Patents
Literature
239 results about "Maskless lithography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
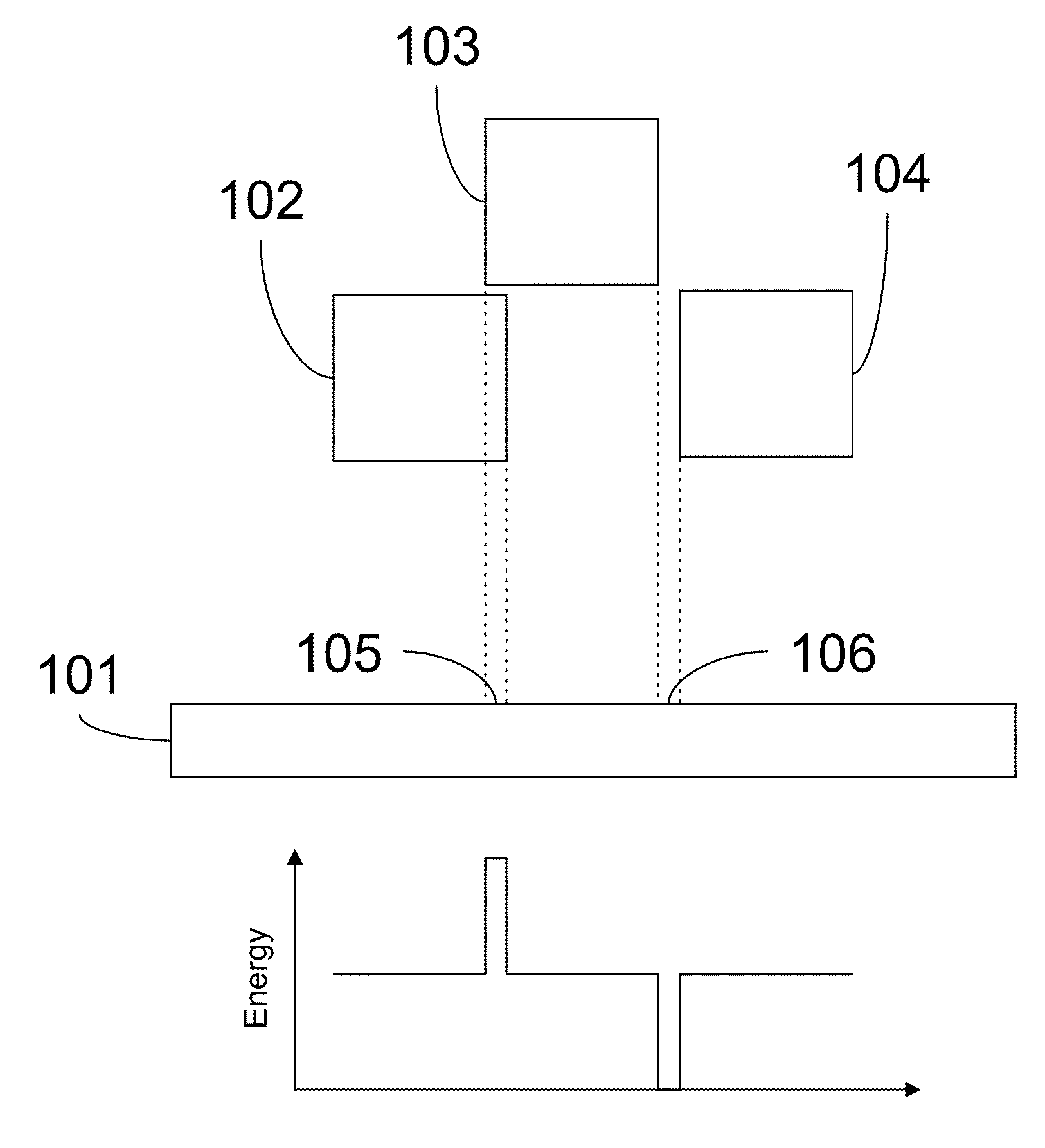
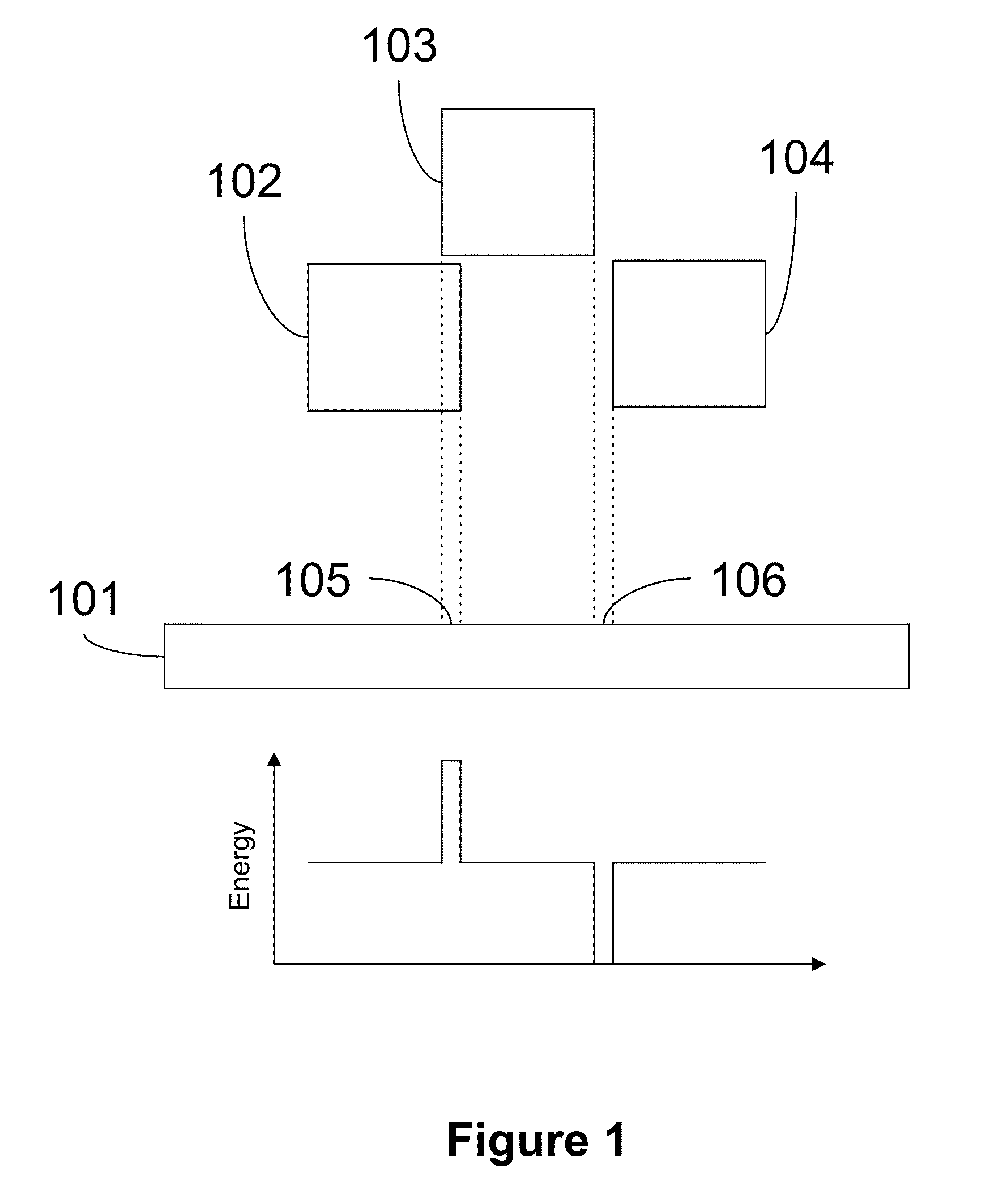
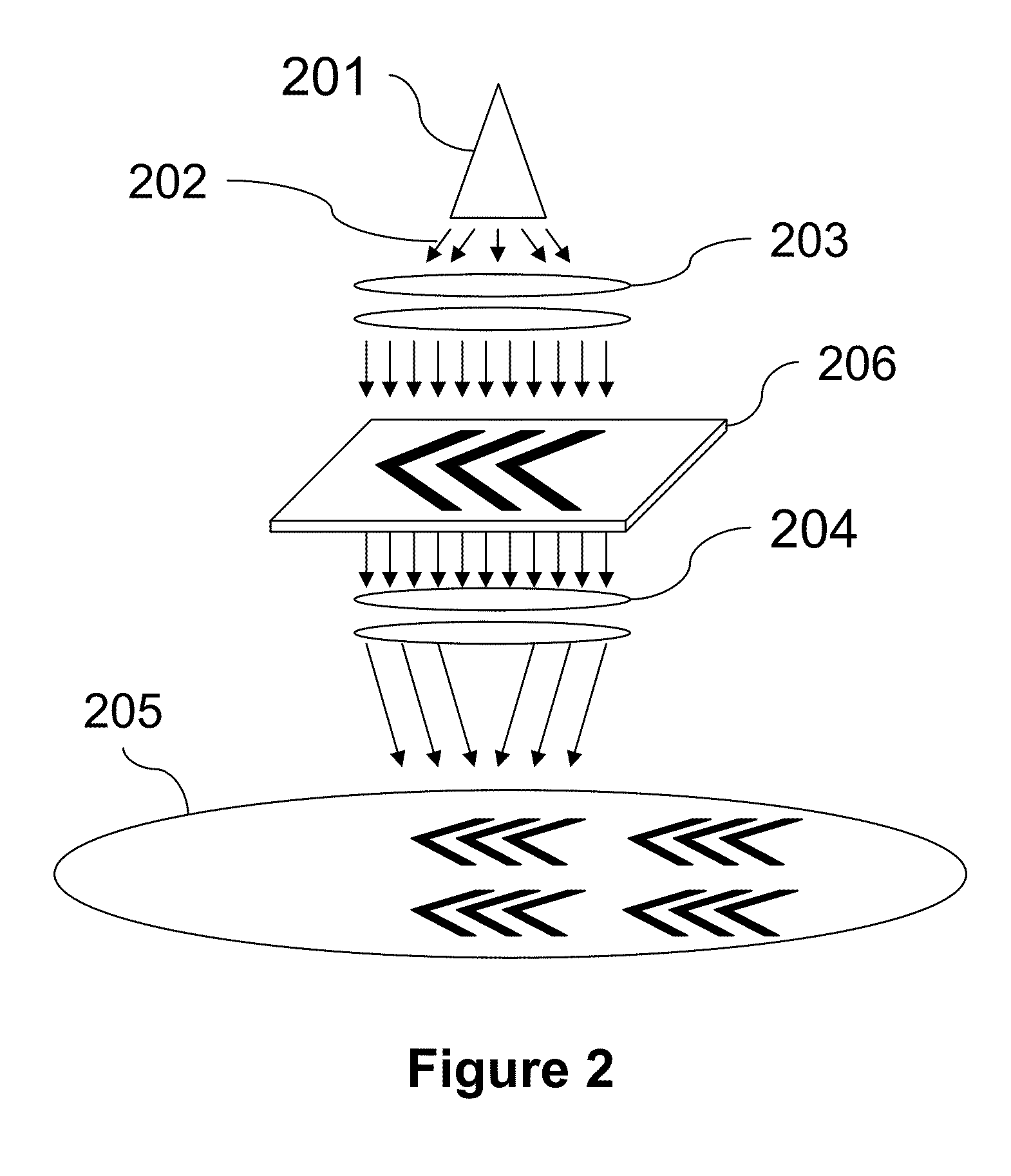
Maskless lithography utilizes methods that directly transfer the information onto the substrate, without utilizing an intermediate static mask, i.e. photomask that is directly replicated. In microlithography typically radiation transfer casts an image of a time constant mask onto a photosensitive emulsion (or photoresist). Traditionally mask aligners, steppers, scanners, but also other non-optical techniques for high speed replication of microstructures are common. The concept takes advantage of high speed or parallel manipulation technologies that have been enabled by large and cheap available computing capacity, which is not an issue with the standard approach that decouples a slow, but precise structuring process for writing a mask from a fast and highly parallel copy process to achieve high replication throughputs as demanded for in industrial microstructuring.
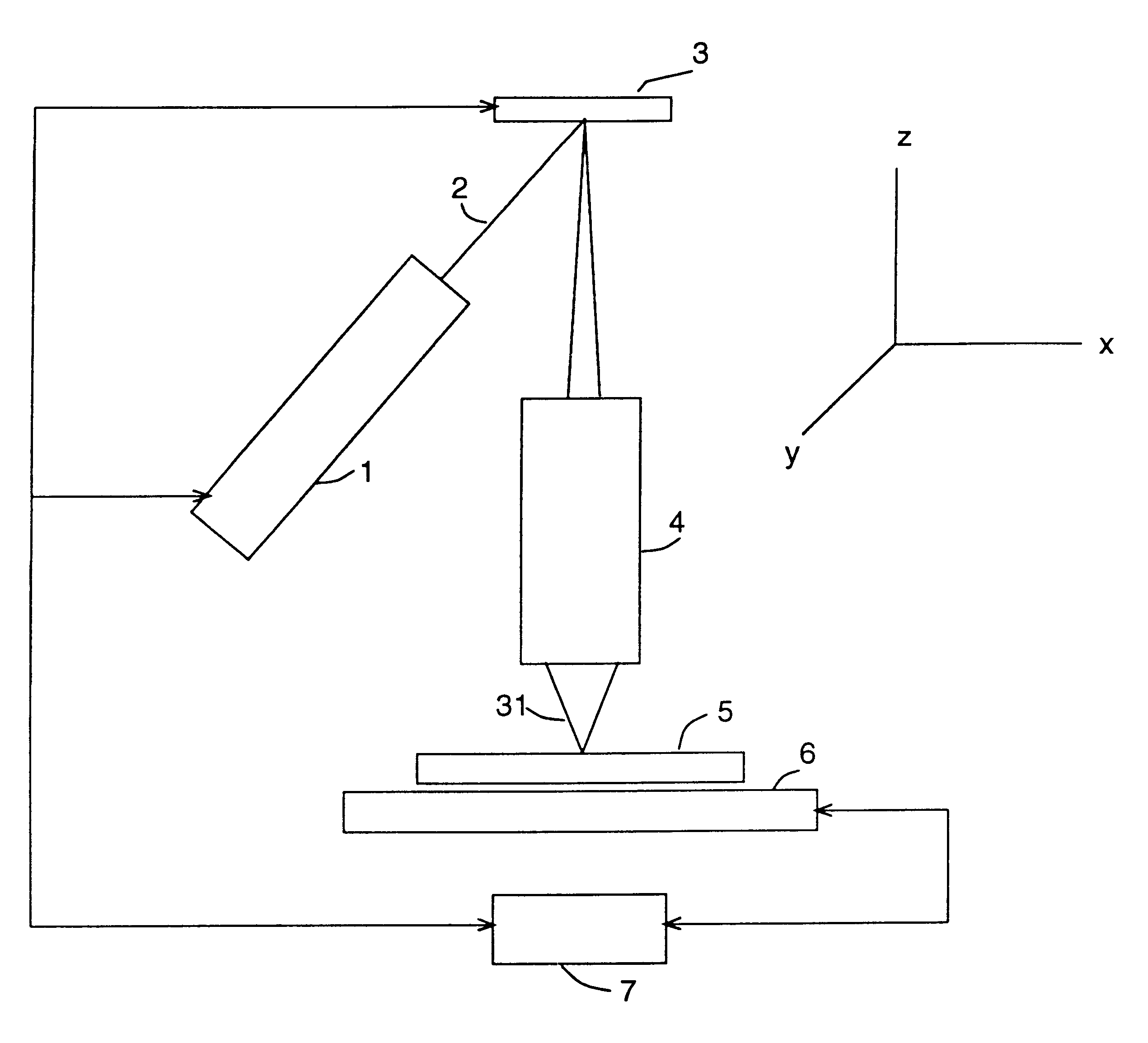
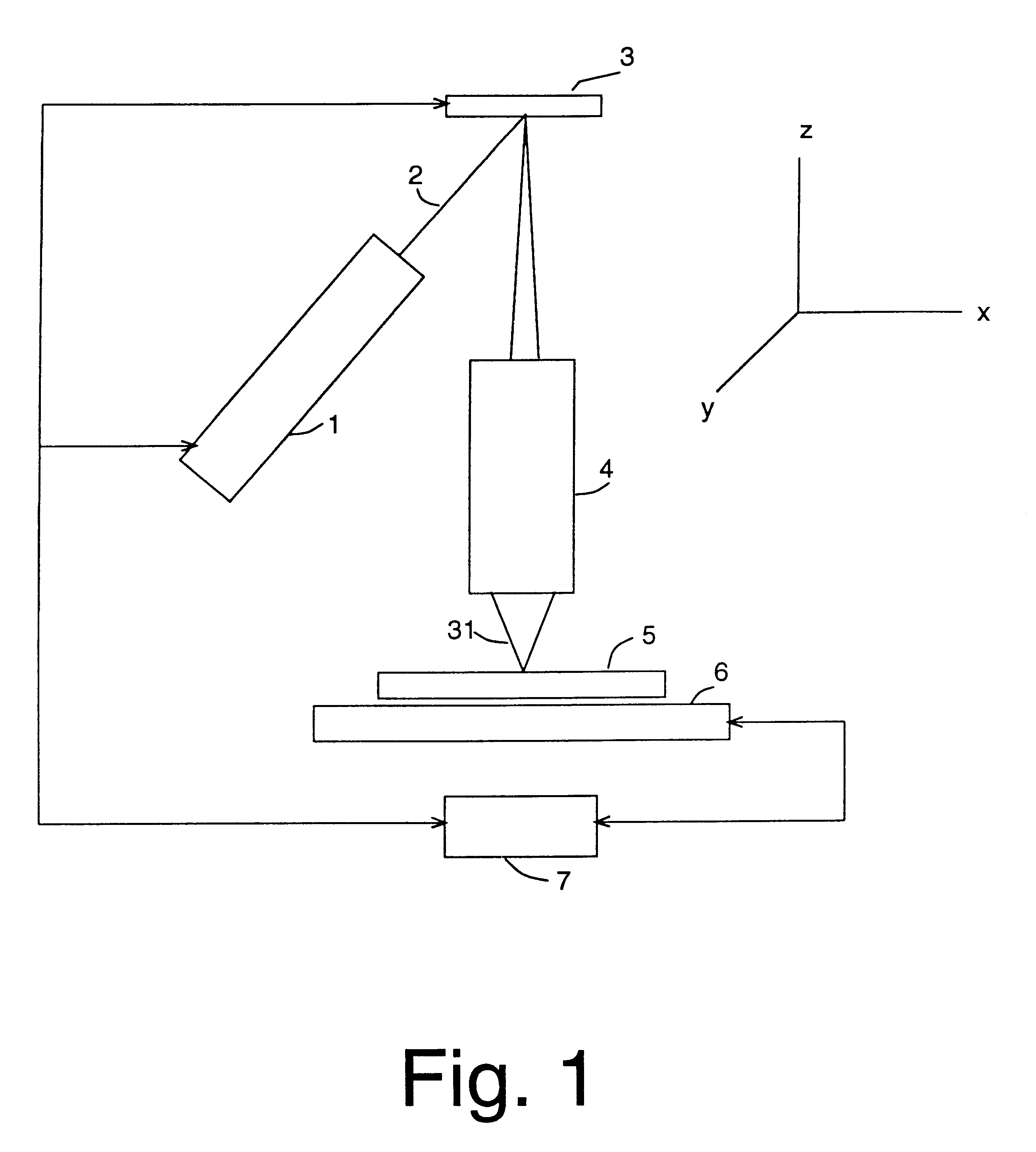
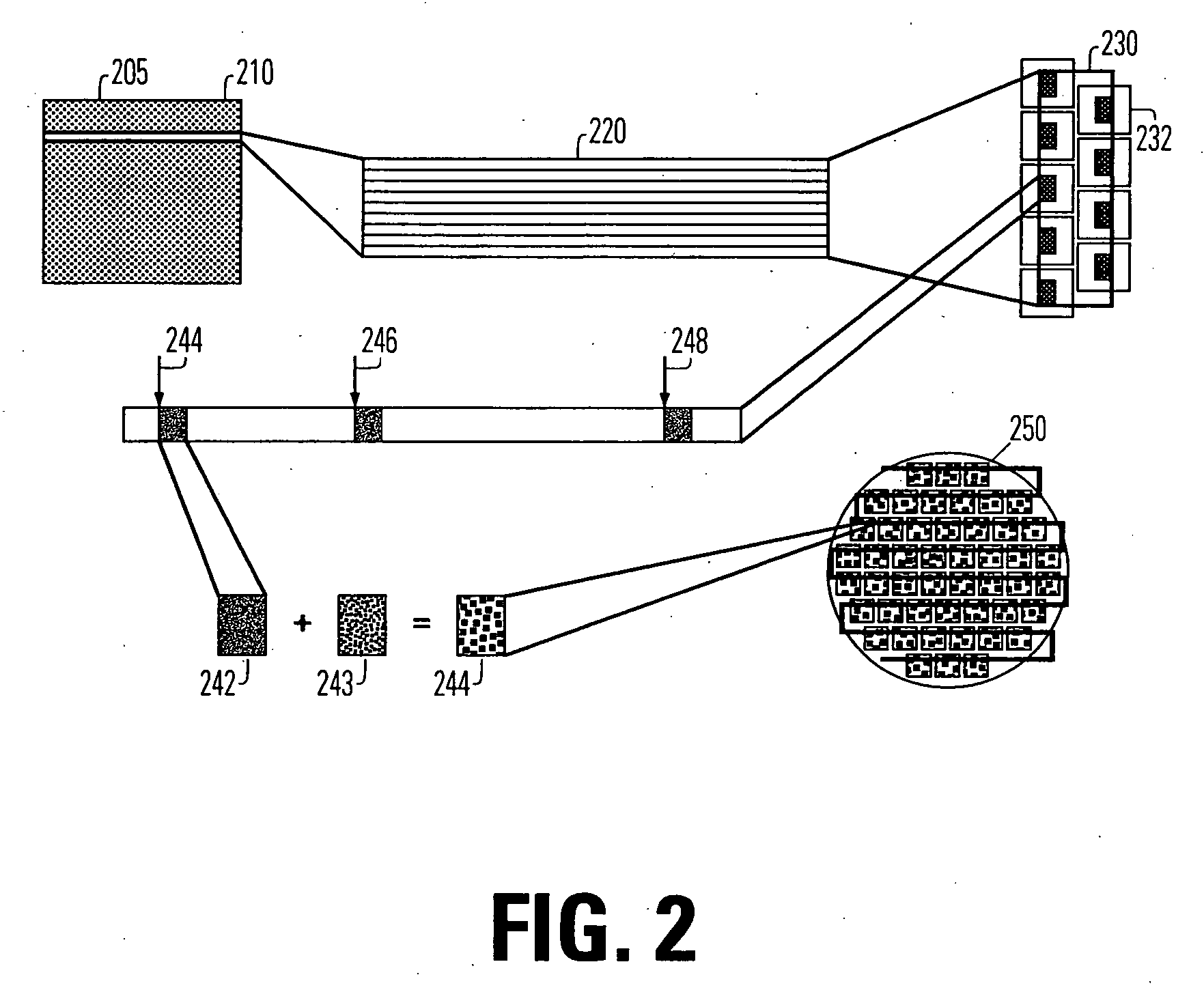
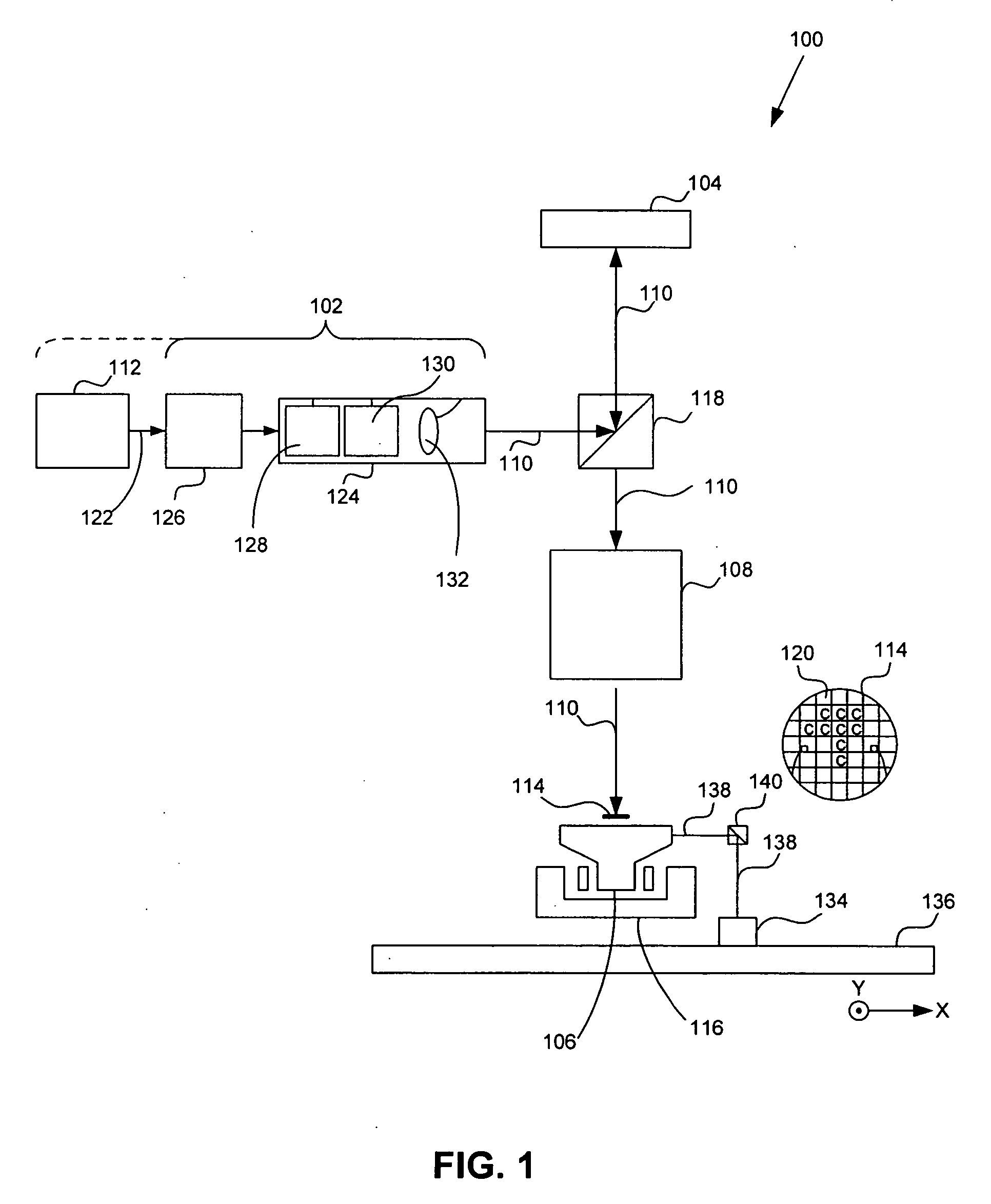
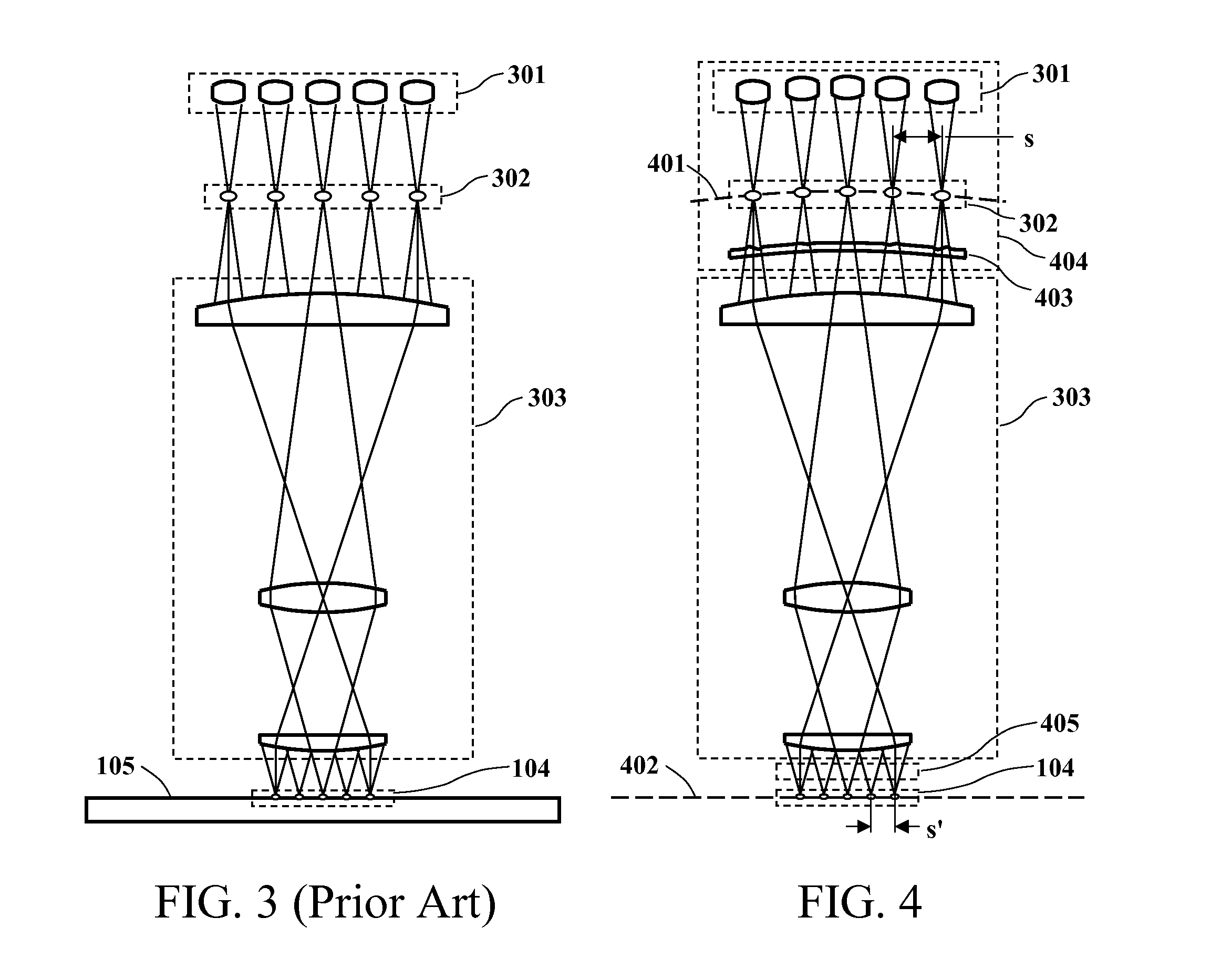
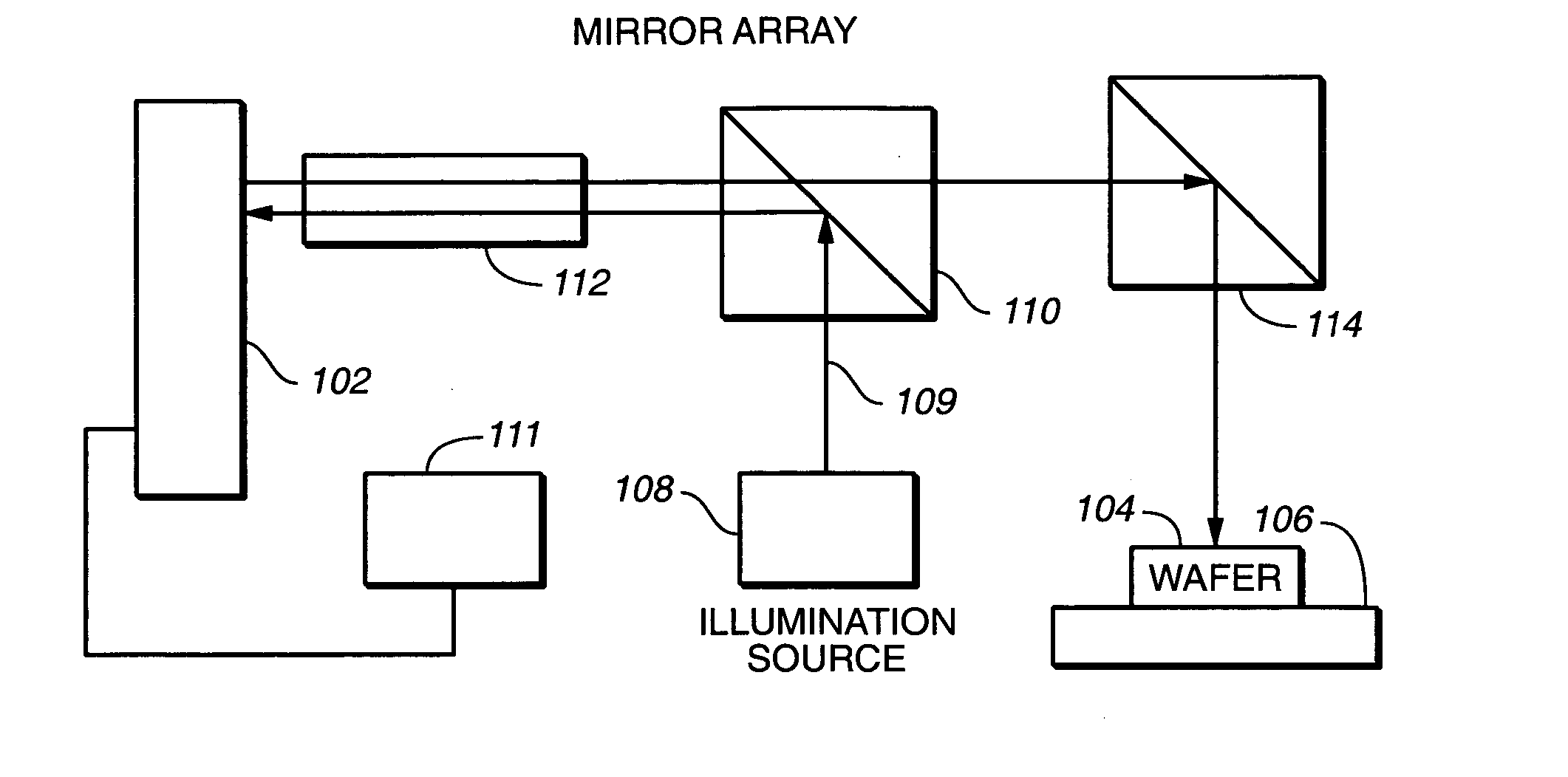
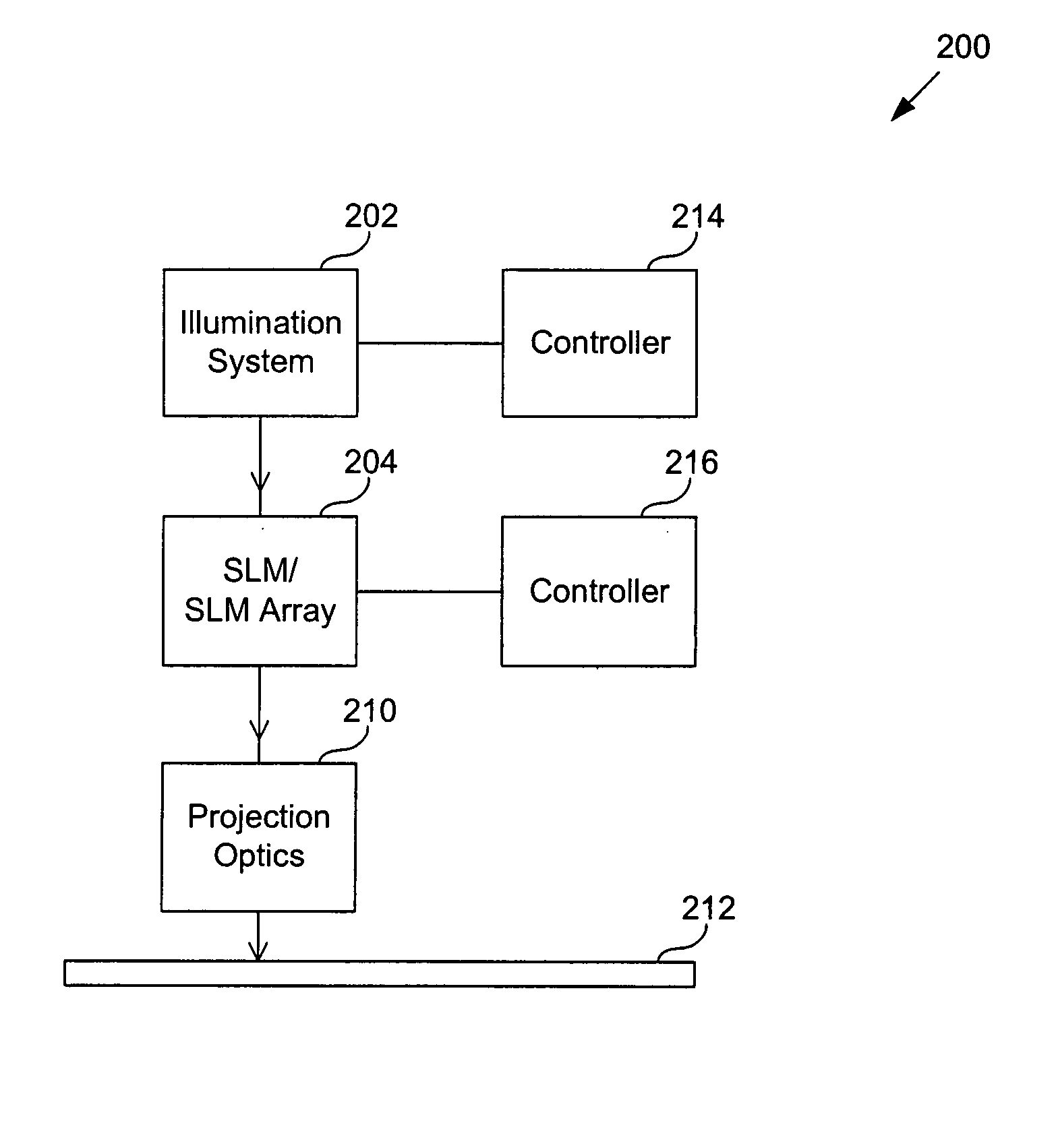
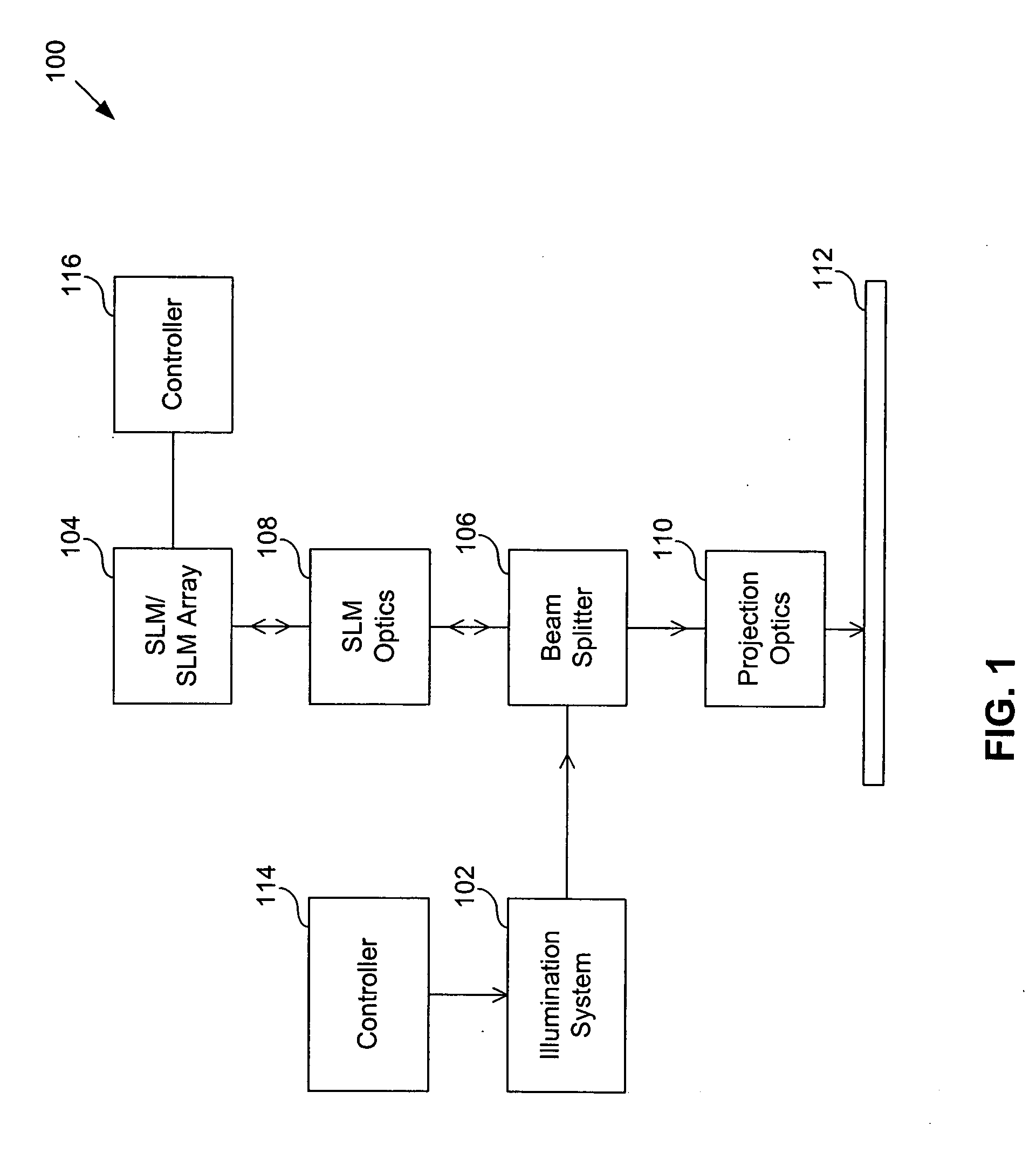
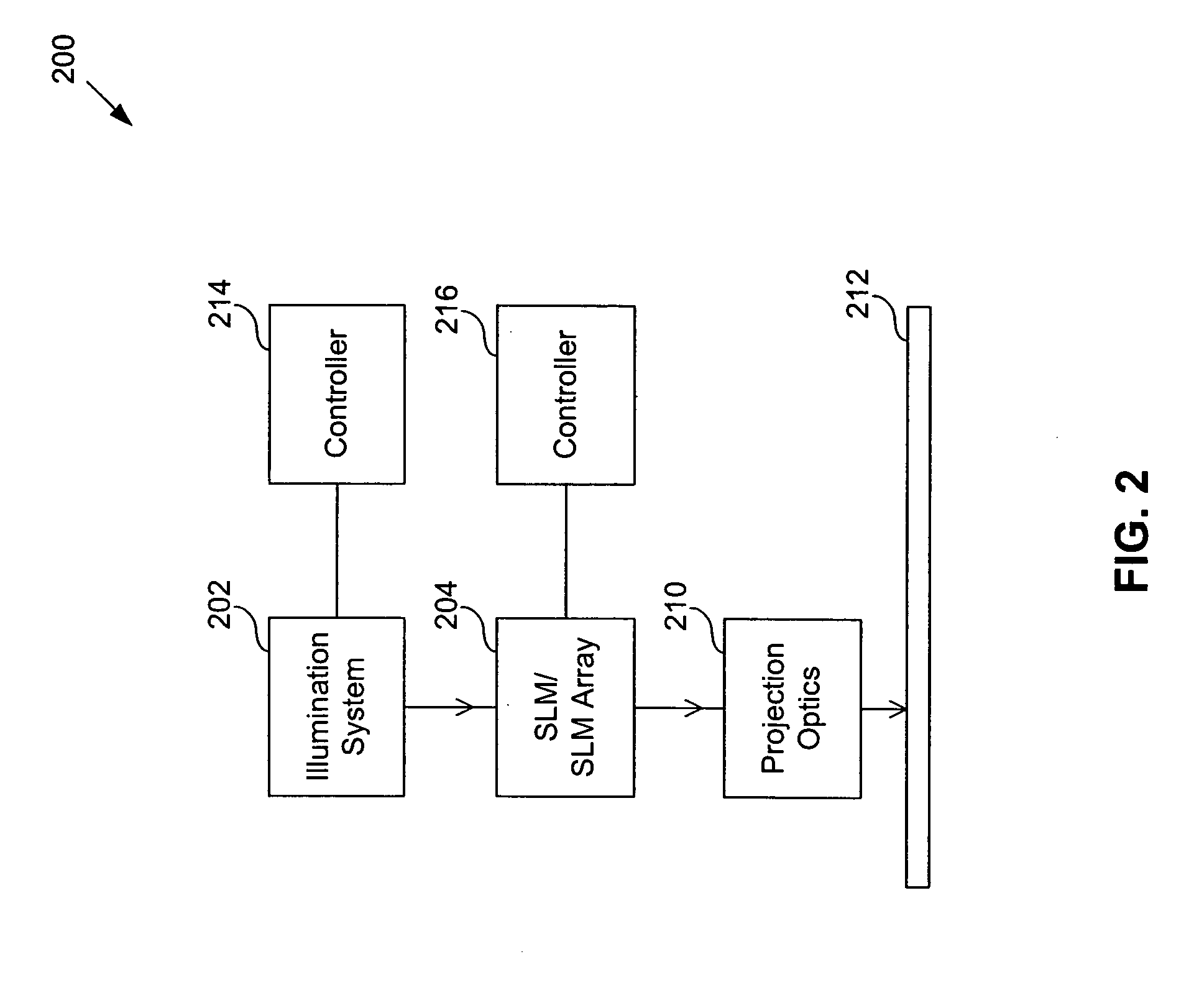
Seamless, maskless lithography system using spatial light modulator
InactiveUS6312134B1Eliminate needImprove processing throughputMirrorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusRadiation DosagesSpatial light modulator
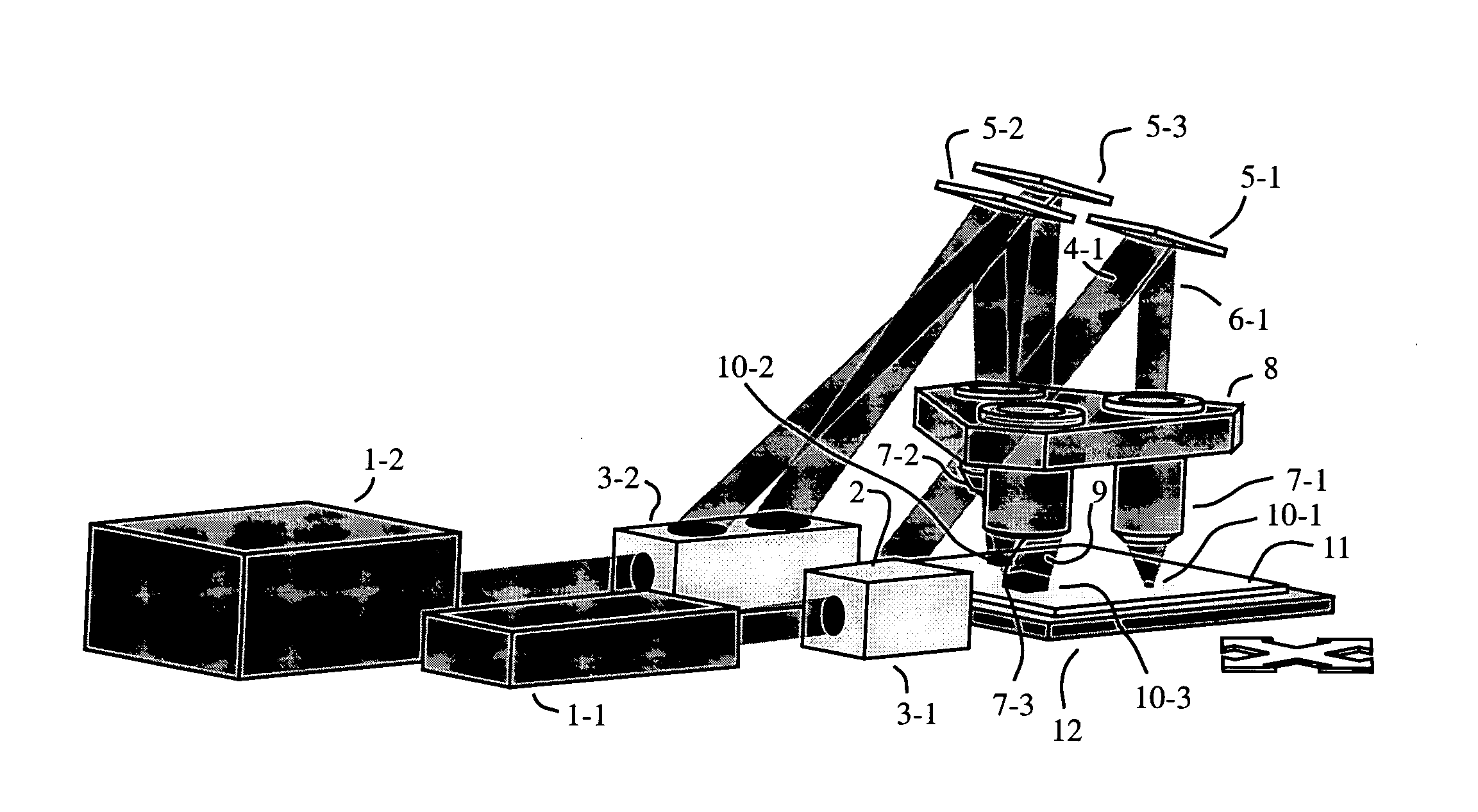
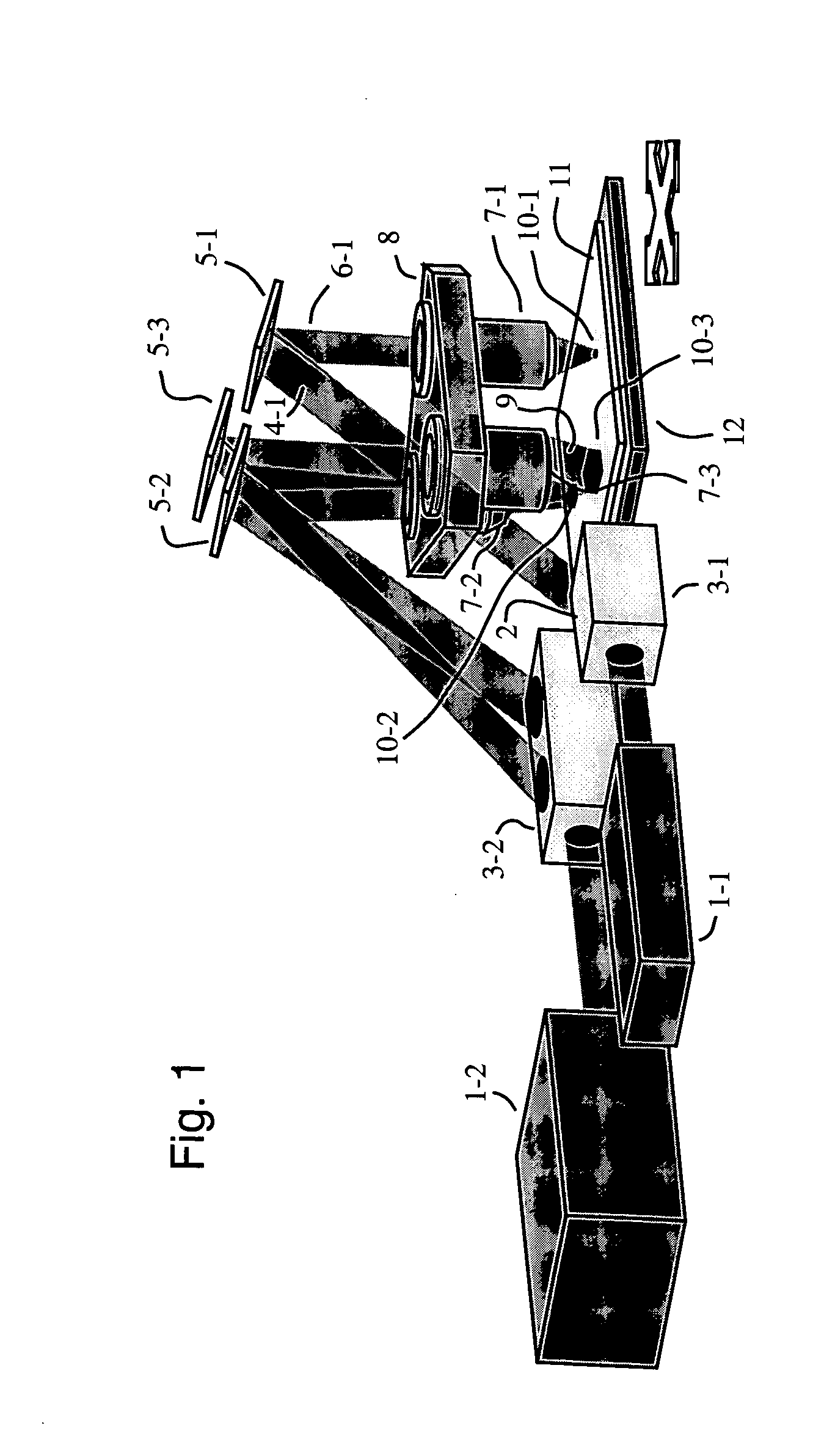
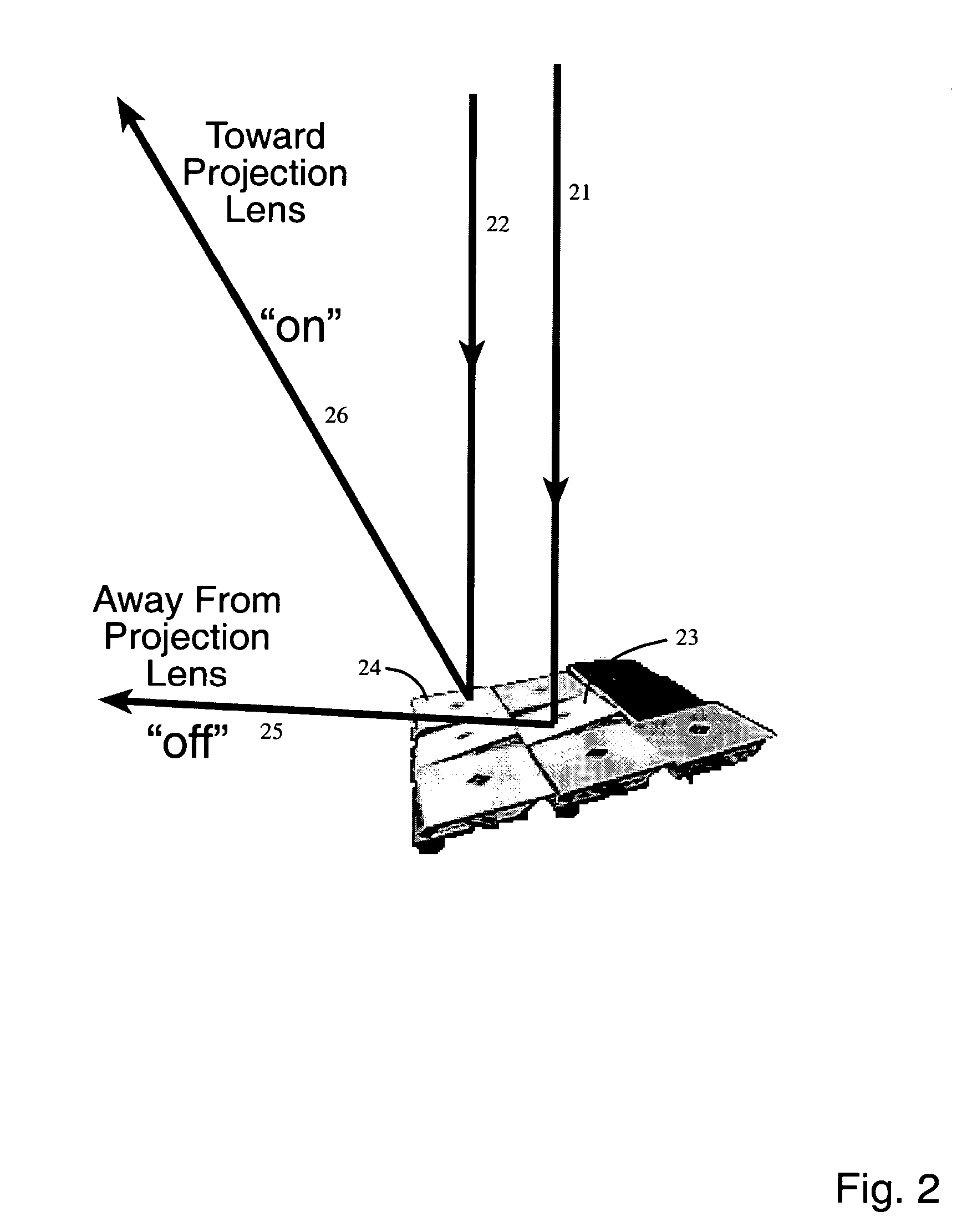
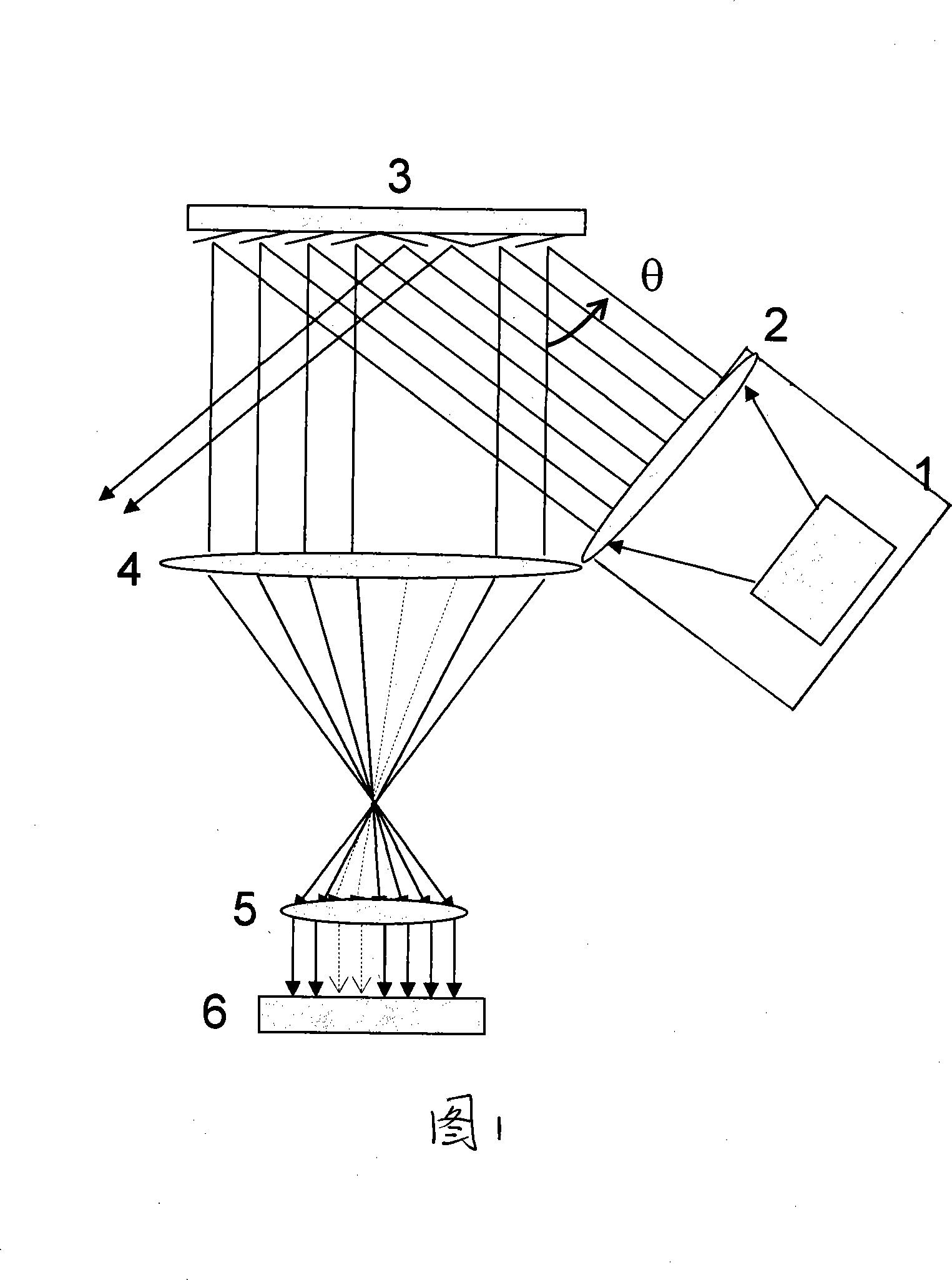
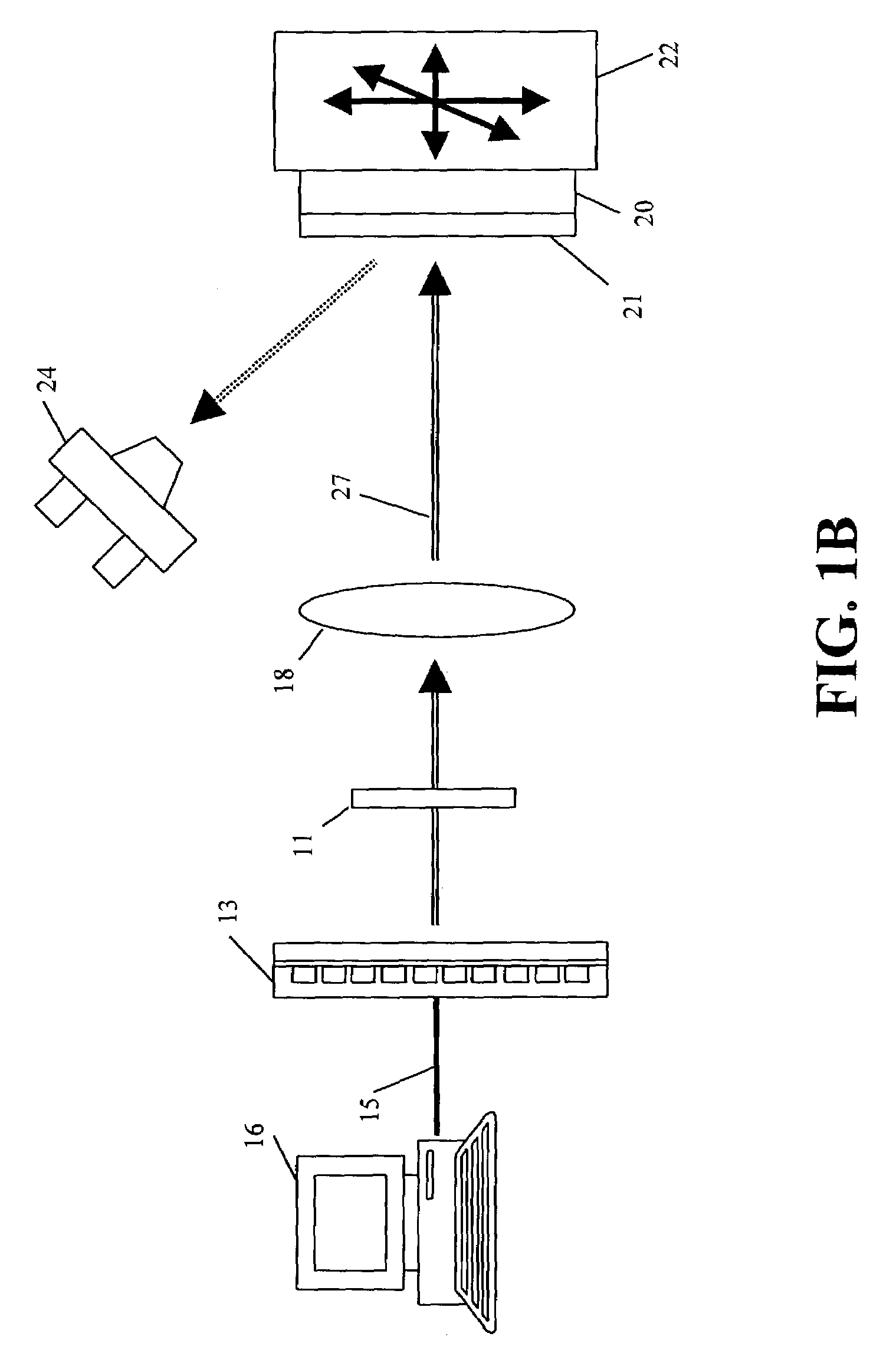
