Patents
Literature
99results about How to "Satisfactory accuracy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
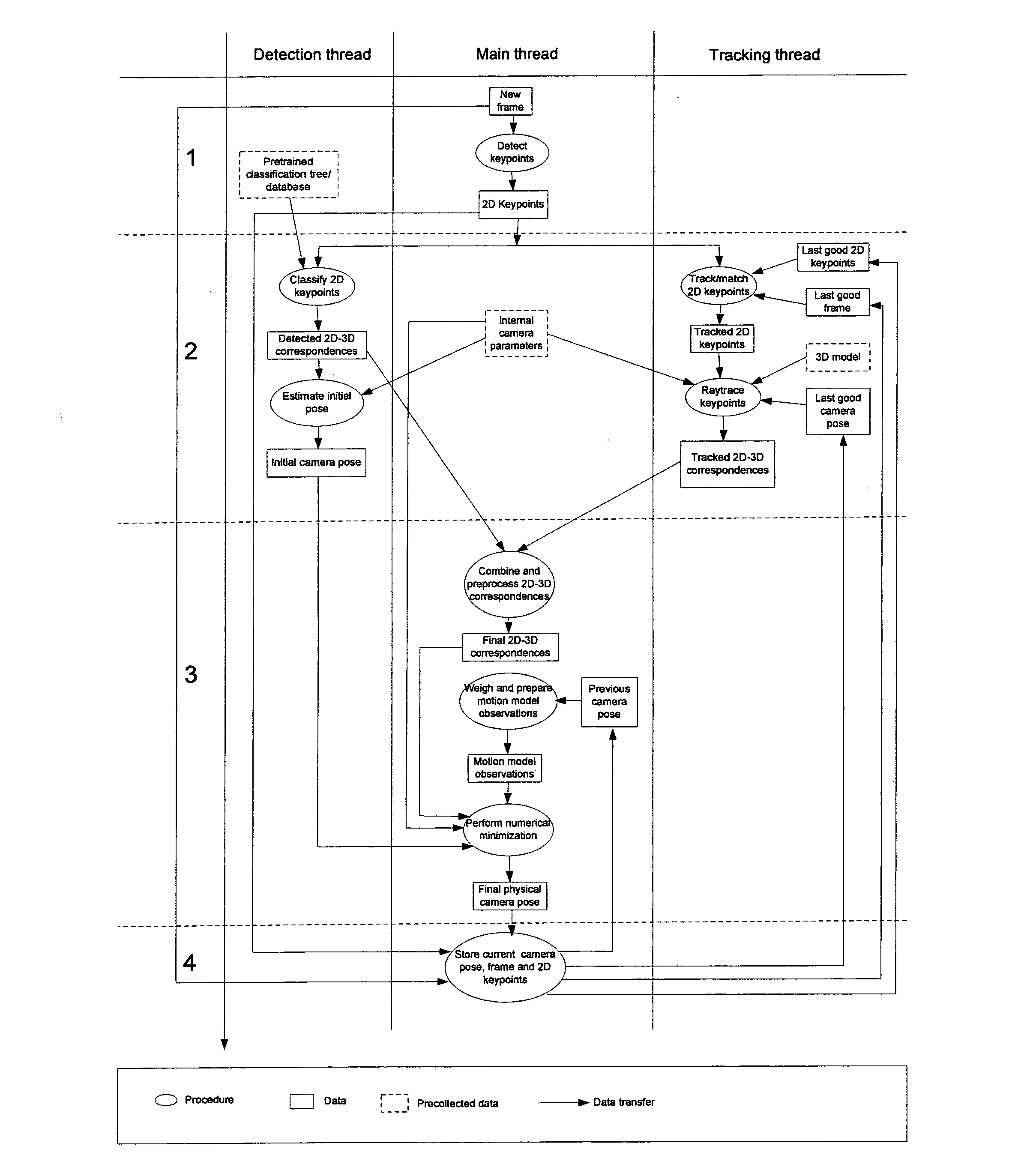
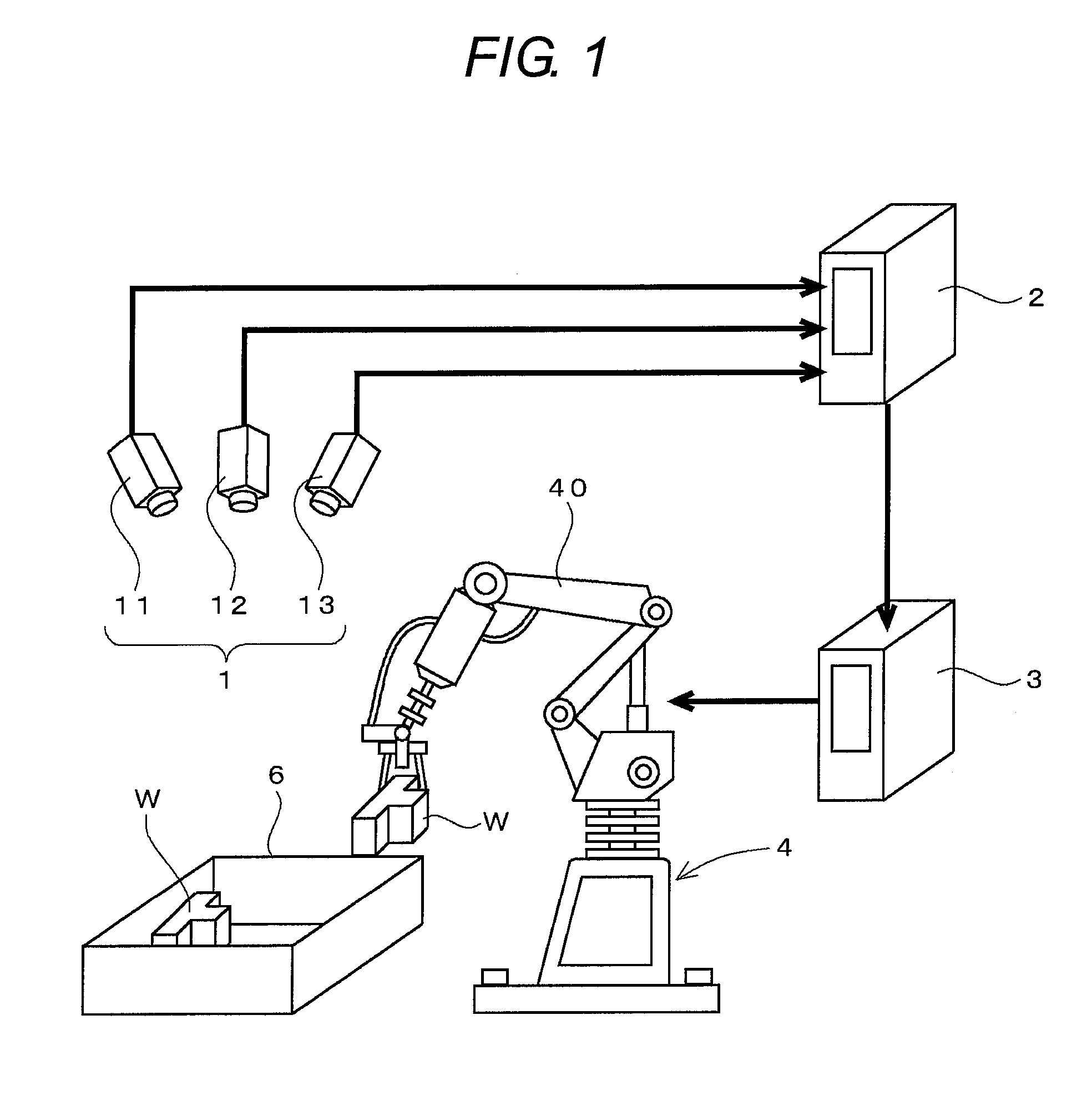
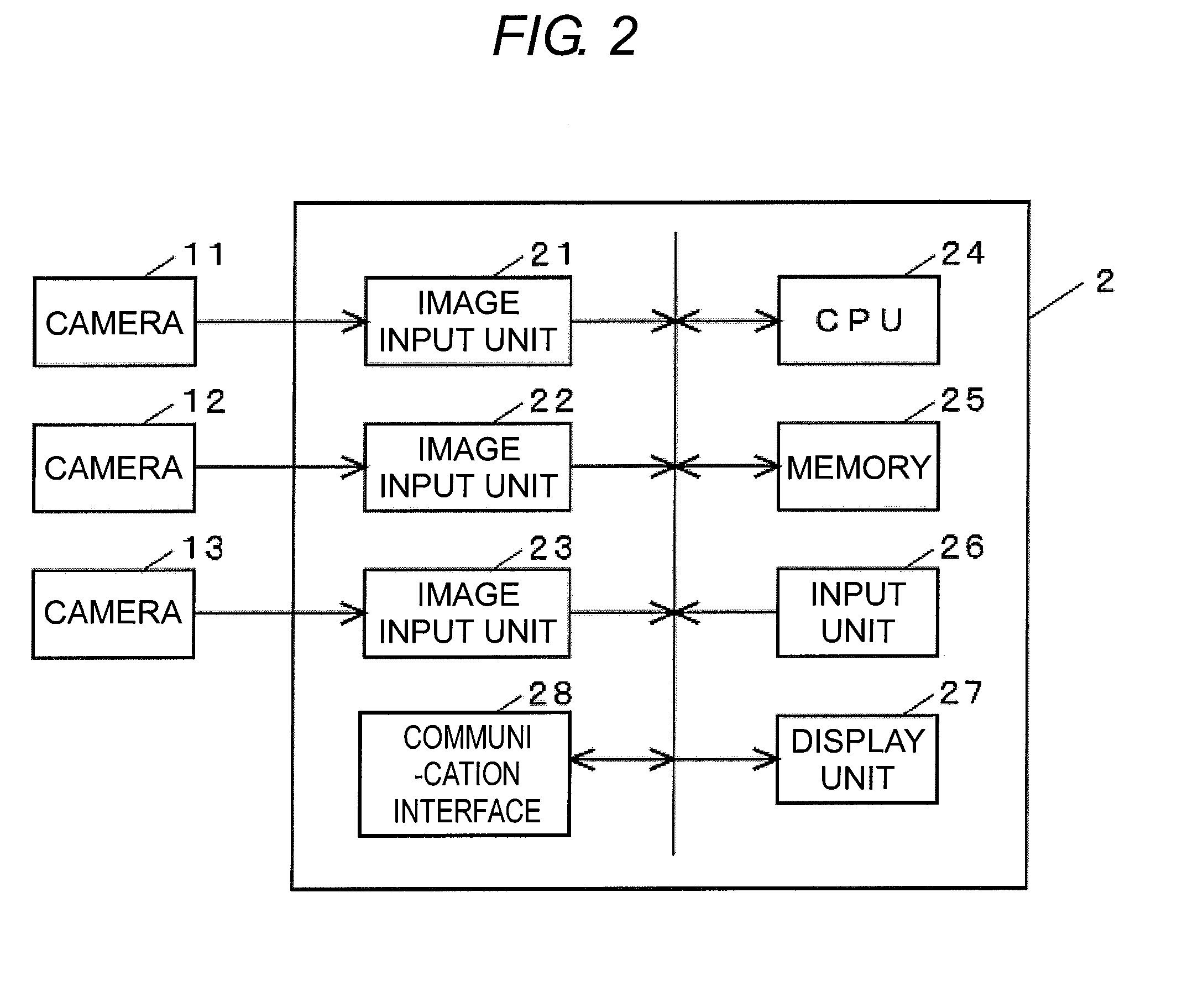
Camera pose estimation apparatus and method for augmented reality imaging
ActiveUS20100232727A1Satisfactory accuracyFast and efficient implementationImage enhancementImage analysis3d cameraCandidate key
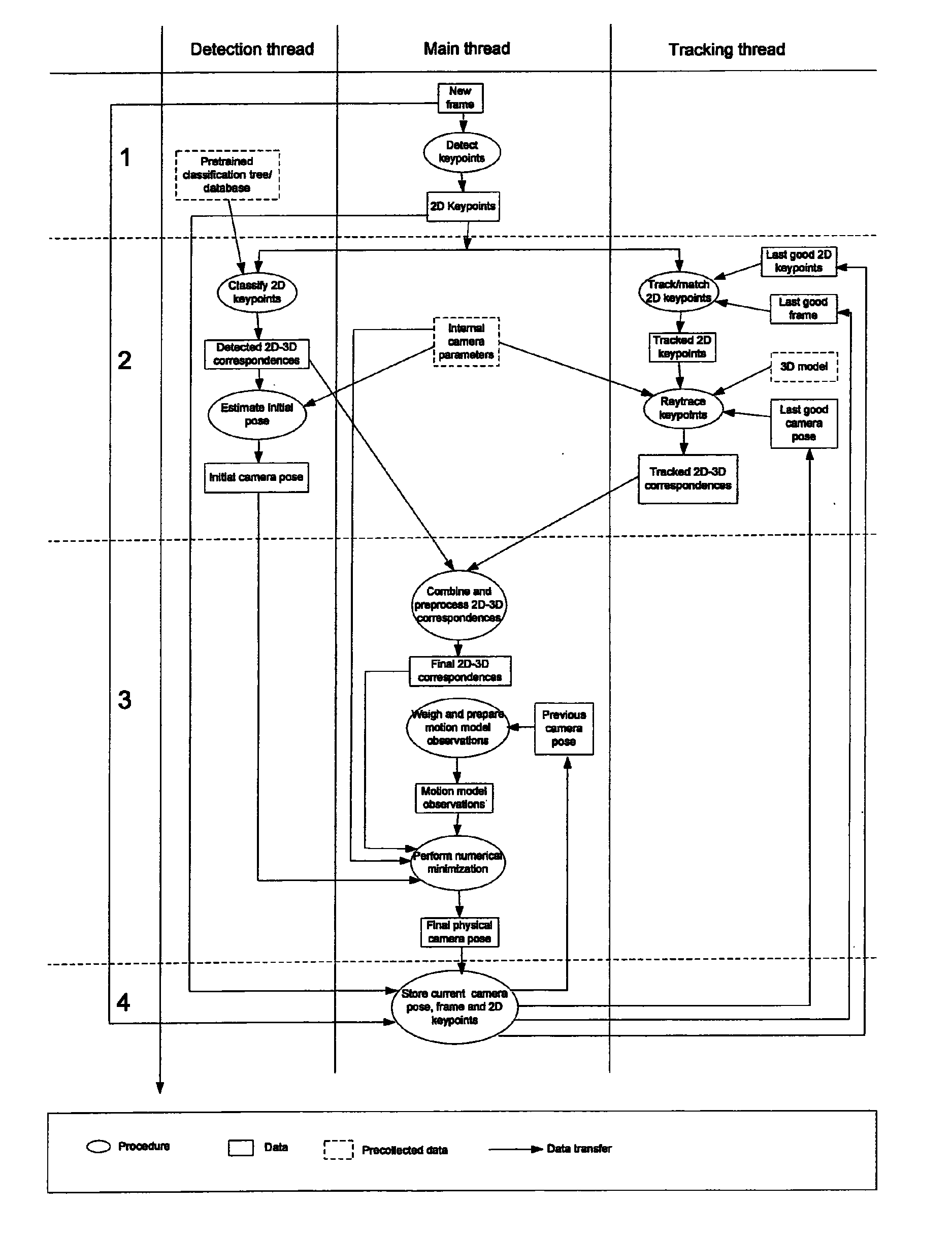
An apparatus for providing an estimate for a 3D camera pose relative to a scene from 2D image data of 2D image frame provided by said camera. A candidate 2D key points detector determines candidate 2D key points from the 2D image frame. A detected 3D observations detector determines detected 3D observations from pre-recorded scene data and the candidate 2D key points. A detected 3D camera pose estimator determines a detected 3D camera pose estimate from the camera data, the detected 3D observations and the candidate 2D key points. A first storage stores the detected 2D candidate key points and the 2D image data, and outputs in response to a 3D camera pose estimate output previous 2D image data and candidate 2D key points related to a previous 3D camera pose estimate output. A second storage stores and outputs a previous 3D camera pose estimate. A tracked 3D observations detector determines tracked 3D observations from the 2D image data, the candidate 2D key points, the camera data, the previous 2D image data and candidate 2D key points, the previous 3D camera pose estimate and 3D scene model data. A pose estimate selector outputs a selected one of the detected camera pose estimate and the previous 3D camera pose estimate. A 3D camera pose estimator computes and outputs the 3D camera pose estimate from the camera data, the detected 3D observations, the tracked 3D observations and the selected 3D camera pose estimate.
Owner:APPLE INC
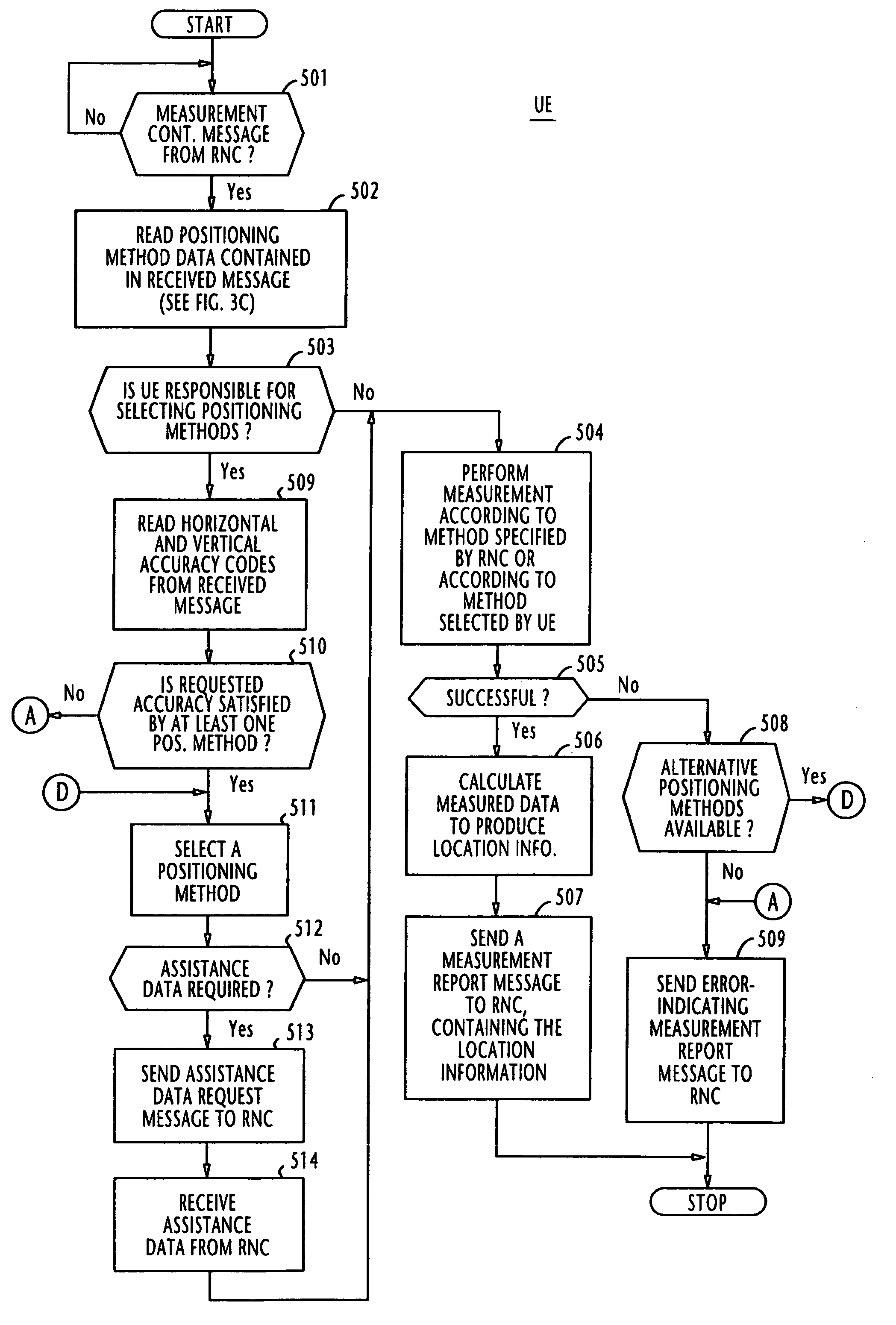
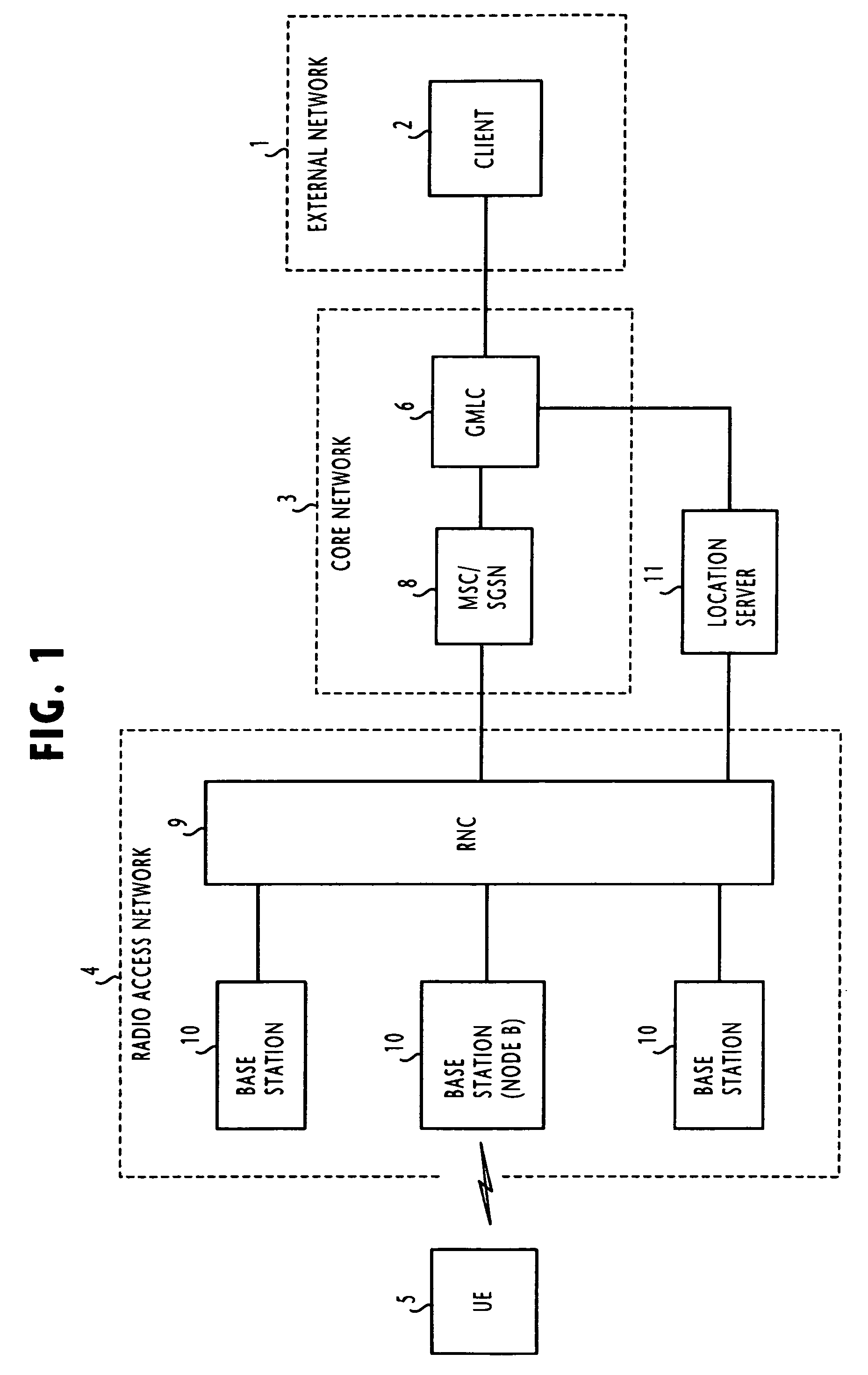
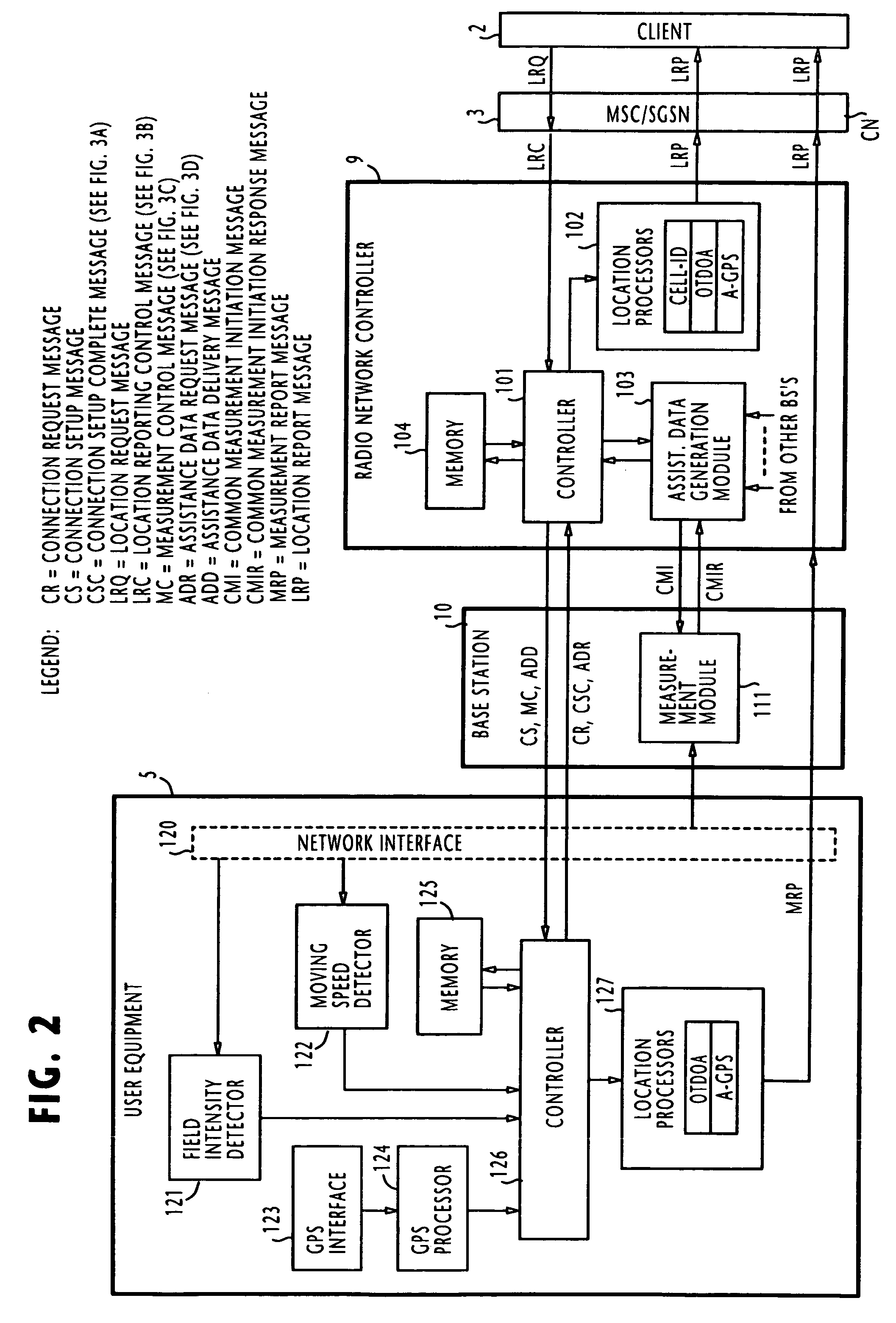
Location system and method for operating mobile terminal as a responsible location for selecting a positioning method
ActiveUS7376430B2Satisfactory accuracyPosition fixationVehicle position indicationEngineeringMobile communication network
In a mobile communication network, a controlling node receives capability information from a mobile terminal, indicating positioning methods supported by the mobile terminal and selectability of the positioning methods. In response to a location request message from a client terminal requesting the location information of a target mobile terminal, the controlling node transmits a first control message via a wireless node to the target mobile terminal, containing a copy of requested accuracy of the location information, if the capability information indicates that the target mobile terminal is capable of selecting positioning methods. The mobile terminal performs measurement according to a positioning method that satisfies the requested accuracy. Otherwise, the controlling transmits a second control message to the mobile terminal, specifying a positioning method. In this case, the mobile terminal performs measurement according to the specified positioning method.
