Patents
Literature
312 results about "Instruction decoder" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
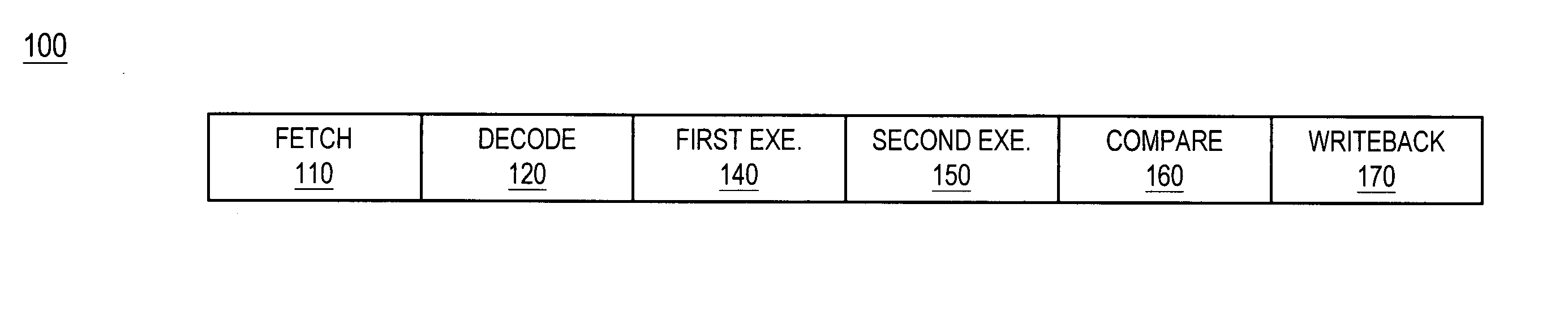
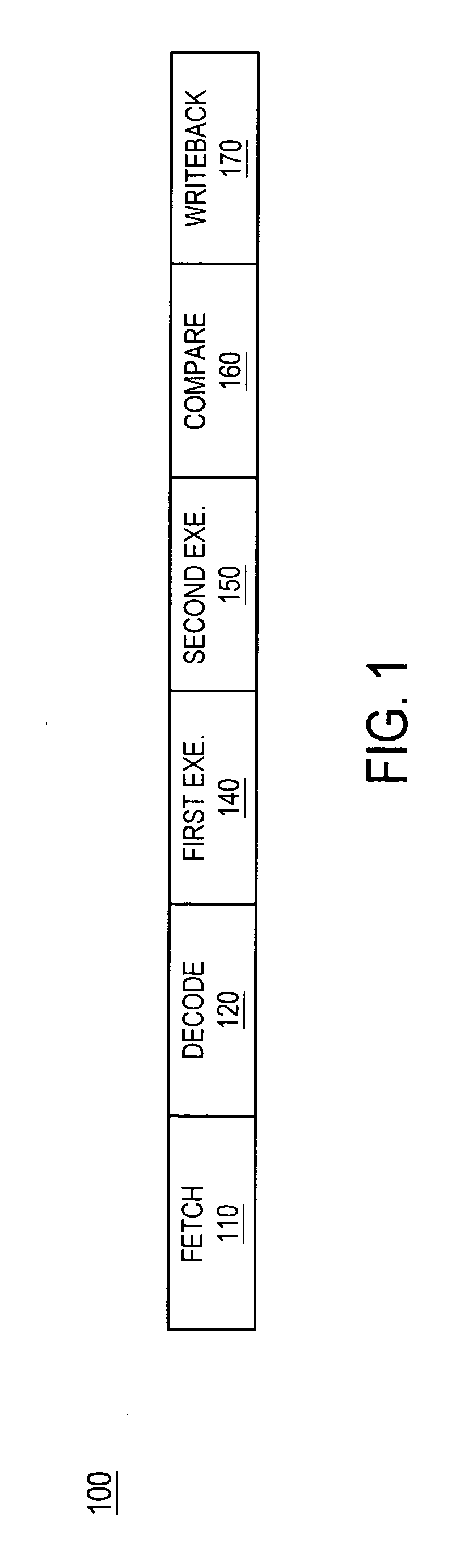
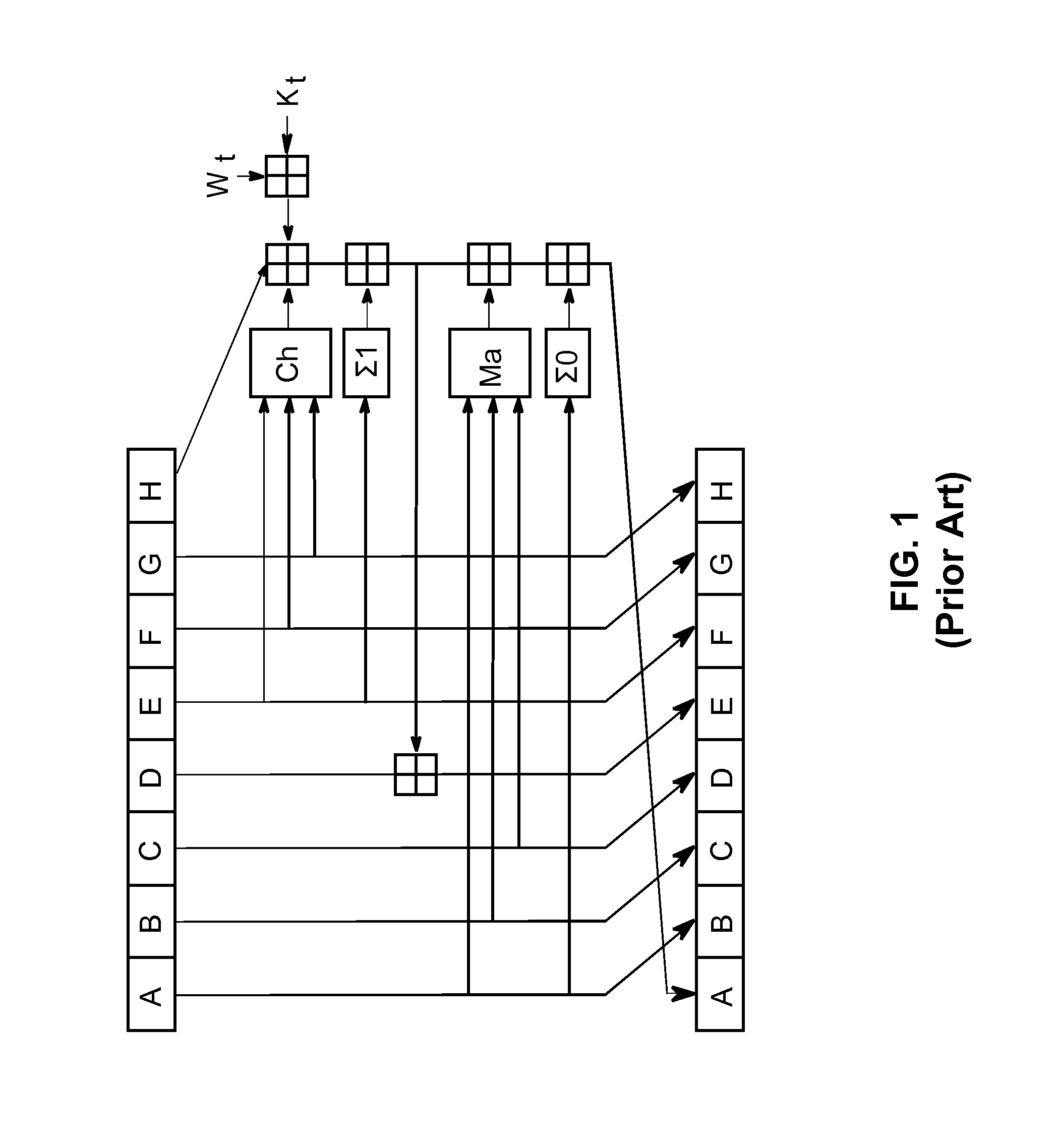
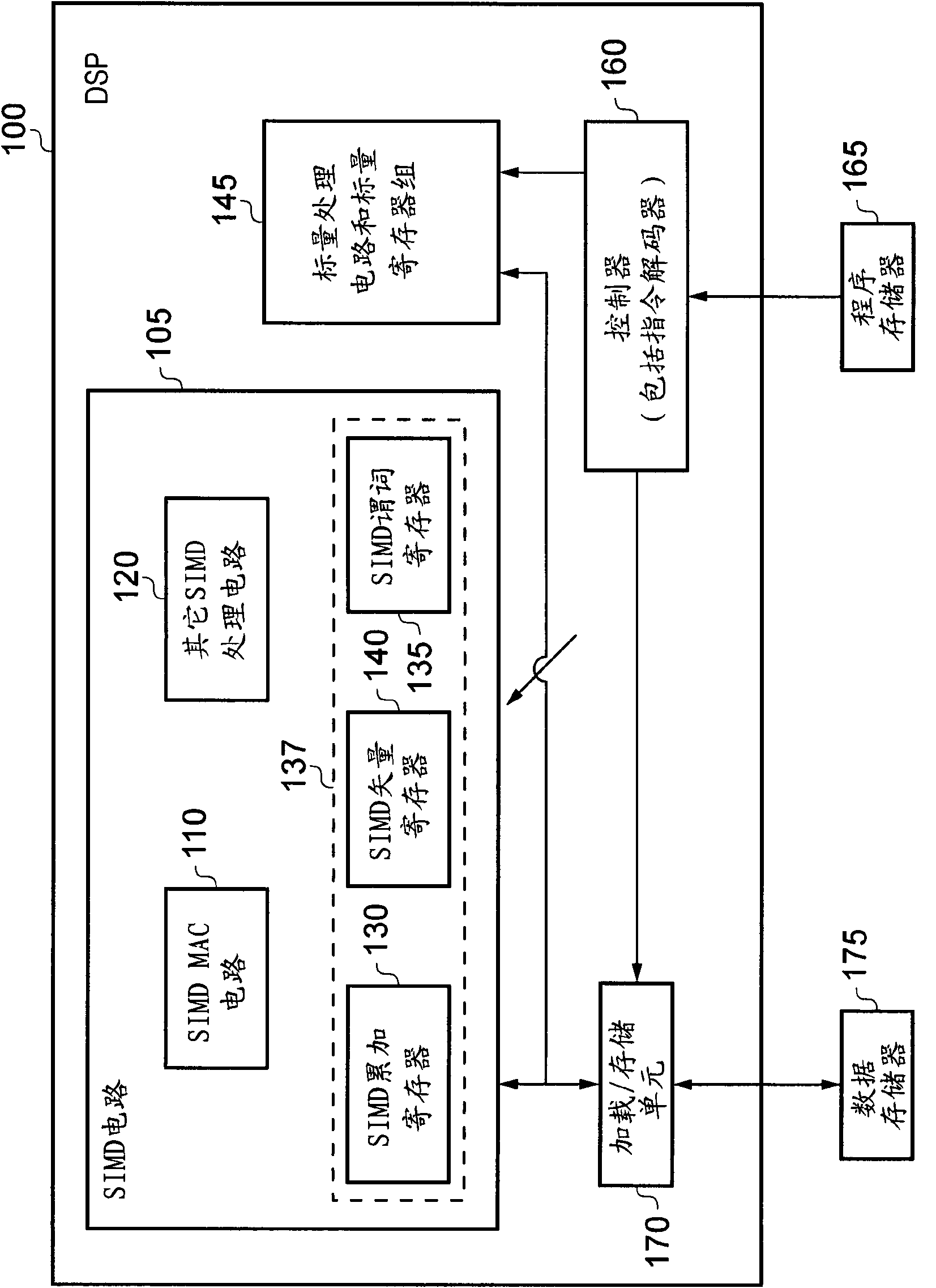
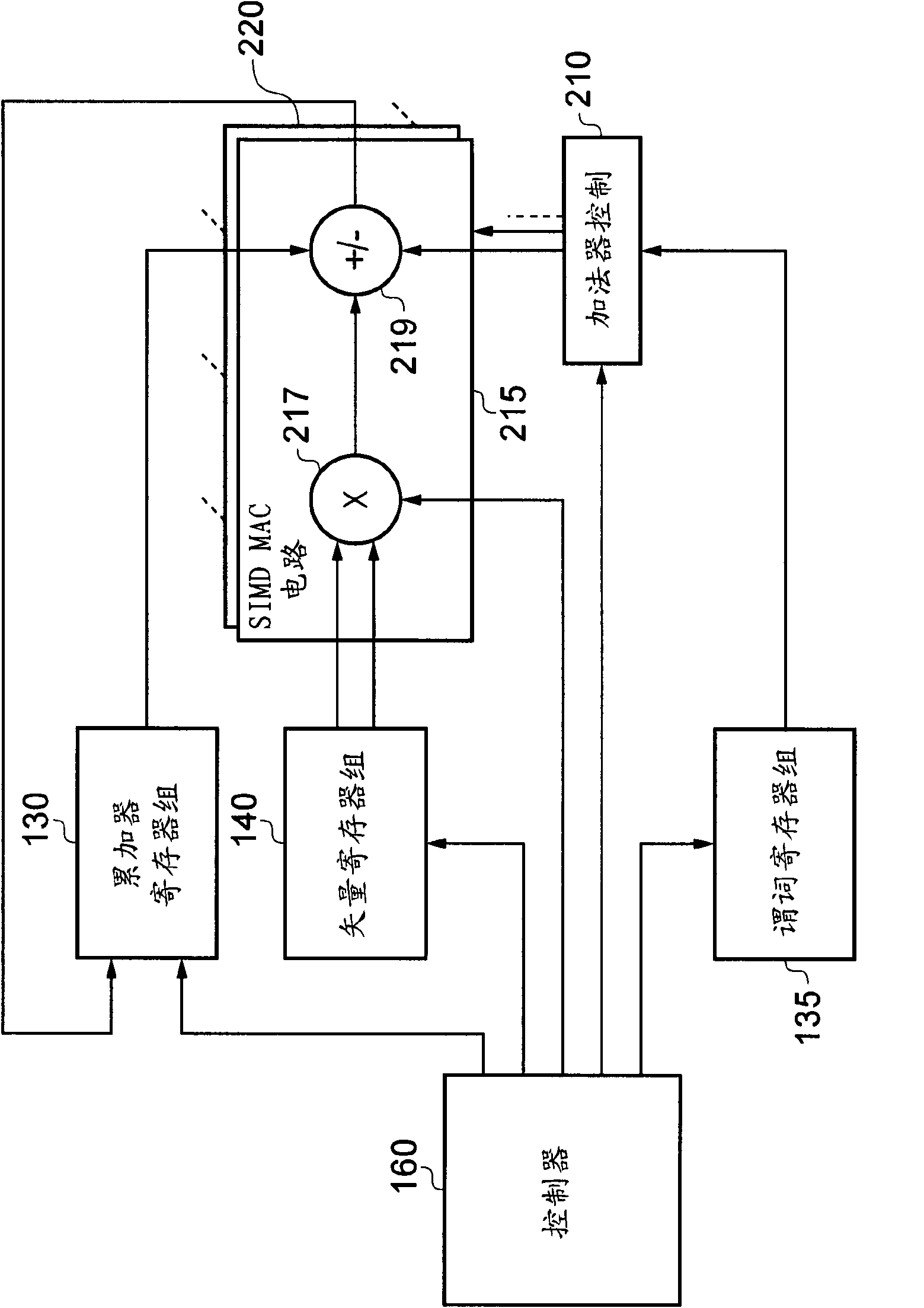
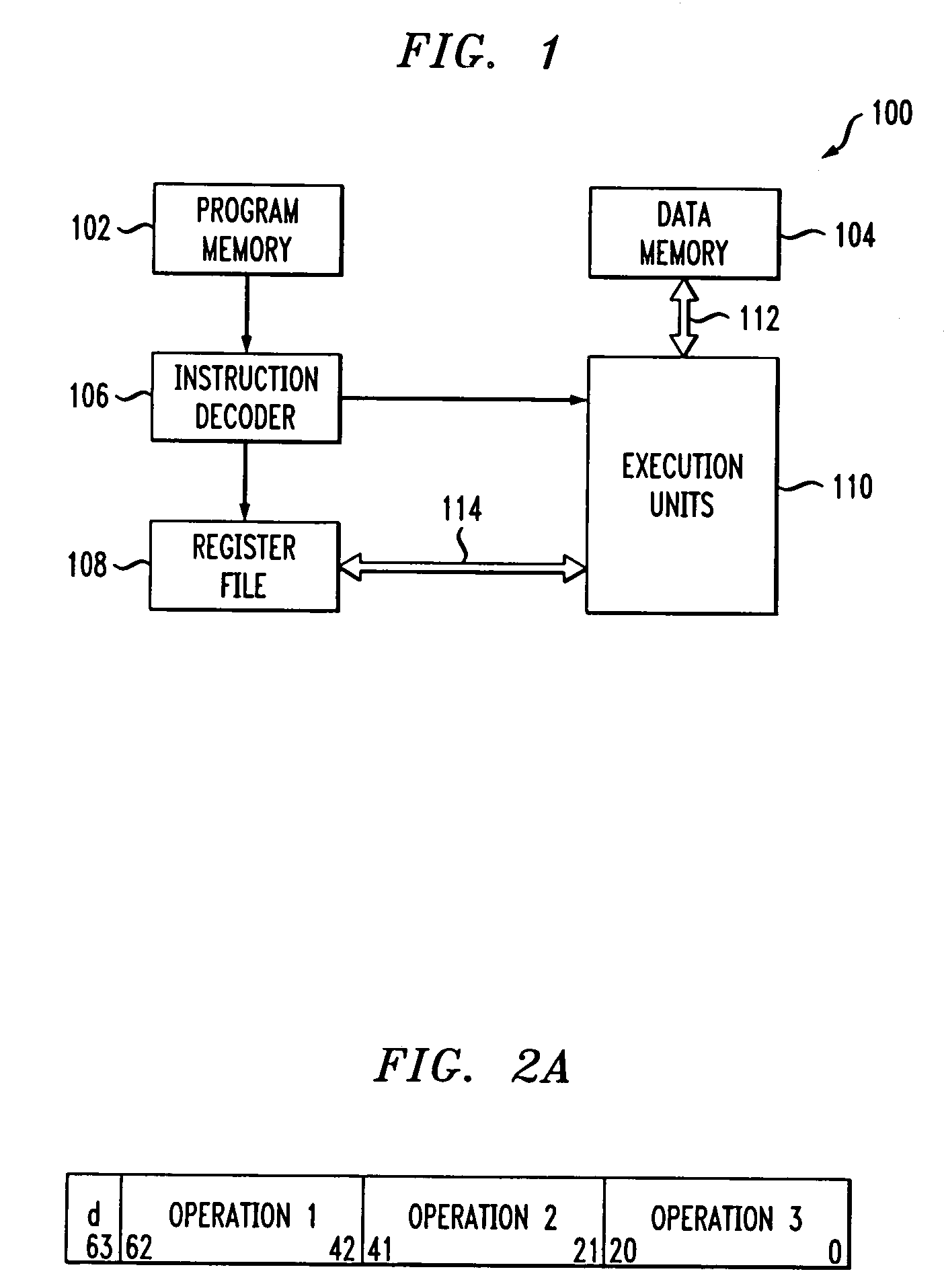
Instruction decoder. The instruction decoder of a processor is a combinatorial circuit sometimes in the form of a read-only memory, sometimes in the form of an ordinary combinatorial circuit. Its purpose is to translate an instruction code into the address in the micro memory where the micro code for the instruction starts.
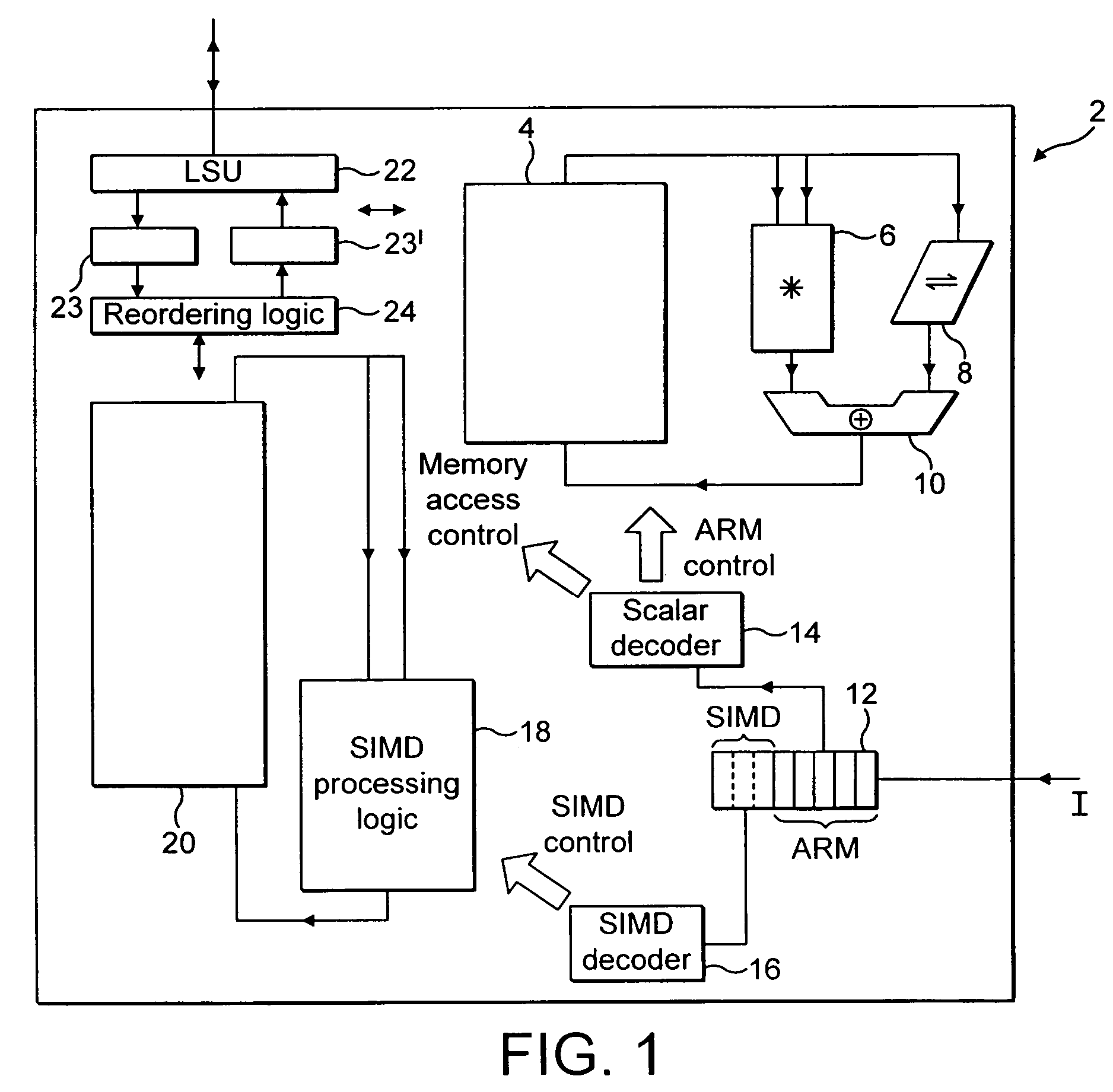
Data processing apparatus and method for performing rearrangement operations
ActiveUS20100106944A1Further flexibilityReduce energy consumptionDigital data processing detailsInstruction analysisControl signalProcessor register
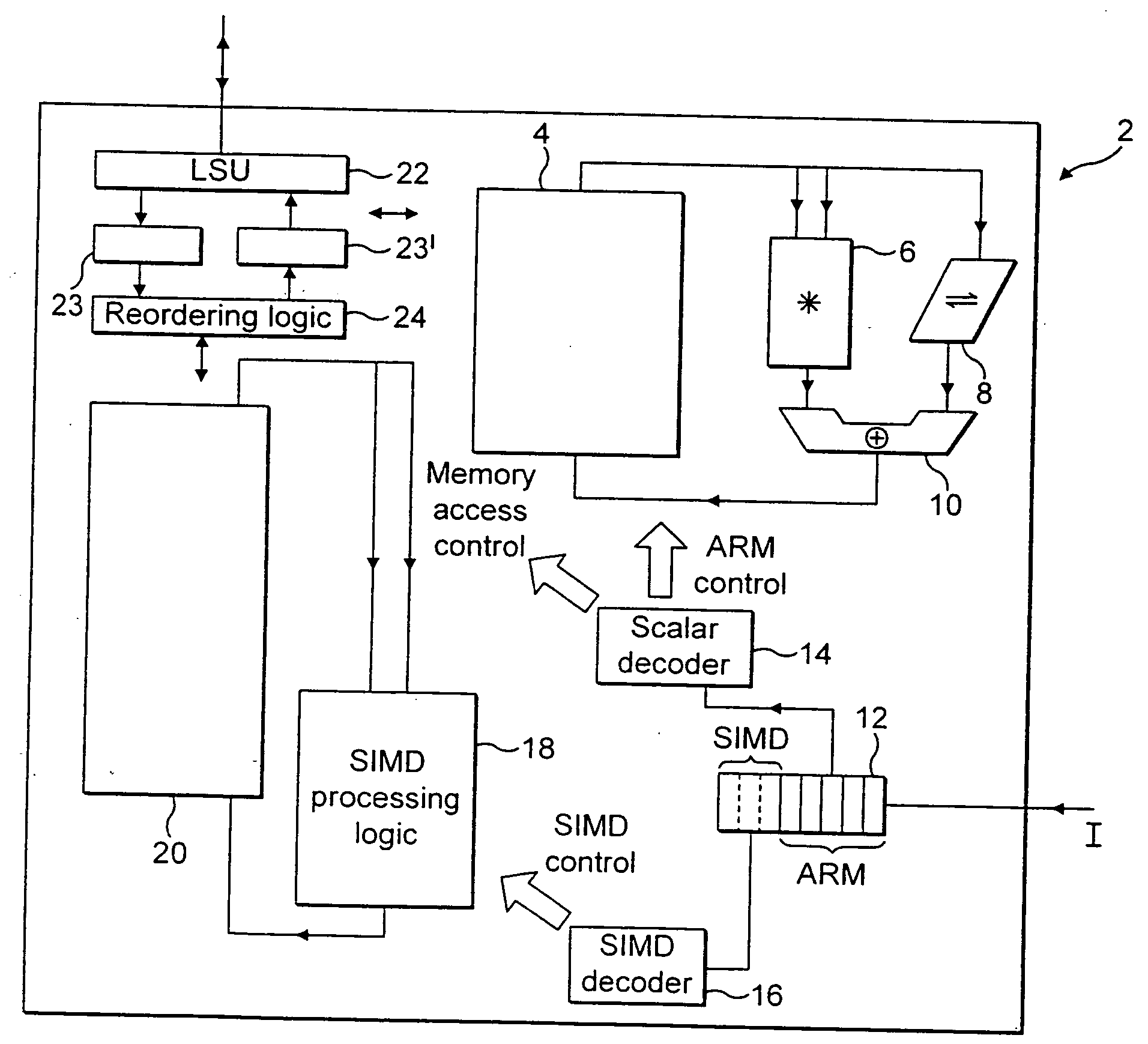
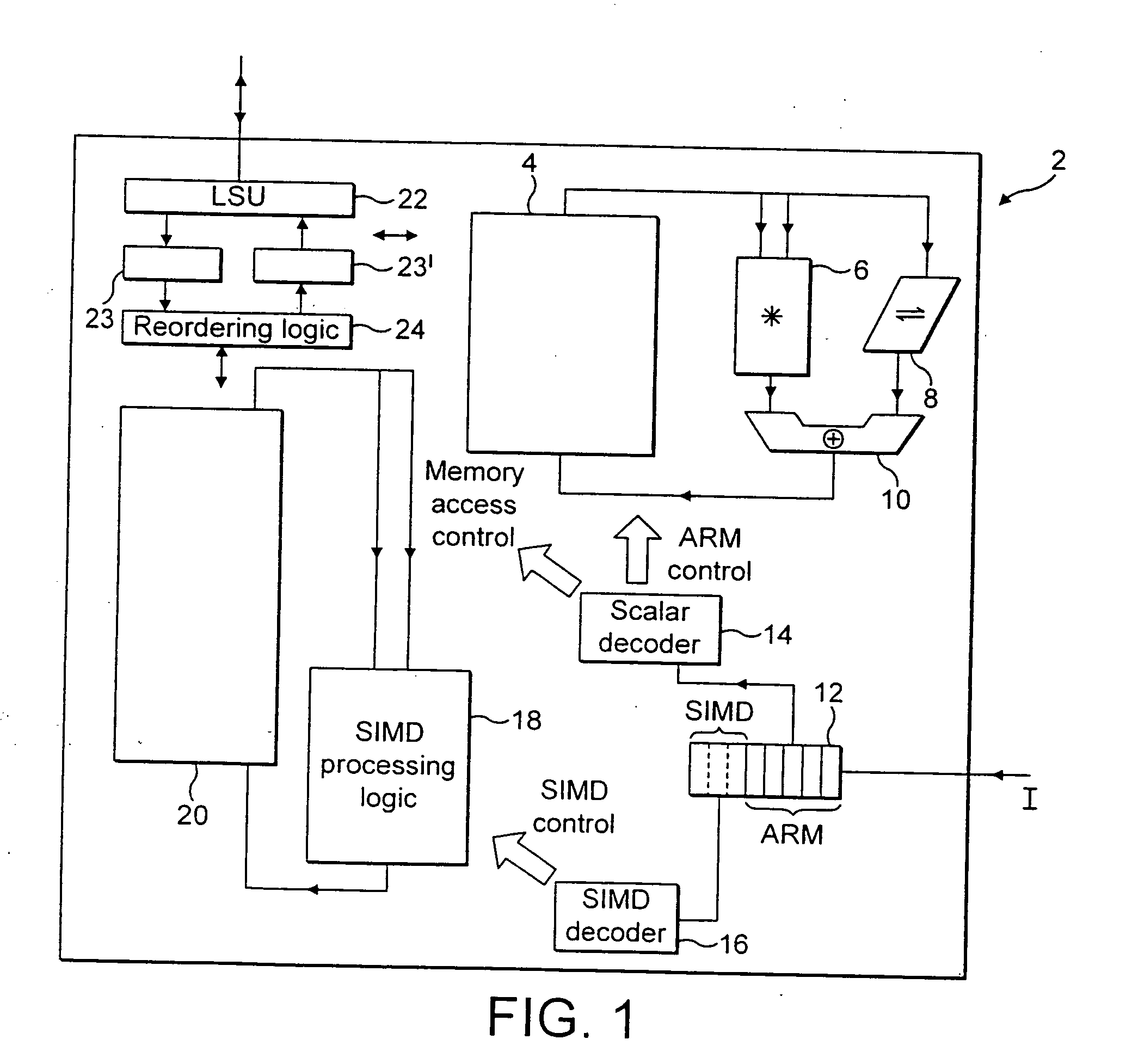
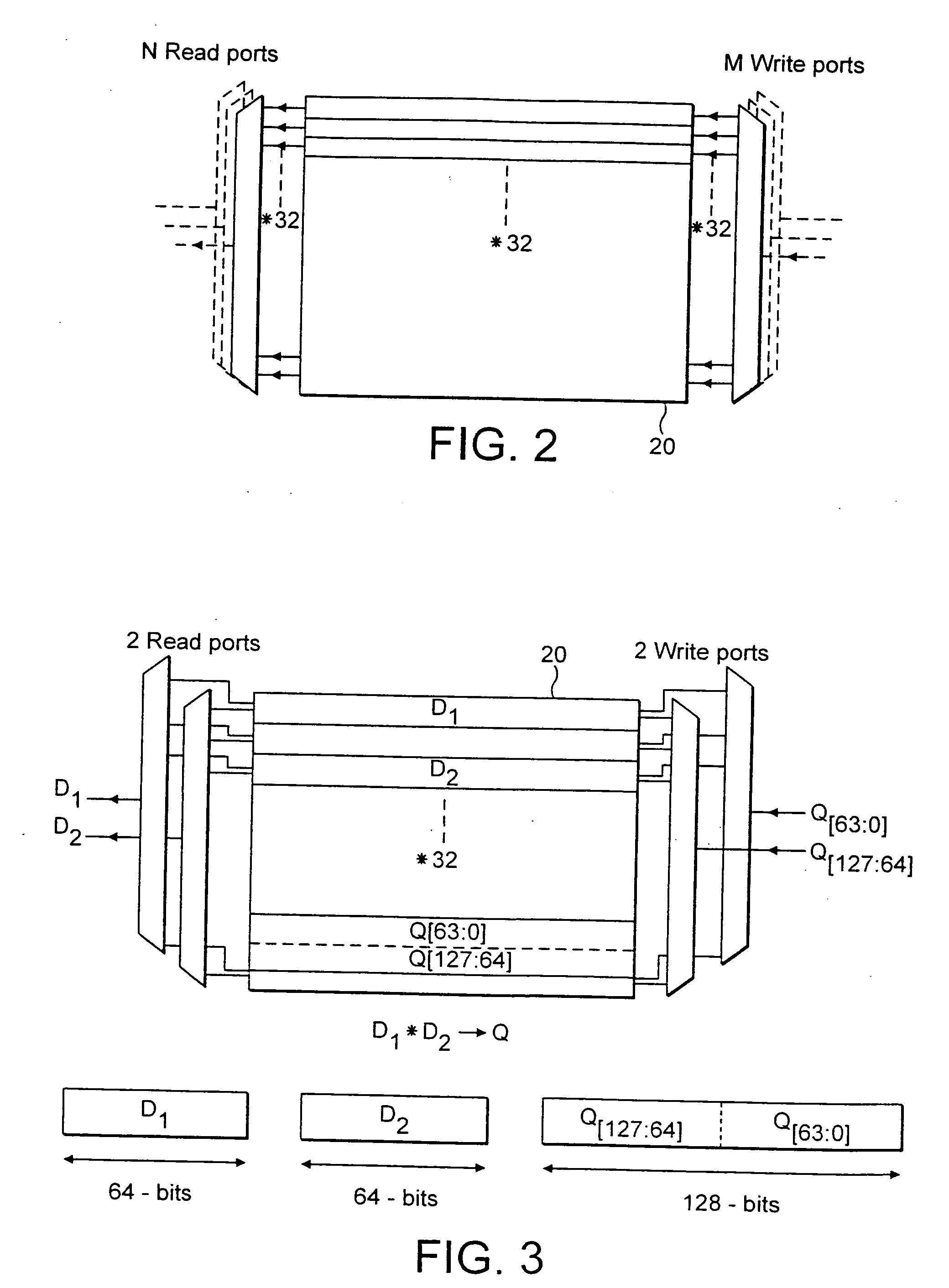
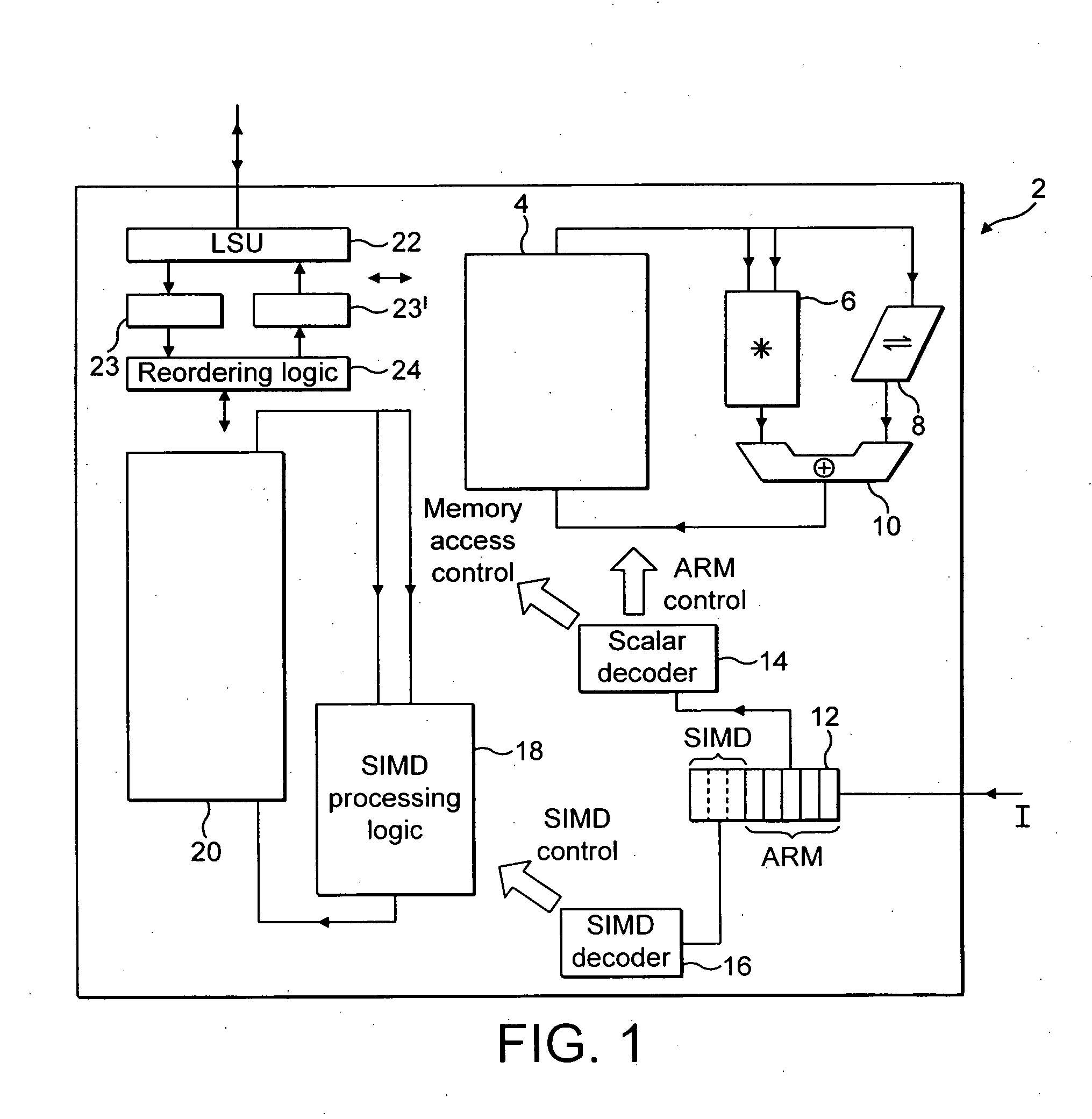
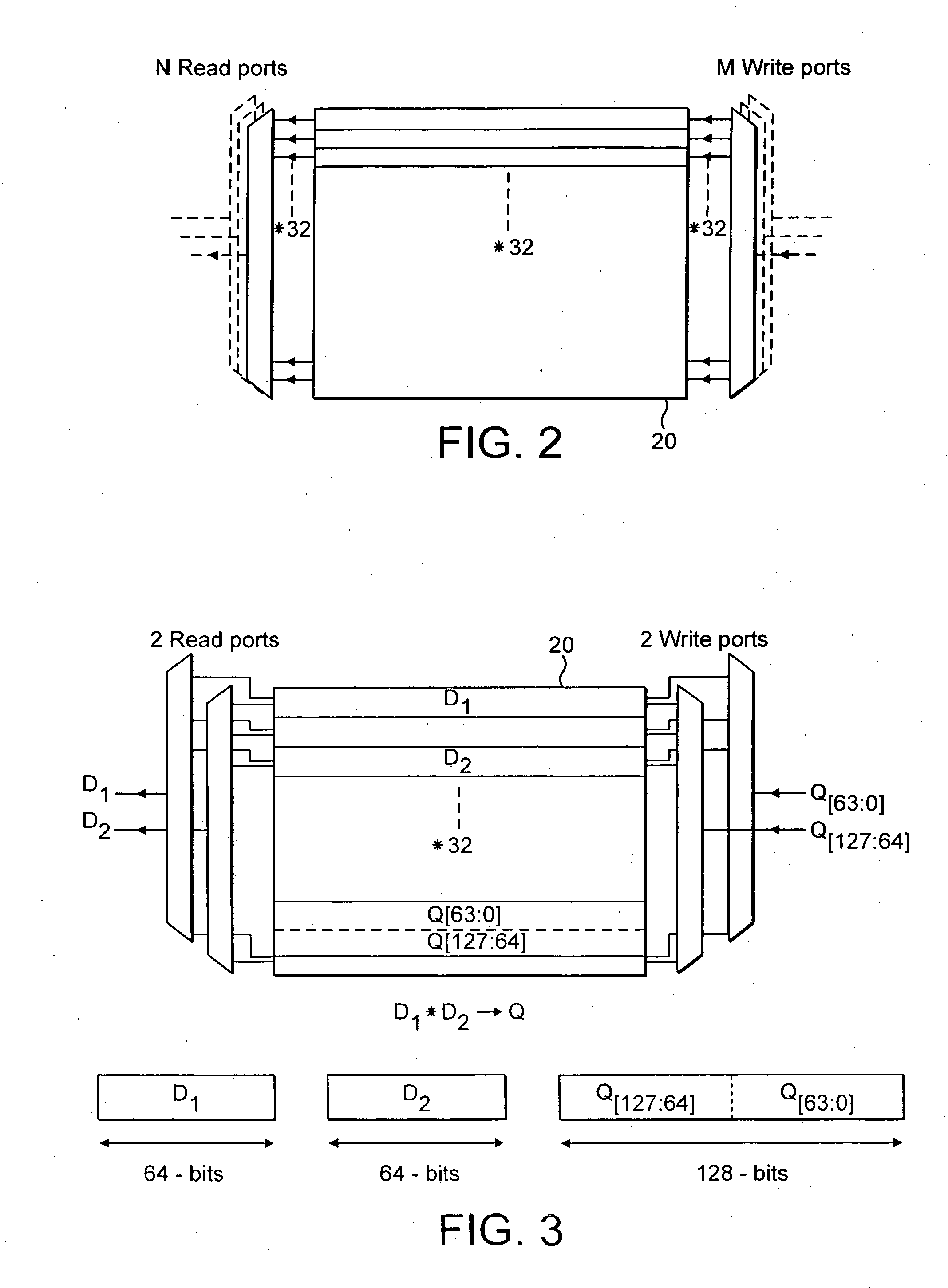
A data processing apparatus and method are provided for performing rearrangement operations. The data processing apparatus has a register data store with a plurality of registers, each register storing a plurality of data elements. Processing circuitry is responsive to control signals to perform processing operations on the data elements. An instruction decoder is responsive to at least one but no more than N rearrangement instructions, where N is an odd plural number, to generate control signals to control the processing circuitry to perform a rearrangement process at least equivalent to: obtaining as source data elements the data elements stored in N registers of said register data store as identified by the at least one re-arrangement instruction; performing a rearrangement operation to rearrange the source data elements between a regular N-way interleaved order and a de-interleaved order in order to produce a sequence of result data elements; and outputting the sequence of result data elements for storing in the register data store. This provides a particularly efficient technique for performing N-way interleave and de-interleave operations, where N is an odd number, resulting in high performance, low energy consumption, and reduced register use when compared with known prior art techniques.
Owner:ARM LTD
Display devices and integrated circuits
InactiveUS20050206585A1Static indicating devicesLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsShift registerEngineering
Owner:RUIZHANG TECH LTD CO
Display devices and integrated circuits
InactiveUS6980184B1Static indicating devicesLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsShift registerProcessor register
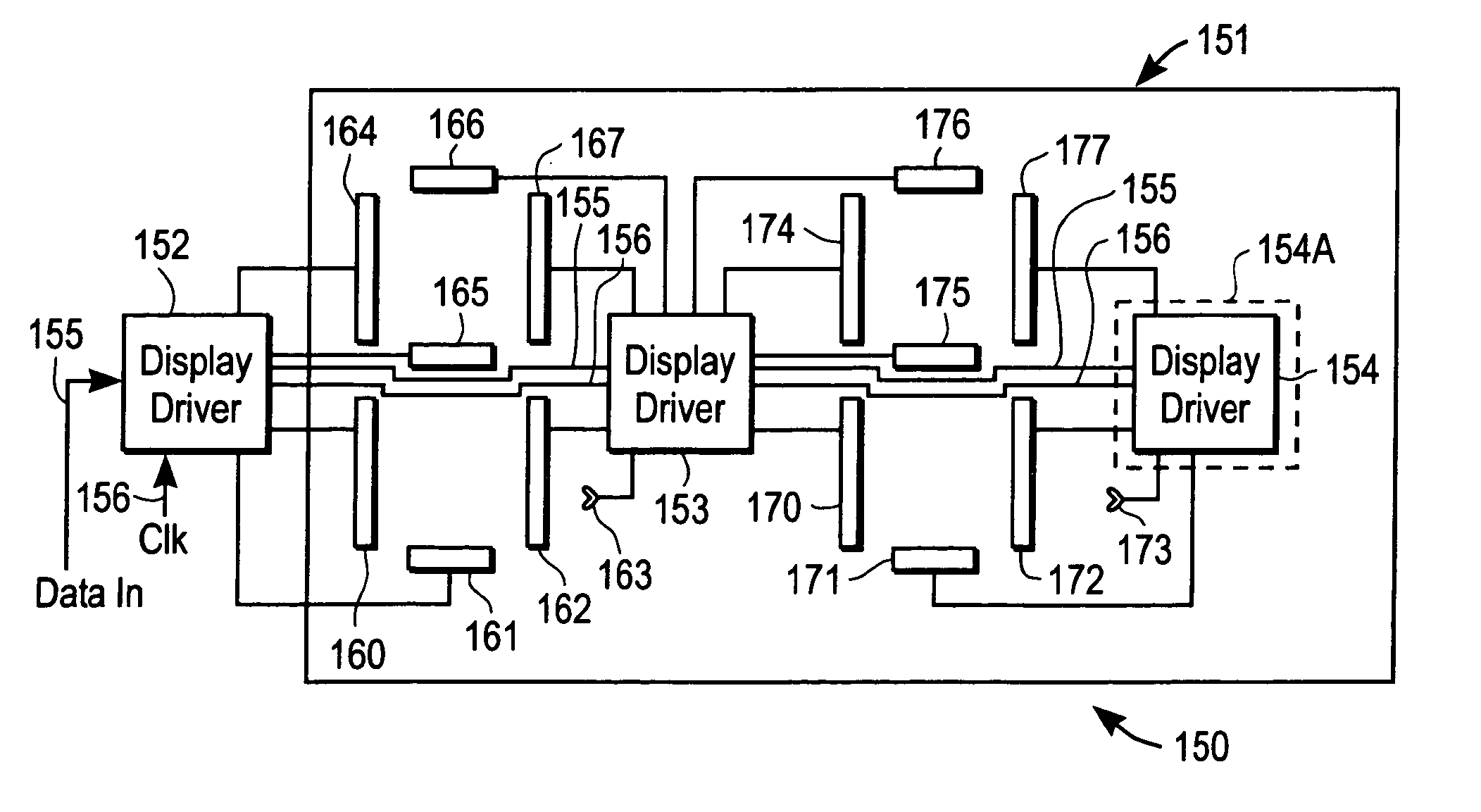
