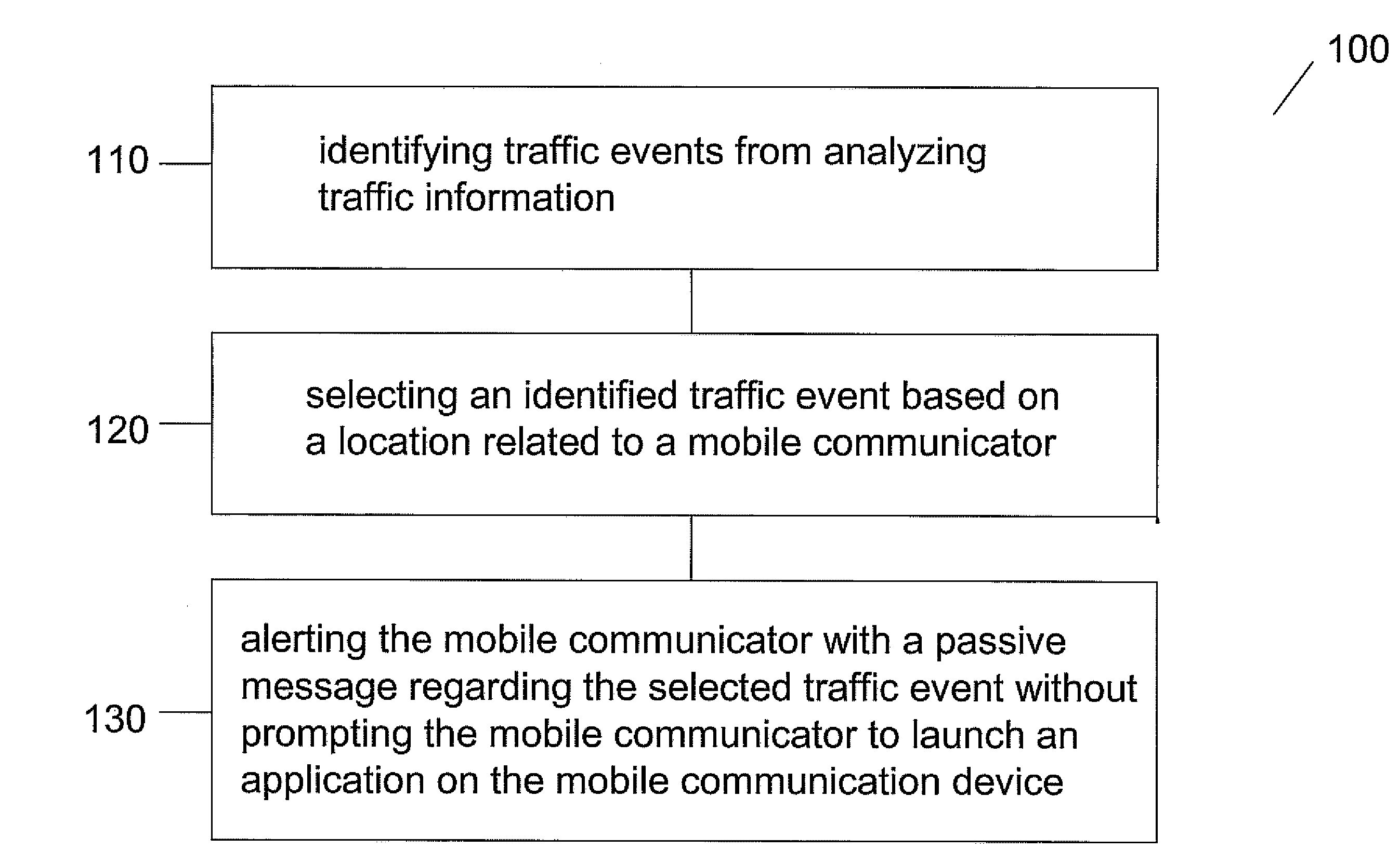
Patents
Literature
828 results about "Register data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
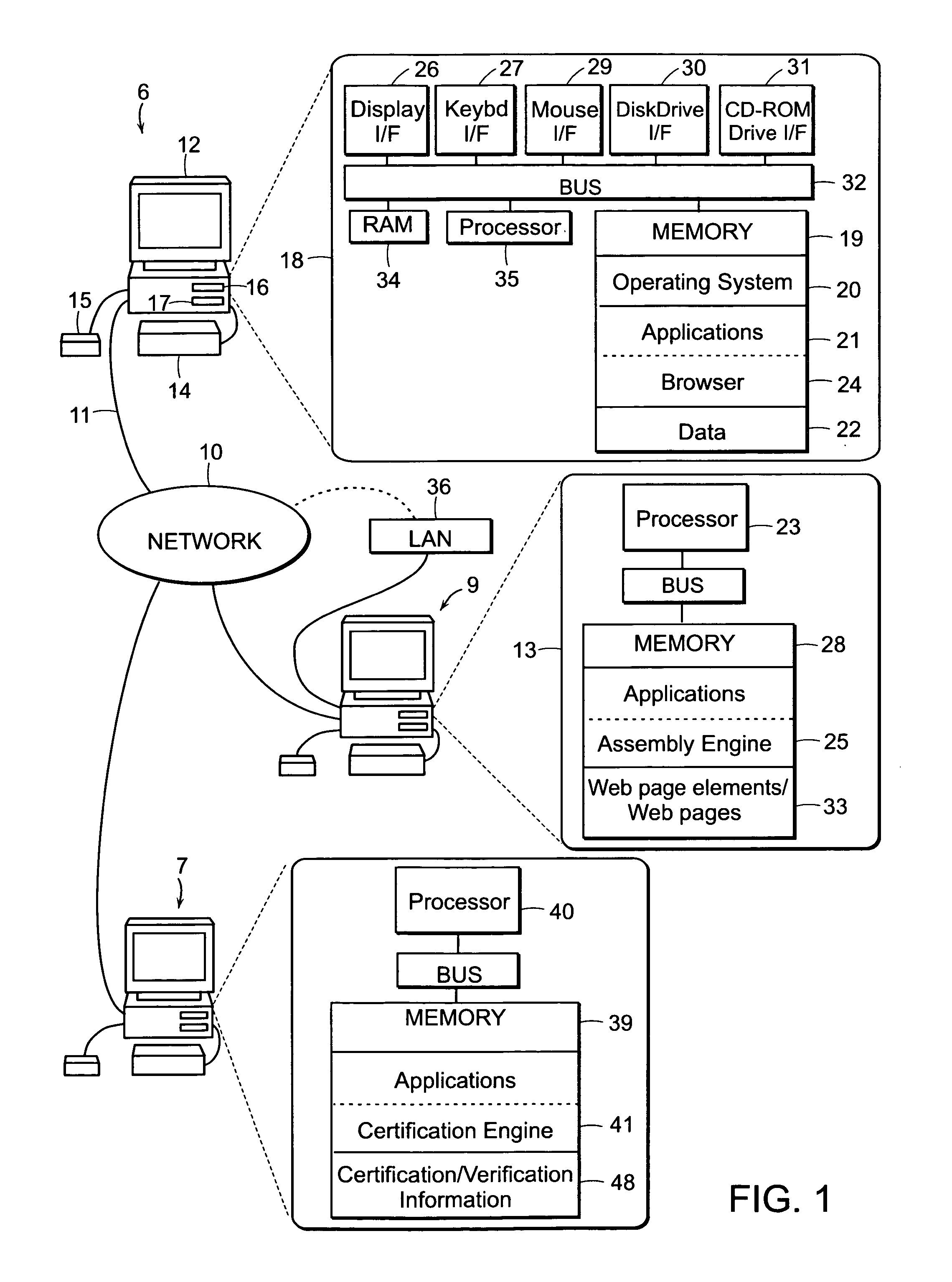
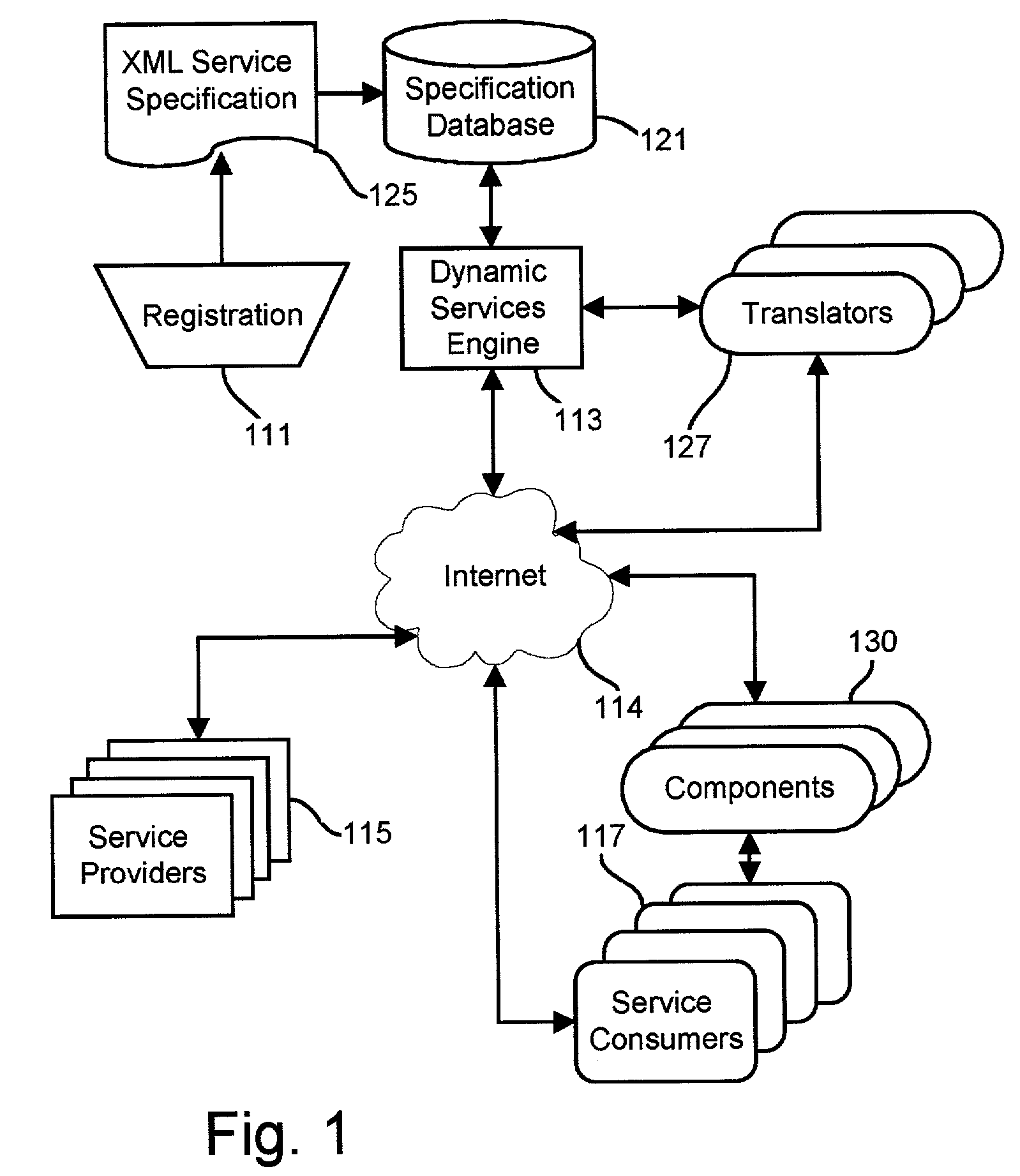
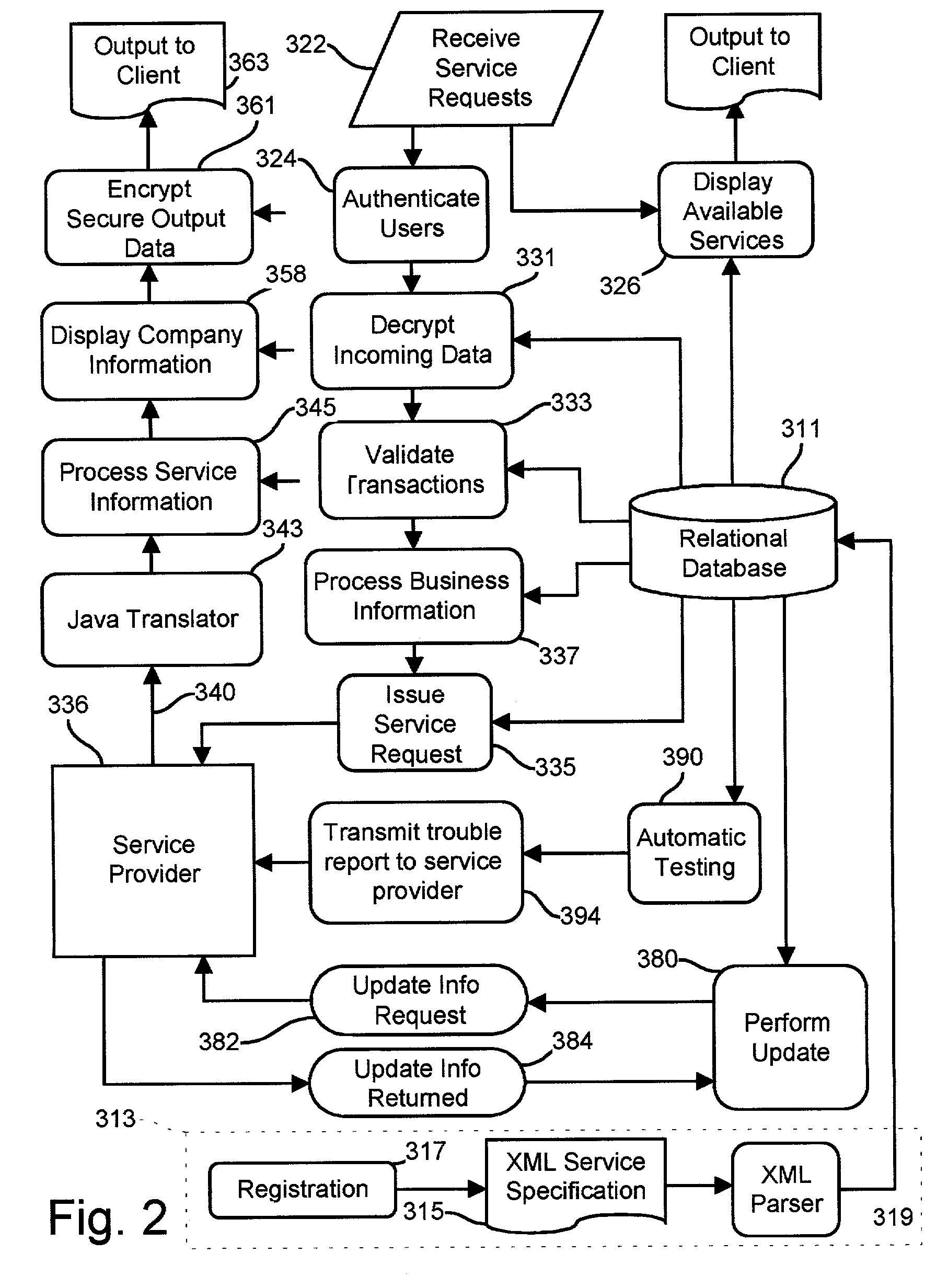
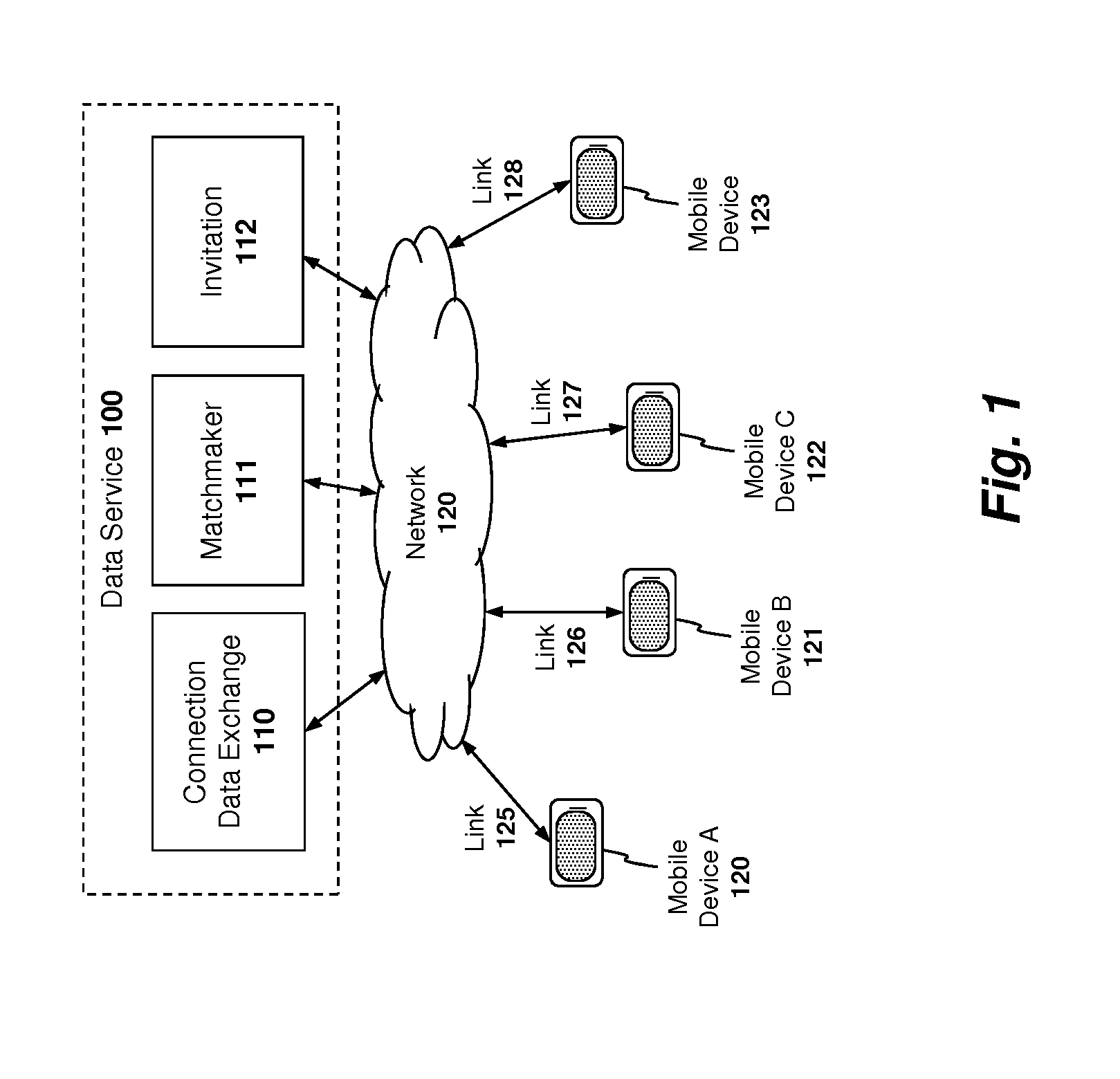
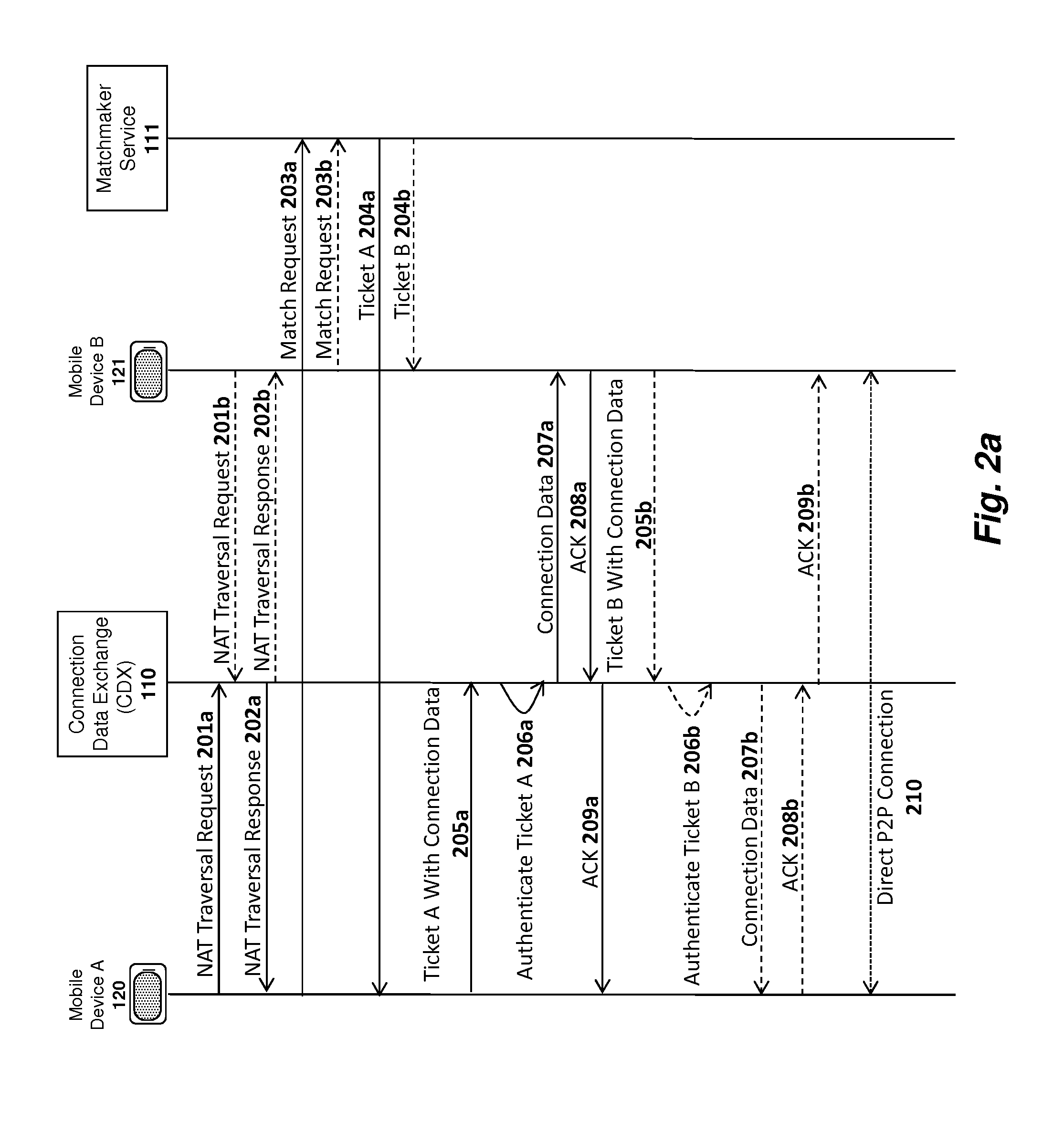
Register data sources. Registration is the process of extracting metadata from the data source and copying that data to the Data Catalog service. The data remains where it currently resides, and it remains under the control of the administrators and policies of the current system. To register a data source, do the following:
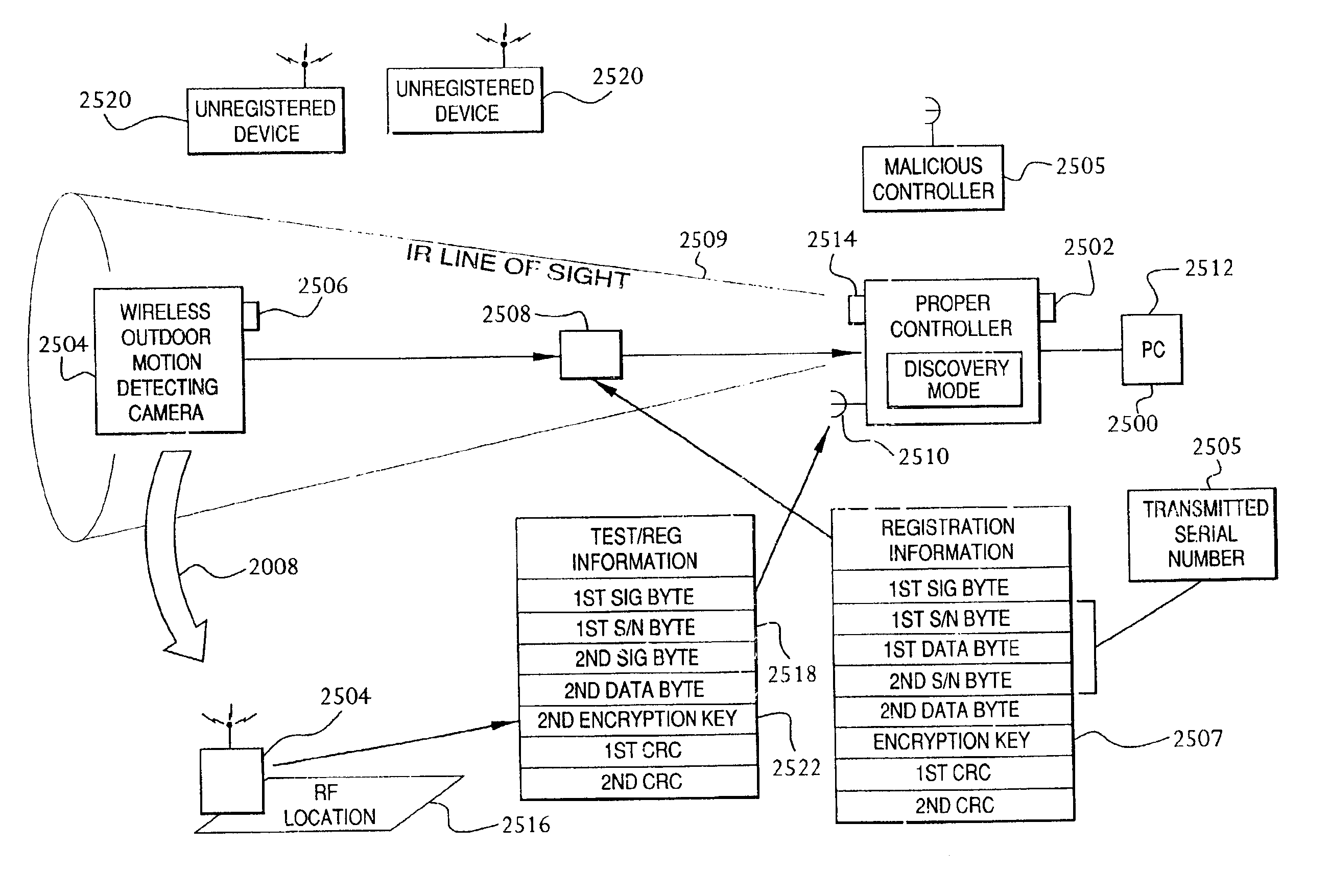
Method and system for communicating with a wireless device
InactiveUS7039391B2Electric signal transmission systemsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionWireless dataOperation mode
A method, system, transmitter, receiver and protocol are disclosed for communicating with wireless receivers. The invention includes providing a controller having a discovery mode and an operating mode, in the discovery mode the controller is capable of registering wireless devices, in the operating mode the controller is capable of receiving transmissions from a wireless device that has been registered. A wireless transmitter is provided which is capable of communicating wirelessly with the controller. The wireless device has an actuator for initiating at least one transmission of registration data. When the controller is placed into the discovery mode, and the actuator of the wireless device is actuated to wirelessly transmit the registration data from the wireless device to the controller, whereby the wireless device is registered with the controller. The wireless data contains data that allows the controller to interface with the wireless device.
