Patents
Literature
179 results about "Message integrity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition of: message integrity. message integrity. The validity of a transmitted message. Message integrity means that a message has not been tampered with or altered. The most common approach is to use a hash function that combines all the bytes in the message with a secret key and produces a message digest that is difficult to reverse.
System and method for secure electronic communication services
InactiveUS20090198997A1Easy accessSecure transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageScalable systemEmail address
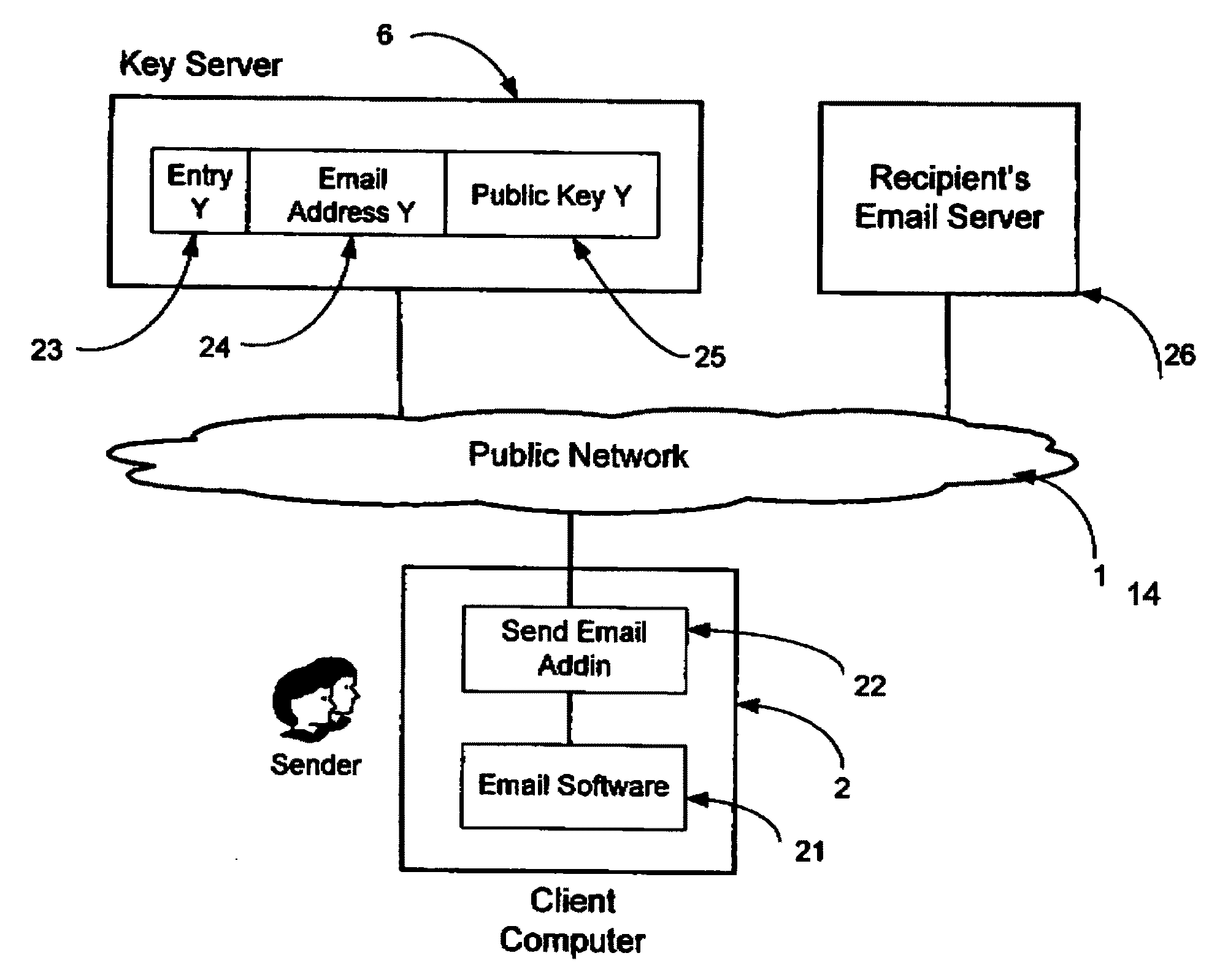
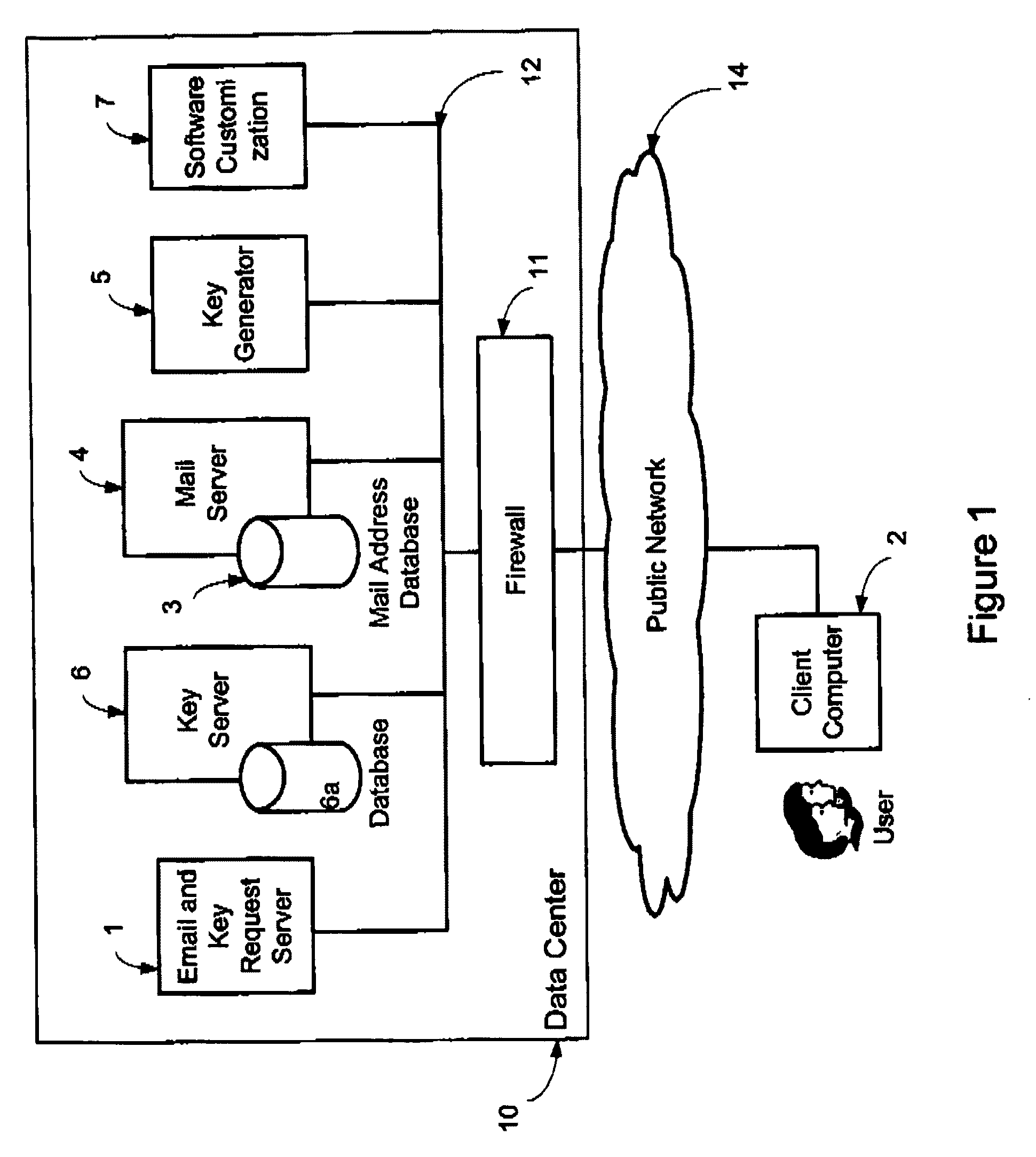
A system, method and software module for secure electronic communication services, wherein a public key (25) of private-public-key pair (30,25) is associated with an email address (24), internet name or other registered unique identifier; the registered user of the unique identifier holds the private-key (30) securely, and the respective public-key (25) is made accessible on a key server (6) for look-up and retrieval by other users, for encryption of communications to be sent to the holder of the private-key, and optionally for message confidentiality, message integrity and authentication of sender and recipient, without requiring certificates. A distributed and scalable system is provided by a server network (600; 401, 501) for registration, key distribution and management preferably using a kDNS server hierarchy (601,602,603) or a key-DNS server hierarchy (701,702,) and associated protocols so that public-keys of recipients can be searched and retrieved over the internet based on the recipients email address or other unique identifier, thus facilitating secure communication between users in different network domains and organizations.
Owner:TOPOSIS CORP
Authentication mechanisms for call control message integrity and origin verification
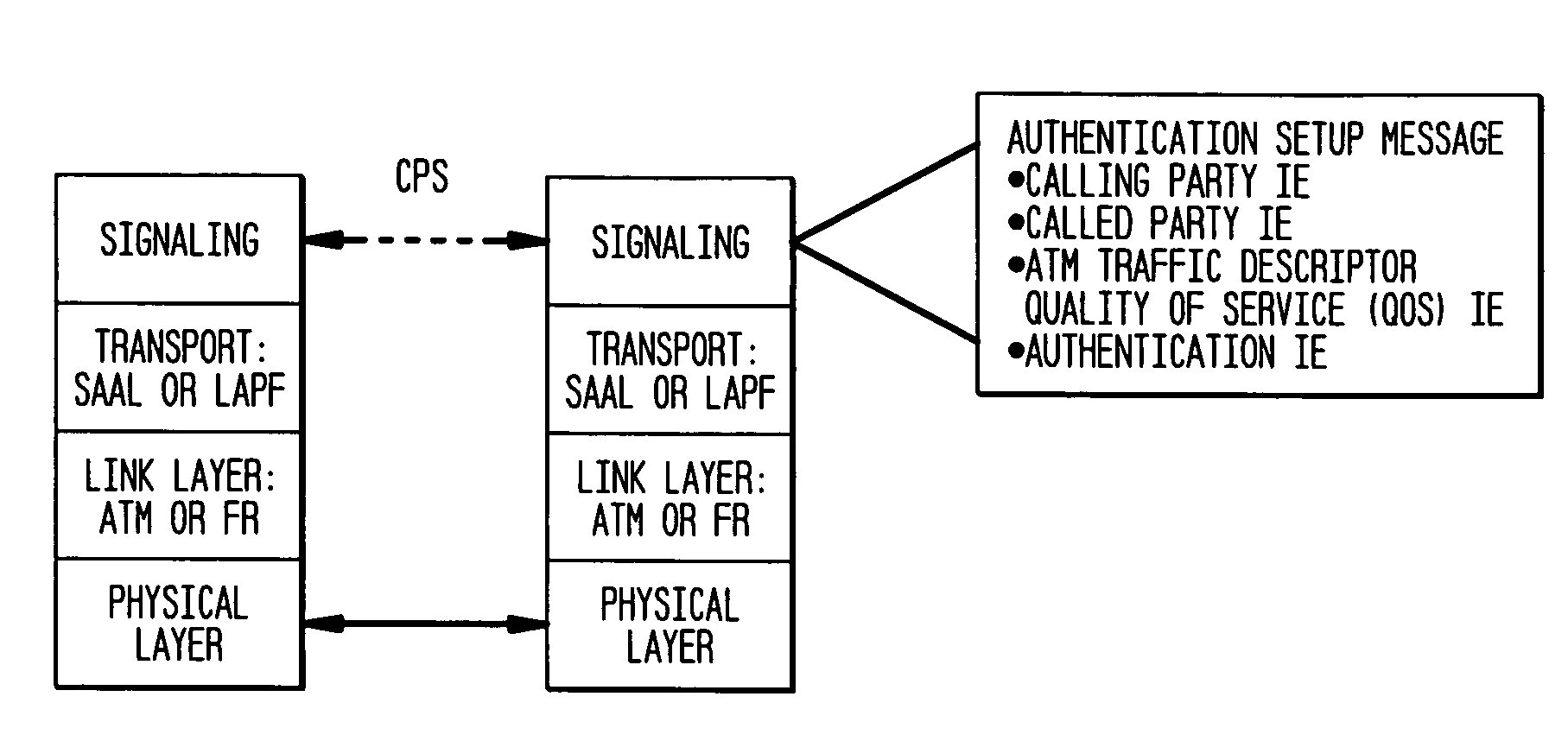
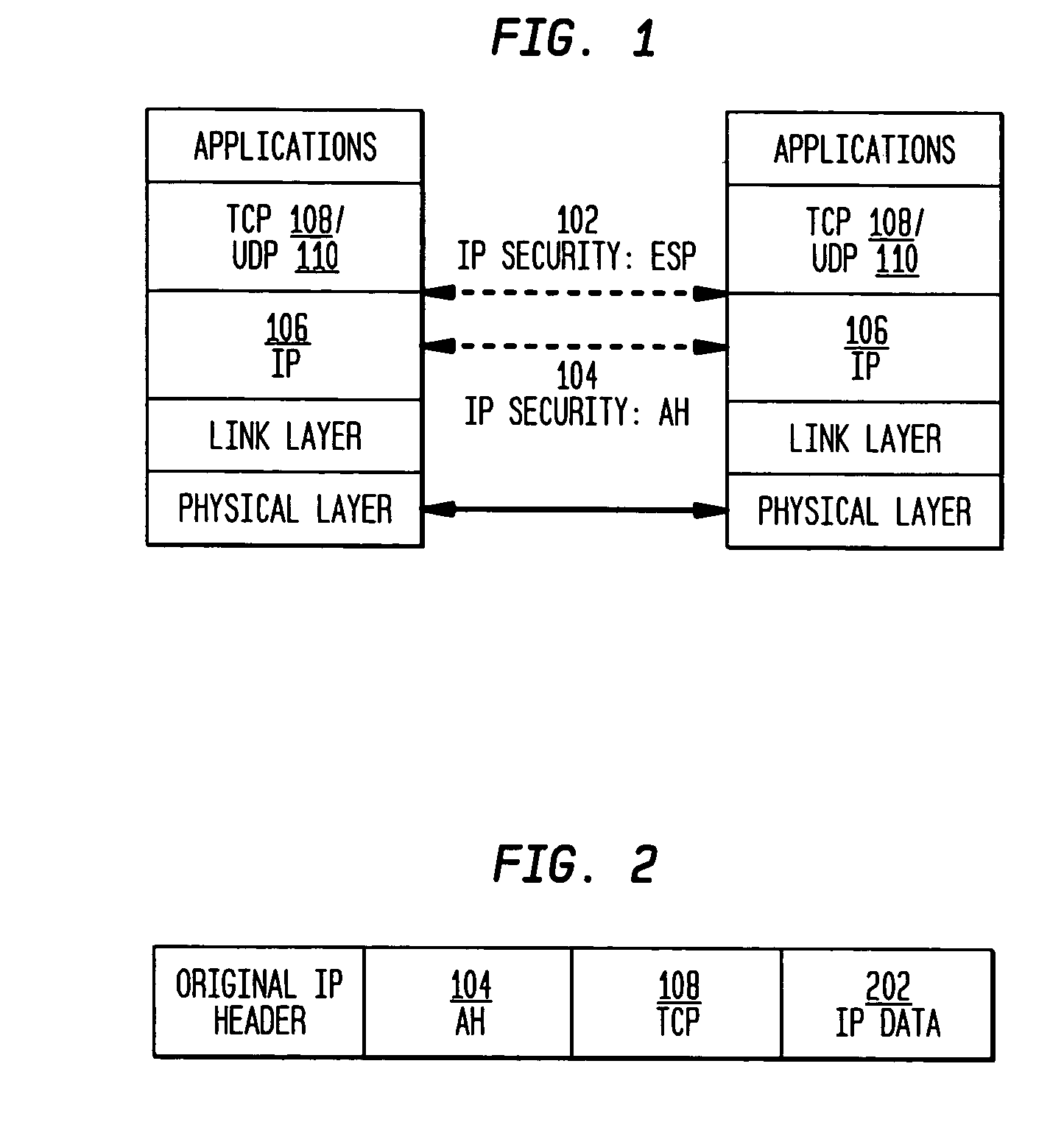
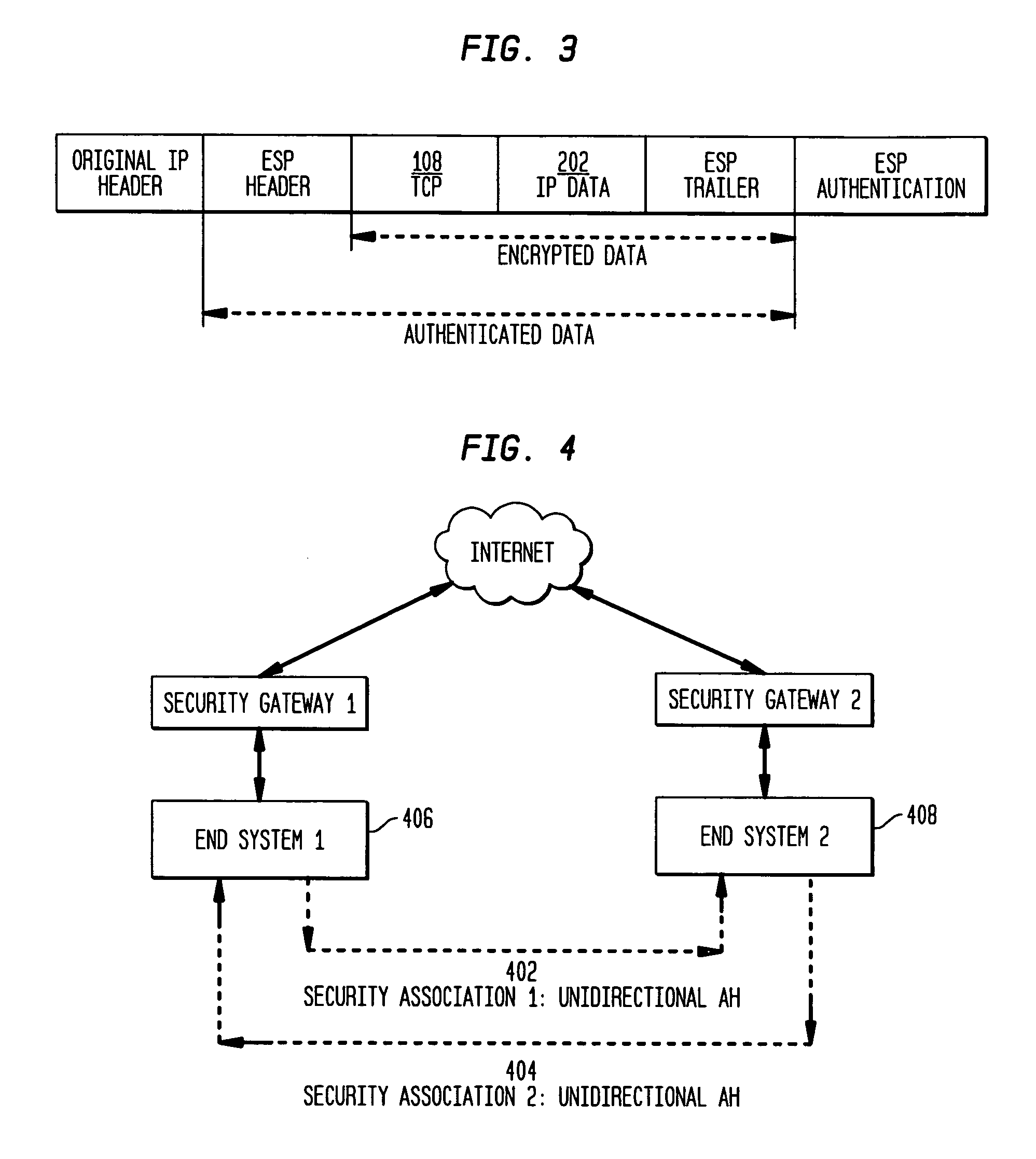
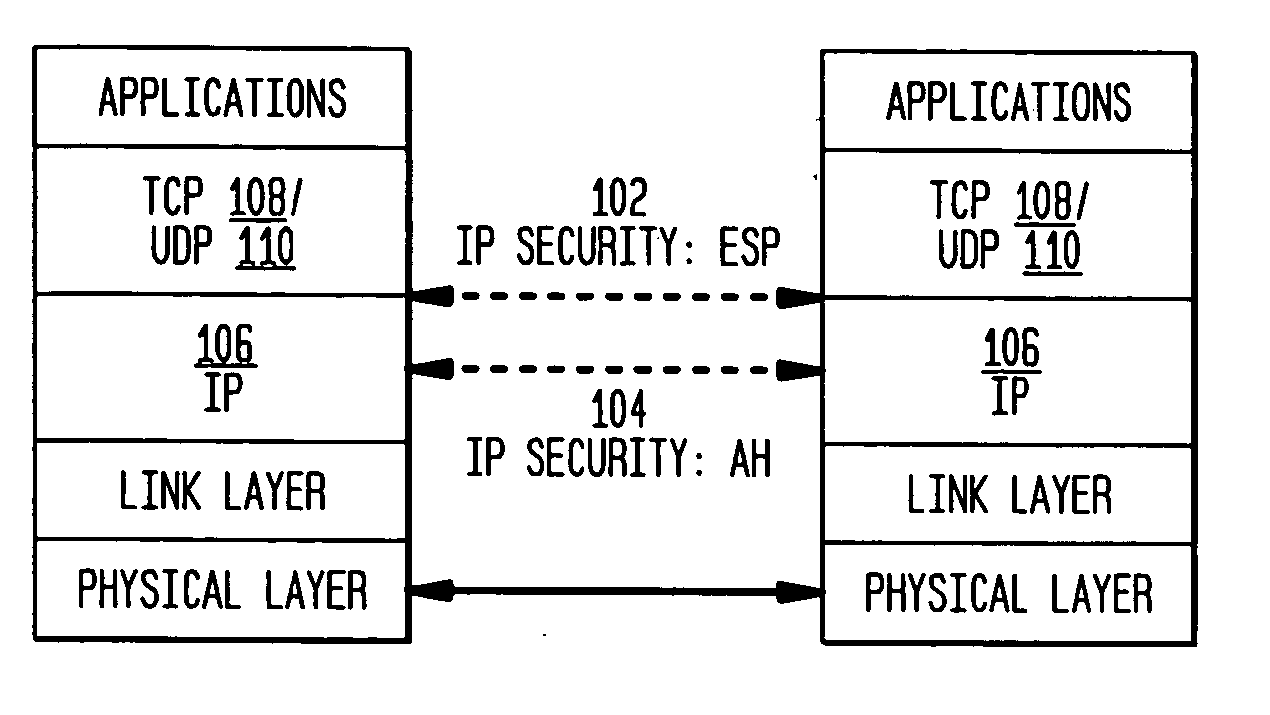
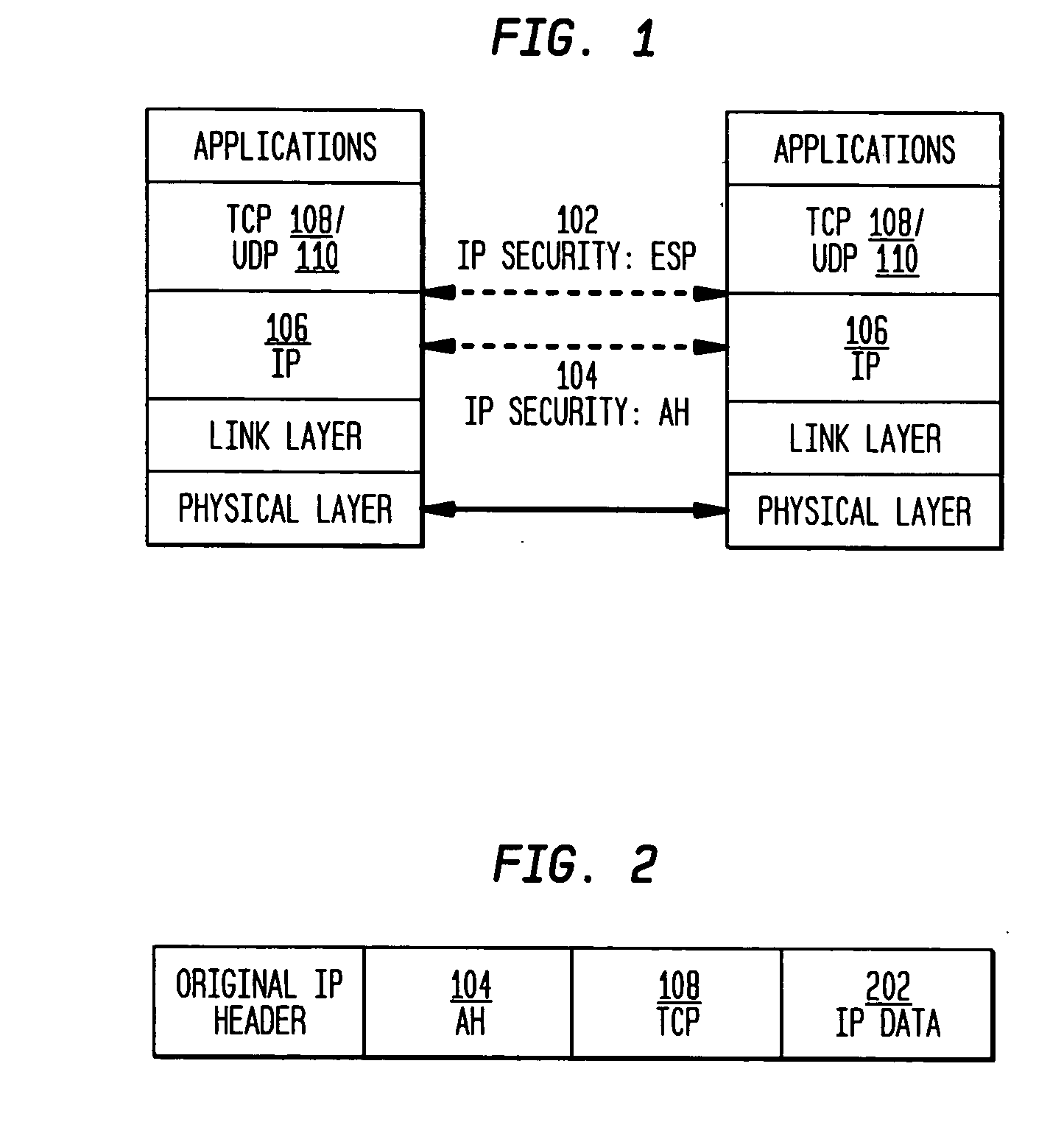
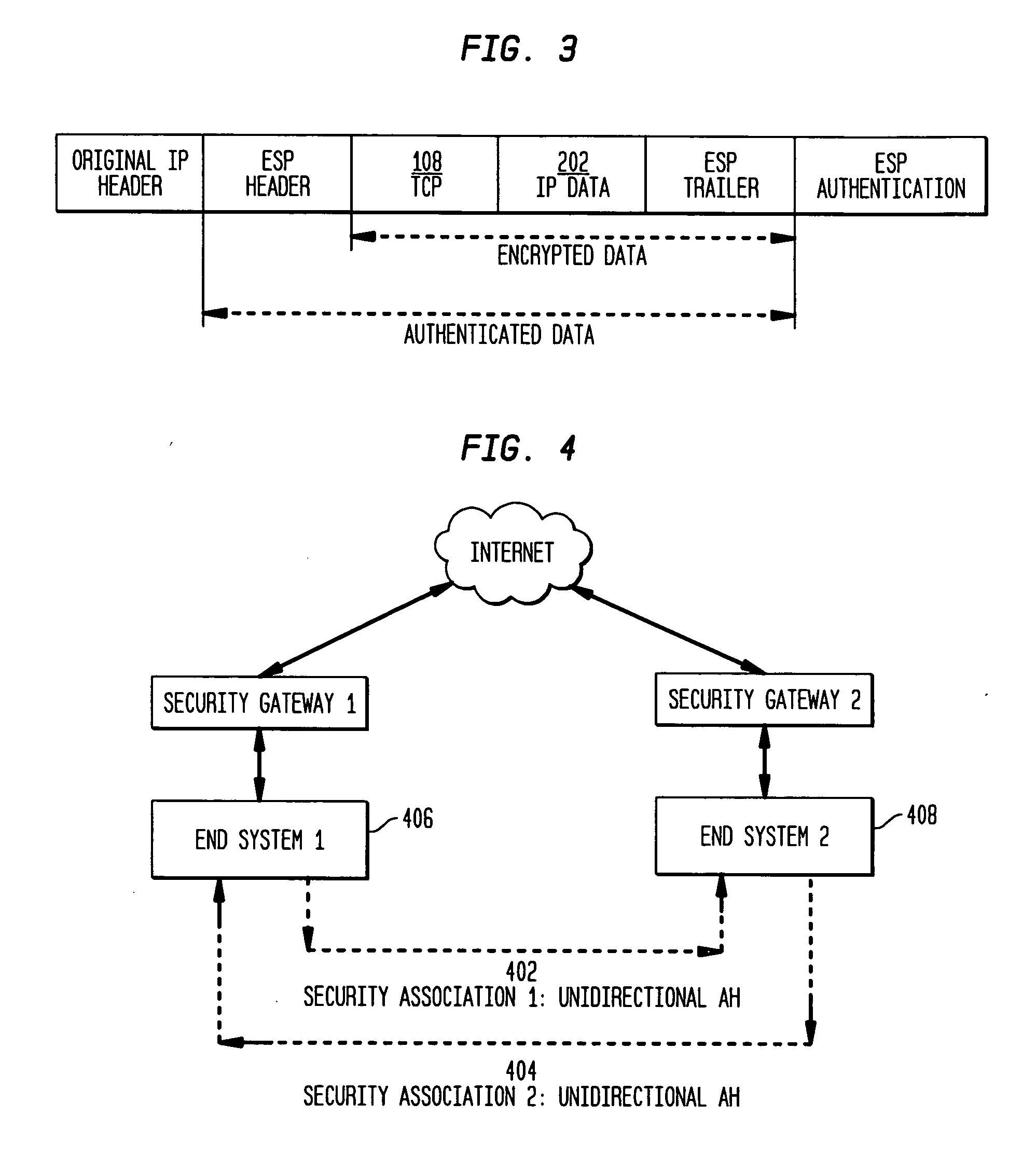
The present invention incorporates methodologies developed in the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Internet Protocol Security (IPSEC) Working Group into asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) and frame relay (FR) signaling to provide message integrity and origin authentication. In one implementation the invention provides a virtual private network (VPN) infrastructure with call control message integrity, origin verification, and transit network filtering. The invention utilizes a set of control plane messages based on the IPSEC authentication header (AH) methodology to provide these security mechanisms for ATM and FR network switching equipment and signaling protocols. This abstract itself is not intended to limit the scope of this patent. The scope of the present invention is pointed out in the appending claims.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
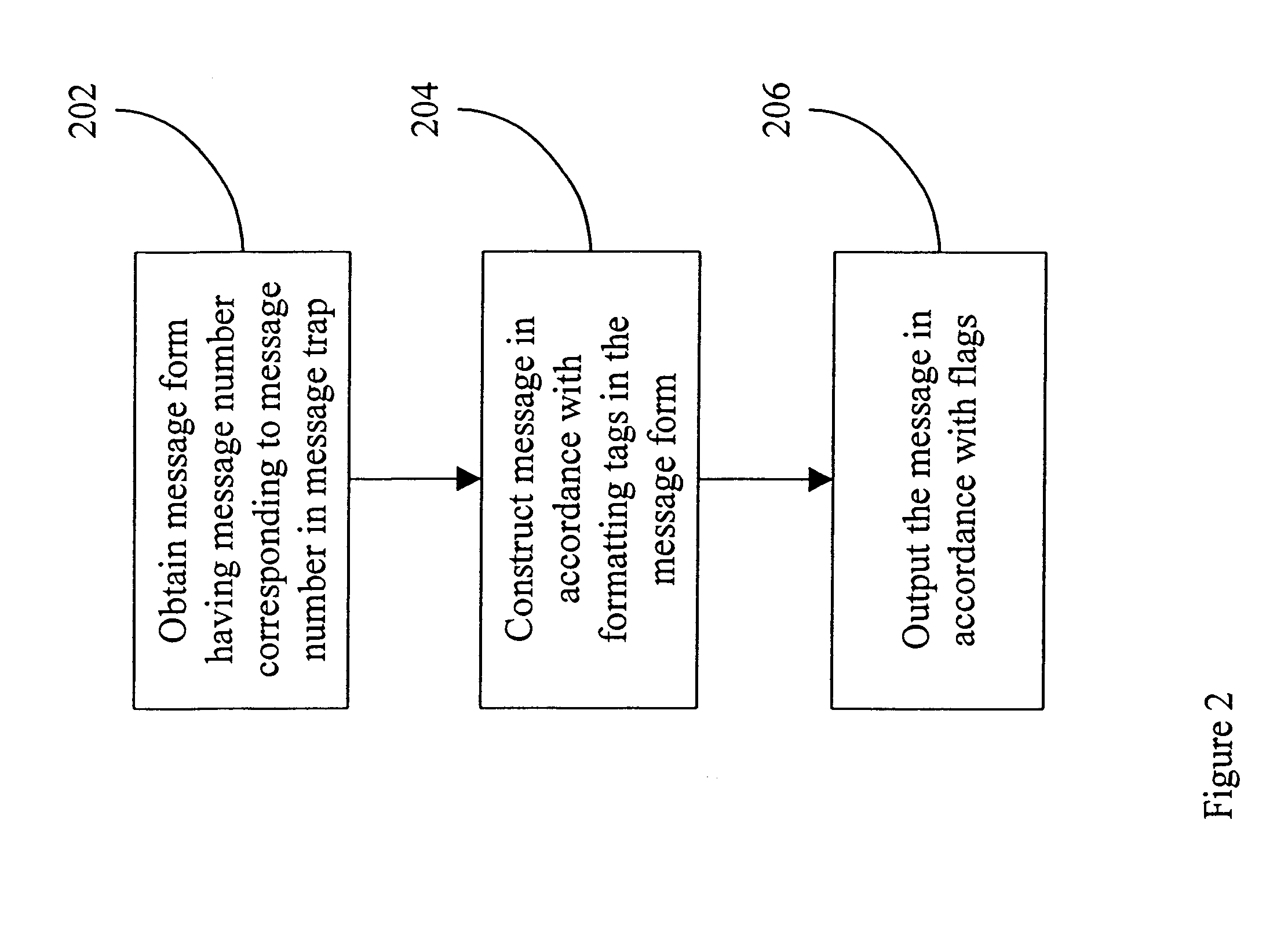
System and method for message handling
InactiveUS6735721B1Multiprogramming arrangementsNon-redundant fault processingComputer hardwareMessage handling
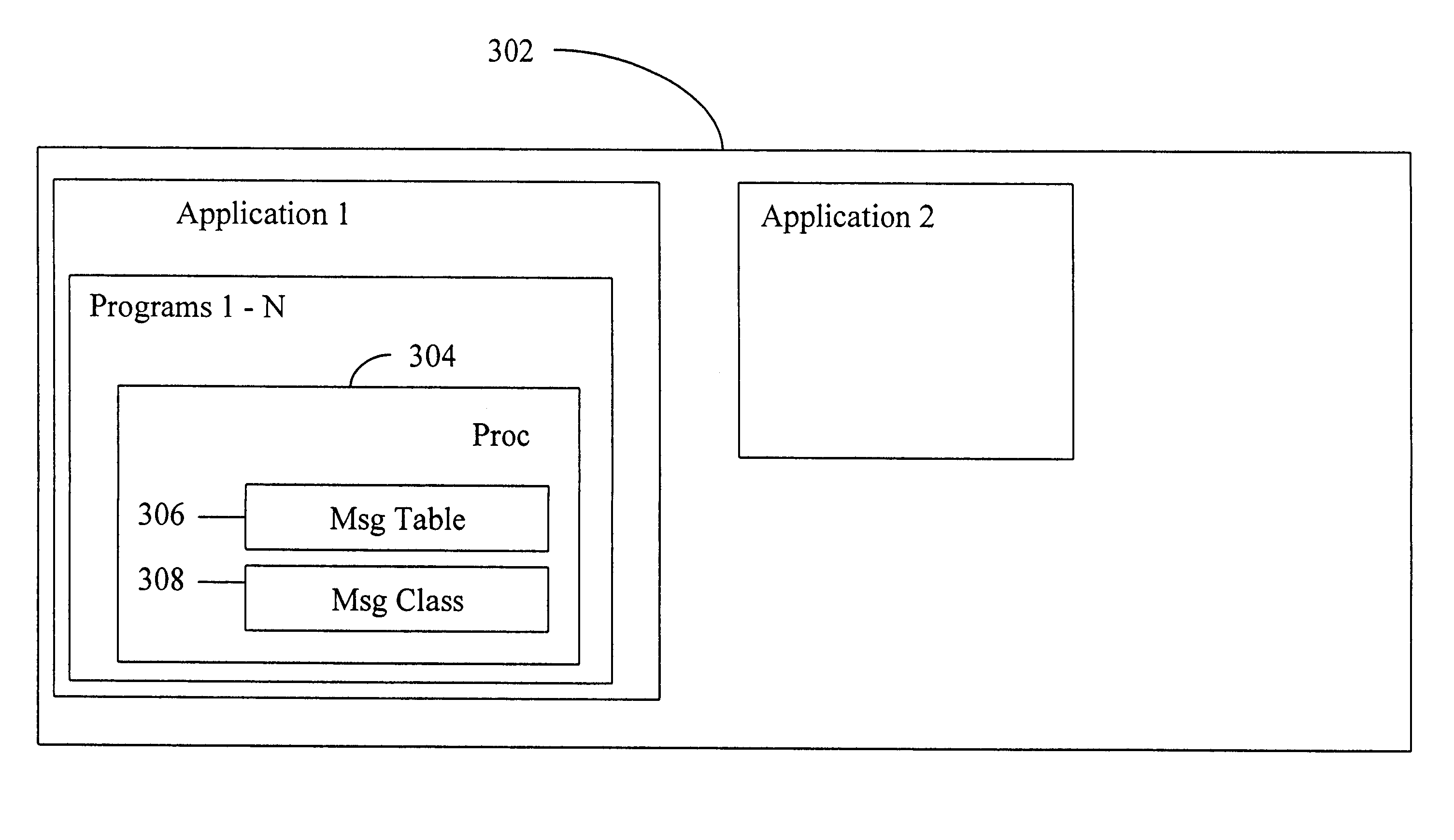
A message handler can dynamically change messages that are output during execution of a computer application. The messages are stored in a message file. When the application begins execution, it opens the message file, extracts the messages, stores them as message entries in a message table in computer memory and closes the file. Message records and message entries have formatting tags that allow dynamic substitution of desired information without expensive recompiling or version releases.
