Patents
Literature
612 results about "Digital micromirror device" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The digital micromirror device, or DMD, is the micro-opto-electromechanical system (MOEMS) that is the core of the trademarked DLP projection technology from Texas Instruments (TI). Texas Instrument's DMD was created by solid state physicist and TI Fellow Emeritus Dr. Larry Hornbeck in 1987. However, the technology goes back to 1973 with Harvey C. Nathanson's (inventor of MEMS c. 1965) use of millions of microscopically small moving mirrors to create a video display of the type now found in digital projectors.
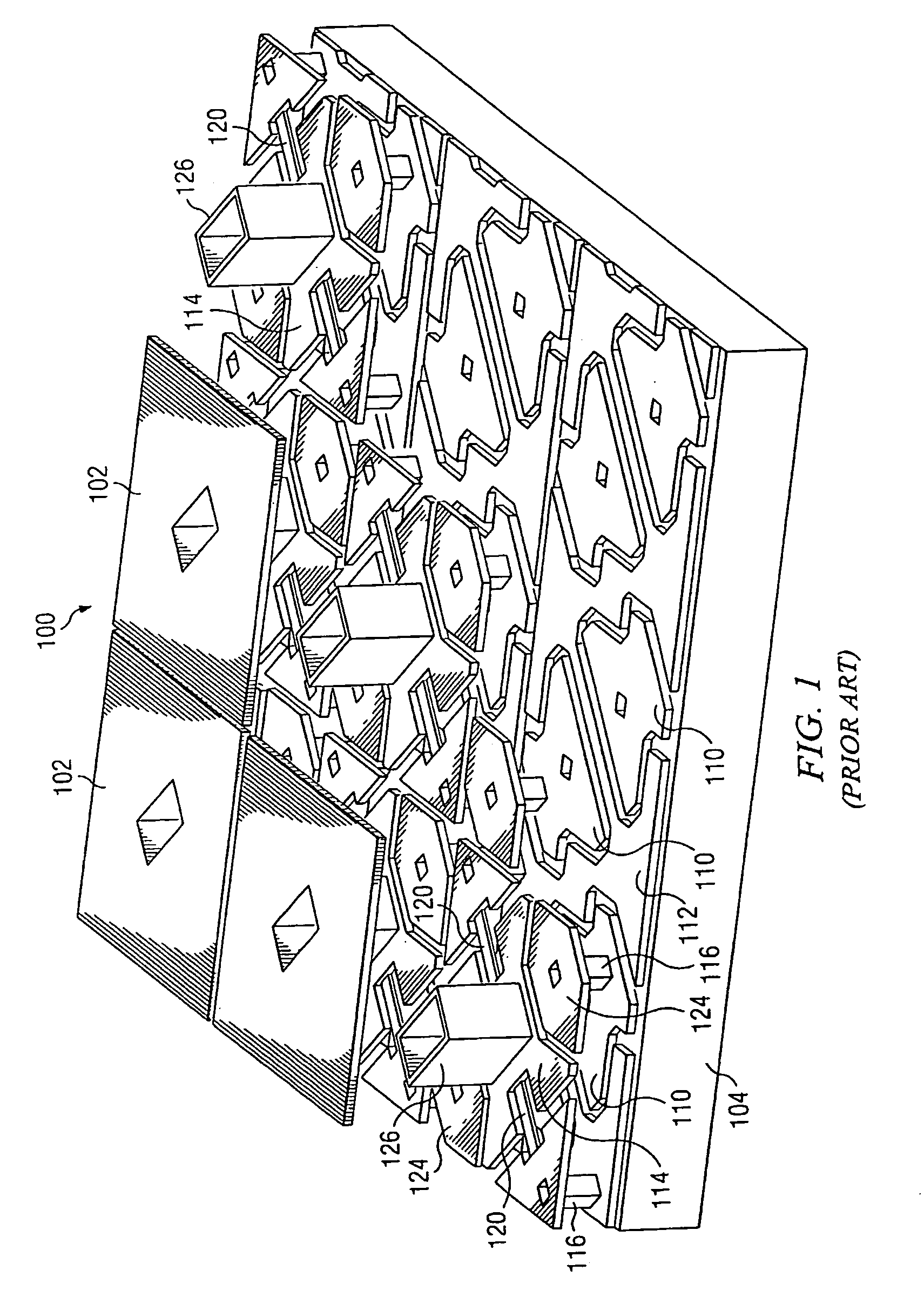
Method of cleaning and treating a semiconductor device including a micromechanical device
InactiveUS6024801ADecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical compoundEngineering
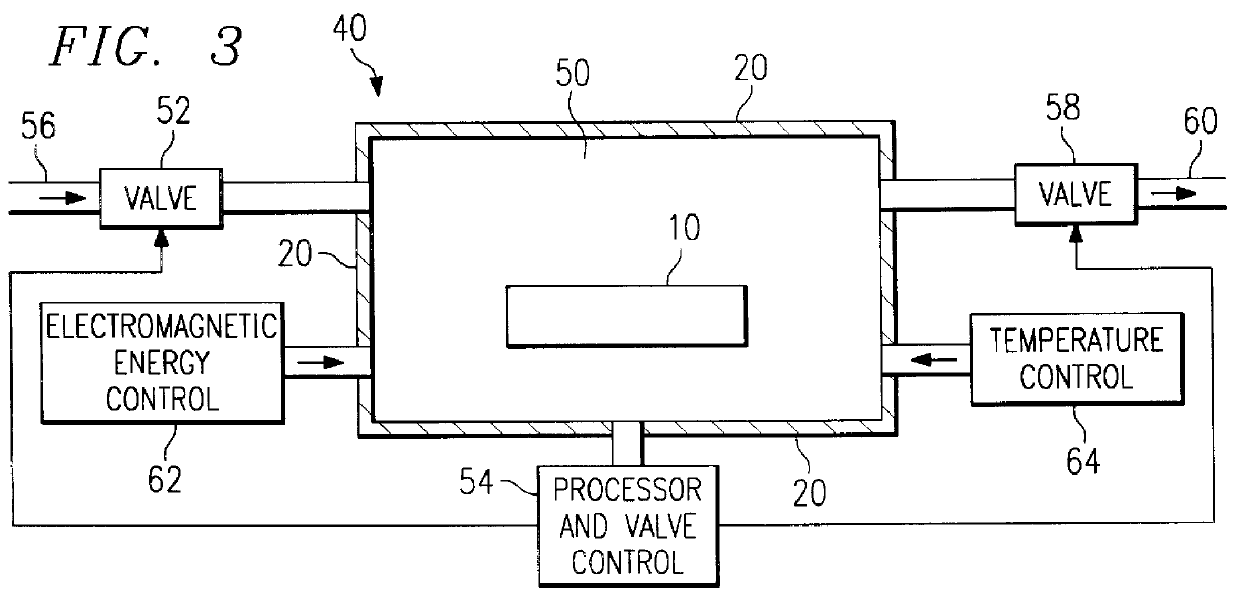
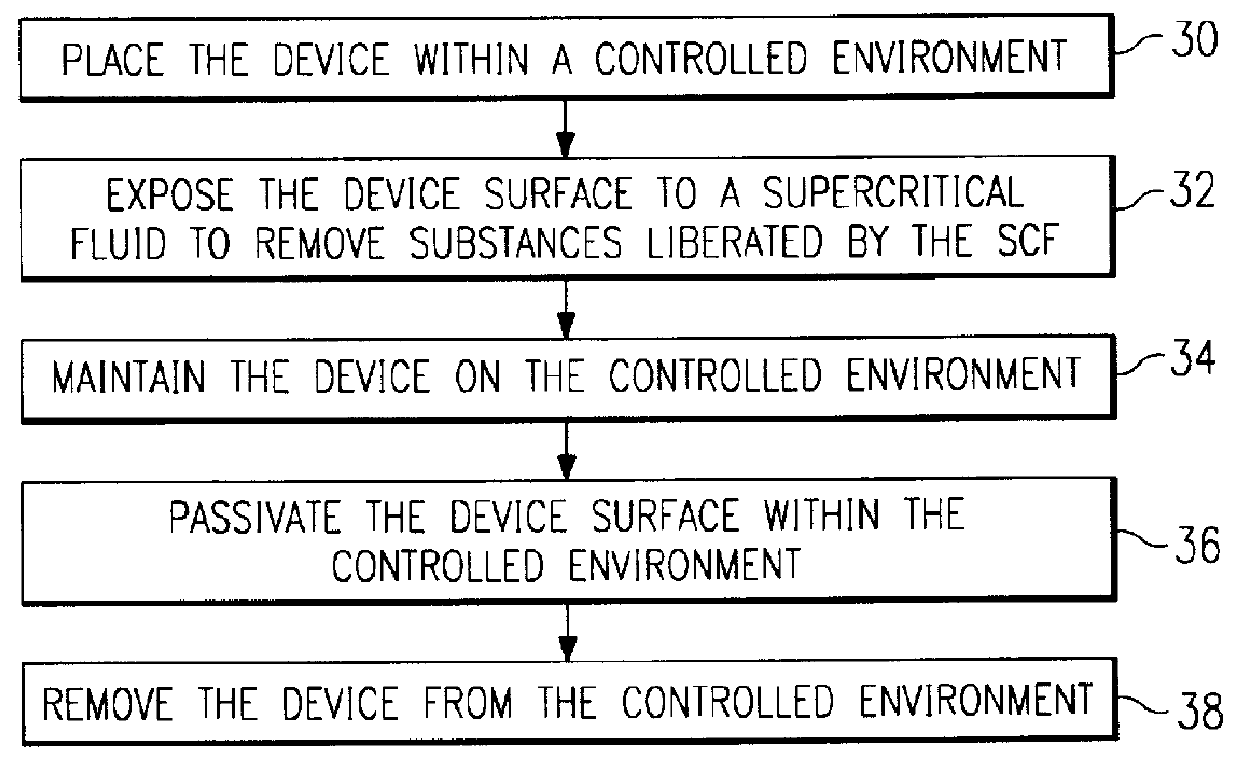
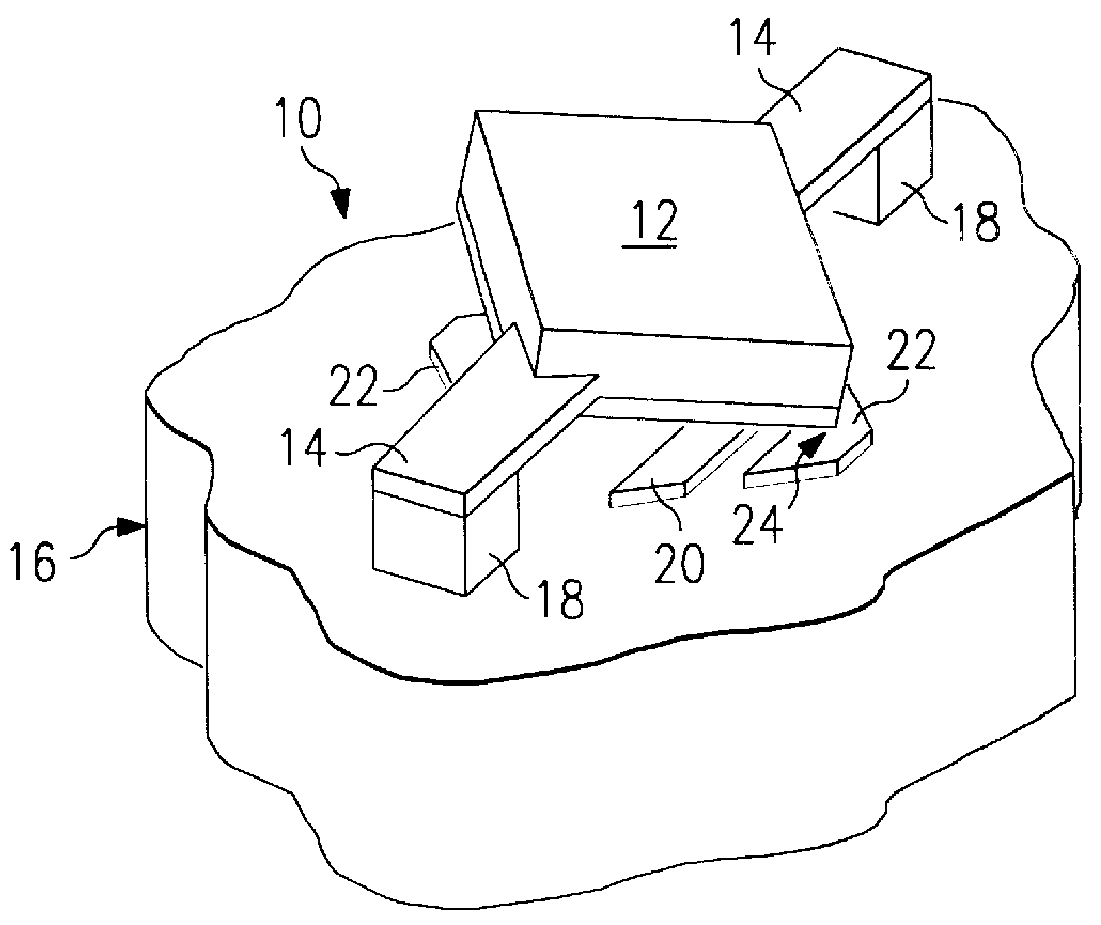
A method of cleaning and treating a device, including those of the micromechanical (10) and semiconductor type. The surface of a device, such as the landing electrode (22) of a digital micromirror device (10), is first cleaned with a supercritical fluid (SCF) in a chamber (50) to remove soluble chemical compounds, and then maintained in the SCF chamber until and during the subsequent passivation step. Passivants including PFDA and PFPE are suitable for the present invention. By maintaining the device in the SCF chamber, and without exposing the device to, for instance, the ambient of a clean room, organic and inorganic contaminants cannot be deposited upon the cleaned surface prior to the passivation step. The present invention derives technical advantages by providing an improved passivated surface that is suited to extend the useful operation life of devices, including those of the micromechanical type, reducing stiction forces between contacting elements such as a mirror and its landing electrode. The present invention is also suitable for cleaning and passivating other surfaces including a surface of semiconductor wafers, and the surface of a hard disk memory drive.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Versatile maskless lithography system with multiple resolutions
InactiveUS20060012766A1Quick selectionEasy to combinePhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingSpatial light modulatorImage resolution
A versatile maskless patterning system with capability for selecting rapidly among a plurality of projection lenses mounted on a turret. This provides the ability to rapidly select multiple choices for resolution and enables optimization of the combination of the imaging resolution and exposure throughput, making possible cost-effective fabrication of microelectronics packaging products. A preferred embodiment uses a digital micromirror device array spatial light modulator as a virtual mask. Another preferred embodiment use multiple closely spaced digital micromirror device array spatial light modulators to enhance throughput.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
Method and apparatus for stereoscopic display using column interleaved data with digital light processing
InactiveUS20070195408A1Quality improvementFast switching timeTelevision system detailsProjectorsVideo processingColumn switching
The invention has two main embodiments, a first called column switching and blanking and a second embodiment called doubling. The first embodiment is a projector for displaying a stereoscopic image with projector using one or more digital micromirror devices positioned into a plurality of columns and rows. The projector itself includes a light source, an optical system, a video processing system and a data system for driving the micromirror devices. The data subsystem provides separate data to a plurality of column pairs of the micromirrors. The projector includes a stereoscopic control circuit having a first state of the control circuit for inputting a first eye view of the stereoscopic image and causing the micromirrors of a first column of each column pair to be in various on and off states during said first eye view of said stereoscopic image and for causing all of said micromirrors of a second column of each column pair to be in an off state during said first eye view of said stereoscopic image. A second state of the control circuit is used for inputting a second eye view of the stereoscopic image and causes the micromirrors of the second column of each column pair to be in various on and off states during the second eye view of the stereoscopic image and for causing all of the micromirrors of the first column of each column pair to be in an off state during the second eye view of said stereoscopic image. The second embodiment is a projector for displaying a stereoscopic image with the projector using one or more digital micromirror devices positioned into a plurality of columns and rows. The projector includes a light source, an optical system, a video processing system and a data system for driving said micromirror devices. The data subsystem provides separate data to a plurality of column pairs of the micromirrors. The projector includes a stereoscopic control circuit having a first state for inputting a first eye view of the stereoscopic image and causing each micromirror of each column pair to be in various but identical on and off states during said first eye view of said stereoscopic image. A second state of the control circuit for inputs a second eye view of the stereoscopic image and causes each micromirror of each column pair to be in various but identical on and off states during the second eye view of the stereoscopic image.
Owner:DIVELBISS ADAM W +1
Miniature three-dimensional contour scanner
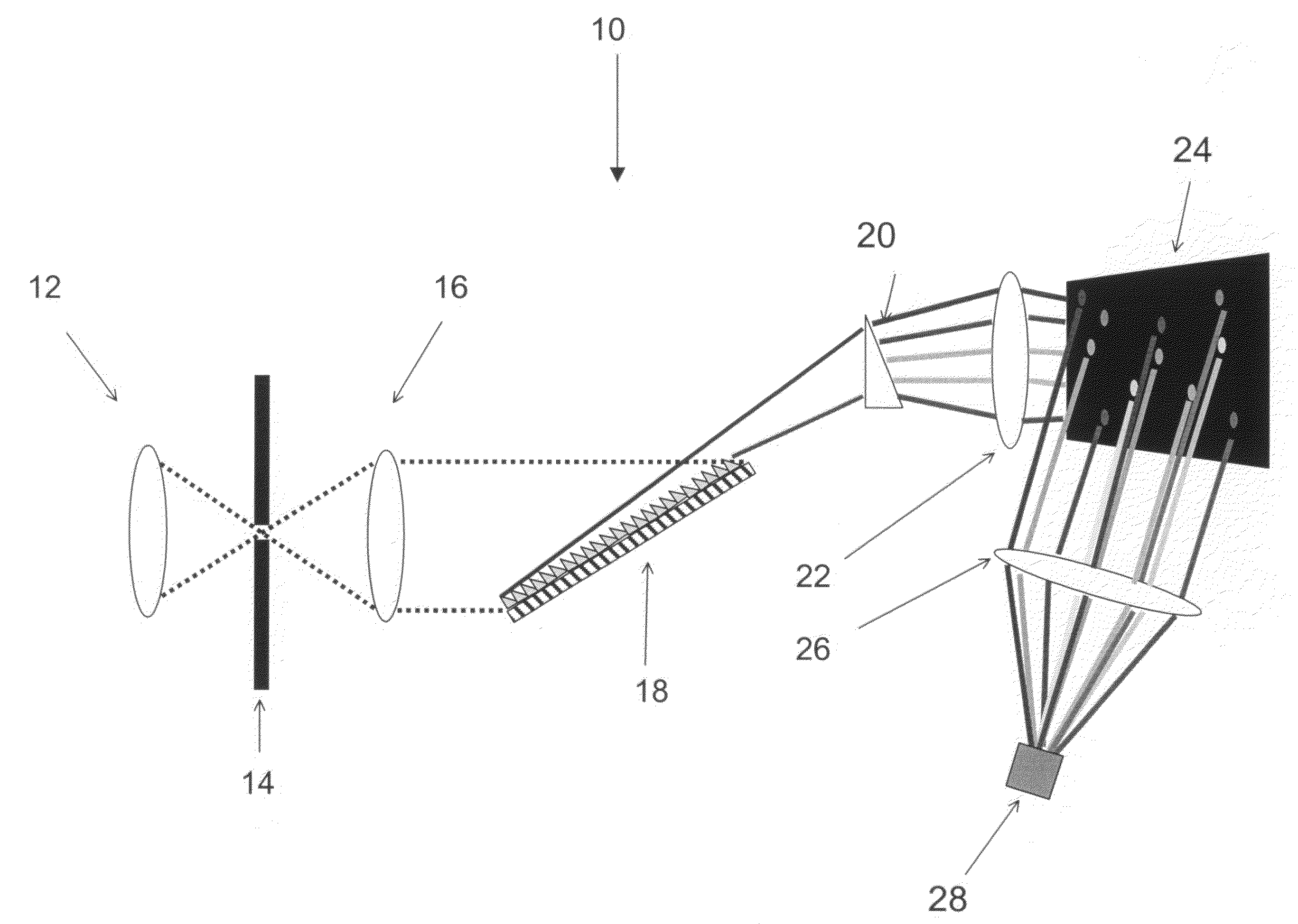
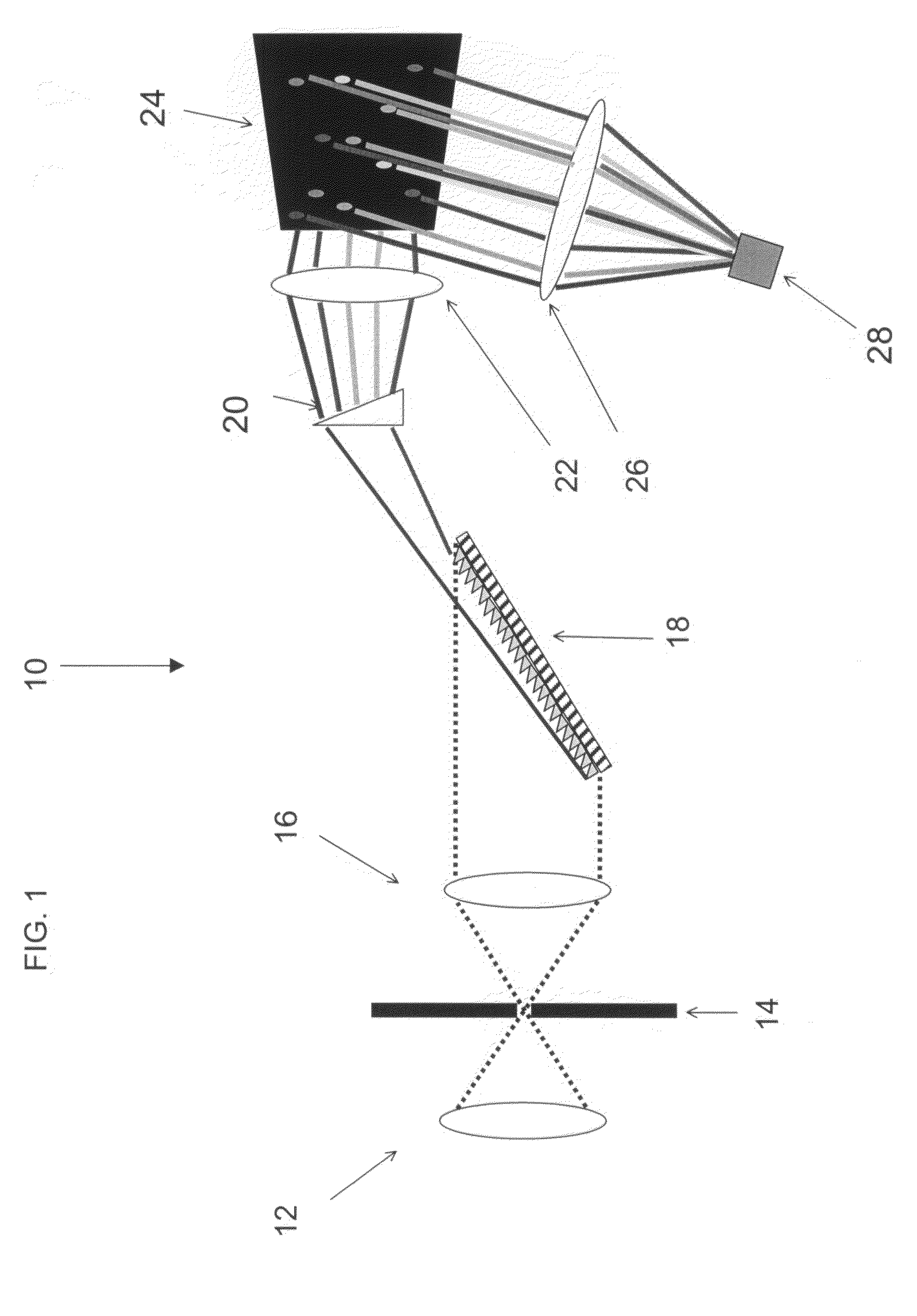
A miniature three-dimensional contour scanner is provided, which integrates the optical element and the set of optical lens of the optical projection module and the image capture module into a miniature measurement device. The device utilizes the optical fiber to guide in the light of outside light source and applies the digital micromirror device (DMD) chip to produce structured light pattern and project it onto the object's surface to be measured. The image sensor element is then used to capture the deformed structured fringe image, and by utilizing this information it is able to obtain the colored two-dimensional image and the three-dimensional contour size of the object. The miniature three-dimensional contour scanner can thus be applied in the measurement of miniature objects in the narrow space.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV +1
Spectrometers using 2-dimensional microelectromechanical digital micromirror devices
InactiveUS20080174777A1Low costSpeed up the time required for analysisEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryGratingSpectroscopy
Echelle gratings and microelectromechanical system (MEMS) digital micromirror device (DMD) detectors are used to provide rapid, small, and highly sensitive spectrometers. The new spectrometers are particularly useful for laser induced breakdown and Raman spectroscopy, but could generally be used with any form of emission spectroscopy. The new spectrometers have particular applicability in the detection of improvised explosive devices.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF WYOMING
Projection system and method including spatial light modulator and compact diffractive optics
ActiveUS20070058143A1Reduce weightLow costTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSpatial light modulatorLight beam
A method and apparatus for a projection display system includes a spatial light modulator and a volume illumination hologram. The spatial light modulator comprises a digital micromirror device, and the projection system includes a laser light source to produce a sequence of collimated, colored, light beams for the illumination hologram. Waste light produced by the spatial light modulator is transmitted to the illumination hologram, and the illumination hologram emits waste light from at least one of its edges. Waste light emitted from an edge of the illumination hologram is absorbed by a light sensor to control the intensity of the light beams. A projection focusing element is mounted proximate a side of the illumination hologram to focus the image beam from the spatial light modulator for viewing. A projection hologram is interposed between the side of the illumination hologram and the projection focusing element to manage waste light.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Pixelated Projection for Automotive Headlamp
An automotive headlamp is provided that includes a digital micromirror device (DMD) headlight module, the DMD headlight module including a DMD, a white light module to provide a white light beam to illuminate the DMD, illumination optics optically coupled between the DMD and the white light module to prepare the white light beam for illuminating the DMD, and projection optics optically coupled to the DMD to receive pixelated light reflected by the DMD and project a pixelated light beam on road, in which at least one of the DMD, the white light module, and the illumination optics shape a beam profile of the white light beam such that the light reflected by the DMD has a pixelated non-uniform beam profile suitable for projecting a white light beam that forms a portion of a white light beam of the headlamp.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Maskless lithography with multiplexed spatial light modulators
InactiveUS6870554B2Improve throughputCathode-ray tube indicatorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSpatial light modulatorEngineering
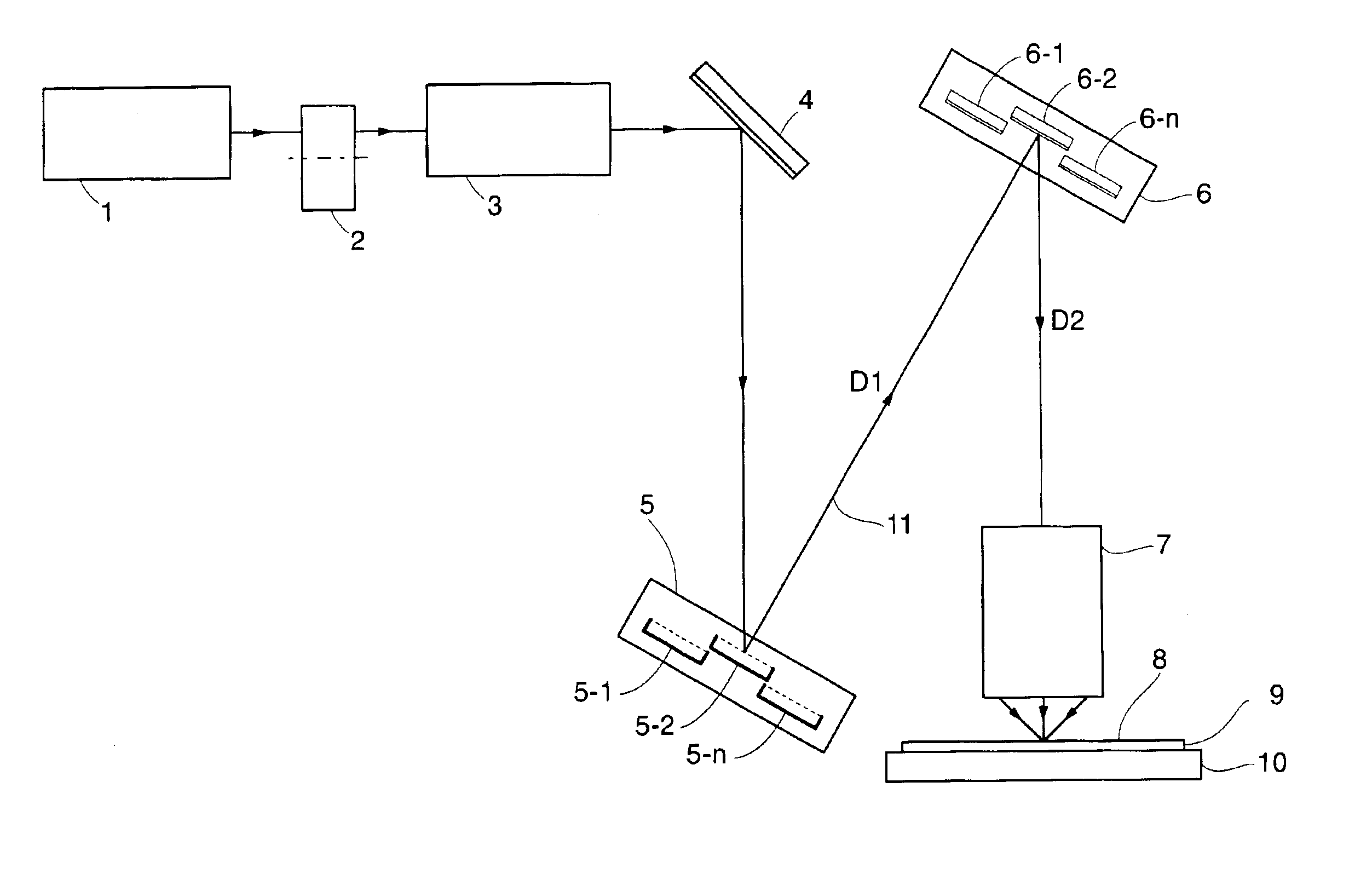
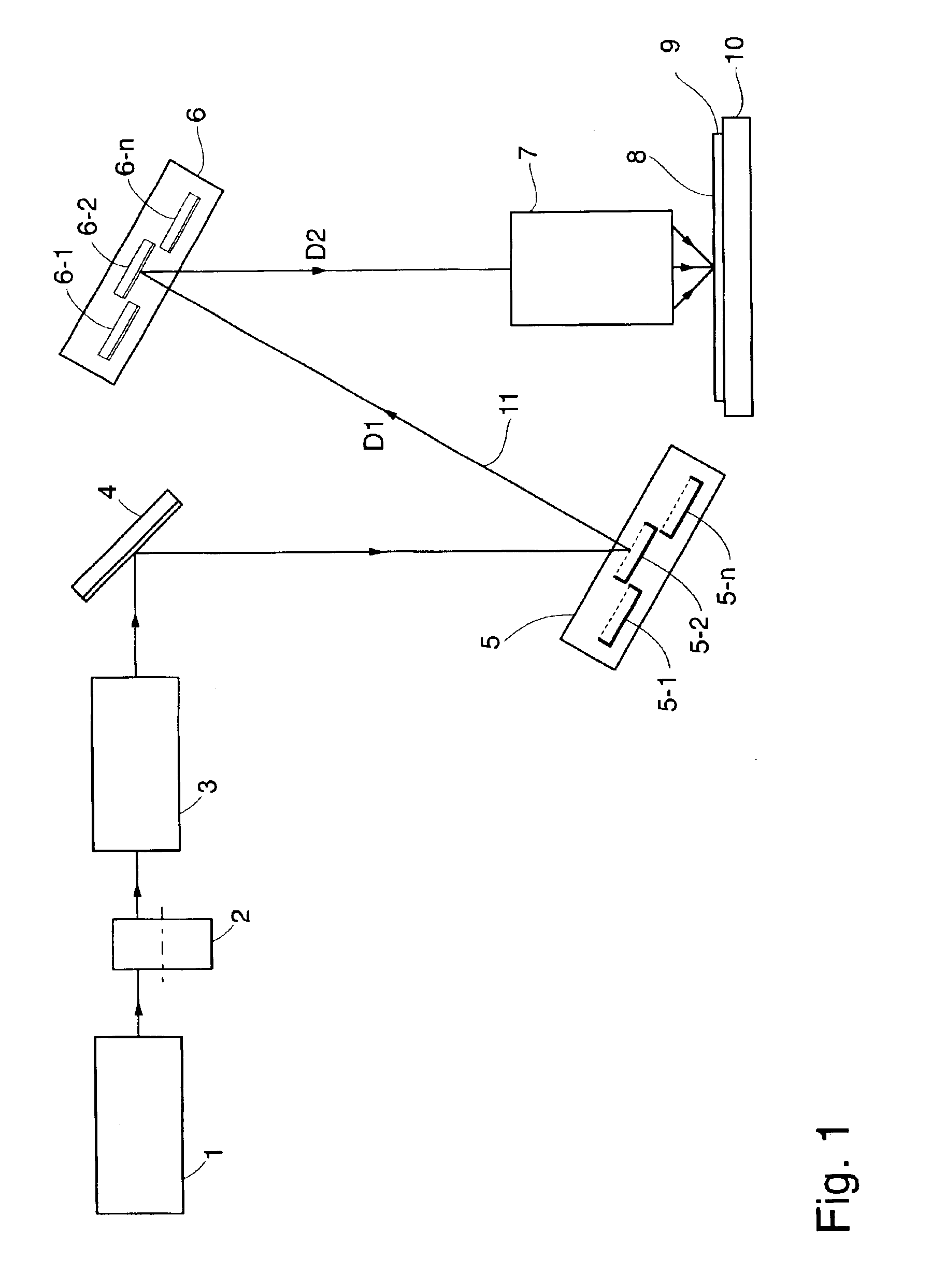
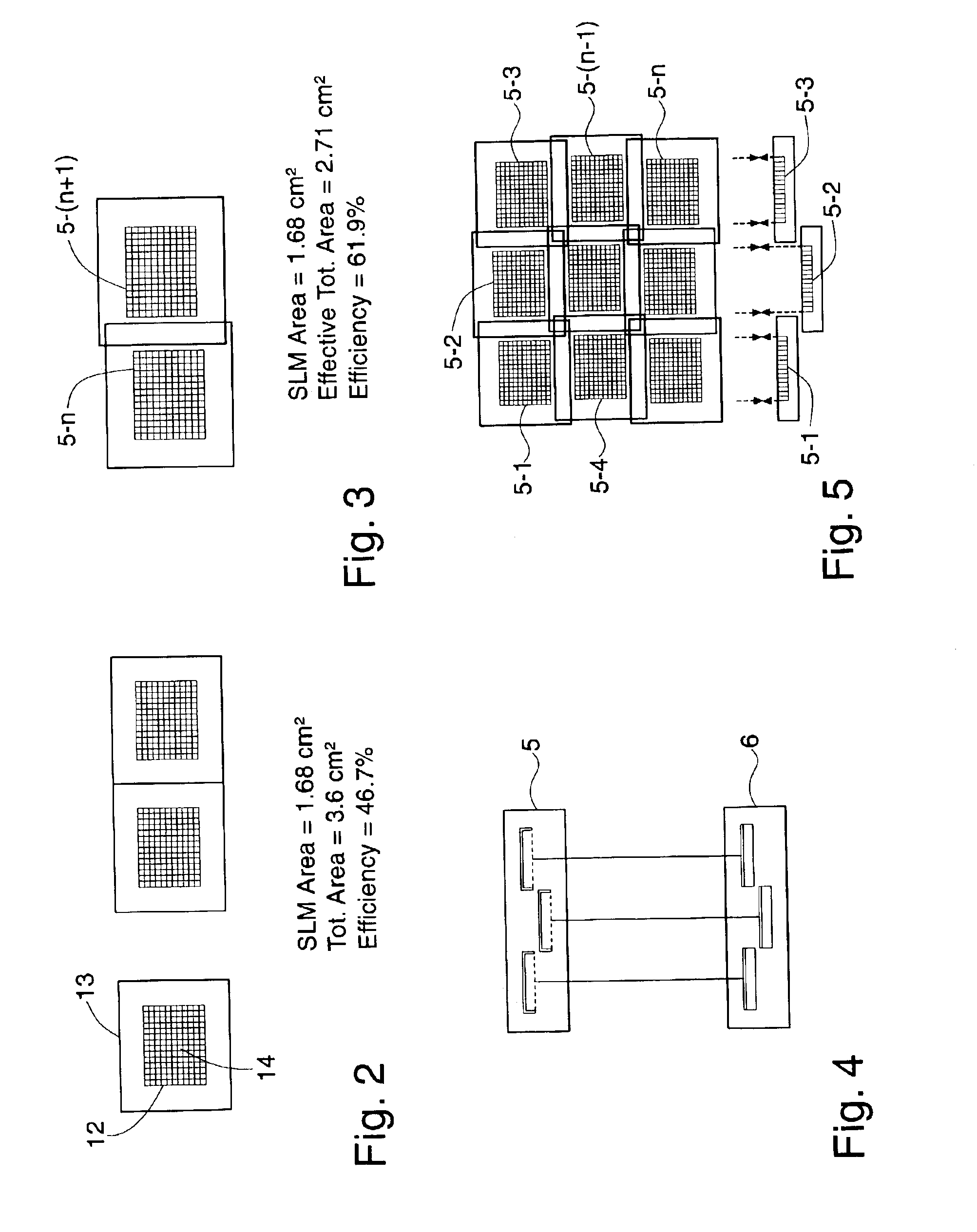
Imaging systems that use a spatial light modulator (SLM), such as maskless lithography systems using a digital micromirror device (DMD), suffer from low throughput at high resolution because of the increase in the number of pixels to be imaged. A possible solution to this problem is provided by using multiple SLMs. However, packaging multiple SLMs on a suitable base is inefficient because, in an SLM, surrounding the active region, a large inactive region is required for the chip kerf and the connector fan-in; these inactive regions thus prevent close packing of the SLMs. This invention enables close packing of a large number of SLMs by arranging them in twin planes, such that the kerf and fan-in regions overlap substantially. Variations in the optical conjugate distances of different SLMs caused by the twin planarity are eliminated by incorporation of a twin-pane compensating mirror array that corresponds to the SLM array, and introduces a pathlength difference between different mirrors that is complementary to the pathlength difference between corresponding SLM chips. Depth-of-focus problems are thus eliminated. The invention enables significant throughput enhancement, up to 82%, in maskless lithography systems.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
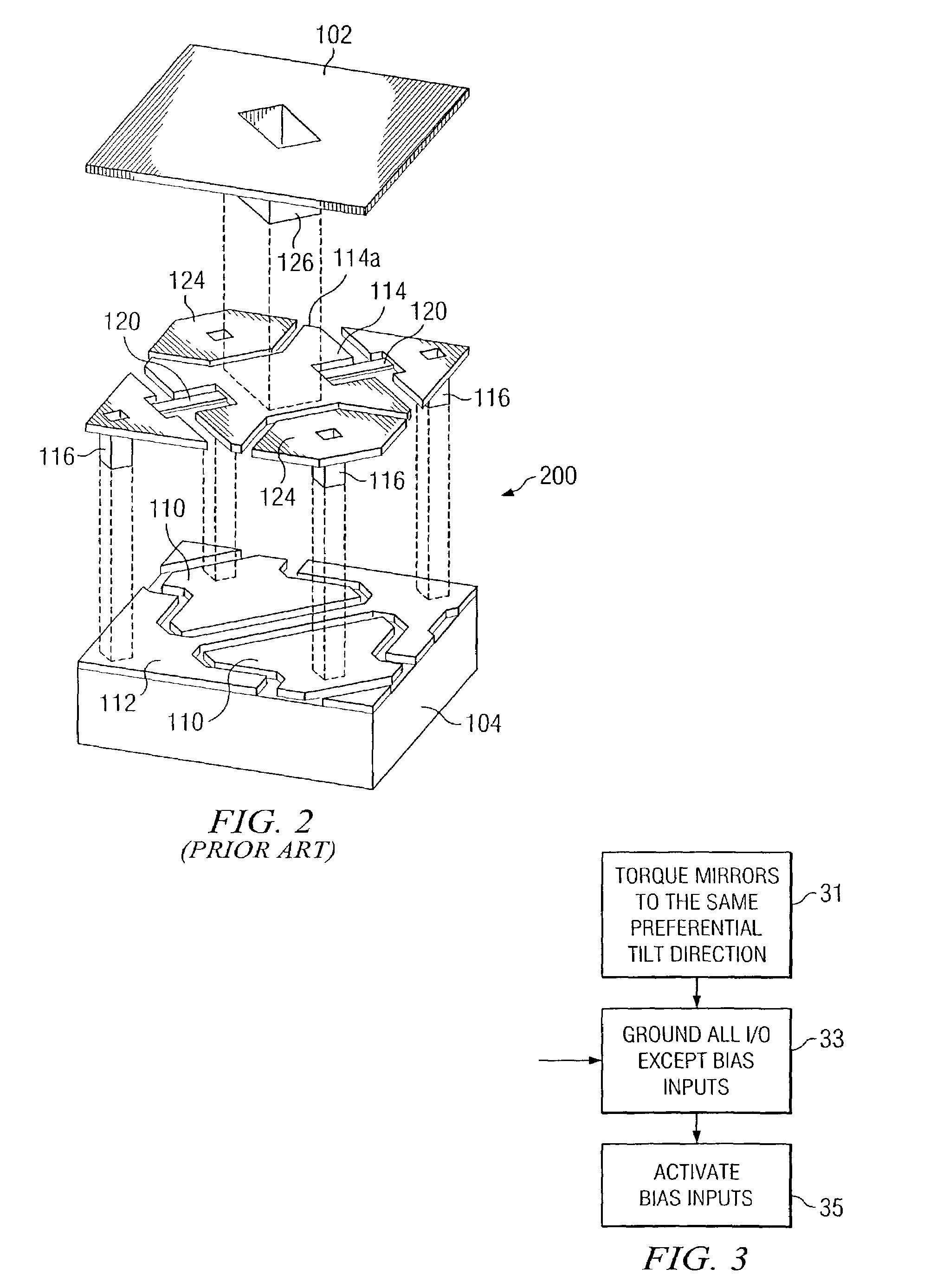
Digital micromirror device with simplified drive electronics for use as temporal light modulator
InactiveUS7187484B2Low costPermit useNon-linear opticsOptical elementsDigital micromirror deviceElectron
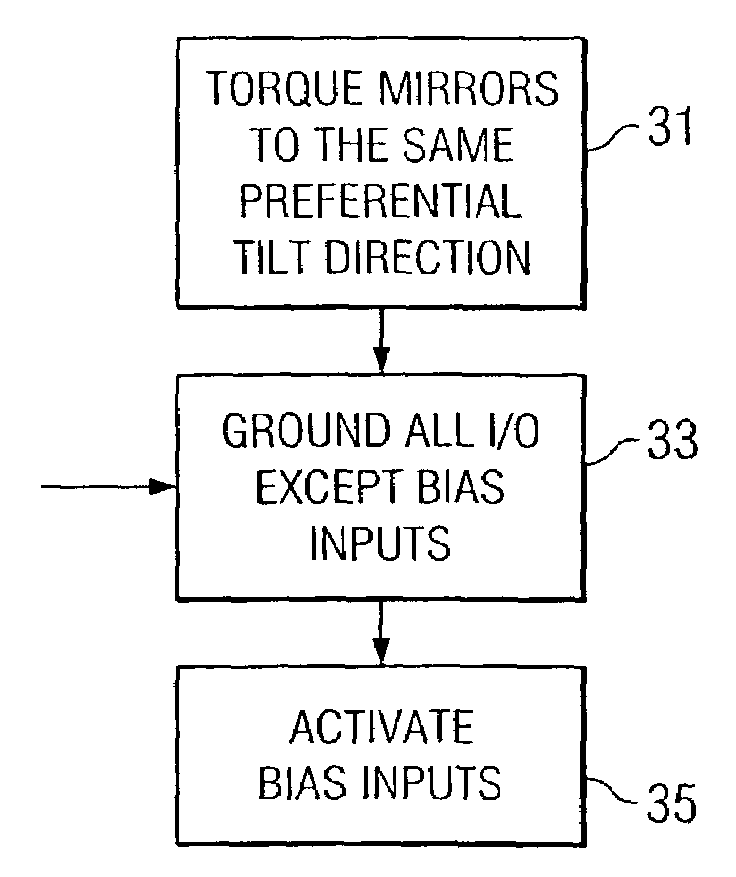
A digital micromirror device (DMD) modified for use as a temporal light modulator. The DMD is modified so that the mirrors of the DMD have a preferential tilt direction. The inputs and outputs of the DMD are connected to common ground, except for the bias input lines. The latter are connected to a common excitation input, which is used to cyclically reposition the mirrors between tilted and flat states.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
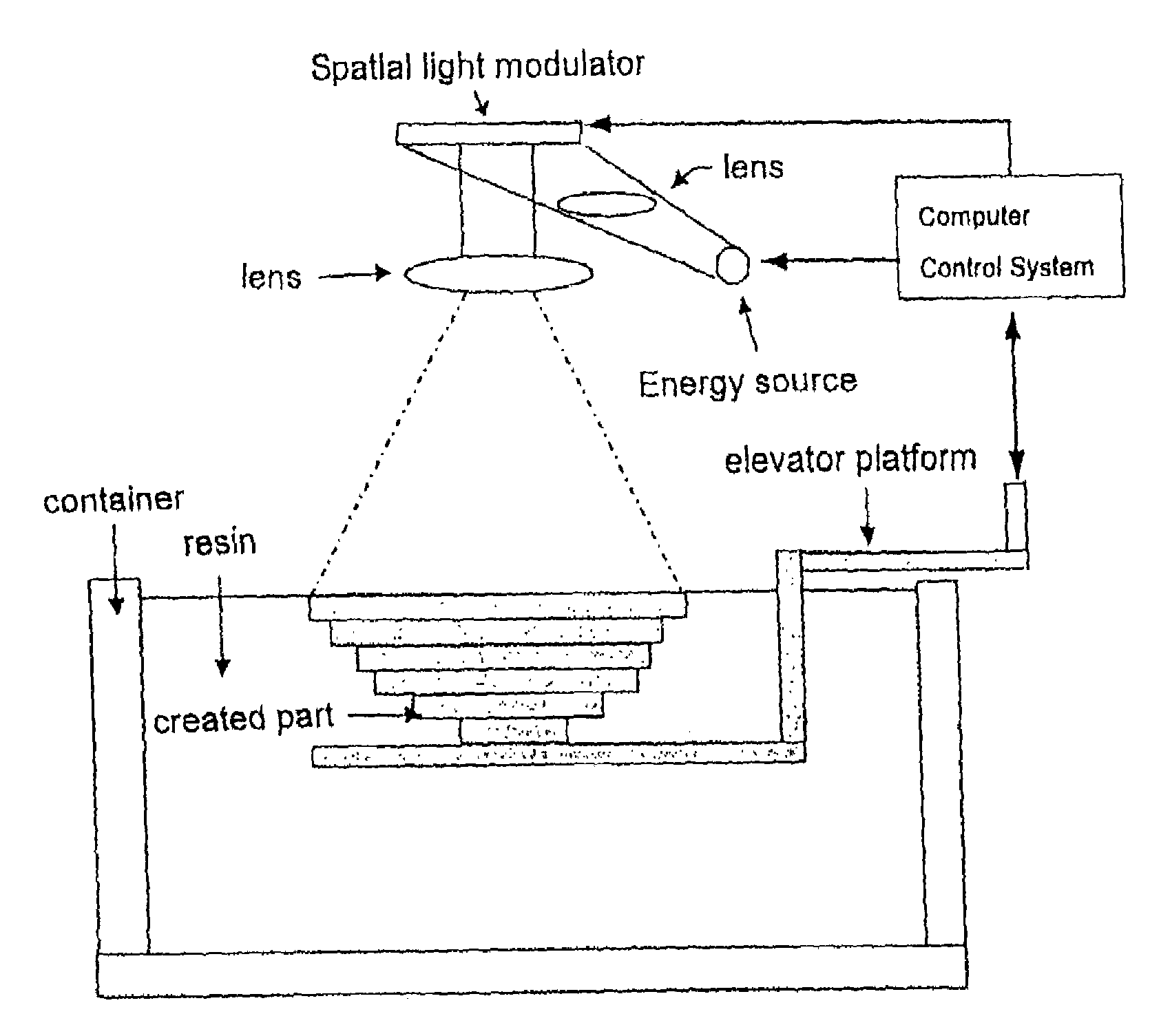
Method for rapid prototyping by using linear light as sources
InactiveUS7158849B2Additive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A method for rapid prototyping by using linear light as sources employs DLP (Radiation Hardening Formation) or LCD, together with the portable devices and linear light source to treat the raw material in two stages. The first stage is to spread the raw material to a selected zone by nozzles or rollers and illuminating the material to let the material being processed and have physical o mechanical changes. The second stage is to use more powerful linear light source with the cooperation of the portable DMD (Digital Micromirror Device) or LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) to illuminate the material to make it have a second times of physical o mechanical changes. By the piling up the layers of the material, a complete 3-D work piece is obtained.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Systems and methods for laser material manipulation
InactiveUS20060119743A1Television system detailsColor television detailsLiquid-crystal displayLaser imaging
A laser material manipulation system is provided for material manipulations such as laser ablation, laser deposition and laser machining. The system includes a laser for emitting laser pulses and a laser imaging device having an array of controllable imaging elements. The laser imaging device receives the laser pulses emitted from the laser, forms a laser image through the controllable imaging elements, and projects the laser image onto a target material which needs to be manipulated. The projected laser image manipulates the material according to a desired manipulation pattern. The laser can be a femtosecond laser. The laser imaging device can be a liquid crystal display (LCD) or a digital micromirror device (DMD). An SEM can be used for monitoring the material distribution and dynamically adjust the laser image according to the monitor result.
