Patents
Literature
416results about How to "Large length" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Porous implant with effective extensibility and methods of forming an implant
The implant includes an outer layer of ePTFE which exhibits extensibility normally not associated with ePTFE. The ePTFE is reduced in length by deforming the fibrils between the nodes while maintaining the nodes in a substantially flat configuration. Various implant configurations that can include the outer layer described are also disclosed.
Owner:EVERA MEDICAL
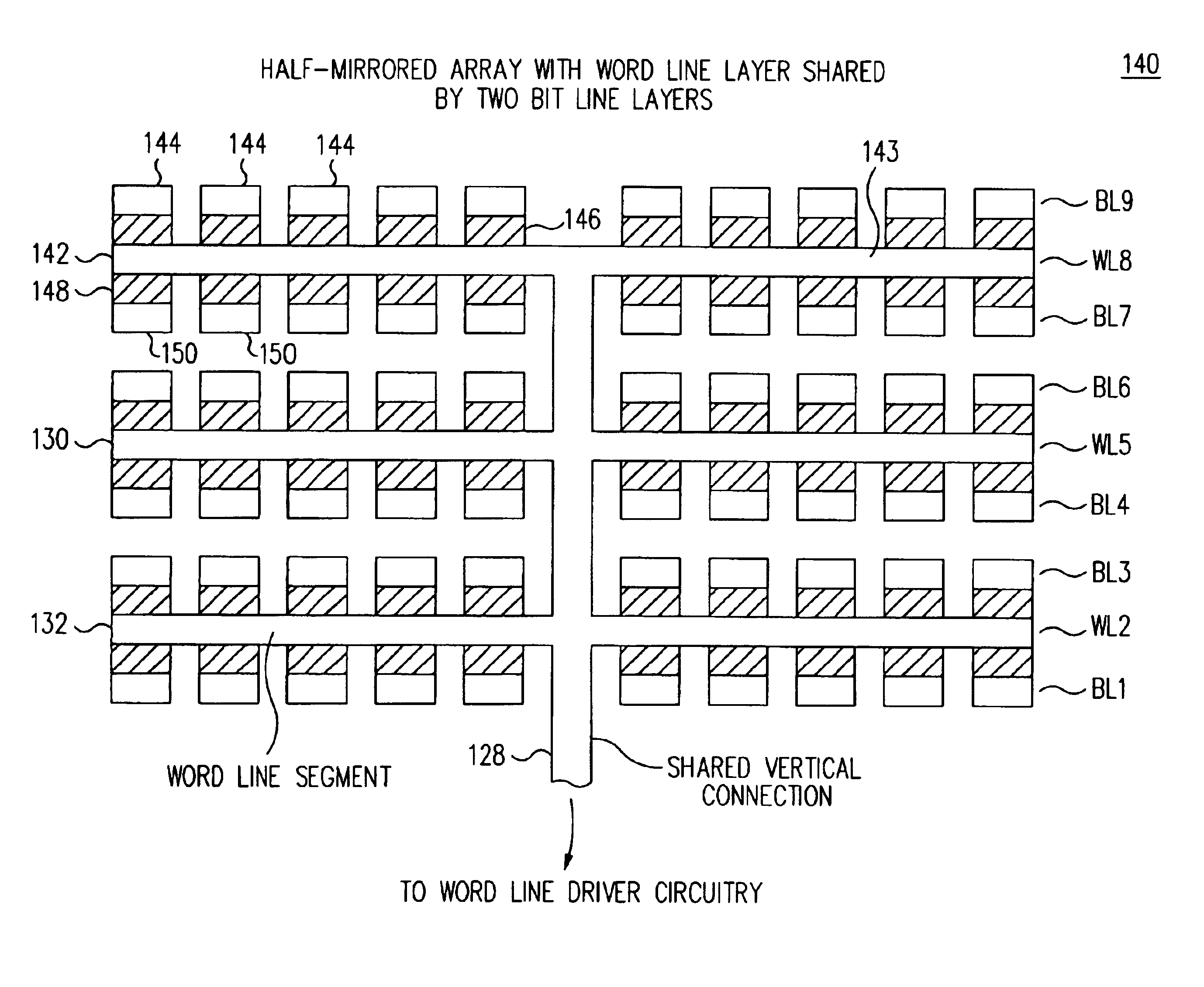
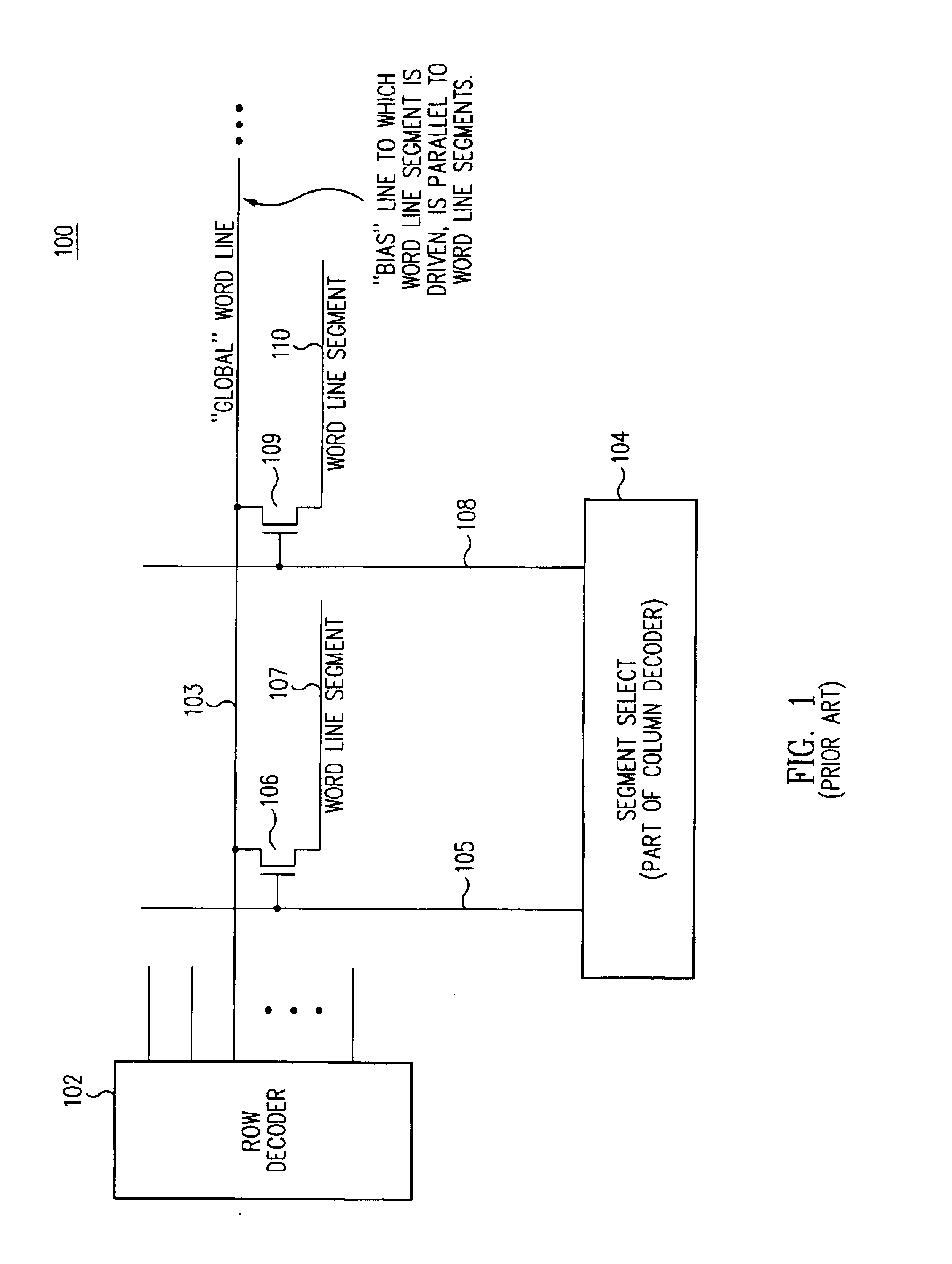
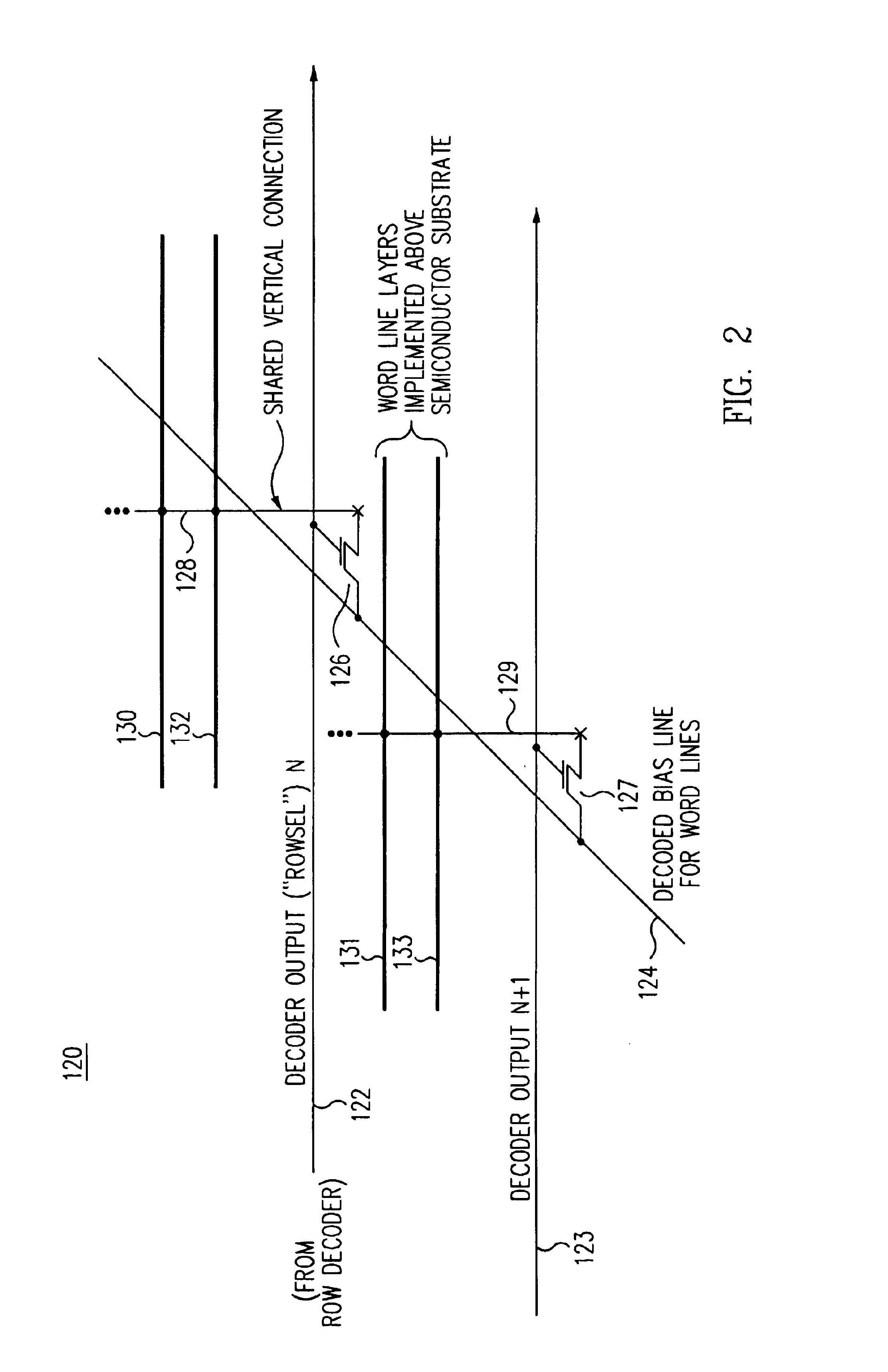
Word line arrangement having multi-layer word line segments for three-dimensional memory array
InactiveUS6879505B2Reduce stress timeDecreasing fan-outSolid-state devicesDigital storageDriver circuitLine driver
A three-dimensional (3D) passive element memory cell array provides short word lines while still maintaining a small support circuit area for efficiency. Short, low resistance word line segments on two or more word line layers are connected together in parallel to form a given word line without use of segment switch devices between the word line segments. A shared vertical connection preferably connects the word line segments together and connects to a word line driver circuit disposed generally below the array near the word line. Each word line driver circuit preferably couples its word line either to an associated one of a plurality of selected bias lines or to an unselected bias line associated with the driver circuit, which selected bias lines are themselves decoded to provide for an efficient multi-headed word line decoder.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
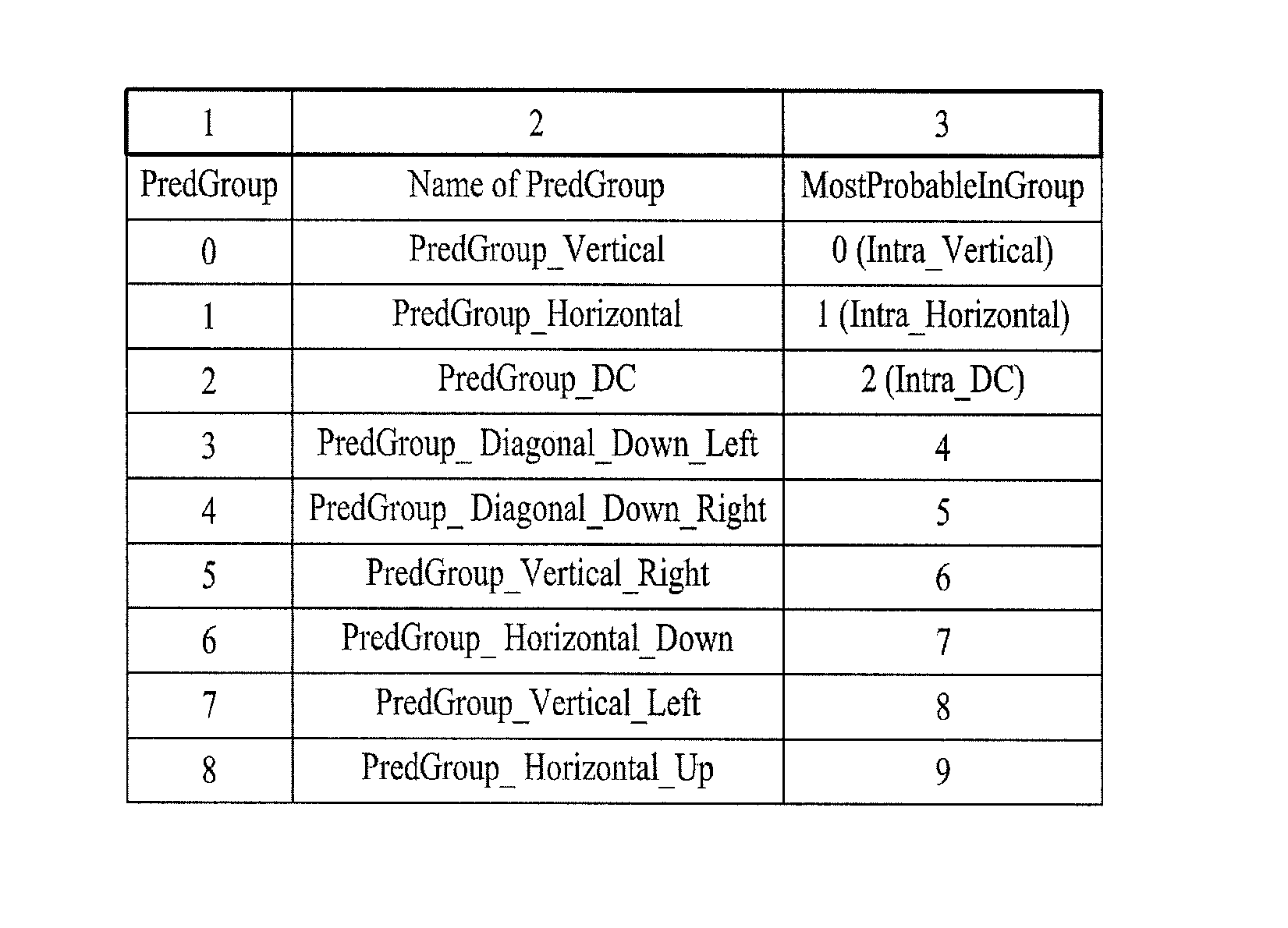
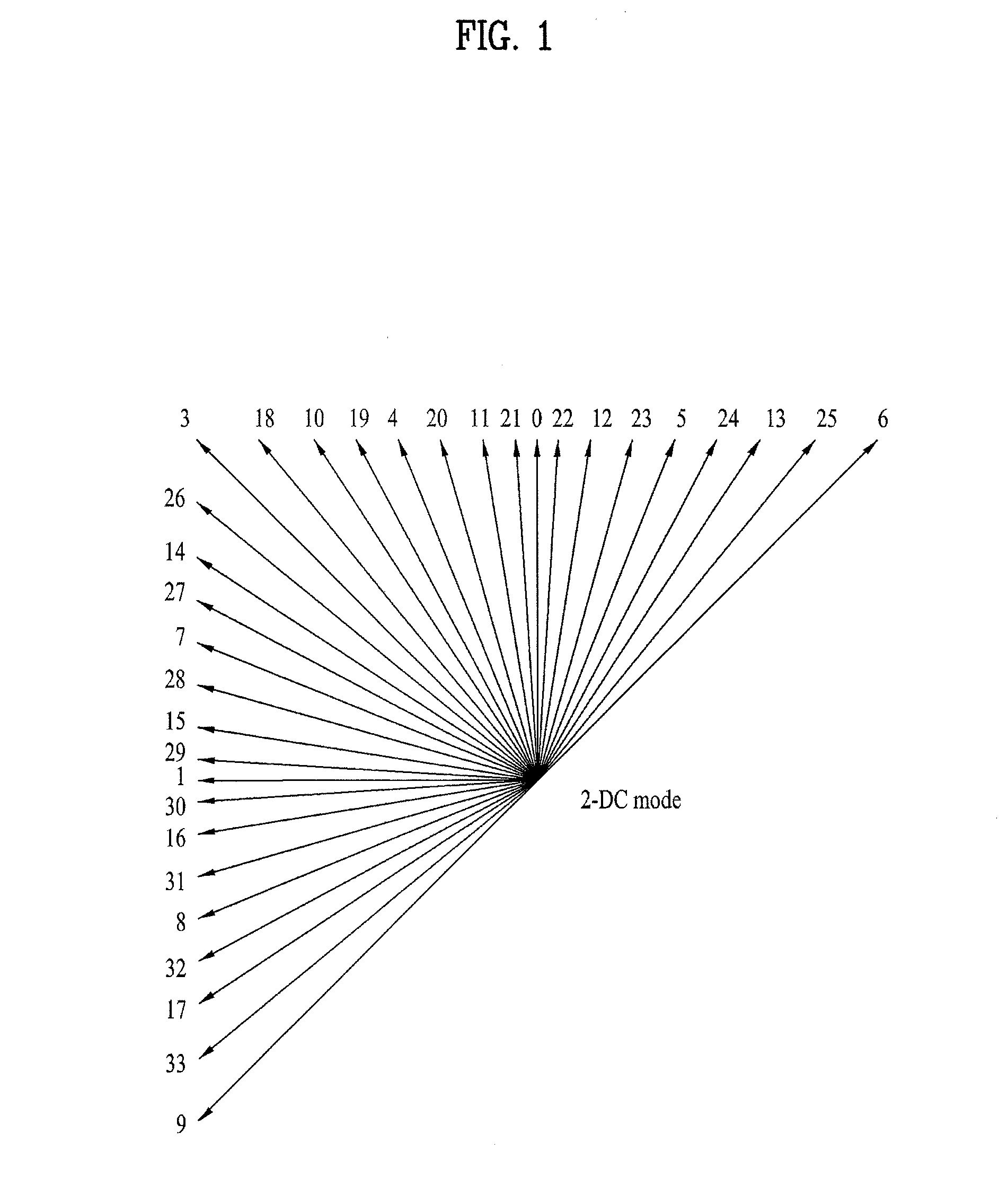
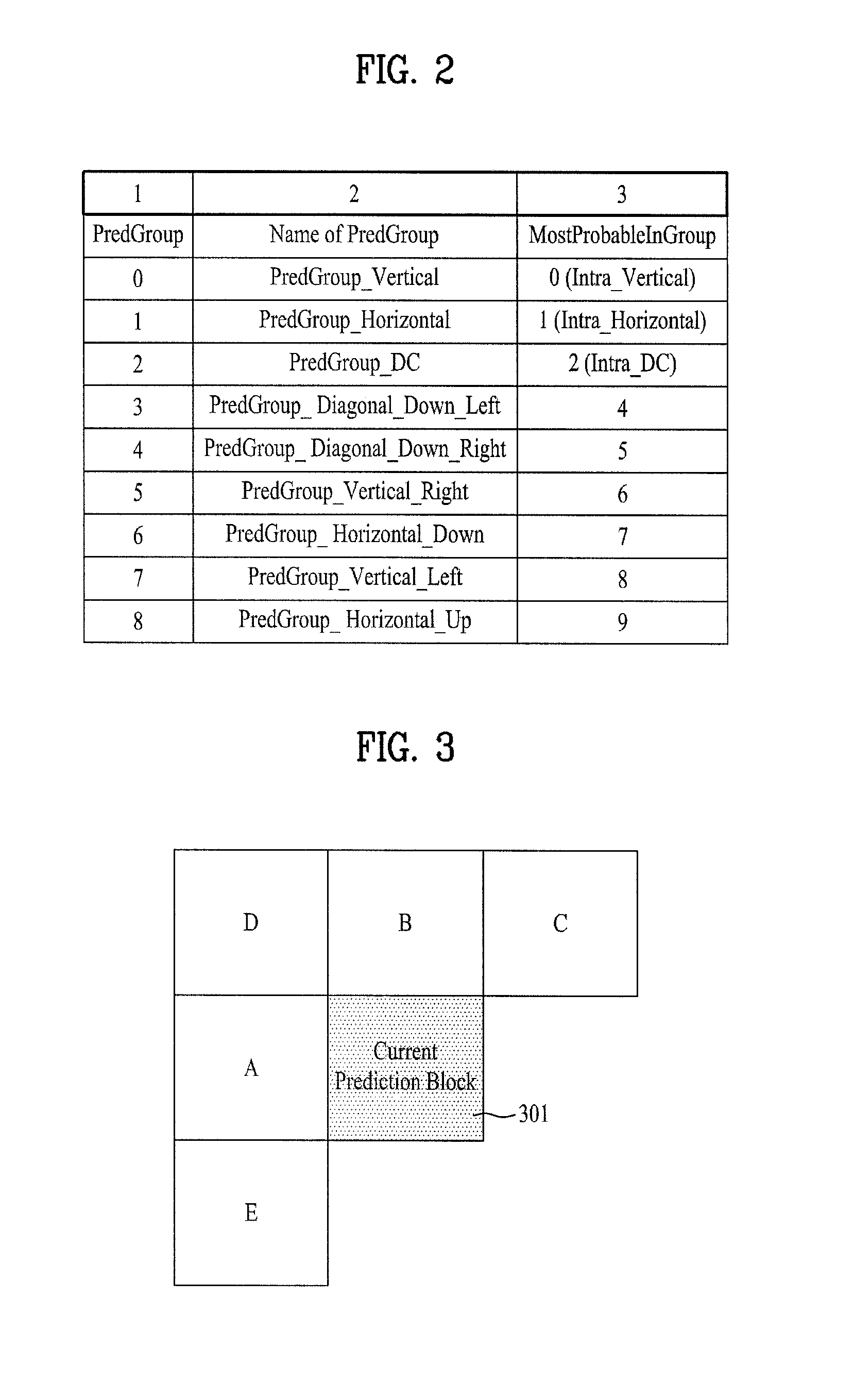
Enhanced intra prediction mode signaling
ActiveUS20110292994A1Reducing maximum lengthIncrease probabilityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionAlgorithm
A method and apparatus for signaling and receiving a video signal for processing is disclosed. Methods for determining a most probable mode for predicting a current prediction block are provided as well as new methods for grouping intra prediction modes into prediction groups. Methods for predicting a prediction block of video data as well as signaling intra prediction modes are also provided.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Depositing organic material onto an OLED substrate
InactiveUS20080131587A1Easy to makeHigh material utilizationSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingLight beamOptoelectronics
A method of depositing organic material onto an OLED substrate, comprising: providing a manifold for receiving vaporized organic material, the manifold including an aperture plate having openings, the aperture plate openings being selected to provide beams of vaporized organic material directed to the substrate, such beams having off-axis components; and providing a mask spaced between the OLED substrate and the manifold, the mask having openings that respectively correspond to the aperture plate openings, the mask openings being selected to skim off at least a portion of the off-axis components of the beams.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
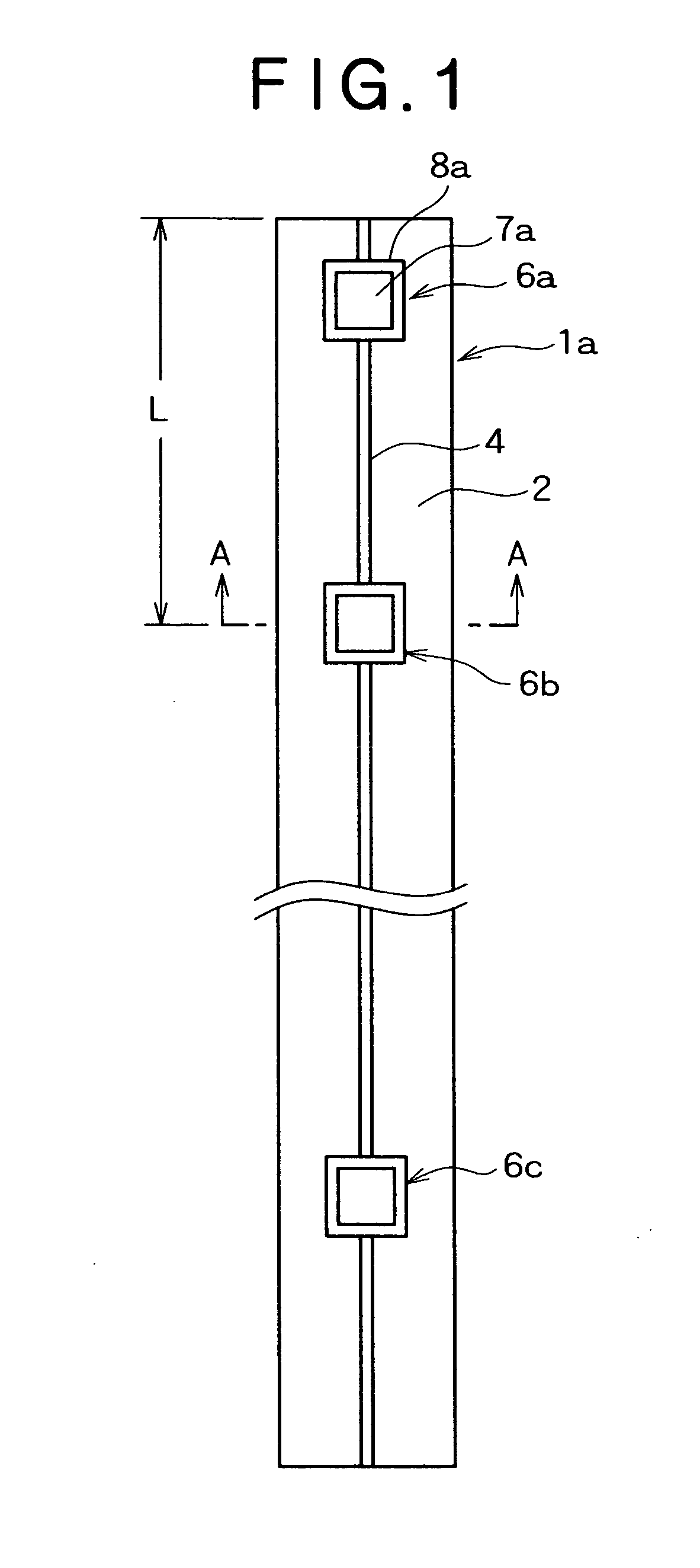