Owner:BENHOV GMBH LLC
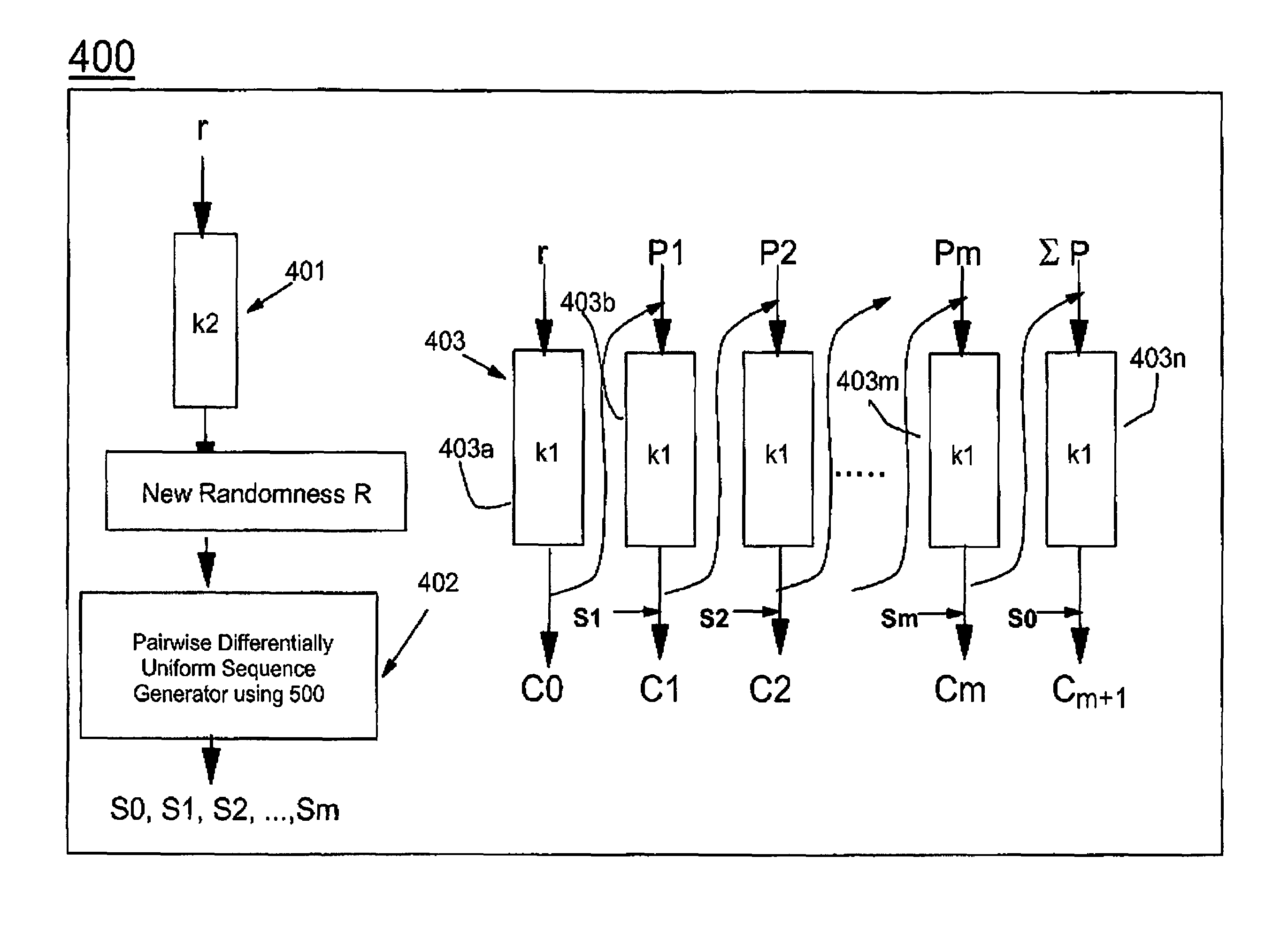
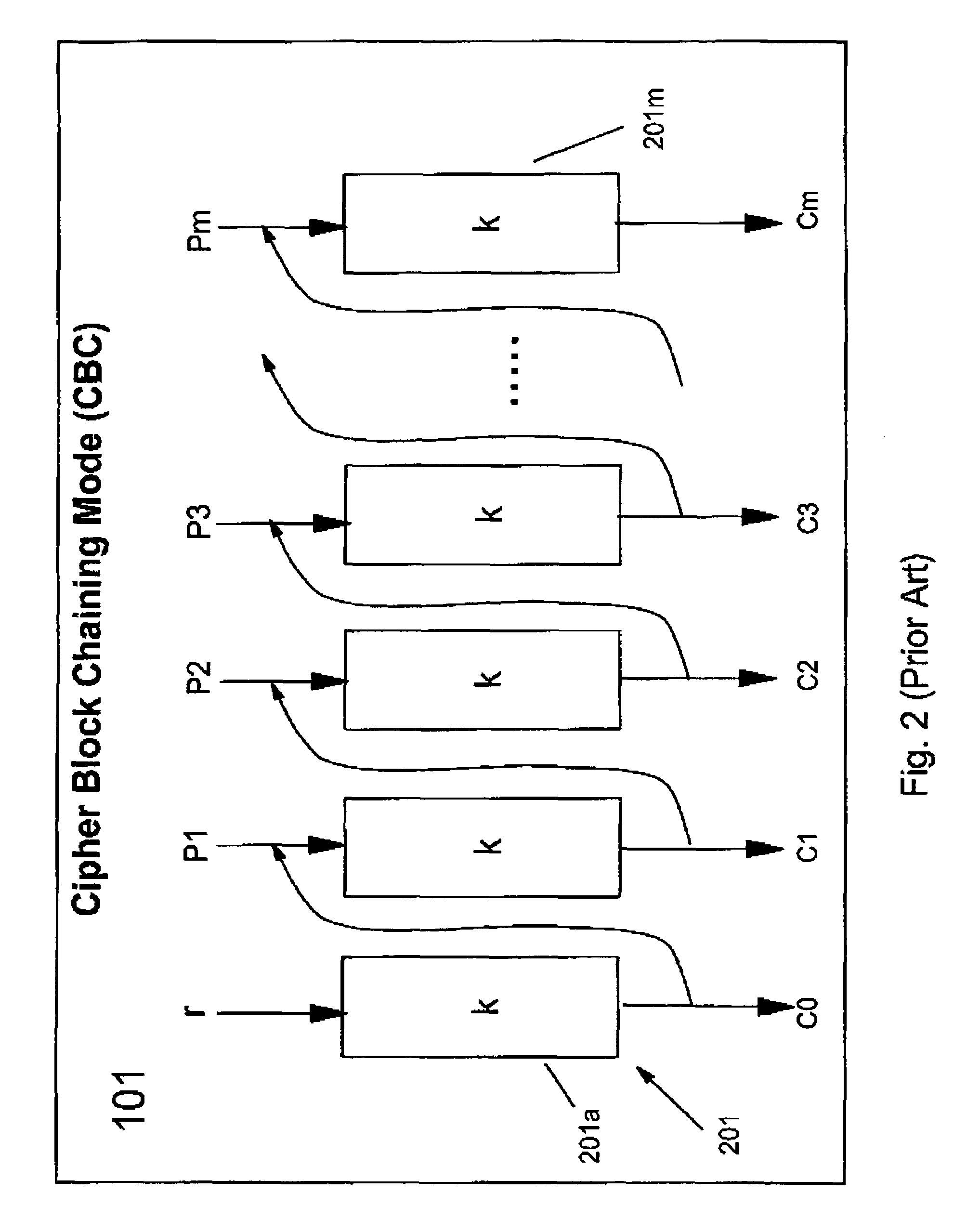
Symmetric key authenticated encryption schemes
InactiveUS6963976B1Low costSame level of securityData processing applicationsEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareCiphertext
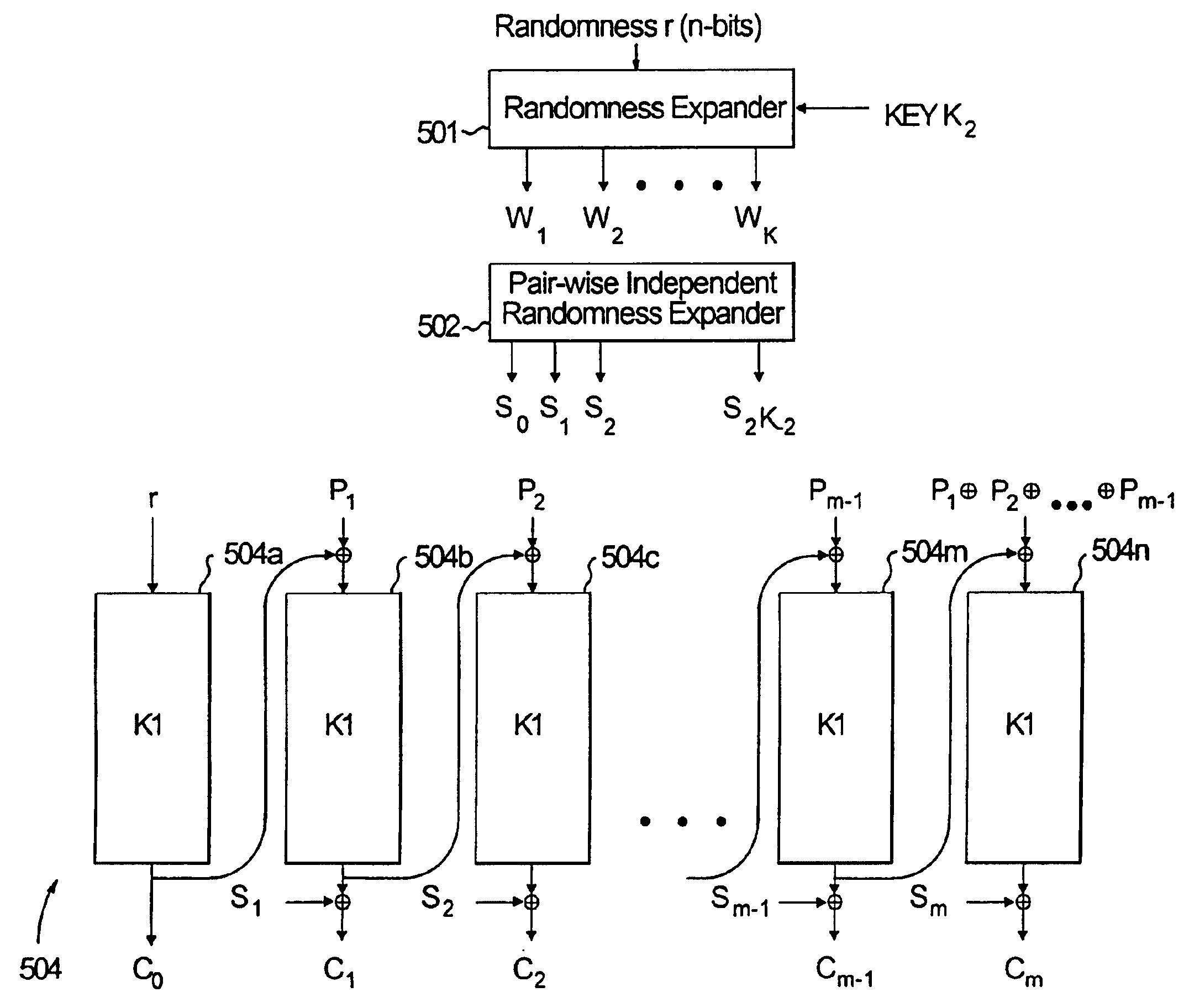
The present invention provides encryption schemes and apparatus which securely generate a cipher-text which in itself contains checks for assuring message integrity. It also provides compatible decryption schemes confirming message integrity. The encryption scheme generates a cipher-text with message integrity in a single pass with little additional computational cost, while retaining at least the same level of security as schemes based on a MAC. One embodiment encrypts a plain-text message by dividing the plain-text message into a multitude of plain-text blocks and encrypting the plain-text blocks to form a multitude of cipher-text blocks. A single pass technique is used in this process to embed a message integrity check in the cipher-text block. A message integrity check is embedded in the cipher-text blocks by embedding a set of pseudo random numbers, which may be dependent, but are pair-wise differentially uniform. We also describe an embodiment which is highly parallelizable.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
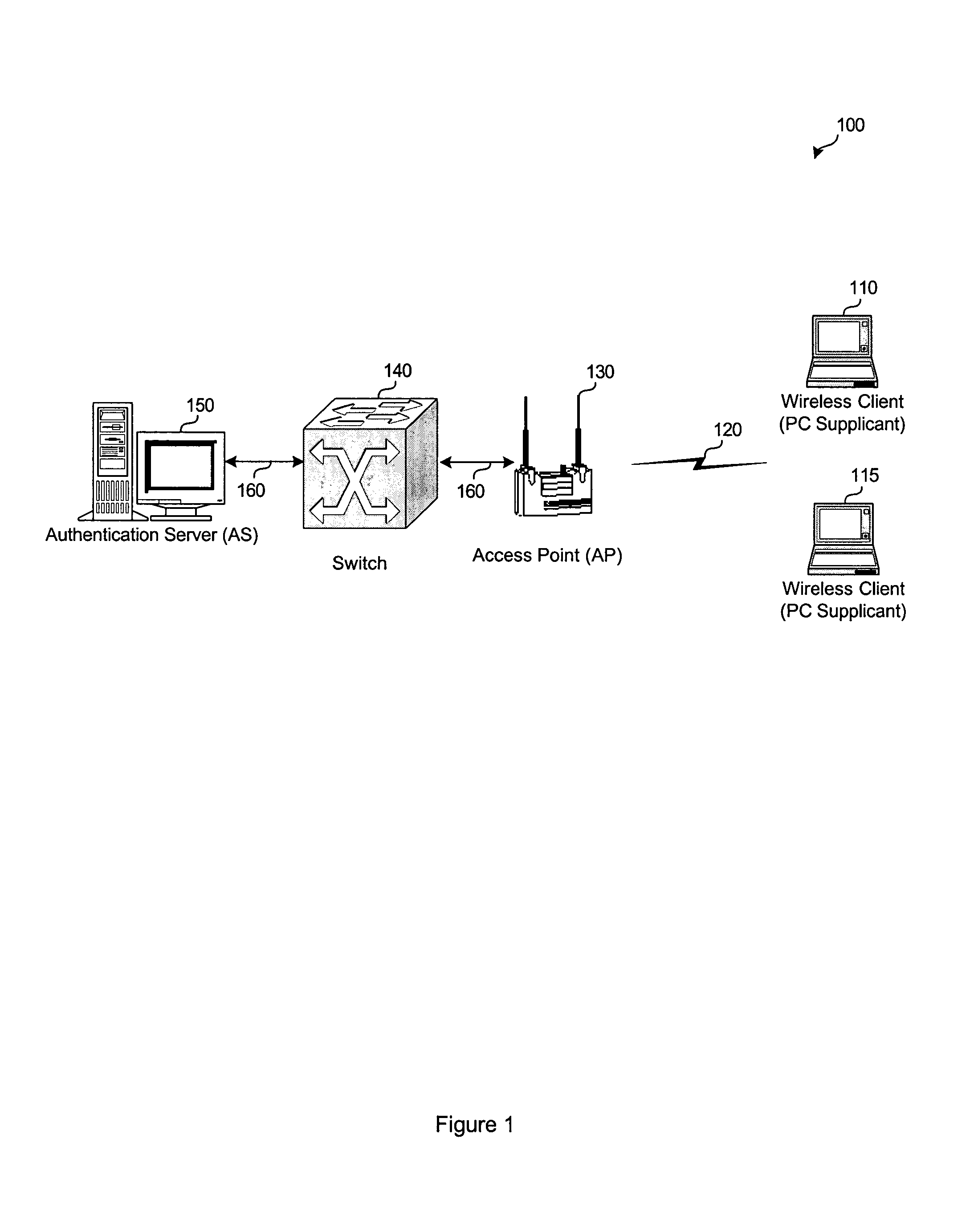
Network infrastructure validation of network management frames
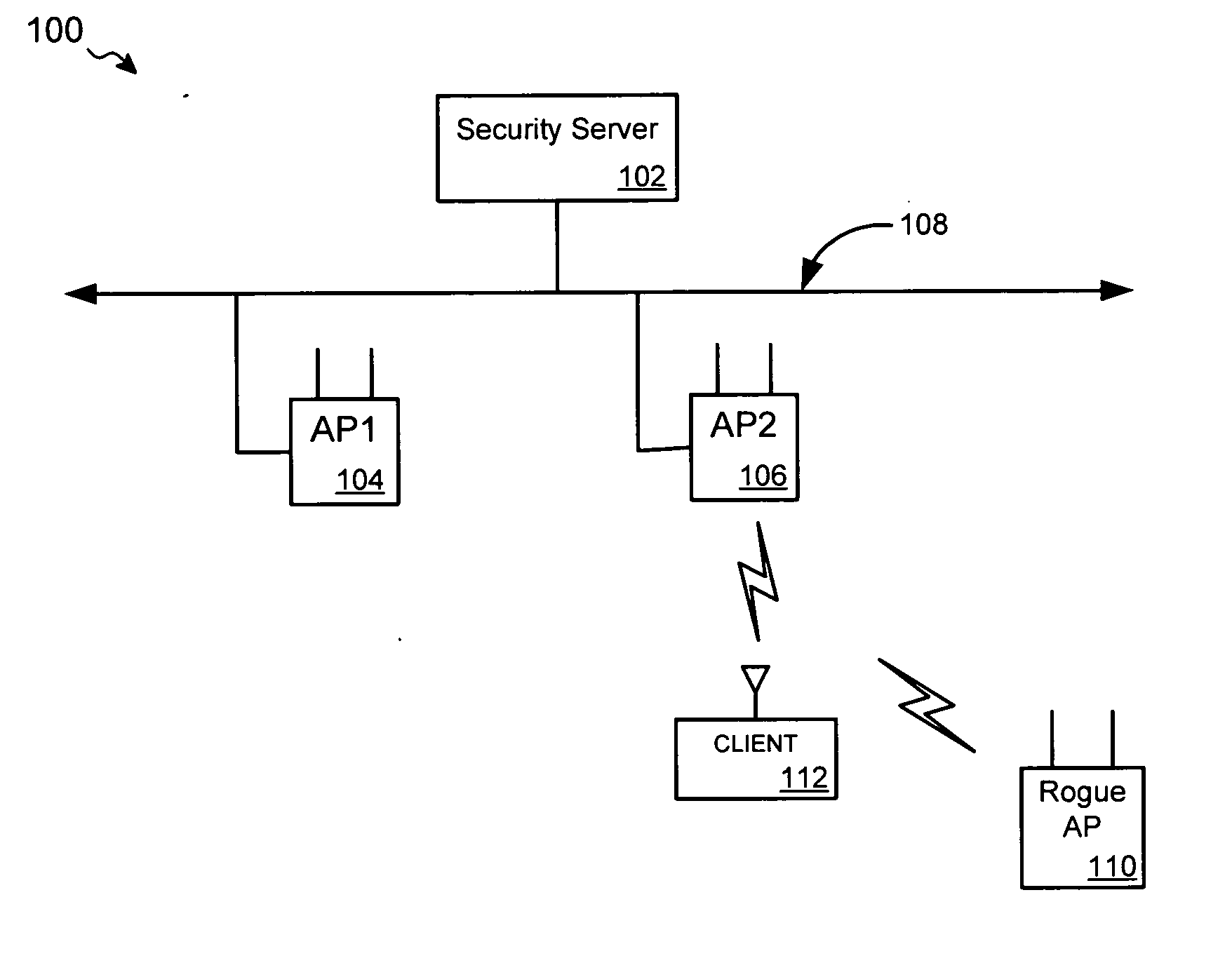
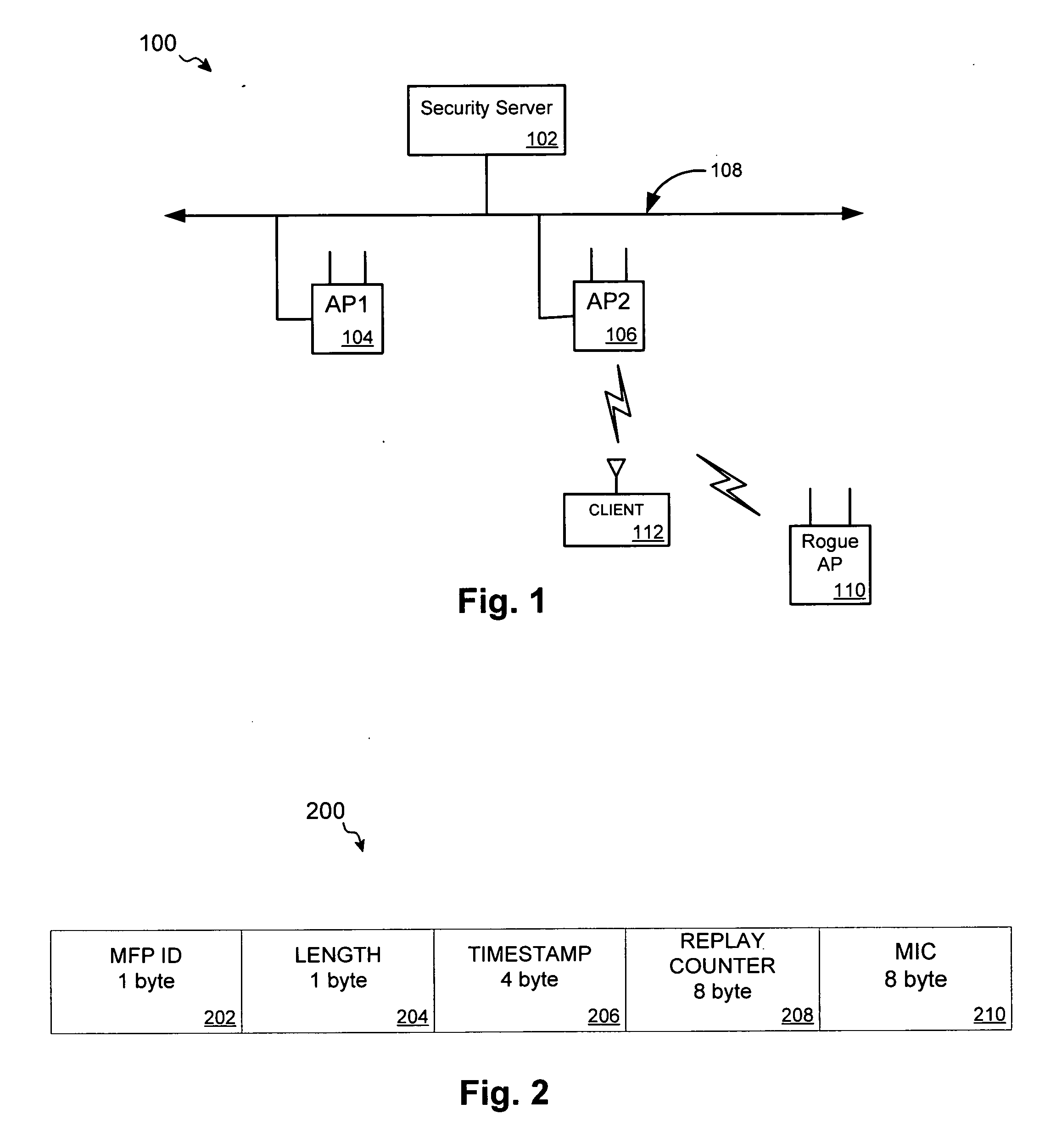
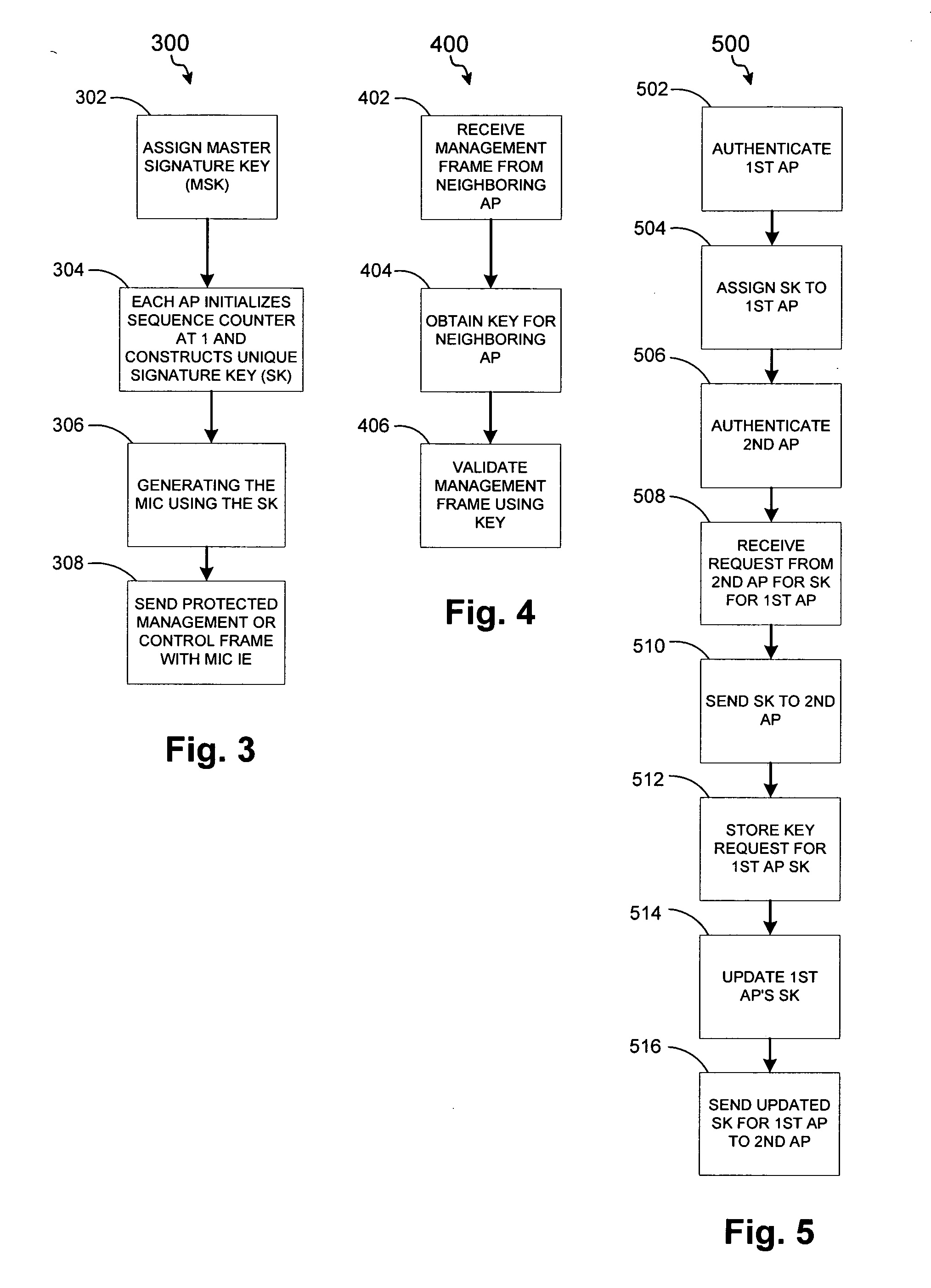
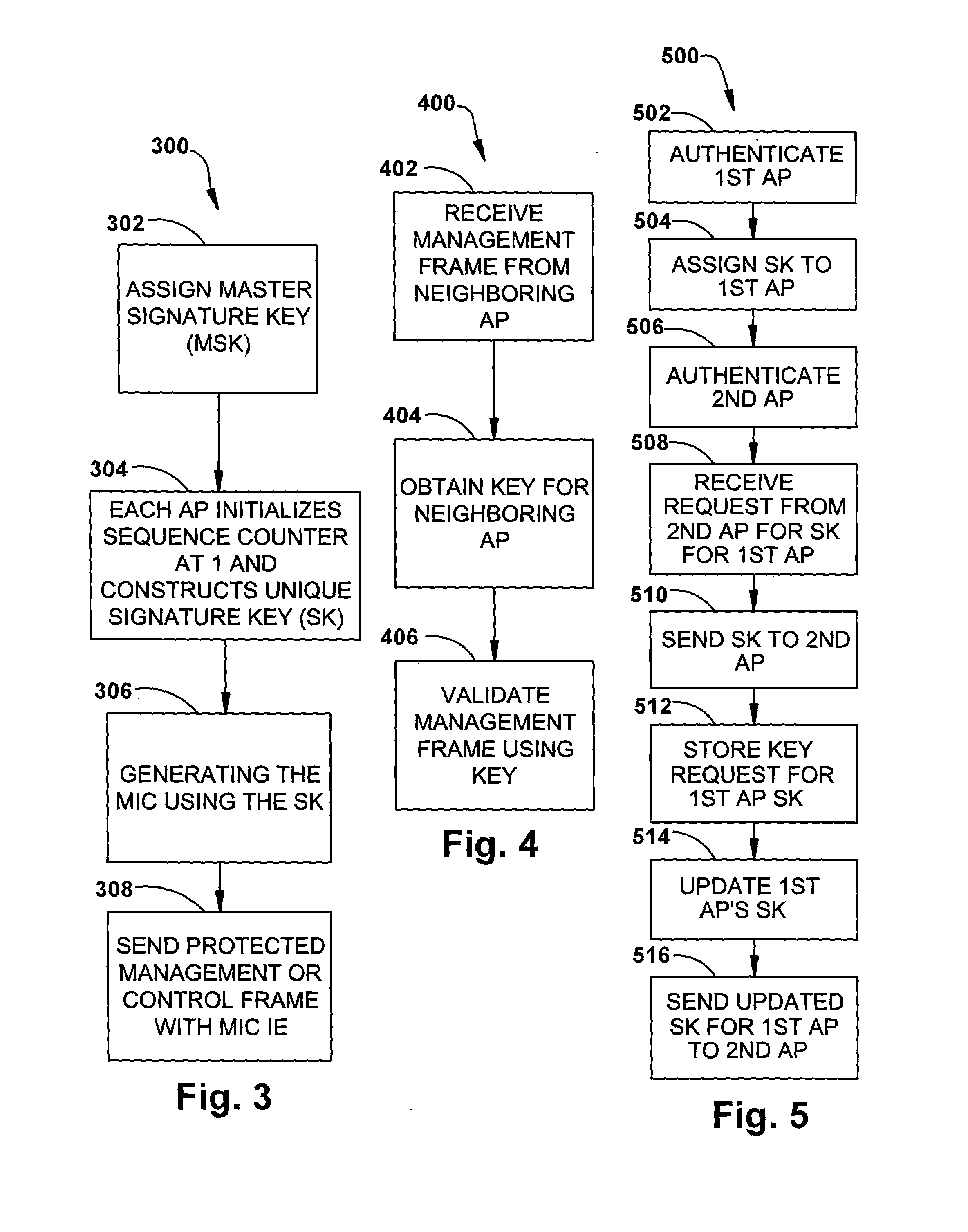
ActiveUS20050141498A1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationNetwork managementMessage integrity
A detection-based defense to a wireless network. Elements of the infrastructure, e.g., access points or scanning-only access points, detect intruders by detecting spoofed frames, such as from rogue access points. Access points include a signature, such as a message integrity check, with their management frames in a manner that enables neighboring access points to be able to validate the management frames, and to detect spoofed frames. When a neighboring access point receives a management frame, obtains a key for the access point sending the frame, and validates the management frame using the key.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
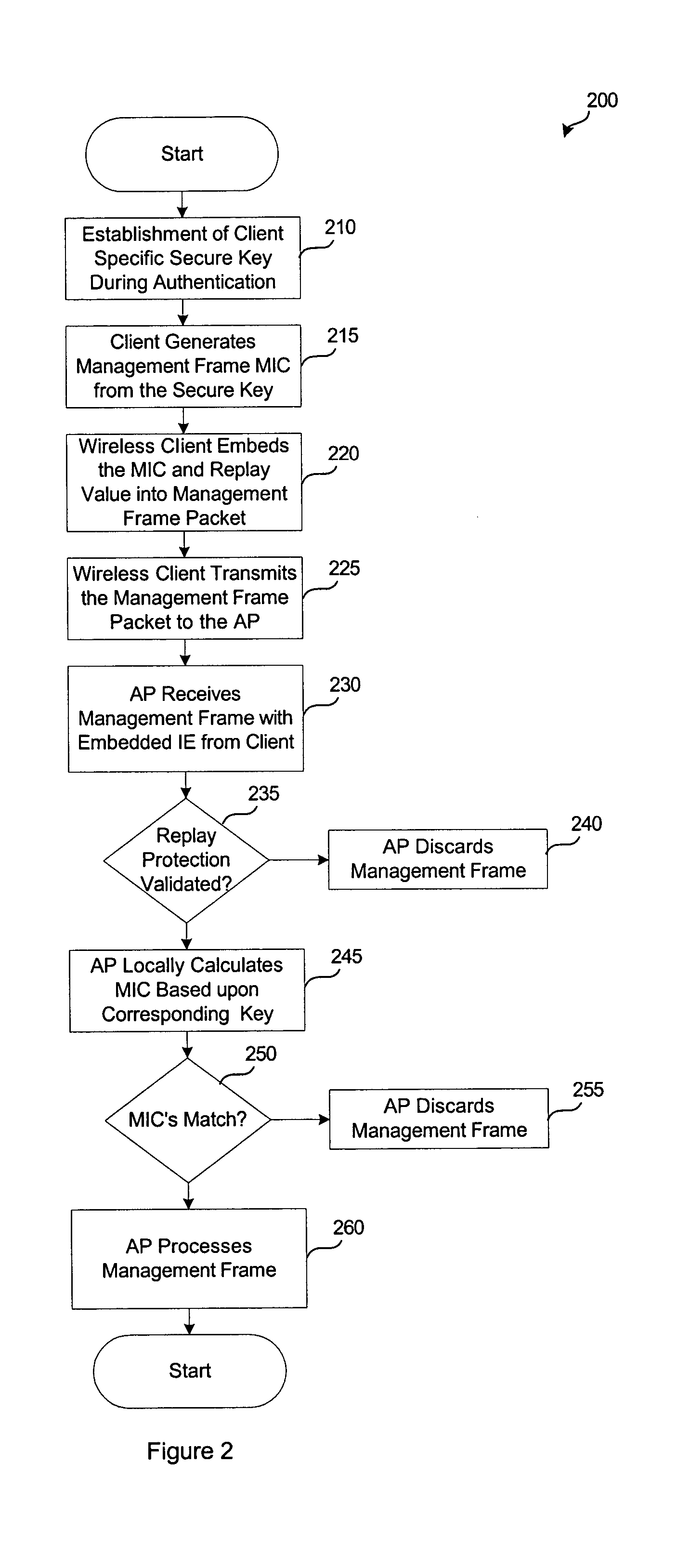
System and method for protecting network management frames
InactiveUS20050086465A1Convenient verificationNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationMessage integrityNetwork communication
System architecture and corresponding method for securing the transmission of management frame packets on a network (e.g. IEEE 802.11) is provided. Once a trust relationship is created between a transmitter and a receiver on the network such that the transmitter is authorized to communicate over the network, a key and corresponding message integrity check may be generated in order to sign management frame communications via the network. The message integrity check and a replay protection value may be transmitted with the management frame packet. Upon receipt, the message integrity check and replay protection value are authenticated to verify permitted transmission of the management frame packet.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
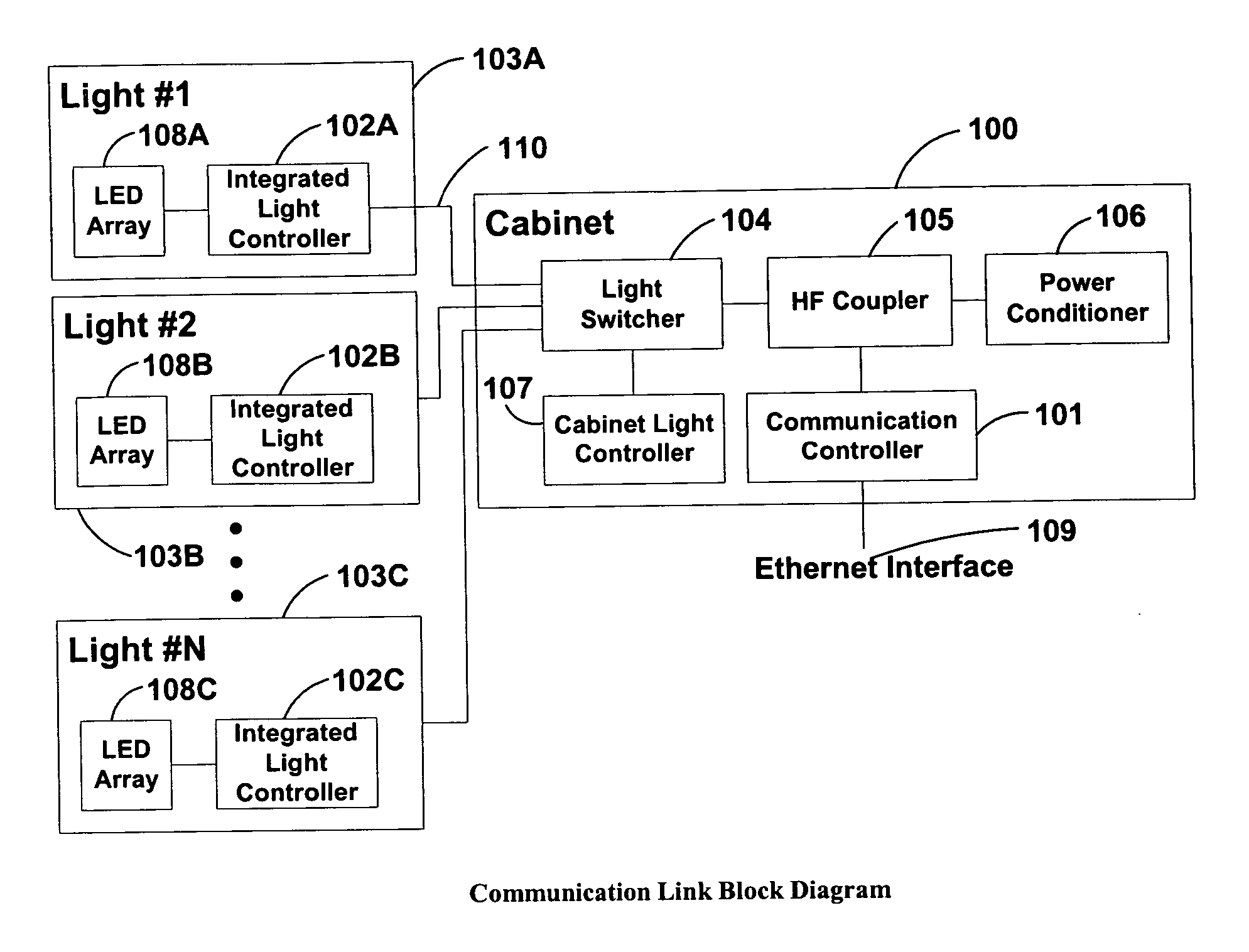
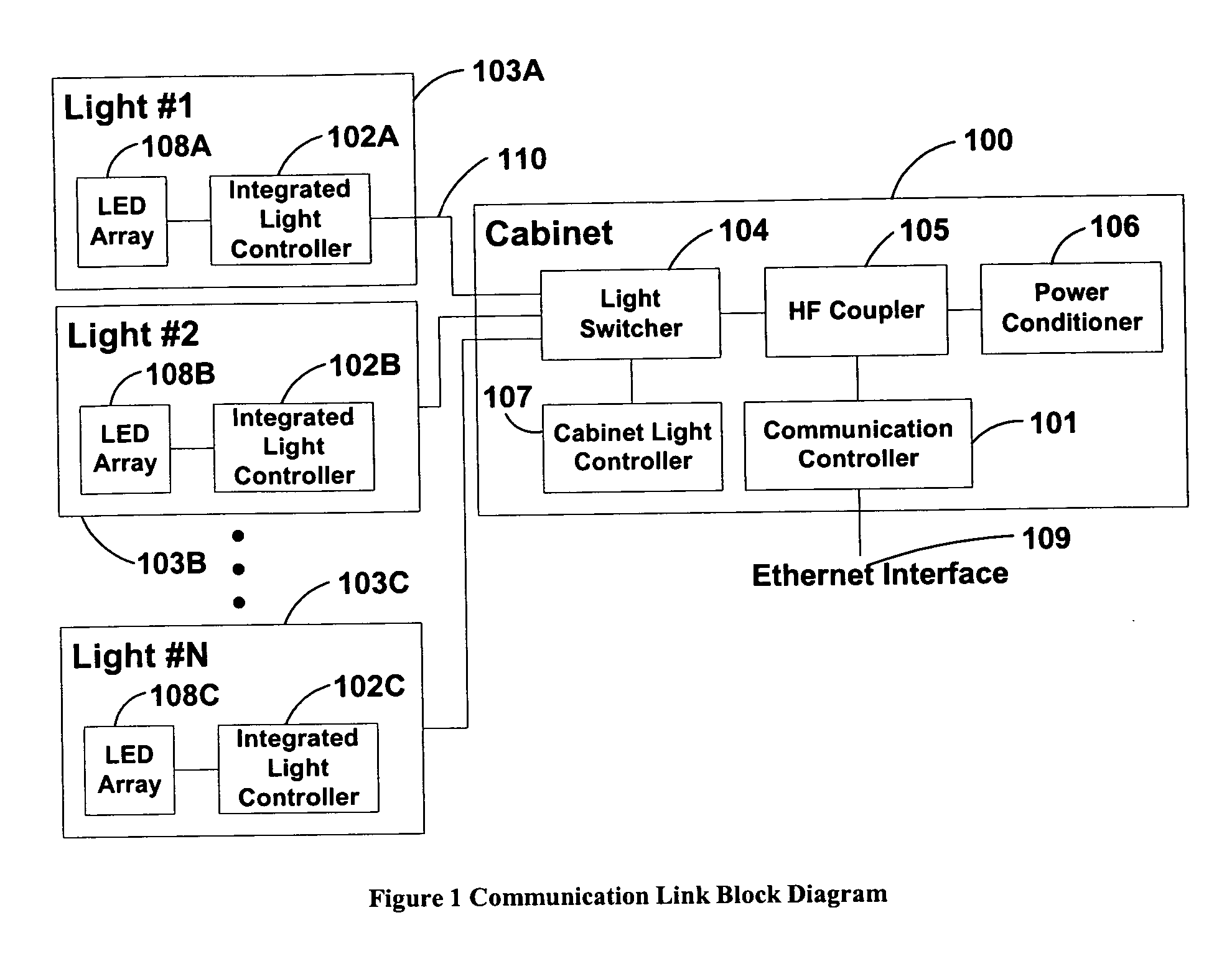
System and method of communications with traffic signals
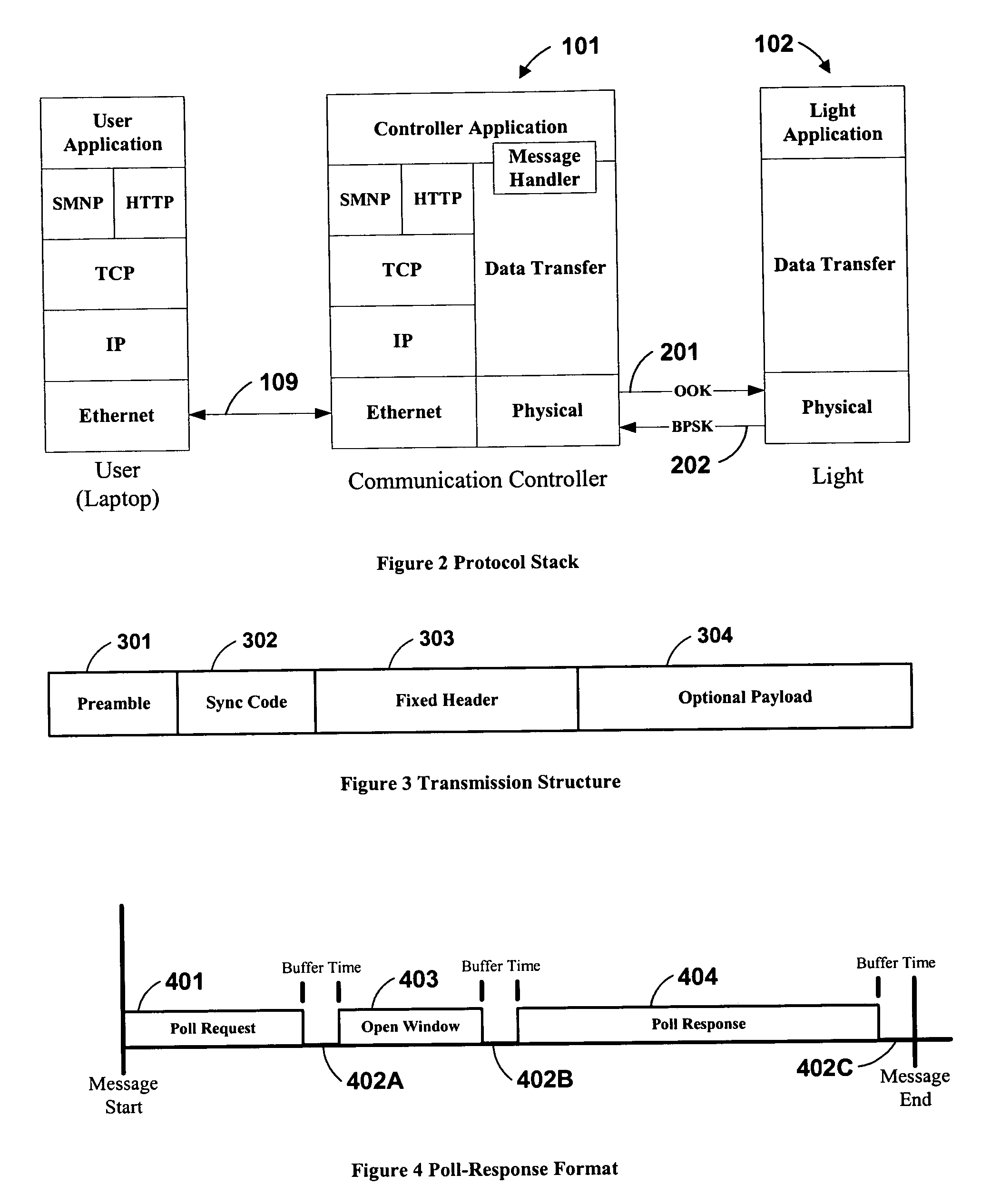
InactiveUS20060039698A1Low costConvenient lengthTransmission monitoringTransmission monitoring/testing/fault-measurement systemsTelecommunications linkTraffic signal