Owner:CHOSEN TECH
Three-dimensional video scanner
ActiveUS20070165246A1Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsInvestigating moving sheets3d shapesLight beam
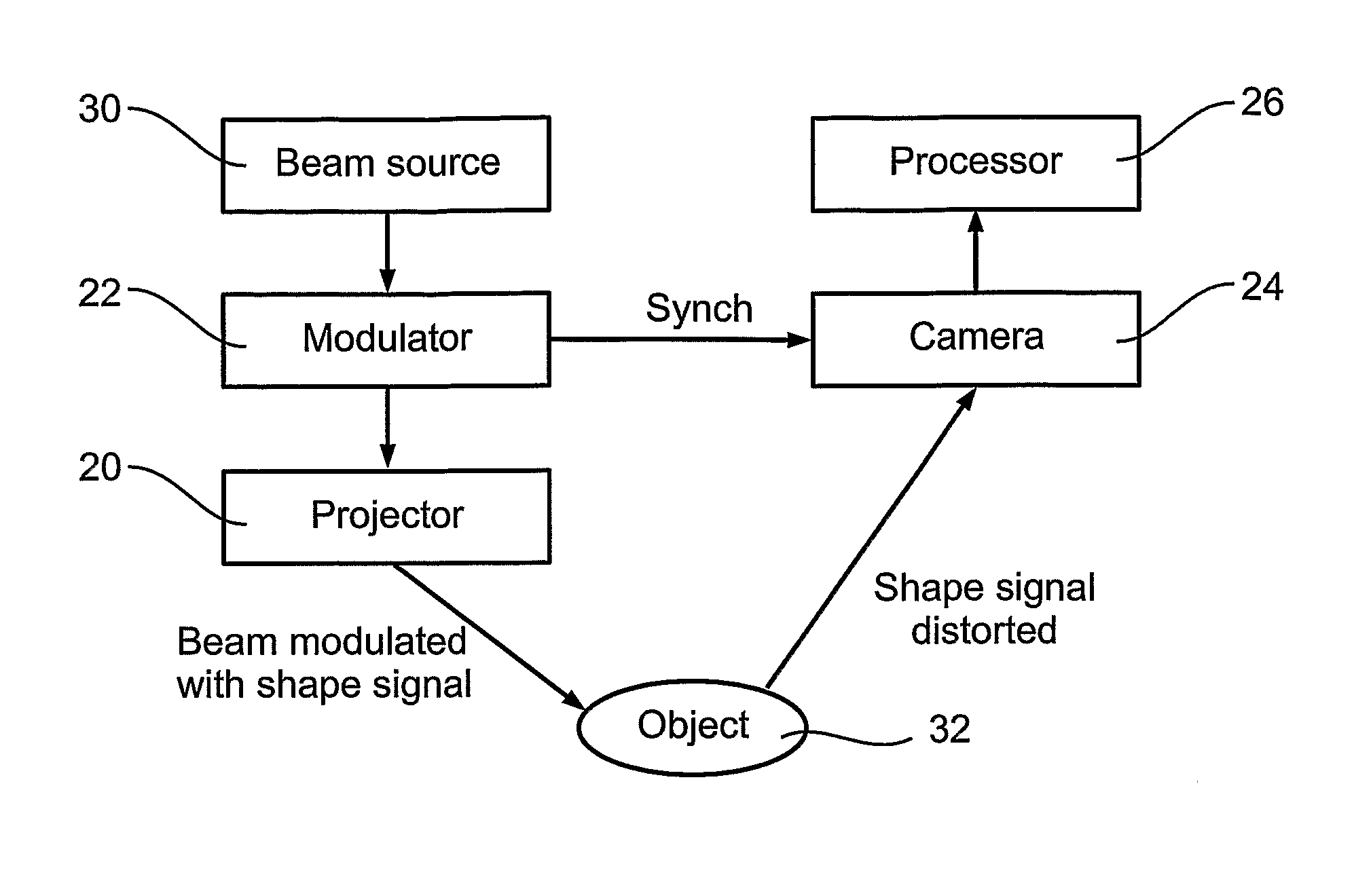
A 3D scanning device comprises: a digital light encoding unit comprising a digital micromirror device for encoding a rapidly changing shape signal onto a light beam directed to an object, a shape of said signal being selected such that distortions thereof by a contoured object reveal three-dimensional information of said contour; a detector synchronized with said digital light processing unit for detecting reflections of said light beam from said object, and a decoder for determining a 3D shape of said object from distortions of said signal in said detected reflections.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD +1
Methods and apparatus for imaging using a light guide bundle and spatial light modulator
InactiveUS7235047B2Reduce the amount of noiseReduce of noise lightPrintersSurgerySpatial light modulatorLight guide
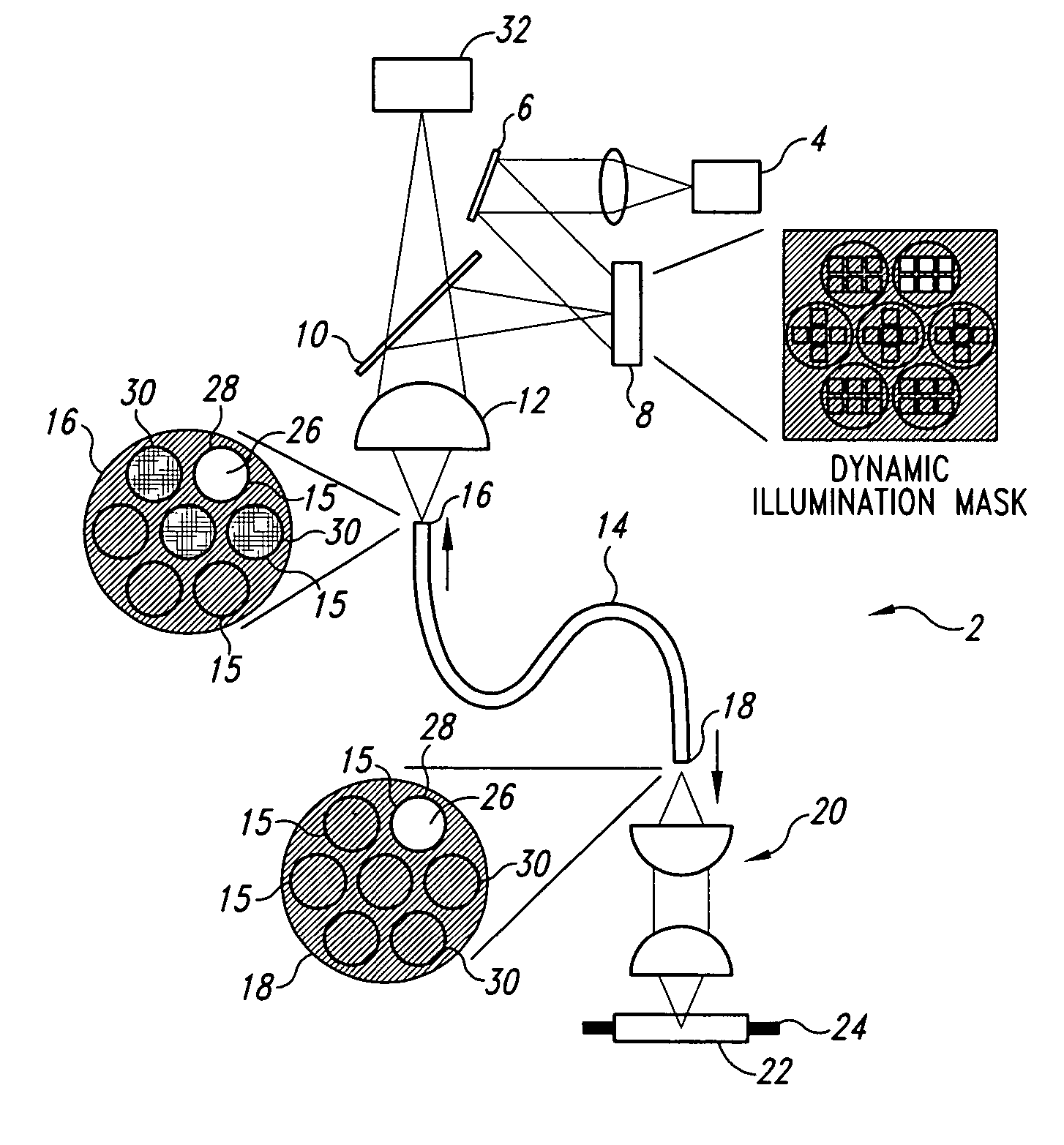
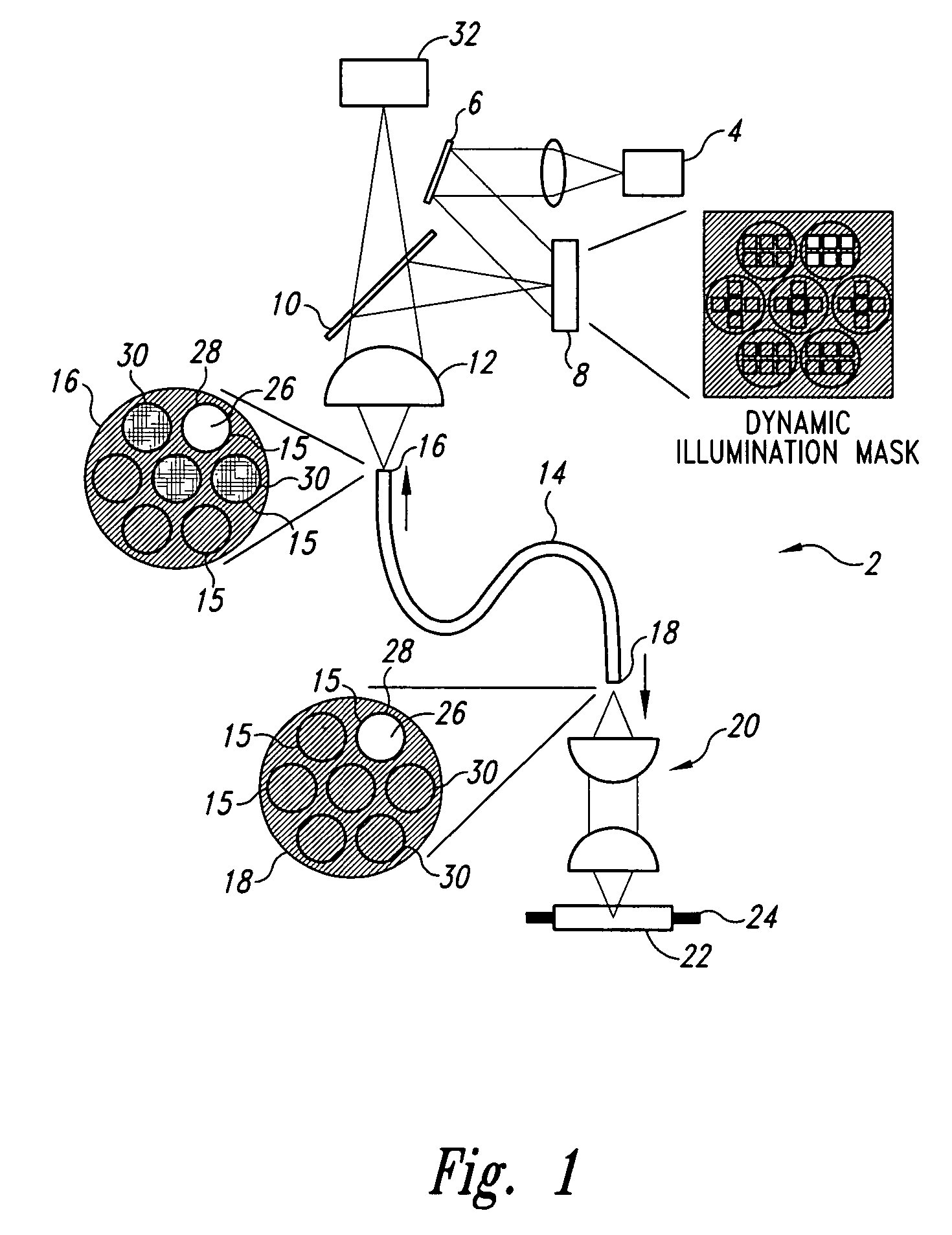
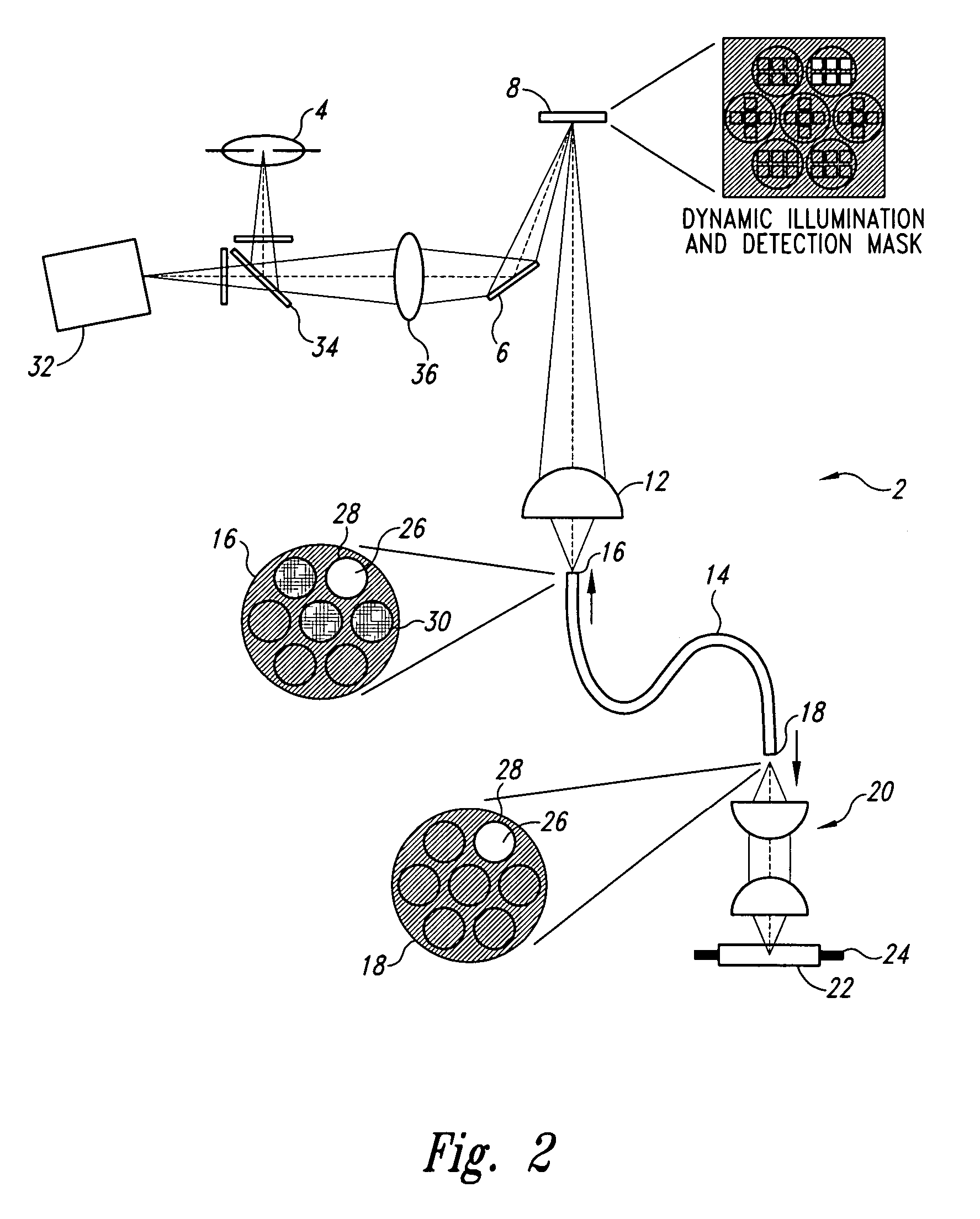
Endoscopes and other viewing devices that control the light that contacts a sample and / or that is detected emanating from a sample. The viewing devices are particularly well suited for in vivo imaging, although other uses are also included. The viewing devices, and methods related thereto, comprise a spatial light modulator in the illumination and / or detection light path so that light transmitted to the target via a bundle of light guides or optical system is transmitted substantially only into the cores of the light guide bundle and not into the cladding surrounding the light guides, filler between the light guides in the bundle, or undesired light guides. Also, methods and apparatus for mapping the pixels of the spatial light modulator to the cores of the light guides in the bundle (preferably at least 3 pixels (e.g., at least 3 mirrors for a digital micromirror device) for each core), as well as for mapping the light guides of one light guide bundle to another.
Owner:MOTIC CHINA GRP CO LTD
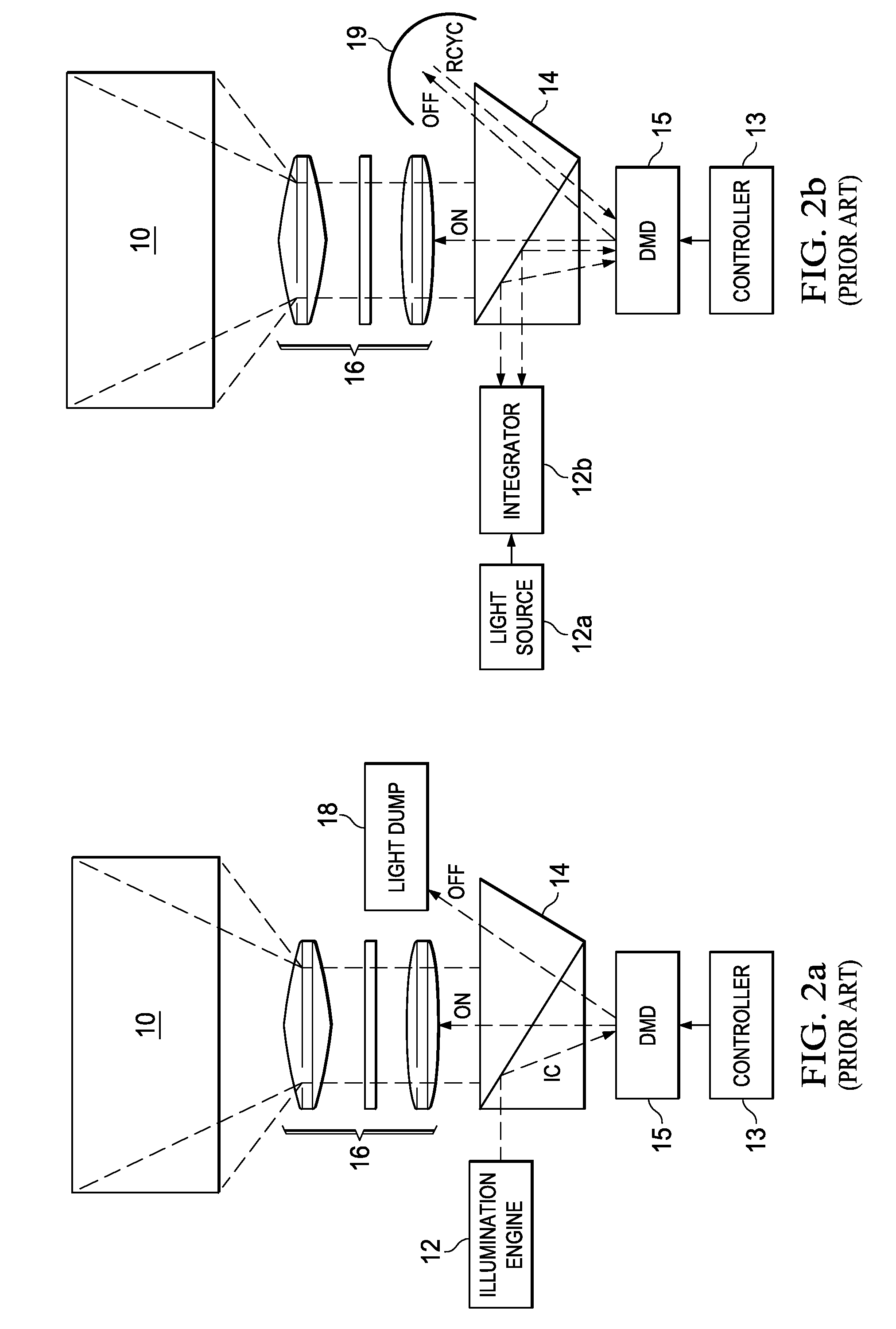
Light Recycling in a Micromirror-Based Projection Display System
ActiveUS20090009730A1Reduce contrastEffective lightingTelevision system detailsCosmonautic condition simulationsIntegratorImage contrast
A digital micromirror projection display system is disclosed in which “off” pixel light is recaptured and recycled. In the disclosed system, a digital micromirror device directs incident light for “on” pixels in the image to be displayed through projection lenses to a projection screen. The digital micromirror device directs incident light for “off” pixels back toward the light source for recapture by a light integrator. Both the incident and projected light can pass through a rear group of projection lenses, with the first projection lens being disposed near the digital micromirror device. A mirror directs the incident light toward the digital micromirror device, and the “off” pixel light from the digital micromirror device toward the light integrator. As a result, “off” pixel light can be recycled without degrading image contrast, in a manner that can place fast projection lenses close to the digital micromirror device to save cost.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
