Patents
Literature
14542 results about "Plastic materials" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
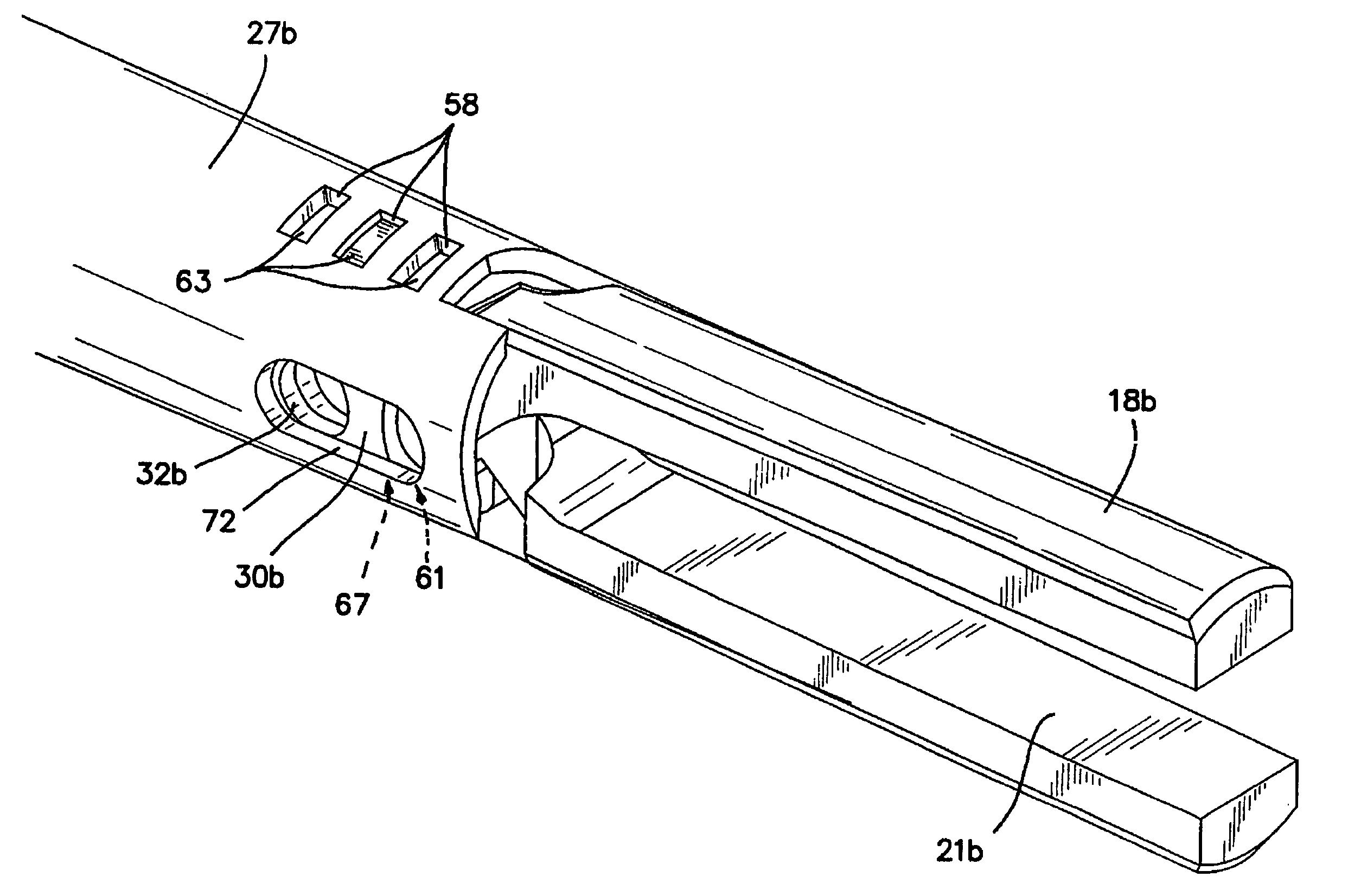
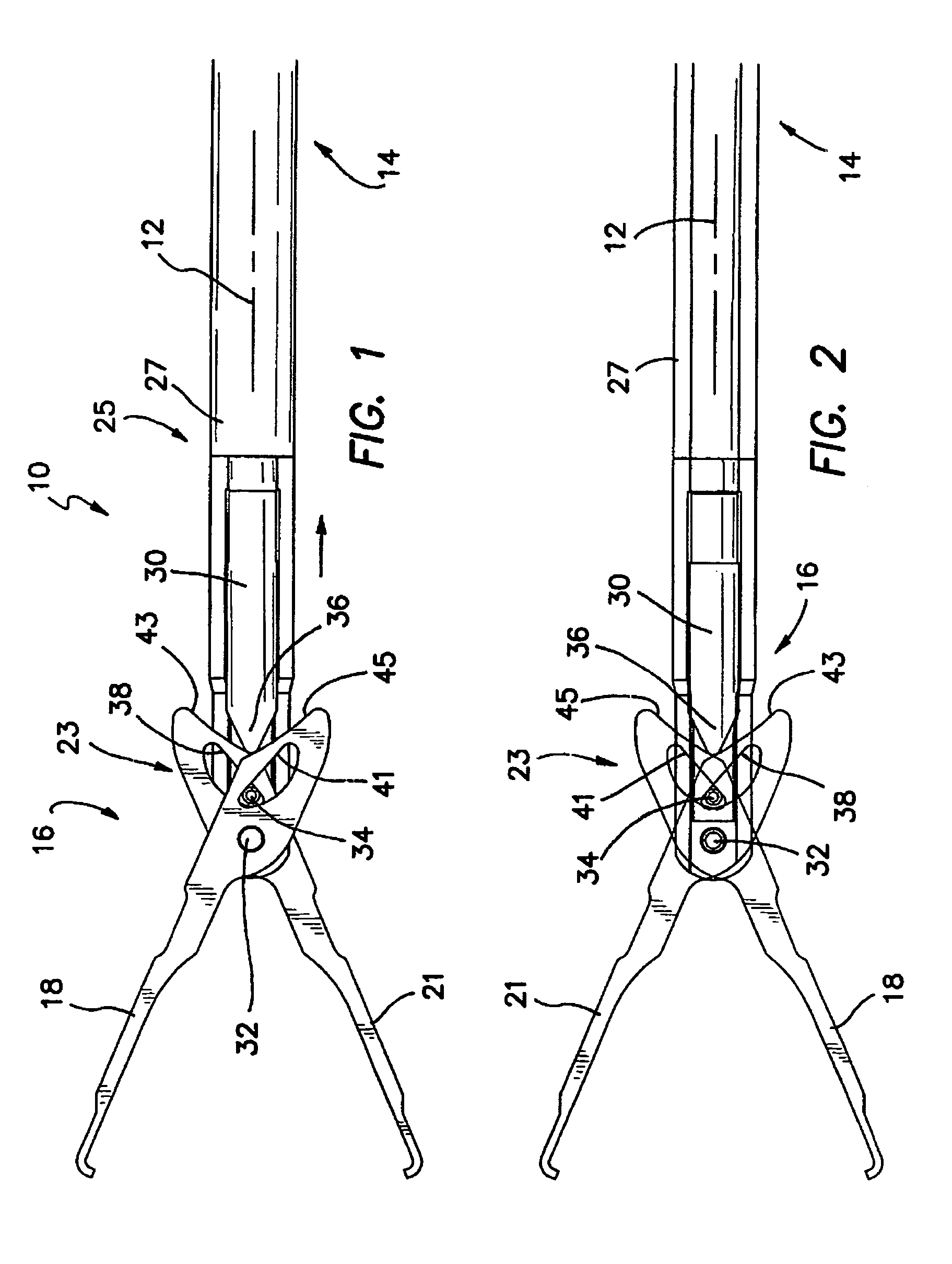
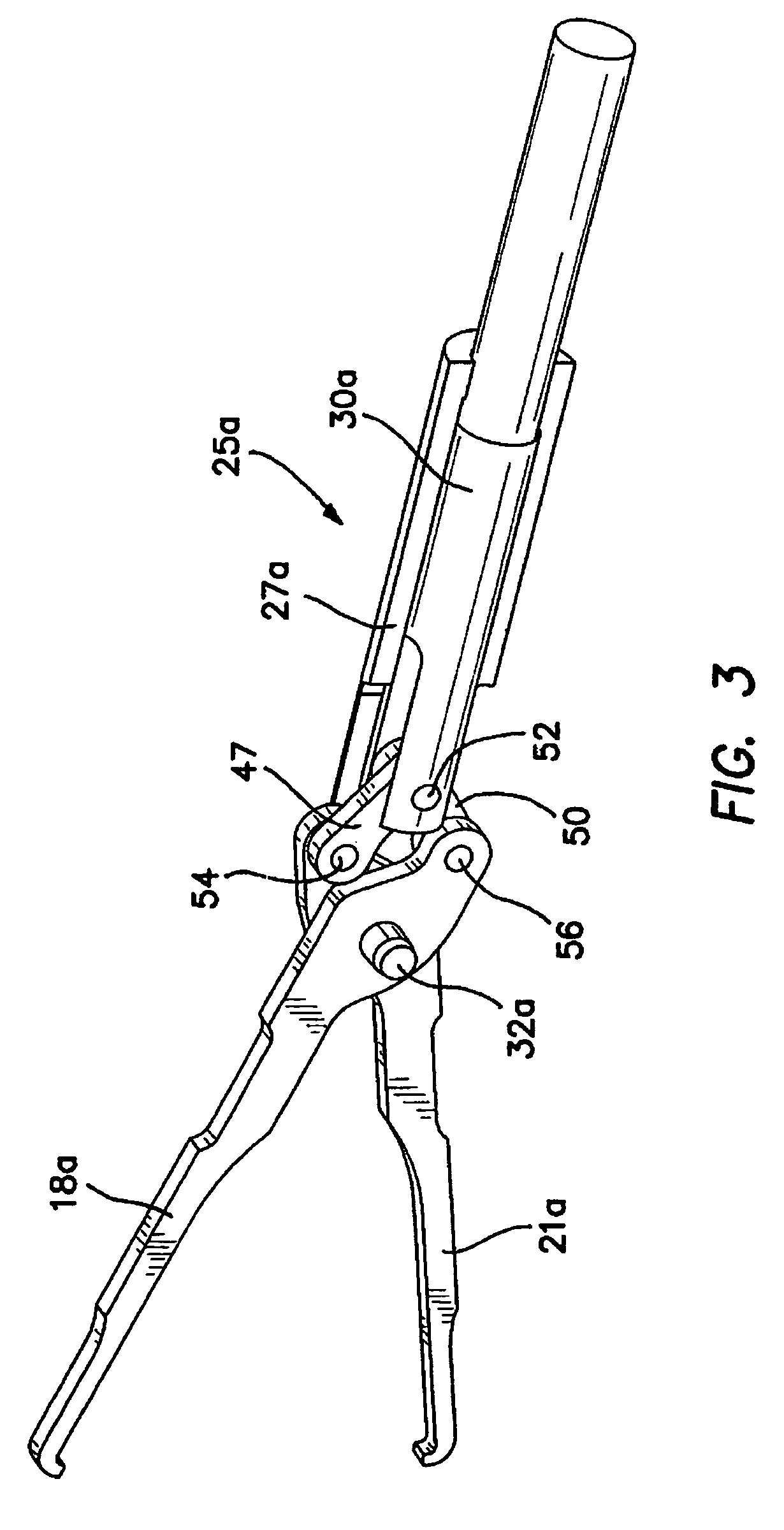
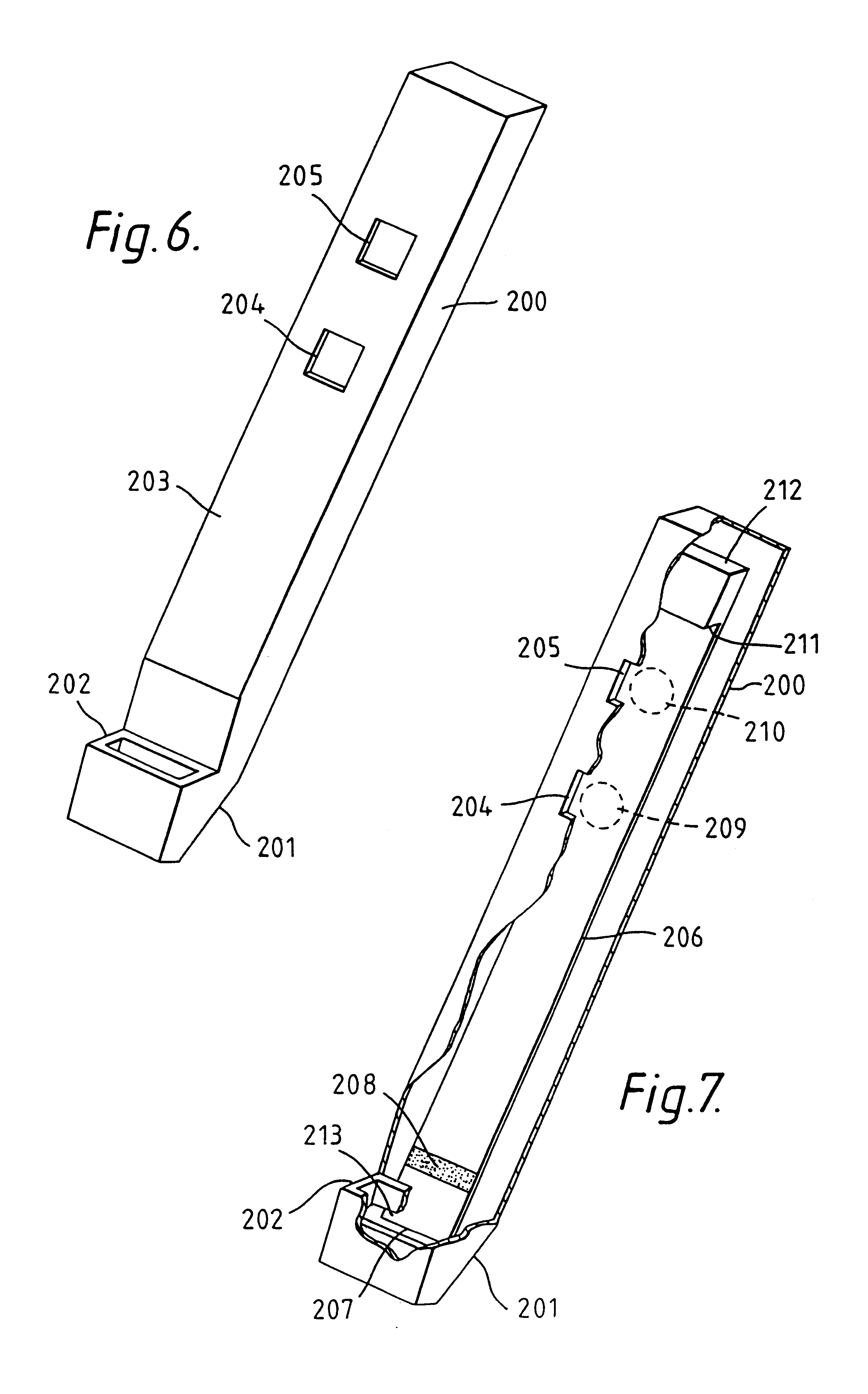
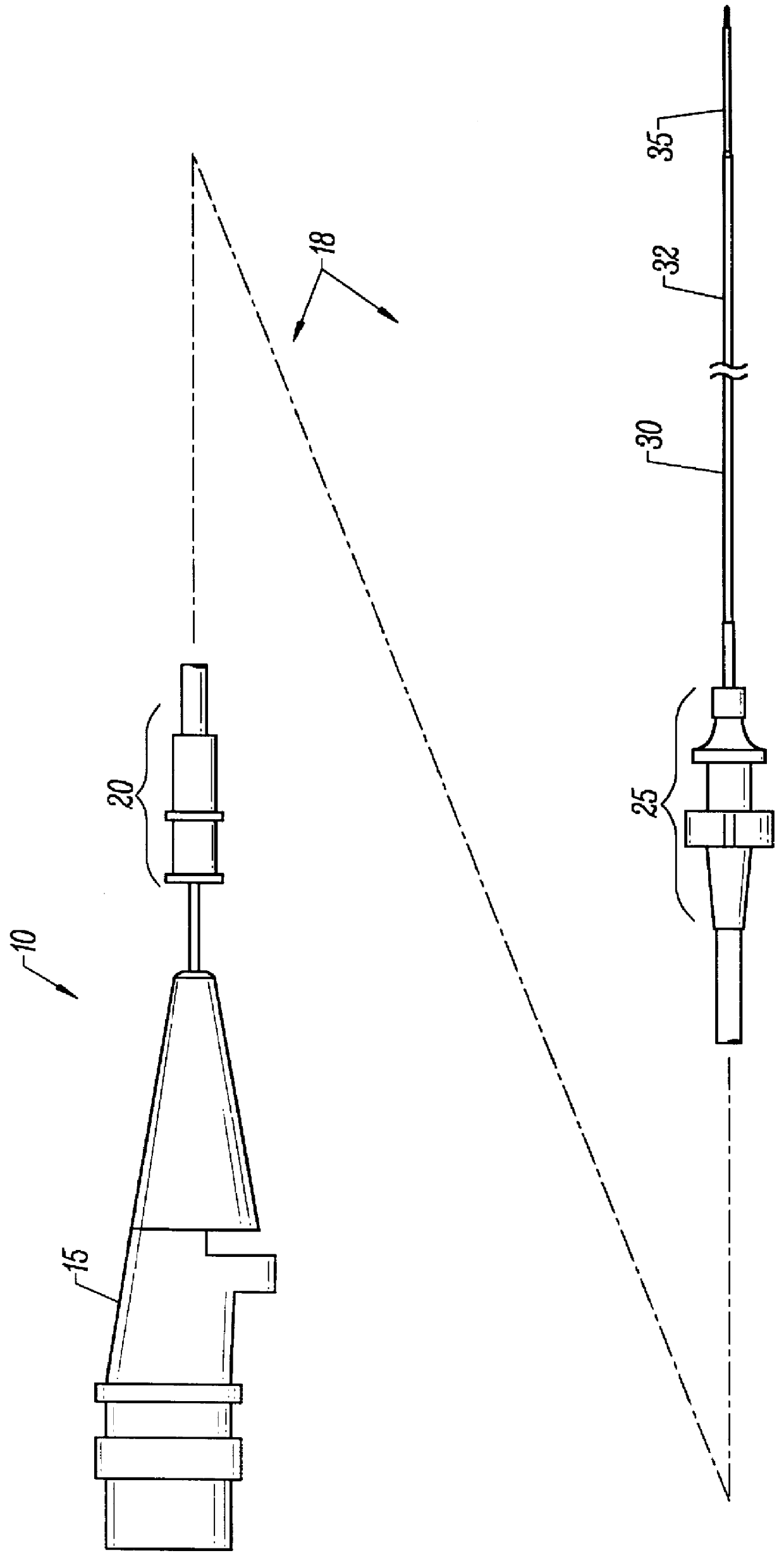
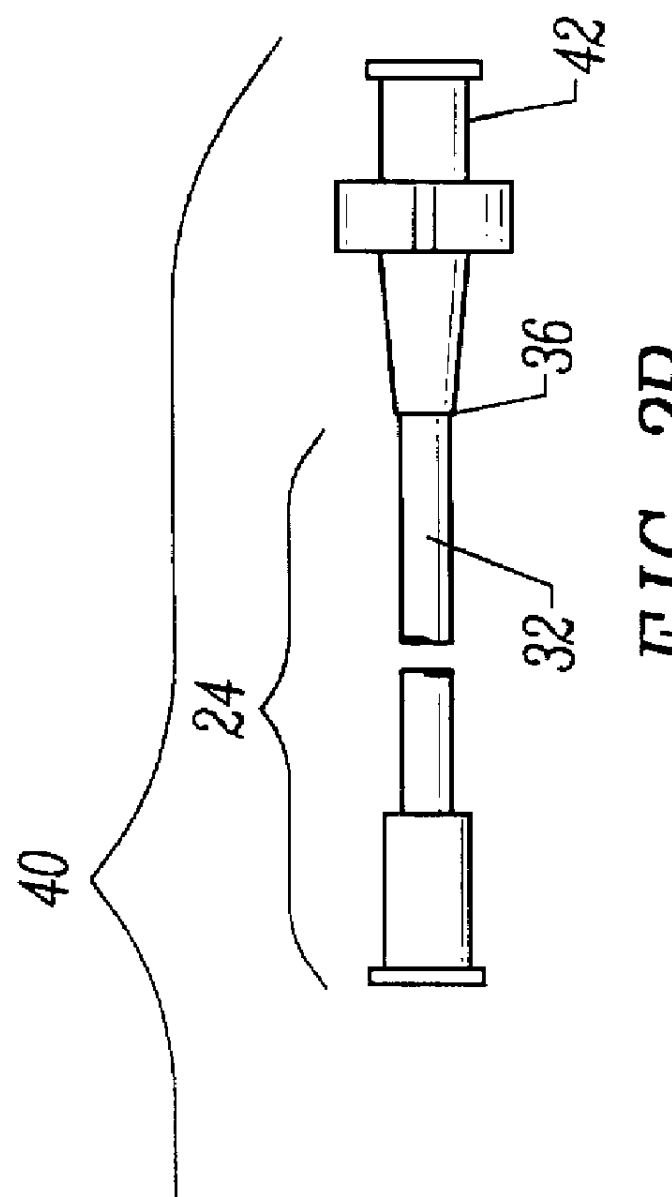
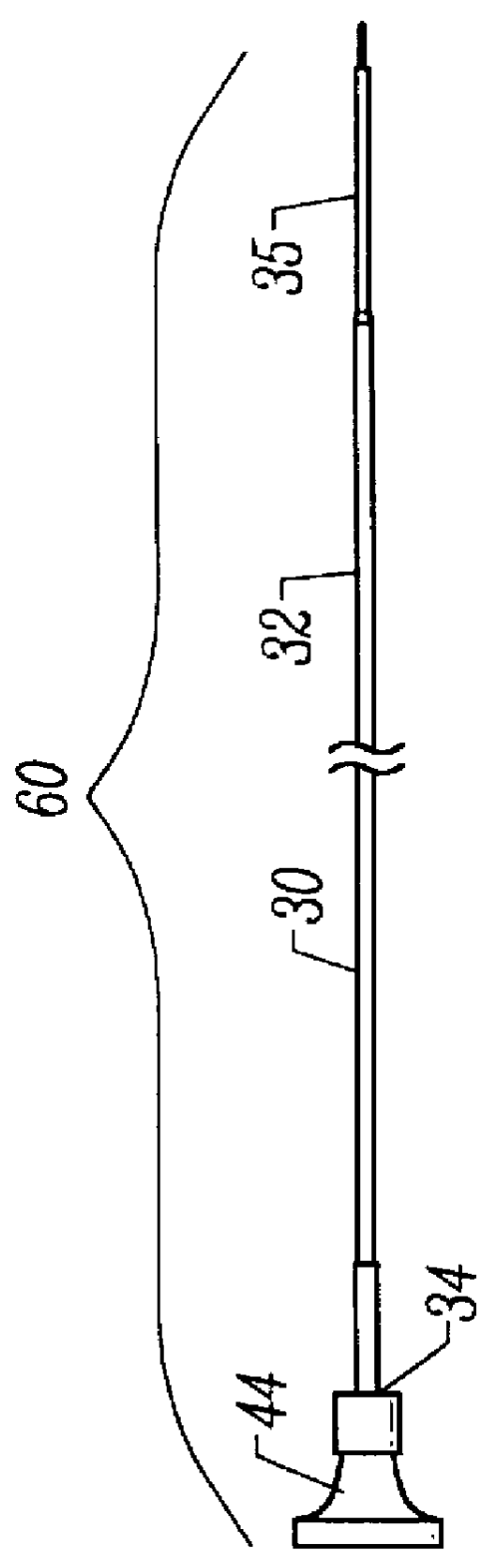
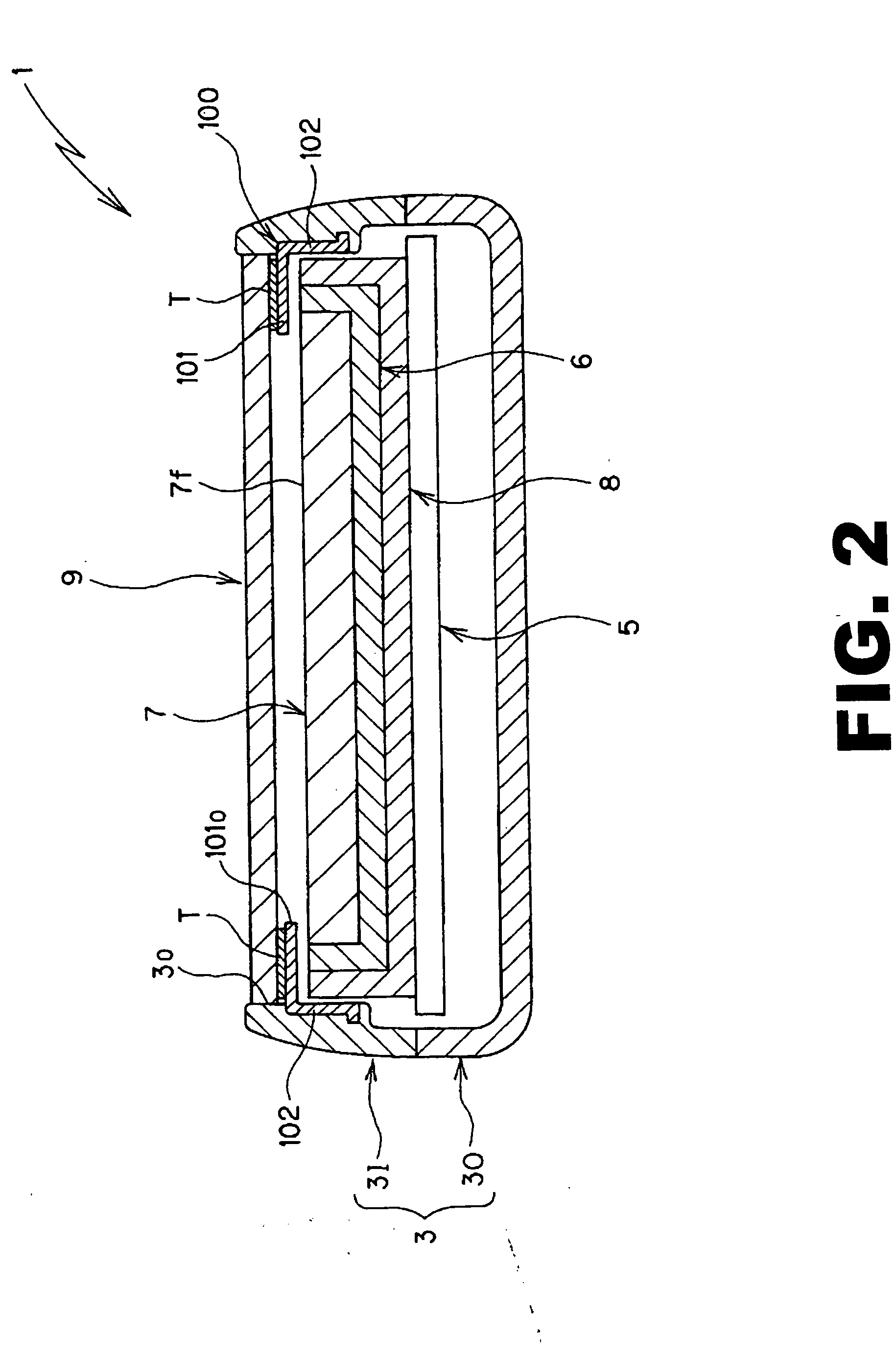
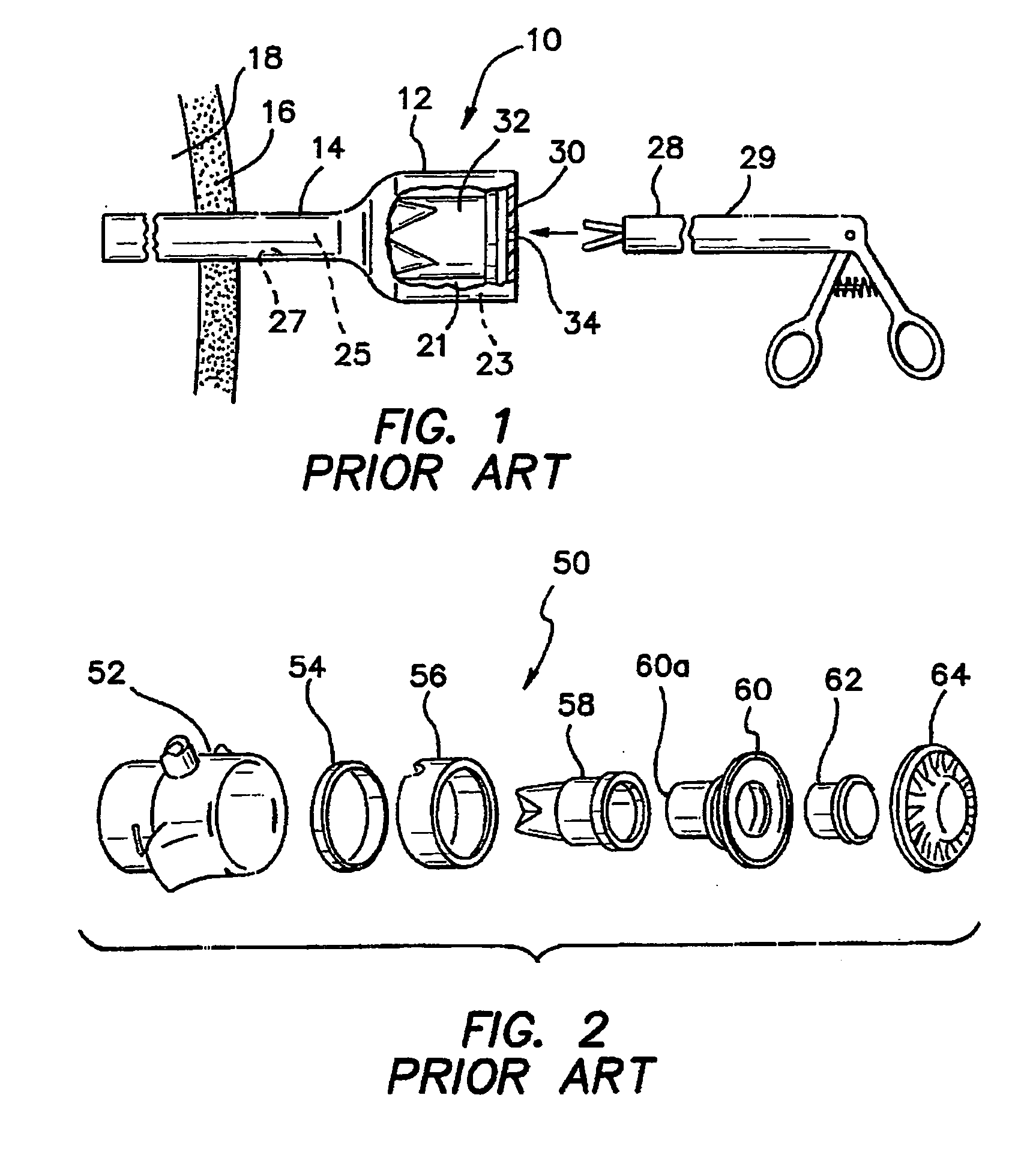
Overmolded grasper jaw
ActiveUS7494501B2Facilitate closing the jaw spinesEnhanced advantageSurgical forcepsPlastic materialsMetallic materials
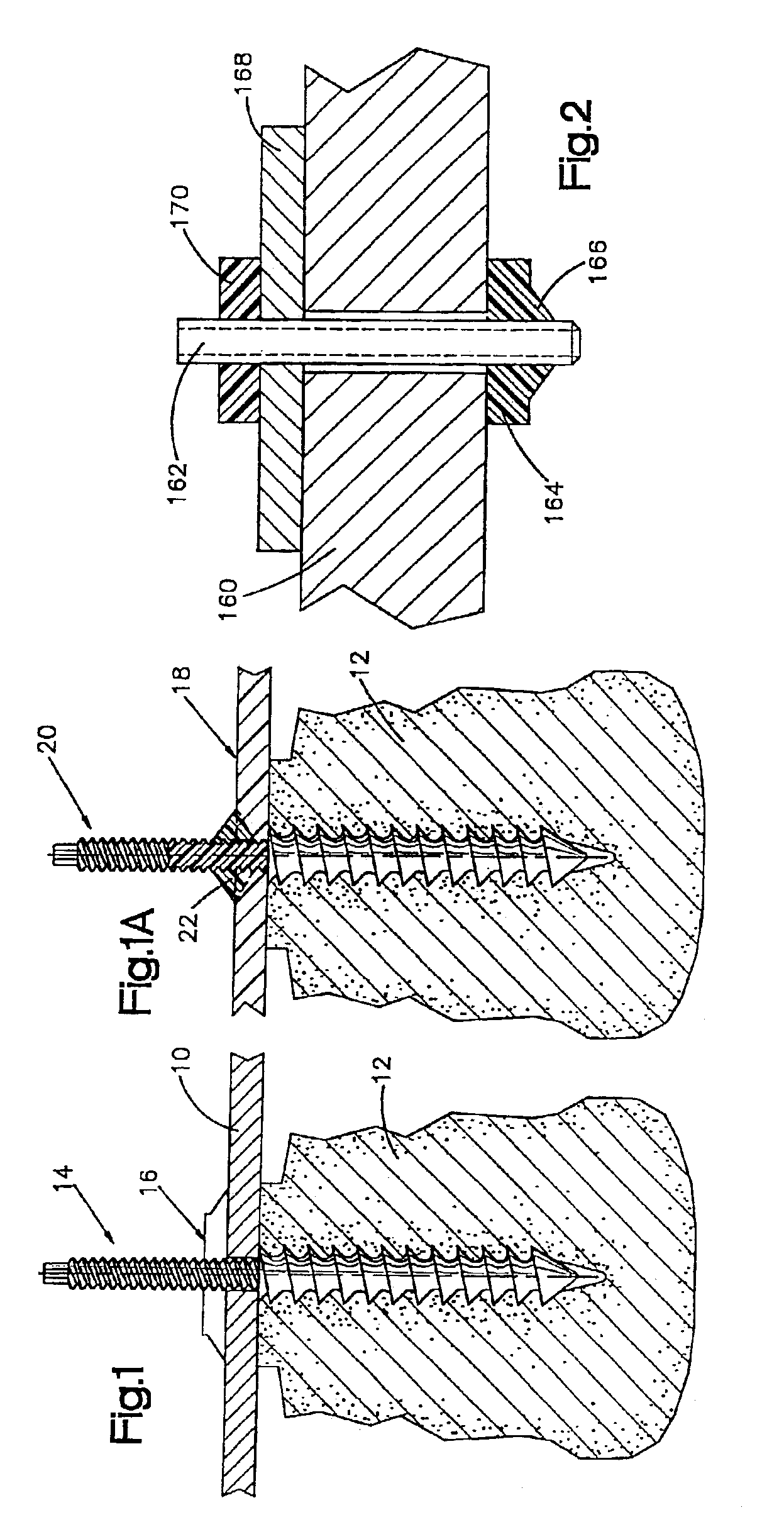
The invention is directed to a surgical instrument comprising an elongate tube extending along an axis including a camming rod and an actuation mechanism operably connected to the camming rod, the camming rod having a camming pin and a camming projection; a first jaw spine having a first cam slot, a first interior camming surface, and a first exterior camming surface; and a second jaw spine having a second cam slot, a second interior camming surface, and a second exterior camming surface, the second jaw spine pivotally connected to the first jaw spine at a common pivot pin operably connected to the elongate tube to open and close the jaw spines in response to movement of the actuation mechanism. The camming pin rides along the first and second interior camming surfaces and operates to close the jaw spines when the camming rod is moved proximally. When the camming rod moves distally, the camming projection rides on the first and second exterior camming surfaces formed on the proximal sides of the respective first and second jaw spines and operates to open the jaw spines. A feature of the invention is one camming surface on each jaw spine can facilitate closing the jaw spines while the other camming surface on each jaw spine can facilitate opening the jaw spines. These two camming surfaces on each jaw spine can be widely separated. The jaw spines can be formed of a metallic material and are overmolded with an atraumatic plastic material. By overmolding the plastic onto the metal spine, an atraumatic outer surface can be formed of the plastic material along with a high degree of detail.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Surgical fasteners and related implant devices having bioabsorbable components
InactiveUS20060142772A1High strengthSufficient flexibilityInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDevice implantPlastic materials
Surgical implants including fasteners and related devices which are partially bioabsorbable. The implants are constructed of a non-bioabsorbable base comprising metals and or high strength plastic materials. The base is partially or completely coated with a bioabsorbable material which can have its own mechanical features, such as the threads on a screw. Attachment elements are provided on the base to enhance the mechanical attachment of the bioabsorbable material to the base. The implants can withstand the torques and stresses encountered during surgery and, following implantation, in the body.
Owner:BIODYNAMICS
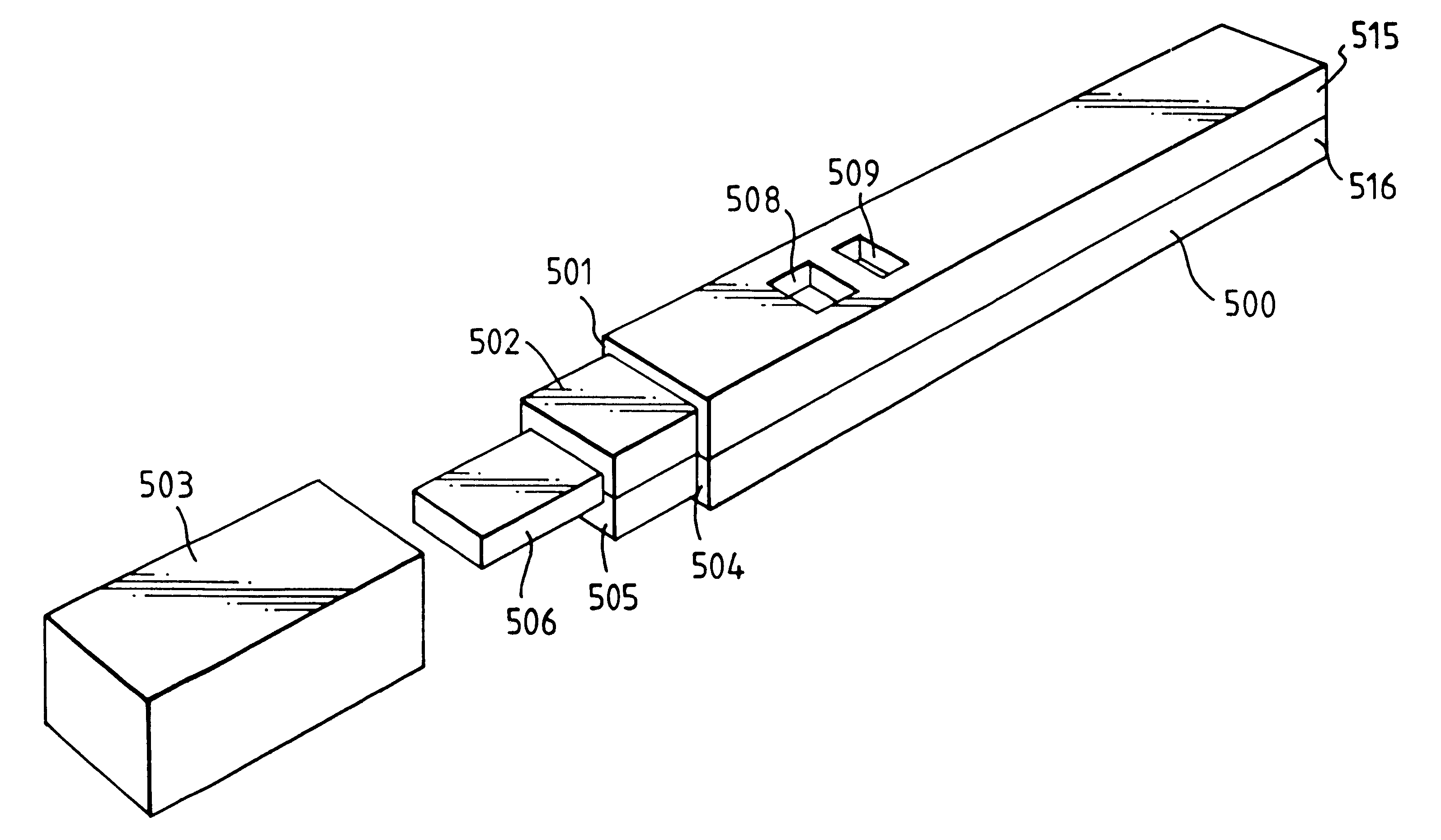
Capillary immunoassay and device therefor comprising mobilizable particulate labelled reagents
InactiveUS6228660B1Improve completenessAnalysis using chemical indicatorsComponent separationParticulatesAnalyte
An analytical test device useful for example in pregnancy testing, comprises a hollow casing (500) constructed of moisture-impervious solid material, such as plastics materials, containing a dry porous carrier (510) which communicates indirectly with the exterior of the casing via a bibulous sample receiving member (506) which protrudes from the casing such that a liquid test sample can be applied to the receiving member and permeate therefrom to the porous carrier, the carrier containing in a first zone a labelled specific binding reagent is freely mobile within the porous carrier when in the moist state, and in a second zone spatially distinct from the first zone unlabelled specific binding reagent for the same analyte which unlabelled reagent is permanently immobilized on the carrier material and is therefore not mobile in the moist state, the two zones being arranged such that liquid sample applied to the porous carrier can permeate via the first zone into the second zone, and the device incorporating means, such as an aperture (508) in the casing, enabling the extent (if any) to which the labelled reagent becomes bound in the second zone to be observed. Preferably the device includes a removable cap for the protruding bibulous member.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Surgical devices assembled using heat bondable materials
