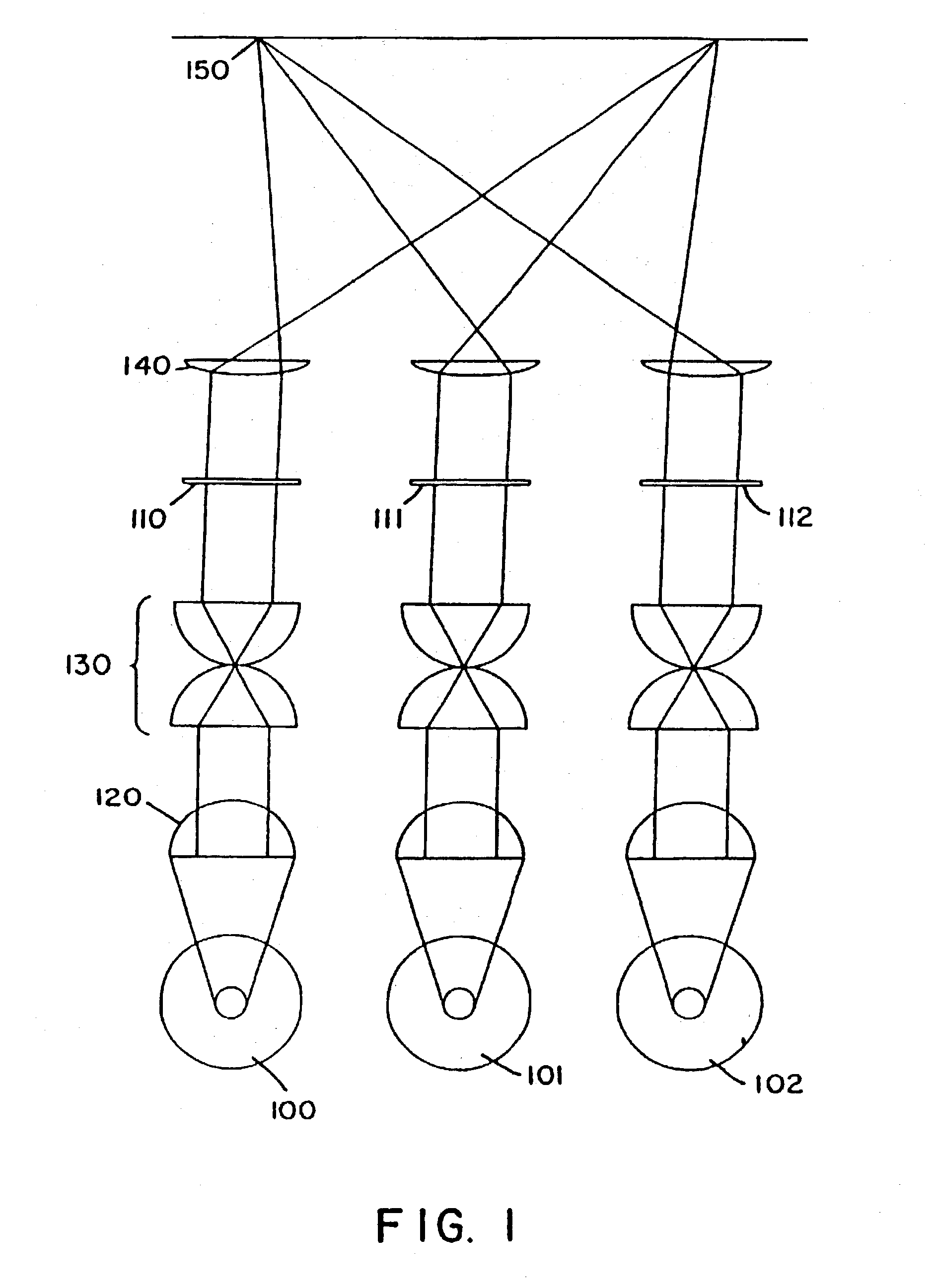
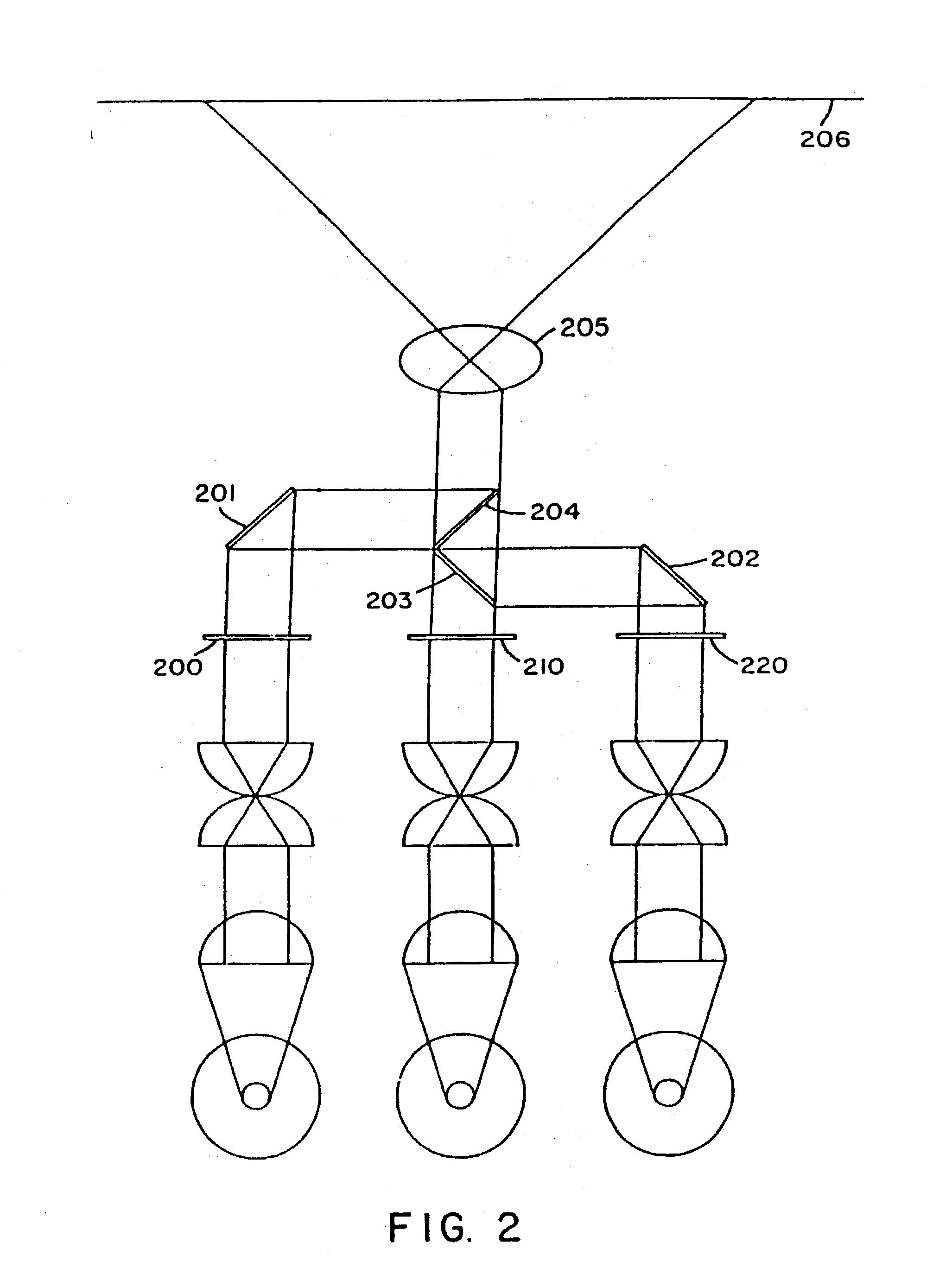
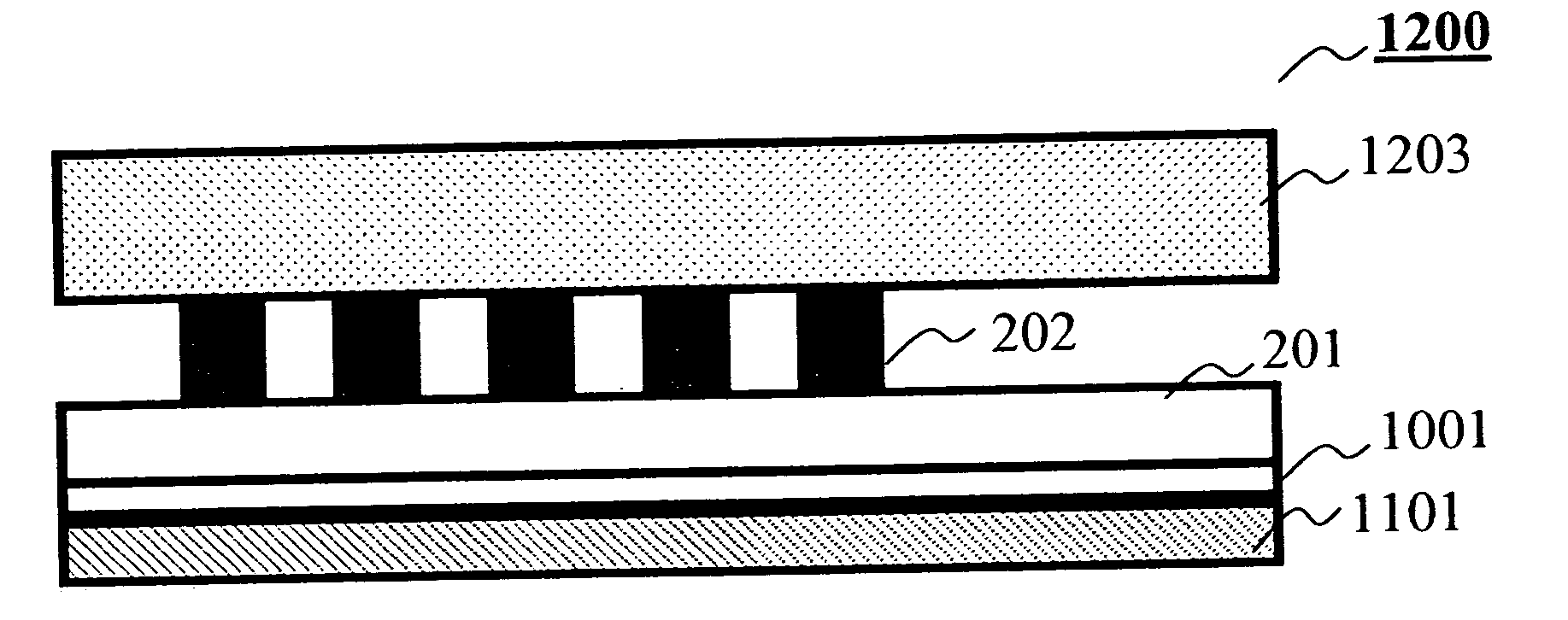
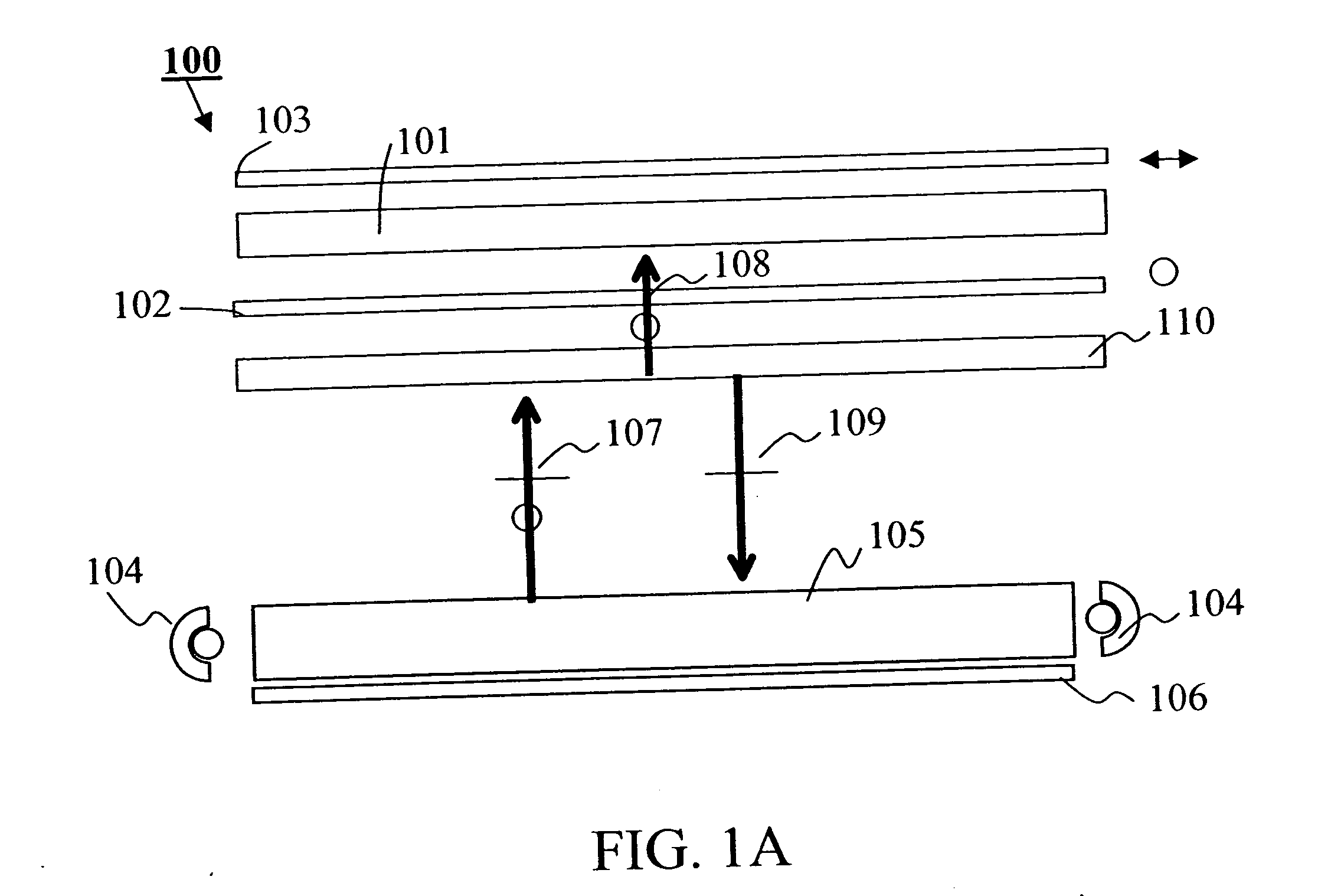
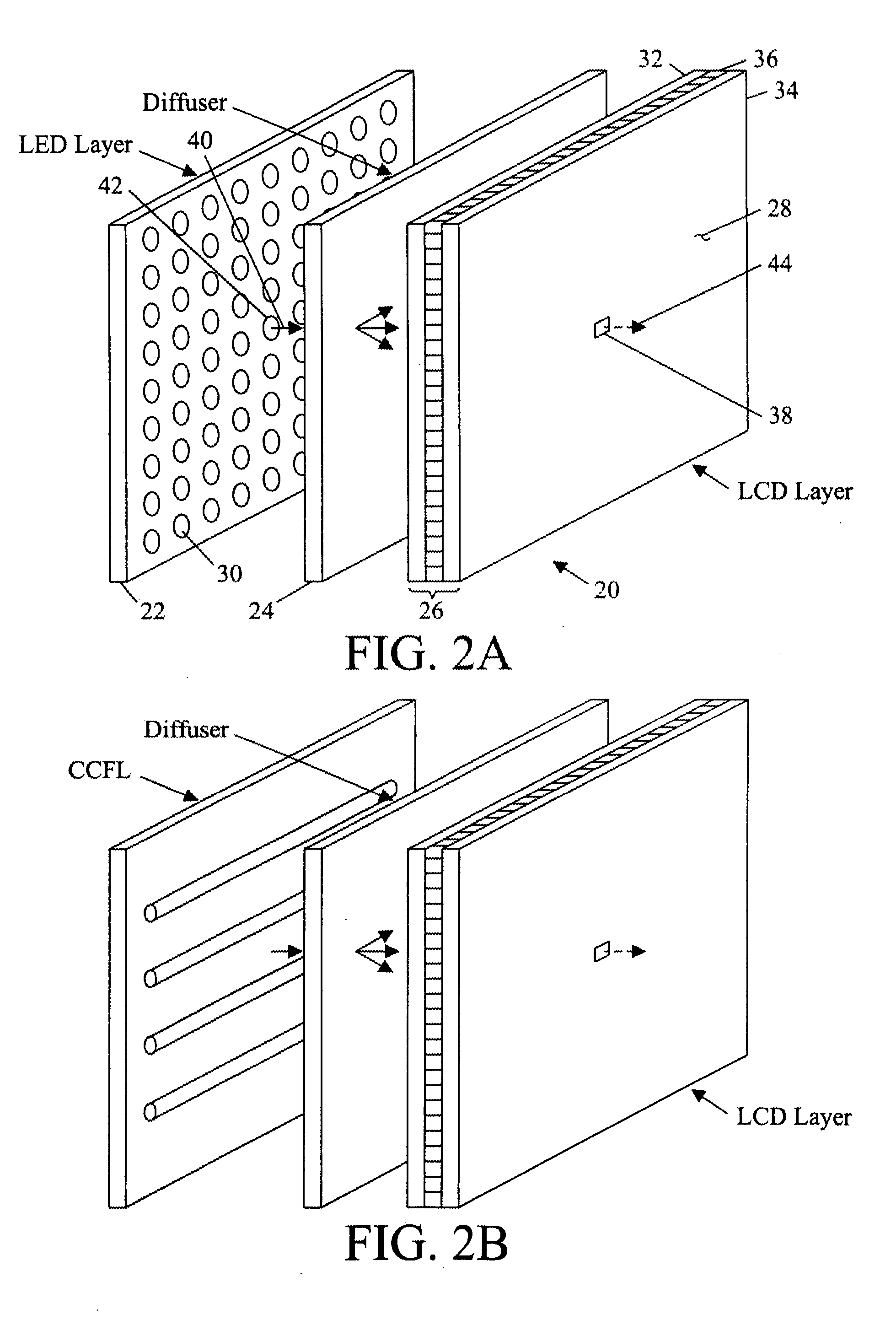
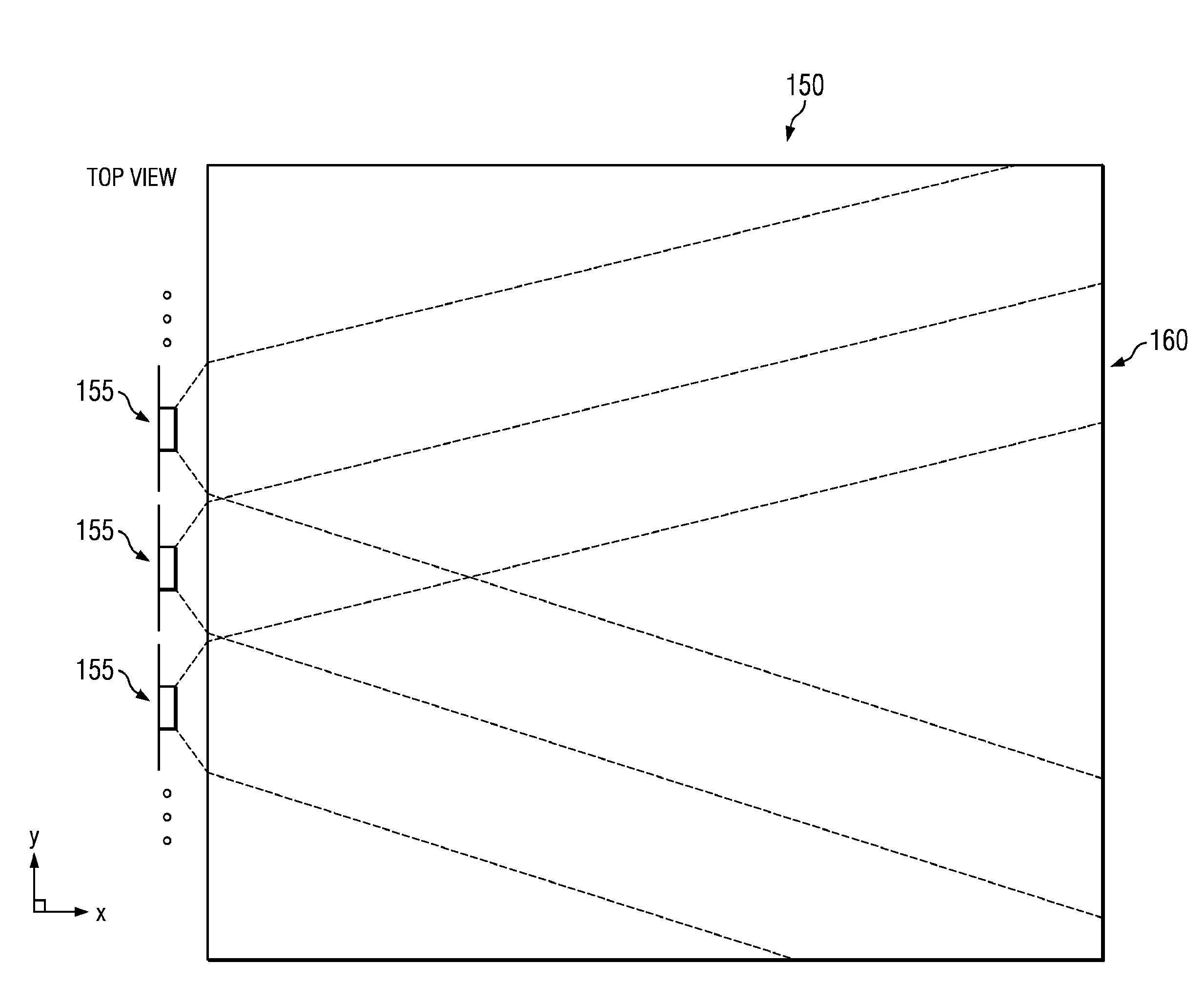
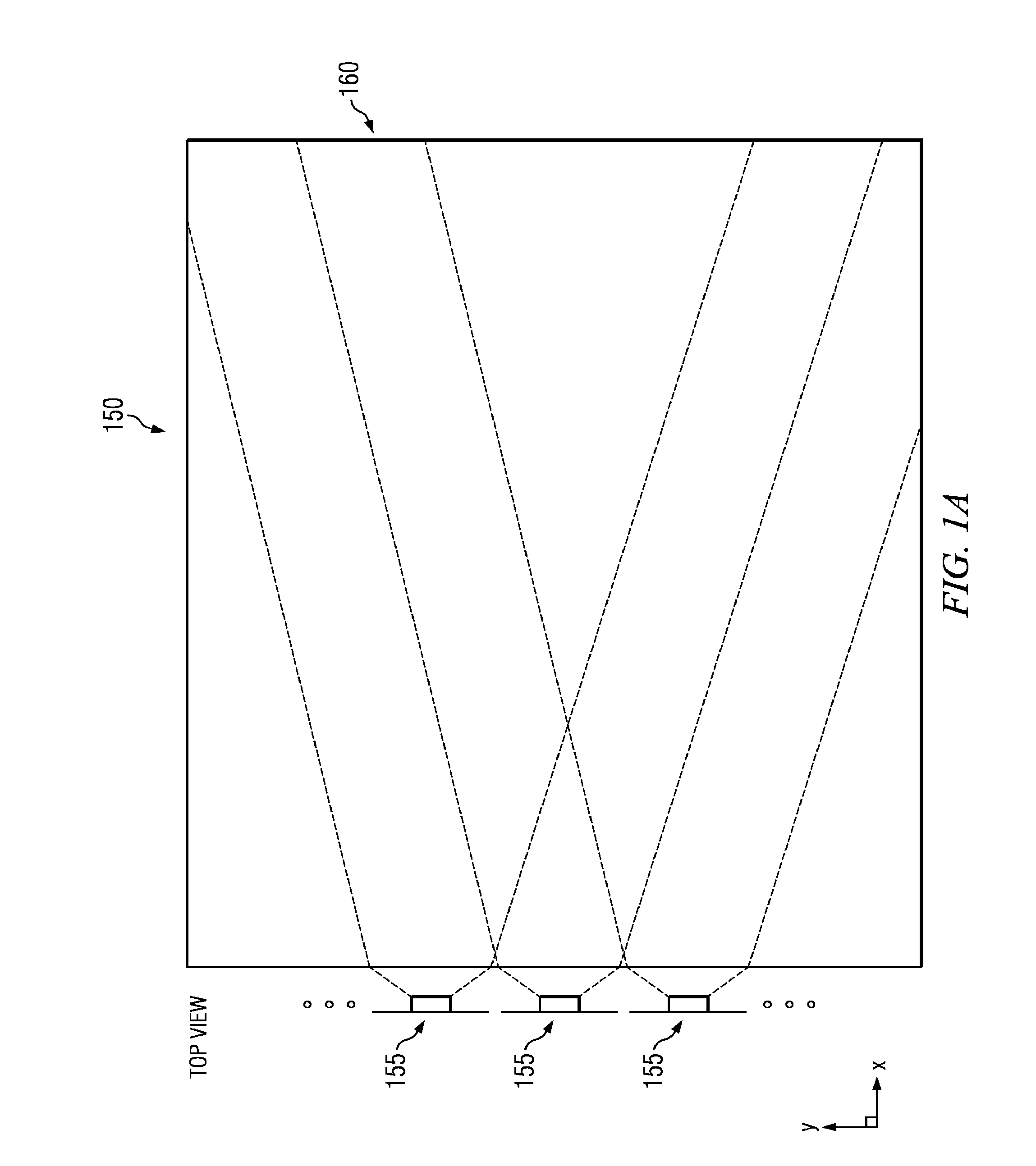
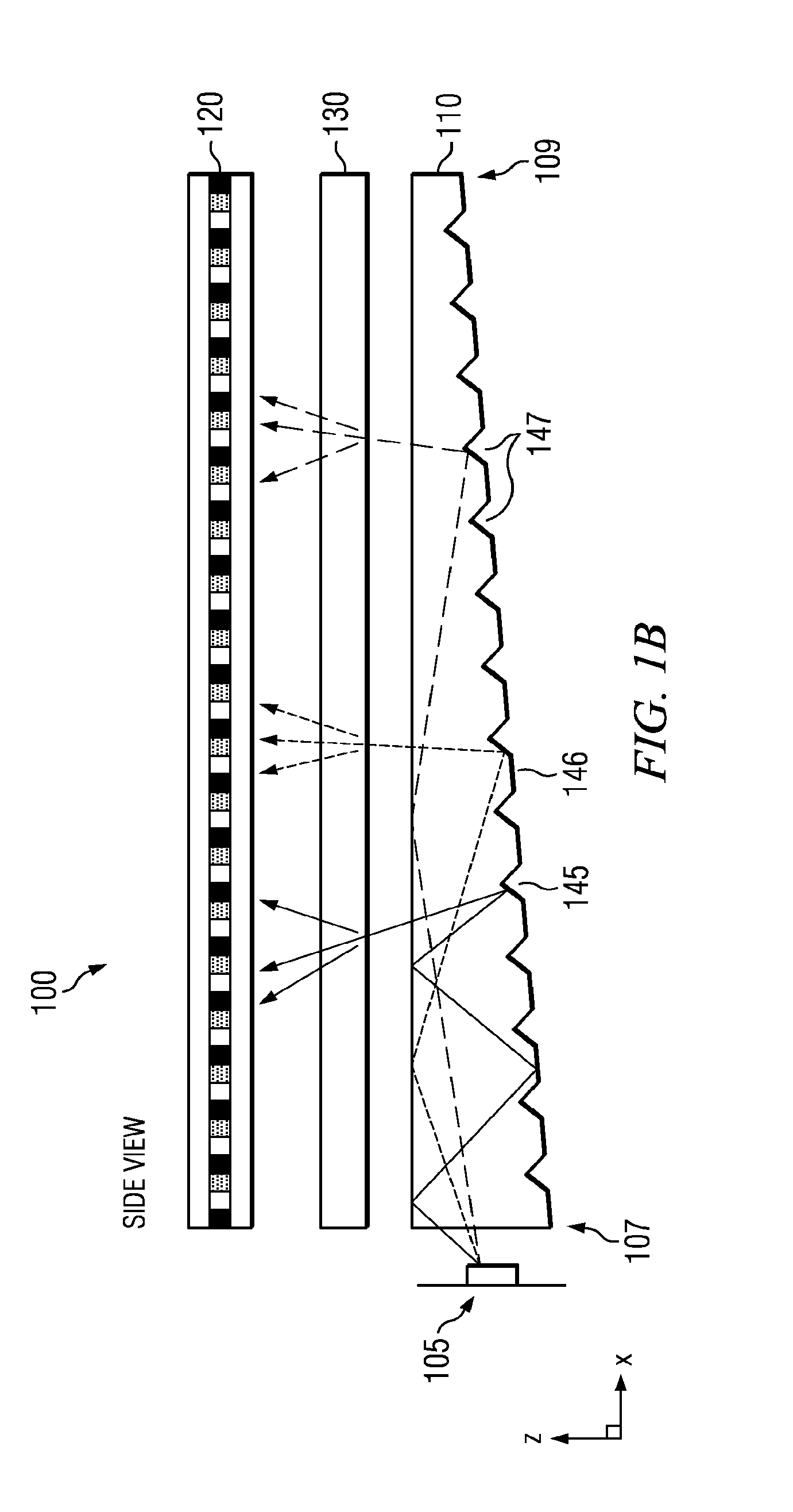
Patents
Literature
1619 results about "Light valve" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A light valve (LV) is a device for varying the quantity of light, from a source, which reaches a target. Examples of targets are computer screen surfaces, or a wall screen in the case of a light projector.
