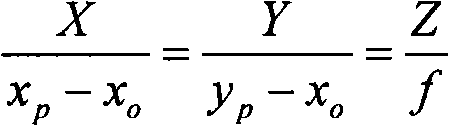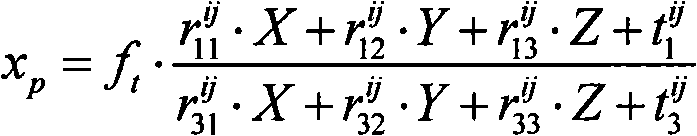Patents
Literature
973 results about "3d camera" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
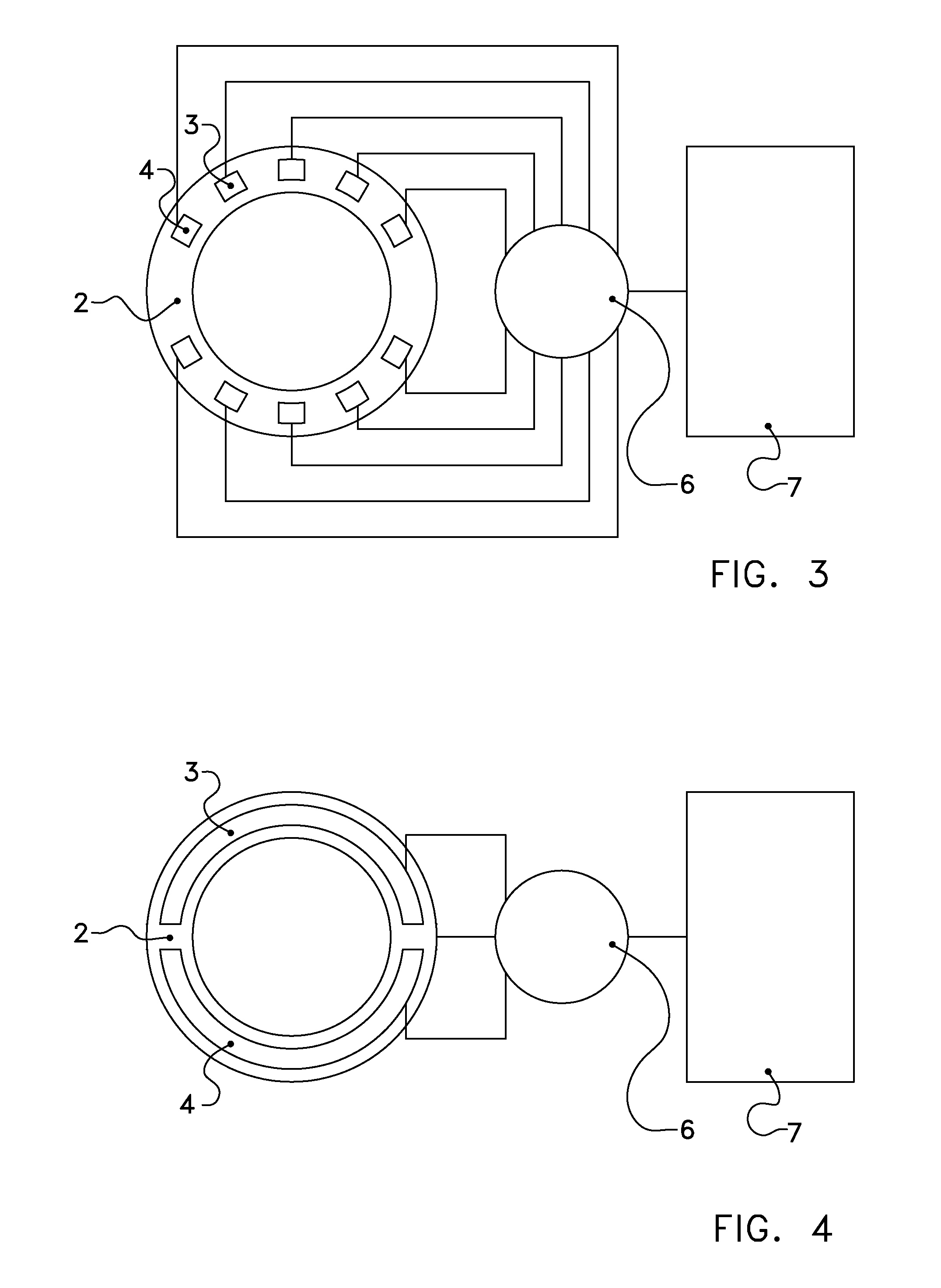
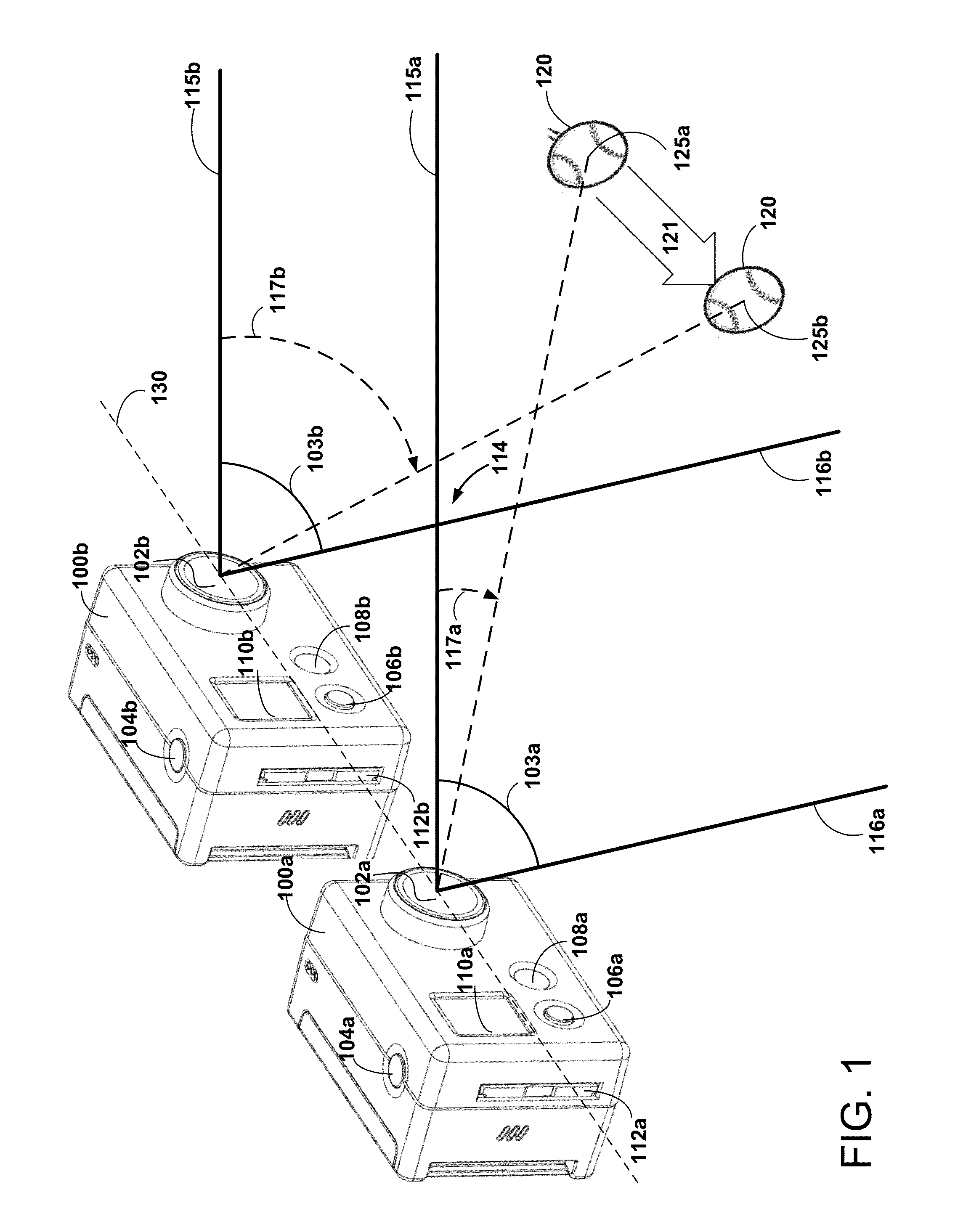
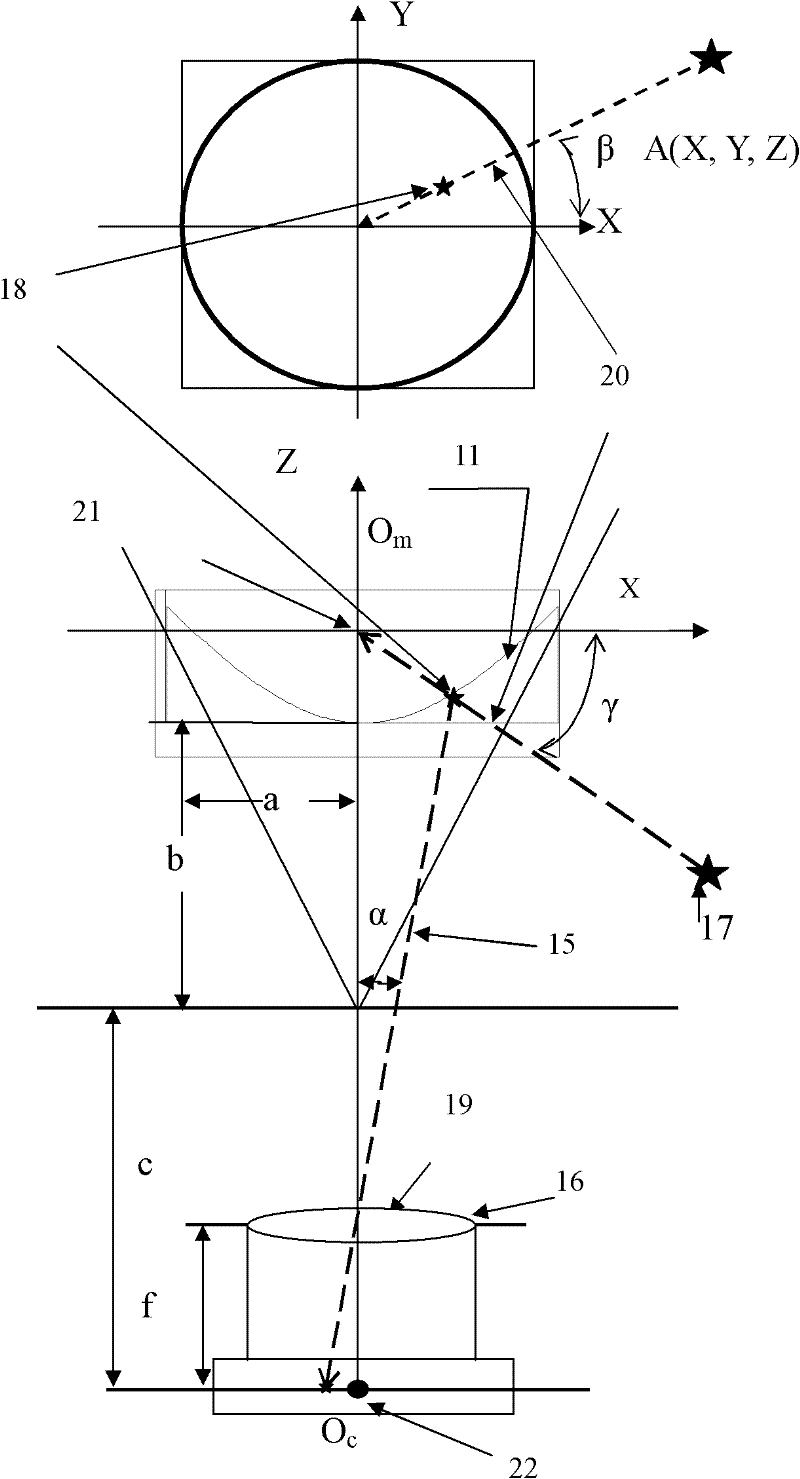
Automatic Scene Modeling for the 3D Camera and 3D Video
InactiveUS20080246759A1Reduce video bandwidthIncrease frame rateTelevision system detailsImage enhancementAutomatic controlViewpoints
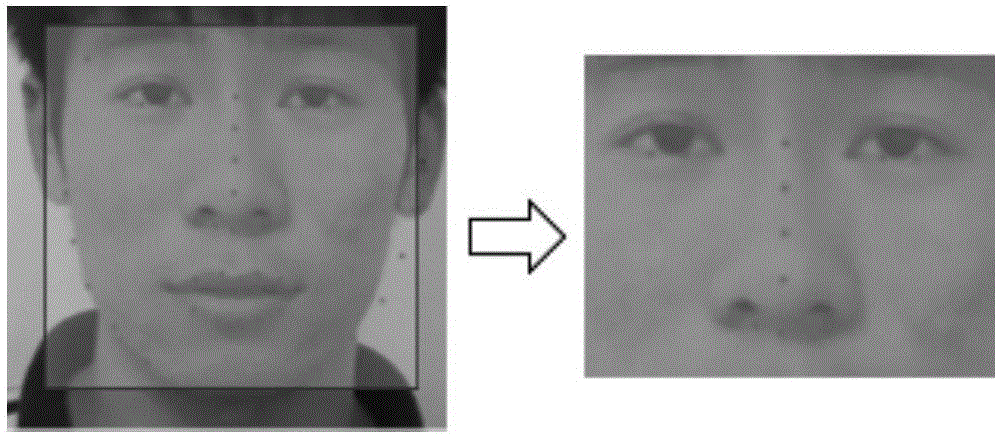
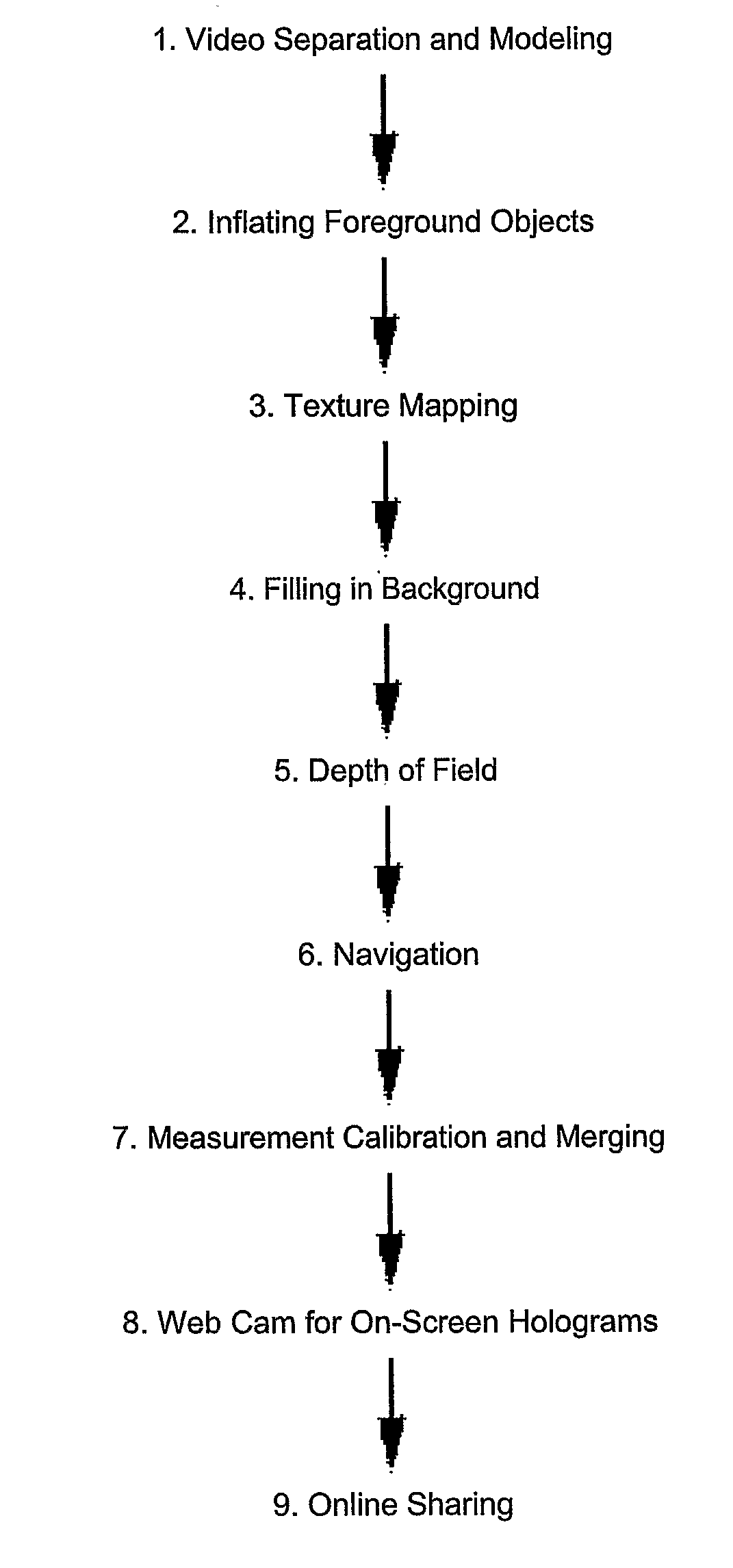
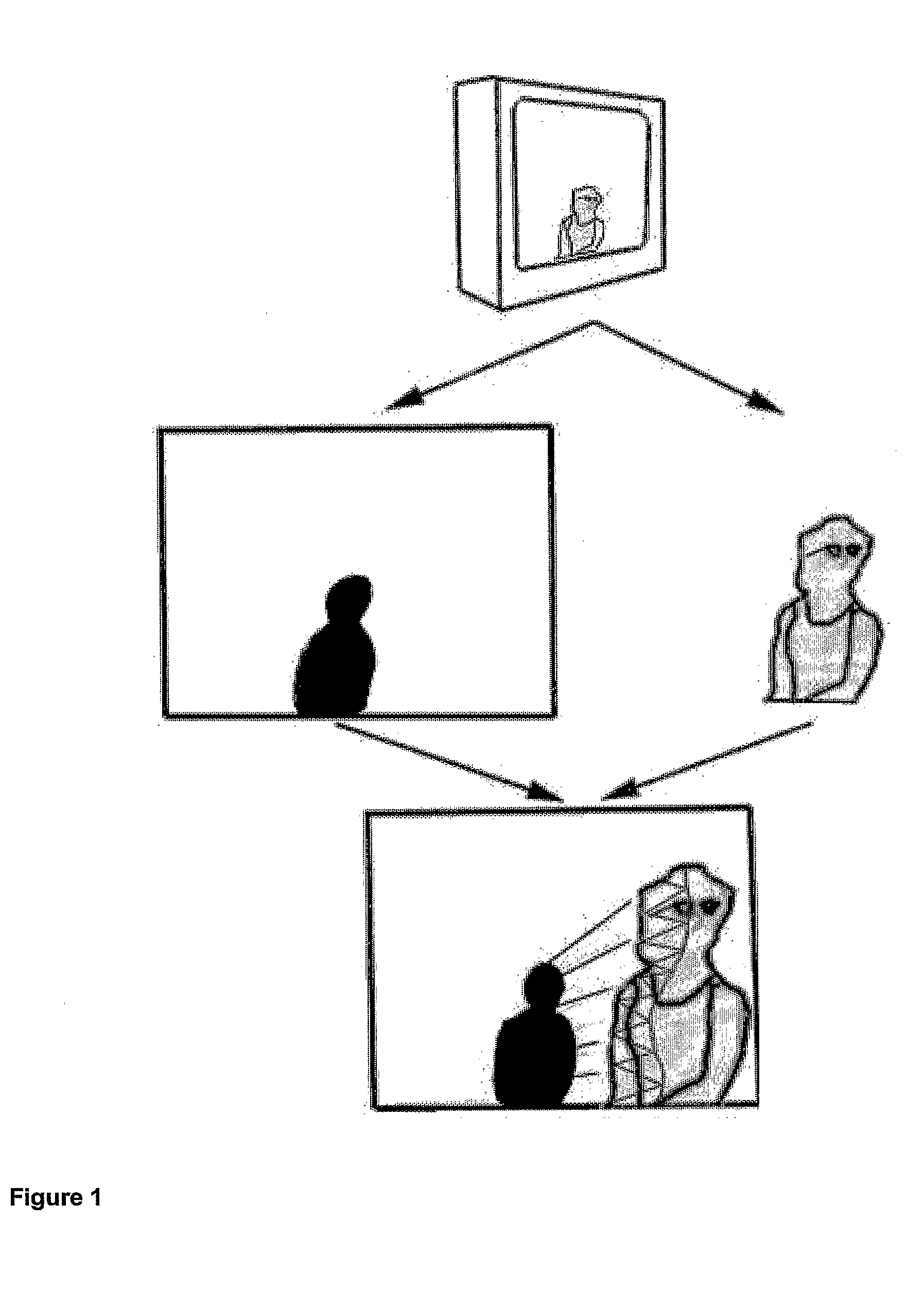
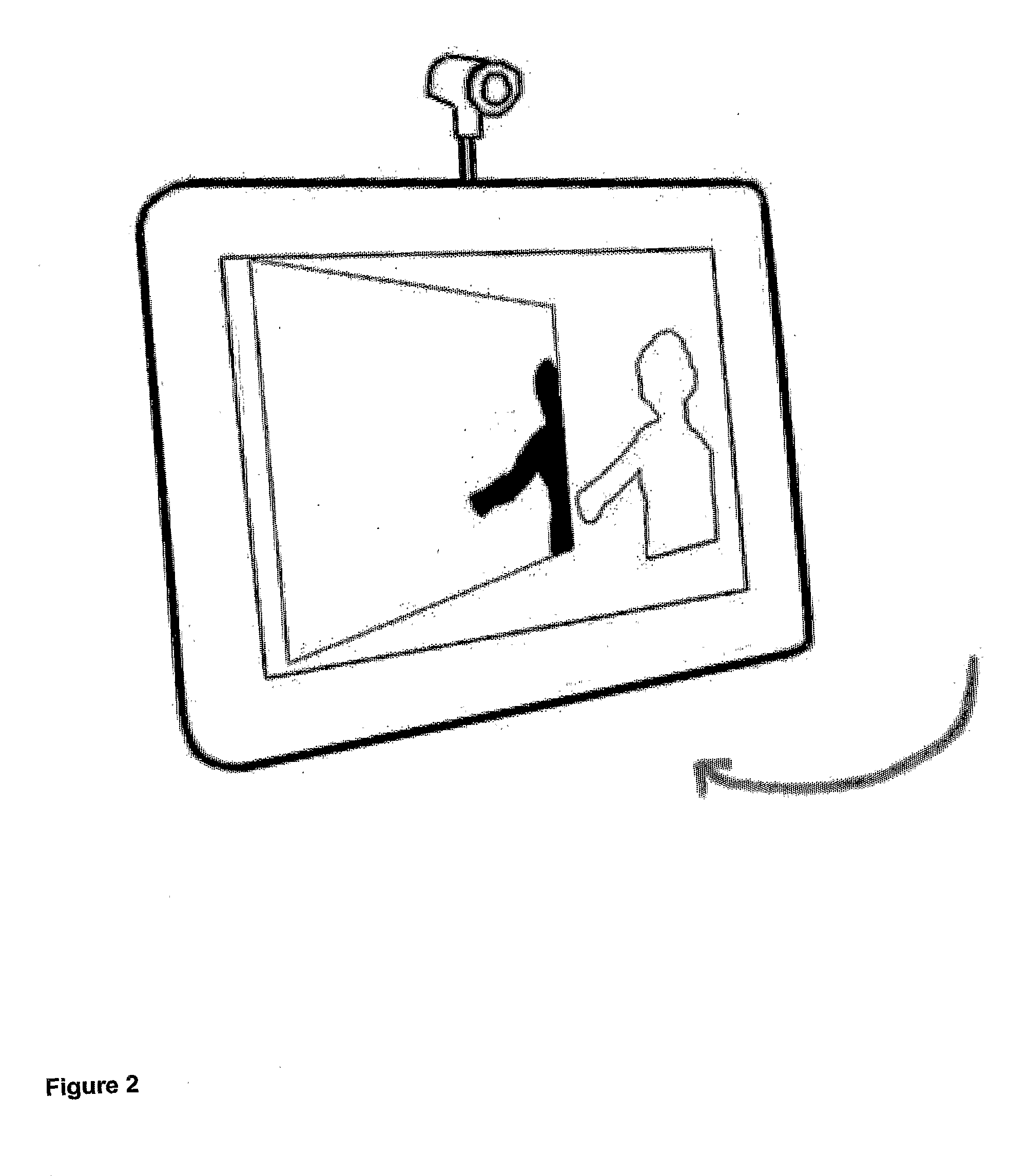
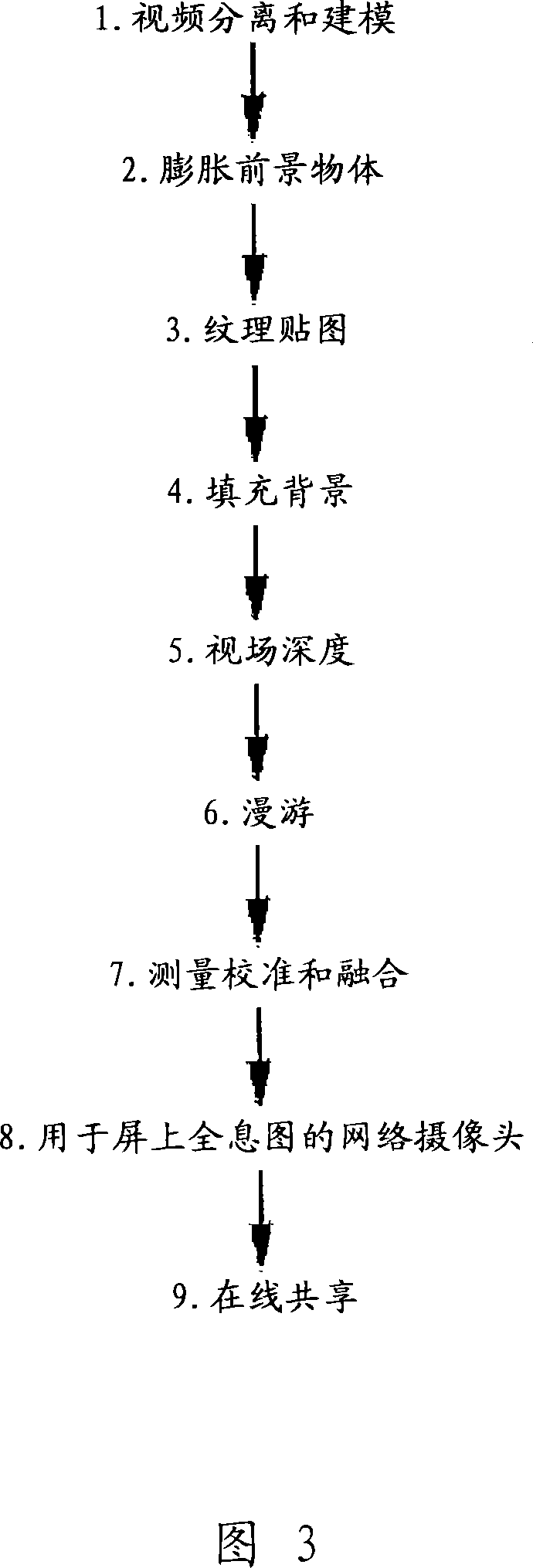
Single-camera image processing methods are disclosed for 3D navigation within ordinary moving video. Along with color and brightness, XYZ coordinates can be defined for every pixel. The resulting geometric models can be used to obtain measurements from digital images, as an alternative to on-site surveying and equipment such as laser range-finders. Motion parallax is used to separate foreground objects from the background. This provides a convenient method for placing video elements within different backgrounds, for product placement, and for merging video elements with computer-aided design (CAD) models and point clouds from other sources. If home users can save video fly-throughs or specific 3D elements from video, this method provides an opportunity for proactive, branded media sharing. When this image processing is used with a videoconferencing camera, the user's movements can automatically control the viewpoint, creating 3D hologram effects on ordinary televisions and computer screens.
Owner:SUMMERS
Safety device for a vehicle
ActiveUS7607509B2Low imageObject detectionBelt control systemsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangement3d cameraObject detection
Owner:IEE INT ELECTRONICS & ENG SA
3-D camera for recording surface structures, in particular for dental purposes
InactiveUS6885464B1Reduced measurement accuracyRequires low equipmentImpression capsOptical rangefindersTriangulationLight beam
A 3-D camera and a method for recording surface structures on an object of interest by triangulation, in particular for dental purposes. The camera provides for producing a group of light beams in order to illuminate the object of interest via a projection optical path, an image sensor for receiving light back-scattered by the object of interest via an observation optical path, and provides, in the projection optical path, for producing a pattern projected onto the object of interest. To avoid ambiguities in the event of large height differences, the camera provides for the projection optical path and / or the observation optical path for altering the triangulation angle, which is defined by the angle between the centroid beam of the projection optical path and the centroid beam of the observation optical path. The proposed process involves the taking of at least two 3-D measurements of the same object of interest with different triangulation angles.
Owner:SIRONA DENTAL SYSTEMS
3D imaging system
InactiveUS7224384B1Easy to controlConvenient amountTelevision system detailsPicture signal generatorsCamera lens3d image
An optical imaging system comprising: a taking lens system that collects light from a scene being imaged with the optical imaging system; a 3D camera comprising at least one photosurface that receives light from the taking lens system simultaneously from all points in the scene and provides data for generating a depth map of the scene responsive to the light; and an imaging camera comprising at least one photosurface that receives light from the taking lens system and provides a picture of the scene responsive to the light.
