Patents
Literature
423 results about "Waiting period" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
What is a Waiting Period. A waiting period is the amount of time an insured must wait before some or all of their coverage comes into effect. The insured may not receive benefits for claims filed during the waiting period. Waiting periods may also be known as elimination periods and qualifying periods.
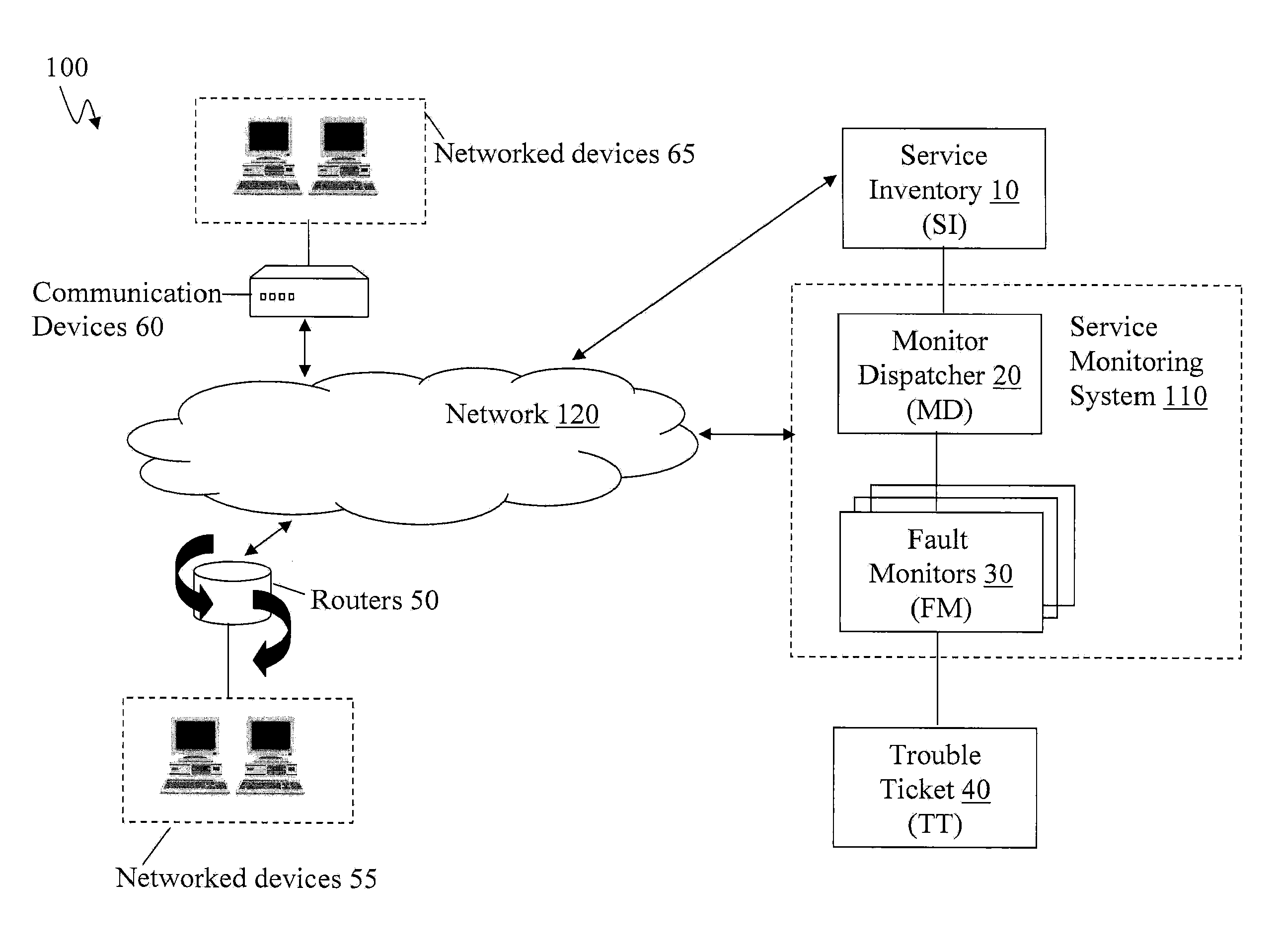
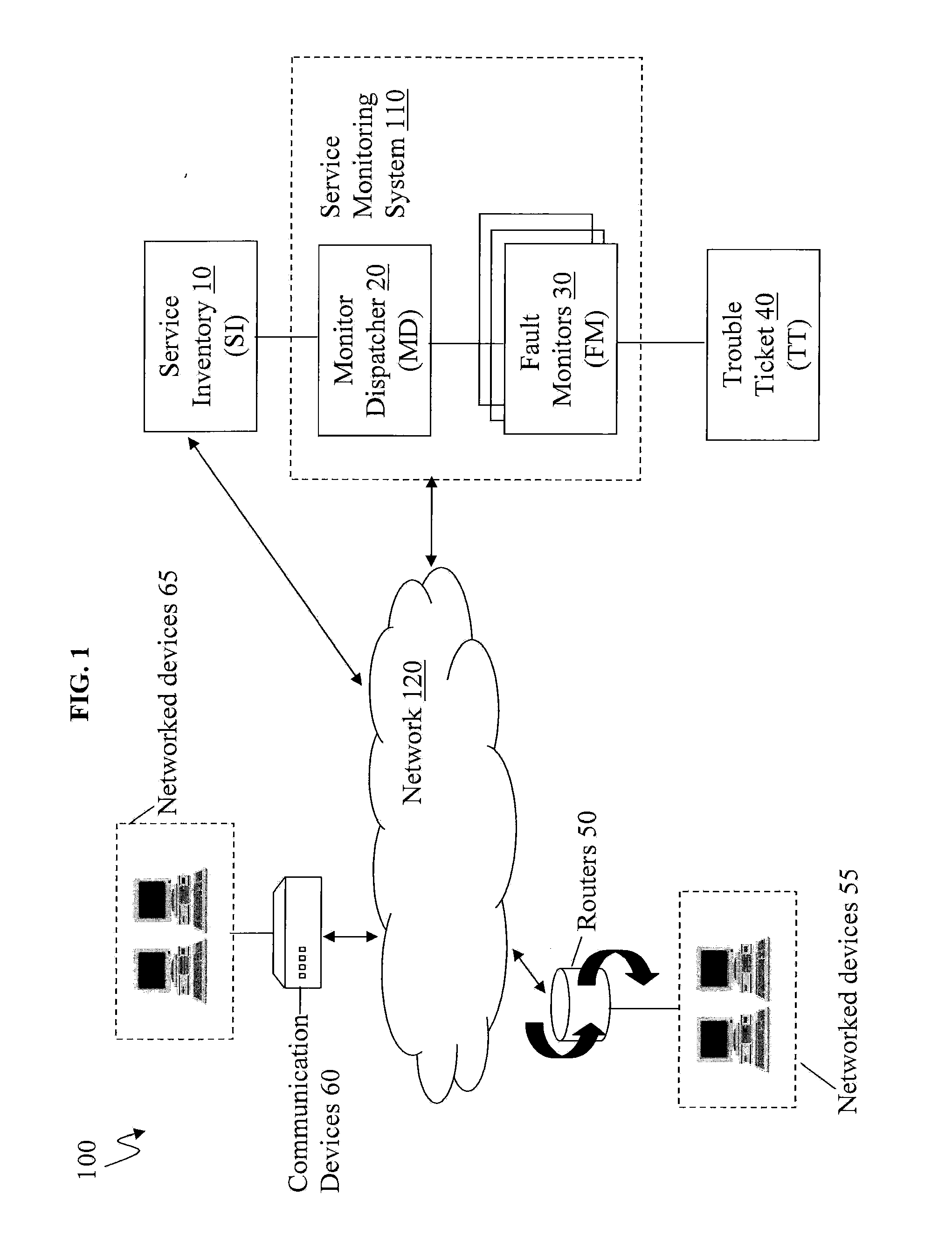
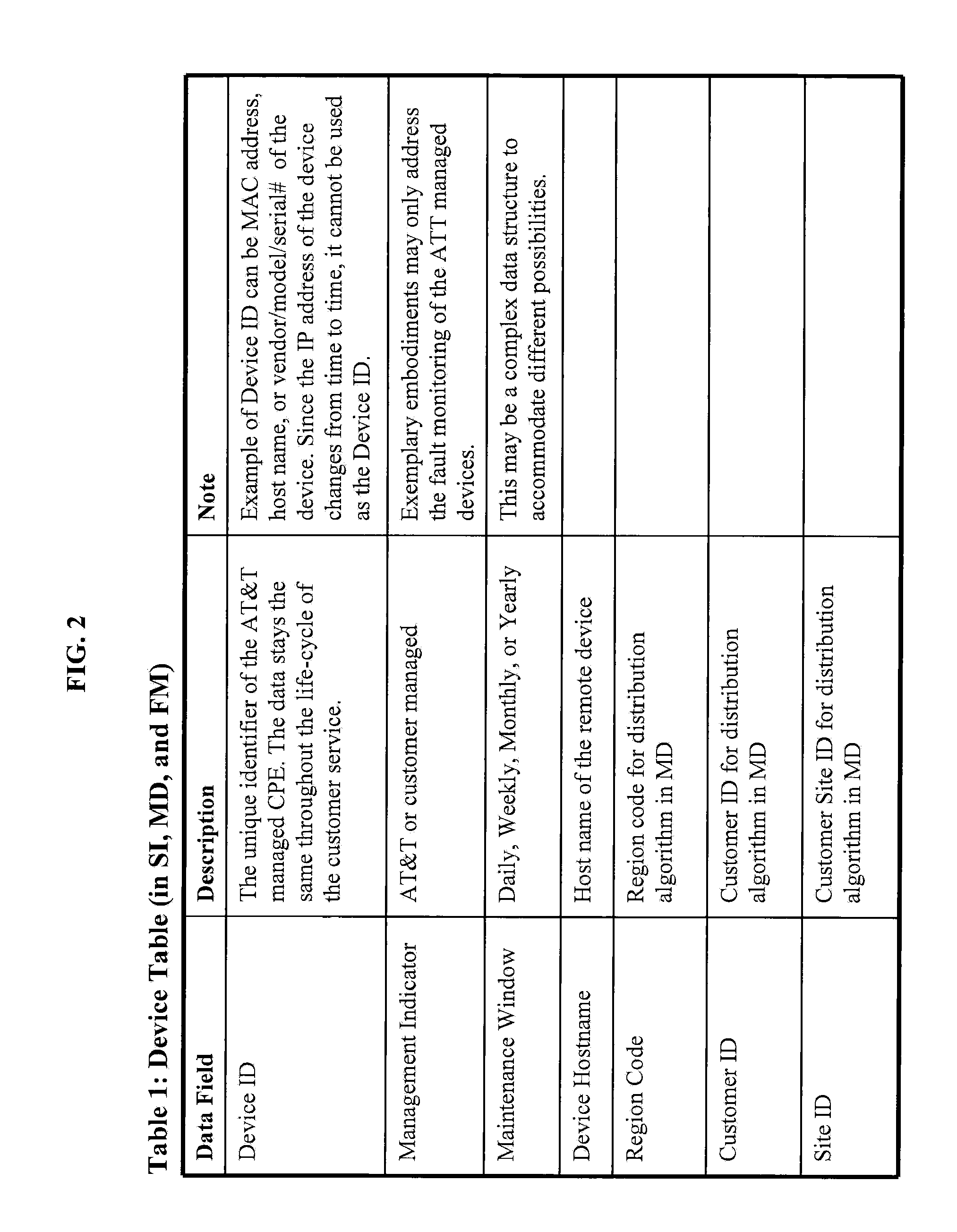
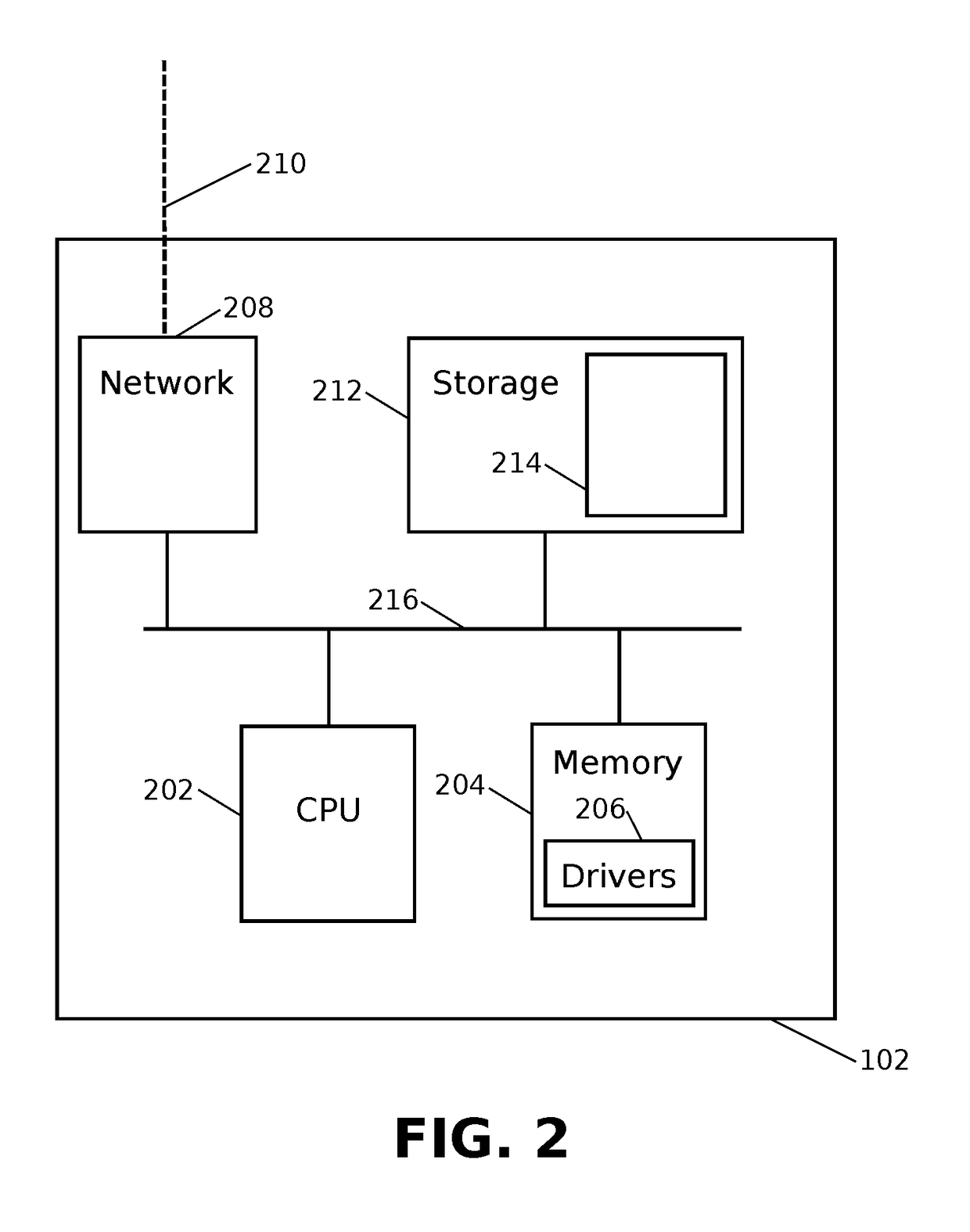
Scalable and Robust Mechanism for Remote IP Device Monitoring With Changing IP Address Assignment
A method is provided for monitoring devices with changing IP addresses. SNMP trap is received from a device at a first IP address to notify that a connection is up, and a SNMP poll is transmitted to the device to obtain an identifier. Predetermined consecutive SNMP GET requests are transmitted to the device in intervals. Responsive to failing to receive from the device predetermined consecutive SNMP GET responses equal to the predetermined consecutive SNMP GET requests, it is determined that there is a connection failure or a device failure and checked whether the device is in a maintenance window. If not in maintenance window, a trouble ticket is generated. Responsive to the failure, there is a predetermined waiting period for another SNMP trap from the device with a second IP address and the same identifier notifying that a connection is back up, and no trouble ticket is generated.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
System and method for replicating data in resource sets
InactiveUS6917951B2Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalManifest fileWaiting period
Described is a system and method for replicating each of a set of resources to a subject computer in a replica set prior to making use of a resource in the set of resources. The set of resources includes resources that are dependent upon each other for a proper functioning of the group. A manifest file that identifies each resource in a group of interrelated resources is used. The manifest file is generated at one computer in the replica set (typically the computer at which a modification to one of the interrelated resources occurred). When the modification occurs to one of the set of resources, the manifest file is transmitted (e.g., itself replicated) to each computer in the replica set. The manifest file includes an indicator that identifies the manifest file as a special file. When received at another computer in the replica set, a service evaluates the manifest file to identify whether the appropriate versions of the identified resources exist at the receiving computer. If not, the service at that computer awaits the receipt of each resource. The wait period may include delaying the execution of an application associated with (or even included within) the manifest file from launching. Alternatively, the FRS could simply disallow access to one or more resources identified in the manifest file until all have arrived. When all have arrived, the FRS releases control of the identified resources, which may then operate or be accessed in the ordinary manner.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Consensus system and method for adding data to a blockchain
ActiveUS20170075941A1Reduce energy consumptionDigital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsTrusted authorityWaiting period
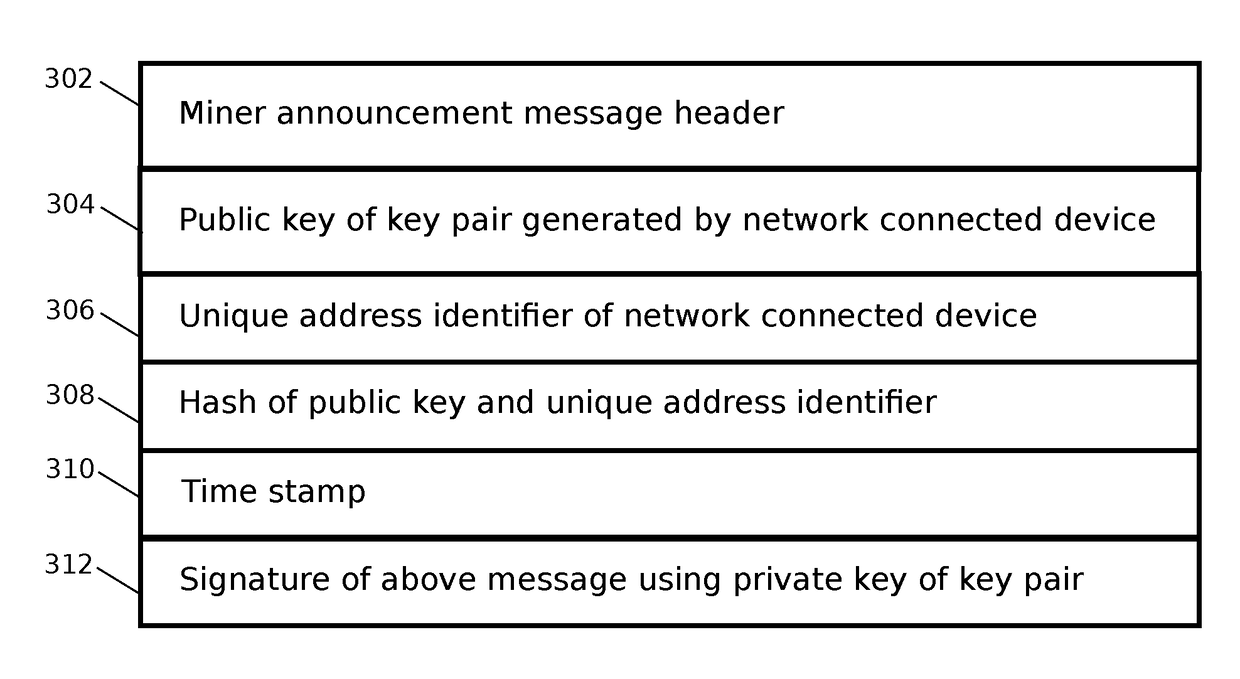
A method and apparatus is presented for reaching consensus on adding data to a distributed ledger system in which no central trusted authority is available, comprising sending an announcement message by a network connected device to a plurality of network connected devices over a peer-to-peer network, said message providing an identification of the network connected device using a public key of a public / private key pair, a unique address identifier, and a hash. Subsequently, after a waiting period measured in, for example, time or blocks of data, the network connected device may submit data for inclusion in the distributed ledger. If the announcement message and preceding data in the distributed ledger satisfy a predetermined condition, the plurality of network connected devices may include the data in the distributed ledger. If the network connected device fails to submit the data when the predetermined condition is satisfied, the announcement message may be canceled.
