Patents
Literature
43results about How to "Reduce Optical Interference" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
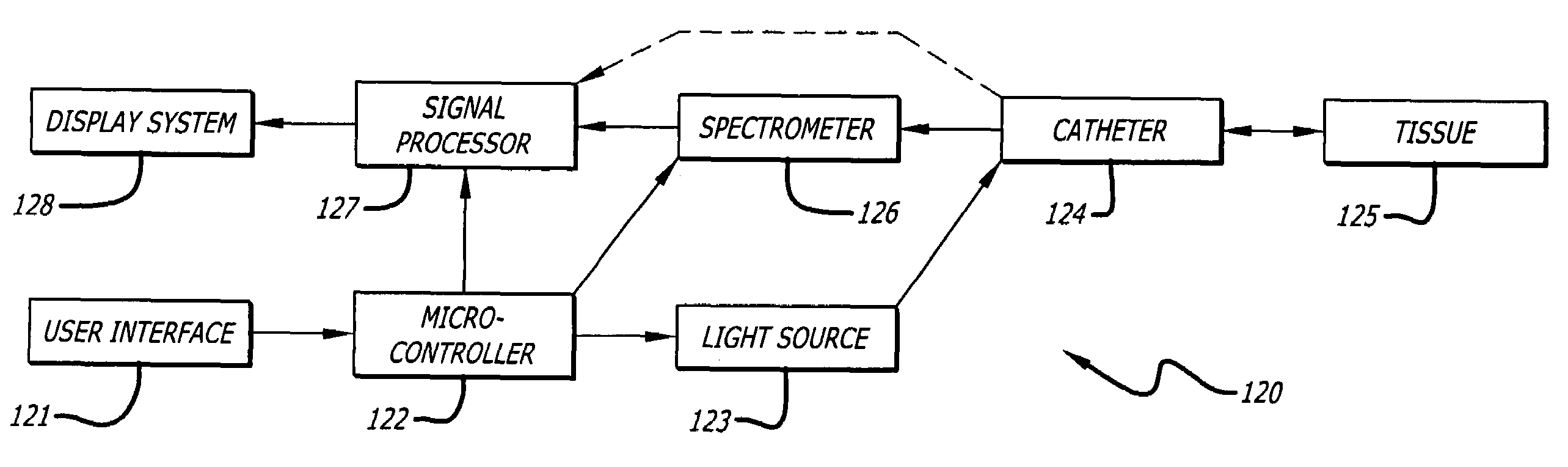
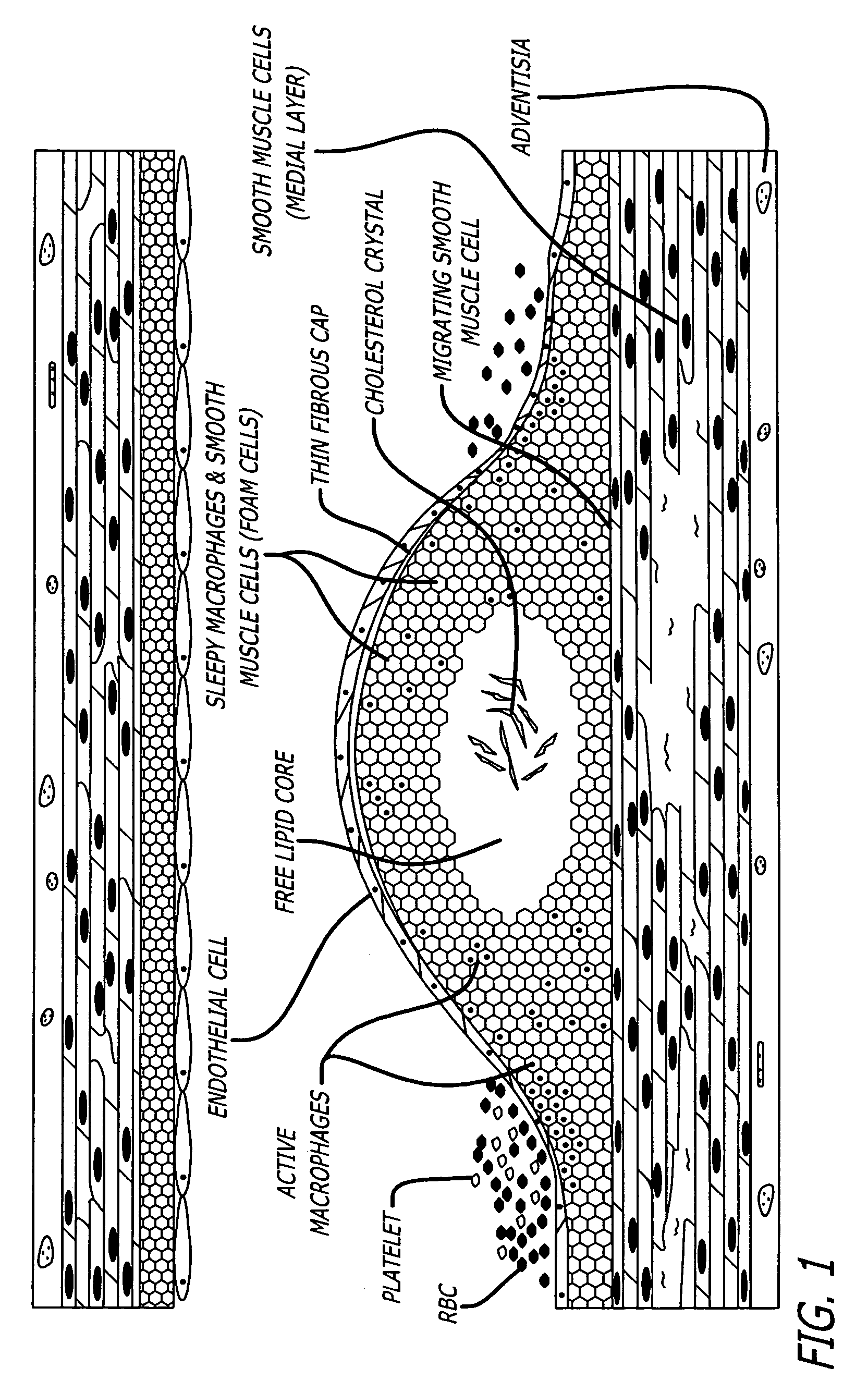
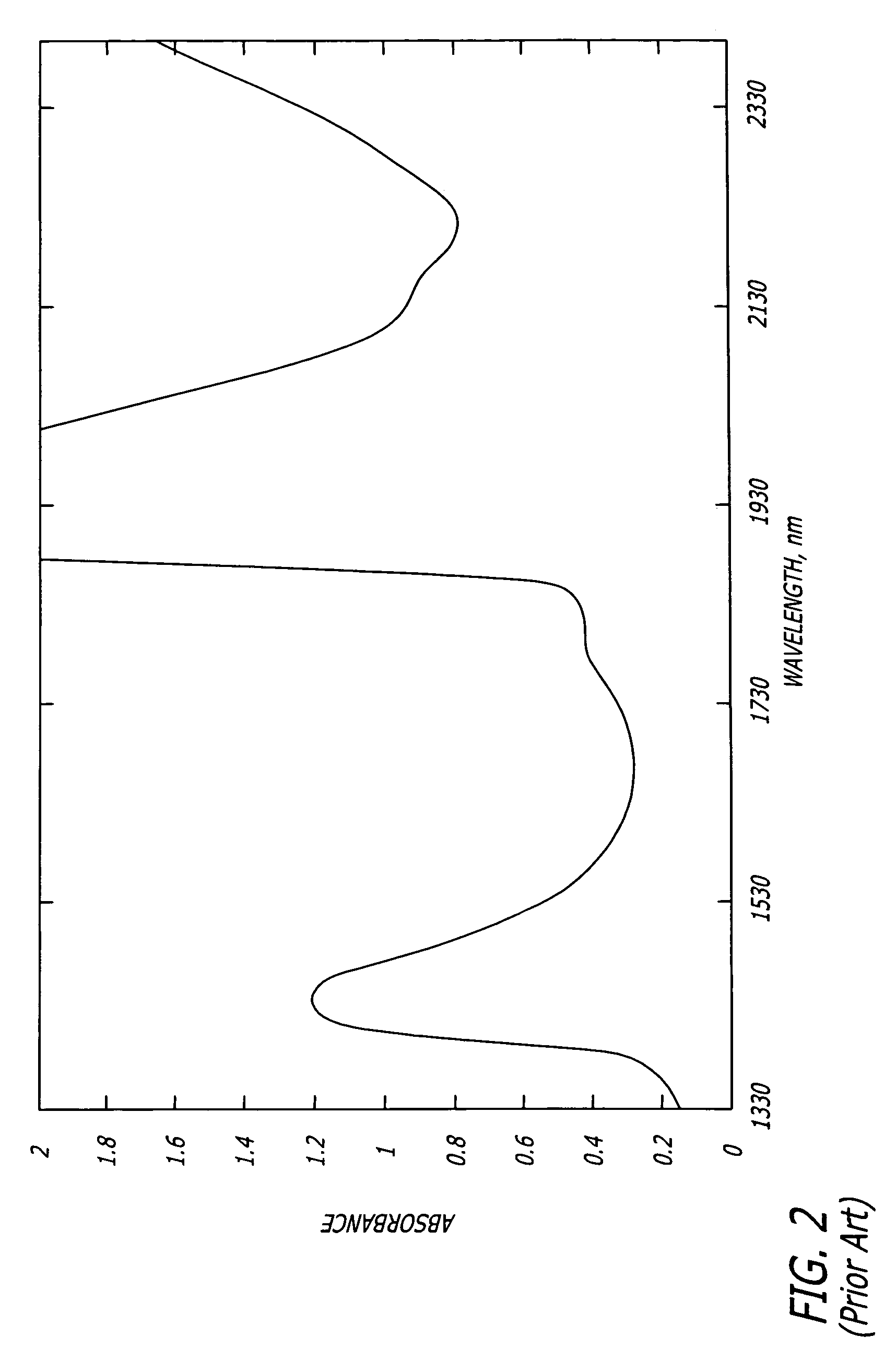
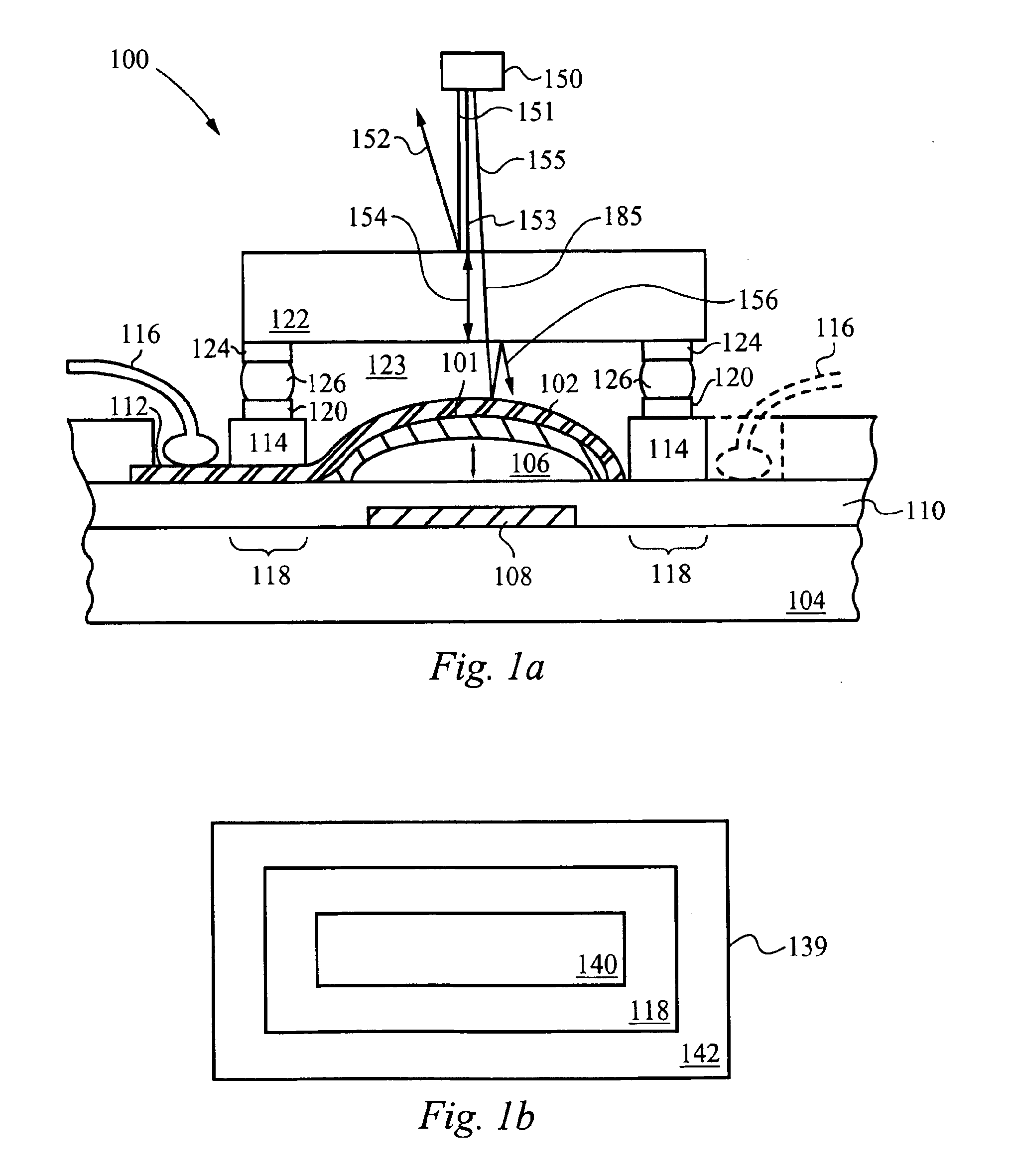
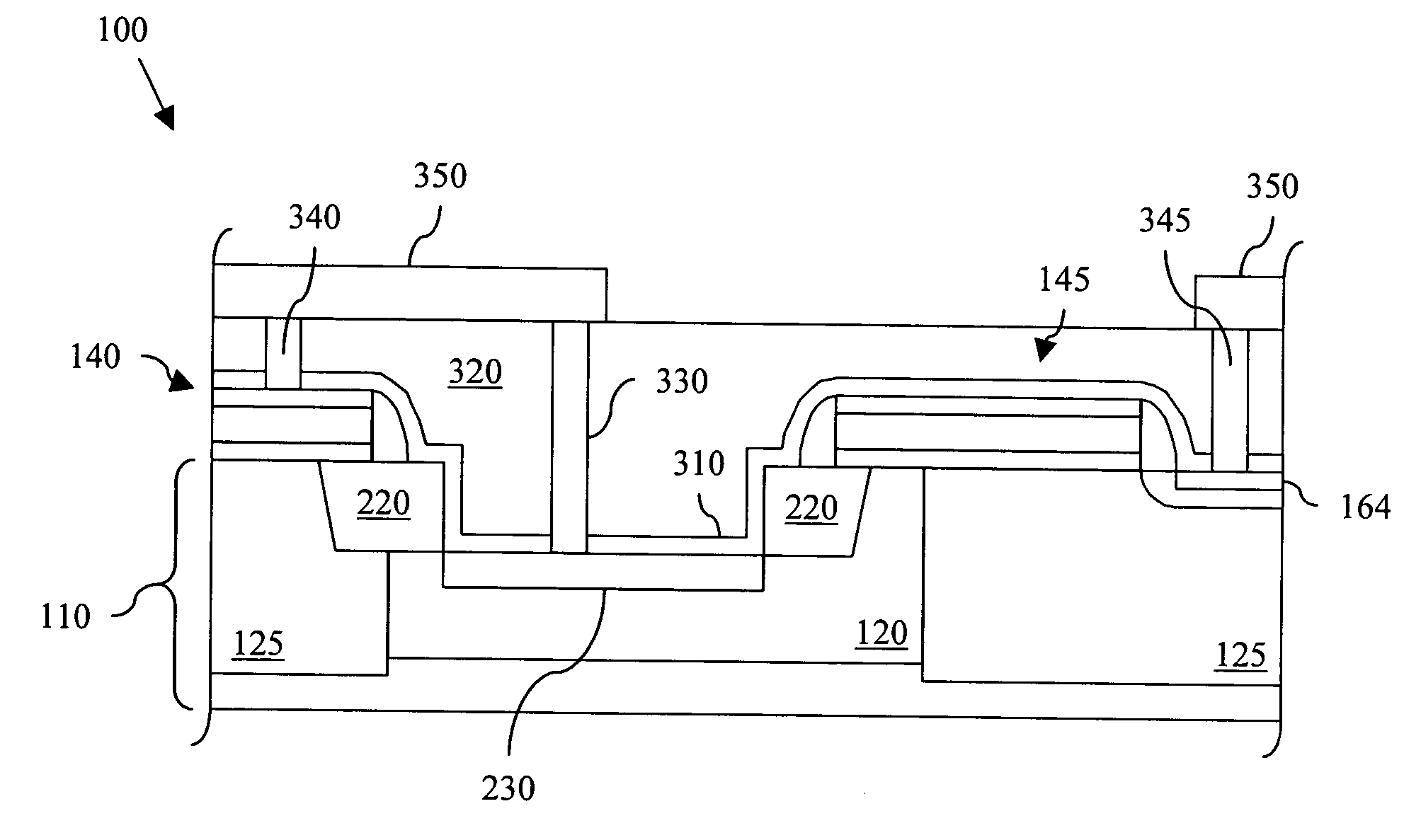
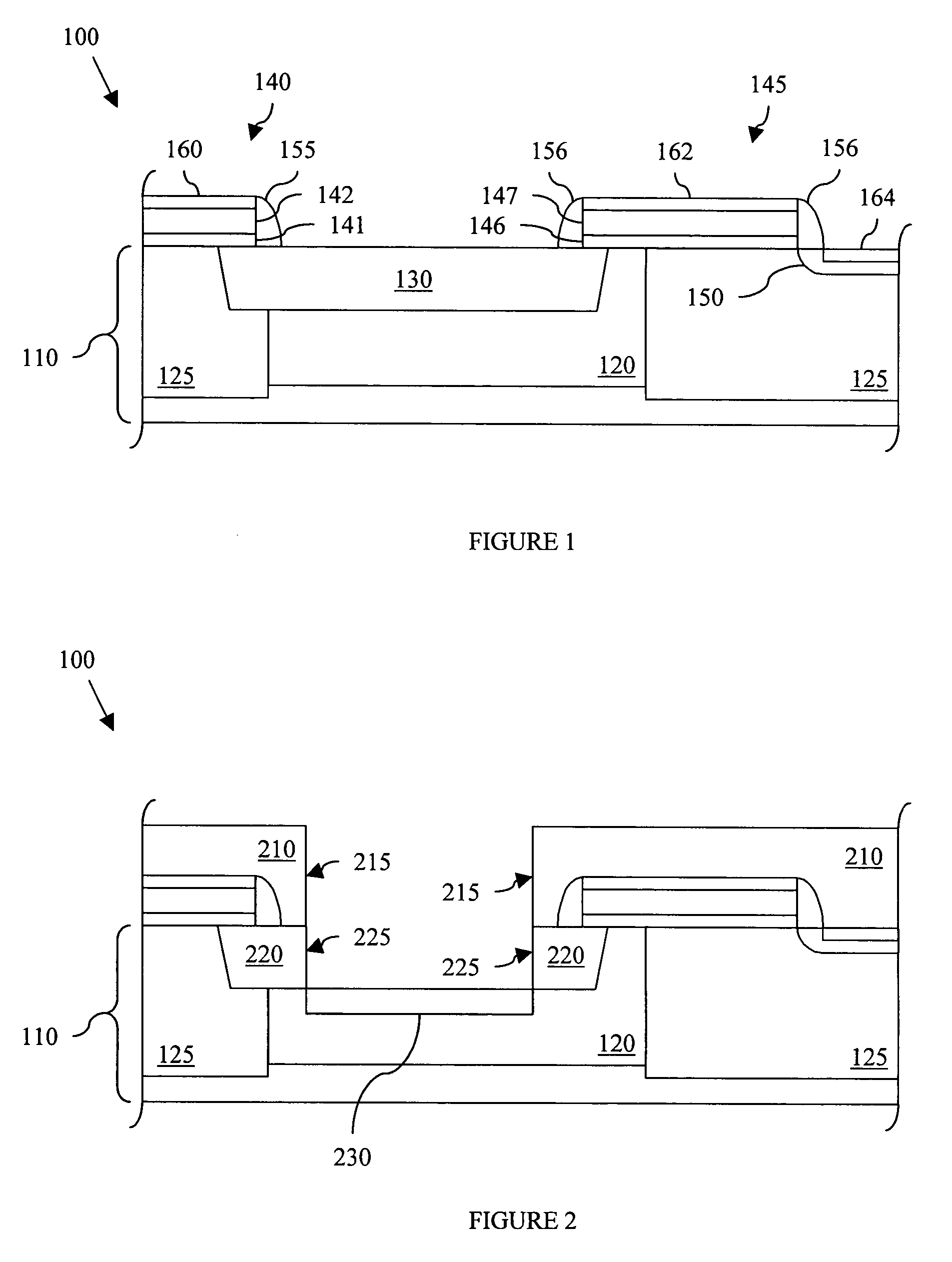
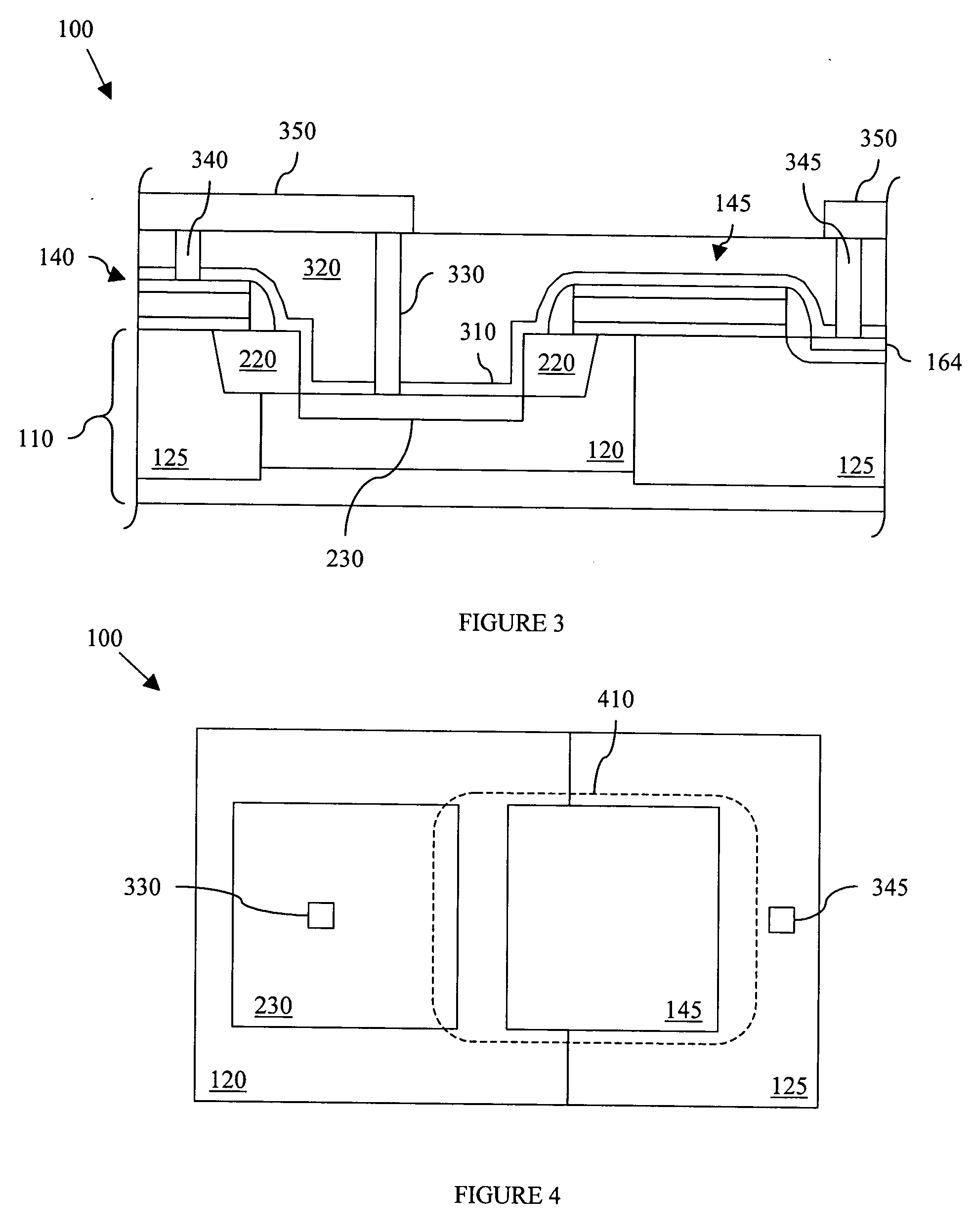
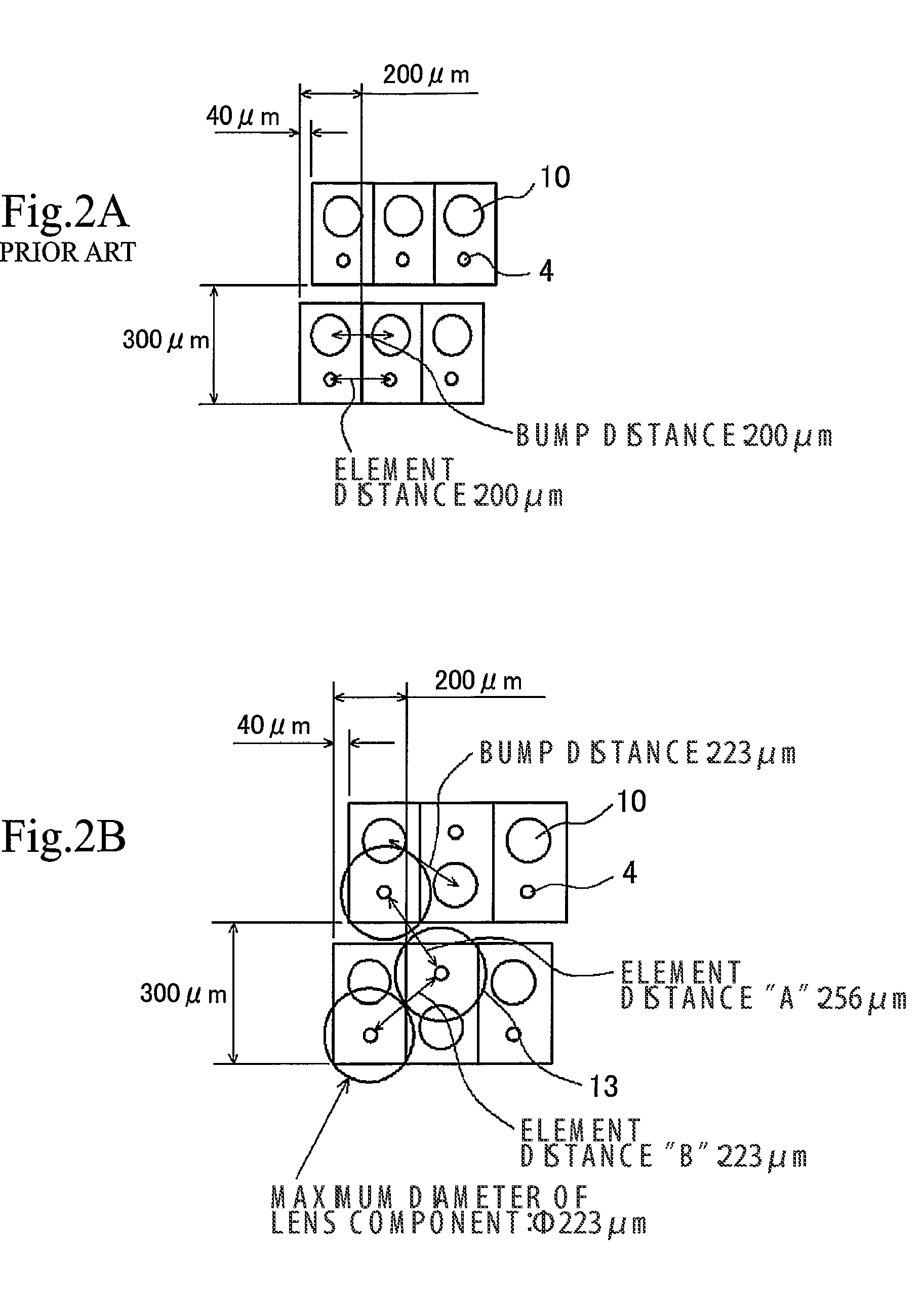
Method and apparatus for detection of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque
InactiveUS7603166B2Early detectionReduce Optical InterferenceRadiation pyrometrySurgeryThrombosisCvd risk
Methods for the detection of inflammation associated with vulnerable atherosclerotic plaque to prevent heart attack and stroke are disclosed. The methods are also applicable to detection of infection, cancer, wounds or auto-immune disease in the body. Certain embodiments of the new methods provide a way of predicting the level of vulnerability of an atherosclerotic plaque to rupture or thrombus formation by assessing via fiber optic NIR spectrophotometry the status of two or more parameters associated with inflamed atherosclerotic plaque in a vessel of a living patient. From these measurements such conditions as low pH, hypoxia, low glucose, oxidative stress or compounds abundant in vulnerable plaque such as oxidized LDL cholesterol and oxidized metabolites of NO, significant active macrophage population, thin plaque cap, as well as senescence and / or apoptosis of smooth muscle or endothelial cells are determined with the assistance of a suitably programmed microprocessor. By considering together the status of some or all of these conditions with respect to successive sites along a vessel wall, particular plaques which are