Owner:MICROSOFT INT HLDG BV
System and method for 3D photography and/or analysis of 3D images and/or display of 3D images
InactiveUS20050053274A1Generate efficientlySolve the real problemProjectorsCharacter and pattern recognitionScale model3d image
When 3D viewing means become much more available and common, it will be very sad that the many great movies that exist today will be able to be viewed in 3D only through limited and partial software attempts to recreate the 3D info. Films today are not filmed in 3D due to various problems, and mainly since a normal stereo camera could be very problematic when filming modern films, since for example it does not behave properly when zooming in or out is used, and it can cause many problems when filming for example smaller scale models for some special effects. For example, a larger zoom requires a correspondingly larger distance between the lenses, so that for example if a car is photographed at a zoom factor of 1:10, the correct right-left disparity will be achieved only if the lenses move to an inter-ocular distance of for example 65 cm instead of the normal 6.5 cm. The present invention tries to solve the above problems by using a 3D camera which can automatically adjust in a way that solves the zoom problem, and provides a solution also for filming smaller models. The angle between the two lenses is preferably changed according to the distance and position of the object that is at the center of focus, and changing the zoom affects automatically both the distance between the lenses and their angle, since changing merely the distance without changing the convergence angle would cause the two cameras to see completely different parts of the image. The patent also shows that similar methods can be used for example for a much better stereoscopic telescope with or without a varying zoom factor. In addition, the patent shows various ways to generate efficiently a 3D knowledge of the surrounding space, which can be used also for example in robots for various purposes, and also describes a few possible improvements in 3d viewing.
Owner:MAYER YARON +1
System for connecting a teat cup to a teat
The invention provides a system for connecting a teat cup to a teat, including a teat cup with an opening for receiving a teat, a robot arm for moving the teat cup, a teat cup positioning system with a 3D-sensor and a sensor device for measuring a control quantity, and for connecting the teat cup under the control of the 3D-camera and the control quantity. The sensor device includes at least two electrodes around the opening and a capacitive sensor configured to measure a quantity connected with the capacitance between the electrodes, in particular the capacitance between two electrodes. This system provides a reliable positioning with respect to a teat by, for example, maximization of the measured capacitance. The positioning system supports an optical 3D-sensor for the first, global positioning.
Owner:LELY PATENT
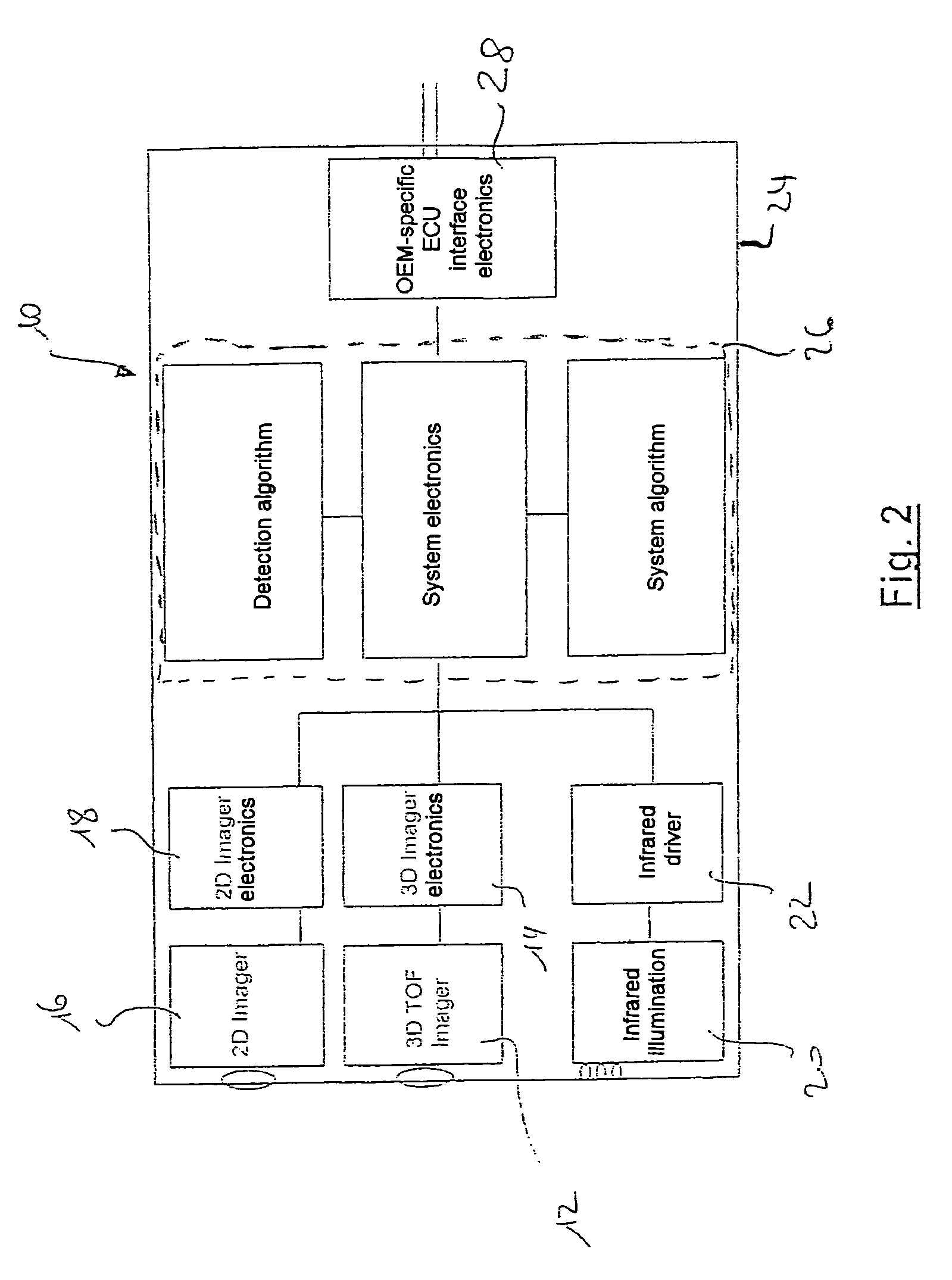
3D camera
InactiveUS7560679B1Easy to determineOptimization definitionTelevision system detailsOptical rangefinders3d cameraComputer science
Owner:NANCHANG O FILM OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Camera pose estimation apparatus and method for augmented reality imaging
ActiveUS20100232727A1Satisfactory accuracyFast and efficient implementationImage enhancementImage analysis3d cameraCandidate key
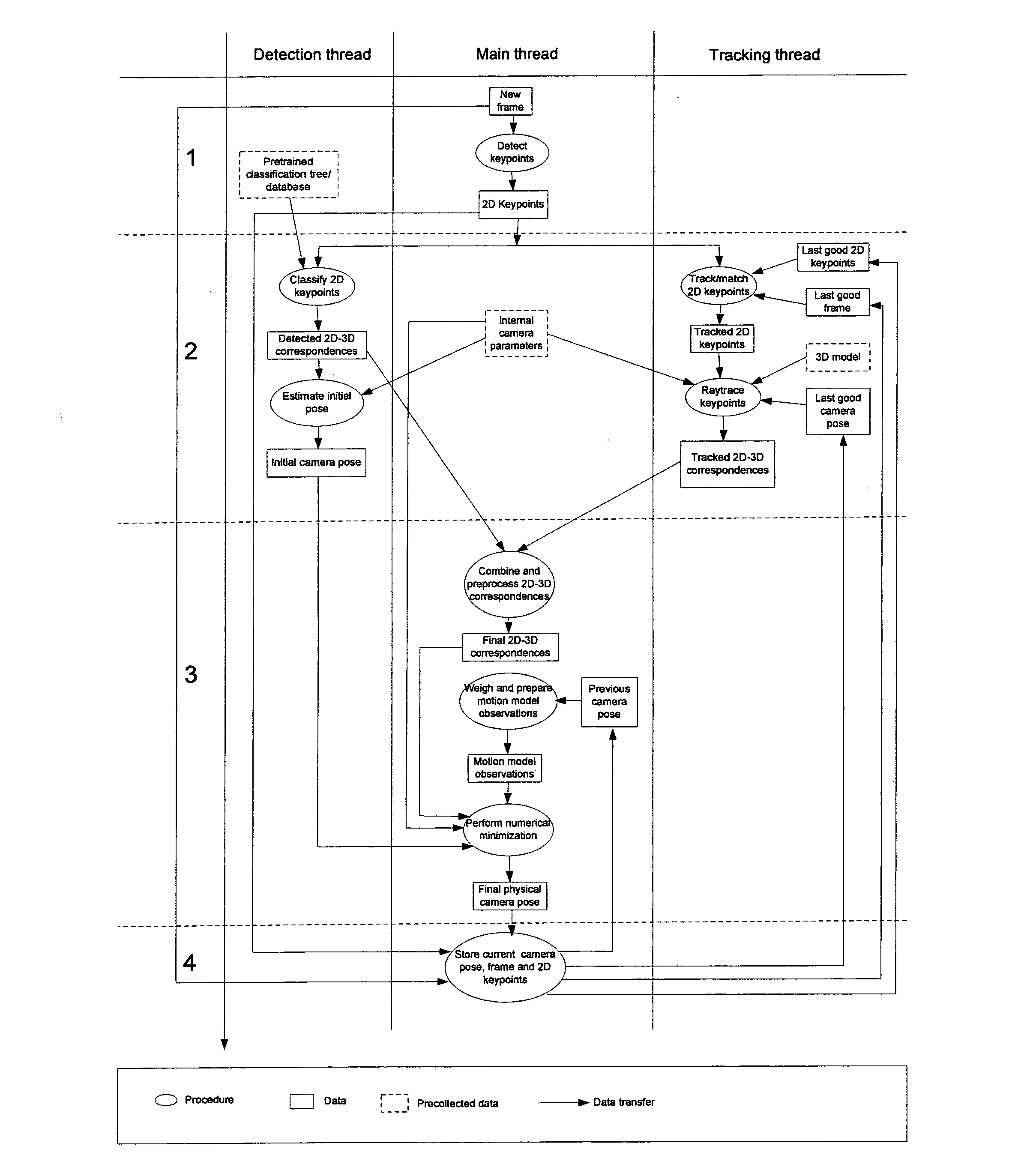
An apparatus for providing an estimate for a 3D camera pose relative to a scene from 2D image data of 2D image frame provided by said camera. A candidate 2D key points detector determines candidate 2D key points from the 2D image frame. A detected 3D observations detector determines detected 3D observations from pre-recorded scene data and the candidate 2D key points. A detected 3D camera pose estimator determines a detected 3D camera pose estimate from the camera data, the detected 3D observations and the candidate 2D key points. A first storage stores the detected 2D candidate key points and the 2D image data, and outputs in response to a 3D camera pose estimate output previous 2D image data and candidate 2D key points related to a previous 3D camera pose estimate output. A second storage stores and outputs a previous 3D camera pose estimate. A tracked 3D observations detector determines tracked 3D observations from the 2D image data, the candidate 2D key points, the camera data, the previous 2D image data and candidate 2D key points, the previous 3D camera pose estimate and 3D scene model data. A pose estimate selector outputs a selected one of the detected camera pose estimate and the previous 3D camera pose estimate. A 3D camera pose estimator computes and outputs the 3D camera pose estimate from the camera data, the detected 3D observations, the tracked 3D observations and the selected 3D camera pose estimate.
Owner:APPLE INC
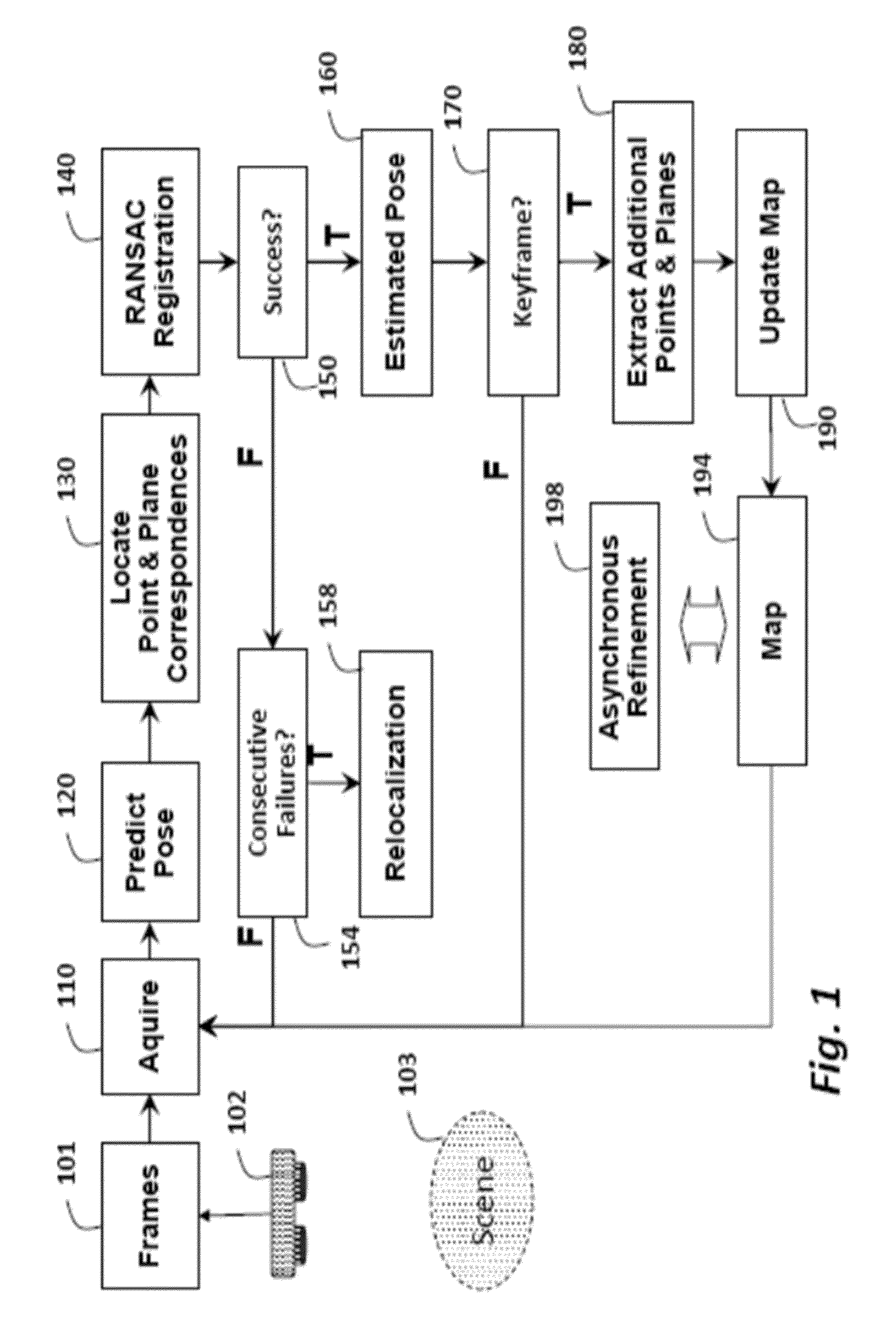
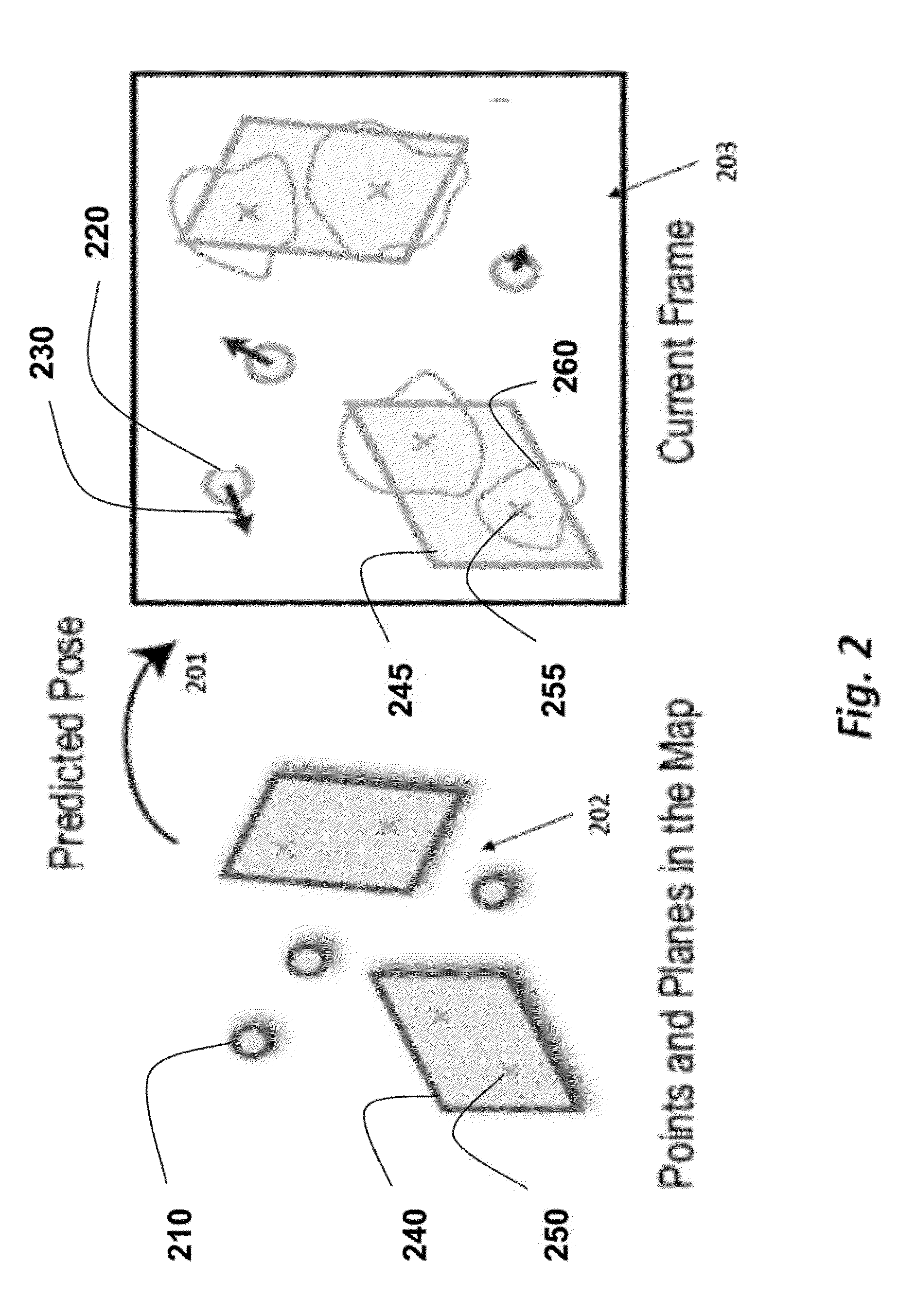
Tracking Poses of 3D Camera Using Points and Planes
ActiveUS20140002597A1Fast and accurate registrationMinimize failureImage enhancementImage analysis3d cameraRegister data
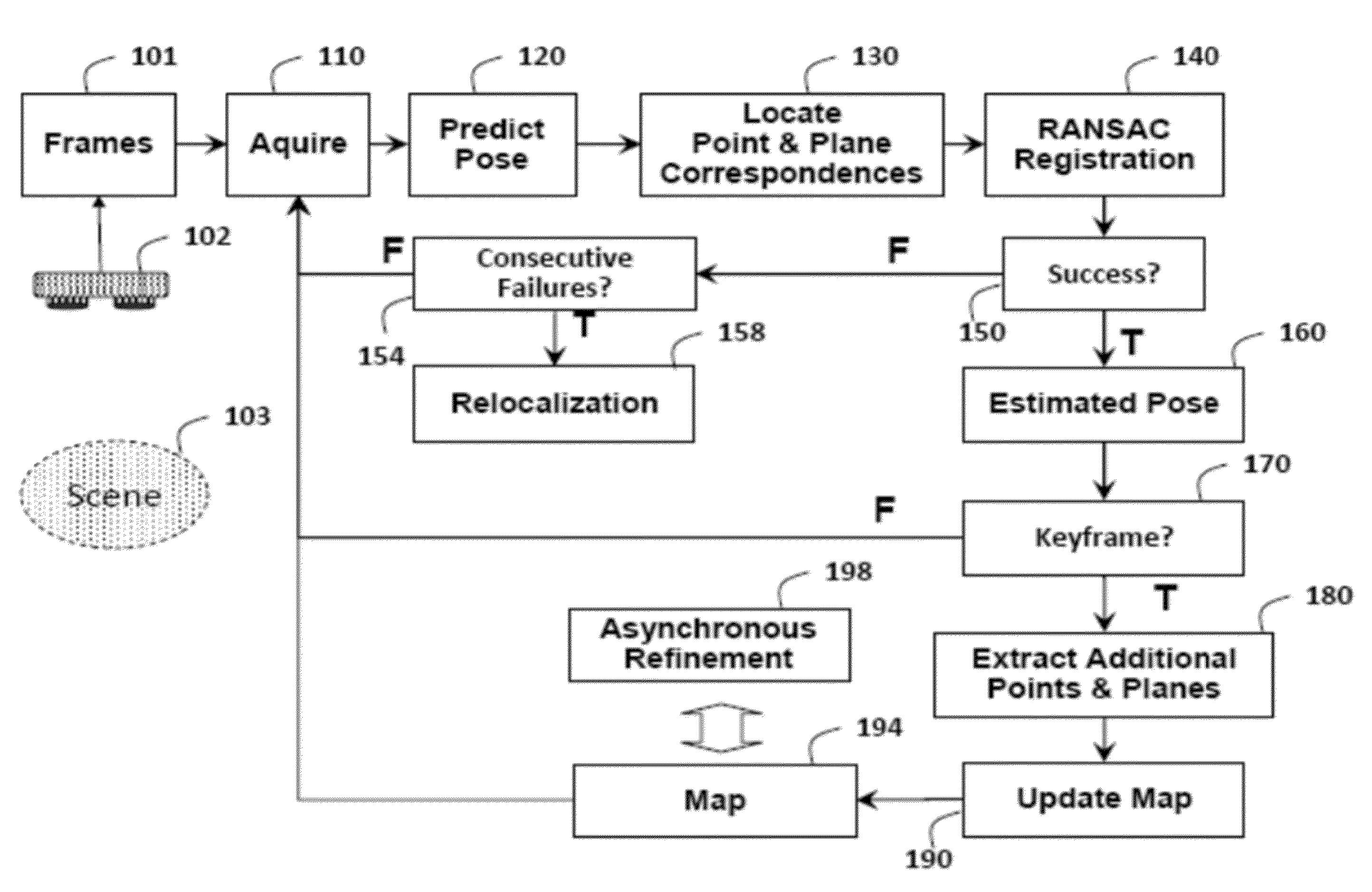