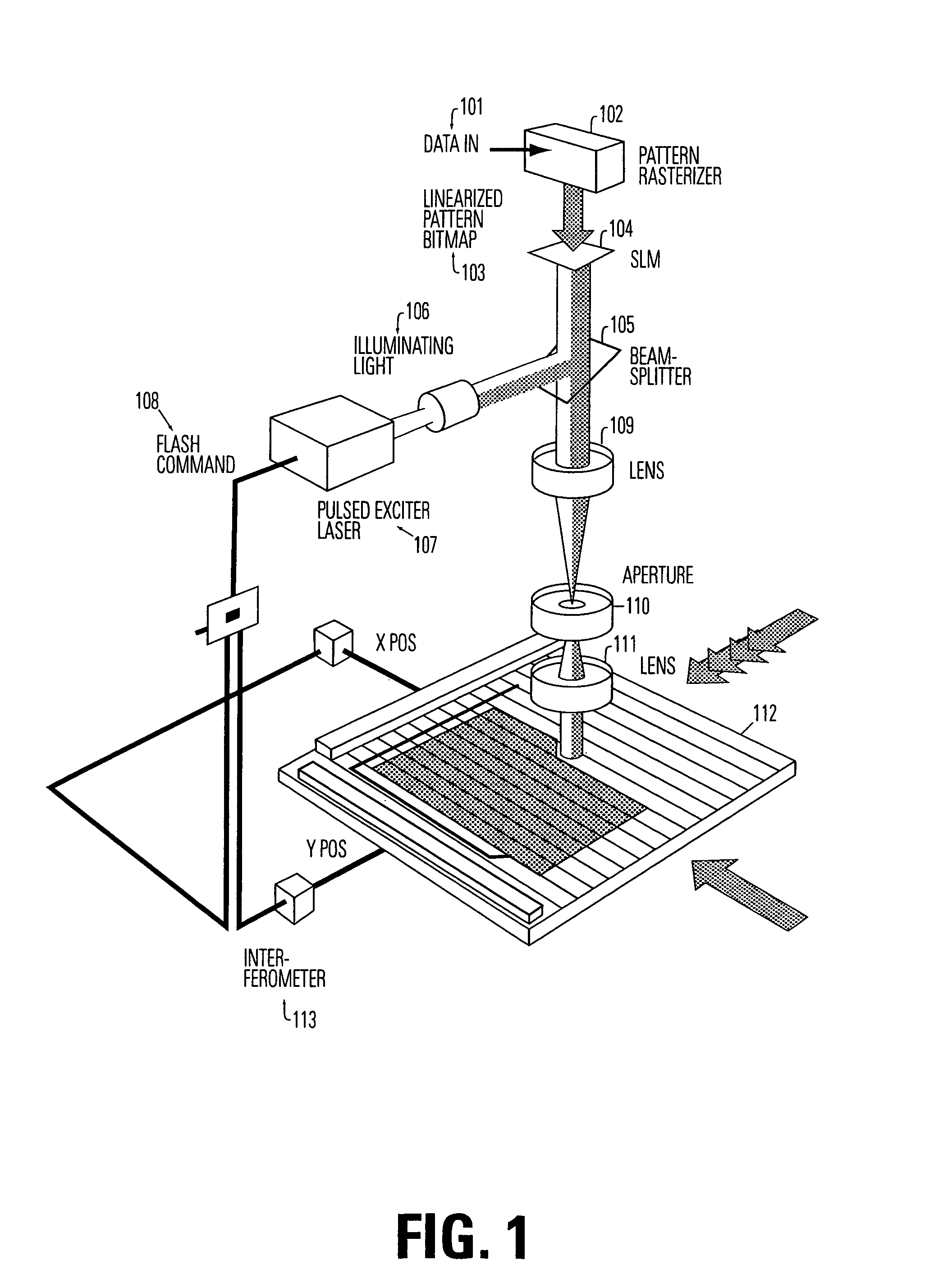
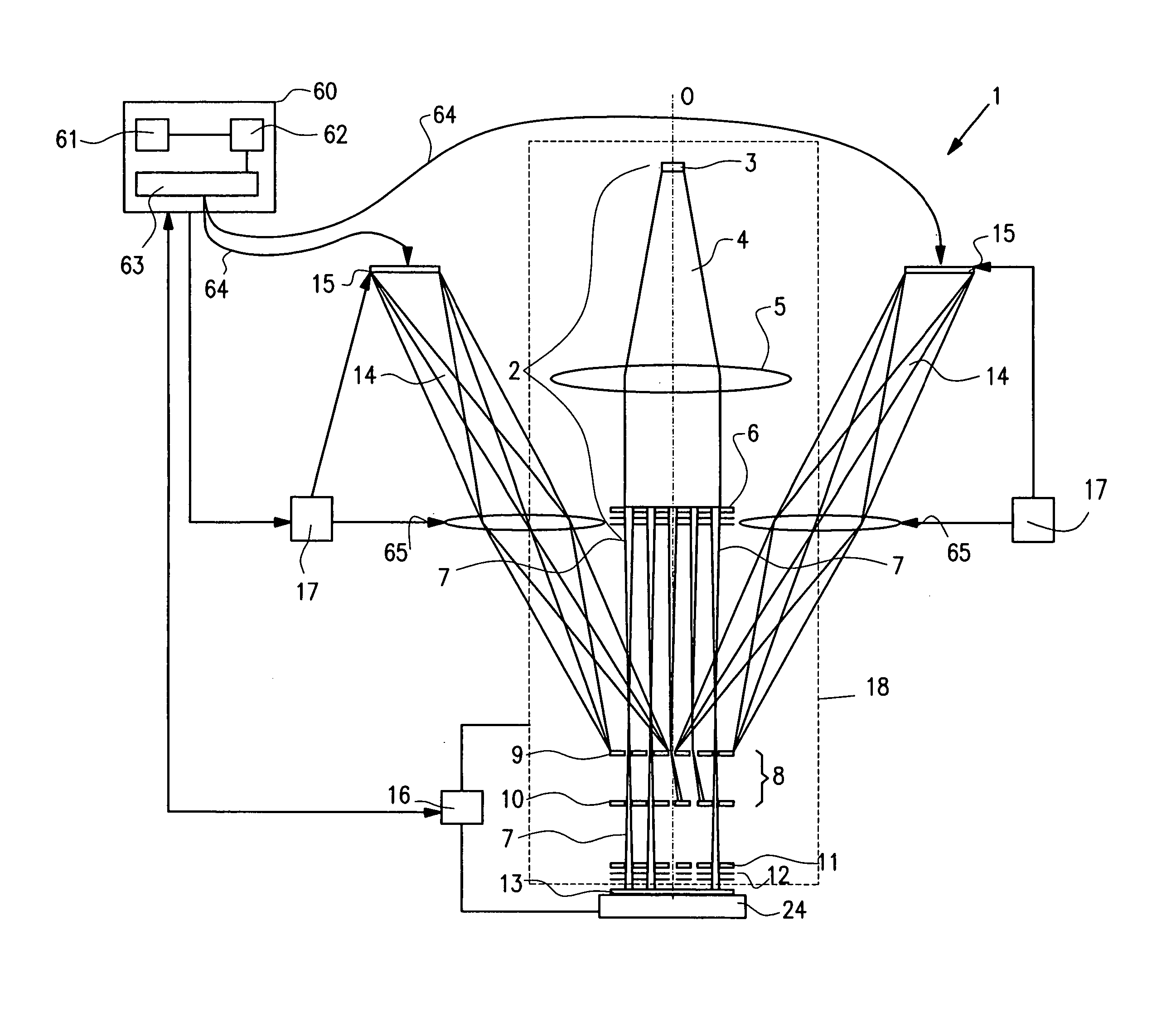
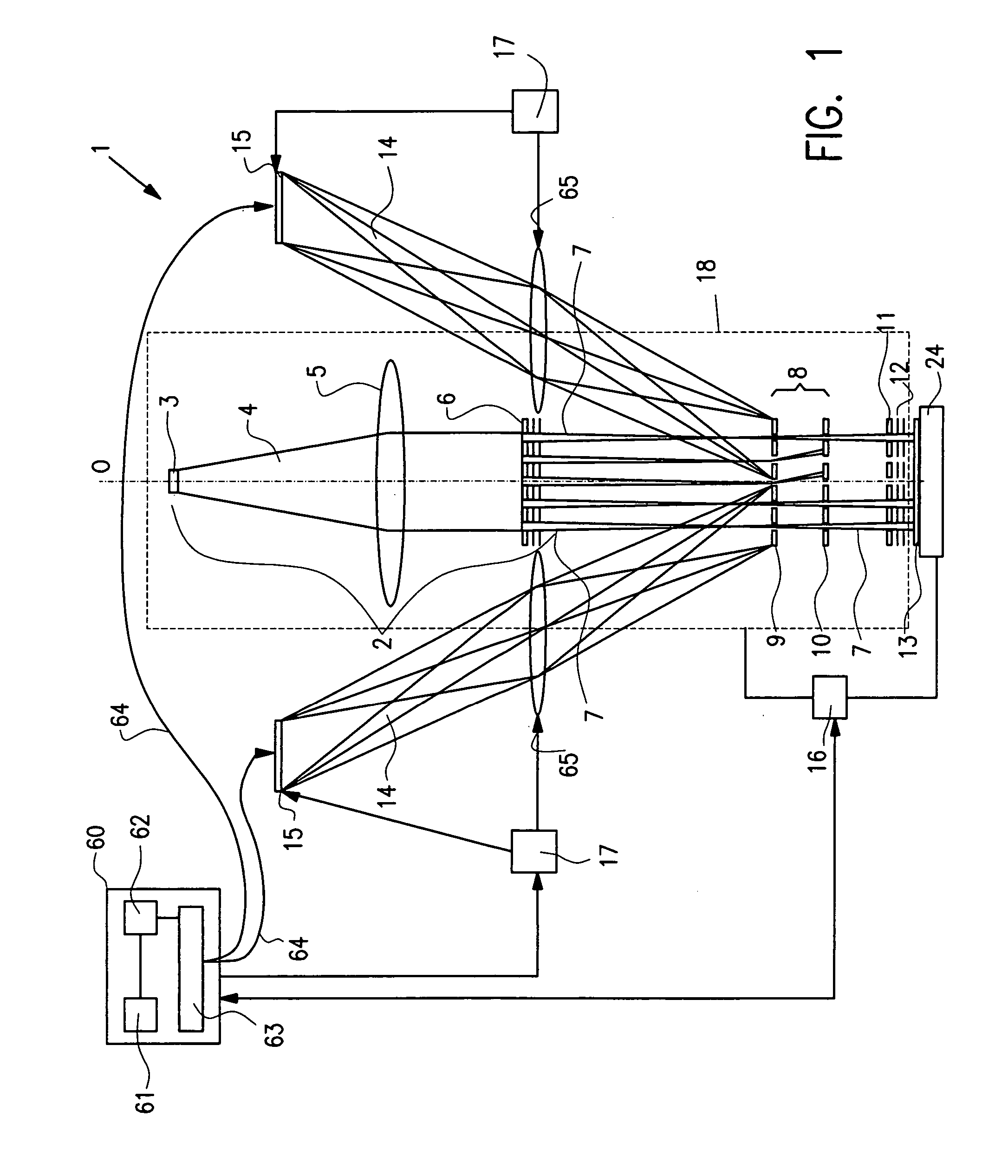
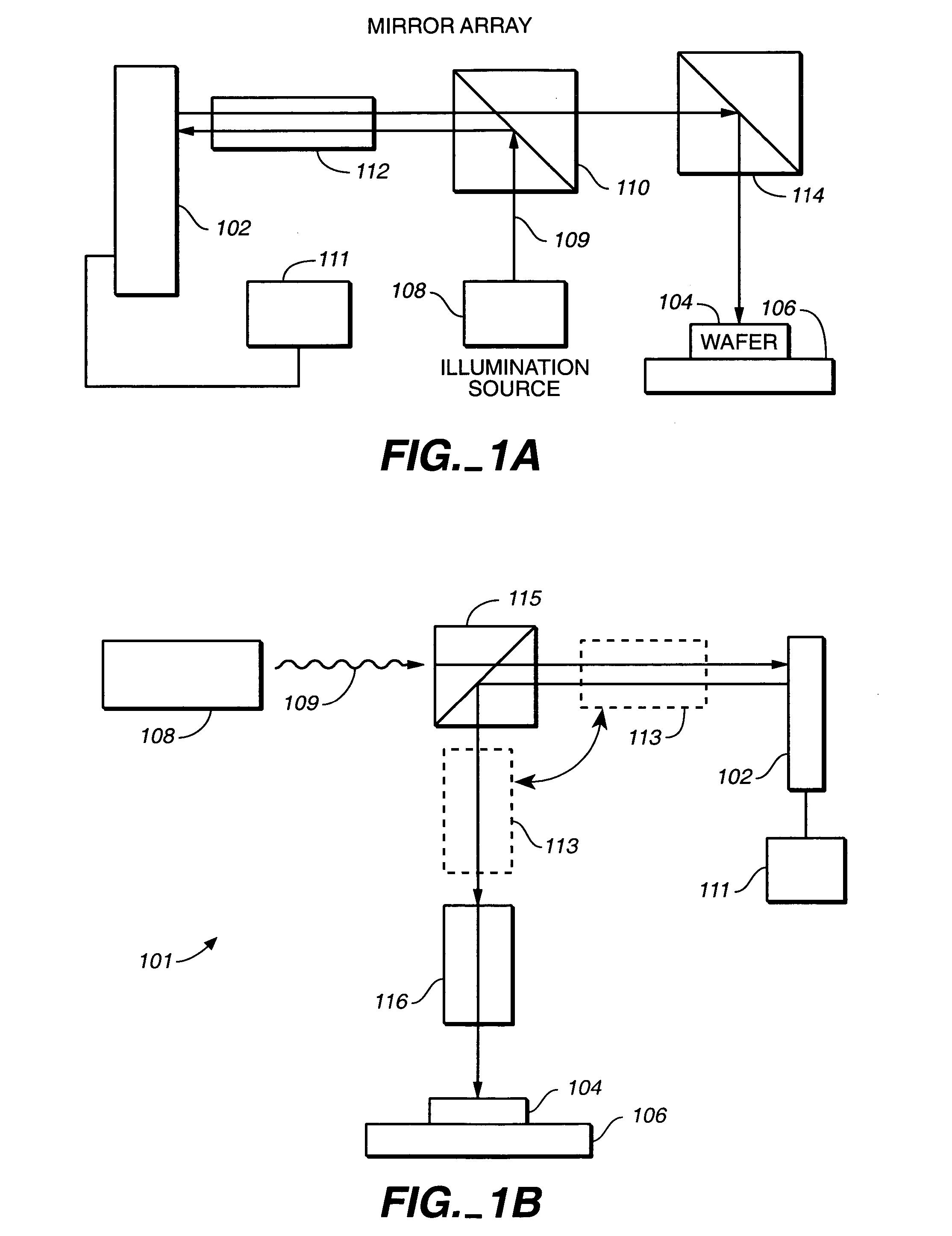
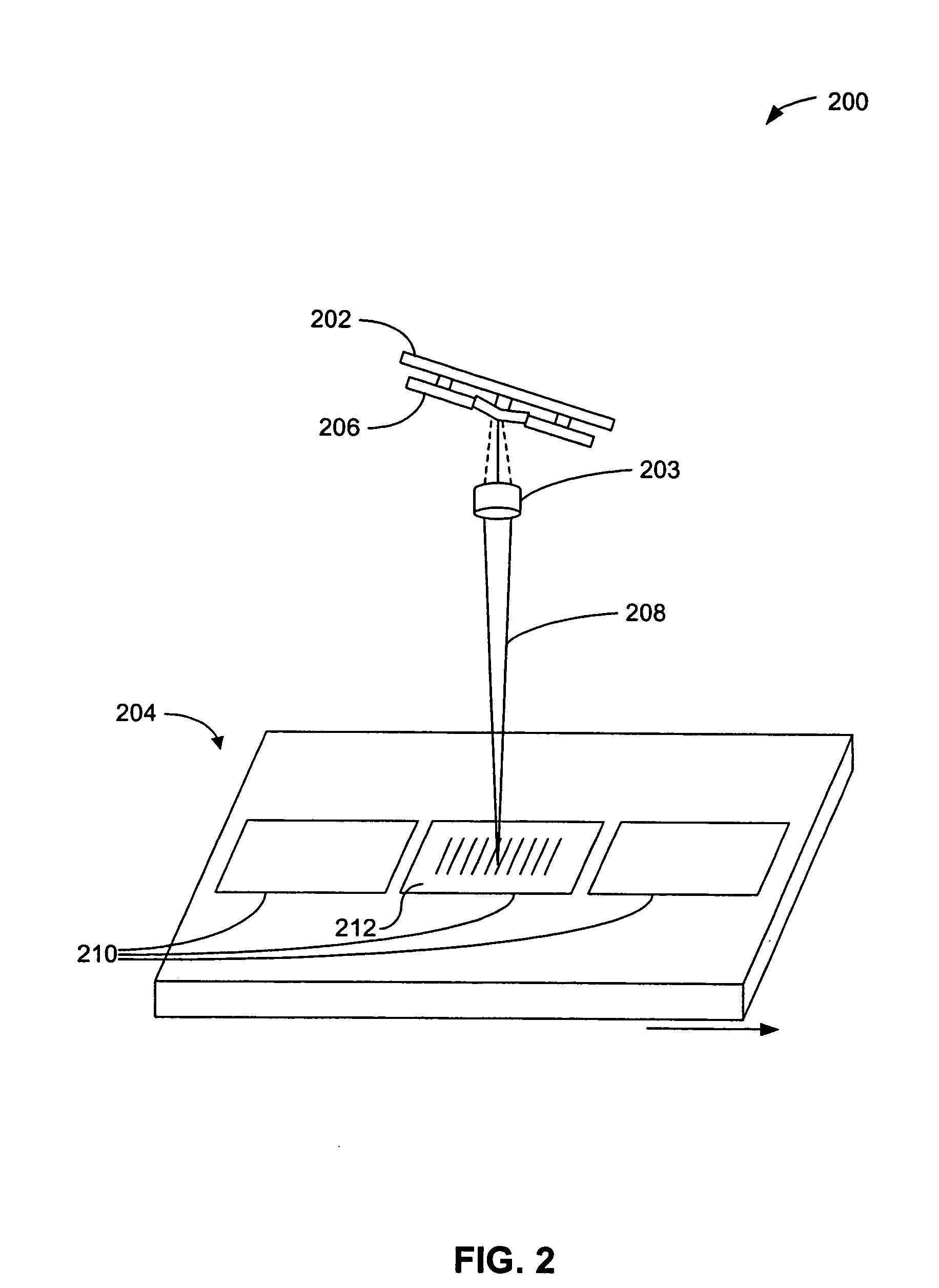
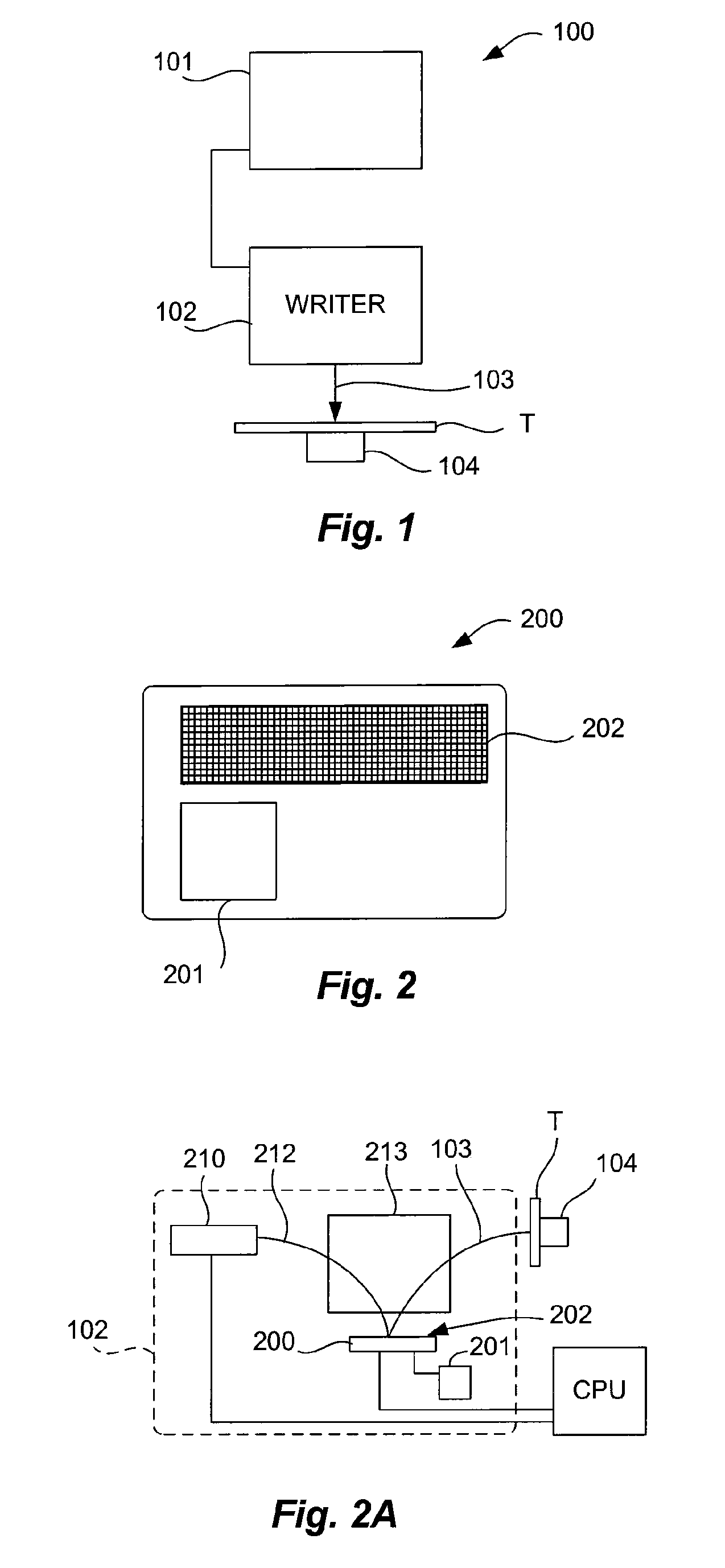
The invention is a seamless projection lithography system that eliminates the need for masks through the use of a programmable Spatial Light Modulator (SLM) with high parallel processing power. Illuminating the SLM with a radiation source (1), which while preferably a pulsed laser may be a shuttered lamp or multiple lasers with alternating synchronization, provides a patterning image of many pixels via a projection system (4) onto a substrate (5). The preferred SLM is a Deformable Micromirror Device (3) for reflective pixel selection using a synchronized pulse laser. An alternative SLM is a Liquid Crystal Light Valve (LCLV) (45) for pass-through pixel selection. Electronic programming enables pixel selection control for error correction of faulty pixel elements. Pixel selection control also provides for negative and positive imaging and for complementary overlapping polygon development for seamless uniform dosage. The invention provides seamless scanning by complementary overlapping scans to equalize radiation dosage, to expose a pattern on a large area substrate (5). The invention is suitable for rapid prototyping, flexible manufacturing, and even mask making.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
Lithography system
ActiveUS6958804B2Location somewhat remoteReduce transmission lossMirrorsElectric discharge tubesLithographic artistLight beam
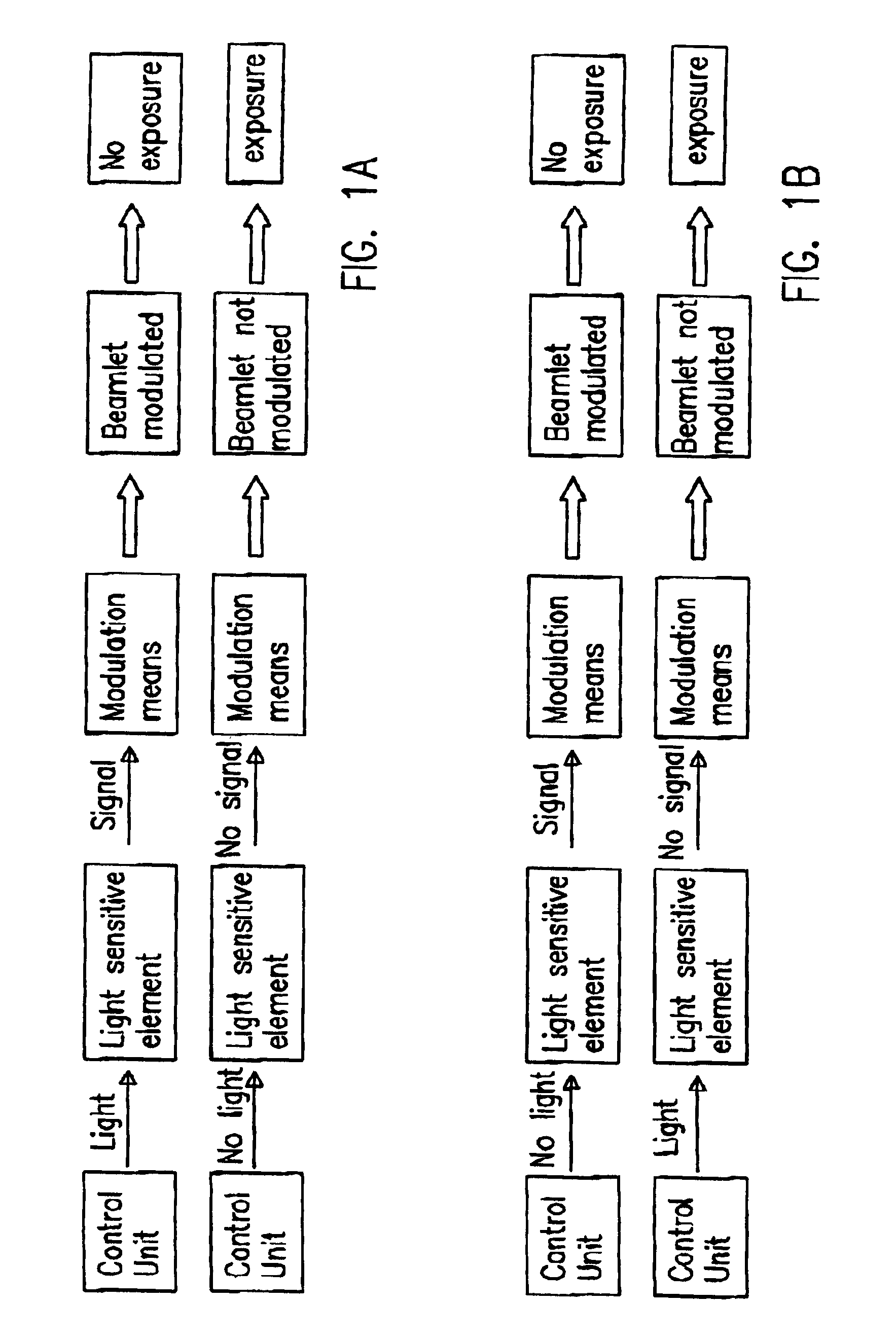
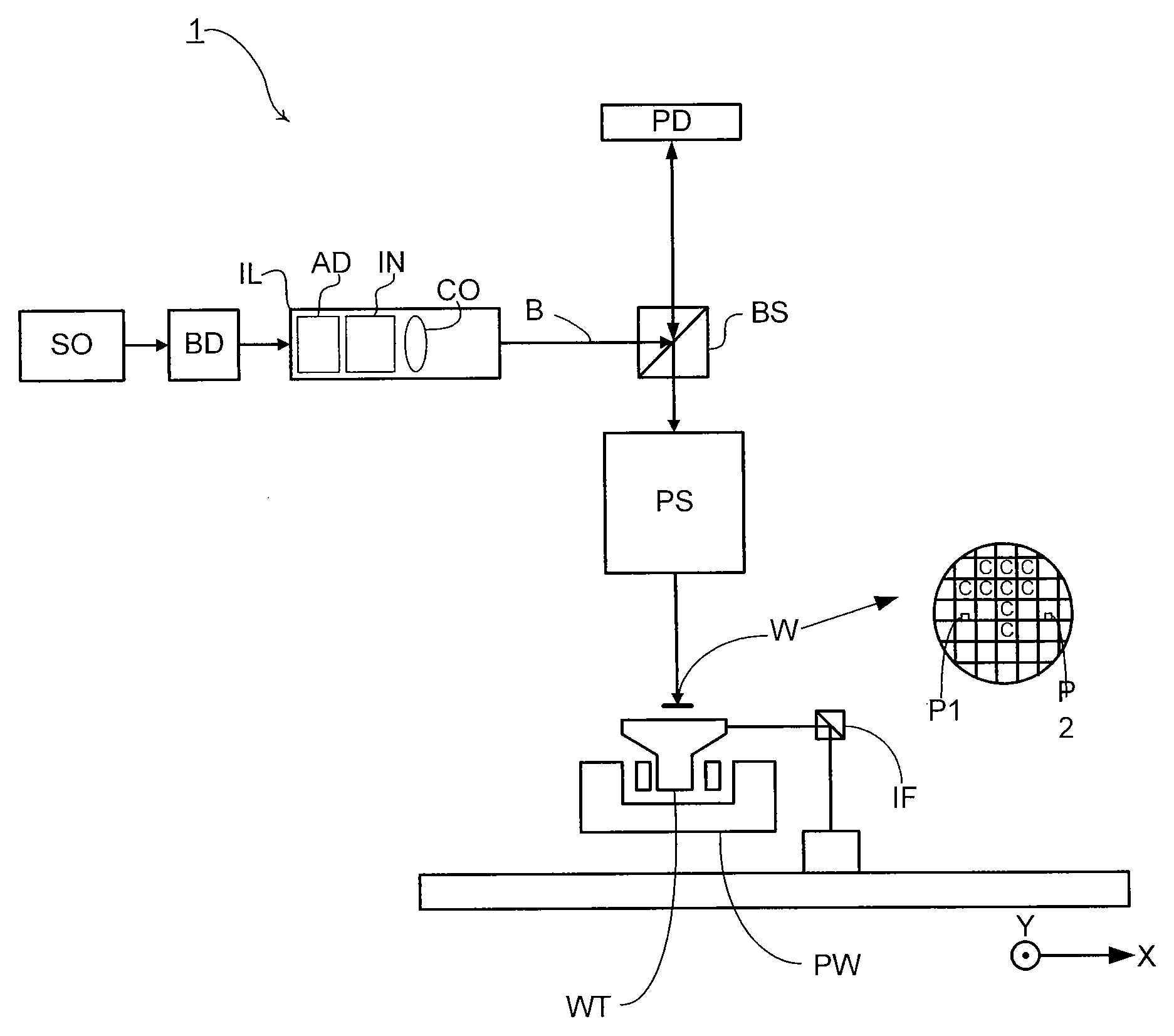
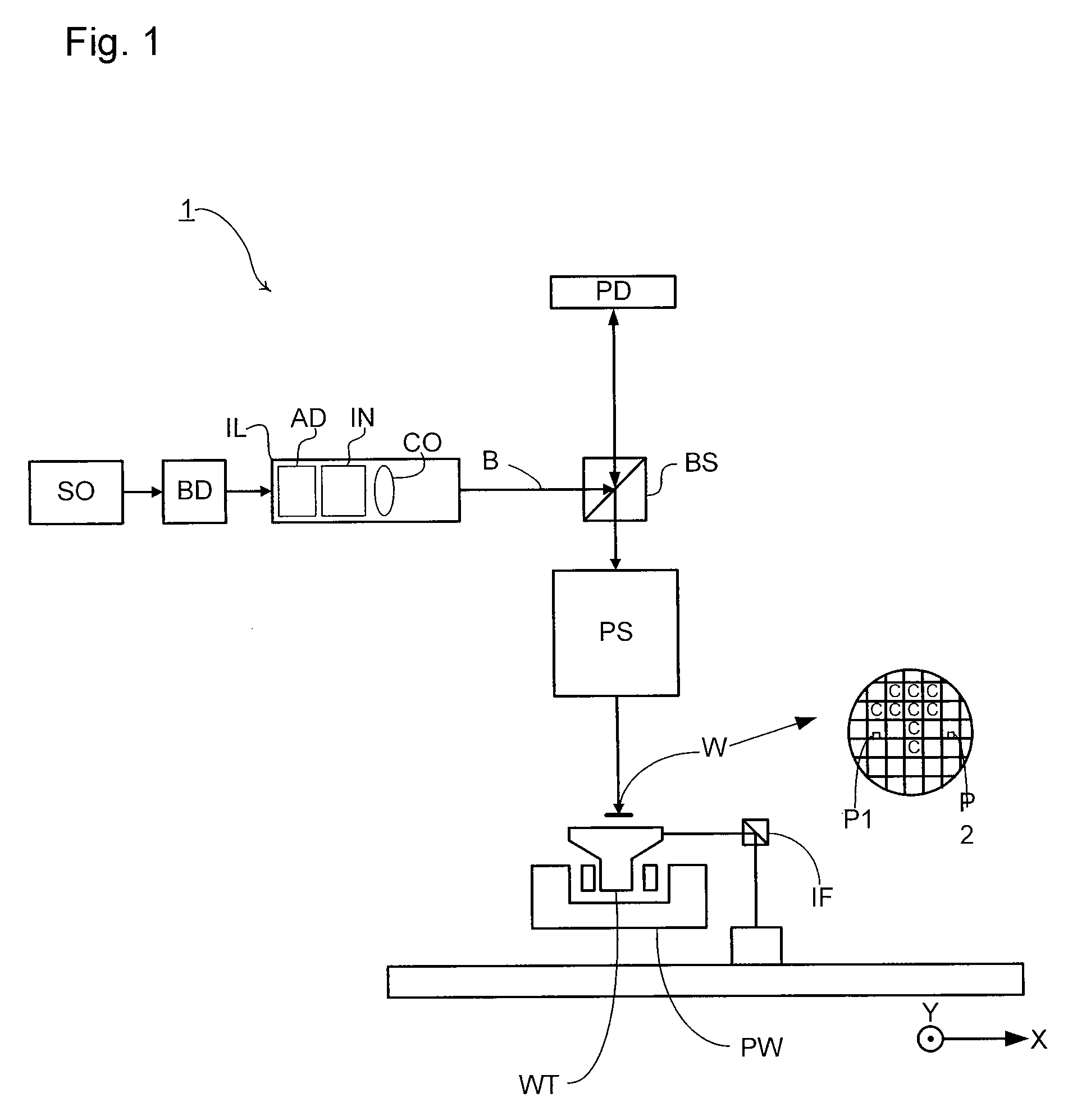
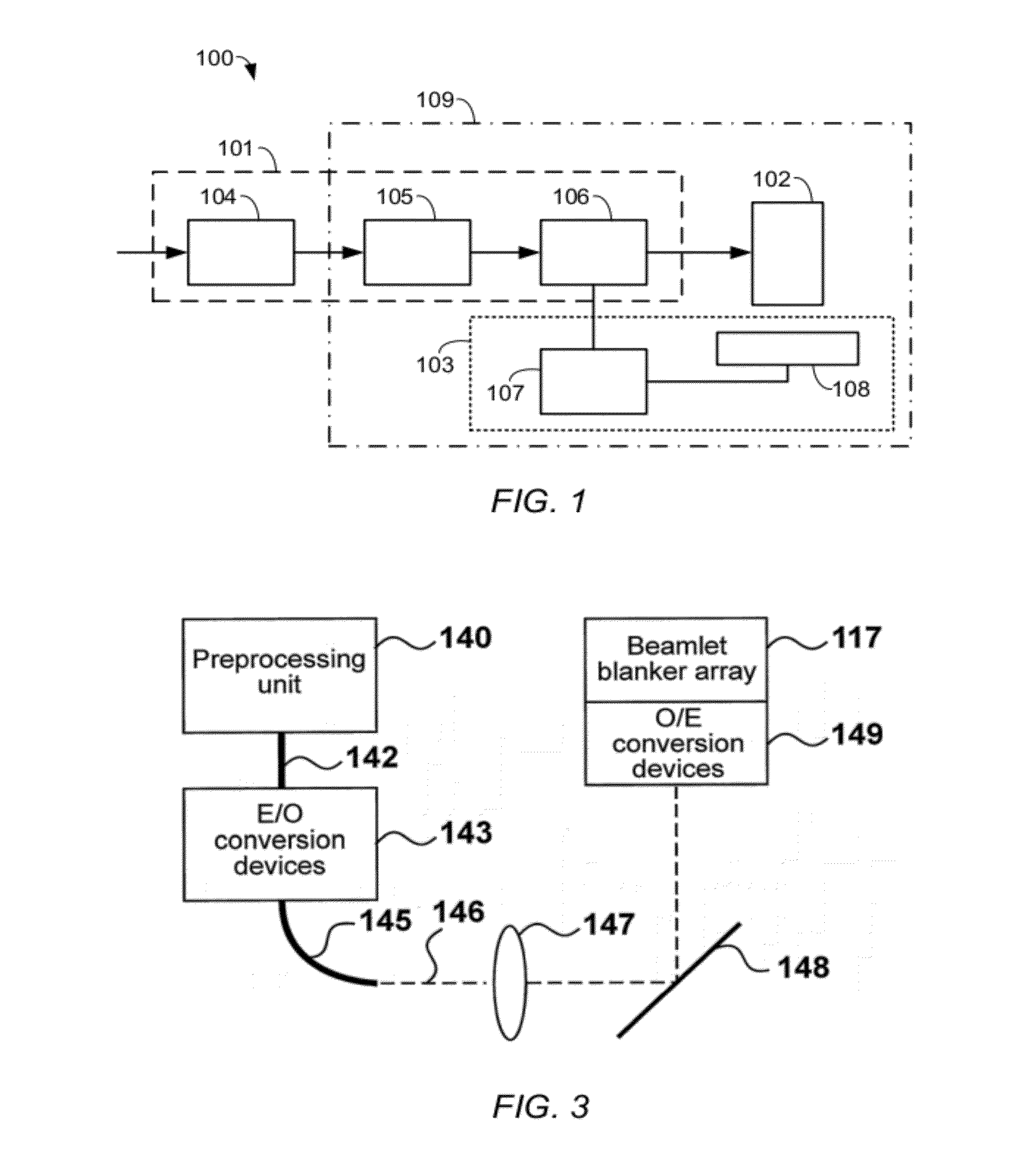
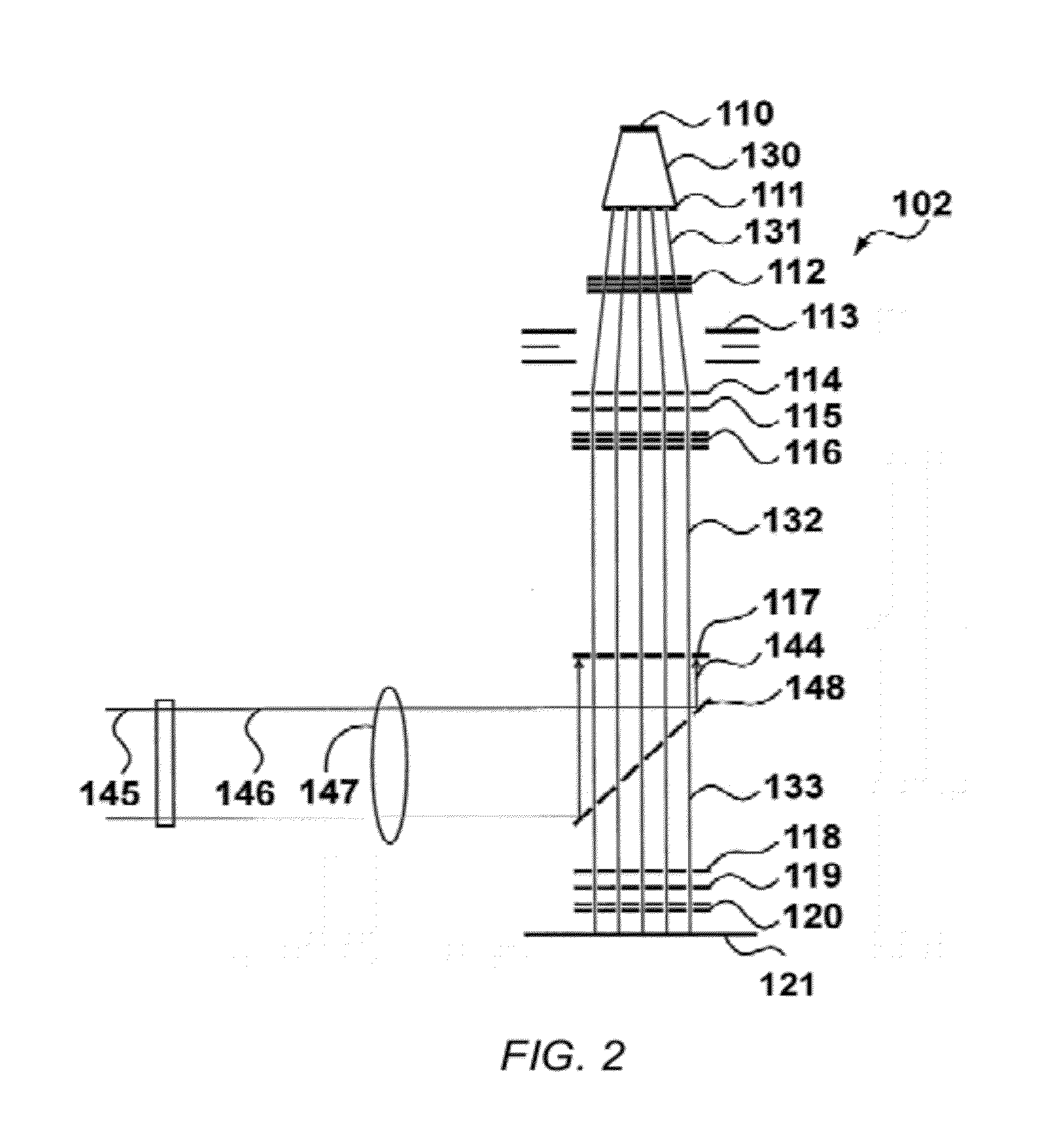
