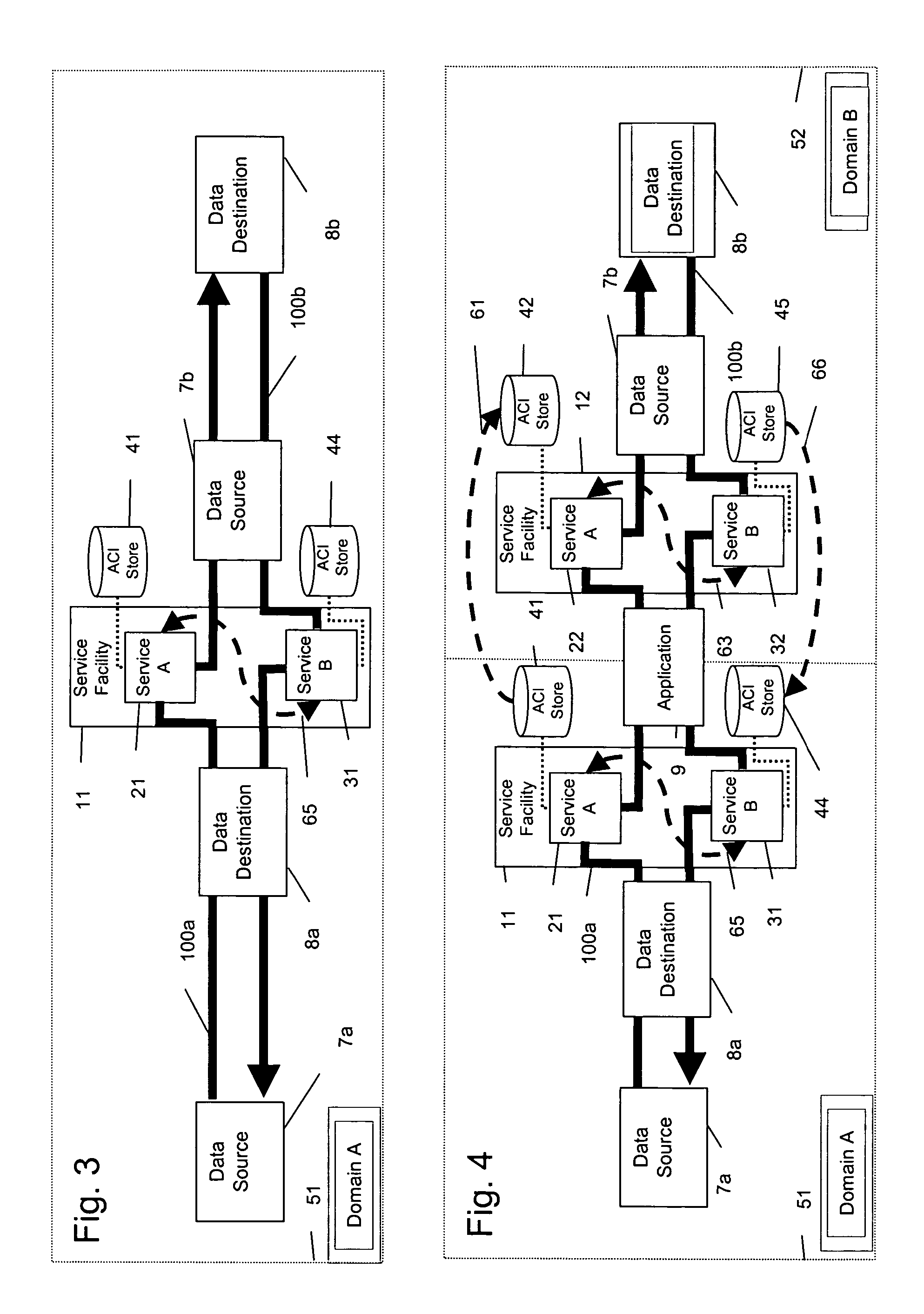
An inter-networking system and method that provides for access control identifier (ACI) metadata utilization for the life of a session even on unknown networks being traversed, allowing for ACI metadata utilization, reutilization, and modification in both the send and receive paths (bi-directional), and allowing for metadata transport over network segments requiring that ACIs be embedded at different layers of the communications stack.