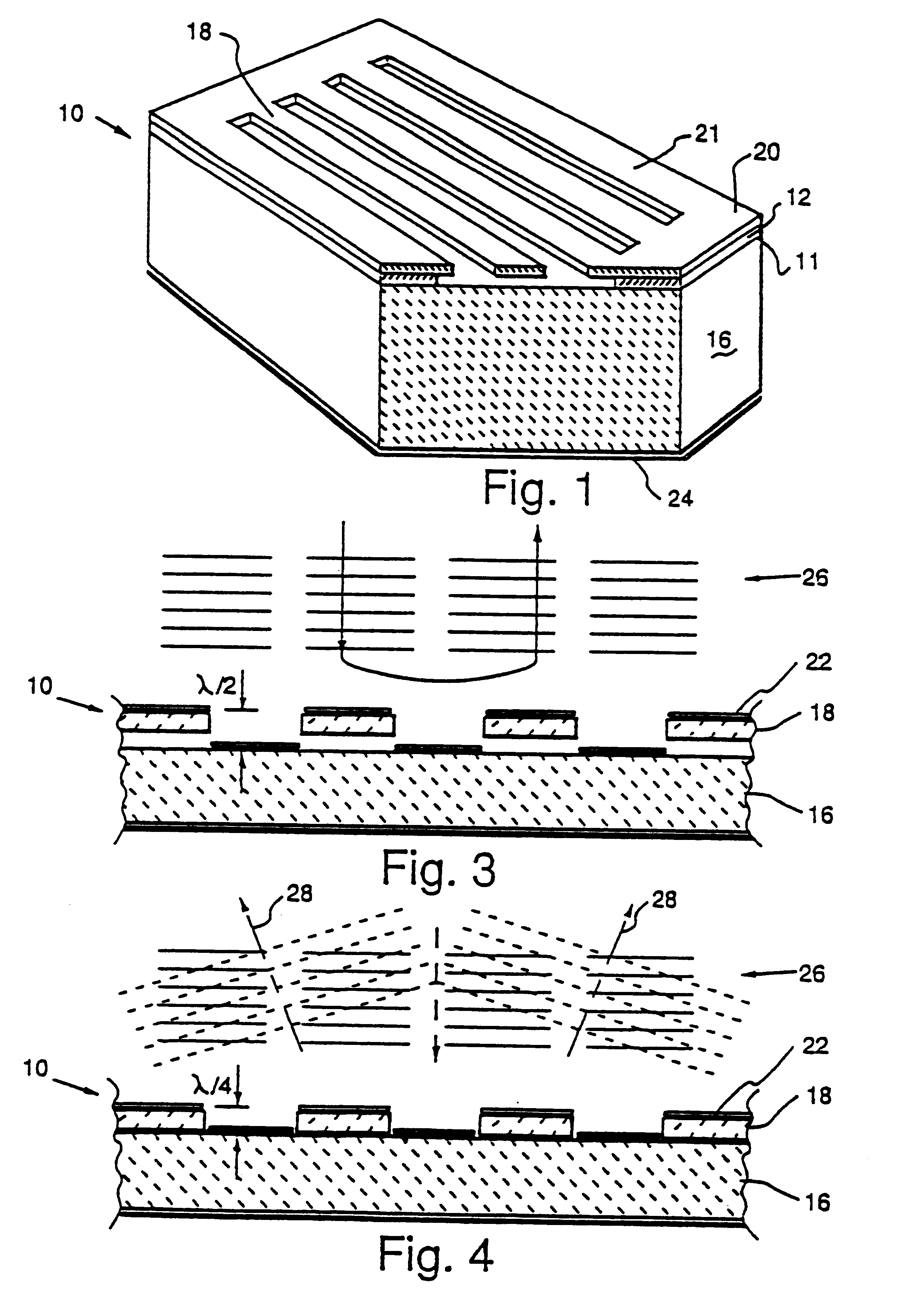
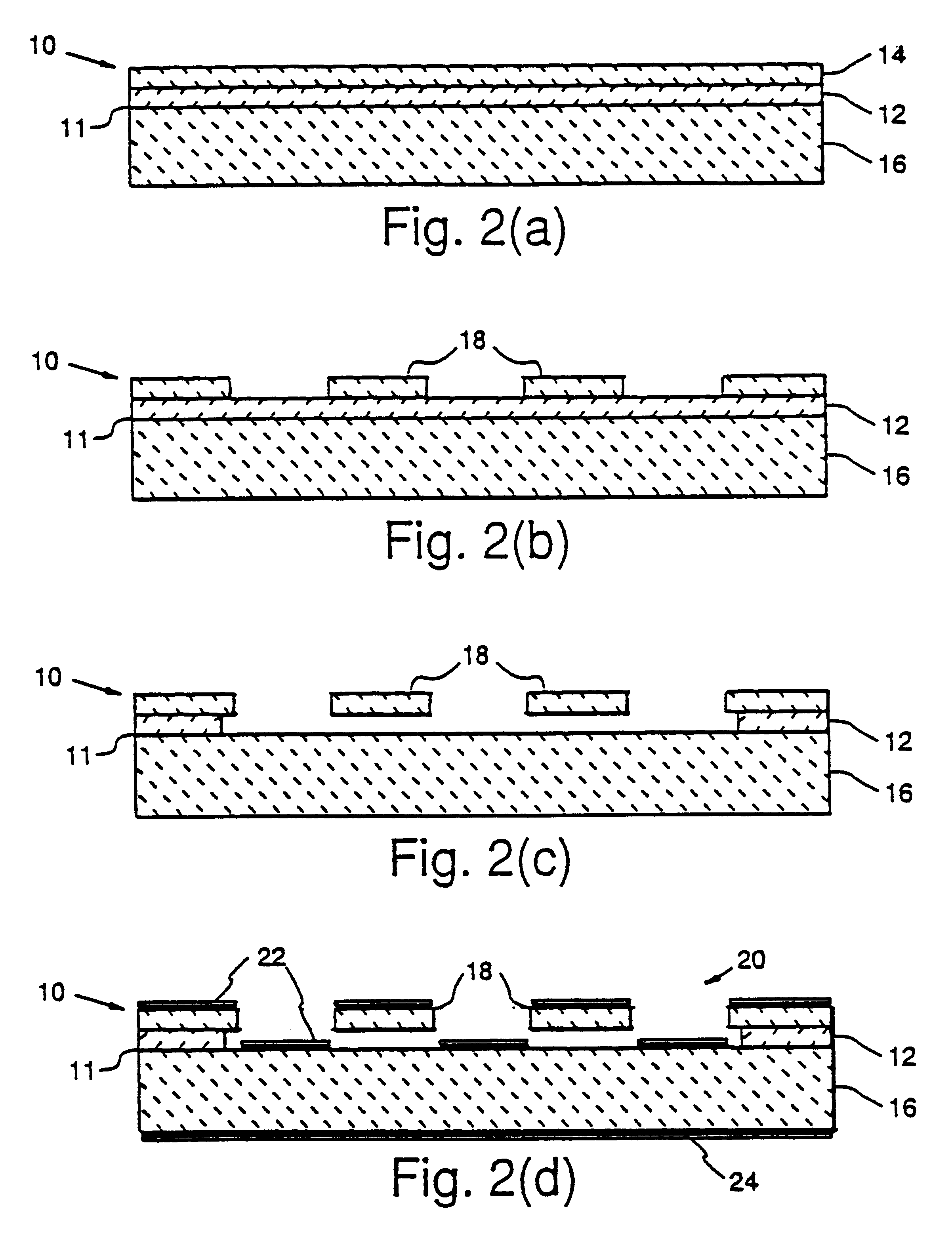
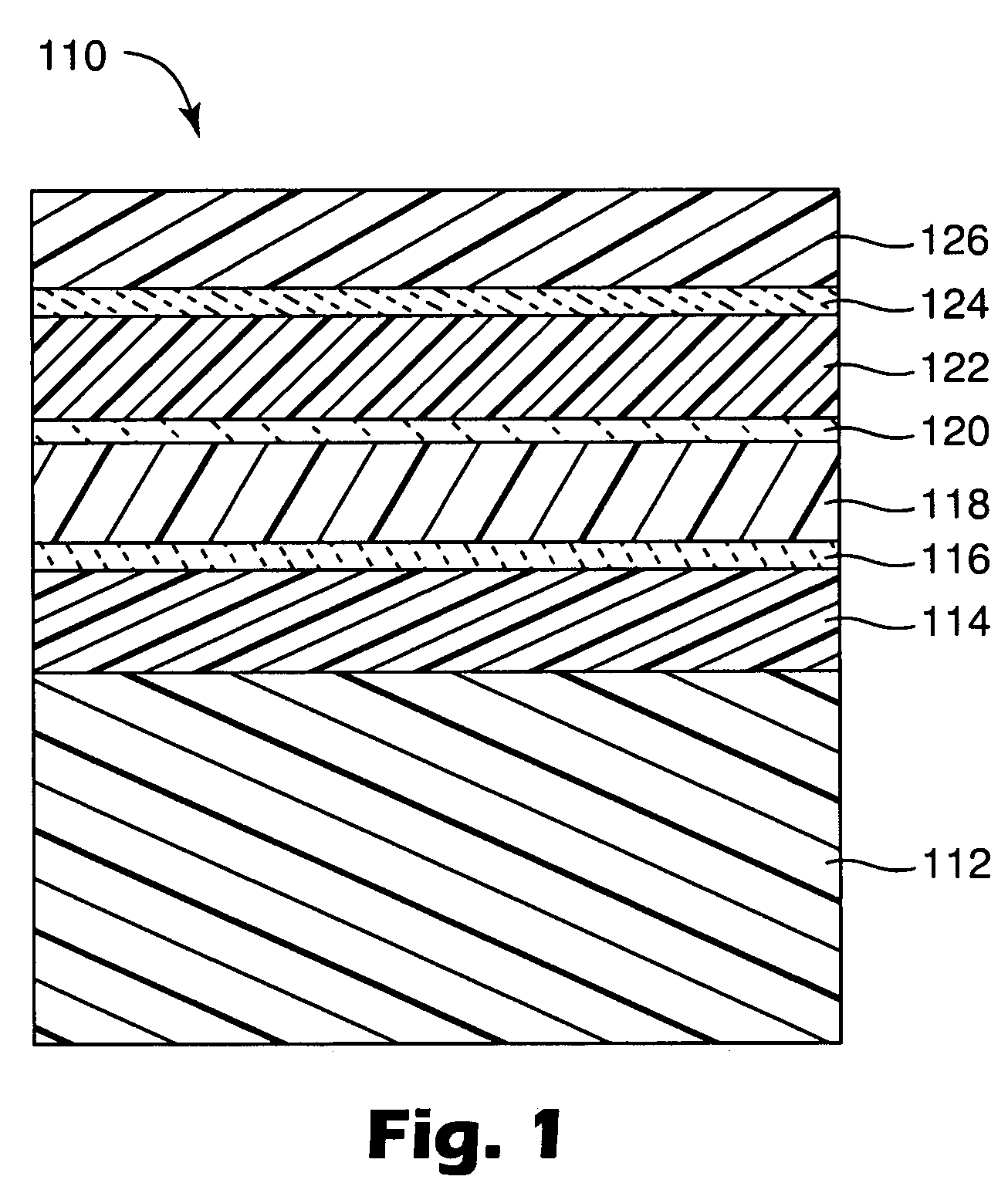
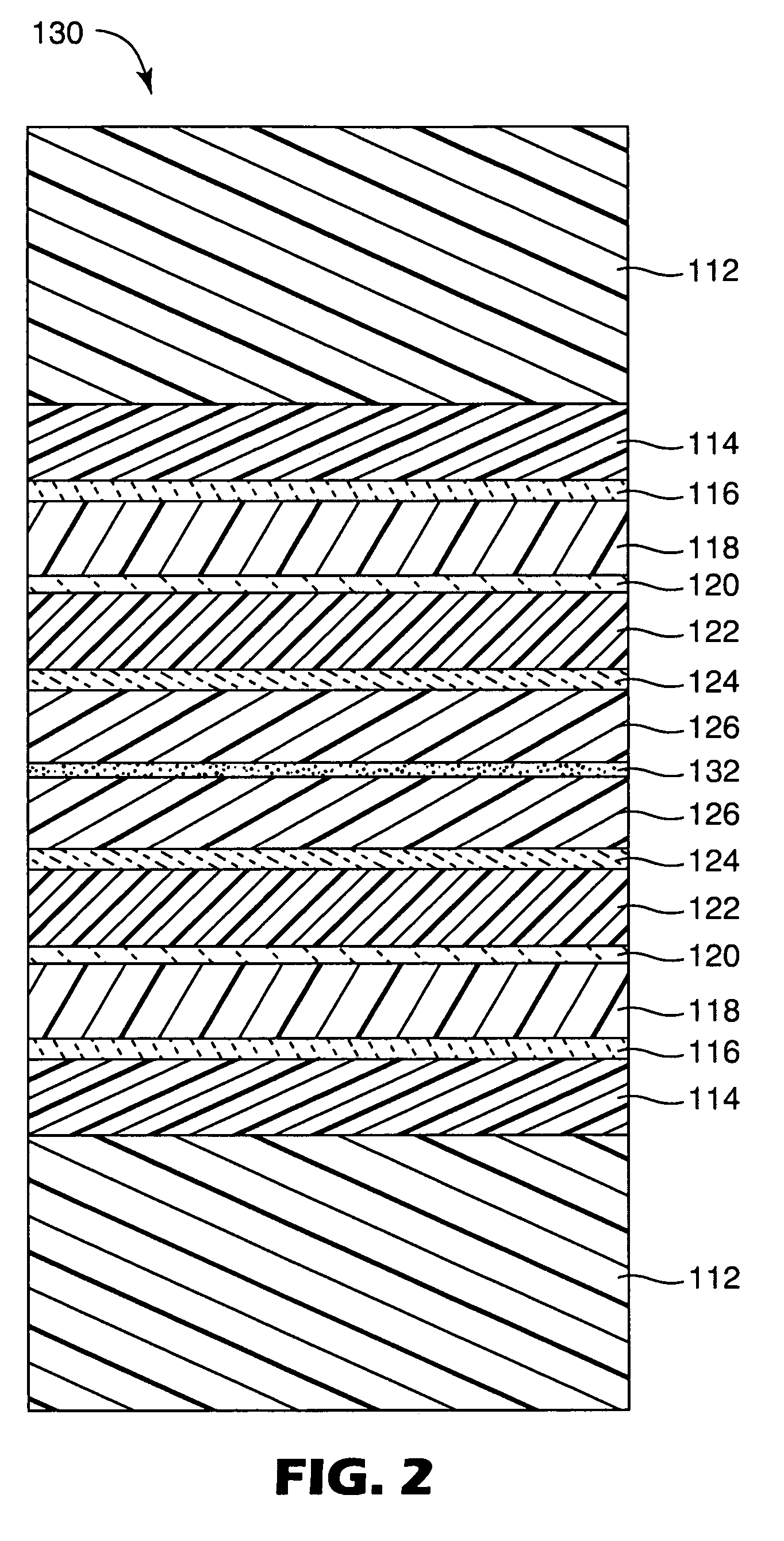
Flexible high-temperature ultrabarrier
InactiveUS7018713B2Final product manufactureSynthetic resin layered productsPolyethylene terephthalateOrganic light emitting device
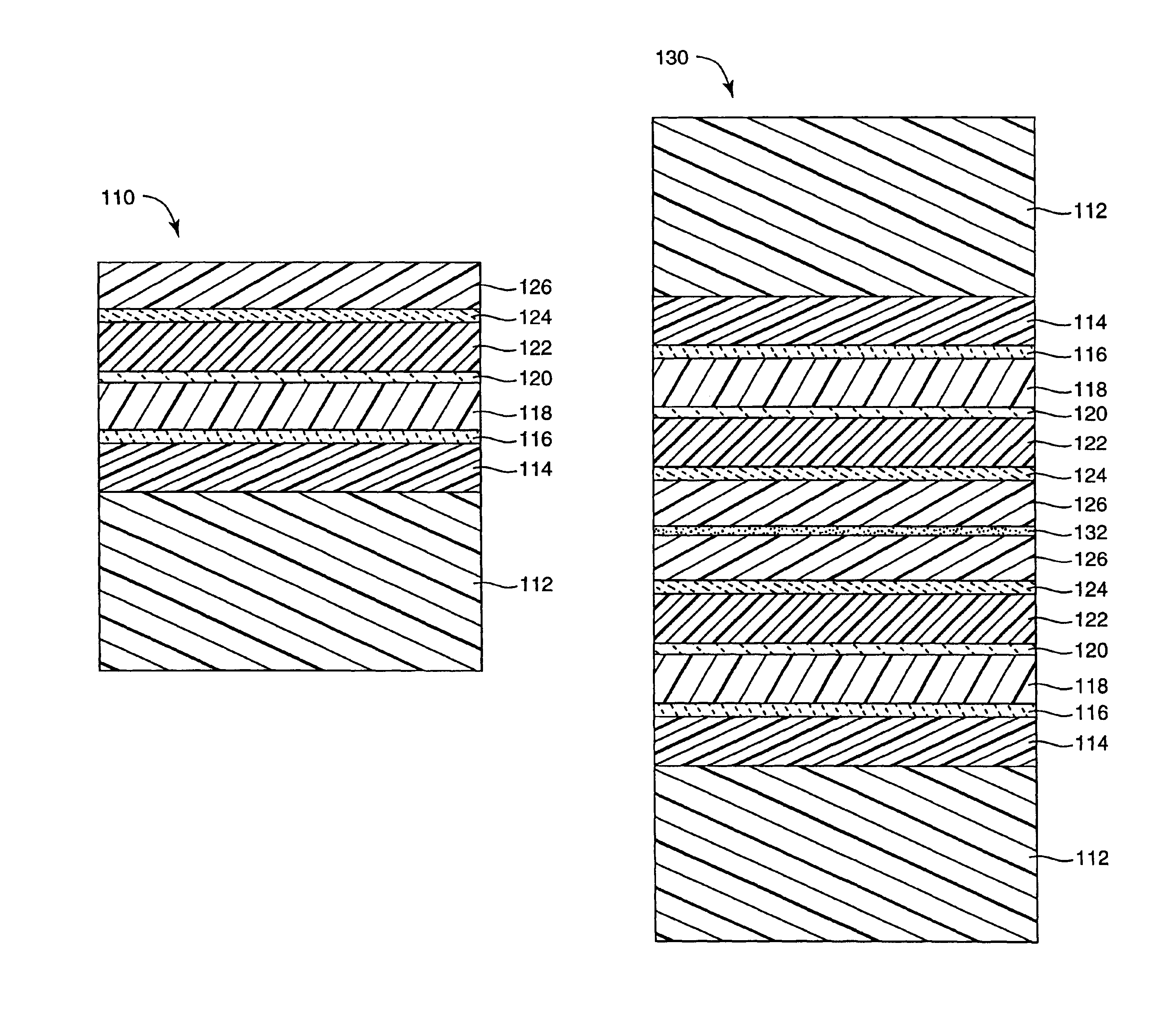
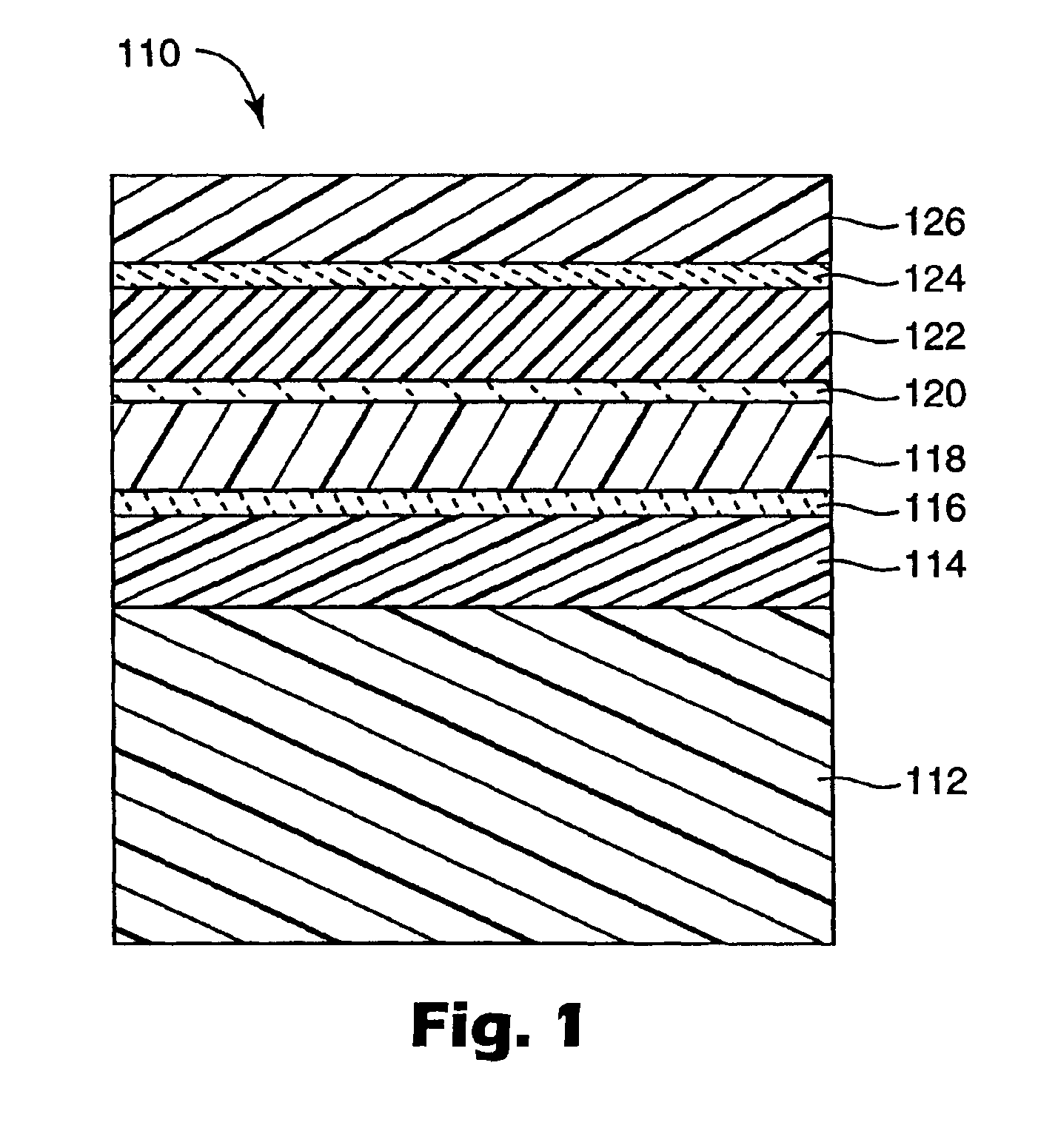
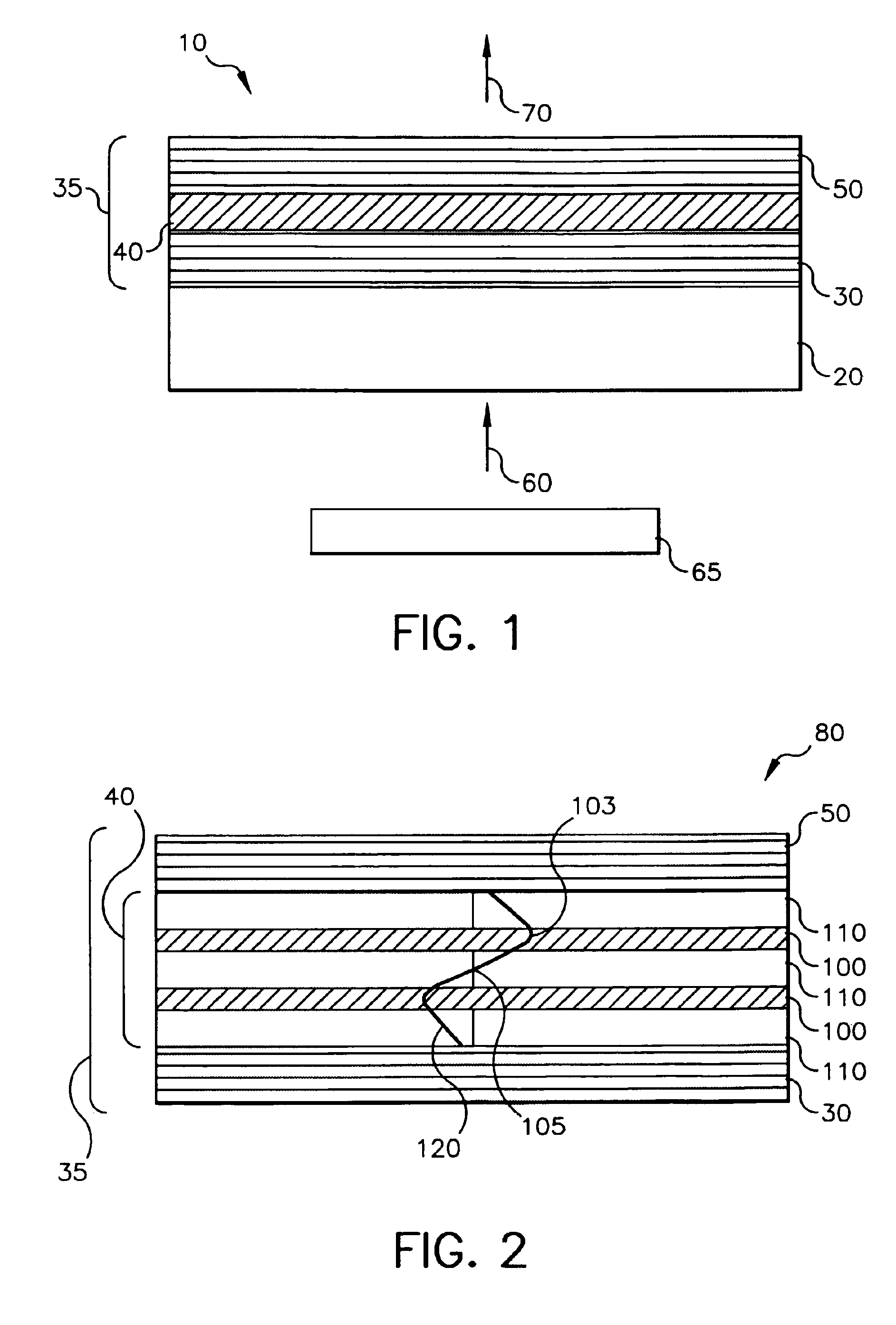
A flexible barrier assembly having a flexible visible light-transmissive substrate having a Tg greater than or equal to that of heat-stabilized polyethylene terephthalate (“HSPET”) overcoated with a first polymer layer having a Tg greater than or equal to that of HSPET and further overcoated with at least two visible light-transmissive inorganic barrier layers separated by at least one second polymer layer having a Tg greater than or equal to that of HSPET can be used to mount, cover, encapsulate or form moisture- and oxygen-sensitive articles such as organic light emitting devices and light valves.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Directional flat illuminators
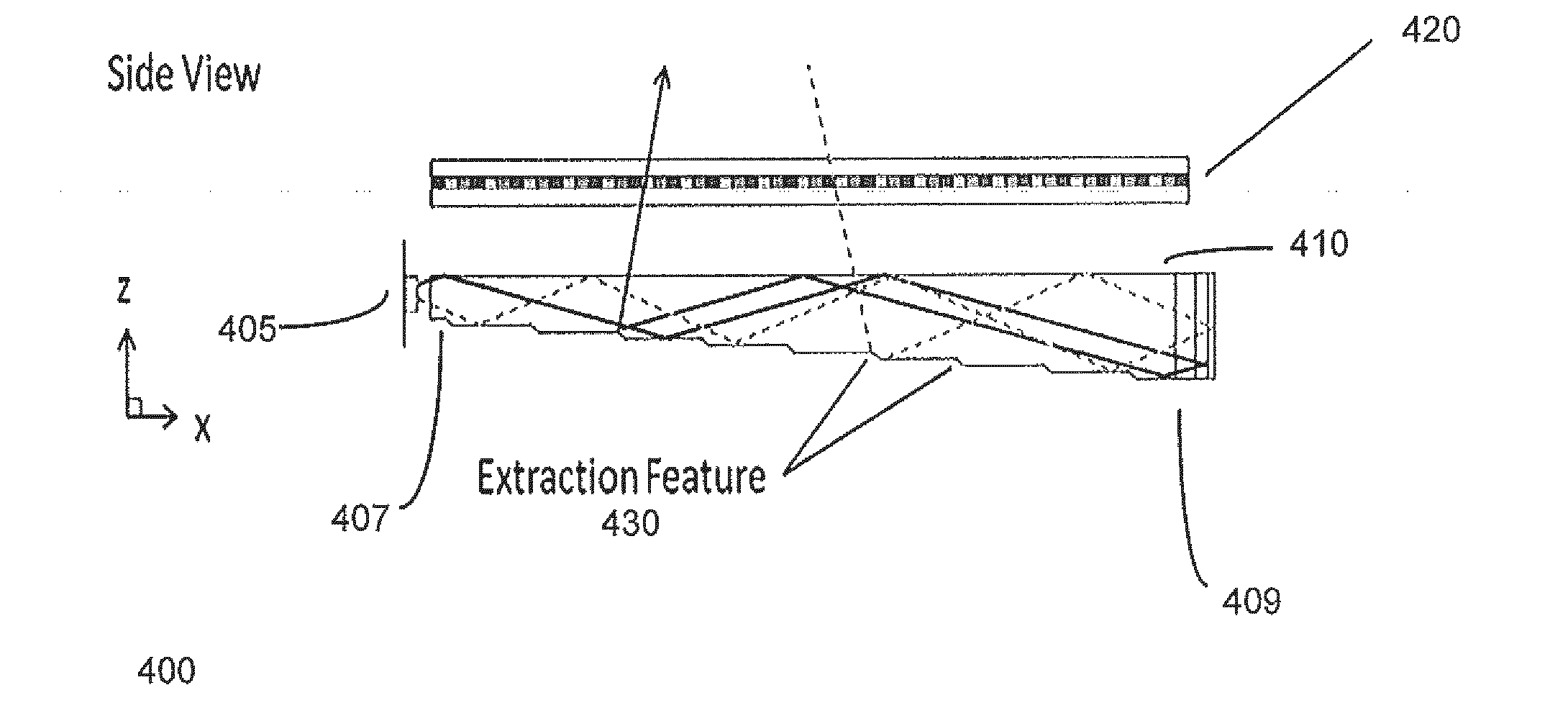
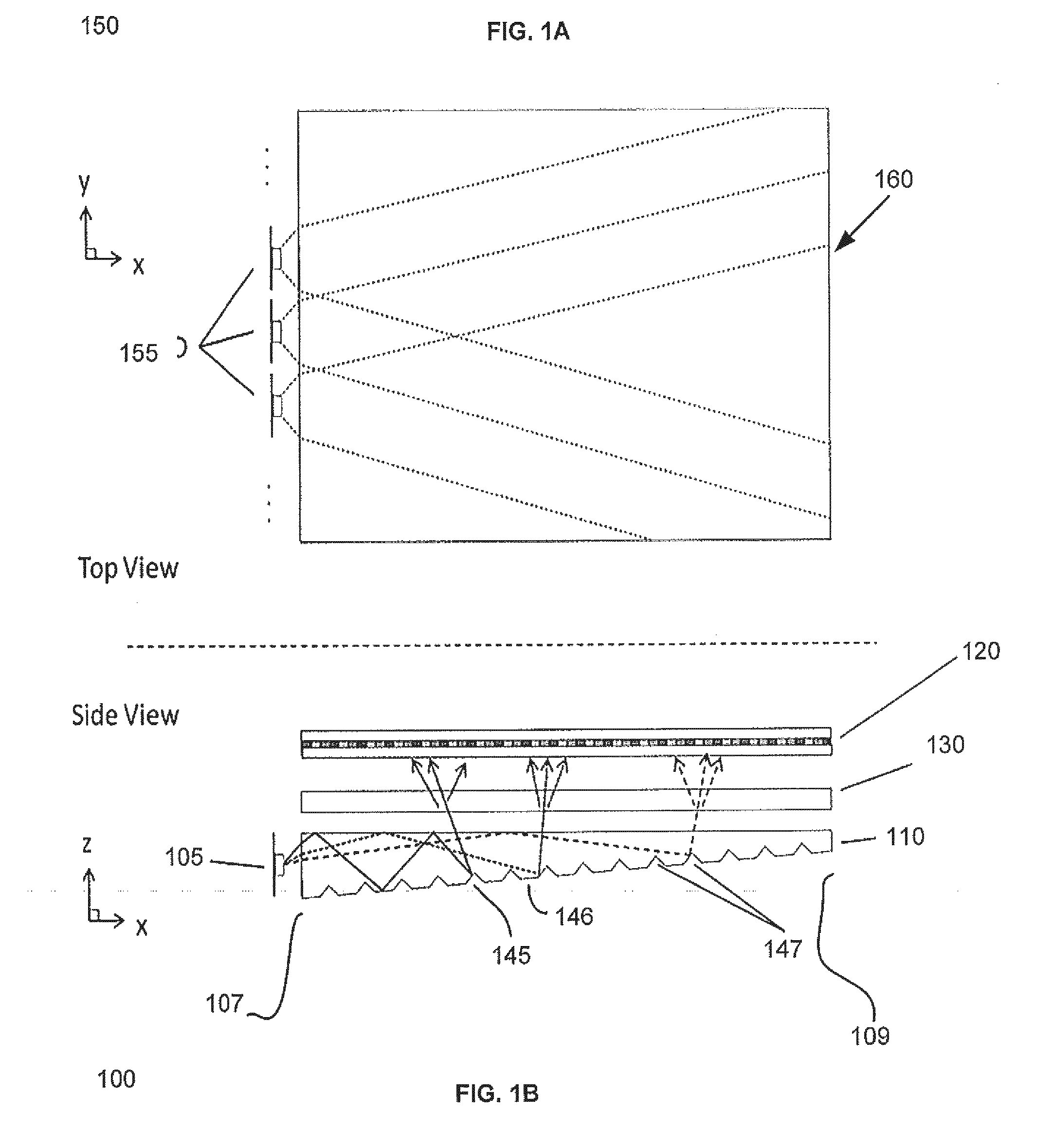
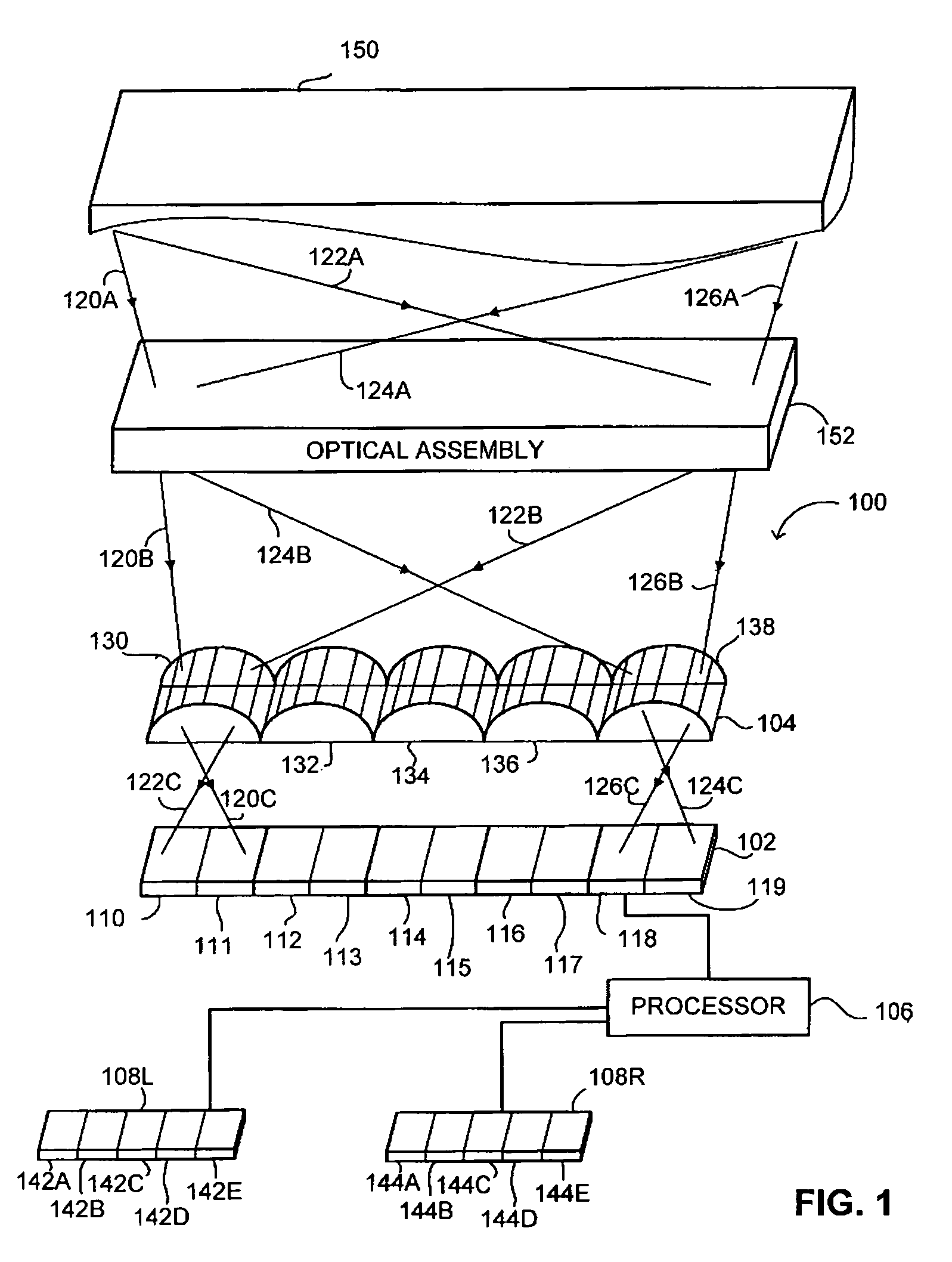
Disclosed is an optical valve or light valve for providing large area collimated illumination from localized light sources, and system and method thereof for 2D, 3D, and / or autosteroscopic displays. An optical valve may include a stepped structure, in which the steps include separated extraction features which may be optically hidden to light propagating in a first direction. Light propagating in a second direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the optical valve. Such controlled illumination may provide for efficient, multi-user autostereoscopic displays as well as improved 2D display functionality.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Enhanced resolution for image generation
InactiveUS7417617B2High resolutionCathode-ray tube indicatorsSteroscopic systemsImage resolutionDisplay device
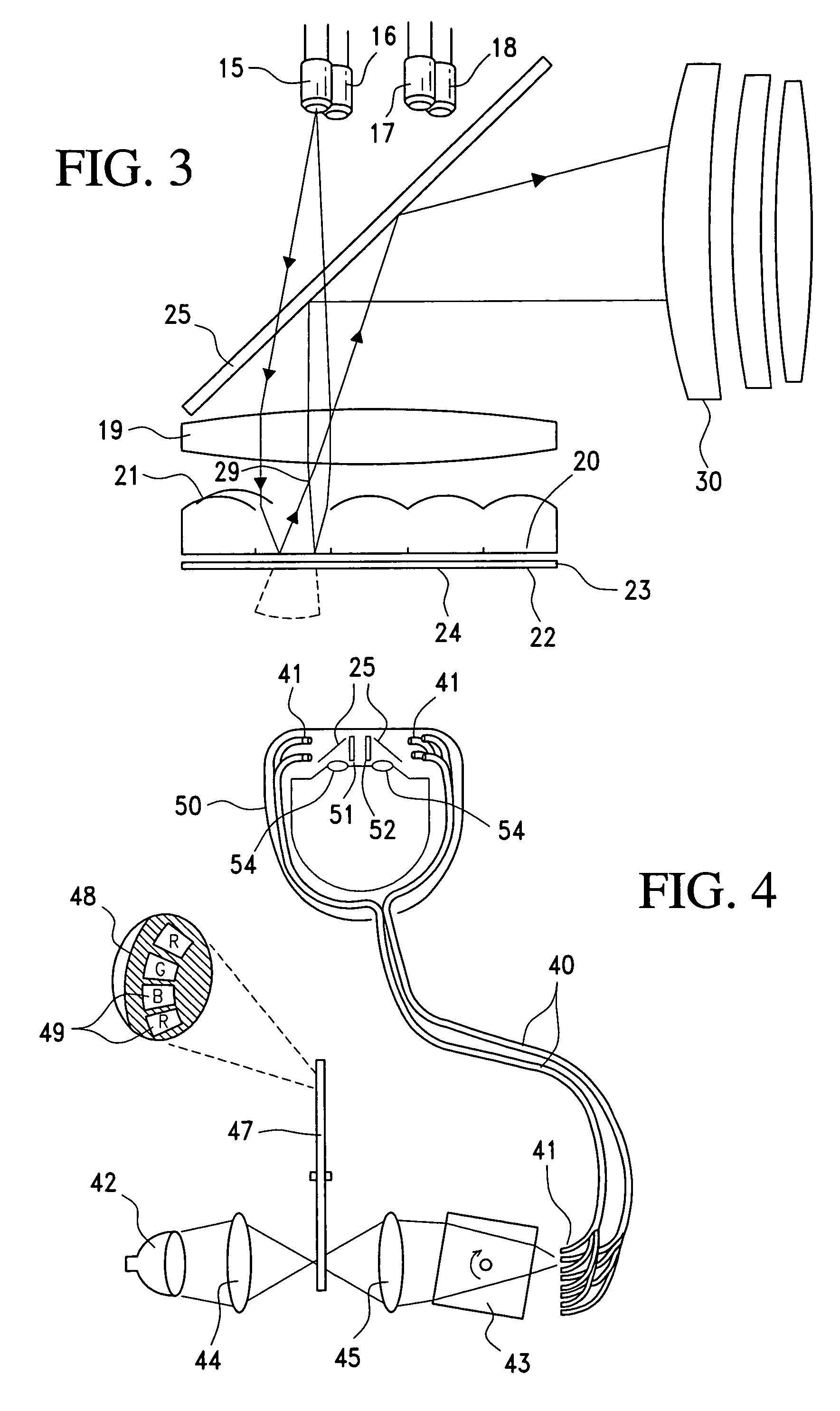
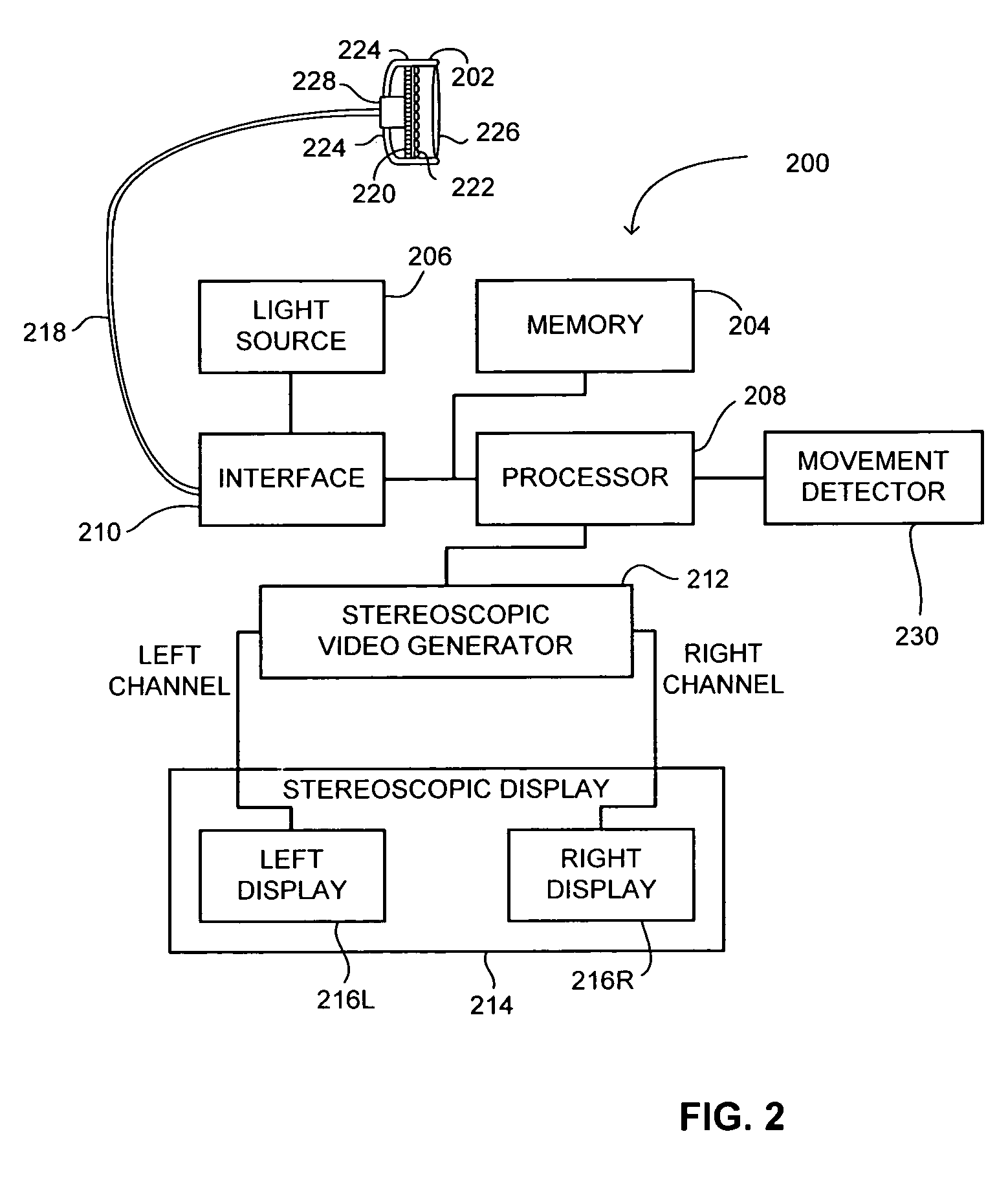
