Patents
Literature
305 results about "Profilometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A profilometer is a measuring instrument used to measure a surface's profile, in order to quantify its roughness. Critical dimensions as step, curvature, flatness are computed from the surface topography.
Magnetic tape
InactiveUS20120196156A1Good electromagnetic characteristicGood characteristic frictionMagnetic materials for record carriersRecord information storageMagnetic tapeNon magnetic
An aspect of the present invention relates to a magnetic tape comprising, on one surface of a nonmagnetic support, a nonmagnetic layer containing a nonmagnetic powder and a binder, and thereon, a magnetic layer containing a ferromagnetic powder and a binder, whereinthe magnetic layer contains a nonmagnetic filler the average particle diameter φ of which satisfies relation (I) below with a thickness t of the magnetic layer:1.0≦φ / t≦2.0 (I);the thickness t of the magnetic layer ranges from 30 to 200 nm;the nonmagnetic layer has a thickness ranging from 30 to 200 nm;a composite elastic modulus as measured on a surface of the magnetic layer ranges from 6.0 to 8.0 GPa; anda centerline average surface roughness Ra of the surface of the magnetic layer, as measured by an optical three-dimensional profilometer, ranges from 0.2 to 1.5 nm.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
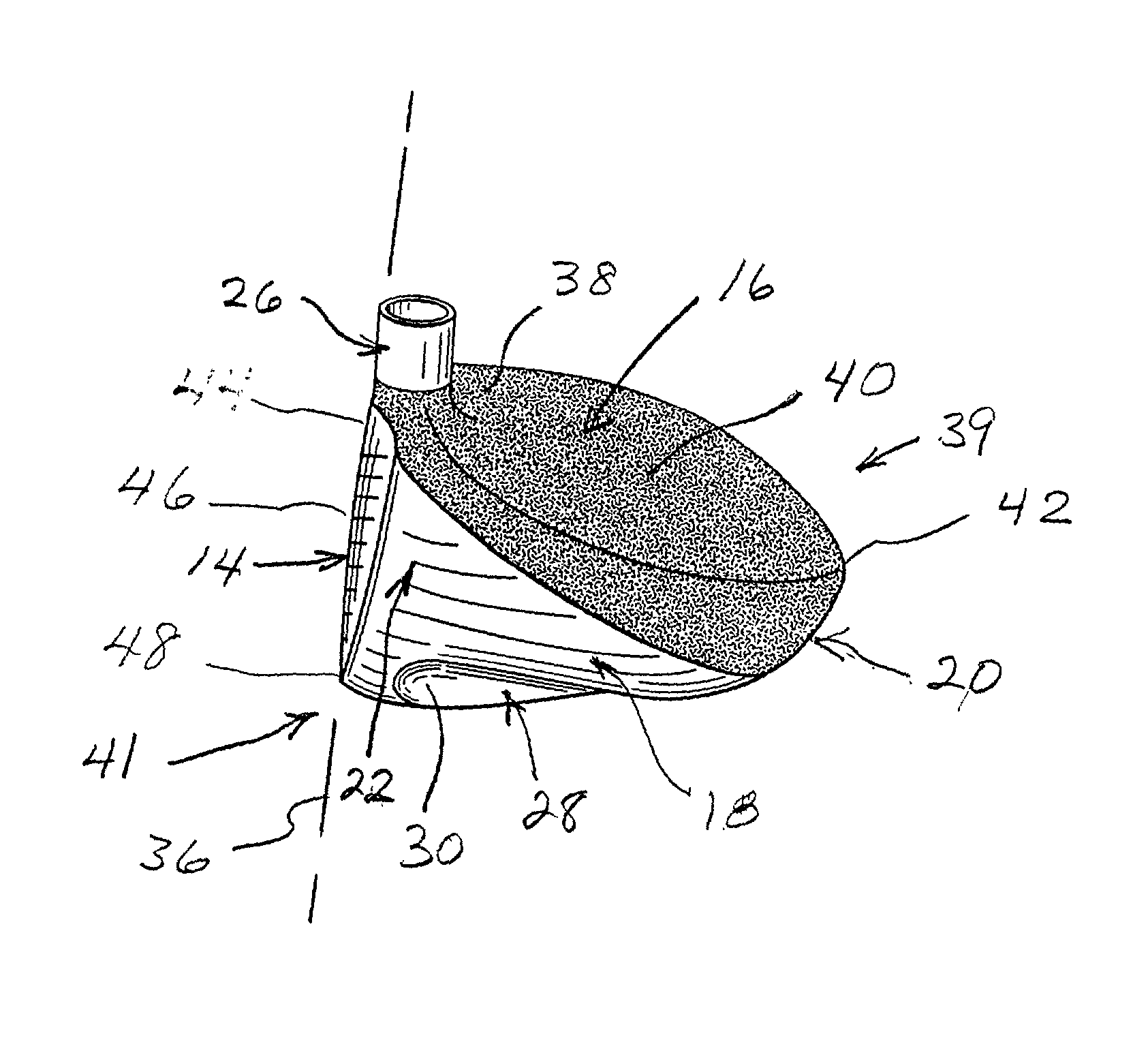
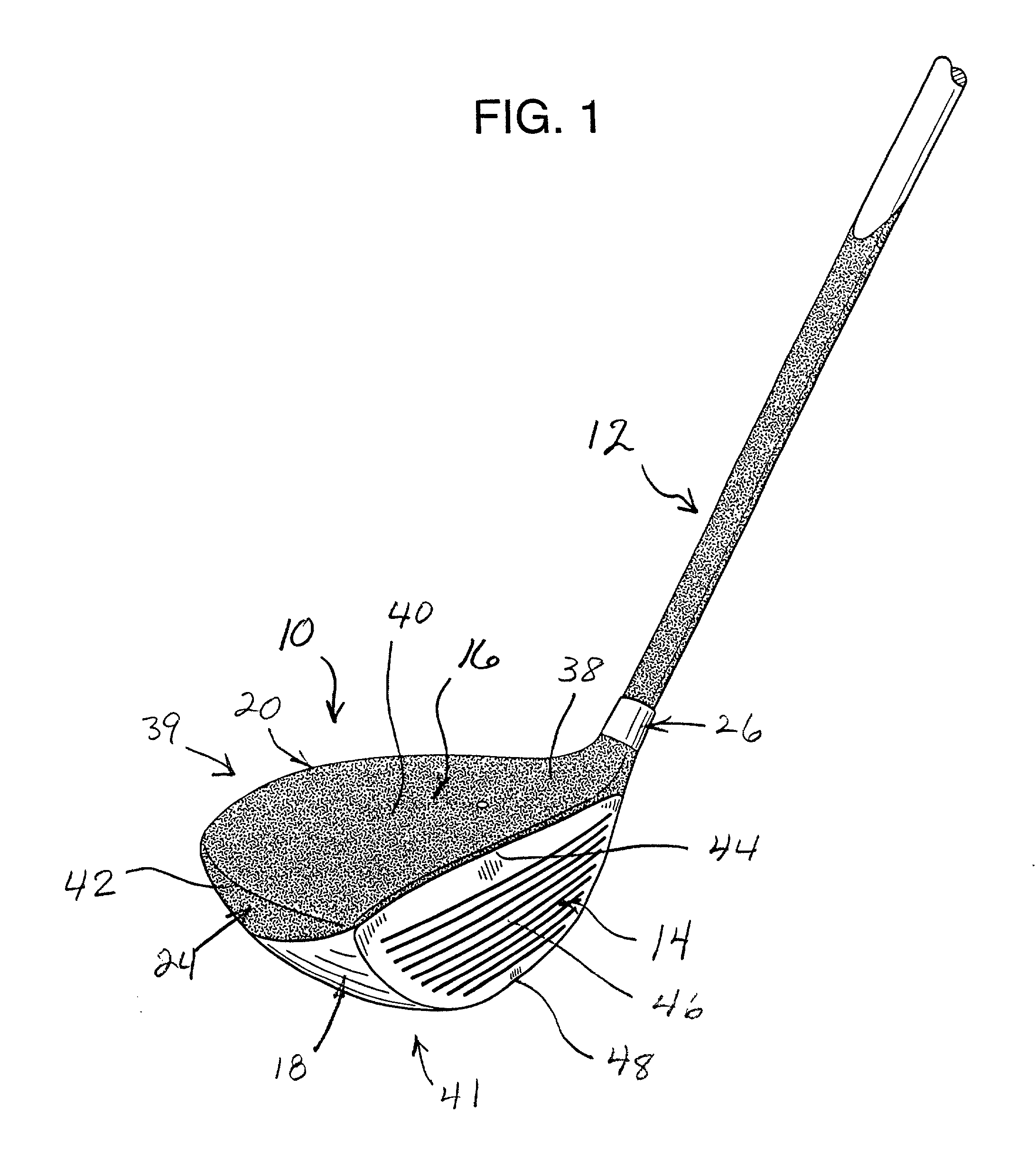
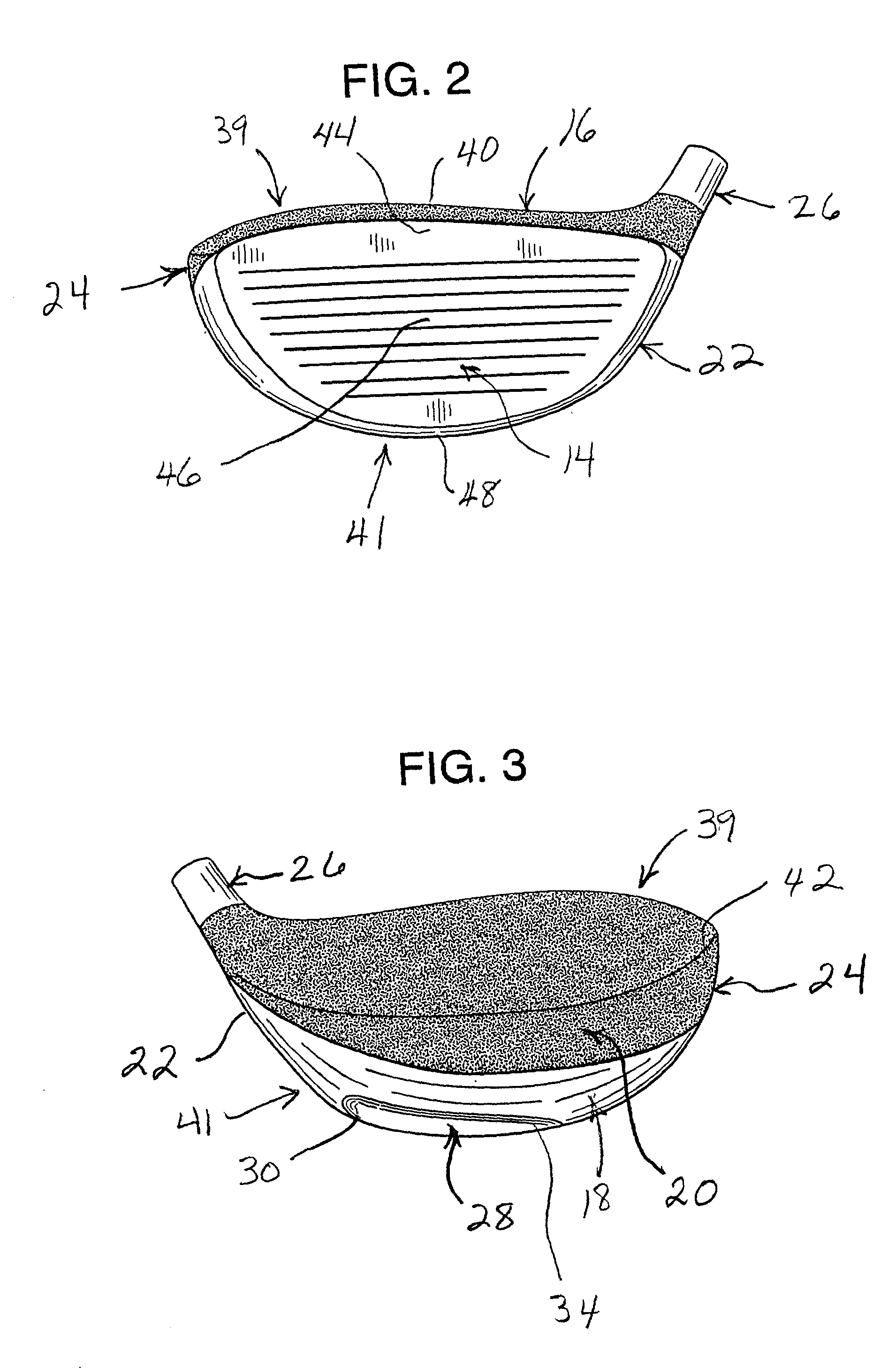
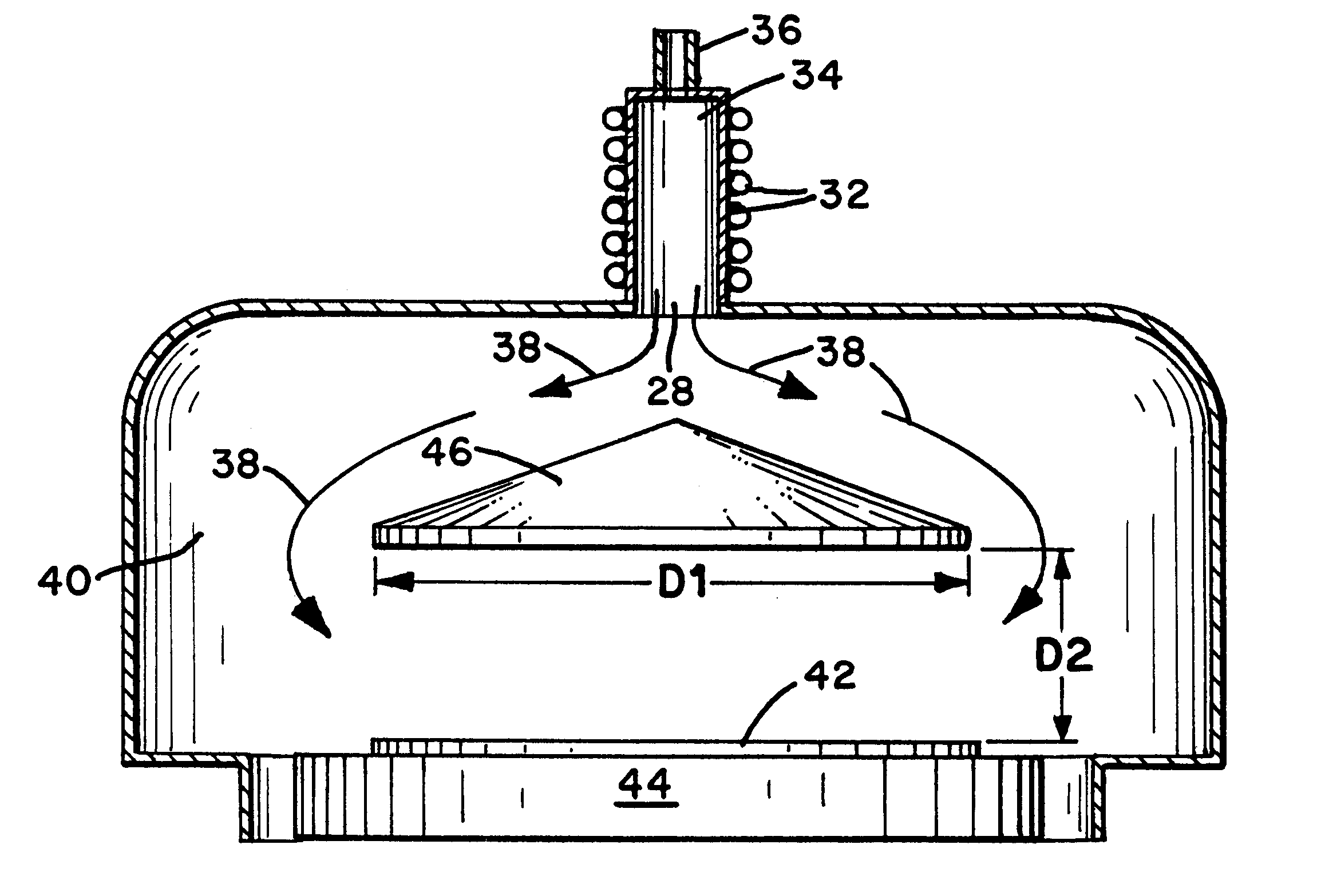
Golf club head
The head of a golf club is improved by reducing the drag and wake turbulence produced in the air when the golf club is swung to strike a golf ball. The club head has a convex sole with an elongated depression defined therein. The inboard end of the depression is located proximate both the heel and the ball-impact face and extends outwardly at a diverging angle from the ball-impact face to an outboard extremity located inboard from the toe of the club head. This depression or channel is thereby closely aligned with the direction of travel of the club head during a normal downswing and follow through of a golf stroke. Also, the top of the club head is covered with a relatively rough coating, such as a textured paint with granules encapsulated therein. The roughness average of the top surface of the club head, as measured by a profilometer, is it least three times as great as that of the ball-impact face and at least three times as great as that of the sole of the club head.