Owner:CRYPTEK INC
Secure virtual network platform for enterprise hybrid cloud computing environments
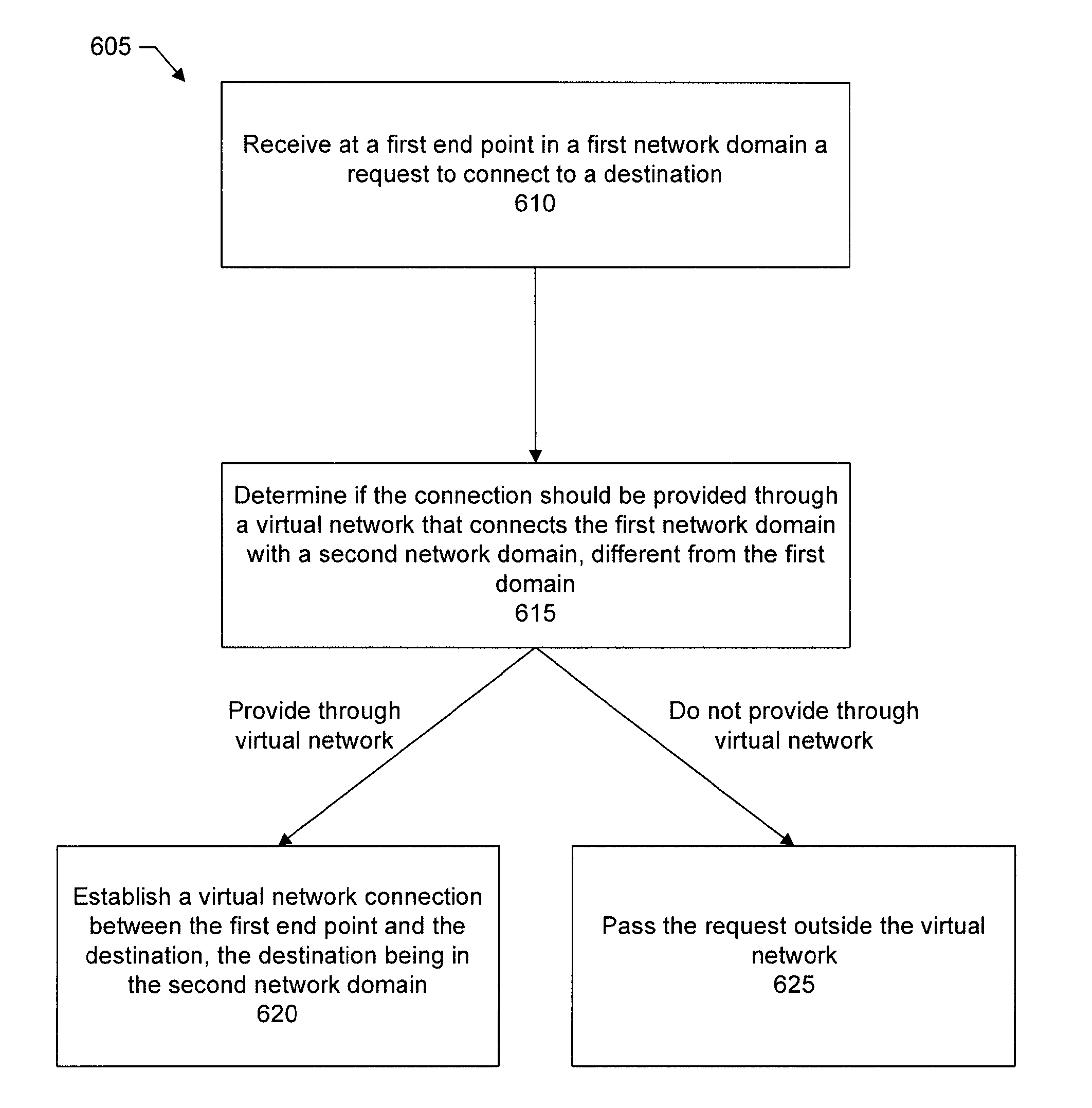
ActiveUS20170064005A1Easy to deployEasy to manageNetworks interconnectionCloud computingNetwork domain
Clusters of virtual network switches (VNS) and controllers are provided. The controller cluster is connected to the VNS cluster which is between first and second network domains. A request is received at a first end point in the first network domain to connect to a second end point in the second network domain. If the connection should be through a virtual network connecting the network domains, a virtual network connection is established as allowed by a controller of the controller cluster. The establishment includes initiating first outbound traffic from the first end point to a VNS of the VNS cluster