at significant risk of rupturing or thrombosing can be distinguished from “normal” vessel wall and from “intermediate” and relatively stable or “lower risk” plaques. Sites having more of the indicator conditions would be considered most in need of prompt intervention, and certain combinations of parameter levels would be suggestive of relatively stable plaque.Also disclosed is a multi-parameter catheter and analytical processing assembly for use in the methods.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
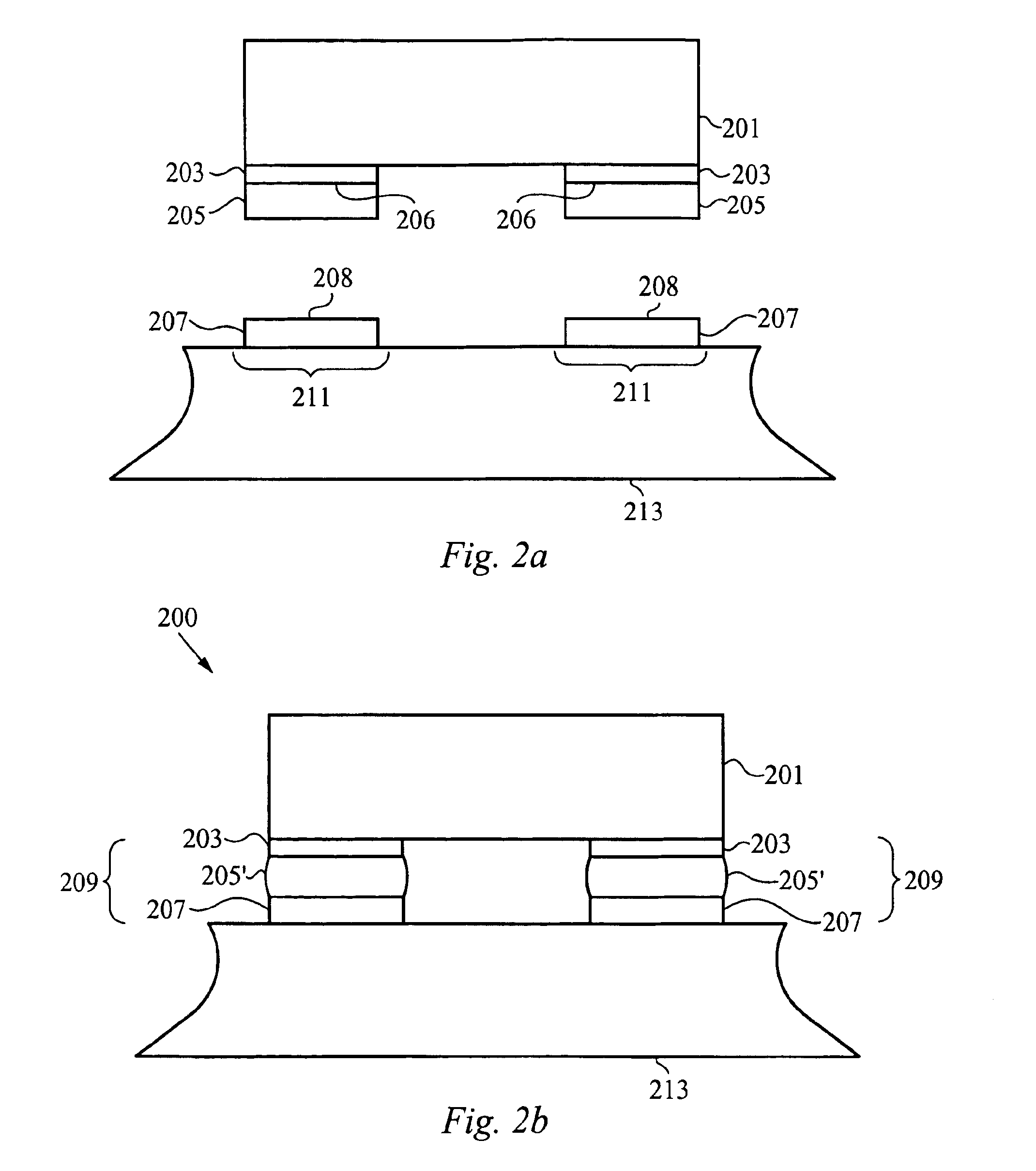
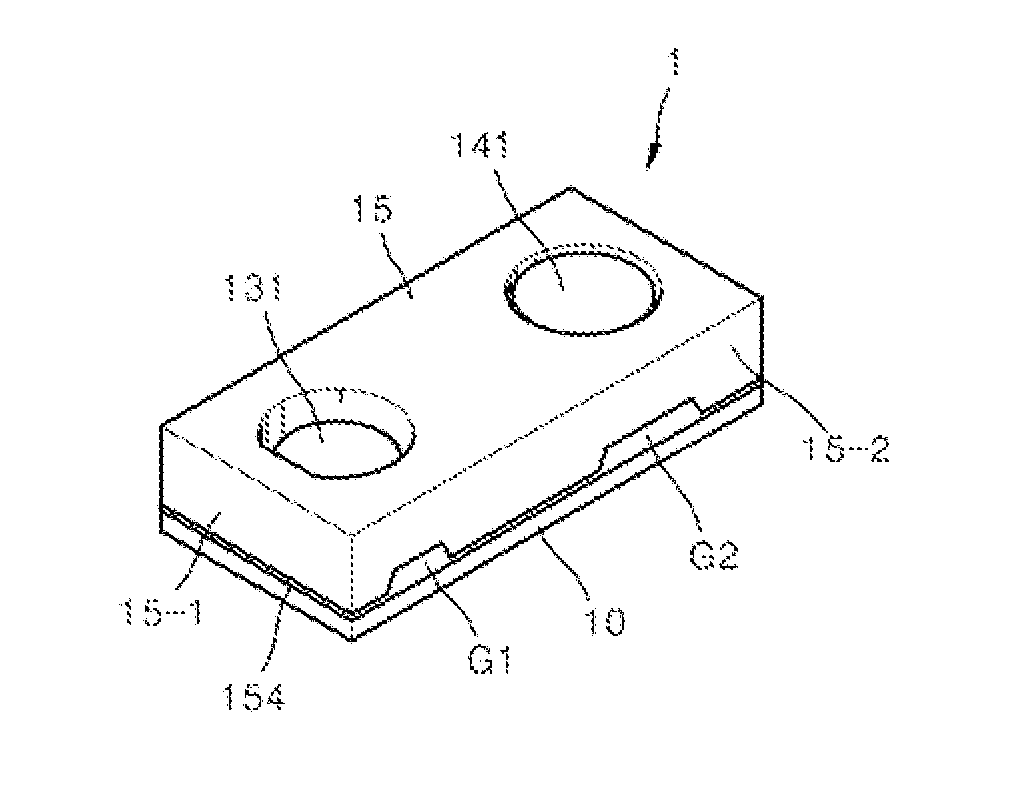
Method of sealing a hermetic lid to a semiconductor die at an angle
InactiveUS6872984B1Reduce Optical InterferenceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHermetic sealAsymmetric distribution
The current invention provides a optical MEM device and system with an angled lid for hermetically sealing an active MEMS structure. The lid is sealed through an asymmetric seal formed with sealing rings having an asymmetric distribution of solder wetting surfaces which tilts the lid, when the lid and a substrate are soldered together. The asymmetric distribution wetting surfaces can be provided by forming one or more edge features, by patterning portions of the sealing rings or both. Preferably, the lid is transparent to one or more wavelengths of light in a range of 300 to 3000 Angstroms and hermetically seals a grating light valve structure having a plurality of movable ribbon for modulating light through the lid.
Owner:SILICON LIGHT MACHINES CORP
CMOS image sensor device and method