Owner:ENTERBRANDS
Apparatus and method for injecting and modifying gas concentration of a meta-stable or atomic species in a downstream plasma reactor
InactiveUS6287643B1Reduce lossesElectric discharge tubesPretreated surfacesRemote plasmaHigh density
An apparatus and method for injecting gas within a plasma reactor and tailoring the distribution of an active species generated by the remote plasma source over the substrate or wafer. The distribution may be uniform, wafer-edge concentrated, or wafer-center concentrated. A contoured plate or profiler modifies the distribution. The profiler is an axially symmetric plate, having a narrow top end and a wider bottom end, shaped to redistribute the gas flow incident upon it. The method for tailoring the distribution of the active species over the substrate includes predetermining the profiler diameter and adjusting the profiler height over the substrate. A coaxial injector tube, for the concurrent injection of activated and non-activated gas species, allows gases to be delivered in an axially symmetric manner whereby one gas can be excited in a high density RF plasma, while the other gas can be prevented from excitation and / or dissociation caused by exposure to the plasma or heated surfaces in the source apparatus. The profiler is used in conjunction with the coaxial injector tube for redistributing the excited gases emerging from the injector tube, while allowing the non-excited gases to pass through its center.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
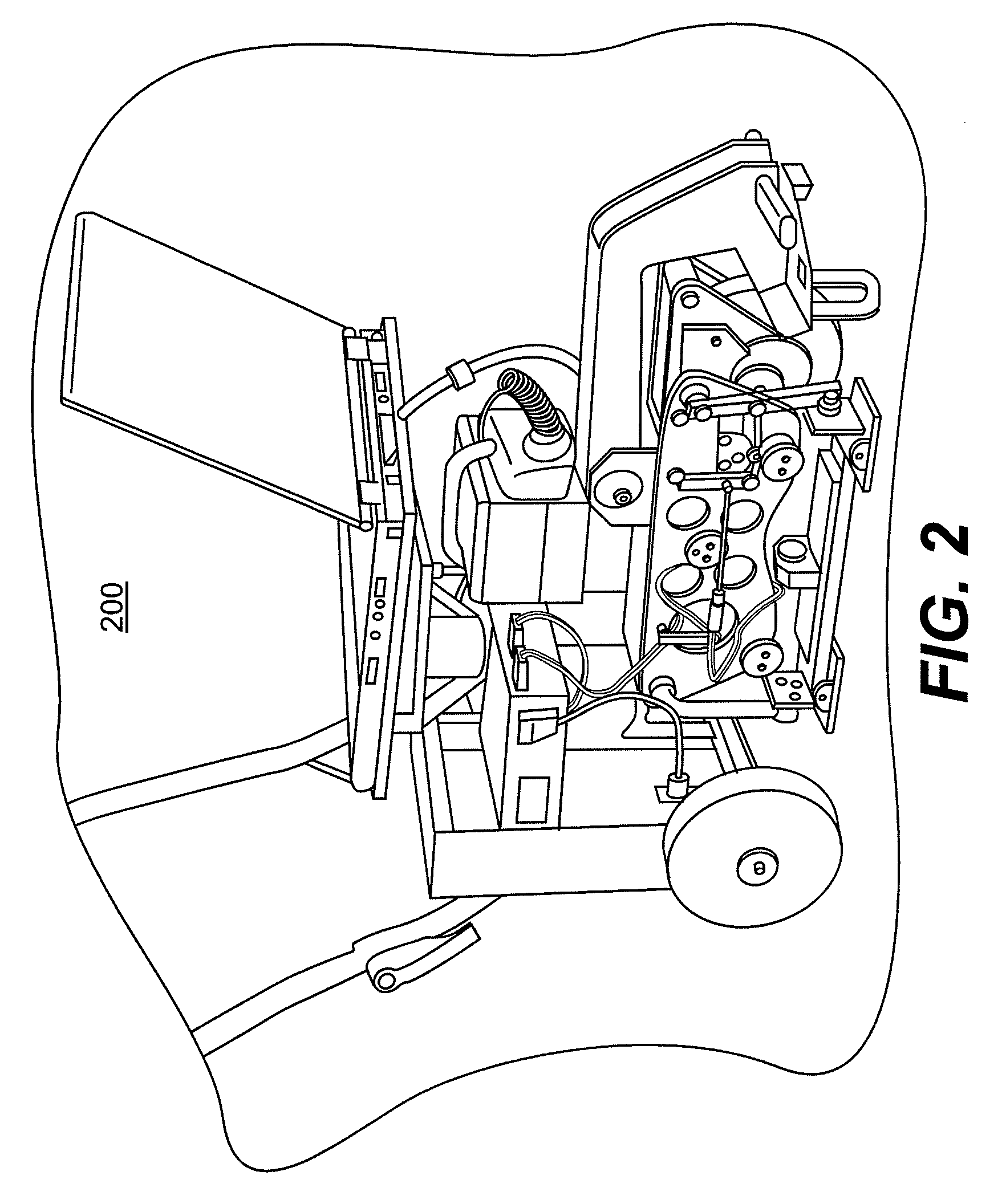
Method and system for surface profile inspection of off-line industrial gas turbines and other power generation machinery
ActiveUS20150300920A1Facilitates of dimensionalGathering informationGas-turbine engine testingMaterial analysis by optical meansIndustrial gasTime profile
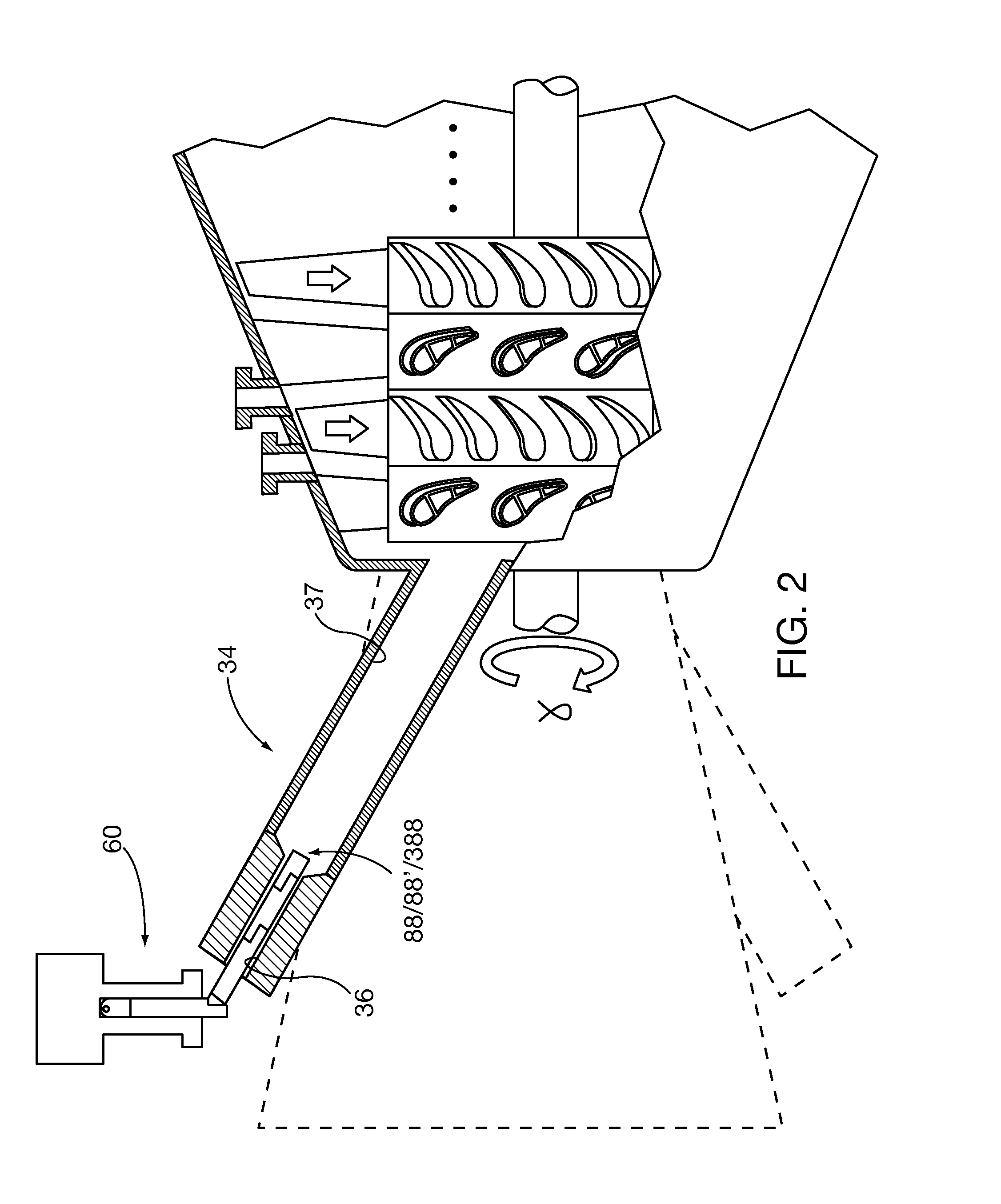
Internal components of power generation machines, such as gas or steam turbines, are inspected with a laser profilometer inspection system that is inserted and positioned within the turbine, for example through an inspection port that is in communication with an open inter-row spacing volume between an opposing turbine vane and turbine blade row. Component surface profile scans are performed to determine relative profile heights along a two-dimensional scan line generated by the profilometer. Three-dimensional profile information is obtained by translating the scan line across the surface. Real time profile information is gathered without physical contact, which is helpful for extracting off-line engineering information about component surface conditions, including surface spallation, perforation, and gaps between components. The system is capable of determining blade tip gap between a turbine blade tip and its opposing abradable surface in the turbine casing.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Method for the production of nanometer scale step height reference specimens
InactiveUS6869480B1Good precisionEliminate needPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsReference sampleSingle crystal substrate
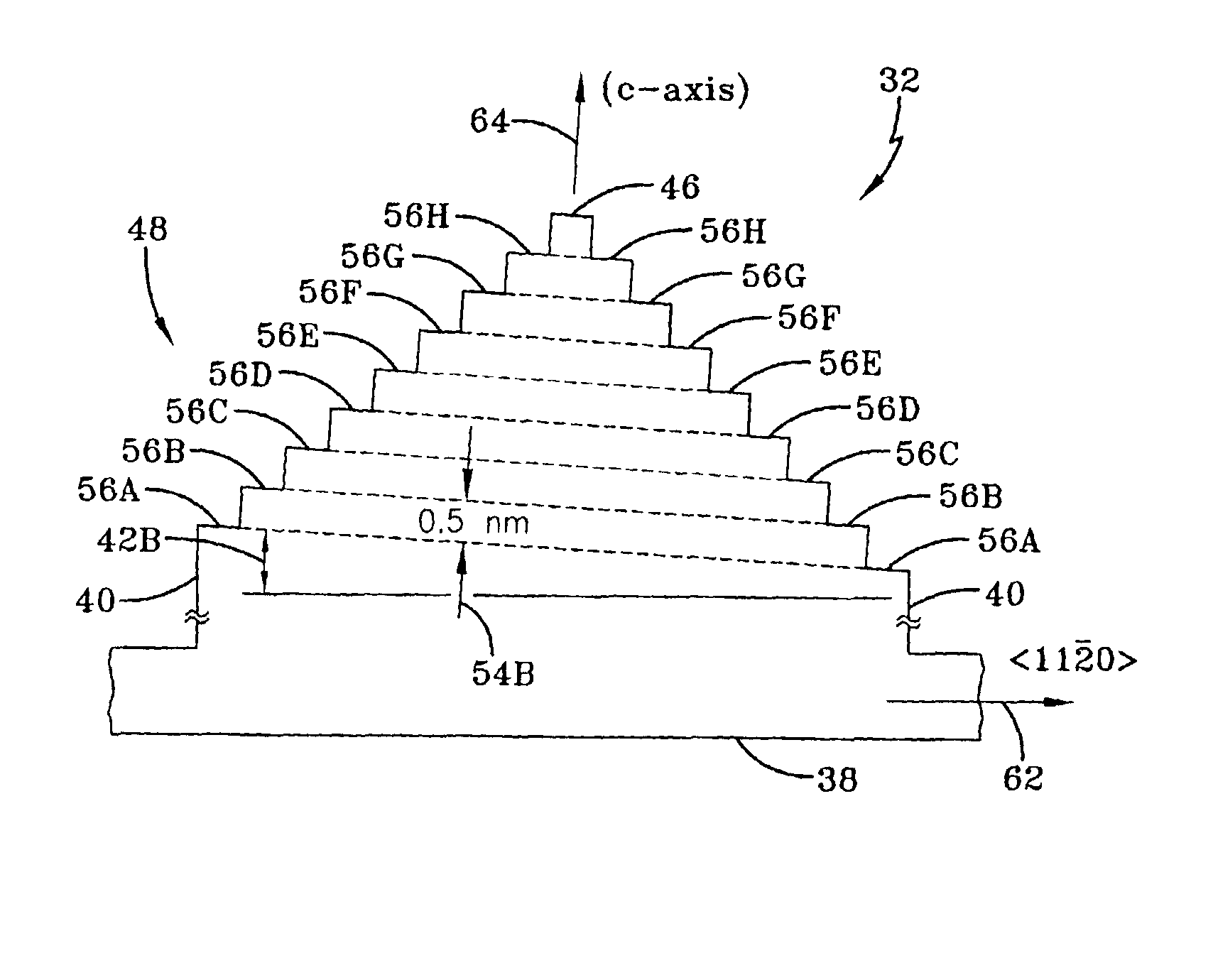