Images with enhanced resolution are created with a display device comprising a non-transmissive light valve including addressable pixels, a light source that directs light to the light valve, and a lens positioned between the light valve and the light source, the lens directing light from the light source to the pixels on the light valve and the light valve directing light to viewing optics. The light valve is an integrated circuit ferroelectric liquid crystal device (ICFLCD), or other light valve arrays such as a digital light processor (DLP) display, having an array of addressable pixels. Such light valves may be mounted in a head mounted display.
Owner:DIMENSION TECH
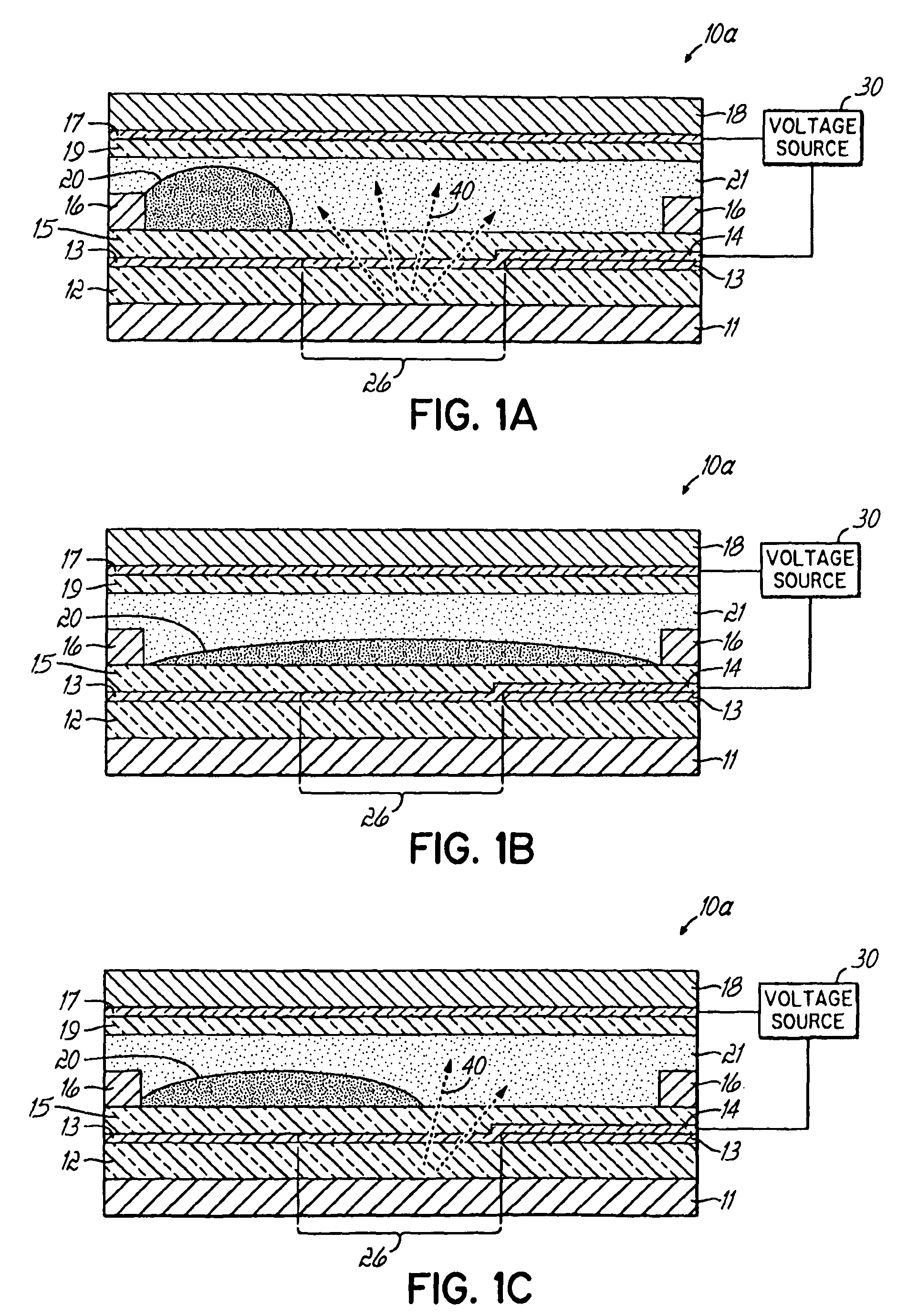
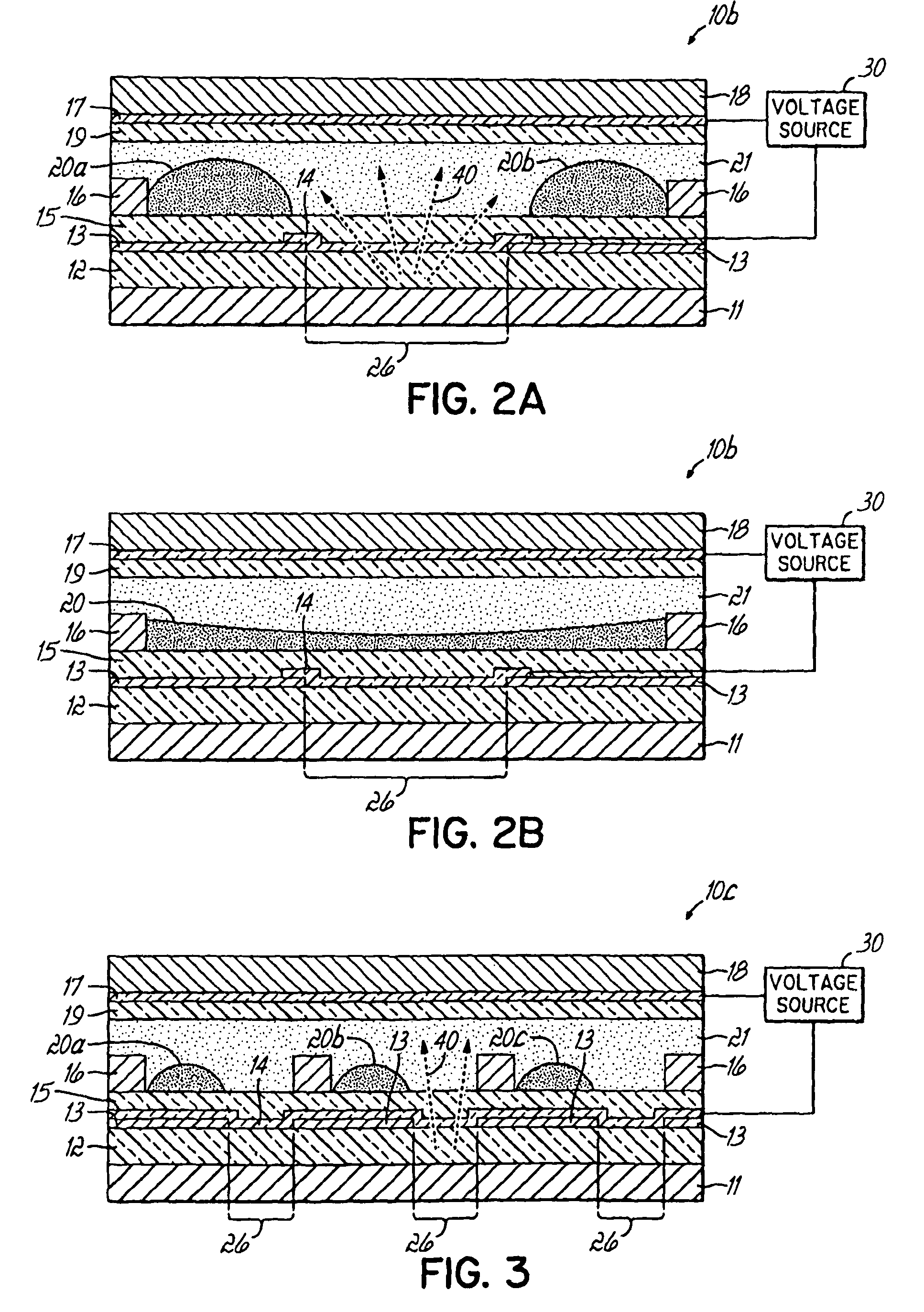
Display Capable Electrowetting Light Valve
ActiveUS20080297880A1High operating requirementsEasy constructionDiffusing elementsNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceFlat panel display
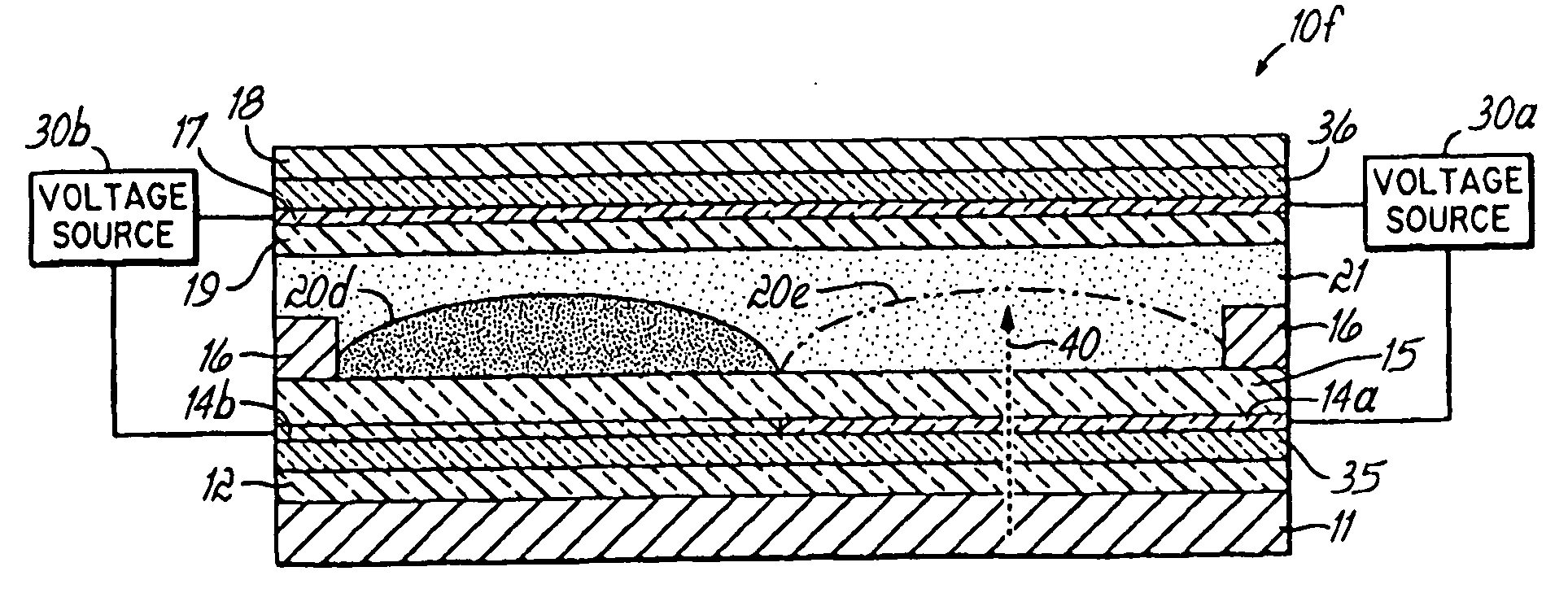
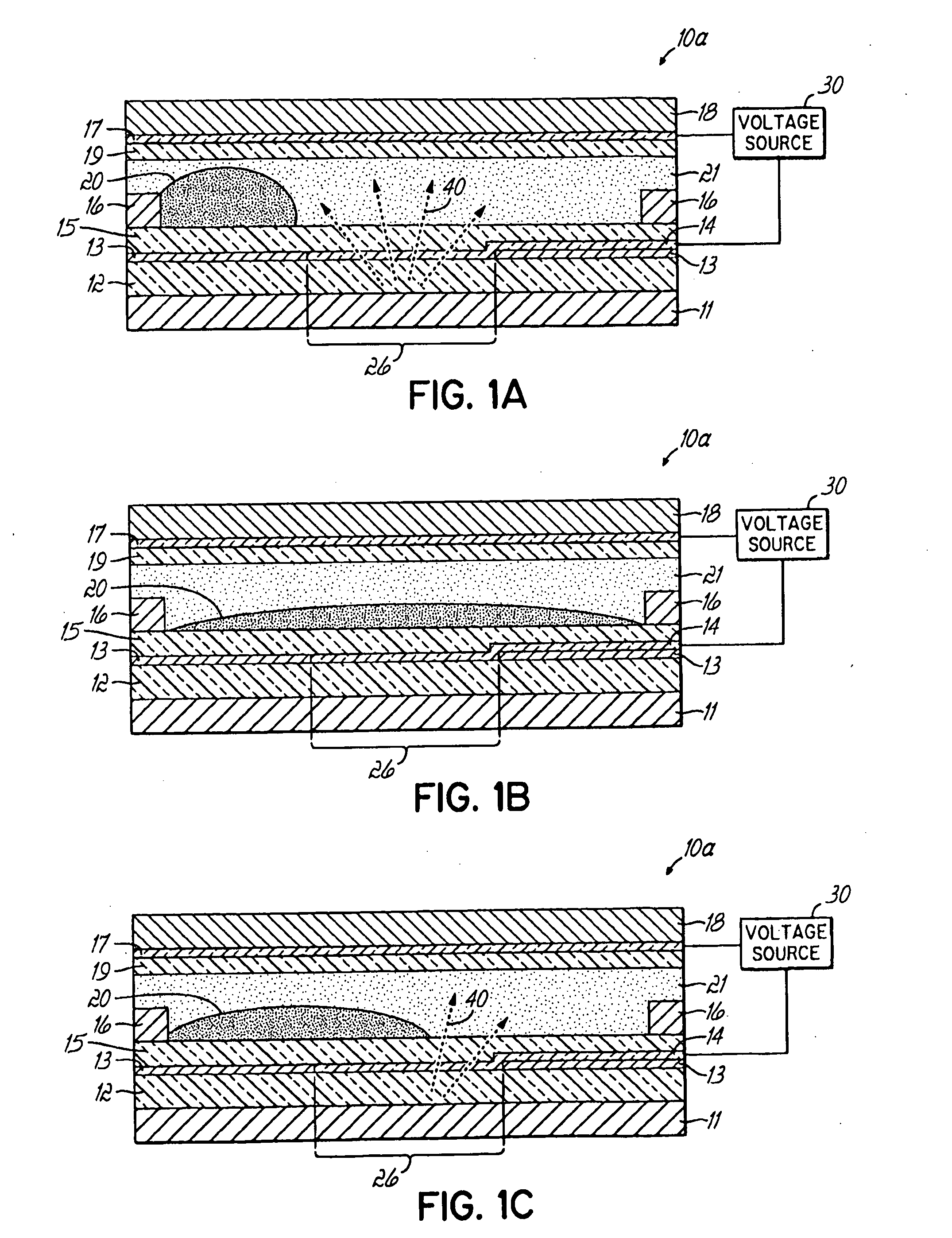
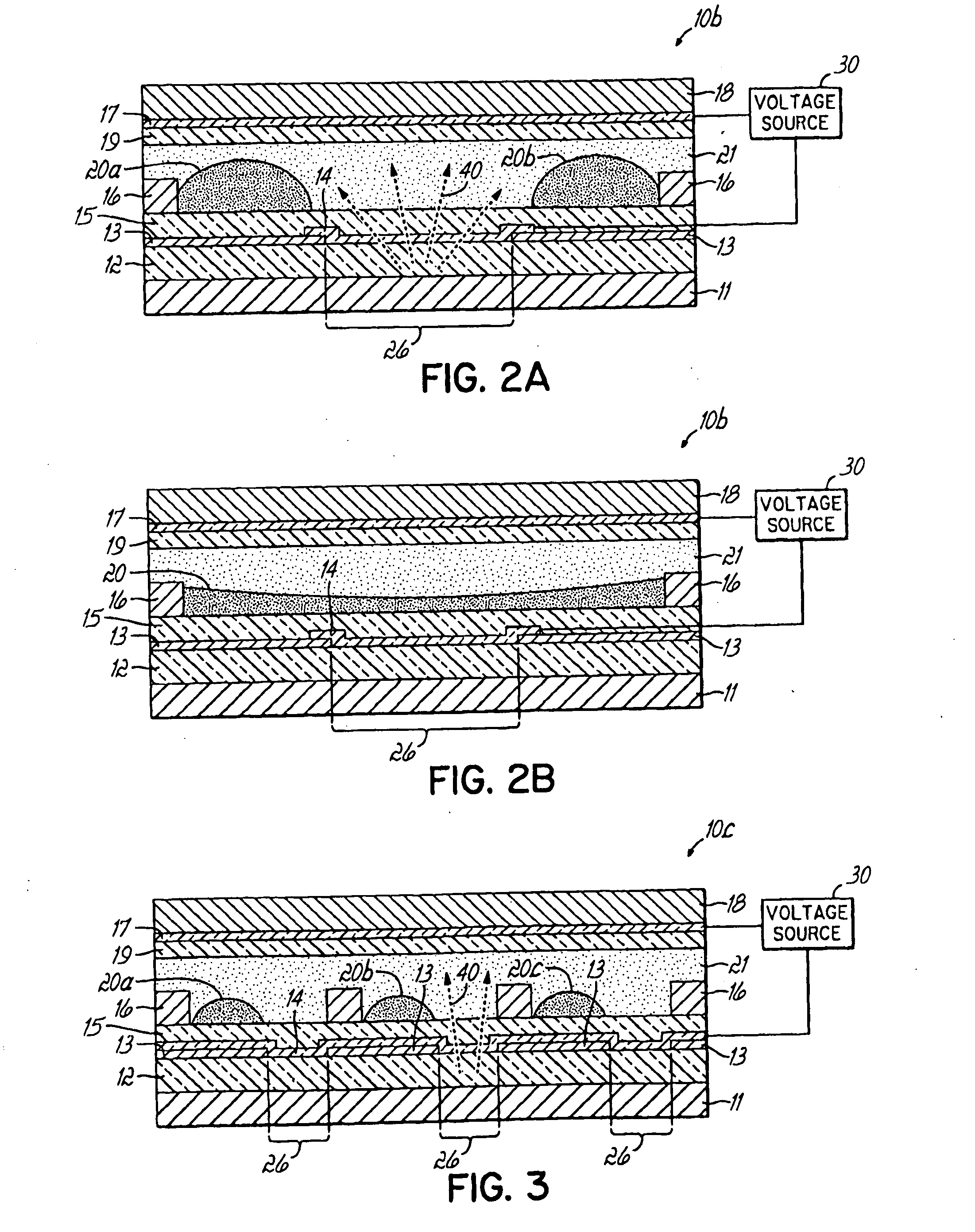
The invention relates to light transmissive, transflective, or reflective flat panel display devices and, more specifically, to light emissive flat panel displays constructed from high performance electrowetting light valve (ELV) devices (10a-g). An array of ELV devices (10a-g) is mounted on or adjacent to a backlight (11), employing a reflector (13) allowing for improved transmission. The backlight (11) may be partially diffusely reflective or translucent as to also allow for creation of a transflective display panel.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Opitcal projection and image sensing apparatus
InactiveUS20070263174A1Reduce manufacturing costProjectorsColor television detailsBeam splitterLight beam
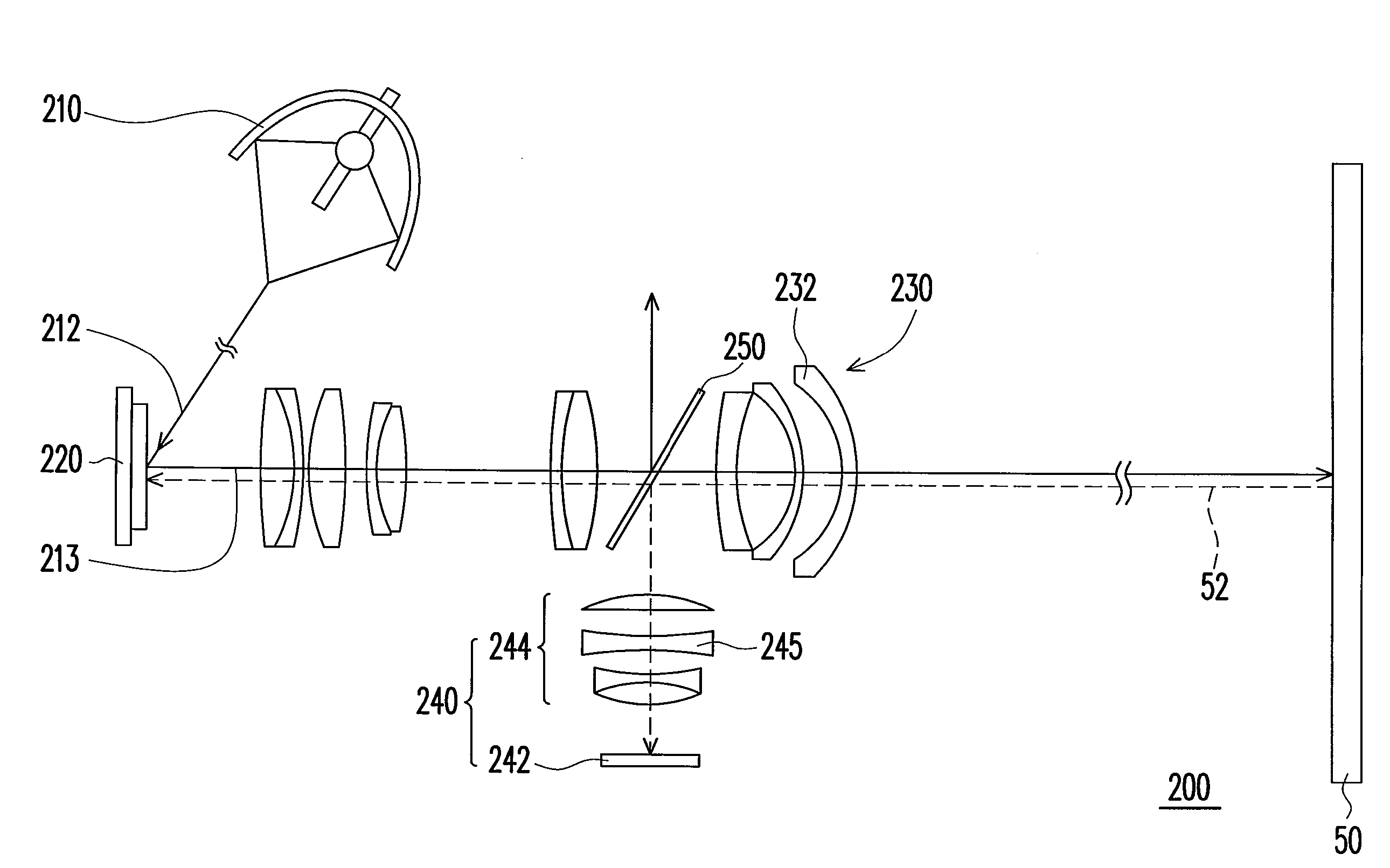
An optical projection and image sensing apparatus including a light source, a light valve, a first lens set, a sensing module, and a beam splitter is provided. The light valve is used to convert an illumination light from the light source to an image light beam. The first lens set is used to project the image light to display an image on a screen, and the sensing module is used to sense a sensing light from the image on the screen. The beam splitter is disposed on the optical paths of the image light and the sensing light from the image on the screen. One of the sensing module and the light valve is disposed on the optical path of the sensing light passing through the beam splitter, and the other is disposed on optical path of the sensing light reflected by the beam splitter.