A photodiode device including a well located in a substrate, a floating node located in the well and shallow trench isolation (STI) regions located over and laterally opposing the floating node. A borderless contact buffer layer is located over at least the floating node, and an interlevel dielectric layer is located over the borderless contact buffer layer. A borderless contact extends through the interlevel dielectric layer and the borderless contact buffer layer to the floating node.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
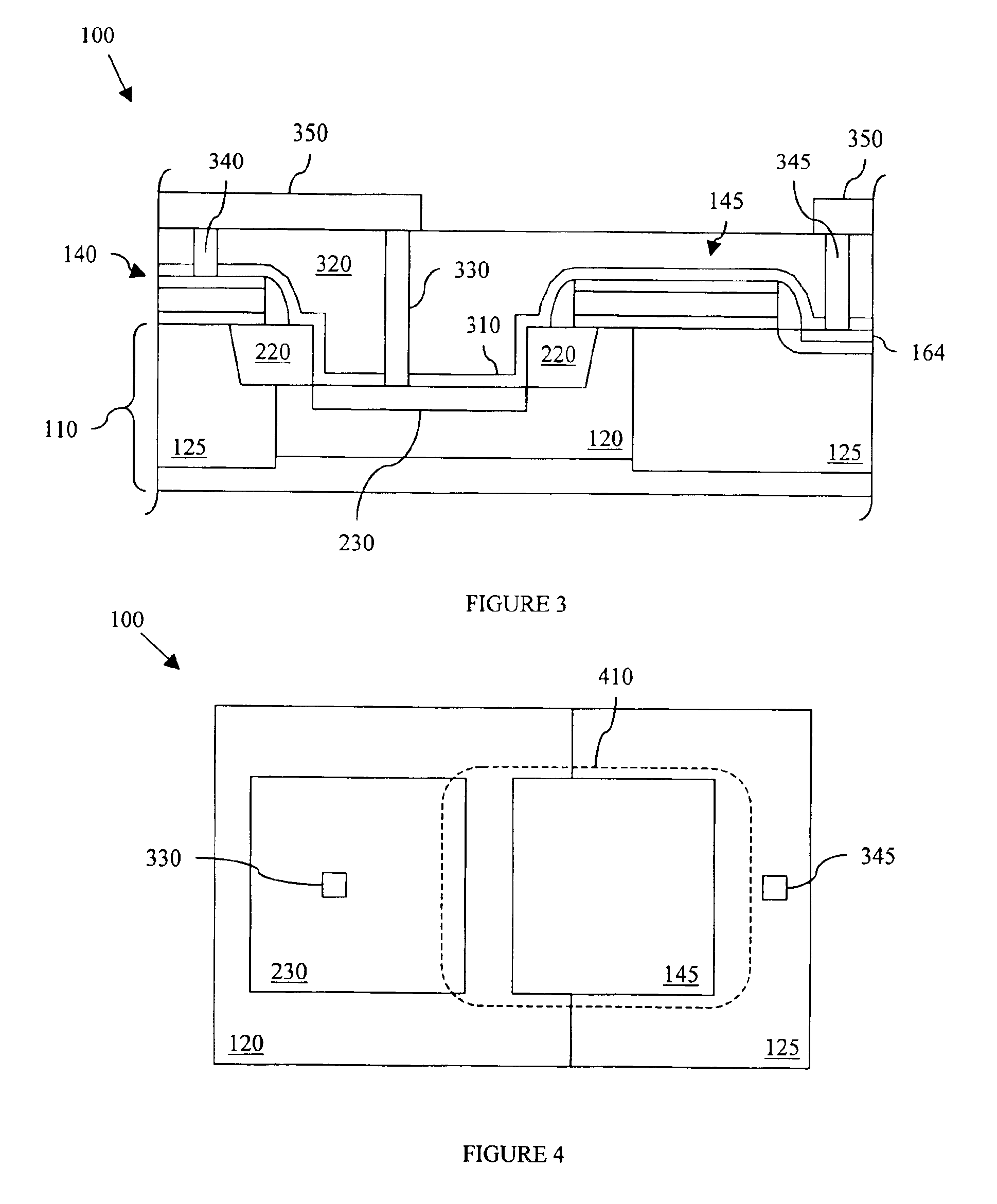
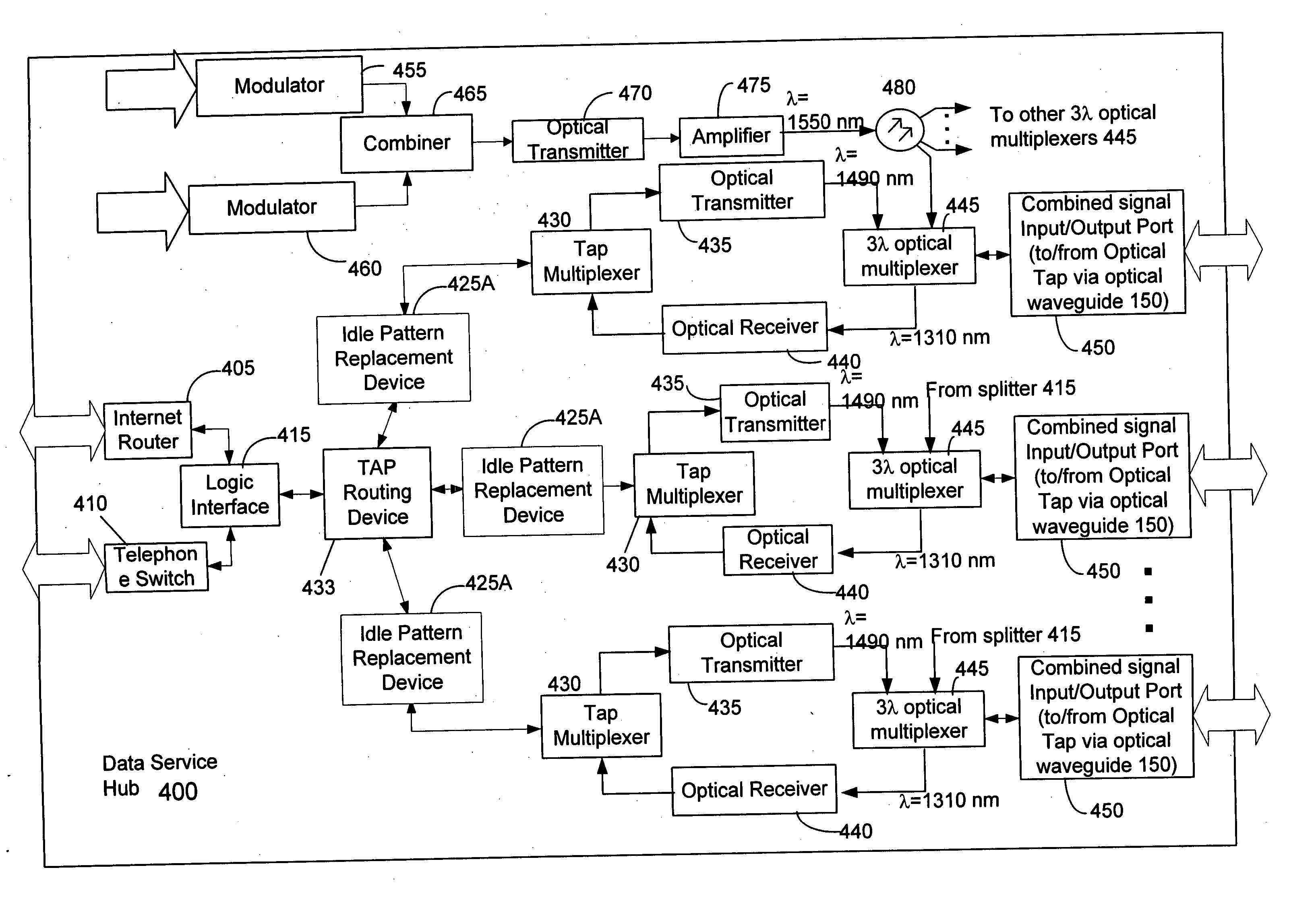
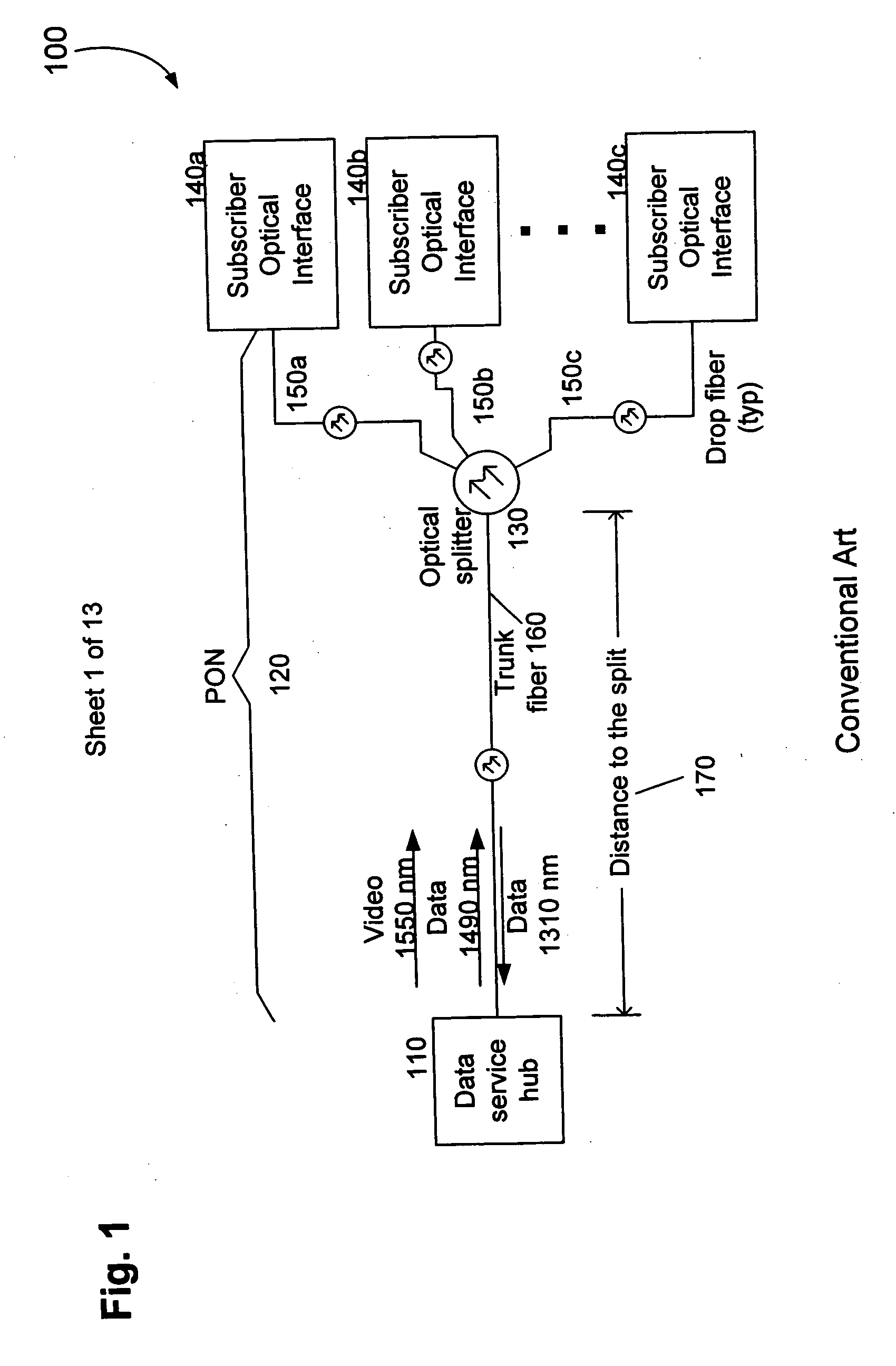
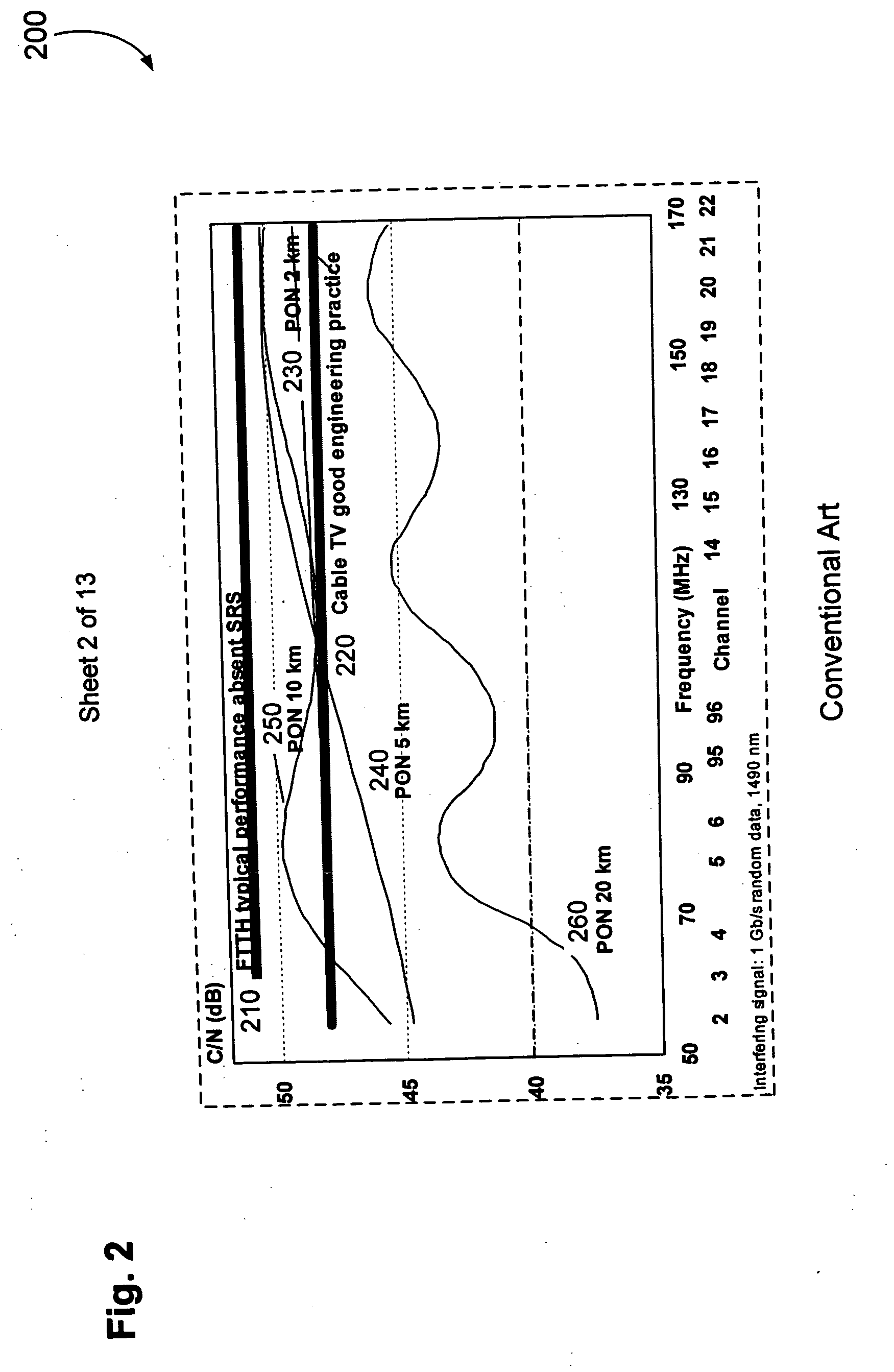
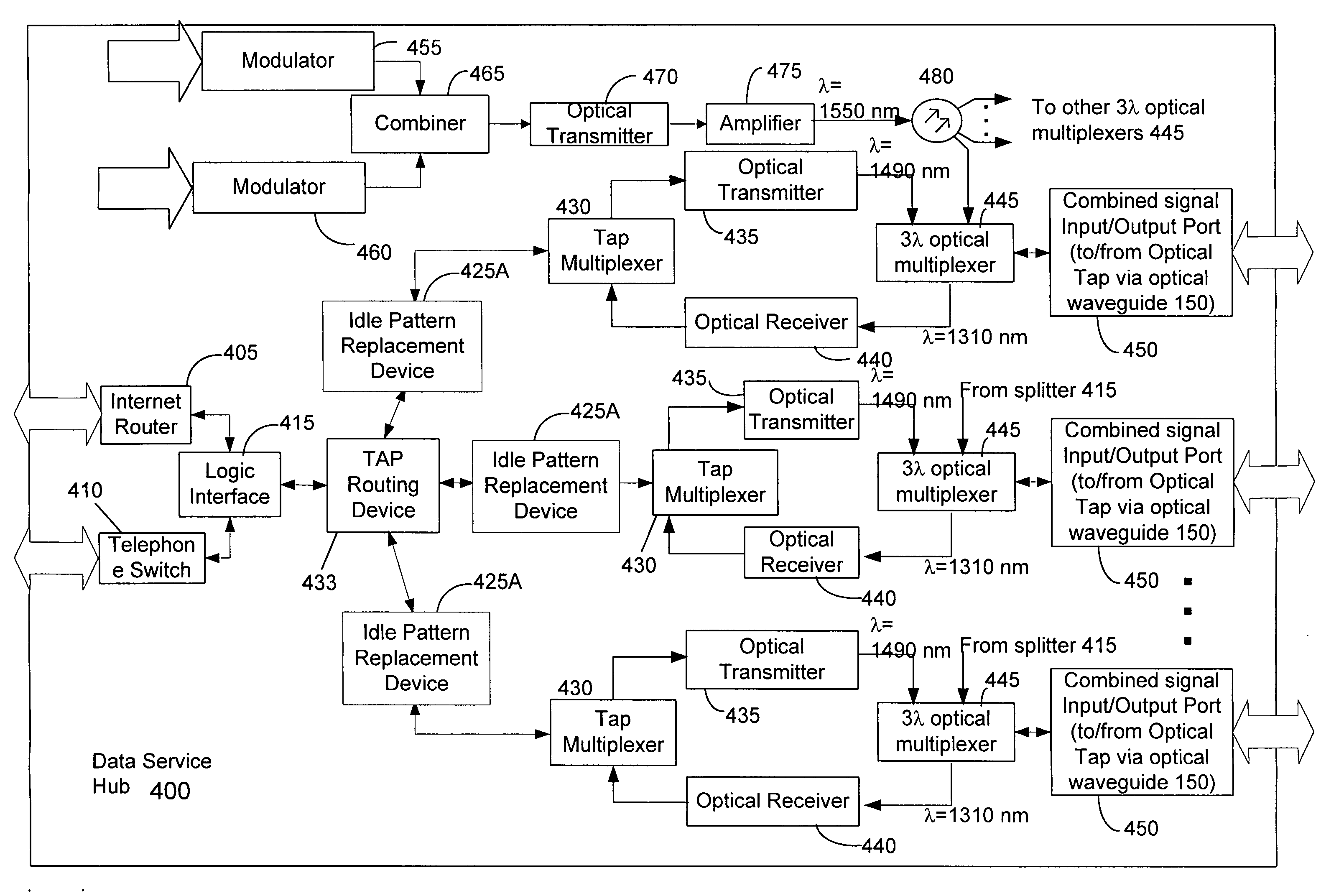
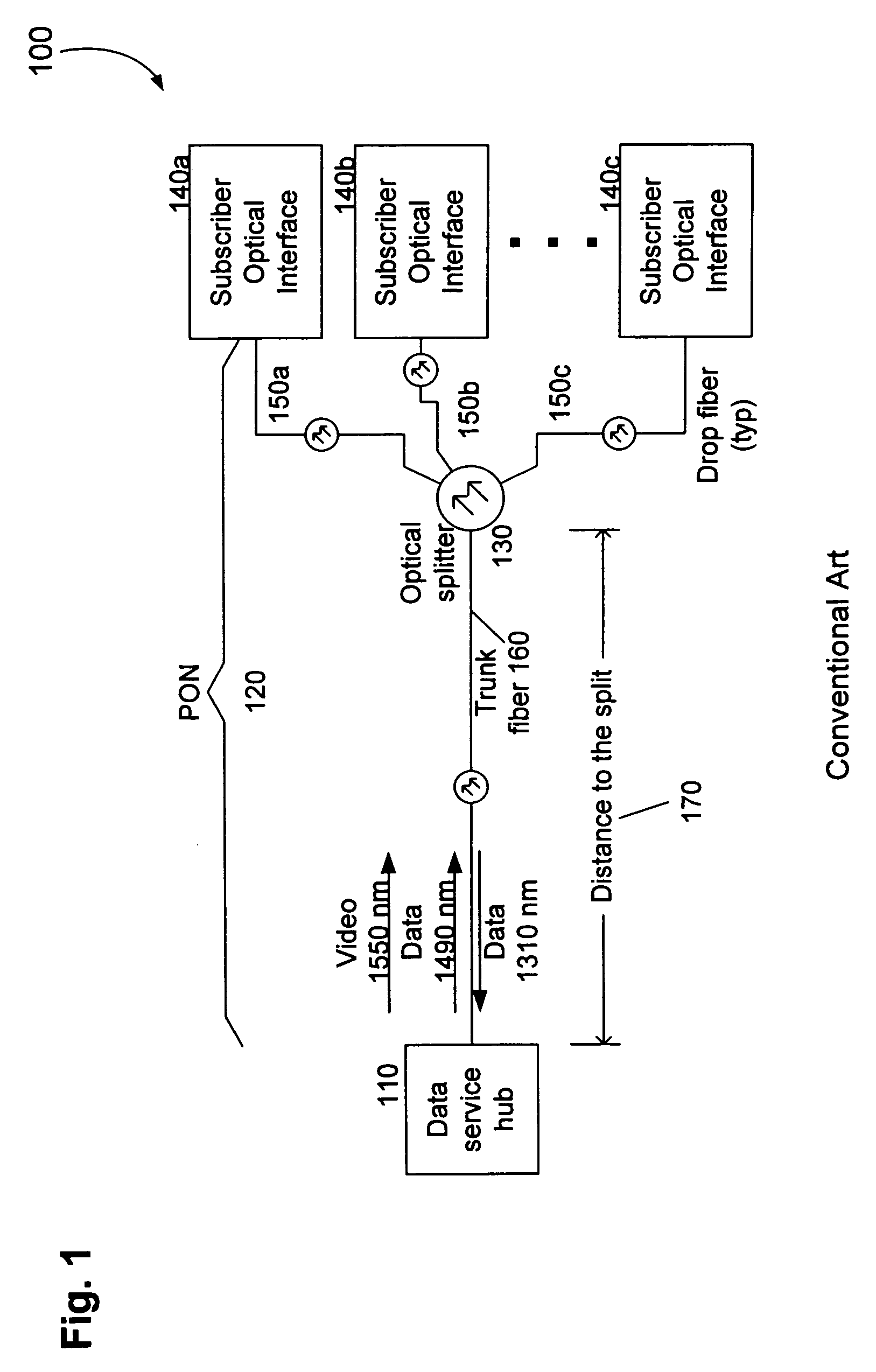
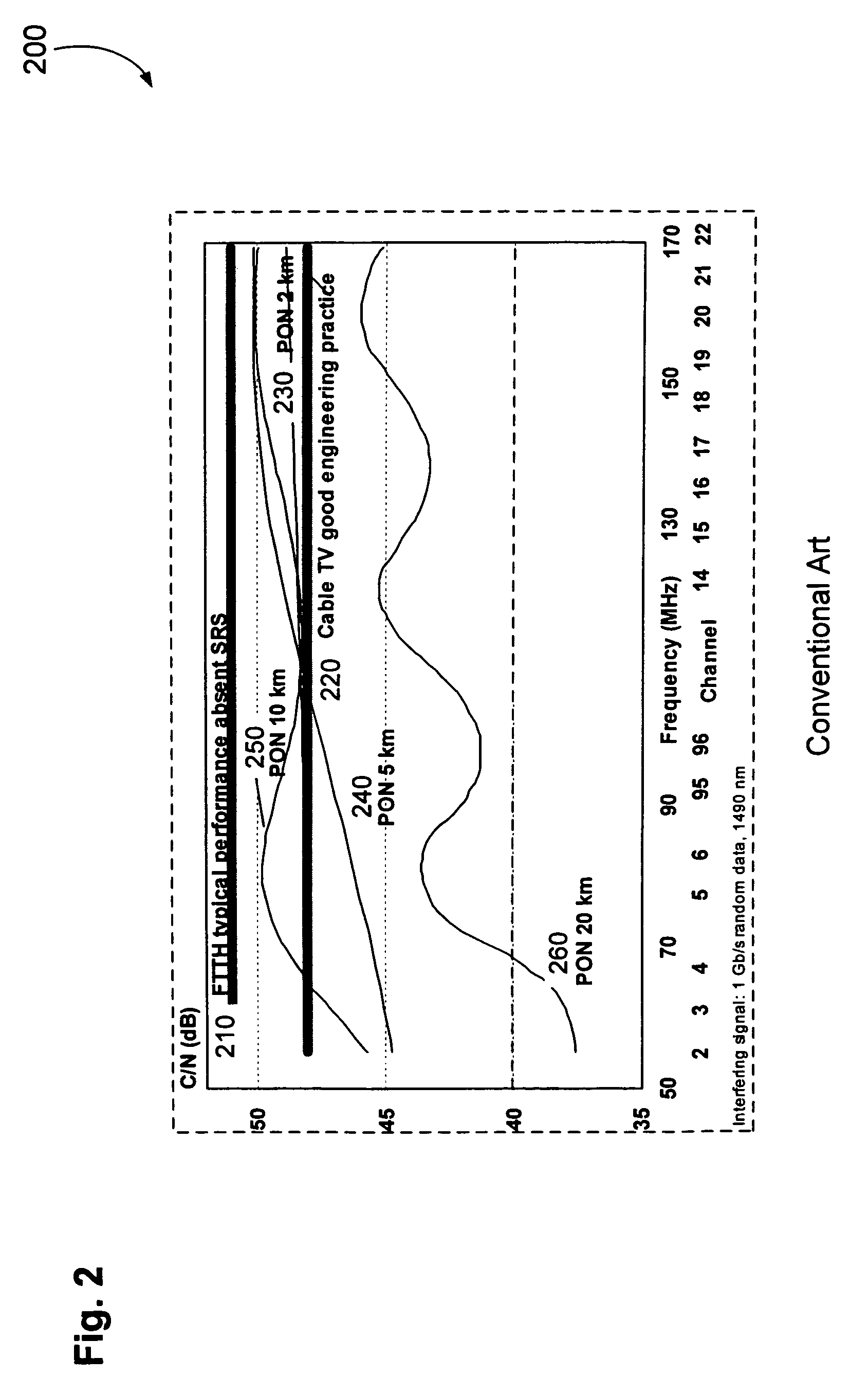
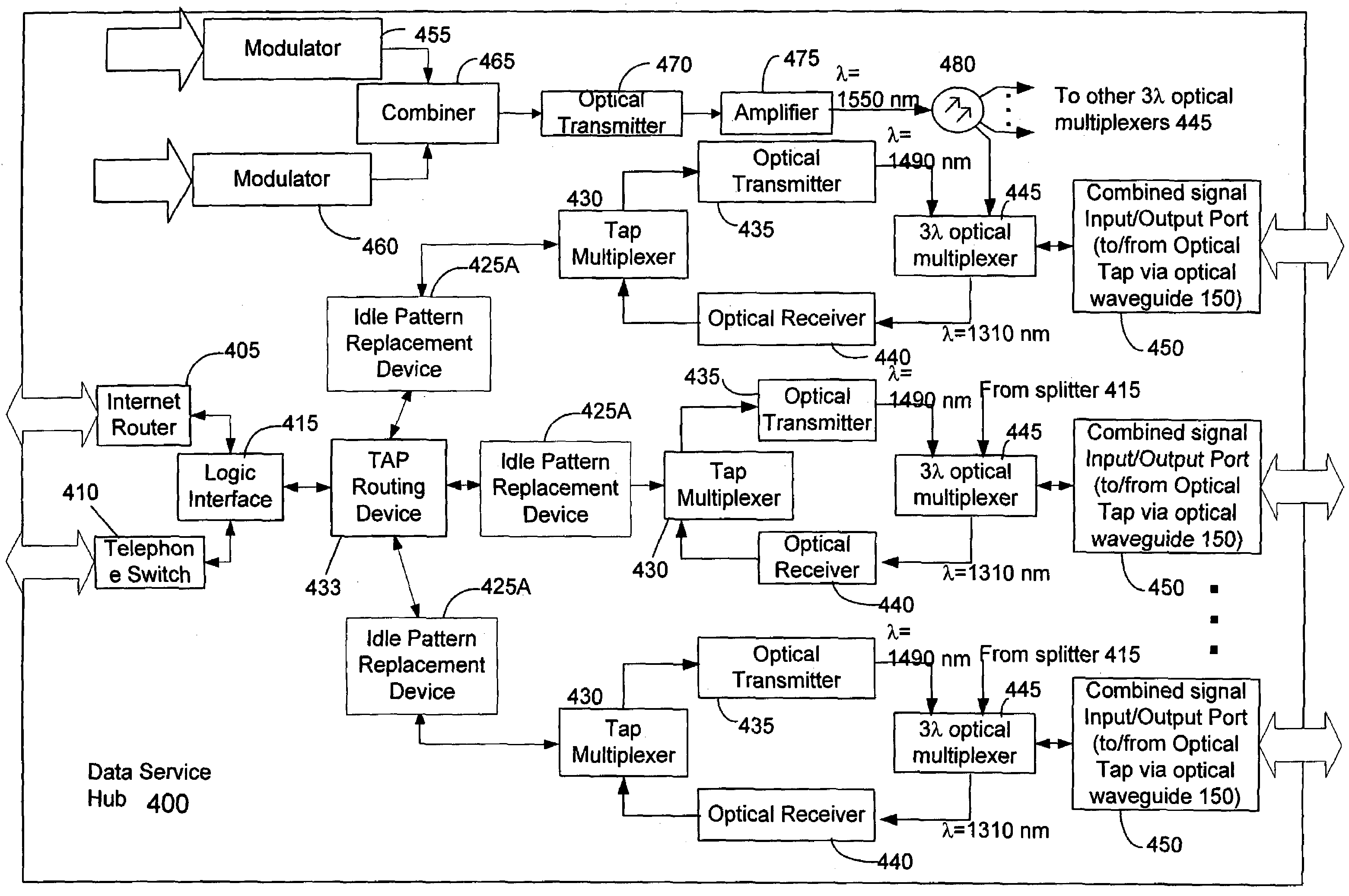
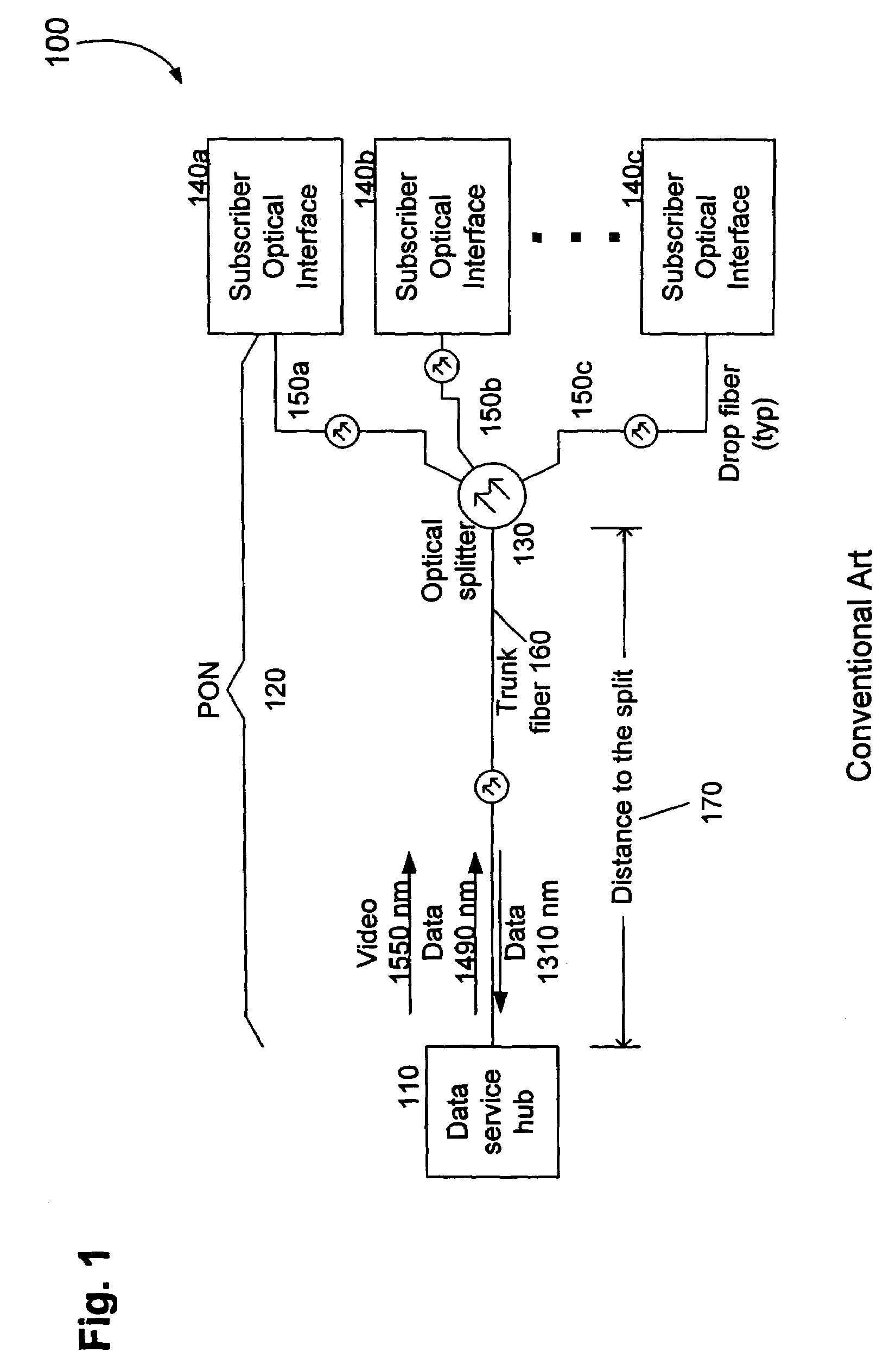
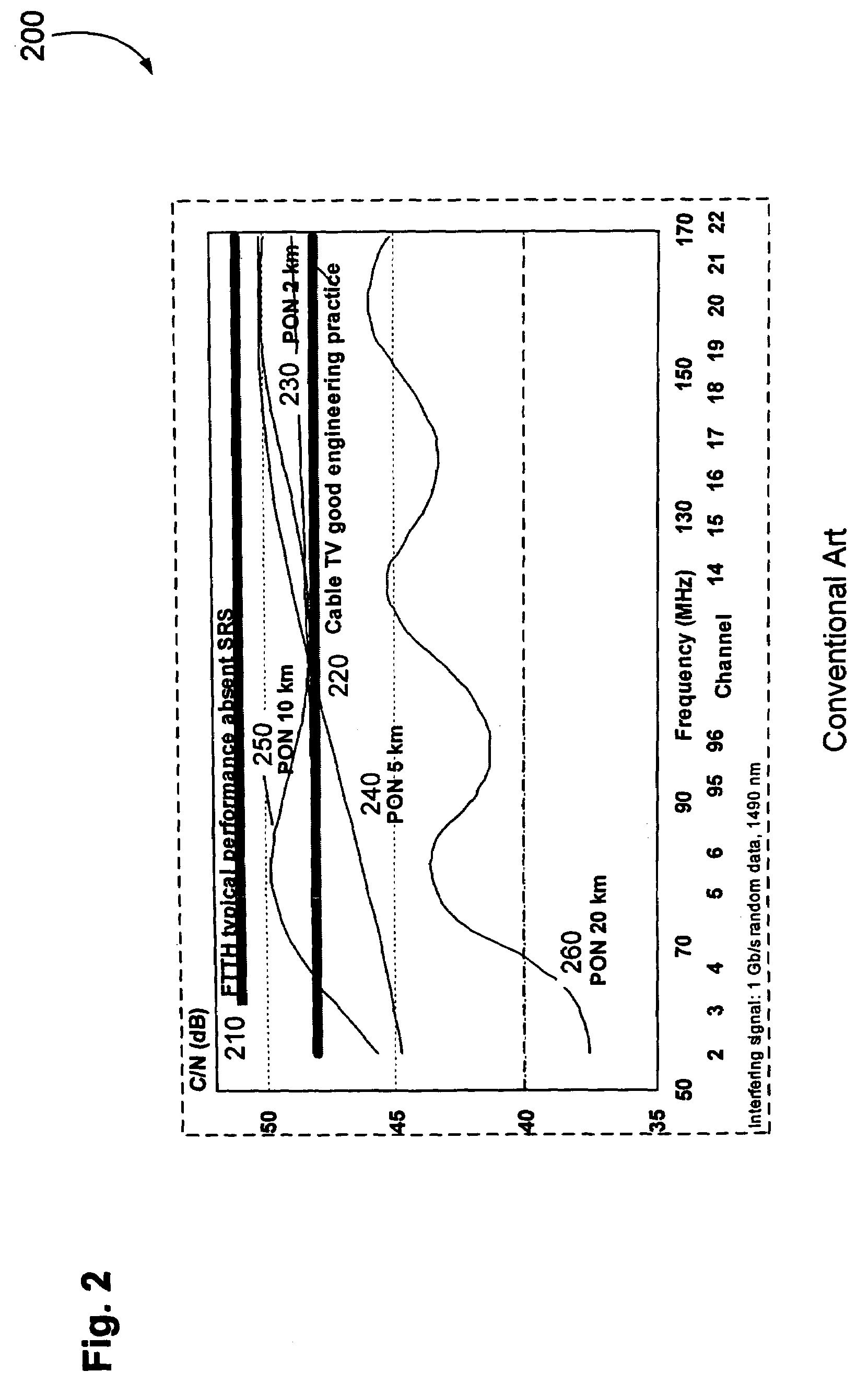
Countermeasures for idle pattern SRS interference in ethernet optical network systems
ActiveUS20060039699A1Reduce effectReduce and eliminate SRS optical interferenceOptical multiplexElectromagnetic transmissionData transmissionSingle-mode optical fiber
Optical networks as defined by the IEEE 802.3ah standard suffer from Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) that causes data transmission at a first optical wavelength to interfere with broadcast video transmission at a second optical wavelength in single mode optical fibers. The problem is exacerbated when data is not being transmitted across the network; and instead, an idle pattern transmission is being transmitted in order to keep the network synchronized. The repetitive nature of the idle pattern transmission leads to the SRS optical interference effect. This optical interference effect is mitigated when countermeasures are implemented to modify the idle pattern transmissions or to transmit random data in place of the idle pattern transmissions.