Owner:FINLOW BATES KEIR
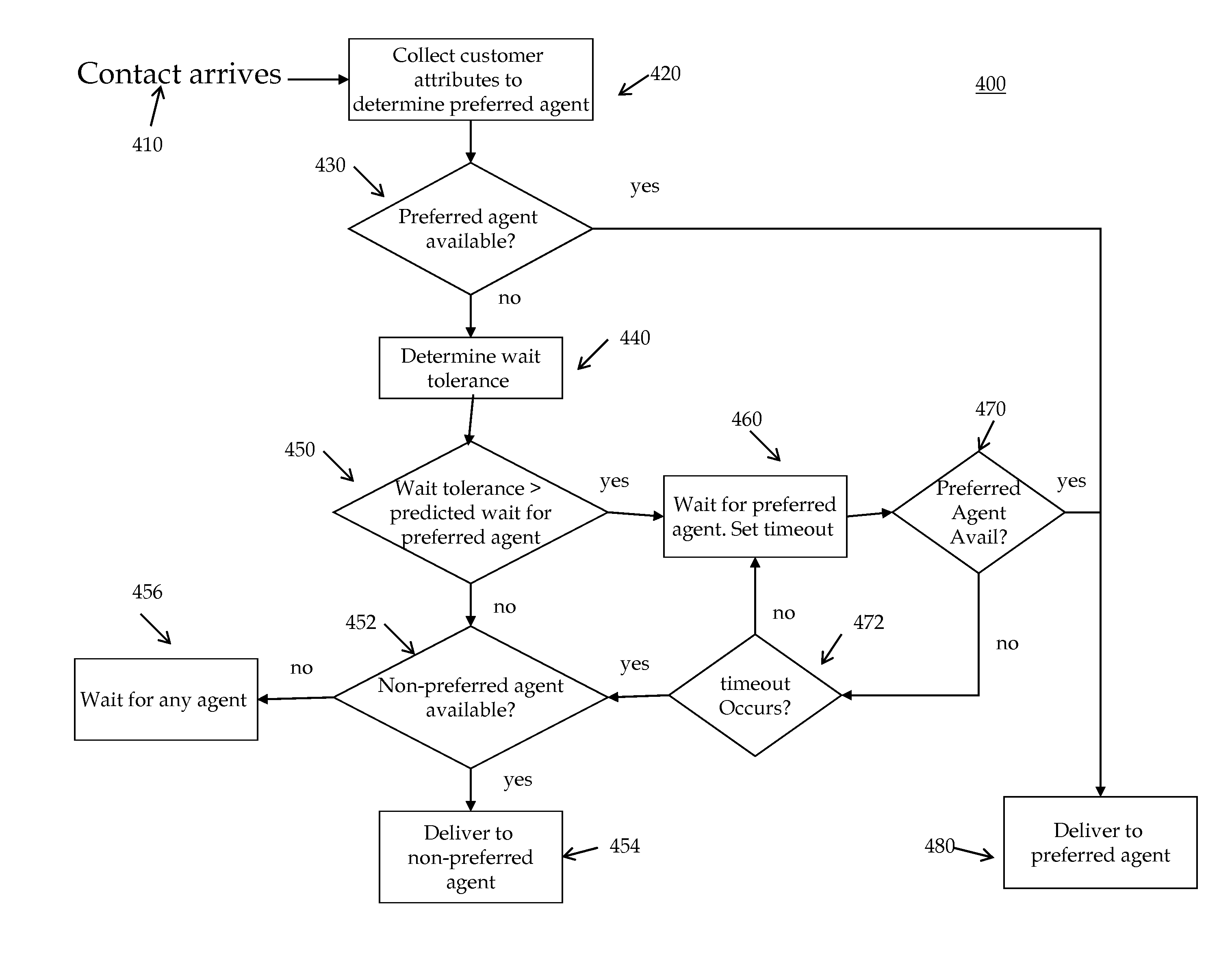
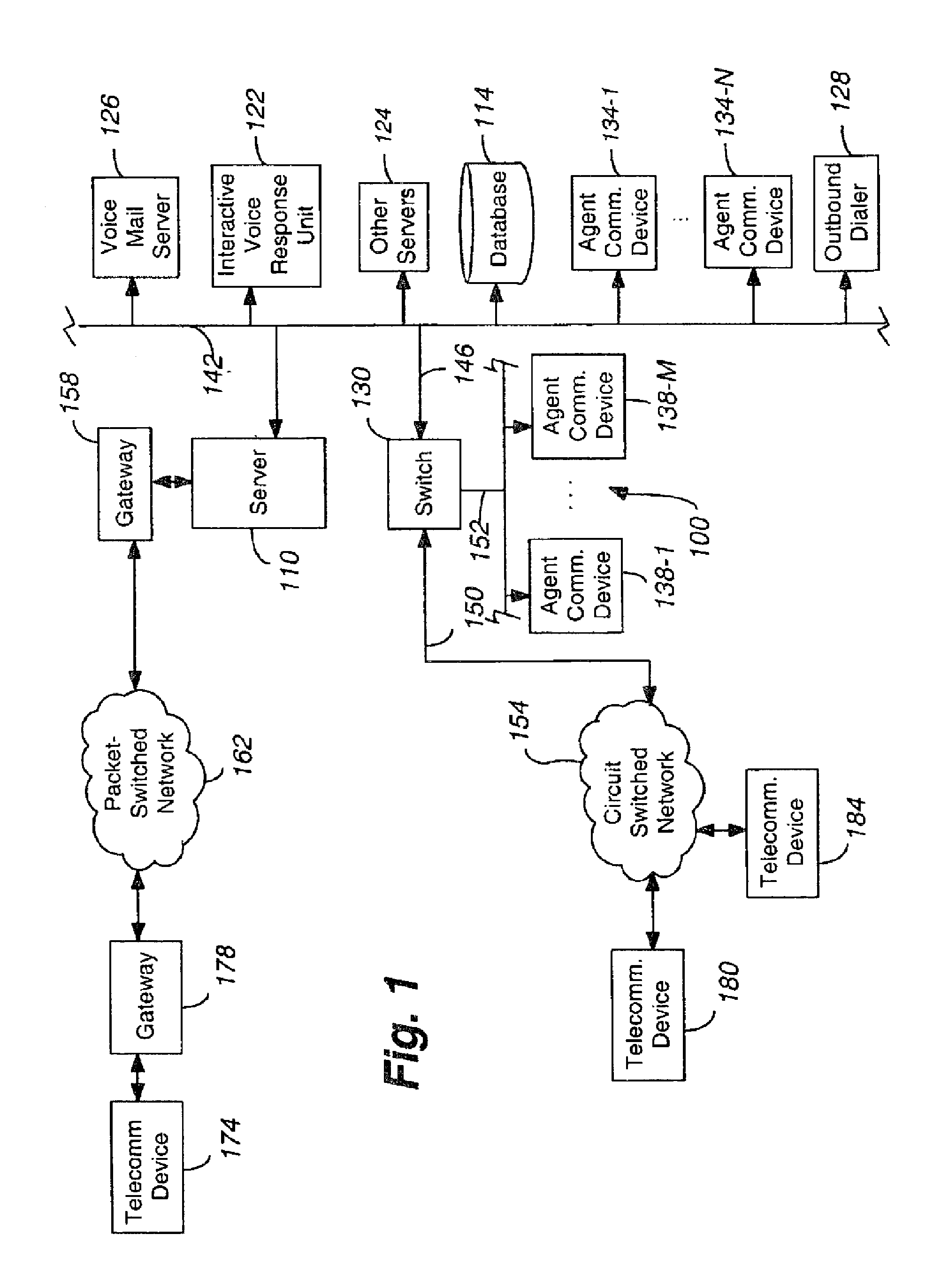
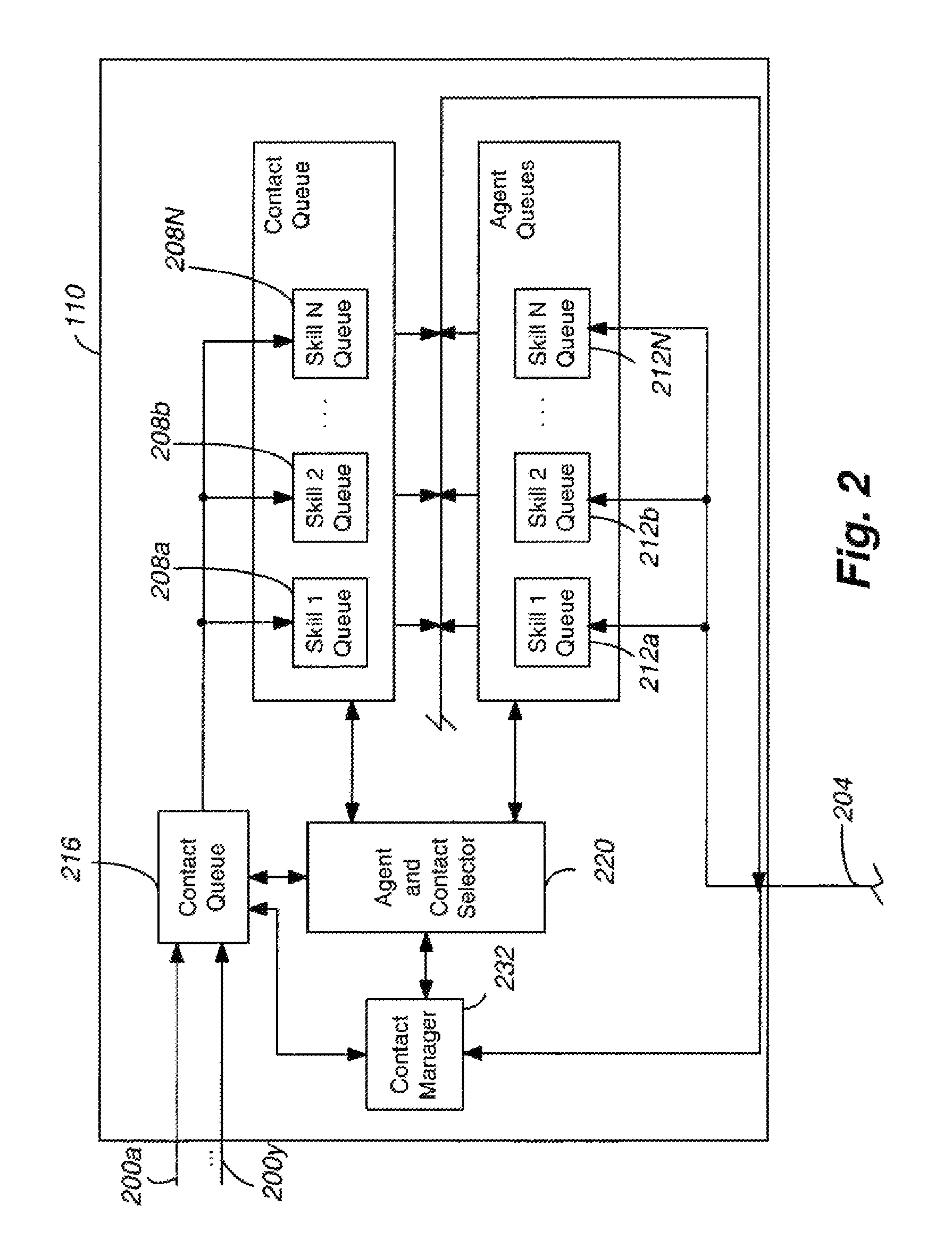
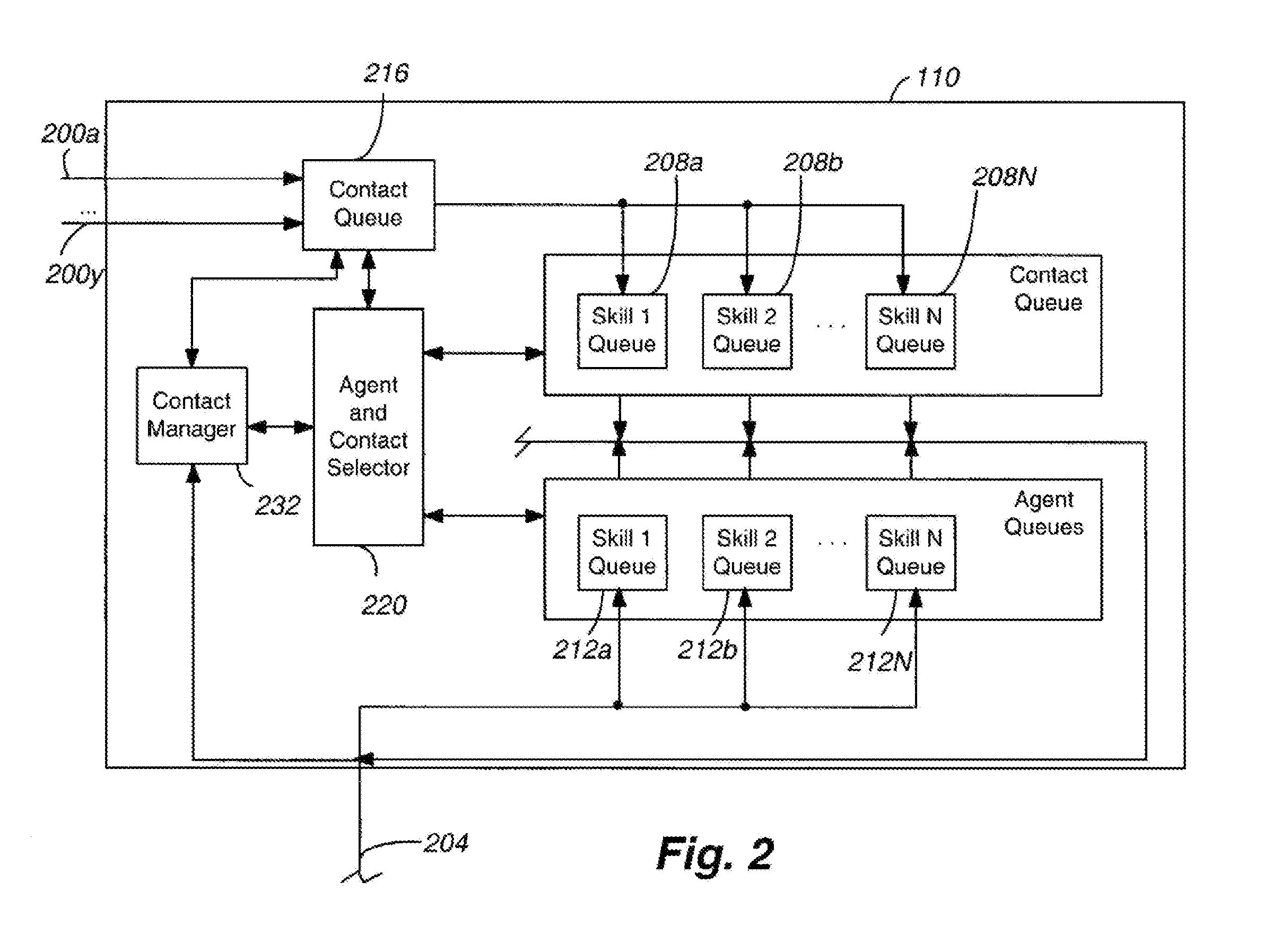
System and method for delivering a contact to a preferred agent after a set wait period
Owner:AVAYA INC
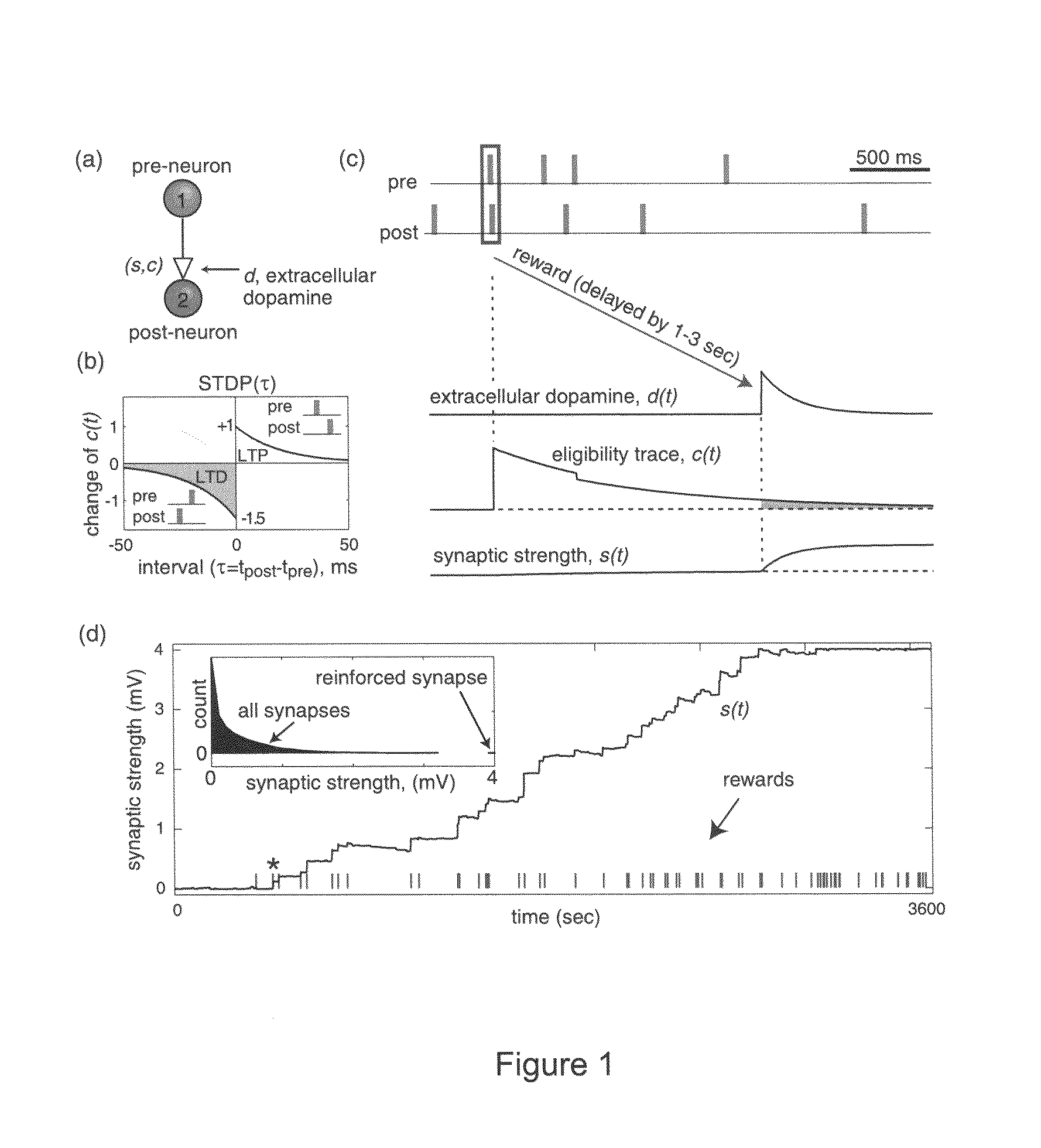
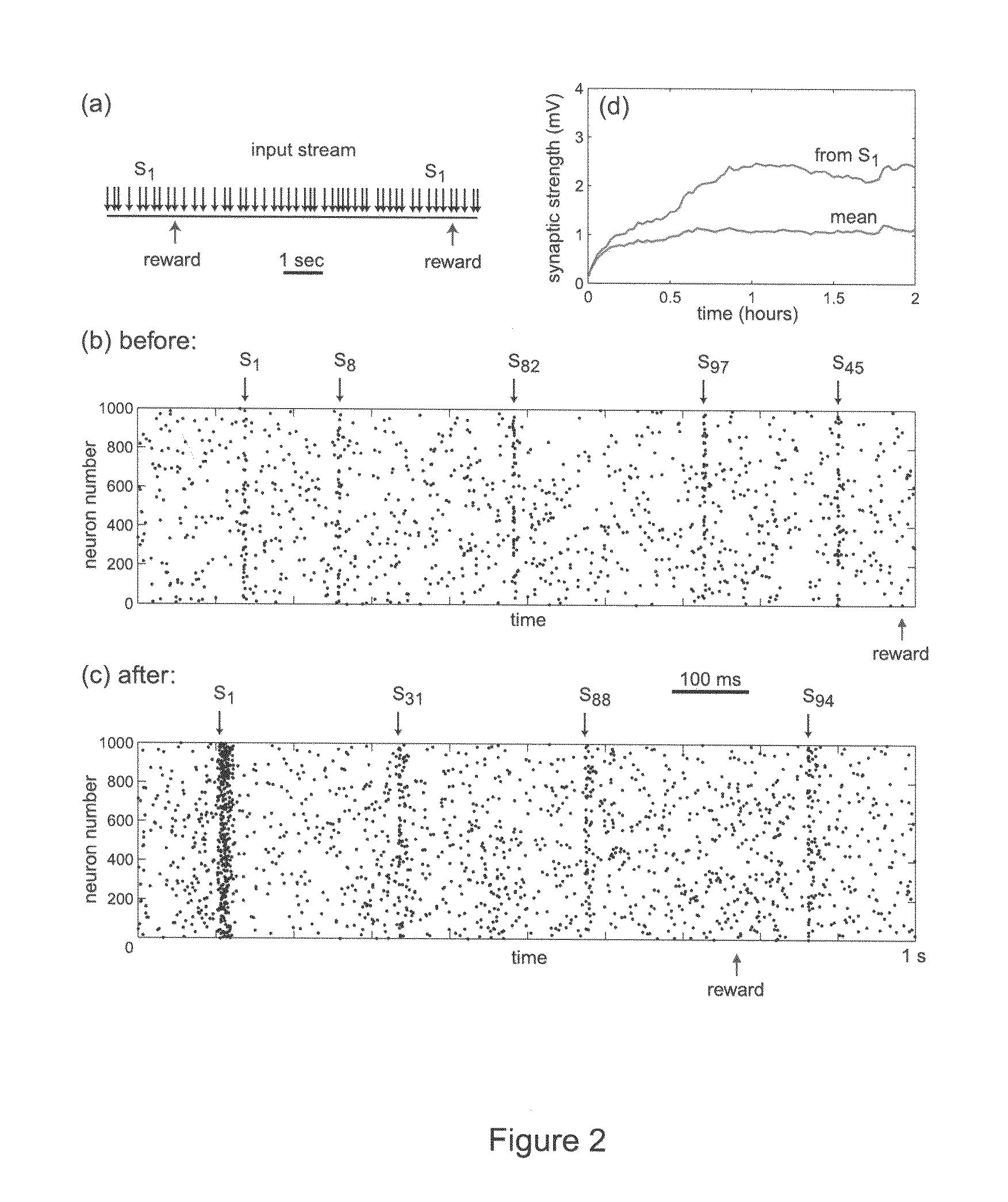
Solving the distal reward problem through linkage of stdp and dopamine signaling
InactiveUS20080162391A1Smooth connectionDigital computer detailsArtificial lifeNerve networkCritical period
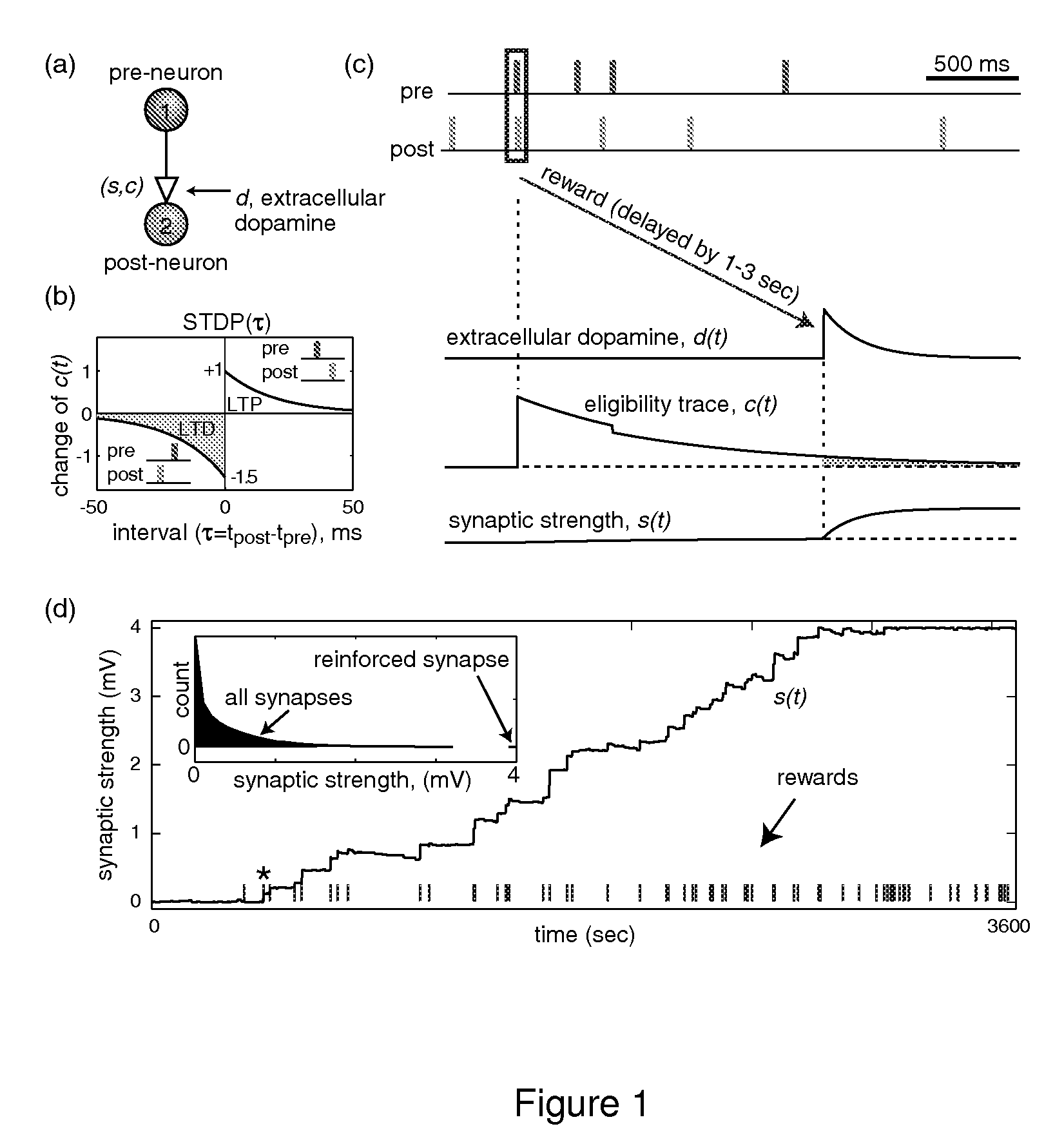
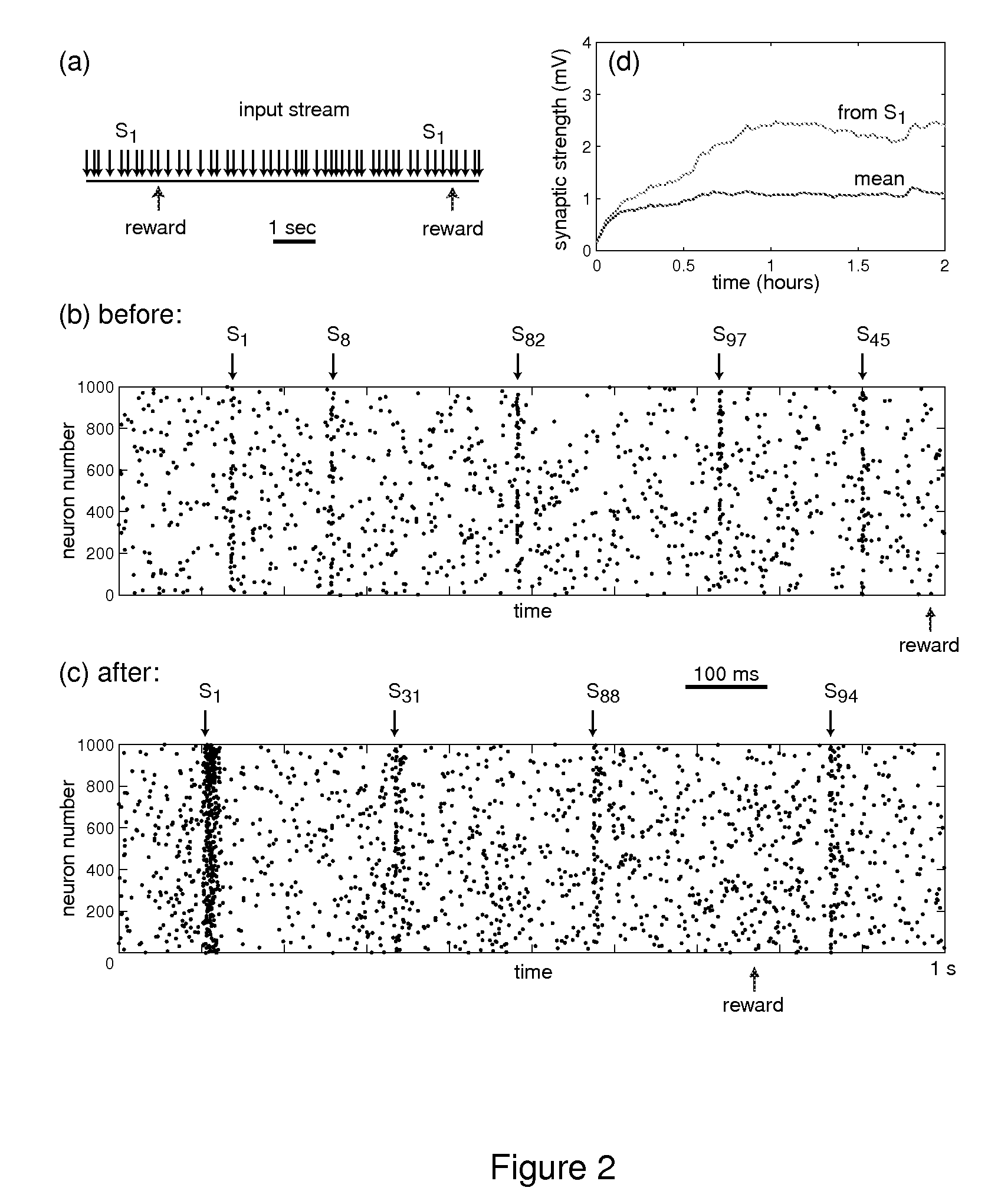
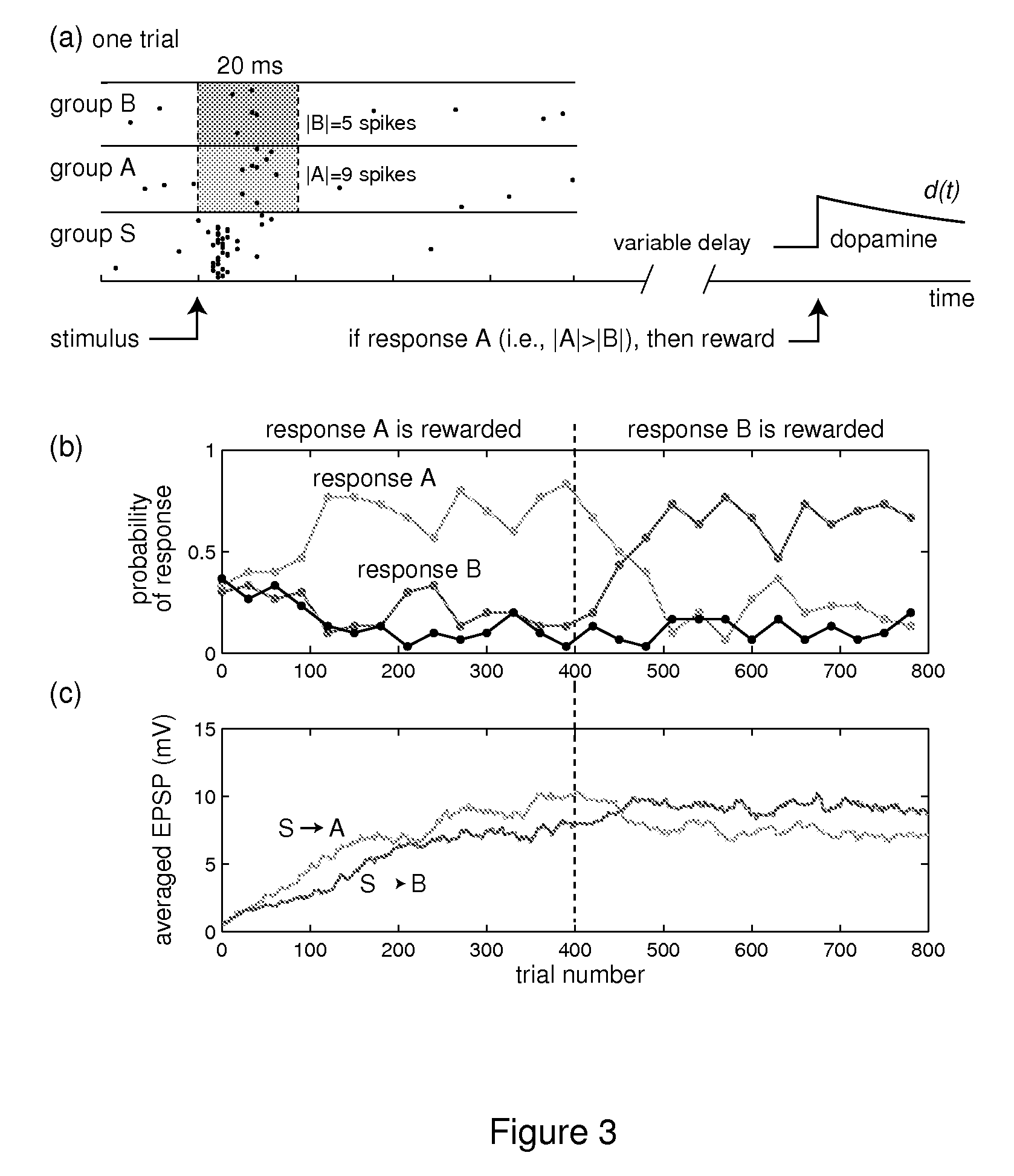
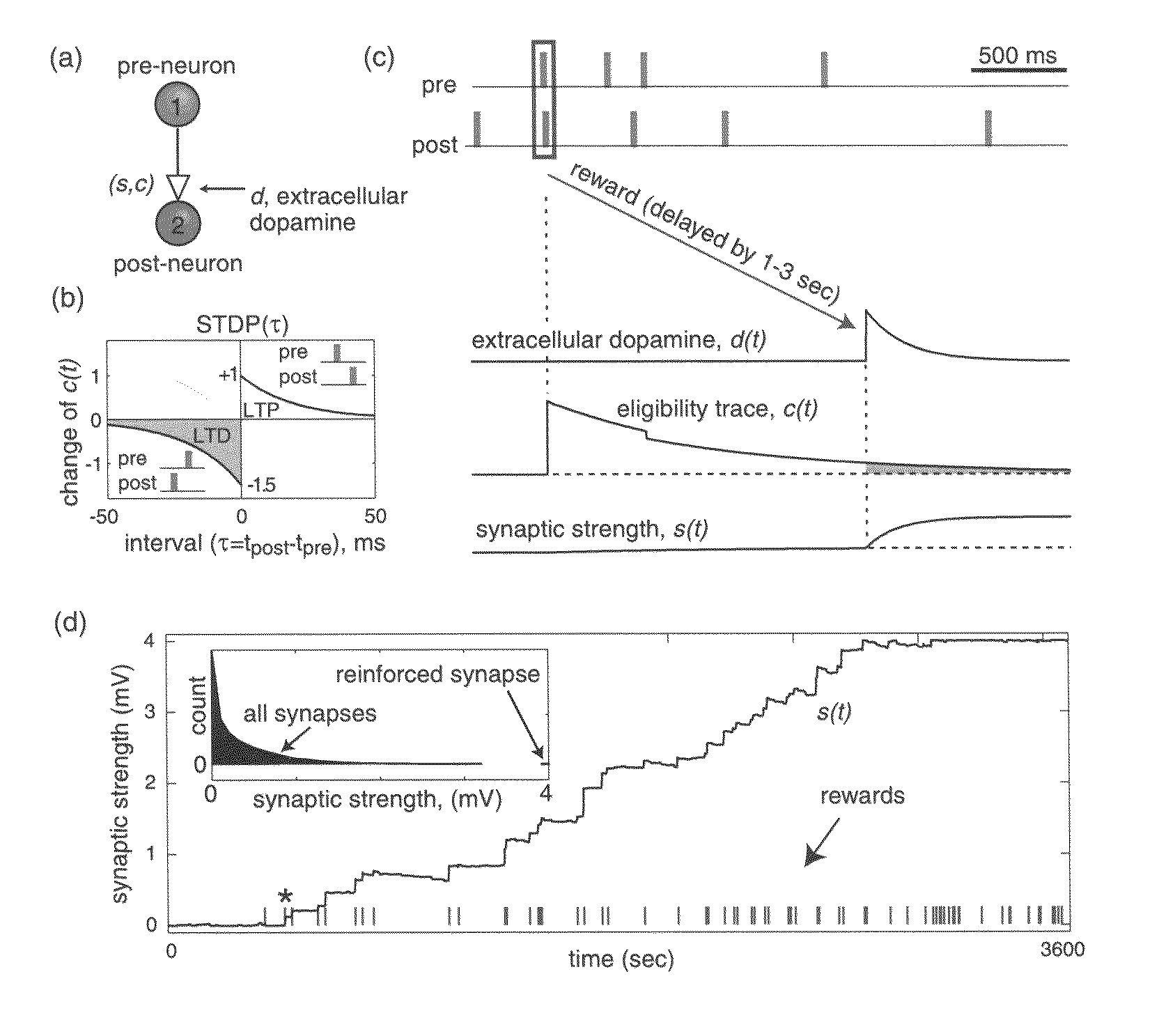
In Pavlovian and instrumental conditioning, rewards typically come seconds after reward-triggering actions, creating an explanatory conundrum known as the distal reward problem or the credit assignment problem. How does the brain know what firing patterns of what neurons are responsible for the reward if (1) the firing patterns are no longer there when the reward arrives and (2) most neurons and synapses are active during the waiting period to the reward? A model network and computer simulation of cortical spiking neurons with spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) modulated by dopamine (DA) is disclosed to answer this question. STDP is triggered by nearly-coincident firing patterns of a presynaptic neuron and a postsynaptic neuron on a millisecond time scale, with slow kinetics of subsequent synaptic plasticity being sensitive to changes in the extracellular dopamine DA concentration during the critical period of a few seconds after the nearly-coincident firing patterns. Random neuronal firings during the waiting period leading to the reward do not affect STDP, and hence make the neural network insensitive to this ongoing random firing activity. The importance of precise firing patterns in brain dynamics and the use of a global diffusive reinforcement signal in the form of extracellular dopamine DA can selectively influence the right synapses at the right time.
Owner:NEUROSCI RES FOUND
Solving the distal reward problem through linkage of STDP and dopamine signaling
InactiveUS8103602B2Smooth connectionDigital computer detailsArtificial lifeCritical periodModel network
In Pavlovian and instrumental conditioning, rewards typically come seconds after reward-triggering actions, creating an explanatory conundrum known as the distal reward problem or the credit assignment problem. How does the brain know what firing patterns of what neurons are responsible for the reward if (1) the firing patterns are no longer there when the reward arrives and (2) most neurons and synapses are active during the waiting period to the reward? A model network and computer simulation of cortical spiking neurons with spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) modulated by dopamine (DA) is disclosed to answer this question. STDP is triggered by nearly-coincident firing patterns of a presynaptic neuron and a postsynaptic neuron on a millisecond time scale, with slow kinetics of subsequent synaptic plasticity being sensitive to changes in the extracellular dopamine DA concentration during the critical period of a few seconds after the nearly-coincident firing patterns. Random neuronal firings during the waiting period leading to the reward do not affect STDP, and hence make the neural network insensitive to this ongoing random firing activity. The importance of precise firing patterns in brain dynamics and the use of a global diffusive reinforcement signal in the form of extracellular dopamine DA can selectively influence the right synapses at the right time.
