Patents
Literature
334 results about "Thread scheduling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and system for recording and replaying the execution of distributed java programs
InactiveUS6832367B1Easy to copyGuaranteed orderError detection/correctionSpecific program execution arrangementsStream socketThread scheduling
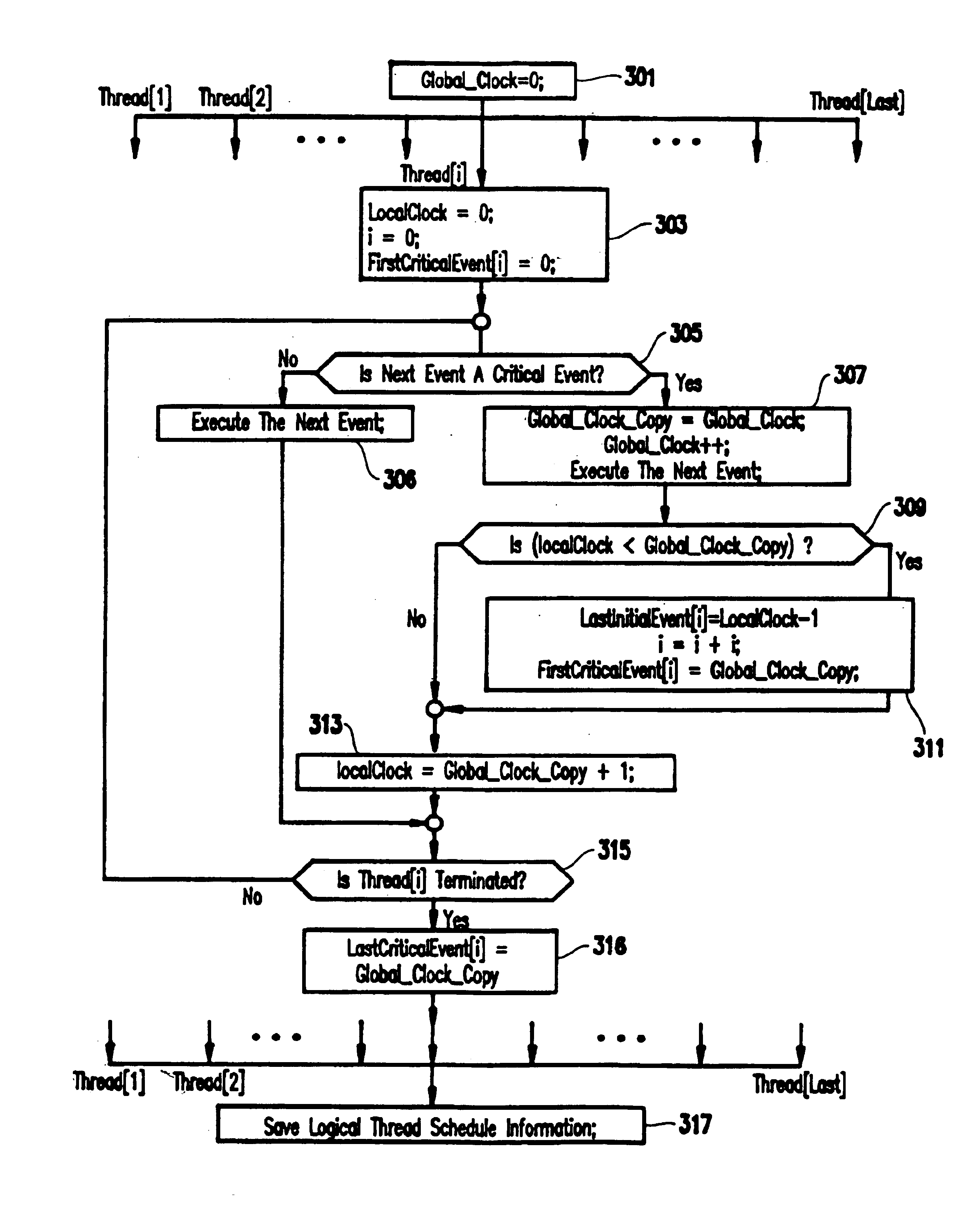
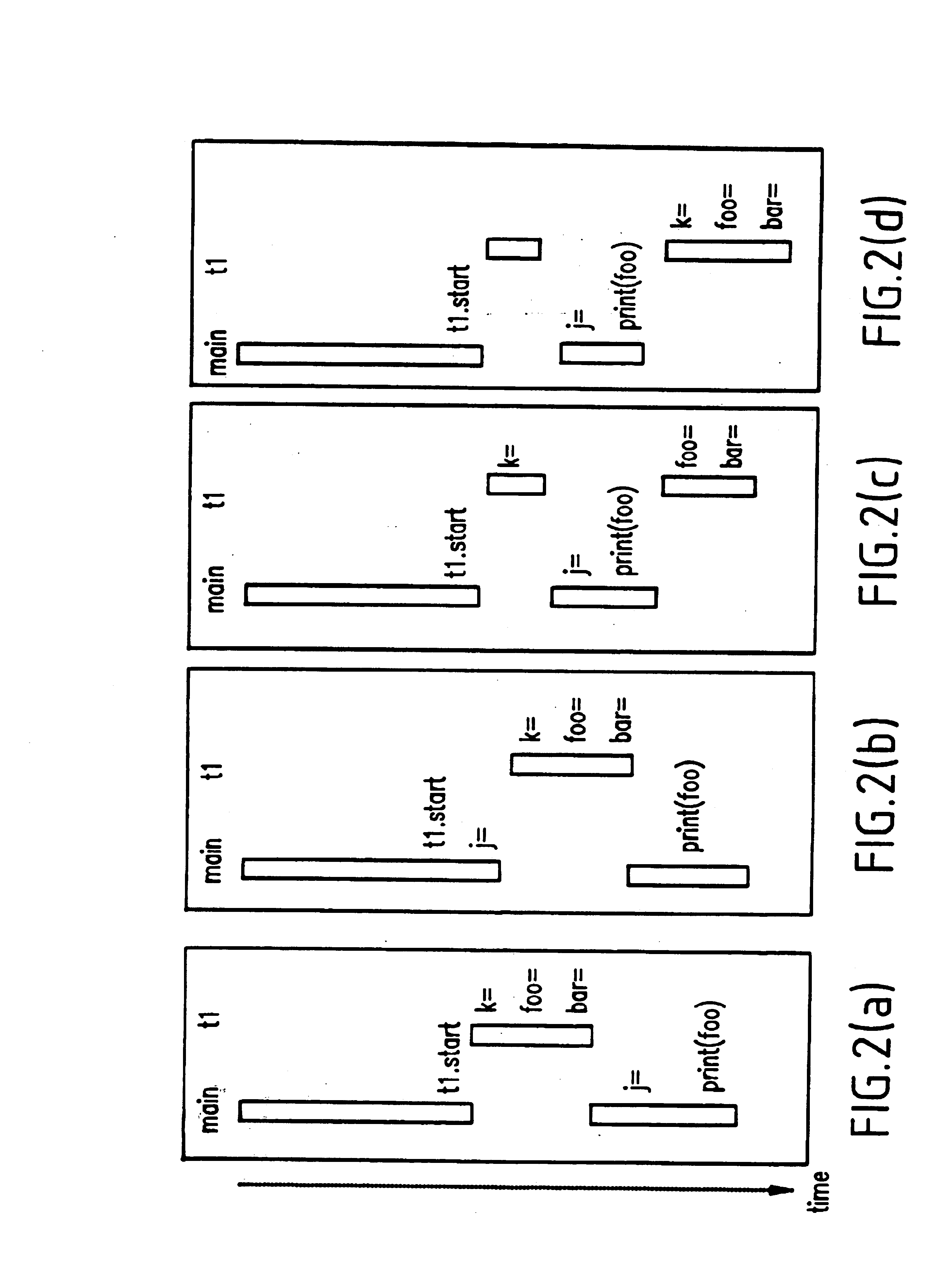
A method for recording and replaying execution of distributed programs on a computer system in a distributed environment, includes identifying an execution order of critical events of a program, generating groups of critical events of the program, wherein for each group, critical events belonging to the group belong to a common execution thread, and generating for each execution thread a logical thread schedule that identifies a sequence of the groups so as to allow deterministically replaying a non-deterministic arrival of stream socket connection requests, a non-deterministic number of bytes received during message reads, and a non-deterministic binding of stream sockets to local ports.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hardware multithreading systems and methods
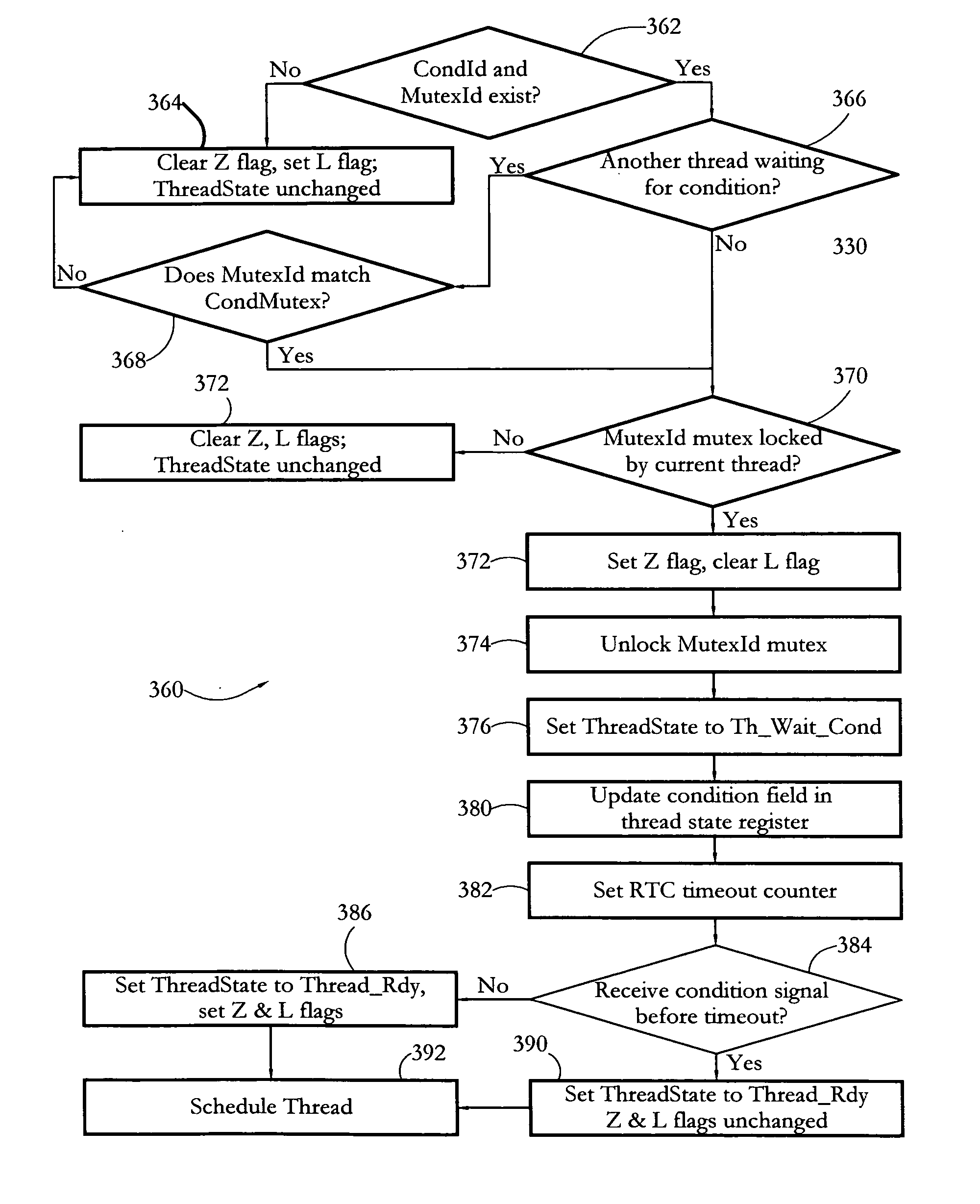
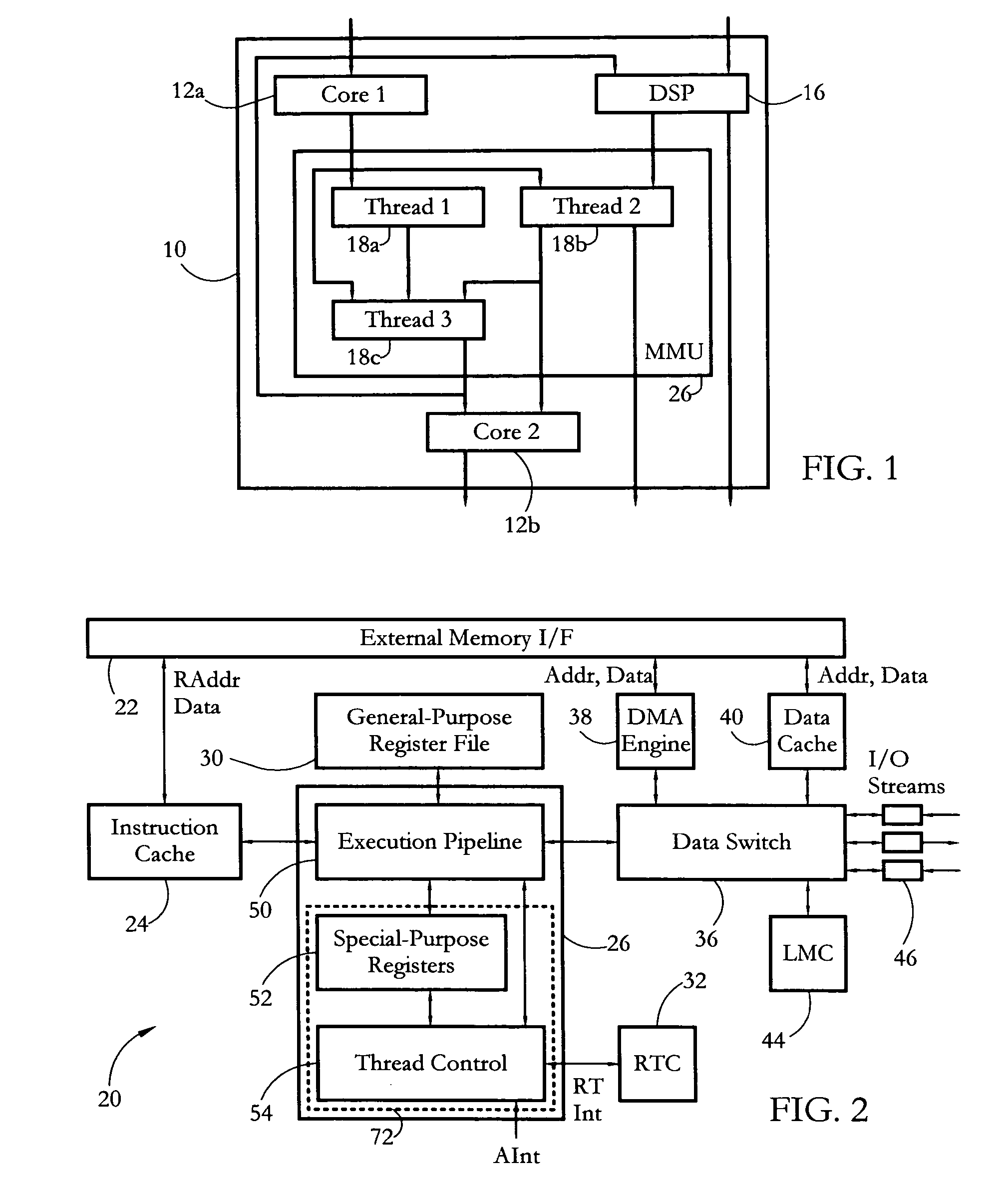
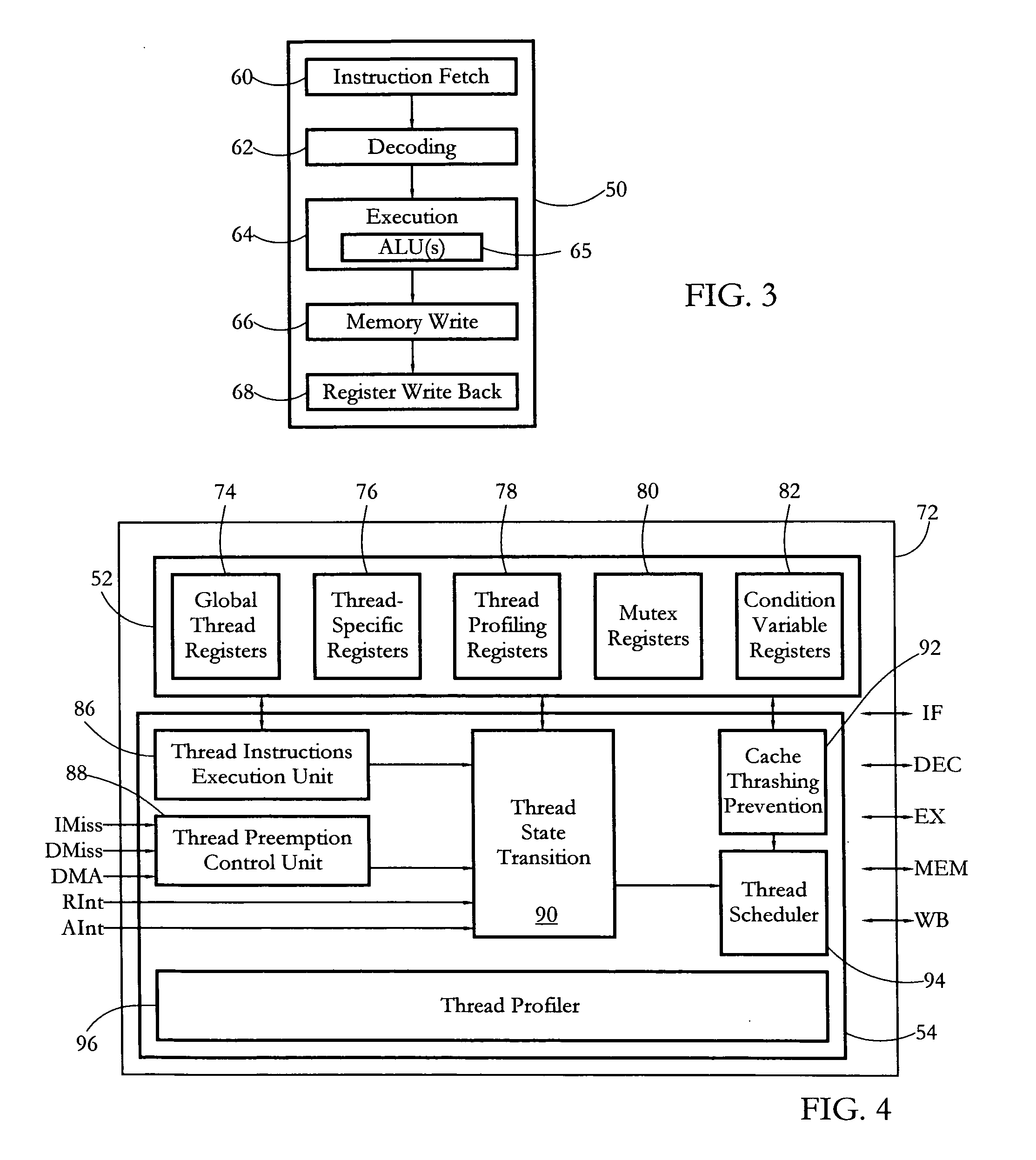
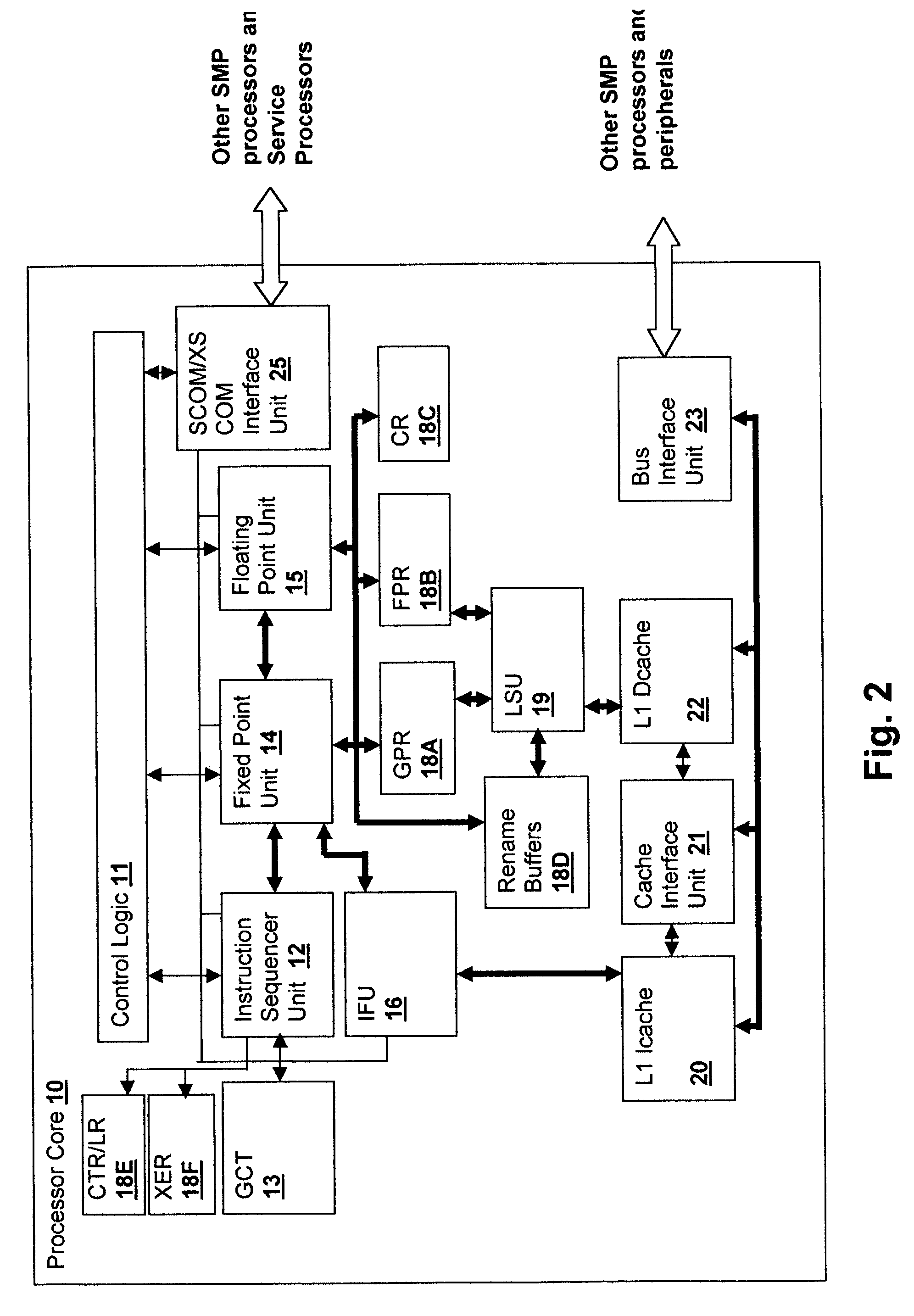
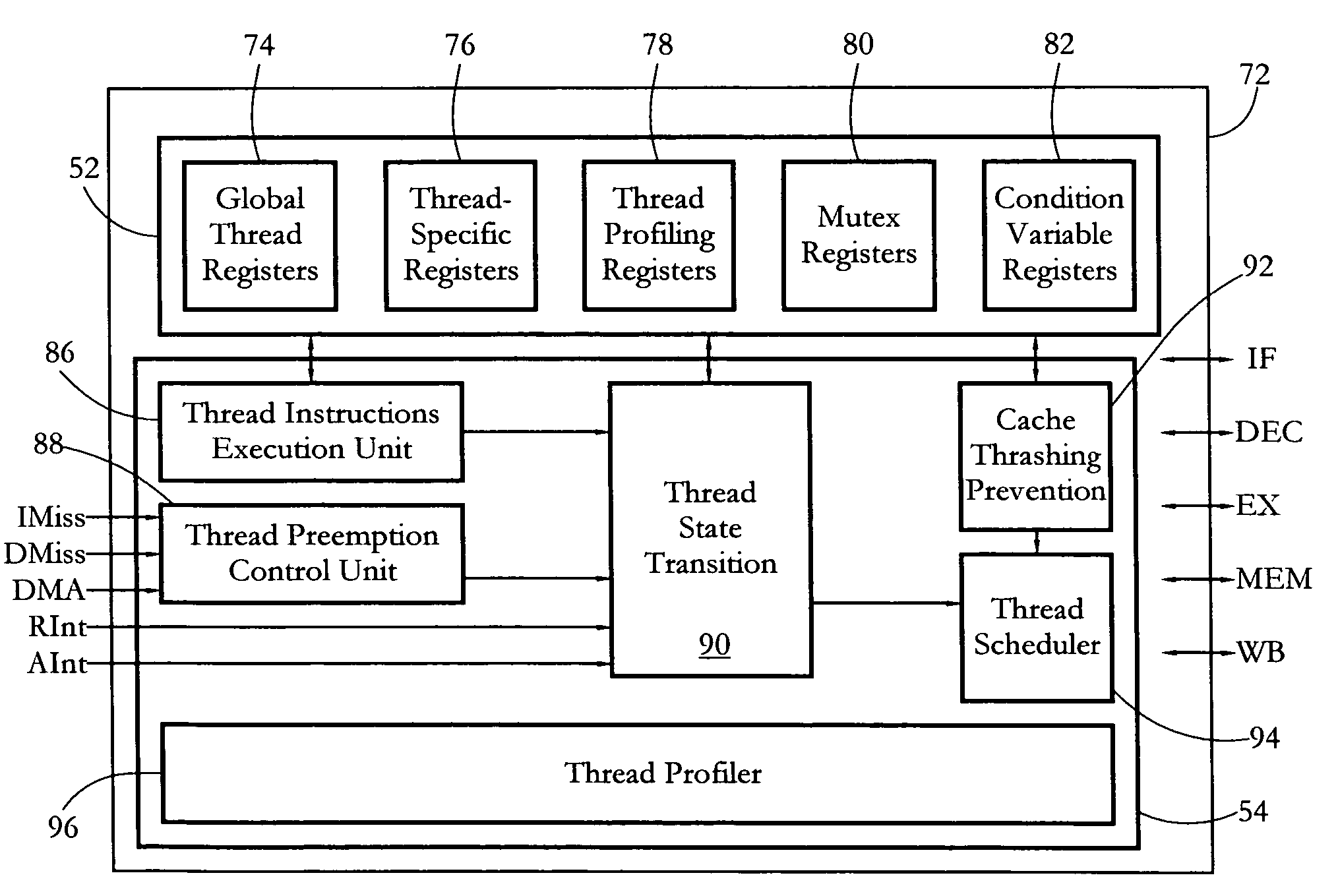
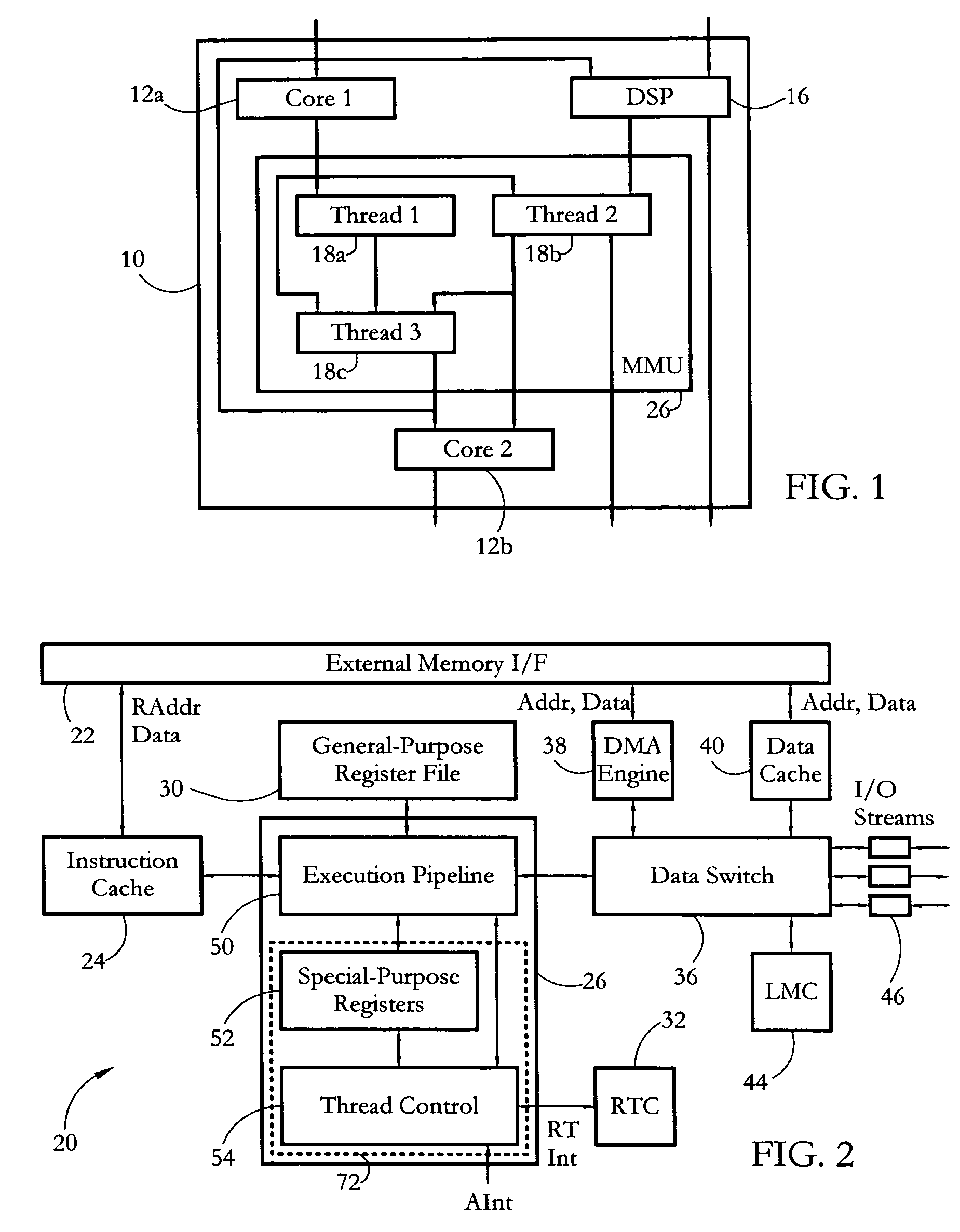
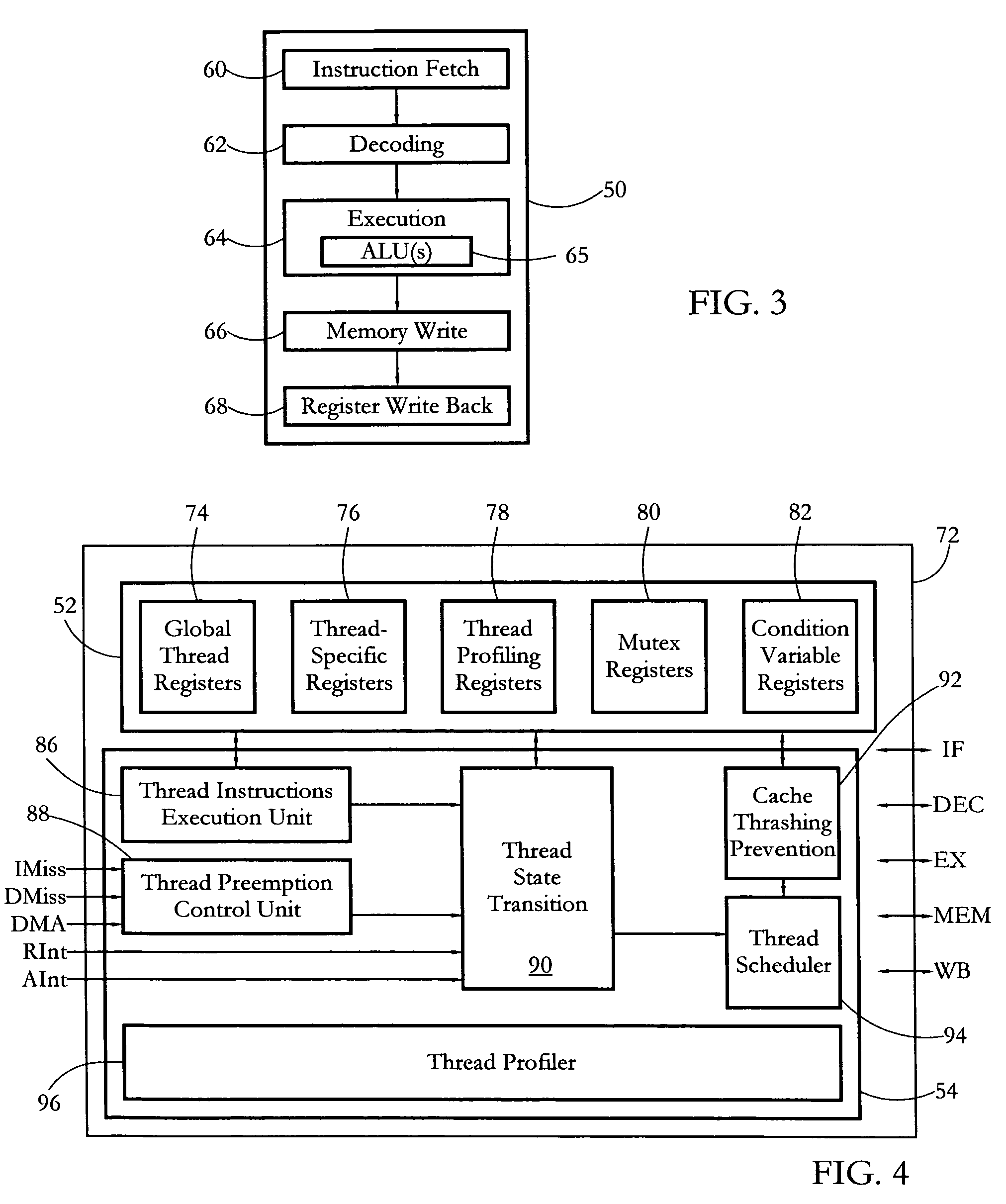
According to some embodiments, a multithreaded microcontroller includes a thread control unit comprising thread control hardware (logic) configured to perform a number of multithreading system calls essentially in real time, e.g. in one or a few clock cycles. System calls can include mutex lock, wait condition, and signal instructions. The thread controller includes a number of thread state, mutex, and condition variable registers used for executing the multithreading system calls. Threads can transition between several states including free, run, ready and wait. The wait state includes interrupt, condition, mutex, I-cache, and memory substates. A thread state transition controller controls thread states, while a thread instructions execution unit executes multithreading system calls and manages thread priorities to avoid priority inversion. A thread scheduler schedules threads according to their priorities. A hardware thread profiler including global, run and wait profiler registers is used to monitor thread performance to facilitate software development.