Owner:AT&T DIGITAL LIFE
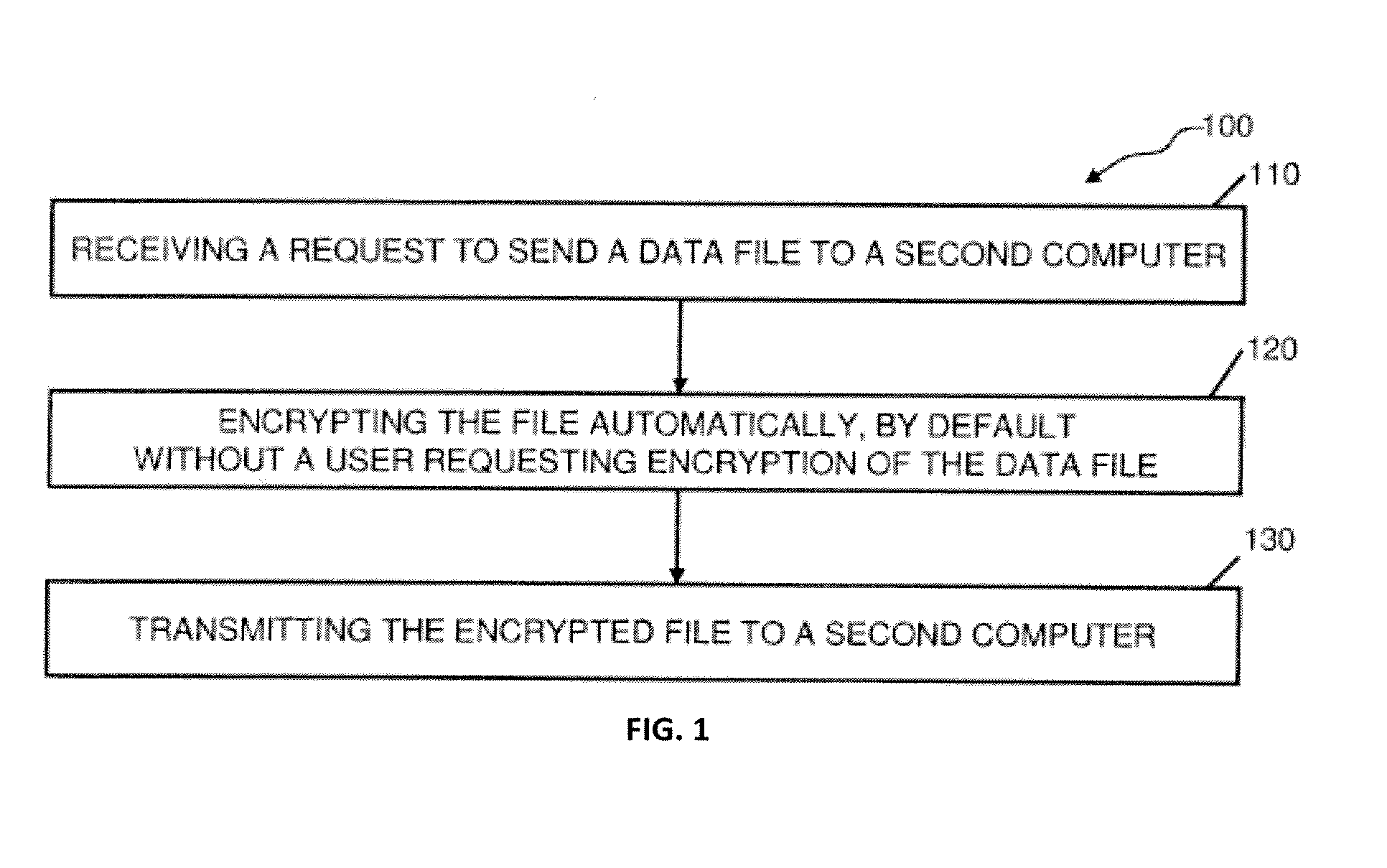
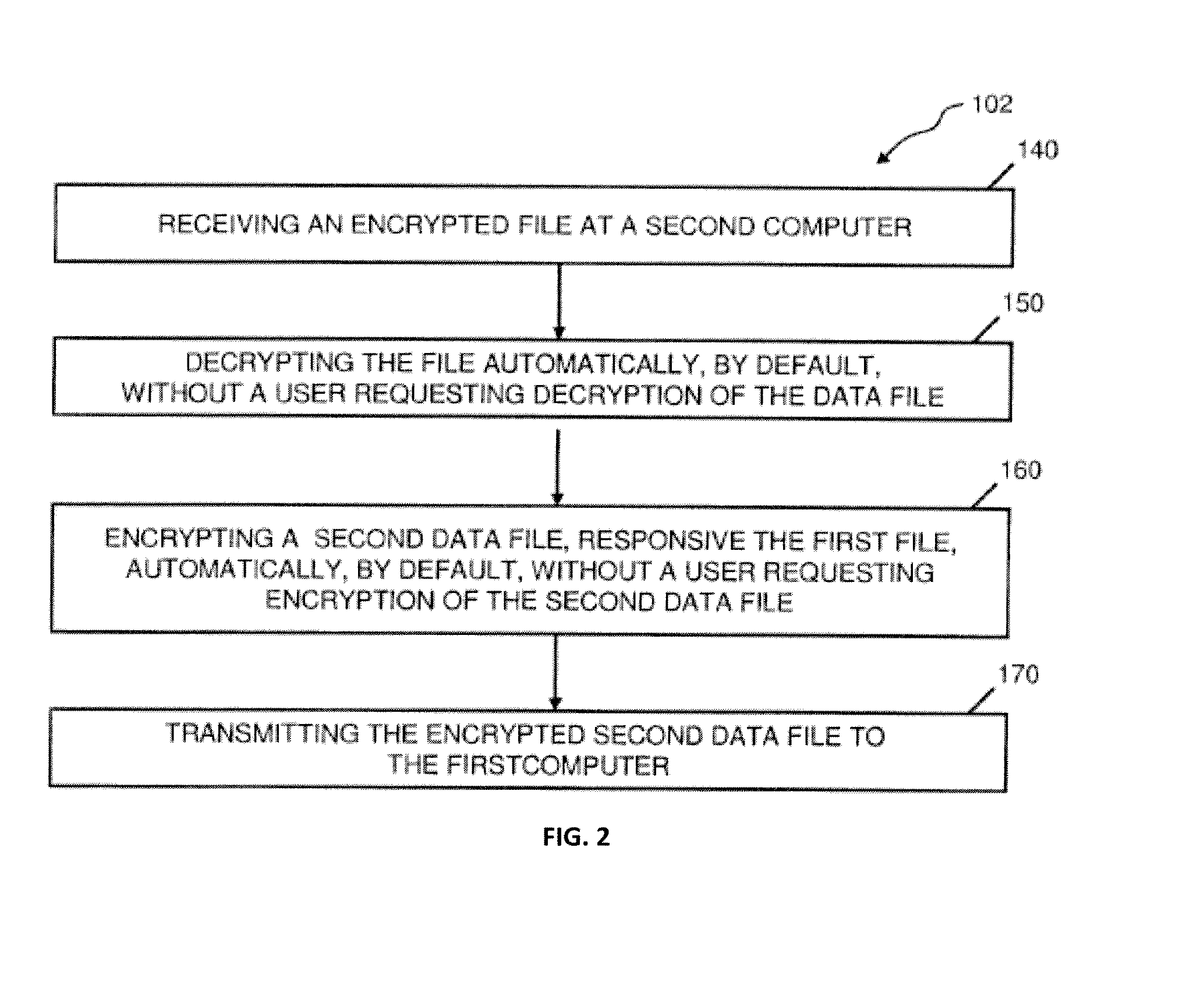
Abstraction layer for default encryption with orthogonal encryption logic session object; and automated authentication, with a method for online litigation
InactiveUS20140304505A1Reduce decreaseData processing applicationsUser identity/authority verificationAbstraction layerSubject matter
Embodiments herein provide methods, apparatus, computer program products, software and means for (1) an abstraction layer for default encryption, (2) with orthogonal encryption logic session object, and (3) automated authentication, (4) with a method for online litigation. In some cases subject matter disclosed herein relates to default data encryption; use a user's registration data to generate an encryption logic and related executable code, including servers and client applications; encryption as an automatic background task occurring through variable encryption logic, with authentication; embodiments are also described for conducting online litigation through pleadings formed as meta-files that trigger litigation related algorithms in order to automate and coordinate litigation.
Owner:VERIDICOM DE
System and method for biometric authorization for check cashing
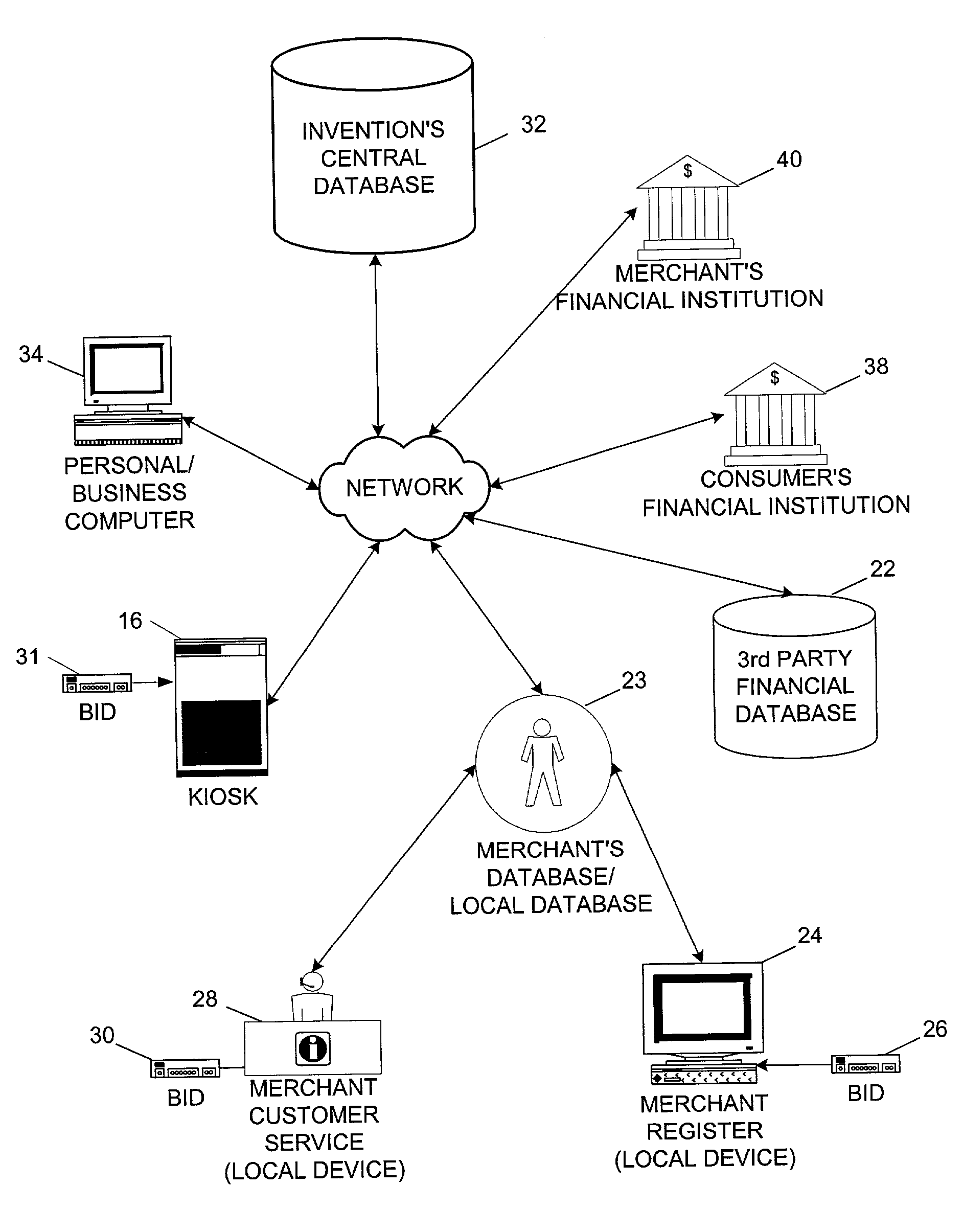
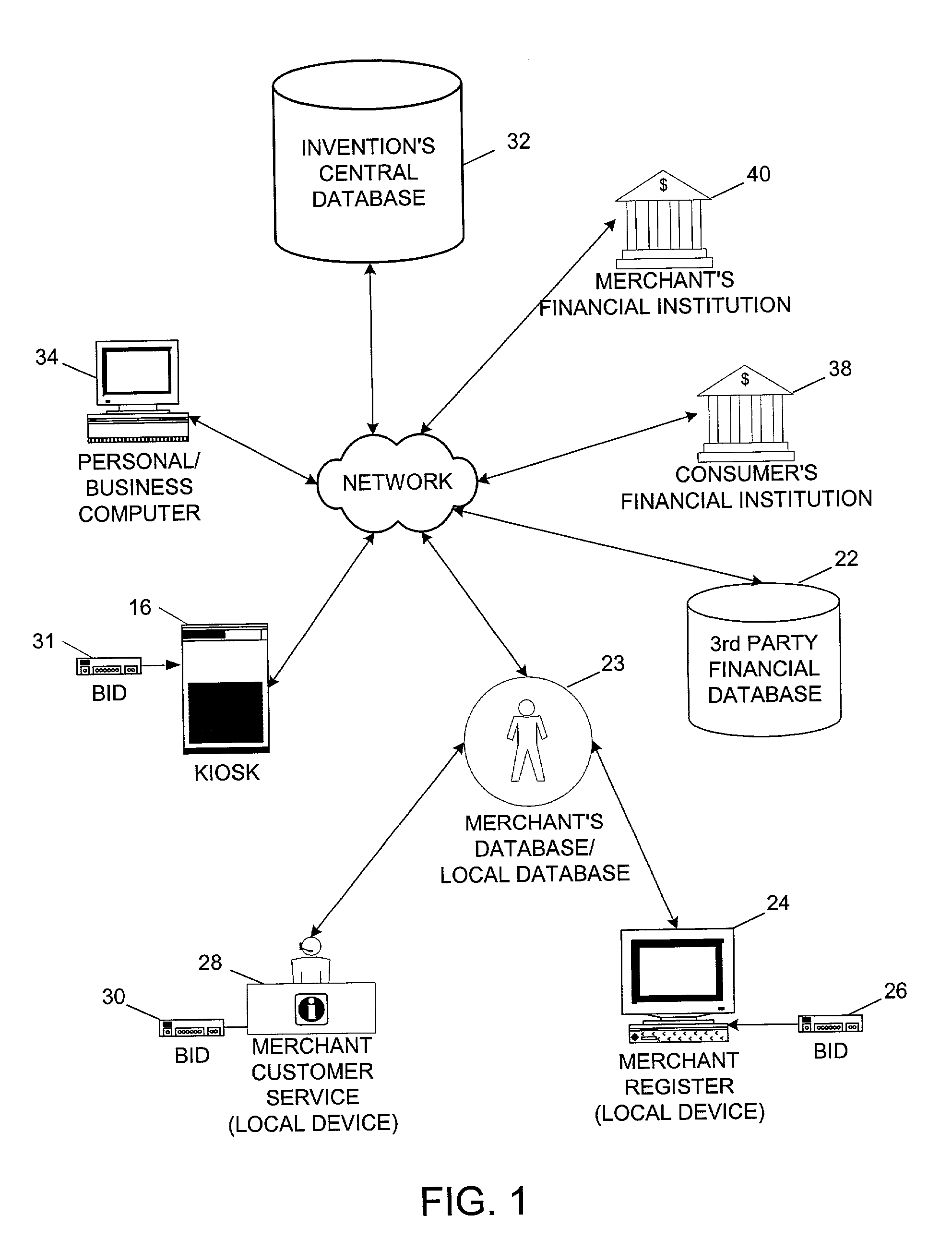
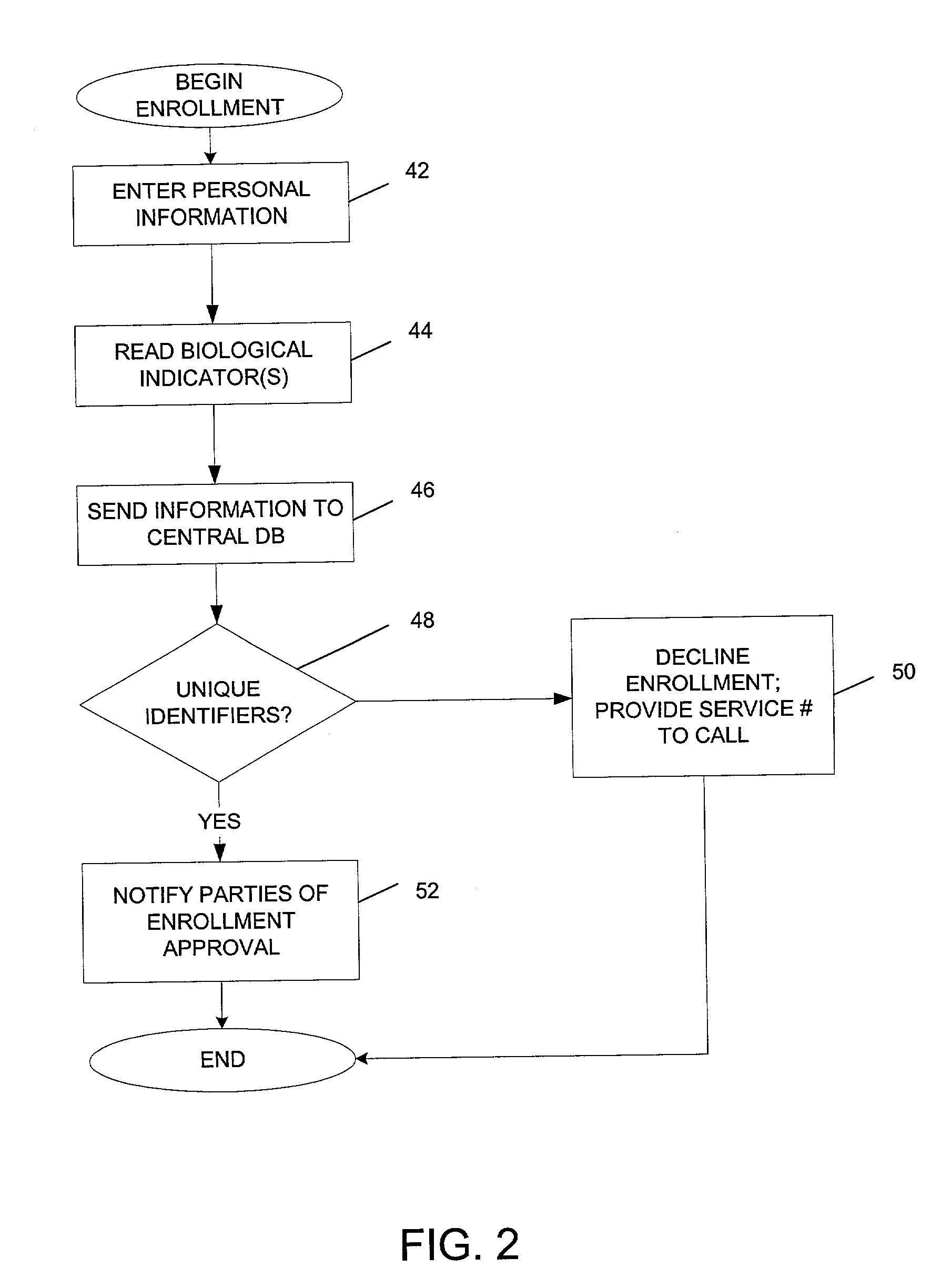
A system for authorizing a check cashing transaction between a consumer and a merchant using identity verification based on biometric information. A system comprises a central biometric information database containing biometric and personal identity-verifying data registered therein by a consumer and containing merchant identity-verifying data registered therein by a merchant. The system further comprises a merchant local device having a biometric reader and linked via a network to the central biometric information database. Using the biometric reader, a consumer desiring to cash a check presents biometric data to the central biometric information database via the biometric reader. The central biometric information database provides an electronic comparison of the present biometric data with the biometric data registered by the consumer. If the presented data and the registered data match, an approval signal is transmitted to the merchant local device.
Owner:VALSOFT CORP INC
Methods and systems for providing a signed digital certificate in real time
ActiveUS20120179907A1User identity/authority verificationApplication programming interfaceService provision
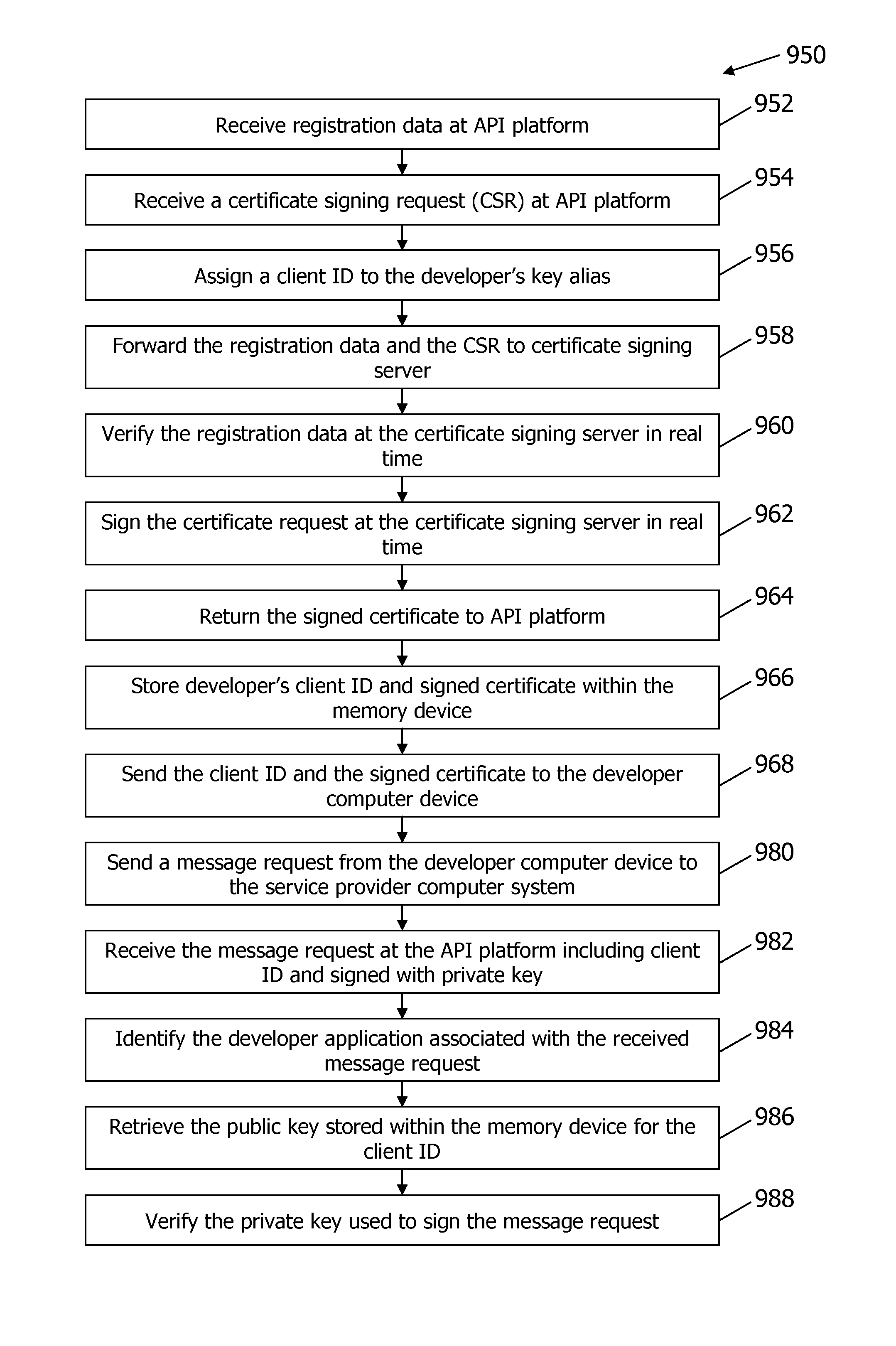
A method and system for signing a digital certificate in real time for accessing a service application hosted within a service provider (SP) computer system through an open application programming interface (API) platform is provided. The API platform is in communication with a memory device. The method includes receiving registration data from a developer computer device wherein the developer computer device is associated with a developer and configured to store a developer application, receiving a certificate signing request (CSR) from the developer computer device wherein the CSR includes a public key associated with the developer, verifying the registration data as being associated with the developer, signing the CSR to produce a signed certificate after verifying the registration data wherein the verifying and signing steps are performed by the SP computer system in real time, and transmitting the signed certificate and a client ID to the developer computer device.
Owner:MASTERCARD INT INC
Method and apparatus for efficient handling of product return transactions
InactiveUS6085172ALow costReduce shipping costsFinanceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsSingle sessionInformation access
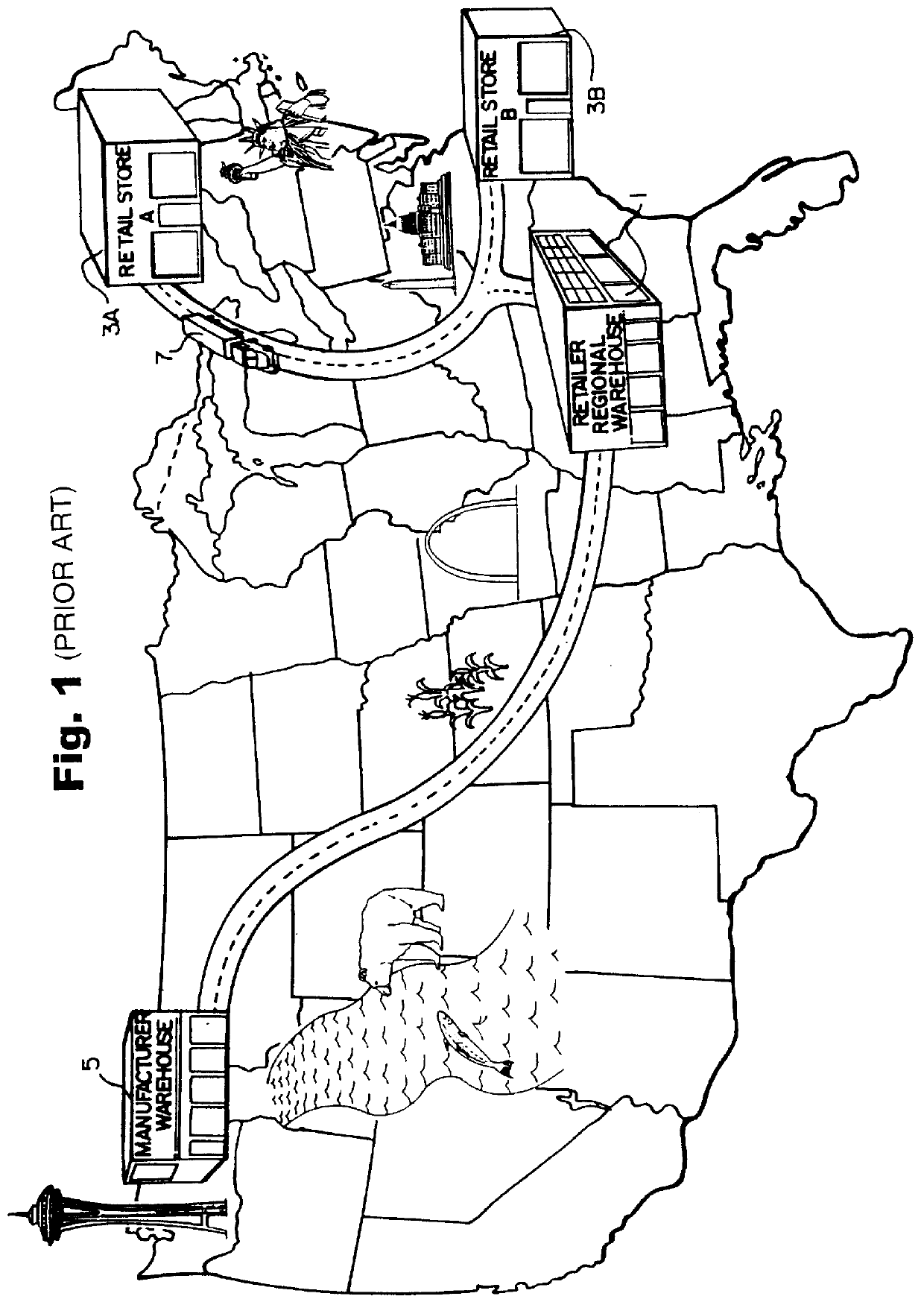
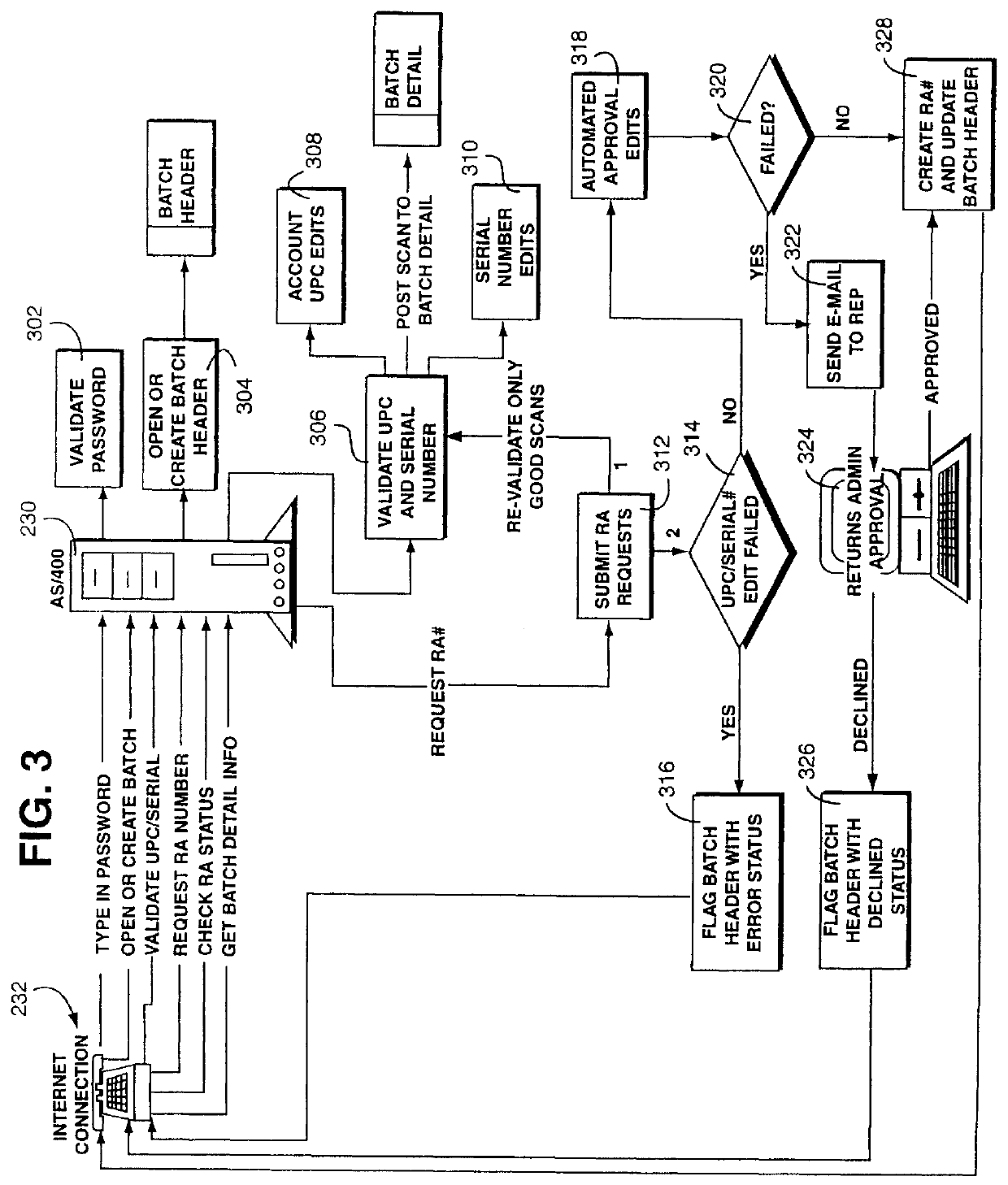
A method and apparatus for efficient handling of product returns to reduce associated costs. A computer system at a regional product return center scans a returned product for identifying information, accesses a manufacturer return approval computer system through the internet or the like, and then submits the identifying information to the manufacturer for return approval. The manufacturer computer system utilizes the identifying information to access an electronic registration database to determine whether the returned product satisfies applicable return criteria. If so, the product is approved for return to the manufacturer. The regional product return center preferably scans a plurality of returned products in a single session. In response to the product identifying information submitted by the regional product return center, the manufacturer provides a list of approved returns and unapproved returns, along with a return authorization number for the batch of approved returns. The regional product return center then assembles the approved product returns into a box, shipping pallet, or the like, applies a label indicating the return authorization label, and ships the batch to the manufacturer. Shipping costs can be saved by omitting rejected product returns from the shipment. The manufacturer can handle the approved product returns from the regional return center as a batch, thereby reducing costs.
