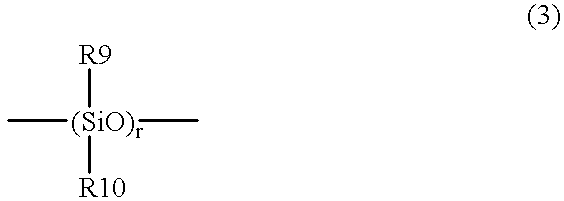Patents
Literature
20986results about "Lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
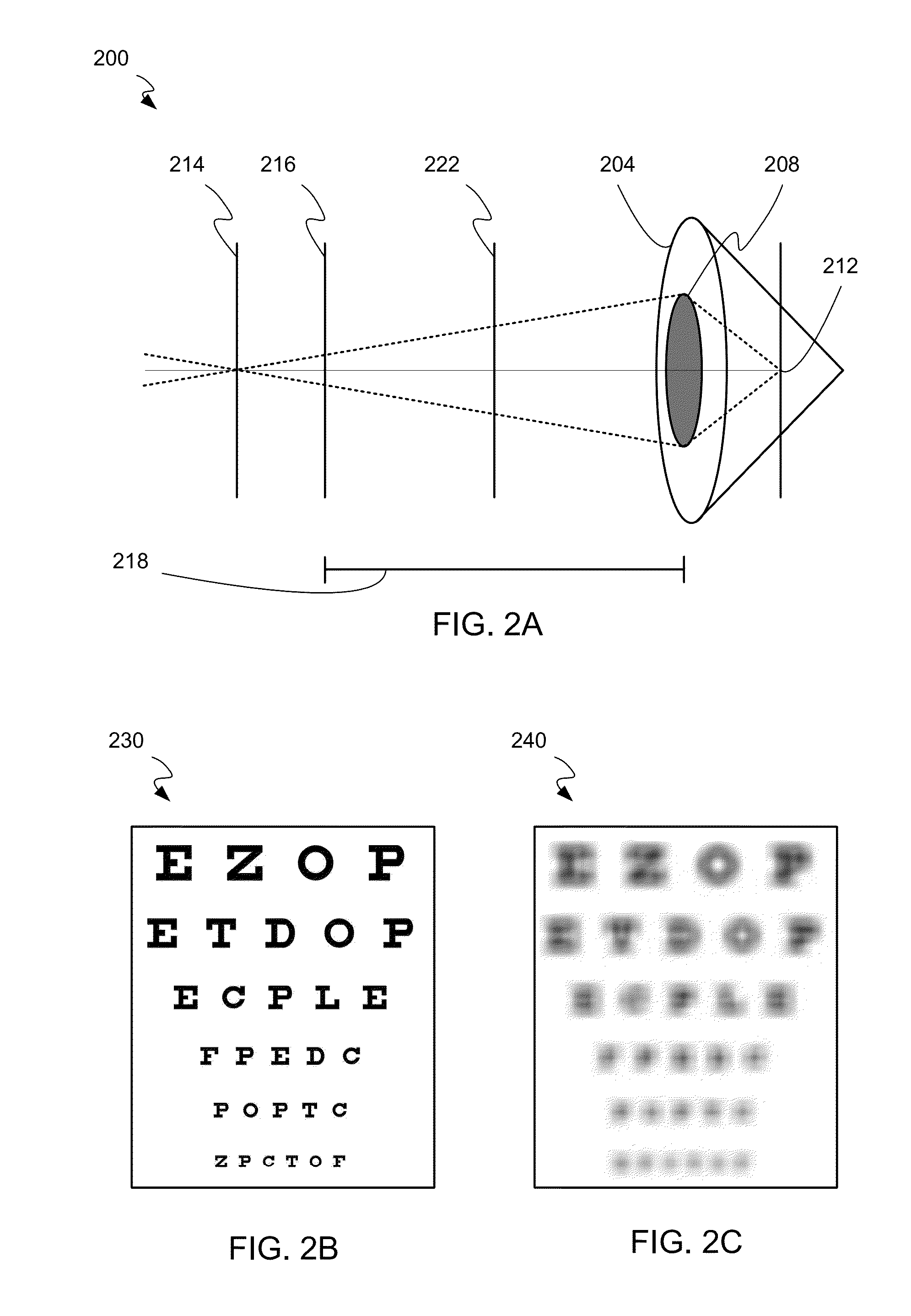
Long wearable soft contact lens
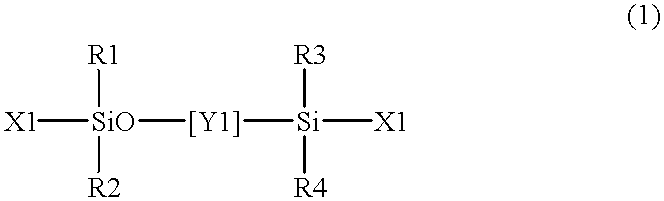
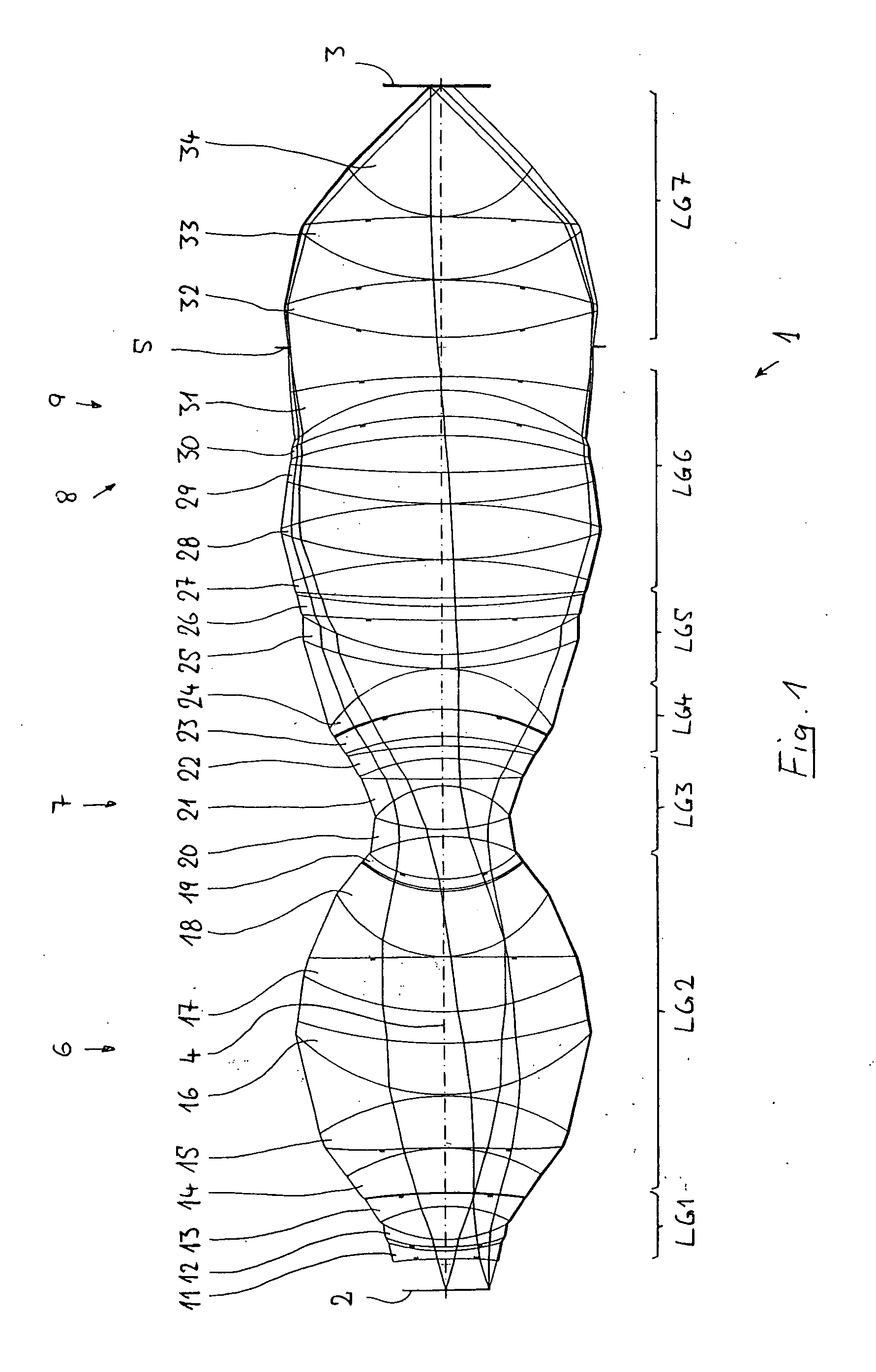
The present invention relates to a soft contact lens, and provides a contact lens which shows small and stable contact angle to water at its surface in water as well as in air, little deposition in wearing, high oxygen permeability, no adhesion of lens to a cornea and superior extended-wearing characteristics. The present invention provides a hydrogel soft contact lens which has contact angle at a lens surface in a range of 10-50° by the captive bubble method in water and 30-90° by the sessile drop method in air, oxygen permeability of not less than 30 and water content of not less than 5%, and also a hydrogel soft contact lens consisting of a polymer comprising a hydrophilic siloxanyl monomer shown by a specified general formula.
Owner:COOPERVISION INT LTD
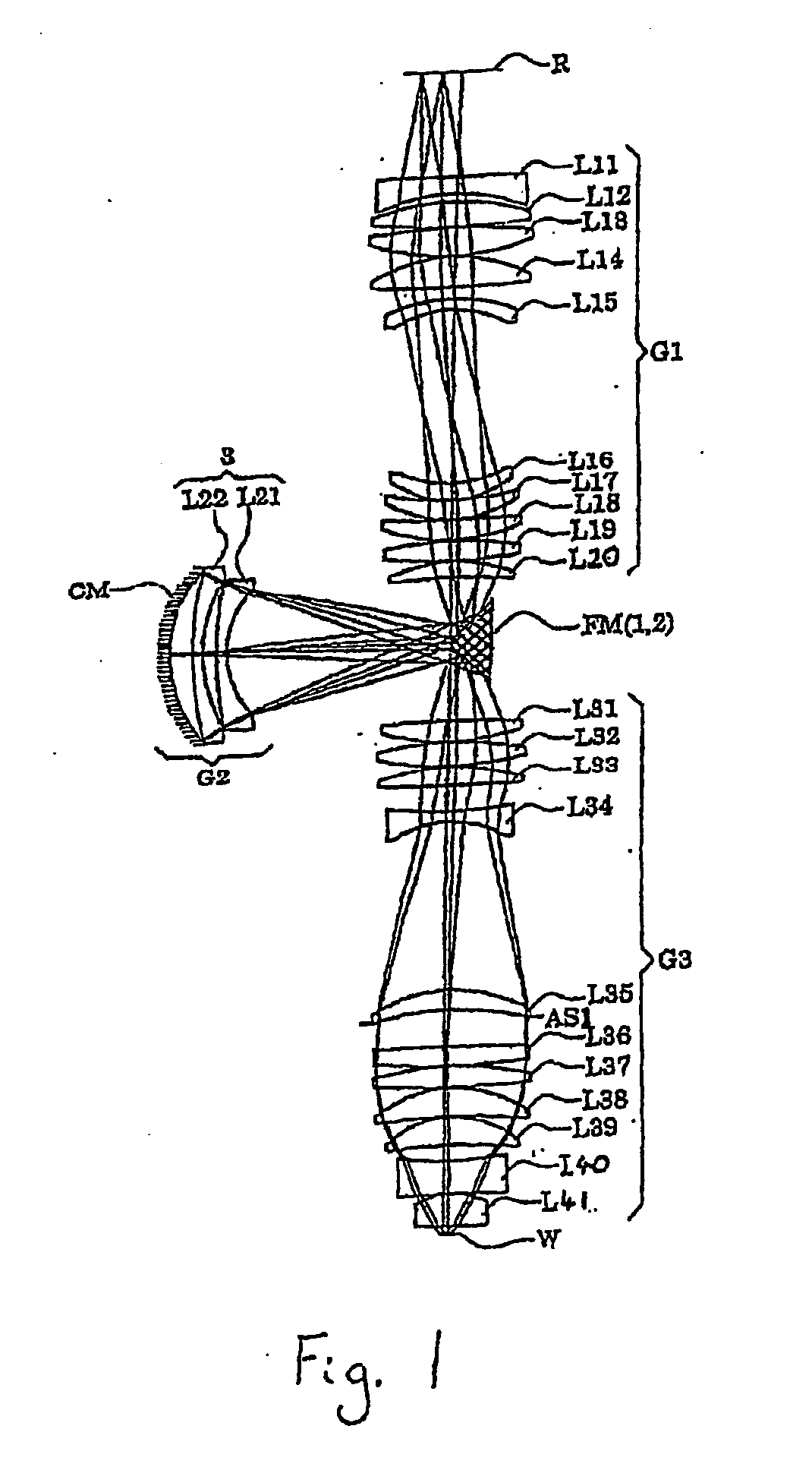
Projection optical system and exposure apparatus having the projection optical system
InactiveUS20030030916A1Avoid stickingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical axisLength wave
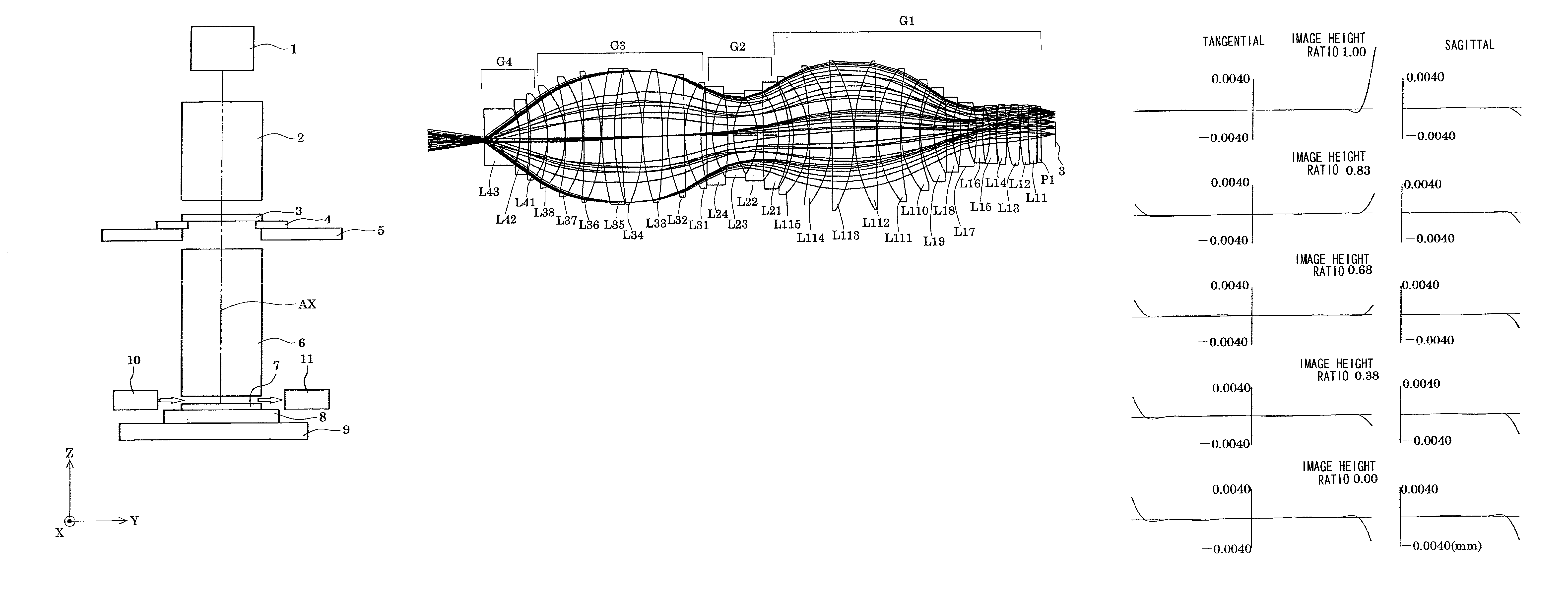
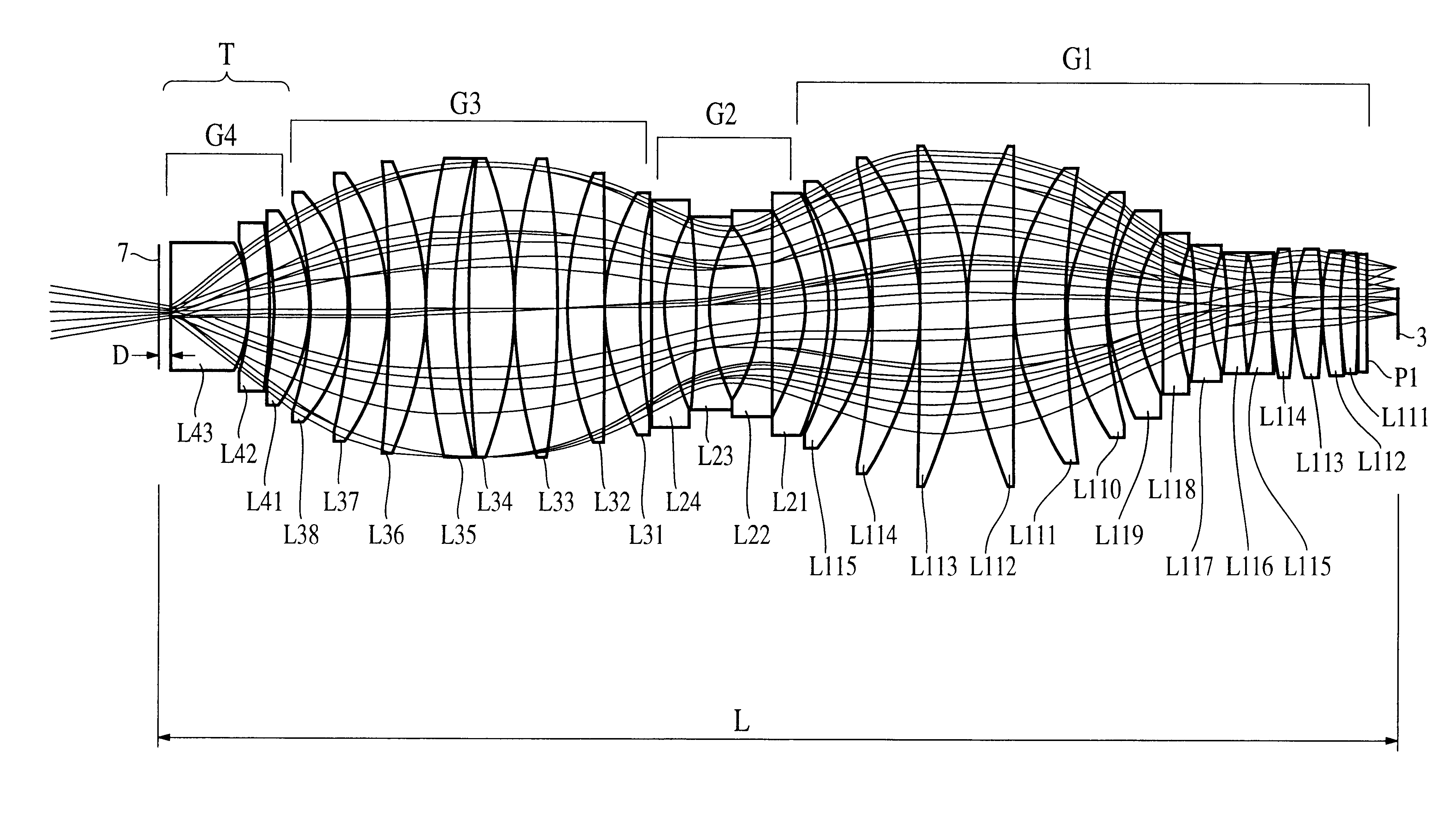
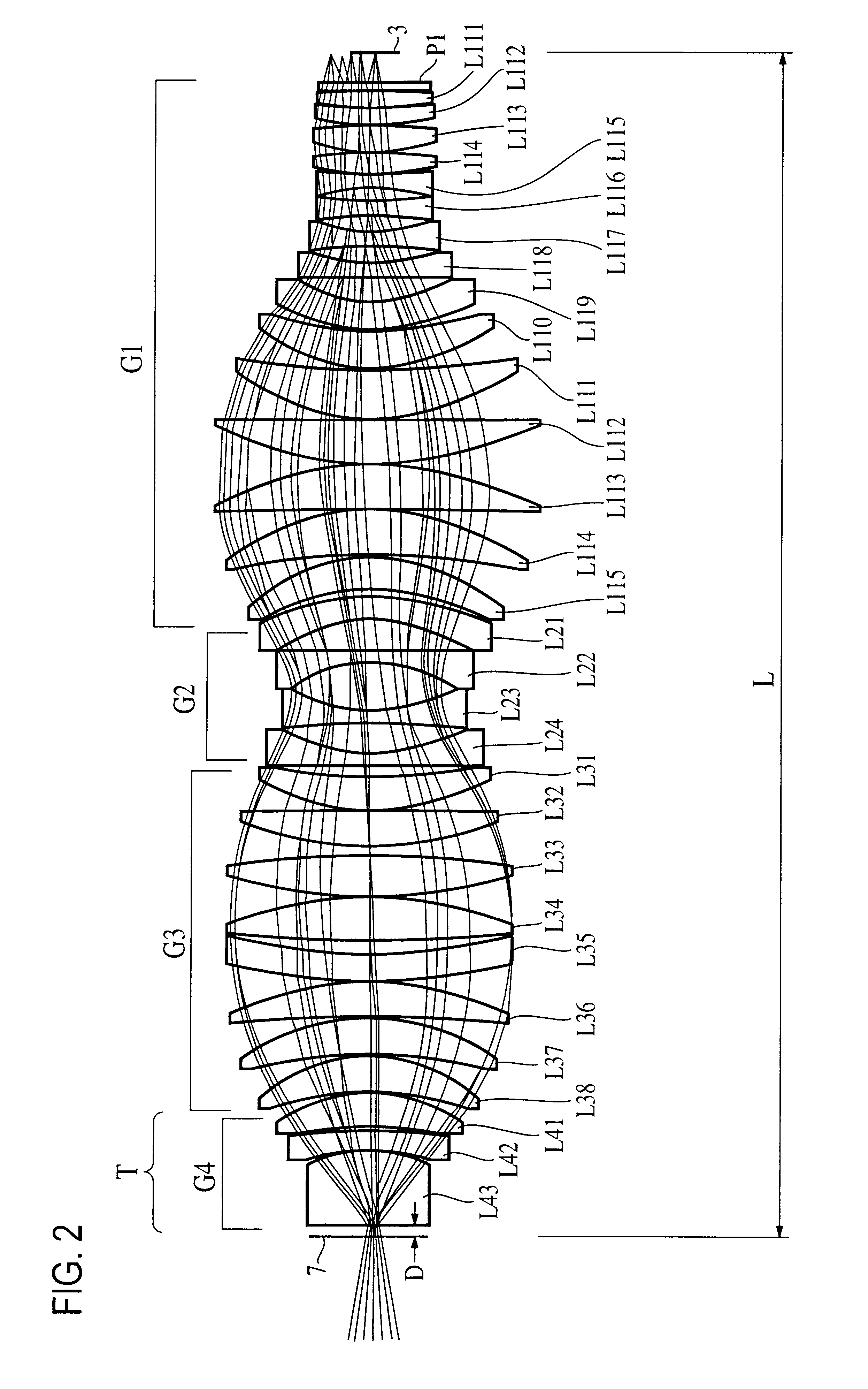
A projection optical system according to the present invention whose image side numerical aperture is greater than or equal to 0.75, and which forms an image of a first object upon a second object using light of a predetermined wavelength less than or equal to 300 nm, comprises: a first lens group G1 of positive refractive power; a second lens group G2 of negative refractive power; a third lens group G3 of positive refractive power; and a fourth lens group G4 of positive refractive power, and: the first lens group G1, the second lens group G2, the third lens group G3 and the fourth lens group G4 are arranged in order from a side of the first object; and a distance D in mm along an optical axis between an optical surface of the fourth lens group G4 closest to the second object, and the second object, satisfies a condition of 0.1<D<5.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Indicia reading terminal including focus element with expanded range of focus distances
ActiveUS8596543B2Television system detailsColor television detailsElectricityPiezoelectric actuators
Embodiments of the present invention comprise an indicia reading terminal including a focus element that extends the range of focus distances at which the indicia reading terminal can decode decodable indicia. In one embodiment, the focus element comprises a variable form element and a variable position element, the combination of which causes an image distance that can change in accordance with a separation distance between these two elements. The focus element can comprise an actuator, e.g., a piezoelectric actuator, which can be coupled to the variable position element in a manner that can cause the variable position element to deform the variable form element, and in one example, the deformation changes the focal length of the variable form element.