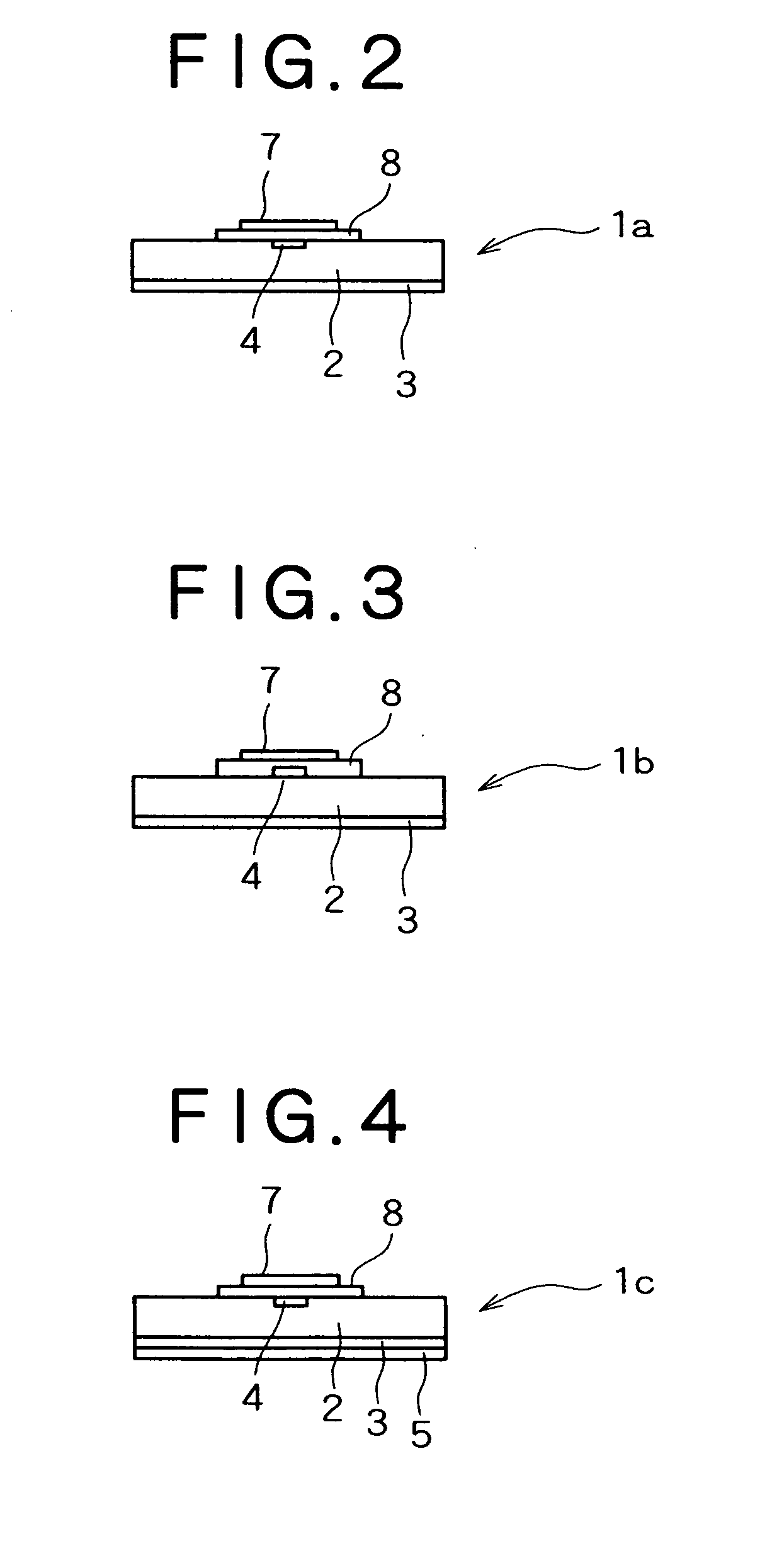
Stent
InactiveUS20050015136A1Avoid less flexibilityLarge lengthStentsSurgeryFlare phenomenonInsertion stent
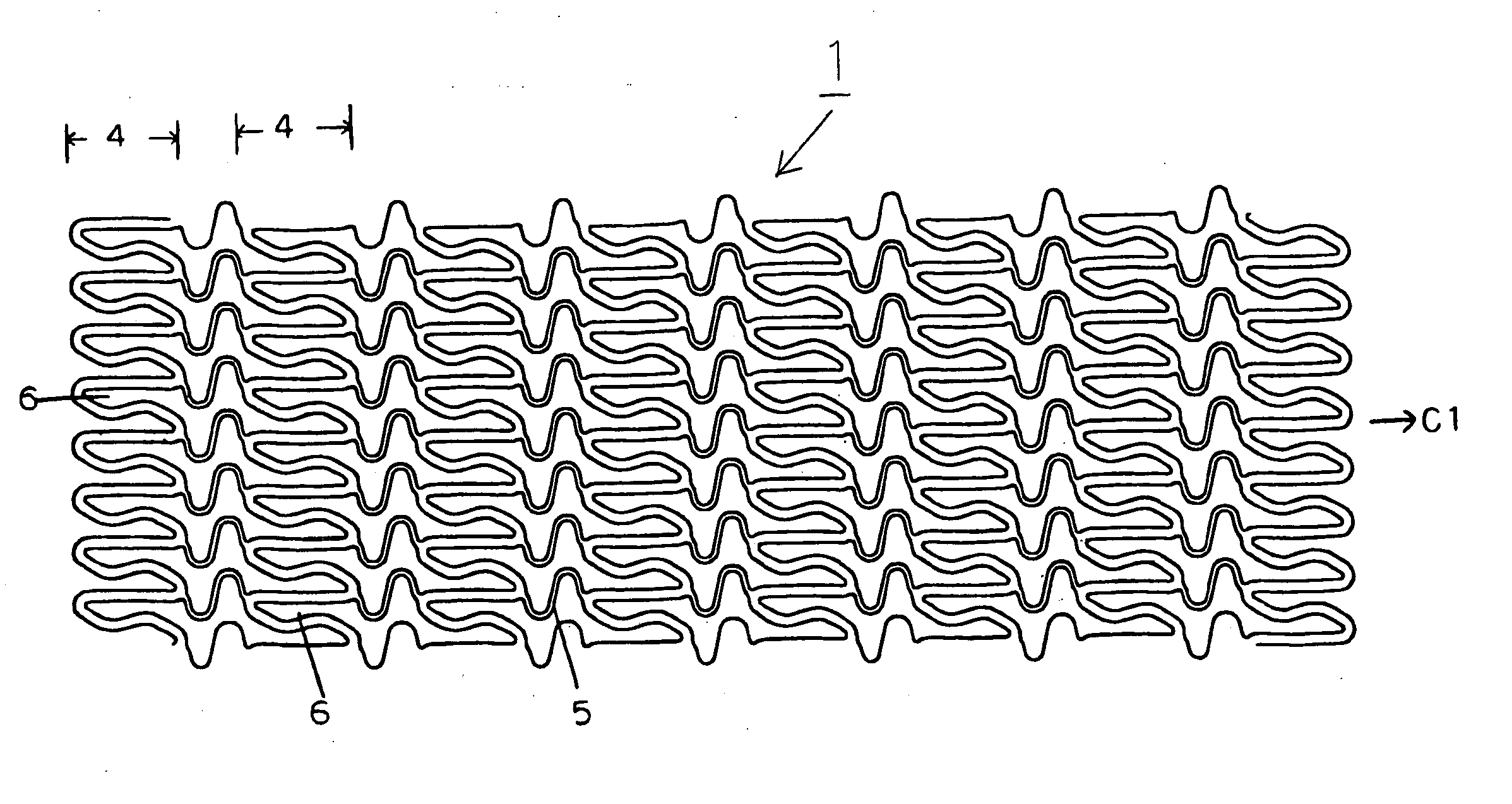
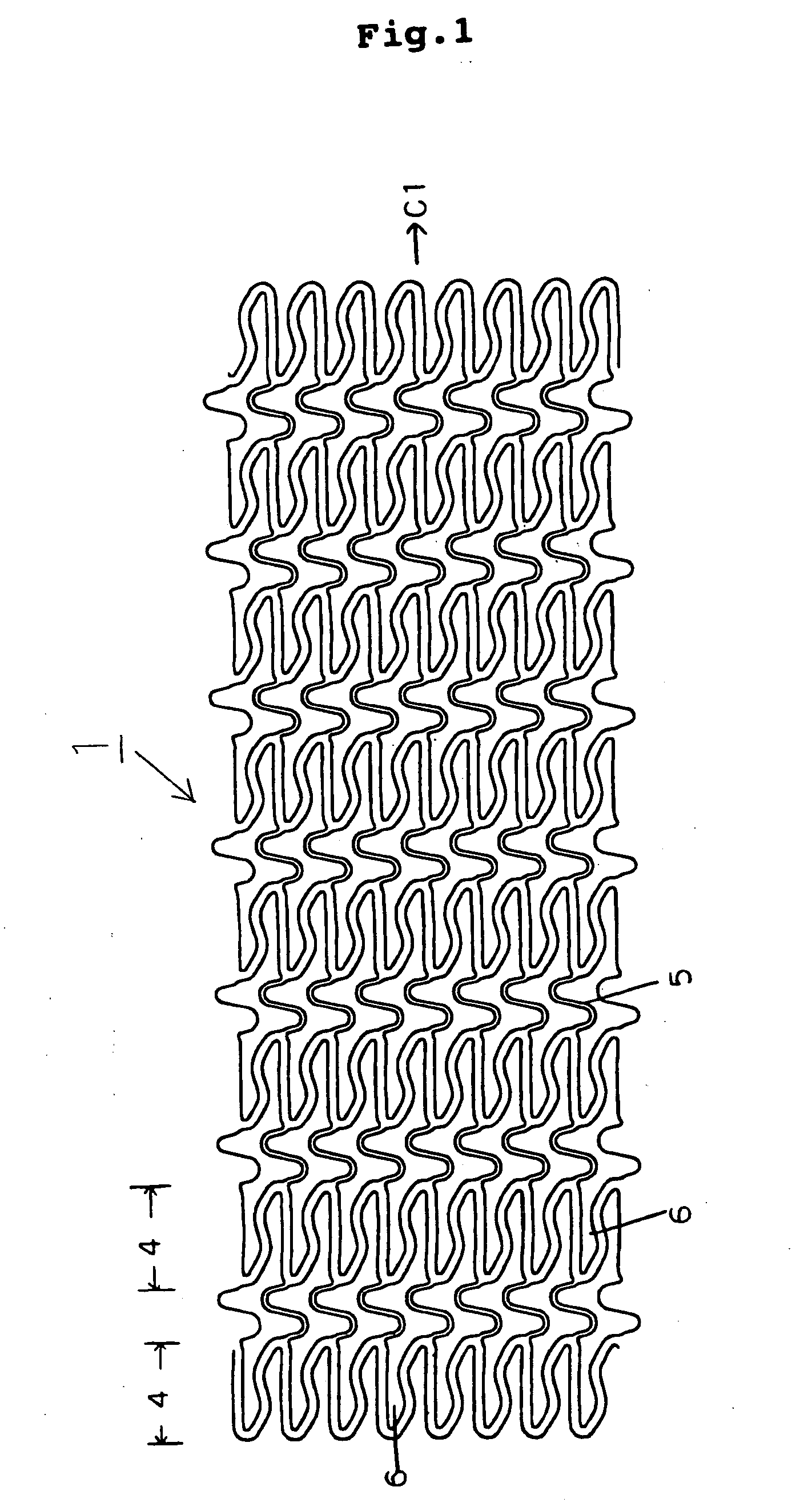
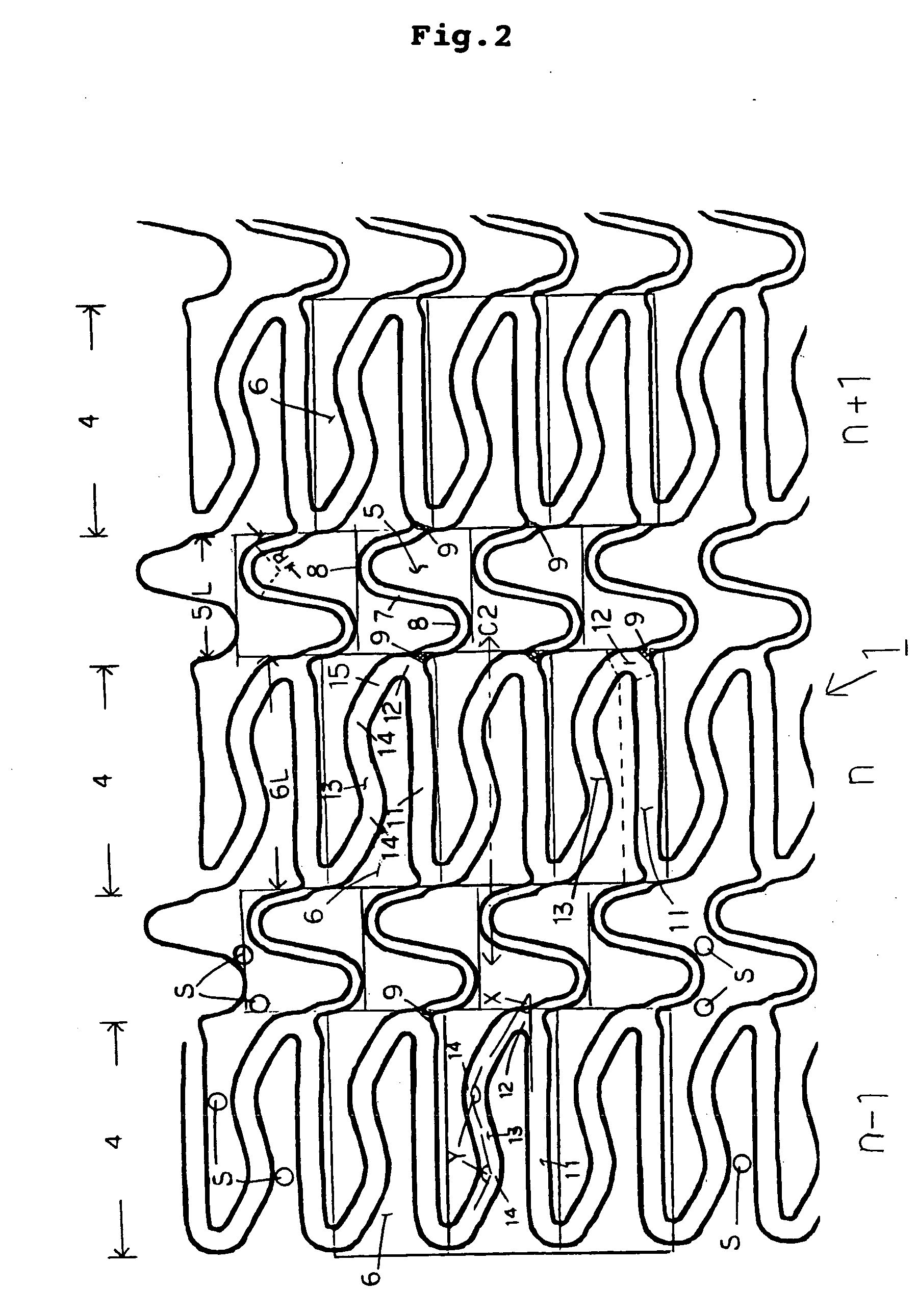
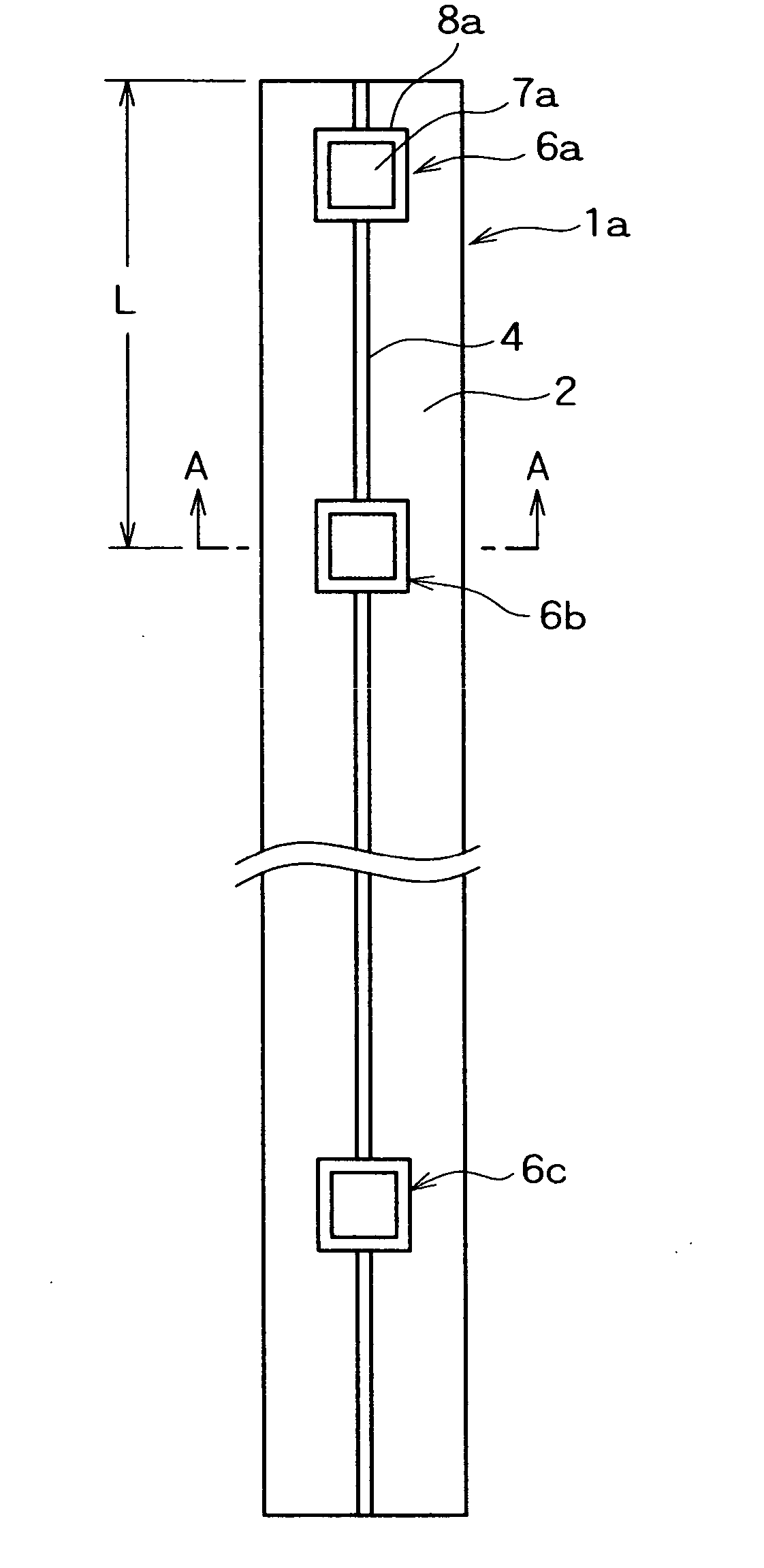
A stent (1) having a generally tubular body formed of ring units formed of a plurality of cells each and being expandable in the radius direction thereof from inside, wherein each ring unit (4) is constituted of the plurality of cells (6) connected to one another above and below and arranged so as to surround the center line (C1) of the stent forming said tubular body, the ring units are arranged in the axial direction of the stent, ring units are connected through at least one site with connector portions (5), each connector portion is formed of curved portions (8) having at least 2 arches and a generally linear portion (7) continued thereto and therefrom, 3 to 8 cells are arranged in the axial direction of the stent per 10 mm of the length of the stent, and the ratio of the length (6L) of the cell in the axial direction of the stent and the length (5L) of the connector portion in the axial direction of the stent is determined such that on the basis that when the length of the cell in the axial direction of the stent is taken as 100, the length of the connector portion in the axial direction of the stent is 50 to 100, thereby high flexibility and radial sustaining force are secured, the stent is improved in capability of dilating a blood vessel, and foreshortening and a flare phenomenon can be prevented.
Owner:KAWASUMI LABORITORIES INC
Radio lan antenna
InactiveUS20070004363A1Improve communication distanceReduce the possibilityAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesNetwork topologiesConductive materialsLayered structure
A high-frequency micro-strip line for transmitting a high-frequency wave for a wireless LAN system has a layered structure where, on a ground layer made of a conductive material, a dielectric layer made of a dielectric material and a signal line made of a conductive material are successively laid. The high-frequency micro-strip line further includes a patch antenna comprising a dielectric plate made of a dielectric material and a patch made of a conductive material, which are successively laid into a layered structure, the patch antenna being electrically connected to the signal line. A wireless-communication RF signal transmission device capable of being applied to such a line is also provided.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
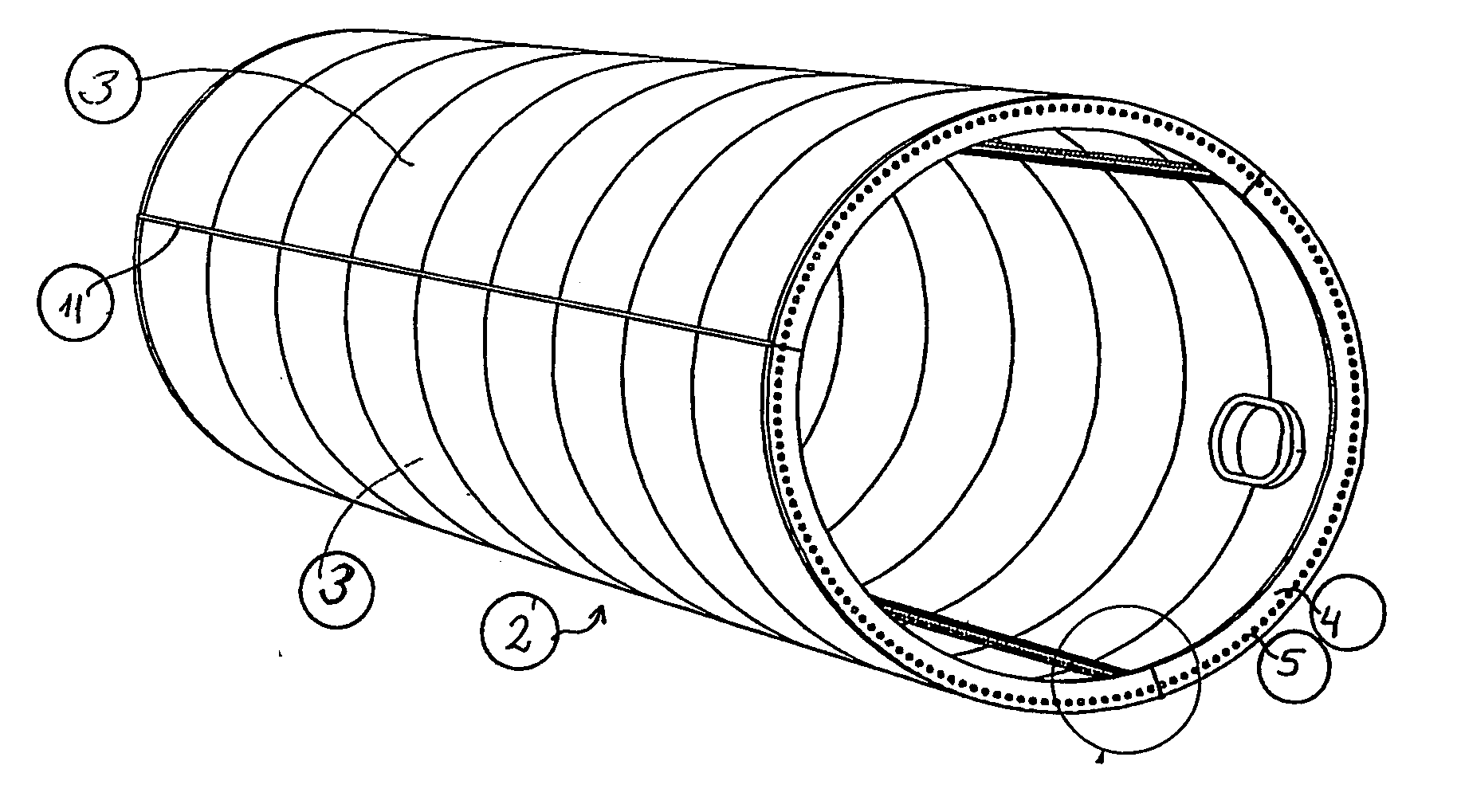
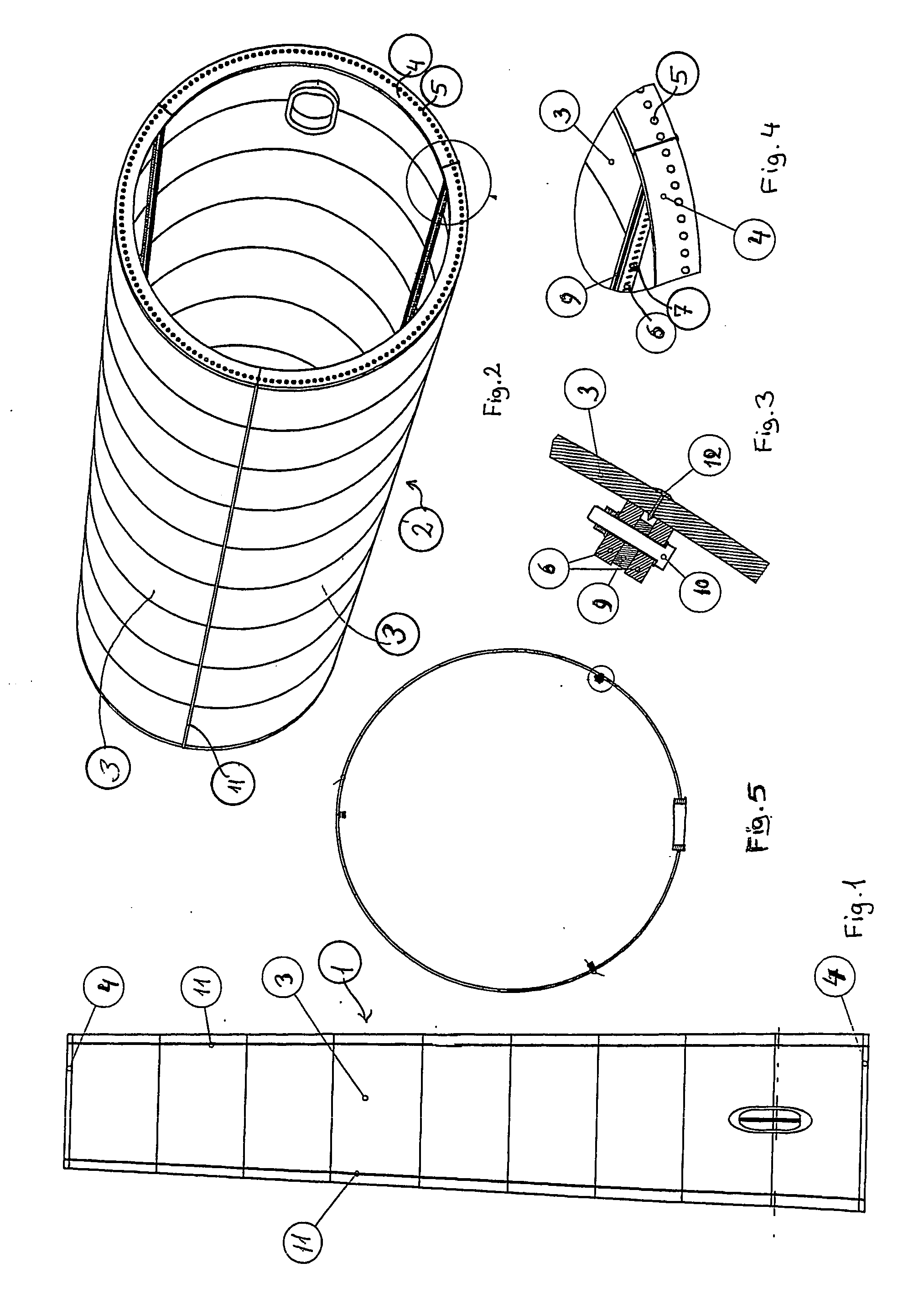
Method of contructing large towers for wind turbines
ActiveUS20060272244A1Large lengthSmooth outer surfaceWind motor assemblyWind motor supports/mountsInterconnectionTower
In order to transport large size windmill towers, the invention suggests a steel tower (1) for a windmill, comprising a number of cylindrical or tapered tower sections (2), at least the wider sections (2) of which being subdivided into two or more elongated shell segments (3), which combine into a complete tower section (2) by means of vertical flanges (6) tightened together, e.g., by bolts (10), said shells being also provided with upper and lower horizontal flanges (4), respectively, to allow interconnection of tower sections (2) one on top of the other.