Owner:NEUROSCI RES FOUND
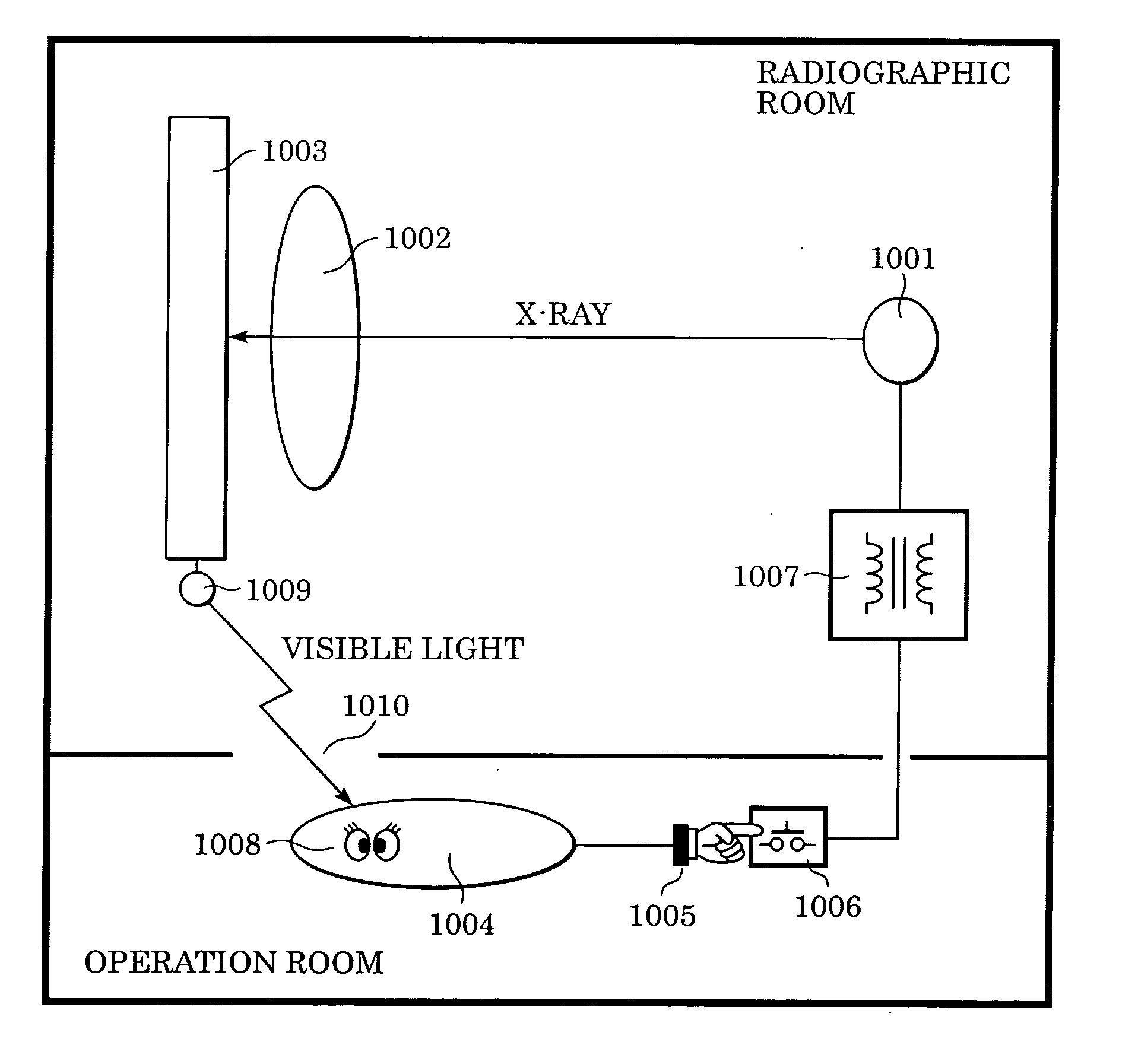
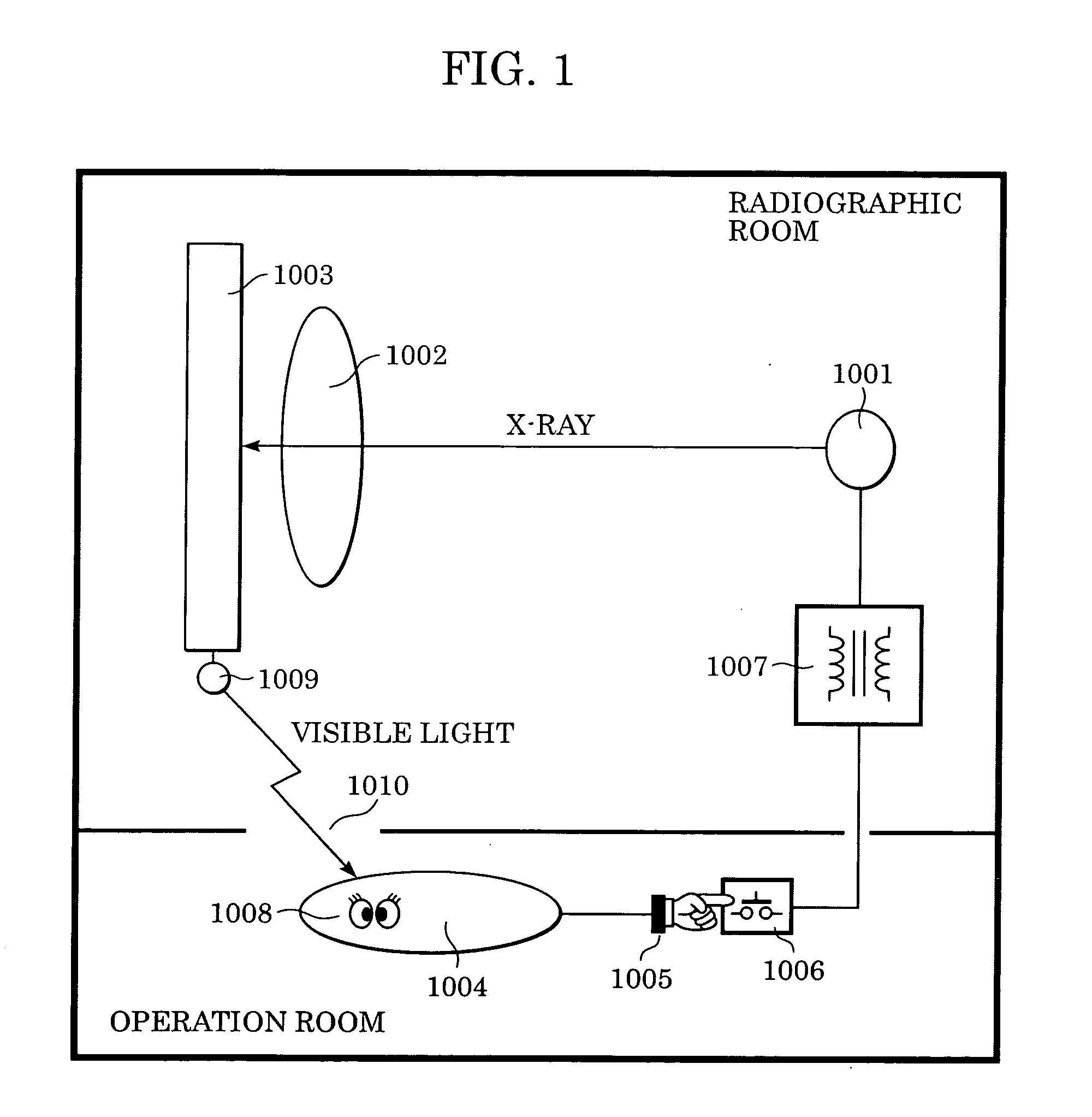
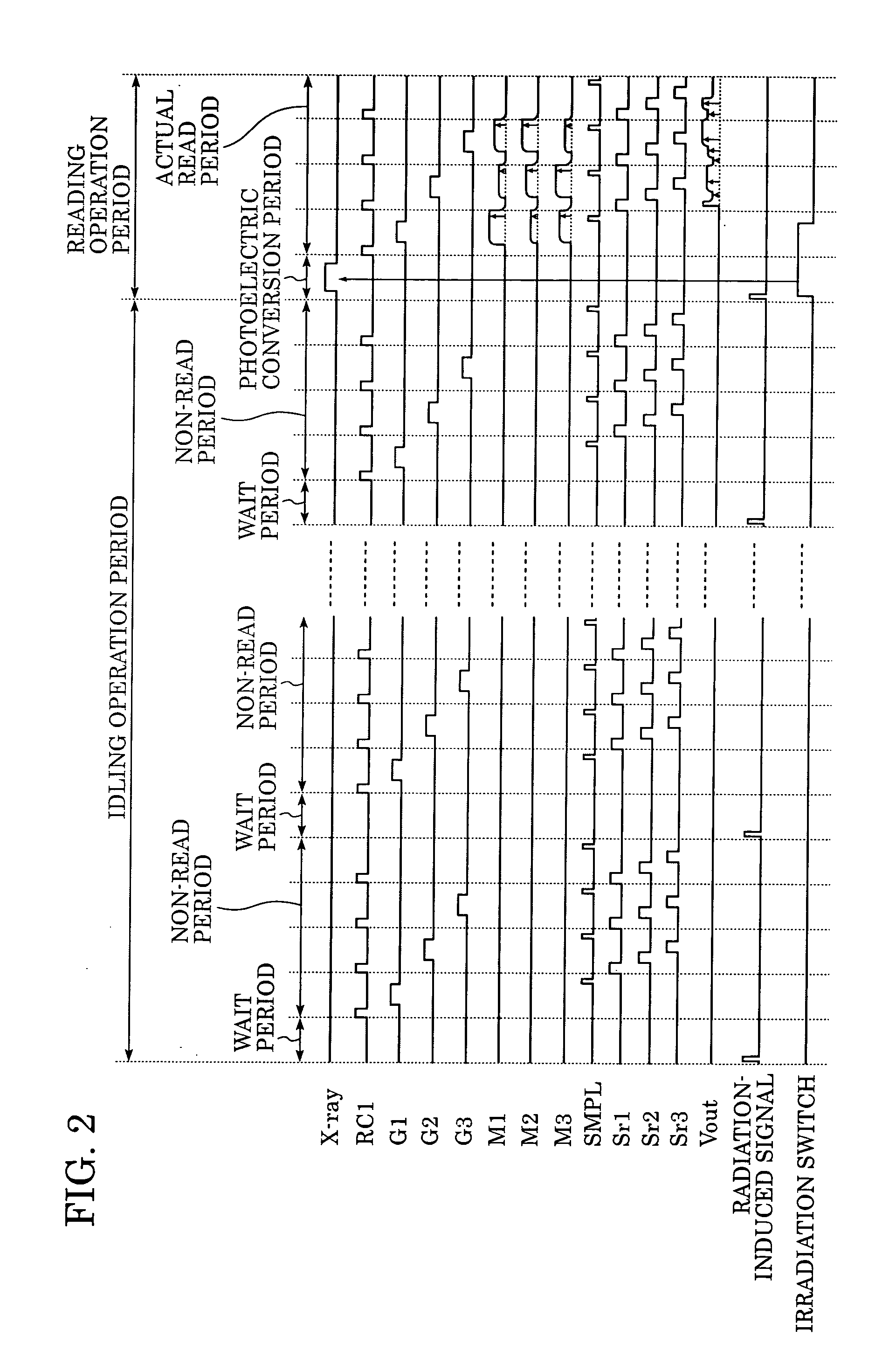
Radiation imaging apparatus and control method therefor
InactiveUS20050220269A1Stably performing radiographyAvoid delayX-ray apparatusRadiation diagnosticsX-rayOpto electronic
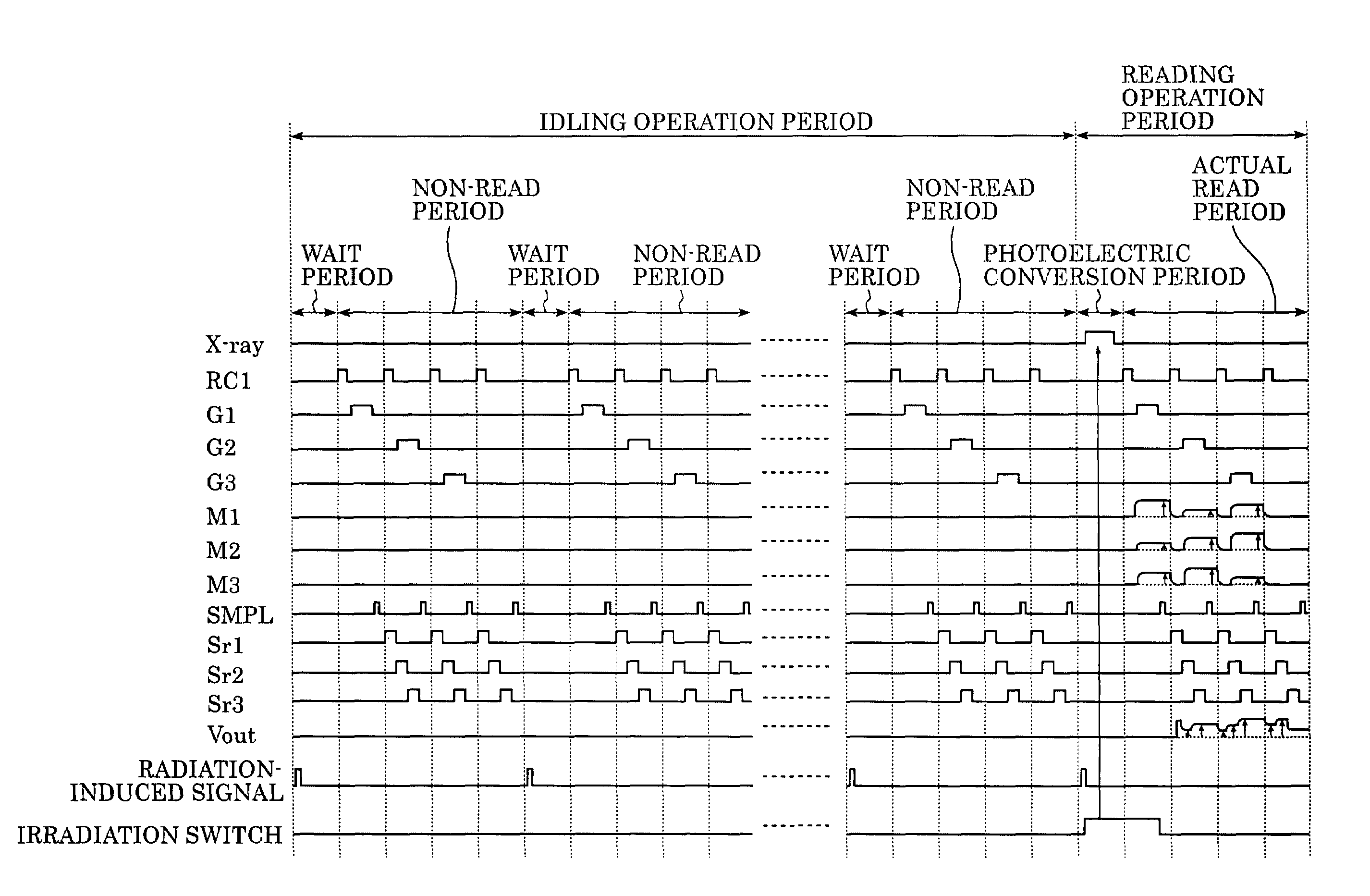
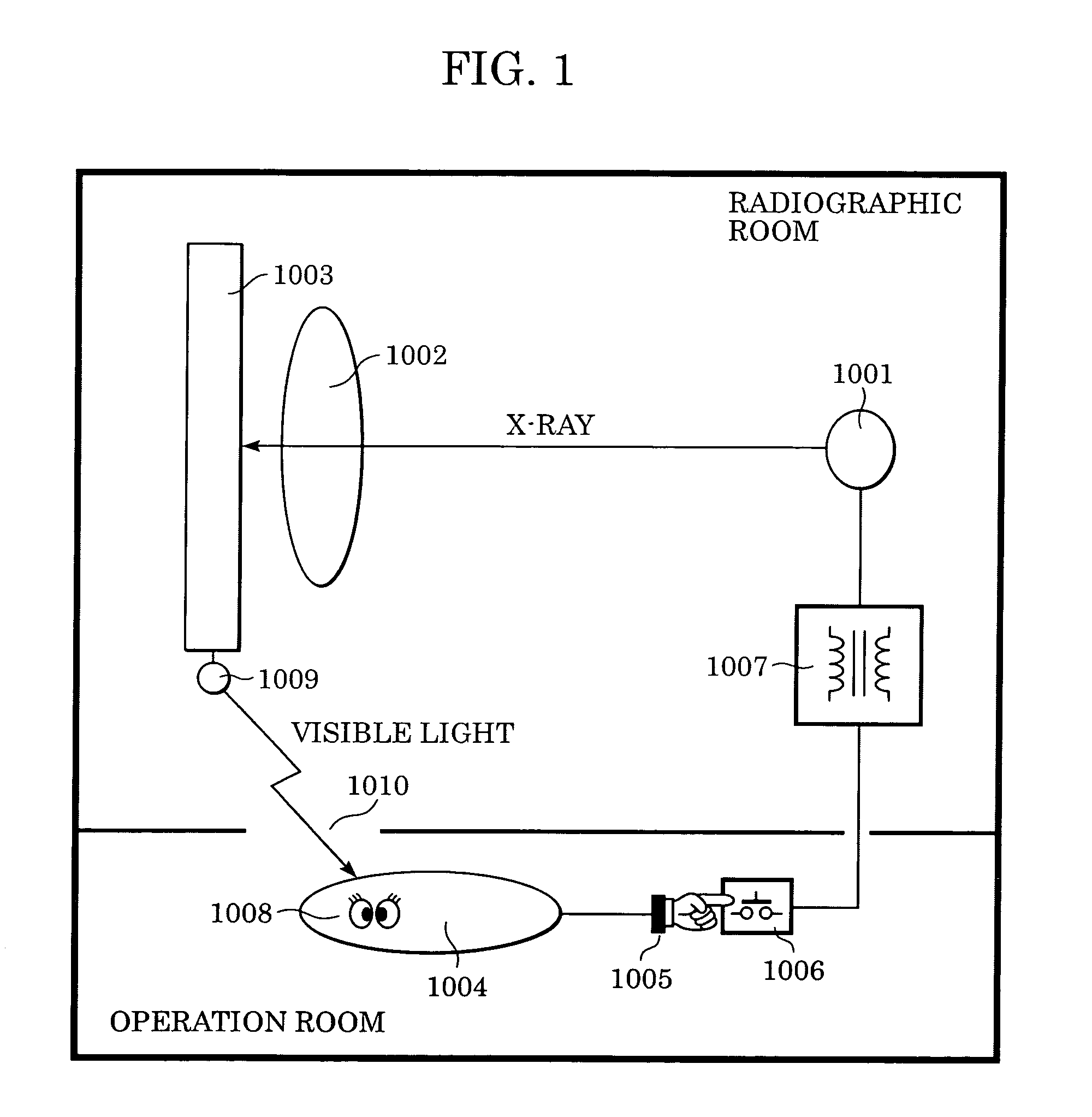
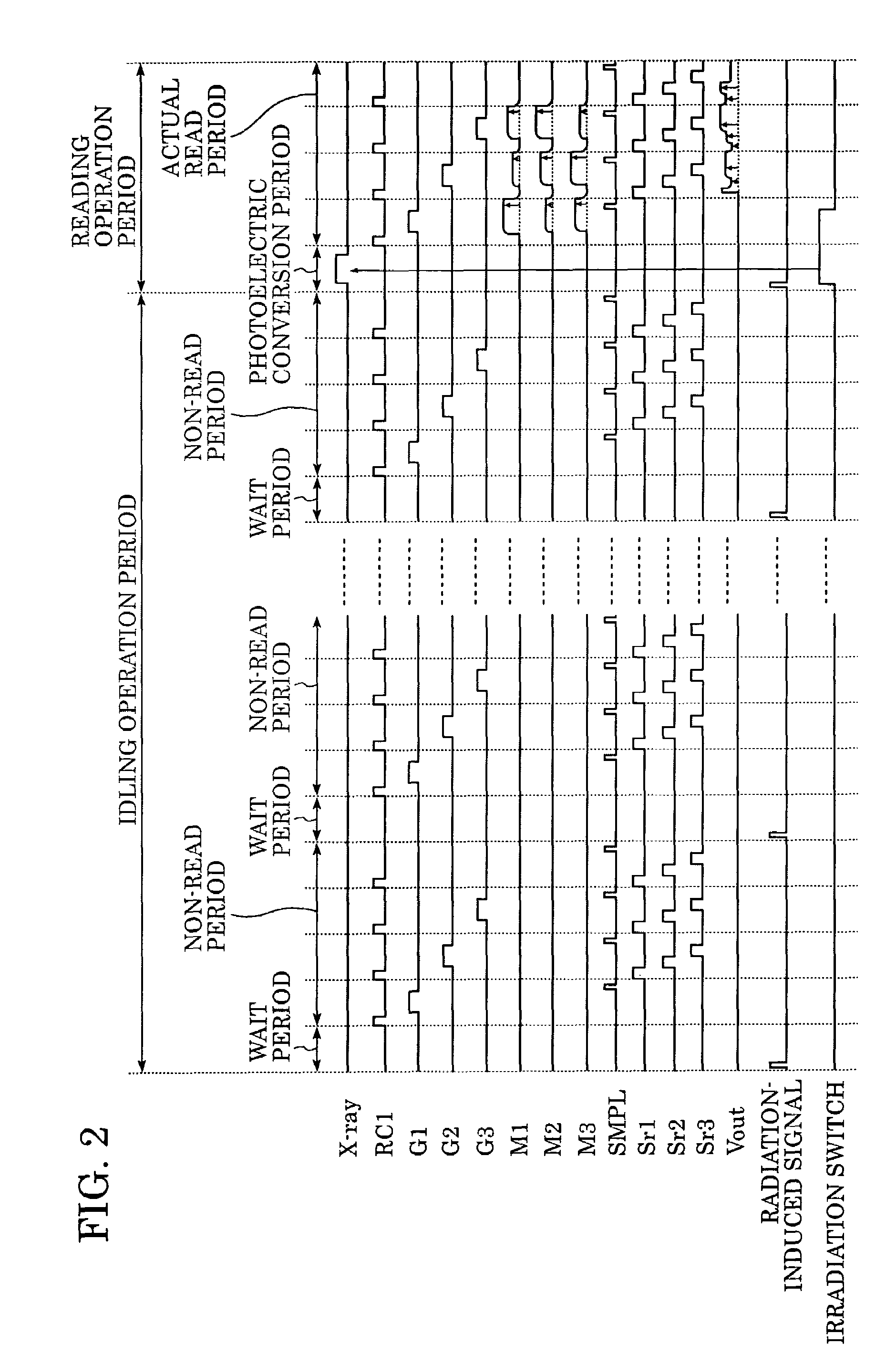
A lamp emits pulse-shaped visible light when a wait period begins. If a radiation emission switch is not pressed in the wait period, X-ray radiation is not emitted from an X-ray source, and no charges are accumulated in photoelectric conversion elements of an X-ray imaging apparatus. In a non-read period, although signals are sequentially read from the photoelectric conversion elements, an output signal does not change. When the radiation emission switch is pressed in synchronization with a radiation-induced signal in a certain wait period, the X-ray source emits X-rays. After irradiation of X-rays, a photoelectric conversion period transitions to an actual read period. In the photoelectric conversion period, X-rays are emitted and transmitted X-ray information of a patient are accumulated in the photoelectric conversion elements of the X-ray imaging apparatus. In the actual read period, the accumulated information is read.
Owner:CANON KK
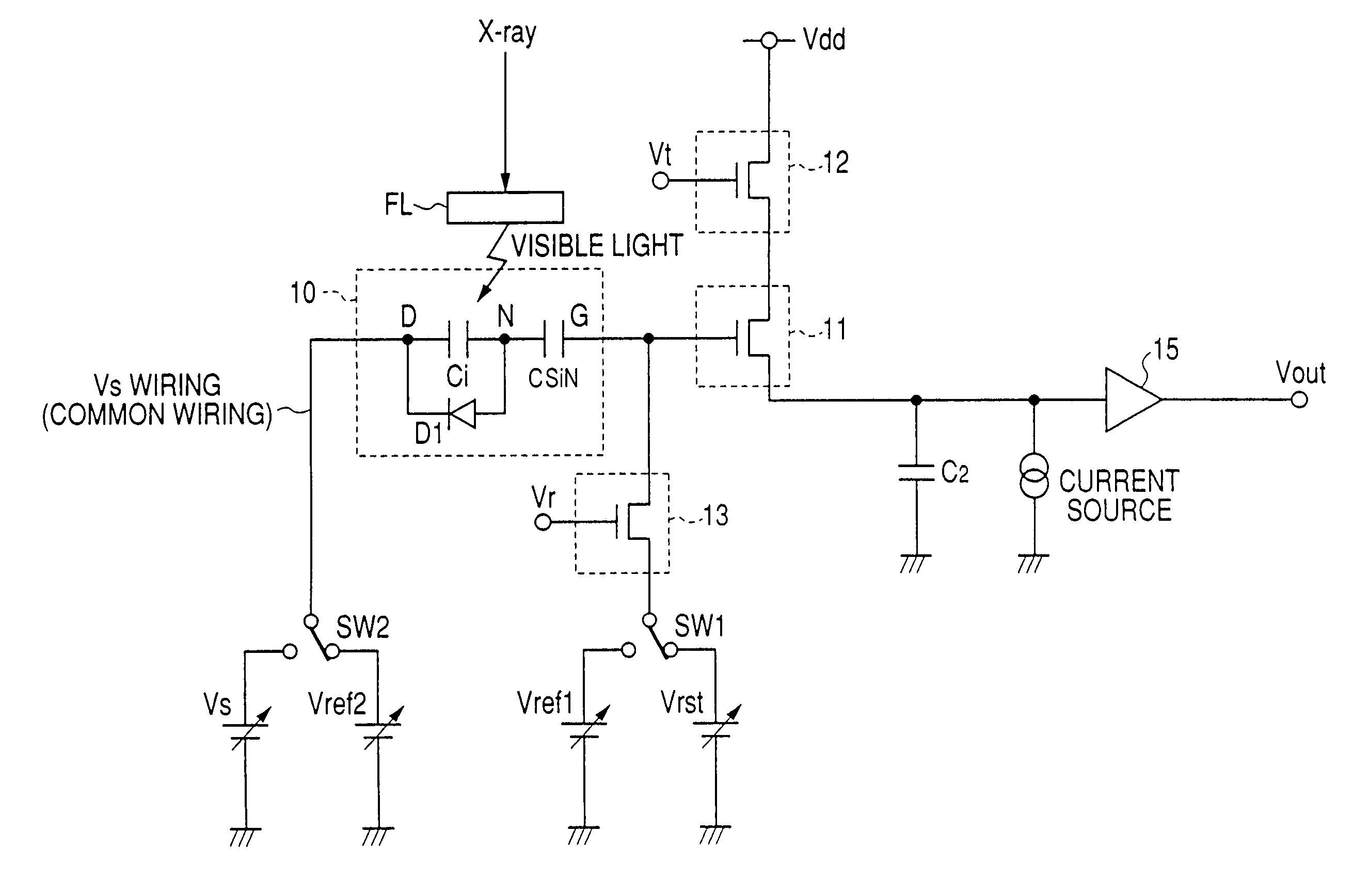
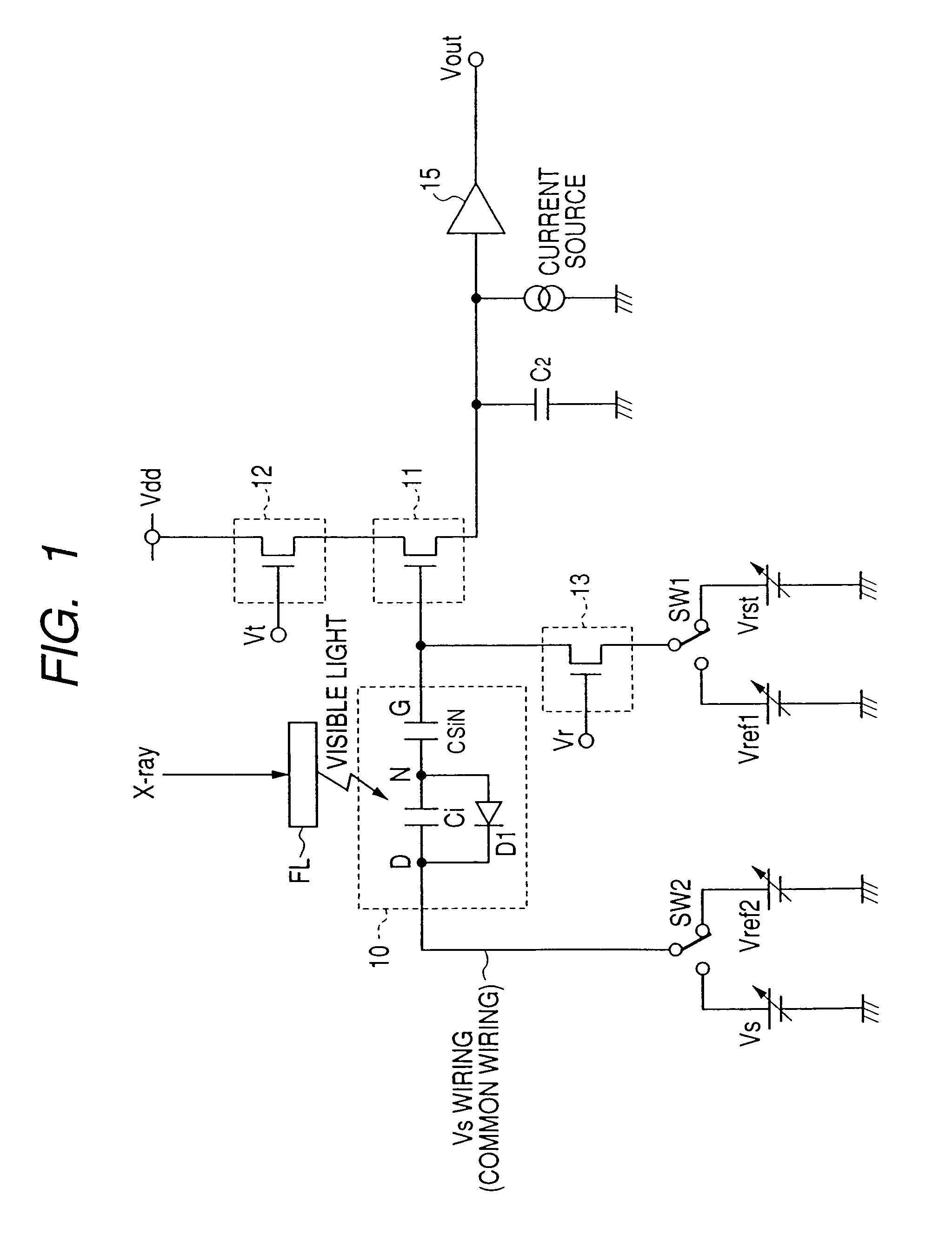
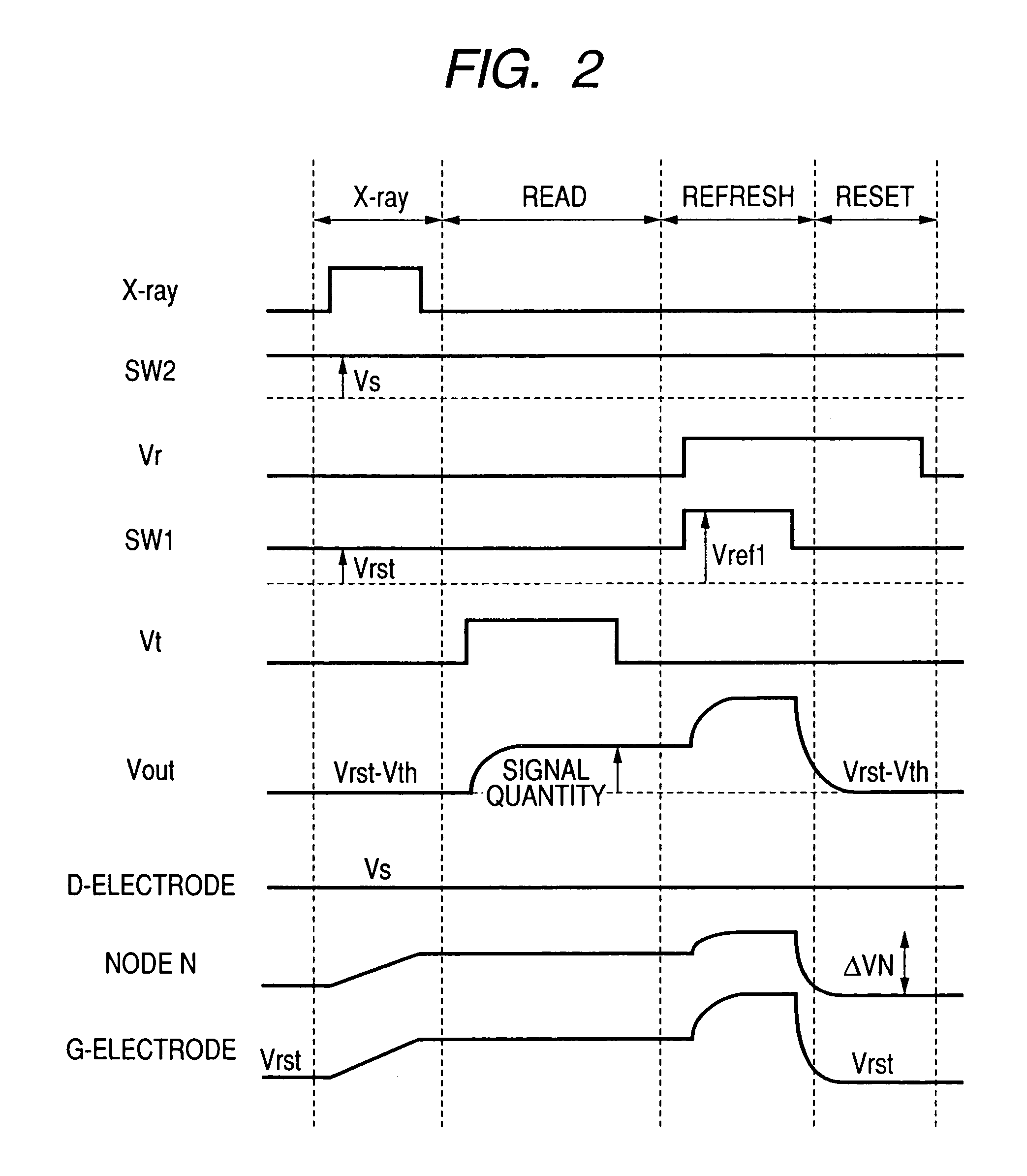
Radiation image pick-up device and radiation image pick-up method
InactiveUS7012260B2Avoid Voltage FluctuationsStable and high speed moving image photographingTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesType conversionWaiting period
A radiation image pick-up device which can restrain voltage fluctuations on GND and power supply lines, dispense with frame-by-frame wait periods, make possible stable and high speed moving image photographing, and are reduced in cost and dark current is to be provided.In pixels for detecting incident radiations, there are provided MIS-type conversion elements for converting the radiations into electric signals, source follower-type first TFTs for reading out the electric signals, second TFTs which so operate as to read out of the first TFTs the electric signals of the conversion elements selected by a drive circuit section on a row-by-row basis, and third TFTs which so operate as to reset or refresh on a row-by-row basis the conversion elements out of which reading by the first TFTs has been accomplished.
Owner:CANON KK
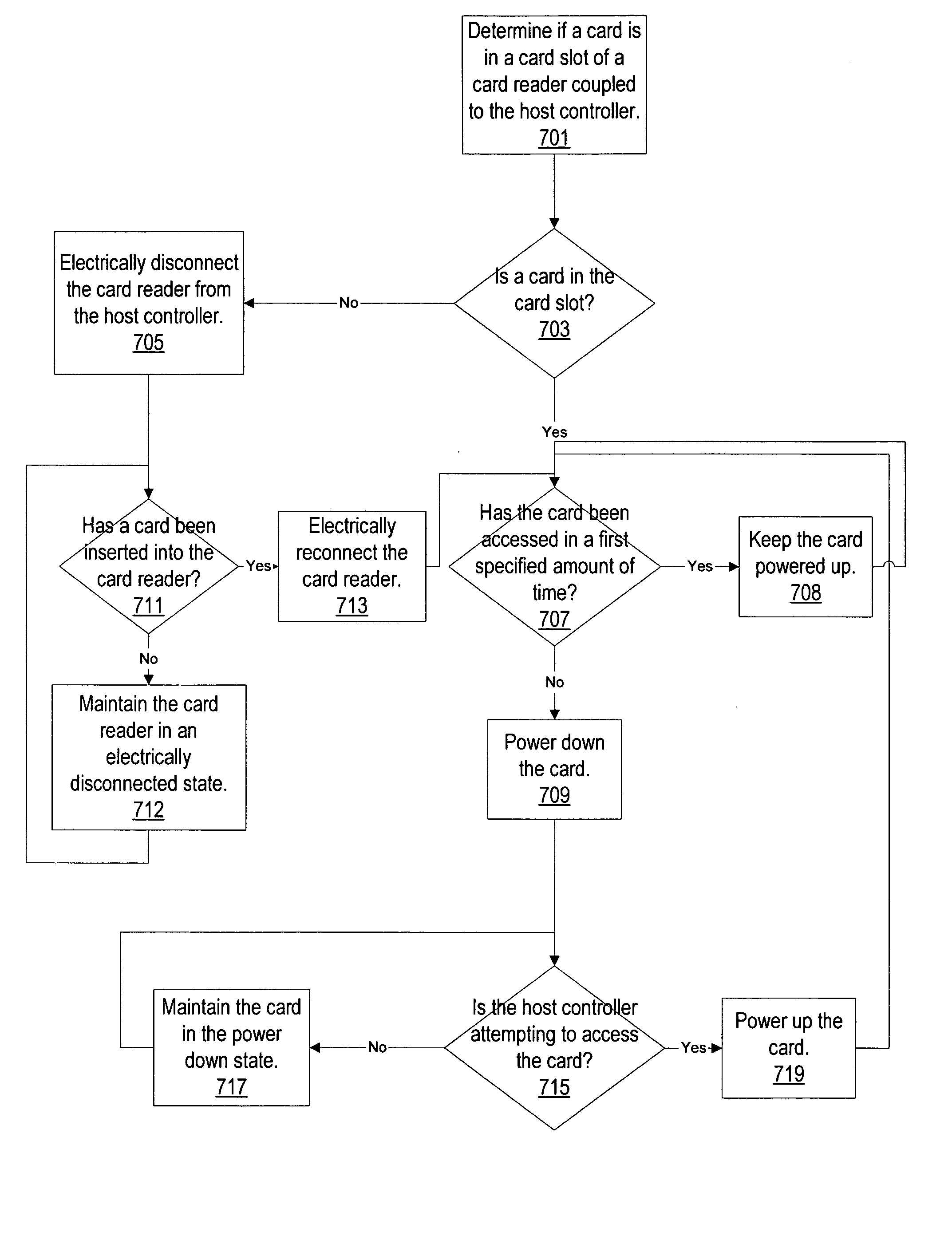
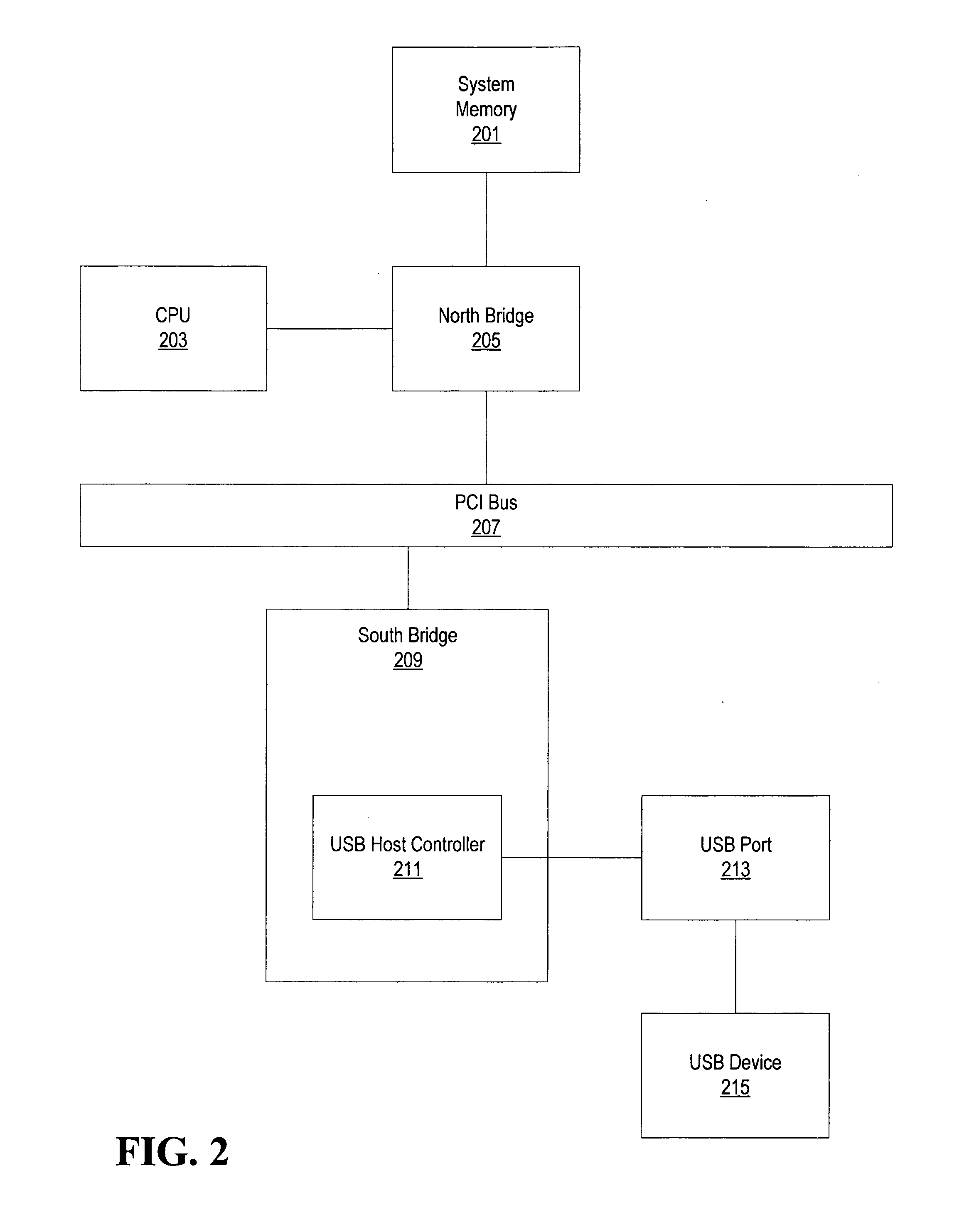
Peripheral device feature allowing processors to enter a low power state
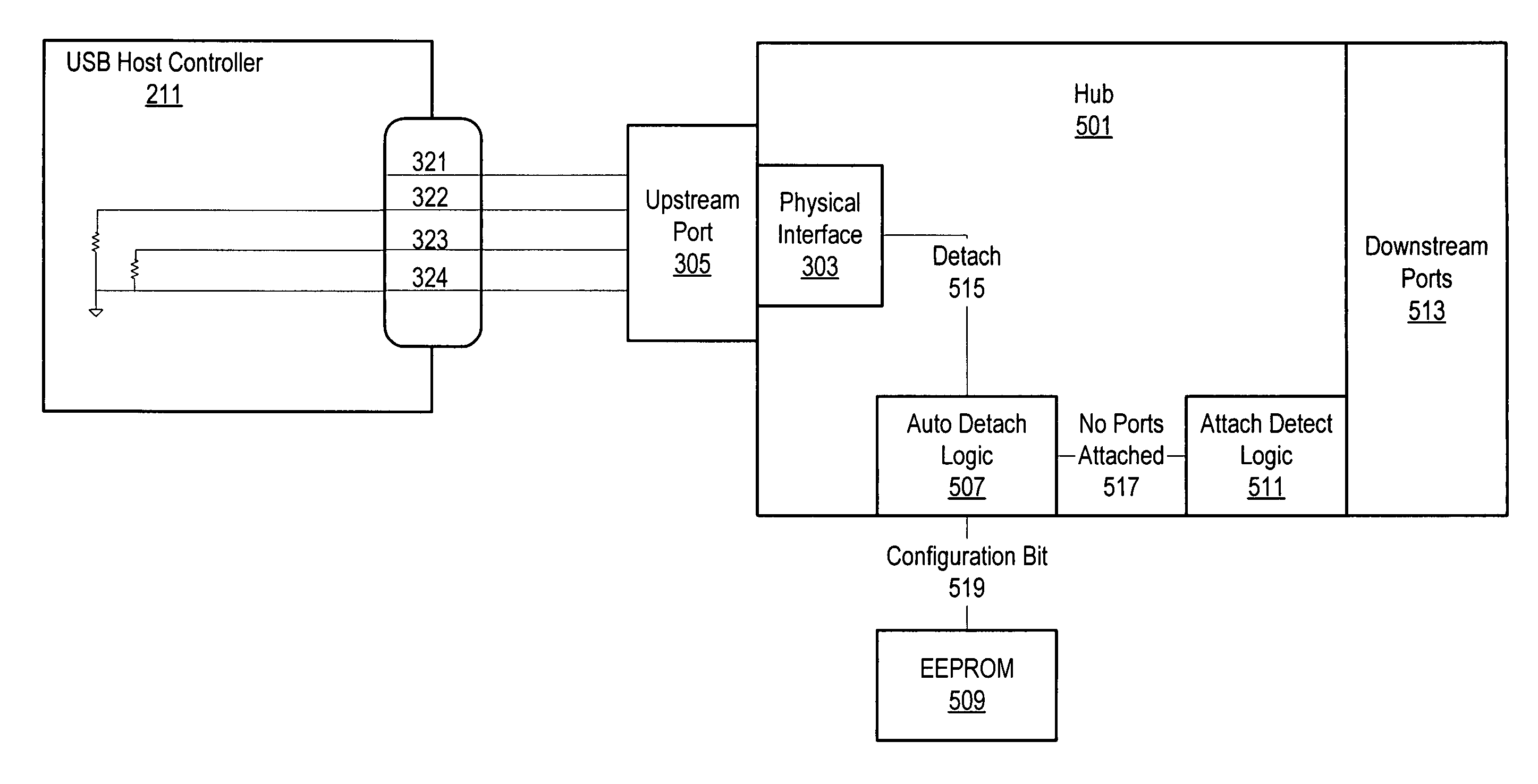
ActiveUS20050156038A1Volume/mass flow measurementCo-operative working arrangementsElectricityWaiting period
If a USB device is turned off or is not active, the device may be electrically disconnected from a USB host controller. The device may be electrically disconnected through a physical interface on the device. In some embodiments, if the device becomes active during a wait period (e.g., 2-3 seconds) prior to electrically disconnecting the device, the device may not be electrically disconnected. In some embodiments, when the device is electrically disconnected from the USB host controller and no system activity of a bus mastering peripheral is occurring, the CPU may enter a low power state if other conditions are met. In some embodiments, if the USB device becomes active after electrically disconnecting, the electrical disconnection may be discontinued.