A maskless lithography system for transferring a pattern onto the surface of a target. At least one beam generator for generating a plurality of beamlets. A plurality of modulators modulate the magnitude of a beamlet, and a control unit controls of the modulators. The control unit generates and delivers pattern data to the modulators for controlling the magnitude of each individual beamlet. The control unit includes at least one data storage for storing the pattern data, at least one readout unit for reading out the data from the data storage, at least one data converter for converting the data that is read out from the data storage into at least one modulated light beam, and at least one optical transmitter for transmitting the at least one modulated light beam to the modulation modulators.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
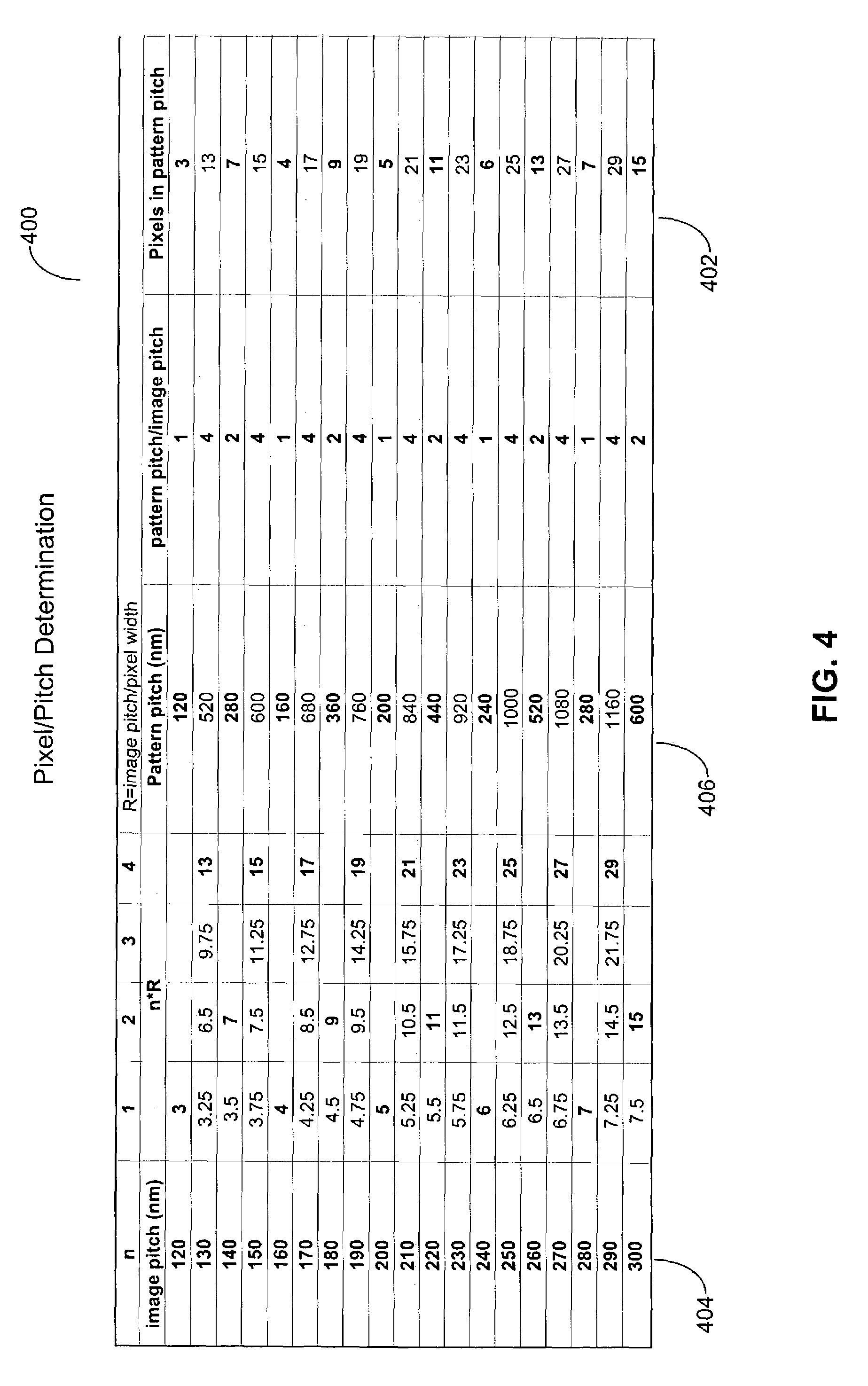
Method for the generation of variable pitch nested lines and/or contact holes using fixed size pixels for direct-write lithographic systems
ActiveUS7063920B2Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusEngineeringMicromirror array
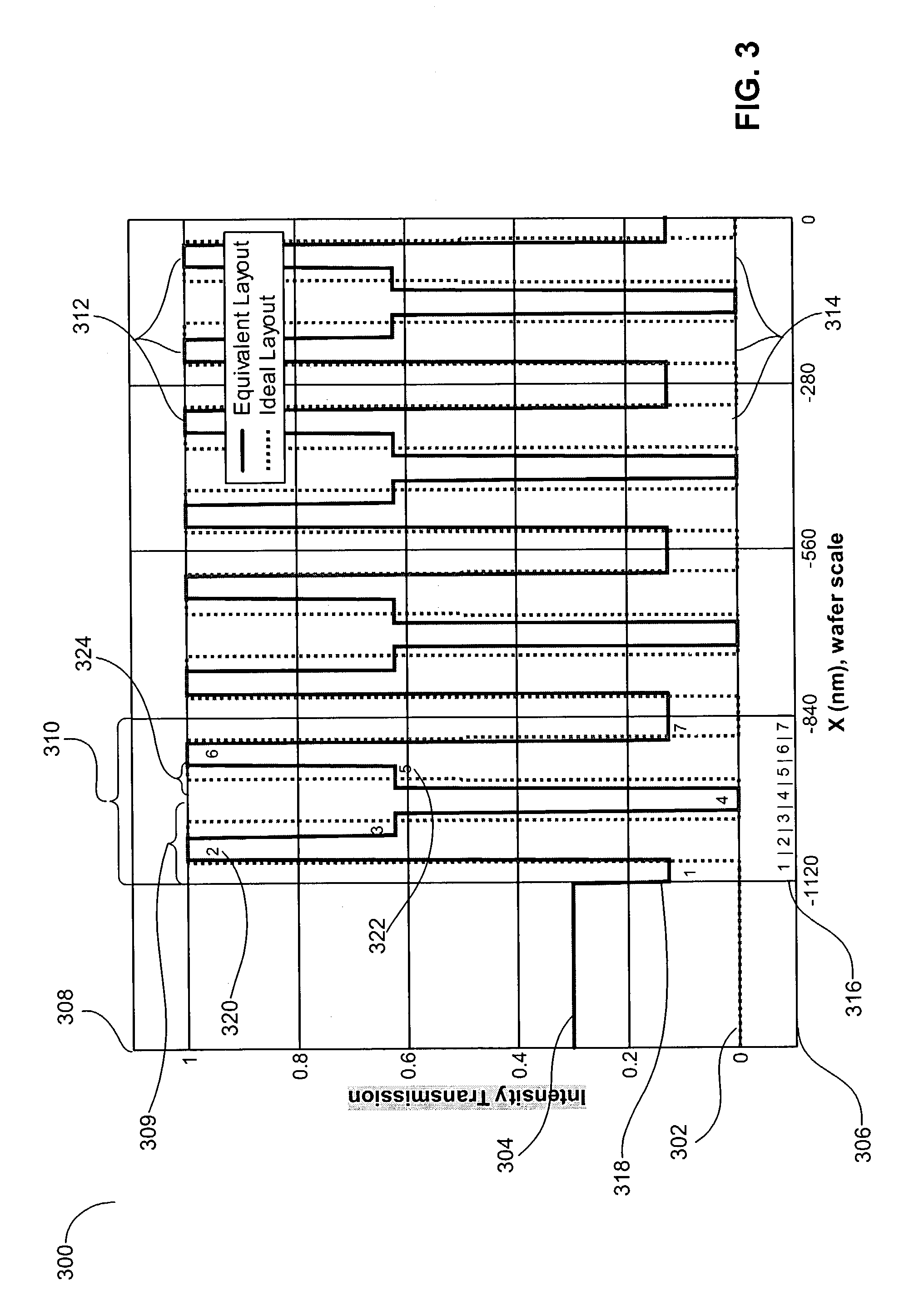
Provided is a method and system for developing a lithographic mask layout. The lithographic mask layout is adapted for configuring an array of micro-mirrors in a maskless lithography system. The method includes generating an ideal mask layout representative of image characteristics associated with a desired image. Next, an equivalent mask is produced in accordance with an average intensity of the ideal mask layout.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Versatile maskless lithography system with multiple resolutions
InactiveUS20060012766A1Quick selectionEasy to combinePhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingSpatial light modulatorImage resolution