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
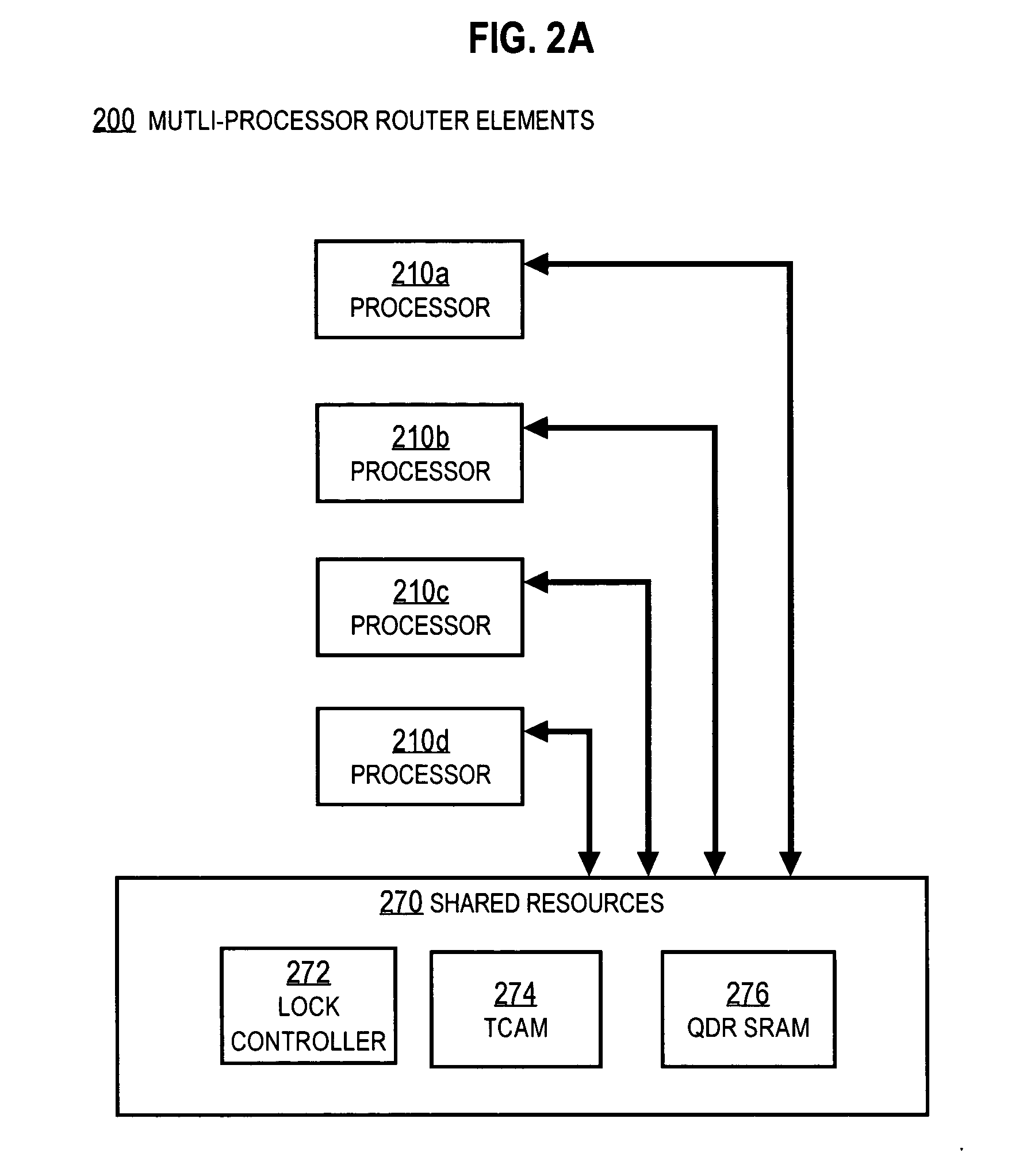
Mechanism for scheduling execution of threads for fair resource allocation in a multi-threaded and/or multi-core processing system
ActiveUS7707578B1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsThread schedulingShared resource
A thread scheduling mechanism is provided that flexibly enforces performance isolation of multiple threads to alleviate the effect of anti-cooperative execution behavior with respect to a shared resource, for example, hoarding a cache or pipeline, using the hardware capabilities of simultaneous multi-threaded (SMT) or multi-core processors. Given a plurality of threads running on at least two processors in at least one functional processor group, the occurrence of a rescheduling condition indicating anti-cooperative execution behavior is sensed, and, if present, at least one of the threads is rescheduled such that the first and second threads no longer execute in the same functional processor group at the same time.
Owner:VMWARE INC
Method and apparatus for optimizing performance in a multi-processing system
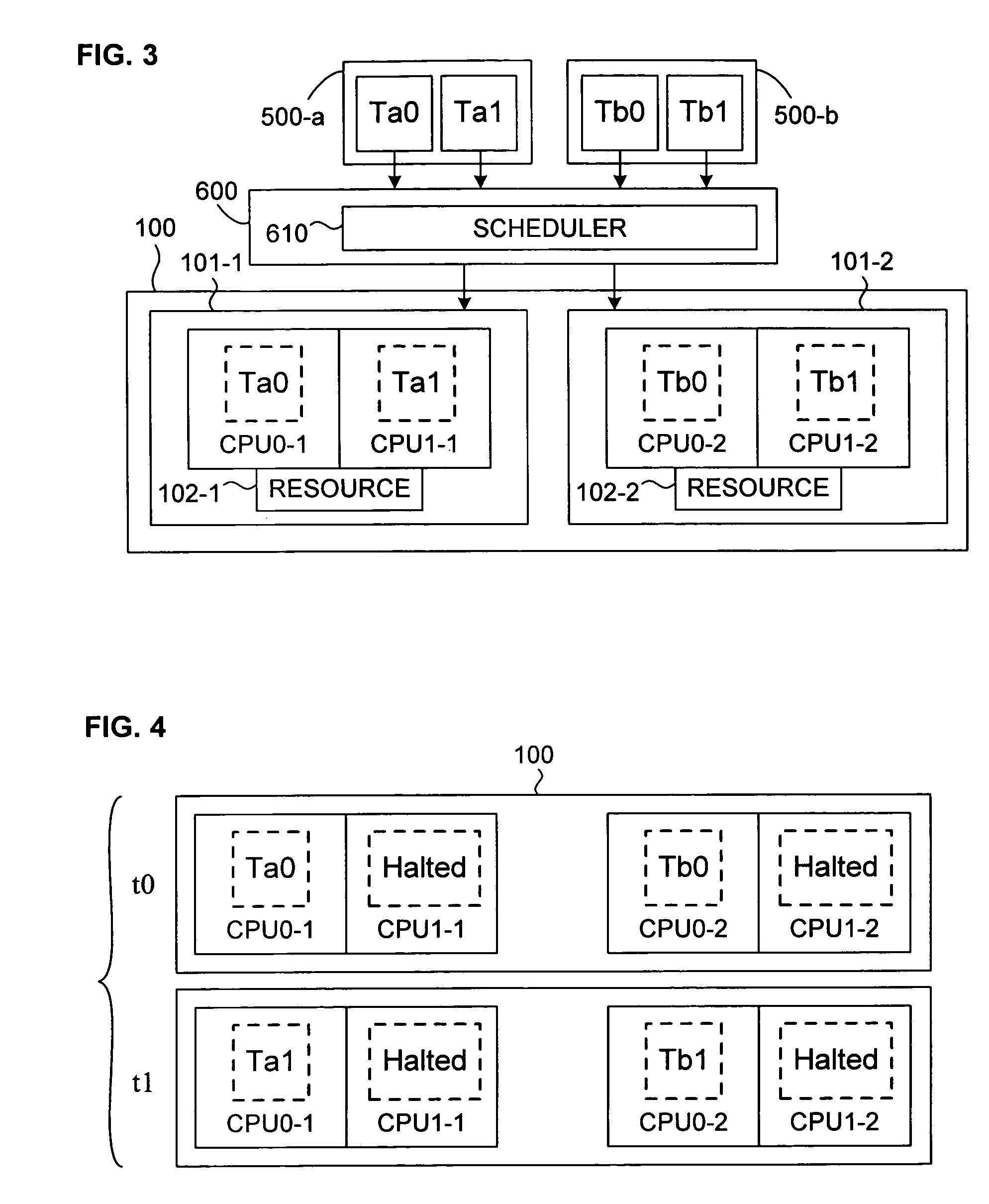
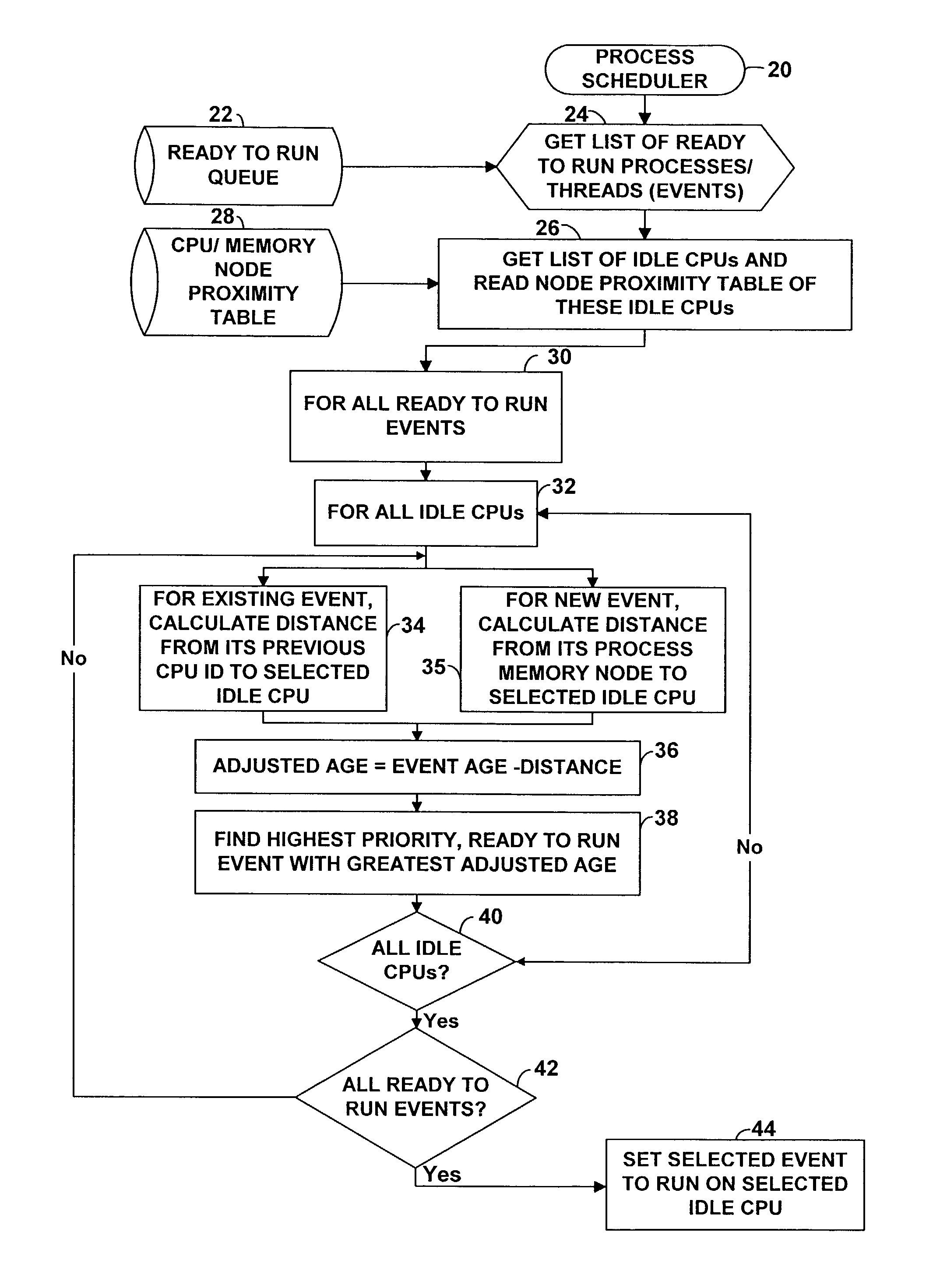
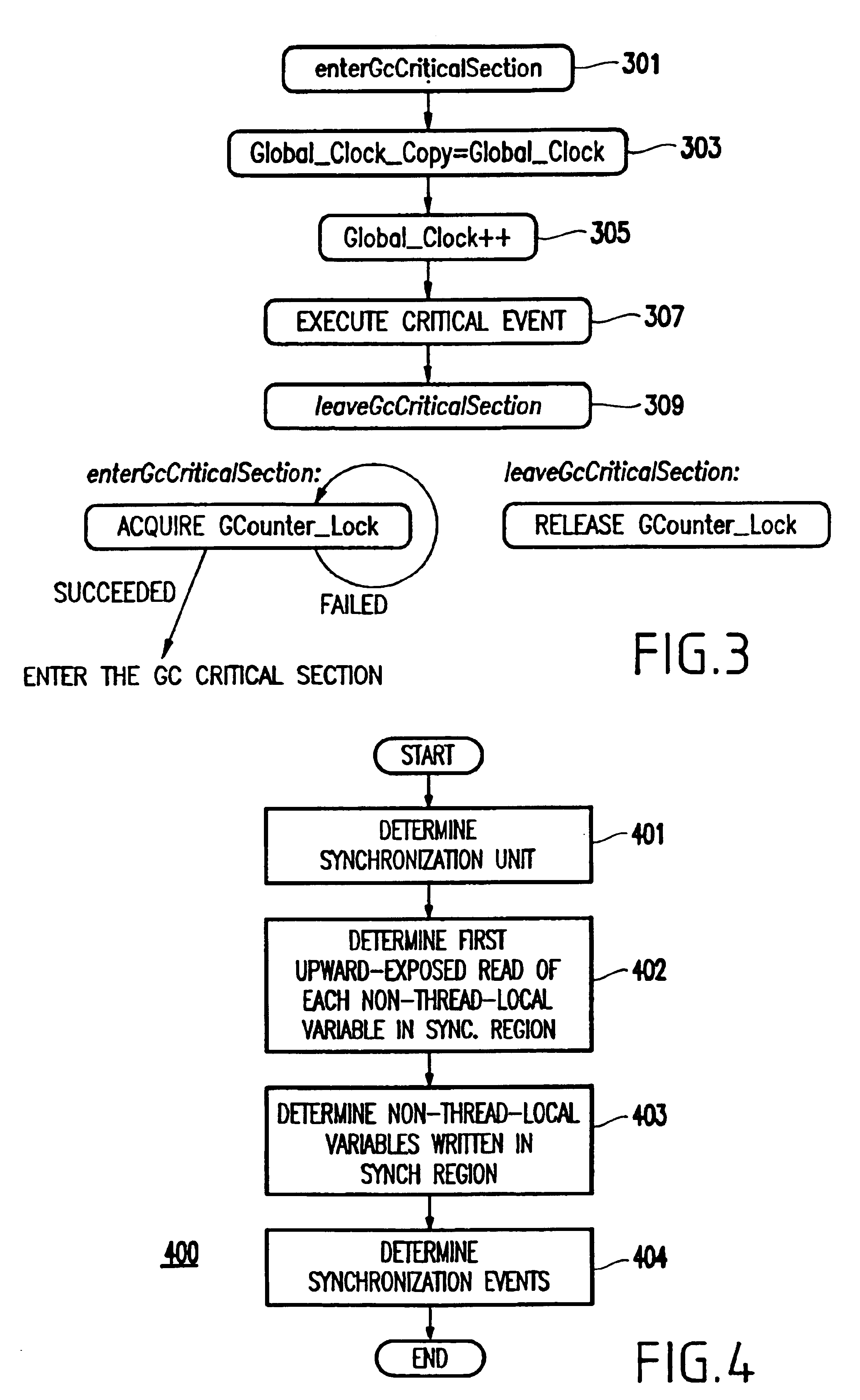
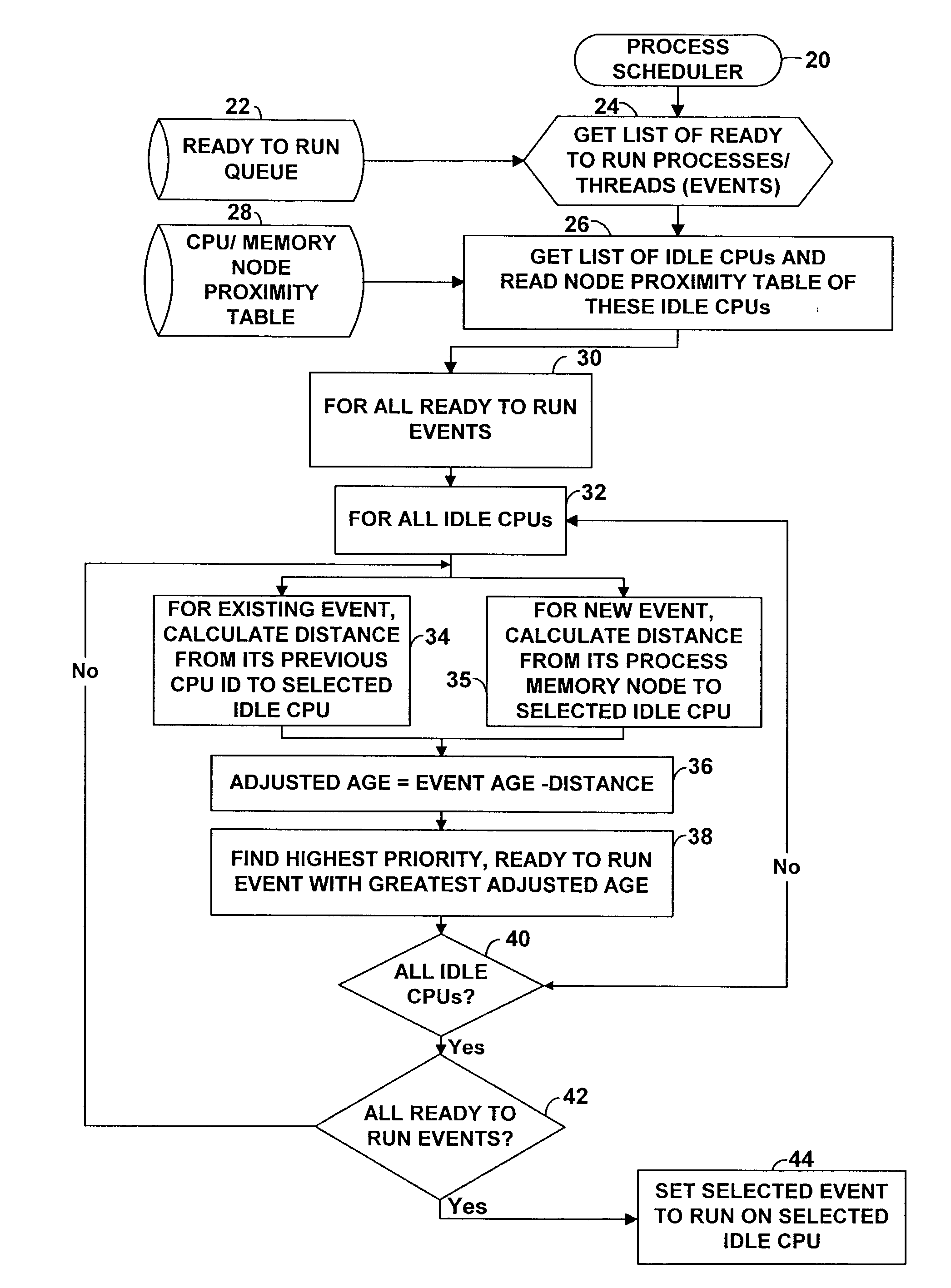
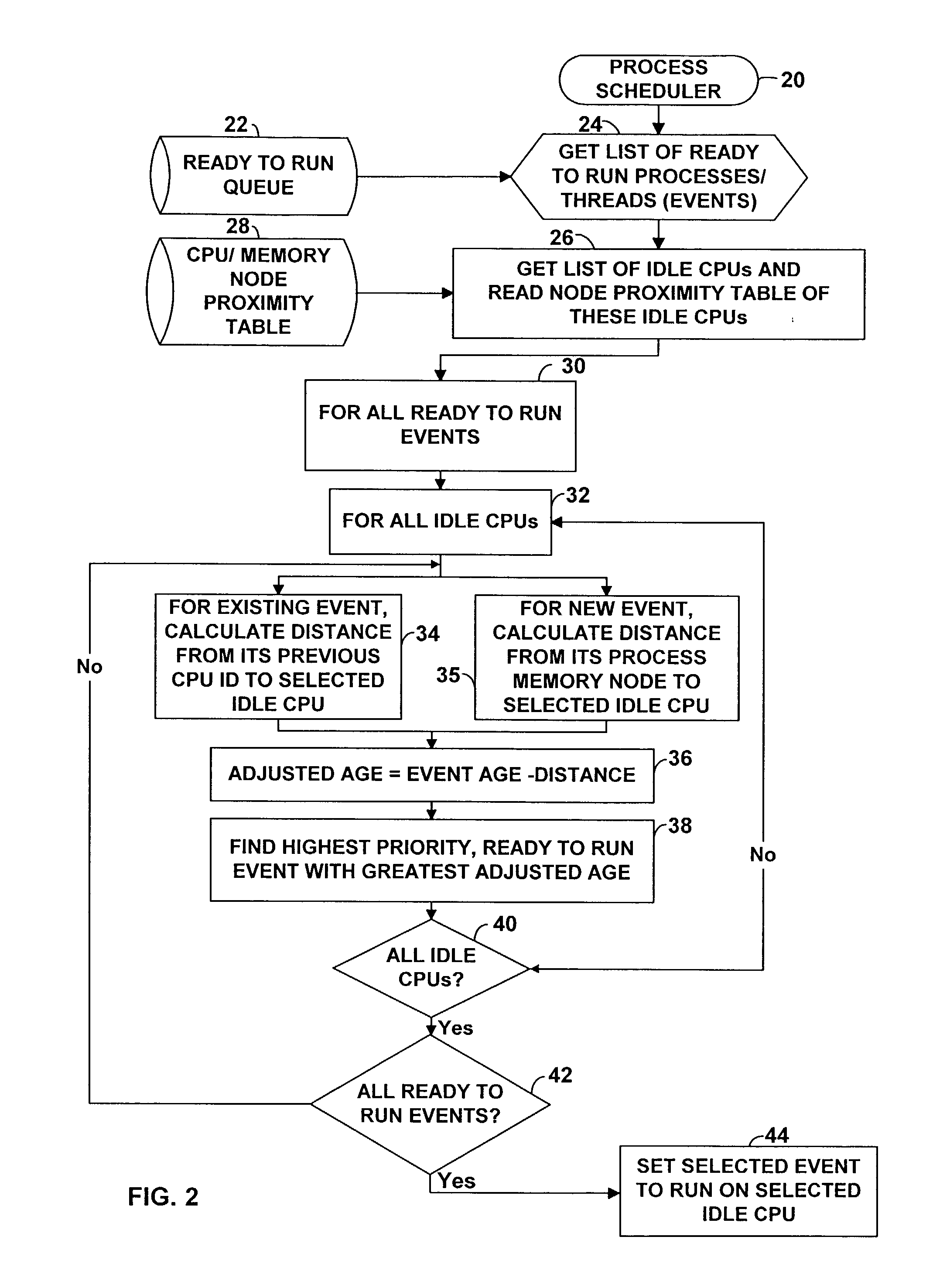
InactiveUS7143412B2Interprogram communicationDigital computer detailsError processingThread scheduling
A technique for improving performance in a multi-processor system by reducing access latency by correlating processor, node and memory allocation. Specifically, a Process / Thread Scheduler is modified such that system mapping and node proximity tables may be referenced to help determine processor assignments for ready-to-run processes / threads. Processors are chosen to minimize access latency. Further, the Page Fault Handler is modified such that free memory pages are assigned to a process based partially on the proximity of the memory with respect to the processor requesting memory allocation.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
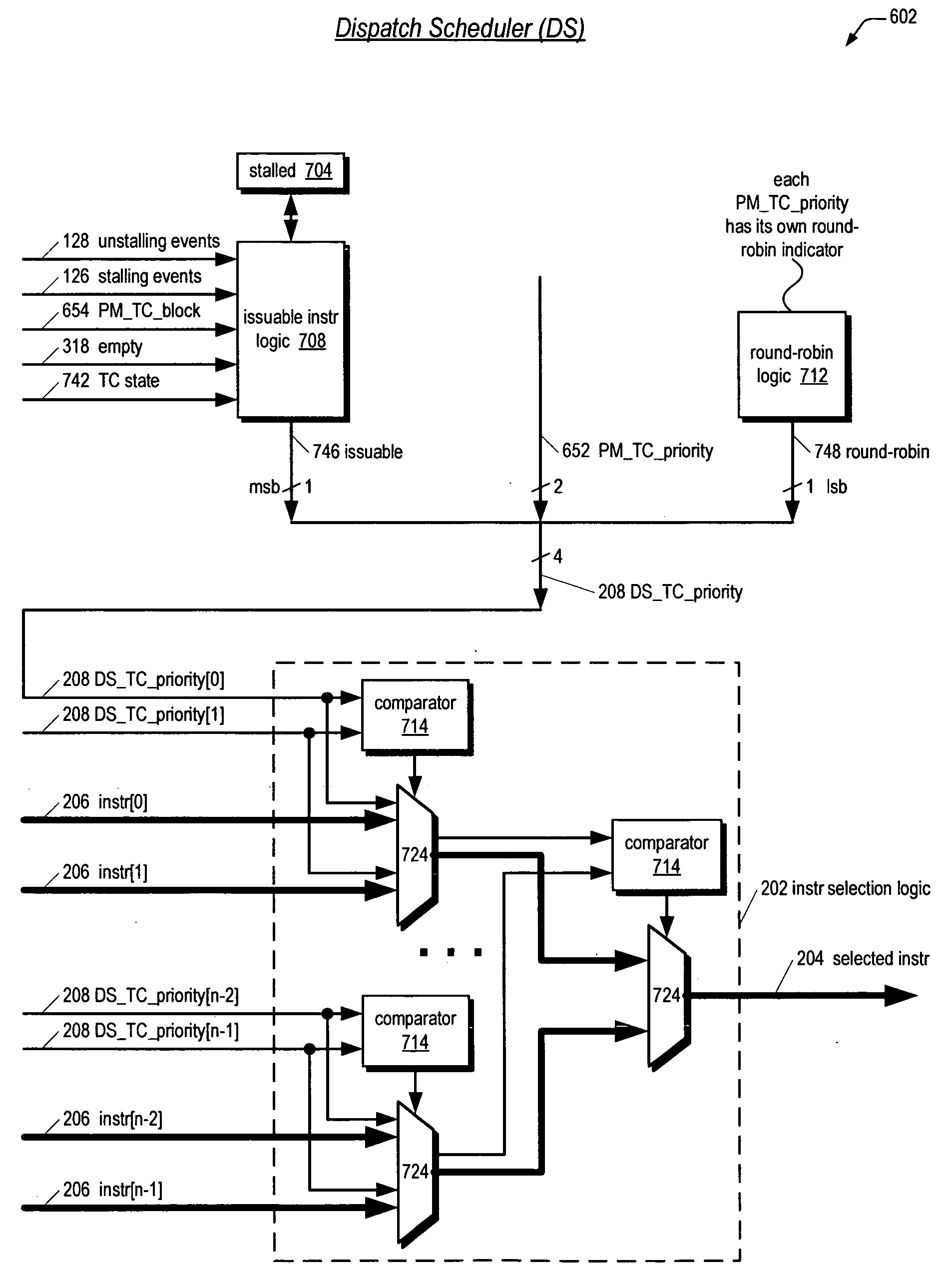
Multithreading instruction scheduler employing thread group priorities
A multithreading processor with an efficient and fair thread scheduler is disclosed. The scheduler enables threads to be grouped and a priority assigned to each group of threads. Round-robin order is maintained for each group. Consequently, the group priorities may be changed relatively frequently in order to obtain the benefits of not starving threads that require relatively low bandwidth and of interleaving instruction dispatch of multiple independent threads to enjoy pipeline efficiencies, and as long as the group populations are changed relatively infrequently, round-robin order fairness is provided within the groups in case multiple threads in a group have issuable instructions.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
Method and apparatus for deterministic replay of java multithreaded programs on multiprocessors
InactiveUS6854108B1Reduce in quantityGood runtime performanceSoftware testing/debuggingSpecific program execution arrangementsMulti processorThread scheduling
A method (and apparatus) of determinstically replaying an observable run-time behavior of distributed multi-threaded programs on multiprocessors in a shared-memory multiprocessor environment, wherein a run-time behavior of the programs includes sequences of events, each sequence being associated with one of a plurality of execution threads, includes identifying an execution order of critical events of the program, wherein the program includes critical events and non-critical events, generating groups of critical events of the program, generating, for each given execution thread, a logical thread schedule that identifies a sequence of the groups associated with the given execution thread, and storing the logical thread schedule for subsequent reuse.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method and apparatus for optimizing performance in a multi-processing system
InactiveUS20040019891A1Interprogram communicationDigital computer detailsError processingThread scheduling
A technique for improving performance in a multi-processor system by reducing access latency by correlating processor, node and memory allocation. Specifically, a Process / Thread Scheduler is modified such that system mapping and node proximity tables may be referenced to help determine processor assignments for ready-to-run processes / threads. Processors are chosen to minimize access latency. Further, the Page Fault Handler is modified such that free memory pages are assigned to a process based partially on the proximity of the memory with respect to the processor requesting memory allocation.