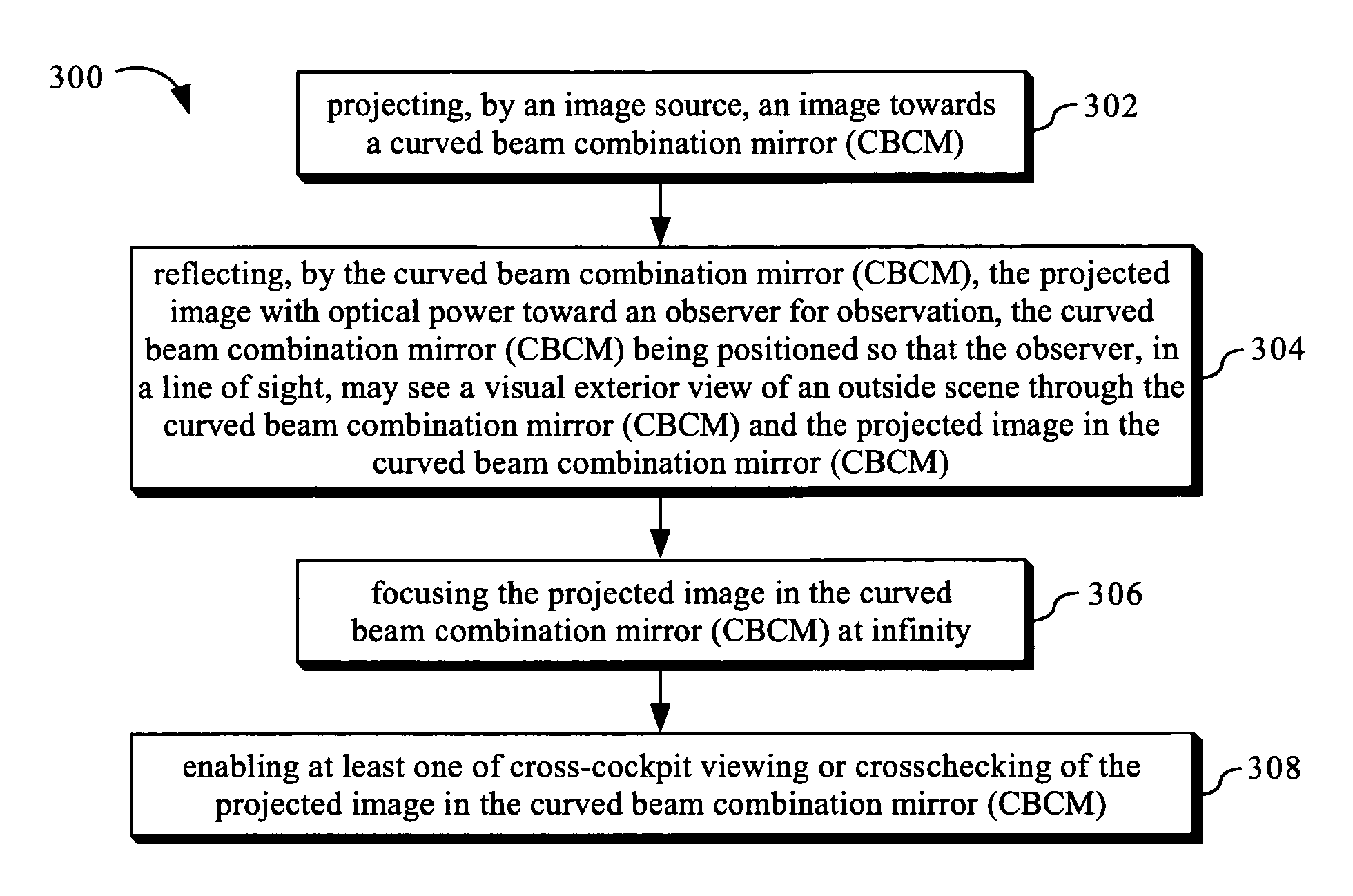
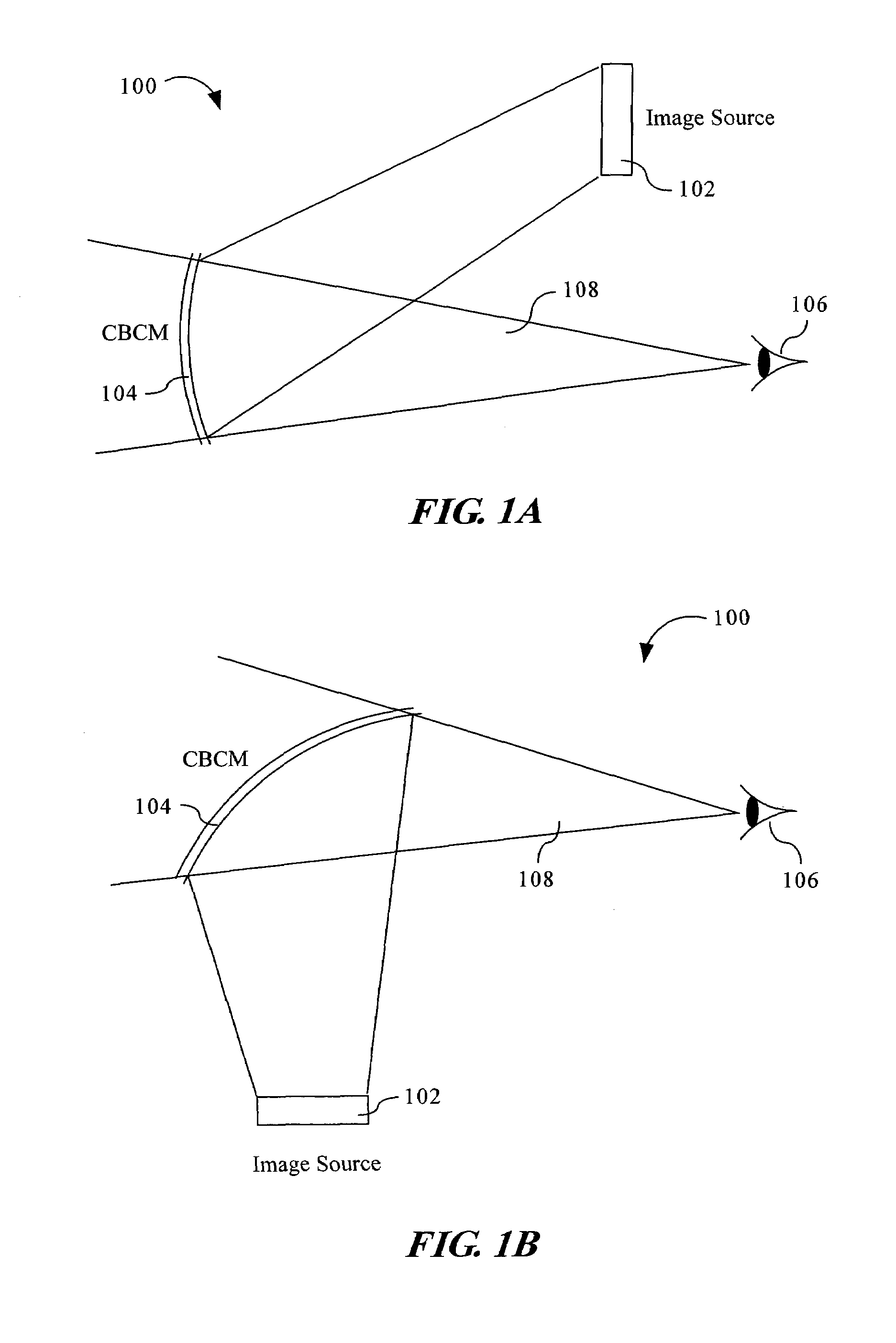
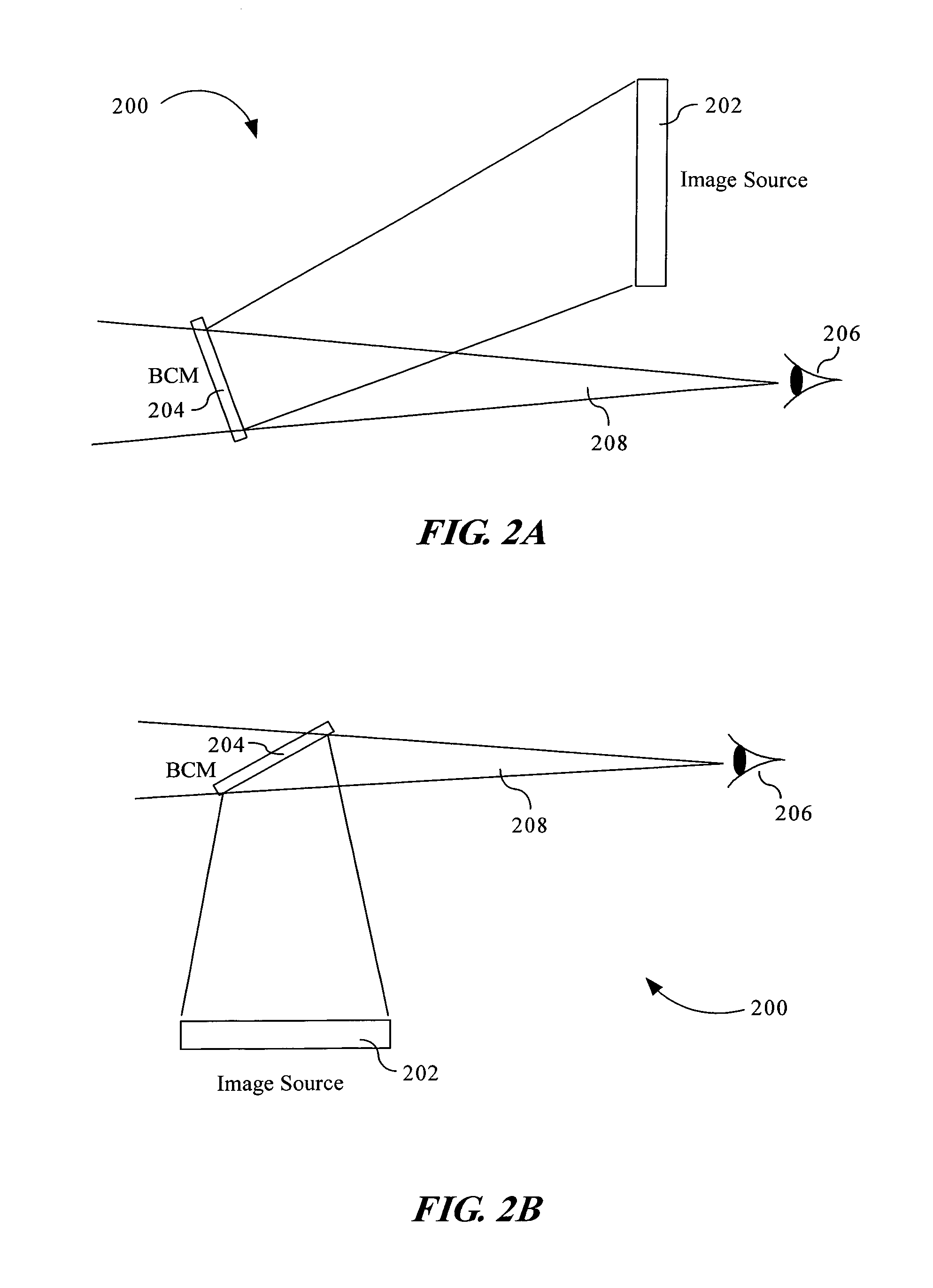
Compact head up display with wide viewing angle
The present invention provides an optical display system and method for producing images and presenting the images for observation in combination with an observer's visual exterior view of an outside scene. The optical display system may include an image source for projecting an image, and a curved beam combination mirror (CBCM) or beam combination mirror (BCM) for reflecting the projected image toward an observer for observation. The image source may be a transmissive LCD, a reflective LCD, a digital micromirror device, a laser display, or the like. The CBCM or BCM may be positioned so that the observer, in a line of sight, may see a visual exterior view of an outside scene through the CBCM or BCM and the projected image in the CBCM or BCM.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
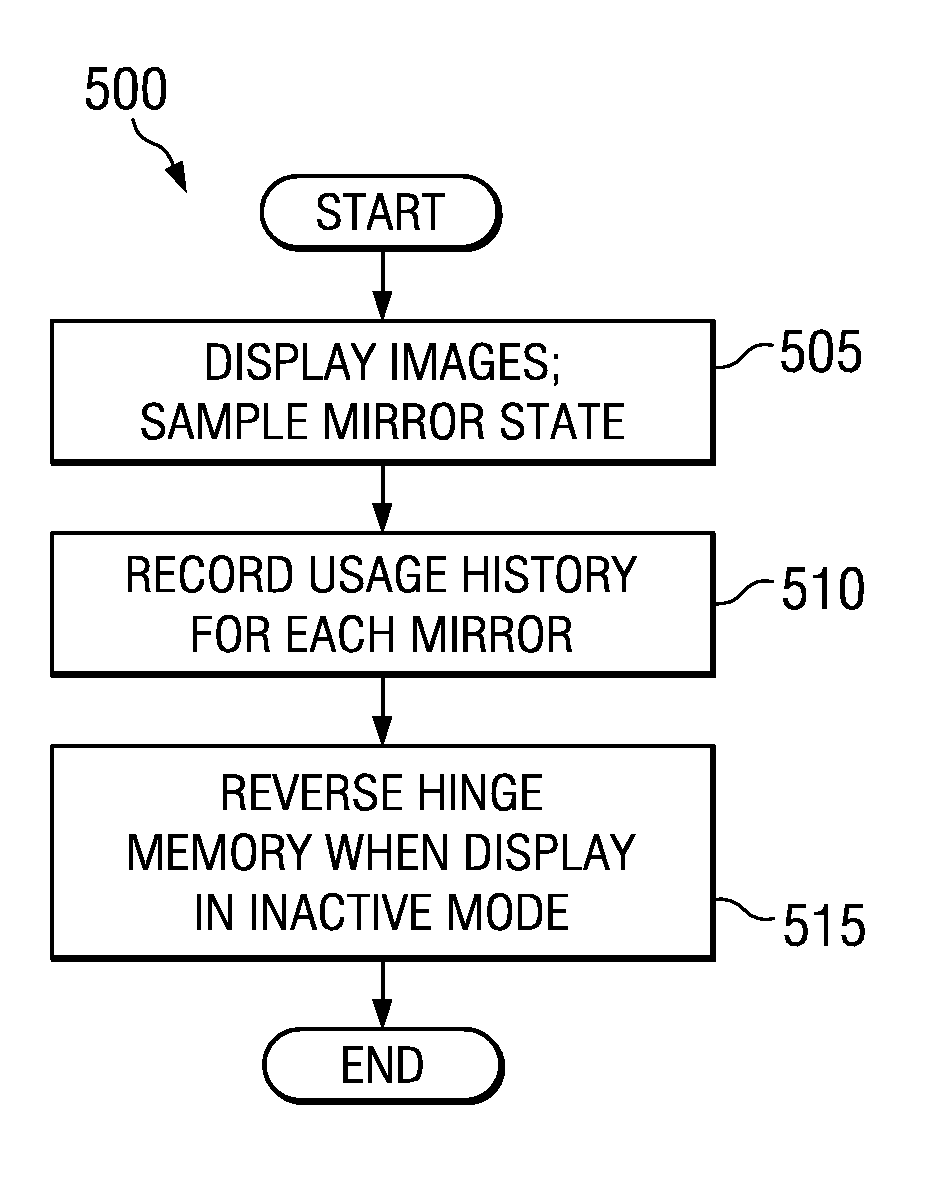
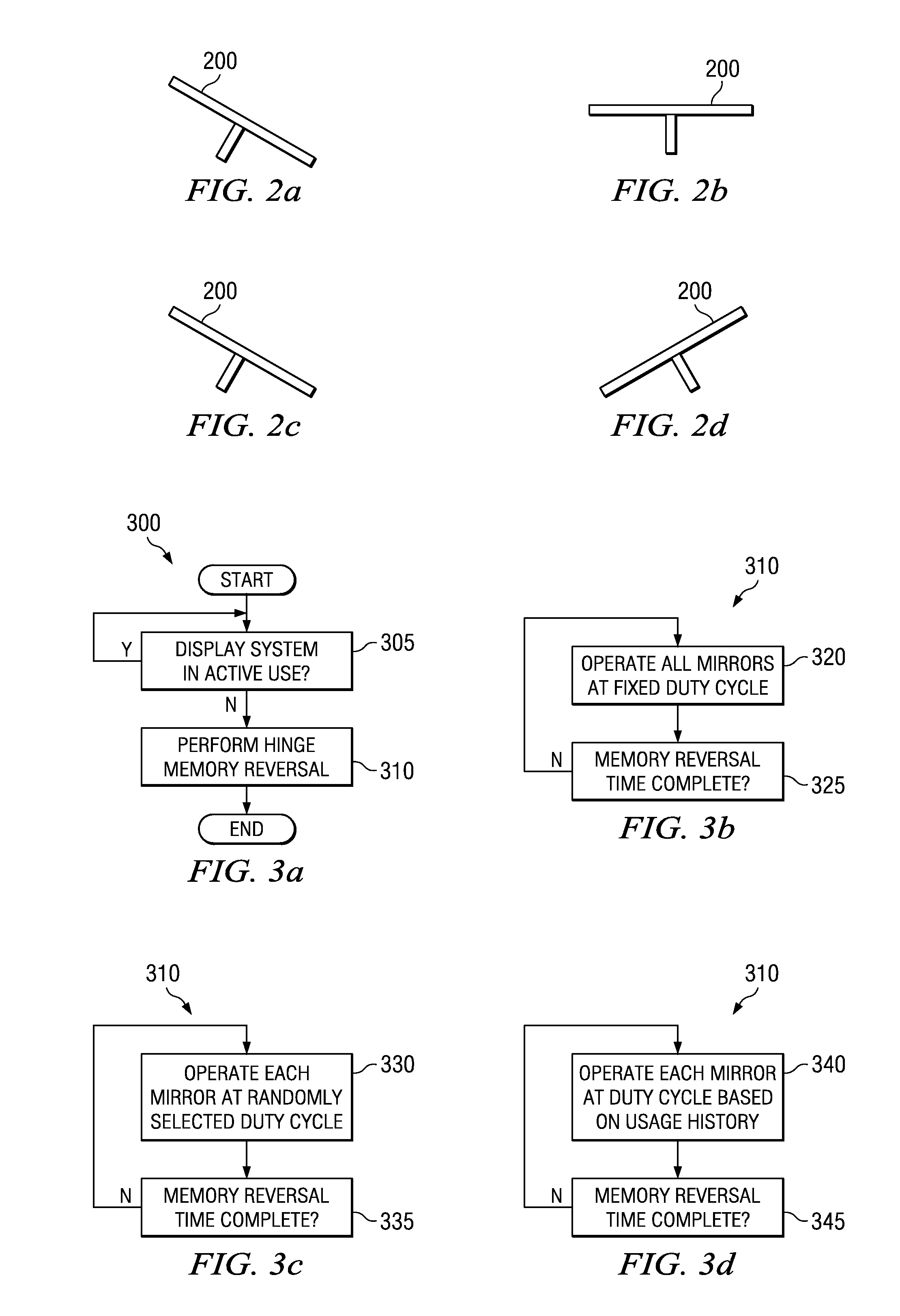
System and method for hinge memory mitigation
ActiveUS7349146B1Reduce failureReduce displayStatic indicating devicesSensing by electromagnetic radiationComputer scienceDigital micromirror device
System and method for reducing failures due to hinge memory in a microdisplay display system. A preferred embodiment includes setting the state of each micromirror in a digital micromirror device based on an image being displayed, recording a usage history for the micromirrors, and providing a sequence of states to each micromirror when the display system is in an inactive mode. The sequence of states provided to a micromirror is based on the micromirror's usage history. The operation of the micromirrors while a display system containing the digital micromirror device is not in active use can help to reverse or eliminate hinge memory, thereby extending the lifetime of the digital micromirror device.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Image projector
InactiveUS20050018145A1Increase brightnessEnhance definitionTelevision system detailsProjectorsColor gelComputer science
An image projector is disclosed. The image projector includes a lamp emitting light rays, a filtering unit having a first device including a plurality of color filters including a white color filter each formed to correspond to a section therein, and a second device including a plurality of color filters except a white color filter each formed to correspond to a section therein and formed at one side of the first device, and filtering the light rays emitted from the lamp through any one of the first device and the second device, a rod lens focusing and projecting the light rays separated from the filtering unit, and a digital micromirror device displaying an image through electric signals in accordance with the projected light rays.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
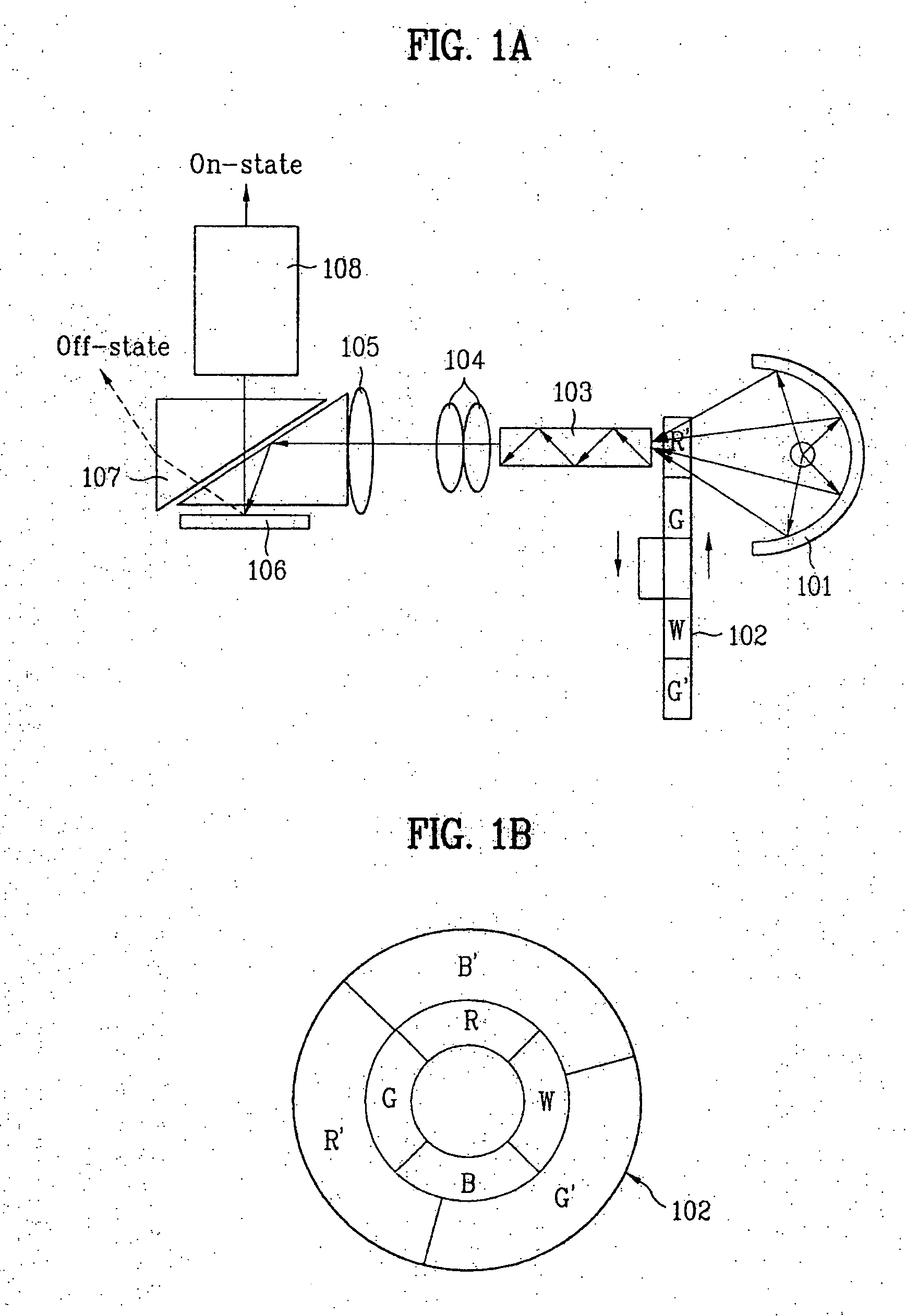
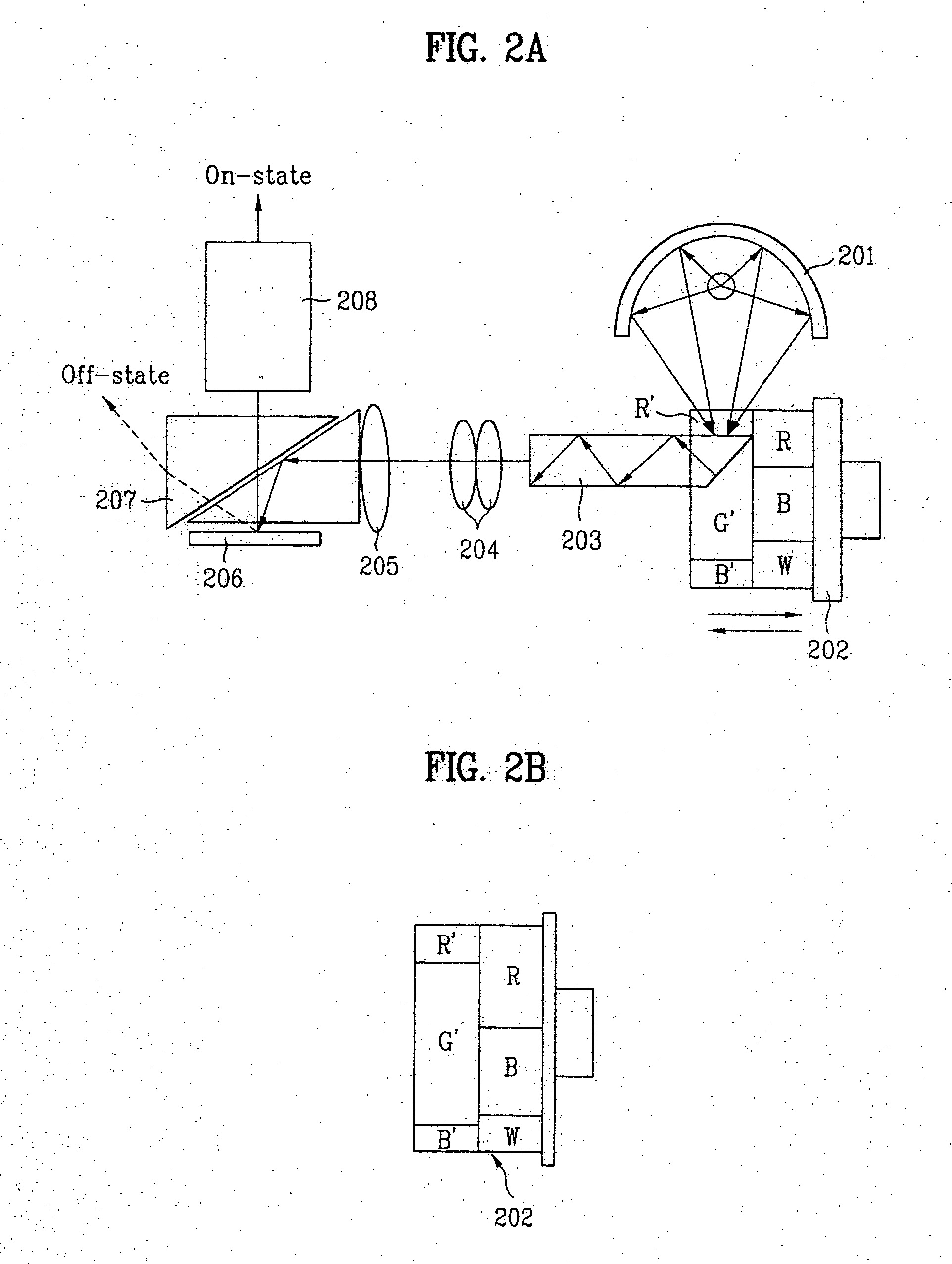
Constant-weight bit-slice PWM method and system for scrolling color display systems
ActiveUS7061512B2Short durationProjectorsPicture reproducers using projection devicesTime segmentDisplay device
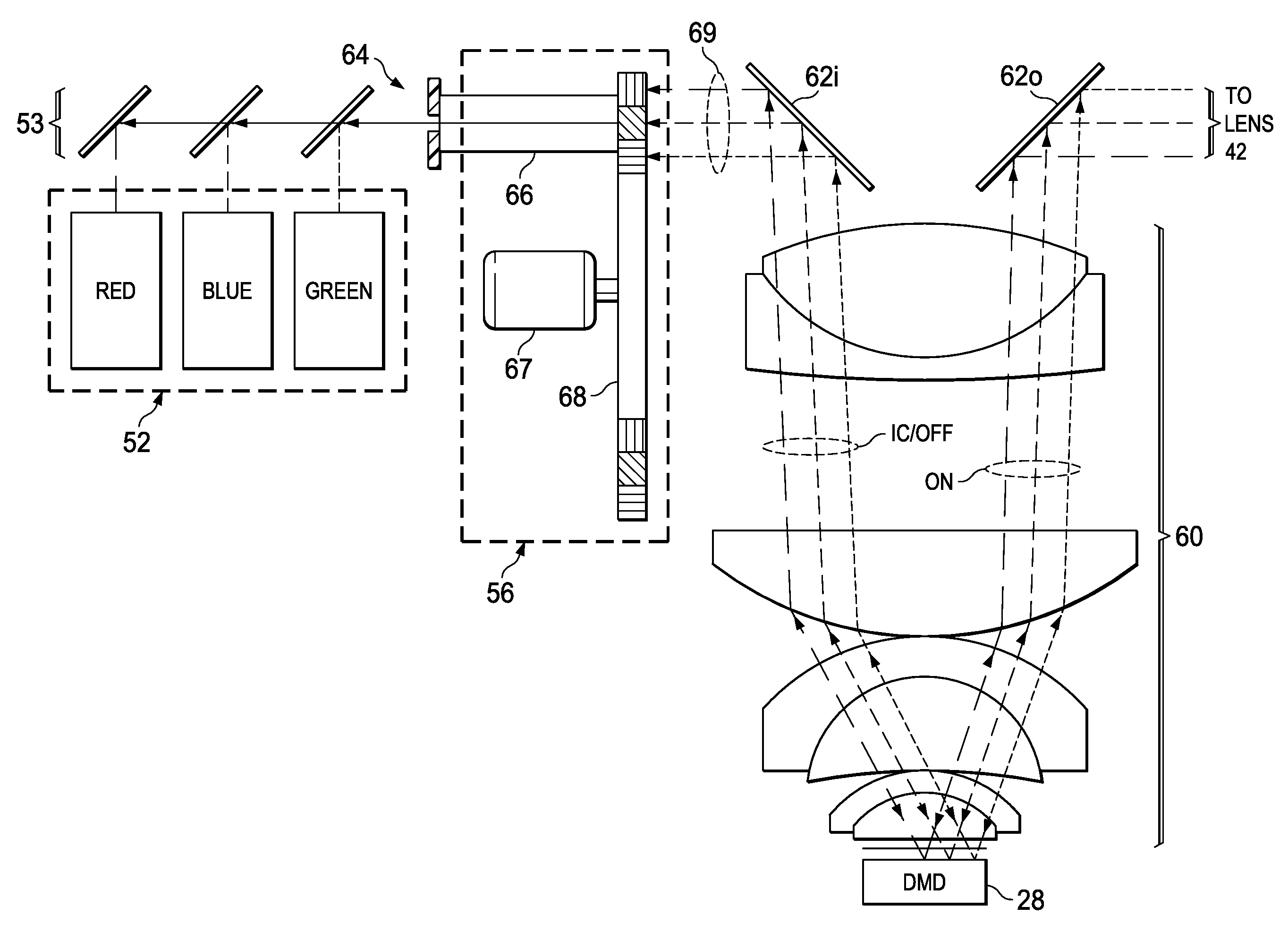