Integrated circuits, assemblies with integrated circuits, display devices and electrical circuits. There are various different aspects and embodiments of these apparatuses described herein. According to one aspect, a display device includes a plurality of display drivers which includes a serial shift register, wherein the display drivers are located in the display area of the display device which is viewable. According to another aspect, an integrated circuit, which has a plurality of functionally symmetric interface pads, includes an instruction decoder which decodes instructions received through at least one of the pads. In another aspect, an integrated circuit (IC) includes a position detector which detects a position of the IC relative to a receptor substrate and provides a signal which is determined by the position; this IC may be used in an assembly which includes the receptor substrate. In another aspect, an IC includes a position detector which detects a position of the IC relative to a receptor substrate and also includes a configurable pad which is configurable, depending upon the position as one of at least two of the following: an input pad, an output pad, or a no-operation pad. According to another aspect, a layout of an IC has a plurality of functionally symmetric interface pads wherein two such pads are configurable pads. According to another aspect, an assembly includes a receptor substrate and an IC attached to the substrate, and the IC includes a first logic circuit which provides a first function, a second logic circuit which provides a second function, and a selector which selects between the two functions such that the IC performs only the selected function. Other aspects and methods are also described.
Owner:RUIZHANG TECH LTD CO
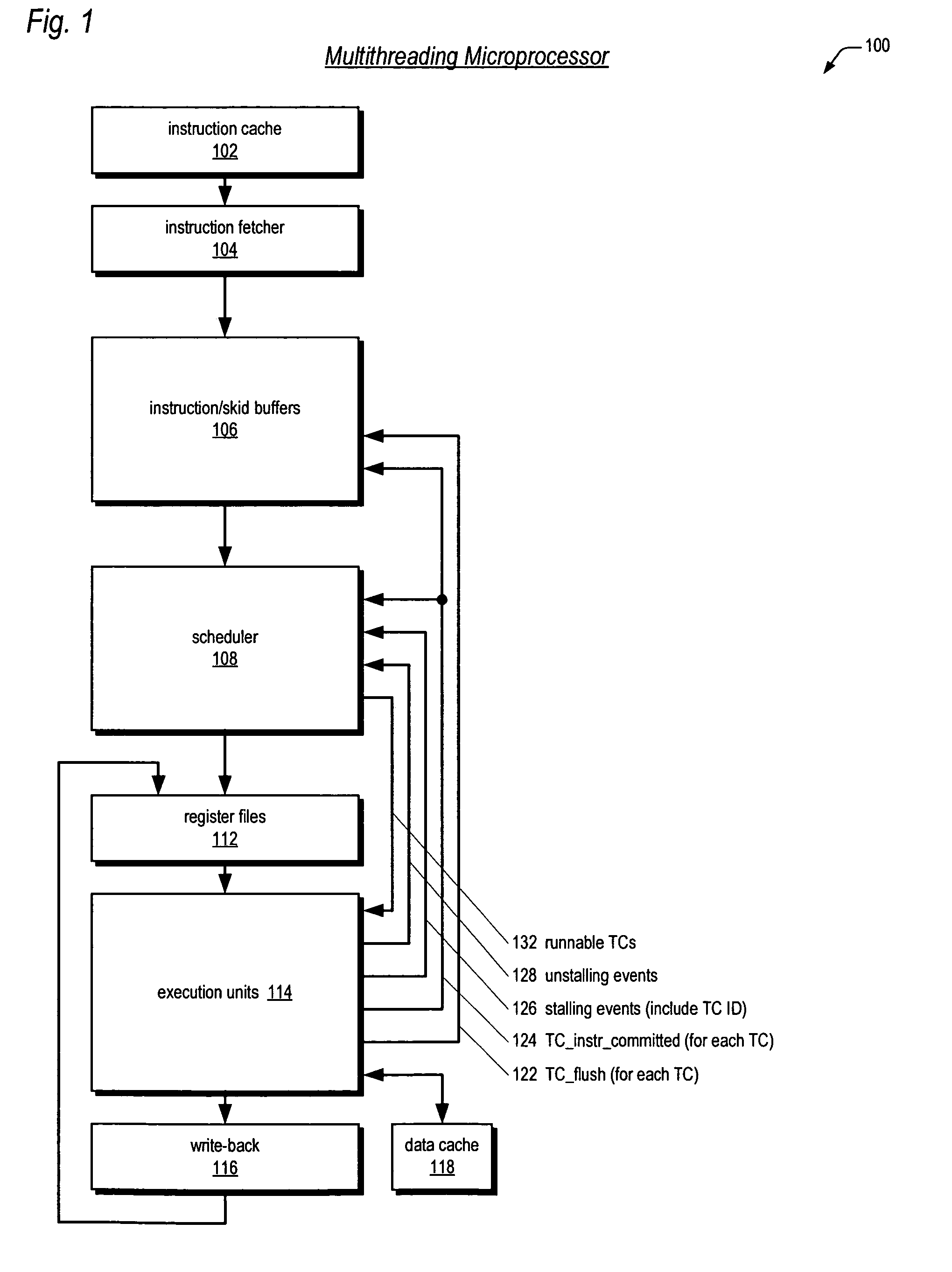
Computer Processors With Plural, Pipelined Hardware Threads Of Execution
InactiveUS20090260013A1Digital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsHardware threadParallel computing
Computer processors and methods of operation of computer processors that include a plurality of pipelined hardware threads of execution, each thread including a plurality of computer program instructions; an instruction decoder that determines dependencies and latencies among instructions of a thread; and an instruction dispatcher that arbitrates, in the presence of resource contention and in accordance with the dependencies and latencies, priorities for dispatch of instructions from the plurality of threads of execution.
Owner:IBM CORP
Coalescing adjacent gather/scatter operations
ActiveUS20140181464A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsMemory addressExecution unit
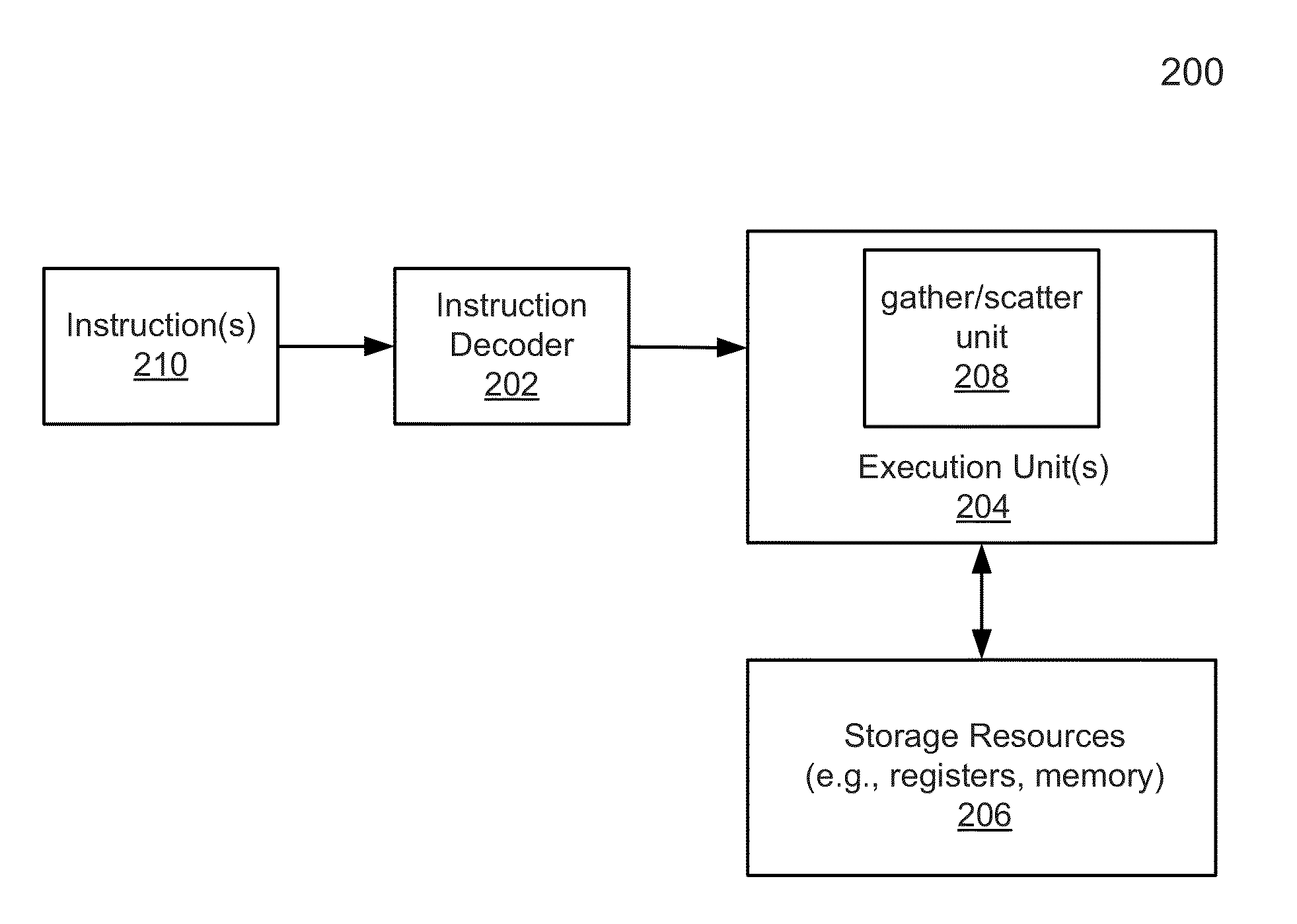
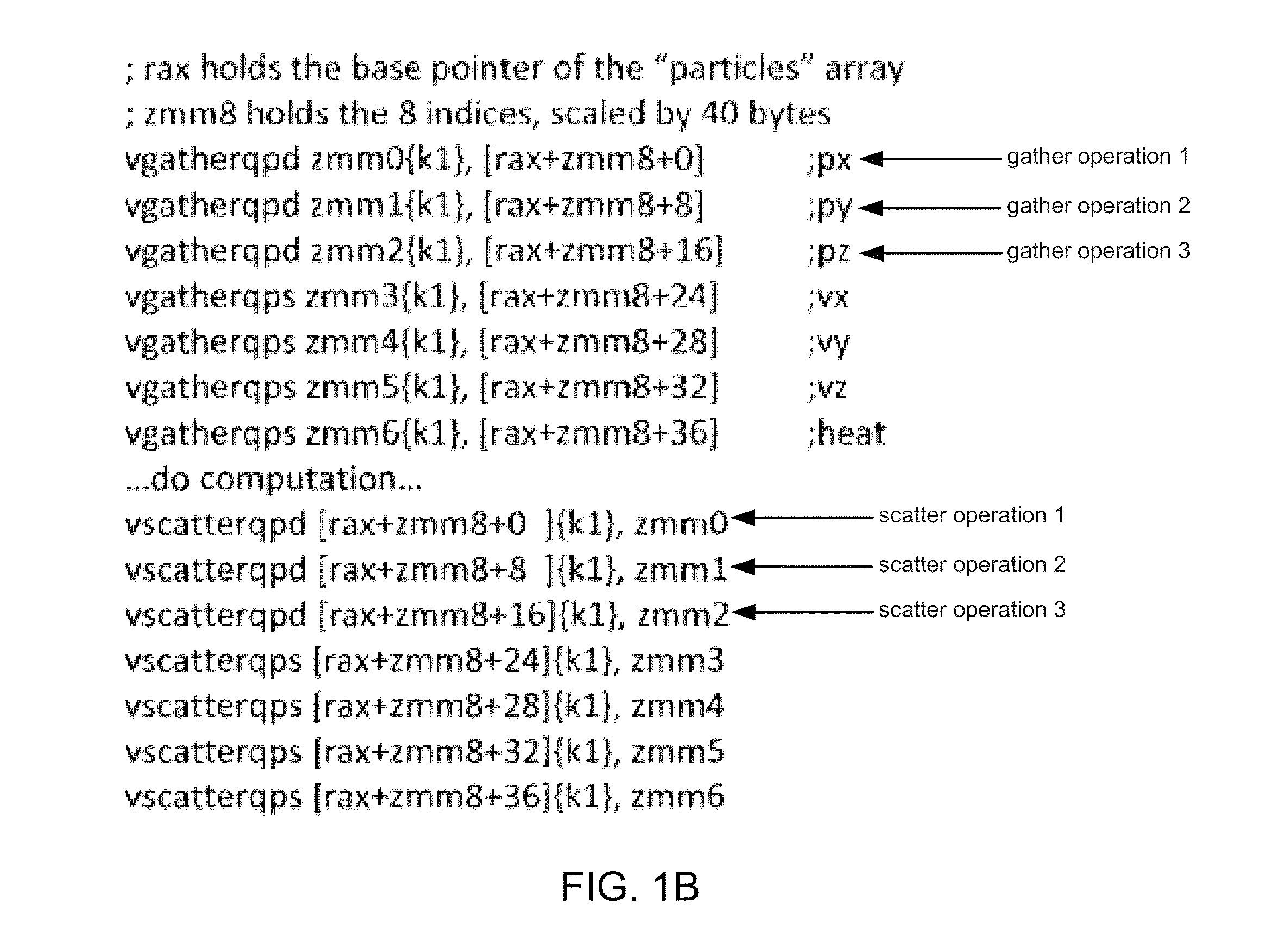
According to one embodiment, a processor includes an instruction decoder to decode a first instruction to gather data elements from memory, the first instruction having a first operand specifying a first storage location and a second operand specifying a first memory address storing a plurality of data elements. The processor further includes an execution unit coupled to the instruction decoder, in response to the first instruction, to read contiguous a first and a second of the data elements from a memory location based on the first memory address indicated by the second operand, and to store the first data element in a first entry of the first storage location and a second data element in a second entry of a second storage location corresponding to the first entry of the first storage location.