Owner:SONRAI MEMORY LTD
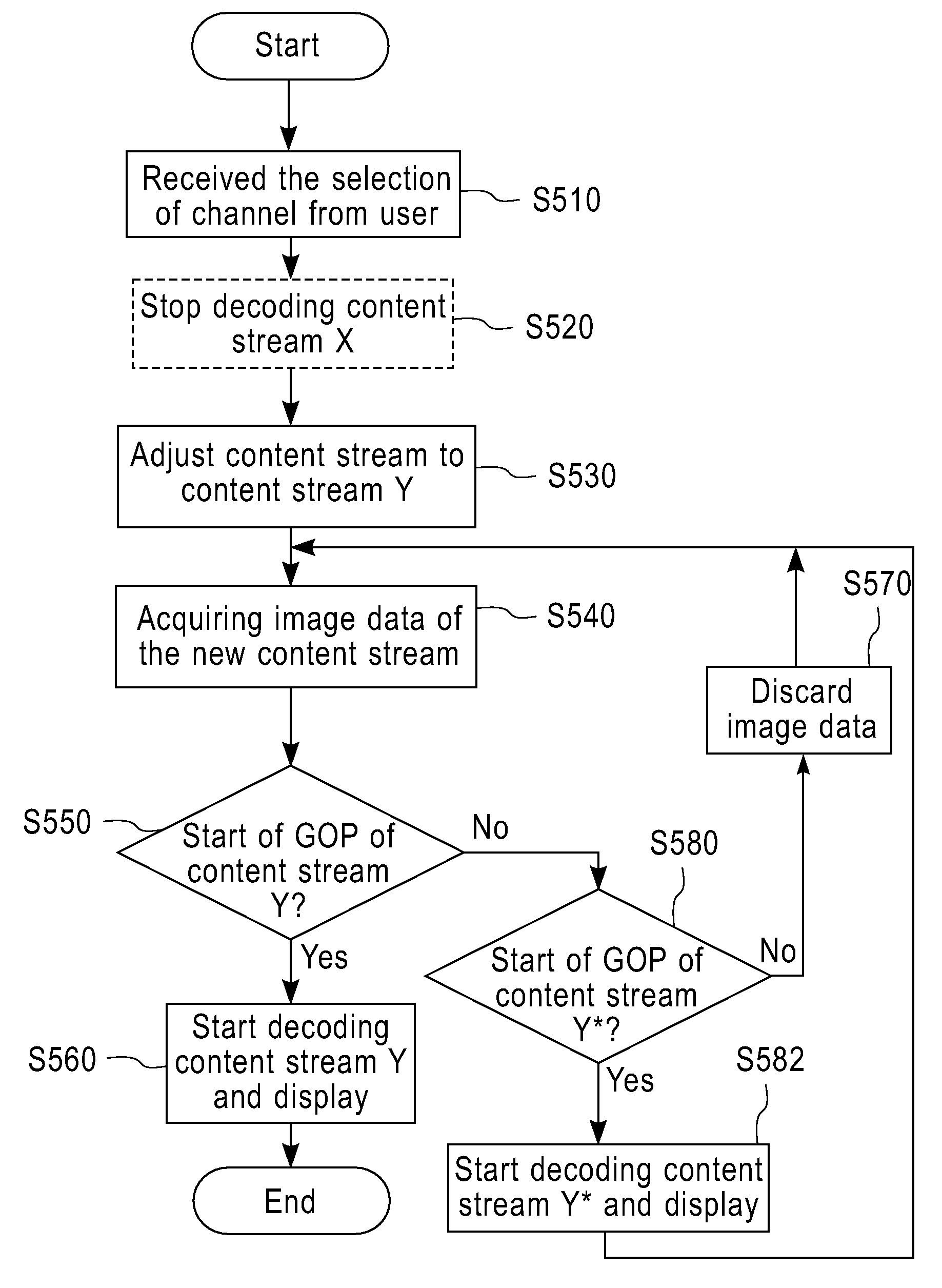
Method and device for processing video stream in digital video broadcasting systems
InactiveUS20080155586A1Improve experienceQuick previewTelevision system detailsElectrical cable transmission adaptationImage resolutionComputer graphics (images)
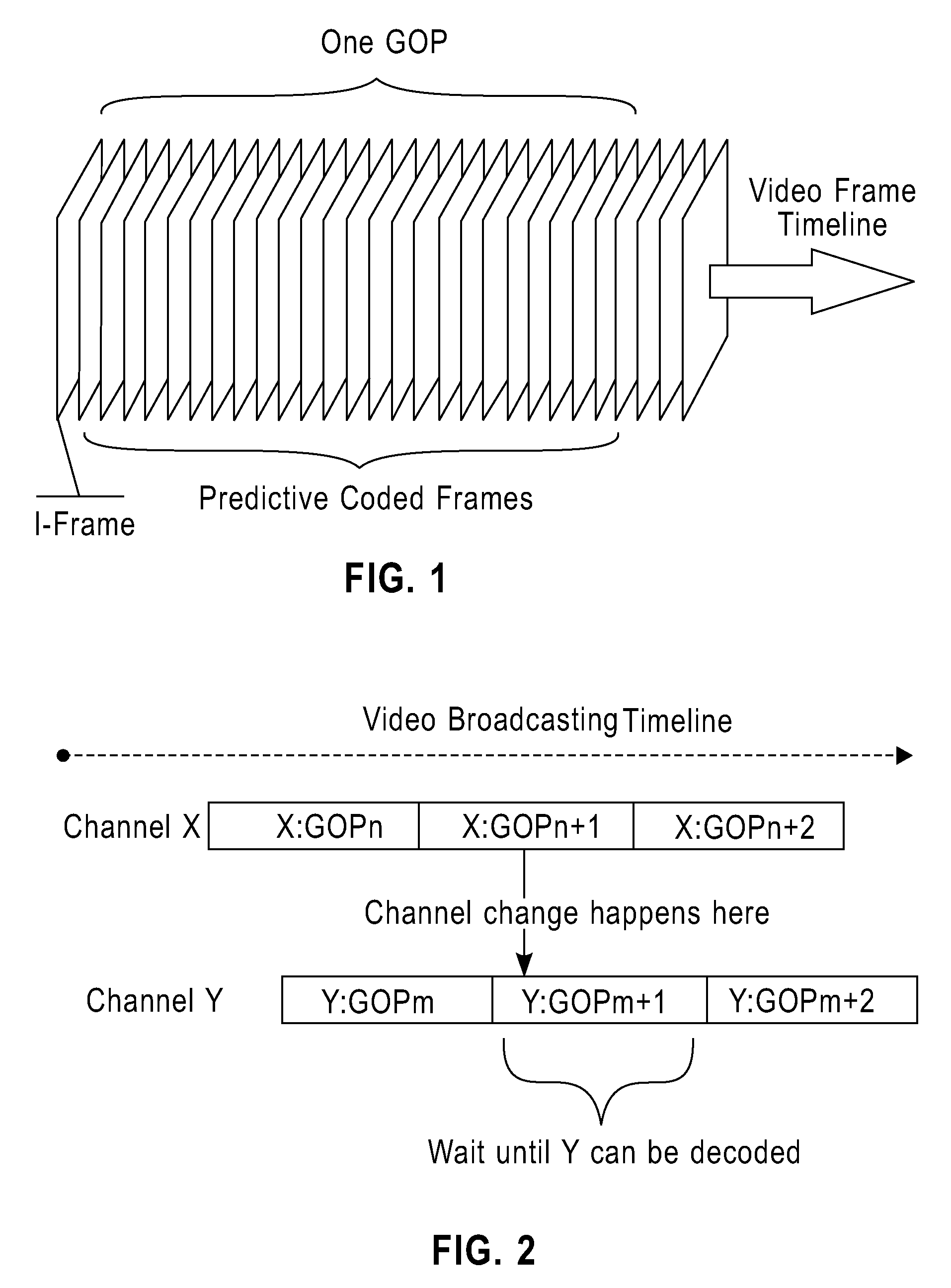
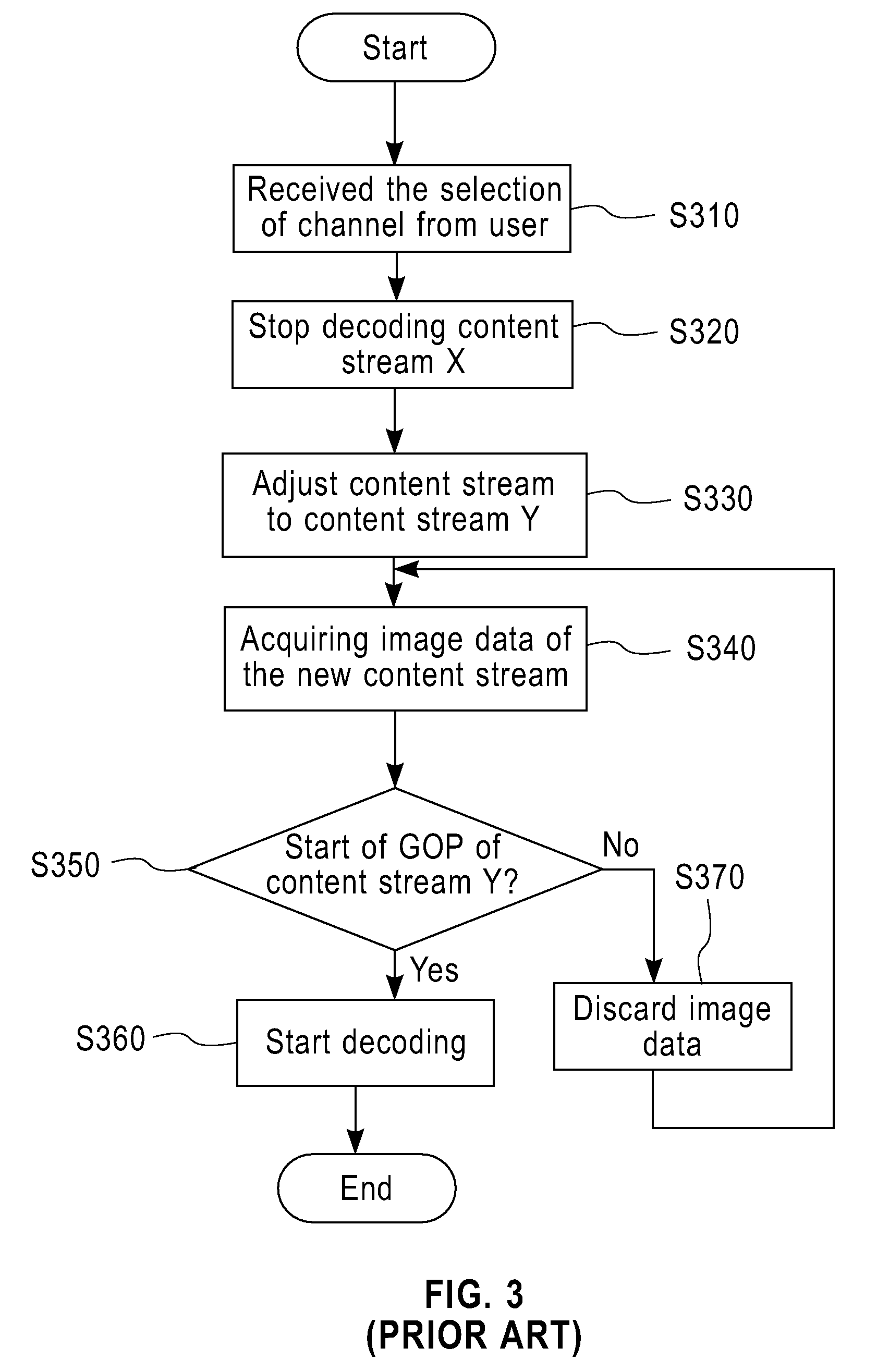
The invention provides a novel method for enhancing user experiences, especially when changing channels, in digital video broadcasting systems. The invention provides a mechanism to show a low resolution version of the contents immediately after the channel change, and then automatically switch to the high resolution content once the new GOP is started, thus the user will not see blank screen during the waiting period.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for delivering a contact to a preferred agent after a set wait period
Owner:AVAYA INC
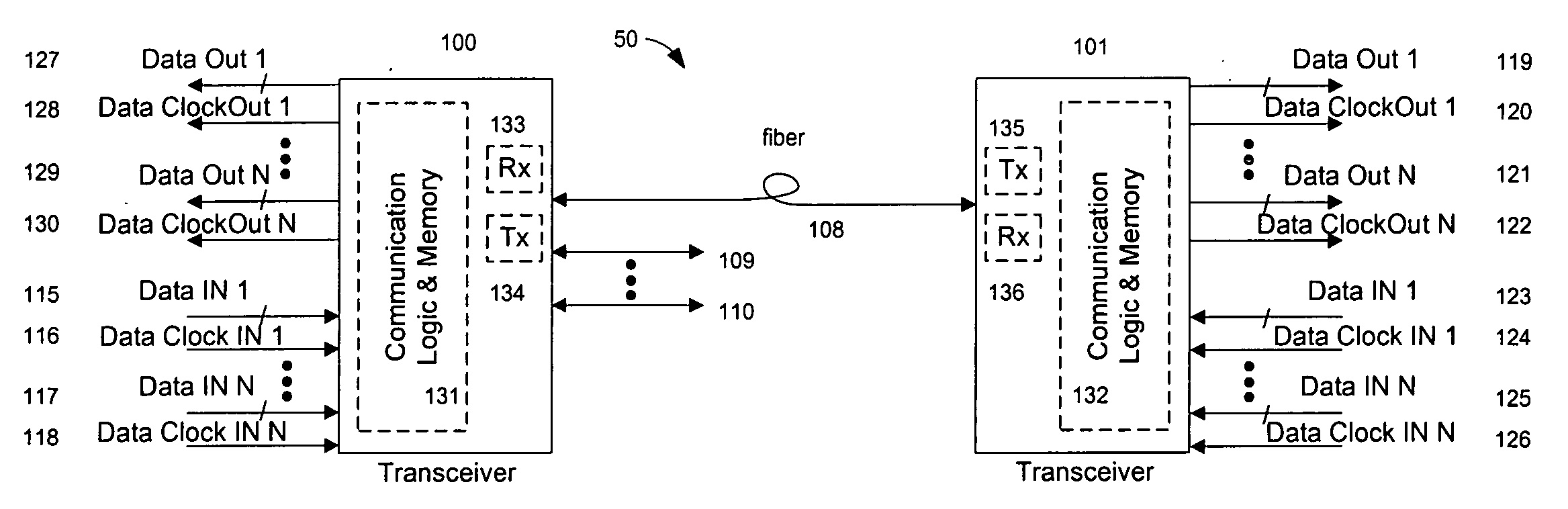
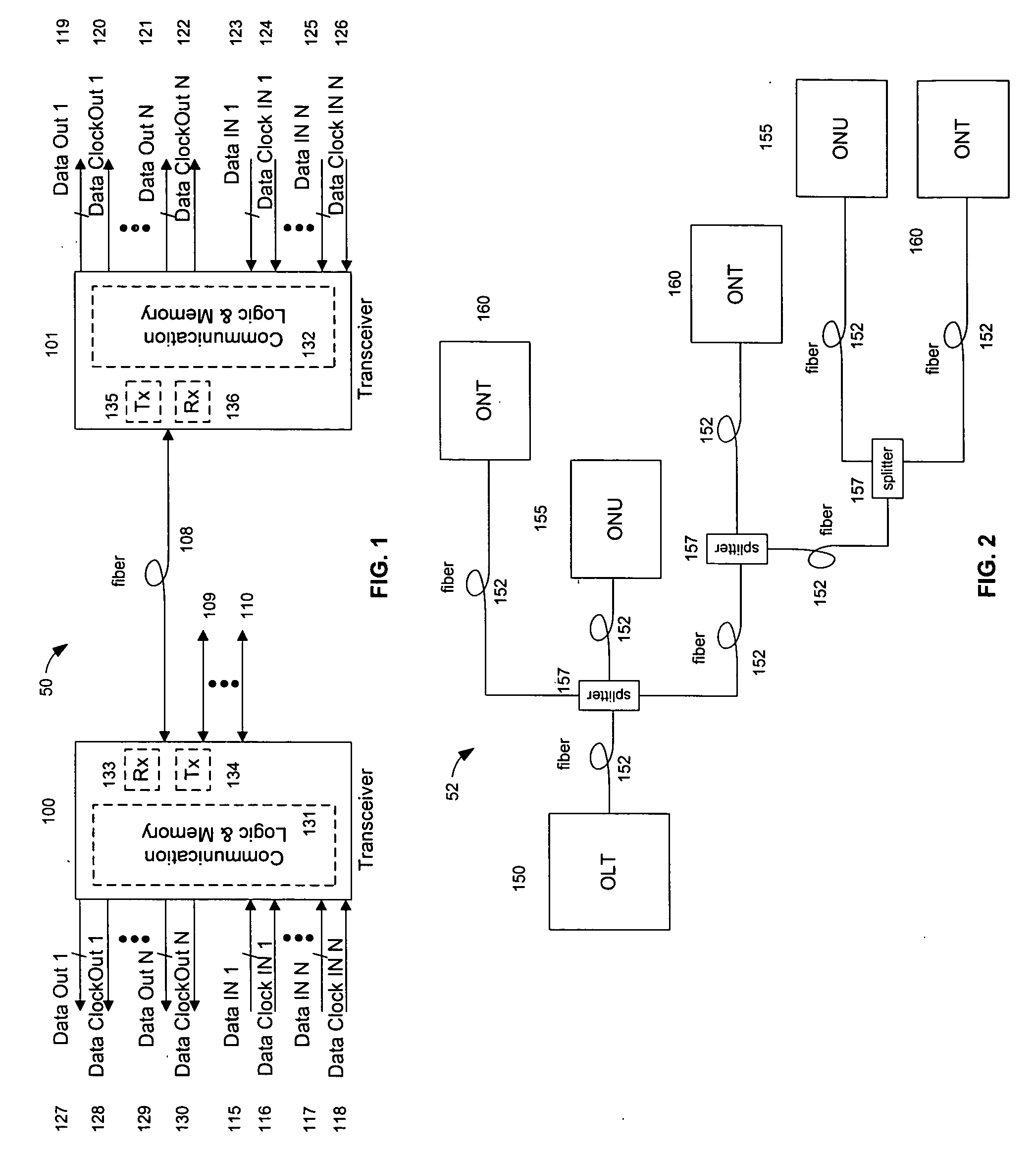
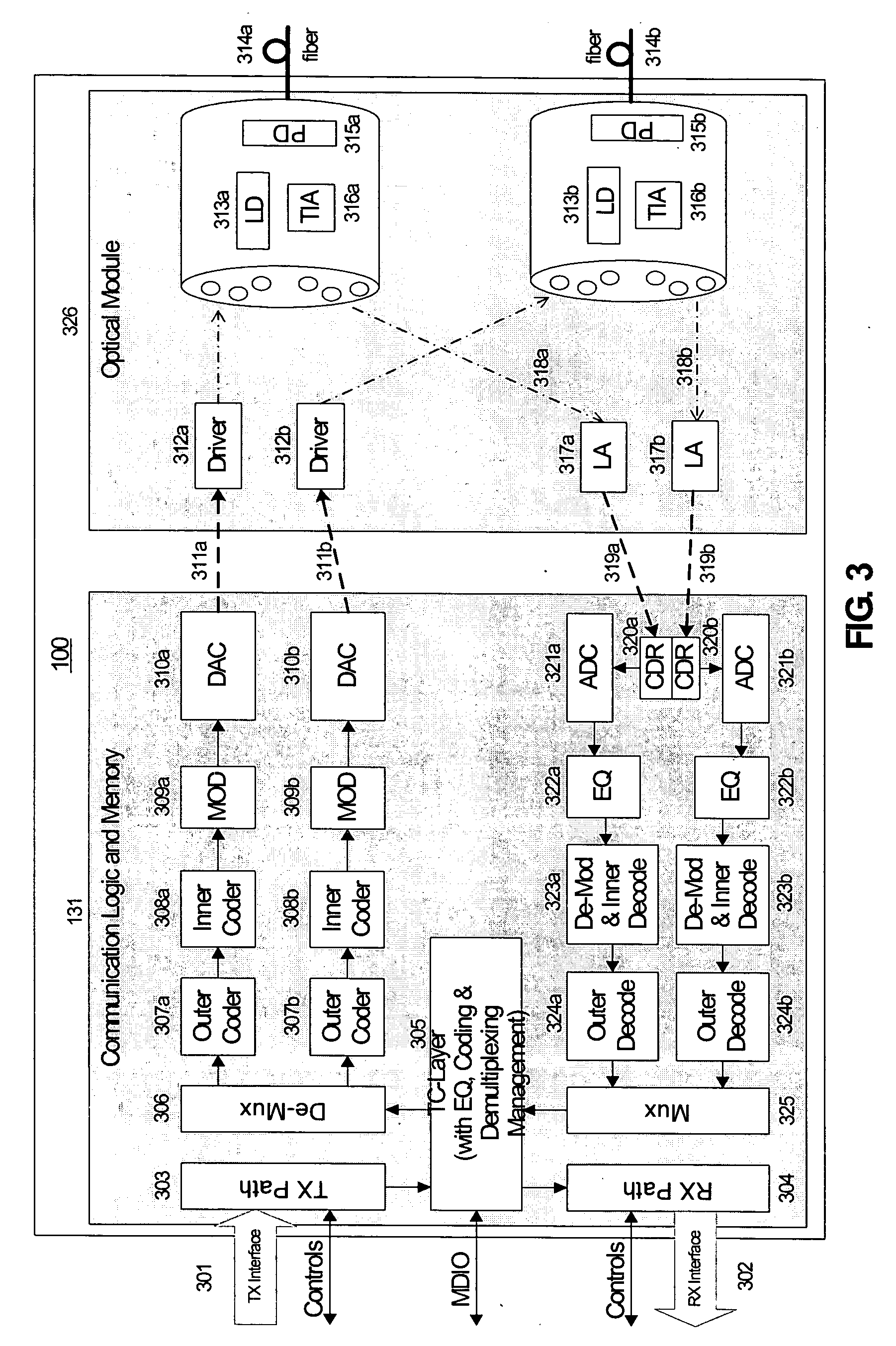
System and method for performing high-speed communications over fiber optical networks
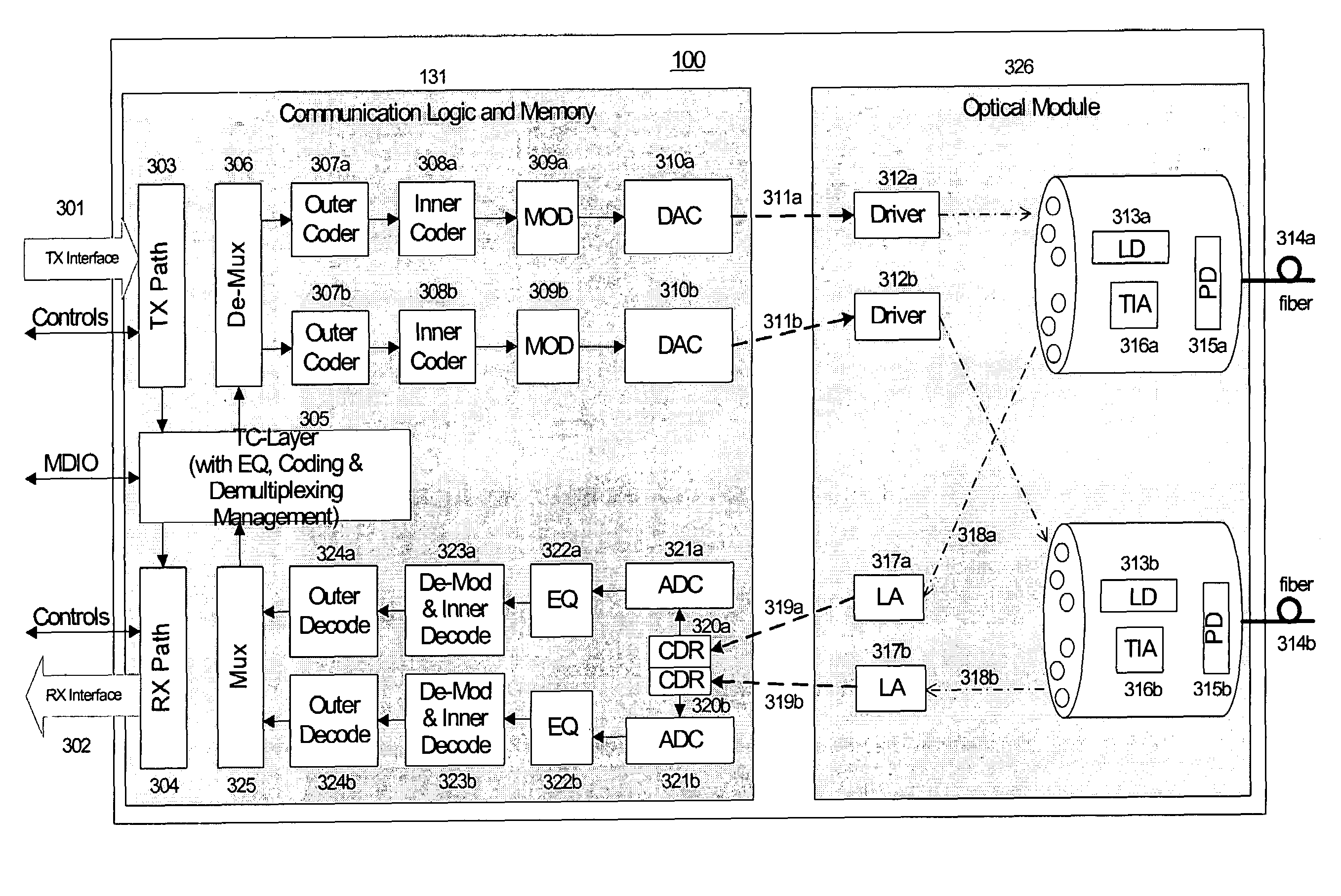
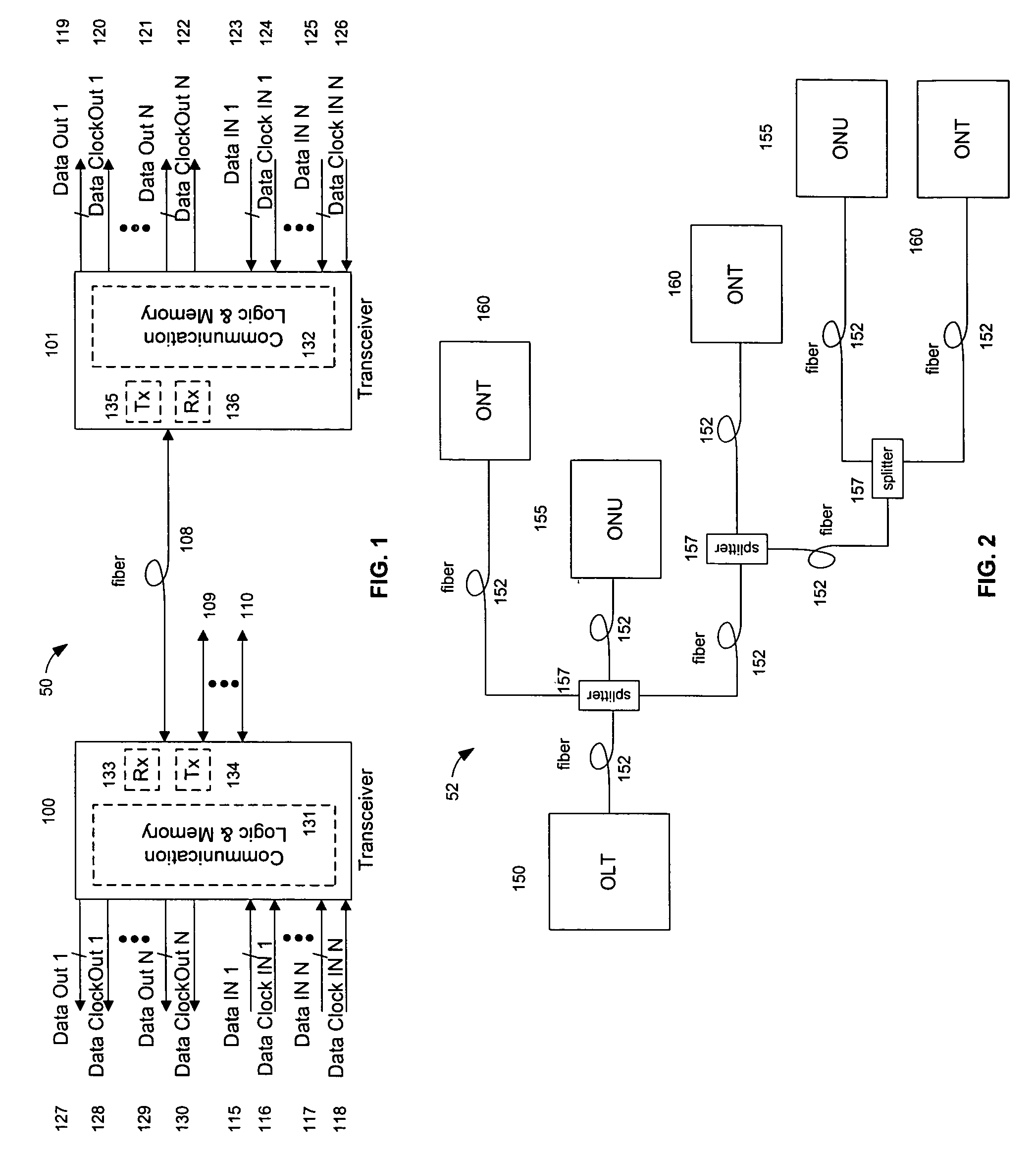
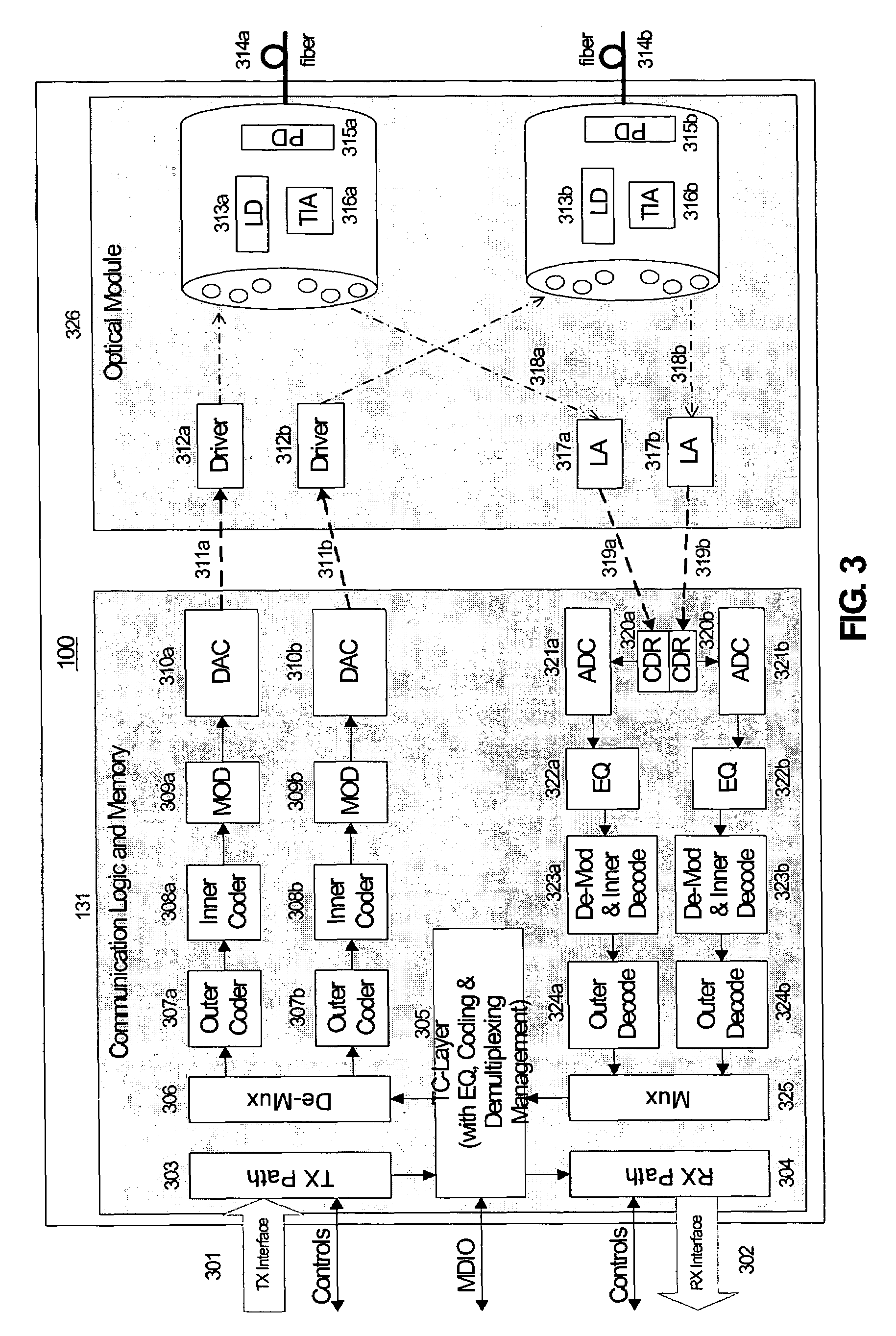
ActiveUS20050019036A1Remove distortionHigh speed communicationMultiple-port networksTransmission path divisionFiberWaiting period
Processing a received optical signal in an optical communication network includes equalizing a received optical signal to provide an equalized signal, demodulating the equalized signal according to an m-ary modulation format to provide a demodulated signal, decoding the demodulated signal according to an inner code to provide an inner-decoded signal, and decoding the inner-decoded signal according to an outer code. Other aspects include other features such as equalizing an optical channel including storing channel characteristics for the optical channel associated with a client, loading the stored channel characteristics during a waiting period between bursts on the channel, and equalizing a received burst from the client using the loaded channel characteristics.