A method registers data using a set of primitives including points and planes. First, the method selects a first set of primitives from the data in a first coordinate system, wherein the first set of primitives includes at least three primitives and at least one plane. A transformation is predicted from the first coordinate system to a second coordinate system. The first set of primitives is transformed to the second coordinate system using the transformation. A second set of primitives is determined according to the first set of primitives transformed to the second coordinate system. Then, the second coordinate system is registered with the first coordinate system using the first set of primitives in the first coordinate system and the second set of primitives in the second coordinate system. The registration can he used to track a pose of a camera acquiring the data.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
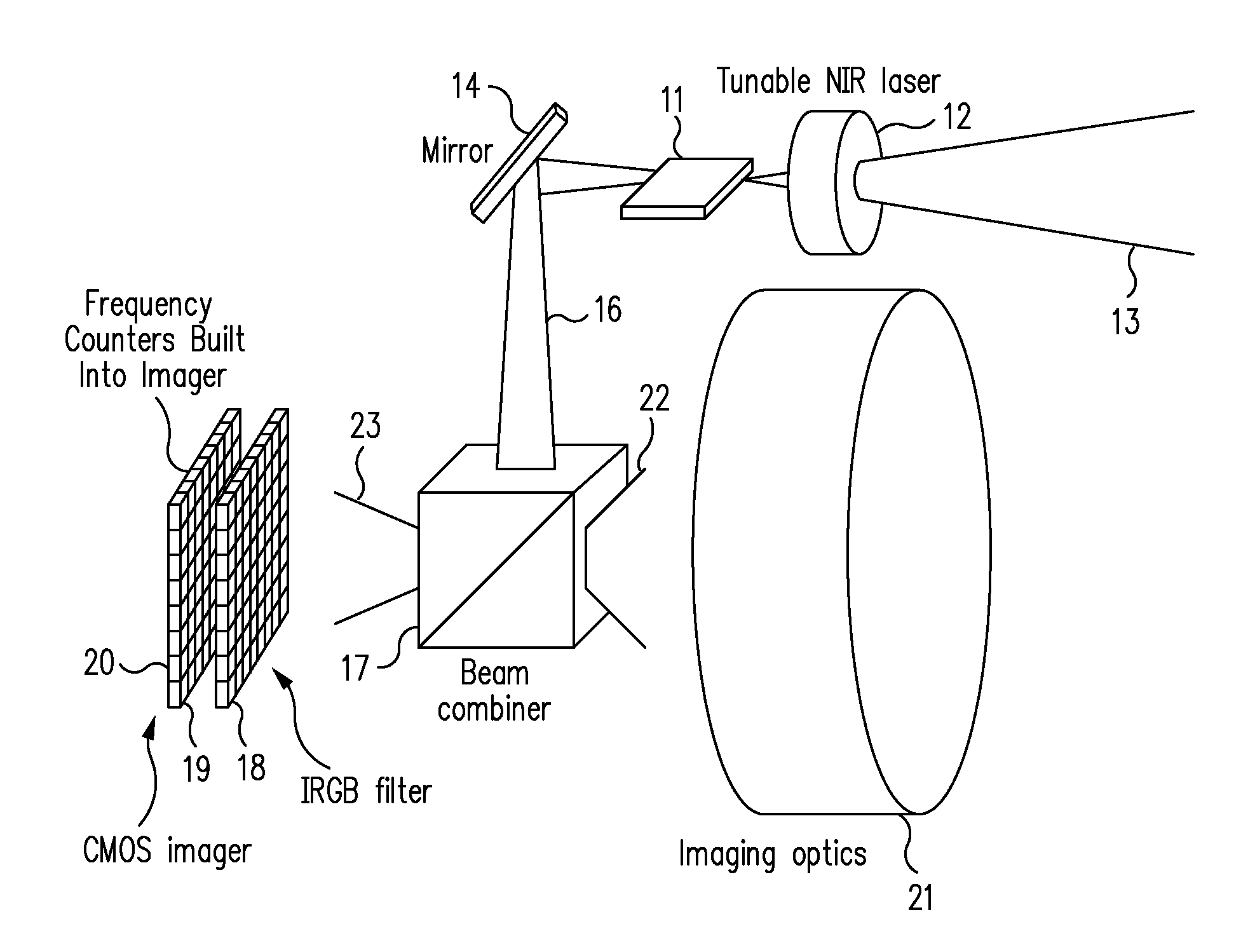
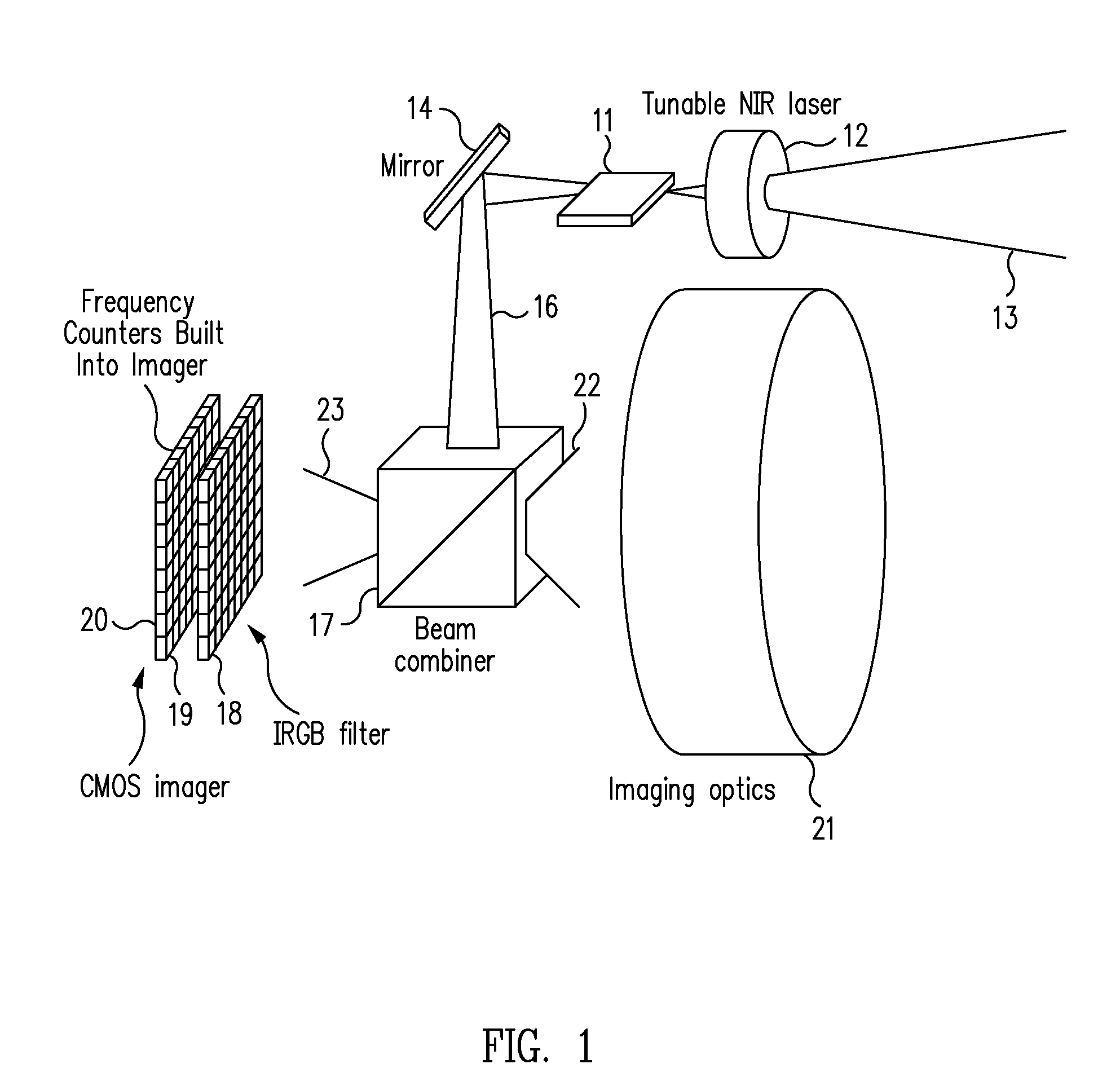
3D camera using flash with structured light
An imaging device capable of capturing depth information or surface profiles of objects is disclosed herein. The imaging device uses an enclosed flashing unit to project a sequence of structured light patterns onto an object and captures the light patterns reflected from the surfaces of the object by using an image sensor that is enclosed in the imaging device. The imaging device is capable of capturing an image of an object such that the captured image is comprised of one or more color components of a two-dimensional image of the object and a depth component that specifies the depth information of the object.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
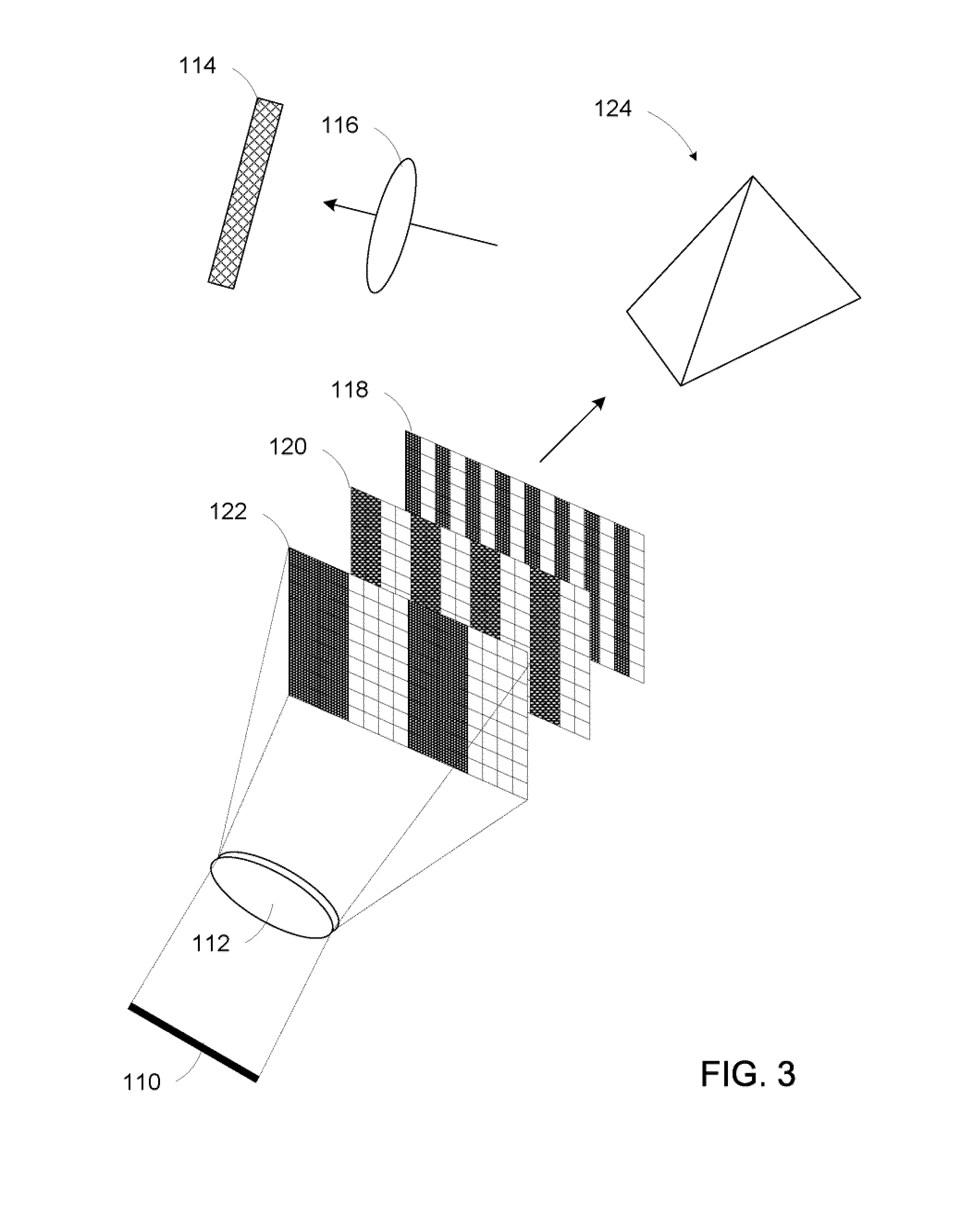
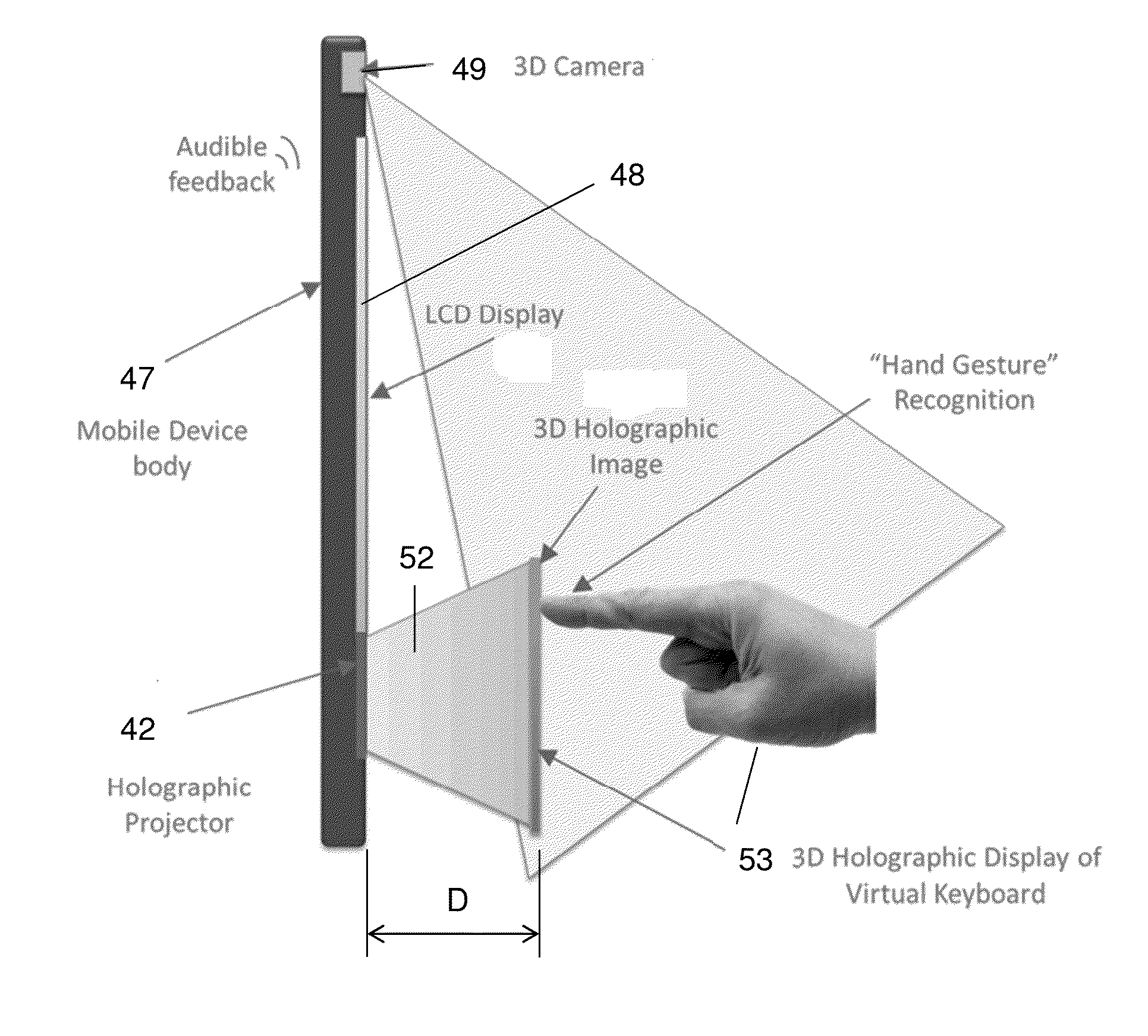
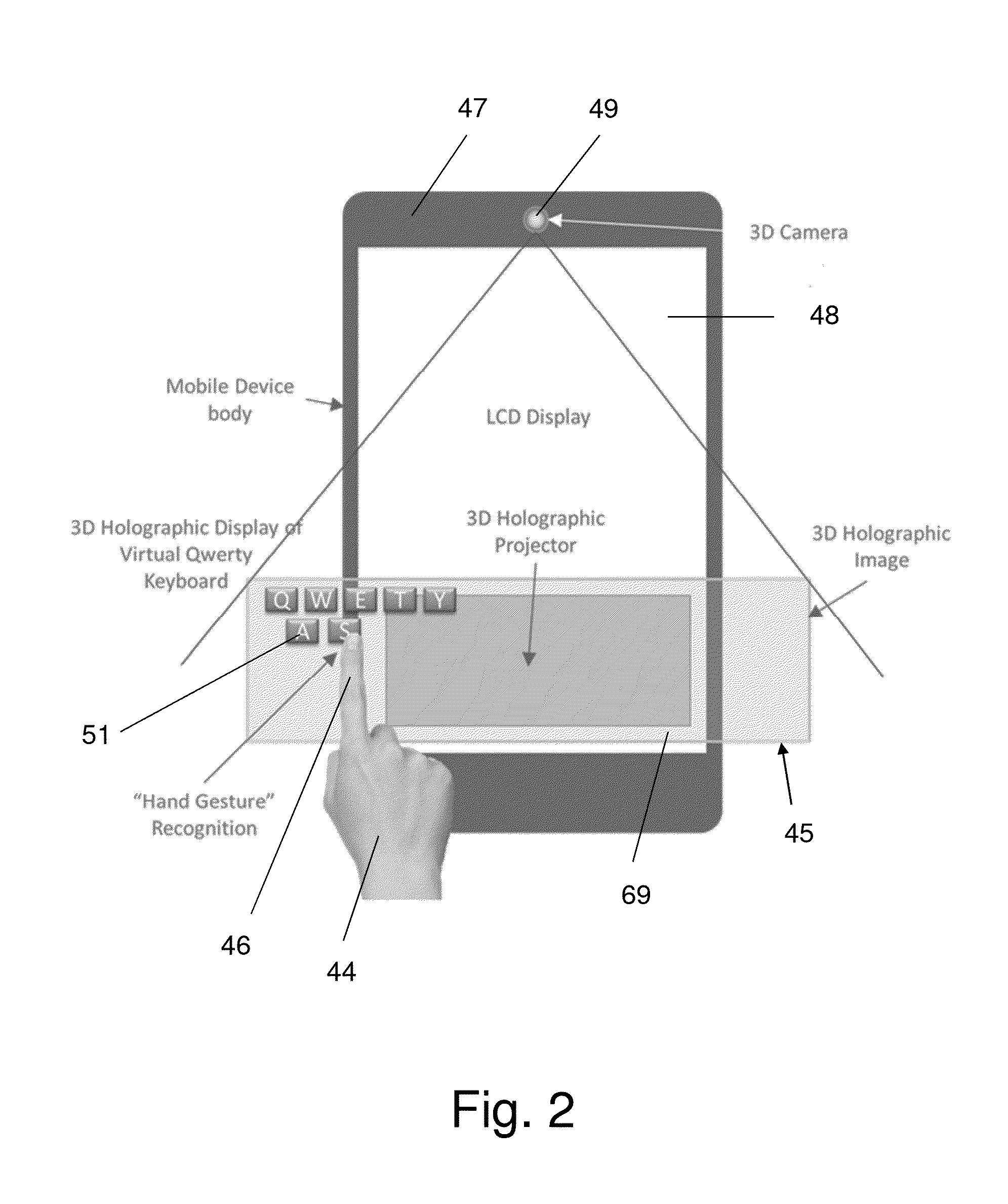
System for generating and controlling a variably displayable mobile device keypad/virtual keyboard
A system for generating and controlling a variably displayable virtual keypad includes a mobile device with a screen on which is displayable selected content, holographic projectors, from image generating data retrievable from a memory, a virtual keypad appearing to be free-floating and suspended in mid-air. An input identification unit identifies a virtual key pressing operation performed in conjunction with the generated virtual keypad, determining which key of the virtual keypad has been virtually pressed, and transmitting an input command in response to the virtual key pressing operation by which the displayed content is modifiable. The input identification unit includes a 3D camera capturing gestures of a user hand and transmitting a signal indicative of gesture related data to a microprocessor for translating the gesture related data into the input command by instructions stored in the memory device. The microprocessor generates feedback in response to the virtual key pressing operation to indicate which key has been virtually pressed and to modify a visualization parameter of the generated virtual keypad. The feedback may be in the form of an ultrasonic beam propagatable to the initiating finger.
Owner:BEN MEIR YORAM
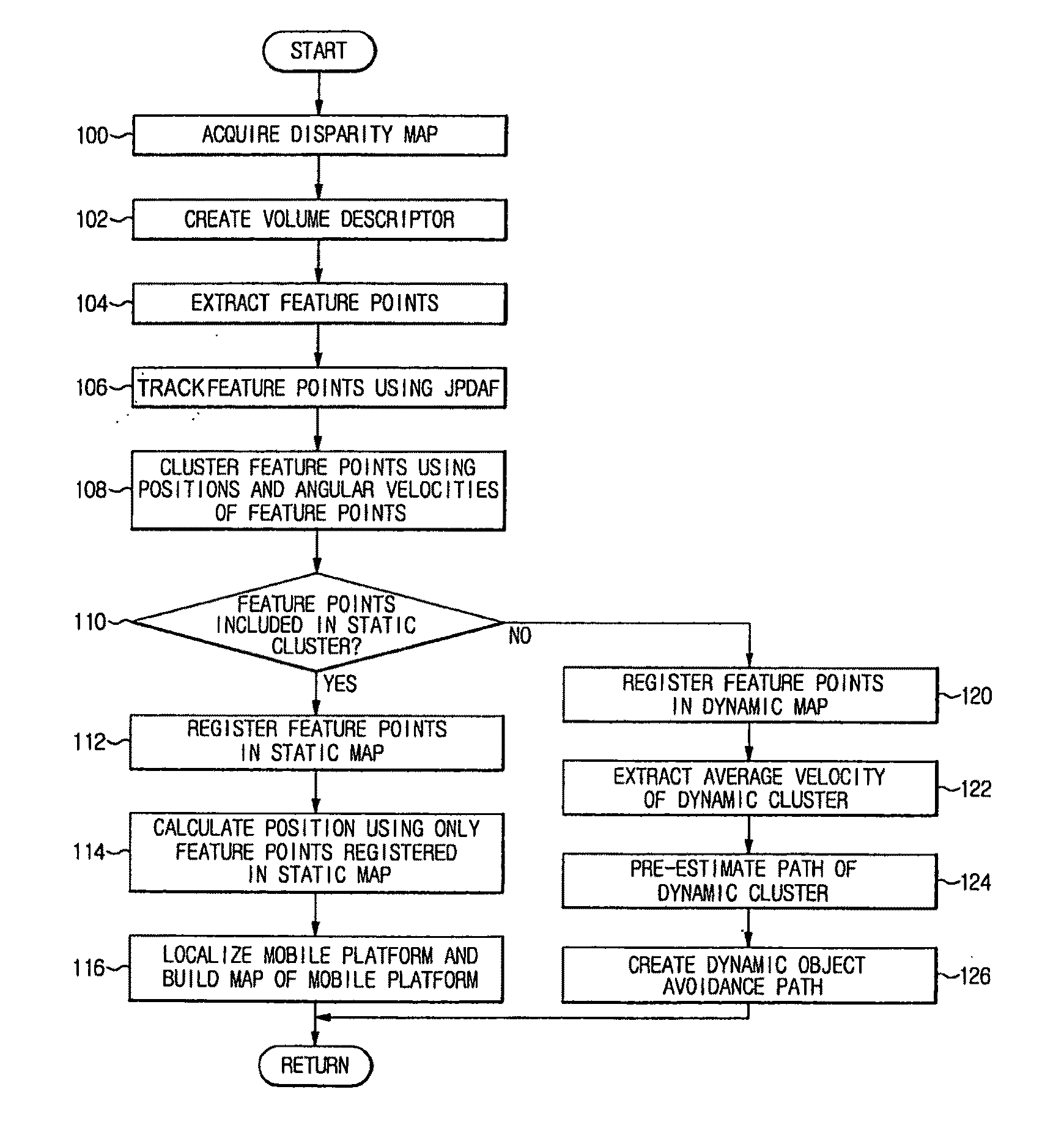
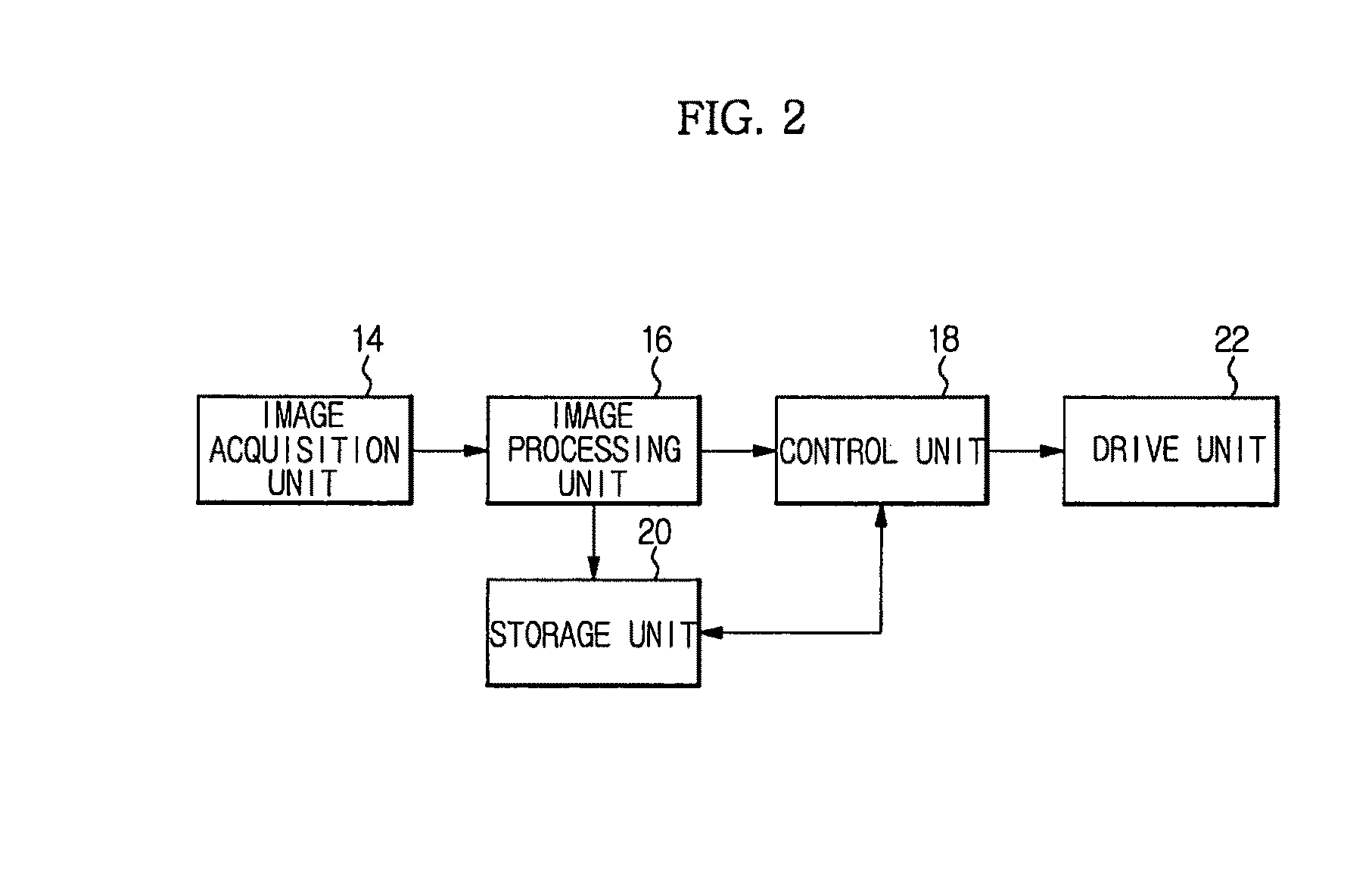
Method of building map of mobile platform in dynamic environment
Disclosed herein is a method of building a map of a mobile platform moving in a dynamic environment and detecting an object using a 3D camera sensor, e.g., an IR TOF camera sensor, for localization. A localization technology to separate and map a dynamic object and a static object is applied to a mobile platform, such as an unmanned vehicle or a mobile robot. Consequently, the present method is capable of accurately building map information based on the static object in a dynamic environment having a large number of dynamic objects and achieving a dynamic object avoidance or chasing function using position information acquired to build the map.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Automatic scene modeling for the 3D camera and 3D video
InactiveCN101208723AReduce computational intensityTexture Mapping EasyTelevision system detailsImage enhancementMediaFLOTelevision set
Single-camera image processing methods are disclosed for 3D navigation within ordinary moving video. Along with color and brightness, XYZ coordinates can be defined for every pixel. The resulting geometric models can be used to obtain measurements from digital images, as an alternative to on-site surveying and equipment such as laser range-finders. Motion parallax is used to separate foreground objects from the background. This provides a convenient method for placing video elements within different backgrounds, for product placement, and for merging video elements with computer-aided design (CAD) models and point clouds from other sources. If home users can save video fly-throughs or specific 3D elements from video, this method provides an opportunity for proactive, branded media sharing. When this image processing is used with a videoconferencing camera, the user's movements can automatically control the viewpoint, creating 3D hologram effects on ordinary televisions and computer screens.