Owner:INTEL CORP
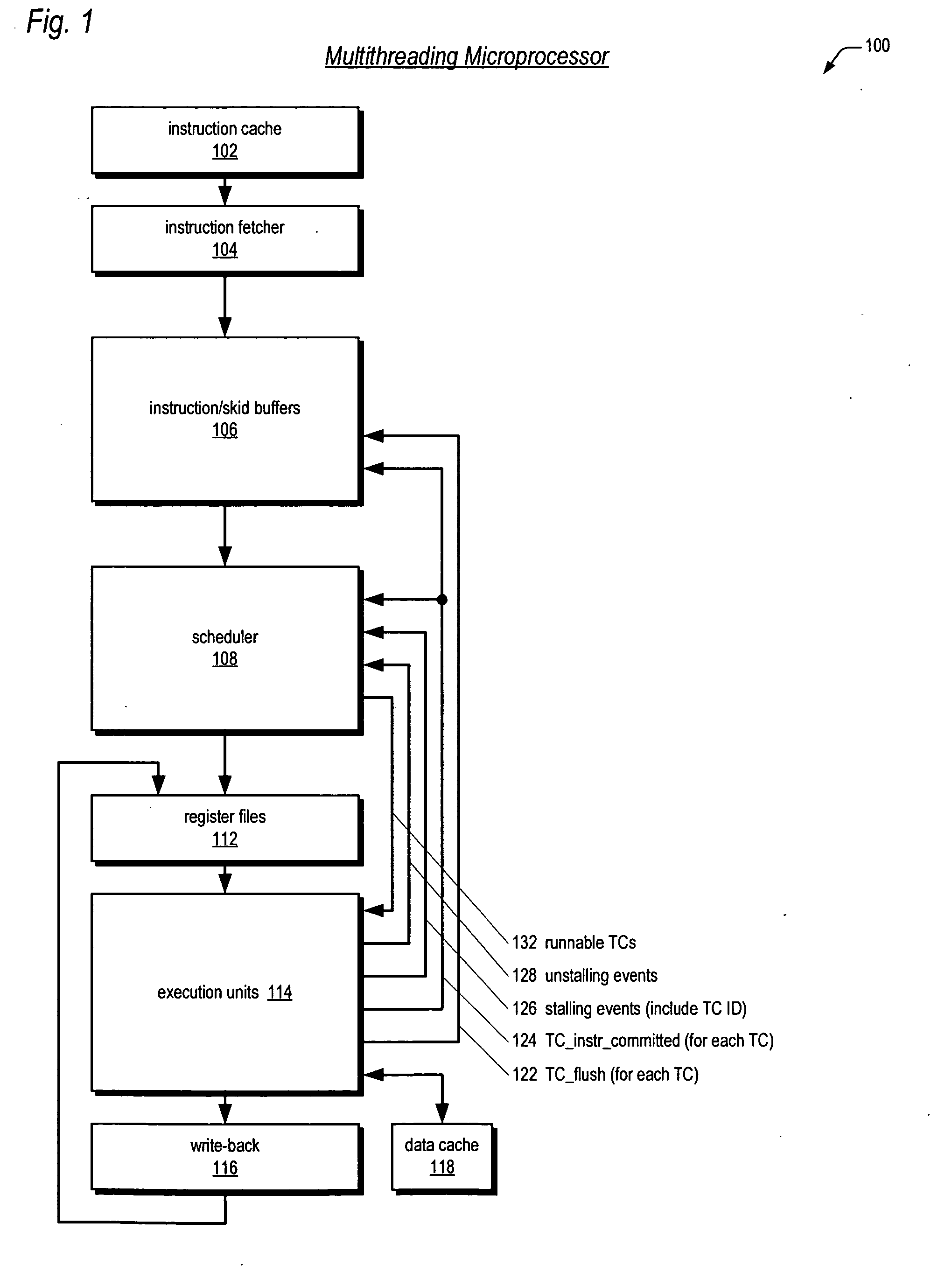
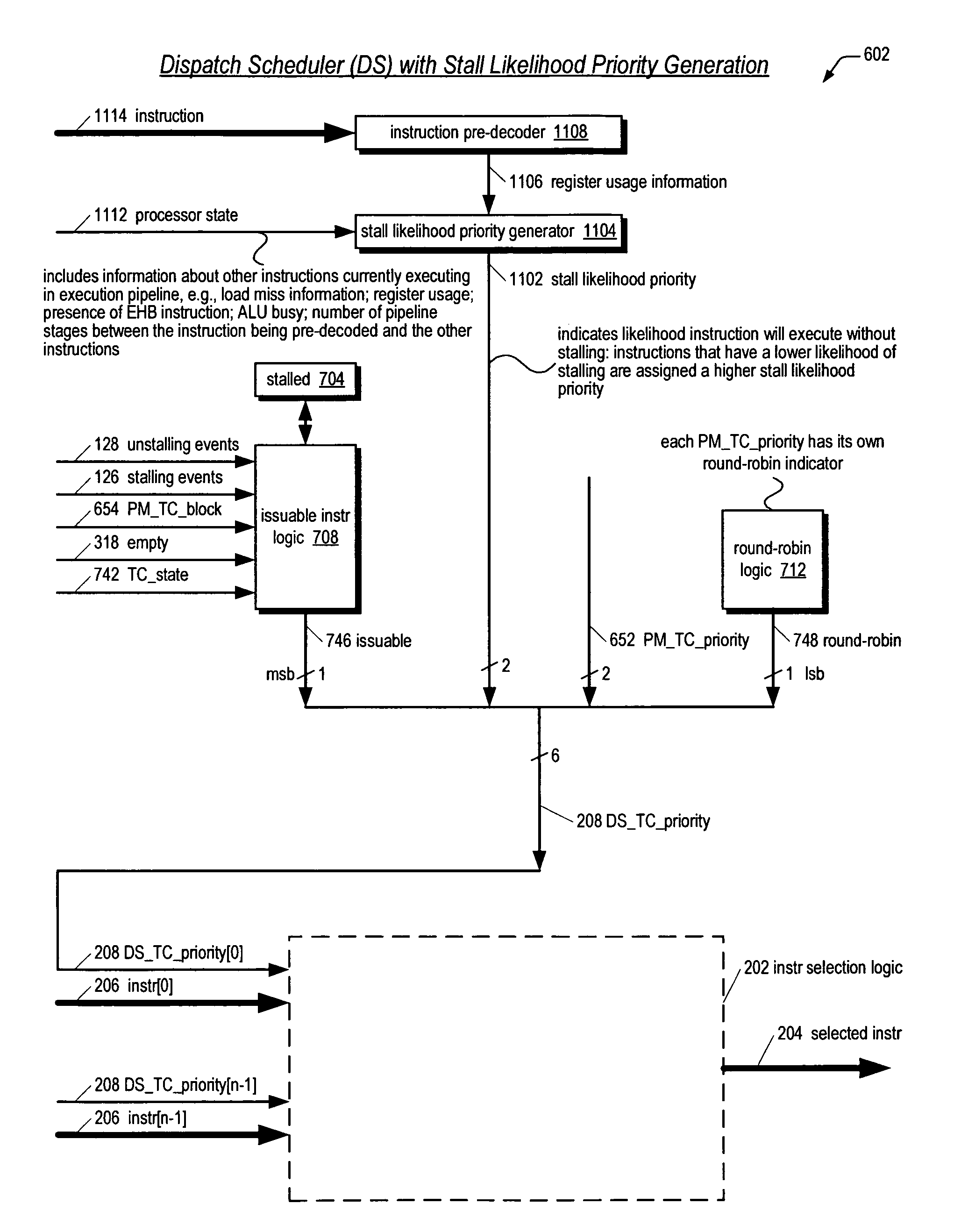
Multithreading processor including thread scheduler based on instruction stall likelihood prediction
ActiveUS20060179280A1Increase processor efficiencyReduce in quantityDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsLoad instructionScheduling instructions
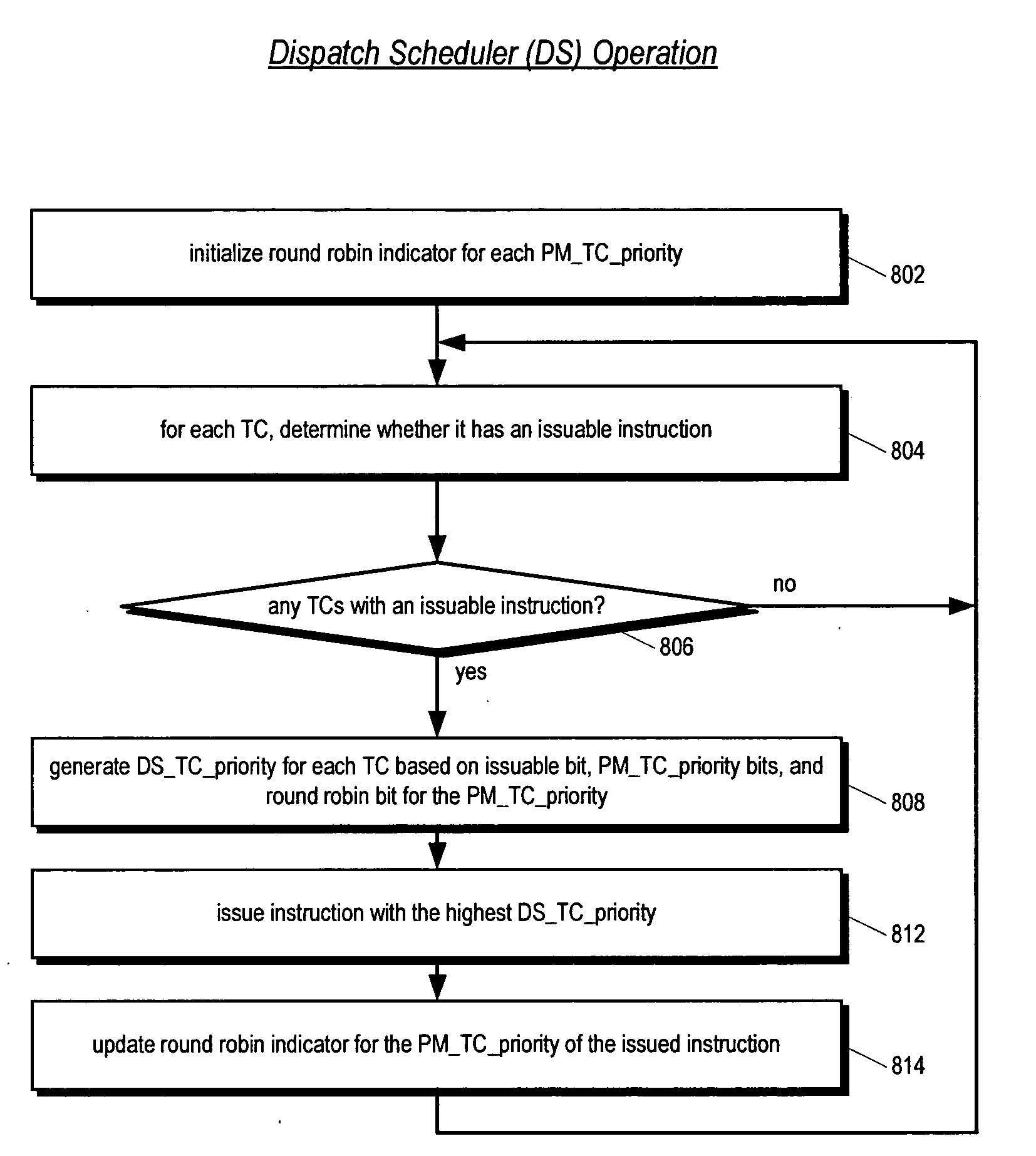
An apparatus for scheduling dispatch of instructions among a plurality of threads being concurrently executed in a multithreading processor is provided. The apparatus includes an instruction decoder that generate register usage information for an instruction from each of the threads, a priority generator that generates a priority for each instruction based on the register usage information and state information of instructions currently executing in an execution pipeline, and selection logic that dispatches at least one instruction from at least one thread based on the priority of the instructions. The priority indicates the likelihood the instruction will execute in the execution pipeline without stalling. For example, an instruction may have a high priority if it has little or no register dependencies or its data is known to be available; or may have a low priority if it has strong register dependencies or is an uncacheable or synchronized storage space load instruction.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
Data processing apparatus and method for performing arithmetic operations in SIMD data processing
ActiveUS20050125476A1Improve accuracyReduce in quantityInstruction analysisComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerData memory
A data processing apparatus, method and a computer program product. A data processing apparatus comprising: a register data store operable to store data elements; an instruction decoder operable to decode an arithmetic returning high half instruction; a data processor operable to perform data processing operations controlled by said instruction decoder wherein: in response to said decoded arithmetic returning high half instruction, said data processor is operable to specify within said register data store, one or more source registers operable to store a plurality of source data elements of a first size, and one or more destination registers operable to store a corresponding plurality of resultant data elements of a second size, said second size being half the size of said first size; and to perform the following operations in parallel on said plurality of source data elements to produce said corresponding plurality of resultant data elements: perform an arithmetic operation on said source registers specified by said instruction to produce a plurality of corresponding intermediate result data elements; form said resultant data elements from information derived from a high half of a corresponding one of said plurality of intermediate result data elements; store said resultant data elements in said destination register.
Owner:ARM LTD
Error detection method and system for processors that employ alternating threads
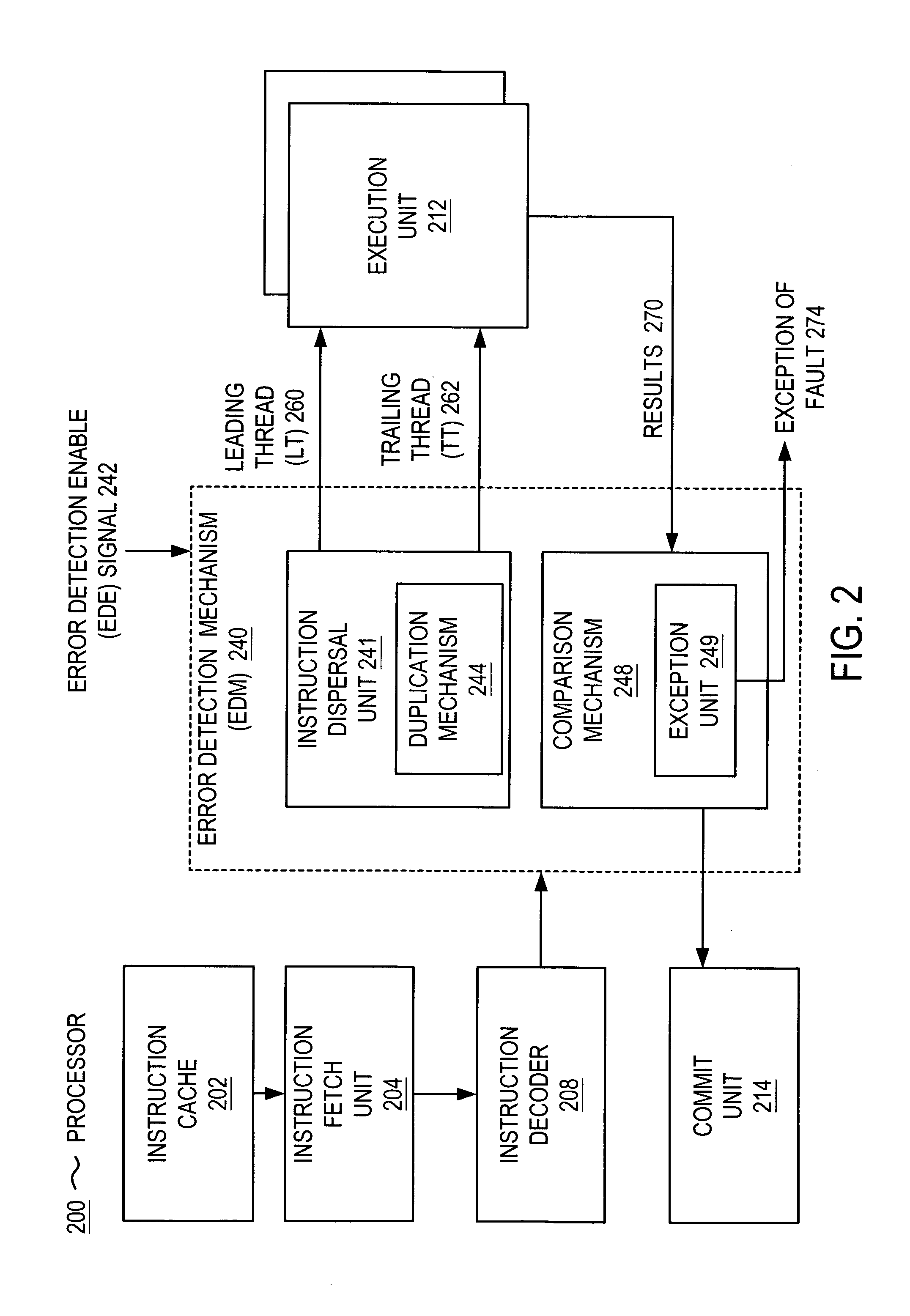
InactiveUS20050138478A1Program controlRedundant operation error correctionParallel computingExecution unit
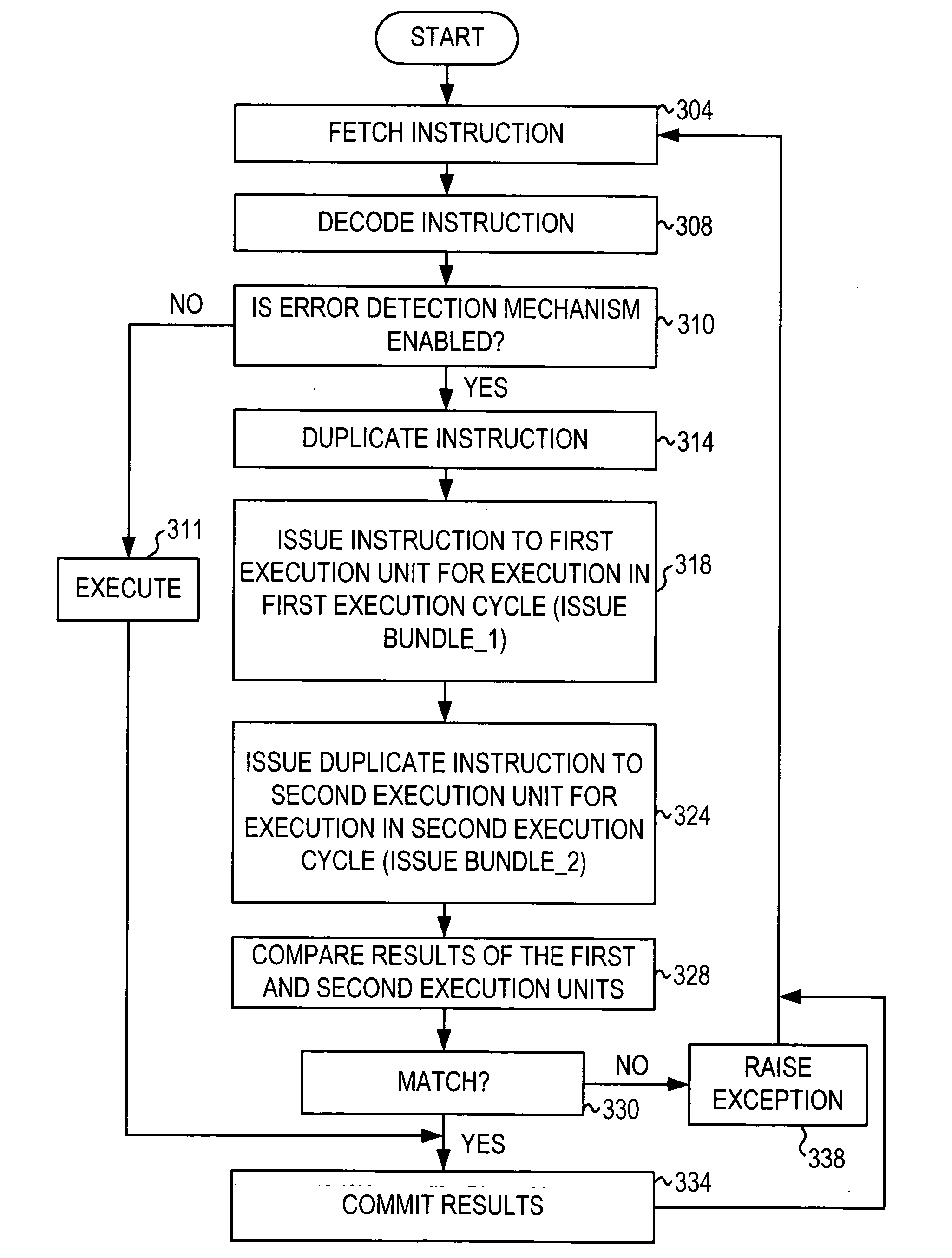
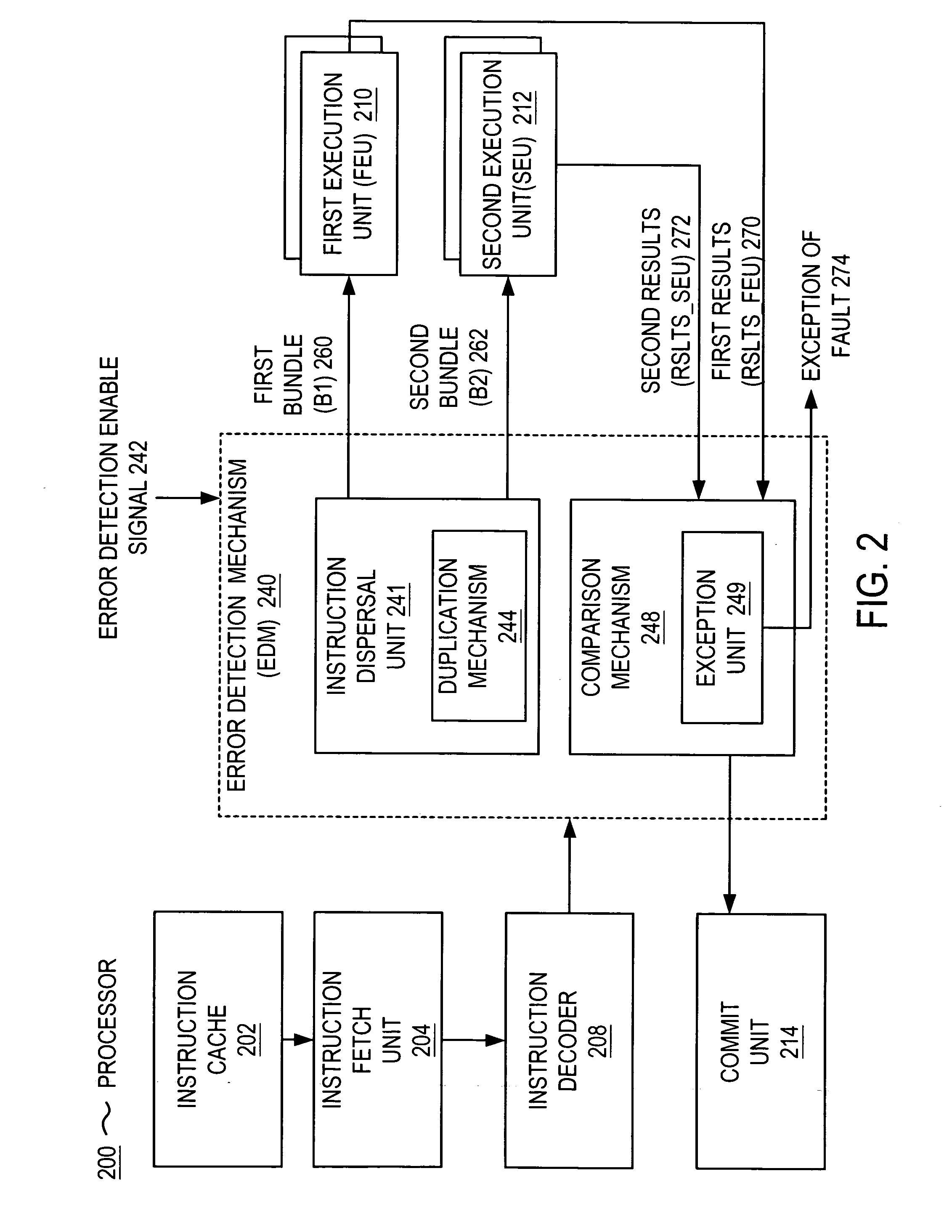
Microprocessor that includes a mechanism for detecting soft errors. The processor includes an instruction fetch unit for fetching an instruction and an instruction decoder for decoding the instruction. The mechanism for detecting soft errors includes duplication hardware for duplicating the instruction and comparison hardware. The processor further includes a first execution unit for executing the instruction in a first execution cycle and the duplicated instruction in a second execution cycle. The comparison hardware compares the results of the first execution cycle and the results of the second execution cycle. The comparison hardware can include an exception unit for generating an exception (e.g., raising a fault) when the results are not the same. The processor also includes a commit unit for committing one of the results when the results are the same.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
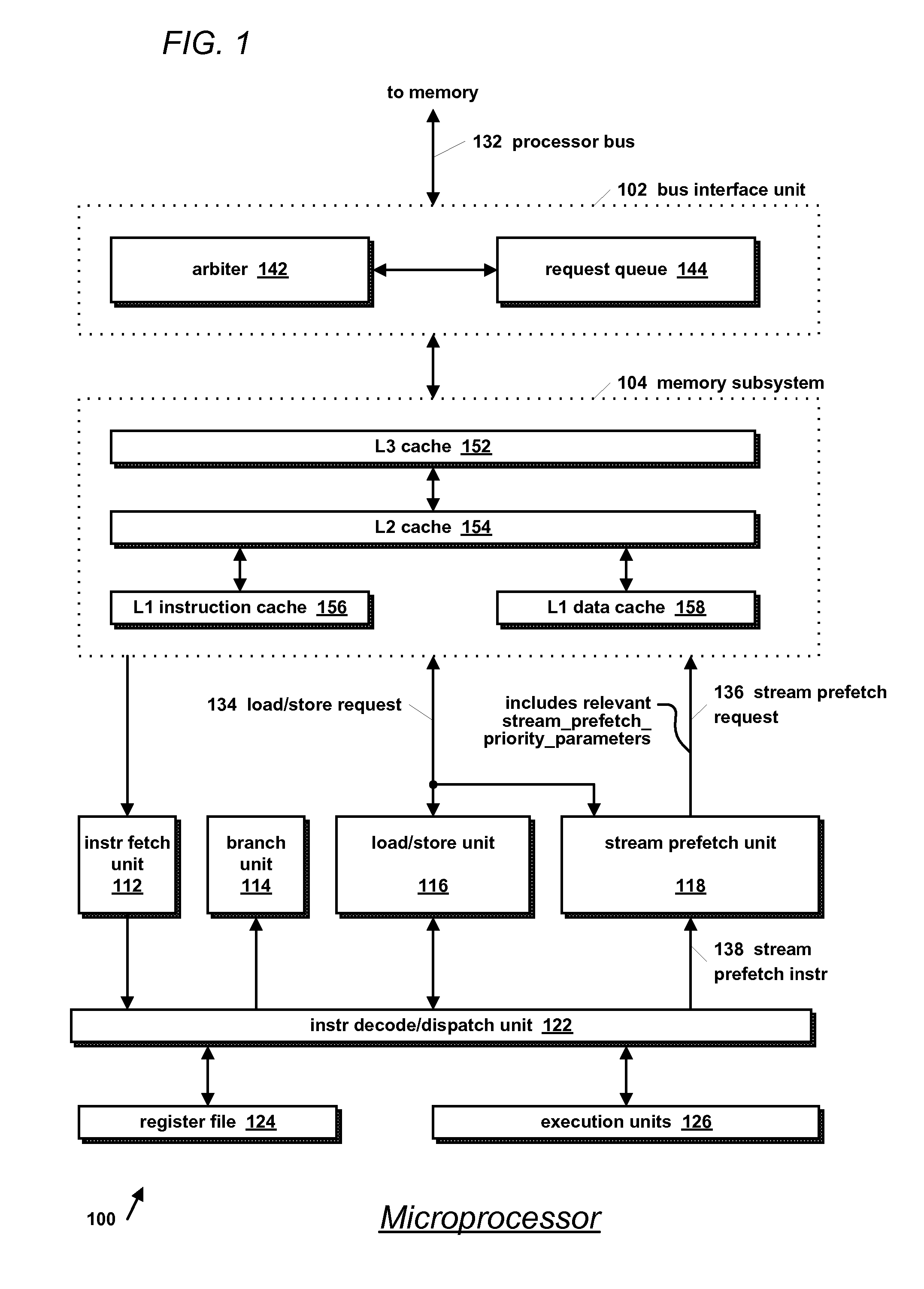
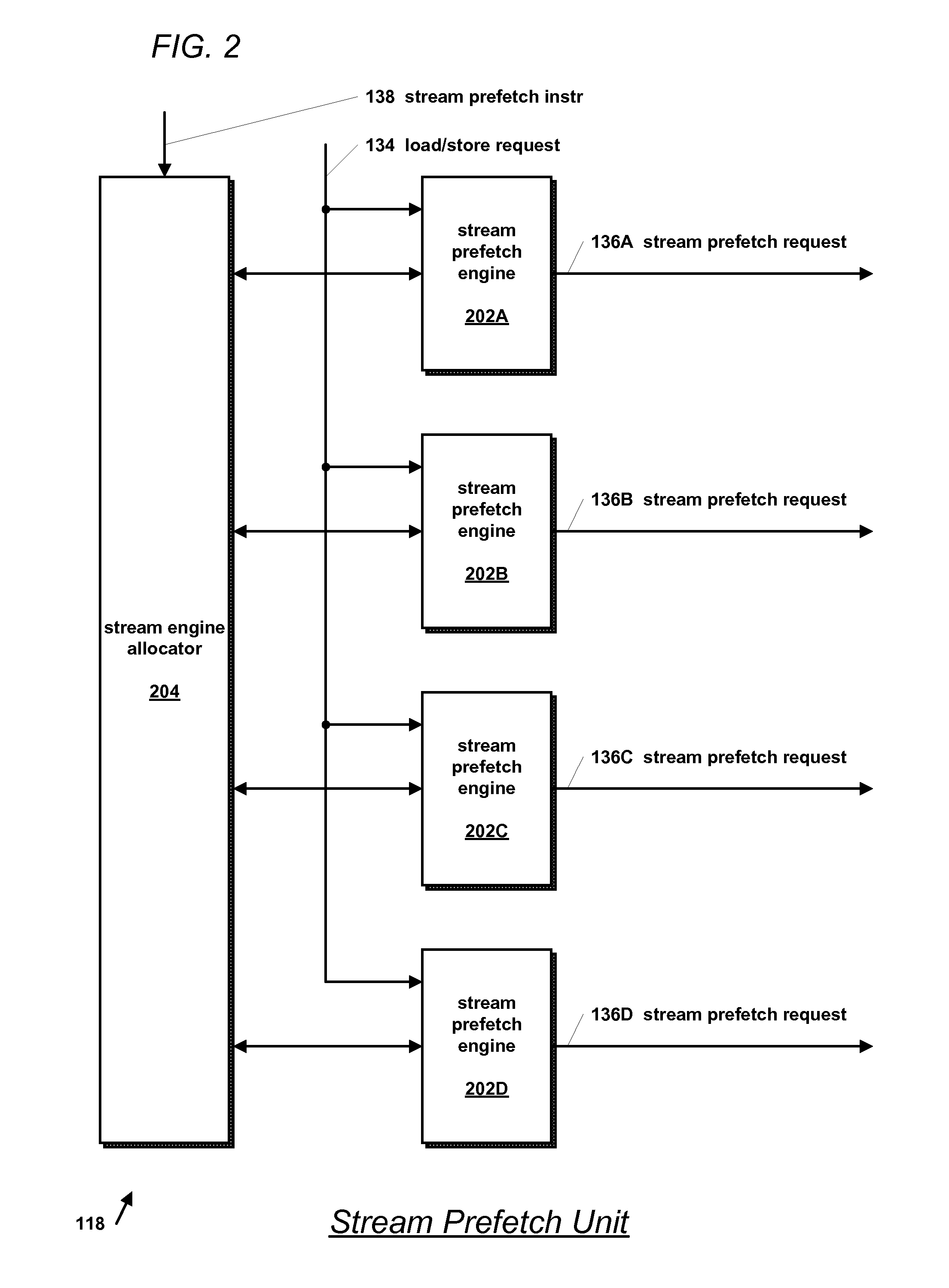
Microprocessor with improved data stream prefetching
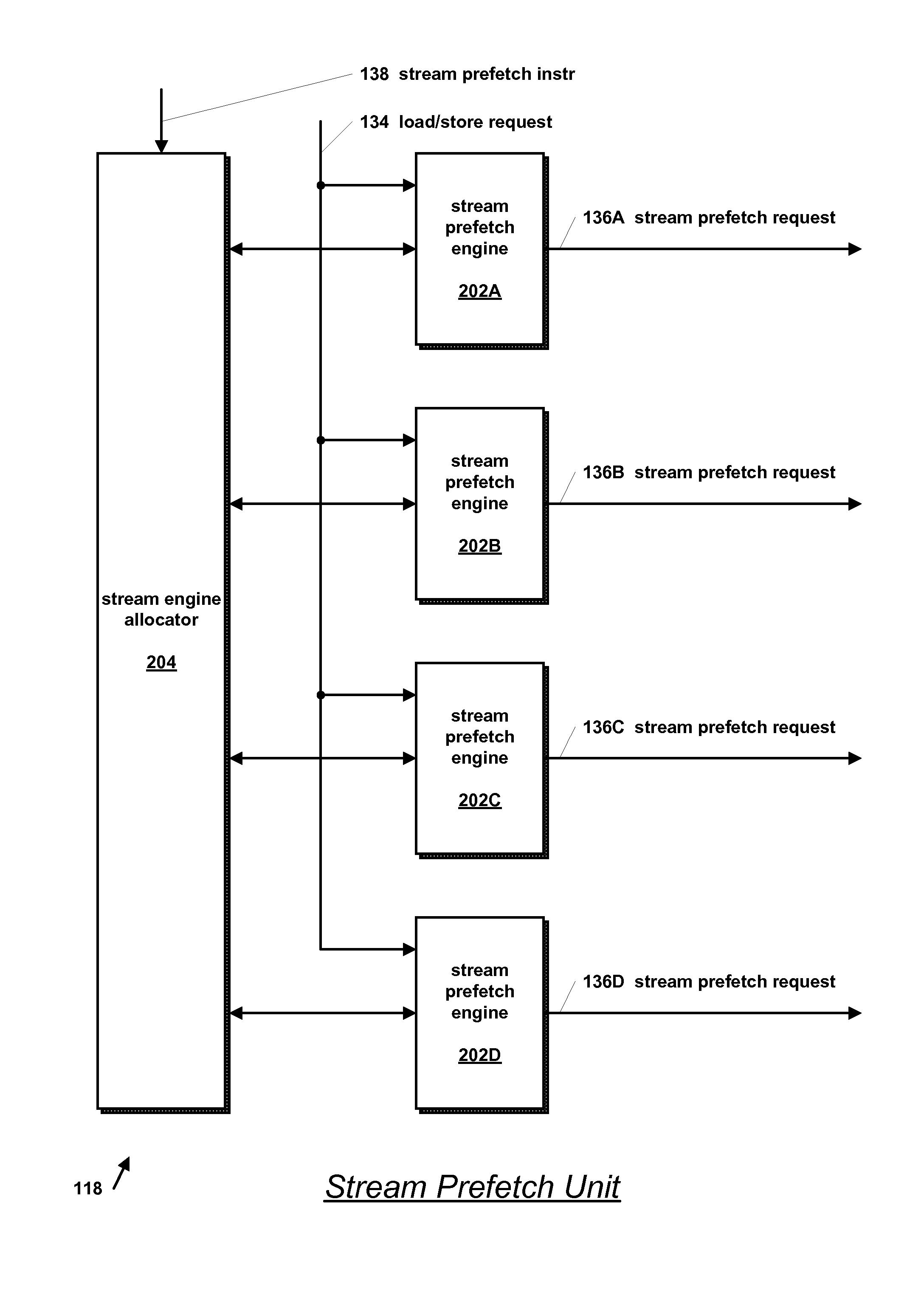
InactiveUS20070043908A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital computer detailsMicroprocessorDataflow
A microprocessor includes a hierarchical memory subsystem, an instruction decoder, and a stream prefetch unit. The decoder decodes an instruction that specifies a locality characteristic parameter. In one embodiment, the parameter specifies a relative urgency with which a data stream specified by the instruction is needed rather than specifying exactly which of the cache memories in the hierarchy to prefetch the data stream into. The prefetch unit selects one of the cache memory levels in the hierarchy for prefetching the data stream into based on the memory subsystem configuration and on the relative urgency. In another embodiment, the prefetch unit instructs the memory subsystem to mark the prefetched cache line for early, late, or normal eviction according to its cache line replacement policy based on the parameter value.