Methods are disclosed that provide for structures and techniques for the fabrication of ordered arrangements of crystallographically determined nanometer scale steps on single crystal substrates, particularly SiC. The ordered nanometer scale step structures are produced on the top surfaces of mesas by a combination of growth and etching processes. These structures, sometimes referred to herein as artifacts, are to enable step-height calibration, particularly suitable for scanning probe microscopes and profilometers, from less than one nanometer (nm) to greater than 10 nm, with substantially no atomic scale roughness of the plateaus on either side of each step.
Owner:NASA
White light interference profile meter
InactiveCN101625231ALarge measuring rangeHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansWhite light interferometryMeasurement plane
The invention discloses a white light interference optical profile meter, comprising a macro / micro two-stage driving and displacement metering device in a vertical direction, white light interference displacement sensors and a universal table, wherein, the white light interference displacement sensors are fixed on the driving and displacement metering device fixed on an upright post, and the upright post is fixed on a vibration isolating table facet on which the universal table is placed. The wide-range three-dimensional optical profile meter based on white light interference and vertical scanning technology realizes rough and fine two-stage driving respectively by a servo motor and piezoelectric ceramic, so as to drive the white light interference displacement sensors to integrally move, adding the servo motor in vertical displacement can enlarge the measurement range, and vertical scanning is accomplished by the piezoelectric ceramic. The measurement of macro / micro displacement is completed by using the same diffraction grating metering system. The profile meter is capable of automatically searching for interference fringes and realizing the three-dimensional profiles of wide-range non-contact measurement planes and curved surfaces, and has the characteristics of high measurement precision, large measurement range, low cost and the like.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method and device for determining grinding brittleness-ductility transformation critical cutting depth of hard and brittle material
InactiveCN103722467AImprove surface qualityHigh precisionGrinding feed controlGrinding machinesHigh surfaceRelative motion
The invention relates to the technical field of hard and brittle material ultra-precision machining. In order to achieve ductility domain grinding of the largest cutting depth, high surface quality of the hard and brittle material, and efficient and high-precision production machining, according to the technical scheme, a method and device for determining the grinding brittleness-ductility transformation critical cutting depth of the hard and brittle material comprises the following steps of (1) according to a grinding wheel used in ultra-precision grinding, determining the number, shape and distance of grains of a homemade multi-grain tool, (2) according to the grain shape, distance and front-angle parameters selected in the step (1), machining three or more grains on a grain base body, (3) controlling the multi-grain tool and a workpiece to generate relative motion, beginning to conduct scratching on the surface of the workpiece, meanwhile, controlling the multi-grain tool to conduct continuous feeding, enabling the depth of the scratch to continuously change, and observing and measuring the workpiece after scratching by utilizing a surface contourgraph and a confocal microscopy. The method is mainly applied to ultra-precision machining.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Swing arm type three-dimensional contourgraph