Owner:YOUNG OPTICS
Method and apparatus for using an array of grating light valves to produce multicolor optical images
InactiveUS6219015B1Improve accuracyMade smallStatic indicating devicesDiffraction gratingsPlane mirrorColored light
A multicolor optical image-generating device comprised of an array of grating light valves (GLVs) organized to form light-modulating pixel units for spatially modulating incident rays of light. The pixel units are comprised of three subpixel components each including a plurality of elongated, equally spaced apart reflective grating elements arranged parallel to each other with their light-reflective surfaces also parallel to each other. Each subpixel component includes means for supporting the grating elements in relation to one another, and means for moving alternate elements relative to the other elements and between a first configuration wherein the component acts to reflect incident rays of light as a plane mirror, and a second configuration wherein the component diffracts the incident rays of light as they are reflected from the grating elements. The three subpixel components of each pixel unit are designed such that when red, green and blue light sources are trained on the array, colored light diffracted by particular subpixel components operating in the second configuration will be directed through a viewing aperture, and light simply reflected from particular subpixel components operating in the first configuration will not be directed through the viewing aperture.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Image capture device
InactiveUS20140104490A1Simple structureImprove ease of useTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptoelectronicsImage capture
An image capture device including a housing, a first lens unit, a second lens unit, an image sensing element, and a beam spliter is provided. The housing includes a body, a first lens barrel, and a second lens barrel. The first lens unit is disposed within the first lens barrel and includes a first switchable light valve. The second lens unit is disposed within the second lens barrel and includes a second switchable light valve. The image sensing element faces to the first lens unit. The beam spliter is configured in front of the image sensing element so that the image sensing element is able to receive a first image light passing through the first lens unit and a second image light passing through the second lens unit. The first switchable light valve and the second switchable light valve present a transparent state at different timings.
Owner:DONGGUAN MASSTOP LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY +1
Directionally illuminated waveguide arrangement
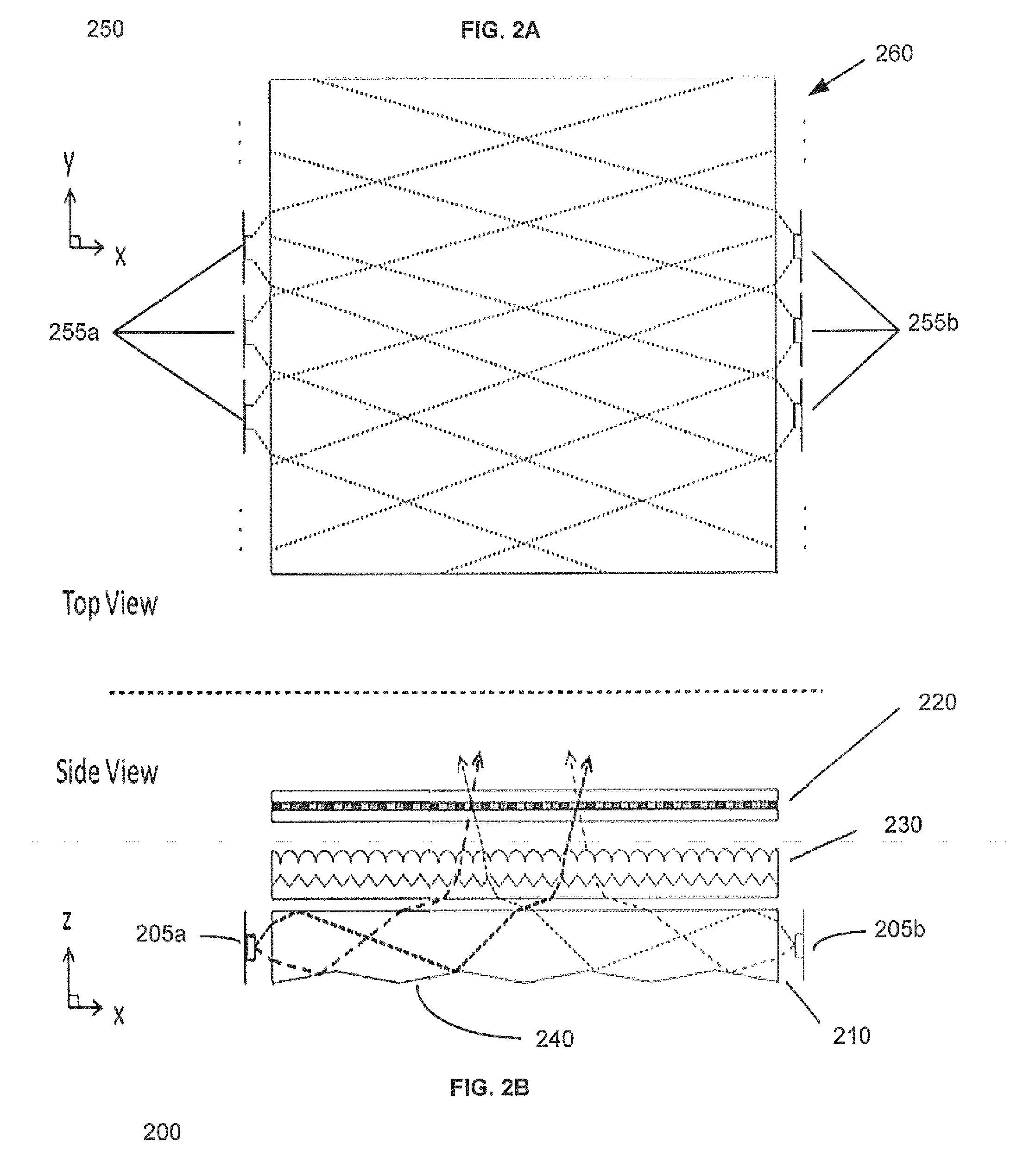
ActiveUS20140036361A1Function increaseCompact display structureMechanical apparatusPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight guideLight beam
Disclosed is a light guiding valve apparatus comprising an optical valve, a two dimensional light source array and a focusing optic for providing large area collimated illumination from localized light sources. A stepped waveguide may be a stepped structure, in which the steps may be extraction features optically hidden to guided light, propagating in a first forward direction. Returning light propagating in a second backward direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide discrete illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the waveguide. A two dimensional array of viewing windows may be produced. Such controlled illumination may provide for efficient, multi-user autostereoscopic displays with wide viewing freedom and low cross talk and near-eye displays that are substantially transparent.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
Method for using a light valve to reduce the visibility of an object within a gaming apparatus
Owner:IGT
Optical element to reshape light with color and brightness uniformity
InactiveUS20030076423A1High resolutionIncrease contrastTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using projection devicesContrast levelActive matrix