Owner:VESTAS WIND SYST AS
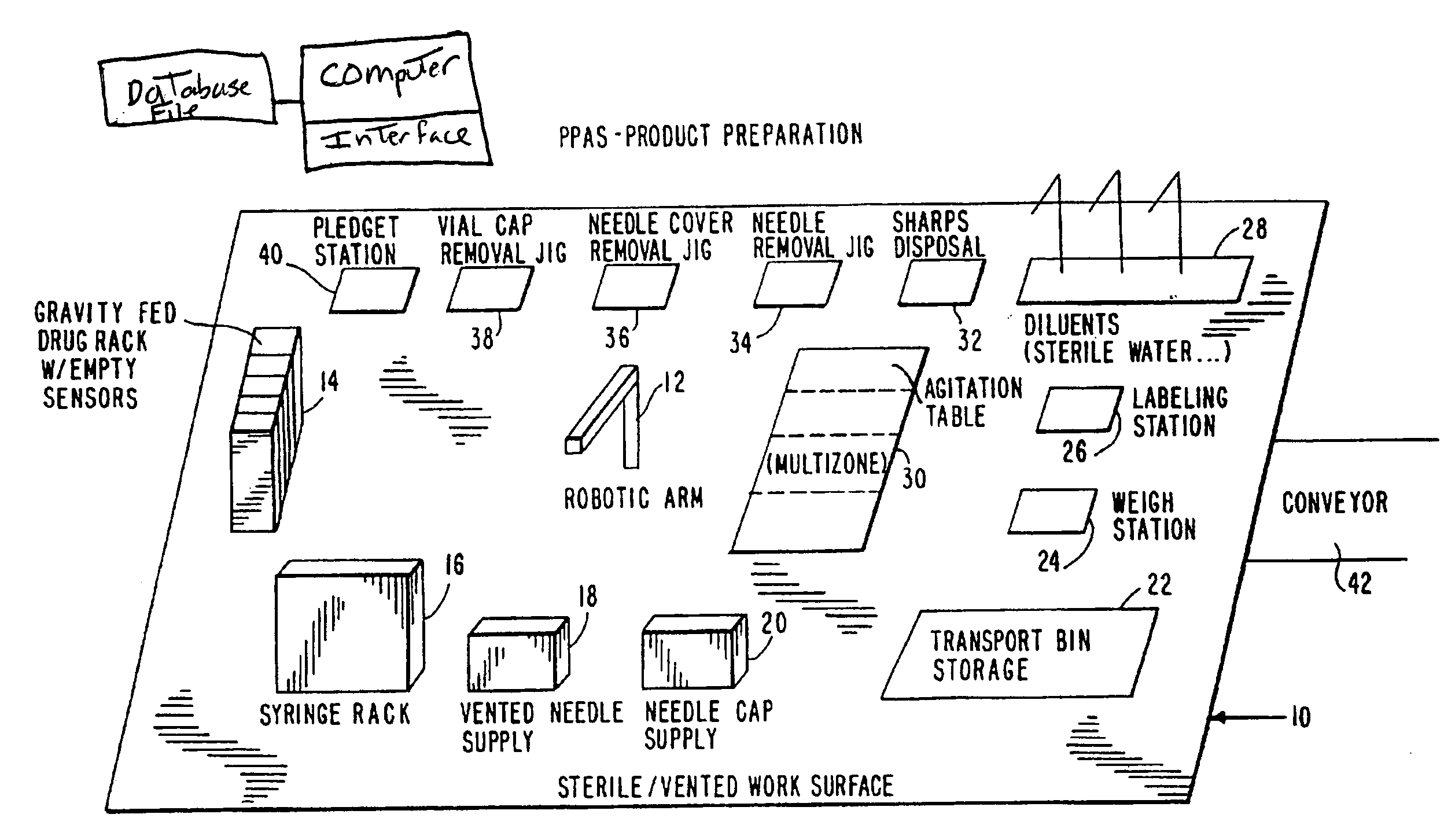
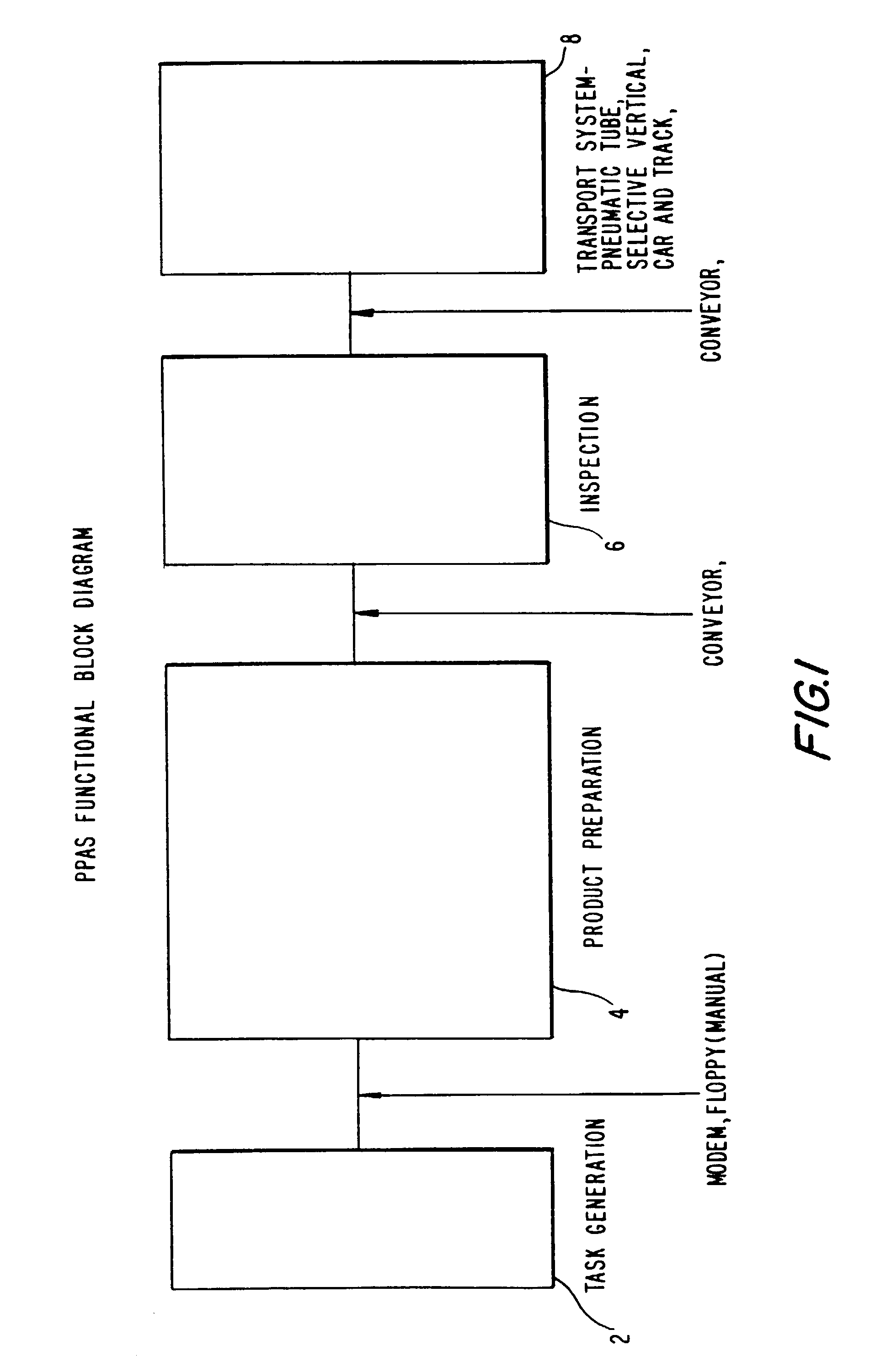
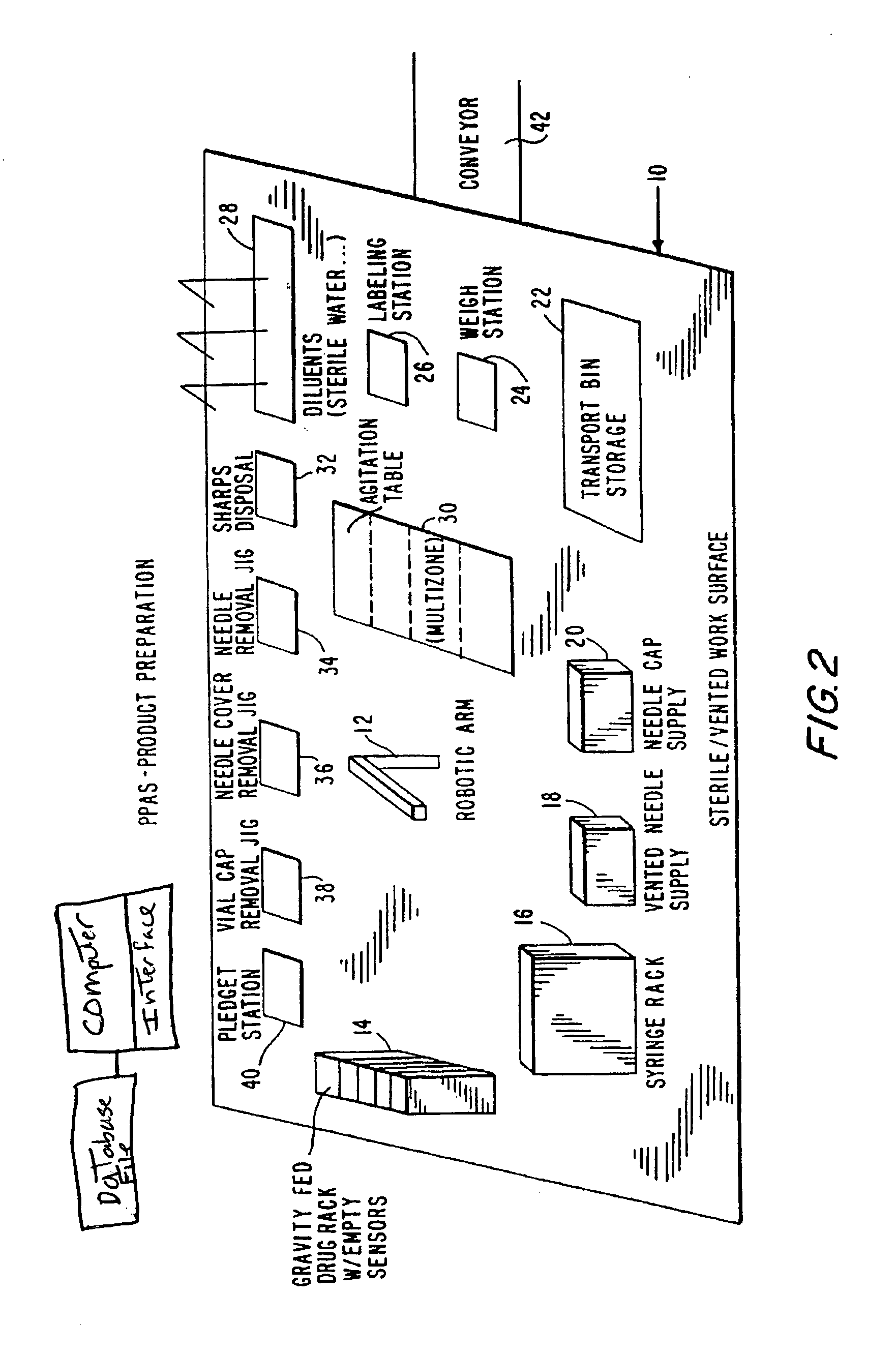
Parenteral products automation system (PPAS)
InactiveUS7260447B2Simple correctionAvoid confusionData processing applicationsConveyorsEngineeringDrug product
An integrated, automated system concerning pharmaceutical products is provided. The system comprises an input queue, a dispensing apparatus comprising a robot device and a number of stations from which the robot device works, and an inspection station. A computer interface provides bi-directional communication between the analytical instruments, robots and peripheral devices and a computer. The robot employed by the system is responsive to computer commands and capable of performing mechanical functions including selection and retrieval of a necessary item and manipulation of retrieved items such that the desired product is produced.
Owner:BAXTER ENGLEWOOD
Cut-out brush for electric hand tool
InactiveUS6087754ACompact designEasy to wearRotary current collectorDynamo-electric machinesElectric machinePigtail
PCT No. PCT / DE98 / 02077 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 20, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 20, 1999 PCT Filed Jul. 23, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO99 / 13538 PCT Pub. Date Mar. 18, 1999A manual electric machine tool (10), having an electric motor (16), whose commutator (20) can be connected to a voltage source via at least one carbon brush (22) pressed against the commutator (20) by spring means (26), wherein the carbon brush (22) includes a head part (34) and a foot part (35) and has an electric pigtail lead (40) and a turn-off device (38), which at a certain wear of the foot part (35) of the carbon brush (22) automatically disconnects the electrical connection between the voltage source and the commutator (20), gains a longer useful life between service intervals for changing carbon brushes in that the carbon brush (22) is lengthened in the region of its head part (34) by a single axial continuation (36), which serves as a socket for the turn-off device (38) and is dimensioned such that the spring (26) enter flush and integrally into the outer contour of the carbon brush (22) between the outermost outer edges of the head part (34) and of the continuation (36), inside these outer edges.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
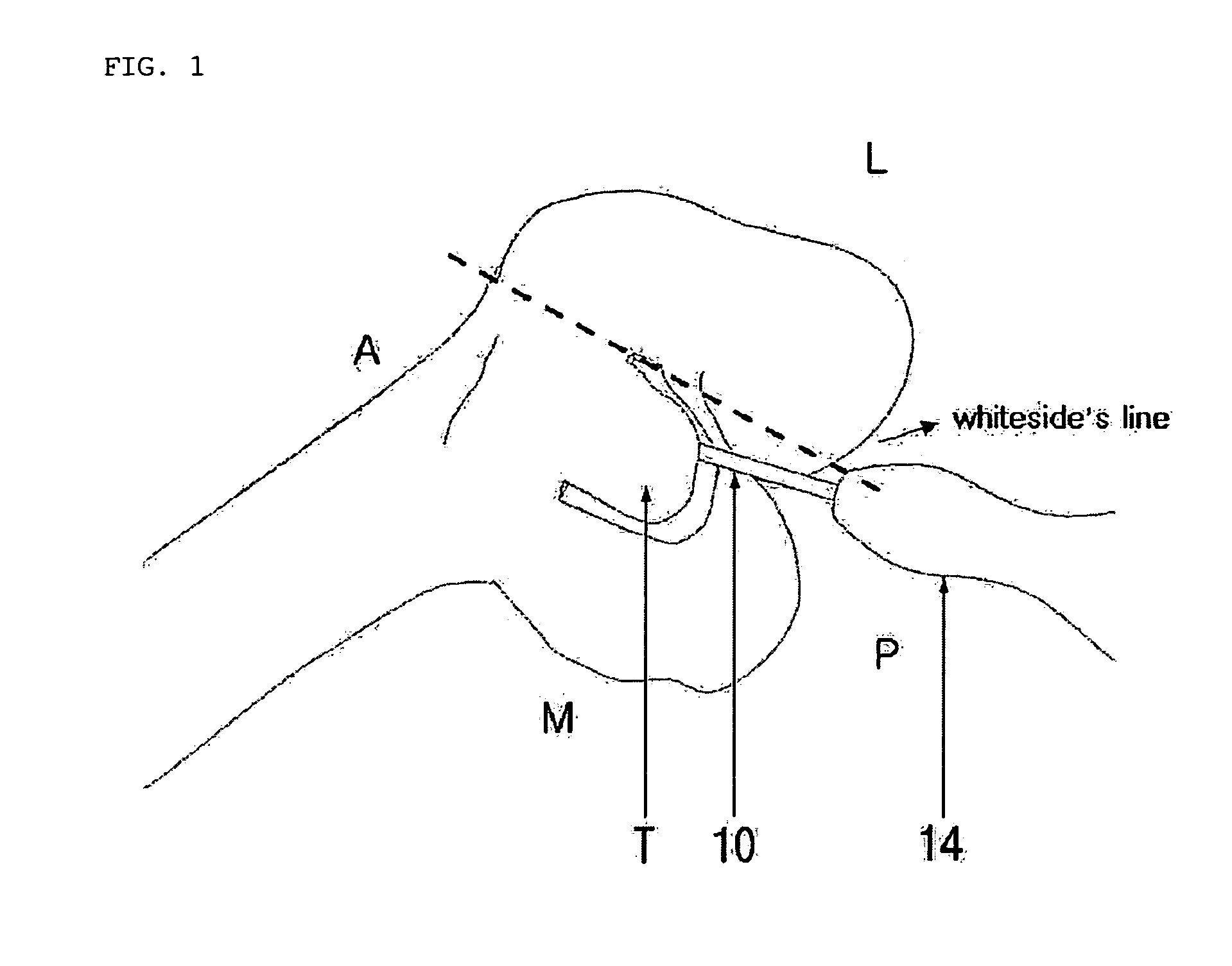
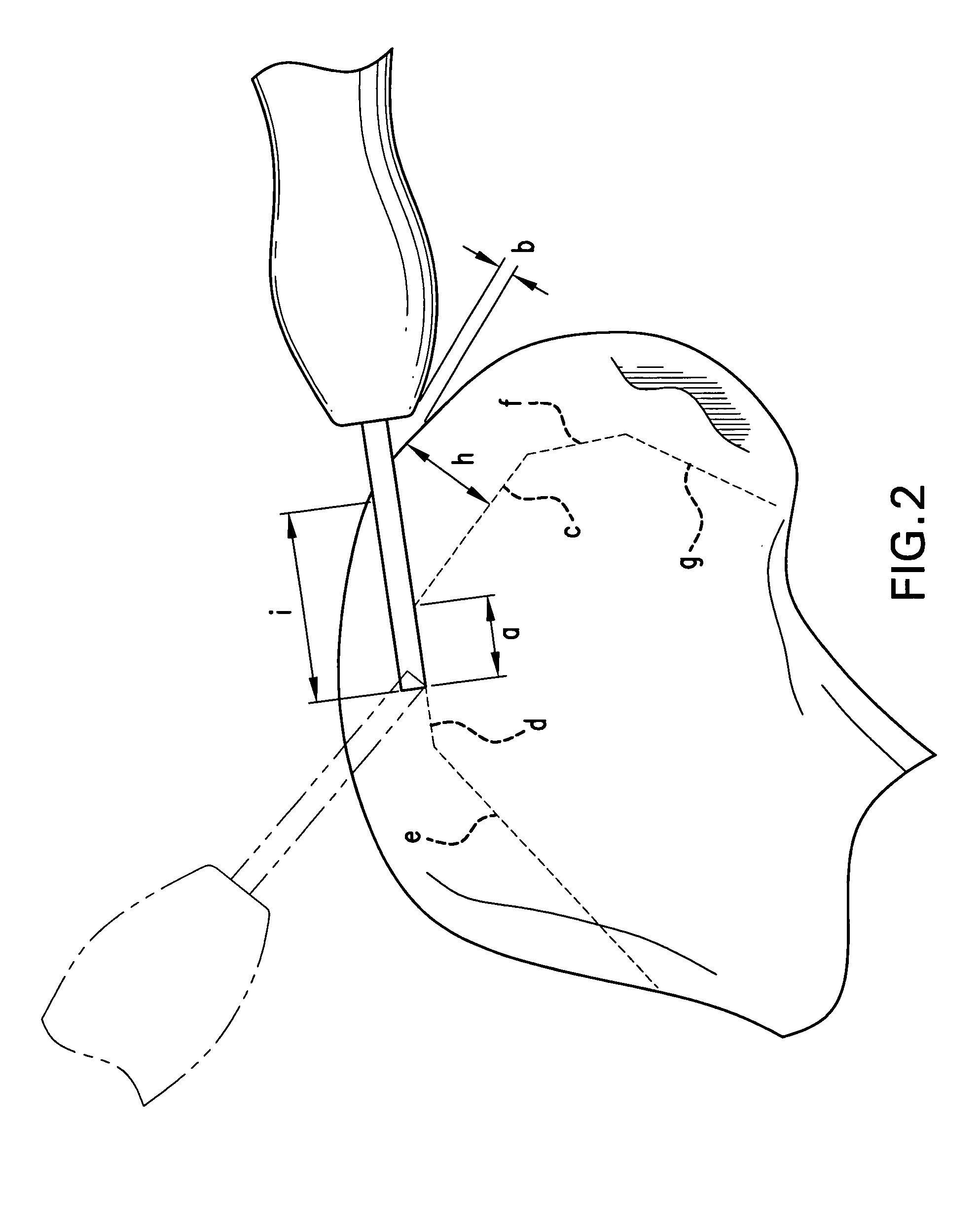
Method and system for cutting knee joint using robot
A method and a system for cutting the knee joint using a robot. A cantilevered cutter is introduced into the knee joint from inside and outside of upper and lower bones of the knee joint to realize a tunnel cutting technique in which cutting is conducted such that tunnels are defined in bone and remnant bone is cleared. The cutter includes a shaft in which a substantial axial portion is fitted into a sleeve and a remaining axial portion serves as a cantilever extending out of the sleeve, and a head which is formed at a distal end of the shaft. A length of the cantilever and a diameter of the head are determined to have minimum sizes as long as the head can be introduced into bone in such a way as to define a tunnel and can be moved in the bone while cutting the bone.