Owner:ARRIS SOLUTIONS
CMOS image sensor device and method
A photodiode device including a well located in a substrate, a floating node located in the well and shallow trench isolation (STI) regions located over and laterally opposing the floating node. A borderless contact buffer layer is located over at least the floating node, and an interlevel dielectric layer is located over the borderless contact buffer layer. A borderless contact extends through the interlevel dielectric layer and the borderless contact buffer layer to the floating node.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
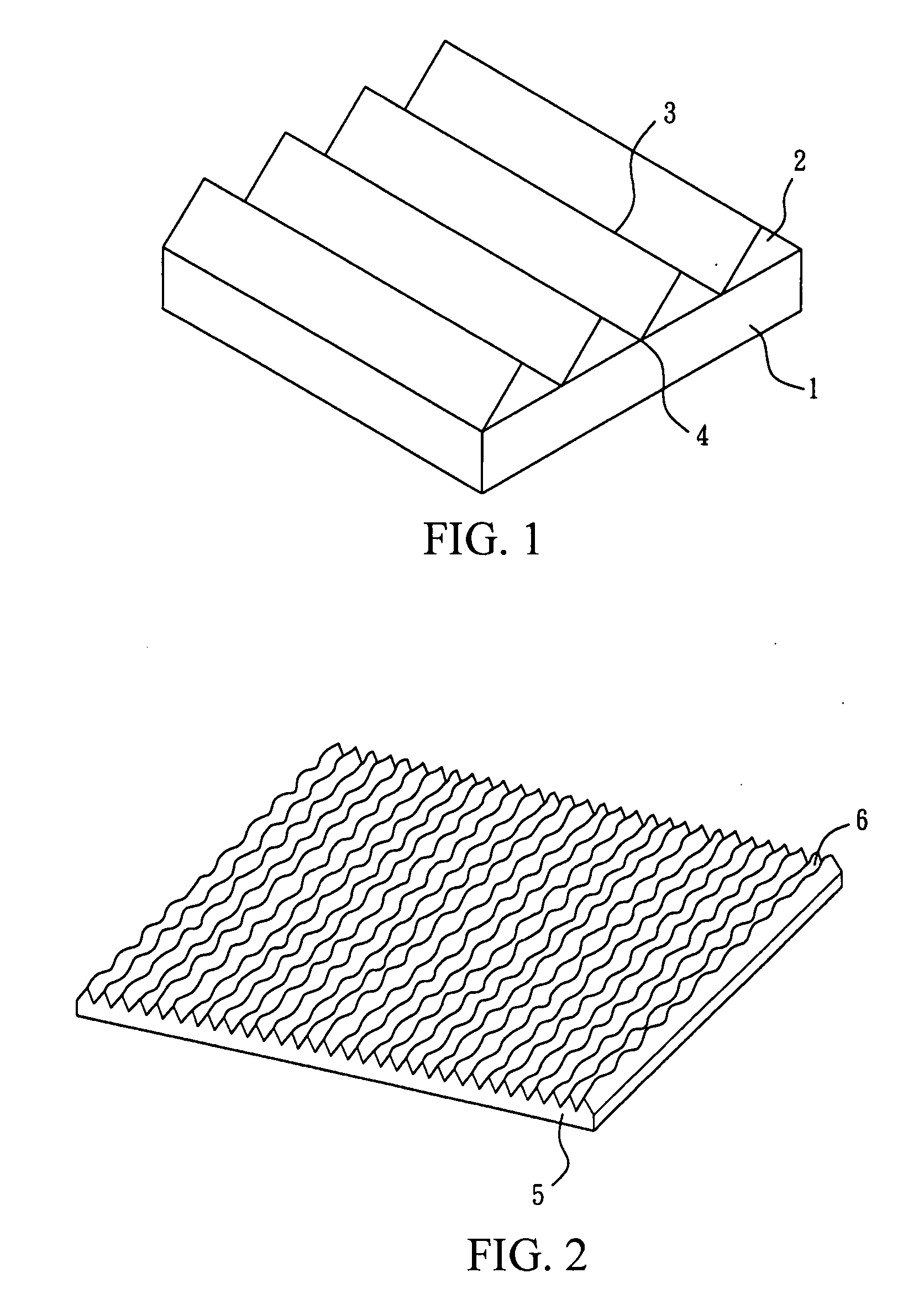
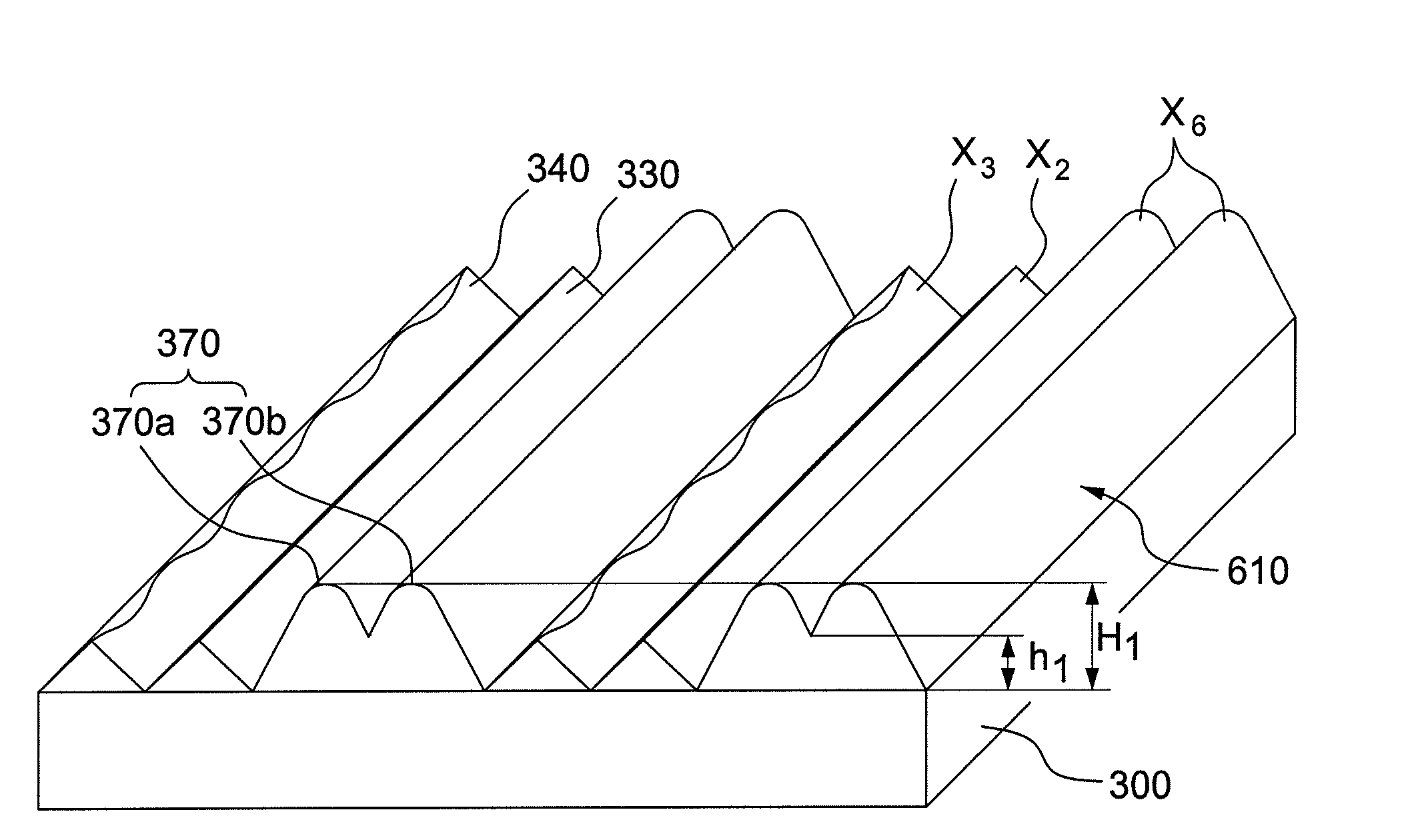
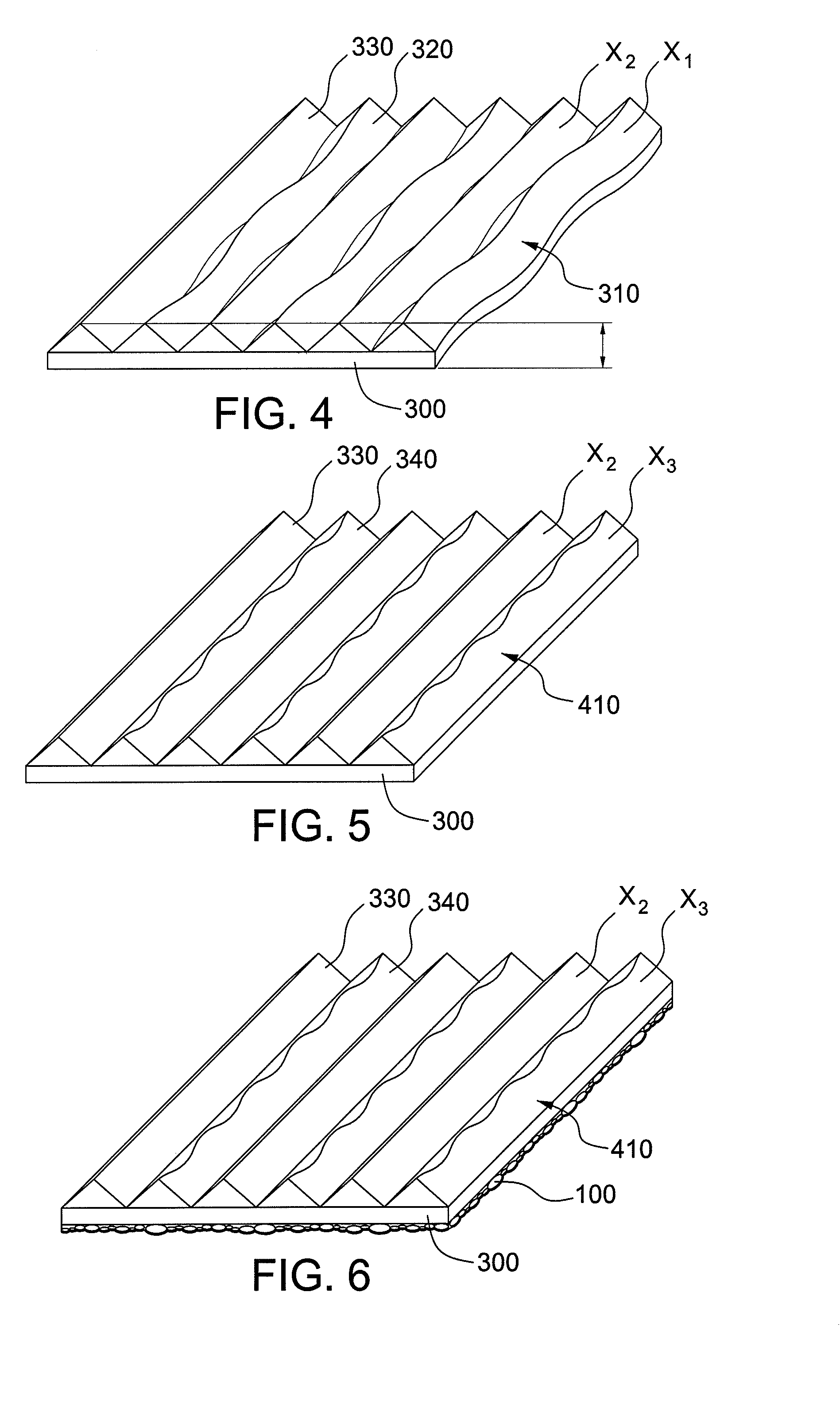
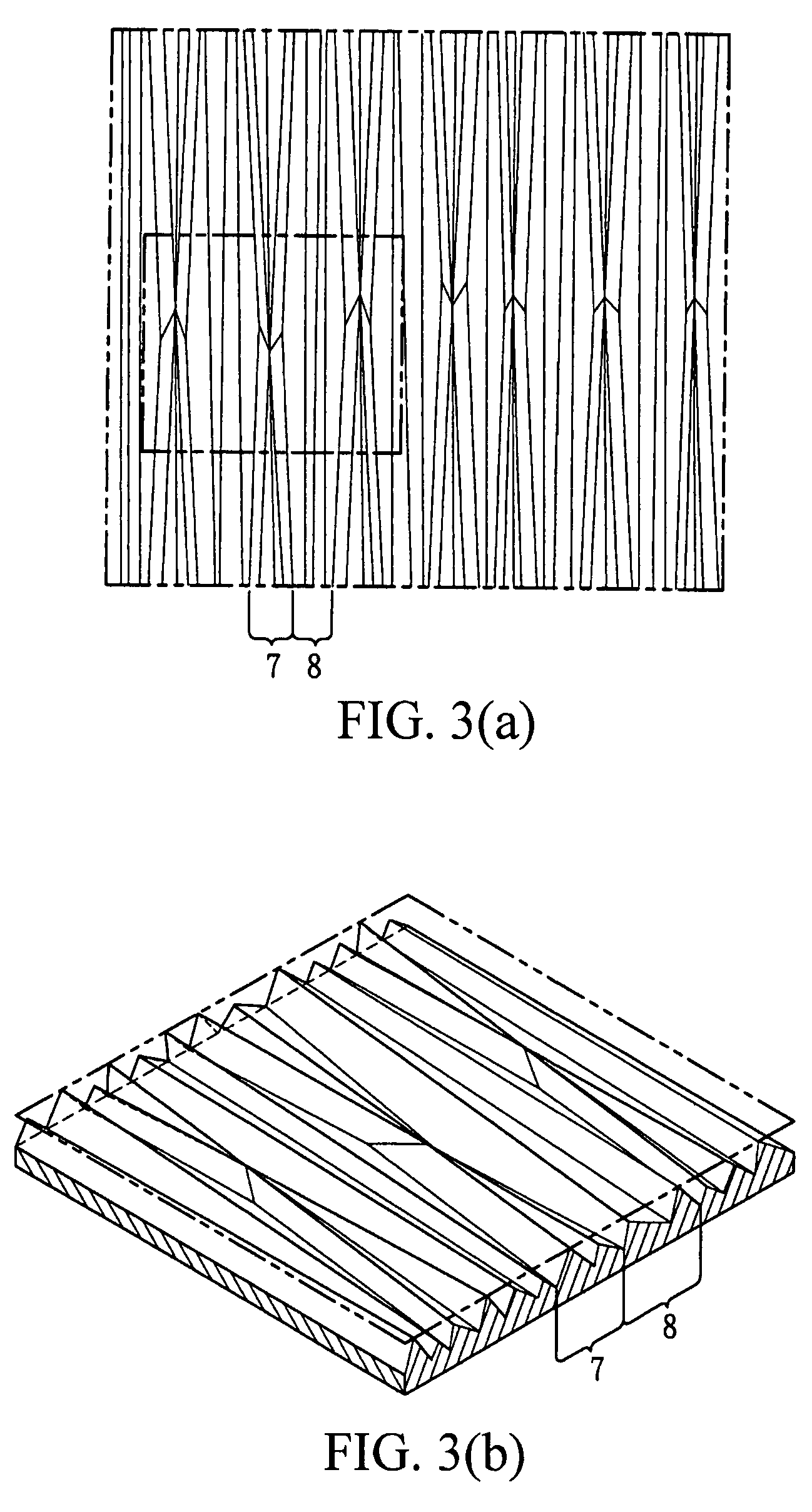
Optical film
ActiveUS20080055937A1Increase brightnessReduce Optical InterferencePrismsMechanical apparatusSurface layerLiquid-crystal display
The subject invention provides an optical film comprising a transparent substrate and a structured surface layer, wherein the structured layer is positioned on the upper surface of the substrate and comprises a plurality of non-parallel, adjacent columnar structures. The optical film according to the subject invention can effectively enhance the brightness of a liquid crystal display and reduce the optical interference.
Owner:ETERNAL MATERIALS CO LTD
Opto-electronic module including a non-transparent separation member between a light emitting element and a light detecting element
ActiveUS20160216138A1Reduce Optical InterferenceReduce crosstalkPoint-like light sourceOptical filtersOpto electronicUV curing
An opto-electronic sensor module (e.g., an optical proximity sensor module) includes a substrate, a light emitter mounted on a first surface of the substrate, the light emitter being operable to emit light at a first wavelength, and a light detector mounted on the first surface of the substrate, the light detector being operable to detect light at the first wavelength. The module includes an optics member disposed substantially parallel to the substrate, and a separation member disposed between the substrate and the optics member. The separation member may surround the light emitter and the light detector, and may include a wall portion that extends from the substrate to the optics member and that separates the light emitter and the light detector from one another. The separation member may be composed, for example, a thermosetting polymer material, a UV-curing polymer material or a visible light-curing polymer material, wherein the separation member further includes one or more inorganic fillers and / or dyes that make the separation member substantially non-transparent to light detectable by the light detector and / or emitted by the light emitter.
Owner:AMS SENSORS SINGAPORE PTE LTD
Mirror Display
ActiveUS20170344166A1Reduce Optical InterferenceStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid crystalEngineering
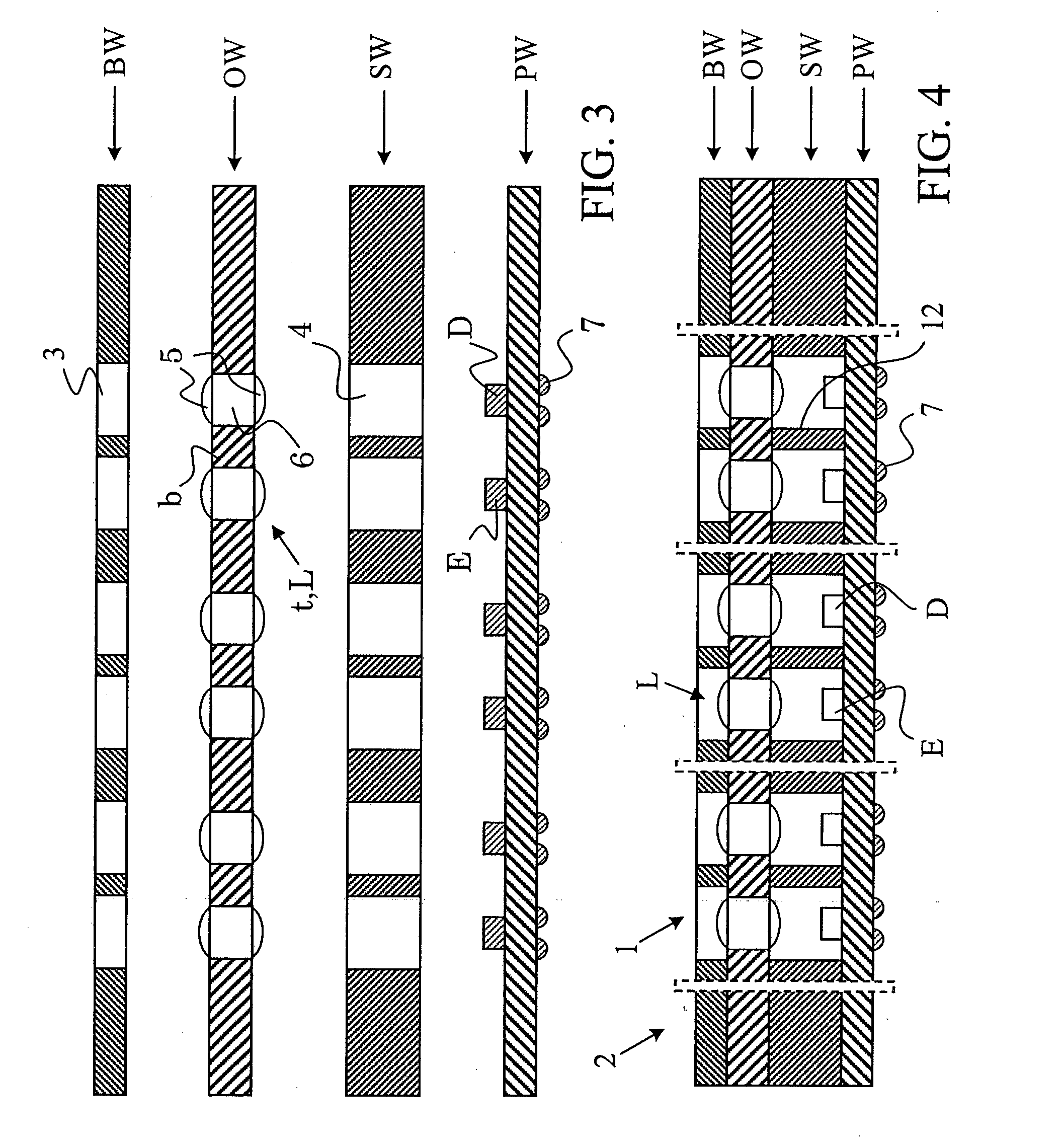
A mirror display is described. The mirror display includes a plurality of first electrodes disposed on a first substrate, a plurality of sensor lines disposed on the first substrate, the plurality of sensor lines connected to the plurality of first electrodes, a plurality of second electrodes disposed on a second substrate, the plurality of second electrodes facing the first substrate, a liquid crystal layer interposed between the plurality of first electrodes and the plurality of second electrodes, a plurality of mirror driving lines on the second substrate, the plurality of mirror driving lines connected to the plurality of second electrodes, and a reflective polarizing film attached to the second substrate.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
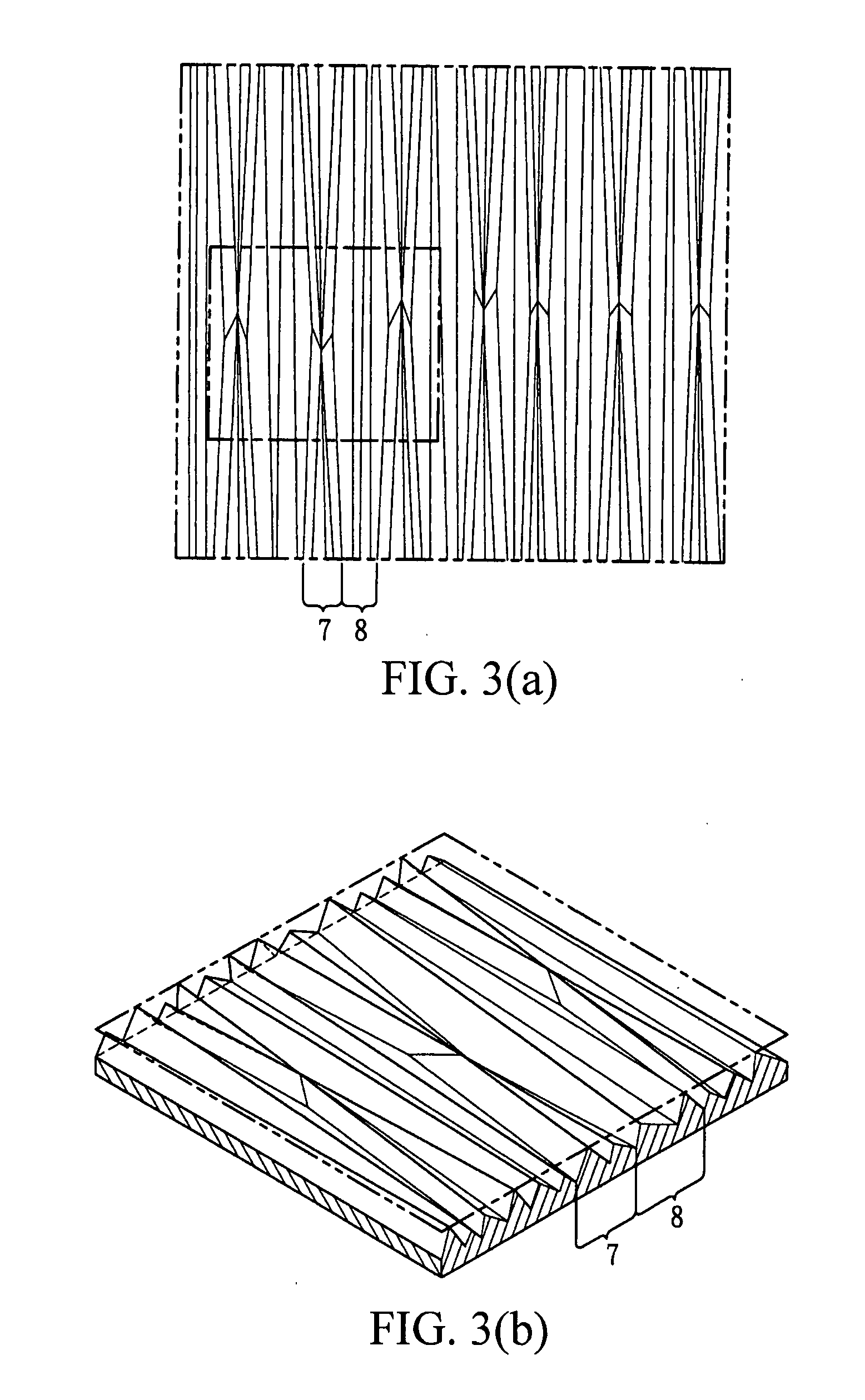
Optical film
The present invention pertains to an optical film comprising a substrate and a microstructured layer on a surface of the substrate, wherein the microstructured layer comprises a plurality of columnar structures and the columnar structures comprise at least two members selected from the group consisting of a linear columnar structure with its height varying along the length direction, a linear columnar structure without its height varying along the length direction, a serpentine columnar structure with its height varying along the length direction, and a serpentine columnar structure without its height varying along the length direction.The optical film of the present invention enhances the brightness and efficiently reduces optical interference.
Owner:ETERNAL MATERIALS CO LTD
Display
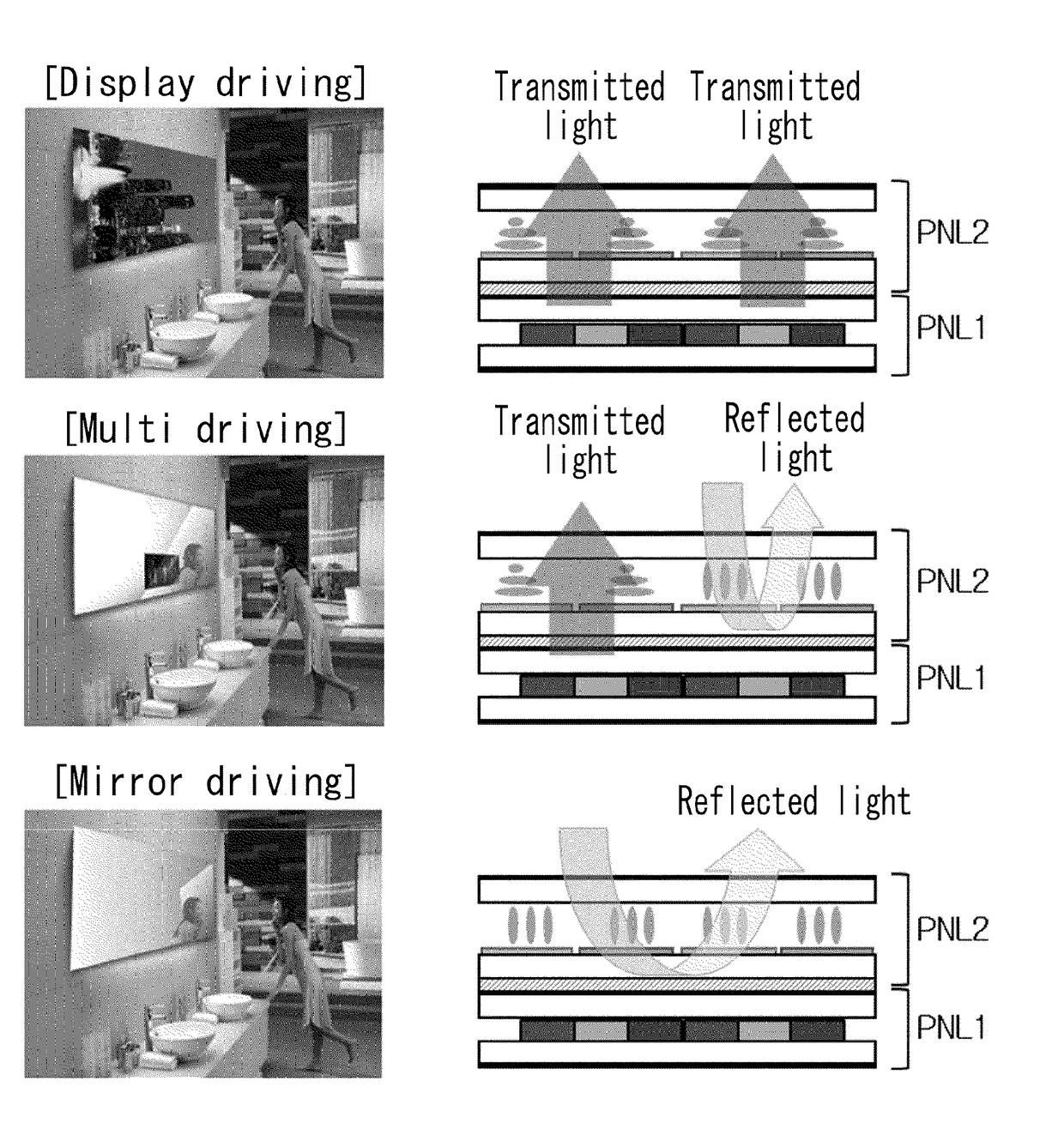
InactiveUS20060238484A1Reduce Optical InterferenceInterference problemStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceEngineering
Owner:INNOCOM TECH SHENZHEN +1
Optical film
ActiveUS7891856B2Increase brightnessReduce Optical InterferencePrismsDiffusing elementsSurface layerLiquid-crystal display
The subject invention provides an optical film comprising a transparent substrate and a structured surface layer, wherein the structured layer is positioned on the upper surface of the substrate and comprises a plurality of non-parallel, adjacent columnar structures. The optical film according to the subject invention can effectively enhance the brightness of a liquid crystal display and reduce the optical interference.
Owner:ETERNAL MATERIALS CO LTD
LED device and LED lamp including the same
ActiveUS20180216787A1Reduce Optical InterferenceElectric circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesEngineeringSurface mounting
An LED device includes a transparent substrate having a bar-like shape and having a first surface and a second surface opposed thereto, a plurality of LED chips mounted on the first surface of the transparent substrate and electrically connected to each other, each of the plurality of LED chips having a reflective layer disposed on a surface mounted in the transparent substrate, a first connection terminal and a second connection terminal disposed on opposing ends of the transparent substrate and electrically connected to the plurality of LED chips, a bonding layer interposed between the plurality of LED chips and the transparent substrate and including a metal filler, and a wavelength conversion portion covering the first surface and the second surface of the transparent substrate and the plurality of LED chips.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
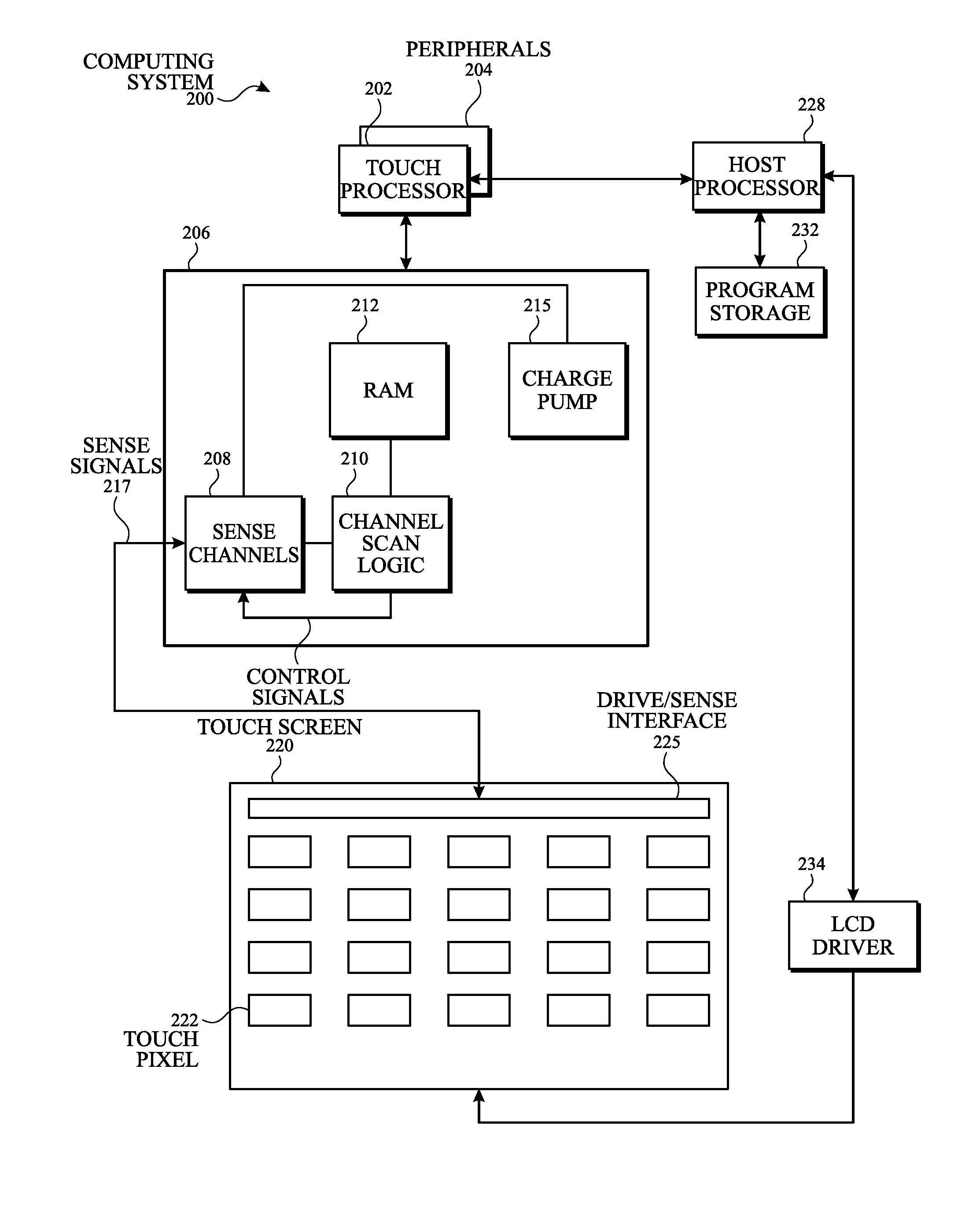
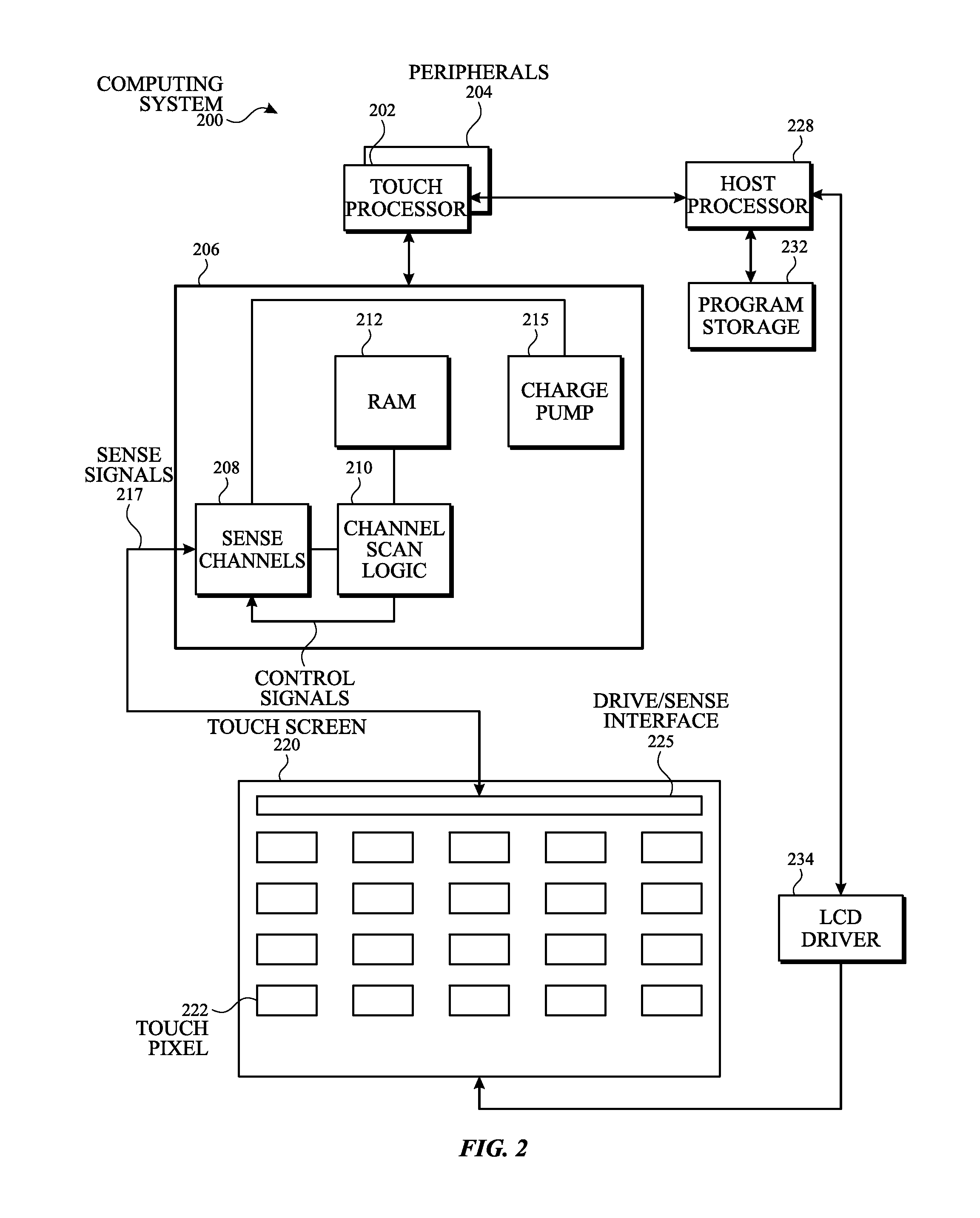
Touch pixel design for reducing visual artifacts
InactiveUS20160062499A1Reduce Optical InterferenceReduce artifactsElectric switchesSelector switchesVisual artifactHuman–computer interaction
A touch sensor panel is disclosed. In some examples, the touch sensor panel comprises a first touch pixel electrode formed in a first layer, the first touch pixel electrode comprising a plurality of electrically coupled touch pixel segments separated by one or more touch pixel gaps. In some examples, the touch sensor panel comprises a sense connection formed in the first layer and coupled to the first touch pixel electrode, the sense connection configured to couple the first touch pixel electrode to sense circuitry. In some examples, the touch pixel segments and the touch pixel gaps are configured to provide optical uniformity on the touch sensor panel.