Owner:E2INTERACTIVE INC D B A E2INTERACTIVE
Method for transmitting voice or data in a wireless network depending on billing account status
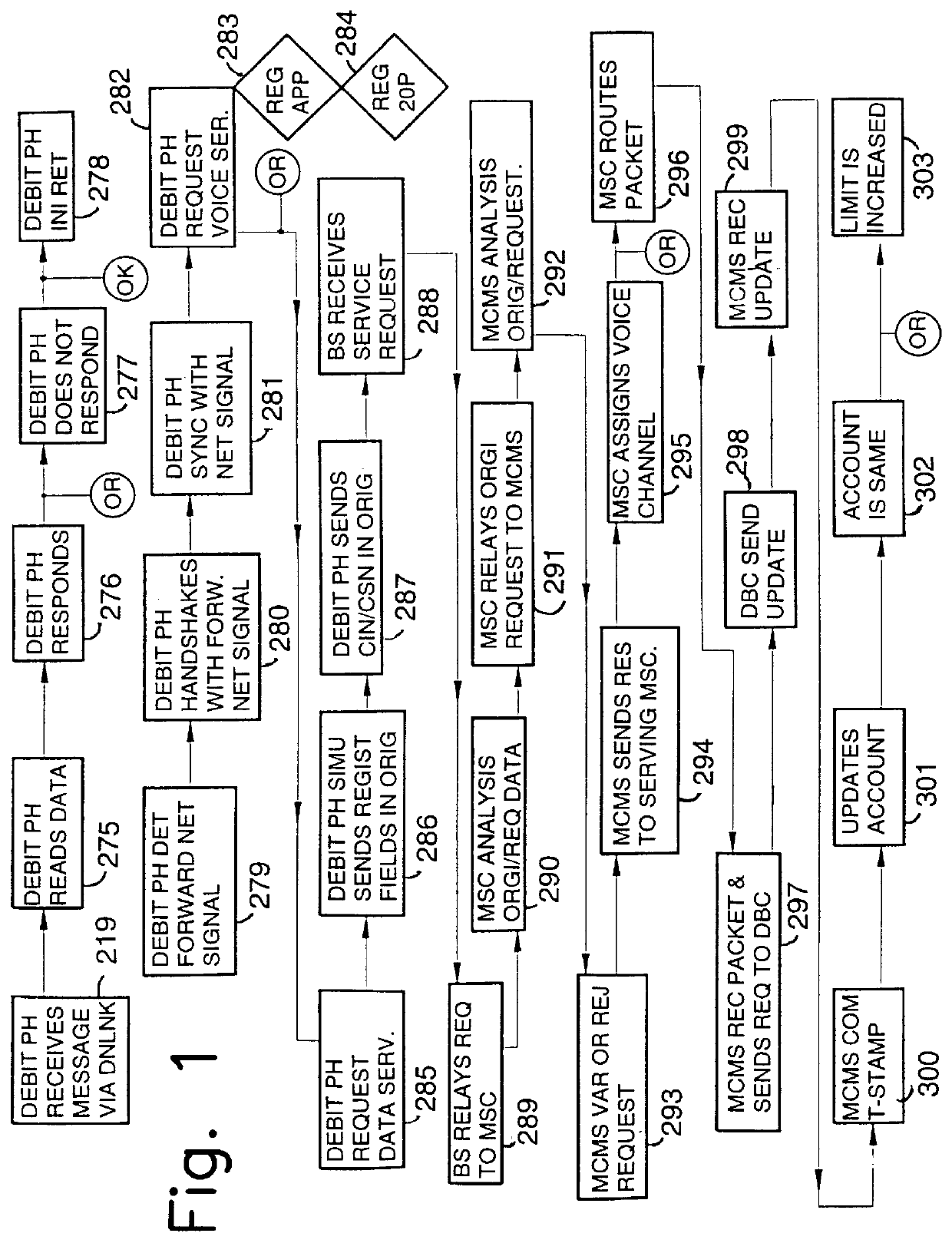
A method for paging network personal communications system voice and data services comprising transmitting a control channel origination data packet including data specifying an identification number, data specifying a user serial number, a voice airtime register data packet, and a sequence of dialed digits for activating a switch to activate a remote feature access control procedure. The control channel origination data packet is then transmitted through control channels or digital access channels of a paging network. The control channel origination data packet is received and stored cellular base station. The control channel origination data packet is relayed to a mobile switching center and then a selected service may be activated if debit information requirements of a user are met by loading and comparing parameter table values for the identification number and the serial number or the user at the mobile switching center. A personal communications apparatus is also disclosed having a housing and circuitry for transmitting a control channel origination data packet. A speaker is mounted in housing and includes a display screen for displaying data messages and a keypad for entering a landline telephone number or mobile number. A plurality of selection keys allow for selecting a data message for transmission from the apparatus.
Owner:AERIS COMM
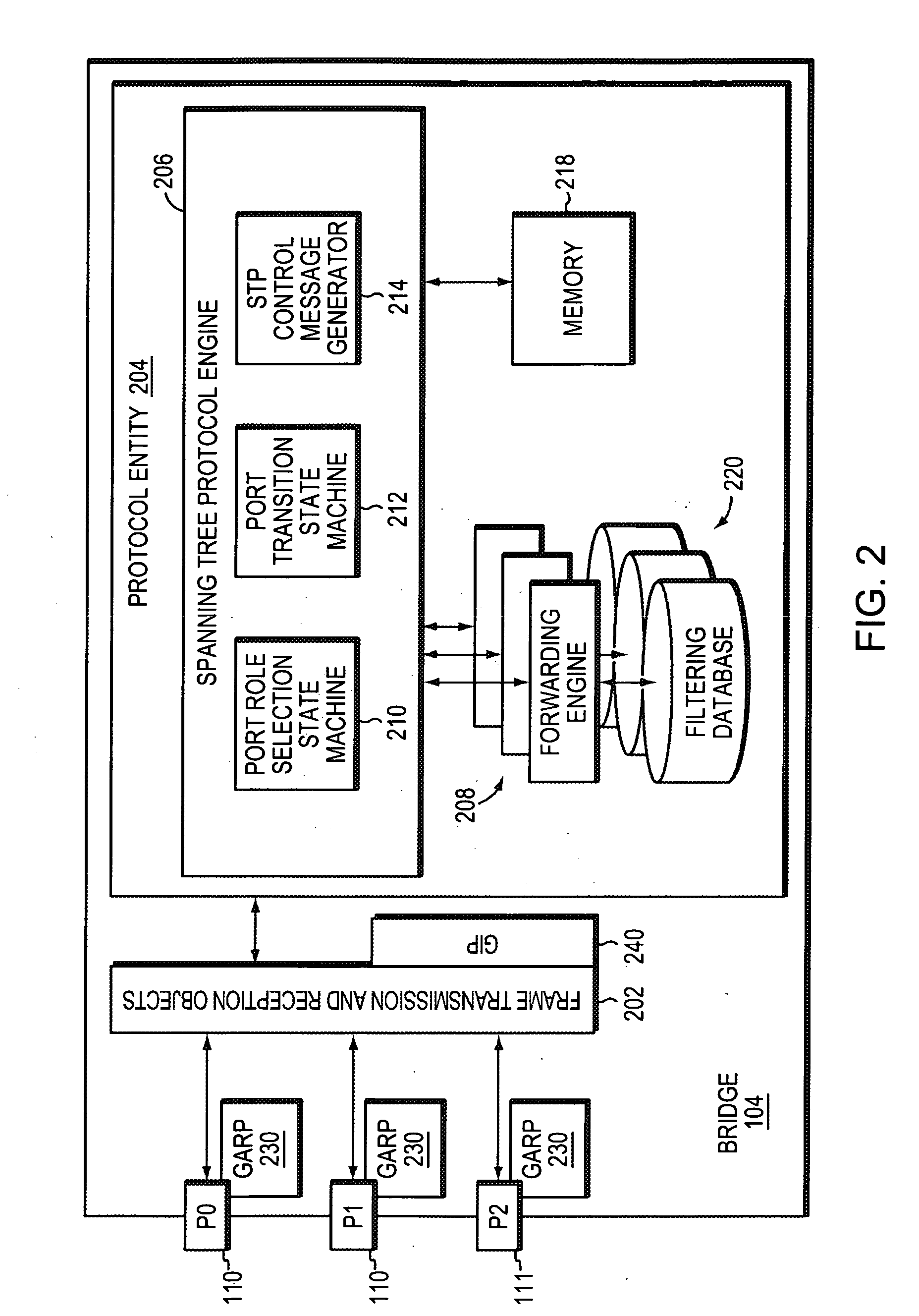
Technique for efficiently managing bandwidth registration for multiple spanning tree options
ActiveUS20070263554A1Efficient managementGreat opportunityData switching by path configurationData streamComputer network
A technique efficiently manages bandwidth (BW) registration for multiple spanning tree options in a computer network. According to the novel technique, an entry bridge determines multiple spanning tree paths to other bridges of the network (namely, one or more available spanning trees rooted at one or more bridges of the network) and determines a utilized (registered) BW on each of those paths. Upon receiving a request to initiate BW registration for a data flow to a destination end point, e.g., from an application source end point, the entry bridge selects one of the spanning tree paths to utilize for the data flow. Selection of the spanning tree path from among the multiple available paths may be based on (i) available bandwidth of the paths, (ii) a shortest of the paths, and (iii) a lowest bridge identifier ID for the bridge root for the path. The entry bridge sends a registration message for the data flow towards the destination end point along the selected spanning tree path. If successful, the data flow is transmitted on the selected path. If not, the entry bridge attempts to register the data flow on a next best alternate spanning tree, e.g., until a successful registration or until a determination that no further alternate spanning trees exist.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
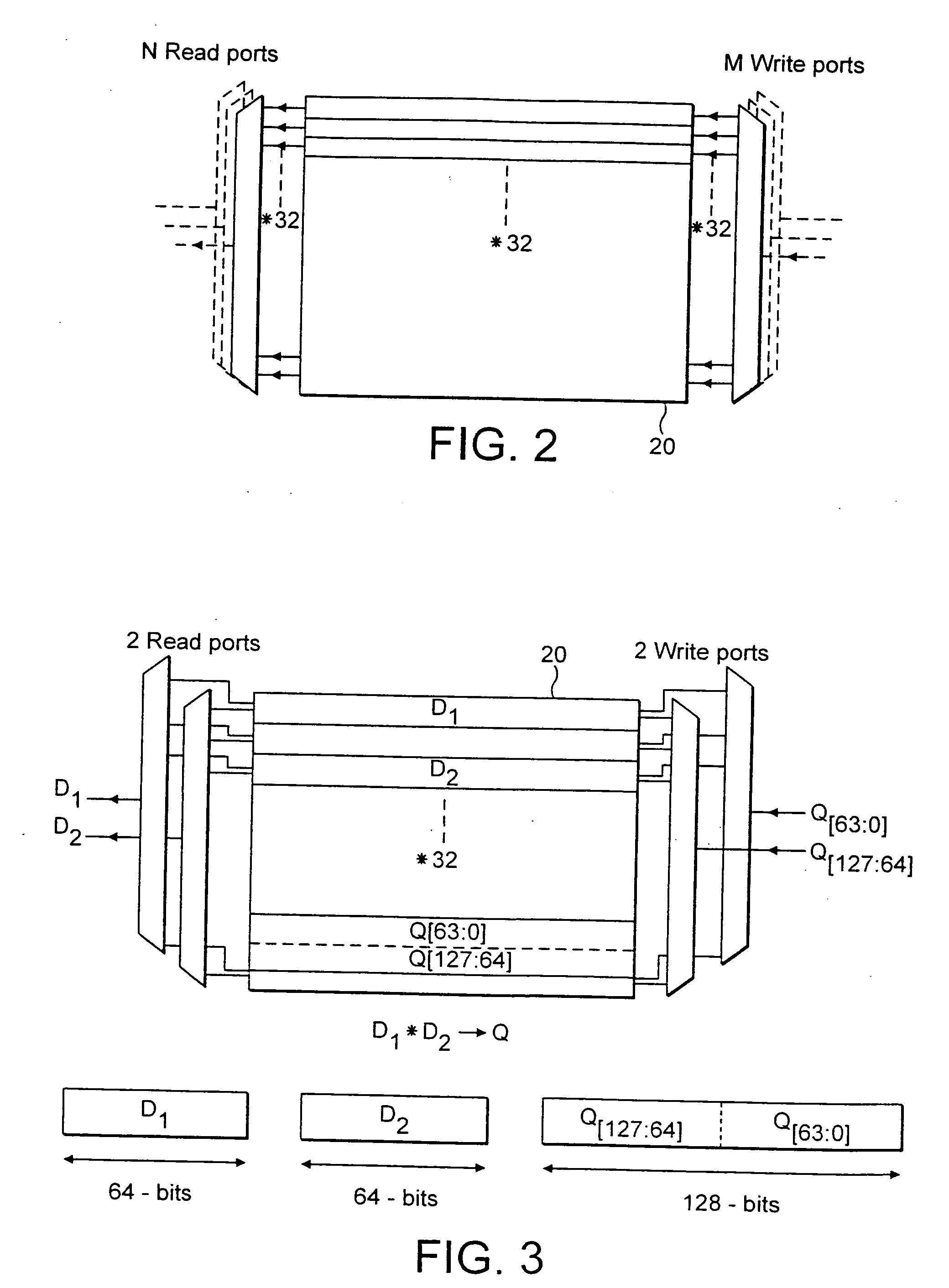
Data processing apparatus and method for performing rearrangement operations
ActiveUS20100106944A1Further flexibilityReduce energy consumptionDigital data processing detailsInstruction analysisControl signalProcessor register
A data processing apparatus and method are provided for performing rearrangement operations. The data processing apparatus has a register data store with a plurality of registers, each register storing a plurality of data elements. Processing circuitry is responsive to control signals to perform processing operations on the data elements. An instruction decoder is responsive to at least one but no more than N rearrangement instructions, where N is an odd plural number, to generate control signals to control the processing circuitry to perform a rearrangement process at least equivalent to: obtaining as source data elements the data elements stored in N registers of said register data store as identified by the at least one re-arrangement instruction; performing a rearrangement operation to rearrange the source data elements between a regular N-way interleaved order and a de-interleaved order in order to produce a sequence of result data elements; and outputting the sequence of result data elements for storing in the register data store. This provides a particularly efficient technique for performing N-way interleave and de-interleave operations, where N is an odd number, resulting in high performance, low energy consumption, and reduced register use when compared with known prior art techniques.
Owner:ARM LTD
Mobile alerting network
ActiveUS20090209233A1Sufficient operationUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionRoad vehicles traffic controlApplication service providerVerification system
A system for providing a mobile application includes a Mobile Subscriber Detection Authorization and Verification System (MSDAVS), to request and receive confidential information from a confidential information owner relating to a user who opted-in to a mobile service application, and to communicate the received confidential information to a mobile application service provider. The MSDAVS can include an opt-in database, to store opt-in or registration data of the opted-in users of the mobile service application and a service policy database. The mobile application service can be a mobile traffic alerting service, the confidential information owner a telephone number database of one of a wireless carrier or a telephone number database operator, and the requested confidential information a list telephone numbers of opted-in users in an alert area, defined by the mobile traffic alerting service.
Owner:GLOBAL TRAFFIC NETWORK INC
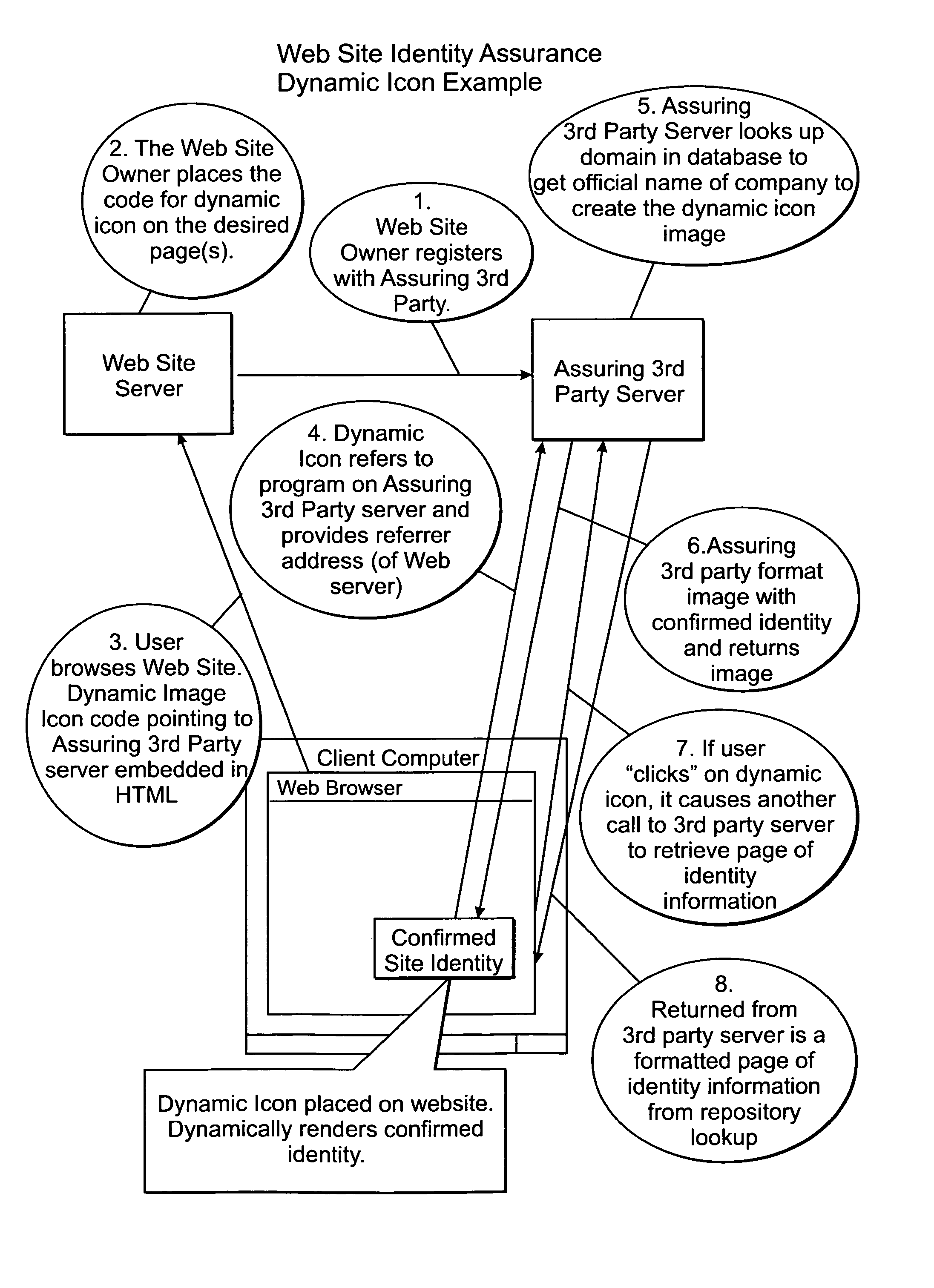
Web site identity assurance
ActiveUS7114177B2Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsDomain nameWeb site
The present invention is a method and system for providing a user with confirmation of the origin of a Web site and related information including the steps of registering a Web site with an assuring 3rd party, saving the registration on a registration server, entering in a database the Web site's Internet domain name and cross-referencing it to the registration data, retrieving the Web site's domain with an Internet browser, and either (1) using a client application tool to call for registration data for the domain name via a secure SSL connection with the registration server, determining if the domain has been registered, and returning and displaying registration data for the domain name as a confirmed identity, or (2) calling a program on the registration server in response to an HTML tag on the domain via a secure SSL connection and passing it the domain name, determining if the domain has been registered, determining if the domain name has been registered, and returning and displaying registration data for the domain name as a confirmed identity.
Owner:DIGICERT
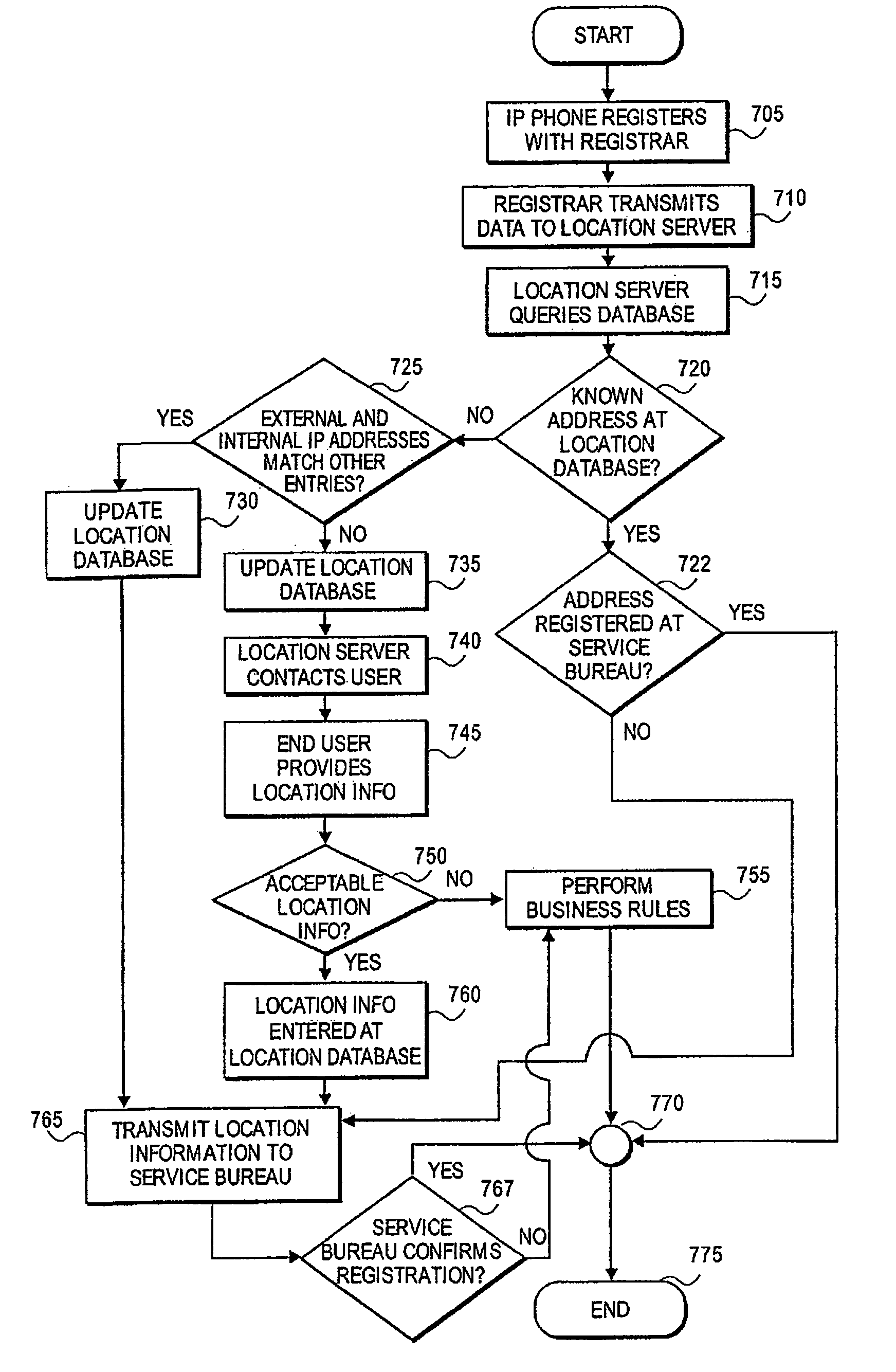
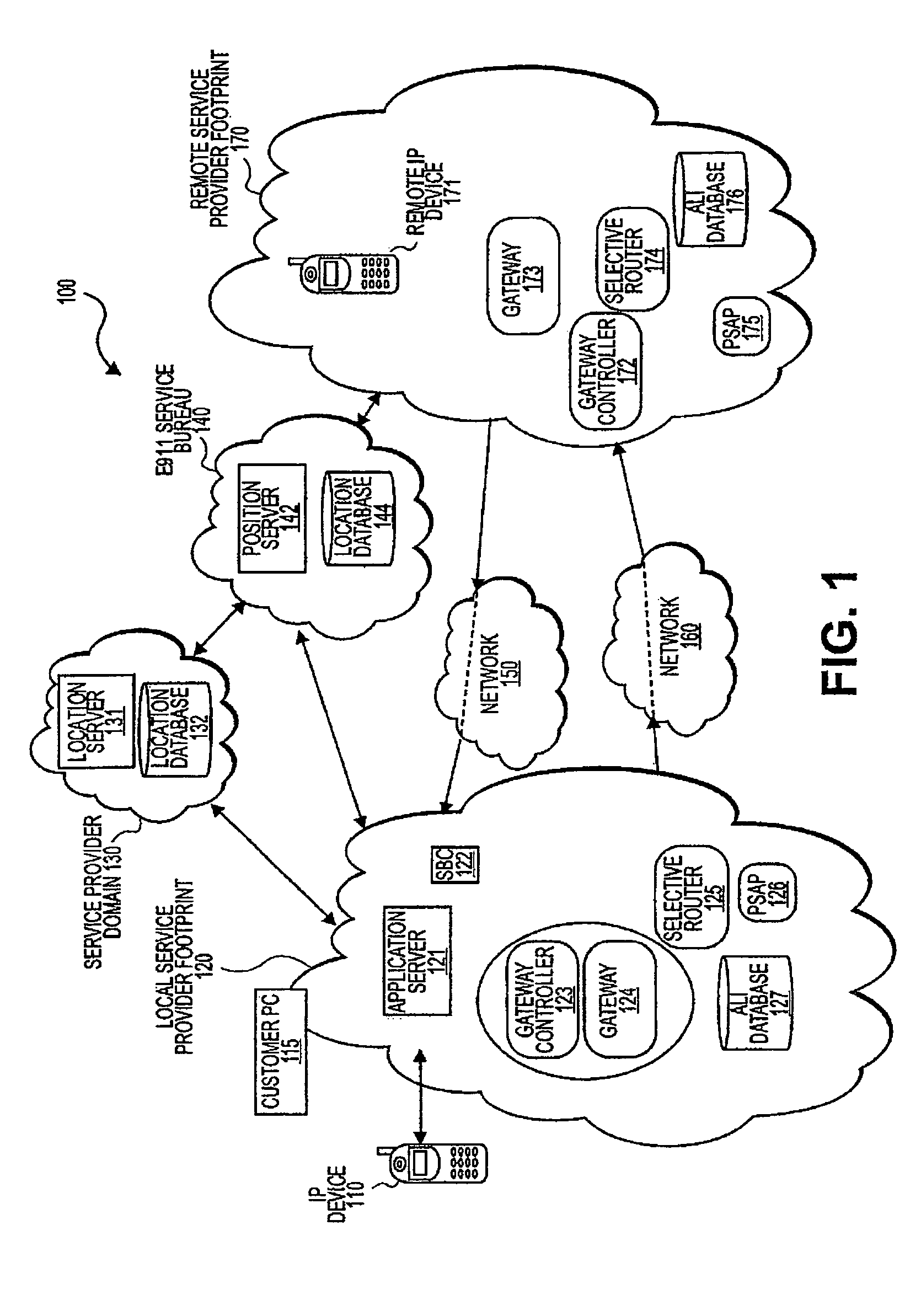
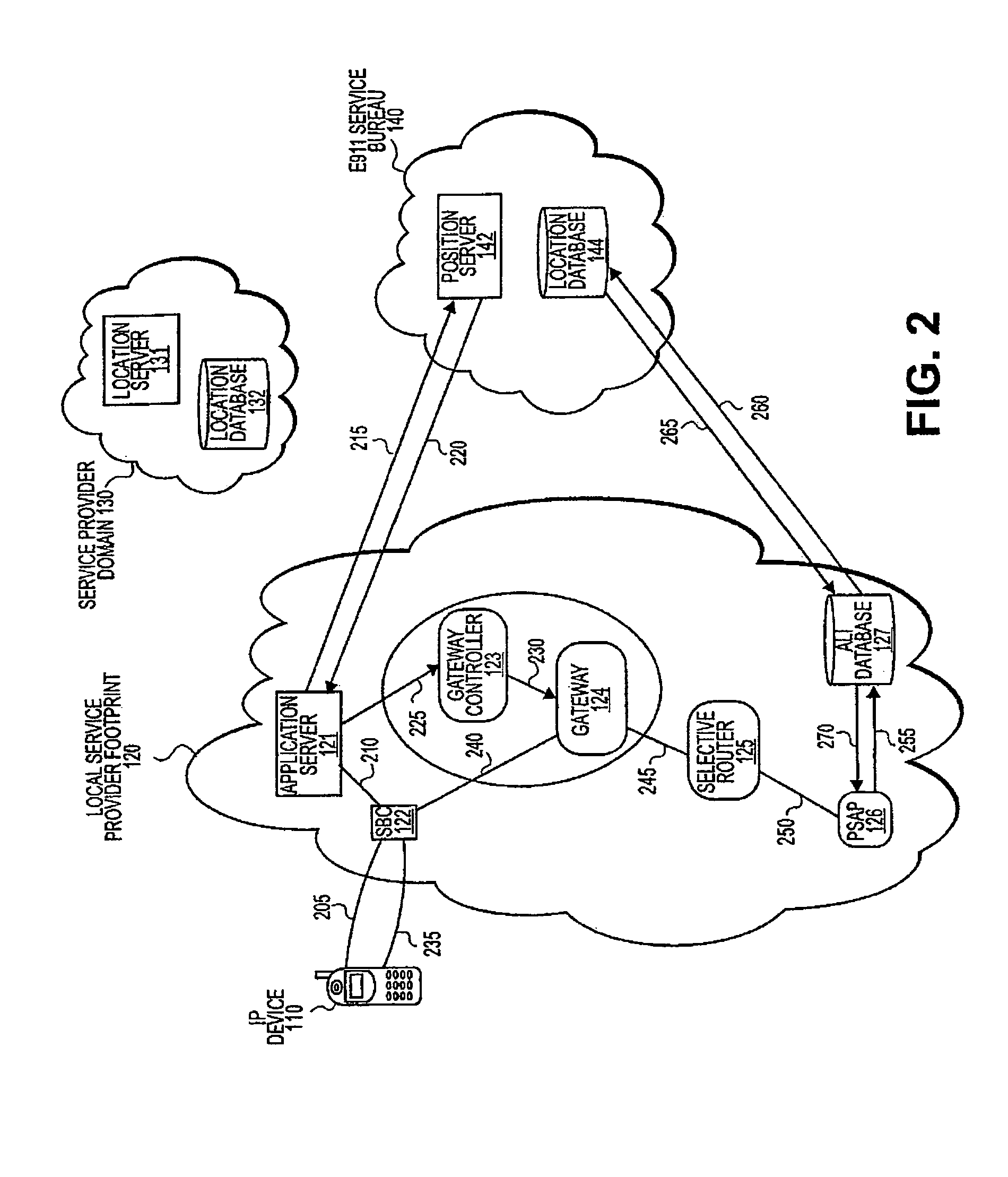
E911 location server
ActiveUS7711094B1Emergency connection handlingAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingService bureauData library
A system including an IP device configured to provide registration data, a Service Bureau configured to store location information of the IP device and provide routing data based on location information of the IP device, location server configured to receive registration data from the IP device, and location database configured to store location information of the IP device, wherein the location server queries the location database to determine whether the registration data matches the location information stored at the location database.
