Adaptive message routing for mobile ad hoc networks
a message routing technology, applied in the field of message routing protocol for mobile ad hoc network, can solve the problems of increasing control overhead in the network, zrp is not readily adaptable to rapid changes in network topology, physical partition of subnets, hardware/spectrum changes,
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
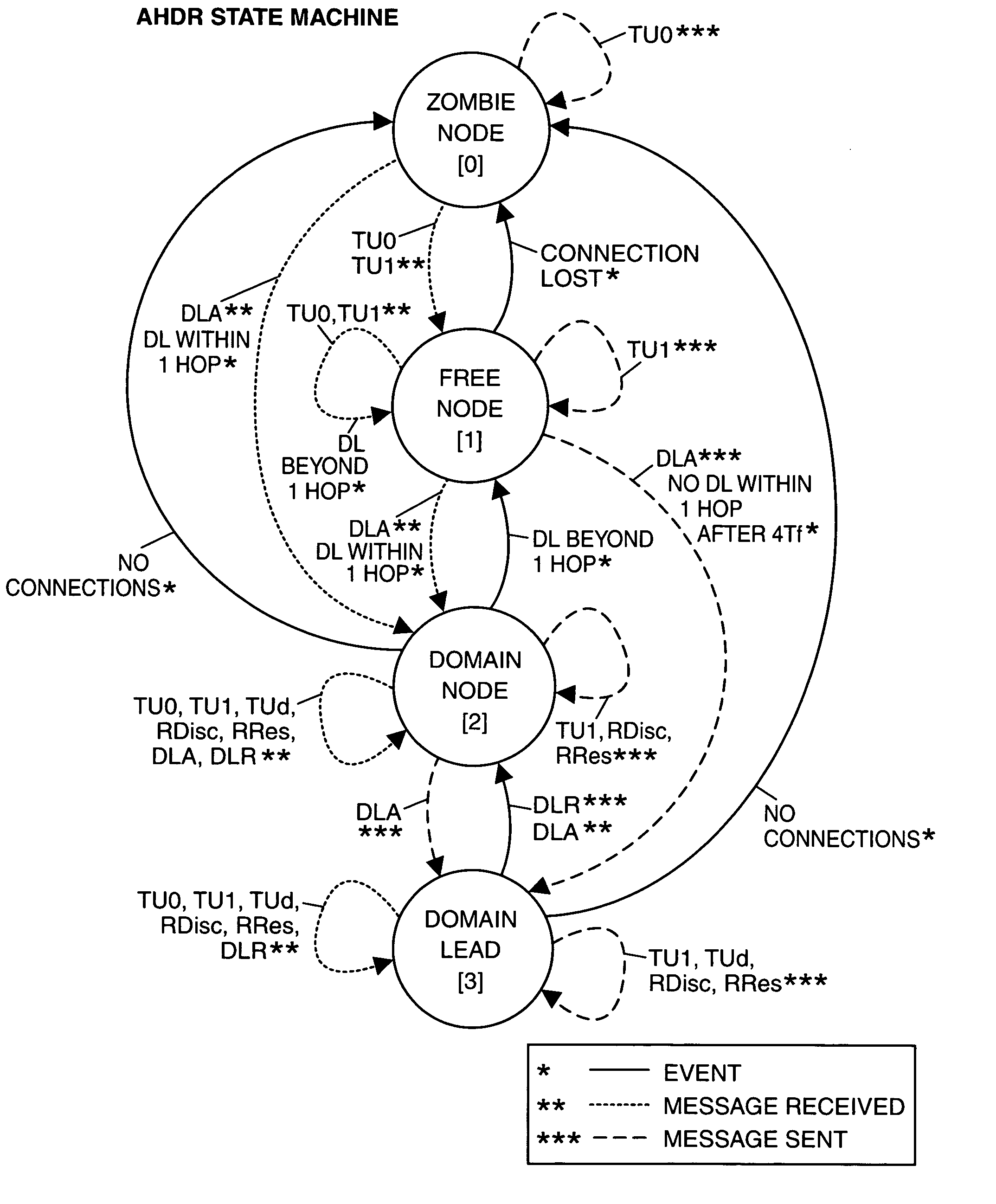
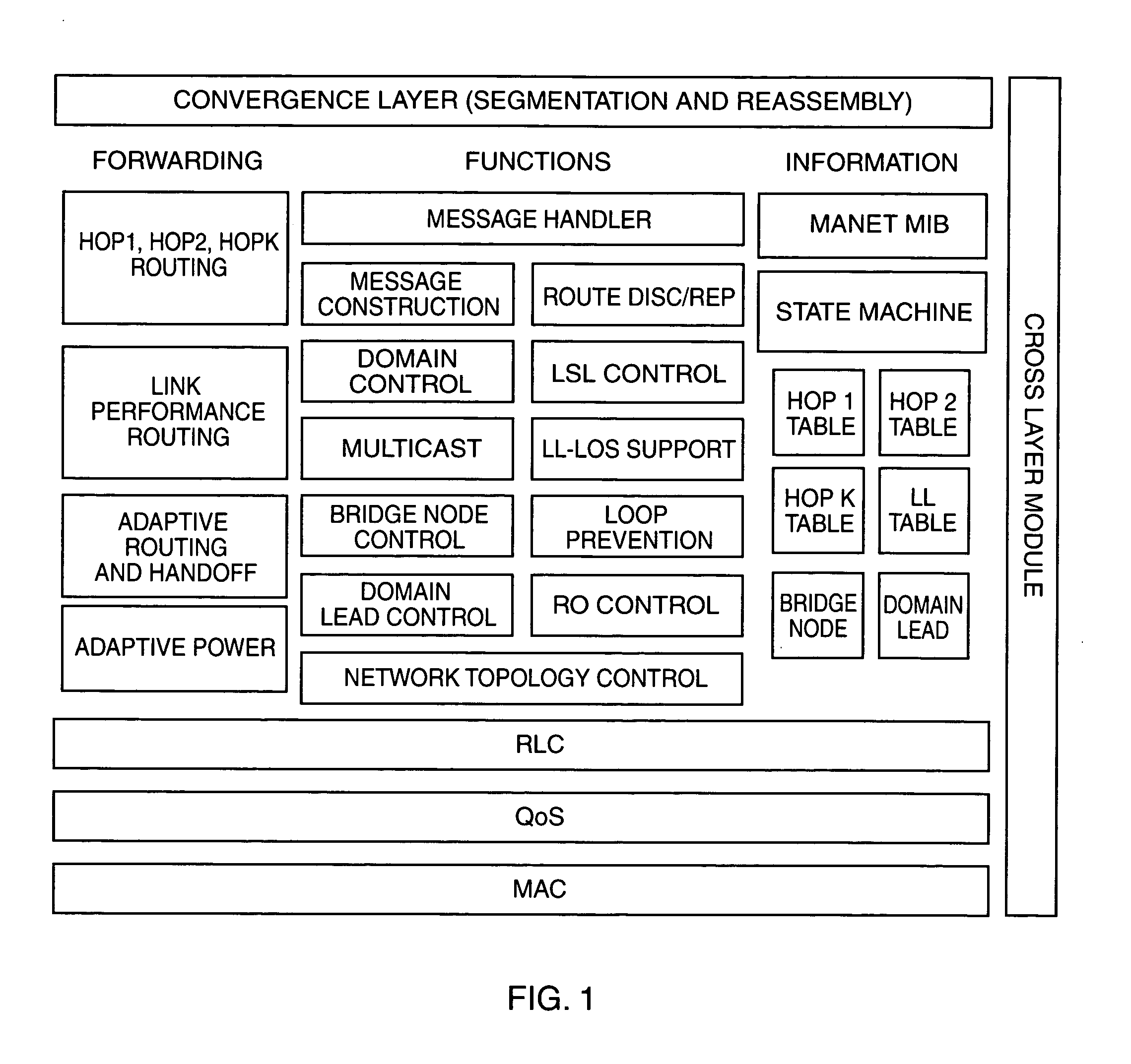
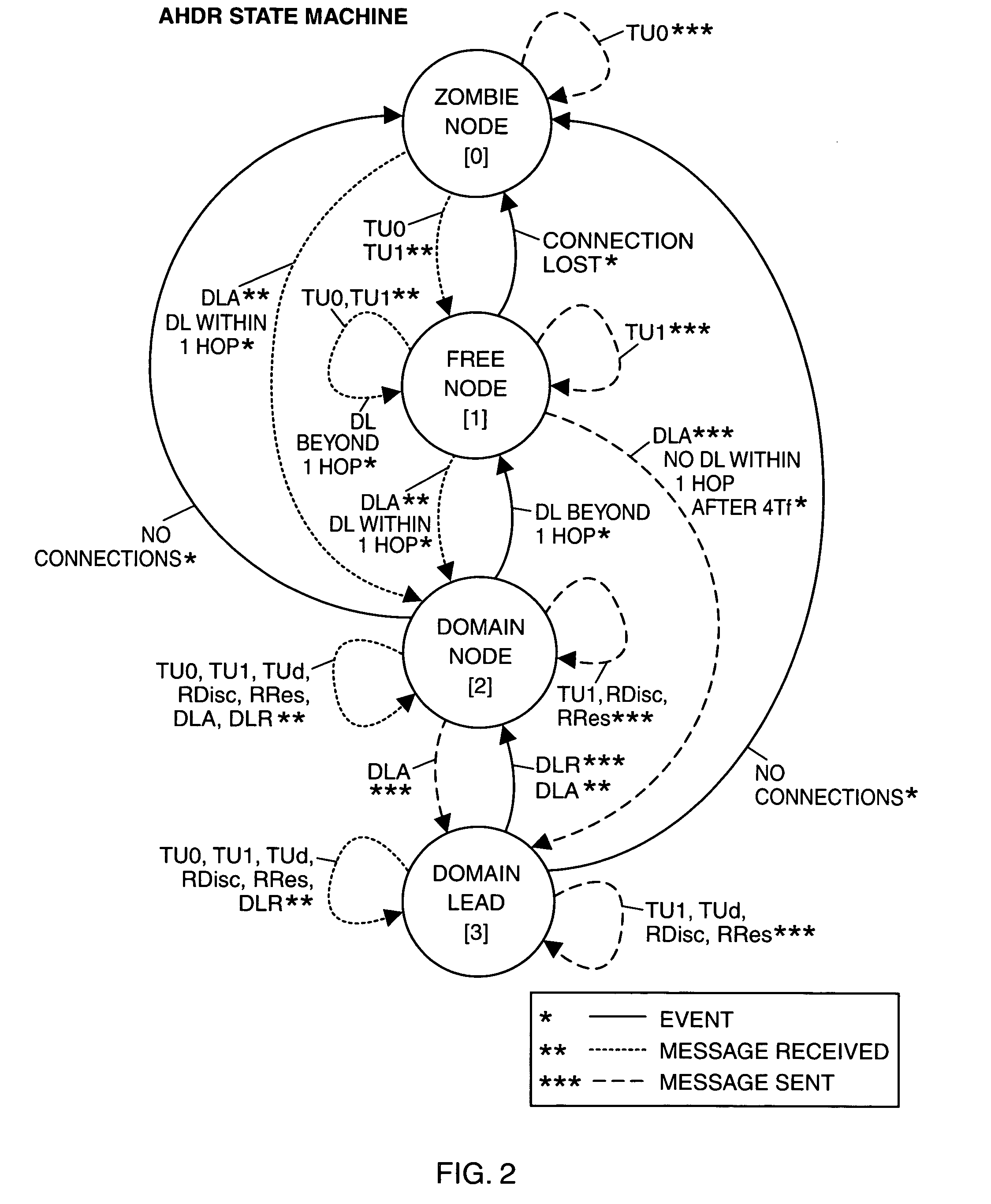
[0037]The present invention concerns a network message routing protocol for use in mobile ad hoc networks (MANETs), especially MANETs deployed in tactical environments wherein the node topology of the network may change rapidly. Referred to herein as adaptive hybrid domain routing (AHDR), the protocol combines proactive and reactive components in such a manner that each node entering the network can readily obtain a current optimal route for messages destined to any other node in the network.
[0038]Basically, AHDR operates by forming a number of network domains each of which contains at least two nodes including a designated domain lead (DL) node. The nodes in each domain proactively exchange local routing information with one another at regular intervals. In addition, all DL nodes in the network inform one another periodically of the node topology in their respective domains. The rates at which the topology information is exchanged may also vary in order to minimize network control ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com