Owner:HAND HELD PRODS
Catadioptric projection objective with geometric beam splitting
InactiveUS20050117224A1Good engineering qualityEasy to installMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusIntermediate imageOptical axis
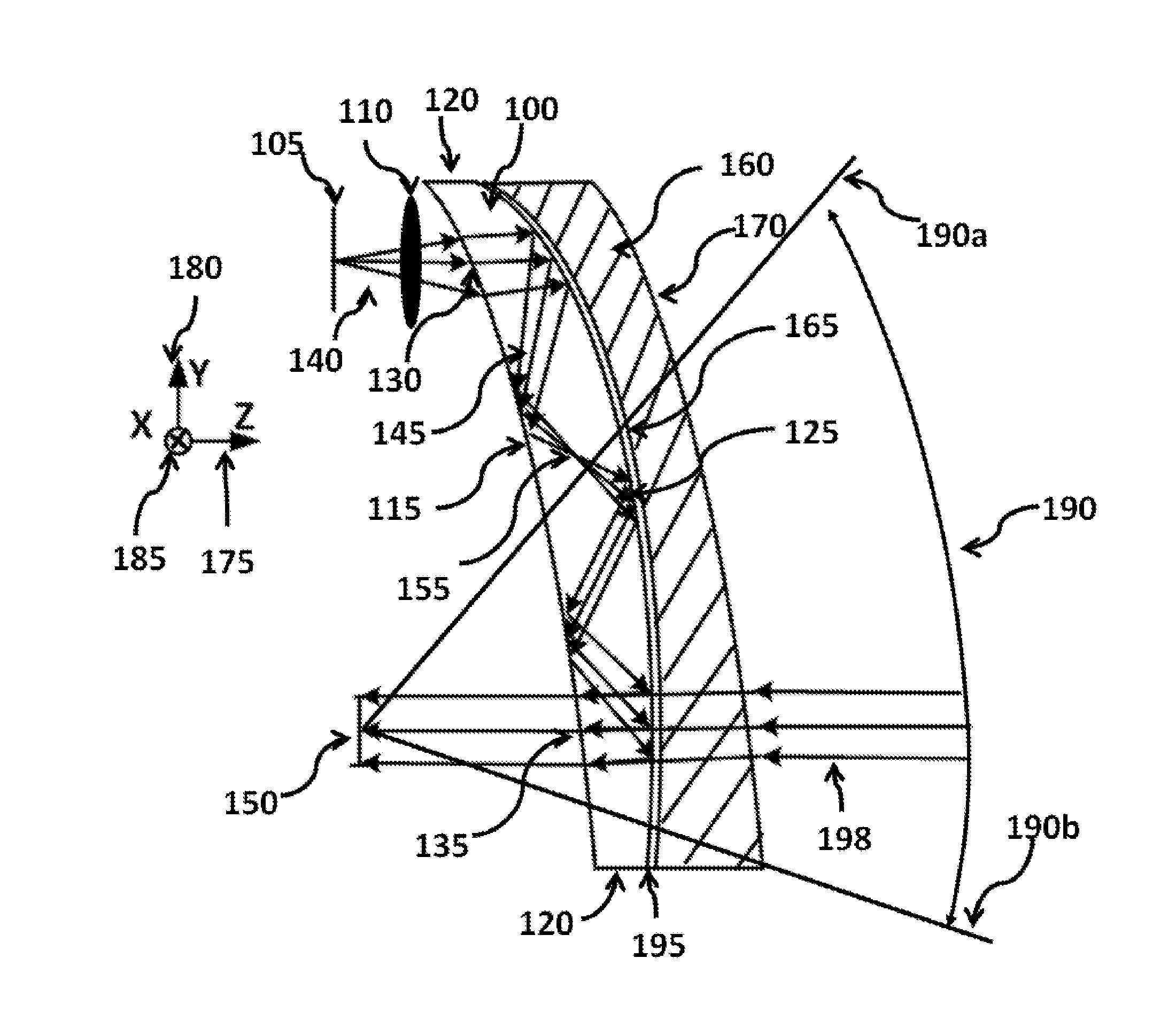
A catadioptric projection objective is used to project a pattern arranged in an object plane of the projection objective into an image plane of the projection objective with the formation of at least one real intermediate image and has an image-side numerical aperture NA>0.7. The projection objective comprises an optical axis and at least one catadioptric objective part that comprises a concave mirror and a first folding mirror. There are a first beam section running from the object plane to the concave mirror and a second beam section running from the concave mirror to the image plane. The first folding mirror is arranged with reference to the concave mirror in such a way that one of the beam sections is folded at the first folding mirror and the other beam section passes the first folding mirror without vignetting, the first beam section and the second beam section crossing one another in a cross-over region.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Contact printing using a magnified mask image
InactiveUS20050068639A1Avoid stickingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusRefractive indexOff-axis illumination
Improvements in the fabrication of integrated circuits are driven by the decrease of the size of the features printed on the wafers. Current lithography techniques limits have been extended through the use of phase-shifting masks, off-axis illumination, and proximity effect correction. More recently, liquid immersion lithography has been proposed as a way to extend even further the limits of optical lithography. This invention described a methodology based on contact printing using a projection lens to define the image of the mask onto the wafer. As the imaging is performed in a solid material, larger refractive indices can be obtained and the resolution of the imaging system can be increased.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Very high-aperture projection objective
InactiveUS20050141098A1Guaranteed true stateIncrease the number ofSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesSpherical shapedOptic system
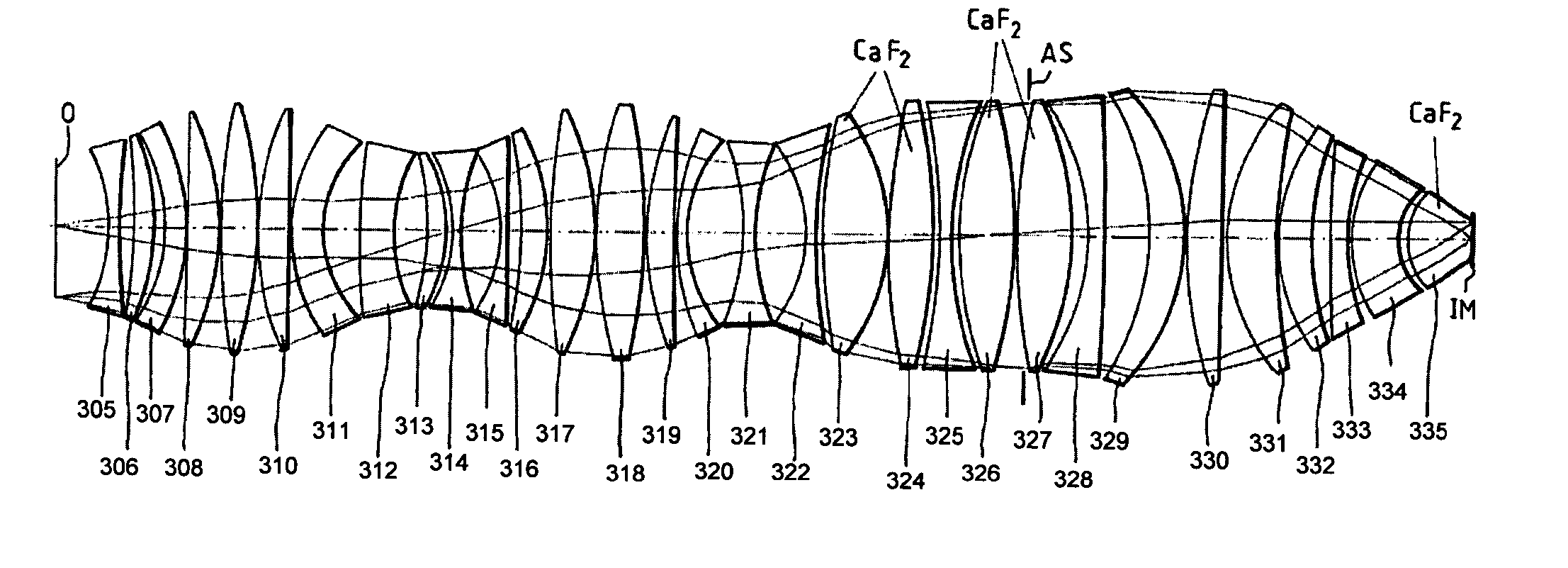
A very high-aperture, purely refractive projection objective having a multiplicity of optical elements has a system diaphragm (5) arranged at a spacing in front of the image plane. The optical element next to the image plane (3) of the projection objective is a planoconvex lens (34) having a substantially spherical entrance surface and a substantially flat exit surface. The planoconvex lens has a diameter that is at least 50% of the diaphragm diameter of the system diaphragm (5). It is preferred to arrange only positive lenses (32, 33, 34) between the system diaphragm (5) and image plane (3). The optical system permits imaging in the case of very high apertures of NA≧0.85, if appropriate of NA≧1.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
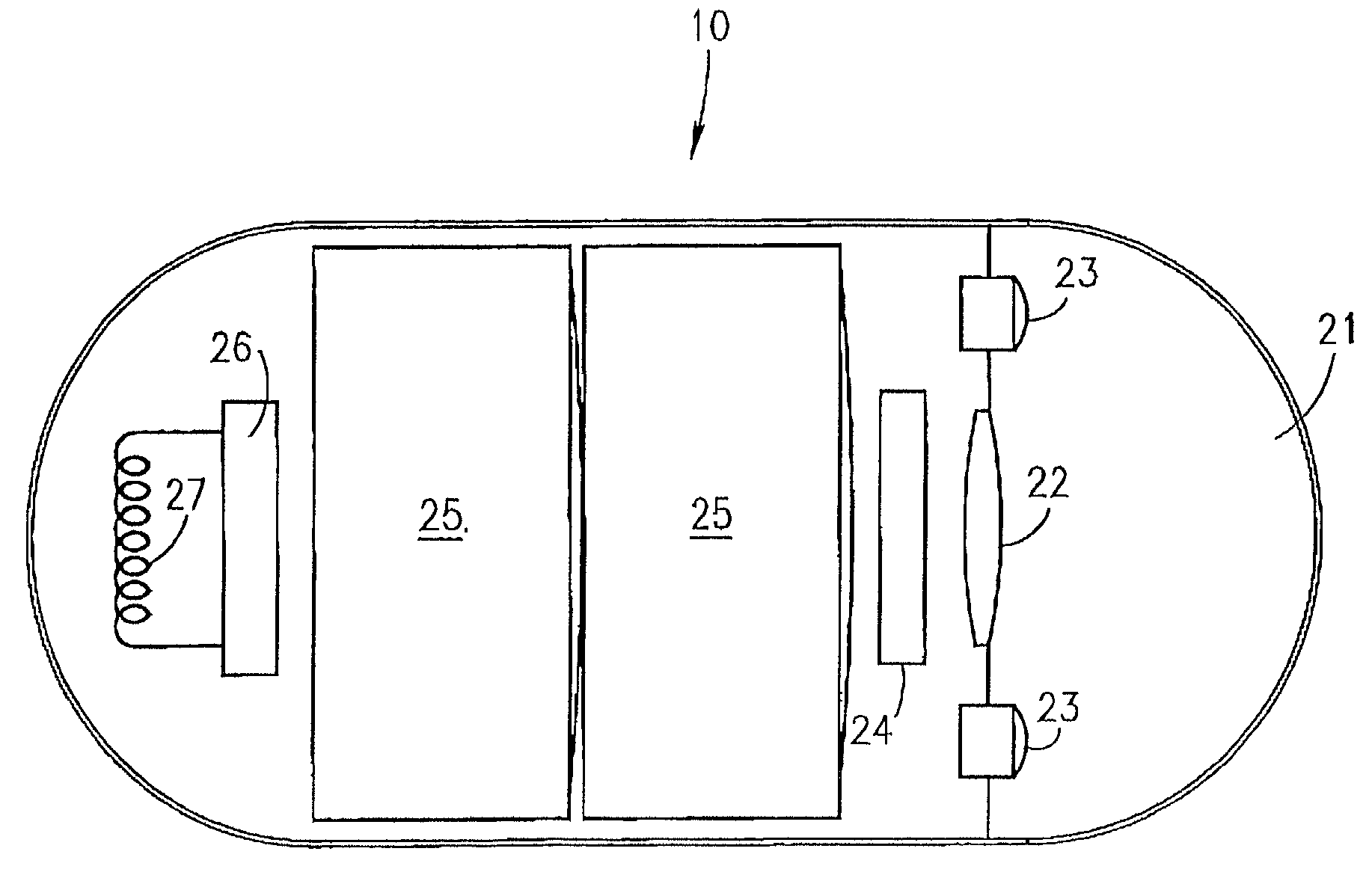
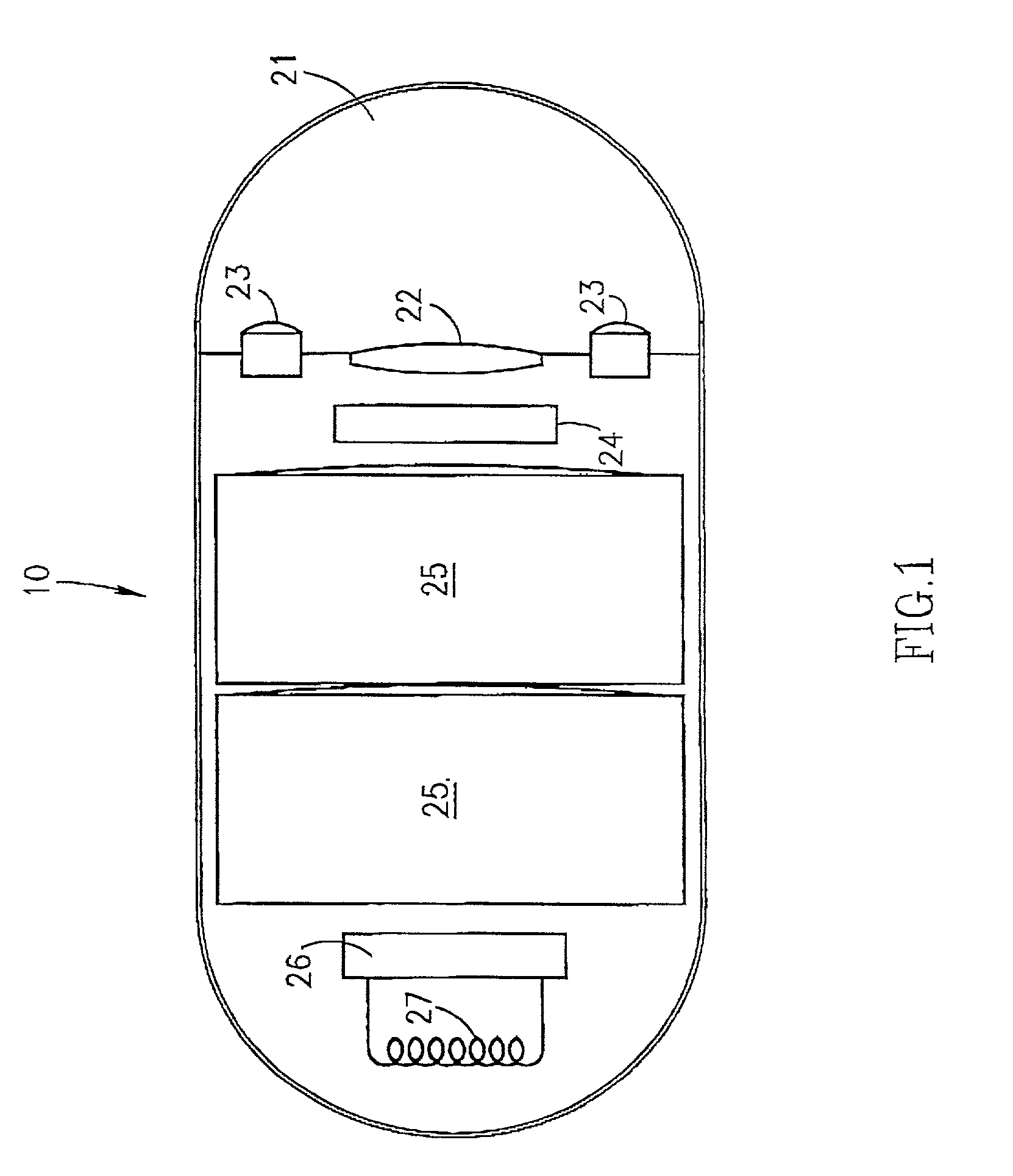
Device for in-vivo imaging
ActiveUS7009634B2Quality improvementTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringIn vivo
The present invention provides a system and method for obtaining in vivo images. The system contains an imaging system and an ultra low power radio frequency transmitter for transmitting signals from the CMOS imaging camera to a receiving system located outside a patient. The imaging system includes at least one CMOS imaging camera, at least one illumination source for illuminating an in vivo site and an optical system for imaging the in vivo site onto the CMOS imaging camera.