Owner:RAKUTEN GRP INC
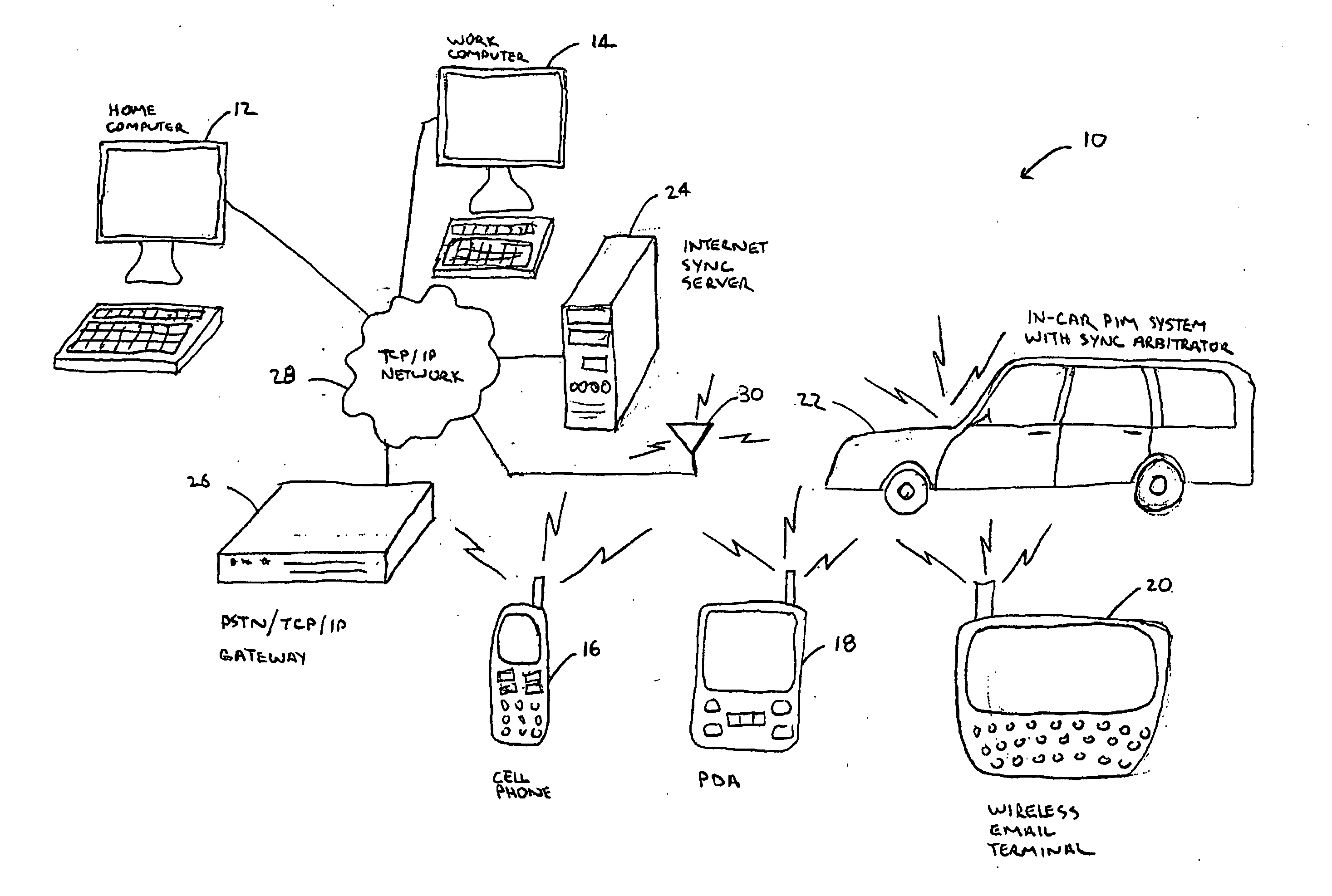
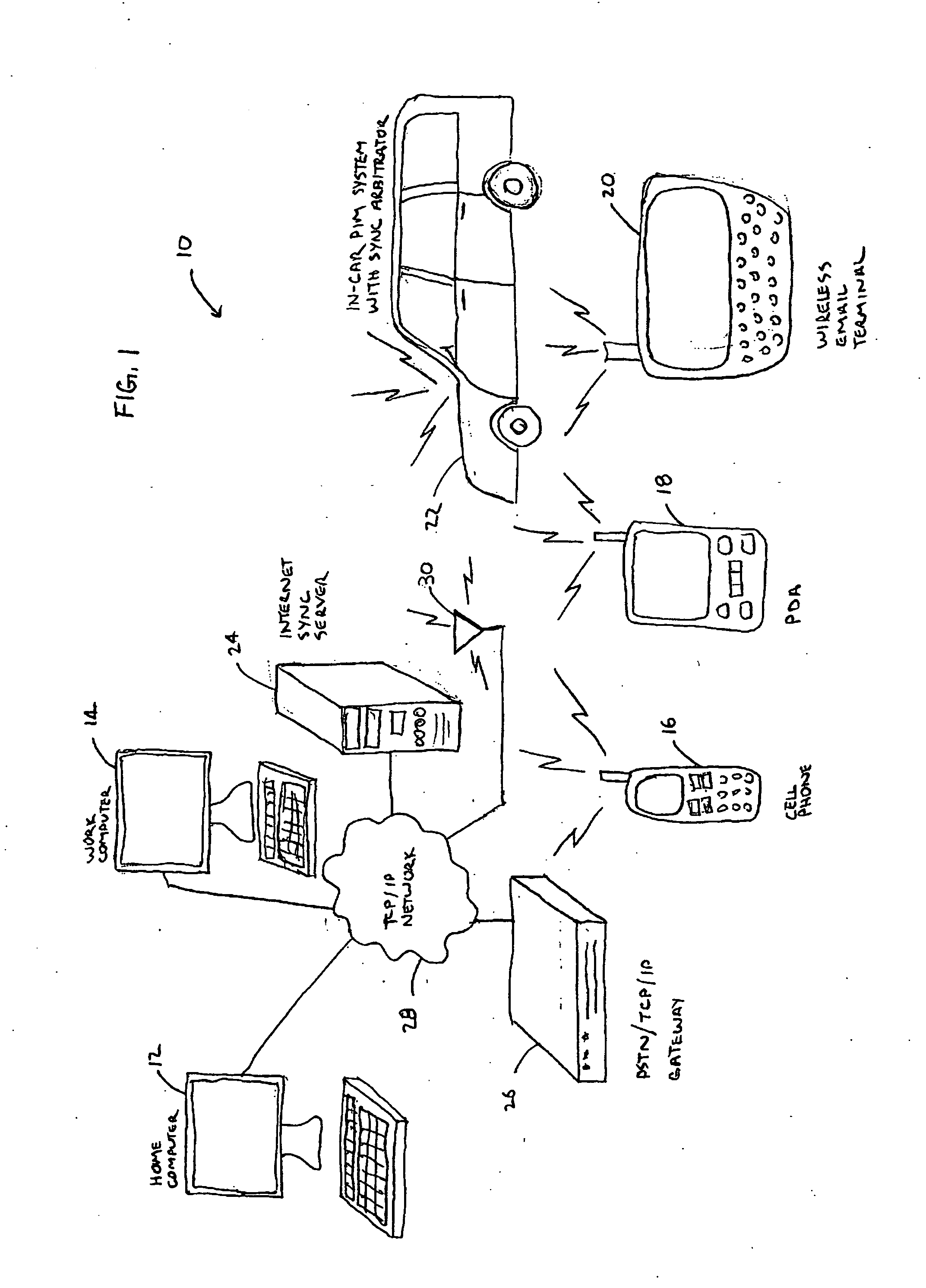
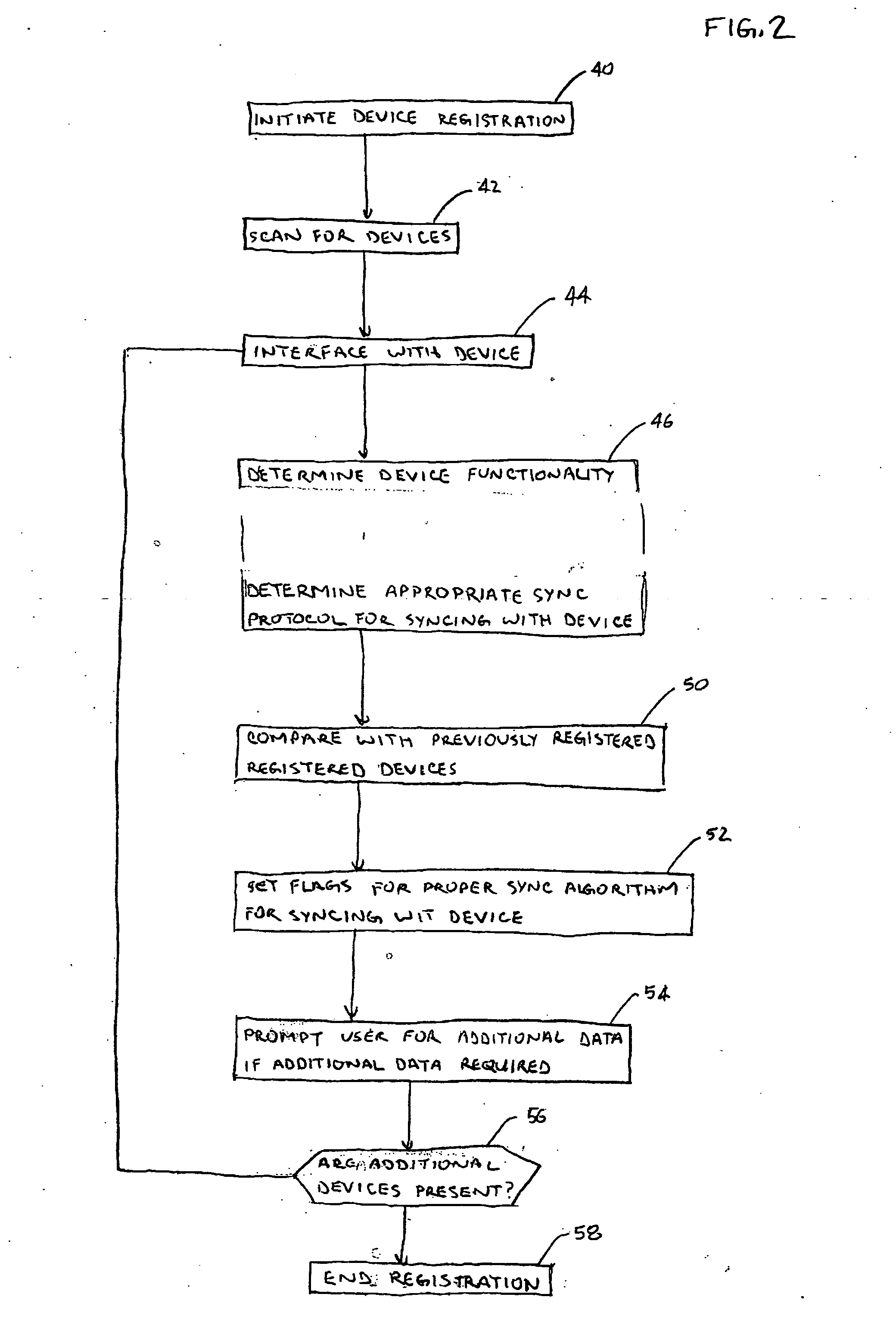
System and method for synchronizing personal data among a plurality of devices storing such data
InactiveUS20070260751A1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsData synchronizationUser device
A system and method for maintaining data synchronization across a plurality of user devices is provided. The system and method manage data synchronization among a plurality of data storage devices includes a mobile personal information system adapted interface with a number of data storage devices. A personal information system supports multiple data synchronization protocols so that the personal information system may synchronize data with a wide range of different data storage devices. A synchronization arbitrator is associated with the personal information system. The synchronization arbitrator is adapted to register all of a user's personal devices which store the user's personal information. The synchronization arbitrator also initiates a data synchronization function with each registered data storage device, employing the synchronization protocol appropriate for each device. The personal information management system may comprise a vehicular mounted personal data storage system. The user devices may include a hand-held personal data storage system and a computer adapted to store personal data.
Owner:ALPS AUTOMOTIVE
Method and apparatus for efficient handling of product return transactions
InactiveUS6269344B1Reduce shipping costsLow costFinanceBuying/selling/leasing transactionsSingle sessionInformation access
A method and apparatus for efficient handling of product returns to reduce associated costs. A computer system at a regional product return center scans a returned product for identifying information, accesses a manufacturer return approval computer system through the internet or the like, and then submits the identifying information to the manufacturer for return approval. The manufacturer computer system utilizes the identifying information to access an electronic registration database to determine whether the returned product satisfies applicable return criteria. If so, the product is approved for return to the manufacturer. The regional product return center preferably scans a plurality of returned products in a single session. In response to the product identifying information submitted by the regional product return center, the manufacturer provides a list of approved returns and unapproved returns, along with a return authorization number for the batch of approved returns. The regional product return center then assembles the approved product returns into a box, shipping pallet, or the like, applies a label indicating the return authorization label, and ships the batch to the manufacturer. Shipping costs can be saved by omitting rejected product returns from the shipment. The manufacturer can handle the approved product returns from the regional return center as a batch, thereby reducing costs.
Owner:E2INTERACTIVE INC D B A E2INTERACTIVE
Web service syndication system
ActiveUS7496637B2Simple taskFunction increaseMultiple digital computer combinationsWebsite content managementDigital assetRegister data
A syndicator for disseminating Web services and other resources from service and content providers to service consumers and for establishing and implementing subscription agreements specifying the terms upon which digital assets are provided to subscribers. A registration database stores a service description for each of a plurality of different Web services and other resources. Each stored service description contains an input processing specification, an output processing specification, and the specification of the business terms upon which the described service or resource is offered by its provider to subscribers. A subscription manager conducts a negotiation with a prospective subscriber and receives from the subscriber an acceptance of the business terms upon which a specified Web service or resource is offered to establish a subscription agreement. Event tracking records information describing the performance of each service on behalf of each subscriber to perform subscription accounting functions.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
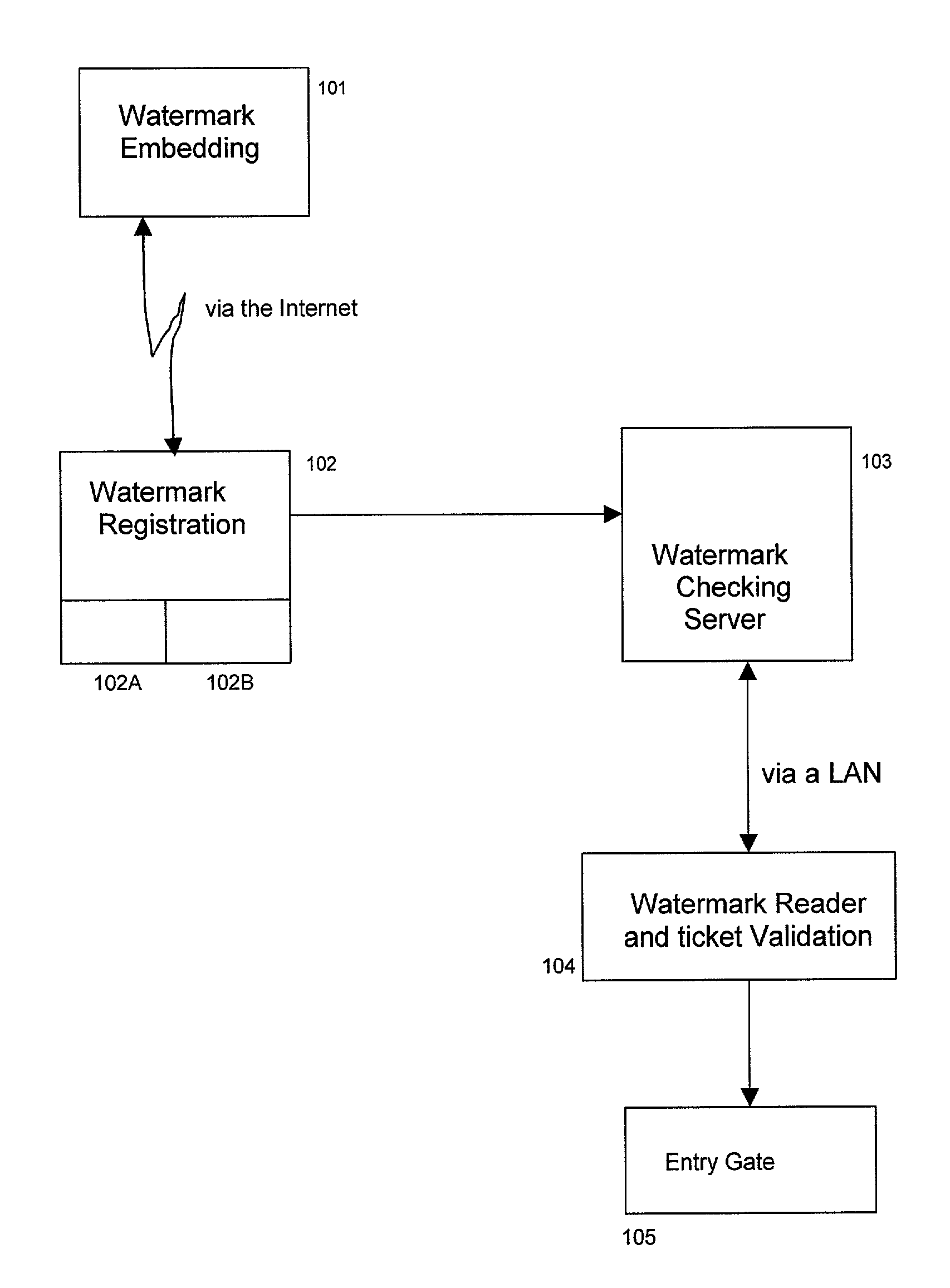
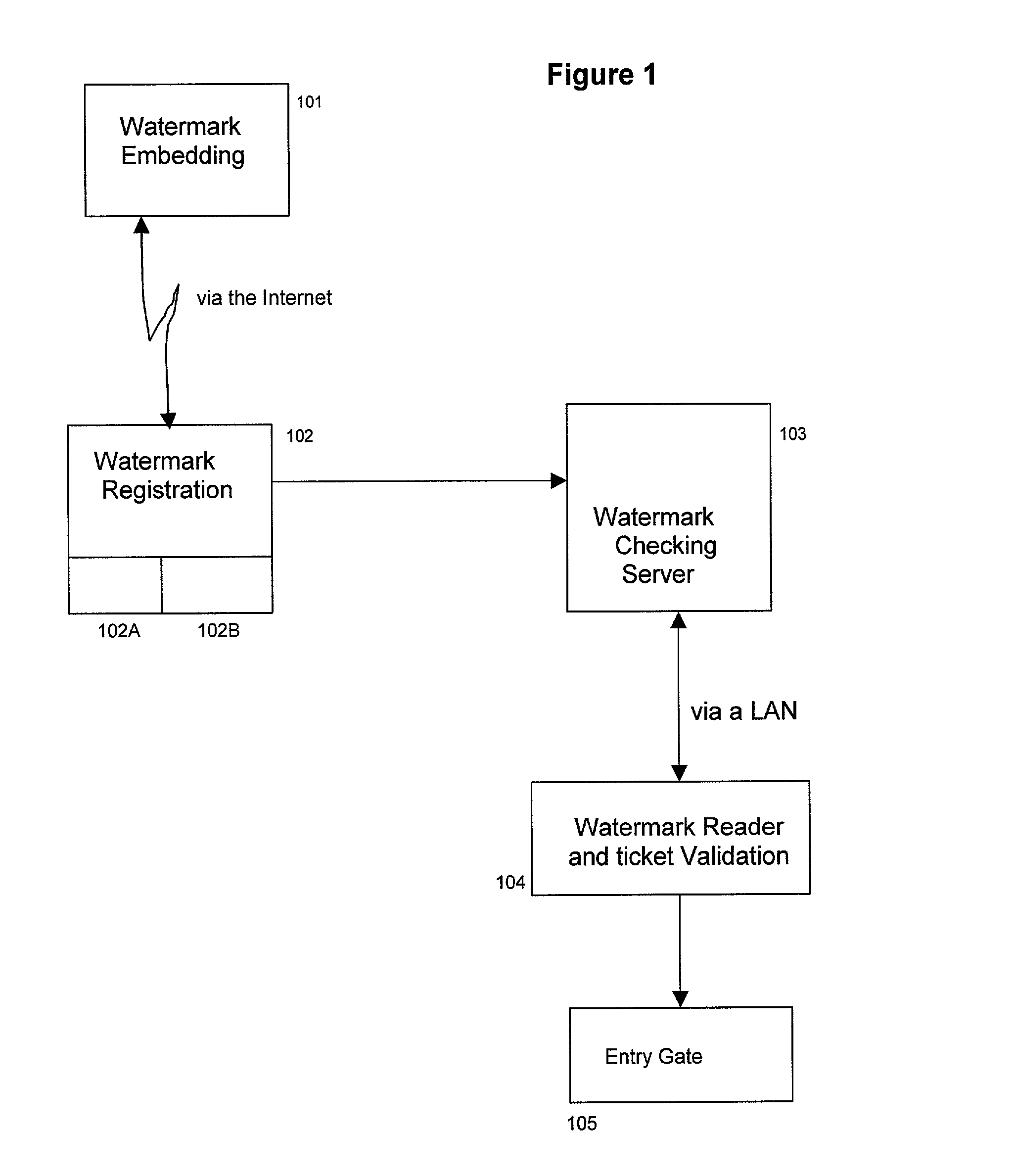
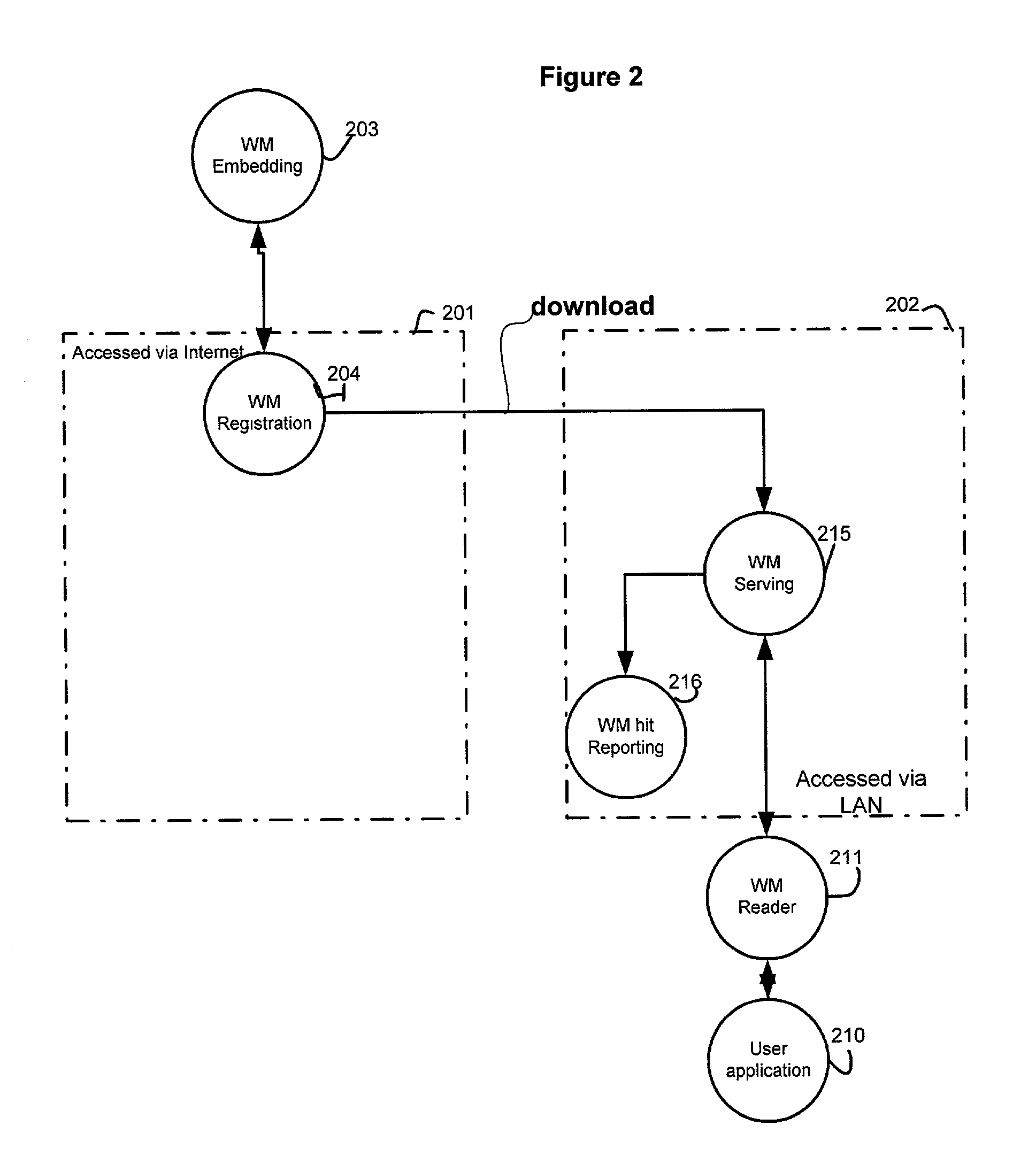
Distributed system for responding to watermarked documents
InactiveUS7111170B2Quick identificationFast authenticationOther printing matterUser identity/authority verificationData matchingThe Internet
A method and system that registers data carried by a watermark with a server, reads watermark data from a document and generates an action string if a watermark read from a document matches registered data. In one embodiment the system includes two servers. Registration is done on one server via the internet the registration data is sent to a second server. The second server is interrogated via a local area network (LAN) to determine if particular watermark data is registered. The LAN allows data carried on documents such as tickets to be authenticated very quickly. In a second embodiment, there are multiple registration servers, each of which registers a different sets of watermark data. The compartmentalization of data increases security and privacy of data.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
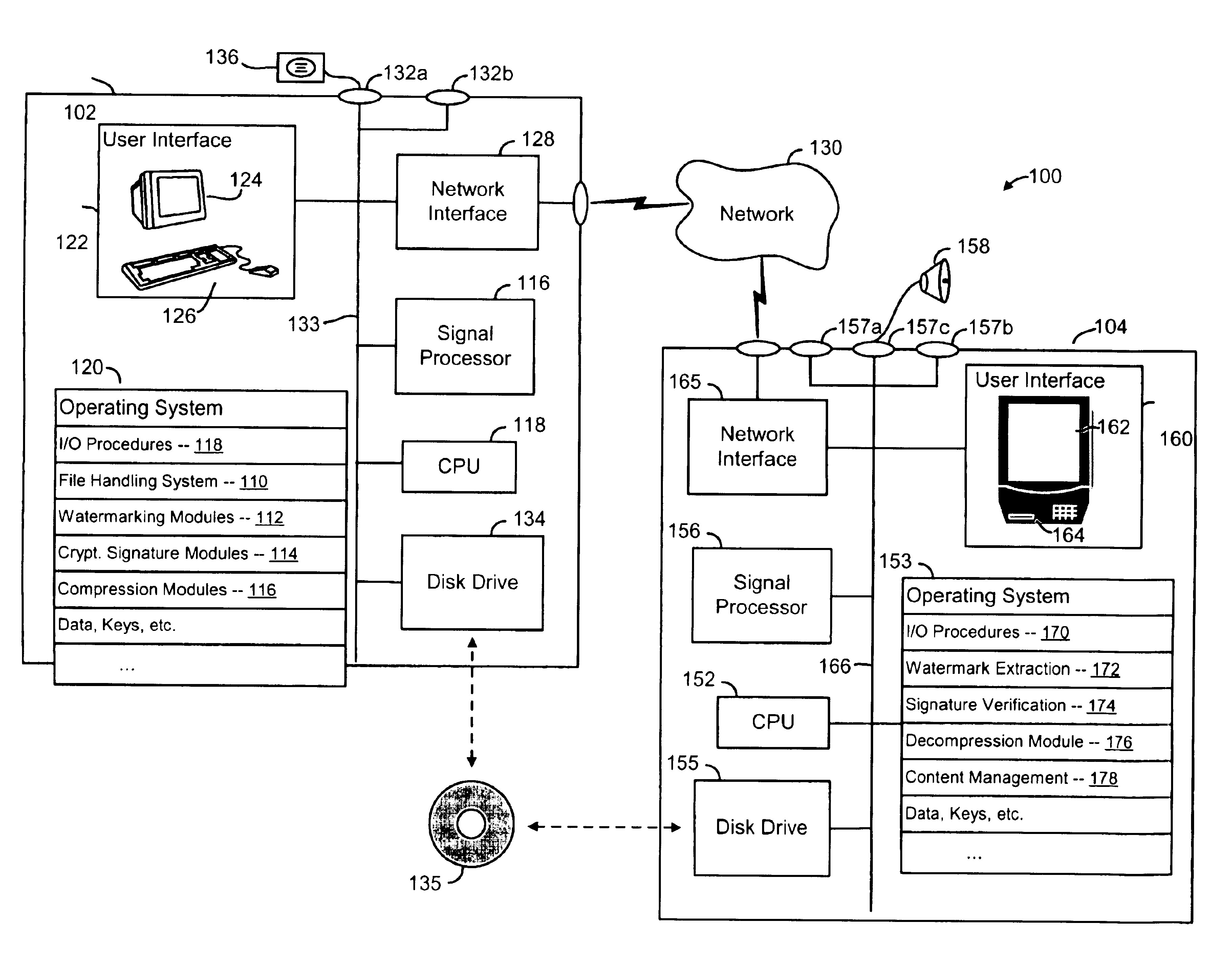
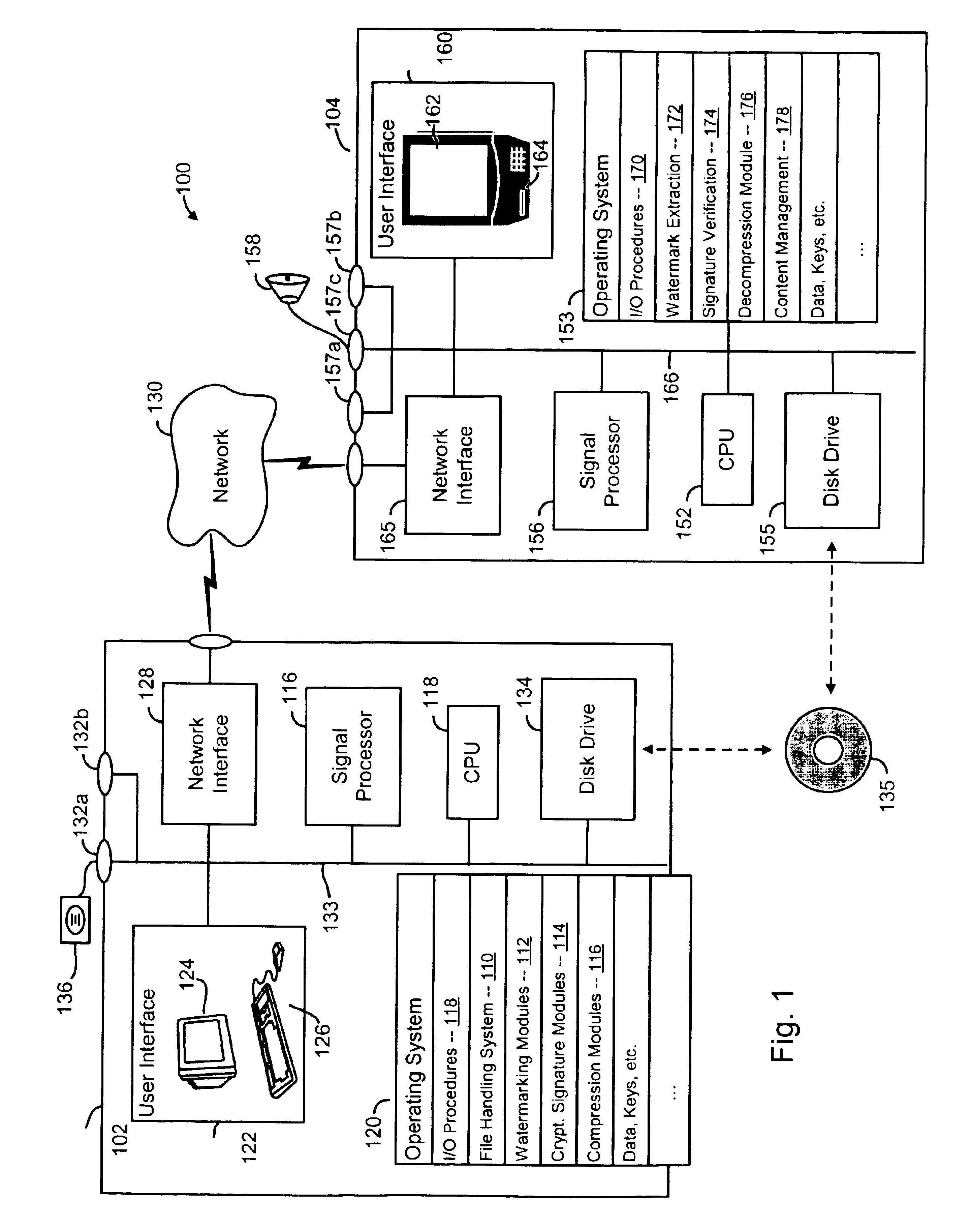
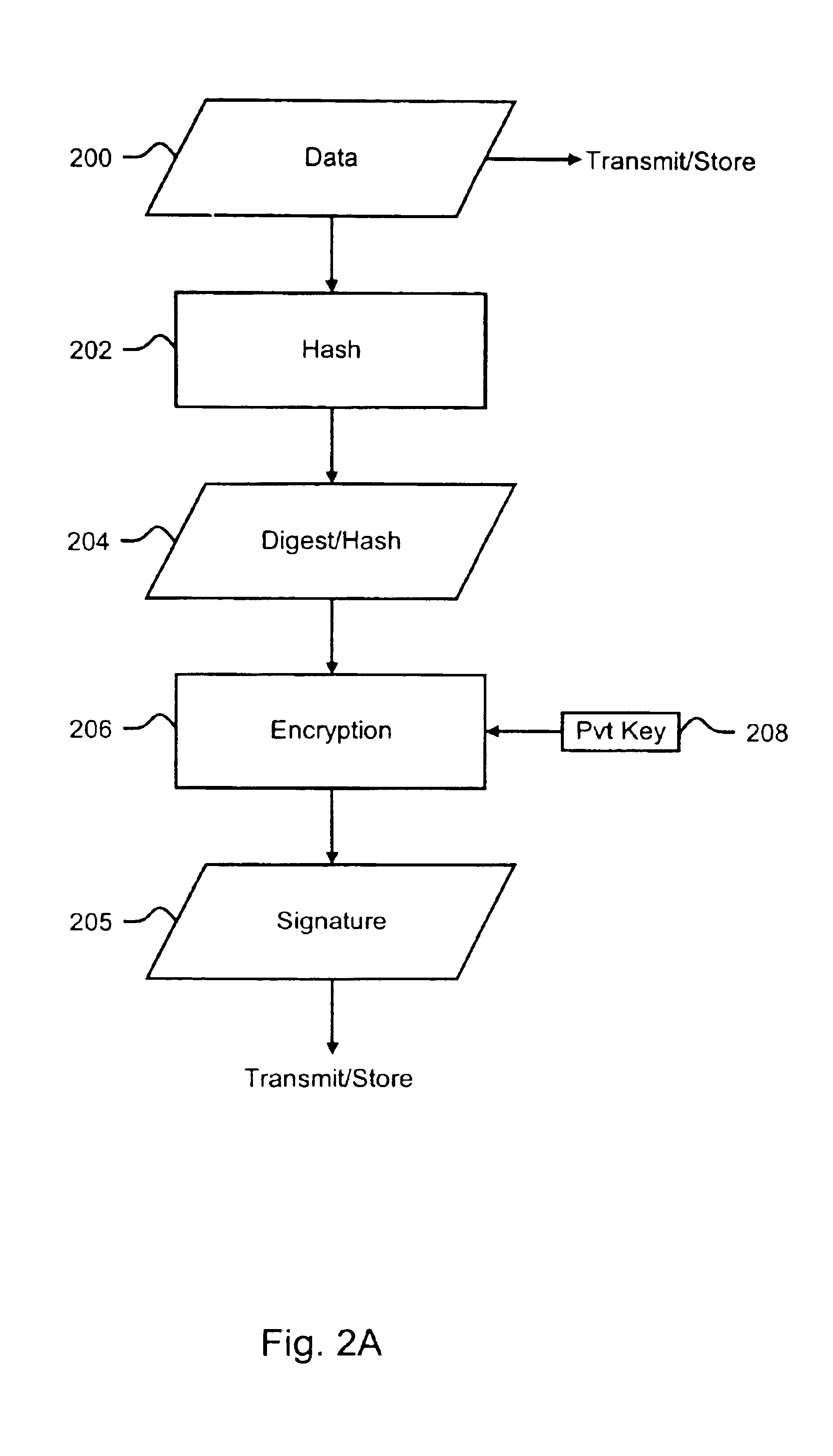
Methods and systems for encoding and protecting data using digital signature and watermarking techniques
InactiveUS6961854B2Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsCompact discDigital signature
Systems and methods are provided for protecting and managing electronic data signals that are registered in accordance with a predefined encoding scheme, while allowing access to unregistered data signals. In one embodiment a relatively hard-to-remove, easy-to-detect, strong watermark is inserted in a data signal. The data signal is divided into a sequence of blocks, and a digital signature for each block is embedded in the signal via a watermark. The data signal is then stored and distributed on, e.g., a compact disc, a DVD, or the like. When a user attempts to access or use a portion of the data signal, the signal is checked for the presence of a watermark containing the digital signature for the desired portion of the signal. If the watermark is found, the digital signature is extracted and used to verify the authenticity of the desired portion of the signal. If the signature-containing watermark is not found, the signal is checked for the presence of the strong watermark. If the strong watermark is found, further use of the signal is inhibited, as the presence of the strong watermark, in combination with the absence or corruption of the signature-containing watermark, provides evidence that the signal has been improperly modified. If, on the other hand, the strong mark is not found, further use of the data signal can be allowed, as the absence of the strong mark indicates that the data signal was never registered with the signature-containing watermark.