Owner:TRABISH MASEI MARTY +1
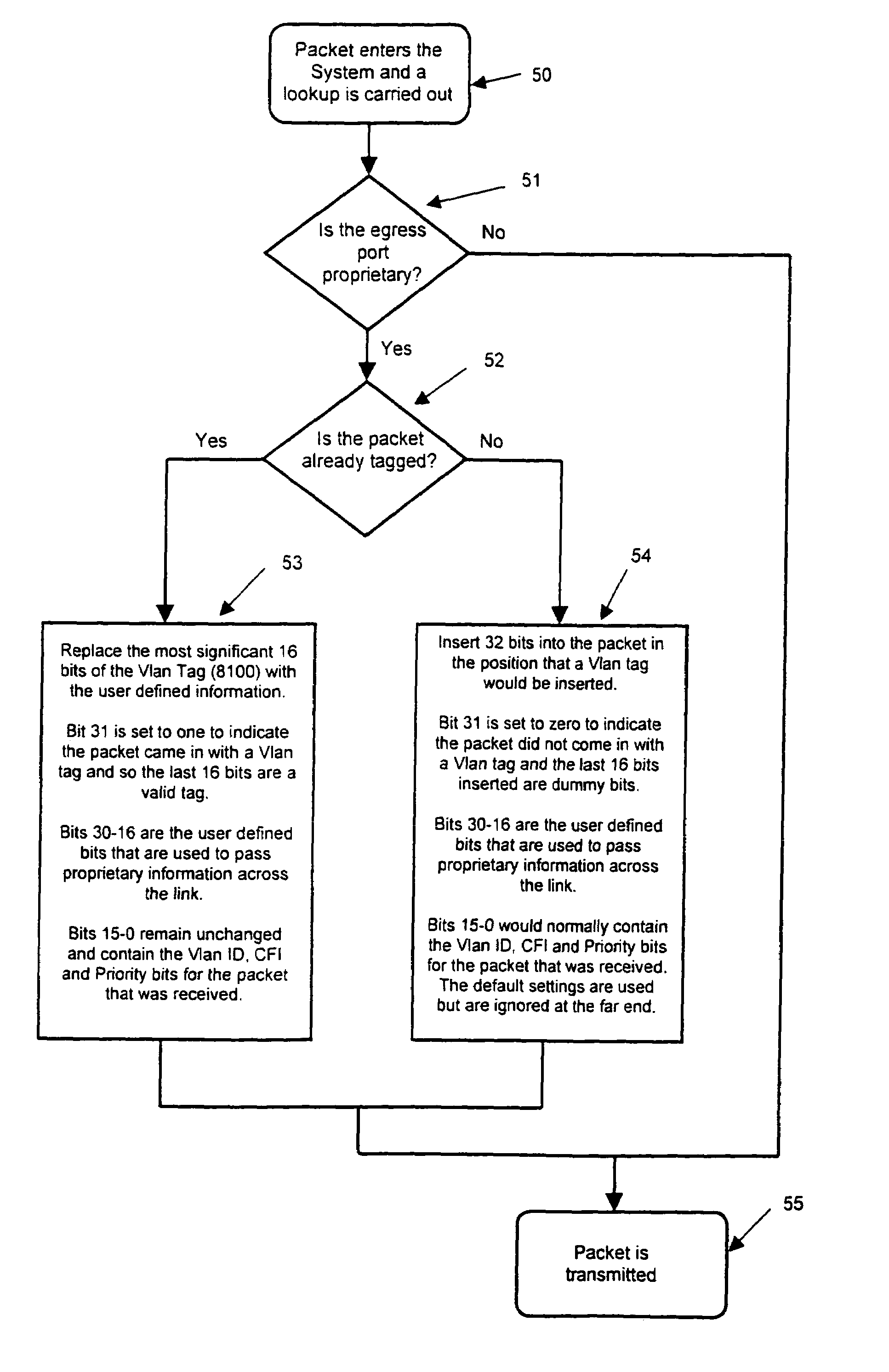
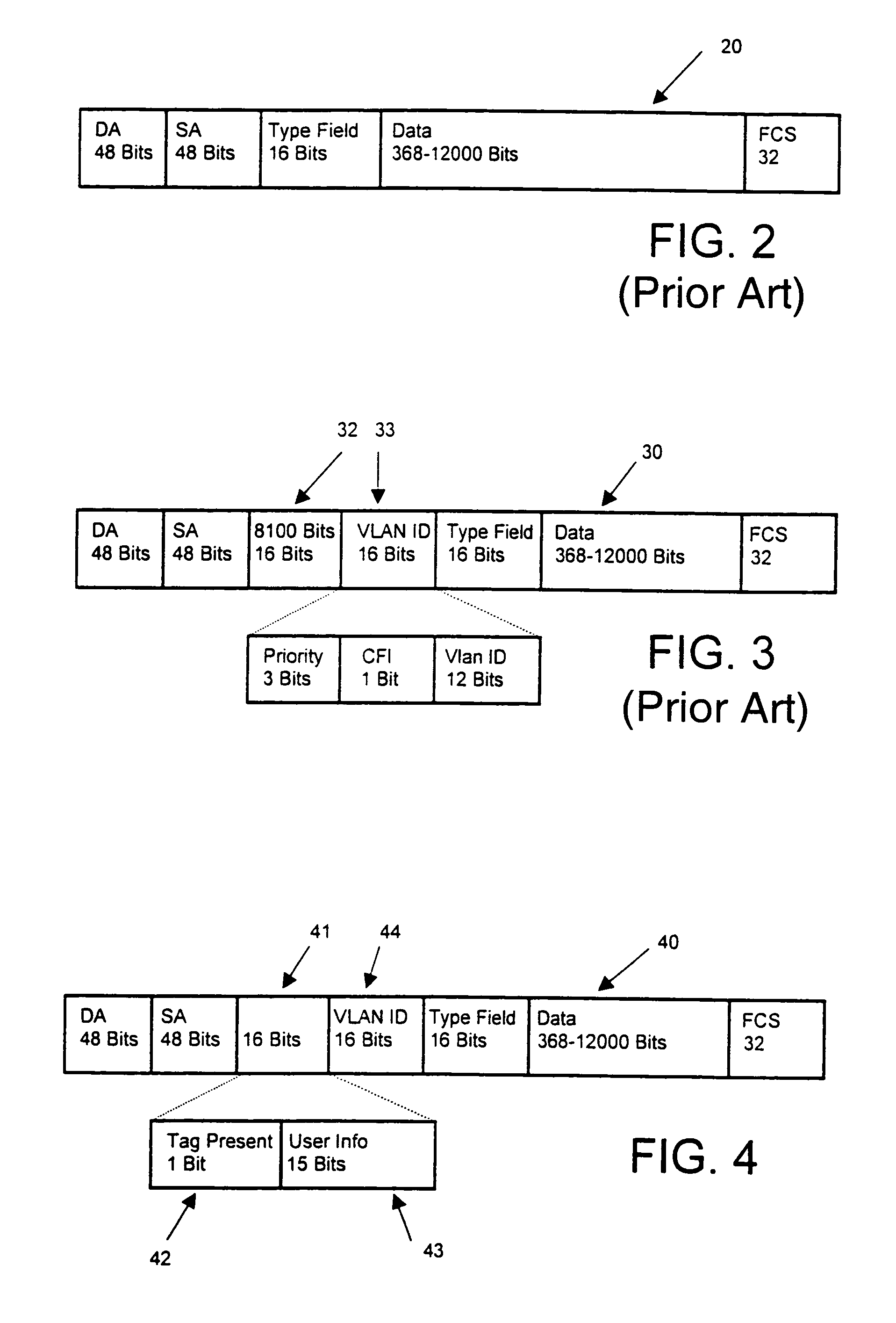
Modification of tag fields in Ethernet data packets
InactiveUS6975627B1Avoid difficultyRedundant informationNetworks interconnectionSecuring communicationNetwork packetEthernet
An Ethernet data packet including a VLAN tag header and a VLAN identification field is modified. The modification is accomplished by inserting in place of the VLAN tag header a field of the same size including selected information. The VLAN identification may be retained. The inserted field may include a first field indicating the presence of the VLAN identification field and a second field of selected information, the second field being longer than the first field.
Owner:3COM TECH +1
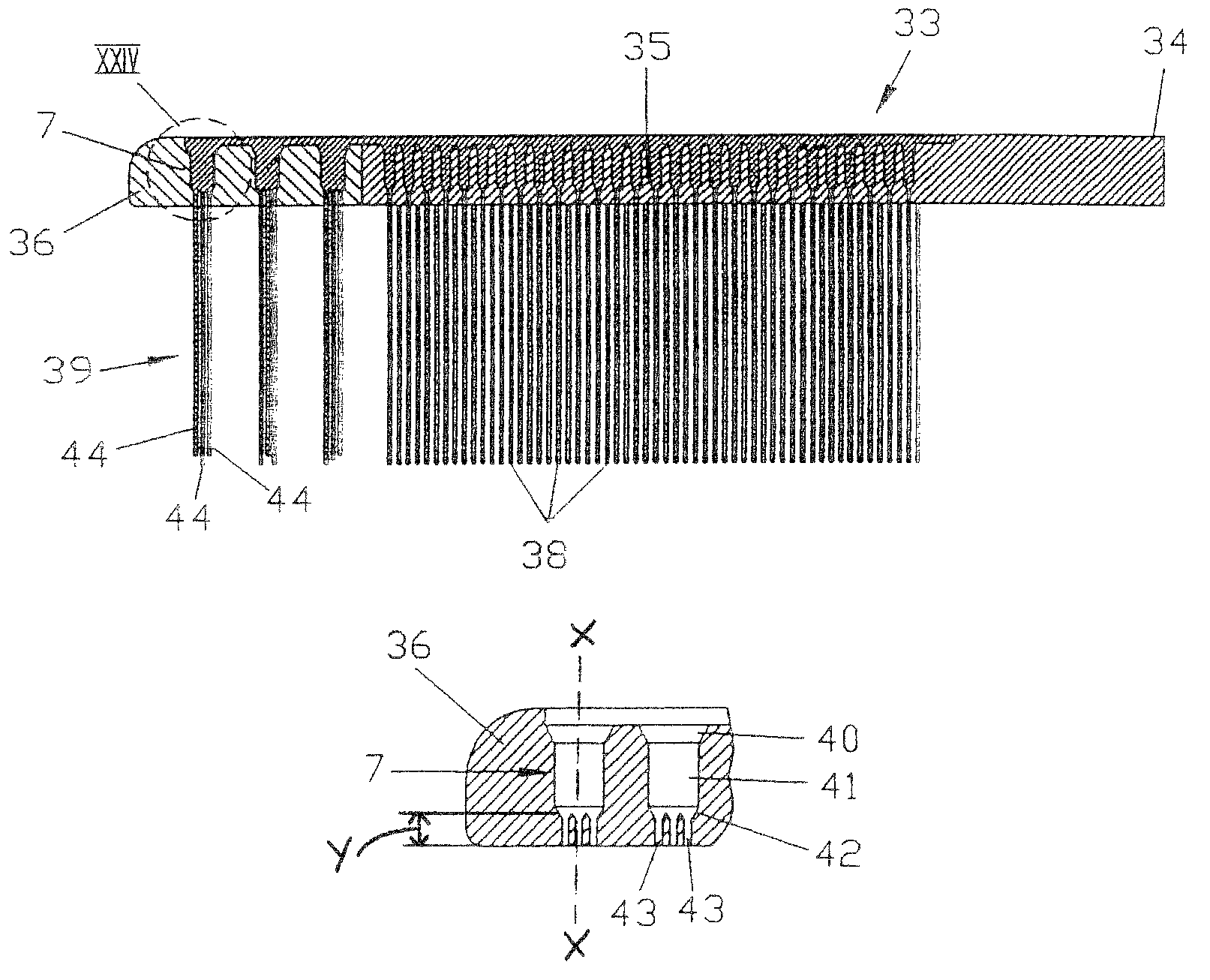
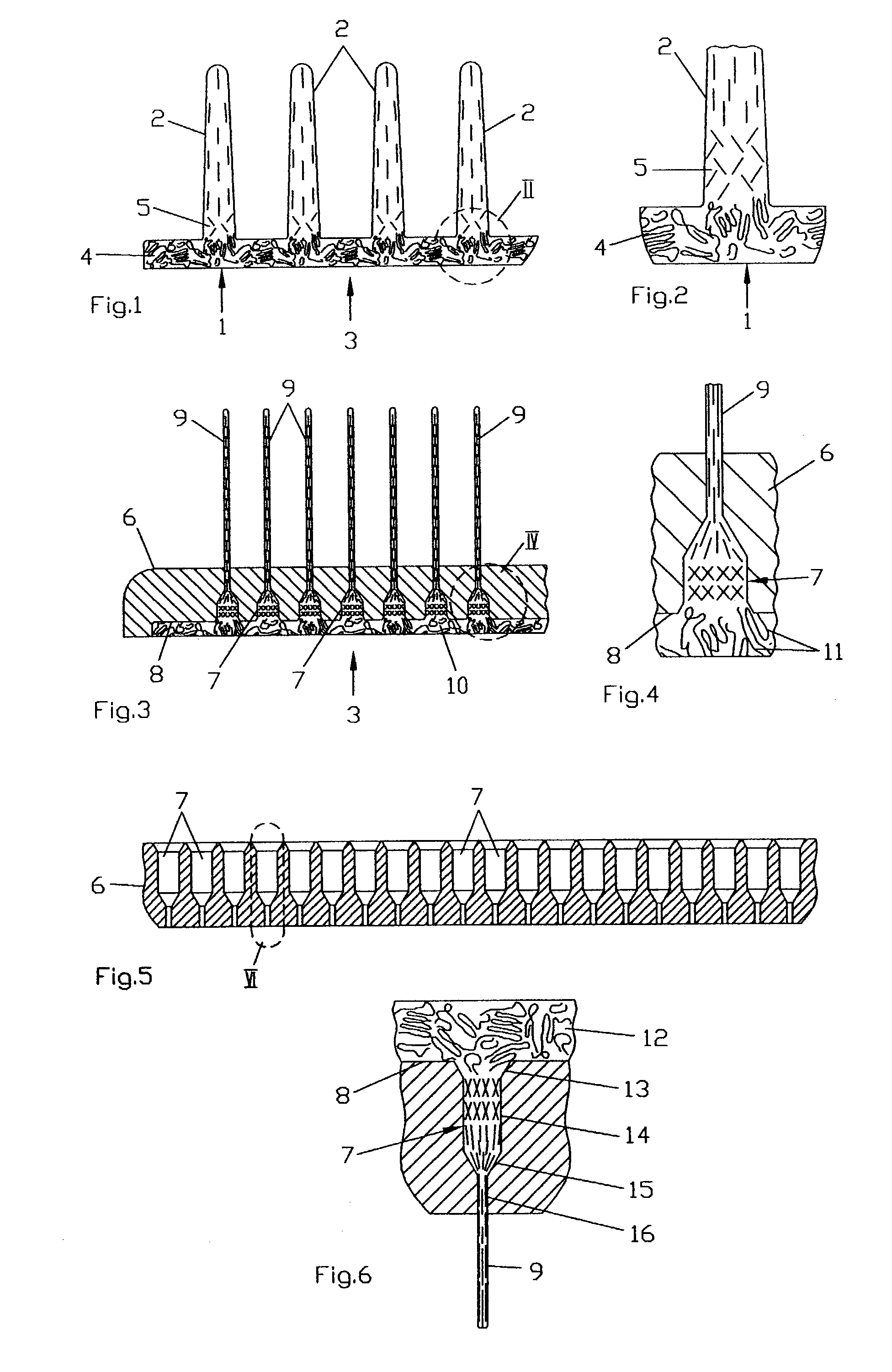
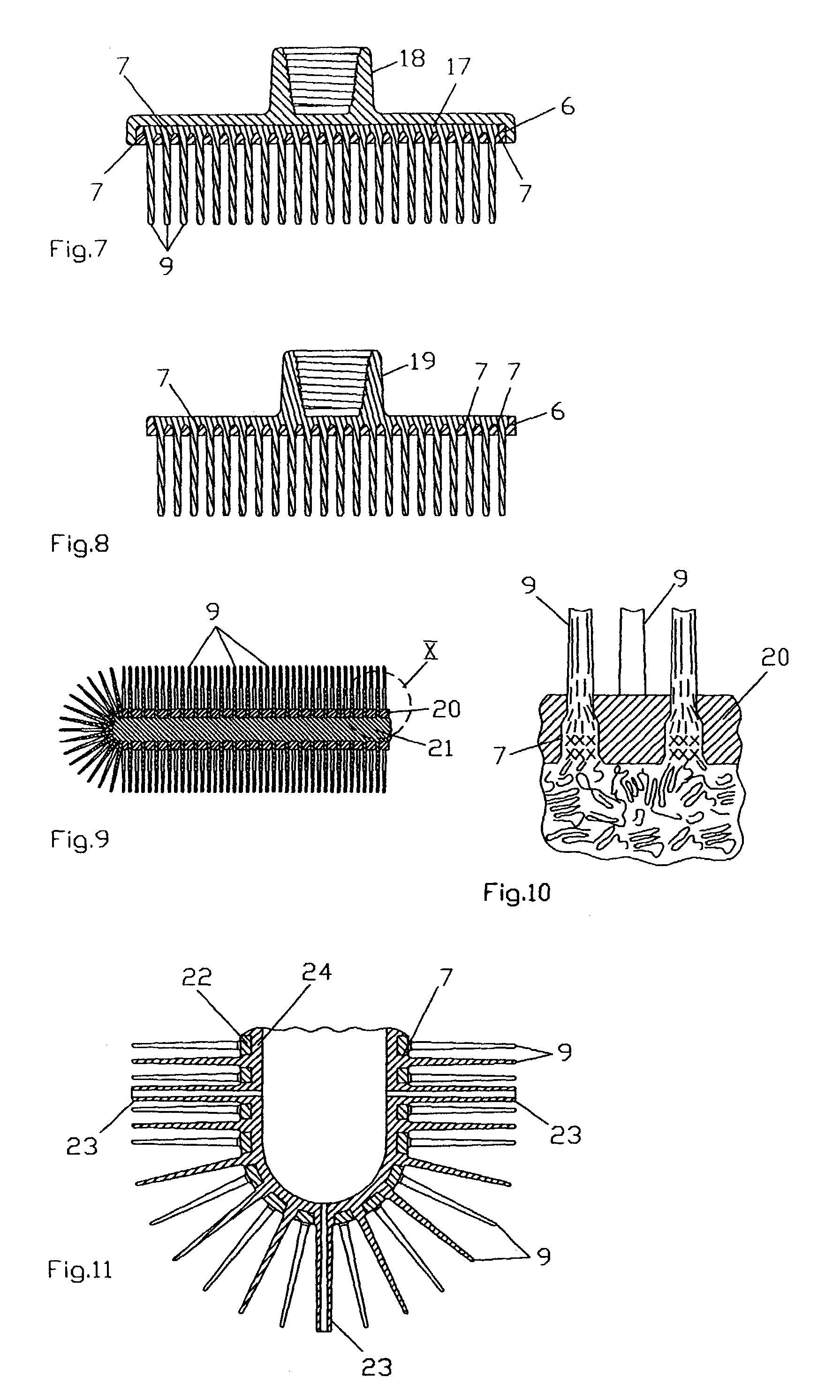
Method and device for producing bristle products and bristle products
InactiveUS7503093B2Improve abilitiesEasy to disassembleBrush bodiesBristle carriersBristlePlastic materials
Brush ware comprising at least one carrier and bristles made from a moldable plastic material disposed thereon, is produced by providing the carrier with through holes acting like spinning nozzles, to which bristle-shaped molding channels join and a plastic melt for the bristles is injected from at least one side of the carrier—the feed side of the melt—through the holes into the channels thereby forming the bristles, wherein the through holes have a minimal width along at least a portion of their length which is ≦3 mm and the ratio between this width and the flow path of the melt resulting from the depth of the through holes plus the length of the channels is ≦1:5. A device for carrying out the method and brush ware produced in accordance with the method is also described.
Owner:GEKA
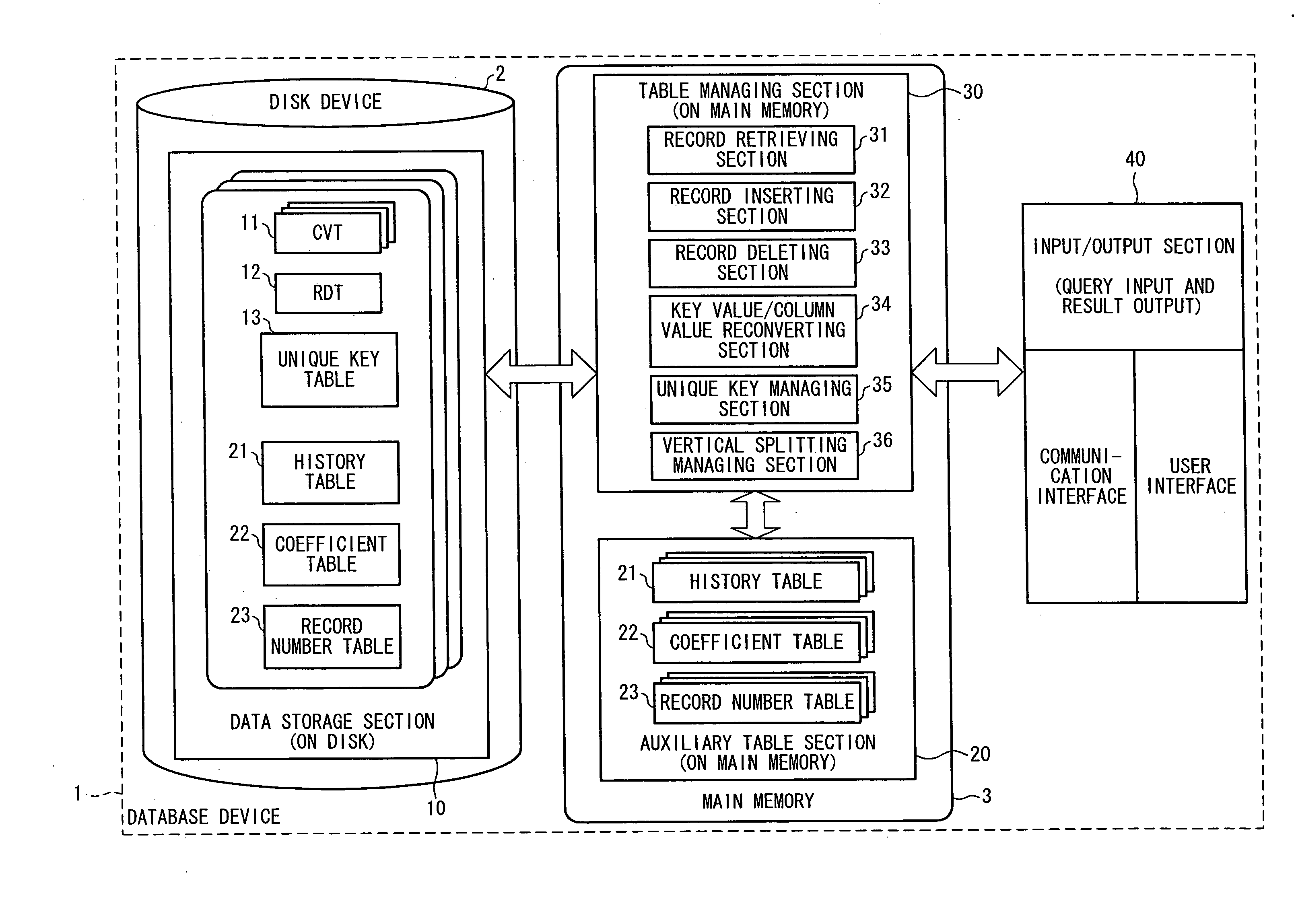
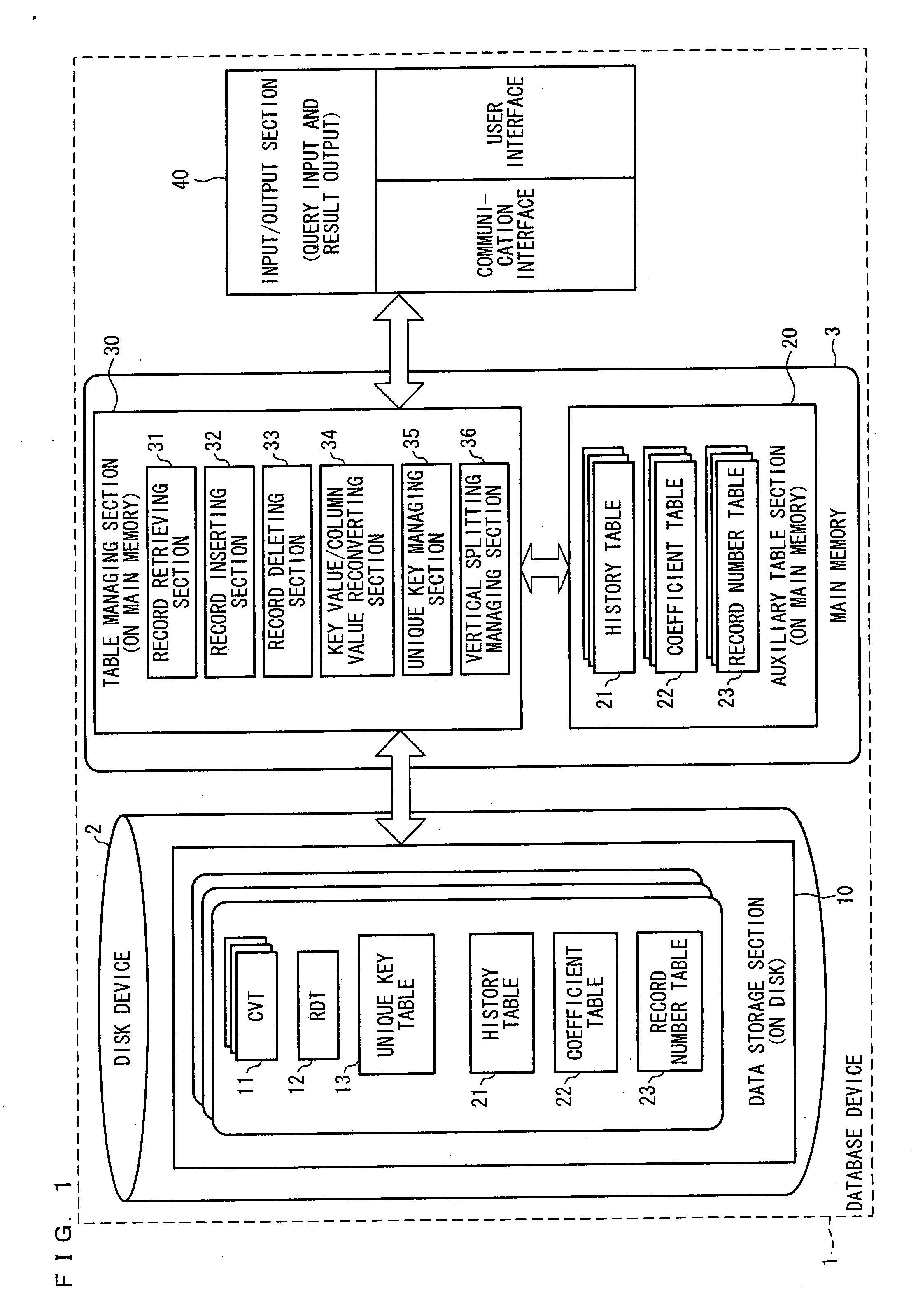
Datebase Device, Database Management Method, Data Structure Of Database, Database Management Program, And Computer-Readable Storage Medium Storing Same Program
InactiveUS20080091691A1Improve memory efficiencyQuick searchRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsRelational databaseData structure
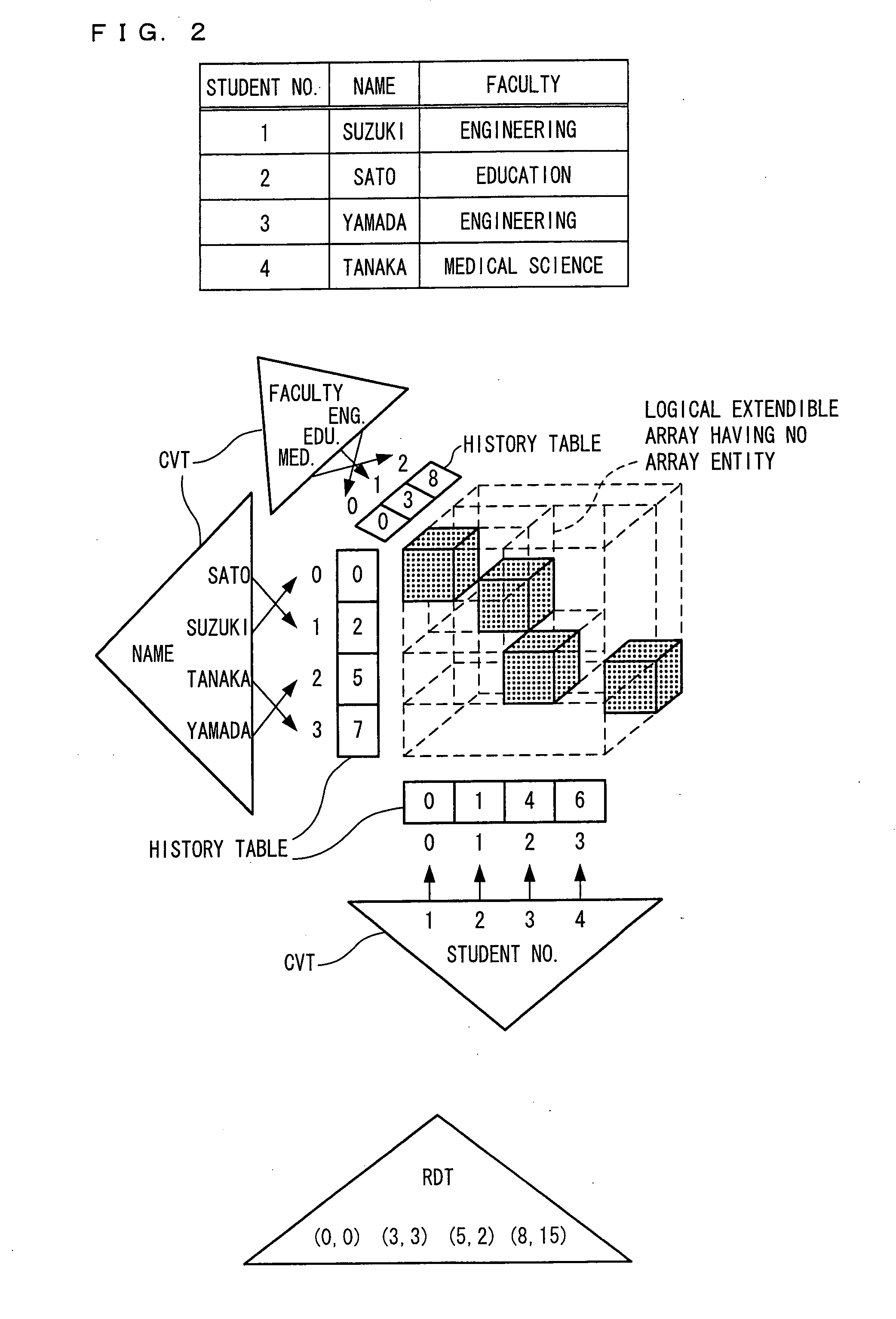
When a record inserting section inserts a record having a new column value, the record inserting section registers the column value in a CVT such that an extendible array is extended; registers, in a history table, a history value indicating a chronological sequence of array extension; registers, in a coefficient table, coefficients of a linear function for calculating an offset of an element in an subarray; registers an initial value in a record number table; and inserts as a key value a 2-tuple expression of the history value and the offset of the element of the extendible array into RDT. This makes it possible to dynamically add, upon operation, a record having a new column value and to register only an existing record, thereby realizing a relational database allowing for fast record retrieval.