Owner:NEC CORP
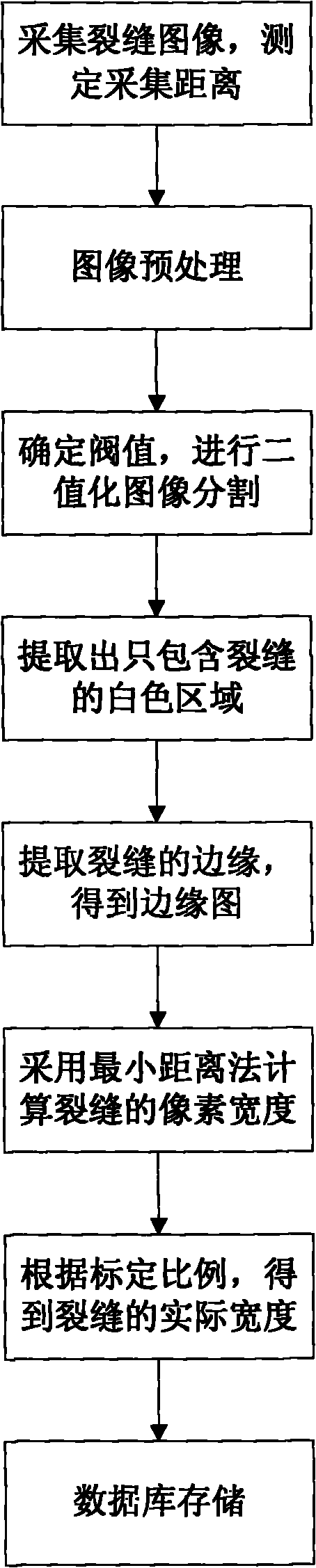
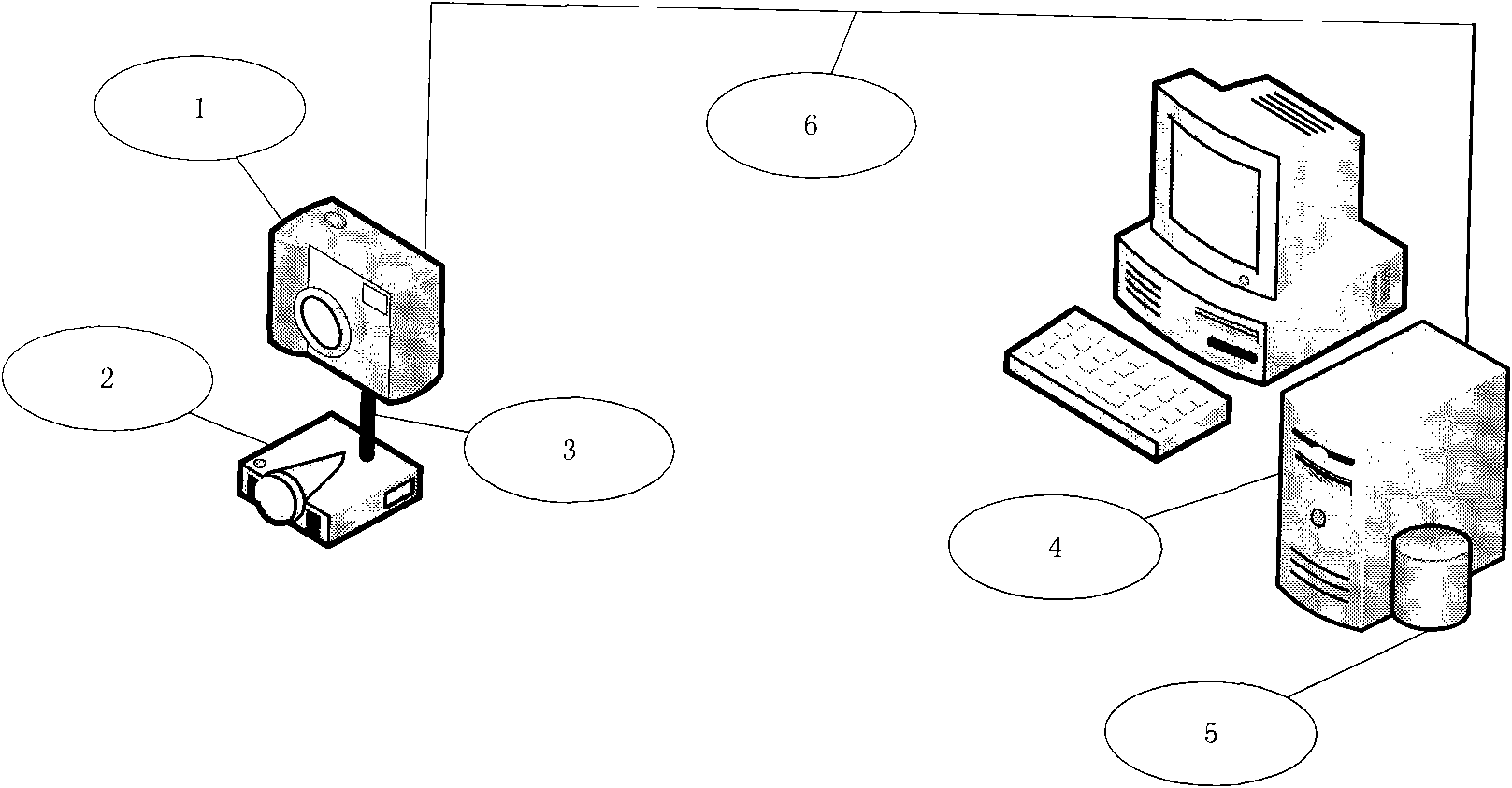
Method and device for measuring tunnel lining cracks
ActiveCN101957178ALow costQuick fixImage analysisUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceImage segmentation
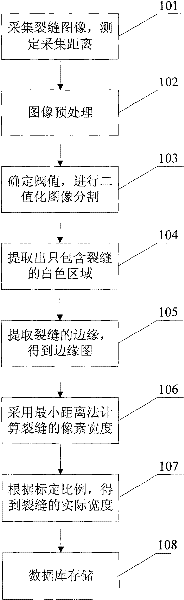
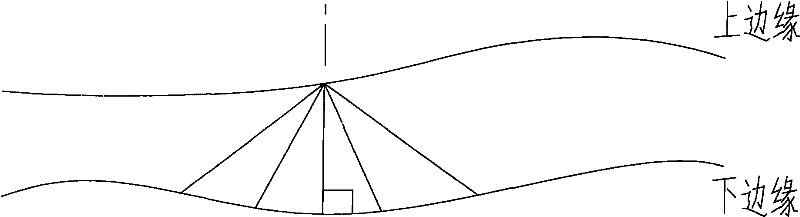
The invention relates to a method for measuring tunnel lining cracks. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring an image of a crack by a digital camera and measuring the acquisition distance by a laser ranger; selecting an area needing to be measured from the acquired image so as to prevent processing deviation due to excessively big picture and relatively small target crack, and changing the selected area into a gray image; determining a threshold for the selected gray image and performing binarization image division to obtain a target area; extracting a white area only comprising the crack from the target area; extracting the border of the crack to obtain a border graph; calculating the pixel width of the crack by a minimum distance method; and obtaining the actual width of the crack according to a predetermined calibration proportion between the actual pixel size and the photographing distance. The method has the advantages of low cost, high speed, convenient carrying and high measurement precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI TONGYAN CIVIL ENGINEERING TECHNOLOGY CORP LTD
Layer-thickness detection methods and apparatus for wafers and the like, and polishing apparatus comprising same
InactiveUS7052920B2Easy to detectHigher diffraction orders is eliminatedSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesCorrelation functionSignal light
Methods and apparatus are disclosed for detecting a thickness of a surficial layer (e.g., metal or insulating layer) on a workpiece (e.g., semiconductor wafer) during a process for planarizing the layer, so as to stop the process when a suitable process endpoint is reached. Layer thickness is detected based on a spectral-characteristic signal of reflected or transmitted signal light, obtained by directing a probe light onto the surface of the workpiece. Example spectral characteristics are local maxima and minima of signal-light waveform, differences or quotients of the same, a dispersion of the signal-light waveform, a component of a Fourier transform of the signal waveform, a cross-correlation function of the signal waveform. Alternatively, the zeroth order of signal light is selected for measurement, or a spatial coherence length of the probe light is compared with the degree of fineness of the pattern on the surface illuminated with the probe light. An optical model can be determined based on the comparison, and at least one of the layer thickness and the process endpoint is detected by comparing the measured signal-light intensity with the calculated theoretical signal light intensity.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Tunnel lining crack width measuring method and device