Owner:GIVEN IMAGING LTD
Refractive projection objective for immersion lithography
InactiveUS20050190455A1Small sizeGood correction stateMicroscopesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusHigh numerical apertureOptoelectronics
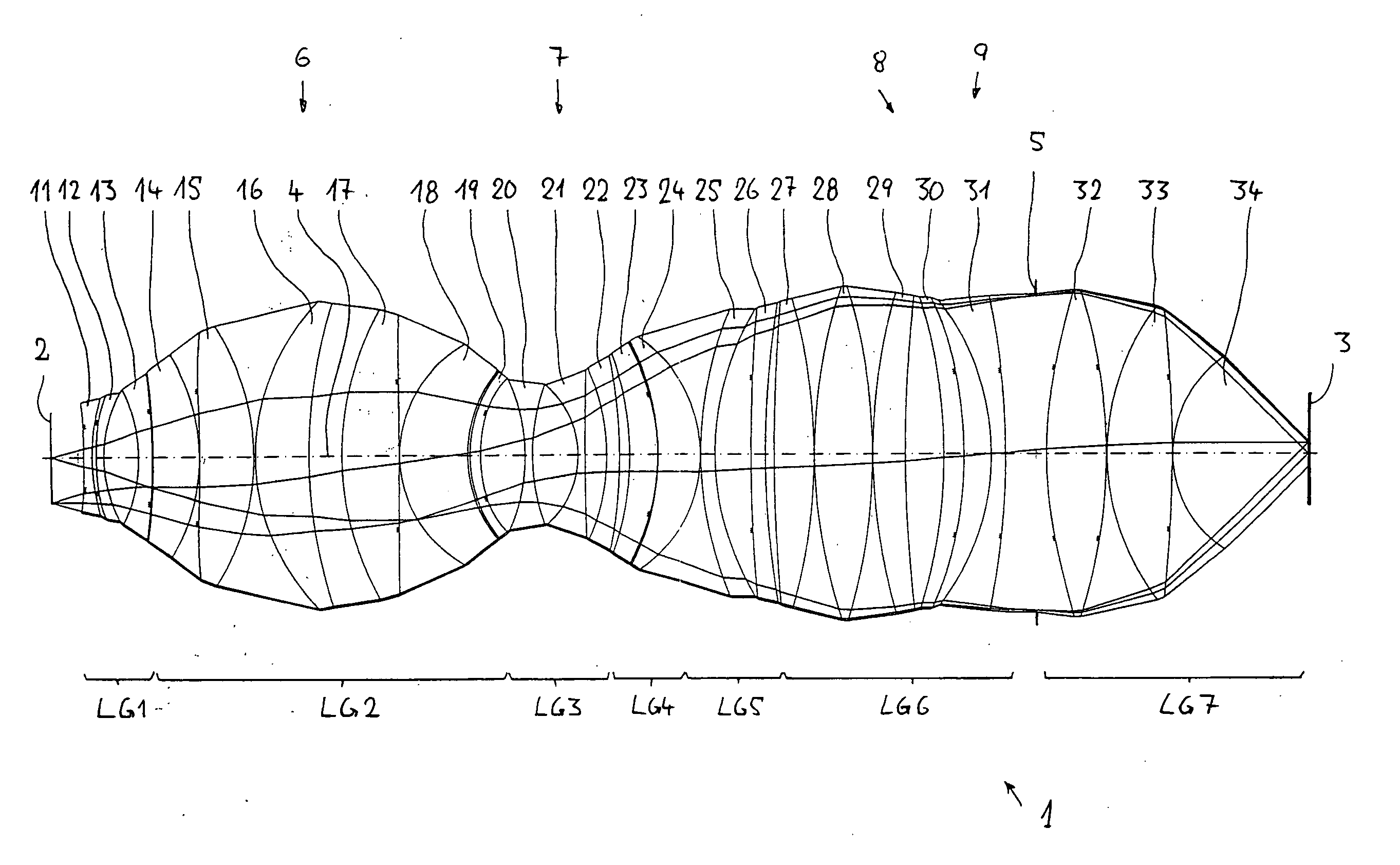
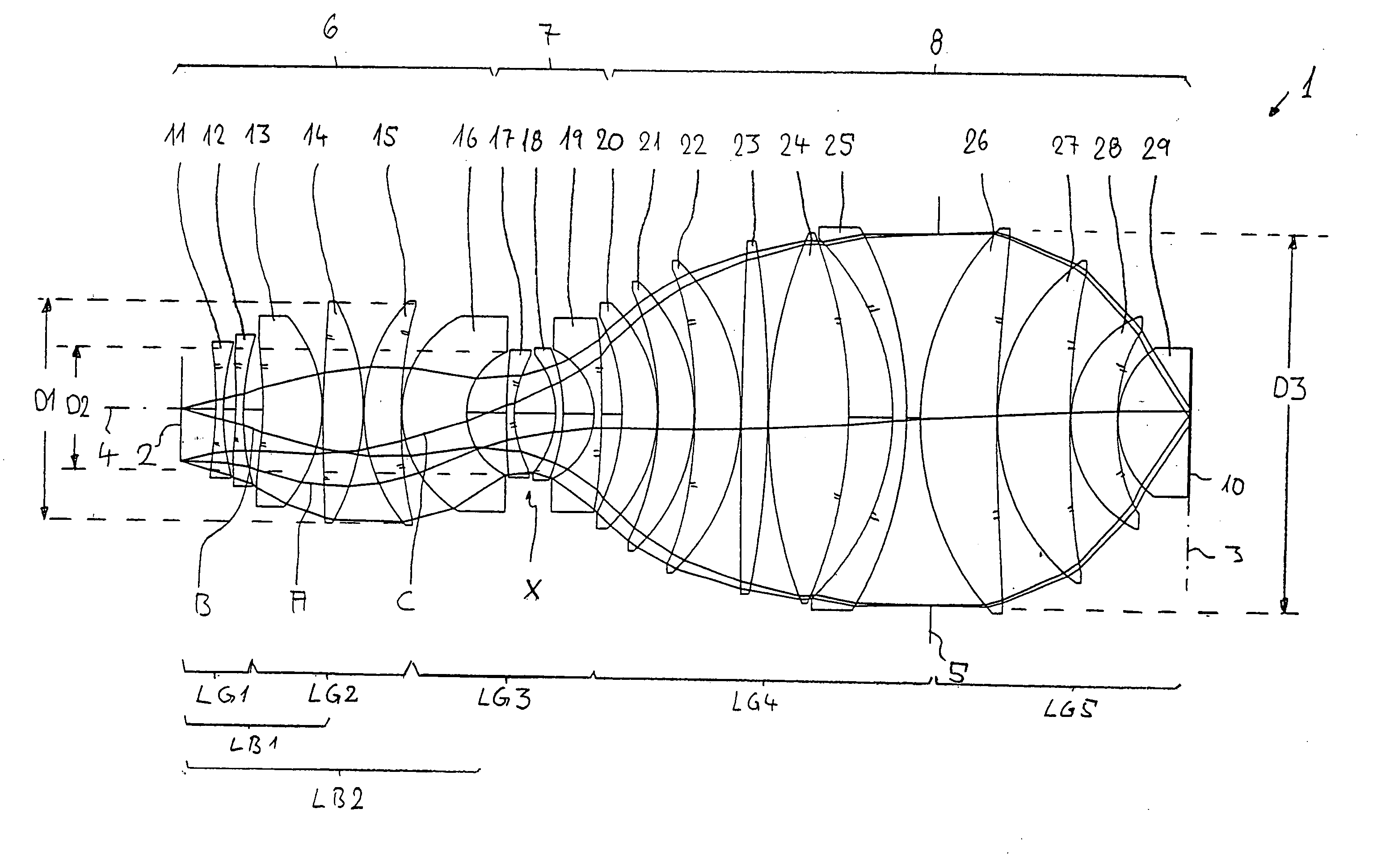
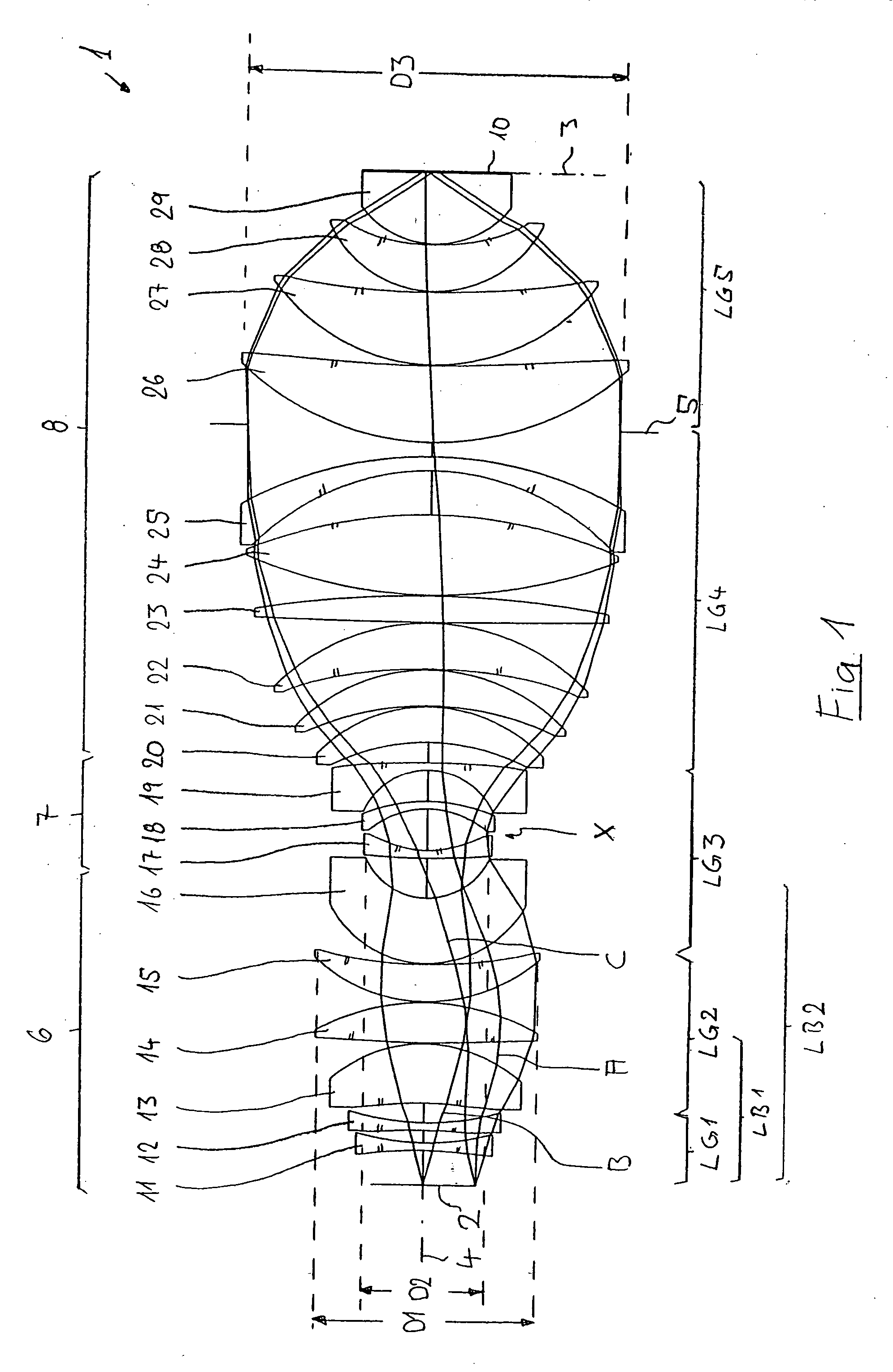
A purely refractive projection objective suitable for immersion microlithography is designed as a single-waist system with five lens groups, in the case of which a first lens group with negative refractive power, a second lens group with positive refractive power, a third lens group with negative refractive power, a fourth lens group with positive refractive power and a fifth lens group with positive refractive power are provided. A constriction site of narrowest constriction of the beam bundle lies in the region of the waist. A waist distance AT exists between the object plane and the constriction site X. The condition AT / L≦0.4 holds for a distance ratio AT / L between the waist distance AT and an object-image distance L of the projection objective. Embodiments of inventive projection objectives reach very high numerical apertures NA>1.1 in conjunction with a large image field and are distinguished by a compact overall size and good correction of the lateral chromatic aberration.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
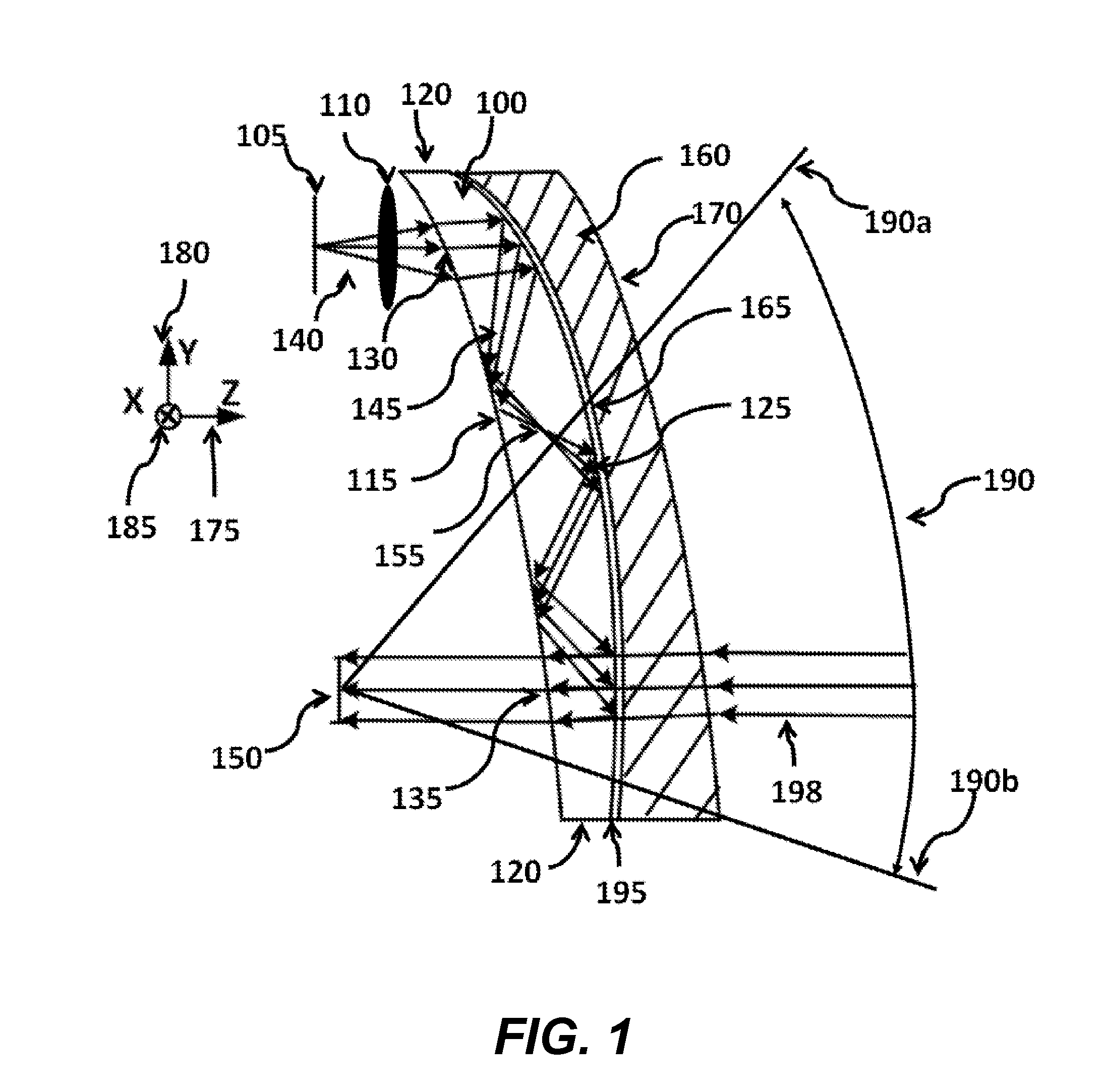
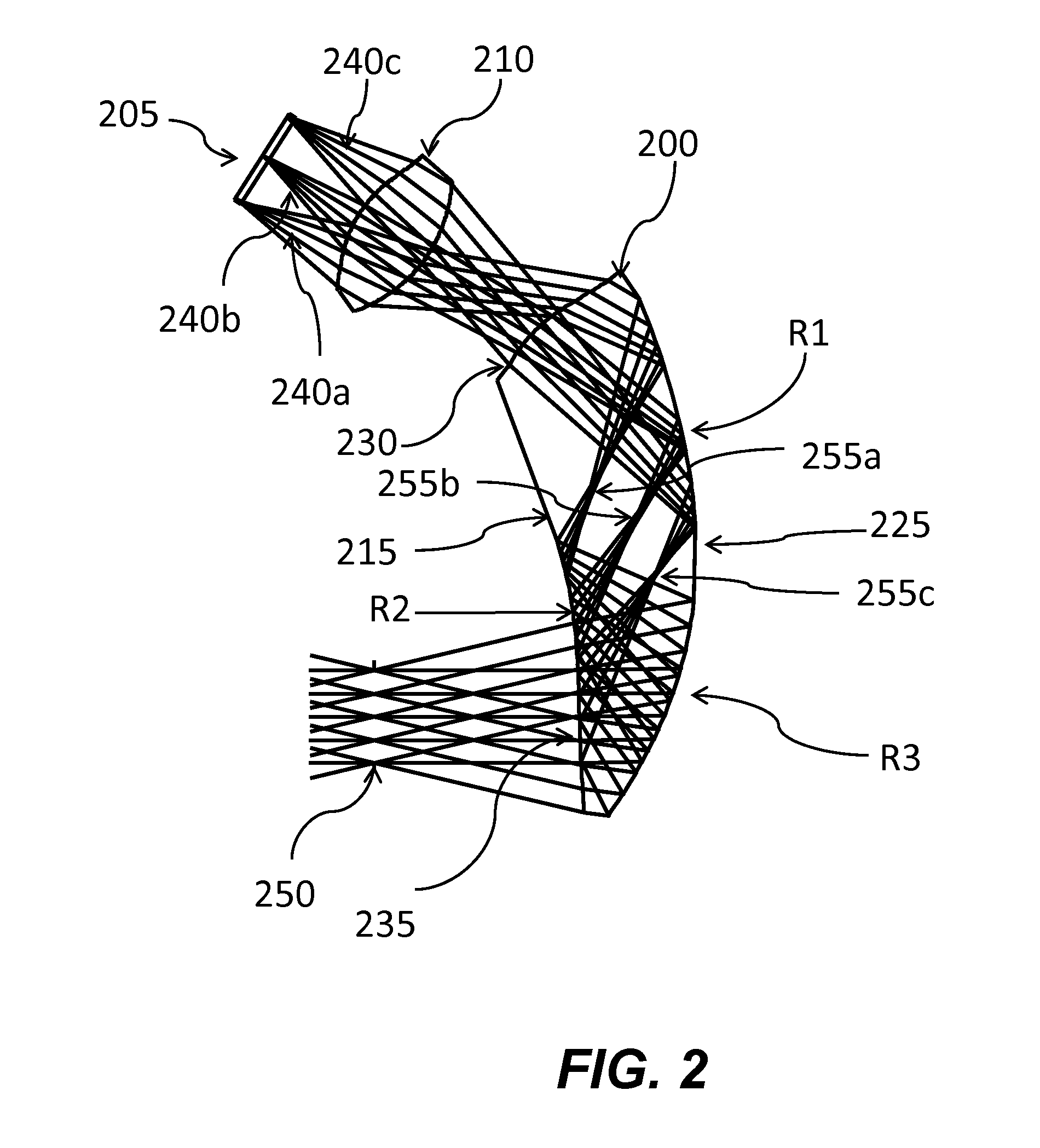
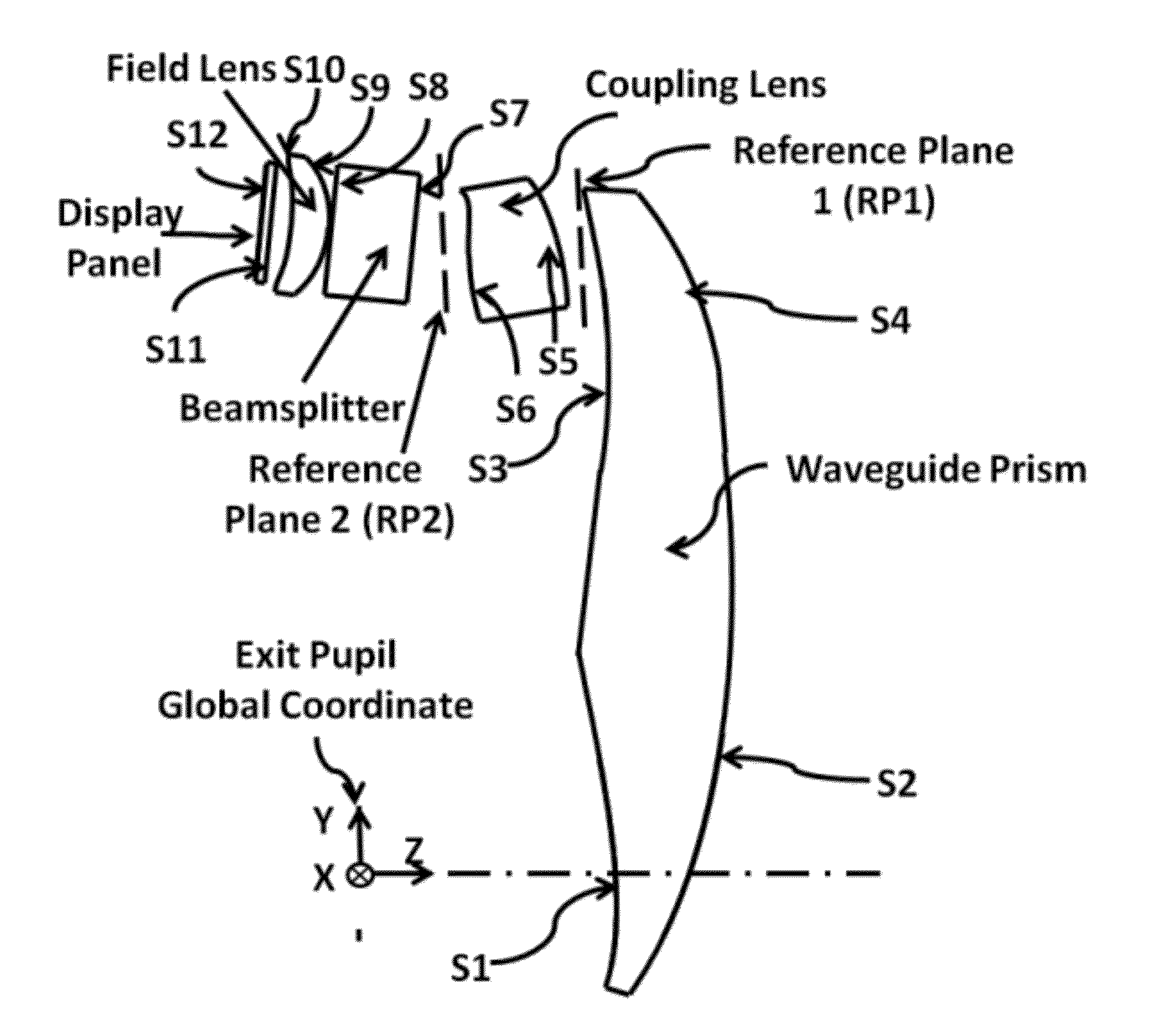
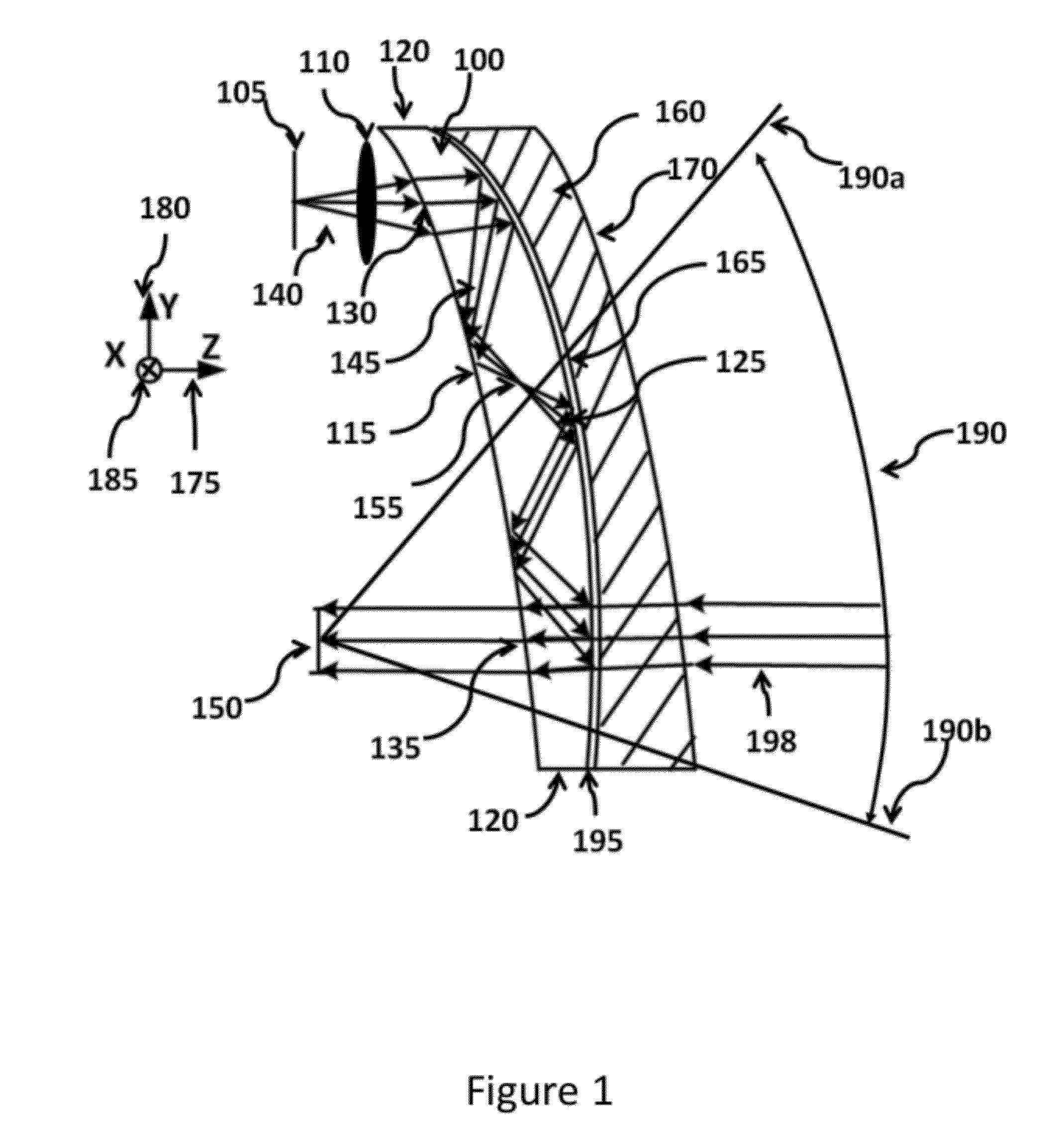
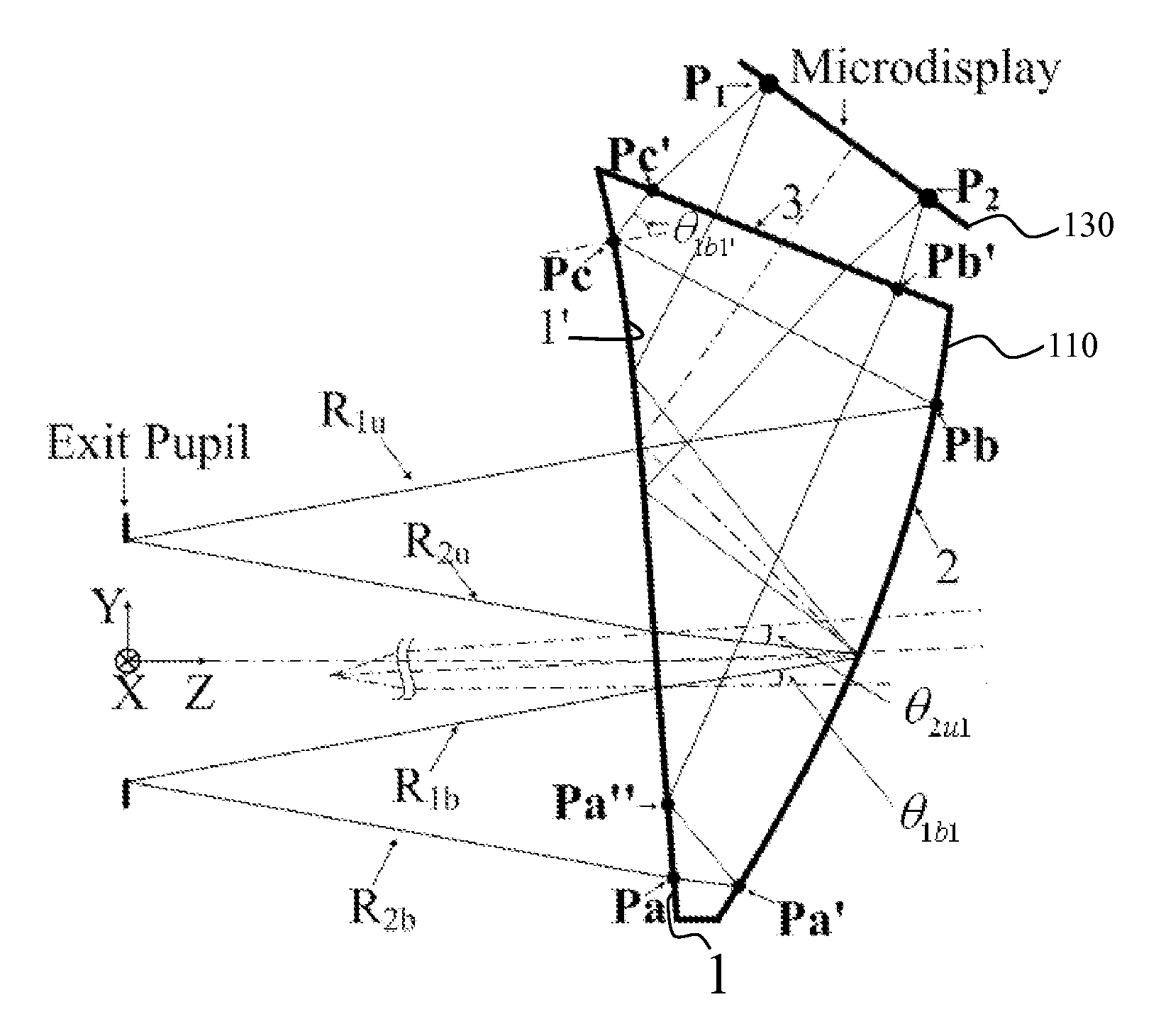
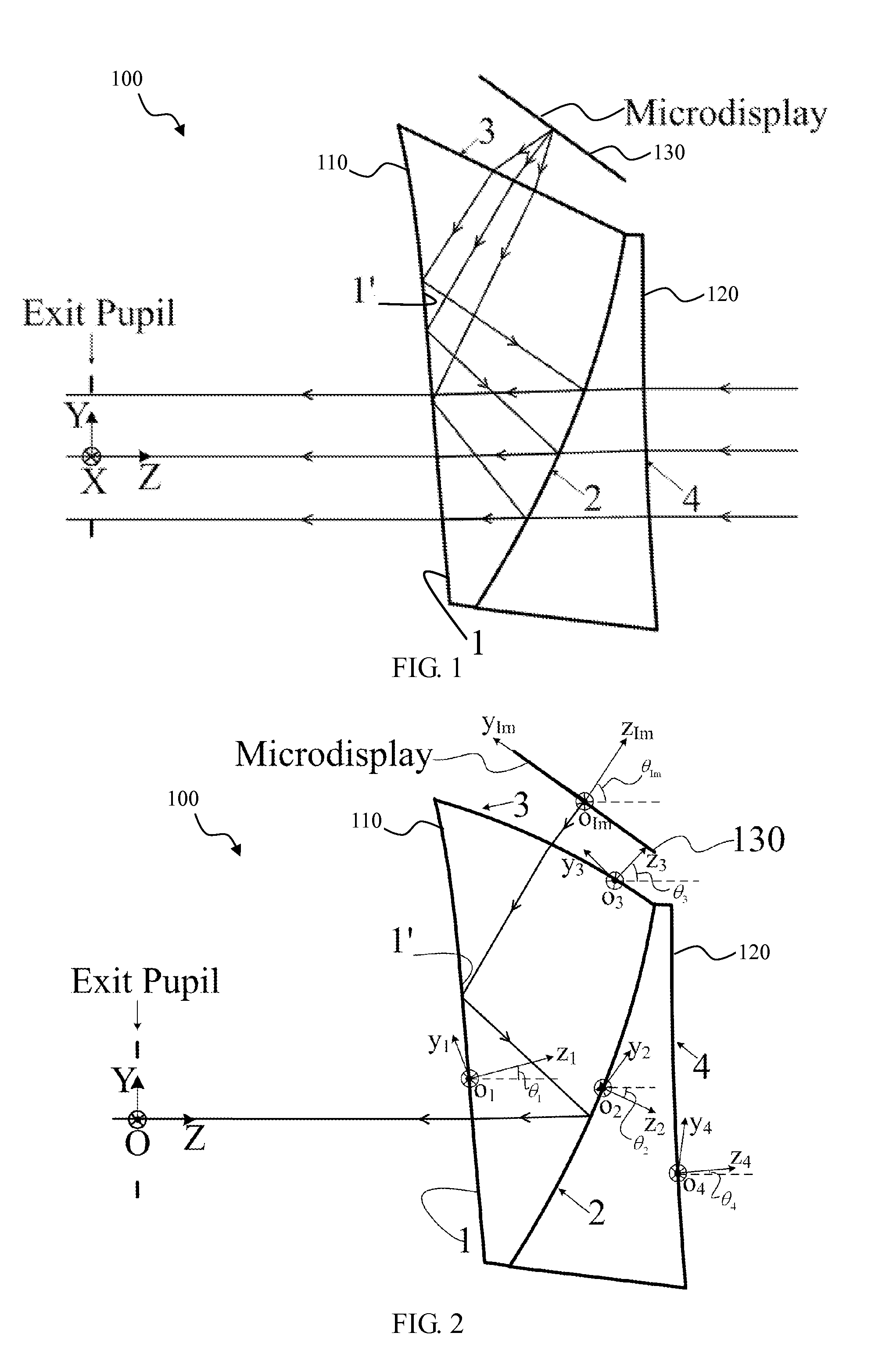
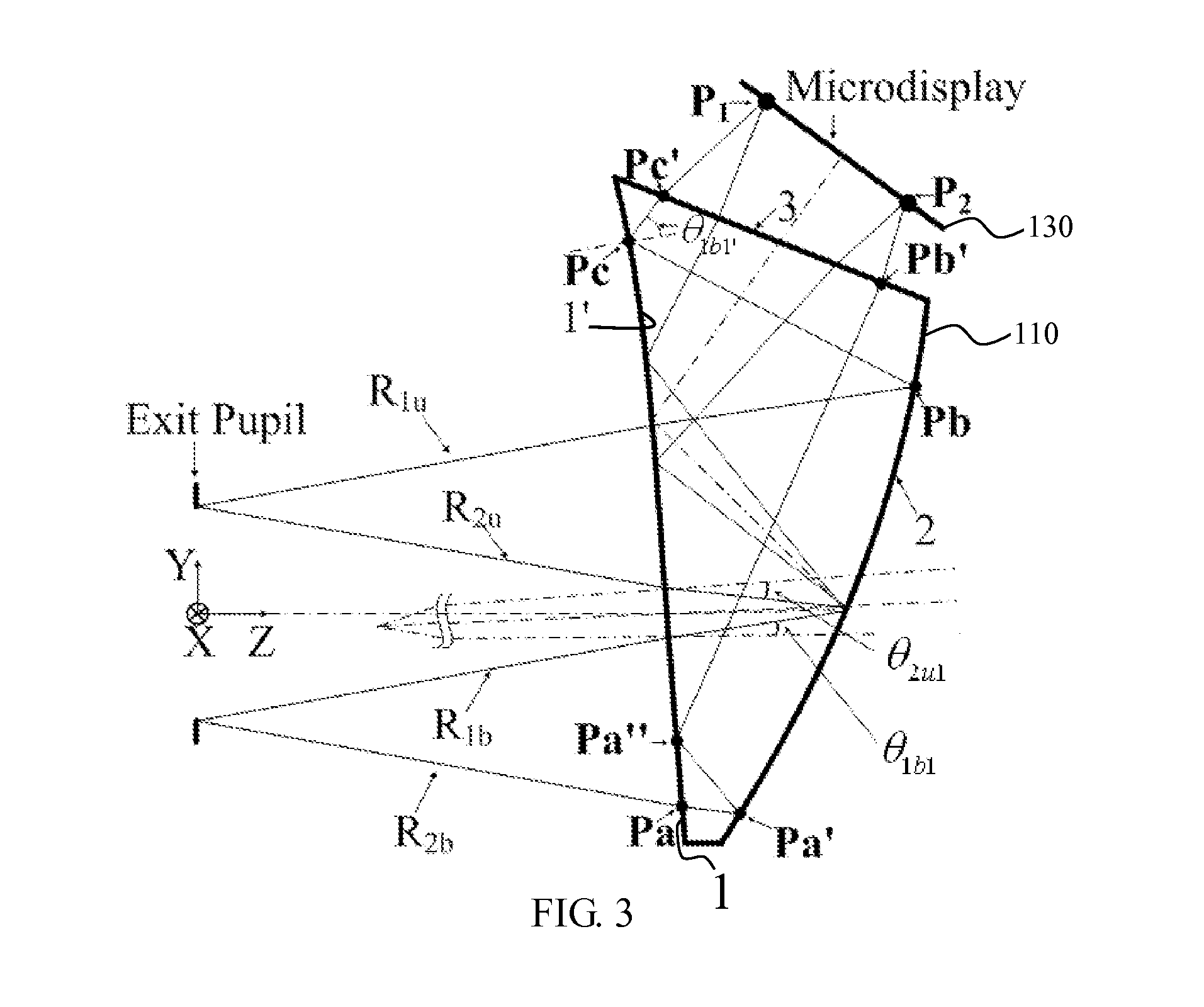
Ergonomic head mounted display device and optical system
Optical systems such as image display systems include a freeform optical waveguide prism and a freeform compensation lens spaced therefrom by a gap of air or index cement. The compensation lens corrects for aberrations which the optical waveguide prism will introduce in light or images from an ambient real-world environment. The optical waveguide prism receives actively projected images at an entry location, and emits the projected images at an exit location after internally reflecting the images along an optical path therein. The image display system may include an image source and coupling optics. The approach permits design of an optical viewing device, for example in optical see-through HMDs, achieving an eyeglass-form appearance and a wide see-through field of view (FOV).
Owner:MAGIC LEAP INC
Ergonomic Head Mounted Display Device And Optical System
ActiveUS20120162549A1Good optical performanceWide field of viewPolarising elementsPlanar/plate-like light guidesDisplay deviceSee-through display
Owner:MAGIC LEAP
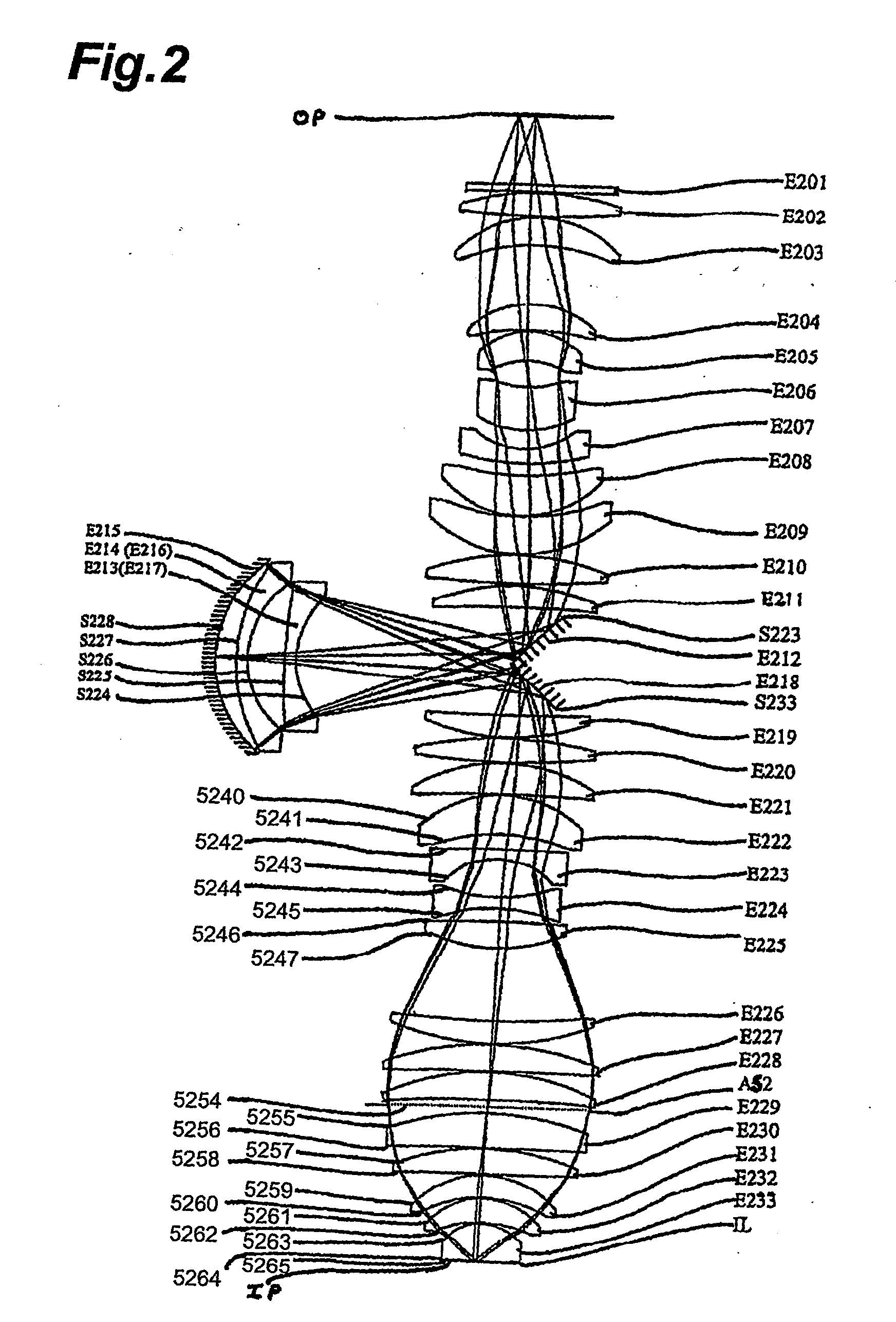