Owner:SOTO ALEXANDER I +1
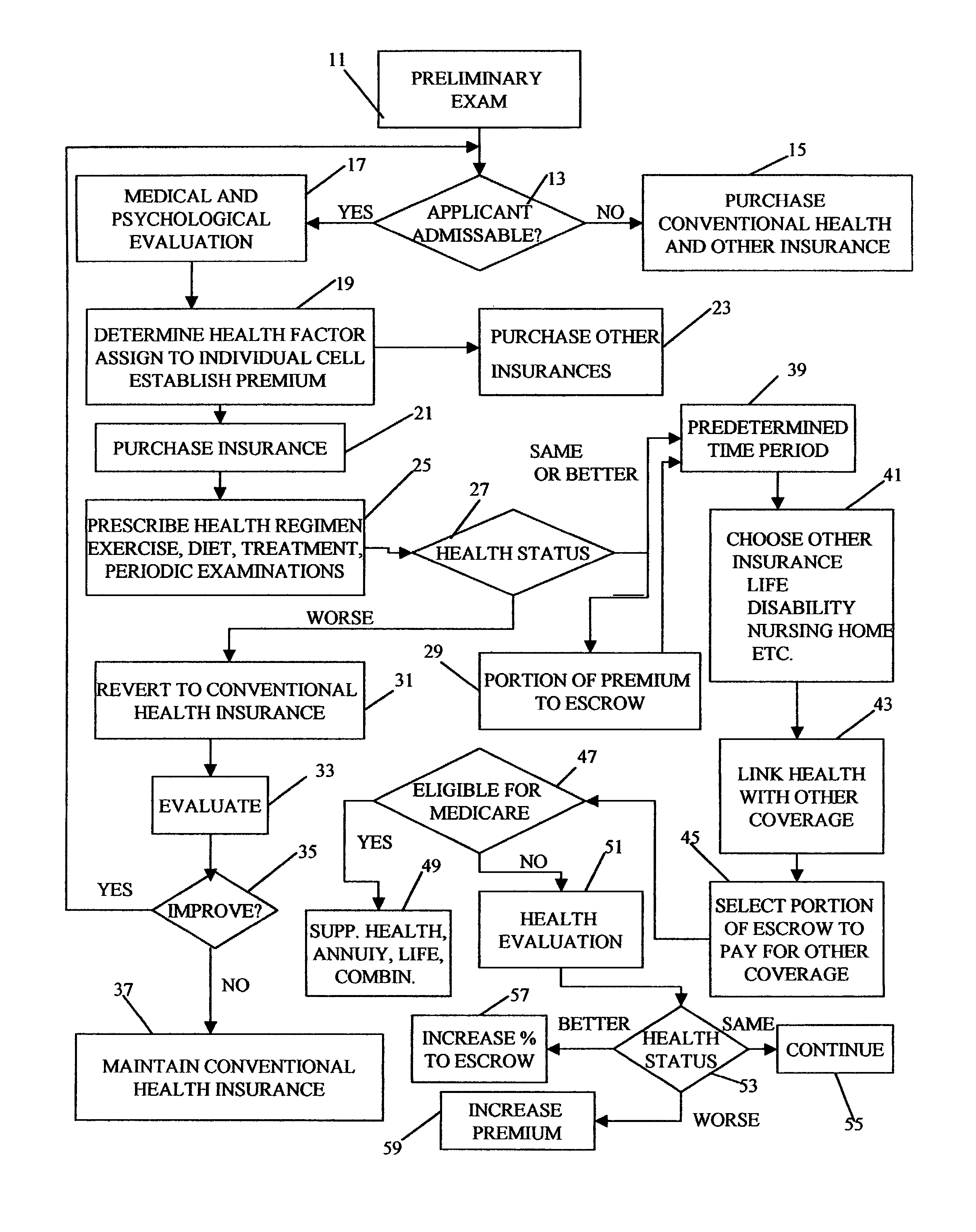
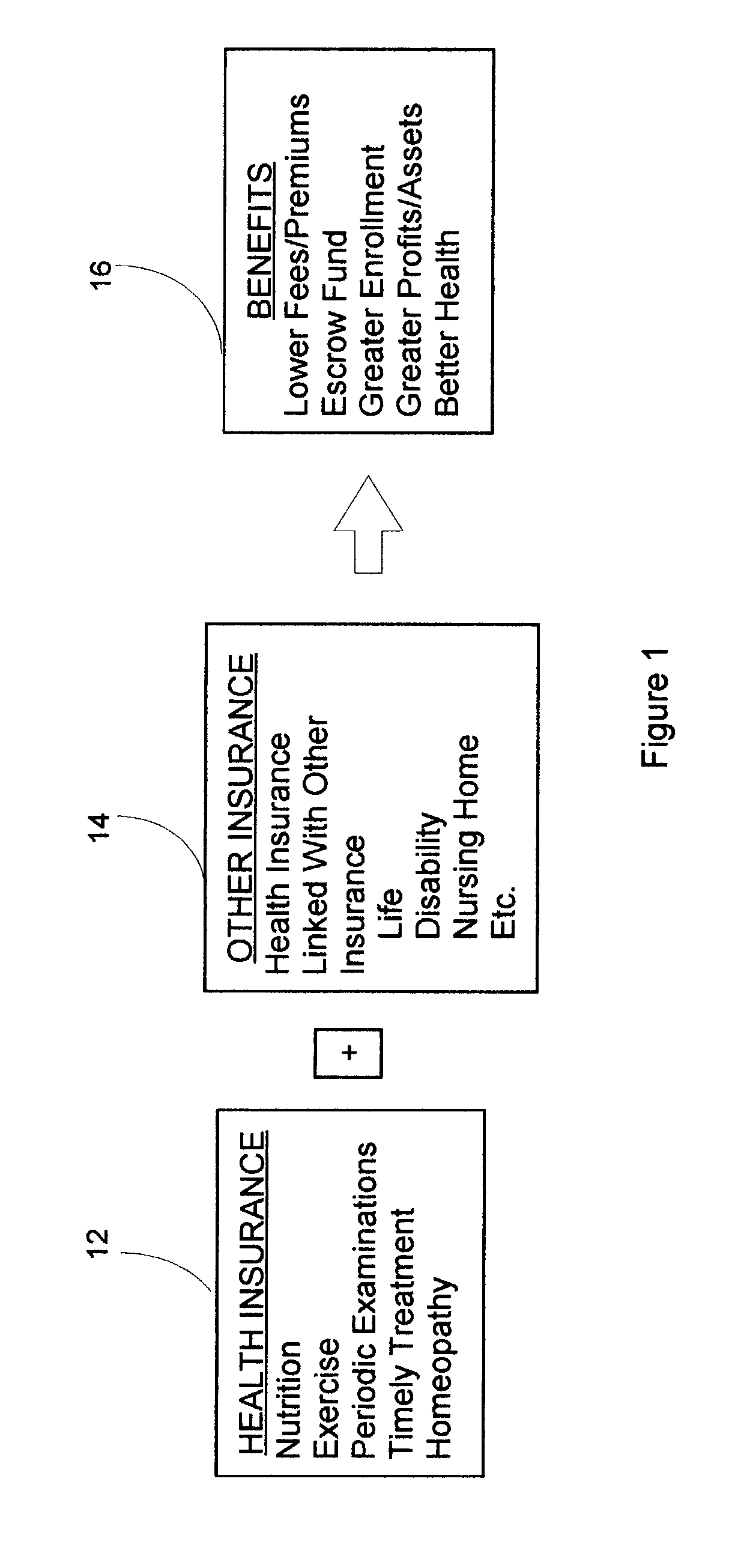
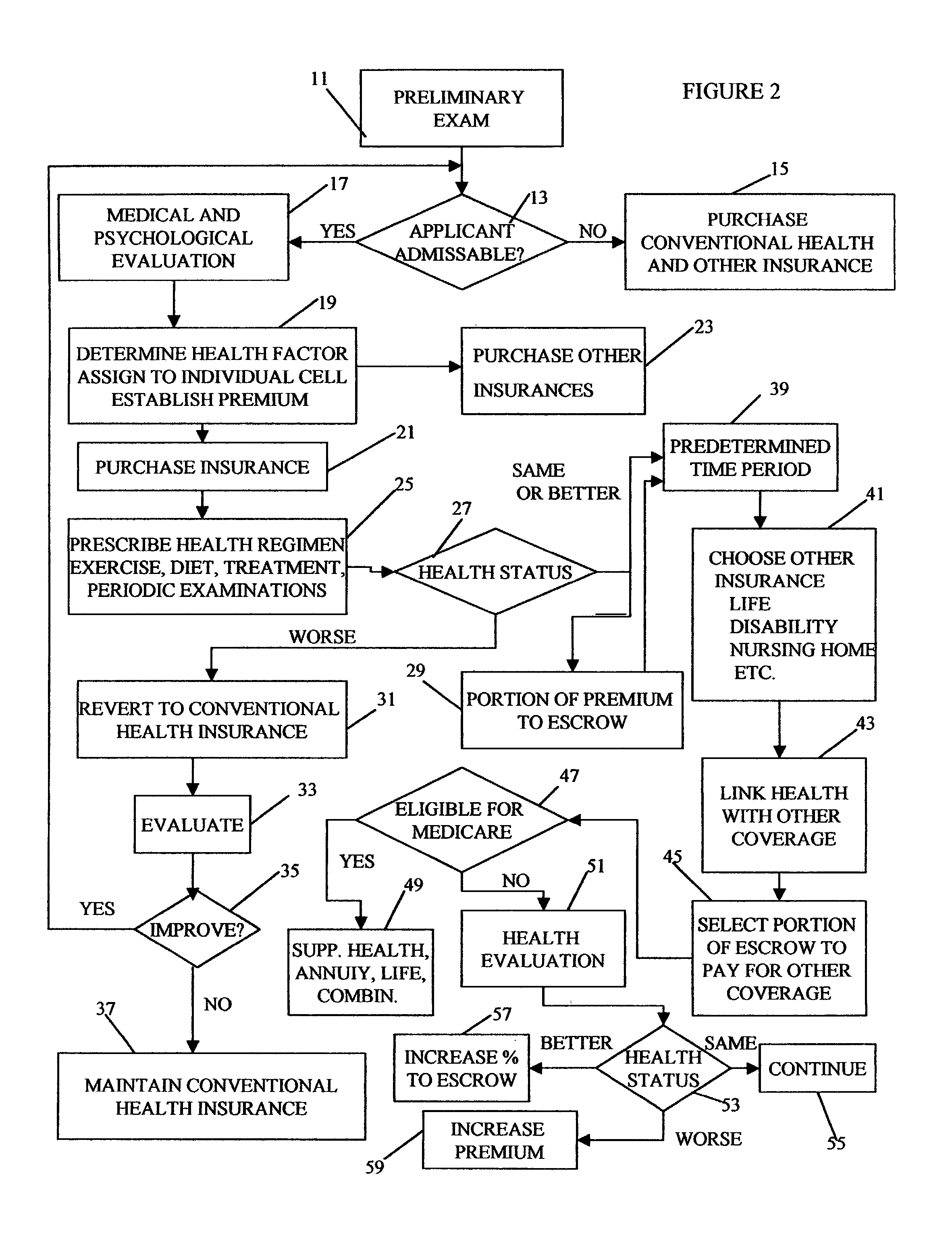
Method for linking insurance policies
ActiveUS7685007B1Reduce morbidityExtend your lifeFinanceHealth insurance managementWaiting periodEscrow
An insurance program that provides improved health care and longevity by emphasizing health improvement and maintenance. After a predetermined waiting period from the time health insurance is purchased, during which the health status of the insured is maintained or improved, the insured may link the health insurance policy with one or more other types of insurance policies, such as; life, disability, nursing home, etc. Throughout the life of the policy, portions of the premiums may be deposited in an escrow account, provided that the health of the insured is maintained or improved, which may be utilized to pay or help pay for the linked insurance and may also be utilized for retirement benefits.
Owner:CHAI INSURANCE CONSULTING GRP
Method and system for embedding information into streaming media
ActiveUS8151298B2Avoid waiting timeTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesWaiting periodWaiting time
A method and system for embedding information into streaming media is disclosed. In order to avoid a prolonged waiting period between the time a video stream is selected for viewing and the time it actually begins to play, information relevant to the content of the video stream is independently obtained and locally stored. This information may be advertising, text, games or any other media which may be of interest to the user. The information is embedded into the video or other media stream to be presented to the viewer and played immediately, so that the user avoids any wait time in viewing the selected stream that may occur due to bandwidth shortages or other system considerations.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method and device for the extraction of a body fluid
InactiveUS7833172B2Easy to collectOptimize withdrawalCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringWaiting periodBody fluid
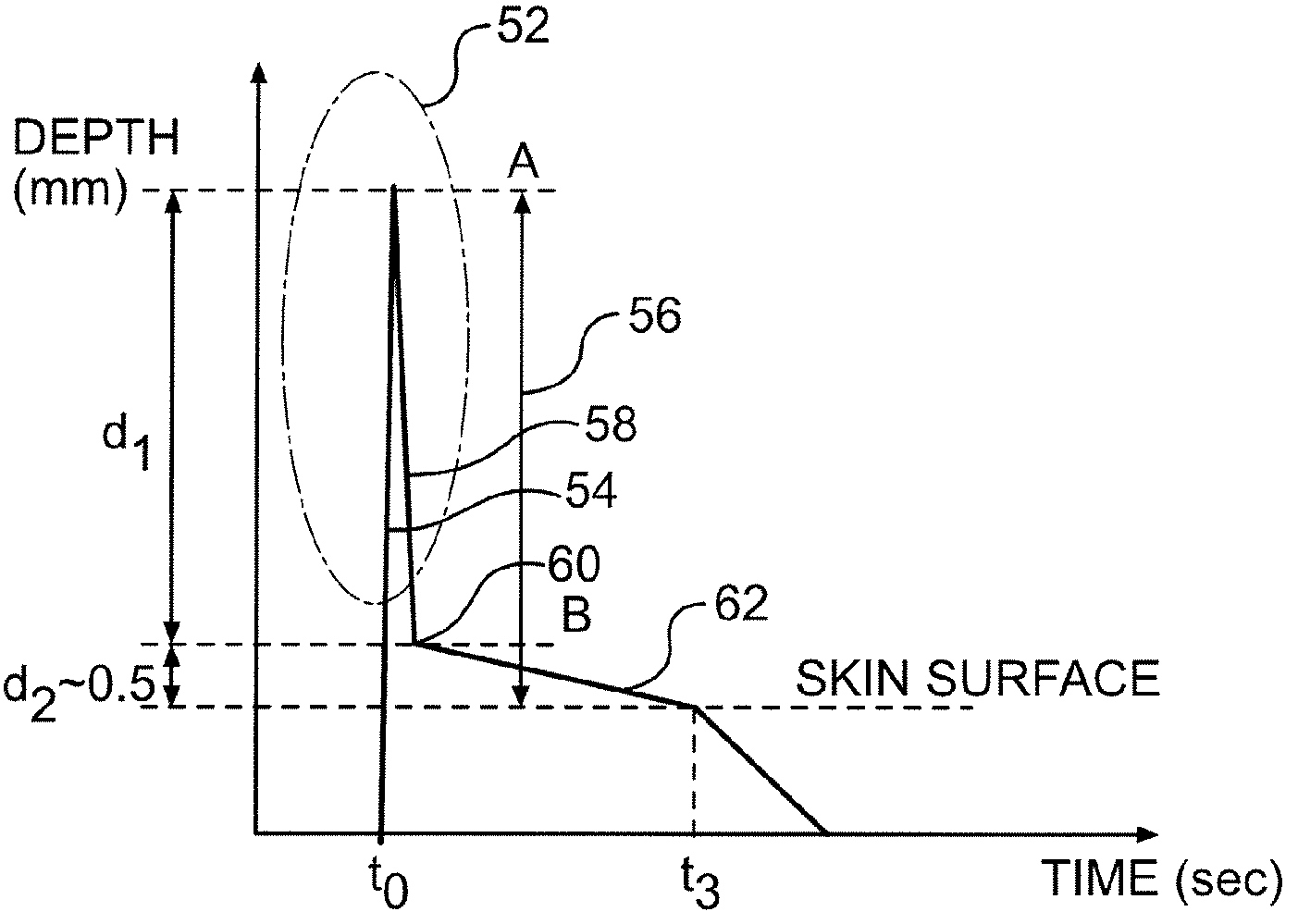
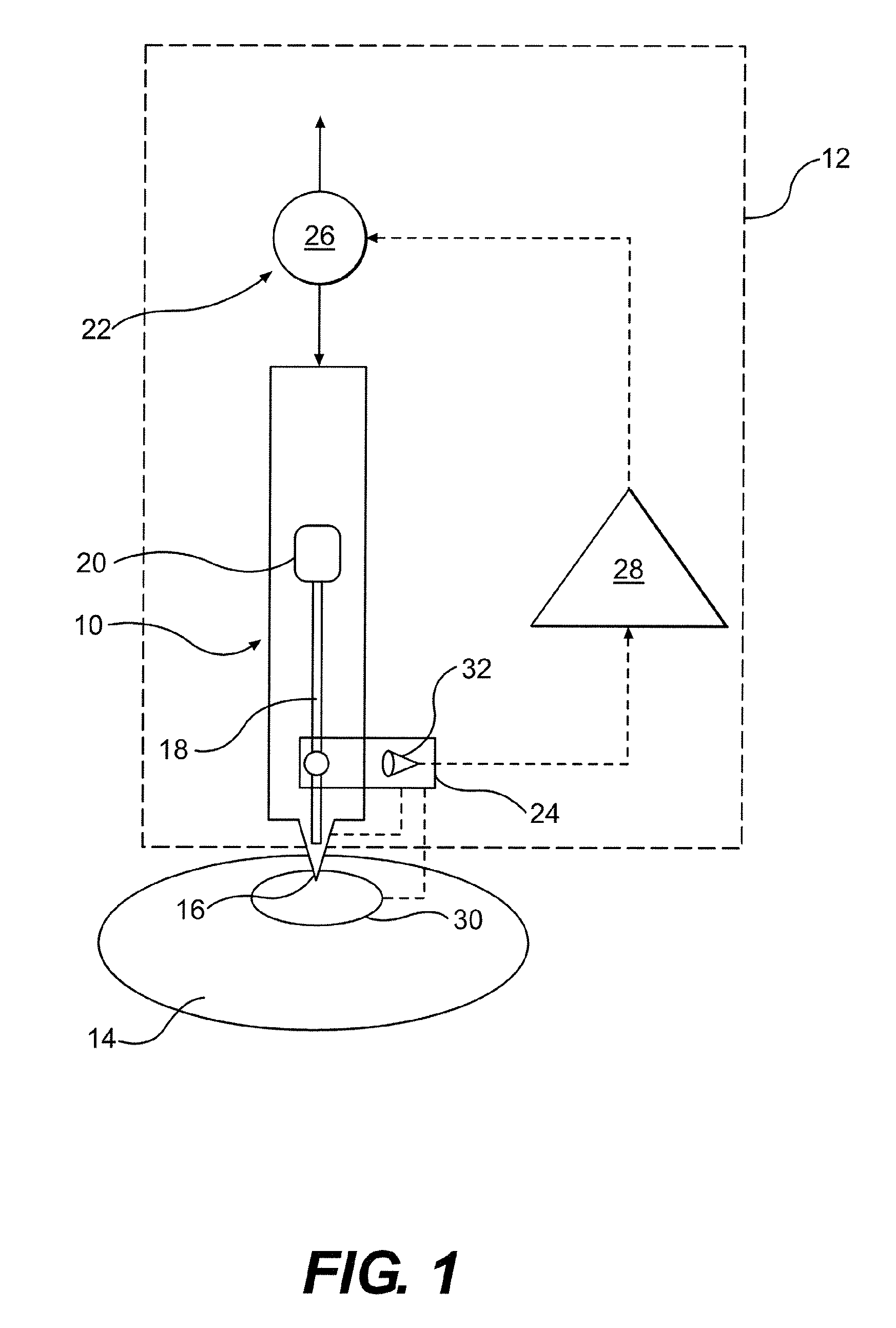
The present invention provides a method and a device for piercing a body part and determining whether a sufficient volume of blood has been withdrawn. A lancing element is rapidly inserted into a body part in a forward phase and retracted quickly to a lesser puncturing depth. Subsequently, the lancing element is retracted slower than during the first retraction movement and the distance retracted during the second retraction is shorter than the first retraction movement. During the second retraction movement, body fluid is collected in a collection phase by a capillary structure of the lancing element. Contact between the lancing element and the body fluid is detected after the forward phase at the beginning and the end of a waiting period.
Owner:ROCHE DIABETES CARE INC
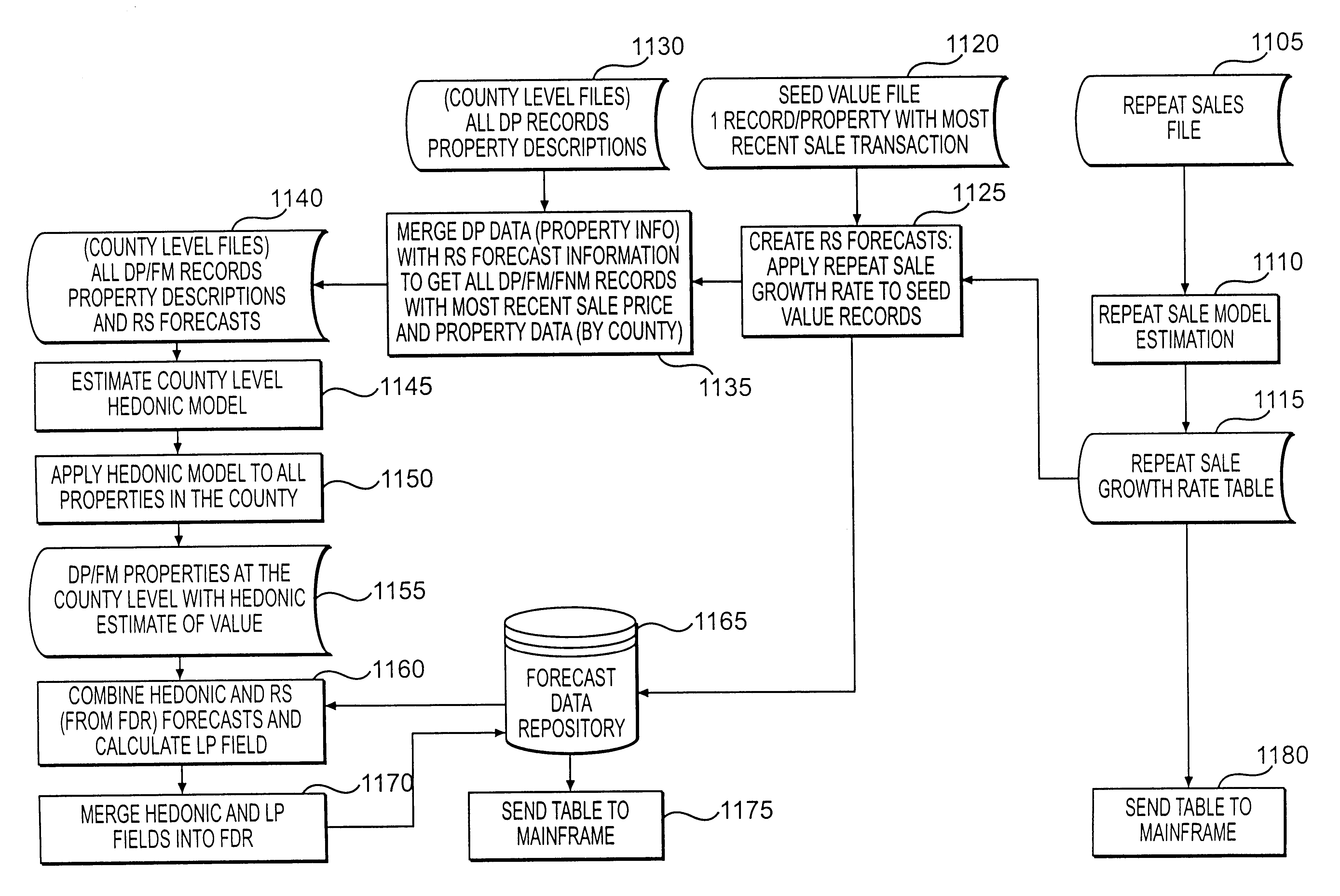
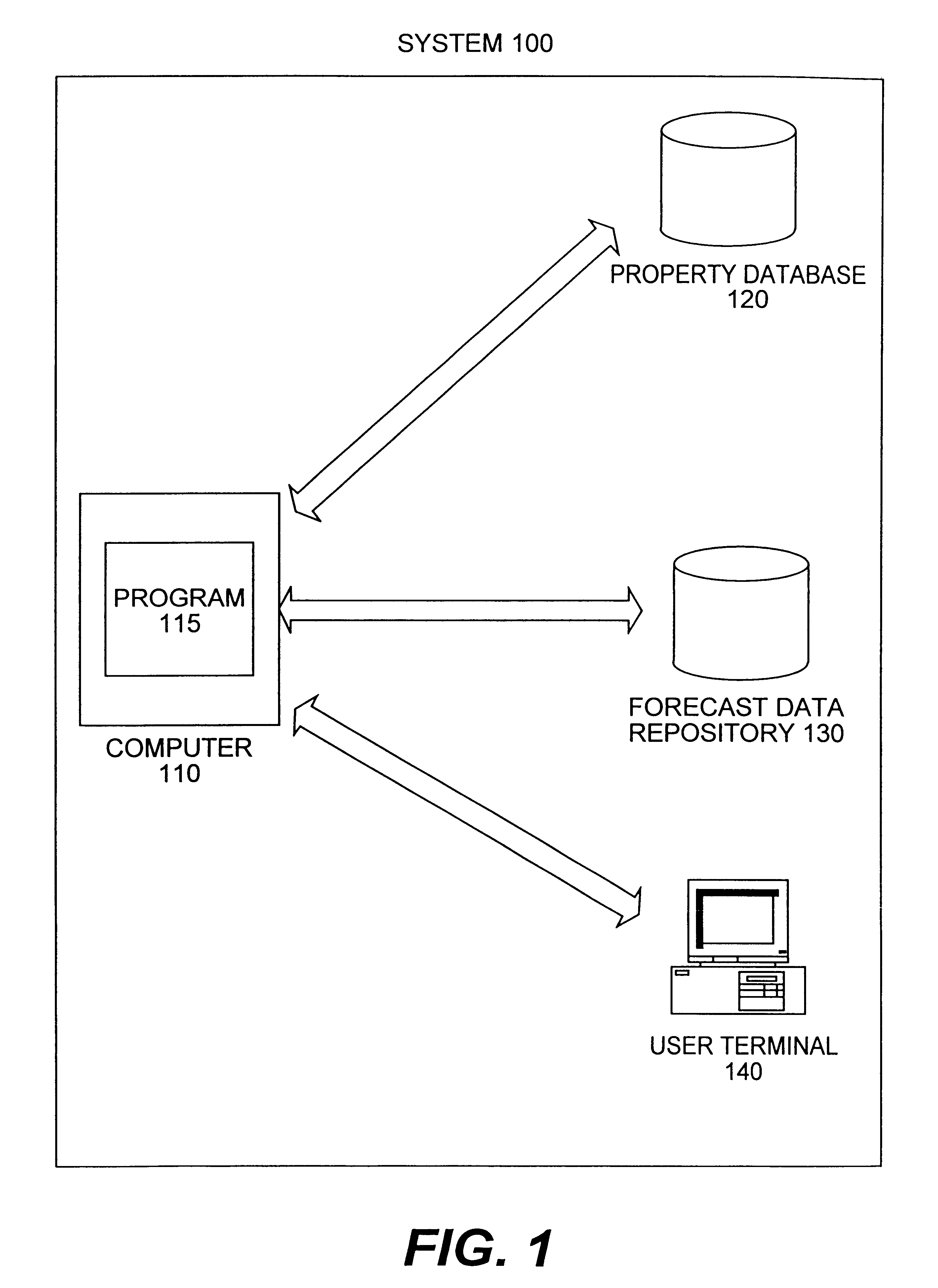
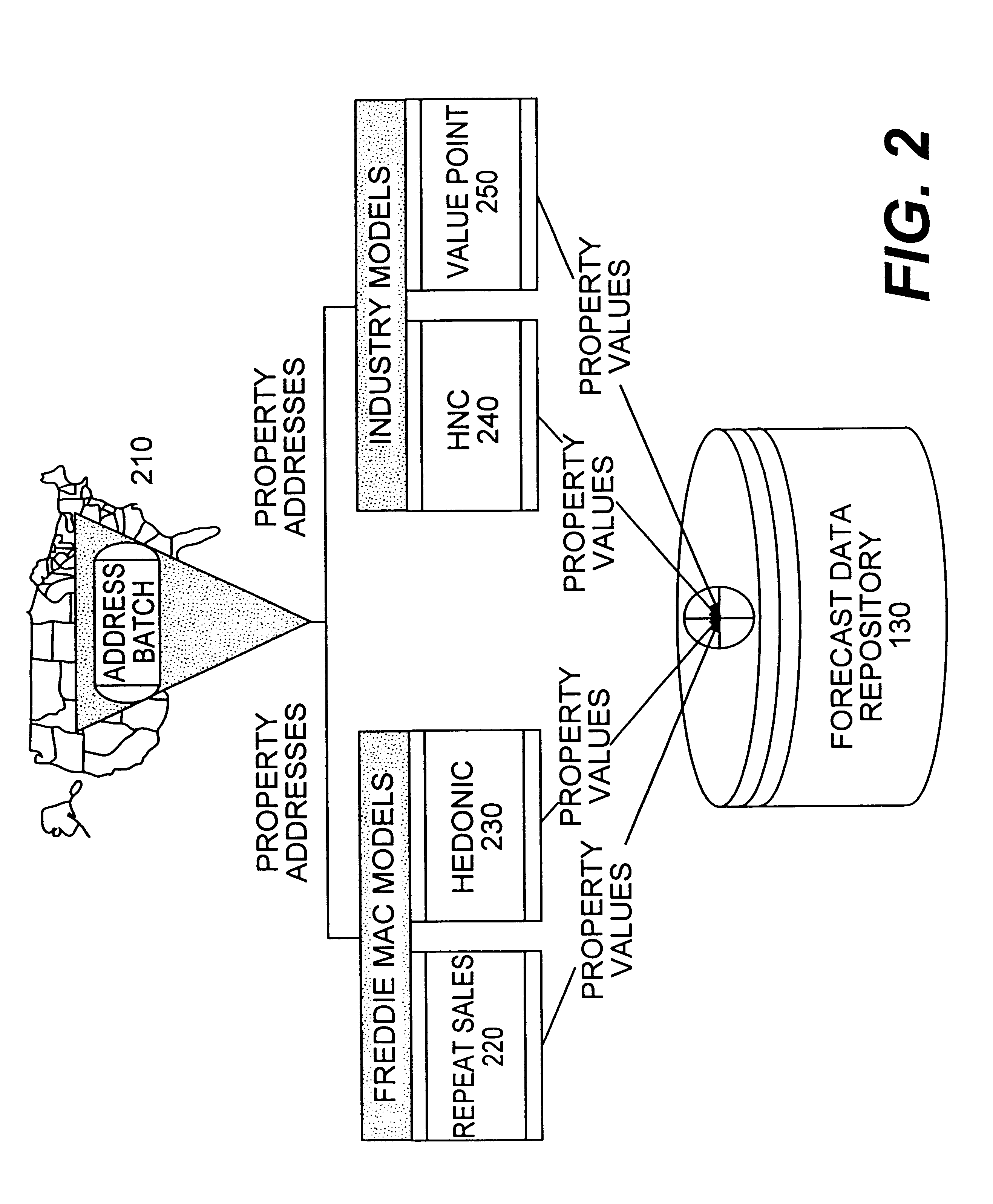
System and method for providing property value estimates
A system preprocesses property value estimates based on stored property data. It stores the computed property value estimates in a forecast data repository. The system obtains updates or new property data and computes new estimates according to a predetermined schedule. Users can instantaneously obtain property value estimates that have been preprocessed, thus eliminating a long wait period necessary for on-line processing.