Surgical devices such as implants or suture fastenings are assembled from a plurality of discrete components, one of which components includes a heat bondable plastic material for bonding the components together. At least two components are bonded to each other by the applying heat to the heat bondable plastic material of one component. The heat bondable plastic material is preferably a polymeric or composite material suitable for surgical applications and implantation in humans, and may be a biodegradable material. A laser may be used as the heat source. The present invention is advantageously embodied in heat bonded fastenings for sutures or K-wires, in which a variety of different suture anchors are usable, including expandable distal suture anchors. Other embodiments include a metal bone plate which is held to bone by a metal bone screw and a nut of bondable material bonded to the plate to secure the connection; a piece of bondable material bonded to a metal prosthesis to custom fit the prosthesis; and a surgical implant custom formed by bonding together a plurality of discrete elements one or more of which is bondable.
Owner:P TECH +1
Capillary immunoassay and device therefor comprising mobilizable particulate labelled reagents
InactiveUS6187598B1Improve completenessBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPlastic materialsCapillary Tubing
An analytical test device useful for example in pregnancy testing, comprises a hollow casing (500) constructed of moisture-impervious solid material, such as plastics materials, containing a dry porous carrier (510) which communicates indirectly with the exterior of the casing via a bibulous sample receiving member (506) which protrudes from the casing such that a liquid test sample can be applied to the receiving member and permeate therefrom to the porous carrier, the carrier containing in a first zone a labelled specific binding reagent is freely mobile within the porous carrier when in the moist state, and in a second zone spatially distinct from the first zone unlabelled specific binding reagent for the same analyte which unlabelled reagent is permanently immobilised on the carrier material and is therefore not mobile in the moist state, the two zones being arranged such that liquid sample applied to the porous carrier can permeate via the first zone into the second zone, and the device incorporating means, such as an aperture (508) in the casing, enabling the extent (if any) to which the labelled reagent becomes bound in the second zone to be observed. Preferably the device includes a removable cap for the protruding bibulous member.
Owner:INVERNESS SWITZERLAND GMBH
Surgical devices assembled using heat bondable materials
Surgical devices such as implants or suture fastenings are assembled from a plurality of discrete components, one of which components includes a heat bondable plastic material for bonding the components together. At least two components are bonded to each other by the applying heat to the heat bondable plastic material of one component. The heat bondable plastic material is preferably a polymeric or composite material suitable for surgical applications and implantation in humans, and may be a biodegradable material. A laser may be used as the heat source. The present invention is advantageously embodied in heat bonded fastenings for sutures or K-wires, in which a variety of different suture anchors are usable, including expandable distal suture anchors. Other embodiments include a metal bone plate which is held to bone by a metal bone screw and a nut of bondable material bonded to the plate to secure the connection; a piece of bondable material bonded to a metal prosthesis to custom fit the prosthesis; and a surgical implant custom formed by bonding together a plurality of discrete elements one or more of which is bondable.