Projection optical system and exposure apparatus having the projection optical system
InactiveUS6633365B2Avoid stickingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusOptical axisLength wave
A projection optical system according to the present invention whose image side numerical aperture is greater than or equal to 0.75, and which forms an image of a first object upon a second object using light of a predetermined wavelength less than or equal to 300 nm, comprises: a first lens group G<HIL><PDAT>1 < / BOLD><PDAT>of positive refractive power; a second lens group G<HIL><PDAT>2 < / BOLD><PDAT>of negative refractive power; a third lens group G<HIL><PDAT>3 < / BOLD><PDAT>of positive refractive power; and a fourth lens group G<HIL><PDAT>4 < / BOLD><PDAT>of positive refractive power, and: the first lens group G<HIL><PDAT>1, < / BOLD><PDAT>the second lens group G<HIL><PDAT>2, < / BOLD><PDAT>the third lens group G<HIL><PDAT>3 < / BOLD><PDAT>and the fourth lens group G<HIL><PDAT>4 < / BOLD><PDAT>are arranged in order from a side of the first object; and a distance D in mm along an optical axis between an optical surface of the fourth lens group G<HIL><PDAT>4 < / BOLD><PDAT>closest to the second object, and the second object, satisfies a condition of 0.1<D<5.
Owner:NIKON CORP
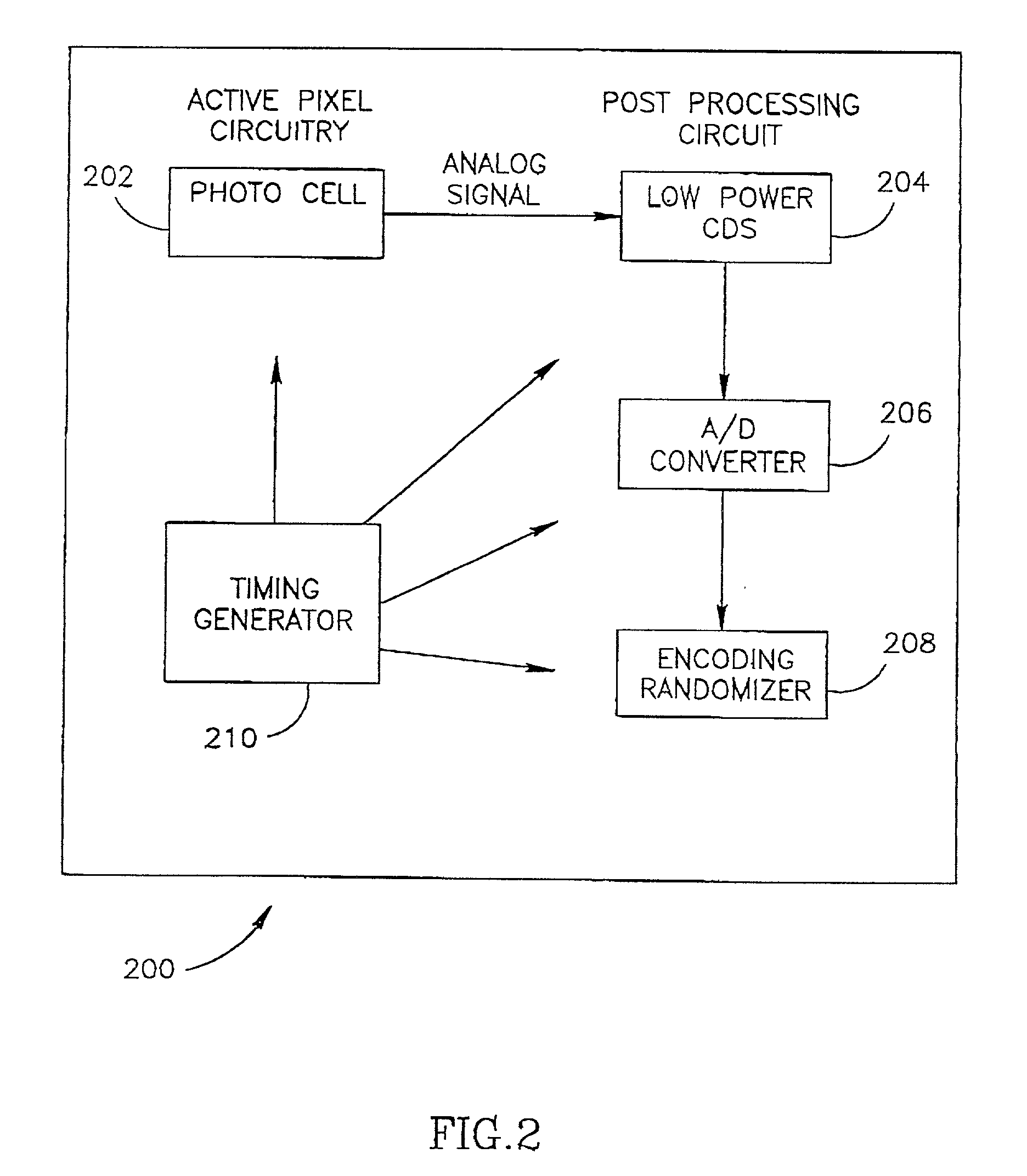
Apparatus for multiple camera devices and method of operating same
InactiveUS20060054782A1Additional imaging capabilityHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhotovoltaic detectorsSignal processing circuits
There are many, many inventions described herein. In one aspect, what is disclosed is a digital camera including a plurality of arrays of photo detectors, including a first array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a first wavelength and a second array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a second wavelength. The digital camera further may also include a first lens disposed in an optical path of the first array of photo detectors, wherein the first lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the first wavelength, and a second lens disposed in with an optical path of the second array of photo detectors wherein the second lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the second wavelength. In addition, the digital camera may include signal processing circuitry, coupled to the first and second arrays of photo detectors, to generate a composite image using (i) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the first array of photo detectors, and (ii) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the second array of photo detectors; wherein the first array of photo detectors, the second array of photo detectors, and the signal processing circuitry are integrated on or in the same semiconductor substrate.