Owner:克雷格・萨默斯
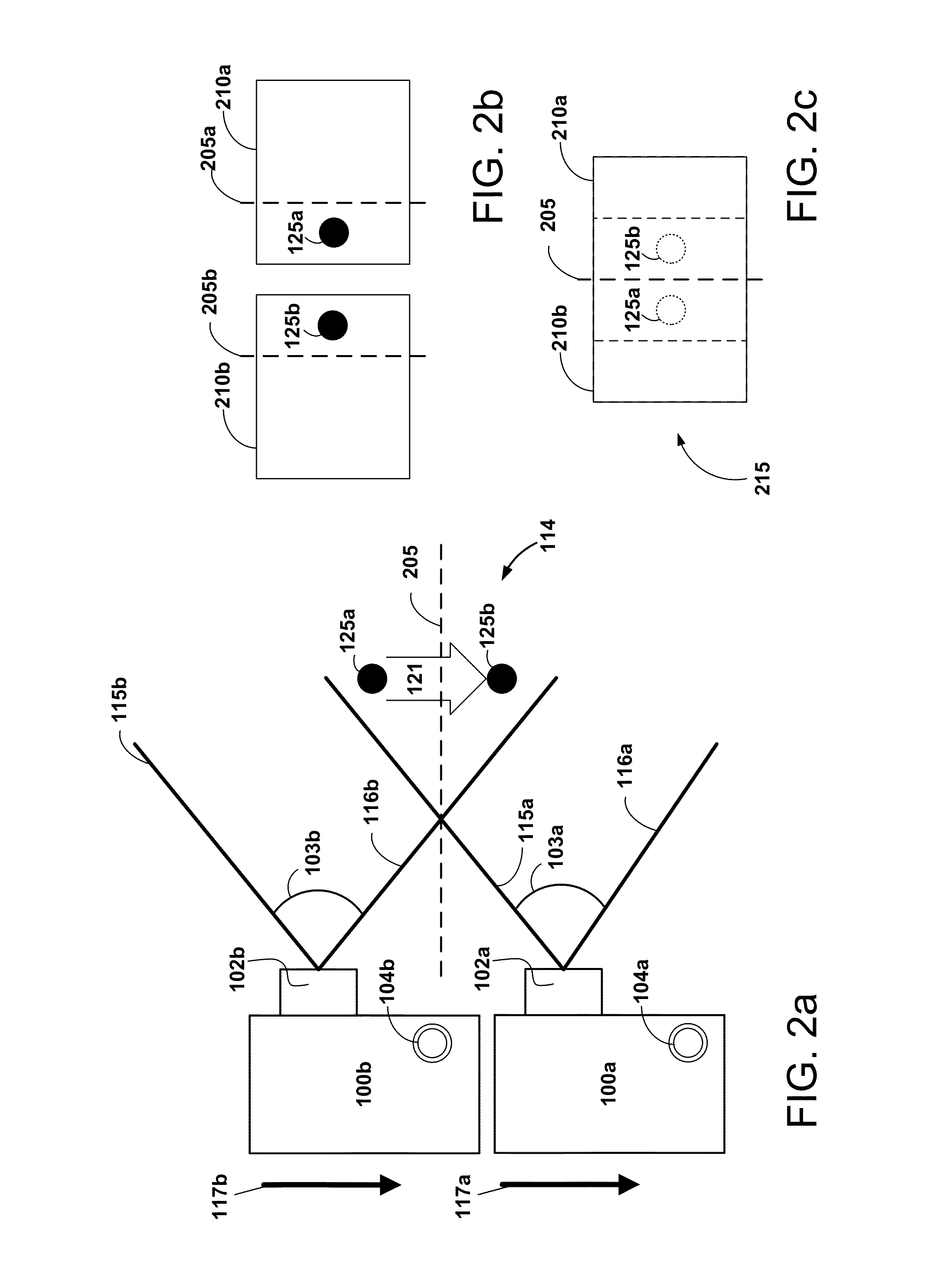
High-speed railroad inspection using coordinated 3D cameras
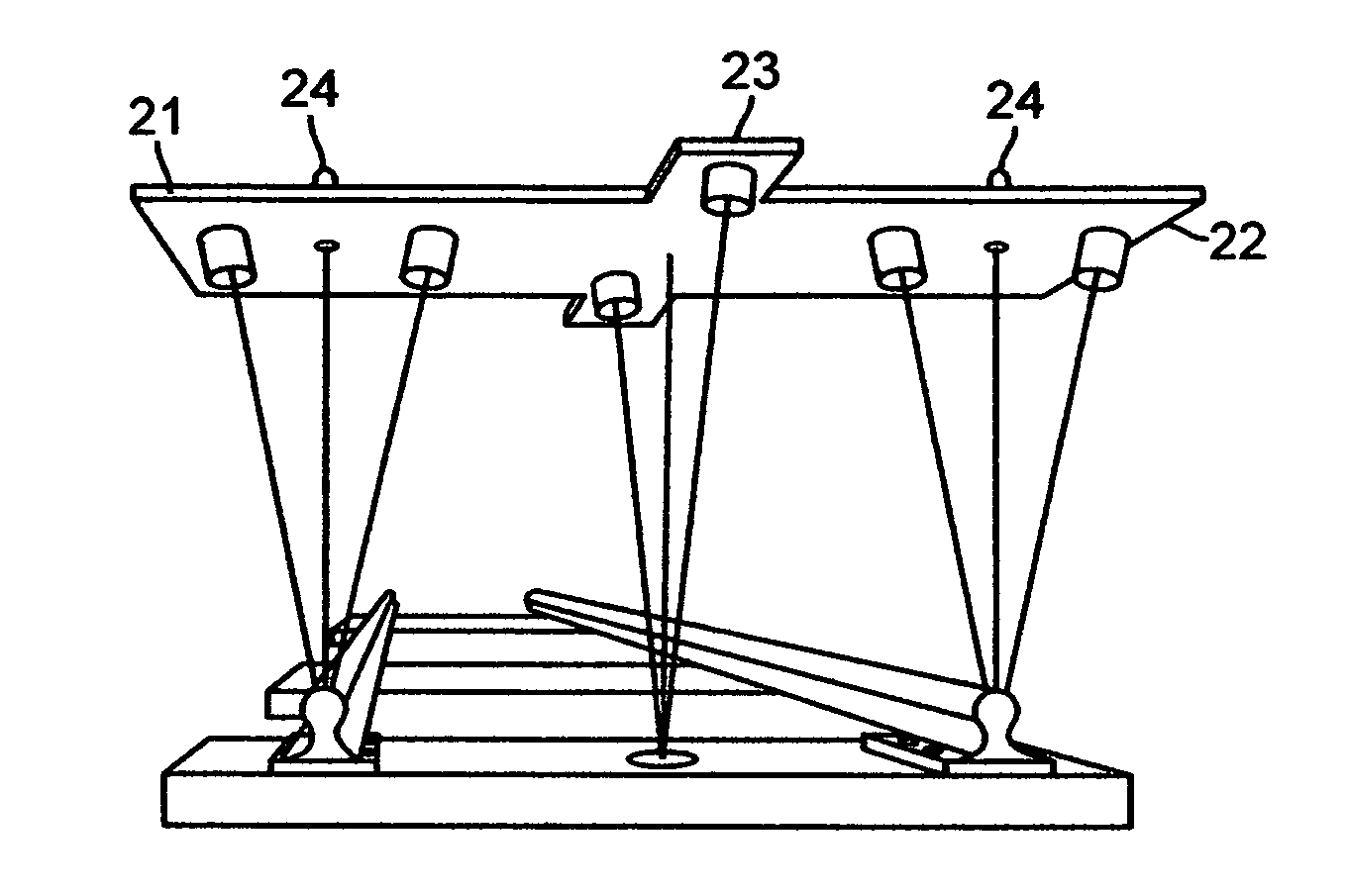
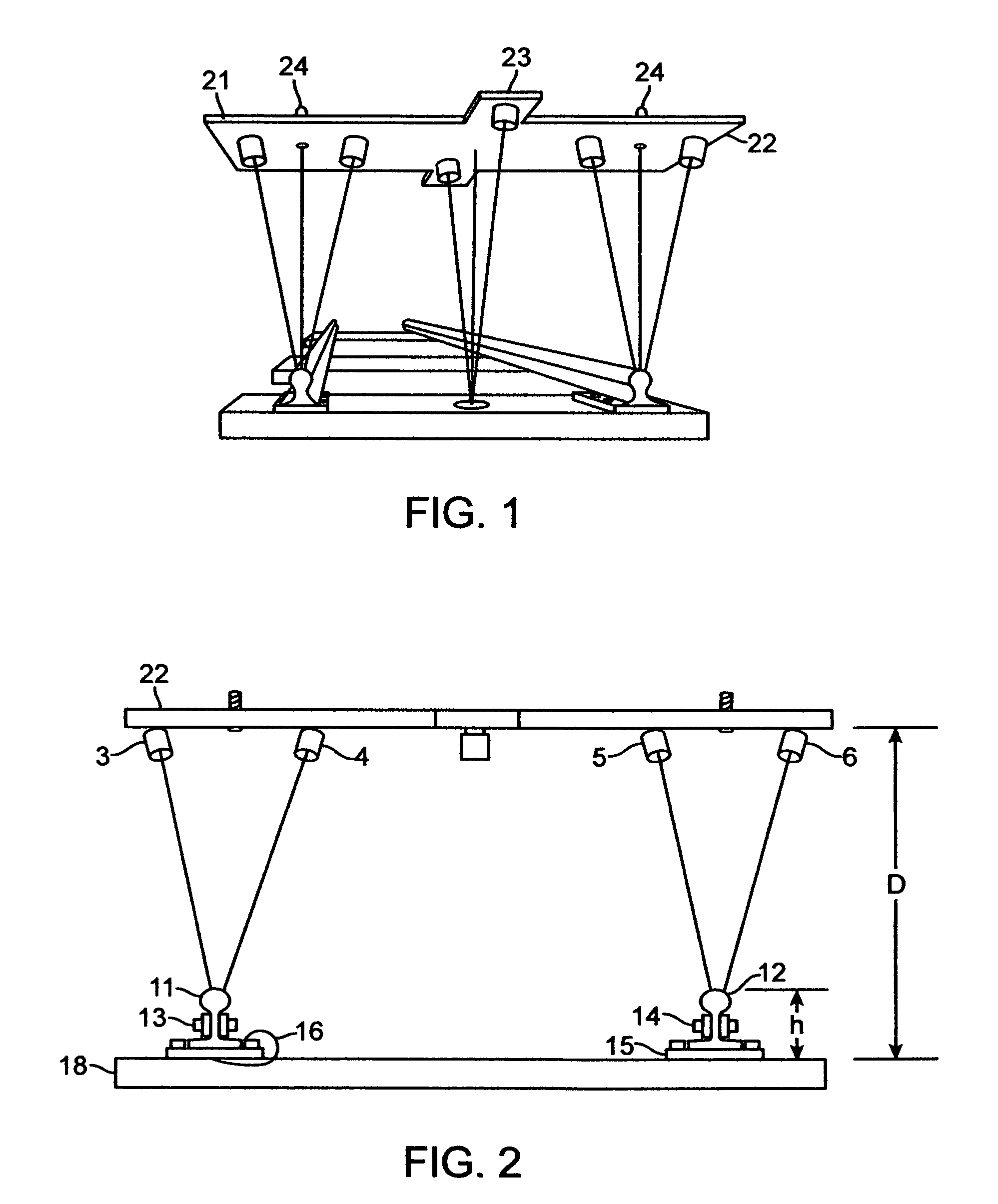
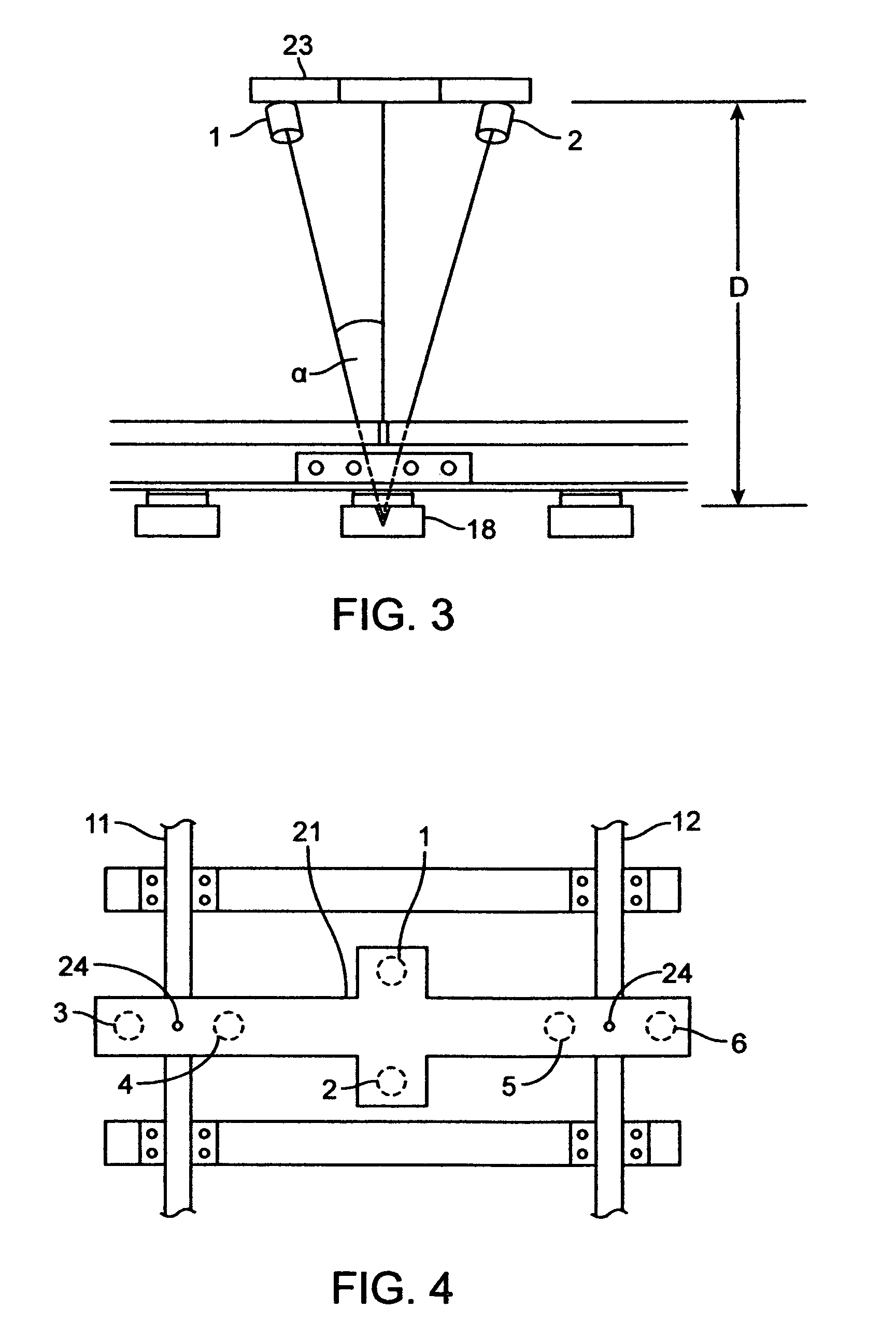
To emulate the 3D visual acuity of an individual track-walker, matched pairs of cameras (which simulate our human eyes) are mounted on a moving vehicle above the tracks. The cameras are mounted both transversely and longitudinally, to create 3D images in two orthogonal orientations, which helps to eliminate visual voids. The location and orientation of each pair of cameras is determined by its specific task, in the present case: (i) to examine each left or right rail for anomalies (two pairs), and (ii) to examine every tie for damage (at least one pair). The camera pairs enable measurements such as defect depth and track width variations. The images are compressed in real time for local storage or high-speed transmission for remote display. The basic arrangement of cameras can be amplified or modified as necessary to circumstances.
Owner:PRINCE JOHN H
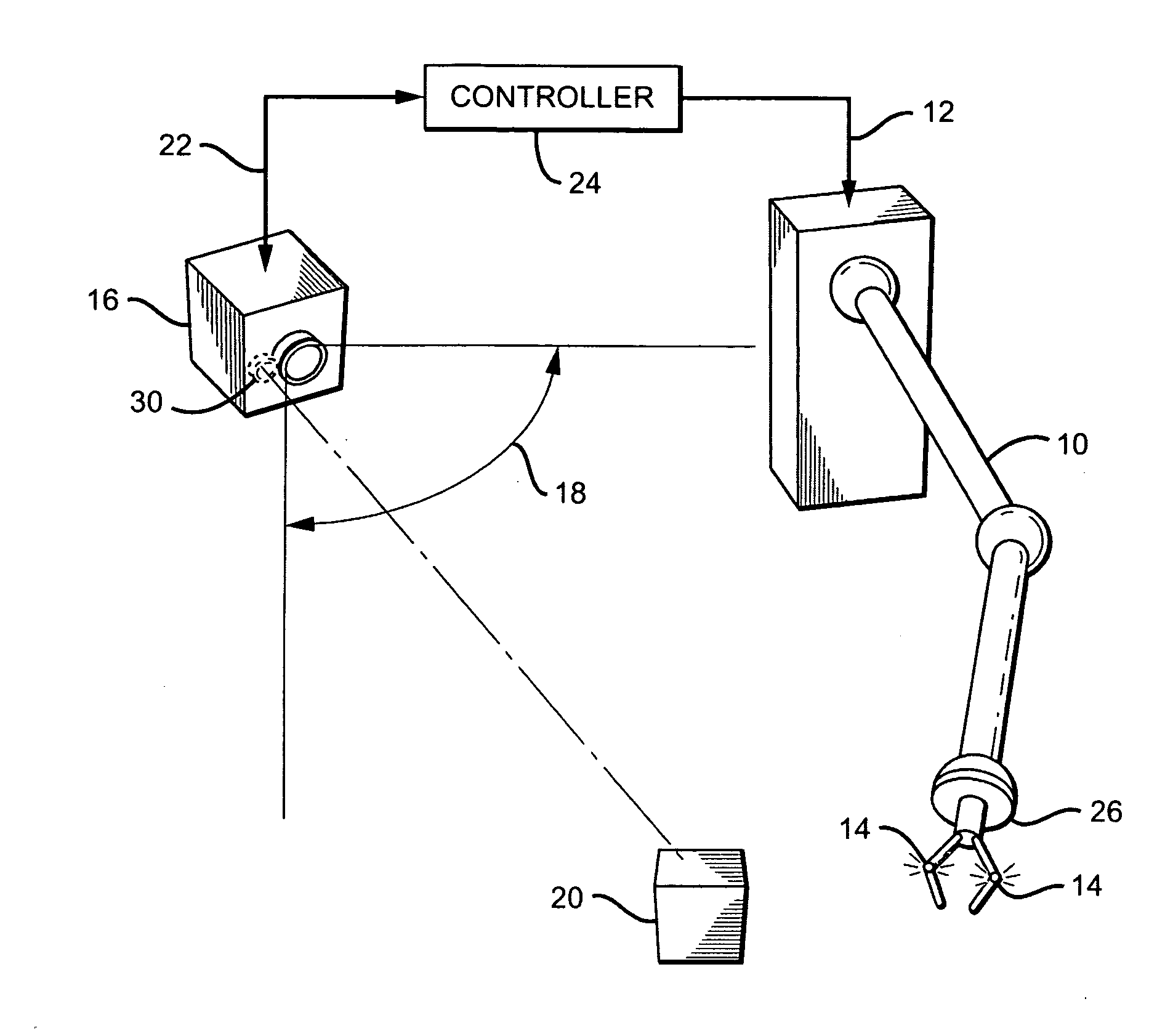
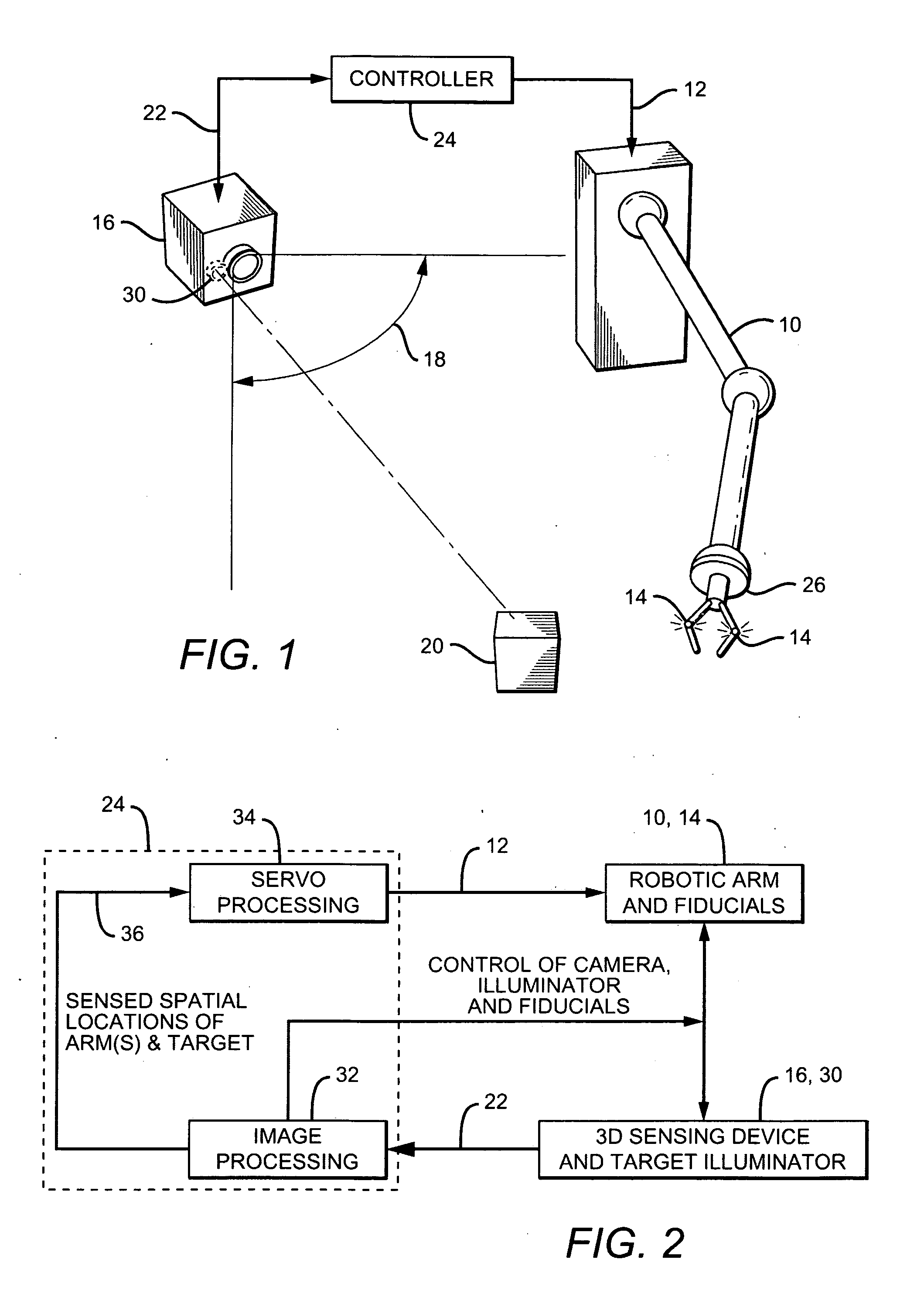
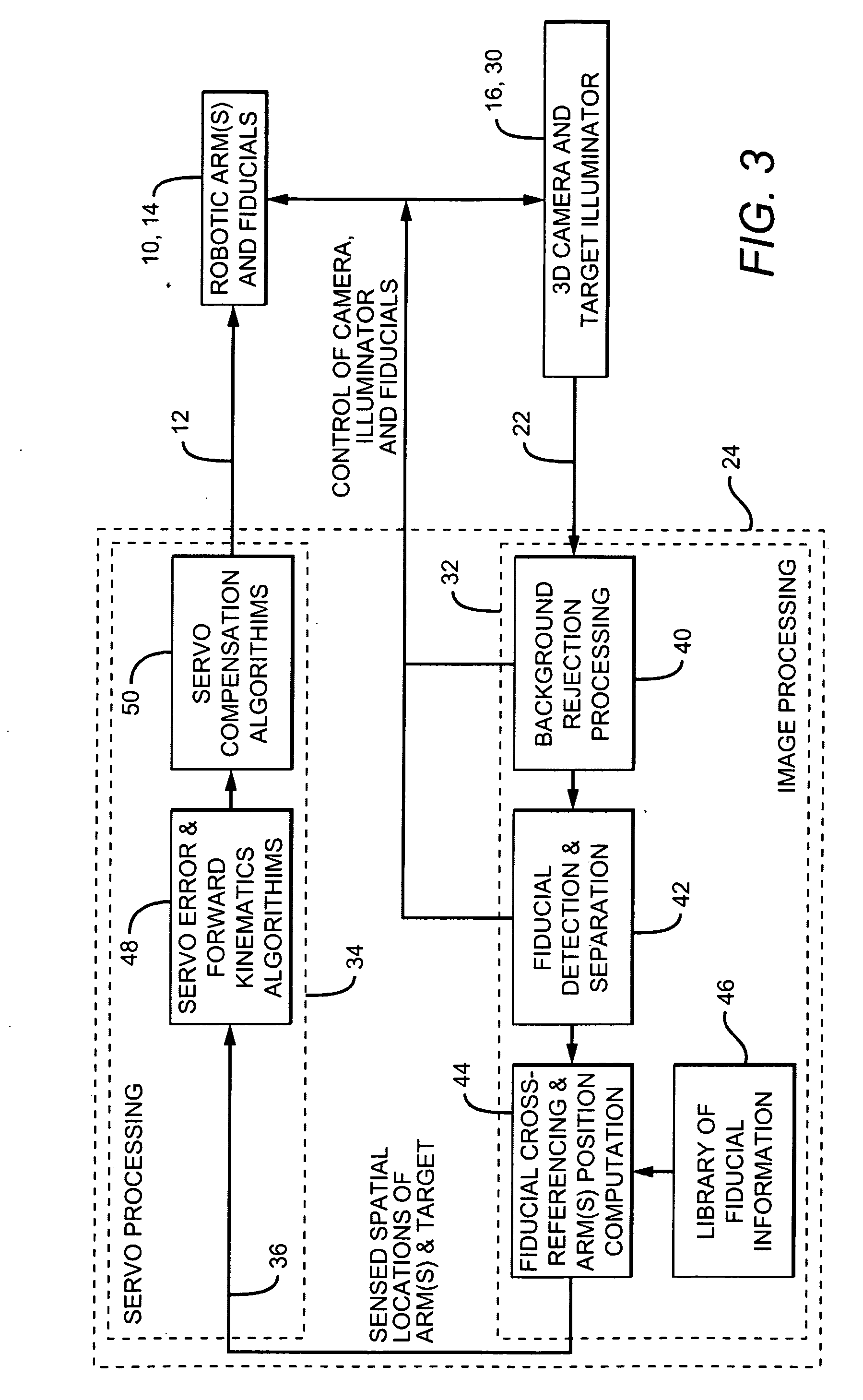
Robotic arm and control system
ActiveUS20090055024A1Efficient and accurate effector positioningEfficient and accurate and movementProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectrotherapyRobotic armControl system
A robotic arm and control system includes a robotic arm which moves in response to one or more command signals. One or more “active” fiducials are located on the arm, each of which emits its own light. A 3D camera having an associated field-of-view is positioned such that at least one fiducial and a target object to be manipulated are in the FOV. To determine their spatial positions, the arm fiducials are activated and the target object is preferably illuminated with a scanning laser; the camera produces output signals which vary with the spatial locations of the fiducials and target object. A controller receives the output signals and uses the spatial position information as feedback to continuously guide the arm towards the target object. Multiple active fiducials may be employed, each having respective characteristics with which they can be differentiated.
Owner:ELITE ENG CORP
Rolling shutter synchronization
A camera system configuration generates 2D or 3D images capable of being stitched together to create panoramic images. The configuration detects a communication coupling of at least two cameras for capturing a sequence of images. The cameras themselves are configured such that their rolling shutters mitigate field of view artifacts from adjacent cameras (2D panoramas) and adjacent 3D camera pairs (3D panoramas) by allowing for the substantially temporally-aligned capture of light in overlap regions between adjacent cameras.
Owner:GOPRO
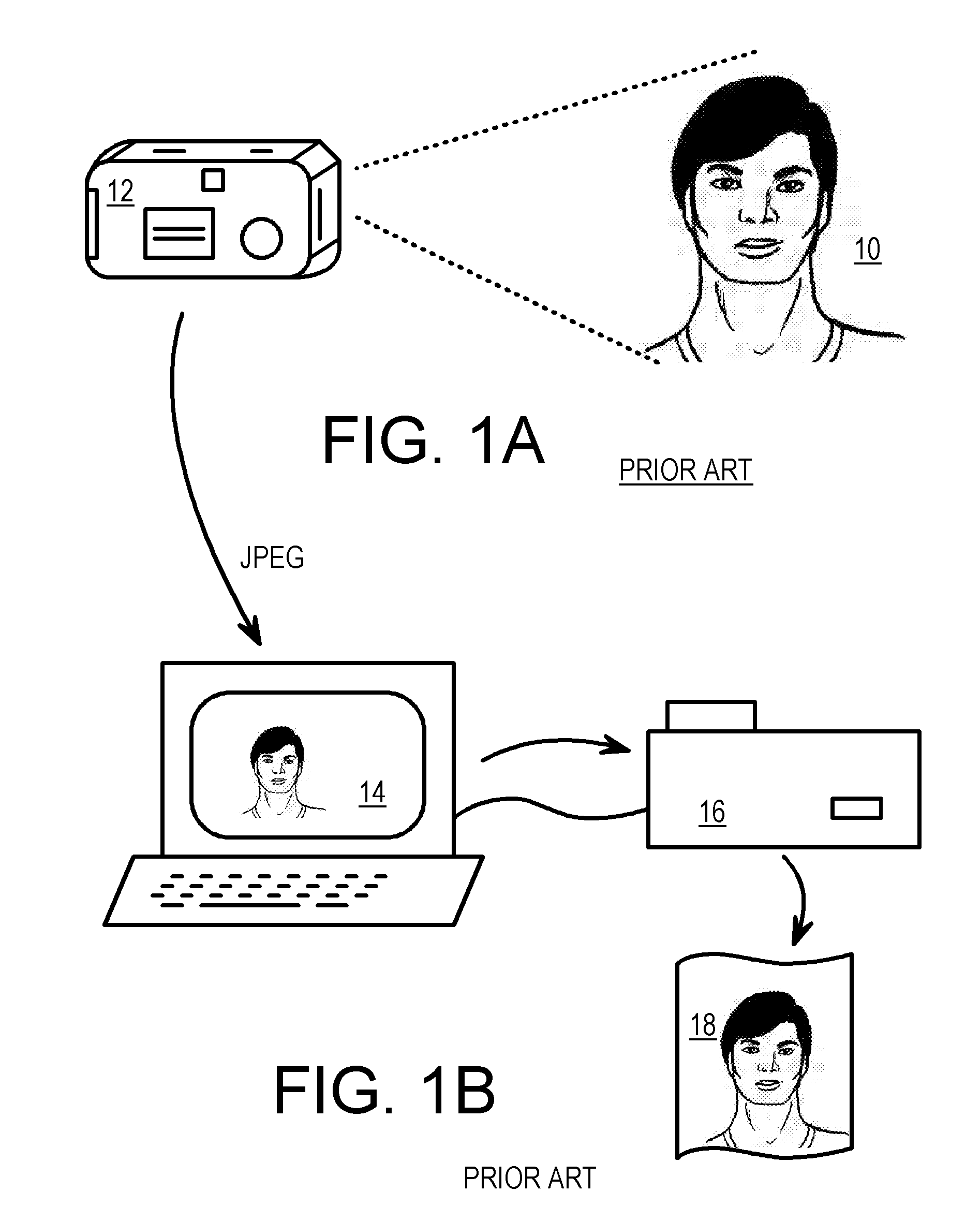
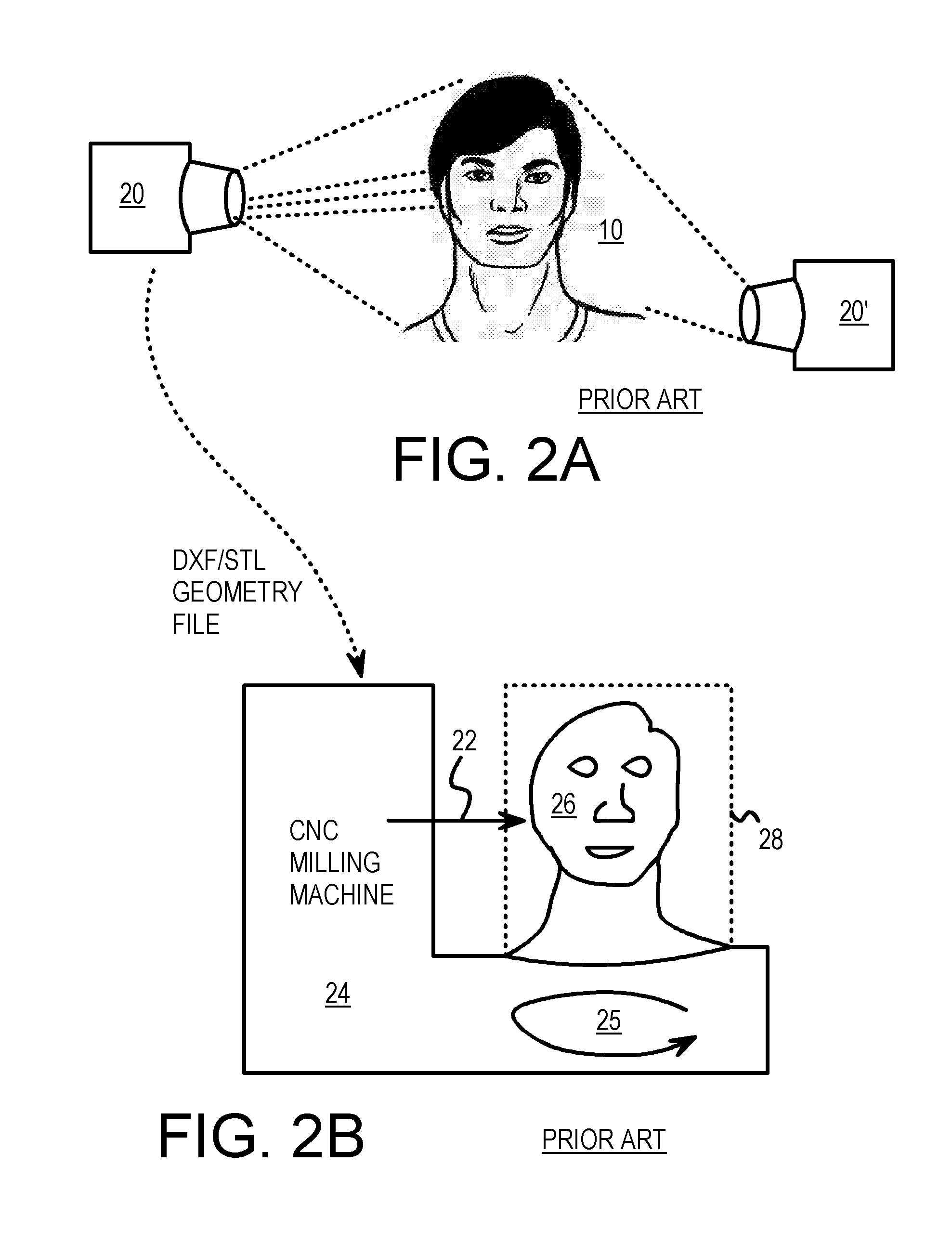
Custom 3-D Milled Object with Vacuum-Molded 2-D Printout Created from a 3-D Camera
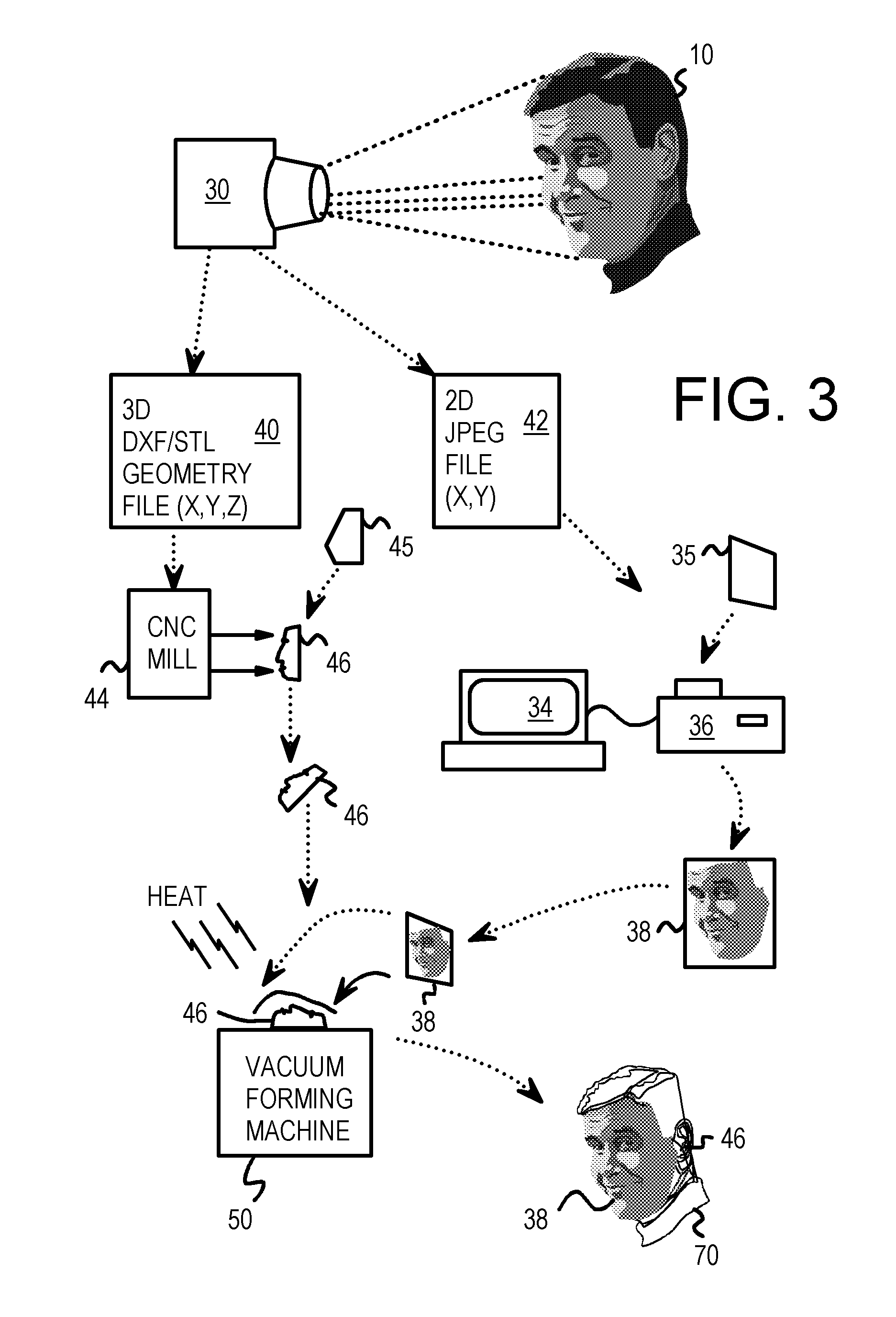
A 3D copy of a 3D subject is made by combining a 3D custom milled shape and a 2D printed 2D image sheet molded to the contours of the 3D custom milled shape. A 3D camera captures 3D details of the 3D subject and also captures a multi-color 2D image of the 3D subject. The 3D camera outputs a geometry file to a CNC milling machine that cuts a milling blank to make a custom milled shape. The 3D camera also outputs a 2D image file to a personal computer that prints the 2D image onto a plastic sheet. The custom milled shape is placed as a mold on a vacuum-forming machine. The plastic sheet is aligned to the custom milled shape and heat and vacuum pressure applied. The 2D image is molded into the 3D shape of the custom milled shape.