Owner:APPLE INC
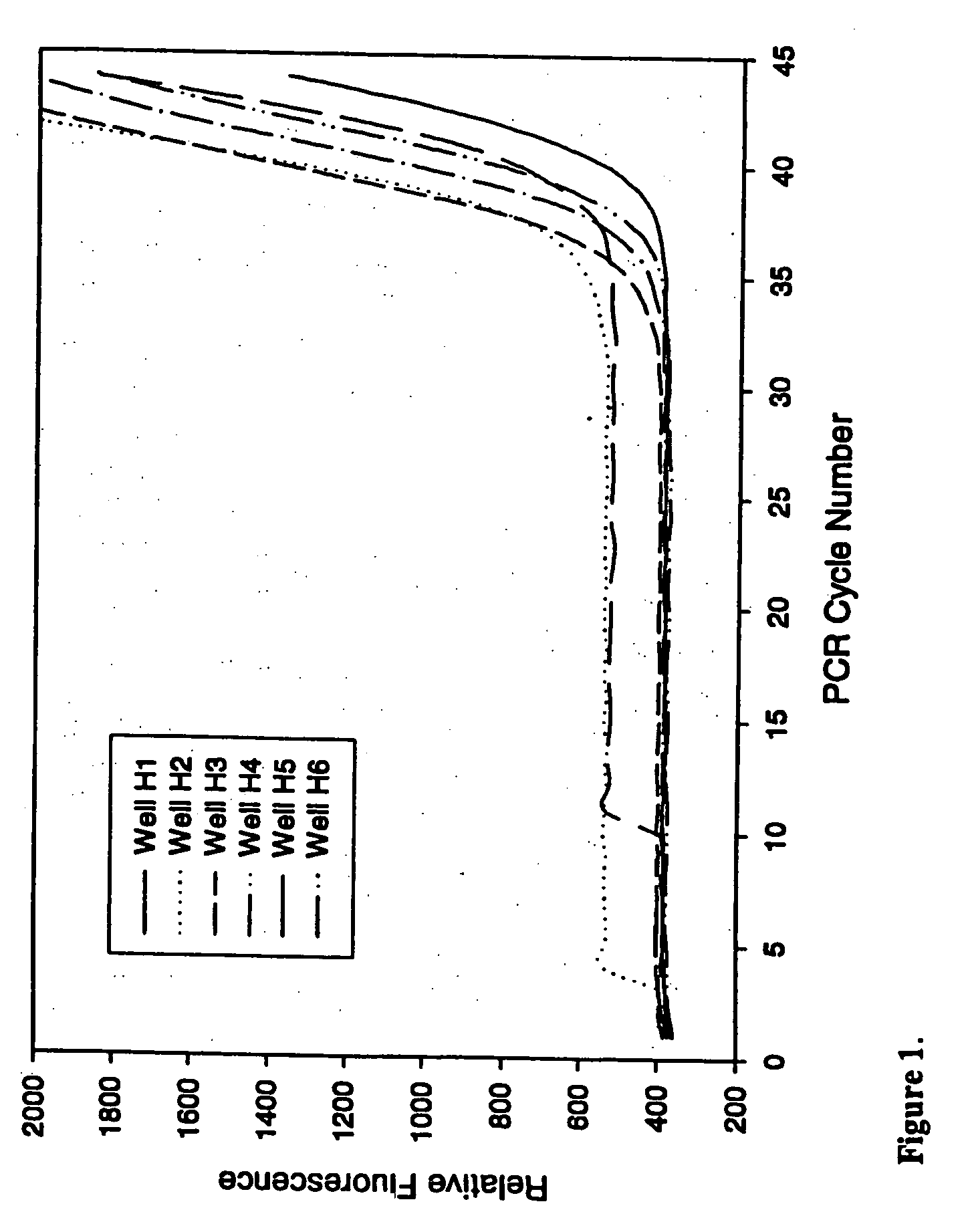
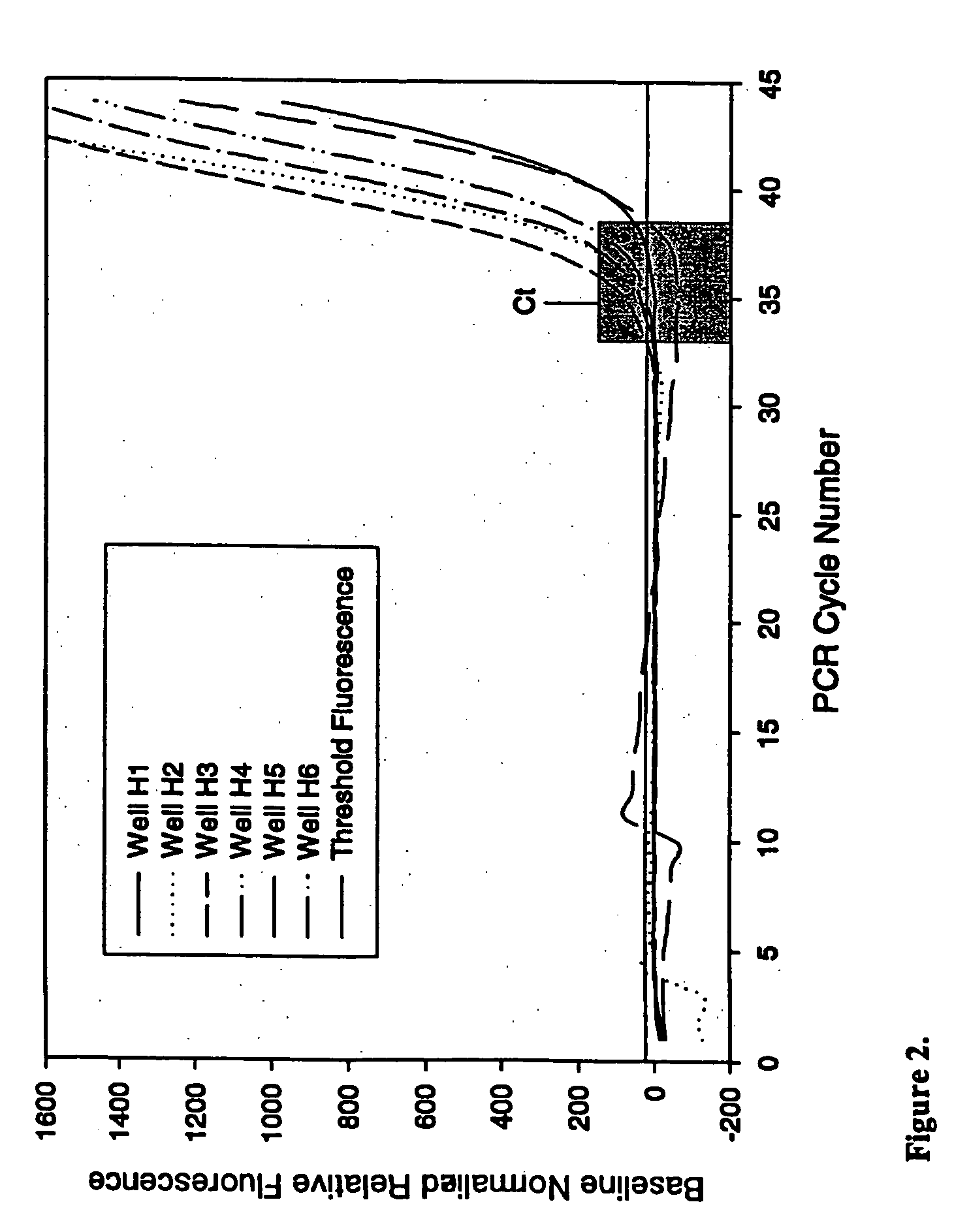
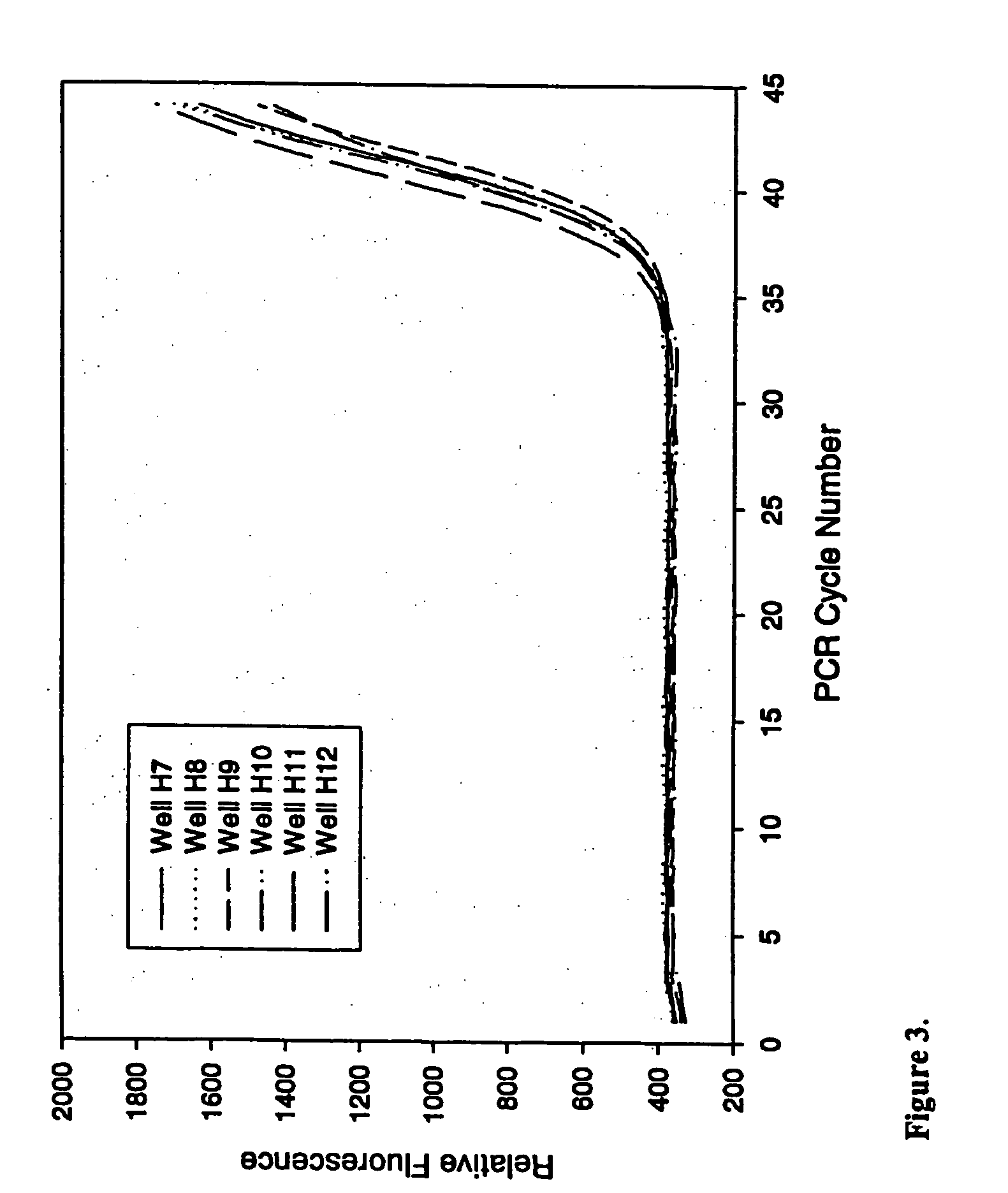
Compositions for in vitro amplification of nucleic acids
InactiveUS20050123924A1Poor precisionStable basal fluorescenceMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationChemistryDna polymerasen
Method and compositions for improving DNA polymerase and reverse transcriptase reactions are provided. Addition of anti-foam reagents to the reactions improves fluid handling, especially of small volumes and allows enhanced accuracy of optical detection, without substantially inhibiting enzymatic activity.
Owner:QUANTA BIOSCI
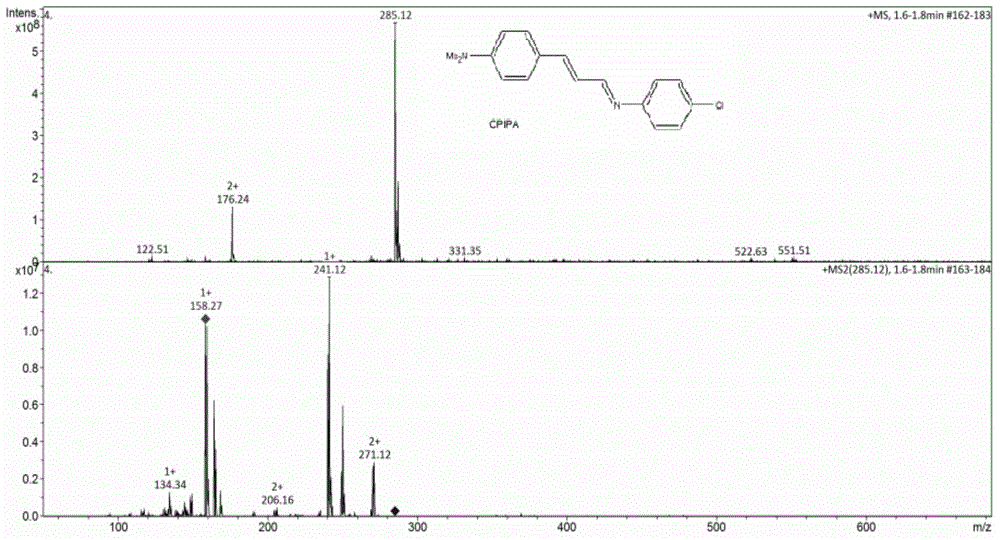
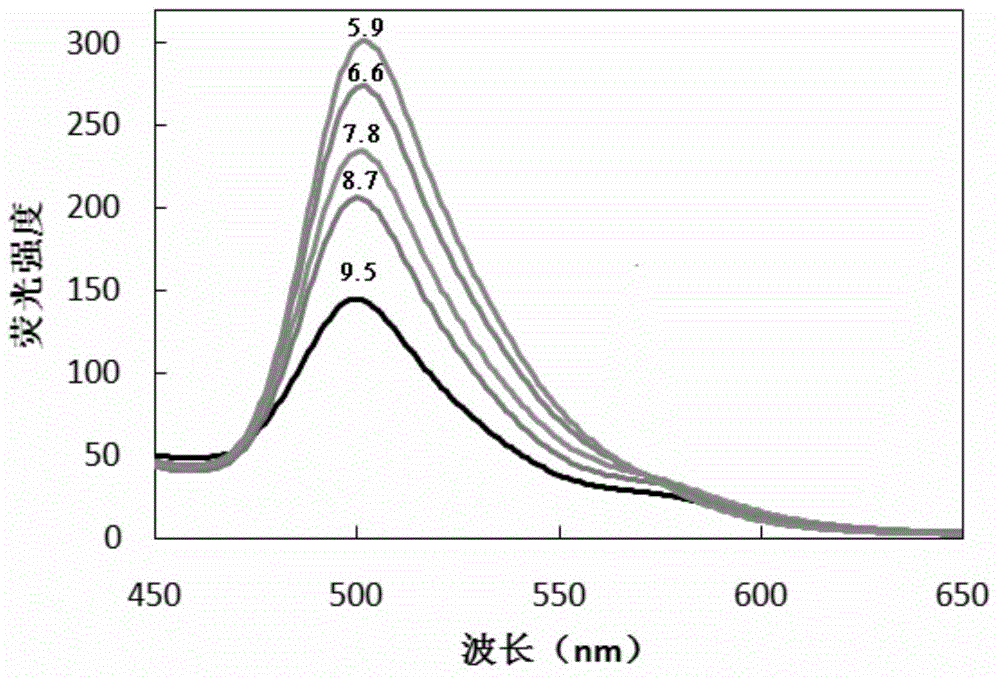
ph fluorescent sensing film and method for detecting ph two-dimensional dynamic distribution of basic sediment
InactiveCN104359884AReduce Optical InterferenceIncrease brightnessFluorescence/phosphorescencePh changesFluorescence
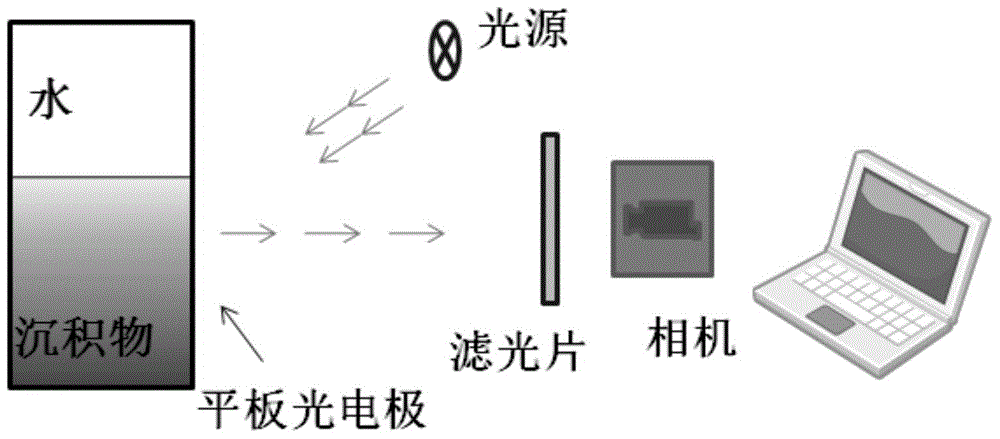
The invention discloses a pH fluorescent sensing film which comprises a film base material and is characterized in that fluorescent dyes of CPIPA (Chloro Phenyl Imino Propenyl Aniline) and fluorandiol 10-GN are uniformly mixed together, and the two fluorescent dyes are fixed on the surface of the film base material by virtue of a chemical embedding method. On the basis of the pH fluorescent sensing film, the invention also discloses a method for detecting pH two-dimensional dynamic distribution of basic sediment, wherein the pH fluorescent sensing film is put into the sediment, spectral information of the two dyes is obtained by virtue of an imaging device under the illumination of exciting light, and distributional characteristics of the pH of the sediment are obtained by virtue of R and B passage fluorescent ratio quantification. According to the sensing film disclosed by the invention, the CPIPA and the fluorandiol 10-GN which has a reference effect and a brightening effect are mixed together to form a fluorescent indicator, and the sensing film has high detection sensitivity and high spatial resolution and is sensitive to respond pH changes. The method adopts a plate electrode technology to realize real-time and in-situ acquisition of pH two-dimensional and dynamic distribution information of the basic sediment by reducing optical interference by virtue of fluorescent ratio quantification.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Optical fingerprint sensor module and forming method thereof
An optical fingerprint sensor module and a method for forming the same. The optical fingerprint sensor module comprises a self-luminous display panel; Optical fingerprint sensor, the optical fingerprint sensor comprises a sensor light-transmitting substrate and a fingerprint sensing circuit layer located on the surface of the sensor light-transmitting substrate, The fingerprint sensing circuit layer includes a first pixel region and a first peripheral region located around the first pixel region, the fingerprint sensing circuit layer includes a first sensing surface, the first sensing surfacefacing away from the sensor light transmitting substrate; A light collimator layer positioned between the optical fingerprint sensor and the self-luminescent display panel, the light collimator layerfacing a first sensing surface of a first pixel region; A light absorbing layer located at a first sensing surface of the first peripheral region. The performance of the optical fingerprint sensor module is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OXI TECH
Countermeasures for idle pattern SRS interference in ethernet optical network systems
ActiveUS20080187313A1Reduce the impactReduce and eliminate SRS optical interferenceOptical multiplexElectromagnetic transmissionCountermeasureVideo transmission
Optical networks as defined by the IEEE 802.3ah standard suffer from Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) that causes data transmission at a first optical wavelength to interfere with broadcast video transmission at a second optical wavelength in single mode optical fibers. The problem is exacerbated when data is not being transmitted across the network; and instead, an idle pattern transmission is being transmitted in order to keep the network synchronized. The repetitive nature of the idle pattern transmission leads to the SRS optical interference effect. This optical interference effect is mitigated when countermeasures are implemented to modify the idle pattern transmissions or to transmit random data in place of the idle pattern transmissions.
Owner:ARRIS SOLUTIONS
Countermeasures for idle pattern SRS interference in ethernet optical network systems
ActiveUS7340180B2Reduce impactReduce and eliminate SRS optical interference in opticalOptical multiplexElectromagnetic transmissionCountermeasureVideo transmission
Optical networks as defined by the IEEE 802.3ah standard suffer from Stimulated Raman Scattering (SRS) that causes data transmission at a first optical wavelength to interfere with broadcast video transmission at a second optical wavelength in single mode optical fibers. The problem is exacerbated when data is not being transmitted across the network; and instead, an idle pattern transmission is being transmitted in order to keep the network synchronized. The repetitive nature of the idle pattern transmission leads to the SRS optical interference effect. This optical interference effect is mitigated when countermeasures are implemented to modify the idle pattern transmissions or to transmit random data in place of the idle pattern transmissions.