A light valve such as an active matrix LCD between crossed polarizers, utilizing, for instance, individual transistors to control each "pixel area" of the LCD and storage elements to store video signal data for each pixel, with optically shielded "dead spaces" between pixels to eliminate electric field cross-talk and non-information-bearing light bleed-through, is illuminated with a bright independent light source which creates a video image projected via specialized projection optics onto an internal or external screen without distortions, regardless of the angle of projection onto the screen. Use of heat sinks, IR reflective coatings, heat absorbing optics, optional fluid and a thermistor controlled pixel transistor bias voltage injection servo circuit stabilizes image performance, maintaining accurate color and contrast levels as the LCD changes temperature. In one embodiment of the invention, use of a multi-color LCD with a stepped cavity, producing different thicknesses of LCD for the different wavelengths that pass through it, allows a linear correspondence between the wavelengths passing through the LCD to produce true black, high contrast and CRT-like color rendition. A dichroic mirror arrangement is used to overlap differently colored pixels in the projected image. Use of striped mirrors duplicate pixels, where necessary, eliminating spaces between pixels, creating a continuous image with no apparent stripes or dots. A special venetian-blind type of screen is also disclosed and methods for using the system to view three-dimensional video are also explained.
Owner:DOLGOFF GENE
Low fill factor wire grid polarizer and method of use
In an example embodiment, a wire grid polarizer includes a plurality of parallel conductors having a pitch (P), a width (W), and a height (H). In example embodiments, a fill-factor (W / P) is greater than approximately 0.18 and less than approximately 0.25. In another example embodiment, a display system includes a light source and a light-valve. The display system also includes a wire grid polarizer that includes a plurality of parallel conductors having a pitch (P), a width (W), and a height (H). In example embodiments, a fill-factor (W / P) is greater than approximately 0.18 and less than approximately 0.25.
Owner:SK MICROWORKS SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Time-sequential colour projection
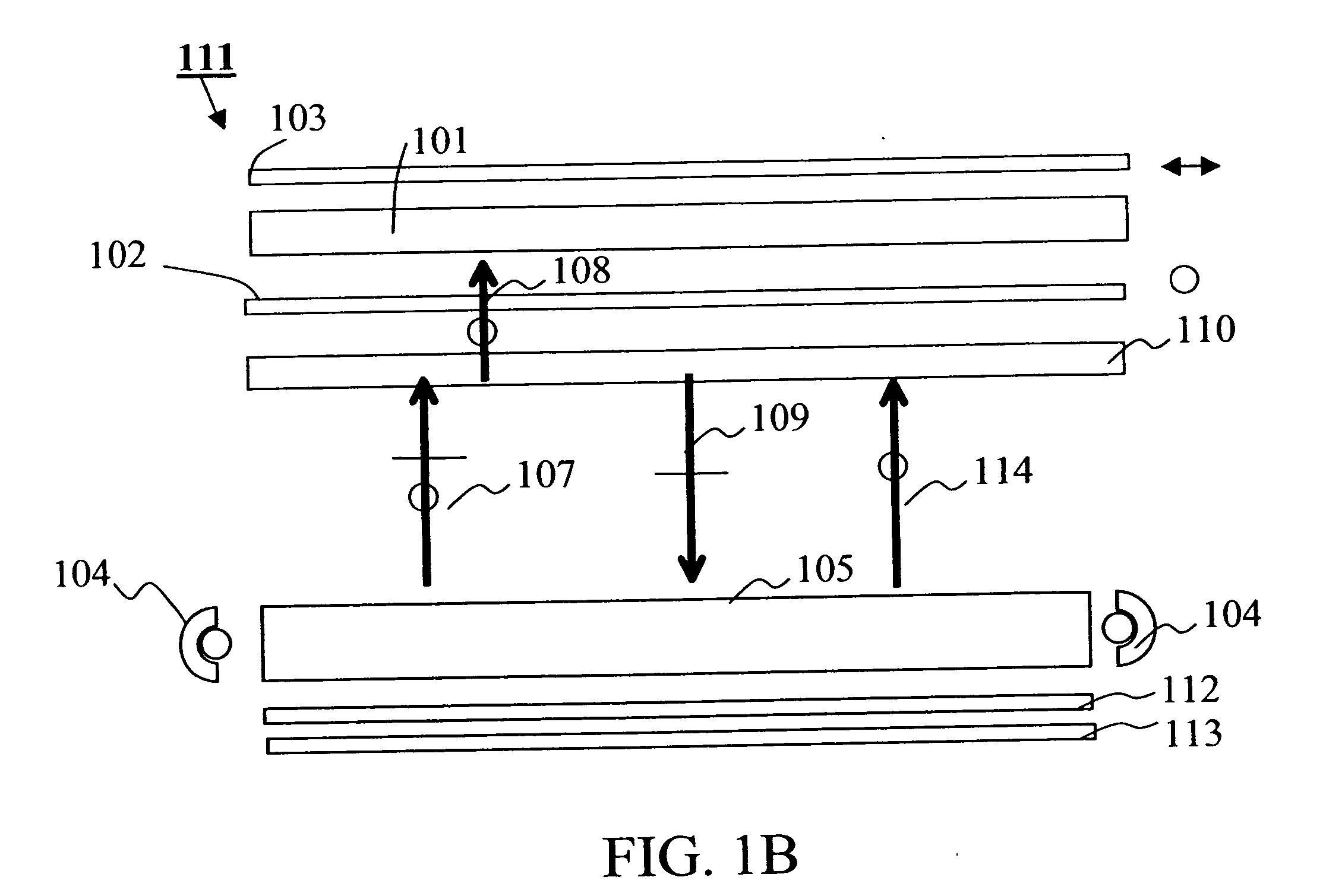
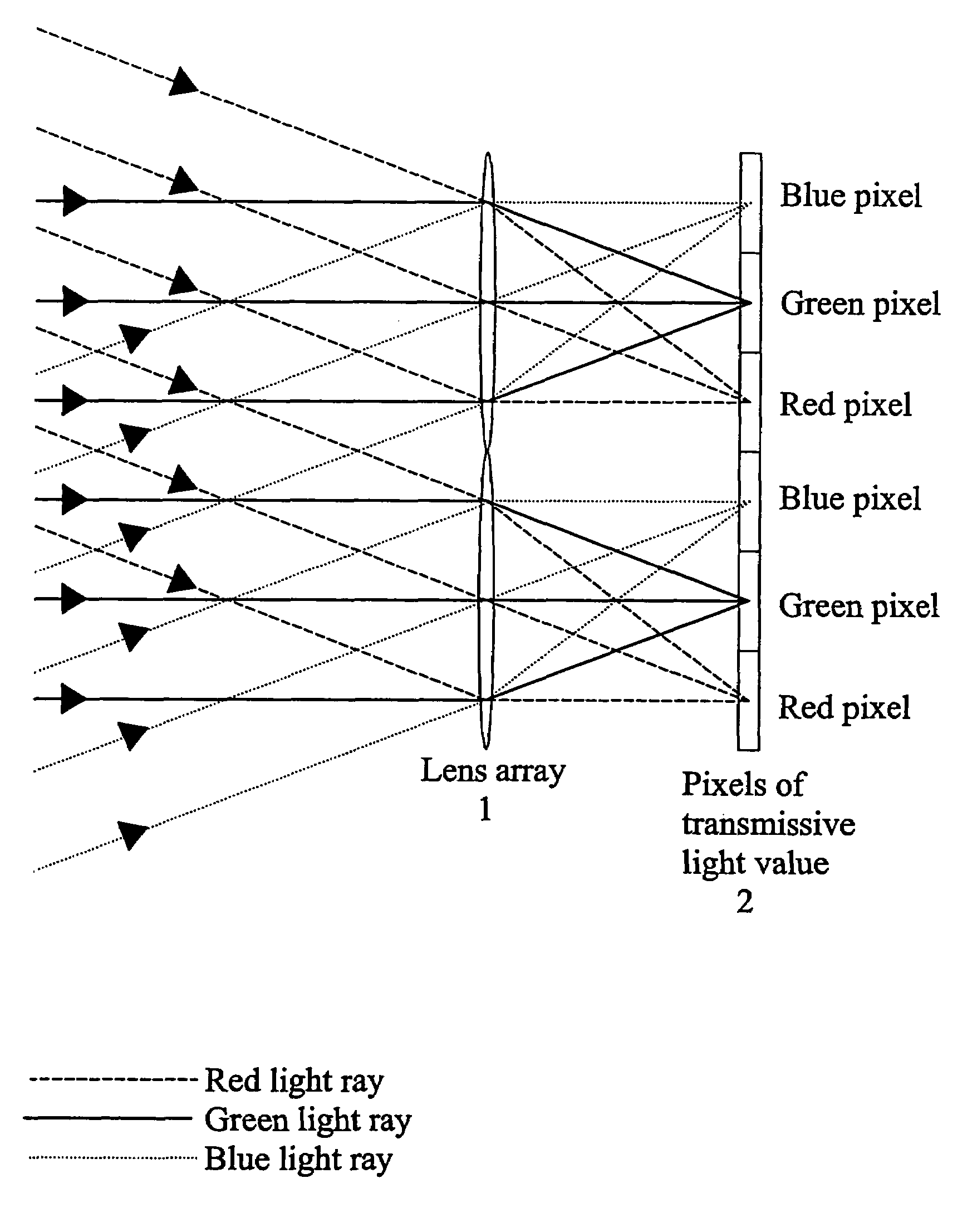
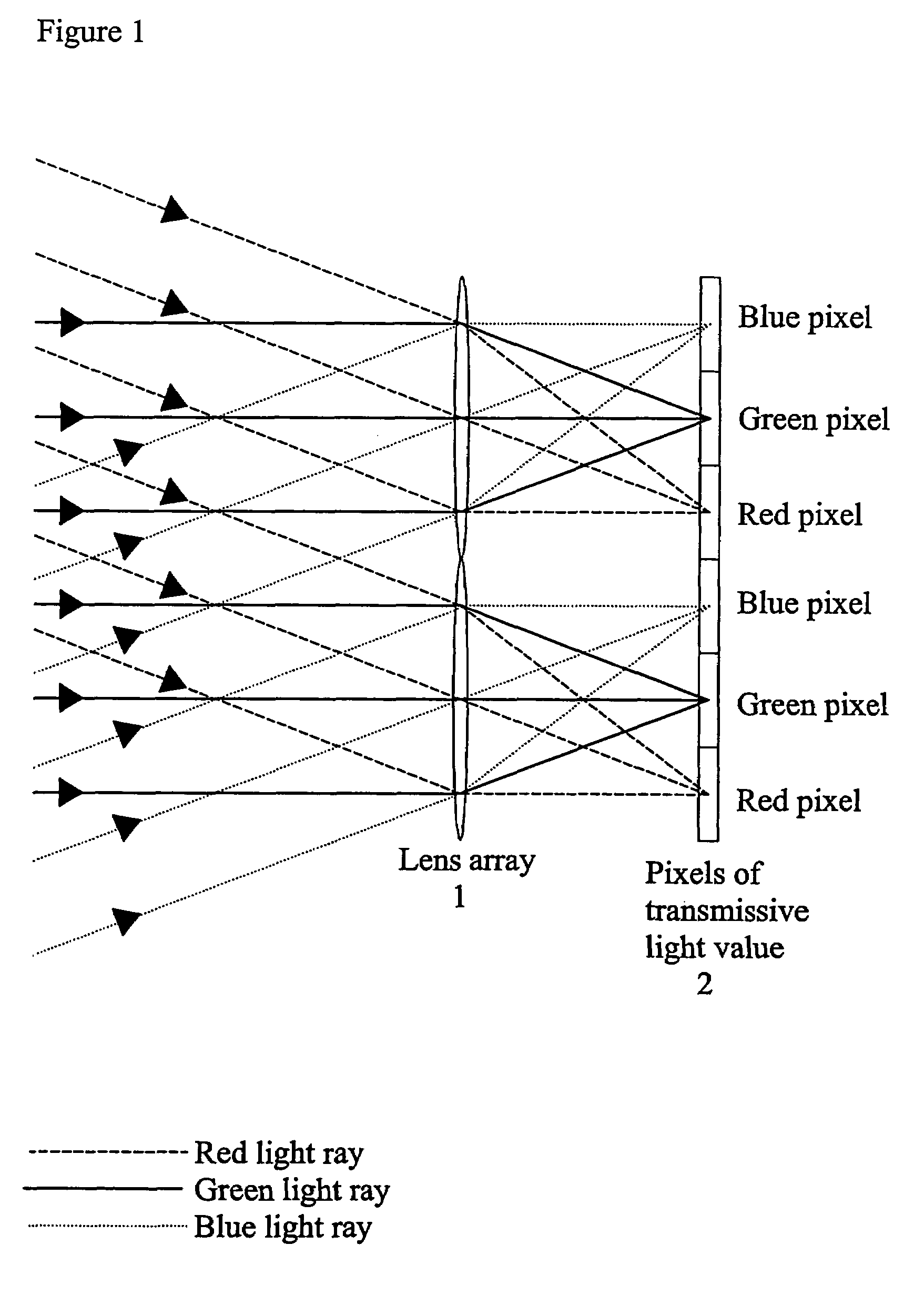
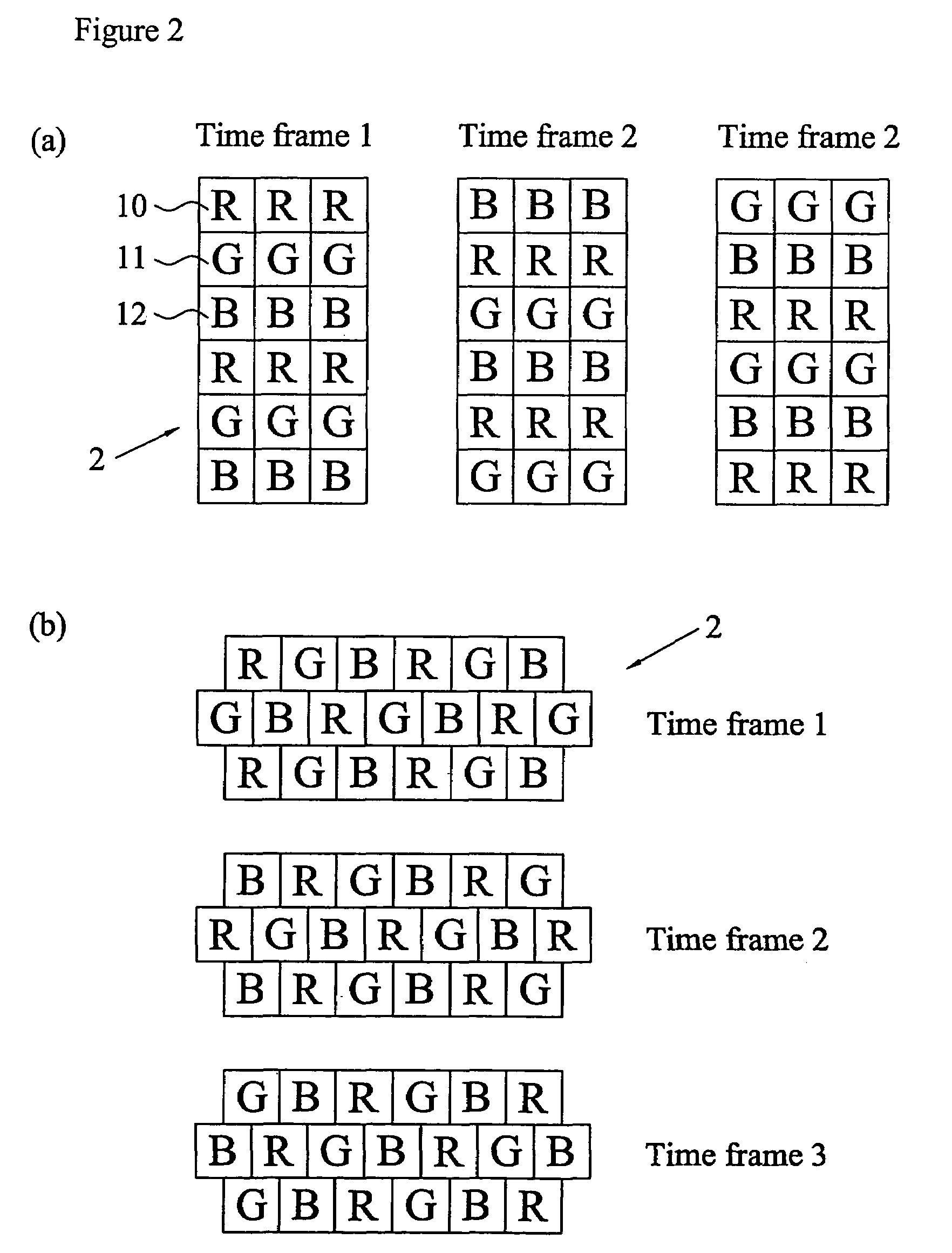
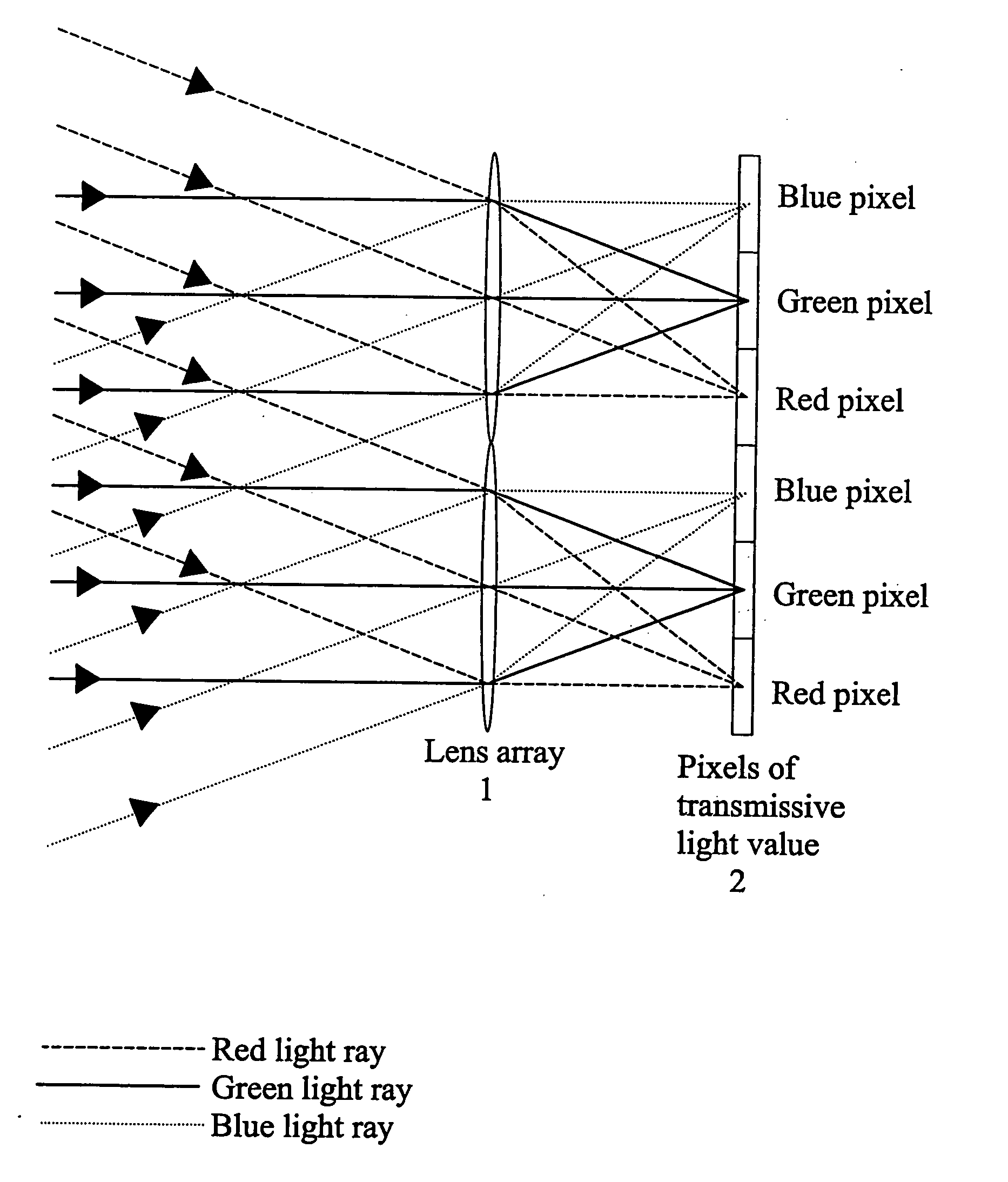
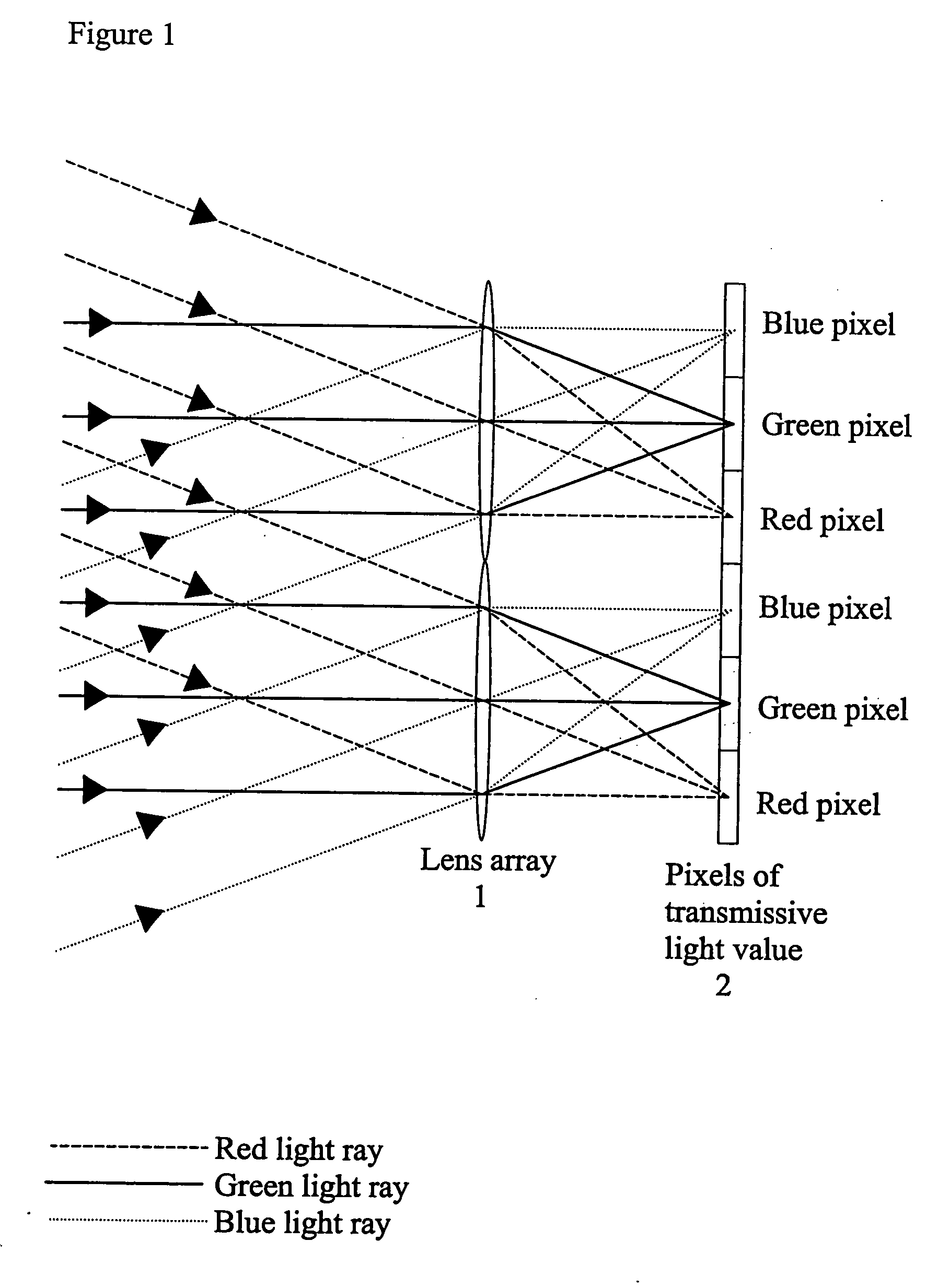
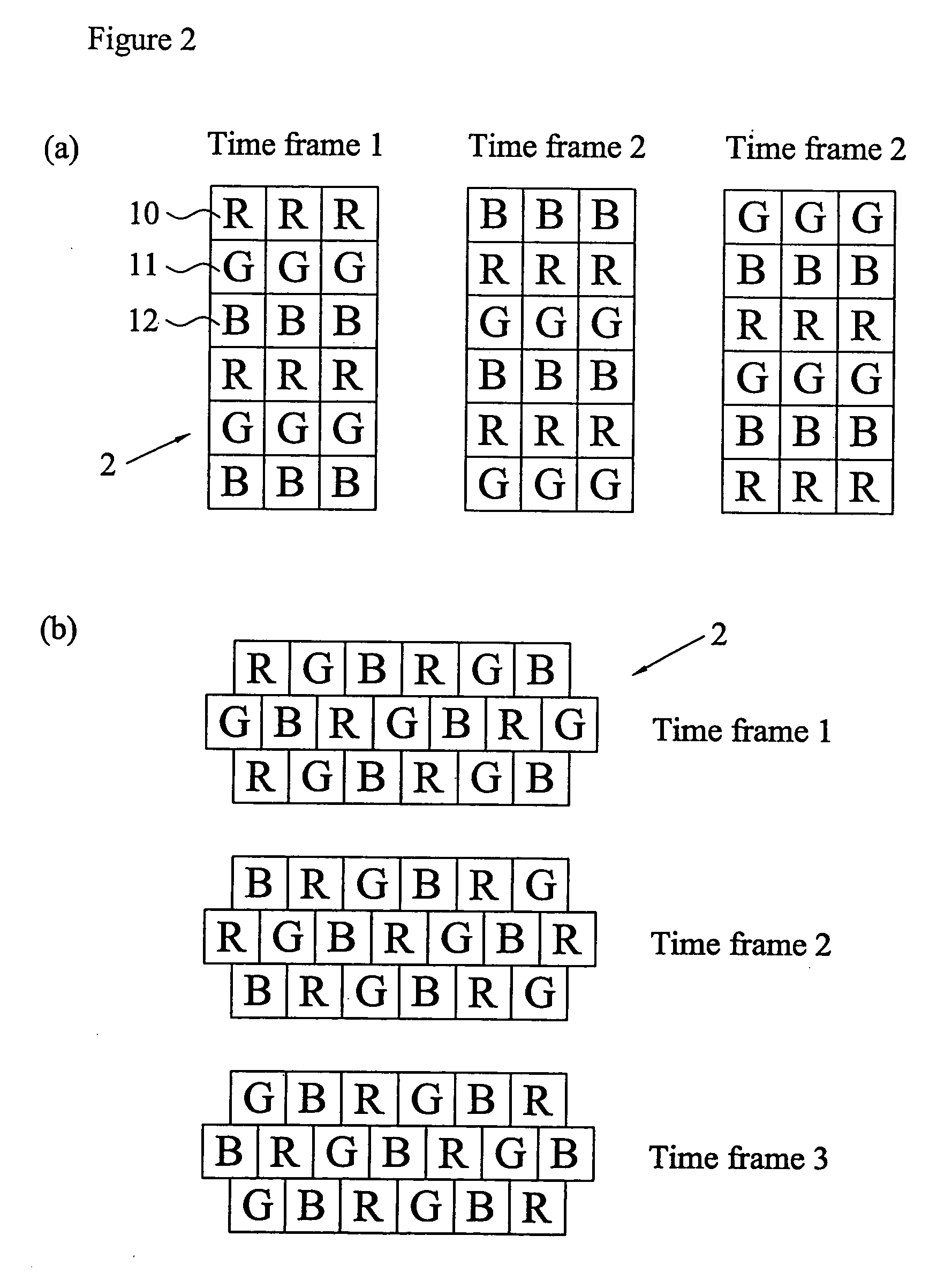
InactiveUS7404644B2High efficiency of illuminationLight-efficiency is relatively highProjectorsPolarising elementsOptoelectronicsLight valve
A time-sequential colour projector comprises a pixellated light valve (2), such as a liquid crystal device, and a plurality of light sources (30, 31, 32). The light sources (30, 31, 32) direct light on different sets of pixels of the light valve (2) via an optical system (1), such as a lens array, which focuses the light on pixels of the light valve (2). At least two of the light sources (30, 31, 32) are multiple colour light sources and the multiple colour light sources emit different colour components during each set of frames making up a complete image frame.
Owner:SHARP KK
Active device having variable energy/optical properties
InactiveUS8035882B2Avoid bendingMounting is thereby simplifiedNon-linear opticsWater vaporLiquid water
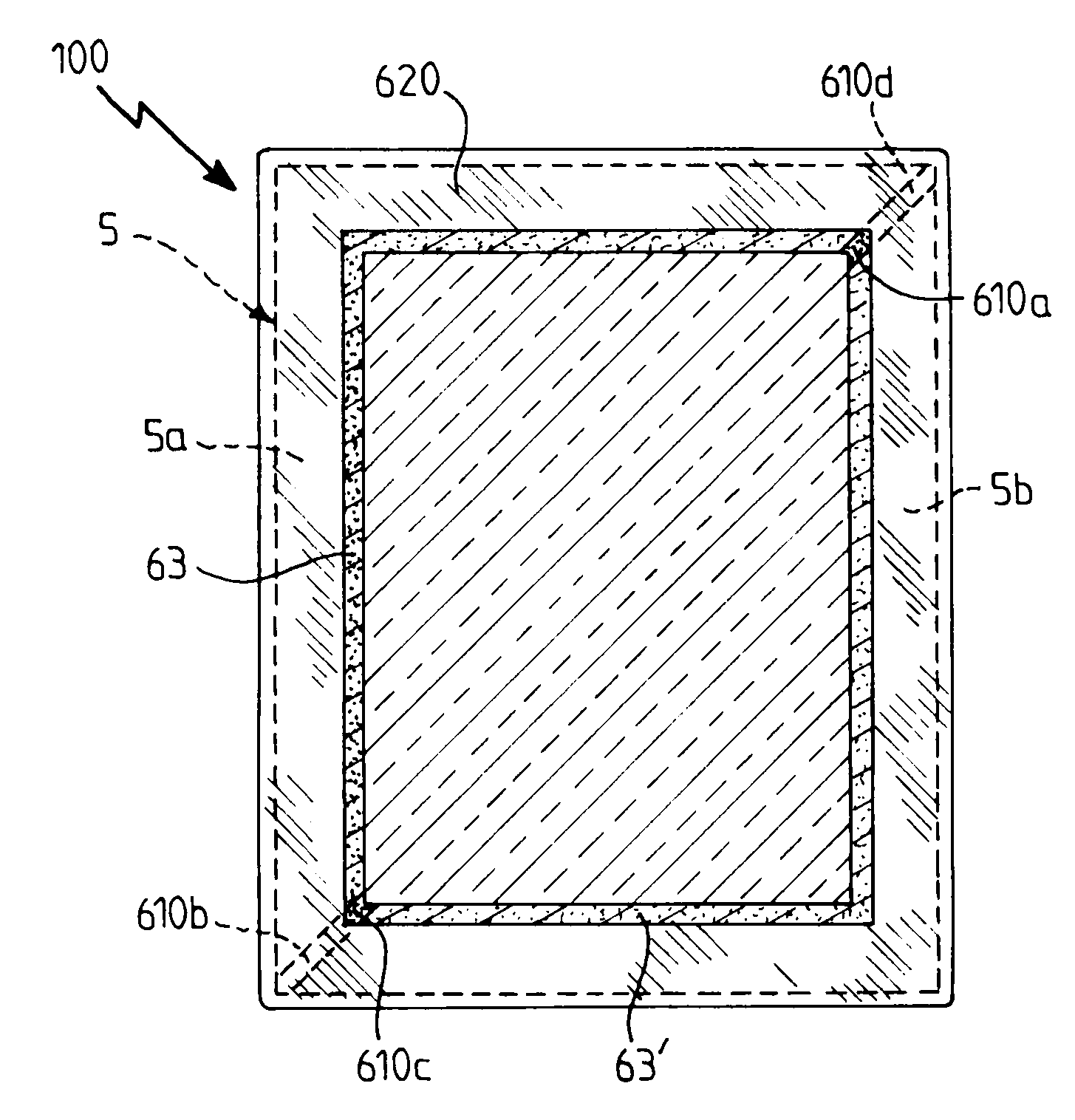
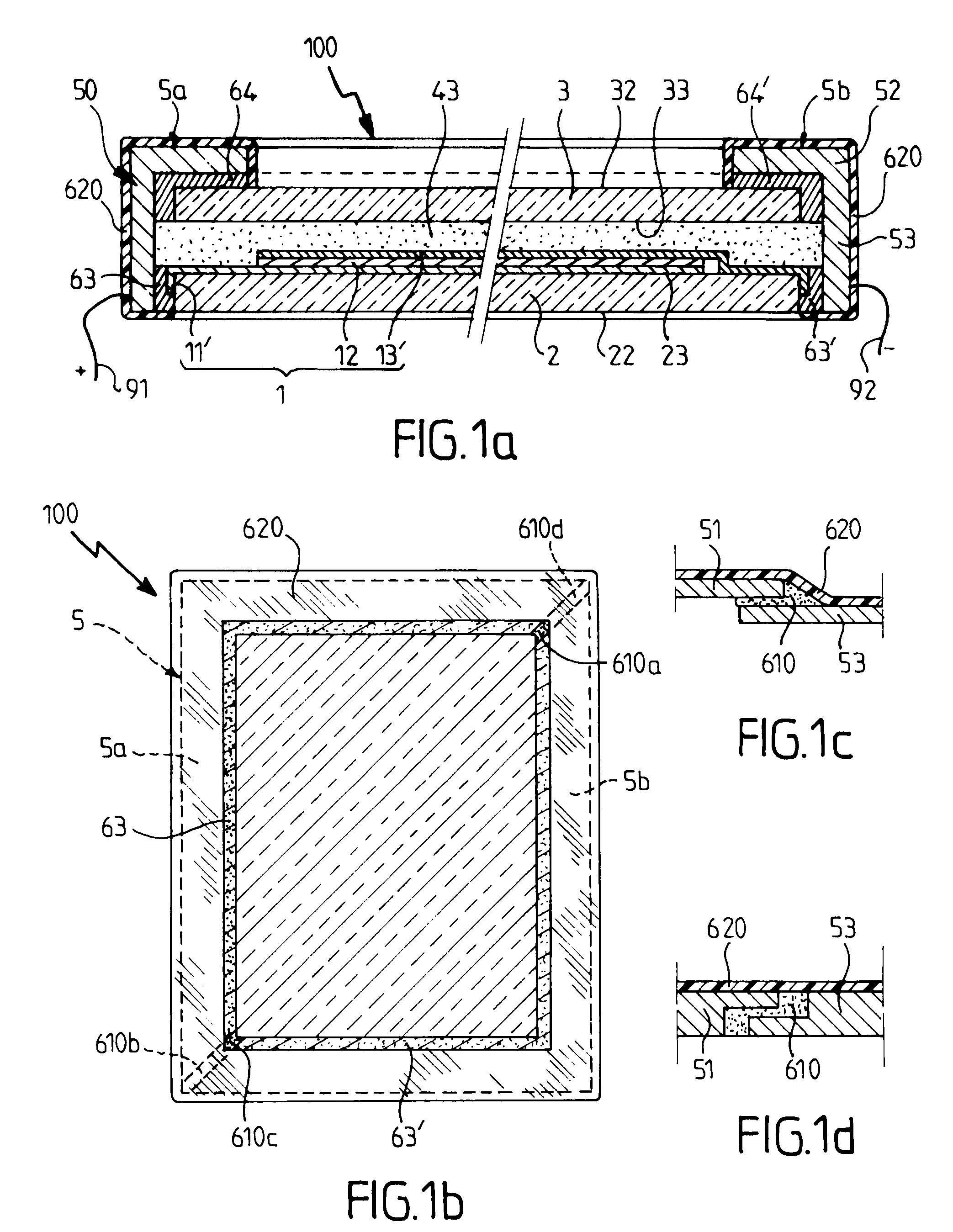
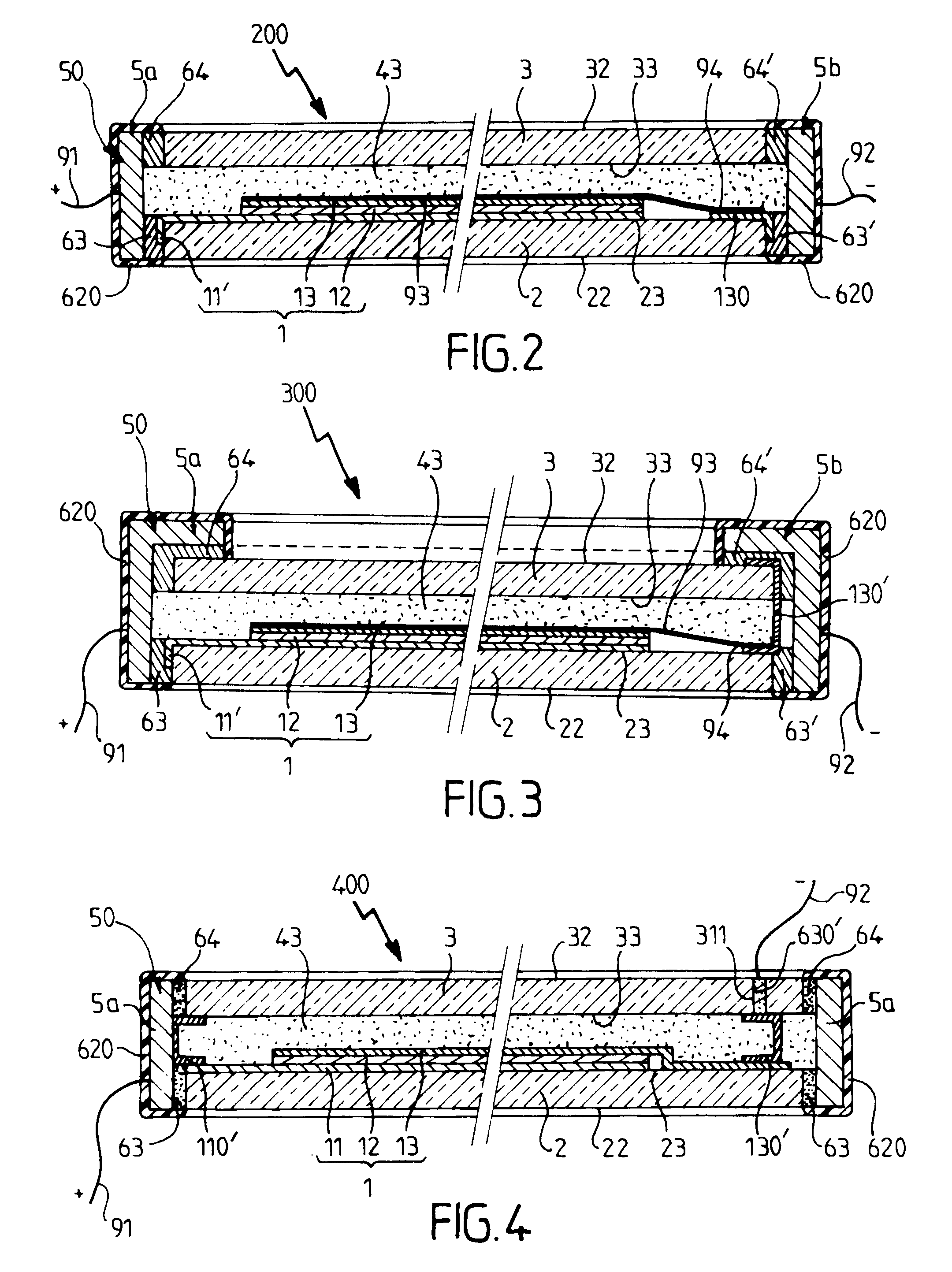
The invention relates to an active device having variable energy / light transmission properties (100) comprising an active system (1, 12) between a protective substrate (2) and a protective cover (3), selected from an essentially inorganic electrochromic system, a light valve system, a liquid crystal system, a gasochromic system, a thermochromic system, means leakproof to liquid water and / or water vapor, a surround (50) made from at least one metal based part (5a, 5b) on the periphery of the device, the surround being assembled with the cover and with the substrate by assembling means (61′ to 64′) forming at least part of the means leakproof to water vapor.