Owner:FREDDIE MAC
Wireless communication system, communication control method and communication node
InactiveUS20100278087A1Effective controlReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower managementCommunications systemWaiting period
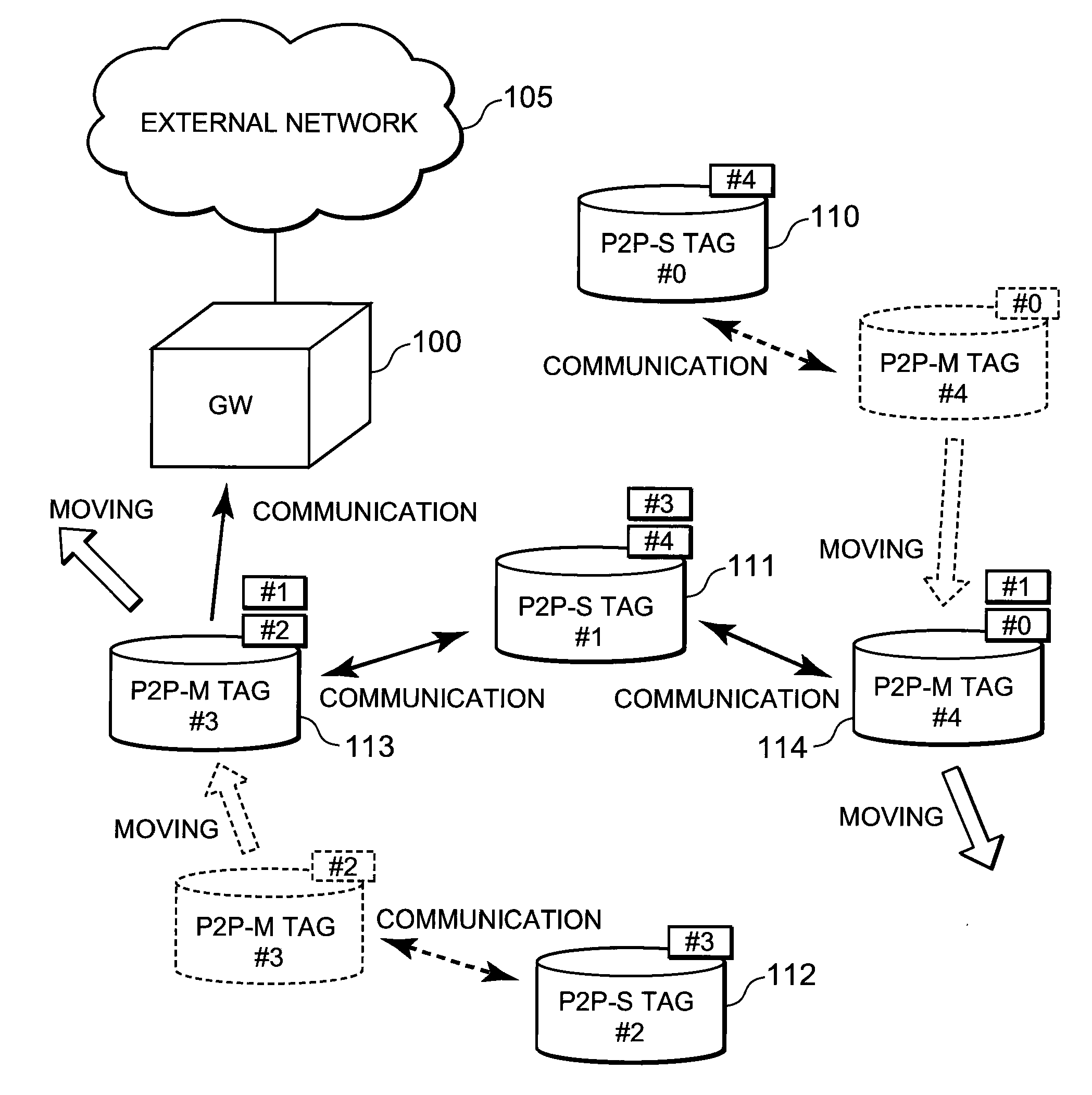
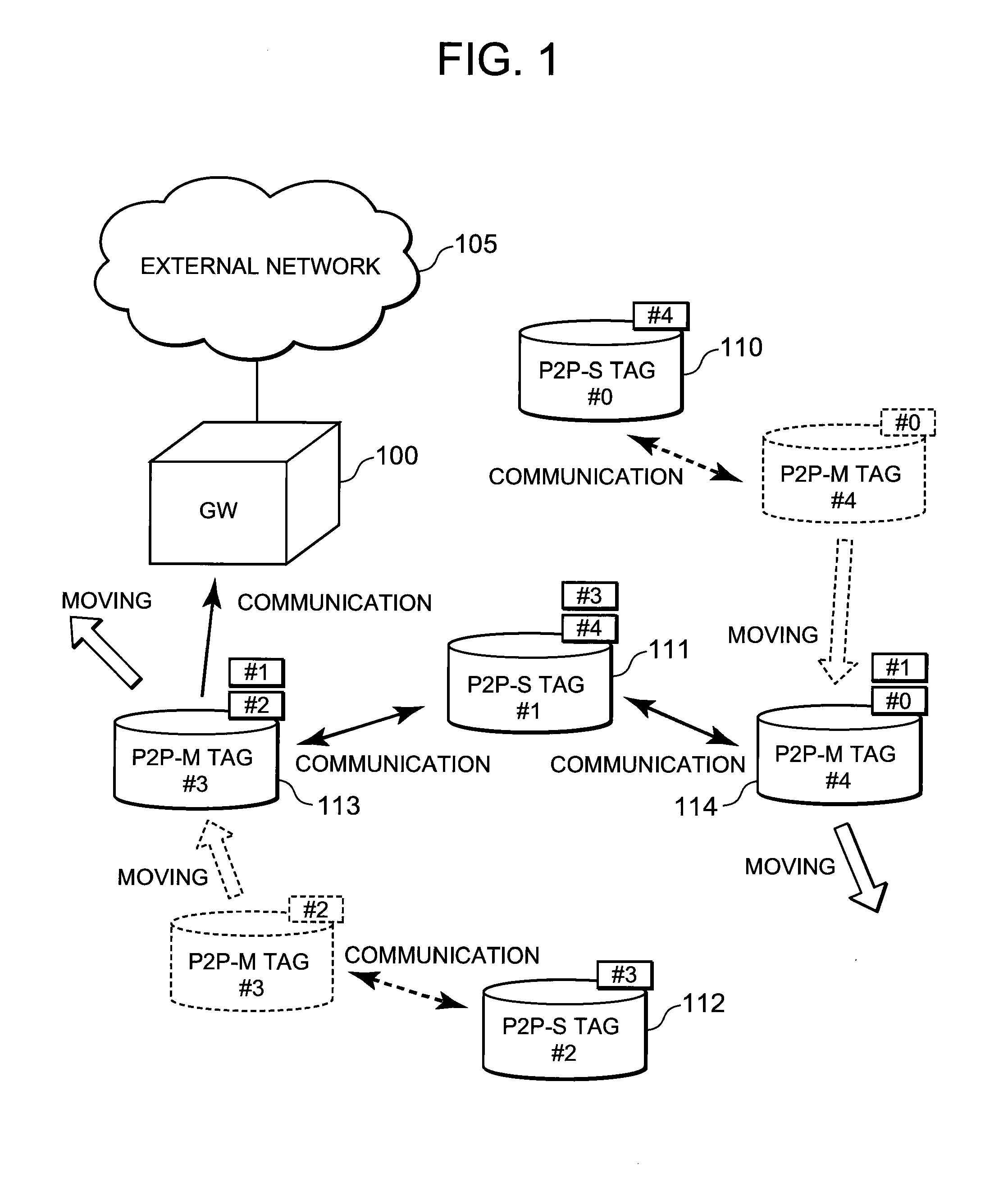
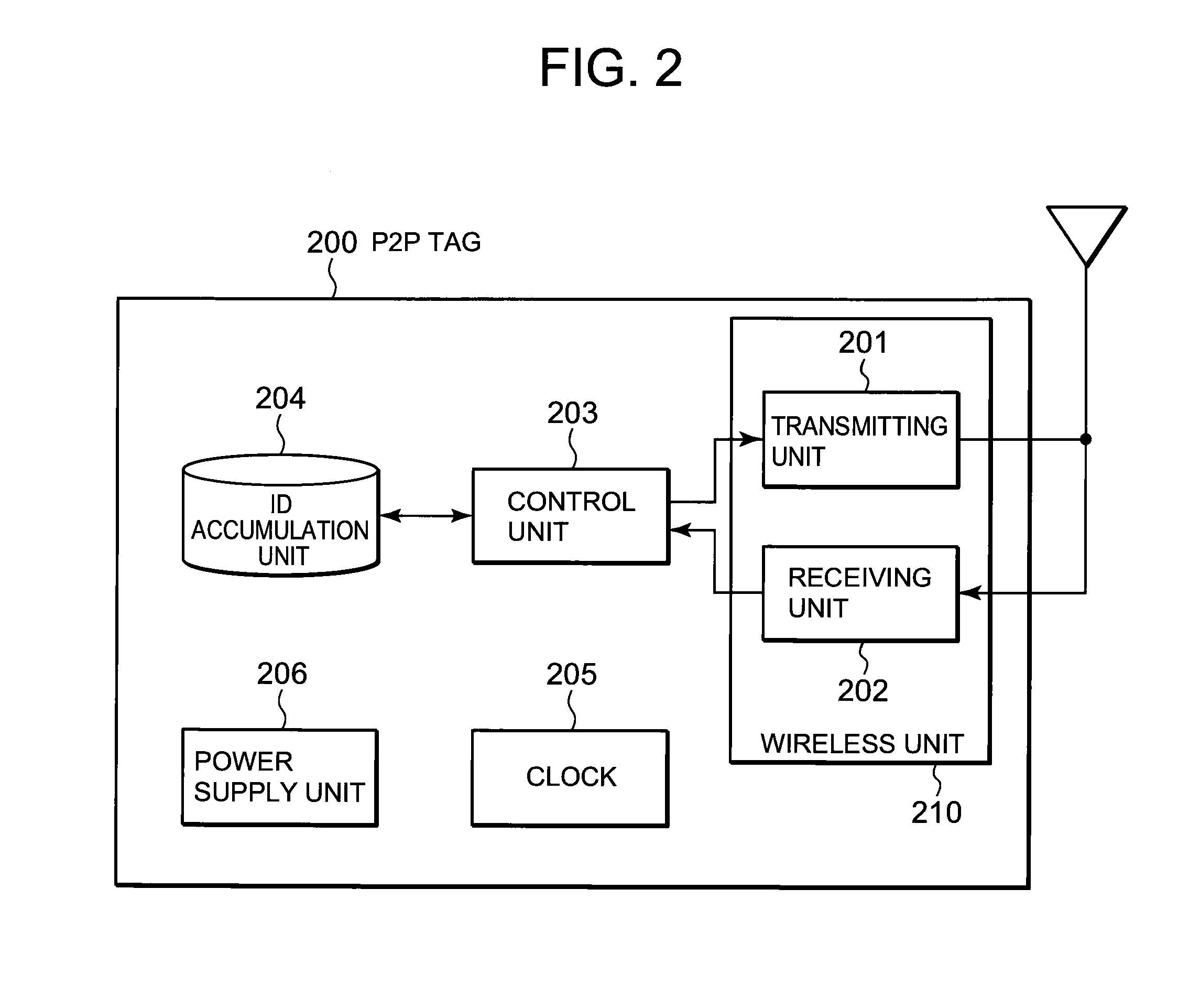
A technique is disclosed, by which it is possible to achieve the reduction of power consumption of each wireless node and to perform efficient access control in wireless communication system. According to this technique, a given period with a beacon transmitted from a gateway (GW) 100 at the foremost position is divided to an active period where each wireless node (P2P tag) transmits and receives a frame and a sleep period where transmitting and receiving of the frames are stopped. Further, the active period is divided to a plurality of timeslots each with a fixed length, and the period is partitioned to sub-periods where each type of a GW, a fixed node (P2P-S tag), and a mobile node (P2P-M tag) can transmit frames respectively. Each of the P2P tags selects a timeslot at random from the period for each type, and after waiting for a waiting period at random at the selected timeslot, it transmits a frame including information to identify the selected timeslot or the waiting period in addition to its own ID.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
System and method for performing high-speed communications over fiber optical networks
ActiveUS7242868B2Remove distortionHigh speed communicationMultiple-port networksTransmission path divisionFiberWaiting period
Processing a received optical signal in an optical communication network includes equalizing a received optical signal to provide an equalized signal, demodulating the equalized signal according to an m-ary modulation format to provide a demodulated signal, decoding the demodulated signal according to an inner code to provide an inner-decoded signal, and decoding the inner-decoded signal according to an outer code. Other aspects include other features such as equalizing an optical channel including storing channel characteristics for the optical channel associated with a client, loading the stored channel characteristics during a waiting period between bursts on the channel, and equalizing a received burst from the client using the loaded channel characteristics.
Owner:SOTO ALEXANDER I +1
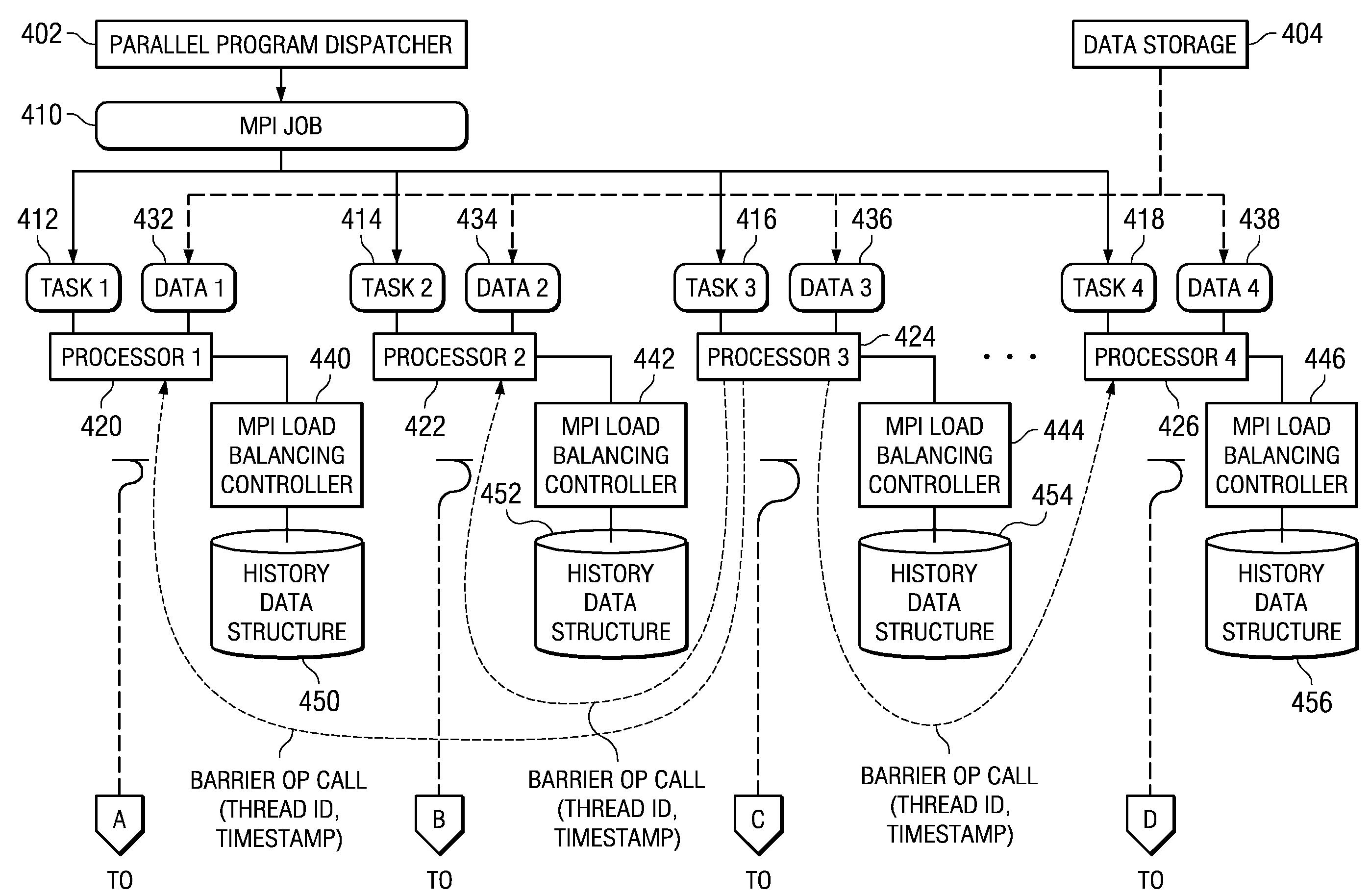
System and Method for Hardware Based Dynamic Load Balancing of Message Passing Interface Tasks By Modifying Tasks
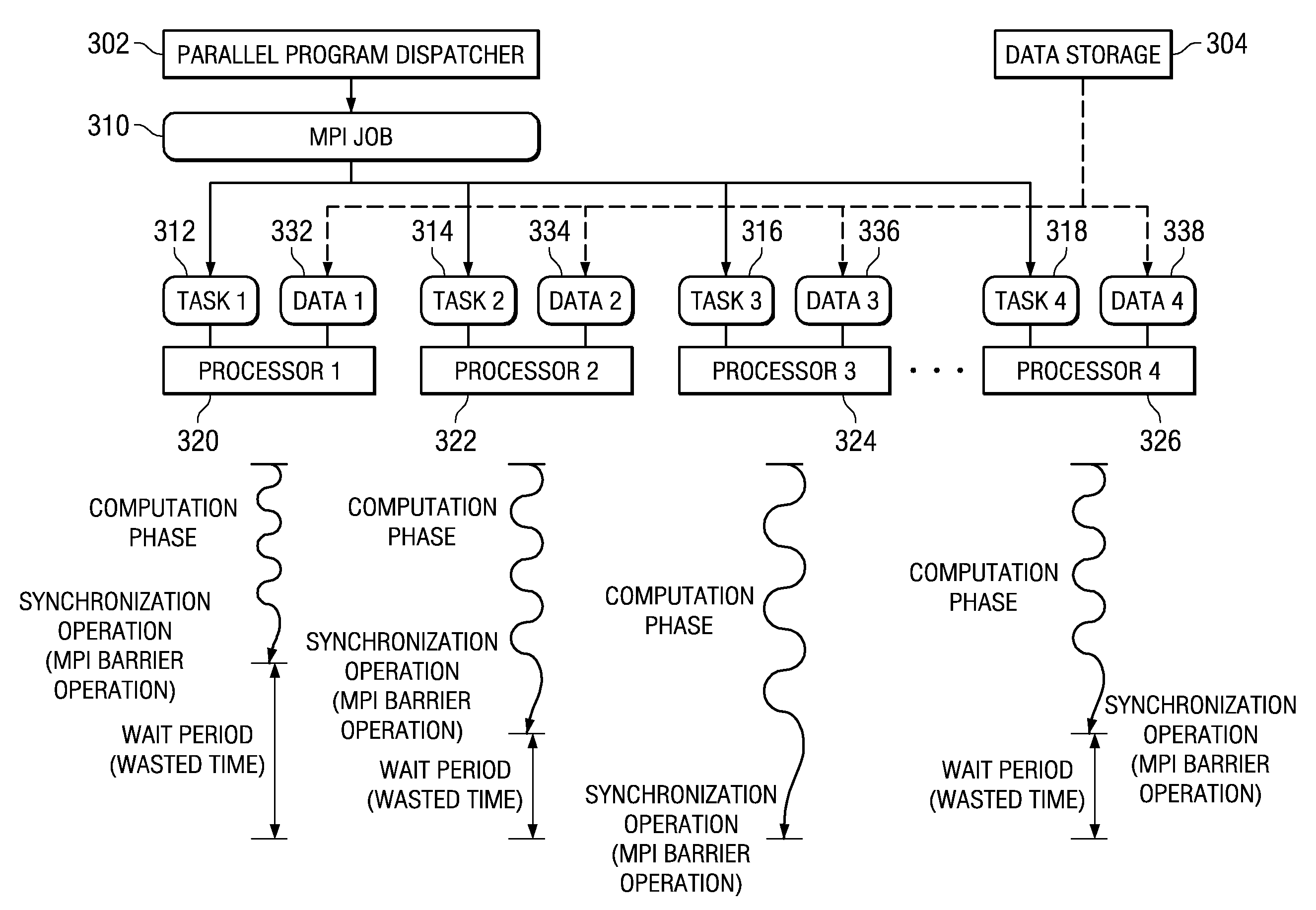
InactiveUS20090064168A1Minimize periodWasted processor cyclesMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsDynamic load balancingMessage Passing Interface
A system and method are provided for providing hardware based dynamic load balancing of message passing interface (MPI) tasks by modifying tasks. Mechanisms for adjusting the balance of processing workloads of the processors executing tasks of an MPI job are provided so as to minimize wait periods for waiting for all of the processors to call a synchronization operation. Each processor has an associated hardware implemented MPI load balancing controller. The MPI load balancing controller maintains a history that provides a profile of the tasks with regard to their calls to synchronization operations. From this information, it can be determined which processors should have their processing loads lightened and which processors are able to handle additional processing loads without significantly negatively affecting the overall operation of the parallel execution system. Thus, operations may be performed to shift workloads from the slowest processor to one or more of the faster processors.
Owner:IBM CORP
Radiation imaging apparatus and control method therefor
InactiveUS7403594B2Stably performing radiographyAvoid delaySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSoft x rayX-ray
A lamp emits pulse-shaped visible light when a wait period begins. If a radiation emission switch is not pressed in the wait period, X-ray radiation is not emitted from an X-ray source, and no charges are accumulated in photoelectric conversion elements of an X-ray imaging apparatus. In a non-read period, although signals are sequentially read from the photoelectric conversion elements, an output signal does not change. When the radiation emission switch is pressed in synchronization with a radiation-induced signal in a certain wait period, the X-ray source emits X-rays. After irradiation of X-rays, a photoelectric conversion period transitions to an actual read period. In the photoelectric conversion period, X-rays are emitted and transmitted X-ray information of a patient are accumulated in the photoelectric conversion elements of the X-ray imaging apparatus. In the actual read period, the accumulated information is read.
Owner:CANON KK
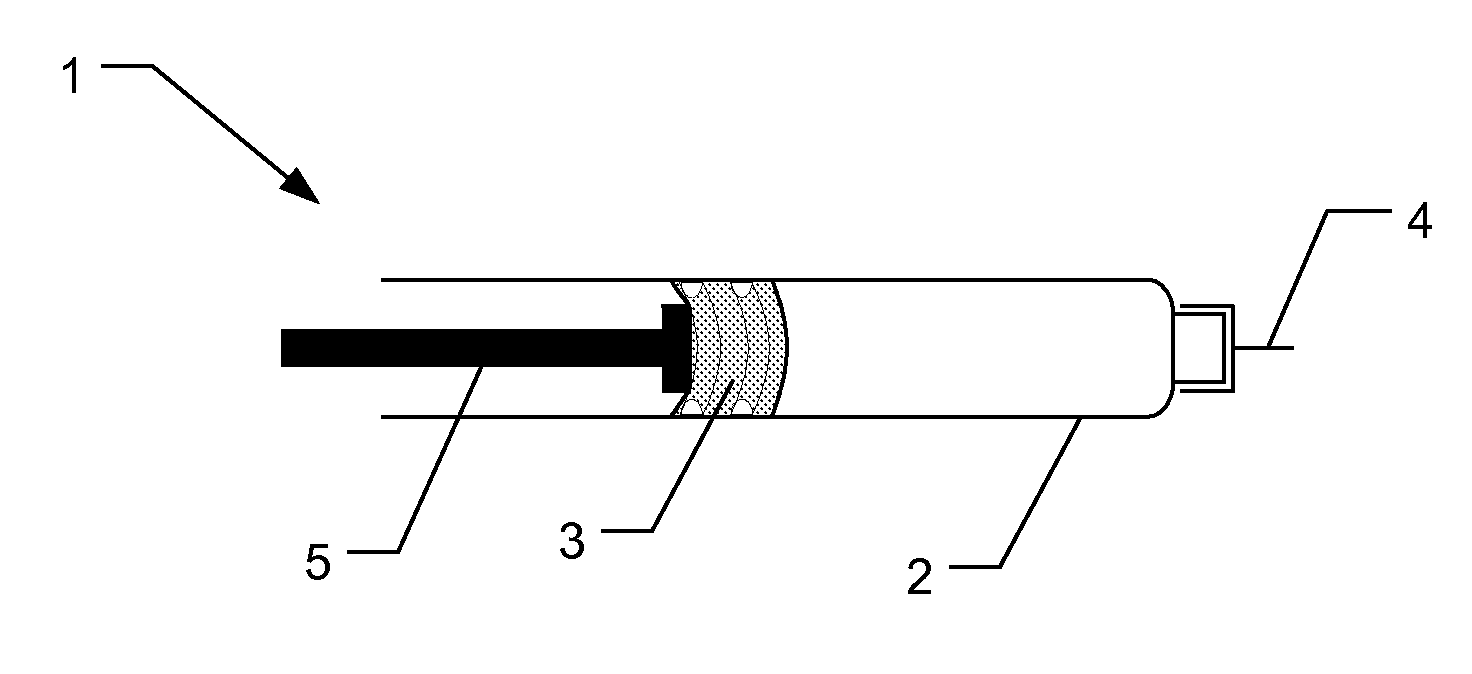
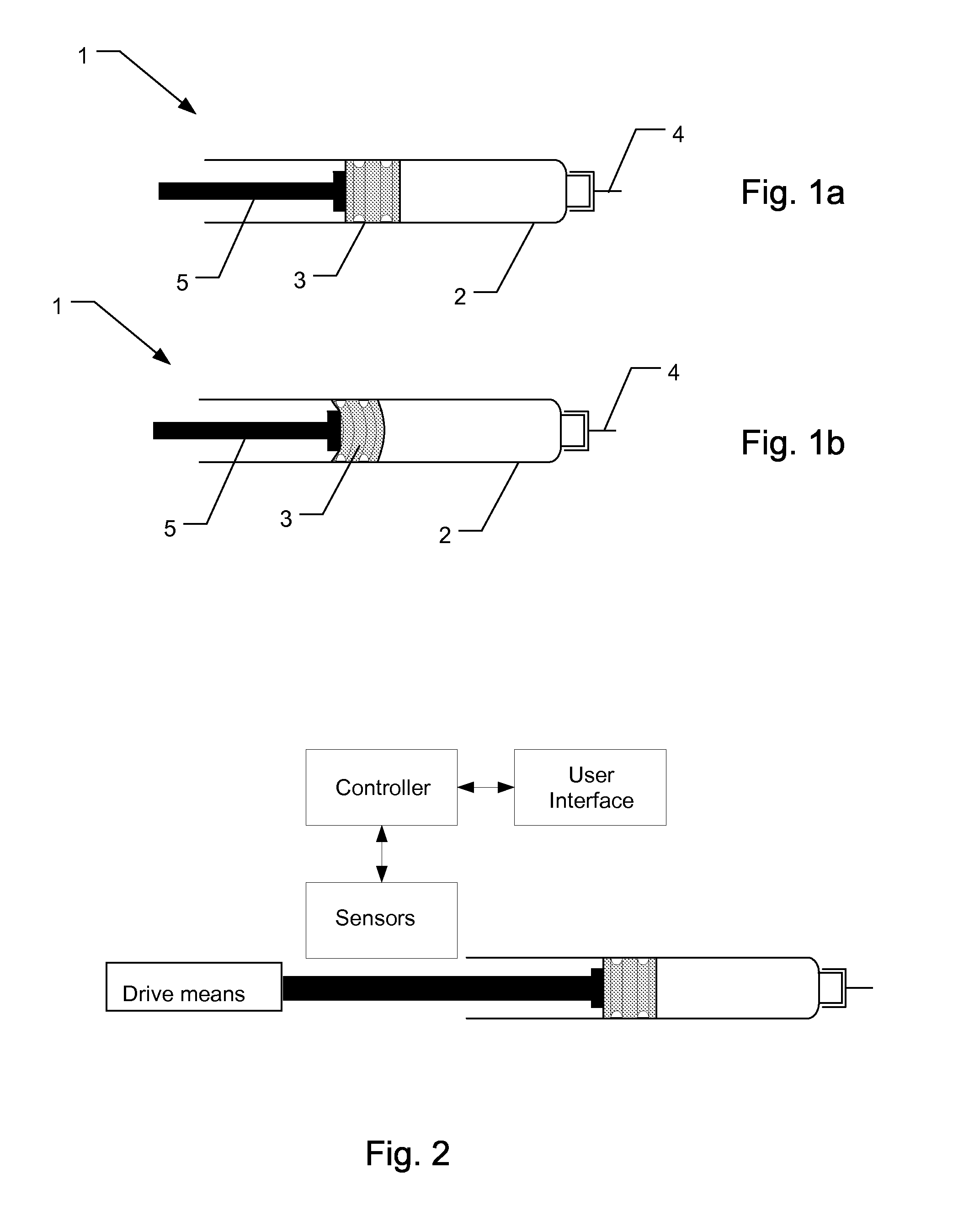
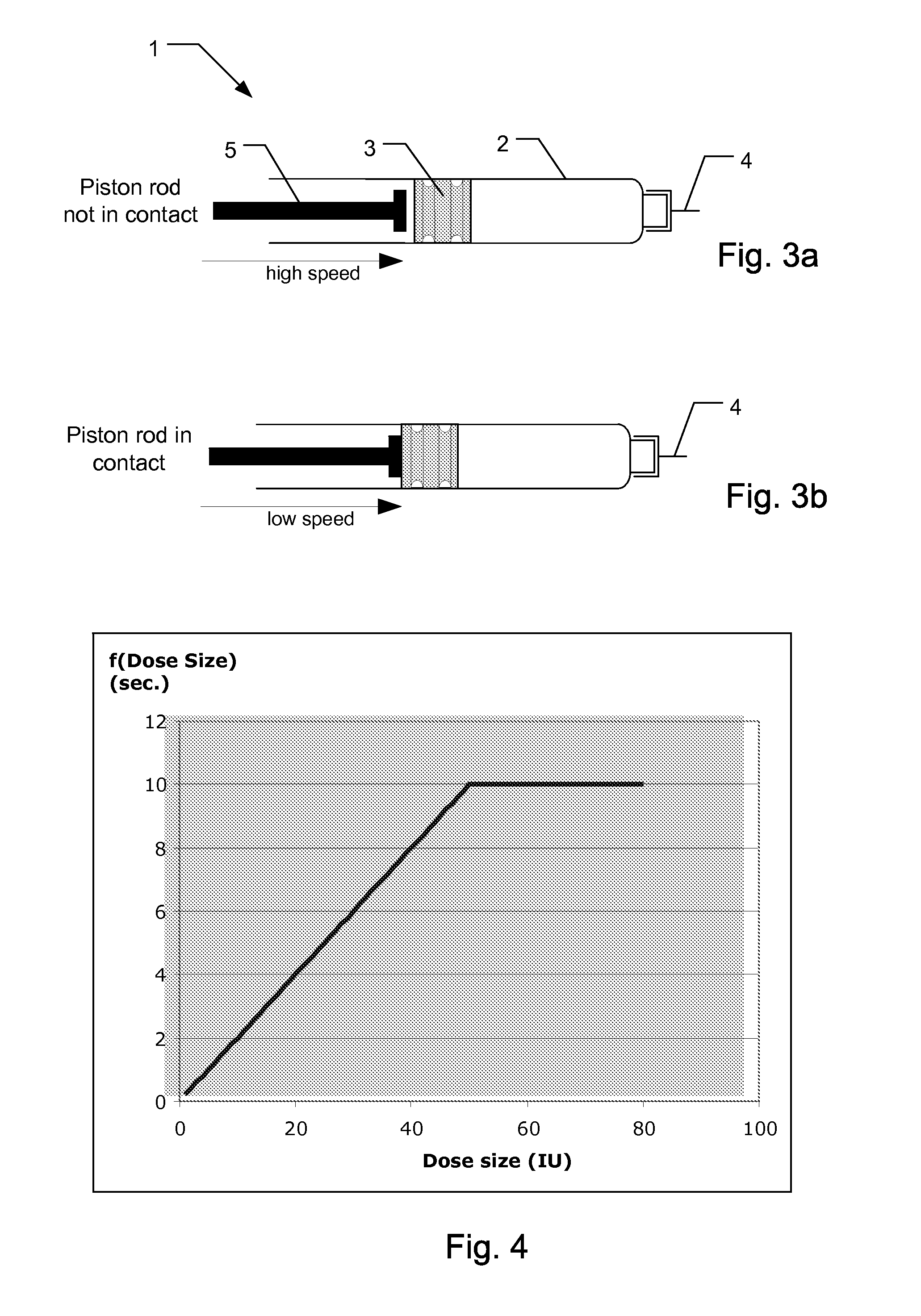
Electronically monitored injection device
ActiveUS20110009821A1Reduce riskHigh accuracy amountAutomatic syringesMedical devicesWaiting periodInjection device