Owner:FUKUI UNIV OF
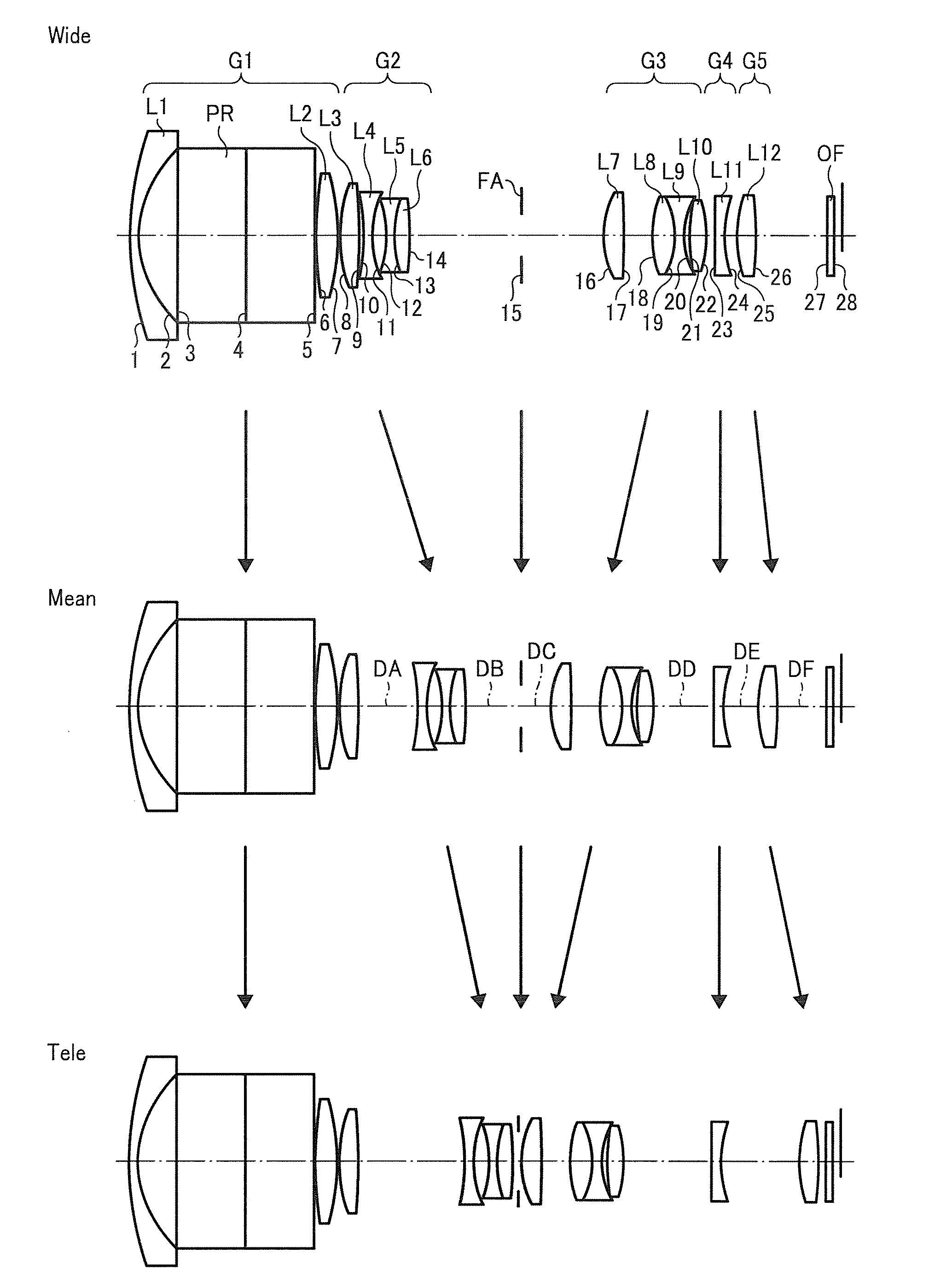
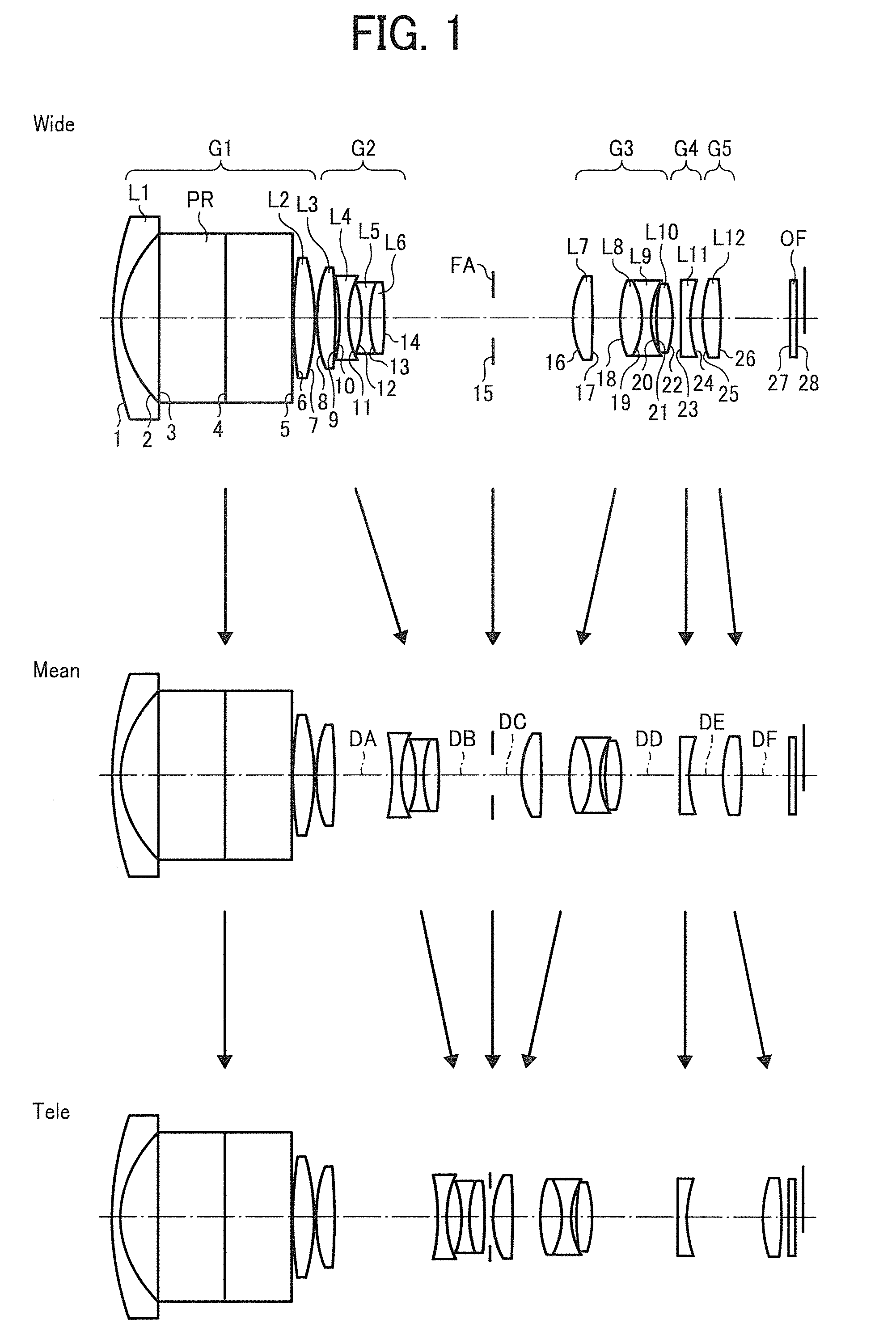
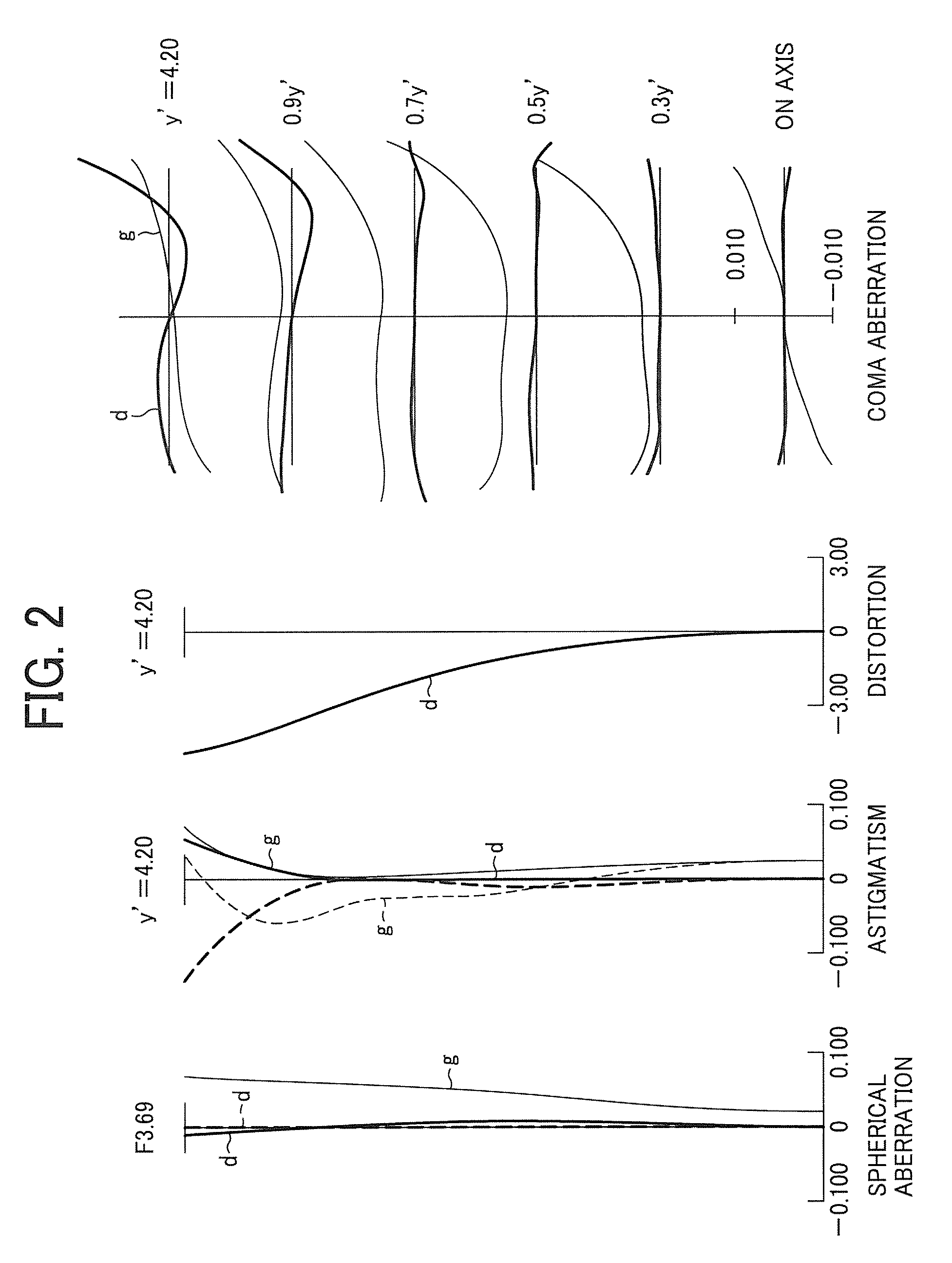
Zoom lens, imaging apparatus, and personal data assistant
A zoom lens includes a first optical system having a positive focal length, the first optical system, a second optical system having a negative focal length, a third optical system having a positive focal length, a fourth optical system having a negative focal length, and a fifth optical system having a positive focal length, which are arranged in order from an object side to an image side and an aperture stop provided at an object side of the third optical system. The following condition is satisfied:0.5<(T23w / Y′) / (ft / fw)<1.0where T23w is an interval between the second optical system and the third optical system at the short focus end, Y′ is a maximum image height of the zoom lens, ft is a focal length of the zoom lens at the long focus end, and fw is a focal length of the zoom lens at the short focus end.
Owner:RICOH KK
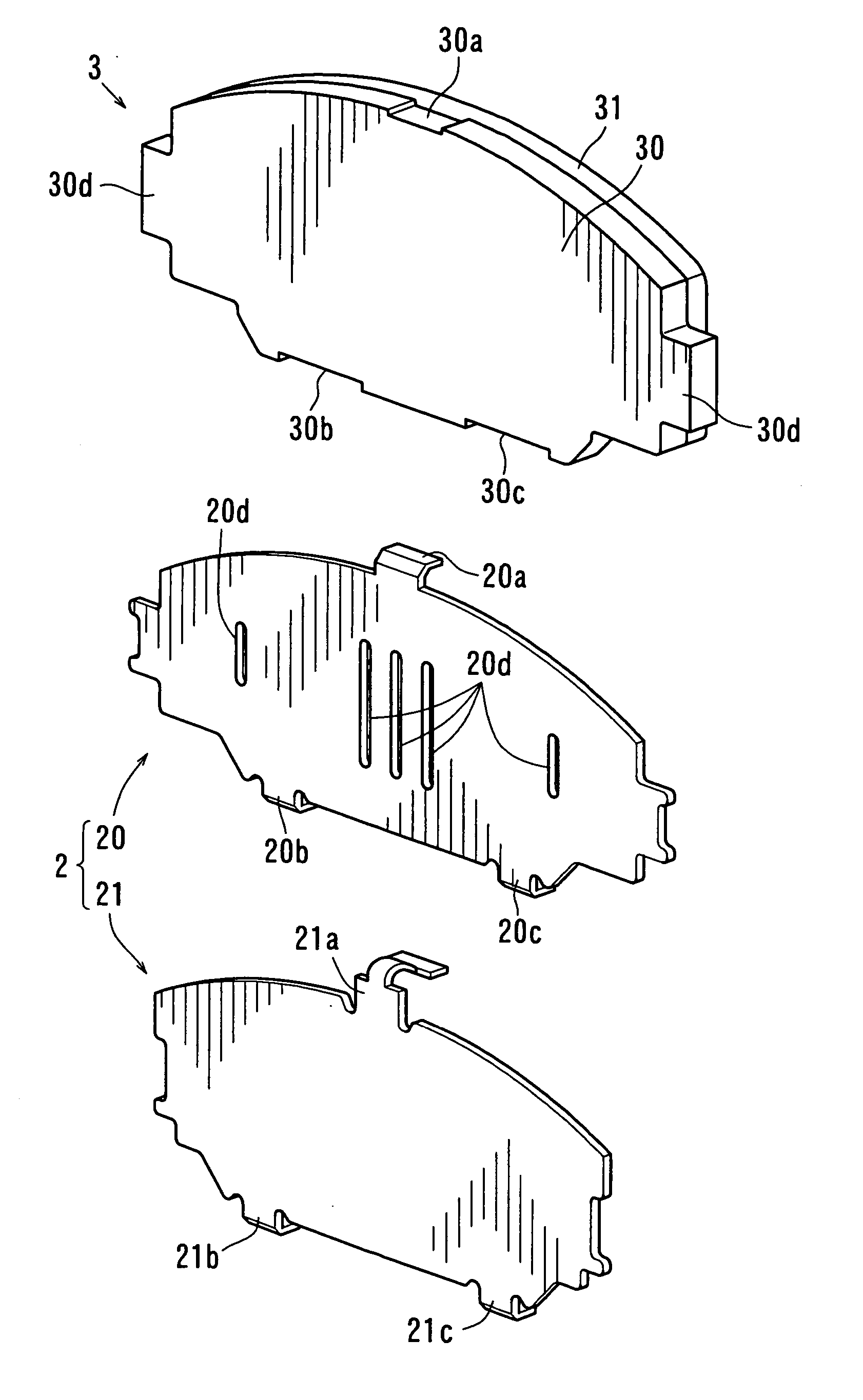
Laminated shim for disk brake and pad unit having the laminated shim
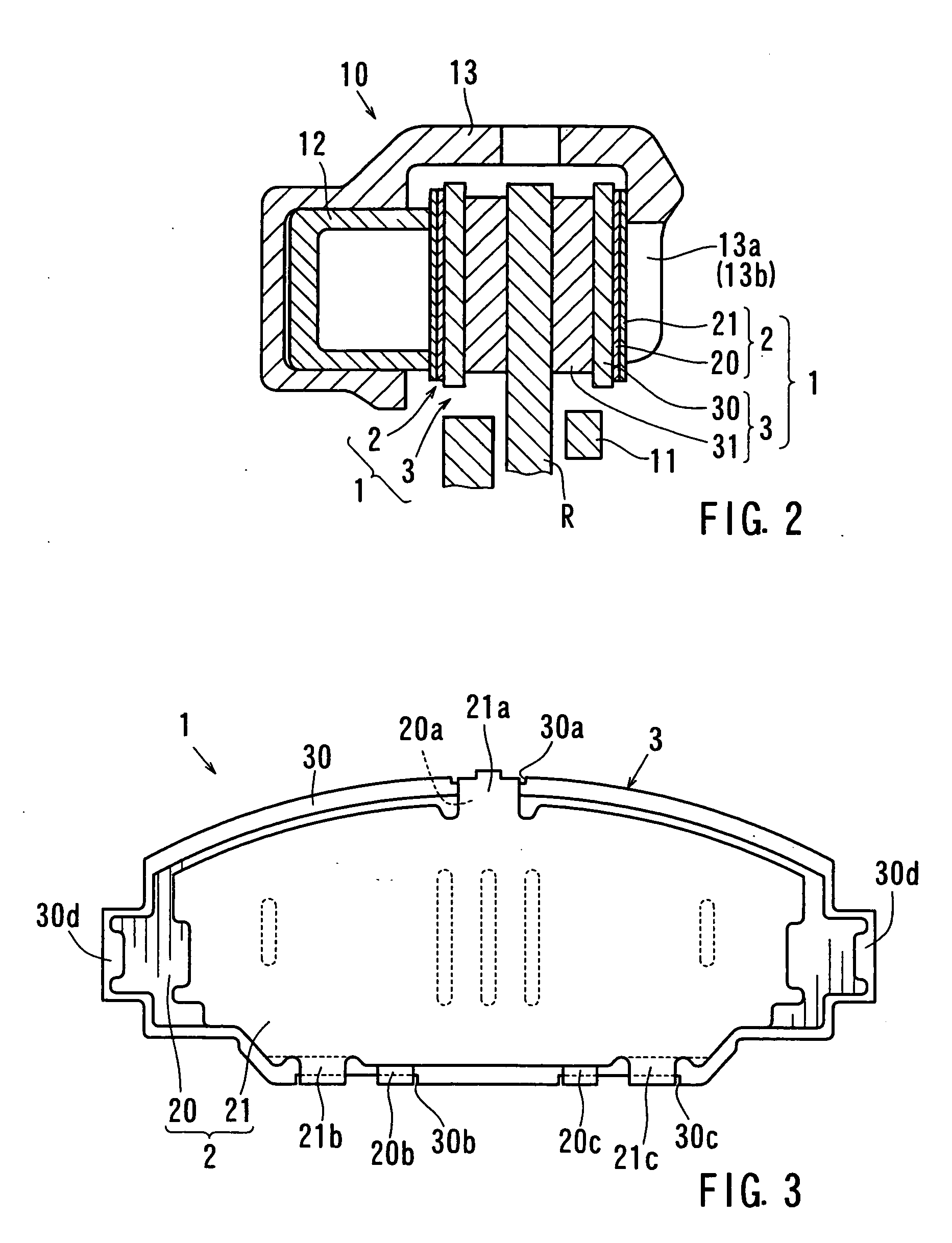
ActiveUS20060027427A1Increase elastic deformationLarge lengthNoise/vibration controlSlack adjustersDisc brakeGasket
A laminated shim for a disk brake has a pad side shim and a pressing member side shim. The pad side shim is provided at a backside of a backing plate of a pad. The pressing member side shim is disposed between the pad side shim and a pressing member used for pressing the pad against a rotor. The pad side shim has hooks that extend over and are hooked onto a peripheral edge of the backing plate. The pressing member side shim has hooks that extend over a surface of a respective pad side hook. The pressing member hooks are slidably contacted to the top of the hooks of the pad side shim so as to be easy to slide in a surface direction with respect to the pad side shim and the backing plate of the pad.
Owner:ADVICS CO LTD
Drying apparatus
InactiveUS20090034946A1Sufficient powerImprove noiseDrying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsMaterial PerforationAirflow
A drying apparatus includes a casing and a cavity formed in the casing for receiving an object to be dried. A fan is located in the casing so as to be capable of creating an airflow, and a motor is provided in the casing for driving the fan. Ducting is provided for carrying the airflow from the fan to at least one opening arranged to emit the airflow into the cavity (12). The ducting includes at least one air duct having a wall in which perforations are provided, and a layer of sound-absorbing material is located on the external surface of the wall so as to cover the perforations. The invention is particularly suitable for use in hand dryers.