The present invention comprises a system and method for communicating with a traffic signal by which at least one communication controller and integrated light controller are coupled by a high frequency (“HF”) coupler to a power line for transmission. In each of the directions of communication, specific transmission methods and data protocols are used over the communication link. The communication link protocol used for communication between the integrated light controller and the communication controller provides a robust method for framing data within a message structure that provides byte-by-byte synchronization and message integrity through a parity check per byte, and a checksum calculation.
Owner:OPTISOFT +2
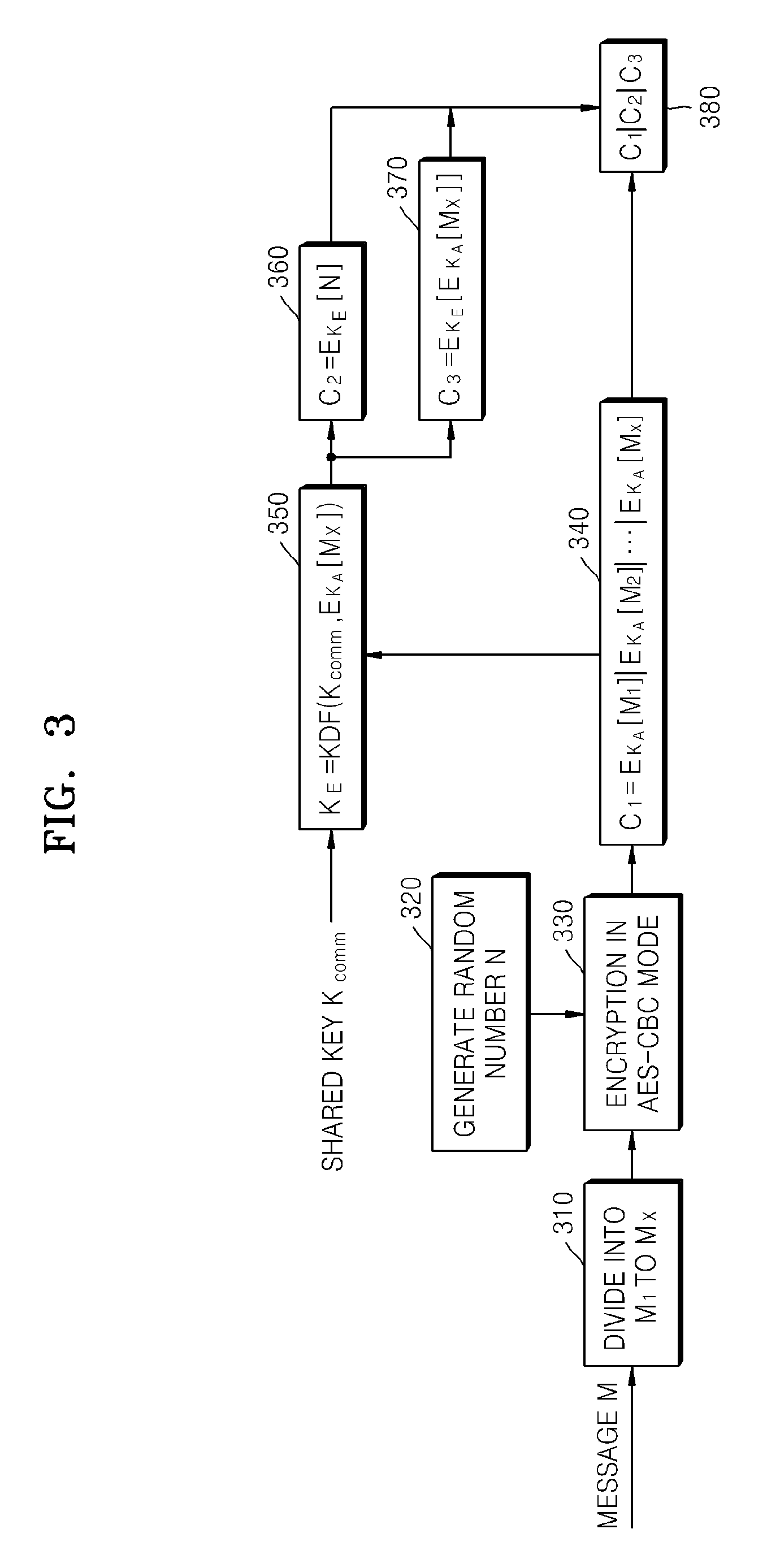
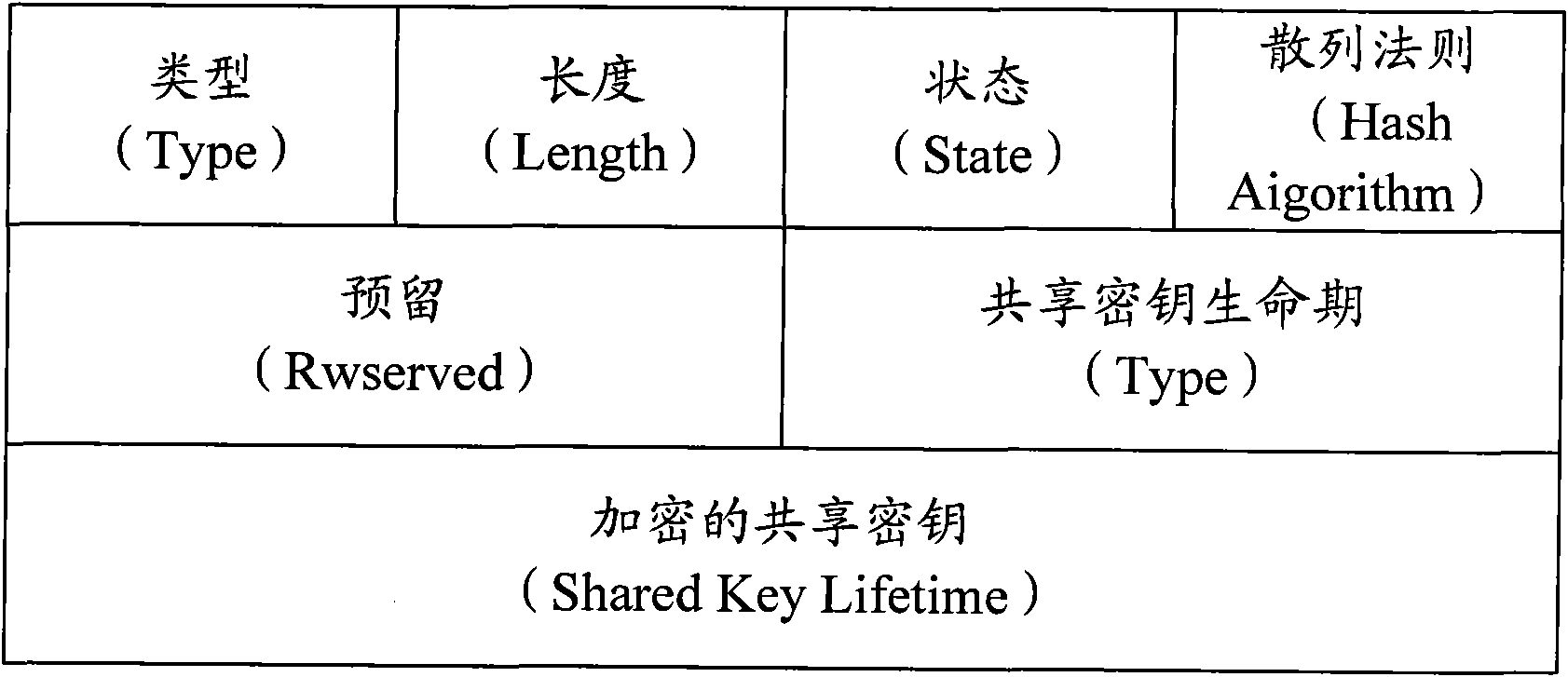
Method and apparatus for encrypting message for maintaining message integrity, and method and apparatus for decrypting message for maintaining message integrity
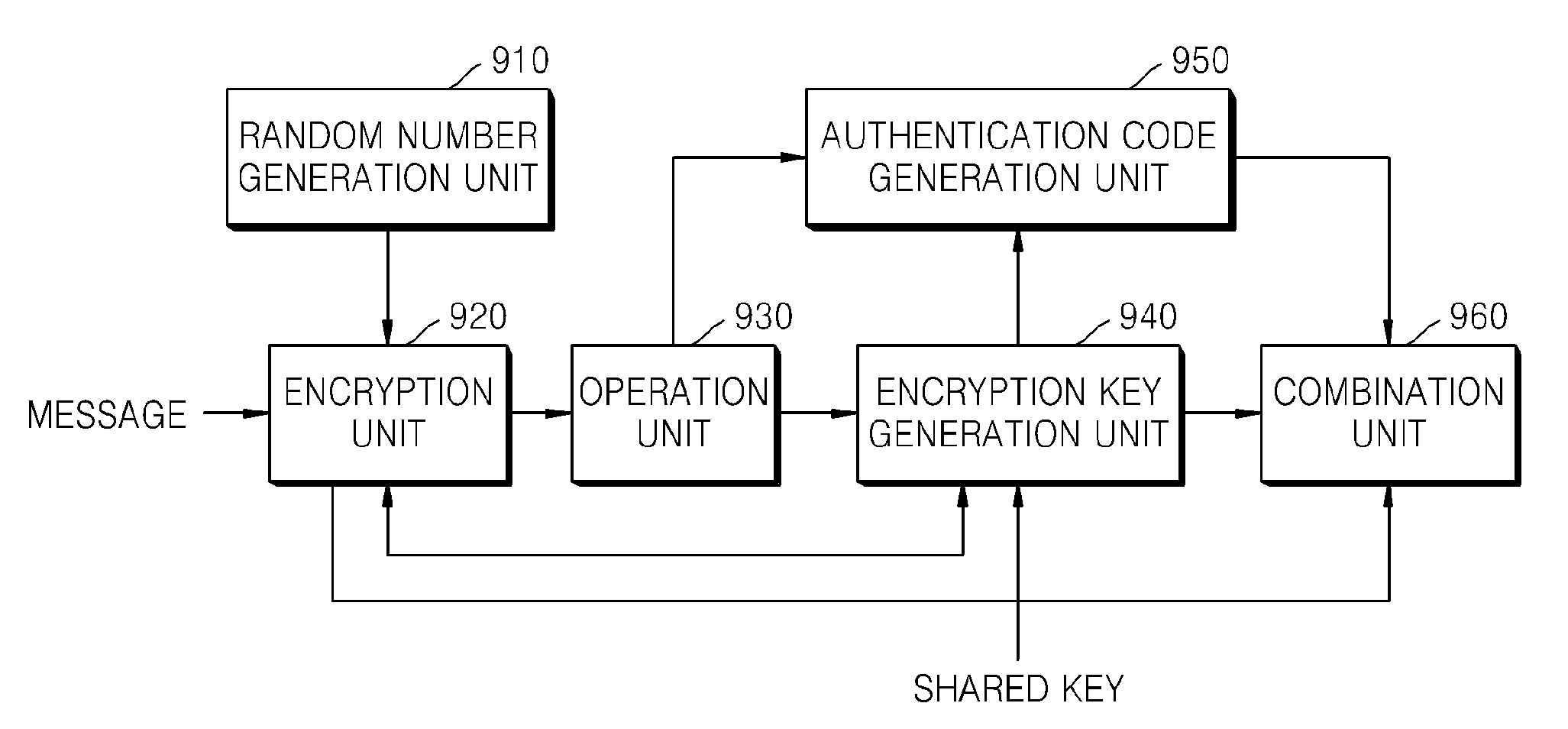
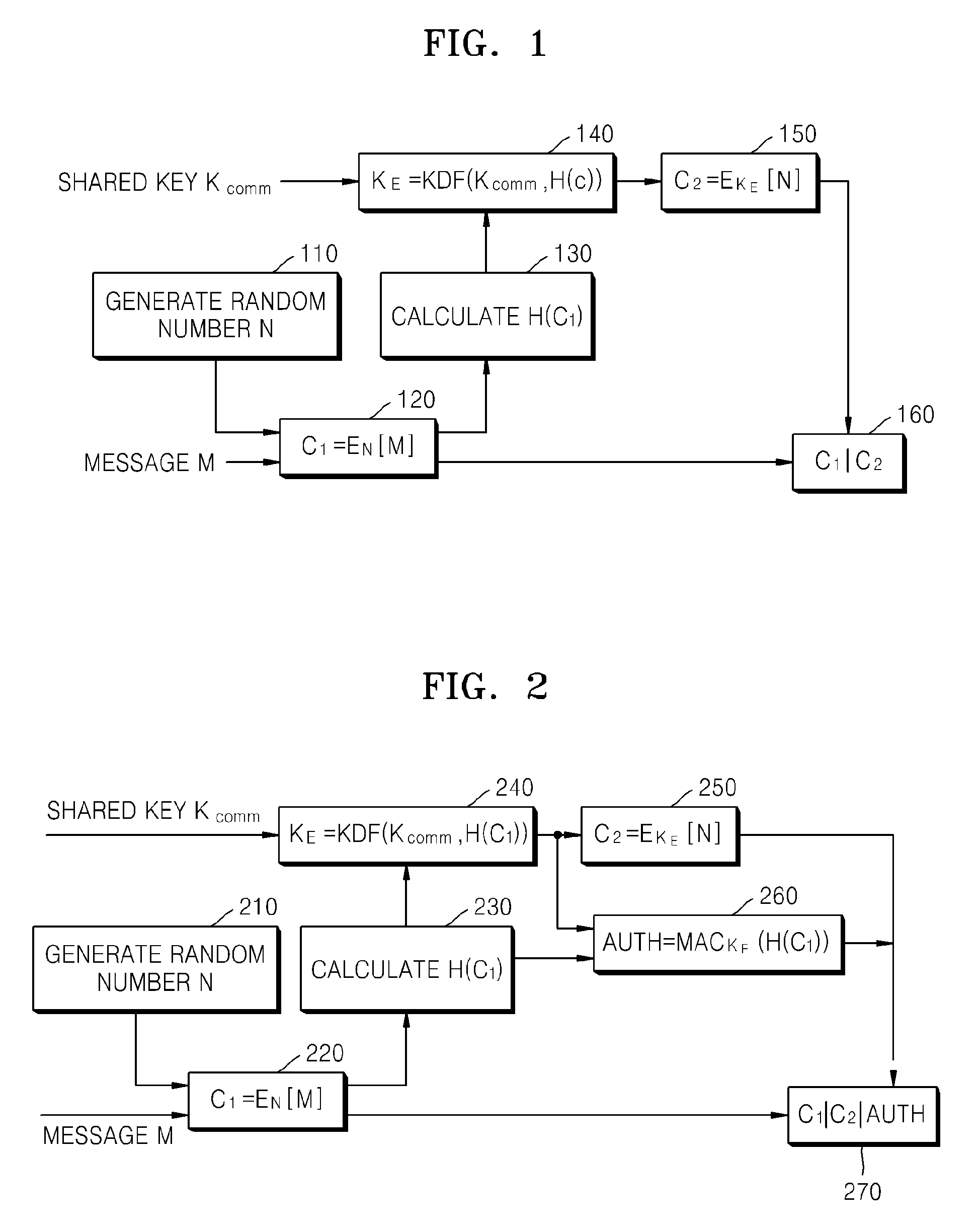
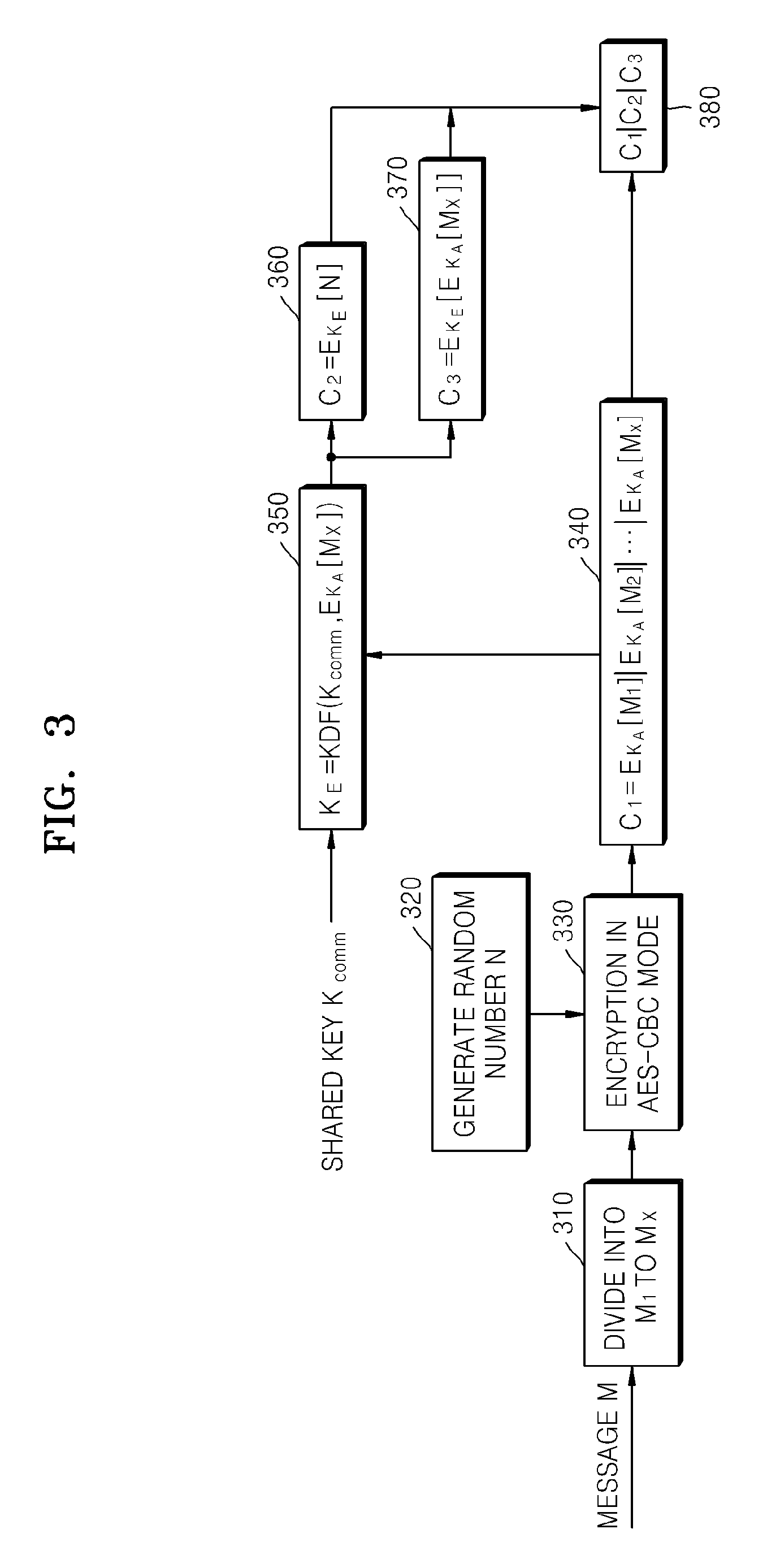
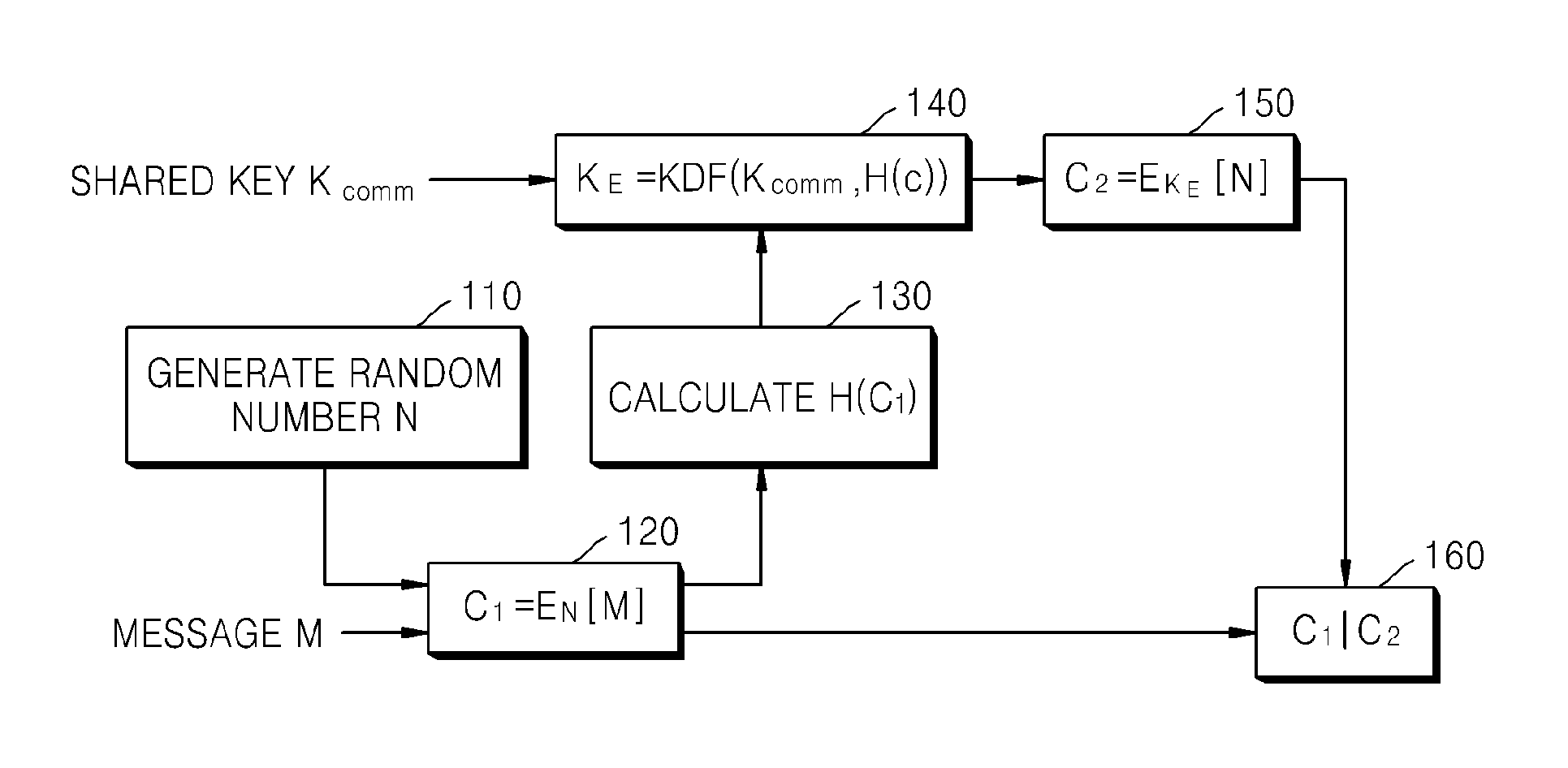
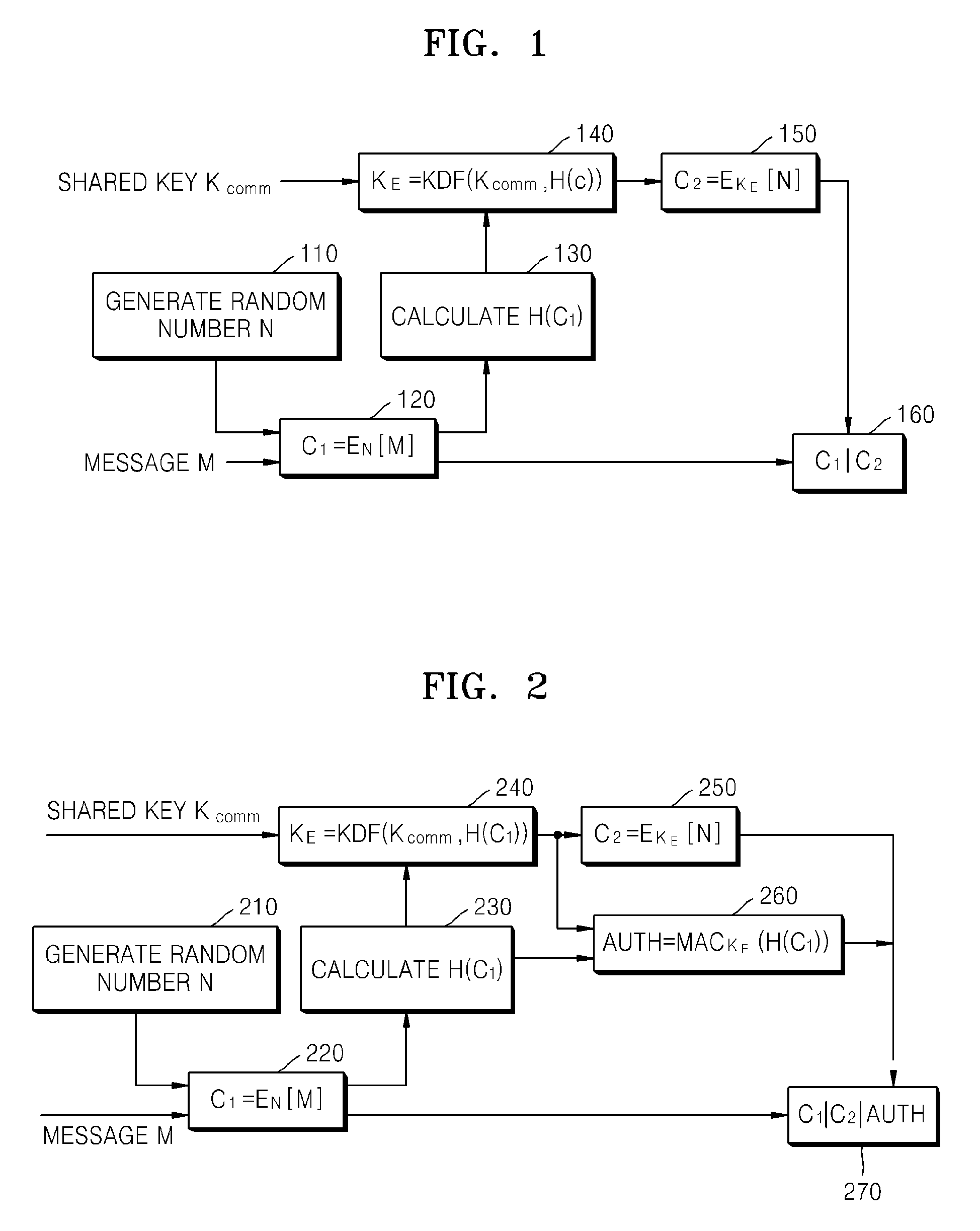
ActiveUS20080260147A1Maintain integrityAvoid reuseMultiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareCiphertext
A method of encrypting a message for message integrity is provided. In the method, a random number is generated, a first ciphertext is generated by encrypting the message by using the generated random number, a hash value of the first ciphertext is calculated, an encryption key is generated by using the hash value of the first ciphertext and a shared key, a second ciphertext is generated by encrypting the random number by using the encryption key, and the first and second ciphertexts are combined.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Authentication scheme for ad hoc and sensor wireless networks
InactiveUS7096359B2Without excessive computational and power consuming overheadKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureChecksum
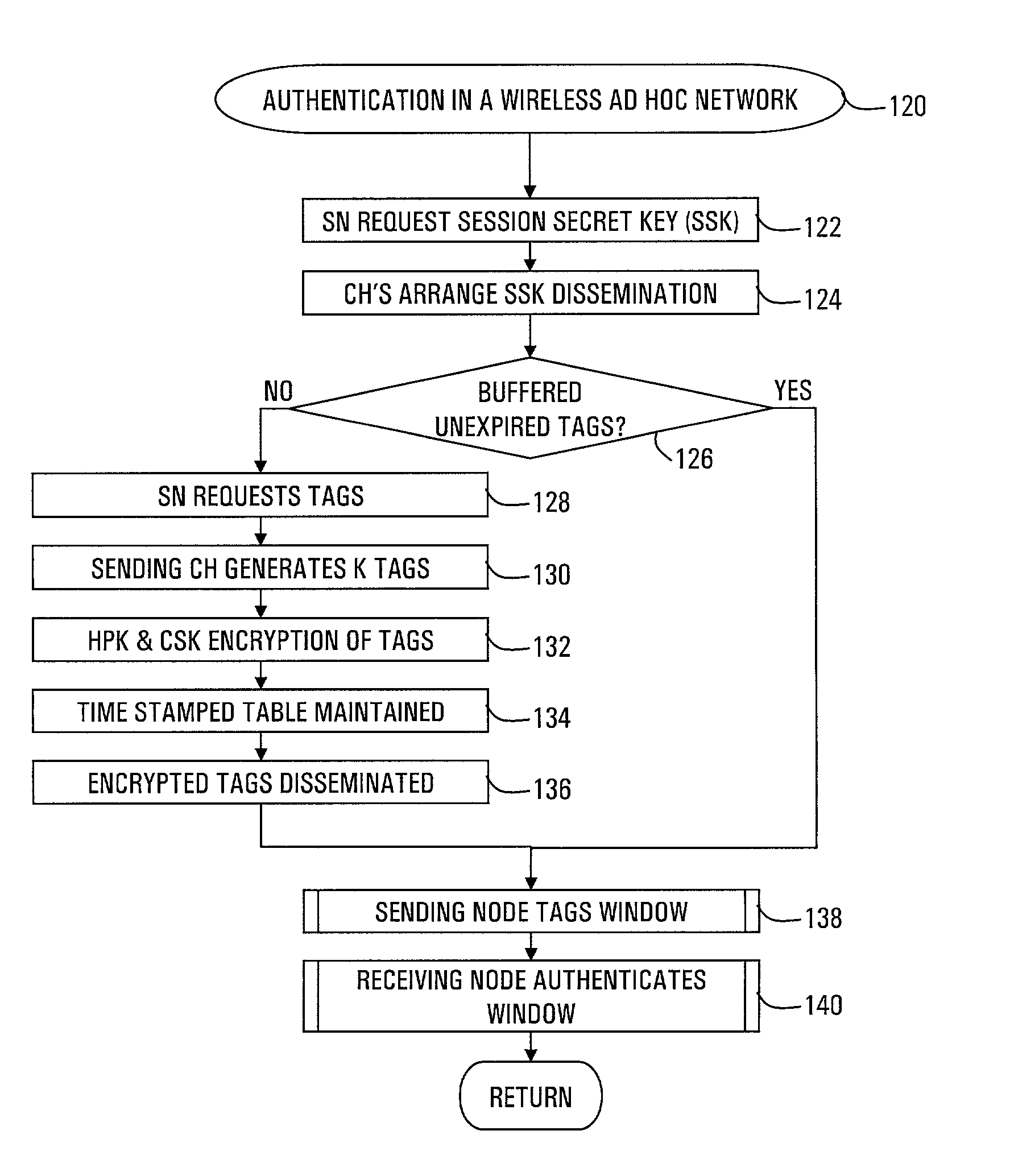
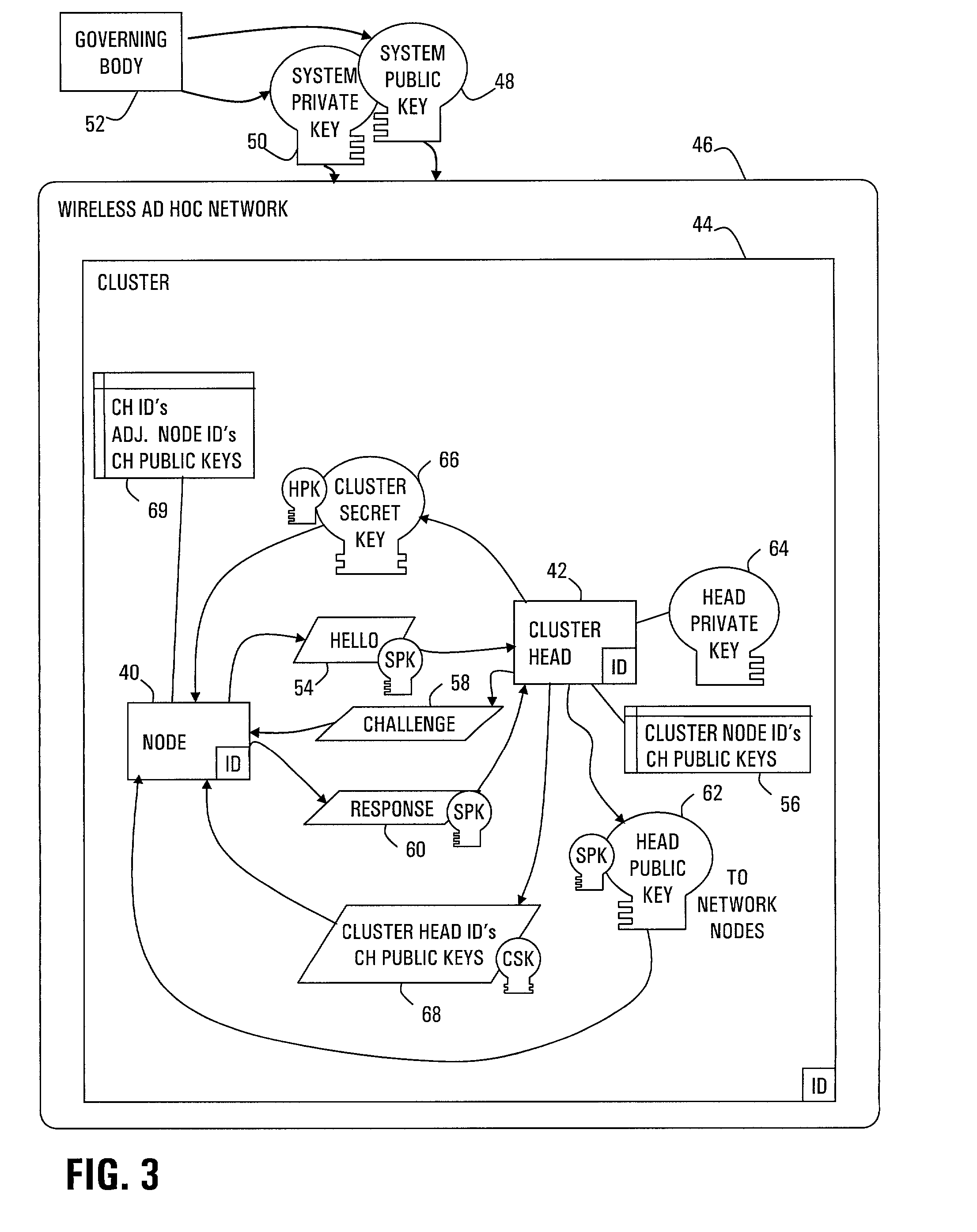
Strong authentication of packets sent between nodes of different clusters in a two-tier ad hoc network is provided by the cluster heads. Each cluster head authenticates nodes that enter the cluster. Thereafter, when a sending node requests a session from its cluster head with a receiving node in another cluster, the cluster head negotiates a session secret key (SSK) with the corresponding cluster head of the receiving node. Further, the cluster head provides authentication tags for the sending node to use with each packet. Each authentication tag is time-stamped, digitally signed by the cluster head, encrypted with the SSK, and includes indicators of message integrity, including a sequence number and TCP header field of checksum. The sending node further calculates a check result from a number of the authentication tags, encrypted with the SSK, so that the receiving node can authenticate the number of packets.
Owner:CINCINNATI UNIV OF
Encryption schemes with almost free integrity awareness
InactiveUS7093126B1Reduce computing costLow costUser identity/authority verificationSpecial data processing applicationsComputer hardwarePlaintext
An encryption / decryption method and system. The method comprises the steps of encrypting a plaintext message by dividing the plaintext message into a multitude of plaintext blocks and encrypting the plaintext blocks to form a multitude of cyphertext blocks. A single pass technique is used in the method to embed a message integrity check in the cyphertext blocks. The method further comprises the steps of decrypting the cyphertext blocks to re-form the plaintext blocks, and testing the message integrity check in the cyphertext blocks to test the integrity of the re-formed plaintext blocks.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for encrypting message for maintaining message integrity, and method and apparatus for decrypting message for maintaining message integrity