The invention relates to a tunnel lining crack width measuring method, which comprises the follow steps of: (1) picking up crack images through a digital camera and measuring pickup distance through a laser distance measuring instrument; (2) selecting a region required to be measured on the picked images and converting selected region images into gray level images; (3) determining the threshold value of the gray level images selected in the second step, cutting binary image cutting, and obtaining a target region; (4) extracting a white region only comprising crack in the target region; (5) extracting the edge of the crack by a sub pixel method, and obtaining sub pixel level edge images; (6) circulating the pixel width of the crack by a minimum distance method; (7) circulating the actual width of the obtained crack according to the calibration proportion of the predetermined actual pixel size and the image pickup distance; and (8) storing the obtained actual width data into a crack data base. Compared with the prior art, the tunnel lining crack width measuring method has the advantages of low cost, high speed, convenience, high precision and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Shower head structure for processing semiconductor
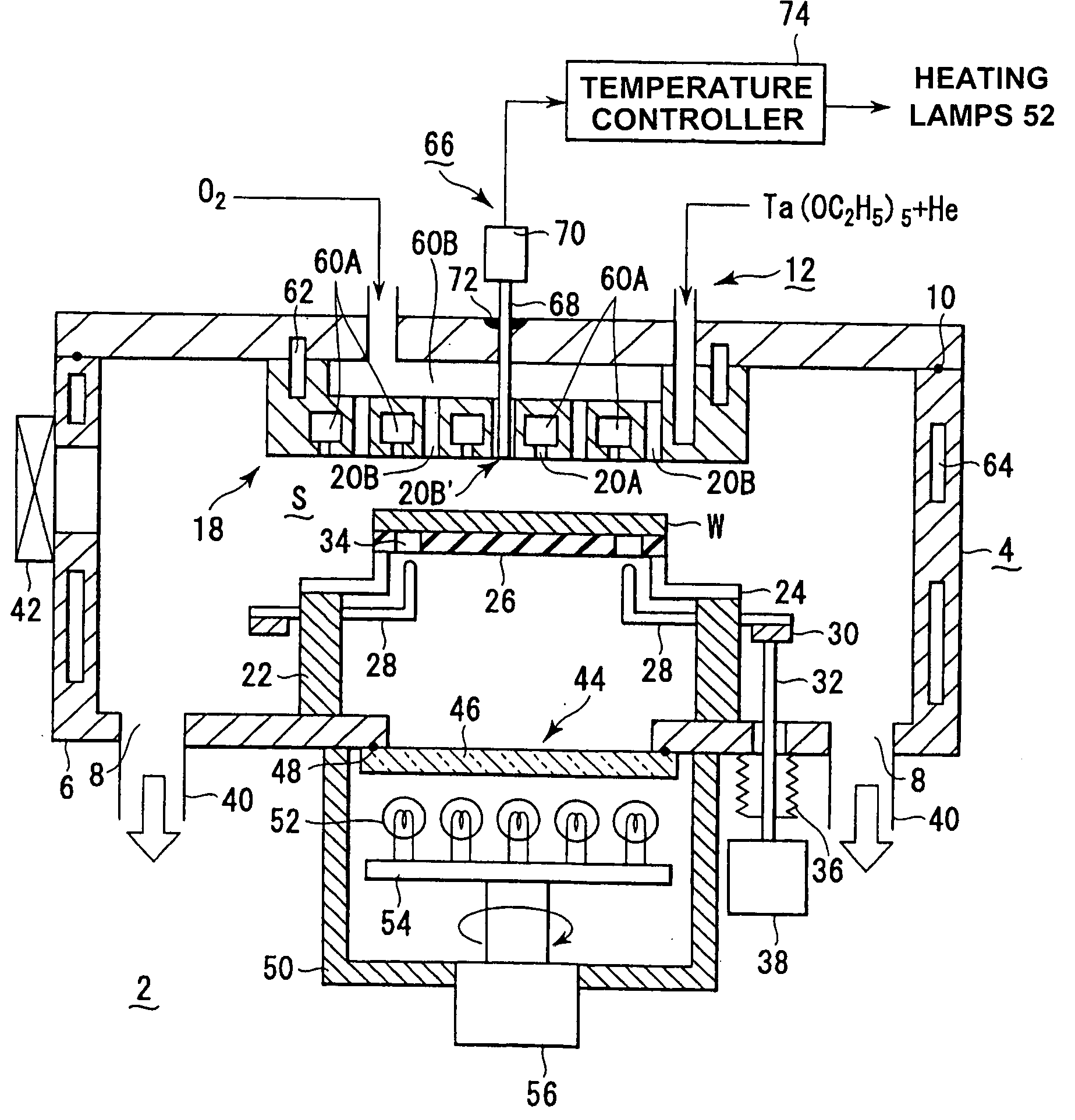
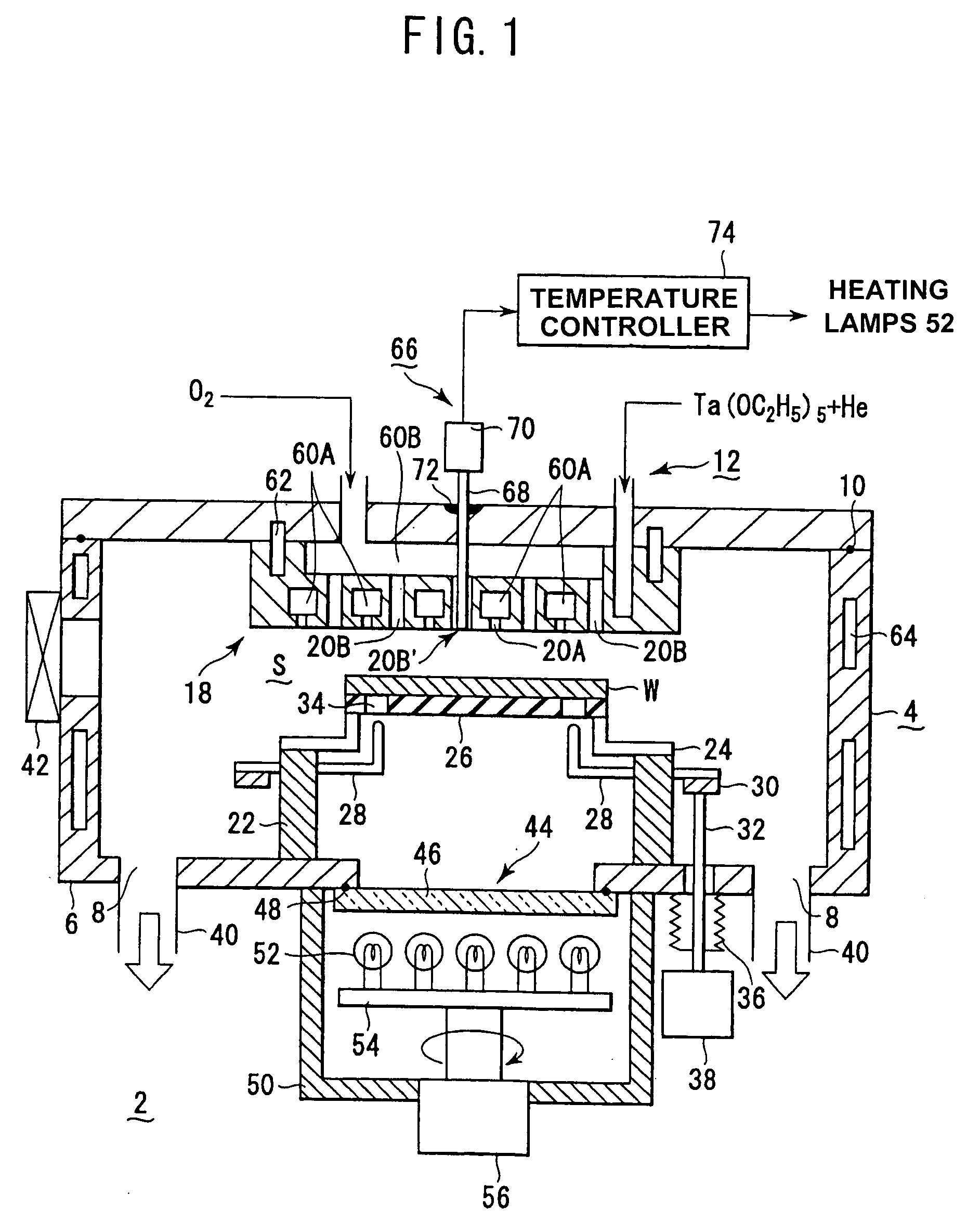
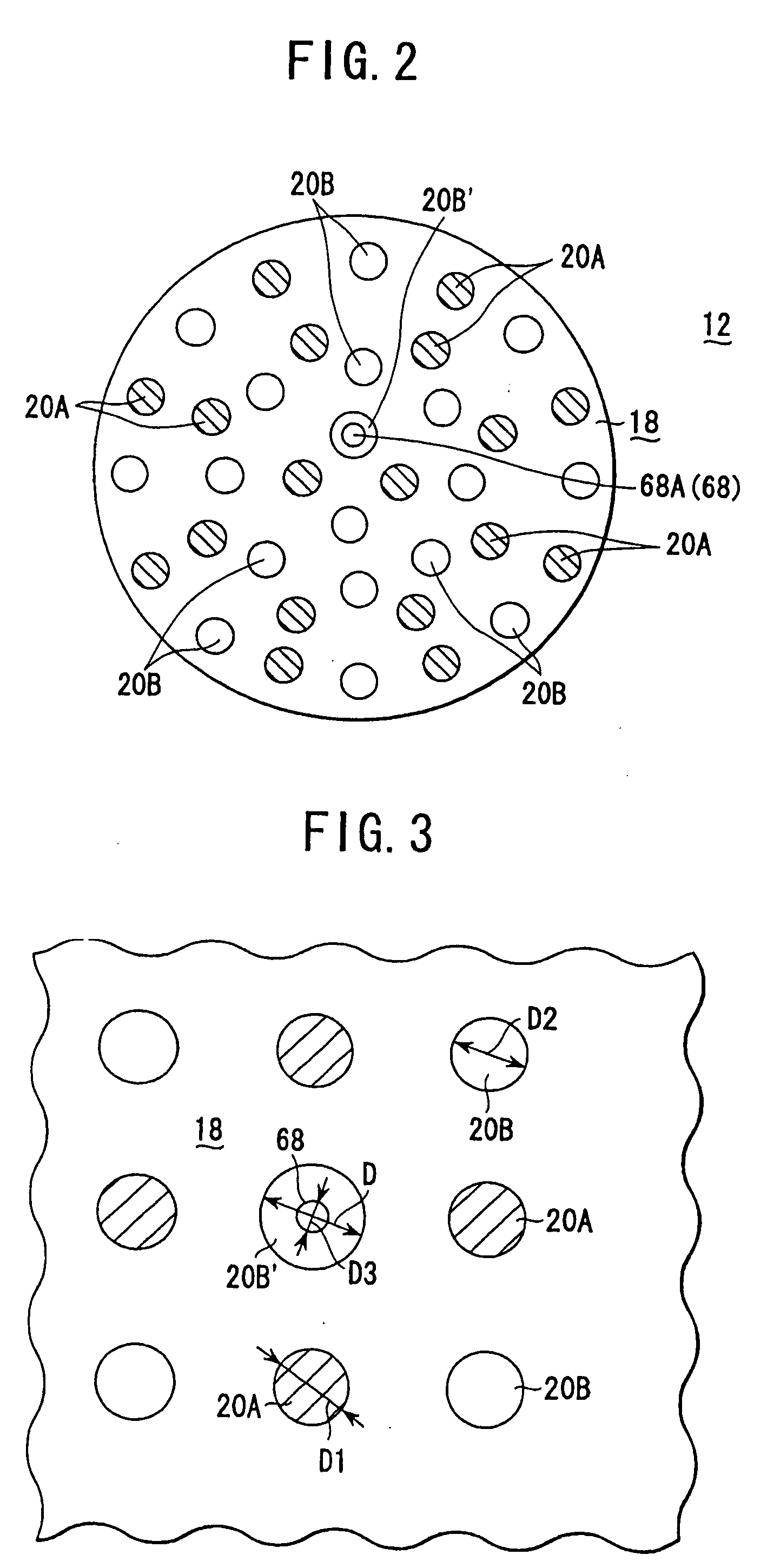
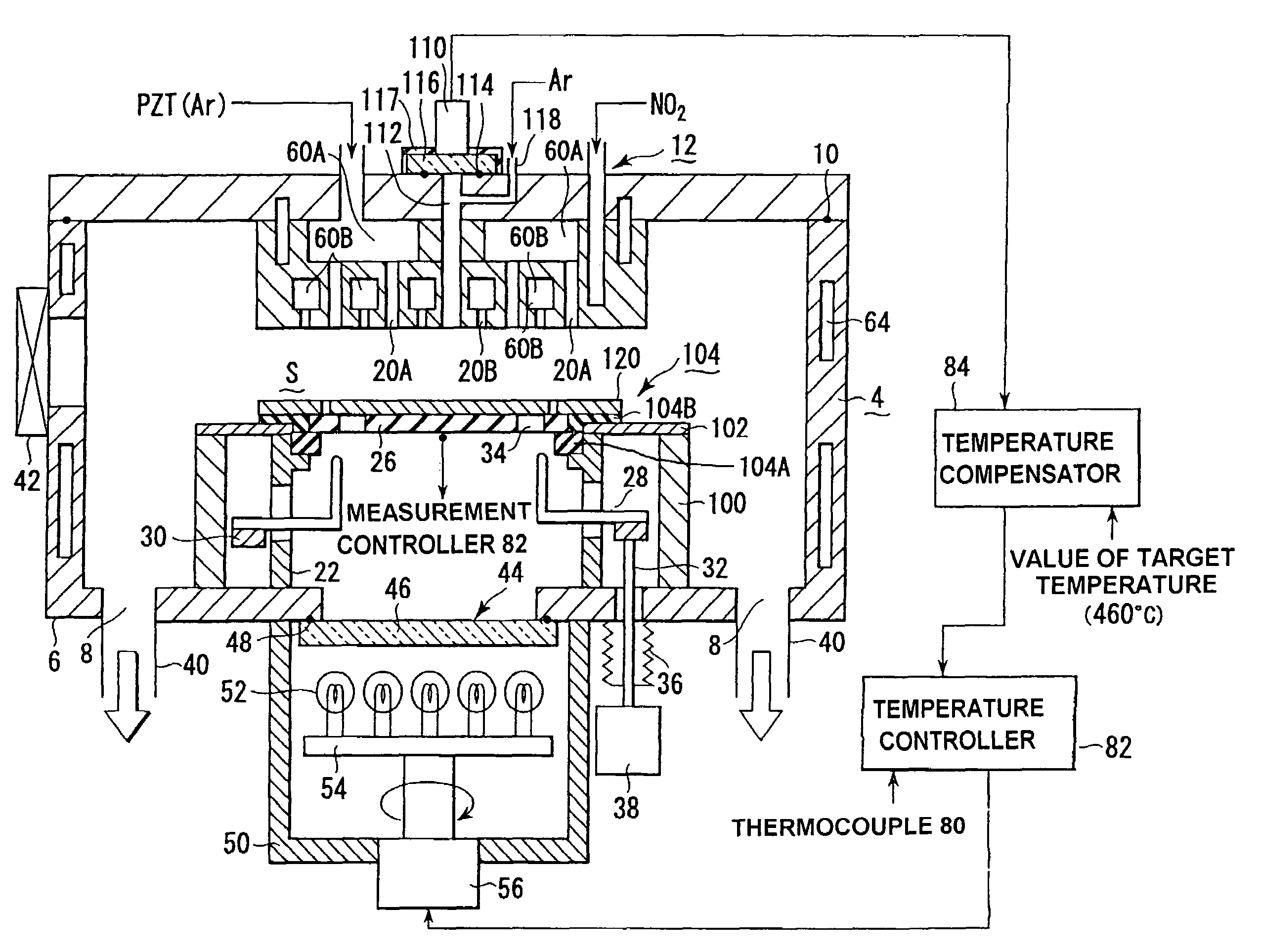
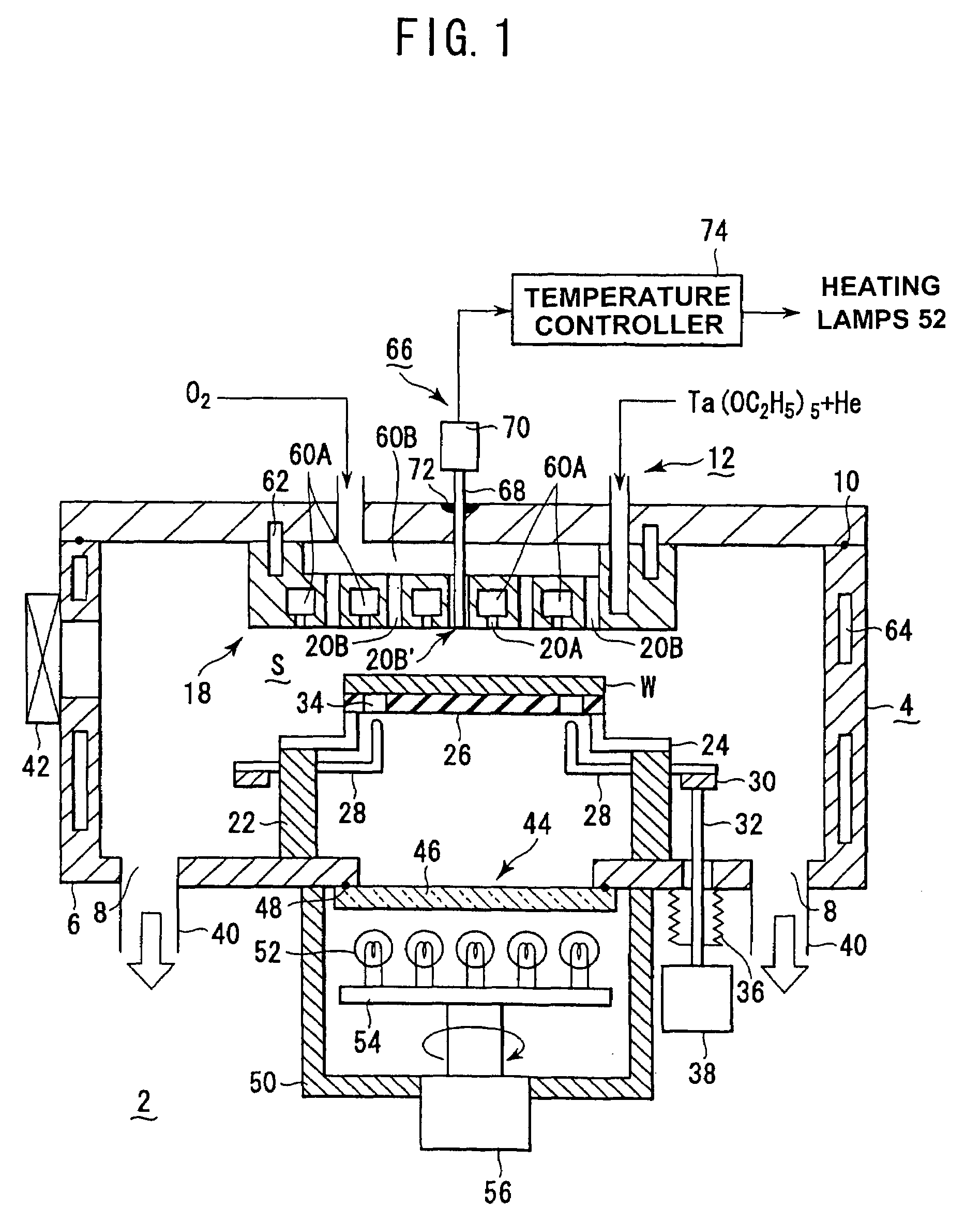
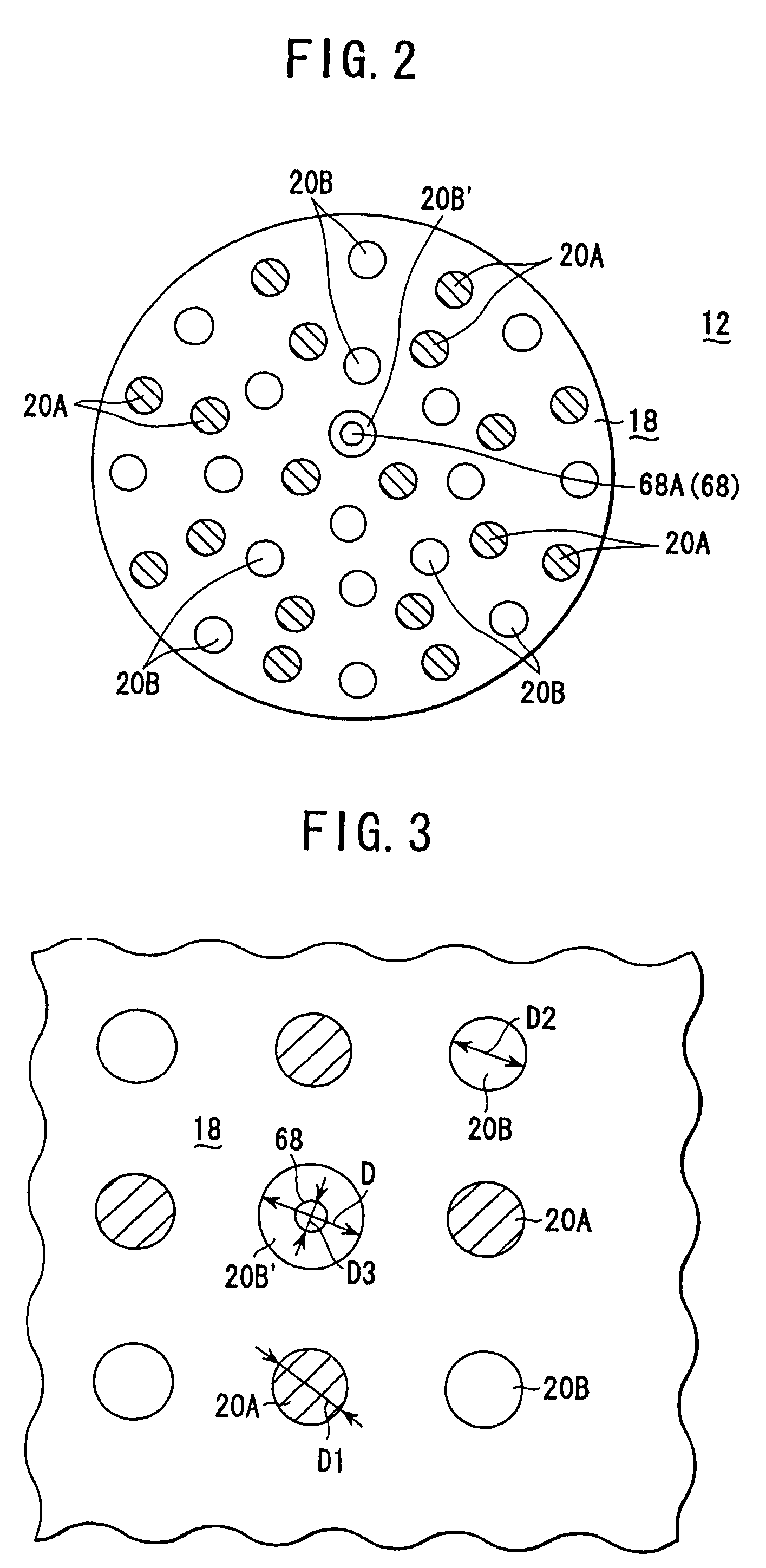
InactiveUS20050118737A1Improve intra-surface uniformityImprove uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesRadiation thermometerEngineering
A shower head structure disposed in a device 2 for processing a semiconductor while supplying processing gas to a processing space S for storing a heated processed substrate W, comprising a shower head 12 having a plurality of gas injection holes 20B for supplying the processing gas and a light introducing rod 68 of a radiation thermometer 66 inserted into at least one of the gas injection holes 20B.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
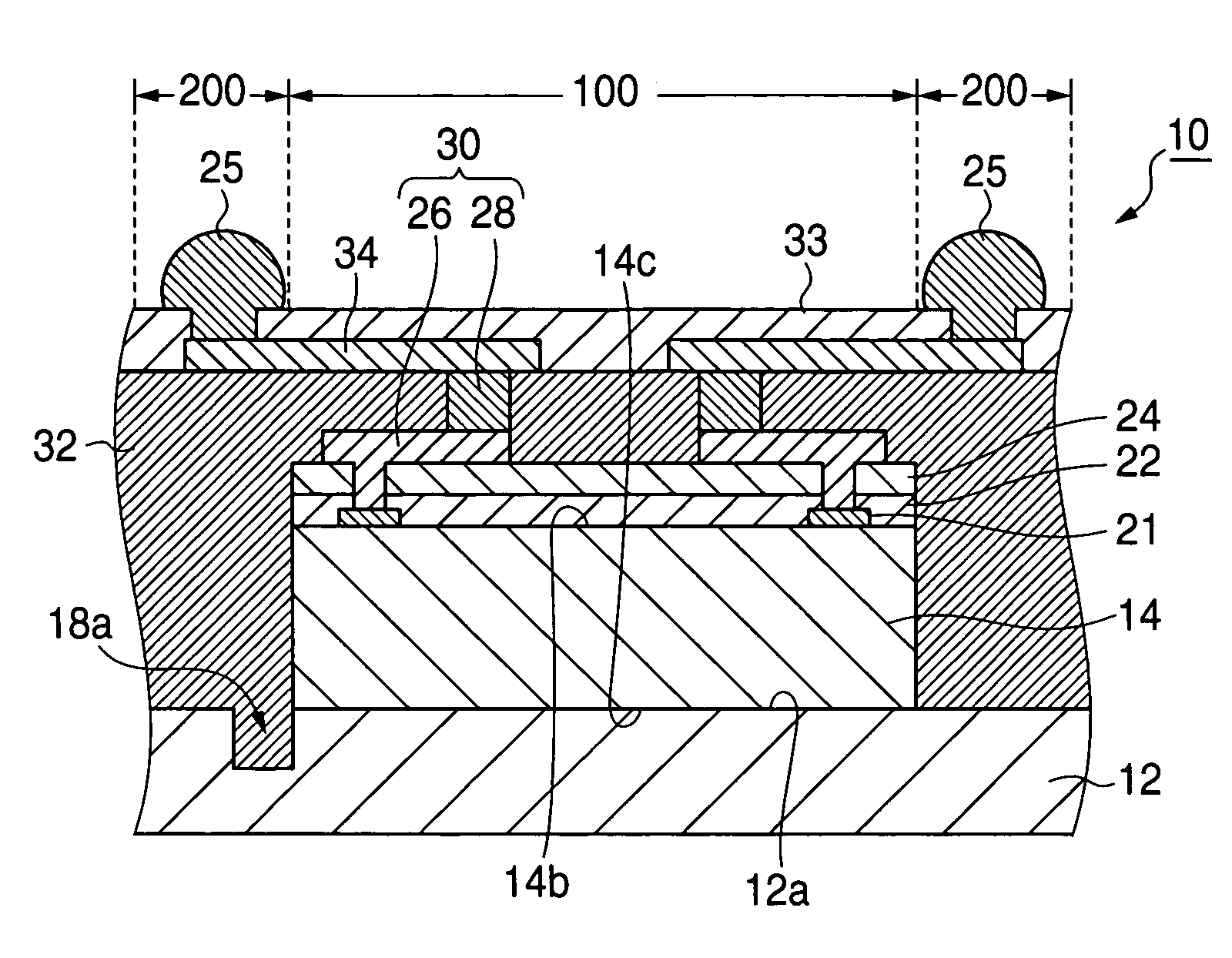
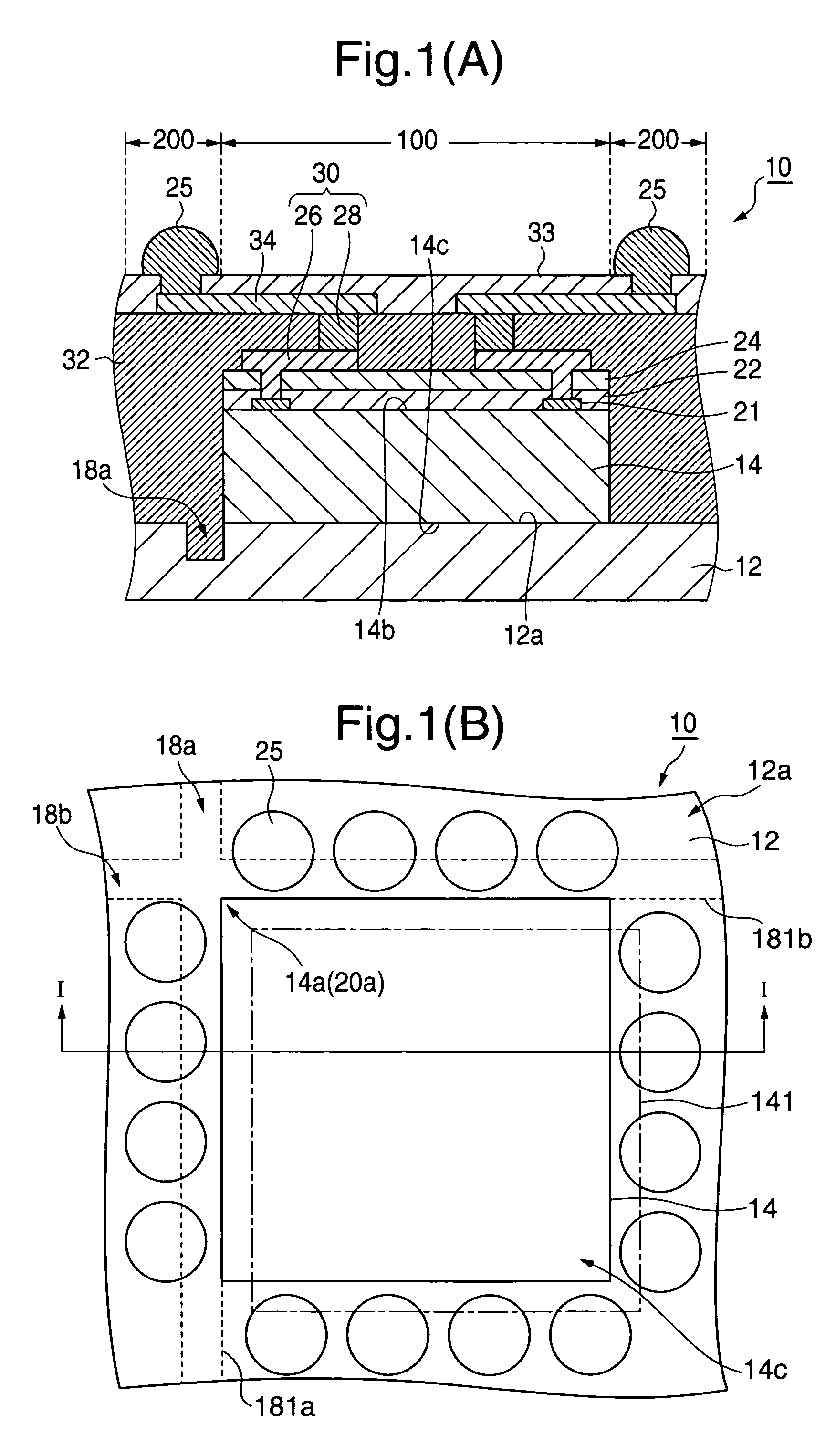
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
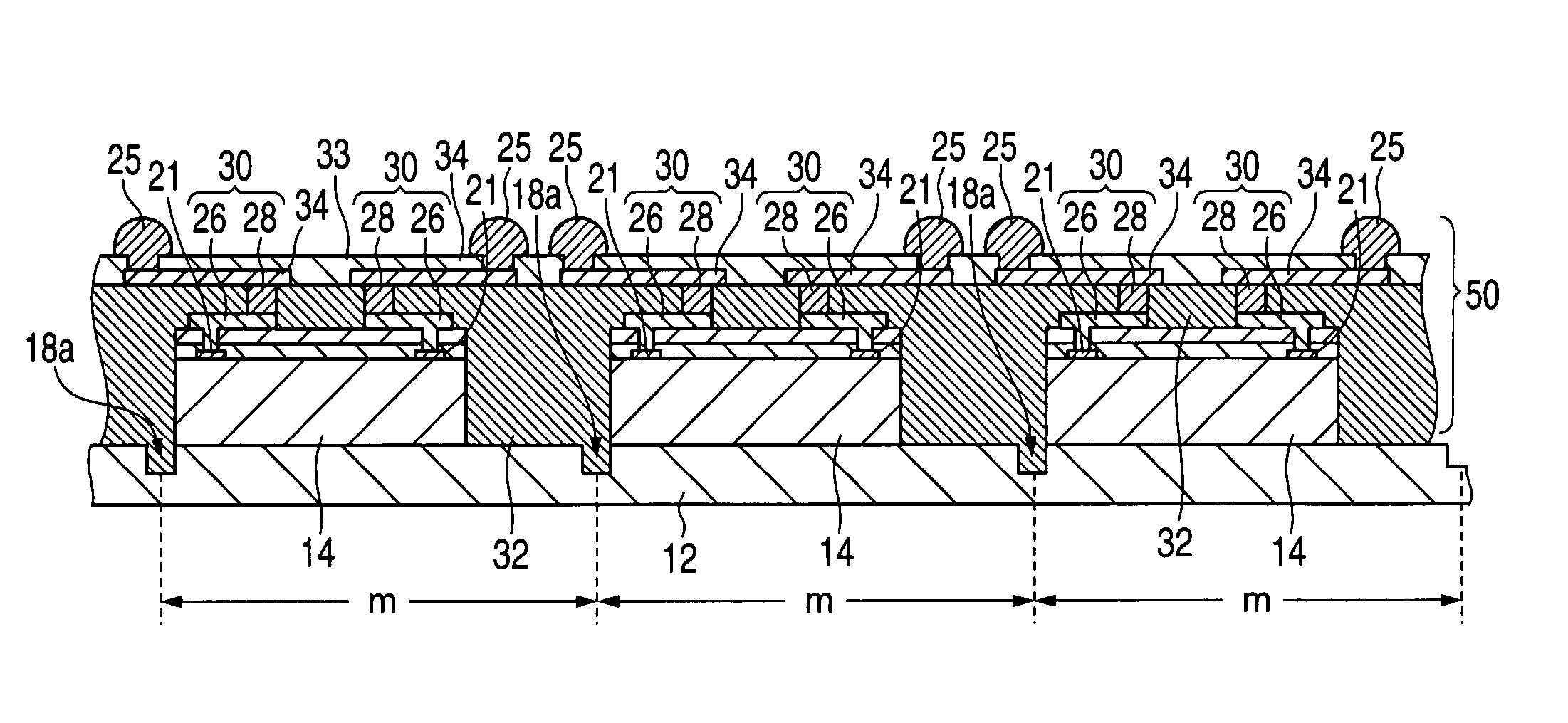
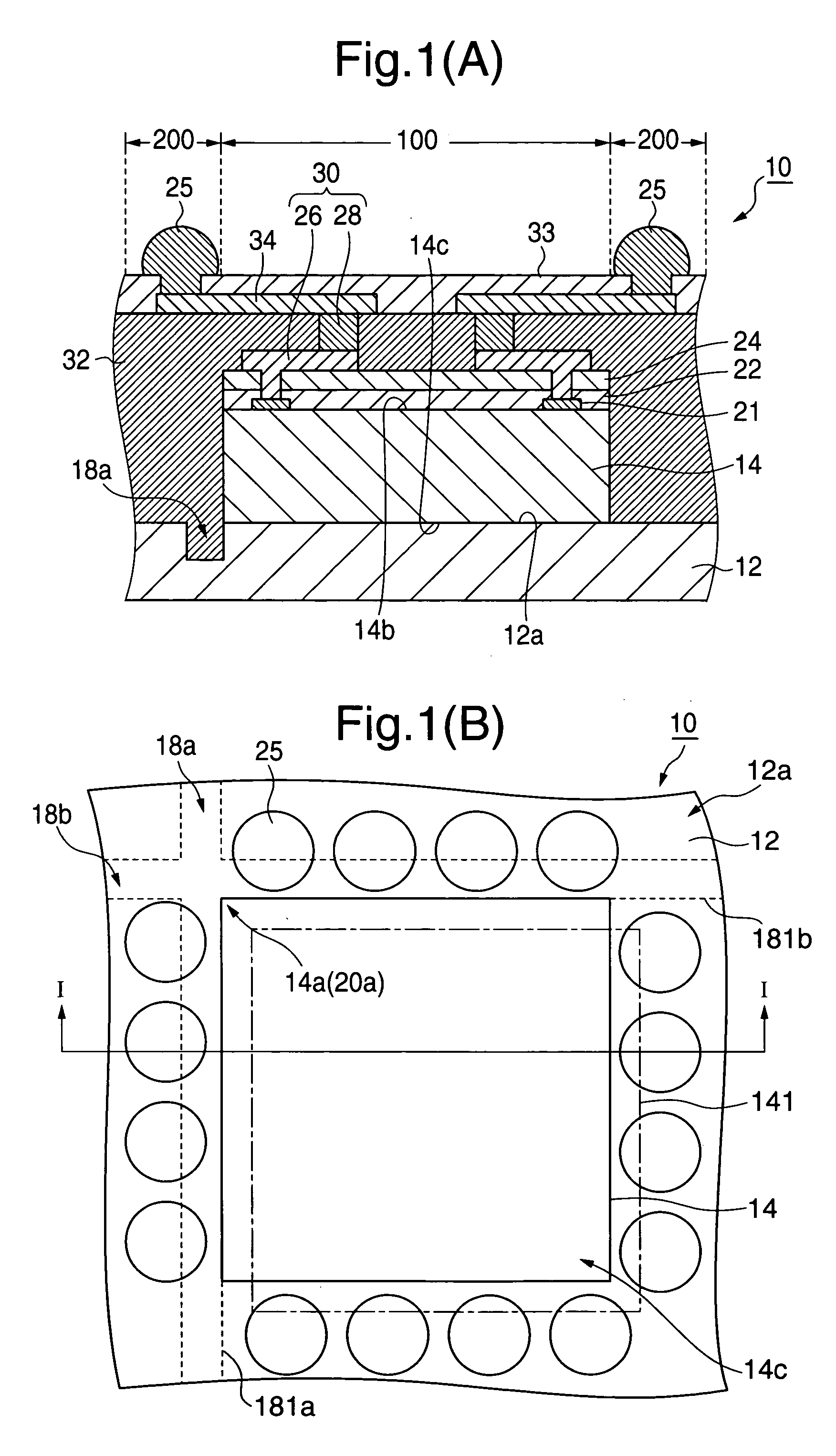
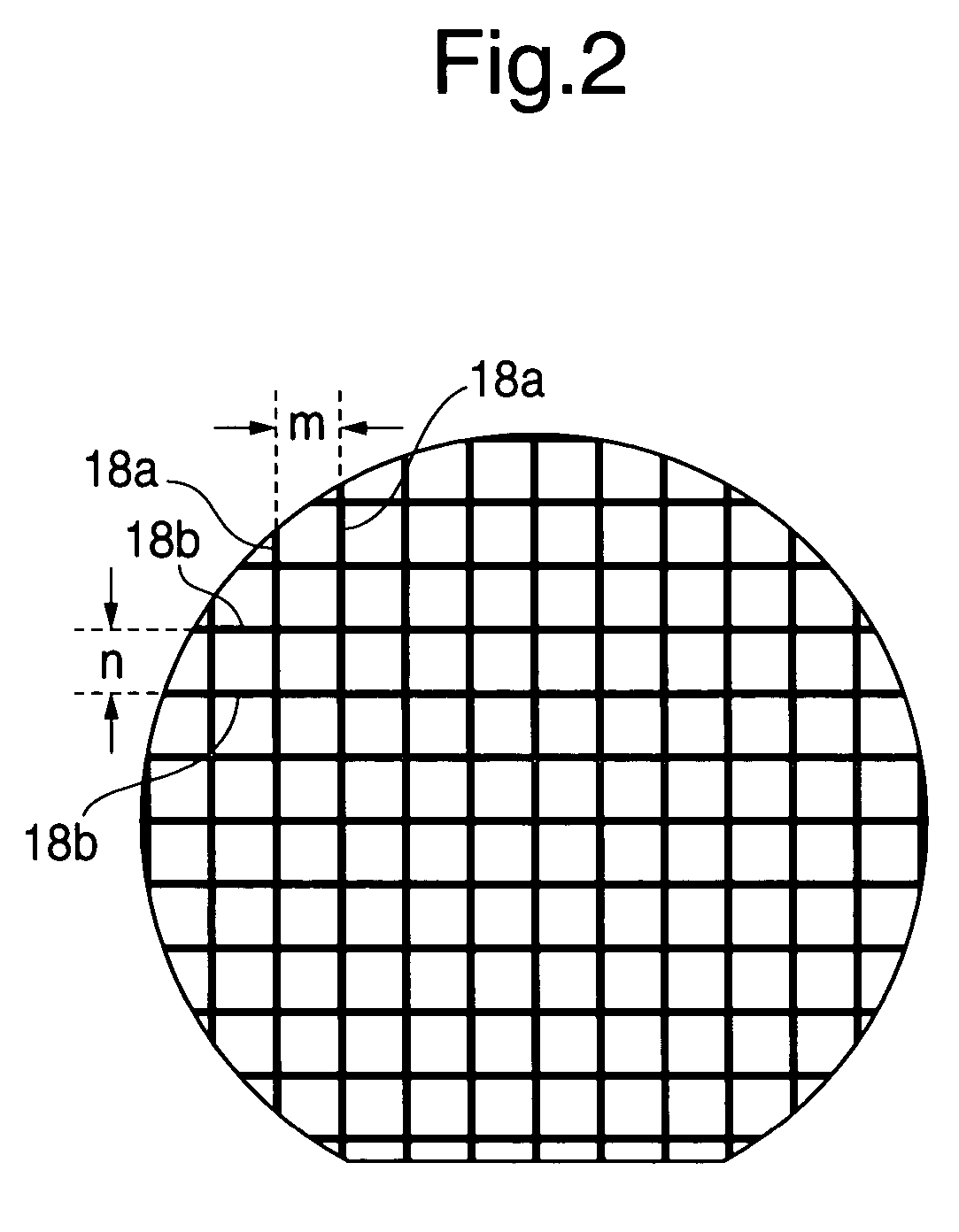
InactiveUS20050116324A1High reliable fan-out structureReduce yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSolder ballSemiconductor chip
A plurality of semiconductor chips (14) each having a first main surface (14b) formed with electrode pads (21) and a second main surface (14c) opposite to the first main surface are respectively mounted on a chip mounting surface (12a) larger in area than the second main surface, of a wafer-shaped mounting substrate (12) at equal intervals so as to extend along first and second trenches (18a, 18b) defined in the chip mounting surface with these trenches as target lines. Thereafter, solder balls (25) electrically connected to the electrode pads of the semiconductor chips are disposed on their corresponding wiring patterns 34 that extend from above first regions (100) located above the semiconductor chips, of a surface region of an encapsulating layer (32) covering the semiconductor chips to above second regions (200) that surround the first regions. Afterwards, the encapsulating layer and the mounting substrate are cut and thereby fractionized into semiconductor devices each having a fan-out structure.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Best-fit affinity sensorless conversion means or technique for pump differential pressure and flow monitoring