Owner:INTERTRUST TECH CORP
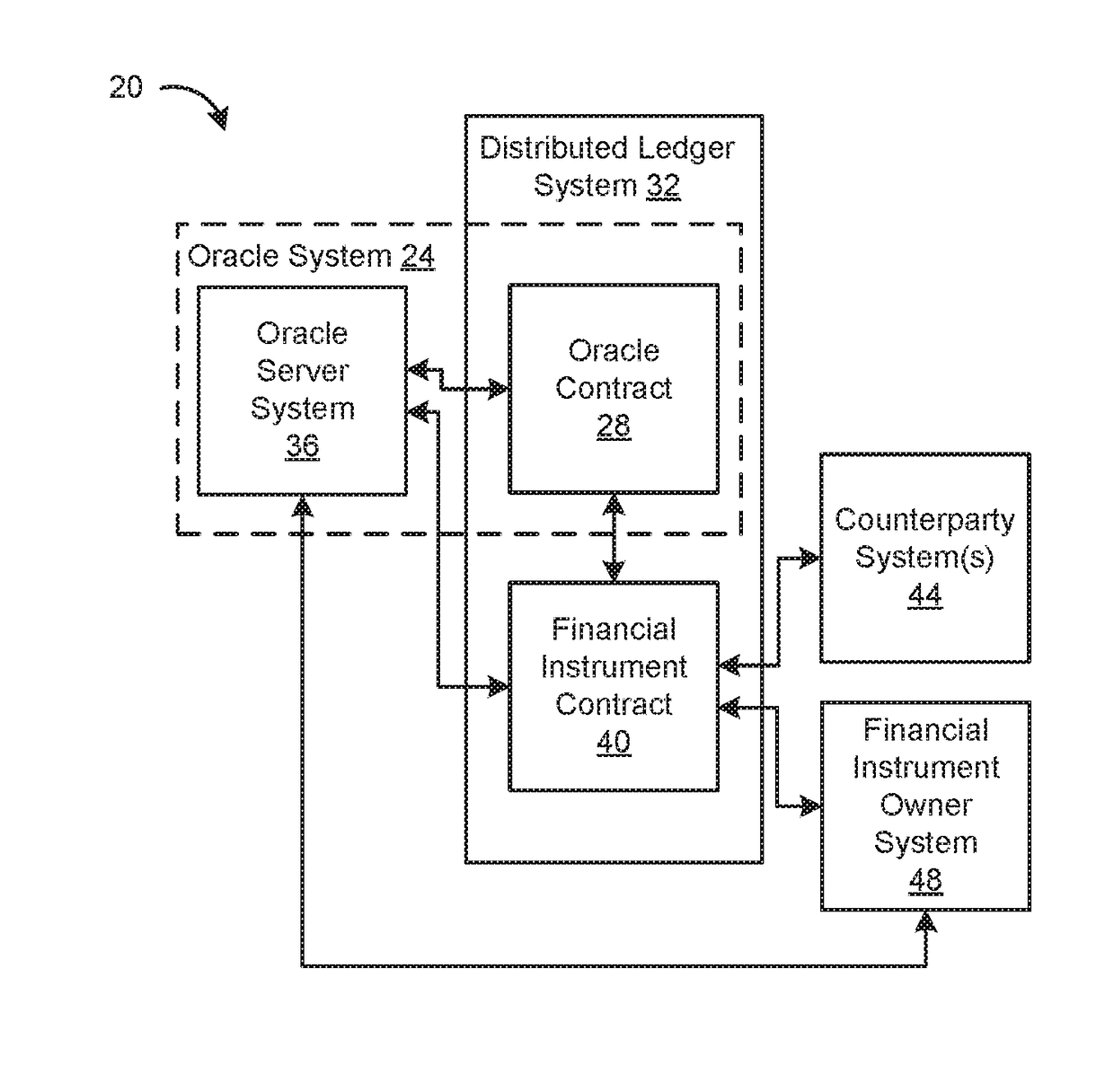
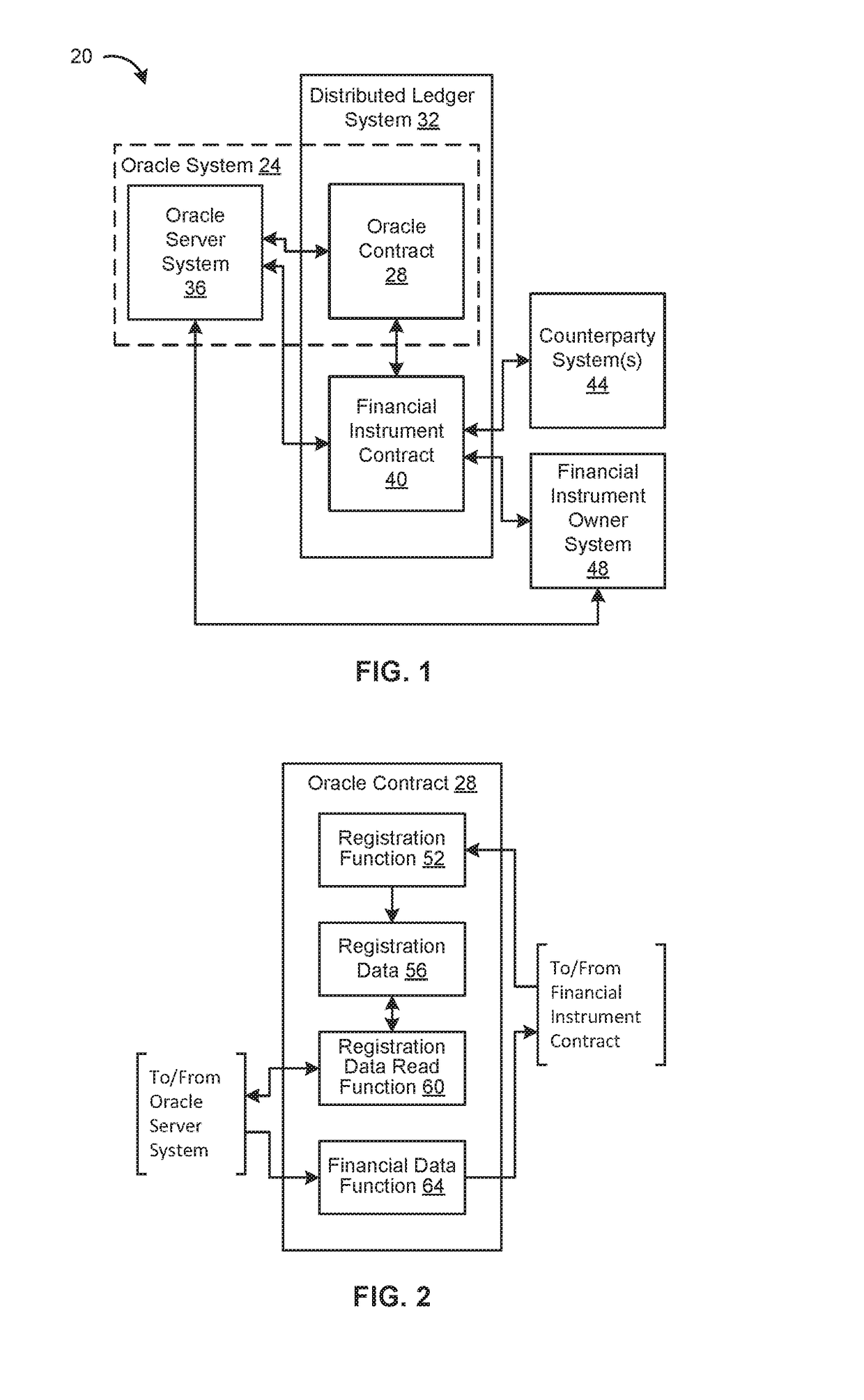
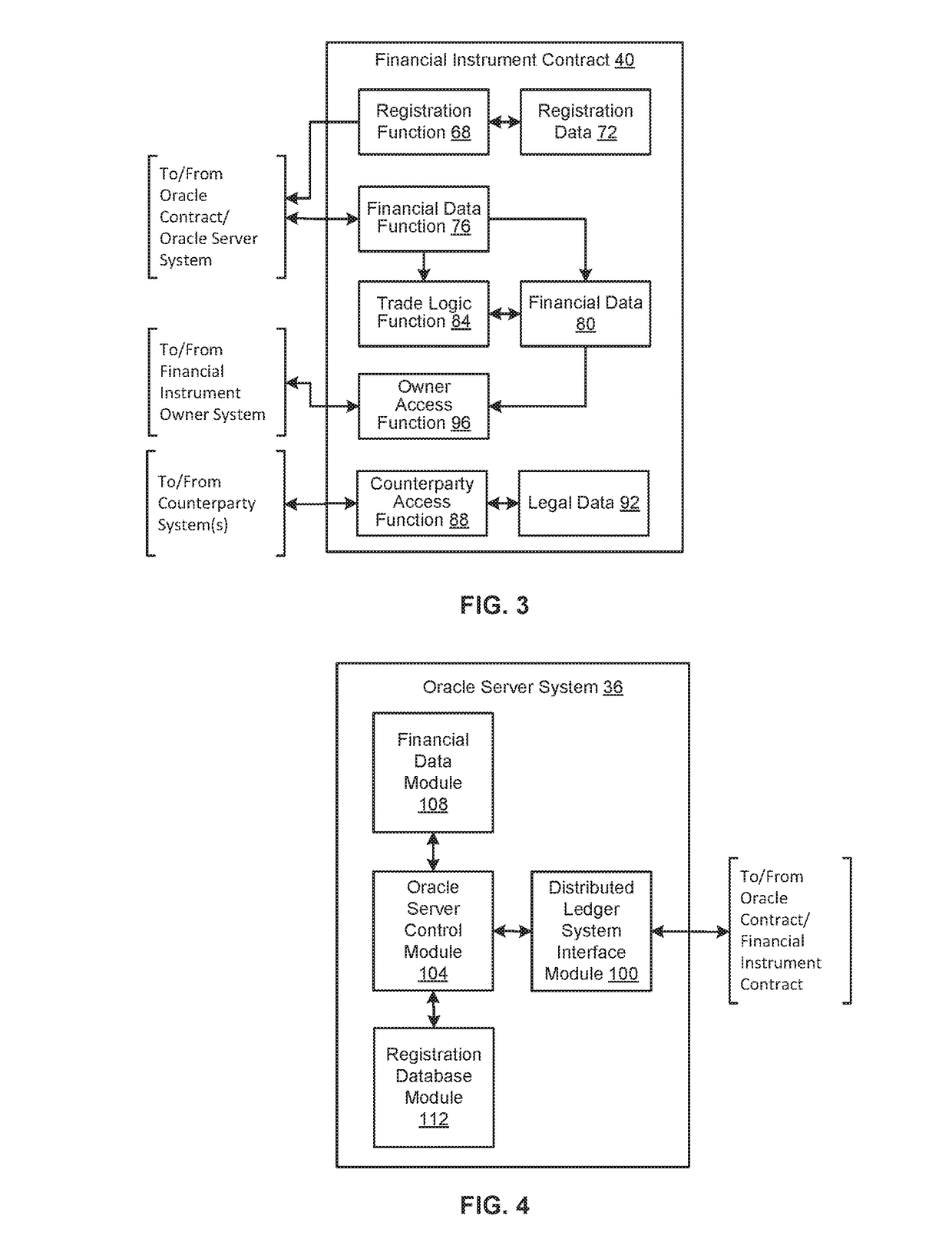
Systems and methods for providing financial data to financial instruments in a distributed ledger system
An embodiment of a method of providing financial data to a financial instrument smart contract in a distributed ledger system includes: receiving, by an oracle smart contract in the distributed ledger system, a transaction from the financial instrument smart contract, the transaction including registration data having an identification of financial data to be delivered and an identification of a schedule on which to deliver the financial data; generating a transaction including the financial data; and transmitting the generated transaction to at least one distributed node of the distributed ledger system according to the requested schedule.
Owner:REFINITIV US ORG LLC
Apparatus and method for managing peer-to-peer connections between different service providers
In one embodiment of the invention, service providers generate bloom filters with the user ID codes of registered users and exchange the bloom filters with one another. In response to a request to locate a first user, a first service provider will query its own registration database to determine if the first user is registered with the first service provider. If the first user is not registered with the first service provider, then the first service provider will query its bloom filters to identify other service providers with which the first user may be registered. A positive response from a bloom filter indicates that the first user may or may not be registered with the service provider associated with that bloom filter, and a negative response indicates with certainty that the first user is not registered with the service provider associated with that bloom filter.
Owner:APPLE INC
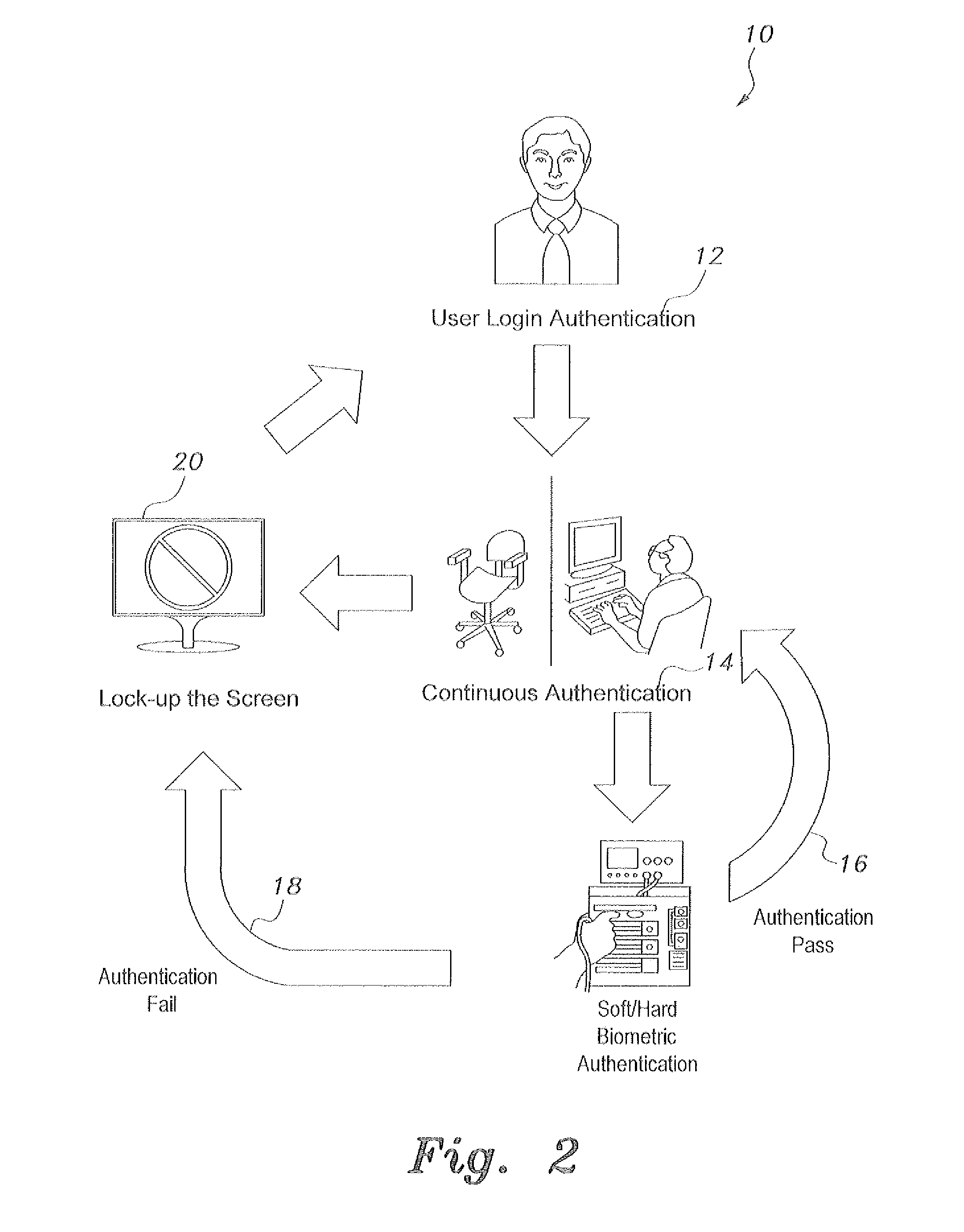
Passive continuous authentication method
InactiveUS20130051632A1Readily apparentTransmissionMultiple biometrics useComputer softwareComputer science
The passive continuous authentication method uses biometric feedback to perform the authentication processes. Computer software and sensors are provided to acquire, memorize, and authenticate both the user's hard (facial) and soft (clothing) biometric information. A registration phase compels the user to register his / her face image into a registration database. Subsequently, the system permits the user to login the system based on facial recognition of the image presented by an attached webcam of the system. During a computing session the system repetitively authenticates the user's identity by comparing the user's acquired face image (hard biometric) to the registered face image in the database. A clothes color histogram (soft biometric) is also computed. The hard biometric recognition mainly decides the authentication result. Otherwise, clothes color histogram matching takes place to decide the result. When the user leaves the terminal the screen locks up. Successful authentication unlocks the screen upon user return.
Owner:KING SAUD UNIVERSITY
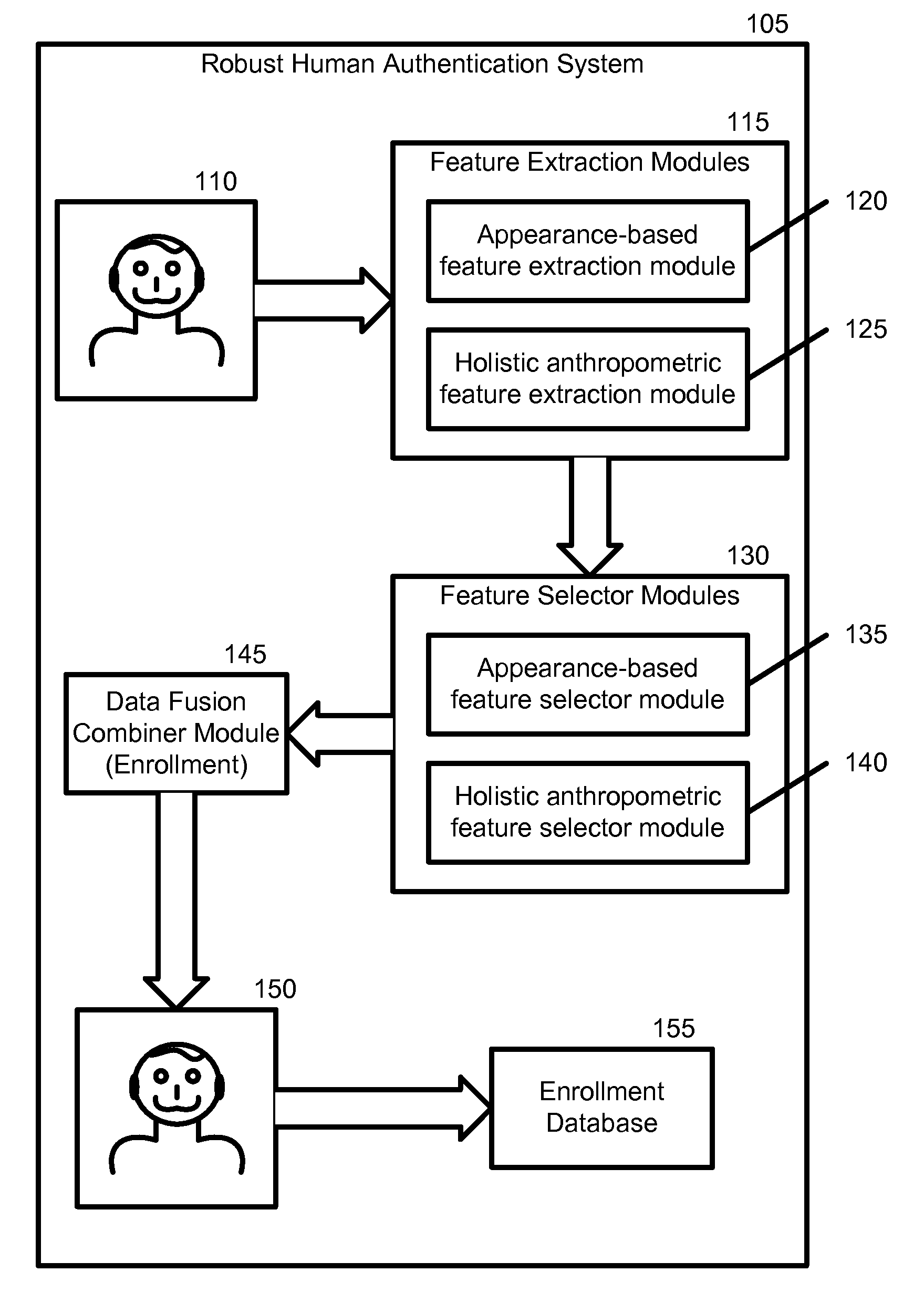
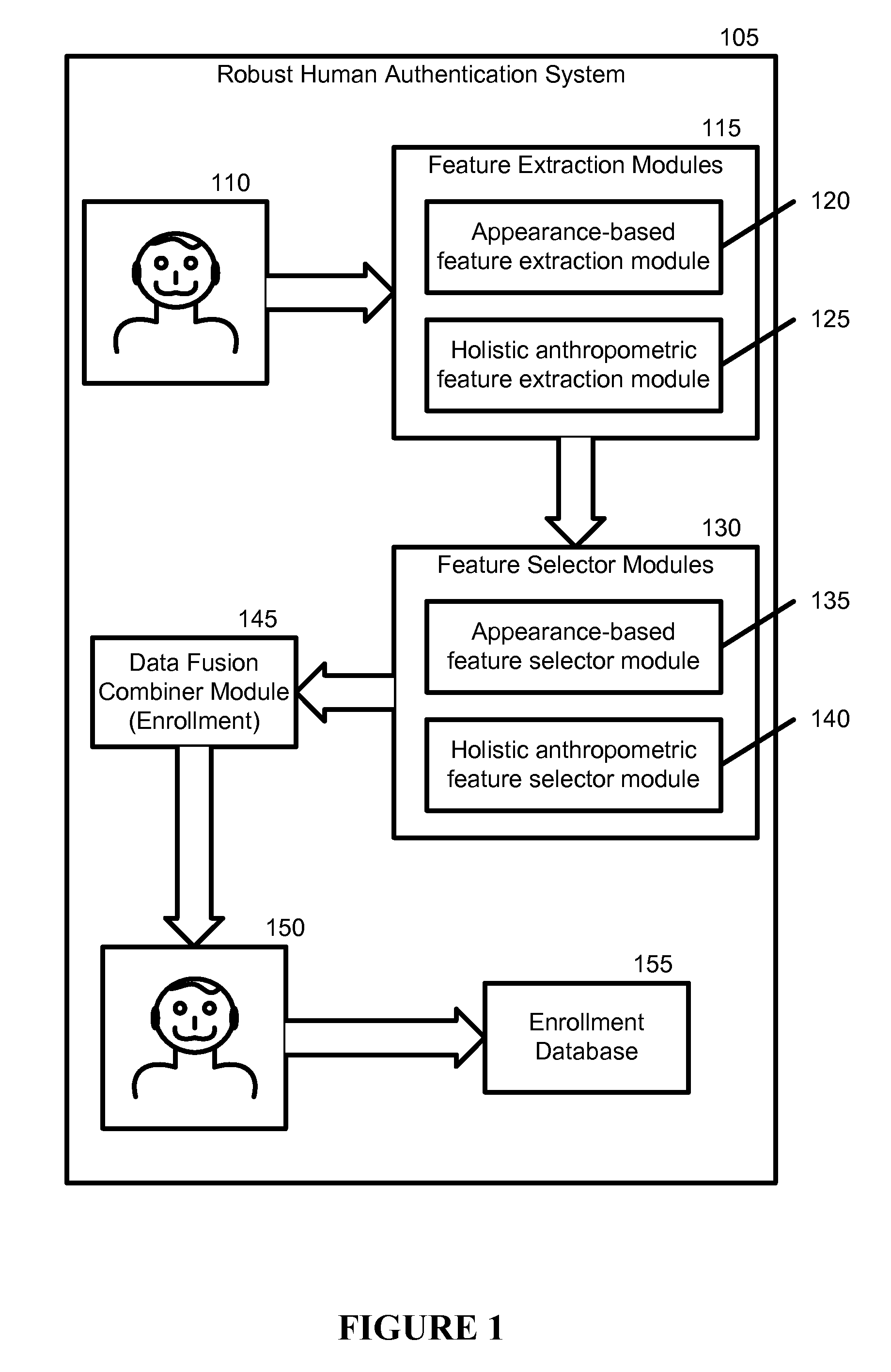
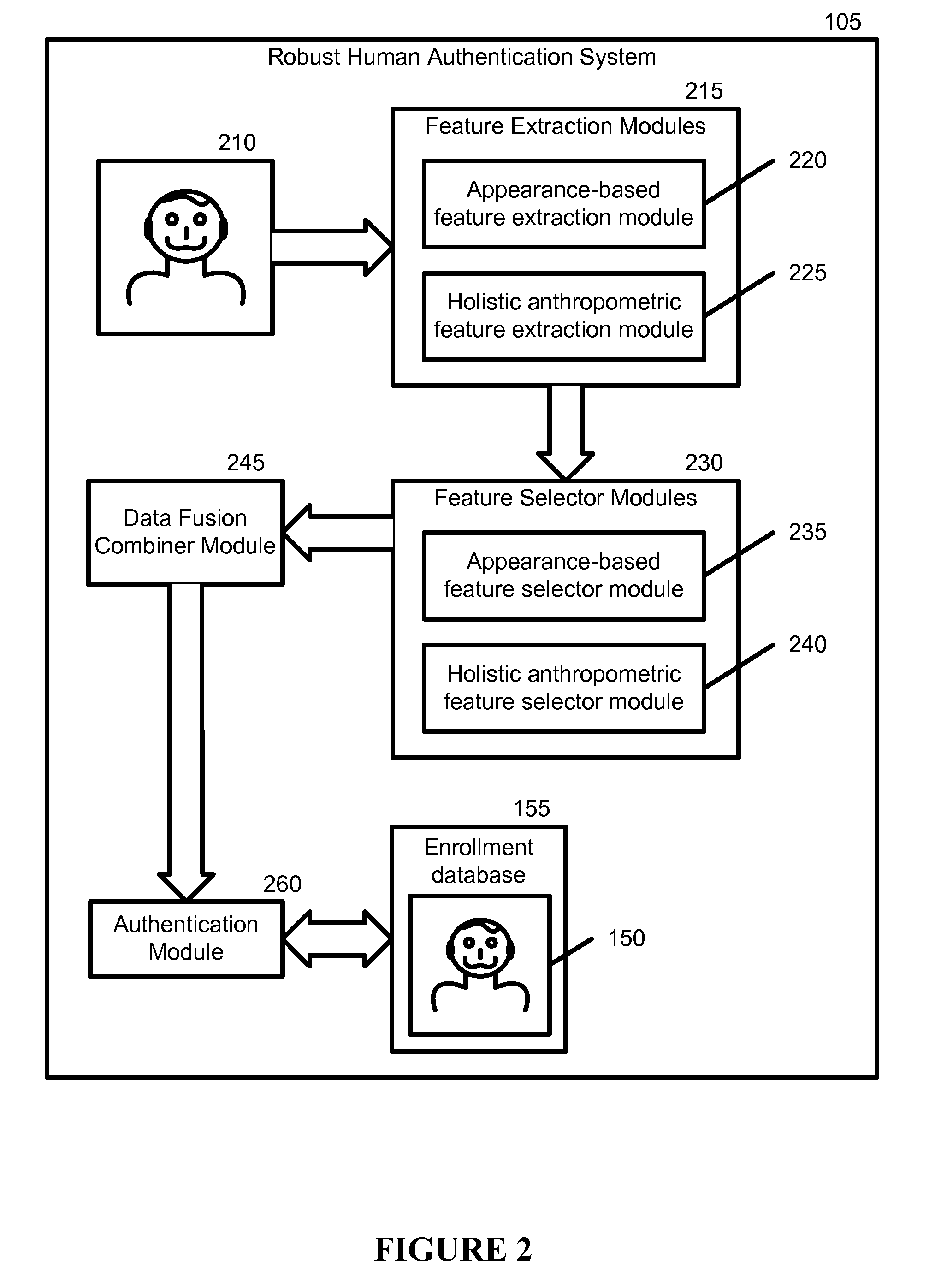
Robust Human Authentication Using Holistic Anthropometric and Appearance-Based Features and Boosting
A new robust human authentication system, device, and instructions, embeddable in a physical and tangible computer readable medium, for determining if at least one test image obtained using an imaging device matches at least one training image in an enrollment database, are disclosed. This invention applies the concepts of appearance (PCA or PCA+LDA) and holistic anthropometrics that include head, face, neck, and shoulder linear and non-linear geometric measurements. The appearance (“eigen”) coefficients and holistic anthropometric measurements selected may be used as feature vectors. A boosting algorithm ranks features as “weak learners” and combines their outputs for “strong” recognition.