Owner:P TECH +1
Golf club having a hollow pressurized metal head
ActiveUS20080188322A1Avoid passingPrevent escapeFilling using counterpressureMetal rolling stand detailsShell moldingPlastic materials
A golf club having a hollow golf club head which is filled with a gas under pressure. The interior surface of the golf club head is coated with a solidified layer of plastic material. The pressurized gas permits the use of thinner face plates by compensating for forces generated when the face plate strikes a golf ball. The plastic layer is preferably applied through the process of rotational molding using a thermoplastic material.
Owner:BLOWERS ALDEN J
Touch Sensitive Screen
ActiveUS20070062739A1Lower impedanceEfficient couplingTransmission systemsInput/output processes for data processingElectrical resistance and conductancePlastic materials
A capacitive sensor for determining the presence of an object, such as a user's finger or a stylus, is provided. The sensor comprises a substrate, for example made of transparent plastics material, such as PET, on which electrodes are deposited. A resistive drive electrode for example formed of transparent ITO, is arranged on one side of the substrate and a resistive sense electrode, which again may be of transparent ITO, is arranged on the other side of the substrate. Thus an overall transparent sensor may be provided. A shorting connection is also provided which is configured to connect between two locations on one of the electrodes. The electrodes are connected to respective drive and sense channels. By providing the shorting connection between two locations on one or other (or both) of the electrodes, a lower resistance connection is provided between other locations on the electrode and the corresponding drive or sense channel.
Owner:NEODRON LTD
Golf club having a hollow pressurized metal head
ActiveUS8663026B2Prevent escapeMetal rolling stand detailsPackaging under special atmospheric conditionsPlastic materialsEngineering
A golf club having a hollow golf club head which is filled with a gas under pressure. The interior surface of the golf club head is coated with a solidified layer of plastic material. The pressurized gas permits the use of thinner face plates by compensating for forces generated when the face plate strikes a golf ball. The plastic layer is preferably applied through the process of rotational molding using a thermoplastic material.
Owner:BLOWERS ALDEN J
Surgical devices having a biodegradable material with a therapeutic agent
Surgical devices such as implants or suture fastenings are assembled from a plurality of discrete components, one of which components includes a heat bondable plastic material for bonding the components together. At least two components are bonded to each other by the applying heat to the heat bondable plastic material of one component. The heat bondable plastic material is preferably a polymeric or composite material suitable for surgical applications and implantation in humans, and may be a biodegradable material. A laser may be used as the heat source. The present invention is advantageously embodied in heat bonded fastenings for sutures or K-wires, in which a variety of different suture anchors are usable, including expandable distal suture anchors. Other embodiments include a metal bone plate which is held to bone by a metal bone screw and a nut of bondable material bonded to the plate to secure the connection; a piece of bondable material bonded to a metal prosthesis to custom fit the prosthesis; and a surgical implant custom formed by bonding together a plurality of discrete elements one or more of which is bondable.
Owner:P TECH +1
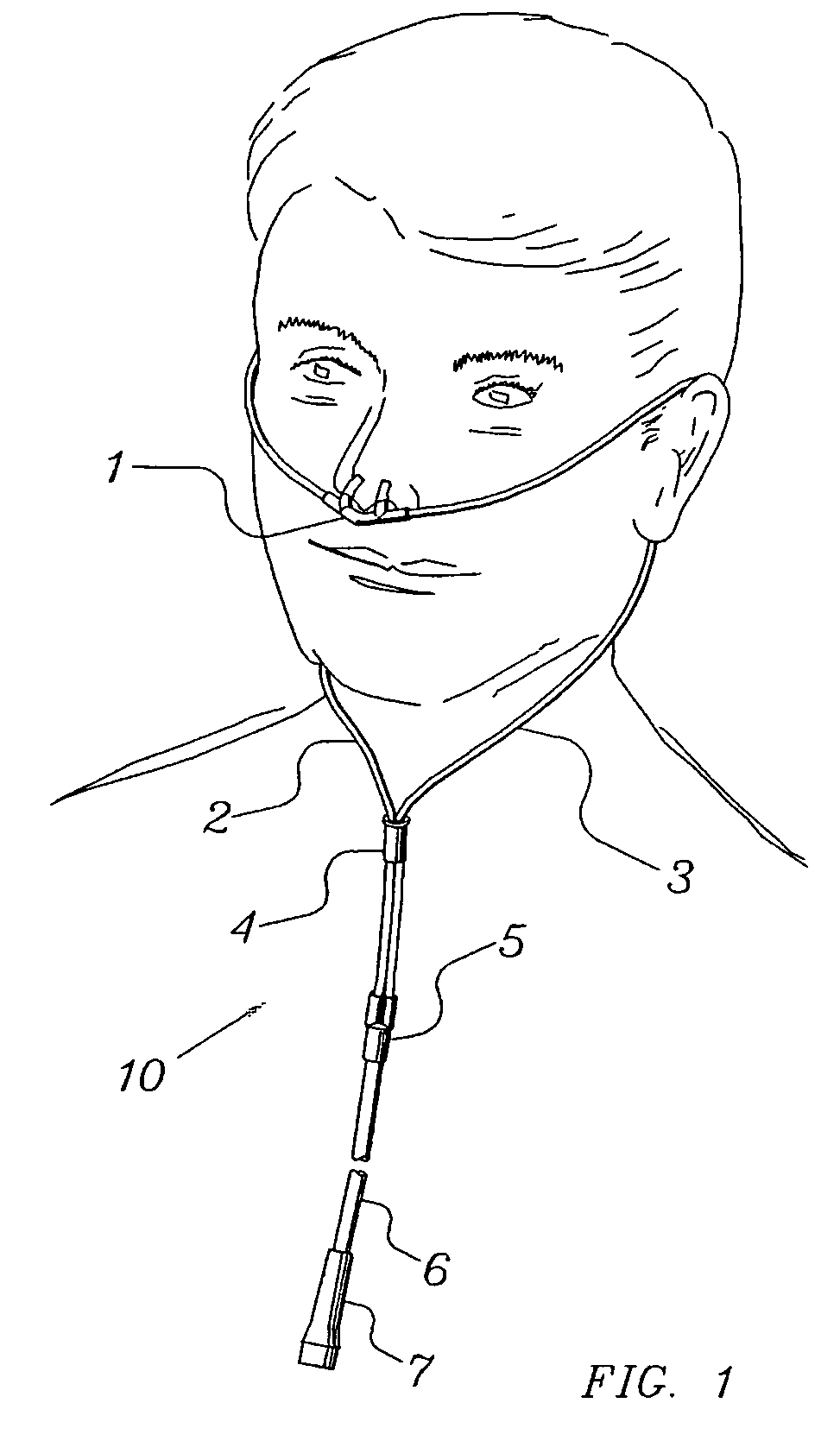
Nasal cannula assembly
A nasal cannula assembly designed for contact with the nasalabidial area of a patient's face comprising a nasal cannula, a pair of oxygen supply tubes connected to opposite ends of the nasal cannula and a main oxygen supply line. The nasal cannula is made of a flexible plastic material molded into a light-weight hollow tubular member having a main body portion formed at an acute angle in the center and having a pair of spaced exterior orifices projecting from the body at an angle and curved upwardly and inwardly for directing gas flow into a patient's nostrils. Attachment points for oxygen supply tubes are above center of gravity of the nasal cannula to make it self-righting thus eliminating need for stiff supply tubing to orient cannula. Oxygen supply tubes made from ultra-high molecular weight PVC possess superior flexibility and low compression set so that little tension on the tubing is required to hold cannula in proper position. A main oxygen supply line made from ultra-high molecular weight PVC resists the formation of twisted loops that tend to block oxygen flow.
Owner:THOMPSON PAUL S
Process and reactor for microwave cracking of plastic materials
InactiveUS6184427B1Indirect and direct heating destructive distillationLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionRadio frequency energyPlastic materials
A process of activated cracking of high molecular organic waste material which includes confining the organic waste material in a reactor space as a mixture with a pulverized electrically conducting material (sensitizer) and / or catalysts and / or "upgrading agents" and treating this mixture by microwave or radio frequency electro-magnetic radiation. Organic waste materials include hydrocarbons or their derivatives, polymers or plastic materials and shredded rubber. The shredded rubber can be the source of the sensitizer and / or catalyst material as it is rich in carbon and other metallic species. This sensitizer can also consist of pulverized coke or pyrolytically carbonized organic feedstock and / or highly dispersed metals and / or other inorganic materials with high dielectric loss which absorb microwave or radio frequency energy.
Owner:HIGHWAVE ACQUISITION
Catheher system having connectable distal and proximal portions
InactiveUS6050949AEnhanced hoop strengthBending stiffnessUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryPlastic materialsUltrasonic imaging
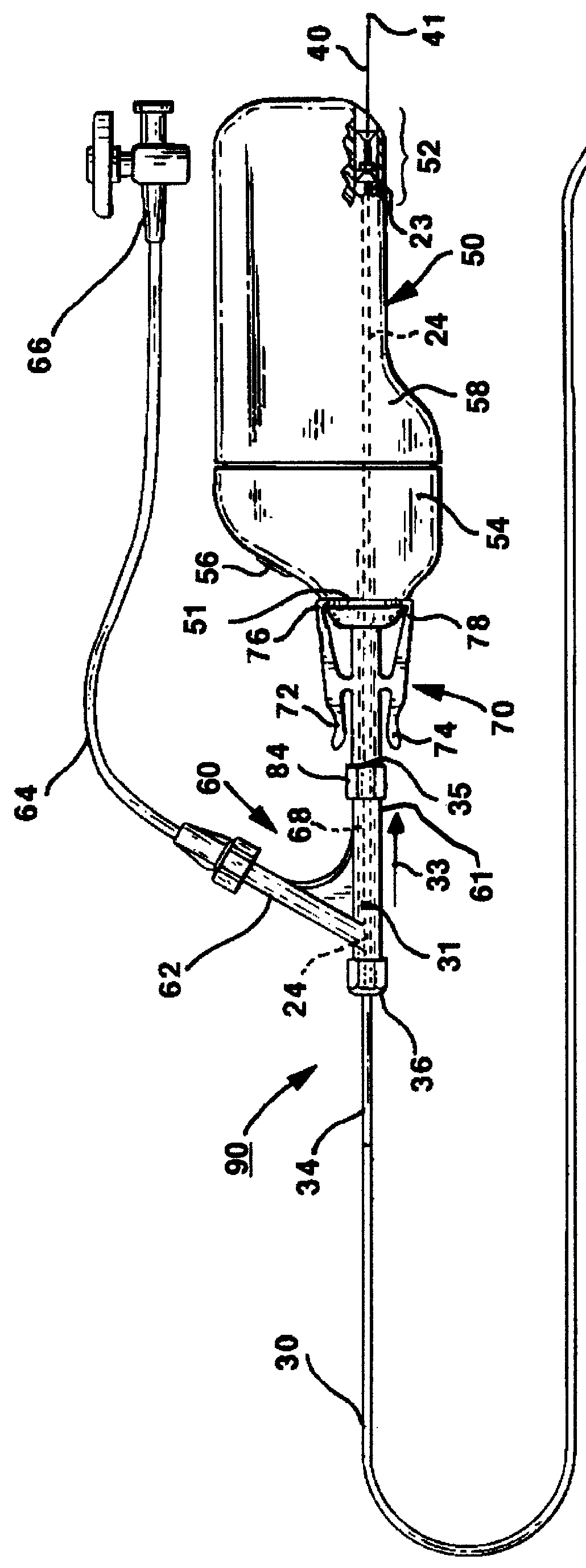
A vascular catheter system comprises a catheter body having a proximal and distal portion and a single common lumen therebetween. The catheter body includes a first connector secured to the distal end of the proximal portion and a second connector secured to the proximal end of the distal portion. The connectors can be selectively connected to each other to join the lumens of the proximal and distal portions together in a continuous, axially fixed relationship. Disposed within the lumens, when the proximal and distal portions are joined together, is a drive cable. The drive cable may be movably, rotatable about its own longitudinal axis and carries at its distal end, a work element, which is typically an ultrasonic imaging transducer or interventional device. The lumen carrying the cable will be sufficiently large along a proximal portion to permit preferential collapse of the cable should rotation of the distal end become impeded. The catheter body may be made of a polymer or plastic material, such as polyetheretherketone (PEEK), which provides adequate bonding stiffness and resistance to kinking from large hoop stresses.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Air gas analyzer window and a method for producing such a window
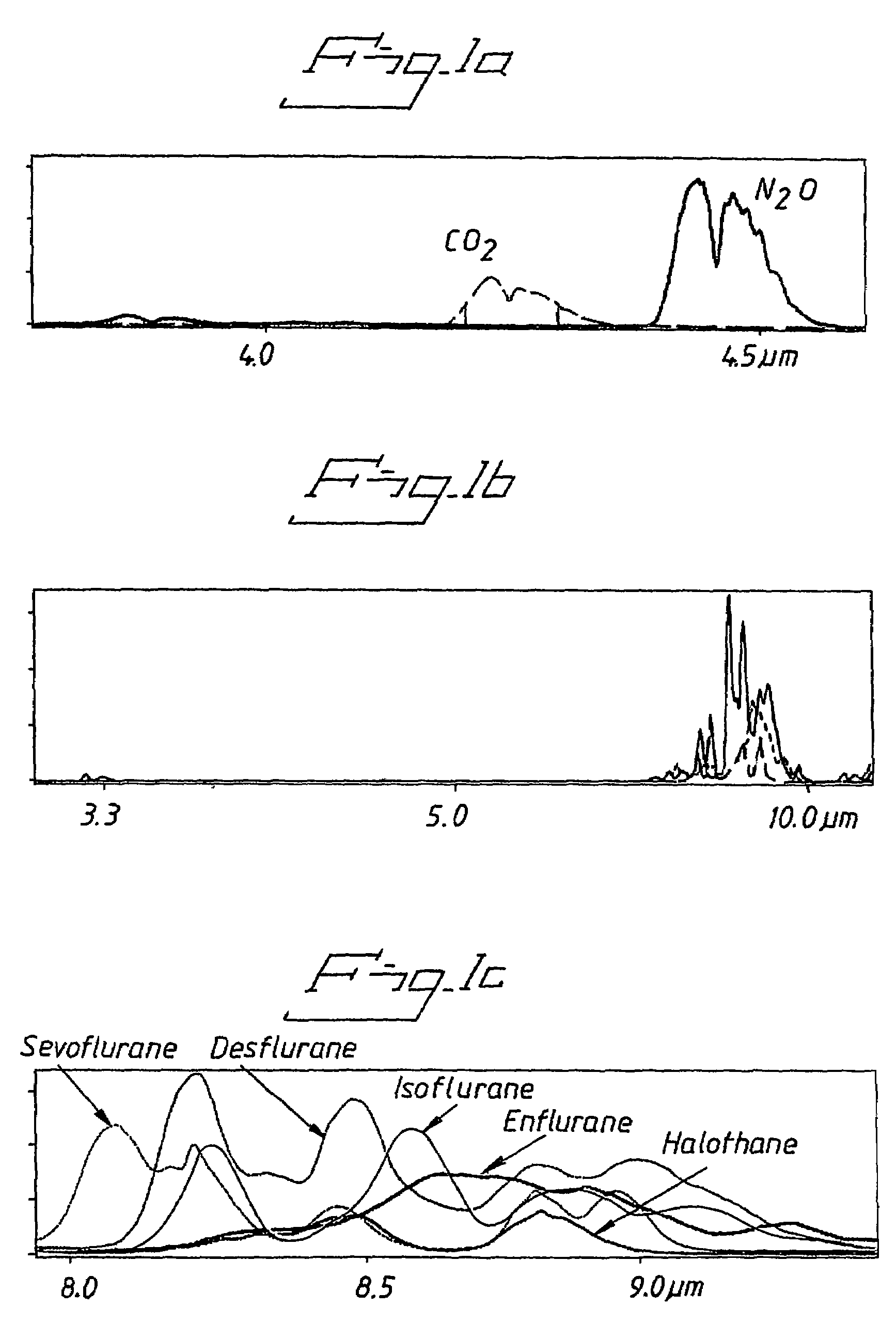
ActiveUS7629039B2Uniform material thicknessSatisfactory transmission propertyLayered productsRespiratory organ evaluationPlastic materialsLight beam
A window for use in an adapter for an IR gas analyser for analysing breathing gases, where the gases flow through a through-penetrating passageway in the adapter, which includes windows disposed on opposite sides of the passageway so as to enable an IR beam to be sent through the windows and through the passageway containing said breathing gases. Each window is a one-piece structure comprised of plastic material and has a round basic shape that includes a surrounding edge and a central part which is sunken in relation to the surrounding edge and which forms the window through which the IR beams or rays shall be able to pass. A method of producing such a window, by injection moulding a thermoplastic material in a mould where injection of the plastic material is also disclosed.
Owner:PHASEIN
Liquid crystal display device protection structure for electronic equipment
InactiveUS20050285991A1Avoid damageOutline size can be minimizedDetails for portable computersElectrical apparatus contructional detailsLiquid-crystal displayPlastic materials
A liquid crystal display device protection structure for electronic equipment having an equipment cabinet made of a plastic material in which a liquid crystal display device is accommodated, the equipment cabinet formed with a viewing window so as to be faced with a display screen of the liquid crystal display device, comprises a reinforcing frame made of a material having a mechanical strength higher than that of the plastic material used for the equipment cabinet, and having a frame shape matched to a periphery of the viewing window, the reinforcing frame being integrally fixed to the equipment cabinet so as to be matched to the periphery of the viewing window, and a display screen protection cover which covers the viewing window and is mounted to the reinforcing frame.