Owner:SAINT-GOBAIN GLASS FRANCE
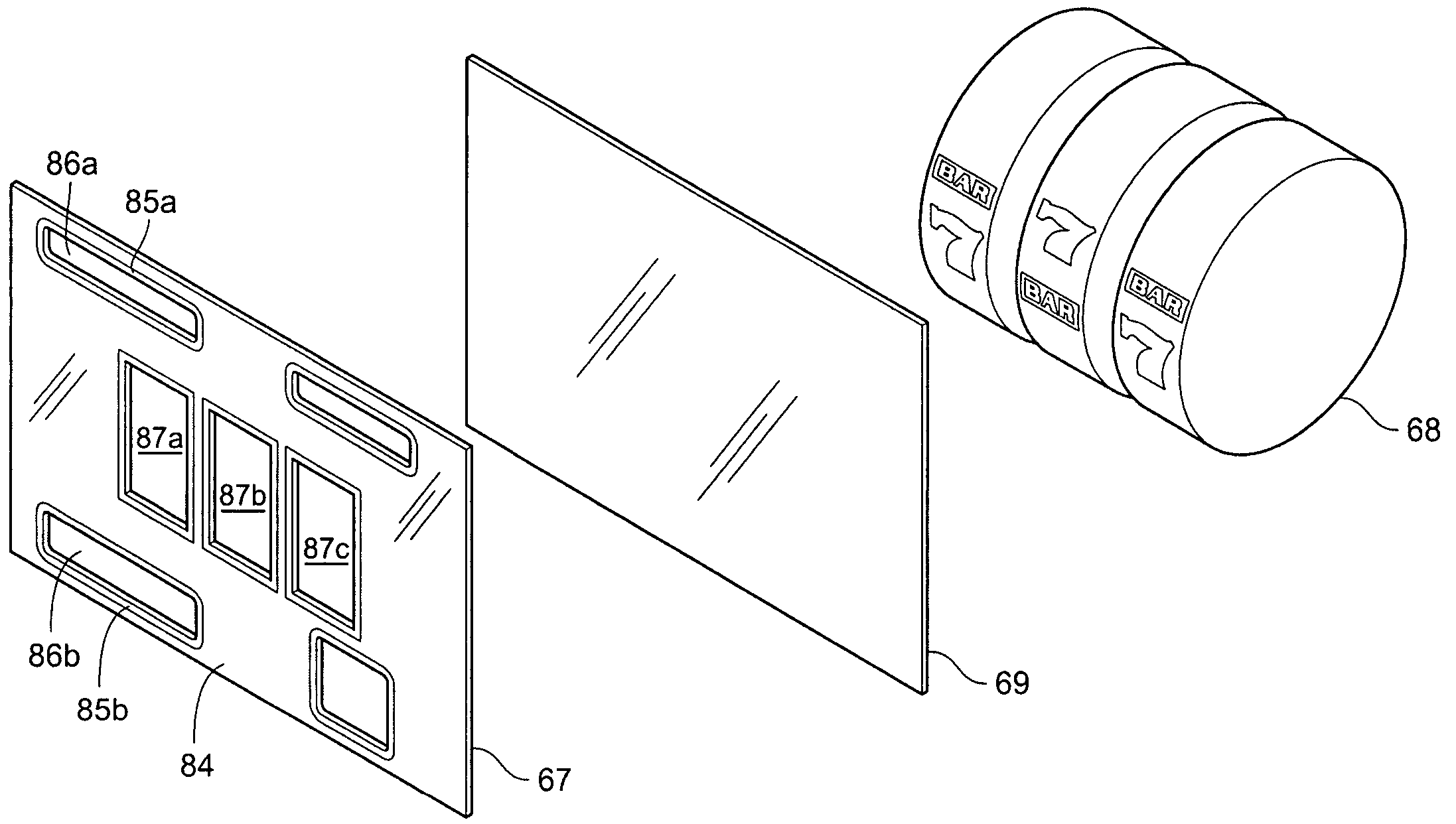
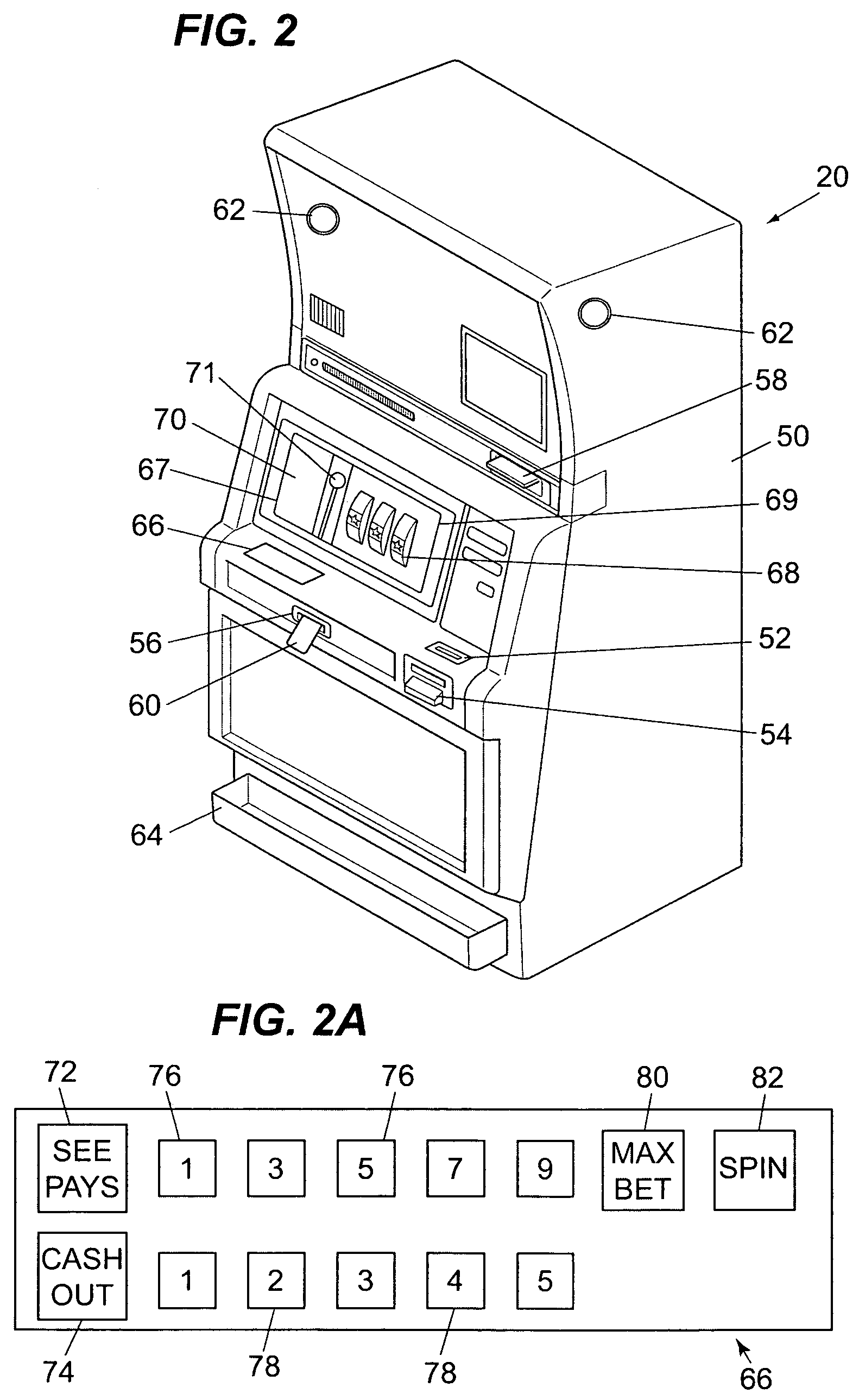
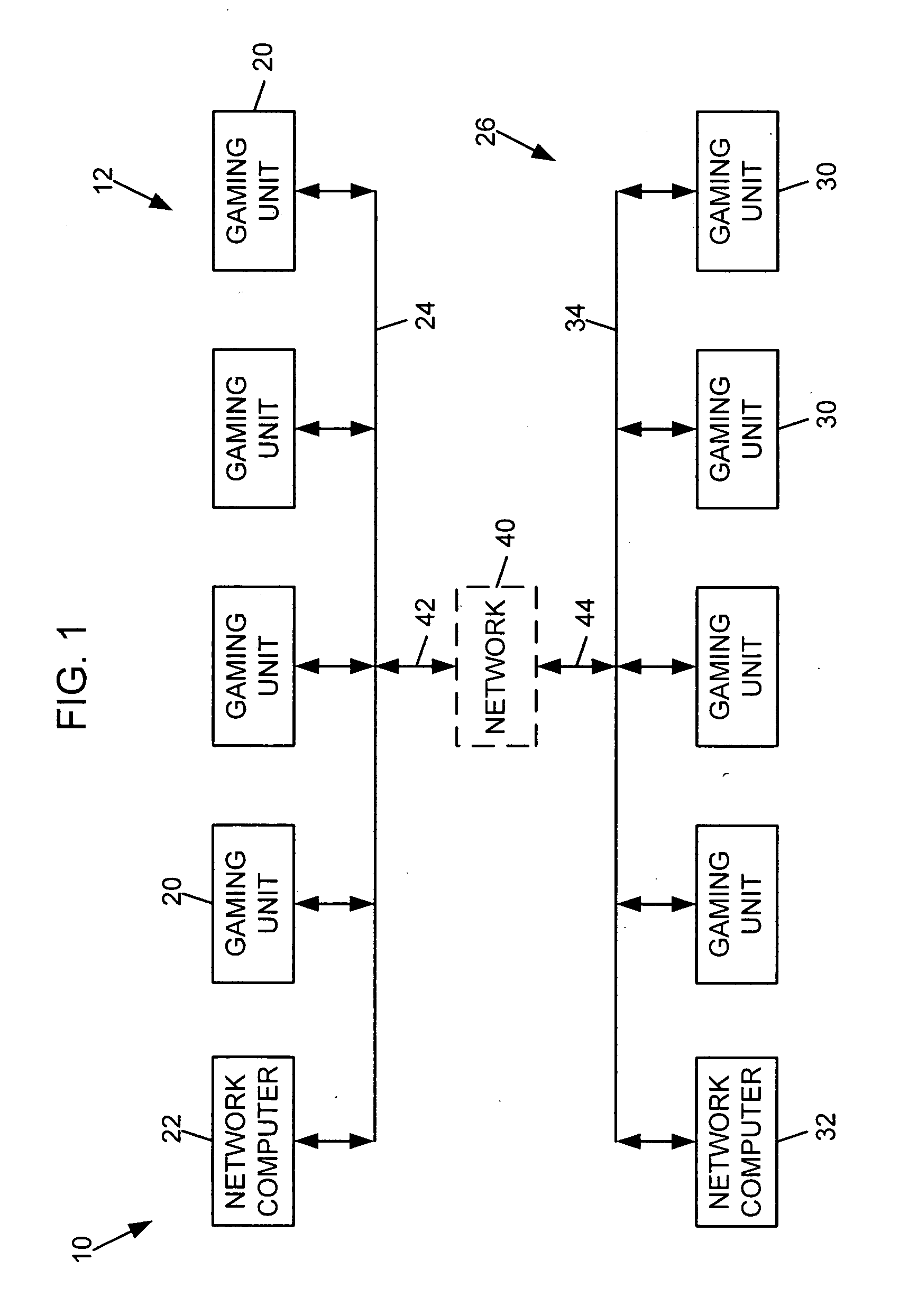
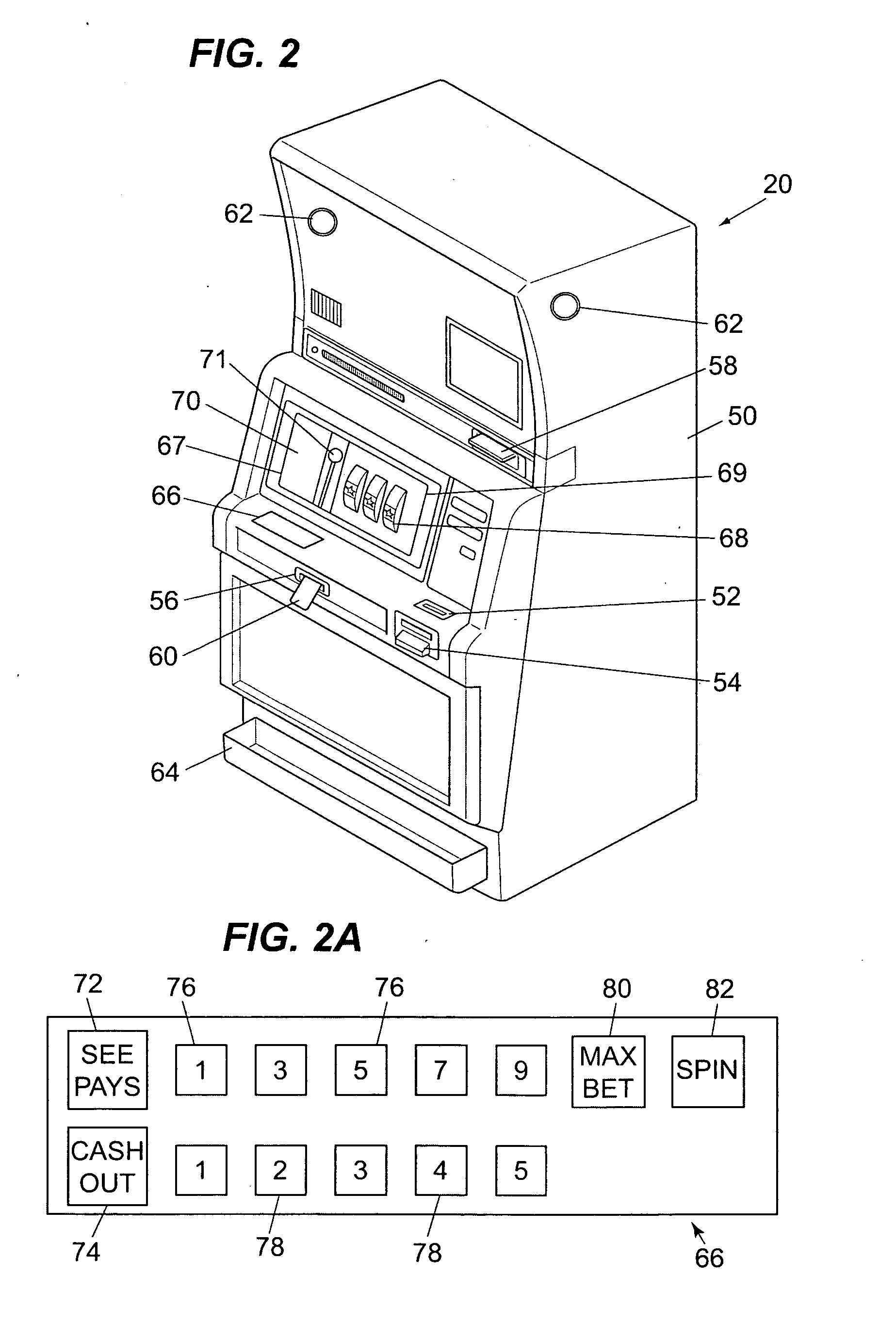
Method and apparatus for using a light valve to reduce the visibility of an object within a gaming apparatus
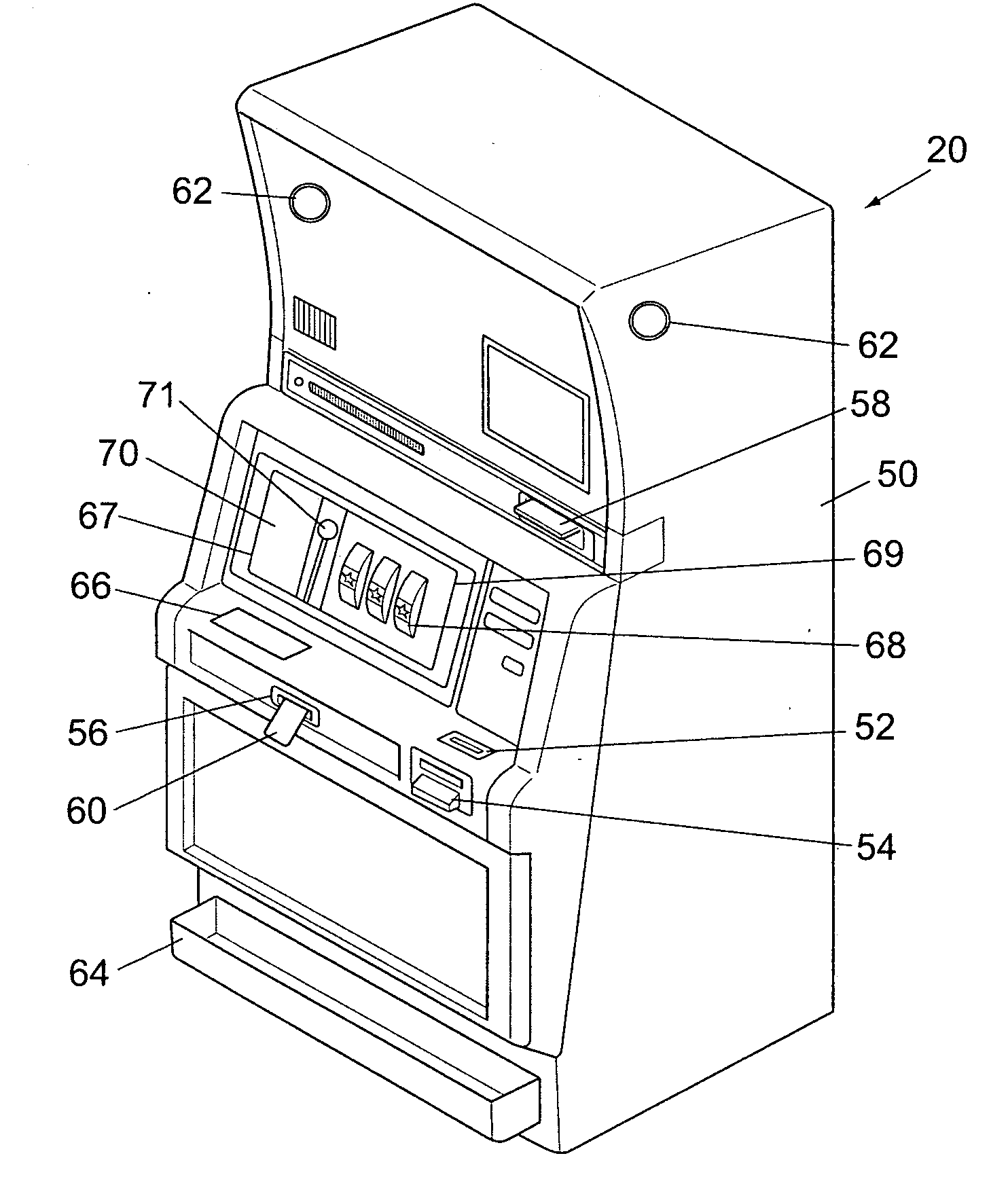
ActiveUS20050153772A1Apparatus for meter-controlled dispensingVideo gamesSuspended particlesVisibility
A gaming apparatus is disclosed that includes a housing, a value input device, a transparent panel having an outer surface and an inner surface, and a plurality of mechanically rotatable slot reels disposed in the housing so that the mechanically rotatable reels are visible to a player through the transparent panel. The gaming apparatus also having a light valve that includes a suspended particle device disposed between the inner surface and the slot reels, and a controller coupled to the light valve to cause the light valve to become opaque to substantially block the view of the slot reels to the player.
Owner:IGT
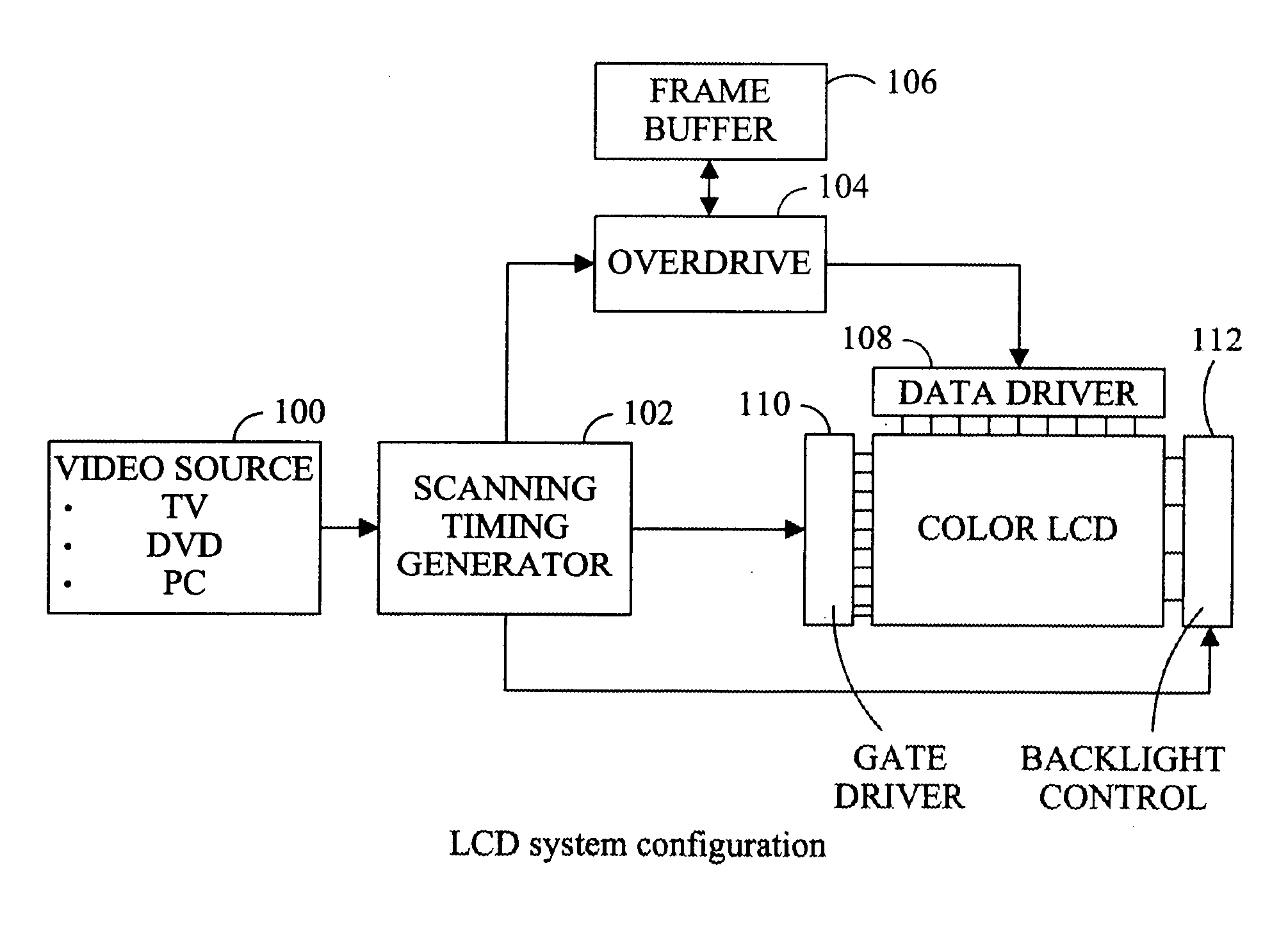
Technique that preserves specular highlights
A method for displaying an image on a liquid crystal display that includes a plurality of light emitting elements and a light valve. A image signal is received and a first light emitting element is illuminated based upon a substantial maximum of a non-uniform image signal in a first region. A second light emitting element is illuminated based upon a substantial maximum of a non-uniform image signal in a second region including, where the first and second light emitting elements are simultaneously illuminated.
Owner:SHARP KK
Directional flat illuminators
Disclosed is an optical valve or light valve for providing large area collimated illumination from localized light sources, and system and method thereof for 2D, 3D, and / or autosteroscopic displays. An optical valve may include a stepped structure, in which the steps include separated extraction features which may be optically hidden to light propagating in a first direction. Light propagating in a second direction may be refracted, diffracted, or reflected by the features to provide illumination beams exiting from the top surface of the optical valve. Such controlled illumination may provide for efficient, multi-user autostereoscopic displays as well as improved 2D display functionality.
Owner:REALD SPARK LLC
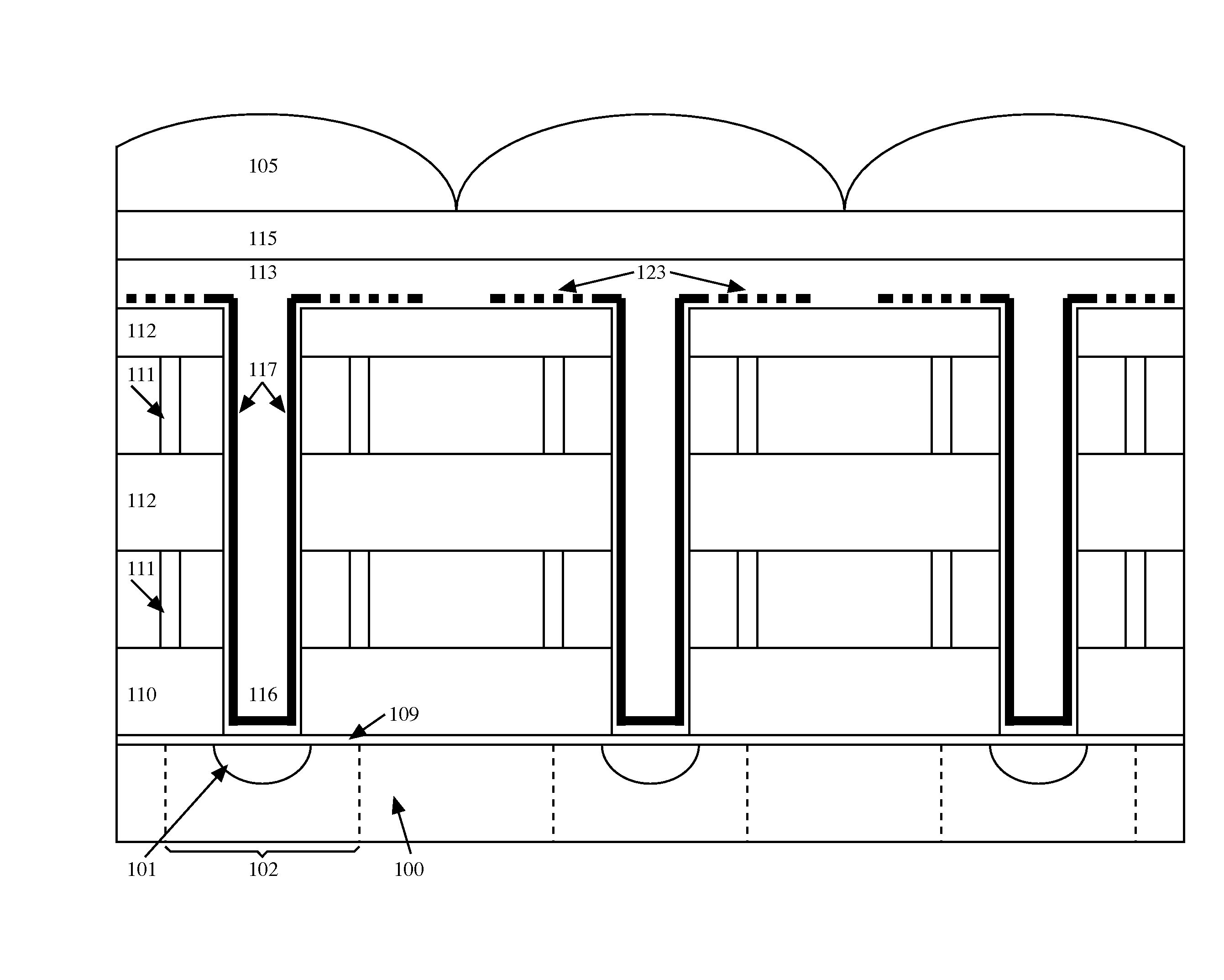
Photonic Via Waveguide for Pixel Arrays
Photonic passive structure to couple and guide light between photonic active devices (101), such as photo-diodes, light emitting devices and light-valves, which may be arranged into 2D arrays, and the top of the metallization layer stack (110,111,112) interconnecting said devices, with said photonic passive structure comprising a hole (116) between the near surface of said photonic active Ndevices and the top of said metallization stack, said hole being filled with a dielectric (113) having embedded metal films (117) and in which the embedded metal thin films are connected to a planar perforated metal film (123,124) formed on top of the metallization stack.
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
Electronic imaging system using organic laser array illuminating an area light valve
InactiveUS6950454B2Good image uniformityFlare can be reducedProjectorsOptical resonator shape and constructionColor imageData stream
An electronic imaging system for providing a viewable color image from an image data stream, including: a plurality of different colored laser light sources arranged in an at least one array with each such colored laser light source including a vertical cavity design; at least one area light valve for receiving the laser light and producing the viewable color image from the image data stream; and a projection lens for projecting the viewable color image onto a target plane.
Owner:IMAX THEATERS INT
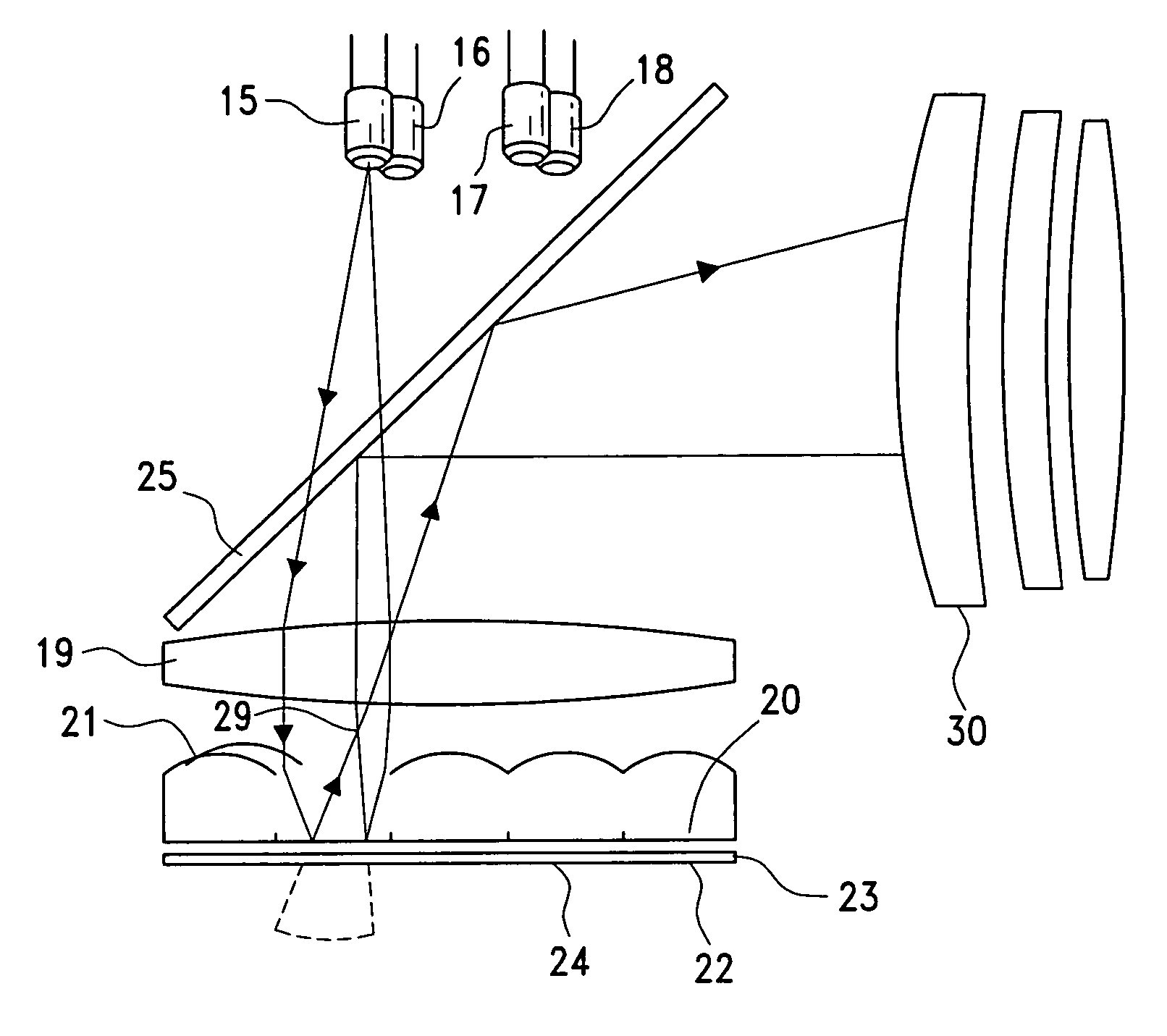
Projection display device
InactiveUS6056407APrevent intrusionEasy to replaceTelevision system detailsProjectorsLiquid-crystal displayFixed frame
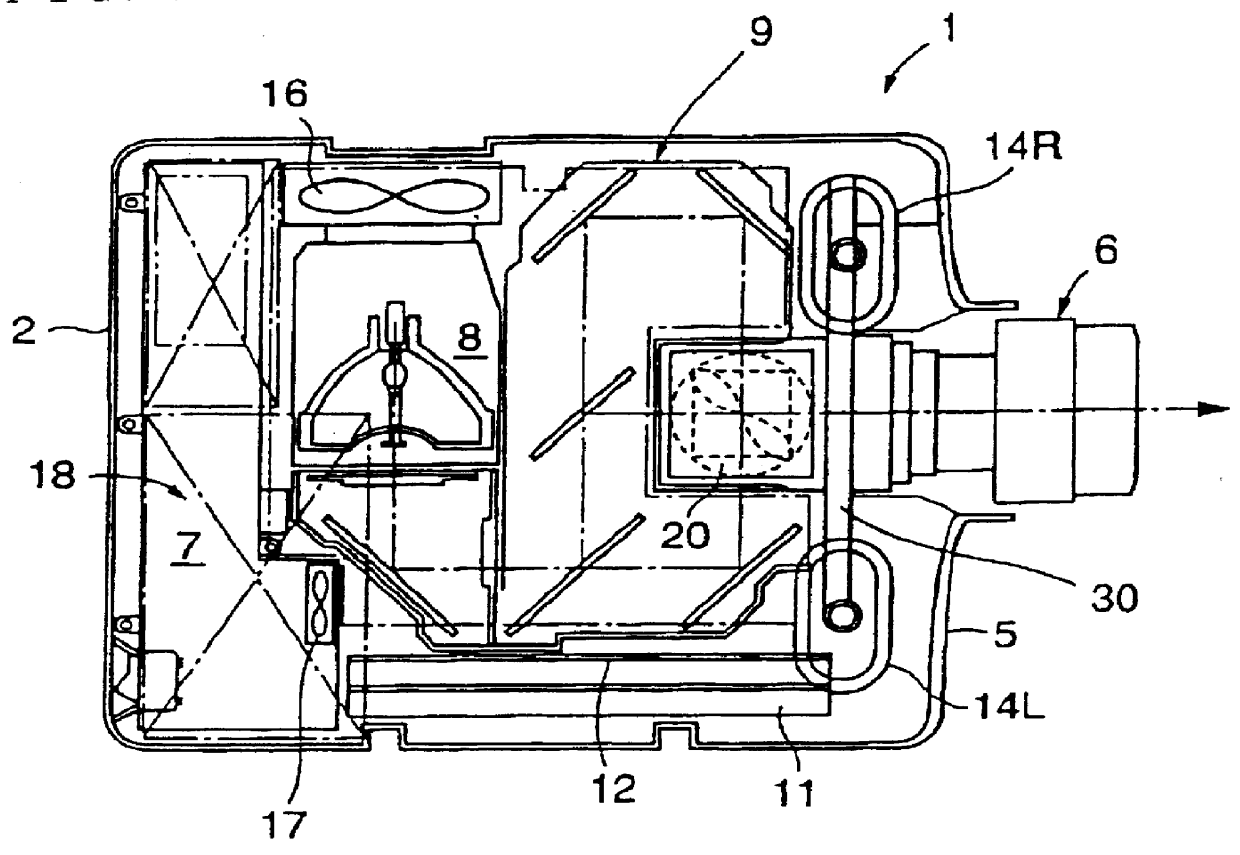
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 04652 Sec. 371 Date Aug. 12, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Aug. 12, 1998 PCT Filed Dec. 17, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 27453 PCT Pub. Date Jun. 25, 1998A liquid crystal panel unit is provided on the light incident face of a prism combining body. The unit has a light valve frame plate for holding a liquid crystal panel and a fixing frame plate fixed onto the light incident face with an adhesive layer. The light valve frame plate is screwed onto the fixing frame plate with a medial frame therebetween. By using wedge members, by adjusting the position of the light valve frame plate on the light incident face, it is possible to precisely position and fix the liquid crystal panel which is held there so that it is possible to control the shifted amount of the pixel alignment and precisely adjust the focus. Thus, it is possible to easily improve the accuracy. Furthermore, the fixing frame plate and the light valve frame plate are composed of materials having linear expansion coefficients ranging from +E,fra 1 / 4+EE to four times that of the prism combining body and from +E,fra 1 / 5+EE to five times that of the fixing frame plate, respectively.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
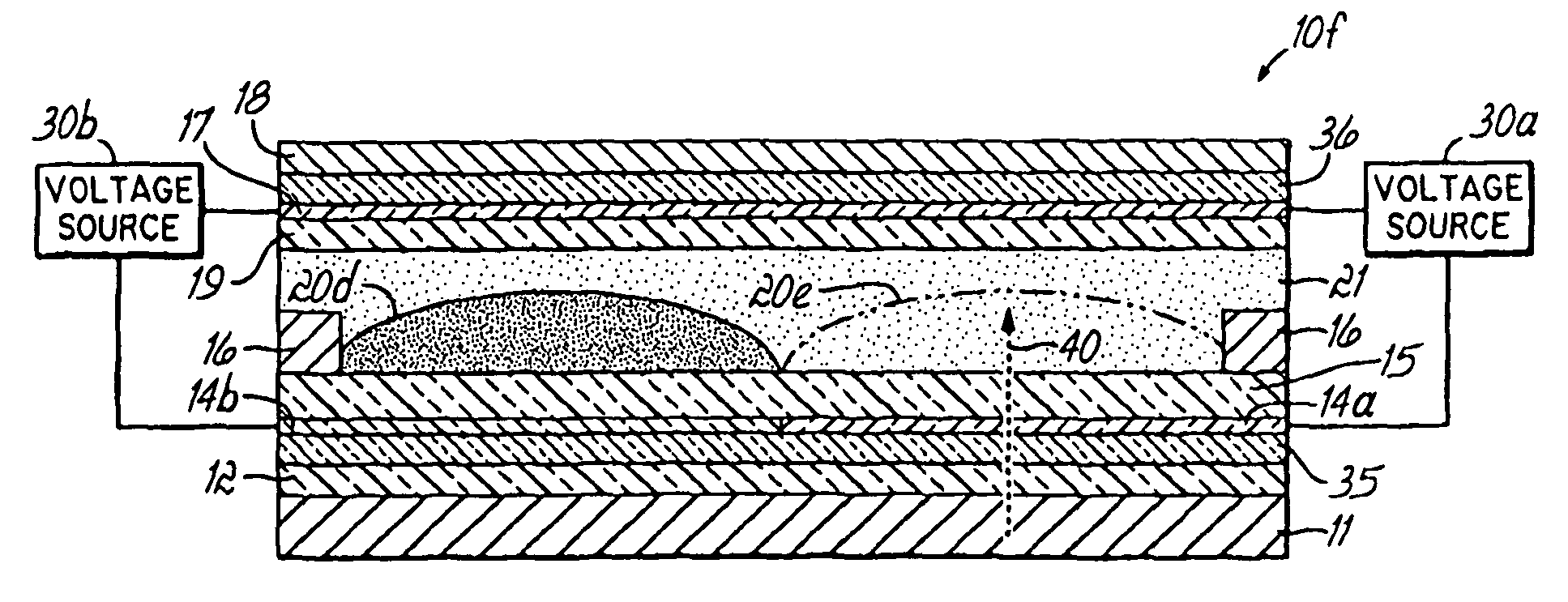
Siloxane matrix polymers and SPD light valve films incorporating same
A film suitable for use as a light-modulating unit of a suspended particle device (SPD) light valve. The film comprises a siloxane matrix polymer which has a refractive index>1.4630 and has droplets of a liquid light valve suspension distributed within the matrix. The liquid light valve suspension preferably comprises a polyalkyl (meth)acrylate and / or fluorinated (meth)acrylate suspending polymer and optionally may comprise one or more non-polymeric liquids.