Owner:NEWPORT IMAGING CORP
Apparatus for multiple camera devices and method of operating same
ActiveUS7199348B2High resolutionExcellent color renditionTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsElectrical conductorPhotovoltaic detectors
There are many, many inventions described herein. In one aspect, what is disclosed is a digital camera including a plurality of arrays of photo detectors, including a first array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a first wavelength and a second array of photo detectors to sample an intensity of light of a second wavelength. The digital camera further may also include a first lens disposed in an optical path of the first array of photo detectors, wherein the first lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the first wavelength, and a second lens disposed in with an optical path of the second array of photo detectors wherein the second lens includes a predetermined optical response to the light of the second wavelength. In addition, the digital camera may include signal processing circuitry, coupled to the first and second arrays of photo detectors, to generate a composite image using (i) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the first array of photo detectors, and (ii) data which is representative of the intensity of light sampled by the second array of photo detectors; wherein the first array of photo detectors, the second array of photo detectors, and the signal processing circuitry are integrated on or in the same semiconductor substrate.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
Light collection and illumination systems employing planar waveguide
ActiveUS20100278480A1Easy to transportEasy to harvestProjectorsCoupling light guidesTotal internal reflectionLighting system
An apparatus for distributing light from a waveguide through a collimating array, or collecting light over a given area into a waveguide. Light received within a waveguide is propagated transmissively and retained by total internal reflection, except in response to impinging upon deflector elements which sufficiently redirect the light to escape the waveguide into a collimator array that aligns and distributes the light. In a light collector, a collection array collects and collimates the received light and directs it at the surface of a waveguide, within which deflectors properly positioned in relation to each collector of the collector array, deflect the angle of the light so that it propagates through the waveguide in response to total internal reflection. The apparatus can be fabricated into an efficient and compact form.
Owner:S V V TECH INNOVATIONS
Four-piece lens assembly
A four-piece lens assembly, from the object side, comprises: an aperture, a first lens, a second lens, a third lens, a fourth lens, a flat parallel glass and an image plane. The first lens is a double convex positive lens. The second lens is a double concave negative lens or a plano-concave lens whose object side surface contacts the image side surface of the first lens. The first and second lenses contact each other in such a manner that the concave surface of the connecting surface faces the object side, and the concave surface (or plano surface) of the second lens faces the image plane. The first and second lenses are made of high refractive index material. The lens assembly not only can ensure a necessary back focus but also can suppress the total length of a portable image taking device.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Led array systems
A light emitting diode (LED) array comprises an array of LEDs mounted to a substrate. The LEDs emit light in a direction generally perpendicular to the substrate. An optical sheet is disposed over the LEDs. At least a portion of light entering one side of the optical sheet from the LEDs is guided within the optical sheet in a direction generally parallel to the substrate. Light extraction features direct light from the optical sheet in a generally forward direction. Such an array is useful for several applications, including space lighting, direct information display and backlighting of liquid crystal displays. The light spreading effect of the optical sheet reduces the amount of black space between LED pixels.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Projection optical system and method for photolithography and exposure apparatus and method using same