Owner:FUJITSU TOSHIBA MOBILE COMM LTD
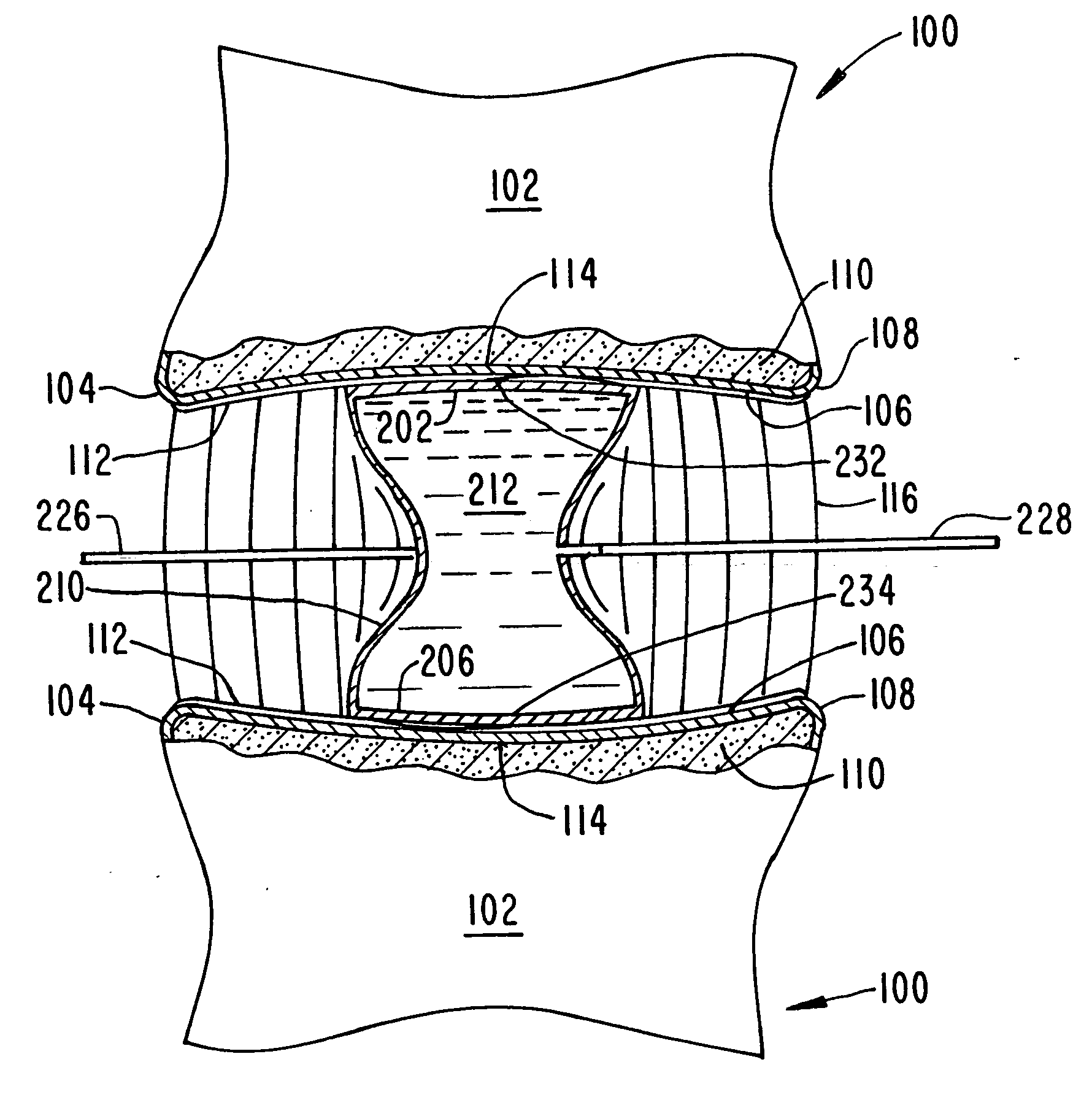
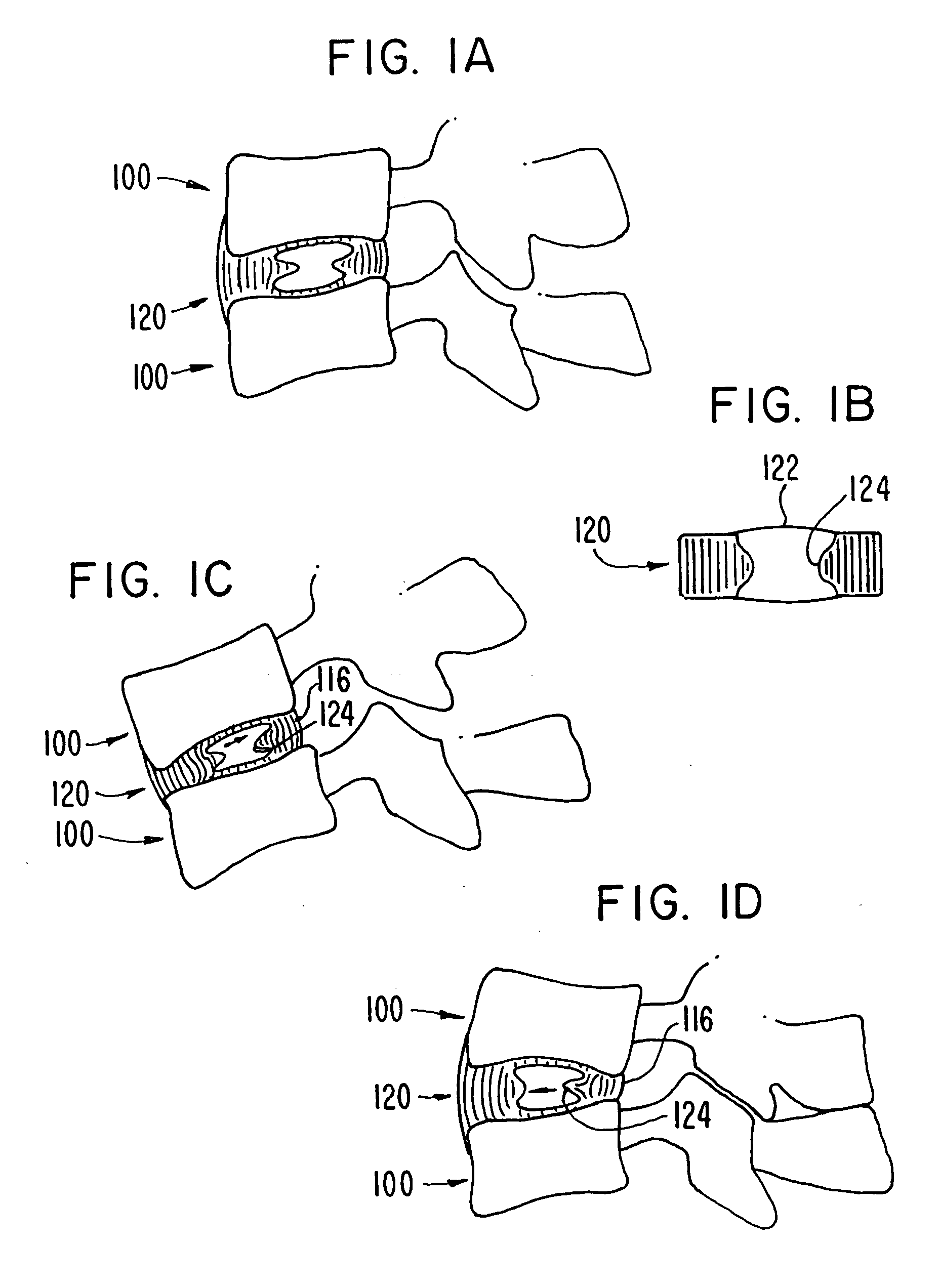
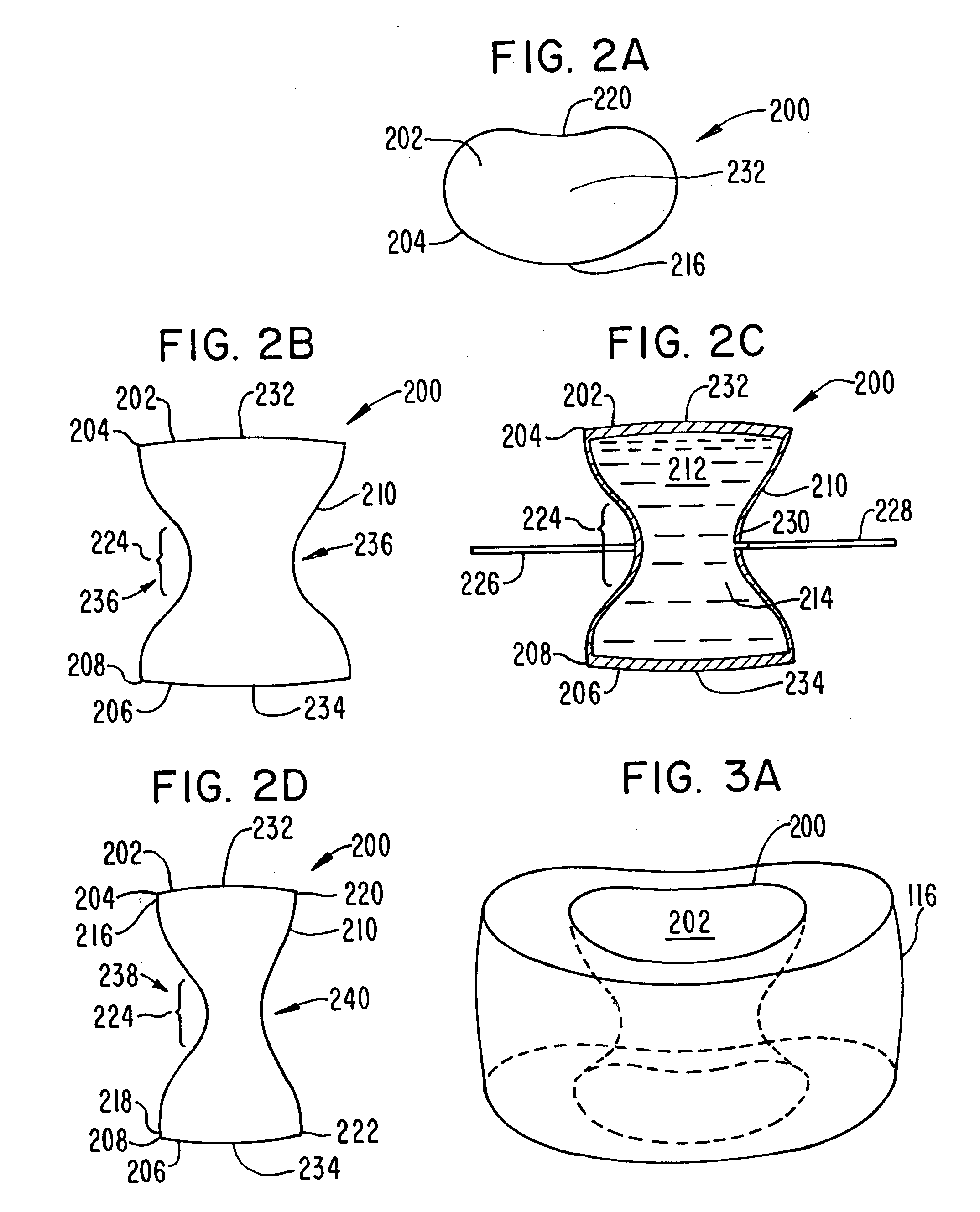
Intervertebral disk and nucleus prosthesis
A prosthetic implant for replacing a nucleus pulposus of an intervertebral disk includes upper and lower endwalls of discoid cross-section, each having an antero-posterior diameter less than its transverse diameter, and an hourglass-shaped sidewall connecting the peripheries of the upper endwall and lower endwall to enclose an interior volume filled with a substantially incompressible liquid or soft plastic material. A total prosthesis for replacing the entire human intervertebral disk has an annular core made of a first biocompatible polymer surrounding a central cavity, transitional plates affixed respectively to the upper and lower surfaces of the annular core, the upper and lower transitional plates being made of a second biocompatible material having an elastic modulus greater than that of the first biocompatible polymer, and upper and lower endplates adapted to contact adjacent vertebrae and affixed respectively to the upper and lower transitional plates.
Owner:K2M
Stretchable and elastic interconnects
InactiveUS7491892B2Reduce mechanical stressSave spaceCircuit bendability/stretchabilityTwo-part coupling devicesElastomerPlastic materials
The present invention relates to stretchable interconnects which can be made in various geometric configurations, depending on the intended application. The stretchable interconnects can be formed of an electrically conducting film or an elastomer material to provide elastic properties in which the interconnects can be reversibly stretched in order to stretch and relax the elastomer material to its original configuration. Alternatively, stretchable interconnects can be formed of an electrically conducting film or a plastic material to provide stretching of the material to a stretched position and retaining the stretched configuration. The stretchable interconnect can be formed of a flat 2-dimensional conductive film covering an elastomeric or plastic substrate. When this structure is stretched in one or two dimensions, it retains electrical conduction in both dimensions. Alternatively, the stretchable and / or elastic interconnects can be formed of a film or stripe that is formed on an elastomeric or plastic substrate such that it is buckled randomly, or organized in waves with long-range periodicity. The buckling or waves can be induced by various techniques, including: release of built-in stress of the conductive film or conductive stripe; pre-stretching the substrate prior to the fabrication of the conductive film or conductive stripe; and patterning of the surface of the substrate prior to the fabrication of the metal film. The stretchable interconnect can be formed of a plurality of conductive films or conductive stripes embedded between a plurality of layers of a substrate formed of an elastomer or plastic.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
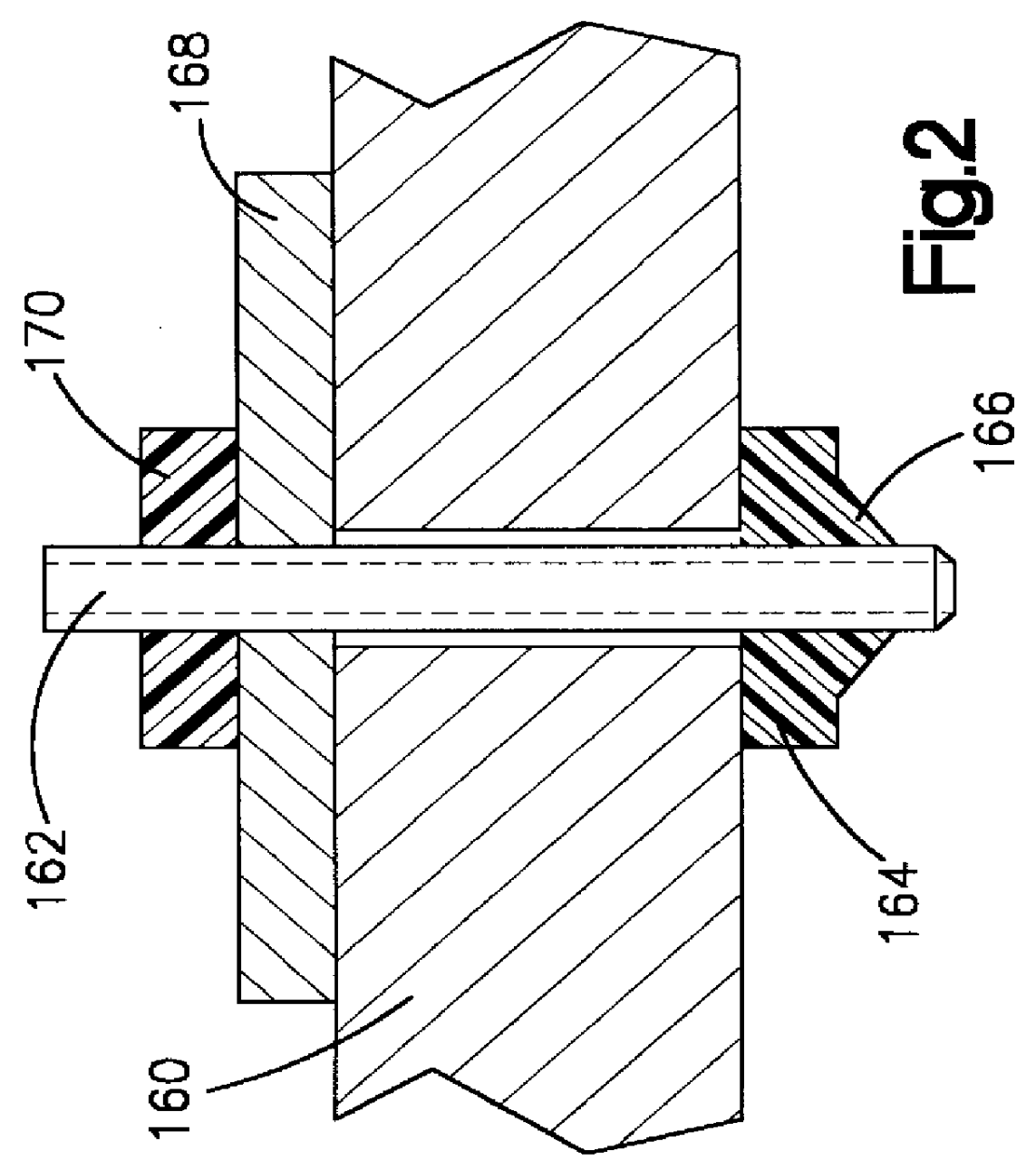
Shielded septum trocar seal
InactiveUS20050131349A1Reduce exerciseReduce forceInfusion syringesSurgical needlesPlastic materialsEngineering
The invention is directed to a trocar assembly having a channel defined along an elongate axis, the trocar assembly being adapted to receive a surgical instrument, the trocar assembly comprising a septum seal disposed in the channel including a seal tip having a proximal facing surface, the seal tip including portions defining an orifice; and a septum shield including a tubular member having a proximal end and a distal end, and a plurality of blades or leaflets protruding distally from the distal end of the tubular member, the septum shield being placed inside the septum seal such that the blades engage the proximal facing surface of the seal tip. The trocar assembly may further comprise a zero closure seal such as a double duckbill valve disposed in the channel outside of the septum seal. The septum shield operates to reduce the drag force and to minimize axial movement of the septum shield and the instrument during insertion and removal of the instrument through the septum seal. The septum shield may be formed from a rigid plastic material, and the septum seal may be formed of an elastomeric material. The blades or leaflets may overlap or offset one another. The orifice may be expandable to accommodate the instrument having a diameter of about 5-15 mm. The blades or leaflets have distal tips that glide or roll against the instrument during placement of the instrument. The distal tips may comprise of a combination of material, durometer and shield geometry to control the behavior of the septum shield. The trocar assembly may further comprise a second septum shield disposed outside of the septum seal.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Adjustable width product display system
InactiveUS6866156B2Adjustable widthEasy to processRacksFolding cabinetsPlastic materialsDisplay device
An adjustable width product display system which includes spaced-apart front and back display supports formed of an engineering plastic material, suitable for food freezer environments. Formed wire side elements, provided with transversely extending mounting portions, are slideably received in transversely disposed recesses in the plastic display supports. Each display support includes a pair of closely adjacent, parallel recesses for receiving the mounting portions in overlapping relation, providing a wide range of width adjustment to accommodate packages of different size. A wire frame, comprising a pair of elongated wire elements extending from front to back of the display system joins the two display supports in spaced relation. These wire elements also function as an underneath support for product packages confined between the side elements. Laterally adjacent elements can be connected in series by intermediate wire side supports provided with transverse mounting elements extending in opposite directions and engagable in plastic display supports on both sides. Product pusher means are easily incorporated into the product display system either in the form of a preassembled pusher device, or the use of a spring-driven pusher sled mounted on the wire elements connecting the front and back display supports. The system, is ideally suited for food freezer environment, because plastic materials are minimally present in the structure and thus can be of a suitable engineering grade material. Additionally, the open wire structure accommodates free circulation of air in a freezer compartment to help maintain the desired environment throughout the compartment.
Owner:TRION IND
Cavity-less film bulk acoustic resonator (FBAR) devices
ActiveUS20050104690A1Manufacturing process is complexPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksCouplingPlastic materials
The film bulk acoustic resonator (FBAR) device comprises a substrate, an acoustic Bragg reflector over the substrate, a piezoelectric element over the acoustic Bragg reflector, and a remote-side electrode over the piezoelectric element. The acoustic Bragg reflector comprises a metal Bragg layer juxtaposed with a plastic Bragg layer. The large ratio between the acoustic impedances of the plastic material of the plastic Bragg layer and the metal of the metal Bragg layer provides sufficient acoustic isolation between the FBAR and the substrate for the frequency response of the FBAR device to exhibit minor, if any, spurious artifacts arising from undesirable acoustic coupling between the FBAR and the substrate.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Cellular plastic material
An improved cellular plastic material comprises a urethane foam that is the reaction product of soy oil, an isocyanate, and a cross linker. The soy oil replaces the polyol typically generally required in the production of urethanes. Because the replaced polyol is a petrochemical, use of a renewable and environmentally friendly material such as soy oil is most advantageous. Further, plastic materials of many final qualities may be formed using a single vegetable oil. In addition to cellular foams, solid plastic elastomers may be formed.