Owner:ARRIS SOLUTIONS LLC
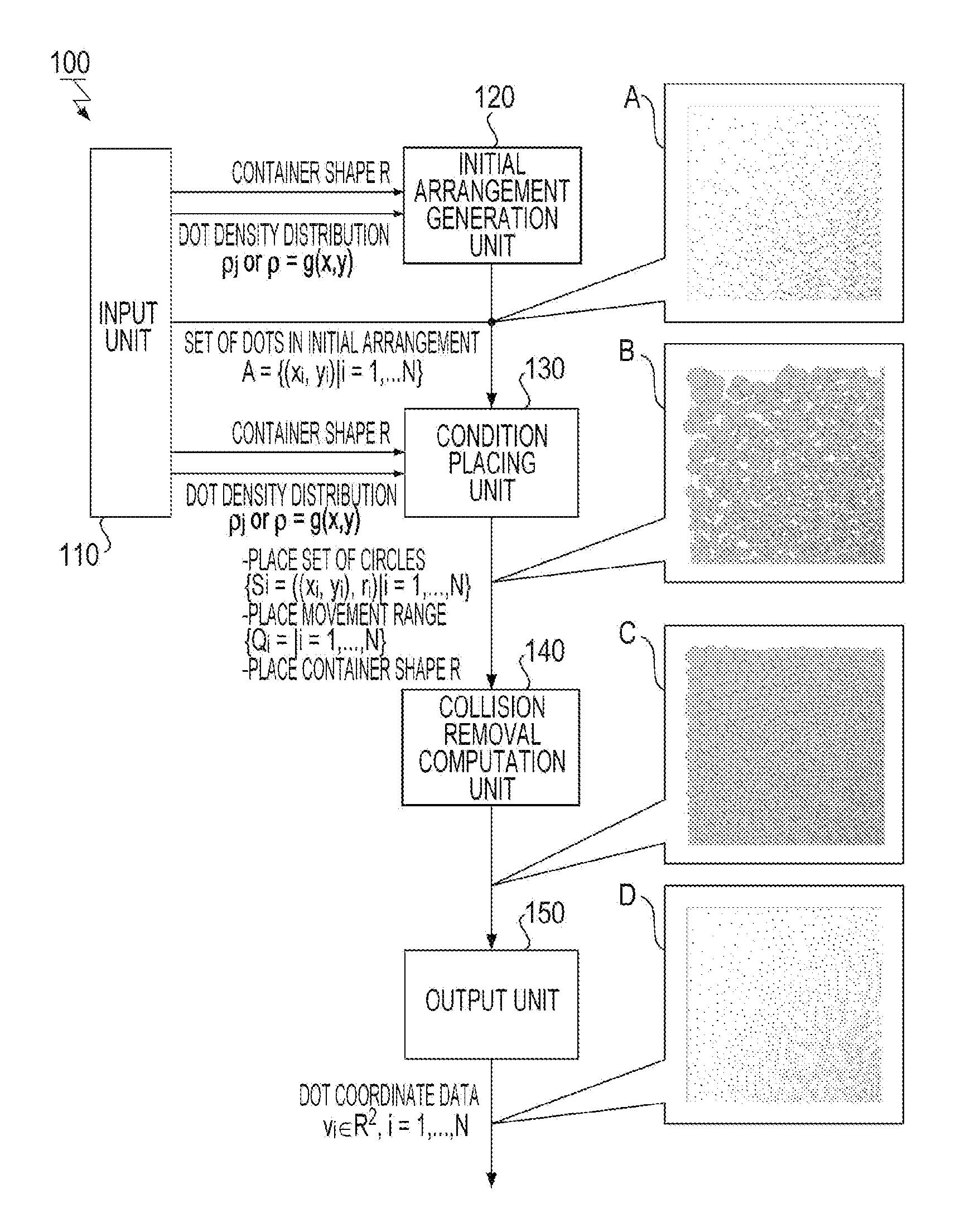
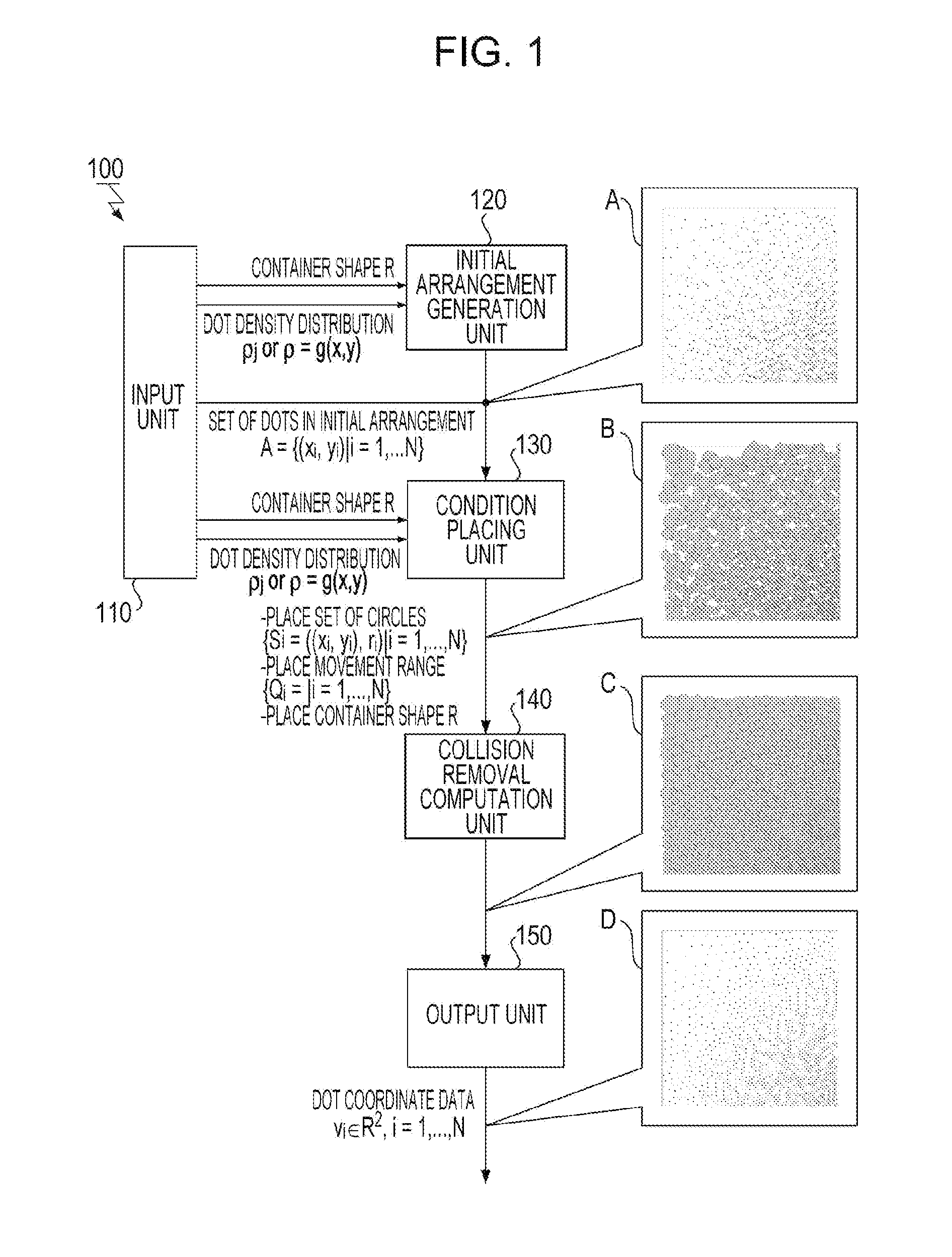
Information processing apparatus, calculation method, program, and storage medium
InactiveUS20120314973A1Light utilization efficiencyReduce Optical Interference2D-image generationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer science
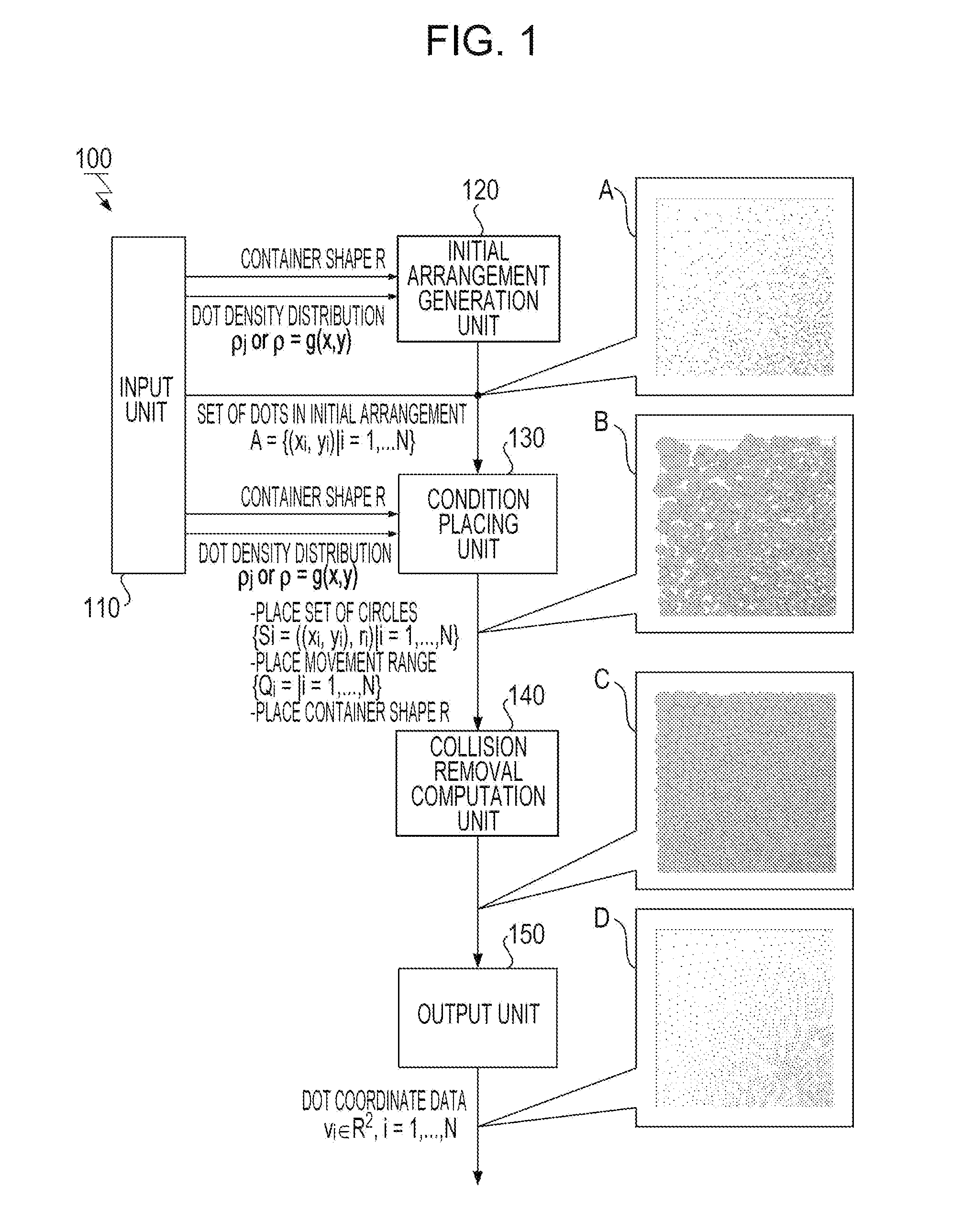
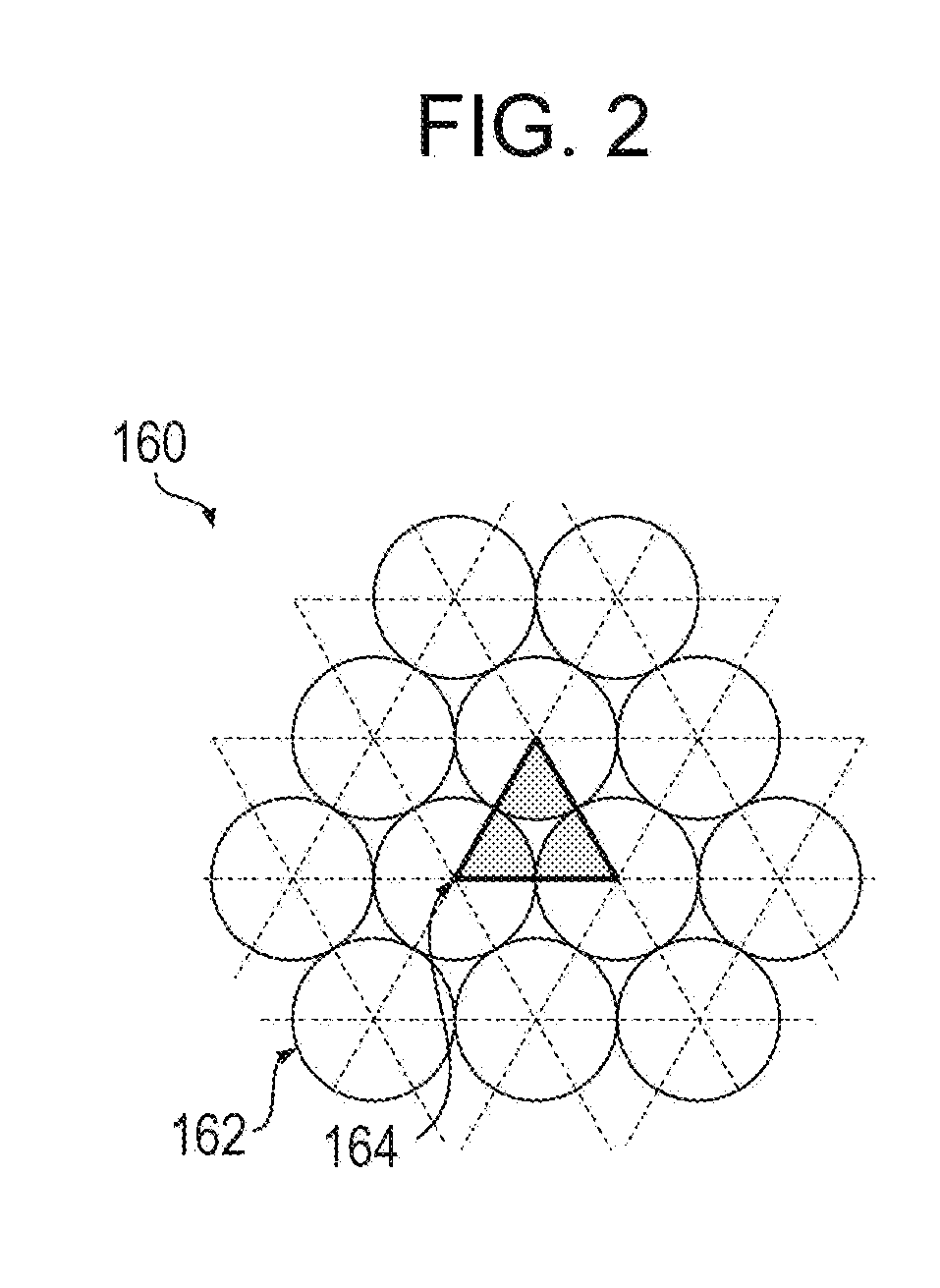
An information processing apparatus, a calculation method, a program, and a storage medium for generating a uniformly distributed discrete pattern. To calculate a spatial arrangement of a plurality of elements of a discrete pattern, the plurality of elements being arranged in a spatially discrete manner, an information processing apparatus according to the present invention determines, for each of the elements, a density in an initial position given to the element from a density distribution of the elements in a region where the elements are arranged in the discrete pattern and places, for the initial position of each of the elements, a figure having a size corresponding to the density and representing a region where the element repels other elements and a movement range of the figure. The information processing apparatus minimizes an objective function, computes an optimal solution, and outputs the optimal solutions.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Ultrasonic and optical double-imaging based transparent member defect detection device and method
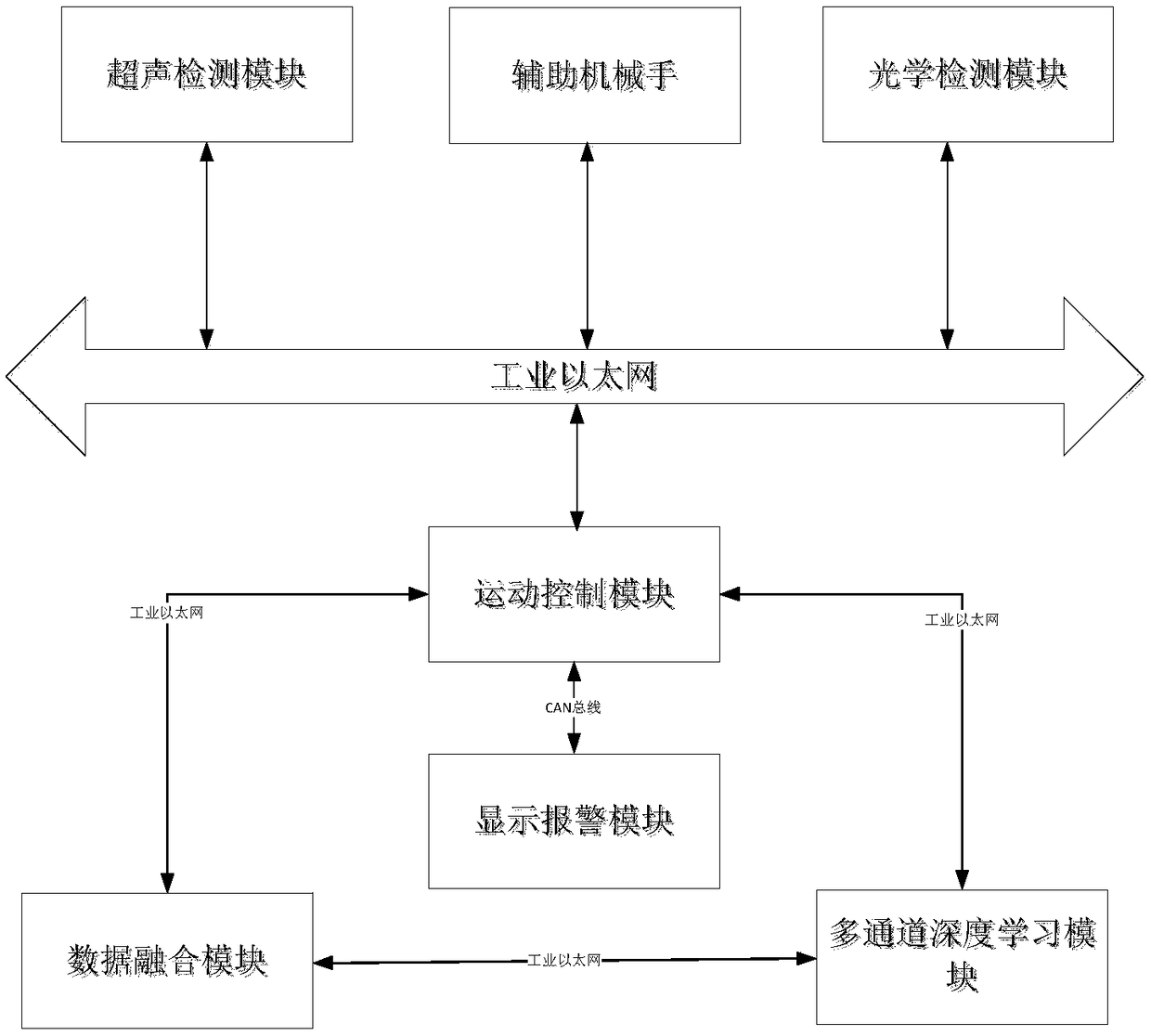
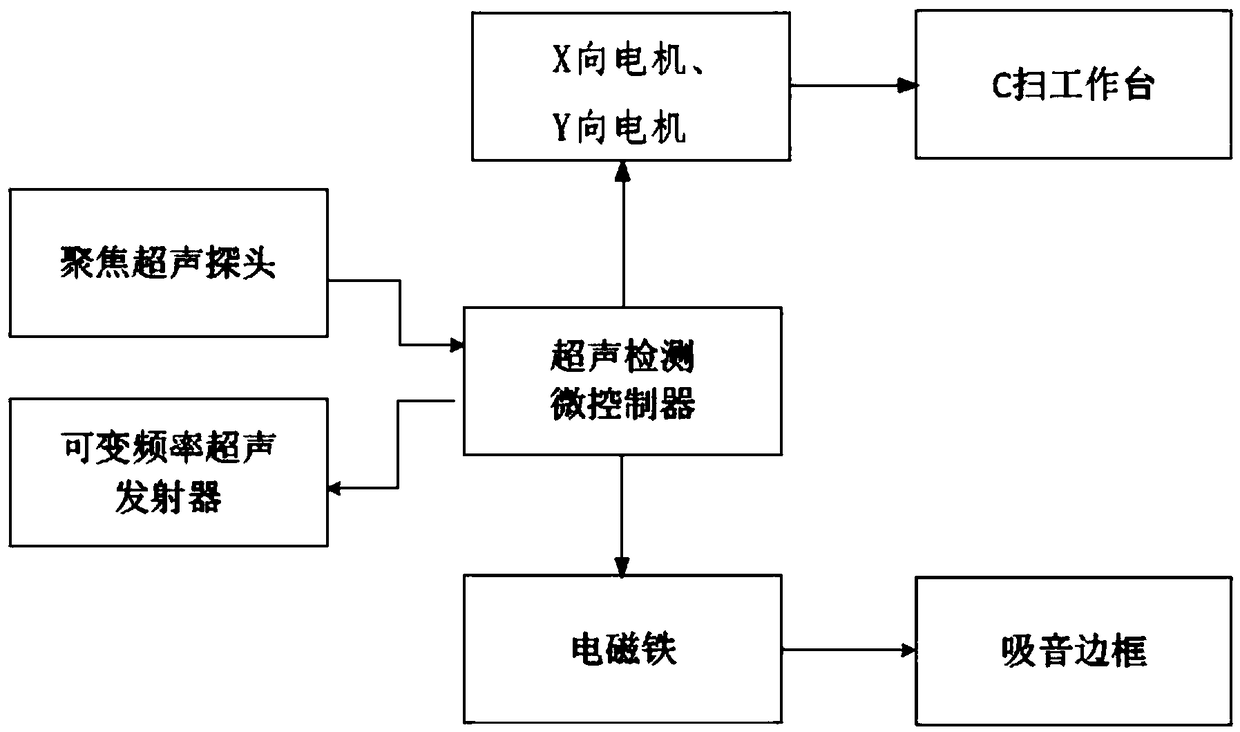
PendingCN109115805AOvercome the shortcomings of a single detection technologyReduce Optical InterferenceAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesMaterial analysis by optical meansMovement controlManipulator
The invention discloses an ultrasonic and optical double-imaging based transparent member defect detection device and method. The device comprises an ultrasonic detection module, an optical detectionmodule, a movement control module, a data fusion module, a multi-channel deep learning module and an auxiliary manipulator; the ultrasonic detection module, the optical detection module and the auxiliary manipulator are in communication connection with the movement control module through the Ethernet; the data fusion module, the multi-channel deep learning module and the movement control module are in communication connection through the Ethernet in pairs; and the movement control module is also in communication connection with a display alarm module through a bus. By utilizing ultrasonic andoptical double-imaging detection, the ultrasonic and optical double-imaging based transparent member defect detection device and the method are more accurate in detection, and the device performs automatic operation and improves the detection efficiency.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUST IND TECH RES INST
Information processing apparatus, calculation method, program, and storage medium
InactiveUS20120262507A1Reduce MoireImprove regularity2D-image generationCathode-ray tube indicatorsGraphicsInformation processing
An information processing apparatus, a calculation method, a program, and a storage medium for generating a uniformly distributed discrete pattern. To calculate a spatial arrangement of a plurality of elements of a discrete pattern, the plurality of elements being arranged in a spatially discrete manner, an information processing apparatus according to the present invention determines, for each of the elements, a density in an initial position given to the element from a density distribution of the elements in a region where the elements are arranged in the discrete pattern and places, for the initial position of each of the elements, a figure having a size corresponding to the density and representing a region where the element repels other elements and a movement range of the figure. The information processing apparatus minimizes an objective function, computes an optimal solution, and outputs the optimal solutions
Owner:IBM CORP
X-ray sensor and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106299017ABarrier damageStrong penetrating powerFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesRefractive indexX-ray
The invention relates to an X-ray sensor and a manufacturing method thereof. The X-ray sensor comprises a sensing substrate and a lead glass substrate, wherein the sensing substrate is provided with a plurality of sensing units; the lead glass substrate comprises a first surface and a second surface which are opposite; the first surface is fixed on the sensing substrate and a plurality of grooves which correspond to the plurality of sensing units one by one are formed in the second surface; the lead glass substrate also comprises a first reflecting layer, scintillator fluorescent powder and a second reflecting layer; the first reflecting layer is arranged on the side walls of the plurality of grooves; the plurality of grooves are filled with the scintillator fluorescent powder; and the second reflecting layer is arranged on the second surface. According to the X-ray sensor provided by the invention, the damage of an X ray to the plurality of sensing units can be effectively blocked through a method of adding lead glass between the scintillator fluorescent powder and the plurality of sensing units; and furthermore, the lead glass has relatively high penetration rate and a high refractive index, so that optical interference caused by light scattering can also be effectively reduced.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS KUNSHAN CO LTD +1
Thin-film photovoltaic cell and manufacturing method thereof
PendingCN110164991AAchieve the effect of one-piece blackReduce optical interferenceFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringMetal
The invention discloses a thin-film photovoltaic cell and a manufacturing method thereof. The thin-film photovoltaic cell comprises a transparent substrate and a photovoltaic unit which is arranged onthe transparent substrate and faces towards an electronic display modules, the photovoltaic unit includes a front electrode arranged on the transparent substrate, a light absorption layer arranged onthe front electrode and a back electrode arranged on the light absorption layer, and the back electrode is provided with a first blackened metal conductive layer on the surface facing towards the transparent substrate, thereby enabling the color of the photovoltaic unit of the thin-film photovoltaic cell to be closer to the background color of the electronic display module, and achieving an effect of black integration of the two.