A display system 100 includes a light source 110 and a color wheel 114. An optical section 112 is arranged to receive light from the light source 110 and to direct the light toward a color wheel 114. A digital micromirror device 122 is arranged to receive the light from the color wheel 114 and to direct image data toward a display. The image data includes an array of pixels arranged in rows and columns. The array of pixels is arranged as curved color bands during a first time period and rectangular color bands during a second time period. The second time period being concurrent with but of a shorter duration than the first time period.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Generation/three g dimensional reconstruction apparatus and method for Laguerre Gaussian vortex beam
InactiveCN106896498AHigh damage thresholdQuick responseOptical elementsGaussian beamInformation transmission
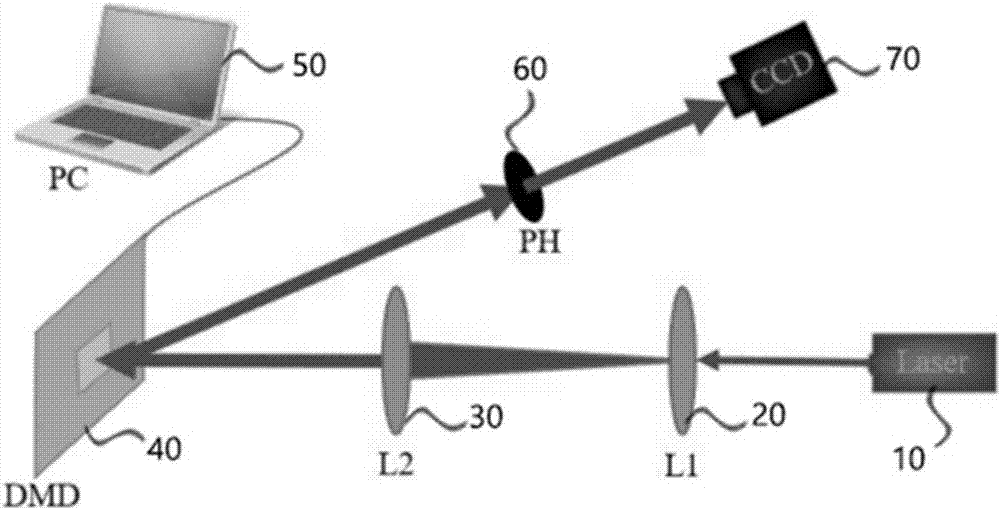
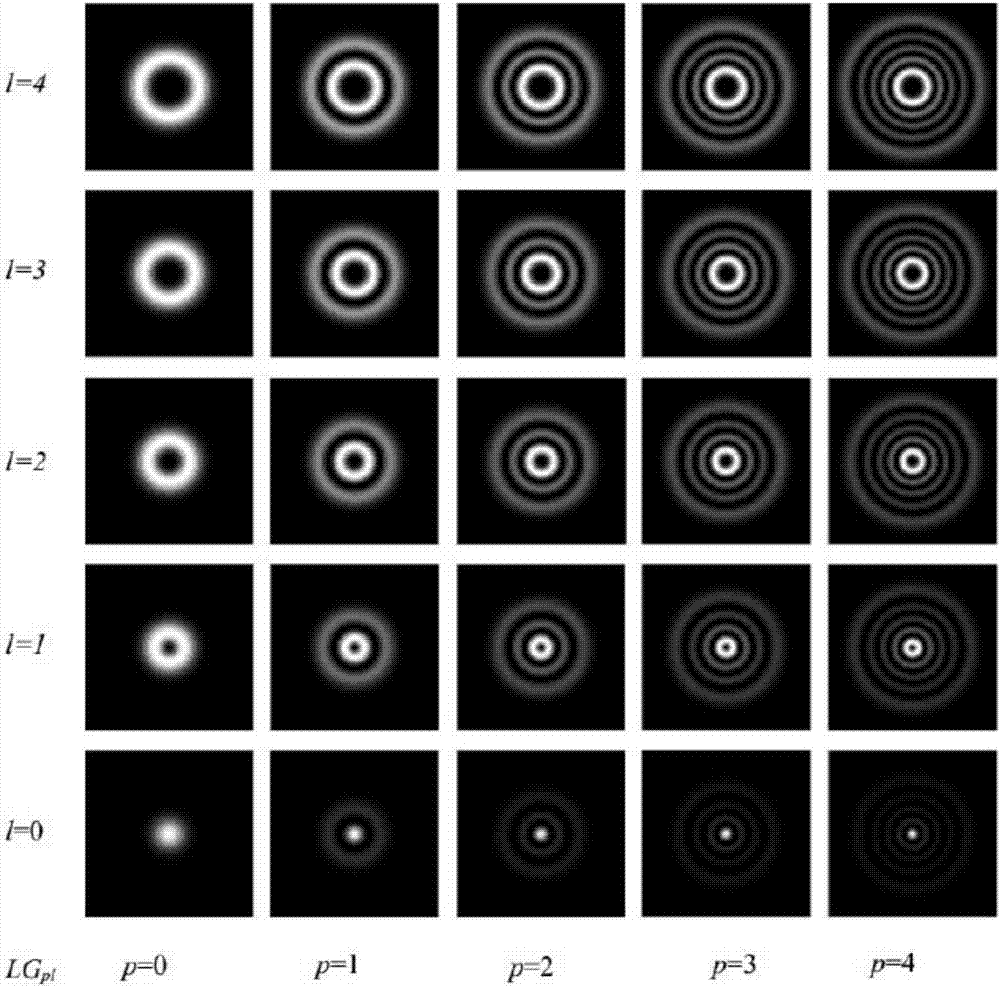
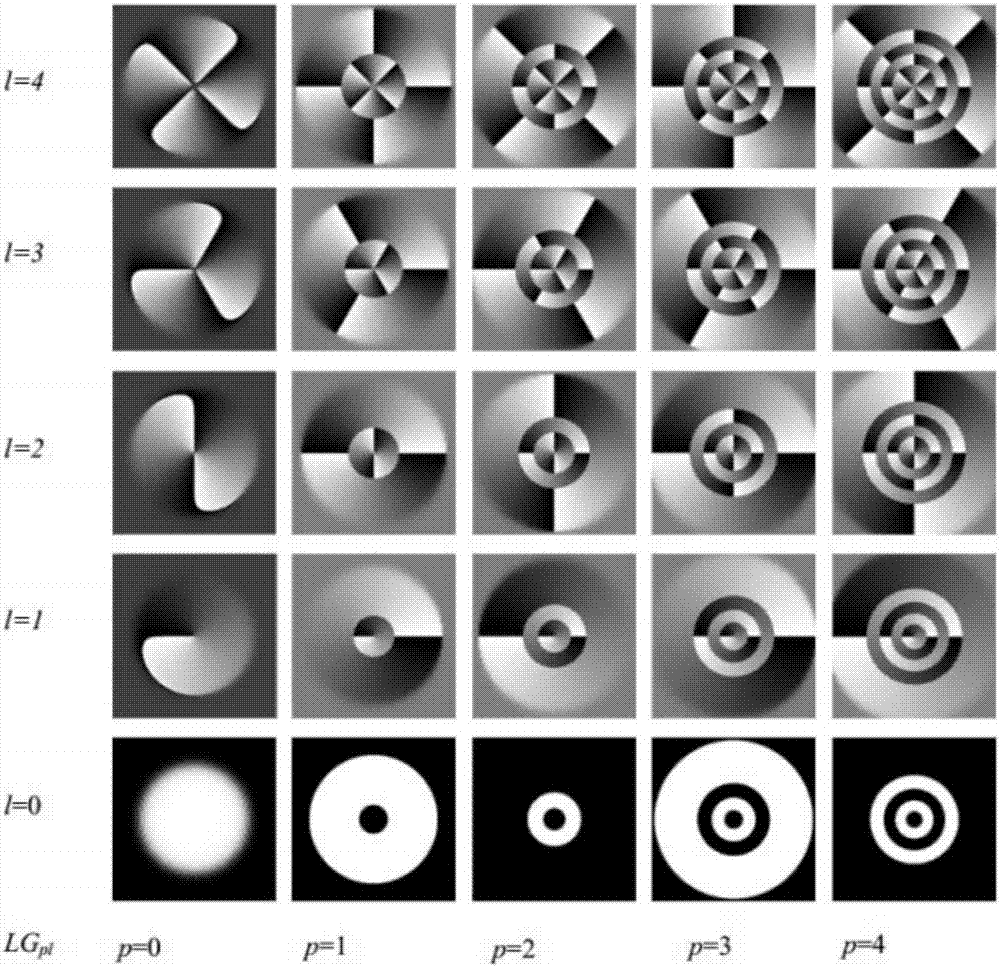
The invention discloses a generation / three-dimensional reconstruction apparatus and method for a Laguerre Gaussian vortex beam. The Laguerre Gaussian vortex beam generation apparatus comprises: a laser for emitting a Gaussian beam; a first convex lens for expanding the Gaussian beam; a second convex lens for collimating the expanded Gaussian beam; a computer for generating a fork-shaped diffraction grating and loading the fork-shaped diffraction grating onto a digital micromirror device, and subjecting the incident beam of the digital micromirror device to amplitude and / or phase modulation; and the digital micromirror device for subjecting a part of the collimated Gaussian beam to amplitude or / and phase modulation to produce Laguerre Gaussian vortex beams with different orders. The generation / three-dimensional reconstruction apparatus has a high damage threshold and a very fast response speed, is simple in structure, good in stability, and low in manufacturing cost, and is widely used in the fields of mechanical processing, biomedical treatment, military field, information transmission, micro-control and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Integrated ocular examination device
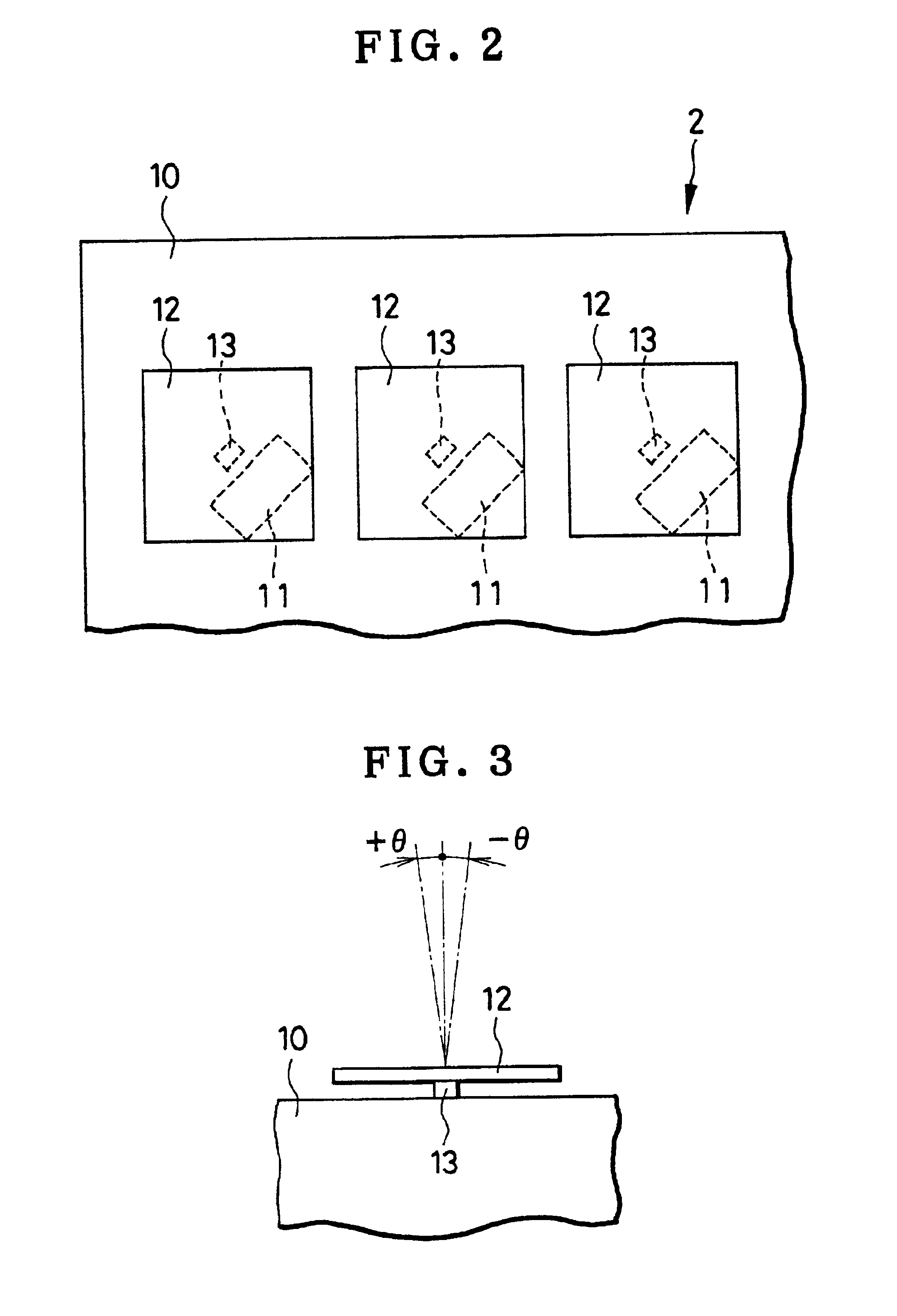
An imaging device for use in ocular investigations and including a body incorporating a light creating projector for issuing a collimated light source. A digital micromirror device being positioned to intercept the collimated light source, the micromirror device reflecting the light source in a specified pattern and in at least one of first and second directions. A control system connected to the micromirror device and interfacing with at least one processor driven input / output device, the control system selectively reflecting the pattern in directions towards and away from a patient's eye.
Owner:SHOWDH
Laser Display Method and System
InactiveUS20120219021A1Television system detailsLaser detailsSpatial light modulatorDigital micromirror device
A laser display system and method that includes some or all of the following parts: an optical apparatus that includes two spatial light modulators and a laser, and switches the laser between the light modulators; two lasers that combine pulses to illuminate one spatial light modulator; controlling a laser Q-switch to stay in CW mode for variable periods of time to generate variable-amplitude pulses; and loading and resetting a digital micromirror device between pulses of light.