Owner:URETHANE SOY SYST +1
Surgical device with tack-free gel and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20050033246A1Significant drag forceImprove complianceCannulasSurgical needlesMolten stateLow-density polyethylene
A process of making a tack-free gel is disclosed comprising the steps of providing a mold defining a mold cavity, the mold cavity comprising a plastic material; pouring or injecting a molten gel having a high molding temperature into the mold cavity; and forming the tack-free gel as a thin layer of plastic of the mold cavity is melted over the gel. The forming step further comprises cooling the gel from the molten state to a solidified state. The melting temperature of the plastic material is lower than the molding temperature of the gel; and the higher the temperature differential, the greater the melting of the plastic material and the thicker the layer of the plastic material on the surface of the gel. The mold may be formed of low-density polyethylene (LDPE). With the process of the invention, the heat of the molten gel at its molding temperature is transferred to the surface of the LDPE mold so as to melt a thin layer of the LDPE. The mold may comprise a mold base having a plurality of mold holes forming a plurality of mold cavities, each of the mold holes comprising an axial pin to mold an axial hole through a center of the gel, an LDPE cylinder providing a predetermined inside diameter for the mold, and an LDPE disc mounted on the axial pin and disposed at the bottom of each mold cavity in the mold base. The process may further comprise the step of dabbing the gel in a low-friction powder such as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and a lubricant. The mold may further comprise a mold top disposed axially of the mold base and comprises a plurality of holes forming a plurality of cavities, each of the mold top holes is adapted to receive the LDPE cylinder, and a second LDPE disc disposed at the top of each mold cavity of the mold top.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Bone anchors with longitudinal connecting member engaging inserts and closures for fixation and optional angulation
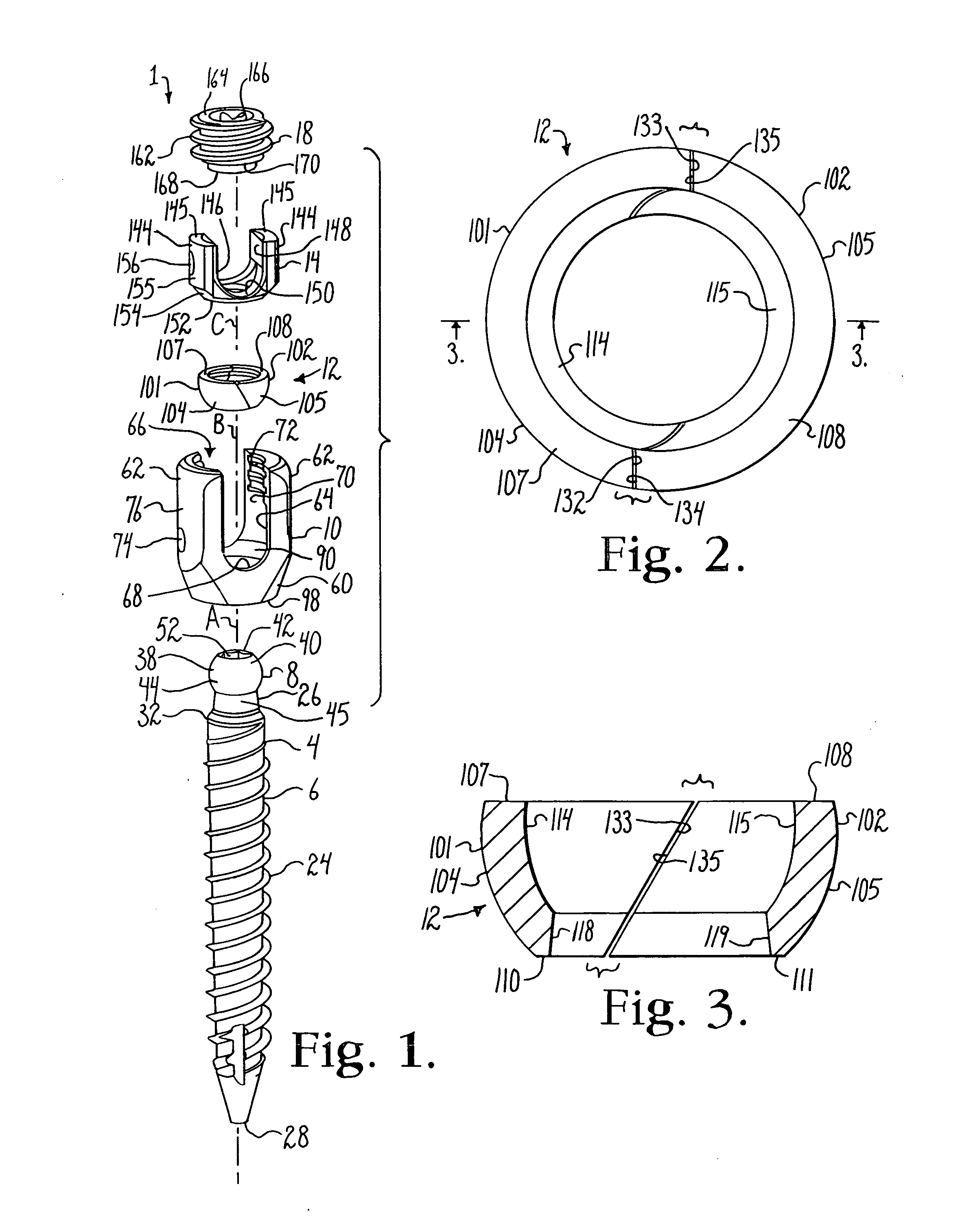
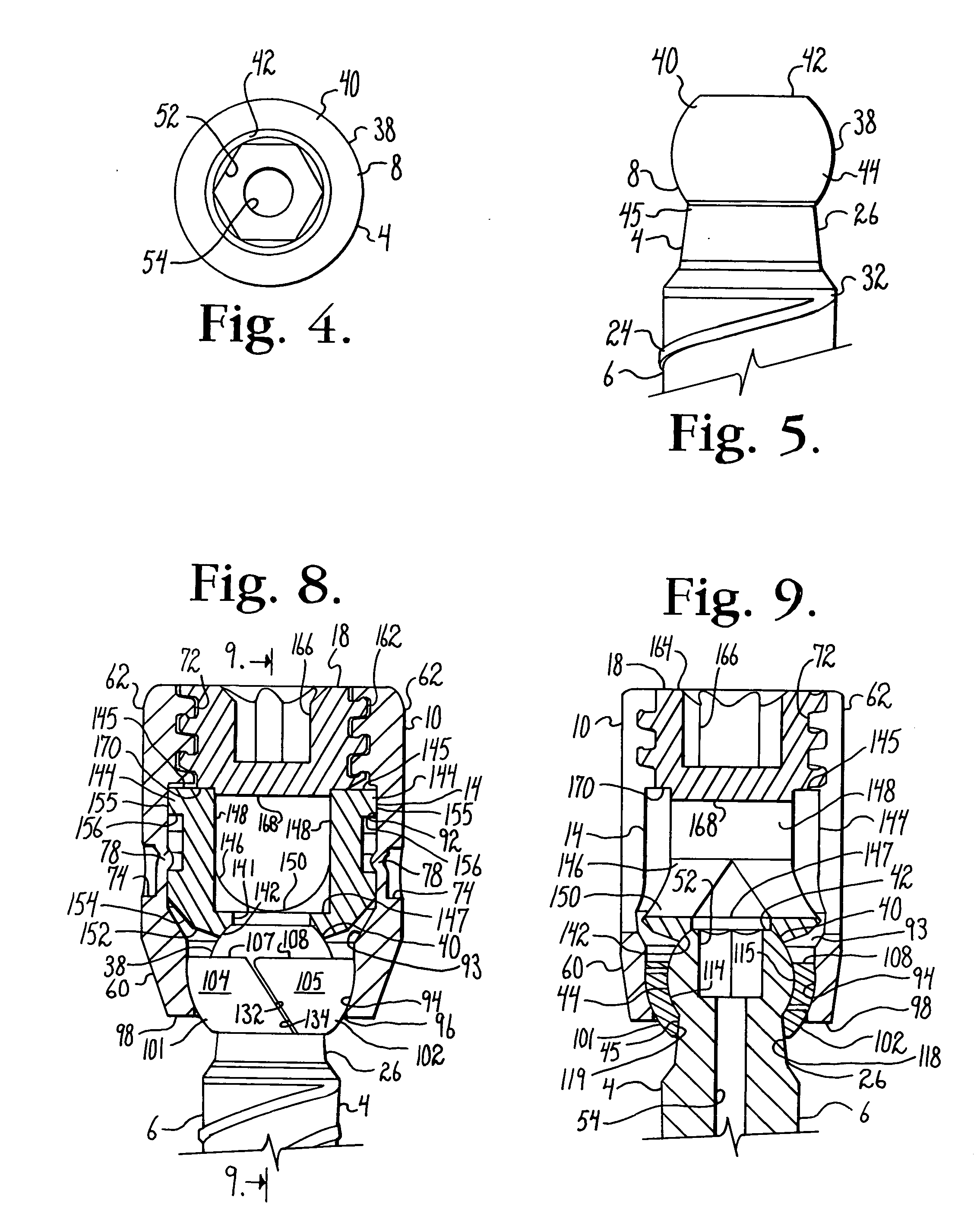
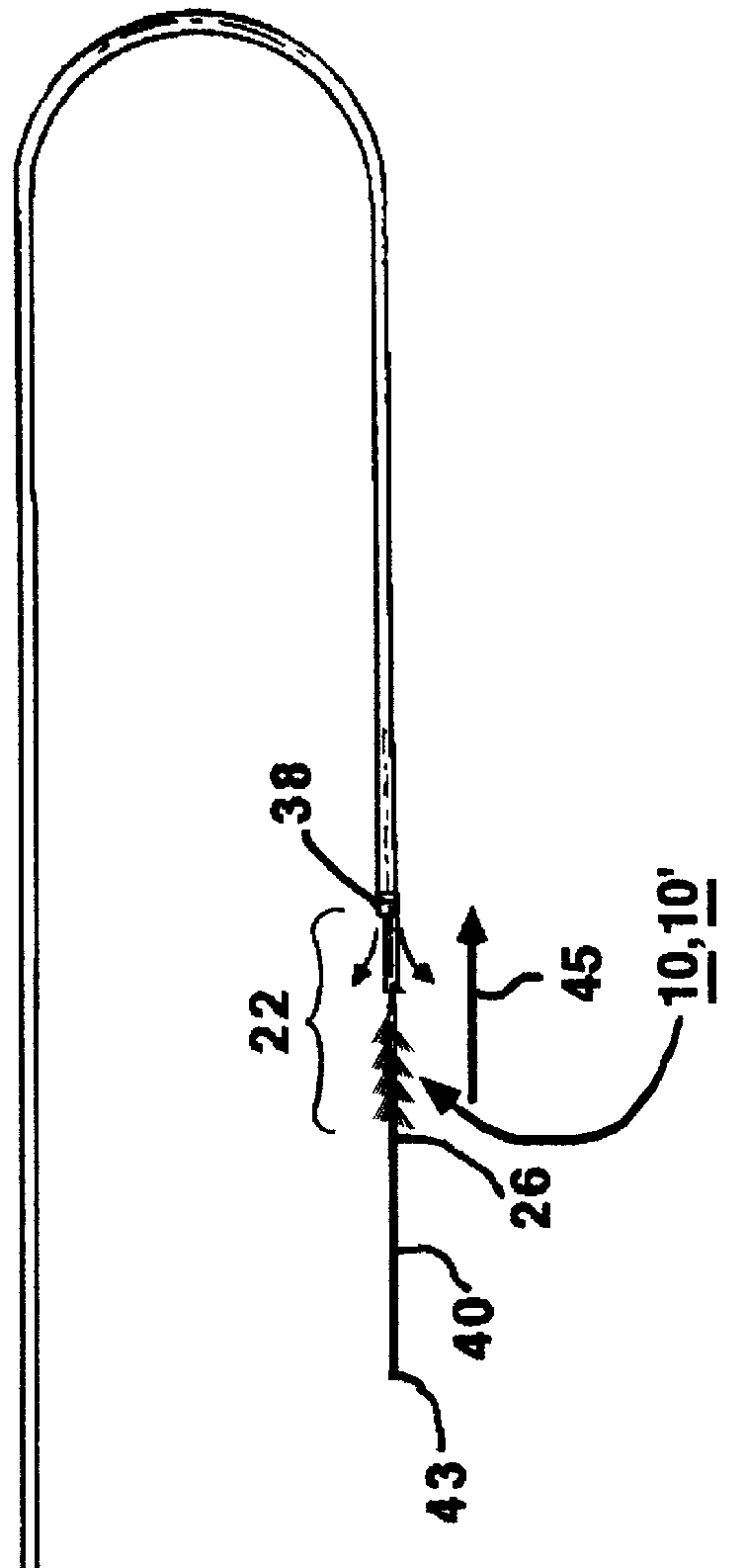
ActiveUS20100298891A1Easy to useLow production costSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSagittal planePlastic materials
Polyaxial bone anchors include a retainer for holding a shank within a receiver, the retainer being in at least two discrete pieces and cooperating with a variety of inserts, some of which independently lock the polyaxial mechanism. Polyaxial and mono-axial bone anchor assemblies include pivot and / or pressure inserts or pads that cooperate with longitudinal connecting members to provide a desired degree of continued control of angulation of the longitudinal connecting member in the sagittal plane or to hold the connecting member in place. Pressure pads for deformable rods may also be made from a deformable plastic material.
Owner:JACKSON
Miniaturized medical brush
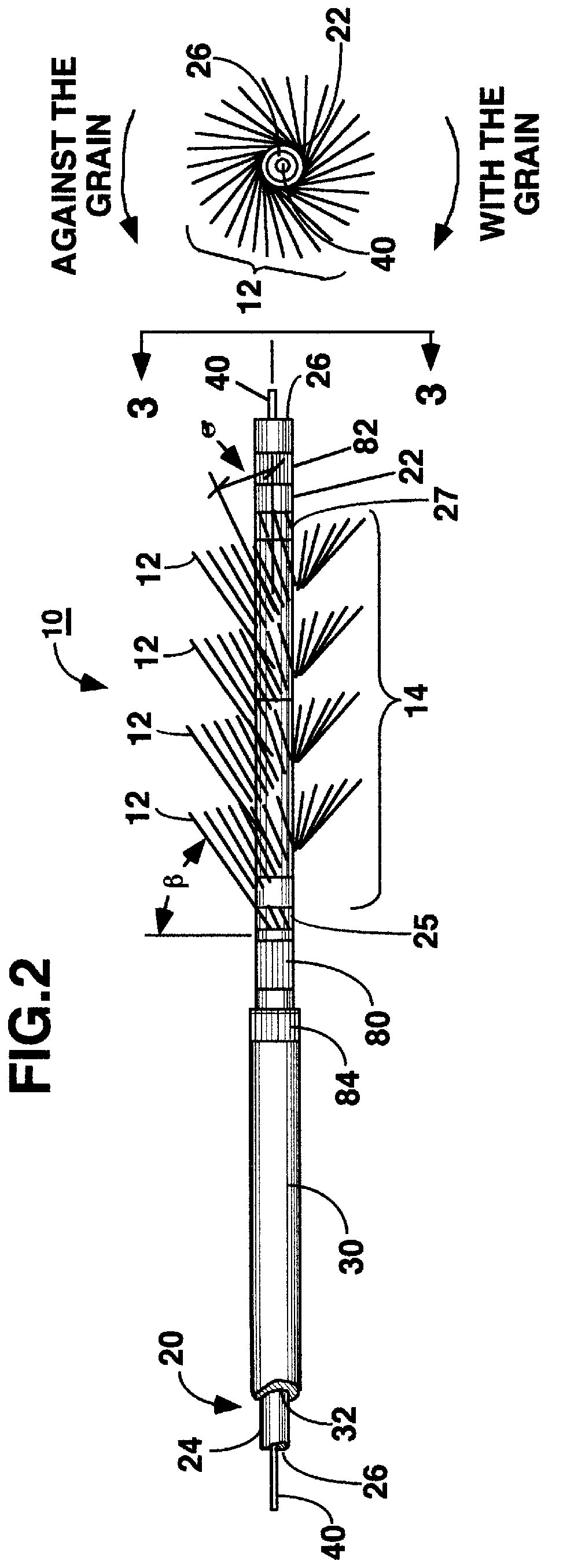
A miniaturized brush particularly adapted for medical use formed at the distal end of an elongated brush drive shaft having a hollow lumen formed therein for introduction over a guidewire. The brush drive shaft is enclosed in the lumen of a brush delivery catheter and other components of a brush sub-assembly adapted to deliver infusate through the catheter lumen and to be coupled to a drive motor unit for rotating the brush drive shaft and brush. The brush bristles of the distal brush are adapted to be garaged in a distal end section of the brush delivery catheter lumen during introduction through a body lumen. The brush bristles are formed of a thin sheet of rigid plastic material that is shaped to have a plurality of fringe elements extending in parallel from a mounting web. The mounting web is wound about and attached to a distal end section of the drive shaft outer circumference so that the fringe elements extend outward from the drive shaft surface and obliquely of the drive shaft axis. Preferably, proximal and distal spiral brush sections are formed in this manner so that fluids are impelled distally and proximally, respectively, between the proximal and distal brush sections as infusate is delivered.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
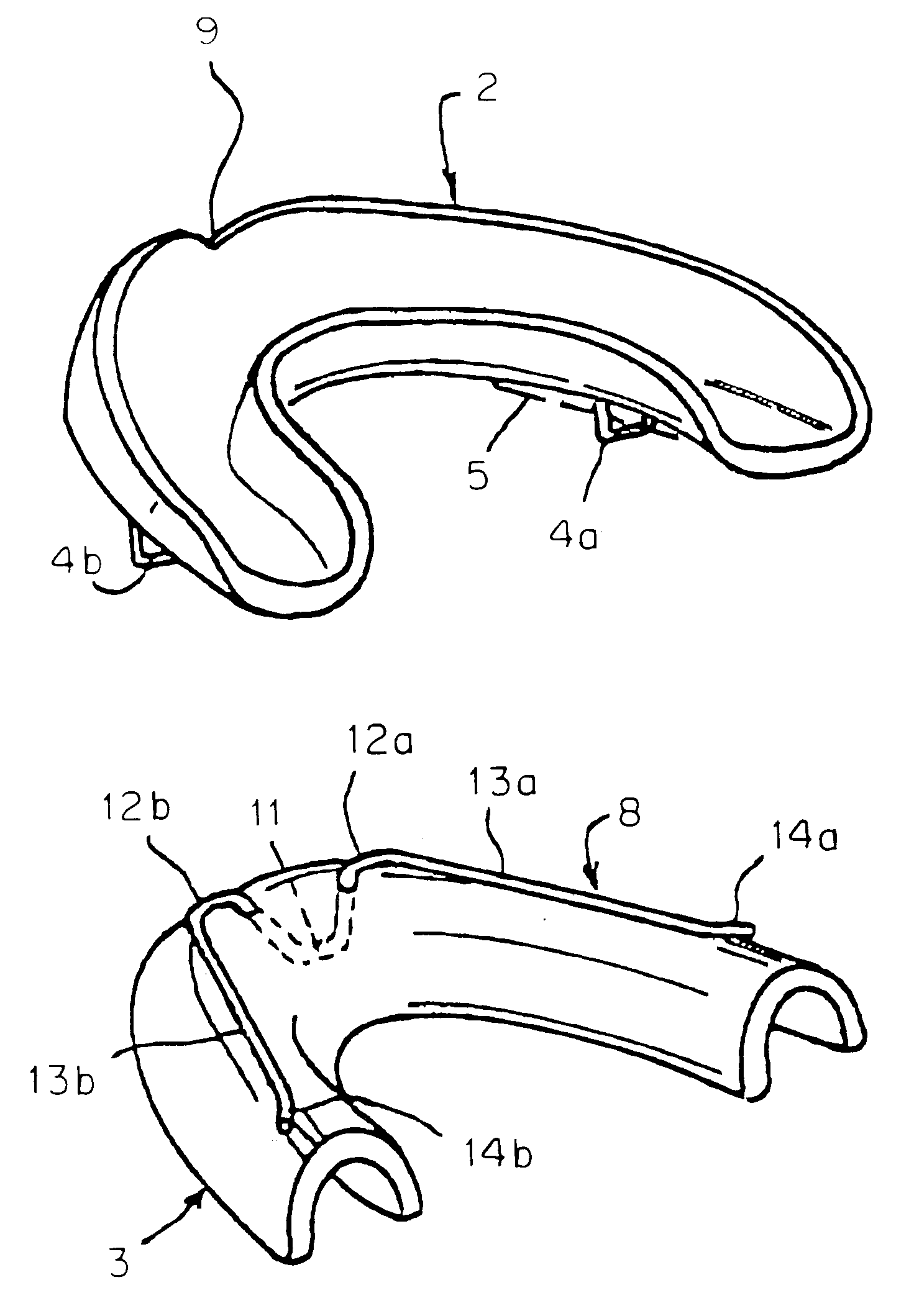
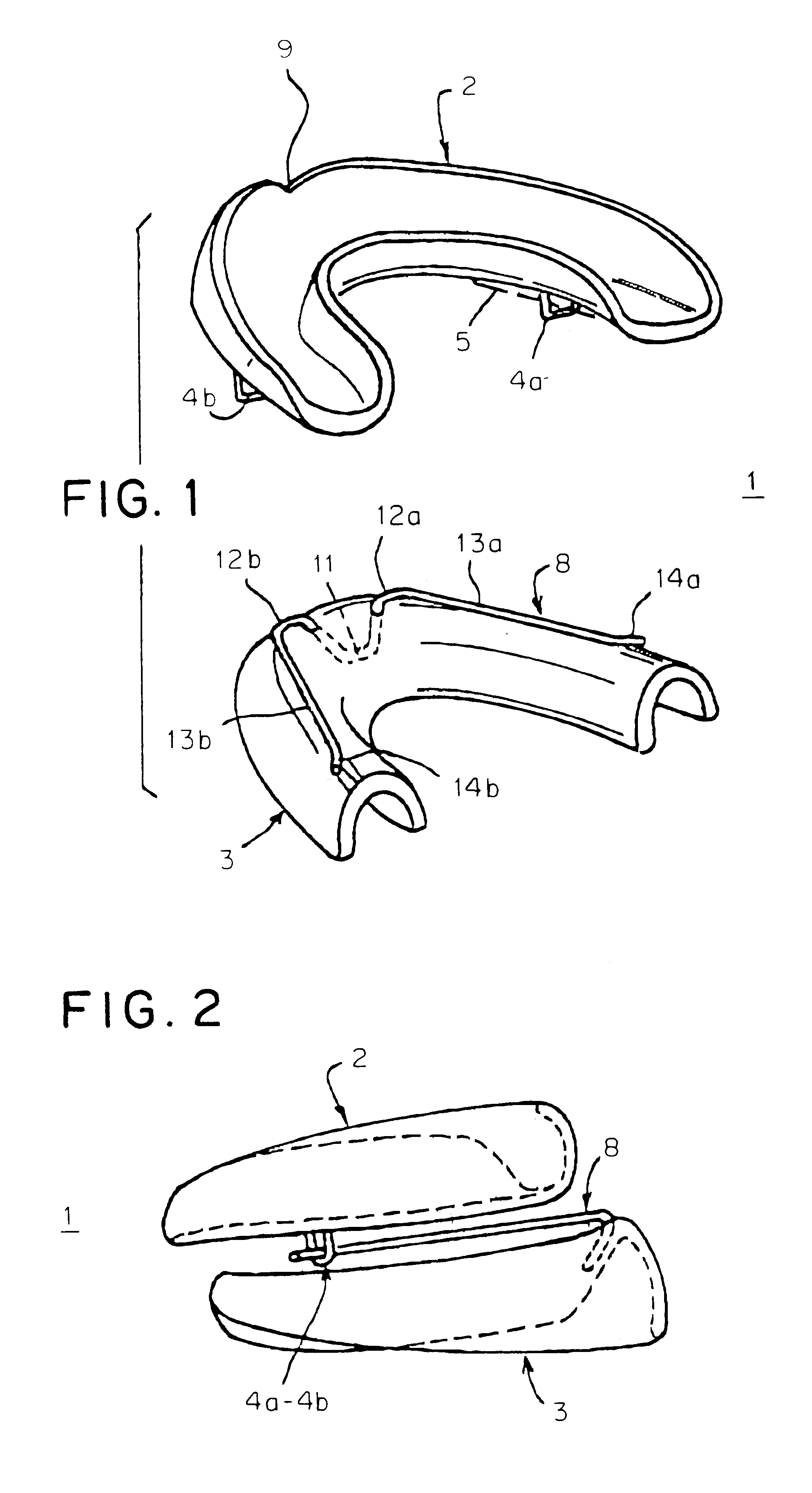
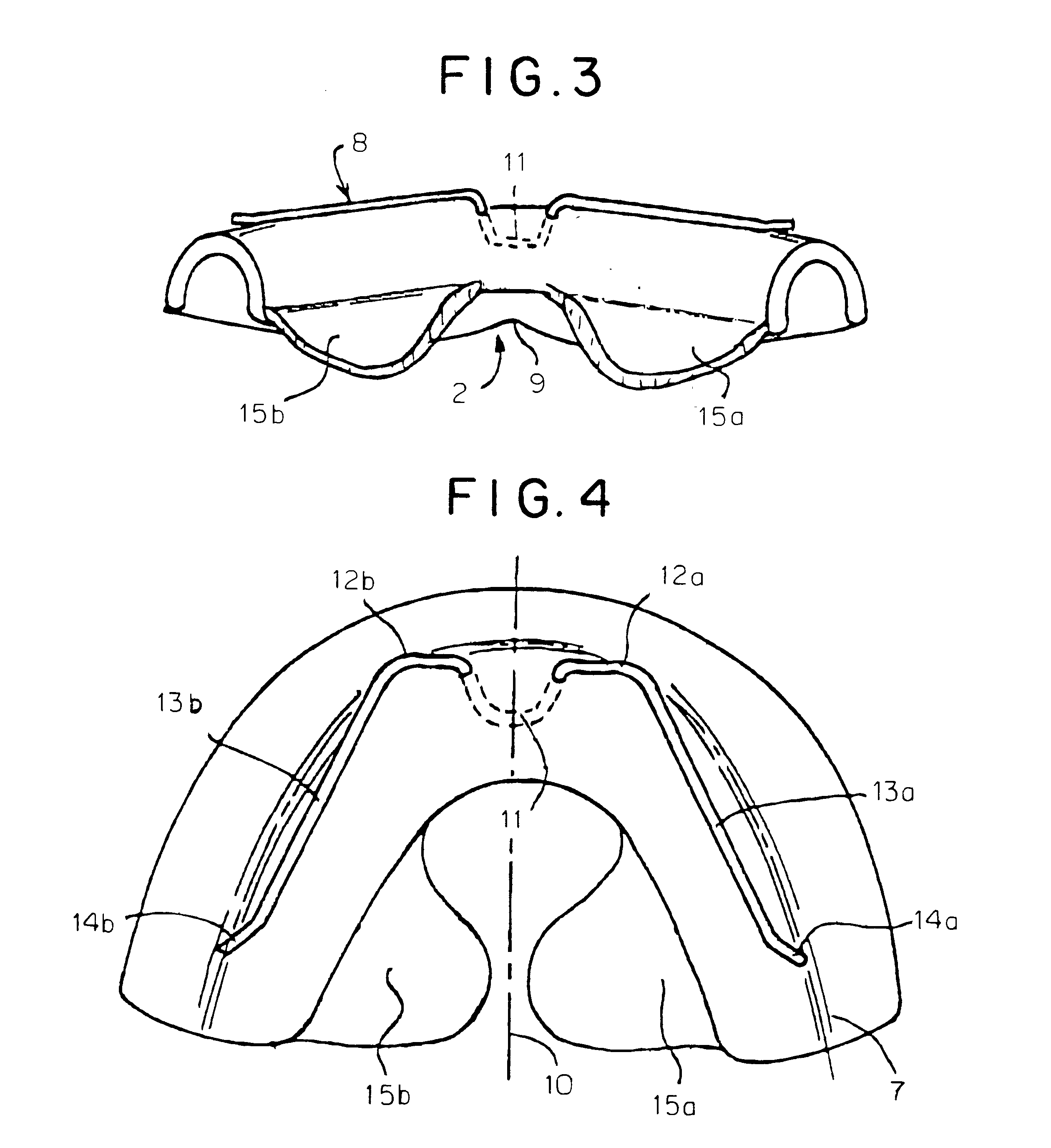
Intraoral device
Intrabuccal device includes two shells (2, 3) made of thermoformed plastic material, the first of which respectively covers the superior arch, and the second of which covers the inferior arch of the oral cavity. This device is provided with (rings and arms) (4a, 4b, 13a, 13b) that act on the said shells (2, 3) and can generate a mandibular propulsion force oriented in the direction of the mandibular propulsion and in the posteroanterior sense, so as to keep a shift of the mandible to the front of the maxilla, while allowing lateral movements.