A versatile maskless patterning system with capability for selecting rapidly among a plurality of projection lenses mounted on a turret. This provides the ability to rapidly select multiple choices for resolution and enables optimization of the combination of the imaging resolution and exposure throughput, making possible cost-effective fabrication of microelectronics packaging products. A preferred embodiment uses a digital micromirror device array spatial light modulator as a virtual mask. Another preferred embodiment use multiple closely spaced digital micromirror device array spatial light modulators to enhance throughput.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
Method for improving photolithography exposure energy homogeneity using grey level compensation
InactiveCN101226343AImprove consistencyReduce designPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusSpatial light modulatorHardness
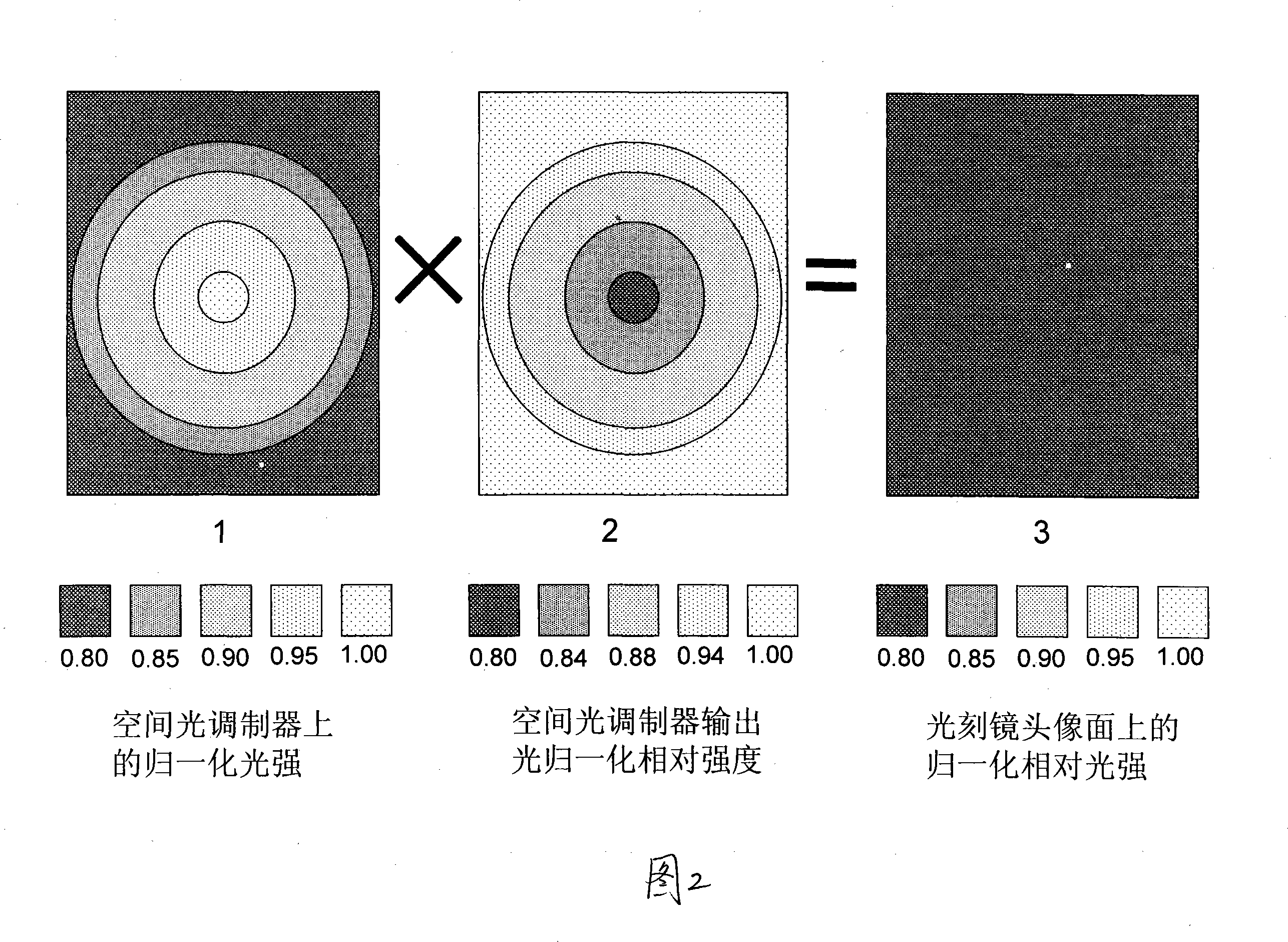
The invention discloses a method for using gray scale compensation to improve photo-etching exposure energy uniformity, with wide application in non-mask photo-etching machine which uses spatial light modulator as image generator. The non-mask photo-etching machine provided with a spatial light modulator as image generator uses the gray scale modulation of the spatial light modulator, according to the image light strength distribution information of photo-etching objective lens collected by a CCD to modulate the light output of each pixel unit of the spatial light modulator to change the emission light field distribution on the image plane of the photo-etching objective lens. The invention uses the light strength distribution measured in the integration of some time or uses the energy distribution of the light emitted from each image plane position in a certain exposure time to make the exposure energy of each position uniform on the image plane. The invention can effectively reduce the design and assembly hardness of the lighting system of traditional photo-etching machine and reach better exposure energy uniformity.