The present invention relates to a medical injection device (1) for use in combination with a medicament filled cartridge (2), the injection device being provided with a spring-assisted injecting mechanism where energy released from the spring moves a plunger (3) of a held cartridge (2). Sensor circuitry is adapted to detect speed related data during injection so at to detect an abnormal speed condition, such as a needle blocking condition, a priming condition or an air purge condition. The invention also relates to a medical injection device comprising sensor circuitry and user communicating means to provide a recommended needle retraction waiting period which is dependent on the speed of injection.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
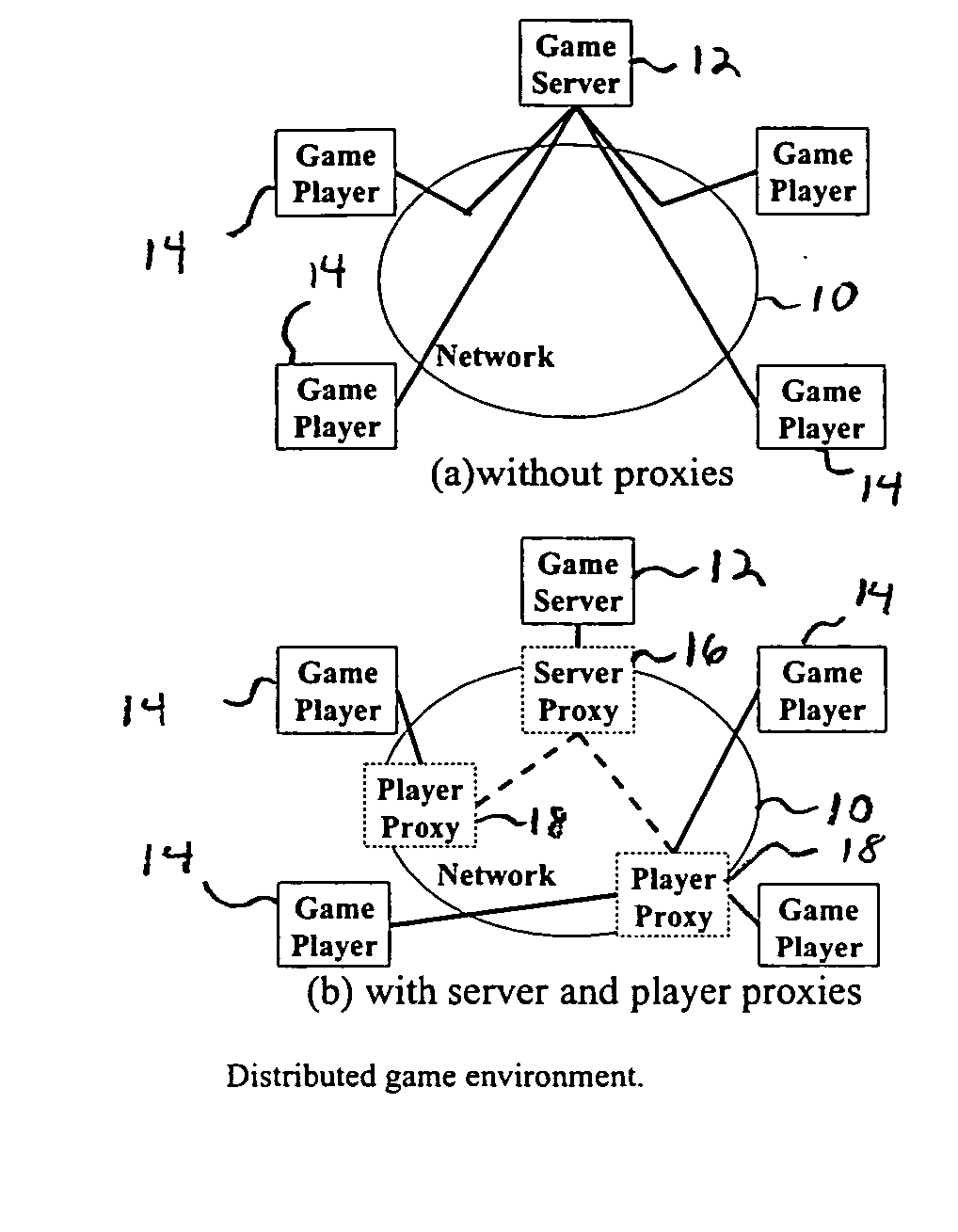
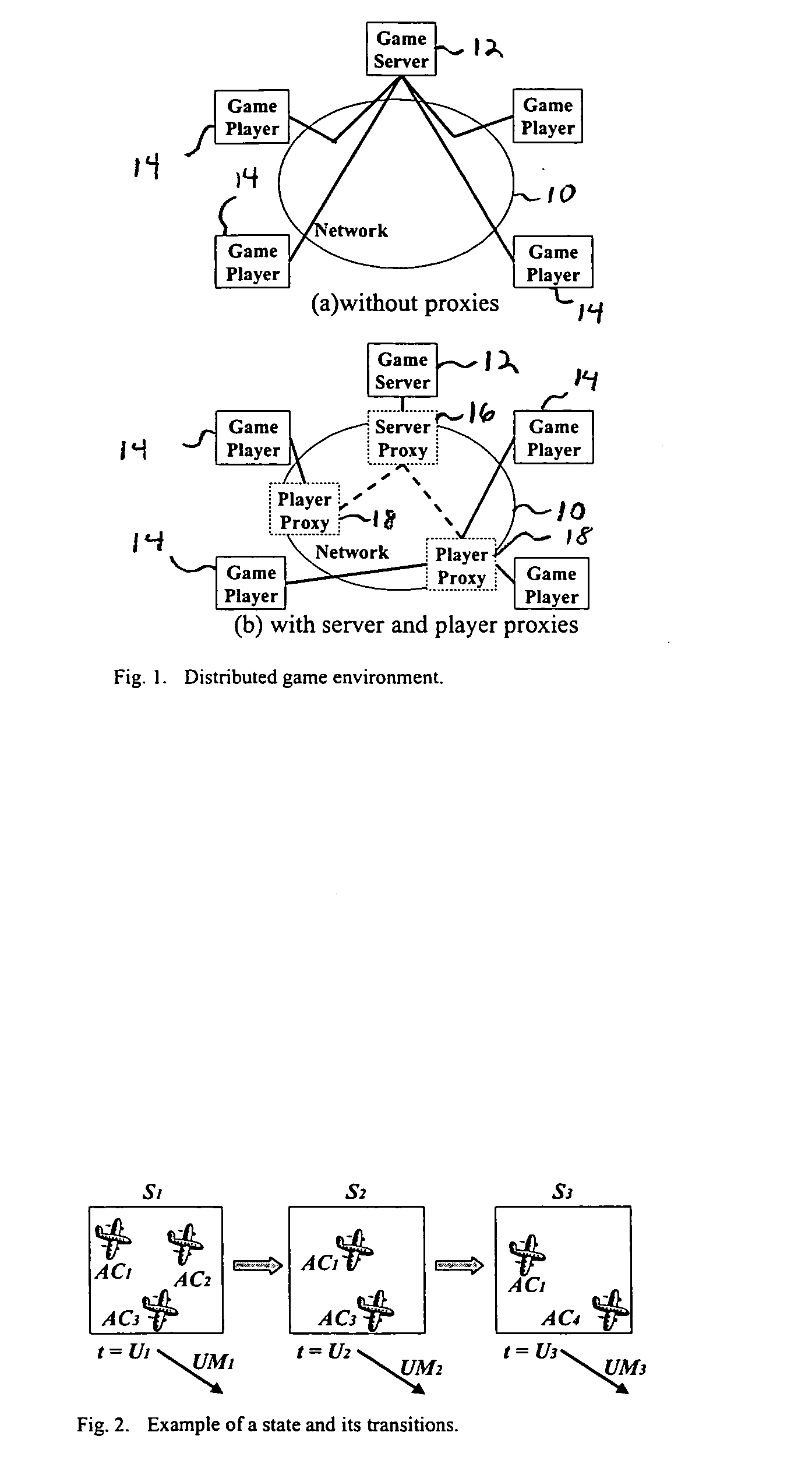
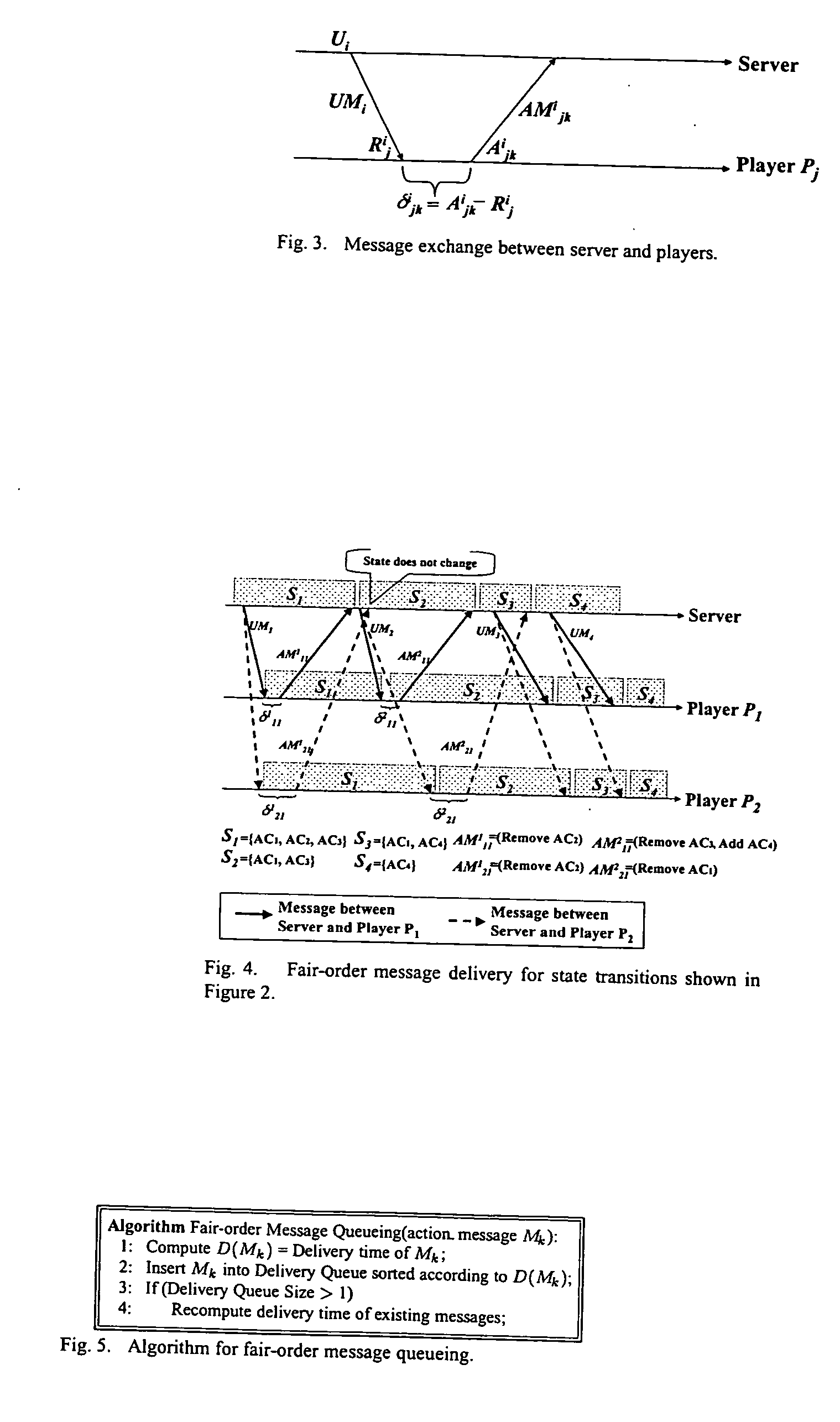
Apparatus and method for fair message exchanges in distributed multi-player games
ActiveUS20050192098A1Guaranteed normal processingMultiple digital computer combinationsApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingWaiting periodApplication software
The Fair-Order Service of the present invention delivers action messages to the server as soon as it is feasible. Because action messages from different players exhibit different reaction times with respect to an update message, the Fair-Ordering Service executed at the server dynamically enforces a sufficient waiting period on each action message to guarantee the fair processing of all action messages. In reality, the waiting period at the server is bounded because of the real-time nature of interactive games. The algorithms that offer Fair Ordering Service take into consideration delayed and out-of-order action messages. When action messages corresponding to multiple update messages are interleaved, the Fair-Ordering Service matches the action message to the appropriate update message. It accomplishes this by maintaining a window of update messages and using the reaction times for an action message for each of the update messages in the window. This enables state changes at the game server to be performed with fairness to all the players. The Fair-Order Service invention is based on a framework that uses a proxy architecture making it transparent to any specific game application. The service is well suited to client-server based, online multi-player games, where a fair order of player actions is critical to the game outcome.
Owner:RPX CORP
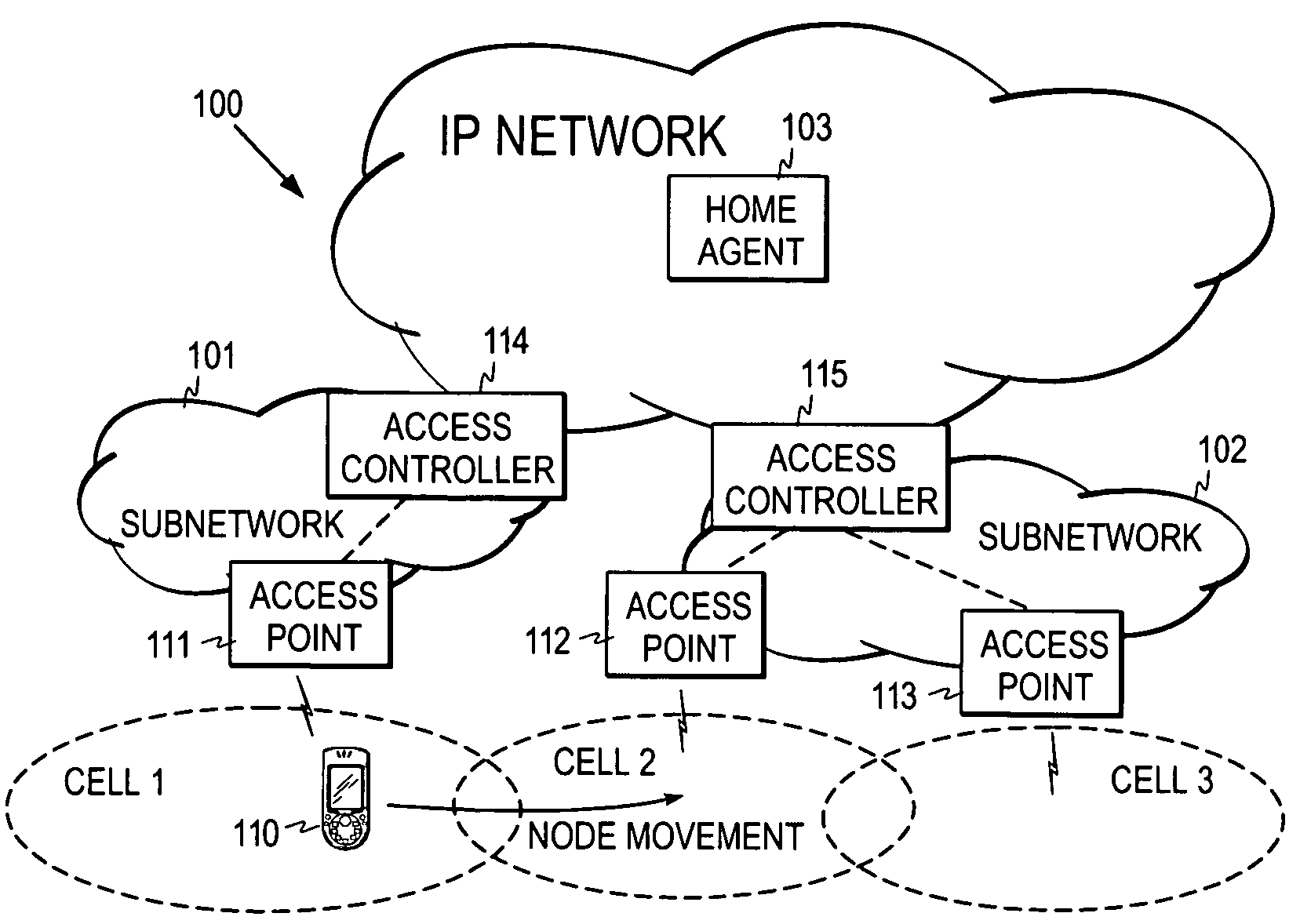
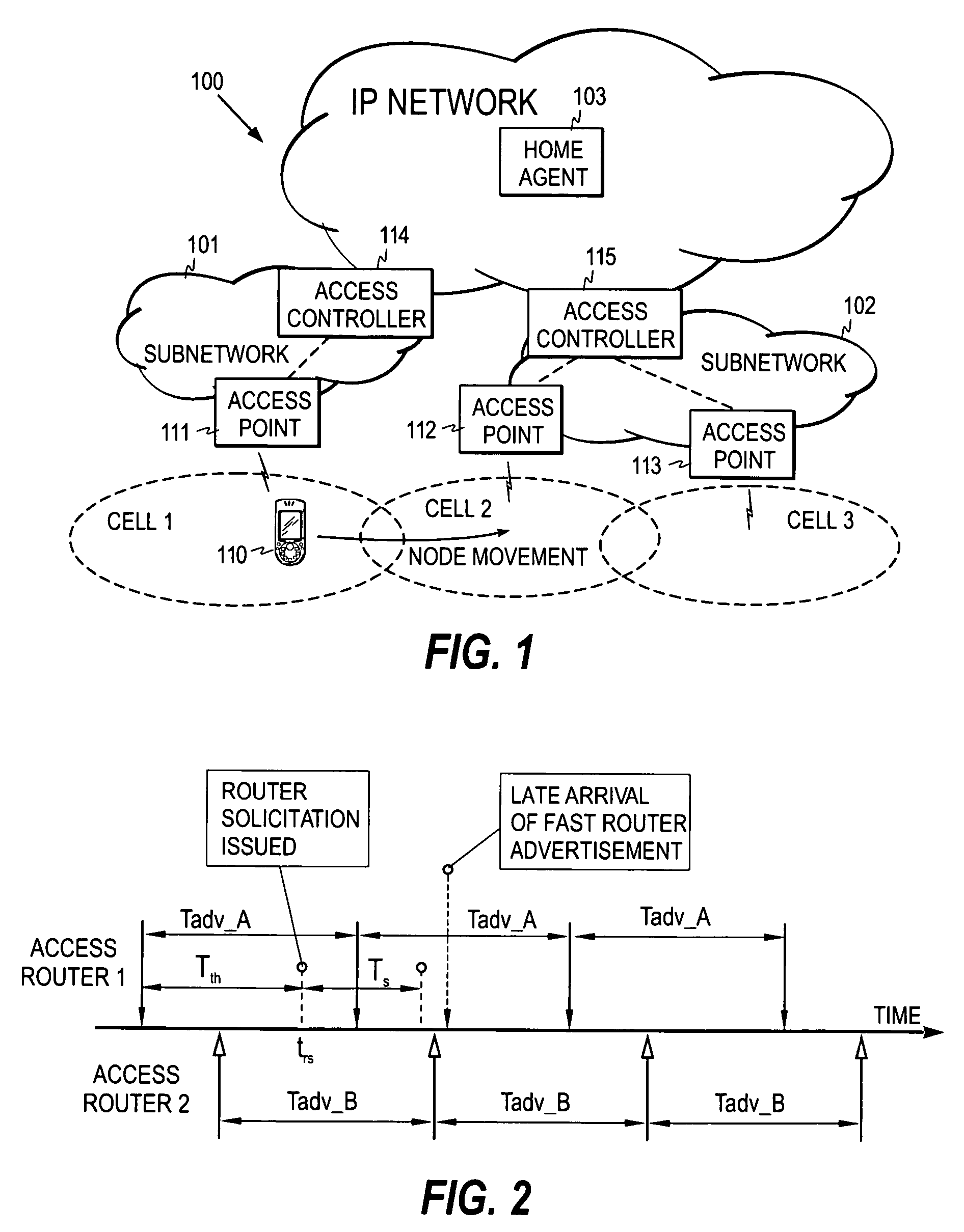
Selection of network access entity in a communication system
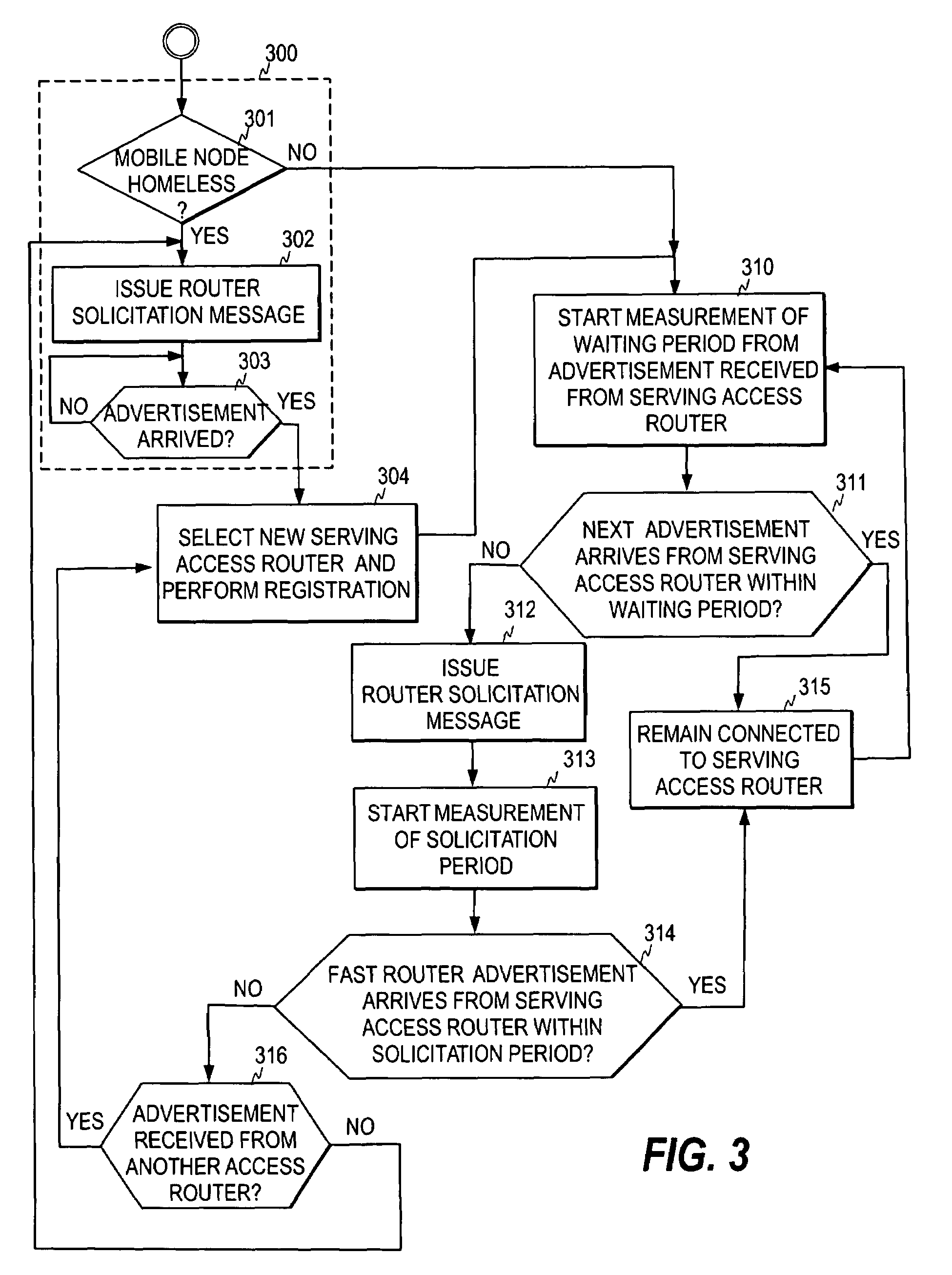
ActiveUS7362731B2Tune performanceAssess restrictionRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsCommunications systemWaiting period
A mechanism for selecting a serving network access entity for a mobile node in a communication system including network access entities broadcasting periodic advertisement messages. The method utilizes a waiting period measured from a first reference moment. When no advertisement message is received within the waiting period from the network access entity being currently the serving network access entity for the mobile node, the node issues a router solicitation message and initiates a measurement of a solicitation period from a second reference moment. The mobile node further monitors whether a response to the router solicitation message is received from the network access entity within the solicitation period, and based on the monitoring step decides whether it remains connected to the said network access entity.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Peripheral device feature allowing processors to enter a low power state
ActiveUS7159766B2Volume/mass flow measurementCo-operative working arrangementsElectricityWaiting period
Owner:SONRAI MEMORY LTD
I/O circuit and data transmission control method
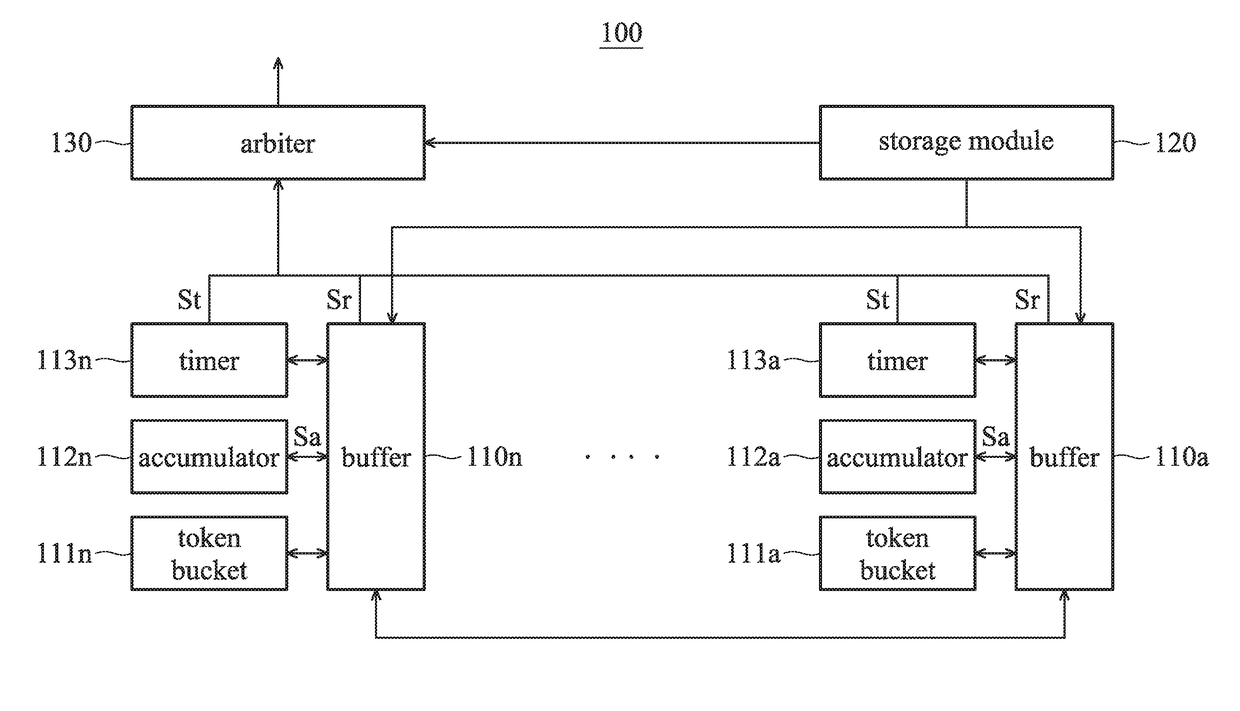
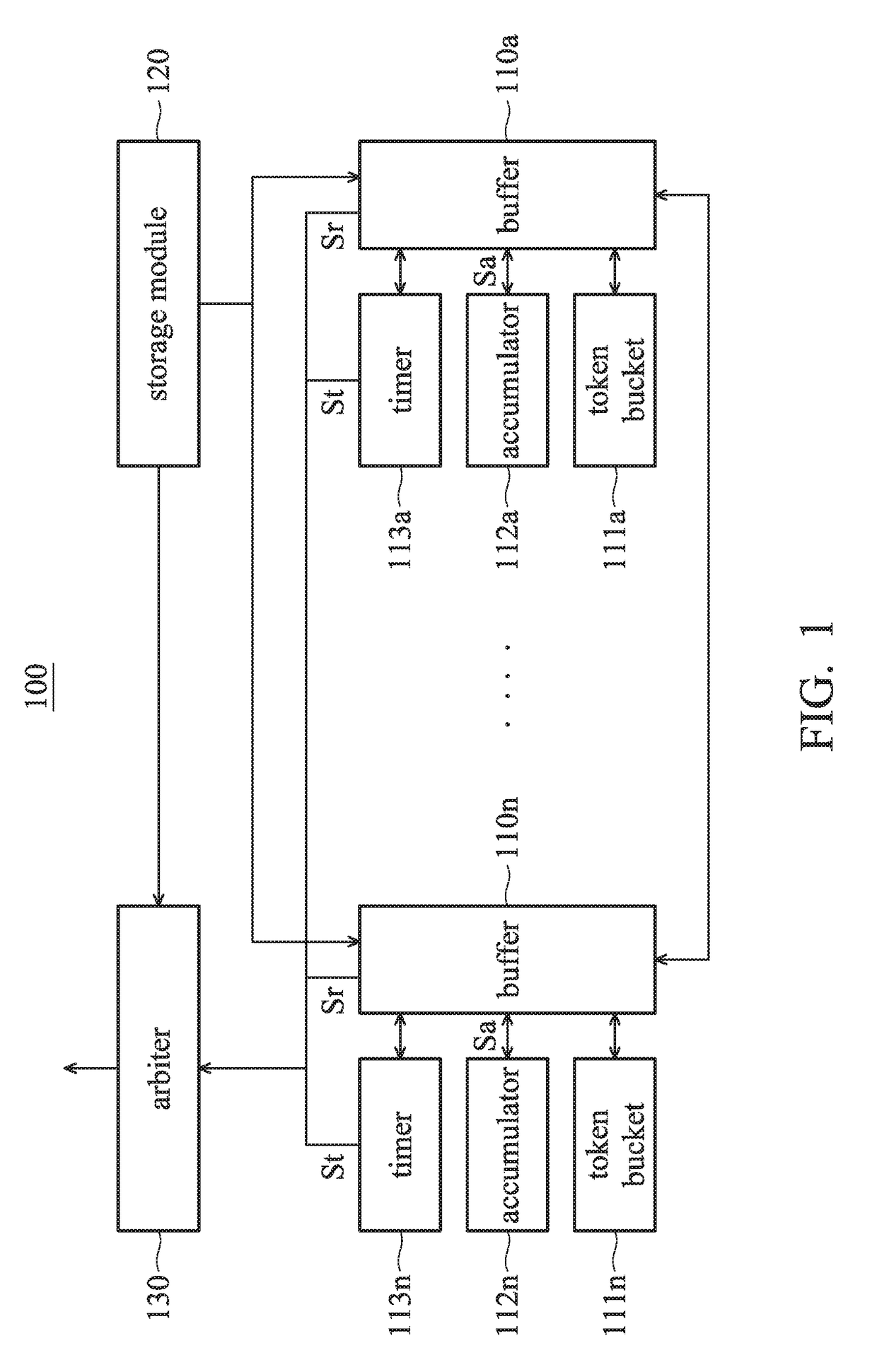
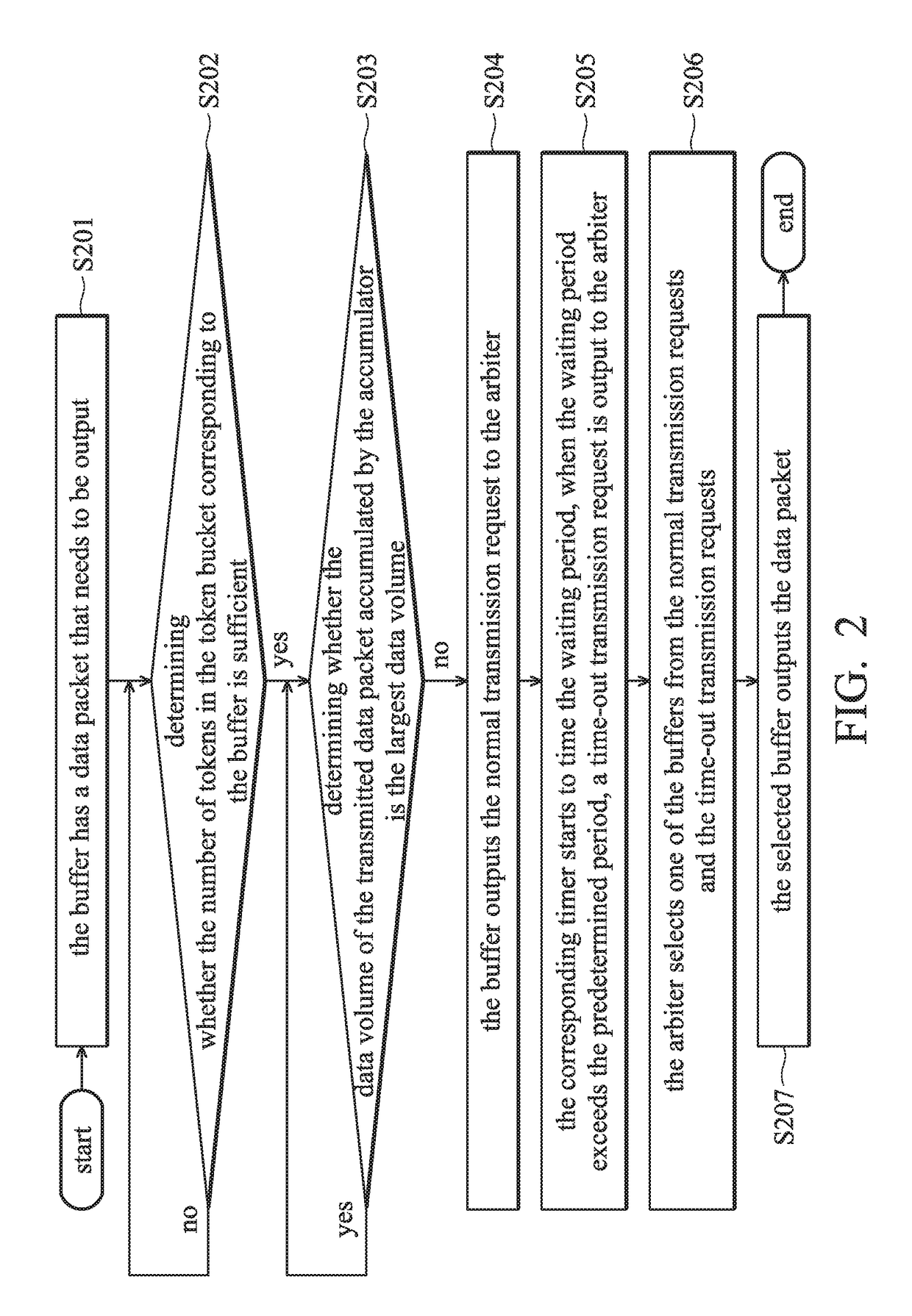
ActiveUS20170163543A1Inefficient data transferEfficiently and fairly offer transmission priorityData switching networksElectric digital data processingComputer hardwareWaiting period
An I / O circuit includes buffers, a storage module, accumulators, timers, and an arbiter. Each buffer corresponds to a respective virtual channel. Each buffer corresponds to a respective token bucket, and outputs a normal transmission request according to the amount of tokens and an accumulating signal. The storage module stores a lookup table including a plurality of weightings. Each accumulator corresponds to a respective buffer, accumulates a data volume according to the corresponding weighting, and outputs the accumulating signal. Each timer corresponds to a respective buffer, times waiting period after the corresponding buffer outputs the normal transmission request, and outputs a time-out transmission request when the waiting period exceeds a predetermined period.The arbiter receives the time-out transmission requests and the normal transmission requests, and selects one of the buffers from all of the time-out transmission requests and the normal transmission requests.