ActiveUS8155311B2Prevent reuseMultiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationComputer hardwareCiphertext
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
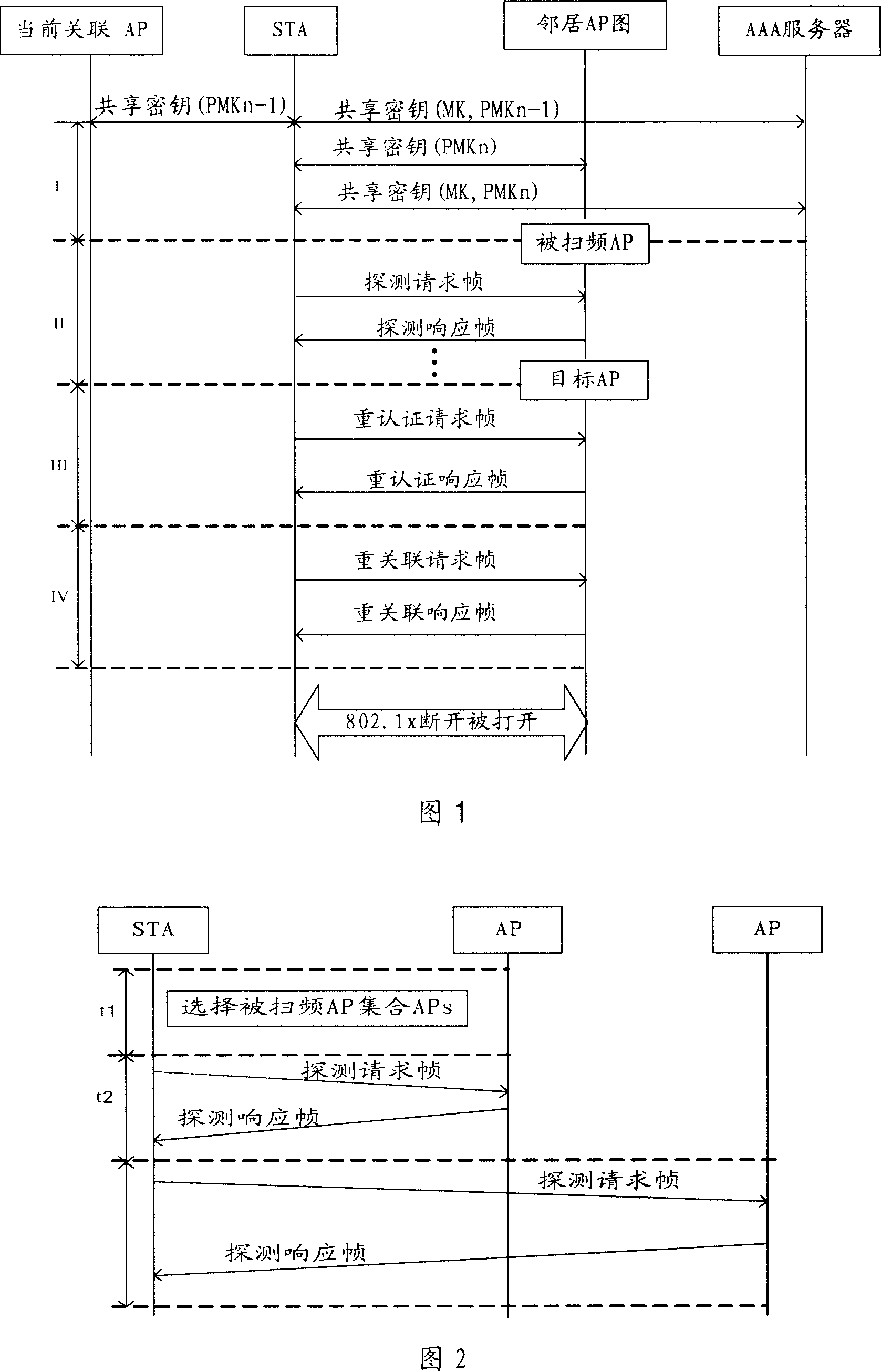
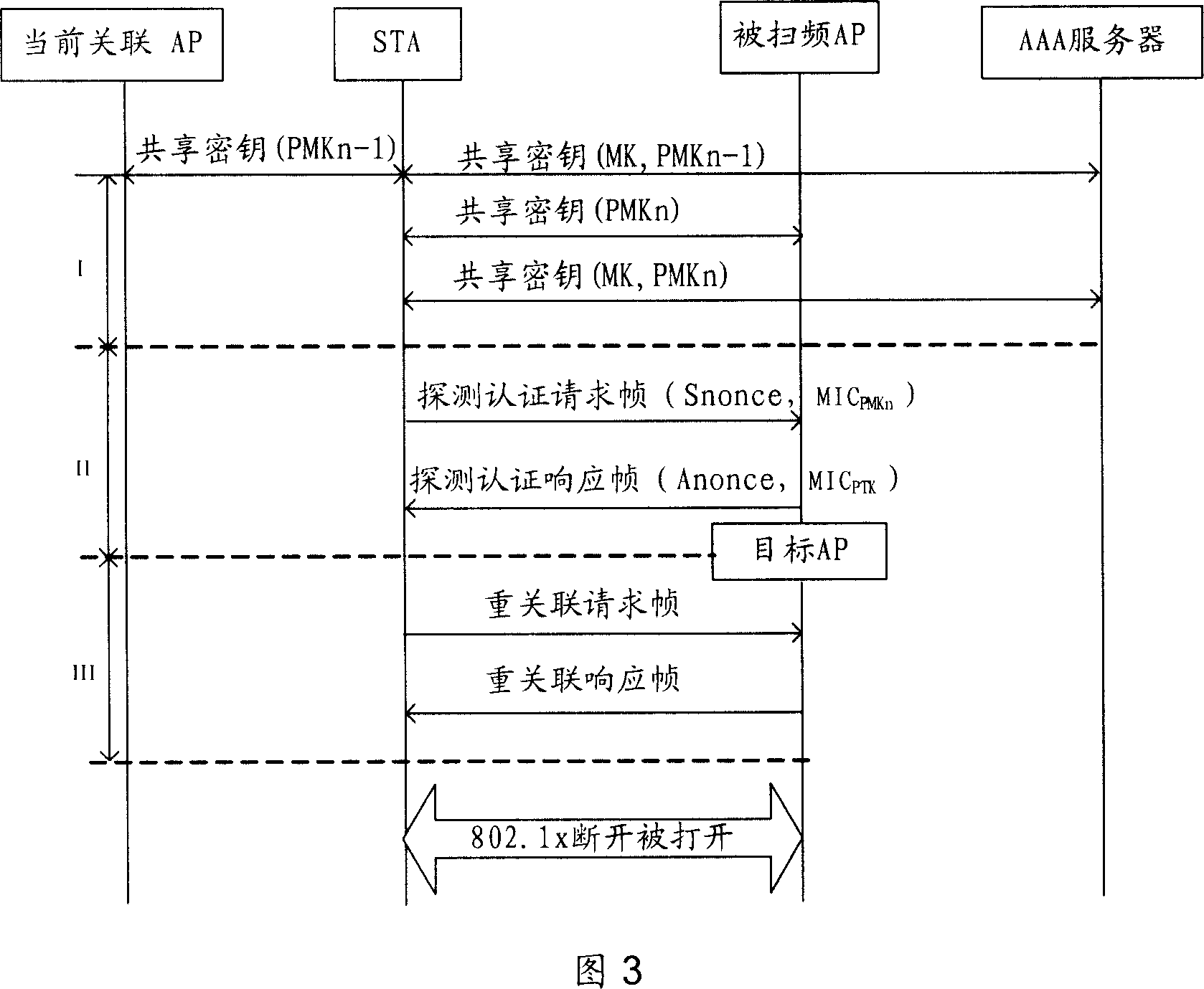
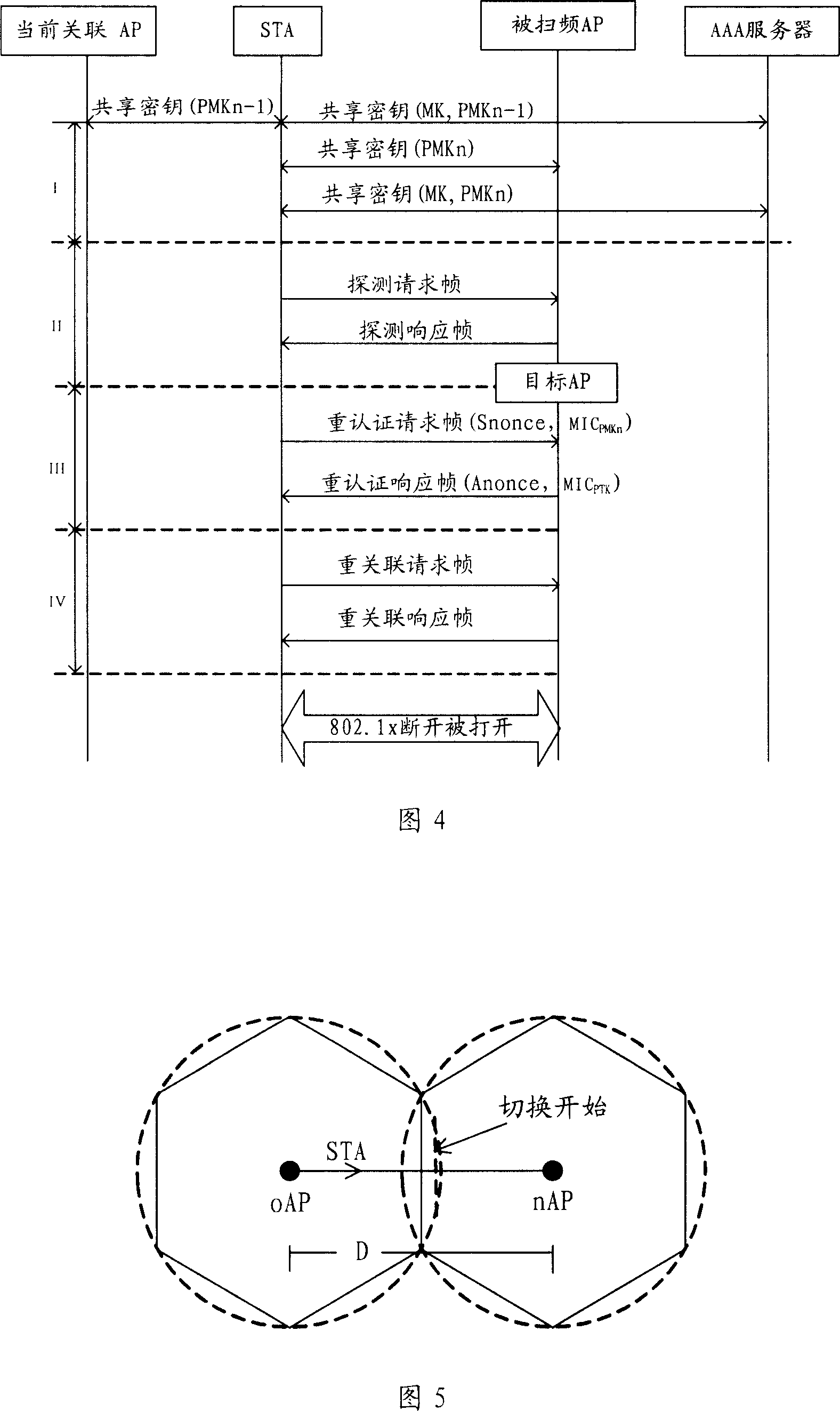
Fast switching method for wireless local area network
InactiveCN101111056AReduce waiting timeReduce switching delayAssess restrictionData switching by path configurationTime delaysMessage integrity
The present invention provides a fast handoff method in a wireless Local Area Network, the method is that a line mobile node STA selects an Access Point aggregation of the Wireless Local Area Network swept the frequency; the STA performs the interaction of the unicast type detecting and authenticating information to the AP aggregation, completes an active frequency sweep process, and selects a goal AP; the STA and the goal AP are associated newly. The present invention also provides a fast handoff method by adopting the unicast type active sweep-frequency and augmenting the safety during the two stages of the re-authentication. A technical proposal provided by the present invention merges the two stages of the sweep-frequency and the re-authentication into one sweep-frequency authentication stage, and the unicast type active sweep-frequency method is also adopted, to effectively decrease the waiting time consumed in a channel and reduce the handover time delay; a Message Integrity Identifying Code is joined during the interaction of the sweep-frequency authentication information, to enhance the safety of the switch. The other technical proposal also decreases the waiting time consumed in the channel, decreases the handover time delay, and enhances the safety of the switch.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV +1
Authentication mechanisms for call control message integrity and origin verification
ActiveUS20050243798A1Provide securityMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlTransit networkFrame Relay
The present invention incorporates methodologies developed in the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) Internet Protocol Security (IPSEC) Working Group into asynchronous transfer mode (ATM) and frame relay (FR) signaling to provide message integrity and origin authentication. In one implementation the invention provides a virtual private network (VPN) infrastructure with call control message integrity, origin verification, and transit network filtering. The invention utilizes a set of control plane messages based on the IPSEC authentication header (AH) methodology to provide these security mechanisms for ATM and FR network switching equipment and signaling protocols. This abstract itself is not intended to limit the scope of this patent. The scope of the present invention is pointed out in the appending claims.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
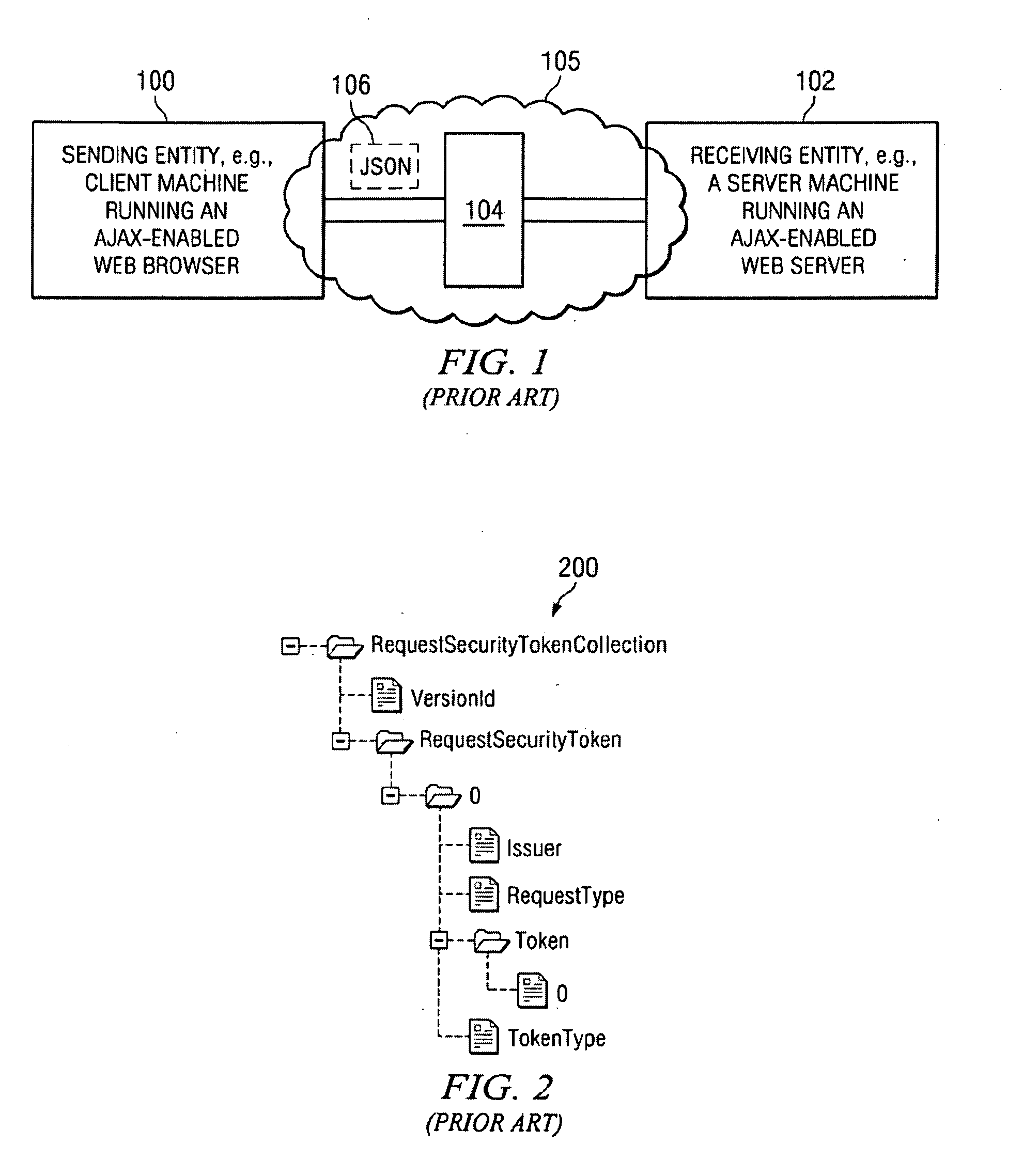
Method and system for signing javascript object notation (JSON) messages
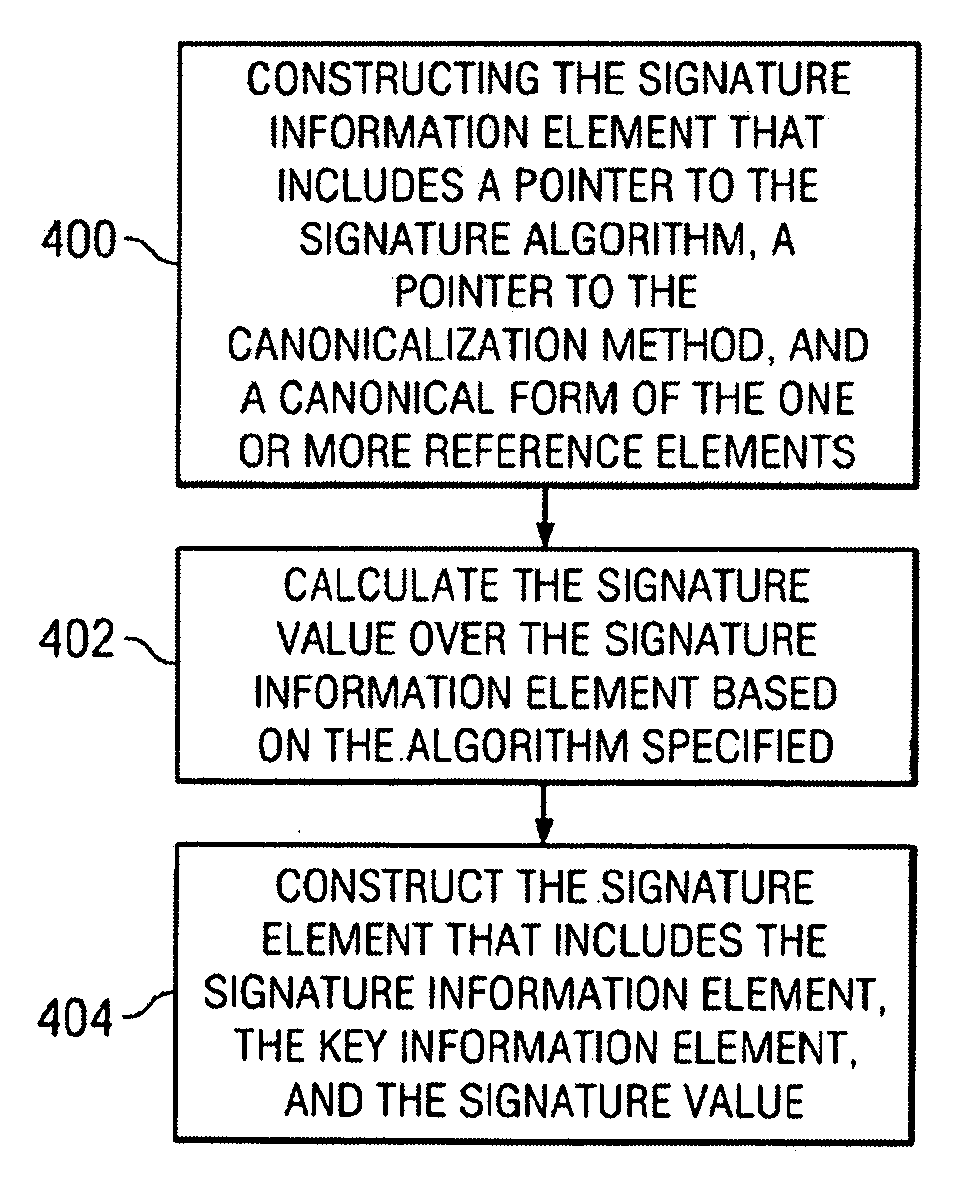