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
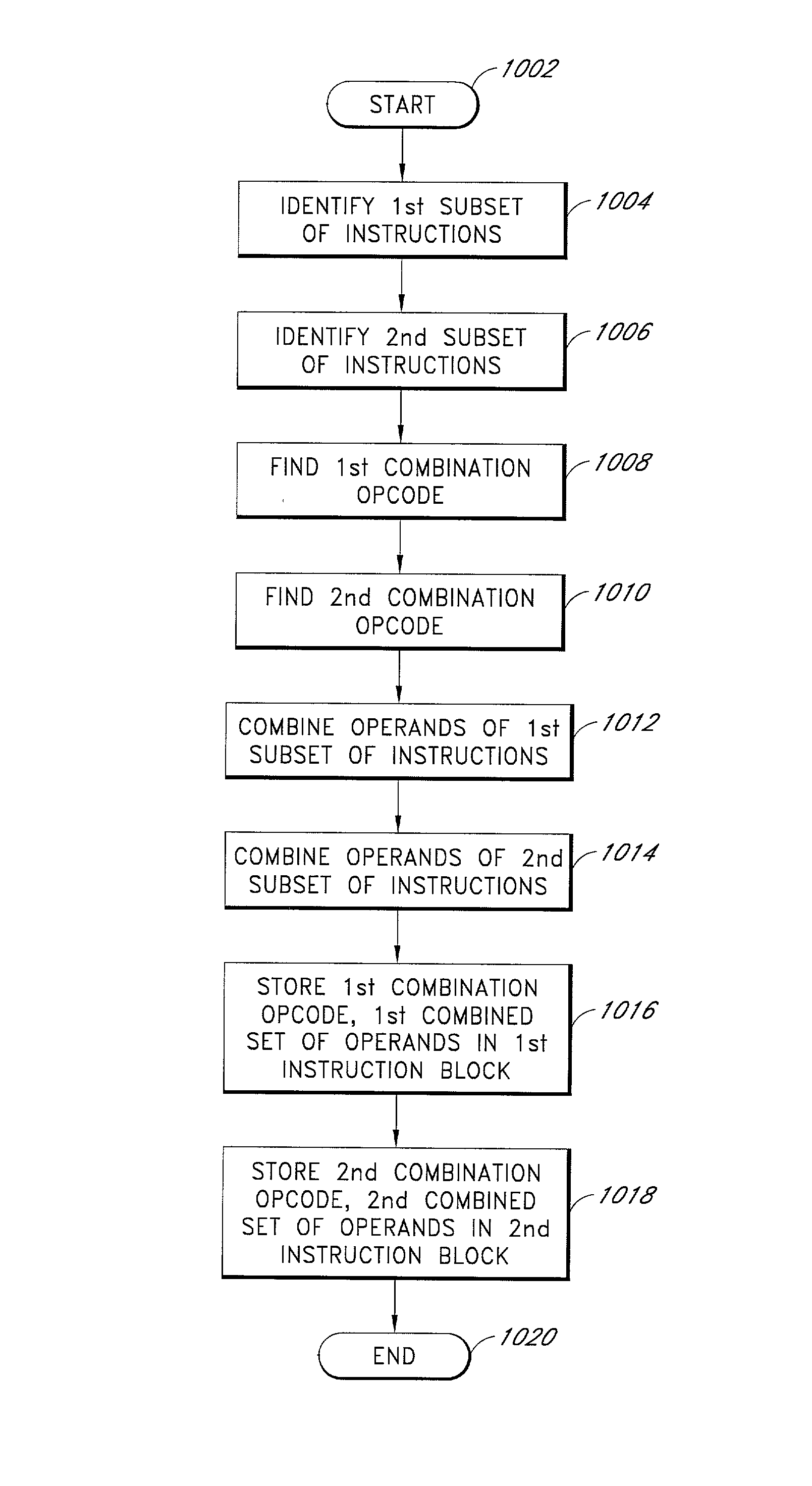
Microprocessor instruction format using combination opcodes and destination prefixes
The present application discloses an instruction format for storing multiple microprocessor instructions as one combined instruction. The instruction format includes a combination opcode field for storing a combination opcode that identifies a combination of the multiple instructions. The application also discloses an instruction format that uses prefix fields to specify the destination functional block for each combined instruction stored in an execute packet. A compiler program or an assembler program obtains from a table a combination opcode that corresponds to a combination of the multiple instructions. The table stores combination opcodes and their corresponding combinations of instructions. The compiler program or assembler program then assigns the found combination opcode to an opcode field of the combined instruction. In a trivial scenario, a single instruction can also be stored as a combined instruction. The compiler program or assembler program also uses prefix fields to identify the destination functional block of each combined instruction in an execute packet. A dispatcher identifies the prefix fields and sends each combined instruction in the execute packet to its destination functional block. An instruction decoder identifies the combination opcode of the combined instruction, separates the combined instruction into the multiple individual instructions, and sends each individual instruction to its respective functional unit for execution.
Owner:AVAZ NETWORKS
Apparatus and method for performing multiplication operations
InactiveUS20020116434A1Reduce power consumptionComputation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsReverse orderParallel computing
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for processing data using a multiplying circuit for performing a multiplication of a W / 2 bit data value by a W bit data value. An instruction decoder is provided which is responsive to a multiply instruction to control the multiplying circuit to generate a multiplication result for the computation MxN, where M and N are W bit data words. The multiplying circuit is arranged to execute a first operation in the which the data word N is multiplied by the most significant W / 2 bits of the data word M to generate a first intermediate result having 3W / 2 bits, and to then execute a second operation in which the data word N is multiplied by the least significant W / 2 bits of the data word M to generate a second intermediate result having 3W / 2 bits. The first intermediate result is shifted by W / 2 with respect to the second intermediate result and added to the second intermediate result to generate the multiplication result. By performing the two parts of the multiplication in reverse order to the conventional approach, it has been found that the complexity of the circuitry can be reduced, and a reduction in power consumption can be achieved.
Owner:ARM LTD
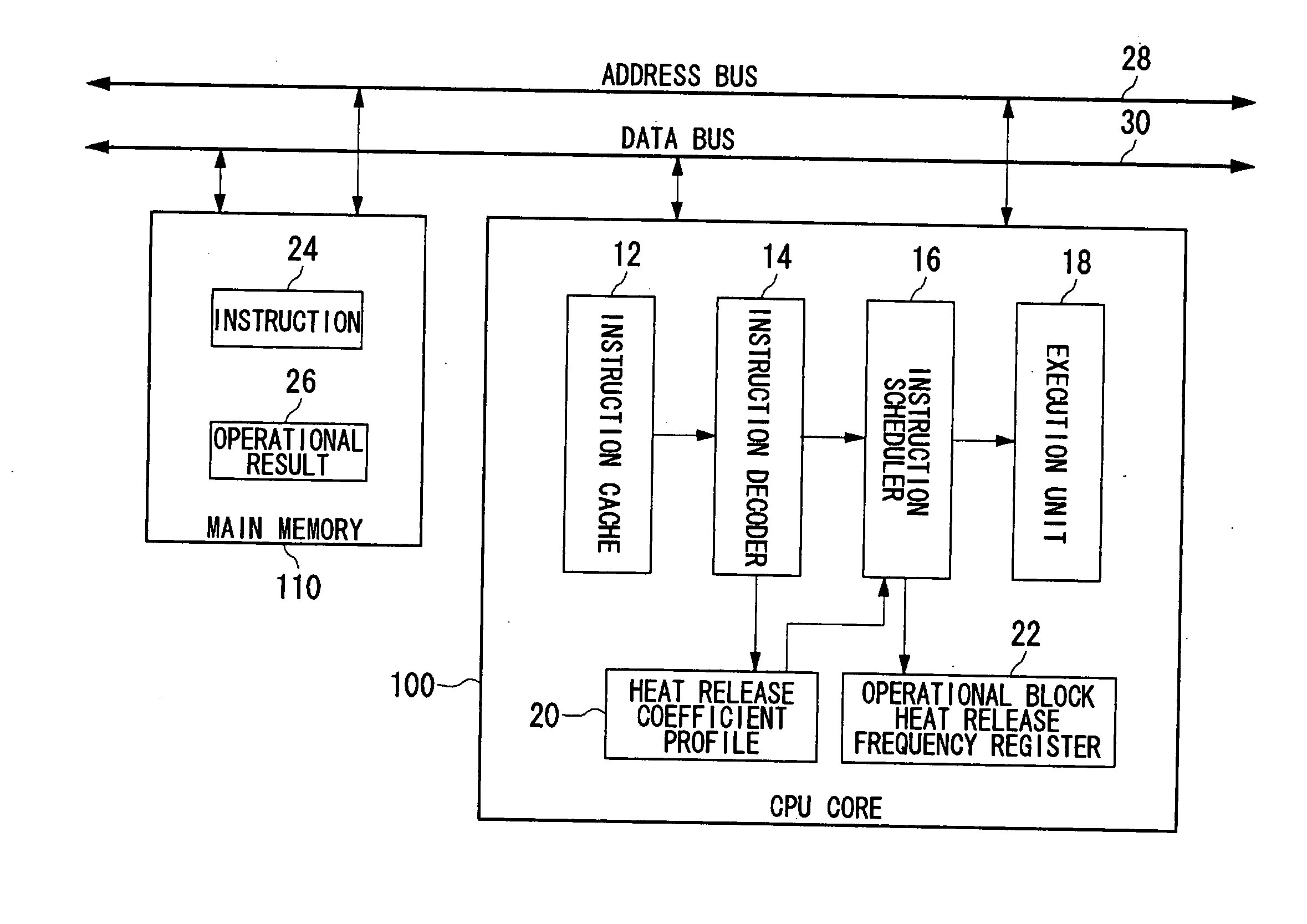
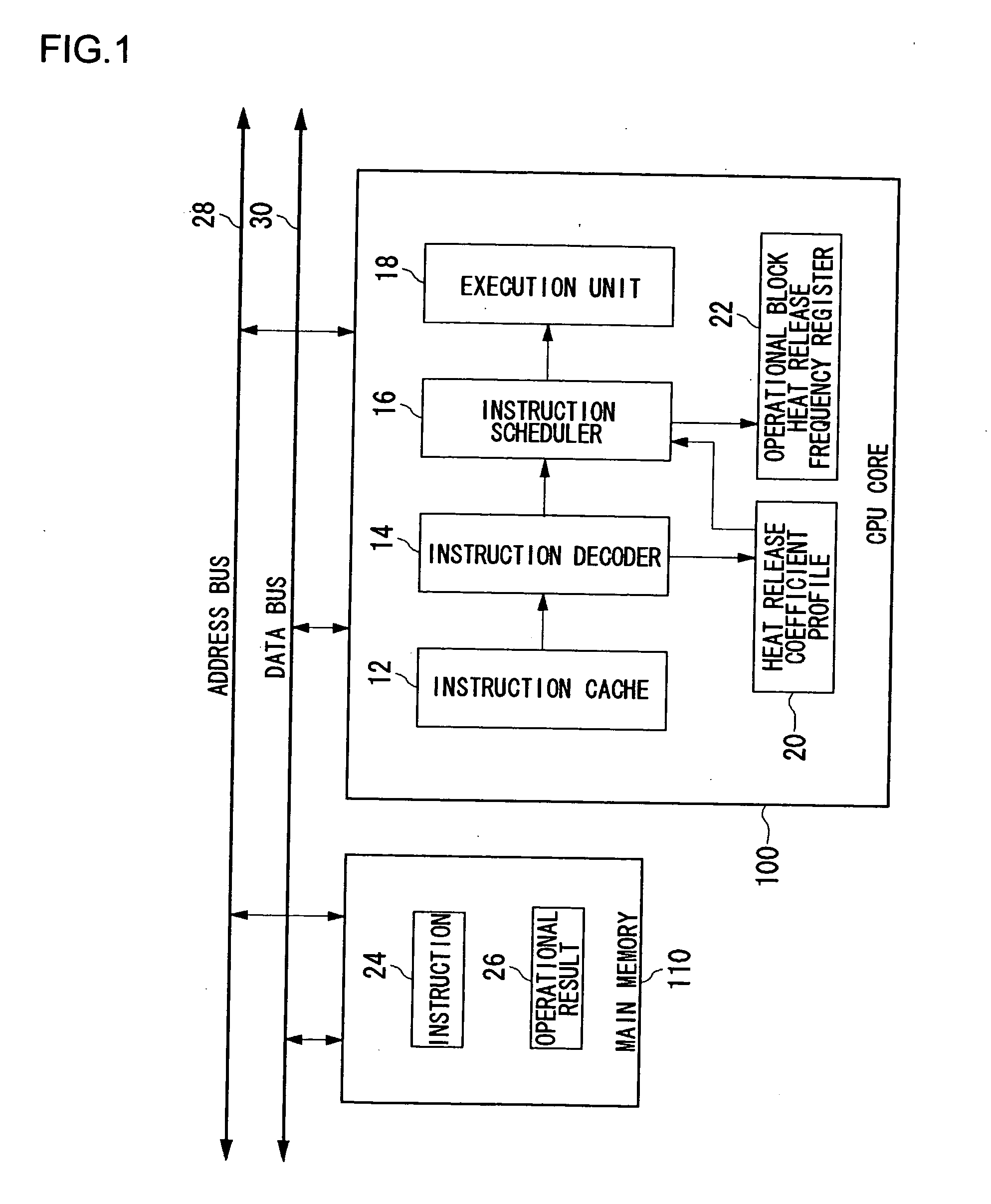
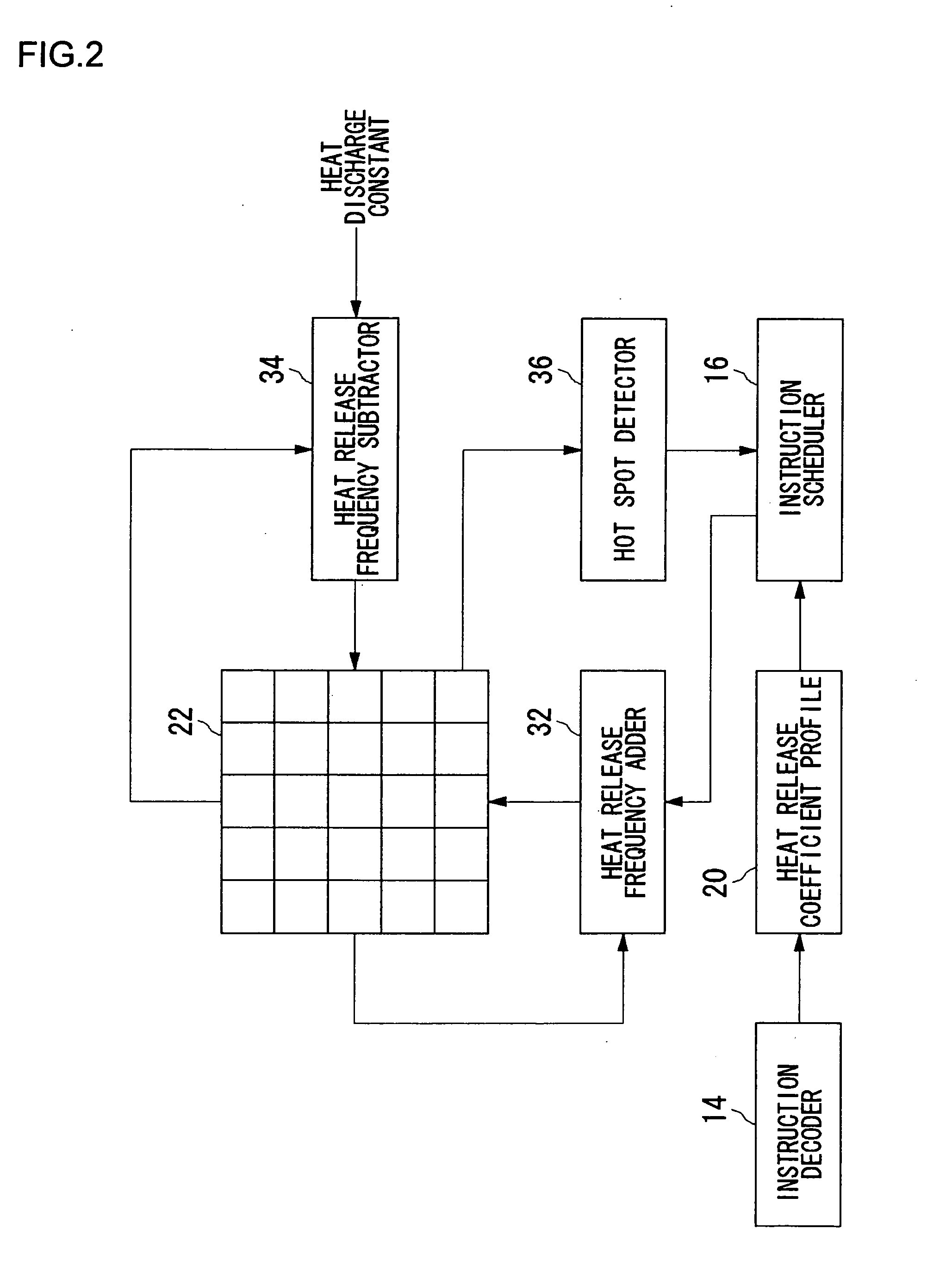
Processor, multiprocessor system, processor system, information processing apparatus, and temperature control method
InactiveUS20070198134A1Avoid misuseWithout incurring degradation in processor performanceEnergy efficient ICTResource allocationTemperature controlInformation processing
An instruction decoder identifies, for each instruction, an operational block involved in the execution of the instruction and an associated heat release coefficient. The instruction decoder stores identified information in a heat release coefficient profile. An instruction scheduler schedules the instructions in accordance with the dependence of the instructions on data. A heat release frequency adder cumulatively adds the heat release coefficient to the heat release frequency of the operational block held in the operational block heat release frequency register as the execution of the scheduled instructions proceeds. A heat release frequency subtractor subtracts from the heat release frequency of the operational blocks in the operational block heat release frequency register in accordance with heat discharge that occurs with time. A hot spot detector detects an operational block with its heat release frequency, held in the operational block heat release frequency register, exceeding a predetermined threshold value as a hot spot. The instruction scheduler delays the execution of the instruction involving for its execution the operational block identified as a hot spot.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
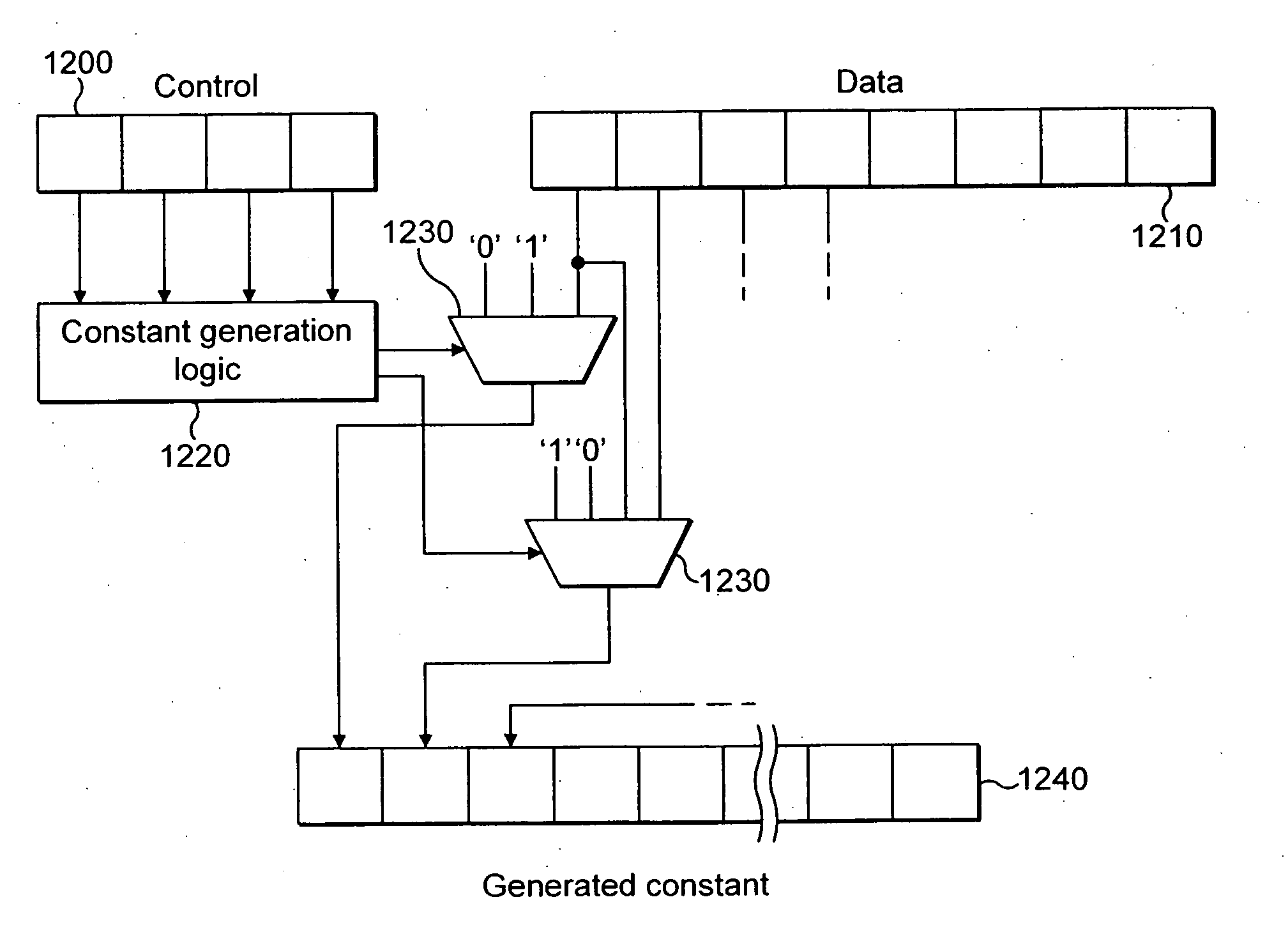
Constant generation in SIMD processing
A data processing apparatus (2) comprising: a register data store operable to store data elements; an instruction decoder (14, 16) operable to decode an instruction with generated constant, said instruction having a data value associated therewith; a data processor. (18) operable to perform data processing operations within parallel processing lanes on at least one source operand in response to a data processing instruction decoded by said instruction decoder (16); and said data processor being operable in response to said decoded instruction with generated constant and associated data value to expand at least a data portion (1210) of said associated data value, said expansion being performed in response to said instruction with generated constant and depending on a selected function, to generate a constant (1240), said generated constant (1240) forming one of said at least one source operands.