Owner:RES FRONTIERS
Time-sequential colour projection
InactiveUS20050254127A1High efficiency of illuminationLight-efficiency is relatively highProjectorsPolarising elementsOptoelectronicsLight valve
A time-sequential colour projector comprises a pixellated light valve (2), such as a liquid crystal device, and a plurality of light sources (30, 31, 32). The light sources (30, 31, 32) direct light on different sets of pixels of the light valve (2) via an optical system (1), such as a lens array, which focuses the light on pixels of the light valve (2). At least two of the light sources (30, 31, 32) are multiple colour light sources and the multiple colour light sources emit different colour components during each set of frames making up a complete image frame.
Owner:SHARP KK
Wavelength-selective photonics device
InactiveUS6891869B2Wide rangeOvercome limitationsSolid-state devicesNanoopticsPhoton emissionPhotonics
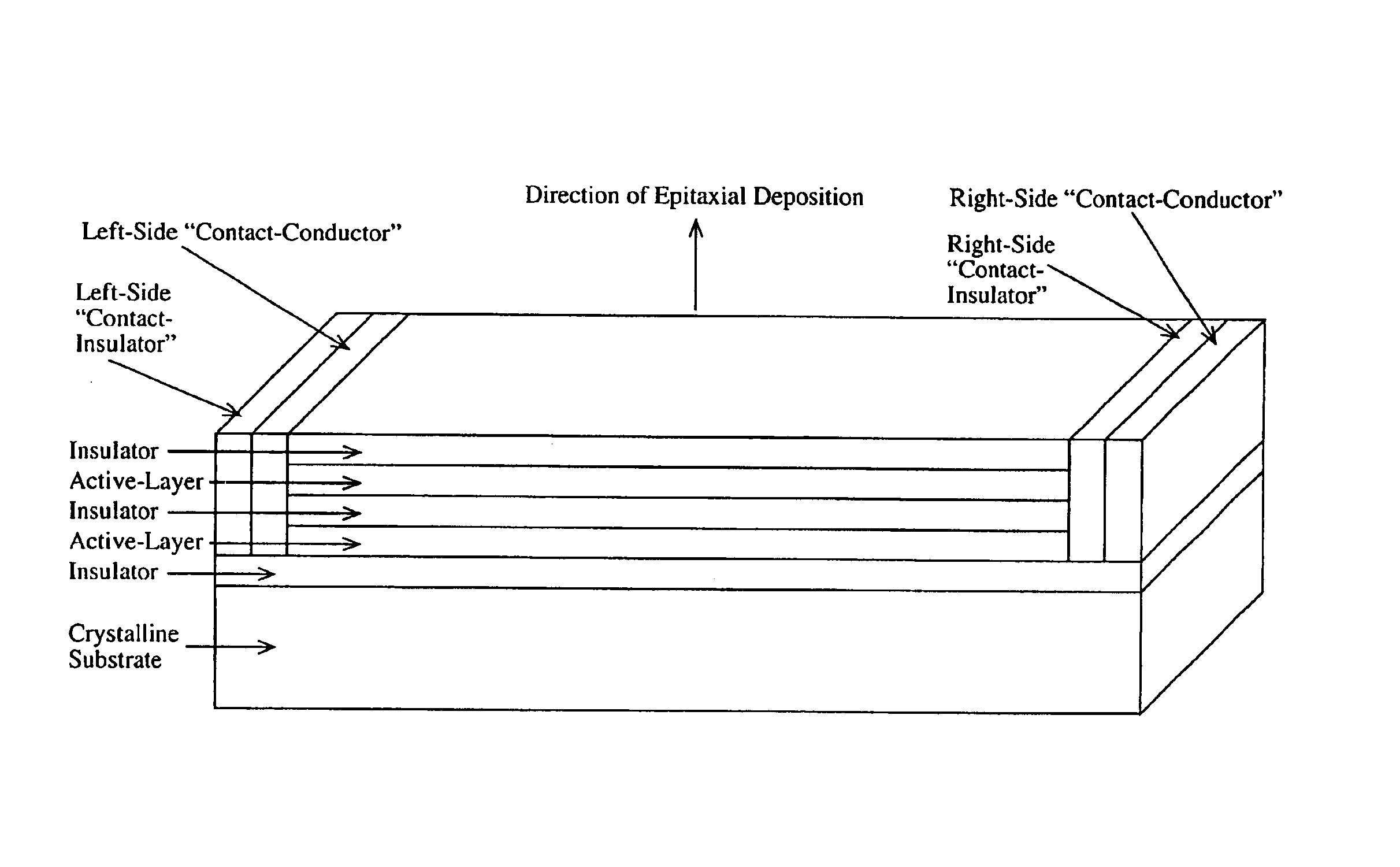
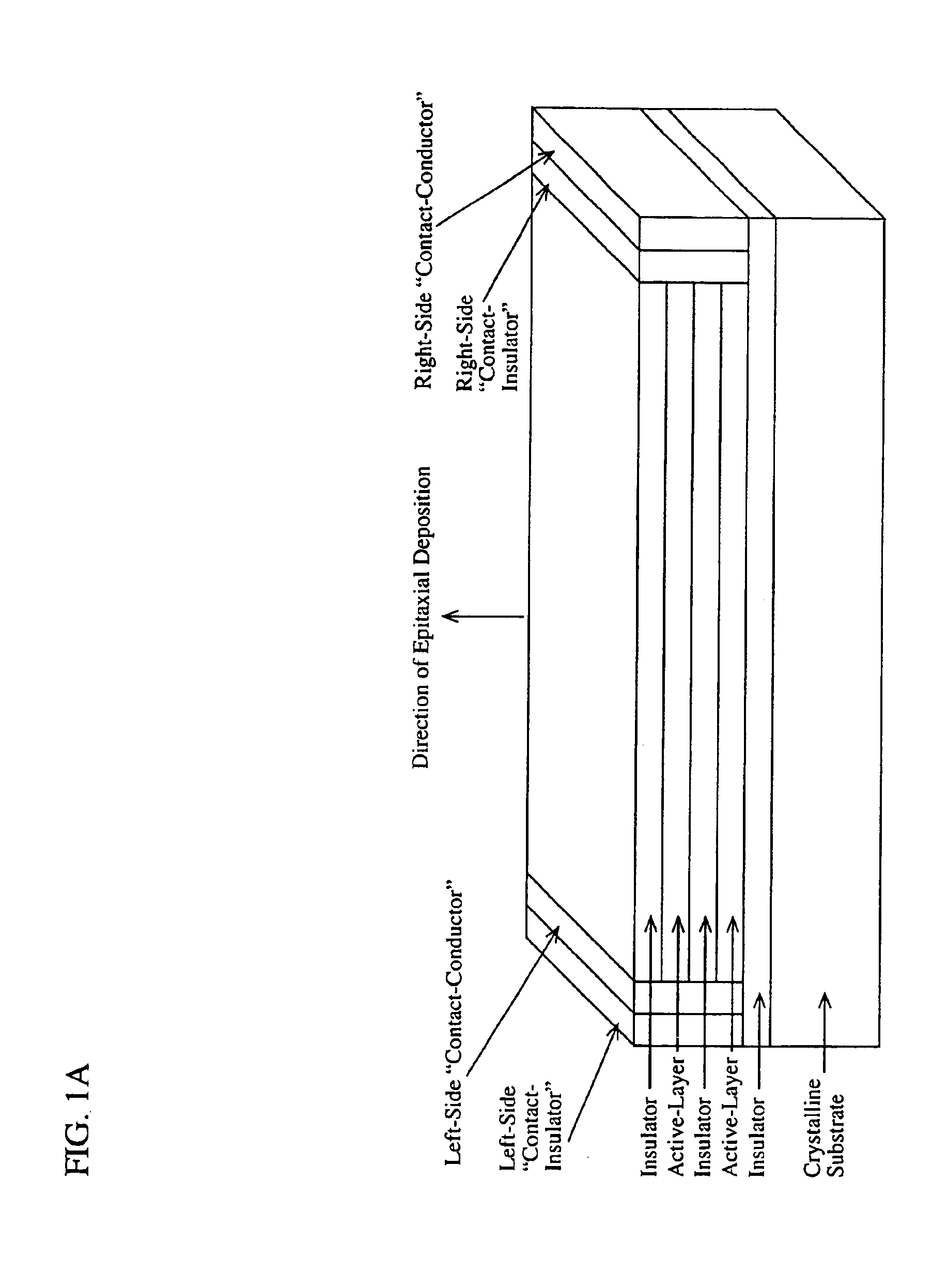
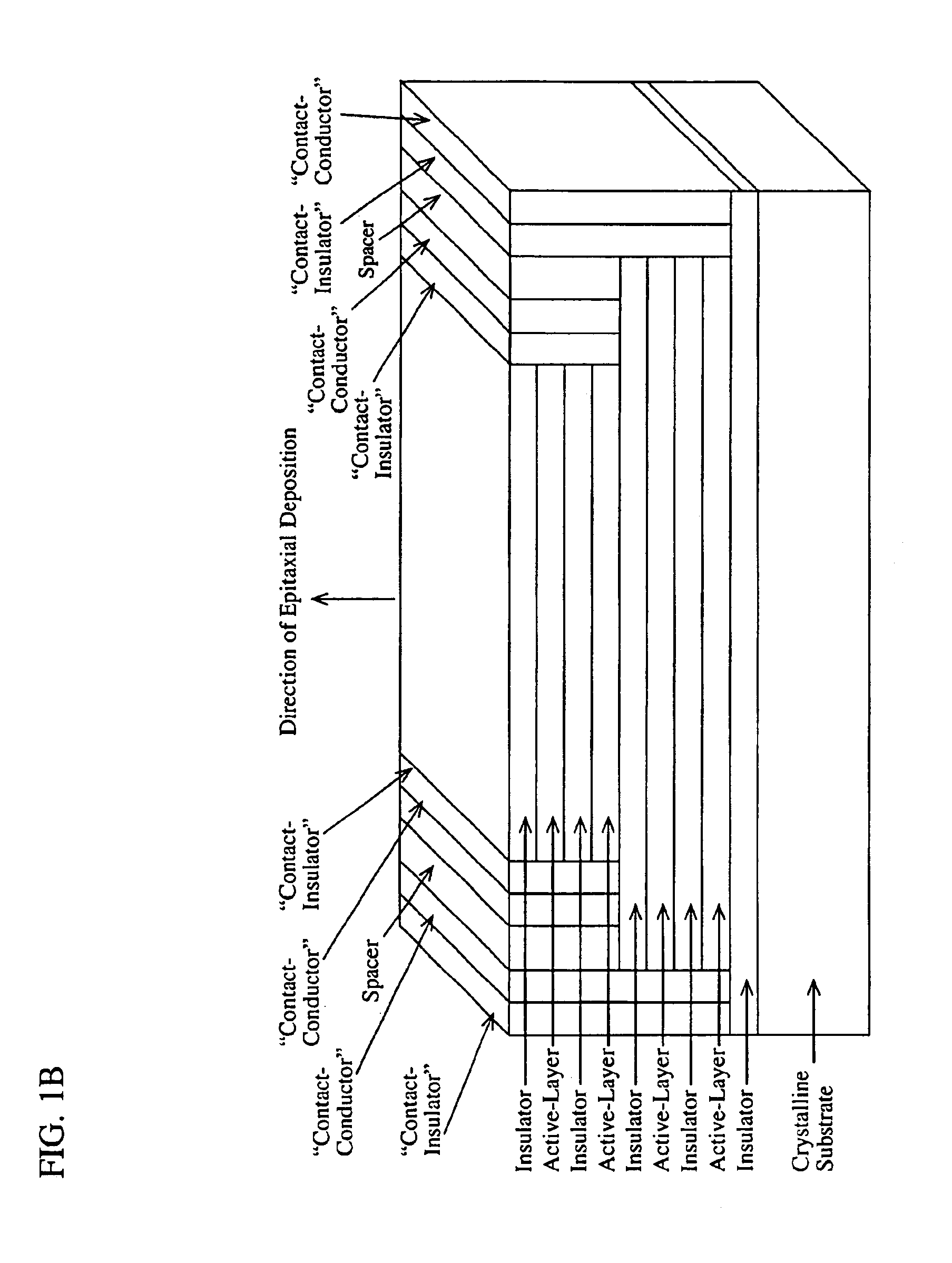
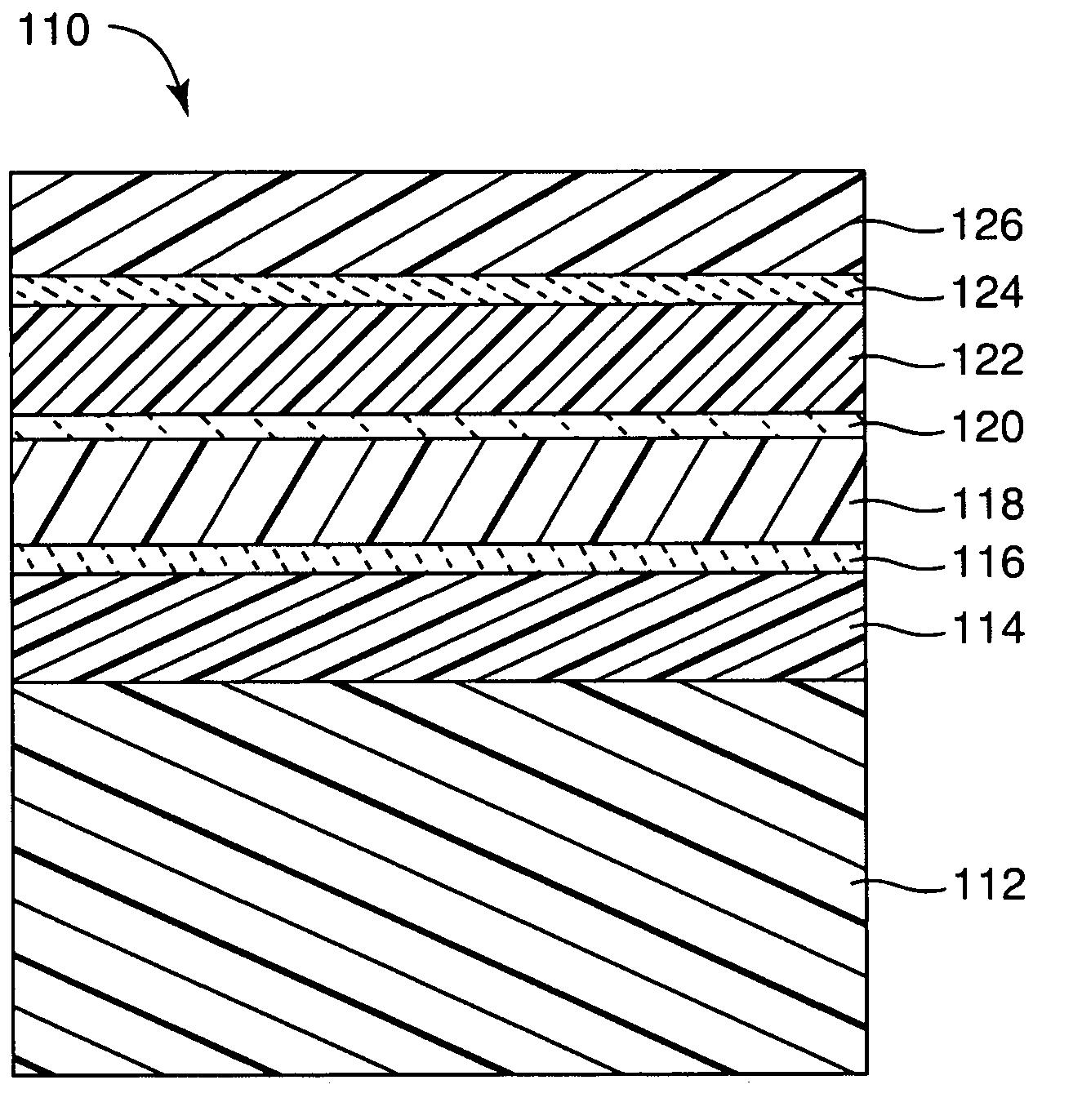
A device comprising a number of different wavelength-selective active-layers arranged in a vertical stack, having band-alignment and work-function engineered lateral contacts to said active-layers, consisting of a contact-insulator and a conductor-insulator. Photons of different energies are selectively absorbed in or emitted by the active-layers. Contact means are arranged separately on the lateral sides of each layer or set of layers having the same parameters for extracting charge carriers generated in the photon-absorbing layers and / or injecting charge carriers into the photon-emitting layers. The device can be used for various applications: wavelength-selective multi-spectral solid-state displays, image-sensors, light-valves, light-emitters, etc. It can also be used for multiple-band gap solar-cells. The architecture of the device can be adapted to produce coherent light.
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
Flexible high-temperature ultrabarrier
ActiveUS20060062937A1Substrate TgLiquid crystal compositionsFinal product manufacturePolyethylene terephthalateOrganic light emitting device
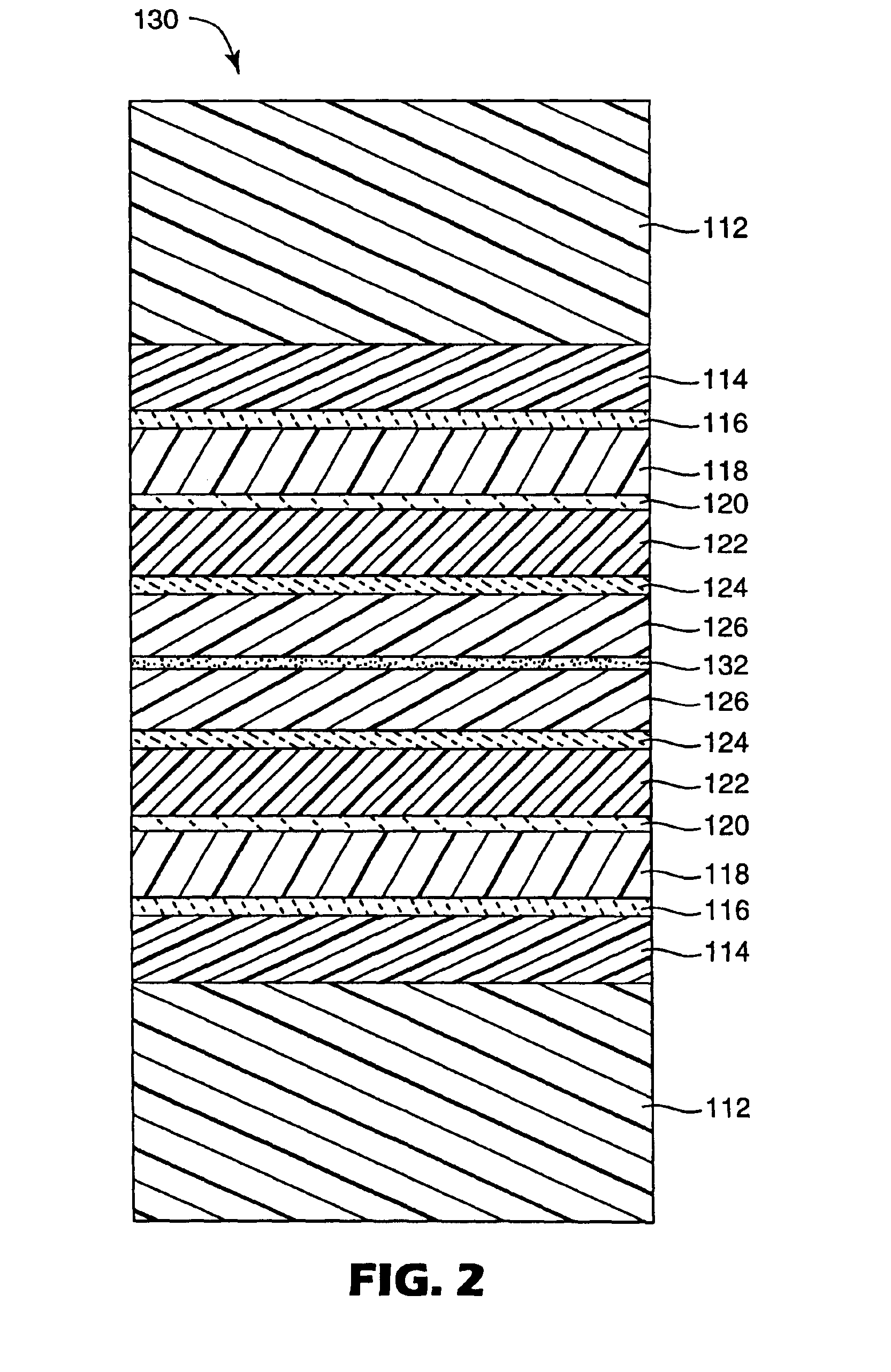
A flexible barrier assembly having a flexible visible light-transmissive substrate having a Tg greater than or equal to that of heat-stabilized polyethylene terephthalate (“HSPET”) overcoated with a first polymer layer having a Tg greater than or equal to that of HSPET and further overcoated with at least two visible light-transmissive inorganic barrier layers separated by at least one second polymer layer having a Tg greater than or equal to that of HSPET can be used to mount, cover, encapsulate or form moisture- and oxygen-sensitive articles such as organic light emitting devices and light valves.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
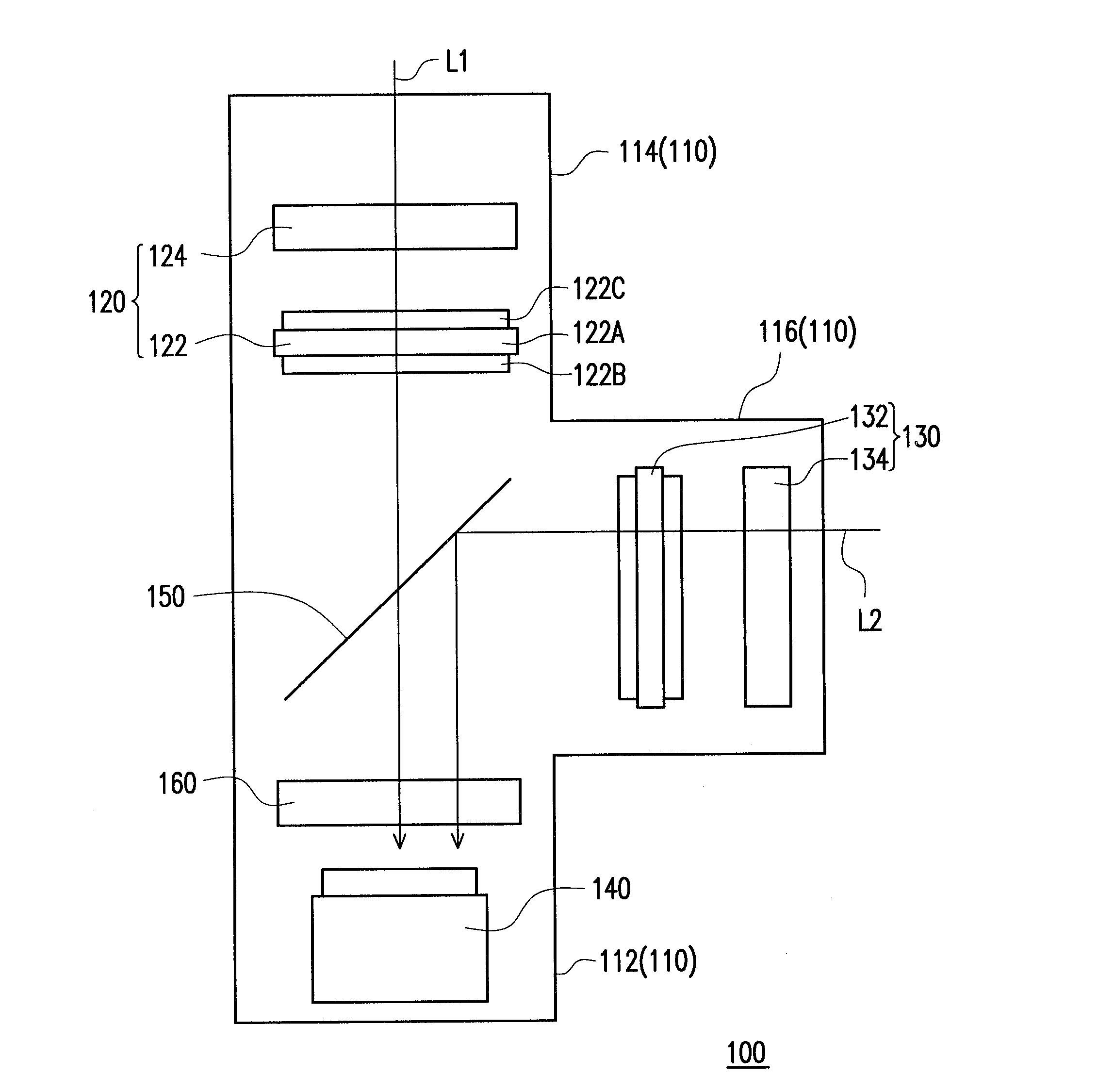
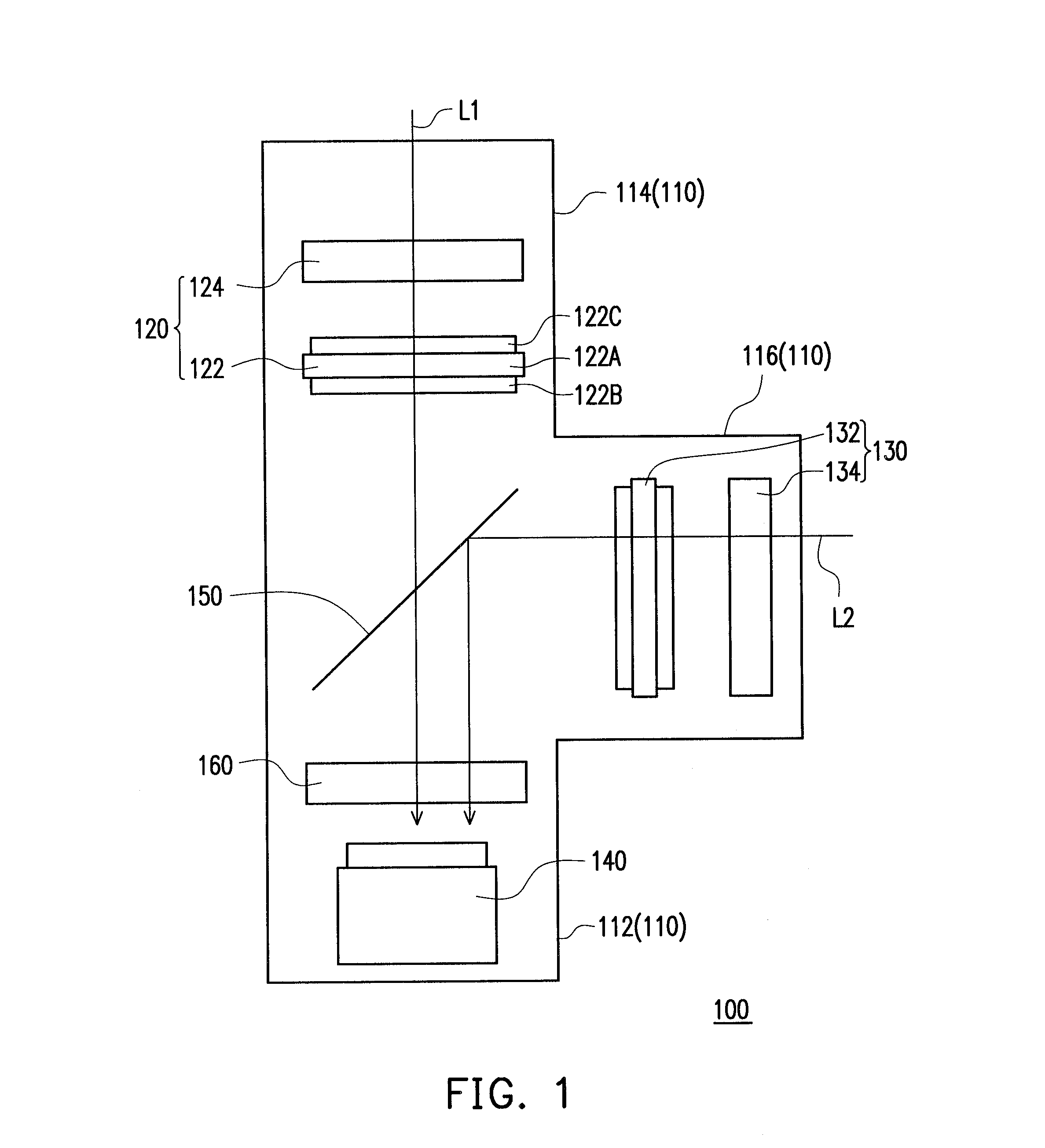
Micro-light-emitting diode backlight system
ActiveUS20170167703A1Improve light uniformityReduce power consumptionLight source combinationsElectrical apparatusContact padPower flow
A backlight system includes a backplane and a plurality of bare die light emitters disposed on the backplane. Each light emitter has a light-emitter substrate and contact pads on the light-emitter substrate through which electrical current is supplied to cause the light emitter to emit light. A plurality of first and second backplane conductors are disposed on the backplane for conducting control signals to control the light emitters through the contact pads. A plurality of light valves is disposed to receive light from the light emitters. The number of light valves is greater than the number of light emitters.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
Method of sealing a hermetic lid to a semiconductor die at an angle
InactiveUS6872984B1Reduce Optical InterferenceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHermetic sealAsymmetric distribution
The current invention provides a optical MEM device and system with an angled lid for hermetically sealing an active MEMS structure. The lid is sealed through an asymmetric seal formed with sealing rings having an asymmetric distribution of solder wetting surfaces which tilts the lid, when the lid and a substrate are soldered together. The asymmetric distribution wetting surfaces can be provided by forming one or more edge features, by patterning portions of the sealing rings or both. Preferably, the lid is transparent to one or more wavelengths of light in a range of 300 to 3000 Angstroms and hermetically seals a grating light valve structure having a plurality of movable ribbon for modulating light through the lid.