Owner:VIA ALLIANCE SEMICON CO LTD
Method and apparatus for automated active sterilization of fully implanted devices
InactiveUS20150011928A1Effective sterilizationPromote resultsUrinary bladderStentsUltravioletProsthetic knee
The current invention provides this advance in infection control via its unique application of active sterilization to a catheter or implant. While most catheters, and many implants, are passive devices, the current invention will provide an active component as a integral part of the implanted catheter or device to continuously or intermittently sterilize the exposed surfaces / areas of the device. This active sterilization may be accomplished by a variety of mechanisms, including, application of heat, RF, microwave, ultrasound, ultraviolet radiation or other energy capable of sterilizing the device or dislodging any problematic Biofilm that may form. The active sterilization may also employ the pumping of a sterilizing chemical from all attached drug reservoir, the use of electricity or freezing temperatures or any other mechanism for either inhibiting, killing or dislodging any infectious material in contact with the implant. One major advantage of this design is that through the use of small, battery powered or inductively powered sterilization element, the implanted catheter or device can be effectively sterilized without requiring the standard removal surgery, waiting period, then replacement of the infected device. This is expected to translate into greatly improved outcomes (particularly for devices where infection may be catastrophic, ie a prosthetic knee or hip), greatly improved costs, and greatly improved longevity of susceptible devices (ie IV ports, etc.).
Owner:THERANOVA LLC
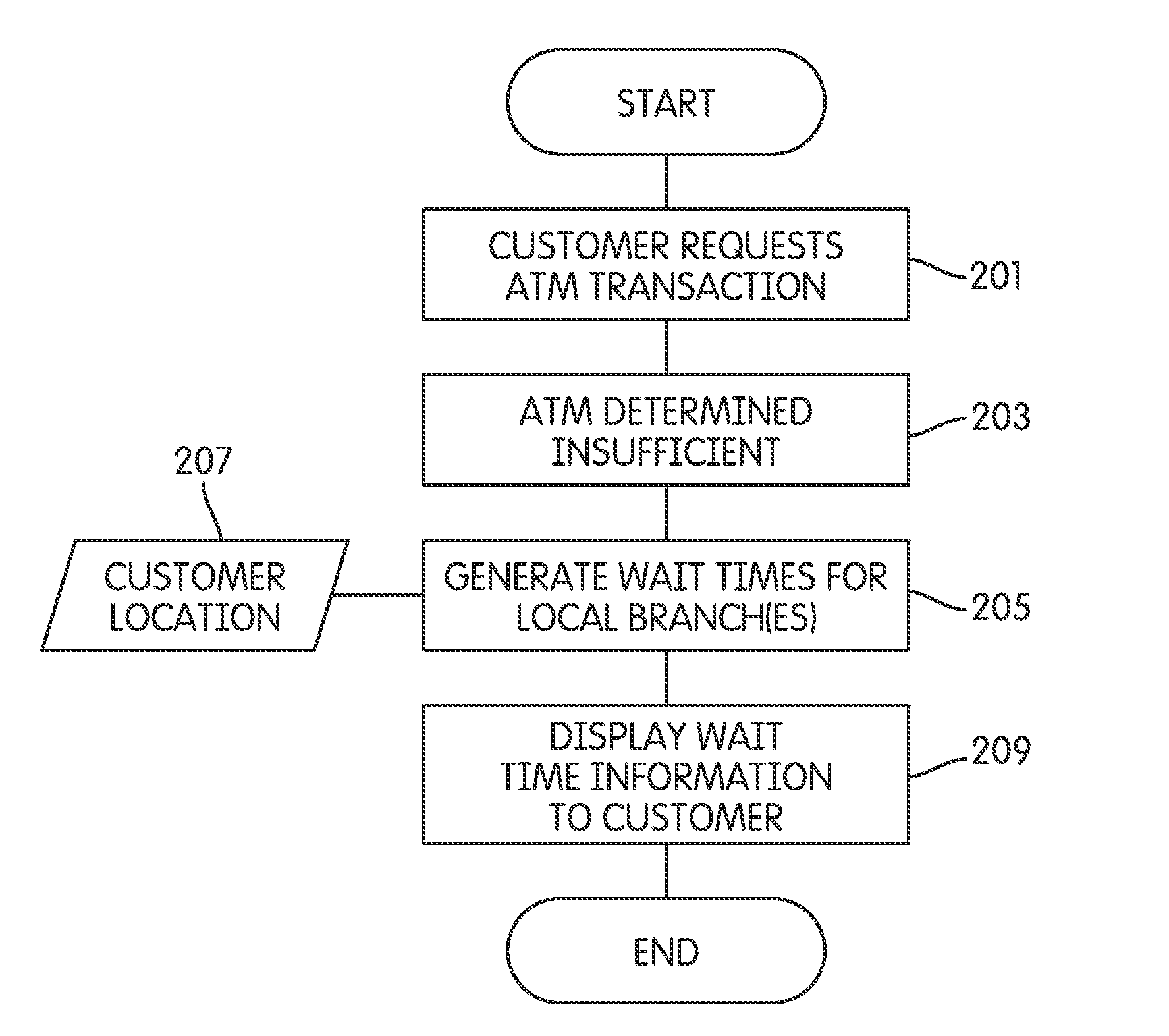
Collection and Distribution of Customer Service Metric Information
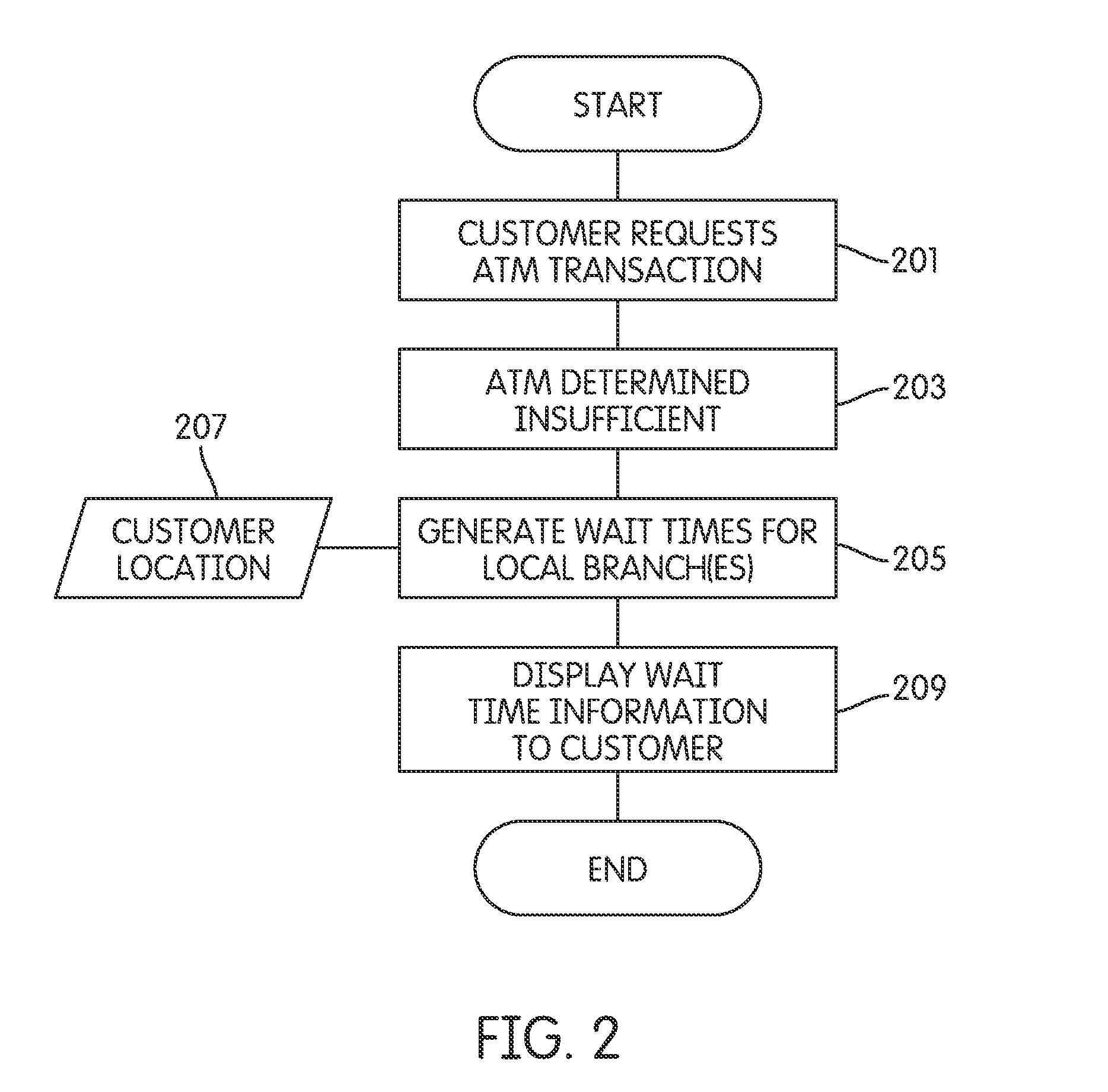
Aspects described herein provide techniques for monitoring, predicting, and providing customer service metrics and wait time information to customers prior to when a customer requests a customer service event that may require a waiting period of otherwise unknown duration. A customer may obtain information regarding a current and / or future predicted wait time for a desired branch of a financial institution. Current wait time information may be provided to help a user determine a branch that is available for immediate service with as short a wait as possible, or that is most time-efficient from the customer's perspective. Wait time information for nearby bank branches may be automatically provided, e.g., when an ATM is out of order. Future and / or predicted wait time information may be provided (e.g., via the Internet) so the customer can plan a convenient time in the future to visit a branch of the financial institution.
Owner:BANK OF AMERICA CORP
System and Method for Performing Setup Operations for Receiving Different Amounts of Data While Processors are Performing Message Passing Interface Tasks
InactiveUS20090064167A1Minimize periodWasted processor cyclesDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsMessage Passing InterfaceWaiting period
A system and method are provided for performing setup operations for receiving a different amount of data while processors are performing message passing interface (MPI) tasks. Mechanisms for adjusting the balance of processing workloads of the processors are provided so as to minimize wait periods for waiting for all of the processors to call a synchronization operation. An MPI load balancing controller maintains a history that provides a profile of the tasks with regard to their calls to synchronization operations. From this information, it can be determined which processors should have their processing loads lightened and which processors are able to handle additional processing loads without significantly negatively affecting the overall operation of the parallel execution system. As a result, setup operations may be performed while processors are performing MPI tasks to prepare for receiving different sized portions of data in a subsequent computation cycle based on the history.
Owner:IBM CORP
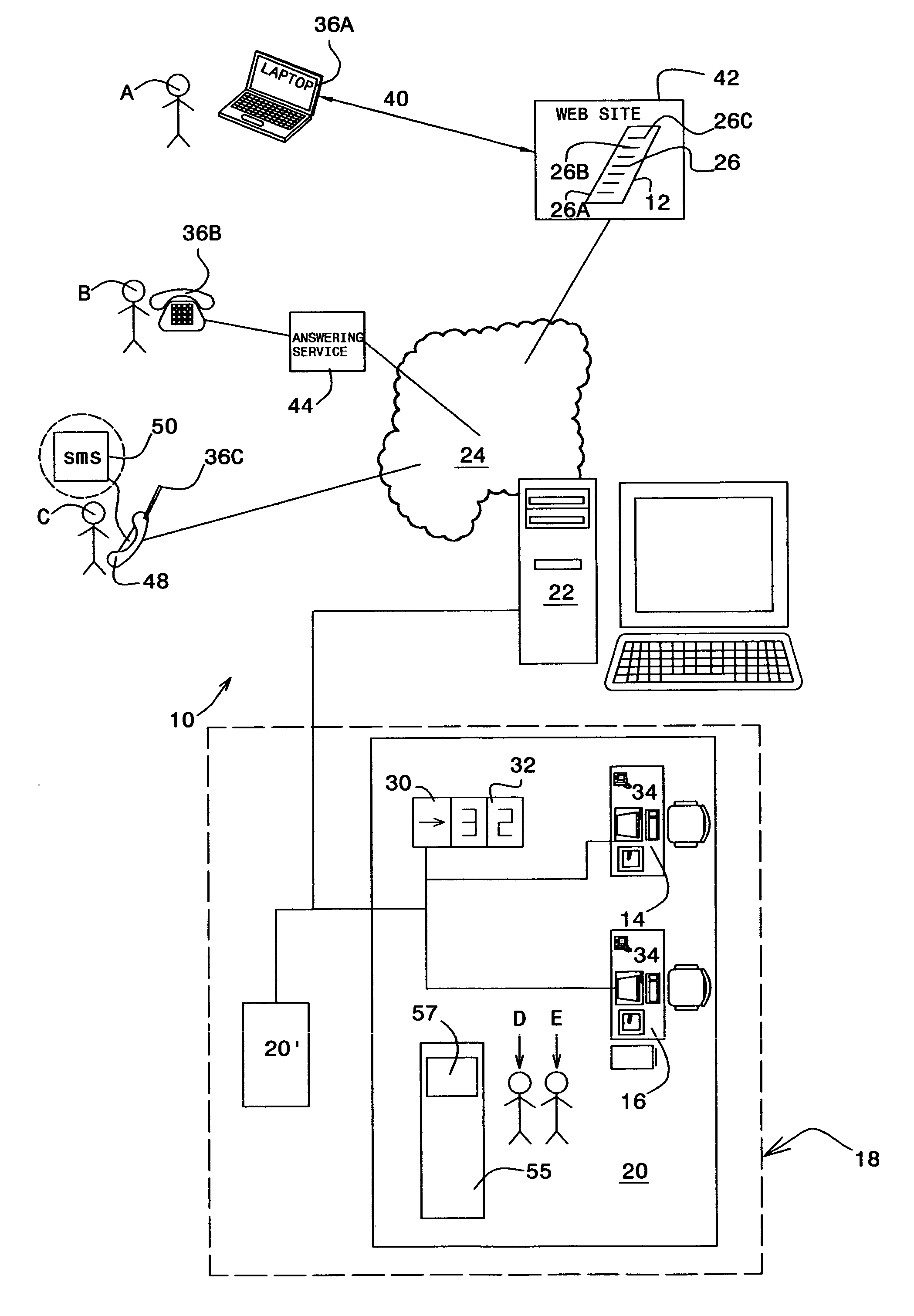
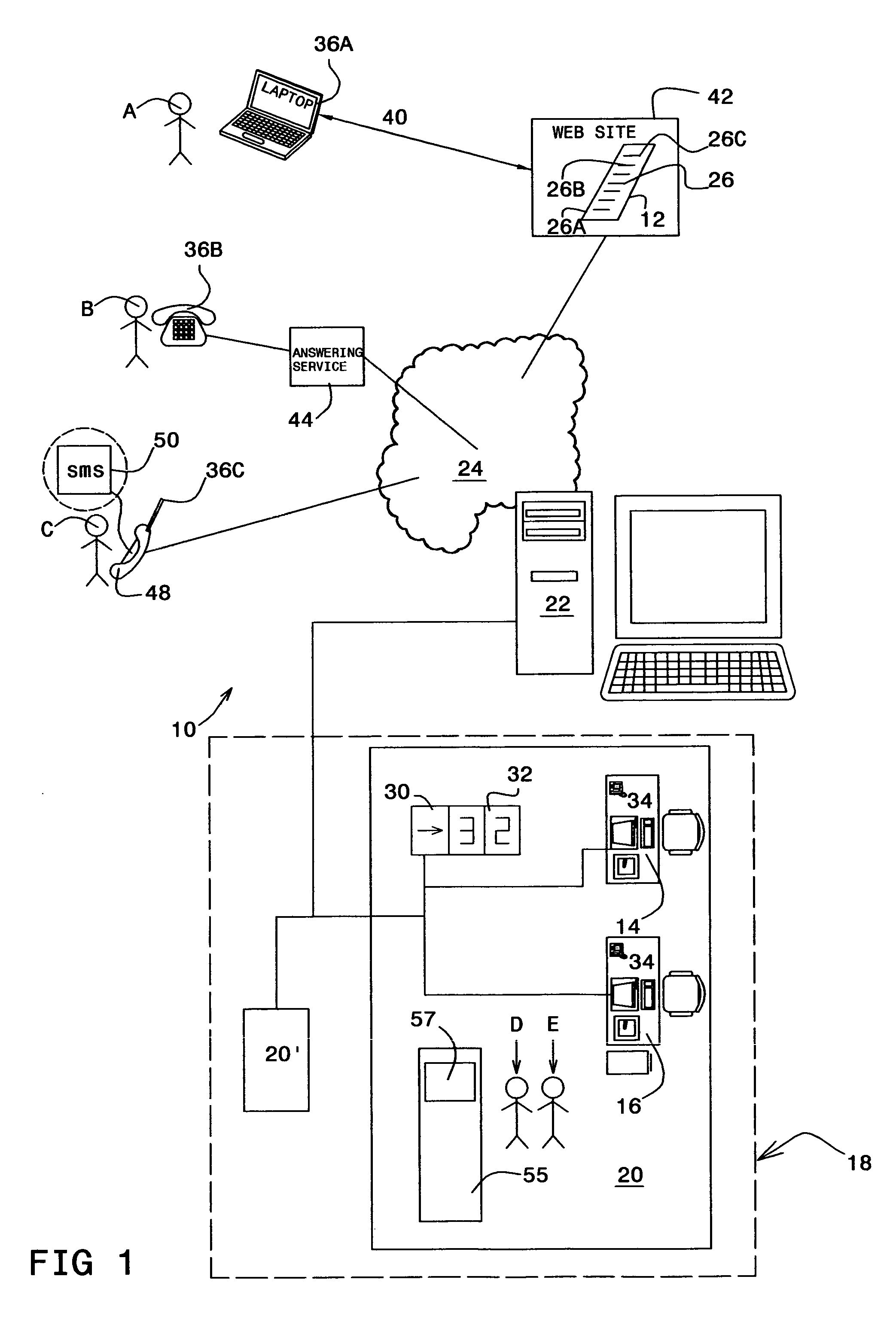
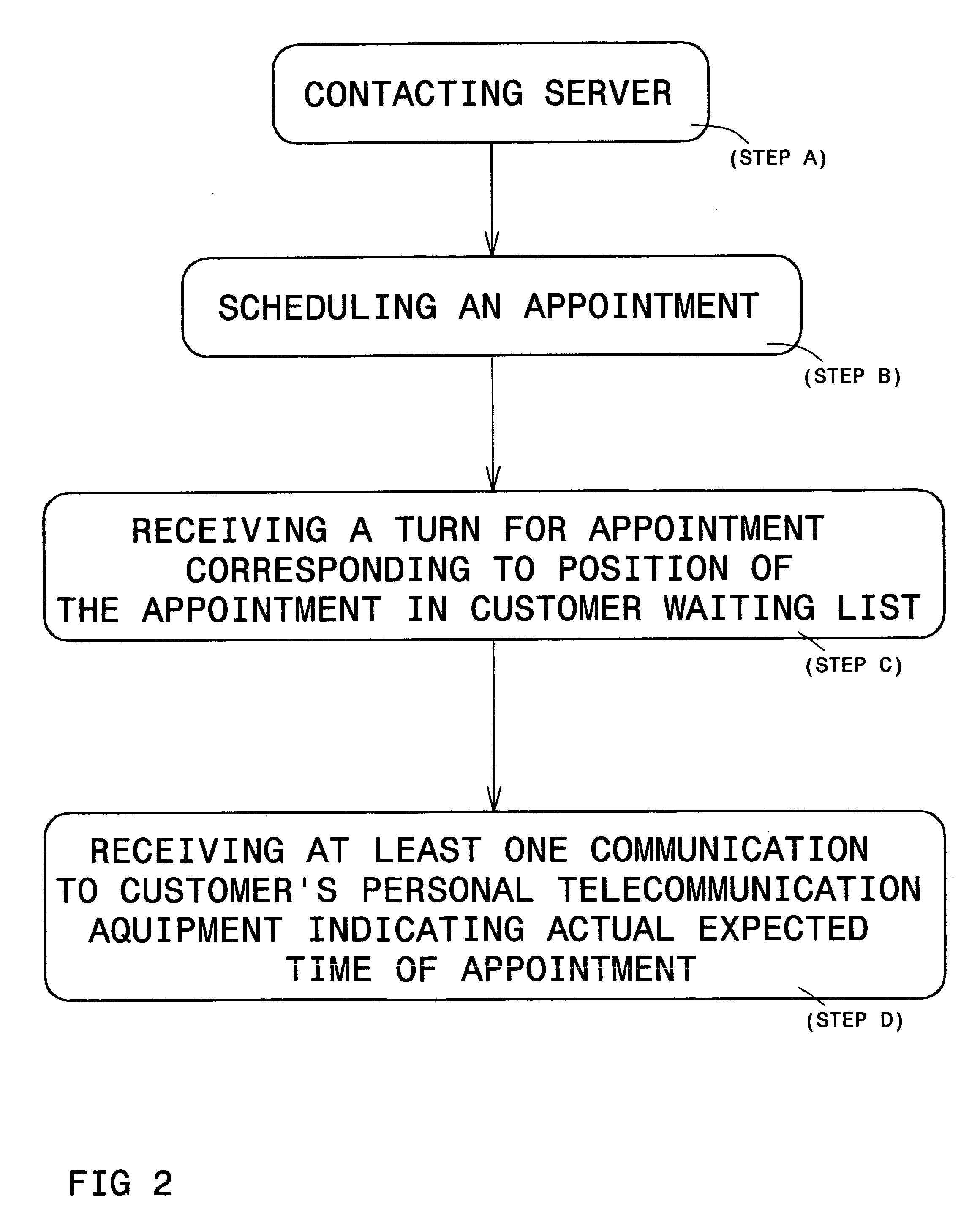
Queuing system
InactiveUS20060147005A1Telephonic communicationChecking apparatusWaiting periodPayment service provider
The present invention is directed to a system and method for organizing customer queues, and particularly to enabling customers to remotely schedule appointments at service stations of a service provider, and to be alerted in real time regarding customer through-flow at the service stations, thereby minimizing physical waiting periods at the service provider's site, and generally improving efficiency.
Owner:TAUB MOSHE
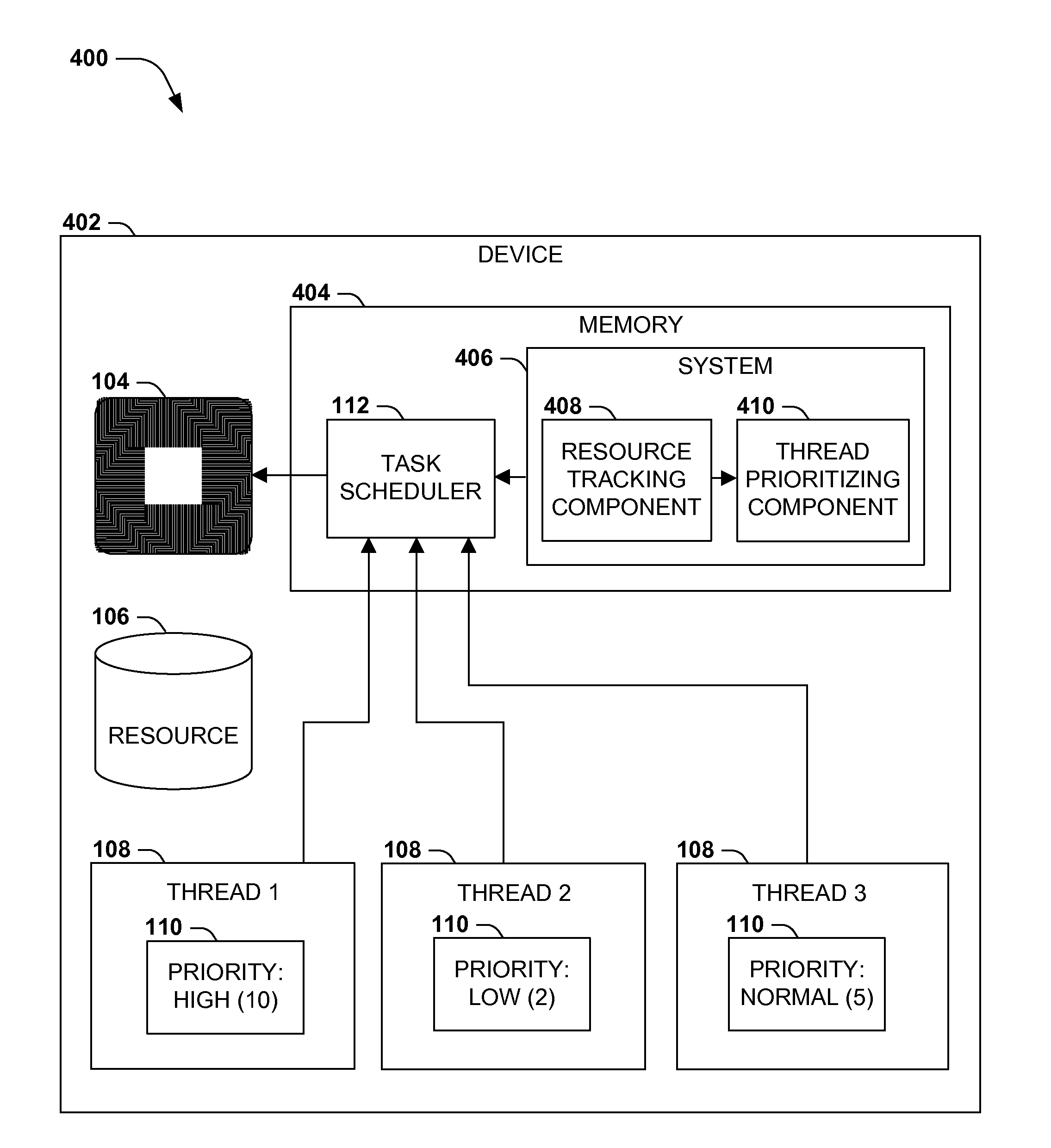
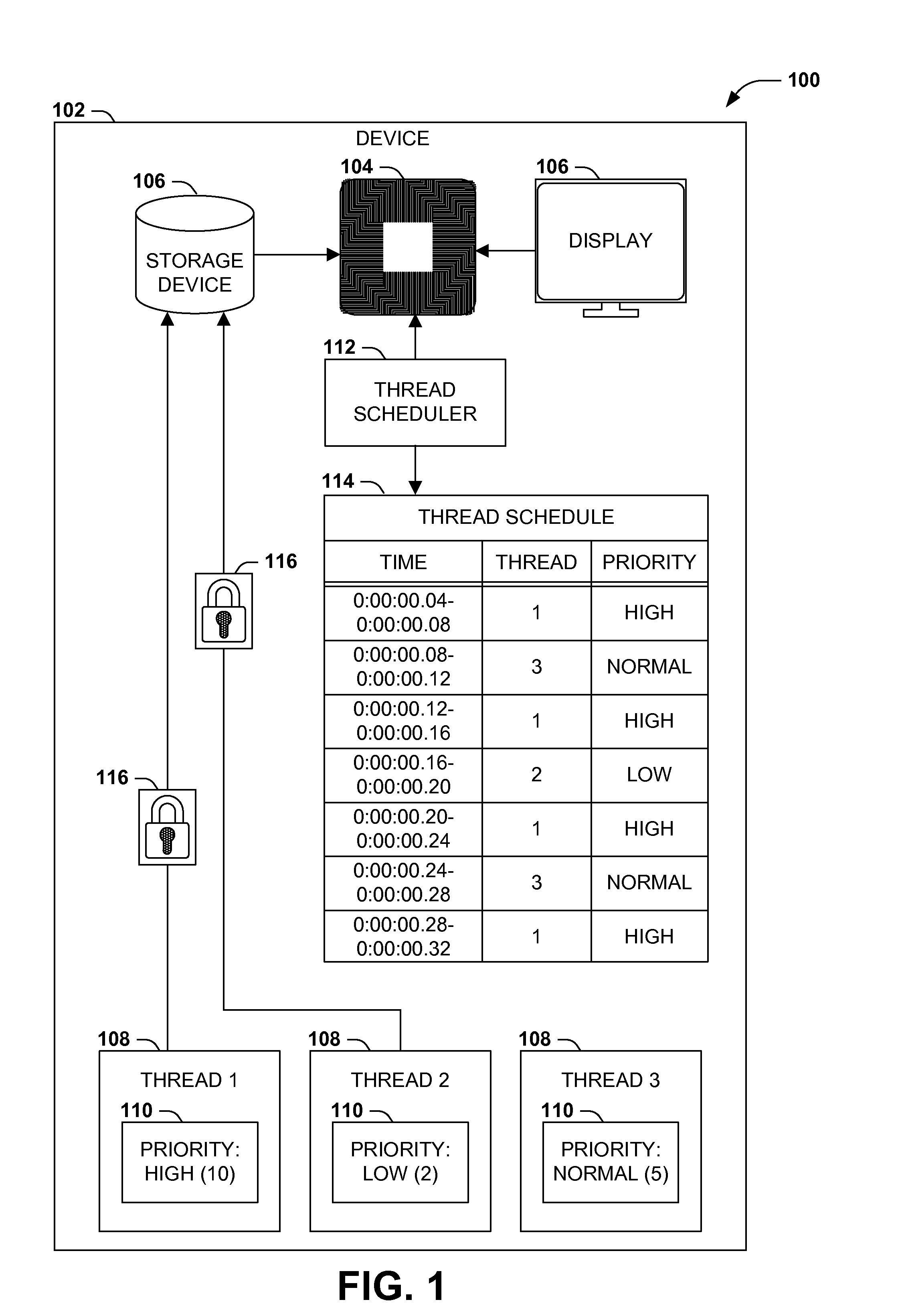
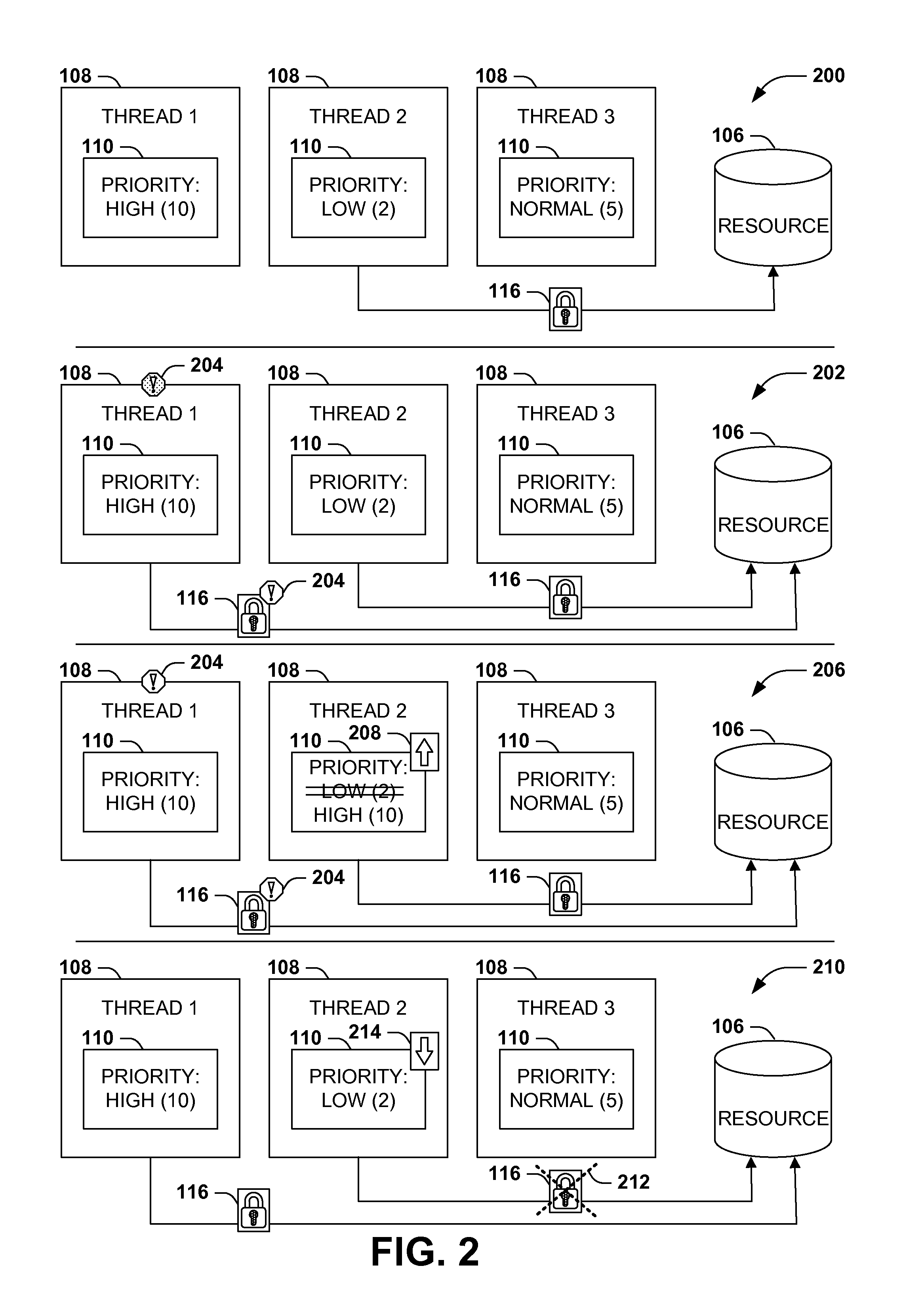
Efficient priority-aware thread scheduling
ActiveUS20140359632A1Reduce morbidityProgram initiation/switchingMemory systemsThread schedulingWaiting period
A priority-based scheduling and execution of threads may enable the completion of higher-priority tasks above lower-priority tasks. Occasionally, a high-priority thread may request a resource that has already been reserved by a lower-priority thread, and the higher-priority thread may be blocked until the lower-priority thread relinquishes the reservation. Such prioritization may be acceptable if the lower-priority thread is able to execute comparatively unimpeded, but in some scenarios, the lower-priority thread may execute at a lower priority than a third thread that also has a lower priority than the high-priority thread. In this scenario, the third thread is effectively but incorrectly prioritized above the high-priority thread. Instead, upon detecting this scenario, the device may temporarily elevate the priority of the lower-priority thread over the priority of the third thread until the lower-priority thread relinquishes the resource, thereby reducing the waiting period of the high-priority thread for the requested resource.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com