Owner:ARM LTD
Data processing circuit with target instruction and prefix instruction
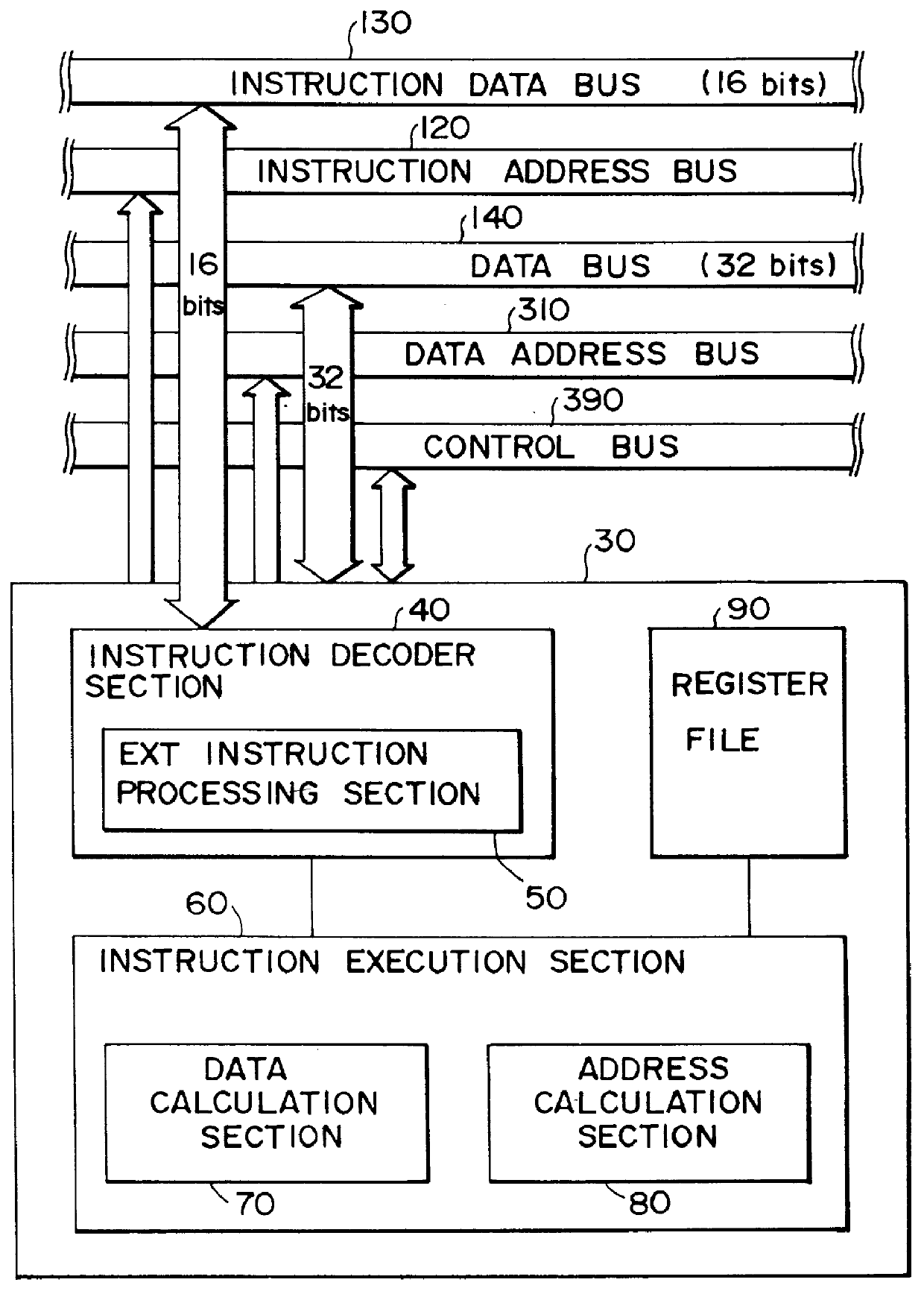
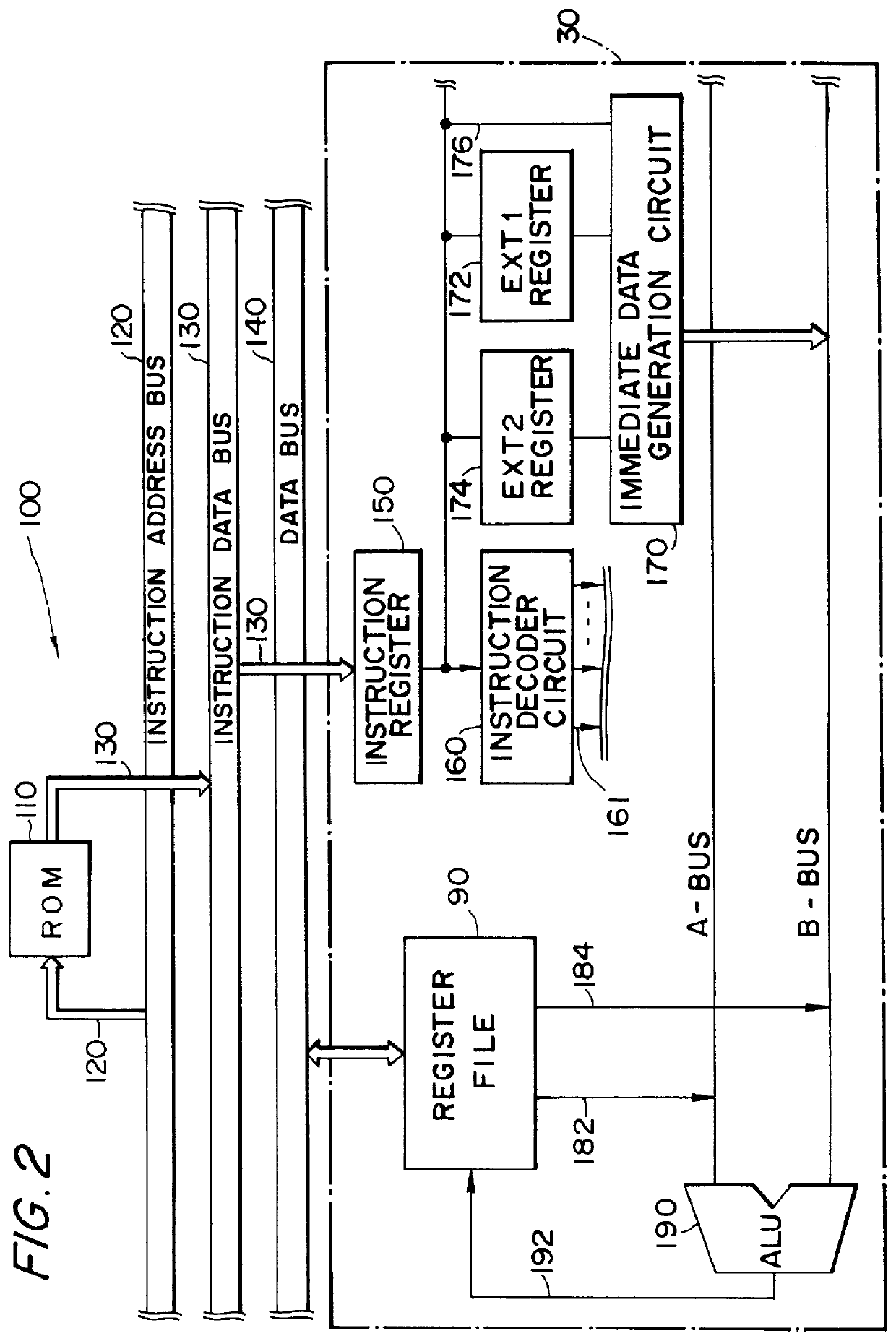
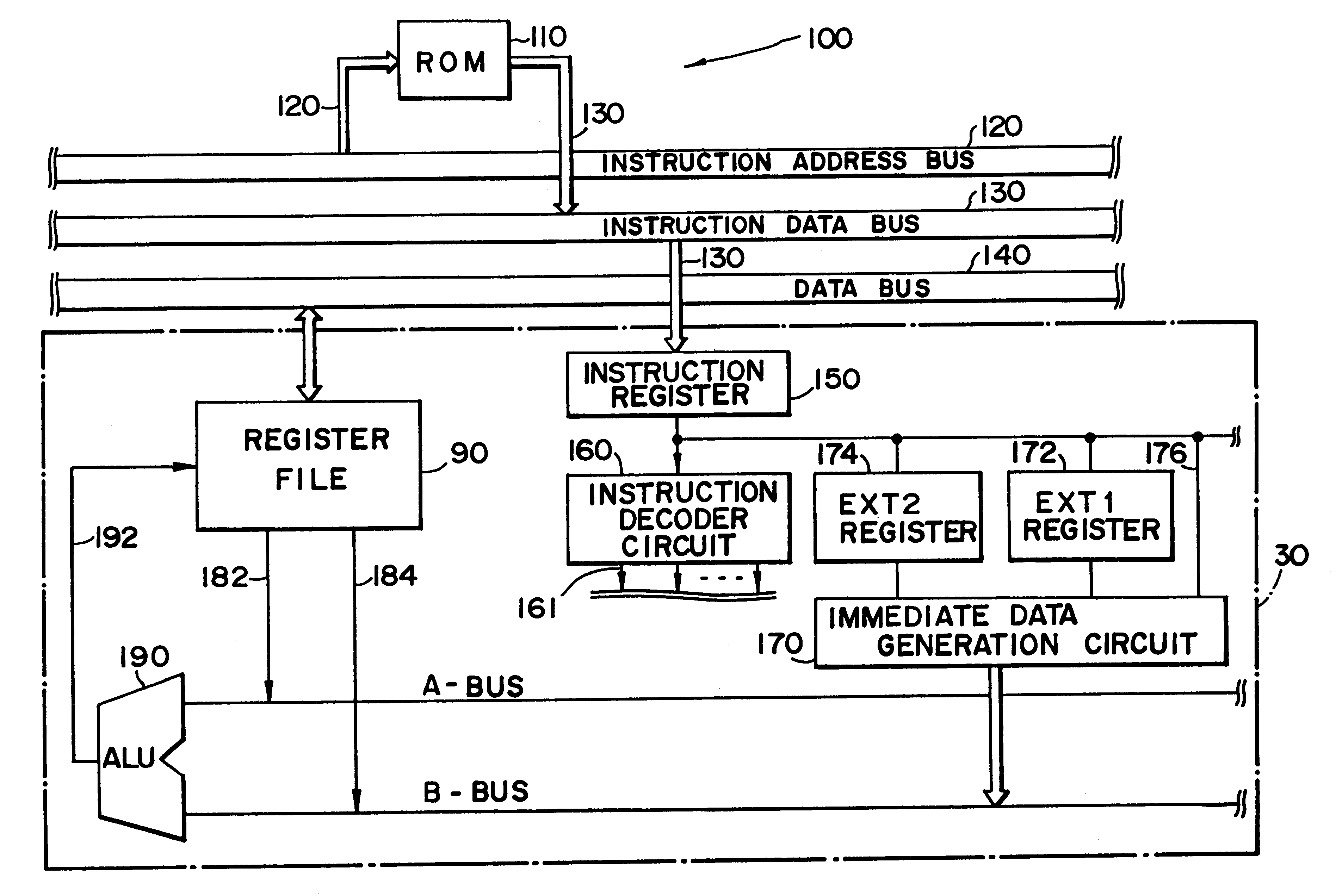
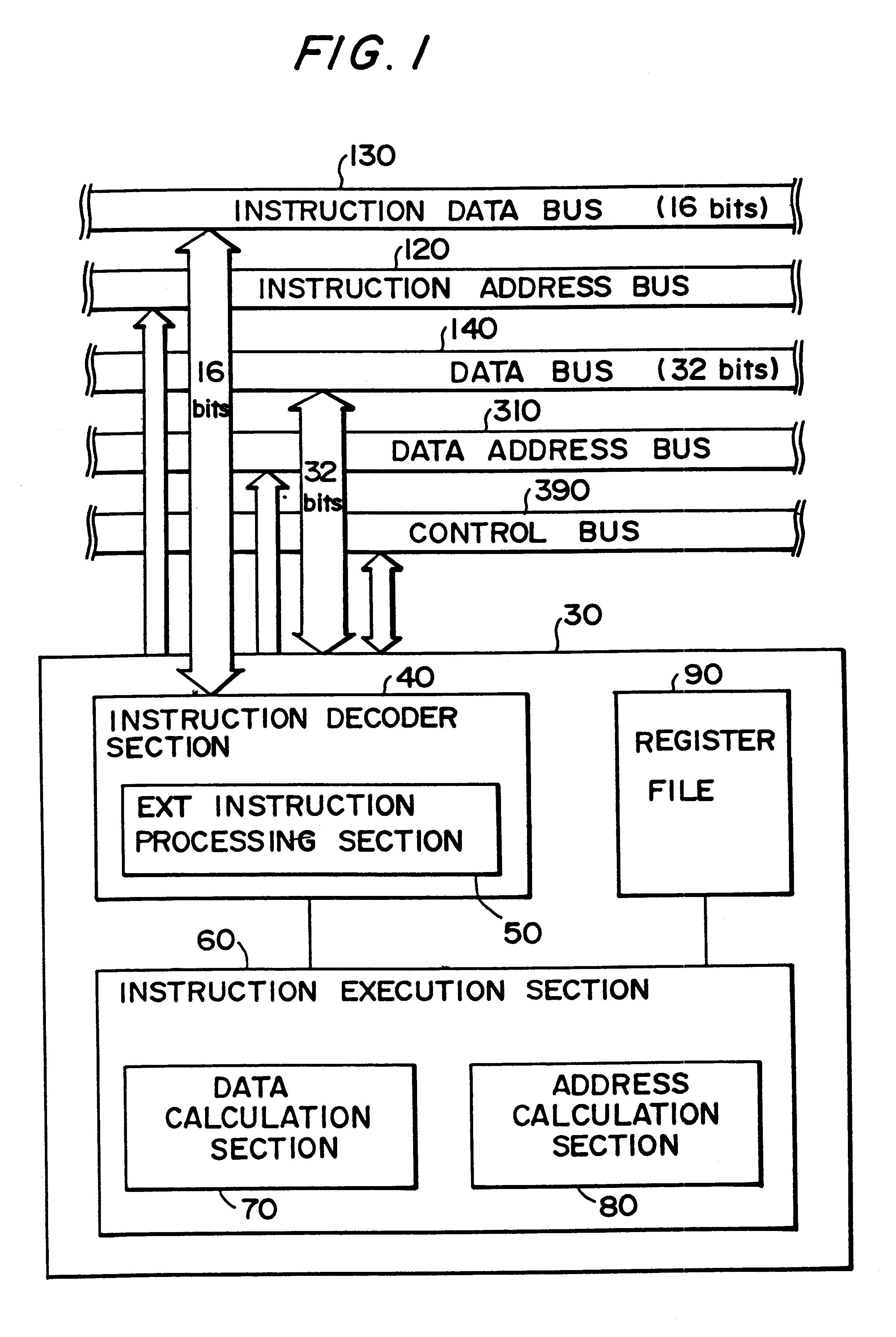
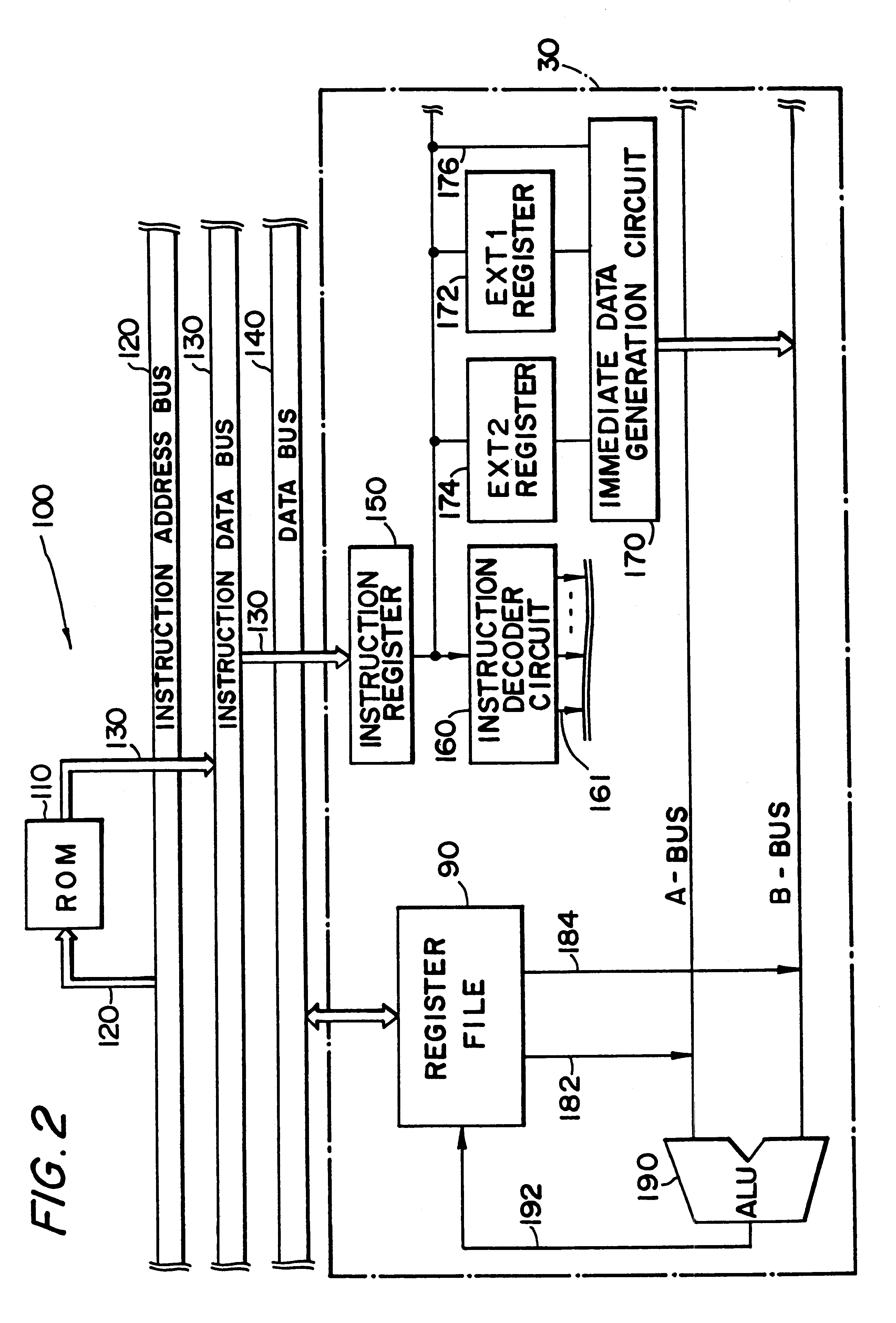
InactiveUS6167505AEasy to operateSimple structureInstruction analysisDigital computer detailsRegister fileInstruction code
A certain target instruction and a prefix instruction for expanding the function of that target instruction are input to the present data processing circuit. The data processing circuit analyzes the thus-input instruction code and performs the processing necessary for the execution of that instruction. The data processing circuit comprises an instruction decoder section, a register file, and an instruction execution section that executes the instruction based on operational details of the instruction analyzed by the instruction decoder section. The instruction decoder section comprises an ext instruction processing section that processed the expansion of immediate data from the prefix instruction.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method and apparatus for modulo scheduled loop execution in a processor architecture
InactiveUS7302557B1Suppresses increase in code sizeReduced Power RequirementsSoftware engineeringDigital computer detailsParallel computingStandard methods
A processor method and apparatus that allows for the overlapped execution of multiple iterations of a loop while allowing the compiler to include only a single copy of the loop body in the code while automatically managing which iterations are active. Since the prologue and epilogue are implicitly created and maintained within the hardware in the invention, a significant reduction in code size can be achieved compared to software-only modulo scheduling. Furthermore, loops with iteration counts less than the number of concurrent iterations present in the kernel are also automatically handled. This hardware enhanced scheme achieves the same performance as the fully-specified standard method. Furthermore, the hardware reduces the power requirement as the entire fetch unit can be deactivated for a portion of the loop's execution. The basic design of the invention involves including a plurality of buffers for storing loop instructions, each of which is associated with an instruction decoder and its respective functional unit, in the dispatch stage of a processor. Control logic is used to receive loop setup parameters and to control the selective issue of instructions from the buffers to the functional units.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Error detection method and system for processors that employs lockstepped concurrent threads
InactiveUS20050108509A1Digital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionExecution unitExecution cycle
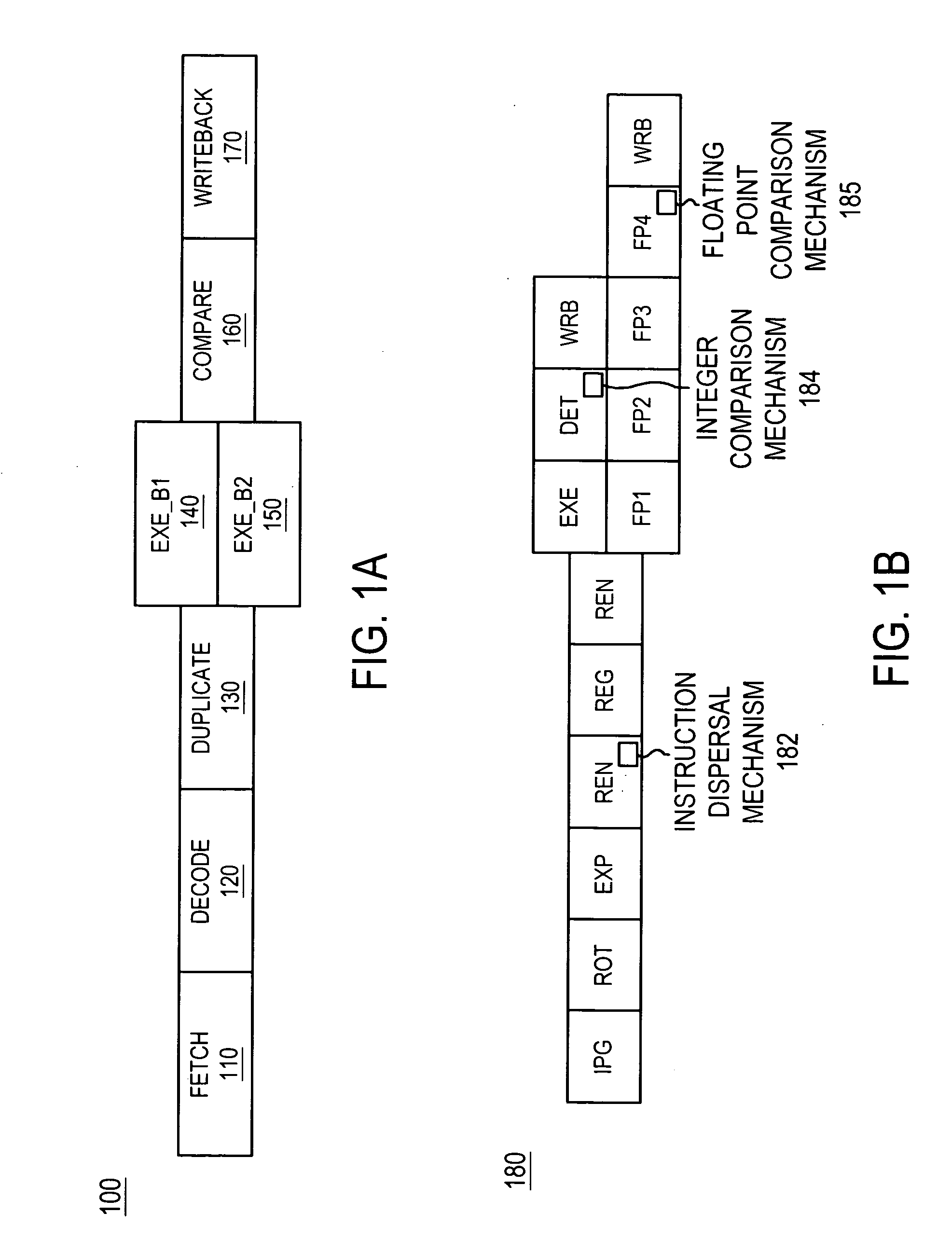
A processor that includes an in-order execution architecture for executing at least two instructions per cycle (e.g., 2n instructions are processed per cycle, where n is an integer greater than or equal to one) and at least two symmetric execution units. The processor includes an instruction fetch unit for fetching n instructions (where n is an integer greater than or equal to one) and an instruction decoder for decoding the n instruction. The error detection mechanism includes duplication hardware for duplicating the n instructions into a first bundle of n instructions and a second bundle of n instructions. A first execution unit for executing the first bundle of instructions in a first execution cycle, and a second symmetric execution unit for executing the second bundle of instructions in the first execution cycle are provided. The error detection mechanism also includes comparison hardware for comparing the results of the first execution unit and the results of the second execution unit. The comparison hardware can have an exception unit for generating an exception (e.g., raising a fault) when the results are not the same. A commit unit is provided for committing one of the results when the results are the same.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
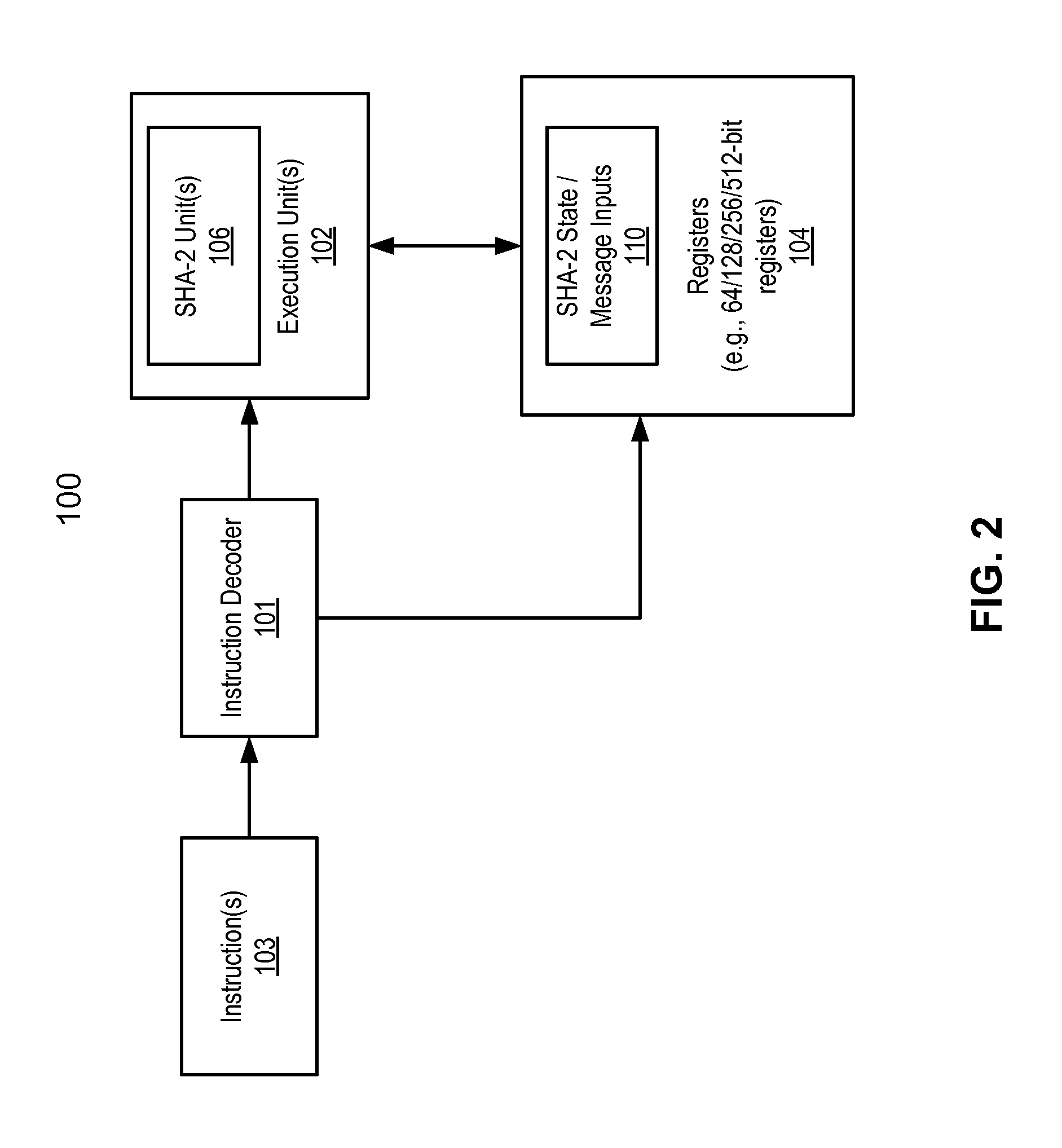
Method and apparatus to process sha-2 secure hashing algorithm
ActiveUS20140195782A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsPosition dependentOperand
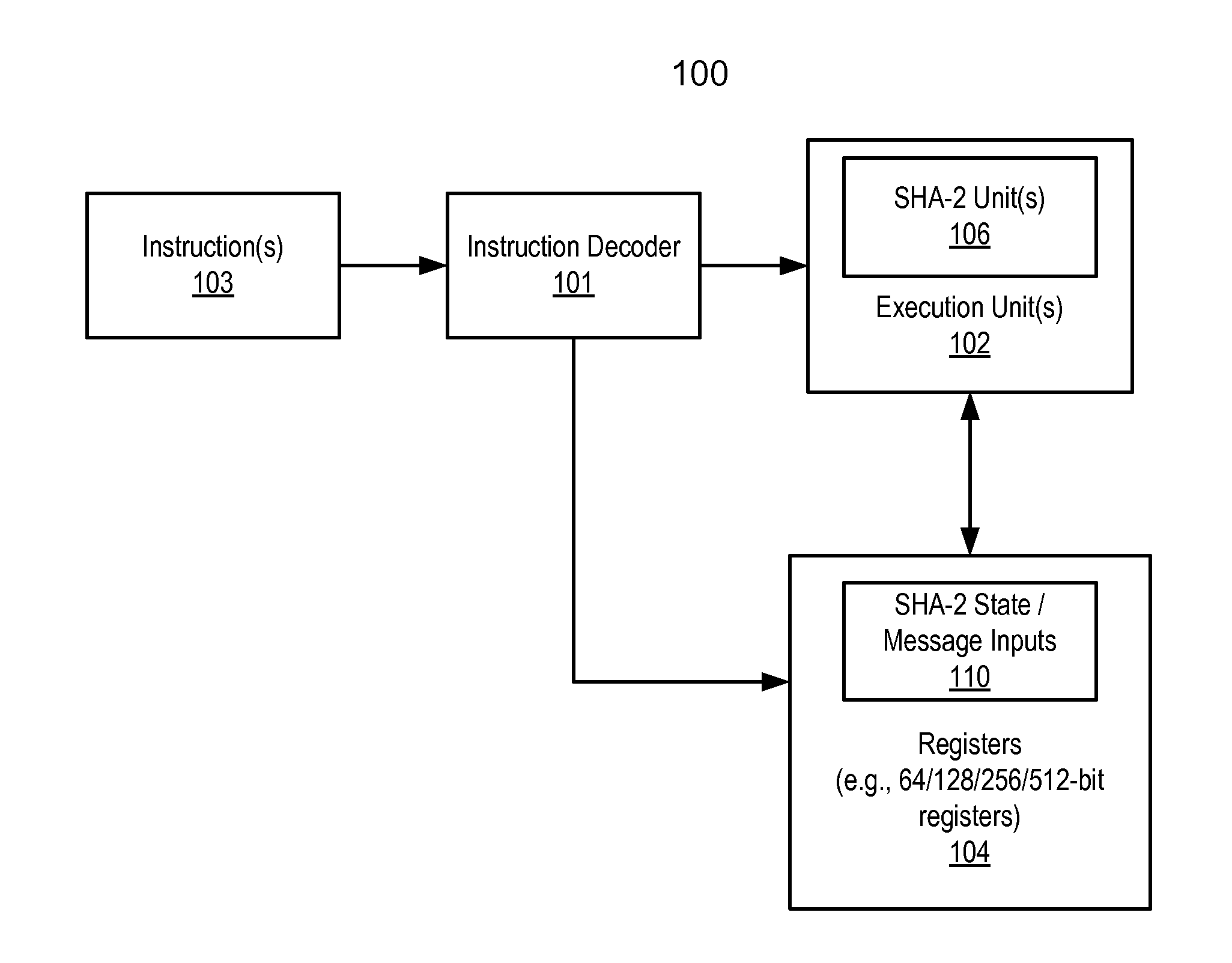
A processor includes an instruction decoder to receive a first instruction to process a secure hash algorithm 2 (SHA-2) hash algorithm, the first instruction having a first operand associated with a first storage location to store a SHA-2 state and a second operand associated with a second storage location to store a plurality of messages and round constants. The processor further includes an execution unit coupled to the instruction decoder to perform one or more iterations of the SHA-2 hash algorithm on the SHA-2 state specified by the first operand and the plurality of messages and round constants specified by the second operand, in response to the first instruction.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Multiply-accumulate instruction which adds or subtracts based on a predicate value
A data processing apparatus and method for performing multiply-accumulate operations is provided. The data processing apparatus includes data processing circuitry responsive to control signals to perform data processing operations on at least one input data element. Instruction decoder circuitry is responsive to a predicated multiply-accumulate instruction specifying as input operands a first input data element, a second input data element, and a predicate value, to generate control signals to control the data processing circuitry to perform a multiply-accumulate operation by: multiplying said first input data element and said second input data element to produce a multiplication data element; if the predicate value has a first value, producing a result accumulate data element by adding the multiplication data element to an initial accumulate data element; and if the predicate value has a second value, producing the result accumulate data element by subtracting the multiplication data element from the initial accumulate data element.