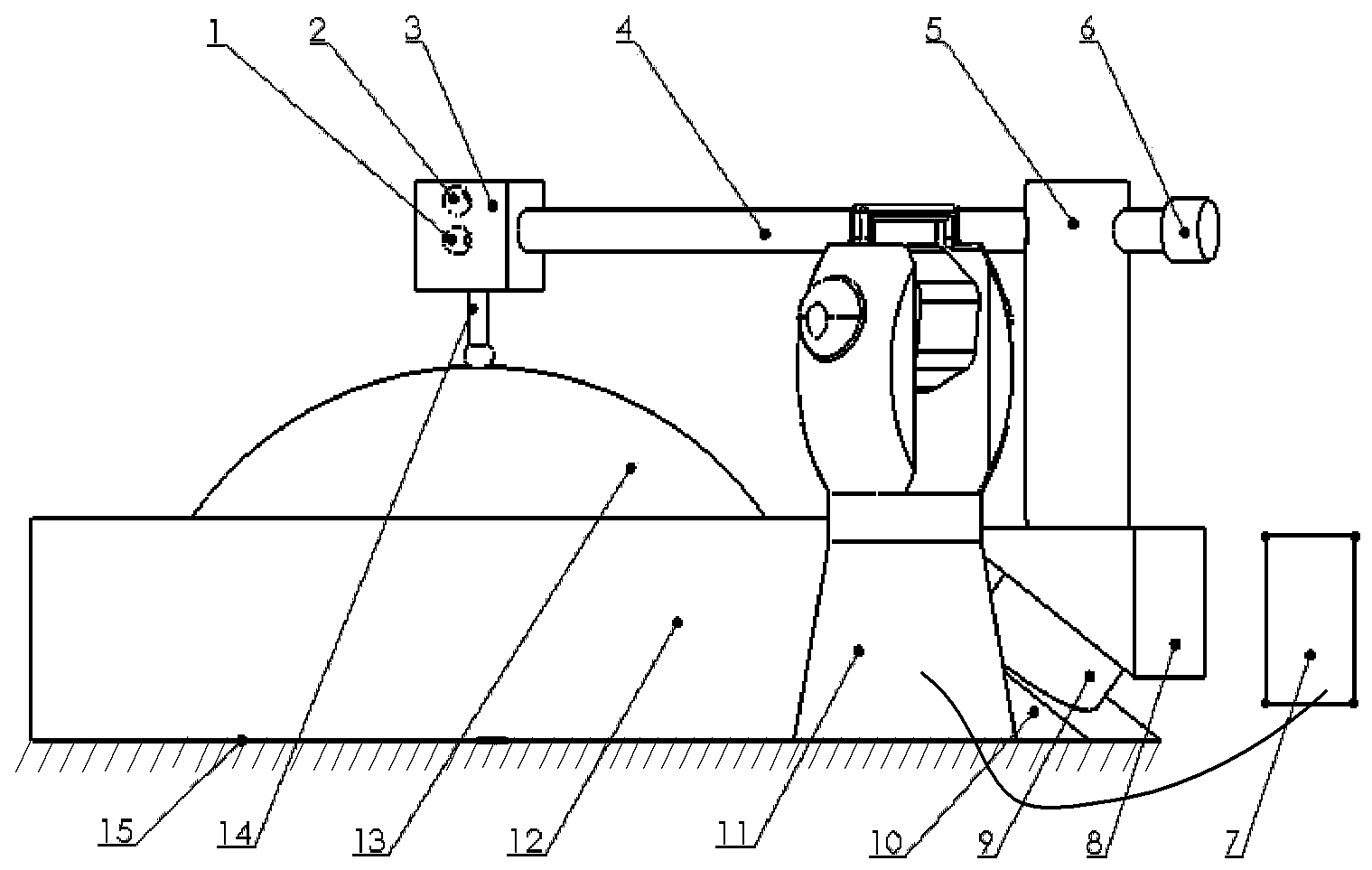
InactiveCN101936699ASolve the problem that only two-dimensional contours can be measuredSolution rangeMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsMechanical roughness/irregularity measurementsThree dimensional morphologyEngineering
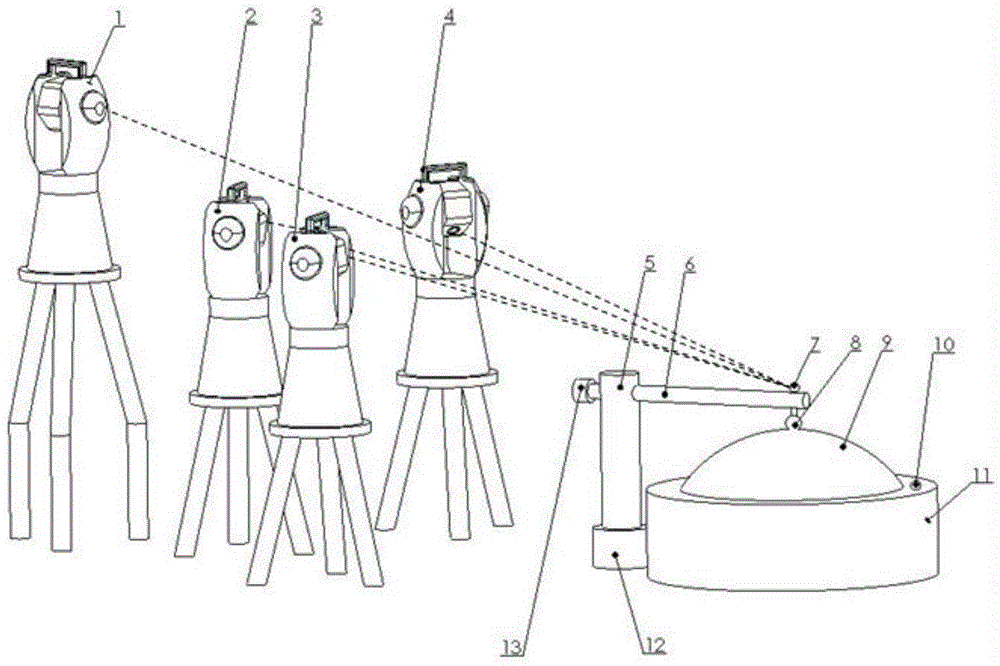
The invention relates to a swing arm type three-dimensional contourgraph which comprises a measuring head system, a transverse arm, an upright post, a counter weight, a measured plane element, a workpiece turntable and a transverse arm turntable, wherein one end part of the upright post is arranged in a mounting hole of the transverse arm turntable and fixedly connected with the transverse arm turntable, and the transverse arm is arranged in another end part mounting hole of the upright post; one end part of the transverse arm is provided with the counter weight, while the other end part of the transverse arm is provided with the measuring head system; the measured plane element is arranged on the workpiece turntable; a detection end of the measuring head system is in contact with the measured plane element; and the transverse arm and the upright post are used for finishing the rotating motion of the measuring head system; and the counter weight is used for balancing the measuring head system and the transverse arm so as to guarantee the transverse arm turntable to maintain stable rotation. The contourgraph can be used for the measurement and the analysis of the three-dimensional surface profile of a heavy-caliber high-precision plane element, wherein measurable parameters comprise three-dimensional morphologies, two-dimensional morphologies, PV (Peak Value), RMS (Root Mean Square) and three-dimensional morphological volumes.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
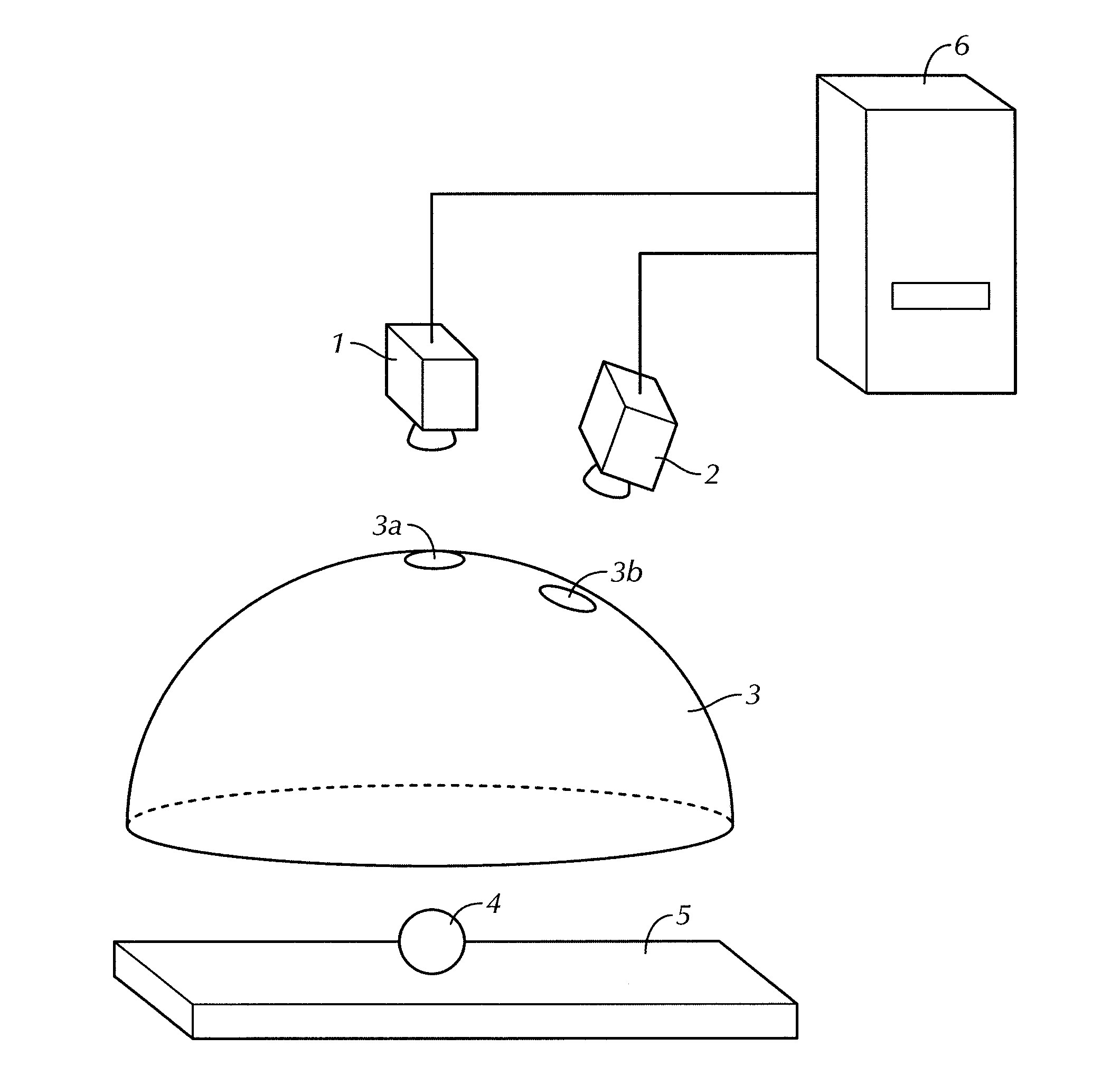
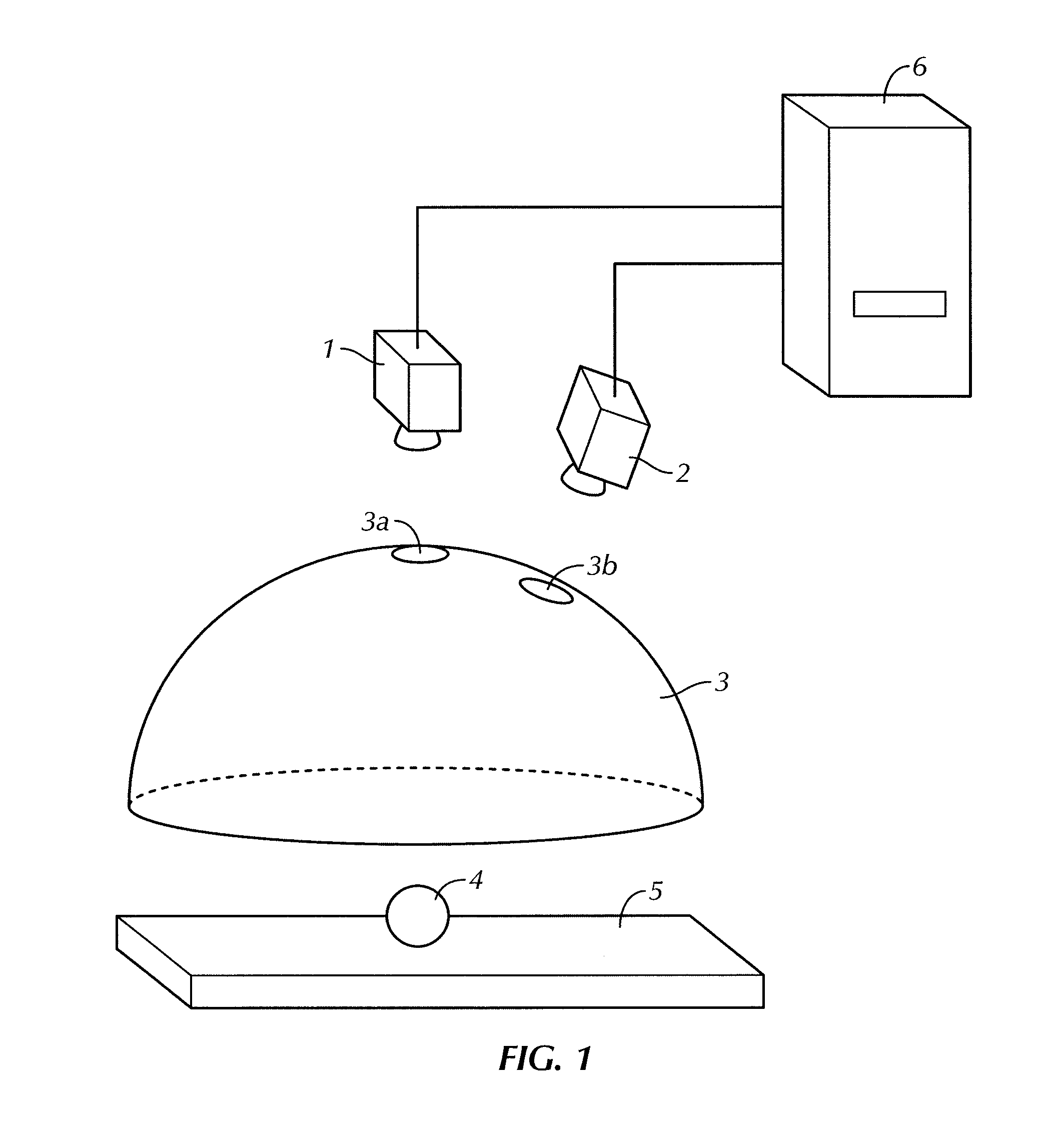
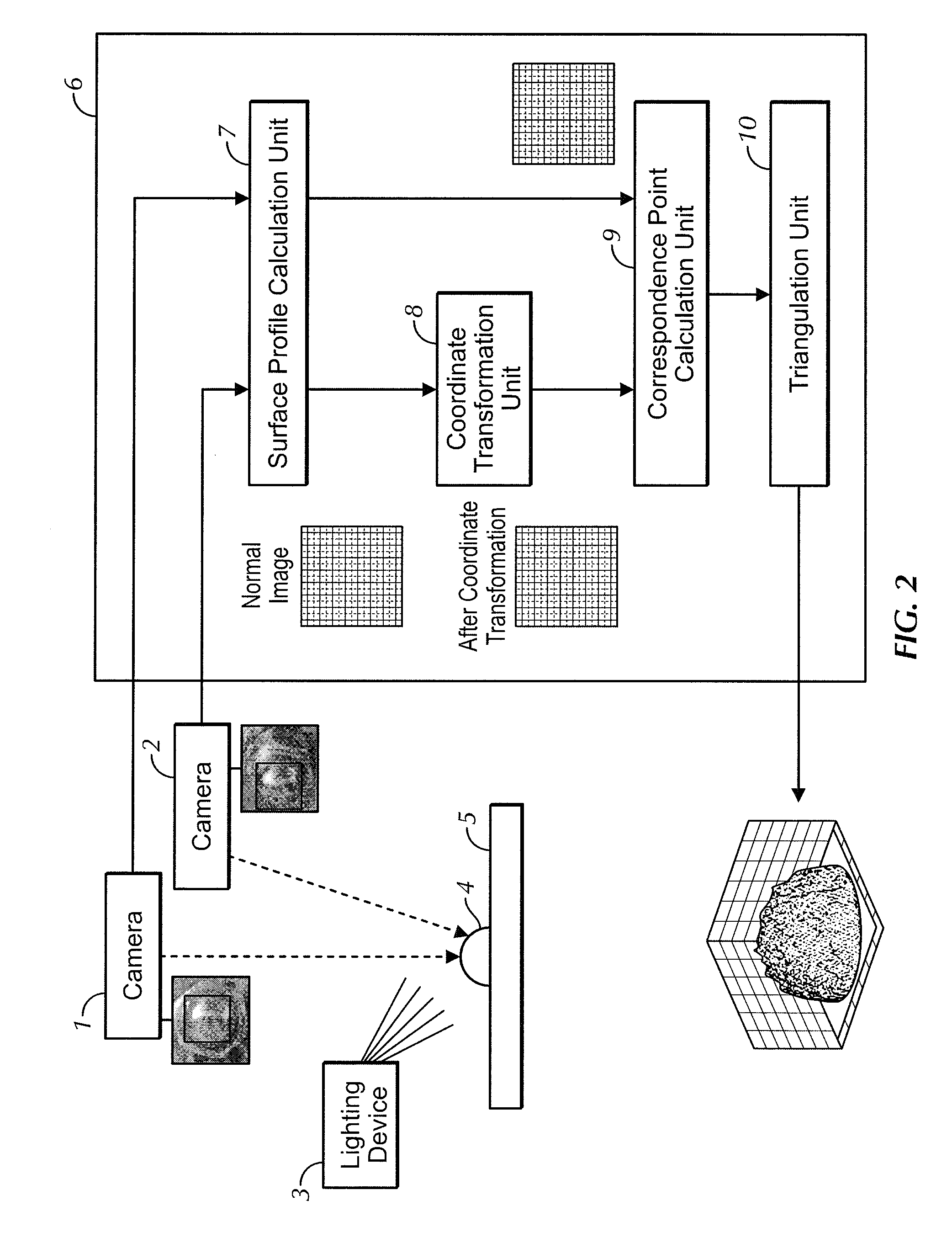
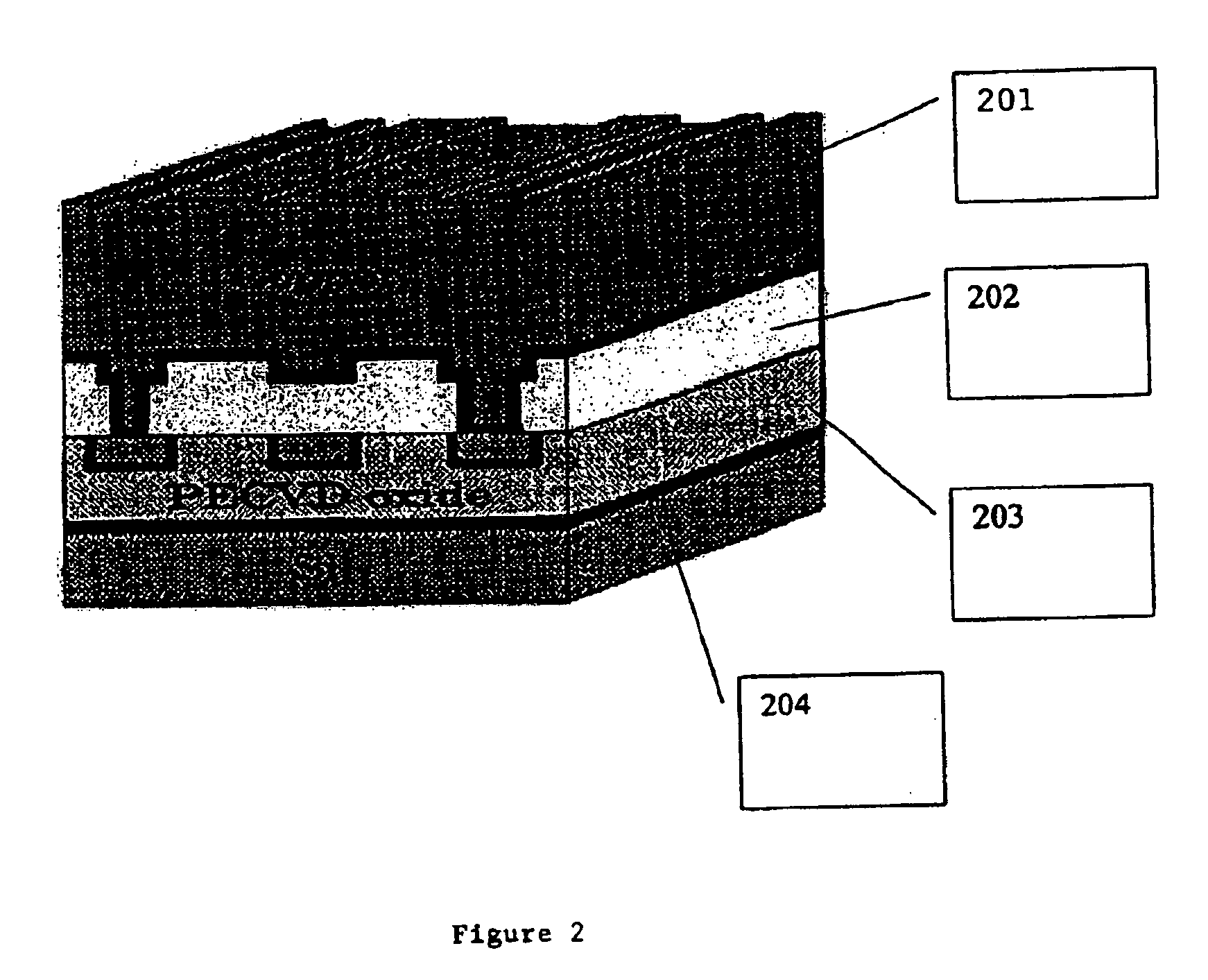
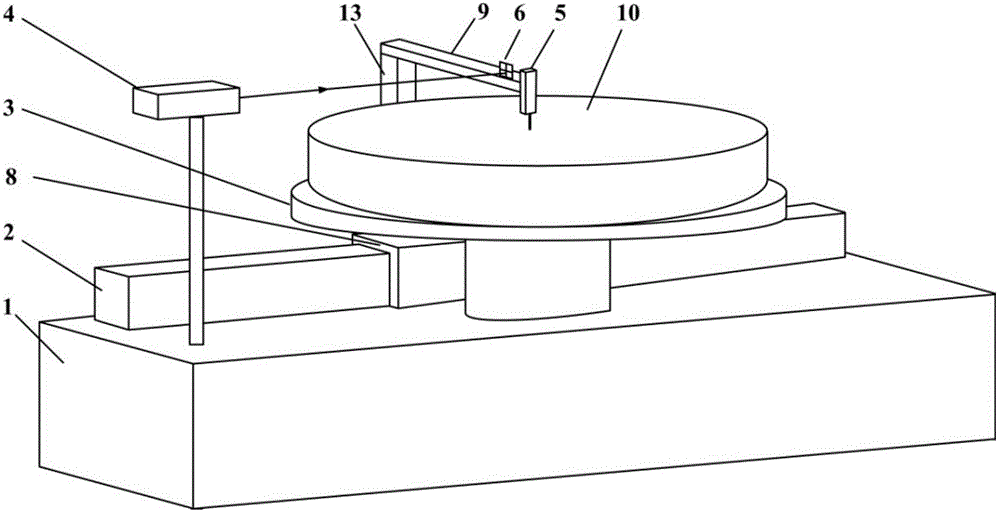
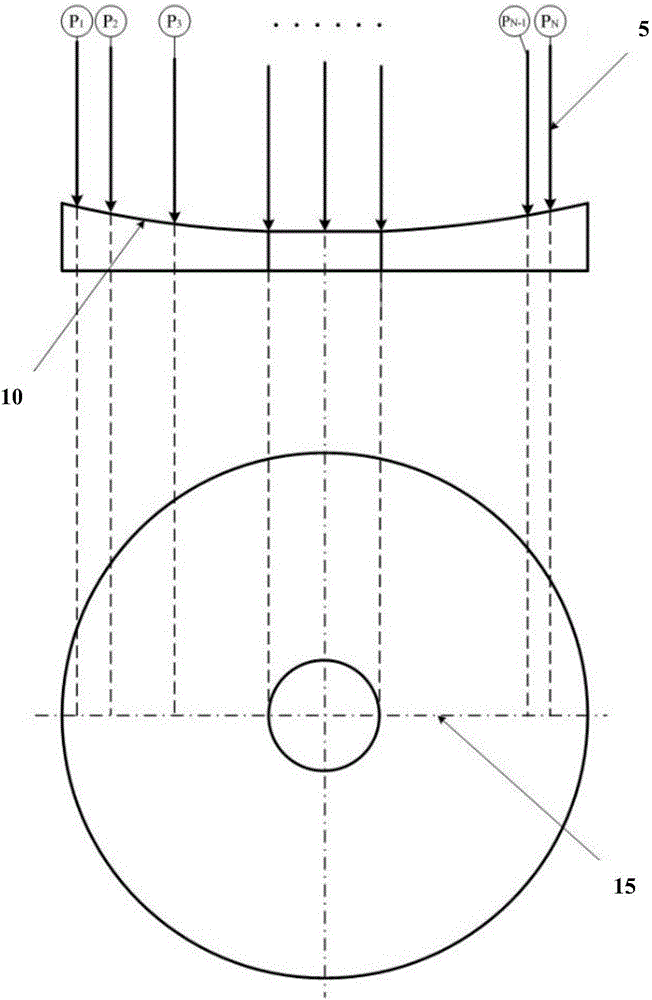
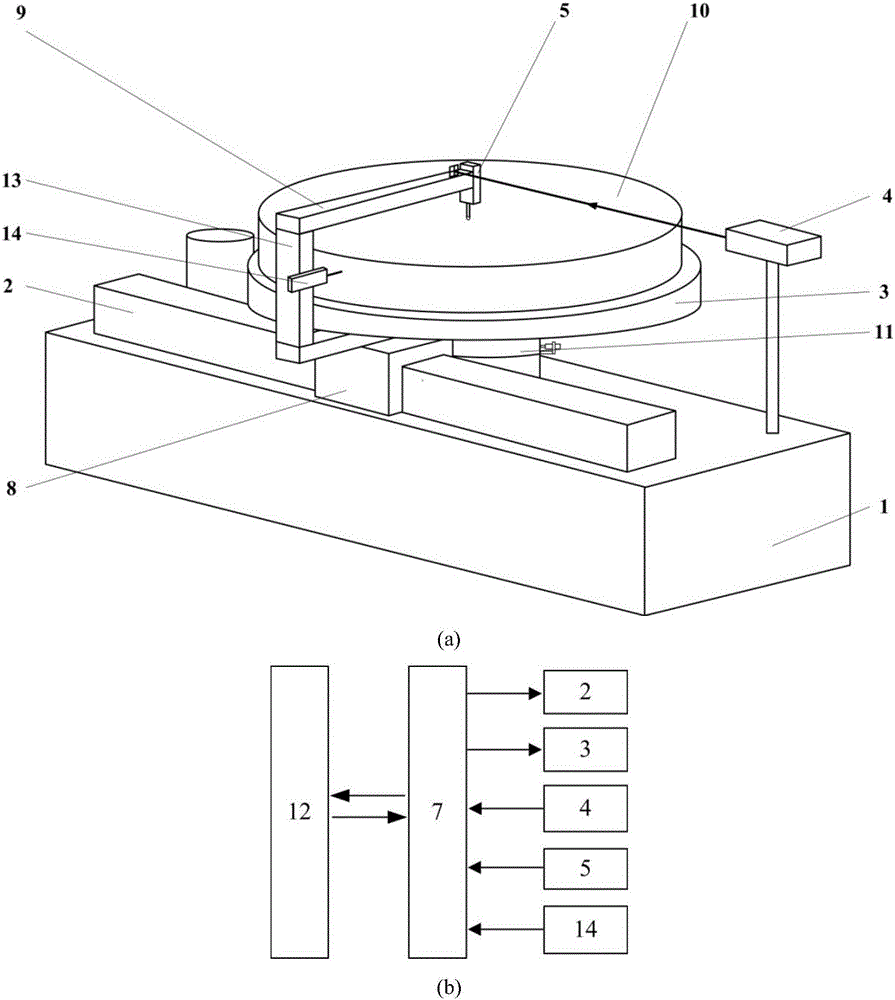
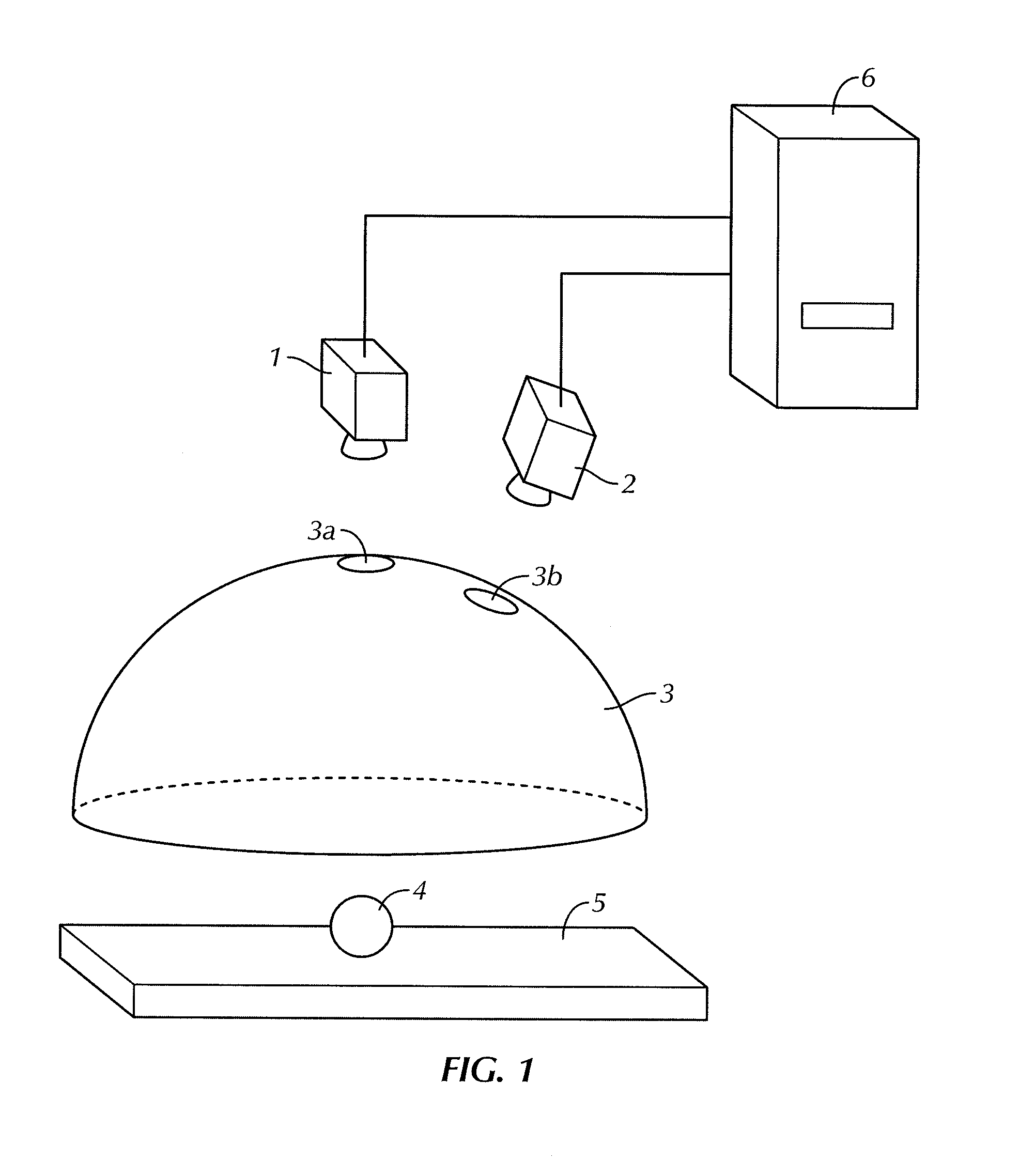
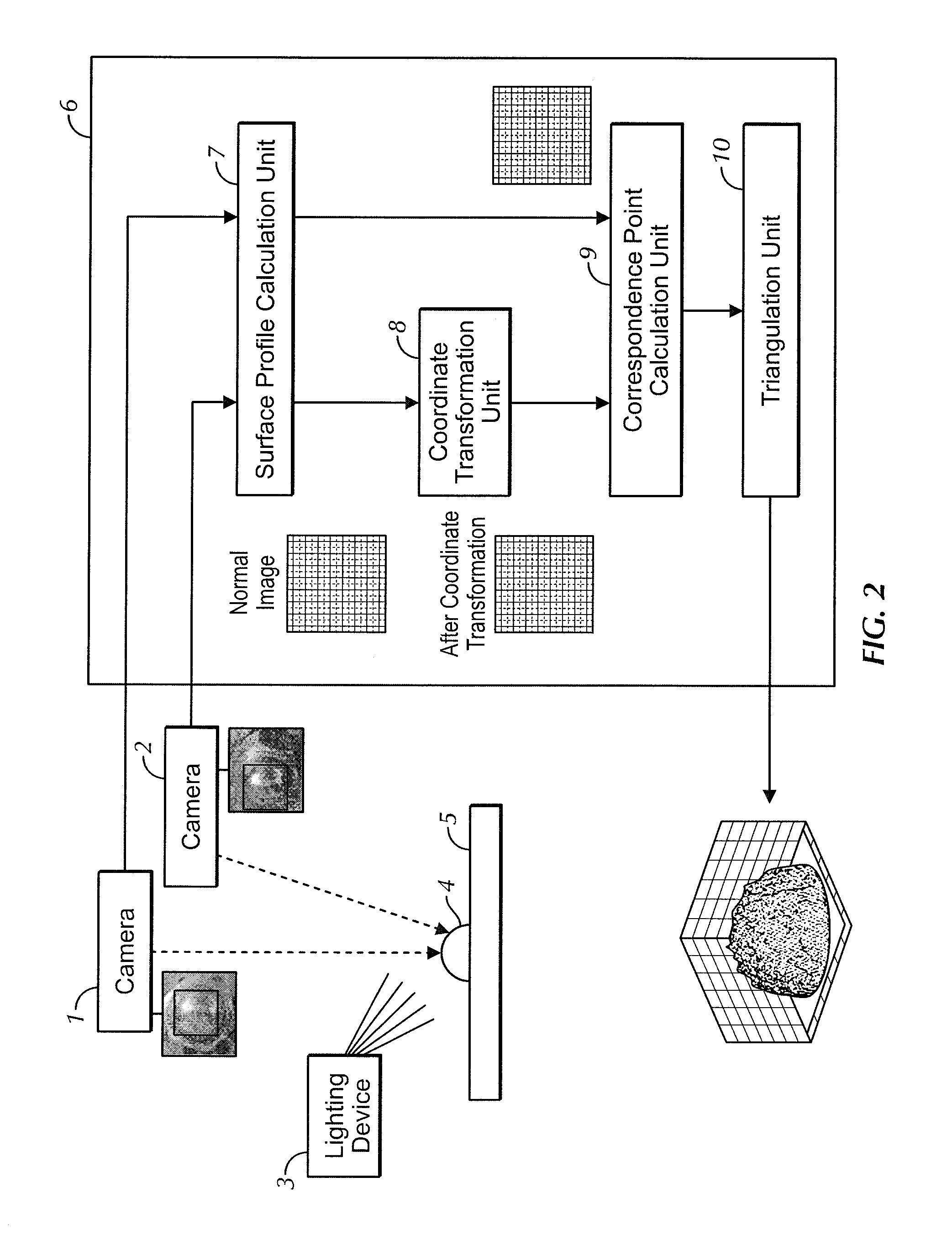
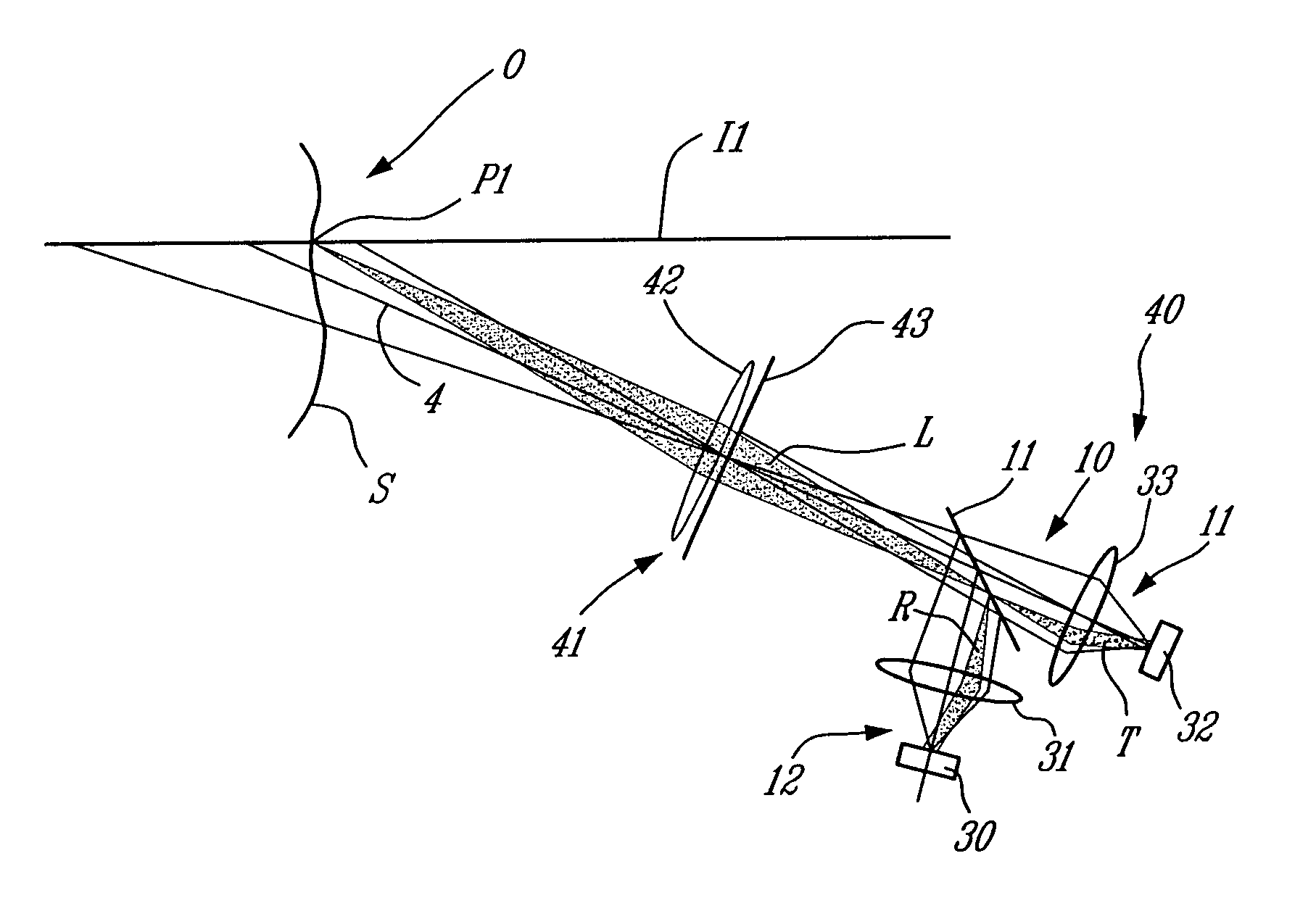
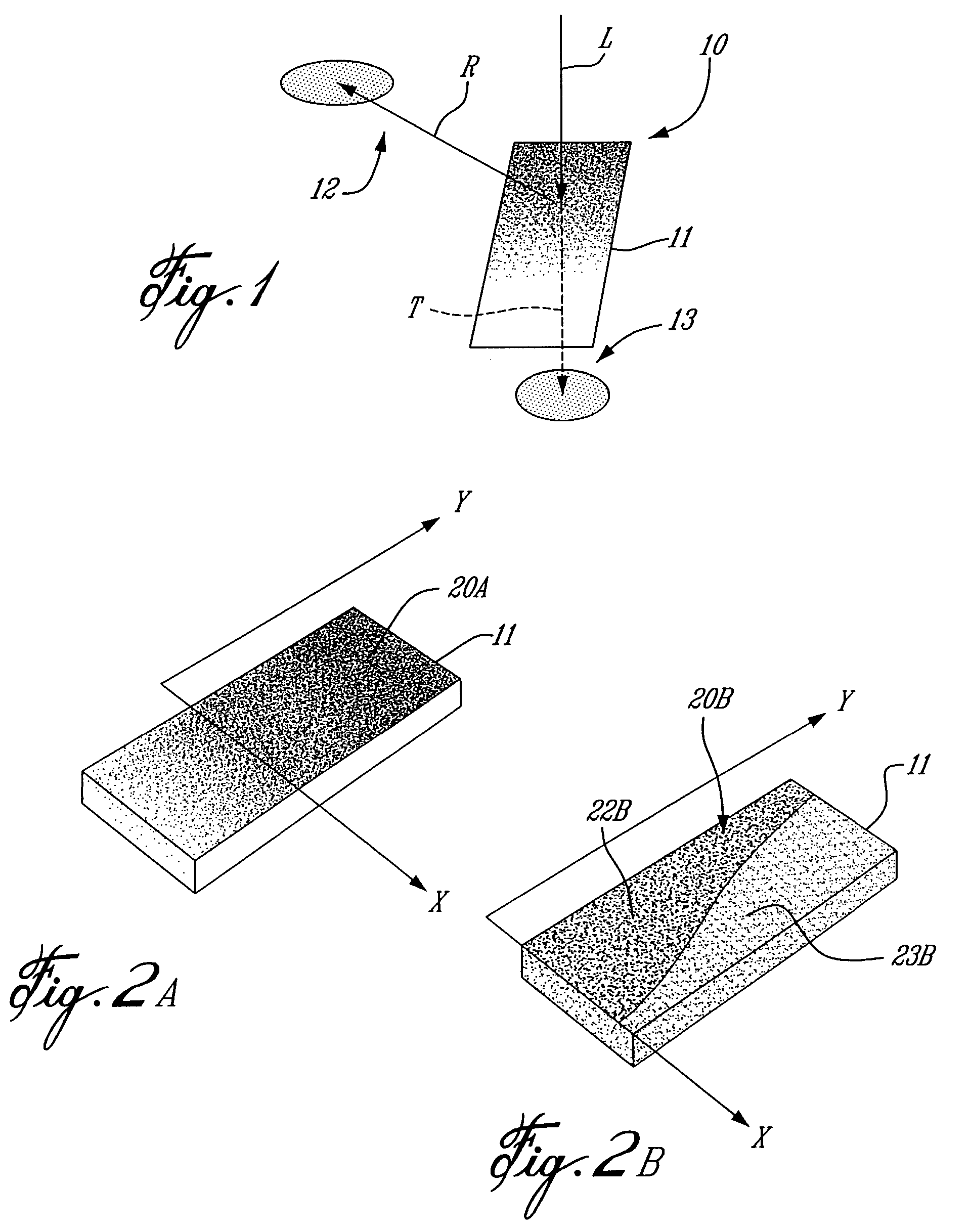
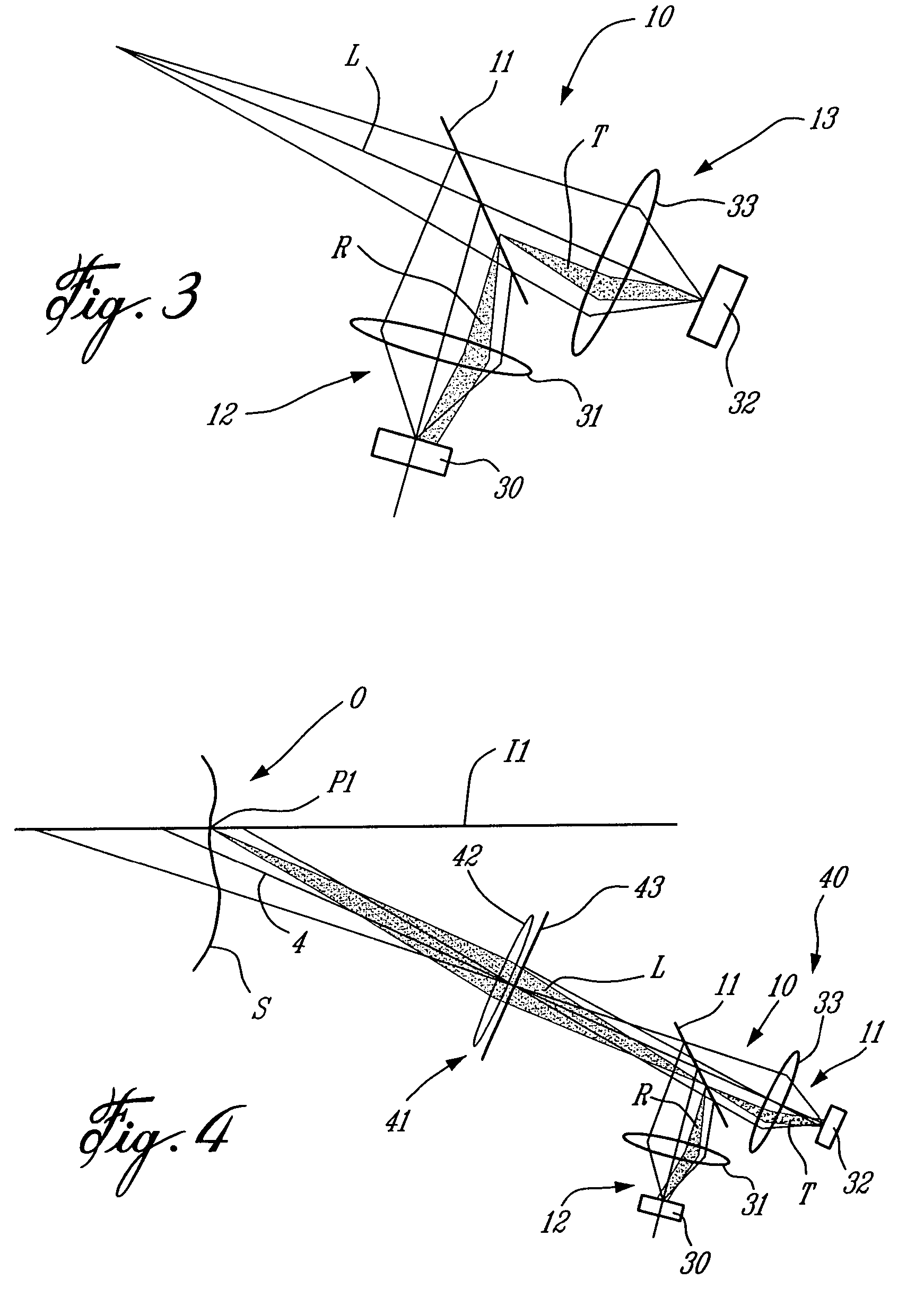
Profilometer
InactiveUS20100259746A1Satisfactory accuracyOptical rangefindersUsing optical meansRadianceLight emission
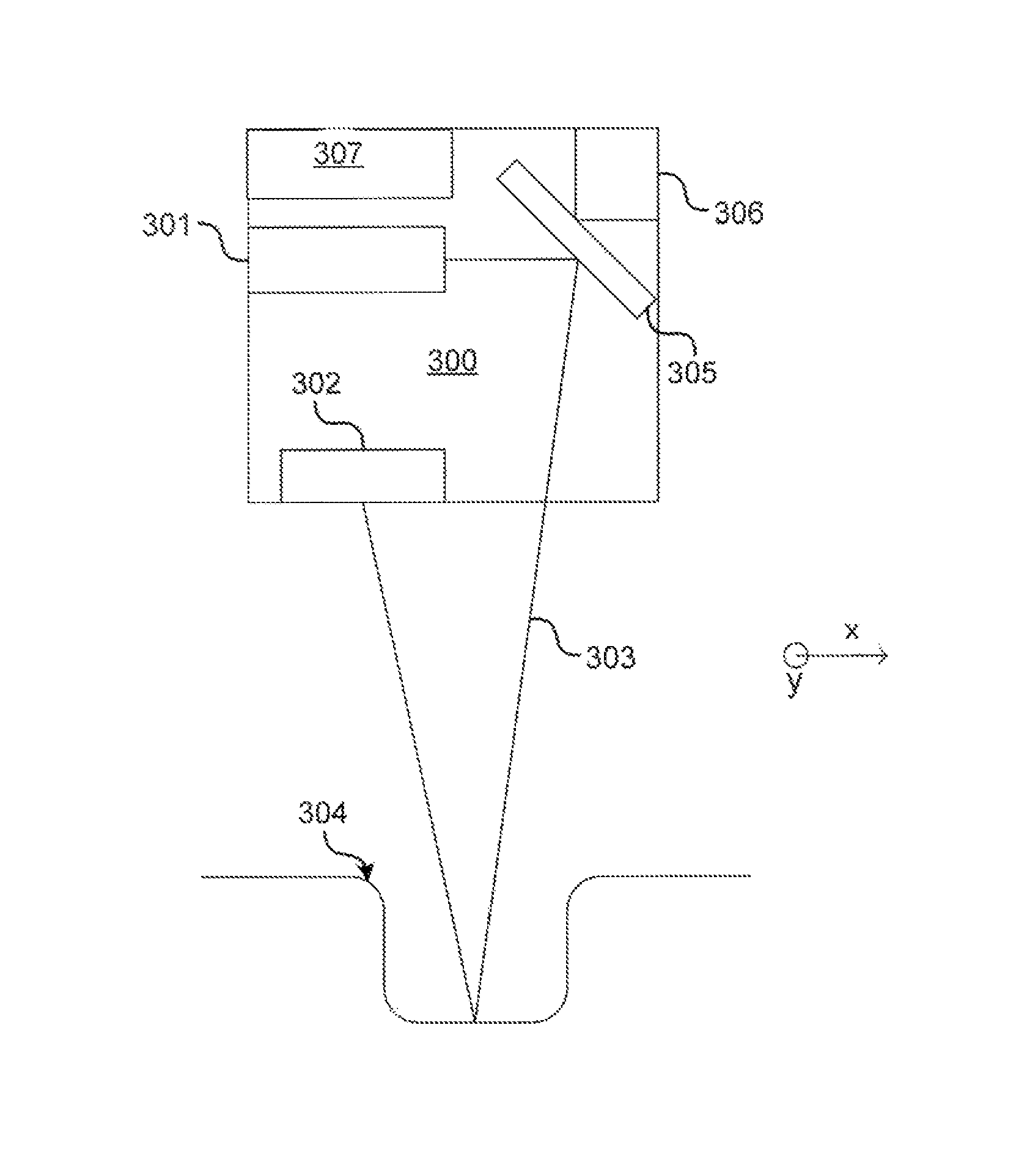
A profilometer for measuring a surface profile of a measuring target has a lighting device for irradiating the measuring target with light, an imaging device for imaging a reflected light from the measuring target, and a normal calculation section for calculating a normal direction of a surface at each position of the measuring target from an imaged image. The lighting device has a light emission region of a predetermined extent. A radiance of center of gravity of a light source distribution of a point symmetric region coincides with a radiance of the center of the point symmetric region in an arbitrary point symmetric region of the light emission region.