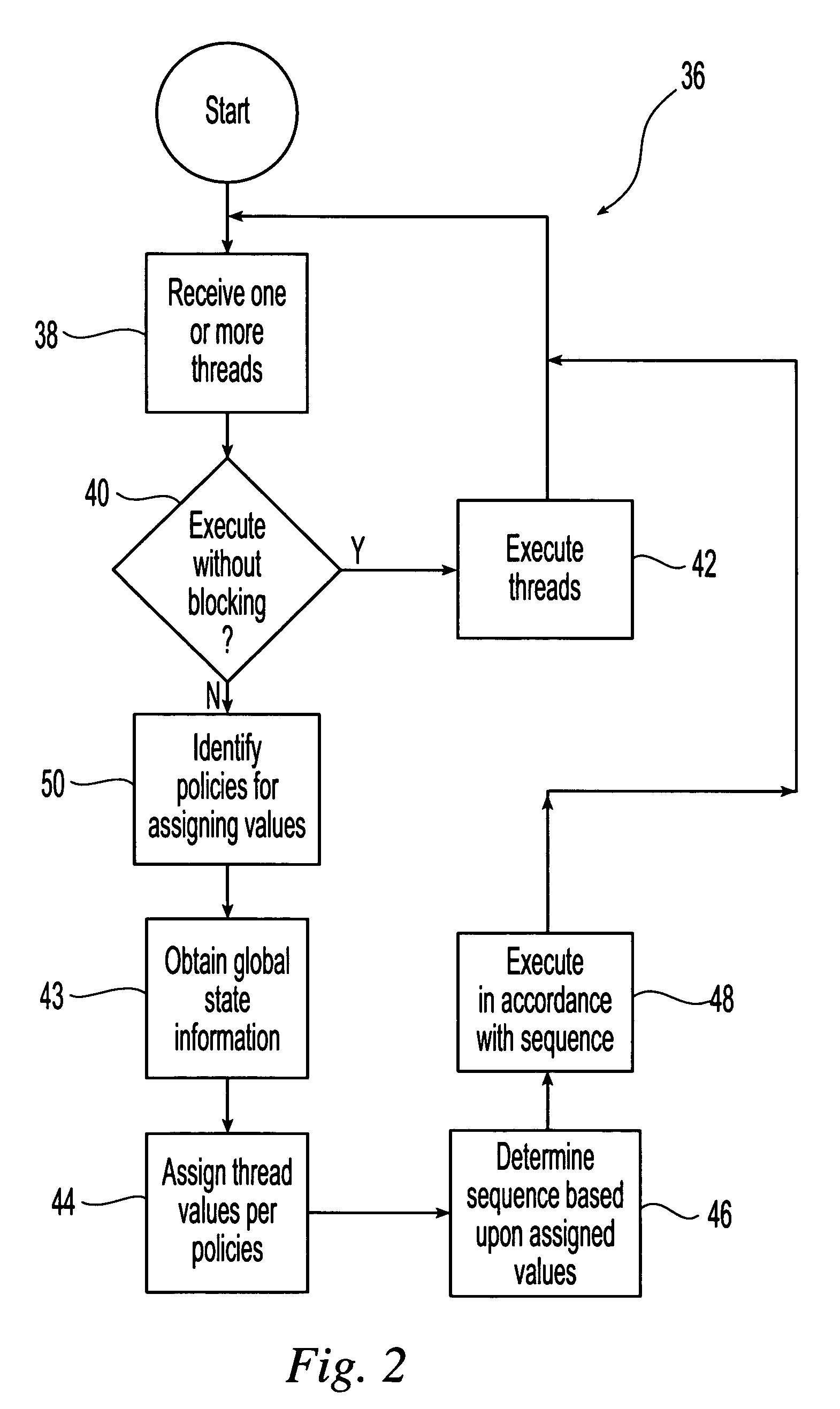
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
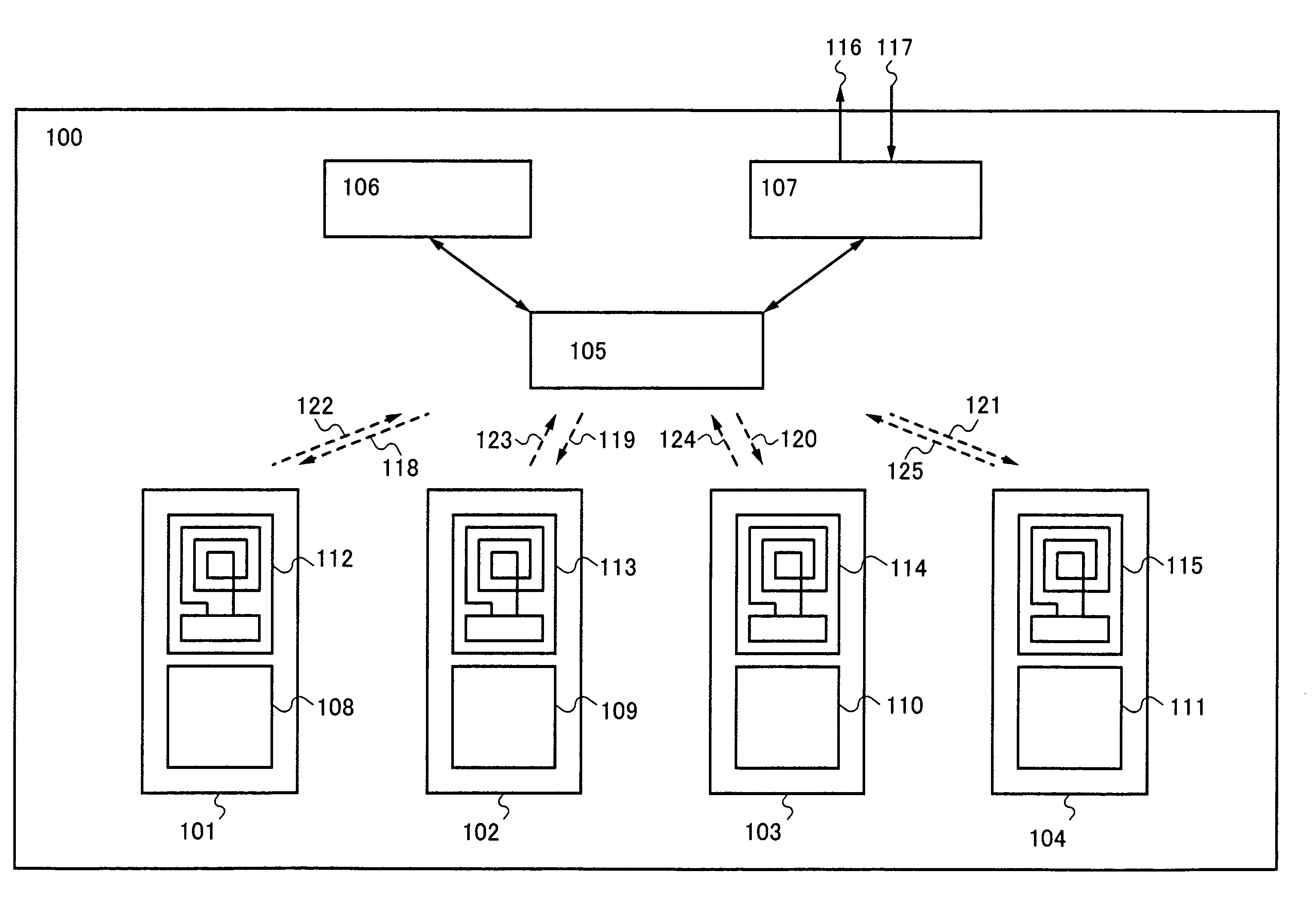
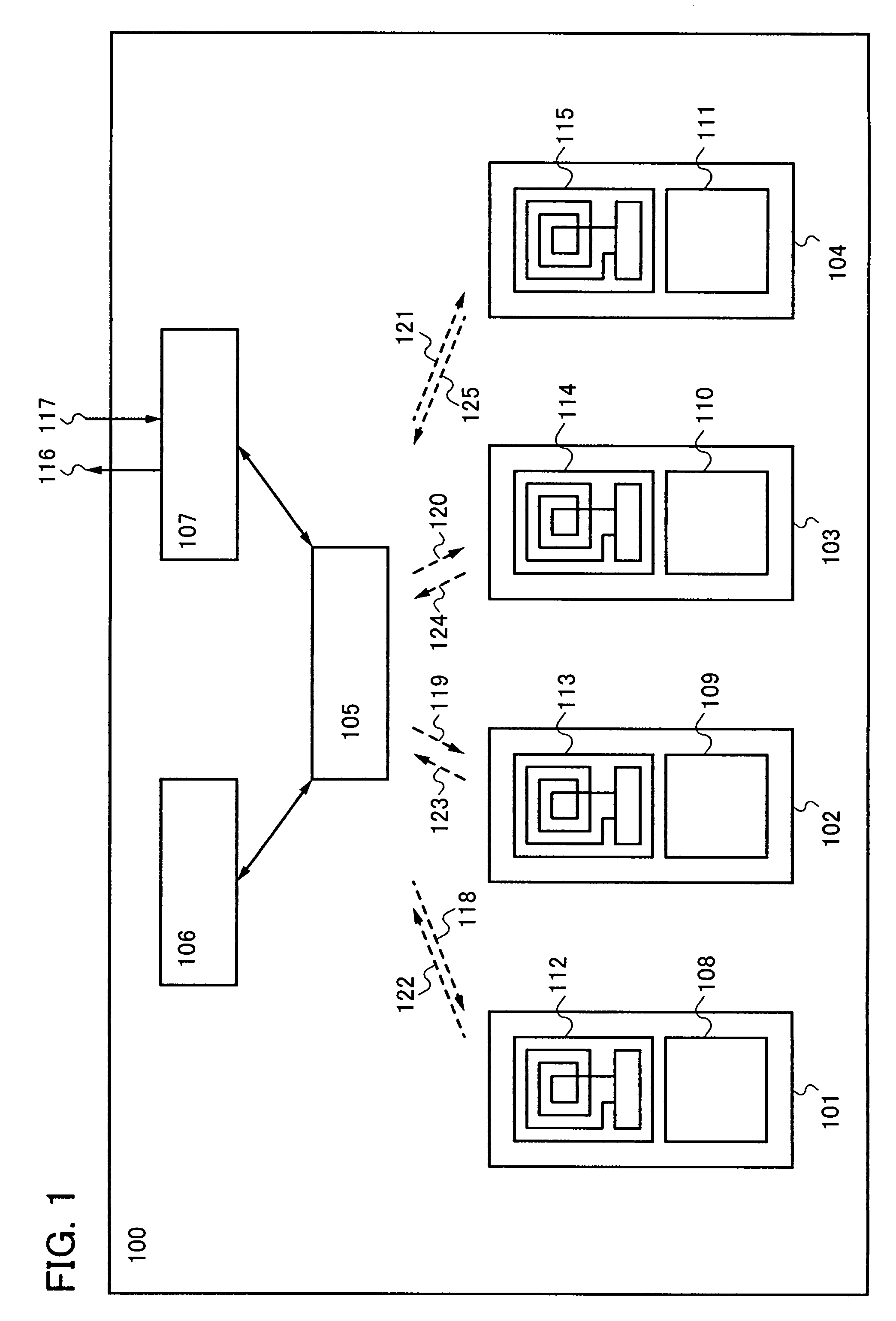
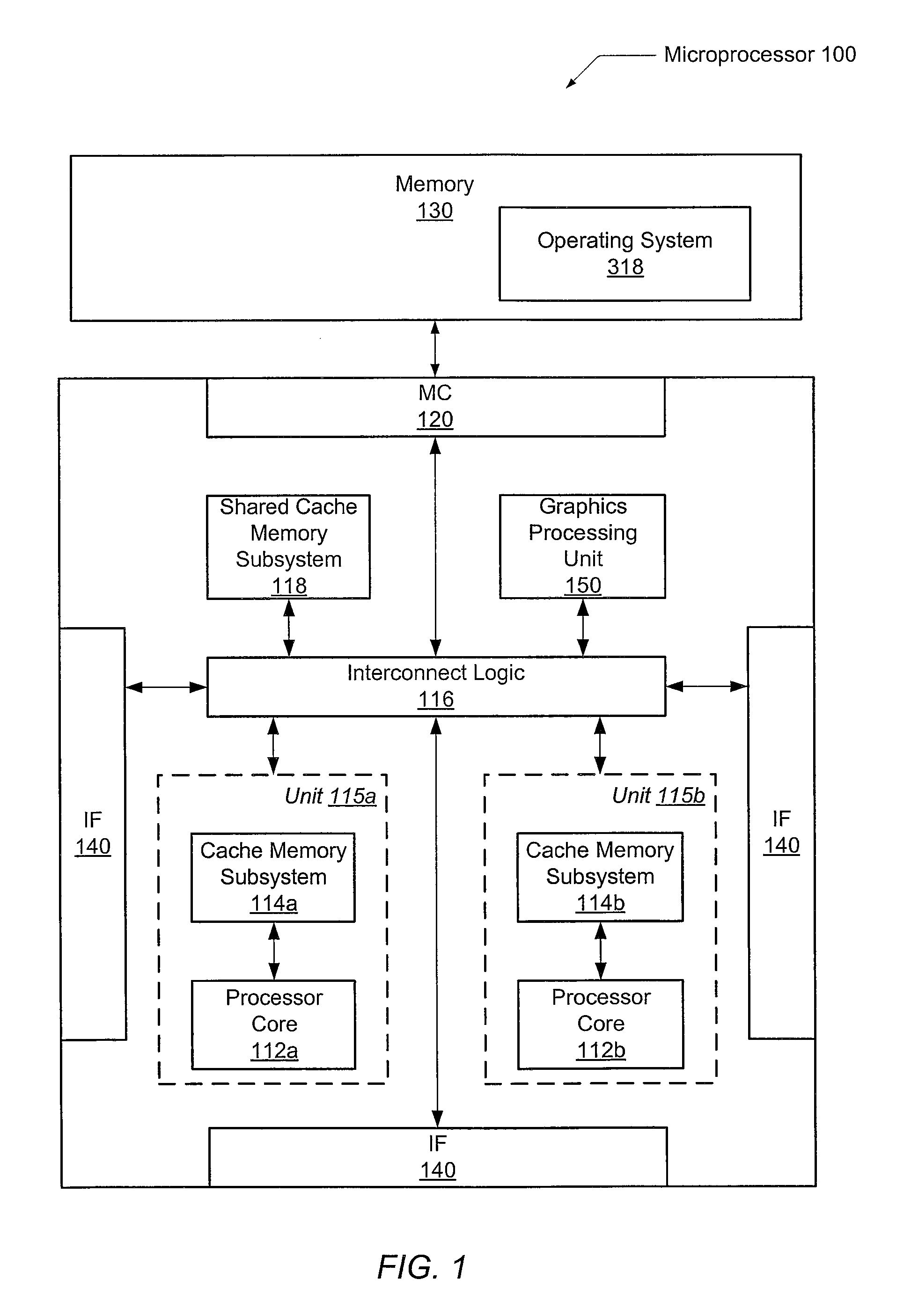
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS7840188B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce total powerEnergy efficient ICTNear-field transmissionThread schedulingControl circuit
In a multi-core semiconductor device, a data bus between CPUs or the like consumes a larger amount of power. By provision of a plurality of CPUs which transmit data by a backscattering method of a wireless signal, a router circuit which mediates data transmission and reception between the CPUs or the like, and a thread control circuit which has a thread scheduling function, a semiconductor device which consumes less power and has high arithmetic performance can be provided at low cost.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
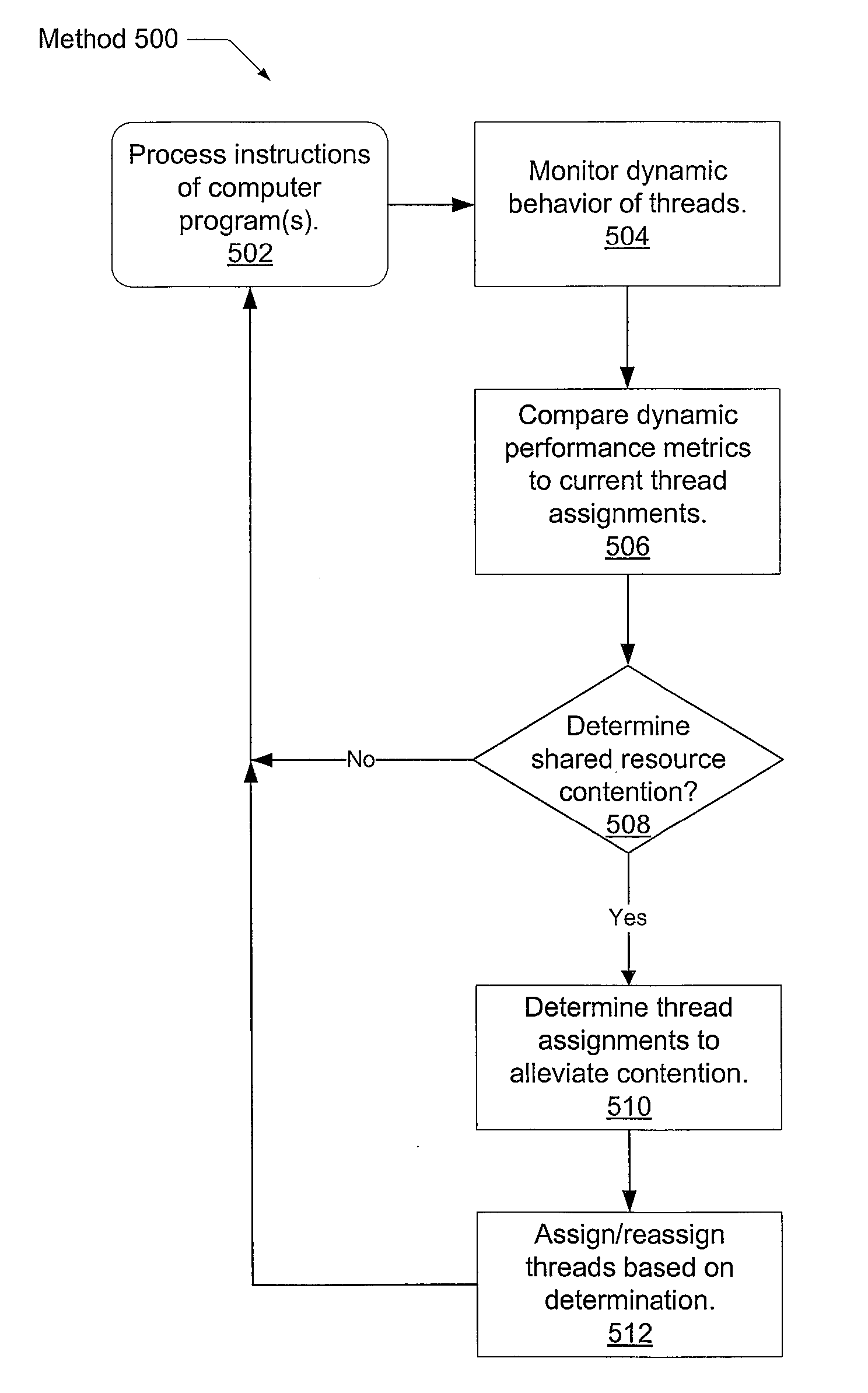
Optimized thread scheduling via hardware performance monitoring
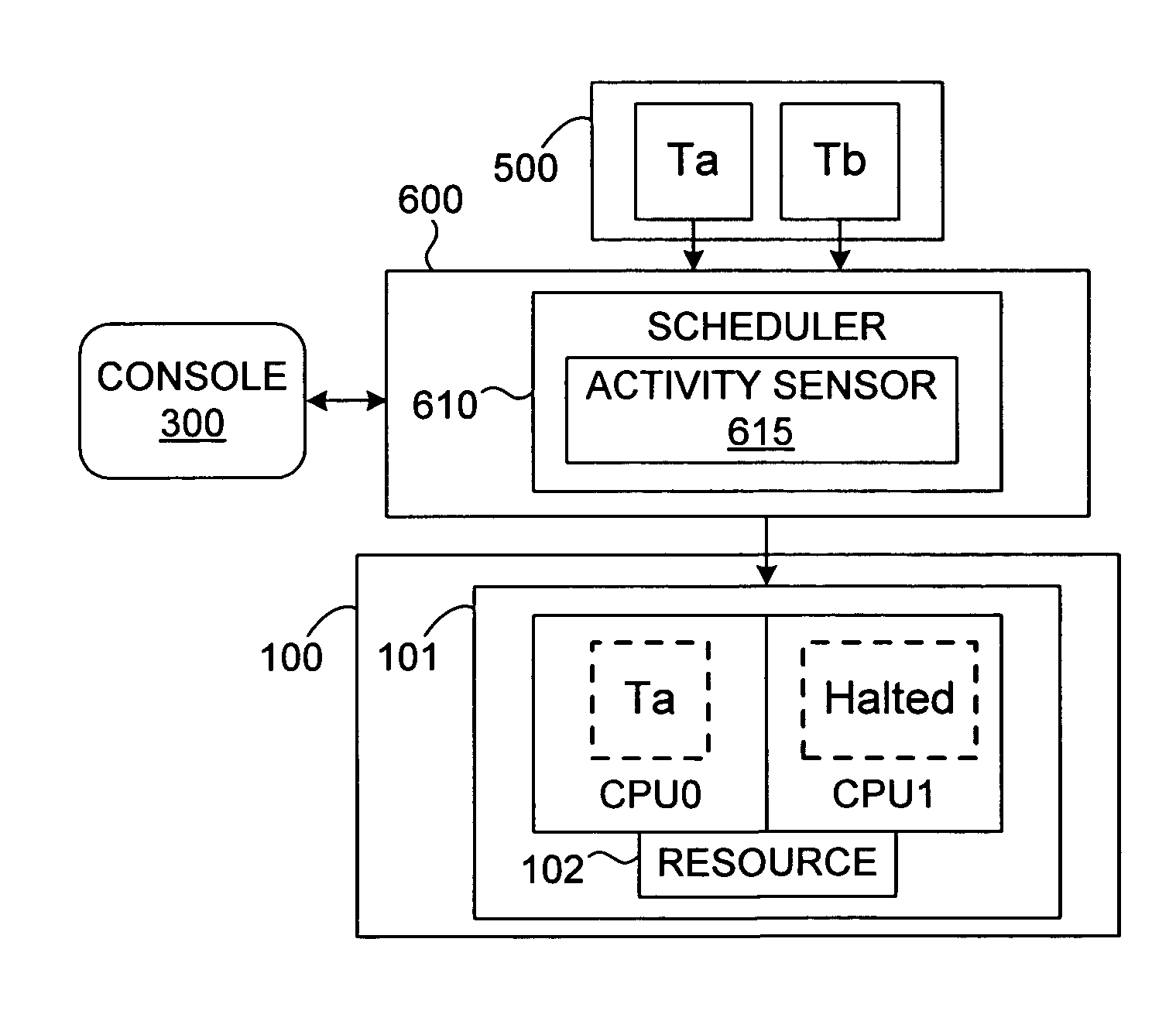
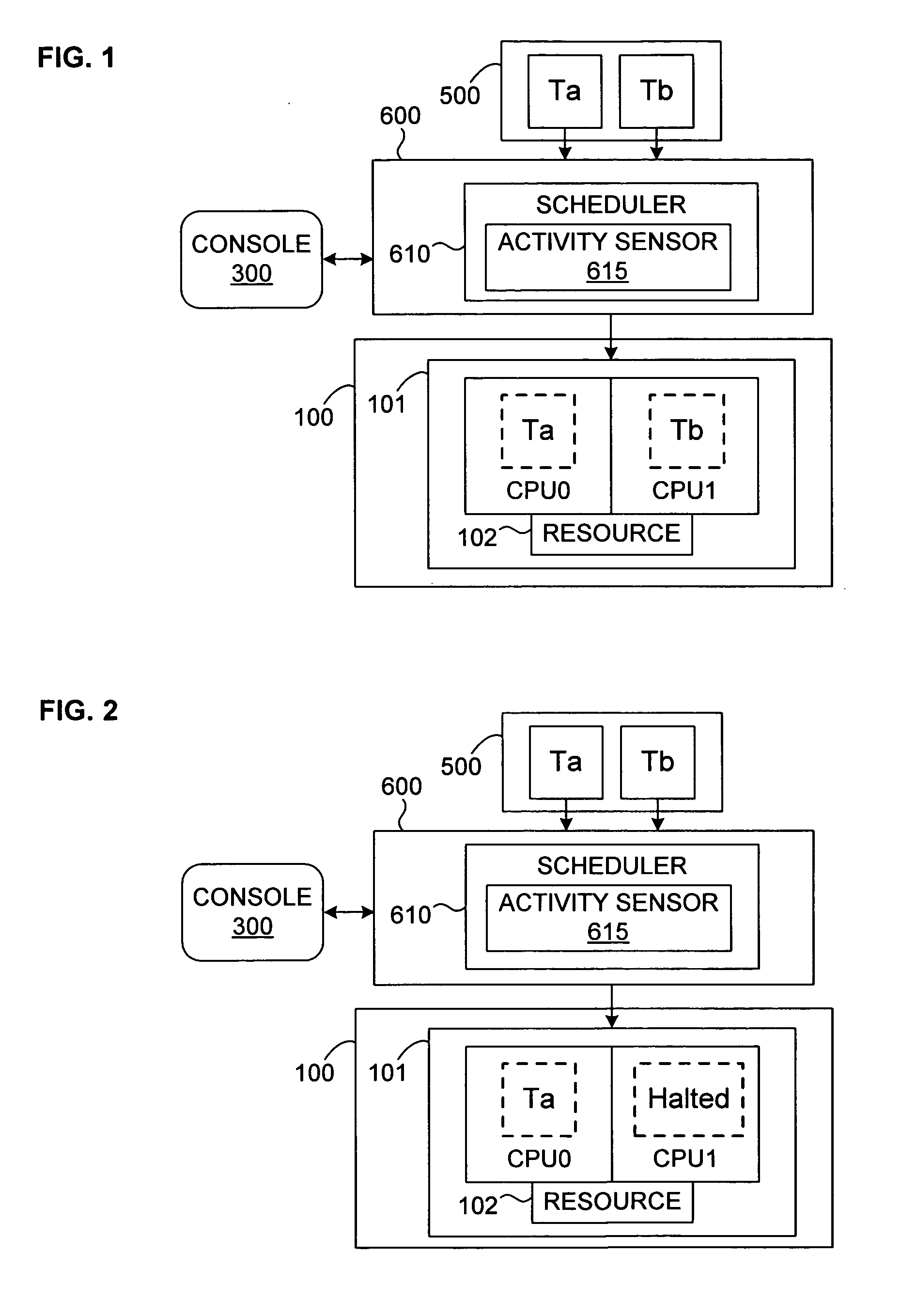
A system and method for efficient dynamic scheduling of tasks. A scheduler within an operating system assigns software threads of program code to computation units. A computation unit may be a microprocessor, a processor core, or a hardware thread in a multi-threaded core. The scheduler receives measured data values from performance monitoring hardware within a processor as the one or more processors execute the software threads. The scheduler may be configured to reassign a first thread assigned to a first computation unit coupled to a first shared resource to a second computation unit coupled to a second shared resource. The scheduler may perform this dynamic reassignment in response to determining from the measured data values a first measured value corresponding to the utilization of the first shared resource exceeds a predetermined threshold and a second measured value corresponding to the utilization of the second shared resource does not exceed the predetermined threshold.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
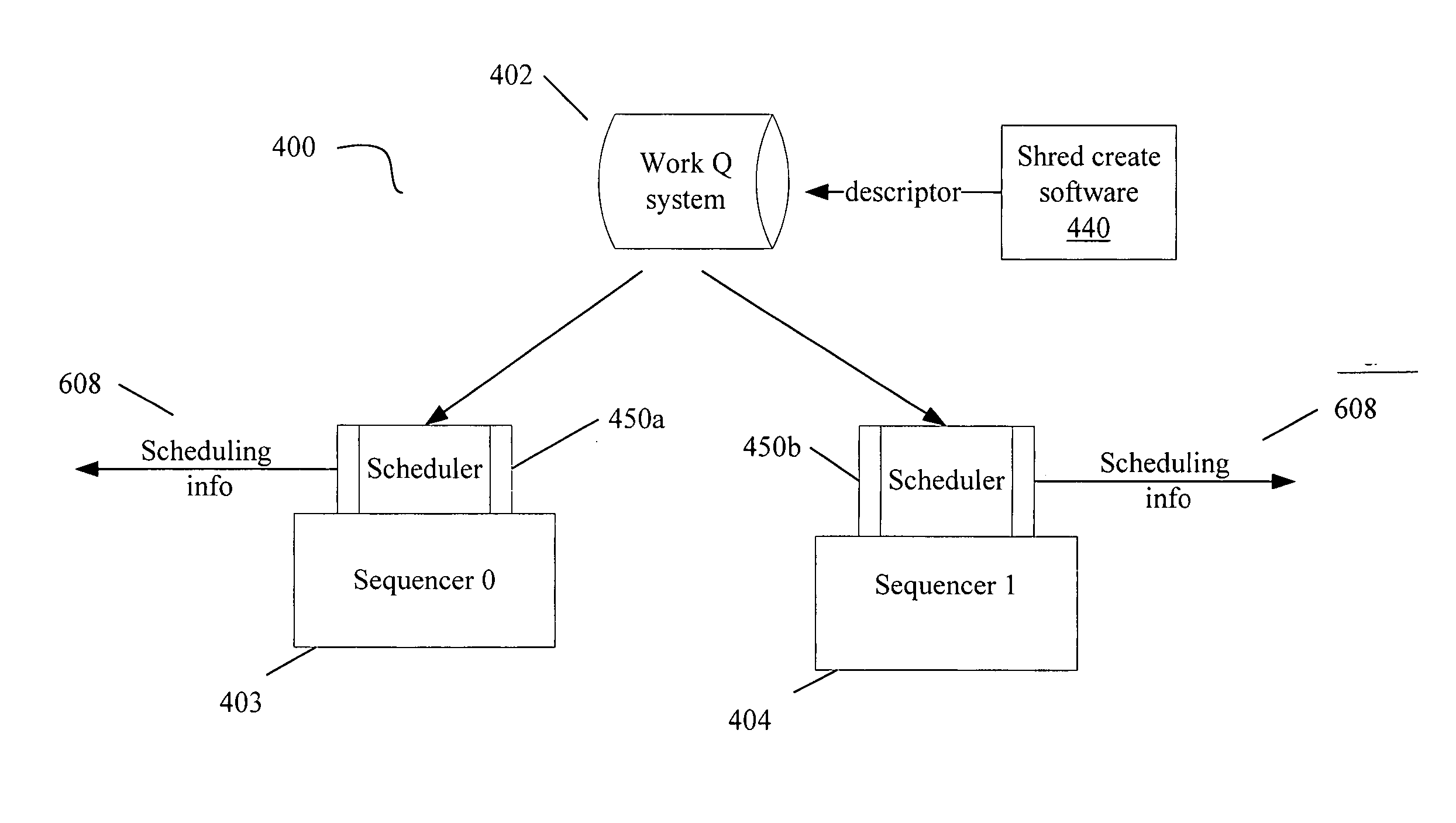
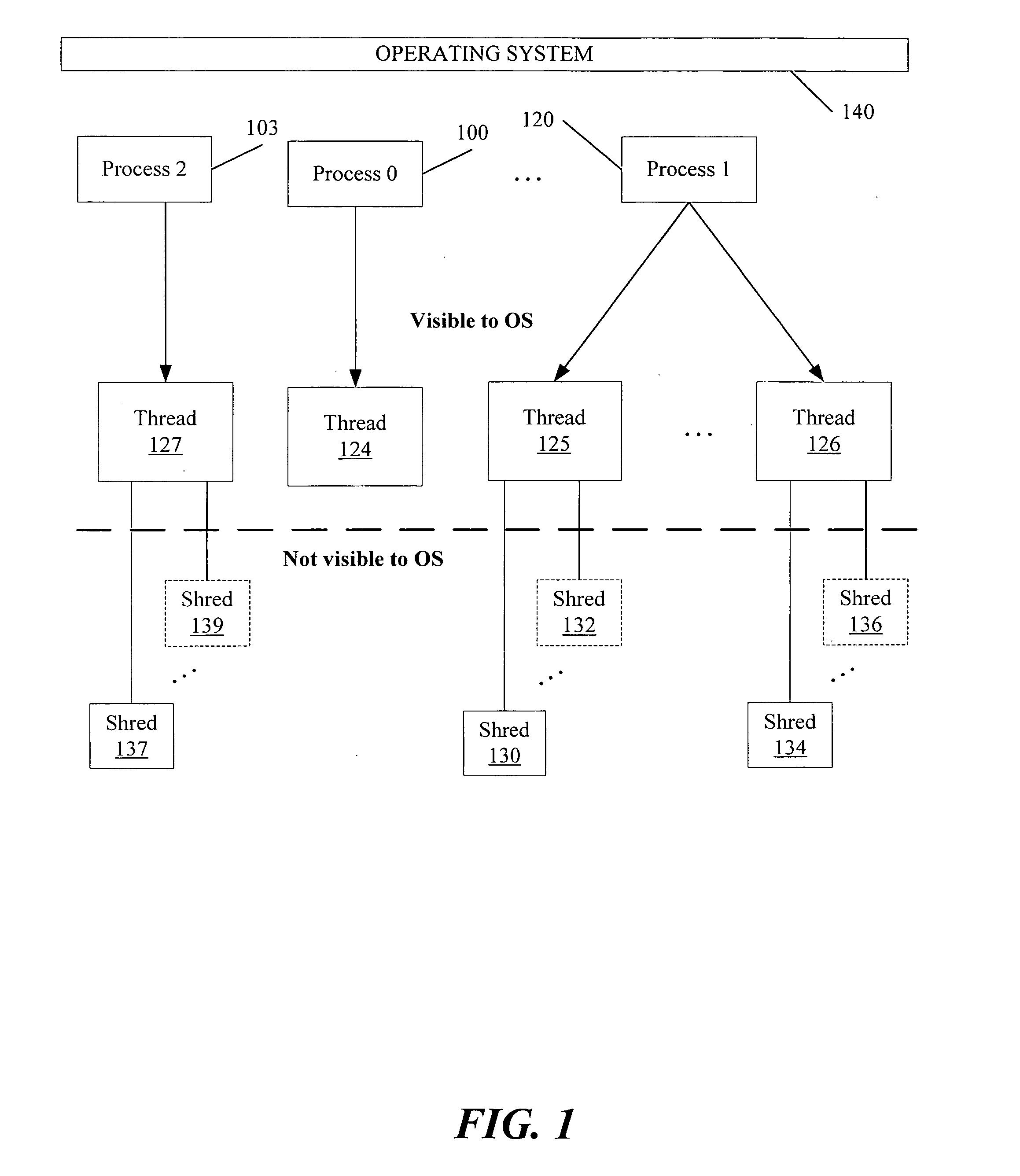
Scheduling optimizations for user-level threads
InactiveUS20070074217A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsOperational systemThread scheduling
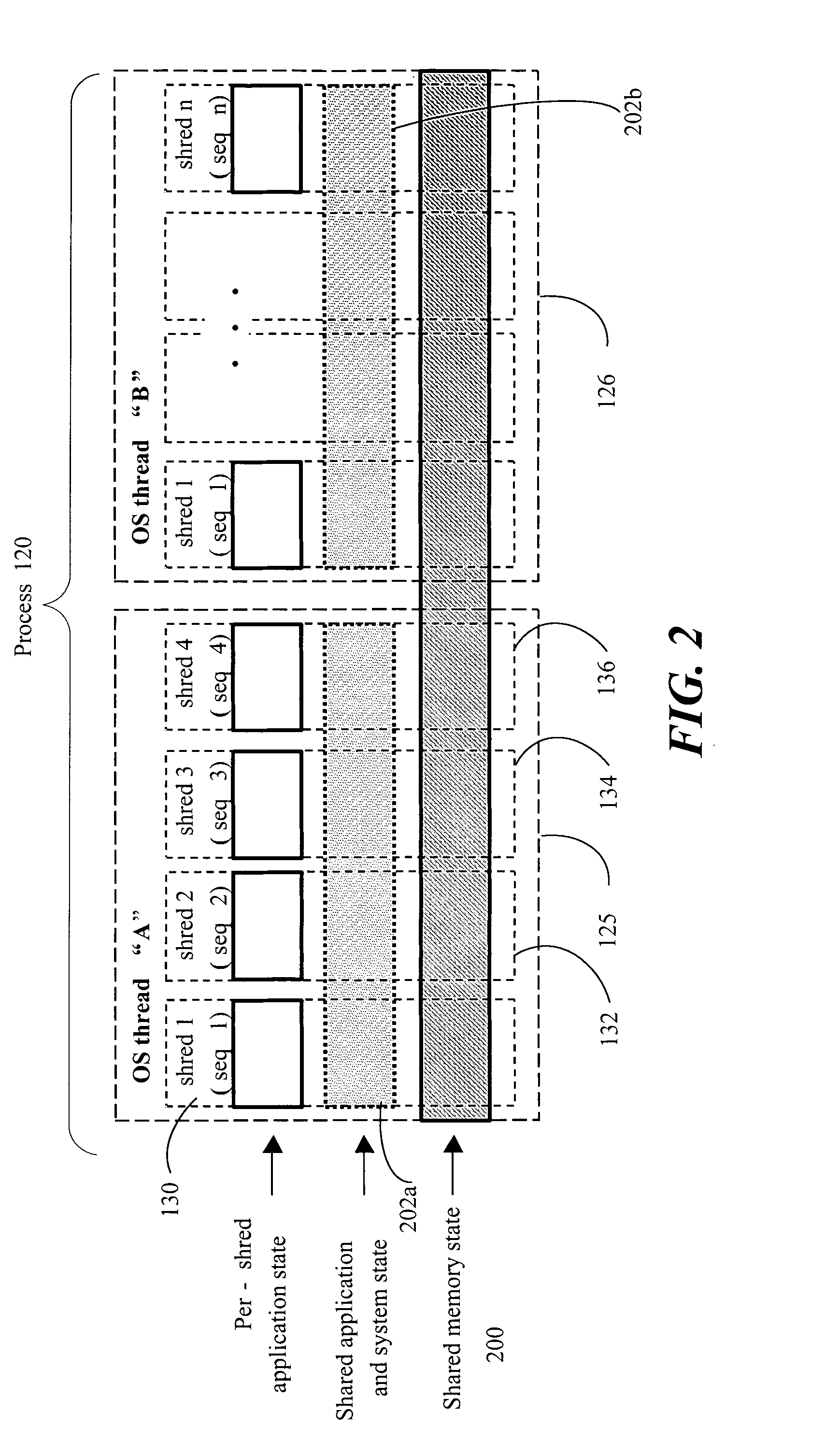
Method, apparatus and system embodiments to schedule user-level OS-independent “shreds” without intervention of an operating system. For at least one embodiment, the shred is scheduled for execution by a scheduler routine rather than the operating system. The scheduler routine resides in user space and may be part of a runtime library. The library may also include monitoring logic that monitors execution of a shredded program and provides scheduling hints, based on shred dependence information, to the scheduler. In addition, the scheduler may further optimize shred scheduling by taking into account information about a system's configuration of thread execution hardware. Other embodiments are also described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Hardware support for thread scheduling on multi-core processors
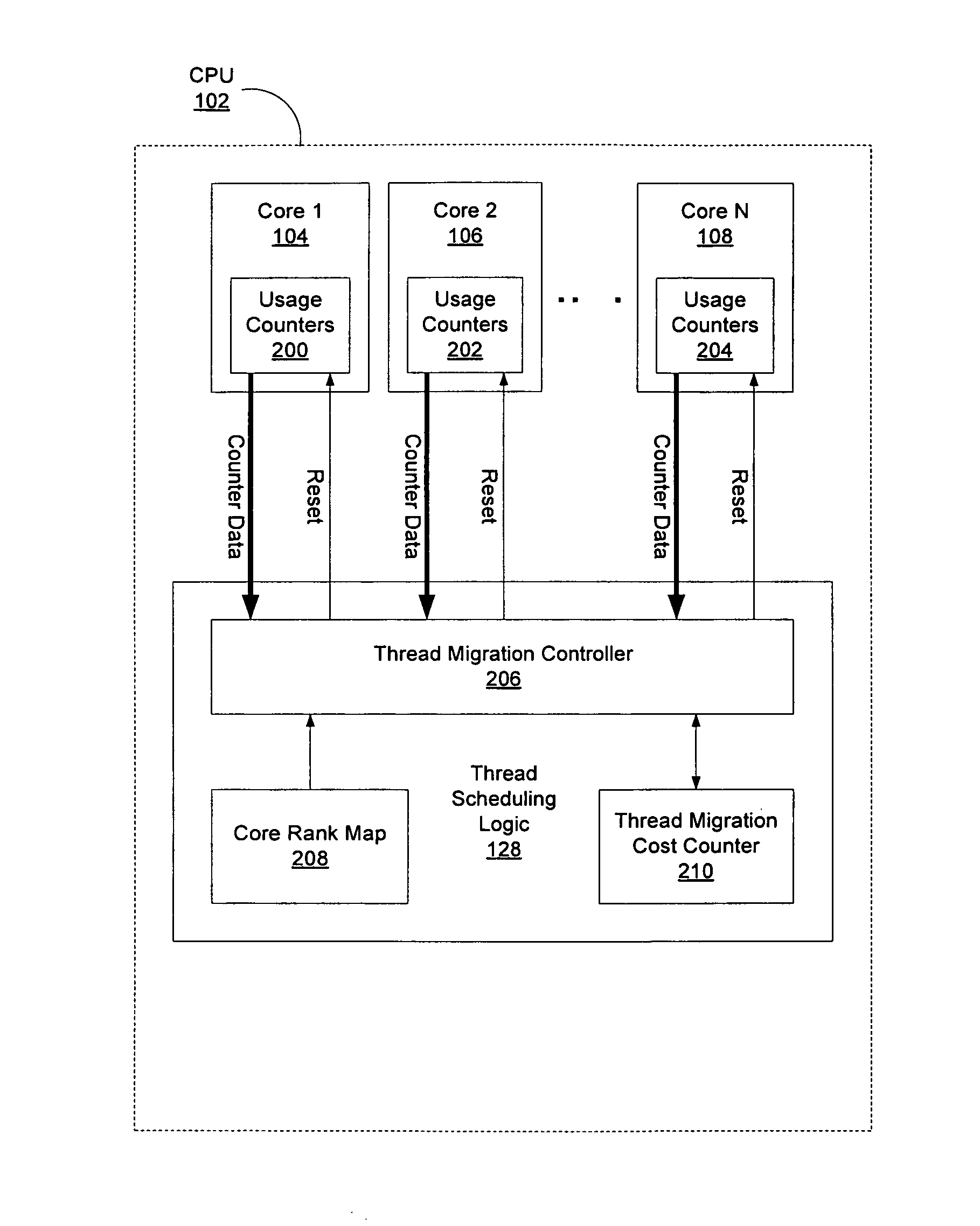
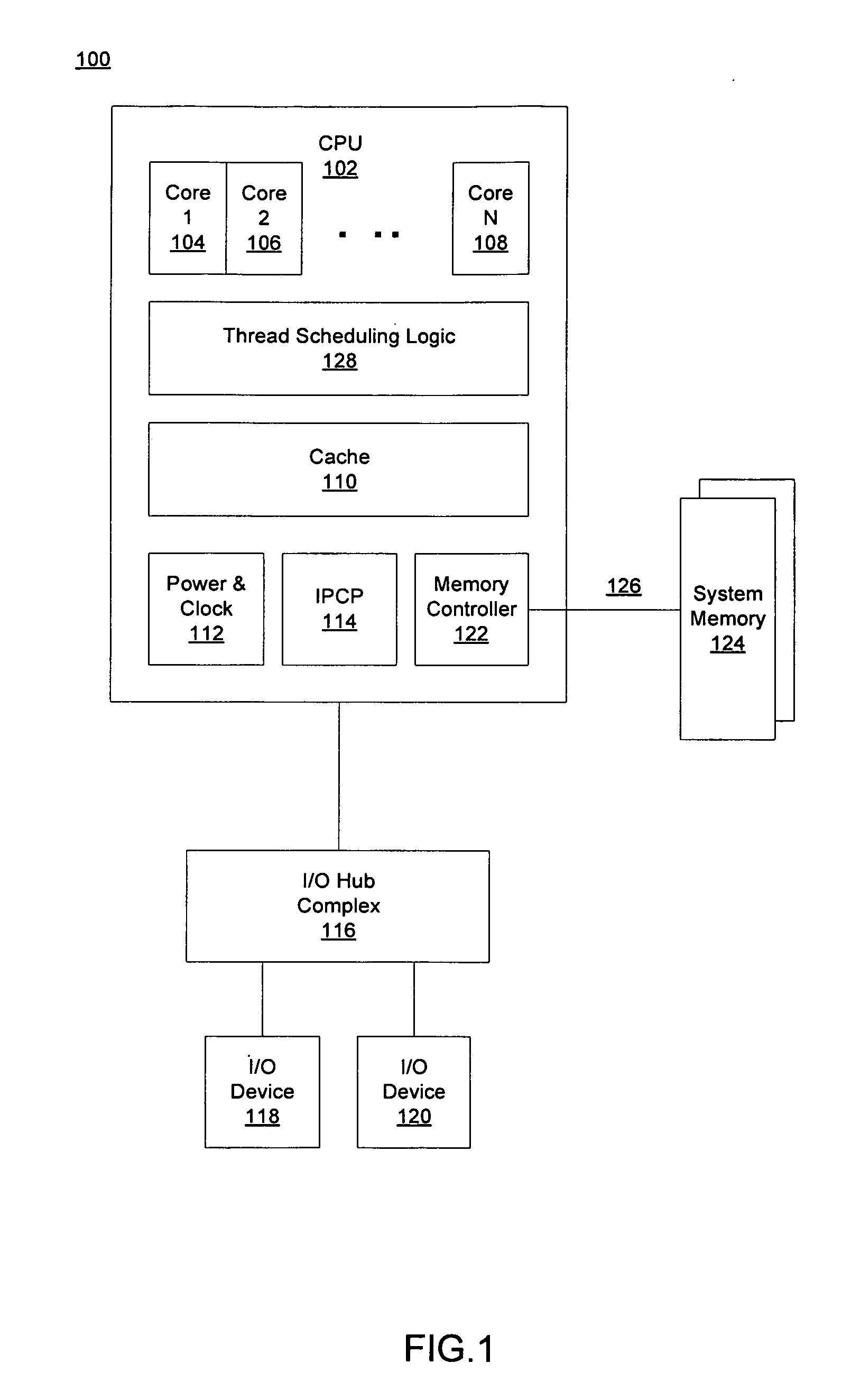
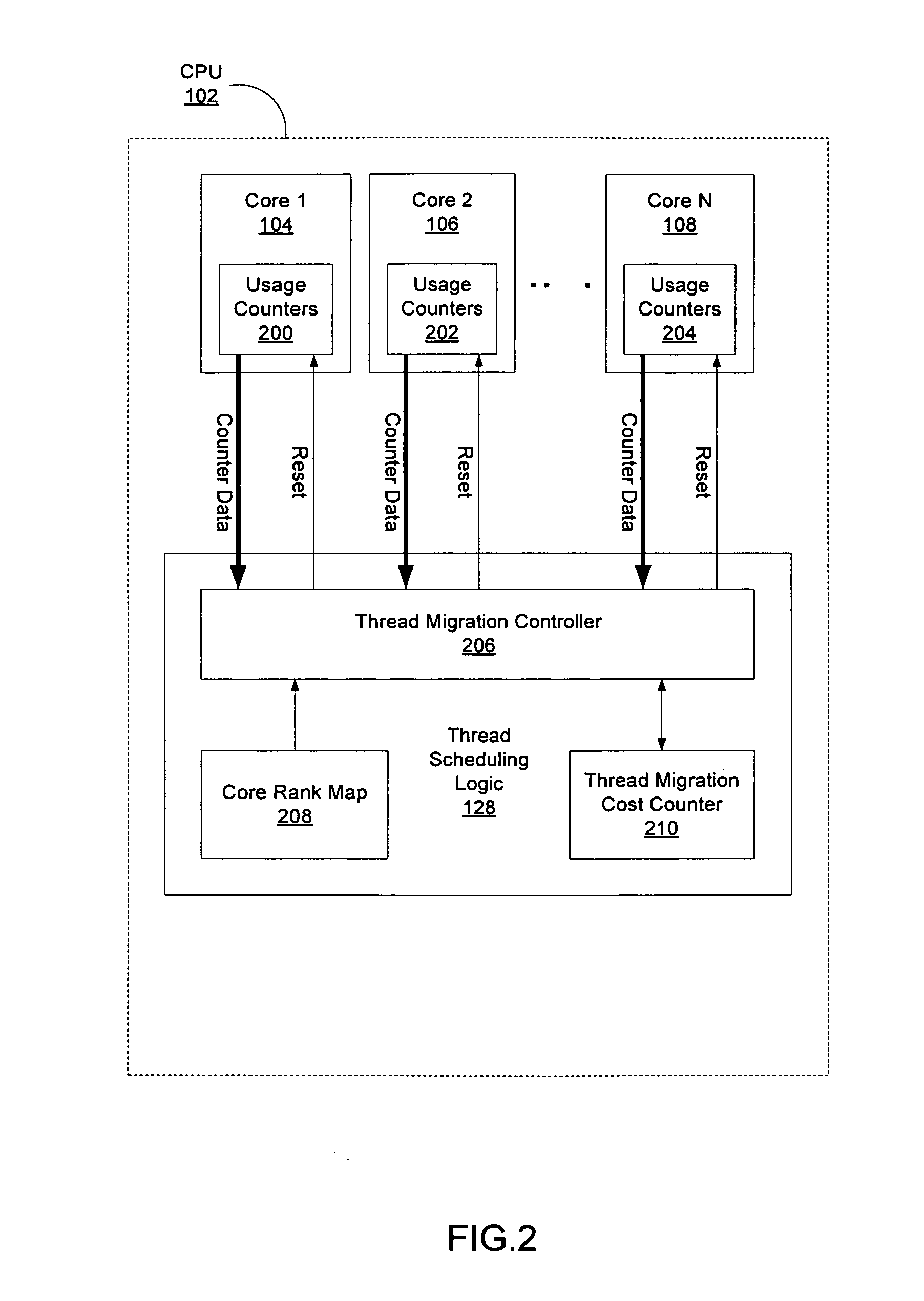
ActiveUS20110088041A1Multiprogramming arrangementsSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationThread schedulingWorkload