ActiveUS20160010639A1Satisfactory accuracyEfficient use ofValve arrangementsPump testingAffinity lawsDifferential pressure
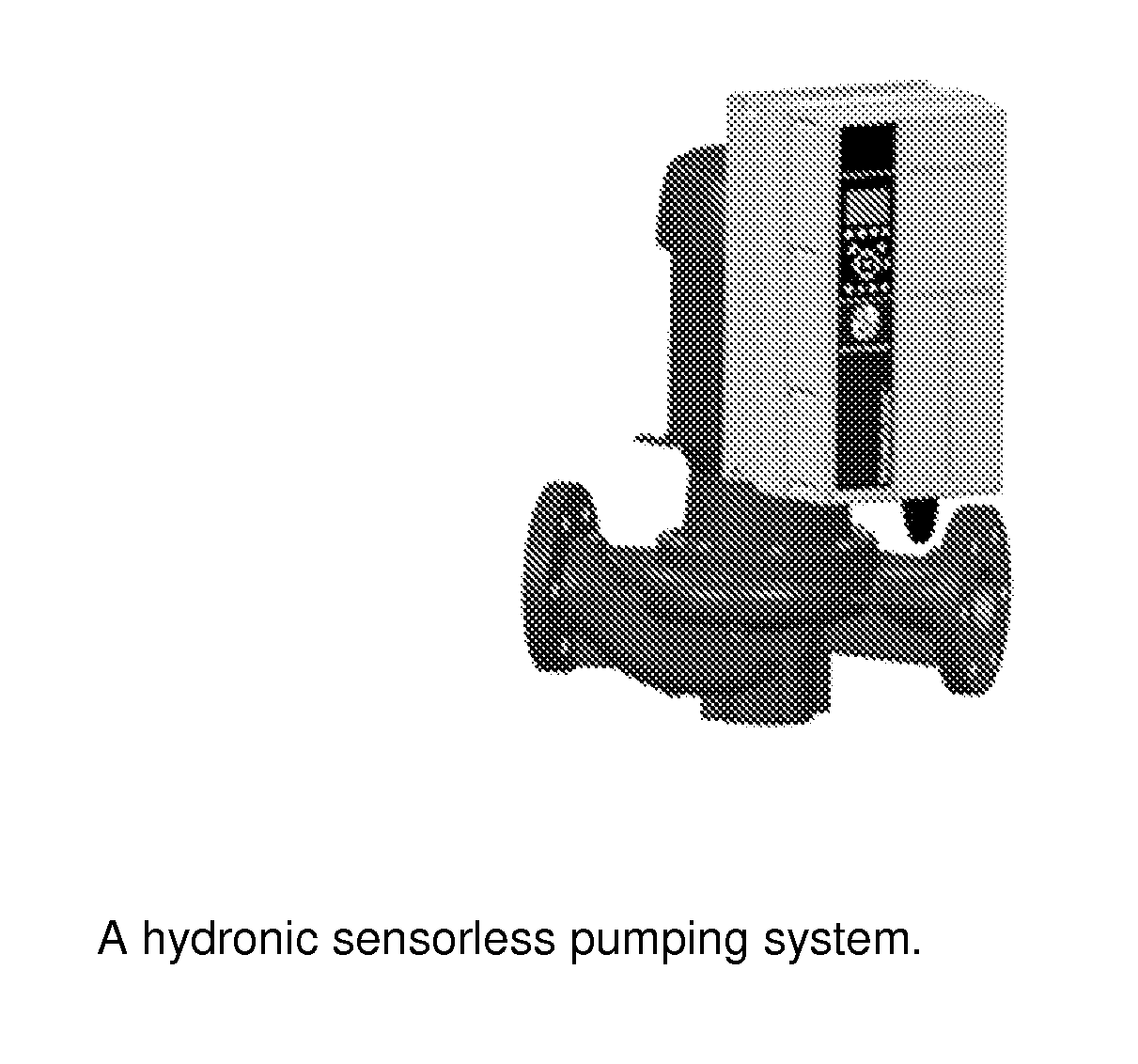
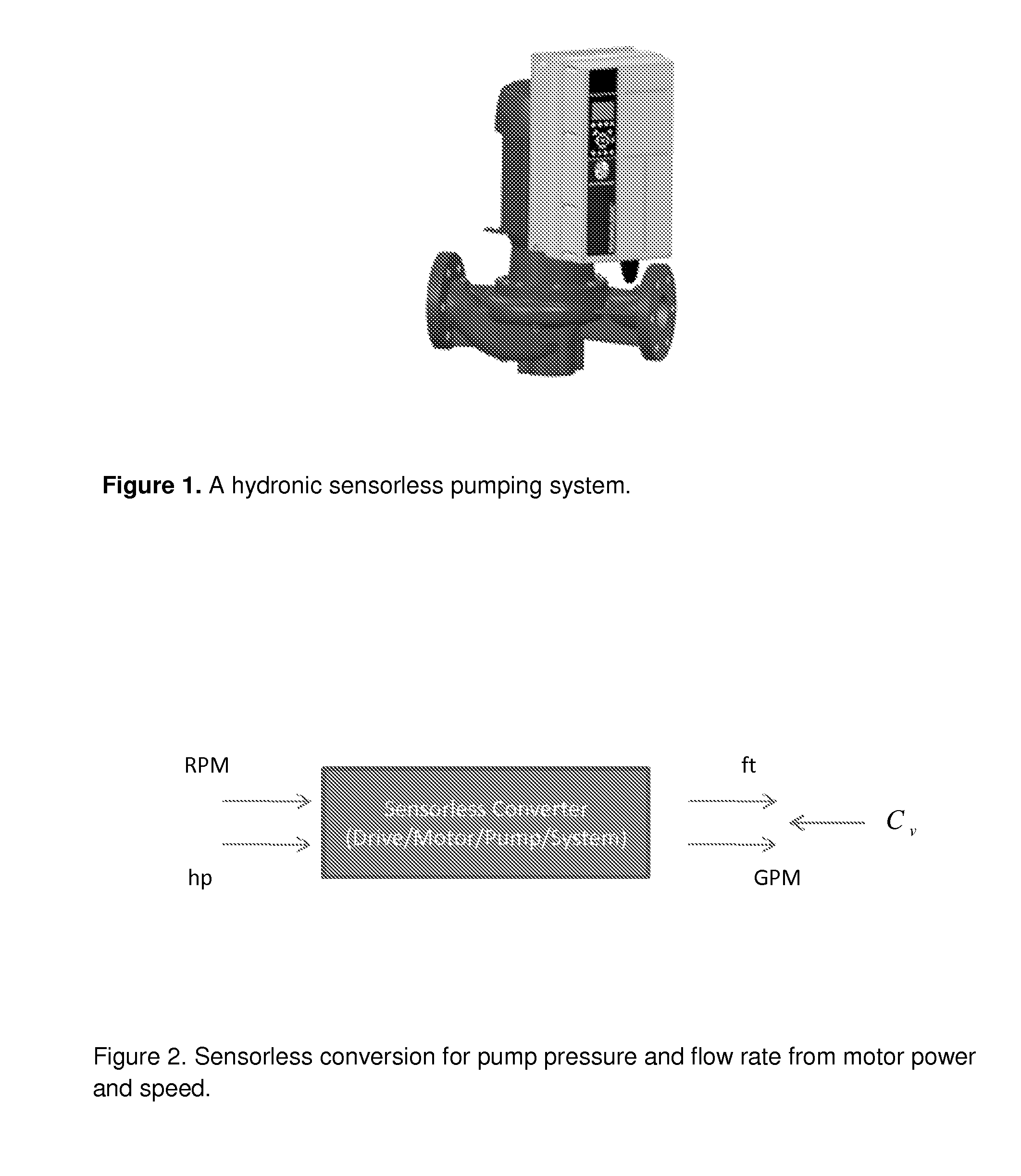
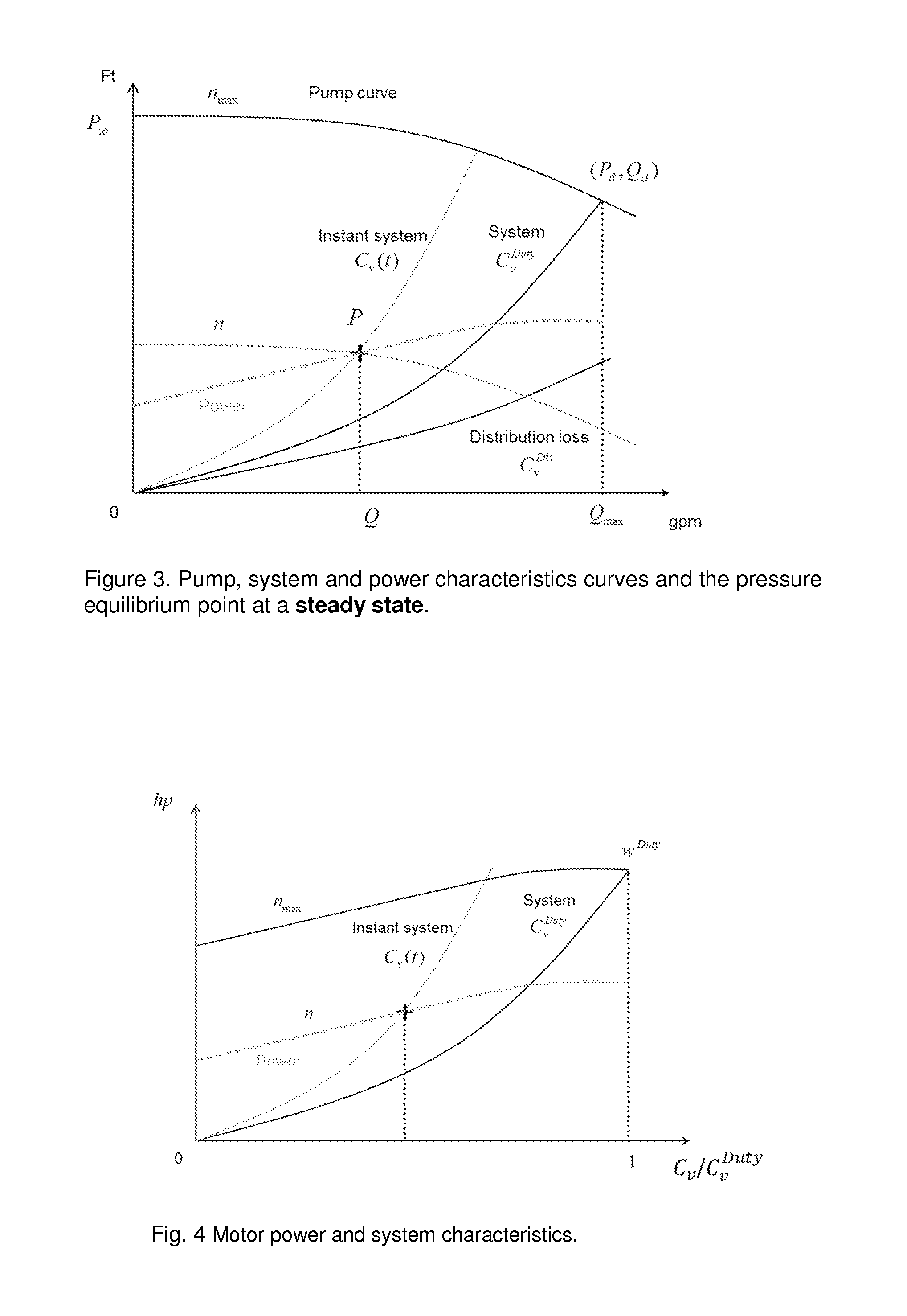
The present invention provides apparatus, including a hydronic sensorless pumping system, that features a signal processor or processing module configured to receive signaling containing information about motor readout values of power and speed, and also about pump and system characteristics equations together with empirical power equations that are constructed by a polynomial best-fit function together with pump affinity laws based upon a pump curve published by a pump manufacturer; and determine corresponding signaling containing information about a pump or system pressure and a flow rate at the motor readout values of power and speed, based upon the signaling received.
Owner:FLUID HANDLING
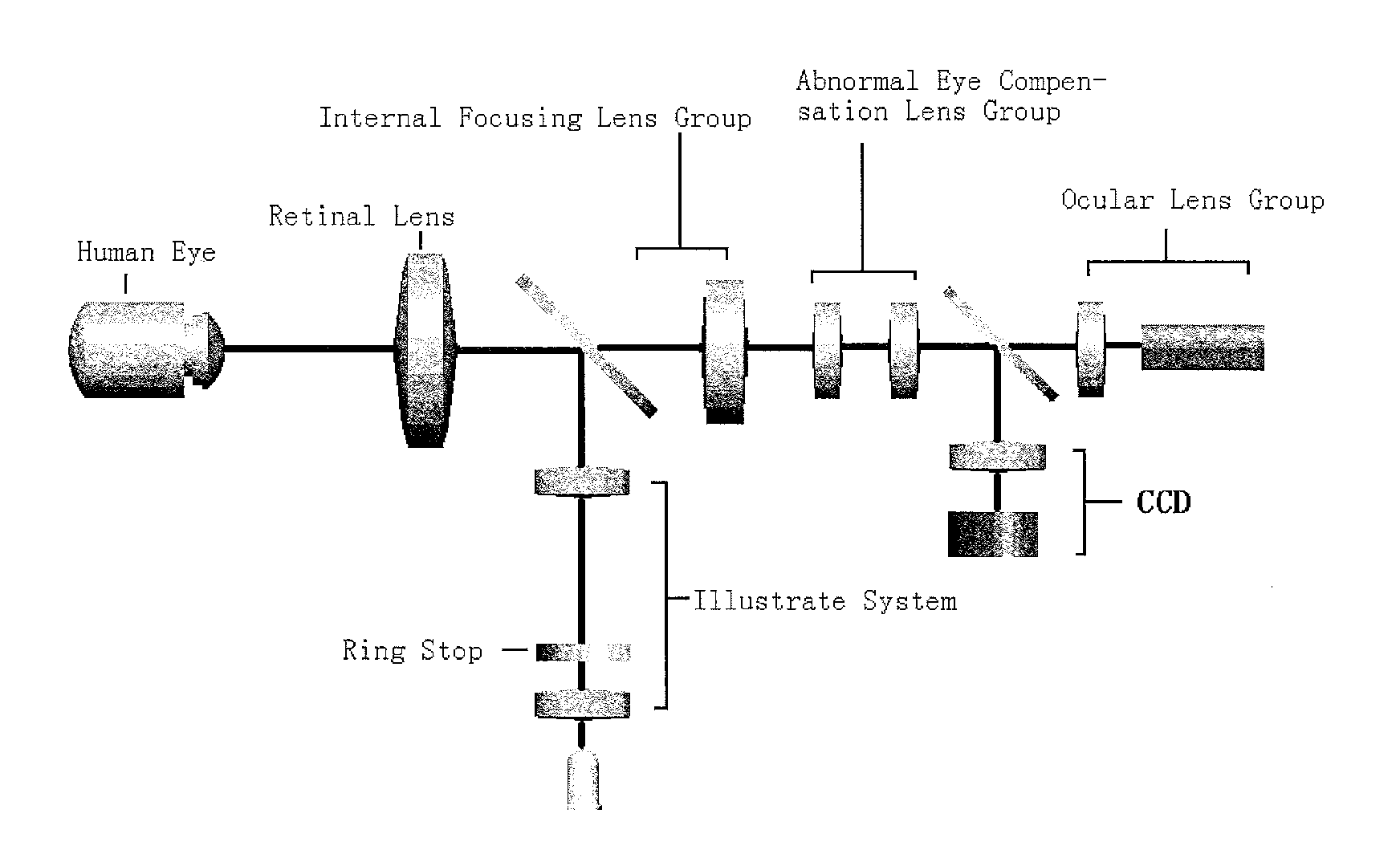
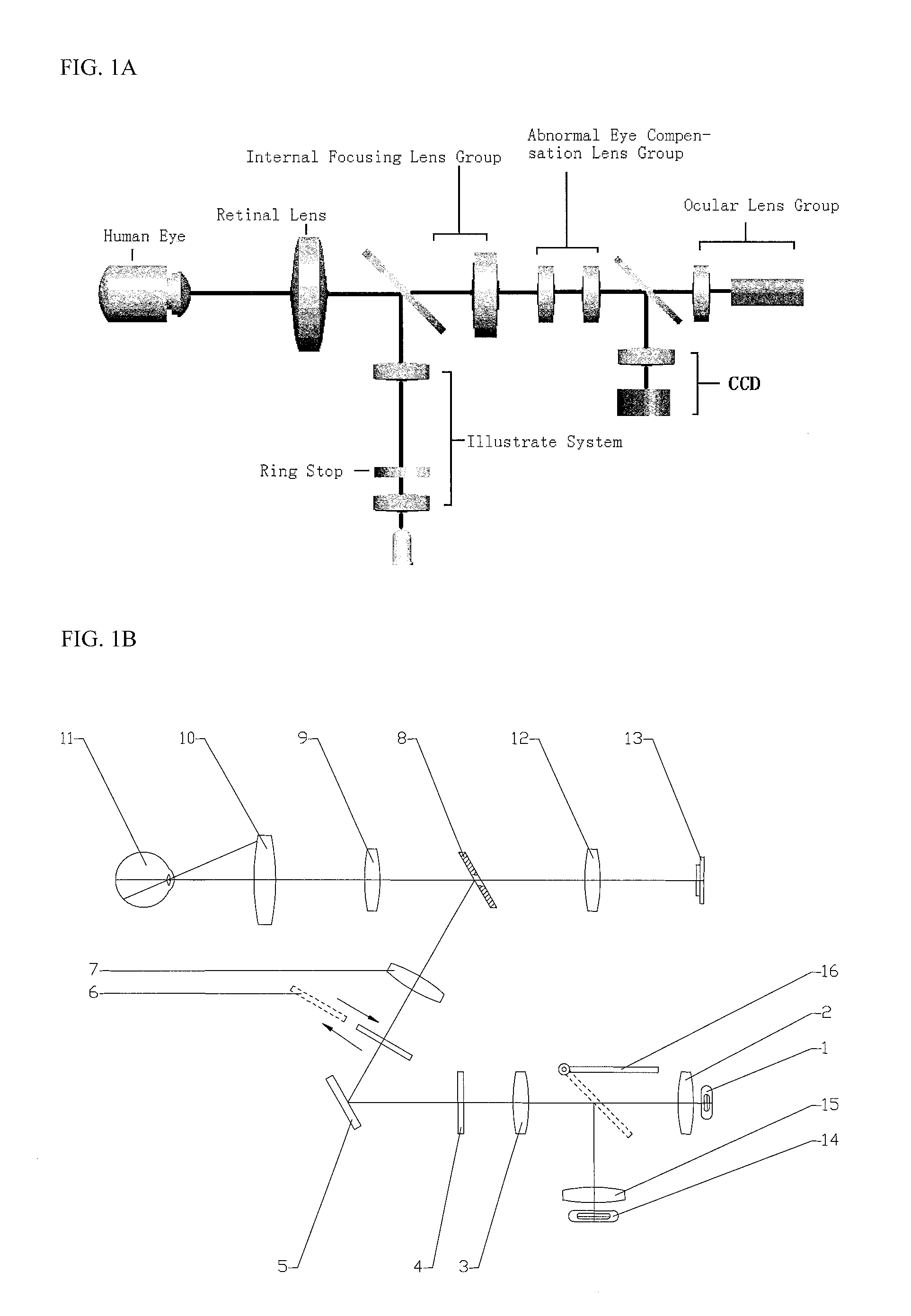
Apparatus and method for non-invasive diabetic retinopathy detection and monitoring
ActiveUS20120249959A1Robust identificationEnhance vesselImage analysisAcquiring/recognising eyesDiabetes retinopathyOphthalmology
A fundus camera using infrared light sources, which included an imaging optical path and an optical path for focusing and positioning and two optical paths share a common set of retina objective lens, and a computer-assisted method for retinal vessel segmentation in general and diabetic retinopathy (DR) image segmentation in particular. The method is primarily based on Multiscale Production of the Matched Filter (MPMF) scheme, which together the fundus camera, is useful for non-invasive diabetic retinopathy detection and monitoring.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
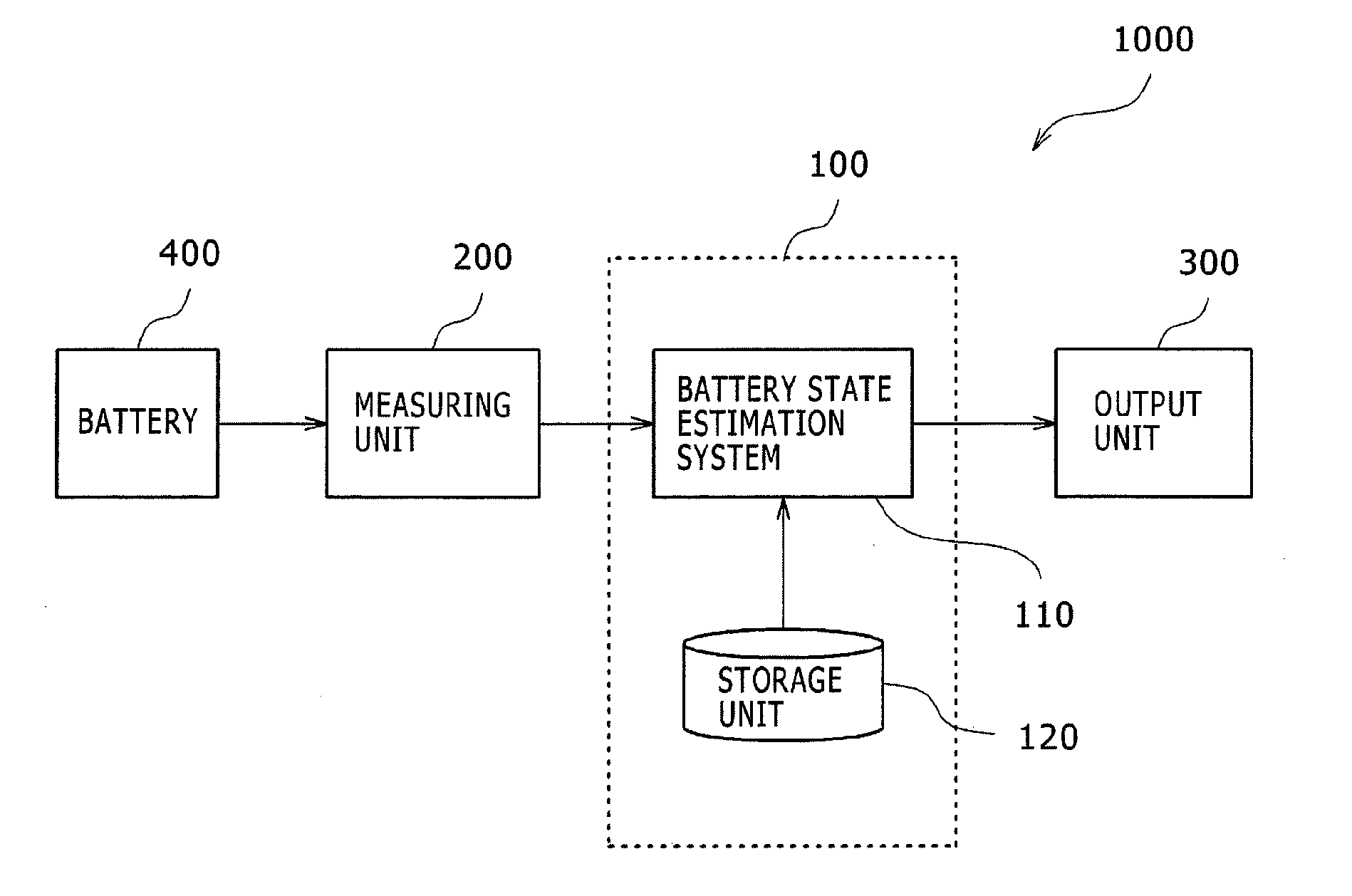
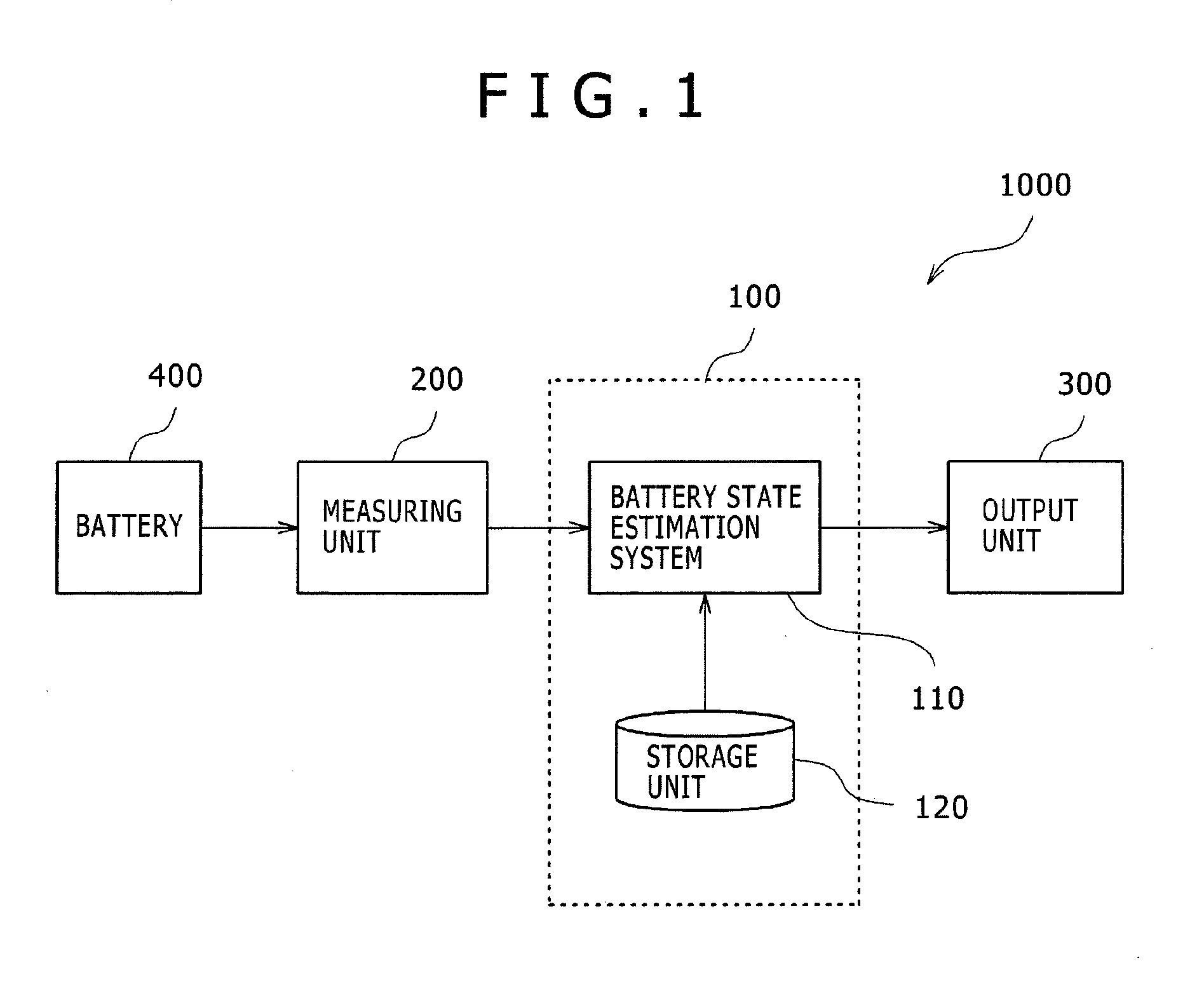
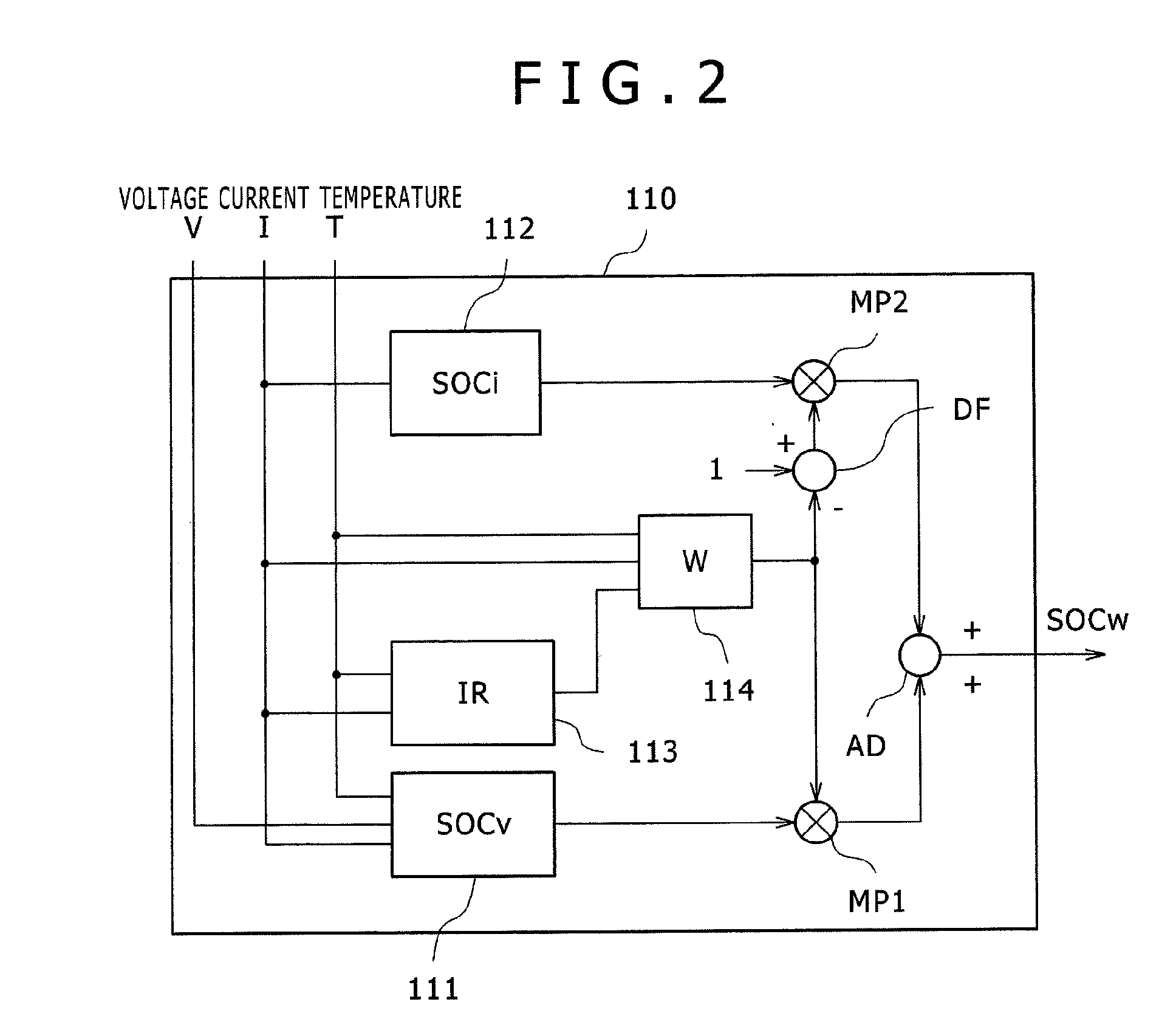
Battery state estimation system, battery control system, battery system, and battery state estimation method
ActiveUS20140055100A1Satisfactory accuracyBatteries circuit arrangementsElectrical testingControl systemEstimation methods
A battery state estimation system estimates a state of charge of a chargeable battery. A SOCv computing unit calculates a state of charge of the battery using a voltage applied across the battery. A SOCi computing unit integrates a current flowing through the battery to calculate a state of charge of the battery. A SOCw computing unit which performs weighted addition to the state of charge of the battery calculated by the SOCv computing unit and the state of charge of the battery calculated by the SOCi computing unit, wherein when the temperature of the battery is a threshold value or less and the current flowing through the battery is a threshold value or less, the SOCw computing unit sets the specific gravity at the state of charge of the battery calculated by the SOCi computing unit larger than that in other cases upon the weighted addition.