Owner:ORMON CORP
Ceramic sheet and process for producing the same
InactiveUS6902790B1Reduce crackingAvoid excessive breakageFinal product manufactureSynthetic resin layered productsOxideZirconia ceramic
A ceramic sheet has a burr height on the periphery of the sheet of ±100 μm or less and / or a dimple height on the sheet surface of 100 μm or less, as determined by irradiating the sheet with a laser beam to measure reflected light, and three-dimensionally analyzing the reflected light with a laser optical three-dimensional profiling instrument. This sheet is highly resistant to stacking-induced loads and thermal stresses. Further, when the ceramic sheet includes a zirconia ceramic partially stabilized with 2.8 to 4.5% by mole of yttria and containing 0.1 to 2% by mass of at least one dispersed reinforcing oxide, in which the grain size of the surface of the sheet has an average of 0.1 to 0.4 μm, a maximum of 0.4 to 0.8 μm, and a coefficient of variation of 30% or less, which grain size is determined by scanning electron microscopic observation, the ceramic sheet has satisfactory strength at room temperature and at high temperatures and satisfactory durability of strength at high temperatures. The ceramic sheet is very useful as, for example, a solid-electrolyte film of a solid oxide fuel cell.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
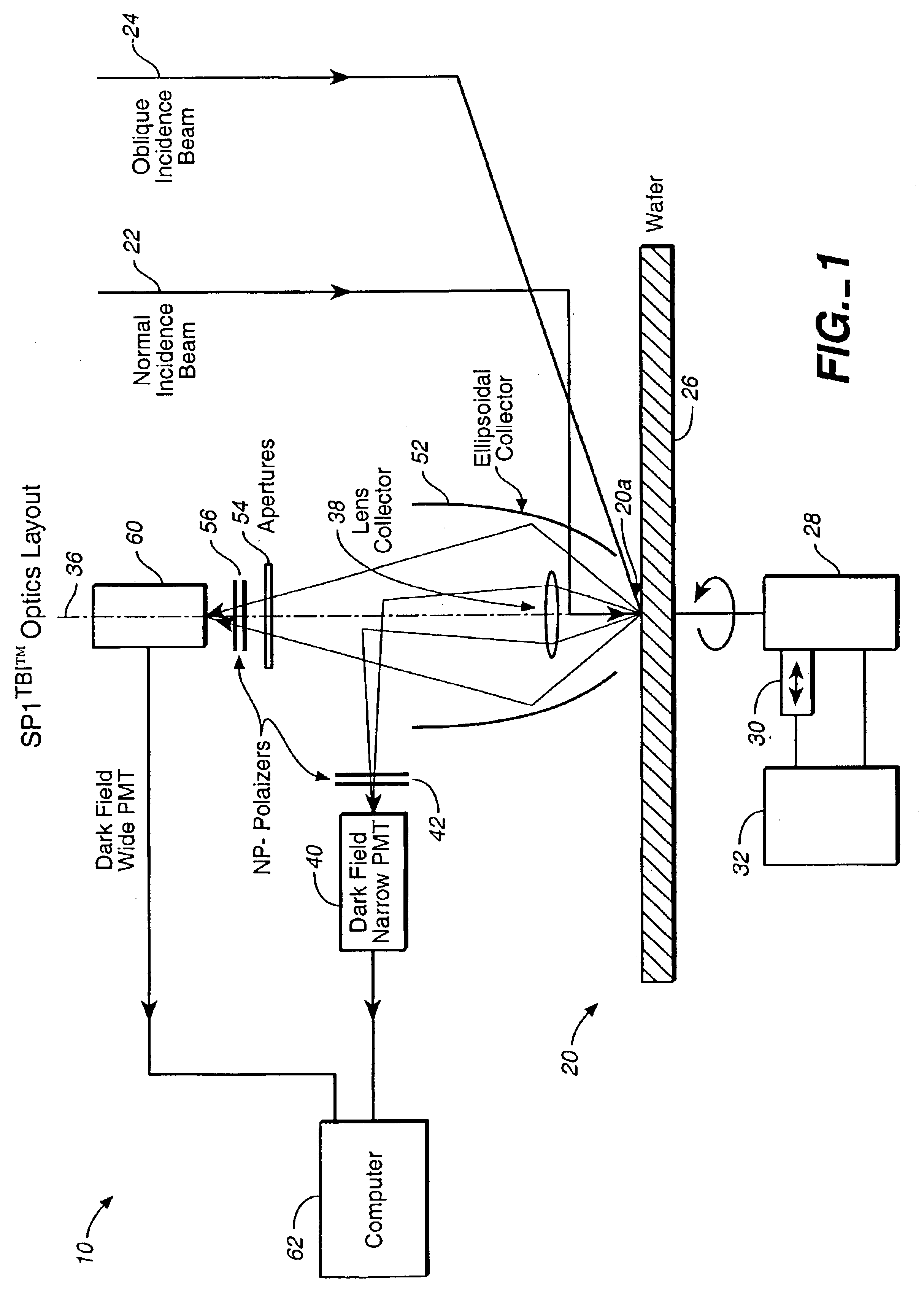
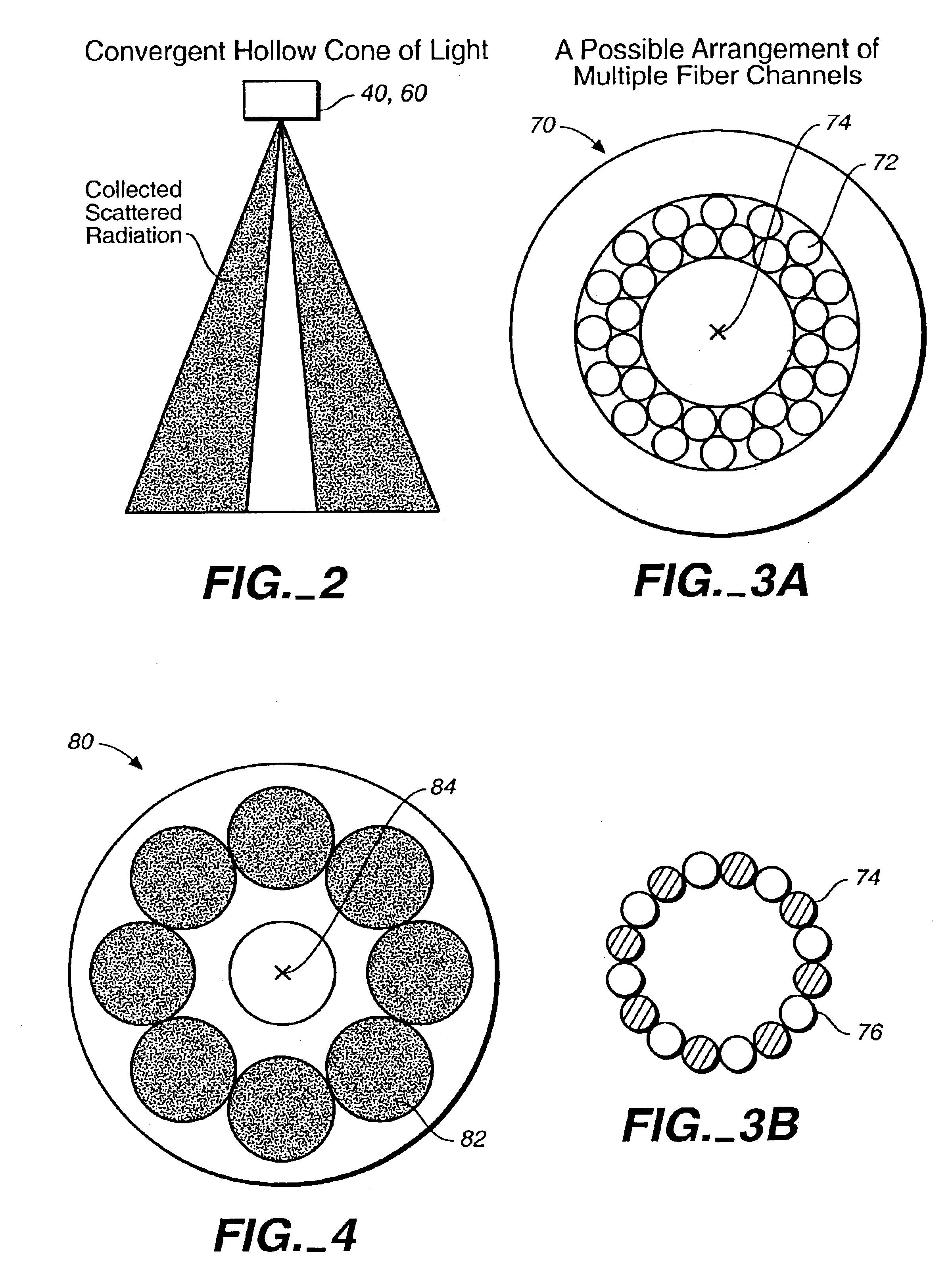
Defect detection system
InactiveUS6862096B2Easy to detectReduce crosstalkPhotometry using reference valuePolarisation-affecting propertiesScanning probe microscopyOptical polarization
Scattered radiation from a sample surface is collected by means of a collector that collects radiation substantially symmetrically about a line normal to the surface. The collected radiation is directed to channels at different azimuthal angles so that information related to relative azimuthal positions of the collected scattered radiation about the line is preserved. The collected radiation is converted into respective signals representative of radiation scattered at different azimuthal angles about the line. The presence and / or characteristics of anomalies are determined from the signals. Alternatively, the radiation collected by the collector may be filtered by means of a spatial filter having an annular gap of an angle related to the angular separation of expected pattern scattering. Signals obtained from the narrow and wide collection channels may be compared to distinguish between micro-scratches and particles. Forward scattered radiation may be collected from other radiation and compared to distinguish between micro-scratches and particles. Intensity of scattering is measured when the surface is illuminated sequentially by S- and P-polarized radiation and compared to distinguish between micro-scratches and particles. Representative films may be measured using profilometers or scanning probe microscopes to determine their roughness and by the above-described instruments to determine haze in order to build a database. Surface roughness of unknown films may then be determined by measuring haze values and from the database.
Owner:KLA CORP
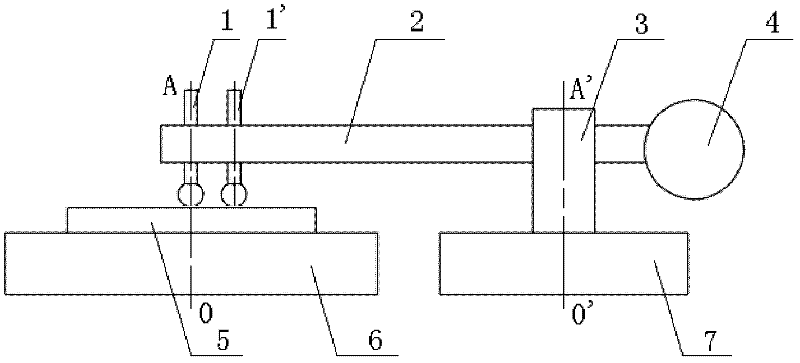
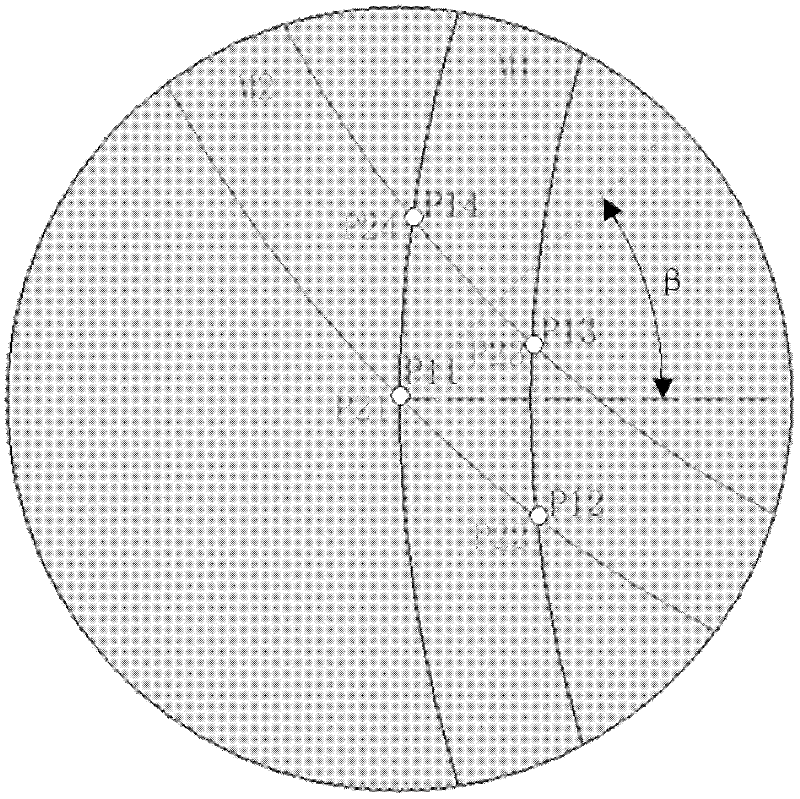
Measuring device of workpiece rotary table error separation based on double-probe scan data splicing and method thereof
InactiveCN102519416AEffective separation and removalHigh measurement accuracyMeasurement devicesOptical processingMotion error
The invention discloses a measuring device of workpiece rotary table error separation based on double-probe scan data splicing and a method thereof. The device employs two sets of probe systems (1, 1') to carry out scanning measurement simultaneously on a swing arm contourgraph which is formed by a probe system (1), a transverse arm (2), a column (3), a counterweight (4), a standard flat crystal (5), a workpiece rotary table (6) and a transverse arm rotary table (7). After two sets of the probe systems scan one time, two scanning loci M1 are obtained, then the workpiece rotary table is rotated with a certain angle beta and scanning is carried out once more, and another two scanning loci M2 are obtained. According to the device and the method, a method of double-probe scan data splicing is employed, influence of a motion error of the workpiece rotary table on a measurement result can be effectively separated and removed, thus measurement precision is raised substantially, and a practical solution scheme is provided for on-position measurement of the swing arm contourgraph at an optical processing field.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Three-dimensional laser scanning on-line detection profiler
InactiveCN101832764AQuick measurementAccurate measurementUsing optical meansImaging processingLaser scanning
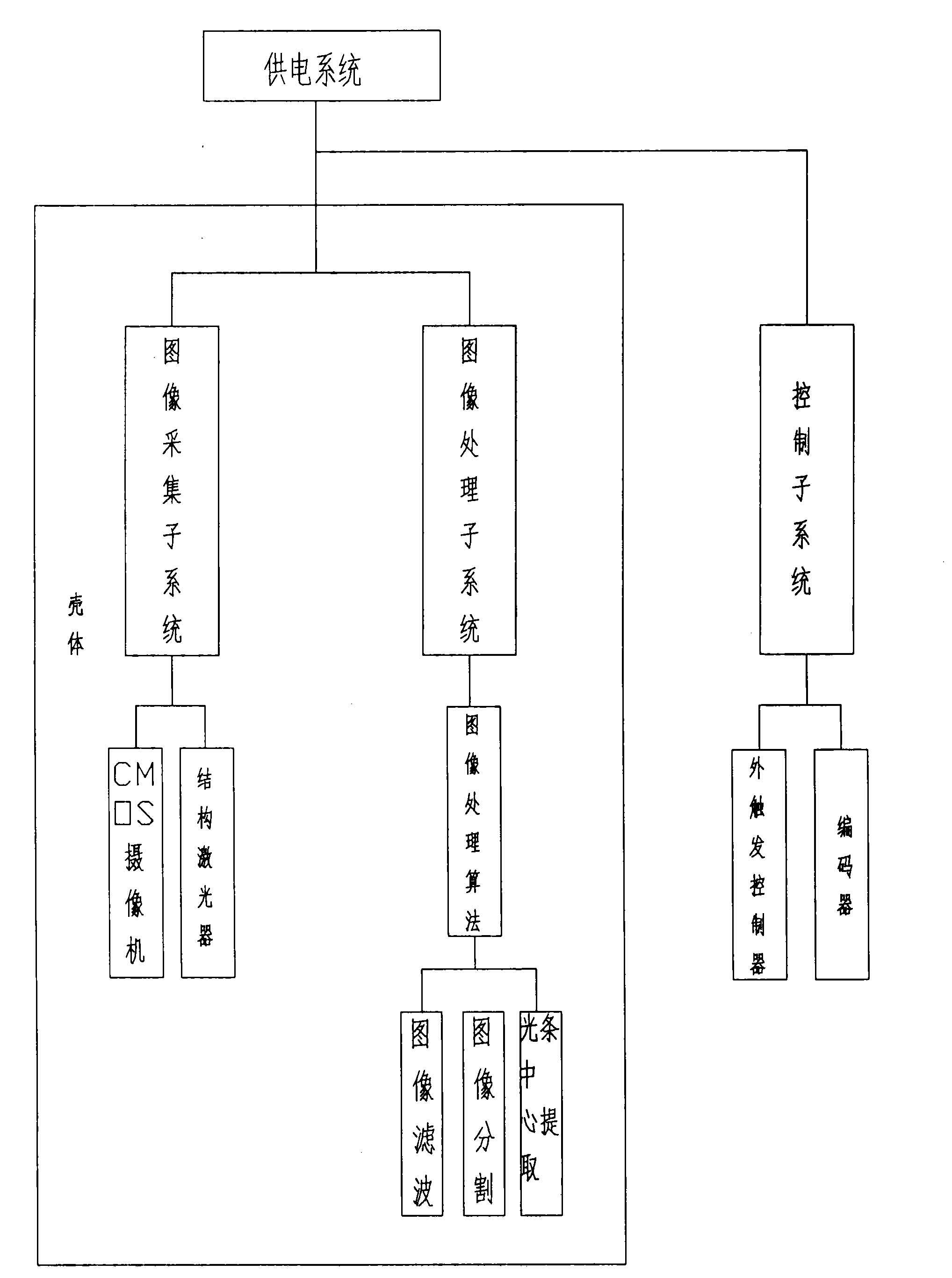
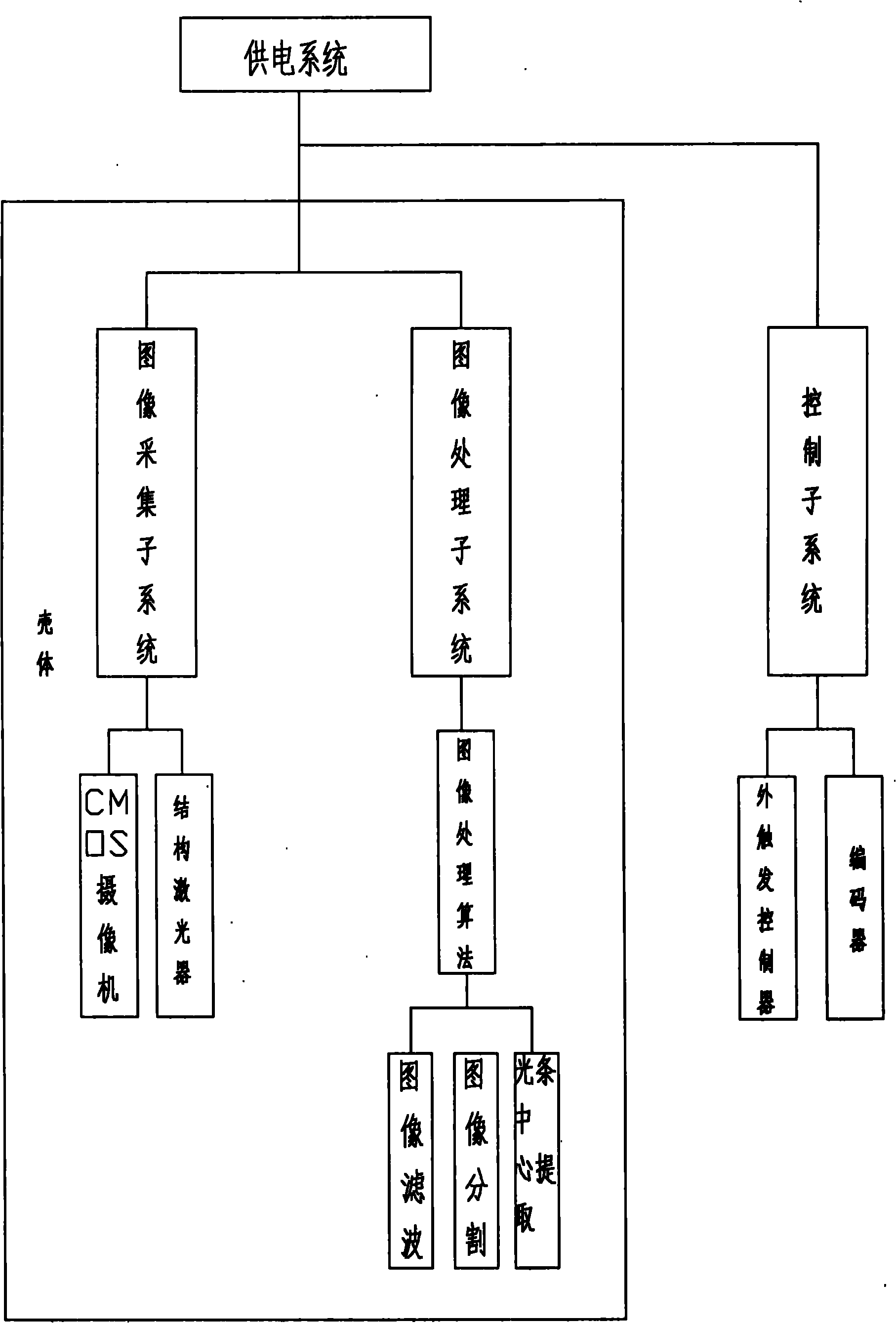
The invention discloses a three-dimensional laser scanning on-line detection profiler, which comprises a shell, wherein an image acquisition sub-system is arranged in the shell. The image acquisition sub-system is used for projecting laser onto a detected object; after being acquired by a camera, an image is transmitted to an image sub-processing system through an Ethernet; the image sub-processing system pre-processes the image transmitted by the image acquisition sub-system through image processing algorithm to highlight the characteristics of a light strip center and then obtain the two-dimensional size of the detected object; the three-dimensional profile size of the detected object is determined by combining the two-dimensional size with a displacement size of the detected object which is provided by an external control sub-system; and the image acquisition sub-system, the image sub-processing system and the control sub-system are commonly connected with a power system. The three-dimensional laser scanning on-line detection profiler of the invention has the advantages of realizing three-dimensional model detection of a product, guaranteeing the quality of the product and improving the production efficiency, along with short detection time.