Owner:PROJECTION VENTURES INC
Projector device
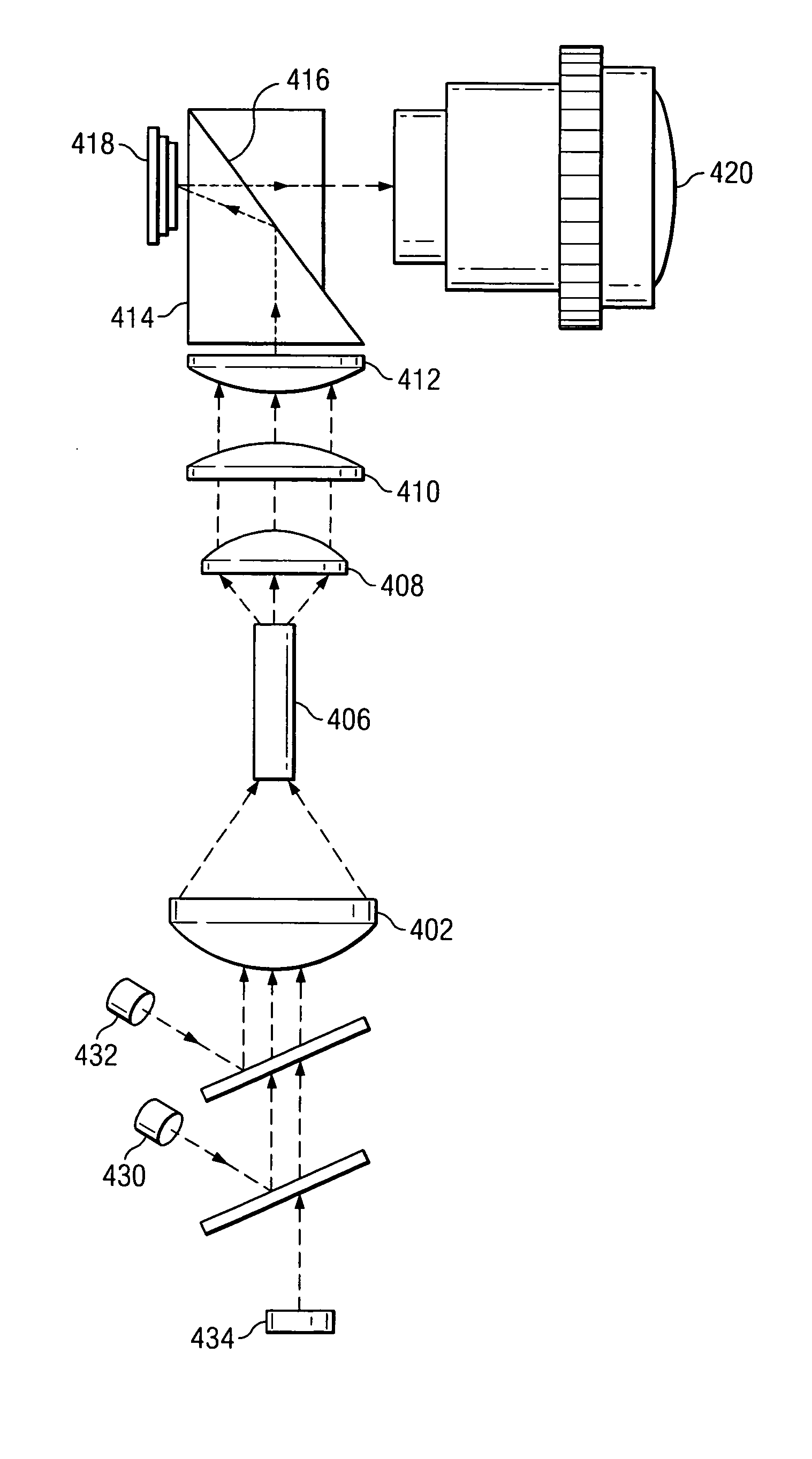
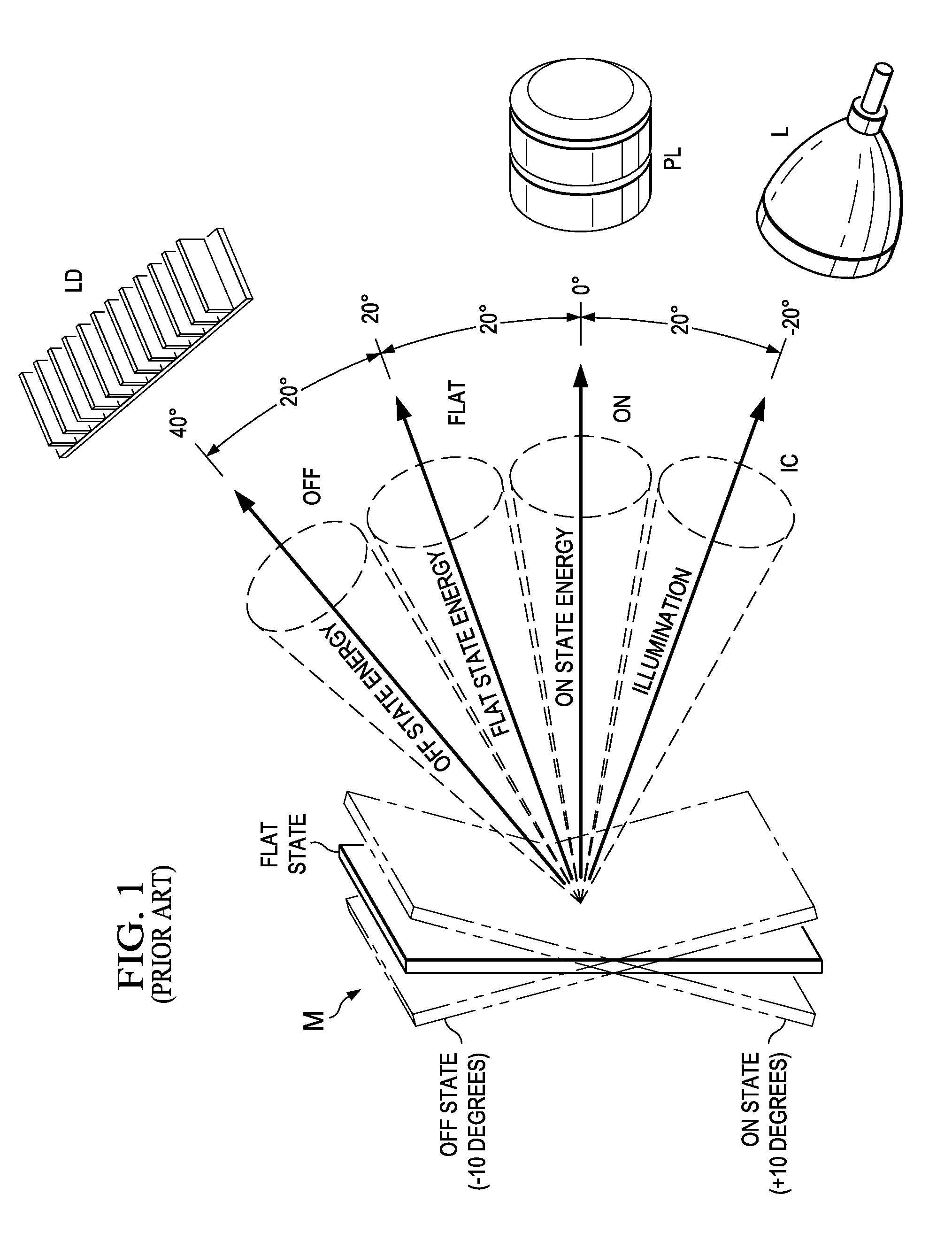
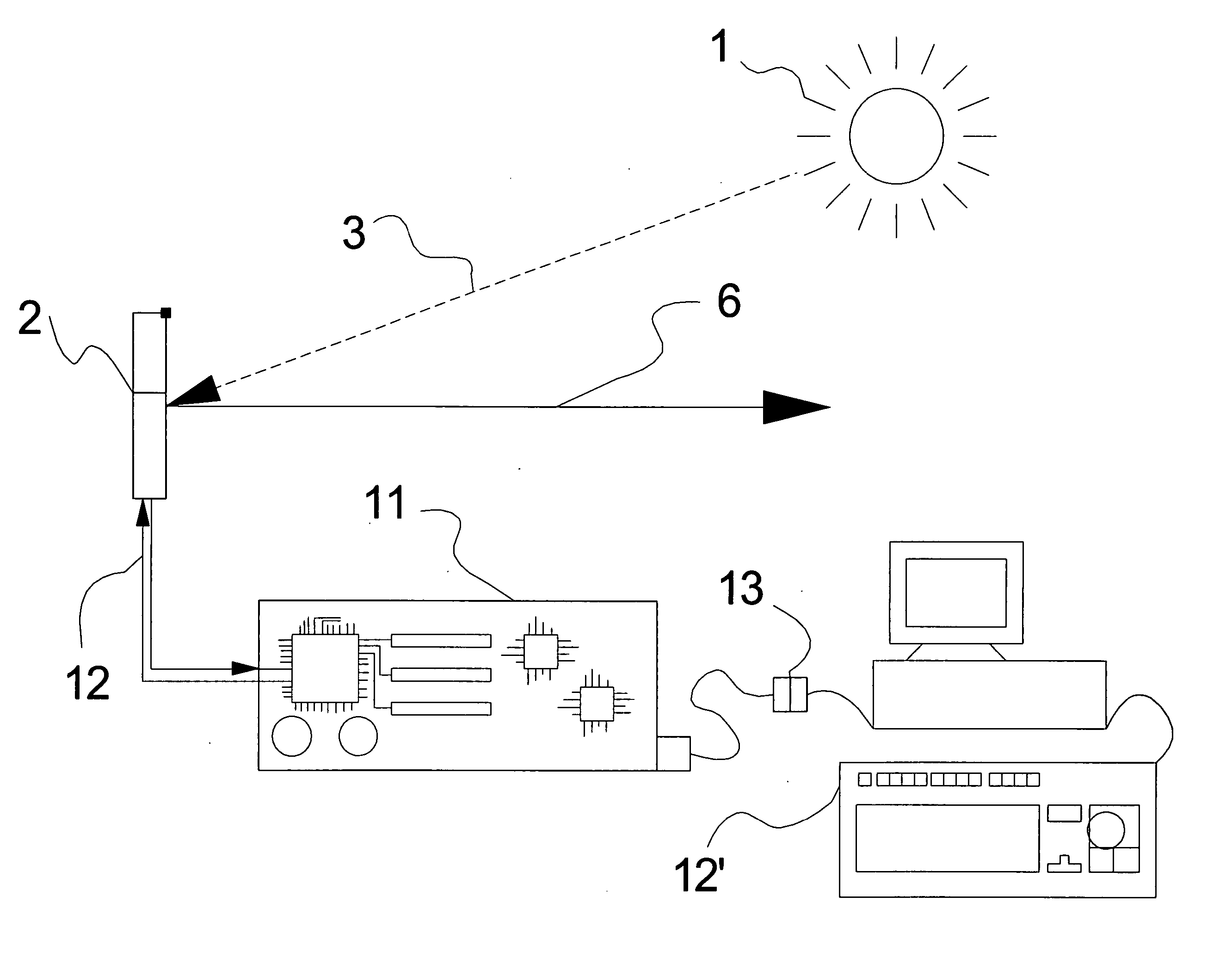
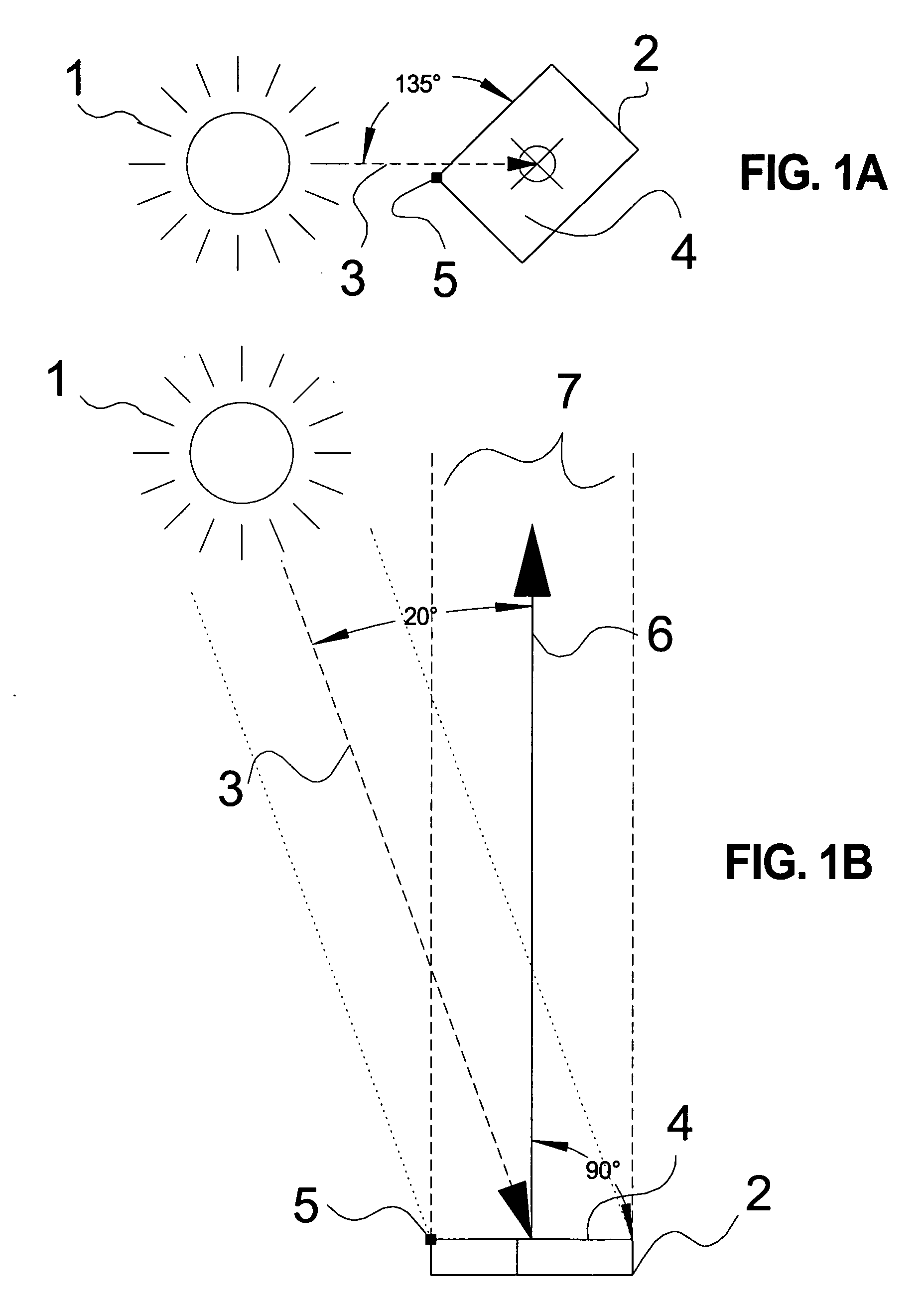
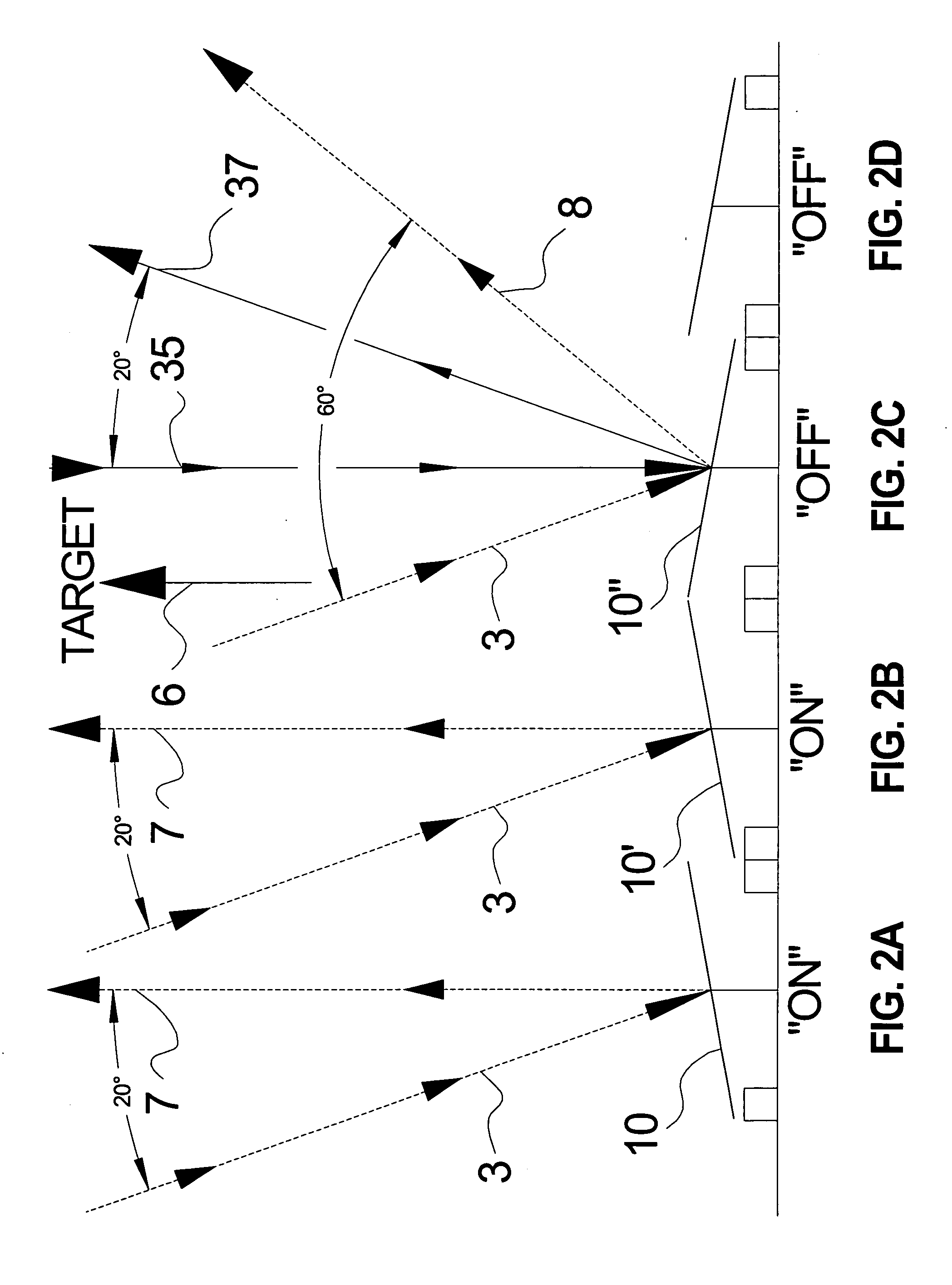
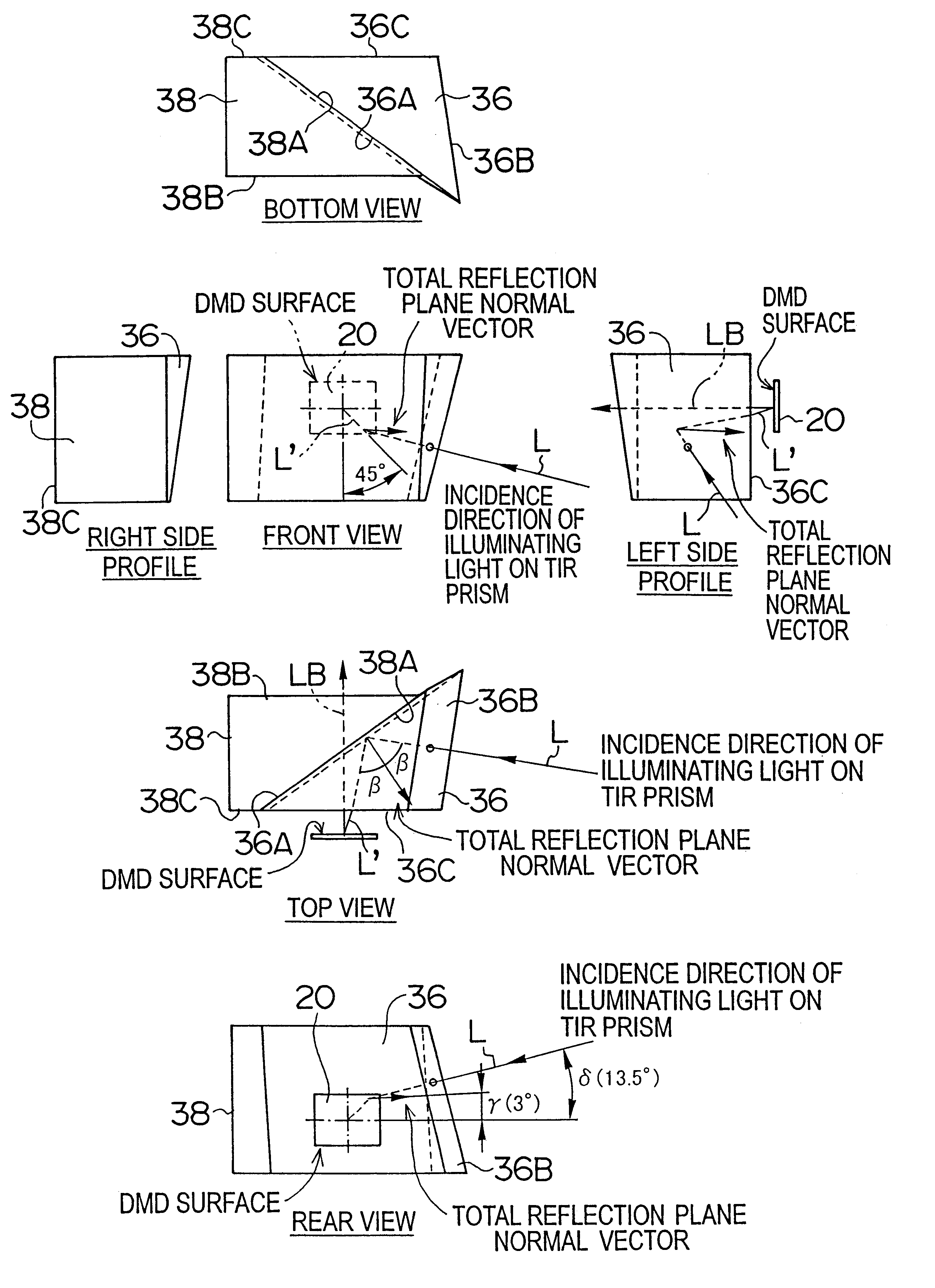
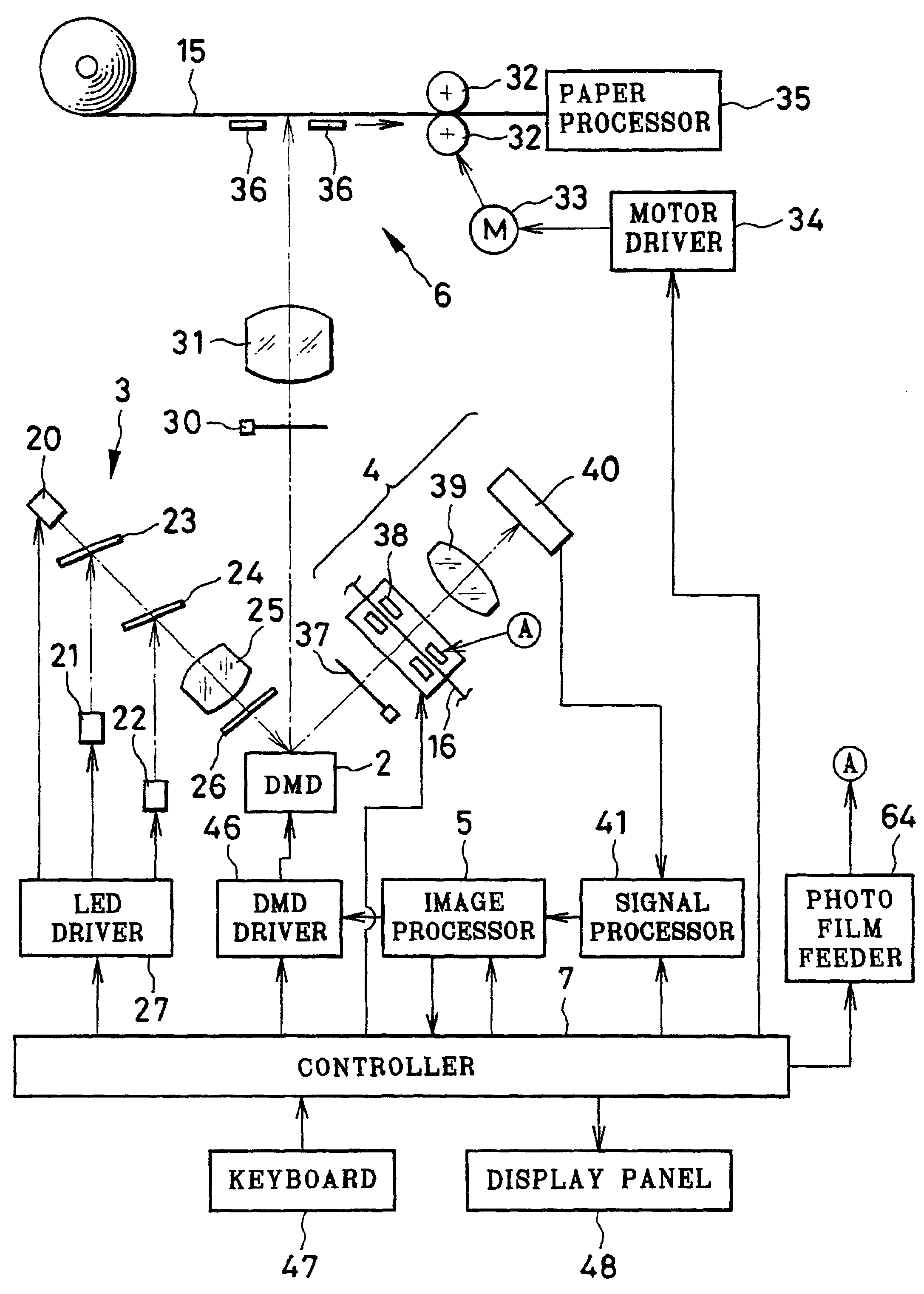
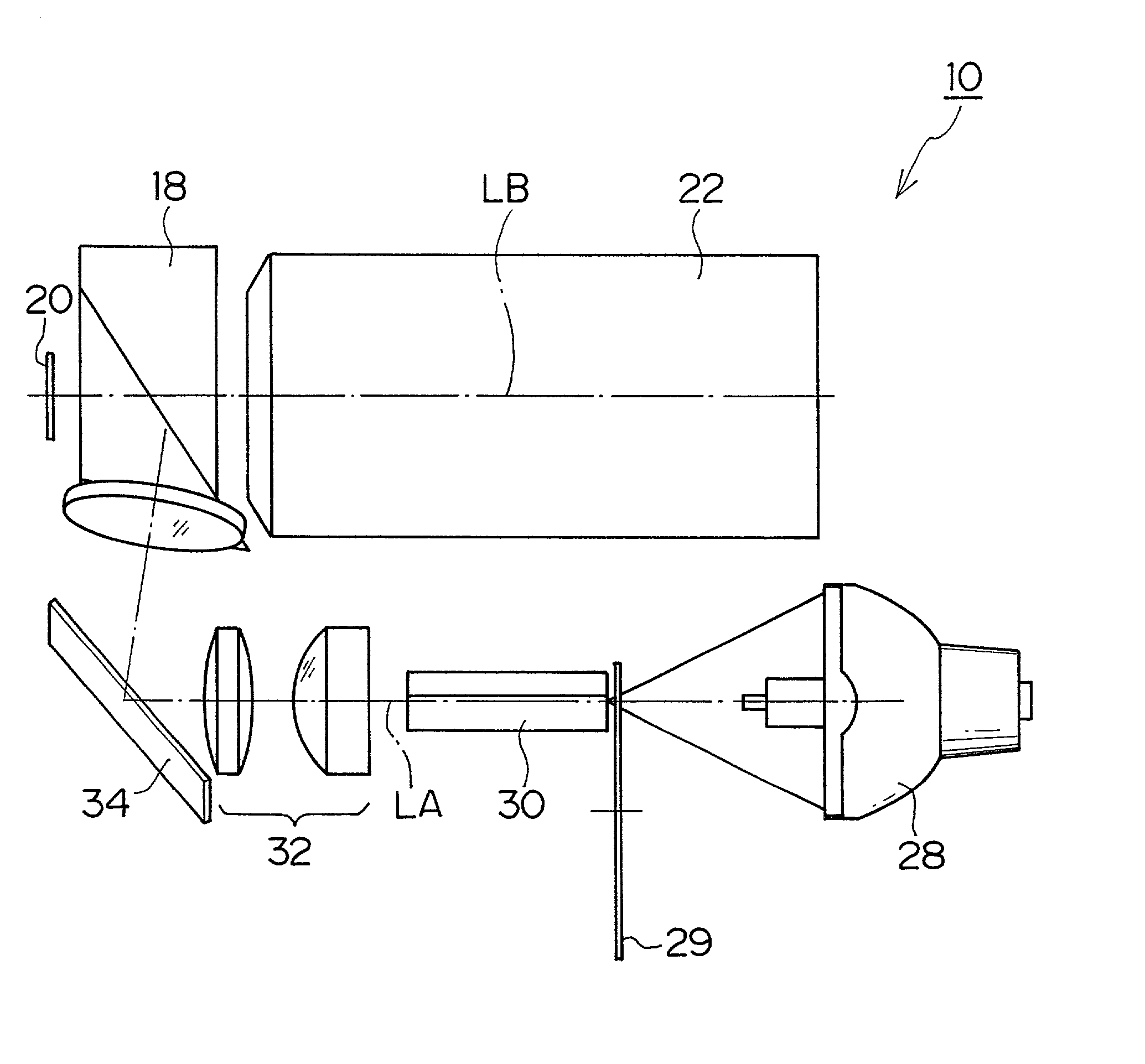
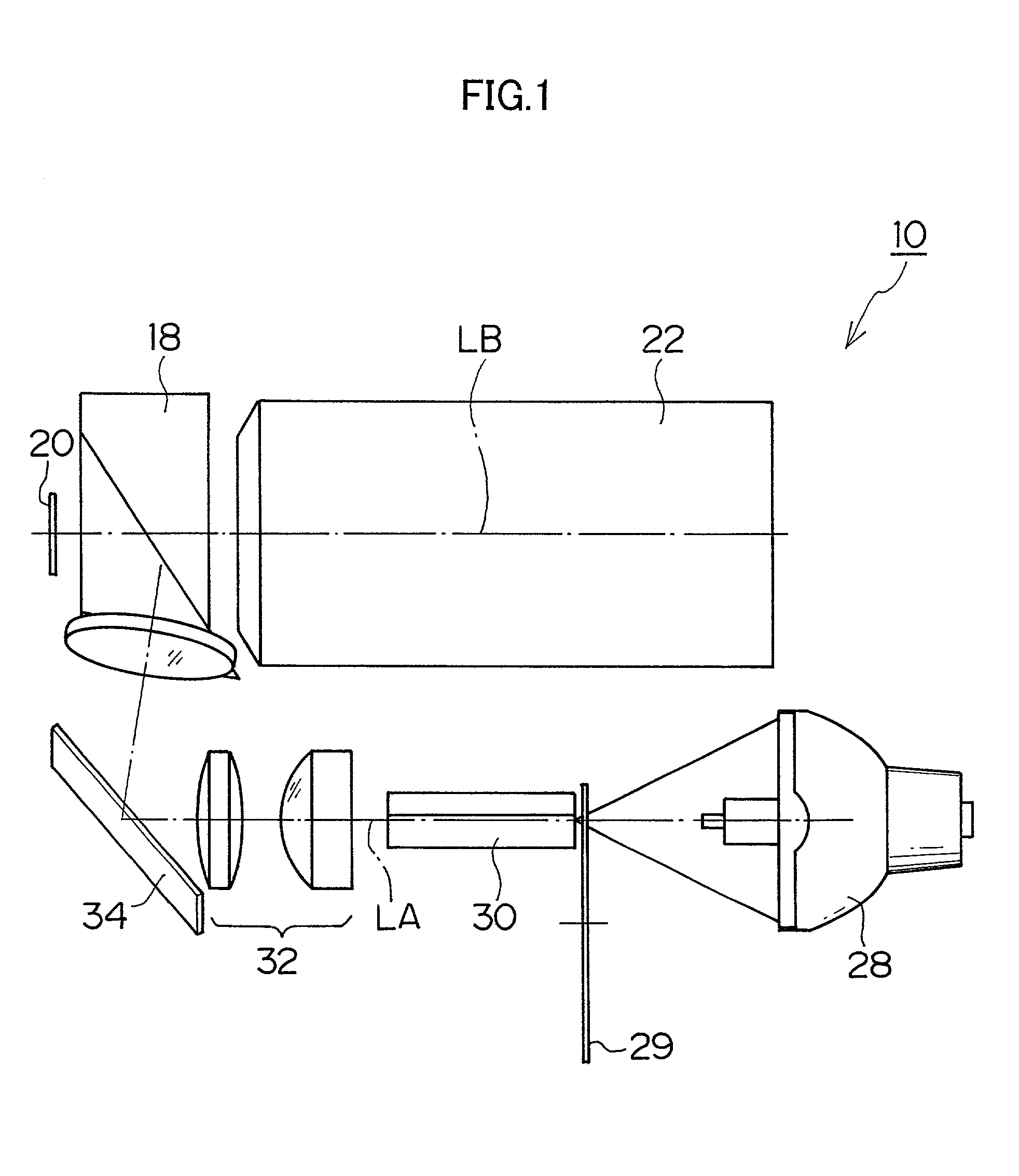
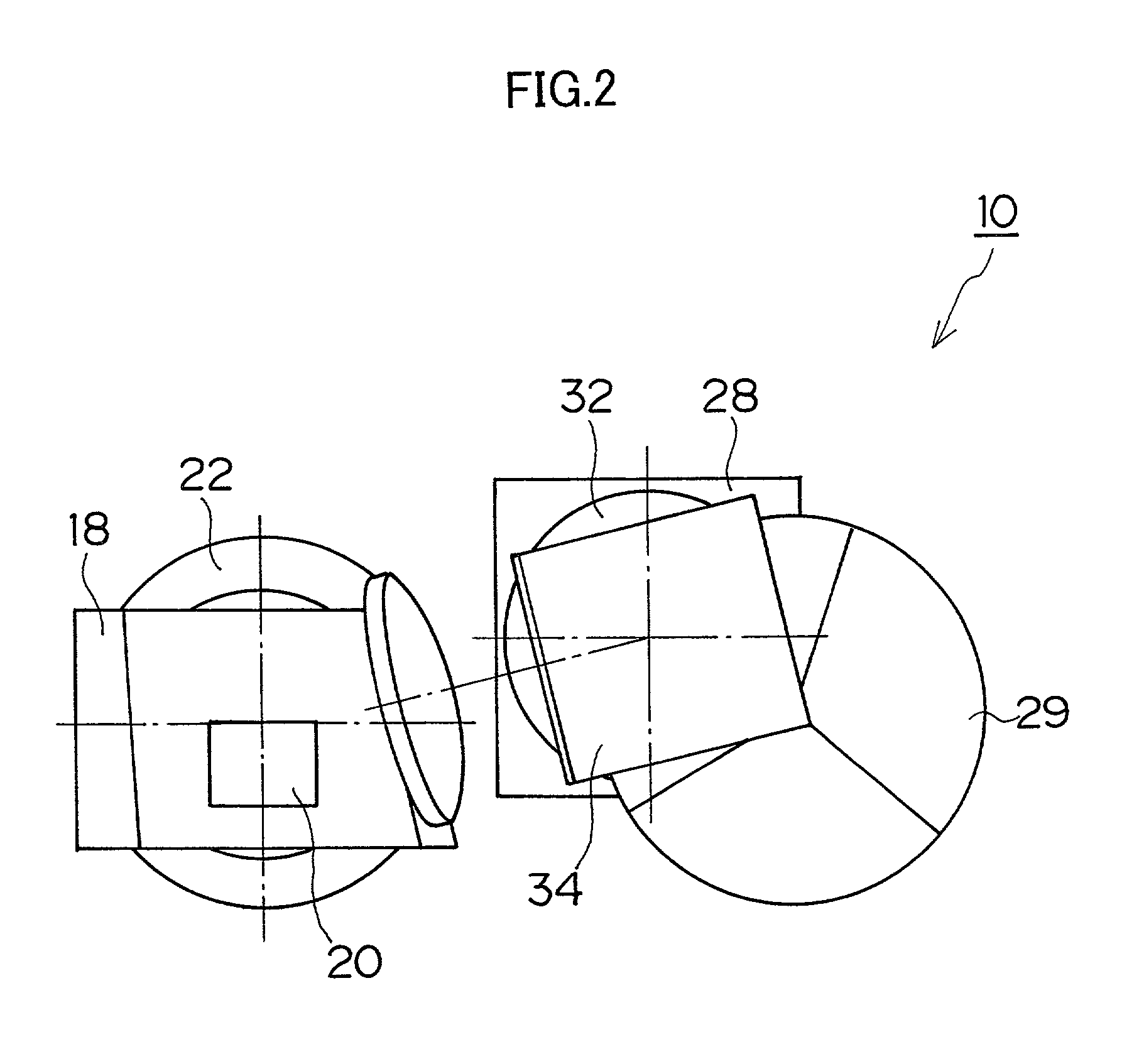
The projector device can be reduced in thickness by using a total internal reflection (TIR) prism wherein the angle formed between a line of projection of the normal vector of the total reflection plane on the surface of a digital micromirror device (DMD) and the long or short side of the DMD is set to be smaller than 45°. The TIR prism has a total reflection plane for totally reflecting illuminating light brought to incidence by an illuminating optical system to guide it to the DMD and totally transmit light optically modulated by the DMD to guide it to a projecting optical system, and this total reflection plane is so arranged relative to the DMD that the angle formed between a line of projection of its normal vector on the surface of the DMD and the long side of the DMD form an angle smaller than 45°. An incidence plane on which the illuminating light is brought to incidence by the illuminating optical system is so formed that the illuminating light brought to incidence vertically on its incidence plane, when totally reflected by the total reflection plane and emitted from an emission plane toward the DMD, be emitted at an incidence angle of 24° to the surface of the DMD in a direction at an angle of 45° to the long side of the DMD.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
Printer and projector equipped with micromirror device
InactiveUS6900825B2Small sizeIncrease speedDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsComputer printingImaging data
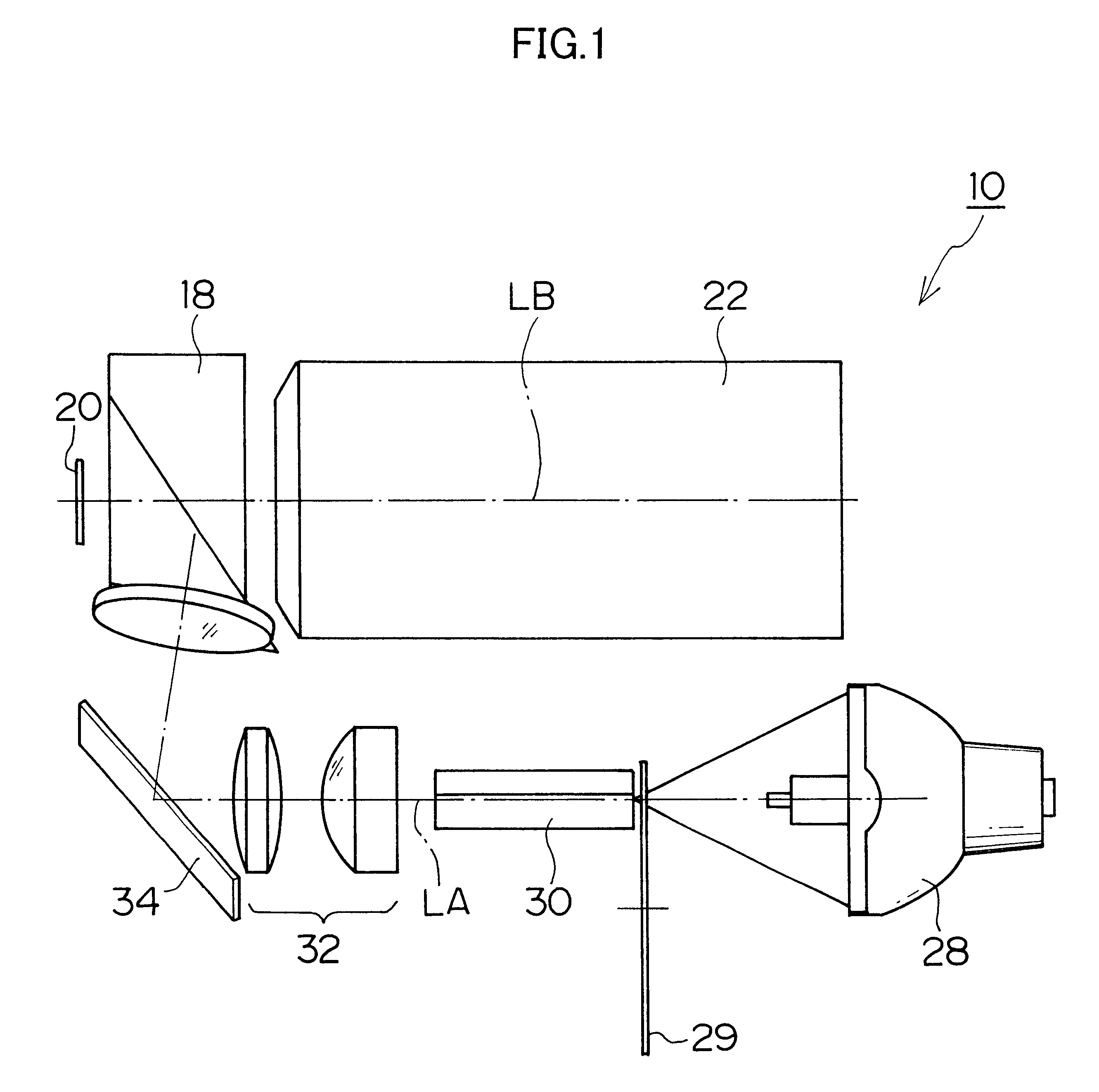
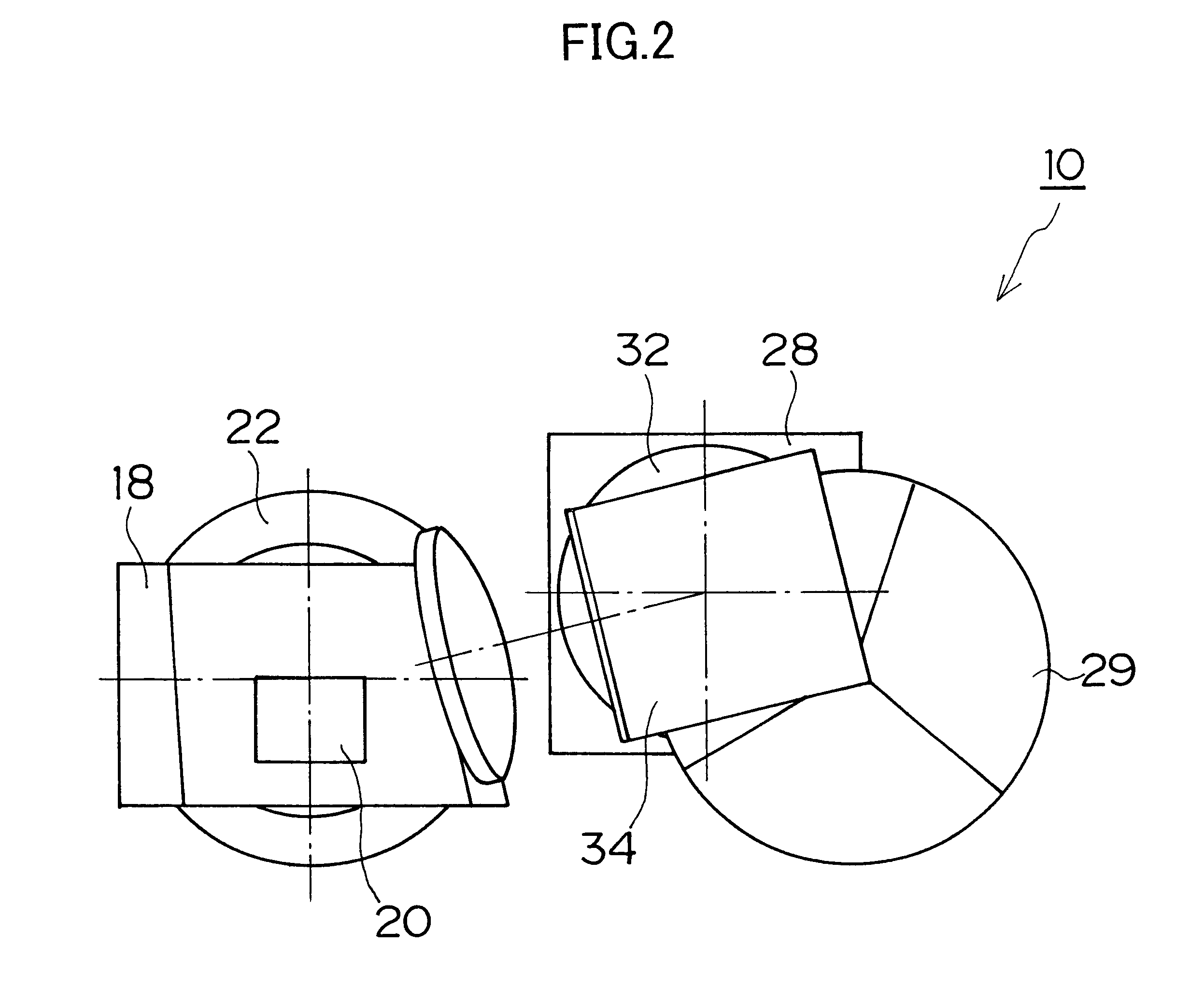
A printer includes an image area sensor for picking up a picture frame in photo film to output image data. A printing projecting lens focuses and records a print frame to color photographic paper. Three LED light sources generate light. A digital micromirror device (DMD) is disposed in a traveling path of the light, includes plural micromirrors arranged in at least one array. The plural micromirrors are individually shiftable between first and second positions different in a direction, and when in the first position, direct the light to the photo film by reflection, and when in the second position, direct the light to the printing projecting lens by reflection. A controller initially sets the plural micromirrors in the first position, to illuminate the picture frame in the photo film while the image area sensor is operated. According to the image data, the controller sets micromirrors in one first group in the DMD to the first position, and sets micromirrors in a second group in the DMD to the second position except for the first group, to modulate the light by reflection on the second group. Thus, the print frame is printed with the printing projecting lens.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