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) message integrity is provided using a digital signature scheme. The digital signature scheme implements a set of processing rules for creating and representing digital signatures using a JSON signature syntax. The syntax preferably comprises a set of named elements, including a reference element, a signature information element, and a signature element. In one embodiment, a machine-implemented method for signing a JSON message begins by constructing a reference element for each data object in the JSON message to be signed. The data object is identified by a reference identifier. The reference element includes the reference identifier, a pointer (such as a URI) to a digest method, and a digest generated by applying the digest method to the data object or a given function of the data object. Then, a signature information element is constructed for one or more of the reference elements corresponding to the one or more data objects in the message that are being signed. The signature information element includes a pointer to a signature method, as well as one or more reference elements, or a canonical form of the one or more reference elements. Then, a signature element is constructed. The signature element includes the signature information element, and a signature value generated by applying the signature method (identified in the signature information element) to the signature information element. The signature element is the JSON message signature. The signature enables a sending entity (such as a Web browser or Web server) to generate a digest on all or parts of a JSON message and then to secure the digests using a signing key.
Owner:IBM CORP
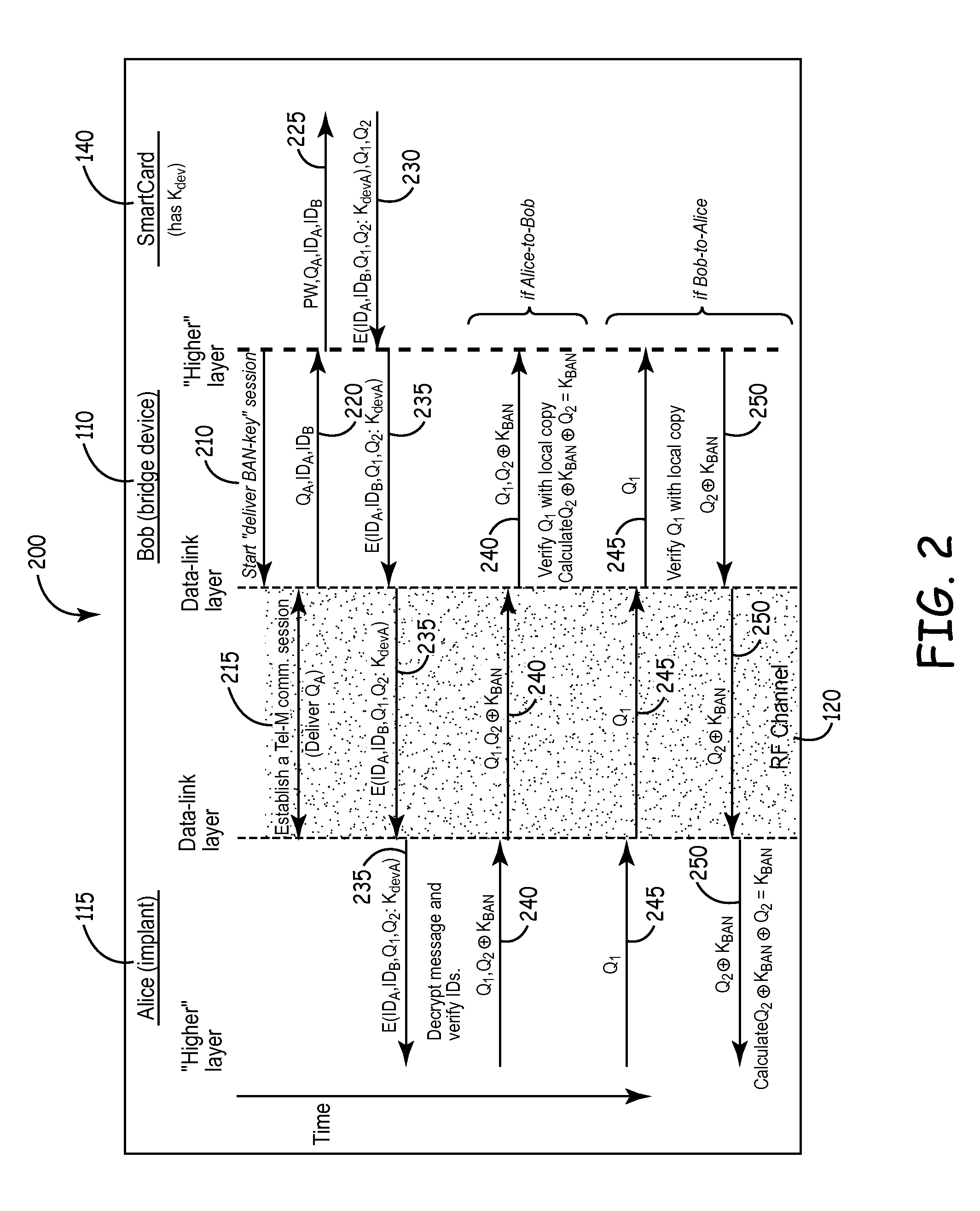
Secure telemetric link
ActiveUS20120330380A1Sufficient powerPrevent adverse health effectElectrotherapyDigital data processing detailsBody area networkNetwork Communication Protocols
A communications protocol is used to provide data privacy, message integrity, message freshness, and user authentication to telemetric traffic, such as to and from implantable medical devices in a body area network. In certain embodiments, encryption, message integrity, and message freshness are provided through use of token-like nonces and ephemeral session-keys derived from device identification numbers and pseudorandom numbers.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
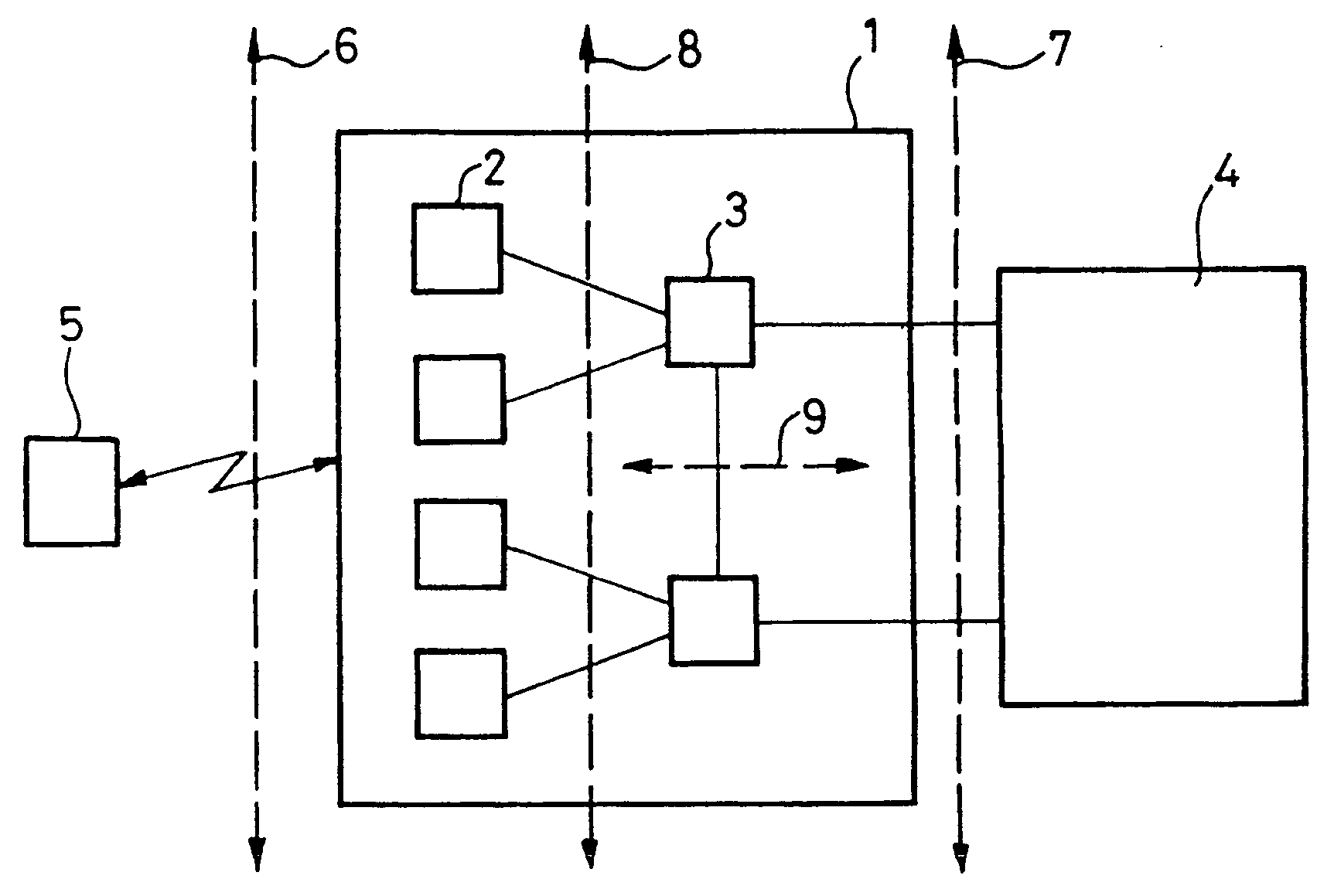
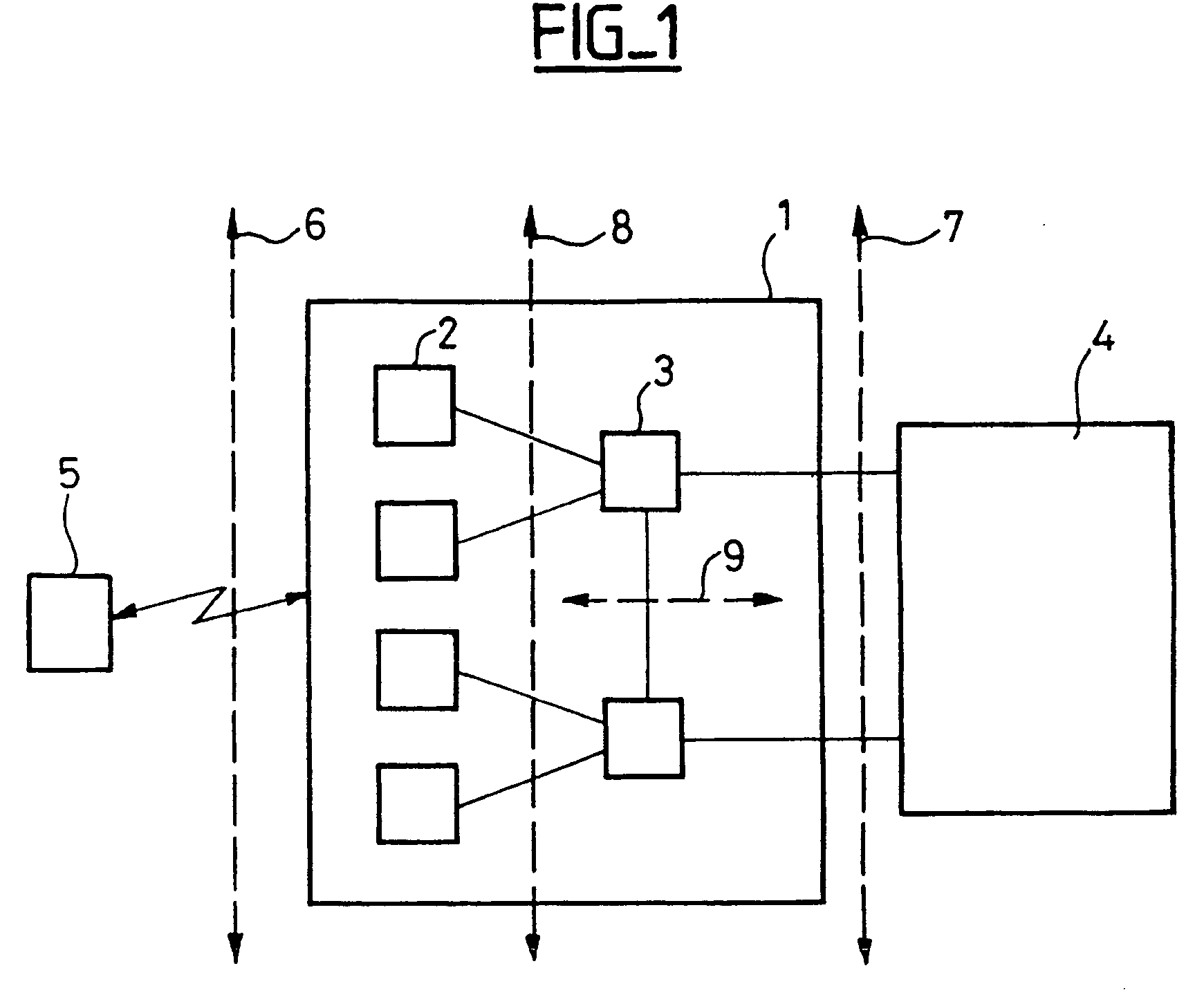
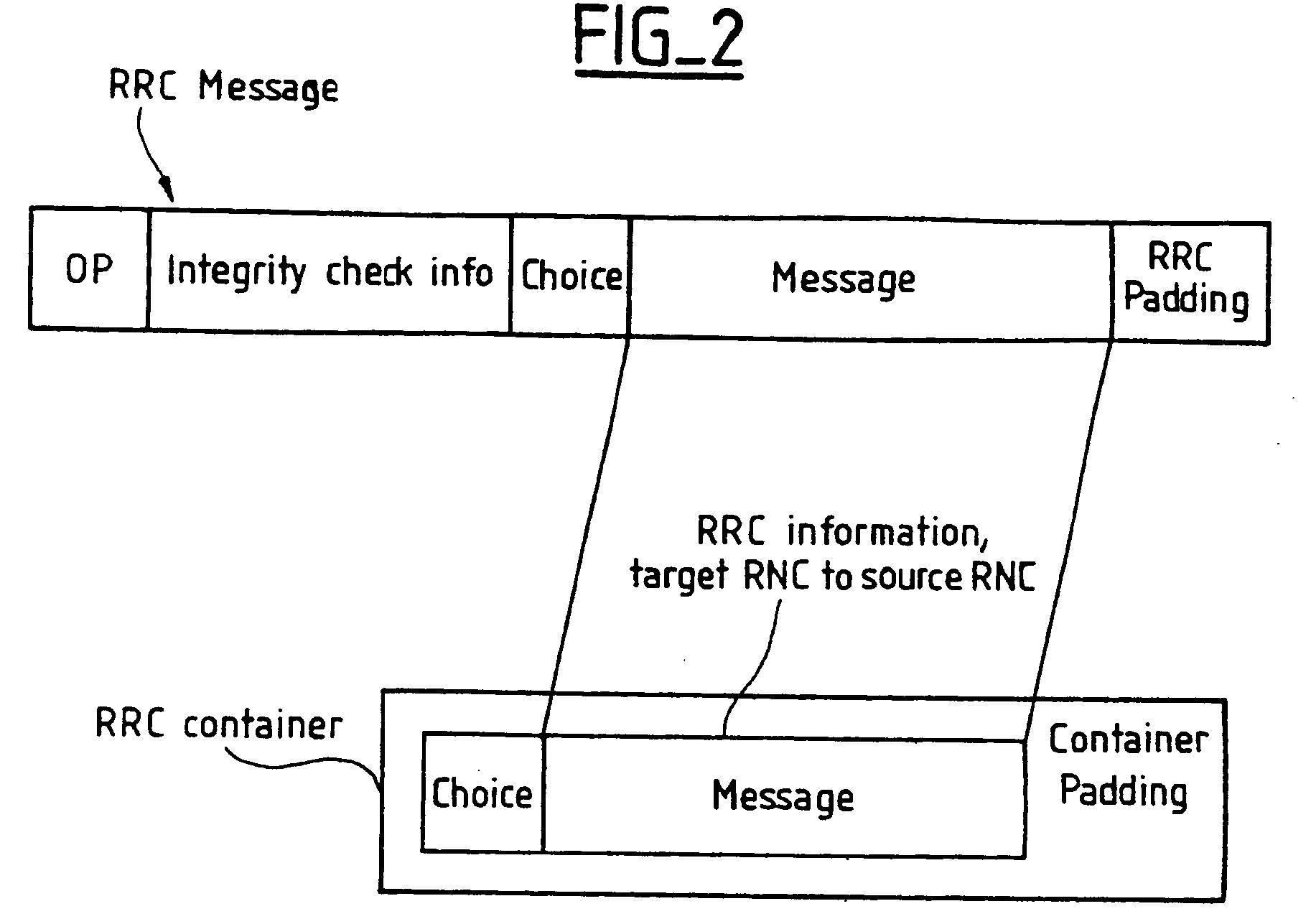
Method of protecting the integrity of messages sent in a mobile radio system
ActiveUS20040137876A1Easy to useUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsRadio access networkMobile radio
The present invention provides a method of protecting the integrity of messages sent between a mobile terminal and a server radio access network controller in a mobile radio system, in which method a message sent is protected by a code calculated on sending and, in the event of a change of server radio access network controller from a source controller to a target controller, a message sent to the mobile terminal by the source controller, for forwarding to the mobile terminal information created in the target controller and then transferred by the target controller to the source controller, is protected by a code calculated in the target controller.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and apparatus for secure aggregated event reporting
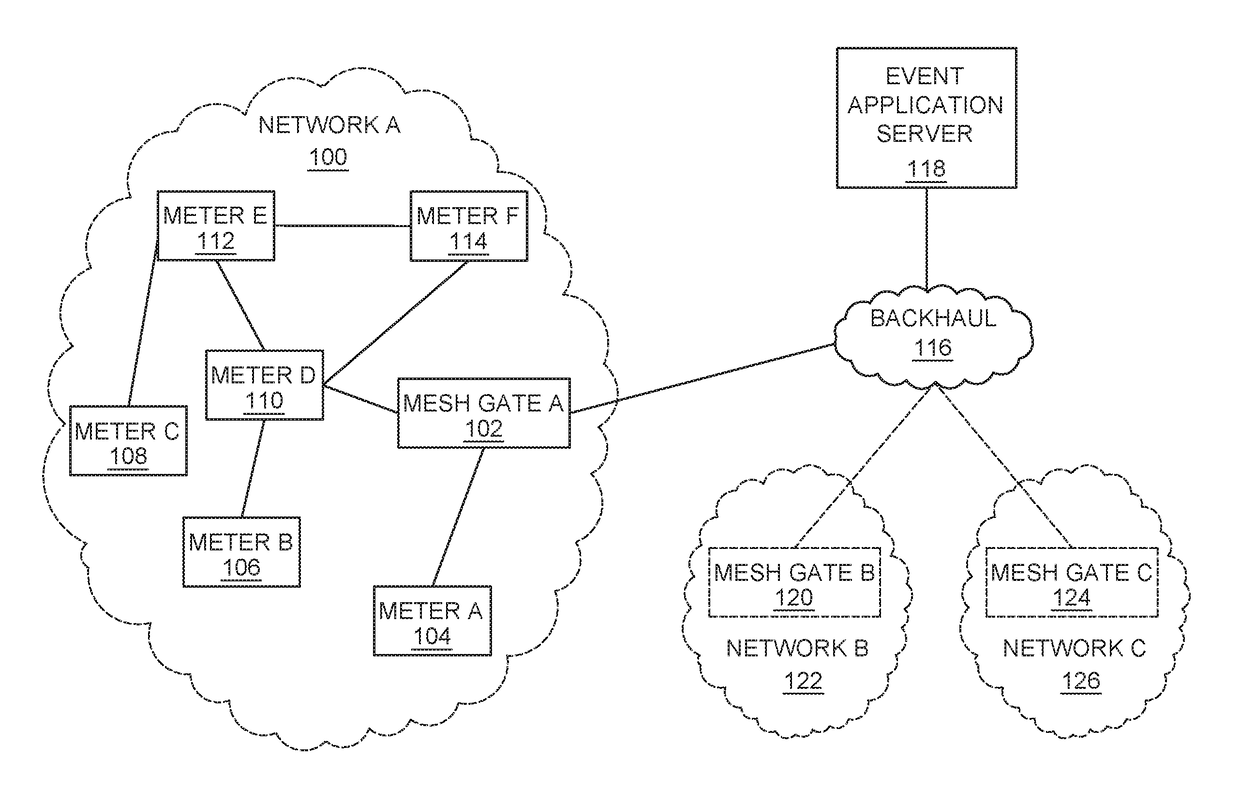
A computer implemented method and system for secure aggregated event reports. The method comprises determining, by a device, that a status change has occurred at the device; receiving, by the device, a status change report from one or more child devices; generating, by the device, a device status change record; generating a record verification field, comprising: combining a nonce, an event type, and a unique device identifier; generating a message integrity check code for the combined nonce, event type and device identifier; and appending the message integrity check code to the device status change record; appending the device status change record to the received status change report; and transmitting, by the device, the status change report to one or more parent devices toward a head end system.