A method, device, and system are disclosed. In one embodiment the method includes scheduling a thread to run on first core of a multi-core processor. The determination as to which core the thread is scheduled on uses one or more processes. These processes may include ranking all of the cores specific to a workload of the thread, establishing a current utilization of each core of the multi-core processor, and calculating an inter-core migration cost for the thread.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
Machine instruction for enhanced control of multiple virtual processor systems
InactiveUS20050108711A1Facilitates increased processor efficiencyEasy to cleanMultiprogramming arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionControl systemThread scheduling
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
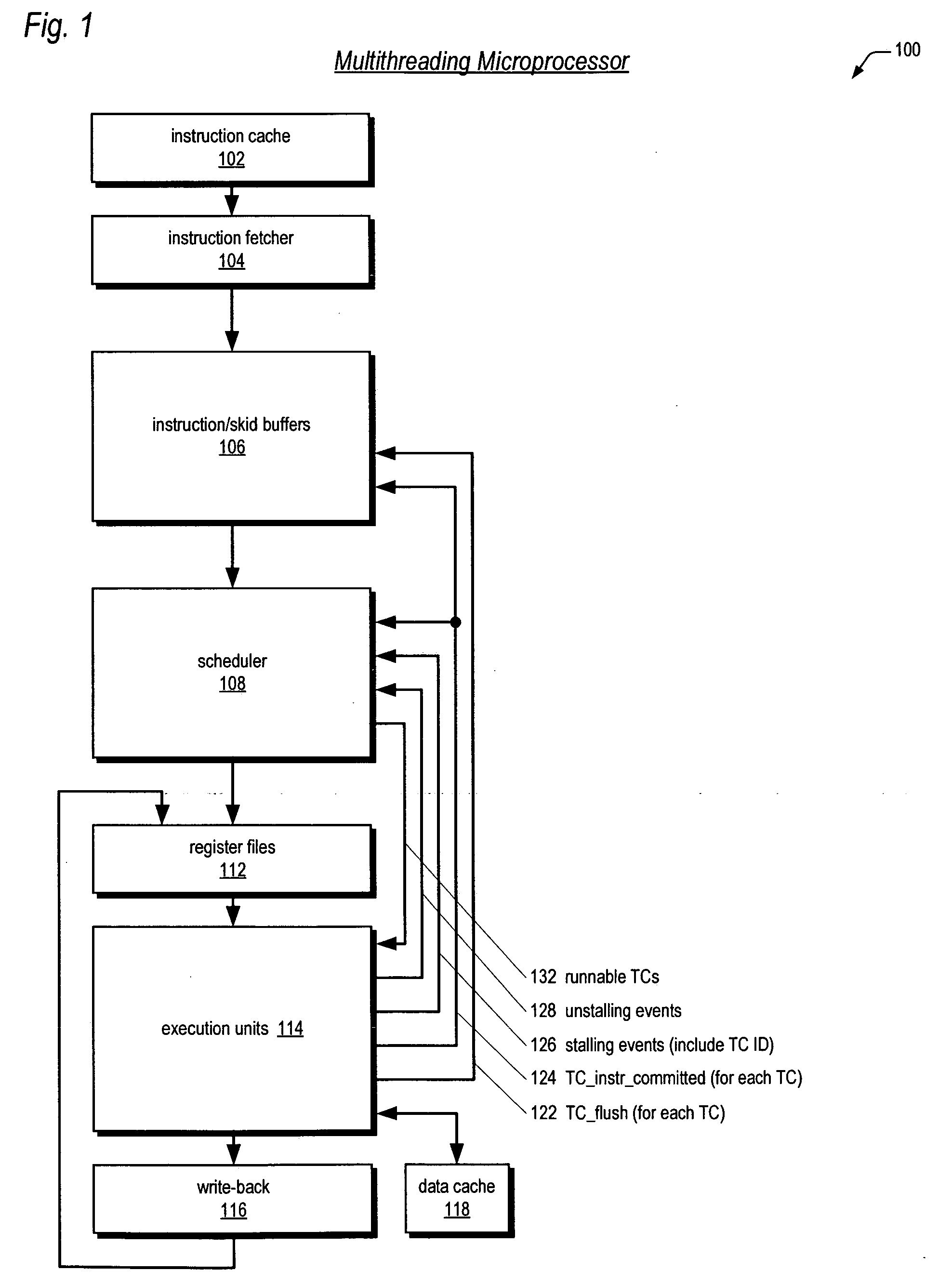
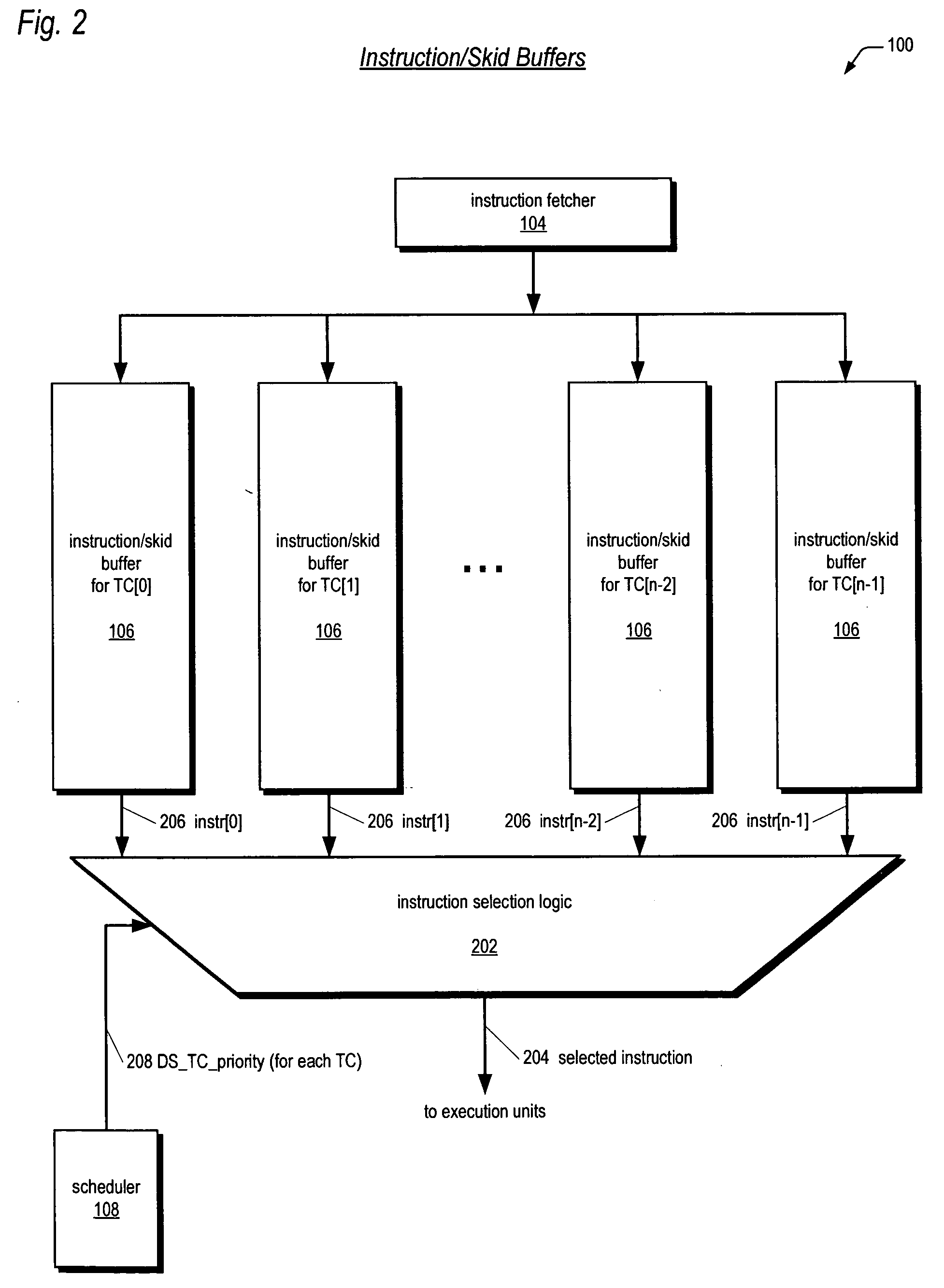
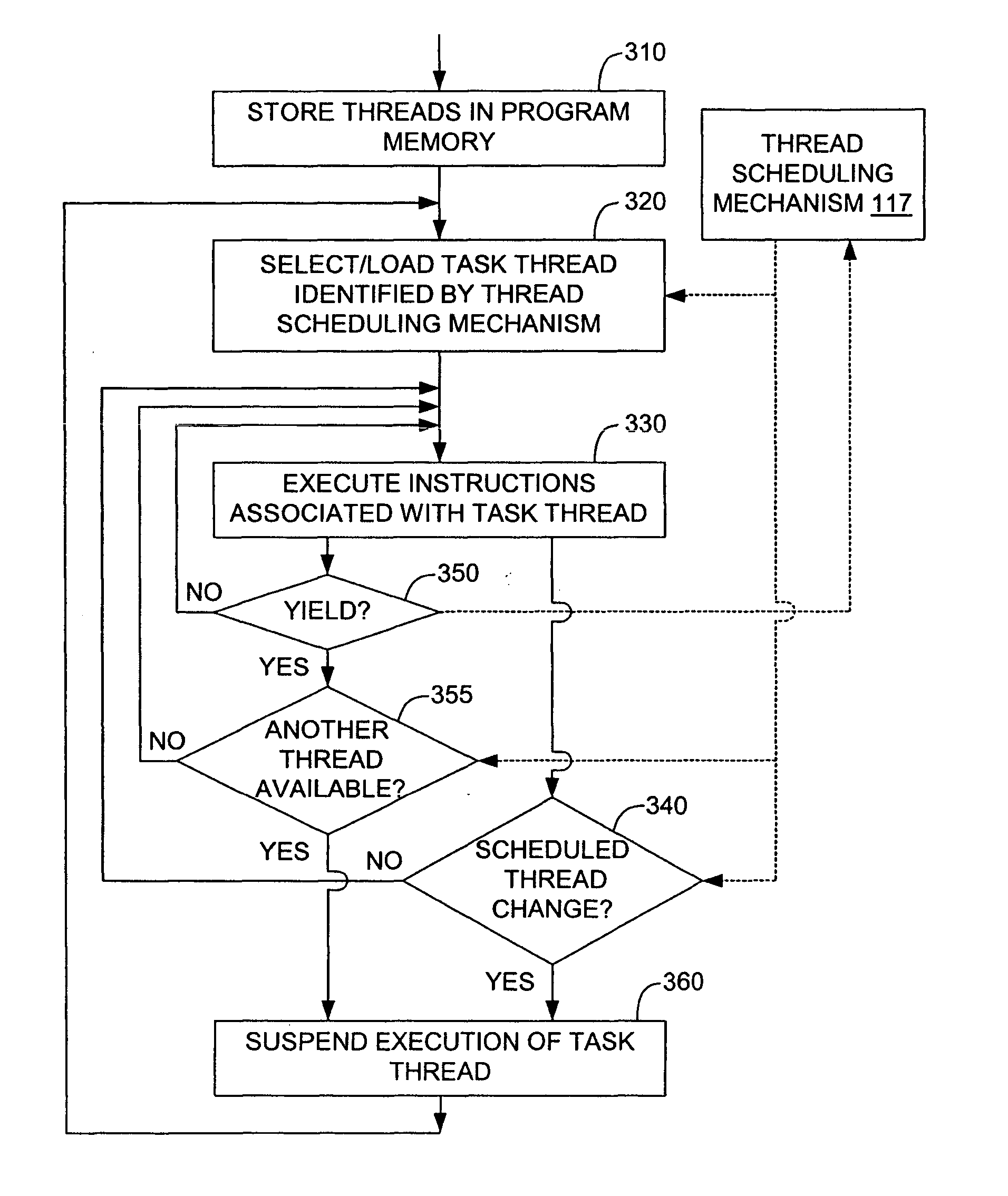
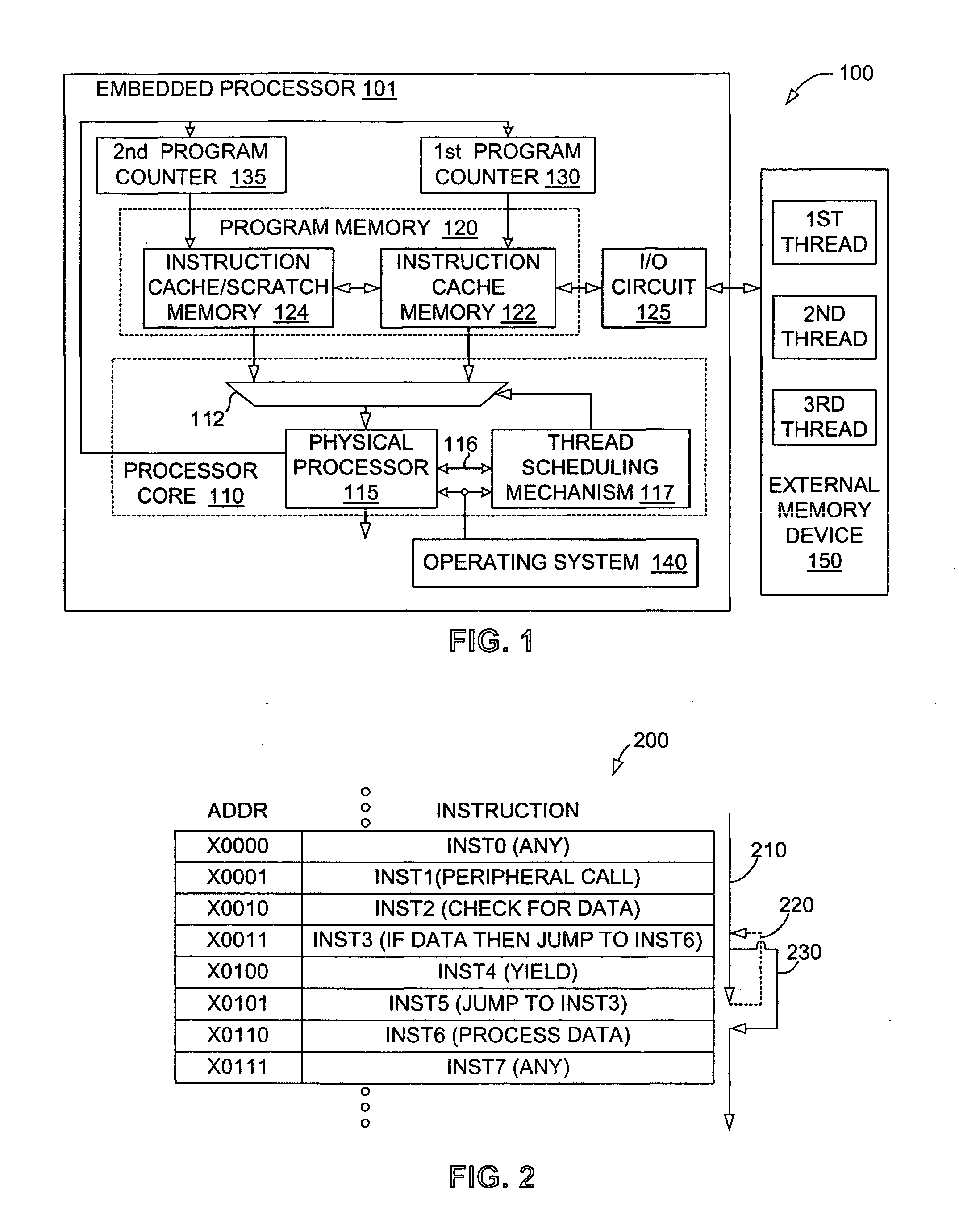
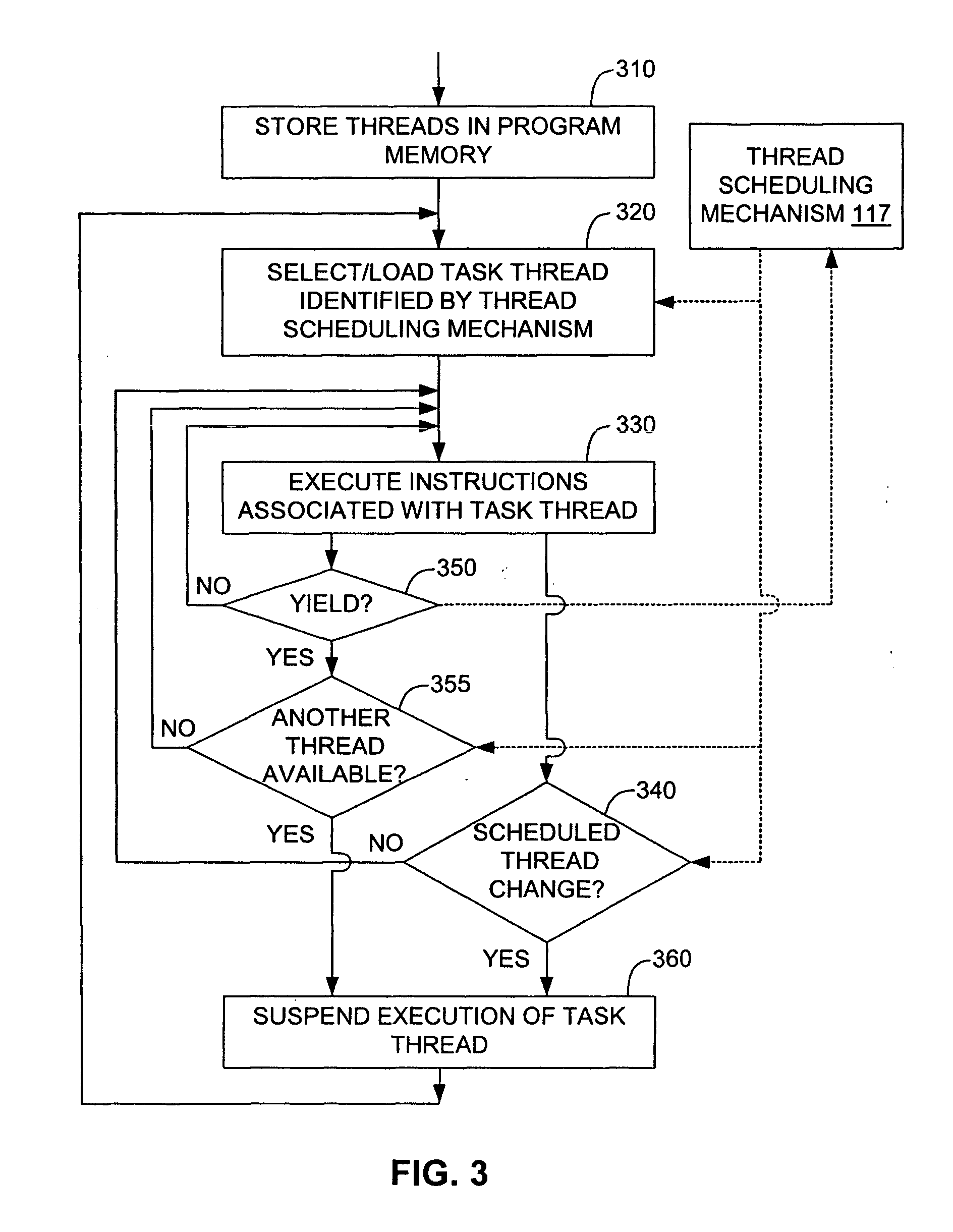
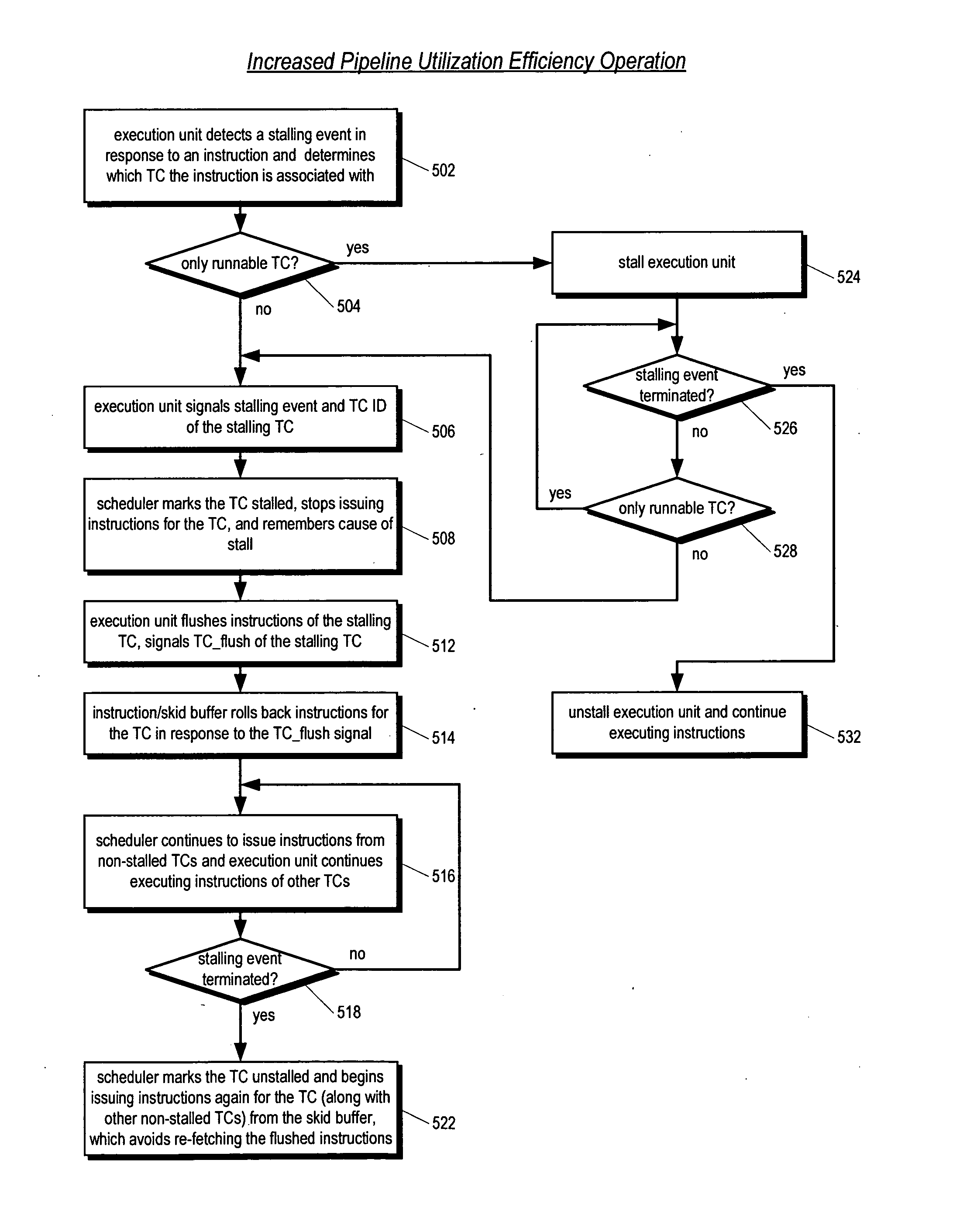
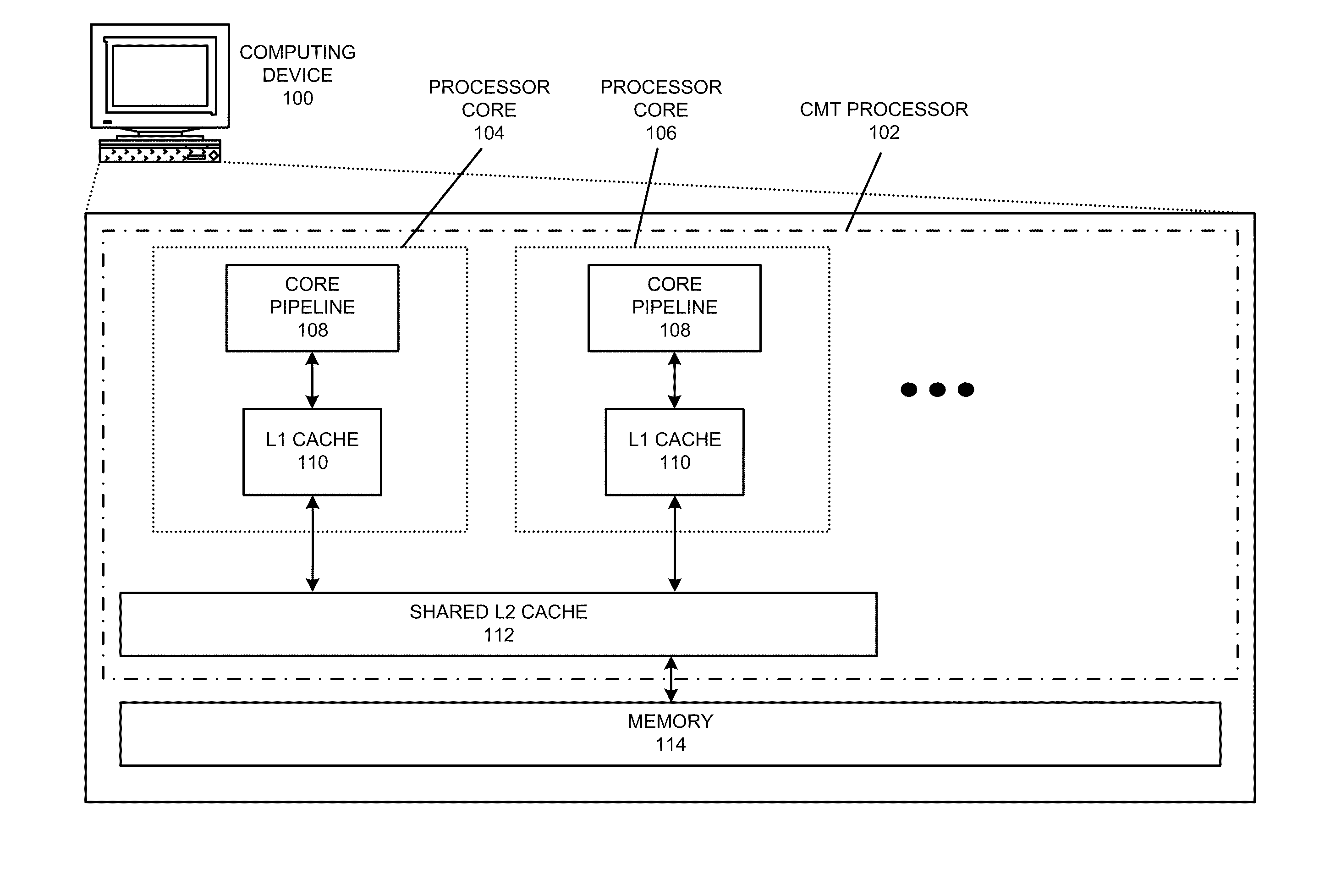
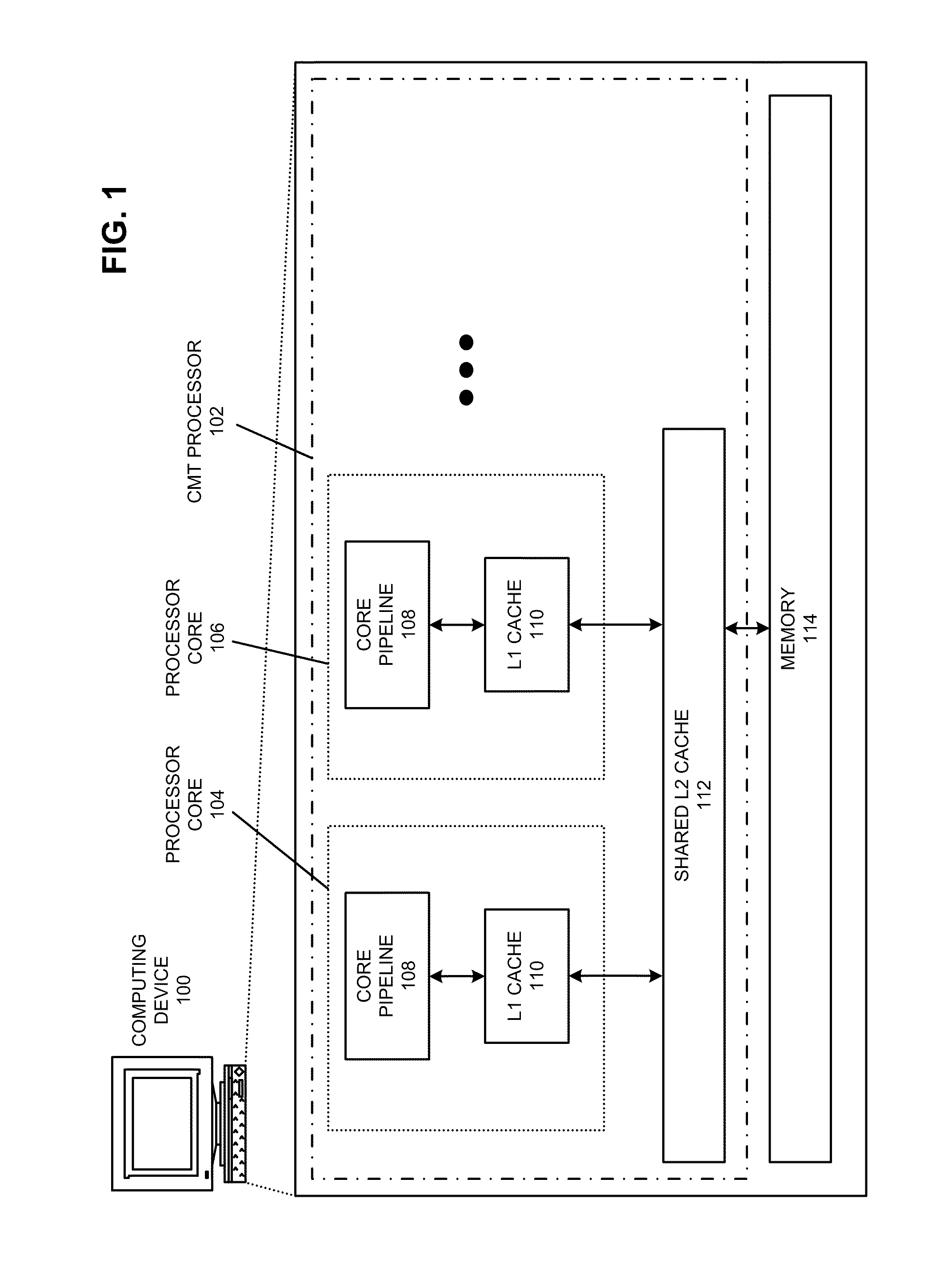
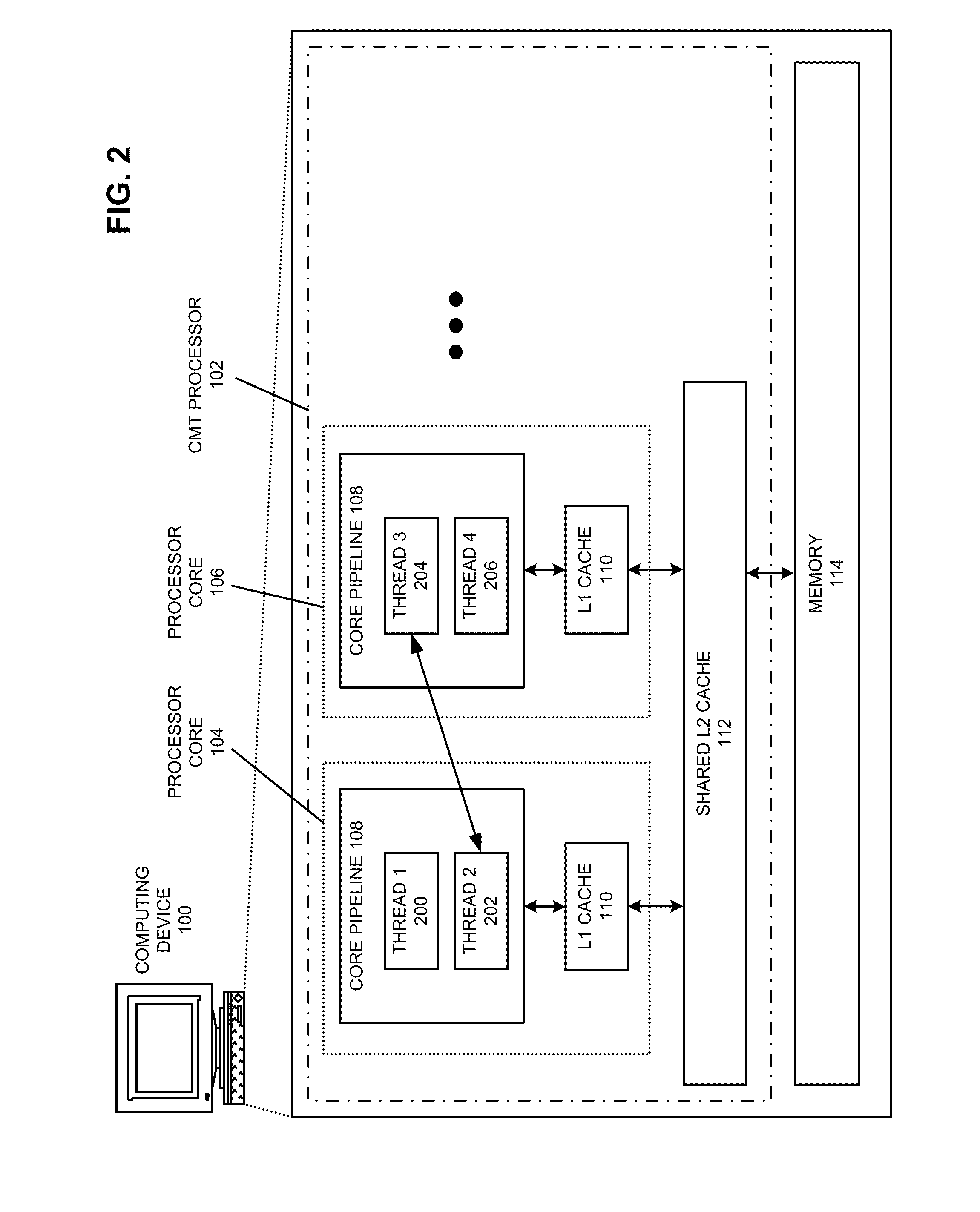
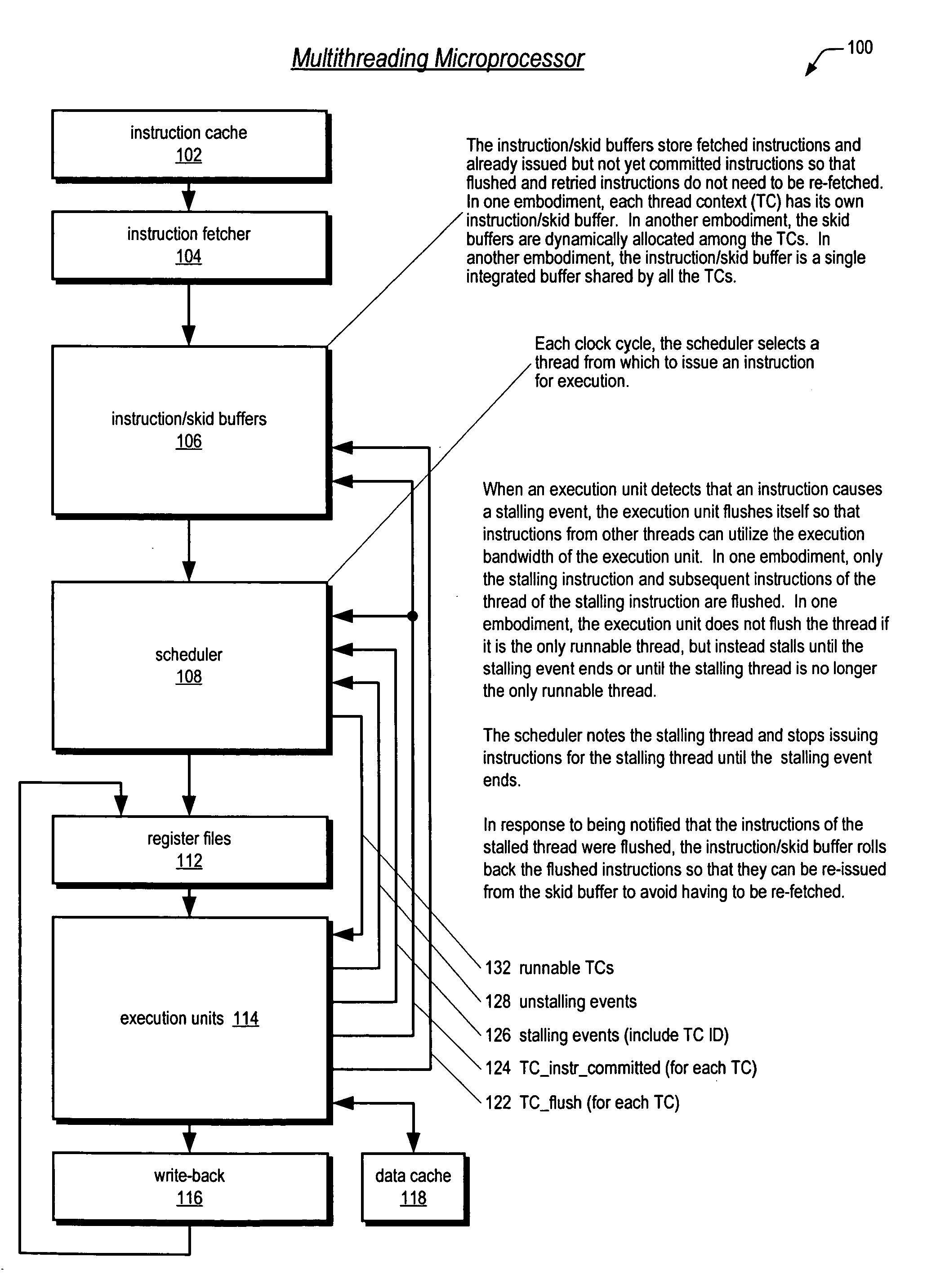
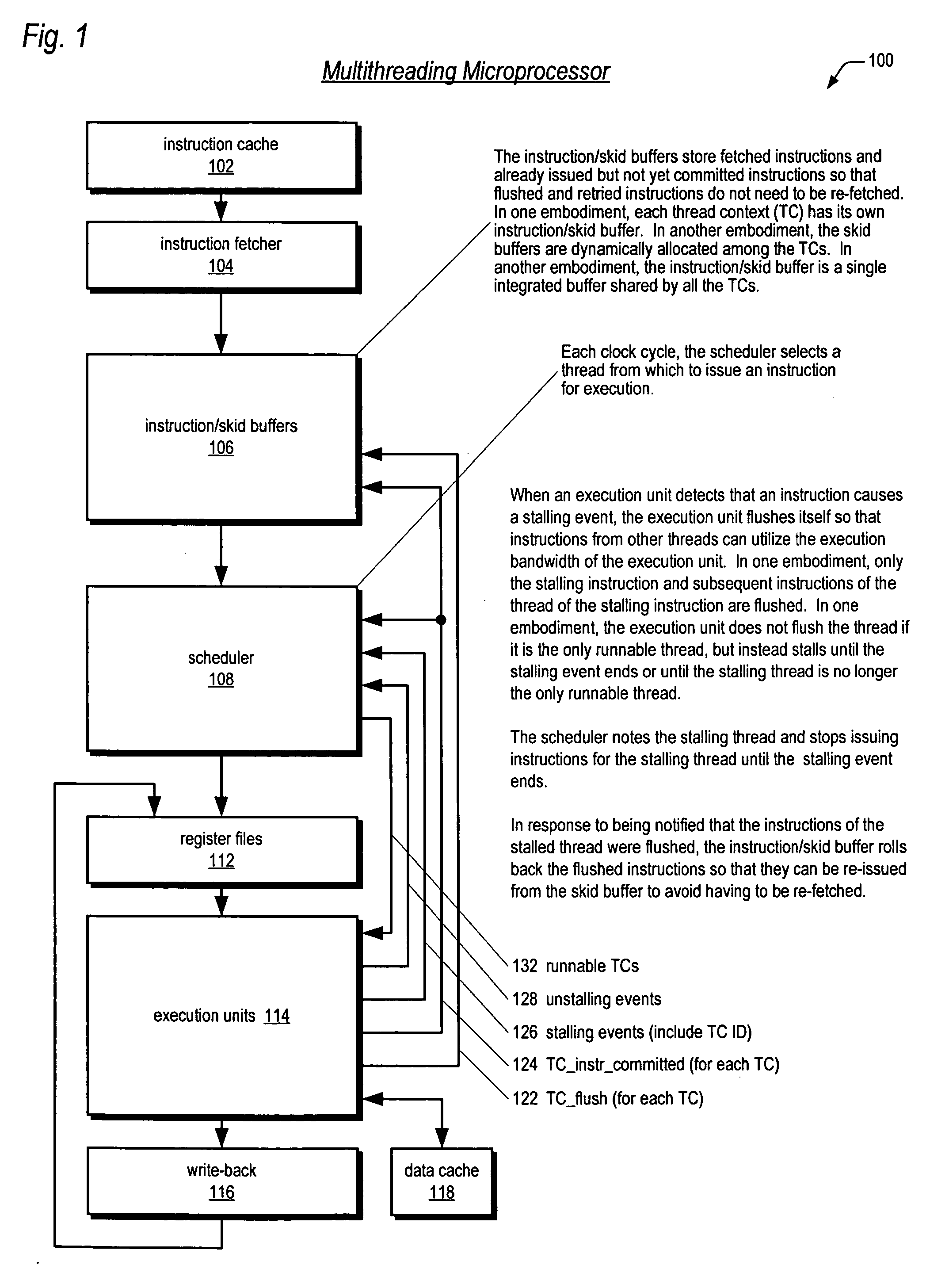
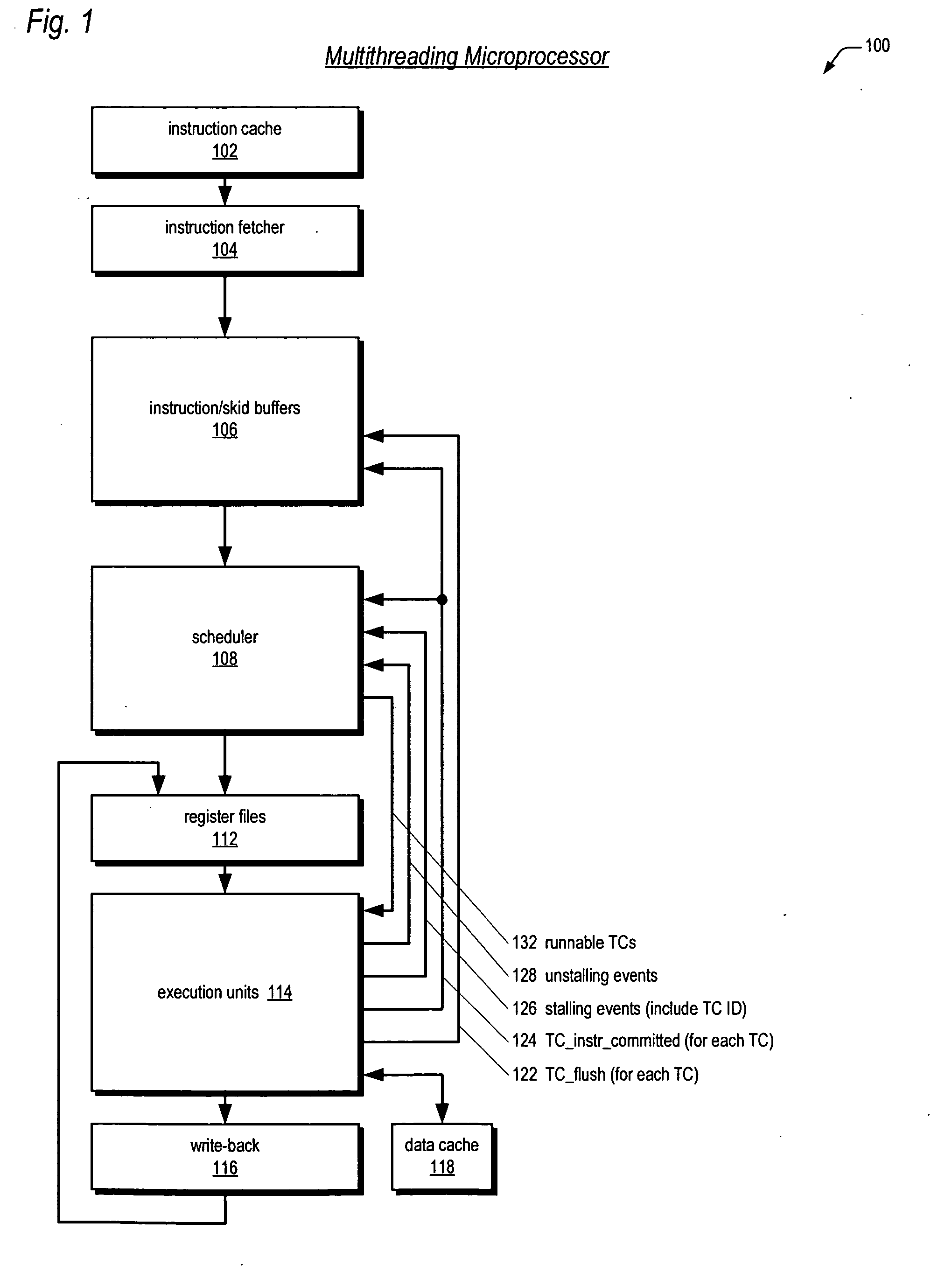
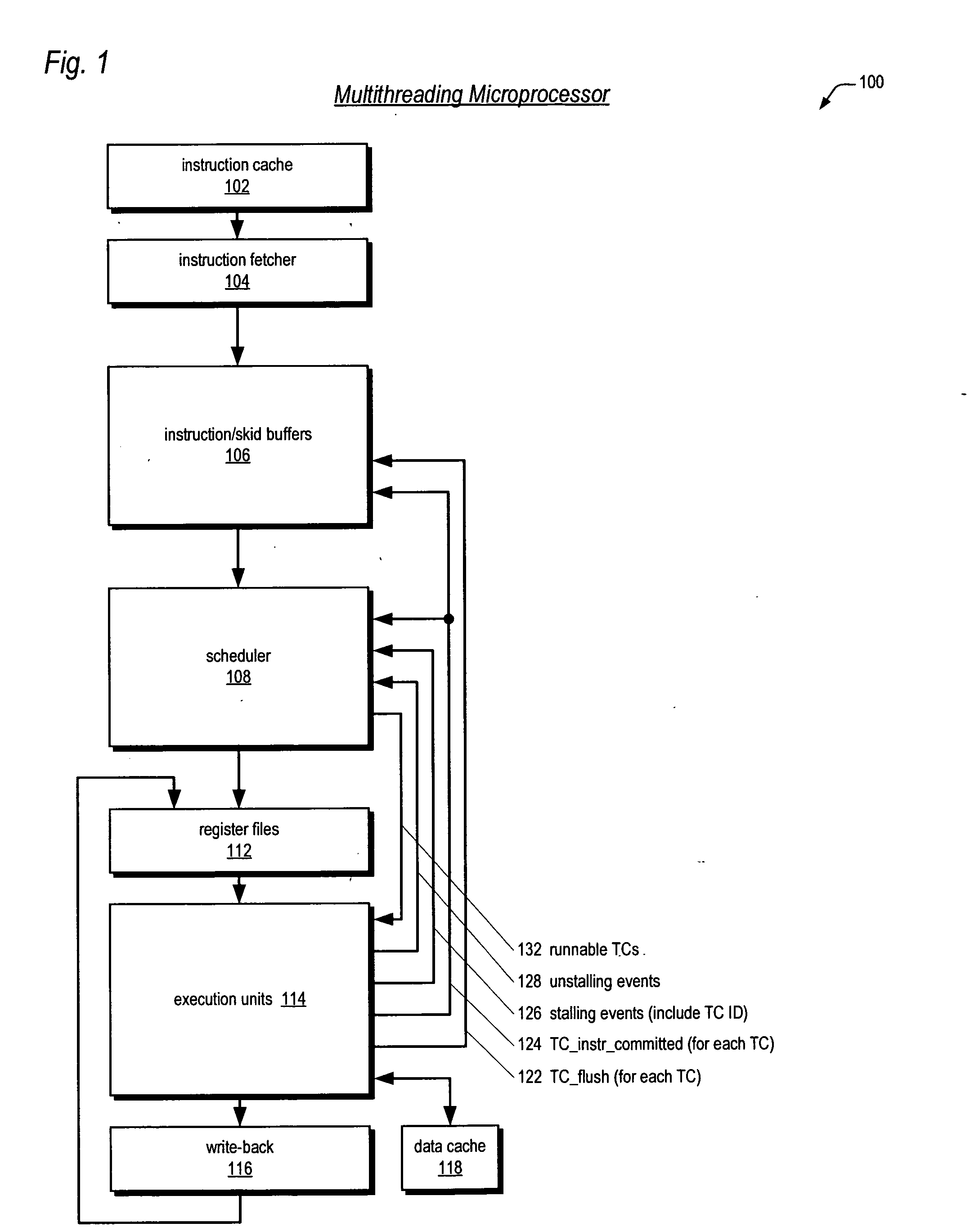
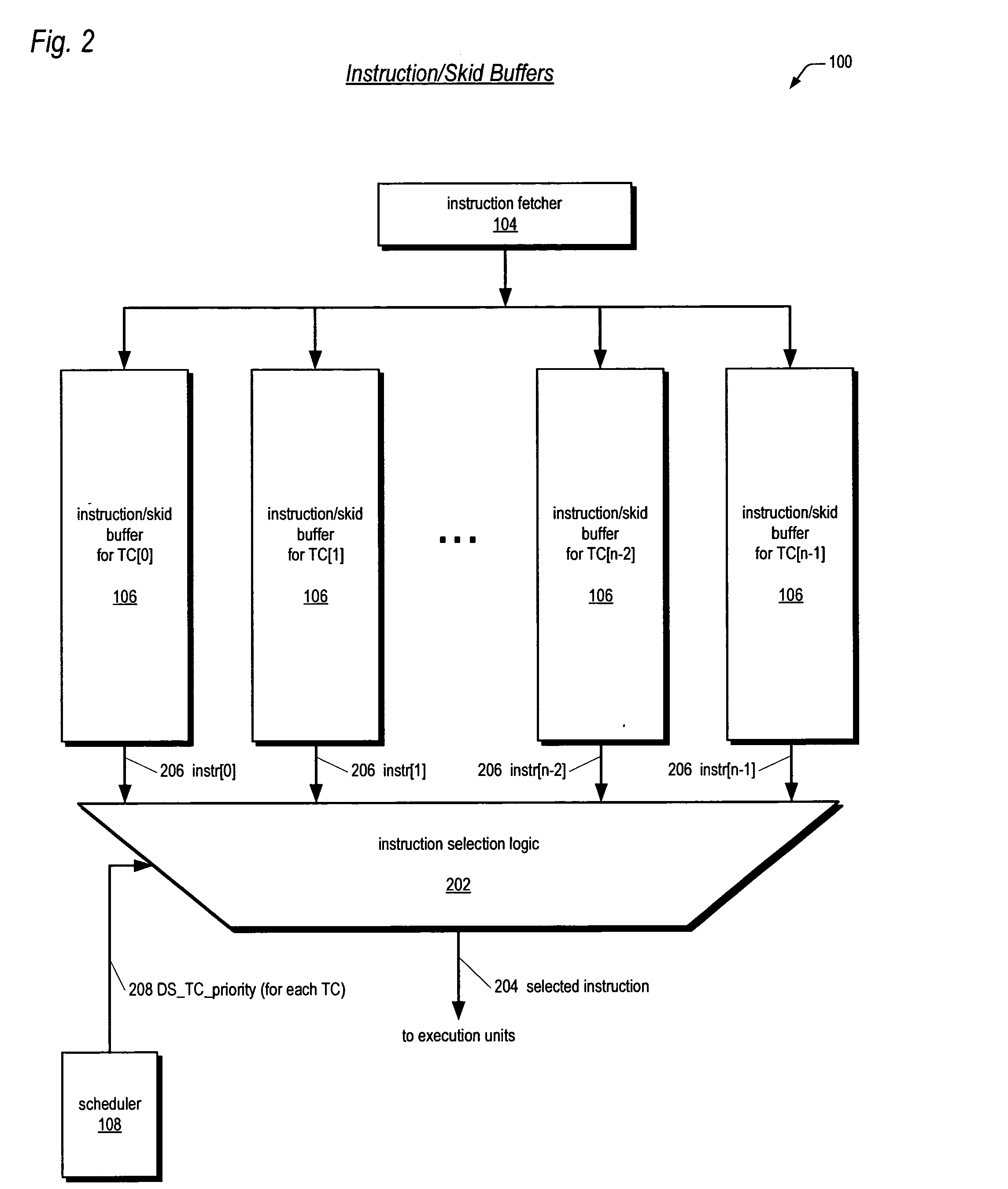
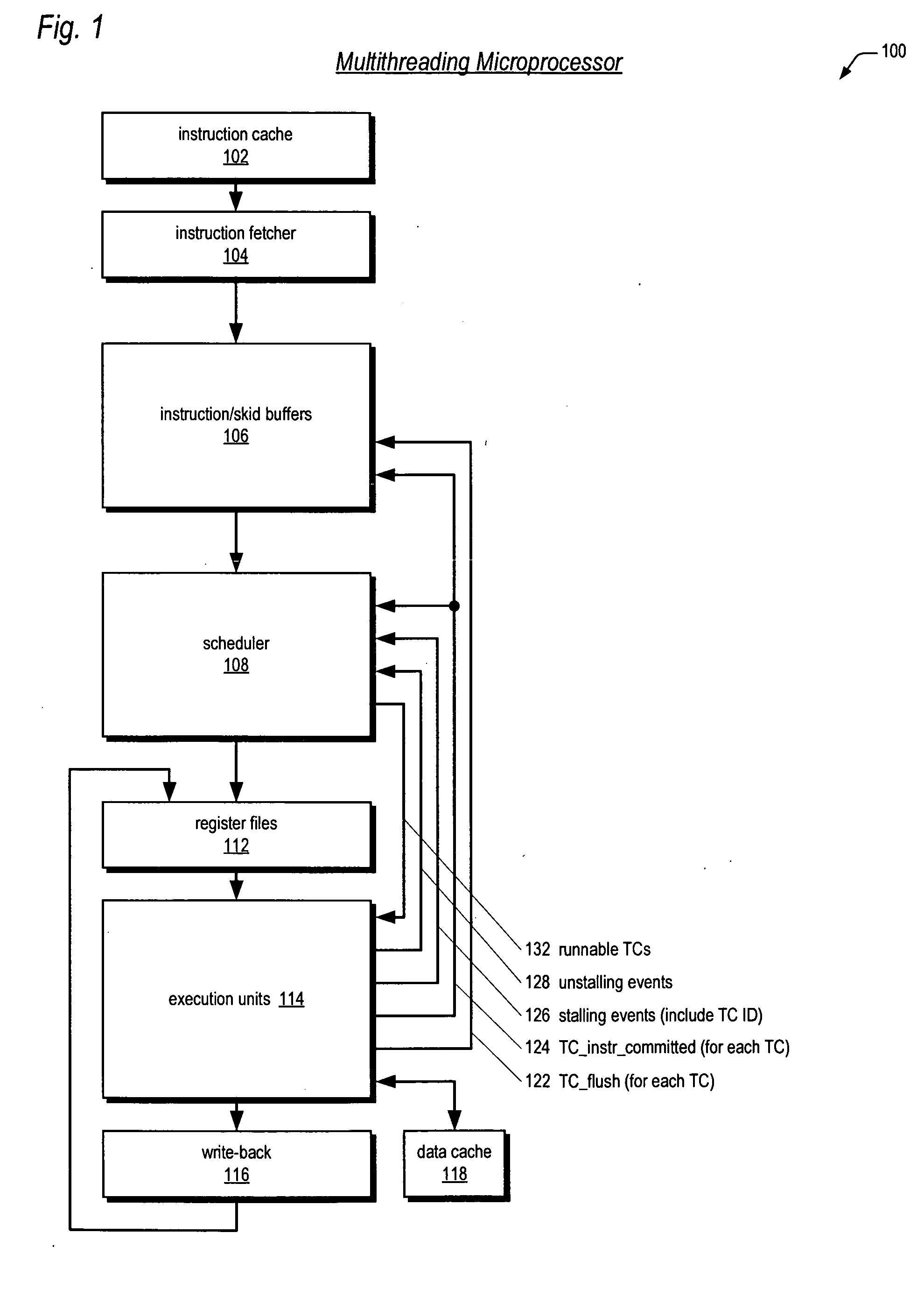
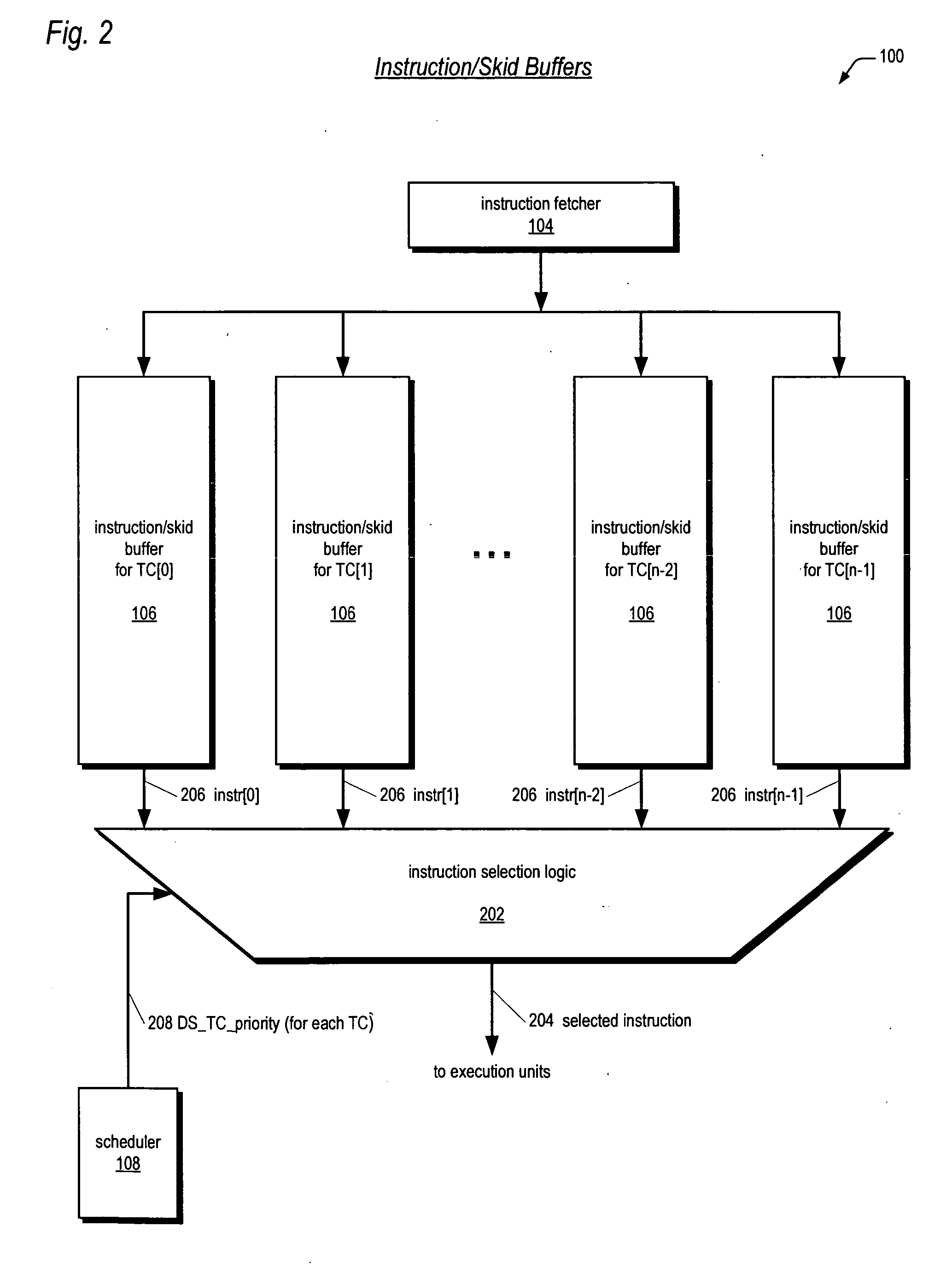
Multithreading microprocessor with optimized thread scheduler for increasing pipeline utilization efficiency
ActiveUS20060179284A1Easy to useAvoiding wasted clock cycleDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsThread schedulingParallel computing
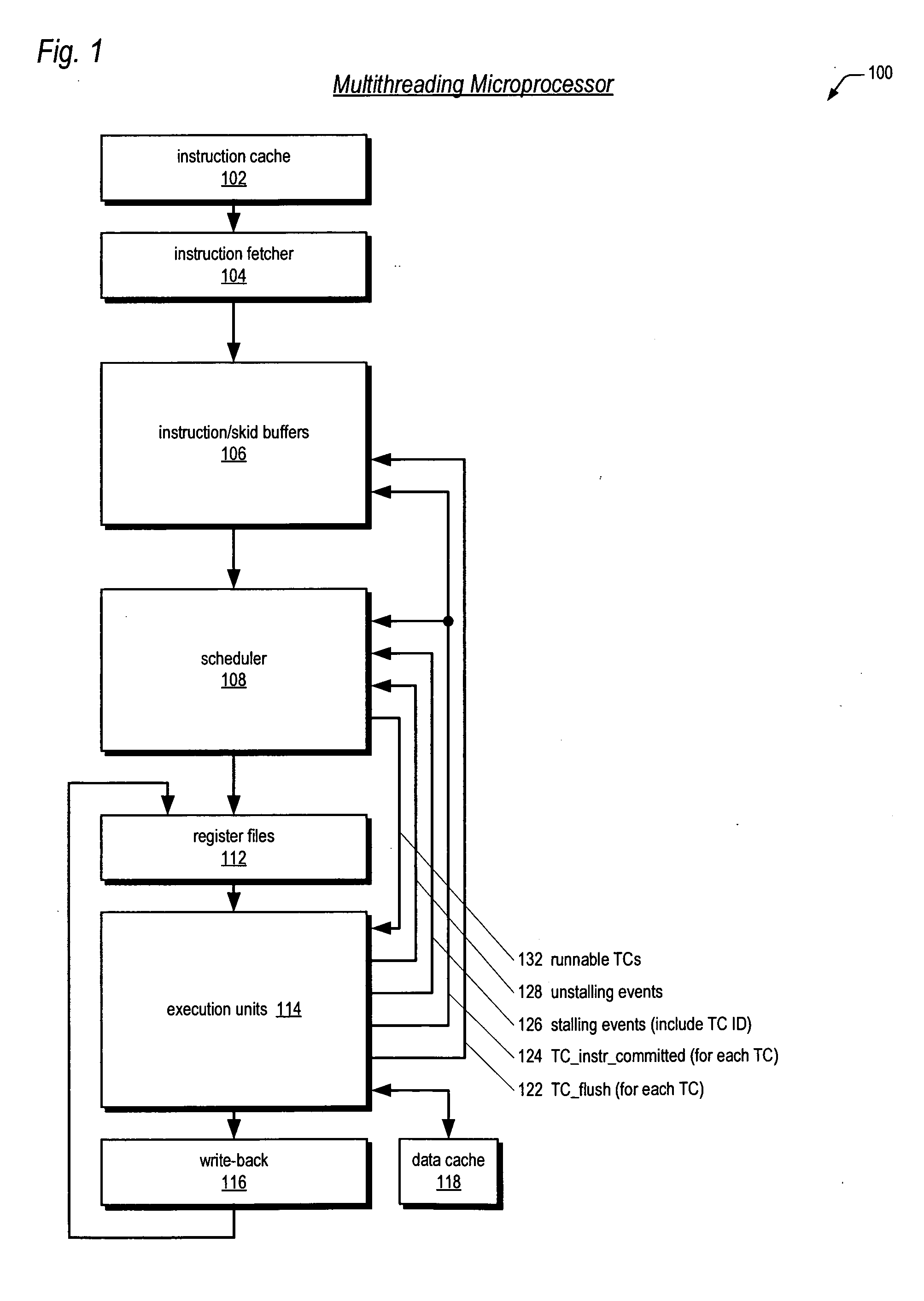
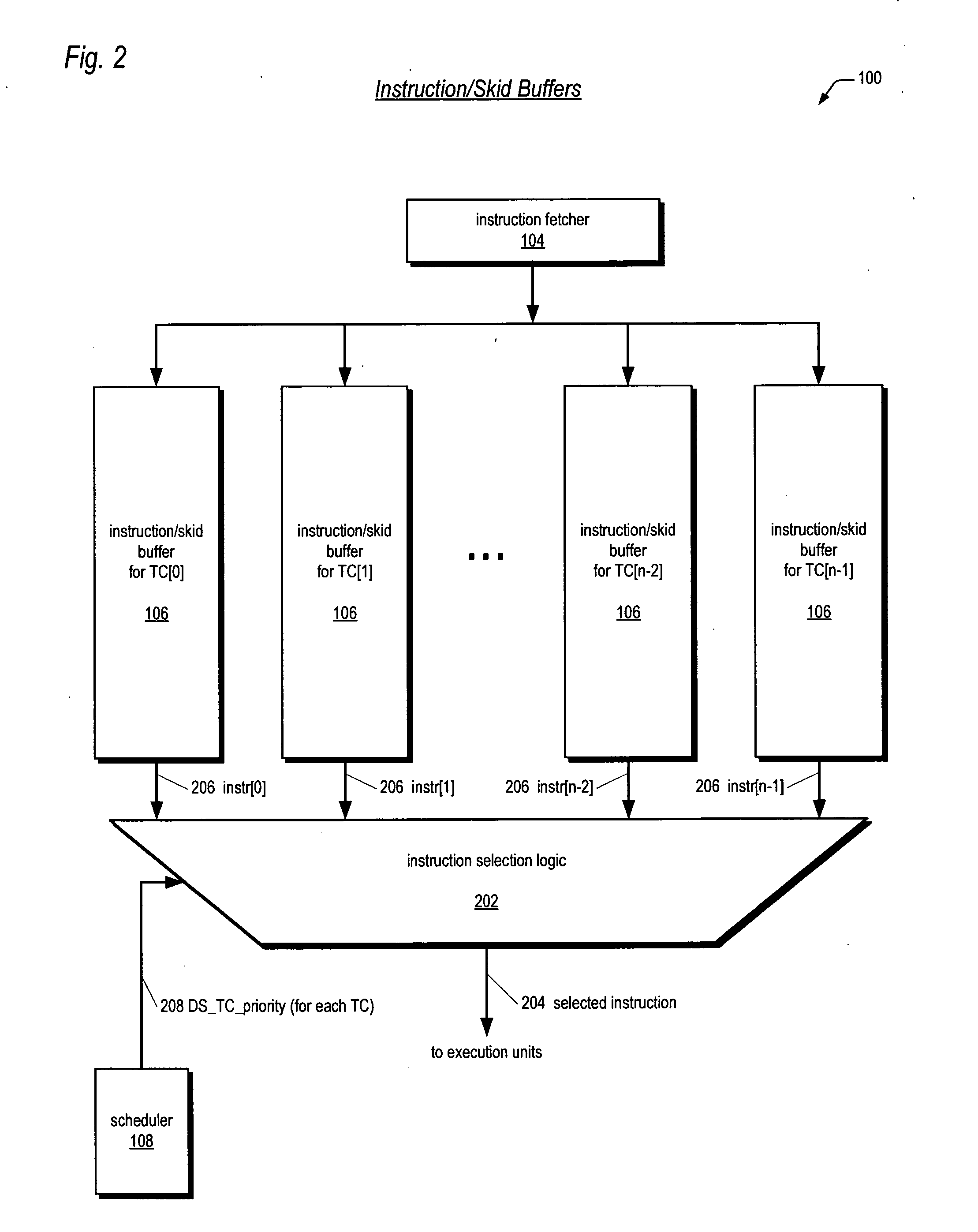
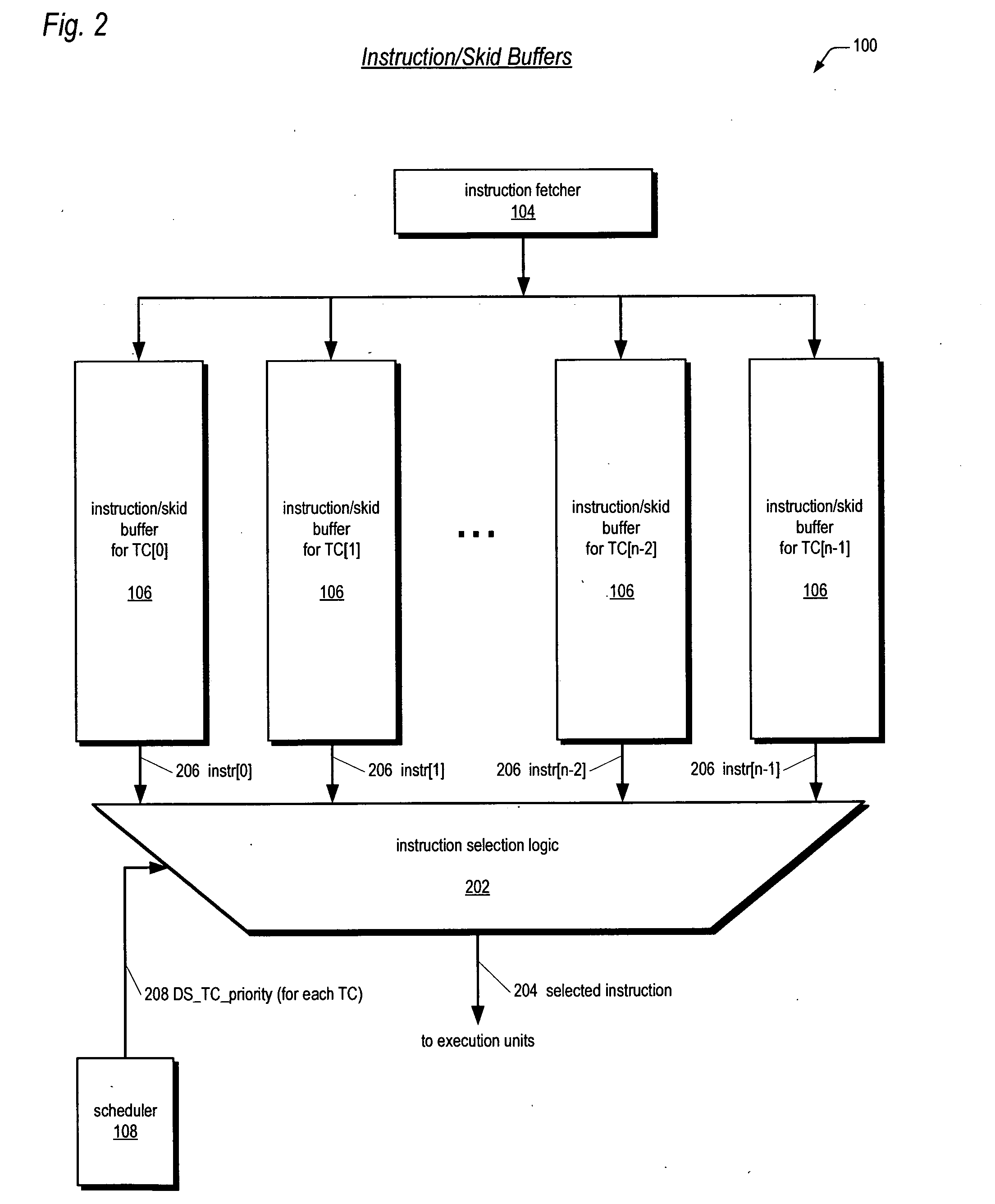
A multithreading processor for concurrently executing multiple threads is provided. The processor includes an execution pipeline and a thread scheduler that dispatches instructions of the threads to the execution pipeline. The execution pipeline detects a stalling event caused by a dispatched instruction, and flushes the execution pipeline to enable instructions of other threads to continue executing. The execution pipeline communicates to the scheduler which thread caused the stalling event, and the scheduler stops dispatching instructions for the thread until the stalling condition terminates. In one embodiment, the execution pipeline only flushes the thread including the instruction that caused the event. In one embodiment, the execution pipeline stalls rather than flushing if the thread is the only runnable thread. In one embodiment, the processor includes skid buffers to which the flushed instructions are rolled back so the instruction fetch pipeline need not be flushed, only the execution pipeline.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
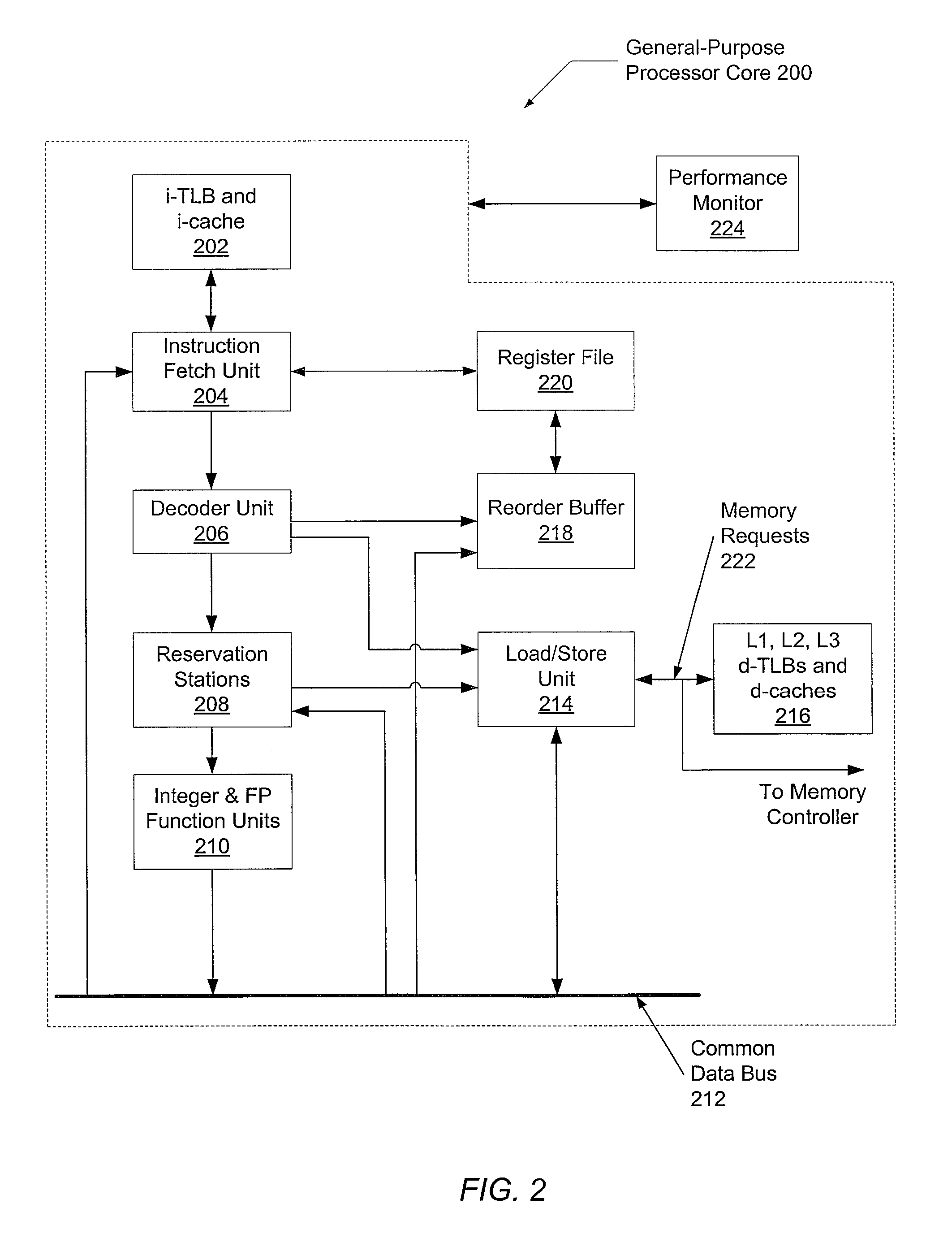
Accounting method and logic for determining per-thread processor resource utilization in a simultaneous multi-threaded (SMT) processor
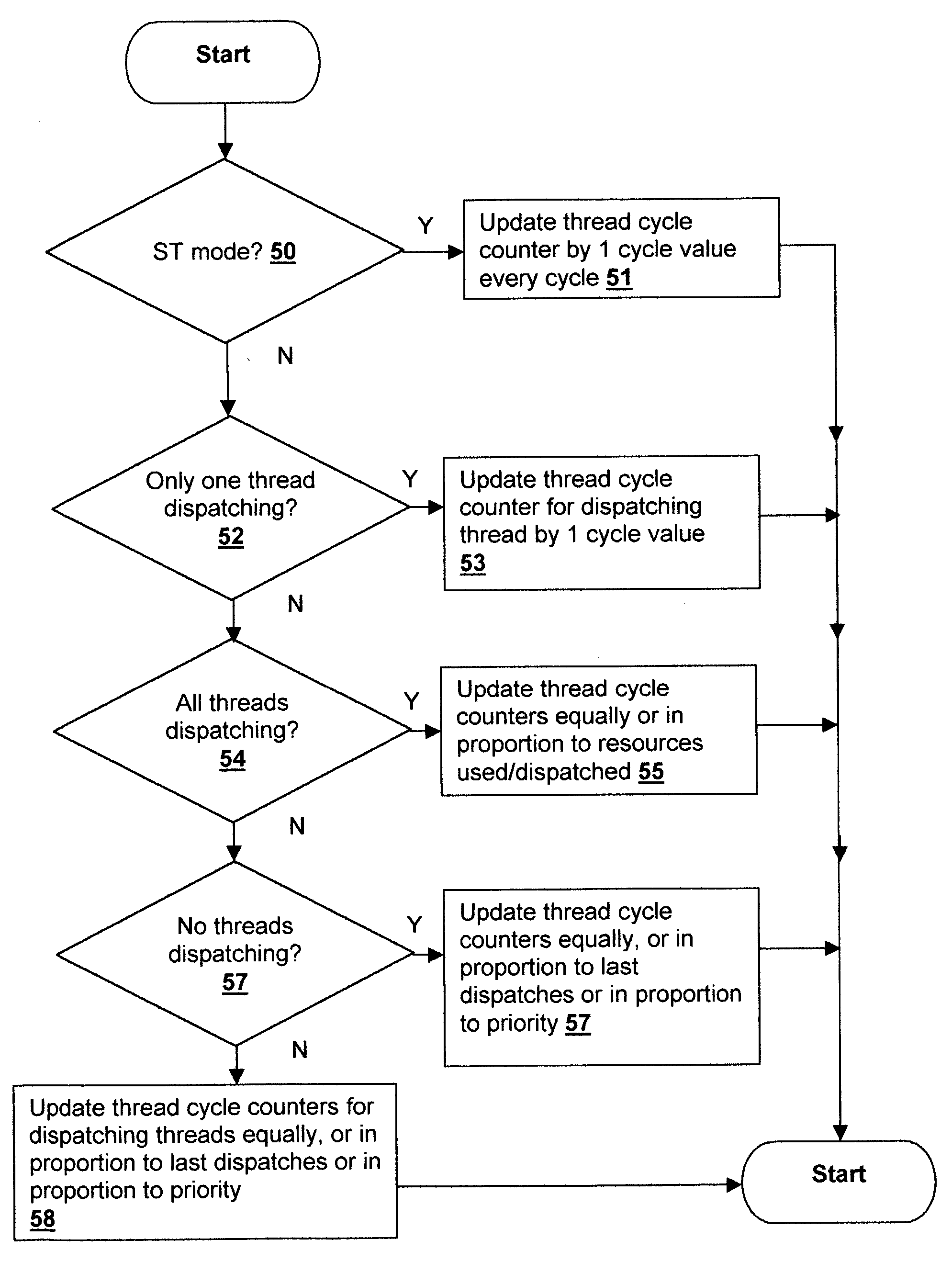
InactiveUS20040216113A1Resource allocationProgram control using stored programsResource utilizationScheduling instructions