Owner:SILICON LIGHT MACHINES CORP
Optical device
Owner:VISIONSENSE LTD
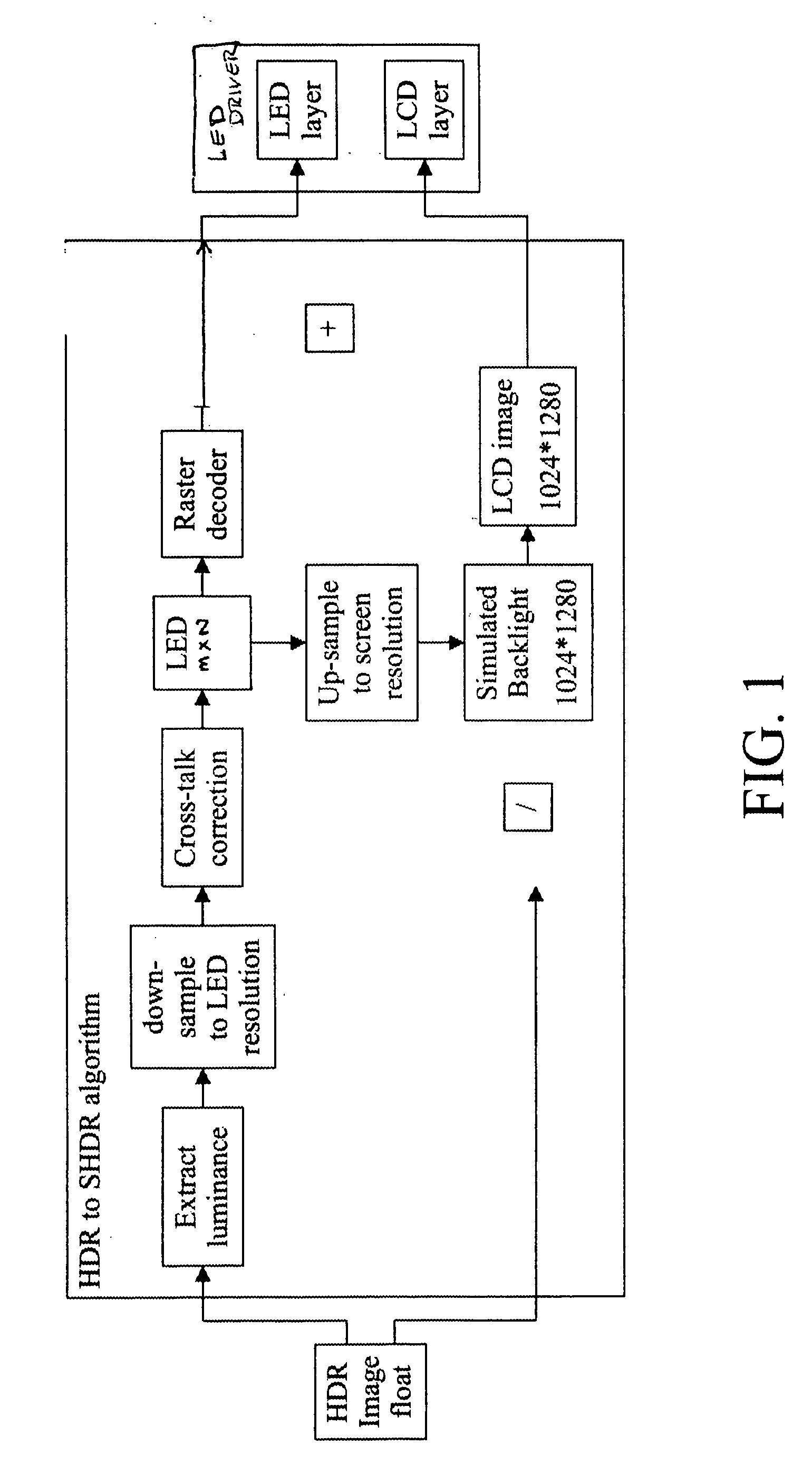
Optically transmissive substrates and light emitting assemblies and methods of making same, and methods of displaying images using the optically transmissive substrates and light emitting assemblies
InactiveUS20100026703A1Improve image qualityBoosting of luminancePoint-like light sourceElectrical apparatusLiquid-crystal displayLight valve
Images are displayed in response to a video signal using a light emitting assembly having one or more optically transmissive substrates, films or sheets, each having at least one pattern of optical elements on or in the substrates, films or sheets. A plurality of light sources are configured to illuminate one or more output areas of one or more of the substrates, films or sheets. The light emitting assembly is configured to emit light through the pattern of optical elements and produce a predetermined luminance profile of the light emitting assembly. At least one of the light sources is dimmed or boosted in response to an input video signal while operating a liquid crystal display as a light valve to illuminate the liquid crystal display by the light emitting assembly. At least some adjacent substrates, films or sheets may have portions that overlap, and at least one pattern of optical elements on or in at least one side of the substrates, films or sheets may be configured so that discontinuities between the adjacent substrates, films or sheets are minimized. A predetermined light output from the light emitting assembly may be produced by varying the electrical input to at least some of the light sources.
Owner:RAMBUS DELAWARE
Projector and projector accessory
ActiveUS7185987B2Input/output for user-computer interactionTelevision system detailsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
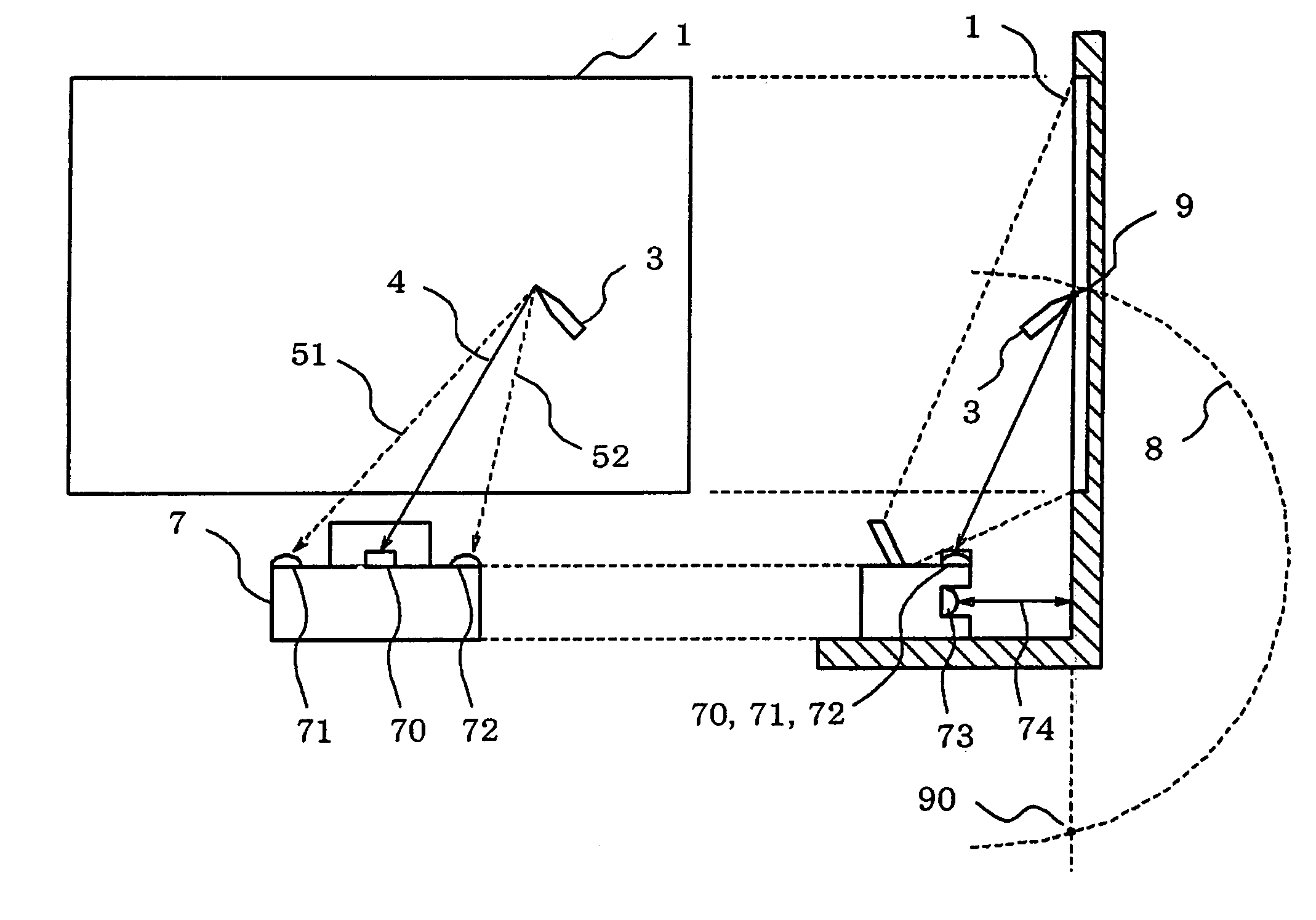
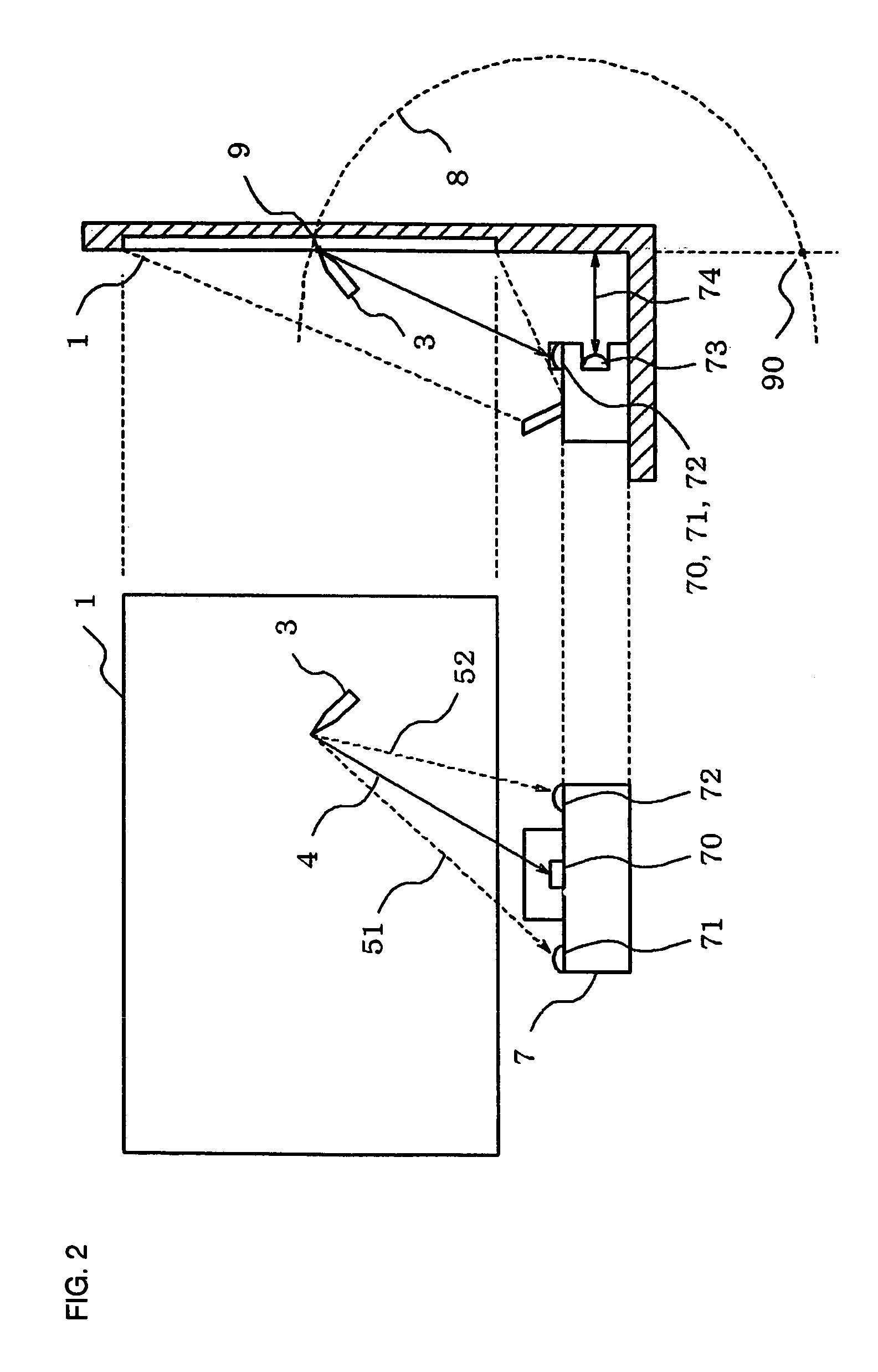
A projector for enlarging and projecting the display image on a light valve onto a screen is provided with: an infrared photodetector for photodetecting infrared light that is emitted by an electronic pen that is manipulated on the screen and that is provided with an infrared light emission device and ultrasonic generator; at least two ultrasonic receivers for detecting ultrasonic waves that are emitted by the electronic pen; means for measuring the distance to a screen; and means for supplying coordinate data in which the position of the electronic pen on the screen, which has been calculated based on output of the infrared photodetector, output of the ultrasonic generator, and output of the means for measuring the distance to the screen, has been normalized by the length of a side of a projected rectangular image that has been enlarged and projected.
Owner:SHARP NEC DISPLAY SOLUTIONS LTD
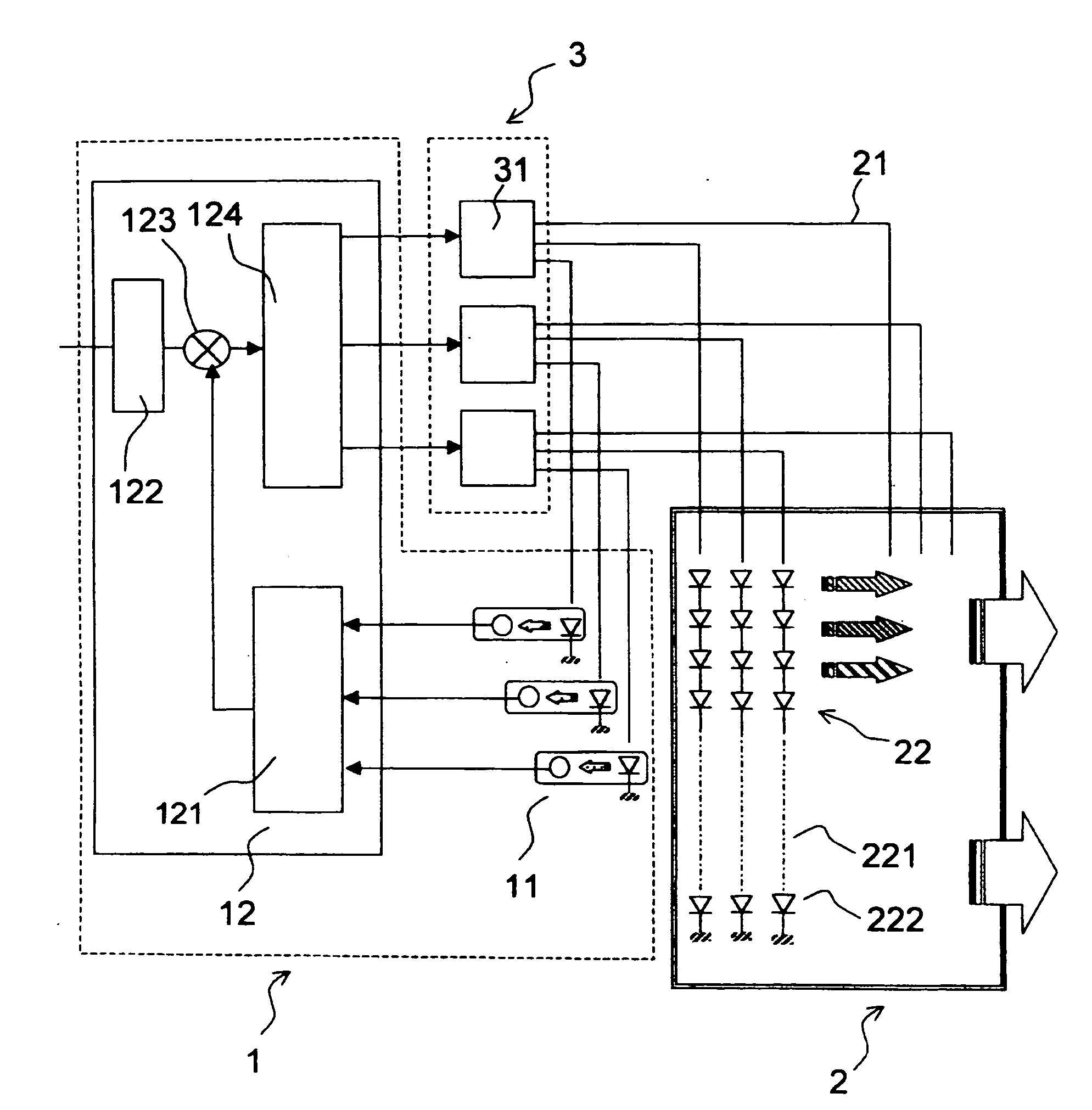
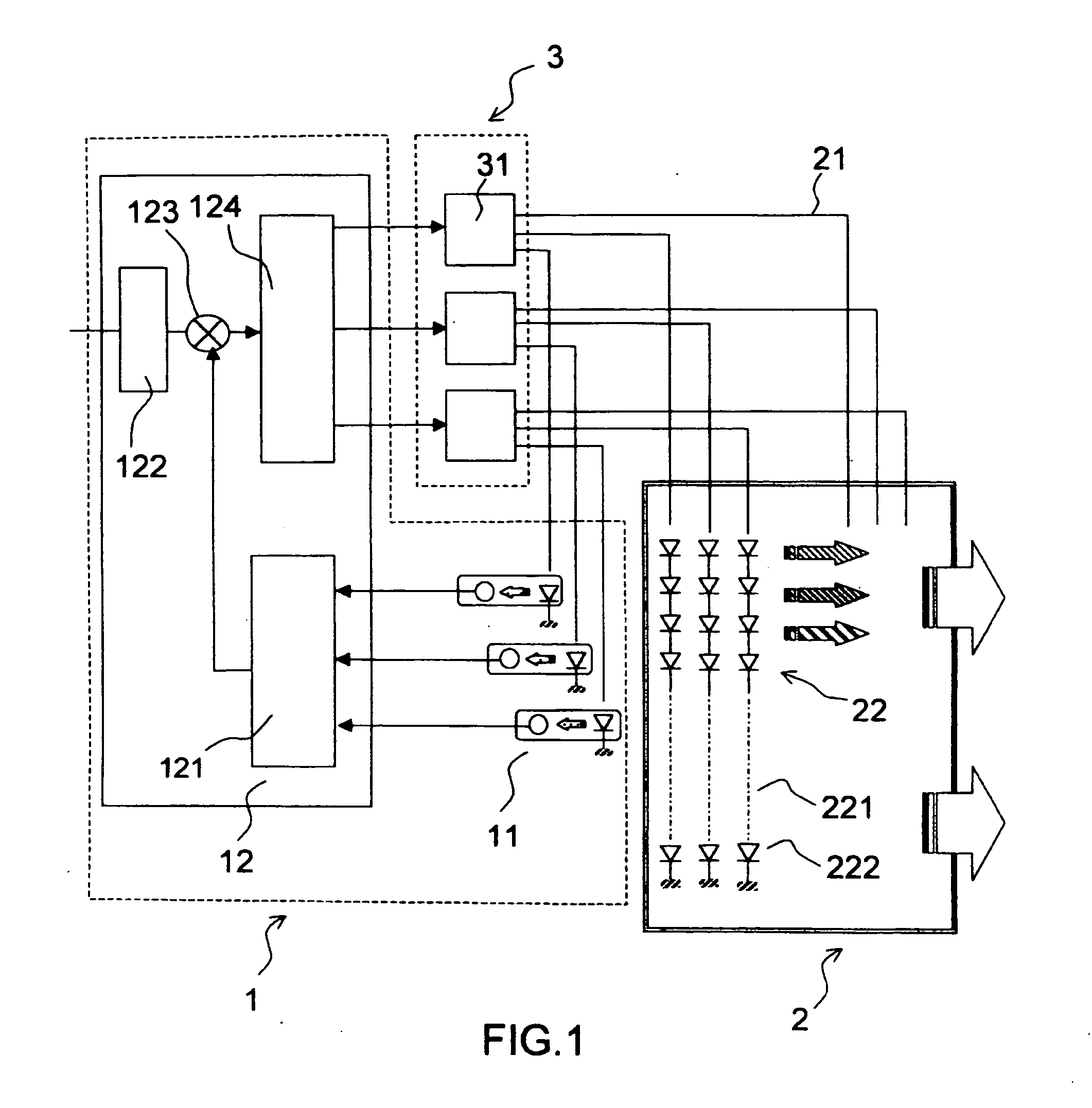
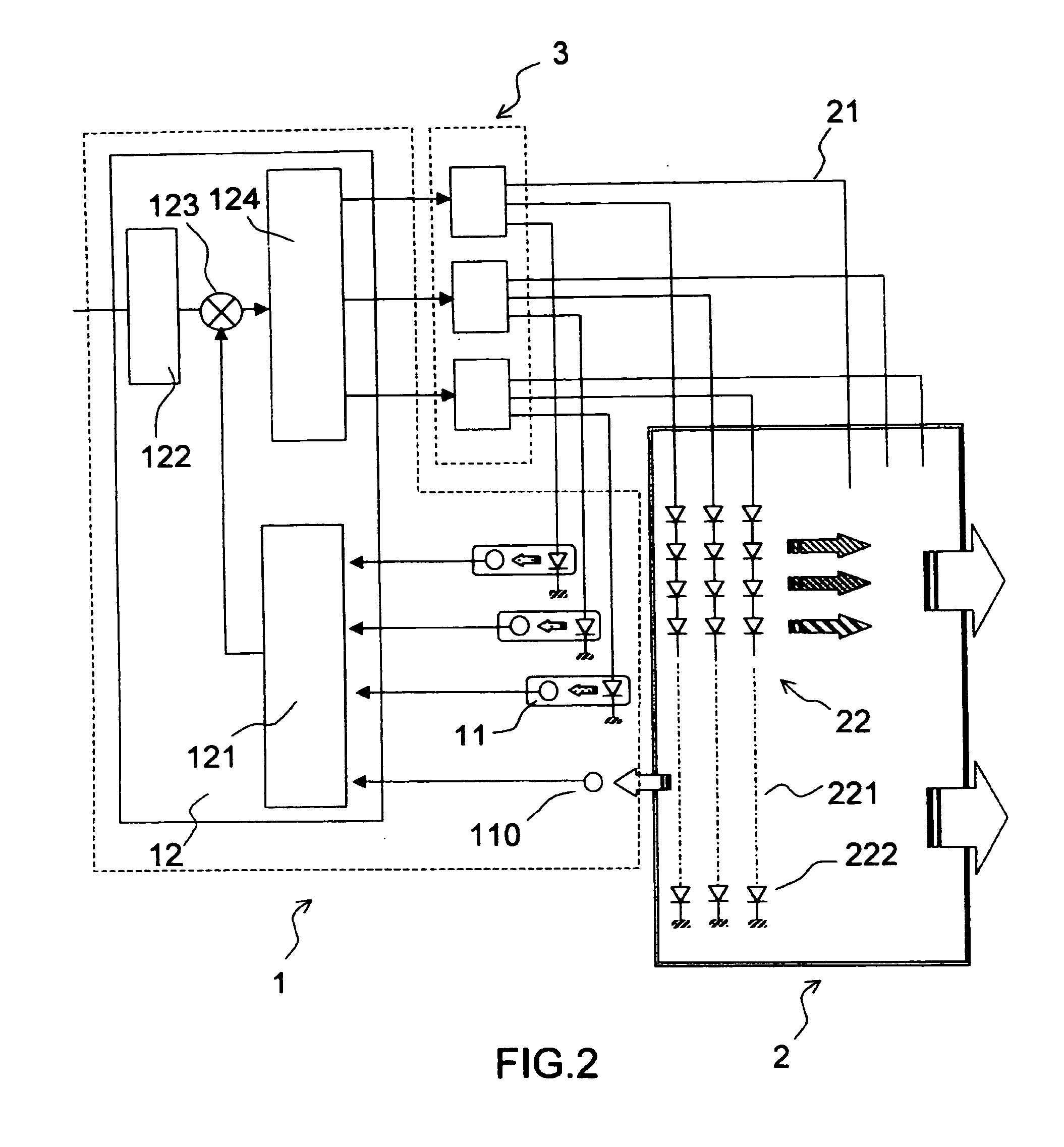
Automatic photo-colorimetric paratmeter control device for light boxes with colour leds
InactiveUS20060256049A1Static indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesSpectral bandsDisplay device
The field of the invention is that of light boxes used for illuminating optical-valve displays, especially matrix liquid-crystal displays (or LCDs). The illumination from light boxes can at the present time be produced by light-emitting diodes that emit in various spectral bands so as to reconstruct white illumination. For a number of applications, in particular aeronautical applications, it is necessary to maintain the photometric and calorimetric characteristics of this illumination independently of the environmental and ageing conditions of the components. The invention provides an electronic feedback control device for maintaining the photometric and calorimetric characteristics of this illumination at given setpoint values without introducing disturbing optoelectronic devices into the light box. Several possible technical solutions are described.
Owner:THALES SA
Display capable electrowetting light valve
ActiveUS7872790B2High operating requirementsEasy constructionDiffusing elementsNon-linear opticsFlat panel displayLight valve
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CINCINNATI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com