and initiating second outbound traffic from the second end point to the VNS. The VNS places a payload from the first outbound traffic into a reply to the second outbound traffic
Owner:ZENTERA SYST
Key management for network elements
ActiveUS20070160201A1Reduce in quantityLow costKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationSecurity parameterMaster key
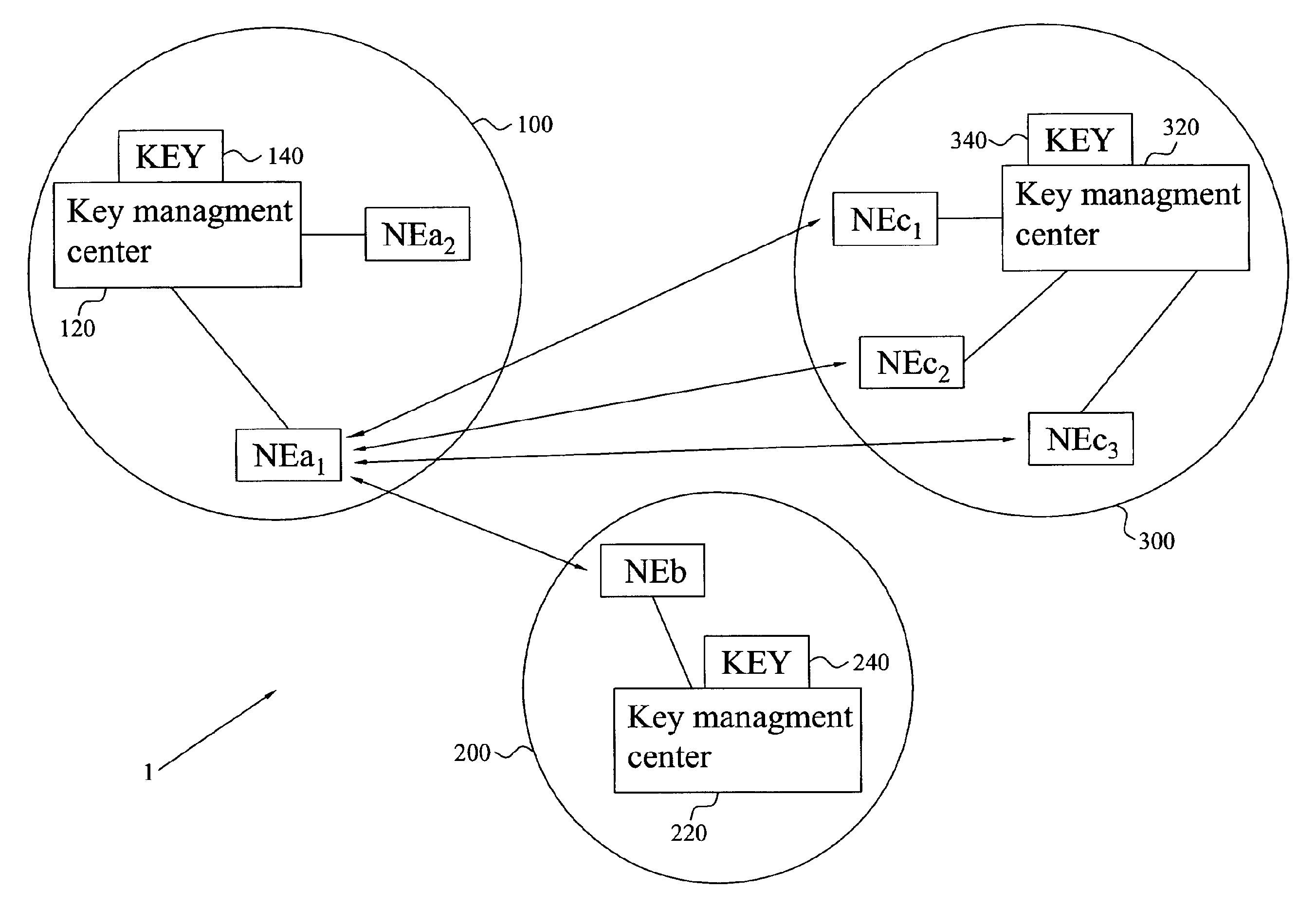
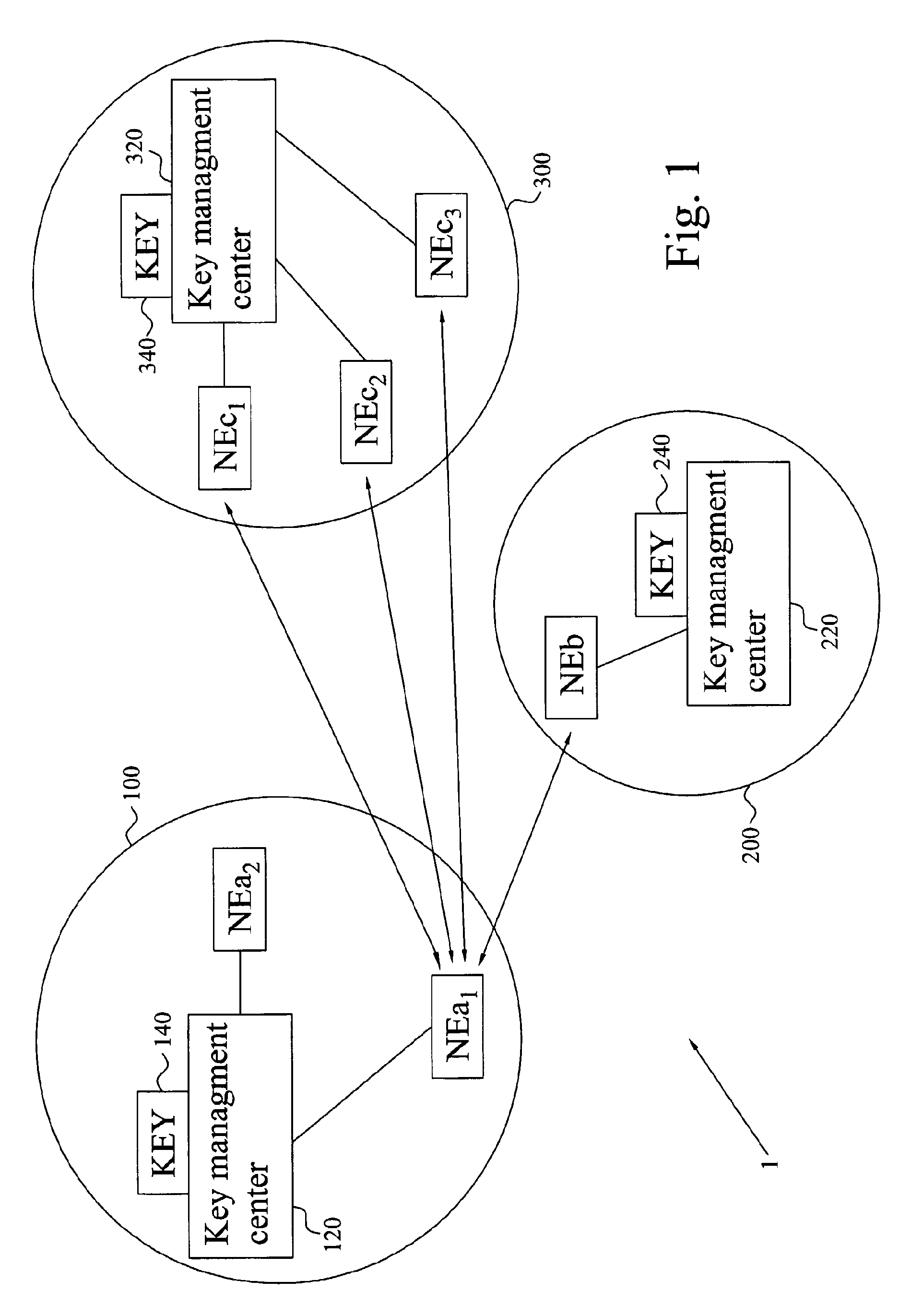
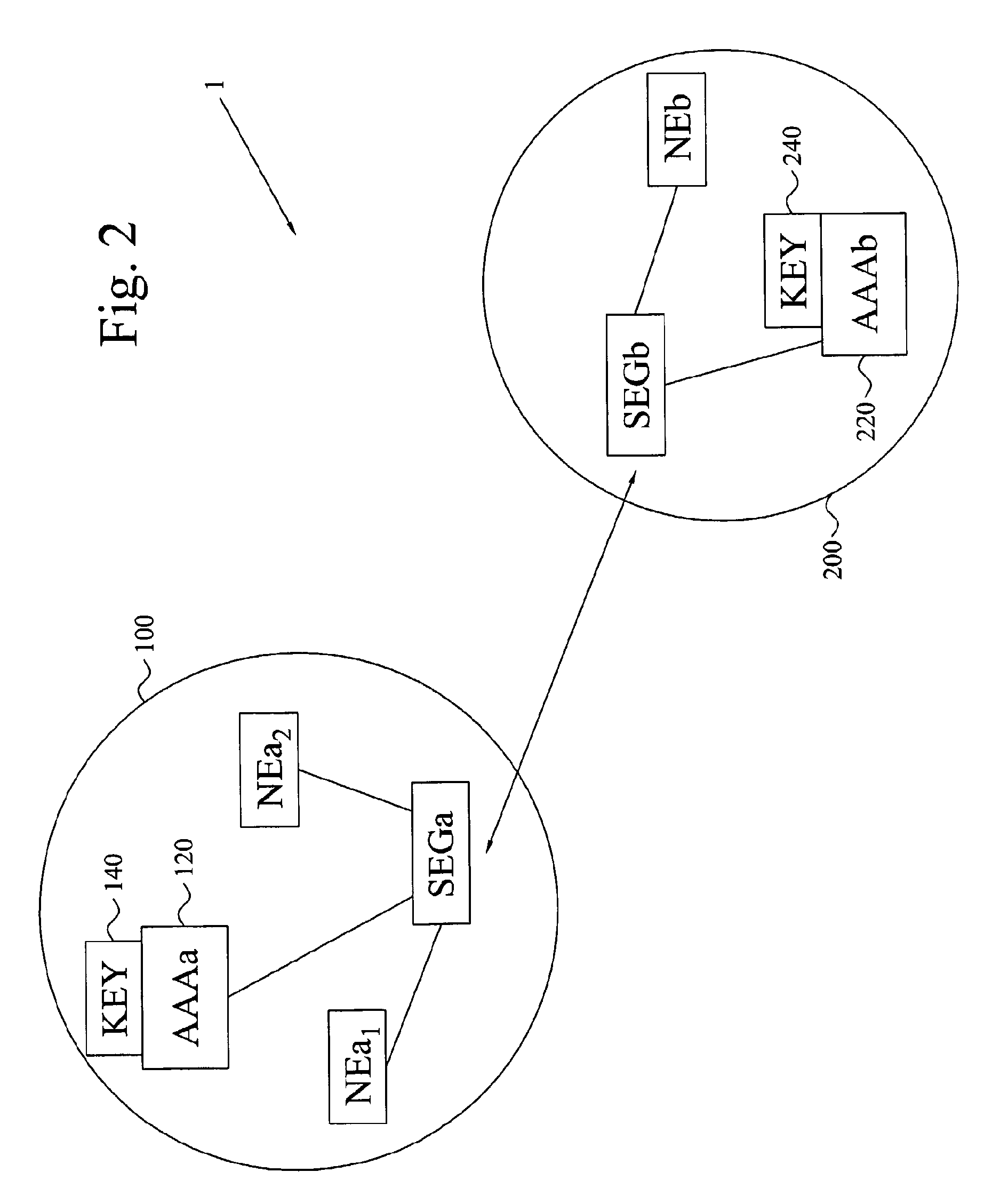
The invention provides an establishment of a secret session key shared Between two network elements (NEa, NEb) belonging to different network domains (NDa, NDb). A first network element (NEa) of a first network domain (NDa) requests security parameters from an associated key management center (KMC) (AAAa). Upon reception of the request, the KMC (AAAa) generates