Owner:HITACHI VEHICLE ENERGY
Coil component
ActiveUS20110260821A1Improve accuracySatisfactory in sizeTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsCoils manufactureEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:SUMIDA CORP
Camera pose estimation apparatus and method for augmented reality imaging
ActiveUS8452080B2Satisfactory accuracyFast and efficient implementationImage enhancementImage analysis3d cameraCandidate key
Owner:APPLE INC
Profilometer
InactiveUS20100259746A1Satisfactory accuracyOptical rangefindersUsing optical meansRadianceLight emission
A profilometer for measuring a surface profile of a measuring target has a lighting device for irradiating the measuring target with light, an imaging device for imaging a reflected light from the measuring target, and a normal calculation section for calculating a normal direction of a surface at each position of the measuring target from an imaged image. The lighting device has a light emission region of a predetermined extent. A radiance of center of gravity of a light source distribution of a point symmetric region coincides with a radiance of the center of the point symmetric region in an arbitrary point symmetric region of the light emission region.
Owner:ORMON CORP
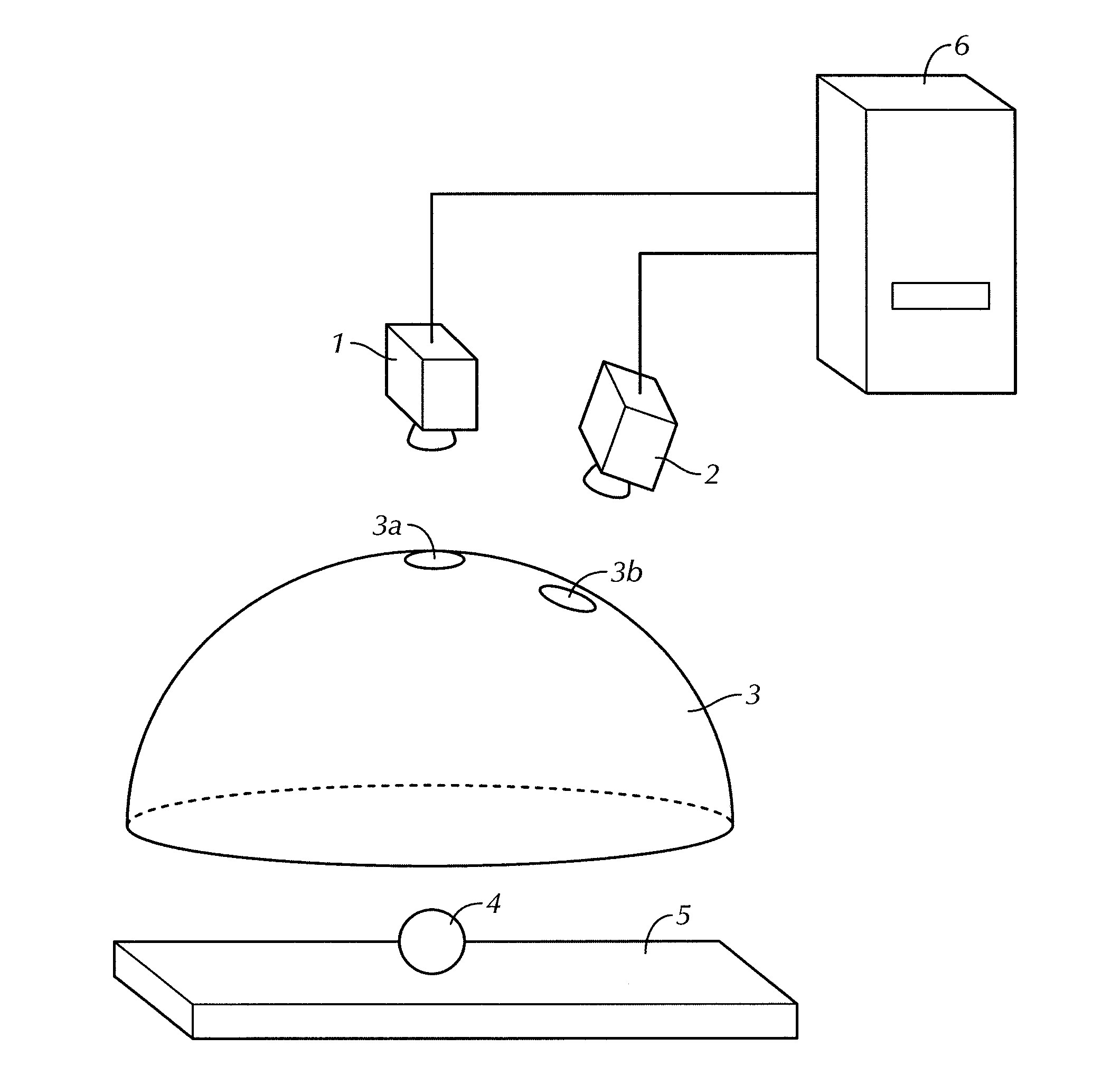
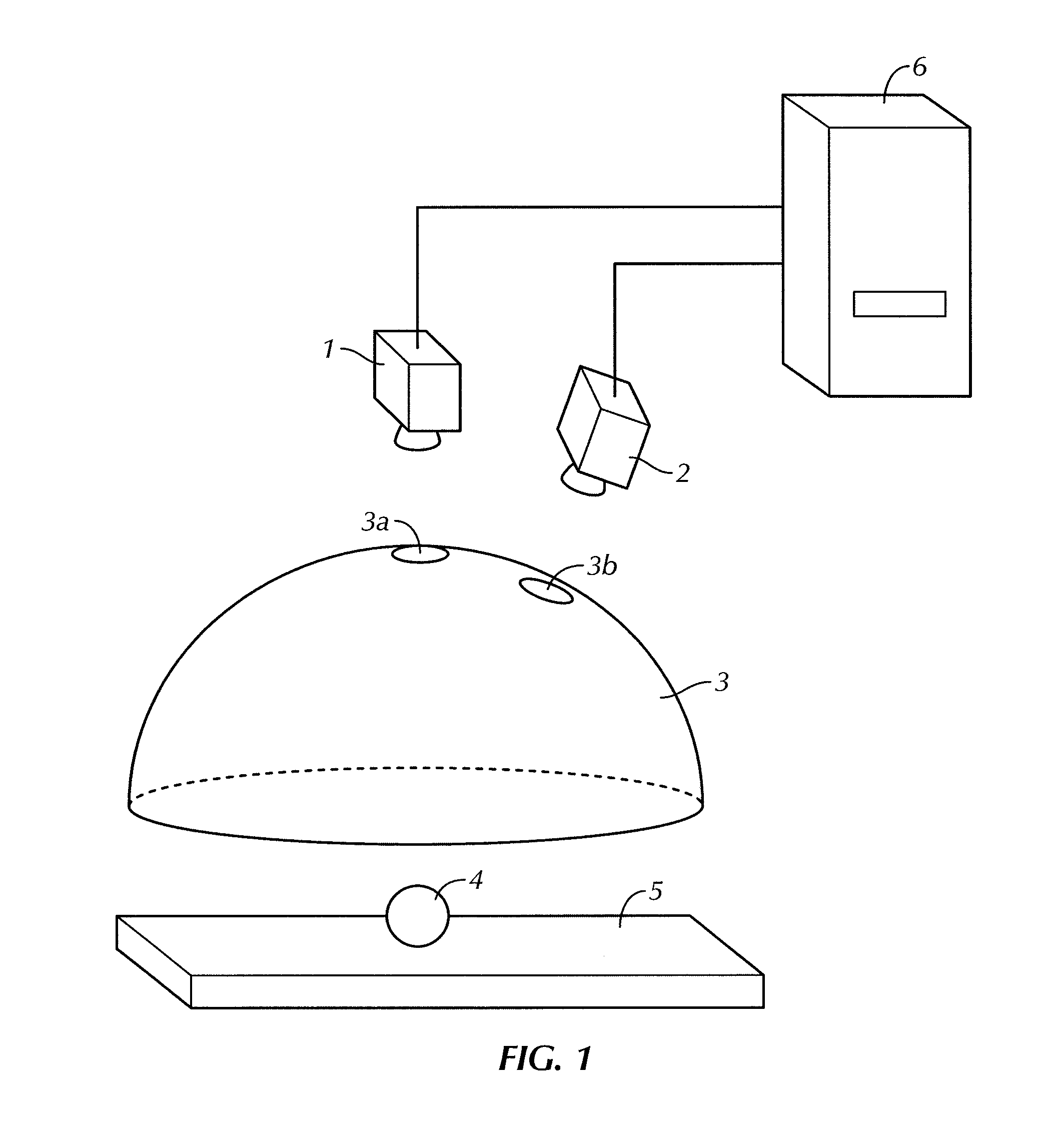
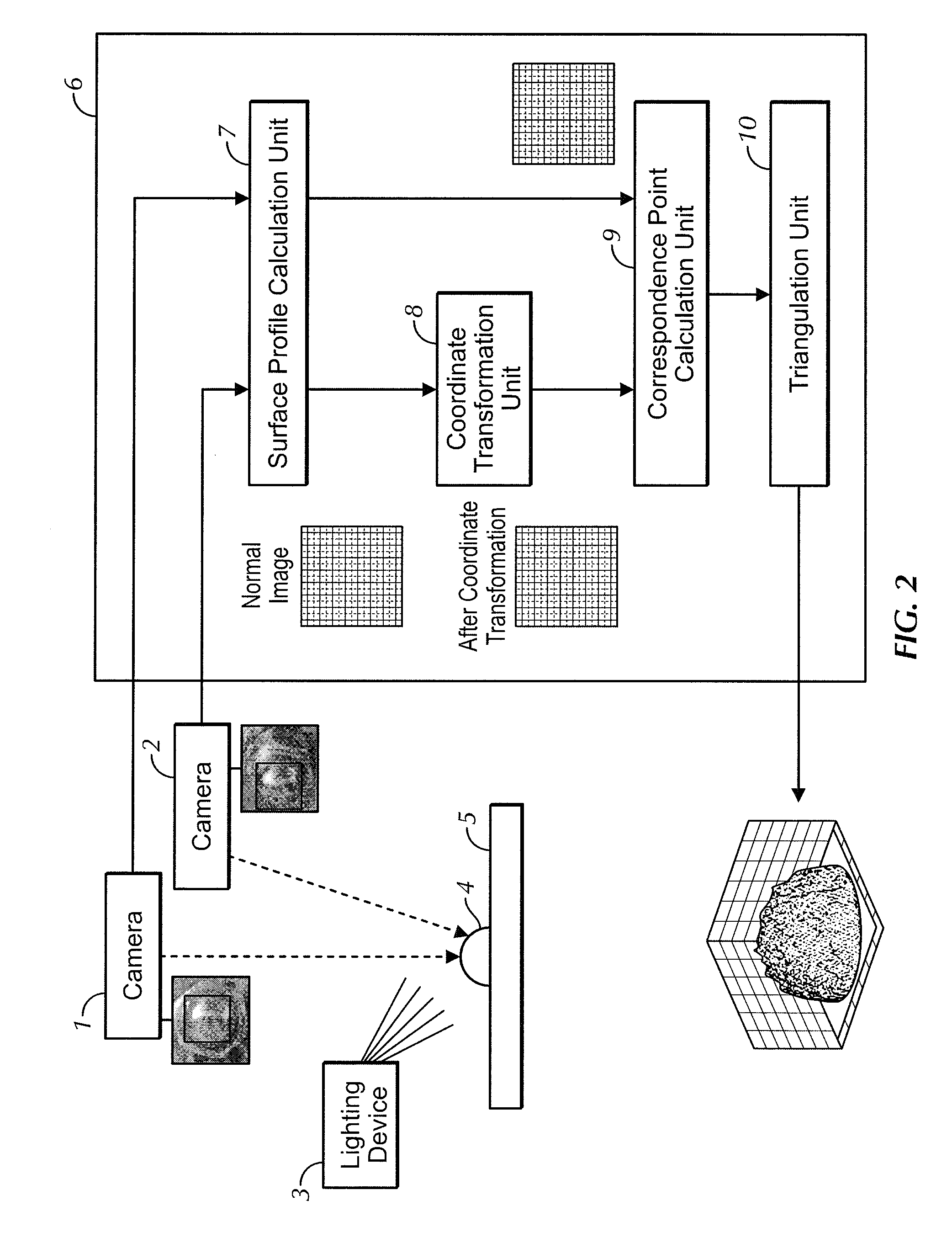
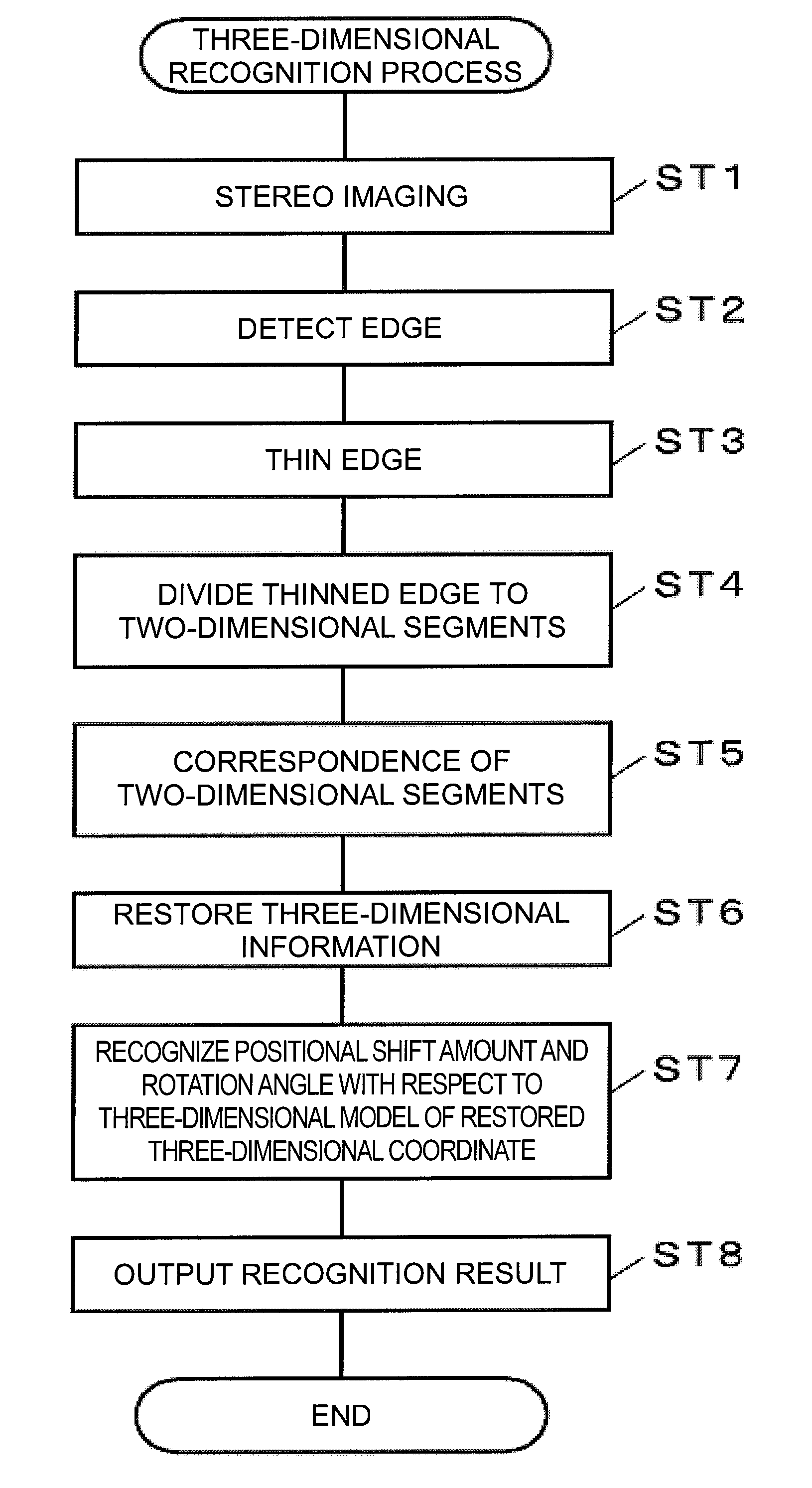
Method of creating three-dimensional model and object recognizing device
ActiveUS20100111364A1Satisfactory accuracyAccurate identificationAquisition of 3D object measurementsThree-dimensional object recognitionComputer graphics (images)Algorithm
Owner:ORMON CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS7193301B2High reliable fan-out structureReduce yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSolder ballSemiconductor chip
A plurality of semiconductor chips (14) each having a first main surface (14b) formed with electrode pads (21) and a second main surface (14c) opposite to the first main surface are respectively mounted on a chip mounting surface (12a) larger in area than the second main surface, of a wafer-shaped mounting substrate (12) at equal intervals so as to extend along first and second trenches (18a, 18b) defined in the chip mounting surface with these trenches as target lines. Thereafter, solder balls (25) electrically connected to the electrode pads of the semiconductor chips are disposed on their corresponding wiring patterns 34 that extend from above first regions (100) located above the semiconductor chips, of a surface region of an encapsulating layer (32) covering the semiconductor chips to above second regions (200) that surround the first regions. Afterwards, the encapsulating layer and the mounting substrate are cut and thereby fractionized into semiconductor devices each having a fan-out structure.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Composite unit of optical semiconductor device and supporting substrate and method for mounting optical semiconductor device on supporting substrate
InactiveUS6087194ASatisfactory accuracyReadily assembleSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSelf alignment
Composite units of an optical semiconductor device and a supporting substrate are disclosed, in which the rear surface of the optical semiconductor device is provided with one or more electrode patterns and the top surface of the supporting substrate is provided with one or more electrode patterns. The optical semiconductor device and the supporting substrate are fixed to each other by once melting and solidifying one or more solder bumps which intervene between the one or more electrode patterns provided on the rear surface of the optical semiconductor device and the one or more electrode patterns provided on the top surface of the supporting substrate. A good grade of accuracy in the mutual geometric position of the optical semiconductor device and the supporting substrate is obtained in a horizontal direction due to a phenomenon called "the self alignment results" in this specification, in which a molten metal is inclined to become a ball based on surface tension. Methods for mounting an optical semiconductor device on a supporting substrate with a good grade of accuracy in the mutual geometric position therebetween in the horizontal direction, based on the same technical principle, are also disclosed. To realize the foregoing results, each of the composite units of an optical semiconductor device and supporting substrate in accordance with this invention is given various structures specific to each of them, and each of the methods in accordance with this invention is given various steps or processes specific to each of them.