InactiveUS20050248856A1Large image-sideWide effective image forming areaSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesWide fieldProjection system
Optical Projection System and Method for Photolithography. A lithographic immersion projection system and method for projecting an image at high resolution over a wide field of view. The projection system and method include a final lens which decreases the marginal ray angle of the optical path before light passes into the immersion liquid to impinge on the image plane.
Owner:NIKON CORP
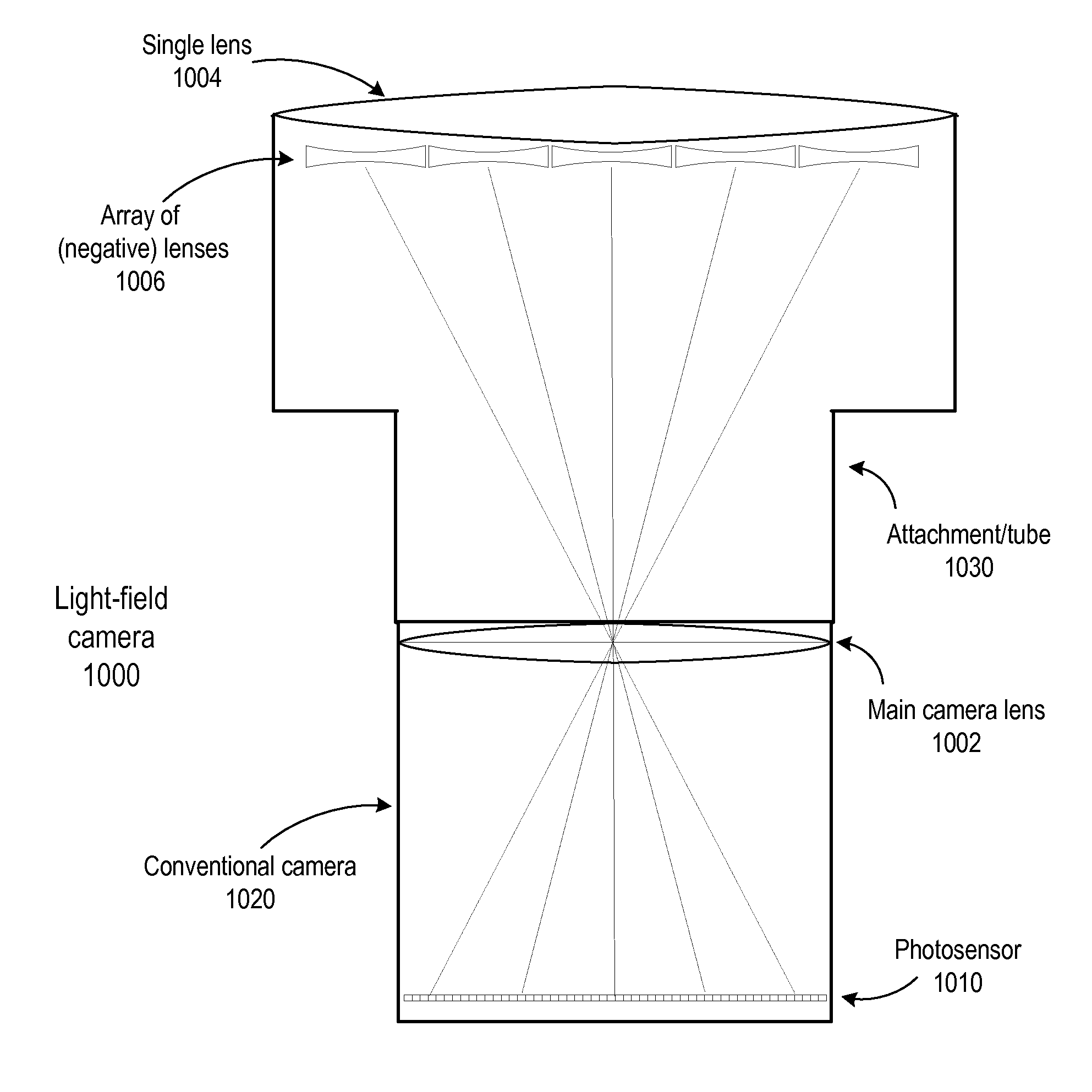
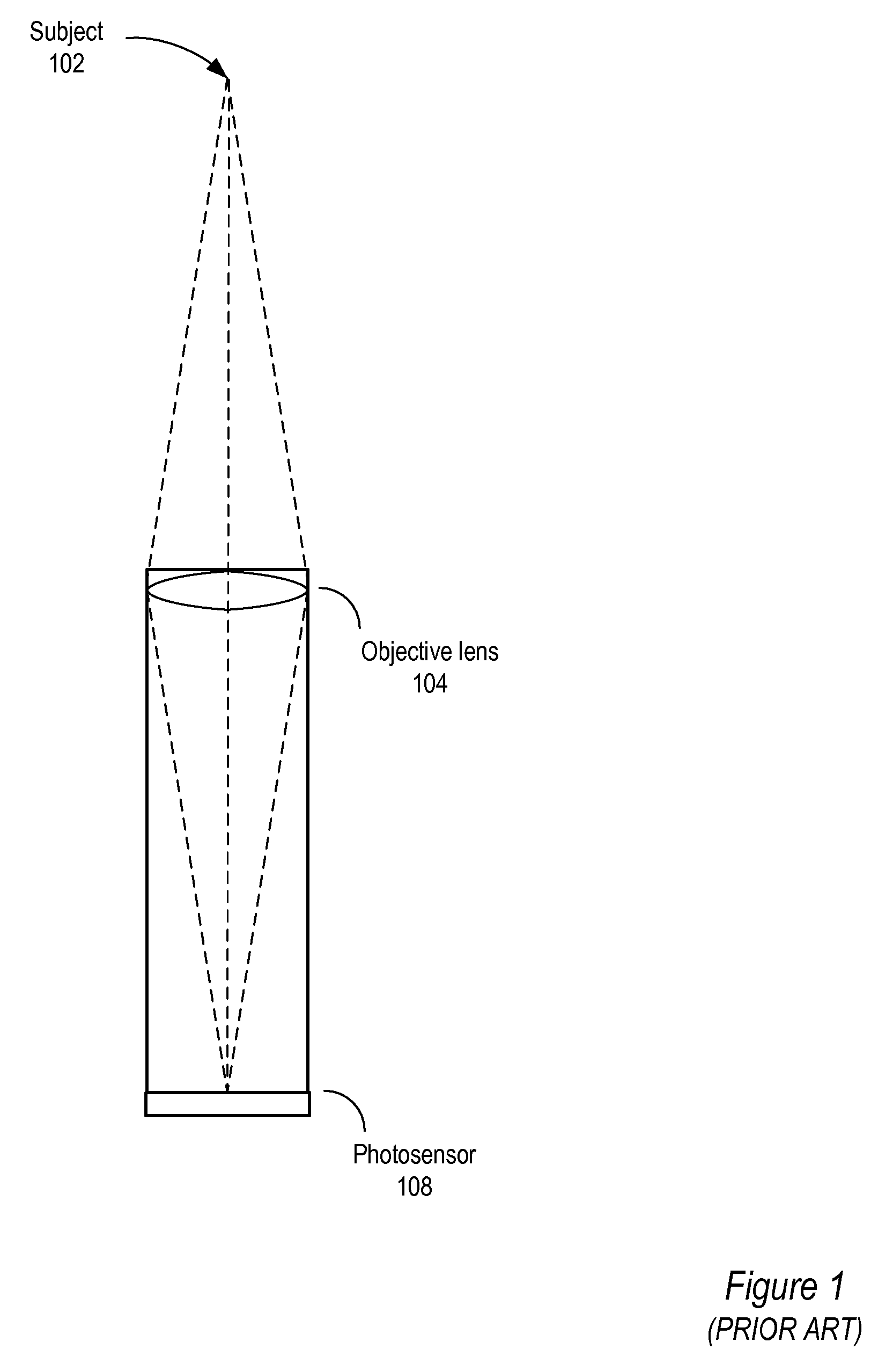
Methods and apparatus for light-field imaging
ActiveUS8290358B1Minimal loss in qualityImprove spatial resolutionStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsCamera lensHand held
Methods and apparatus for light-field imaging. Light-field camera designs are described that produce higher spatial resolution than conventional plenoptic camera designs, while trading-off the light-field's angular sampling density. This lower angular resolution may be compensated for by a light-field image processing method that inserts data synthesized by view interpolation of the measured light-field. In one embodiment, a light-field image processing method that performs three-view morphing may be used to interpolate the missing angular samples of radiance. The light-field camera designs may be implemented in hand-held light-field cameras that may capture a light-field with a single exposure. Some of the light-field camera designs are internal to the camera, while others are external to the camera. One light-field camera design includes a single, relatively large lens and an array of negative lenses that are placed in front of (external to) the main lens of a conventional camera.
Owner:ADOBE SYST INC
Resin composition for production of optical element, the optical element, and projection screen
InactiveUS6650471B2Increase crosslink densityHigh refractive indexProjectorsOptical articlesTemperature curveProjection screen
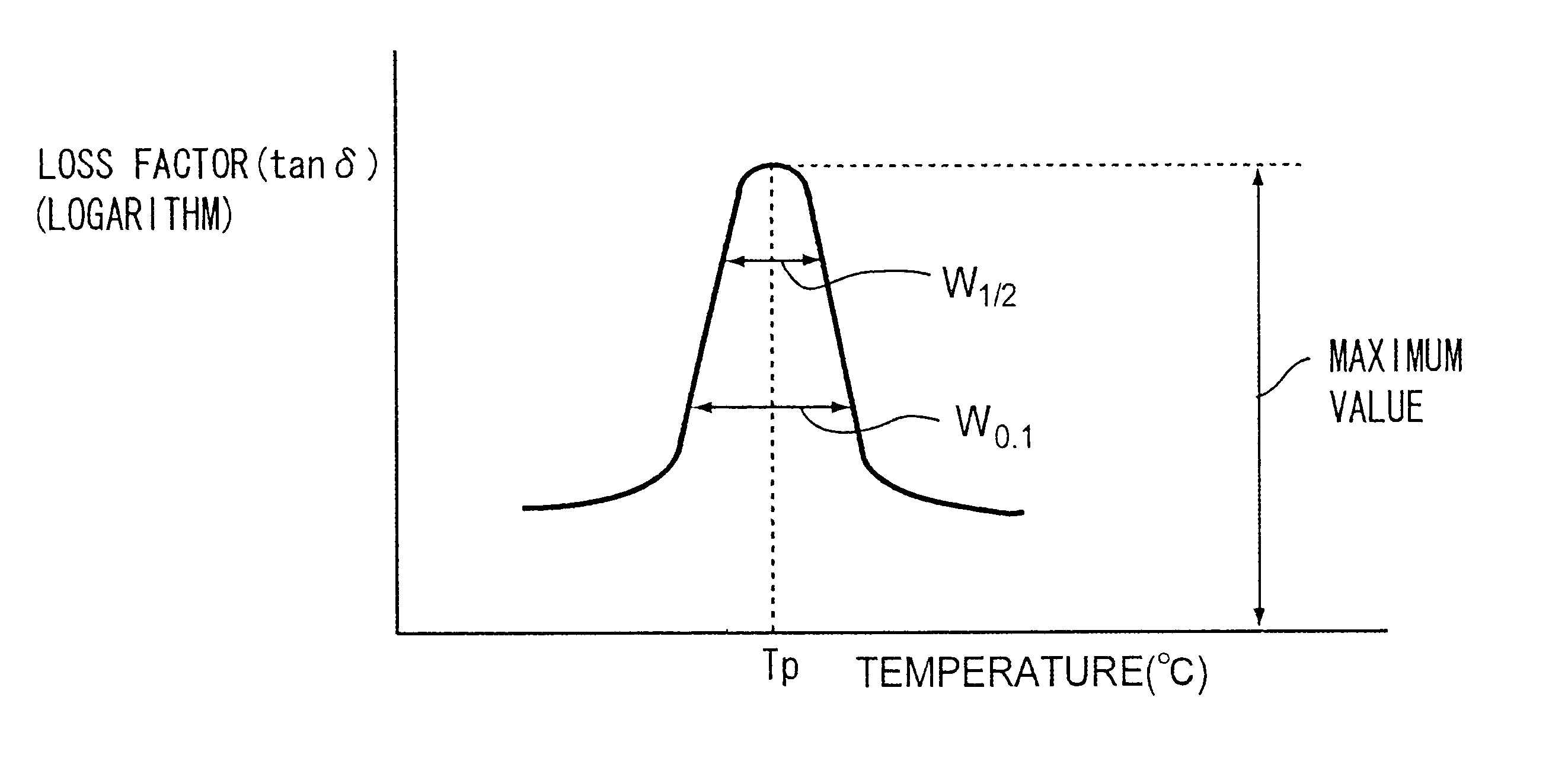
A resin composition for production of an optical element being adapted to form the optical element has a characteristics of which, when W1 / 2 (° C.) represents, regarding a crest portion in a loss factor / temperature curve obtained by measuring the loss factor of the resin composition relative to a change in the temperature, the width of the crest portion at the position of ½ of the maximum value of the loss factor in the crest portion temperature range; W0.1 (° C.) represents, regarding the crest portion, the width of the crest portion at the position of 0.1 of the maximum value of the loss factor; and DeltaW (° C.), the difference between the widths of the two crest portions, is set to be DeltaW=W0.1-W1 / 2, the DeltaW is in the range of from 16° C. to 31° C.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
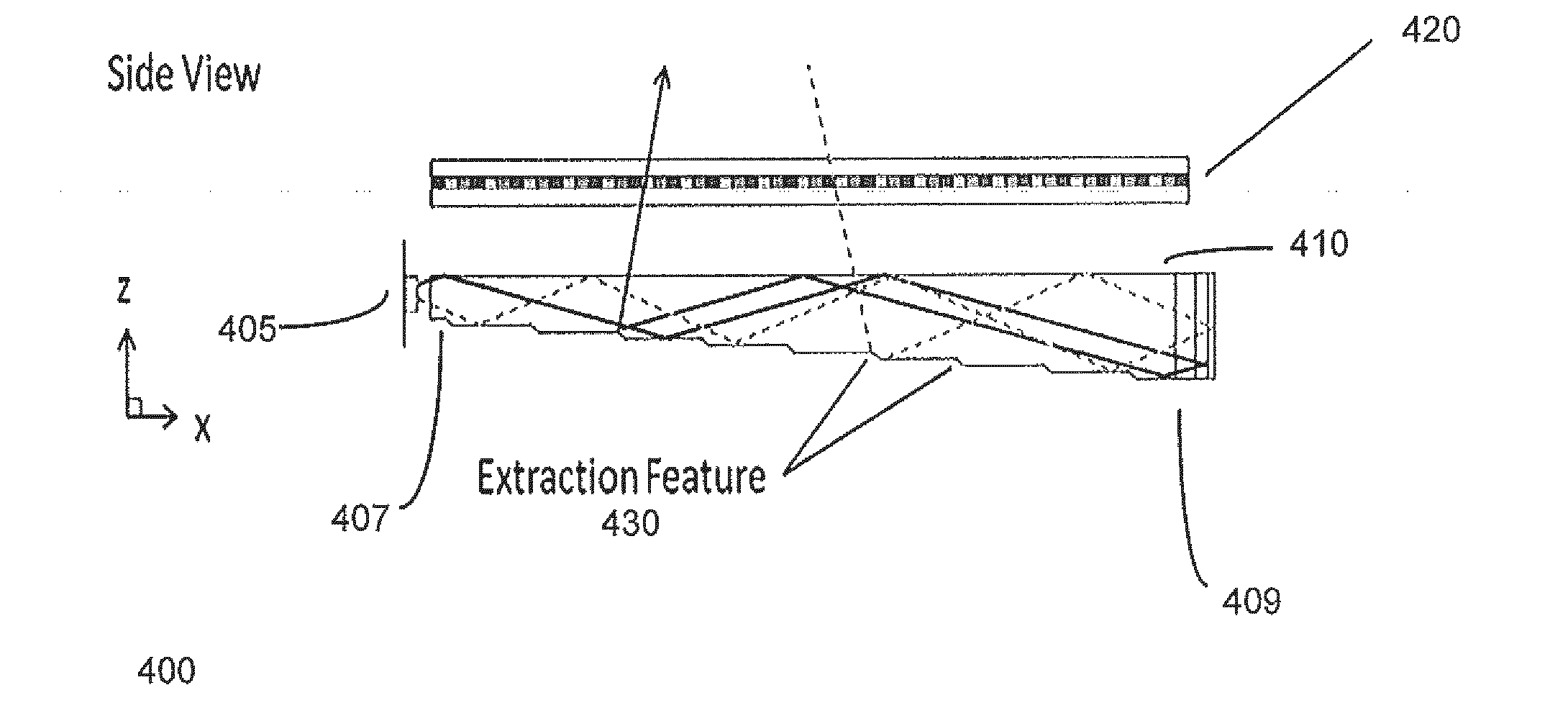
Directional flat illuminators
Disclosed is an optical valve or light valve for providing large area collimated illumination from localized light sources, and system and method thereof for 2D, 3D, and / or autosteroscopic displays. An optical valve may include a stepped structure, in which the steps include separated extraction features which may be optically hidden to light propagating in a first direction. Light propagating in a second direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the optical valve. Such controlled illumination may provide for efficient, multi-user autostereoscopic displays as well as improved 2D display functionality.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
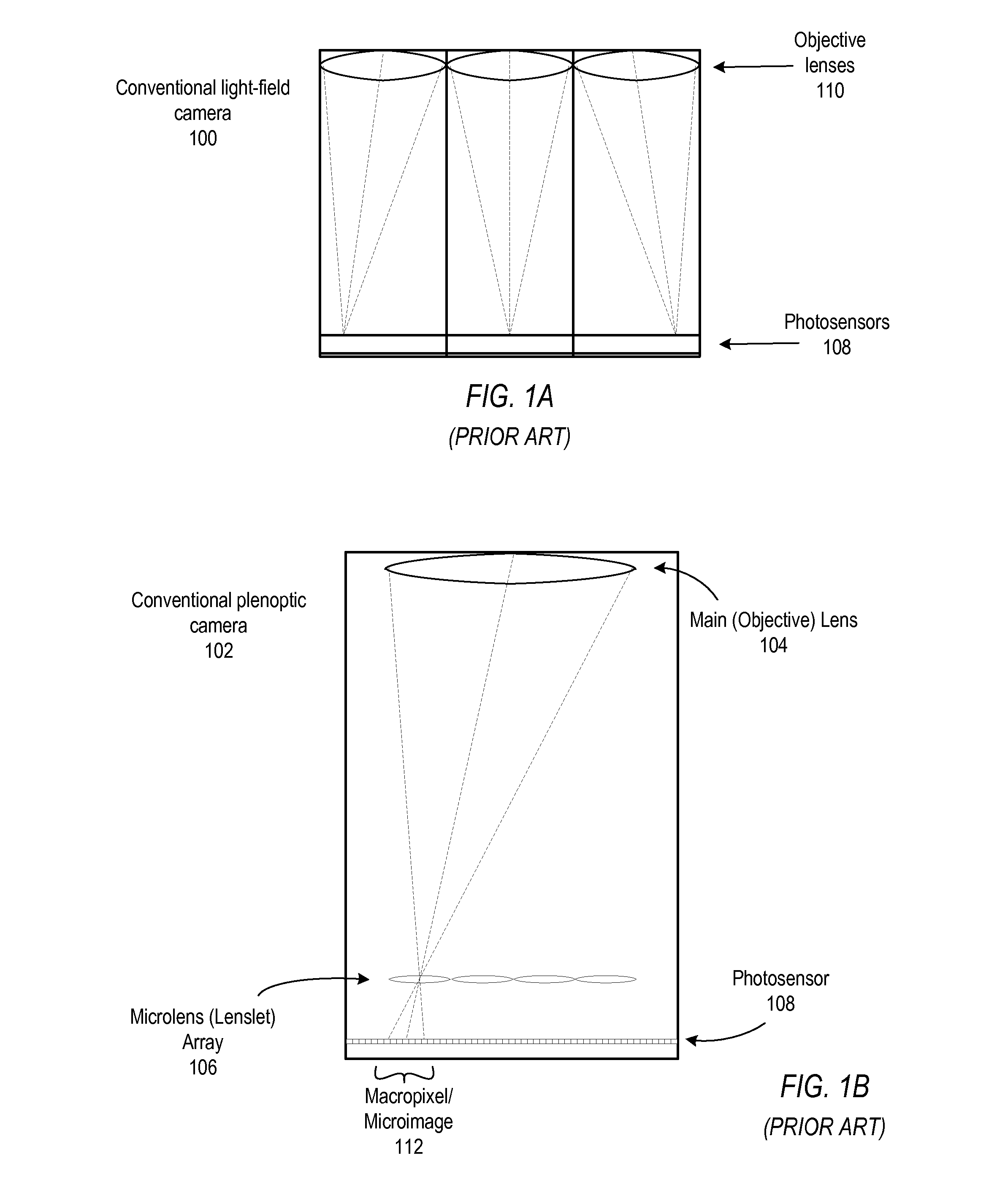
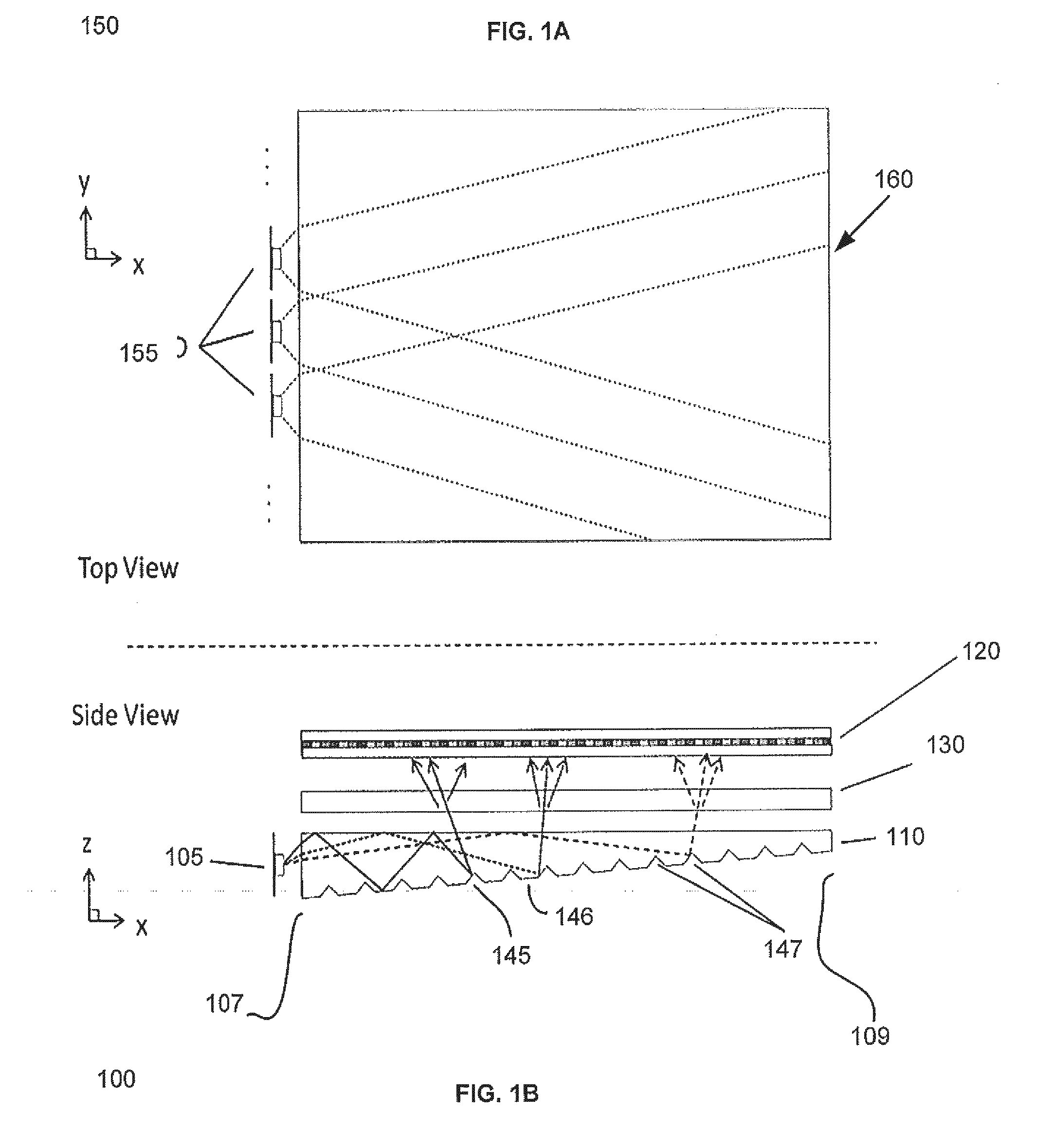
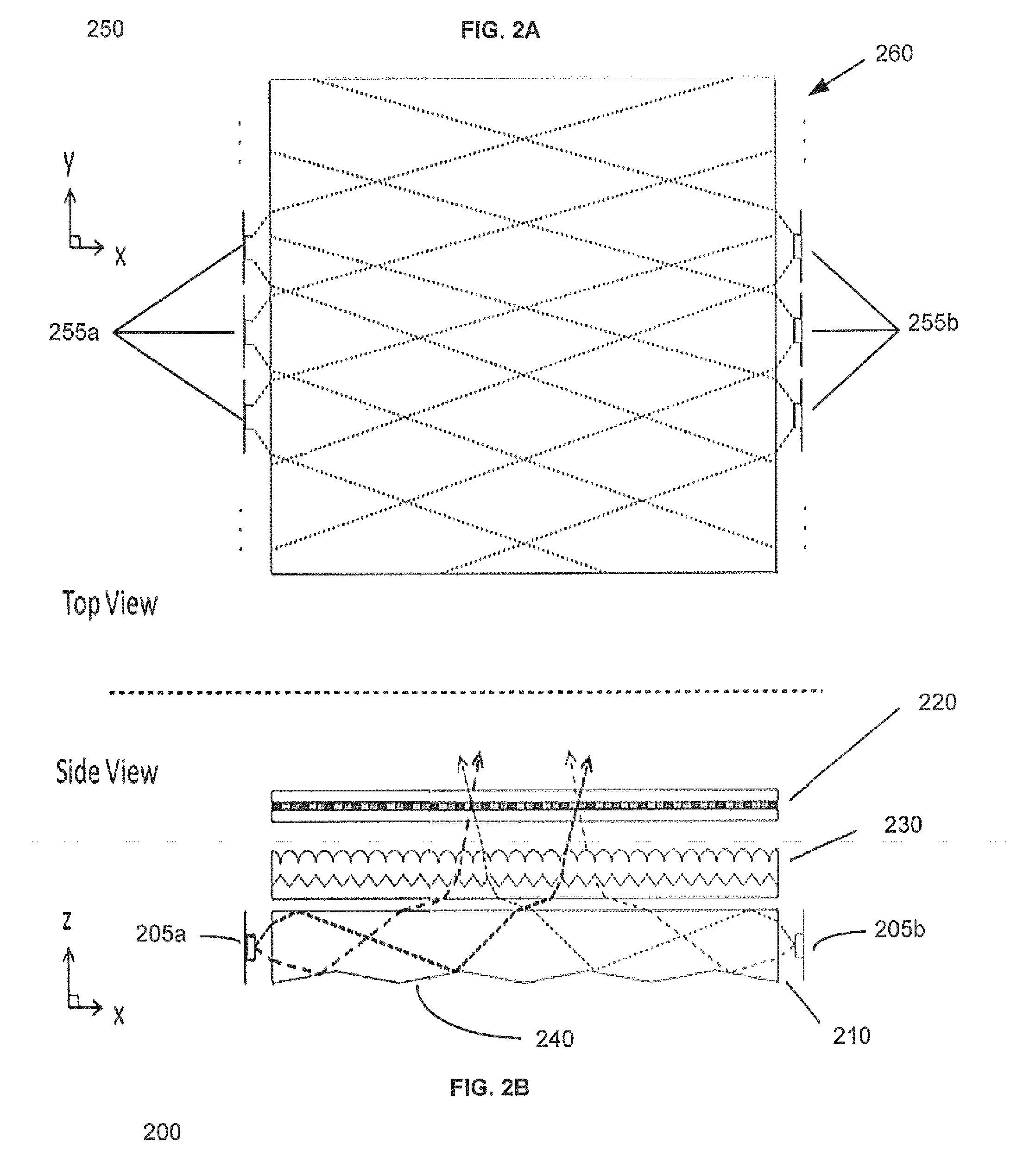
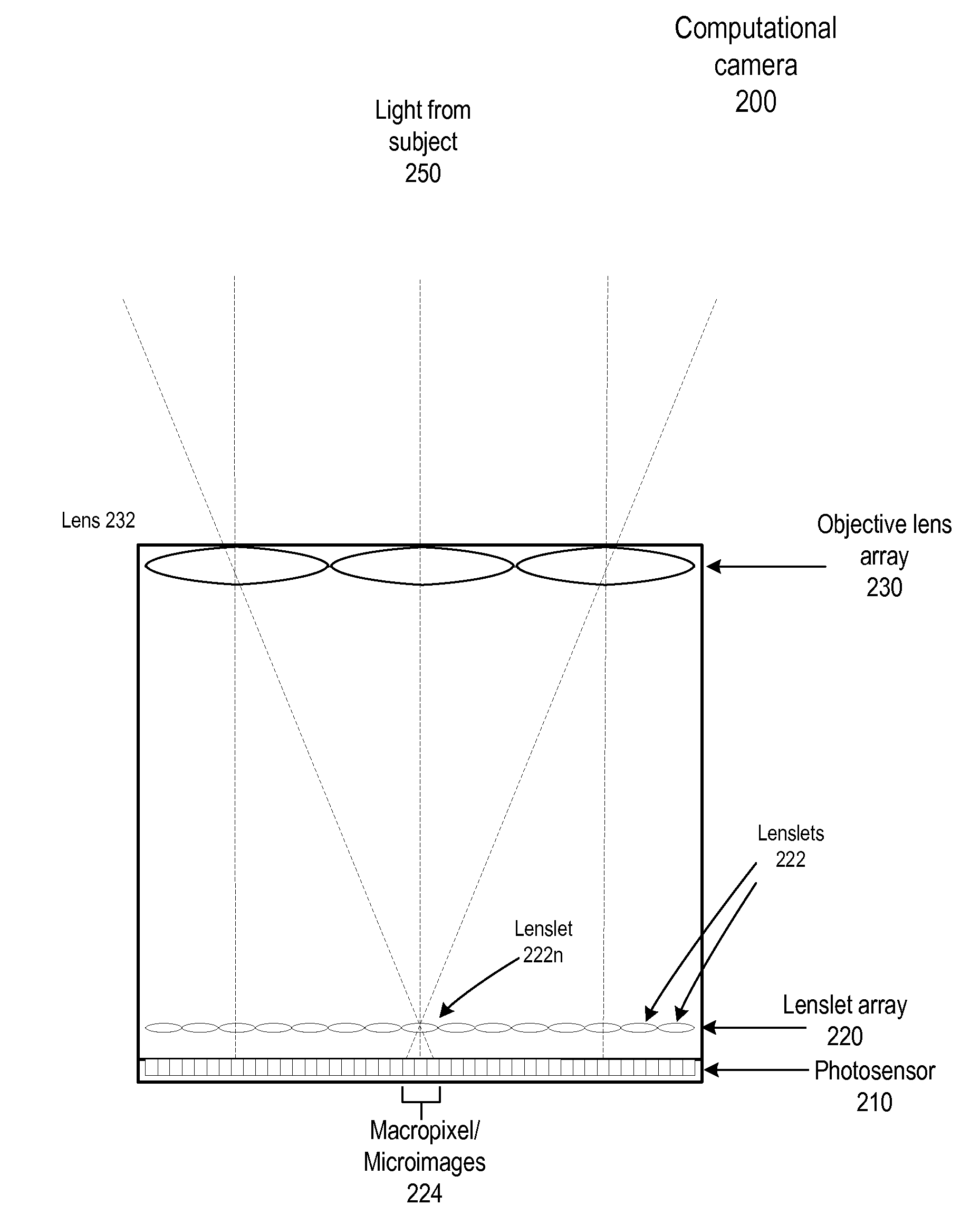
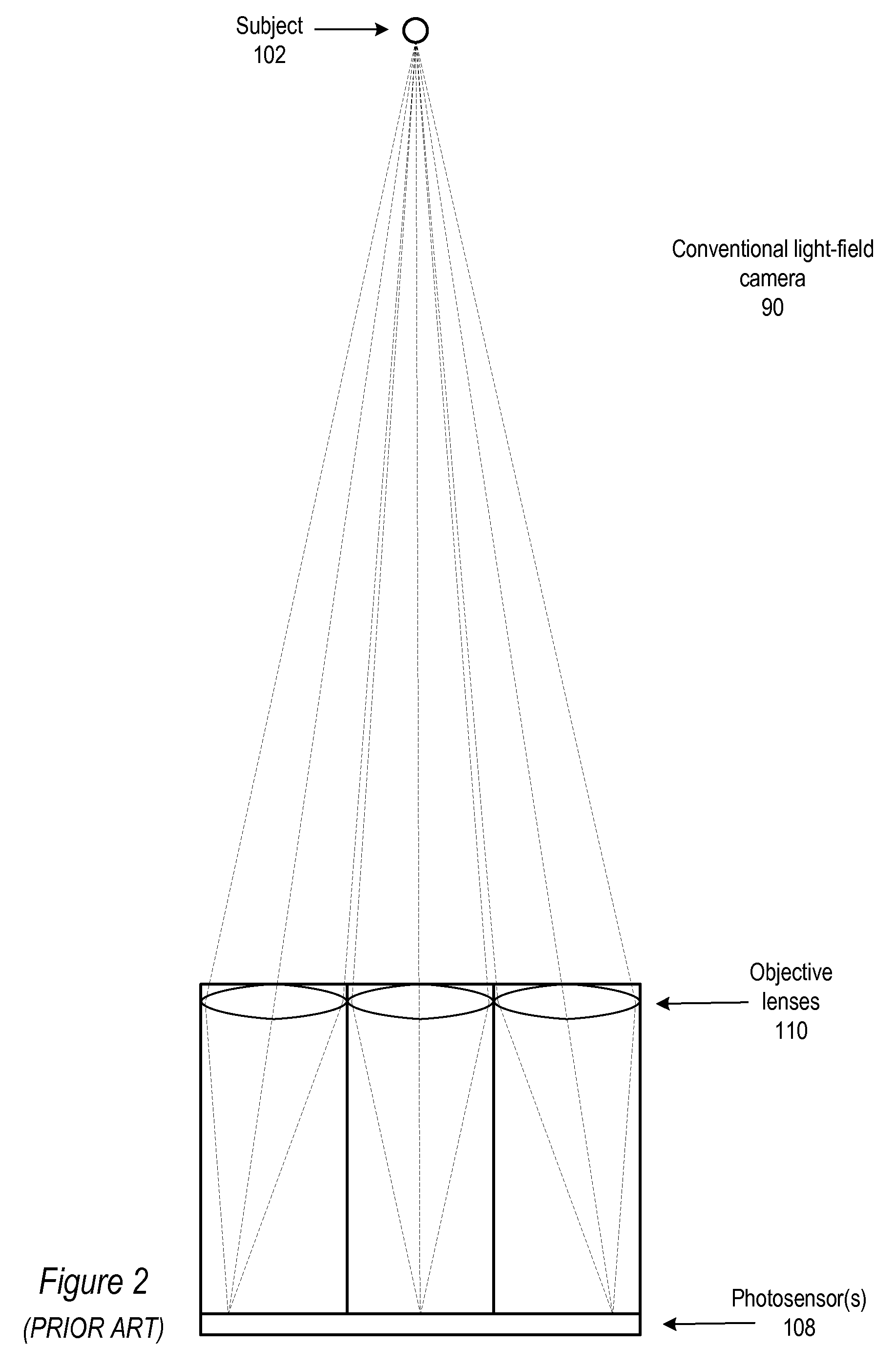
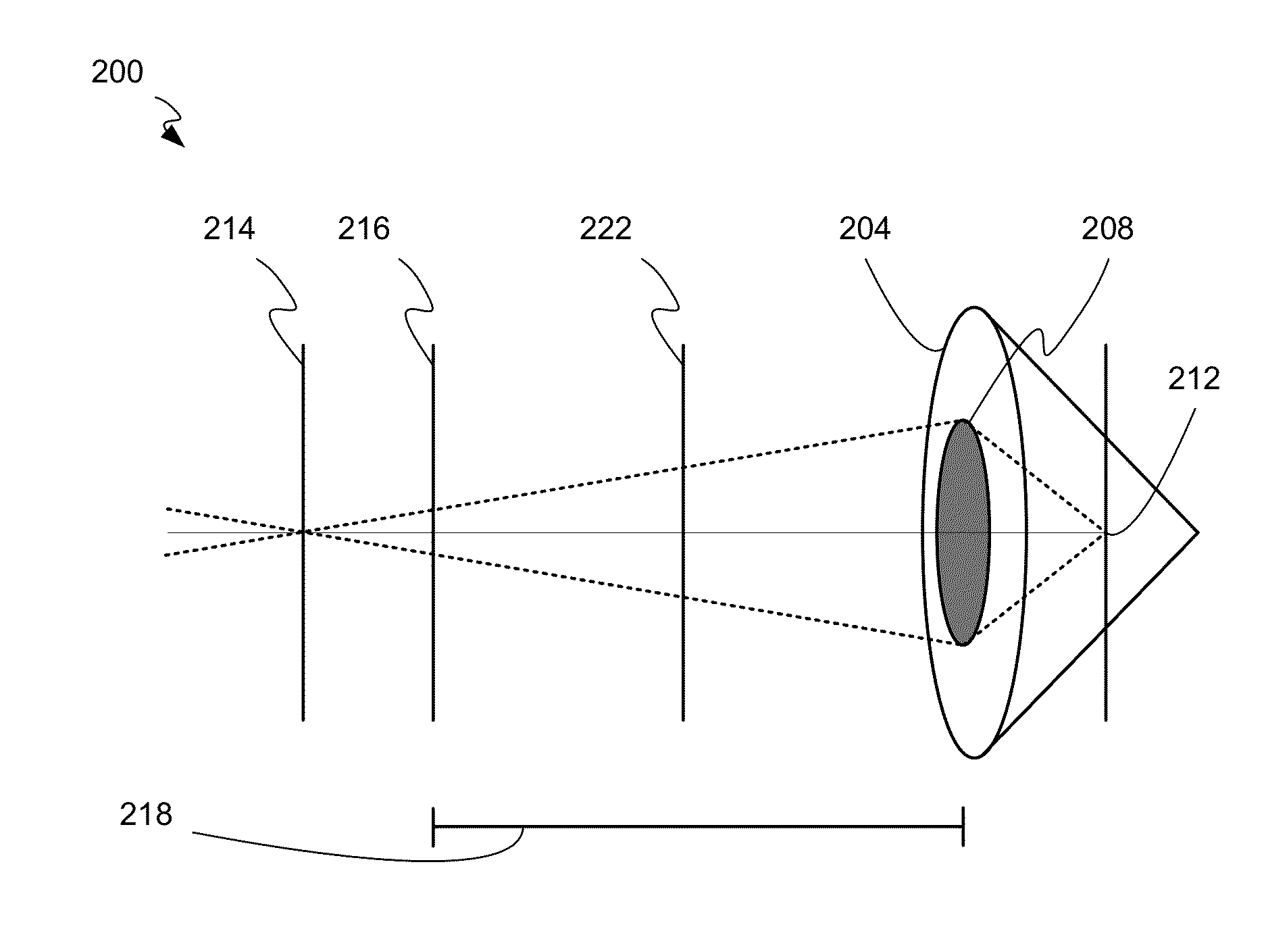
Fast Computational Camera Based On Two Arrays of Lenses
ActiveUS20090102956A1Less expenseQuality improvementTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsRadianceInformation capture