Owner:TRILLIANT NETWORKS
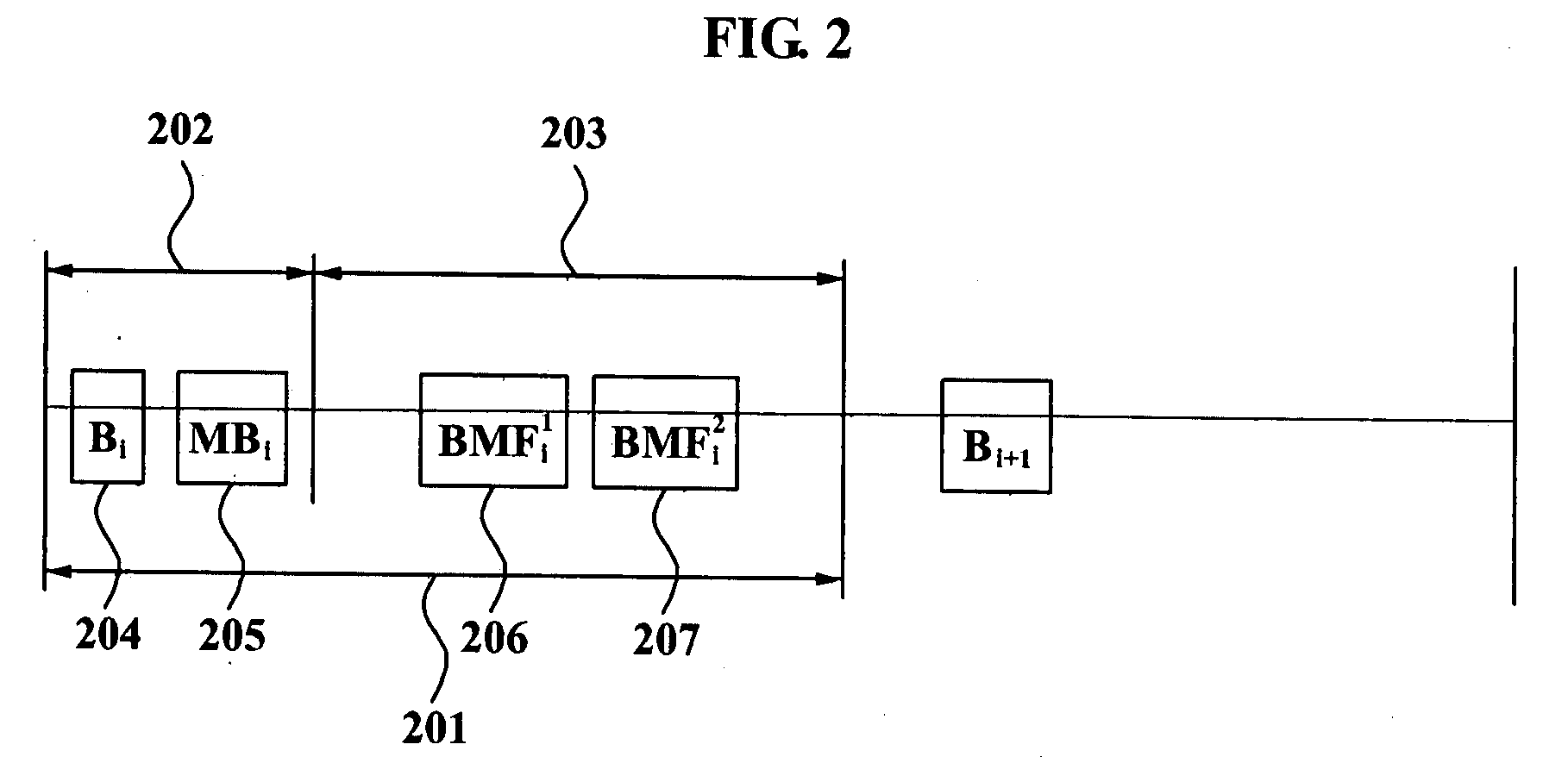
Method of protecting broadcast frame, terminal authenticating broadcast frame, and access point broadcasting broadcast frame
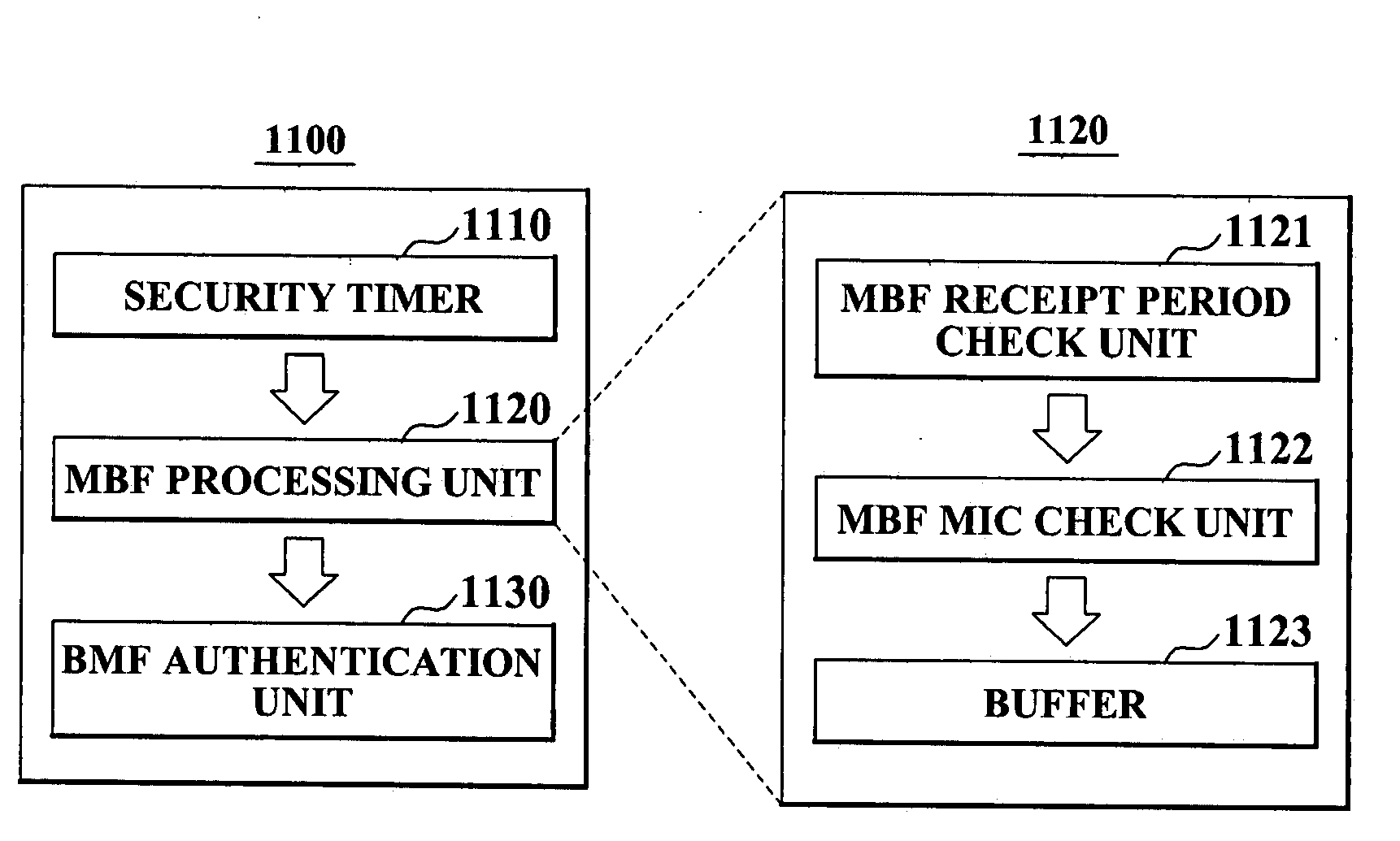
ActiveUS20080159535A1Increase the number ofMultiple keys/algorithms usageDigital data processing detailsBeacon frameWaiting period
A method of protecting a broadcast frame, the method comprising broadcasting a beacon and a maintenance beacon frame (MBF) from an access point (AP) to a plurality of terminals during a maintenance beacon waiting period (MBWP); and broadcasting broadcast management frames (BMFs) from the AP to the plurality of terminals during a broadcast management frame waiting period (BMFWP), wherein the MBF comprises a BMFs message integrity code (MIC) field including a BMFs MIC calculated from concatenated BMFs to be sent in a current beacon interval.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
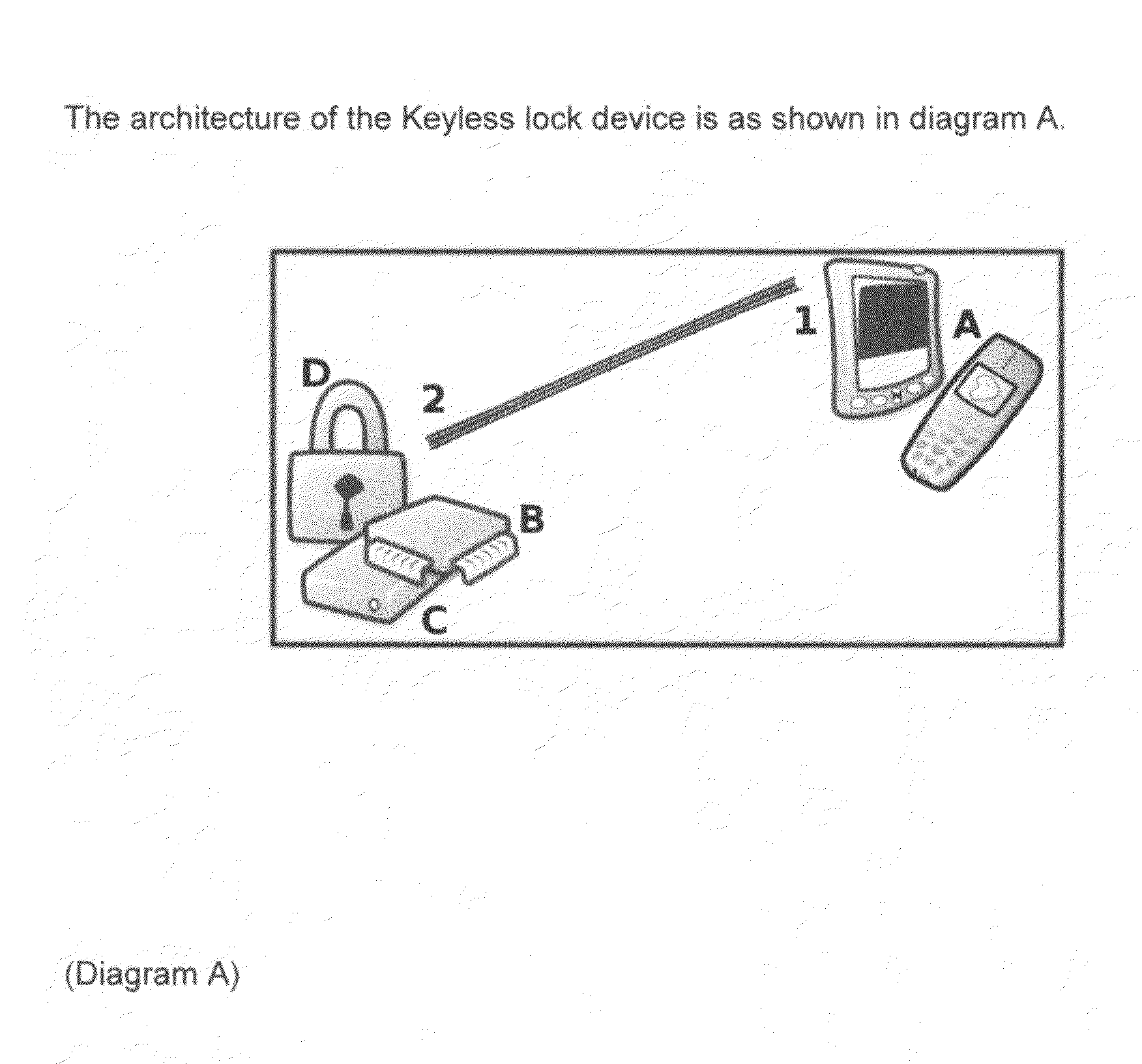
DigiKey and DigiLock
InactiveUS20080303630A1Avoid problemsImproved locking mechanismElectric signal transmission systemsDigital data processing detailsConfidentialityLocking mechanism
The present invention discloses an improvement in conventional lock and key mechanical fastening devices. This complete electronic security system utilizes a radio standard and communications protocol such as bluetooth, asymmetric cryptography encryption algorithms for authentication, confidentiality and non-repudiation purposes such as GPG, and a magnetic lock mechanism.A magnetic lock is mounted on the frame and can be set between locked and unlocked positions. The lock mechanism selectively blocks and unblocks the access opening depending on the authenication communication provided by both the emmiter (I.E. Cell Phone) and the magnetic lock. The receiving device (GPG de-encryptor) will be embedded inside the lock itself and will be responsible for verifying message integrity and origin by calculating the hash value of the received message and comparing it against the decoded signature (the original hash). If the hash from the emitter (IE Cell Phone) and the hash on the receiver (IE Magnetic Lock) side do not match, then the received message is not identical to the message which the sender “signed”, or the sender's identity is wrong, thus the magnetic lock device will not open, and an signal can be emitted via SMS thus allerting of an anomality.The emmiter (I.E. Cell Phone) will be provided with a software code for it to encrypt the message signaling a lock / unlock status to the magnetic lock using his private key, then a second encryption is performed using the receiver's public key thus achieving authentication, non-repudiation, and confidentiality.
Owner:MARTINEZ DANILO JOSE
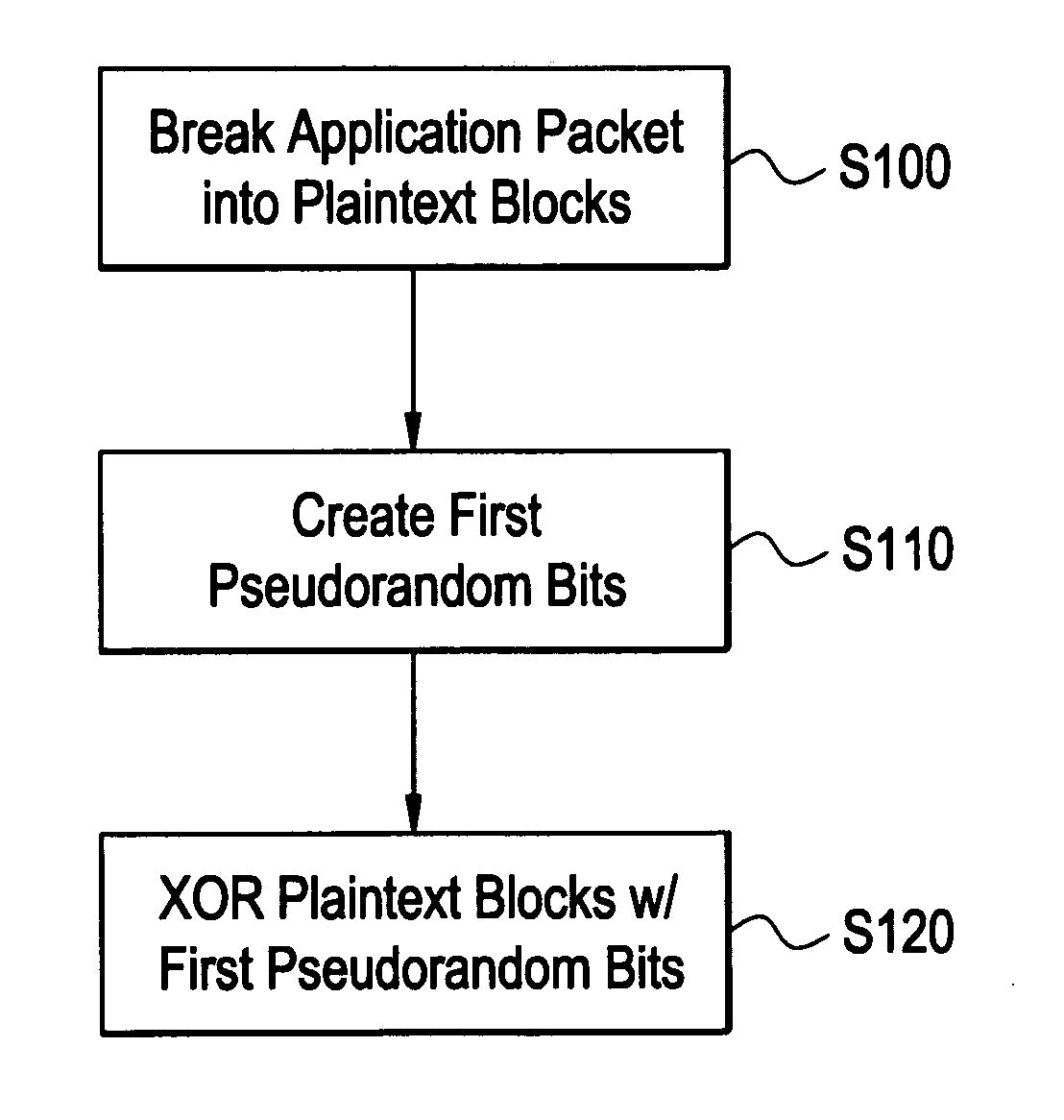
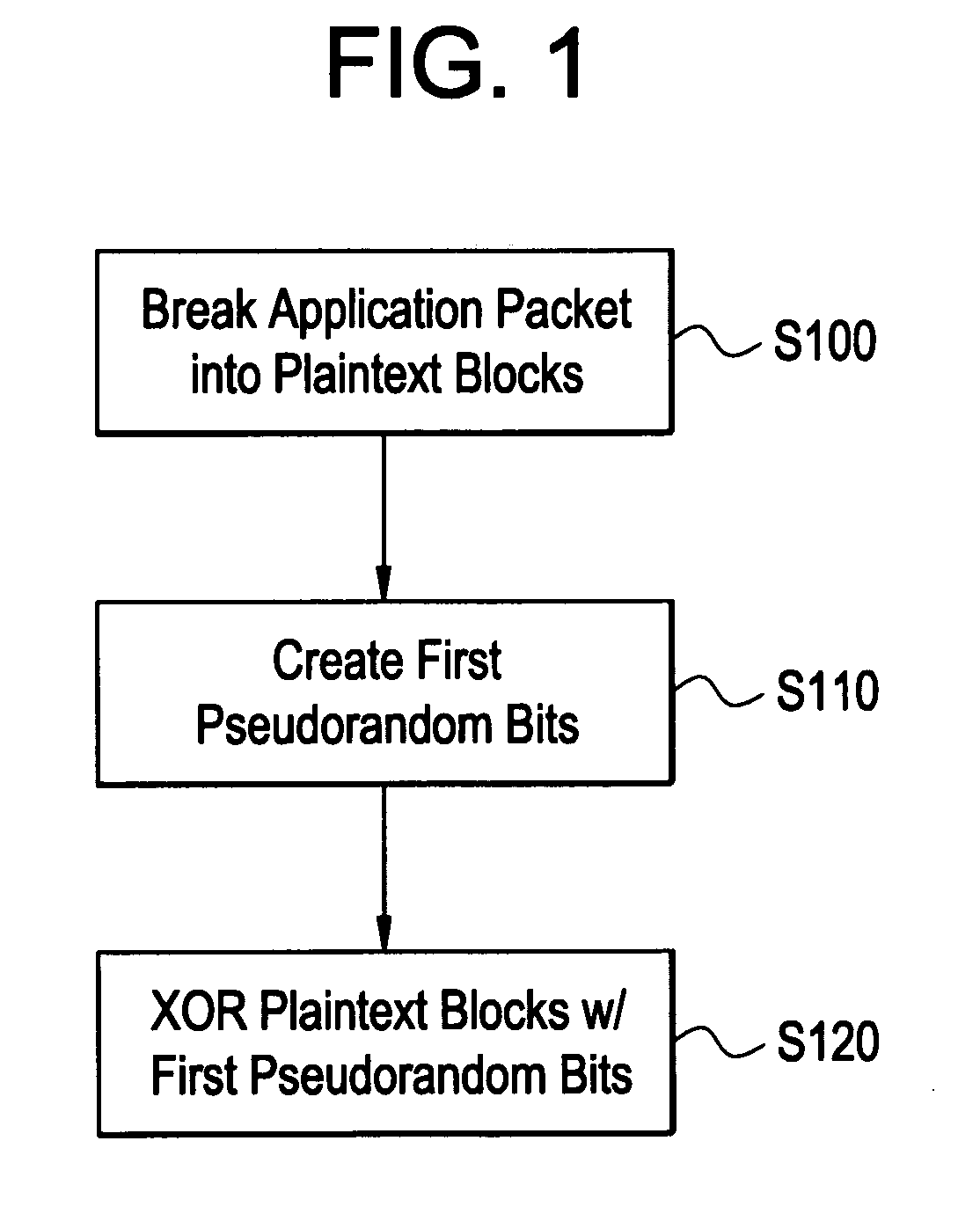
Processing method for message integrity with tolerance for non-sequential arrival of message data
ActiveUS20080165953A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareMessage integrity
One example embodiment of the present invention discloses a method for processing an application packet for transmission, includes breaking the application packet into a plurality of segments, creating first pseudorandom bits, and generating partial tags based on each of the plurality of segments and portions of the first pseudorandom bits associated with each of the plurality of segments. The method further including combining the partial tags including a last partial tag associated with a last segment of the application packet to create an accumulated tag, generating an authentication tag based on the accumulated tag and second pseudorandom bits, storing the authentication tag, and transmitting the plurality of segments including the authentication tag.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
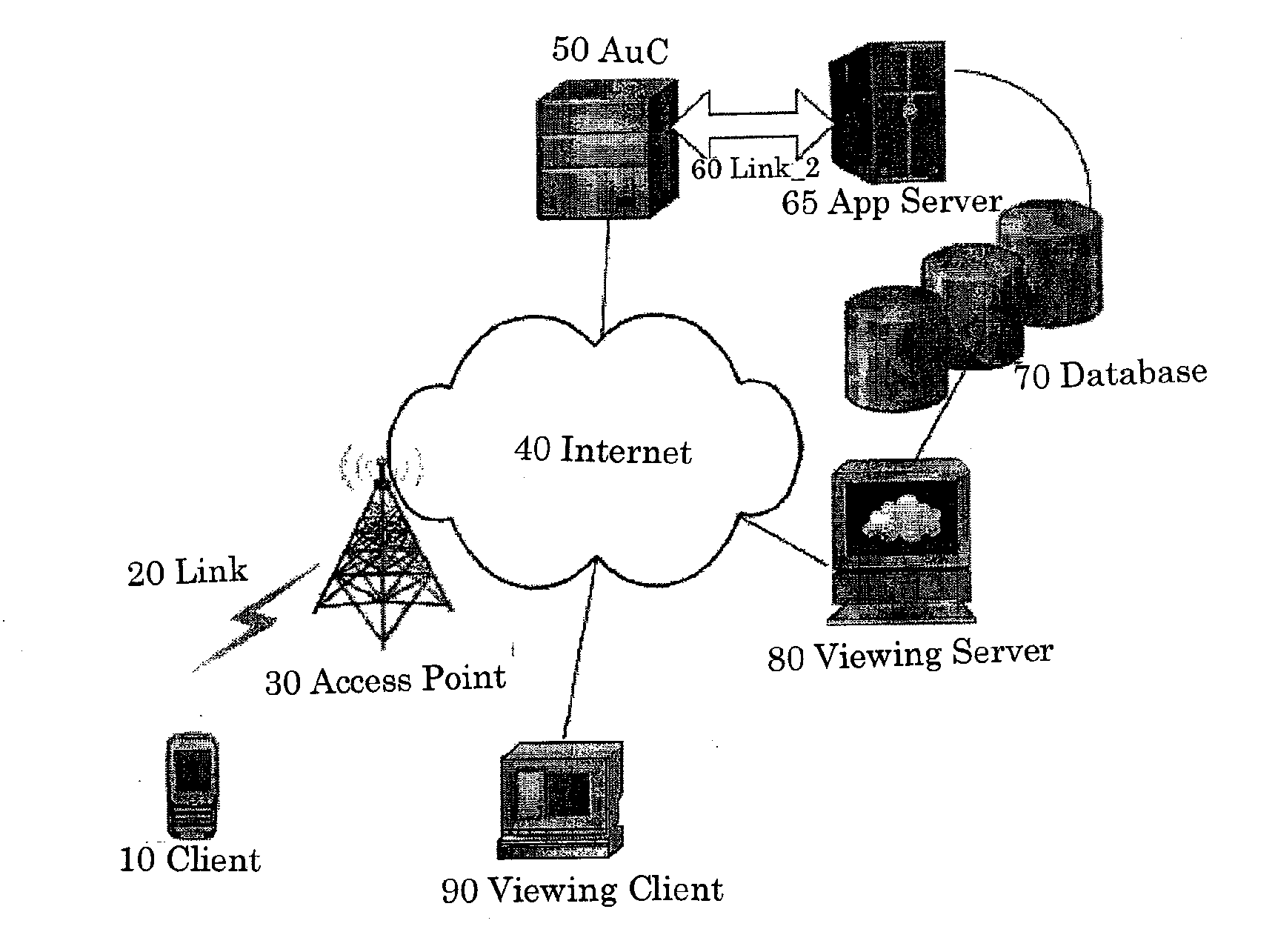
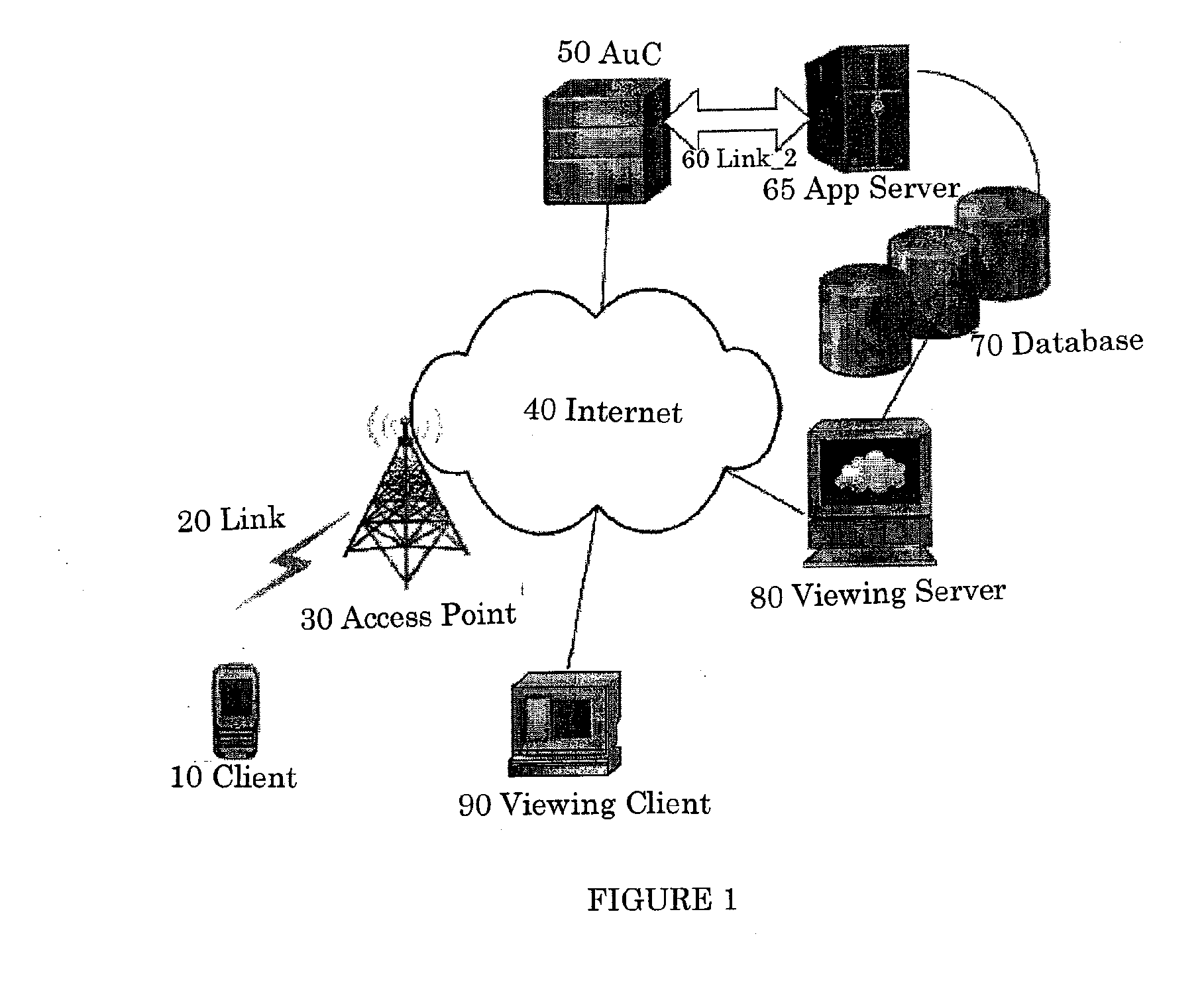
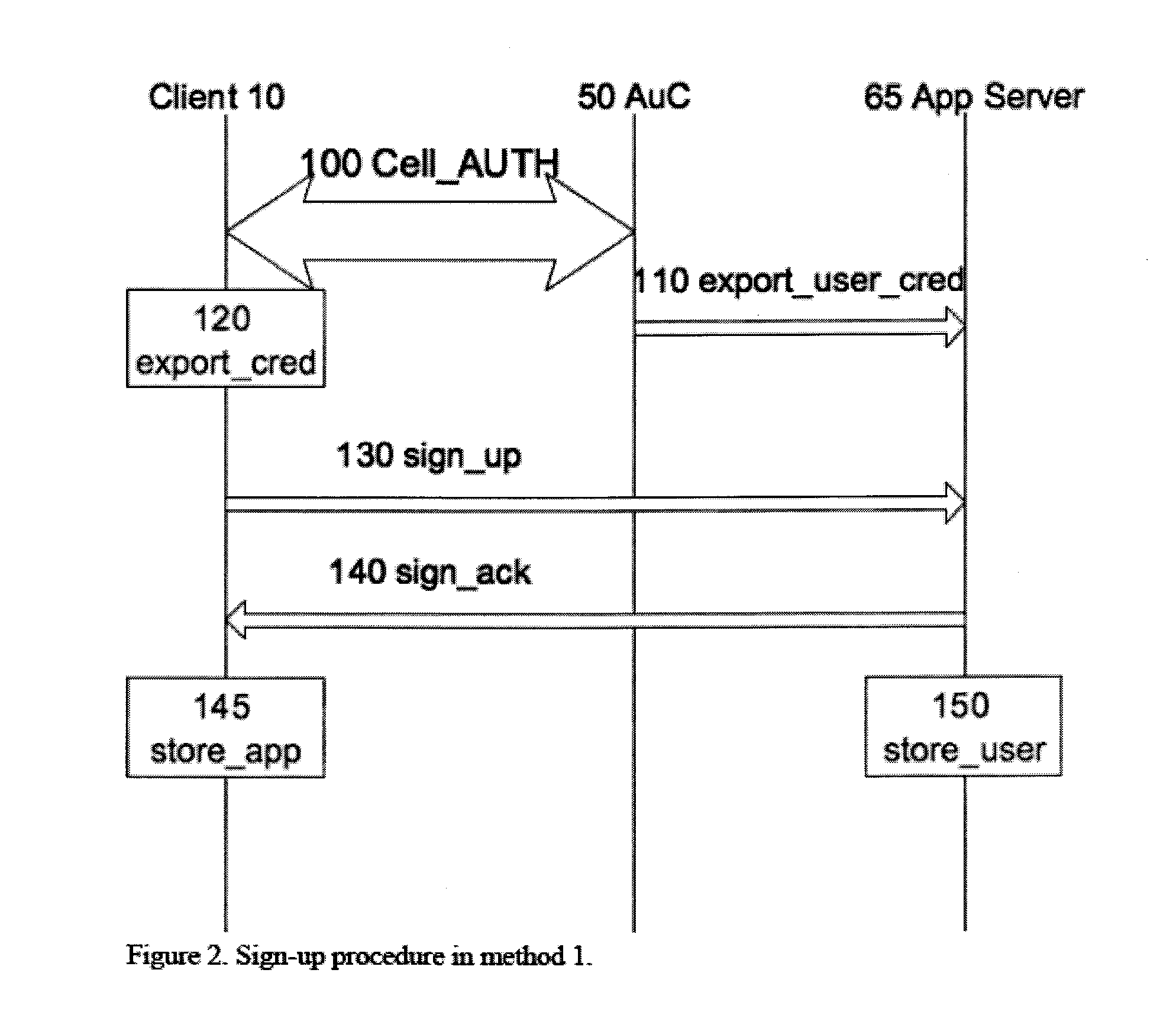
Systems and Methods for Secure Sign-Up Procedures for Application Servers in Wired and Wireless Environments
InactiveUS20090260070A1Strong mutual authenticationShort timeDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationApplication serverMessage integrity
Systems and methods of providing strong authentication for a client device to sign-up with an online service. Authentication can involve verifying user's identity, message authentication, message integrity and nonrepudiation. The security procedures may, in some cases, be sufficient to verify all of these parameters. In other cases, the sign-up procedure needs to be combined with other information in order to verify the user's real identity.