An accounting method and logic for determining per-thread processor resource utilization in a simultaneous multi-threaded (SMT) processor provides a mechanism for accounting for processor resource usage by programs and threads within programs. Relative resource use is determined by detecting instruction dispatches for multiple threads active within the processor, which may include idle threads that are still occupying processor resources. If instructions are dispatched for all threads or no threads, the processor cycle is accounted equally to all threads. Alternatively if no threads are in a dispatch state, the accounting may be made using a prior state, or in conformity with ratios of the threads' priority levels. If only one thread is dispatching, that thread is accounted the entire processor cycle. If multiple threads are dispatching, but less than all threads are dispatching (in processors supporting more than two threads), the processor cycle is billed evenly across the dispatching threads. Multiple dispatches may be detected for the threads and a fractional resource usage determined for each thread and the counters may be updated in accordance with their fractional usage.
Owner:IBM CORP
Hardware multithreading systems with state registers having thread profiling data
According to some embodiments, a multithreaded microcontroller includes a thread control unit comprising thread control hardware (logic) configured to perform a number of multithreading system calls essentially in real time, e.g. in one or a few clock cycles. System calls can include mutex lock, wait condition, and signal instructions. The thread controller includes a number of thread state, mutex, and condition variable registers used for executing the multithreading system calls. Threads can transition between several states including free, run, ready and wait. The wait state includes interrupt, condition, mutex, I-cache, and memory substates. A thread state transition controller controls thread states, while a thread instructions execution unit executes multithreading system calls and manages thread priorities to avoid priority inversion. A thread scheduler schedules threads according to their priorities. A hardware thread profiler including global, run and wait profiler registers is used to monitor thread performance to facilitate software development.
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Cache-aware thread scheduling in multi-threaded systems
ActiveUS20110246995A1Facilitates predictively schedulingImprove performanceEnergy efficient ICTGeneral purpose stored program computerThread schedulingParallel computing
The disclosed embodiments provide a system that facilitates scheduling threads in a multi-threaded processor with multiple processor cores. During operation, the system executes a first thread in a processor core that is associated with a shared cache. During this execution, the system measures one or more metrics to characterize the first thread. Then, the system uses the characterization of the first thread and a characterization for a second, second thread to predict a performance impact that would occur if the second thread were to simultaneously execute in a second processor core that is also associated with the cache. If the predicted performance impact indicates that executing the second thread on the second processor core will improve performance for the multi-threaded processor, the system executes the second thread on the second processor core.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Apparatus and method for automatic low power mode invocation in a multi-threaded processor
A processor comprises a processor core executing multiple threads. A bifurcated thread scheduler includes an internal processor core component and an external processor core component. The bifurcated thread scheduler identifies when all of the multiple threads are blocked and thereafter automatically enters a default low power sleep mode.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
Multithreading processor including thread scheduler based on instruction stall likelihood prediction