Owner:TSENG TAN
System for evaluating an image
In a system for evaluating an image, a processing device includes an input for receiving image data representing the image and another input for receiving distance information on a distance of an object relative to an image plane of the image. The distance information may be determined based on a three-dimensional image including depth information captured utilizing a 3D camera device. The processing device is configured for resampling at least a portion of the image data based both on the distance information and on a pre-determined reference distance to generate resampled image data, the portion of the image data to be resampled representing at least part of the object.
Owner:HARMAN BECKER AUTOMOTIVE SYST
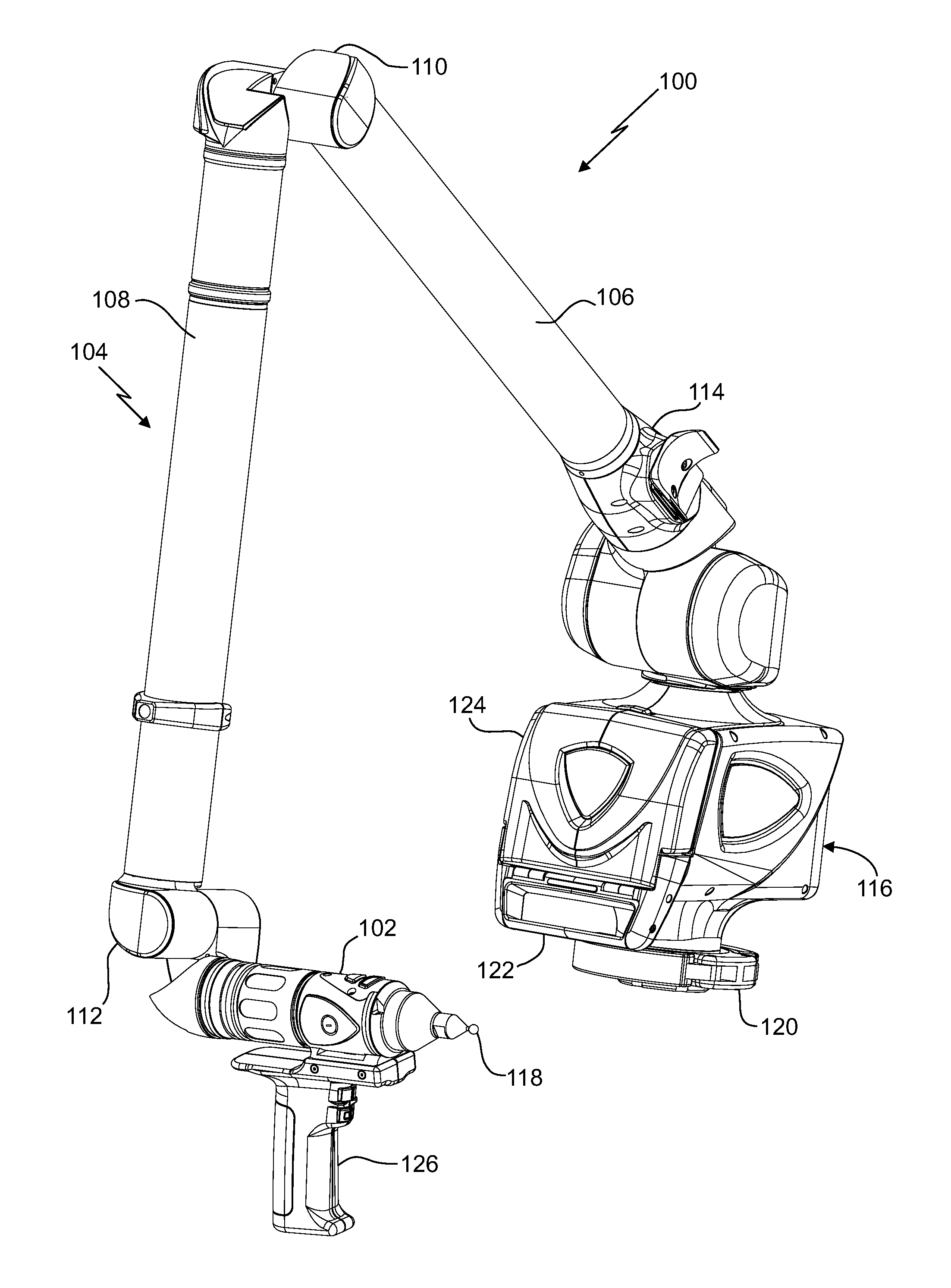
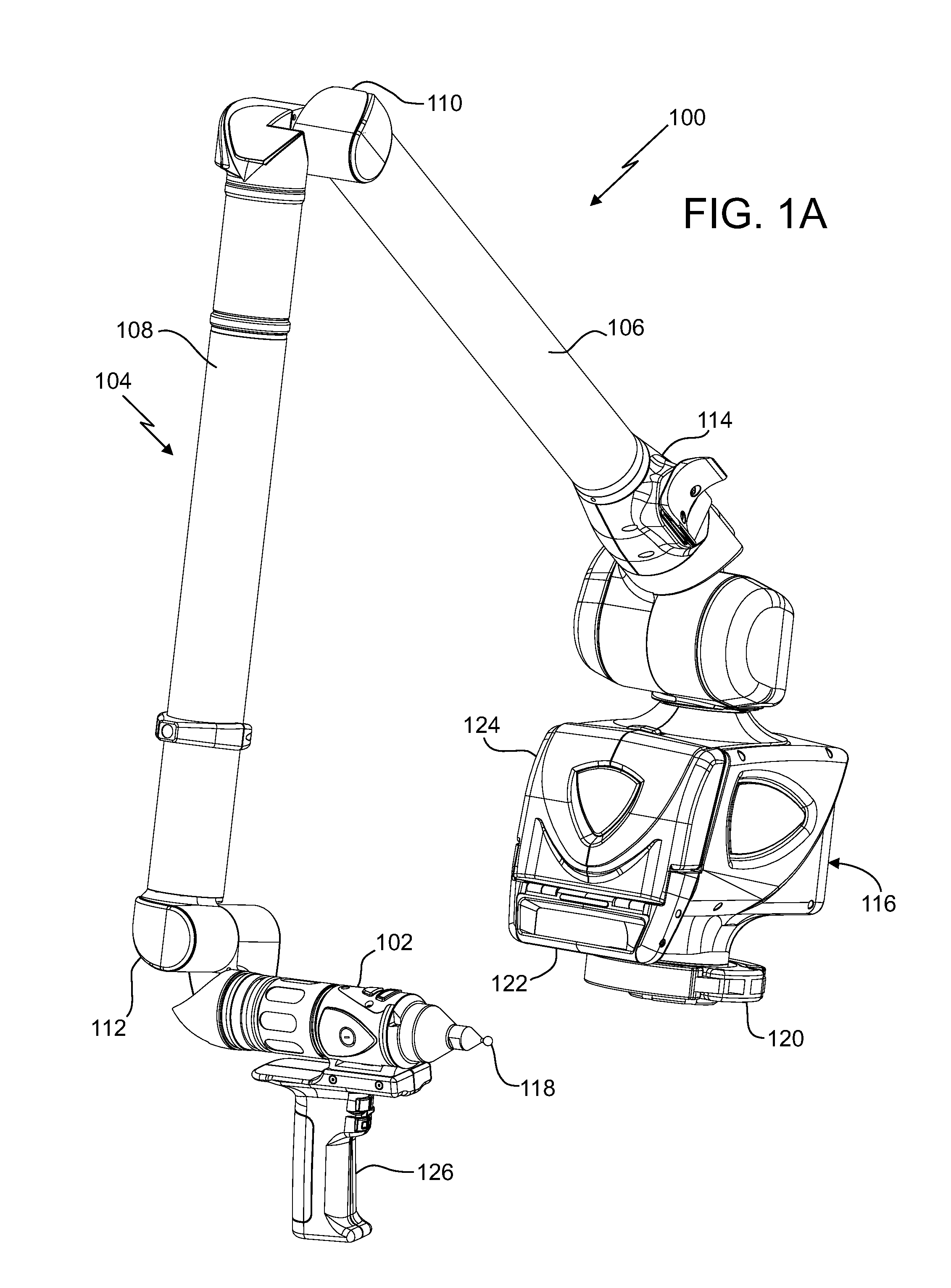
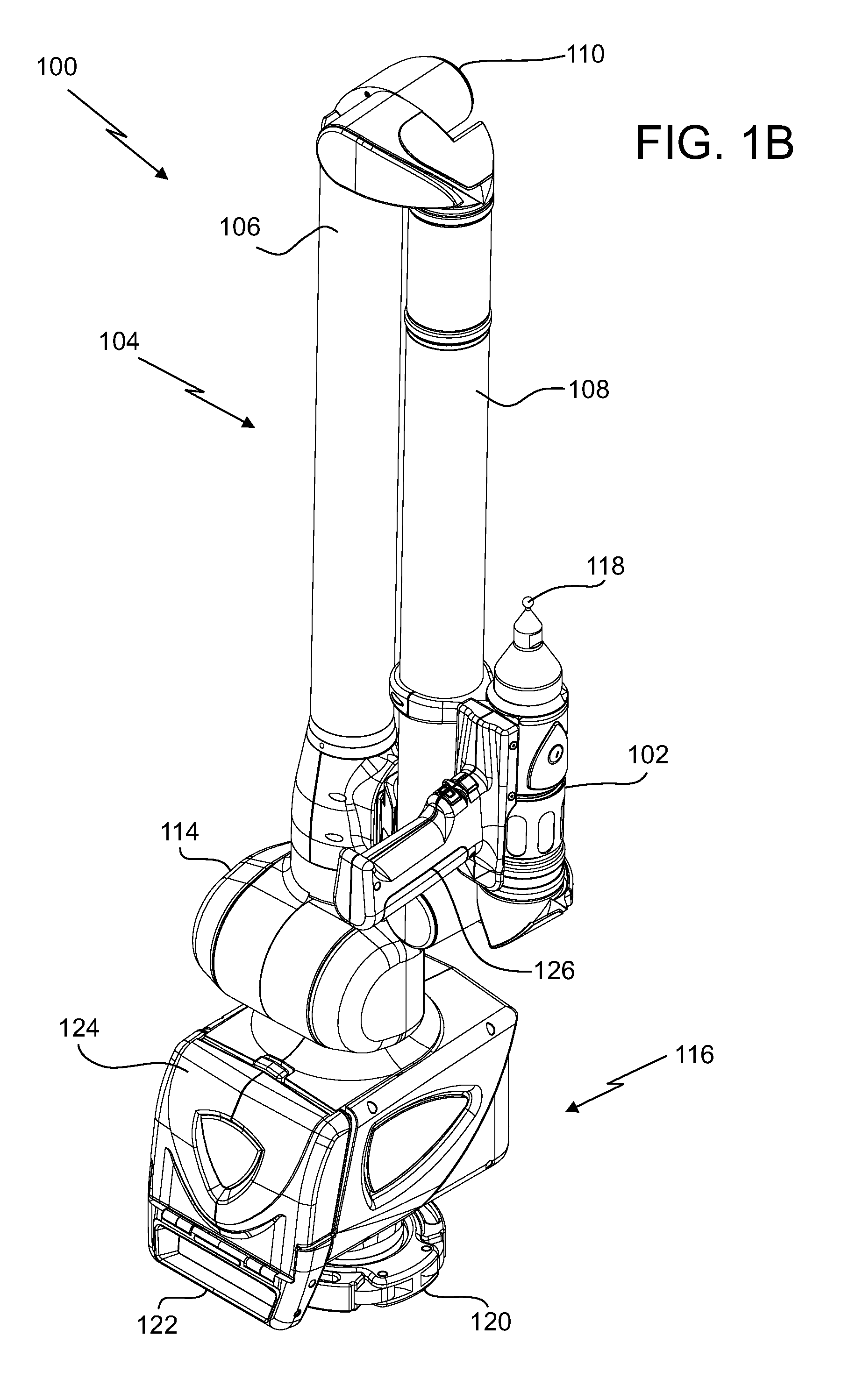
Coordinate measurement machine with distance meter and camera to determine dimensions within camera images
An articulated arm coordinate measurement machine (AACMM) that includes a noncontact 3D measurement device, position transducers, a camera, and a processor operable to project a spot of light to an object point, to measure first 3D coordinates of the object point based on readings of the noncontact 3D measurement device and the position transducers, to capture the spot of light with the camera in a camera image, and to attribute the first 3D coordinates to the spot of light in the camera image.
Owner:FARO TECH INC
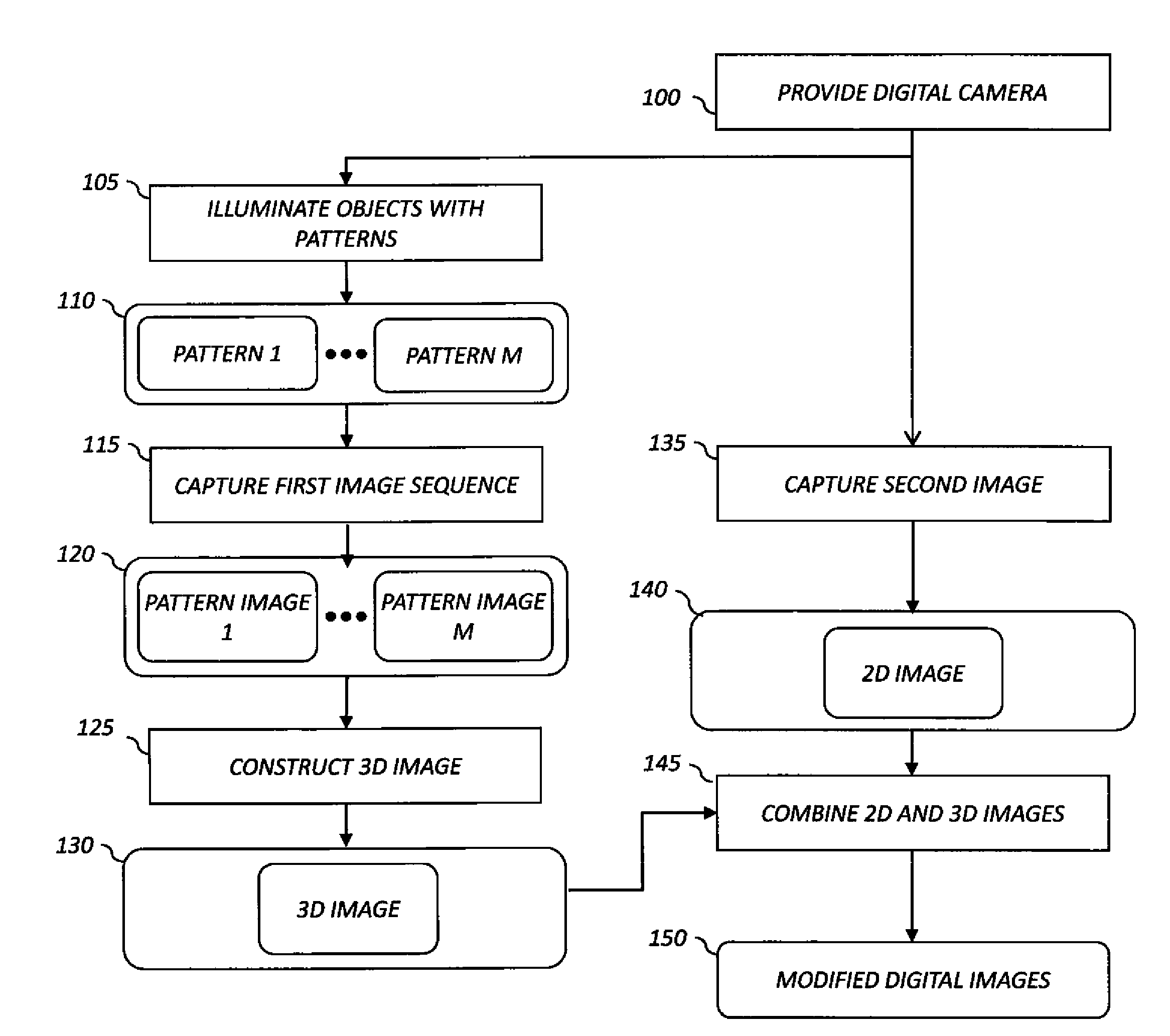
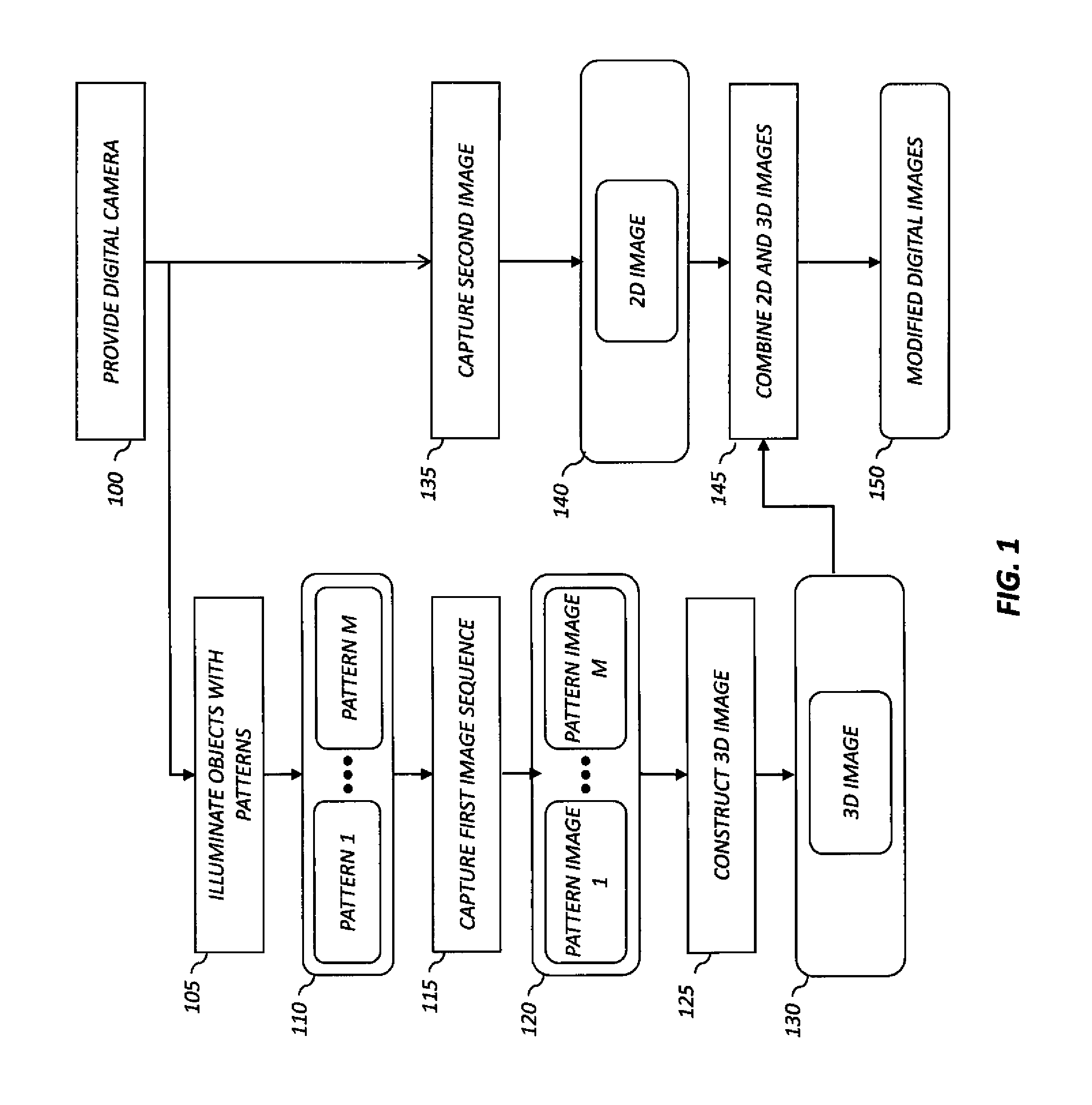
Digital 3D camera using periodic illumination
A method of operating a digital camera, includes providing a digital camera, the digital camera including a capture lens, an image sensor, a projector and a processor; using the projector to illuminate one or more objects with a sequence of patterns; and capturing a first sequence of digital images of the illuminated objects including the reflected patterns that have depth information. The method further includes using the processor to analyze the first sequence of digital images including the depth information to construct a second, 3D digital image of the objects; capturing a second 2D digital image of the objects and the remainder of the scene without the reflected patterns, and using the processor to combine the 2D and 3D digital images to produce a modified digital image of the illuminated objects and the remainder of the scene.