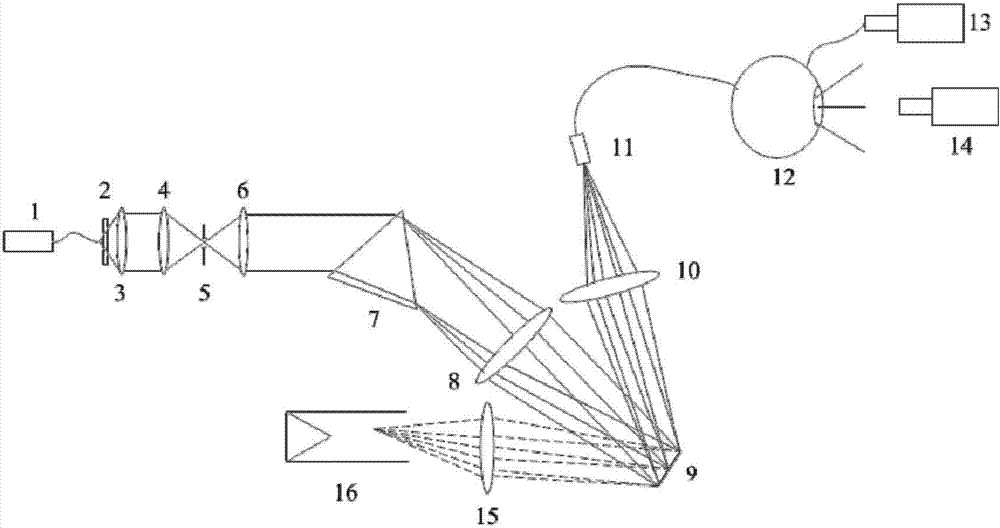
Spectrum programmable light source system applied to hyper-spectrum calibration
ActiveCN103196555AReduce uncertaintyAccurate RadiometryRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsOptical radiationRadiometer
The invention discloses a spectrum programmable light source system applied to hyper-spectrum calibration. The spectrum programmable light source system applied to hyper-spectrum calibration comprises a light source. An optical filter, a collimation system, a cylindrical lens coupled system, a slit, a collimation objective and a dispersion element are sequentially placed on a light path in front of the light source, an imaging system and a digital micromirror device are sequentially arranged on a light path in front of the dispersion element, a light collection lens and an optical fiber coupler are arranged on a light path of useful light modulated by the digital micromirror device, wherein the optical fiber coupler is connected with a integrating sphere, a light splitting radiometer is arranged on the integrating sphere, and feedback control is conducted and target spectrums are simulated through a spectrum simulation program and monitoring the light splitting radiometer. A focusing system and a garbage light collector are sequentially arranged on a light path of garbage light modulated by the digital micromirror device, and the garbage light is eliminated. The spectrum programmable light source system applied to hyper-spectrum calibration can simulate accurately the target spectrums and reduce the effect of inconsistence of calibration light source spectrums and the target spectrums to a calibration result. The spectrum programmable light source system applied to hyper-spectrum calibration accurately measures radiation quantity, and is favorable to improving optical radiation calibration accuracy of a sensor.
Owner:合肥中科九衡科技有限公司
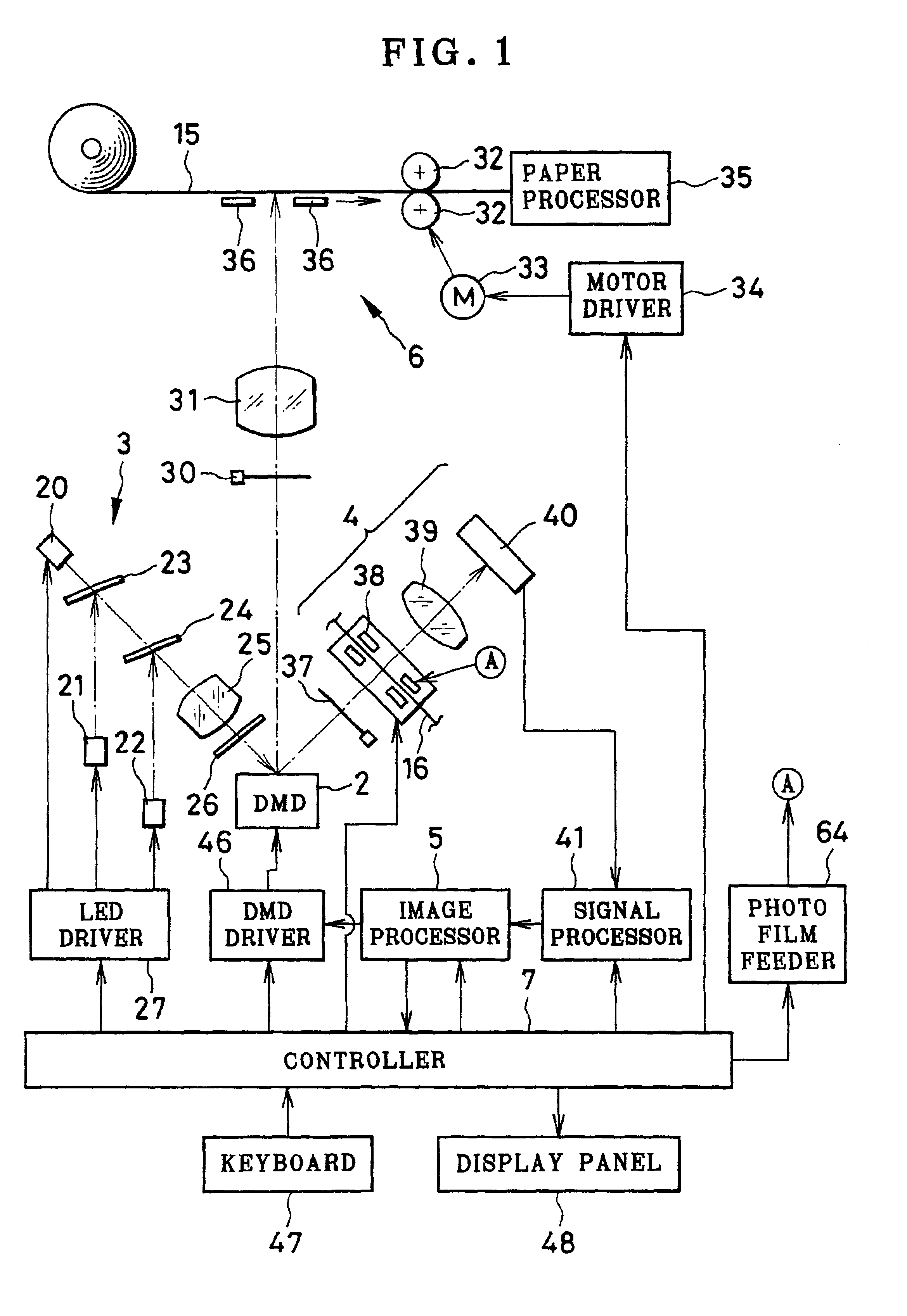
Projector device
The projector device can be reduced in thickness by using a total internal reflection (TIR) prism wherein the angle formed between a line of projection of the normal vector of the total reflection plane on the surface of a digital micromirror device (DMD) and the long or short side of the DMD is set to be smaller than 45°. The TIR prism has a total reflection plane for totally reflecting illuminating light brought to incidence by an illuminating optical system to guide it to the DMD and totally transmit light optically modulated by the DMD to guide it to a projecting optical system, and this total reflection plane is so arranged relative to the DMD that the angle formed between a line of projection of its normal vector on the surface of the DMD and the long side of the DMD form an angle smaller than 45°. An incidence plane on which the illuminating light is brought to incidence by the illuminating optical system is so formed that the illuminating light brought to incidence vertically on its incidence plane, when totally reflected by the total reflection plane and emitted from an emission plane toward the DMD, be emitted at an incidence angle of 24° to the surface of the DMD in a direction at an angle of 45° to the long side of the DMD.