ActiveUS20060179280A1Increase processor efficiencyReduce in quantityDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsLoad instructionScheduling instructions
An apparatus for scheduling dispatch of instructions among a plurality of threads being concurrently executed in a multithreading processor is provided. The apparatus includes an instruction decoder that generate register usage information for an instruction from each of the threads, a priority generator that generates a priority for each instruction based on the register usage information and state information of instructions currently executing in an execution pipeline, and selection logic that dispatches at least one instruction from at least one thread based on the priority of the instructions. The priority indicates the likelihood the instruction will execute in the execution pipeline without stalling. For example, an instruction may have a high priority if it has little or no register dependencies or its data is known to be available; or may have a low priority if it has strong register dependencies or is an uncacheable or synchronized storage space load instruction.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
Vector crossing multithread processing method and vector crossing multithread microprocessor
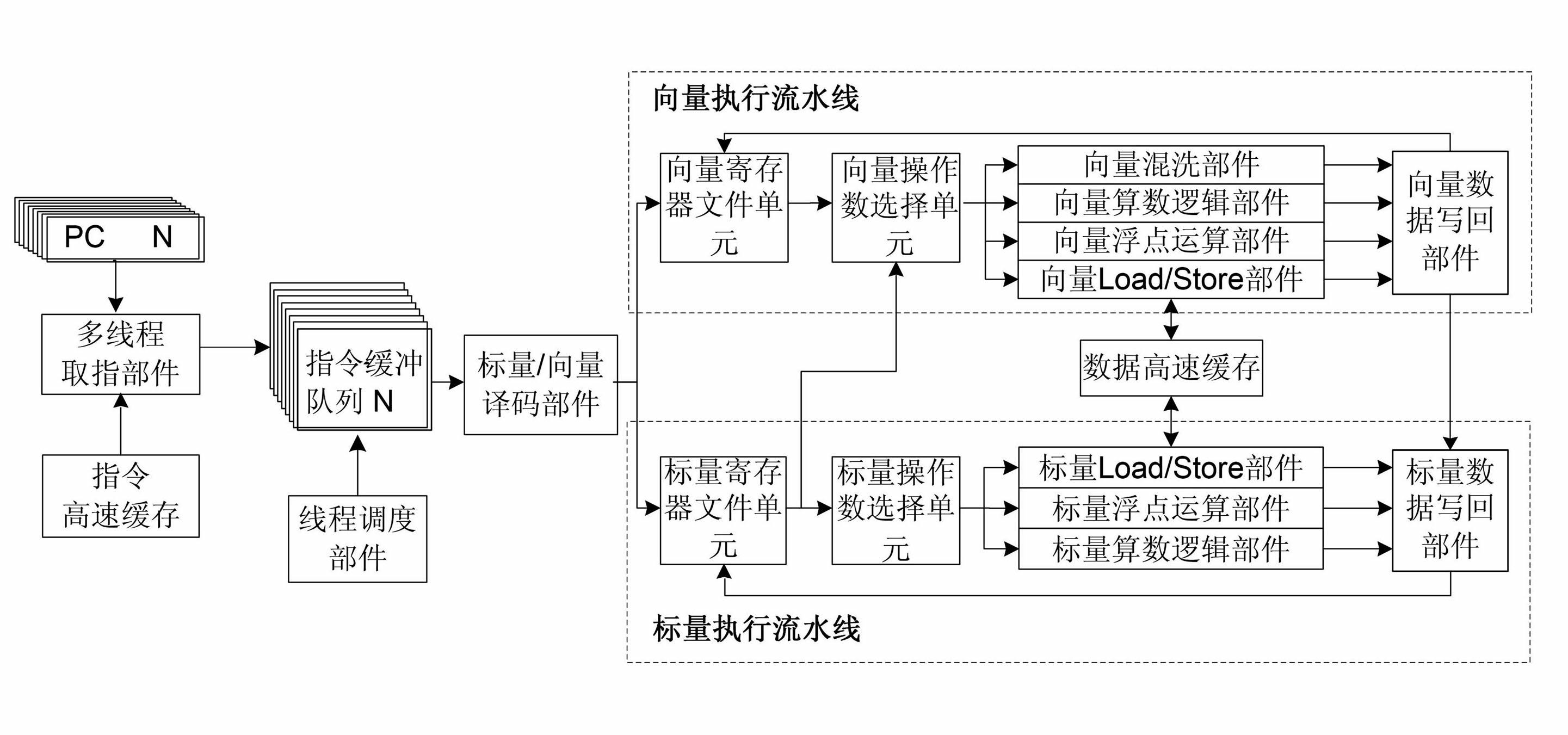
InactiveCN102156637AImprove peak performanceGive full play to computing powerMultiprogramming arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionHardware structureThread scheduling
The invention discloses a vector crossing multithread processing method and a vector crossing multithread microprocessor. The processing method comprises the following steps: using a multithread instruction-acquiring part to choose a vector thread from N vector threads for reading an instruction and storing the read instruction to a corresponding instruction buffer array of the vector thread; using a thread scheduling part to choose an instruction buffer array from N instruction buffer arrays and taking out an instruction from the instruction buffer array for the purpose of decoding; and sending a decoded instruction to a vector executing streamline or scalar executing streamline so as to execute. The method can be realized by using hardware structure by the vector crossing multithread microprocessor. The method and the microprocessor provided by the invention have the advantages that the vector processing technique and multithread technique are combined, the hardware structure is simple, the operation capability is strong, the compatibility and expansibility are excellent, and the like.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Mechanism for Scheduling Execution of Threads for Fair Resource Allocation in a Multi-Threaded and/or Multi-Core Processing System
InactiveUS20100205602A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital computer detailsThread schedulingShared resource
A thread scheduling mechanism is provided that flexibly enforces performance isolation of multiple threads to alleviate the effect of anti-cooperative execution behavior with respect to a shared resource, for example, hoarding a cache or pipeline, using the hardware capabilities of simultaneous multi-threaded (SMT) or multi-core processors. Given a plurality of threads running on at least two processors in at least one functional processor group, the occurrence of a rescheduling condition indicating anti-cooperative execution behavior is sensed, and, if present, at least one of the threads is rescheduled such that the first and second threads no longer execute in the same functional processor group at the same time.