Owner:ARM LTD
Multithreaded processor with multiple concurrent pipelines per thread
ActiveUS20060095729A1Improve concurrencyControl consumptionGeneral purpose stored program computerConcurrent instruction executionHardware threadExecution unit
A multithreaded processor comprises a plurality of hardware thread units, an instruction decoder coupled to the thread units for decoding instructions received therefrom, and a plurality of execution units for executing the decoded instructions. The multithreaded processor is configured for controlling an instruction issuance sequence for threads associated with respective ones of the hardware thread units. On a given processor clock cycle, only a designated one of the threads is permitted to issue one or more instructions, but the designated thread that is permitted to issue instructions varies over a plurality of clock cycles in accordance with the instruction issuance sequence. The instructions are pipelined in a manner which permits at least a given one of the threads to support multiple concurrent instruction pipelines.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Arithmetic decoding apparatus
InactiveUS20100134330A1Excellent effect of capabilityImprove processing speedCode conversionDigital video signal modificationParallel computingArithmetic coding
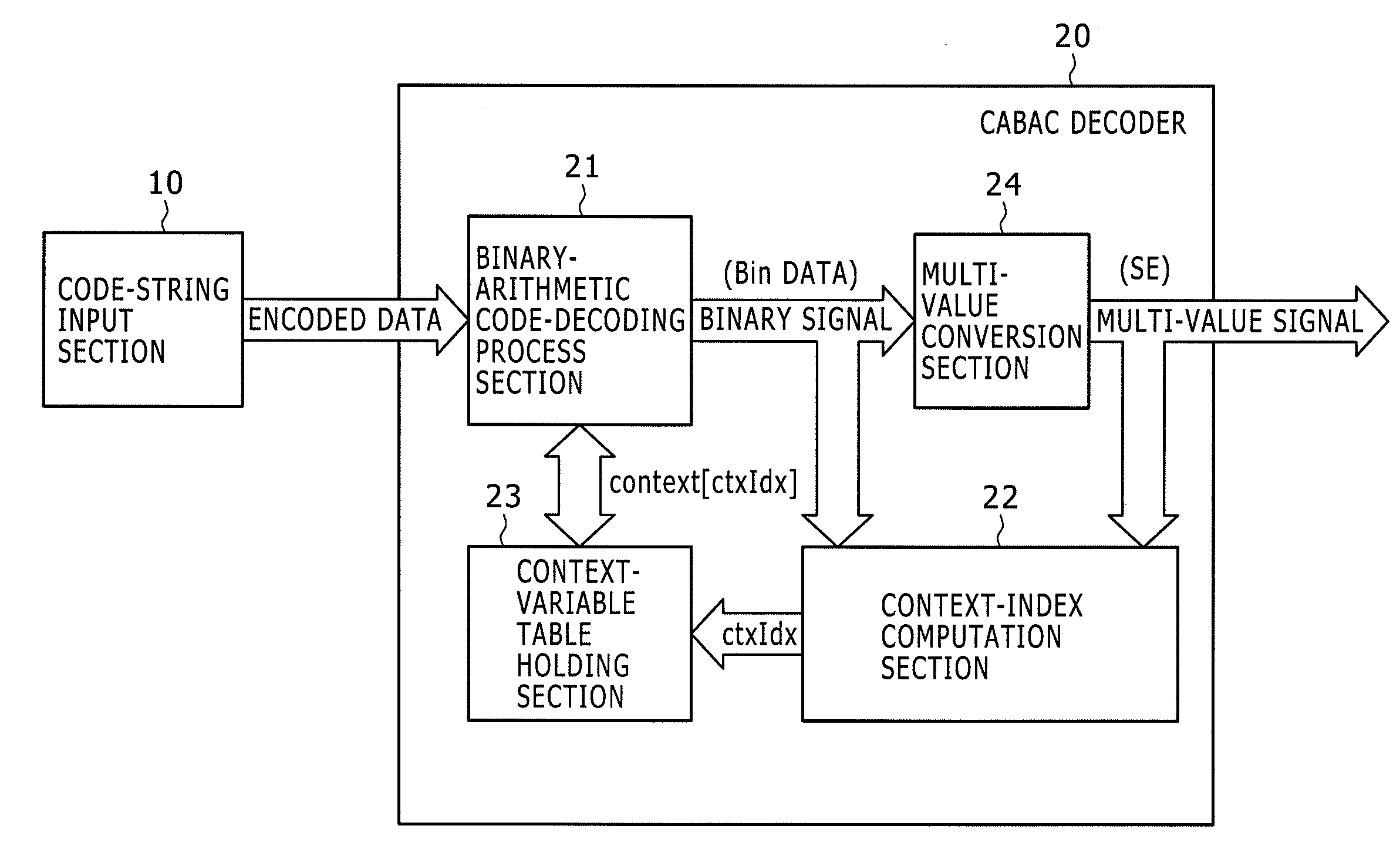
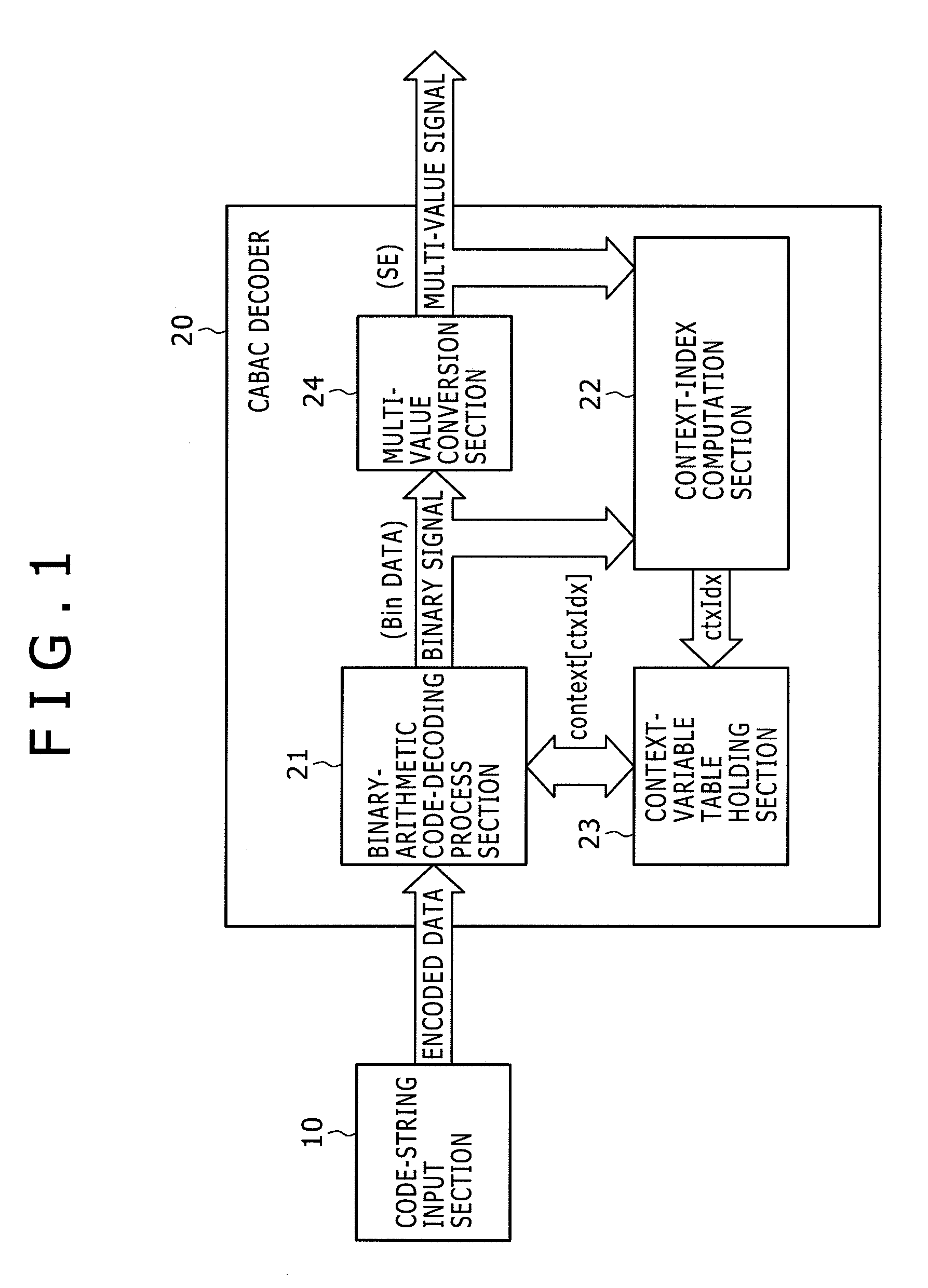
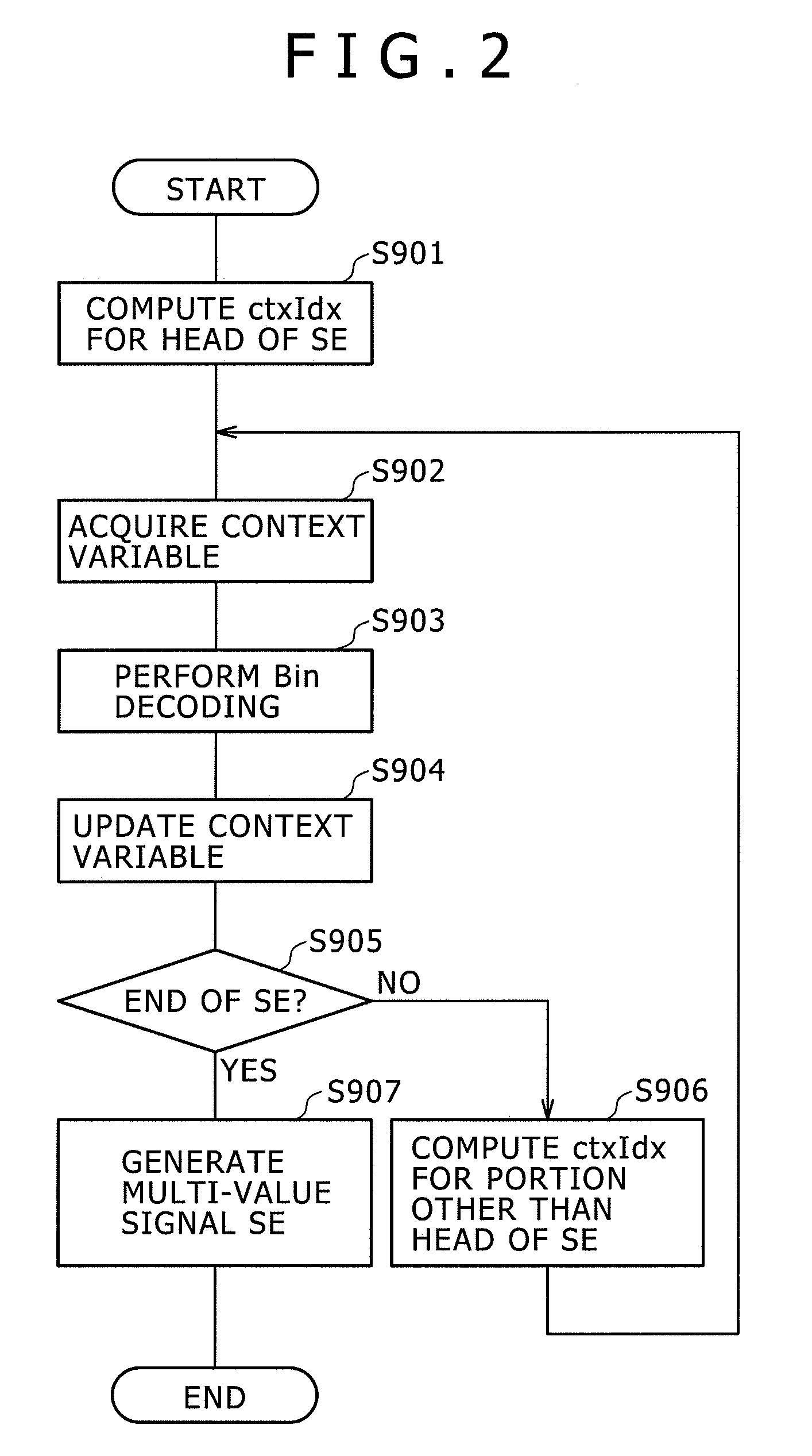
Disclosed herein is an arithmetic decoding apparatus including an instruction decoder configured to decode an arithmetically encoded data decoding instruction to be executed for carrying out an arithmetic-decoding process of arithmetically decoding arithmetically encoded data into a binary signal; an execution condition code holding section configured to hold the binary signal obtained as a result of an immediately preceding arithmetic-decoding process as an execution condition code; and an arithmetic decoding execution section configured to determine whether a context number specified by the arithmetically encoded data decoding instruction is to be used as a context index as it is or the specified context number incremented by 1 is to be used as the context index in accordance with the execution condition code, and carry out the arithmetic decoding process by making use of the determined context index.
Owner:SONY CORP
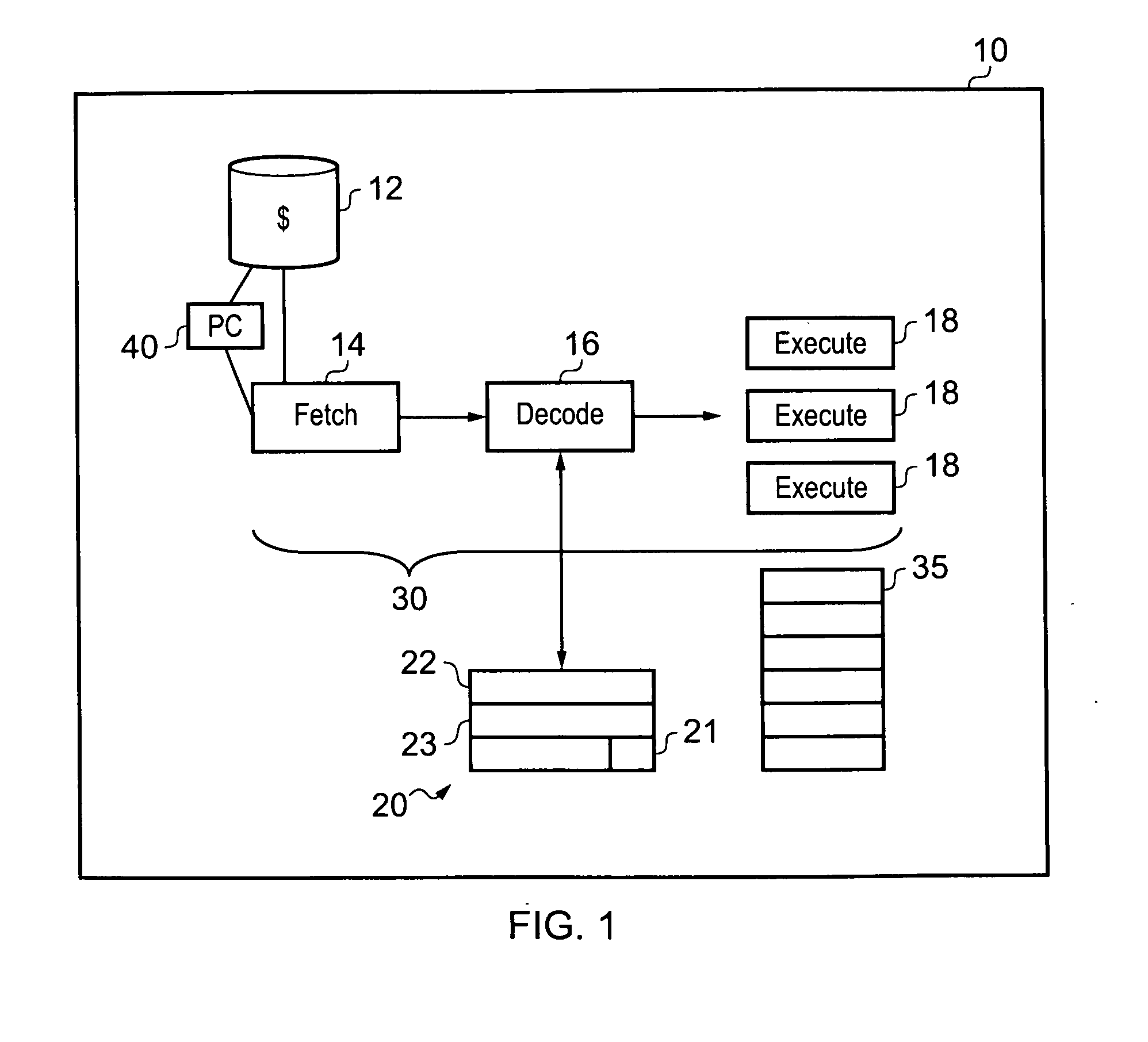
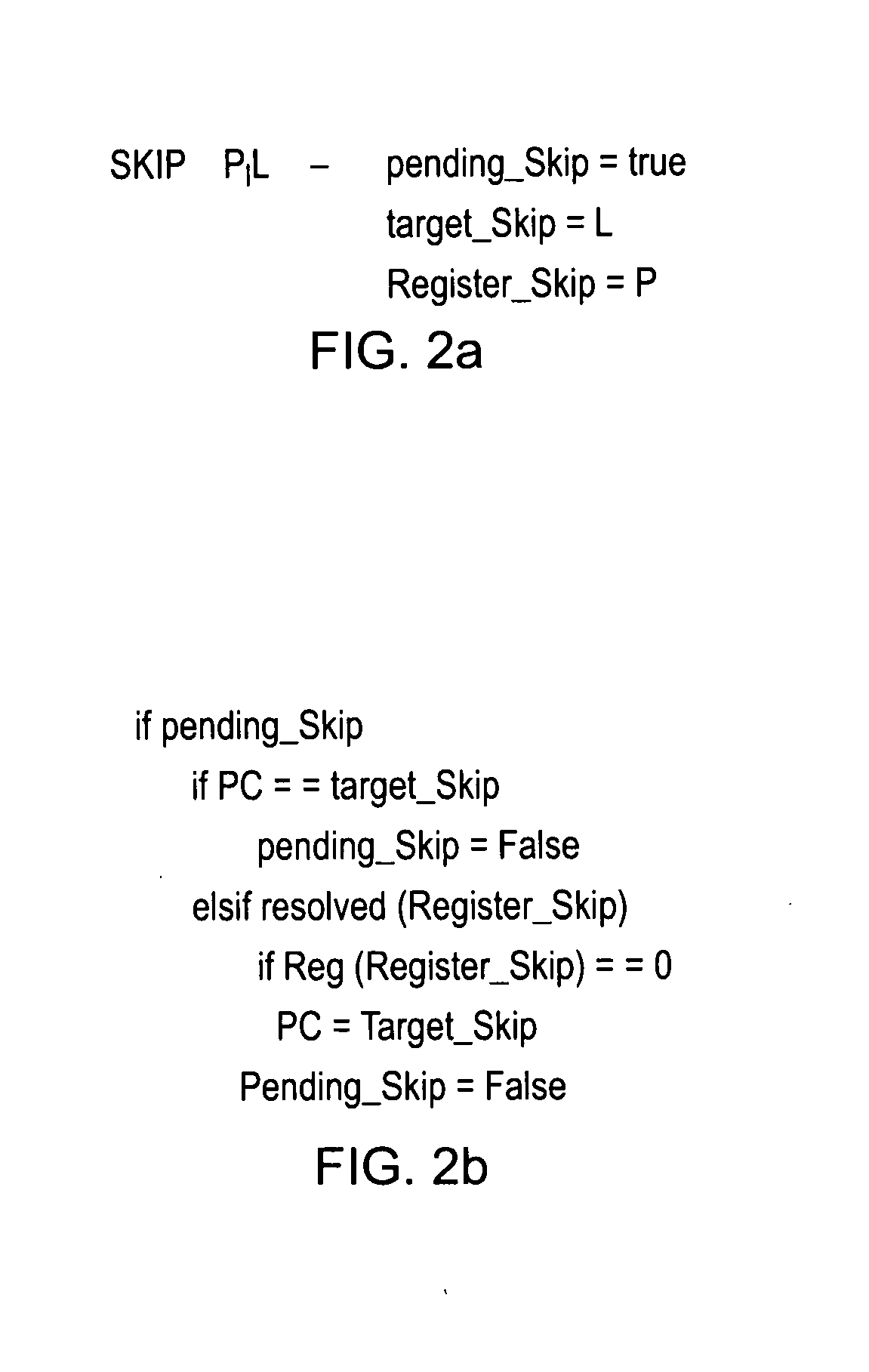
Controlling the execution of adjacent instructions that are dependent upon a same data condition
ActiveUS20120204007A1Improve processor performanceSuitable for useConditional code generationDigital computer detailsParallel computingInstruction decoder
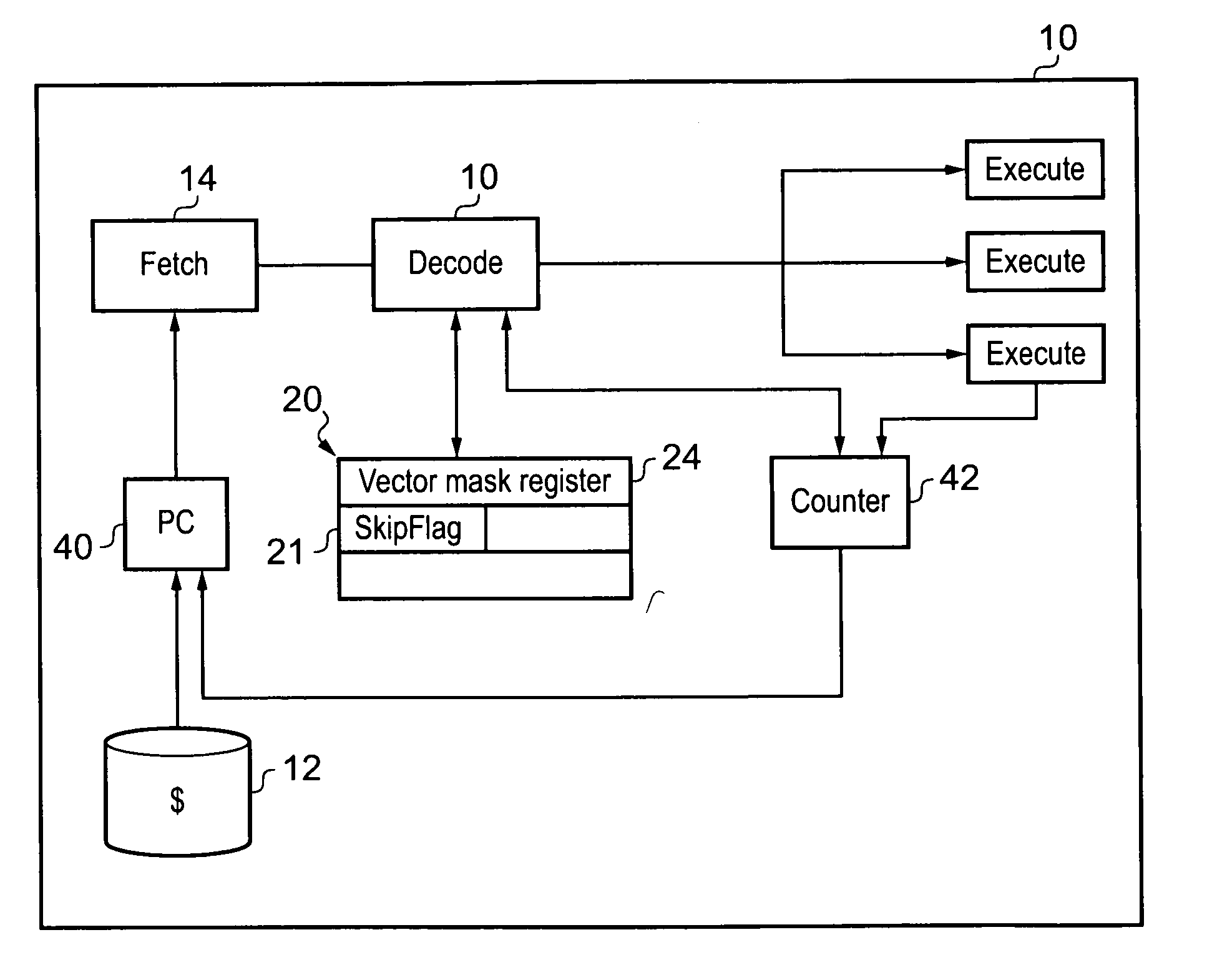
A data processing apparatus is disclosed, having: an instruction decoder configured to decode a stream of instructions, a data processor configured to process the decoded stream of instructions; wherein in response to a plurality of adjacent instructions within the stream of instructions execution of which is dependent upon a data condition being met and whose execution when said data condition is not met does not change a state of said processing apparatus, the processor is configured to: commence determining whether the data condition is met or not; and commence processing said plurality of adjacent instructions; and in response to determining that said data condition is not met; skip to a next instruction to be executed after said plurality of adjacent instructions without executing any intermediate ones of said plurality of adjacent instructions not yet executed and continue execution at the next instruction.
Owner:ARM LTD
Method and apparatus for constant generation in SIMD processing
A data processing apparatus (2) comprising: a register data store operable to store data elements; an instruction decoder (14, 16) operable to decode an instruction with generated constant, said instruction having a data value associated therewith; a data processor (18) operable to perform data processing operations within parallel processing lanes on at least one source operand in response to a data processing instruction decoded by said instruction decoder (16); and said data processor being operable in response to said decoded instruction with generated constant and associated data value to expand at least a data portion (1210) of said associated data value, said expansion being performed in response to said instruction with generated constant and depending on a selected function, to generate a constant (1240), said generated constant (1240) forming one of said at least one source operands.