Owner:DYSON TECH LTD
Hand-held wand mixer
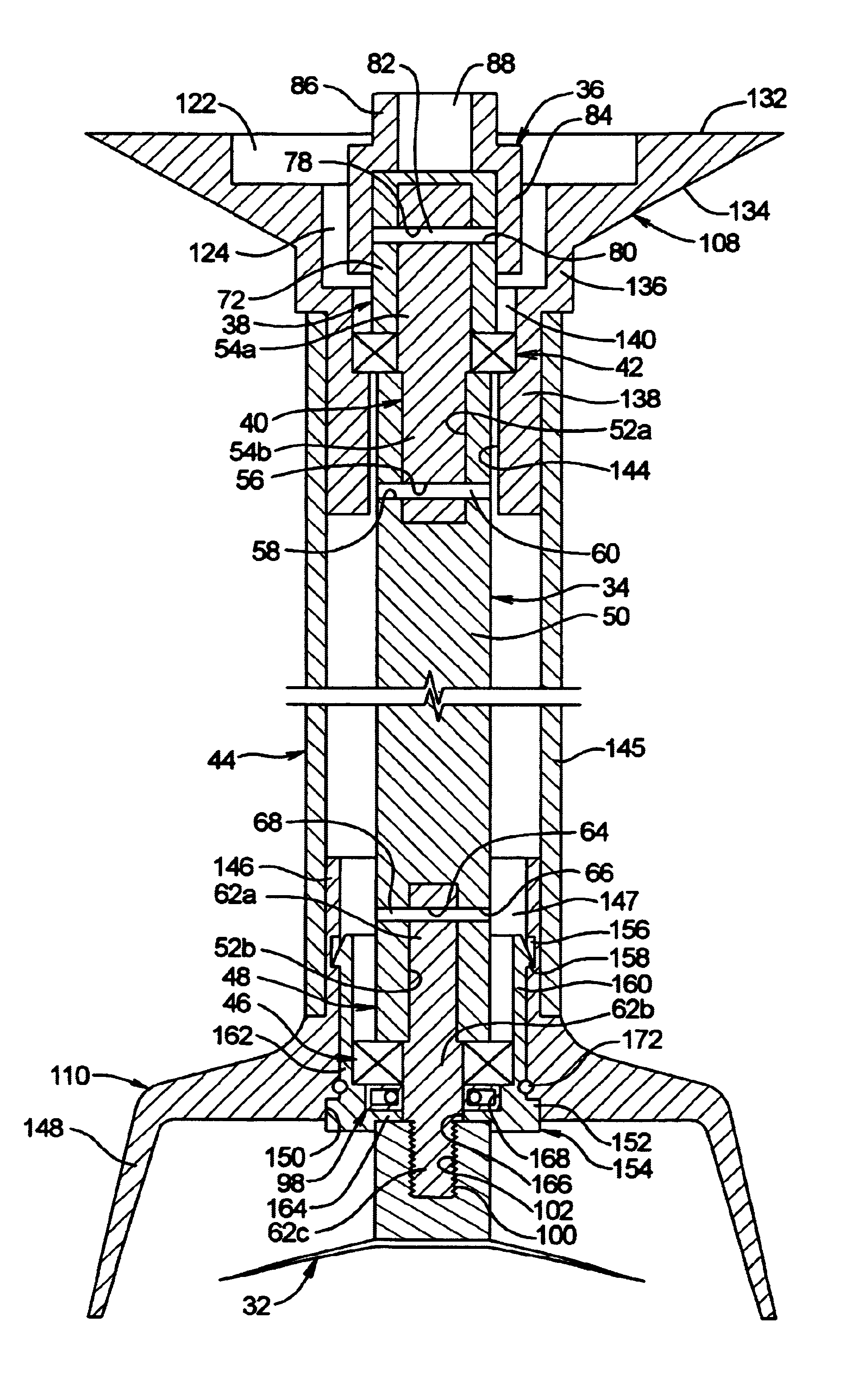
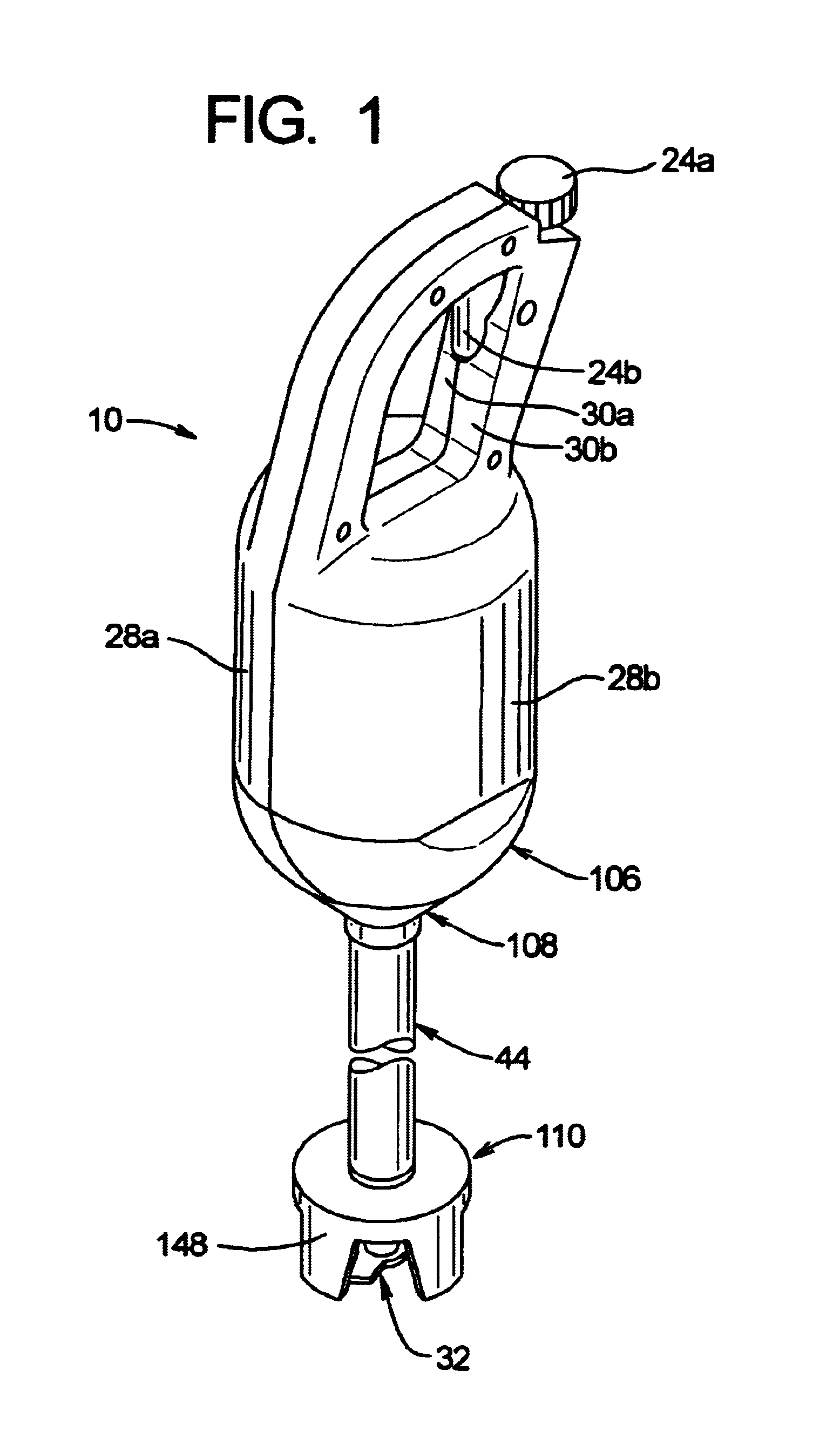
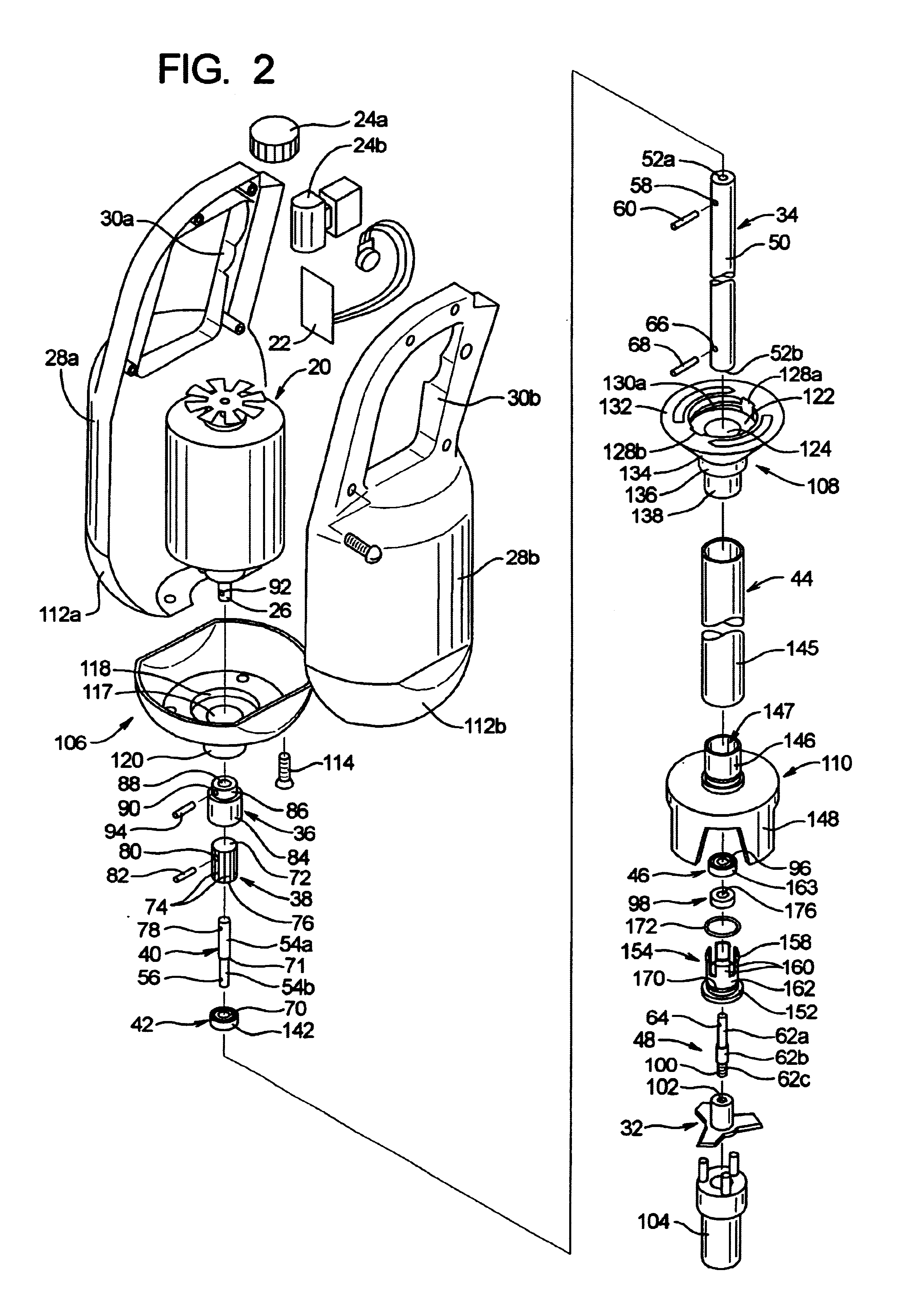
InactiveUS6974244B1Easily remove and exchangeLoad be therefore reducedRotary stirring mixersMixer accessoriesHand heldDrive shaft
A wand mixer having a wand assembly that is detachable from the motor assembly as a single unit. The wand assembly includes a drive shaft that is enclosed within a tubular housing having a seal at the lower end for preventing entry of fluids and debris. First and second bearings at the ends of the tubular housing support both ends of the shaft so as to prevent deformation and damage of the seal when the wand assembly is removed from the motor assembly for cleaning. The wand assembly mounts to the motor assembly using a bayonet-type connection, and the motor and drive shafts are interconnected by an externally splined member that is received axially in an internally splined sleeve. The wand assembly can therefore be removed or mounted to the motor assembly by a convenient, manual turning and axial movement of the components.
Owner:LIN KING YUAN
Balloon catheter having a shaft with a variable stiffness inner tubular member
ActiveUS7273485B2Reduce wall thicknessIncrease wall thicknessStentsBalloon catheterVariable stiffnessAxial compression
A catheter having an elongated shaft and a balloon on a distal shaft section, the elongated shaft comprising an outer tubular member, and an inner tubular member which has a bonded portion along which an outer surface of the inner tubular member is bonded to an inner surface of the outer tubular member. The inner tubular member has a proximal portion proximal to the bonded portion, and a distal portion distal to the bonded portion with higher axial compression stiffness and column strength than the proximal portion thereof. The catheter has improved traceability, axial collapse resistance, pushability, and crossability, for improved ability to position the balloon at a desired location in a patient's body lumen.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
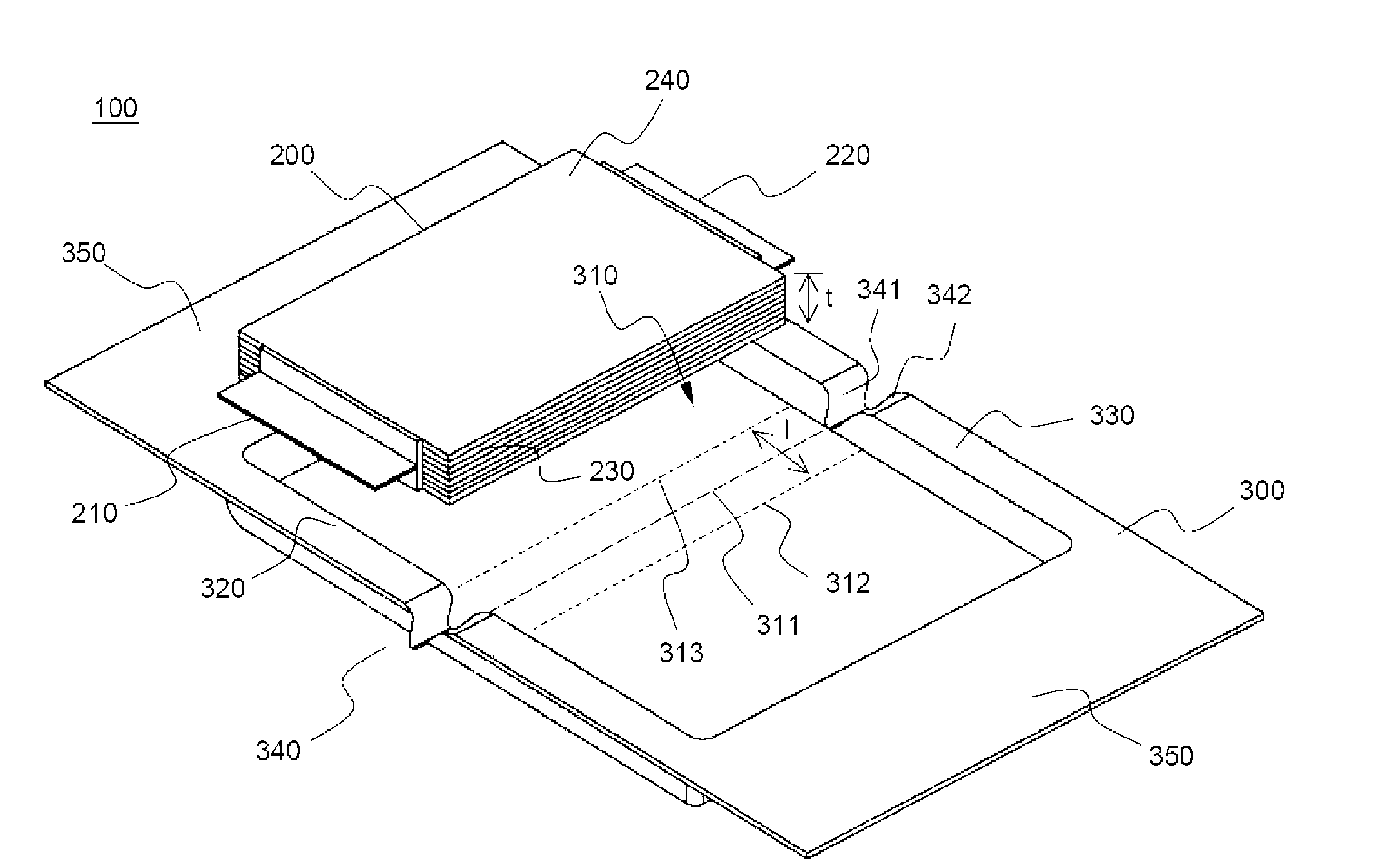
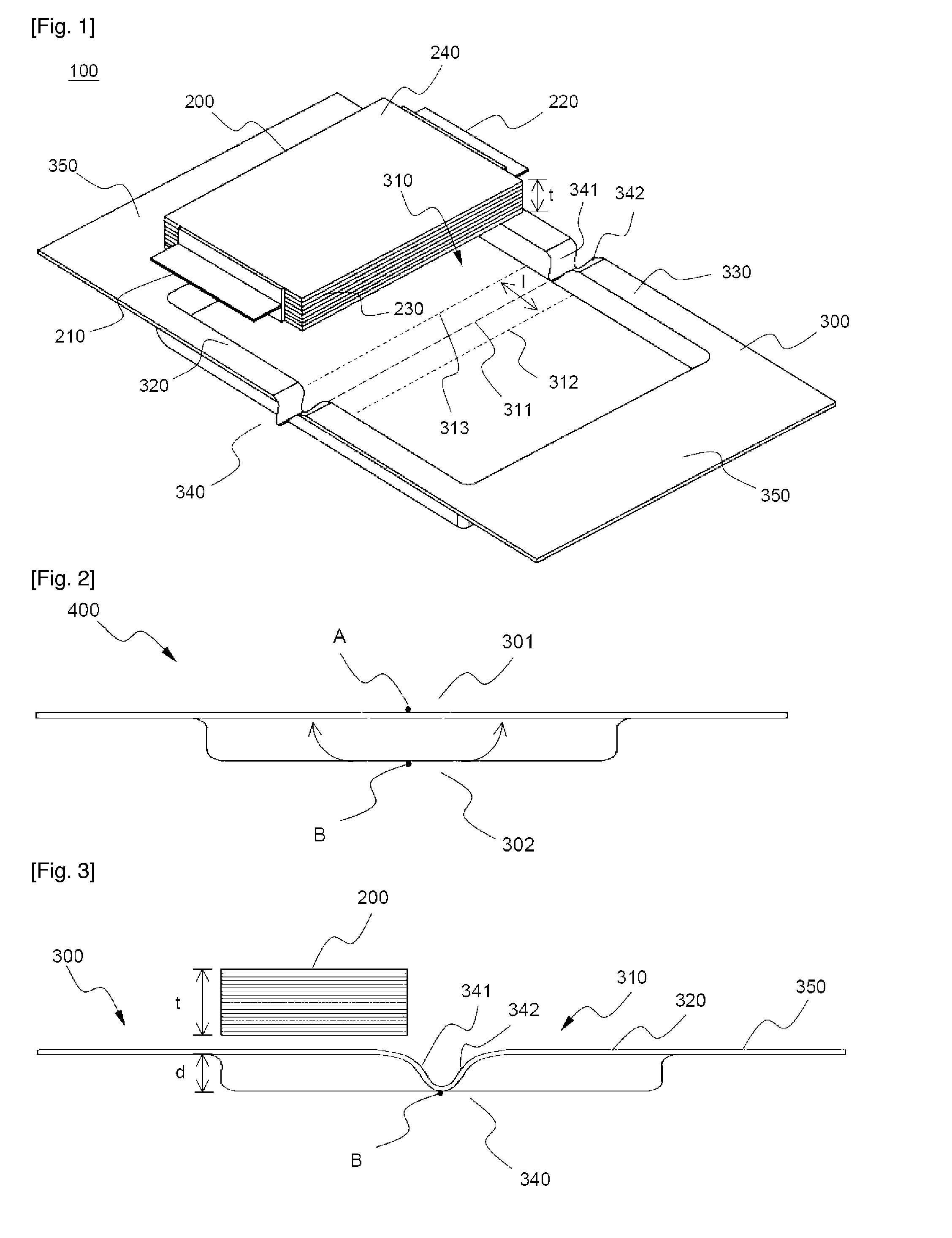
Pouch-type battery
ActiveUS20090311592A1Avoid breakingExtended service lifeFinal product manufactureSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsEngineeringCathode
Disclosed herein is a pouch-type battery including a cathode and an anode protruding from opposite sides of a battery case in opposite directions, wherein the pouch-type battery is constructed in a structure in which two receiving parts are formed at a one-unit sheet-type battery case in a symmetrical fashion such that an electrode assembly is received in the receiving parts, the battery case is bent between the two receiving parts (along a bending line) such that one of the receiving parts overlaps with the other receiving part while the electrode assembly is received in the other receiving part, the bent battery case being scaled, the two receiving parts are continuously formed while the two receiving parts are in contact with the bending line, and the battery case is provided at the edge thereof where the bending line runs with bent depression parts having a depth equivalent to that of the receiving parts. The pouch-type battery is manufactured with a capacity equivalent to twice that of a conventional battery through a simple assembly process, and is constructed in a structure in which the battery case is prevented from breakage during the assembly process.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
Piezoelectric structure, liquid ejecting head and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveUS20020140320A1Durable devices can be providedMaintain strengthPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesLiquid jetSingle crystal
A piezoelectric structure includes a vibrational plate; a piezoelectric film; the vibrational plate including a layer of a monocrystal material, a polycrystal material, a monocrystal material doped with an element which is different from an element constituting the monocrystal material, or a polycrystal material doped with an element which is different from an element constituting the polycrystal materials, and oxide layers sandwiching the aforementioned layer, the piezoelectric film has a single orientation crystal or monocrystal structure.