Owner:VMWARE INC
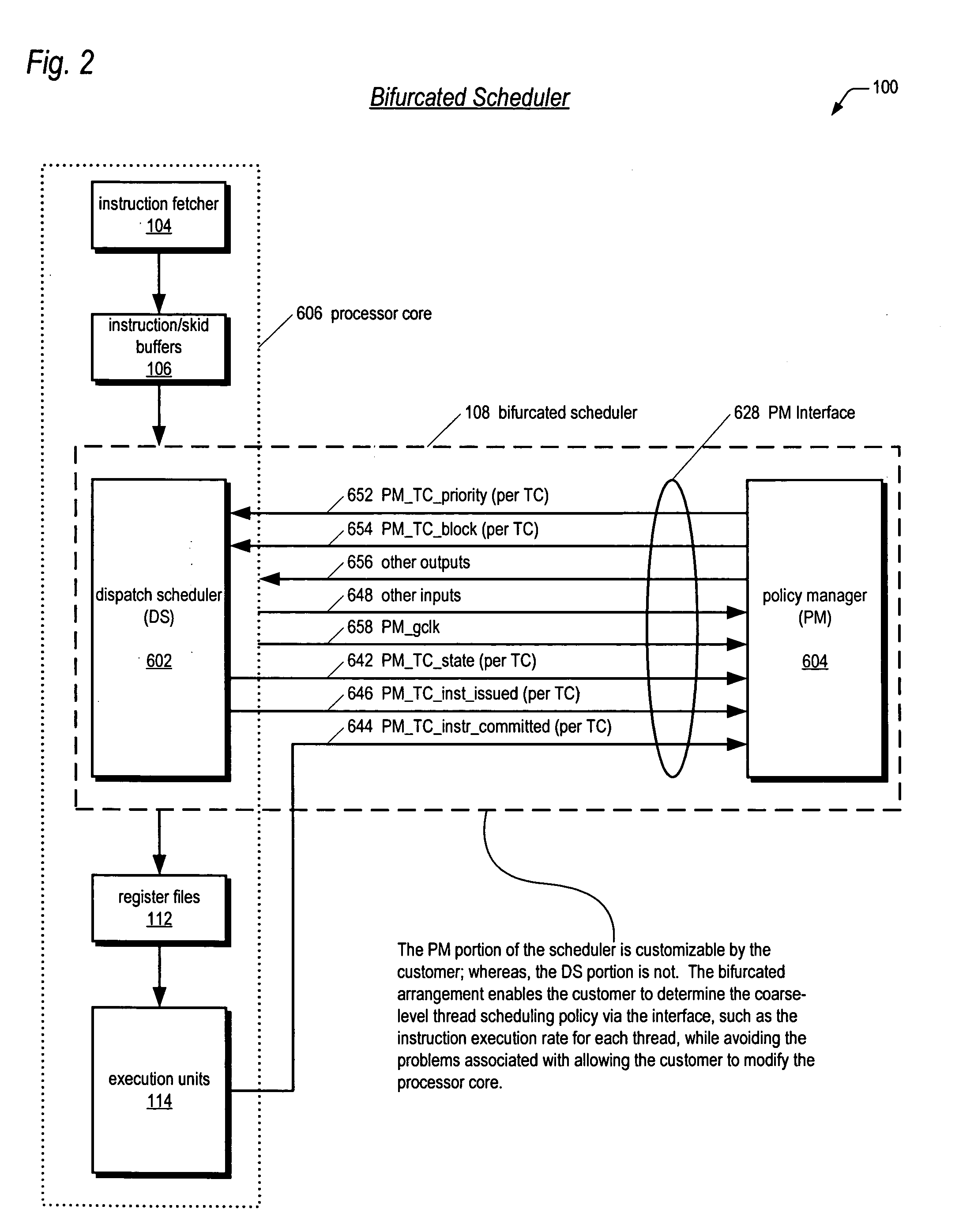
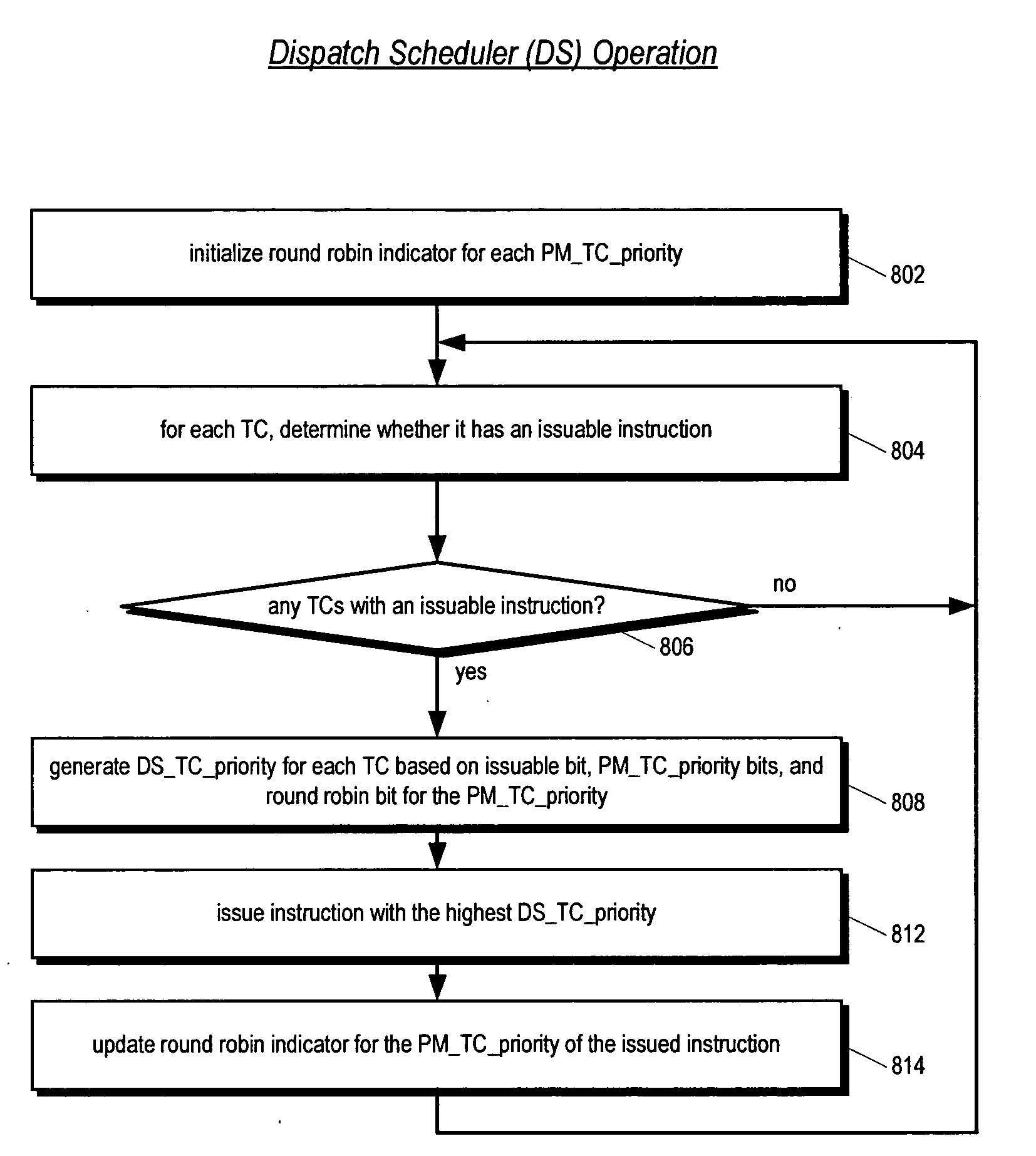
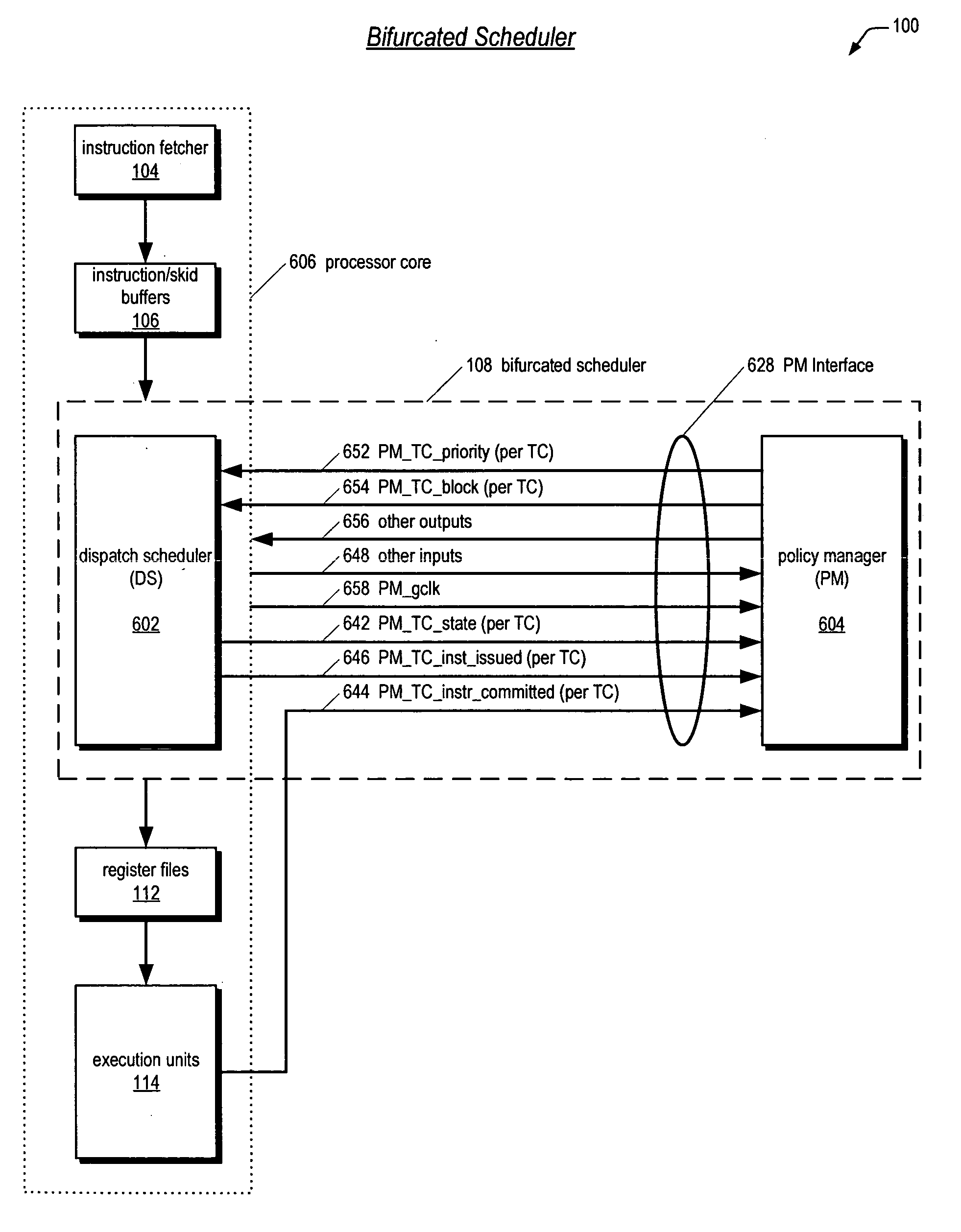
Bifurcated thread scheduler in a multithreading microprocessor
ActiveUS20060179279A1Accurate operationSafely modified by the customerProgram control using stored programsDigital computer detailsThread schedulingExecution unit
A bifurcated instruction scheduler for dispatching instructions of multiple threads concurrently executing in a multithreading processor is provided. The scheduler includes a first portion within a reusable core that is not customizable by a customer, a second portion outside the core that is customizable, and an interface coupling the second portion to the core. The second portion implements a thread scheduling policy that may be customized to the customer's particular application. The first portion may be scheduling policy-agnostic and issues instructions of the threads each clock cycle to execution units based on the scheduling policy communicated by the second portion. The second portion communicates the scheduling policy via a priority for each of the threads. When the core commits an instruction for execution, the core communicates to the second portion which thread the committed instruction is in to enable the second portion to update the priorities in response thereto.
Owner:MIPS TECH INC
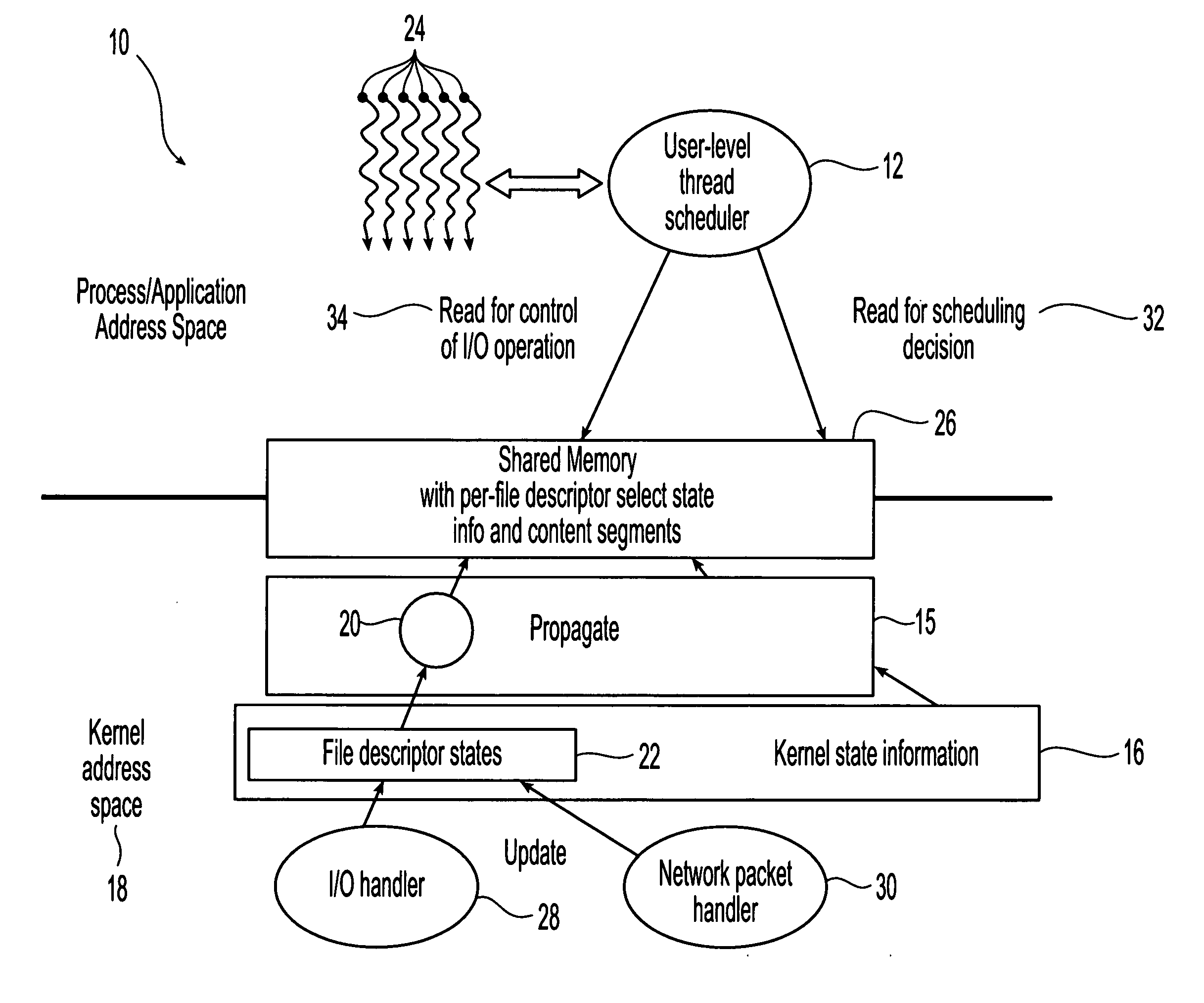
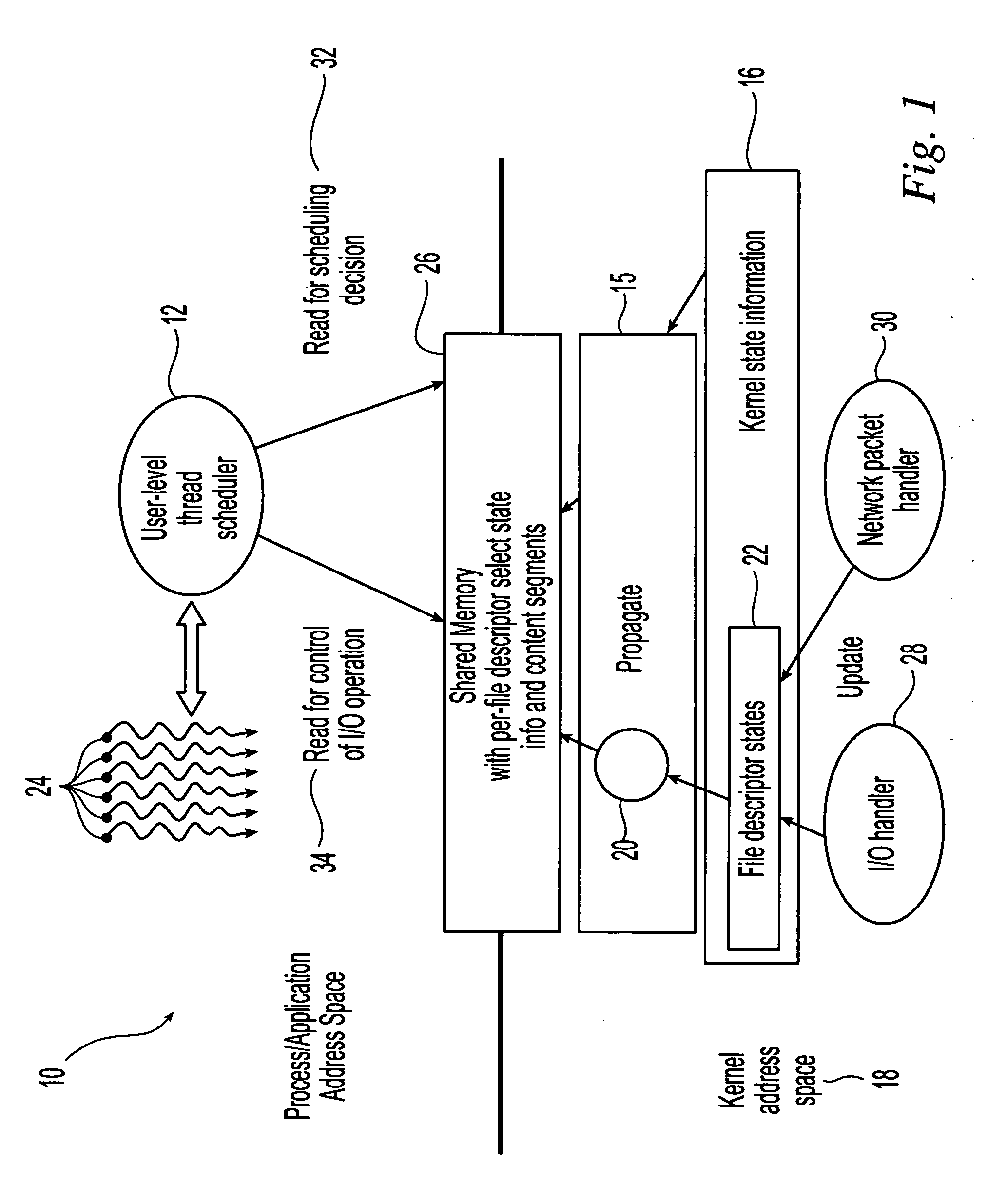
Method and system for scheduling user-level I/O threads
InactiveUS20060075404A1Efficiently determineReduce in quantityMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsThread schedulingKernel level
The present invention is directed to a user-level thread scheduler that employs a service that propagates at the user level, continuously as it gets updated in the kernel, the kernel-level state necessary to determine if an I / O operation would block or not. In addition, the user-level thread schedulers used systems that propagate at the user level other types of information related to the state and content of active file descriptors. Using this information, the user-level thread package determines when I / O requests can be satisfied without blocking and implements pre-defined scheduling policies.
Owner:IBM CORP
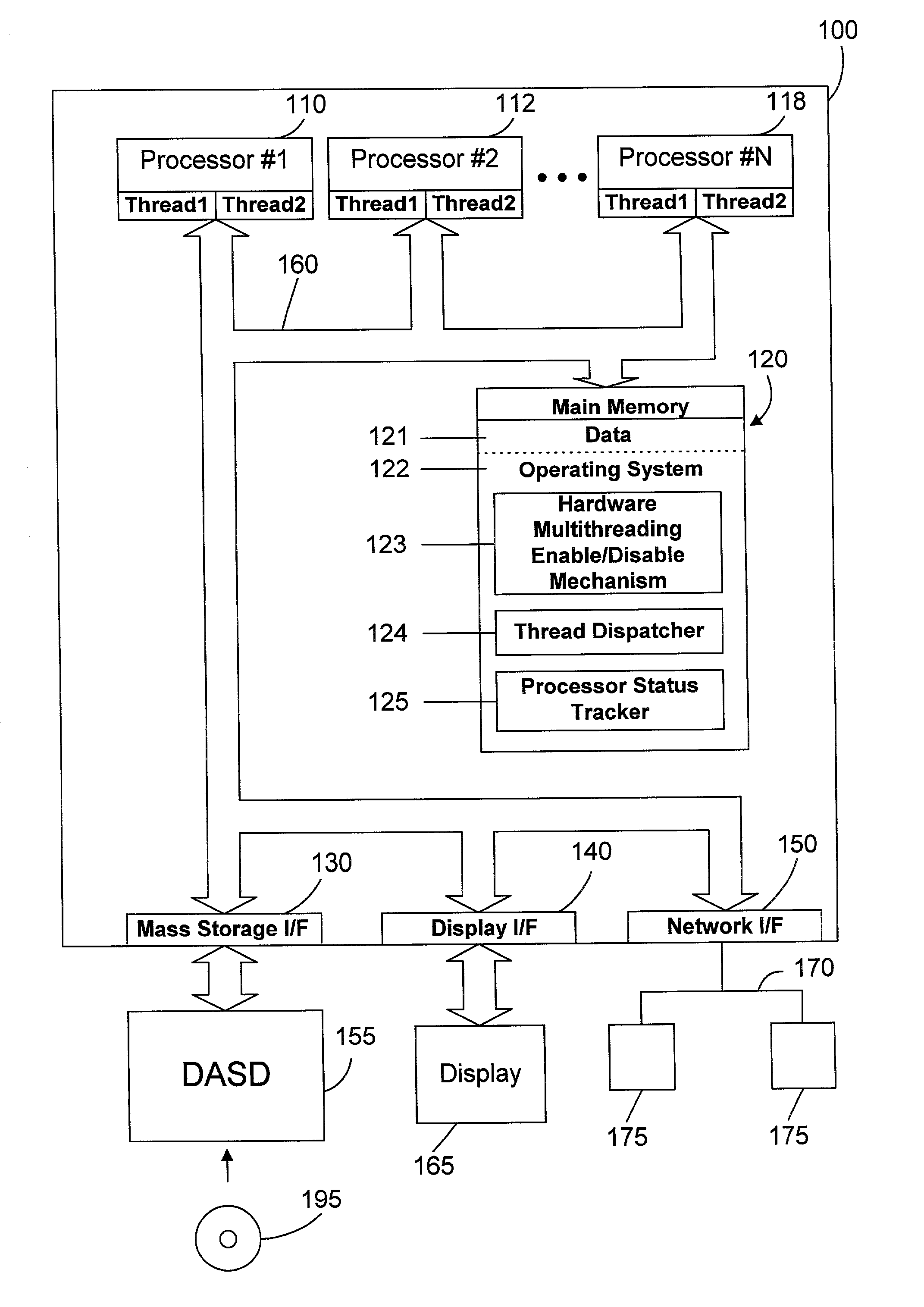
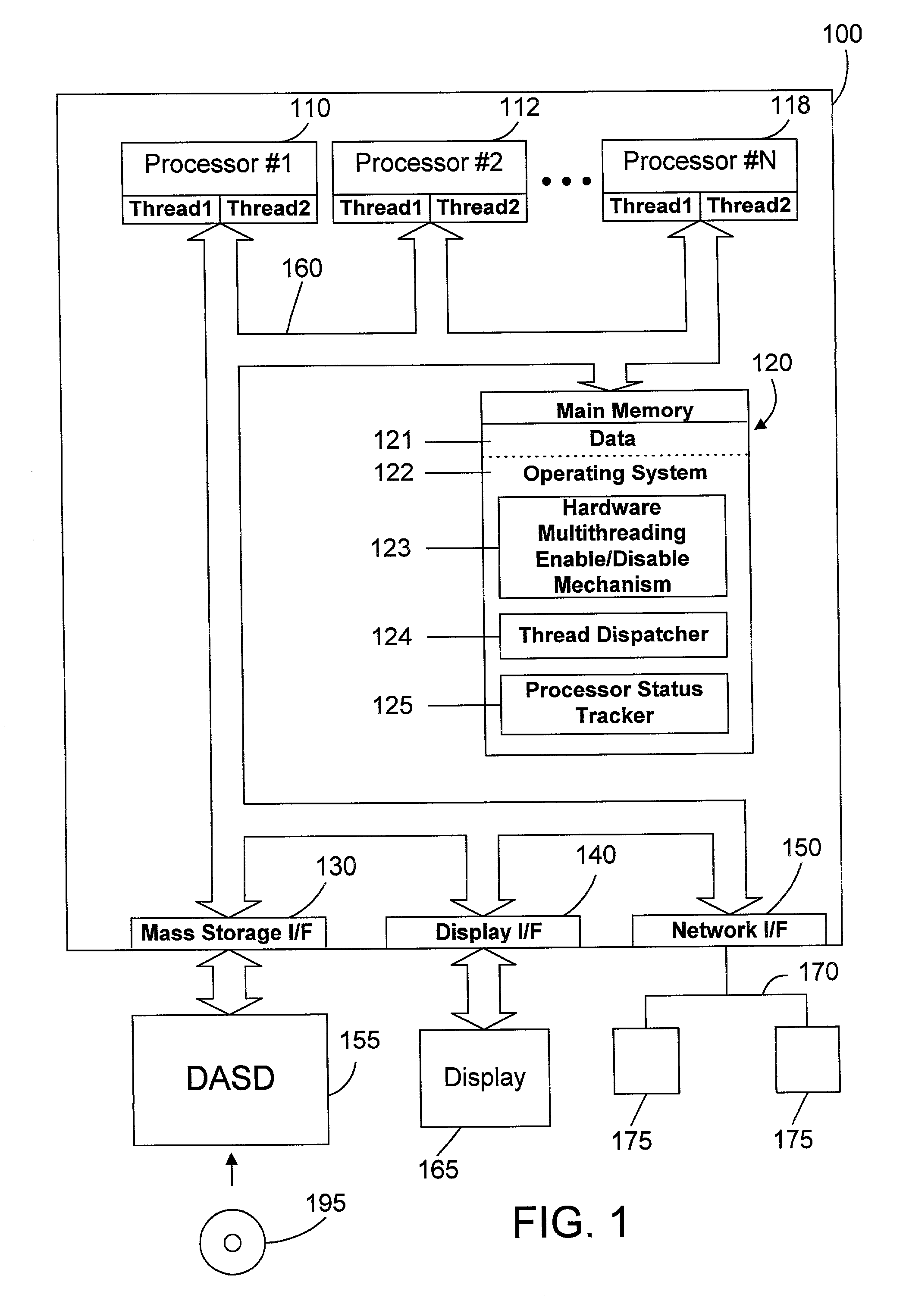
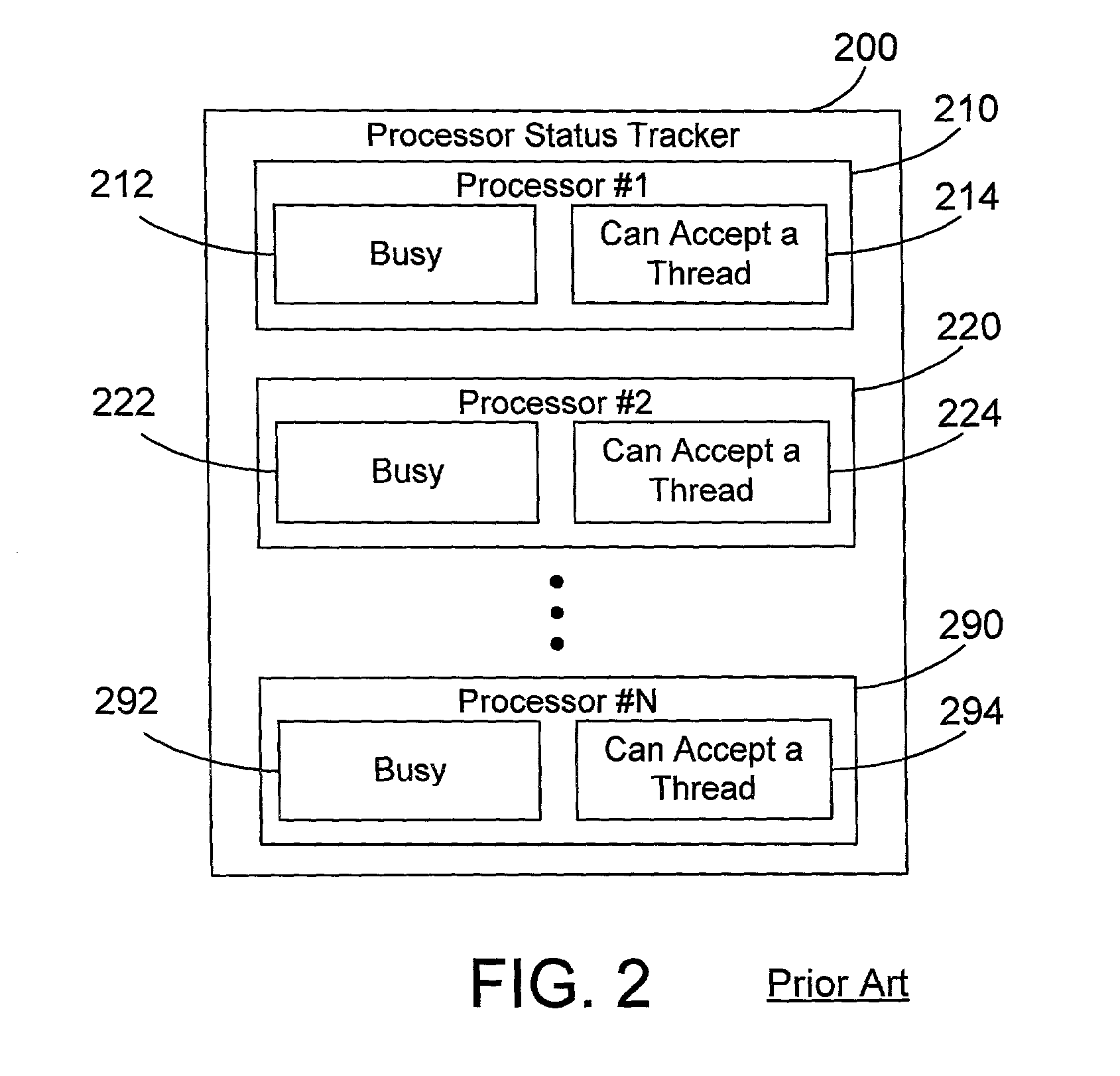
Thread dispatch mechanism and method for multiprocessor computer systems
InactiveUS20030149716A1Minimizing thread spreadHuman perceptionOperational speed enhancementResource allocationMulti processorThread scheduling
A thread dispatch mechanism dispatches threads in a multiprocessor computer system that has hardware multithreading enabled, thereby allowing each processor to execute multiple threads. The thread dispatch mechanism determines which processors are busy and cannot execute an additional thread, which processors are working on a thread but can still accept an additional thread, and which processors are idle. As threads are ready to be dispatched, each is dispatched to an idle processor instead of a processor that is already working on another thread. If there are no idle processors, the thread is dispatched to a processor working on one or more threads that can still process the new thread. In this manner the thread dispatch mechanism and method of the present invention provides greatly improved consistency in response times between threads and higher throughput compared to prior art methods of dispatching threads.