Owner:DAVID MICHEL +2
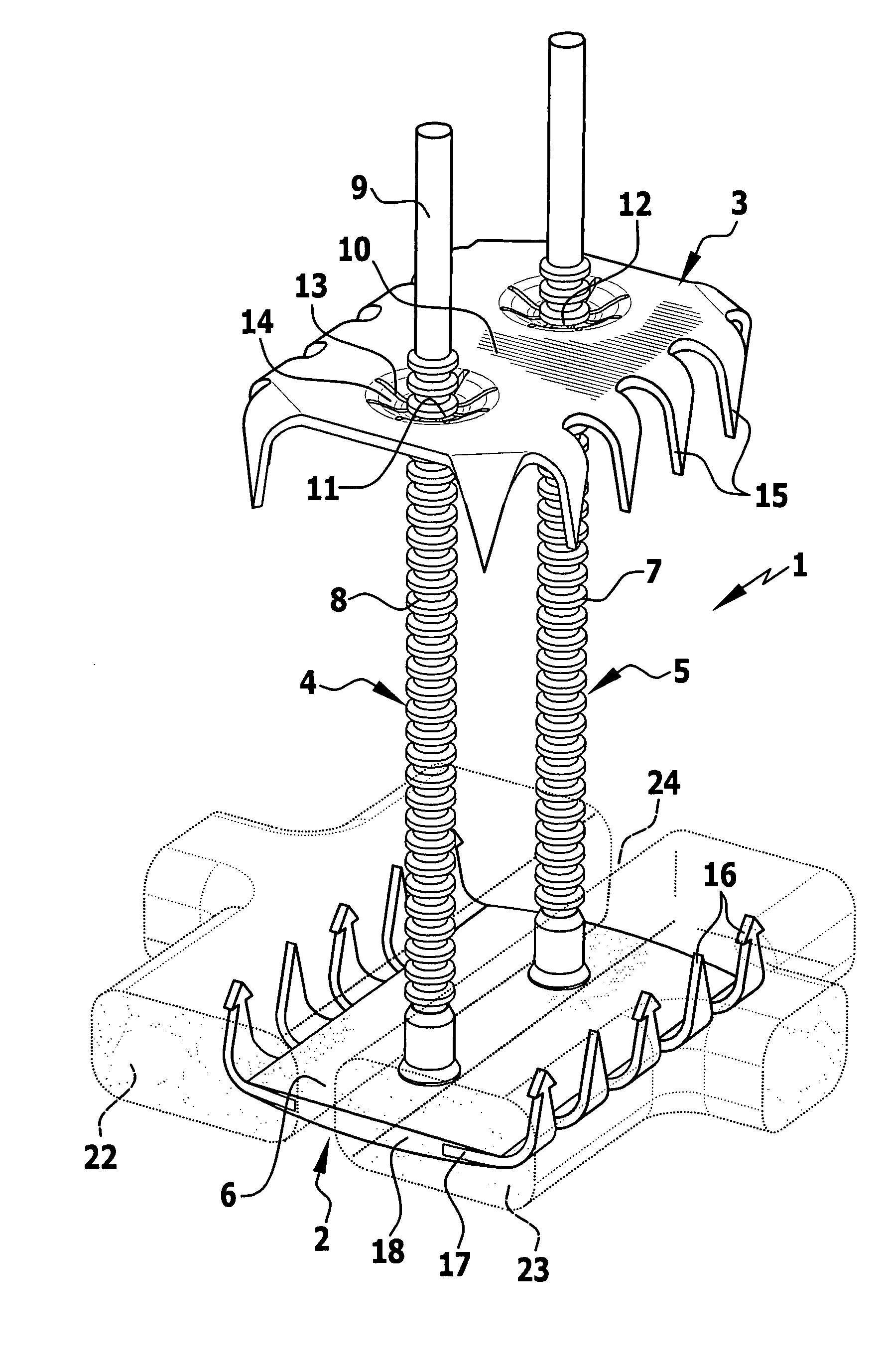
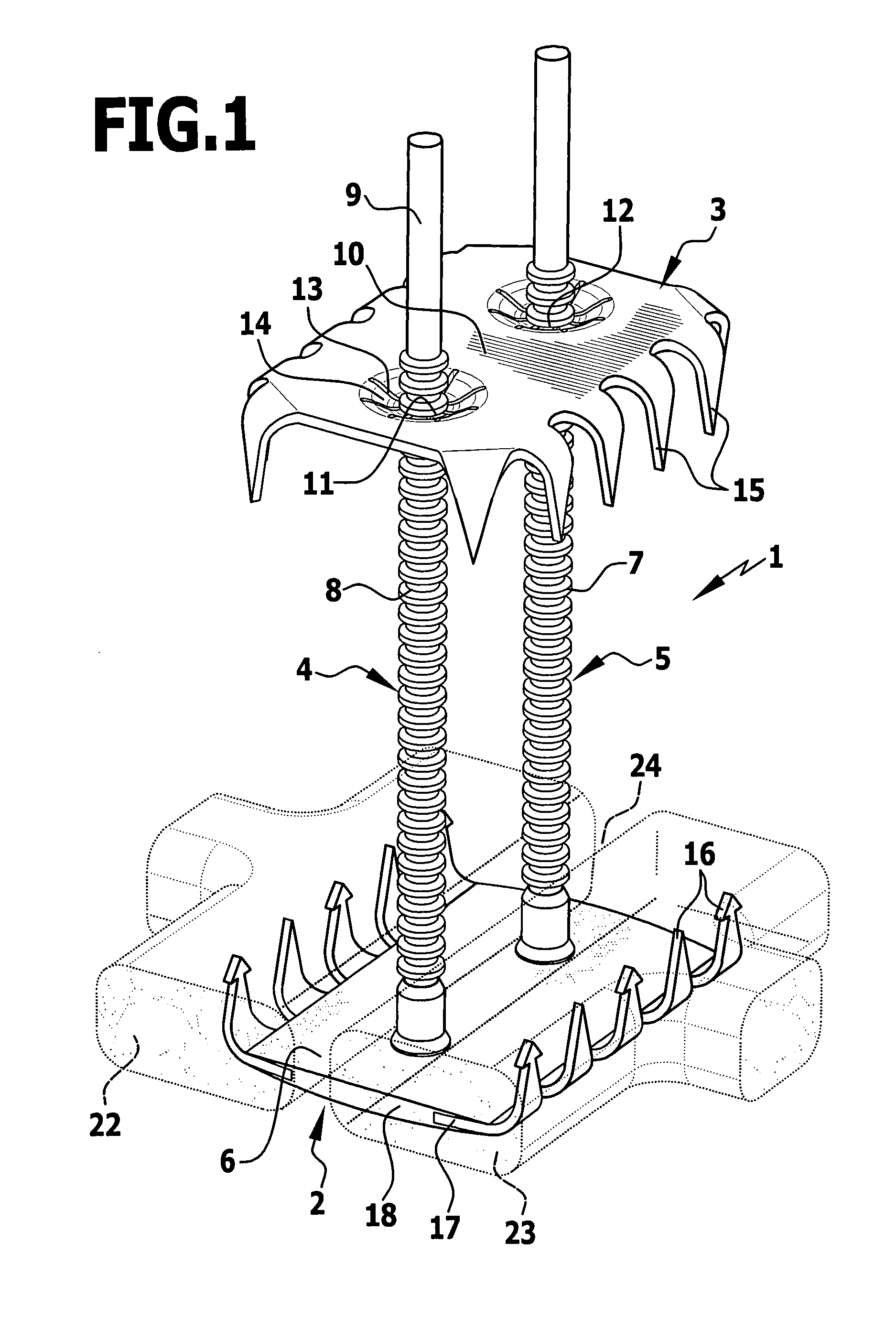
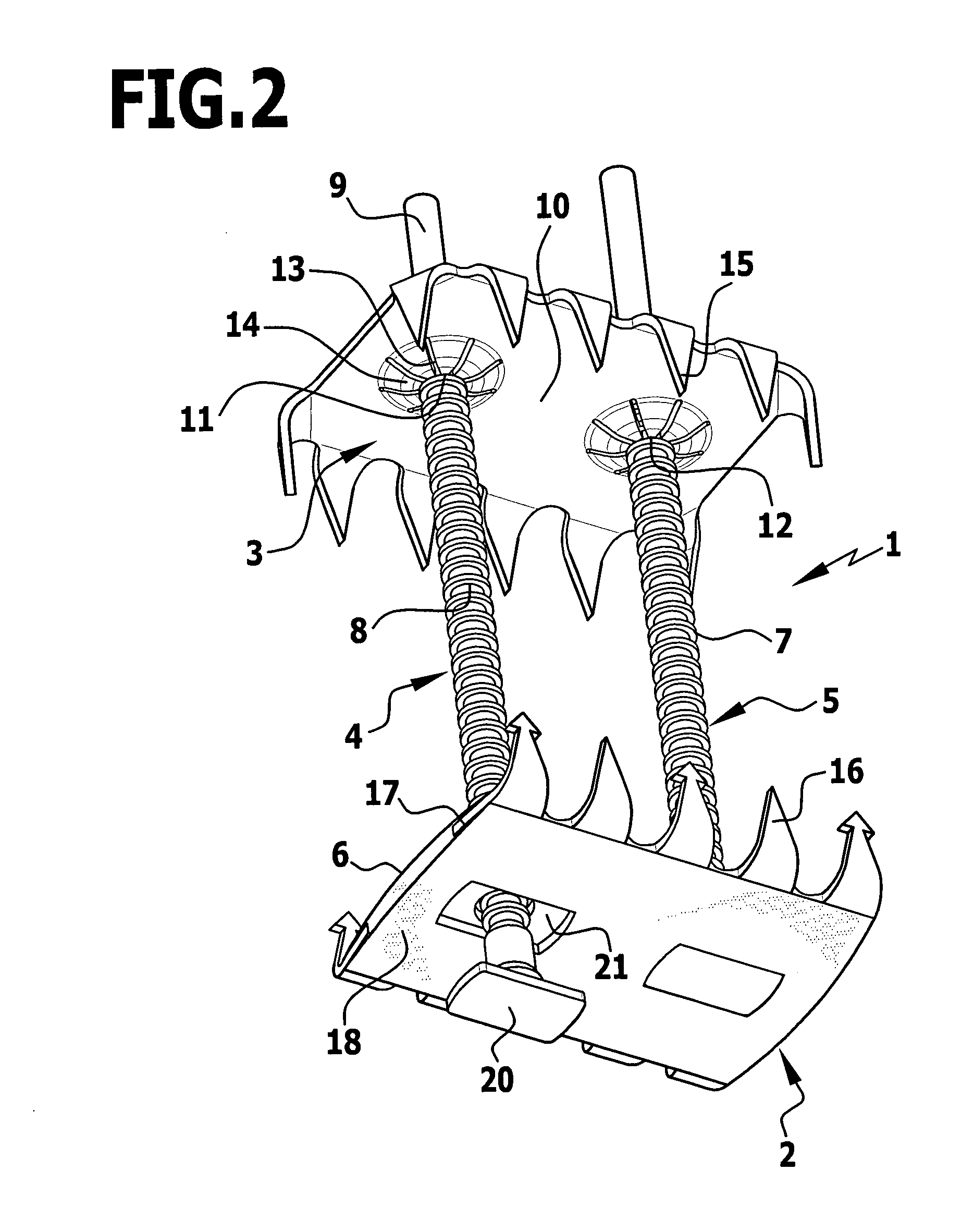
Sternum closure device
InactiveUS20090234357A1Easy to spreadInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSternum partPlastic materials
In a sternum closure device for securing two sternum parts to be connected to one another, comprising an inner contact element to abut the inner face of the sternum, at least one clamping element secured thereto and projecting transversely therefrom, and comprising an outer contact element for abutment on the outer side of the sternum and which can be clamped by means of the clamping element guided through the intermediate space between the sternum parts against the inner contact element, in order to reduce the obstruction by the sternum closure device in the event of a renewed separation of the sternum parts, it is proposed that the inner contact element consists at least partially of a biocompatible plastics material.
Owner:AESCULAP AG
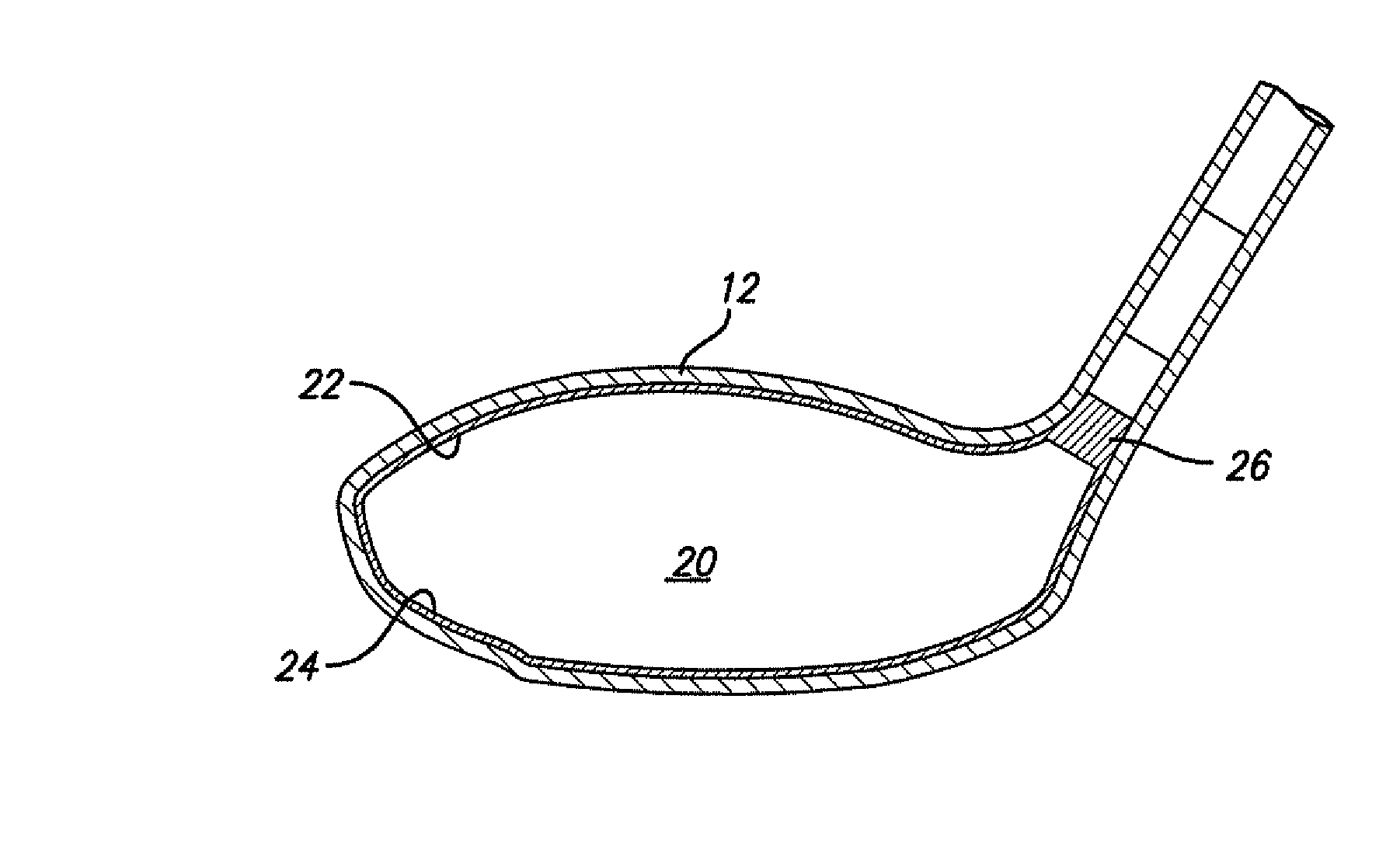
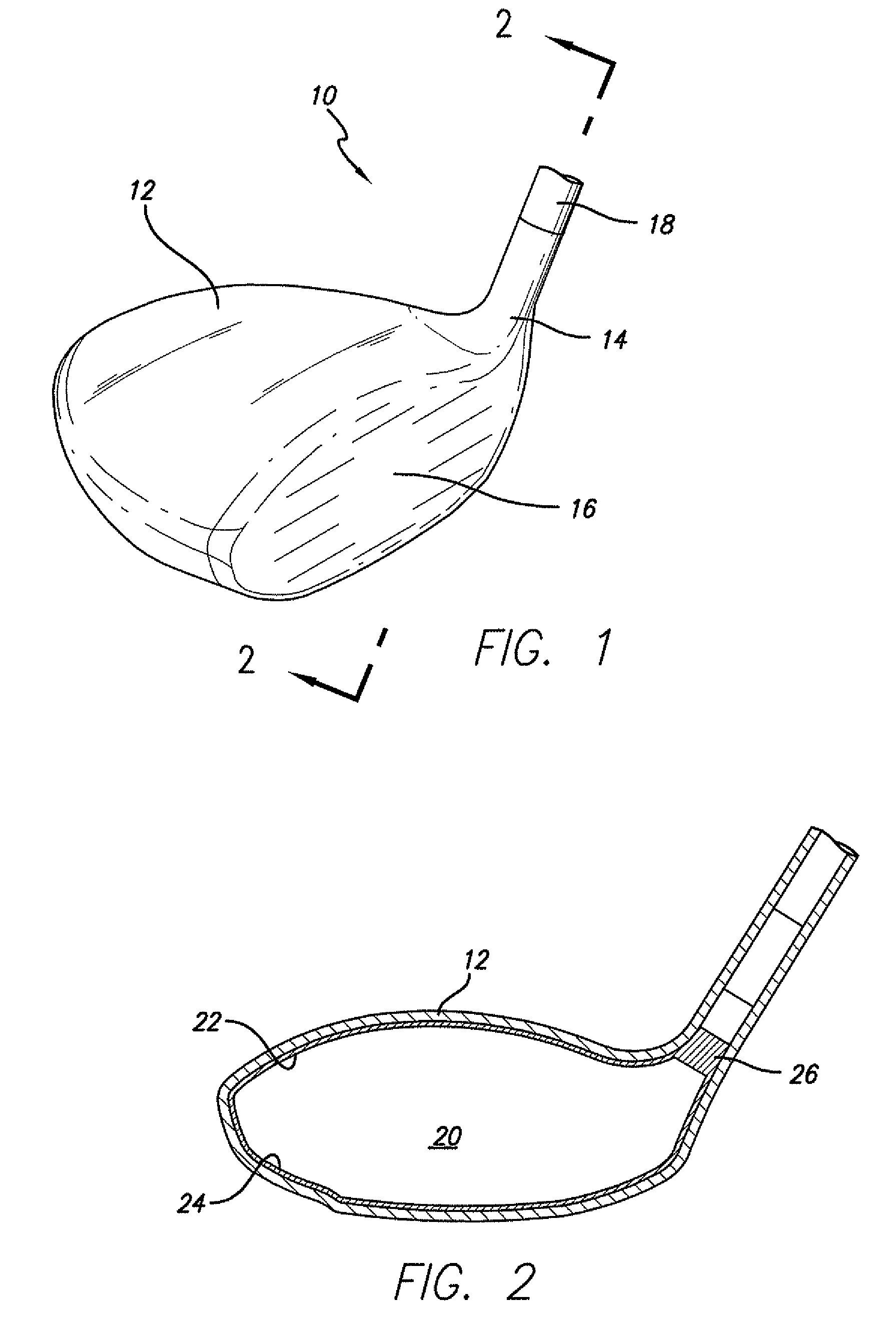
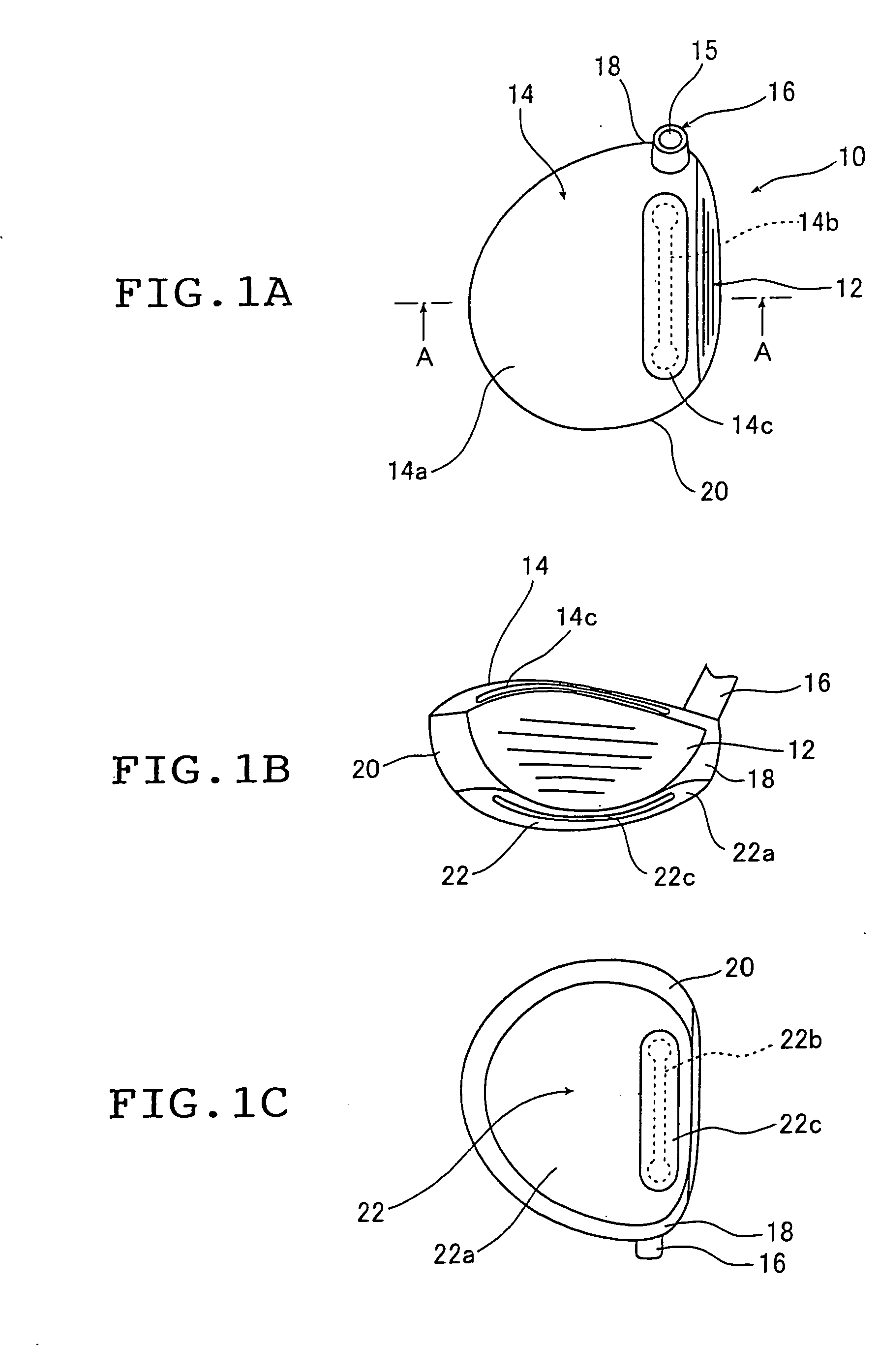
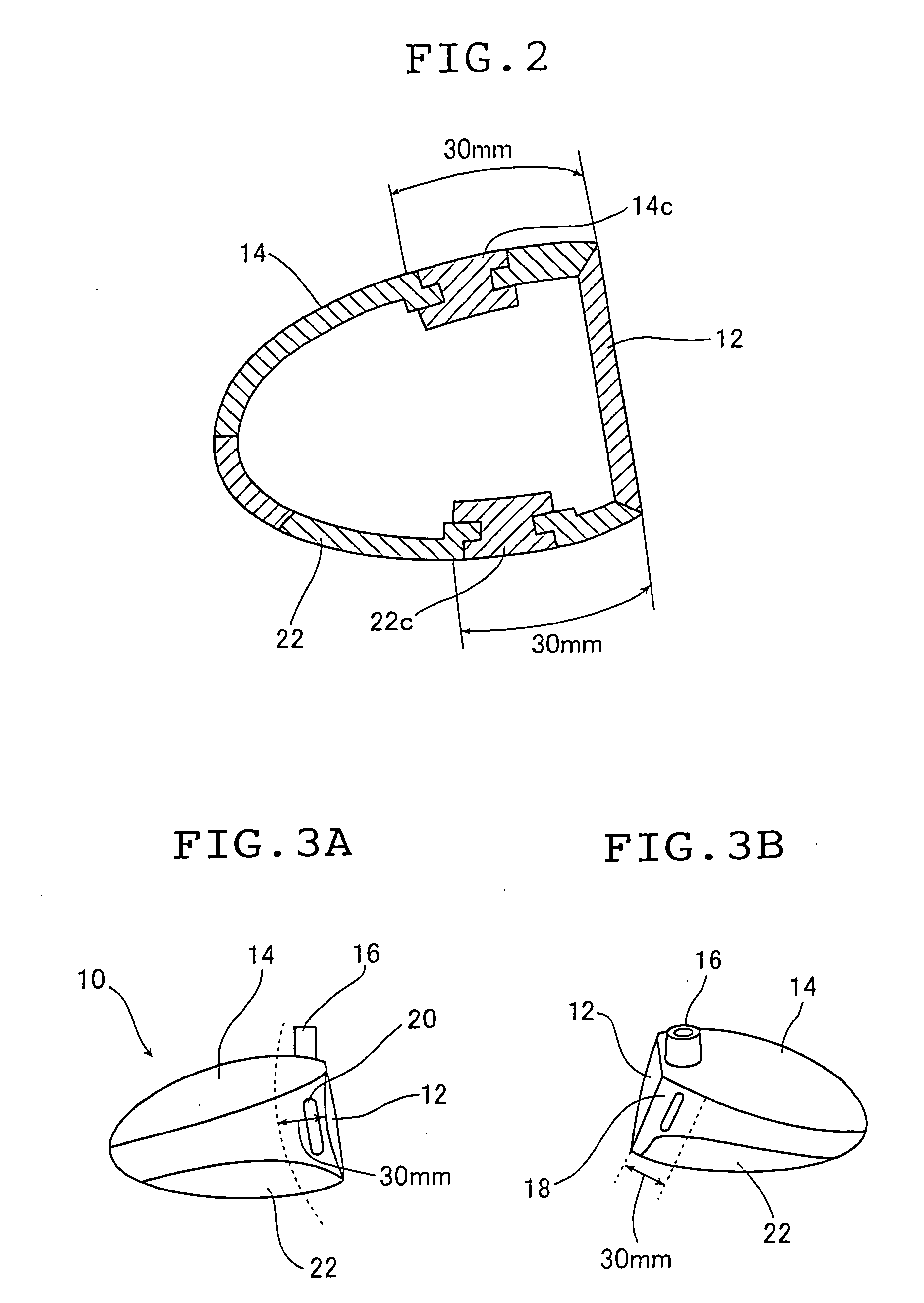
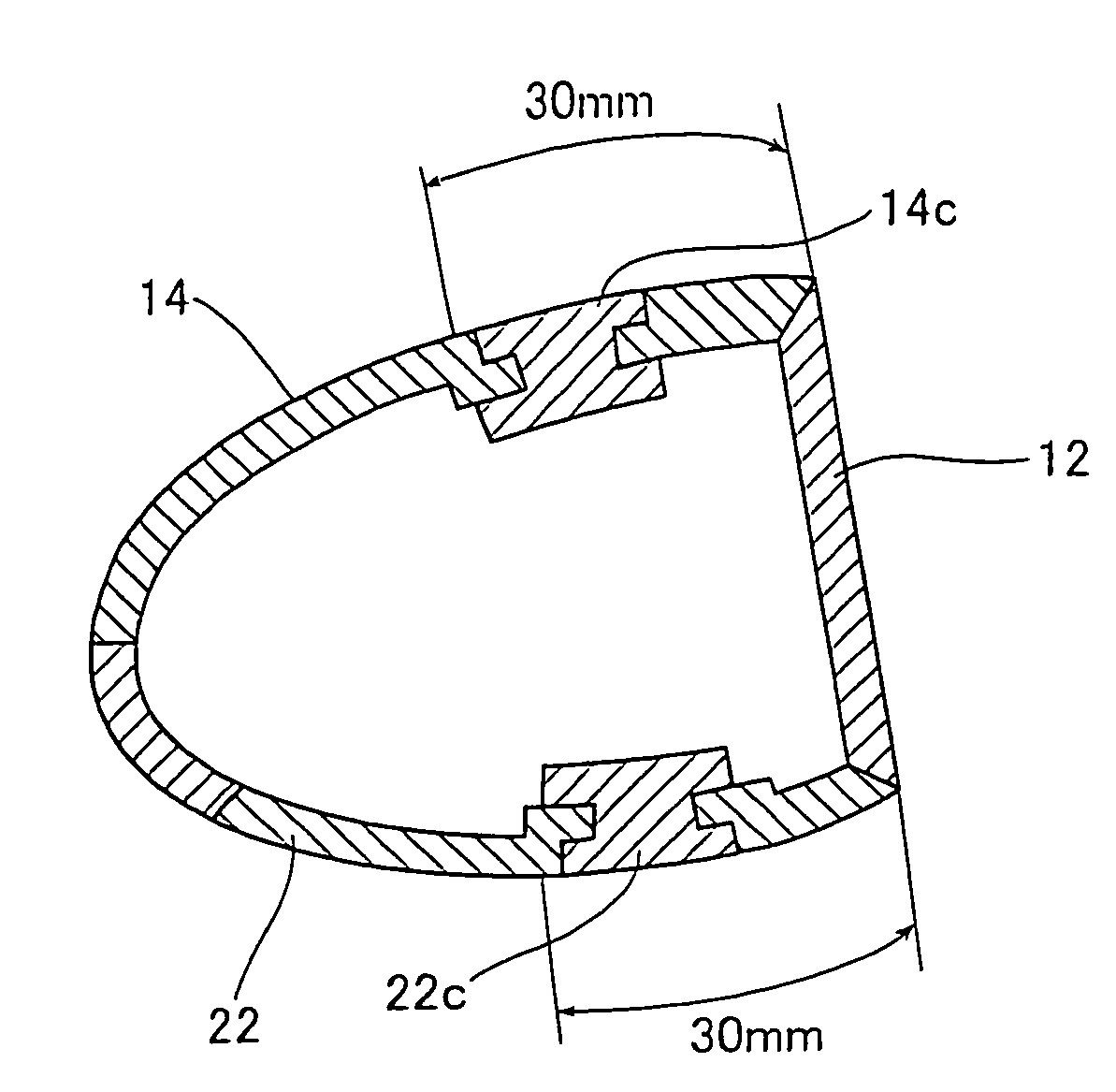
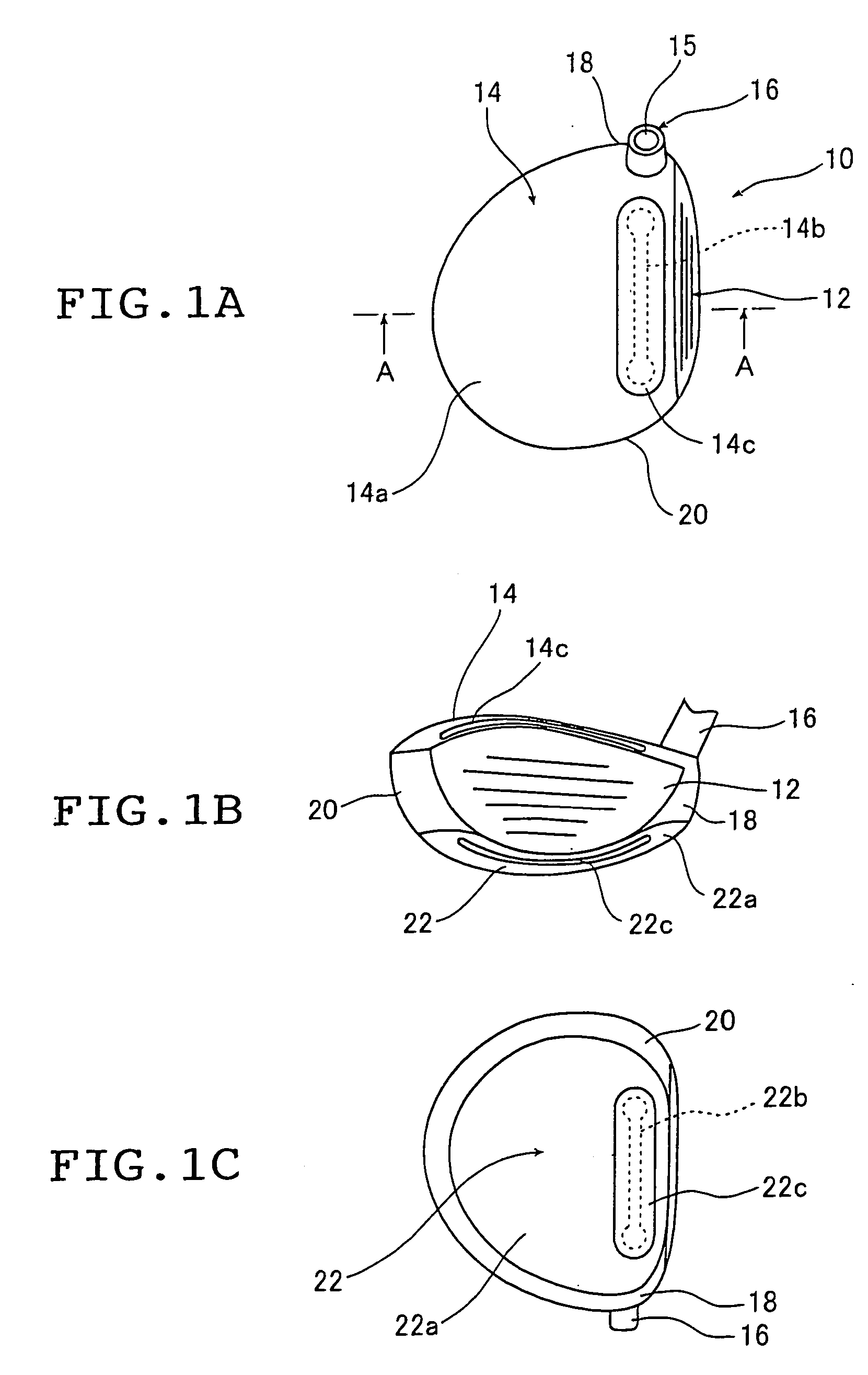
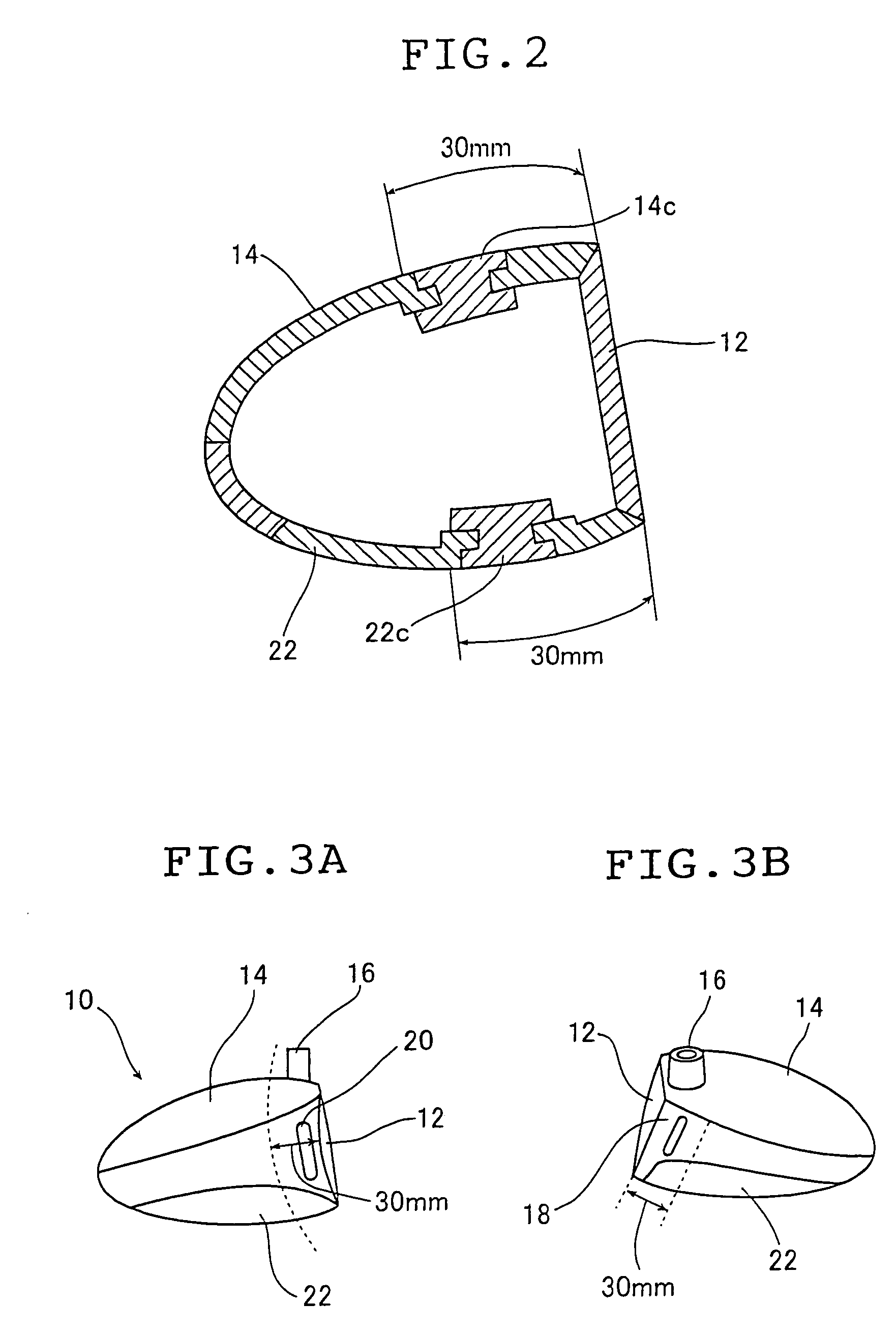
Hollow golf club head
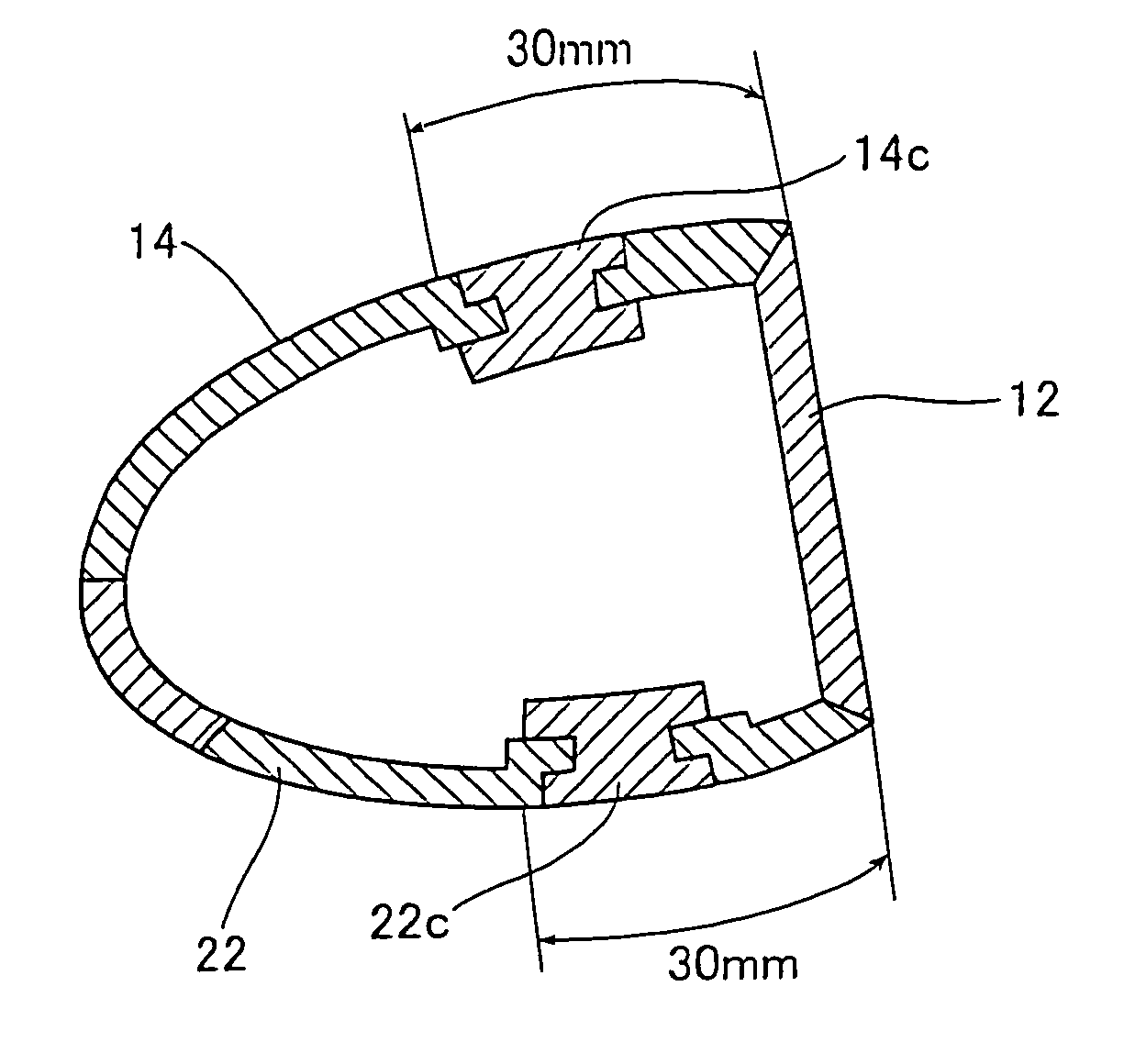
InactiveUS20060052177A1Improve the overall coefficientIncrease the carrying distanceGolf clubsRacket sportsFiberPlastic materials
A golf club head of the present invention includes a face portion having an impact surface that impacts a golf ball and is made from a metallic material, and a crown portion, a heel portion, a sole portion, and a toe portion that are adjacent to the face portion. In at least two portions from among the crown