a freshness token (FRESH) and calculates the session key (K) based on this token (FRESH) and a master key (KAB) shared with a second network domain (NDb). The security parameters are (securely) provided to the network element (NEa), which extracts the session key (K) and forwards the freshness token (FRESH) to the KMC (AAAb) of the second domain (NDb) through a second network element (NEb). Based on the token (FRESH) and the shared master key (KAB), the KMC (AAAb) generates a copy of the session key (K), which is (securely) provided to the second network element (NEb). The two network elements (NEa, NEb) now have shares the session key (K), enabling them to securely communicate with each other.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Secure virtual network platform for enterprise hybrid cloud computing environments
ActiveUS9525564B2Easy to deployEasy to manageDigital computer detailsNetworks interconnectionCloud computingNetwork domain
Owner:ZENTERA SYST
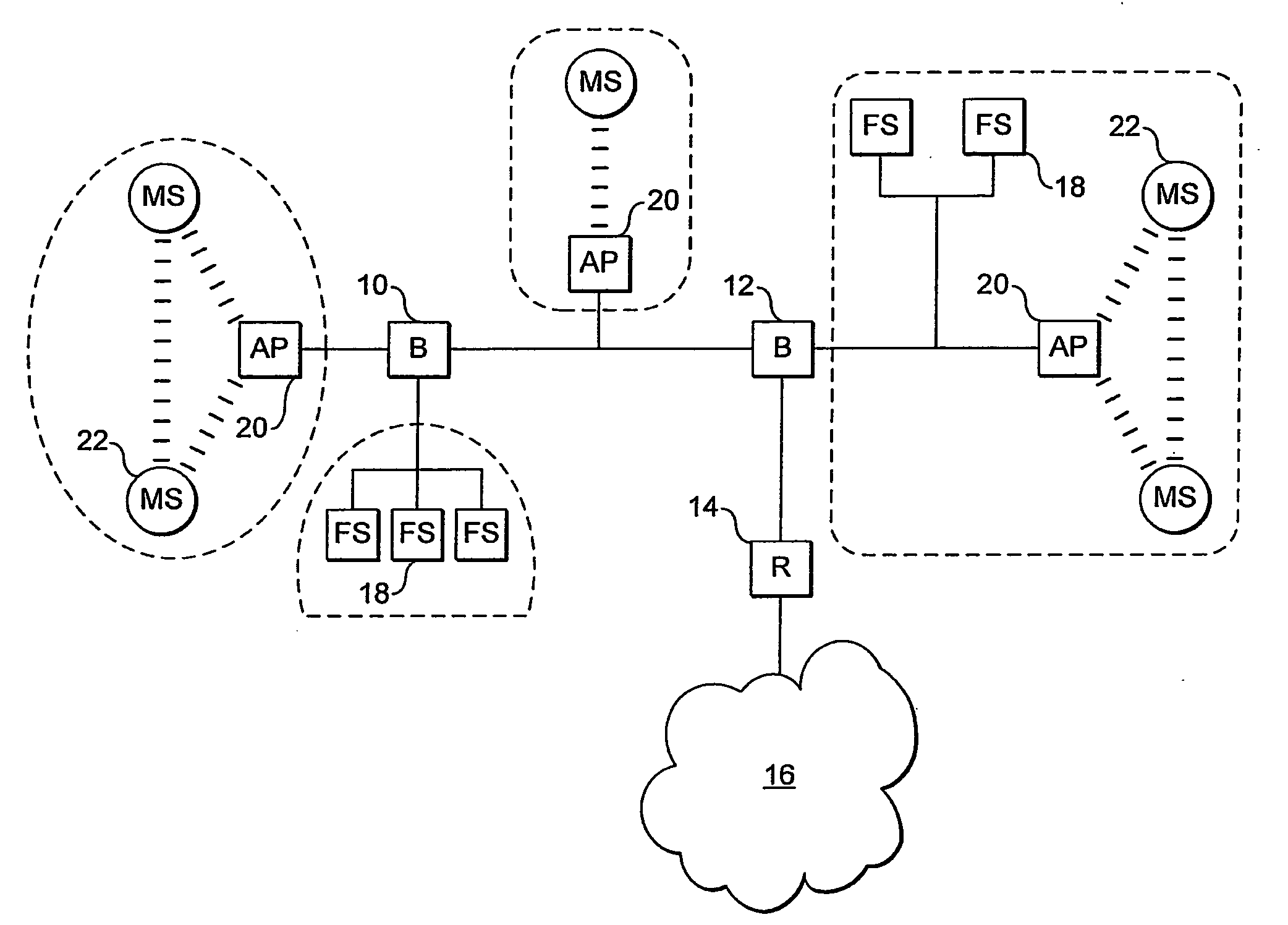
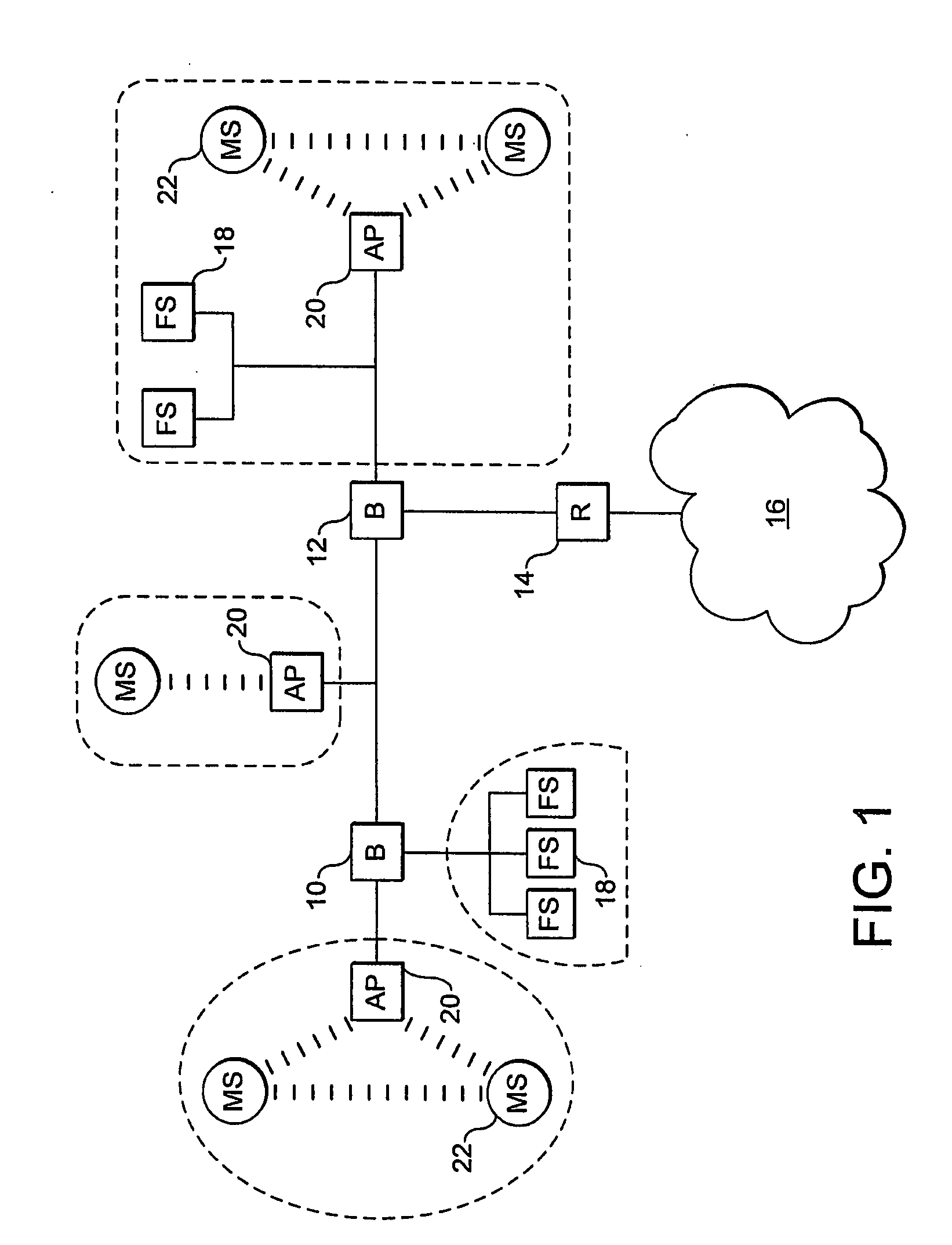
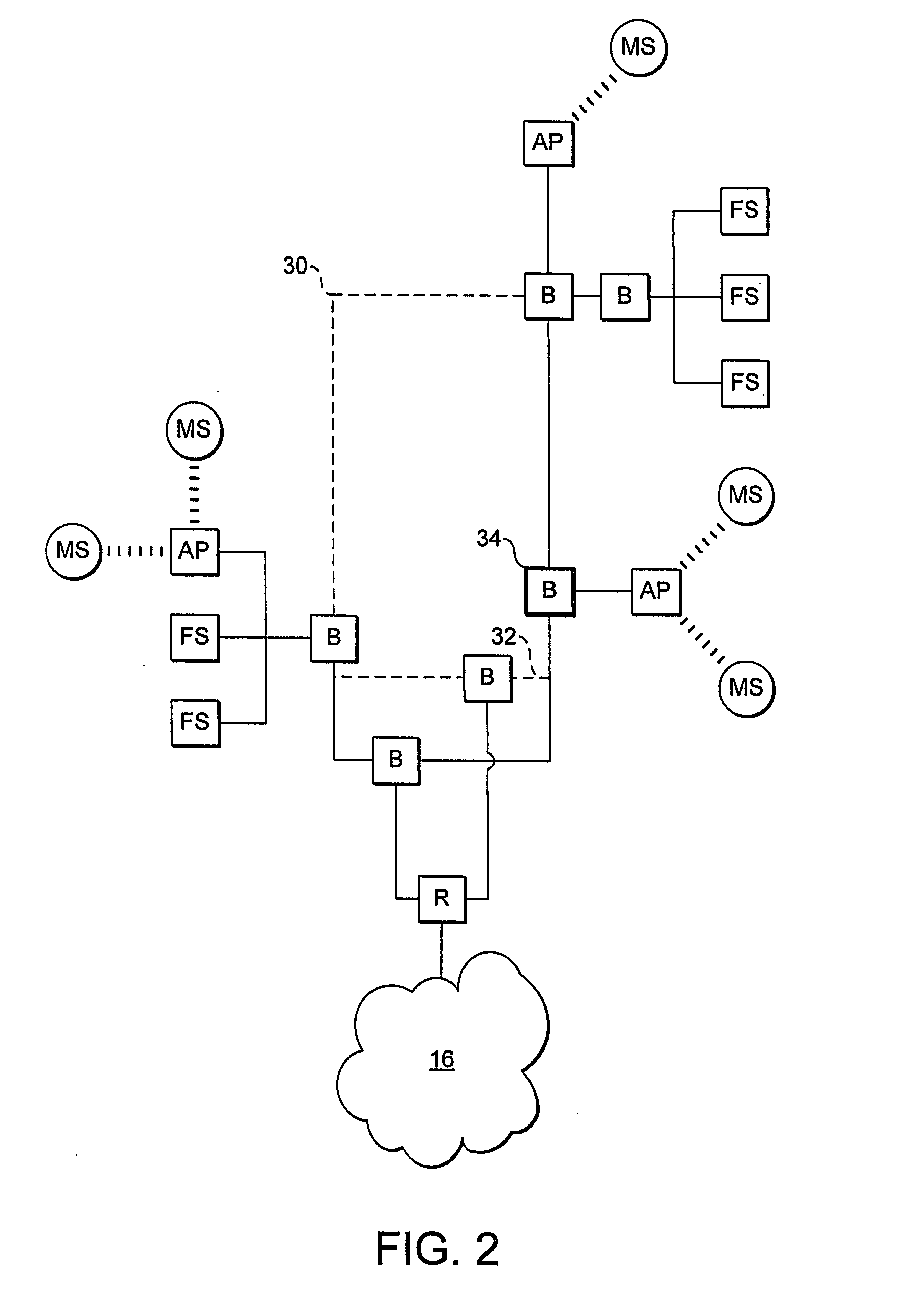
Roaming Network Stations Using A Mac Address Identifier To Select New Access Point
There is disclosed a method of helping mobile stations such as voice over IP devices to roam between wireless access points, by each access point transmitting the MAC address of a spanning tree algorithm root switch of the local network domain. This MAC address is used by mobile stations to detect if two access points are in a common network domain.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS (RES & DEV) LTD
Method and apparatus for distributing and updating private keys of multicast group managers using directory replication