Owner:NEOPHOTONICS SEMICON GK
Alignment device for fabricating optical disk
InactiveUS20050173072A1Satisfactory accuracyPrecise positioningRecord carriersMechanical working/deformationEngineeringPush out
In an optical disc fabricating apparatus, when the disc substrate is lowered from the tip of a disc inserting portion at a center pin down to a disc supporting portion, a disc urging portion of an alignment lever is pressed by a disc substrate, to be thus pushed in toward an inner periphery and a sheet urging portion is pushed out toward an outer periphery, so as to press the inner peripheral surface of a cover sheet so that both of the cover sheet and the disc substrate are urged in an alignment direction. Thus, it is possible to eliminate play generated between the inner peripheral surface of the cover sheet and the outer peripheral surface of a sheet inserting portion and play generated between the inner peripheral surface of the disc substrate and the outer peripheral surface of the disc inserting portion.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Method and device of mobile augmented reality of underground engineering based on mixed registration
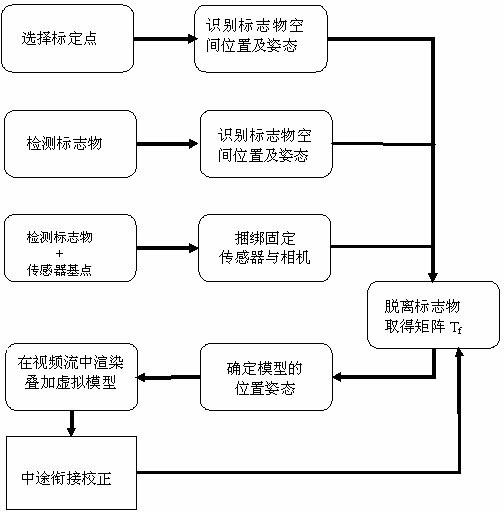
InactiveCN102222333AGet rid of dependenceImprove registration accuracyImage analysisUsing optical meansTwo stepGlobal Positioning System
The invention relates to a method and a device of mobile augmented reality of an underground engineering based on a mixed registration. The method comprises the following steps of: standardizing the inner parameters of a video camera via two-step calibration method; designing a landmark and regarding the landmark as the initial base point of the coordinates; firstly realizing the augmented reality registration based on the landmark; binding the video camera and the tracking sensor to form a rigid body; reading the landmark based on the photogrammetric technology so as to calculate the offset between the center of the video camera and the rigid body of the tracking sensor; adding virtual information and mixing the information with the environmental scene; rendering and outputting so as to realize the augmented reality; fixing a set relay marker within the functional range of the tracking sensor; calculating out the relative coordinates of the relay marker via marking point identification and photogrammetry; calculating the offset value of the relay marker and the initial base point; and converting the offset value into the coordinate extendable matrix to be loaded to the system so as to realize the extension of the coordinate system. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages of low cost, no simple dependence on the landmark or tracking sensor, no need of a global positioning system (GPS), high speed, convenience, high precision and the like, and creates conditions for enhancing the mobility of the reality technology.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for optimizing a number of kernels used in a sum of coherent sources for optical proximity correction in an optical microlithography process
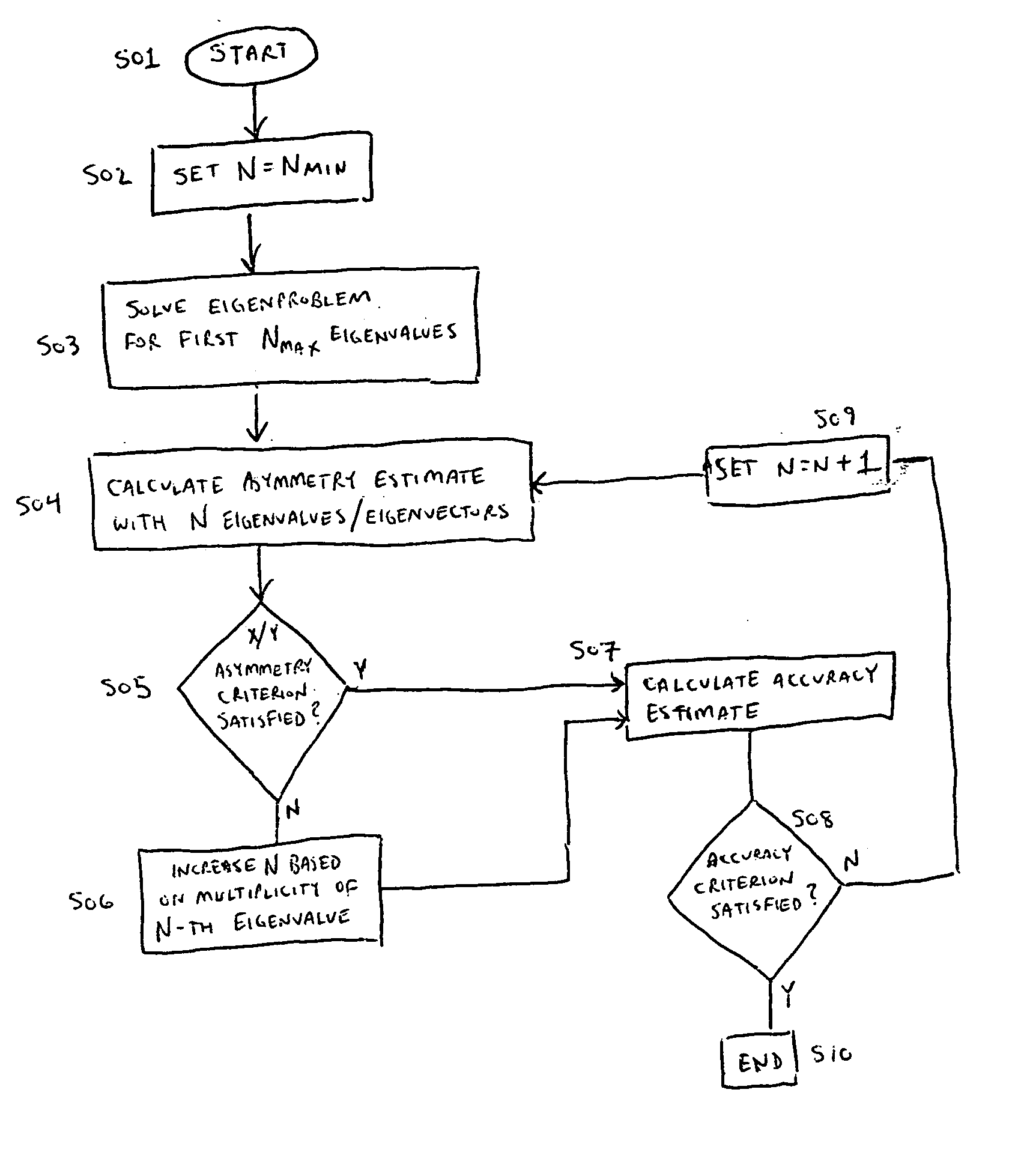
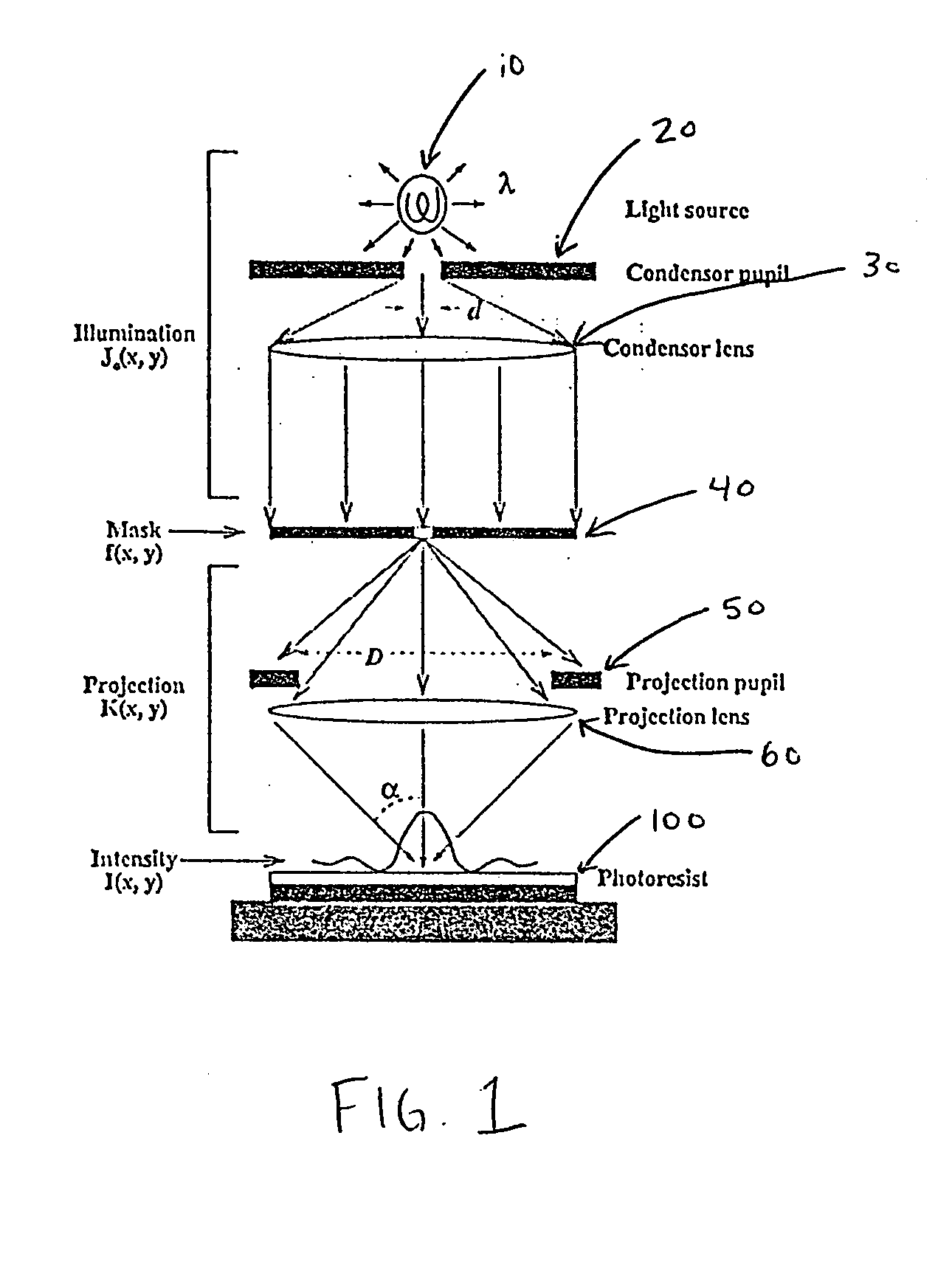
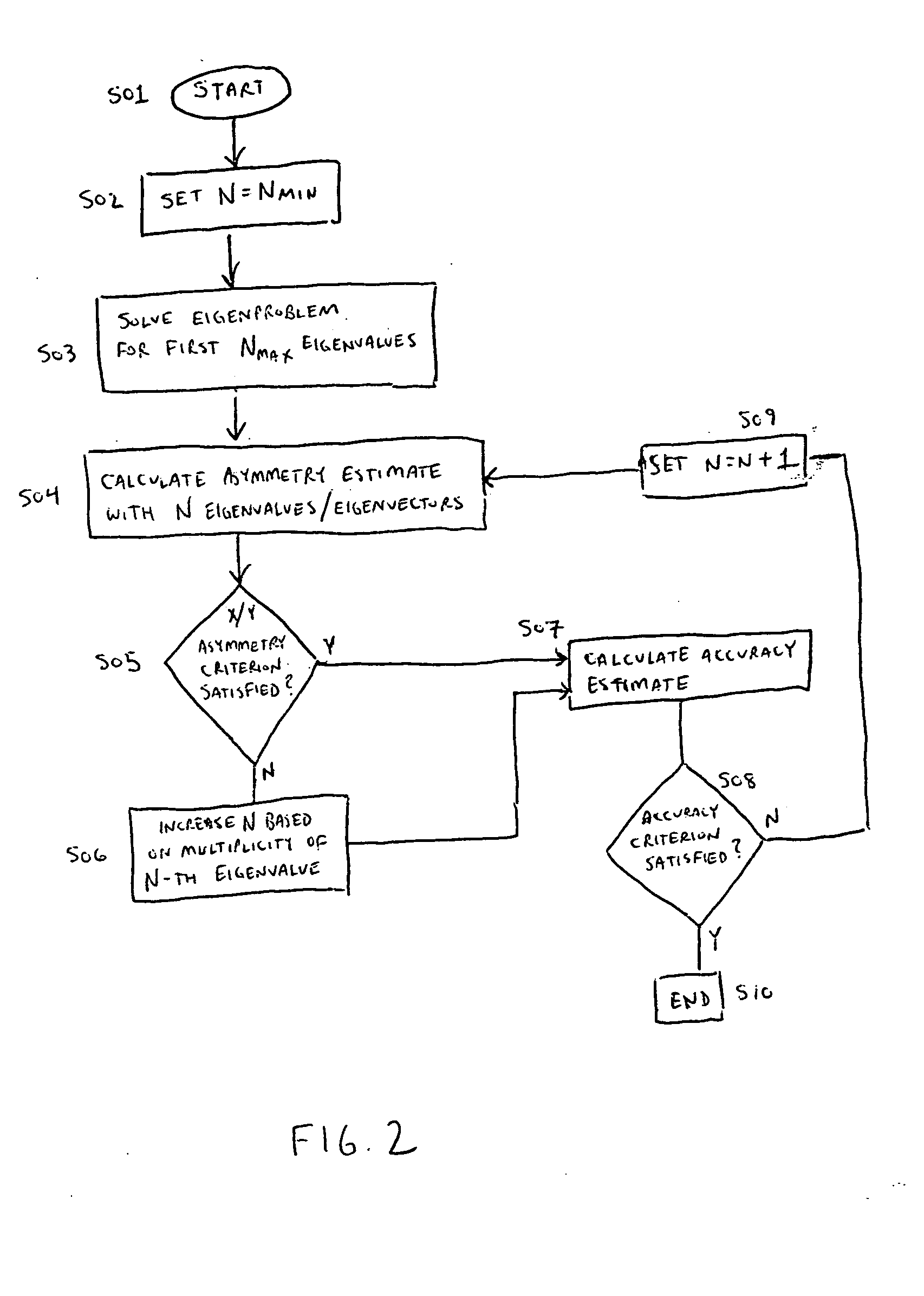
InactiveUS20050132310A1Required accuracySatisfactory accuracyComputation using non-denominational number representationOriginals for photomechanical treatmentComputer scienceOptical proximity correction
A method for optimizing the number of kernels N used in a sum of coherent sources (SOCS) for optical proximity correction in an optical microlithography process including setting the number of kernels N to a predetermined minimum value Nmin. A determination is made as to whether an accuracy estimate of calculated intensity is within a tolerable value. A determination is also made as to whether an added X / Y asymmetry estimate of the calculated intensity is negligible.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Shower head structure for processing semiconductor
InactiveUS7540923B2Improve uniformitySatisfactory accuracyLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesRadiation thermometerProduct gas