Owner:TRULY SEMICON
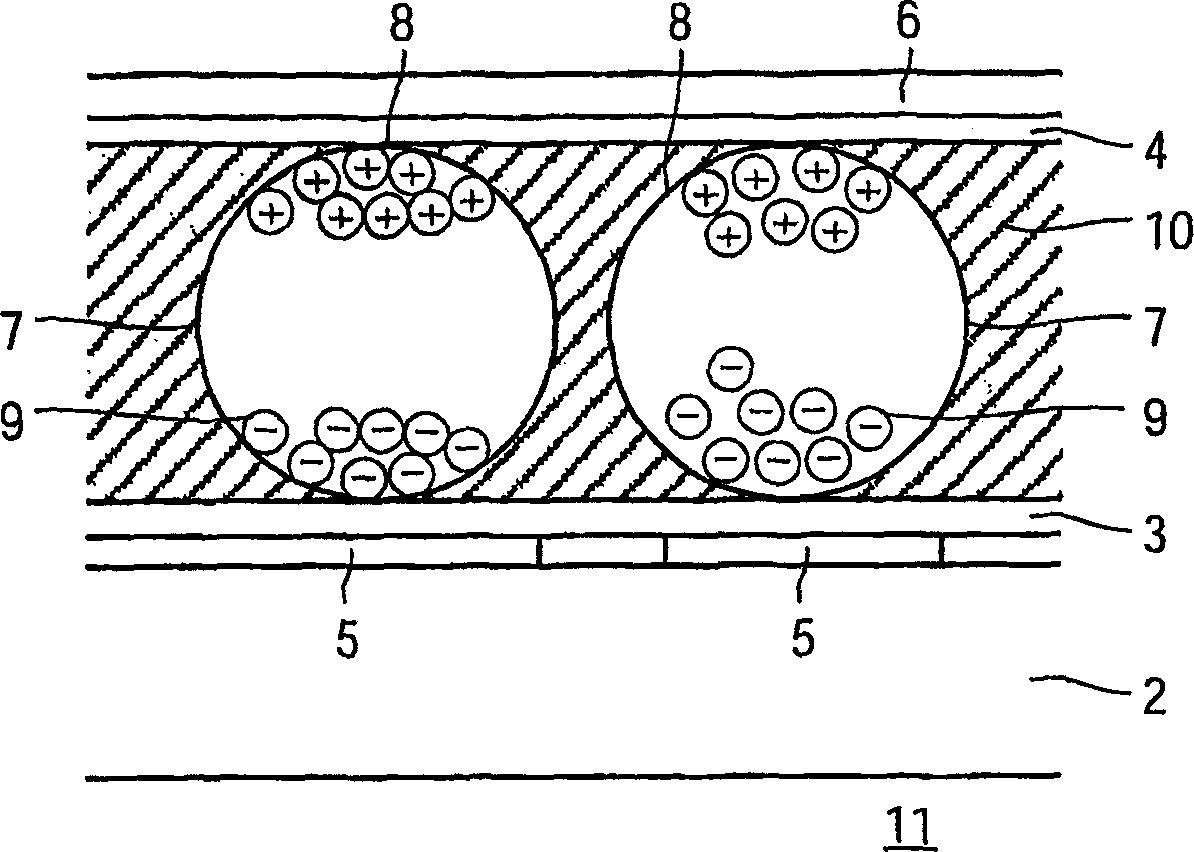
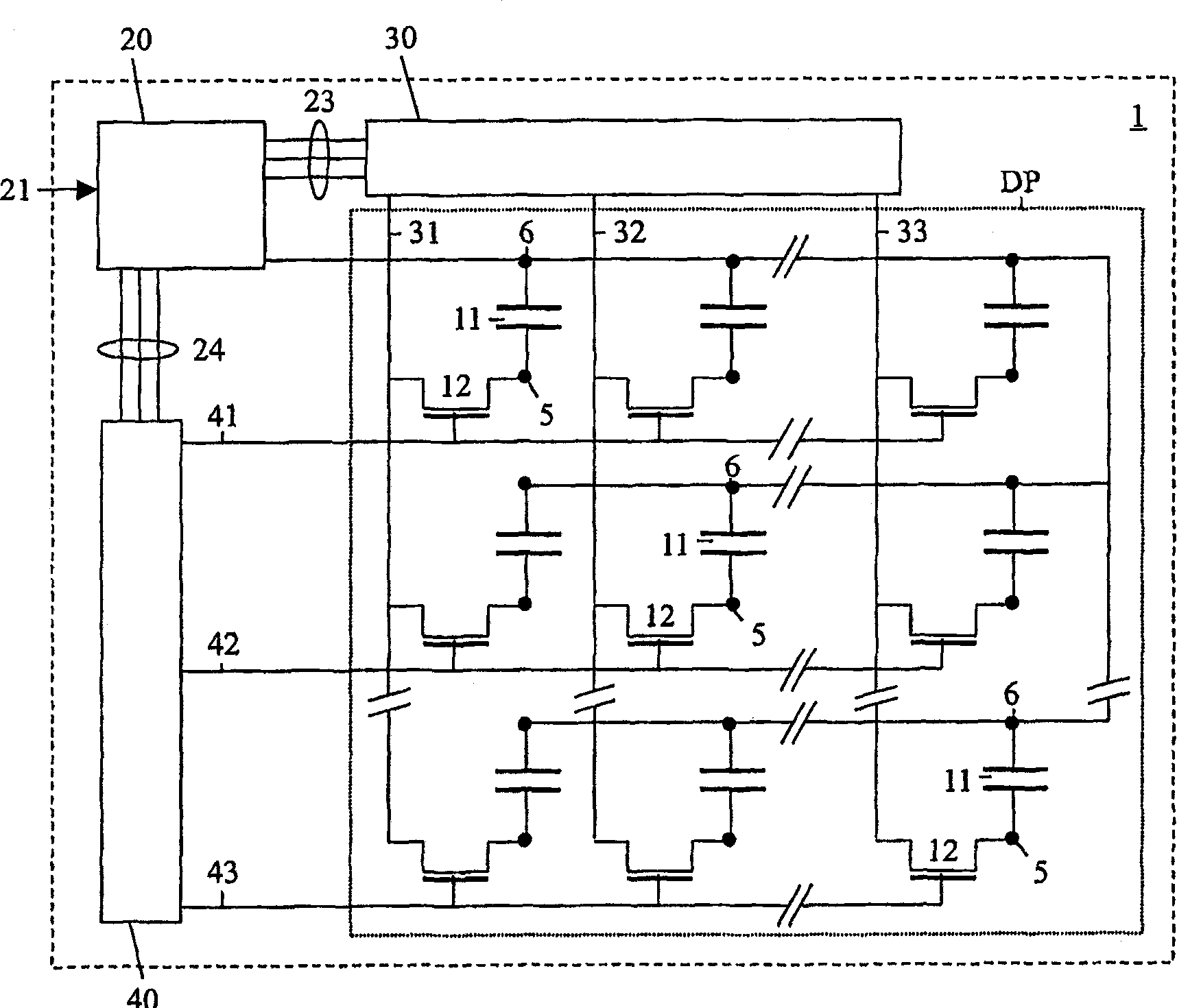
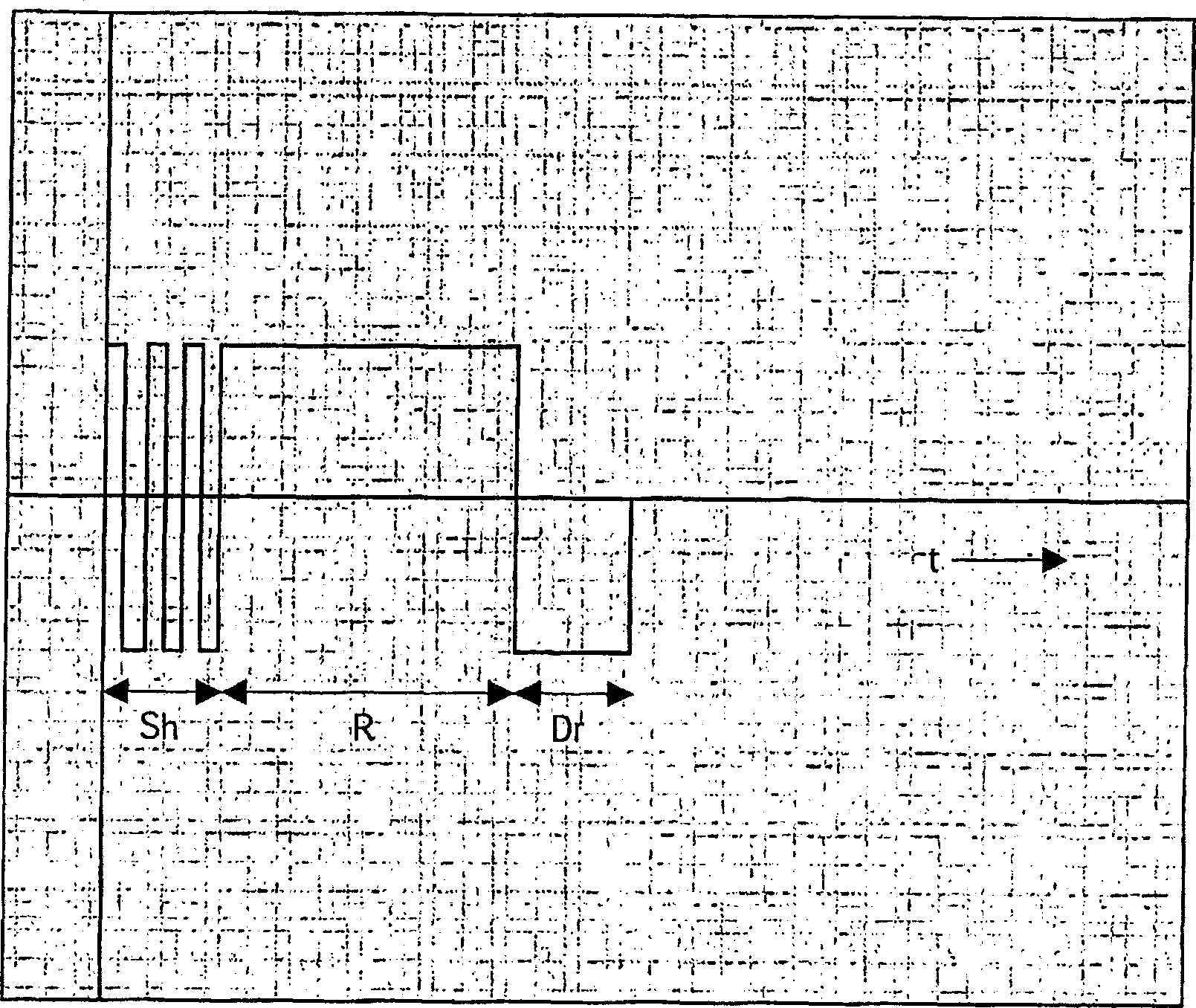
Electrophoretic display unit
InactiveCN1820299AFlexible driveReduce Optical InterferenceStatic indicating devicesElectrophoresisFixed frame
Electrophoretic display units (1) having fixed frame times are driven relatively unflexibly. By introducing line driving signals having timing parameters, the frame rates can be made variable. With variable frame rates, the optical disturbance from shaking pulses (Sh) is reduced and the number of gray values is increased. The timing parameters comprise delays of starts of line driving signals and / or comprise durations of line driving signals. The lines preferably comprise rows. All possible column driving signals and, per column driving signal or per frame, a row delay parameter defining a row delay time, are stored in a memory coupled to the controller (20). Shaking pulses (Sh) are supplied at minimum row delay time, reset pulses (R) are supplied at maximum row delay time, and driving pulses (Dr) are supplied at flexible row delay time, which corresponds with a product of a predefined timeinterval and a step value defined by a number of bits.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
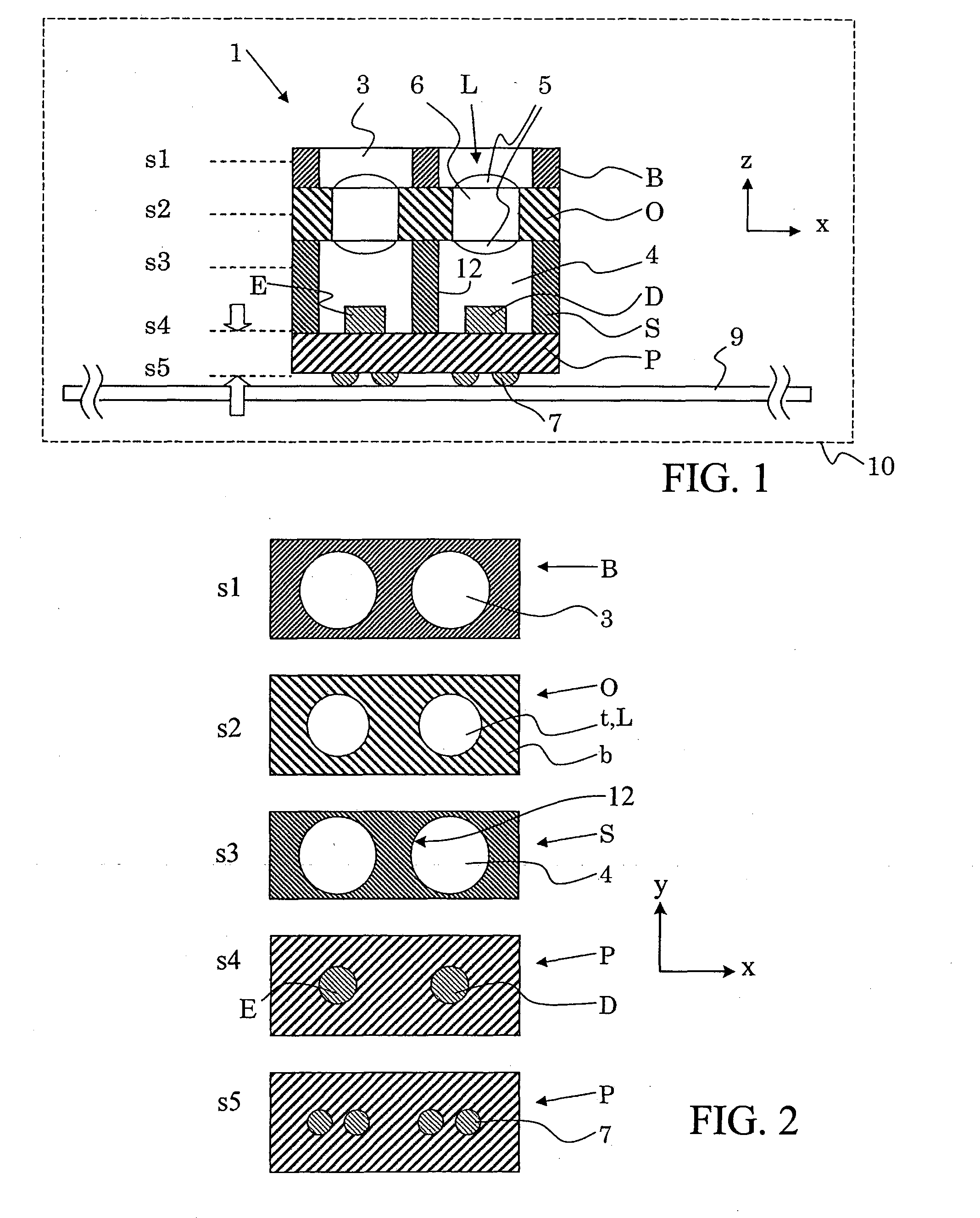
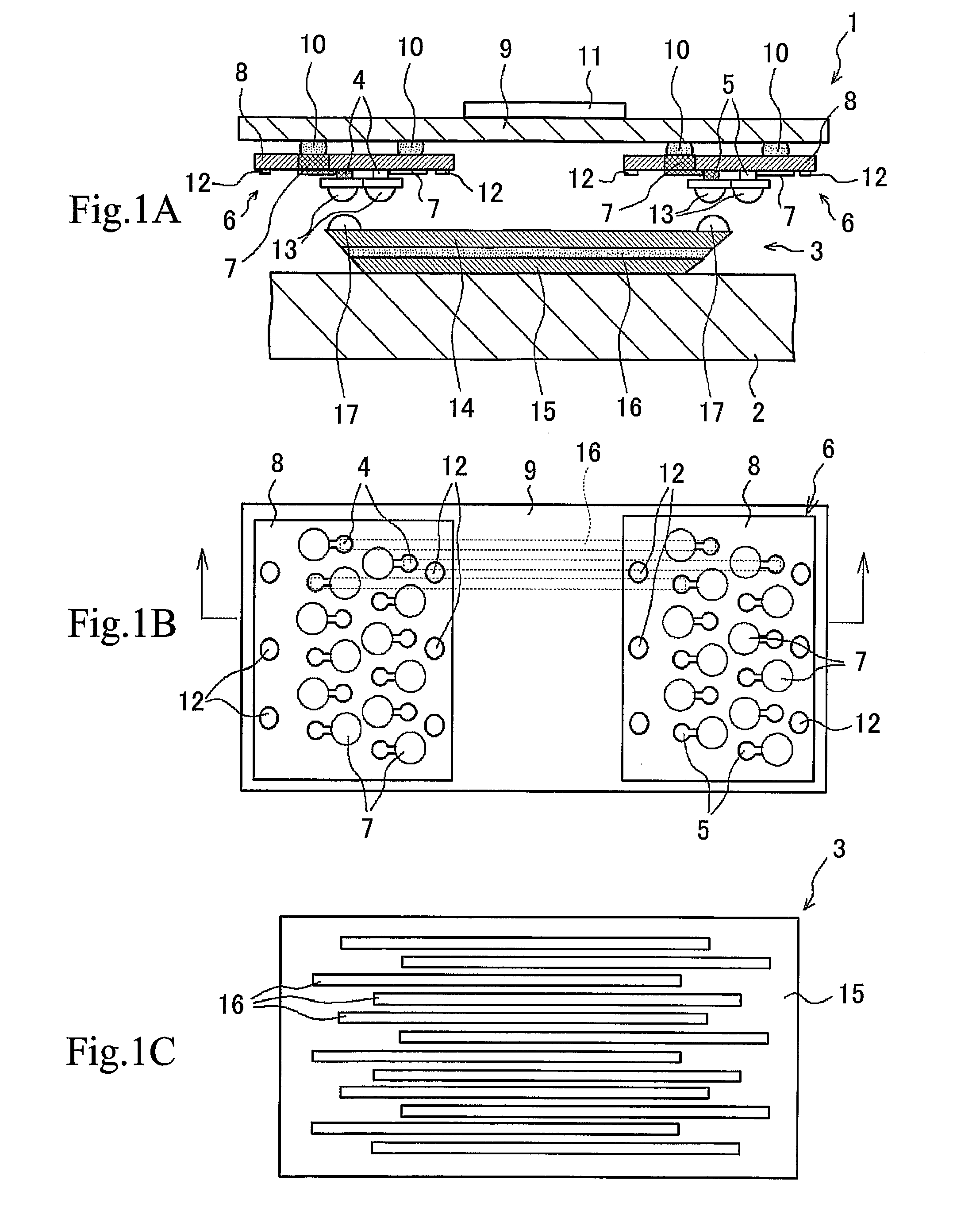
Photo-Electric Conversion Element Array, Integrated Apparatus Of The Same, Mounted Structures Of Them, And Optical Information Processing Apparatus
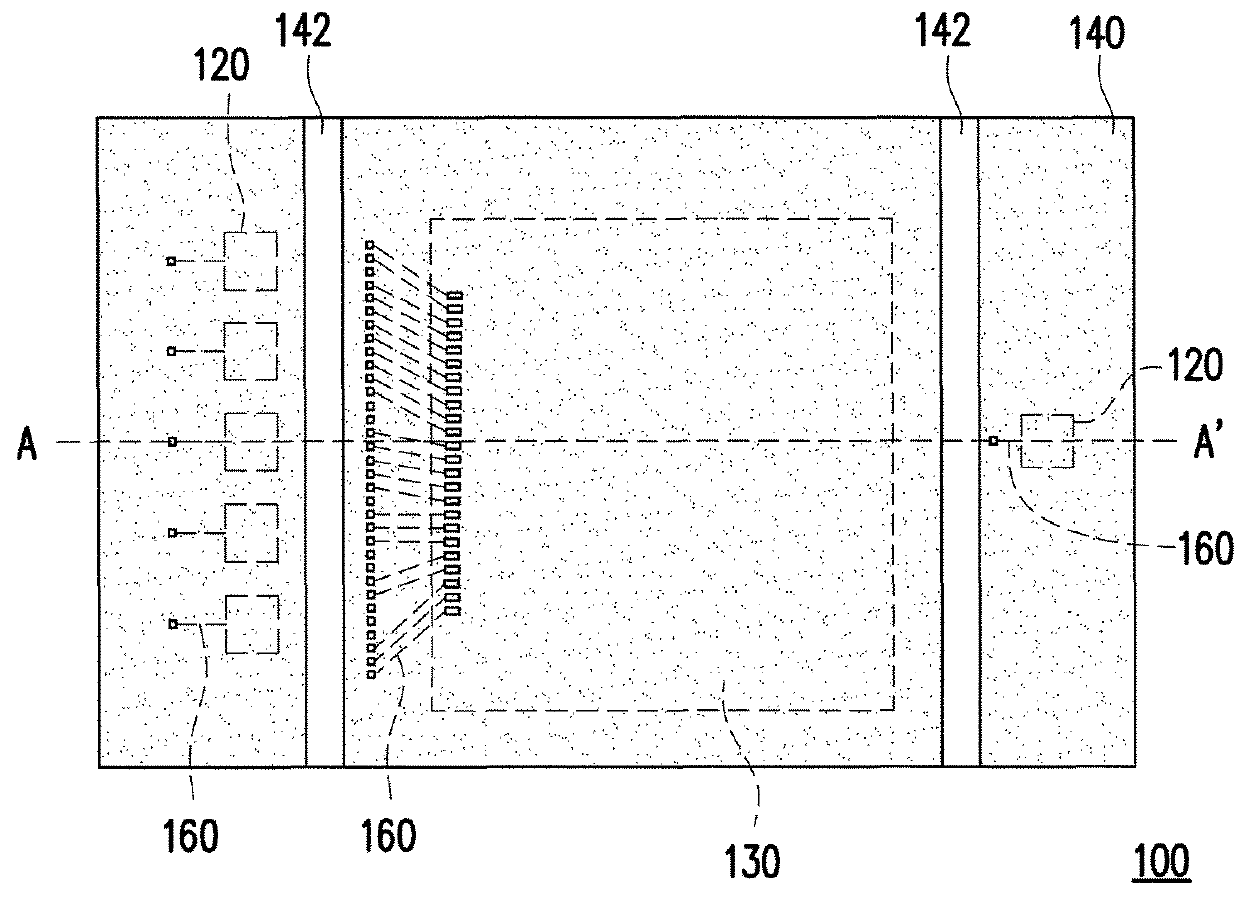
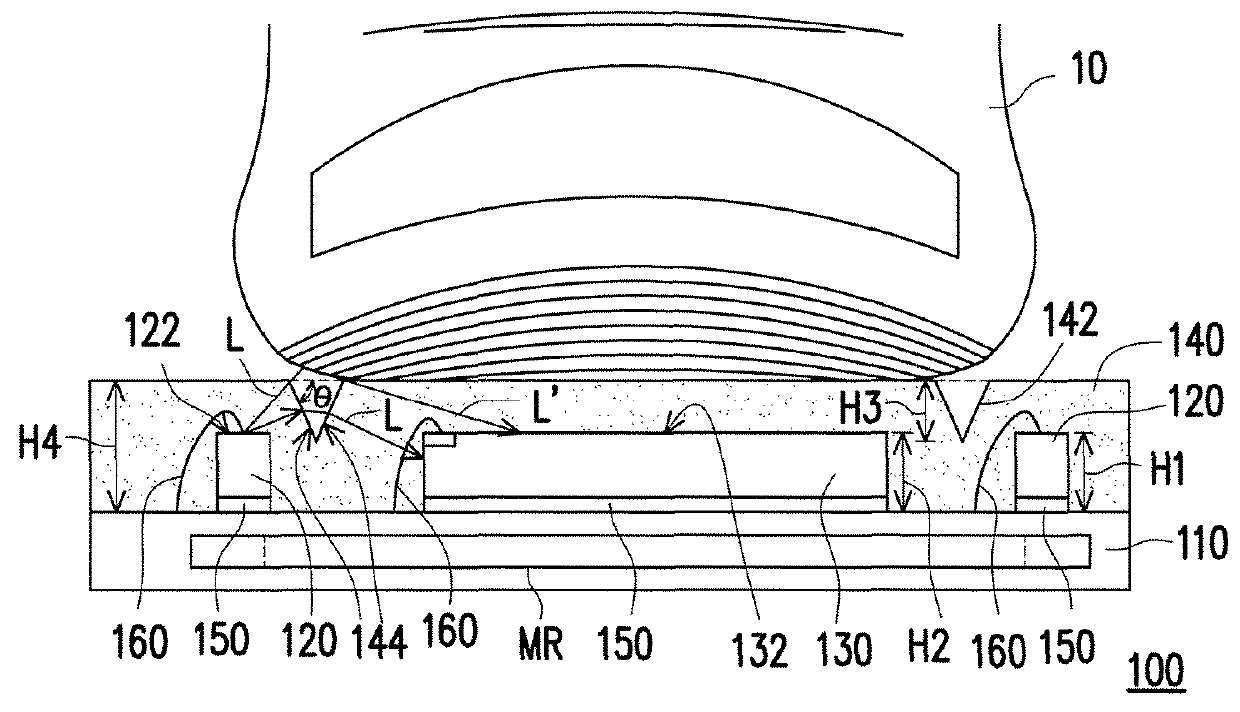
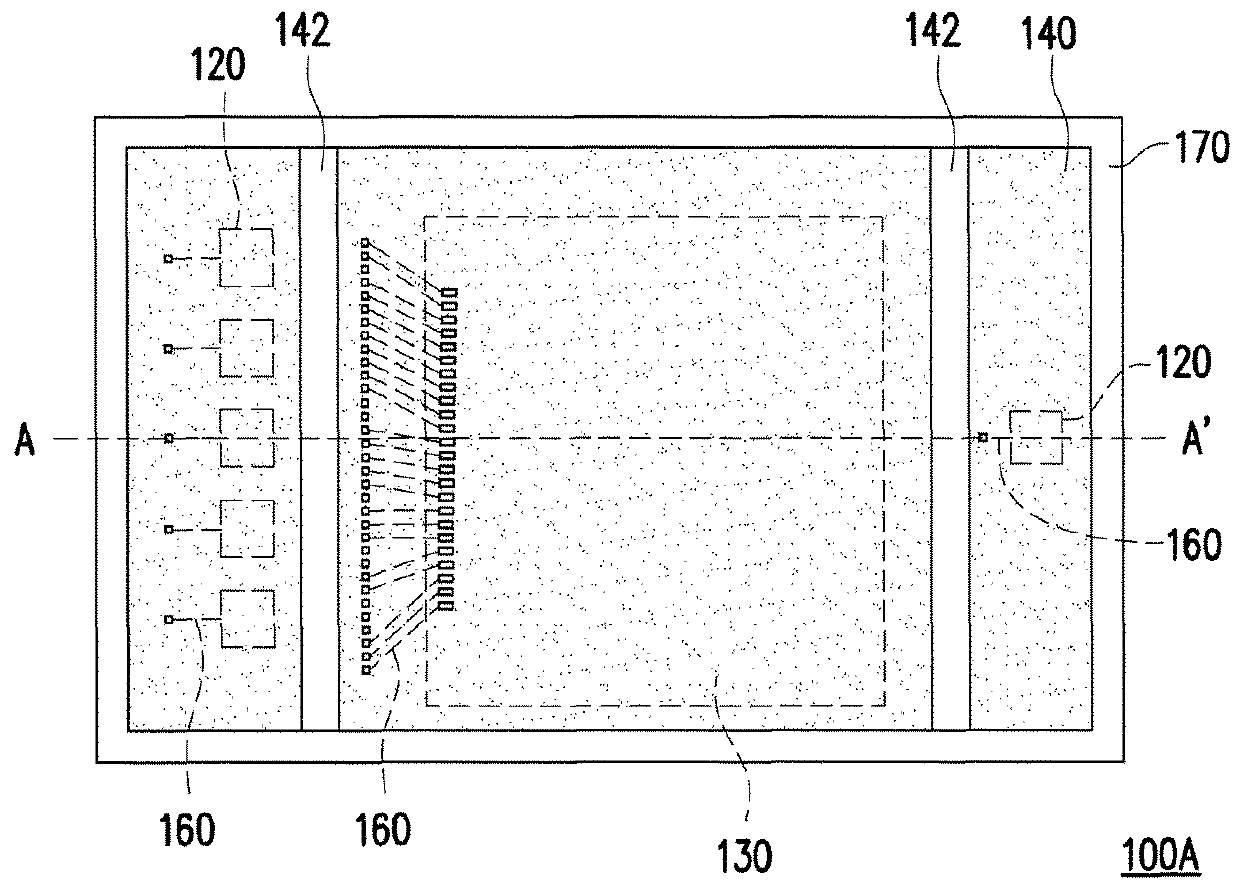
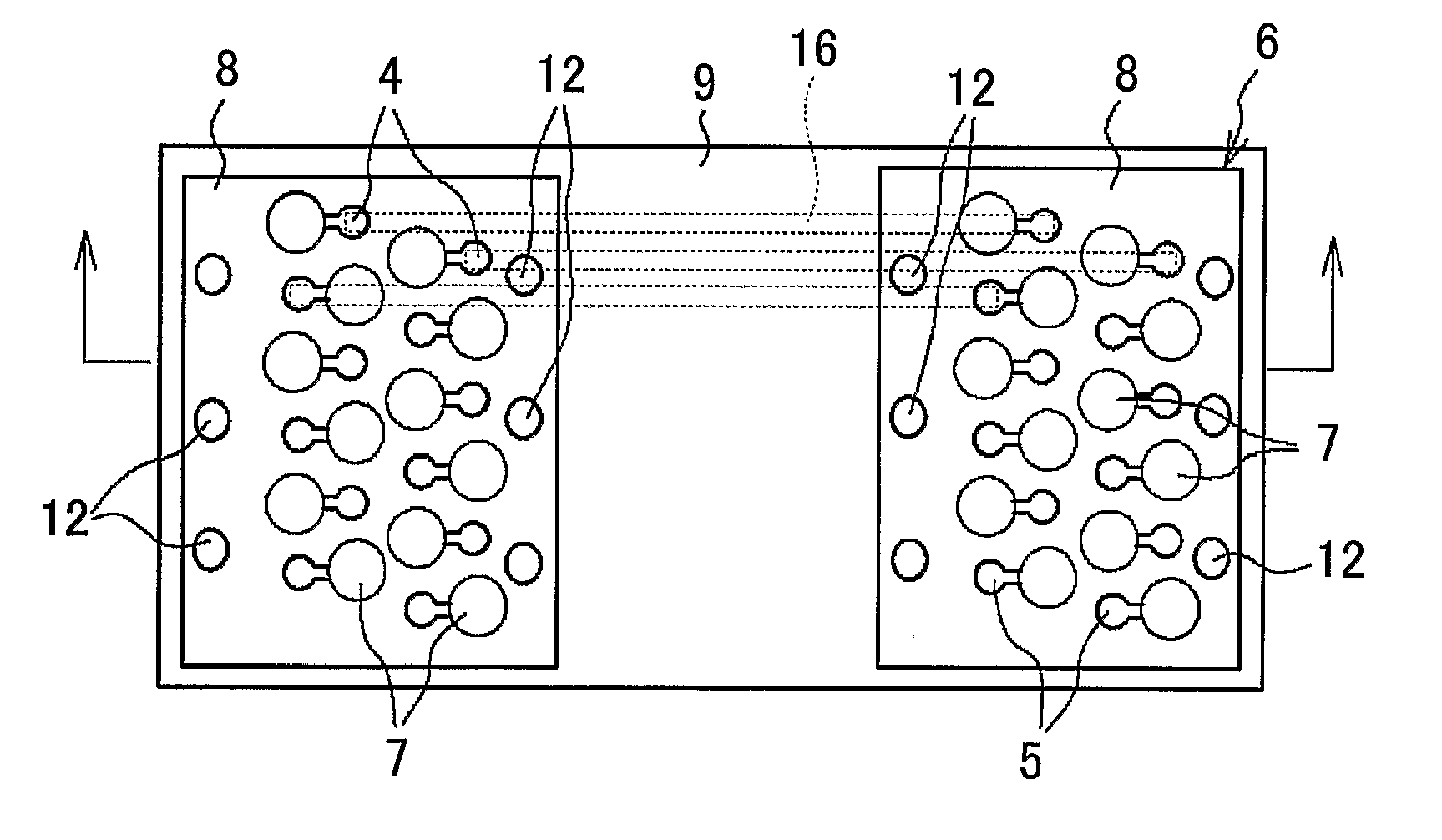
ActiveUS20070215790A1Sufficient level of distanceLarge transmission capacityTelevision system detailsLaser detailsInformation processingHigh density
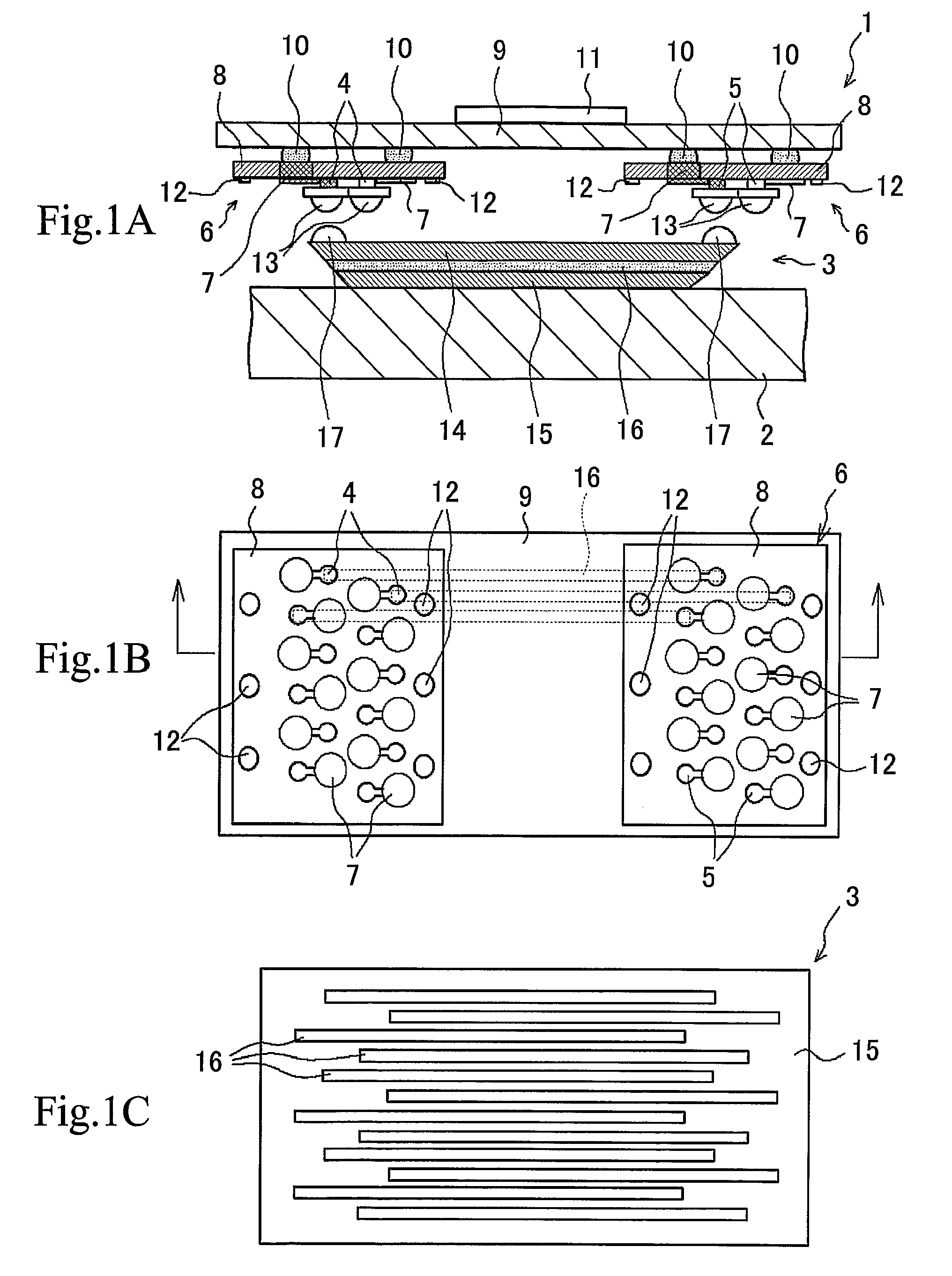
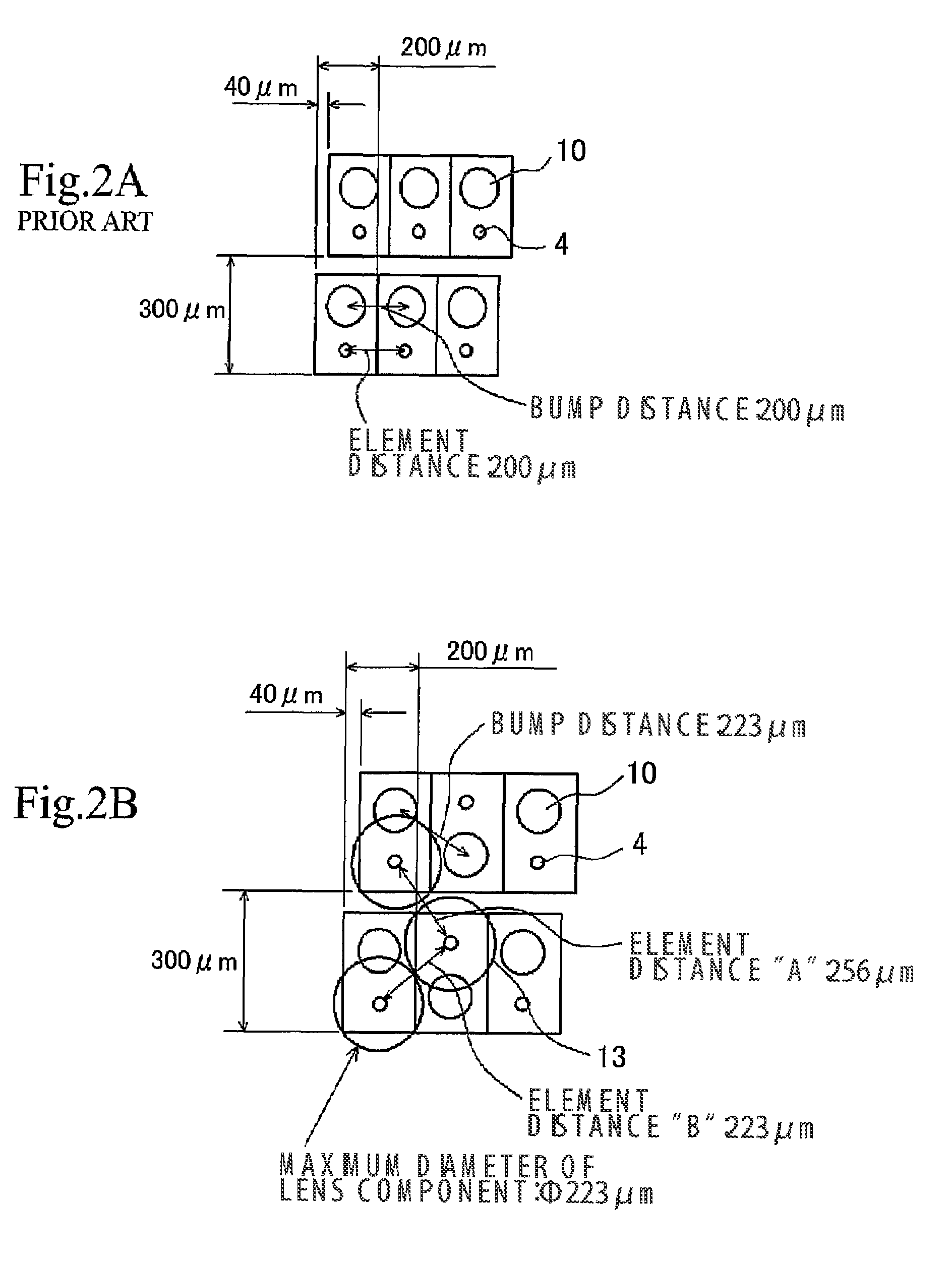
A photoelectric conversion element array having a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements (emitting optics 4, receiving optics 5) arranged in an array, and the photoelectric conversion elements 4, 5 are arranged alternately at different positions so that every second one is aligned on the same line in the direction of array. A mounted structure of photoelectric conversion element array, having the emitting optics array and the receiving optics array in the photoelectric conversion element array of this invention, arranged on an interposer substrate 9 so as to oppose therewith, and these arrays are mounted on the interposer substrate 9 through the external connection terminals 7. An optical information processing apparatus 1 having the photoelectric conversion element array of the present invention, and an optical wave guide 3 opposed to the respective optics of the photoelectric conversion element arrays. These configurations not only allow high-density integration of optical interconnects, but also reduce optical interference or crosstalk due to the photoelectric conversion element, and can thereby provide a photoelectric conversion element array allowing efficient propagation of light, an integrated apparatus thereof, a mounted structure of them, and an optical information processing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
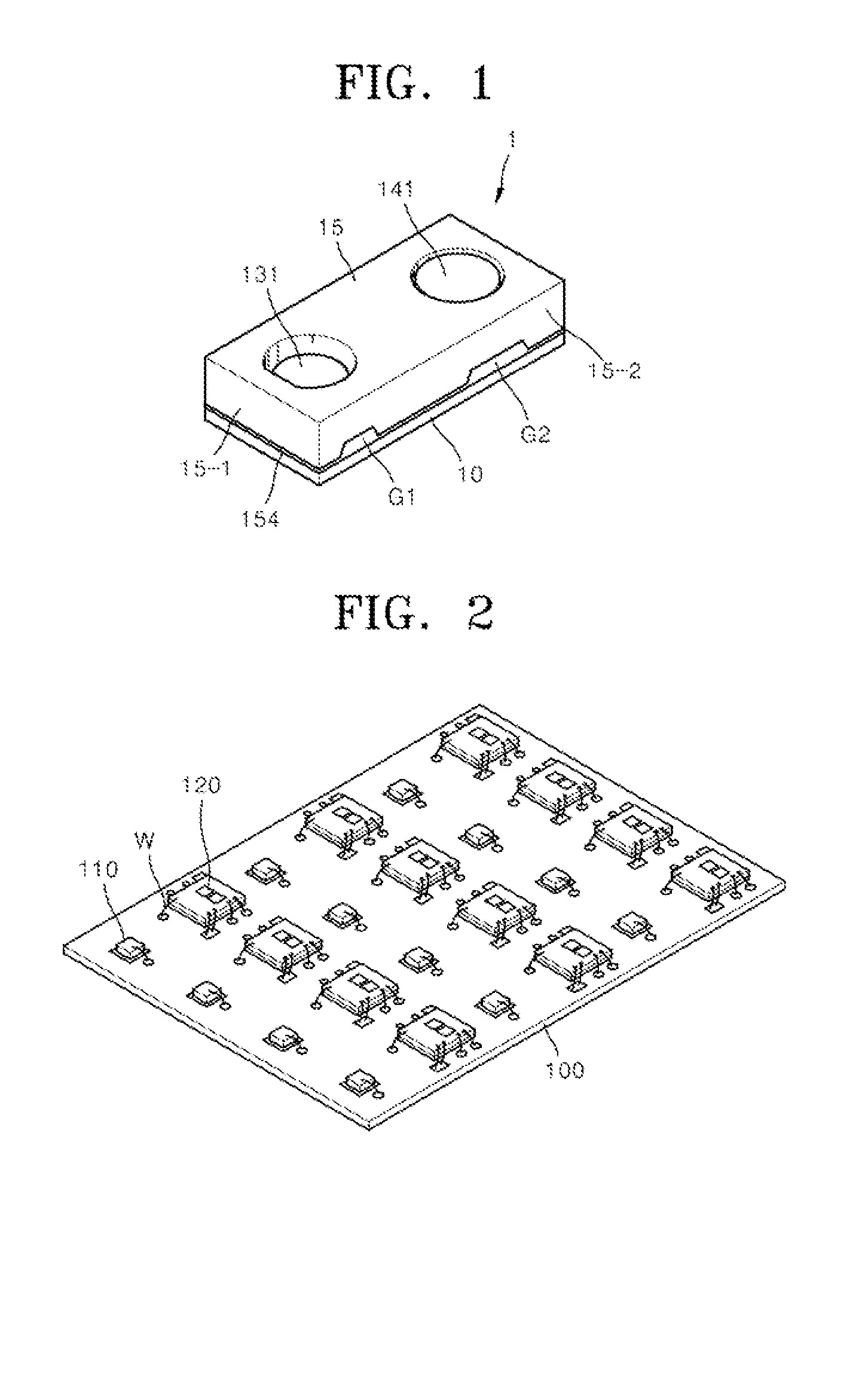
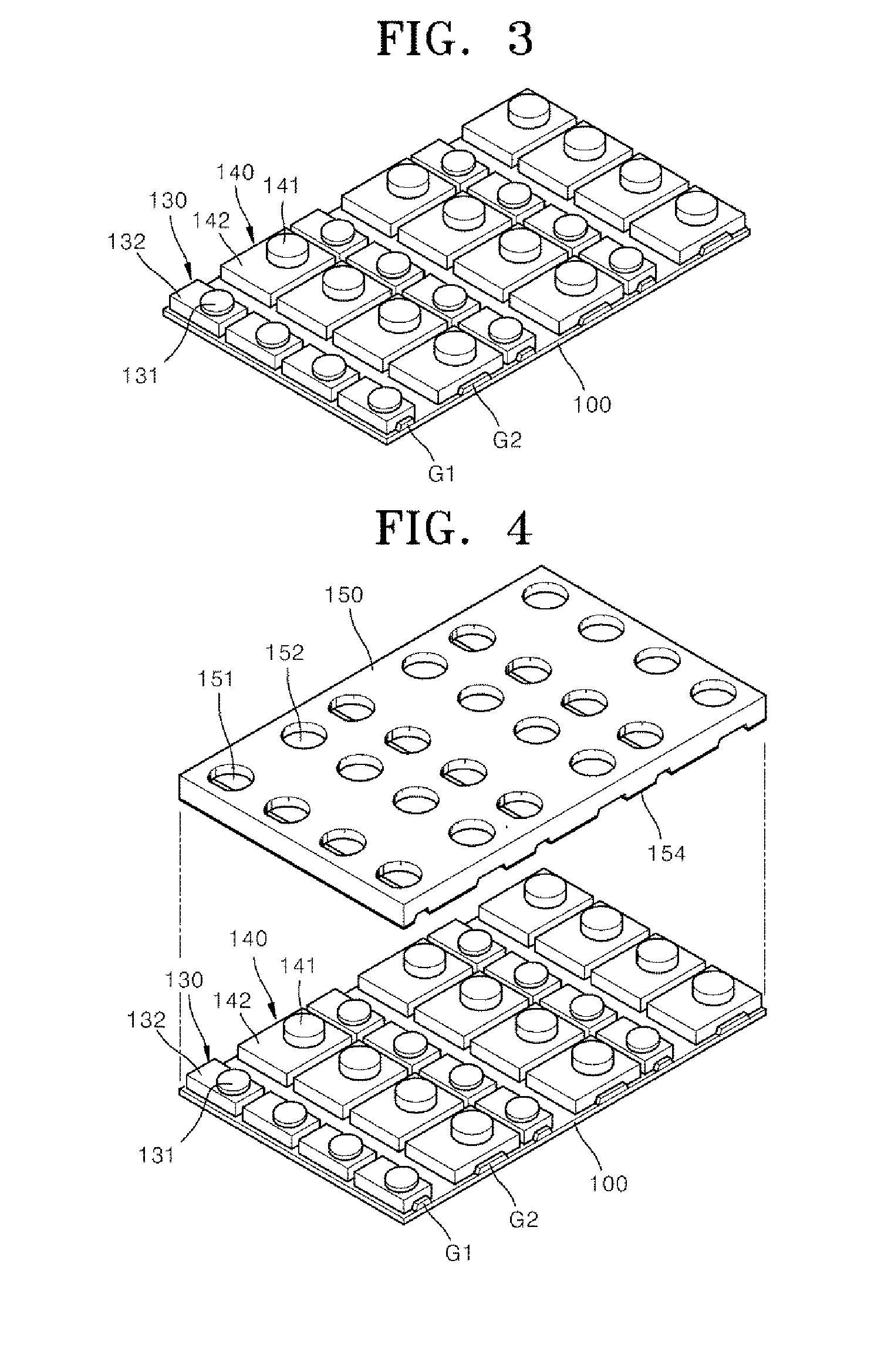
Proximity luminance sensor and method for manufacturing same
InactiveUS20160305817A1Avoid contaminationAvoid damageSolid-state devicesPhotometry electrical circuitsInterference phenomenonEngineering