portion, the heel portion, the sole portion, and the toe portion, at least one from among dissimilar metallic materials that differ from the metallic material of the impact surface and fiber reinforced plastic materials is used in regions along ends that are adjacent to the face portion, within a range of 30 mm from the adjacent ends. Thereby, the golf club has a structure that easily deforms with respect to golf ball impacts, and the face portion deforms more than conventional face portions. The coefficient of restitution of a struck golf ball therefore increases, the initial velocity of the golf ball increases, and the carry distance increases.
Owner:YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Hollow golf club head
InactiveUS7470201B2Improve the overall coefficientIncrease distanceGolf clubsRacket sportsPlastic materialsMetallic materials
A golf club head of the present invention includes a face portion having an impact surface that impacts a golf ball and is made from a metallic material, and a crown portion, a heel portion, a sole portion, and the toe portion that are adjacent to the face portion. In at least two portions from among the crown portion, the heel portion, the sole portion, and the toe portion, at least one from among dissimilar metallic materials that differ from the metallic material of the impact surface and fiber reinforced plastic materials is used in regions along ends that are adjacent to the face portion, within a range of 30 mm from the adjacent ends. Thereby, the golf club has a structure that easily deforms with respect to golf ball impacts, and the face portion deforms more than conventional face portions. The coeffecient of restitution of a struck golf ball therefore increases, the initial velocity of the golf ball increases, and the carry distance increases.