Owner:ARM LTD
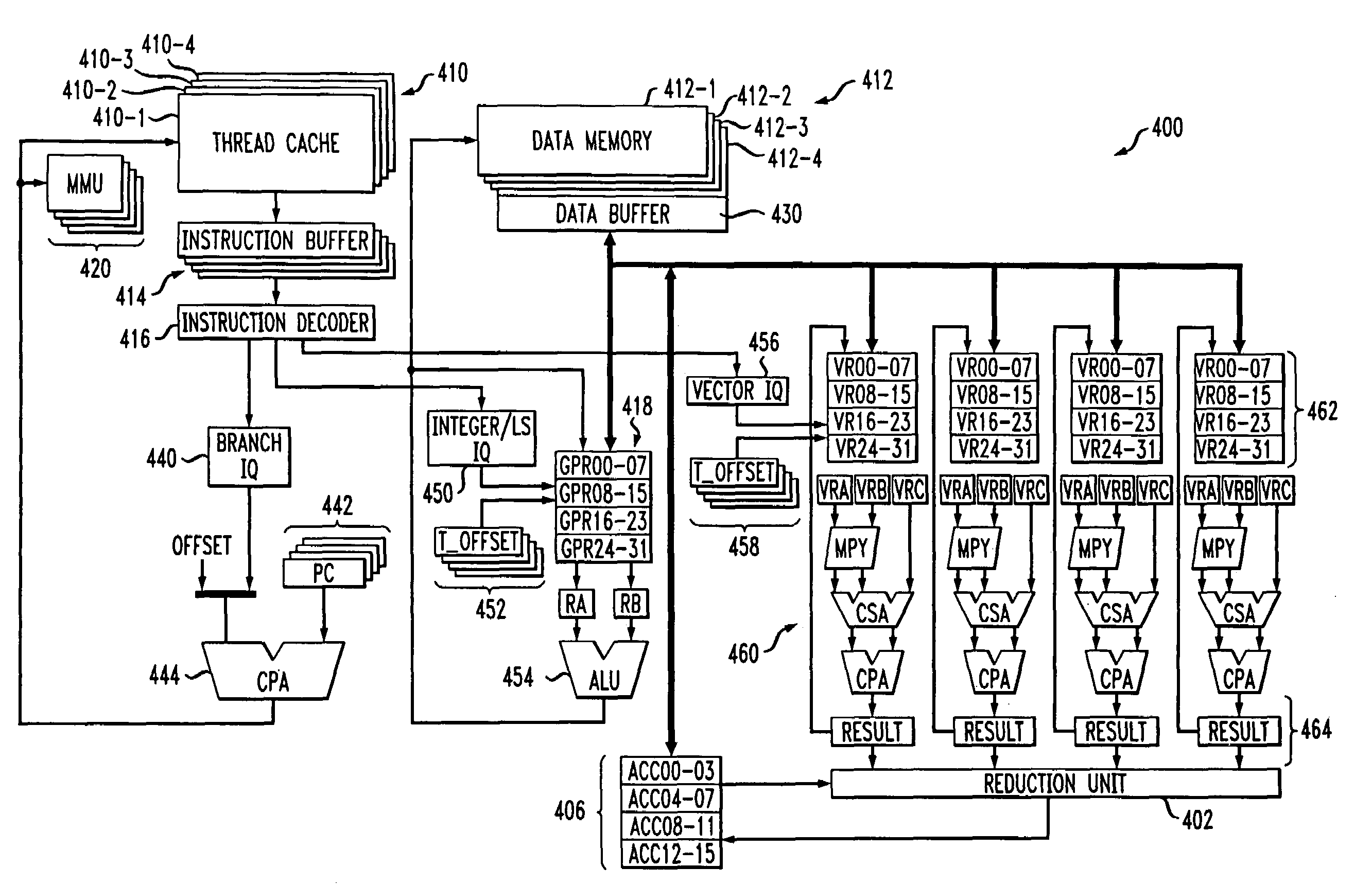
Multithreaded processor with efficient processing for convergence device applications
ActiveUS6968445B2Executing controlEfficient executionMultiprogramming arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionInstruction unitExecution control
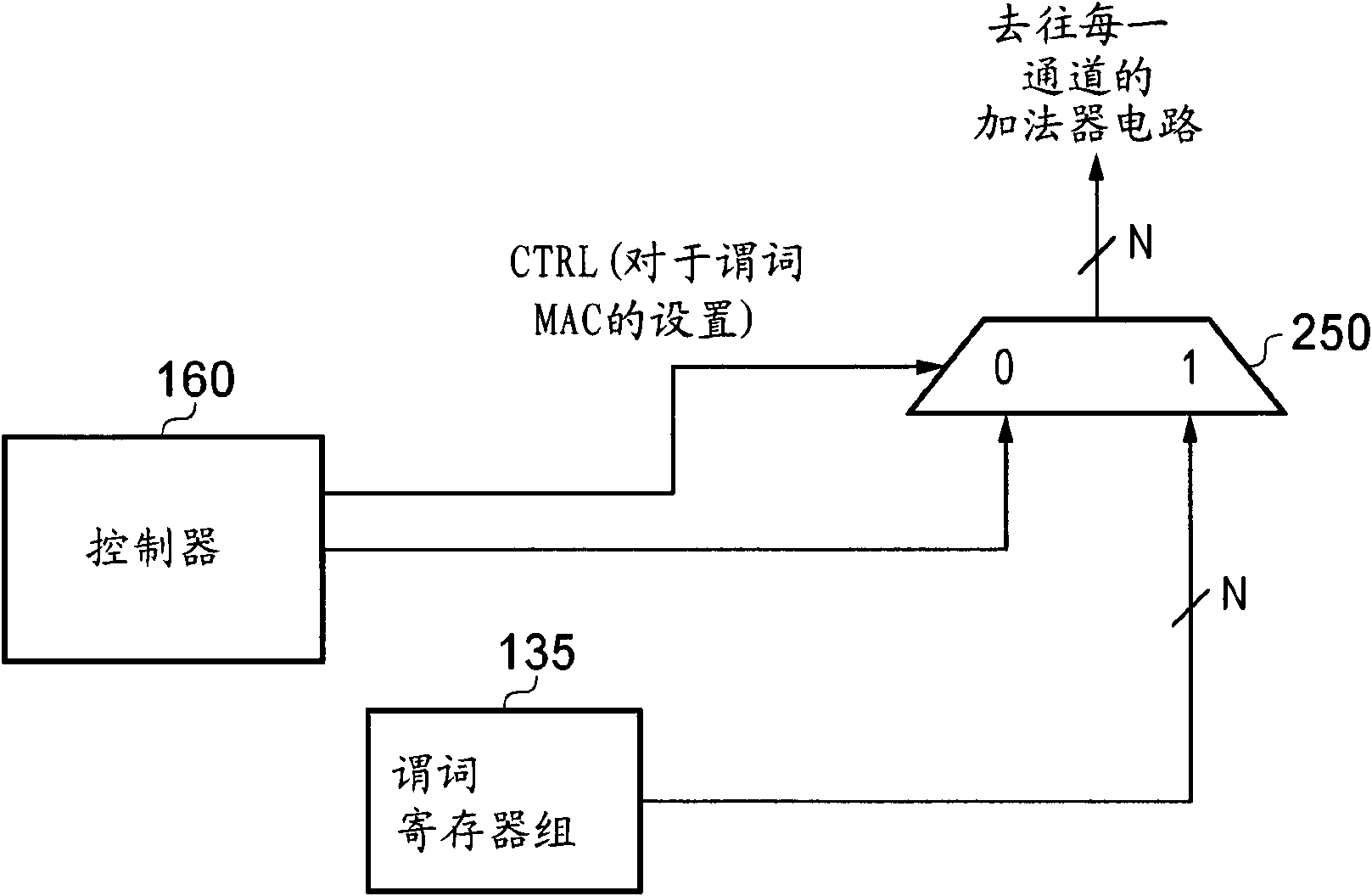
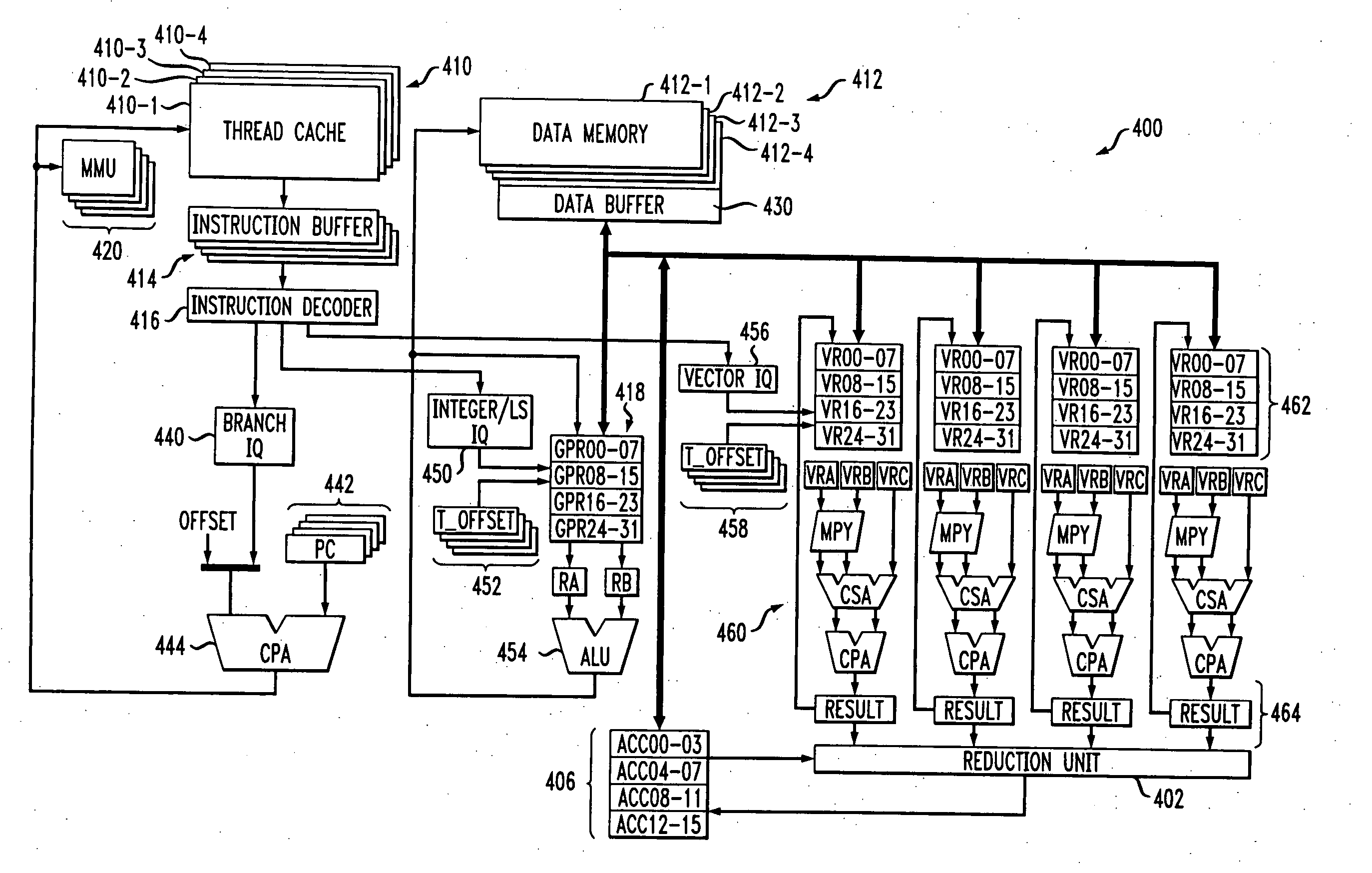
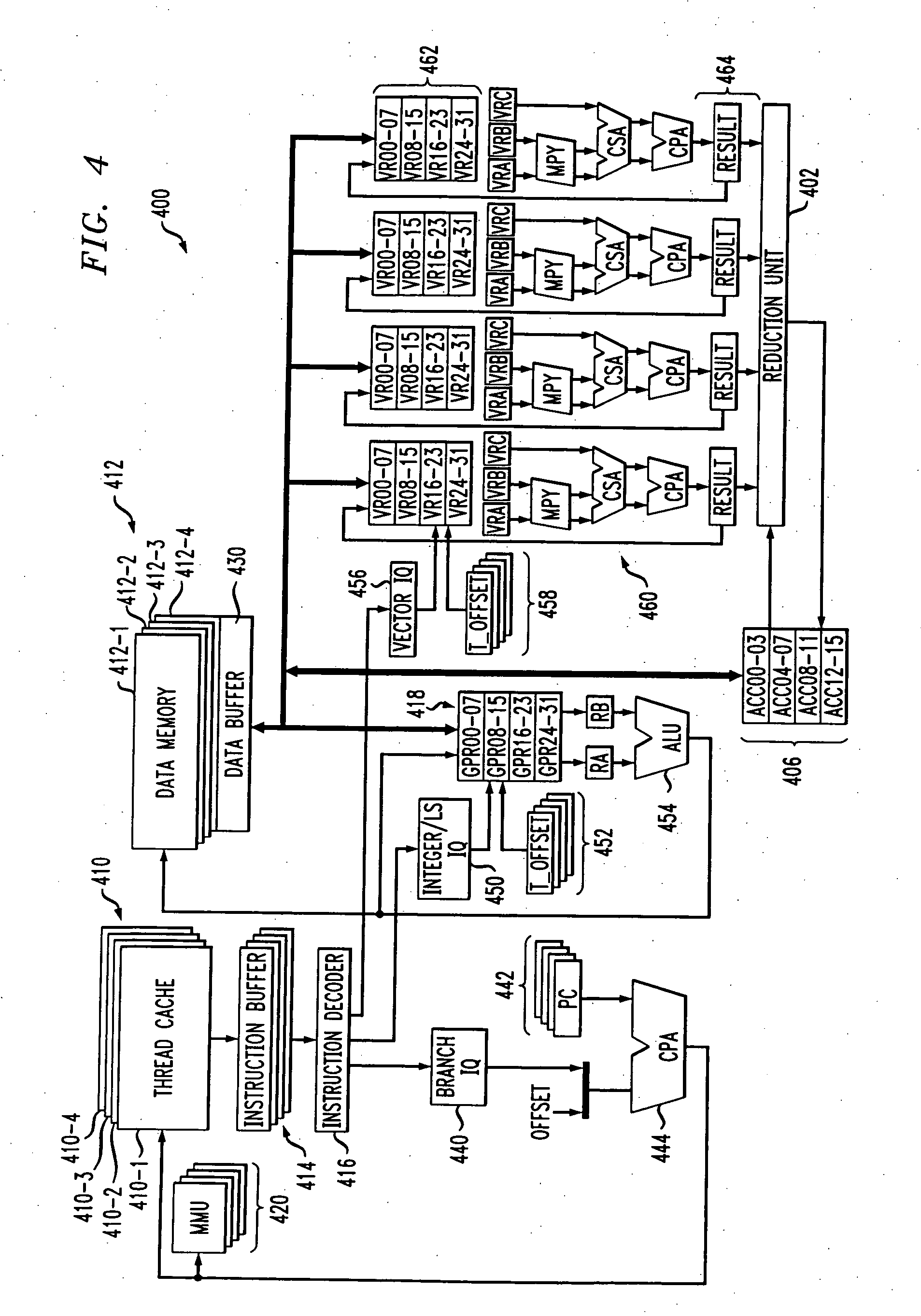
A multithreaded processor includes an instruction decoder for decoding retrieved instructions to determine an instruction type for each of the retrieved instructions, an integer unit coupled to the instruction decoder for processing integer type instructions, and a vector unit coupled to the instruction decoder for processing vector type instructions. A reduction unit is preferably associated with the vector unit and receives parallel data elements processed in the vector unit. The reduction unit generates a serial output from the parallel data elements. The processor may be configured to execute at least control code, digital signal processor (DSP) code, Java code and network processing code, and is therefore well-suited for use in a convergence device. The processor is preferably configured to utilize token triggered threading in conjunction with instruction pipelining.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Data processing circuit with target instruction and prefix instruction
InactiveUS6308258B1Simple structureUses memory efficientlyInstruction analysisDigital computer detailsRegister fileInstruction decoder
A certain target instruction and a prefix instruction for expanding the function of that target instruction are input to the present data processing circuit. The data processing circuit analyses the thus-input instruction code and performs the processing necessary for the execution of that instruction. The data processing circuit comprises an instruction decoder section, a register file, and an instruction execution section that executes the instruction based on operational details of the instruction analyzed by the instruction decoder section. The instruction decoder section comprises an ext instruction processing section that processed the expansion of immediate data from the prefix instruction.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
A Remote Control System of Air Conditioner Based on Wireless Network
InactiveCN102287893AEnsure proper temperatureImprove comfortSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusWireless mesh networkControl system
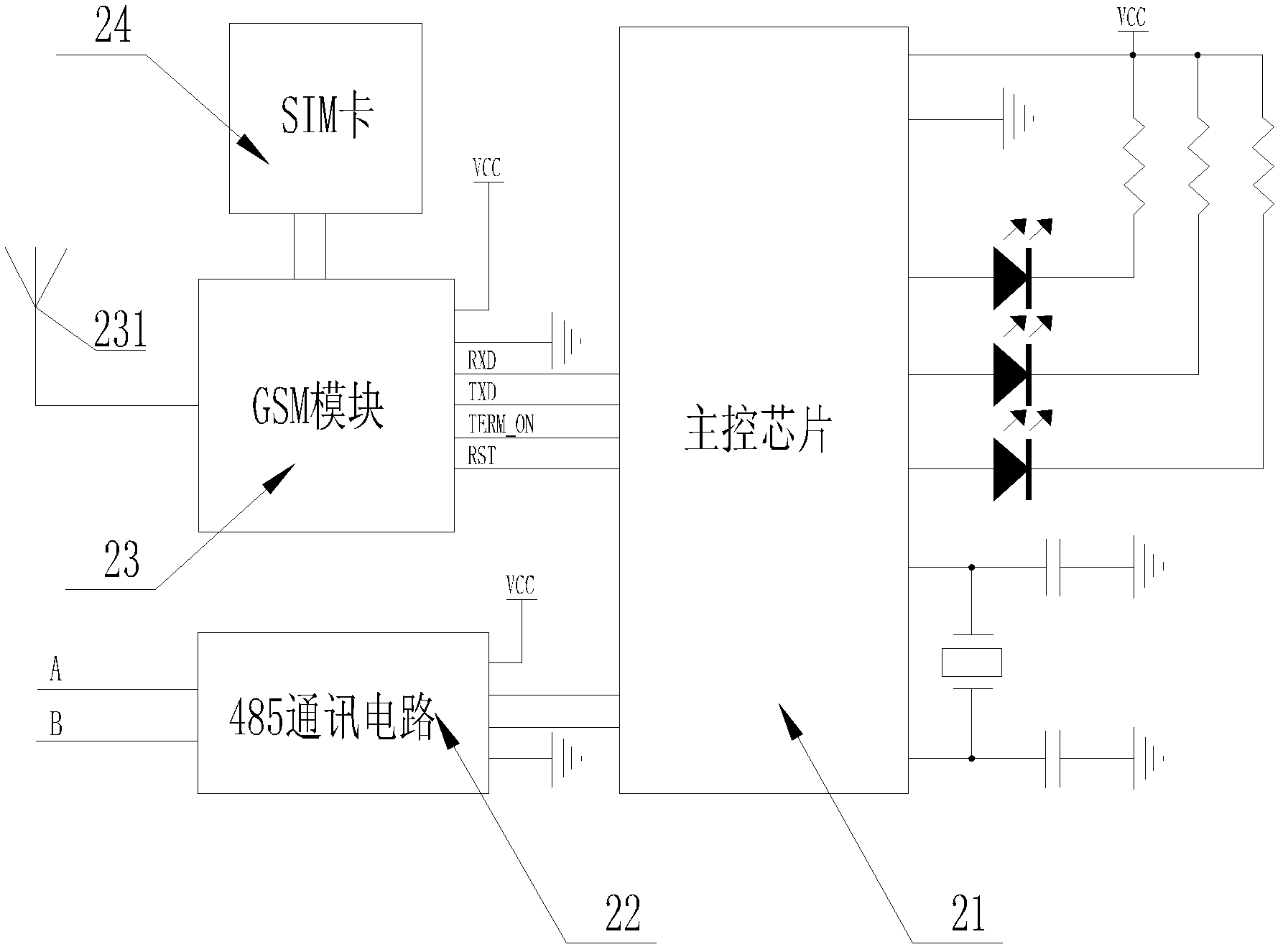
The invention discloses a remote control system for an air conditioner based on a wireless network, which includes a control terminal and a controller connected through a wireless network, and the controller is connected to the air conditioner with a communication line, wherein the controller is used for: receiving the control The query information of the terminal is decoded to generate a query instruction, and the operating status of the air conditioner is queried accordingly, and the query result is returned to the control terminal; the control information of the control terminal is received, and a control instruction is generated after decoding, according to which The air conditioner executes the corresponding operation, and feeds back the execution result to the control terminal; receives the fault signal of the air conditioner, generates an alarm message after encoding, and sends it to the control terminal for corresponding processing. The remote air conditioner control system of the present invention can inquire and control the operating state of the air conditioner in real time, and automatically alarm when the air conditioner fails to operate.
Owner:GUANGDONG CHIGO AIR CONDITIONING
Prioritizing thread selection partly based on stall likelihood providing status information of instruction operand register usage at pipeline stages
ActiveUS7664936B2Improve efficiencyReduce in quantityResource allocationDigital computer detailsLoad instructionProcessor register
Owner:ARM FINANCE OVERSEAS LTD
Instruction set for supporting wide scalar pattern matches
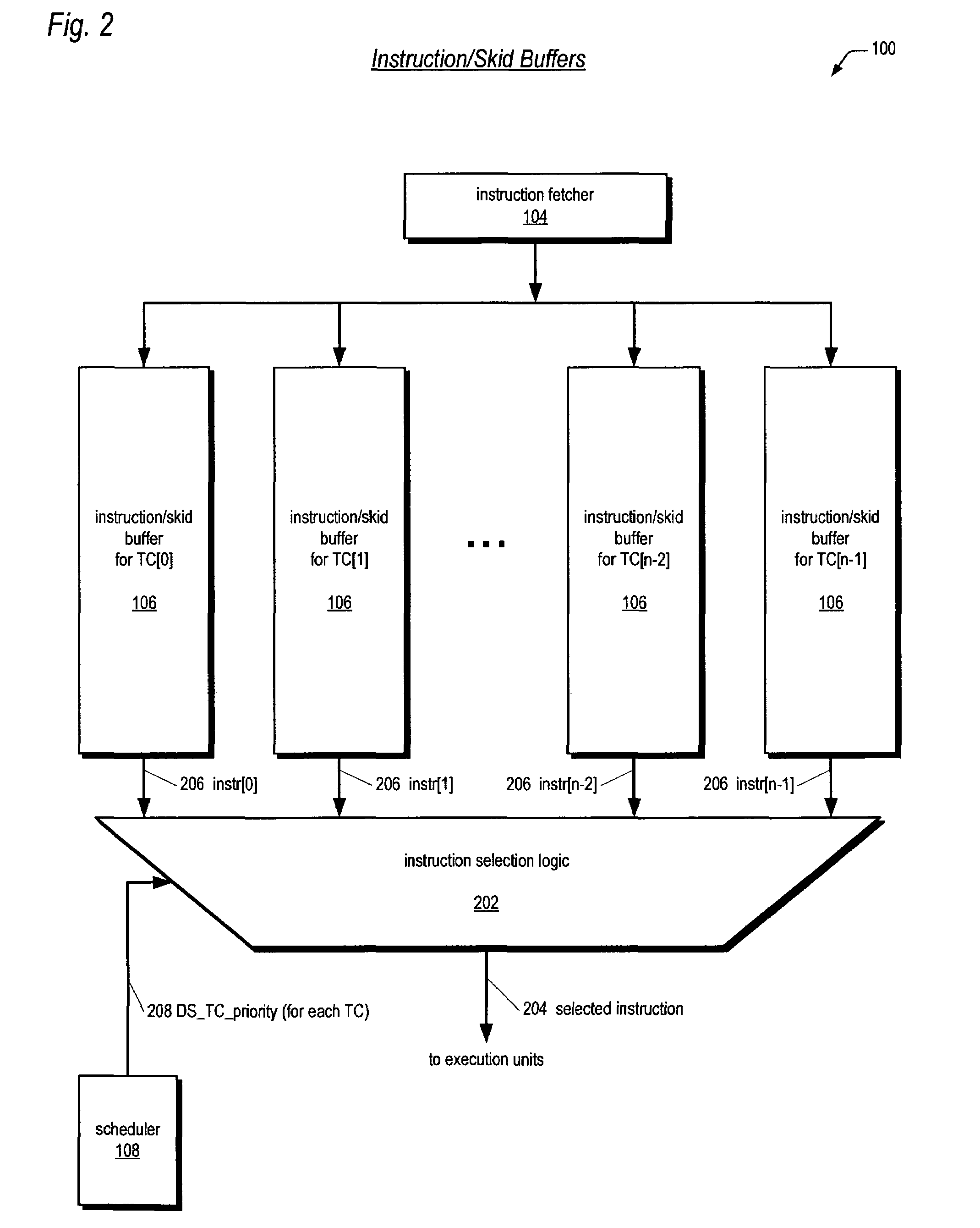
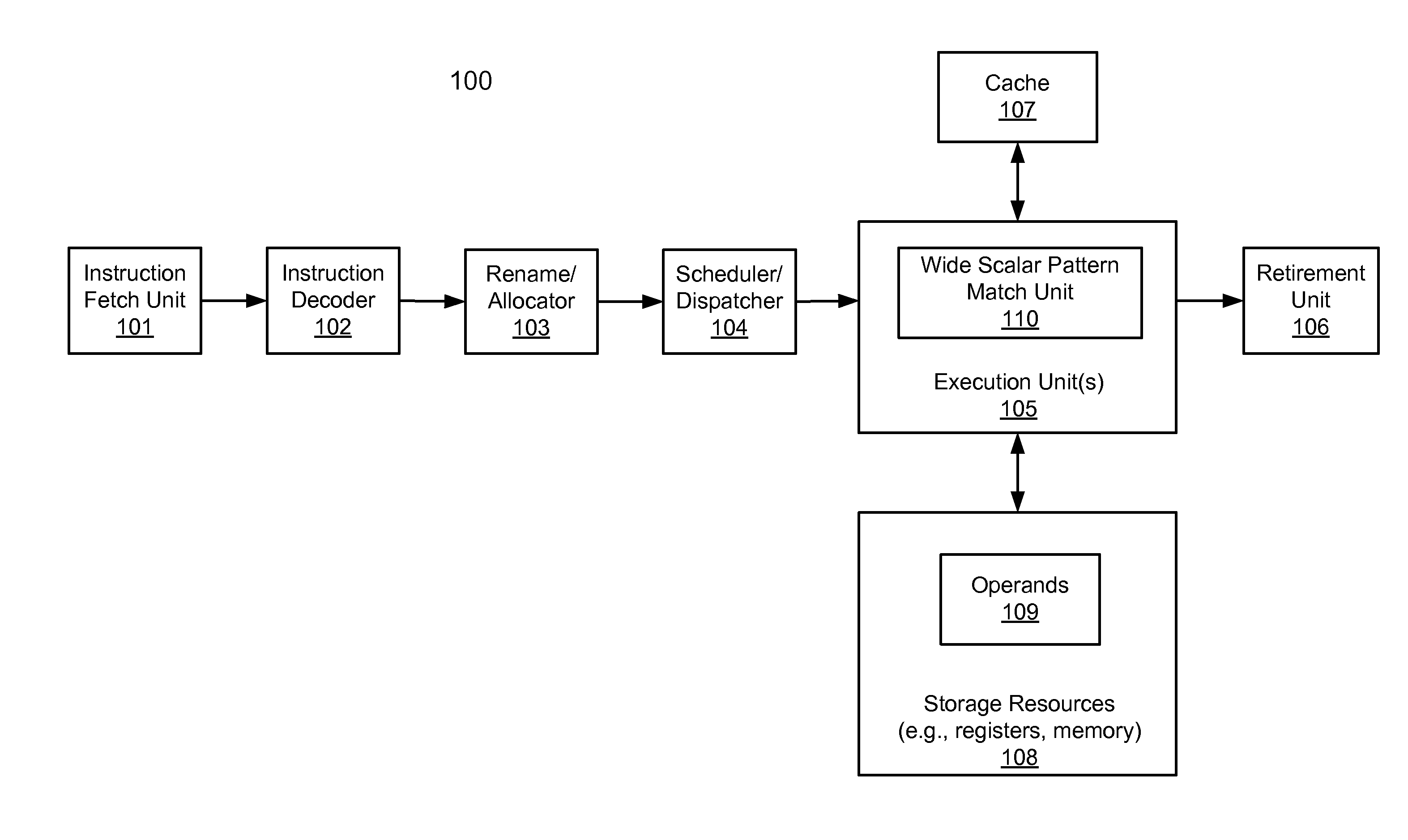
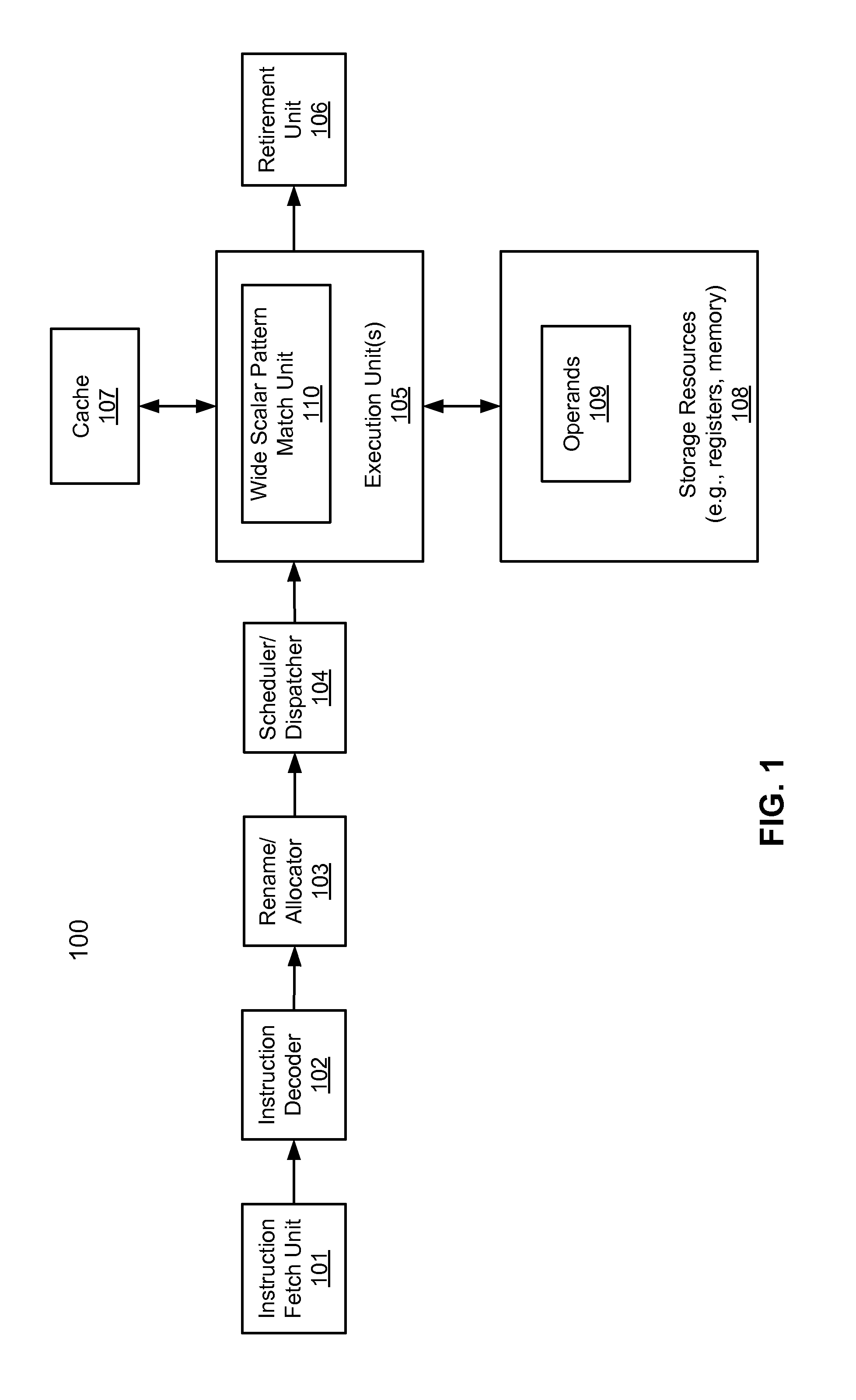
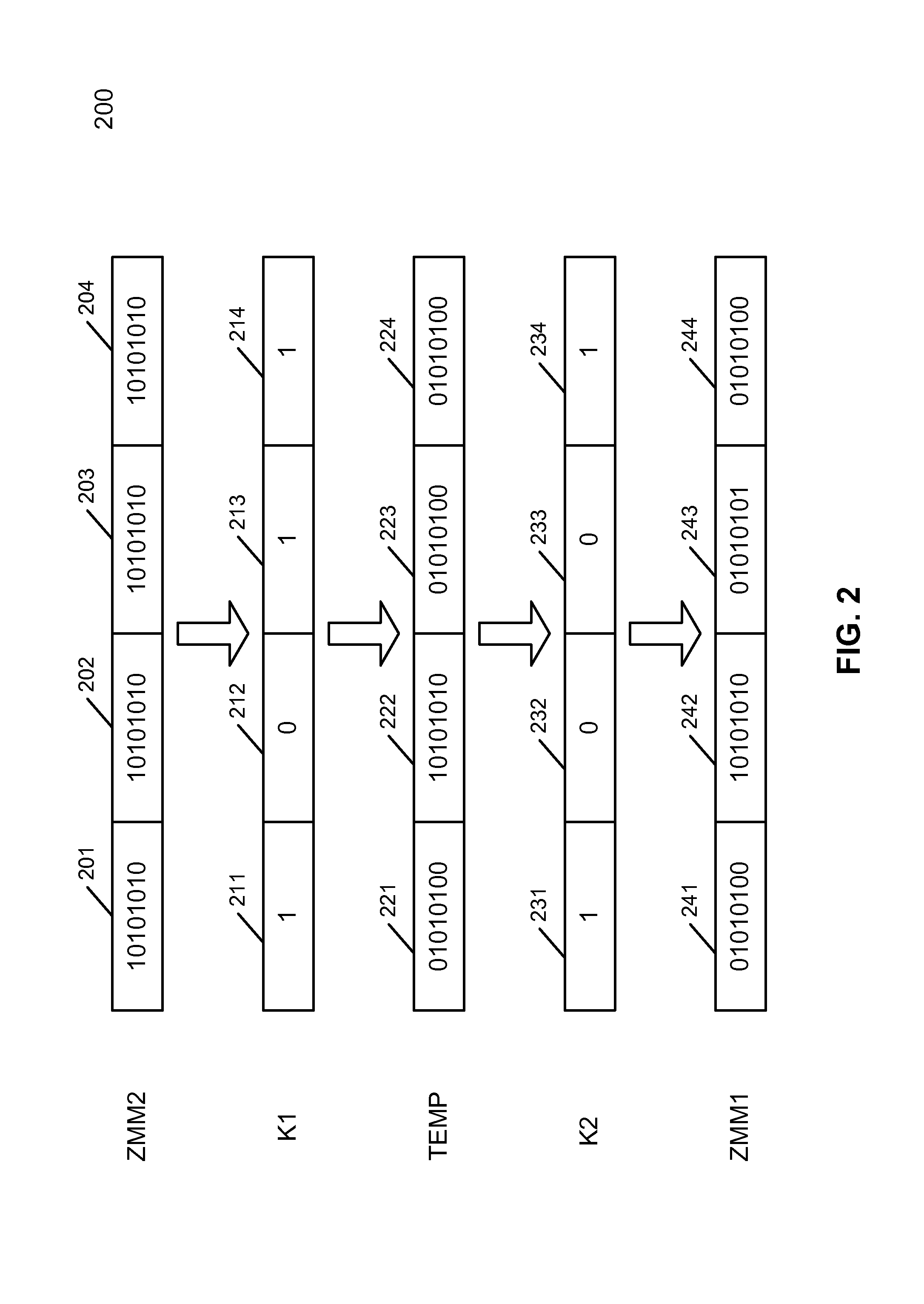
A processor includes an instruction decoder to receive an instruction having a first operand, a second operand, and a third operand, and an execution unit coupled to the instruction decoder to execute the instruction, the execution unit to individually perform a shift operation by at least one bit for each of a plurality of data elements stored in a storage location indicated by the second operand, for each of the data elements that has an overflow in response to the shift-left operation, to carry over the overflow into an adjacent data element based on a first bitmask obtained from the third operand, generating a final result, and to store the final result in a storage location indicated by the first operand.