Owner:NANTONG NORTHERN LIGHTS AUTOMATION TECH
Three-dimensional profilometer
Profilometers for industrial metrology and other applications are described. A line is projected on a surface to be profiled. The line is scanned to build a three dimensional point cloud allowing the three-dimensional (3D) profile of the surface to be determined. In some embodiments, the line is projected by a laser system. In other embodiments, the line is projected by a digital micromirror device (DMD). In still further embodiments, multiple lines, or other patterns are projected.
Owner:INTELLISENSE SYST INC
Combined high speed optical profilometer and ellipsometer
InactiveUS20060066854A1Ability to detectSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementOptically investigating flaws/contaminationSiliconProfilometer
A system and method for measuring defects, film thickness, contamination, particles and height of a thin film disk or a silicon wafer.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
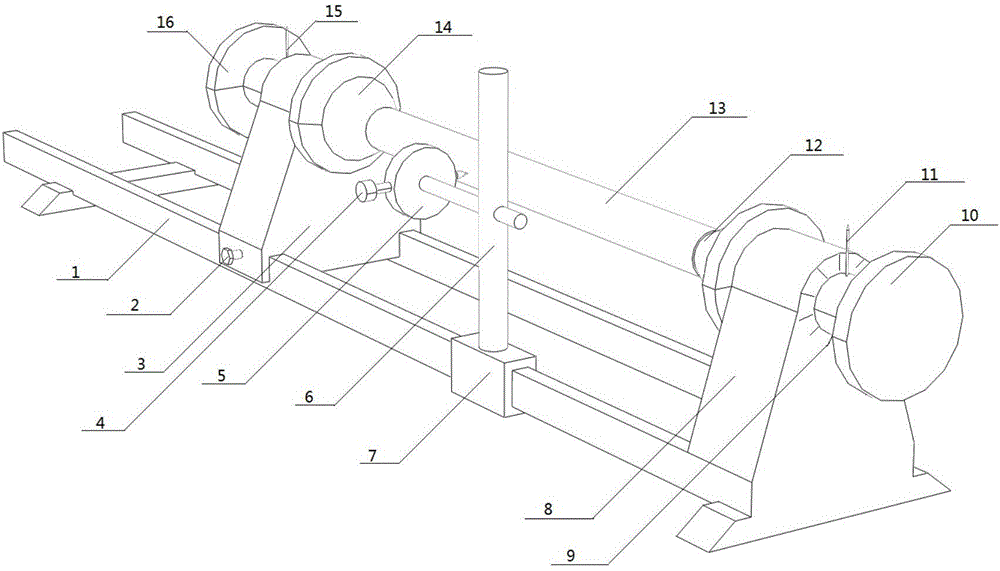
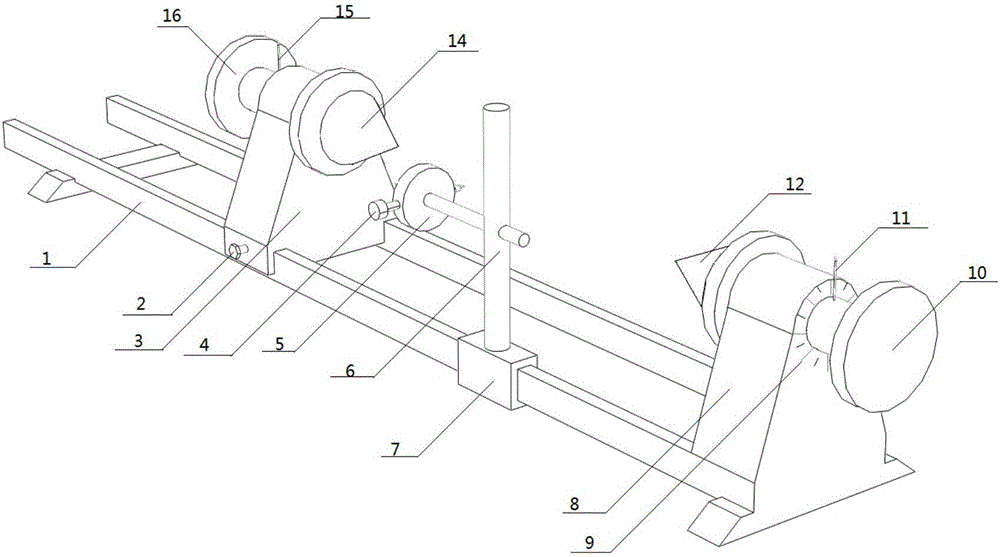
Pipeline contourgraph and scribing instrument
InactiveCN106767325AHigh precisionThe principle is simpleMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsOther workshop equipmentRotating discProfilometer
The present invention discloses a pipeline contourgraph. The pipeline contourgraph is used for measuring the outer contour of a pipe 13 to be measured. The pipeline contourgraph comprises a guide rail 1, a fixed bracket 8 and a first sliding bracket 3; the first sliding bracket 3 is arranged on the guide rail 1; two identical circular groove openings are formed at the top ends of the fixed bracket 8 and the first sliding bracket 3 respectively; one rotation shaft of which the diameter is matched with the corresponding circular groove opening is arranged in each of the two identical circular groove openings; positioning pushing cones are fixed onto the inner sides of the two rotation shafts; the outer sides of the two rotation shafts are fixedly connected with two rotating discs respectively used for rotating the pipe to be measured; an angle rotating disc is arranged around the circular groove opening of the fixed bracket 8 or the first sliding bracket 3; an angle pointer is located on the rotation shaft so as to determine the rotation angle of the pipeline; a displacement dial plate 5 of a depth gauge is arranged on one slide channel of the guide rail 1; and the displacement probe 4 of the depth gauge points to the pipe 13 to be measured and is located at the same horizontal plane with the axis of the pipe 13 to be measured. The present invention also provides a pipeline scribing instrument.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
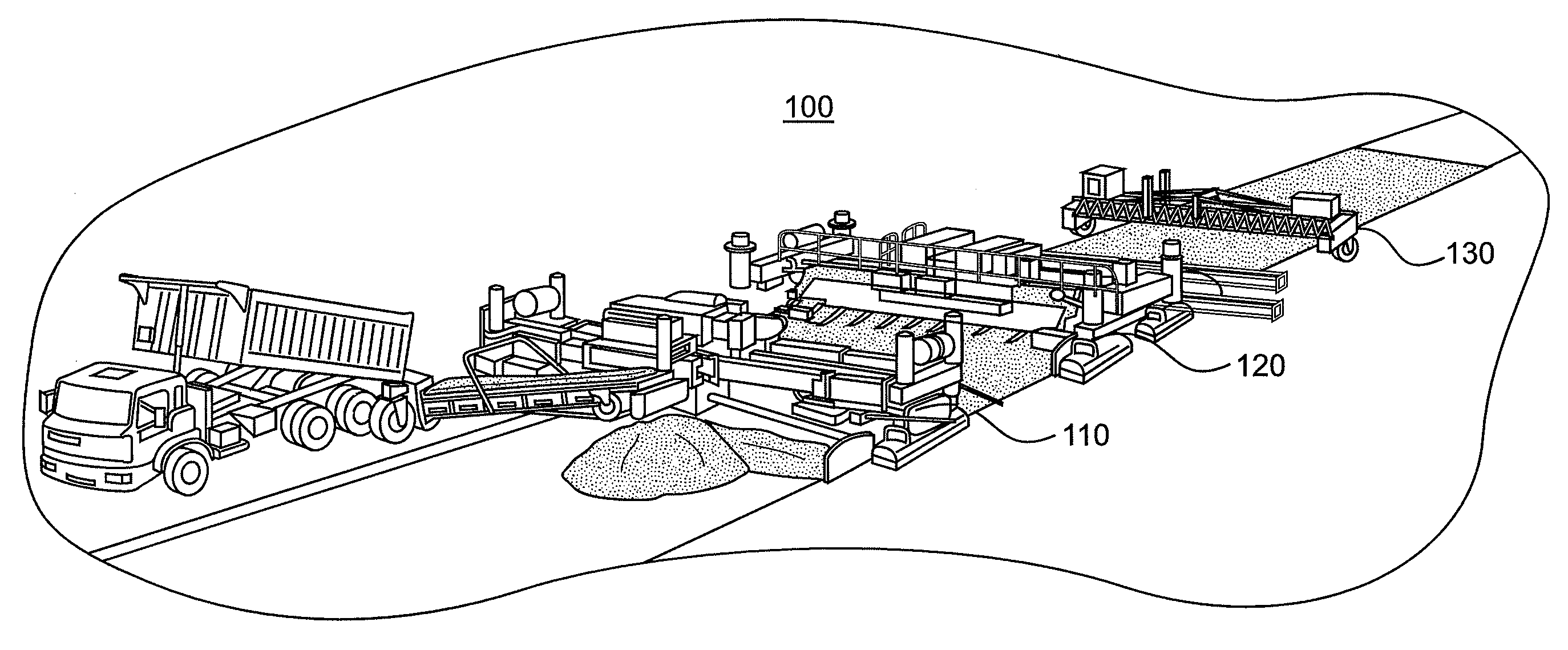
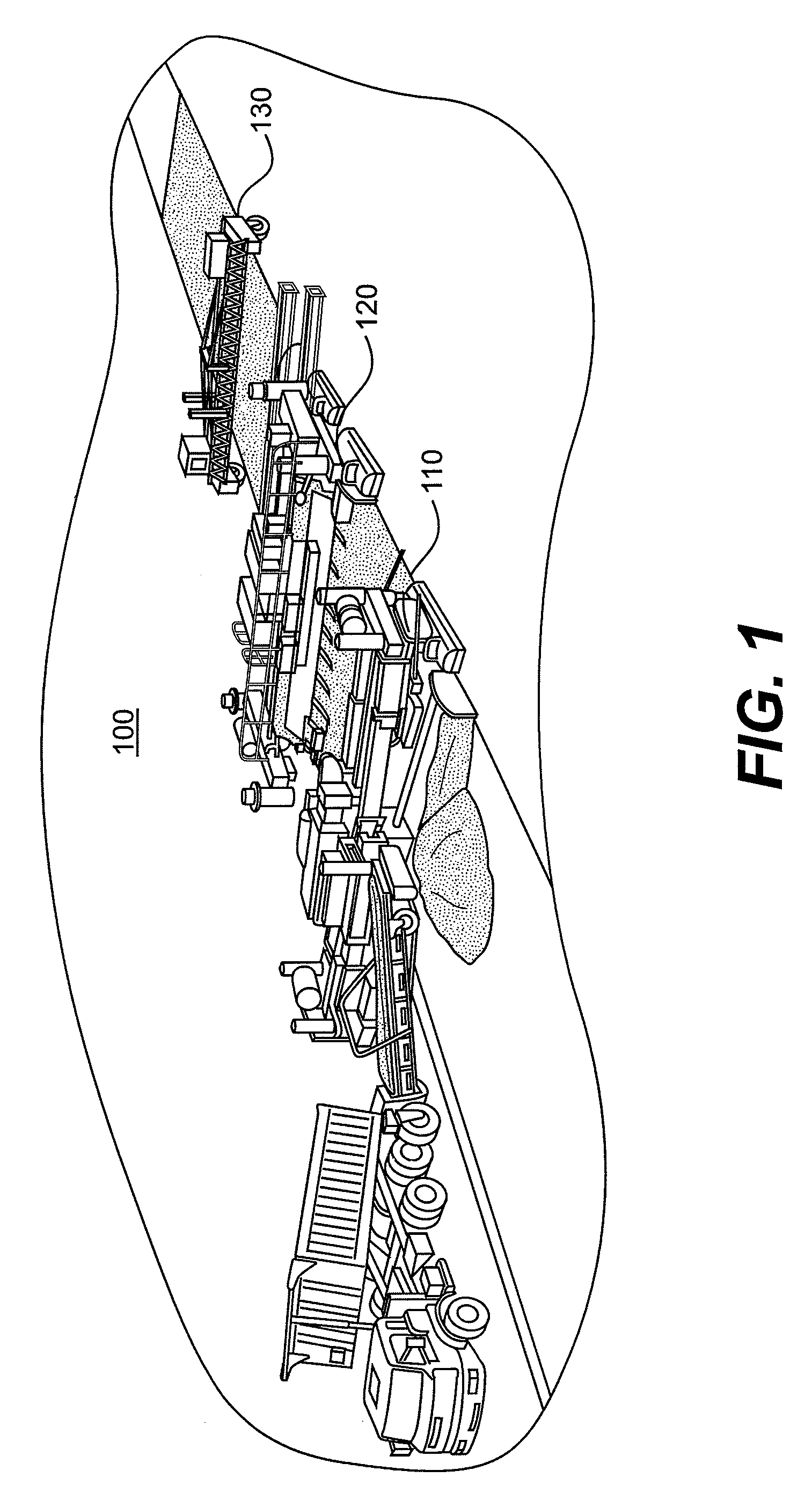
Method and apparatus to perform profile measurements on wet cement and to report discrepancies
InactiveUS20090103978A1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyPaving detailsRoads maintainenceEngineeringCement
An apparatus, method, and system are disclosed, which provide a means of real time surface profile evaluation in wet cement. The sliding profiler can be pulled behind various stages in a paving train. The user is alerted to profile discrepancies while the cement is still pliable and afforded the opportunity to make adjustments to the paving process, to include additional finishing. The system is made of affordable components and thus is appropriate for construction projects of different scale. In addition, multiple sliding profilers can measure the profile of multiple wheel paths simultaneously. The system can measure profile changes of less than 150 mils. Use of the system described herein will contribute to better roadways at lower costs.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
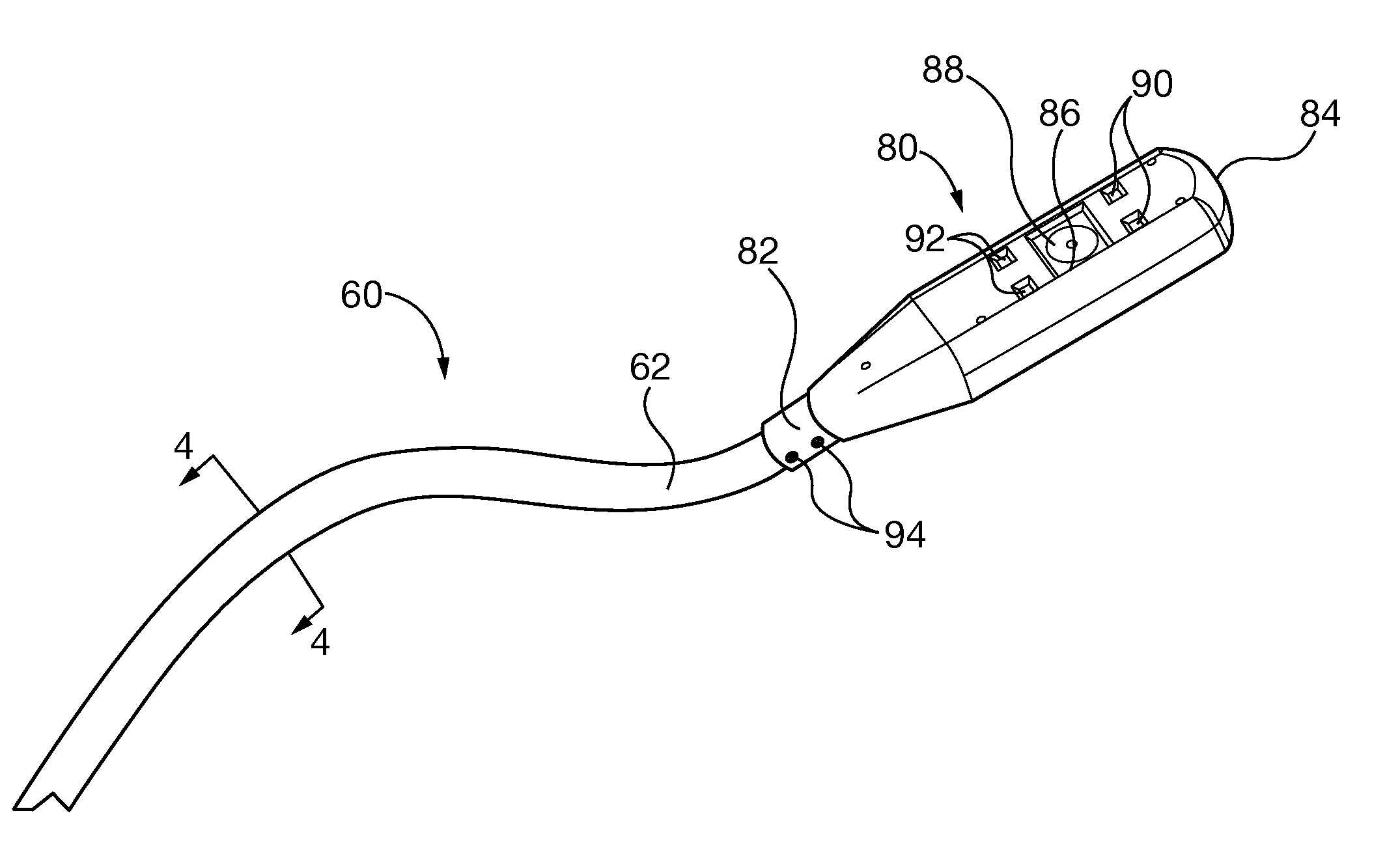
Optical inspection scope with deformable, self-supporting deployment tether
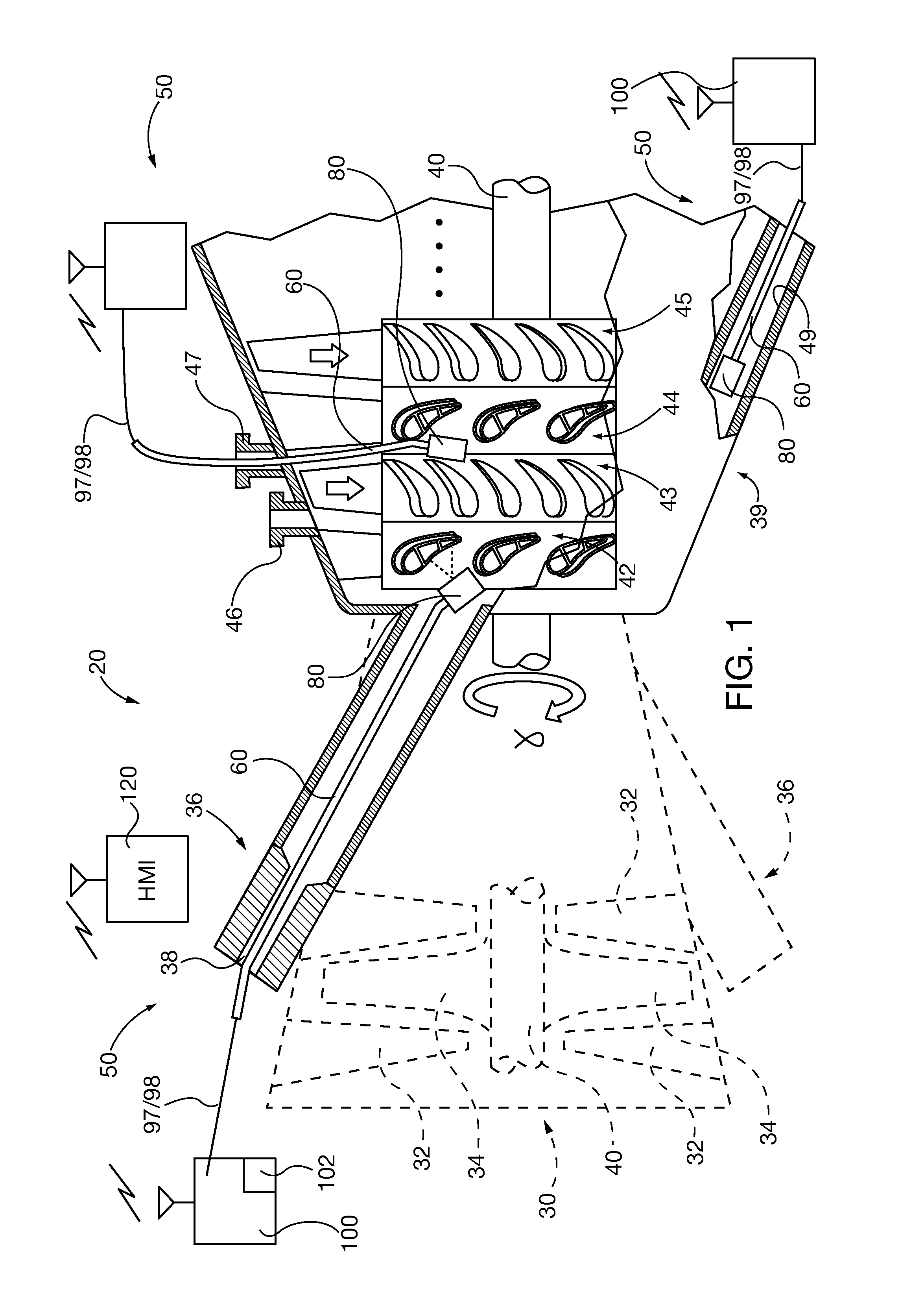
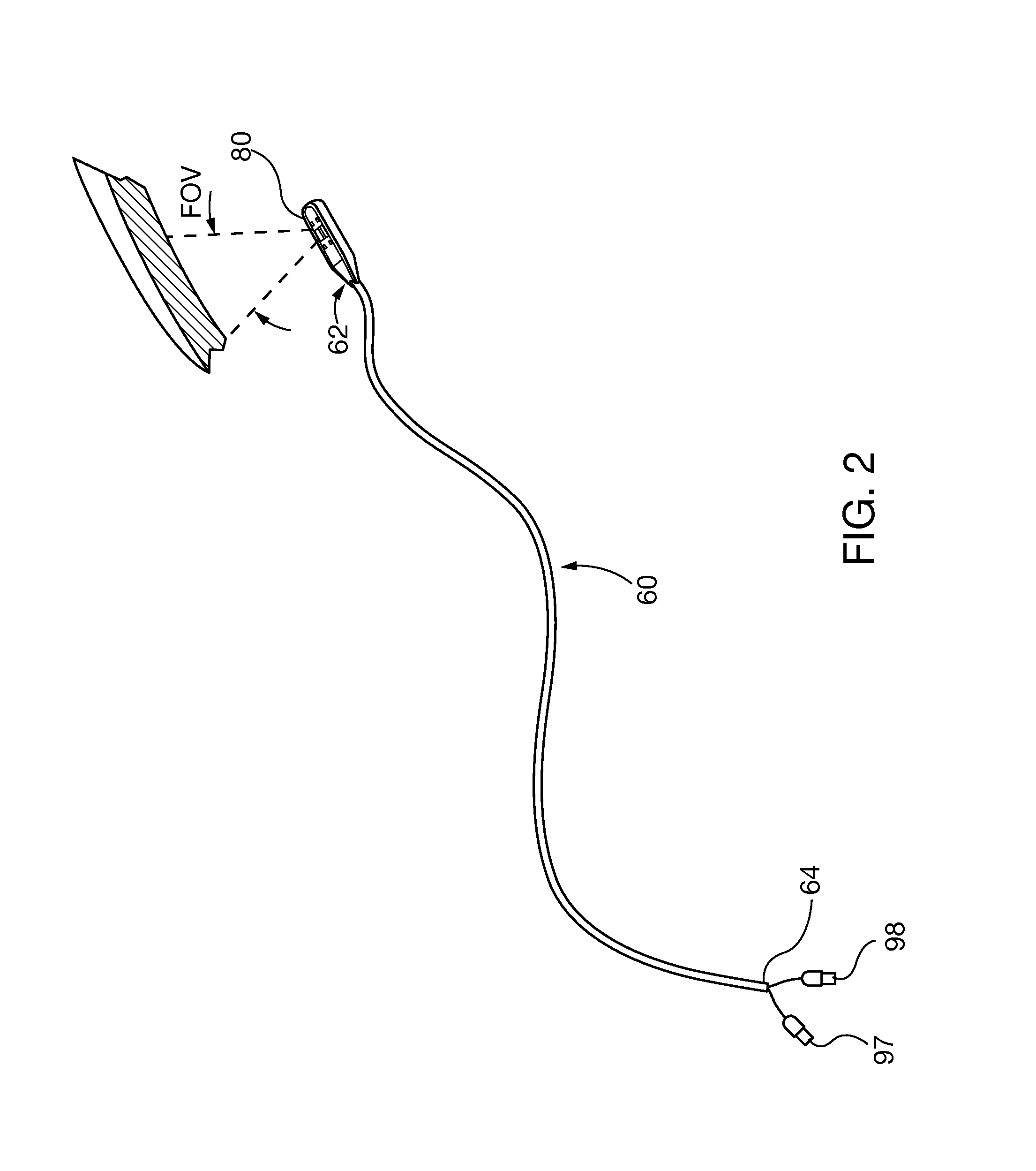
InactiveUS20150338353A1Easy to insertTelevision system detailsGas-turbine engine testingNon destructiveEngineering
Non-destructive evaluation optical inspection systems include video cameras or other reflective-photonic optical instruments, such as laser profilometers or 3D white light laser dimensional scanners, which are incorporated in a camera head. The camera head is coupled to a distal end of a self-supporting and shape-retaining elongate deformable deployment tether. The deployment tether is bendable, for insertion through cavities of power generation machines and orientation of the camera head field of view on the internal area of interest. The deployment tether is capable of being deformed repeatedly, for inspection of different areas of interest. In some embodiments, interchangeable camera heads are selectively coupled to the deployment tether, so that a kit or family of different optical inspection instruments are available to carry out multiple types of inspections within a single or multiple types of power generation machinery.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Remote sampling system
InactiveUS6916219B2Improve efficiencyExtension of timeWater treatment parameter controlWaterborne vesselsCommunications systemSample water
An automated system for periodically sampling water bodies, such as lakes, and delivering the test results to a remote computer using a communication system. In particular, the system has a variable buoyancy profiler with a dynamic buoyancy compensator responding approximately linear to a water pressure created by an external water body so as to actively or passively interact with an external force or pressure thereby moving the profiler to a target depth.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Rotation axis spatial state calibrating method for swinging arm-type contourgraph
The invention discloses a rotation axis spatial state calibrating method for a swinging arm-type contourgraph. According to the calibrating method, the rotation axis spatial state of the swinging arm-type contourgraph is calibrated by combining a three-side measurement principle with a four-laser tracker redundant self-calibrating technology. A target ball (cat eye) is mounted on a cross arm (workpiece turntable) of the contourgraph; the positions of four laser trackers are fixed, so that the four laser trackers are positioned at the optimal measurement positions. When the cross arm (workpiece turntable) rotates by a certain angle, the four laser trackers track the target ball (cat eye) to perform scanning measurement; a cross arm circular rotating surface (workpiece turntable circular rotating surface) is fit by the acquired three-dimensional coordinates of a point on a high-precision rotating arc to obtain a normal vector which passes through a circle center; the rotation axis spatial state relationship of the swinging arm-type contourgraph can be obtained by calculating the spatial state relationship between two normal lines. According to the method, the state relationship of a spatial axis can be calibrated with high precision.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Device and method for detecting contours of large-caliber aspheric surface components
ActiveCN106441153ARealize high-precision detectionReduce mistakesUsing optical meansCommon baseMotion accuracy