The present invention relates to a proximity luminance sensor obtained by assembling a housing array to a printed circuit board array using an adhesive layer, prior to separation into individual proximity luminance sensors, thereby preventing contamination or damage to lenses, decreasing the optical interference phenomenon, reducing the manufacturing cost and manufacturing time, and thus substantially improving productivity. The proximity luminance sensor may comprise: a printed circuit board; a light-emitting chip mounted on the printed circuit board; a light-receiving chip mounted on the printed circuit board; a light-emitting lens unit surrounding the light-emitting chip; a light-receiving lens unit surrounding the light-receiving chip; a housing shaped to surround the light-emitting chip and the light-receiving chip and provided with a light-emitting window, which corresponds to the light-emitting lens unit, and a light-receiving window, which corresponds to the light-receiving lens unit; and an adhesive layer installed between the housing and the printed circuit board.
Owner:ITM SEMICON CO LTD
Image capturing module and electrical apparatus
ActiveUS10043847B2Easy to identifyReduce Optical InterferenceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingColloidLight emitting device
An image capturing module including a substrate, a plurality of light emitting devices, a sensor, and a transparent colloid curing layer is provided. The light emitting devices and the sensor are disposed on the substrate and are respectively electrically connected to the substrate. The transparent colloid curing layer is disposed on the substrate and covers the sensor and the light emitting devices. At least one trench is provided at a side of the transparent colloid curing layer opposite to the sensor. The at least one trench is located between the sensor and the light emitting devices, and a depth of the at least one trench is less than a thickness of the transparent colloid curing layer. An electrical apparatus is also provided.
Owner:GINGY TECH
Photo-electric conversion apparatus with alternating photoelectric conversion elements
ActiveUS7622700B2Reduce Optical InterferenceDistanceTelevision system detailsLaser detailsInformation processingHigh density
A photoelectric conversion element array having a plurality of photoelectric conversion elements (emitting optics 4, receiving optics 5) arranged in an array, and the photoelectric conversion elements 4, 5 are arranged alternately at different positions so that every second one is aligned on the same line in the direction of array. A mounted structure of photoelectric conversion element array, having the emitting optics array and the receiving optics array in the photoelectric conversion element array of this invention, arranged on an interposer substrate 9 so as to oppose therewith, and these arrays are mounted on the interposer substrate 9 through the external connection terminals 7. An optical information processing apparatus 1 having the photoelectric conversion element array of the present invention, and an optical wave guide 3 opposed to the respective optics of the photoelectric conversion element arrays. These configurations not only allow high-density integration of optical interconnects, but also reduce optical interference or crosstalk due to the photoelectric conversion element, and can thereby provide a photoelectric conversion element array allowing efficient propagation of light, an integrated apparatus thereof, a mounted structure of them, and an optical information processing apparatus.
Owner:SONY CORP
LED device and LED lamp including the same
ActiveUS10281088B2Reduce Optical InterferenceElectric circuit arrangementsSolid-state devicesSurface mountingEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Organic light emitting device
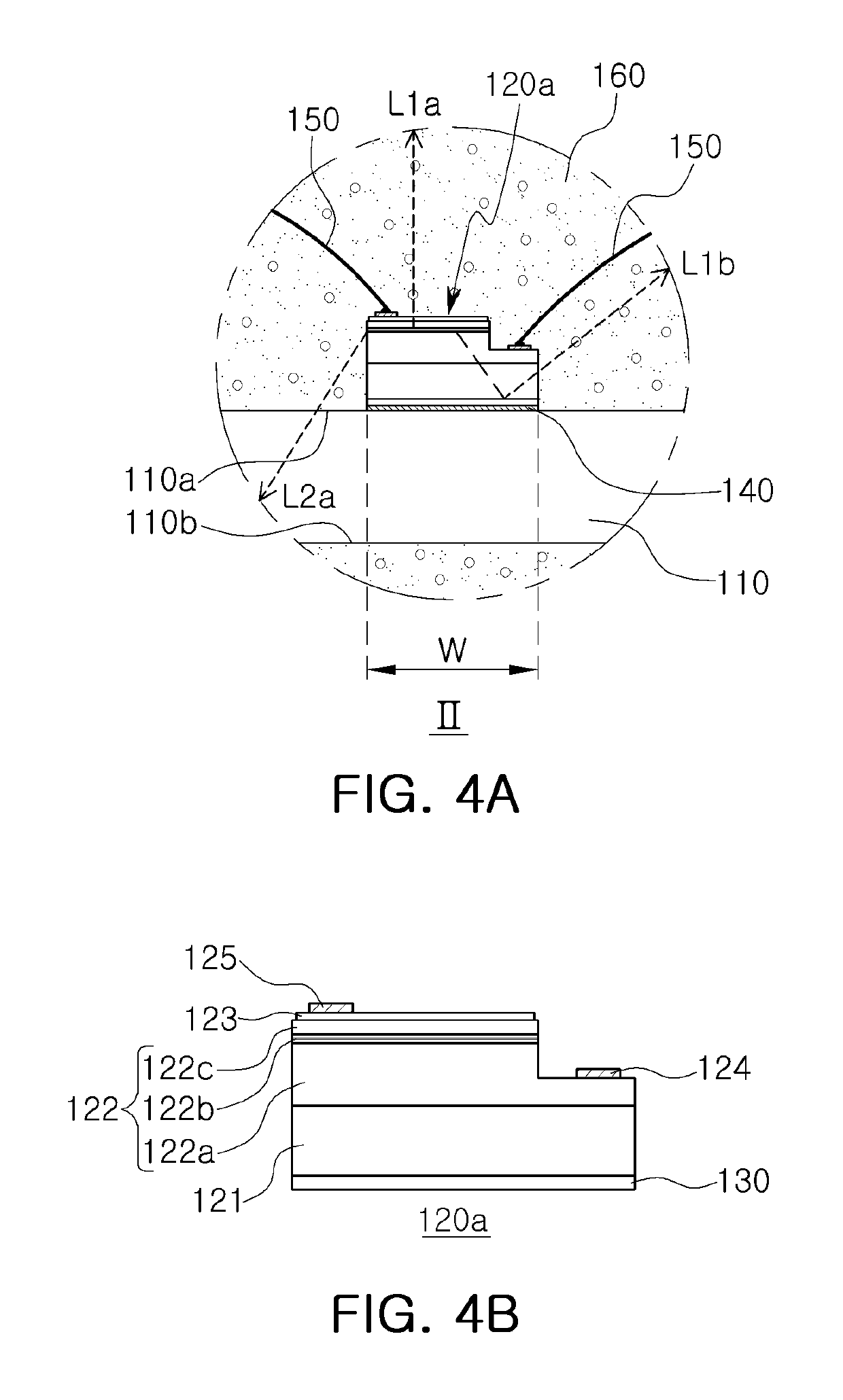
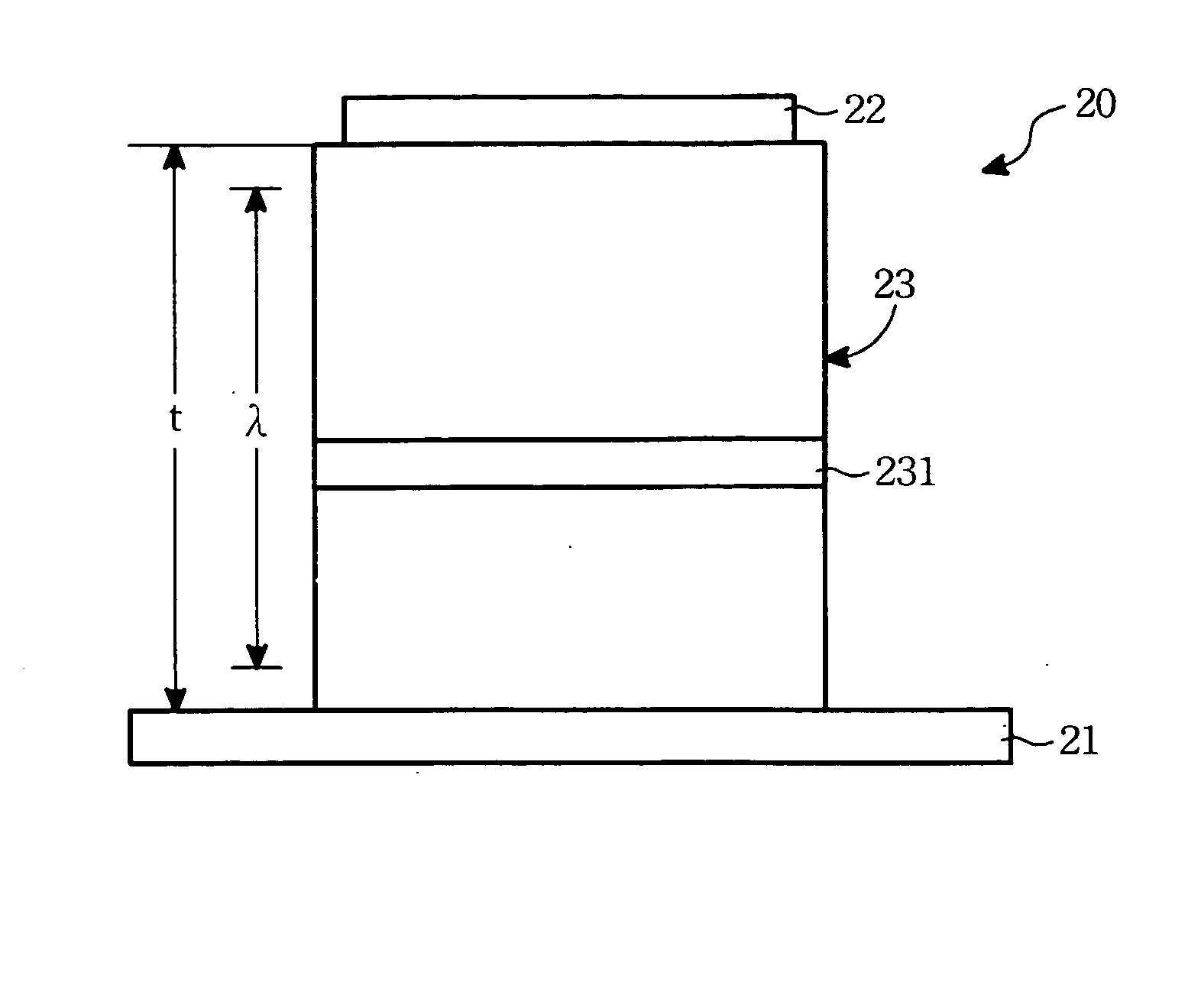
InactiveUS20060163991A1Increasing the thicknessAvoid light interferenceIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensDopantOrganic light emitting device
An organic light emitting device includes a transparent electrode, a reflective electrode, and an organic light emitting element. The organic light emitting element includes an emissive material layer doped with an emissive dopant, and is disposed between the transparent electrode and the reflective electrode. The total thickness of the organic light emitting element is greater than the wavelength of the light from the emissive material layer.
Owner:AU OPTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com