Owner:INTEL CORP
CPU, information processing device including the CPU, and controlling method of CPU
ActiveUS7266641B2Easy to handleReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTVolume/mass flow measurementInformation processingExternal storage
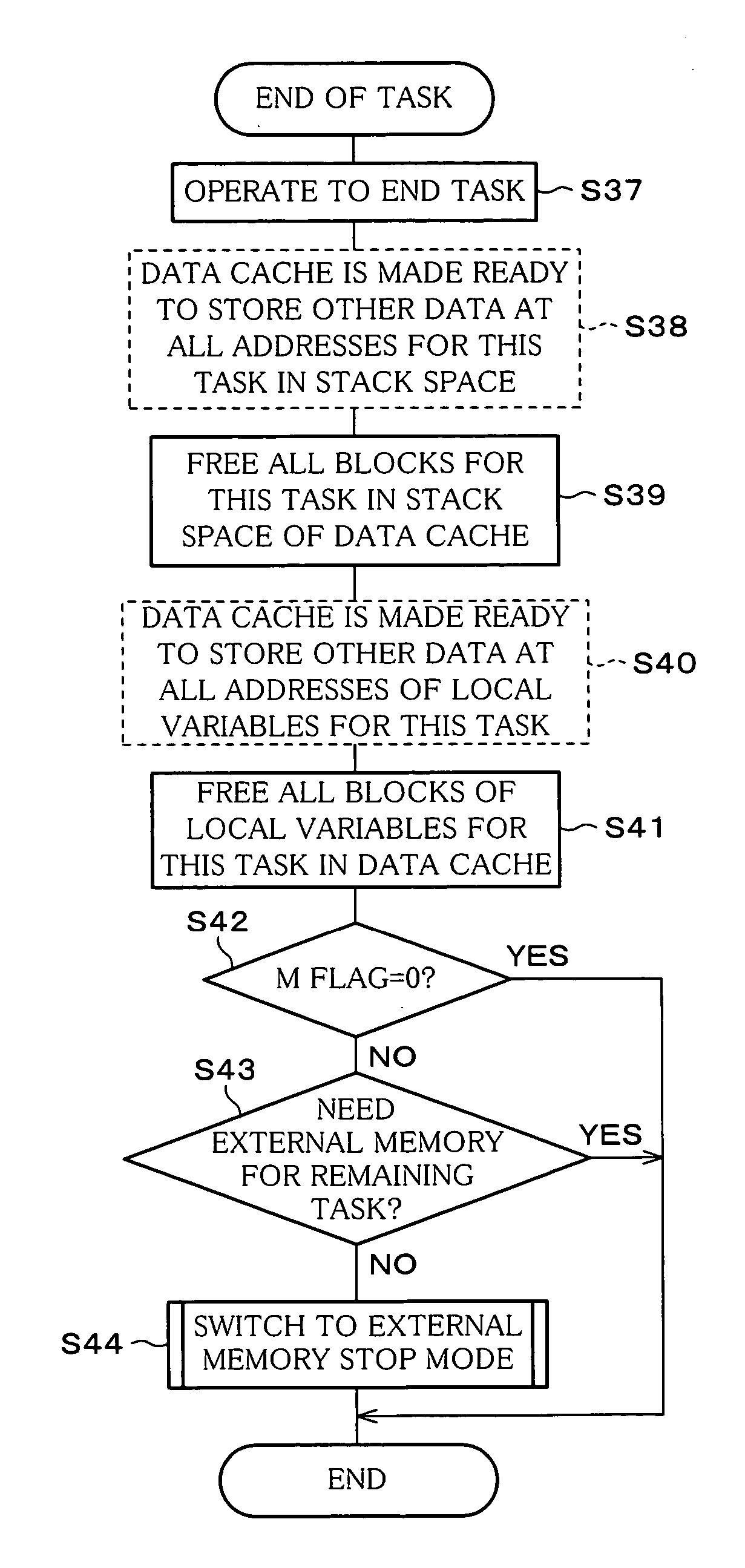
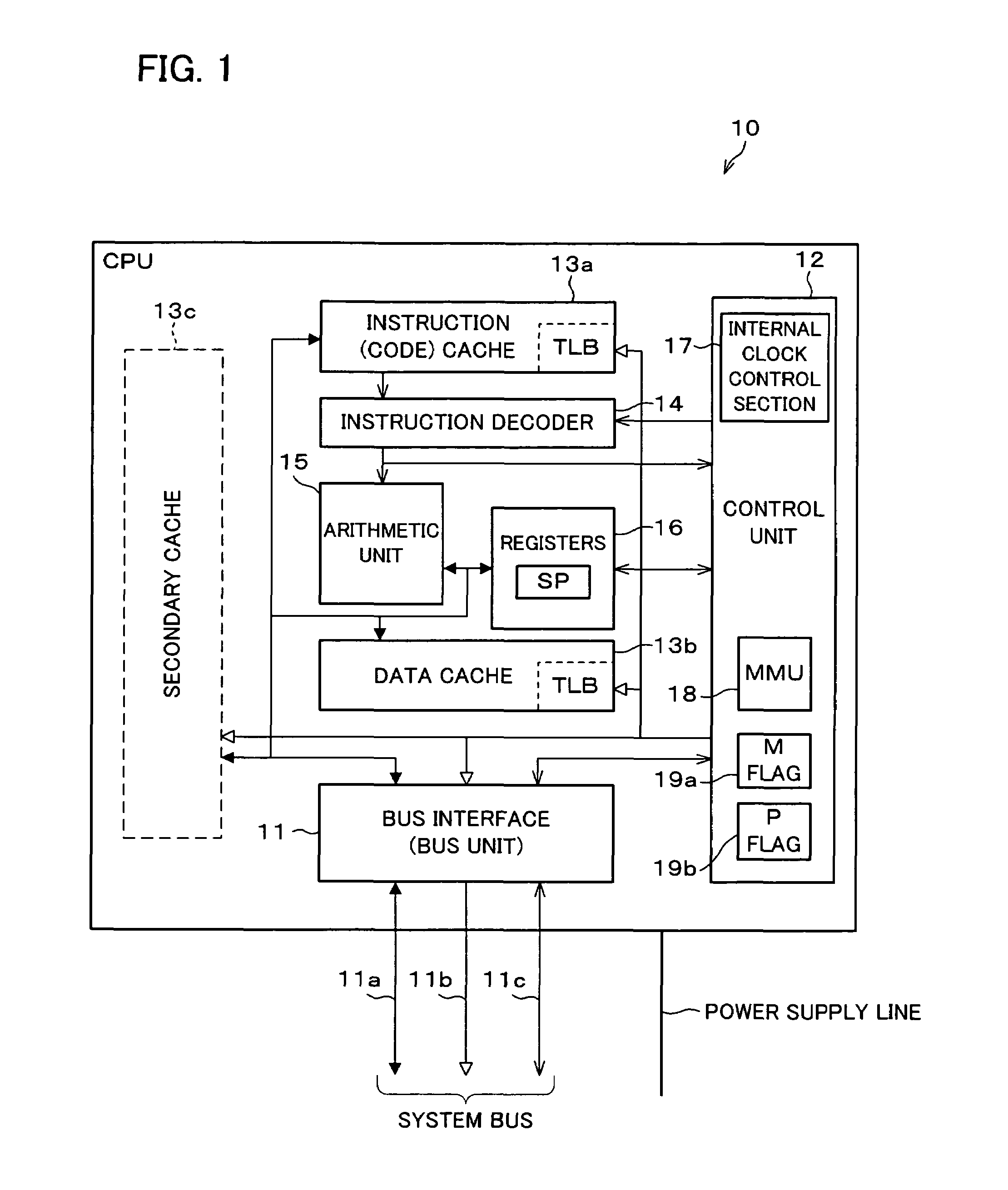
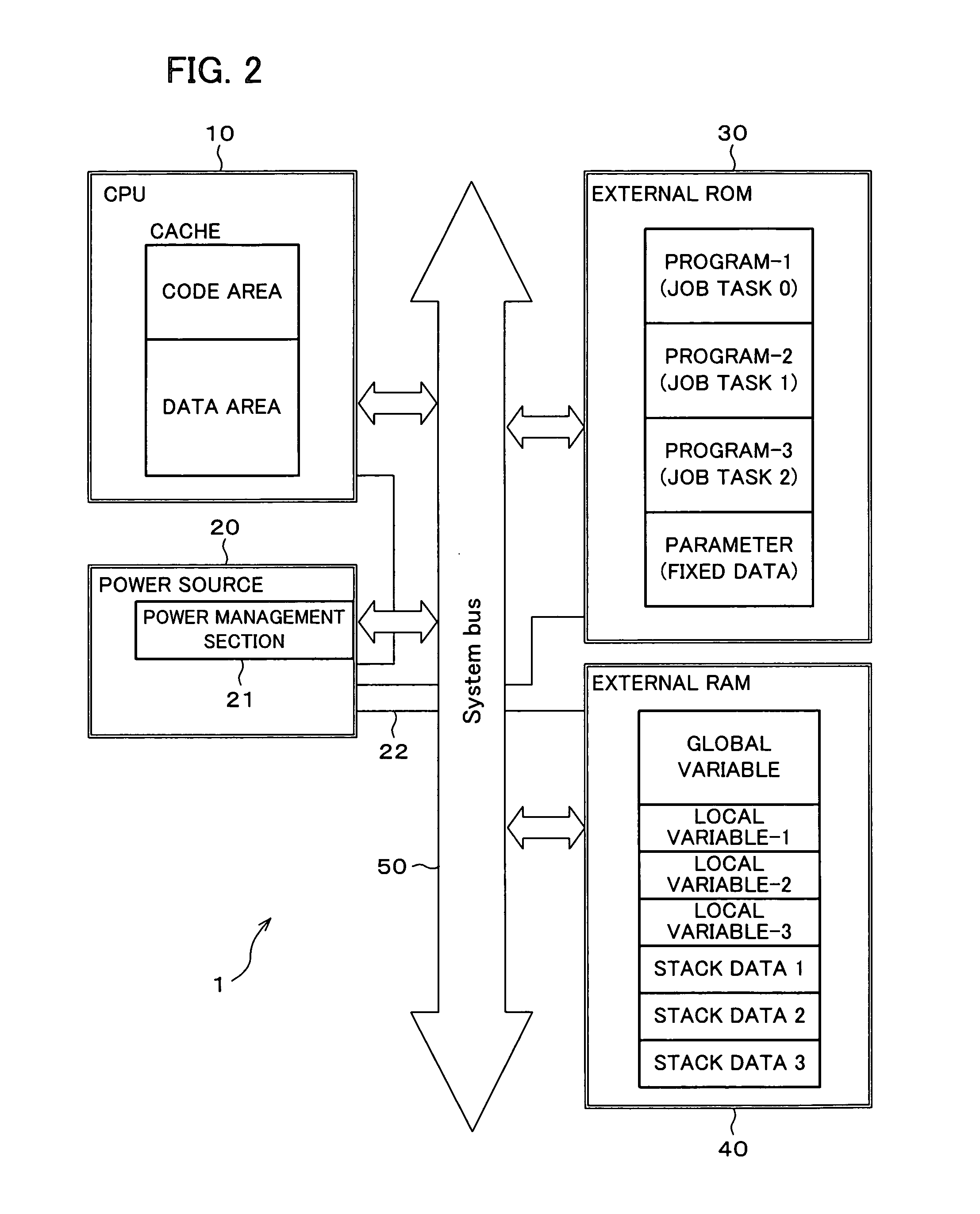
A CPU includes a bus interface, a control unit, an instruction cache, a data cache, a secondary cache, an instruction decoder, an arithmetic unit, and registers. When operations can be performed only with the cache, the CPU inhibits access to external memory and stops power supply to the external memory. With this arrangement, by performing operations in the CPU without using the external memory, it is possible to realize a speedy processing and to stop power supply to the external memory, thus allowing for reduction in power consumption.
Owner:SHARP KK
Microprocessor that detects erroneous speculative prediction of branch instruction opcode byte
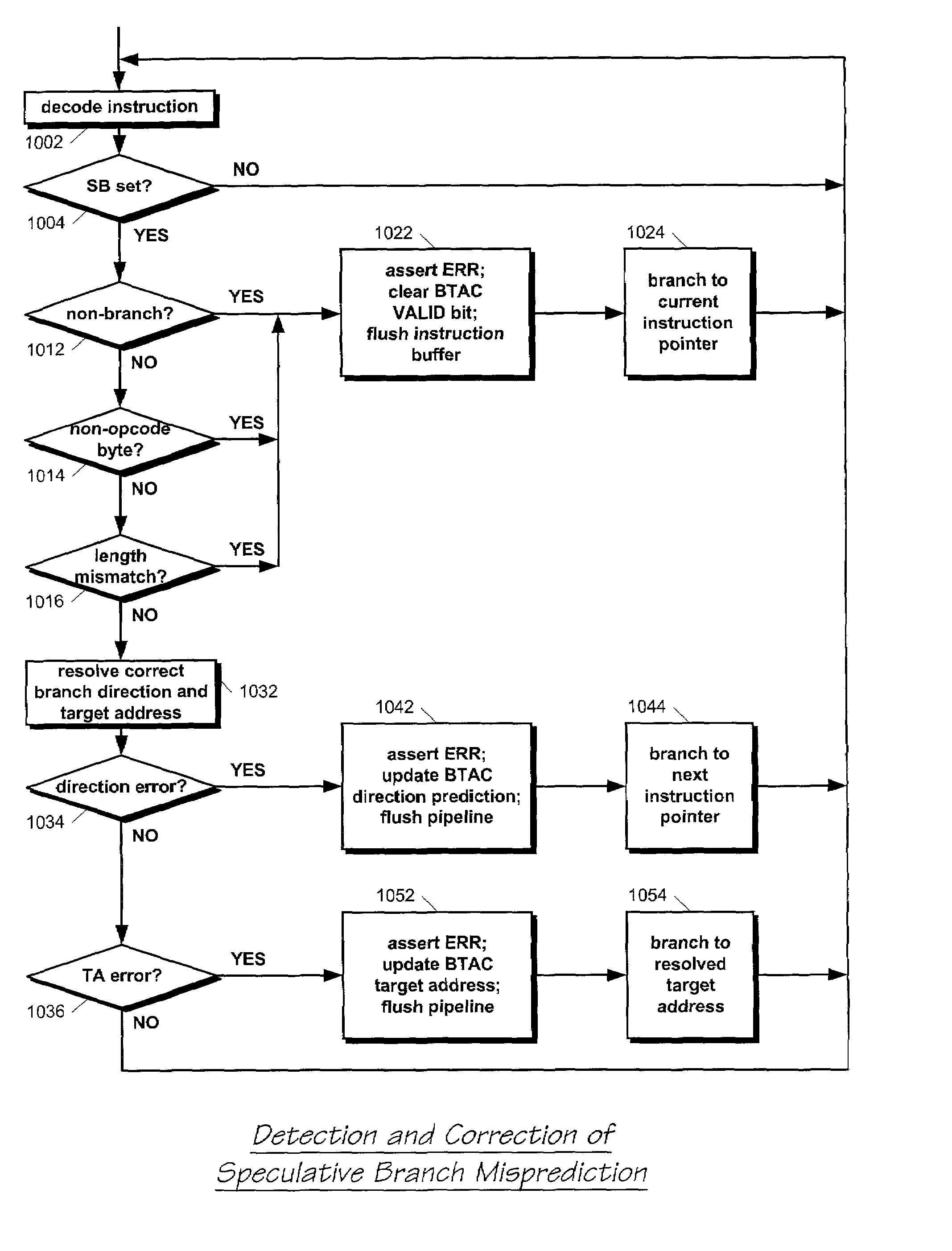
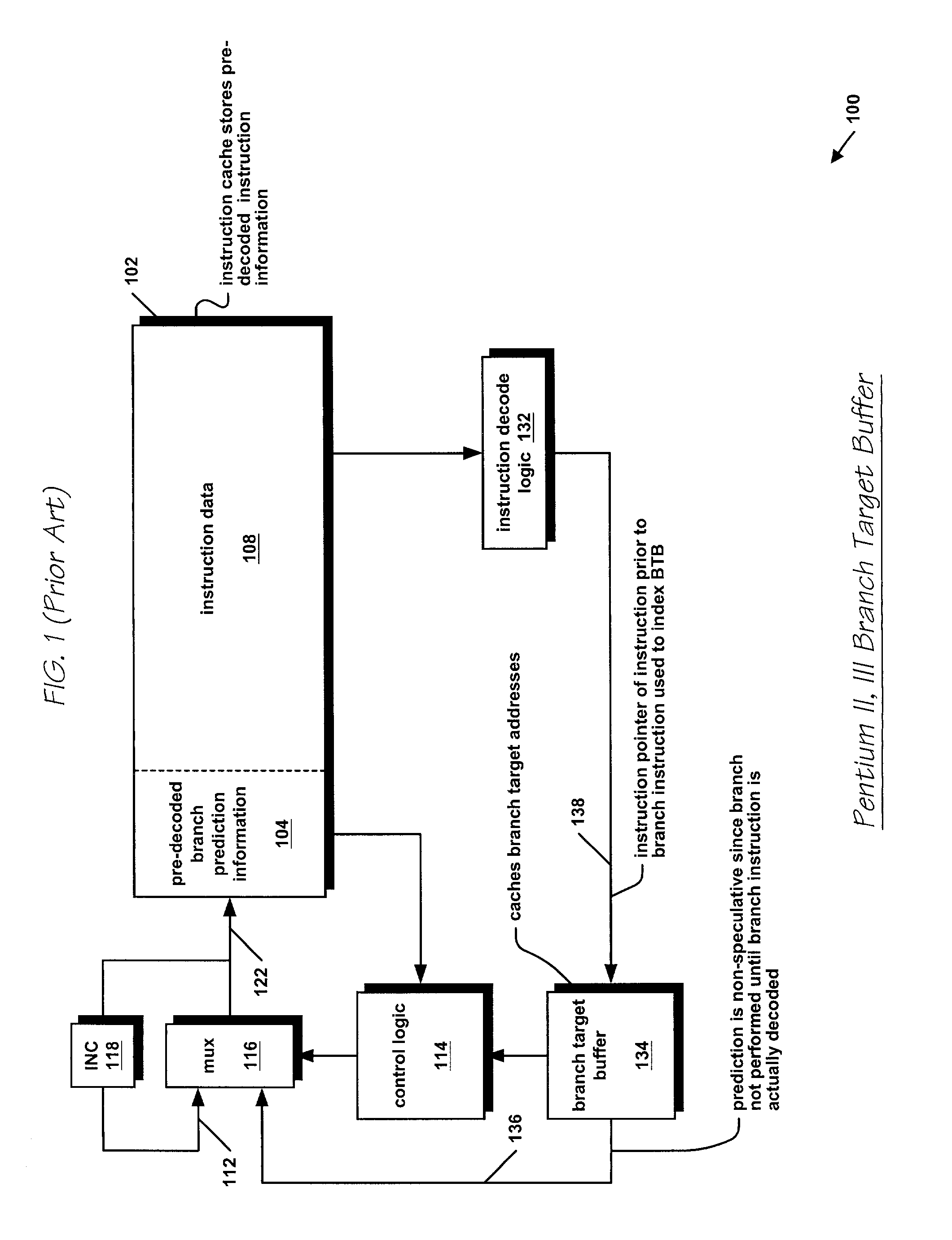
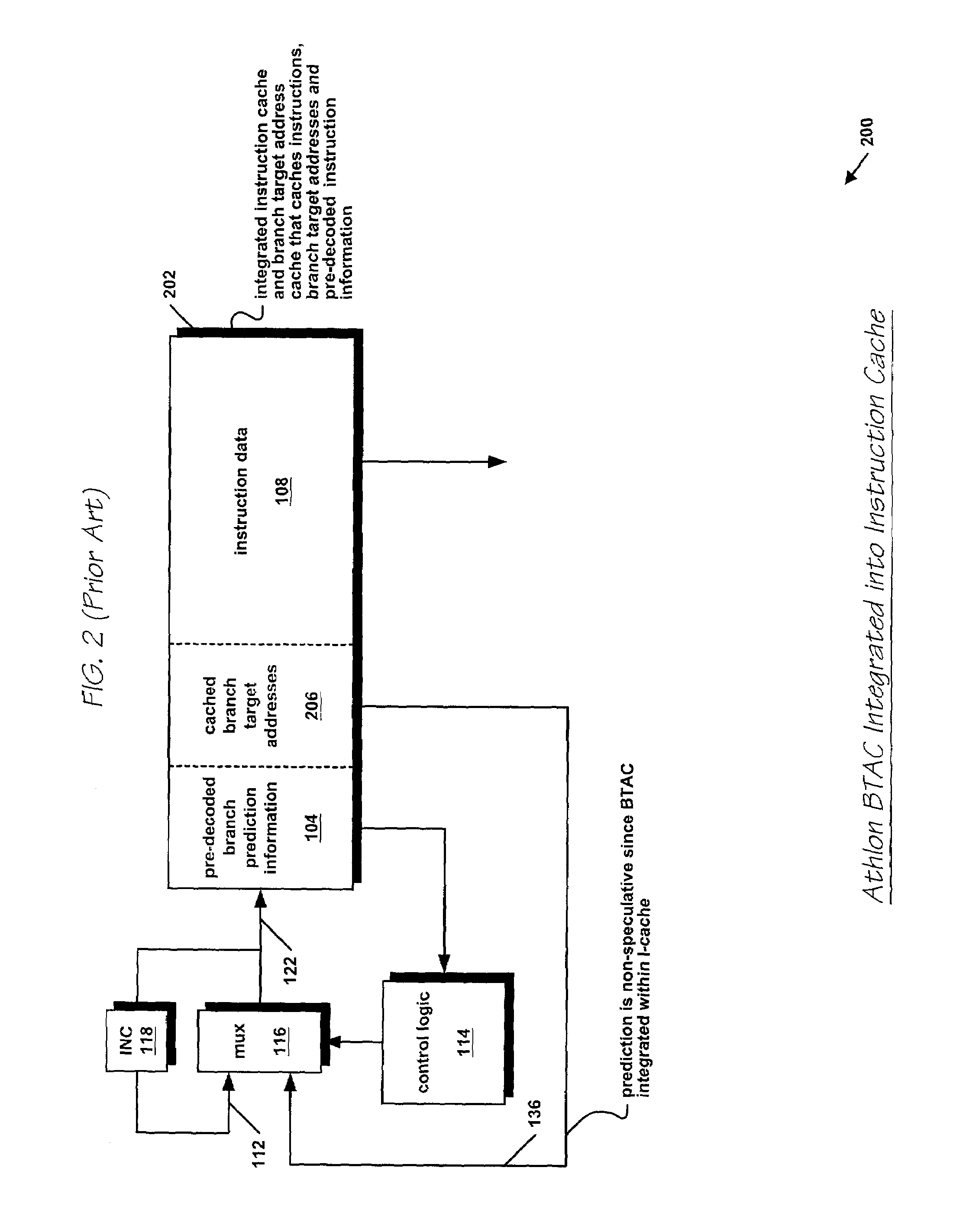
InactiveUS7134005B2Easy to useImproved processor cycle timeDigital computer detailsConcurrent instruction executionParallel computingBranch target address cache
A microprocessor caches in a branch target address cache (BTAC), for each of a plurality of previously executed branch instructions: a prediction of whether the branch instruction will be taken and is present in a cache line of instruction bytes provided by an instruction cache in response to a fetch address, a target address of the branch instruction, and a location of an opcode byte of the branch instruction within the cache line. The instruction cache provides the cache line to an instruction buffer and the BTAC provides the prediction, the target address, and the location in response to the fetch address. The microprocessor branches to the target address. A byte in the cache line within the instruction buffer indicated by the location provided by the BTAC is marked. An instruction decoder formats the instruction bytes in the cache line. The microprocessor erroneously branched to the target address if the instruction decoder indicates the marked byte is in a non-opcode location within one of the formatted instructions.
Owner:IP FIRST
Multi-threaded processor having compound instruction and operation formats
ActiveUS7475222B2Instruction analysisGeneral purpose stored program computerParallel computingExecution unit
A processor comprises a memory, an instruction decoder coupled to the memory for decoding instructions retrieved therefrom, and a plurality of execution units for executing the decoded instructions. One or more of the instructions are in a compound instruction format in which a single instruction comprises multiple operation fields, with one or more of the operation fields each comprising at least an operation code field and a function field. The operation code field and the function field together specify a particular operation to be performed by one or more of the execution units.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com