Owner:IBM CORP
Techniques for hardware-assisted multi-threaded processing
ActiveUS20070294694A1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsThread schedulingProcessor register
Techniques for processing each of multiple threads that share a core processor include receiving an intra-thread register address from the core processor. This address contains C bits for accessing each of 2c registers for each thread. A thread ID is received from a thread scheduler external to the core processor. The Thread ID contains T bits for indicating a particular thread for up to 2T threads. A particular register is accessed in a register bank that has 2(C+T) registers using an inter-thread address that includes both the intra-thread register address and the thread ID. The particular register holds contents for the intra-thread register address for a thread having the thread ID. Consequently, register contents of all registers of all threads reside in the register bank. Thread switching is accomplished rapidly by simply accessing different slices in the register bank, without swapping contents between a set of registers and memory.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
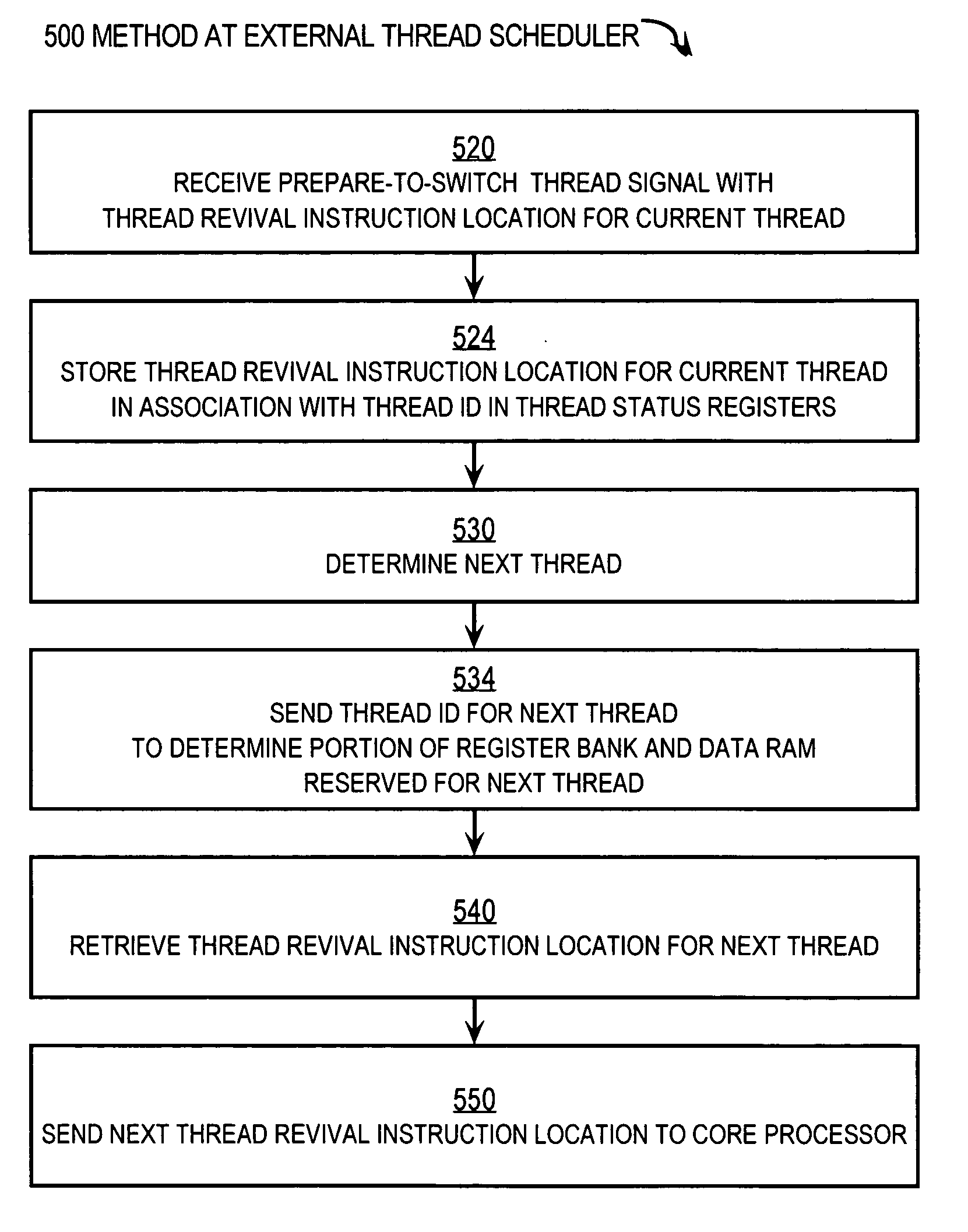
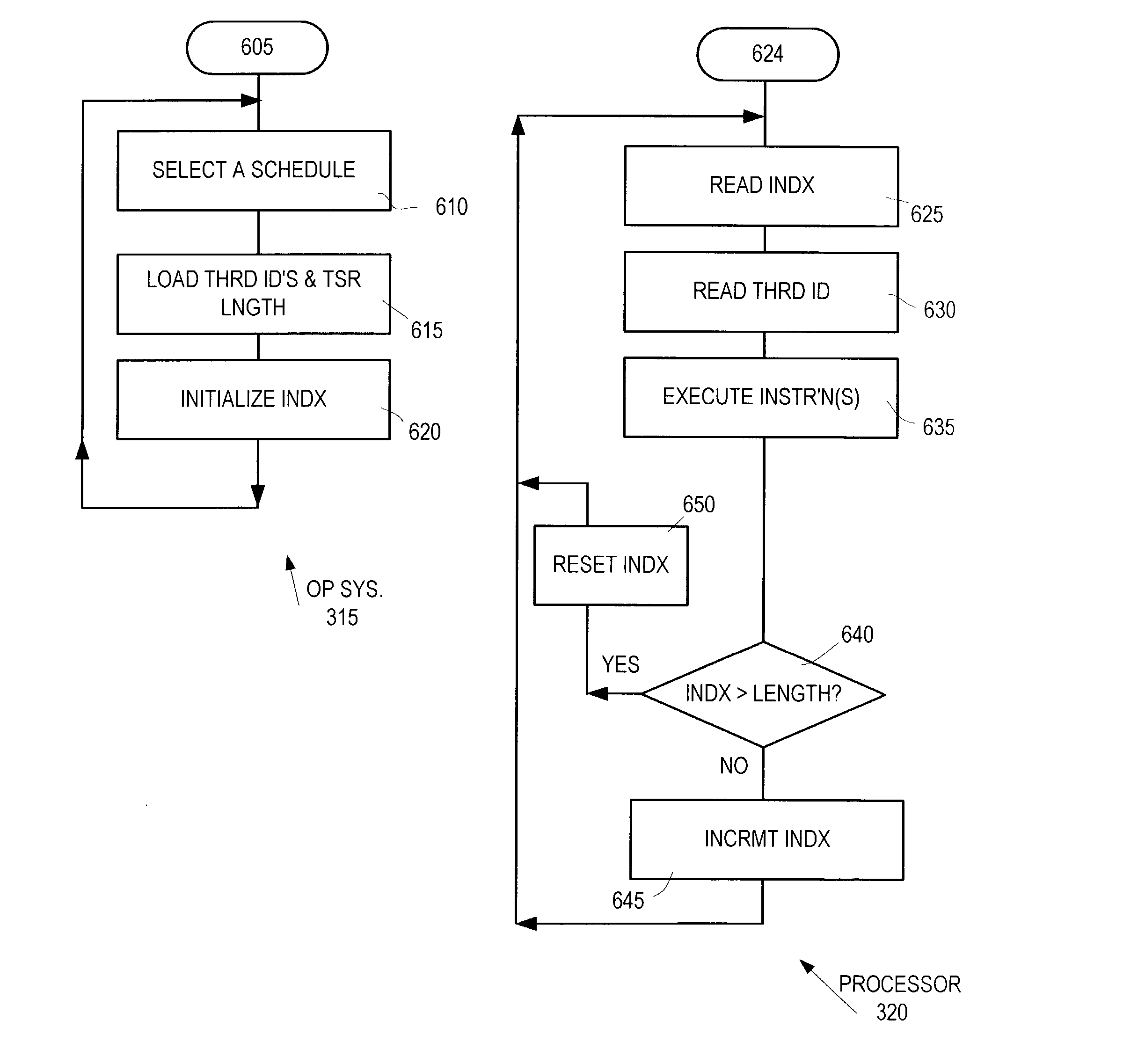
Method, apparatus and computer program product for scheduling multiple threads for a processor
InactiveUS20040015684A1Program initiation/switchingDigital computer detailsComputer architectureProcessor scheduling
In one form of the invention, a method for scheduling multiple instruction threads for a processor in an information handling system includes communicating, to processor circuitry by an operating system, a selected schedule of instruction threads for a set of instructions. The processor circuitry switches from executing one of the threads with one of the contexts to executing another of the threads with another of the contexts, responsive to the schedule received from the operating system.
Owner:IBM CORP
Thread dispatcher for multi-threaded communication library
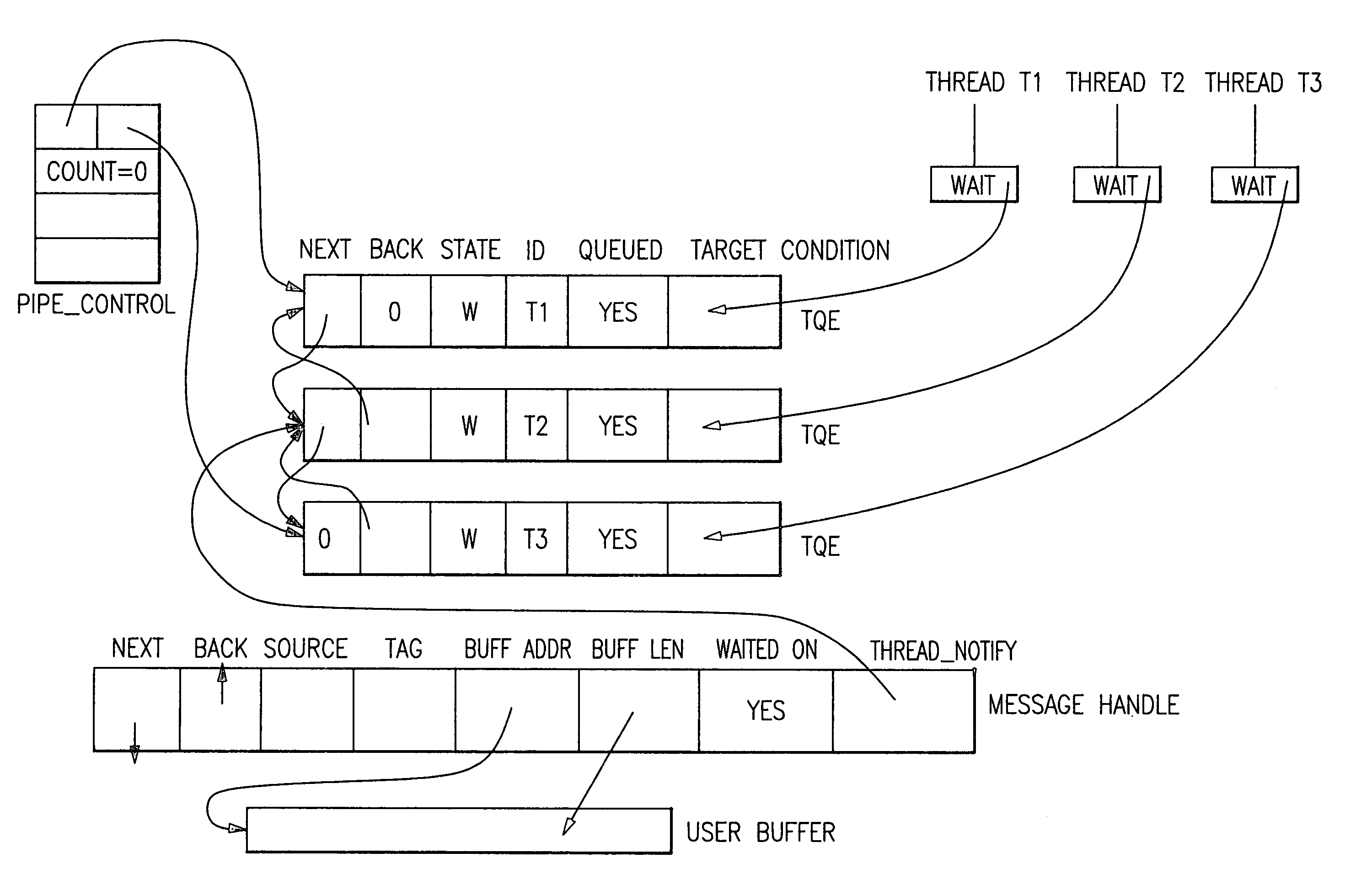
InactiveUS6934950B1Improve efficiencyRaise priorityMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsPOSIX ThreadsThread scheduling
Method, computer program product, and apparatus for efficiently dispatching threads in a multi-threaded communication library which become runnable by completion of an event. Each thread has a thread-specific structure containing a “ready flag” and a POSIX thread condition variable unique to that thread. Each message is assigned a “handle”. When a thread waits for a message, thread-specific structure is attached to the message handle being waited on, and the thread is enqueued, waiting for its condition variable to be signaled. When a message completes, the message matching logic sets the ready flag to READY, and causes the queue to be examined. The queue manager scans the queue of waiting threads, and sends a thread awakening condition signal to one of the threads with its ready flag set to READY. The queue manager can implement any desired policy, including First-In-First-Out (FIFO), Last-In-First-Out (LIFO), or some other thread priority scheduling policy. This ensures that the thread which is awakened has the highest priority message to be processed, and enhances the efficiency of message delivery. The priority of the message to be processed is computed based on the overall state of the communication subsystem.
Owner:IBM CORP
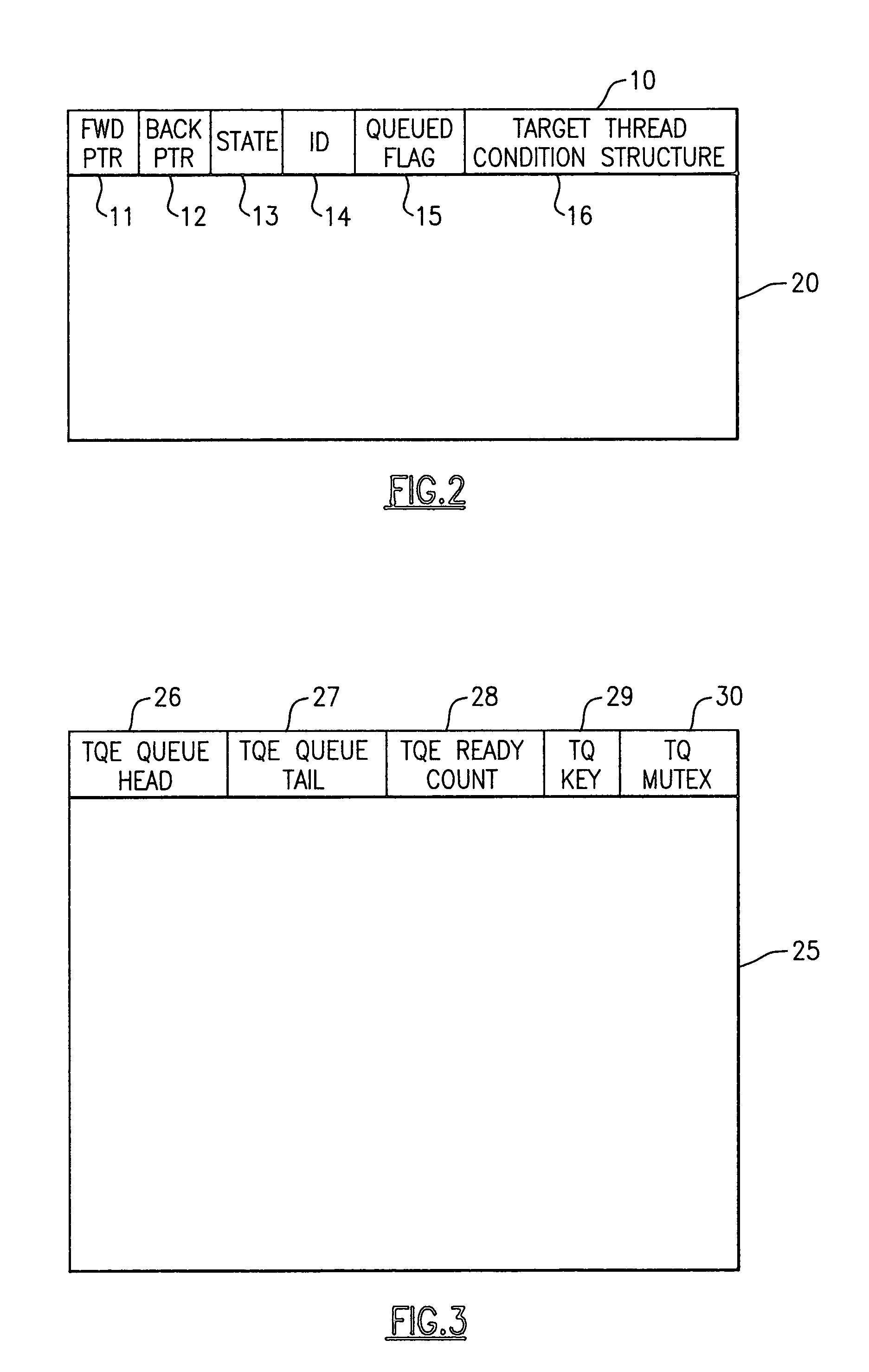
Leaky-bucket thread scheduler in a multithreading microprocessor
ActiveUS20060179439A1Energy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsThread schedulingParallel computing
A leaky-bucket style thread scheduler for scheduling concurrent execution of multiple threads in a microprocessor is provided. The execution pipeline notifies the scheduler when it has completed instructions. The scheduler maintains a virtual water level for each thread and decreases it each time the execution pipeline executes an instruction of the thread. The scheduler includes an instruction execution rate for each thread. The scheduler increases the virtual water level based on the requested rate per a predetermined number of clock cycles. The scheduler includes virtual water pressure parameters that define a set of virtual water pressure ranges over the height of the virtual water bucket. When a thread's virtual water level moves from one virtual water pressure range to the next higher range, the scheduler increases the instruction issue priority for the thread; conversely, when the level moves down, the scheduler decreases the instruction issue priority for the thread.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
Method and system for scheduling multitasking thread pools
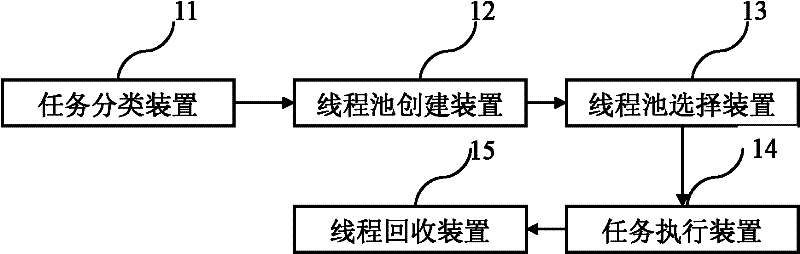
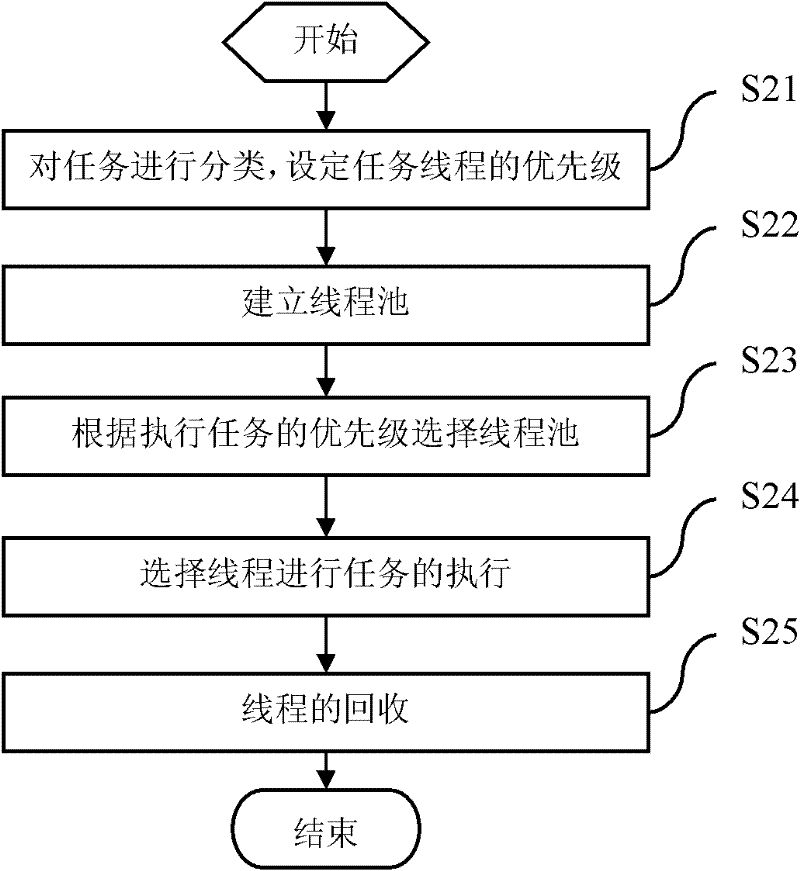
InactiveCN102541653AIncrease profitAvoid wastingResource allocationProcessor architectures/configurationThread schedulingThread pool
The invention relates to a method and a system for scheduling multitasking thread pools, which create task threads according to the number of real central processing units (CPUs) of a computer, set up the thread pools according to priority of the task threads, choose threads in the thread pools corresponding to priority according to the priority of the task threads to be executed, finally relate task algorithm to the threads and start thread scheduling algorithm to execute the tasks. By adopting the method and the system for scheduling multitasking thread pools, users can create the thread pools according to the priority of the task threads and classify and manage the threads. Due to a thread creating and recovering device of threads arranged in the method and the system, utilization ratio of the threads is improved, and resource waste is avoided.
Owner:CHINA DIGITAL VIDEO BEIJING
Method and apparatus for reconfiguring thread scheduling using a thread scheduler function unit
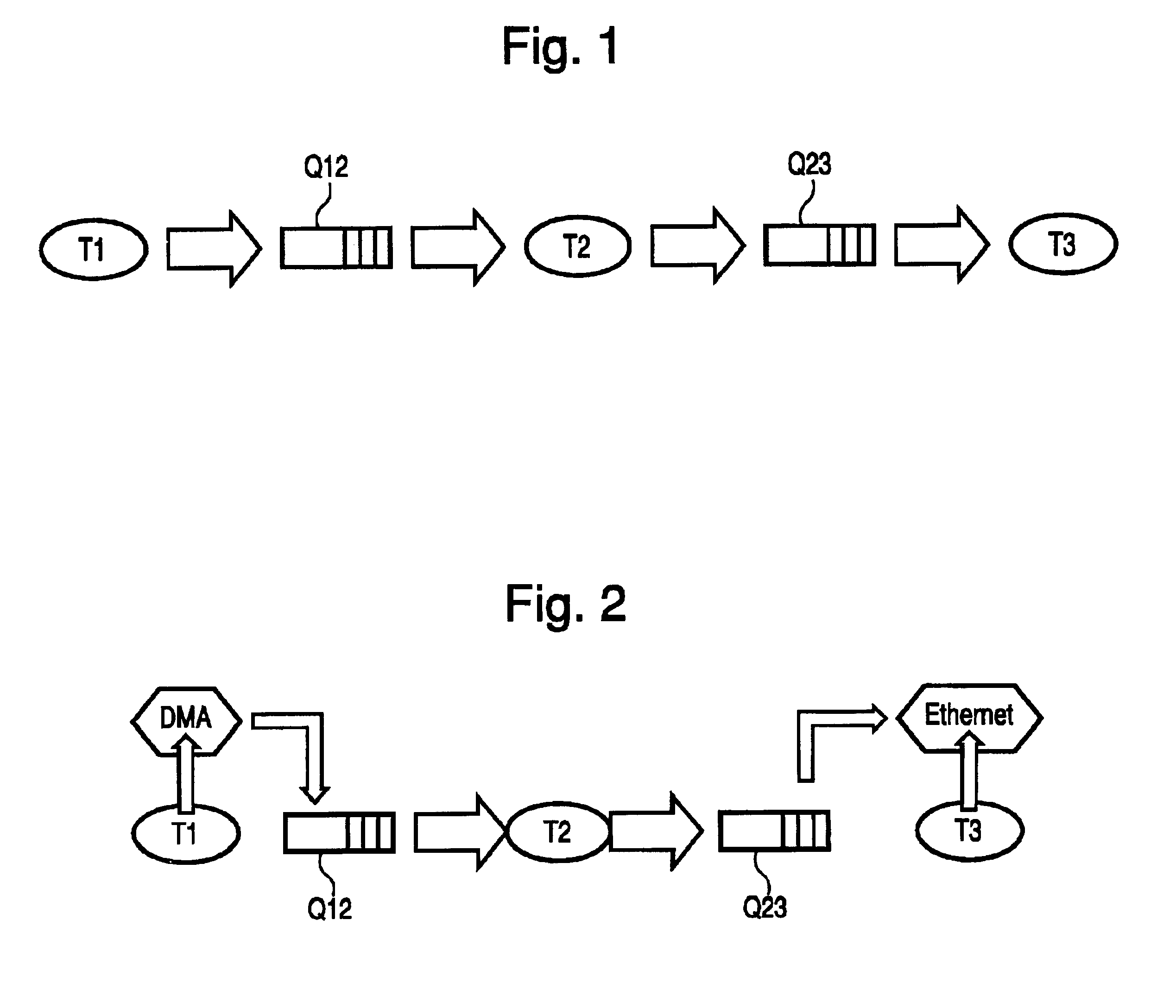
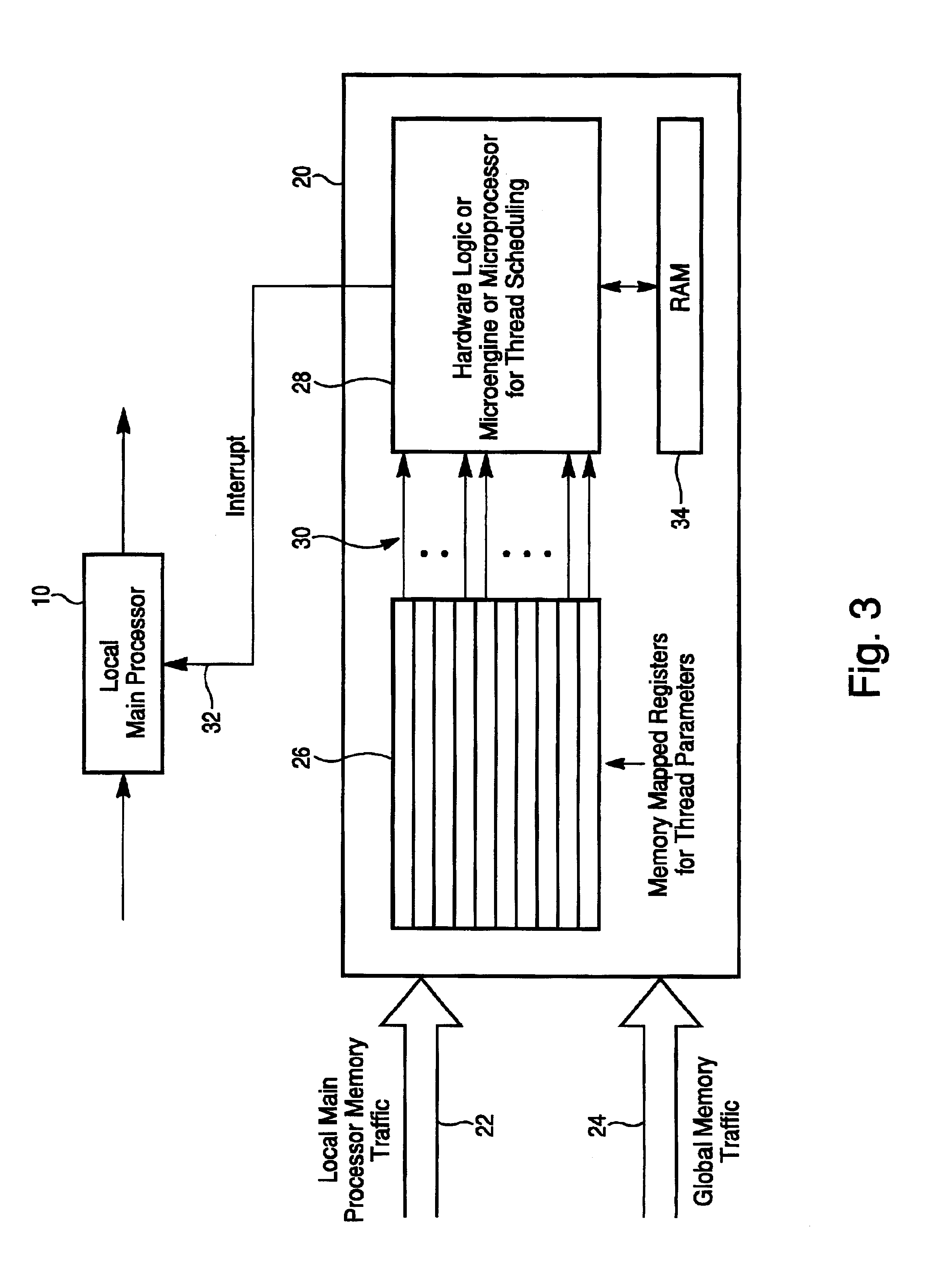
InactiveUS6918116B2Multiprogramming arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionTraffic capacityProcessor register
A method and system for thread scheduling to run in parallel with a main processor, comprising: obtaining parameter values for a plurality of different threads; performing logic functions, in parallel with, but without interrupting the main processor, on said parameter values to determine if thread scheduling should be reconfigured, and if so, which thread should be enabled; and sending an interrupt signal to interrupt the main processor if thread scheduling is to be reconfigured. The parameters may be obtained by monitoring the values from thread processes held in registers with fixed addresses, or by snooping memory traffic for selected parameters. The logic functions, in a preferred embodiment, may be implemented using reconfigurable hardware logic.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
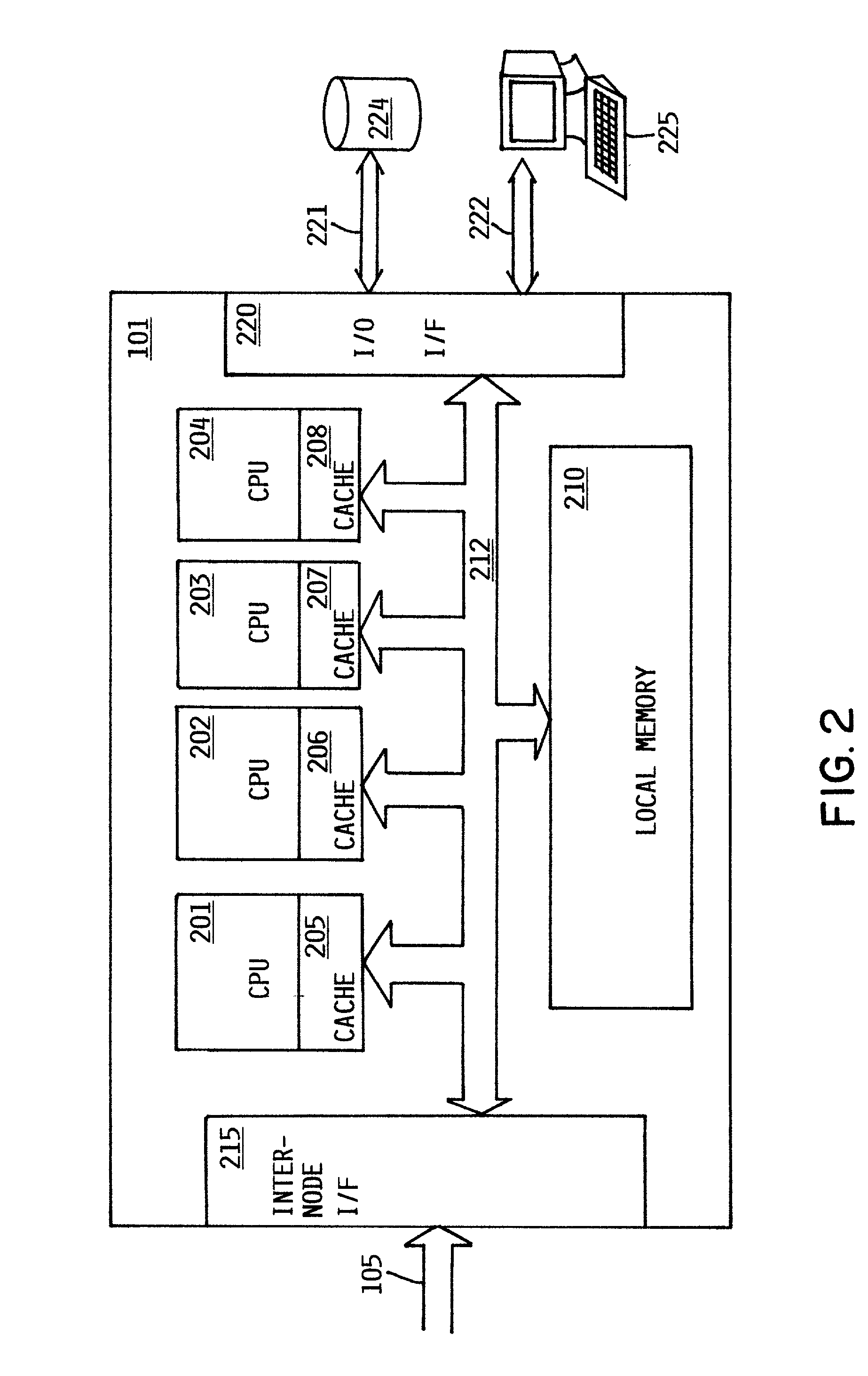
Method and apparatus for dispatching tasks in a non-uniform memory access (NUMA) computer system
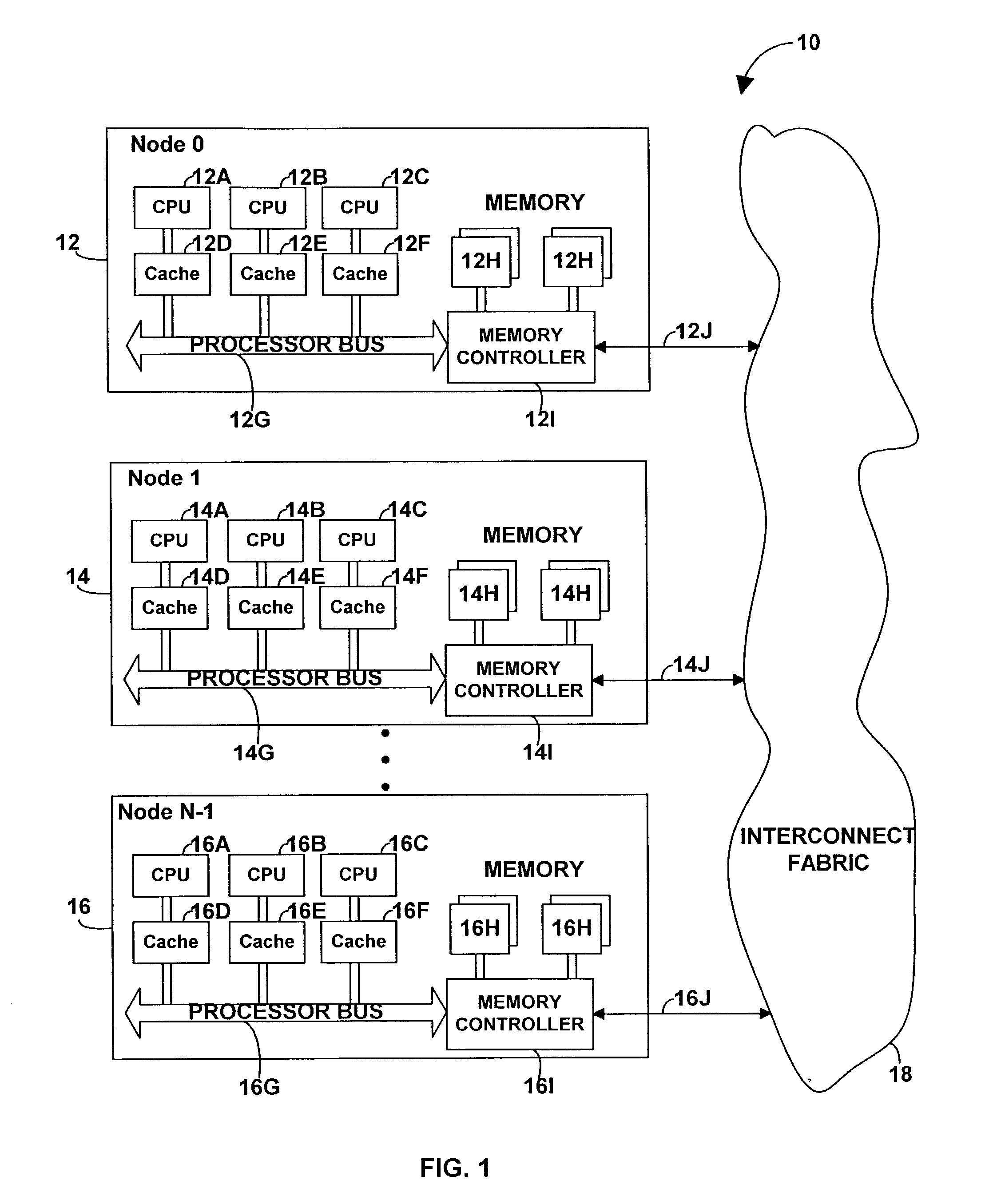
InactiveUS7159216B2Avoid starvationShort timeProgram initiation/switchingMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDistributed memoryAccess time
A dispatcher for a non-uniform memory access computer system dispatches threads from a common ready queue not associated with any CPU, but favors the dispatching of a thread to a CPU having a shorter memory access time. Preferably, the system comprises multiple discrete nodes, each having a local memory and one or more CPUs. System main memory is a distributed memory comprising the union of the local memories. A respective preferred CPU and preferred node may be associated with each thread. When a CPU becomes available, the dispatcher gives at least some relative priority to a thread having a preferred CPU in the same node as the available CPU over a thread having a preferred CPU in a different node. This preference is relative, and does not prevent the dispatch from overriding the preference to avoid starvation or other problems.
Owner:DAEDALUS BLUE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com