Owner:HEFEI ADVANTOOLS SEMICON
RET for optical maskless lithography
The present invention relates to Optical Maskless Lithography (OML). In particular, it relates to providing OML with a recognizable relationship to mask and phase-shift mask techniques.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
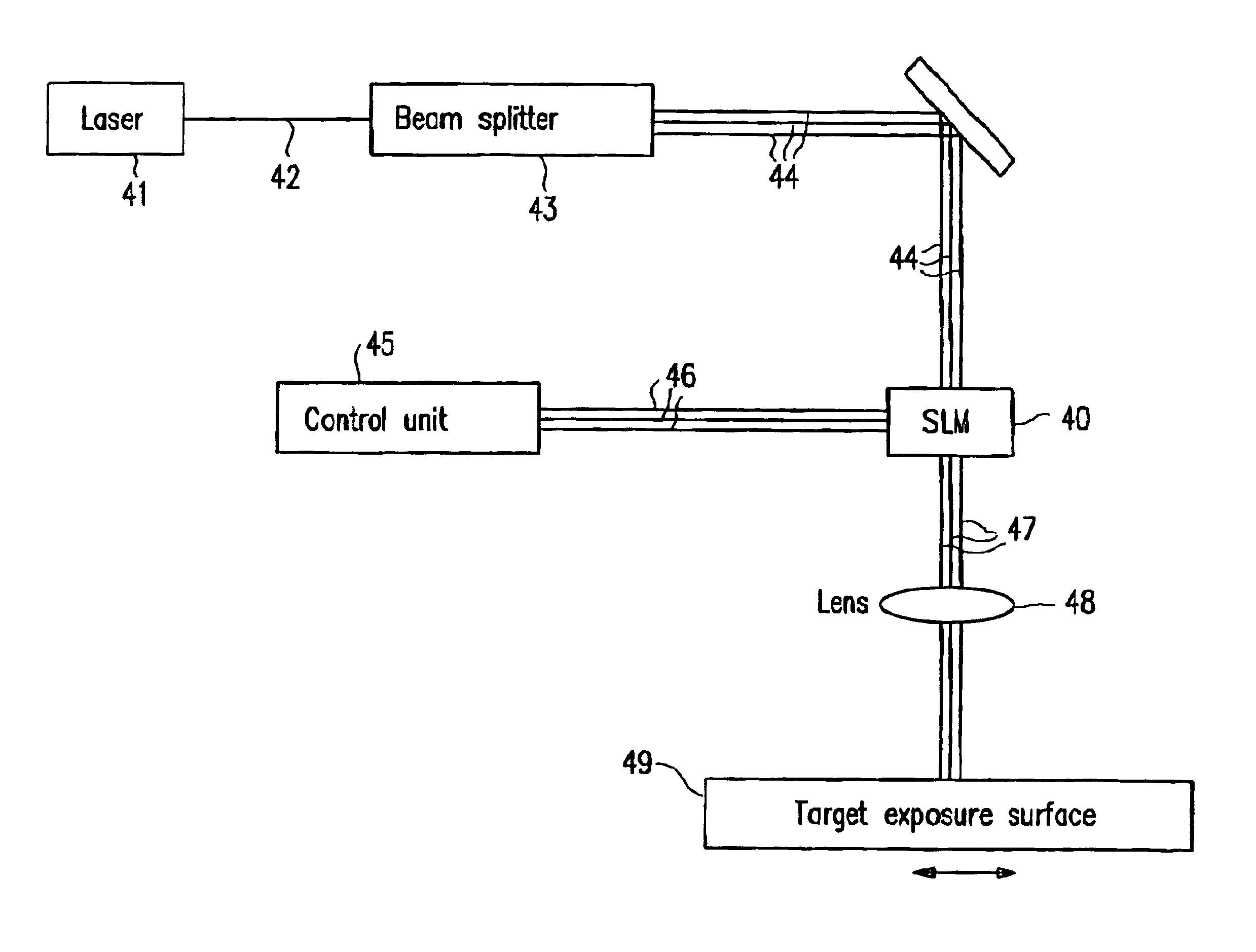
Maskless lithography with multiplexed spatial light modulators
InactiveUS6870554B2Improve throughputCathode-ray tube indicatorsPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSpatial light modulatorEngineering
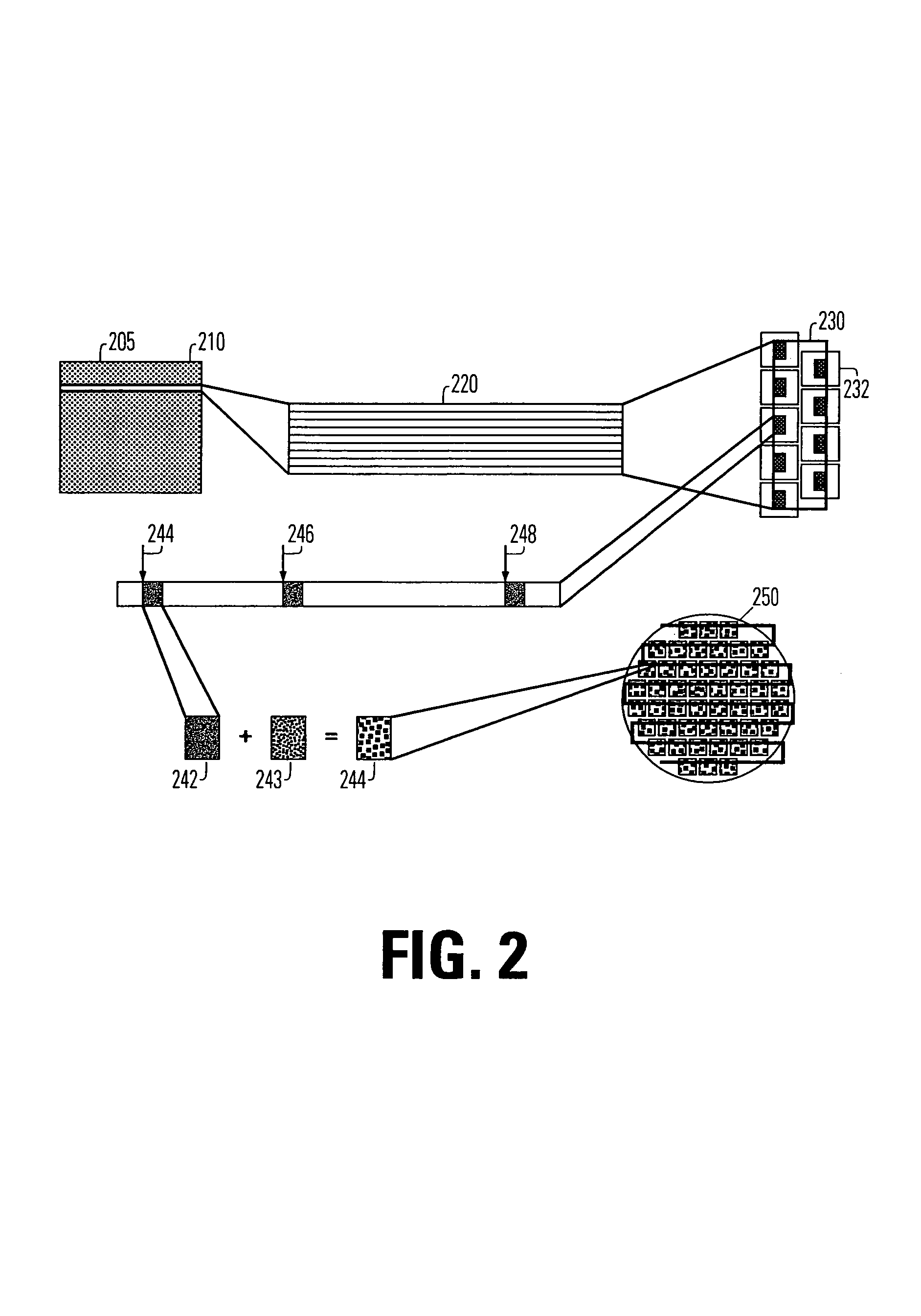
Imaging systems that use a spatial light modulator (SLM), such as maskless lithography systems using a digital micromirror device (DMD), suffer from low throughput at high resolution because of the increase in the number of pixels to be imaged. A possible solution to this problem is provided by using multiple SLMs. However, packaging multiple SLMs on a suitable base is inefficient because, in an SLM, surrounding the active region, a large inactive region is required for the chip kerf and the connector fan-in; these inactive regions thus prevent close packing of the SLMs. This invention enables close packing of a large number of SLMs by arranging them in twin planes, such that the kerf and fan-in regions overlap substantially. Variations in the optical conjugate distances of different SLMs caused by the twin planarity are eliminated by incorporation of a twin-pane compensating mirror array that corresponds to the SLM array, and introduces a pathlength difference between different mirrors that is complementary to the pathlength difference between corresponding SLM chips. Depth-of-focus problems are thus eliminated. The invention enables significant throughput enhancement, up to 82%, in maskless lithography systems.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
Microphotonic maskless lithography
ActiveUS20080014534A1Improve scalabilityIncrease the number ofSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction gratingsWaveguidePhoton beam
A maskless lithography system and method to expose a pattern on a wafer by propagating a photon beam through a waveguide on a substrate in a plane parallel to a top surface of the wafer.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Lithographic apparatus and device manufacturing method
In a maskless lithography apparatus light deflected by a patterning array out of a path towards a substrate is directed onto a detector that detects malfunctions of the patterning array. If the patterning array is of a type which selectively diverts radiation in order to pattern the beam, the detector can use the radiation that is diverted out of the beam. Alternatively, a second beam of radiation, additional to the exposure radiation, can be provided.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
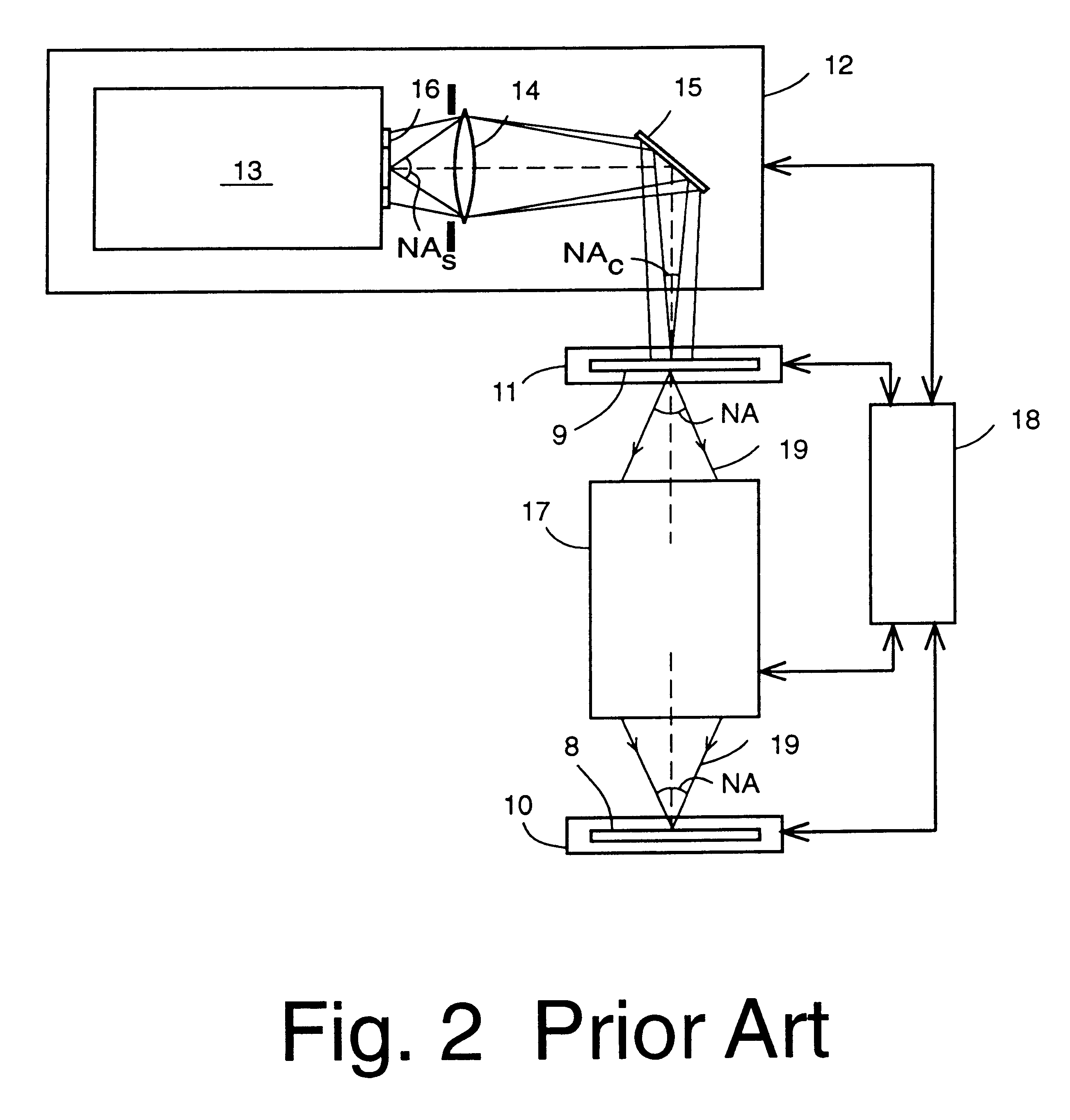
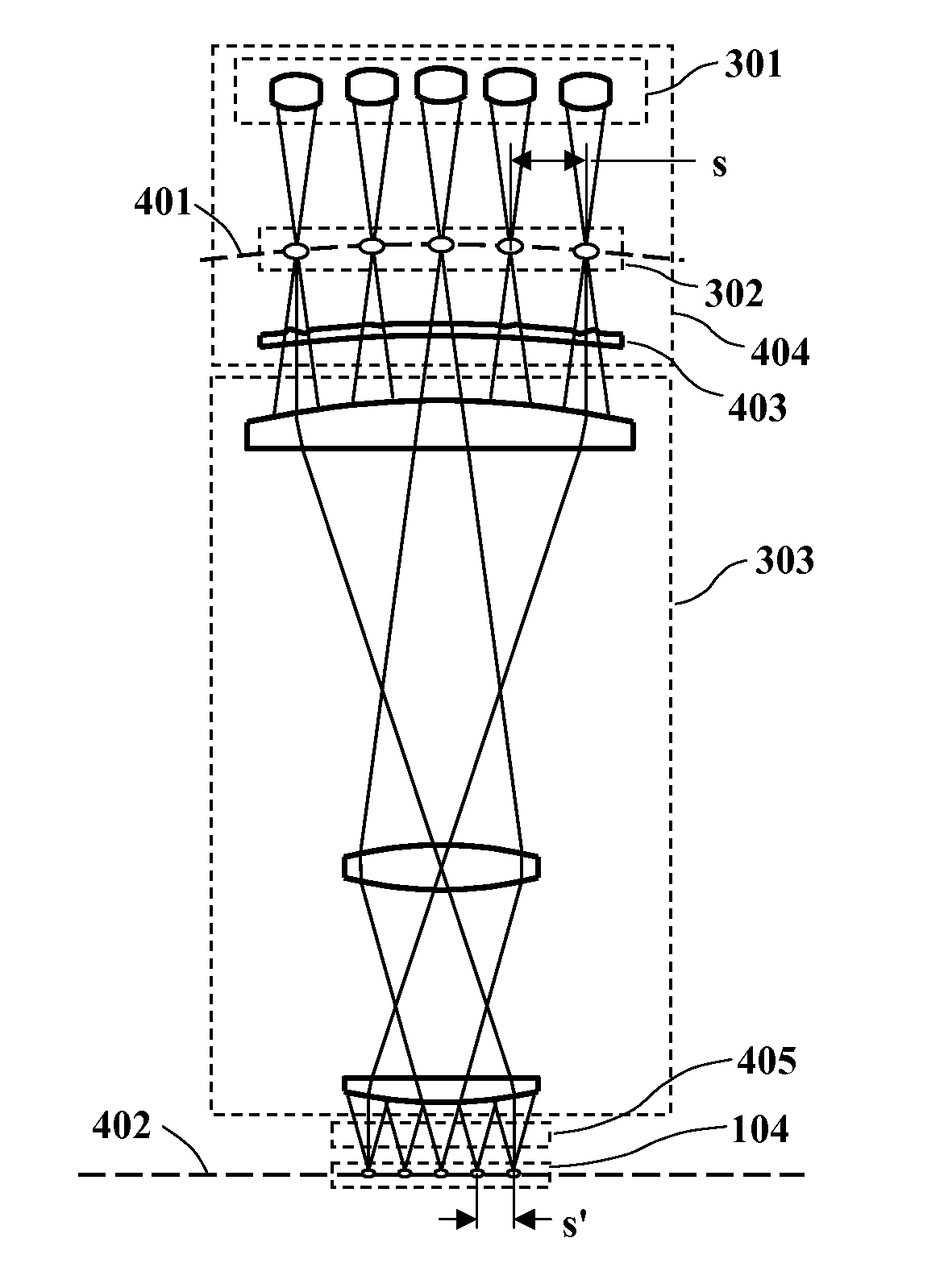
Spot-array imaging system for maskless lithography and parallel confocal microscopy
ActiveUS9188874B1Ensure correct executionCorrect chromatic aberrationOptically investigating flaws/contaminationMicroscopesCamera lensGrating
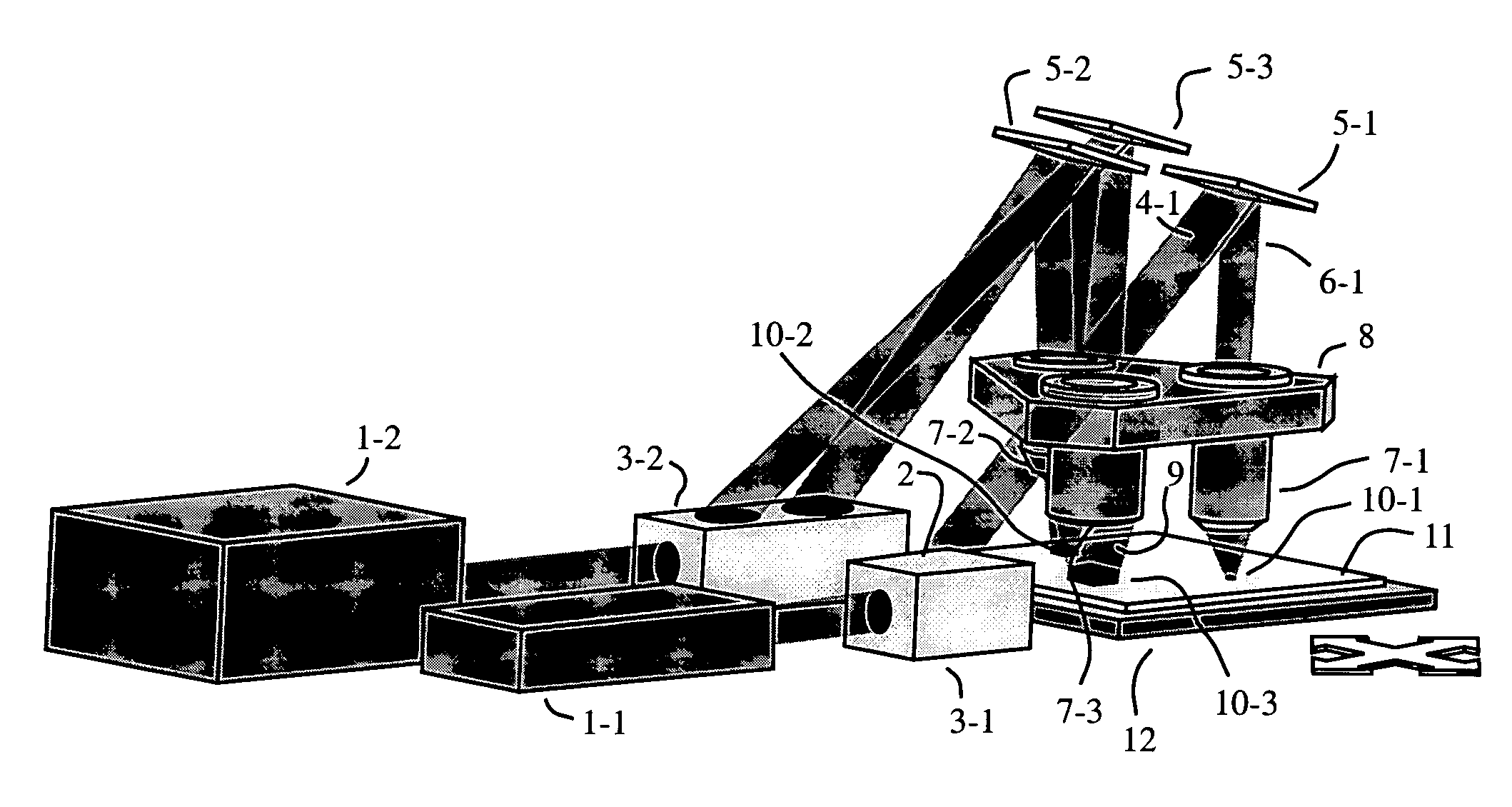
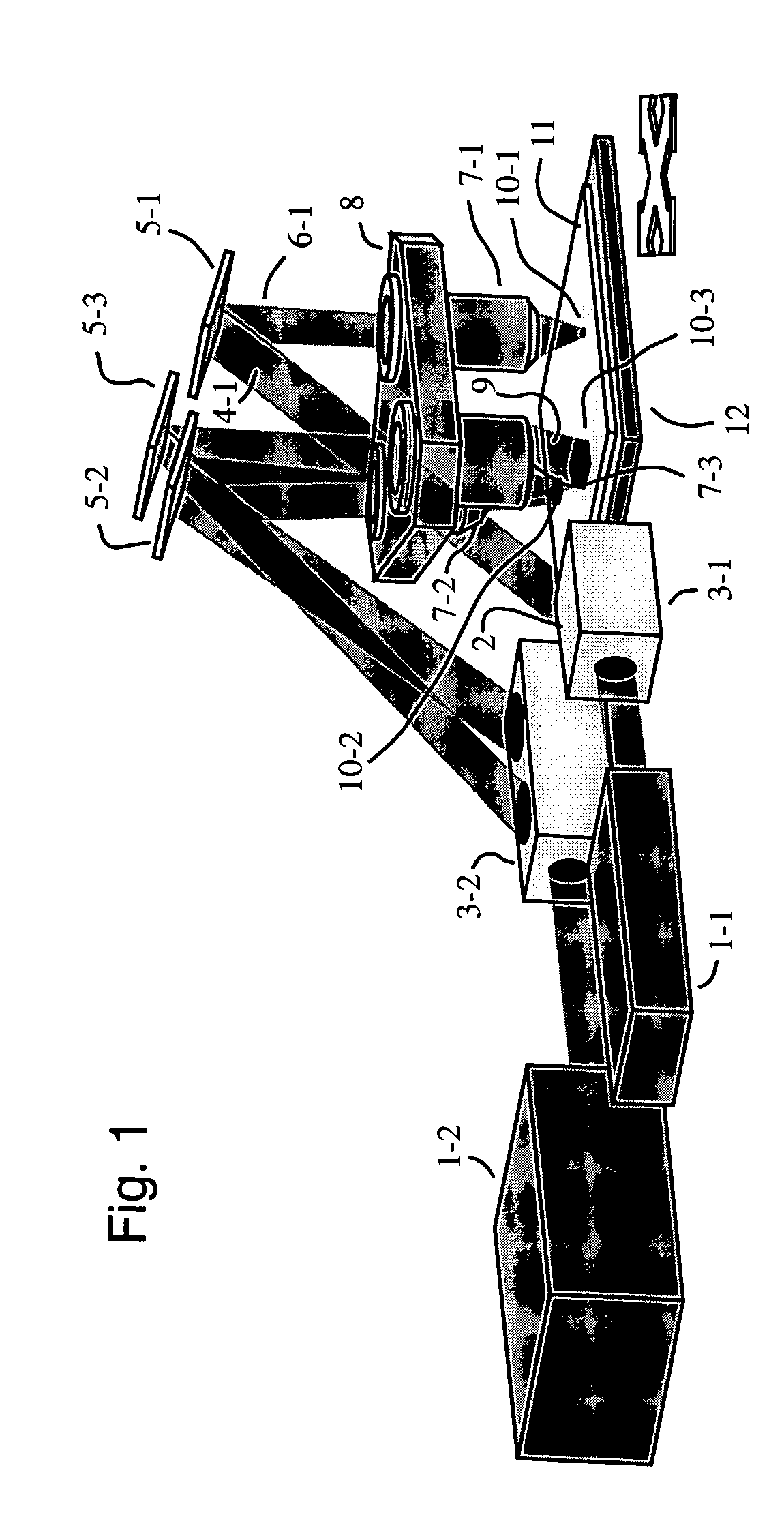
In a scanned-spot-array lithography system, a modulated array of radiant-energy source spots is imaged by a projection lens onto a printing surface, which is scanned in synchronization with the spot modulation to print a synthesized, high-resolution raster image. Similarly, in a scanned-spot-array microscopy system, an array of radiant-energy source spots is imaged by a projection lens onto an inspection surface, and radiation reflected from or transmitted through the image spots is collected and detected to acquire a synthesized, high-resolution raster image of the surface. In either case, the spot-generation optics can be configured to counterbalance and neutralize imperfect imaging characteristics of the projection lens, enabling perfectly flat-field, distortion-free, and aberration-free point imaging of the entire spot array. The spot-generation optics can also be further configured to achieve narrow-band achromatization of the optical system, and to optimally control the intensity and polarization characteristics of the image-plane radiation.
Owner:JOHNSON KENNETH C
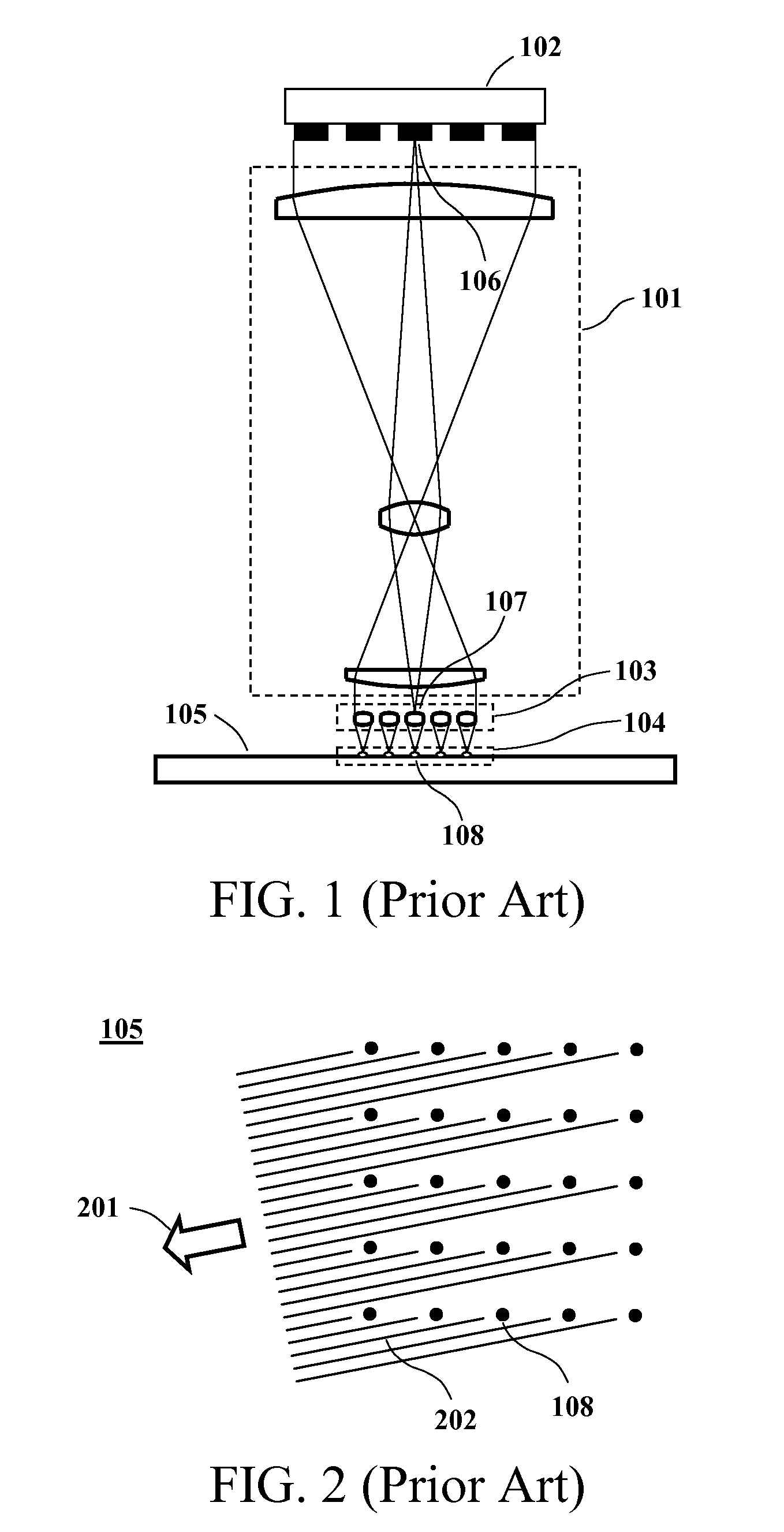
Direct write lithography system
InactiveUS6919952B2Easy to produceFast transferDecorative surface effectsNanoinformaticsLithographic artistElectron source
The mask-less lithography system has a converter that includes an array of light controllable electron sources. Each electron source is arranged for converting light into an electron beam and has an activation area. Individually controllable light sources are included where each light source is arranged for activating one electron source. A Controller controls each light source individually and each electron beam is focused on an object plane with a diameter smaller than the diameter of an individually controllable light source.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
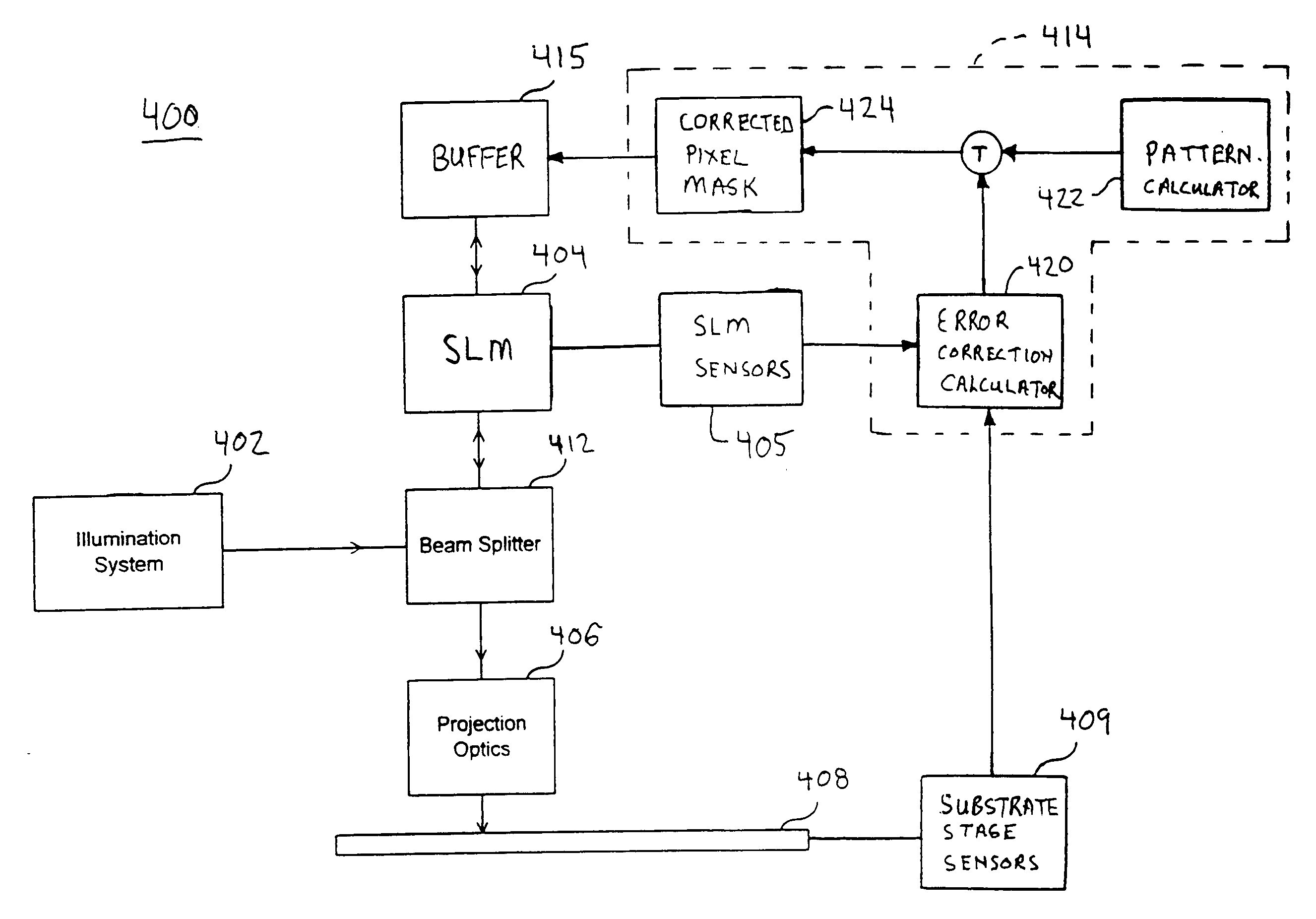
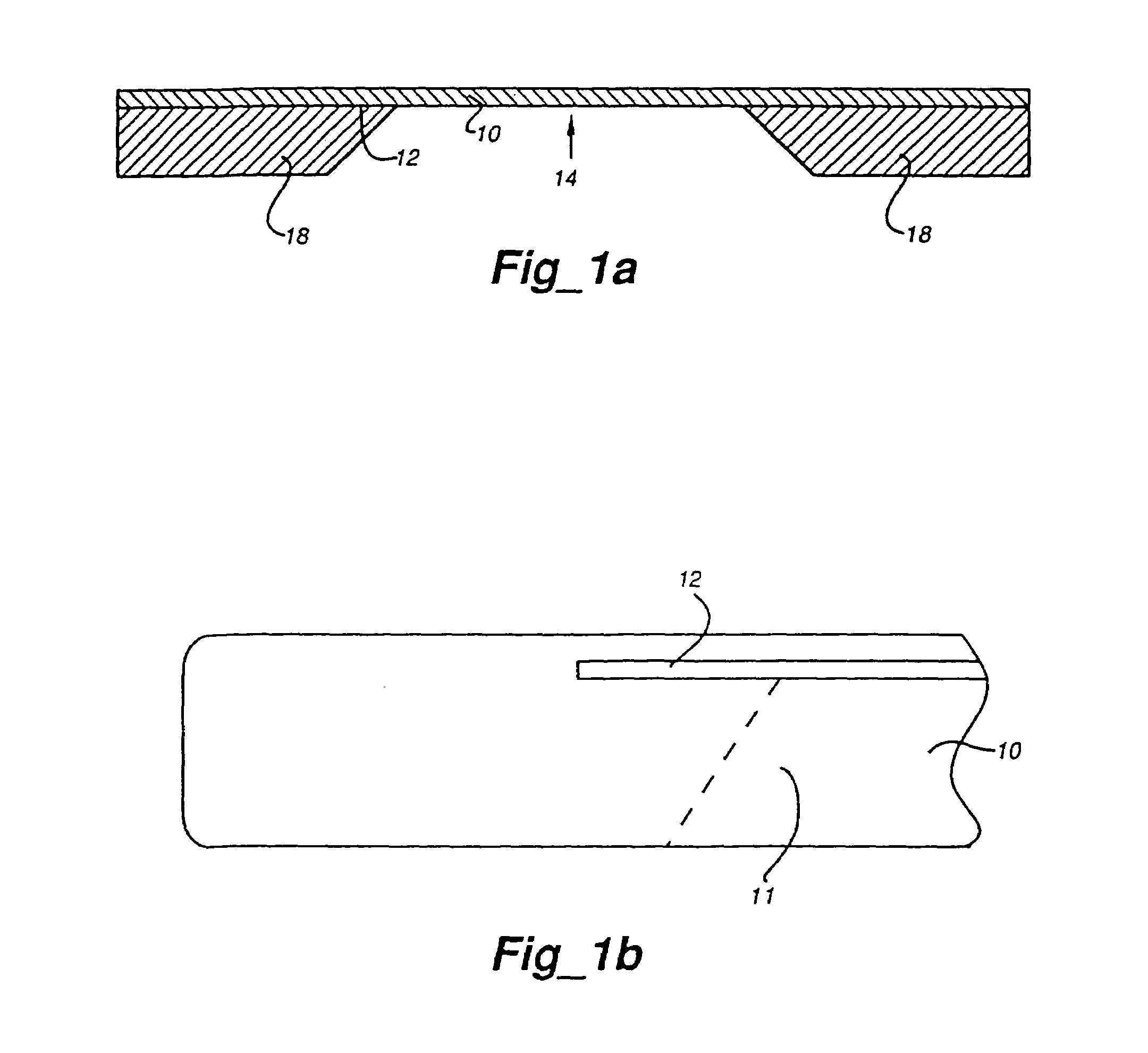
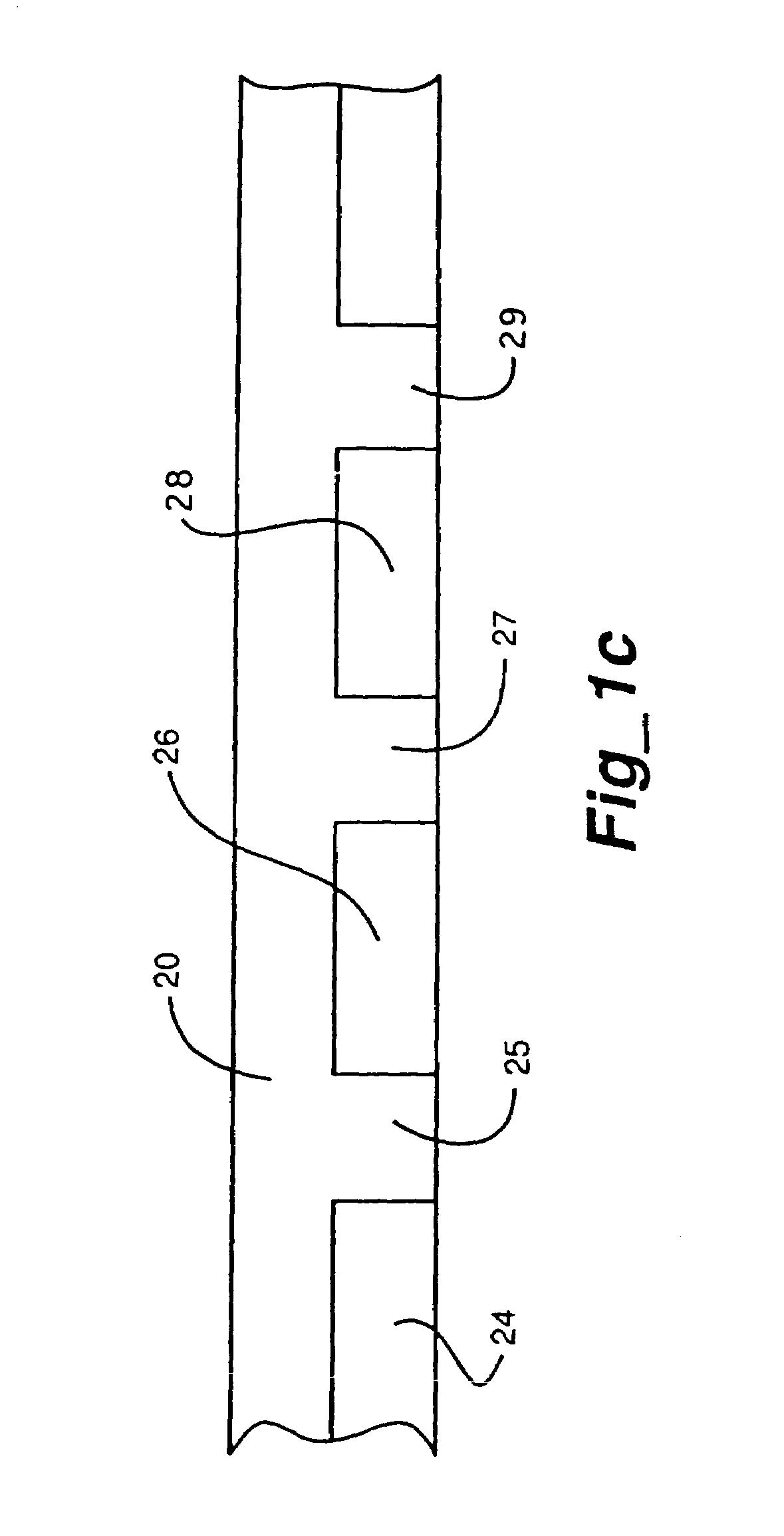
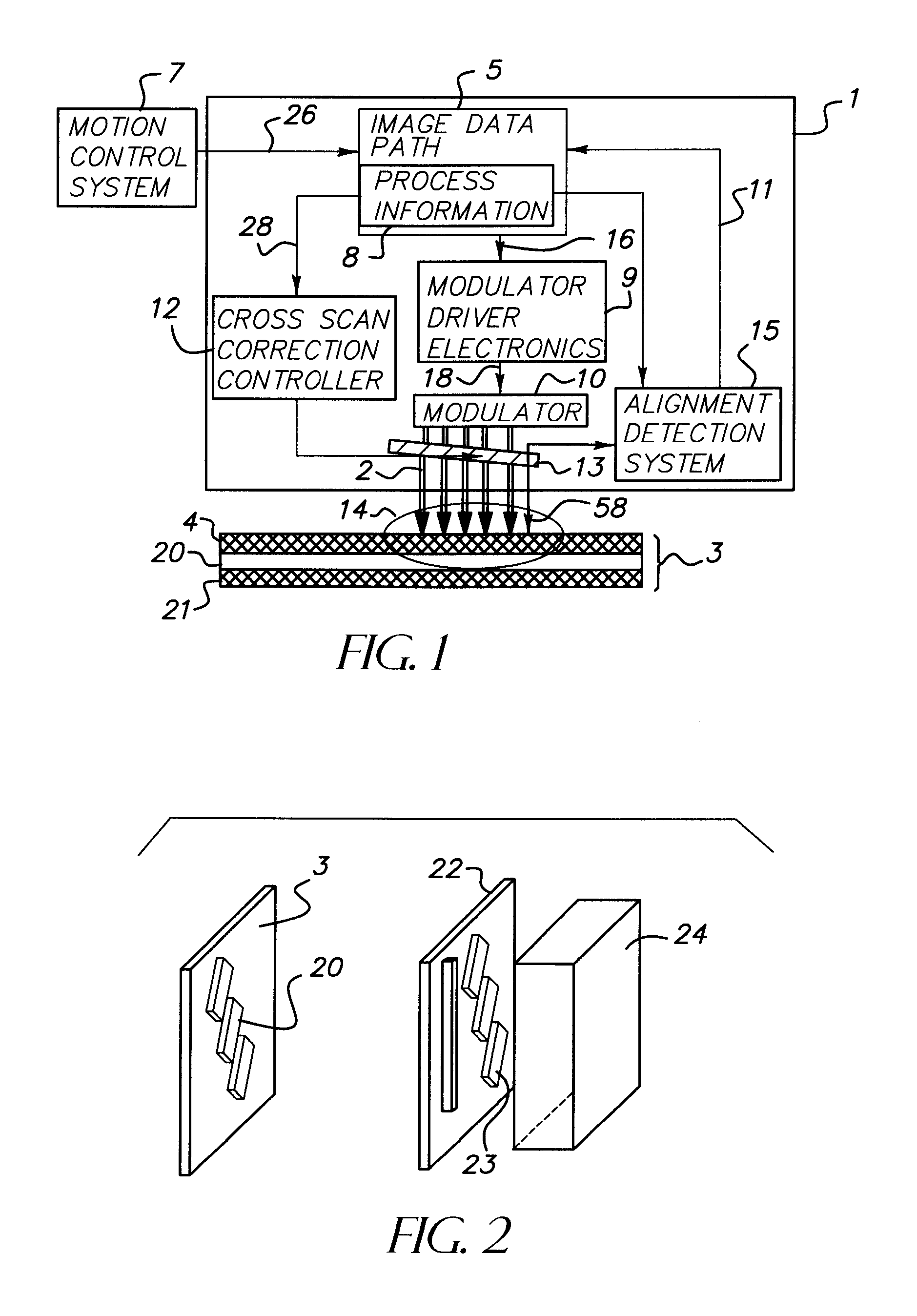
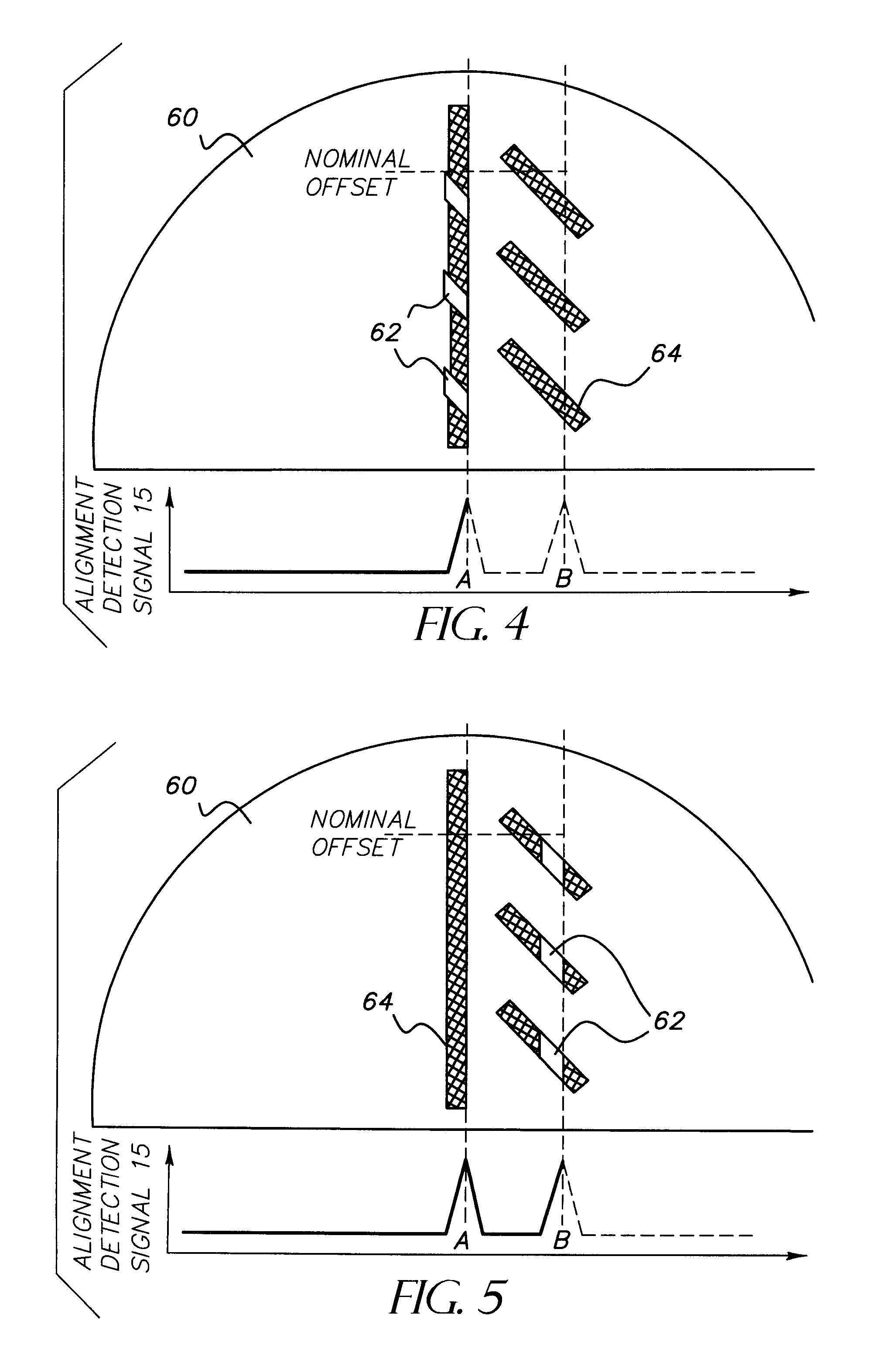