Owner:ELEVATE TECH
Method and device for checking management frames in wireless local area networks
InactiveCN101616412APrevent spoofing attacksNetwork topologiesSecurity arrangementMessage integrityInformation integration
The invention discloses a method and a device for checking management frames in wireless local area networks. The method comprises: judging whether a management frame carries an MIC (message integrity checkout) message when receiving the management frame; utilizing a pre-configured key to check the message integrity of parts in the management frame except the MIC message when the MIC message is carried and obtaining an MIC check value; and judging the management frame legal when the MIC check value is identical with the MIC message carried by the management frame, otherwise judging the management frame illegal. In the invention, by adding the MIC message to the management frame, a management frame receiver can judge the legitimacy of the received management frame so as to avoid spoofing attack based on the management frame.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
Network infrastructure validation of network management frames
ActiveUS7558960B2User identity/authority verificationNetwork topologiesRogue access pointNetwork management
A detection-based defense to a wireless network. Elements of the infrastructure, e.g., access points or scanning-only access points, detect intruders by detecting spoofed frames, such as from rogue access points. Access points include a signature, such as a message integrity check, with their management frames in a manner that enables neighboring access points to be able to validate the management frames, and to detect spoofed frames. When a neighboring access point receives a management frame, obtains a key for the access point sending the frame, and validates the management frame using the key.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Updating method of air key, terminal and base station
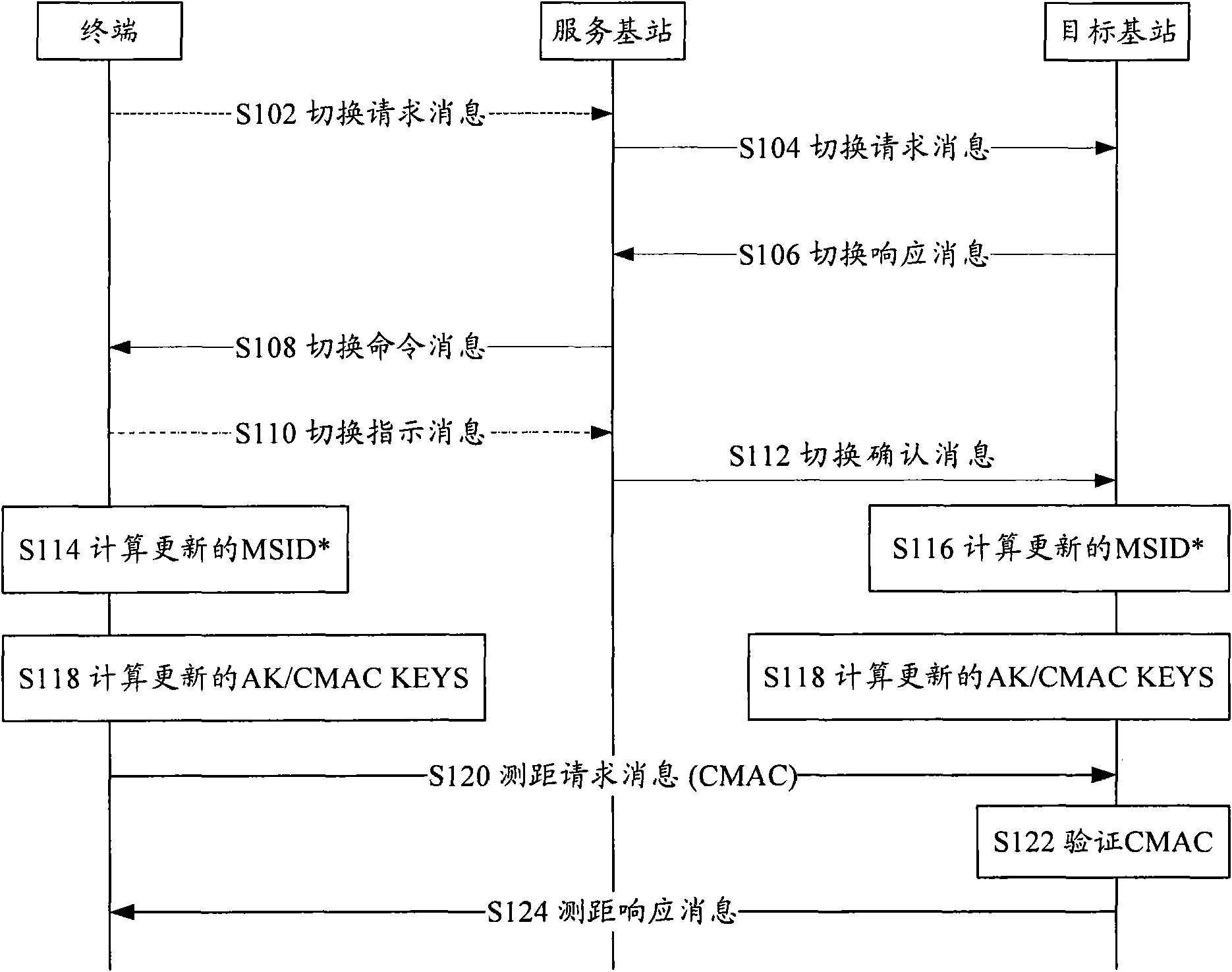
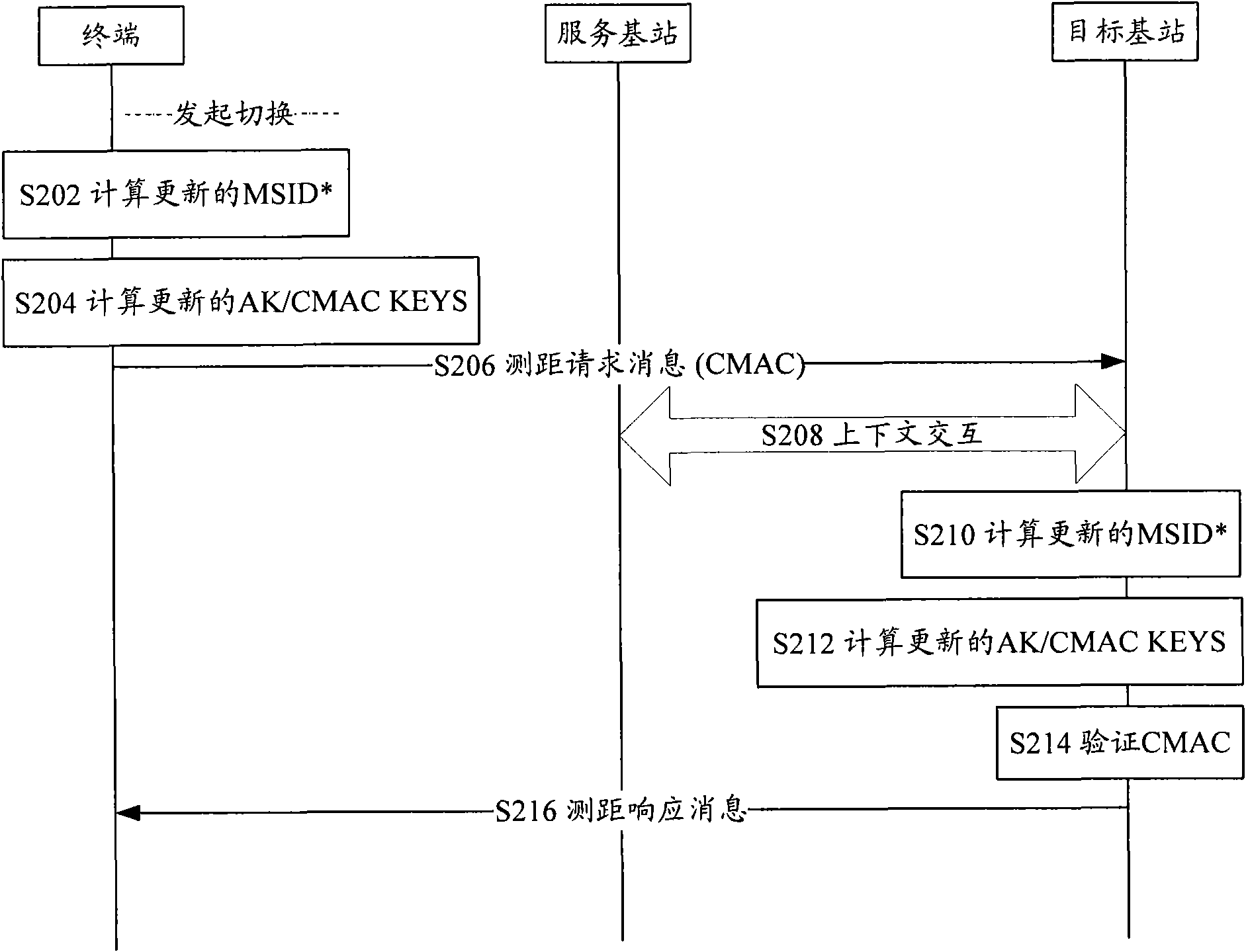
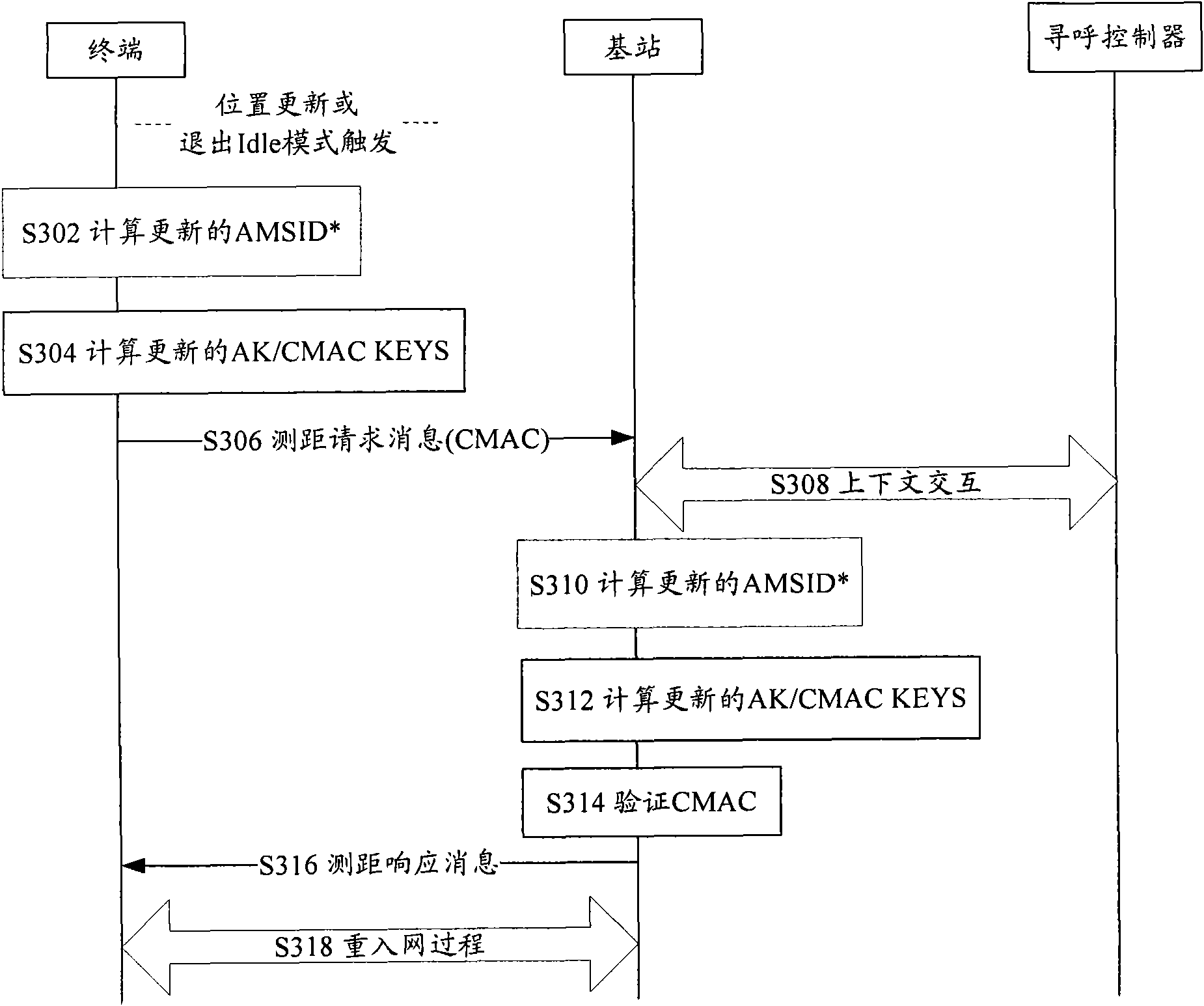
InactiveCN101631306ASolving problems for which no clear definition is givenImplement updateSecurity arrangementMessage integrityAuthorization
The invention discloses an updating method of an air key, a terminal and a base station. The method comprises the following step: the terminal updates a hashing computing value AMSID <*> of a terminal identification when switching or updating the position or exiting an idle mode, and the updated AMSID <*> computes authorization keys AK and message integrity protection keys CMAC KEYS and / or a traffic stream encryption keys TEK. The invention realizes the updating of the air key.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Authentication and Encryption for Secure Data Transmission
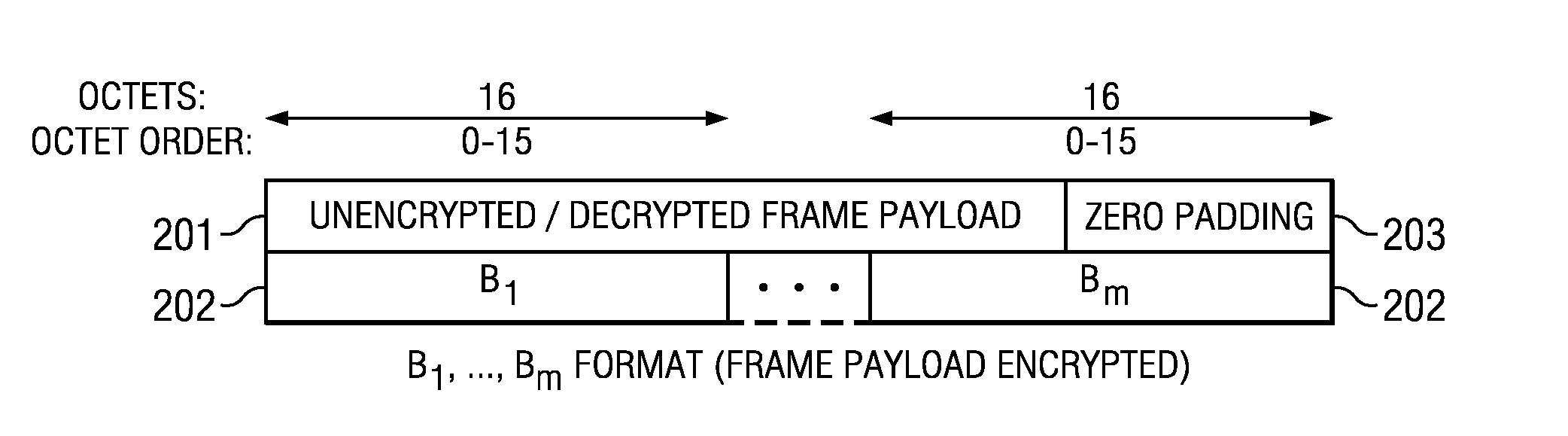
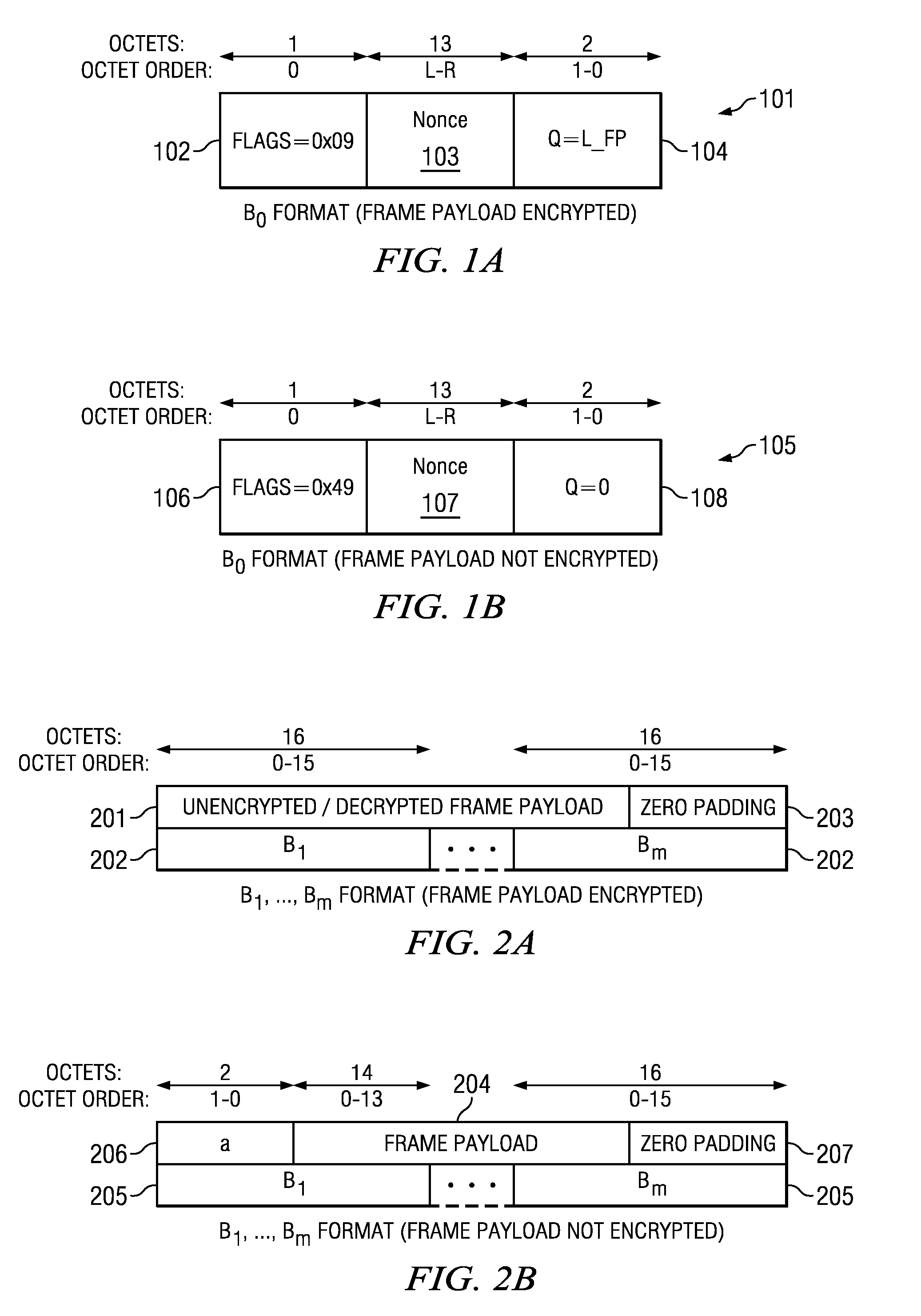
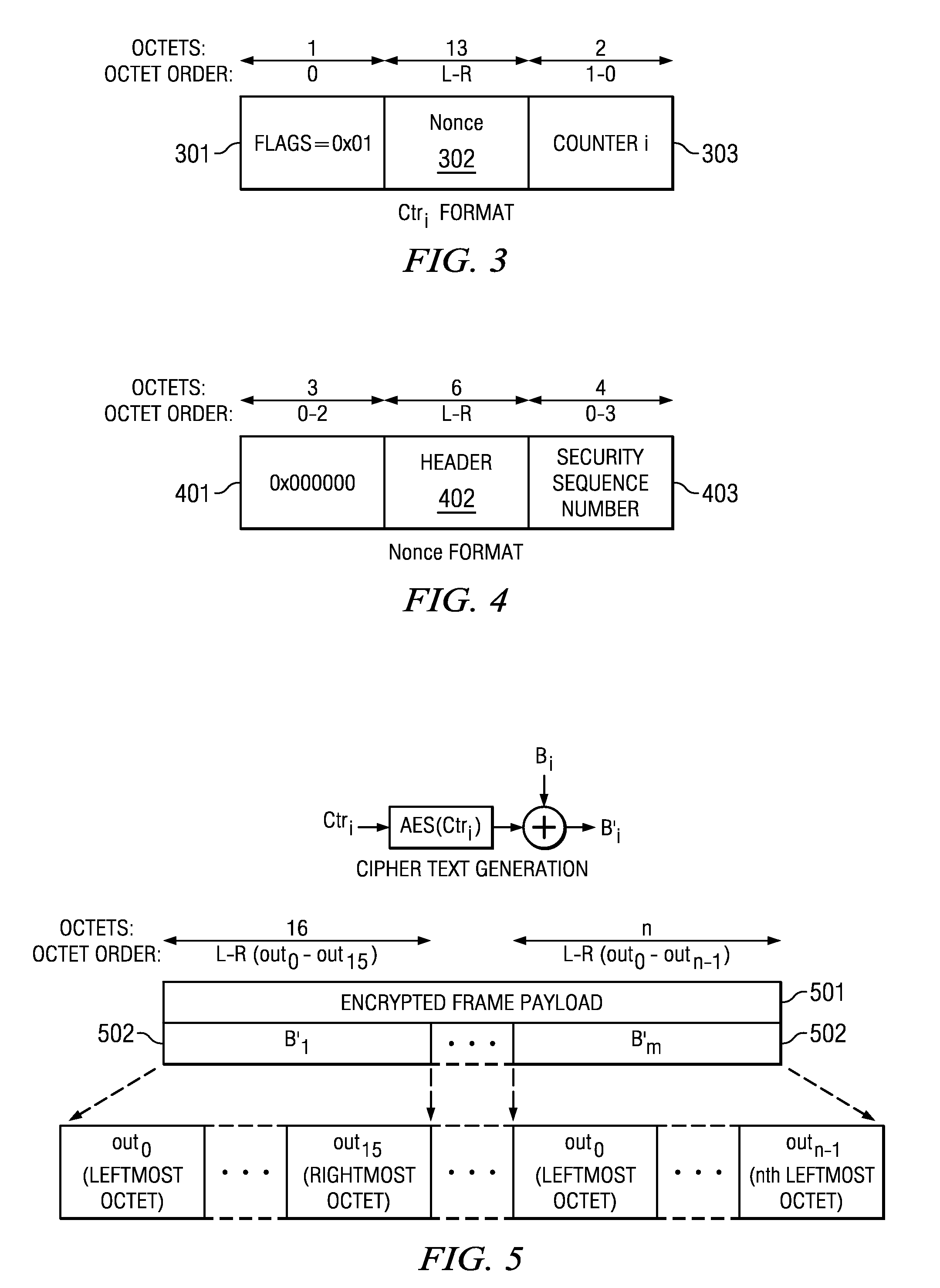
A system and method for authenticating and encrypting messages for secure transmission is disclosed. A frame to be transmitted between devices comprises a frame header and a frame body. The frame body includes a security sequence number (SSN), frame payload, and message integrity code (MIC). The SSN is incremented by one for each frame transmitted using a same pairwise temporal key (PTK). A nonce is formed using the frame header and the SSN. Counter blocks Ctri and a first input block B0 are created using the nonce. Payload blocks Bi are created from the frame payload. The frame payload encrypted by sequentially applying the blocks of payload data Bi and corresponding counter blocks Ctri to a cipher function. The MIC is computed by cipher block chaining a cipher function applied to blocks B0 and Bi, and counter block Ctr0. The cipher functions all use the PTK.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
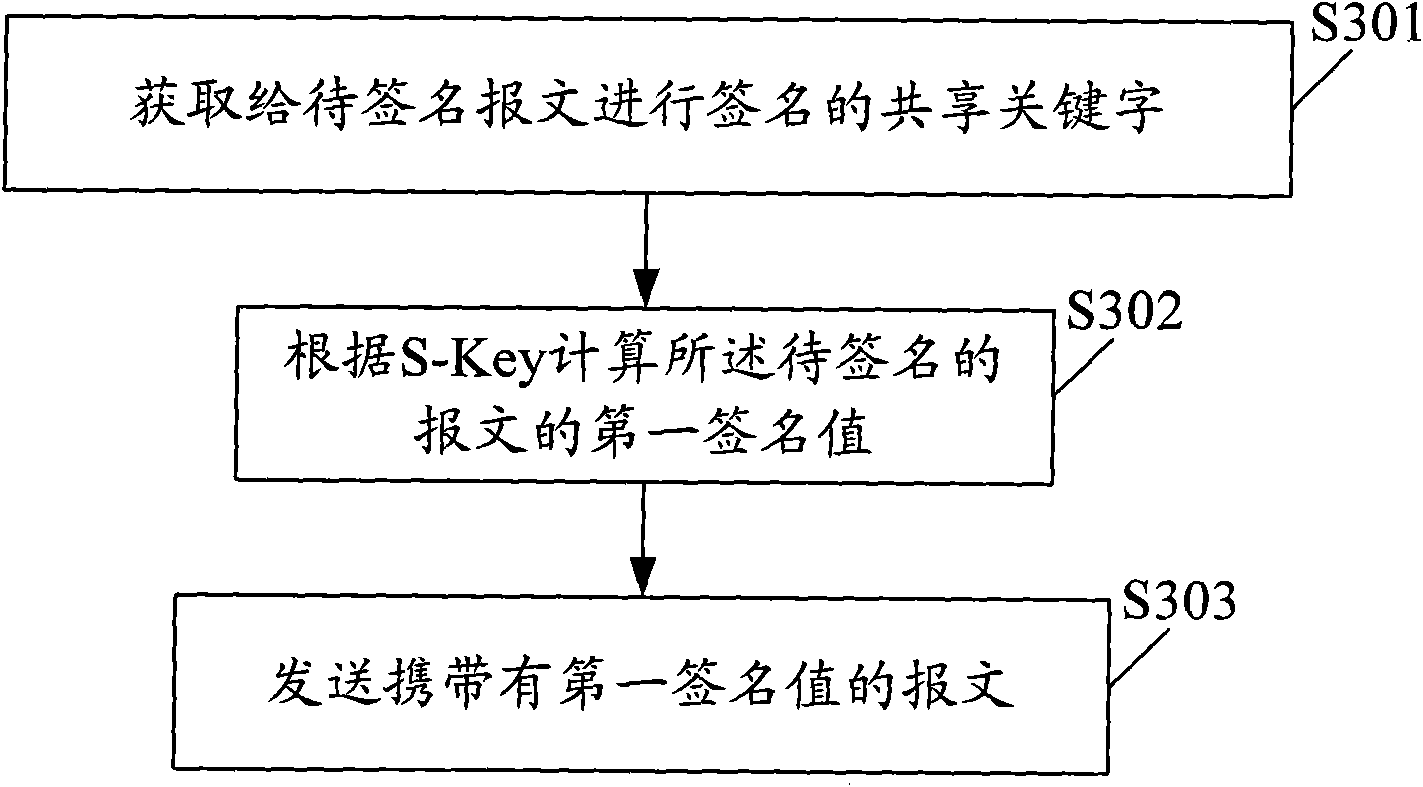
Communication system, verification device, and verification and signature method for message identity
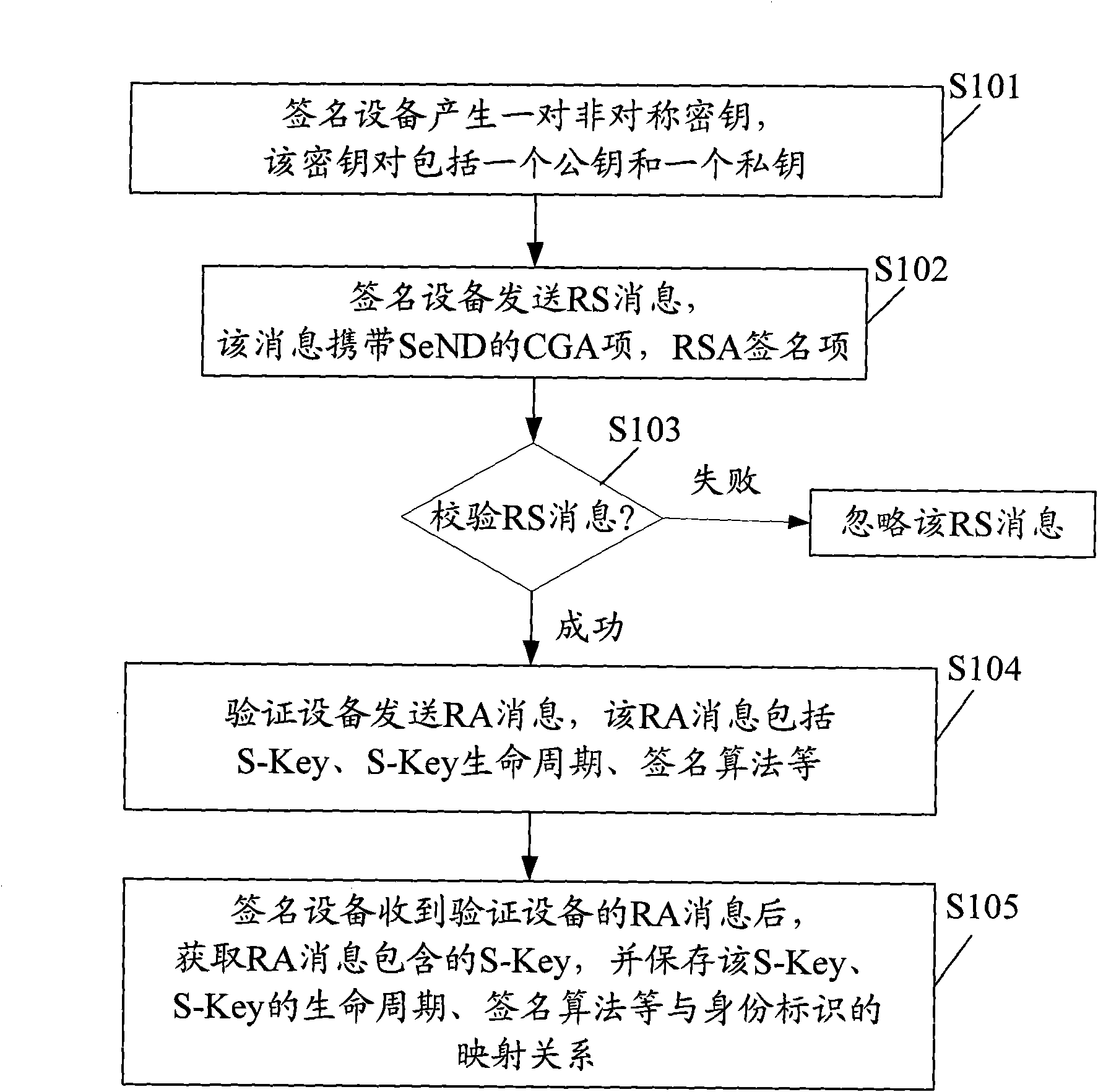
InactiveCN101848085ASatisfy advanced security requirementsImprove verification efficiencyUser identity/authority verificationData switching networksCommunications systemMessage integrity
The embodiment of the invention provides a communication system, a verification device, and a verification and signature method for message identity, and relates to the technical field of communication. The invention provides a mobile access user terminal, and verification of message identity transmitted by the access user terminal in the form of PON and radio broadcasting. The system comprises a signature device and a verification device, wherein the signature device is used for transmitting a message carrying a first signature value; and the verification device is used for receiving the message, which carries the first signature value and is transmitted by the signature device, acquiring sharing key words for verifying the message, computing a second signature value of the message according to the sharing key words and comparing the second signature value with the first signature value, if the second signature value is equal to the first signature value, the message is valid, otherwise, the IP message is invalid. The technical scheme can be widely used in communication systems or computer networks.