Method and apparatus for a fast (low F / number) computational camera that incorporates two arrays of lenses. The arrays include a lenslet array in front of a photosensor and an objective lens array of two or more lenses. Each lens in the objective lens array captures light from a subject. Each lenslet in the lenslet array captures light from each objective lens and separates the captured light to project microimages corresponding to the objective lenses on a region of the photosensor under the lenslet. Thus, a plurality of microimages are projected onto and captured by the photosensor. The captured microimages may be processed in accordance with the geometry of the objective lenses to align the microimages to generate a final image. One or more other algorithms may be applied to the image data in accordance with radiance information captured by the camera, such as automatic refocusing of an out-of-focus image.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Near-eye microlens array displays
In embodiments of the invention, an apparatus may include a display comprising a plurality of pixels and a computer system coupled with the display and operable to instruct the display to display images. The apparatus may further include a microlens array located adjacent to the display and comprising a plurality of microlenses, wherein the microlens array is operable to produce a light field by altering light emitted by the display to simulate an object that is in focus to an observer while the display and the microlens array are located within a near-eye range of the observer.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
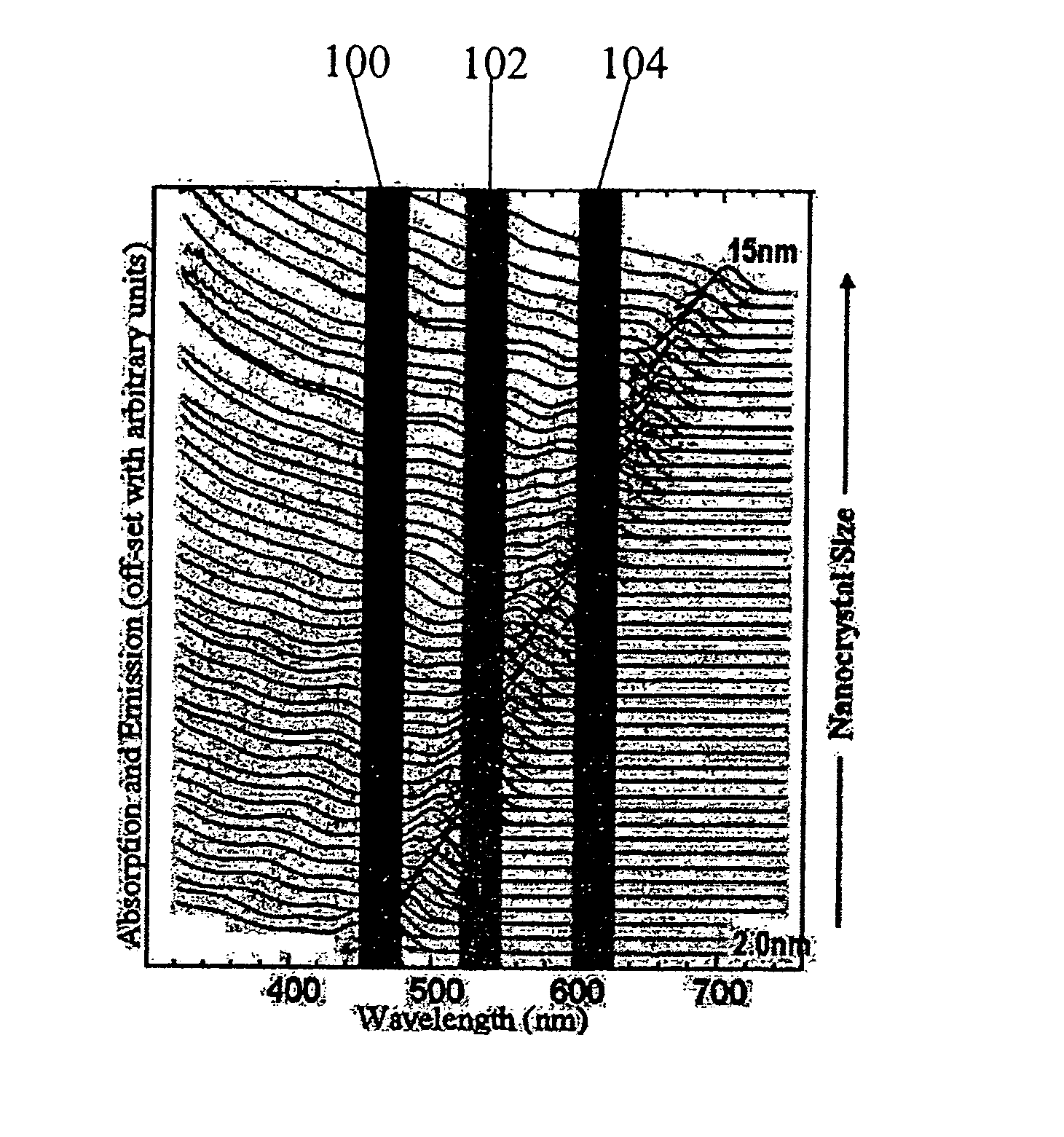
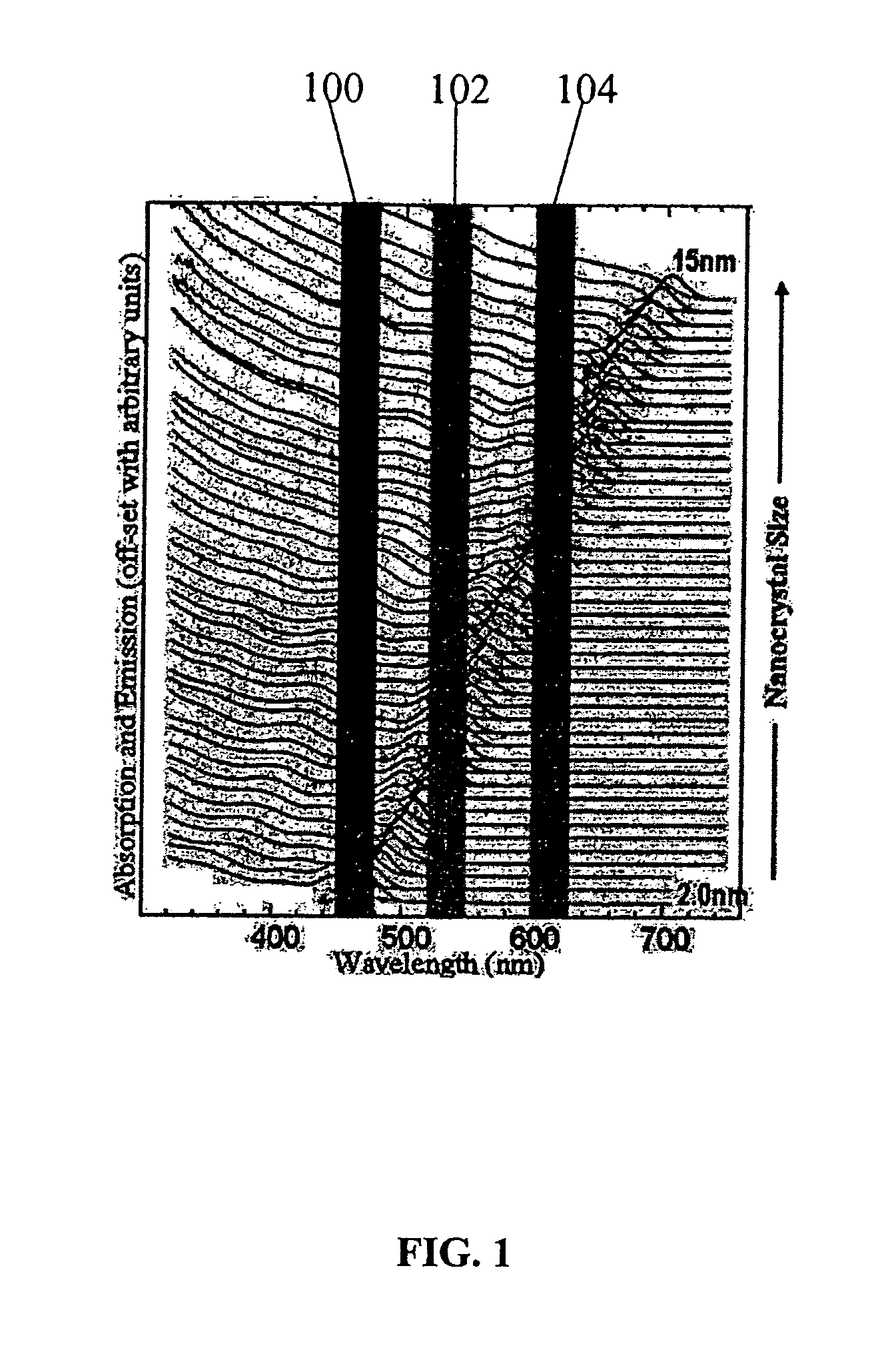
Nanocrystal doped matrixes
ActiveUS20070034833A1Good miscibilityInhibit aggregationMaterial nanotechnologyIndividual molecule manipulationAnti-reflective coatingSemiconductor nanocrystals
Matrixes doped with semiconductor nanocrystals are provided. In certain embodiments, the semiconductor nanocrystals have a size and composition such that they absorb or emit light at particular wavelengths. The nanocrystals can comprise ligands that allow for mixing with various matrix materials, including polymers, such that a minimal portion of light is scattered by the matrixes. The matrixes of the present invention can also be utilized in refractive index matching applications. In other embodiments, semiconductor nanocrystals are embedded within matrixes to form a nanocrystal density gradient, thereby creating an effective refractive index gradient. The matrixes of the present invention can also be used as filters and antireflective coatings on optical devices and as down-converting layers. Processes for producing matrixes comprising semiconductor nanocrystals are also provided. Nanostructures having high quantum efficiency, small size, and / or a narrow size distribution are also described, as are methods of producing indium phosphide nanostructures and core-shell nanostructures with Group II-VI shells.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Optical see-through free-form head-mounted display
A see-through free-form head-mounted display including a wedge-shaped prism-lens having free-form surfaces and low F-number is provided.
Owner:CHENG DEWEN +2
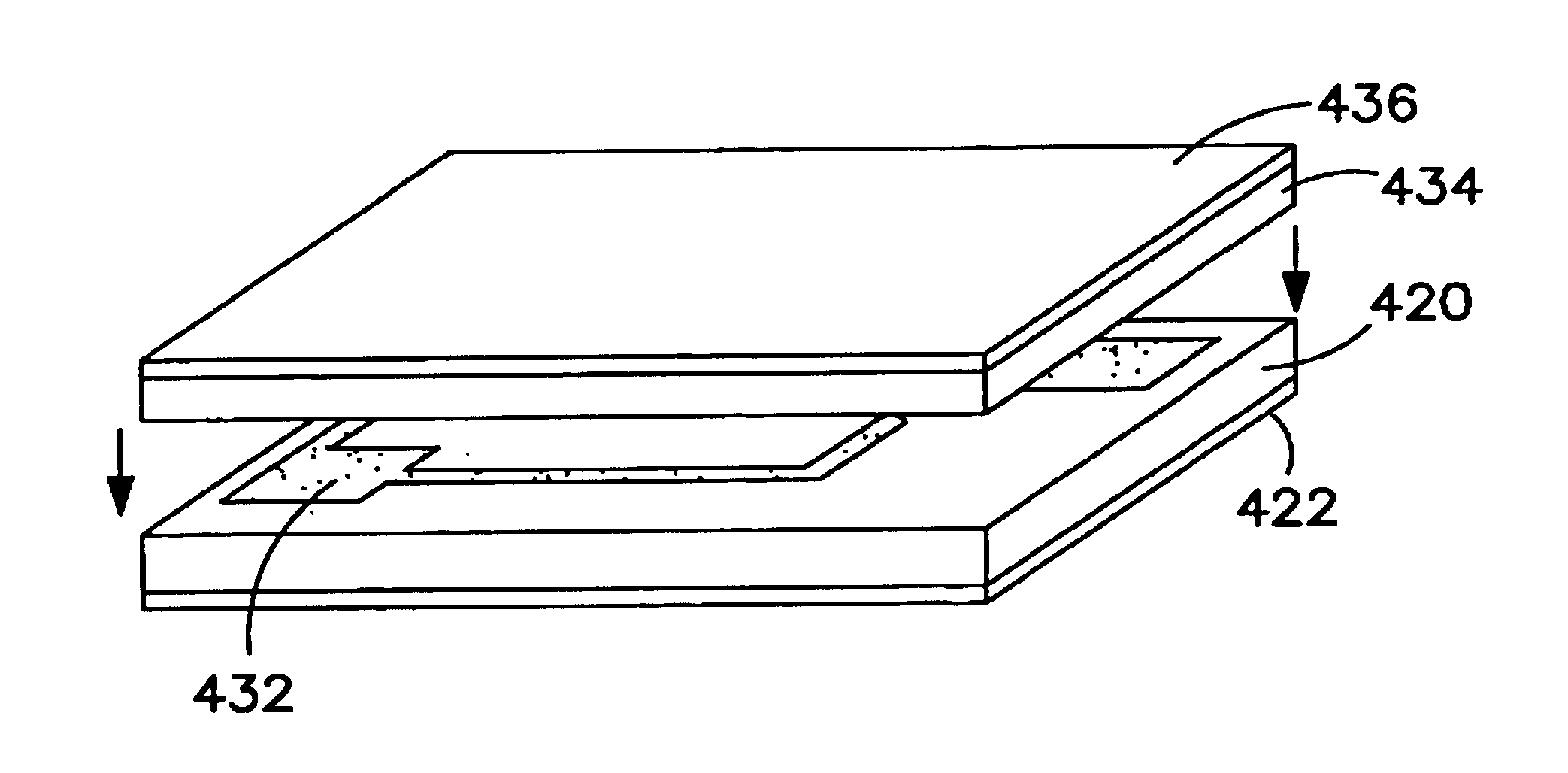
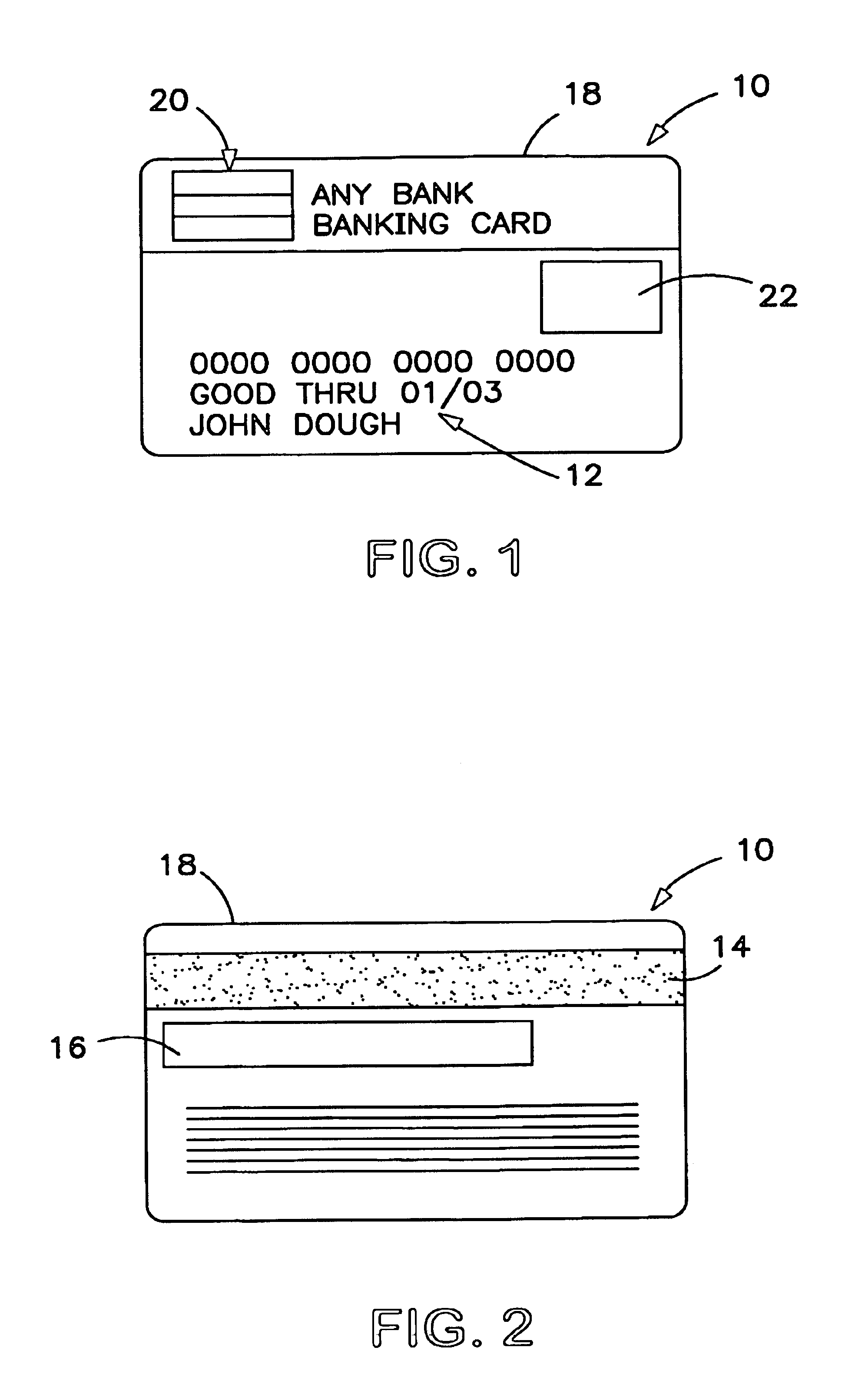
Method for making a financial transaction card with embedded electronic circuitry
InactiveUS6902116B2Complete banking machinesOther printing matterComputer hardwareFinancial transaction
Financial transaction and similar cards are fabricated with a split core adapted to received embedded electronic circuitry. The card core has two or more laminated layers. The cavity is milled into one or more of the layers to receive the electronic circuitry. The core layers are then laminated together, along with protective overlays. Alternative fabrication methods include co-extrusion and injection molding.
Owner:INNOVATIVE CARD TECH
Compact folded-optics illumination lens
The present embodiments provide for apparatuses, and methods for manufacturing apparatuses to convert a first distribution of an input radiation to a second distribution of output radiation. The apparatus can be defined in some embodiments by generating a two-dimensional representation of three active optical surfaces including calculating a segment of first, entry and second surfaces based on first second, and third generalized Cartesian ovals, respectively, and successively repeating the calculating of the segments of the first and second surfaces, and rotationally sweeping the two-dimensional representation about a central axis providing a three-dimensional representation. In some embodiments, portion of the first and / or second surfaces can be totally internally reflective.