The invention belongs to the technical field of optical precision tests, and relates to a device and a method for precisely detecting large-caliber aspheric surfaces. The device and the method can be used for detecting the contours of large aspheric surface components in precision optical systems in a high-precision manner. The device is of an open type contour instrument structure with rotary-linear datum common base planes on the basis of linear / rotary datum technologies and the like, so that the contours of the large-caliber aspheric surface components can be detected on the basis of precision flotation rotary centers in the high-precision manner. The device and the method have the advantages that common base plane designs for rotary-linear datum systems, turning designs for measurement frames and designs for open type non-gantry structures are adopted, Abbe errors of instruments can be reduced, the movement precision of a precision linear flotation guide rail can be realized to the greatest extent, and parameters of the contour of a mother line of each to-be-detected aspheric surface can be directly measured by a sensing measuring system which synchronously moves with the precision linear flotation guide rail; the contours of multiple mother lines of the to-be-detected aspheric surfaces can be measured by the aid of precision flotation rotary technologies, and the contours of the large-caliber aspheric surfaces can be quickly detected in the high-precision manner by means of fitting.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
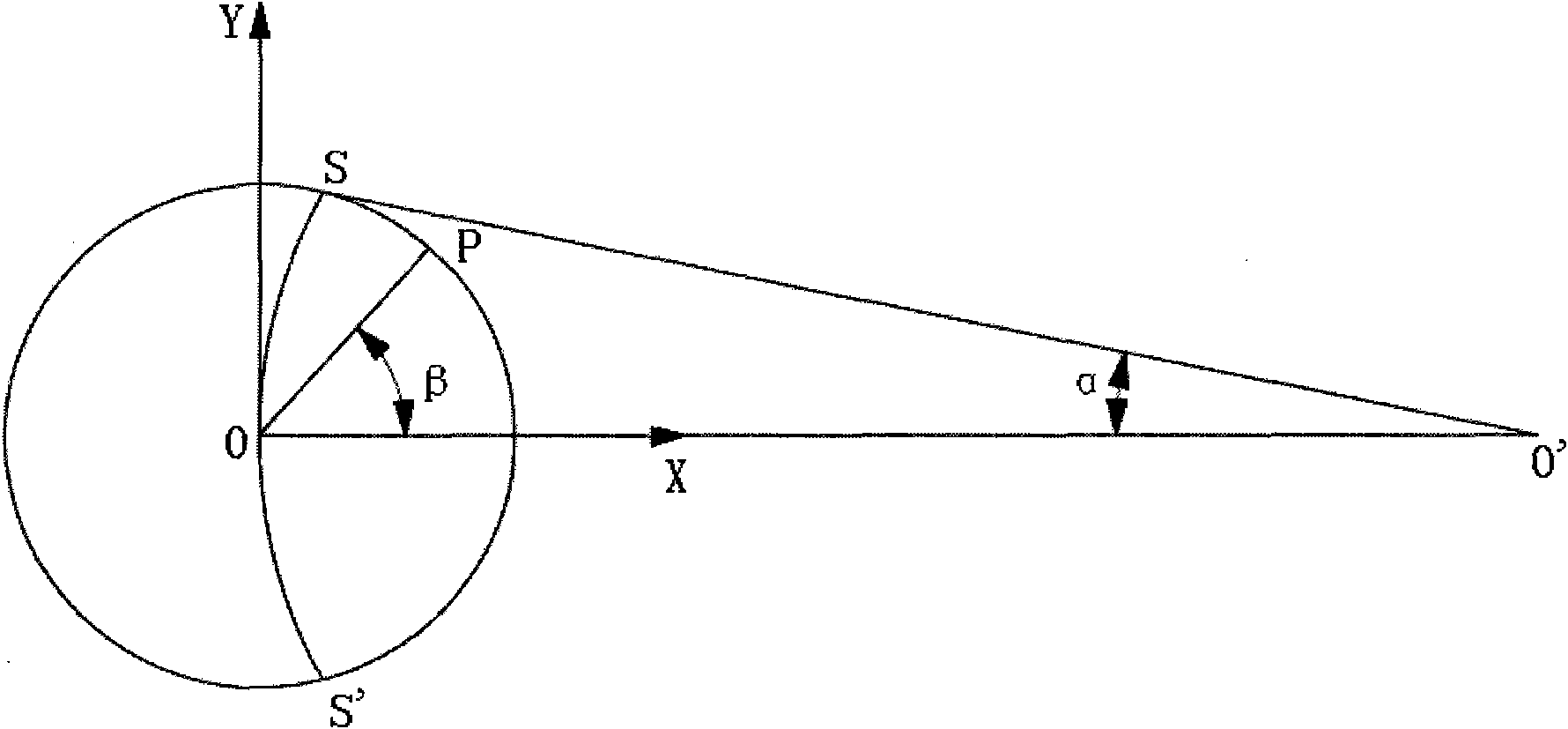
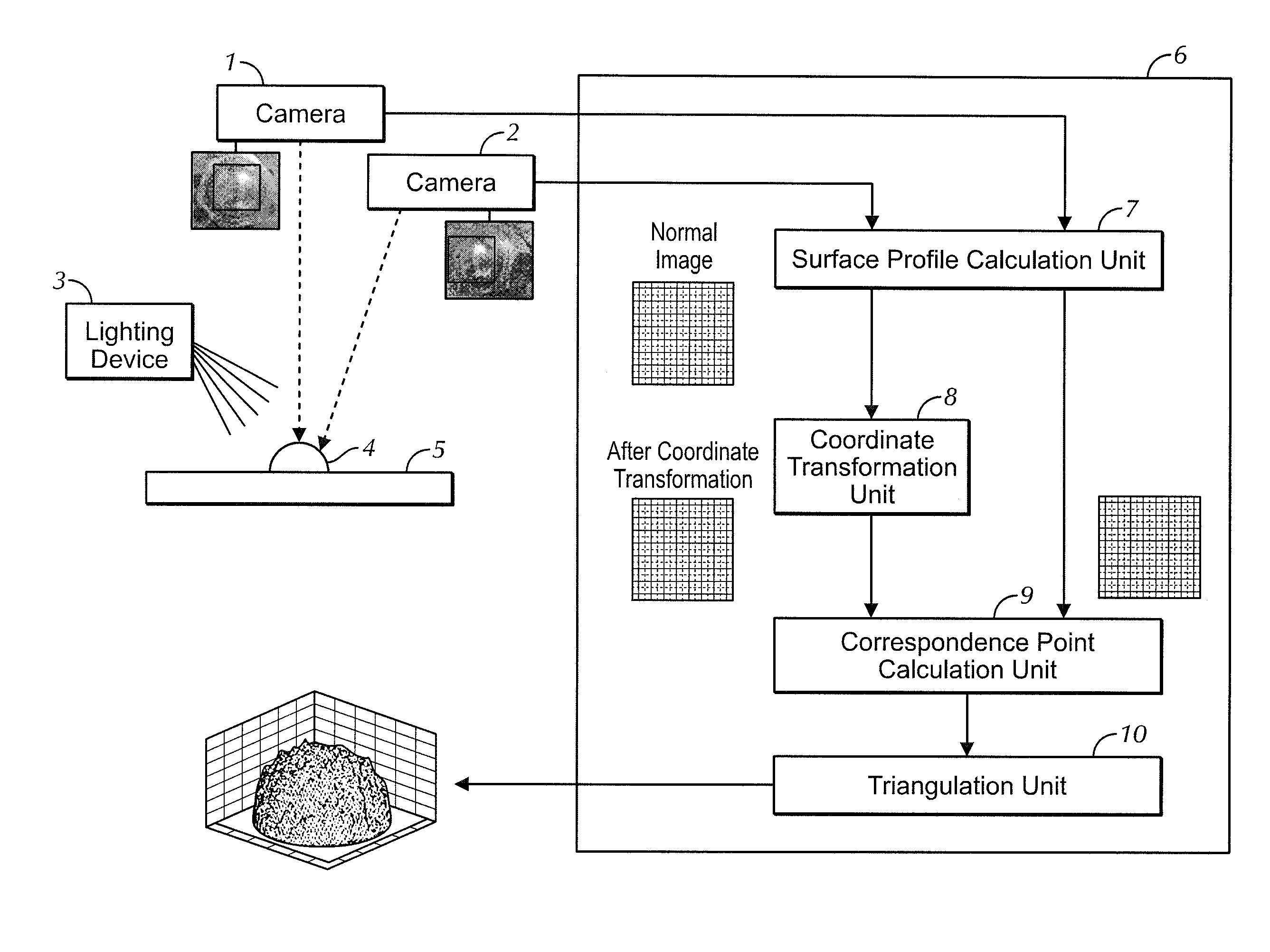
Profilometer, measuring apparatus, and observing apparatus
ActiveUS20120044504A1Satisfactory accuracyInformation obtainedUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceMeasurement point
An observing apparatus includes a lighting device for irradiating a surface of a measuring target with light having a first light source distribution, and an imaging section for imaging the surface of the measuring target. Considering a first plane passing through a measurement point, the first light source distribution is set such that: (1) a radiance L11(θ) changes in a continuous or stepwise manner according to an angle θ, and (2) the radiance L11(θ) is not zero in a local region of a predetermined range of ±σ having a point located at a predetermined angle θc as a center on the first plane when viewed from the measurement point, and the following equation substantially holds for arbitrary a satisfying 0<a≦σ; L11(θc−a)+L11(θc+a)=2×L11(θc).
Owner:ORMON CORP
Method for measuring a high accuracy height map of a test surface
ActiveUS20160027194A1Minimize timeDrawing from basic elementsUsing optical meansHeight mapMeasurement test
Method for measuring a height map of a test, including measuring a coarse height map of the test surface with a pre-map sensor provided to an optical profiler with a relatively long working distance and / or a large field of view, storing the coarse height map in a memory, subdividing the coarse height map into sections appropriate for the field of view of a high resolution optical profiler sensor provided to the optical profiler, calculating corresponding X, Y and Z positions for the optical profiler sensor with respect to the test surface, calculating a trajectory in the X, Y, Z-direction for the optical profiler sensor with respect to the test surface using the calculated X, Y, Z-positions, moving the optical profiler in the X, Y, Z-direction with respect to the test surface according to the trajectory, and measuring a high accuracy height map with the high resolution optical profiler sensor.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Polar coordinate-based profilometer and methods
InactiveUS6895682B2Accurate measurementAvoid interferenceMechanical counters/curvatures measurementsWind musical instrumentsRotary stageTransducer
A polar coordinate-based profilometer includes a base, a rotary stage, a linear stage, and a probe device. The rotary stage is mounted on the base and includes a rotary table rotatable about a vertical axis oriented orthogonal to the base. The linear stage is mounted on the rotary table and is rotatable therewith. The linear stage includes a linear slide member that is translatable along a radial axis orthogonal to the vertical axis. The probe device is mounted on the linear slide member and is translatable therewith. The probe device includes a probe tip that is linearly displaceable along the radial direction and communicates with a linear displacement-sensing transducer. Alternatively, the probe device scans an object without contacting the object. Methods are provided for measuring an object based on polar coordinates, and correcting for misalignment prior to measurement.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA STATE UNIV
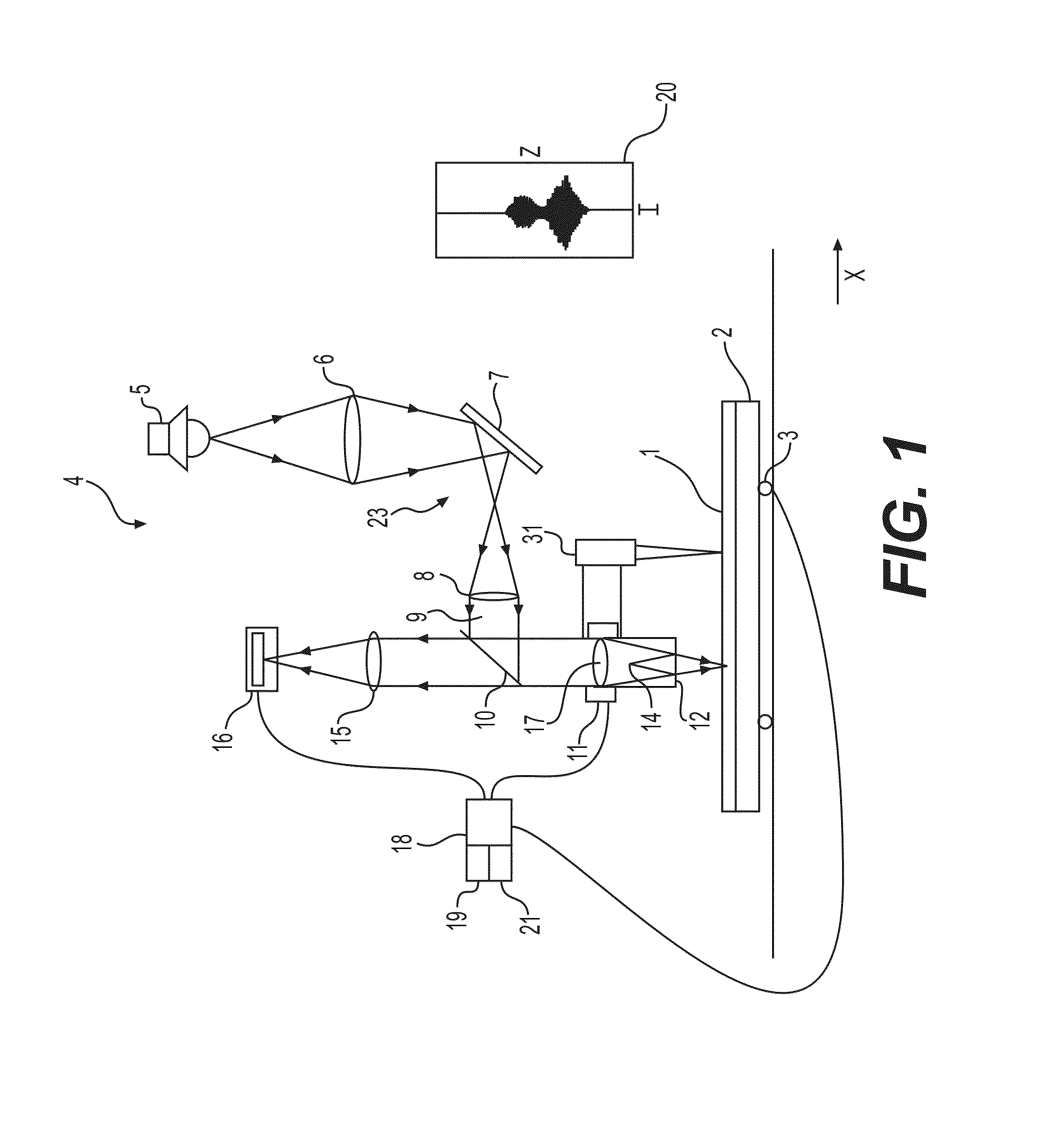
Position-sensing device for 3-D profilometers
InactiveUS6985239B2Improve data acquisition speedIncrease speedInvestigating moving sheetsUsing optical meansBeam splitterTransmission channel
An apparatus for sensing position data of a light pattern created by a known light source on an object, comprising an optical system for collecting an incident light beam of the light pattern and transmitting the incident light beam to a beam splitter. The beam splitter has a known reflection / transmission ratio, such that the incident light beam from the light pattern received on the surface of the beam splitter results in a transmission channel, transmitted through the beam splitter, and a reflective channel, reflected from the beam splitter, with intensities of the transmission channel and the reflective channel varying as a function of a position of the incident light beam on the surface of the beam splitter. Detectors detect the intensities of the reflective channel and of the transmission channels. Dimensions of points of the light pattern on the object are calculable as a function of the intensity of the reflective channel and of the intensity of the transmission channel.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL D'OPTIQUE
Method for machining off-axis aspherical mirror
ActiveCN105690187ADifficult to processImprove processingOptical surface grinding machinesEngineeringFace shape
The invention discloses a method for machining an off-axis aspherical mirror. The method comprises the steps that 1, a rotary aspherical matrix structure is designed; 2, a through hole for inlaying of a daughter structure is excavated in a matrix blank; 3, a cylindrical integral workpiece is formed by combining a matrix and a daughter; 4, an initial spherical surface is machined; 5, grinding is guided through the surface shape error detecting result of a contourgraph, and the surface shape error between the initial spherical surface and a rotary aspheric surface is corrected; and 6, polishing is guided through the surface shape error detecting result of an interferometer or knife-edge tester, and the off-axis aspherical daughter is taken out after polishing is completed. The method is characterized in that the caliber D of the initial spherical surface is equal to the diameter of a cylinder of the integral workpiece, and the curvature radius R of the initial spherical surface is equal to the radius of a circumcircle of a triangle formed by a vertex in a rotary aspheric bus equation and a first point and a second point which are located at the position with the caliber of 1.414 D on a rotary aspheric bus. According to the method, the problem of the influence of the fringe effect in the prior art is solved, the efficiency of aspherical surface machining is improved, and machining difficulty is reduced.