InactiveUS7103185B1Optimize allocationKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesGroup sessionSecure multicast
An approach for establishing secure multicast communication among multiple multicast proxy service nodes is disclosed. The multicast proxy service nodes, which can be distributed throughout an enterprise domain, are organized in a logical tree that mimics the logical tree arrangement of domains in a directory server system. The attributes of the multicast proxy service nodes include the group session key and the private keys of the multicast proxy service nodes that are members of the multicast or broadcast groups. The private keys provide unique identification values for the multicast proxy service nodes, thereby facilitating distribution of such keys. Because keys as well as key version information are housed in the directory, multicast security can be achieved over any number of network domains across the entire enterprise. Key information is stored in, and the logical tree is supported by, a directory service. Replication of the directory accomplishes distribution of keys. Multicast proxy service nodes may obtain current key information from a local copy of the replicated directory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
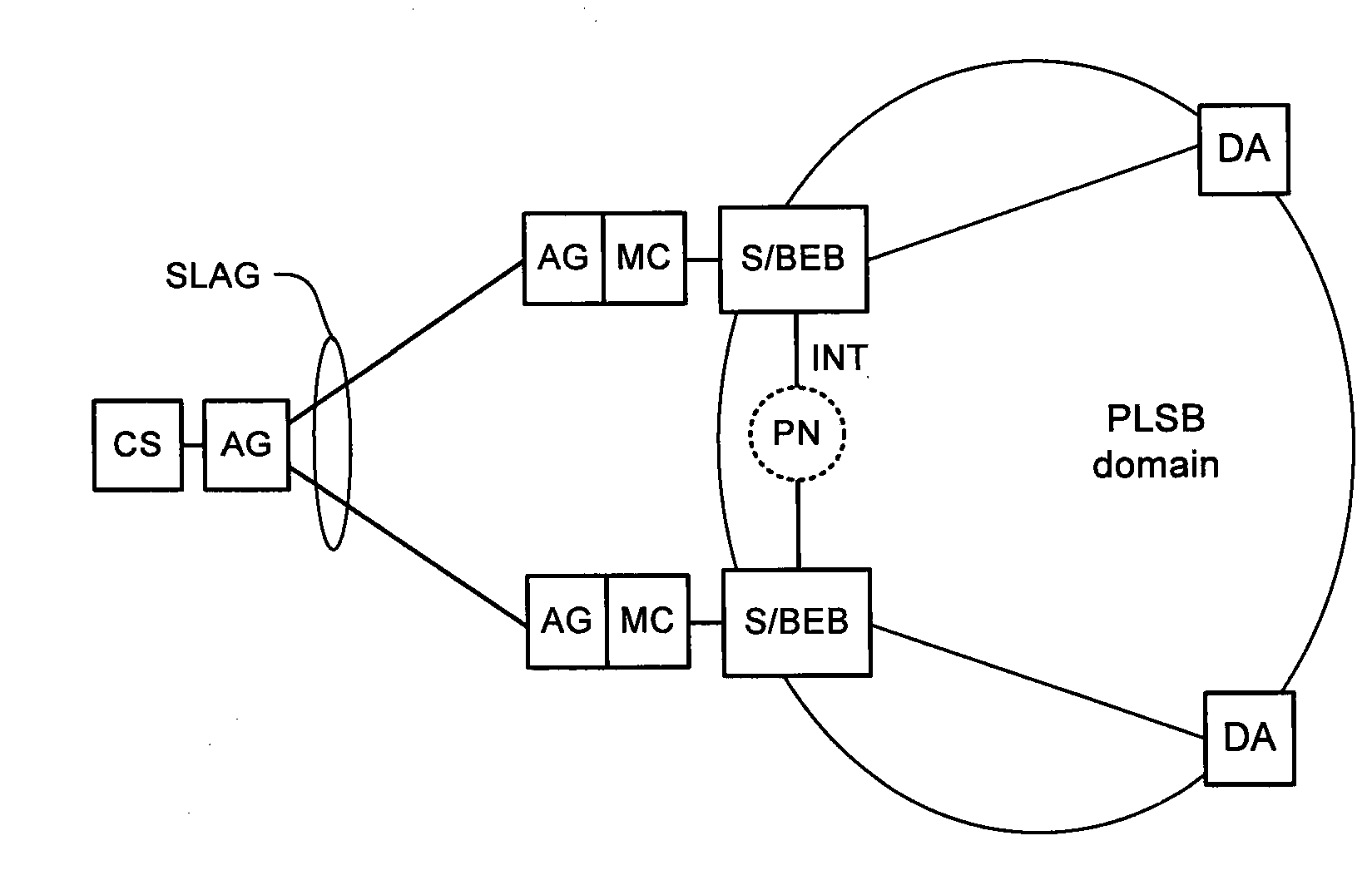
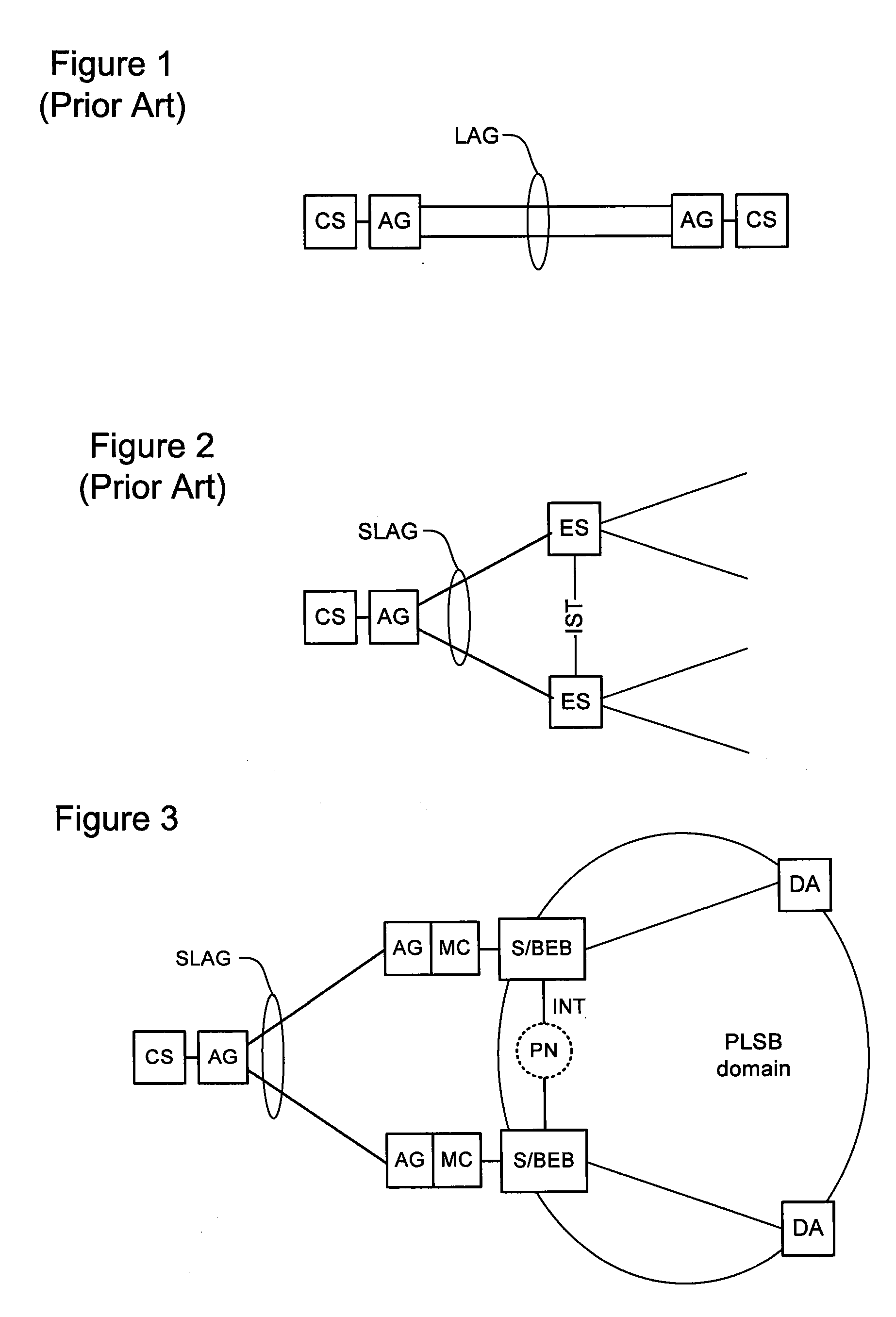
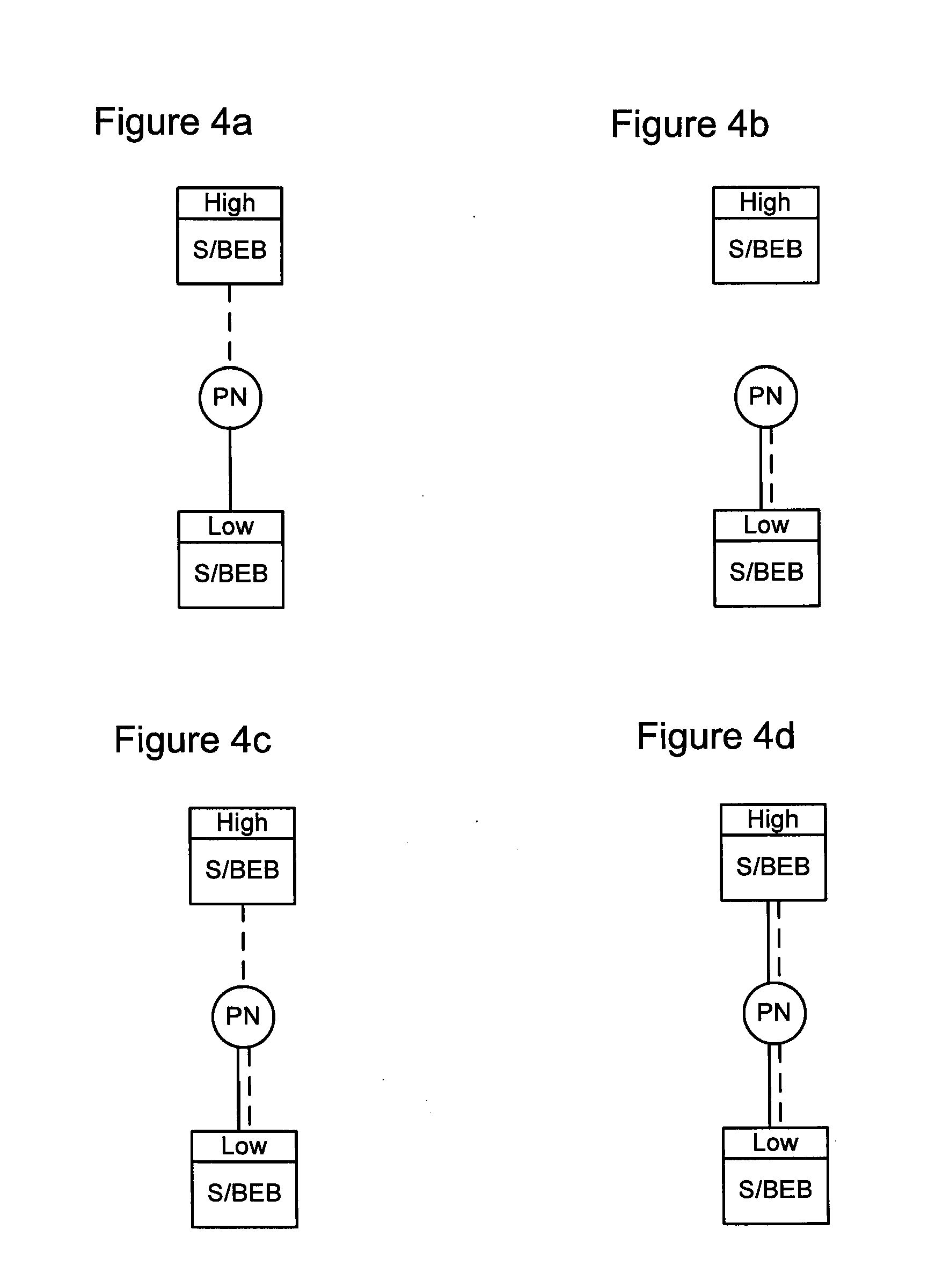
Resilient attachment to provider link state bridging (PLSB) networks
A method system for interfacing a client system in a first network domain with a Provider Link State Bridging (PLSB) network domain. At least two Backbone Edge Bridges (BEBs) of the PLSB domain 20 are provided. Each BEB is an end-point of a connection in the first network domain to the client system and an end-point of at least a unicast path defined within the PLSB domain 20. An inter-node trunk is provided in the PLSB domain 20 for interconnecting the at least two BEBs. A phantom node is defined in the PLSB domain 20. The phantom node has a unique address in the PLSB domain 20 and is notionally located on the inter-node trunk one hop from each of the BEBs. Each of the BEBs is configured such that: an ingress packet received from the client system via the connection in the first network domain is forwarded through a path notionally rooted at the phantom node; and an egress subscriber packet destined for the client system is forwarded to the client system through the connection in the first network domain.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com