Owner:KODAK ALARIS INC
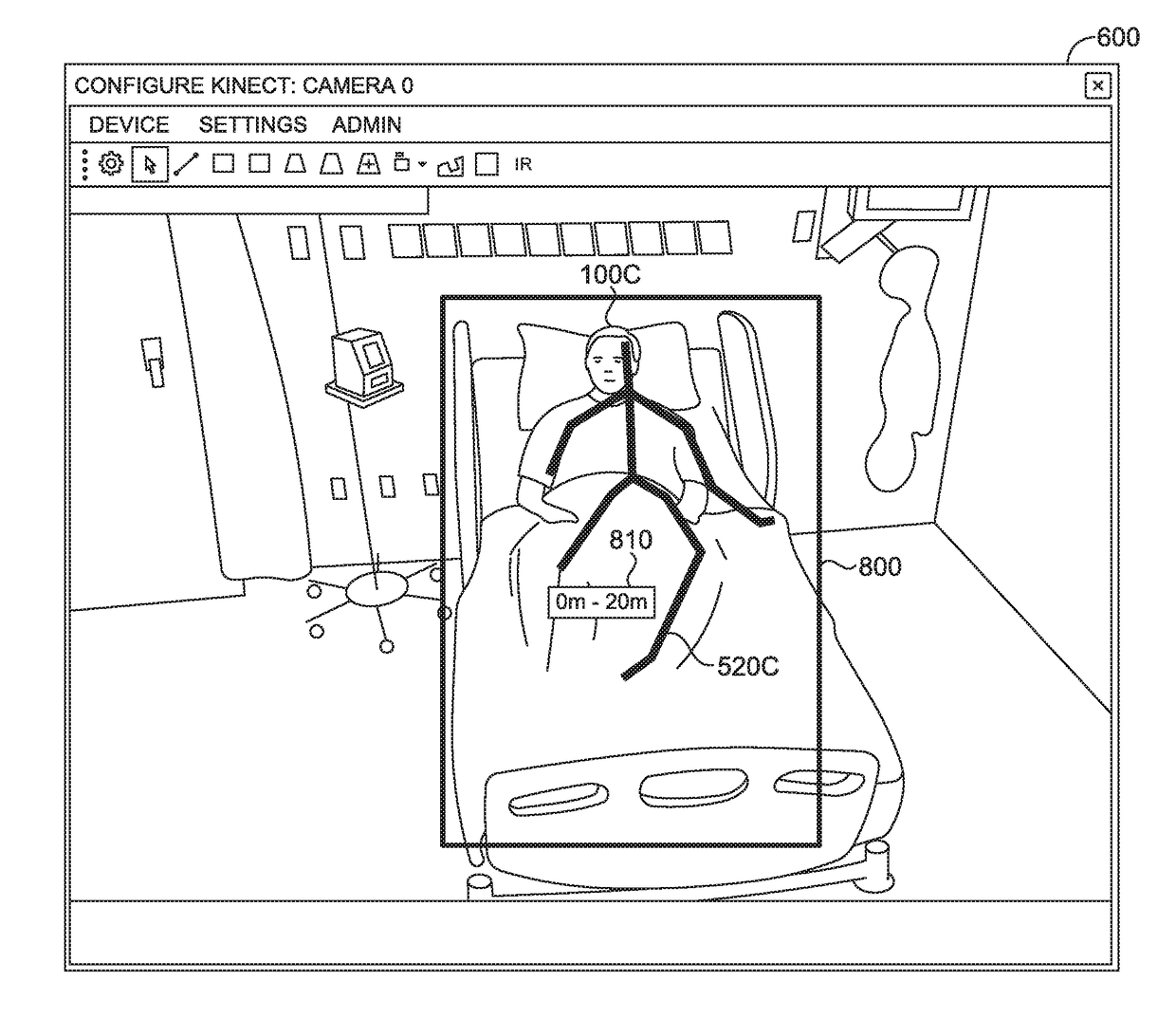
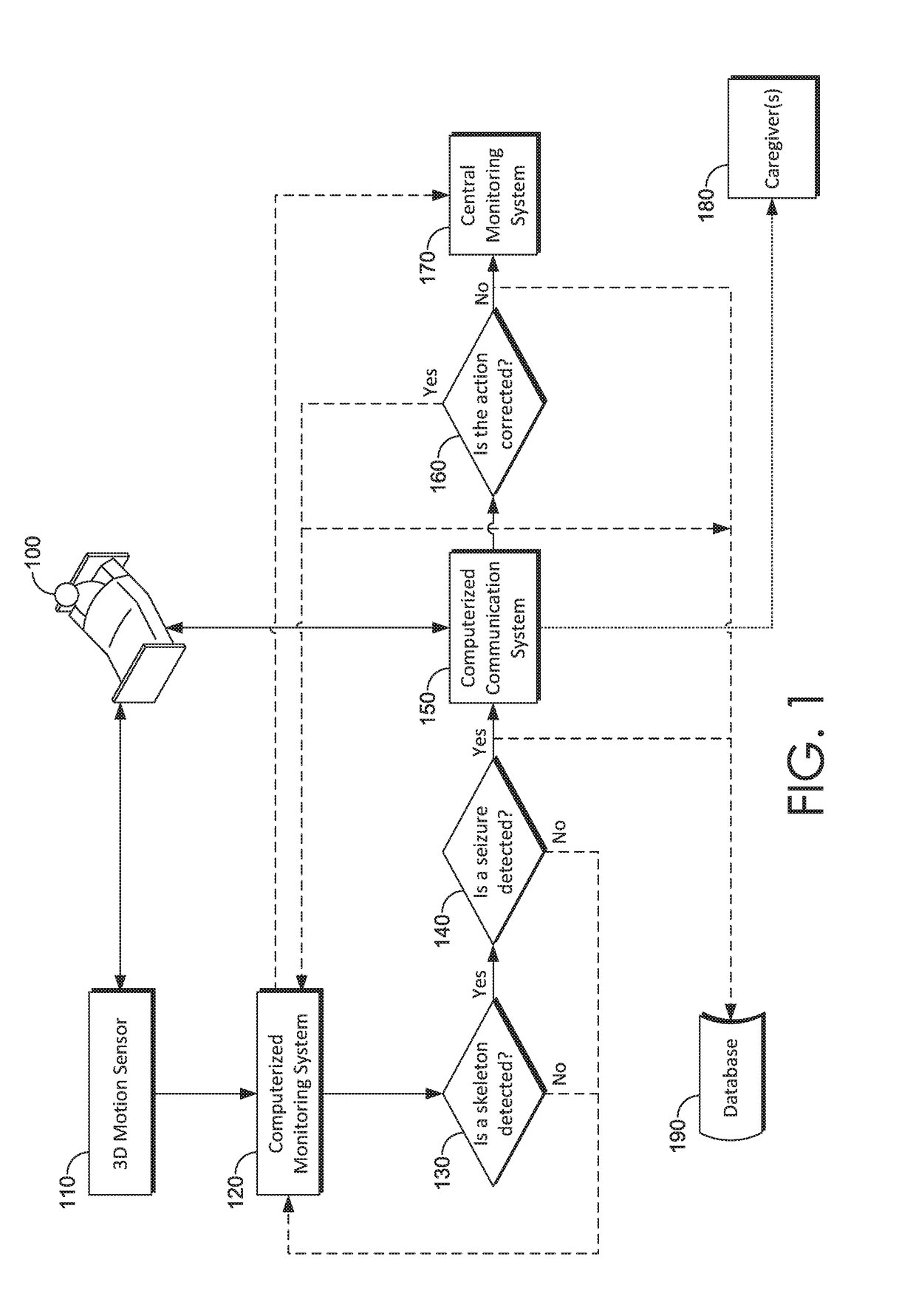
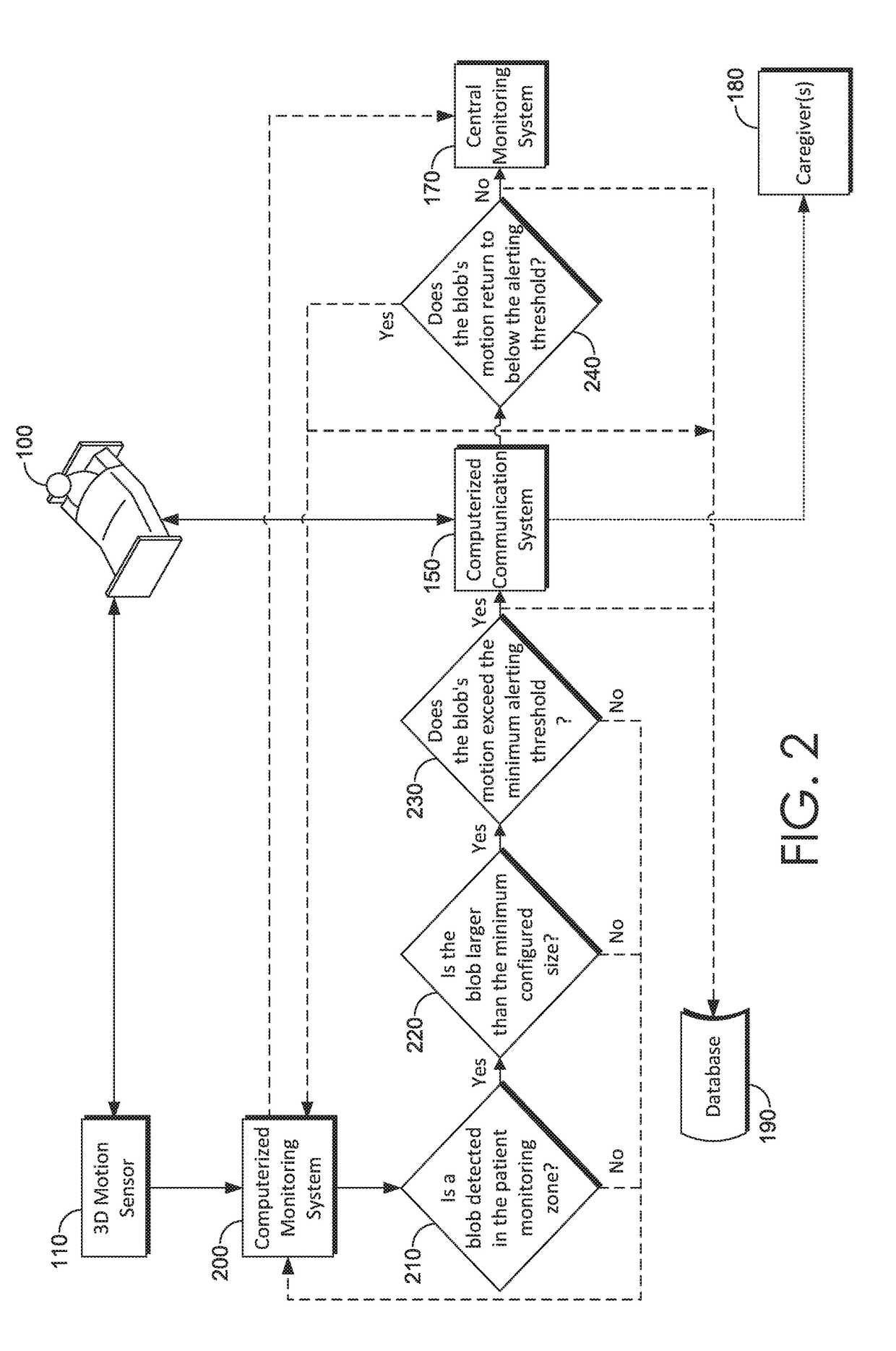
Seizure detection
ActiveUS20180189946A1Not identifyImage enhancementImage analysisSeizure detectionPhysical medicine and rehabilitation
Systems, methods and media for detecting a seizure use one or more 3D cameras to monitor an individual. The 3D cameras may detect rigidity and / or rapid movements associated with the tonic or clonic phases of a seizure. Body position and / or movements consistent with a seizure may cause the system or media to alert the individual, a central monitoring system, caregivers, and / or others.
Owner:CERNER INNOVATION
Rolling Shutter Synchronization
Owner:GOPRO
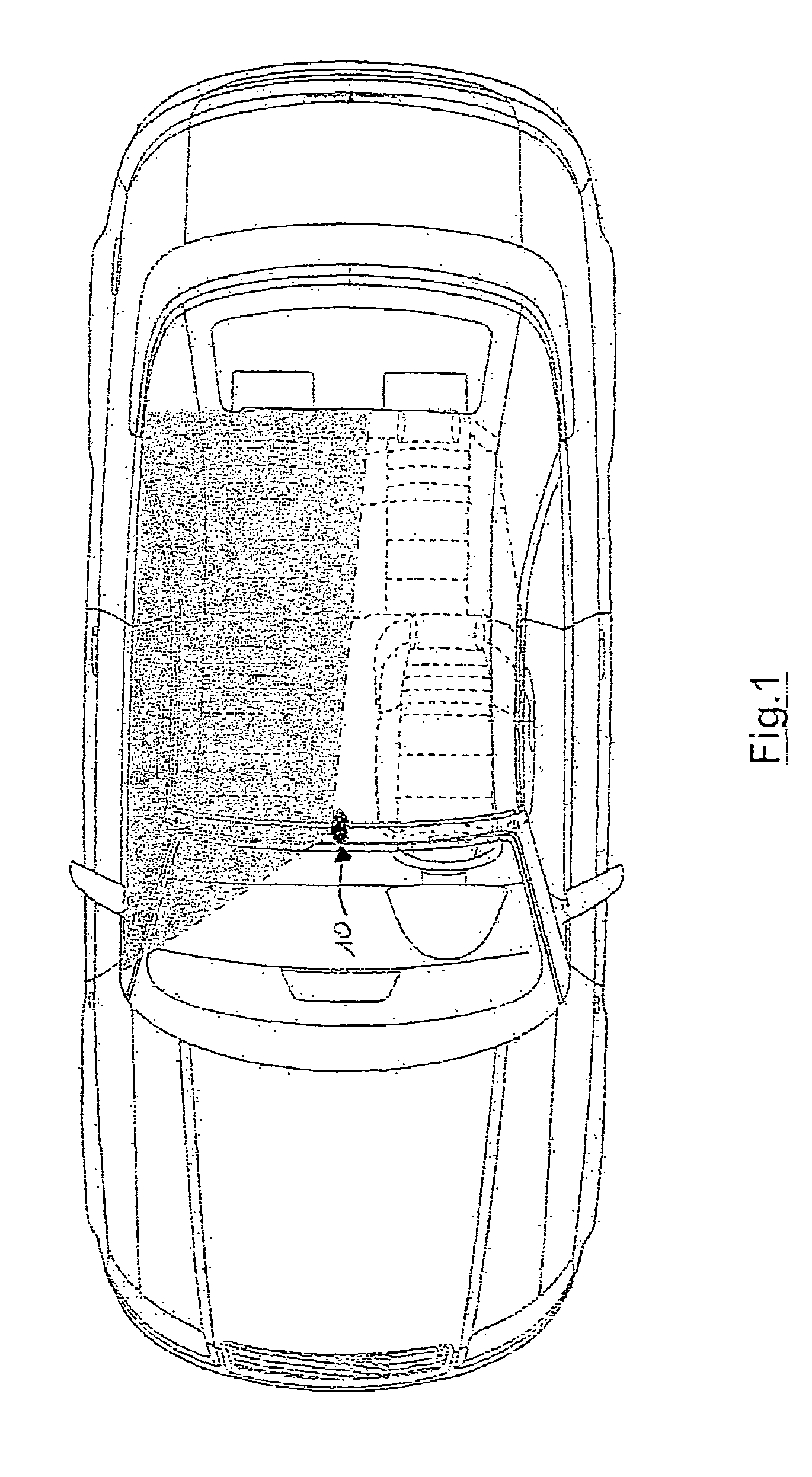
Occupant detection system, alarm system, brake system and vehicle
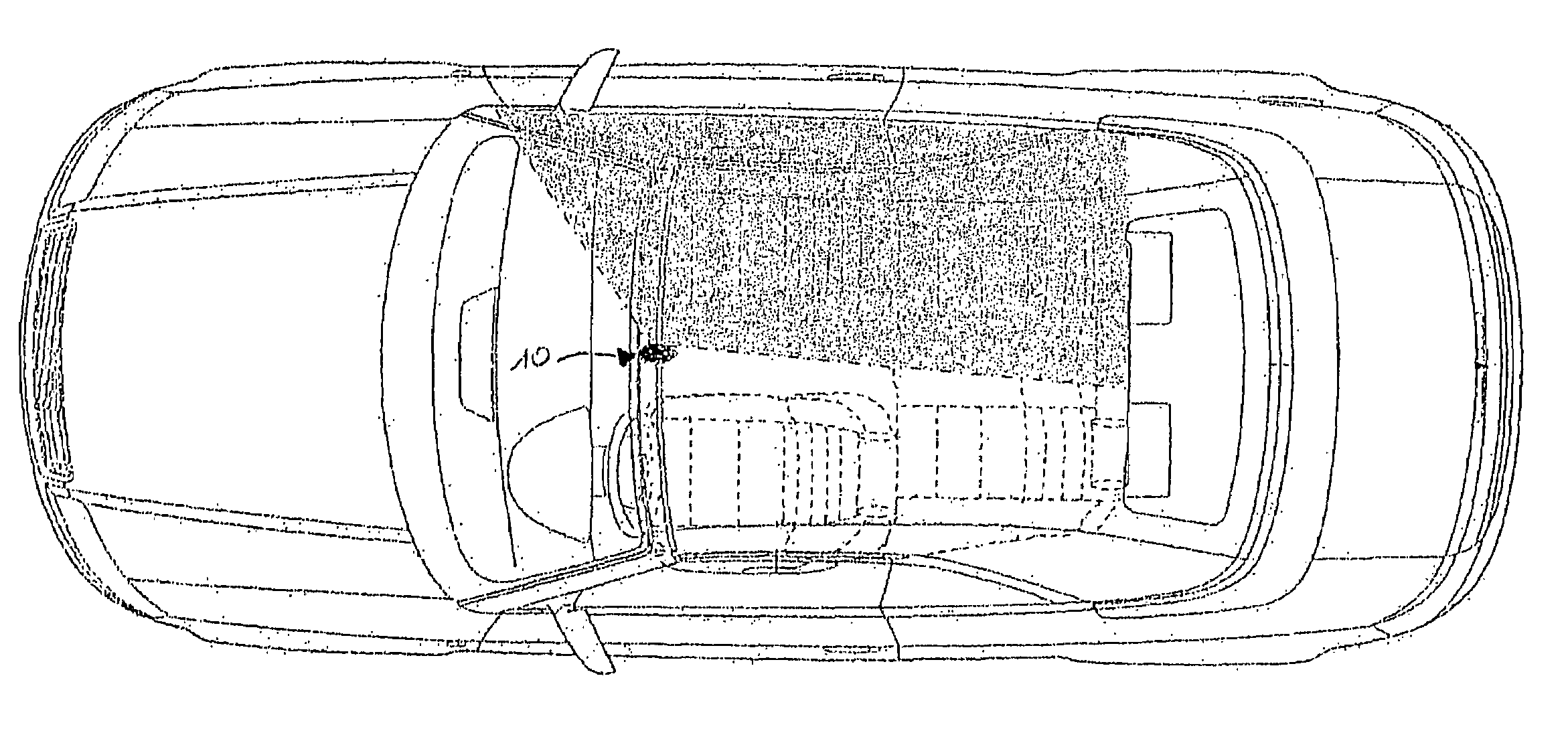
InactiveCN101153798ADetect attentionReduce concentrationPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryDriver/operatorIn vehicle
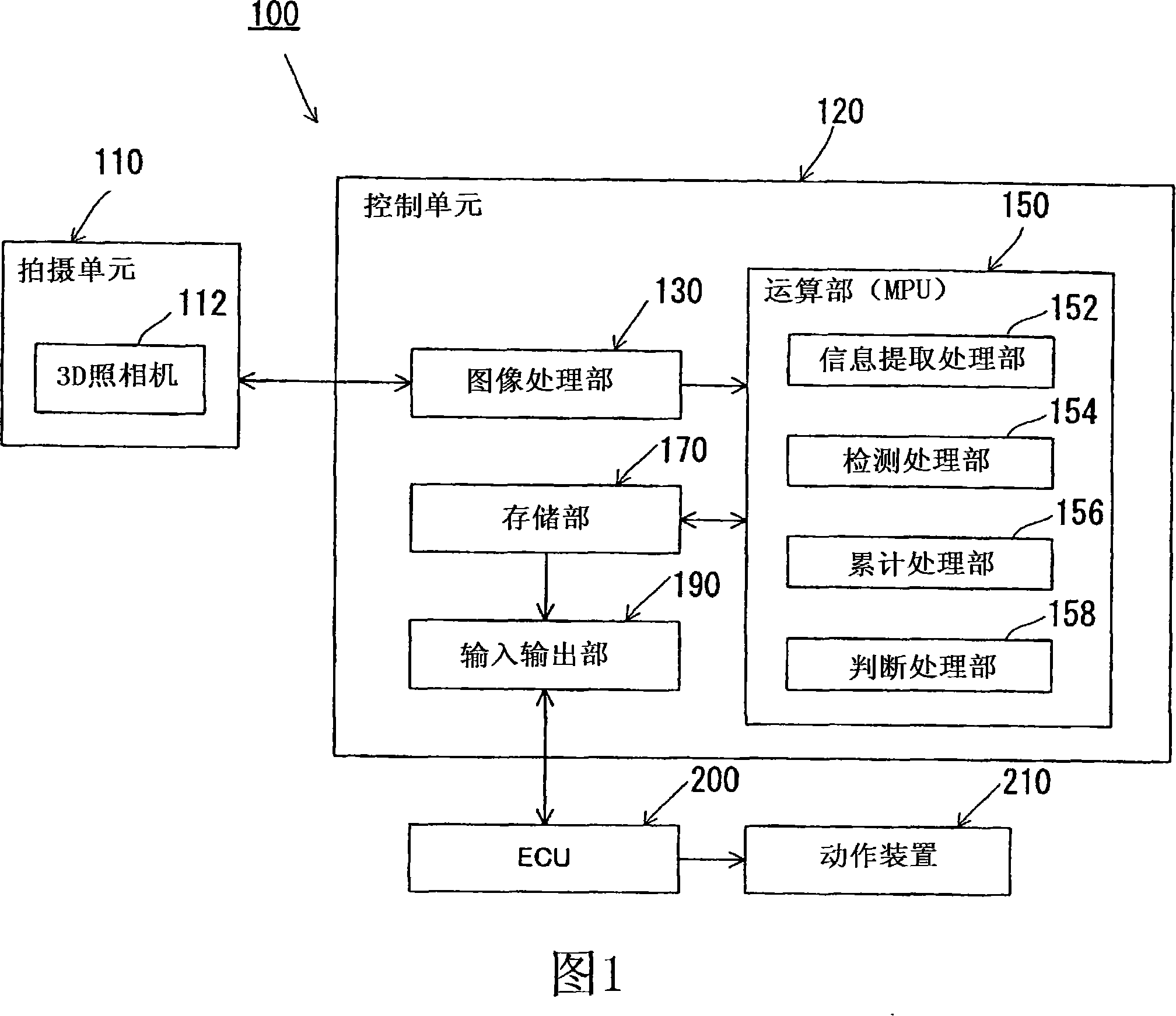
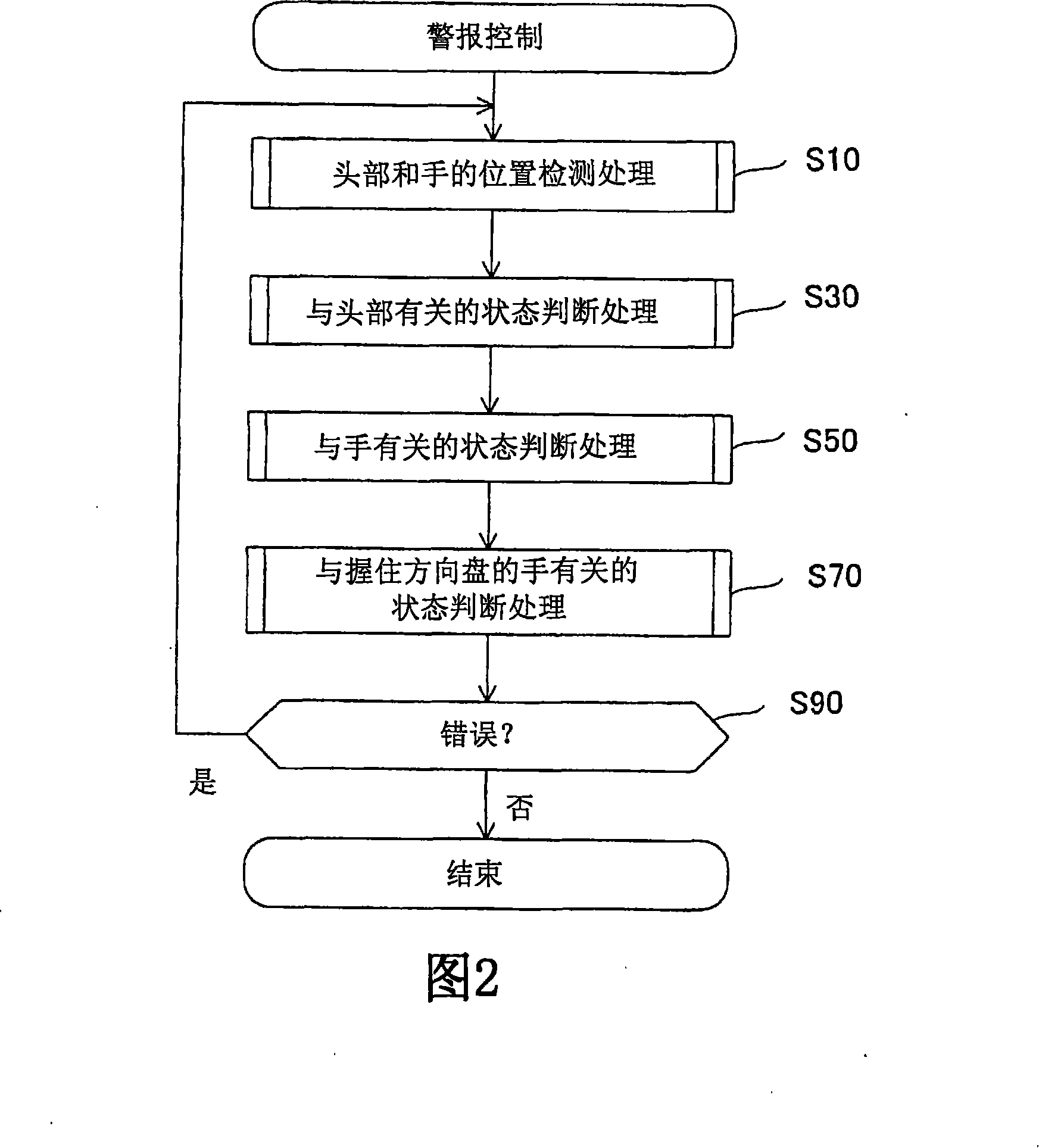
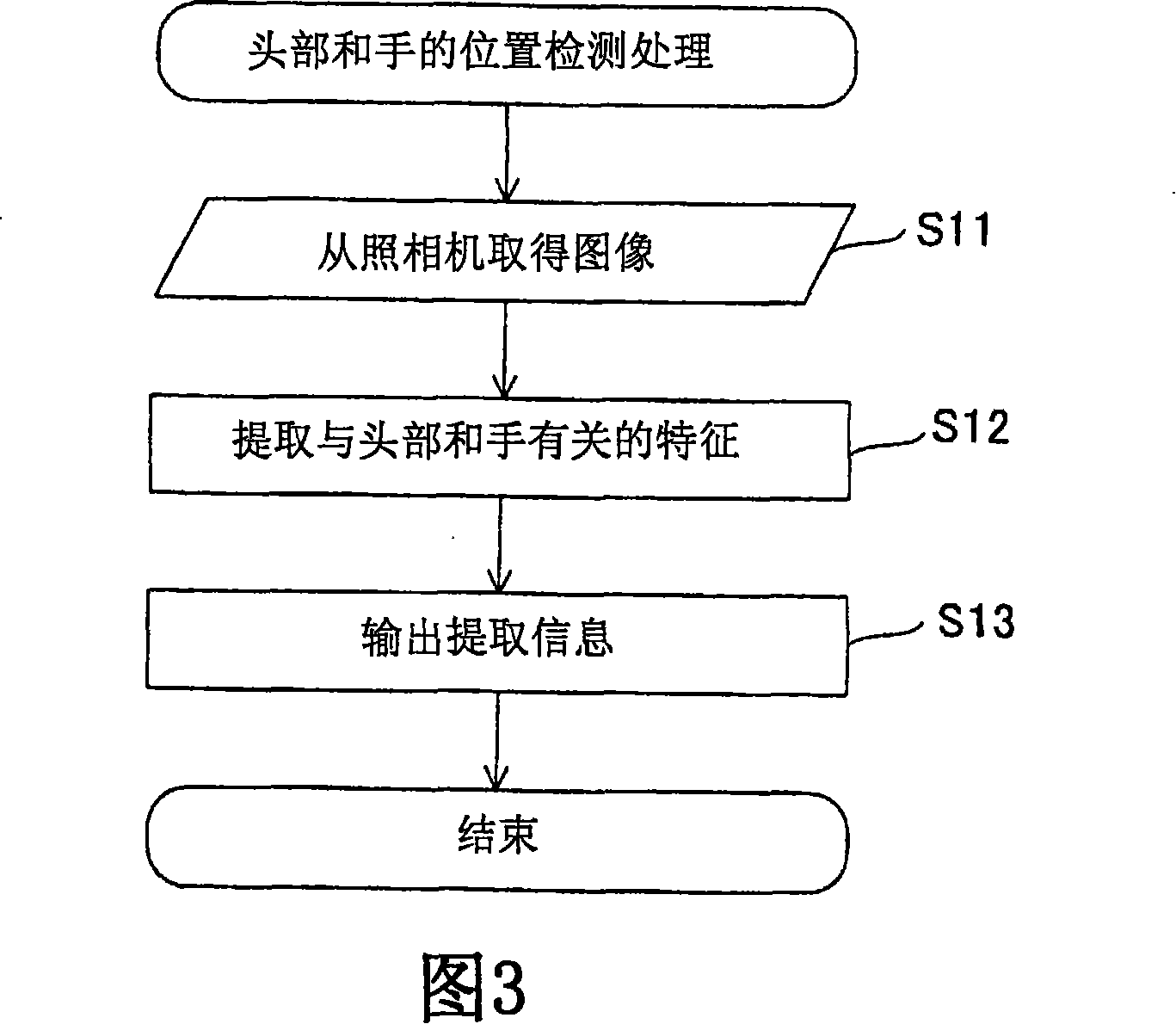
In order to provide an occupant detection system (100) to be installed in a vehicle, provided with a technology which is effective for precisely detecting whether or not the attention of a driver is diminished, the occupant detection system (100) of the present invention comprises a 3D camera (112), an information extracting section (152) for extracting information about the head and hand(s) of a driver based on three-dimensional images taken by the 3D camera (112), a detection processing section (154) for detecting whether or not the positions or movement of the head and hand(s) of the driver are in predetermined specified states based on the information extracted by the information extracting section (152), an integration processing section (156) which, when at least either the driver's head or the driver's hand(s) is out of the specified state, adds up time in which the head or hand(s) is not in the specified state, and a determination processing section (158) which, based on the time added up by the integration processing section (156), determines that the driver's attention is diminished when the time added up exceeds a preset reference value and determines that the driver's attention is not diminished when the time added up is equal to or less than the preset reference value.