Owner:深圳市智通天下科技服务有限公司
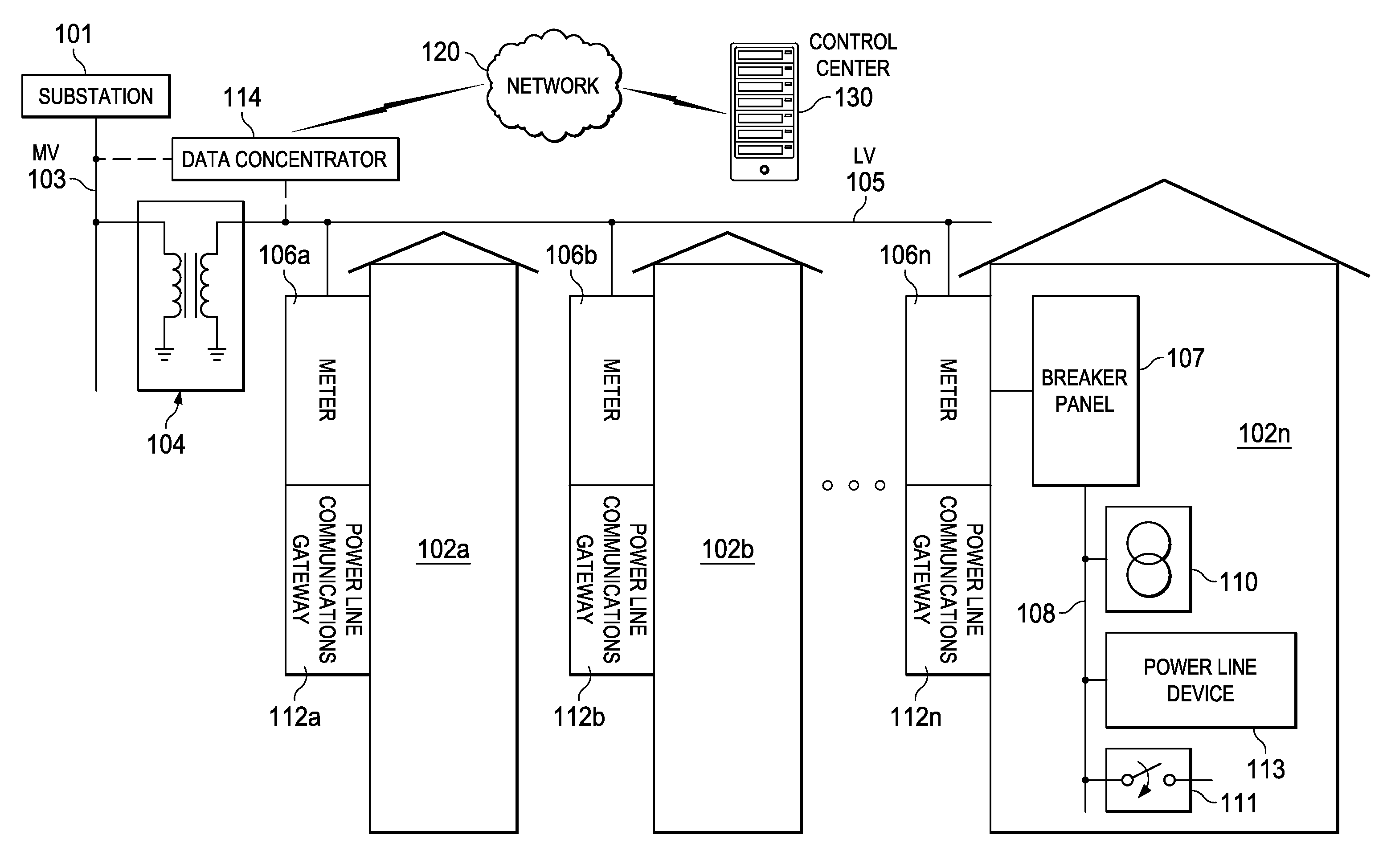
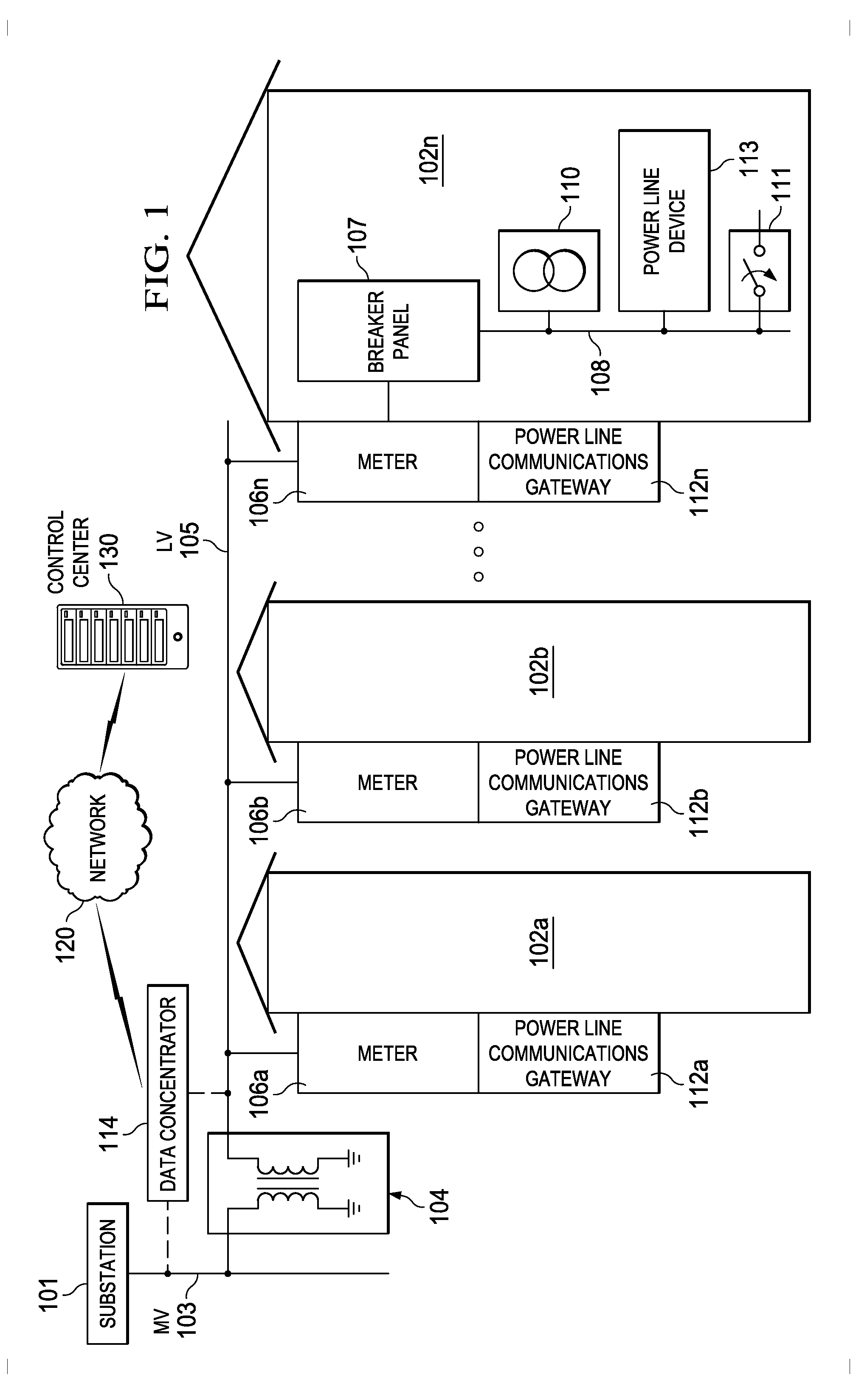
Power Line Communication (PLC) Network Nodes Using Cipher Then Segment Security
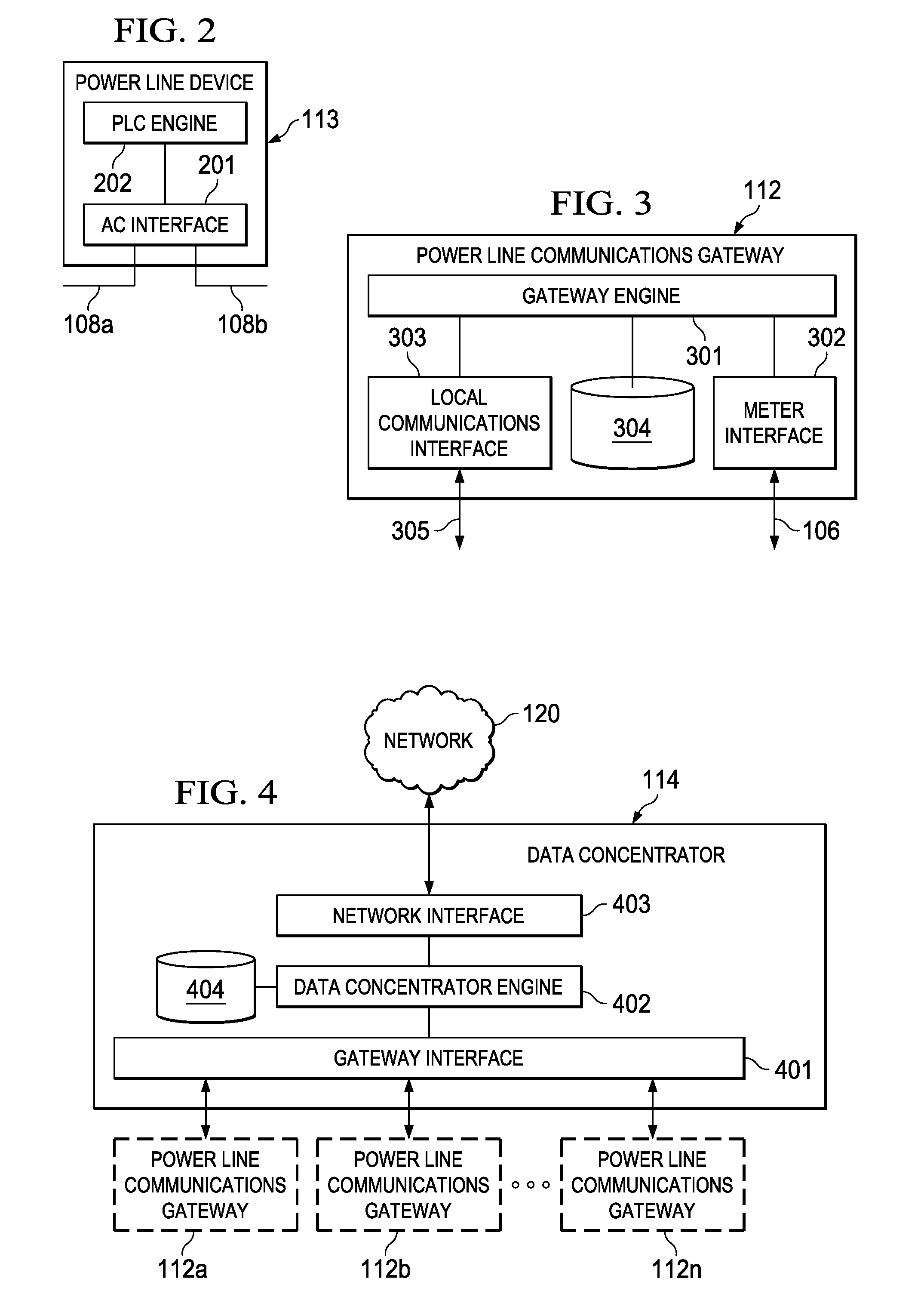
ActiveUS20150098569A1Public key for secure communicationPower distribution line transmissionComputer hardwareMessage integrity
Embodiments of the invention provide systems and methods for a cipher then segment approach in a Power Line Communication (PLC). A node or device generates frames to be transmitted to a destination node in the PLC network. A processor in the node is configured to generate a data payload comprising data to be sent to the destination node. The processor divides the data payload into two or more payload segments and encrypts the payload segments. The processor creates a frame for each of the encrypted payload segments, wherein each frame comprises a message integrity code. The processor creates a segment identifier for each frame using the message integrity code and an authentication key that is shared with the destination PLC node. The segment identifier is added to each frame.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
WAPI single broadcasting key negotiation method
ActiveCN101159543APrevent forgeryImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationMessage integrityProtocol for Carrying Authentication for Network Access
The invention relates to a WAPI unicast key negotiation method, which comprises the following steps: (1) an identifier entity adds a message integrity code to a unicast key negotiation request group and sends to an identification requester entity; (2) the identification requester entity receives the unicast key negotiation request group and then checks, if incorrect, the identification requester entity directly discards the group, otherwise performs other checks, if the check succeeds, the identification requester entity responses a unicast key negotiation response group; (3) the identifier entity receives unicast key negotiation request group and checks, if the check succeeds, response a unicast key negotiation acknowledgement group to the requester entity; (4) the identifier entity receives the unicast key negotiation acknowledgement group and then checks, if the check succeeds, the agreement of a unicast session key is reached. The invention solves the DoS attack problem of the unicast key management protocol in the existing WAPI security mechanism.
Owner:CHINA IWNCOMM
Navigation integrity monitoring system and method based on leo constellation
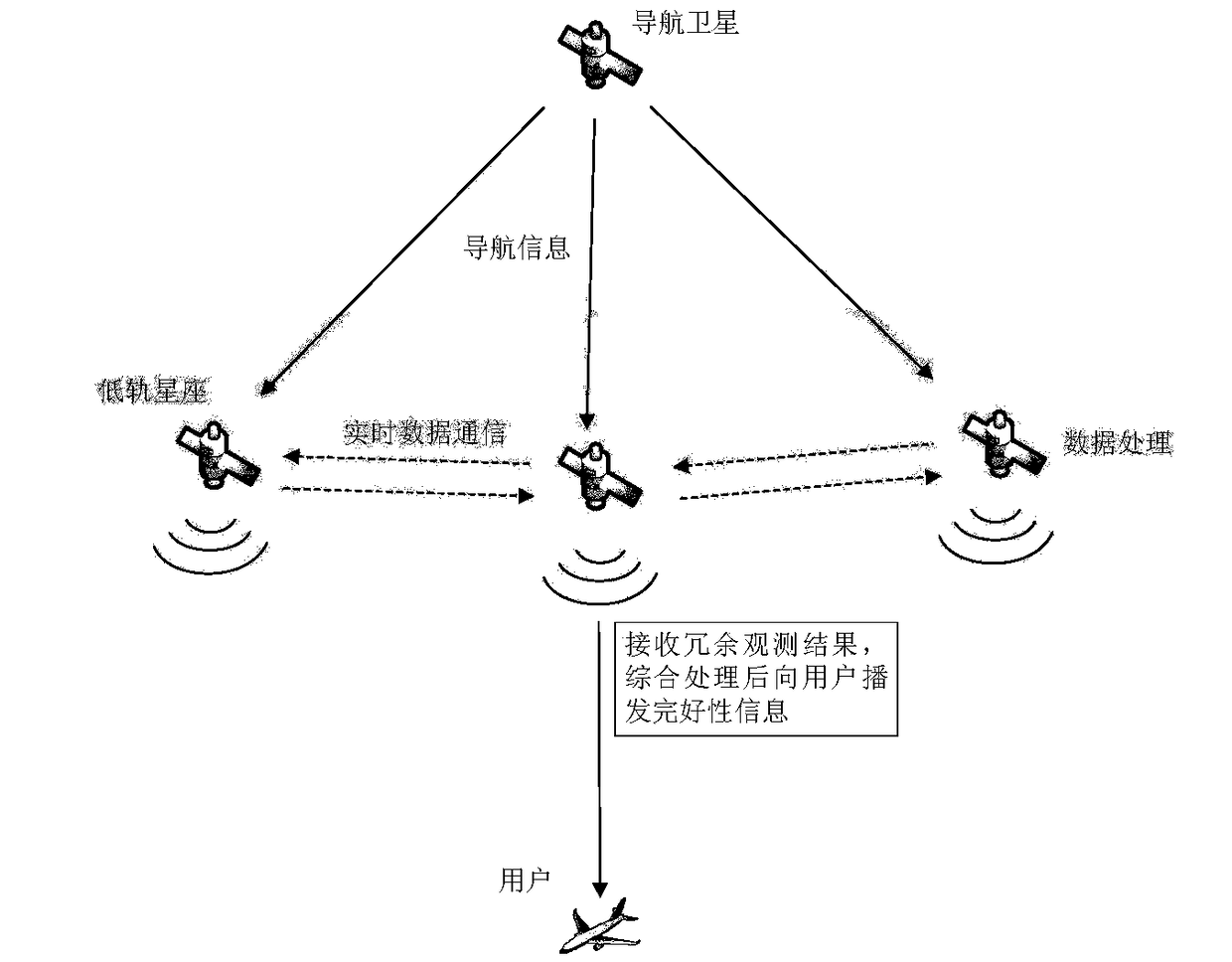
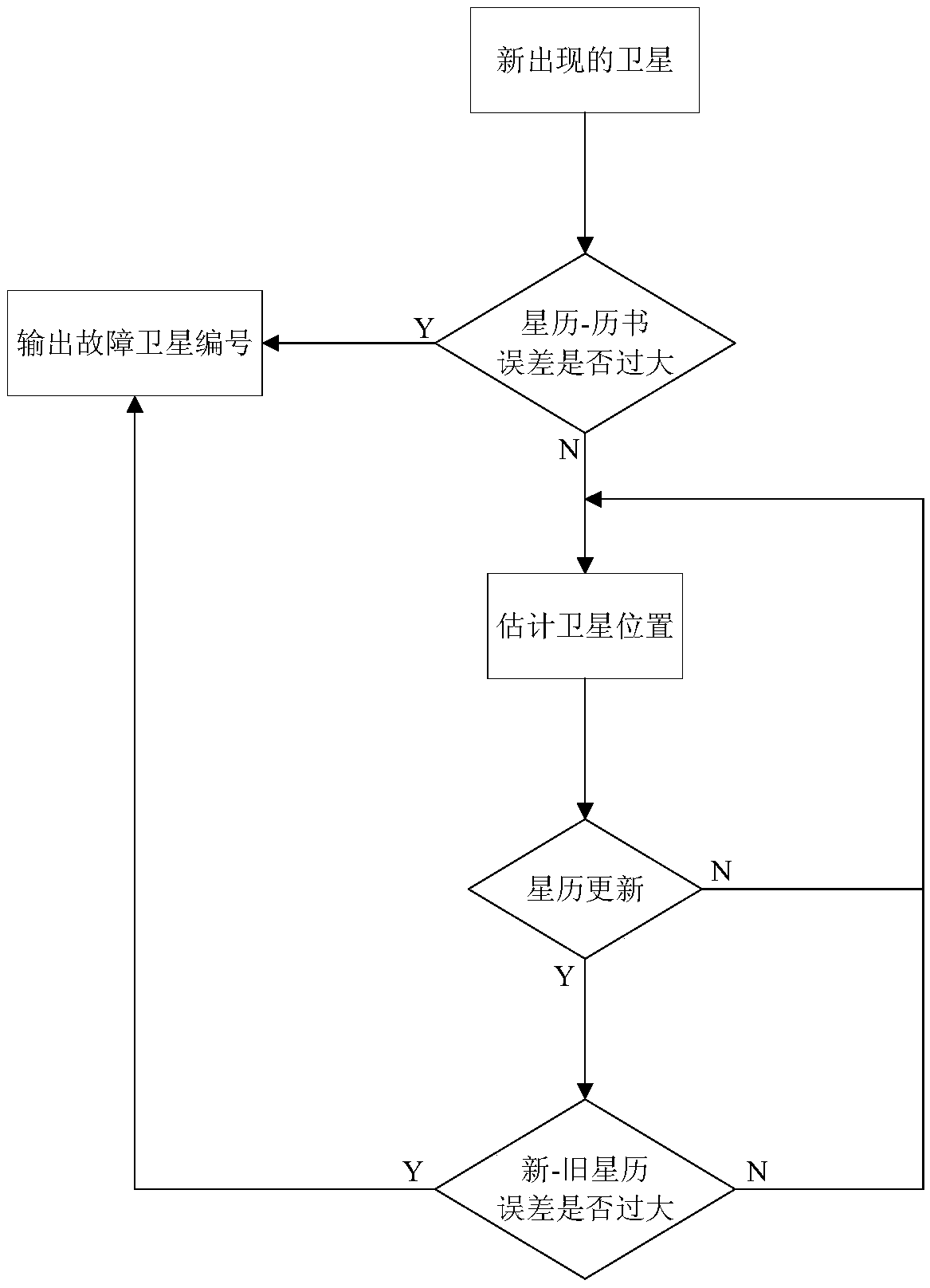
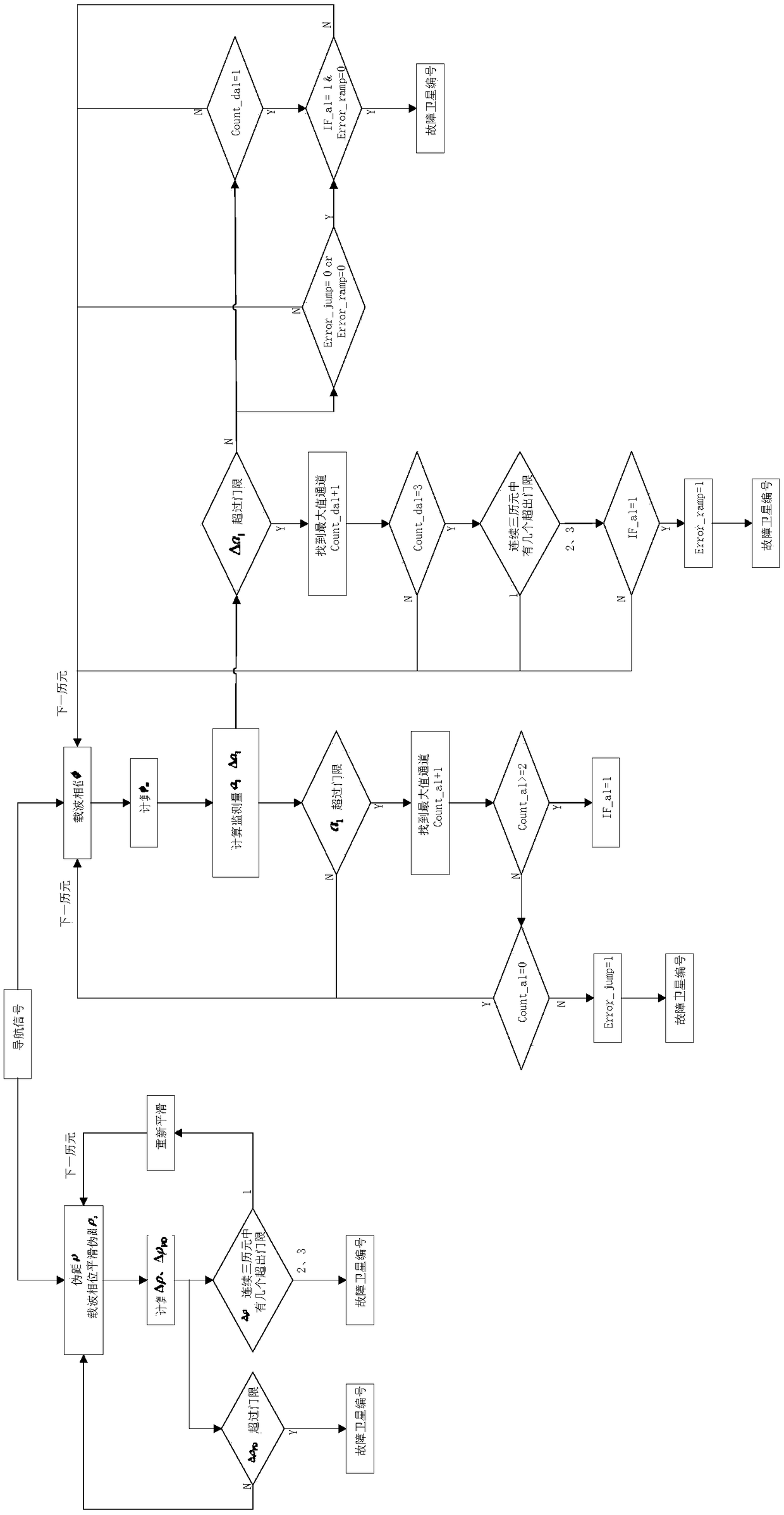
ActiveCN109100748AIncrease coverageReduce dependenceSatellite radio beaconingMonitoring systemMessage integrity
The invention discloses a navigation integrity monitoring system and method based on a leo constellation. The system comprises a plurality of leo satellites; each leo satellite serves as a space-basedmonitoring station to receive a navigation signal; each receiving channel of each leo satellite is provided with a data processing module; the data processing modules perform navigation message integrity monitoring and observed quantity integrity monitoring on the received navigation signals, and communicate with the leo satellites which can observe the same navigation satellite nearby through inter-satellite links; and redundancy judgment is carried out on processing results of all the leo satellites capable of observing the same navigation satellite through a comprehensive processing logicmodule arranged on any leo satellite, thereby giving a final navigation integrity monitoring result.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Communication apparatus and method for secure low power transmission
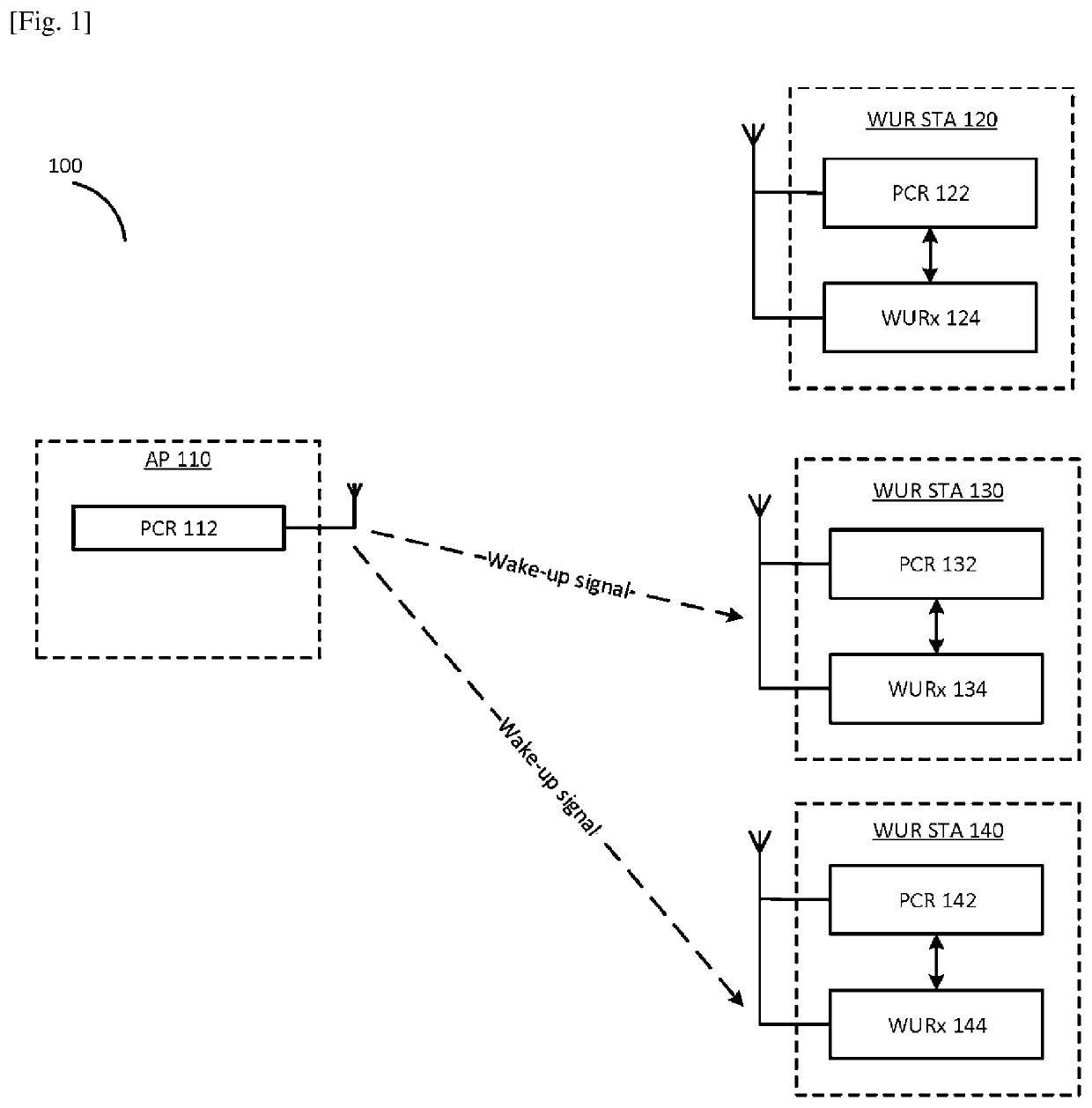
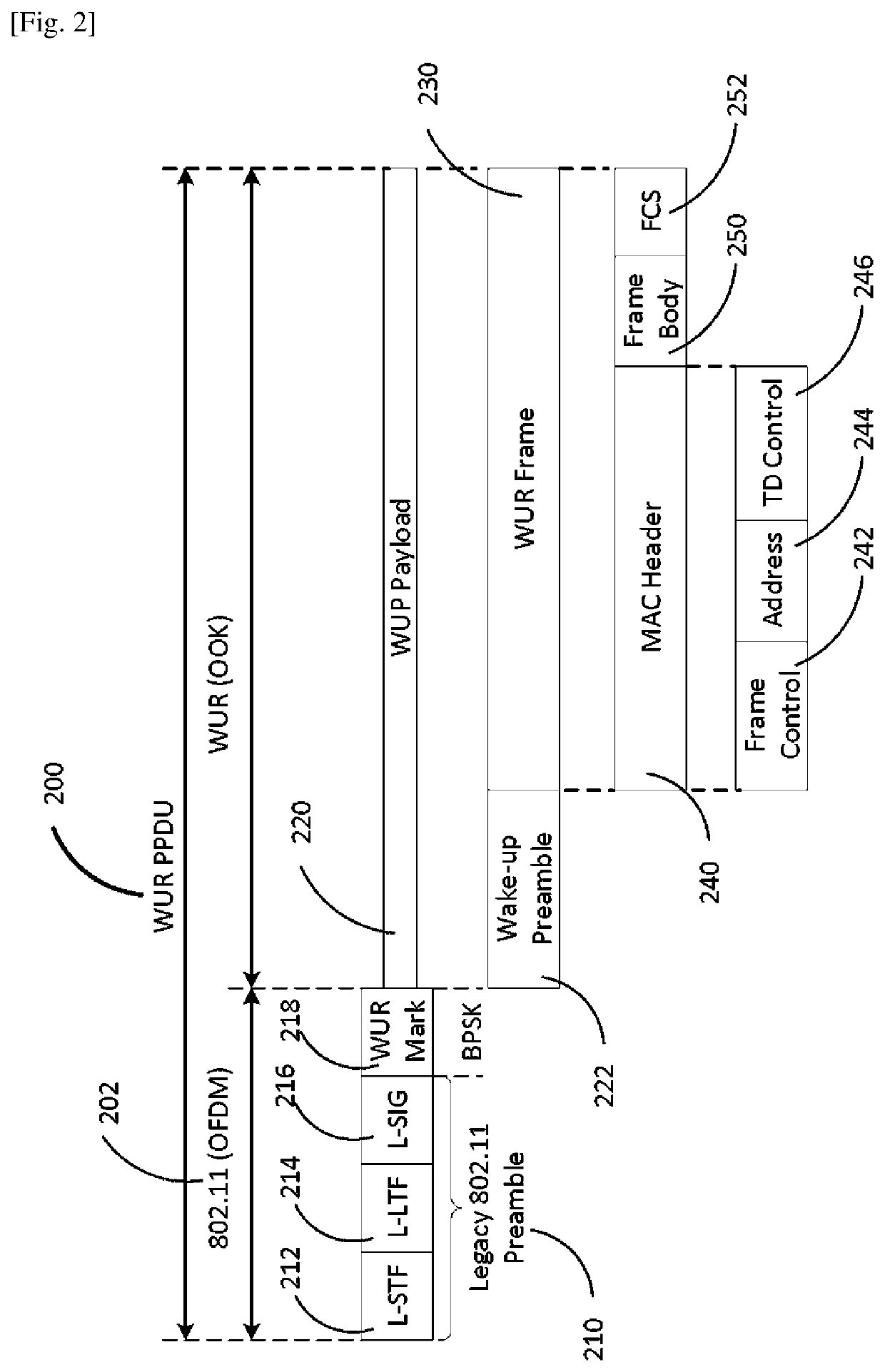
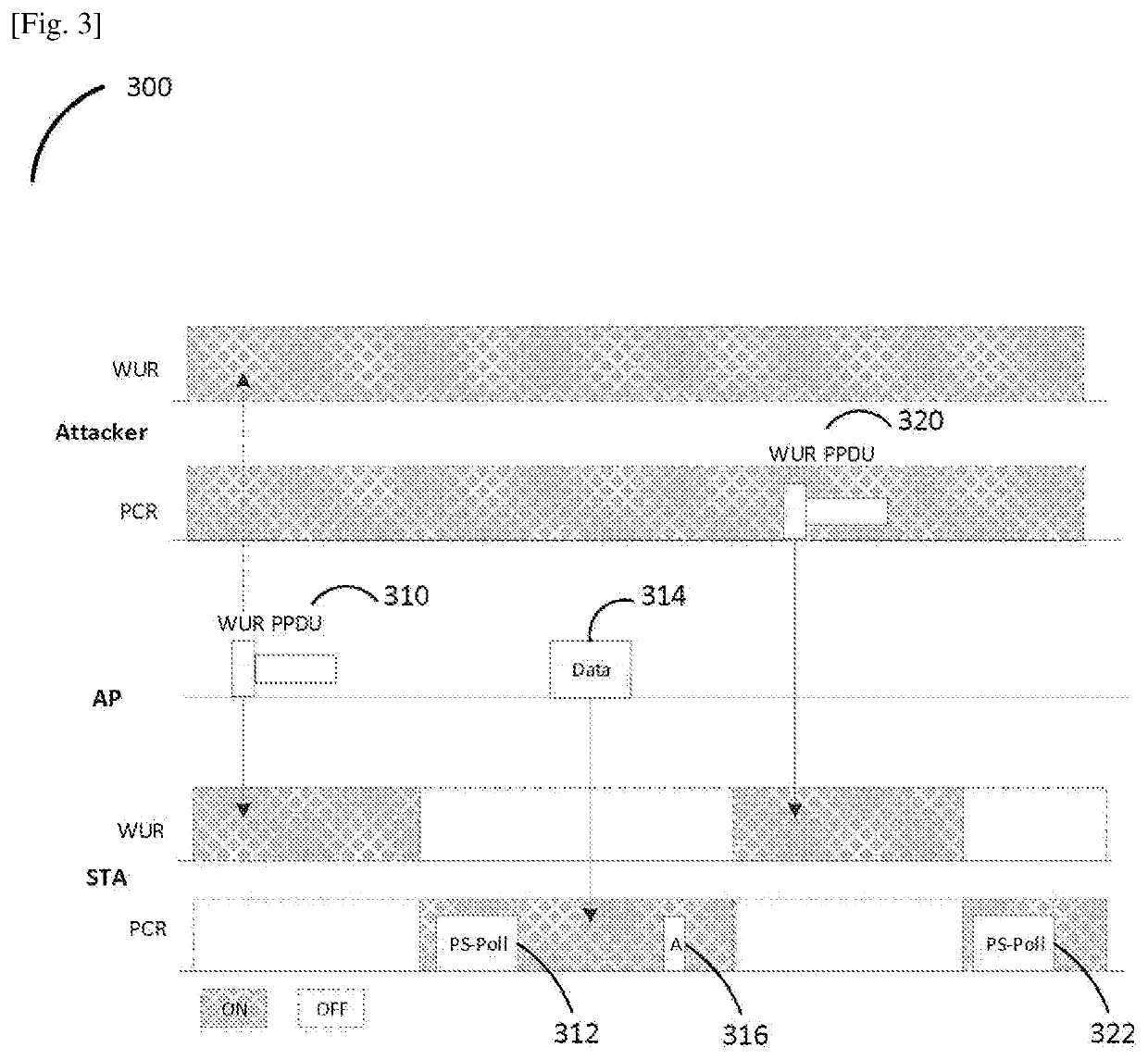
ActiveUS20200245137A1Prevent malicious attacksPower managementNetwork topologiesMessage integritySignal generator
The present disclosure provides a communication apparatus comprising a cryptographic circuitry which, in operation, uses a shared cryptographic secret Key and a cryptographic salt to generate a cryptographically encoded Message Integrity Code (MIC) that is computed over the address field of a Wake Up Radio (WUR) frame; and a transmission signal generator which, in operation, generates a secure WUR signal by replacing the address field of the WUR frame with the MIC; and a transmitter which, in operation, transmits the secure WUR signal.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY CORP OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com