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
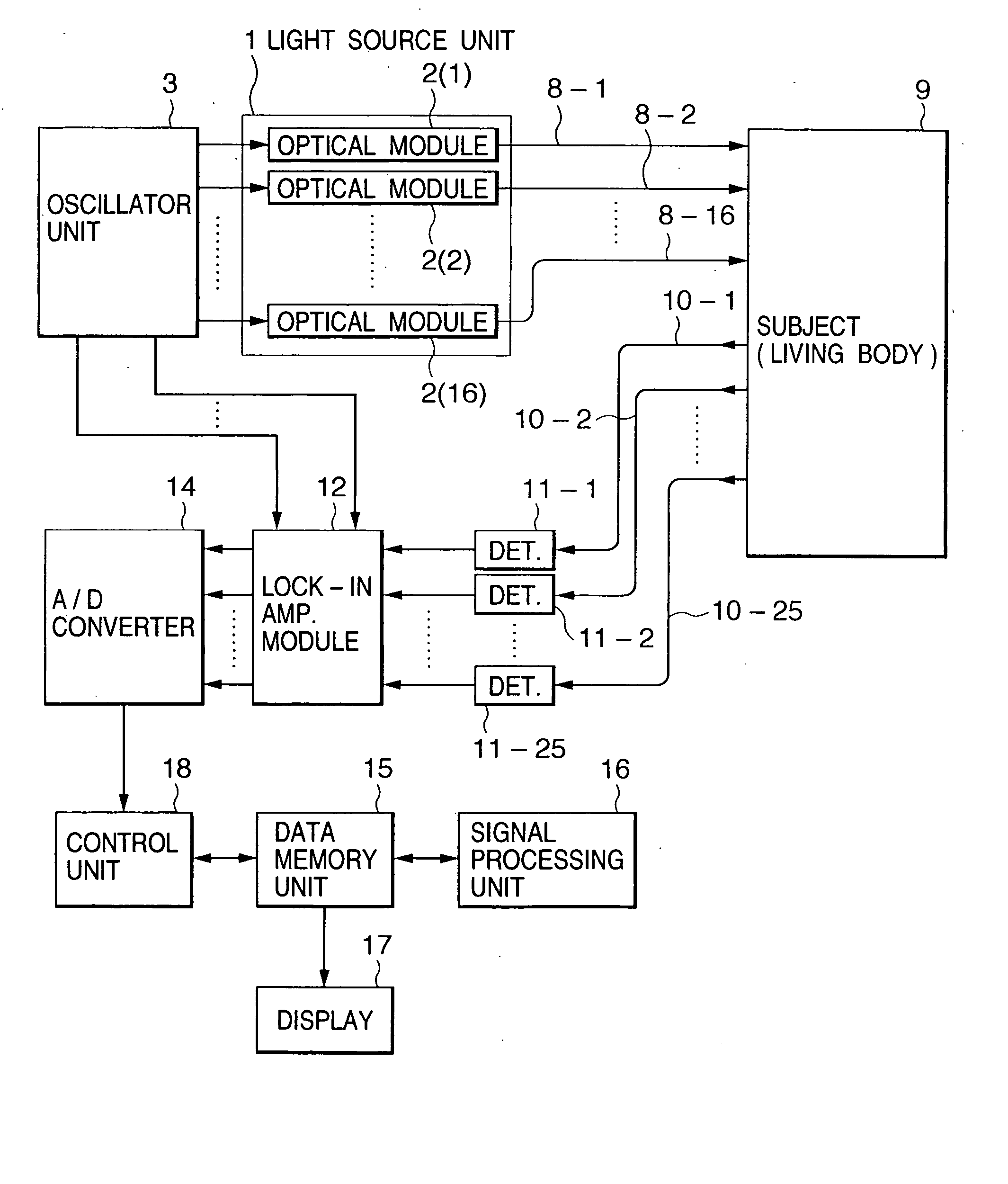
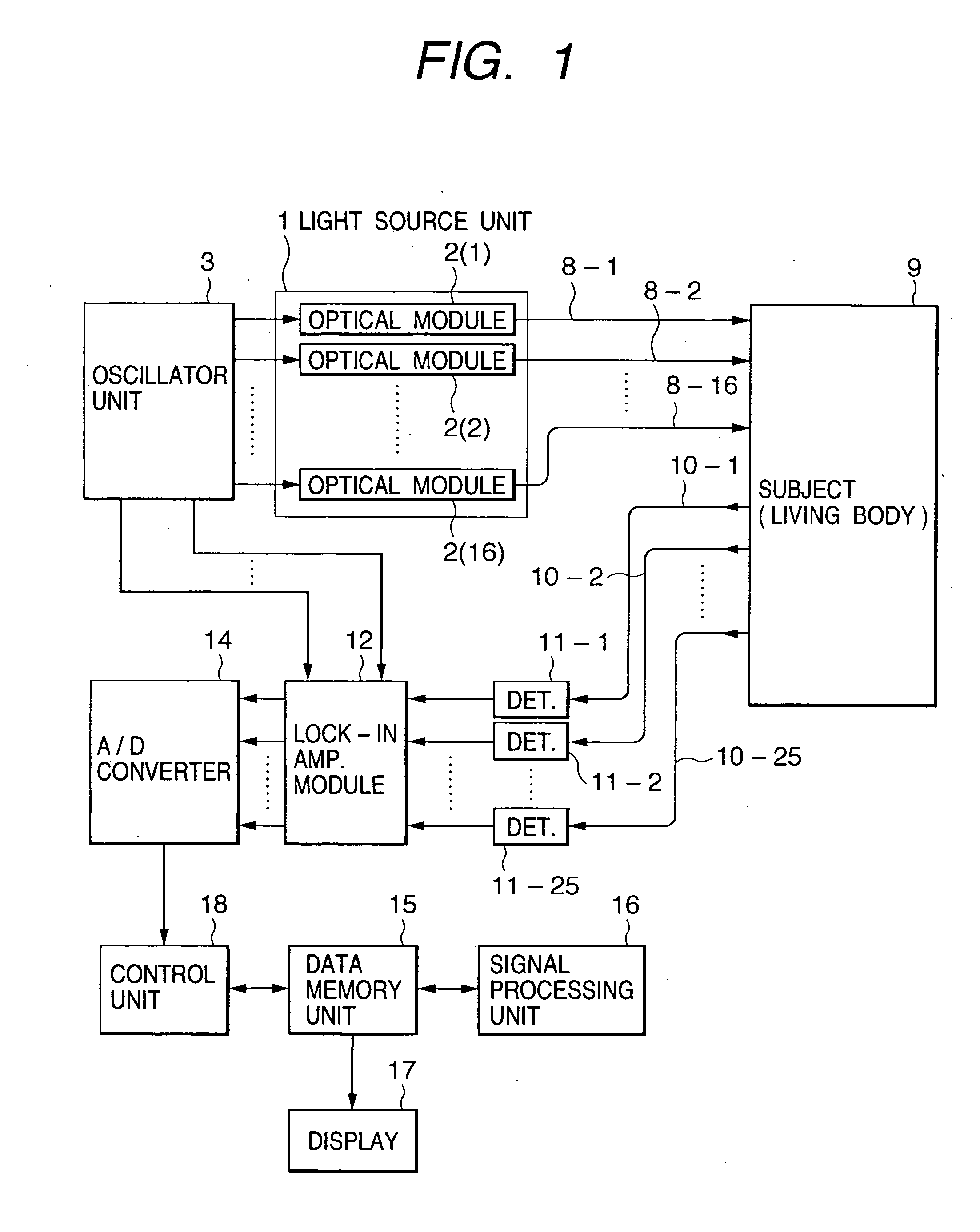
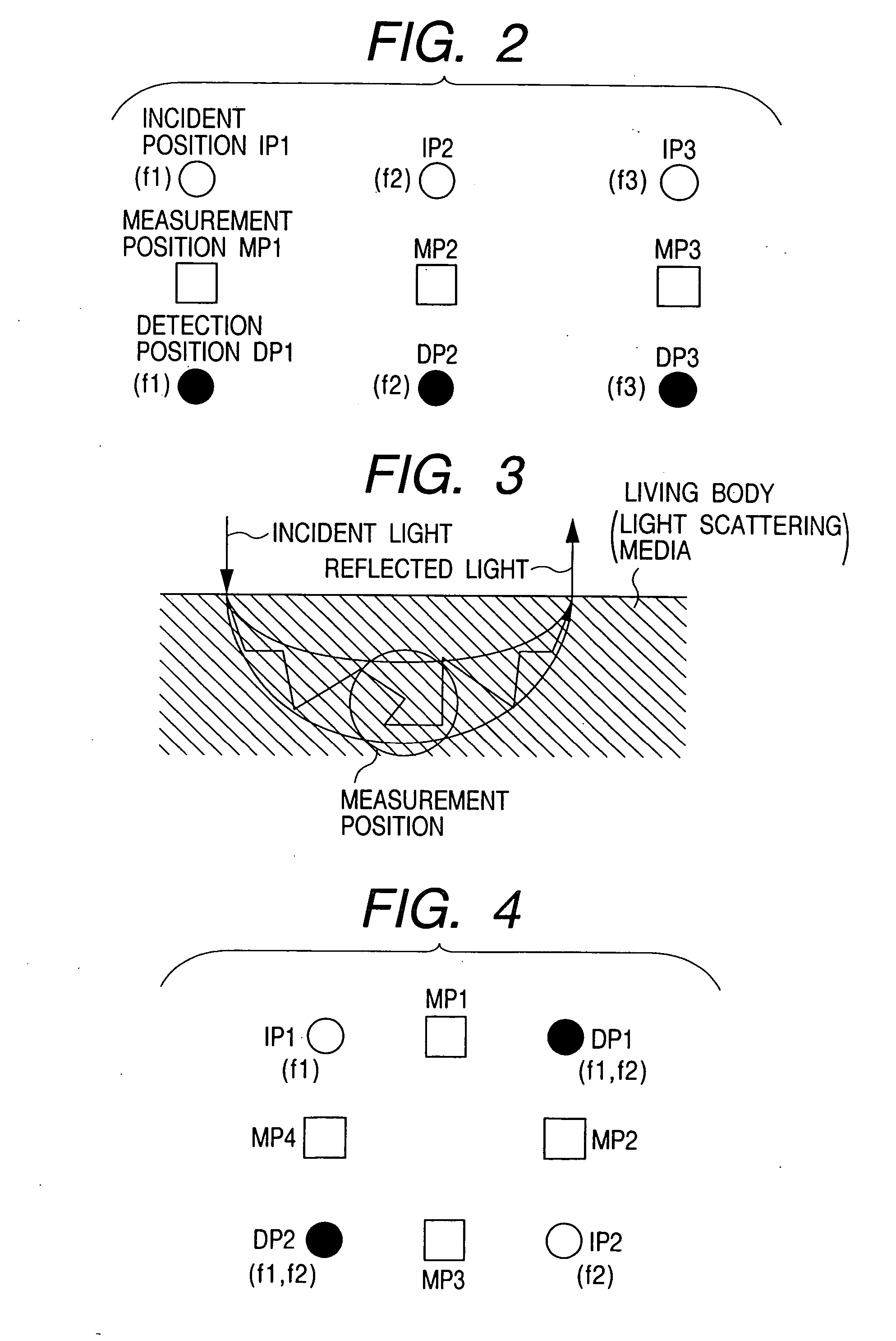
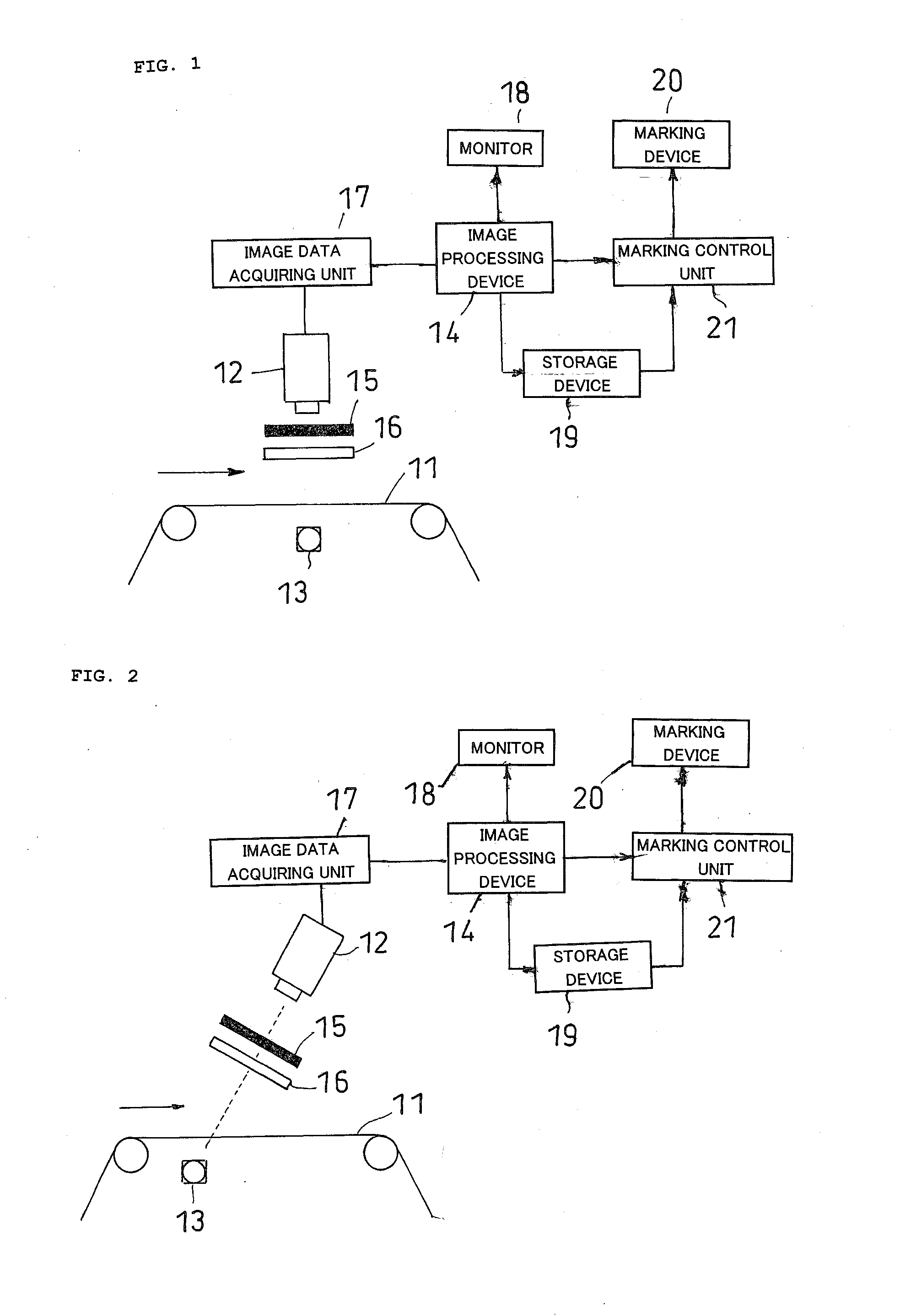
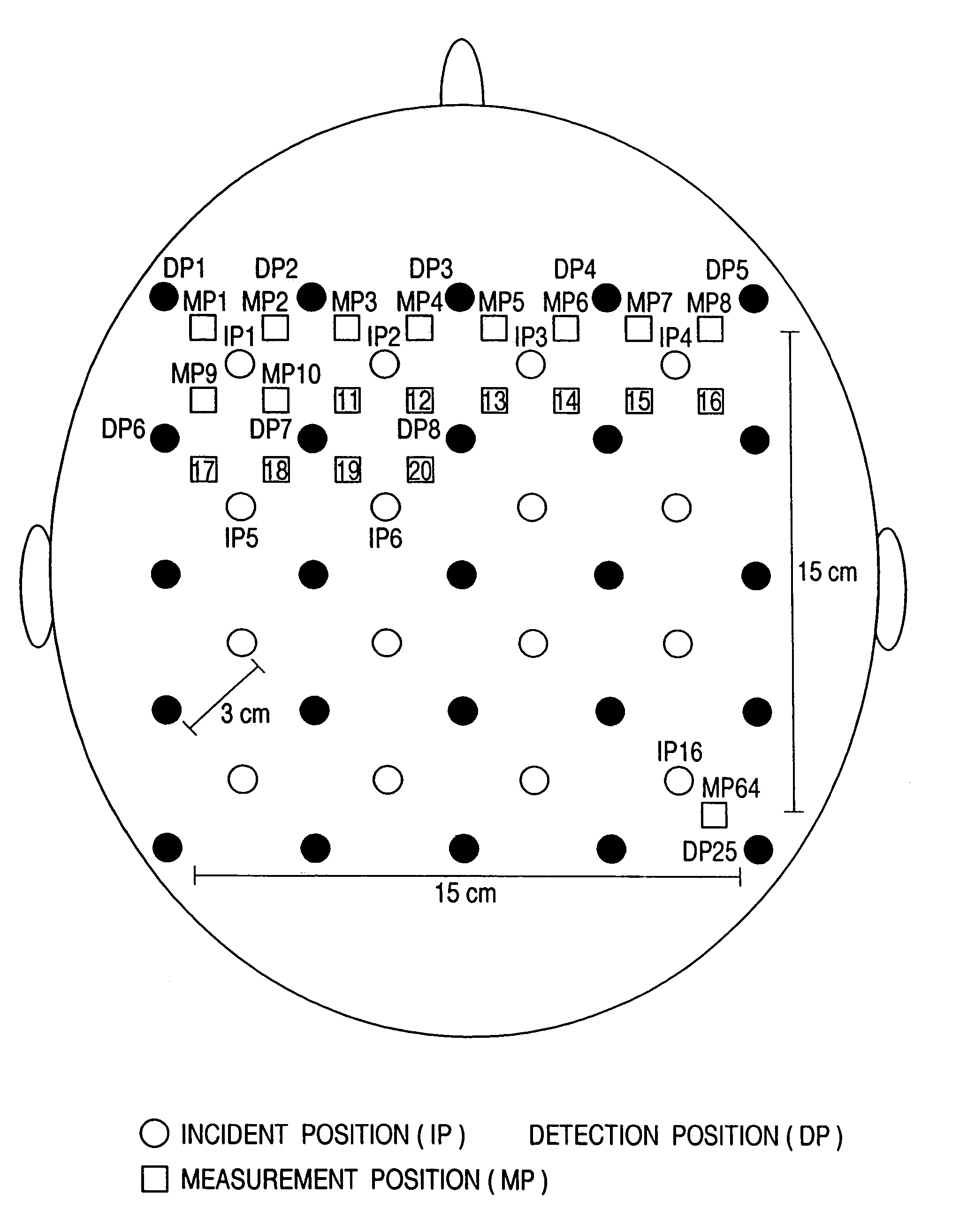
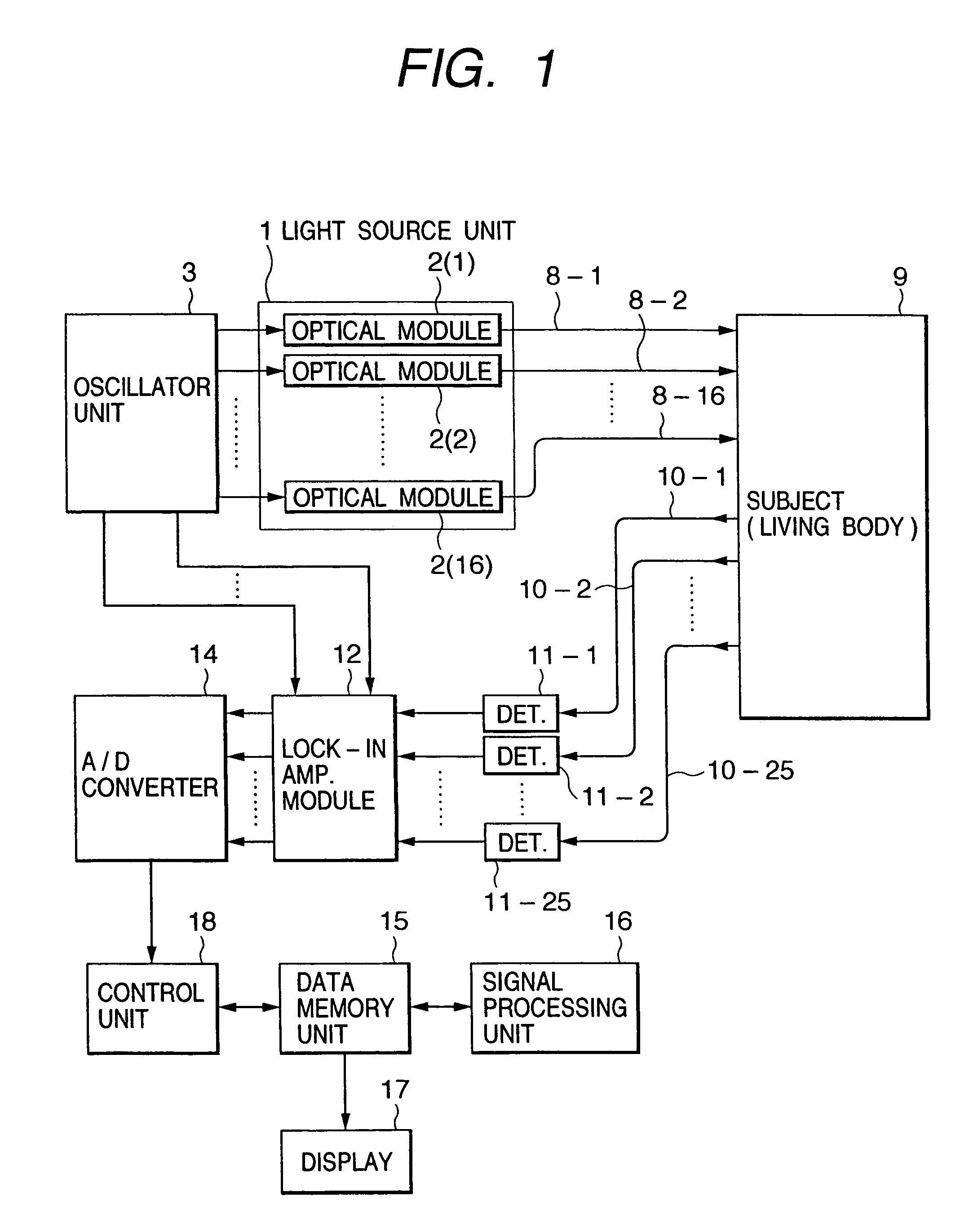
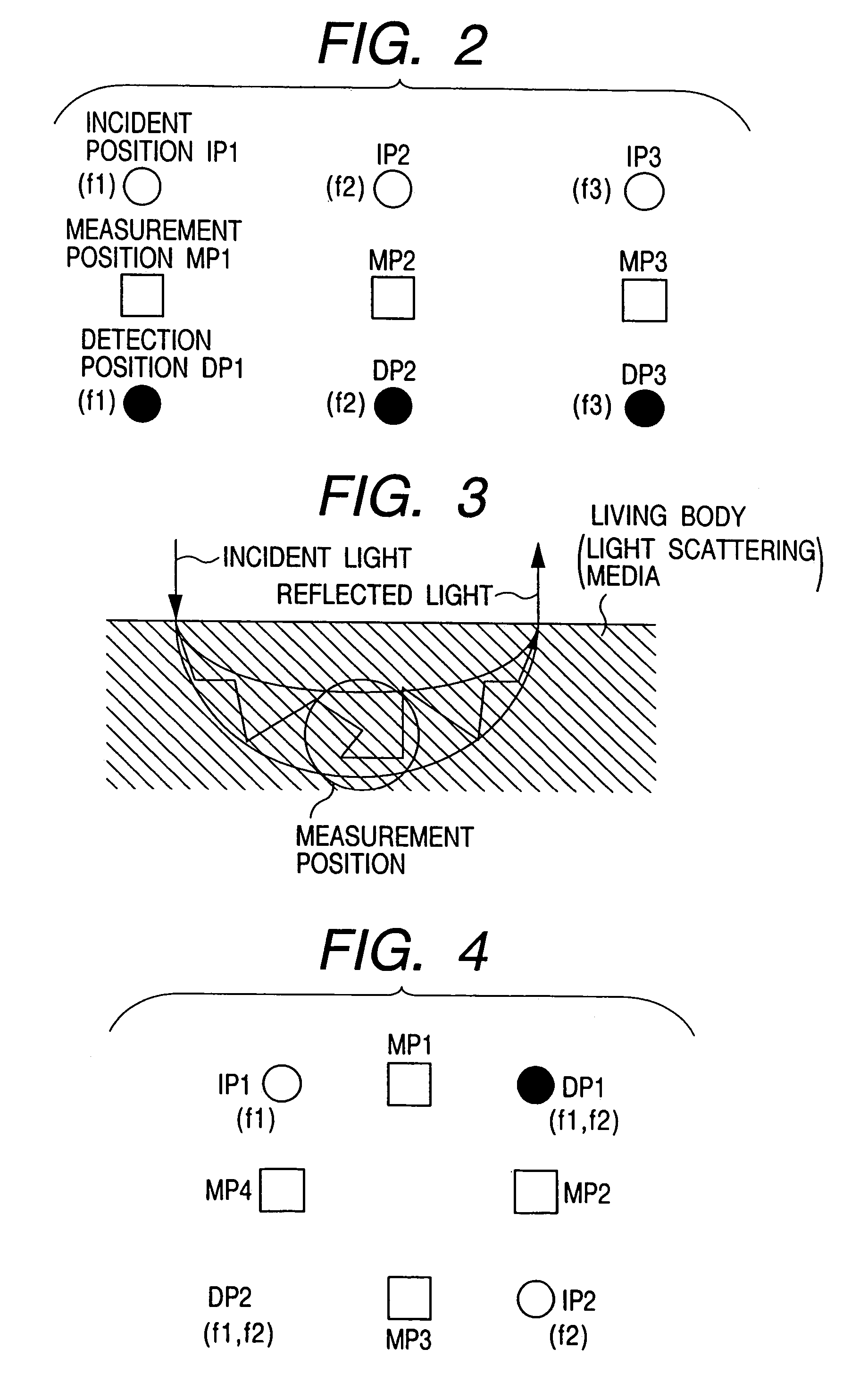
Optical measurement instrument for living body
InactiveUS20060184047A1Improve efficiencySatisfactory accuracyDiagnostics using lightComputerised tomographsBiological bodyMeasuring instrument
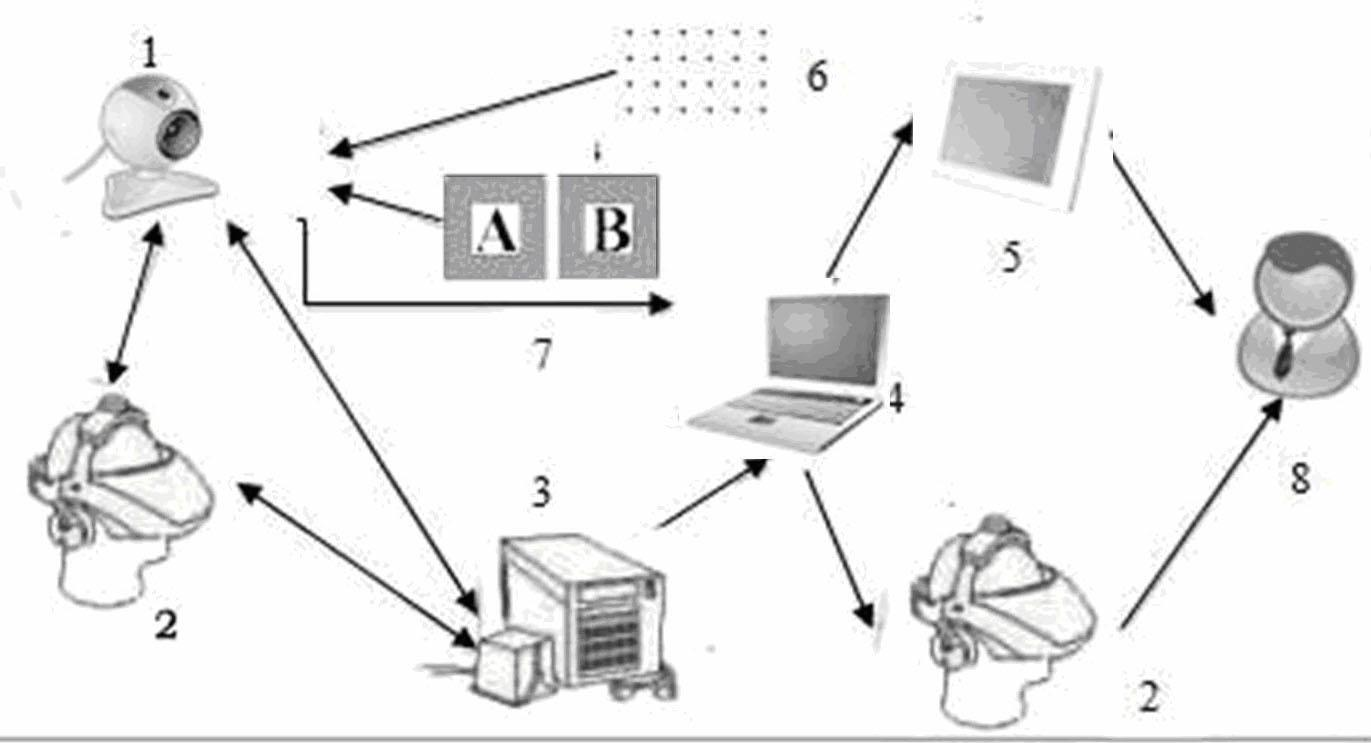
An input instrument for a living body, using an optical measurement system for the living body, includes first and second light incident units arranged on a head of a living body, and first and second light detectors which are paired with the first and the second light incident units respectively, and which are provided to collect light which passes through the living body based on the light irradiated onto the head of the living body by the light incident means. Measurement signals are obtained by measuring a plurality of regions of the living body by the first and the second light incident units, the first and the second light detectors, and characteristic parameters of the signals of an arbitrary time interval of the measured signals are calculated.
Owner:YAMASHITA YUICHI +2
Technique for video quality estimation
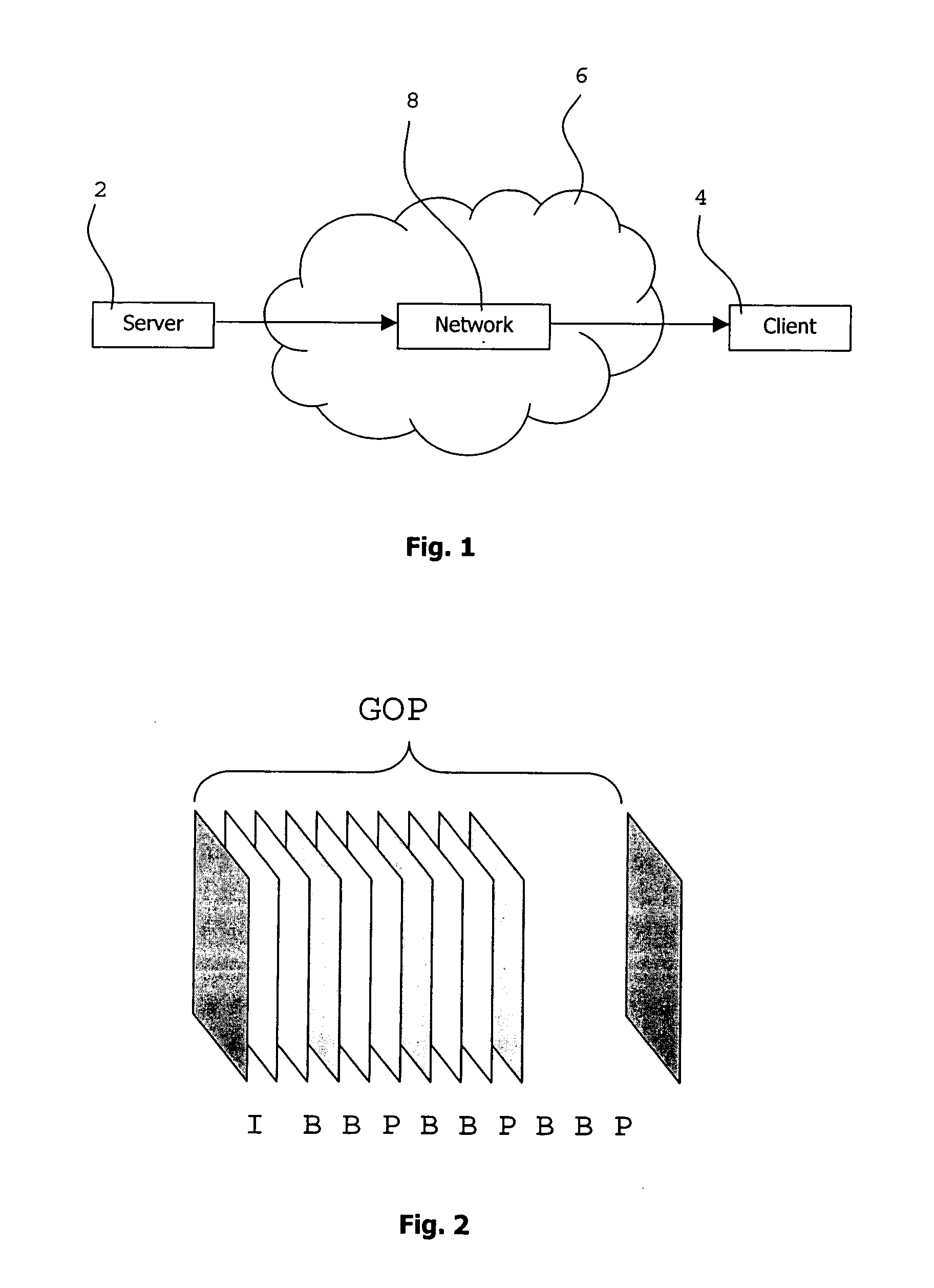
ActiveUS20120281142A1Satisfactory accuracyConsumes few computational resourceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsVideo bitstreamVideo encoding
An objective video quality estimation technique is disclosed. The technique may be based on a video bitstream model, using parameters taken from the video coding layer of the bitstream for estimating the quality of the video. The technique can be implemented as a method, a computer program, a computer program product, a device, or any one of a server node, a client terminal and a network node comprising the device. As a method embodiment, the technique comprises receiving a video bitstream comprising a series of picture frames; determining an error occurrence in a picture frame of the video bitstream; determining at least one of a temporal propagation and a spatial propagation of the error; and estimating the quality of the video bitstream based on result of the determination.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for detecting the presence of inhomogeneities in an interior of a turbid medium and device for imaging the interior of turbid media
InactiveUS9341569B2Satisfactory accuracySimple calculationScattering properties measurementsDiagnostics using tomographyLight source
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
OFDM receiver and doppler frequency estimating circuit
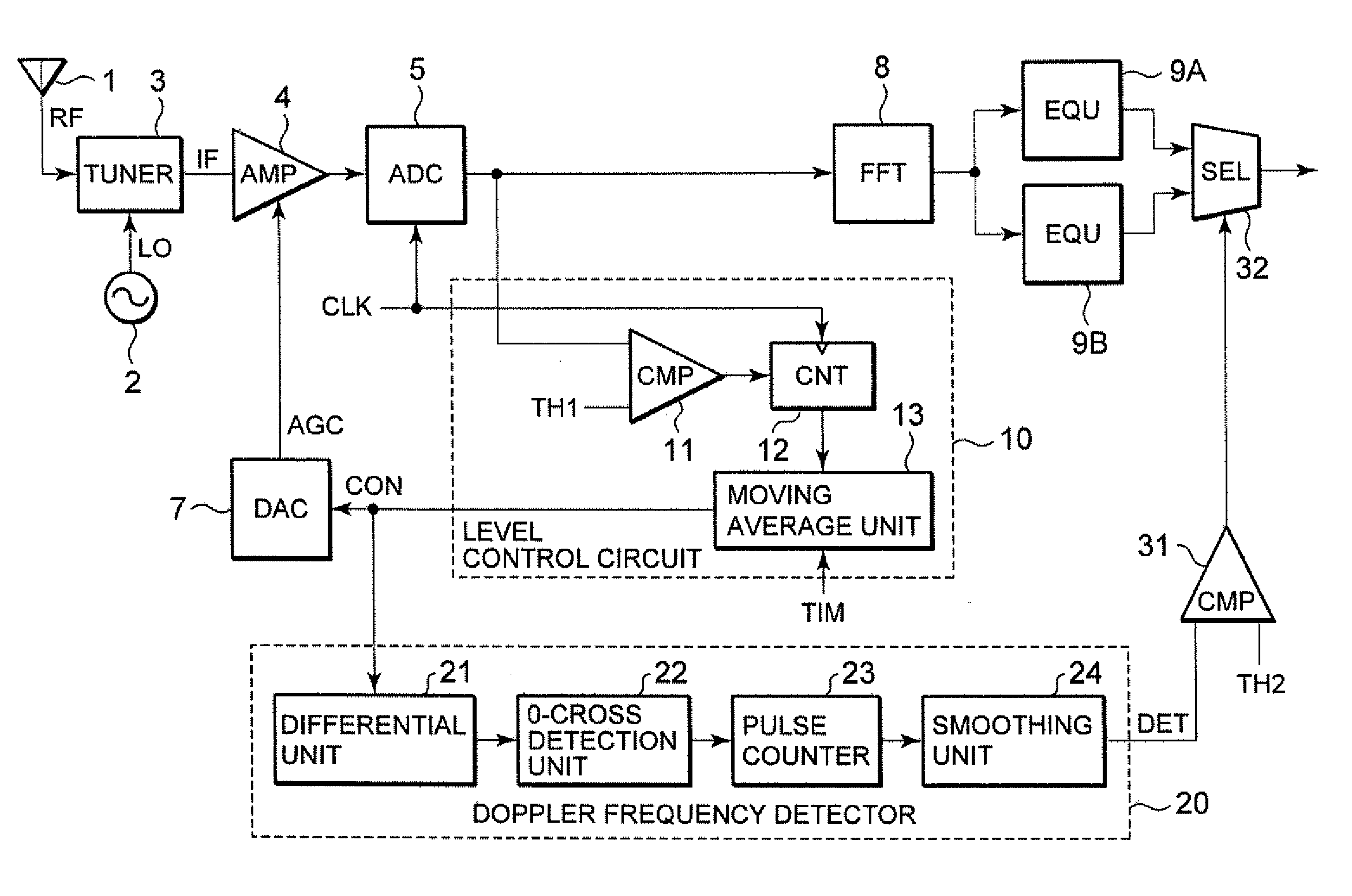
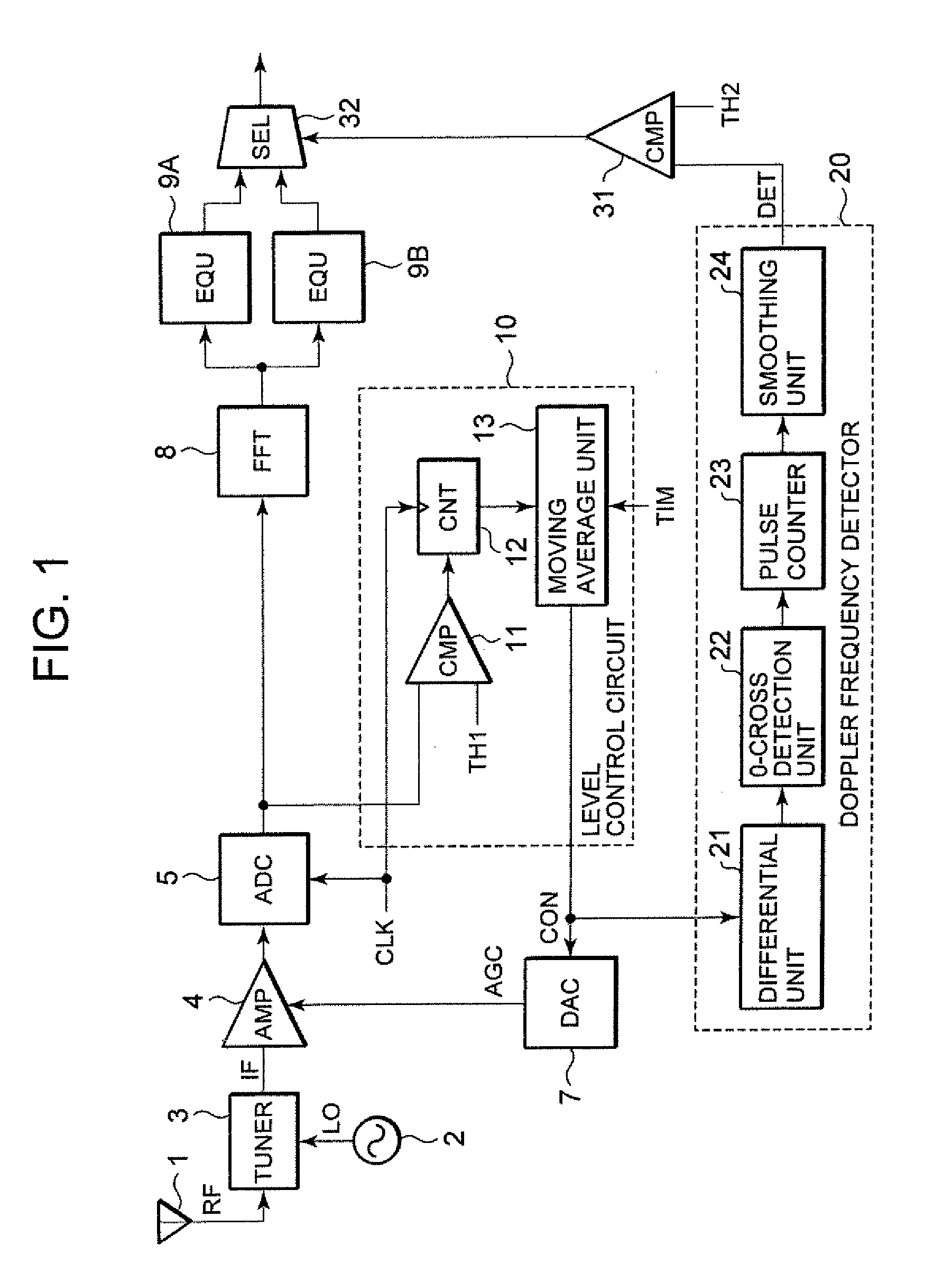
ActiveUS20080101215A1Suitable receptionReduce problem sizeGain controlAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsAudio power amplifierVariable-gain amplifier
A radiofrequency signal is converted to an intermediate frequency signal by a tuner, which is amplified by a variable gain amplifier. The so-amplified signal is converted into a digital signal by an ADC, which is supplied to an FFT, where it is separated into signals set every carrier, followed by being supplied to equalizers different in characteristic. The digital signal outputted from the ADC is further supplied to a level converting circuit from which a control signal is generated. The control signal is supplied to a DAC and a Doppler frequency detector. The DAC generates a gain control signal and supplies the same to the variable gain amplifier. The Doppler frequency detector outputs a frequency component of the control signal as a Doppler detection signal. The Doppler detection signal is compared with a threshold value by a comparator. A selector selects one of signals outputted from the equalizers, in accordance with a select signal indicative of the result of comparison.