Owner:TAKATA CORPORATION
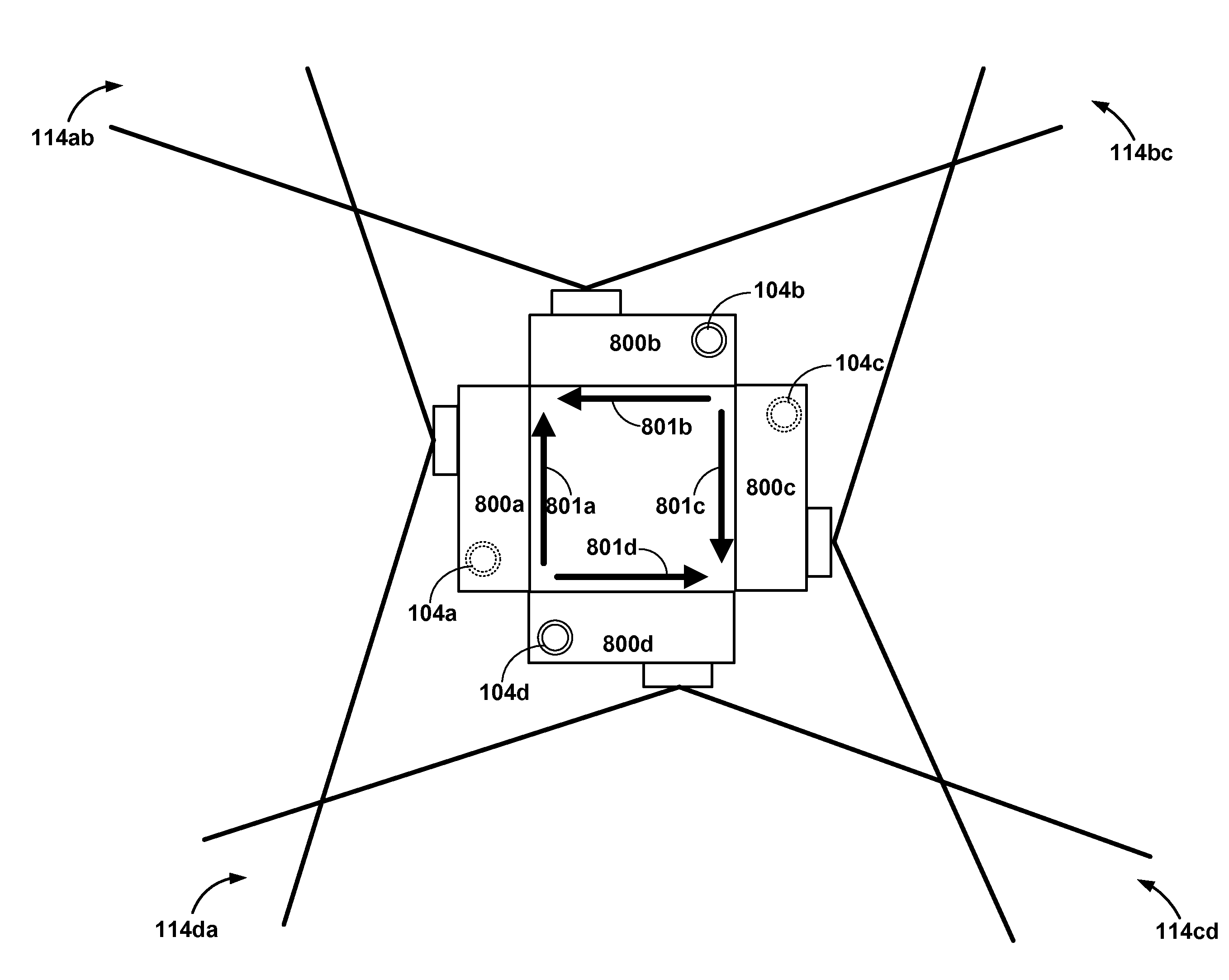
Intelligent 3D Stereo Camera Equipment Based on 3D Panoramic Vision
InactiveCN102289145AThe shooting process is simple and convenientHigh degree of intelligenceStereoscopic photographyPanoramic photographyStereoscopic imagingImaging processing
An intelligent three-dimensional stereo camera device based on 3D panoramic vision, including a group of 3D panoramic camera devices composed of 4 omnidirectional camera devices, a group of 3D camera devices composed of 2 high-definition cameras, and 4 omnidirectional camera devices. A computer for panoramic stereo imaging processing of images; it can simultaneously acquire real-time 3D panorama and 3D video images, and the shooting process is extremely simple and convenient. Just click on the object you want to shoot on the panoramic image and the device will automatically complete the focus, horizontal rotation, vertical Actions such as rotation and 3D depth adjustment can be widely used in many application fields such as live stereoscopic shooting of major sports events, theatrical performances, and animation movies.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
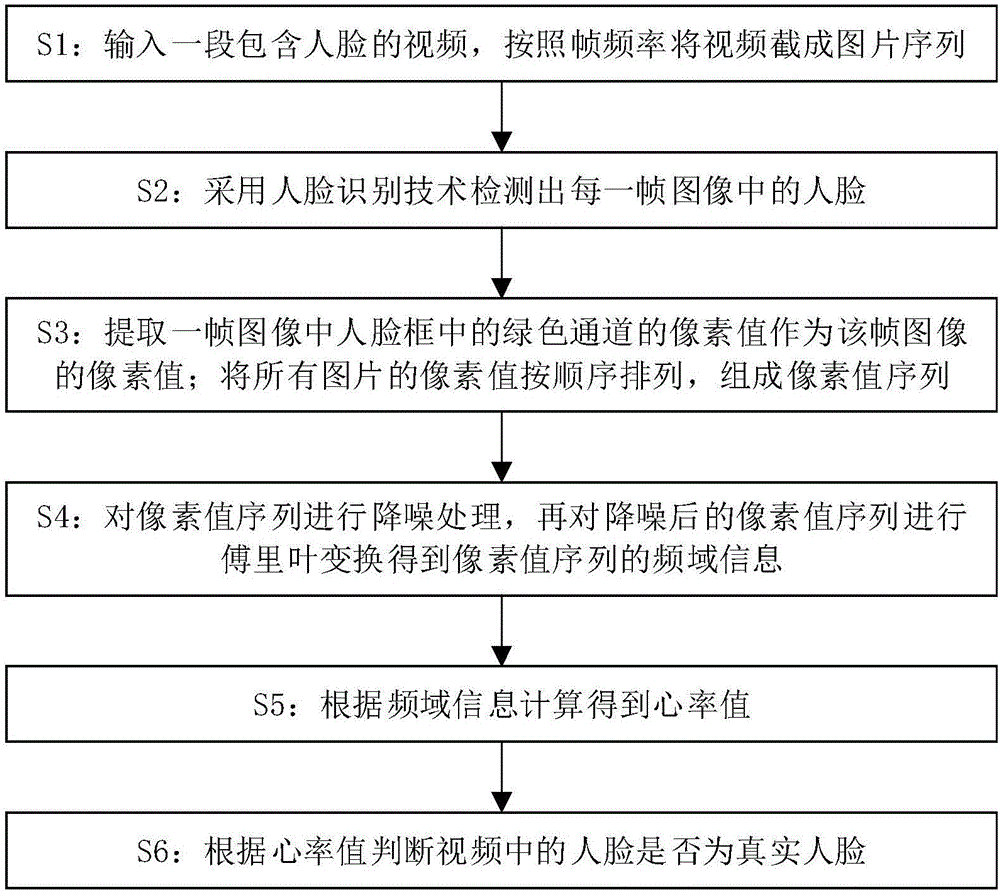
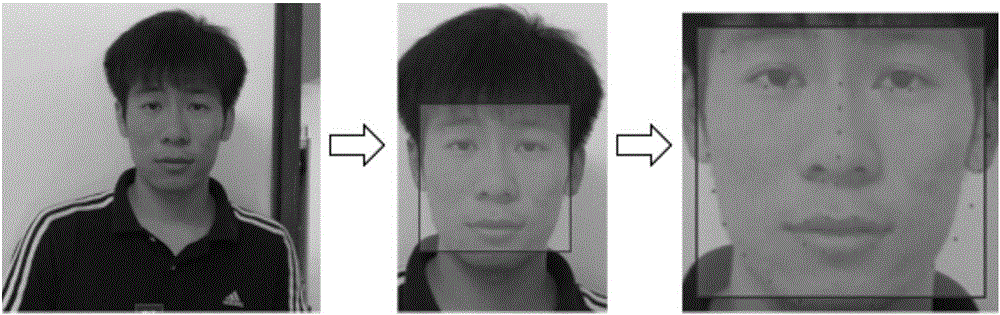
Method for carrying out in-vivo detection based on human face recognition
The invention relates to a method for carrying out in-vivo detection based on human face recognition. The method comprises the following steps that a video including human faces is input, and the video is cut into picture sequences according to frame frequency; the human face in each frame of picture is detected out through the human face recognition technology; the pixel value of a green channel in a human face frame in one frame of picture is extracted to serve as the pixel value of the picture, the pixel values of all the pictures are ranked according to the sequence, and a pixel value sequence is formed; the pixel value sequence is subjected to noise reduction, then Fourier transform is carried out, and frequency domain information of the pixel value sequence is obtained; a heart rate value is calculated according to the frequency domain information; whether the human faces in the video are real human faces or not is judged according to the heart rate value. Heartbeat information reflected by the human faces is utilized, human face in-vivo detection is carried out faster in a better interaction mode, a tester does not need to carry out operation according to a voice instruction, and the detection speed is high. Hardware equipment such as infrared cameras or 3D cameras is not needed, the cost is low, and the method can be widely applied.
Owner:北京飞搜科技有限公司
Deep learning-based quick automatic capture and placement method
ActiveCN108399639ABeneficial degree of automationEasy to deployProgramme-controlled manipulatorImage analysisTransfer matrix3d camera
The invention discloses a deep learning-based quick automatic capture and placement method. The method can quickly and accurately determine positions and attitudes of articles in combination with a GPU and a 3D camera by adopting a deep learning scheme. Through a quick calibration scheme, a transfer matrix from a coordinate system of the 3D camera to a coordinate system of a mechanical arm can beobtained. The transfer matrix can convert the positions and attitudes of the articles to the coordinate system of the mechanical arm, and then operate the mechanical arm to perform capture. For accurately placing the articles in a specific mode, the articles are subjected to secondary attitude estimation. A secondary attitude estimation process comprises the steps of firstly capturing the articlesto an estimation position by fixed attitude; at the moment, segmenting out the articles more completely by only using depth information; projecting the articles to a placement plane; and performing accurate attitude estimation for information on the plane, thereby enabling the mechanical arm to perform placement.