Owner:GEORGE MASON INTPROP INC
Personal Identification Device and Personal Identification Method
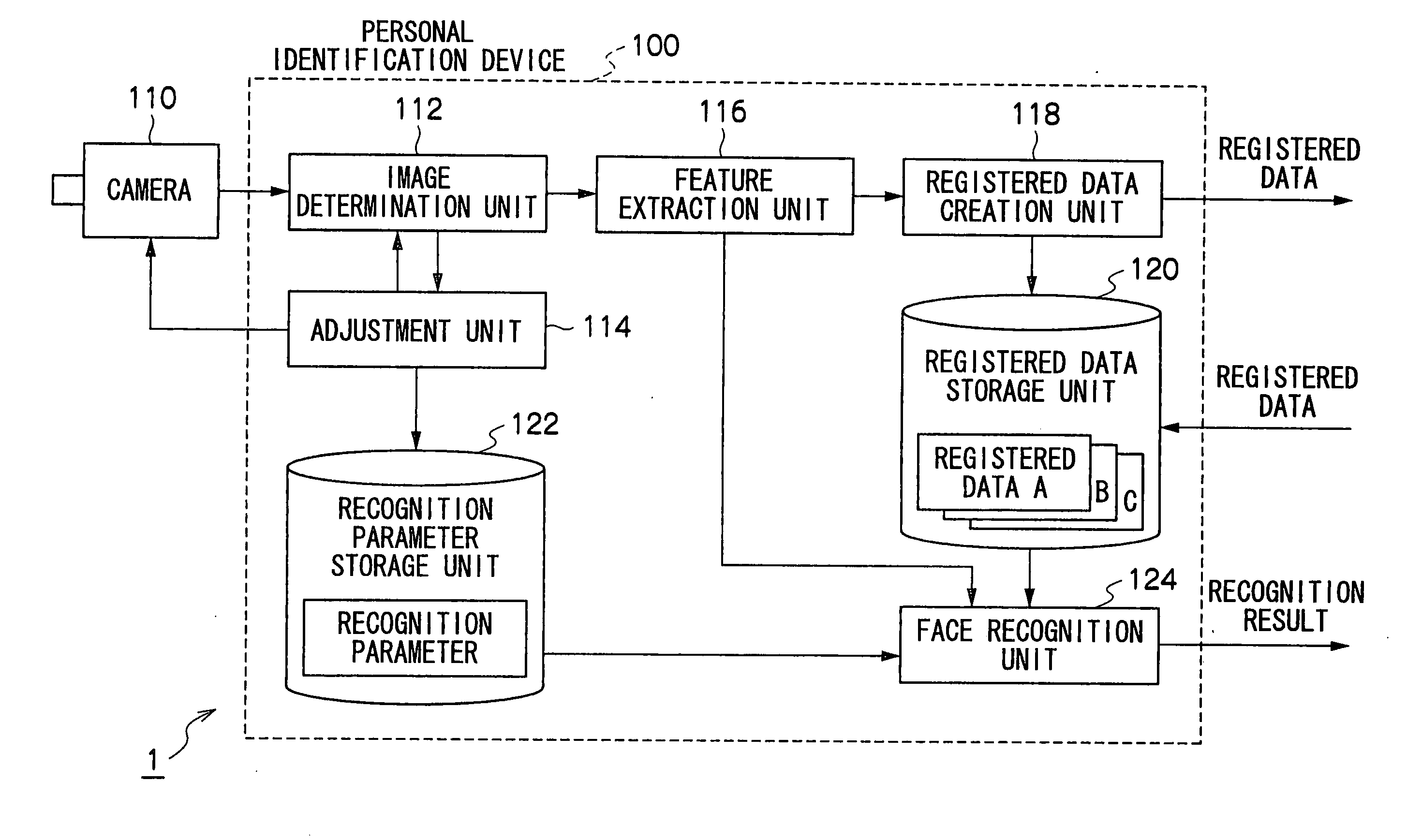
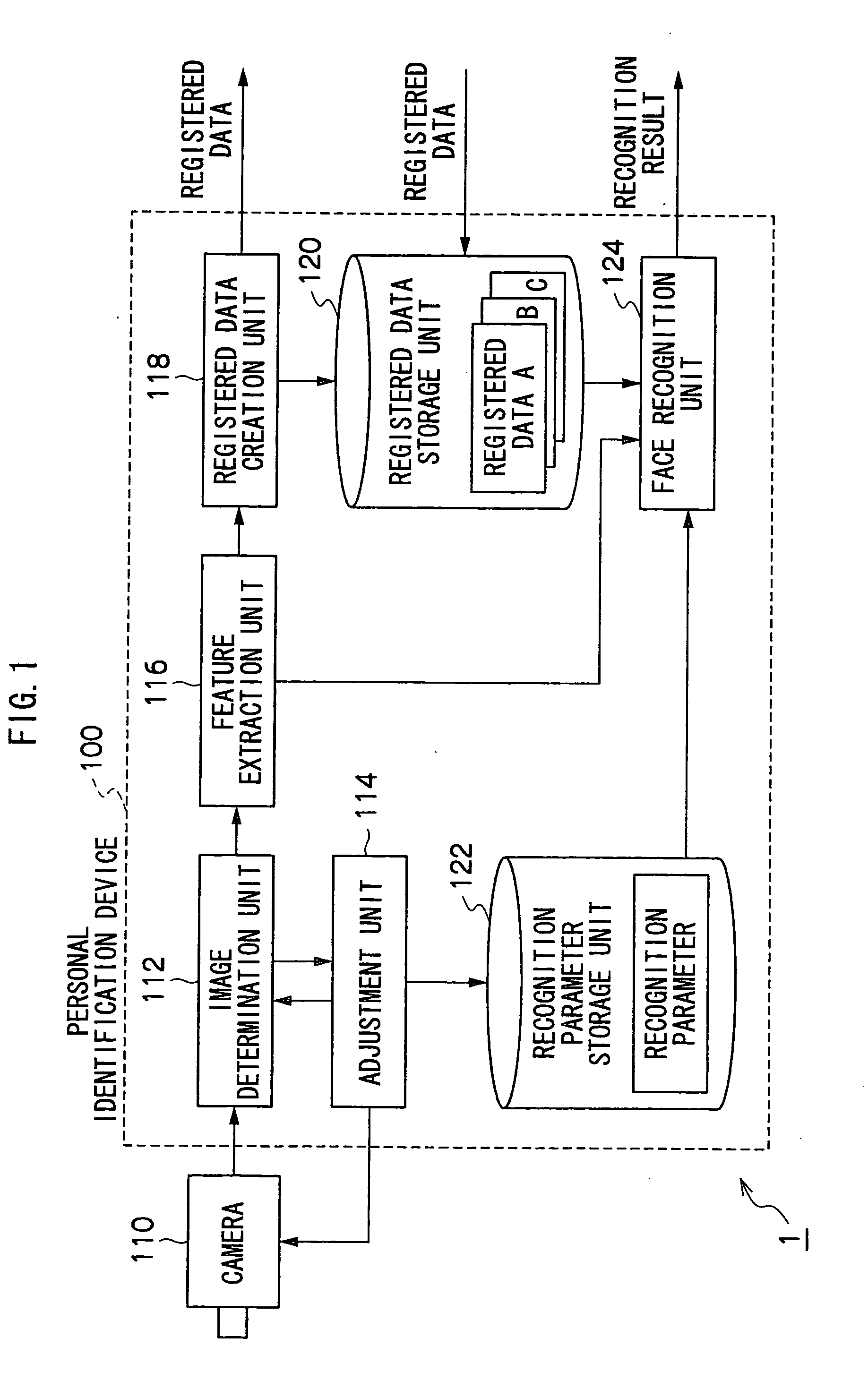
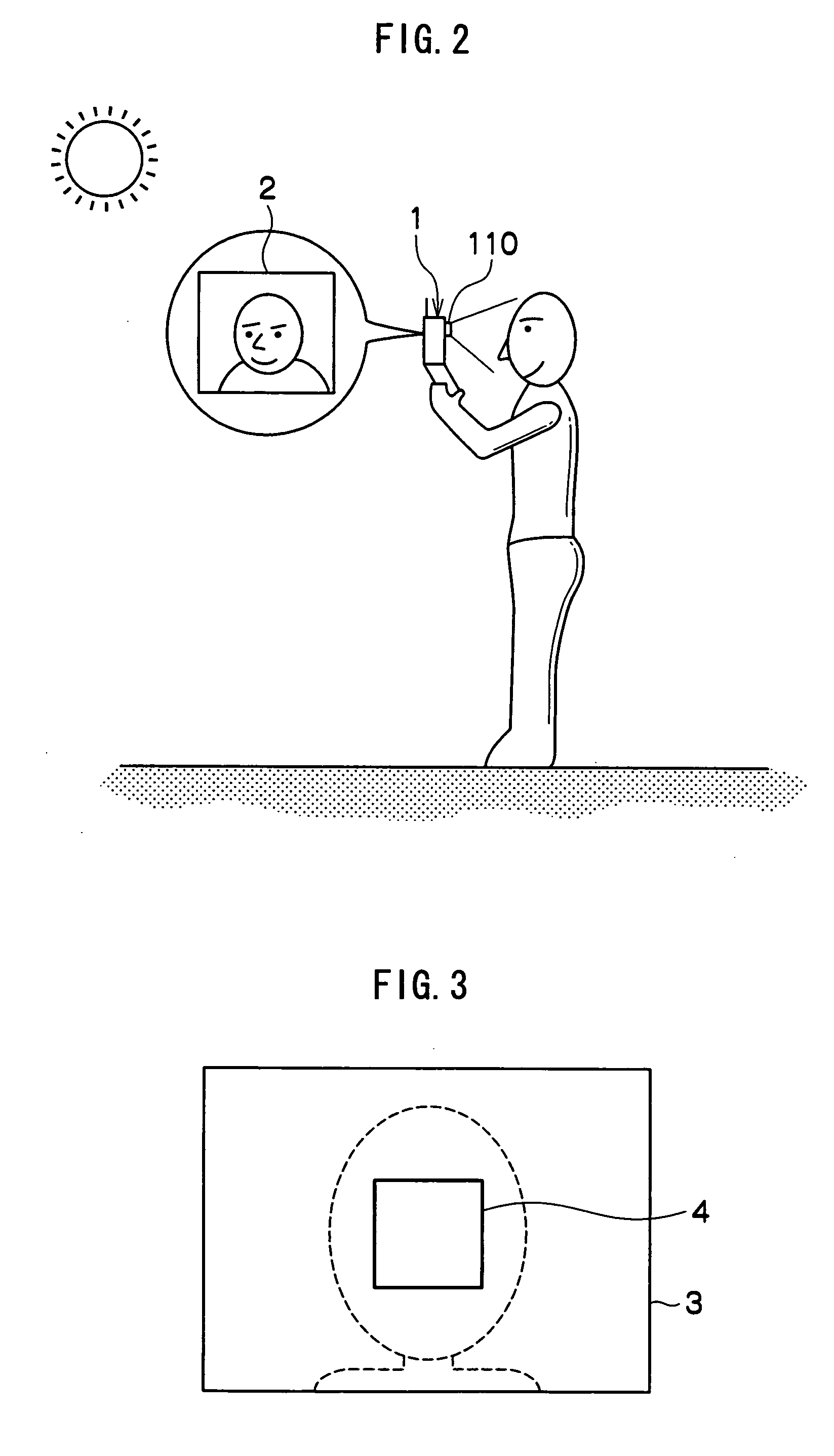
InactiveUS20090060293A1Improve performanceImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionImage extractionFeature extraction
A personal identification device of the present invention is provided with a registered data storage unit for storing registered data containing facial feature data for a registered user, a recognition parameter storage unit for storing recognition parameters, a image determination unit for determining whether or not the image quality of a user facial image input from an imaging device is appropriate, an adjustment unit for adjusting the settings of the imaging device or modifying the recognition parameters, in accordance with the result of determination carried out in the image determination unit, a feature extraction unit for extracting user facial feature data from a facial image, and a face recognition unit for comparing the extracted feature data with the registered data to determine whether or not the user is a registered user based on the result of comparison and the recognition parameters.
Owner:OKI ELECTRIC IND CO LTD
Tracking Poses of 3D Camera Using Points and Planes
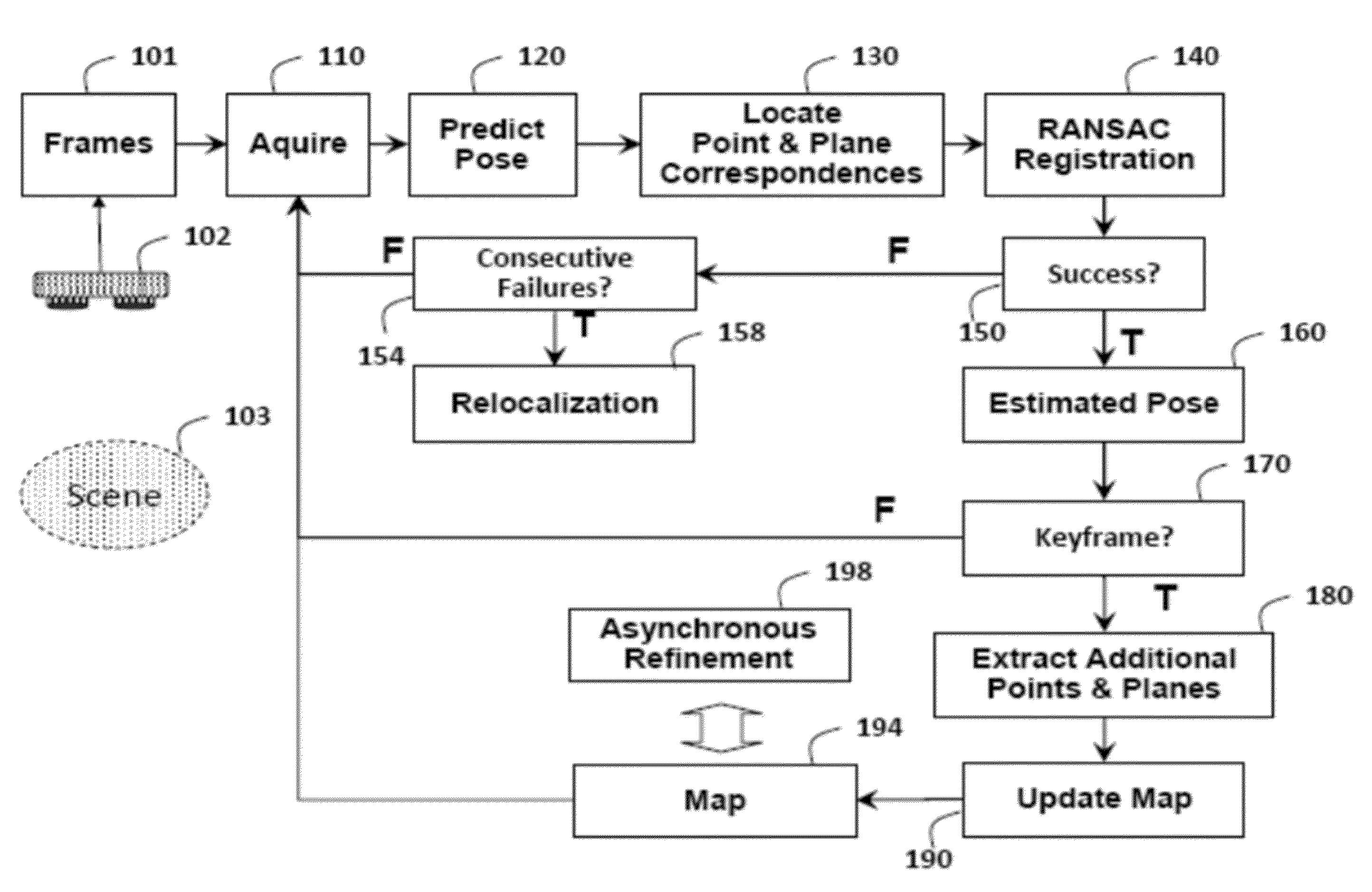
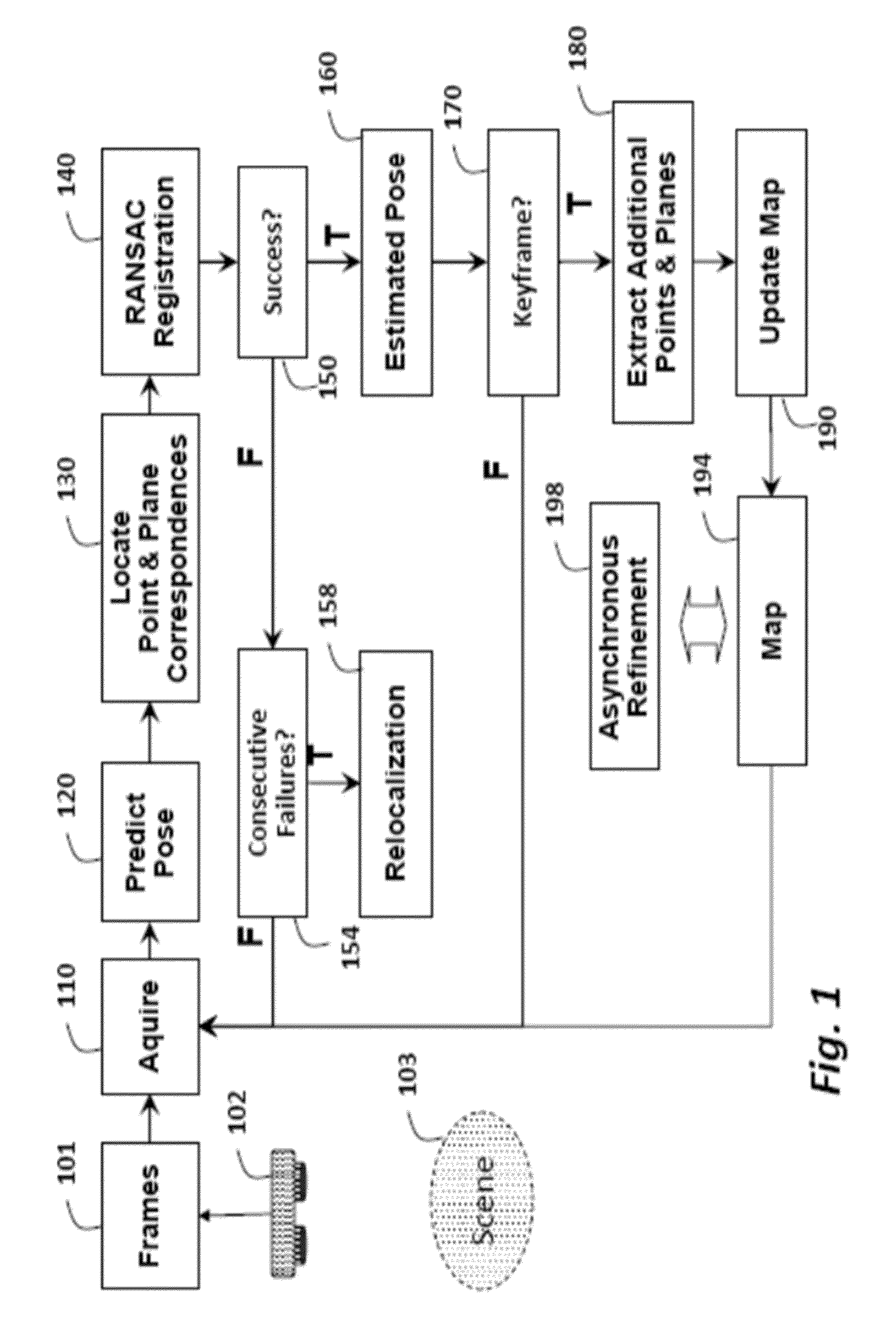
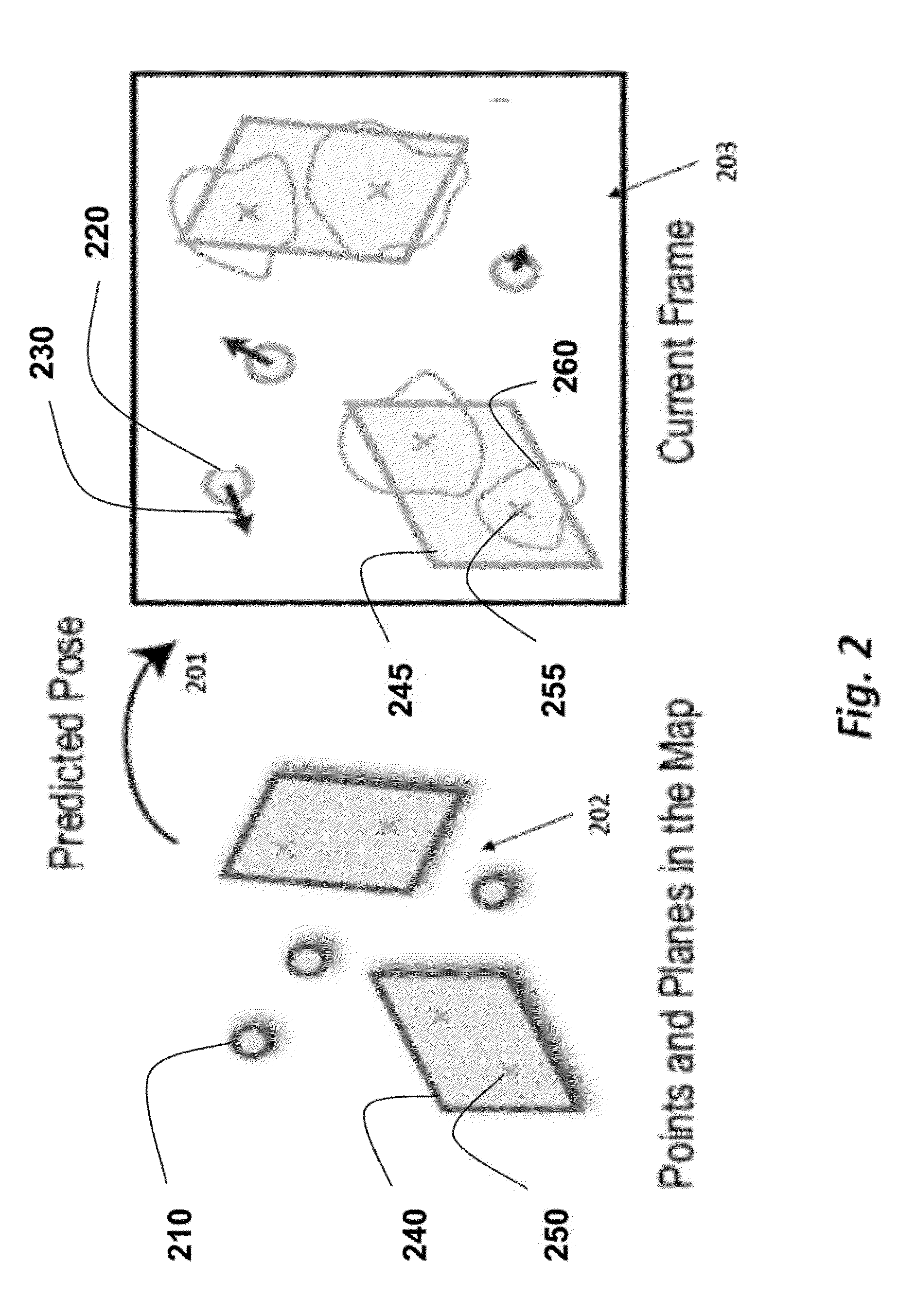
ActiveUS20140002597A1Fast and accurate registrationMinimize failureImage enhancementImage analysis3d cameraRegister data
A method registers data using a set of primitives including points and planes. First, the method selects a first set of primitives from the data in a first coordinate system, wherein the first set of primitives includes at least three primitives and at least one plane. A transformation is predicted from the first coordinate system to a second coordinate system. The first set of primitives is transformed to the second coordinate system using the transformation. A second set of primitives is determined according to the first set of primitives transformed to the second coordinate system. Then, the second coordinate system is registered with the first coordinate system using the first set of primitives in the first coordinate system and the second set of primitives in the second coordinate system. The registration can he used to track a pose of a camera acquiring the data.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
System and method for providing user mobility handling in a network telephony system
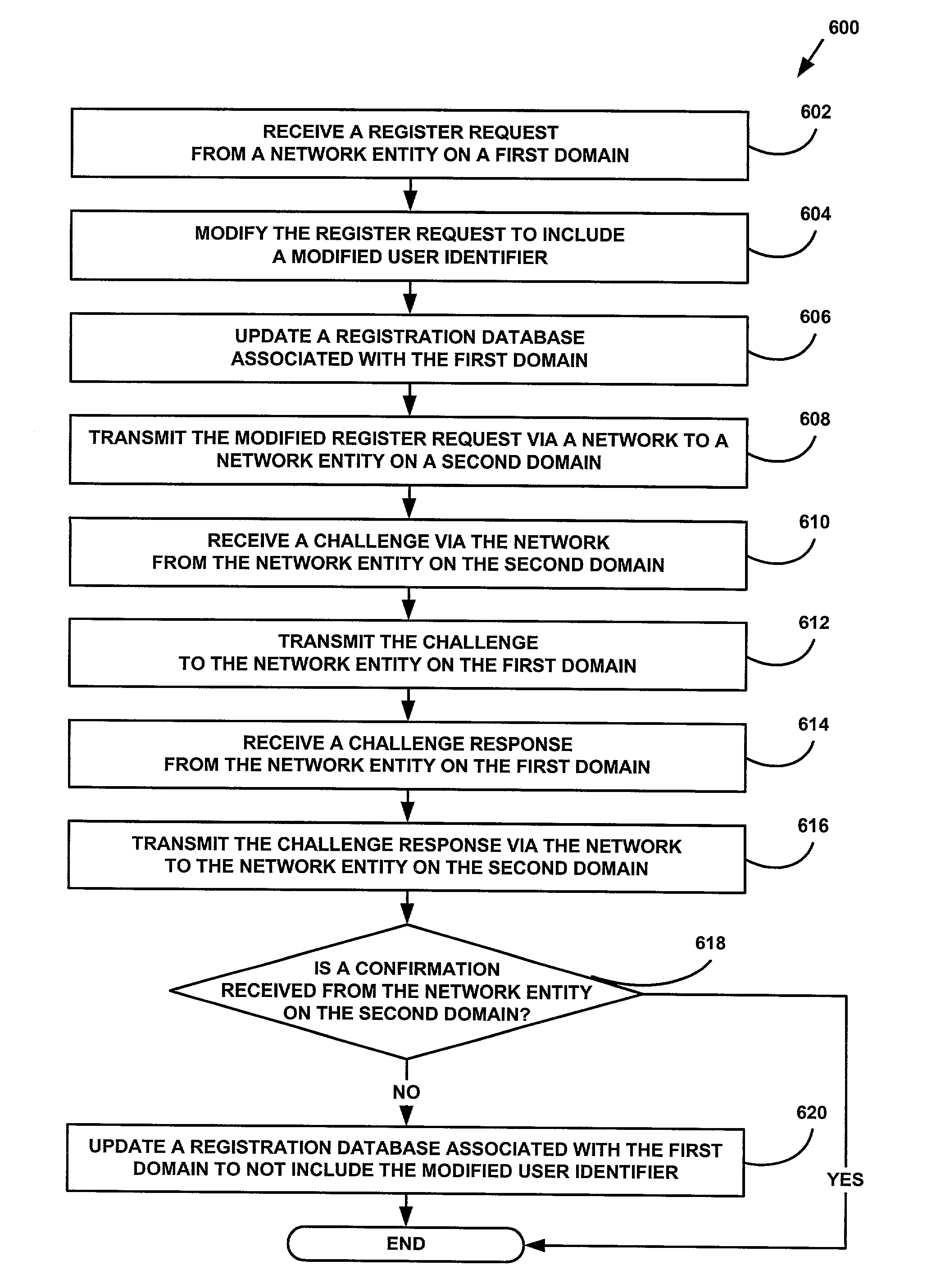
ActiveUS7110393B1Data switching by path configurationNetwork connectionsRegister dataUser identifier
A system and method for providing user mobility handling in a network telephony system is provided. In one embodiment, the method includes receiving a register request from a network entity on a first domain and modifying a user identifier in the register request. A registration database is preferably updated with the modified user identifier. The modified register request is transmitted via a network to a network entity on a second domain. An authentication process preferably takes place between the network entity on the first domain and the network entity on the second domain. If successful, a confirmation is received via the network from the network entity on the second domain. Various embodiments of the invention may, for example, allow a user typically located in a home domain to temporarily move to a visiting domain, while maintaining the user's home domain user identifier. Preferred embodiments utilize the Session Initiation Protocol.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD
Method and apparatus for protecting digital contents stored in USB mass storage device
InactiveUS20080247540A1User identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsMass storageDigital content
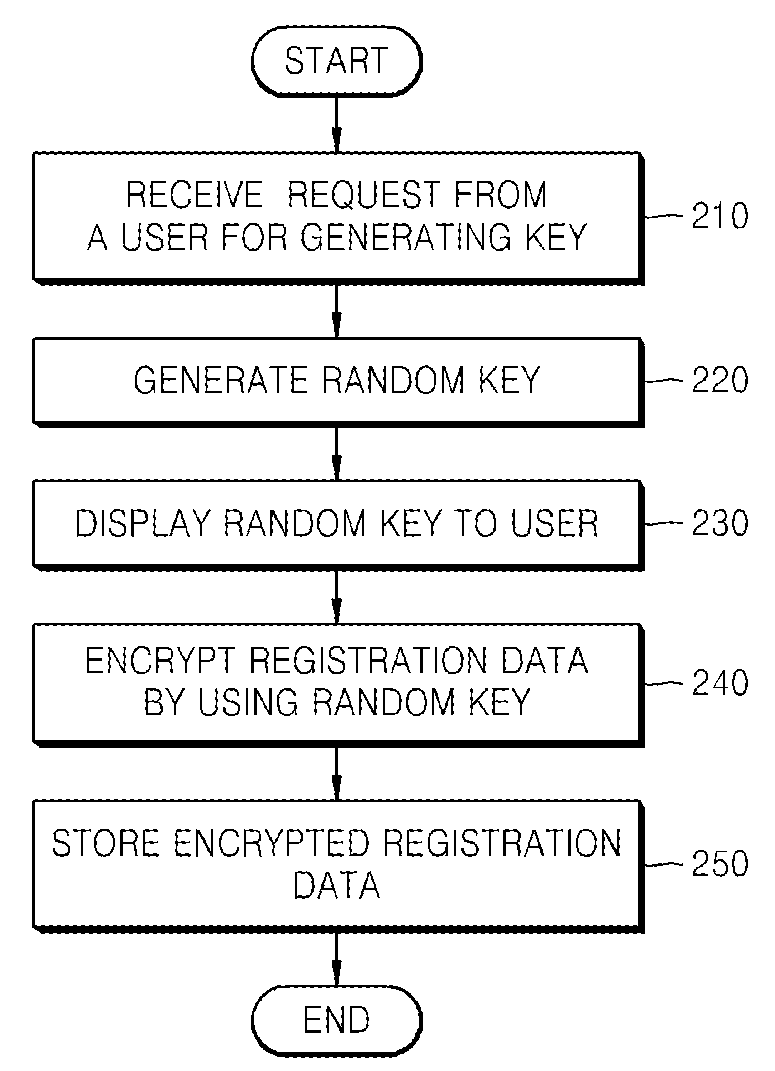
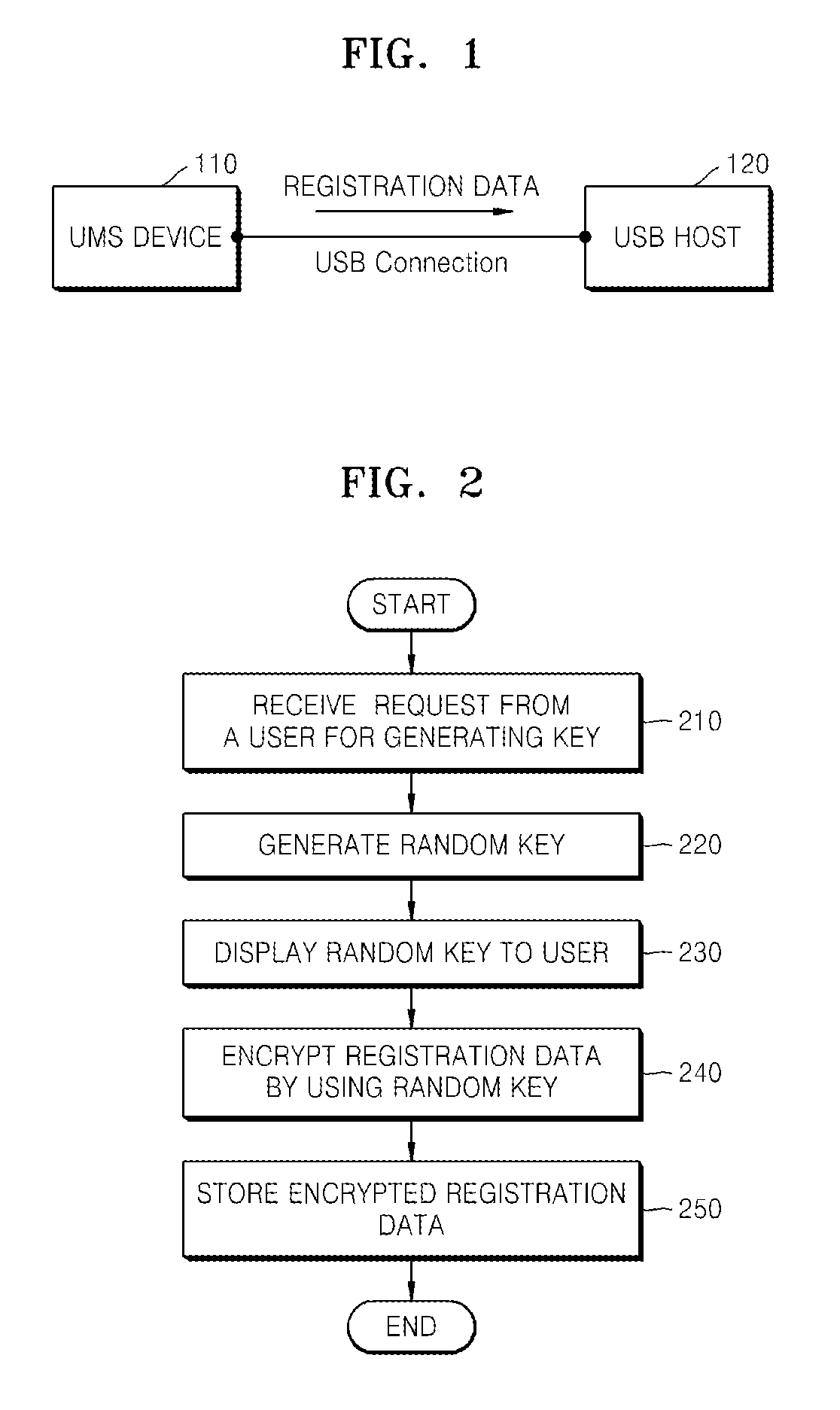
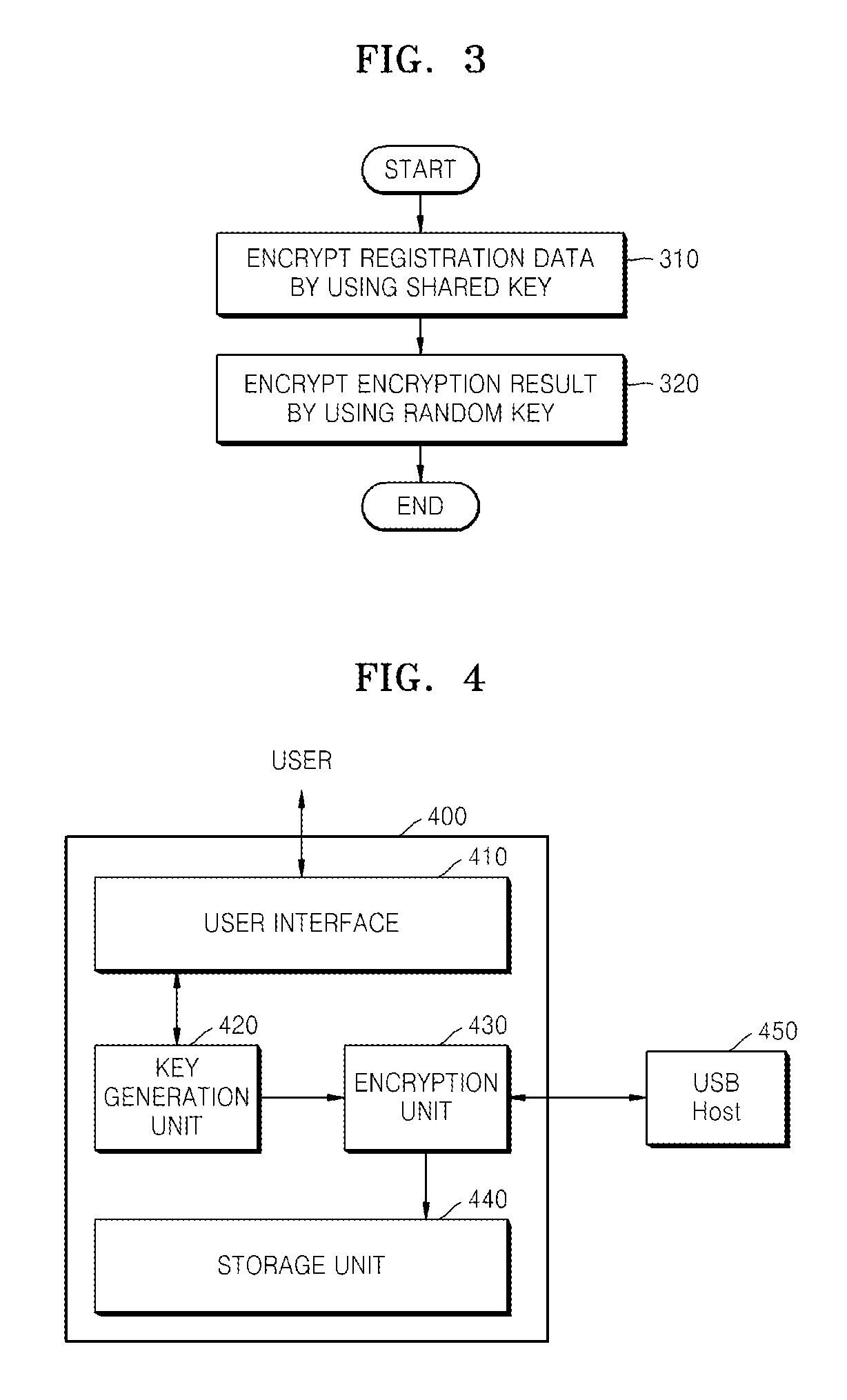
A method and apparatus for protecting digital content stored in a universal serial bus (USB) mass storage (UMS) device from unlimited distribution are provided. According to the method and apparatus, a UMS device generates a random key according to a request from a user and shows the generated random key to the user, and then, by using the random key, registration data is encrypted. Accordingly, only a USB host that registers the UMS device after the user connects the USB host directly to the UMS device, can freely use digital content of the UMS device, and even if encrypted registration data of the UMS is leaked out, unauthorized devices cannot register the UMS device.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
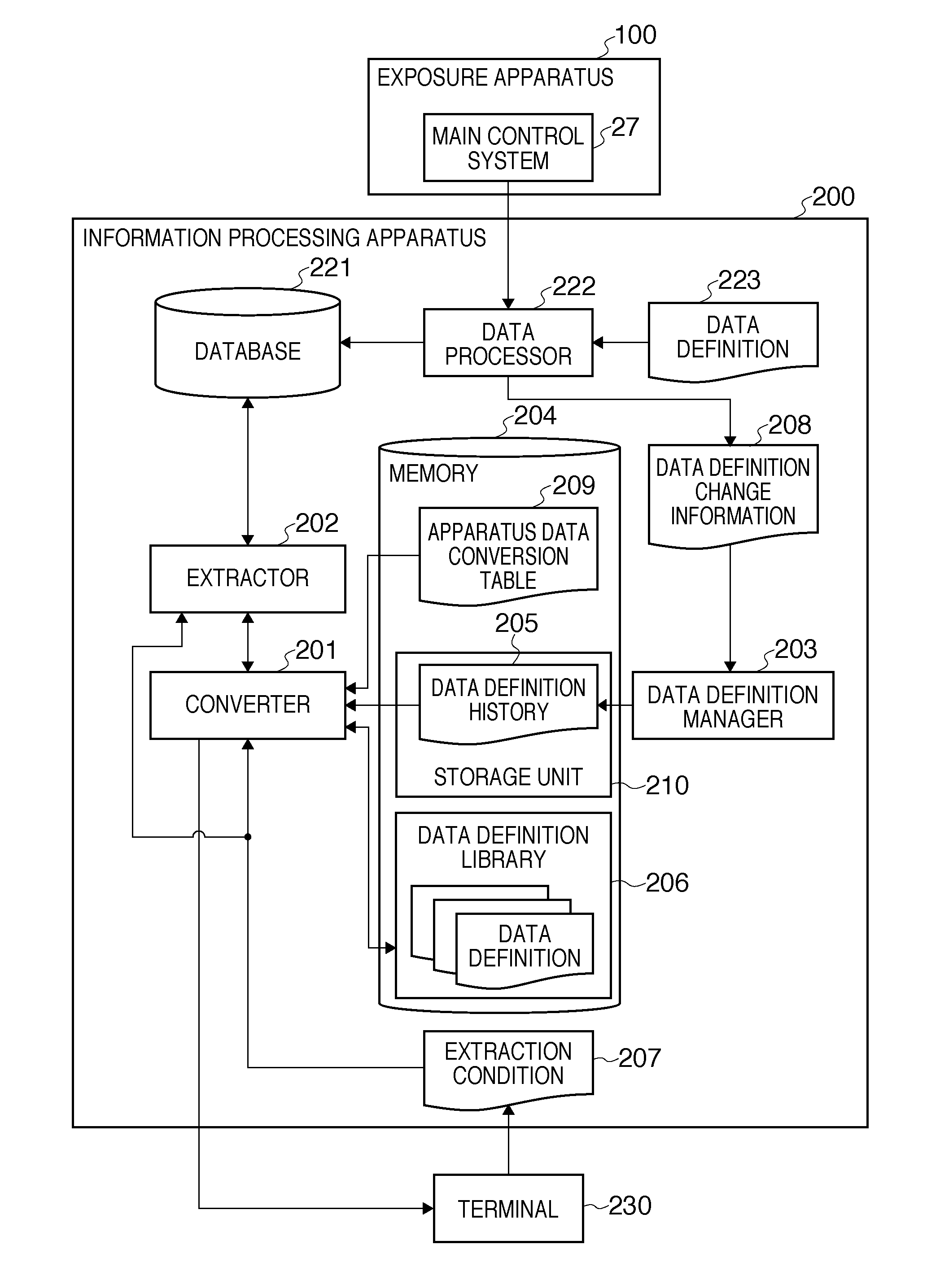
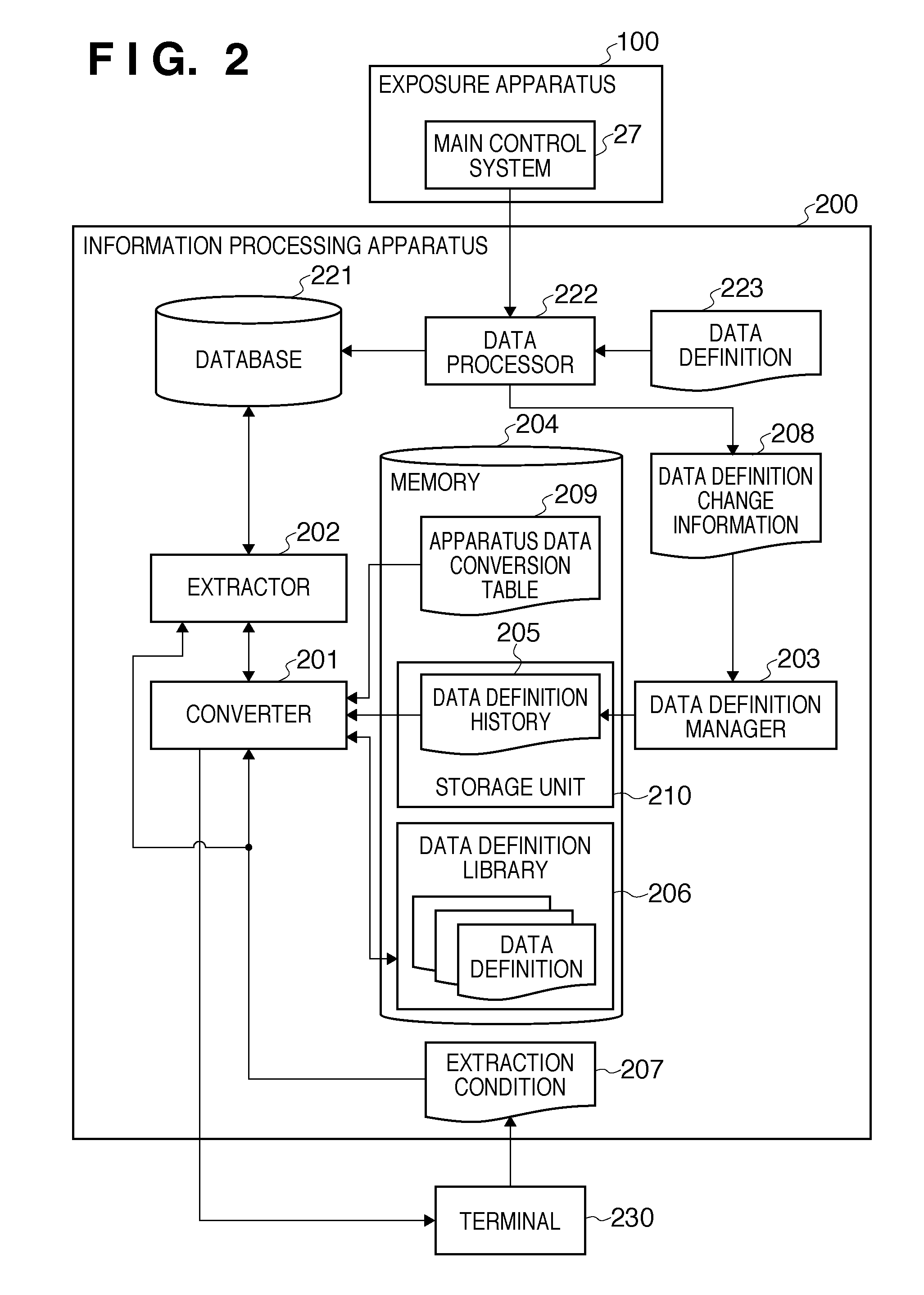
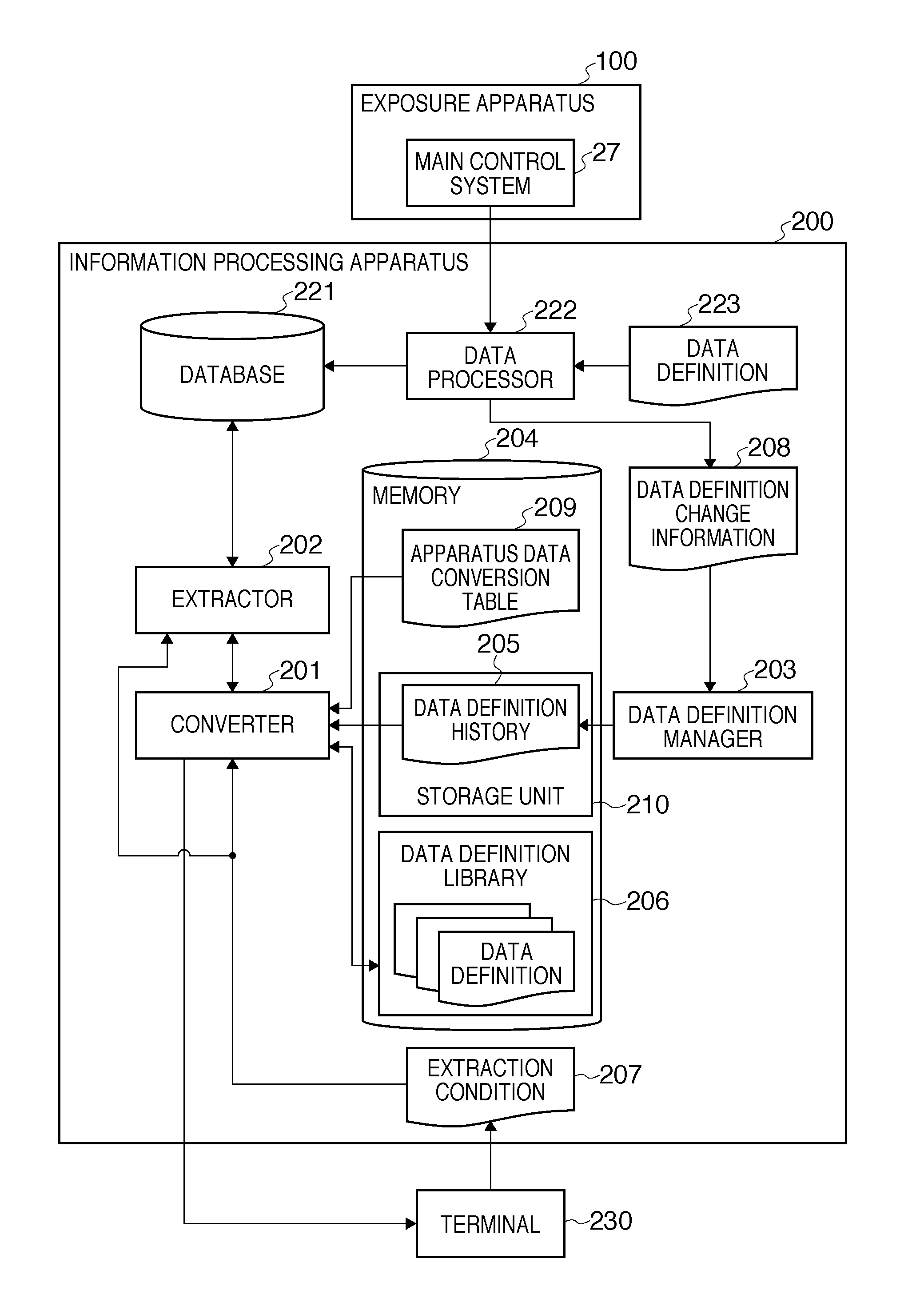
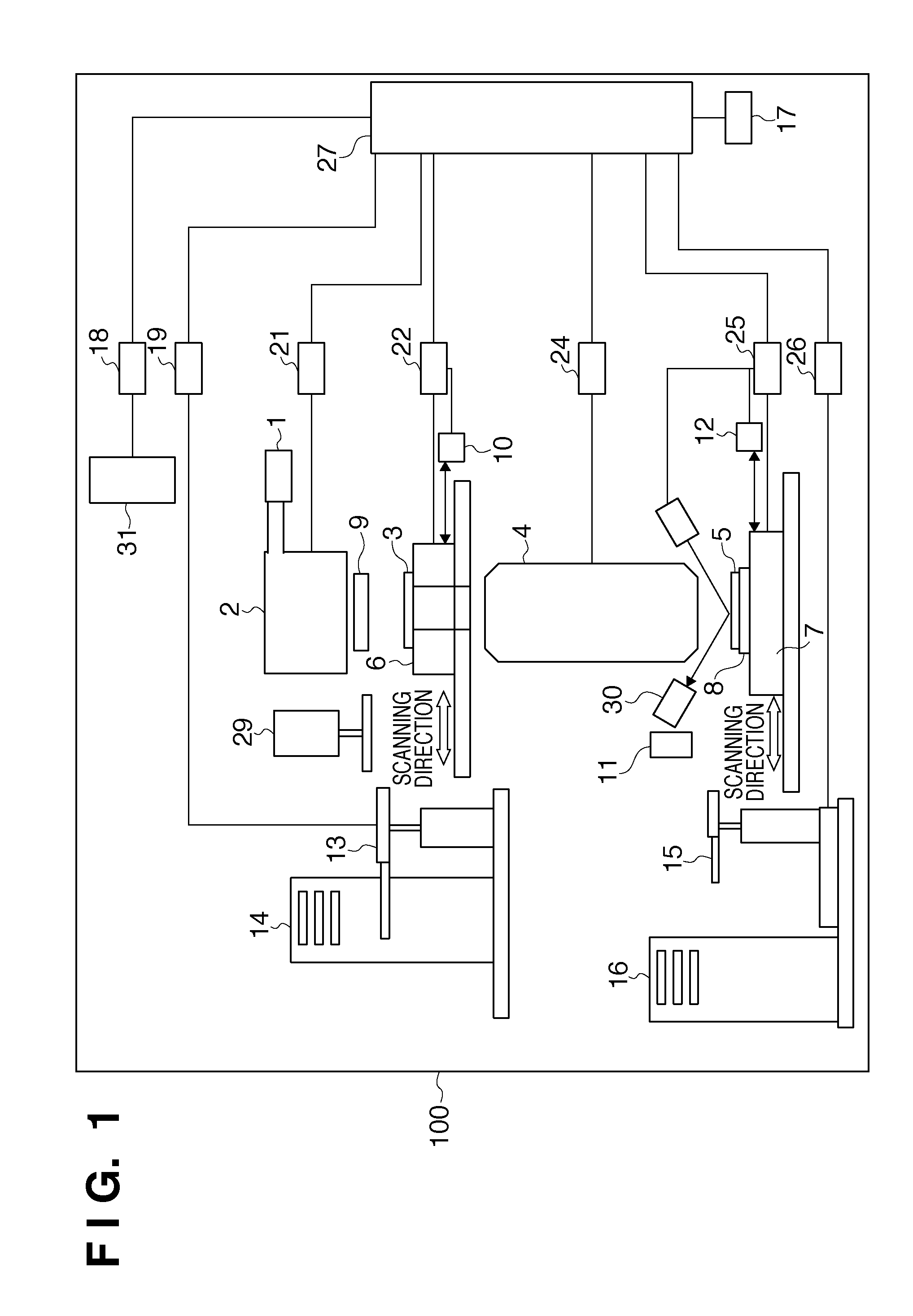
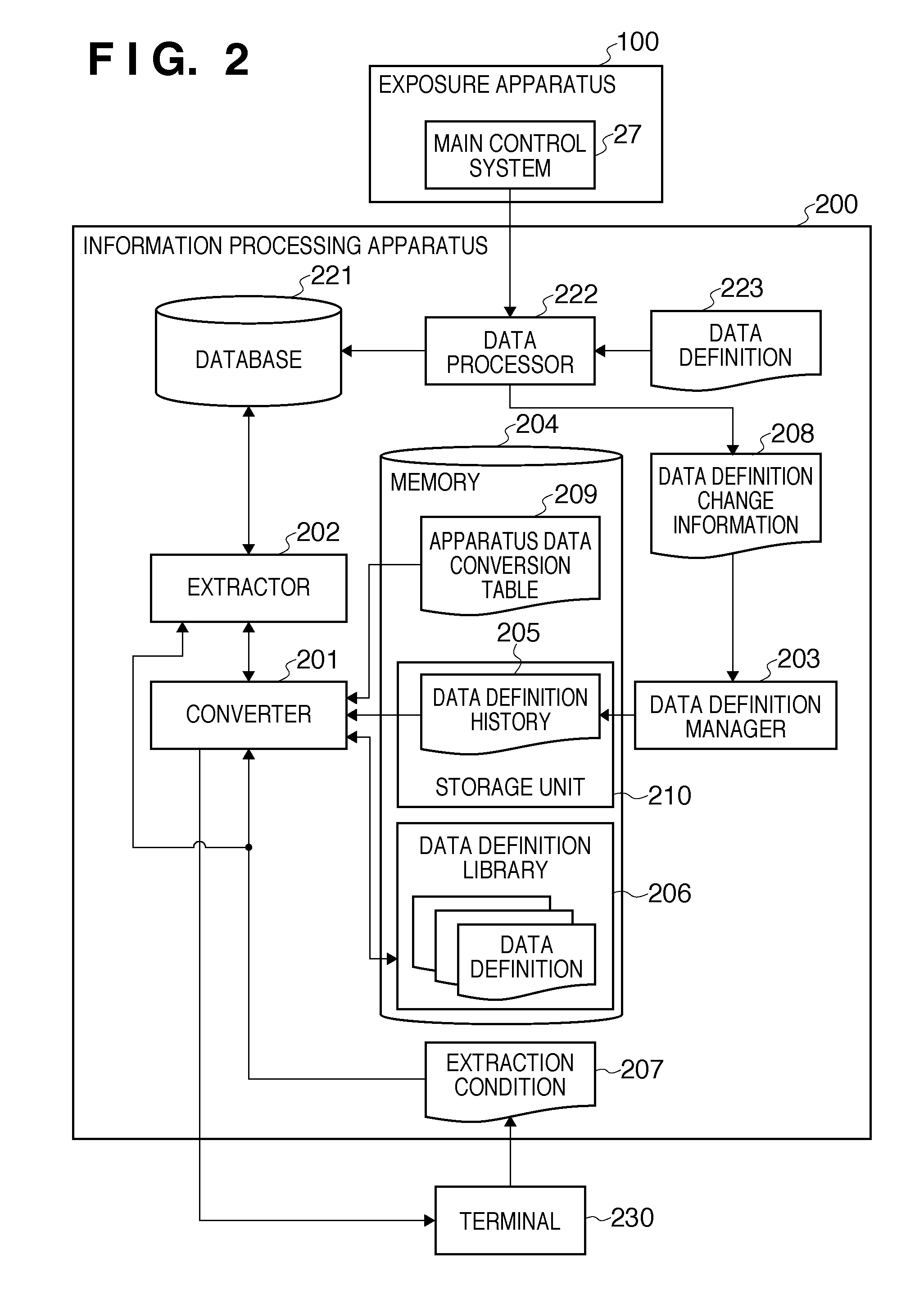
Information processing system, information processing method, and computer-readable storage medium
InactiveUS8060472B2Digital data processing detailsPhotomechanical apparatusData ingestionInformation processing
An information processing system which utilizes apparatus data recorded in a database in conformity with a data definition which can be updated as needed, comprises a storage unit configured to store a data definition history in which a data definition version is associated with a period for which a data definition in the data definition version is used, a data definition library configured to register a data definition version and a data definition in the data definition version in association with each other, an extractor configured to extract, from the database, apparatus data which meets an extraction condition including an extraction period designated via a user interface, and a converter configured to convert an expression of the apparatus data extracted by the extractor into an expression conforming to a data definition designated via the user interface.
Owner:CANON KK
Information processing system, information processing method, and computer-readable storage medium
InactiveUS20100235384A1Photomechanical apparatusStructured data retrievalInformation processingData ingestion
An information processing system which utilizes apparatus data recorded in a database in conformity with a data definition which can be updated as needed, comprises a storage unit configured to store a data definition history in which a data definition version is associated with a period for which a data definition in the data definition version is used, a data definition library configured to register a data definition version and a data definition in the data definition version in association with each other, an extractor configured to extract, from the database, apparatus data which meets an extraction condition including an extraction period designated via a user interface, and a converter configured to convert an expression of the apparatus data extracted by the extractor into an expression conforming to a data definition designated via the user interface.