System and method to compensate for static and dynamic misalignments and deformations in a maskless lithography tool
ActiveUS20060033902A1Compensate for misalignmentImprove matchPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingSpatial light modulatorEngineering
The present invention provides systems and methods for maskless lithographic printing that compensate for static and / or dynamic misalignments and deformations. In an embodiment, a misalignment of a pattern formed by a spatial light modulator is measuring during printing. Rasterizer input data is generated based on the measured misalignment and passed the rasterizer. The rasterizer generates pattern data, based on the rasterizer input data, that is adjusted to compensate for the measured misalignment. The pattern data generated by the rasterizer is passed to the spatial light modulator and used to form a second pattern, which includes compensation for the measured misalignment. In an embodiment, deformations caused, for example, by a warping a surface of the spatial light modulator are measured and used by the rasterizer to generate pattern data that compensates for the deformations.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
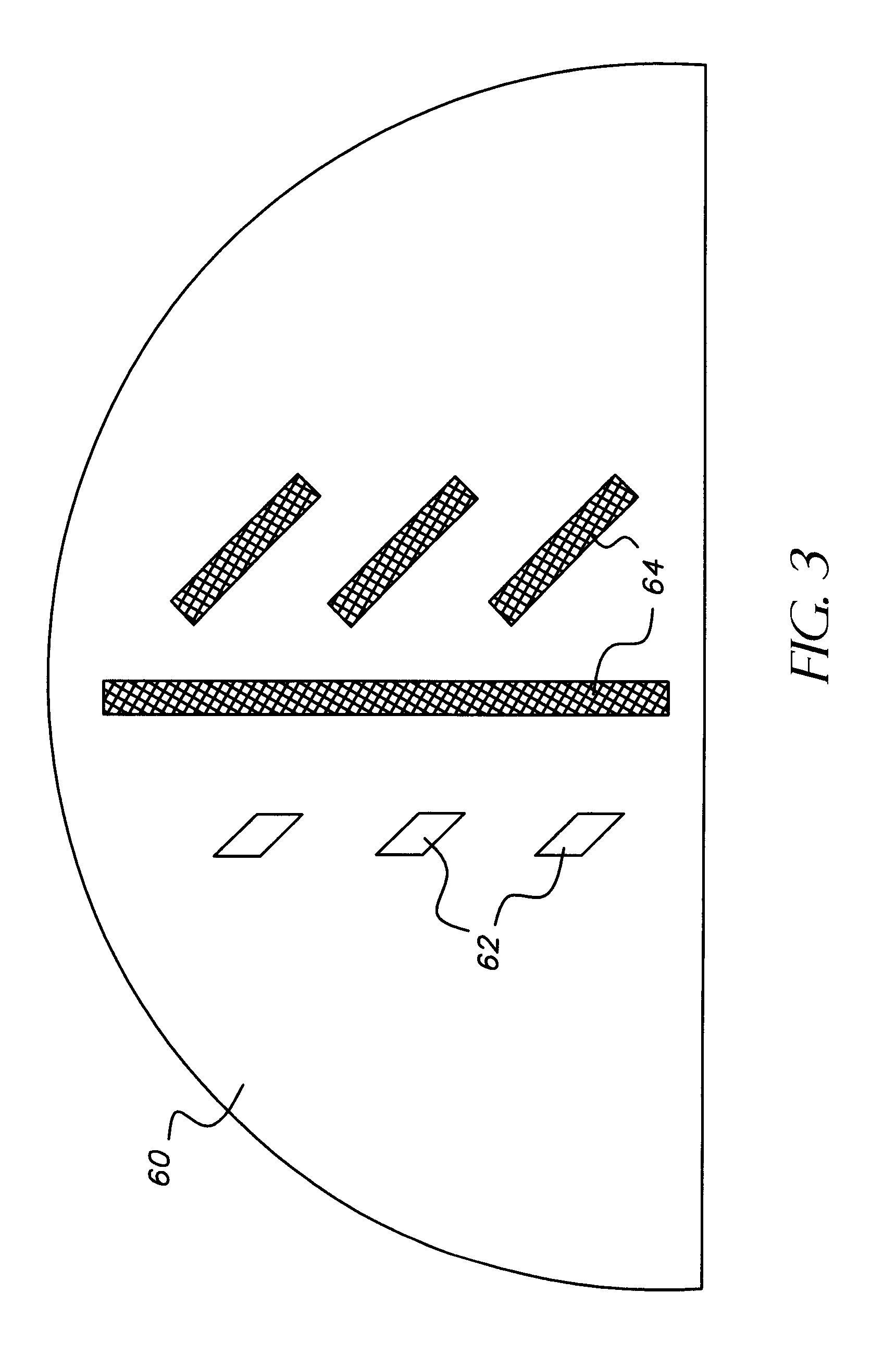
Segmented MEMS mirror for adaptive optics or maskless lithography
ActiveUS20060126151A1Less stringent requirementsLarge lengthOptical elementsParallel plateDevice form
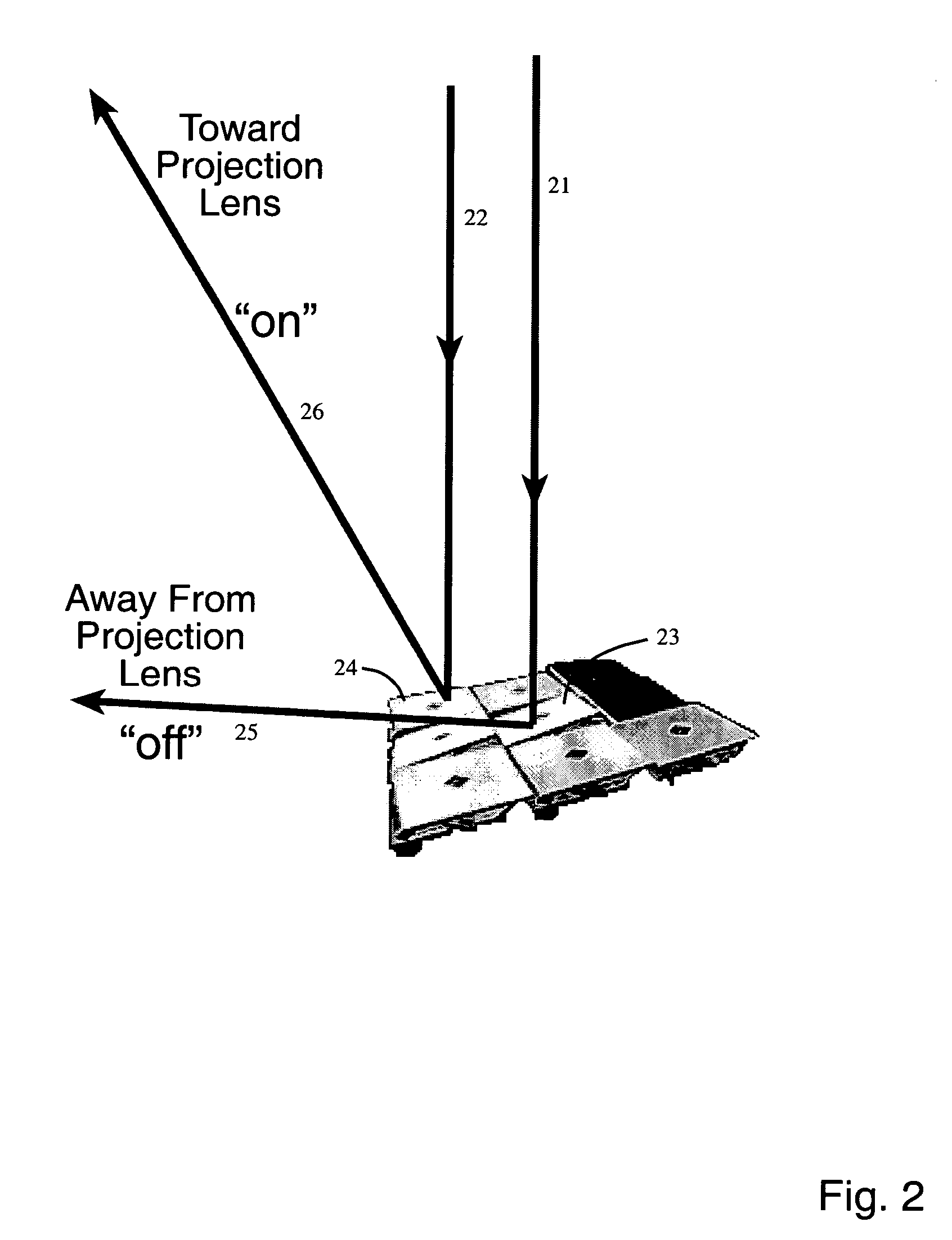
An apparatus having a plurality of arrayed MEMS devices, each device having a parallel-plate actuator and a reflective plate, both of which are mechanically coupled to a flexible beam attached between two anchors. Advantageously, the use of parallel-plate actuators in the apparatus alleviates stringent requirements for the alignment of lithographic masks employed in the fabrication process. In one embodiment, each flexible beam has a relatively small thickness and a relatively large length to effect a relatively large displacement range for the corresponding reflective plate. Movable electrodes of different parallel-plate actuators are configured to act as an electrical shield for the flexible beams, which reduces inter-device crosstalk in the apparatus. Reflective plates of different MEMS devices form a segmented mirror, which is suitable for adaptive-optics and / or maskless lithography applications.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method and apparatus for maskless photolithography
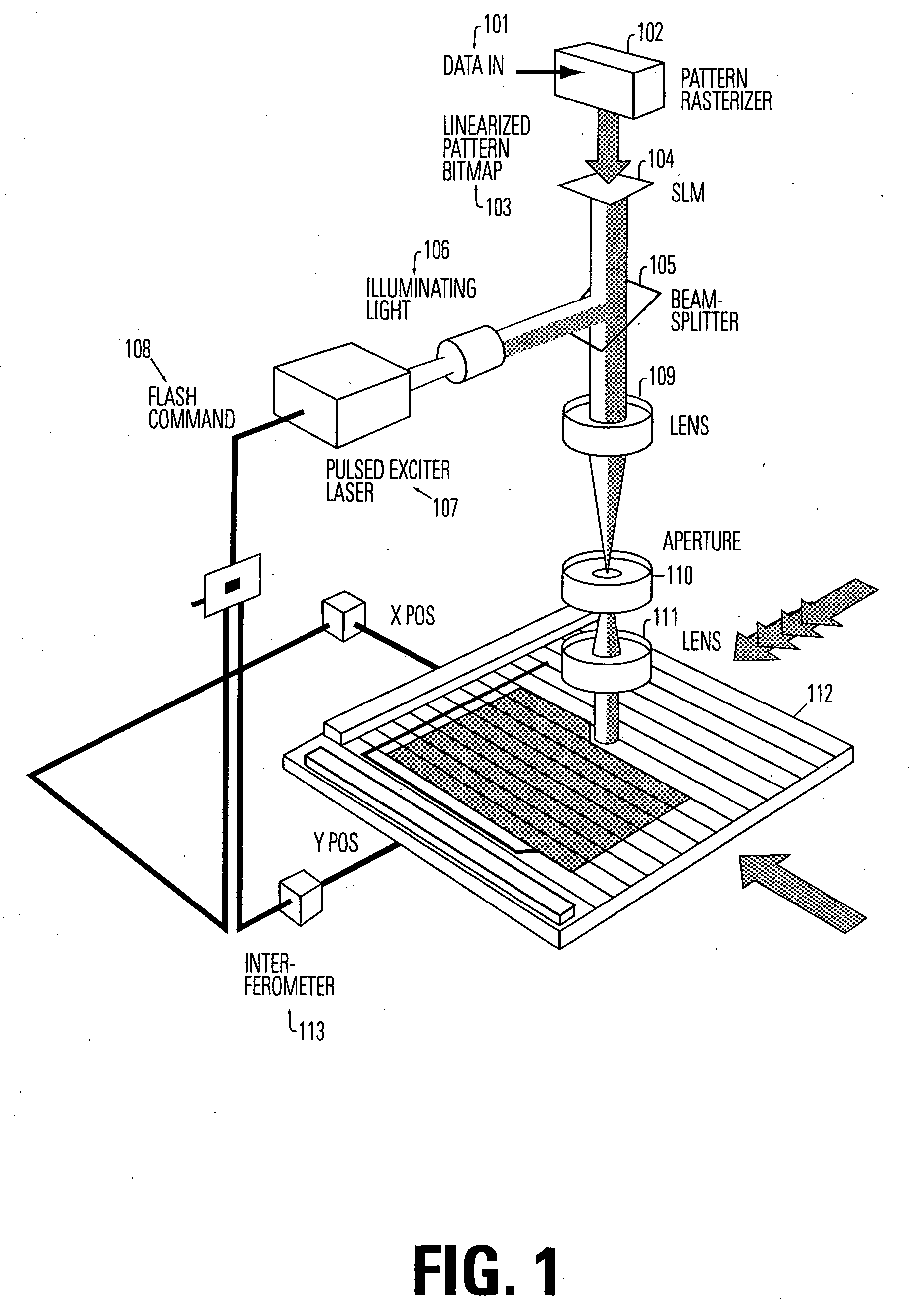
InactiveUS7095484B1Create efficientlyEasily and quickly be createdPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingVariable thicknessComputer-aided
A method and apparatus to create two dimensional and three dimensional structures using a maskless photolithography system that is semi-automated, directly reconfigurable, and does not require masks, templates or stencils to create each of the planes or layers on a multi layer two-dimensional or three dimensional structure. In an embodiment, the pattern generator comprises a micromirror array wherein the positioning of the mirrors in the micromirror array and the time duration of exposure can be modulated to produce gray scale patterns to photoform layers of continuously variable thickness. The desired pattern can be designed and stored using conventional computer aided drawing techniques and can be used to control the positioning of the individual mirrors in the micromirror array to reflect the corresponding desired pattern. A fixture for mounting of the substrate can be incorporated and can allow the substrate to be moved three dimensions. The fixture can be rotated in one, two, or three directions.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Optimal Rasterization for Maskless Lithography
InactiveUS20080224251A1Photosensitive materialsPhotomechanical apparatusEngineeringMaskless lithography
A lithographic system is provided in which an extent of overlap between pattern sections is adjusted in order to match a size of a pattern section to a size of a repeating portion of the pattern to be formed.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV +1
Pattern data conversion for lithography system
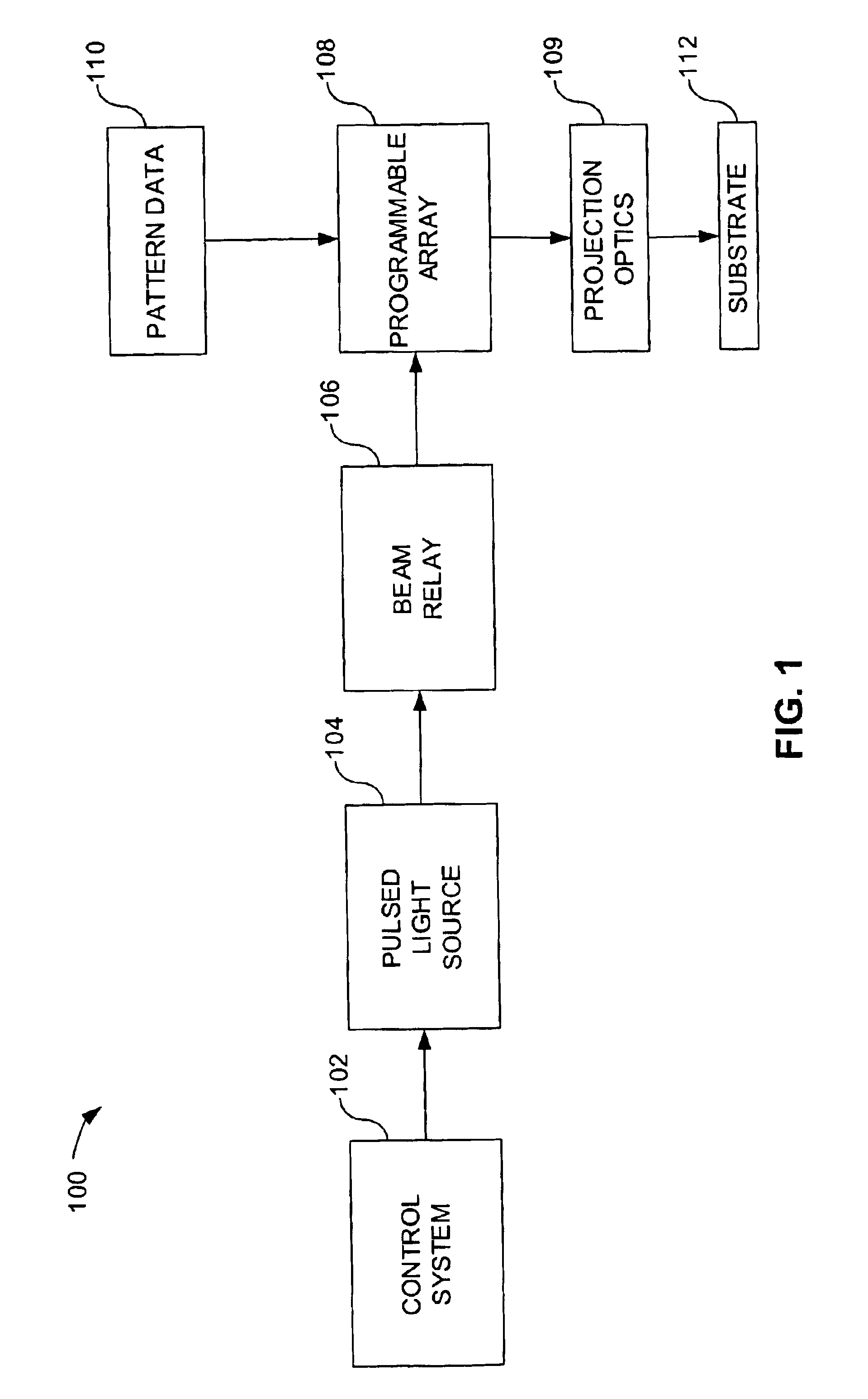
ActiveUS20120286173A1Improve performanceLower performance requirementsElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsGraphicsPattern recognition
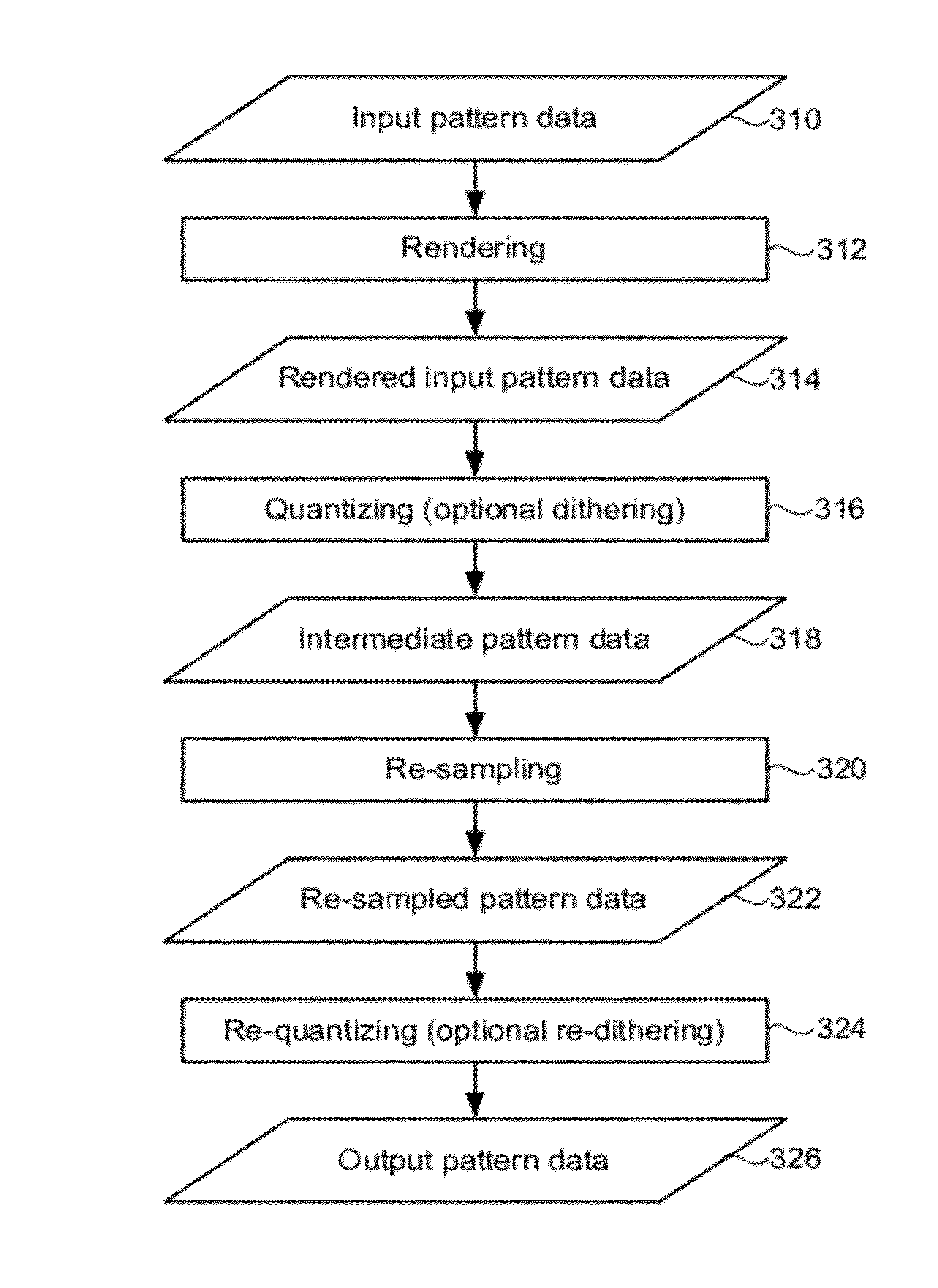
A method and system for exposing a target according to pattern data in a maskless lithography machine generating a plurality of exposure beamlets for exposing the target. The method comprises providing input pattern data in a vector format, rendering and quantizing the input pattern data to generate intermediate pattern data, and re-sampling and re-quantizing the intermediate pattern data to generate output pattern data. The output pattern data is supplied to the lithography machine, and the beamlets generated by the lithography machine are modulated on the basis of the output pattern data.
Owner:MAPPER LITHOGRAPHY IP +1
RET for optical maskless lithography
The present invention relates to Optical Maskless Lithography (OML). In particular, it relates to providing OML with a recognizable relationship to mask and phase-shift mask techniques.