Owner:LIGHT ENGINE
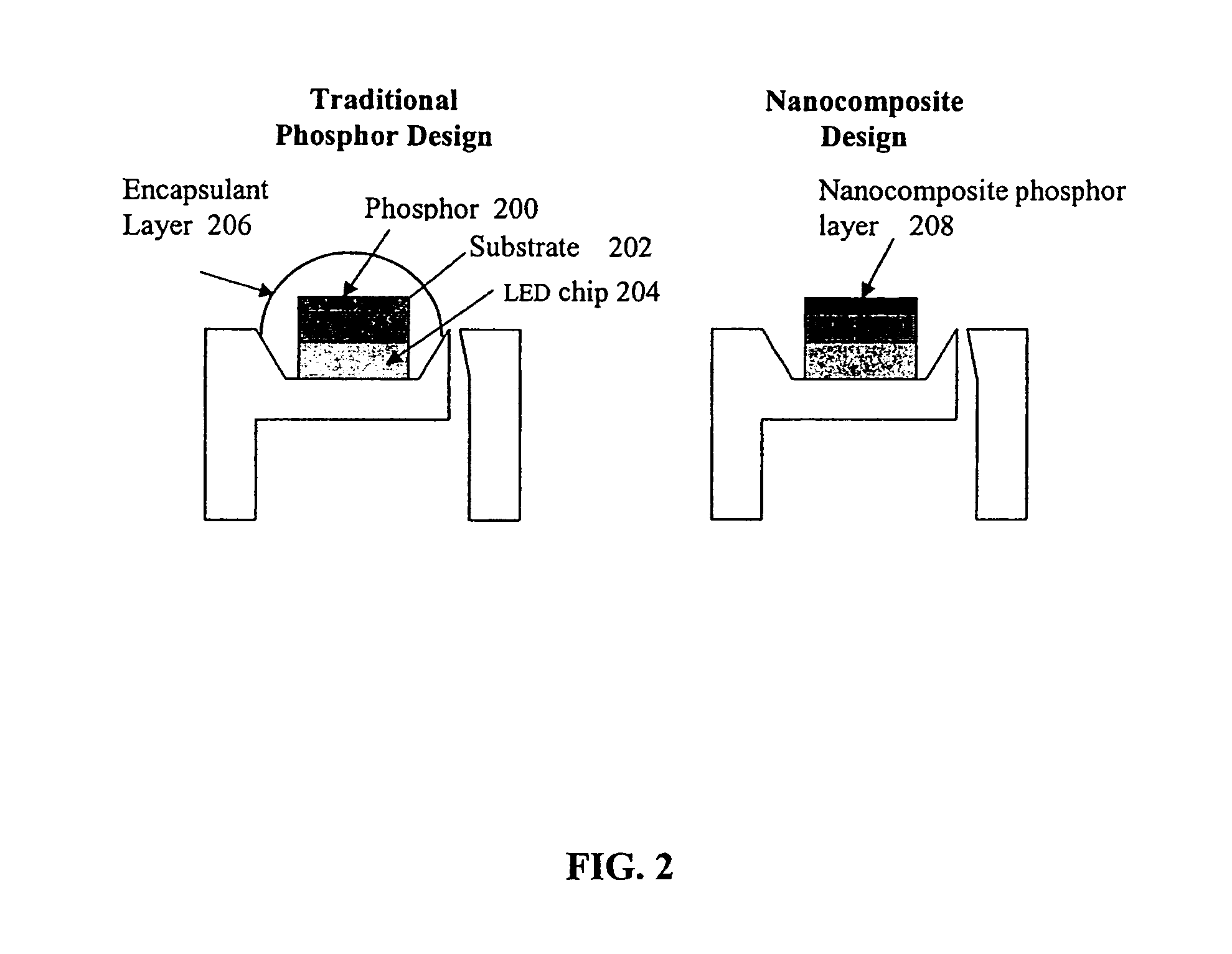
Optical manifold for light-emitting diodes
ActiveUS20050243570A1Cost-effectiveImprove throughputMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourcePhotoluminescencePhosphor
An optical manifold for efficiently combining a plurality of LED outputs into a single, substantially homogeneous output, in a small, cost-effective package. The optical manifolds can be used to combine multiple LEDs of the same color and provide a high intensity output aperture with very high uniformity and sharp borders, or they can be used to generate a multiwavelength output, such as red, green, and blue LEDs that are combined to generate white light. Embodiments are also disclosed that use a single or multiple LEDs and a remote phosphor and an intermediate wavelength-selective filter arranged so that backscattered photoluminescence is recycled to boost the luminance and flux of the output aperture. The optical manifolds are designed to alleviate substantial luminance inhomogeneities inherent to LEDs. The optical manifold utilizes principles of non-imaging optics to transform light and provide directed, substantially uniform light sources.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Methods and apparatus for capturing and/or processing images
ActiveUS20140192253A1Enhance the imageImproved video generation resultTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLight beamMultiple sensor
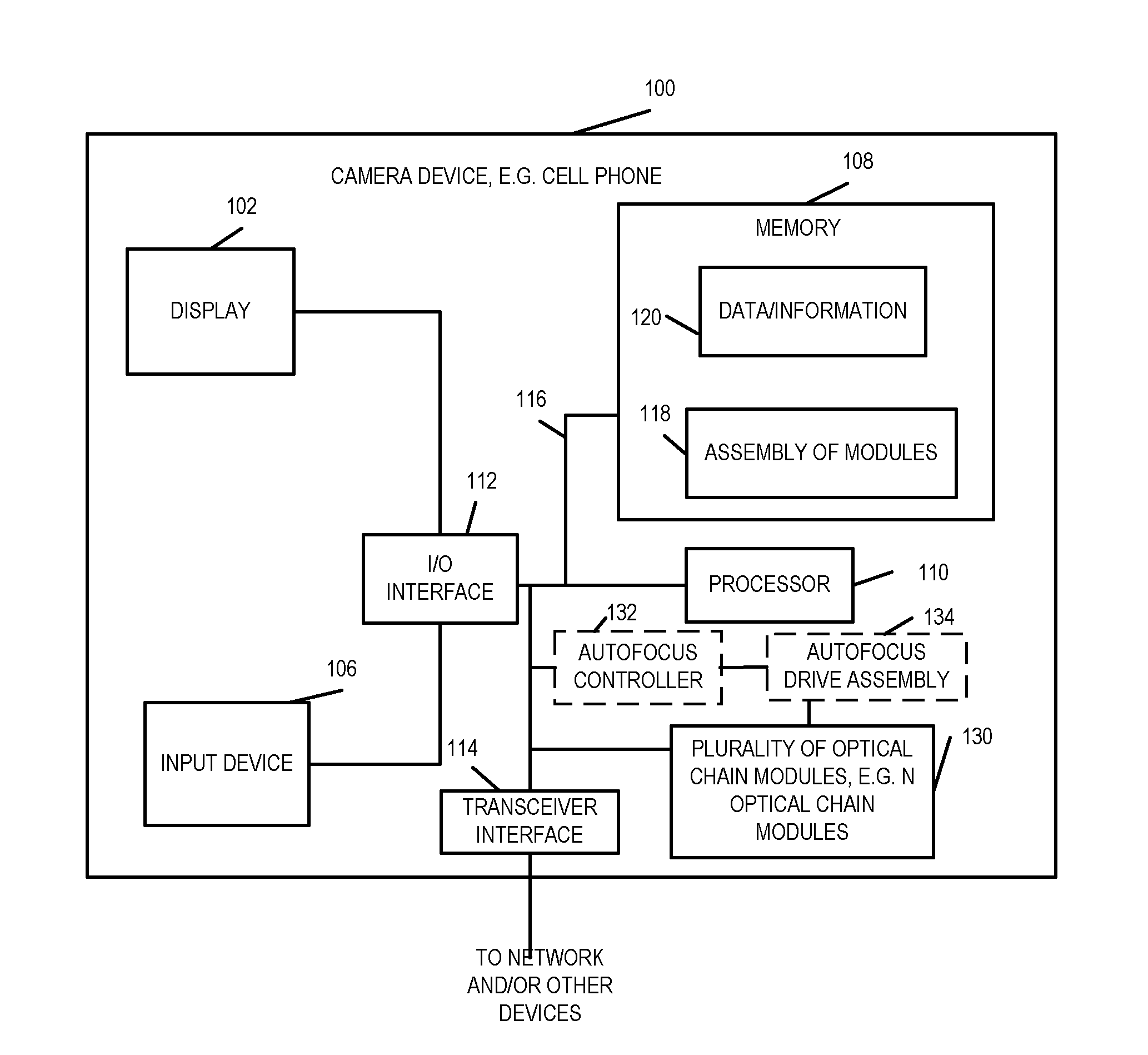
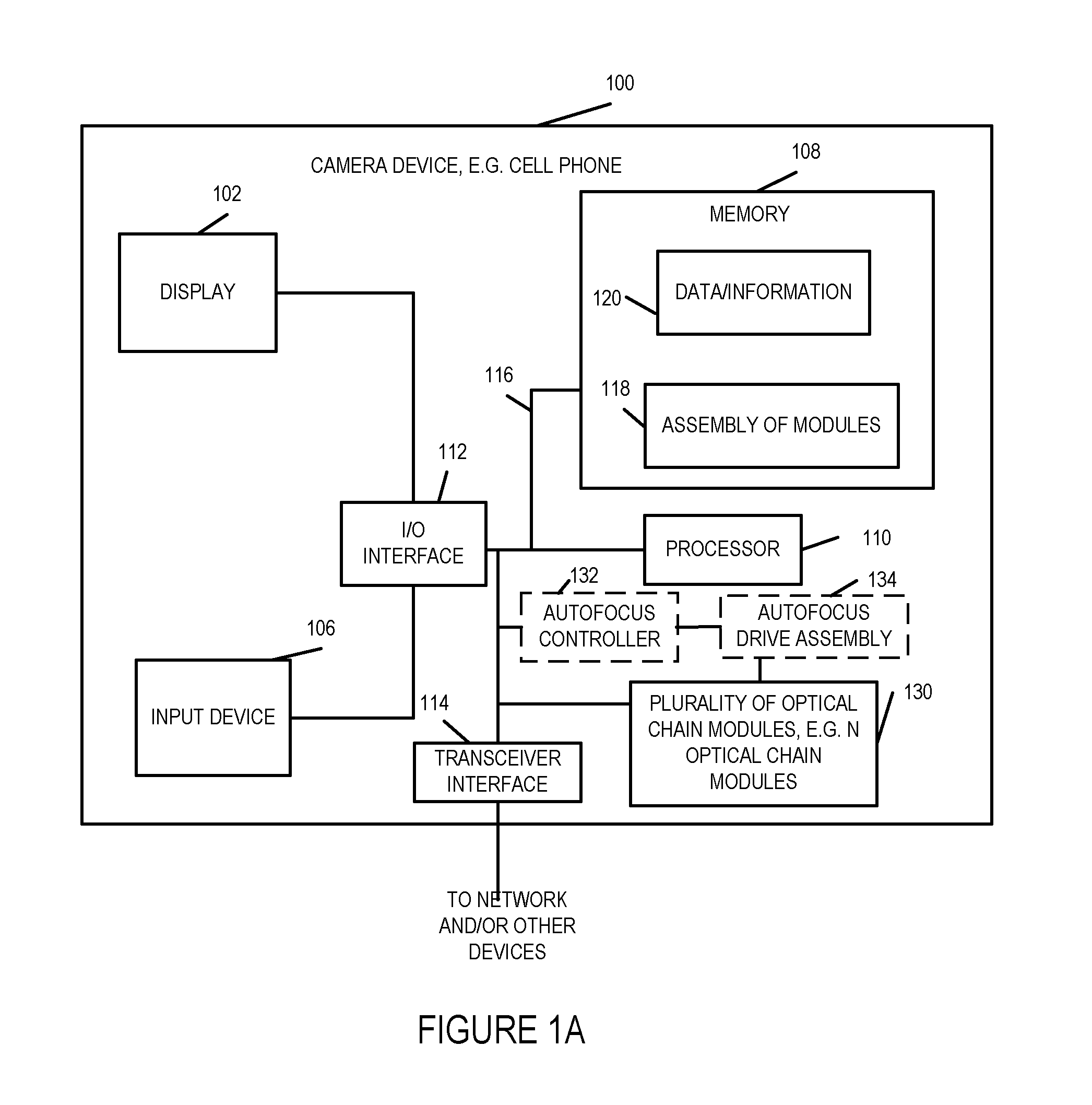
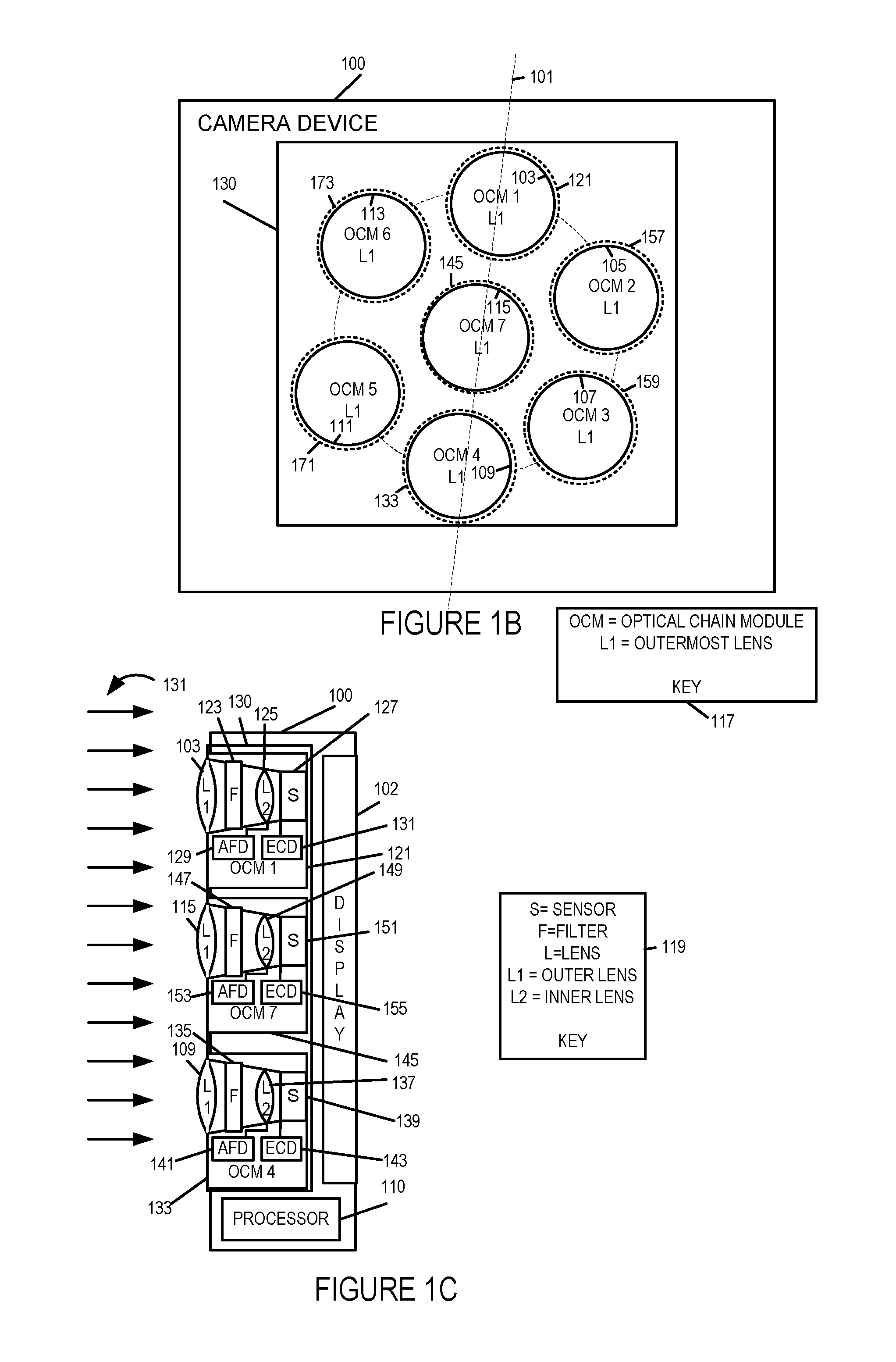
Methods and apparatus for capturing or generating images using multiple optical chains operating in parallel are described. Pixel values captured by individual optical chains corresponding to the same scene area are combined to provide an image with at least some of the benefits which would have been provided by capturing an image of the scene using a larger lens than that of the individual lenses of the optical chain modules. By using multiple optical chains in parallel at least some benefits normally obtained from using a large lens can be obtained without the need for a large lens. Furthermore in at least some embodiments, a wide dynamic range can be supported through the use of multiple sensors with the overall supported dynamic range being potentially larger than that of the individual sensors. Some lens and / or optical chain configurations are designed for use in small handheld devices, e.g., cell phones.
Owner:BLUE RIVER TECH
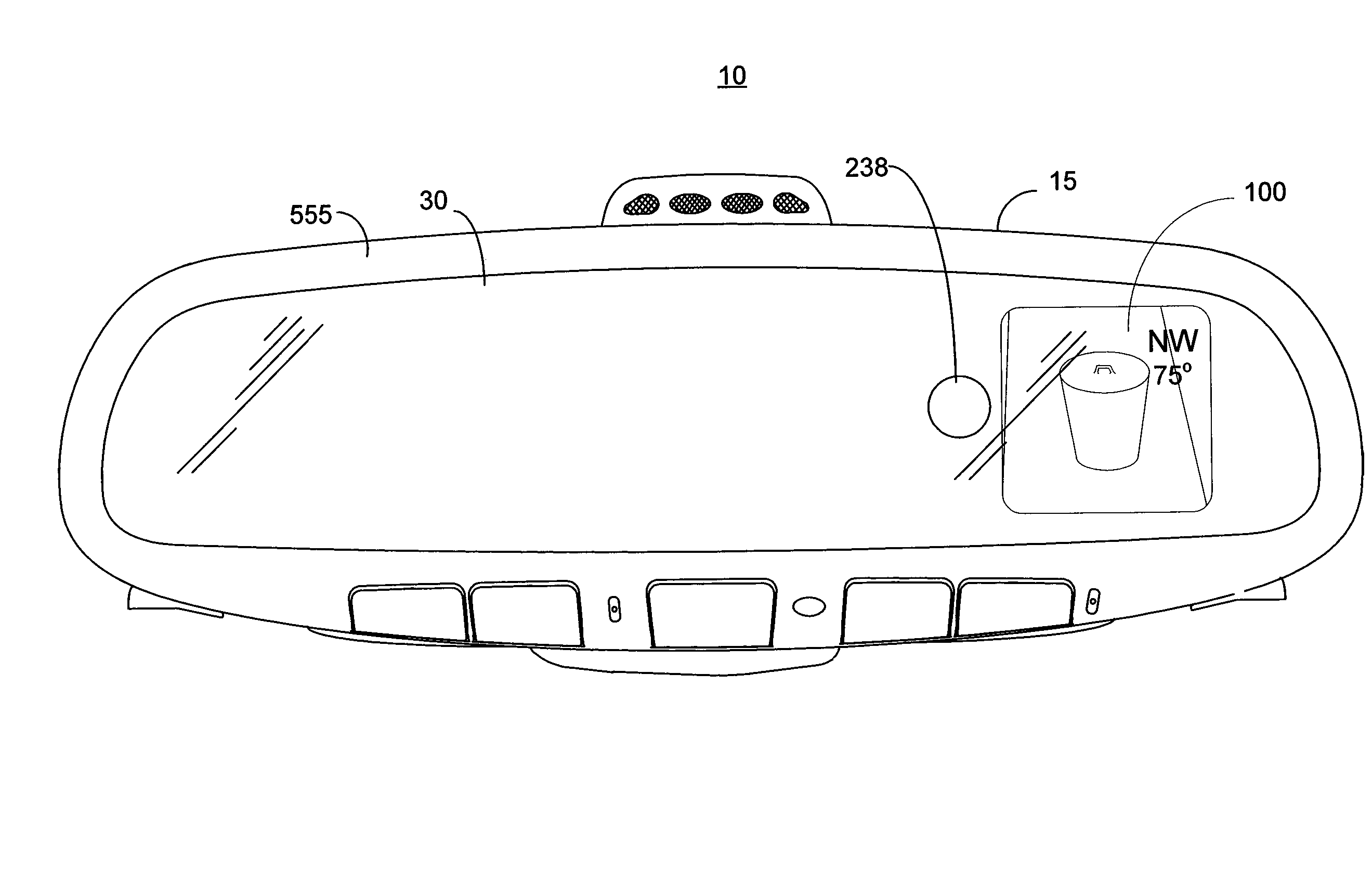
Vehicle Rearview Mirror Assembly Including a High Intensity Display
ActiveUS20080068520A1Eliminate effect of losingNon-linear opticsOptical viewingTransmittanceDisplay device
An inventive rearview assembly for a vehicle may comprise a mirror element and a display including a light management subassembly. The subassembly may comprise an LCD placed behind a transflective layer of the mirror element. Despite a low transmittance through the transflective layer, the inventive display is capable of generating a viewable display image having an intensity of at least 250 cd / m2 and up to 3500 cd / m2. The display includes a novel backlighting subassembly and novel optical components including a magnifying system, a depolarizer, a reflector, and a reflective polarizer. The display may be configured to display an image having edges contoured to correspond to the edges of the mirror element.
Owner:GENTEX CORP
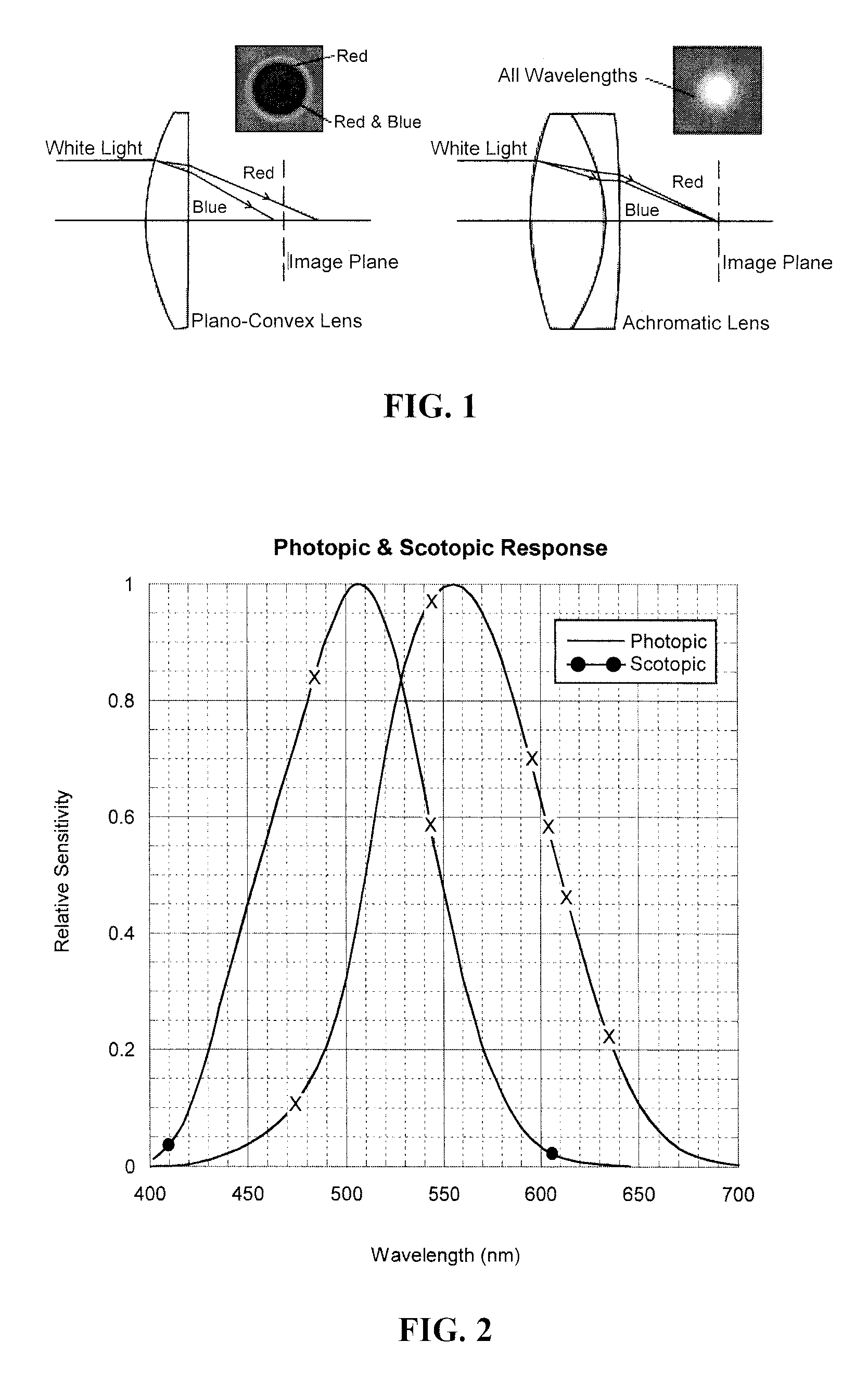
Methods and lenses for correction of chromatic aberration
ActiveUS20080088793A1Reduce overall chromatic aberrationEasy to useOptical articlesEye diagnosticsOptoelectronicsChromatic aberration
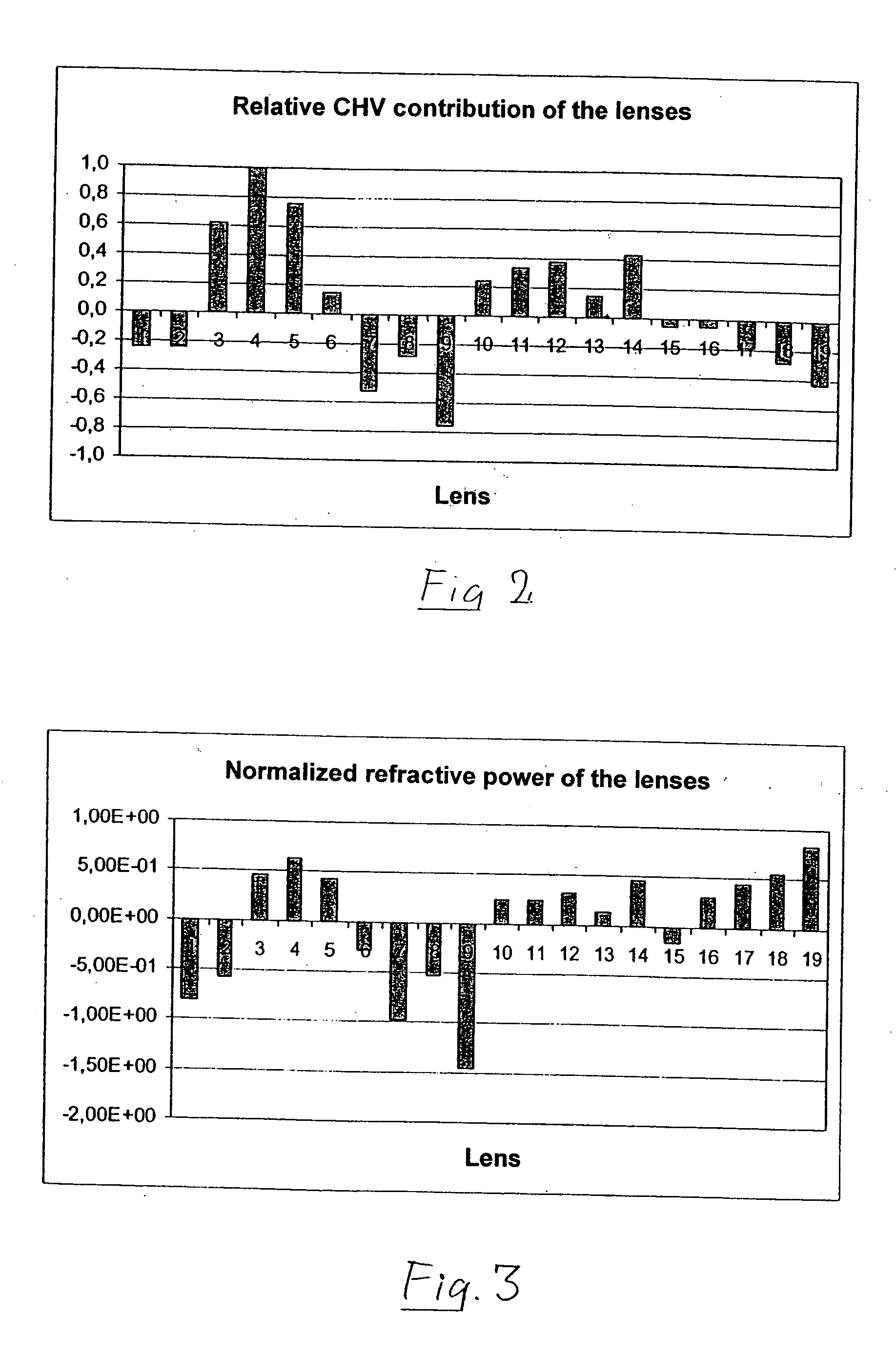
The subject invention provides lenses, and methods for designing and manufacturing these lenses, with reduced chromatic aberration. Advantageously, these lenses are specifically designed to correct chromatic aberration that results as multichromatic light passes through the lenses.
Owner:ESSILOR INT CIE GEN DOPTIQUE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com