Owner:CANON KK +1
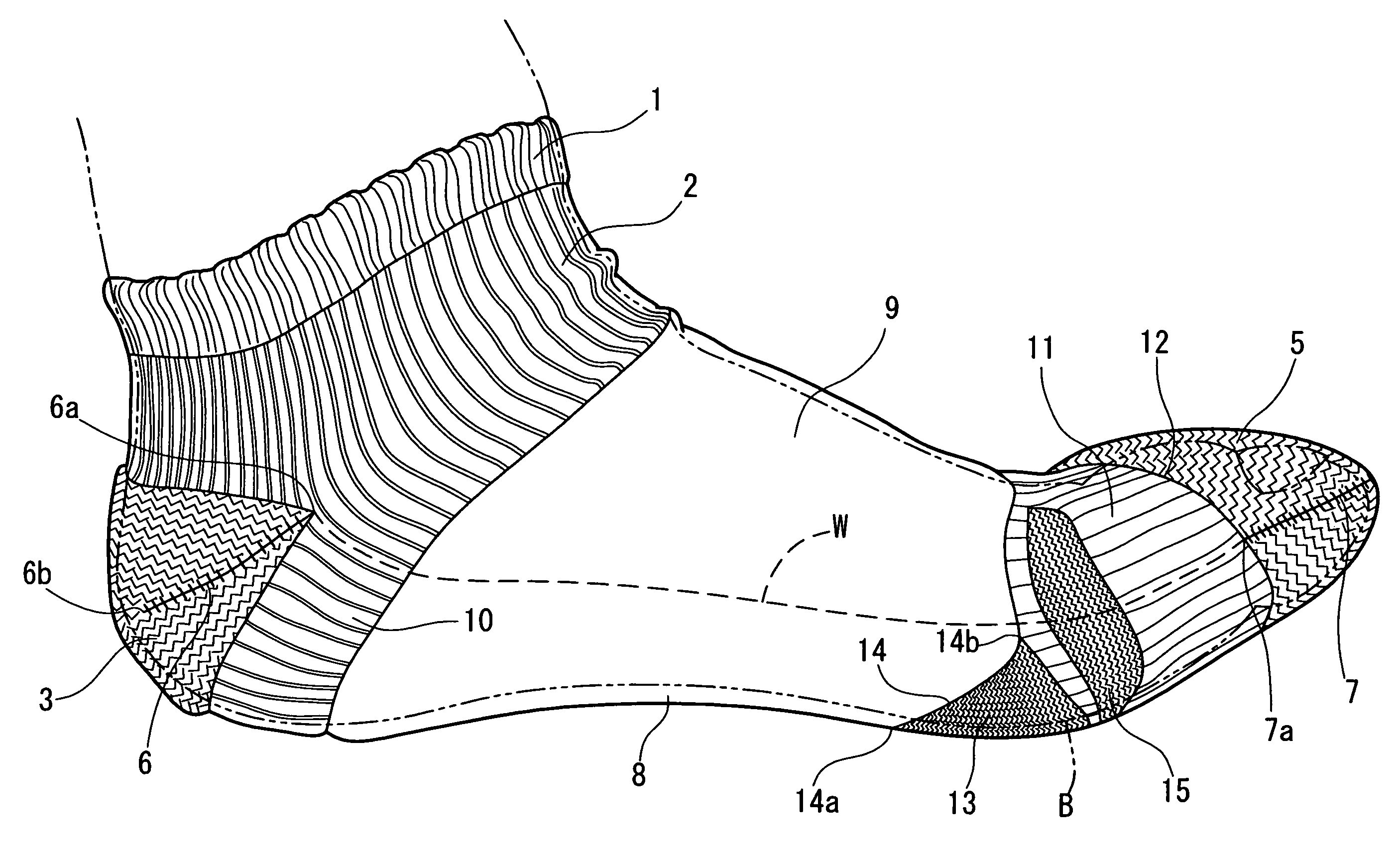
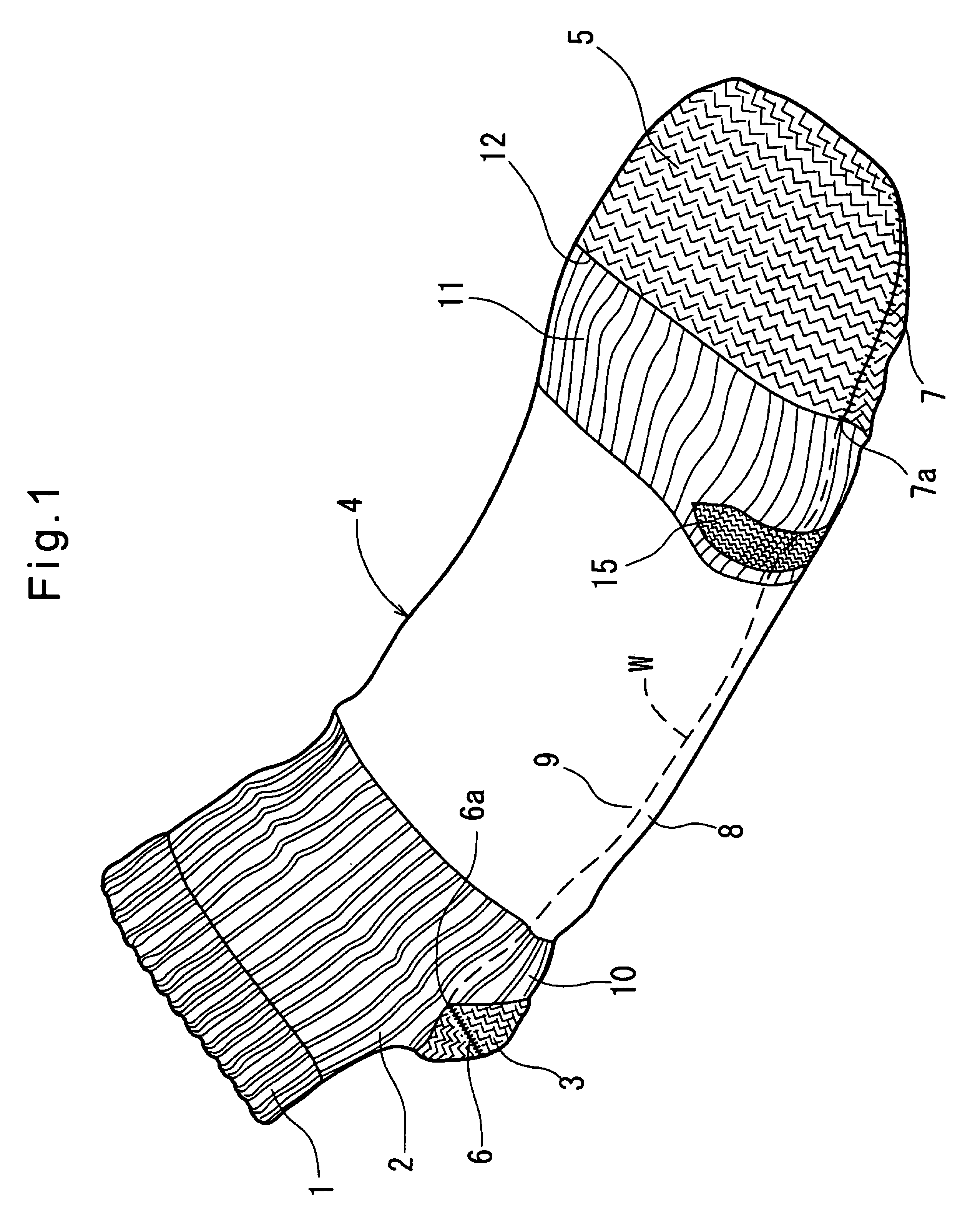
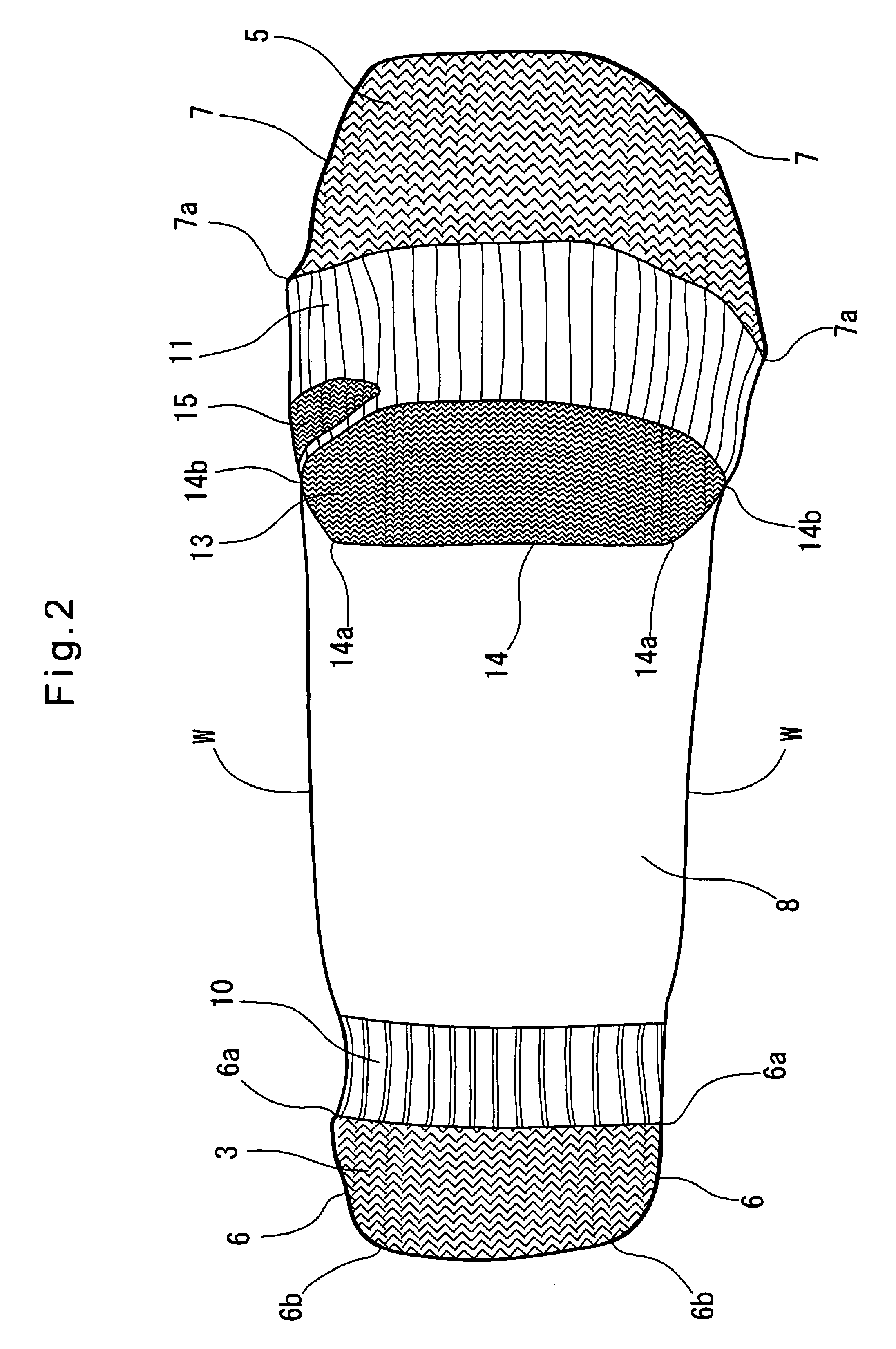
Socks
Owner:OKAMOTO INDS
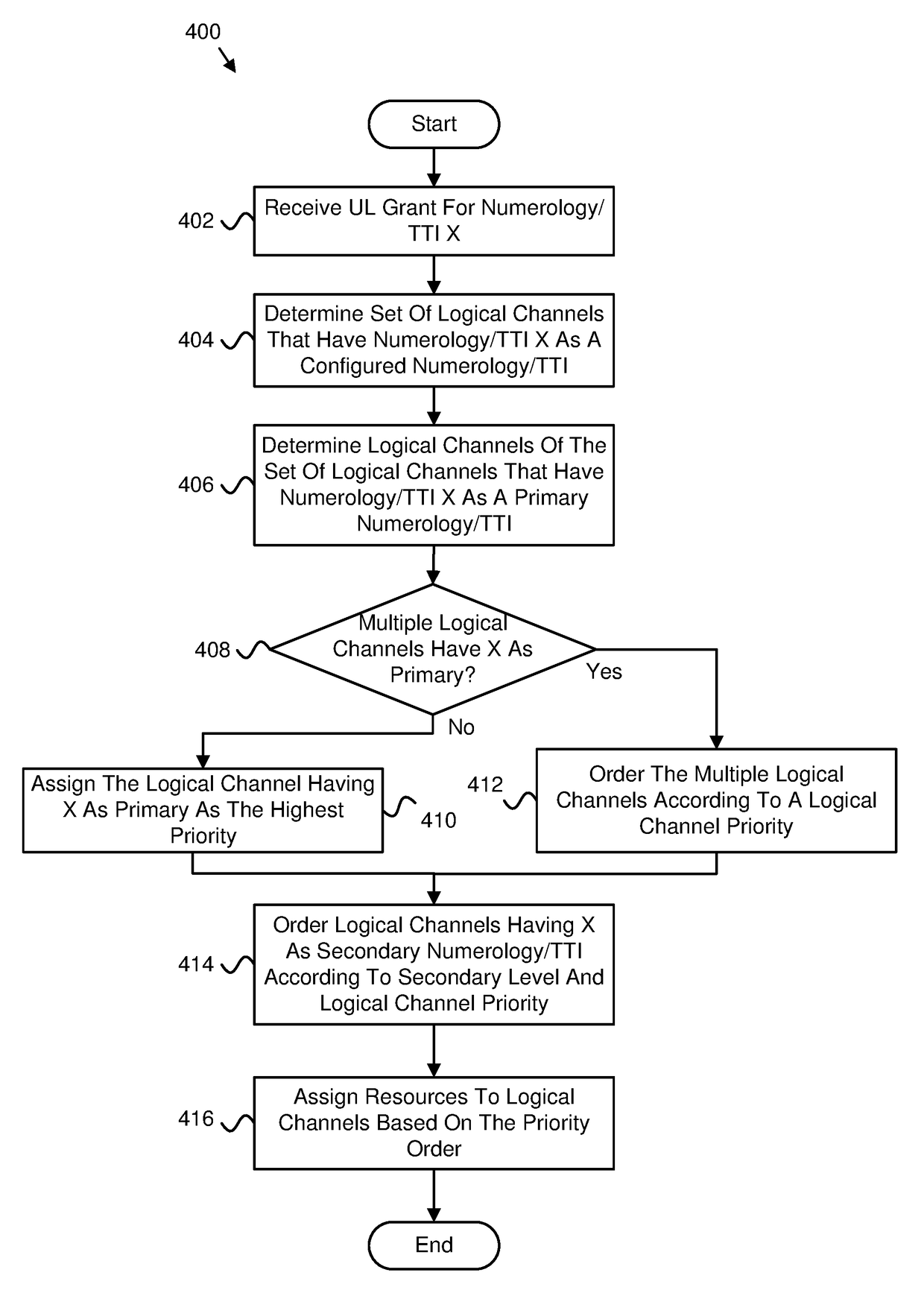
Determining a priority order based on uplink transmission parameters
ActiveUS20180310308A1Large lengthTransmission path divisionSignal allocationUplink transmissionResource allocation
Apparatuses, methods, and systems are disclosed for determining a priority order based on uplink transmission parameters. One apparatus includes a receiver that receives an uplink grant corresponding to uplink transmission parameters that include an indication of a numerology and a transmission time interval length. The apparatus includes a processor that determines a priority order of multiple logical channels based on the uplink transmission parameters and a logical channel priority of the multiple logical channels. The processor assigns resources to logical channels of the multiple logical channels based on the priority order.
Owner:MOTOROLA MOBILITY LLC
Toothed washer for a tube coupler device, a method of making a toothed washer, and a coupler device of the quick coupling type
ActiveUS7273235B2Improving tube retentionImprove stressSleeve/socket jointsFluid pressure sealed jointsCouplingFree edge
Owner:LEGRIS
Work vehicle with engine compartment and exhaust gas treatment arrangement
ActiveUS8505661B2Reduce cooling efficiencySufficient reliabilityExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusExhaust fumesAir blast
In a work vehicle, an engine compartment is disposed forwards of a cab. An exhaust gas treatment device is disposed over an engine in the engine compartment. A radiator is disposed forwards of the exhaust gas treatment device (33) in the engine compartment. A blower is configured to generate an airflow passing through the radiator from back to front of the radiator. The exhaust gas treatment device is slanted with respect to a vehicle width direction for increasing a distance between the exhaust gas treatment device and the radiator towards a first lateral face portion. Further, the first lateral face portion includes air inlets facing a space between the exhaust gas treatment device and the radiator.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
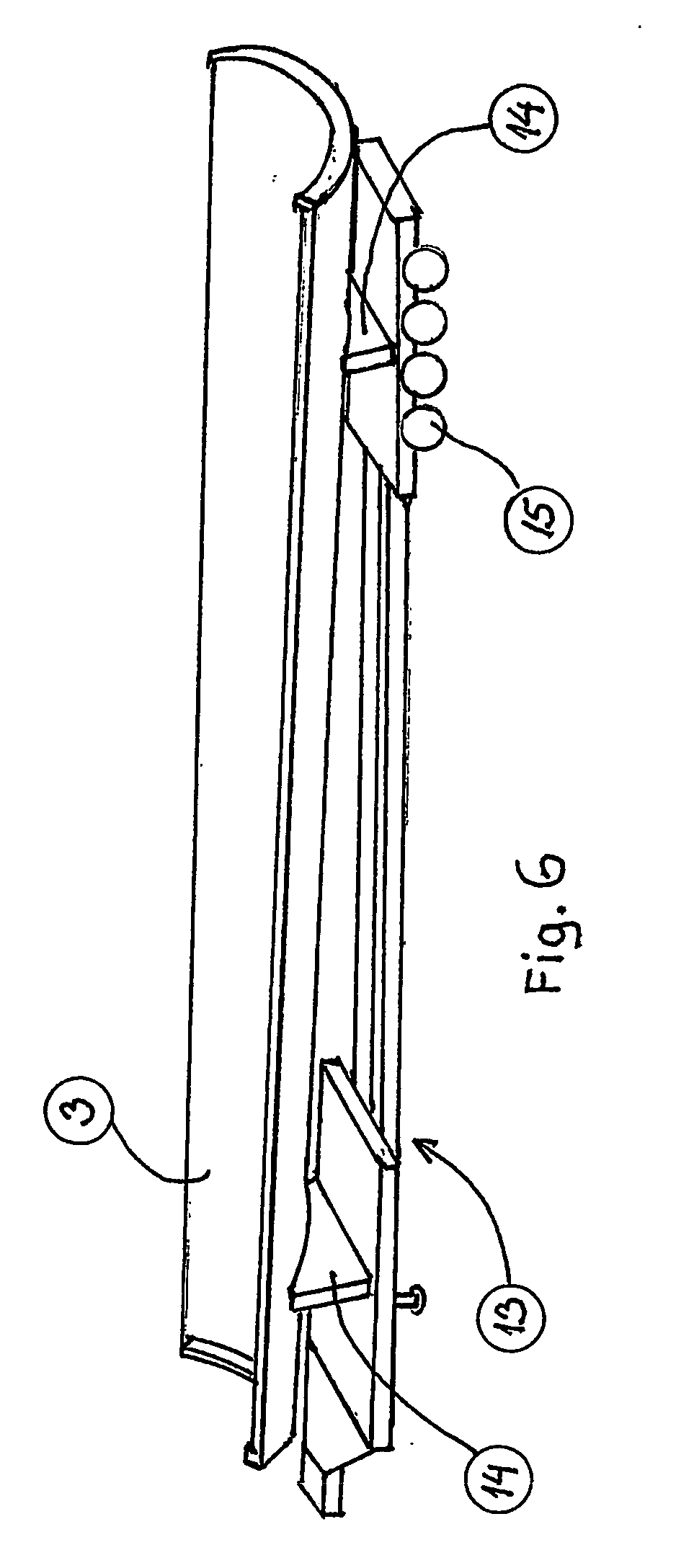
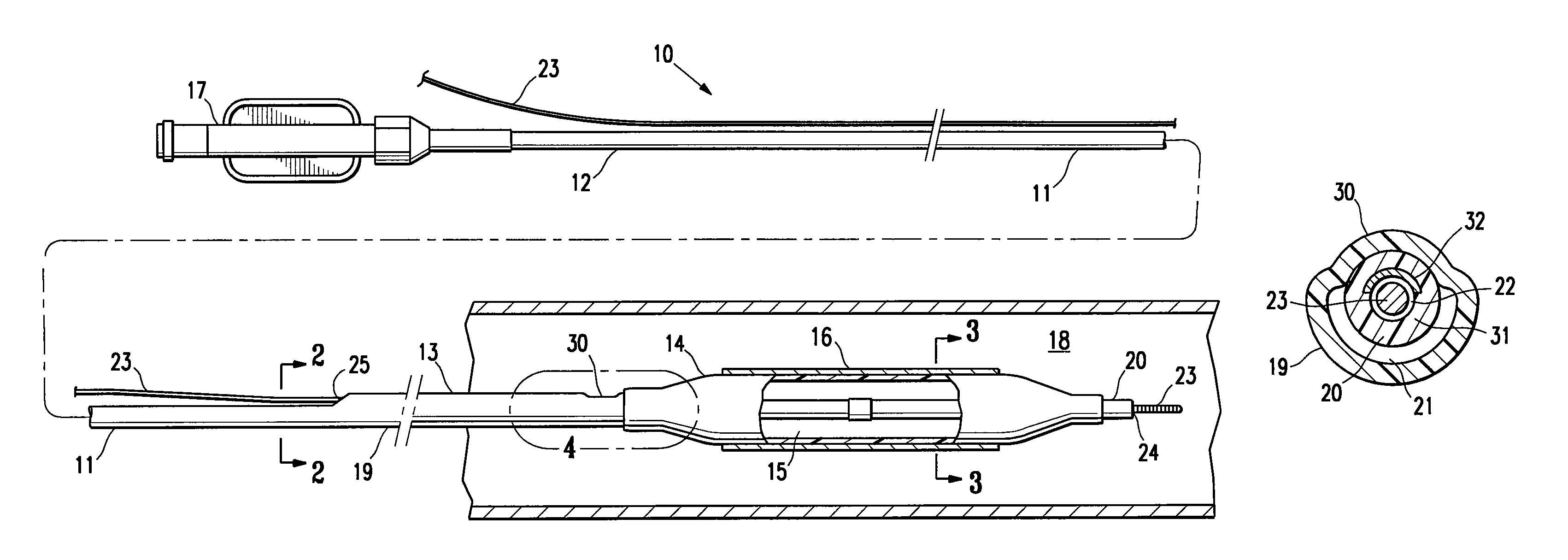
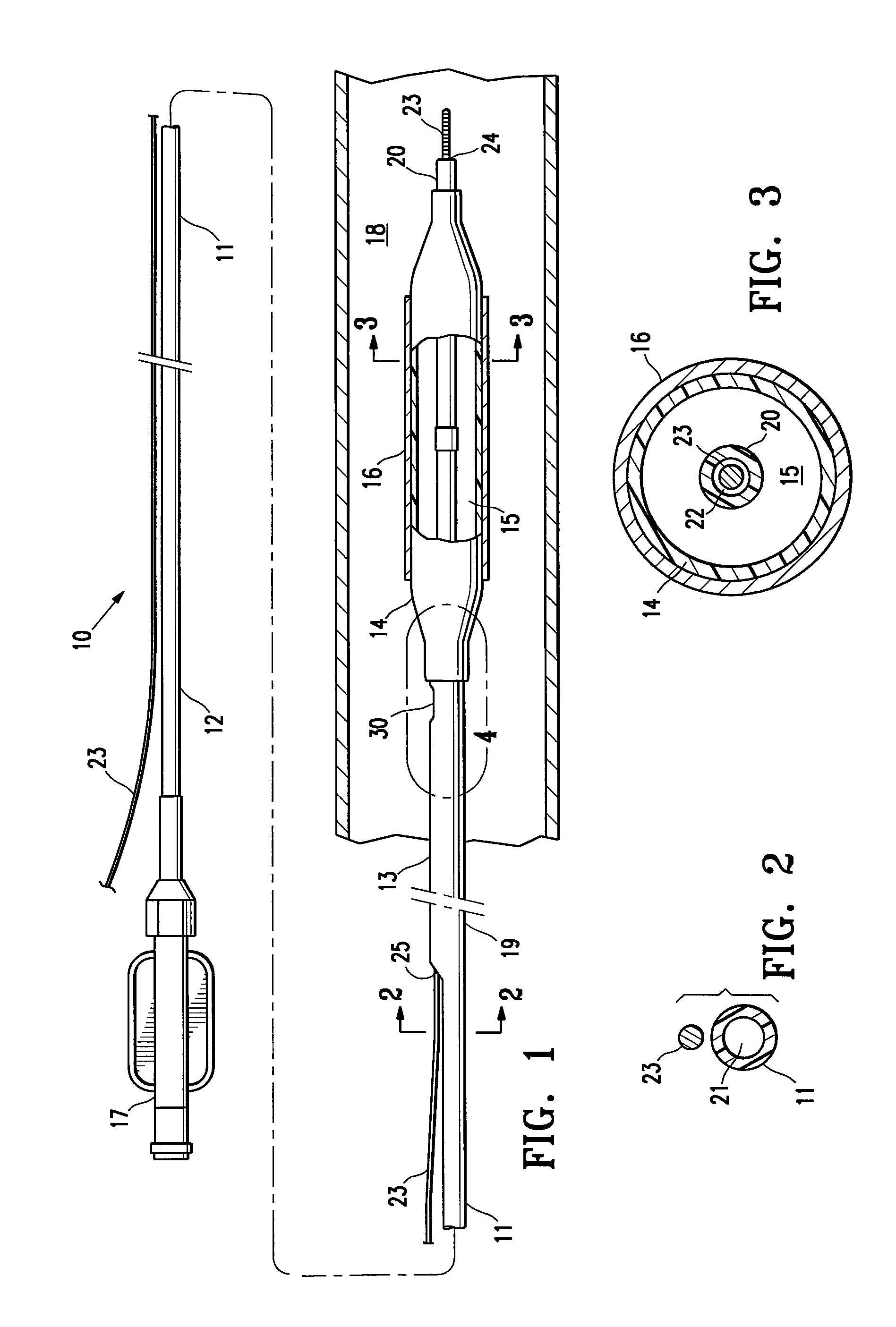
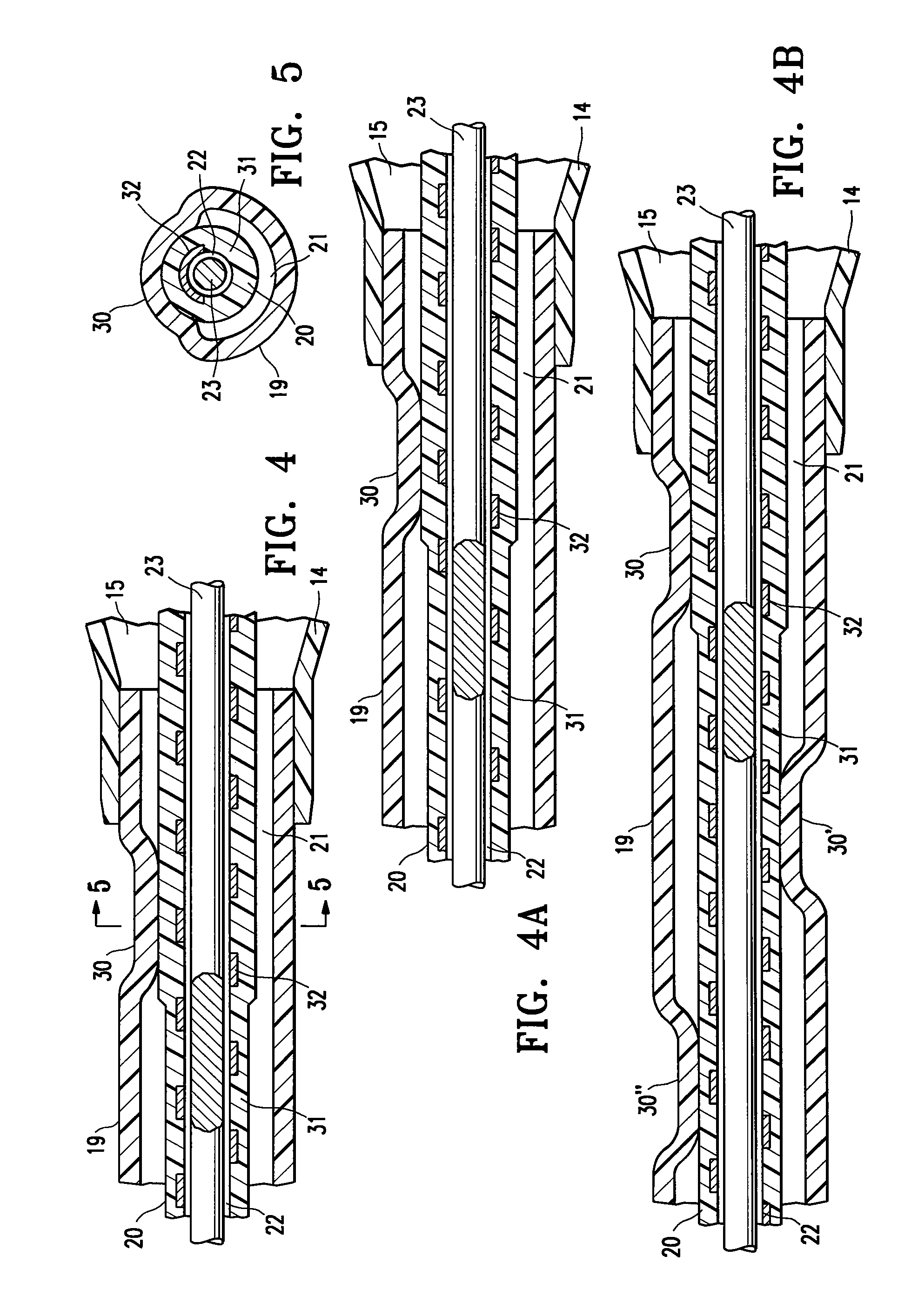
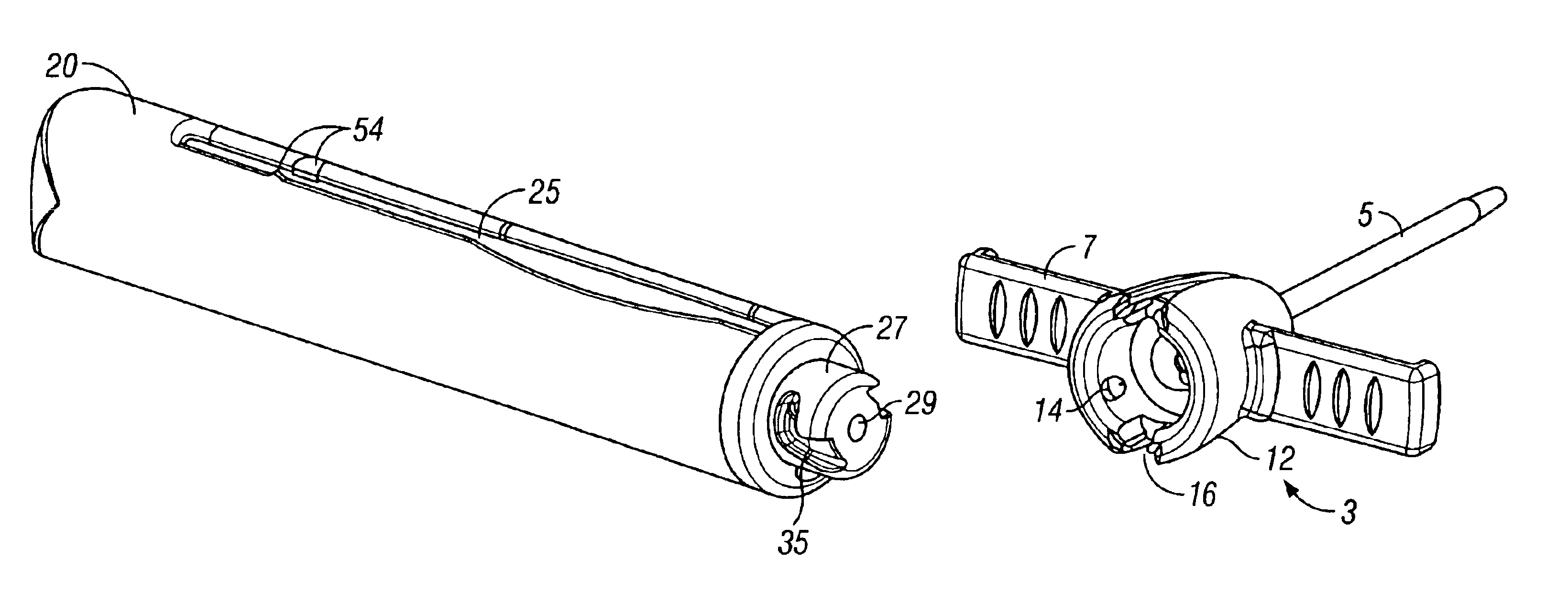
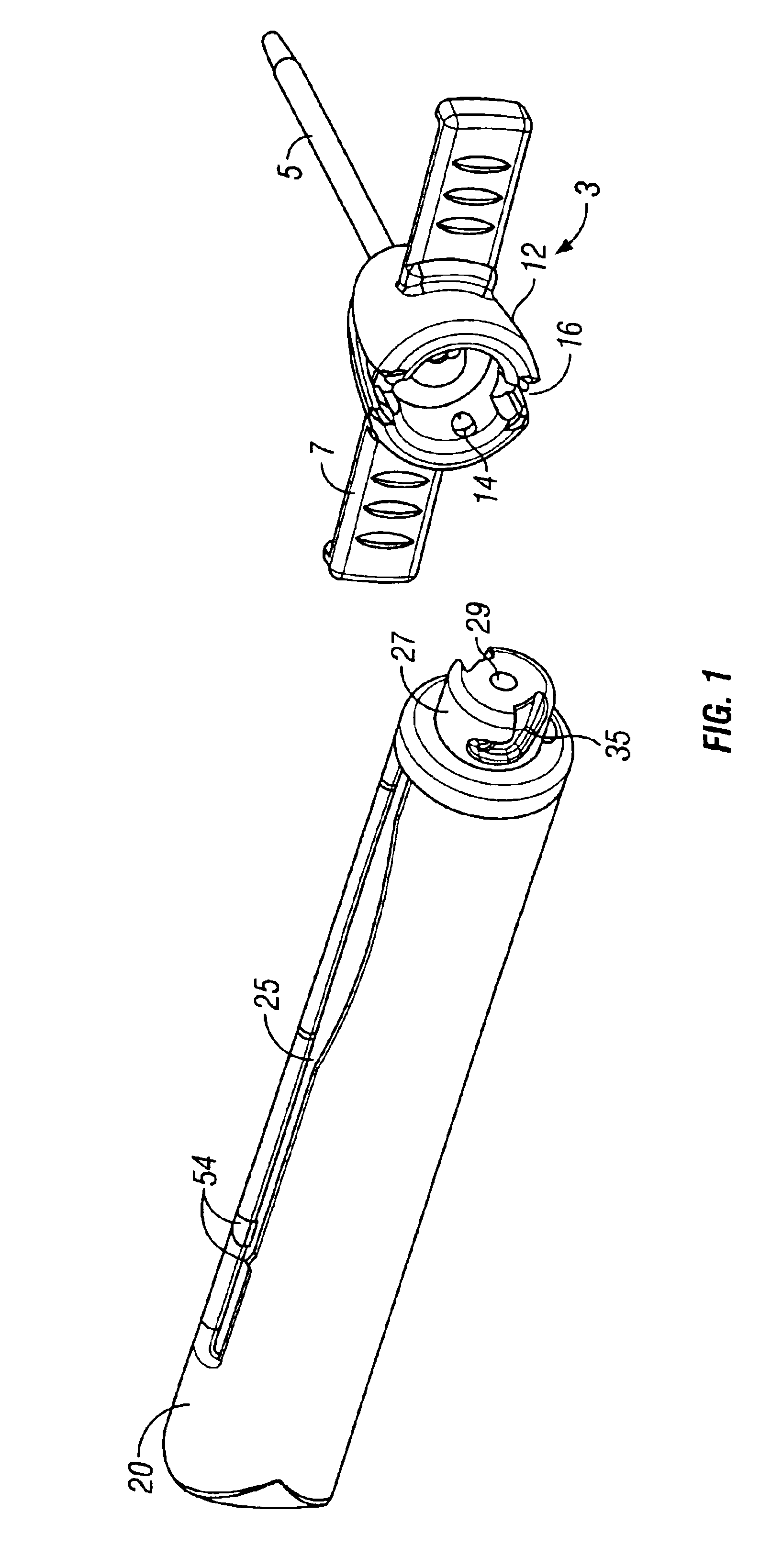
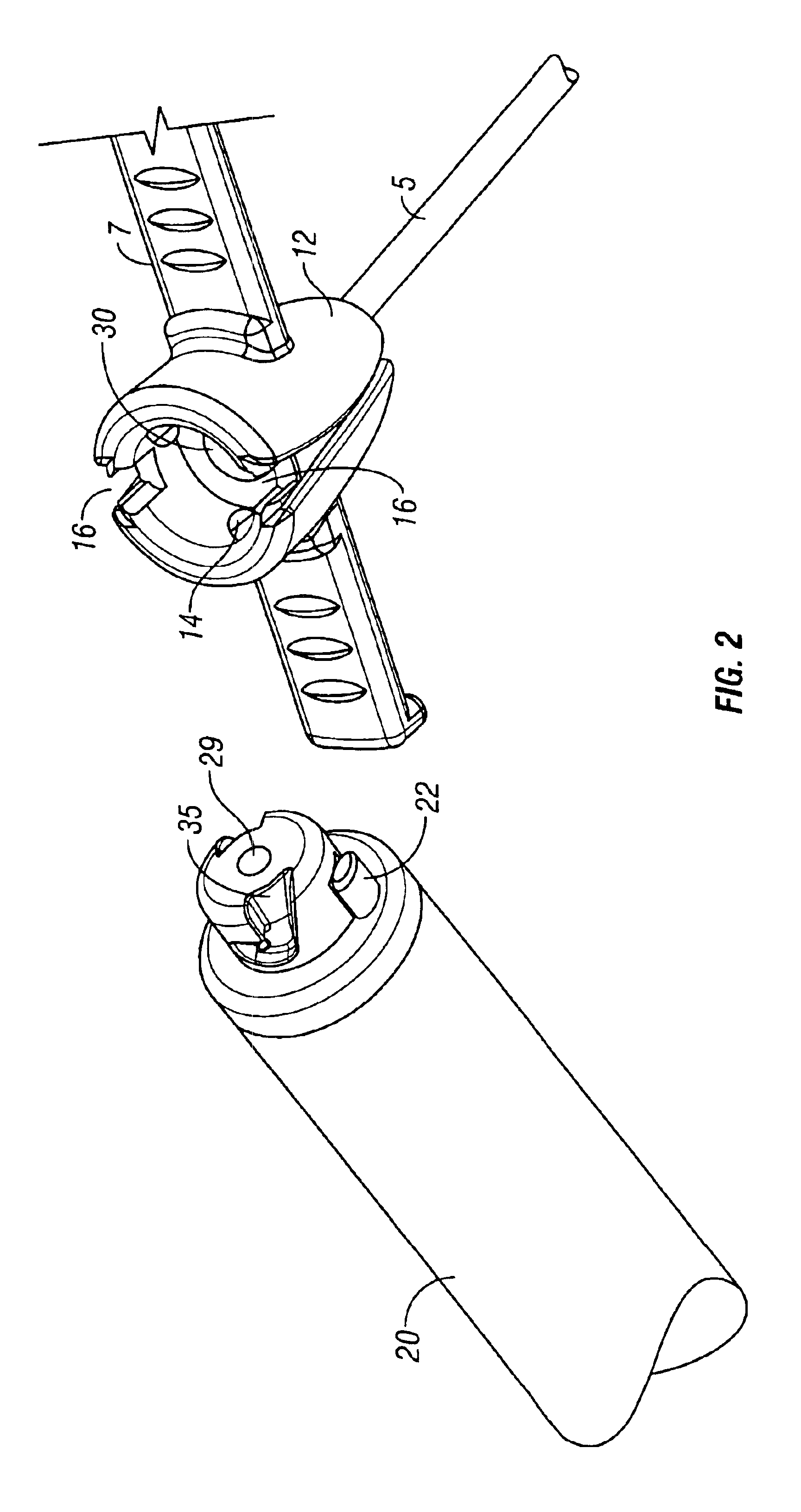
Safety needle assembly with locking retraction
Provided is an assembly in which a needle is safely housed in a cover. A safety mechanism prevents the needle from being removed from a device, unless the needle is in a “needle safe position”.
Owner:ARAGON MEDICAL
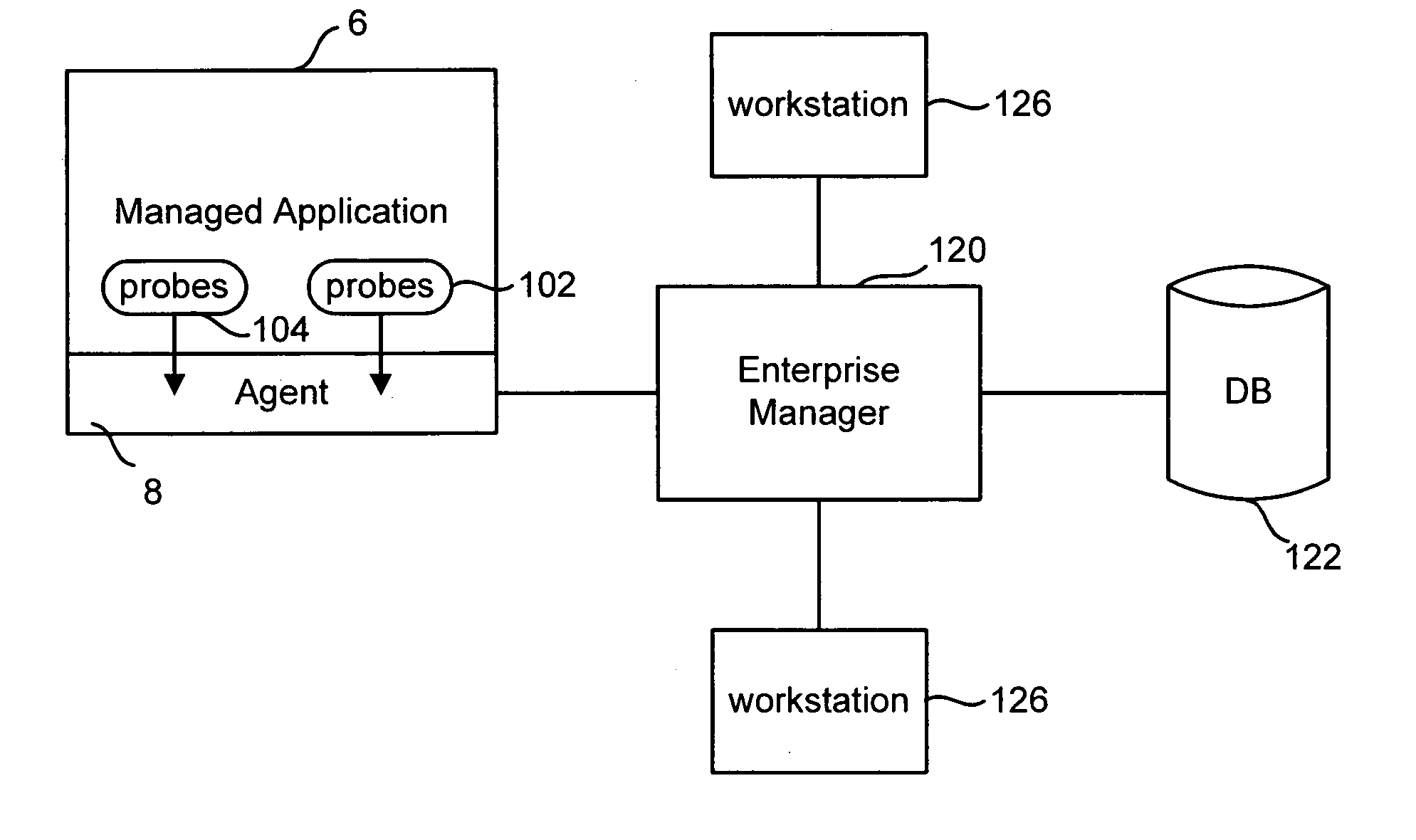
Efficient processing of time series data
InactiveUS20060173878A1Improve performanceReduce in quantityDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsDatabaseTime series
A system receiving time series data will store the data in a first format suited for quick writing. That data will subsequently be converted from the first format to a second format better suited than the first format for compact storage and queries. Over time, the data in the second format can be aggregated and / or down sampled. In one embodiment, the first format includes a set of blocks of information, with each block of information storing data for a set of metrics during a time period. The second format includes a header, a set of blocks of data and a footer. Each bock of data in the second format stores information for a metric over multiple time periods. The footer includes pointers to each block of data.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Method and device for the quantitative gas analysis