Owner:MICRONIC LASER SYST AB
Synchronous pulse exposure method for maskless lithography equipment and digital laser direct-writing system
InactiveCN104865800AExtend effective lifeImprove and increase contrastPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusUv laserDigital micro mirror device
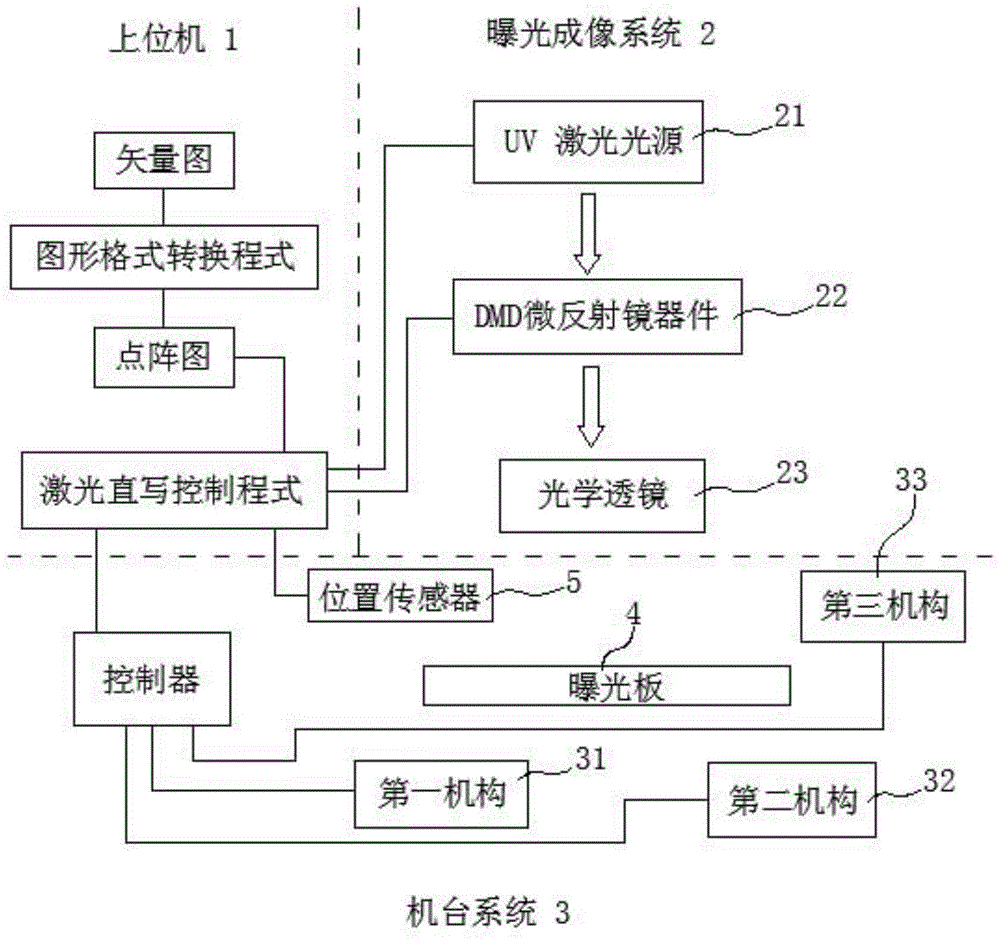
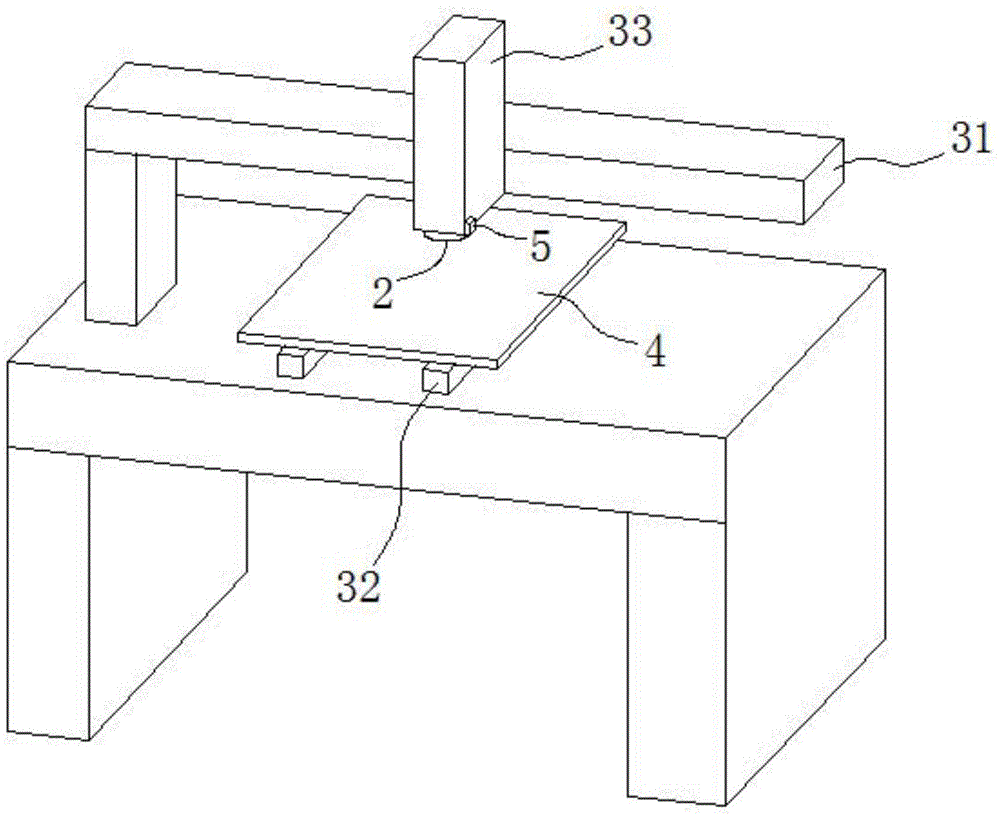
The invention provides a synchronous pulse exposure method for maskless lithography equipment. The maskless lithography equipment adopts an exposure imaging system consisting of a UV (ultraviolet) laser or UV LED light source, a DMD (digital micro-mirror device) and an optical lens; the synchronous pulse exposure method is characterized in that a series of pulse synchronization signals are generated, the DMD and the UV laser or UV LED light source are triggered to synchronously work, and the pulse interval of the pulse synchronization signals depends on the replacement or refreshing cycle of the DMD to graphs; a digital laser direct-writing system comprises an upper computer in charge of outputting digital lattice patterns and the series of pulse synchronization signals to the exposure imaging systems, and one or more exposure imaging systems arranged side by side. According to the method, a synchronous control problem of parts of the lithography equipment is solved, more effective and reasonable exposure and refreshing time is convenient to design, and the shortcomings of low production capacity and poor system adaptability of a conventional exposure machine are overcome.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN AISCENT TECH
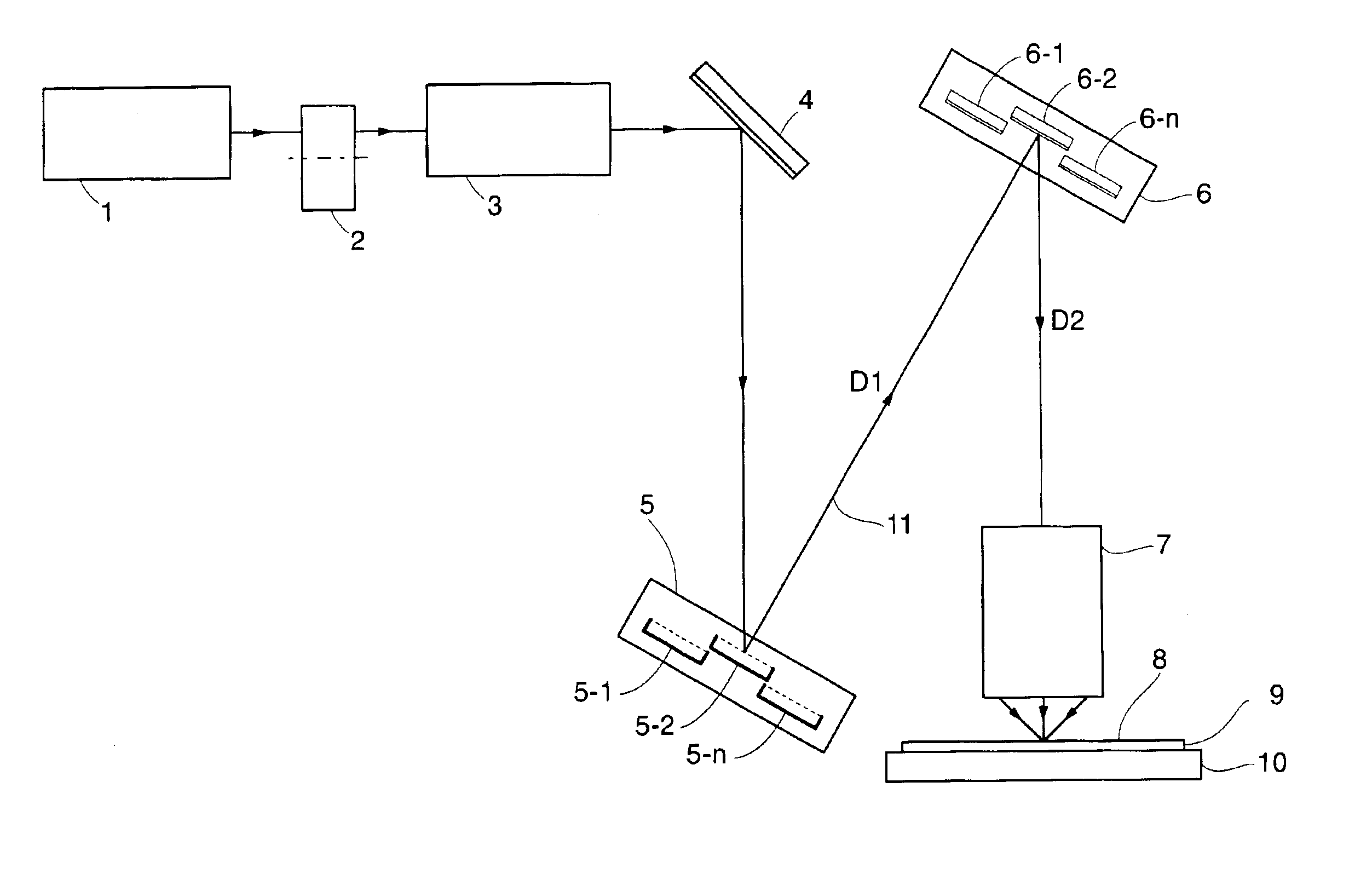
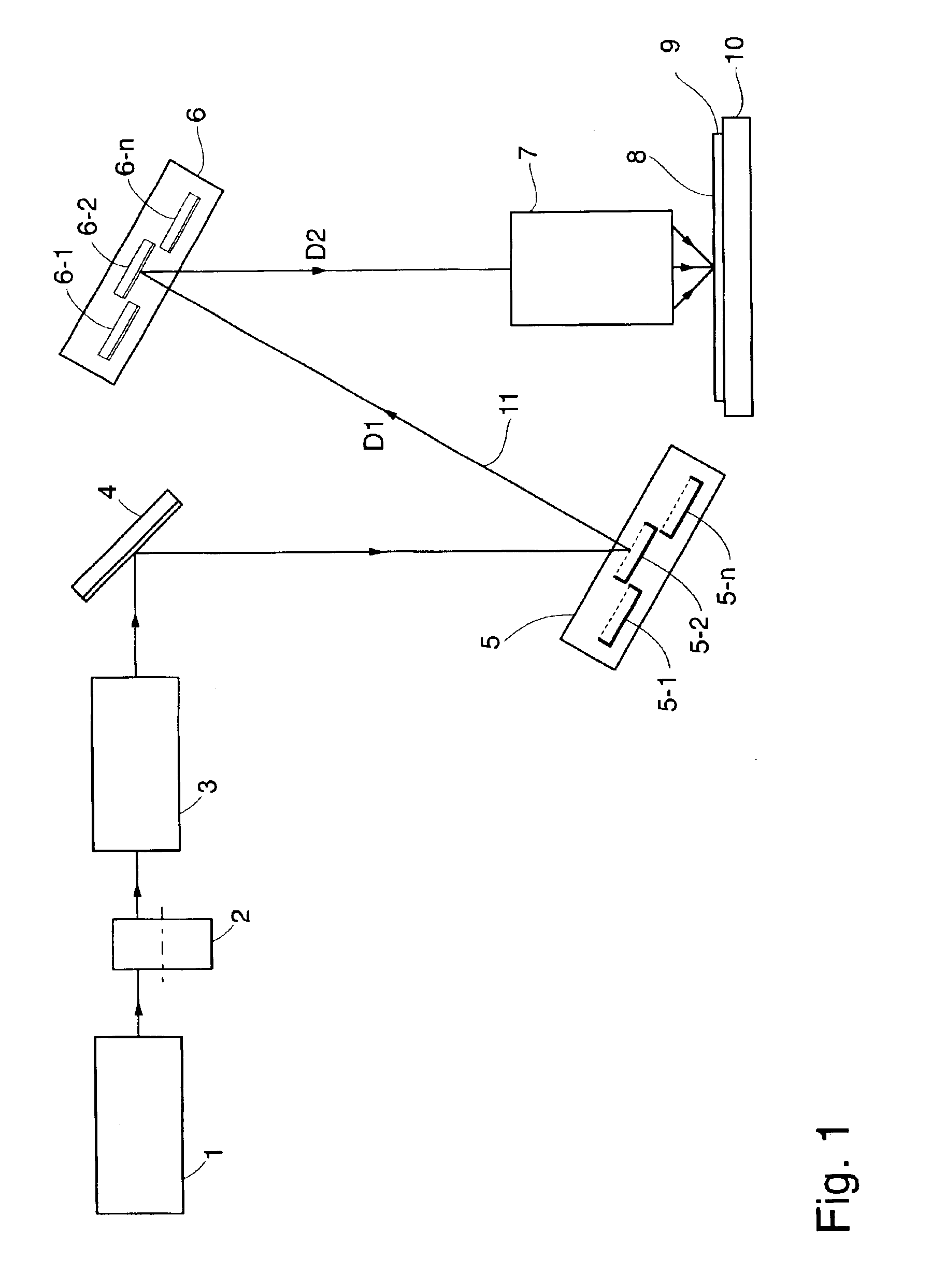
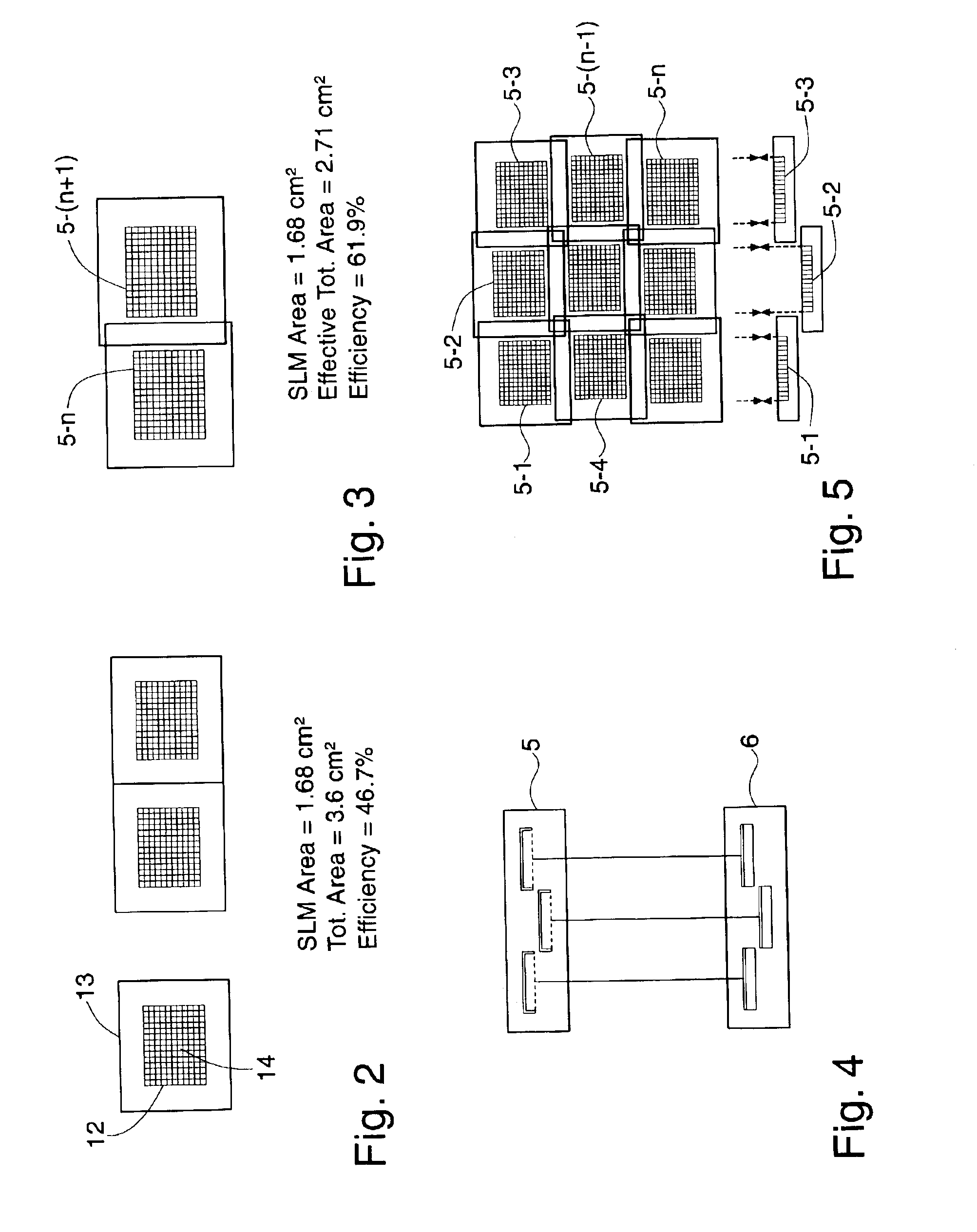
Reliability in a maskless lithography system
ActiveUS20070029507A1Reduce partReduce impactElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsTarget surfaceProperty value
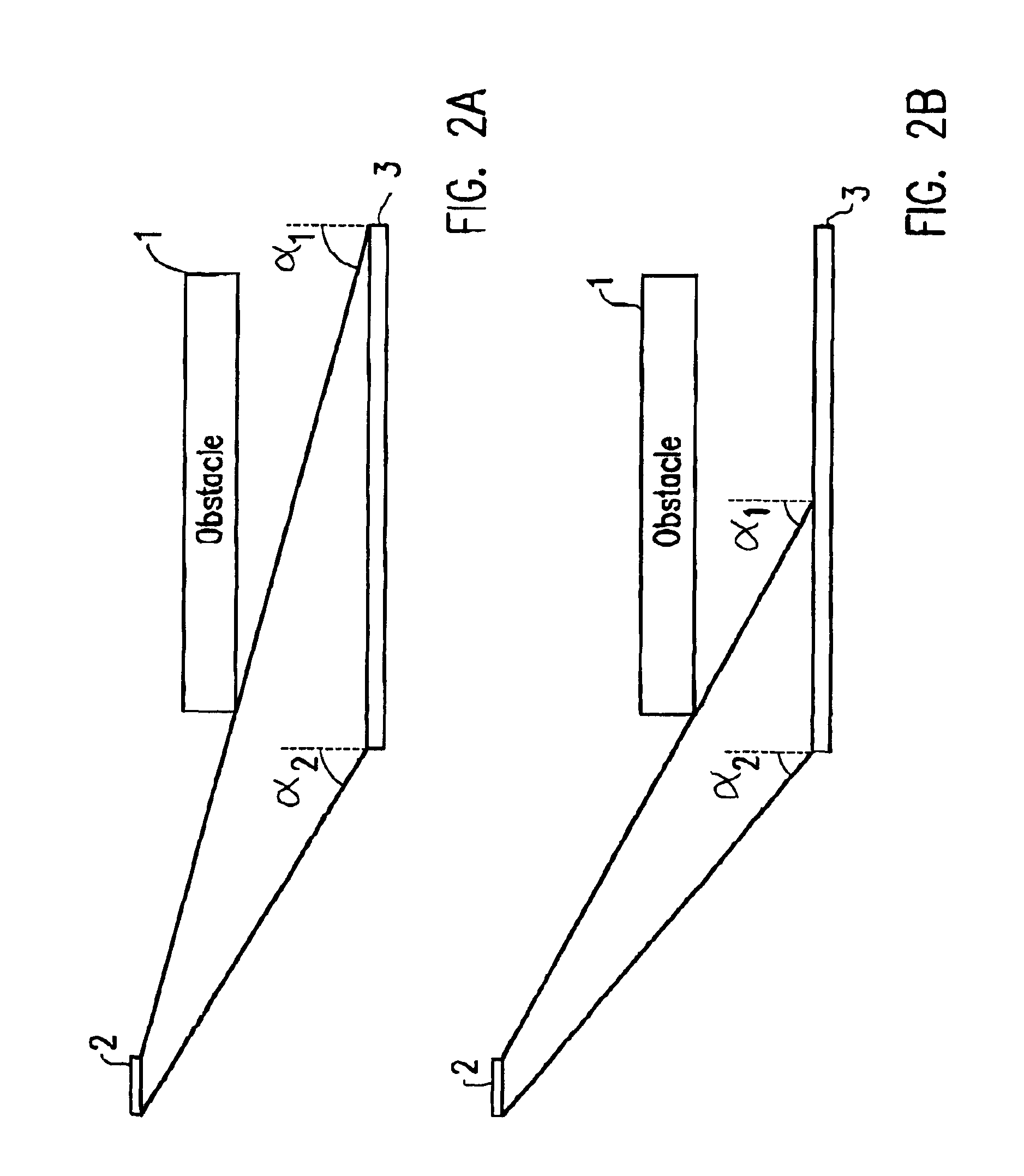
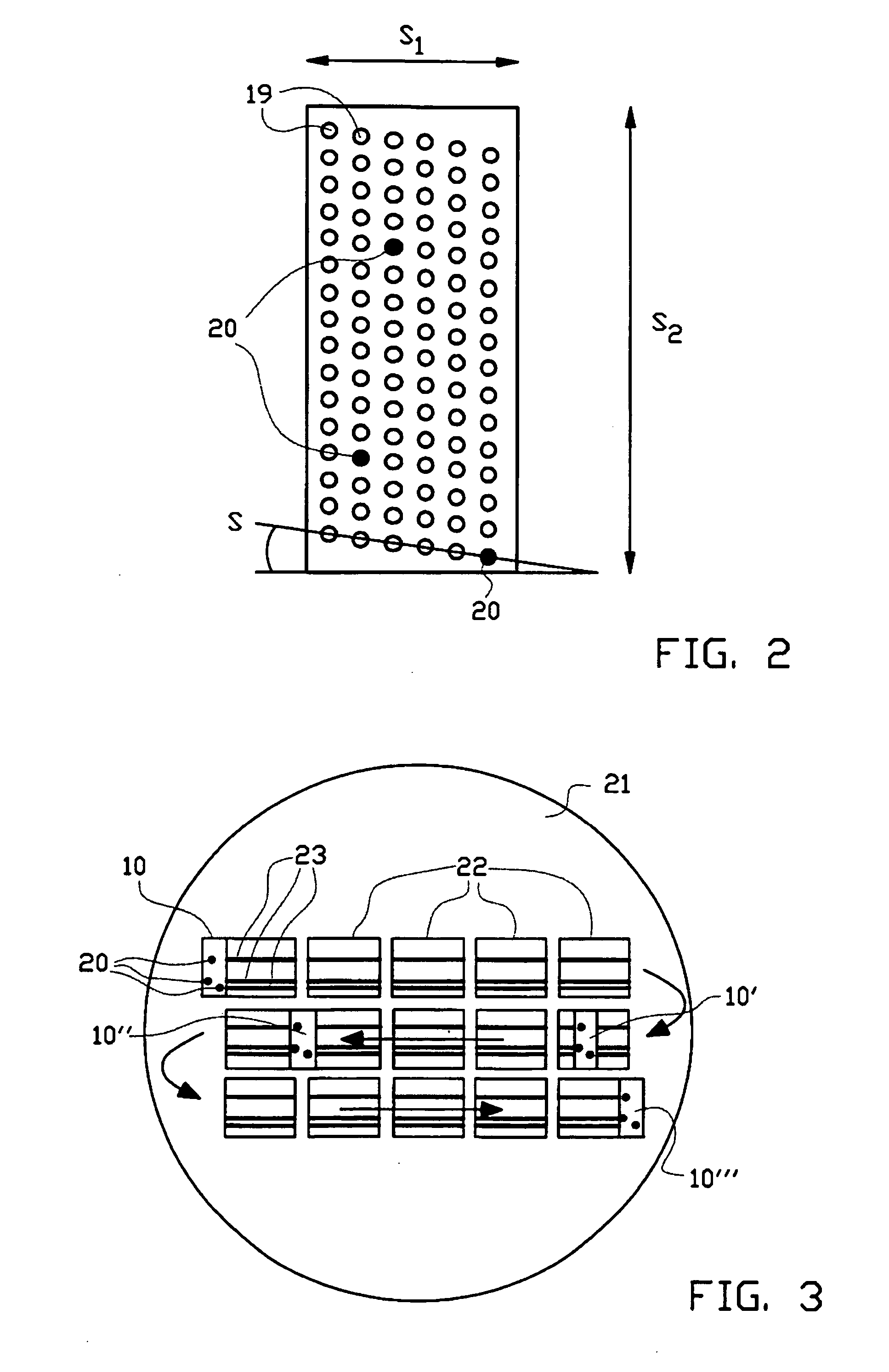
The invention pertains to a maskless lithography system for transferring a pattern onto a surface of a target, comprising at least one beamlet optical unit for generating a plurality of beamlets, at least one measuring unit for measuring properties of each beamlet, at least one control unit for generating and delivering pattern data to said beamlet optical unit, said control unit being operationally coupled to said measuring unit for identifying invalid beamlets which have a measured property value outside a predefined range of values for said property at least one actuator for inducing a shift of said beamlet optical unit and said target with respect to one another, wherein said actuator is operationally coupled with said control unit, said control unit determining said shift, positioning valid beamlets at the position of said invalid beamlets, thus replacing said invalid beamlets with valid beamlets.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
Process and apparatus for generating a strong phase shift optical pattern for use in an optical direct write lithography process
ActiveUS20050153246A1Increase exposureLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLithographic artistLithography process
The present invention provides methods and apparatus for accomplishing a strong phase shift direct write lithography process using reconfigurable optical mirrors. A maskless lithography system is provided. The maskless direct-write lithography system provided uses an array of mirrors configured to operate in a tilting mode, a piston-displacement mode, or both in combination. The controlled mirror array is used to generate strong phase shift optical patterns which are directed onto a photoimageable layer of a substrate in order to facilitate pattern transfer. In order to avoid constraining the system to forming edges of patterns aligned with the array of mirrors, gray-scale techniques are used for subpixel feature placement.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
Methods and systems to compensate for a stitching disturbance of a printed pattern in a maskless lithography system utilizing overlap without an explicit attenuation
A method and system are provided for printing a pattern on a photosensitive surface using a maskless lithography system including a spatial light modulator (SLM). The method includes defining two or more exposure areas within a predetermined region of the surface, each area corresponding to selected pixels of the SLM. An overlap region is formed between the two or more exposure areas, the overlapping region being defined by respective overlapping edges of the exposure areas, the overlapping edges corresponding to overlapping pairs of the selected pixels from each area. The pixels within each pair are alternately activated such that only one of the pixels within the pair is used to produce the pattern.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Versatile maskless lithography system with multiple resolutions
InactiveUS7164465B2Easy to combineQuick selectionPhotomechanical apparatusPhotographic printingSpatial light modulatorImage resolution
A versatile maskless patterning system with capability for selecting rapidly among a plurality of projection lenses mounted on a turret. This provides the ability to rapidly select multiple choices for resolution and enables optimization of the combination of the imaging resolution and exposure throughput, making possible cost-effective fabrication of microelectronics packaging products. A preferred embodiment uses a digital micromirror device array spatial light modulator as a virtual mask. Another preferred embodiment use multiple closely spaced digital micromirror device array spatial light modulators to enhance throughput.