Owner:苏州普锐仕精密光学科技有限公司
Internal weld profile gauge
Owner:BAREFOOT BYRON G
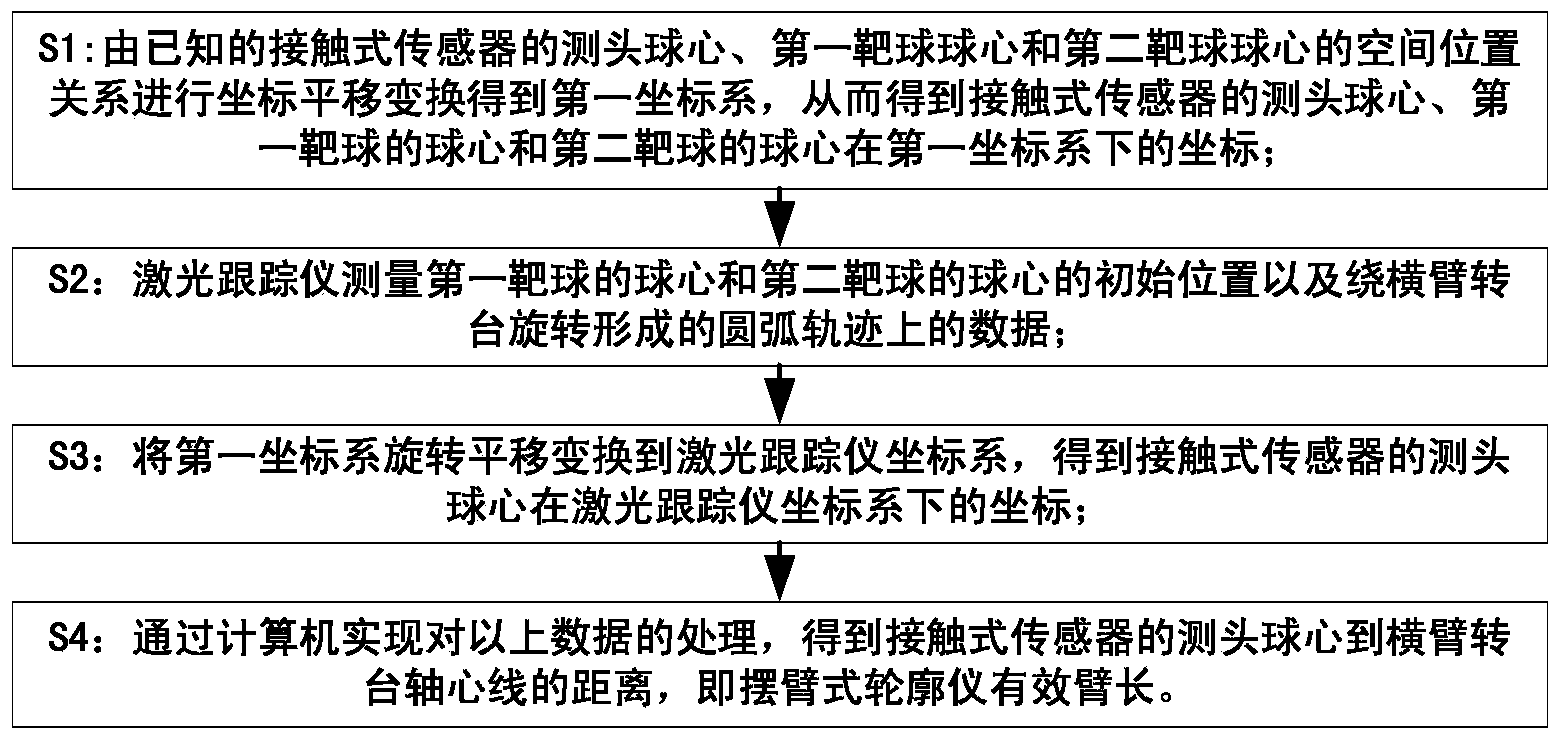
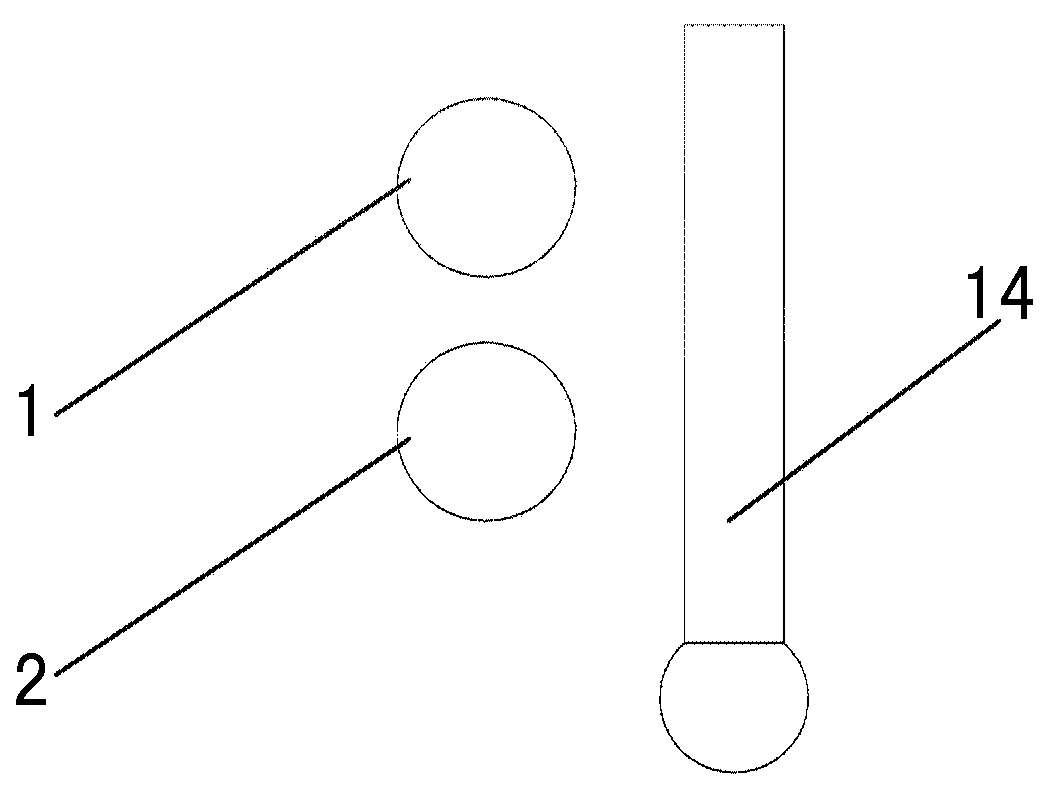
Device and method for measuring effective arm length of swing arm type contourgraph
ActiveCN104019750AAccurate measurementEasy to measureUsing optical meansMeasurement deviceEngineering
The invention provides a device and method for measuring the effective arm length of a swing arm type contourgraph. The device comprises a first target ball, a second target ball, a fine-tuning mechanism, a cross arm, a cross arm support, a balance weight block, a computer, a first angle block, a cross arm turntable, a second angle block, a laser tracking instrument, a workpiece turntable, a mirror face to be tested, a touch type sensor and a work table face. The cross arm rotates around the axis of the cross arm turntable, a measurement head ball center of the touch type sensor, the ball center of the first target ball and the ball center of the second target ball form an arc track rotating around the axis of the cross arm turntable in space, and the laser tracking instrument respectively tracks and measures the arc track of the ball center of the first target ball and the ball center of the second target ball in the space. By means of data processing of the computer, the distance between the measurement head ball center of the touch type sensor and the axis of the cross arm turntable, namely the effectively arm length of the swing arm type contourgraph, is obtained.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Powder coating composition
InactiveUS20090252869A1High appearance requirementsImprove smoothnessLiquid surface applicatorsPolyester coatingsCross-linkCoated surface
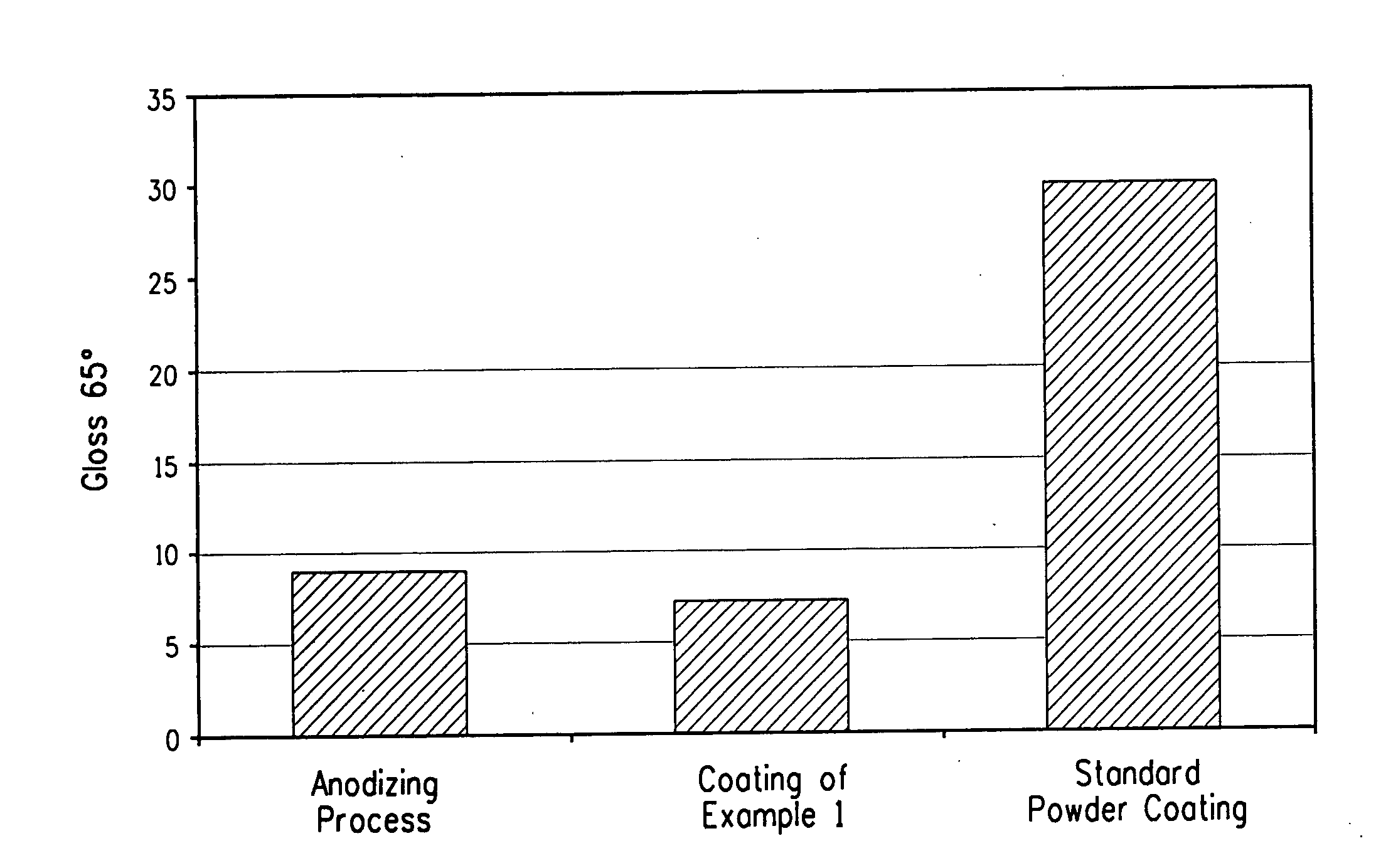
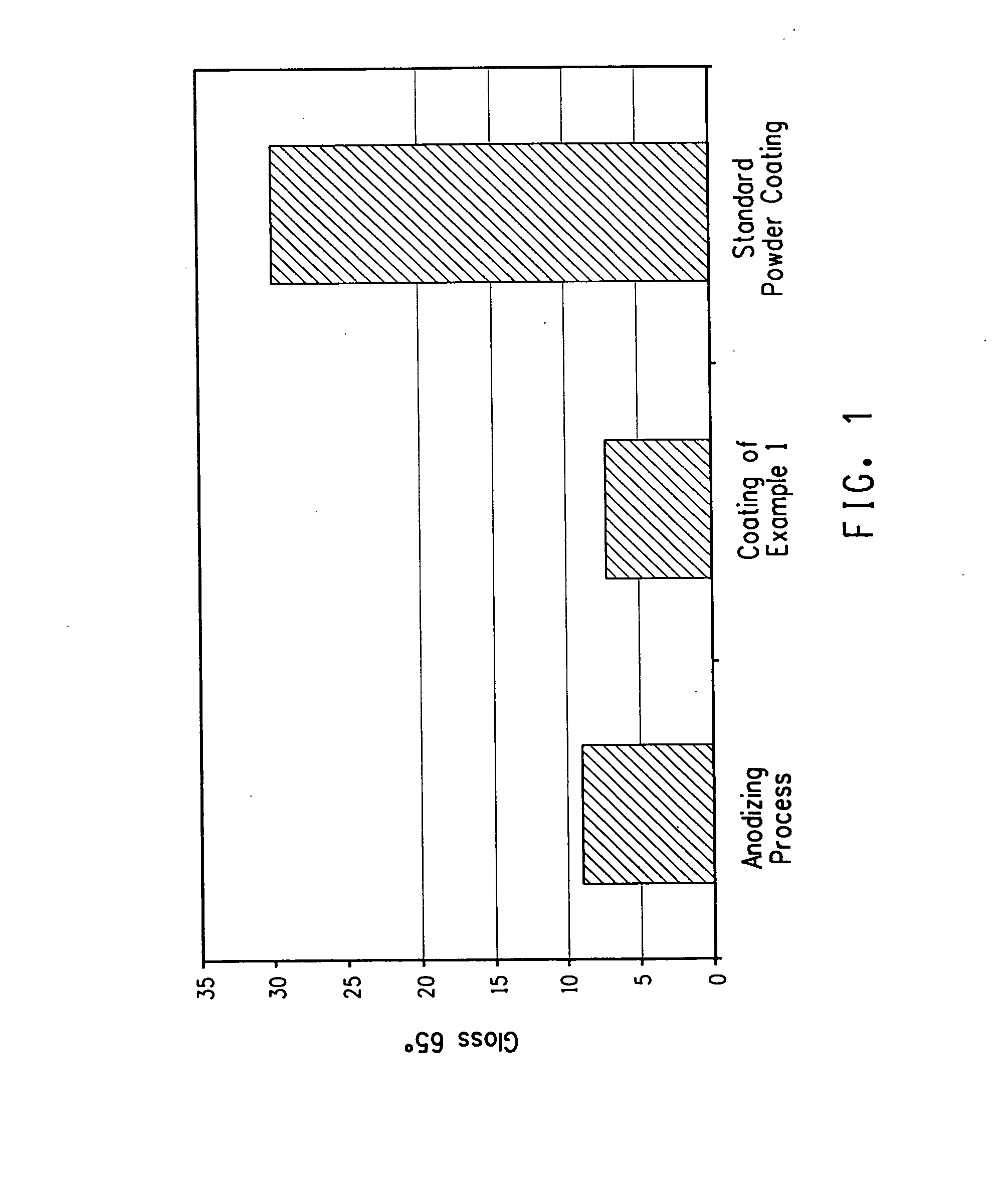
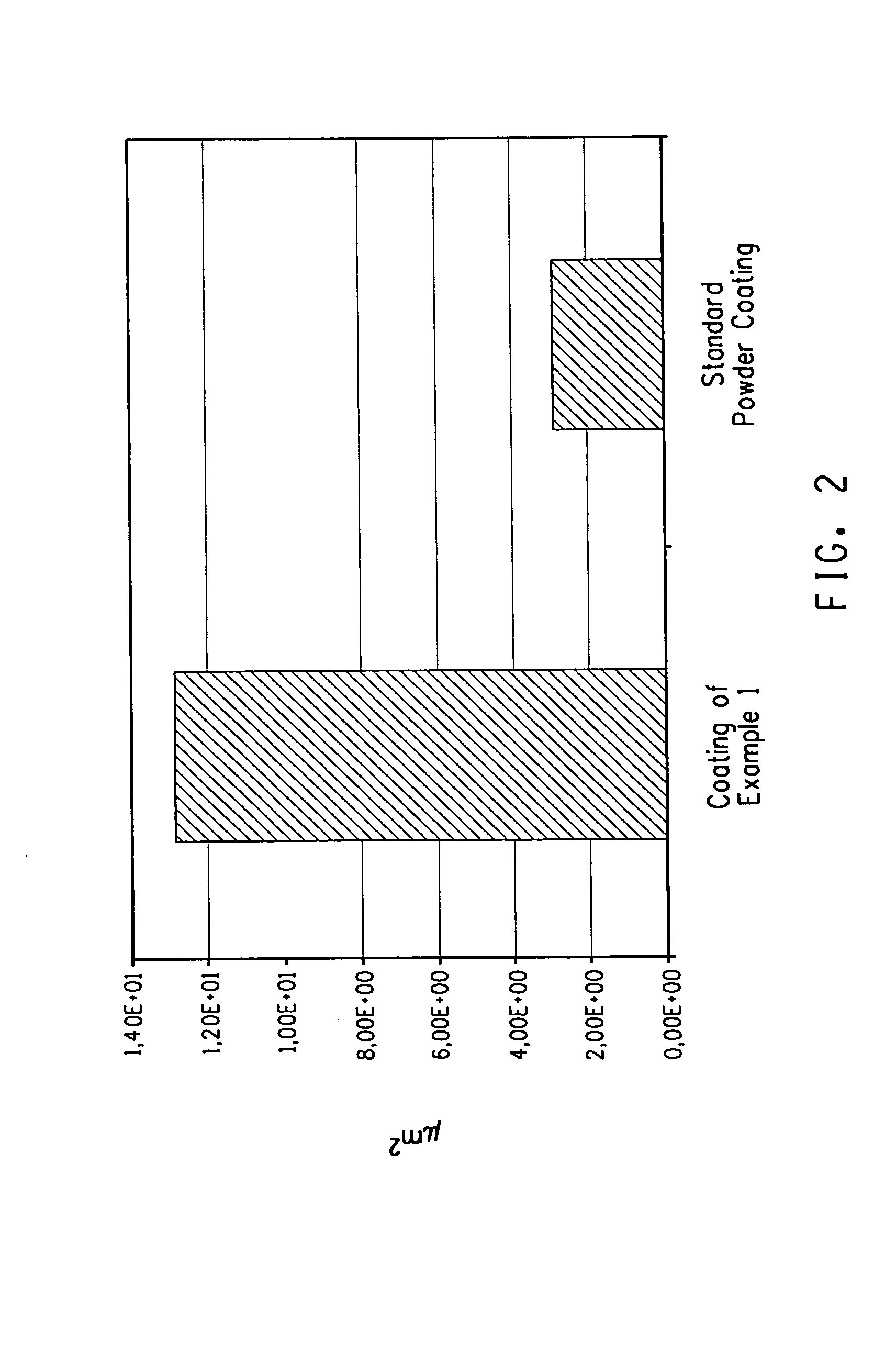
A powder coating composition of an intimate mixture comprising(A) 60 to 99 wt % of a mixture comprising at least one polyester resin and at least one (meth)acrylate resin,(B) 0 to 30 wt % of at least one cross-linking agent,(C) 0.1 to 10 wt % of at least one pigment,component (A) and component (C) are selected to provide the cured-powder coating composition with a low gloss of 1 to 20 gloss units at 60° angle according to DIN 67530 (ISO2813) and a surface structure having a value of Integral 1 in the range of higher than 8.00E+00 measured by the mechanical profilometry Fourier analysis, and the wt % are based on the total weight of the powder coating composition. The powder coating composition provides the desired special metallic effect of the coated surface which meets the metallic effect resulted with anodized aluminium.
Owner:DUPONT POWDER COATINGS IBERICA
Phased array ultrasonic contact transducer, with a flexible wedge and a profilometer
InactiveUS20110032800A1Improve featuresSmall sizeMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDirection finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveUltrasonic beam
Phased array ultrasonic contact transducer, with a flexible wedge and a profilometer. This transducer applies to the non-destructive monitoring of an object and comprises: a set of elements that are rigidly integral with each other, at least part of the elements serving as ultrasound transmitters, a wedge whereof at least the front face is flexible to be applied against the surface of the object and the rear face of which is made integral with the set of elements, and a profilometer to measure surface variations and supply signals representative thereof to allow the transmitters to create a focused ultrasonic beam whereof the characteristics are controlled in relation to the object.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com