Owner:CANON KK
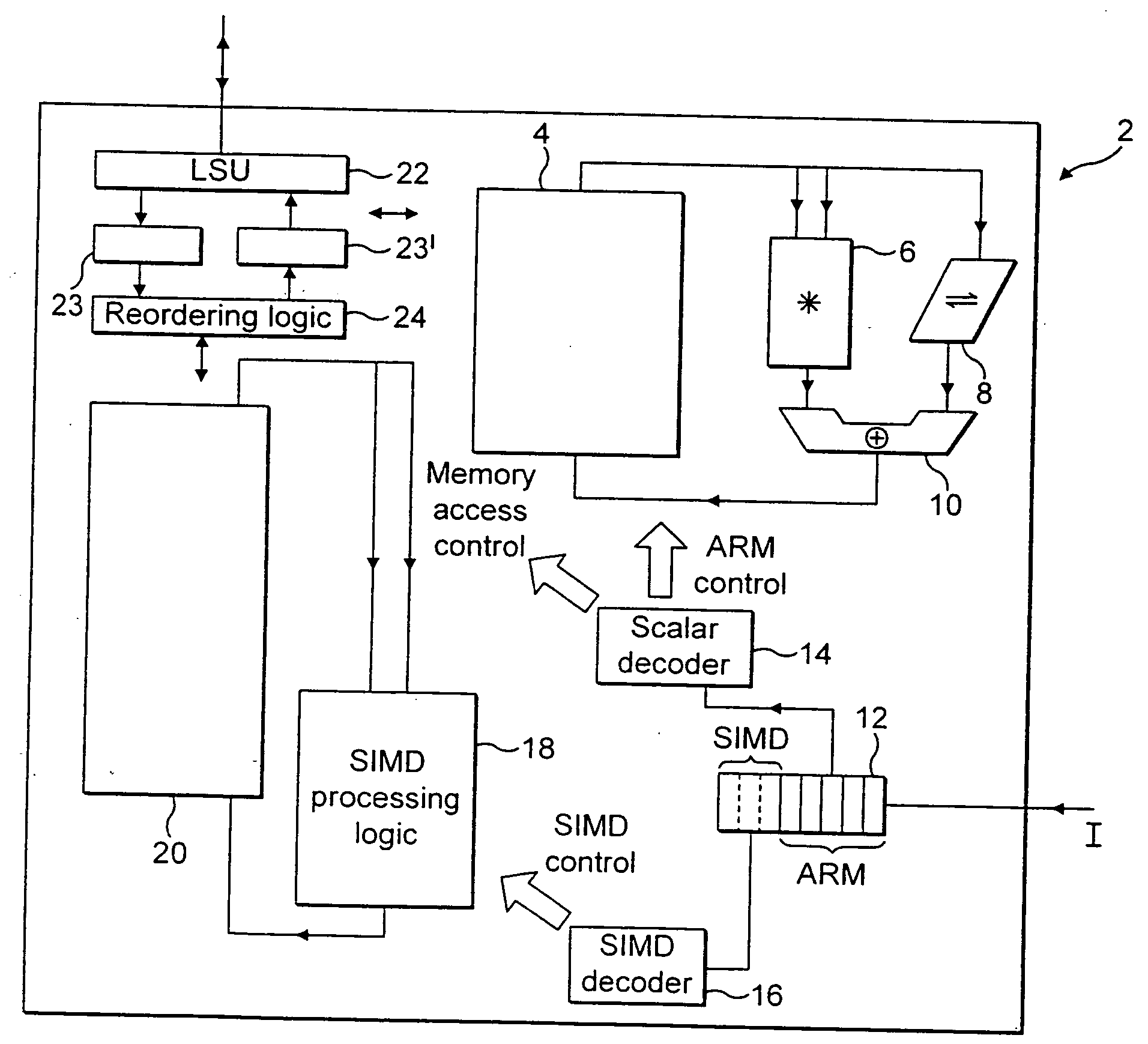
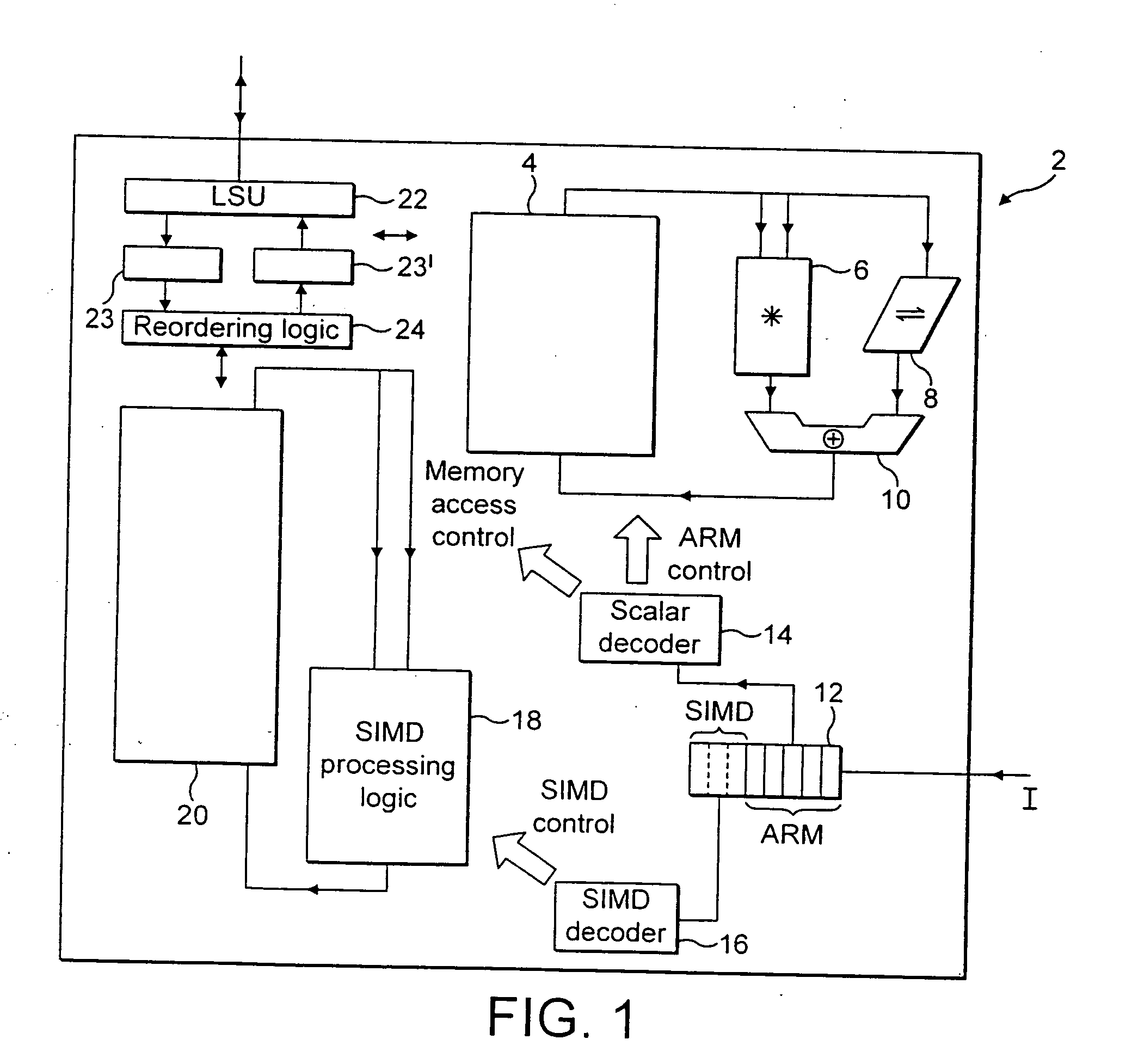
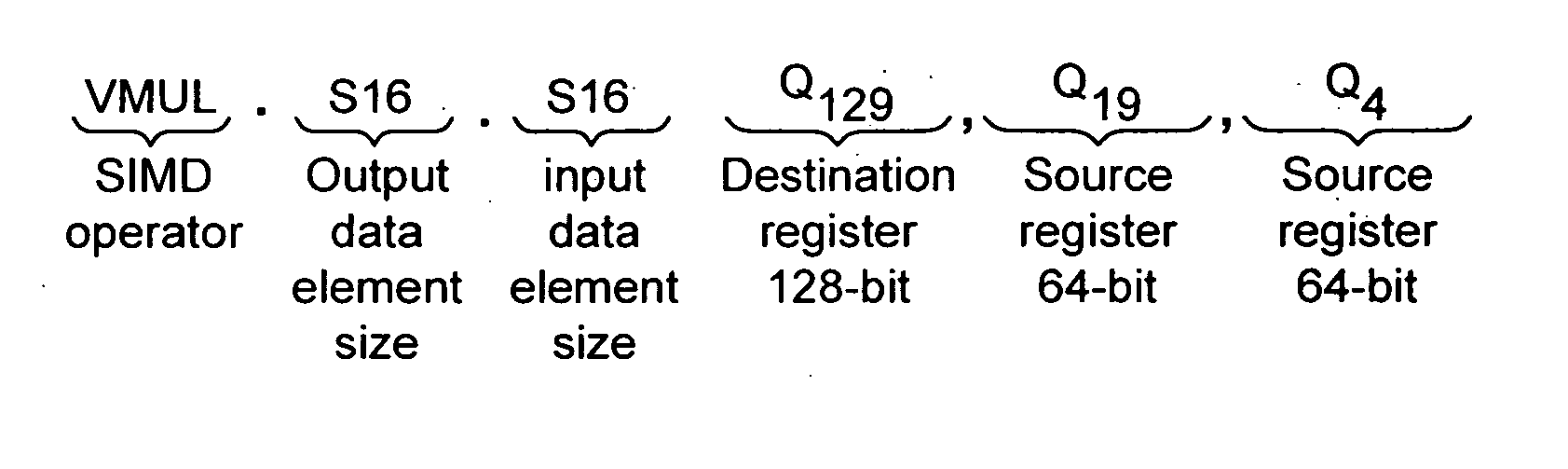
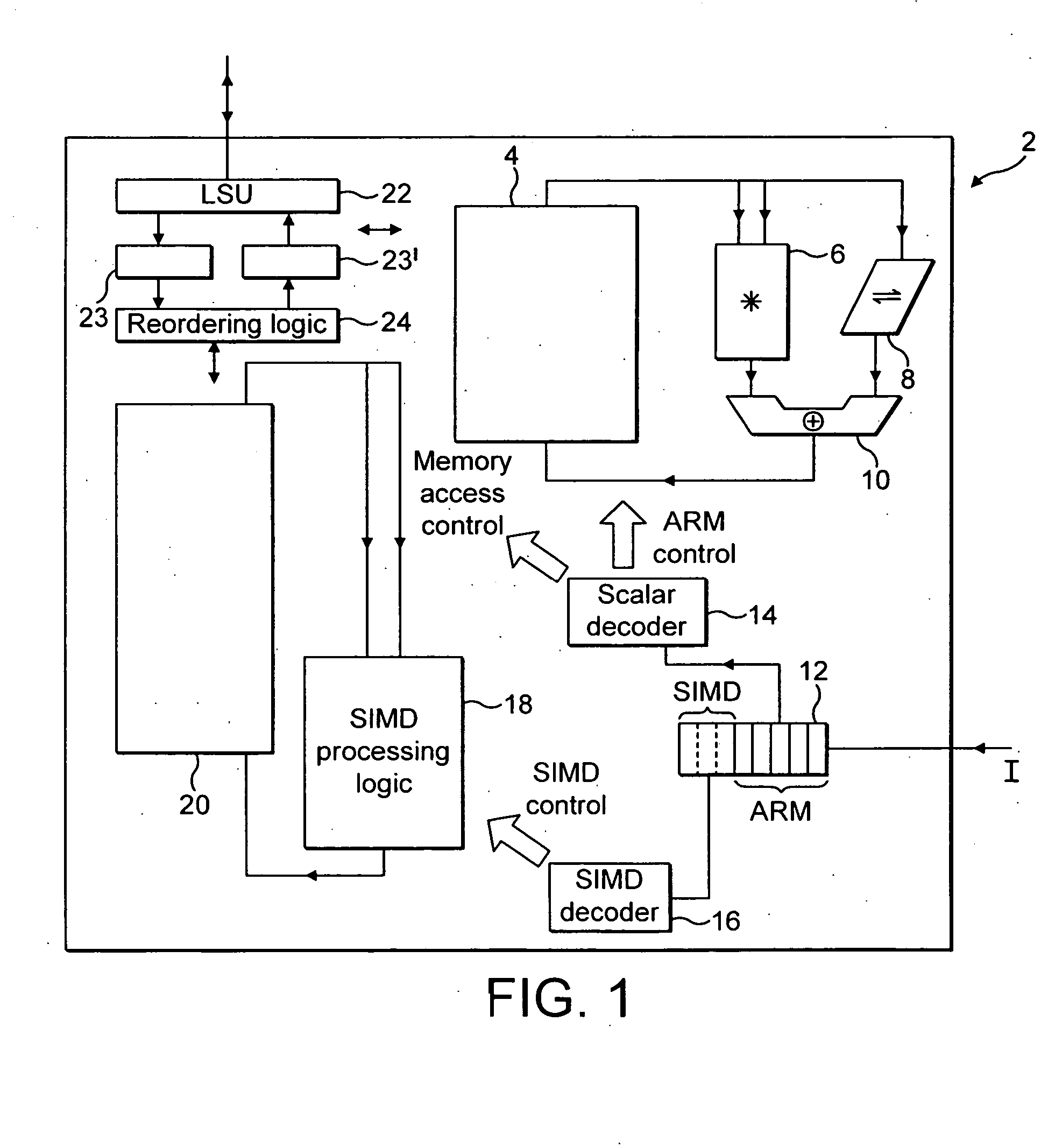
Data processing apparatus and method for performing arithmetic operations in SIMD data processing
ActiveUS20050125476A1Improve accuracyReduce in quantityInstruction analysisComputation using non-contact making devicesProcessor registerData memory
A data processing apparatus, method and a computer program product. A data processing apparatus comprising: a register data store operable to store data elements; an instruction decoder operable to decode an arithmetic returning high half instruction; a data processor operable to perform data processing operations controlled by said instruction decoder wherein: in response to said decoded arithmetic returning high half instruction, said data processor is operable to specify within said register data store, one or more source registers operable to store a plurality of source data elements of a first size, and one or more destination registers operable to store a corresponding plurality of resultant data elements of a second size, said second size being half the size of said first size; and to perform the following operations in parallel on said plurality of source data elements to produce said corresponding plurality of resultant data elements: perform an arithmetic operation on said source registers specified by said instruction to produce a plurality of corresponding intermediate result data elements; form said resultant data elements from information derived from a high half of a corresponding one of said plurality of intermediate result data elements; store said resultant data elements in said destination register.
Owner:ARM LTD
Debug interface including timing synchronization logic
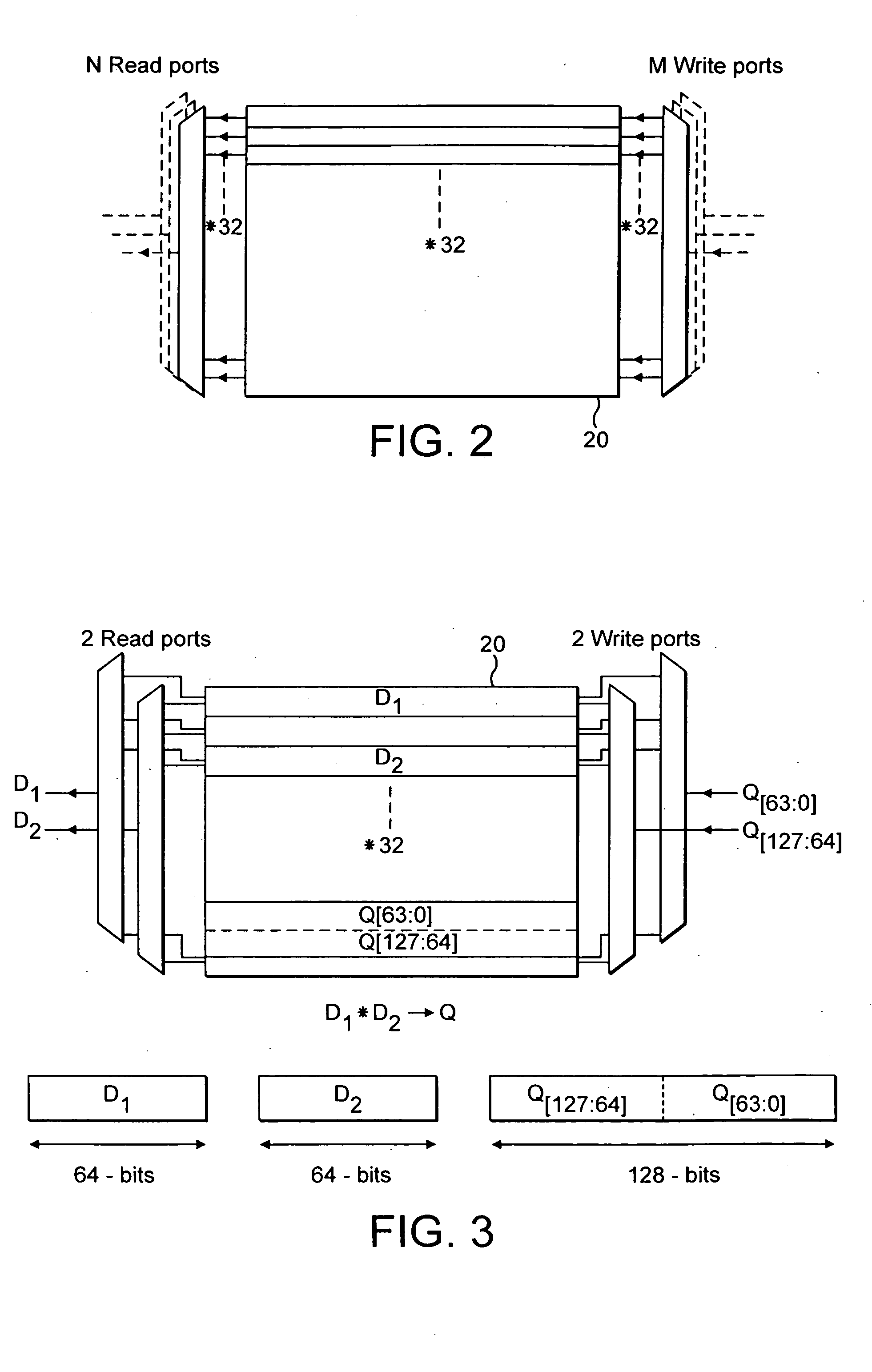
A system for debugging a processor includes a logic circuit for communicating commands and data between an input / output port which operates at a first clock frequency, and trace control logic which operates at a second clock frequency that is different from the first clock frequency. In some embodiments, the input / output port is a JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) port operating at a maximum clock frequency of 25 MHz and the trace control logic operates at a clock frequency of 33 Mhz, 66 MHz, 99 MHz, or 133 mhz. A suitable JTAG clock frequency is a minimum of either half the CPU internal clock frequency or 2.25 Mhz for synchronizing the internal signals between different clock frequencies. When the input / output port, which is typically a serial / parallel input / output port, writes data to debug registers, including ITCR, DCSR, soft-address, and RX-DATA registers, timing strobe signals to the registers are synchronized to a processor clock to reduce the synchronization logic for register bits that are used by the processor and trace control logic. By synchronizing the debug register data write operations to the processor clock timing, the data bits of the registers are used by the processor and the trace logic without further synchronization. Advantageously, the amount of synchronization logic is reduced. Synchronizing the signals that cross the blocks with different clock timing facilitates communication between the processor, the trace control logic, and the serial and parallel input / output ports and reduces the amount of synchronization logic.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method and system for providing fast handoff in a wlan-like communication system using active neighboring sets
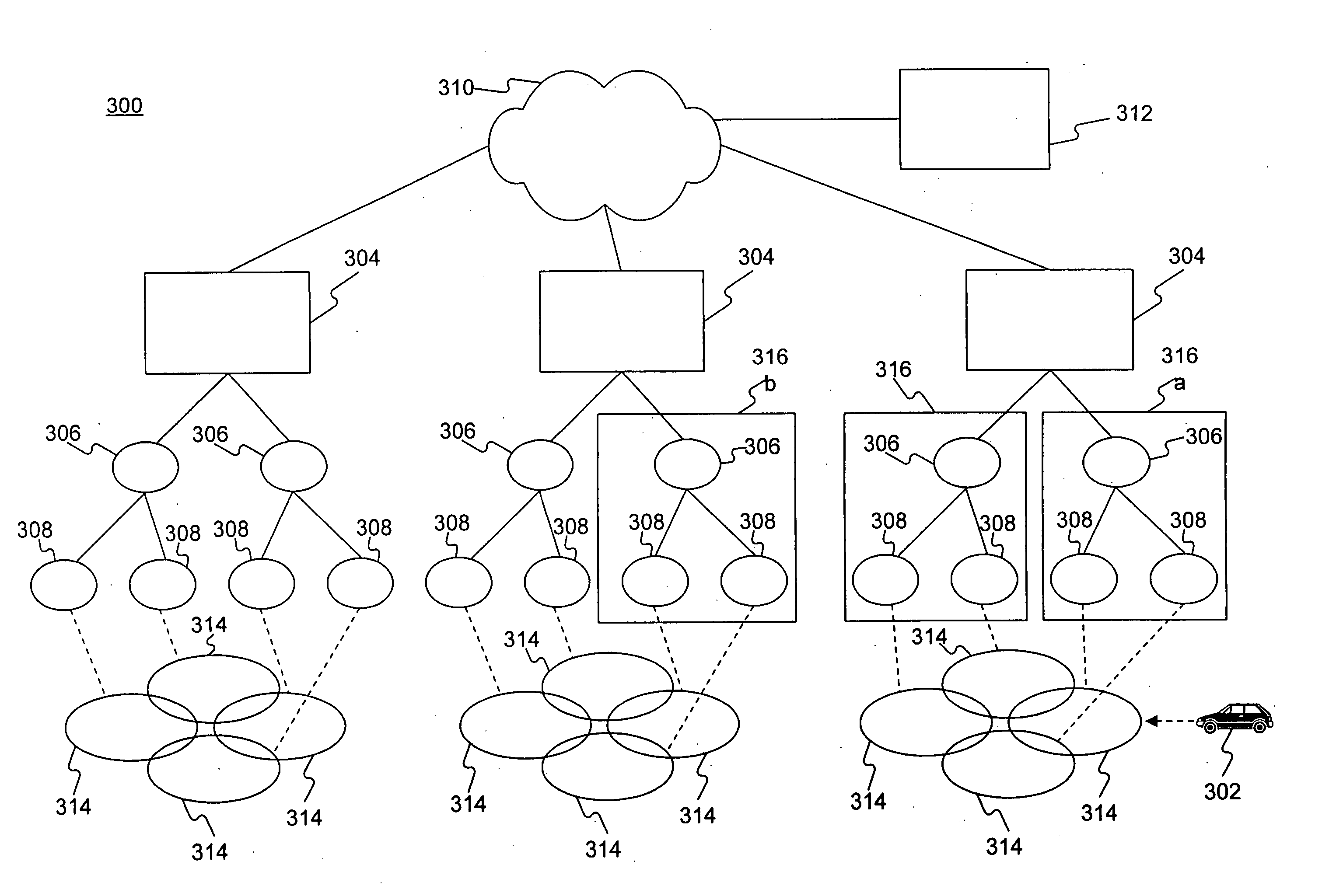
ActiveUS20050282546A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesCommunications systemSignal quality
Methods and systems for providing fast handoff in WLAN-like communications system construct a caching candidate set based upon a weighted handoff tendency coefficient. The weighted handoff tendency coefficient is based upon the handoff matrix and the weighting factor. The handoff matrix is an adaptive two-dimensional array that provides a list of nearby access points relative to a mobile station and the weighting factor is a value that prioritizes the nearby access points based upon a signal quality indication. A home access point, once it is triggered to initialize proactive caching, provides the caching candidate set with registration data of the mobile station before a transfer of a connection between the home access point and one of the access points on the caching candidate set.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
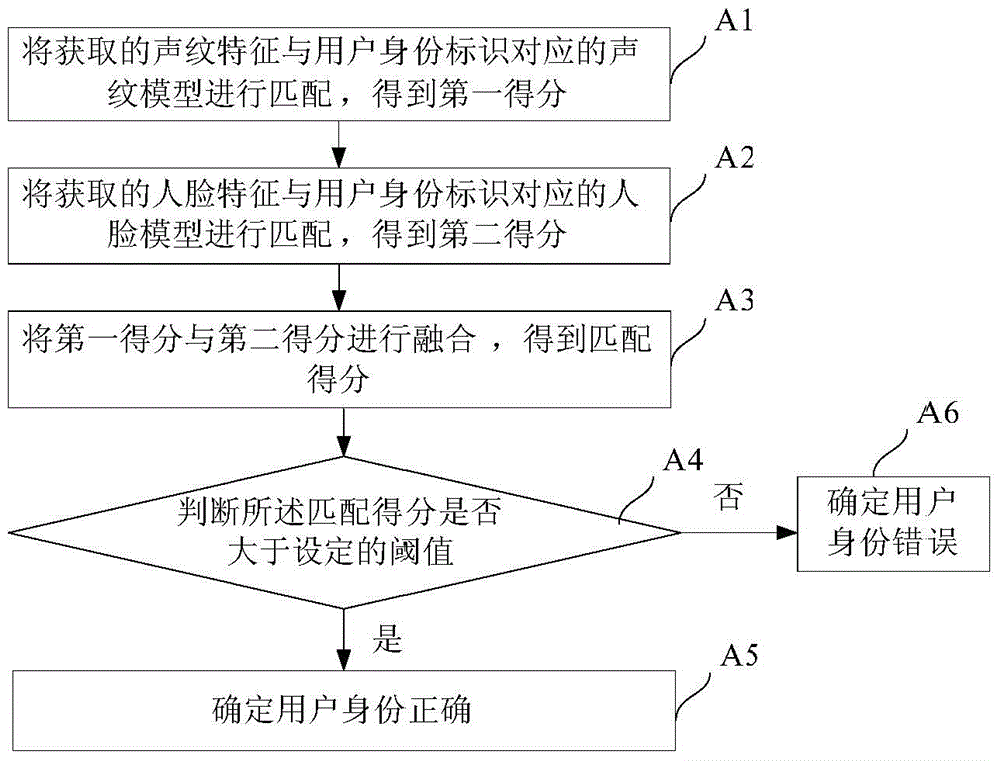
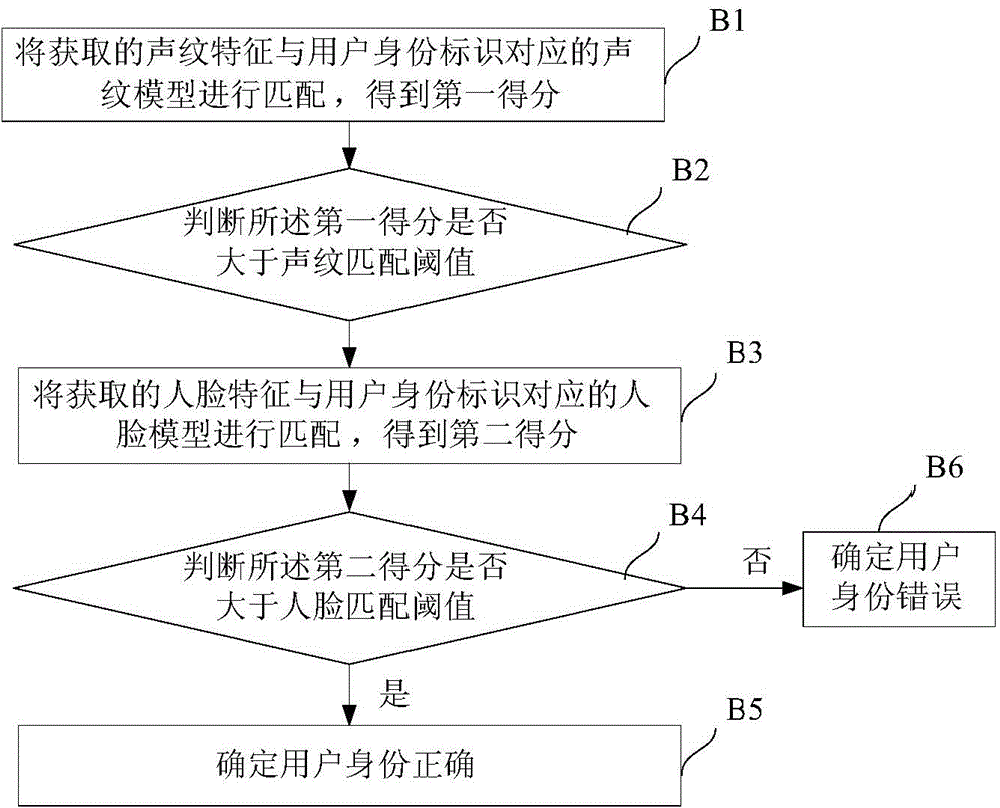
Method and system for identifying identity
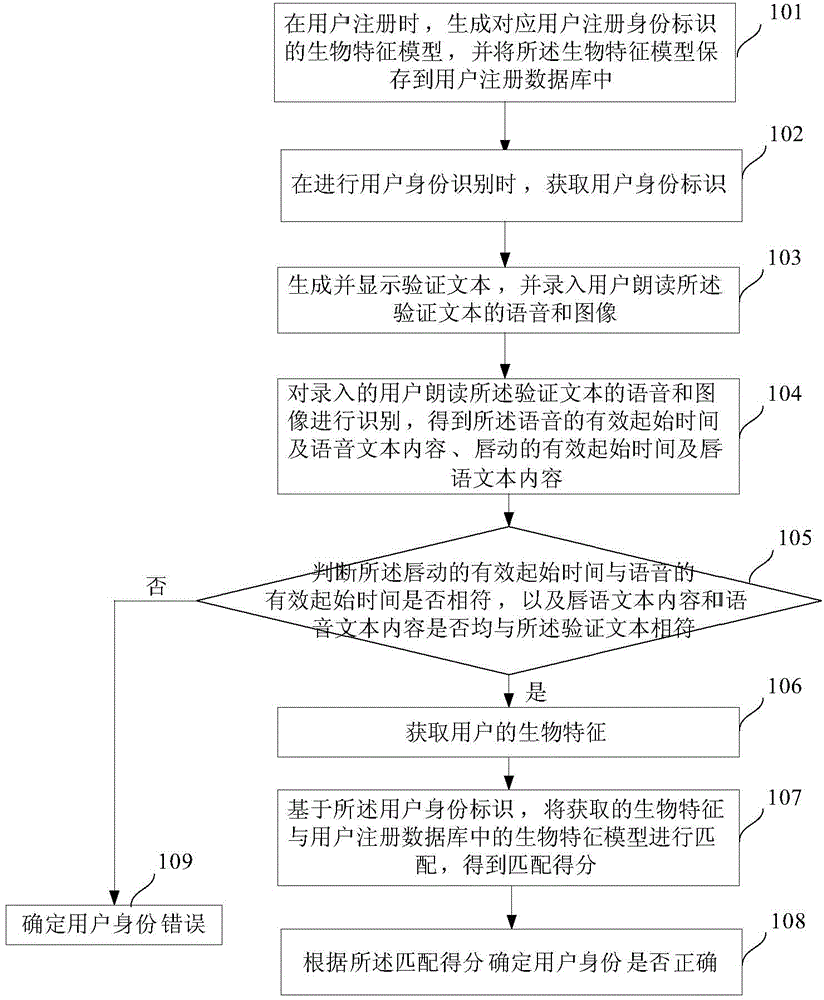
ActiveCN104598796AImprove securityImprove convenienceDigital data authenticationStart timeSpeech sound
The invention discloses a method and a system for identifying an identity. The method comprises the following steps: generating a biological characteristic model corresponding to a user registration identity mark when a user registers; generating and displaying a verification text and recording a voice and an image of a user reading verification text when the user identity is identified; identifying the recorded voice and image of the user reading verification text, thereby acquiring a valid starting time of the voice, the text content of the voice, the valid starting time of lip motion and a lip language text content; acquiring biological characteristics of the user if the valid starting time of lip motion conforms to the valid starting time of the voice and the lip language text content and the text content of the voice both conform to the verification text; matching the acquired biological characteristics with the biological characteristic model in a user register database, thereby acquiring a matching score; confirming if the user identity is correct according to the matching score. The method provided by the invention can be utilized to effectively increase the safety of the identity identification.
Owner:IFLYTEK CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com