Owner:HANGZHOU LANXIN TECH CO LTD
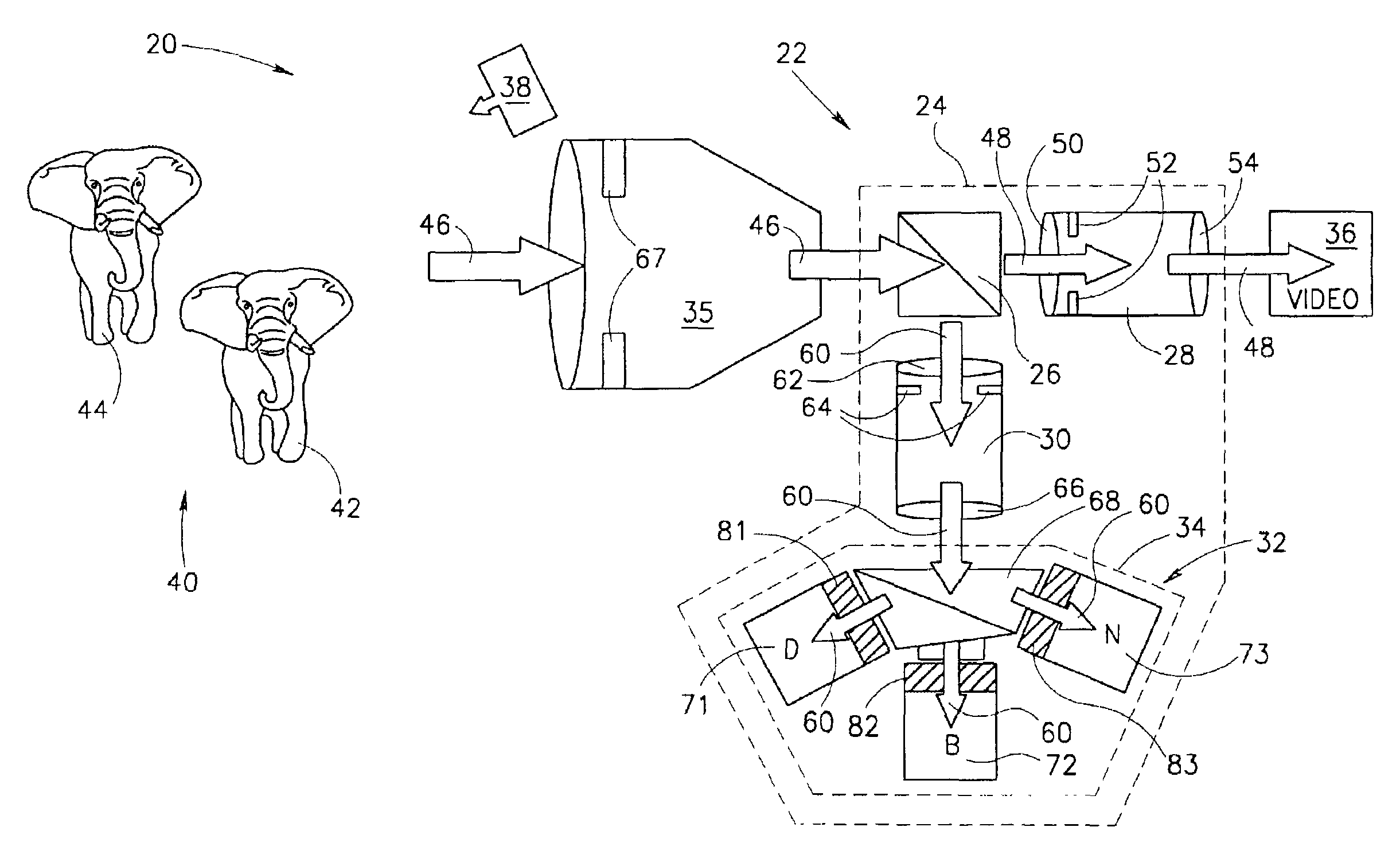
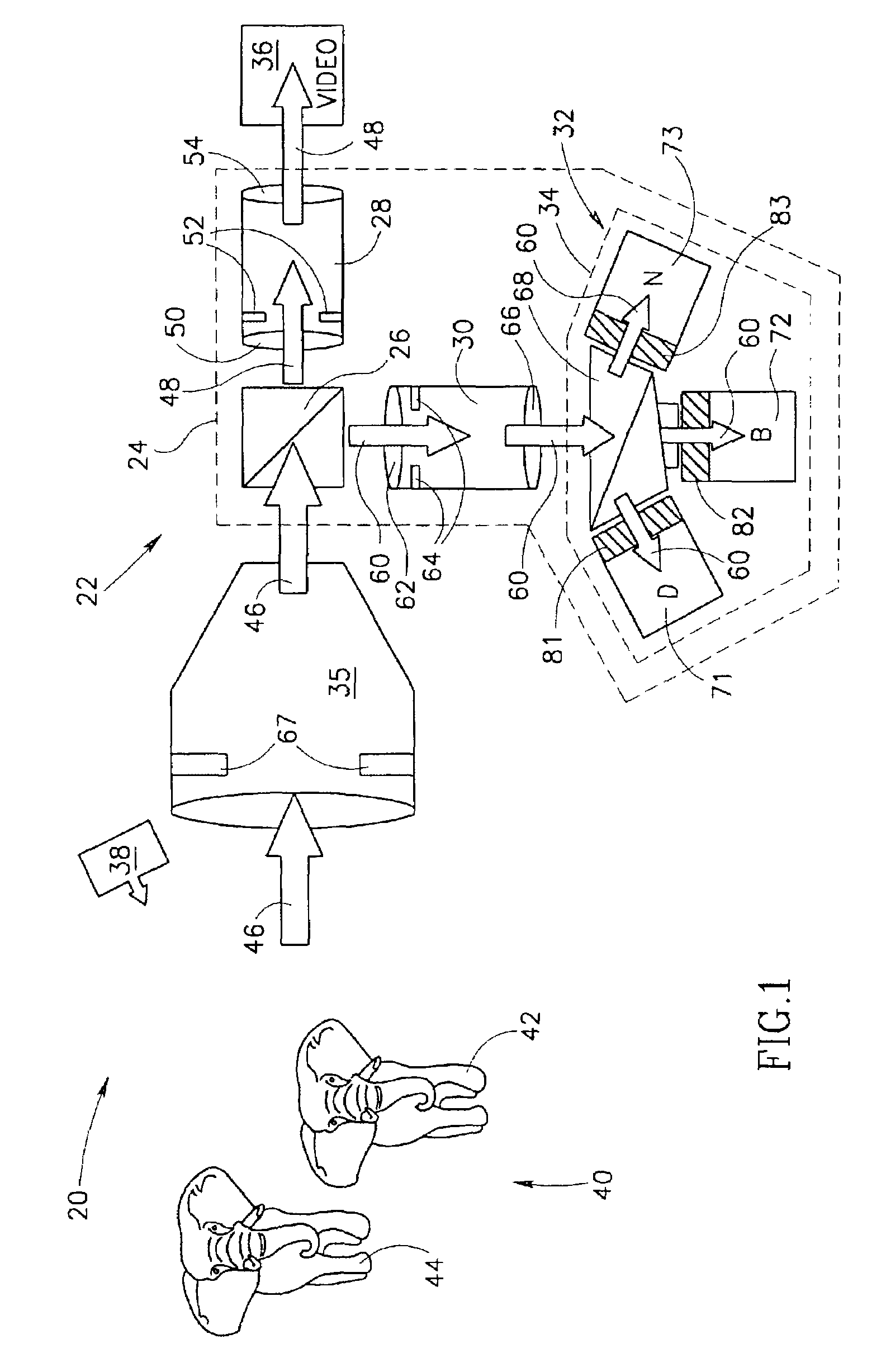
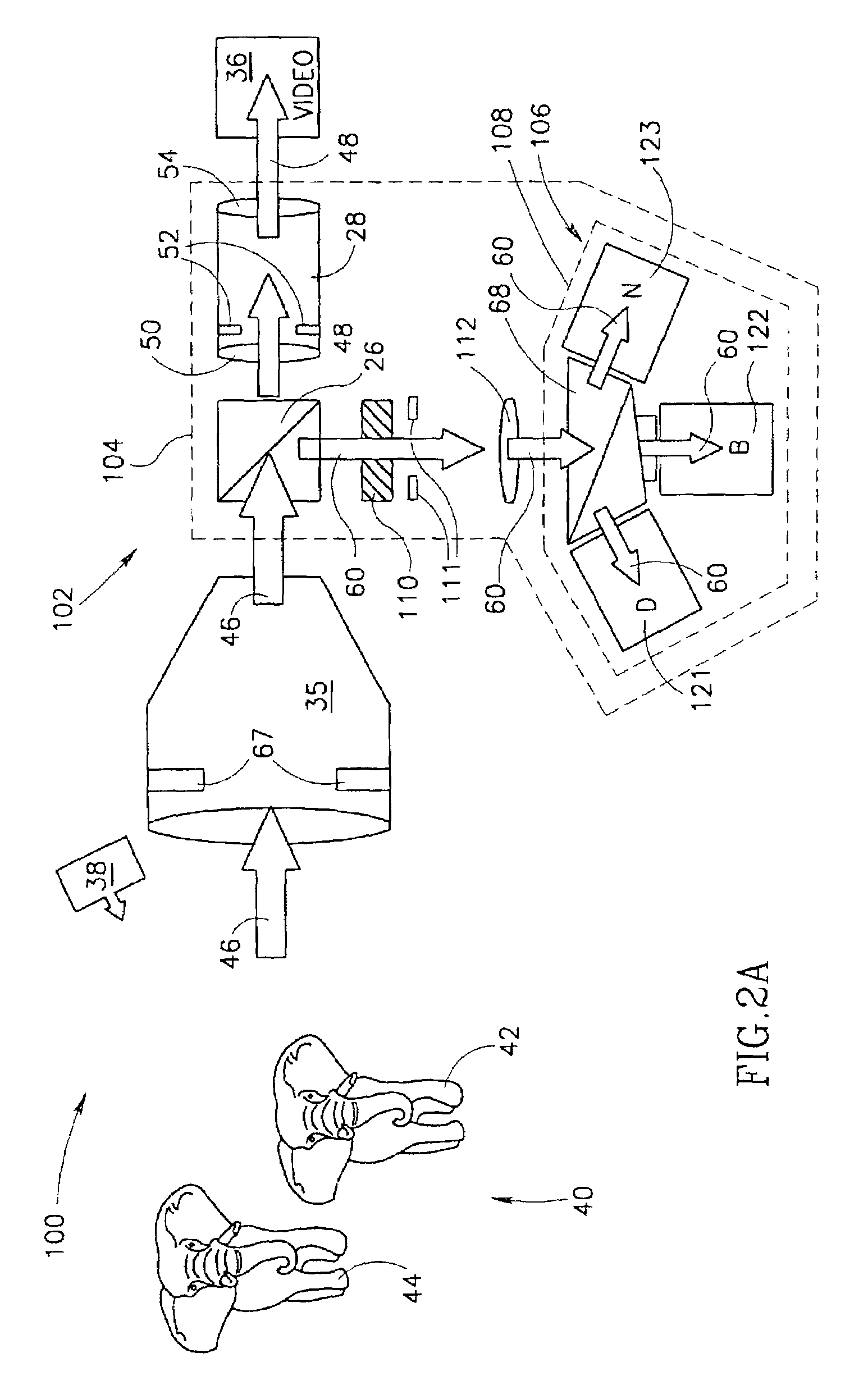
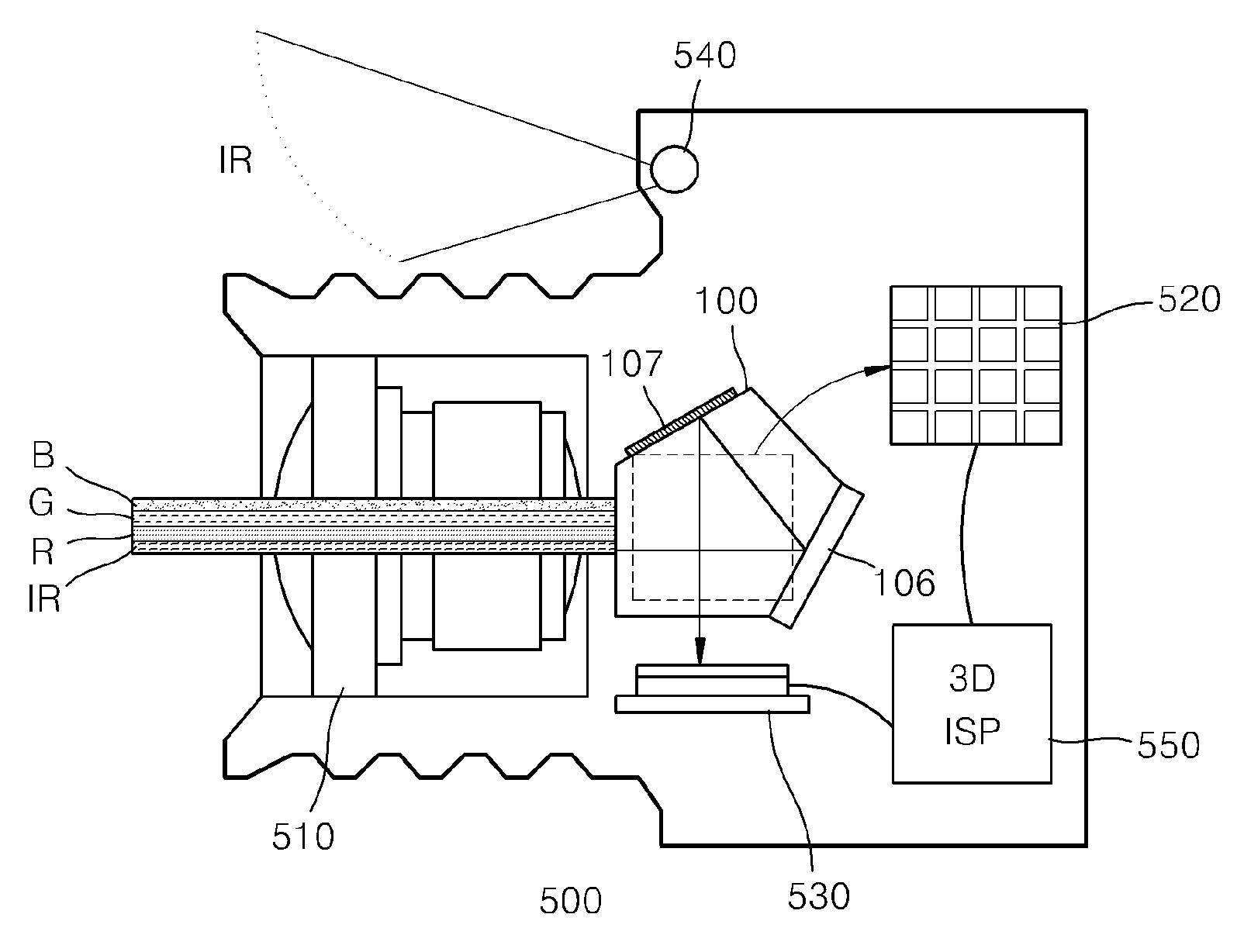
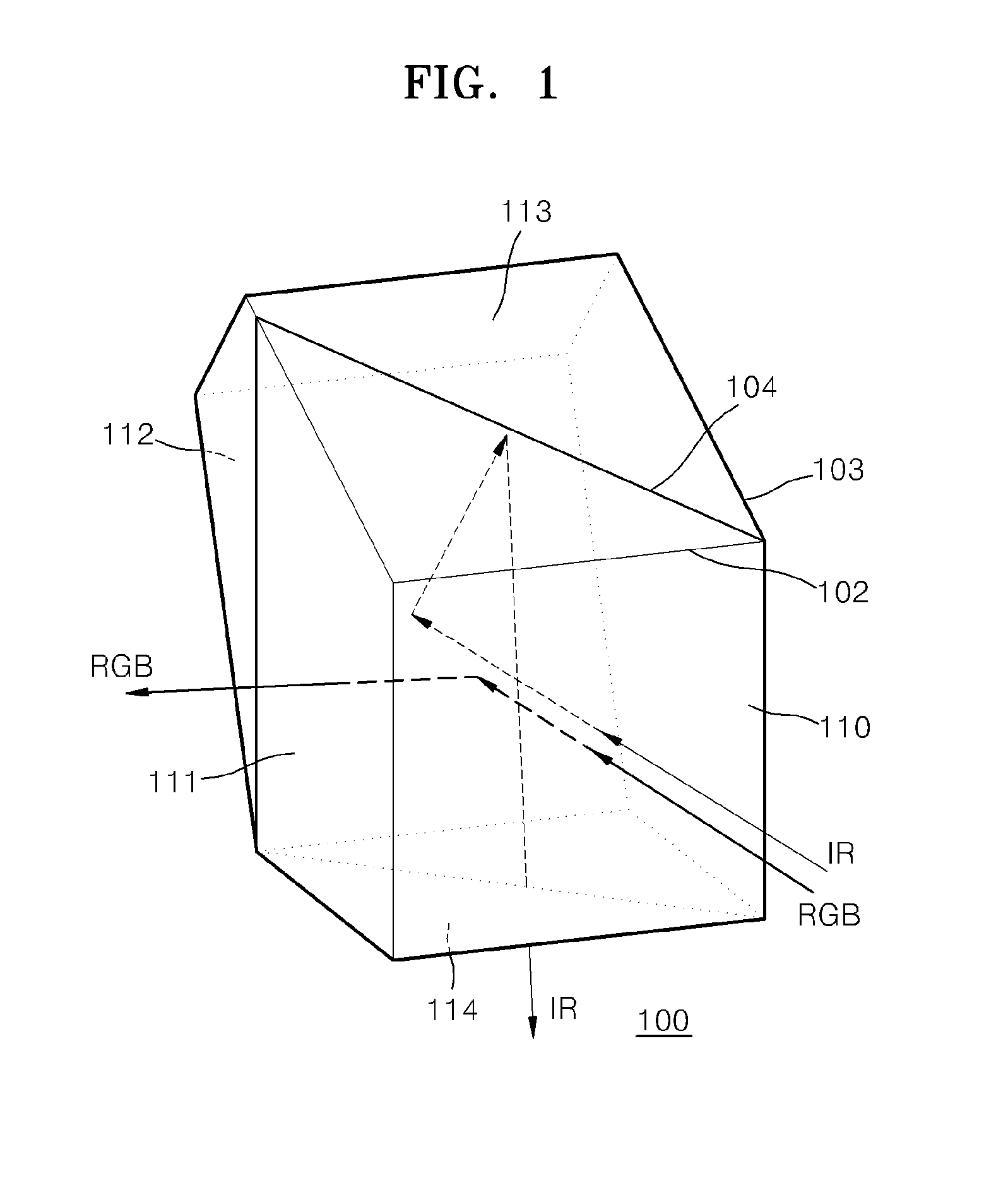
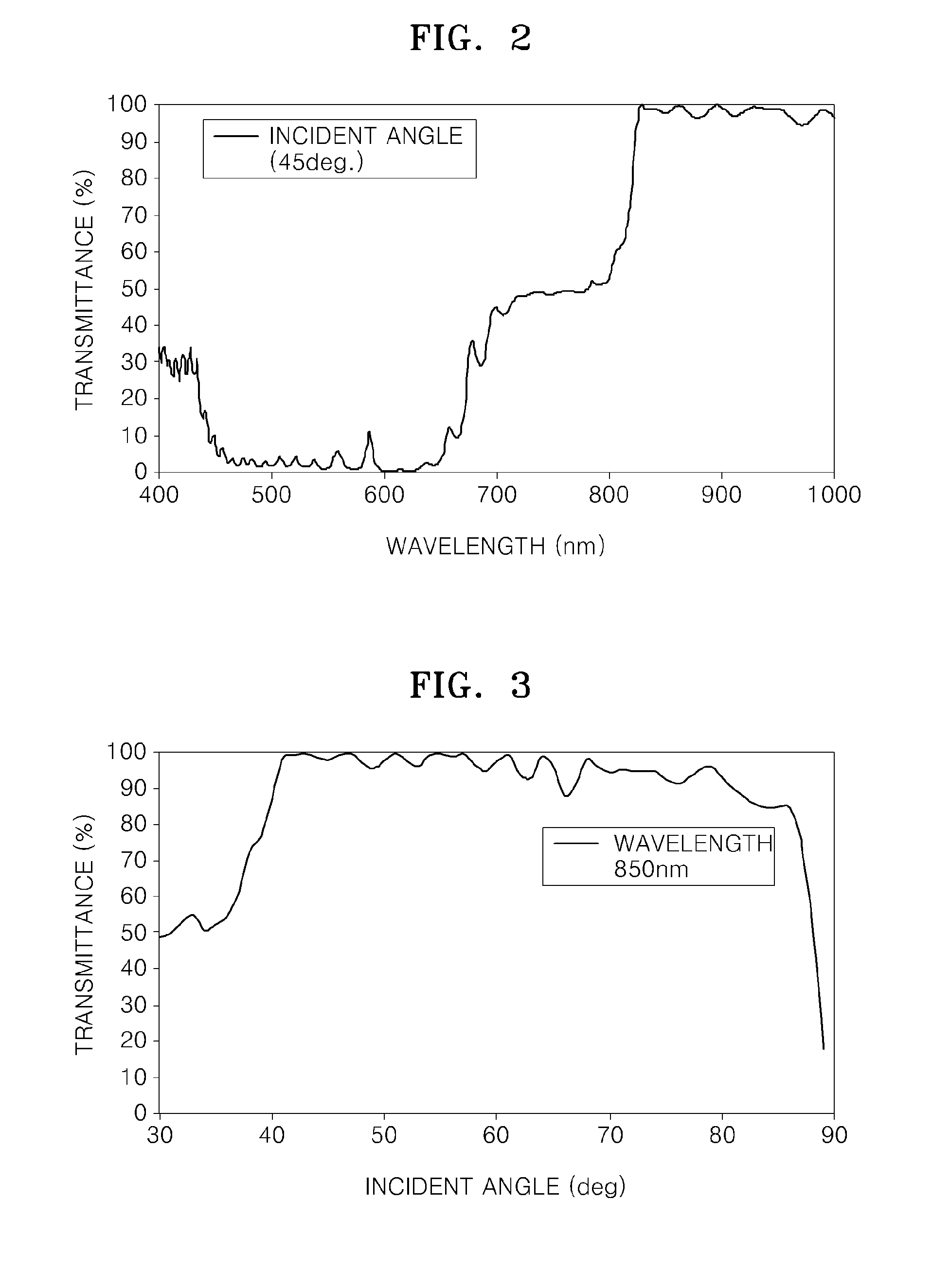
Beam splitter for 3D camera, and 3D image acquisition apparatus employing the beam splitter
ActiveUS20120105594A1Television system detailsStatic indicating devicesBeam splitterAcquisition apparatus
A beam splitter and a 3D image acquisition apparatus including the beam splitter are provided. The beam splitter includes a light incident surface on which light having a first wavelength and light having a second wavelength are incident; a beam splitting surface which is inclined to the light incident surface and reflects the light having the first wavelength and transmits the light having the second wavelength; a first light exit surface through which the light having the first wavelength reflected from the beam splitting surface exits; a first reflective surface which reflects the light having the second wavelength transmitted by the beam splitting surface; a second reflective surface which reflects the light having the second wavelength reflected from the first reflective surface; and a second light exit surface through which the light having the second wavelength reflected from the second reflective surface exits.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
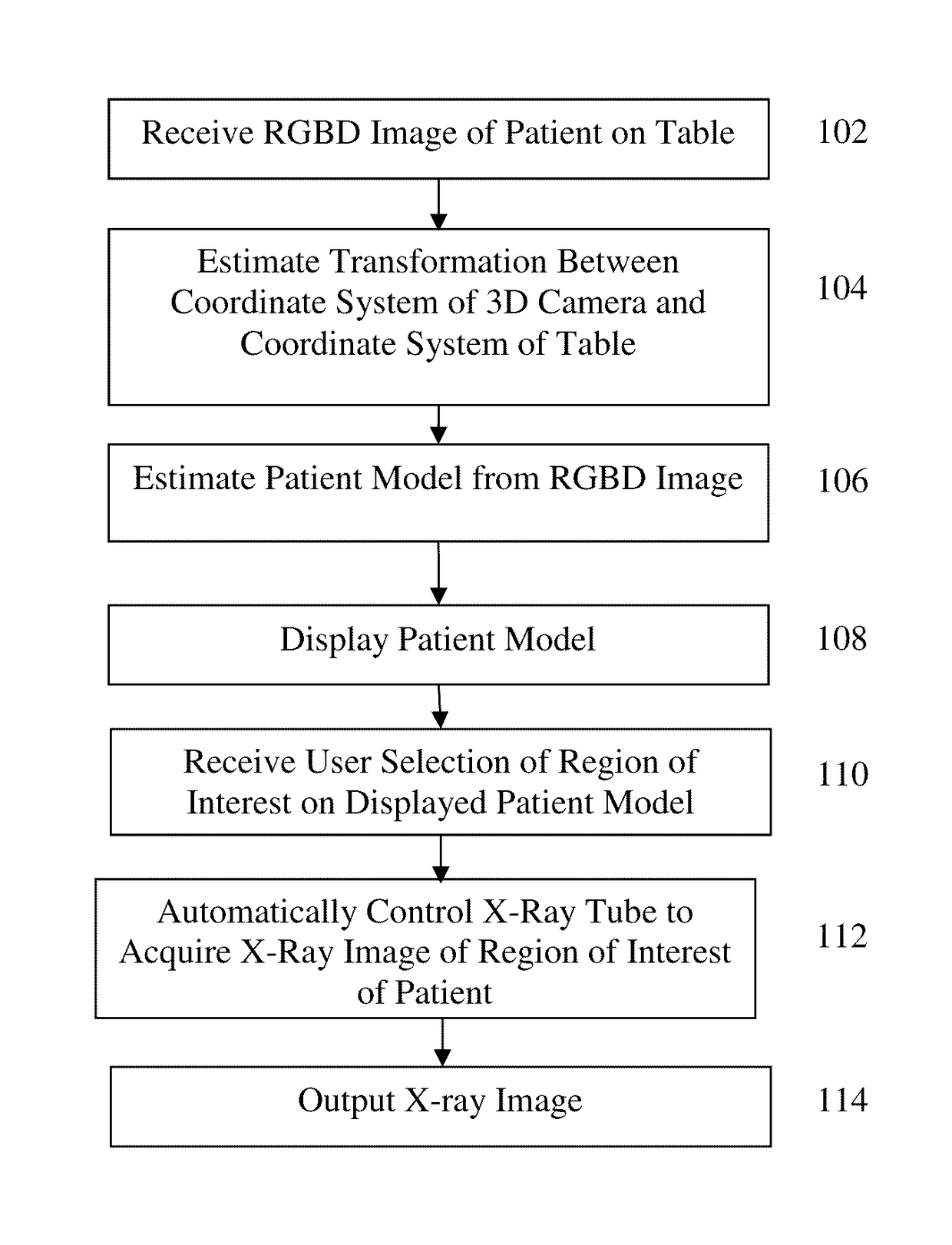
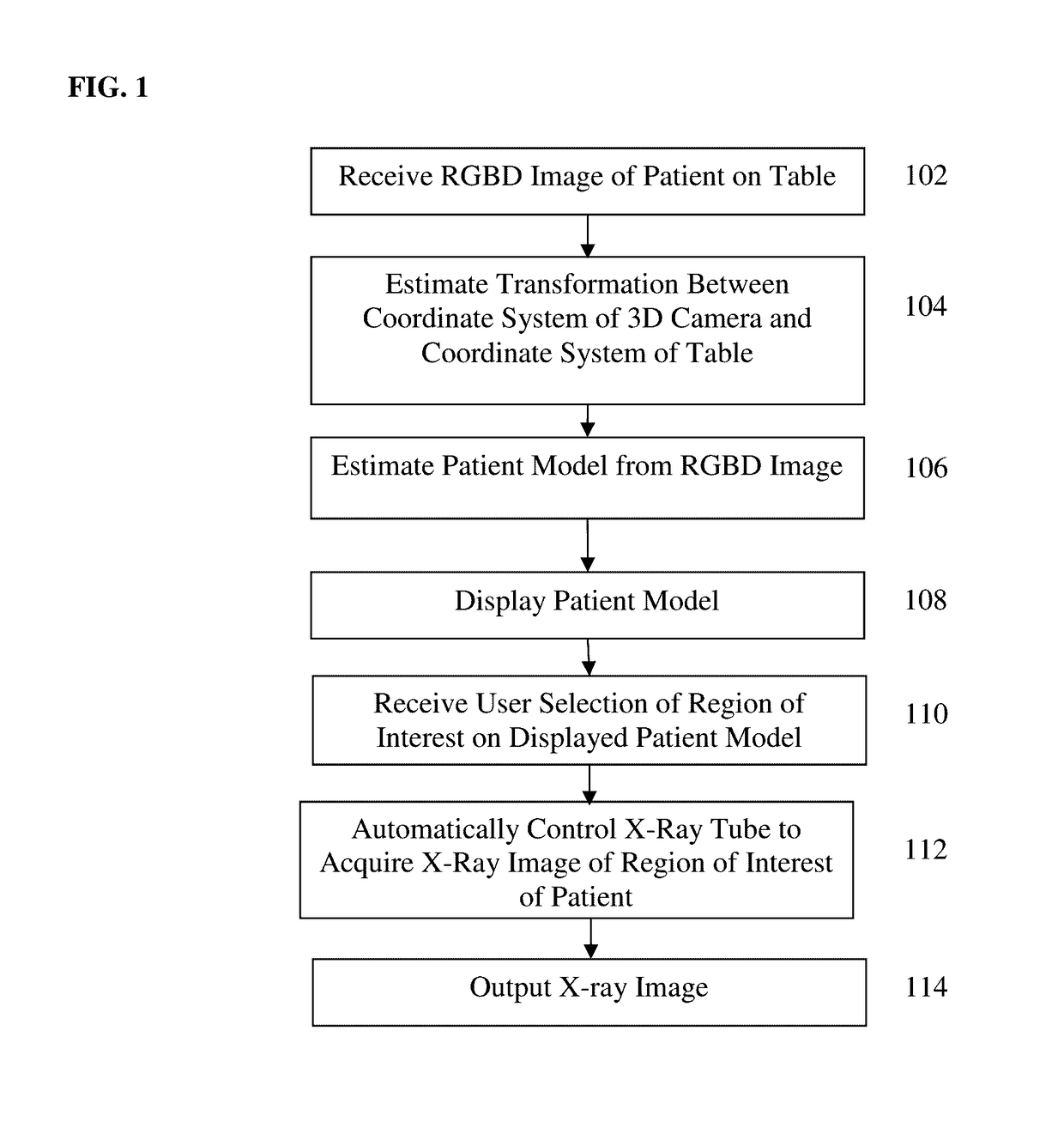
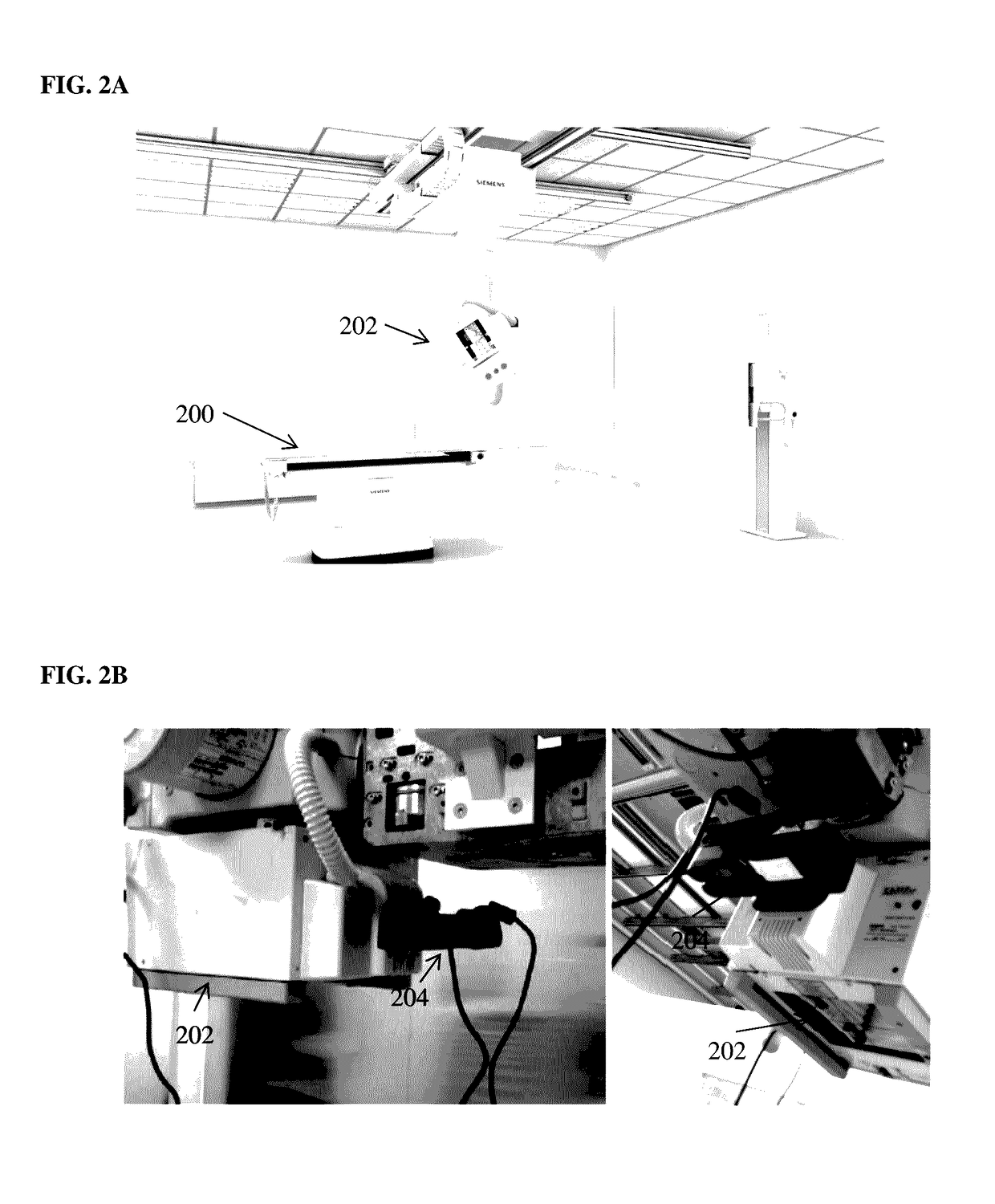
Method and System of Scanner Automation for X-Ray Tube with 3D Camera
A method and apparatus for X-ray tube scanner automation using a 3D camera is disclosed. An RGBD image of a patient on a patient table is received from a 3D camera mounted on an X-ray tube. A transformation between a coordinate system of the 3D camera and a coordinate system of the patient table is calculated. A patient model is estimated from the RGBD image of the patient. The X-ray tube is automatically controlled to acquire an X-ray image of a region of interest of the patient based on the patient model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
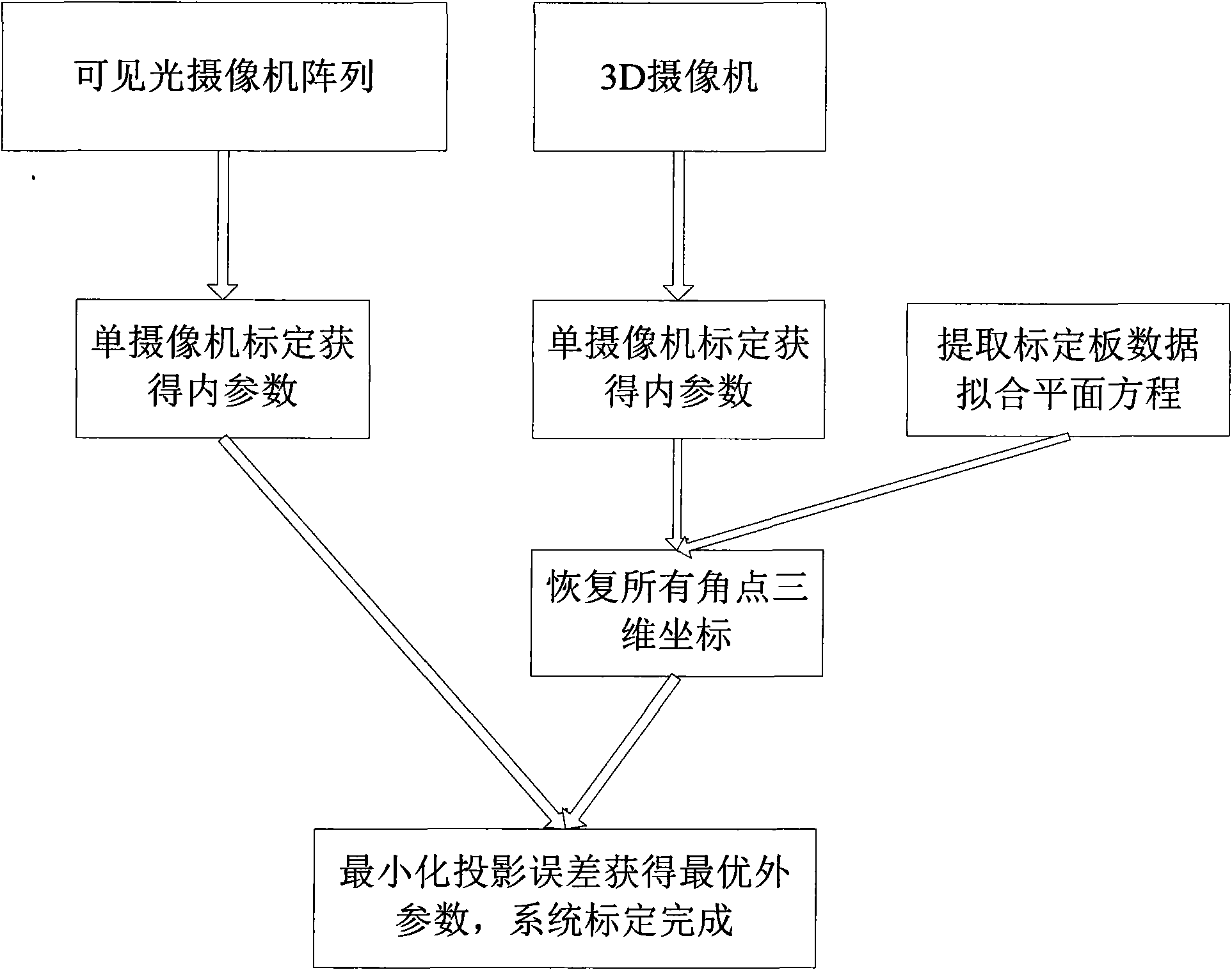
Camera array calibration algorithm based on gray level image and spatial depth data
The invention provides a camera array calibration algorithm capable of calibrating a 3D camera and obtaining relatively precise extrinsic parameters between the 3D camera and a visible light camera. The algorithm comprises the following steps: firstly, internally calibrating the visible light camera and the 3D camera to obtain intrinsic parameters of the cameras; secondly, adopting the intrinsic parameters of and a depth map provided by the 3D camera to restore the spatial locations of corner points of calibration boards, adopting minimum corner point projection error to obtain the optimum extrinsic parameters from the 3D camera to the required visible light camera, thereby completing the calibration of the whole camera array.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and device for increasing patient safety in clinical scanners
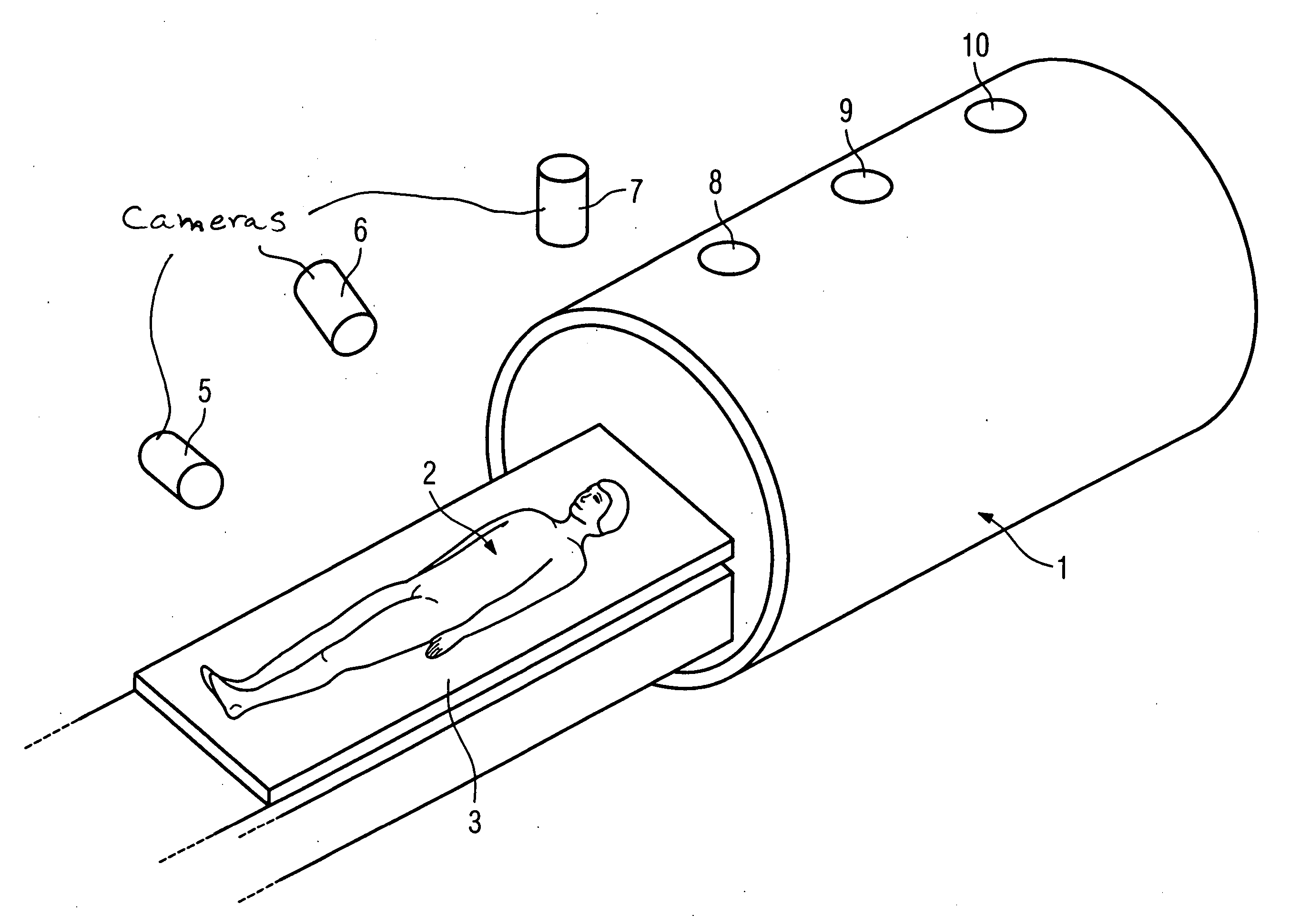
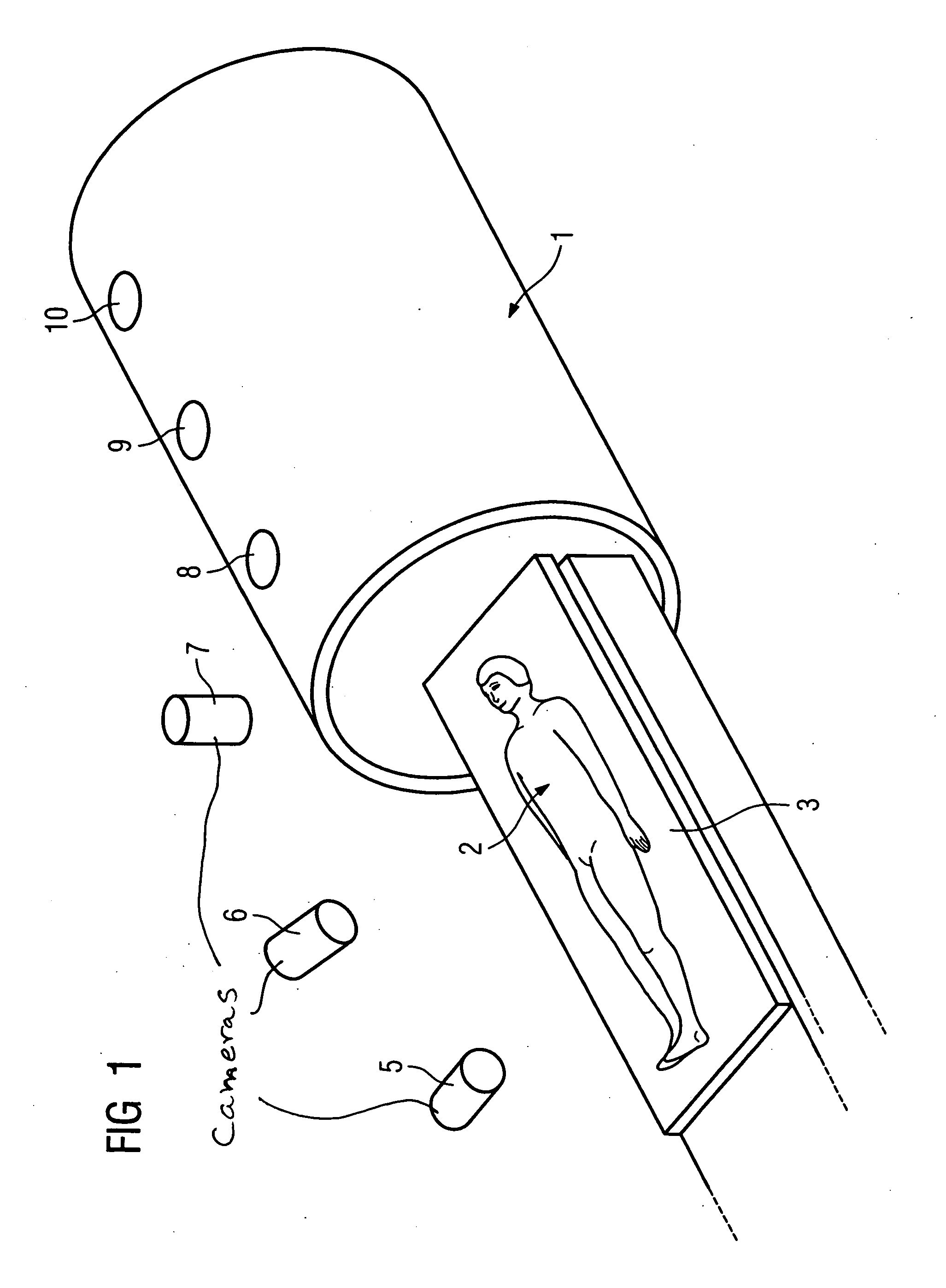
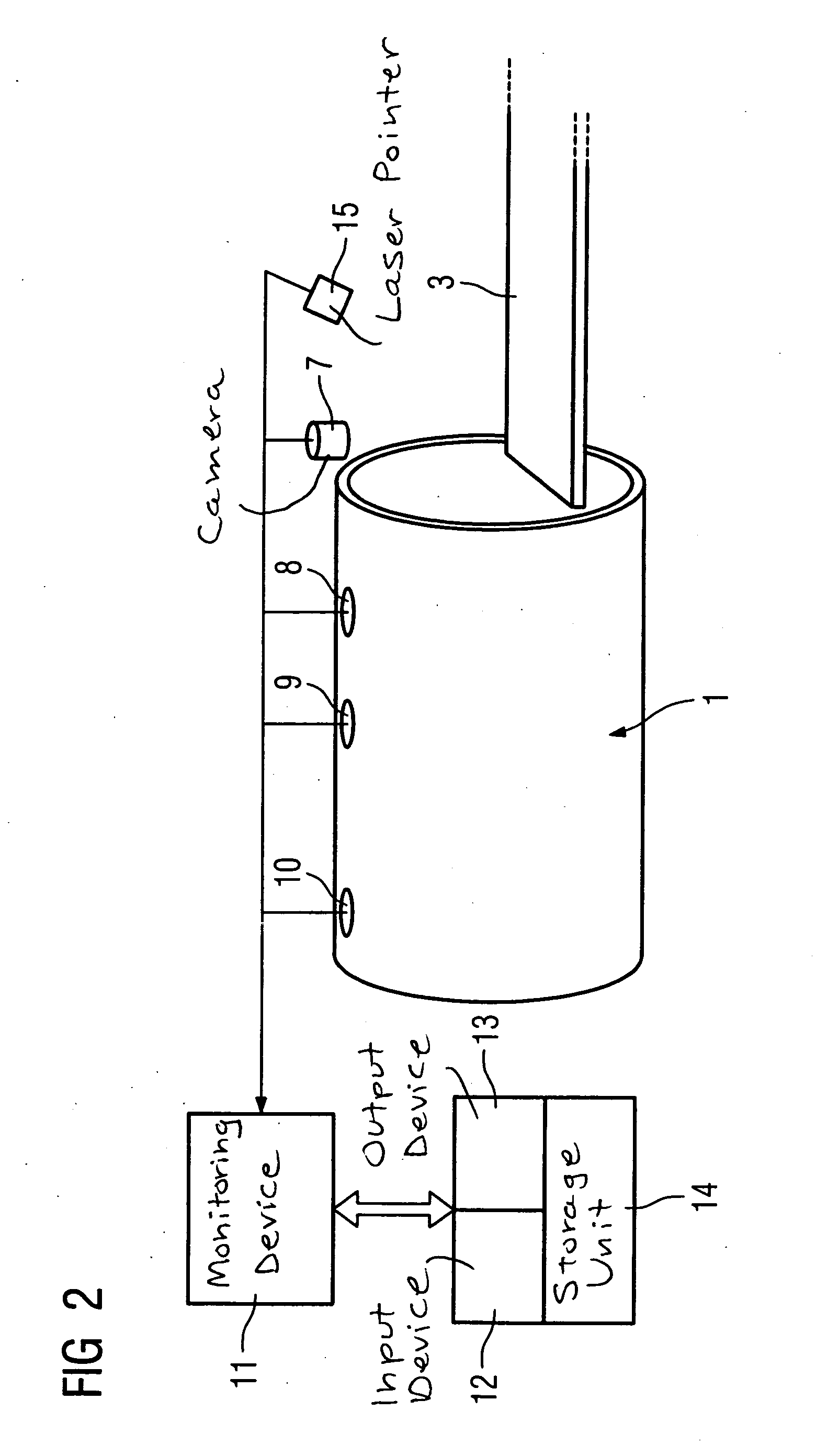
InactiveUS20050265516A1Precise positioningMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingMedicine3d camera
In a method and device for increasing patient safety in clinical scanners, the positioning of the patient during the preparation and the implementation of the examination is monitored by a 3D camera system, and incorrect positions are automatically detected by comparison of the current image with standard specifications, and corresponding corrections are prompted.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com