Owner:FUJI PHOTO OPTICAL CO LTD
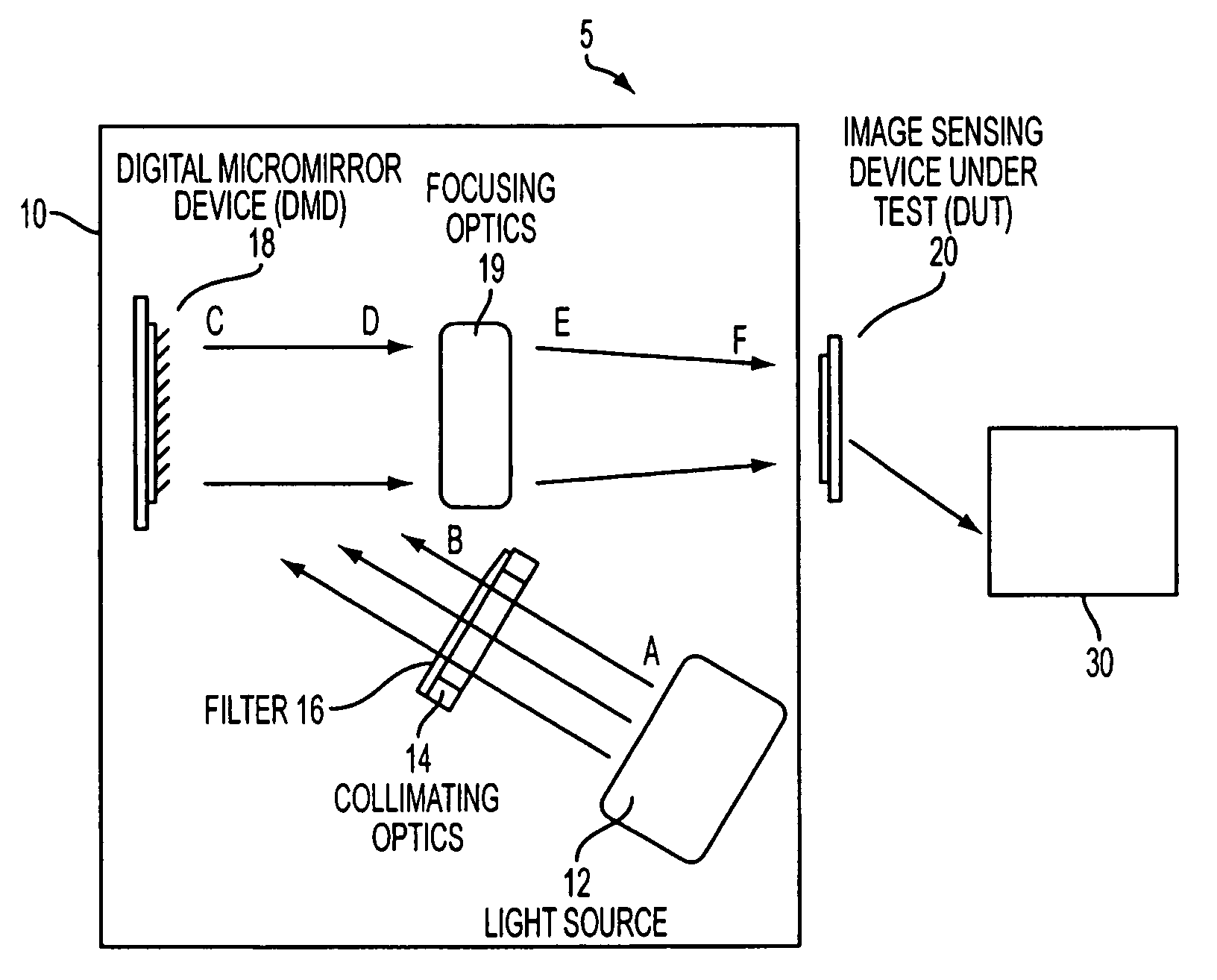
Method and apparatus for testing image sensors
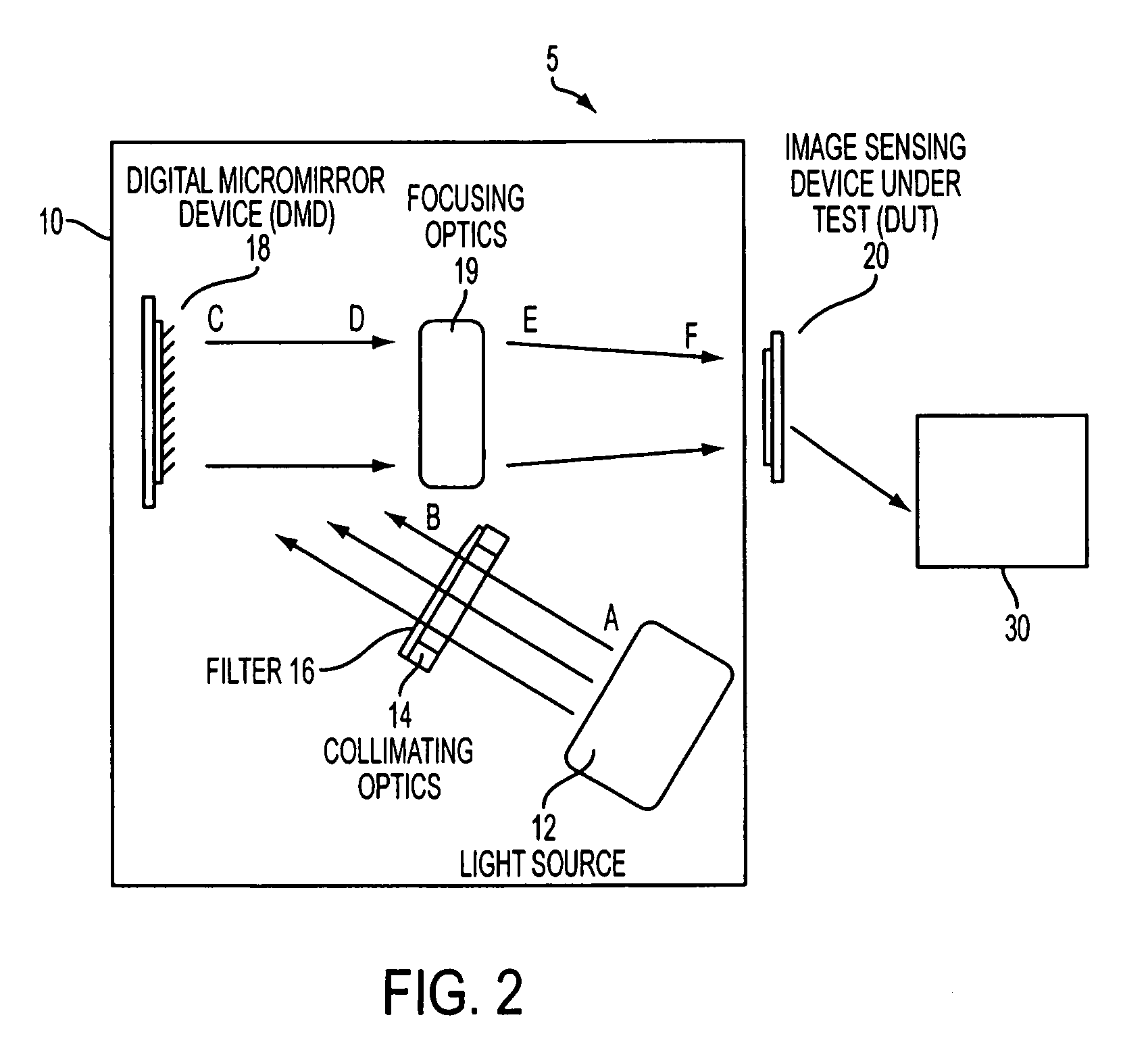
ActiveUS7136157B2Television system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansProjection systemDigital micromirror device
Methods and apparatuses for testing image sensors are disclosed. Desirable apparatuses of the present invention include image sensor testing devices comprising a digital light projection system capable of projecting static or dynamic images onto an image sensing device under test and an image sensor signal detection means for analyzing the output of said image sensing device under test. The digital light projection system comprises a light source, collimating optics, a digital micromirror device, and focusing optics. Other desirable methods and apparatuses of the present invention include image sensor testing devices employing a digital light projection system capable of simultaneously testing a plurality of image sensors. According to the present invention, the light source is calibrated and converted to a desired test image by the digital micromirror device. The test image is then focused onto an image sensor, the output of which is read by a detector and correlated with the input digital test image.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
High-speed Binary Laser Beam Shaping and Scanning
ActiveUS20170082845A1High shapingHigh scanning rateTelevision system detailsColor television detailsFrequency spectrumLight beam
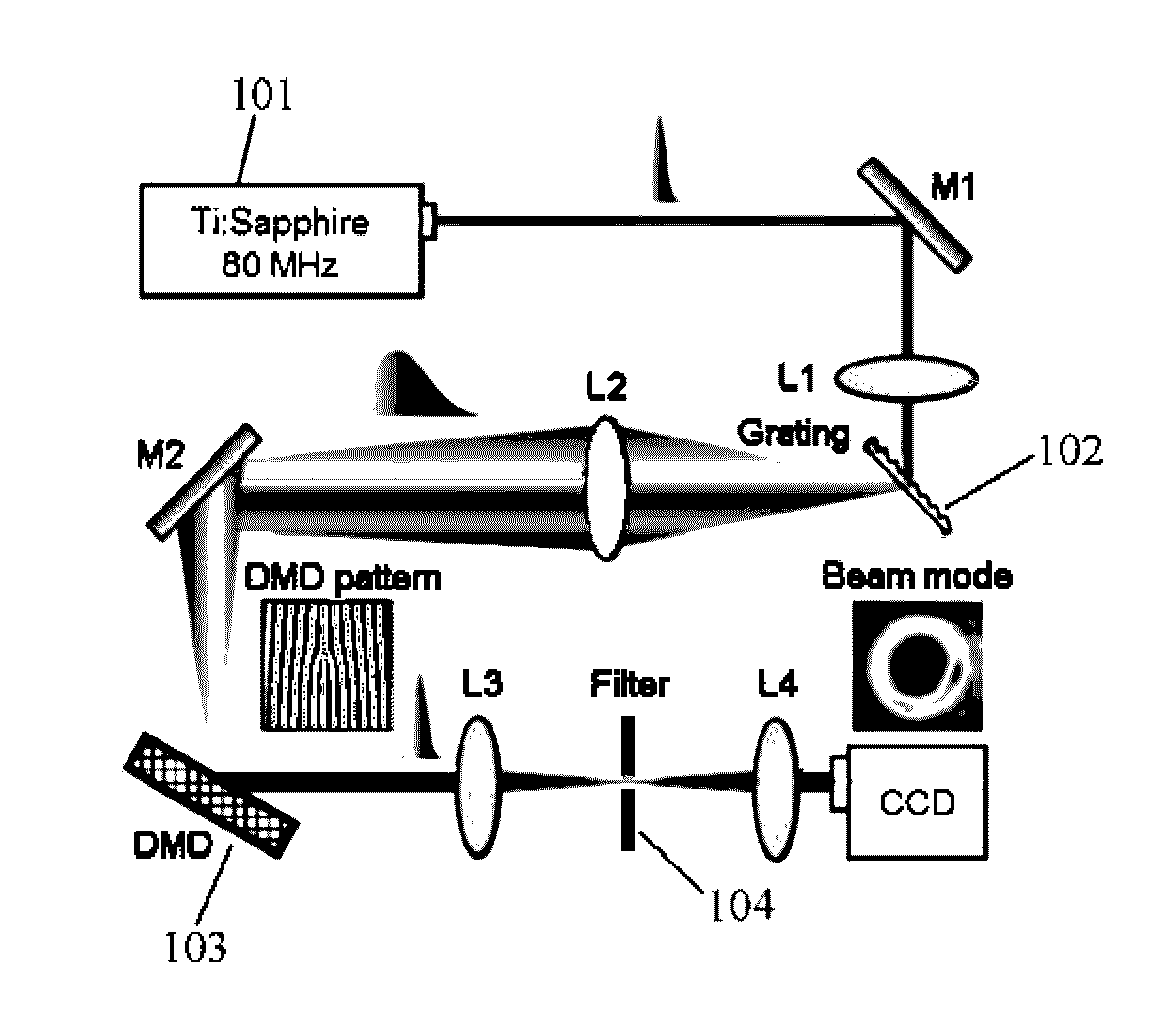
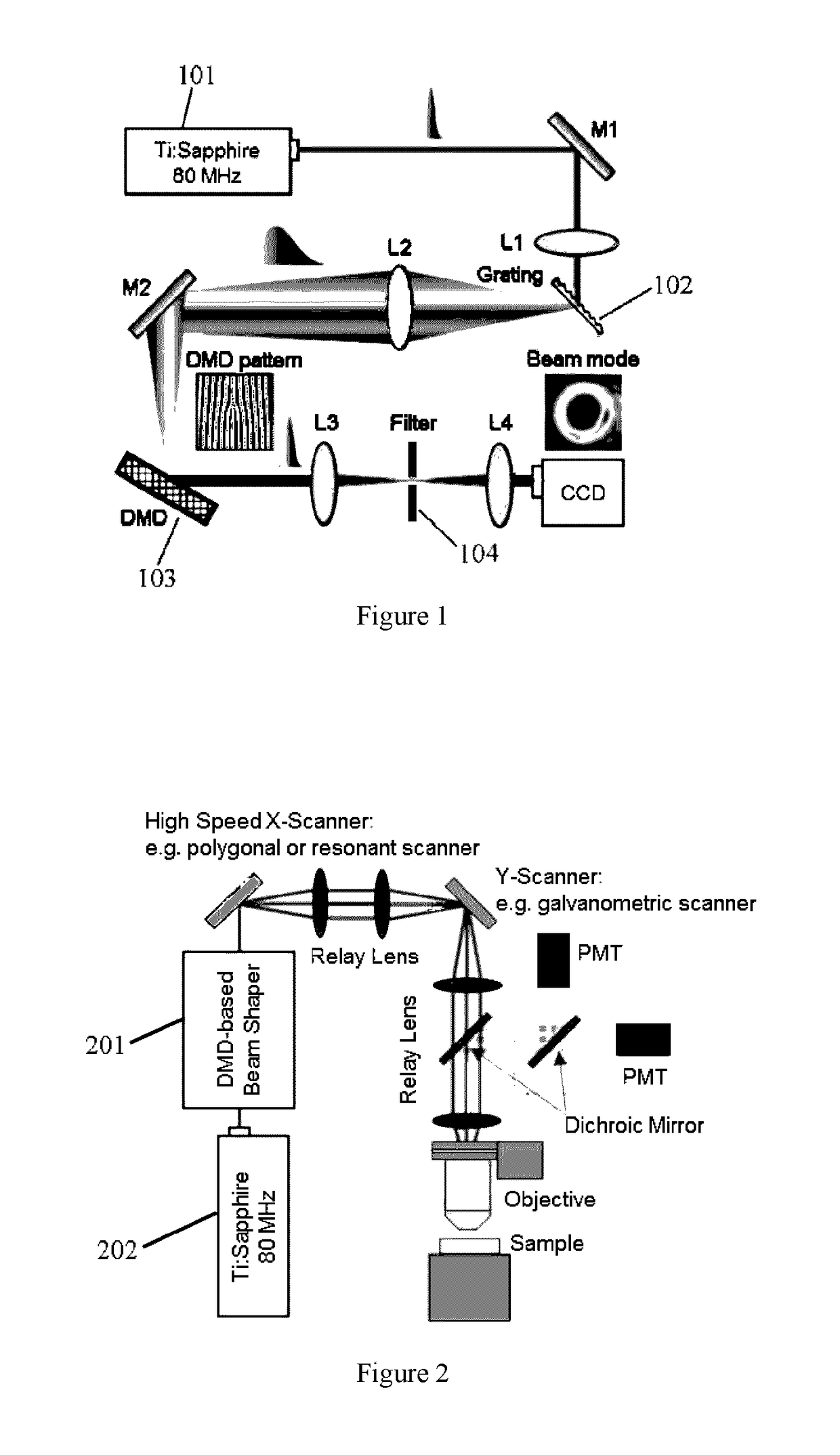
A device for shaping and scanning an ultrafast laser beam including a laser source configured to output a pulsed laser beam containing different frequency spectrum; a digital micromirror device (DMD) consisting of a plurality of micromirrors, configured to receive the laser beam and shape the received laser beam with a first angular dispersion; and a dispersion compensation unit, arranged before or after the DMD, configured to transfer the laser beam from the laser source to the DMD with a second angular dispersion for neutralizing the first angular dispersion.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Portable raman spectrometer based on spectral analysis of micro electro mechanical system
InactiveCN103196889AMaintain detection resolutionHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringRayleigh scatteringLine width
The invention provides a portable raman spectrometer based on spectral analysis of a micro electro mechanical system. On the basis of the micro electro mechanical system, the portable raman spectrometer comprises a laser light source, a raman probe head and a spectrum detection system of a spectrograph, wherein the laser light source comprises a semiconductor laser which is used for generating lasers, the power of the generated lasers is not less than 200 milliwatts, and the line width of the generated lasers is not greater than 0.2 nanometers; the raman probe head comprises a laser outputting optical path and a raman scattered light collecting optical path which does not comprise a light filter for filtering rayleigh scattered light; and the spectrograph comprises the spectrum detection system which sequentially consists of a focusing lens I, a digital micromirror device (DMD) module I, a collimating lens, a chromatic dispersion optical grid, a focusing lens II, a digital micromirror device (DMD) module II, a de-chromatic dispersion optical grid, a focusing lens III, a single-point detector and a signal processor. The portable raman spectrometer has the advantages of being capable of keeping the resolution ratio of spectrum detection and improving the sensitivity of spectrum detection, being suitable for detection on weak signals such as raman signals, and the like.
Owner:许春 +2
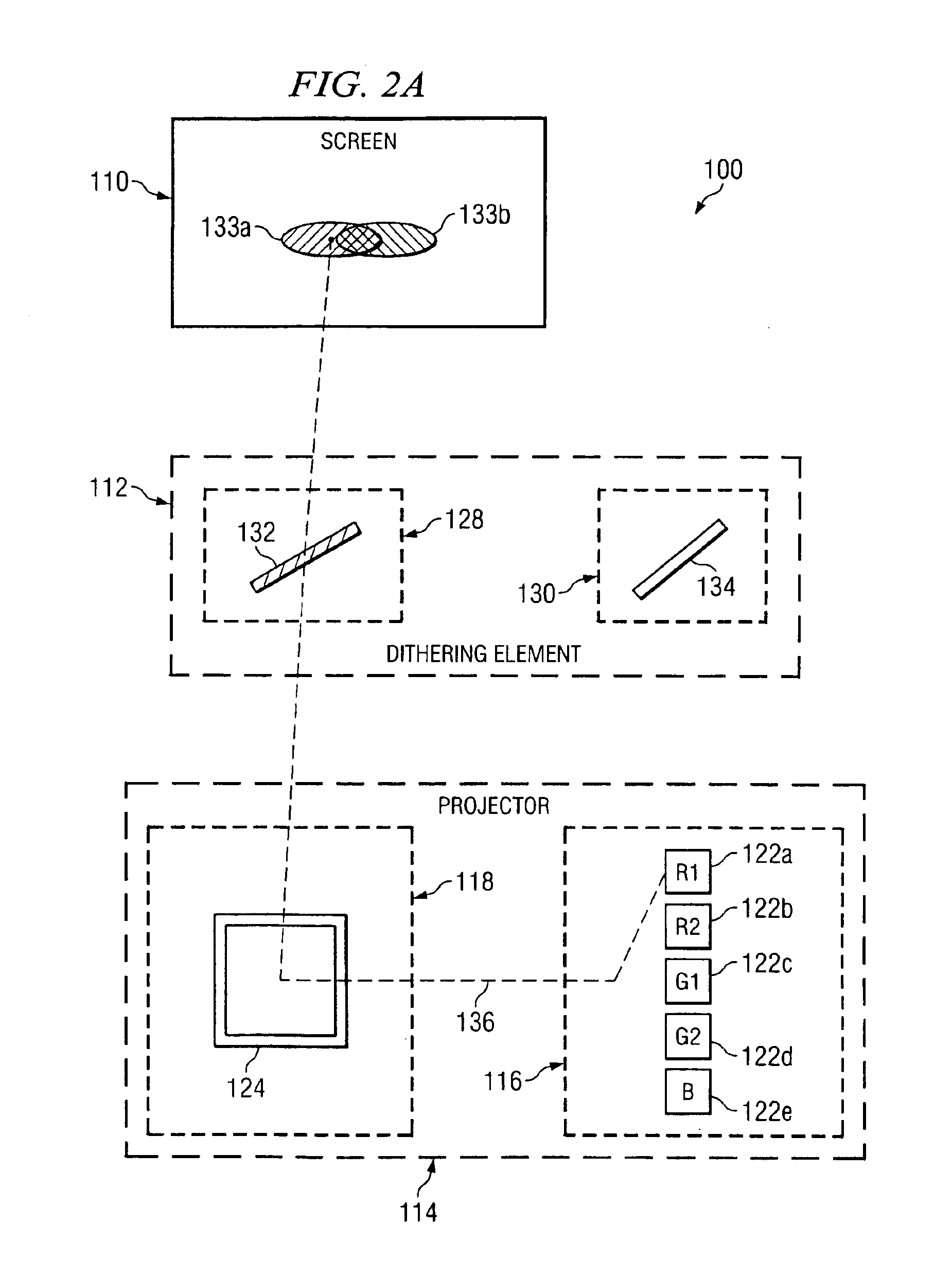
Wavelength discriminated image dithering
ActiveUS6906852B1Enhance the imageTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesLight beamLength wave
A method and system for providing a dithered image is provided. In one embodiment, a projector system for providing a dithered image includes a light source comprising a first and a second light emitting diode (LED). The first LED is operable to transmit a first light beam at a first peak wavelength. The second LED is operable to transmit a second light beam at a second peak wavelength. The first peak wavelength is disparate from the second peak wavelength. A digital micromirror device (DMD) is operable to receive the first beam and the second beam and selectively pass a first portion of the first beam and a second portion of the second beam along a projection path. A dichroic reflector operable to receive the first portion and the second portion, passively pass the first portion along the projection path, and substantially reflect the second portion within a wavelength range. An optical mirror operable to receive the substantially reflected second portion and reflect the substantially reflected second portion along an offset path.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
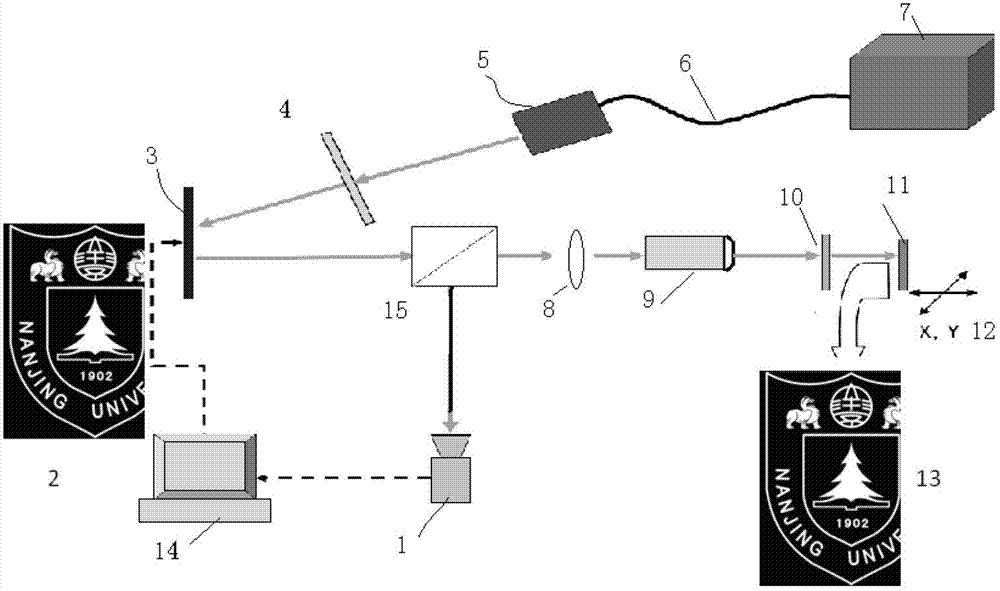
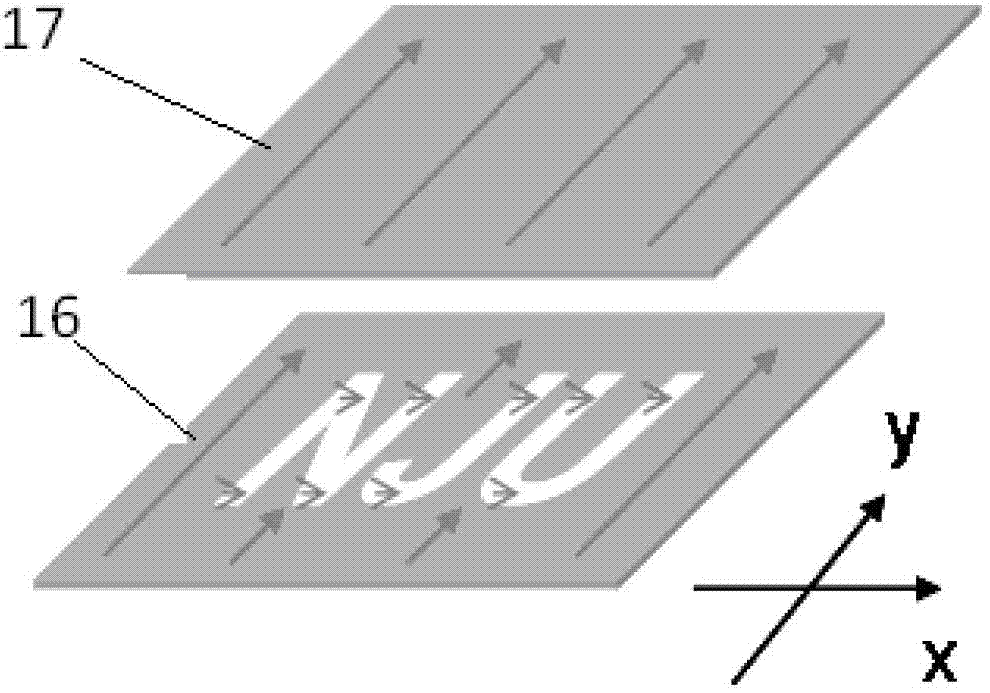
Method and device for realizing liquid crystal arbitrary orientation control through numerical control micromirror array photoetching
InactiveCN102768472AReduce manufacturing costAvoid graphic distortionPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusNumerical controlUltraviolet
A method for realizing liquid crystal arbitrary orientation control through numerical control micromirror array photoetching utilizes a set of projection photoetching system based on a digital micromirror device (DMD), so the collimated ultraviolet or blue light beams are uniformly irradiated to the surface of the numerical control micromirror array DMD, a computer outputs a shape signal to control all the DMD pixels, i.e. single micromirrors are in different reflection states for realizing intermediate photomask, so the all the DMD pixel reflected lights carry out the shape signal control; the beams are demagnified by a microobjective, and then are projected onto a substrate which has the surface coated with a light-operated orientation material through a polarizing film, exposure is completed through controlling the light intensity and time, and the liquid crystal of an exposure pattern area is reorientated; and another substrate is utilized to form a liquid crystal cell, the liquid crystal cell is filled with the liquid crystal, so preset orientation is realized. The method realizes the control and production of arbitrary patterns and orientation directions, and has a potential important application in the fields of wide viewing angle liquid crystal display, adjustable optical communication devices, wavefront correction, light beam control and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com