Owner:ANVIK CORP
Mirror arrays for maskless photolithography and image display
ActiveUS20100255426A1Low costLamination ancillary operationsMirrorsSelective reflectionElectromagnetic radiation
Micromirrors and micromirror arrays described herein are useful, for example in maskless photolithography systems and methods and projection display devices and methods. According to one aspect, the micromirrors comprise a polymer structural layer and a reflective dielectric multilayer for selective reflection and / or redirection of incoming electromagnetic radiation. According to another aspect, incorporation of a reflective dielectric multilayer allows for use of polymer structural materials in micromirrors and prevents damage to such polymer materials due to excessive heating from absorption of electromagnetic radiation, as the reflective dielectric multilayers are highly reflective and minimize heating of the micromirror components. According to yet a further aspect, top down fabrication methods are described herein for making a micromirror comprising a polymer structural layer and a reflective dielectric multilayer.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
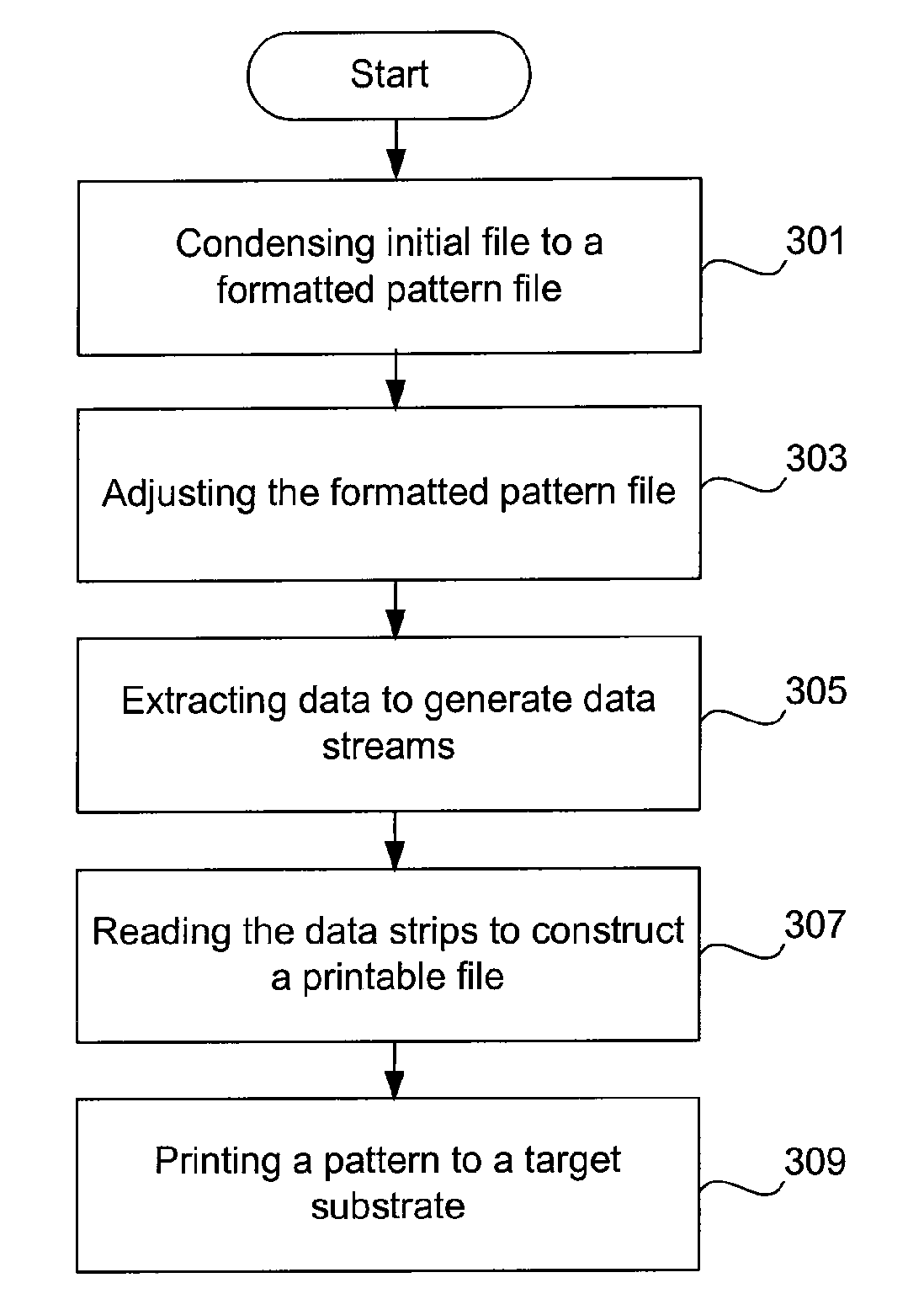
Method of data encoding, compression, and transmission enabling maskless lithography
InactiveUS20080145767A1Electric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsPattern recognitionLithographic artist
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
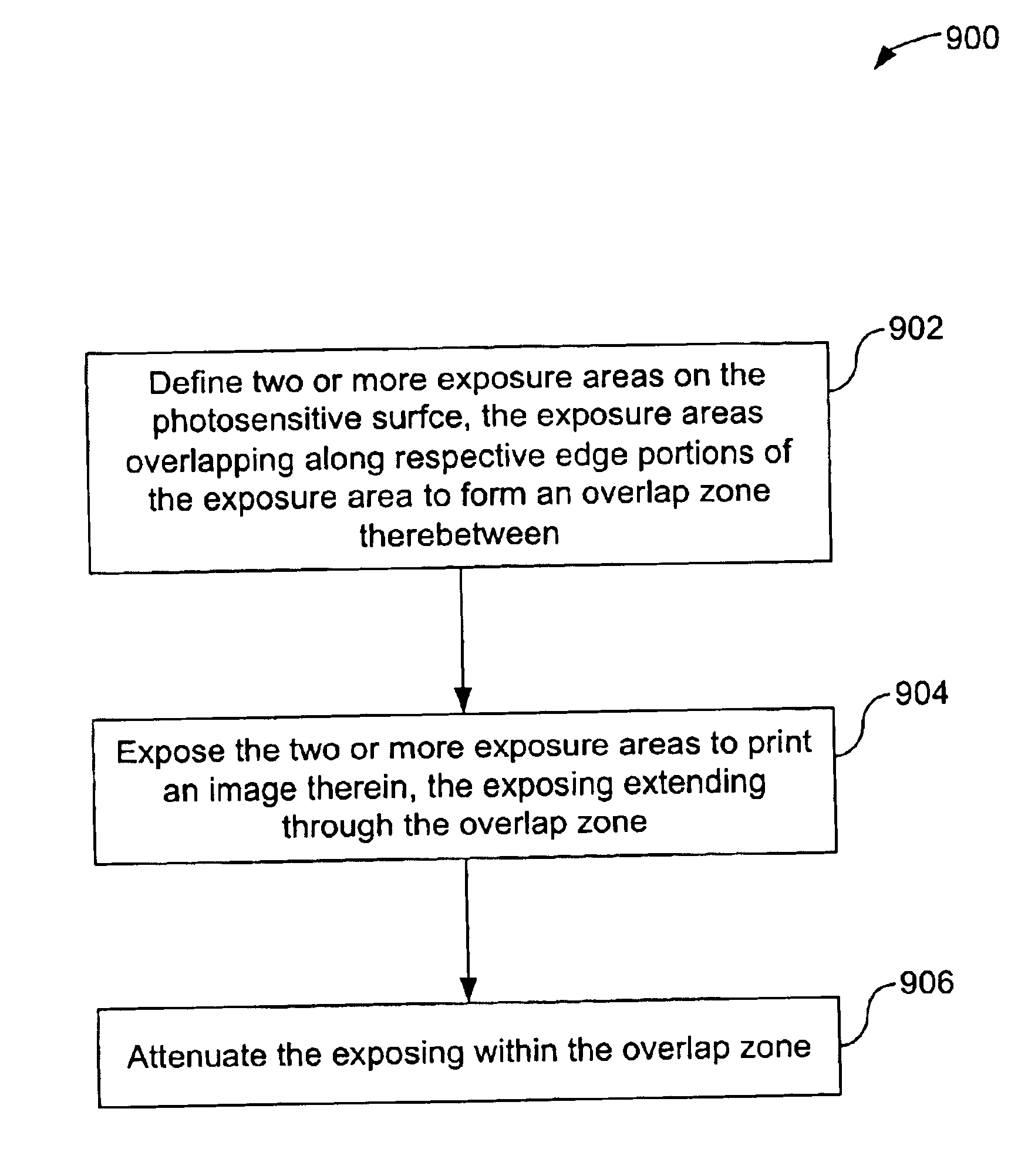
Methods and systems to compensate for a stitching disturbance of a printed pattern in a maskless lithography system utilizing overlap of exposure zones with attenuation of the aerial image in the overlap region
A method and system are provided for printing a pattern on a photosensitive surface using a spatial light modulator (SLM). An exemplary method includes defining two or more exposure areas on the photosensitive surface, the exposure areas overlapping along respective edge portions of the exposure areas to form an overlap zone therebetween. Two or more exposure areas are exposed to print an image therein, the exposing extending through the overlap zone. The exposing within the overlap zone is then attenuated.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Plasmonic array for maskless lithography
In various embodiments, a photolithography system comprises a spatial light modulator and a plasmonic lens array. The spatial light modulator comprises a plurality of pixels, and the plasmonic lens array comprises a plurality of plasmonic lenses. The pixels are optically aligned with the plasmonic lenses such that light from the pixels is substantially focused by the lenses. The plasmonic lenses each comprise an optical aperture and a plurality of metal features proximal to the aperture. The metal features have a dimension and arrangement configured to couple optical energy incident on one side of the plasmonic lens into plasmon excitation supported by the metal and to reemit optical energy through the aperture.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Maskless lithography systems and methods utilizing spatial light modulator arrays
InactiveUS20050046819A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSpatial light modulatorControl signal
A maskless lithography system that writes patterns on an object. The system can include an illumination system, the object, spatial light modulators (SLMs), and a controller. The SLMs can pattern light from the illumination system before the object receives the light. The SLMs can include a leading set and a trailing set of the SLMs. The SLMs in the leading and trailing sets change based on a scanning direction of the object. The controller can transmit control signals to the SLMs based on at least one of light pulse period information, physical layout information about the SLMs, and scanning speed of the object. The system can also correct for dose non-uniformity using various methods.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
Methods for maskless lithography
InactiveUS7223696B2Cost effectiveImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMOSFETDevice material
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
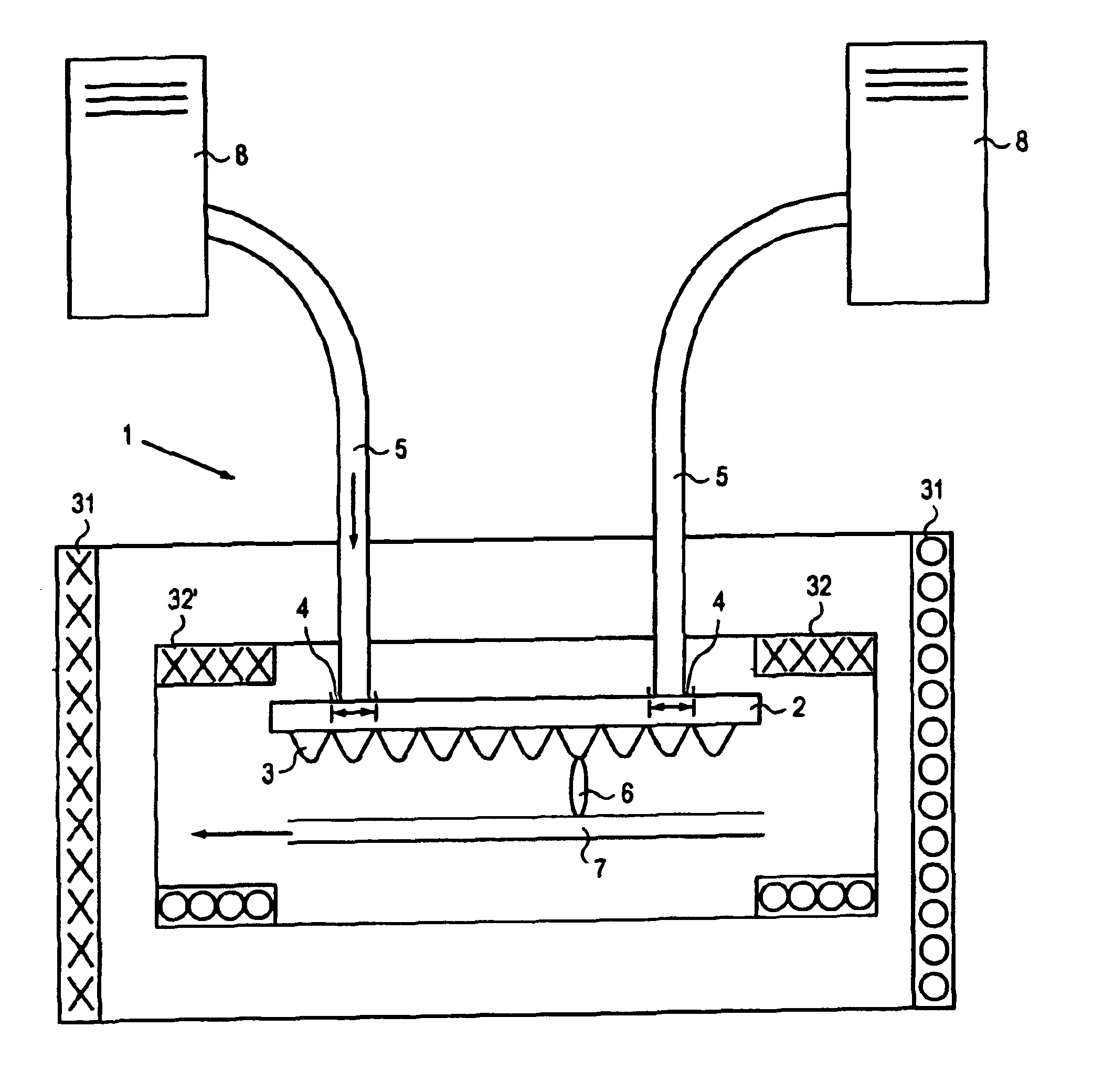
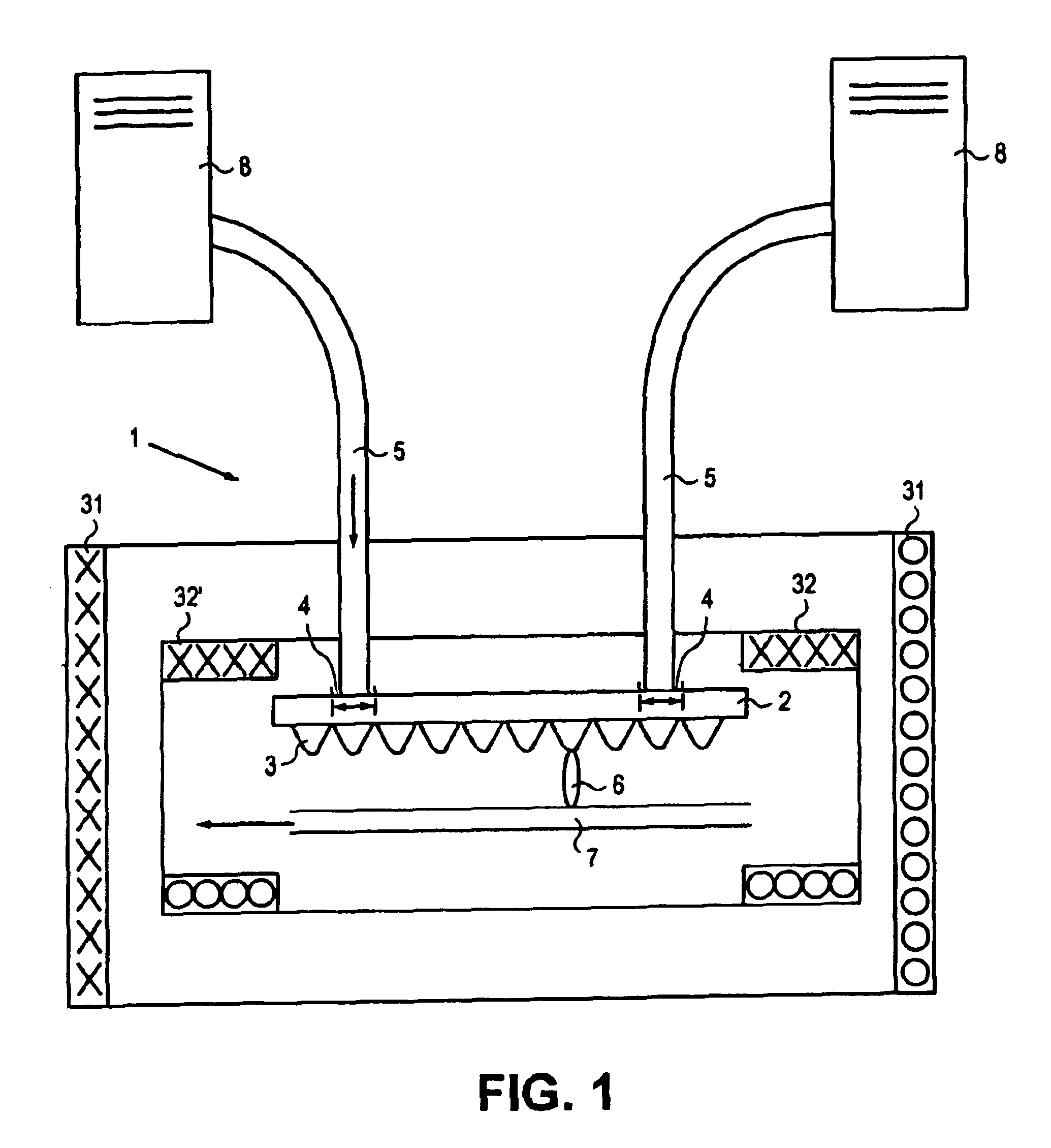
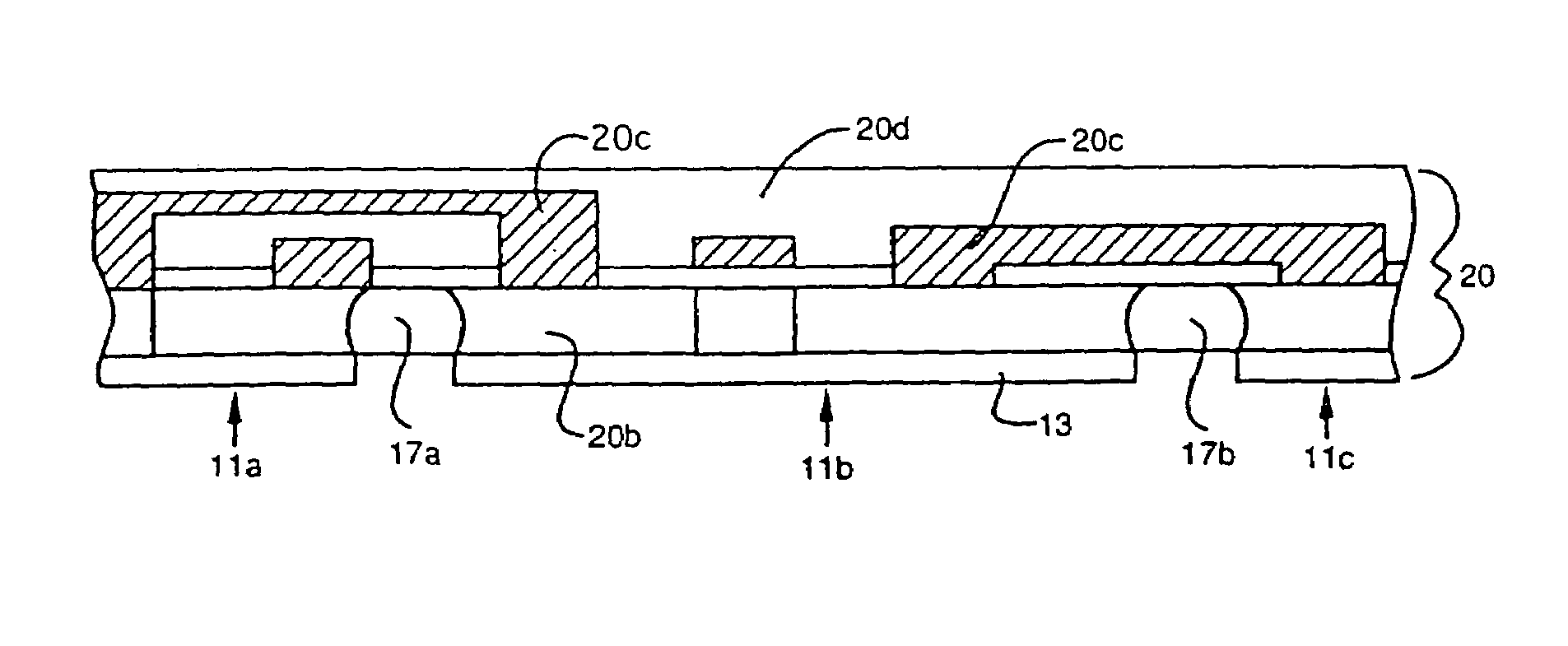
Dynamic compensation system for maskless lithography
InactiveUS20070231717A1Convenient registrationIncrease speedPhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaskless lithographyElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method for dynamically registering multiple patterned layers on a substrate (3) comprises: depositing a first layer on the substrate; printing a first pattern (20) on the first layer; depositing a second layer on the first pattern; and printing a second pattern on the second layer while dynamically detecting the first pattern to align the second pattern with the first pattern.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
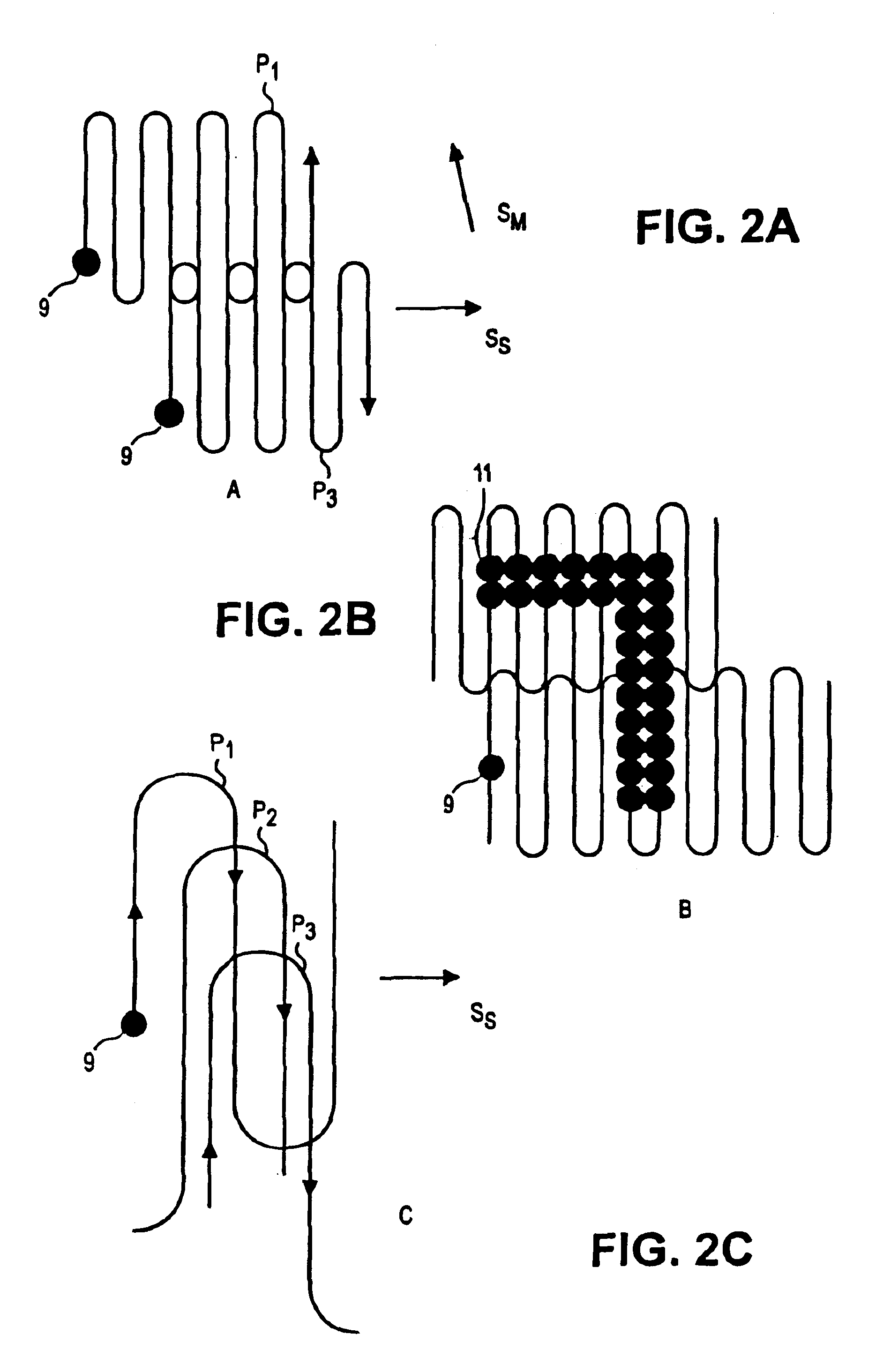
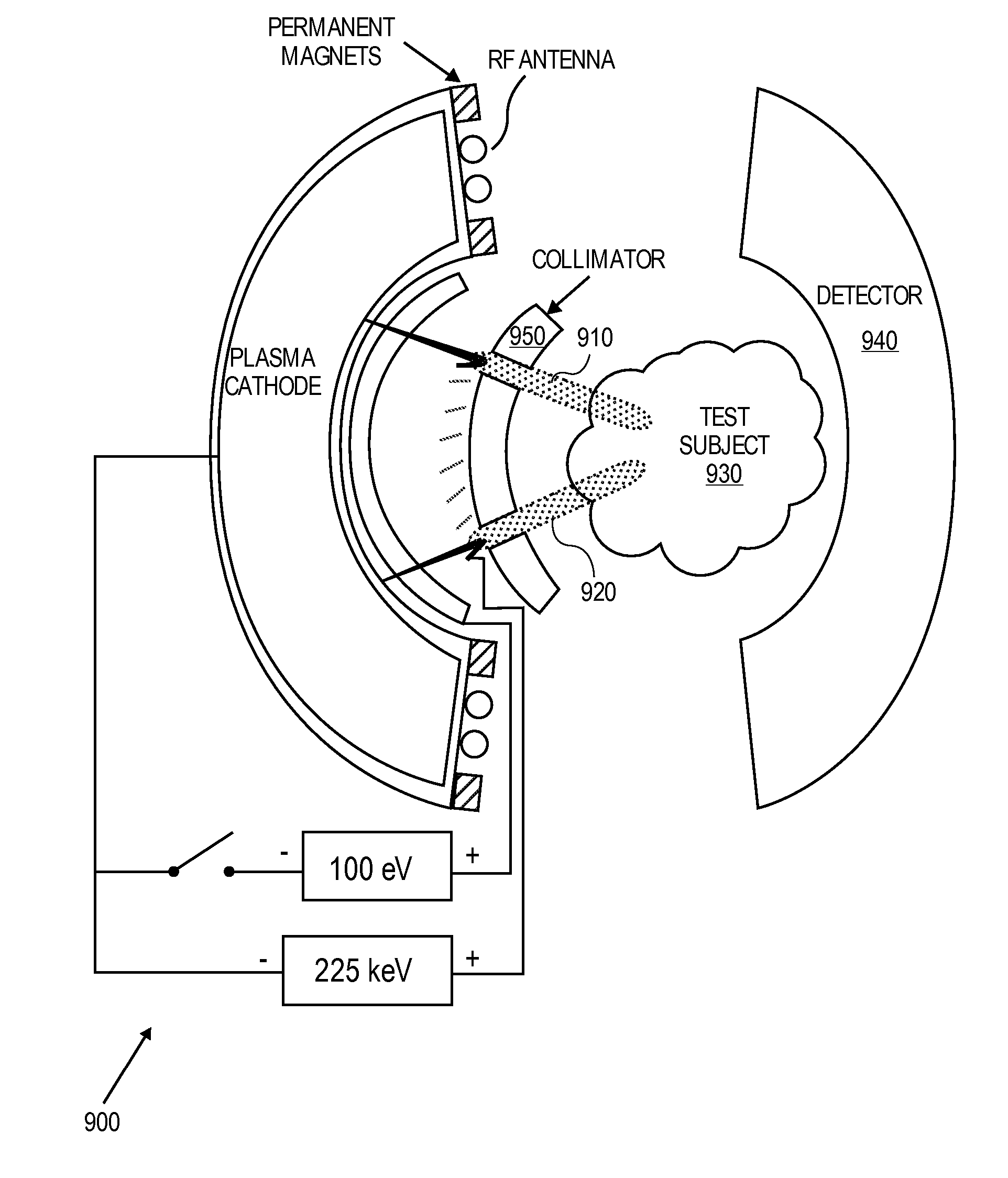
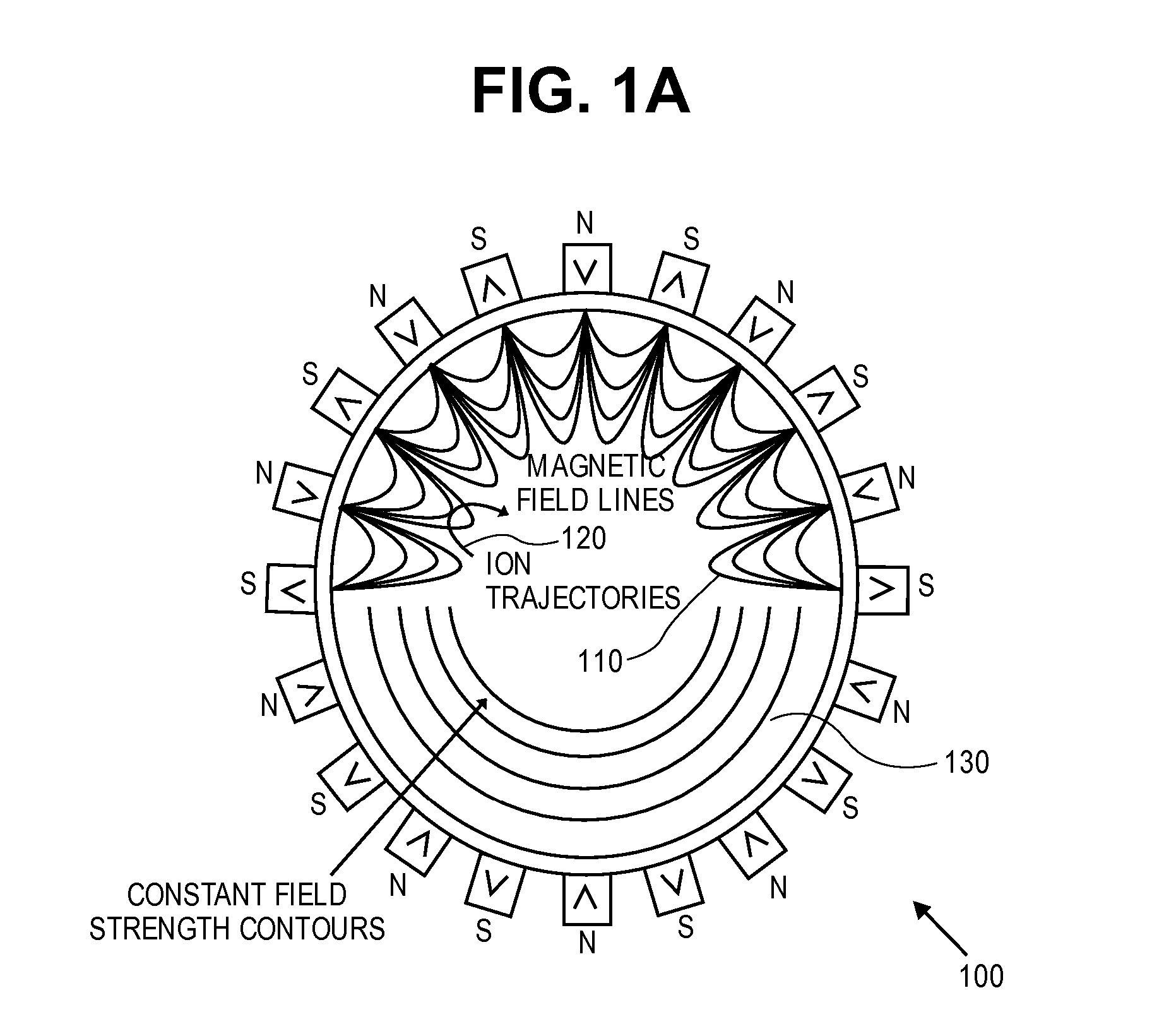
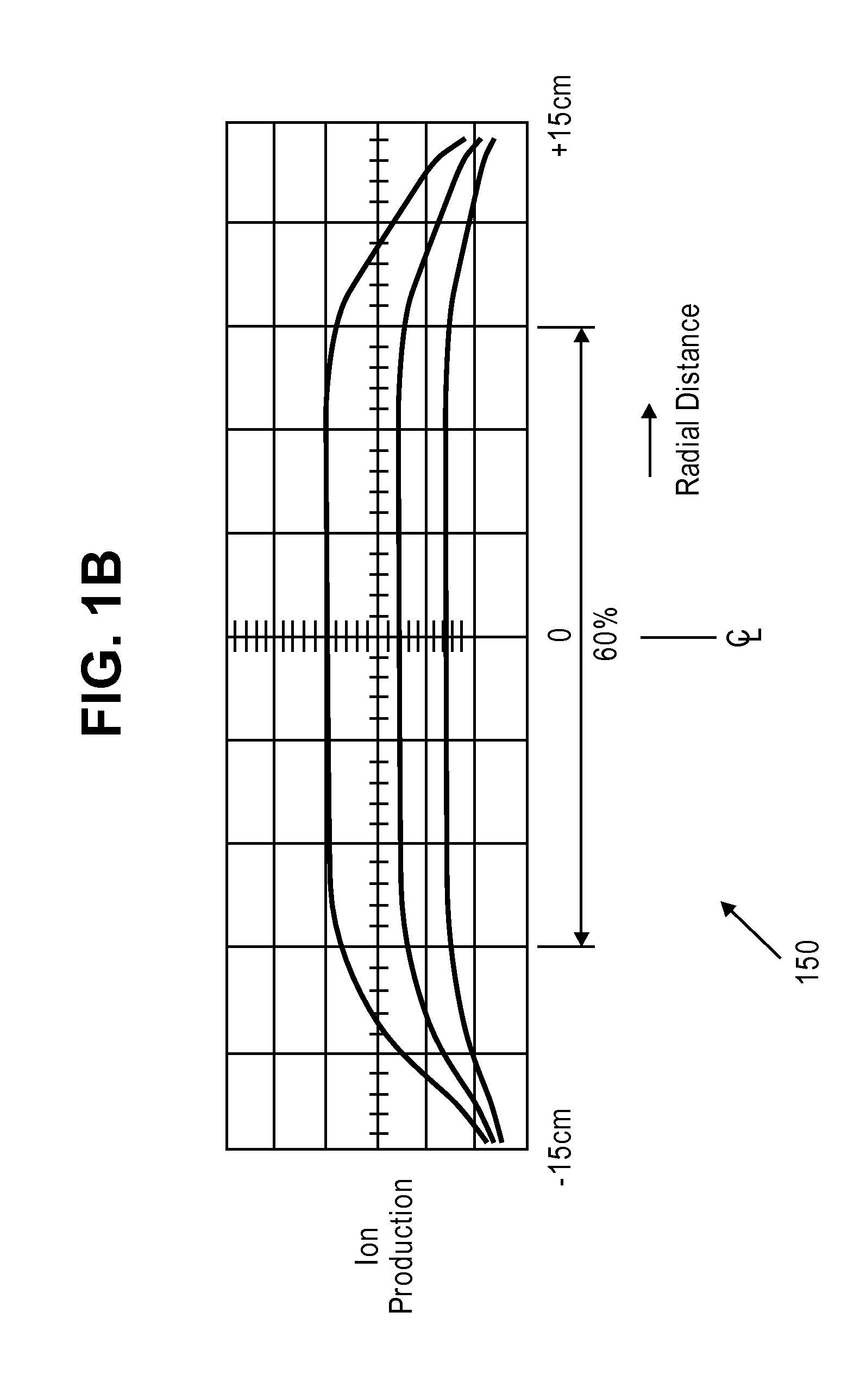
High Brightness - Multiple Beamlets Source for Patterned X-ray Production
InactiveUS20080049888A1Reduce aberrationImprove concentrationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray tube electrodesX-rayIon beam
Techniques for controllably directing beamlets to a target substrate are disclosed. The beamlets may be either positive ions or electrons. It has been shown that beamlets may be produced with a diameter of 1 μm, with inter-aperture spacings of 12 μm. An array of such beamlets, may be used for maskless lithography. By step-wise movement of the beamlets relative to the target substrate, individual devices may be directly e-beam written. Ion beams may be directly written as well. Due to the high brightness of the beamlets from extraction from a multicusp source, exposure times for lithographic exposure are thought to be minimized. Alternatively, the beamlets may be electrons striking a high Z material for X-ray production, thereafter collimated to provide patterned X-ray exposures such as those used in CAT scans. Such a device may be used for remote detection of explosives.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com