Owner:LAPIS SEMICON CO LTD
Method and device for express analysis of acetone traces in gases
InactiveUS20090290161A1Satisfactory accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorTransmissivity measurementsGlucose polymersD-Glucose
Owner:POSITIVEID CORP
Layered film fabrication method, layered film defect detection method, layered film defect detection device, layered film, and image display device
InactiveUS20090288754A1Effectively cancellingSatisfactory accuracyLamination ancillary operationsControlling laminationPhase differenceDisplay device
When inspecting a defect of a layered film having a polarizer by using an inspection polarizing filter or an inspection phase difference filter, members to be arranged in the imaging optical path are arranged in an appropriate order. A defect detection method of a layered film (11) having a polarizing plate (1) and an optical compensation layer includes: a step of applying light from a light source arranged at the polarizing plate layer side of the film surface of the layered film (11); a step of imaging a transmitting light image of the layered film (11) by an imaging unit (12) arranged at the optical compensation layer side of the film surface; and a defect detection step for detecting a defect existing on the layered film (11) according to the transmitting light image captured by the imaging unit (12). The imaging unit (12) performs imaging via an inspection polarizing filter (15) arranged on the optical path between the light source (13) and the imaging unit (12) and adjacent to the imaging unit (12); and an inspection phase difference filter (16) arranged on the optical path between the light source (13) and the imaging unit (12) and between the inspection polarizing filter (15) and the layered film (11).
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Optical measurement instrument for living body
InactiveUS7142906B2Improve efficiencySatisfactory accuracyDiagnostics using lightScattering properties measurementsBiological bodyMeasuring instrument
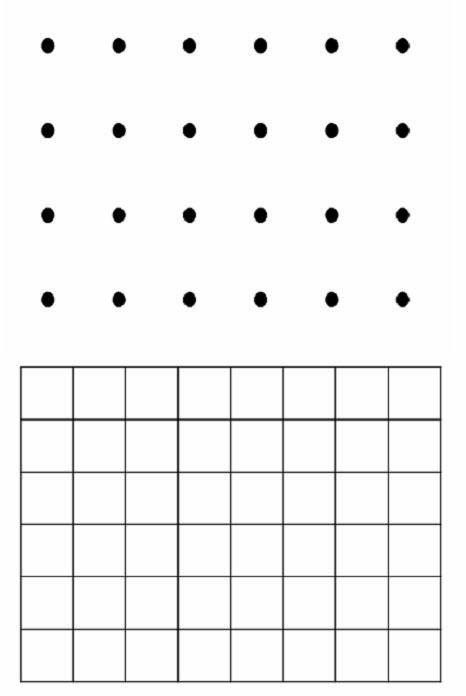
A control device and measurement system for a living body applies lights of at least one wavelength in a visible-infrared region to a plurality of incident positions on a surface of the living body, and a light detector detects lights transmitted through the living body at a plurality of detection positions on the surface of the living body. An operation unit determines a type of output signal, based on an intensity of the transmitted light and pre-stored reference data, and outputs a signal indicative thereof as the type of output signal. An external equipment executes a functional operation according to the type of output signal from the operation unit. The incident positions and the detection positions are alternately disposed in square lattice form and middle points between the incident positions and detection positions adjacent to one another are defined as measurement positions.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Photomask blank, photomask, and methods of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090214961A1Good shading effectConsumption amount can be reducedVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingTantalum nitrideOptoelectronics
A photomask blank has a light-shielding film composed of at least two layers on a transparent substrate. The light-shielding film includes a light-shielding layer made of a material mainly containing tantalum nitride and further containing xenon and a front-surface antireflection layer formed on the light-shielding layer and made of a material mainly containing tantalum oxide and further containing argon.
Owner:HOYA CORP
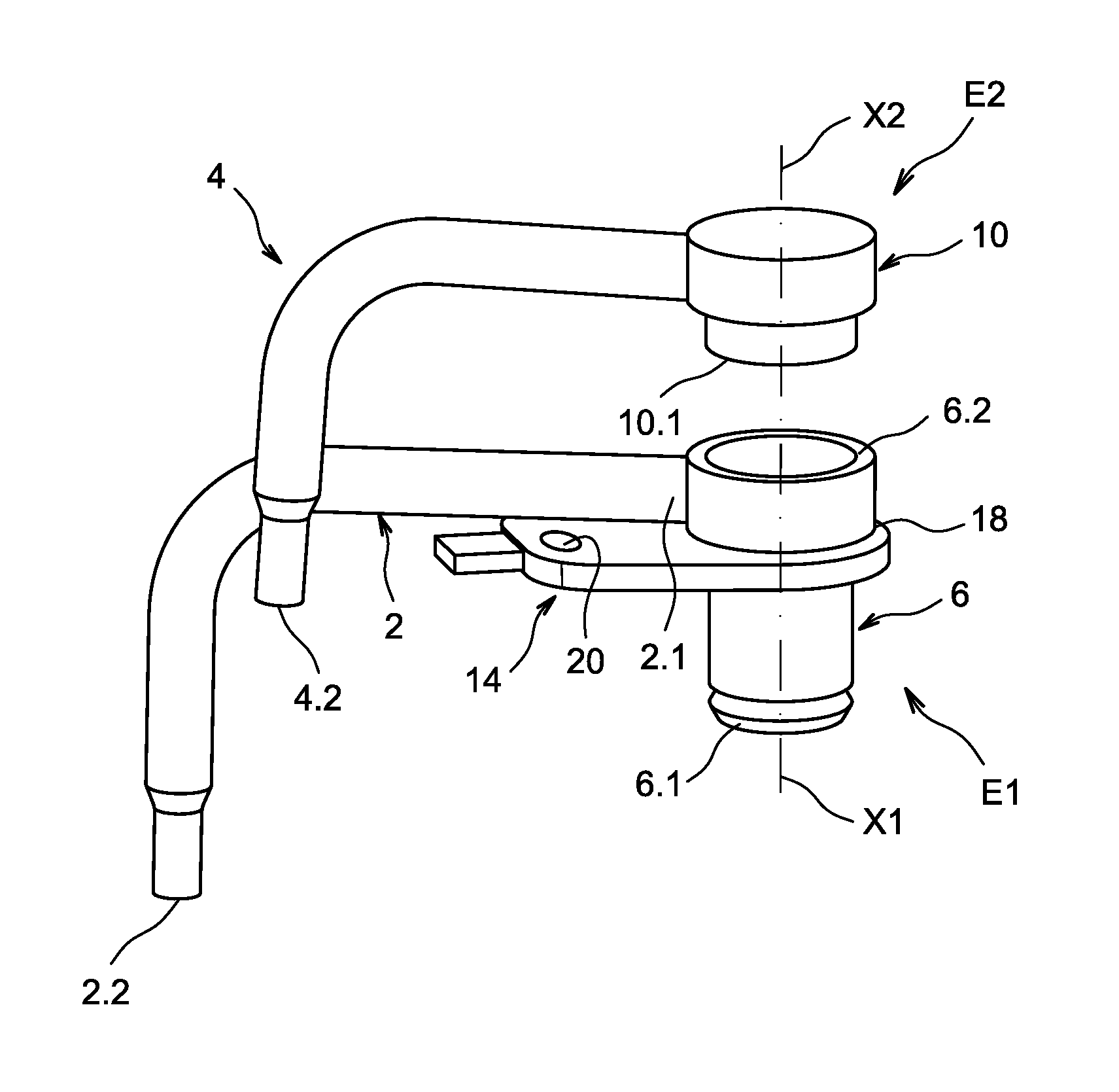
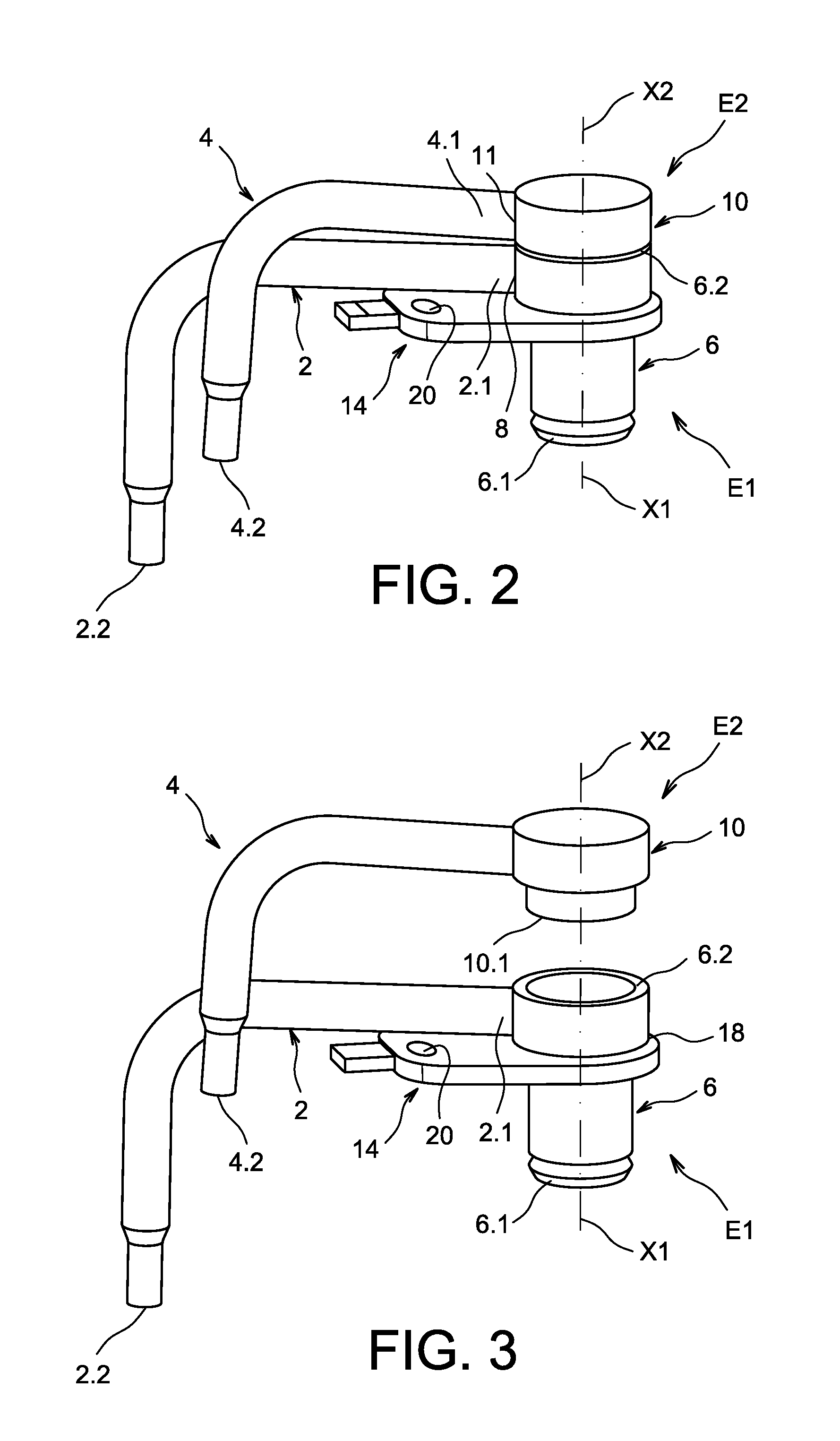
Compact Cooling Device for an Internal Combustion Engine and Method for Manufacturing Such a Device
ActiveUS20140305392A1Satisfactory target accuracySimple manufacturing methodLiquid coolingAir coolingInternal combustion engineCooling fluid
A cooling device for a motor vehicle engine connected to a cooling fluid feed system, where said cooling device comprises two superposed subassemblies, where the first subassembly comprises a feed body connected to the feed aperture and a tube connected to the feed body, the free end of which forms a first evacuation end, where the tube extends laterally relative to the feed body and is shaped so as to have a desired orientation, where the second subassembly comprises a feed body connected to the feed aperture and a tube connected to the feed body the free end of which forms the second evacuation end, where the tube extends laterally relative to the feed body and is shaped so as to have a desired orientation, and where the feed bodies are securely attached to one another in sealed fashion.
Owner:BONTAZ CENT
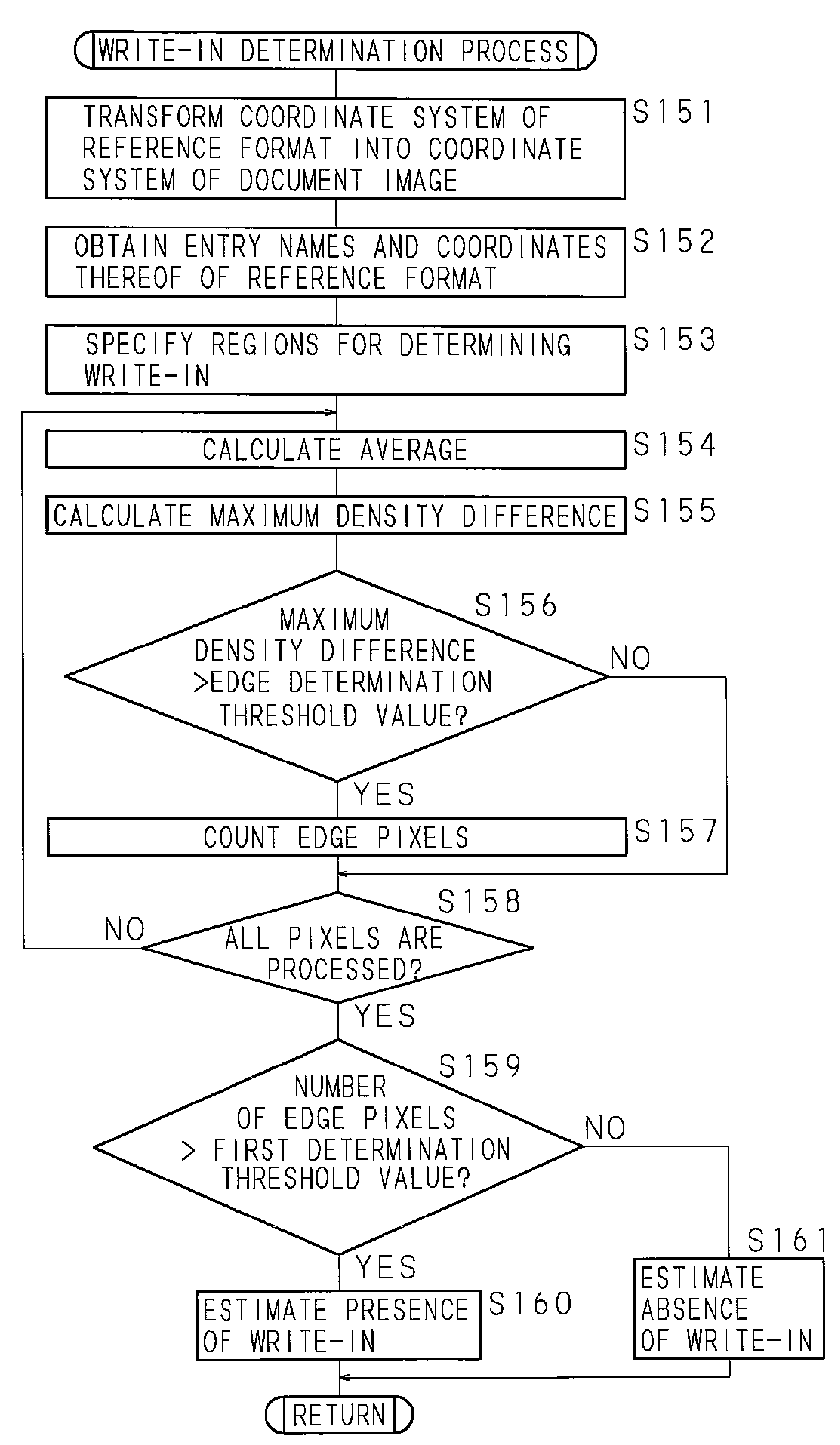
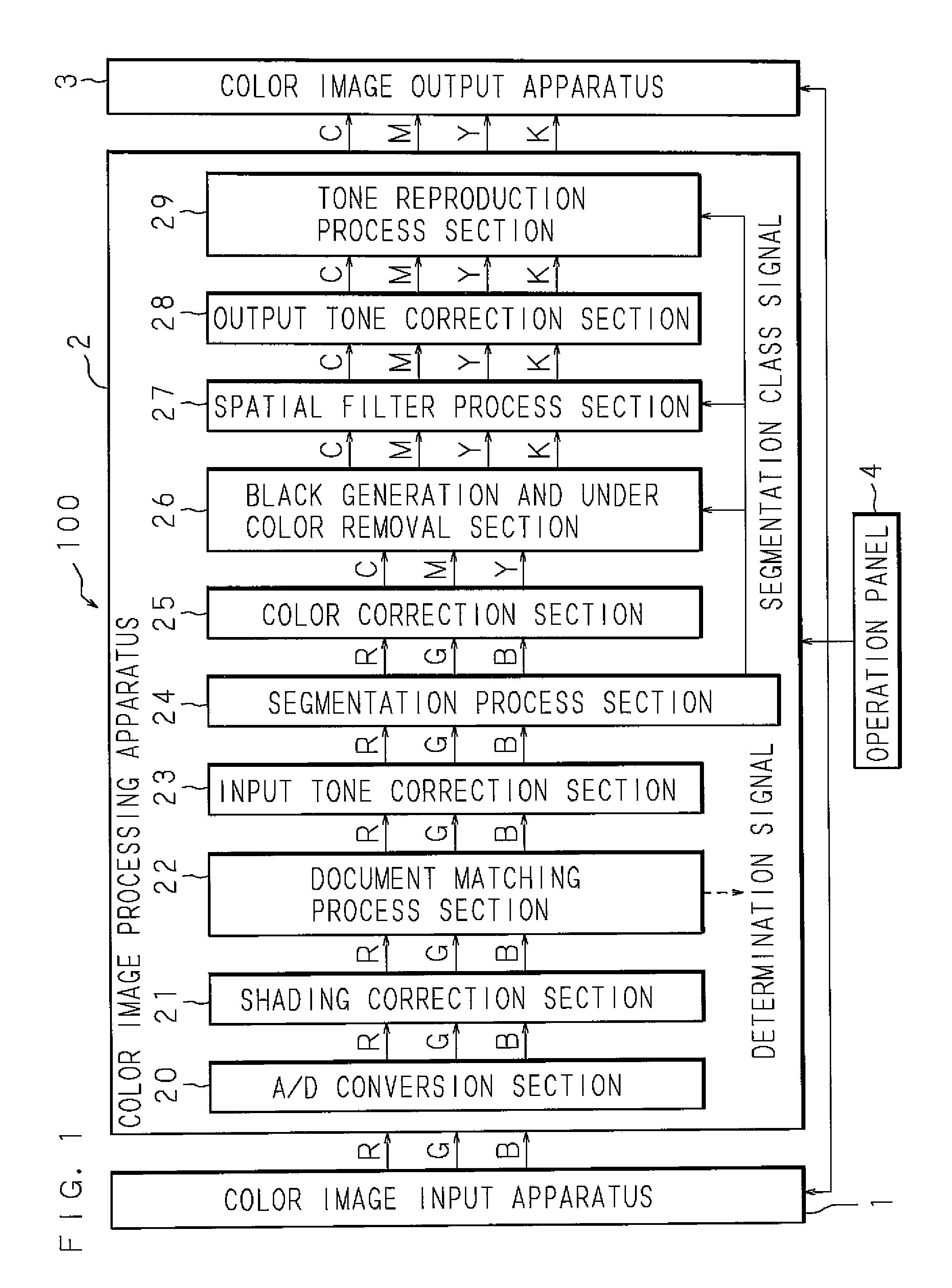
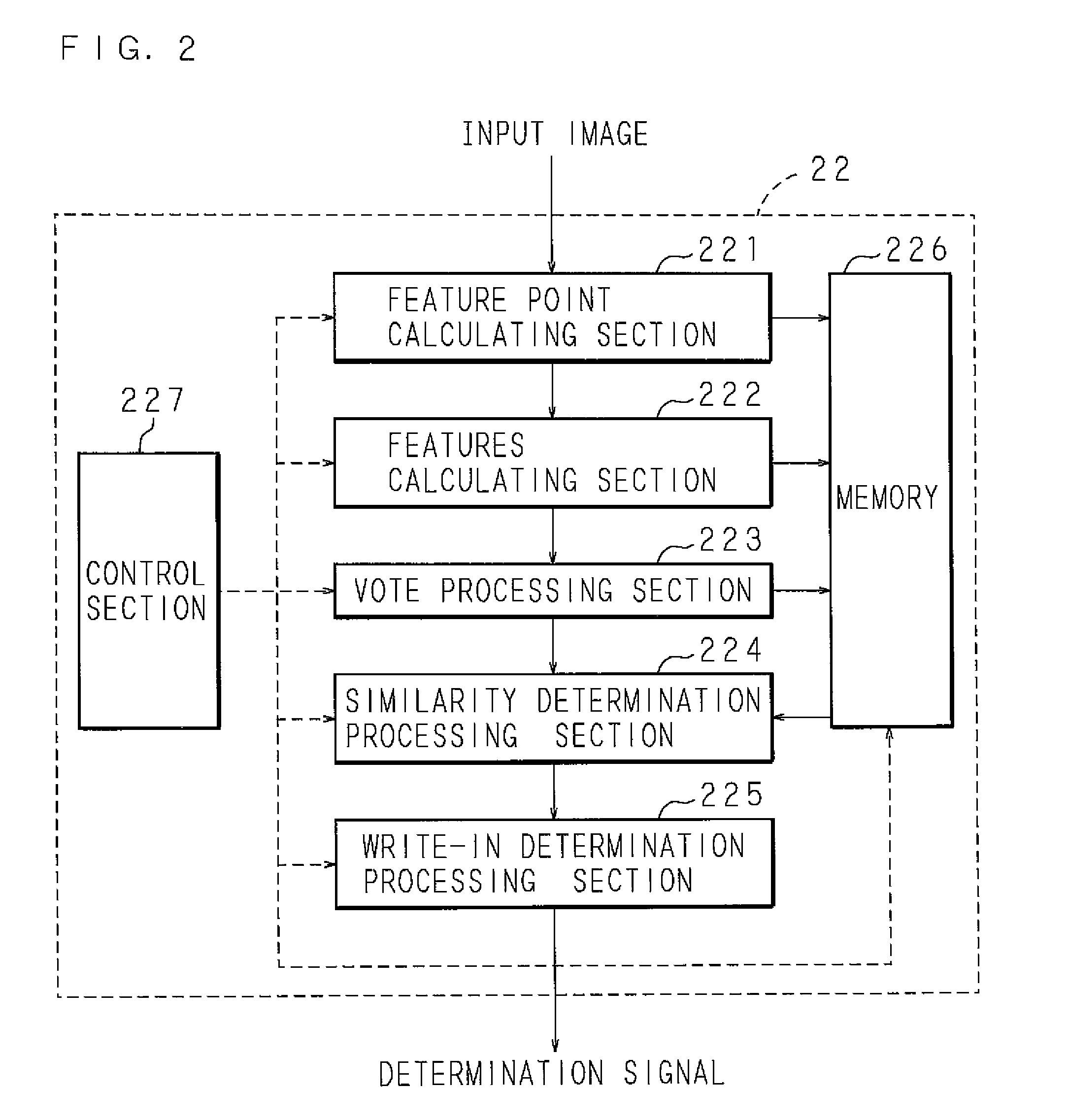
Image processing method, image processing apparatus, image forming apparatus, and image reading apparatus
ActiveUS20080118112A1Inhibit outputPrevent leakageDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImaging processingImage formation
A document matching process section calculates feature points (e.g., the centroid) on the basis of an inputted document image, then selects a plurality of feature points from among the calculated feature points, and then calculates a hash value on the basis of the selected feature points. Then, on the basis of the calculated features, the document matching process section determines whether the document image is similar to a preliminary reference format (reference image). When it is determined as being similar, the document matching process section determines whether write-in is present in the document image, and then outputs a determination signal (a determination result indicating the presence or absence of write-in). In the determination of similarity of the document image, permission or non-permission for processing such as copying is determined more accurately than in the prior art.
Owner:SHARP KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com