Owner:THE YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
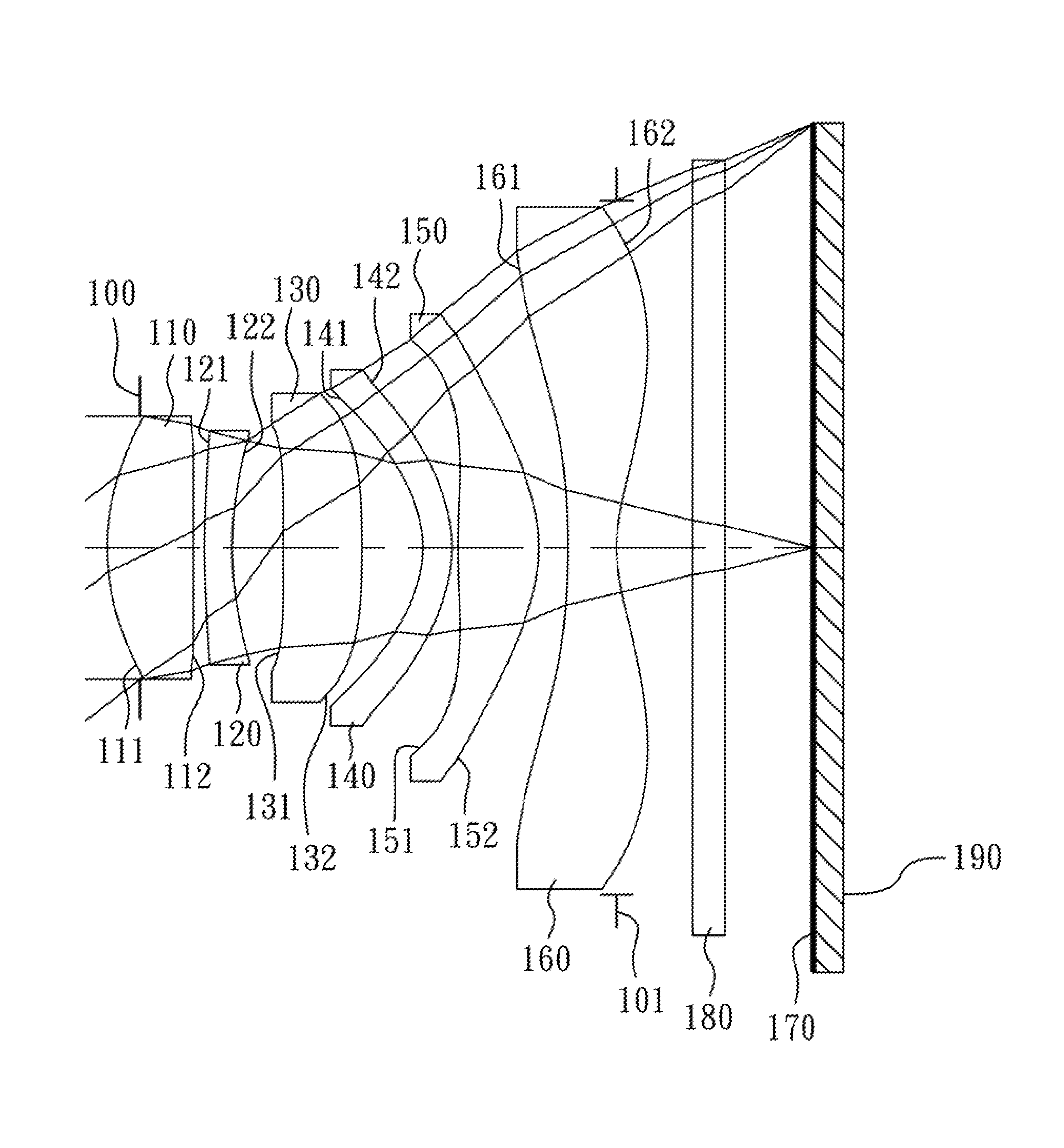
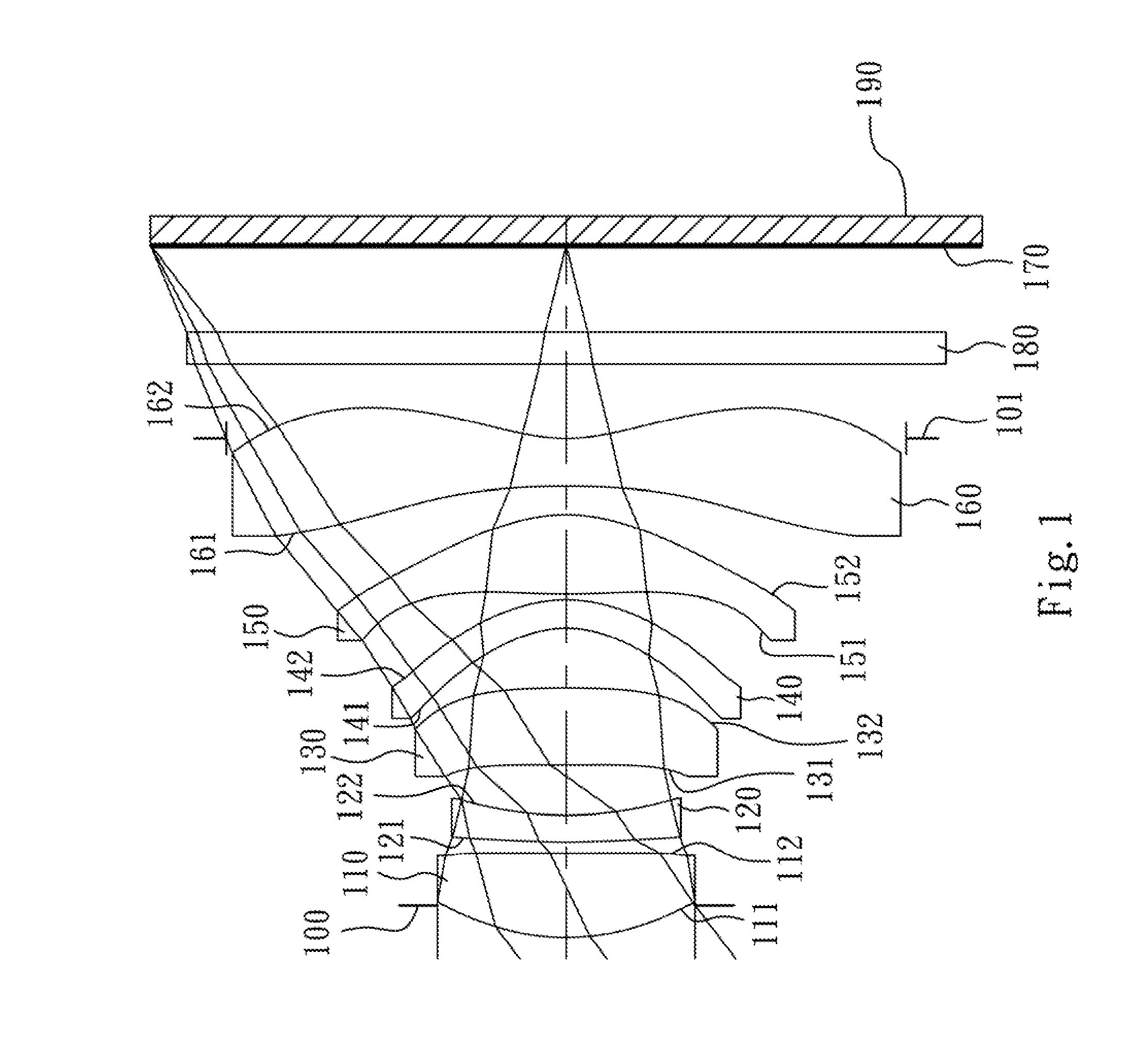
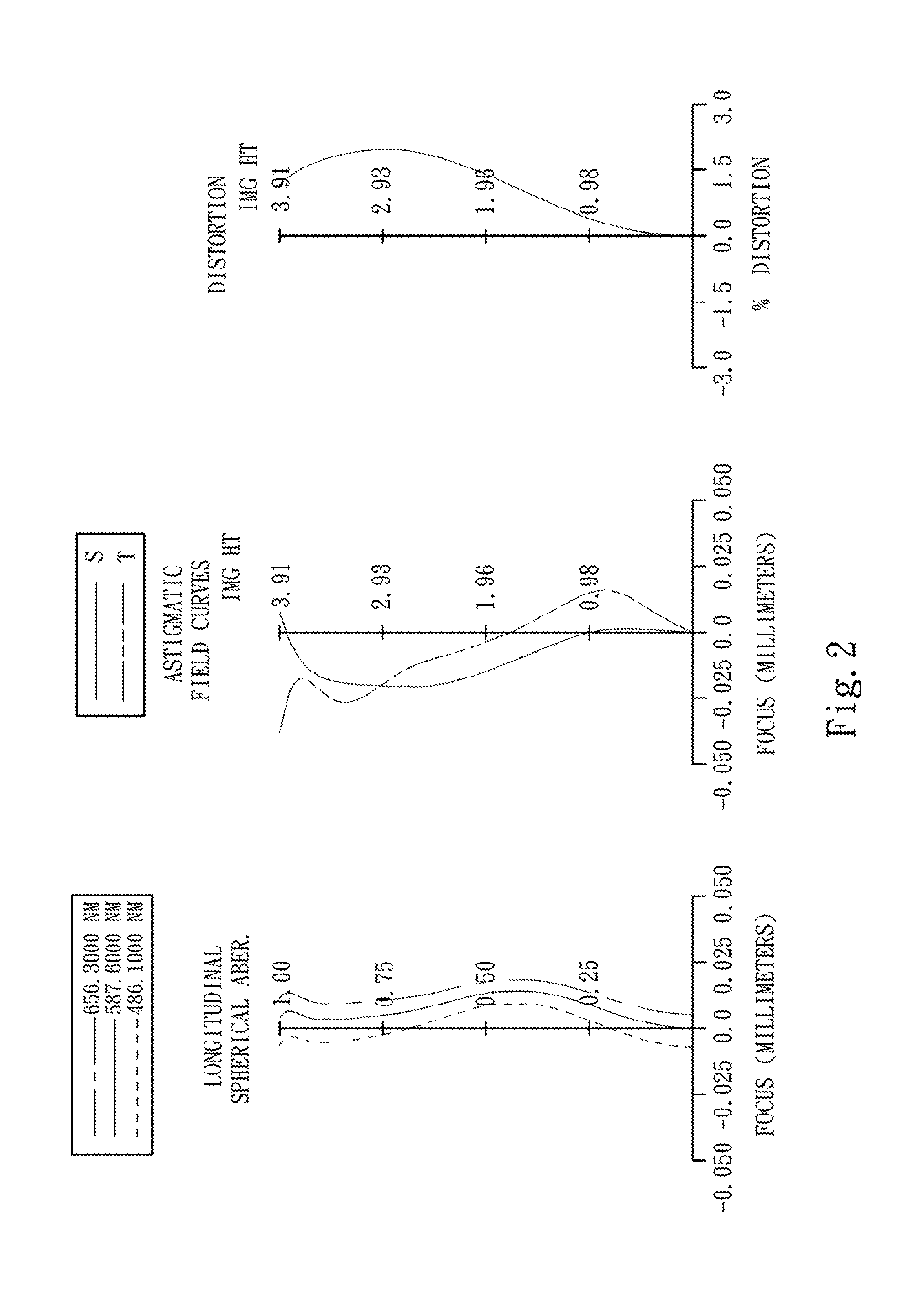
Optical image capturing lens assembly
An optical image capturing lens assembly includes, in order from an object side to an image side, the first lens element with positive refractive power having a convex object-side surface, the second lens element with refractive power, the third lens element with refractive power, the fourth lens element with refractive power having a concave object-side surface and a convex image-side surface, the fifth lens element with refractive power having a convex image-side surface, the object-side surface and the image side surface of the fifth lens element being aspheric, and the sixth lens element with negative refractive power made of plastic material and having a concave image-side surface. The object-side surface and the image-side surface of the sixth lens element are aspheric, and at least one surface thereof has at least one inflection point.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
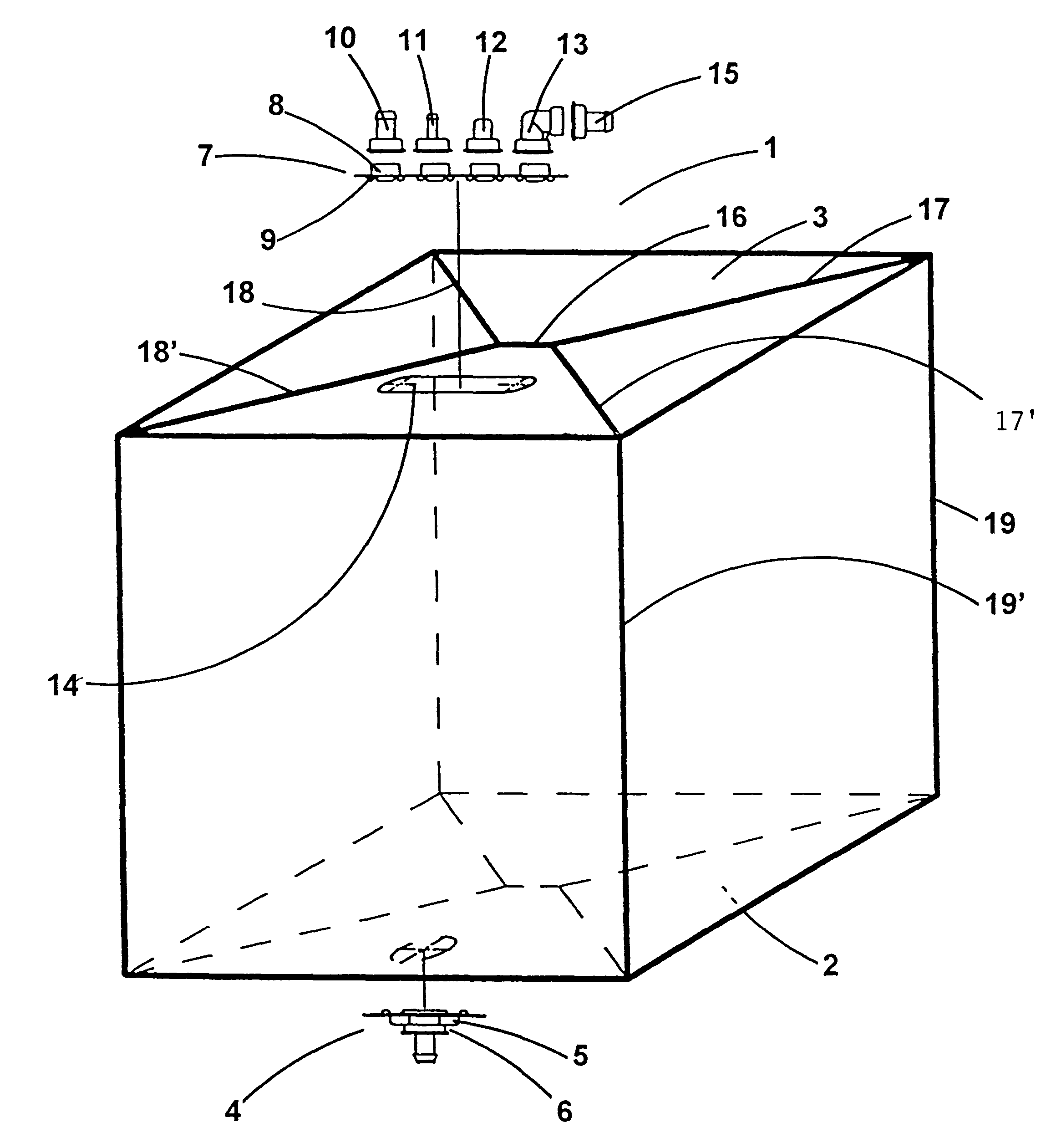
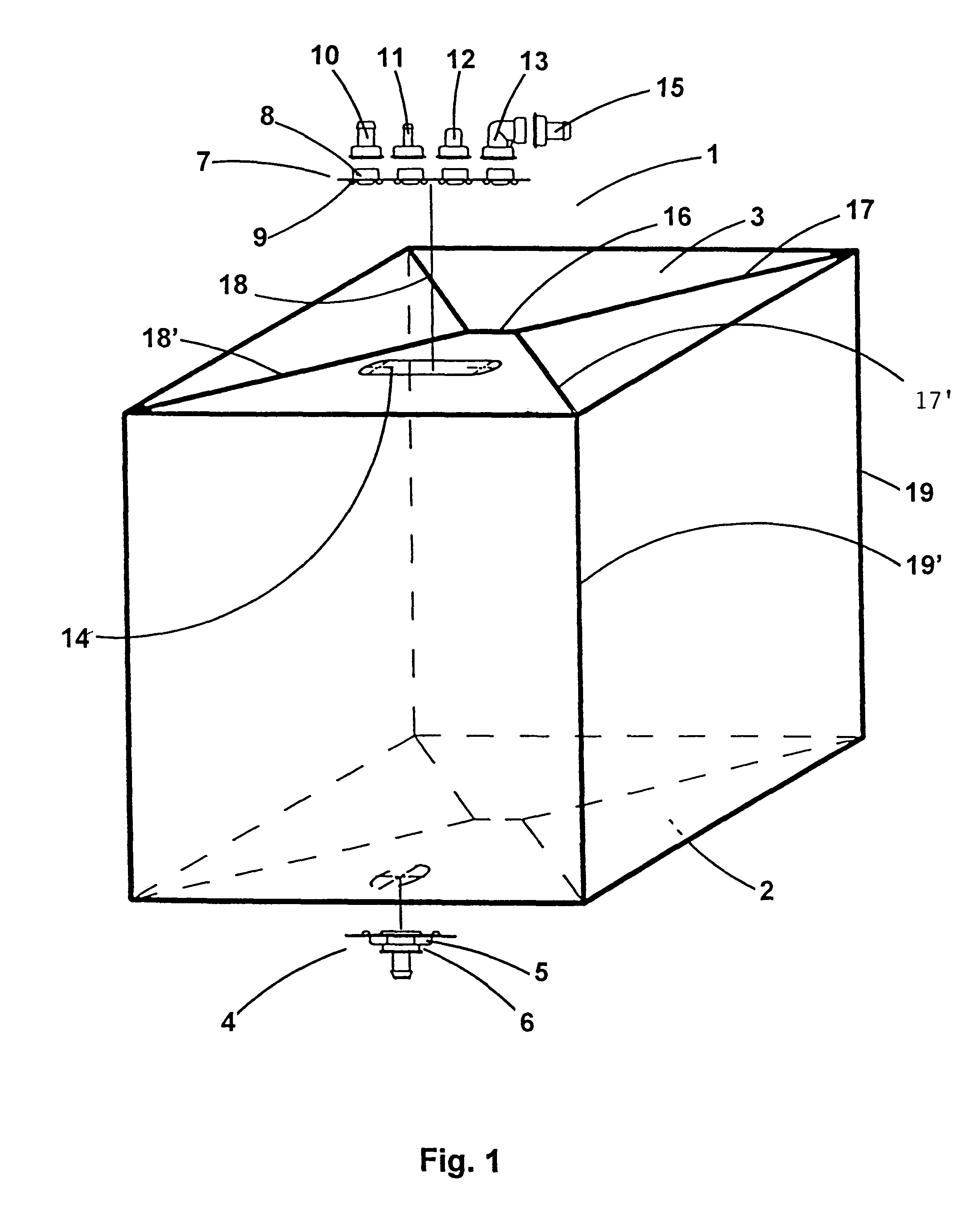
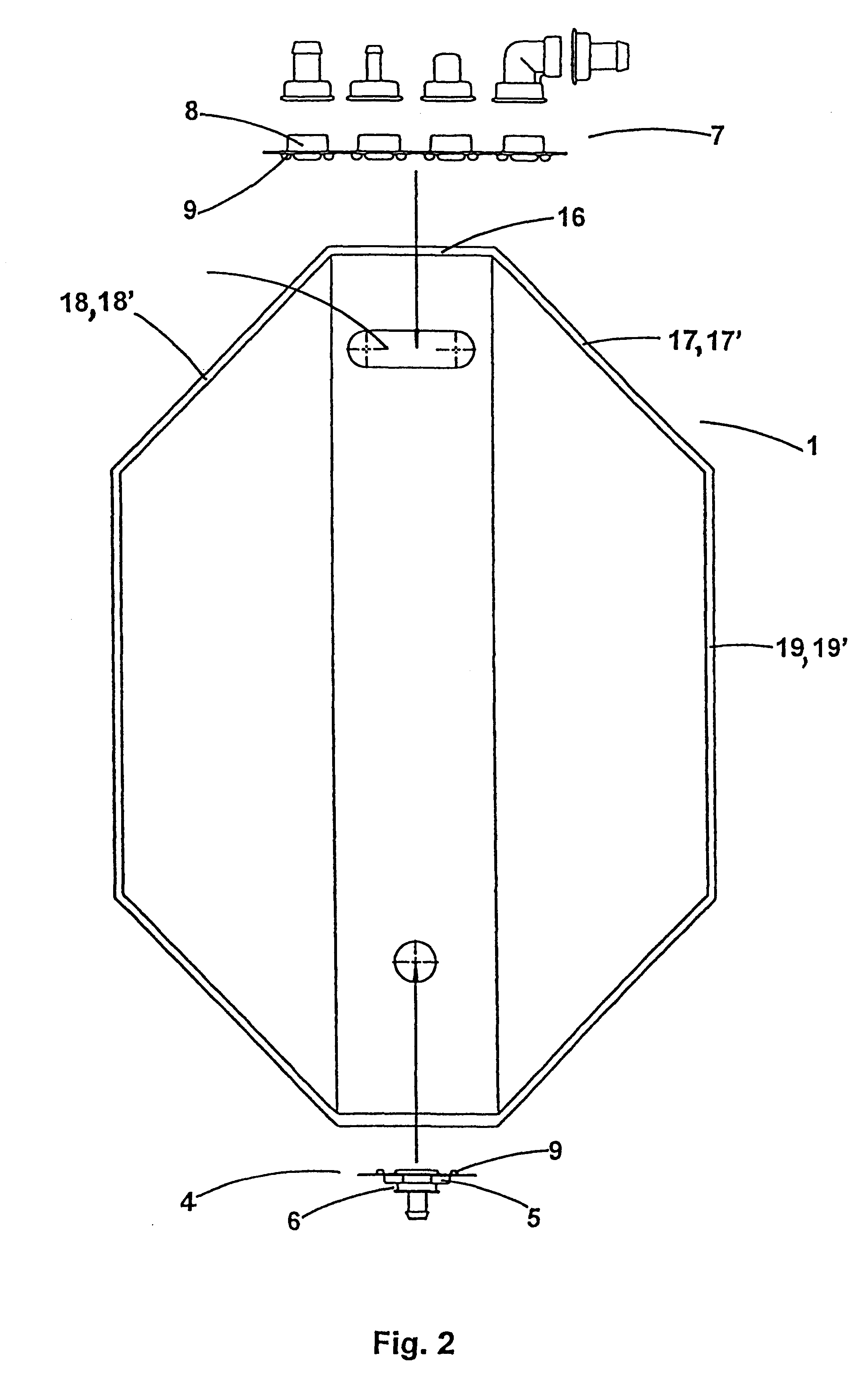
Sachets for bio-pharmaceutical fluid products
InactiveUS6186932B1Easily customizedImprove convenienceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsEnvelopes/bags making machineryPlastic materialsEngineering
A flexible sachet for transporting bio-pharmaceutical liquids with a volume of 50 liters or more, of the bellows type, assumes when filled a substantially parallelepiped shape. It comprises a bottom wall, a top wall and four lateral walls. It is made of a single laminated film with three or more layers, the innermost layer being a plastics material layer that can be heat welded and is biocompatible with the media transported. A method of manufacturing the sachet is also disclosed.
Owner:SARTORIUS STEDIM FMT SAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com