InactiveUS6903823B1Economical and simpleLarge lengthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGas analysisDiffusion
The invention relates to a device and a method for the quantitative gas analysis in which the gas analysis of a sample atmosphere is implemented by means of a sensor device, a diffusion seal being produced between the sample atmosphere contained in a sample system and a measuring chamber and the gas analysis of the sample atmosphere which is diffused into the measuring chamber being implemented with the sensor device, the sensor head (5) being able to be coupled to the measuring adapter (4) and the radiation source (16) and the detector device (17) being fixed to the measuring chamber (9) in a defined orientation and the measuring radiation (24) emitted from the radiation source (16) traversing at least once through the measuring chamber (9) and being detected by the detector device (17) after leaving the measuring chamber (9).
Owner:MULLER HOLGER +1
Balloon catheter having a shaft with a variable stiffness inner tubular member
InactiveUS20080045895A1High axial compression stiffness and column strengthImproved crossabilityStentsBalloon catheterVariable stiffnessDistal portion
A catheter having an elongated shaft and a balloon on a distal shaft section, the elongated shaft comprising an outer tubular member, and an inner tubular member which has a bonded portion along which an outer surface of the inner tubular member is bonded to an inner surface of the outer tubular member. The inner tubular member has a proximal portion proximal to the bonded portion, and a distal portion distal to the bonded portion with higher axial compression stiffness and column strength than the proximal portion thereof. The catheter has improved trackability, axial collapse resistance, pushability, and crossability, for improved ability to position the balloon at a desired location in a patient's body lumen.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
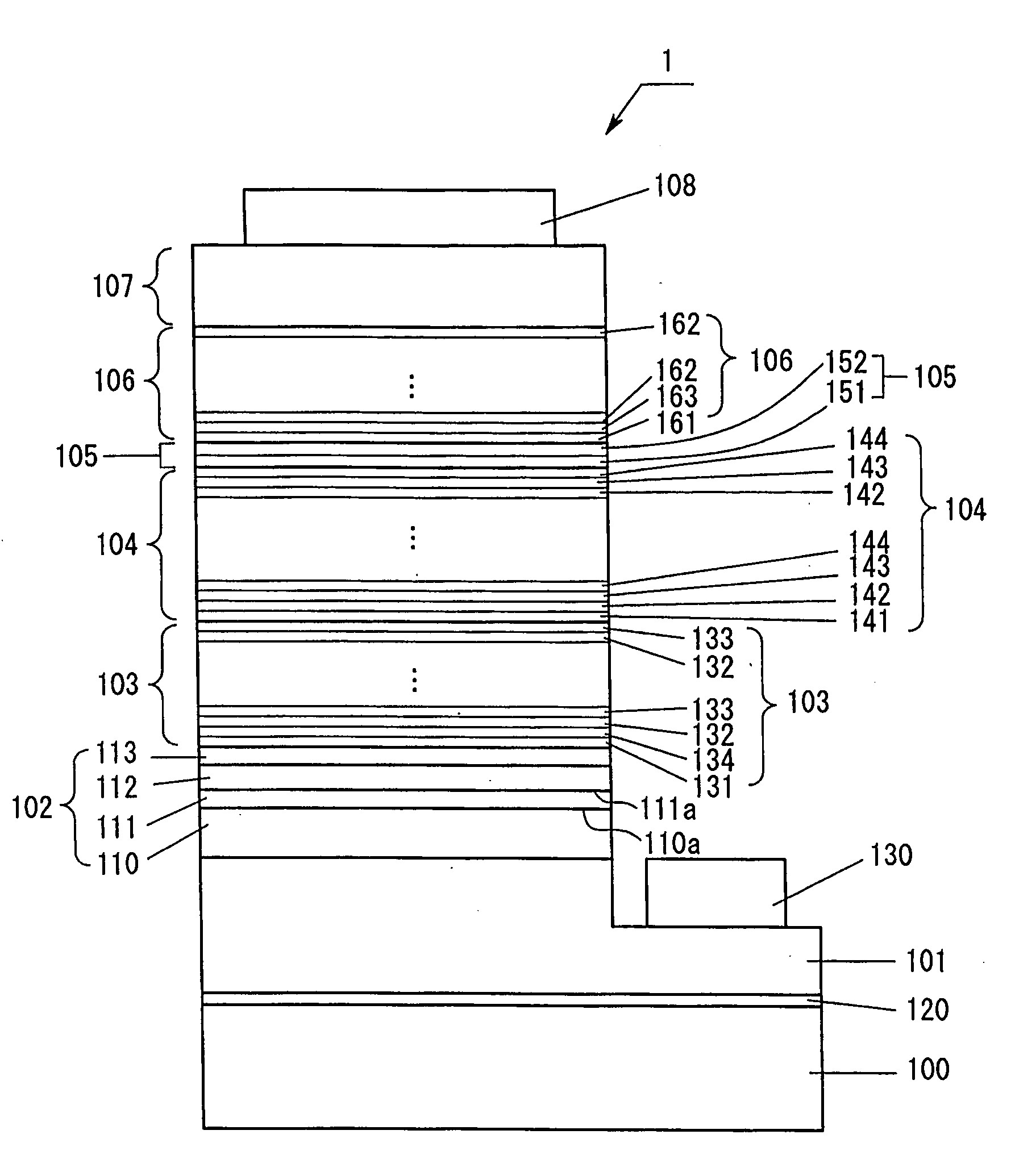
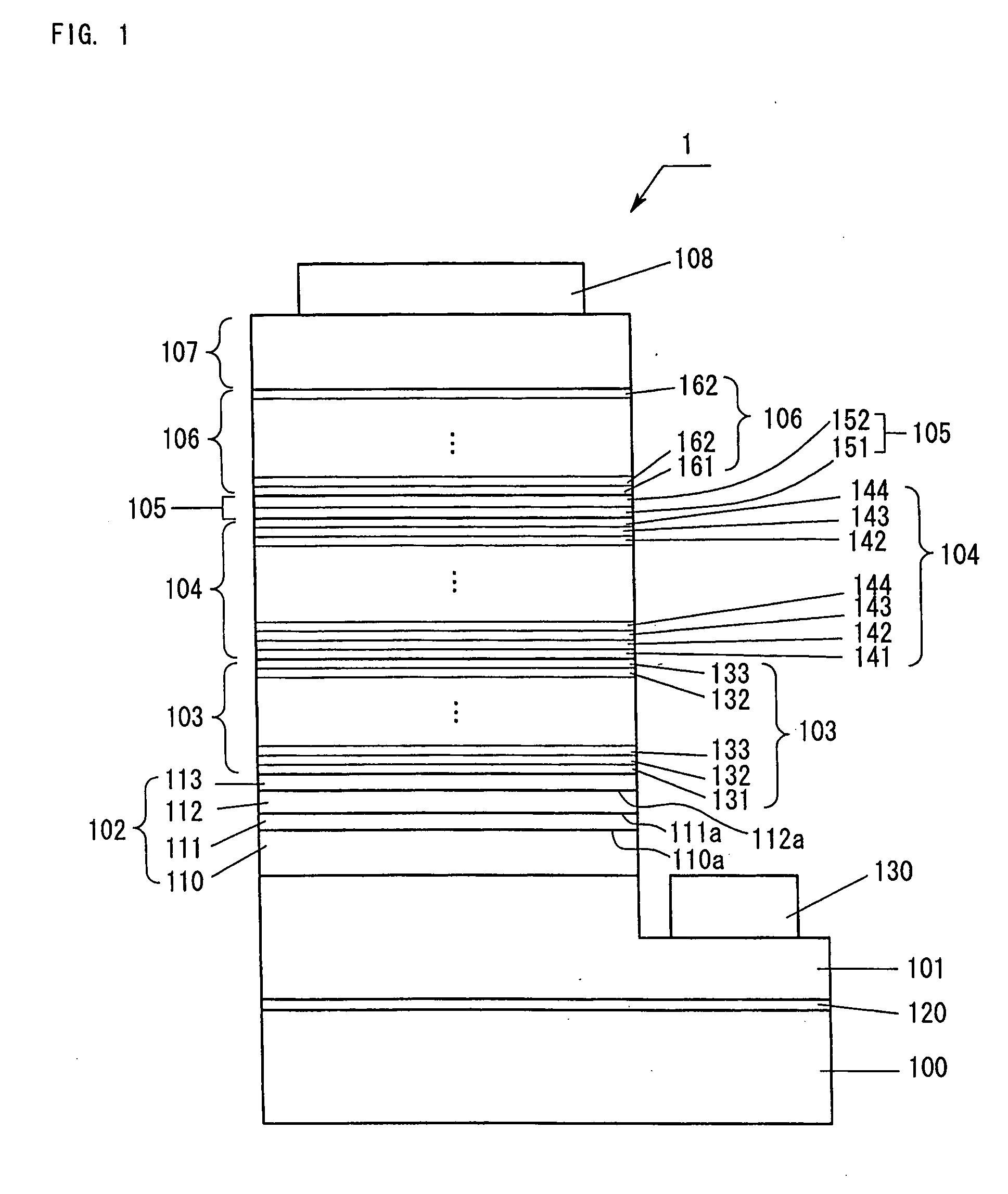
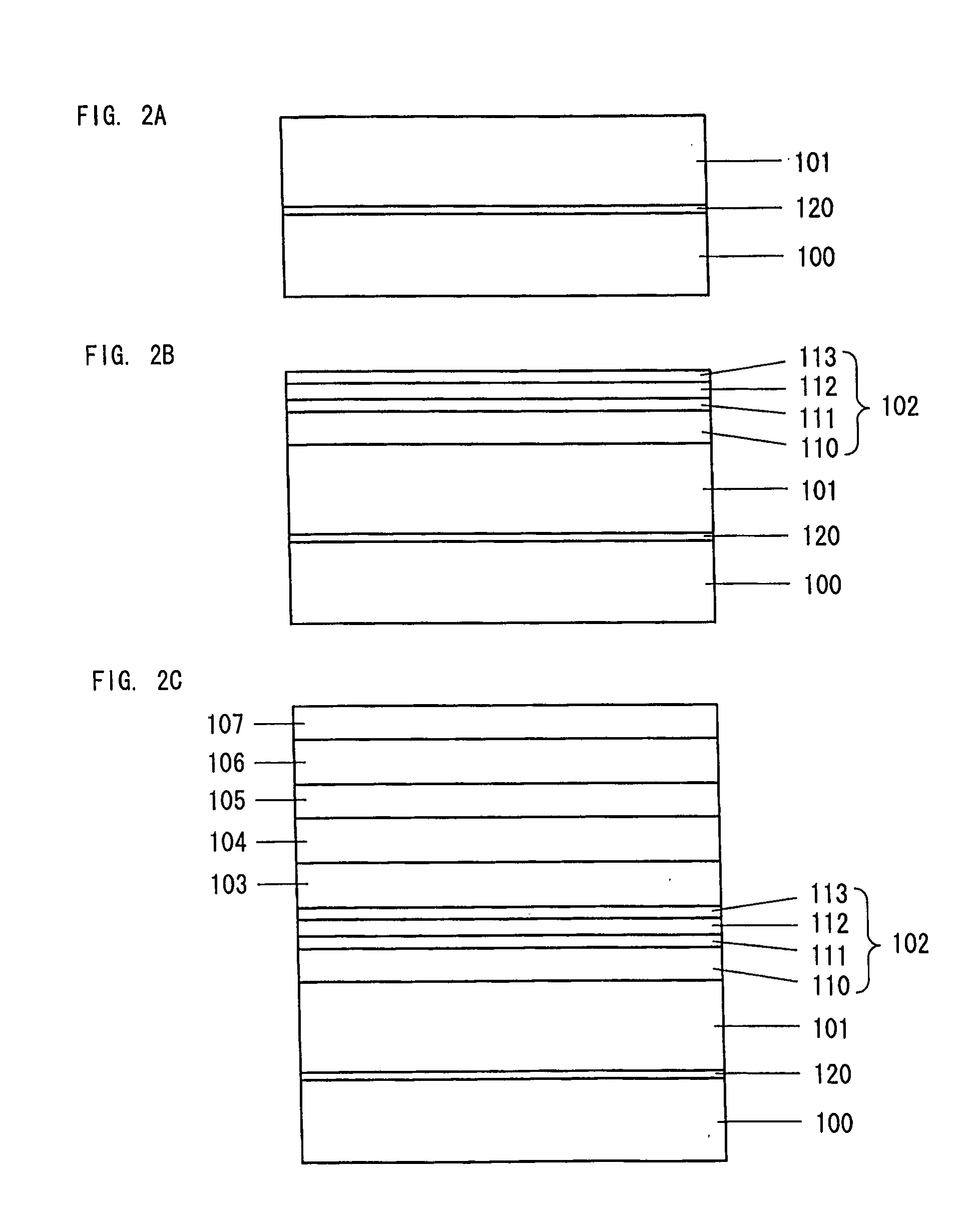
Group lll nitride semiconductor light-emitting device
InactiveUS20110240957A1Improve performanceIncrease in drive voltageSemiconductor devicesVoltageSuperlattice
The present invention provides a Group III nitride semiconductor light-emitting device exhibiting improved emission performance without increasing driving voltage. The Group III nitride semiconductor light-emitting device includes at least an n-type-layer-side cladding layer, a light-emitting layer, and a p-type-layer-side cladding layer, each of the layers being formed of a Group III nitride semiconductor. The n-type-layer-side cladding layer is a superlattice layer having a periodic structure including an InyGa1-yN (0<y<1) layer, an AlxGa1-xN (0<x<1) layer, and a GaN layer. The AlxGa1-xN (0<x<1) layer has such a thickness that electrons tunnel through the AlxGa1-xN layer and holes are confined in the light-emitting layer.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com